Patents
Literature
602 results about "Qubit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
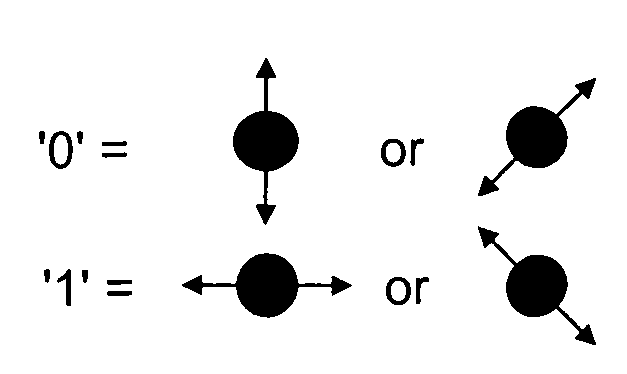
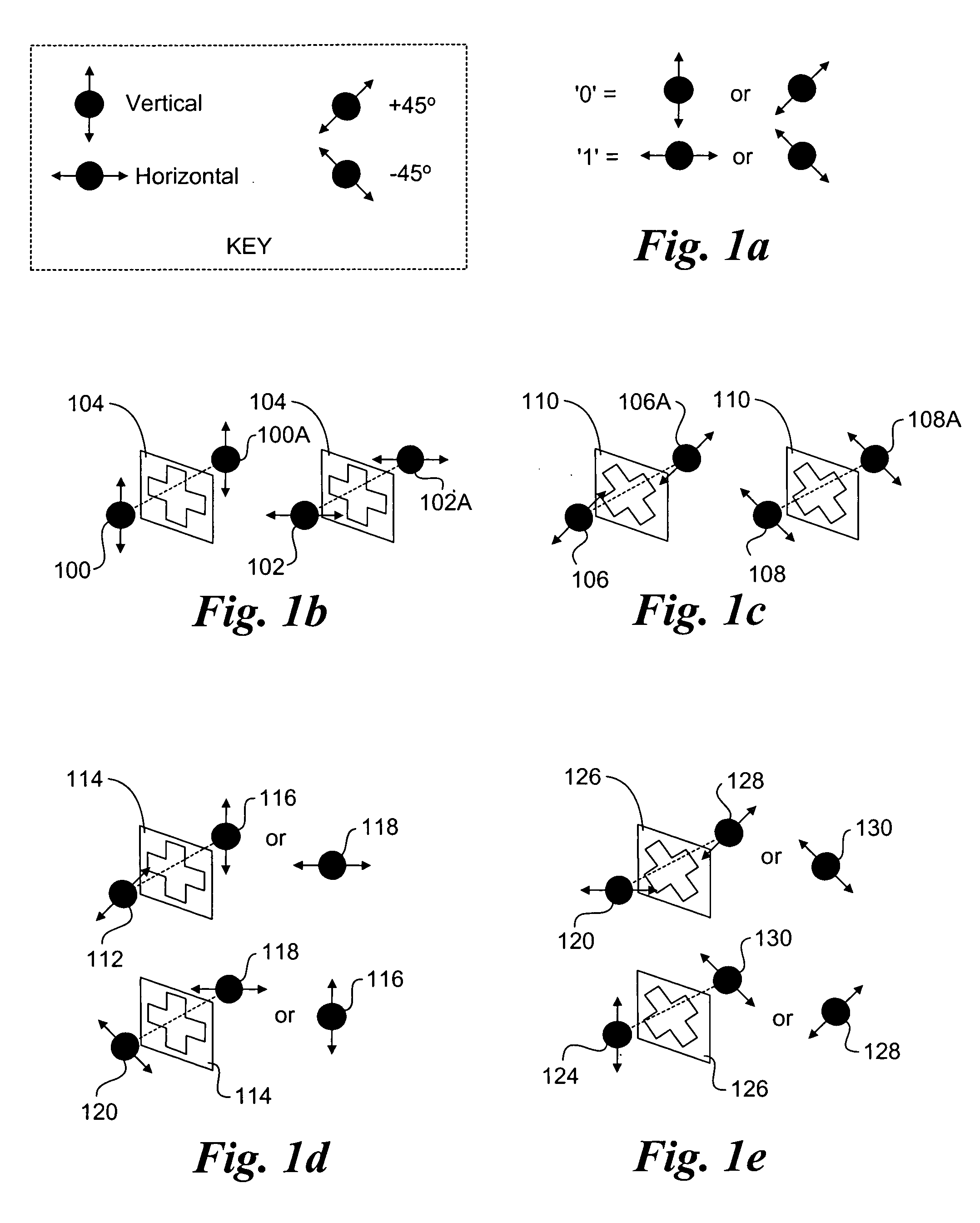
In quantum computing, a qubit (/ˈkjuːbɪt/) or quantum bit (sometimes qbit) is the basic unit of quantum information—the quantum version of the classical binary bit physically realized with a two-state device. A qubit is a two-state (or two-level) quantum-mechanical system, one of the simplest quantum systems displaying the peculiarity of quantum mechanics. Examples include: the spin of the electron in which the two levels can be taken as spin up and spin down; or the polarization of a single photon in which the two states can be taken to be the vertical polarization and the horizontal polarization. In a classical system, a bit would have to be in one state or the other. However, quantum mechanics allows the qubit to be in a coherent superposition of both states/levels simultaneously, a property which is fundamental to quantum mechanics and quantum computing.
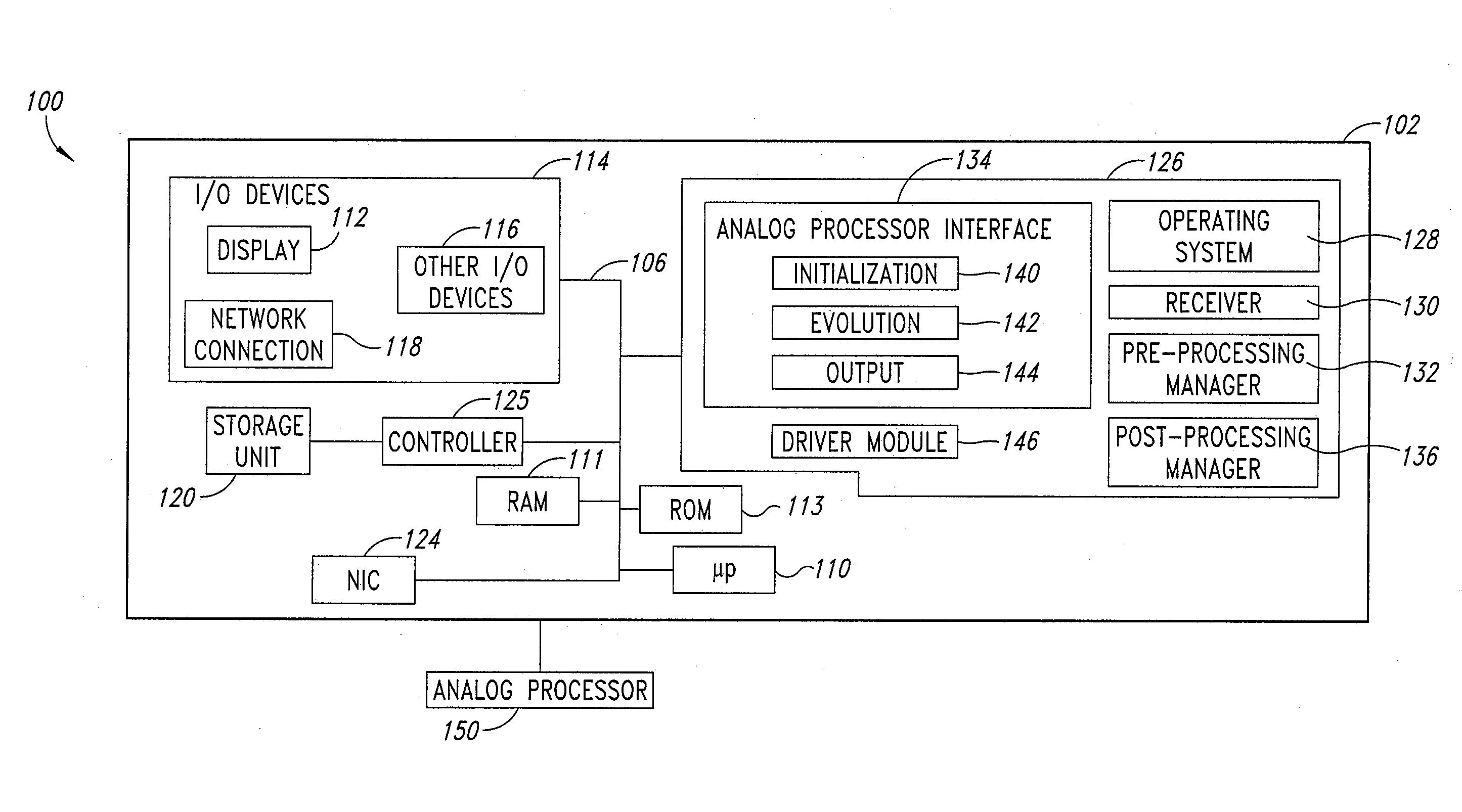
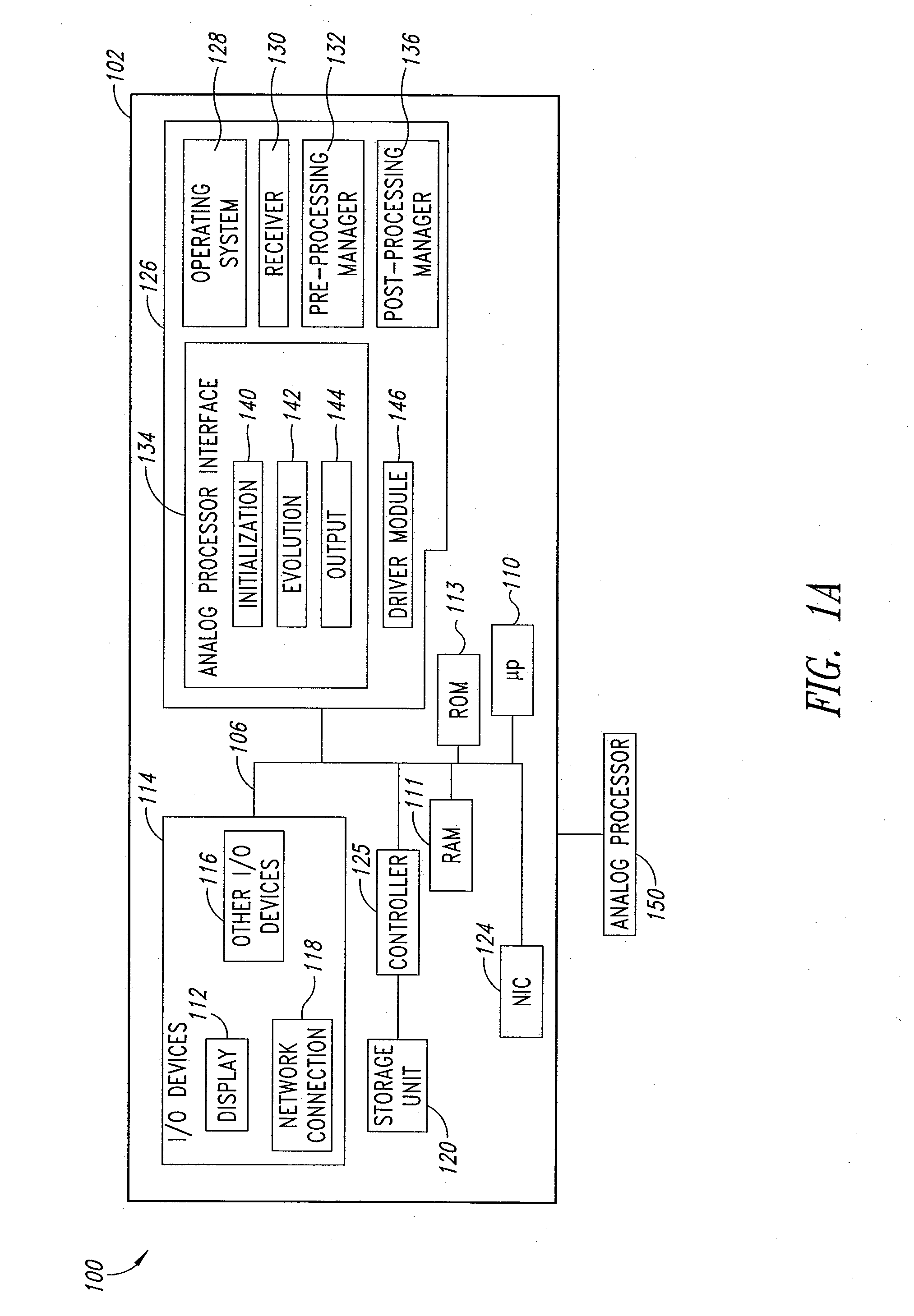
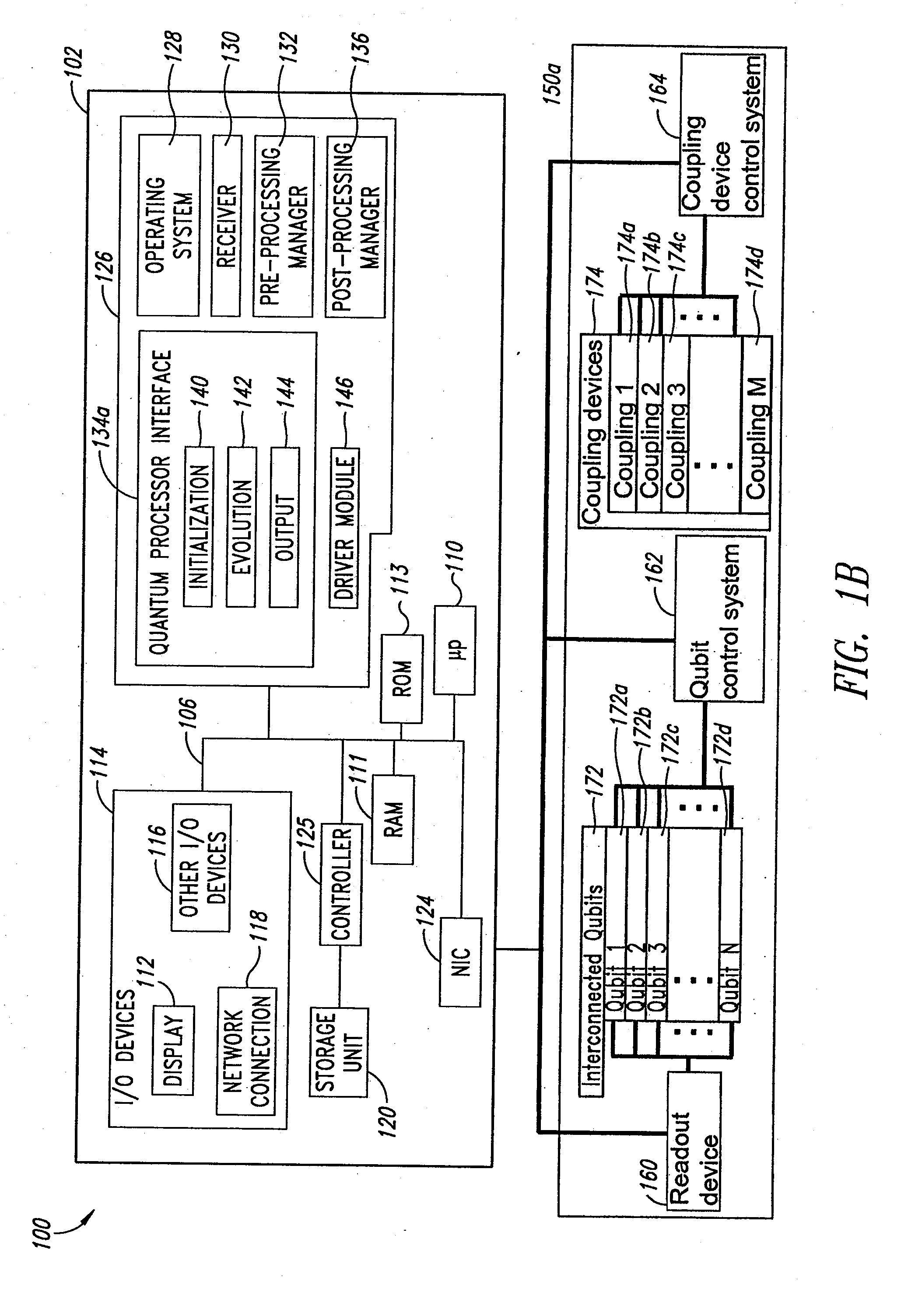
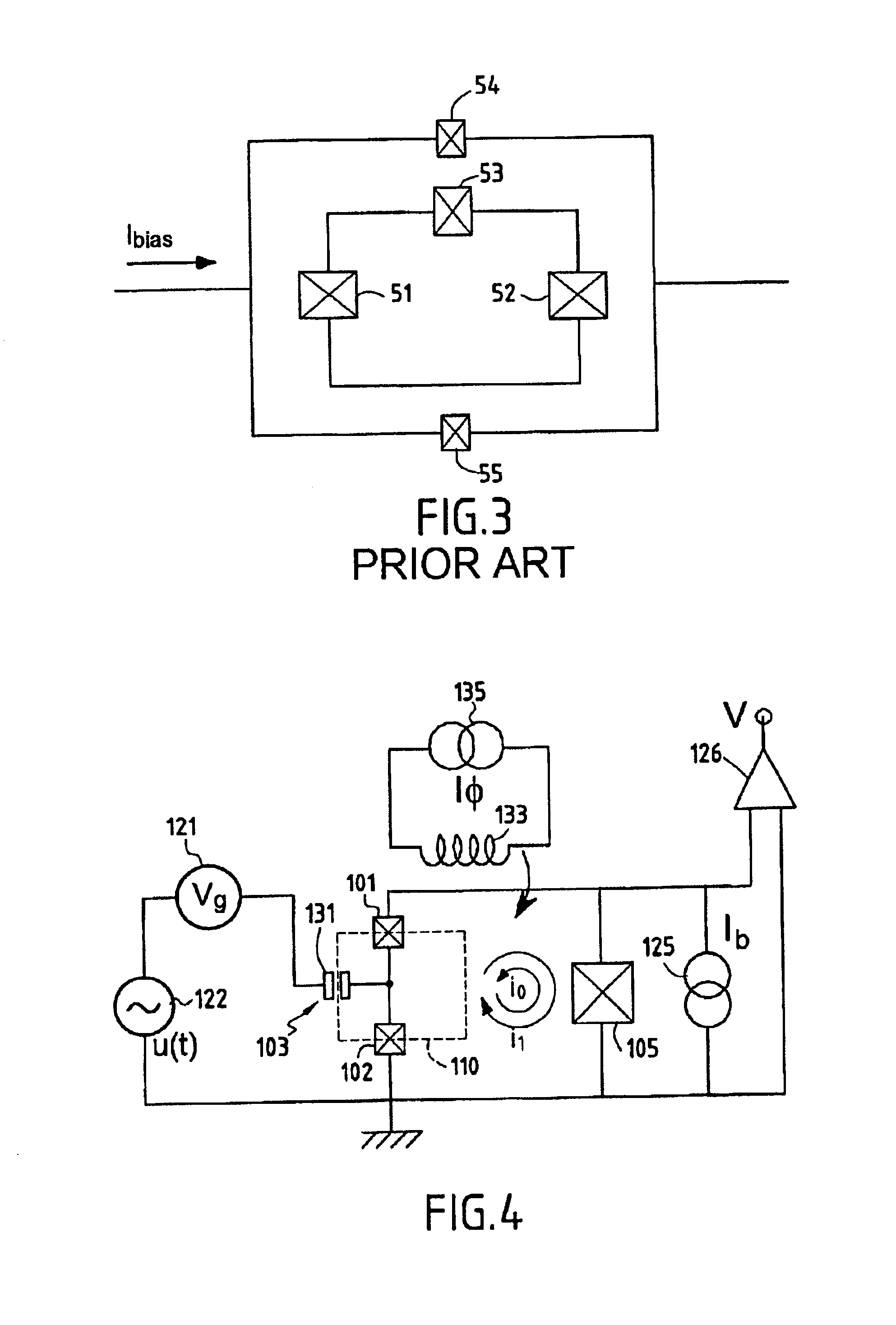
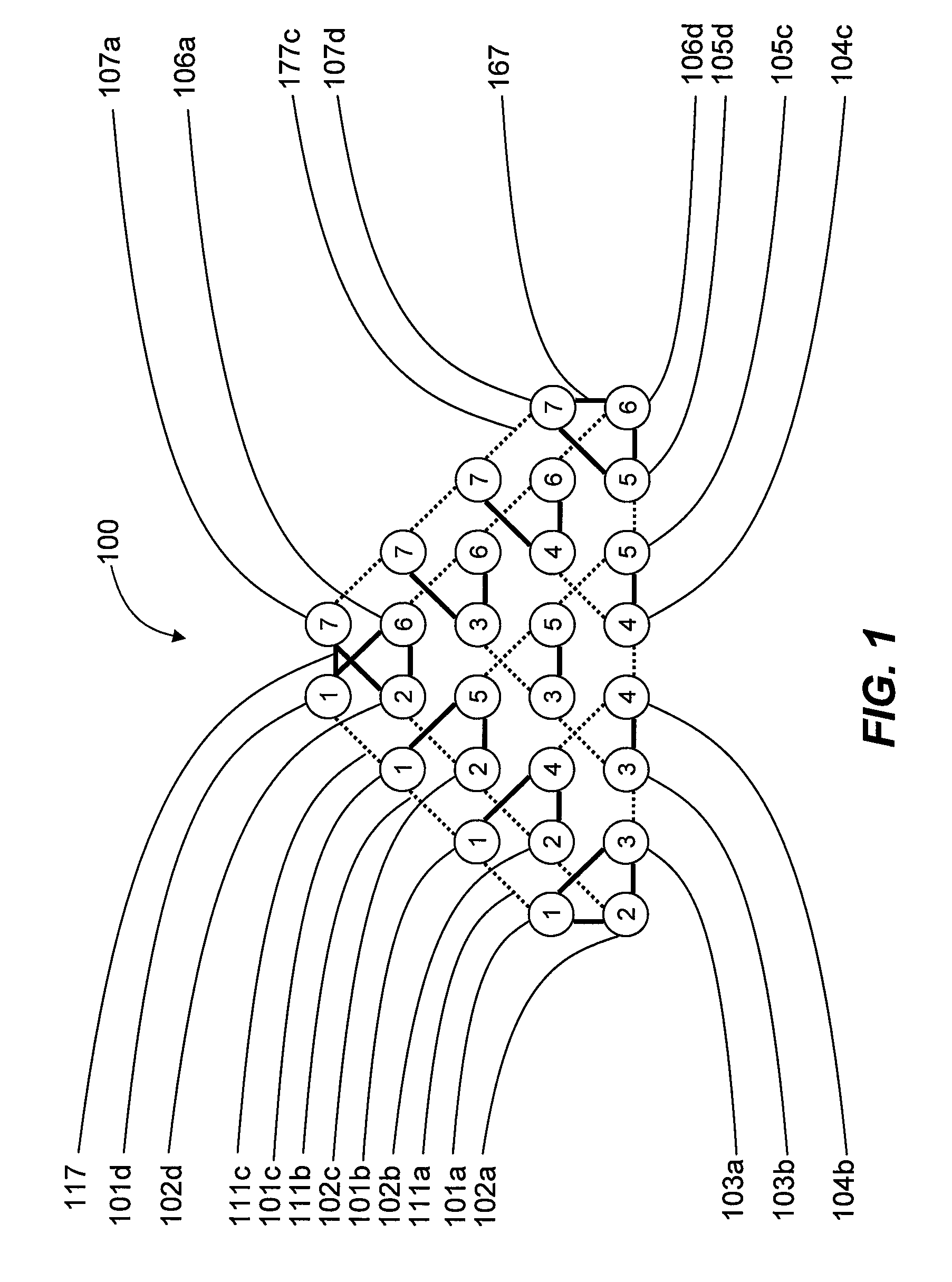
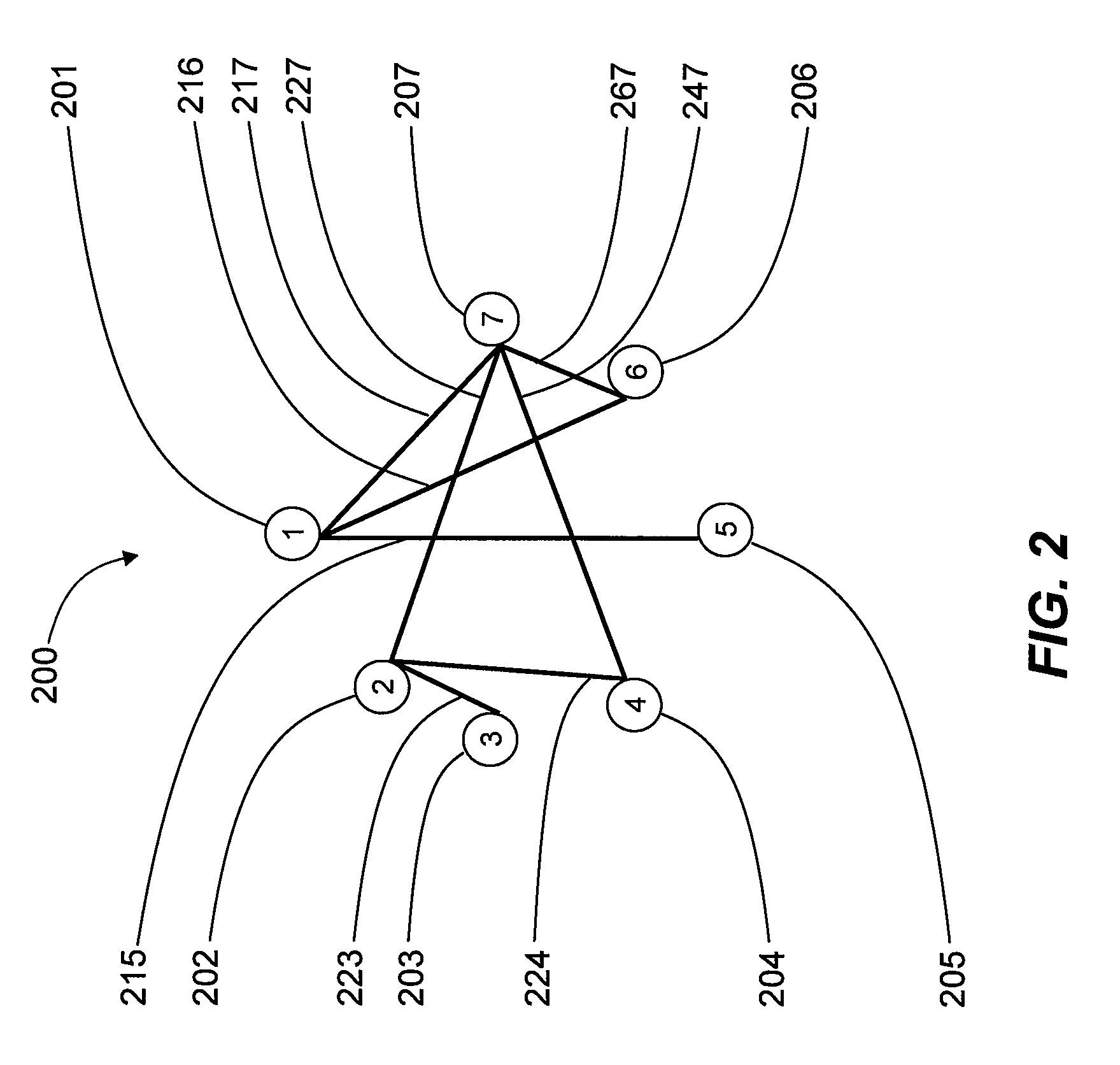
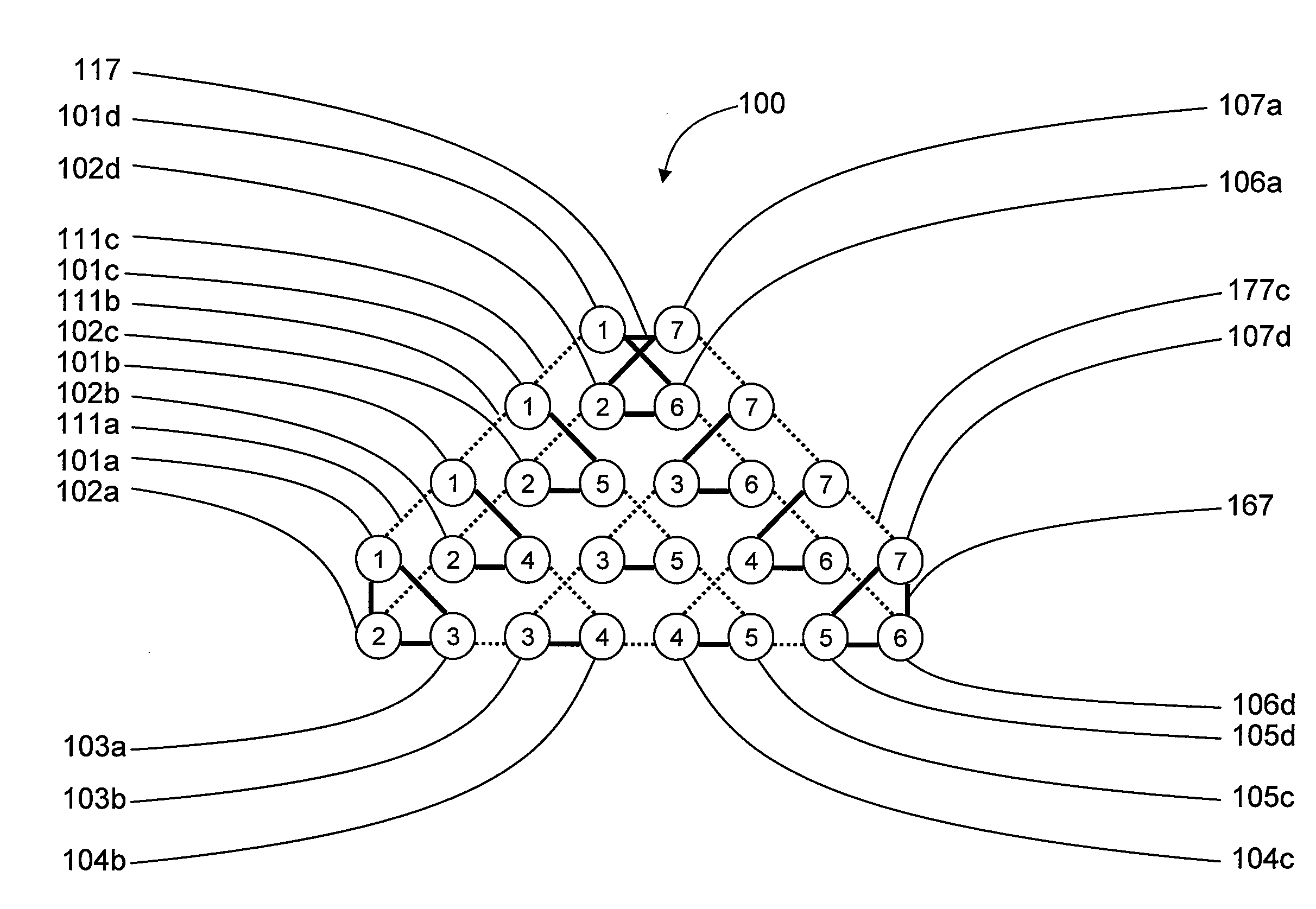
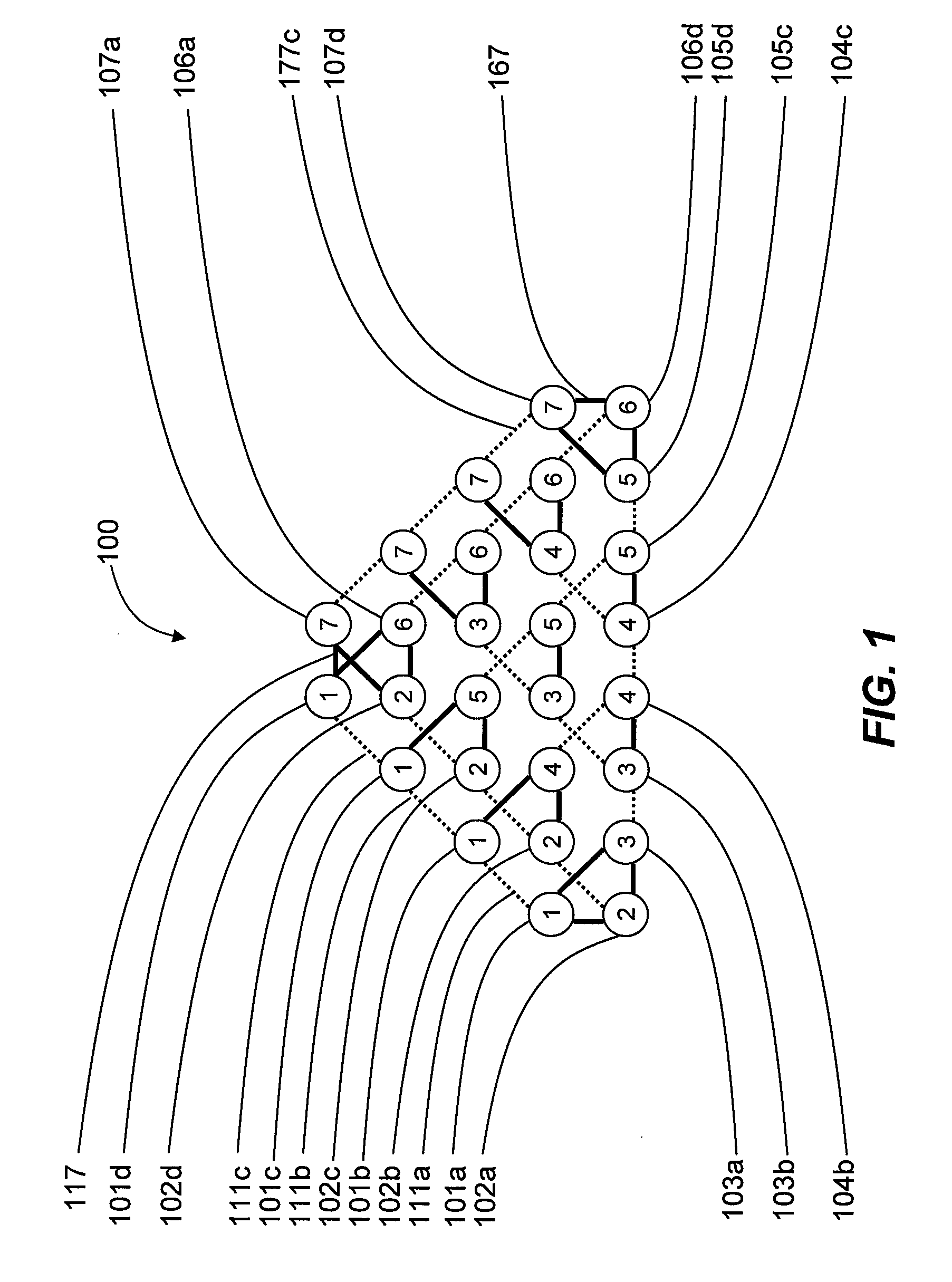
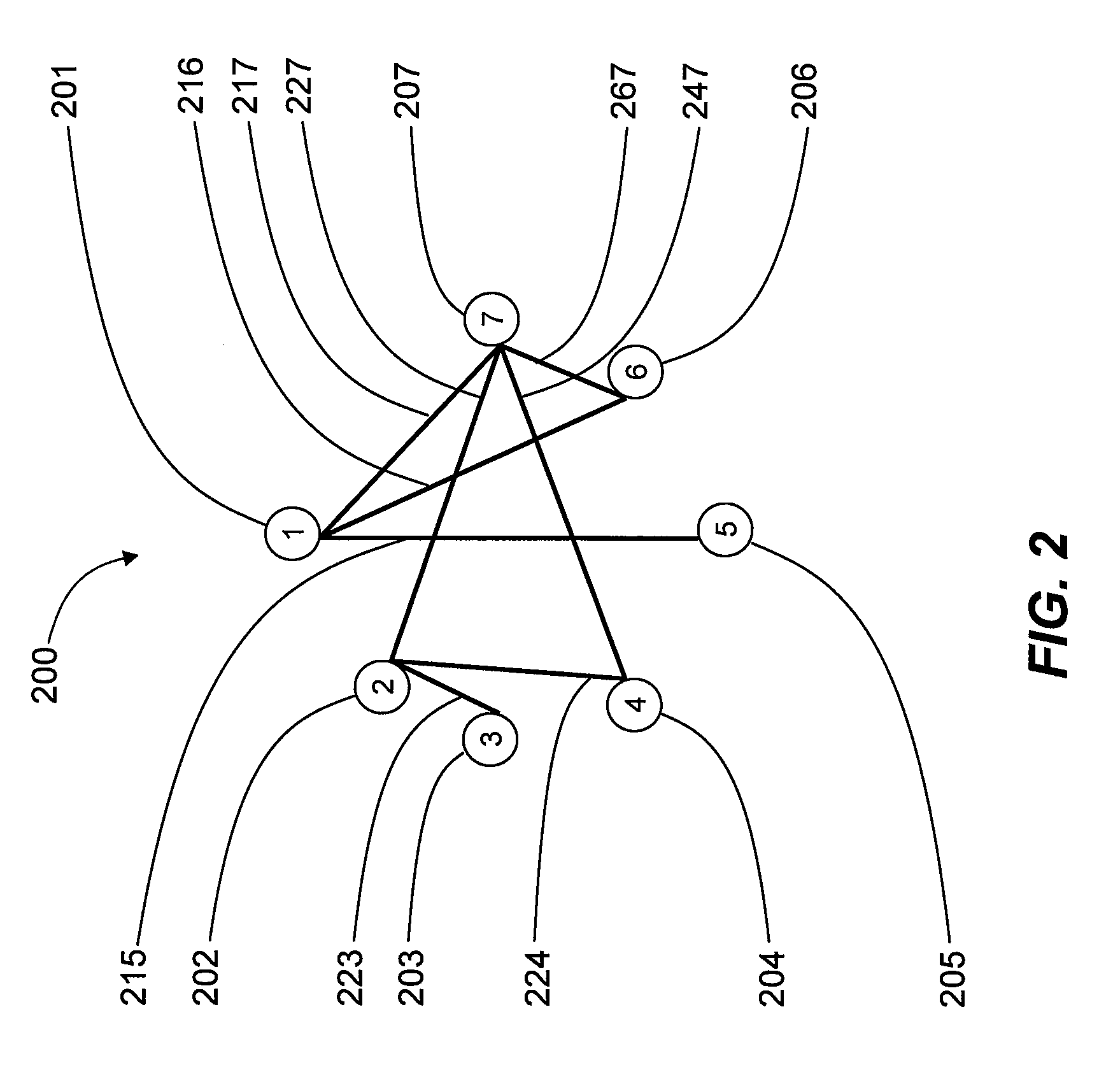
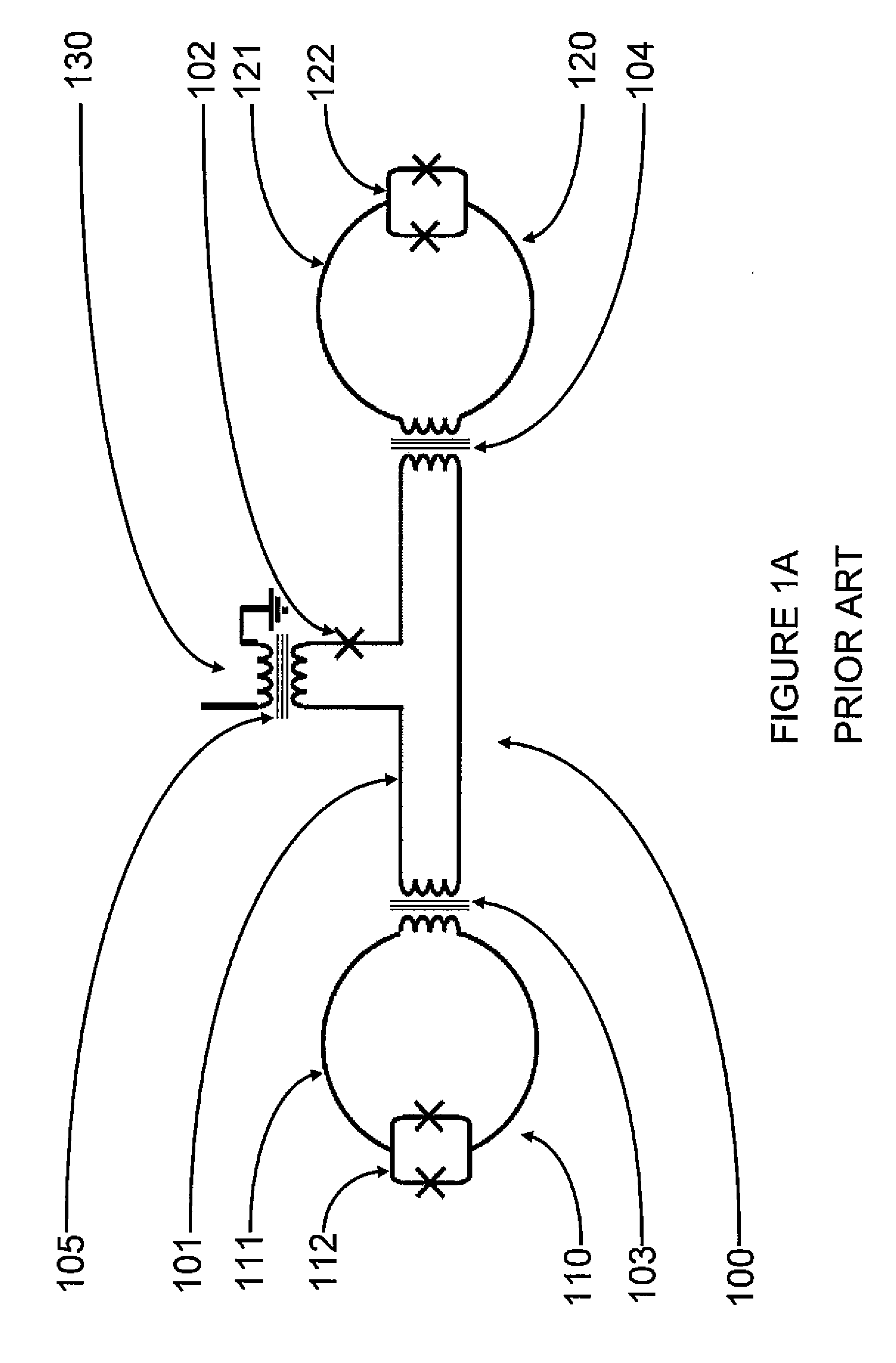
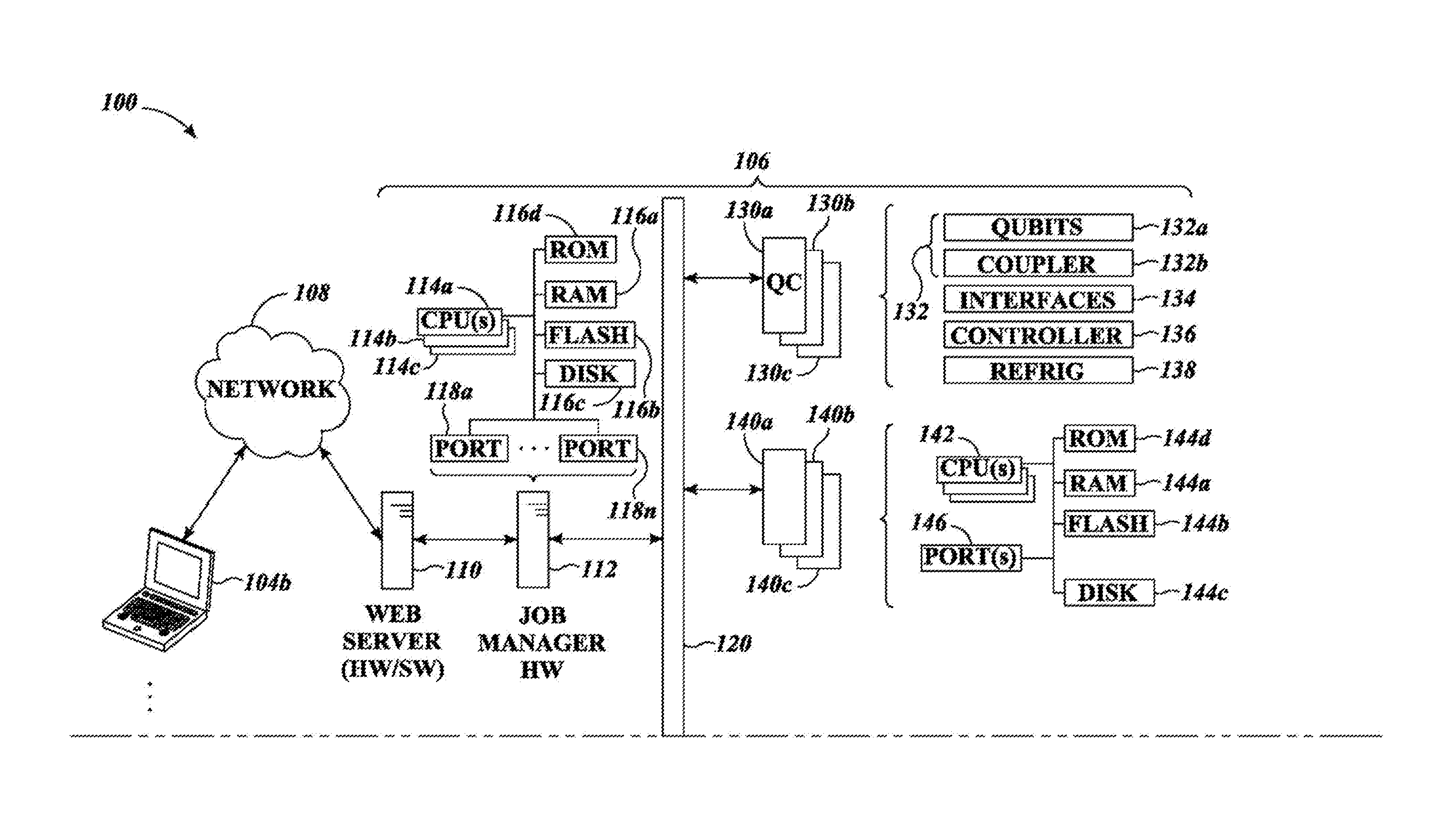
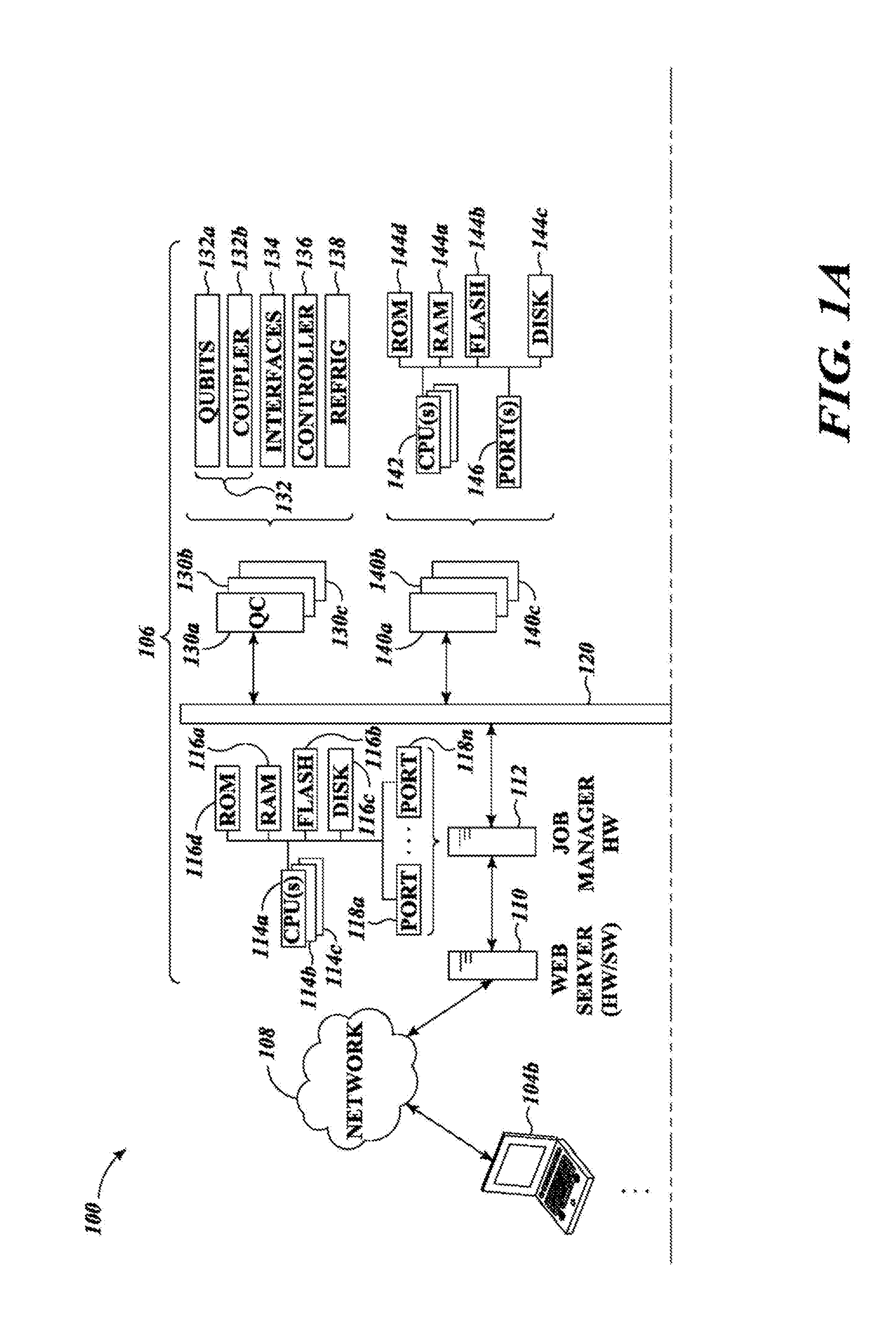
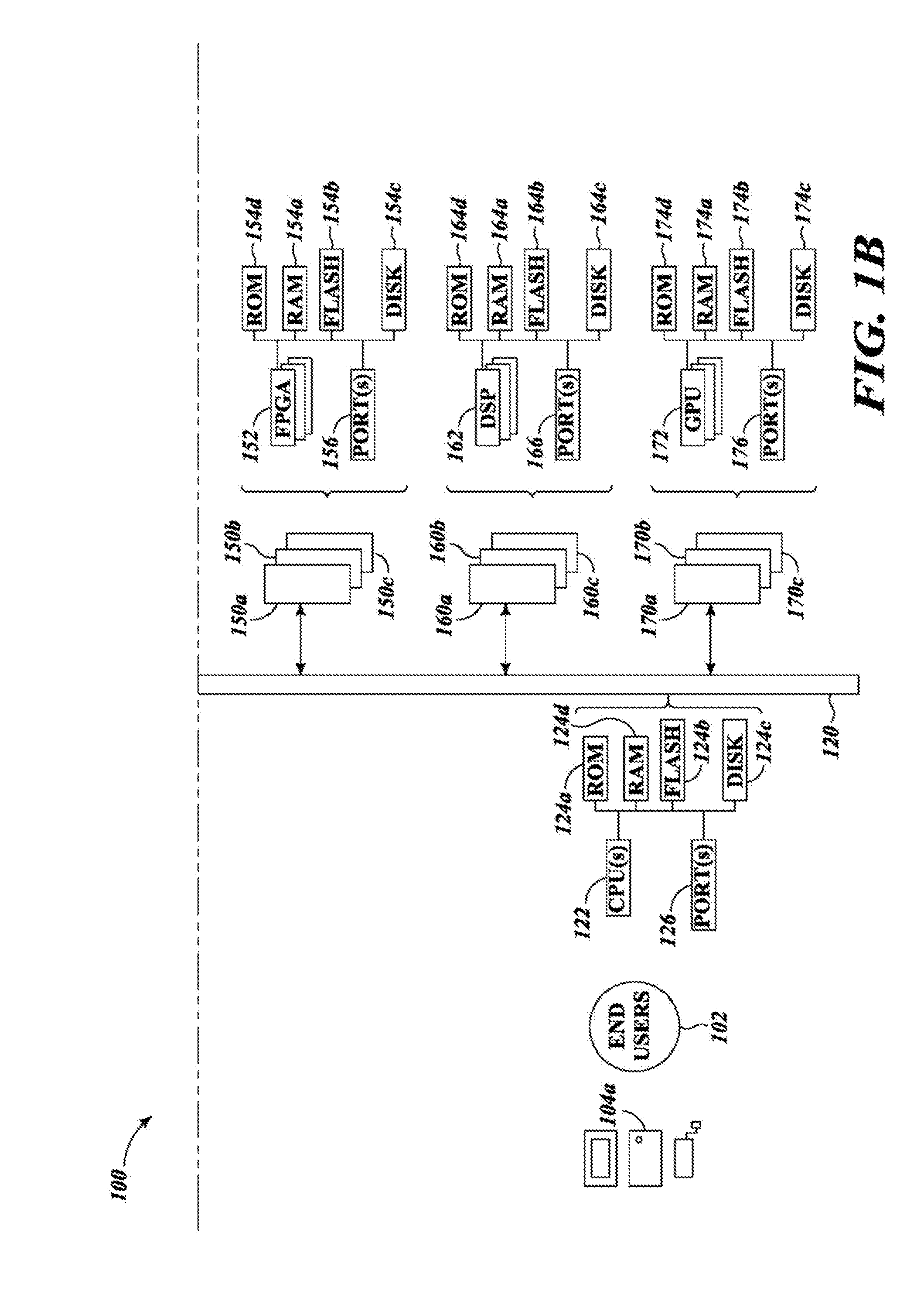
Systems, devices, and methods for interconnected processor topology
ActiveUS20080176750A1Improve legibilityQuantum computersProgram control using wired connectionsAnalog processorCoupling
An analog processor, for example a quantum processor may include a plurality of elongated qubits that are disposed with respect to one another such that each qubit may selectively be directly coupled to each of the other qubits via a single coupling device. Such may provide a fully interconnected topology.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
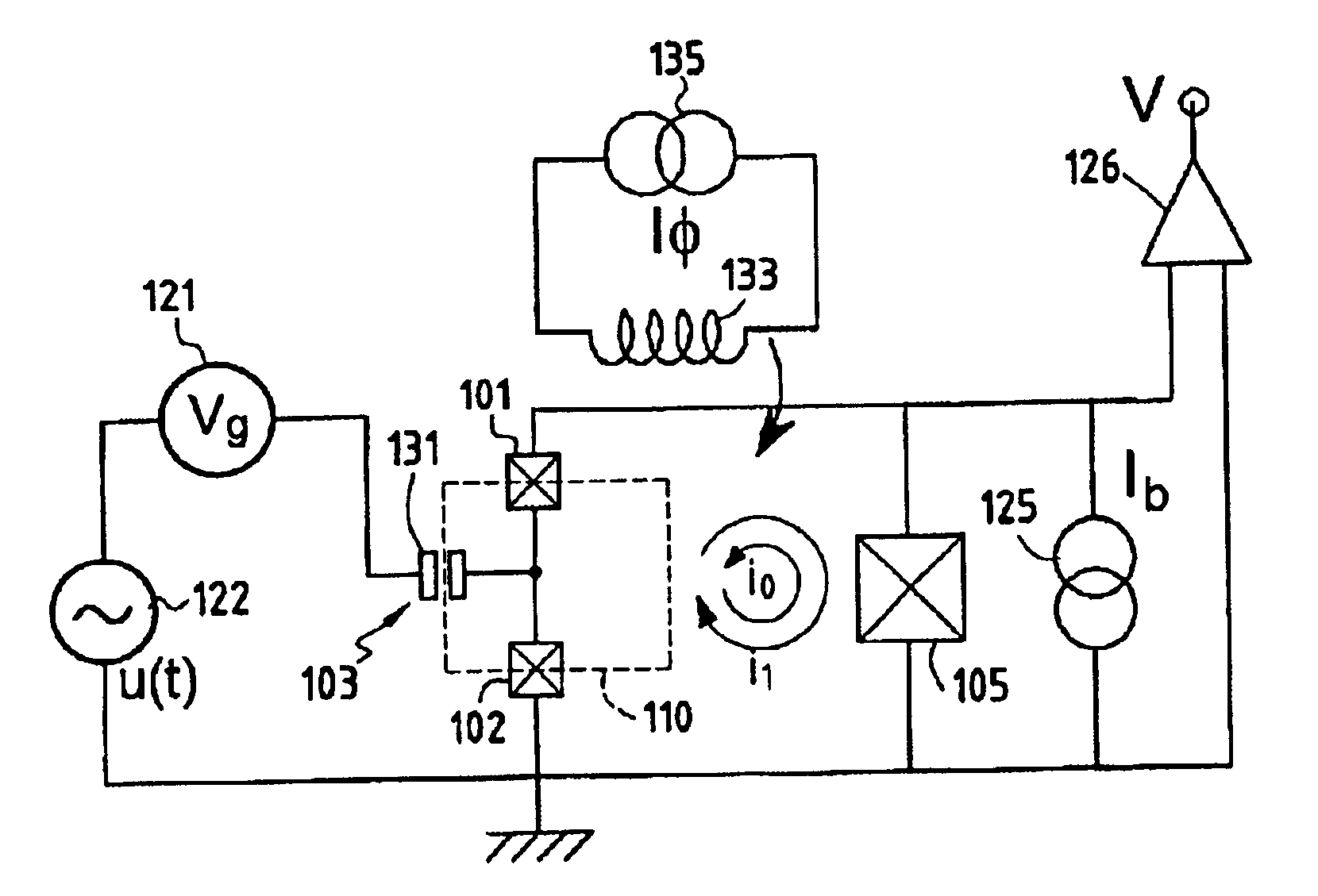
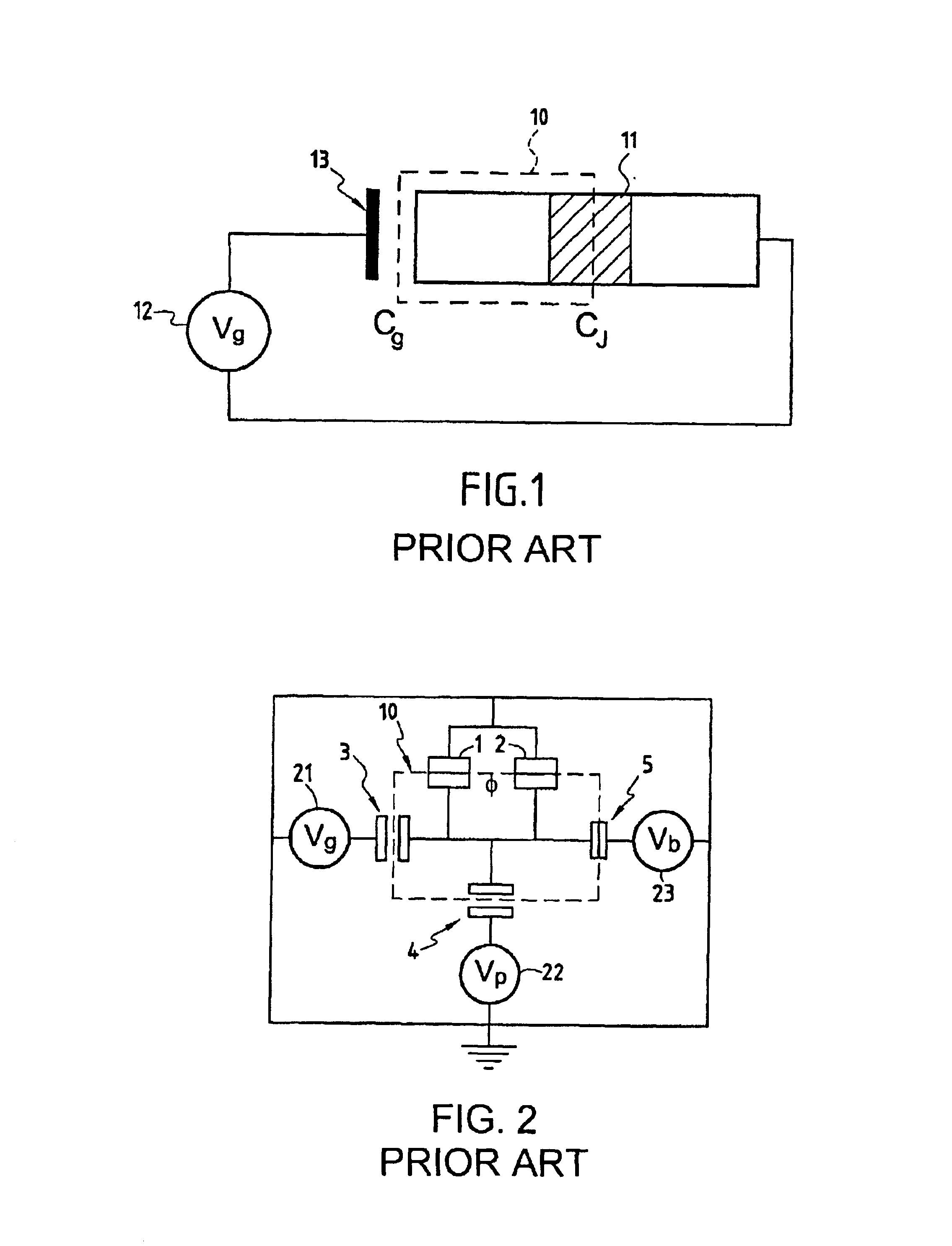
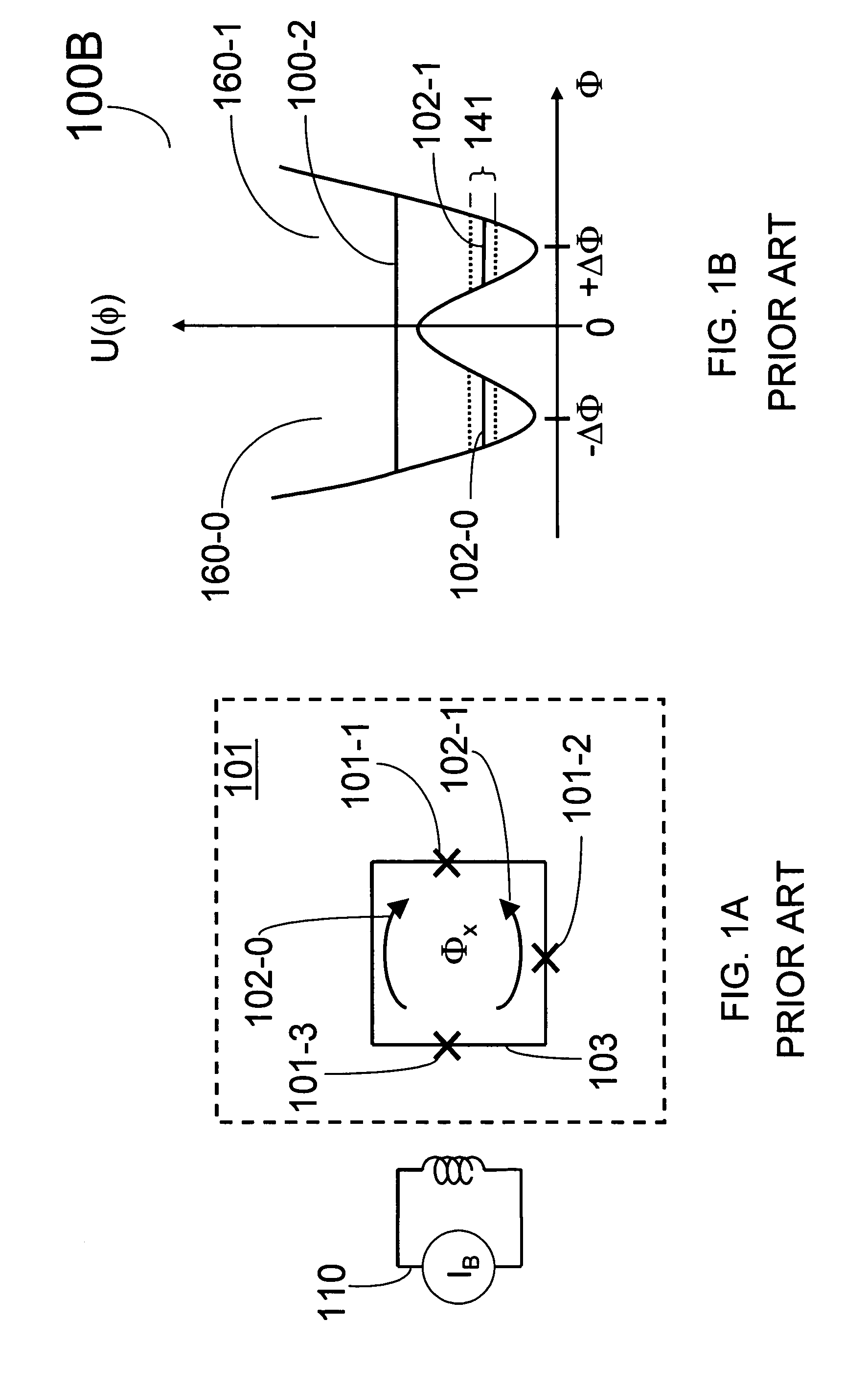
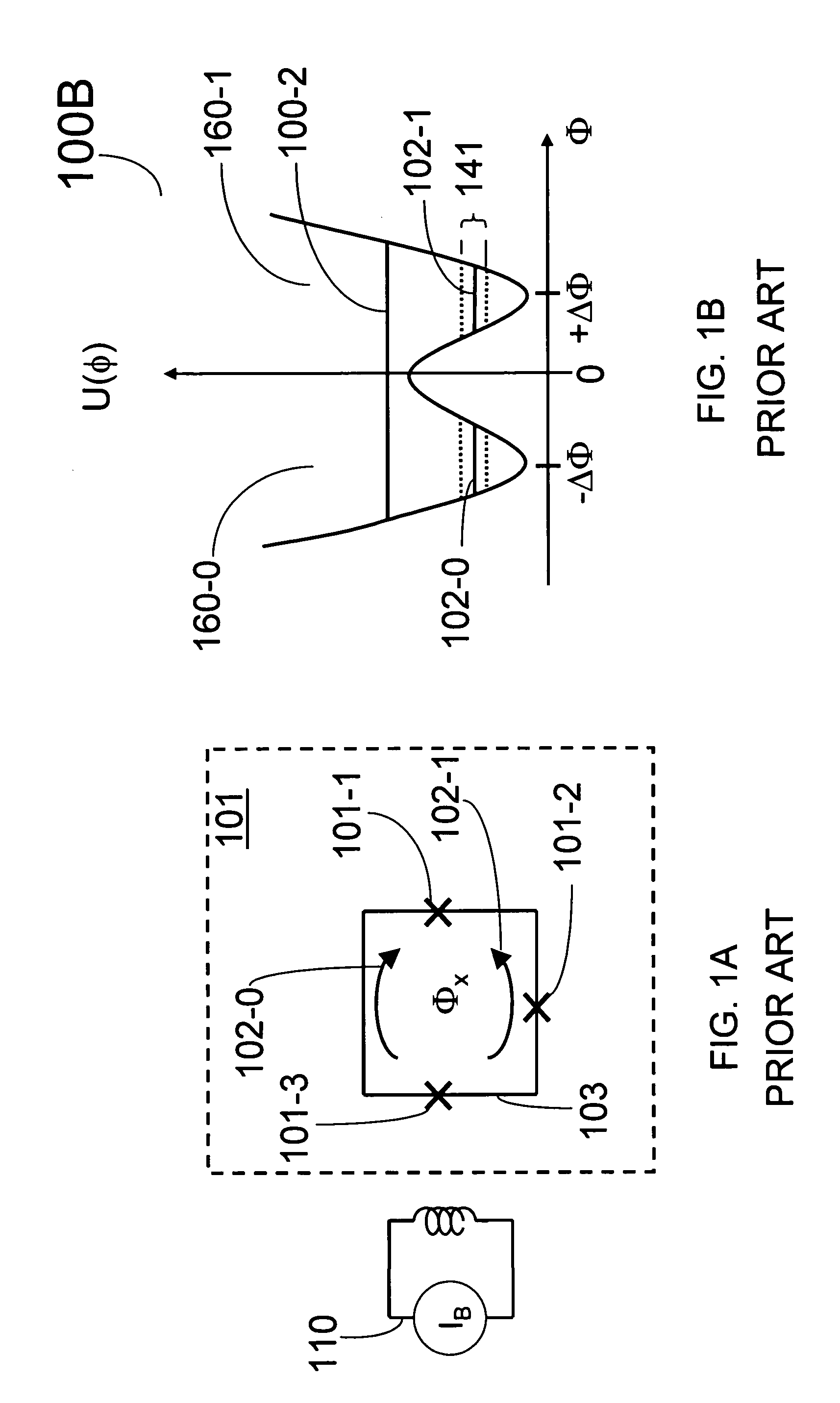
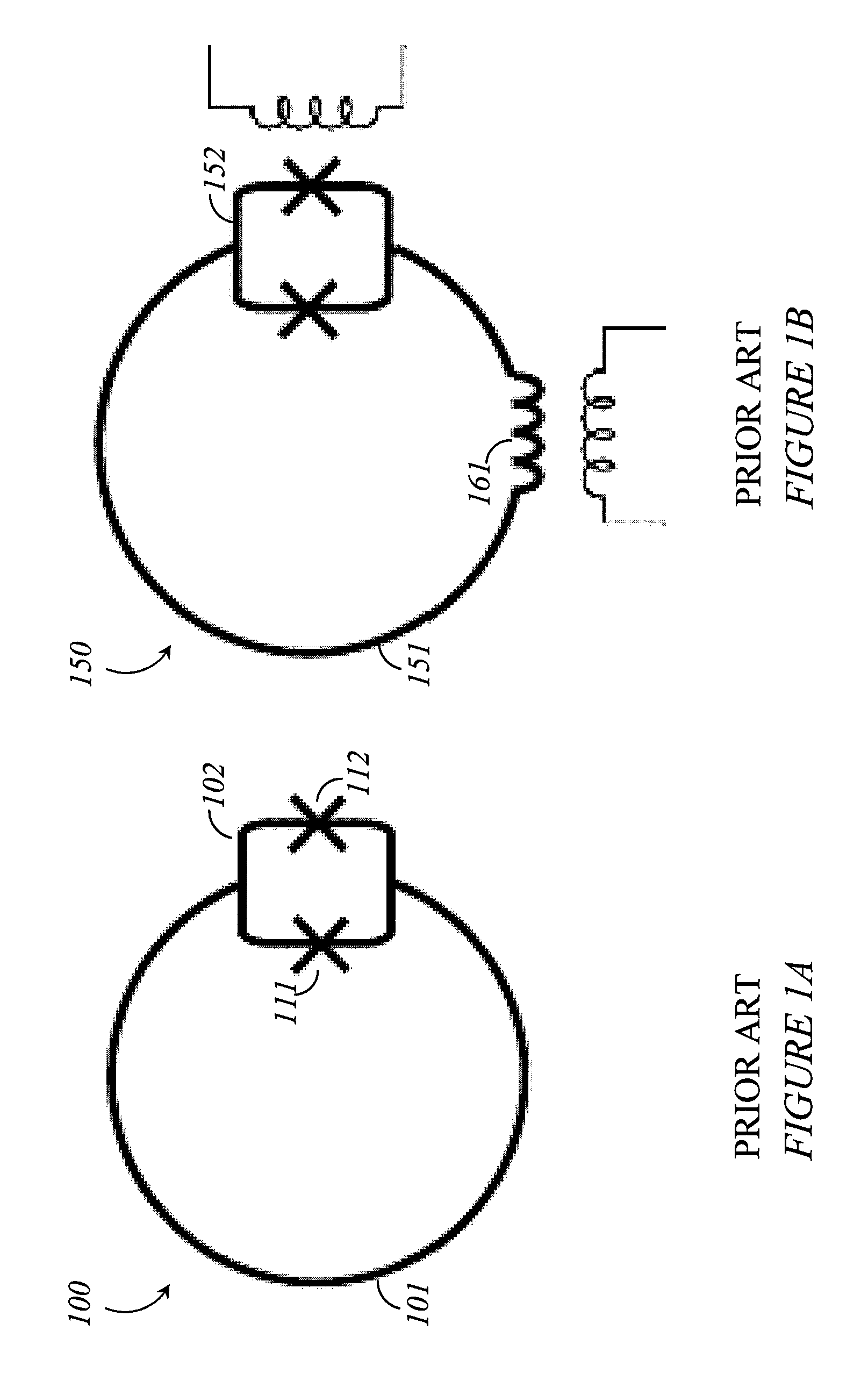
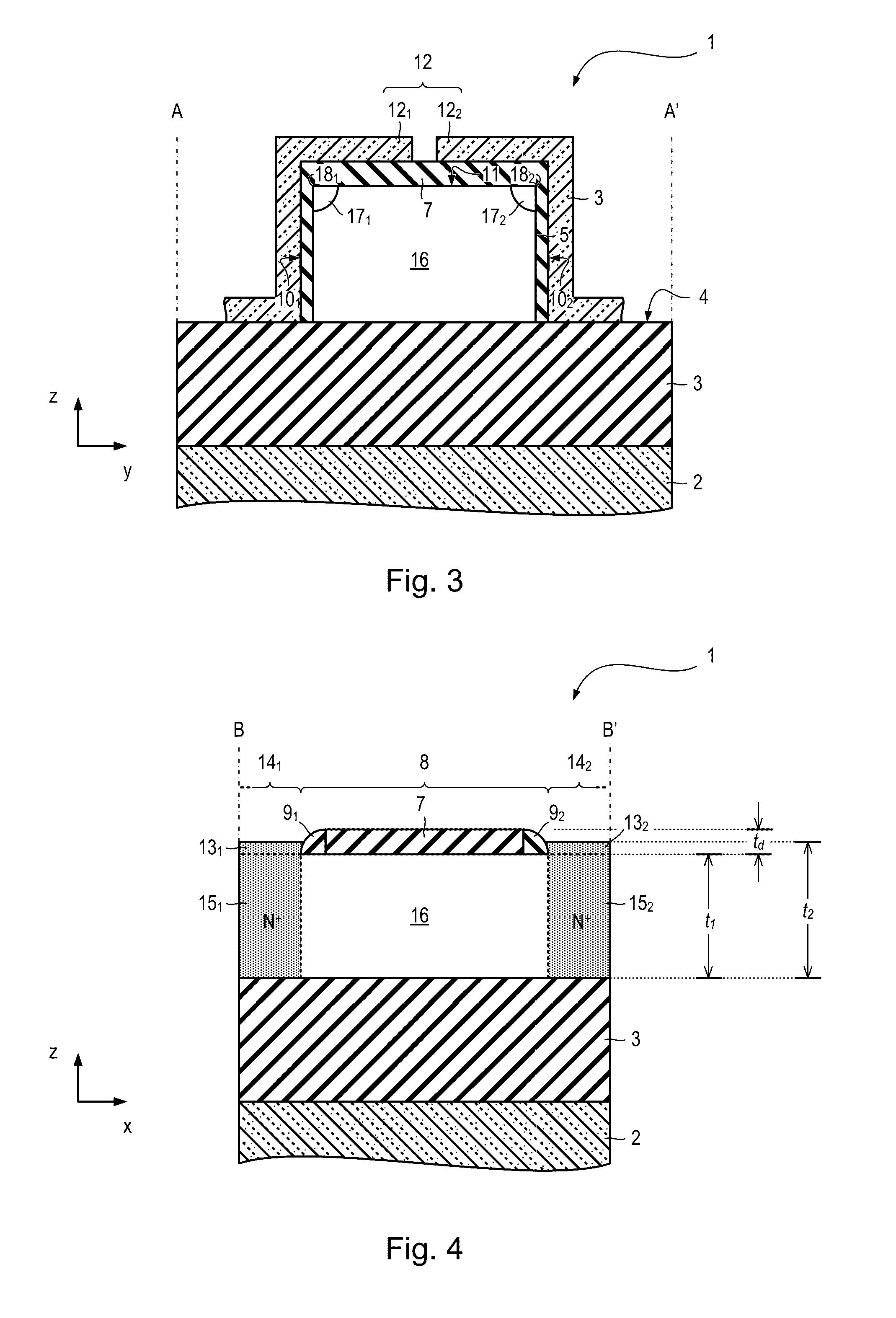
Superconducting quantum-bit device based on Josephson junctions
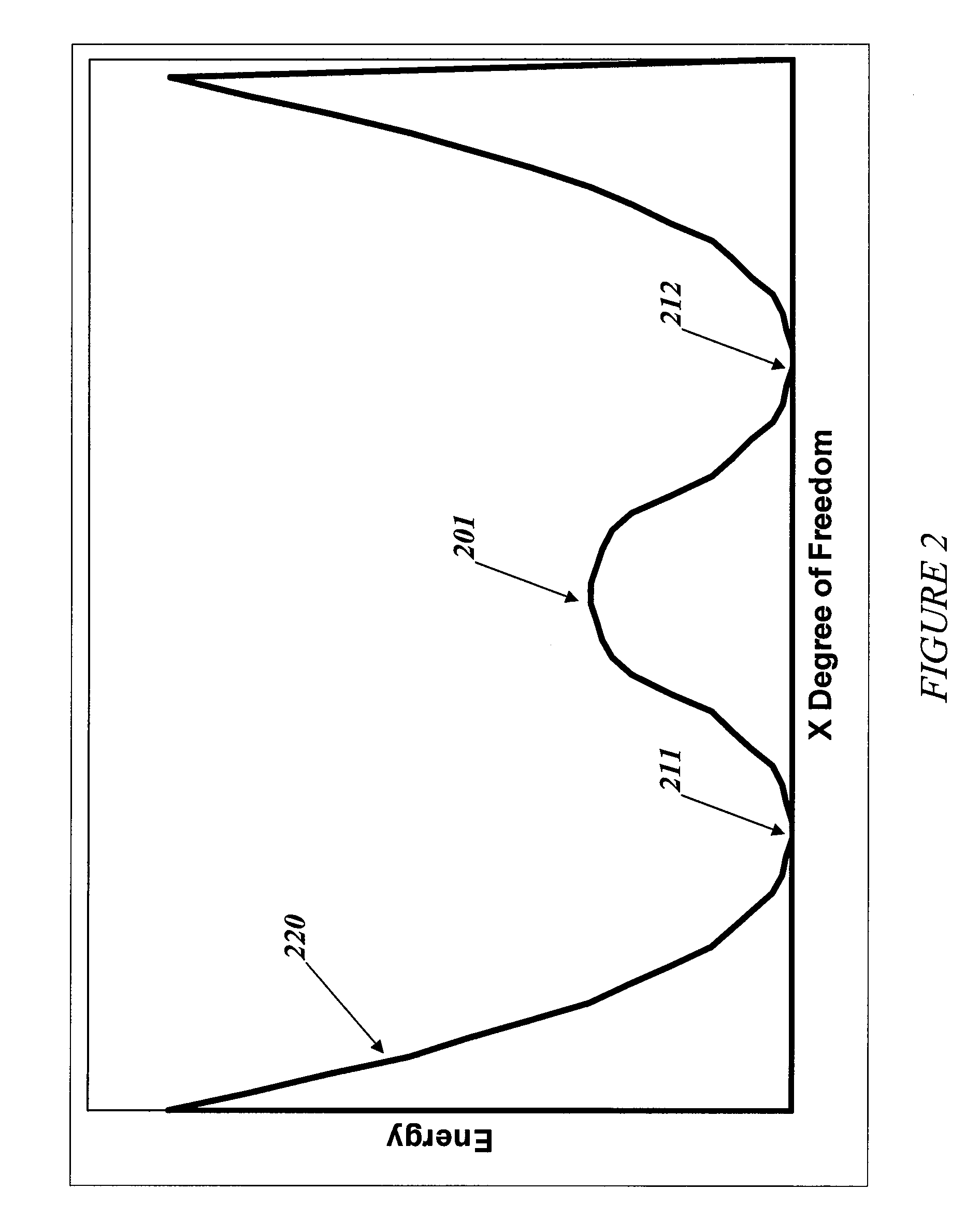
InactiveUS6838694B2Enhanced couplingShortness of the coherence timeQuantum computersNanoinformaticsCooper pairDegrees of freedom
A superconducting quantum-bit device based on Josephson junction has a charge as a first principal degree of freedom assigned to writing and a phase as a second principal degree of freedom assigned to reading. The device comprises a Cooper-pair box comprising first and second Josephson junctions defining a charge island of the Cooper-pair box closing up onto a superconducting loop. A read circuit comprises a read Josephson junction JL inserted into the superconducting loop and having a Josephson energy Ej at least 50 times greater than the Josephson energy of each of the first and second Josephson junctions.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Systems, devices, and methods for analog processing
ActiveUS8190548B2Quantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsQuadratic unconstrained binary optimizationComputer science
A system employs a plurality of physical qubits, each having a respective bias operable to up to six differentiable inputs to solve a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization problem. Some physical qubit couplers are operated as intra-logical qubit couplers to ferromagnetically couple respective pairs of the physical qubits as a logical qubit, where each logical qubit represents a variable from the Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization problem. The logical qubits may include two or more physical qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems, devices, and methods for interconnected processor topology
An analog processor, for example a quantum processor may include a plurality of elongated qubits that are disposed with respect to one another such that each qubit may selectively be directly coupled to each of the other qubits via a single coupling device. Such may provide a fully interconnected topology.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Adiabatic quantum computation with superconducting qubits
ActiveUS20050224784A1Increasing effective charging energyQuantum computersNanoinformaticsAdiabatic quantum computationComputational problem
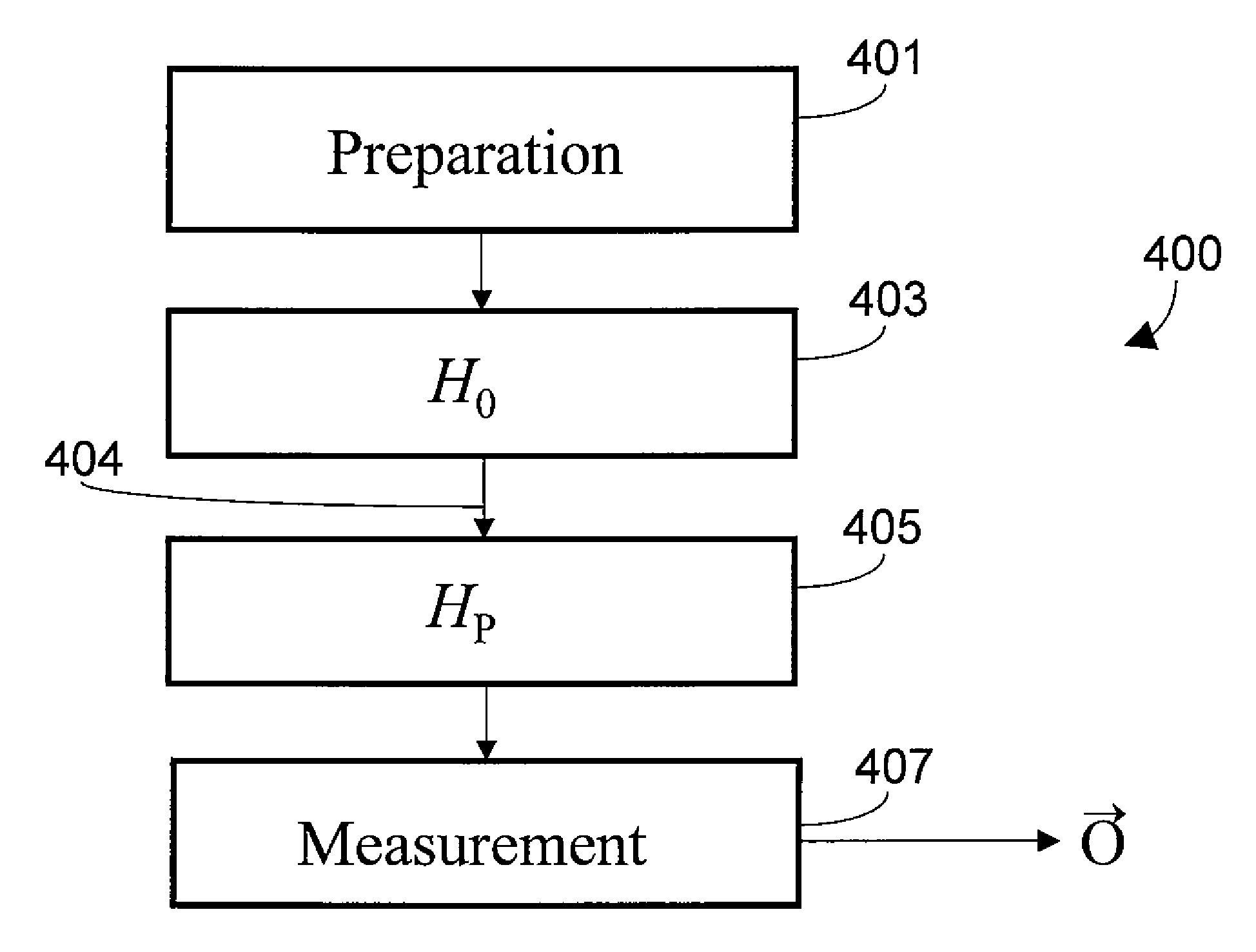
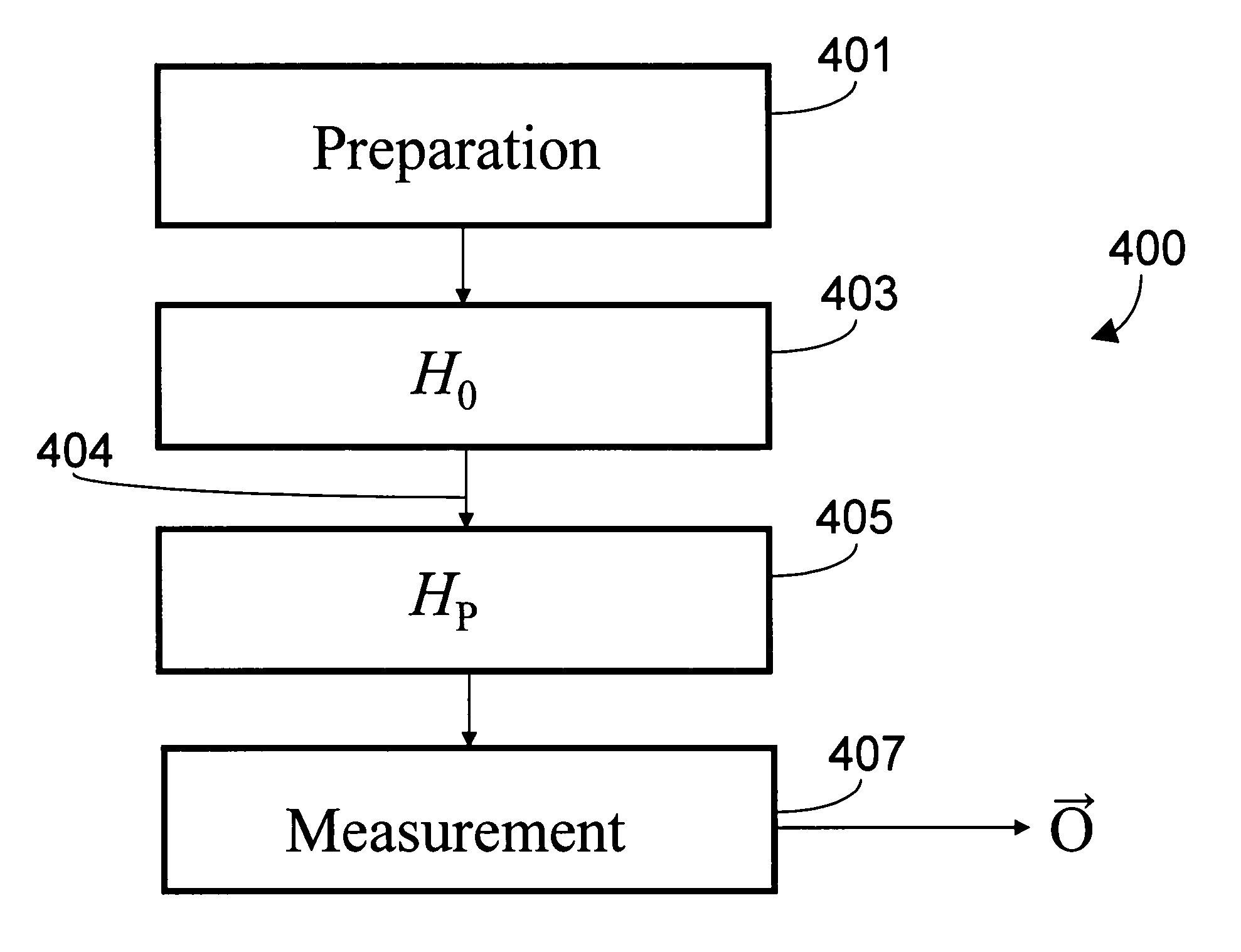
A method for computing using a quantum system comprising a plurality of superconducting qubits is provided. Quantum system can be in any one of at least two configurations including (i) an initialization Hamiltonian H0 and (ii) a problem Hamiltonian HP. The plurality of superconducting qubits are arranged with respect to one another, with a predetermined number of couplings between respective pairs of superconducting qubits in the plurality of qubits, such that the plurality of superconducting qubits, coupled by the predetermined number of couplings, collectively define a computational problem to be solved. In the method, quantum system is initialized to the initialization Hamiltonian HO. Quantum system is then adiabatically changed until it is described by the ground state of the problem Hamiltonian HP. The quantum state of quantum system is then readout thereby solving the computational problem to be solved.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems, devices, and methods for analog processing
ActiveUS20090121215A1Quantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsQuadratic unconstrained binary optimizationComputer science
A system employs a plurality of physical qubits, each having a respective bias operable to up to six differentiable inputs to solve a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization problem. Some physical qubit couplers are operated as intra-logical qubit couplers to ferromagnetically couple respective pairs of the physical qubits as a logical qubit, where each logical qubit represents a variable from the Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization problem. The logical qubits may include two or more physical qubits
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Methods of adiabatic quantum computation
ActiveUS20070180586A1Increasing effective charging energyIncrease the gap sizeQuantum computersDigital data processing detailsAdiabatic quantum computationComputational problem
A method for quantum computing using a quantum system comprising a plurality of qubits is provided. The system can be in any one of at least two configurations at any given time including one characterized by an initialization Hamiltonian H0 and one characterized by a problem Hamiltonian HP. The problem Hamiltonian HP has a final state. Each respective first qubit in the qubits is arranged with respect to a respective second qubit in the qubits such that they define a predetermined coupling strength. The predetermined coupling strengths between the qubits in the plurality of qubits collectively define a computational problem to be solved. In the method, the system is initialized to H0 and is then adiabatically changed until the system is described by the final state of the problem Hamiltonian HP. Then the state of the system is read out by probing an observable of the σX Pauli matrix operator.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
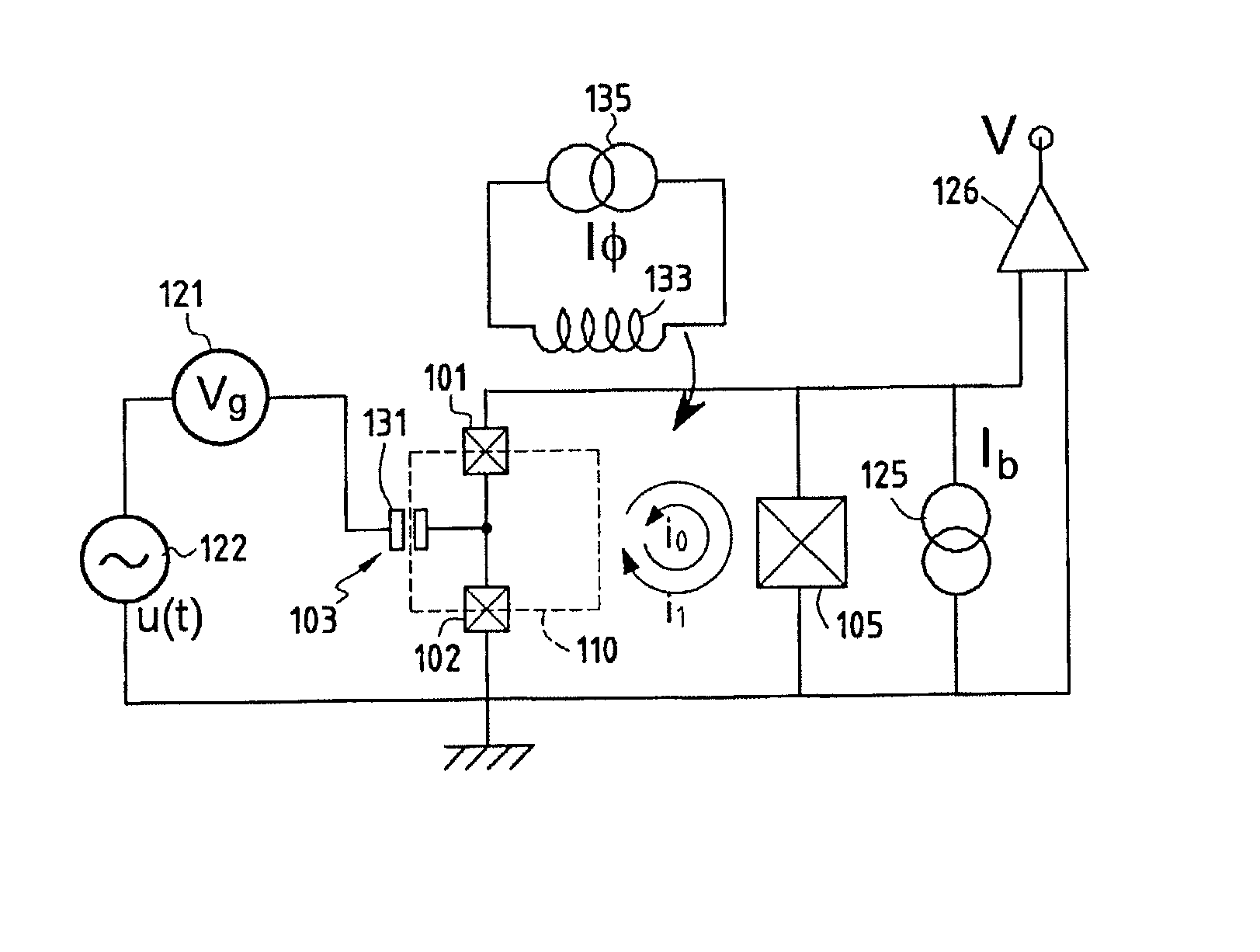
Conditional Rabi oscillation readout for quantum computing
A method for determining whether a first state of a quantum system is occupied is provided. A driving signal is applied to the system at a frequency corresponding to an energy level separation between a first and second state of the system. The system produces a readout frequency only when the first state is occupied. A property of a measurement resonator that is coupled to the quantum system is measured when the quantum system produces the readout frequency, thereby determining whether the first state of the quantum system is occupied. A structure for detecting a qubit state of a qubit is provided. The structure comprises a quantum system that includes the qubit. The qubit has first and second basis states and an ancillary quantum state. The ancillary quantum state can be coupled to the first or second basis states. The structure has a measurement resonator configured to couple to Rabi oscillations between (i) one of the first and second basis states and (ii) the ancillary state in the quantum system.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
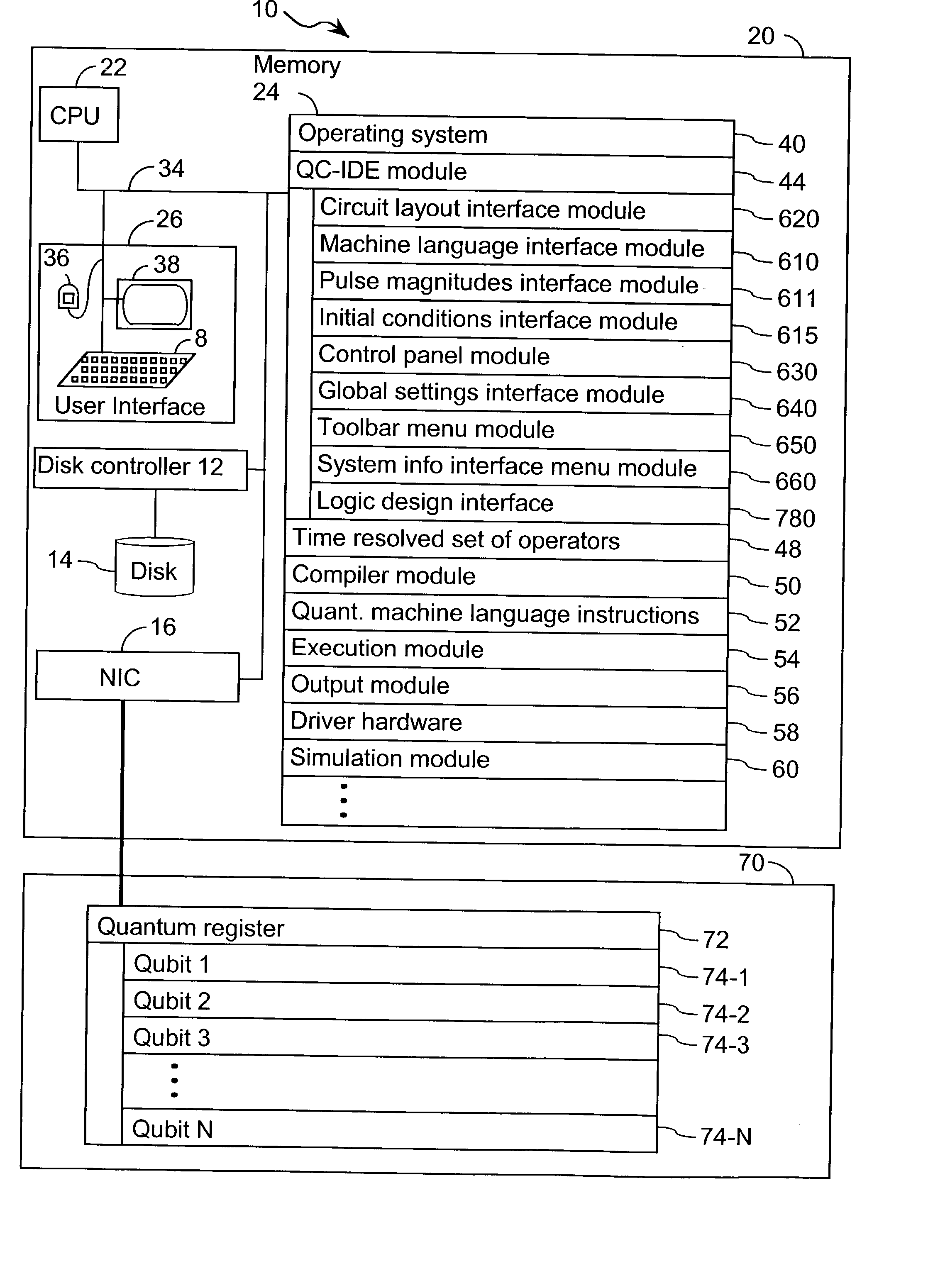
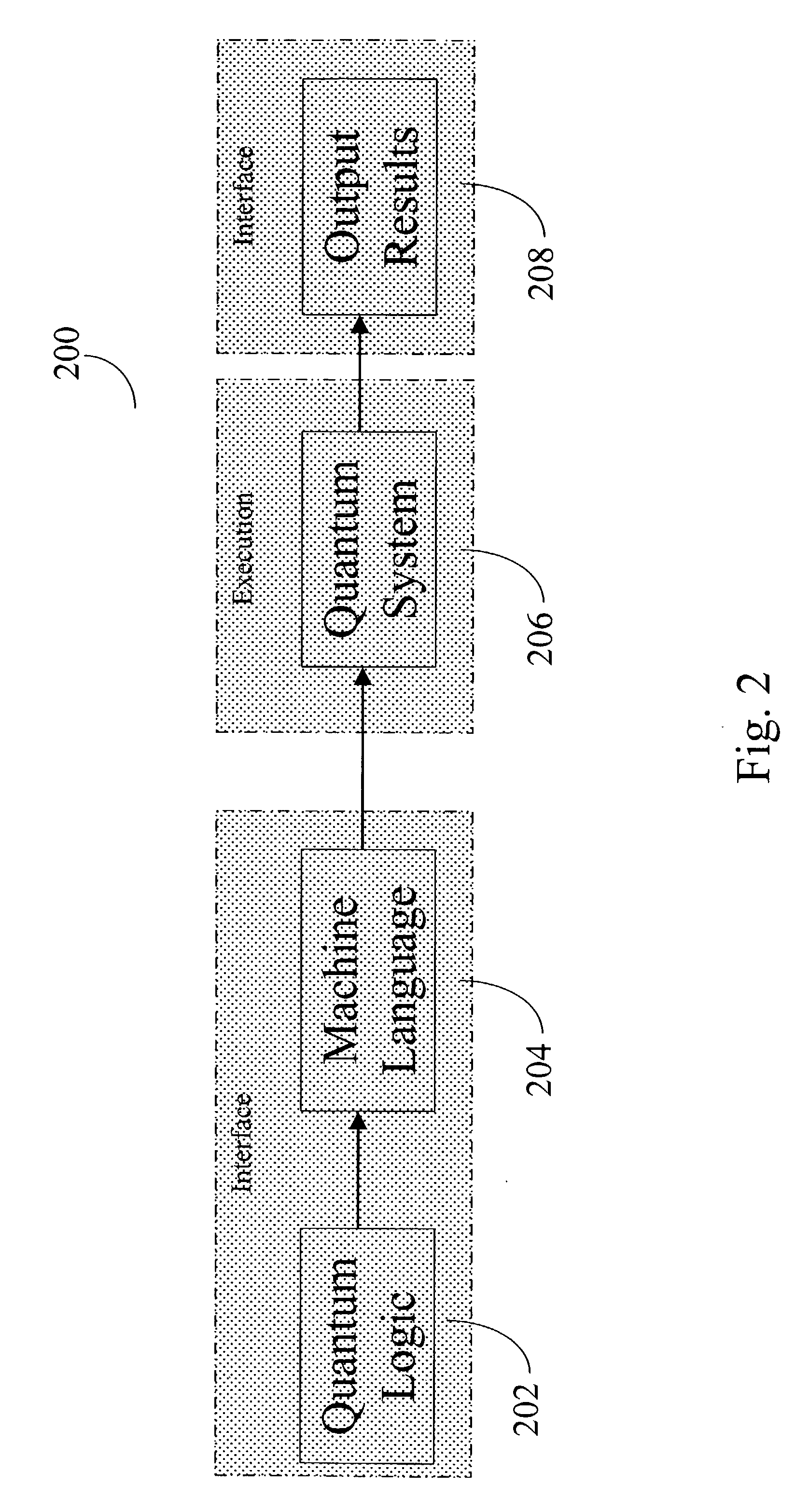
Quantum computing integrated development environment
A computer program product for use in conjunction with a computer system, the computer program product comprising a computer readable storage medium and a computer program mechanism embedded therein. The computer program mechanism comprises a quantum computing integrated development environment (QC-IDE) module and a compiler module. The QC-IDE module is used to design a quantum logic for a plurality of qubits. The QC-IDE module includes instructions for generating a time resolved set of operators. The compiler module includes instructions for compiling the time resolved set of operators into a set of quantum machine language instructions.
Owner:D WAVE SSTEMS INC +1
Adiabatic quantum computation with superconducting qubits
InactiveUS20050250651A1Quantum computersNanoinformaticsAdiabatic quantum computationComputational problem
A computer program product with computer program mechanism embedded therein is provided. The mechanism has instructions for initializing a quantum system, which includes a plurality of qubits, to an initialization Hamiltonian HO. The system is capable of being in one of at least two configurations at any give time including HO and a problem Hamiltonian HP. Each respective first qubit in the plurality of qubits is arranged with respect to a respective second qubit in the plurality of qubits such that the first respective qubit and the second respective qubit define a predetermined coupling strength. The predetermined coupling strengths between the qubits in the plurality of qubit collectively define a computational problem to be solved. The mechanism further comprises instructions for adiabatically changing the system until it is described by the ground state of the problem Hamiltonian HP and instructions for reading out the state of the system.
Owner:AMIN MOHAMMAD H S +4
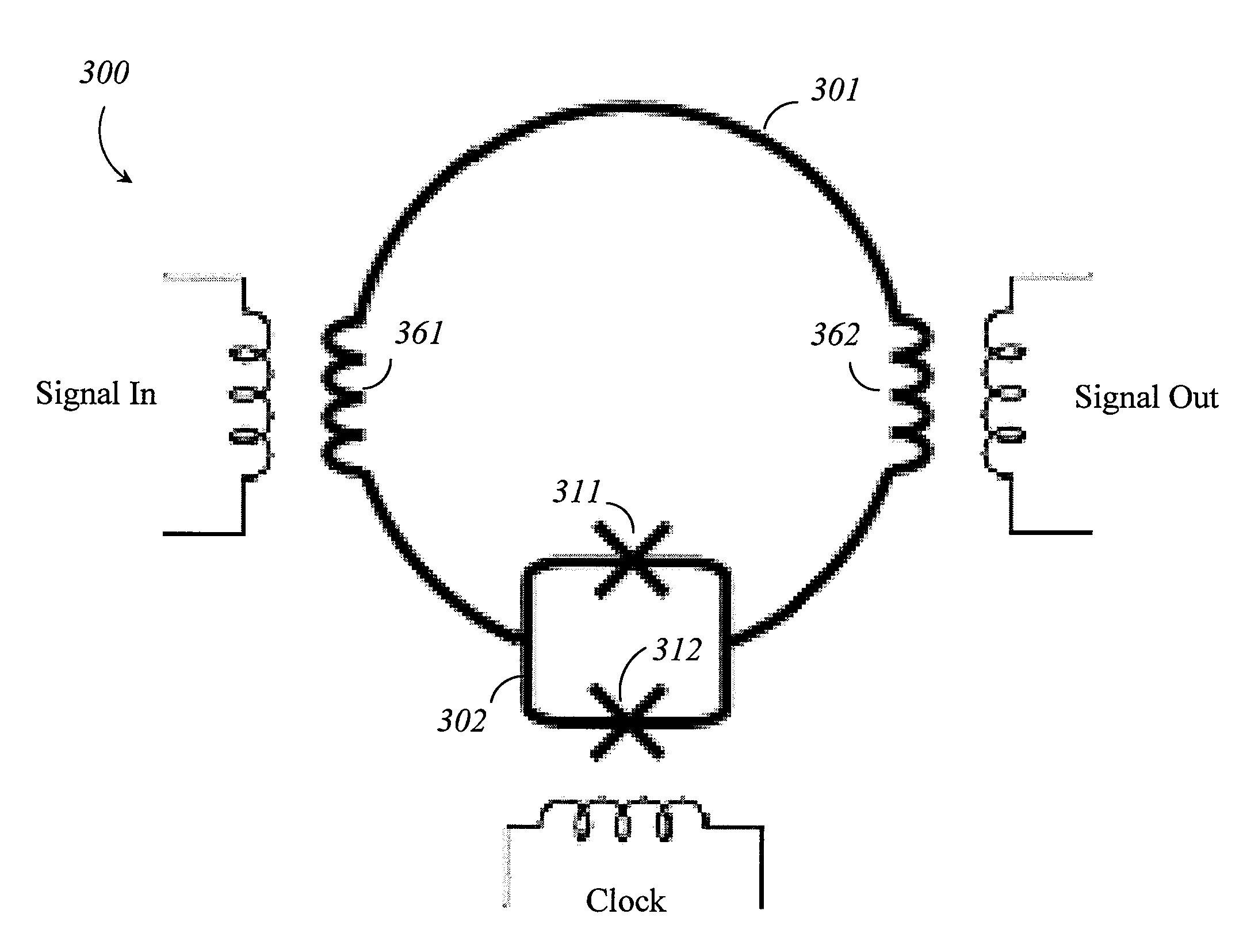
Systems, methods, and apparatus for qubit state readout
A superconducting readout system includes a computation qubit; a measurement device to measure a state of the computation qubit; and a latch qubit that mediates communicative coupling between the computation qubit and the measurement device. The latch qubit includes a qubit loop that includes at least two superconducting inductors coupled in series with each other; a compound Josephson junction that interrupts the qubit loop that includes at least two Josephson junctions coupled in series with each other in the compound Josephson junction and coupled in parallel with each other with respect to the qubit loop; and a first clock signal input structure to couple clock signals to the compound Josephson junction.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
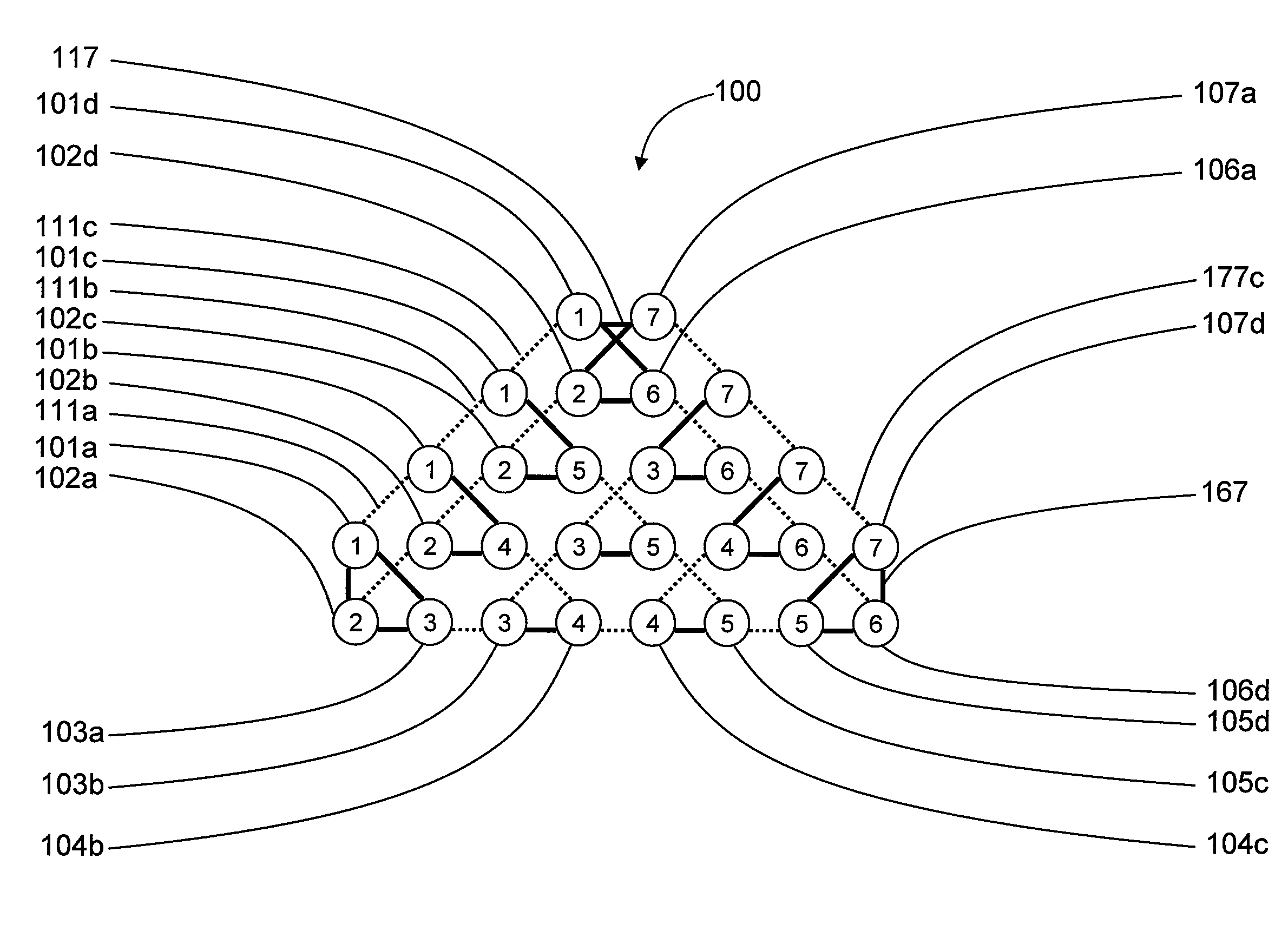
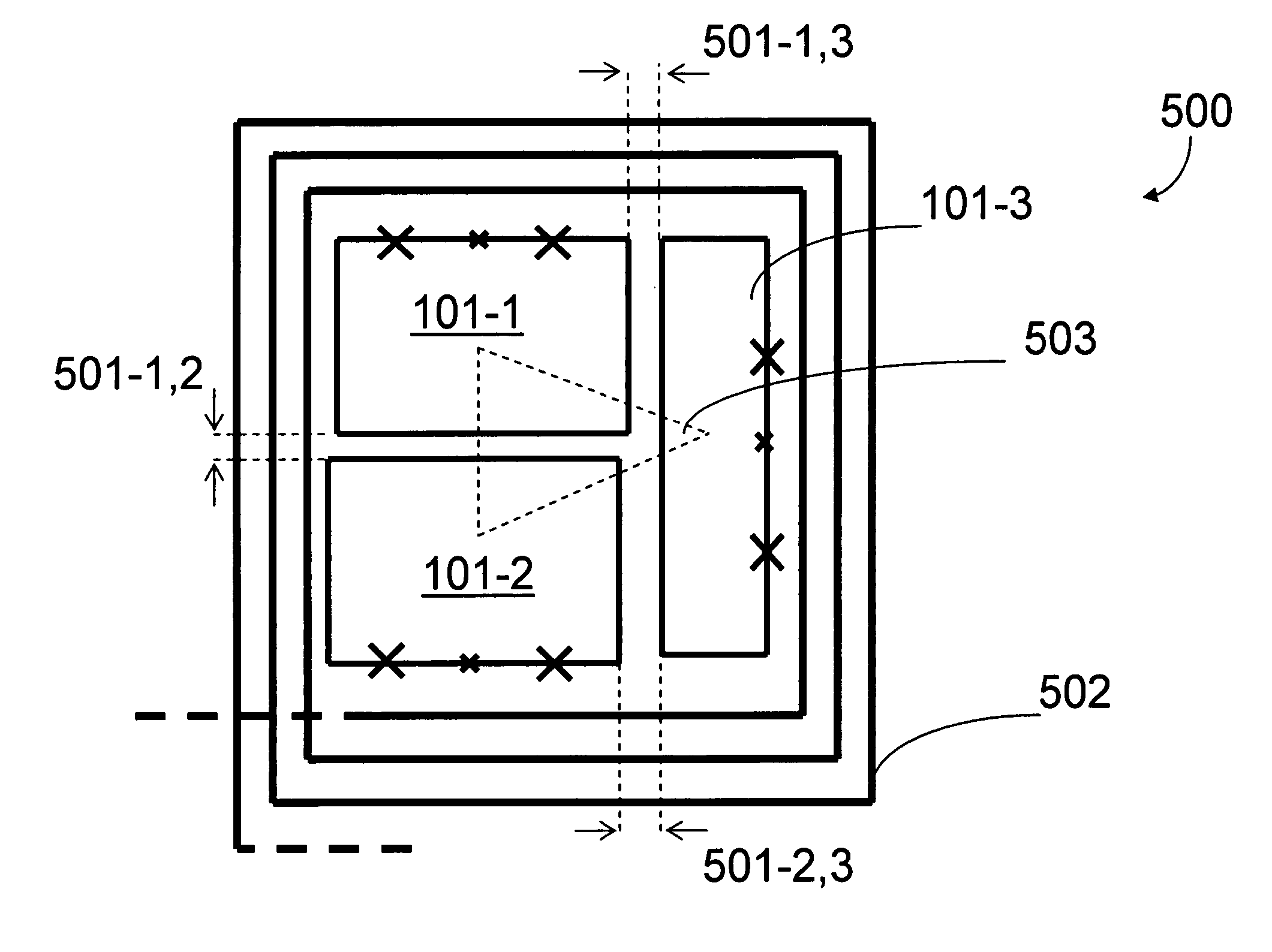
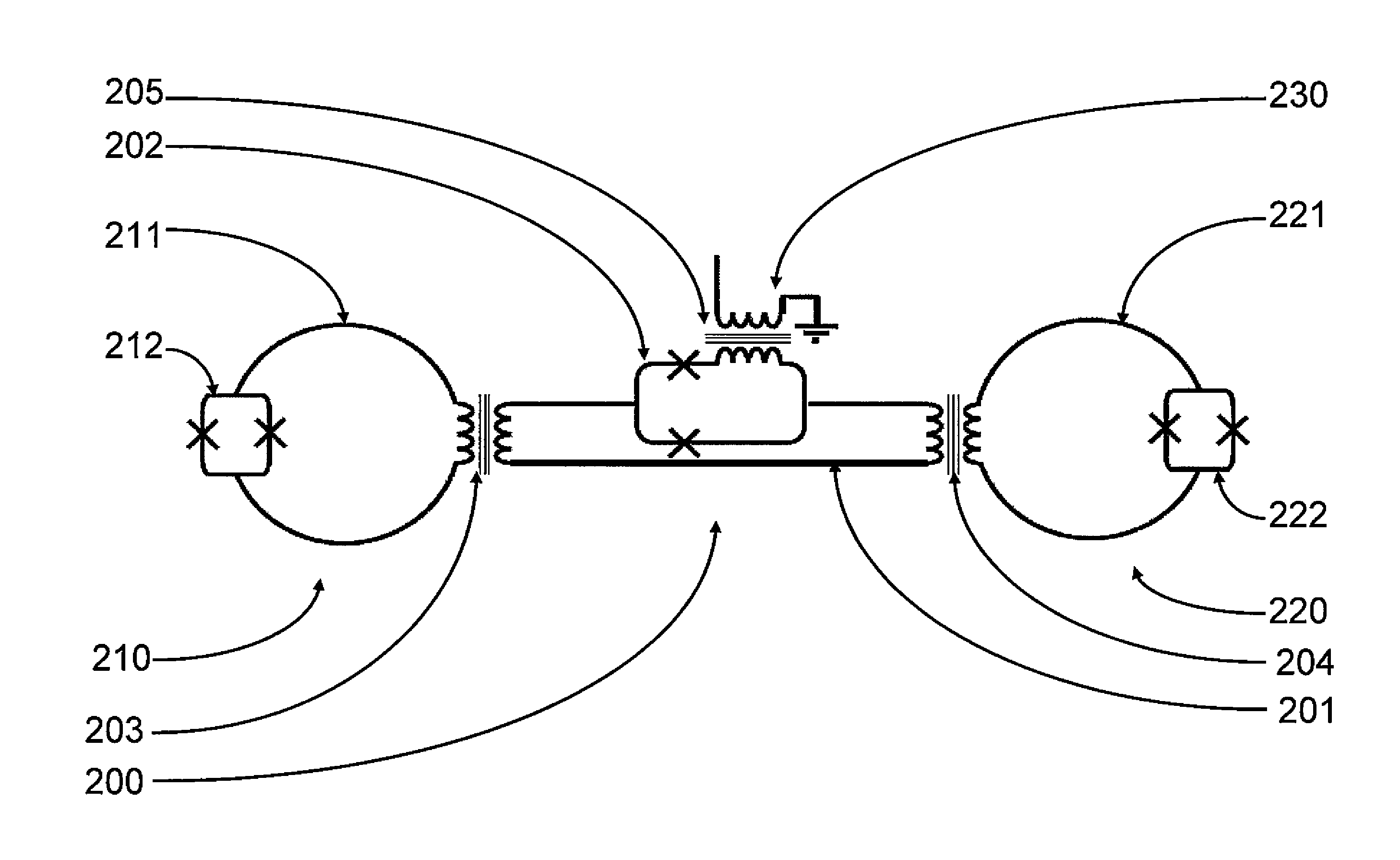
Systems, devices, and methods for controllably coupling qubits
InactiveUS20080238531A1Improve drawing legibilityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsCoupling systemInductor
A coupling system may include an rf-SQUID having a loop of superconducting material interrupted by a compound Josephson junction; and a first magnetic flux inductor configured to selectively provide a mutual inductance coupling the first magnetic flux inductor to the compound Josephson junction, wherein the loop of superconducting material positioned with respect to a first and second qubits to provide respective mutual inductance coupling therebetween. The coupling system may further include a second magnetic flux inductor configured to selectively provide a second magnetic flux inductor mutual inductance coupling the second magnetic flux inductor to the compound Josephson junction. A superconducting processor may include the coupling system and two or more qubits. A method may include providing the first, the second and the third mutual inductances.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
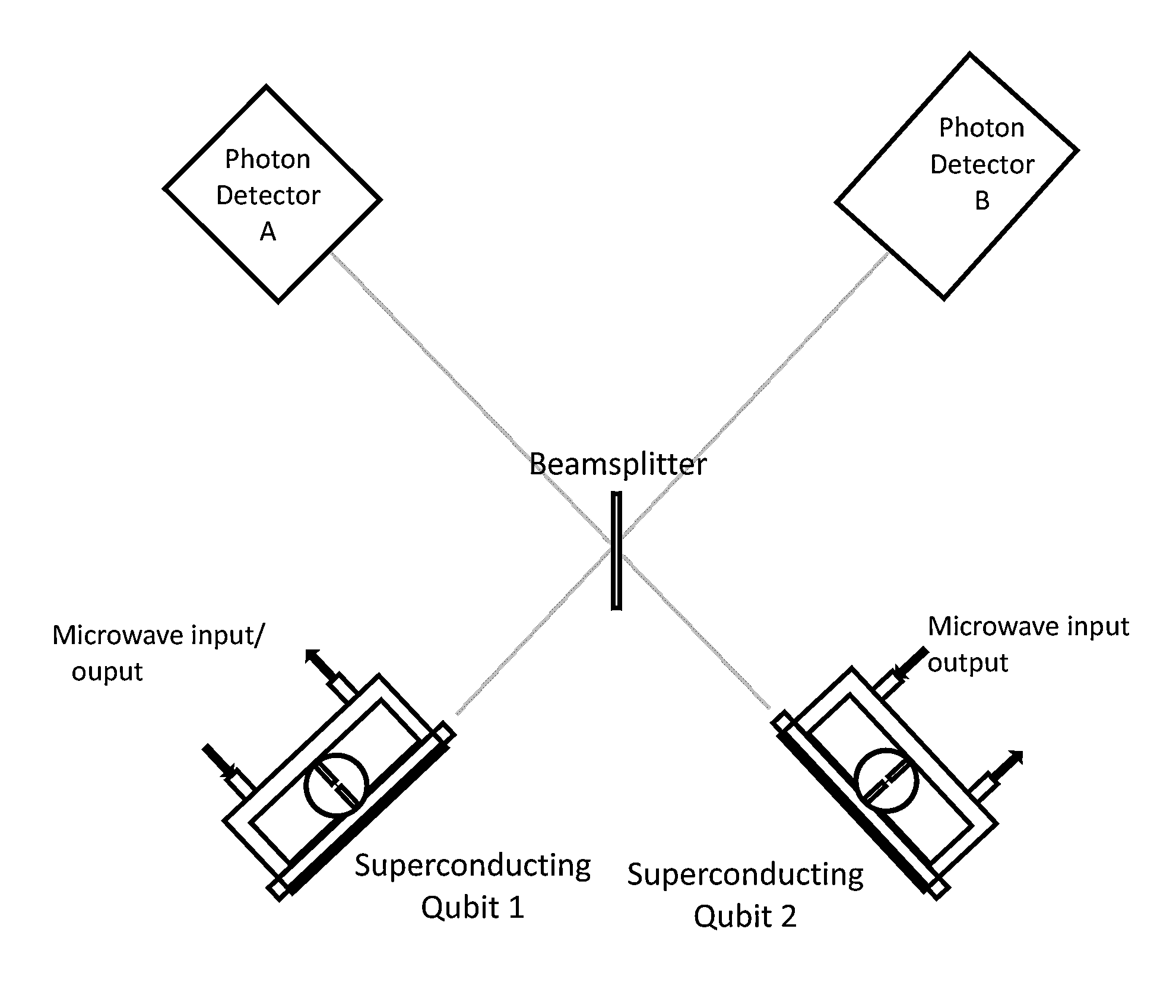
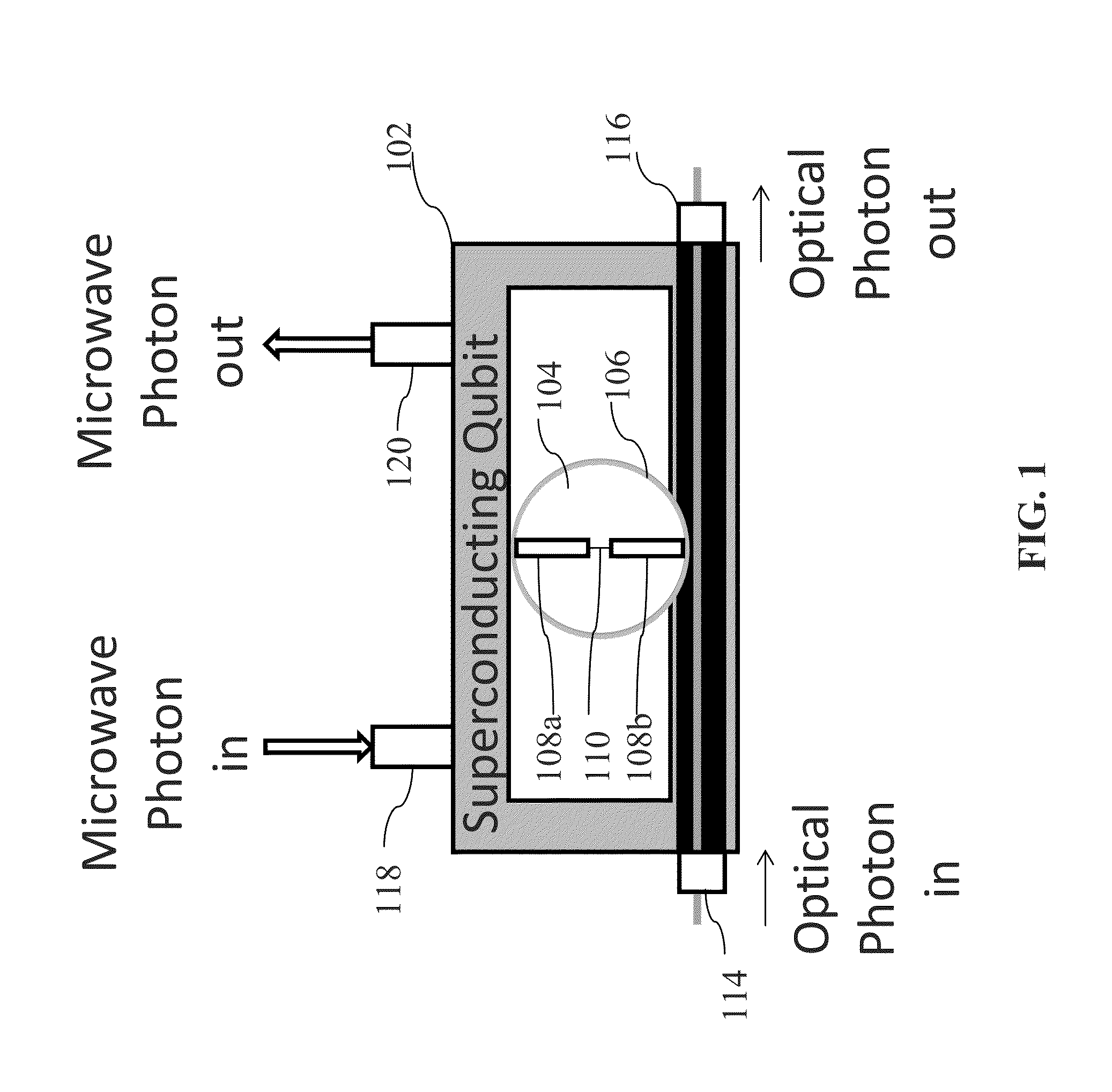
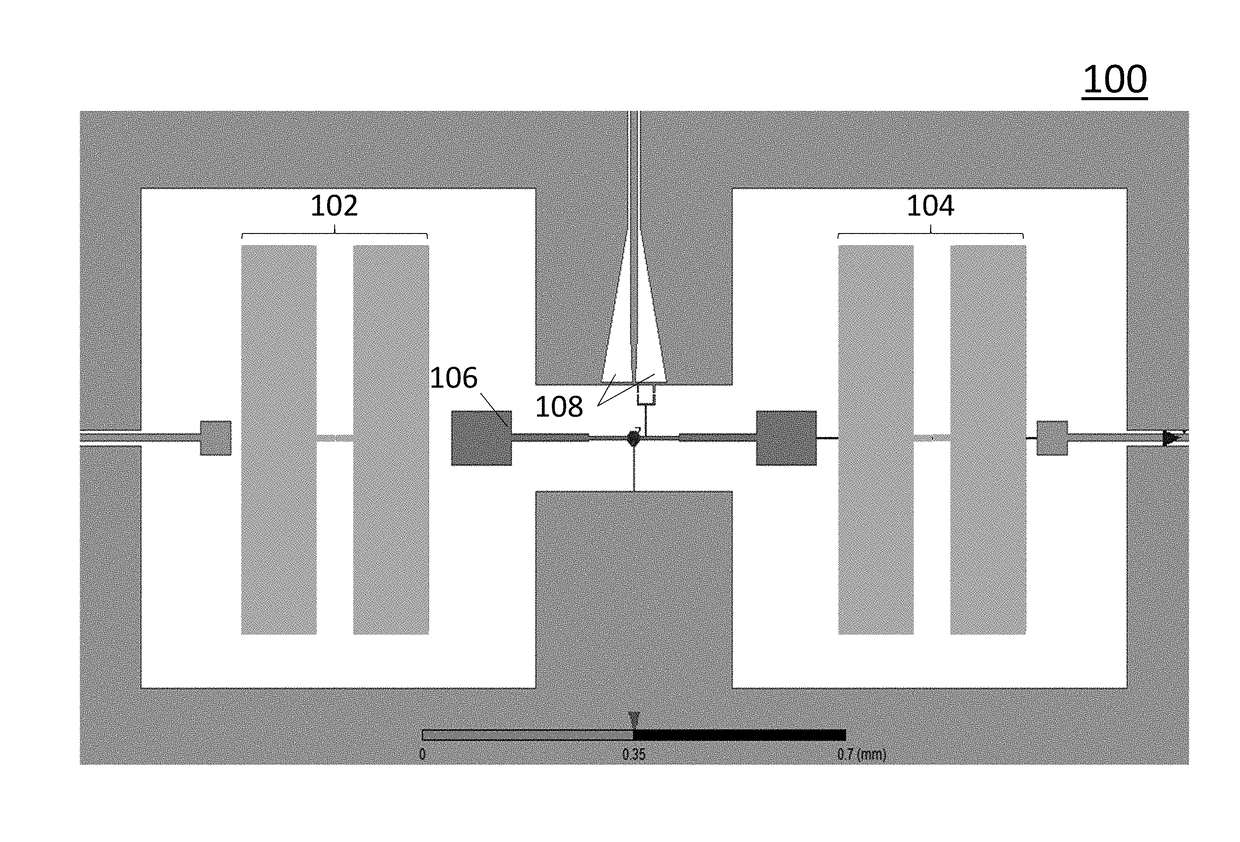
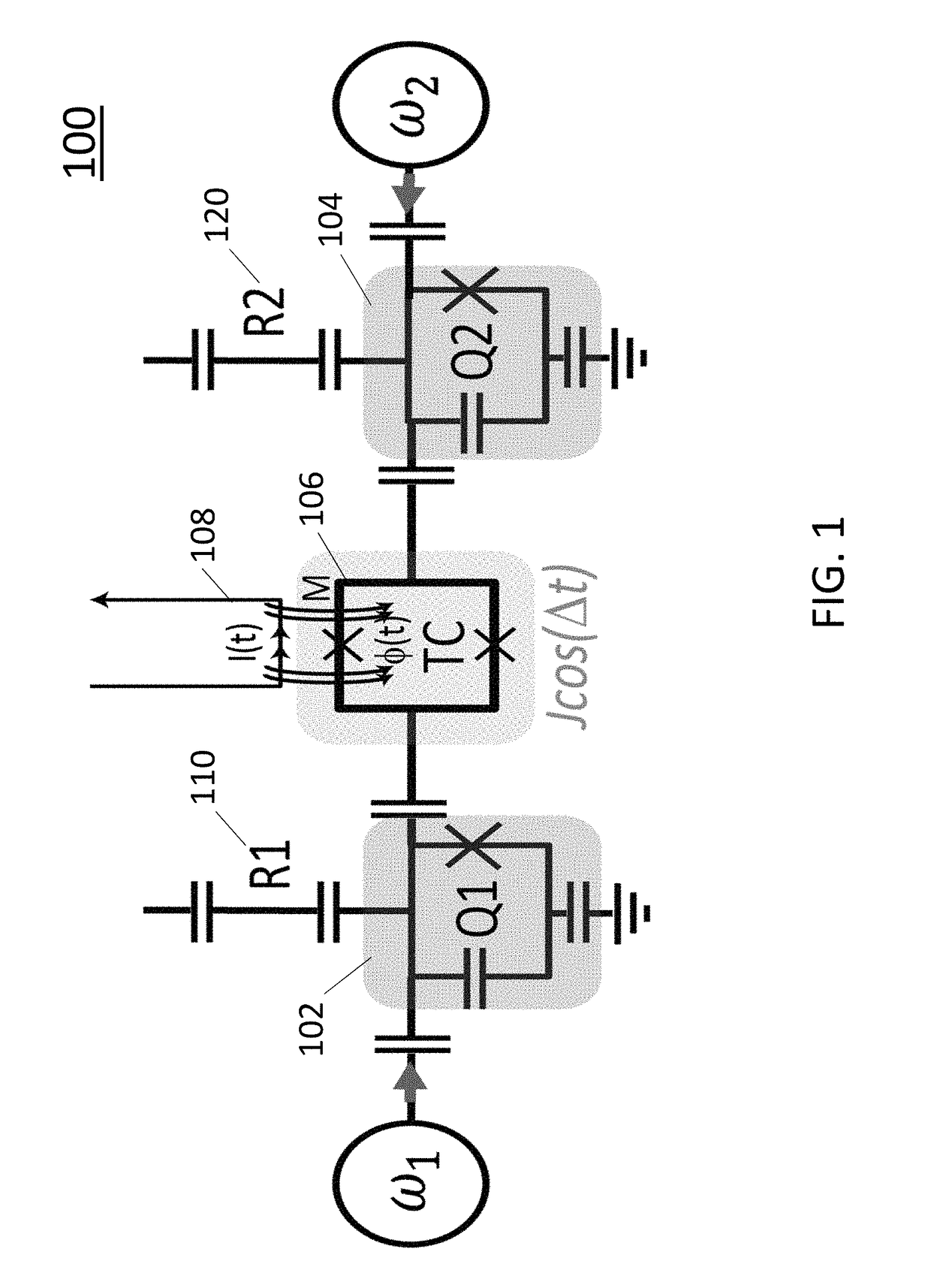
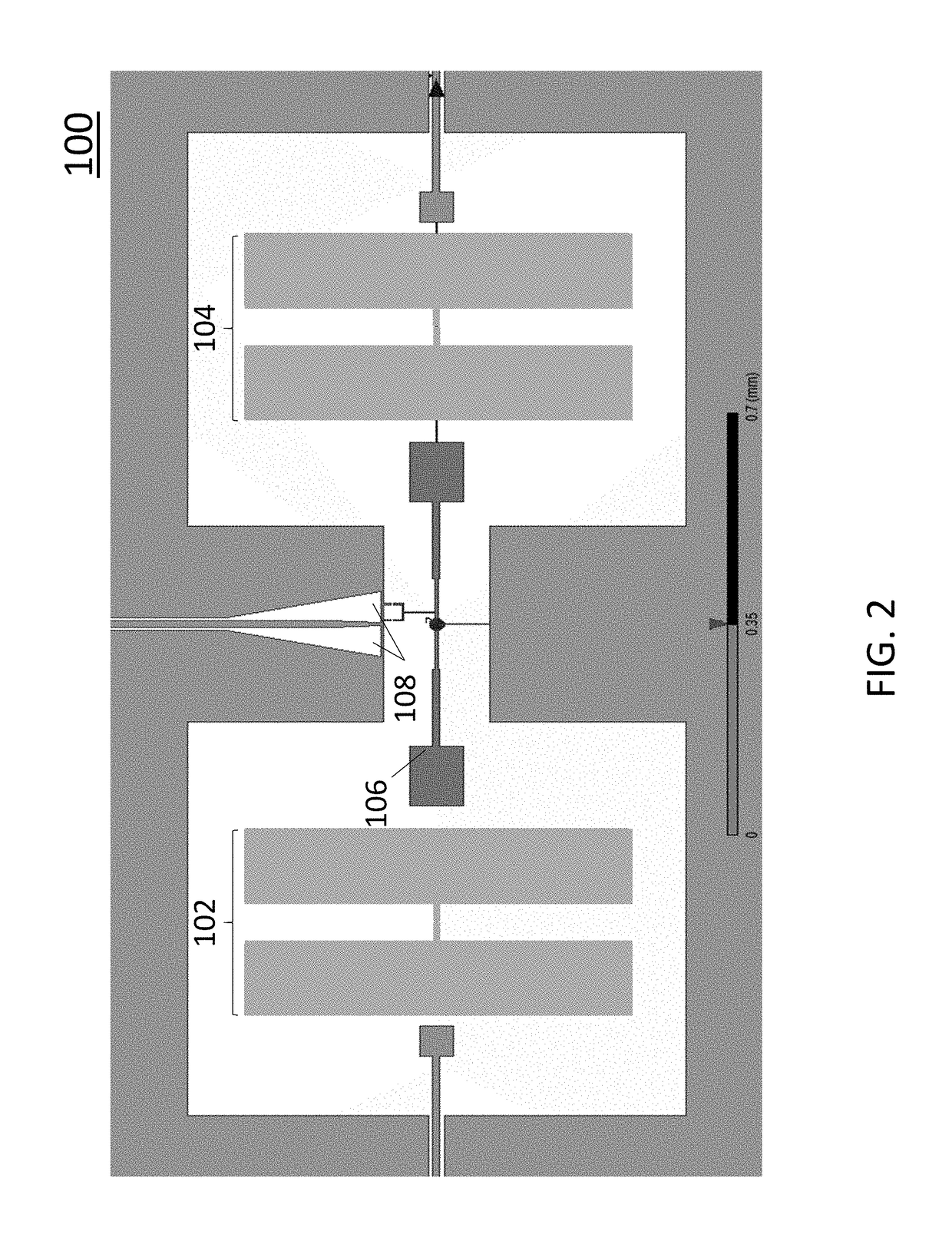
System and method for quantum information transfer between optical photons and superconductive qubits
ActiveUS20140314419A1Modulation frequencyQuantum computersNanoinformaticsMicrowave cavityDirect coupling
An electro-optical system for exchanging quantum information between optical qubits and including a superconductive microwave cavity; an electro-optical material: a superconductive qubit circuit formed on the electro-optical material including a superconductive qubit; a dipole antenna, formed on the electro-optical material for directly coupling the superconductive qubit to the superconductive microwave cavity; an optical input for receiving input optical photons; a microwave input for receiving input microwave photons; and an optical output for outputting modulated optical photons, wherein a frequency and a phase of the optical photon is modulated with a state of the superconducting qubit by the dipole antenna.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Systems, methods, and apparatus for qubit state readout
A superconducting readout system includes a computation qubit; a measurement device to measure a state of the computation qubit; and a latch qubit that mediates communicative coupling between the computation qubit and the measurement device. The latch qubit includes a qubit loop that includes at least two superconducting inductors coupled in series with each other; a compound Josephson junction that interrupts the qubit loop that includes at least two Josephson junctions coupled in series with each other in the compound Josephson junction and coupled in parallel with each other with respect to the qubit loop; and a first clock signal input structure to couple clock signals to the compound Josephson junction.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
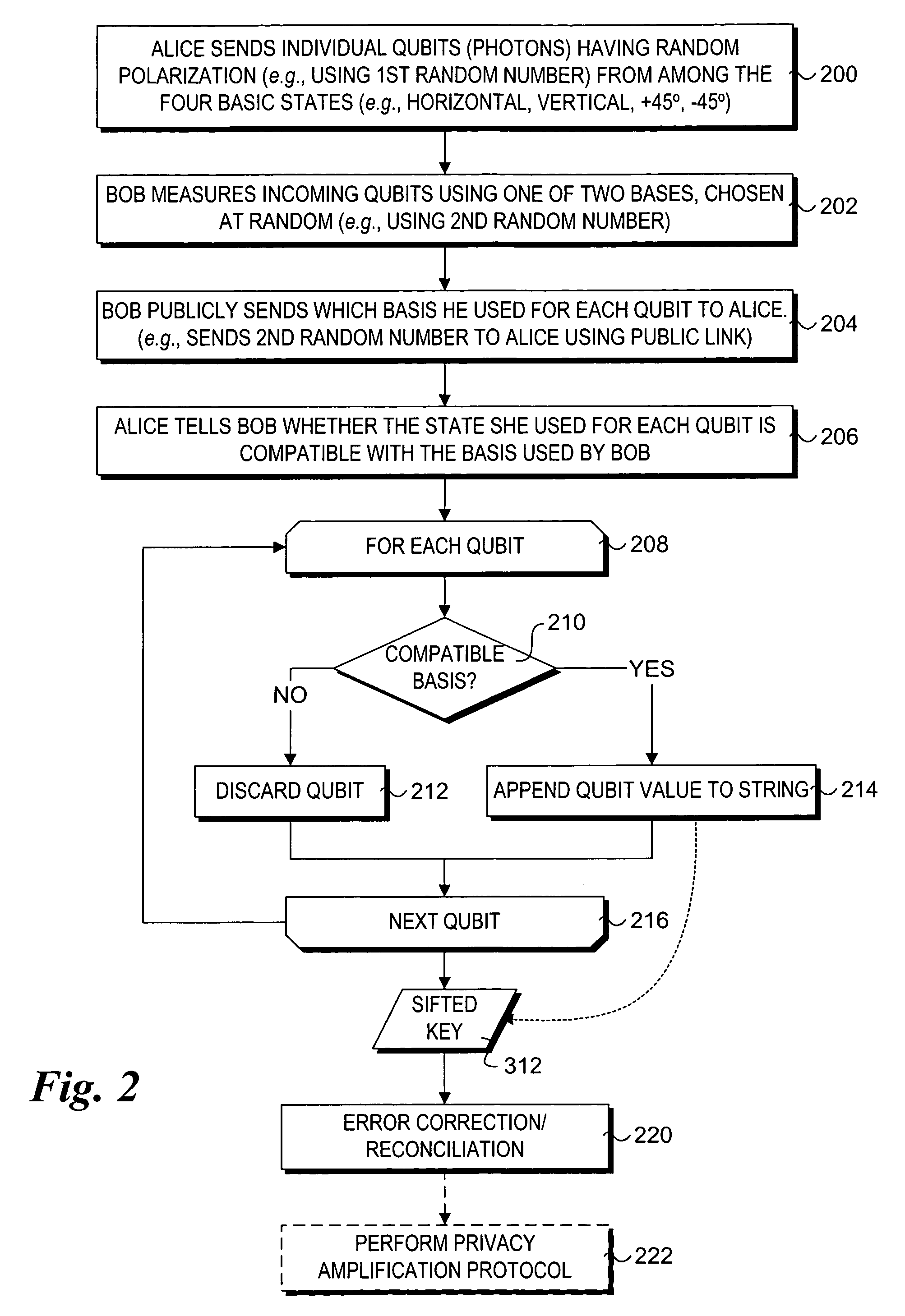
Method to support secure network booting using quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution
A method and system to support secure booting and configuration. The mechanism employs an optical link comprising a quantum channel that is used to send data encoded as quantum bits (qubits) via respective photons. Qubits encoded using a first random basis at the client and are sent to the boot server, which processes the qubits using a second random basis to extract the encoded data. A public channel is used to send data indicative of the second random basis to the client. A symmetric quantum key is then derived a both the client and the boot server using a comparison of the random basis' and the original and extracted data. The scheme enables the presence of an eavesdropper to be detected on the quantum channel. A DHCP message exchange is employed to obtain a network address, and, optionally, be provided with a network address for one or more boot servers. A boot image request is made to the boot server by the client, and a subsequent boot image is downloaded via a secure channel facilitated by the symmetric quantum key.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Microwave readout for flux-biased qubits
A method for determining whether a quantum system comprising a superconducting qubit is occupying a first basis state or a second basis state once a measurement is performed is provided. The method, comprising: applying a signal having a frequency through a transmission line coupled to the superconducting qubit characterized by two distinct, separate, and stable states of differing resonance frequencies each corresponding to the occupation of the first or second basis state prior to measurement; and measuring at least one of an output power or phase at an output port of the transmission line, wherein the measured output power or phase is indicative of whether the superconducting qubit is occupying the first basis state or the second basis state.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Resonant controlled qubit system
Methods for coupling a superconducting qubit to a resonant control circuit. An interaction term between the qubit and the circuit initially has a diagonal component. A recoupling operation is applied to the qubit. The circuit is tuned so that a frequency of the qubit and circuit match. A second recoupling operation transforms the term to have only off-diagonal components. A method for entangling a state of two qubits coupled to a bus with a control circuit. An interaction term between at least one of the qubits and the circuit has a diagonal component. A recoupling operation is applied to at least one of the qubits such that the term has only off-diagonal components. The frequency of the circuit is tuned to the frequency of the first qubit, and then tuned to the frequency of the second qubit. The recoupling operation is reapplied to at least one of the qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Superconducting qubit with a plurality of capacitive couplings
A first qubit having a superconducting loop interrupted by a plurality of Josephson junctions is provided. Each junction interrupts a different portion of the superconducting loop and each different adjacent pair of junctions in the plurality of Josephson junctions defines a different island. An ancillary device is coupled to the first qubit. In a first example, the ancillary device is a readout mechanism respectively capacitively coupled to a first and second island in the plurality of islands of the first qubit by a first and second capacitance. Quantum nondemolition measurement of the first qubit's state may be performed. In a second example, the ancillary device is a second qubit. The second qubit's first and second islands are respectively capacitively coupled to the first and second islands of the first qubit by a capacitance. In this second example, the coupling is diagonal in the physical basis of the qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
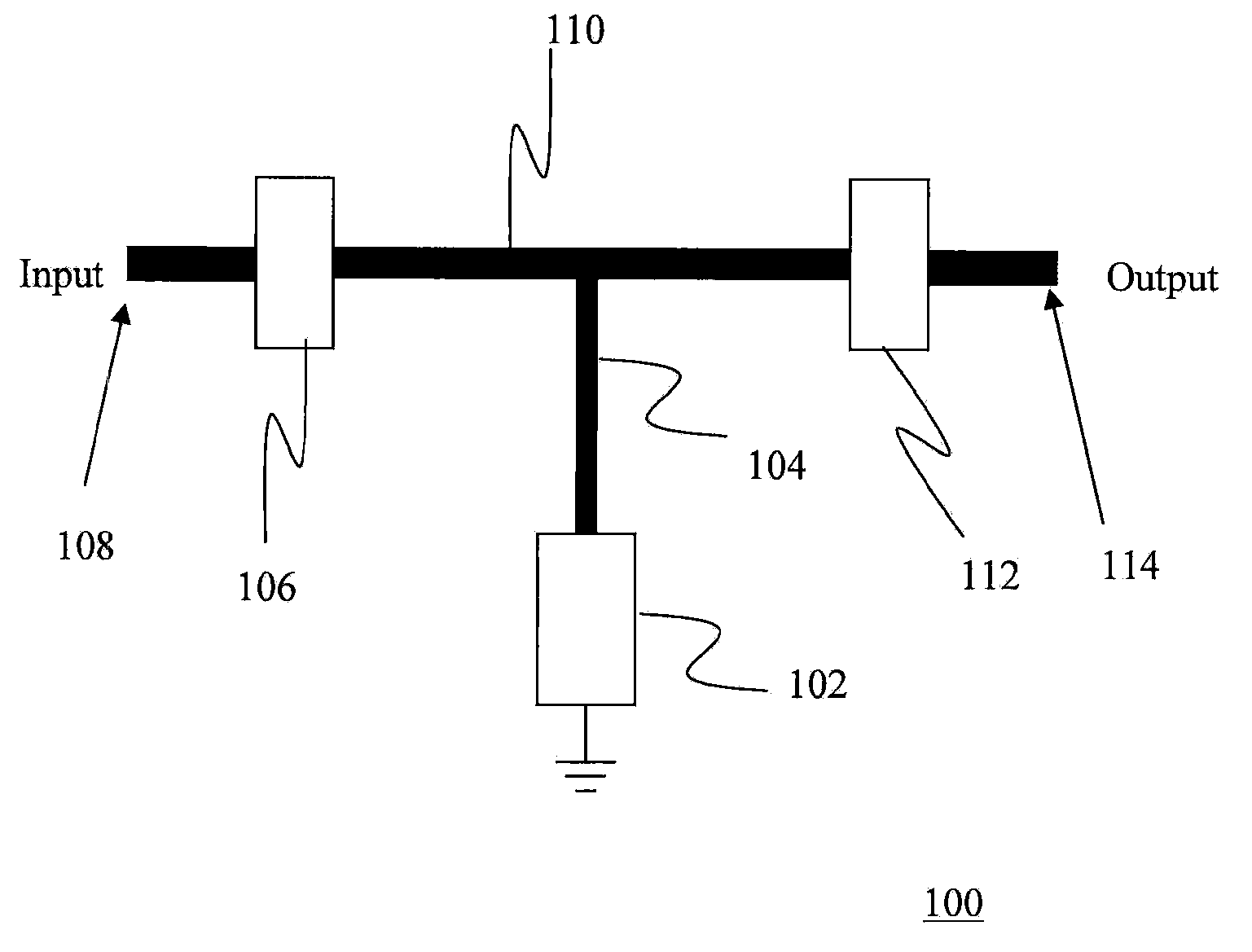
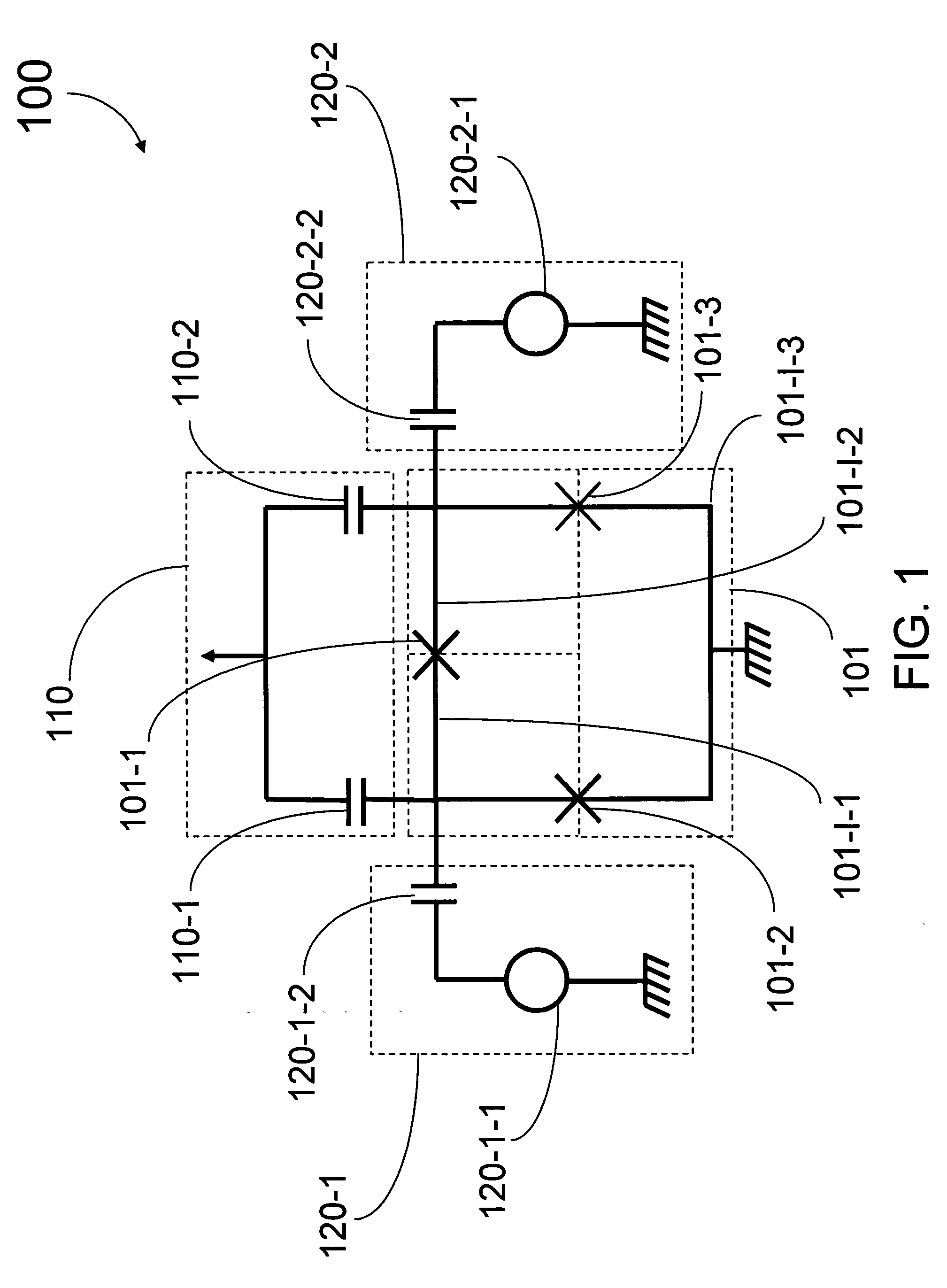
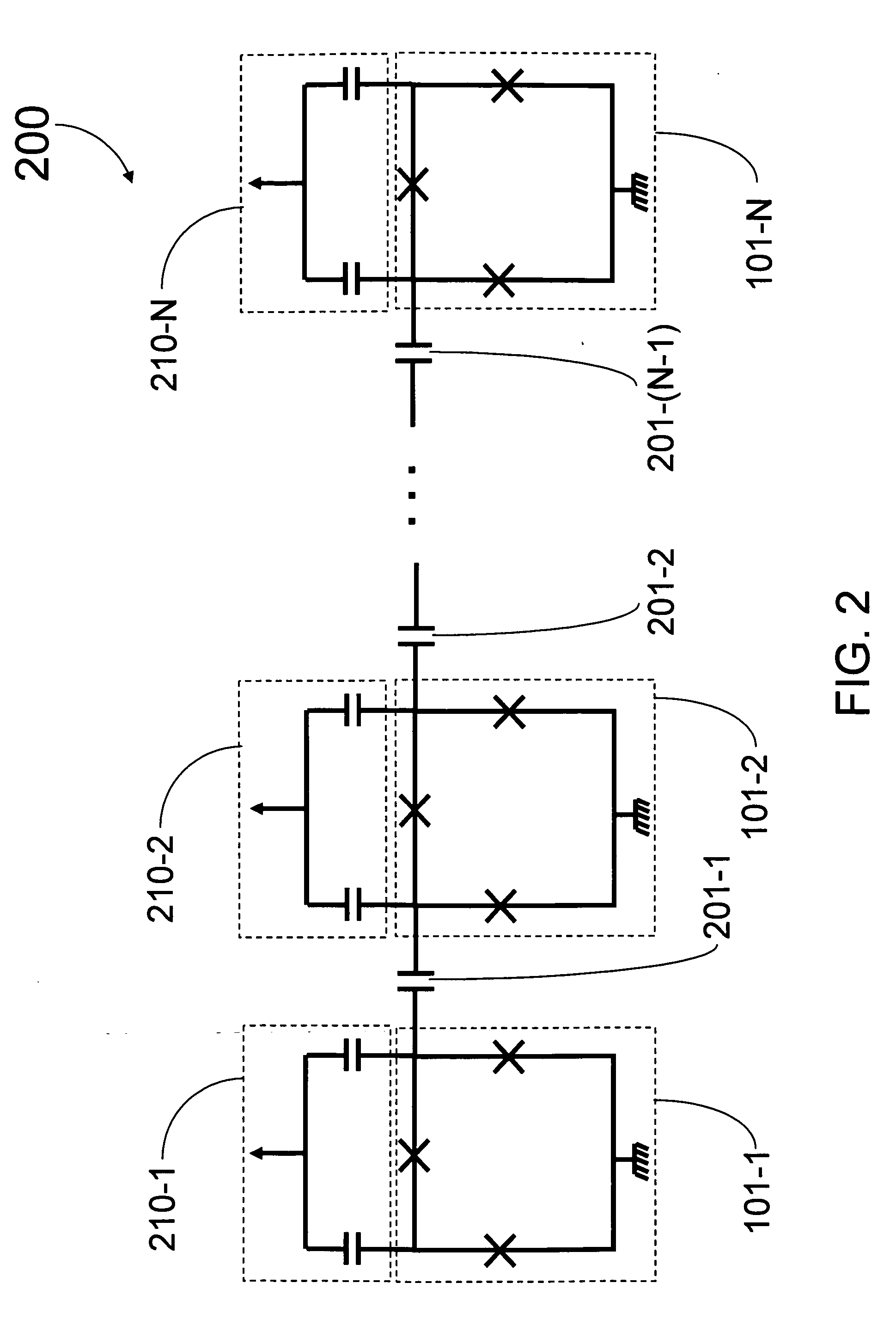
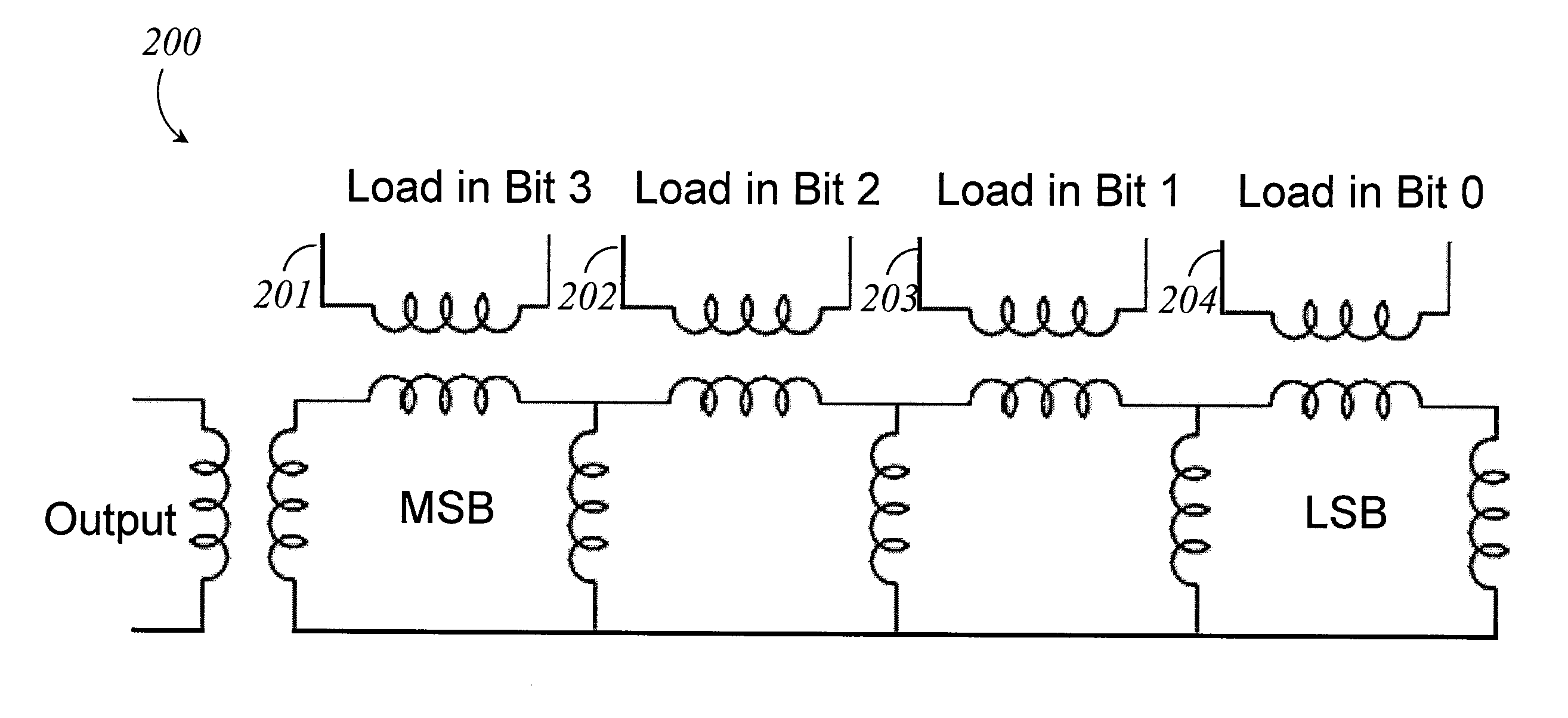
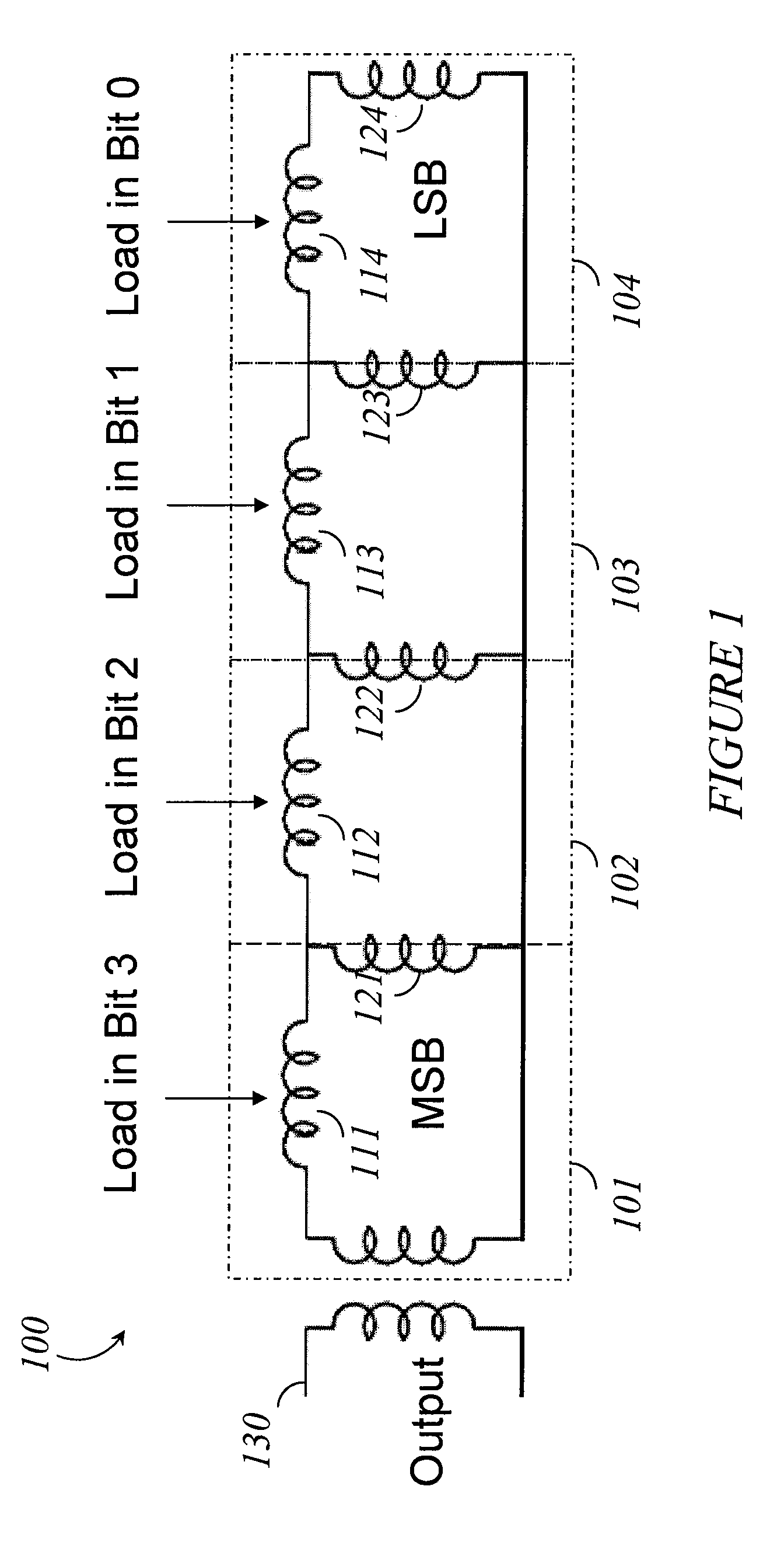
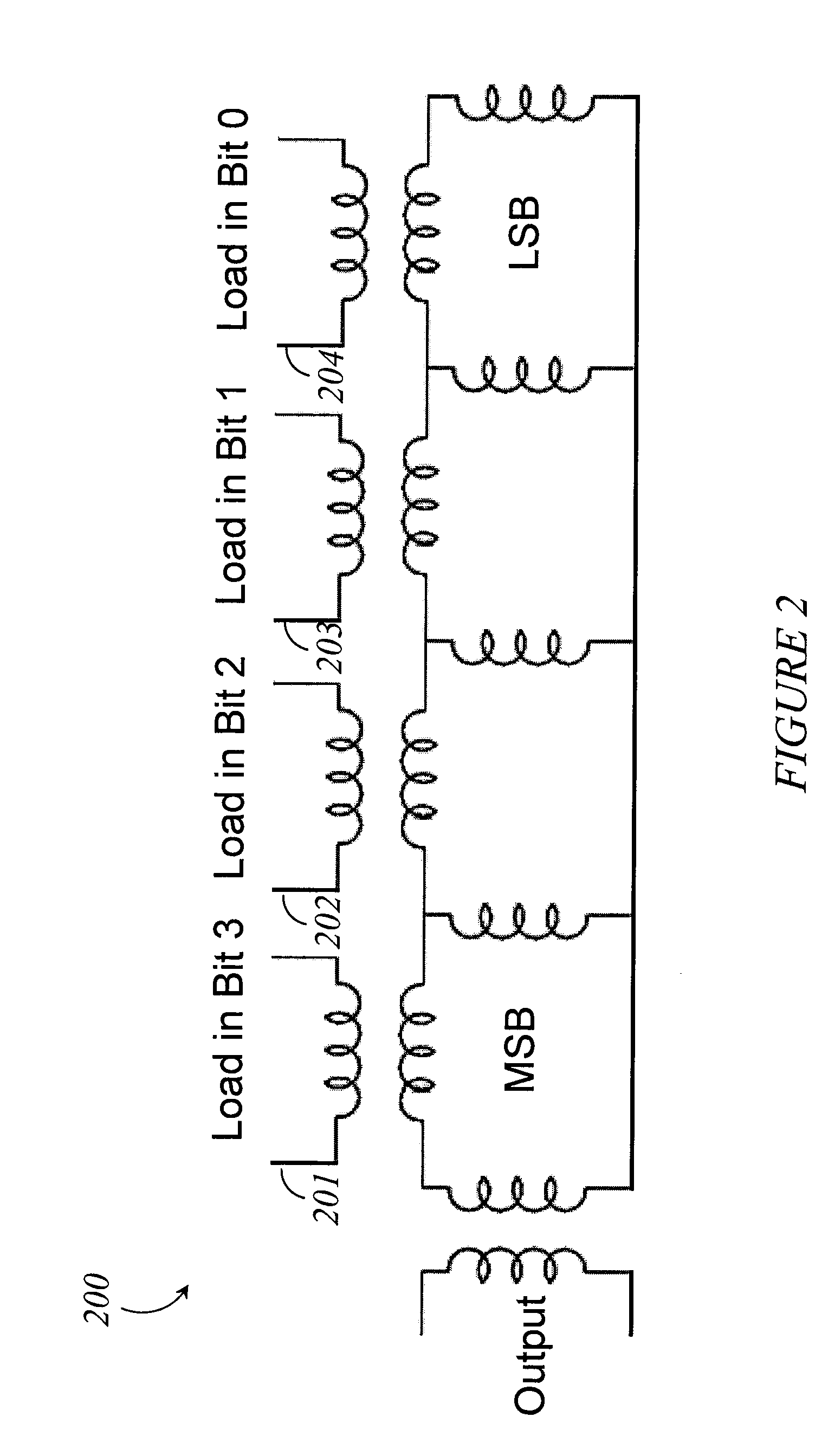
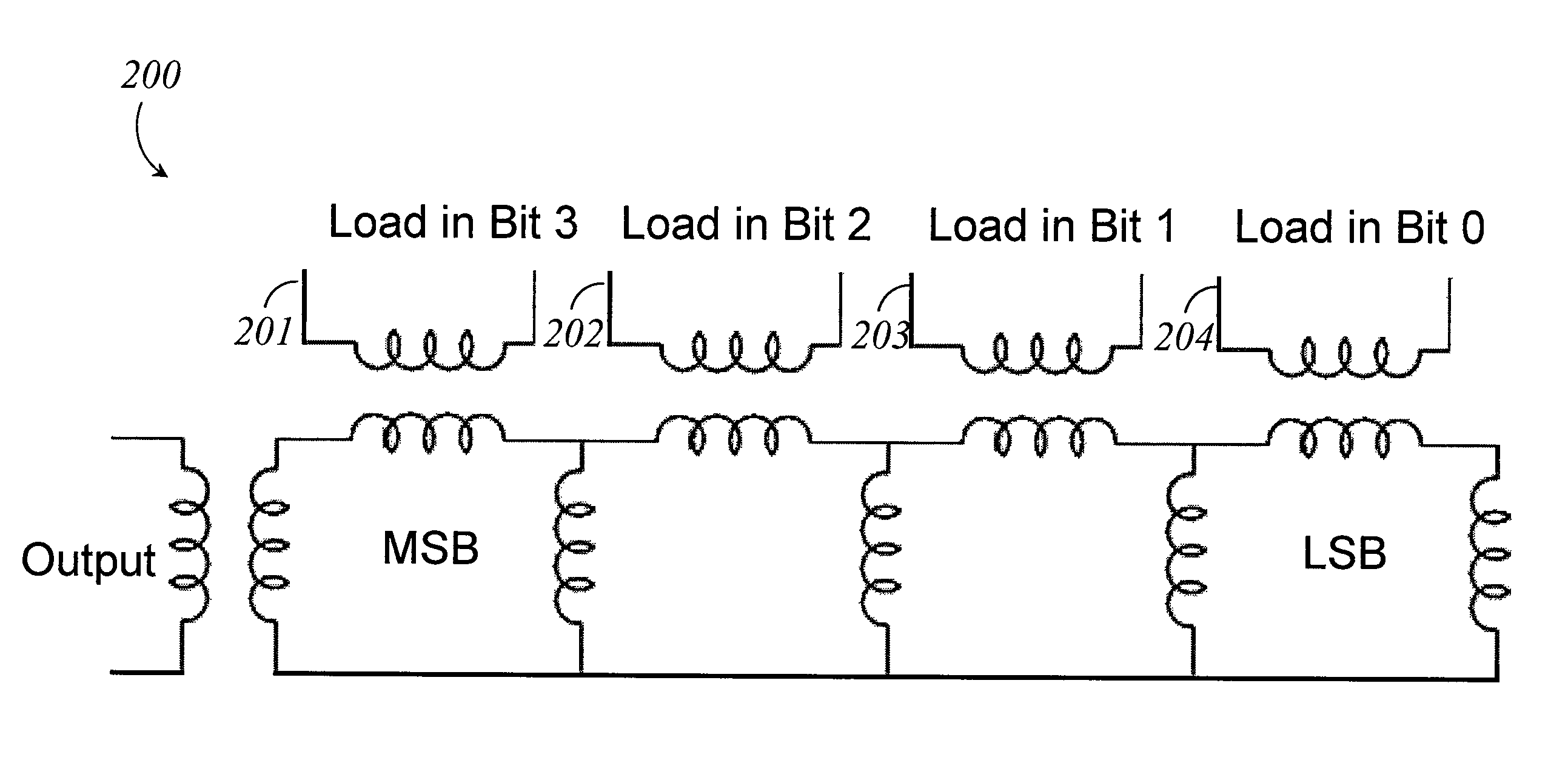
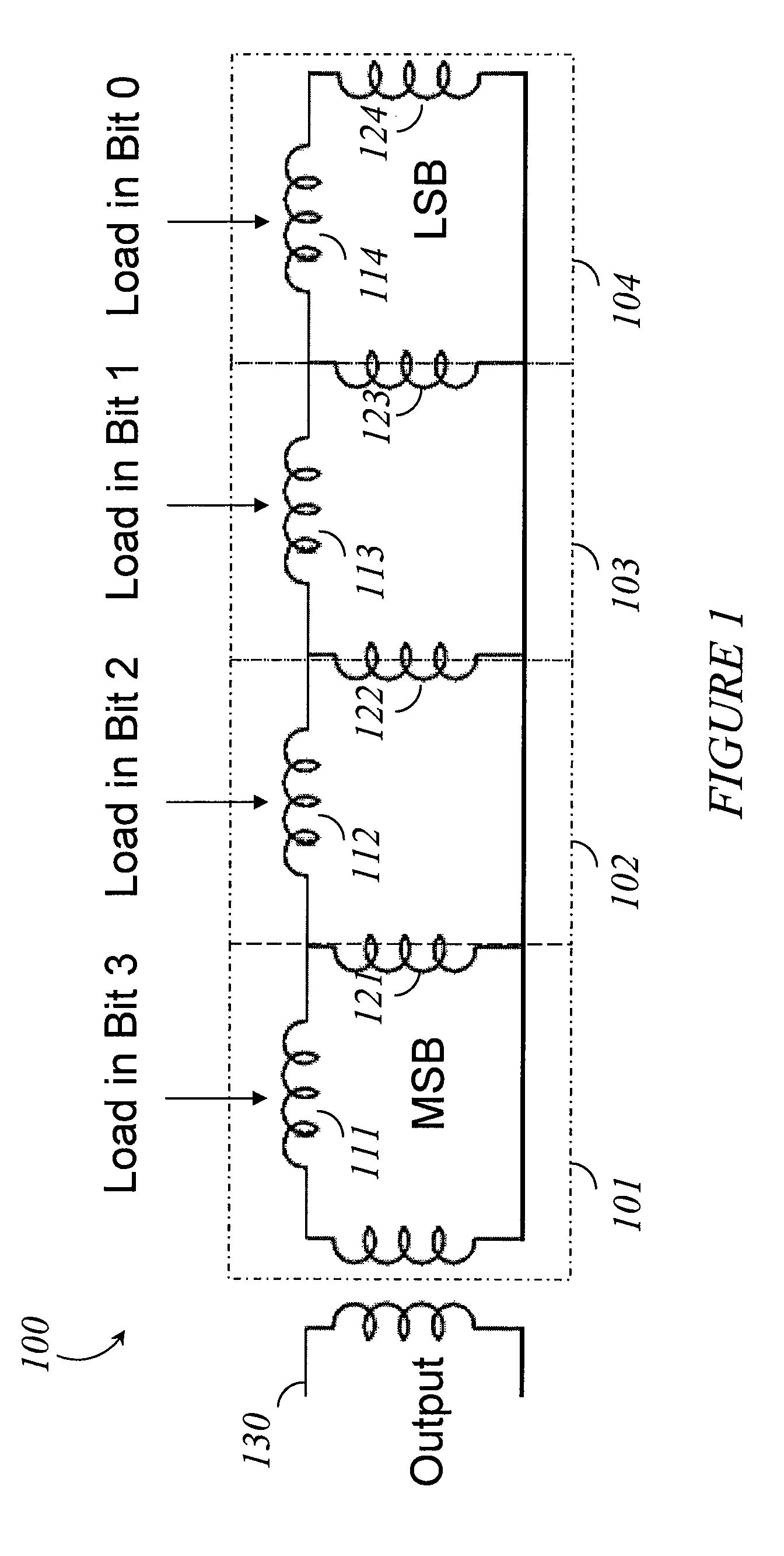
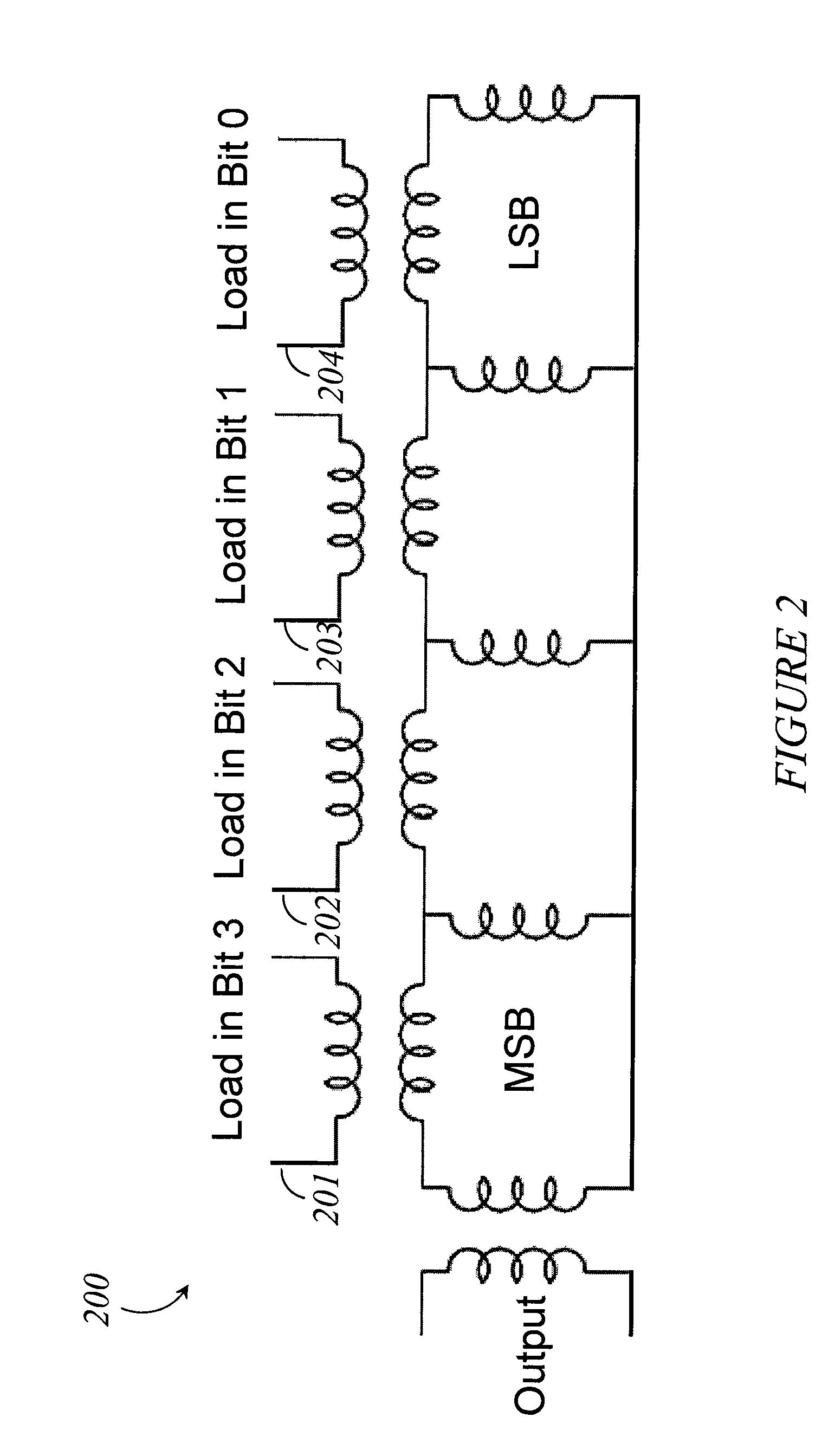
Systems, methods and apparatus for digital-to-analog conversion of superconducting magnetic flux signals
ActiveUS20090082209A1Fast switching speedShort calculation timeElectric signal transmission systemsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShift registerData signal
A superconducting flux digital-to-analog converter includes a superconducting inductor ladder circuit. The ladder circuit includes a plurality of closed superconducting current paths that each includes at least two superconducting inductors coupled in series to form a respective superconducting loop, successively adjacent or neighboring superconducting loops are connected in parallel with each other and share at least one of the superconducting inductors to form a flux divider network. A data signal input structure provides a respective bit of a multiple bit signal to each of the superconducting loops. The data signal input structure may include a set of superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). The data signal input structure may include a superconducting shift register, for example a single-flux quantum (SFQ) shift register or a flux-based superconducting shift register comprising a number of latching qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
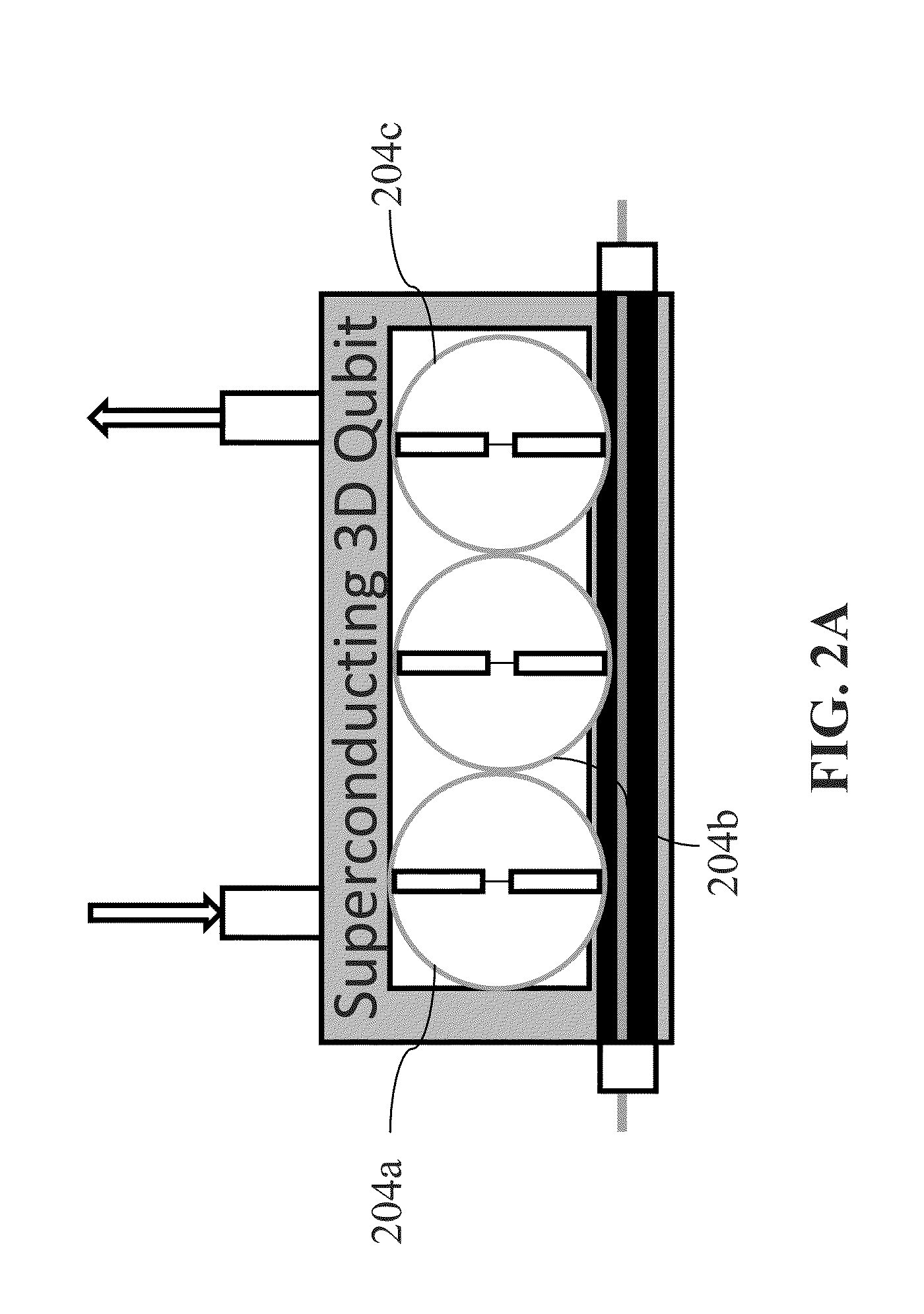
Multi-qubit tunable coupling architecture using fixed-frequency superconducting qubits
Various embodiments provide a coupling mechanism, method of activation and a square lattice. The coupling mechanism comprises two qubits and a tunable coupling qubit that activates an interaction between the two qubits by modulation of a frequency of the tunable coupling qubit. The tunable coupling qubit capacitively couples the two qubits. The tunable coupling qubit is modulated at a difference frequency of the two qubits. The difference frequency may be significantly larger than an anharmonicity of the two qubits. The tunable coupling qubit may be coupled to the two qubits by two electrodes separated by a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) loop having two Josephson junctions or by a single electrode with a SQUID loop coupling to ground. The SQUID loop is controlled by an inductively-coupled flux bias line positioned at the center of the tunable coupling qubit.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for improving the performance of a quantum processor via reduced readouts
ActiveUS20160071021A1Quantum computersGeneral purpose stored program computerComposite sampleComputer science
Techniques for improving the performance of a quantum processor are described. The techniques include reading out a fraction of the qubits in a quantum processor and utilizing one or more post-processing operations to reconstruct qubits of the quantum processor that are not read. The reconstructed qubits may be determined using a perfect sampler to provide results that are strictly better than reading all of the qubits directly from the quantum processor. The composite sample that includes read qubits and reconstructed qubits may be obtained faster than if all qubits of the quantum processor are read directly.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems, methods and apparatus for digital-to-analog conversion of superconducting magnetic flux signals
A superconducting flux digital-to-analog converter includes a superconducting inductor ladder circuit. The ladder circuit includes a plurality of closed superconducting current paths that each includes at least two superconducting inductors coupled in series to form a respective superconducting loop, successively adjacent or neighboring superconducting loops are connected in parallel with each other and share at least one of the superconducting inductors to form a flux divider network. A data signal input structure provides a respective bit of a multiple bit signal to each of the superconducting loops. The data signal input structure may include a set of superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). The data signal input structure may include a superconducting shift register, for example a single-flux quantum (SFQ) shift register or a flux-based superconducting shift register comprising a number of latching qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Superconducting low inductance qubit
A superconducting structure that can operate, for example, as a qubit or a superconducting switch is presented. The structure includes a loop formed from two parts. A first part includes two superconducting materials separated by a junction. The junction can, for example, be a 45° grain boundary junction. The second part can couple the two superconducting materials across the junction. The second part includes a superconducting material coupled to each of the two superconducting materials of the first part through c-axis junctions. Further embodiments of the invention can be as a coherent unconventional superconducting switch, or a variable phase shift unconventional superconductor junction device.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
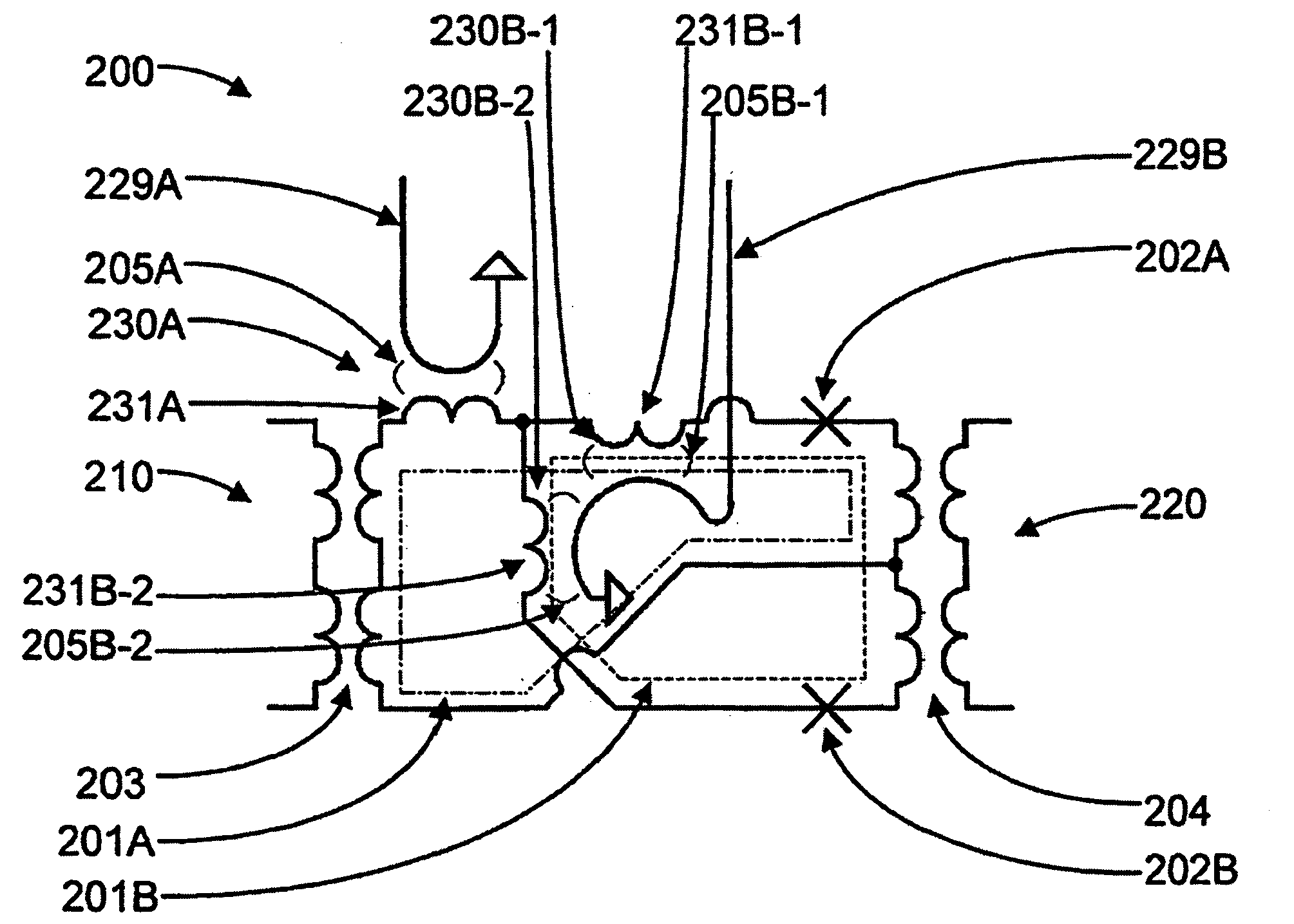
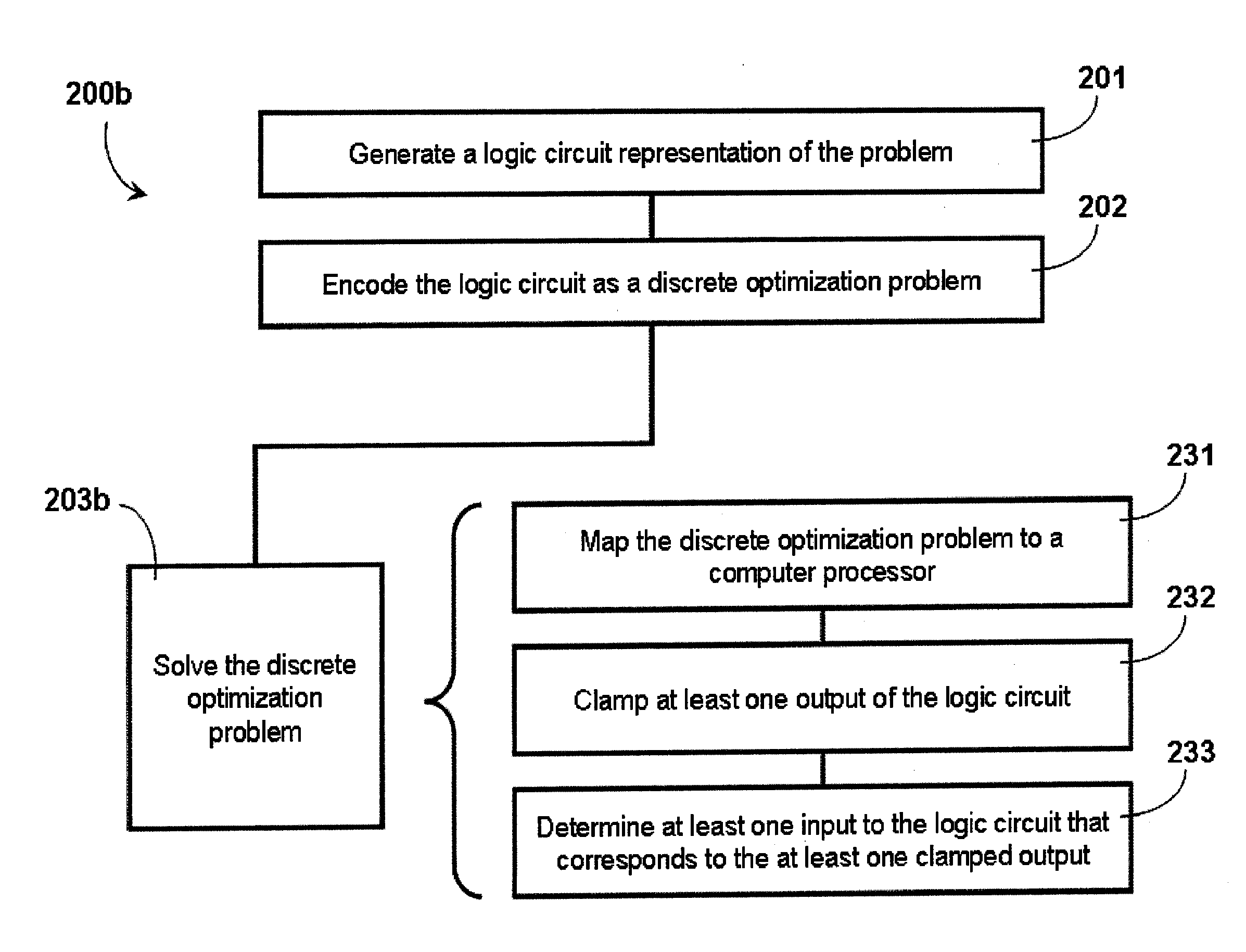
Systems and methods for solving computational problems
ActiveUS20110231462A1Quantum computersNanoinformaticsComputational problemTheoretical computer science
Solving computational problems may include generating a logic circuit representation of the computational problem, encoding the logic circuit representation as a discrete optimization problem, and solving the discrete optimization problem using a quantum processor. Output(s) of the logic circuit representation may be clamped such that the solving involves effectively executing the logic circuit representation in reverse to determine input(s) that corresponds to the clamped output(s). The representation may be of a Boolean logic circuit. The discrete optimization problem may be composed of a set of miniature optimization problems, where each miniature optimization problem encodes a respective logic gate from the logic circuit representation. A quantum processor may include multiple sets of qubits, each set coupled to respective annealing signal lines such that dynamic evolution of each set of qubits is controlled independently from the dynamic evolutions of the other sets of qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Quantum information processing
Quantum information processing apparatus and methods are described. The apparatus comprises a device for defining a qubit and a reflectometry circuit for reading out a state of the qubit. The device comprises a semiconductor nanowire extending along a first direction having first and second obtuse or acute edges running along the first direction, gate dielectric overlying the first and second edges of the nanowire and a split gate running across a section of the nanowire in a second, transverse direction, the split gate comprising first and second gates overlying the first and second edges respectively. The reflectometry circuit comprises a resonator coupled to the first or second gate.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Superconducting quantum-bit device based on josephson junctions
InactiveUS20030207766A1Quantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsCooper pairDegrees of freedom
A superconducting quantum-bit device based on Josephson junction has a charge as a first principal degree of freedom assigned to writing and a phase as a second principal degree of freedom assigned to reading. The device comprises a Cooper-pair box comprising first and second Josephson junctions defining a charge island of the Cooper-pair box closing up onto a superconducting loop. A read circuit comprises a read Josephson junction JL inserted into the superconducting loop and having a Josephson energy Ej at least 50 times greater than the Josephson energy of each of the first and second Josephson junctions.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Apparatus and method for quantum processing
ActiveUS20160125311A1Minimizes quantum controlMinimizes characterization complexityQuantum computersSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsSpins
The present disclosure provides a quantum processor realised in a semiconductor material and method to operate the quantum processor to implement error corrected quantum computation. The quantum processor comprises a plurality of qubit elements disposed in a two-dimensional matrix arrangement. The qubits are implemented using the nuclear or electron spin of phosphorus donor atoms. Further, the processor comprises a control structure with a plurality of control members, each arranged to control a plurality of qubits disposed along a line or a column of the matrix. The control structure is controllable to perform topological quantum error corrected computation.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD +1
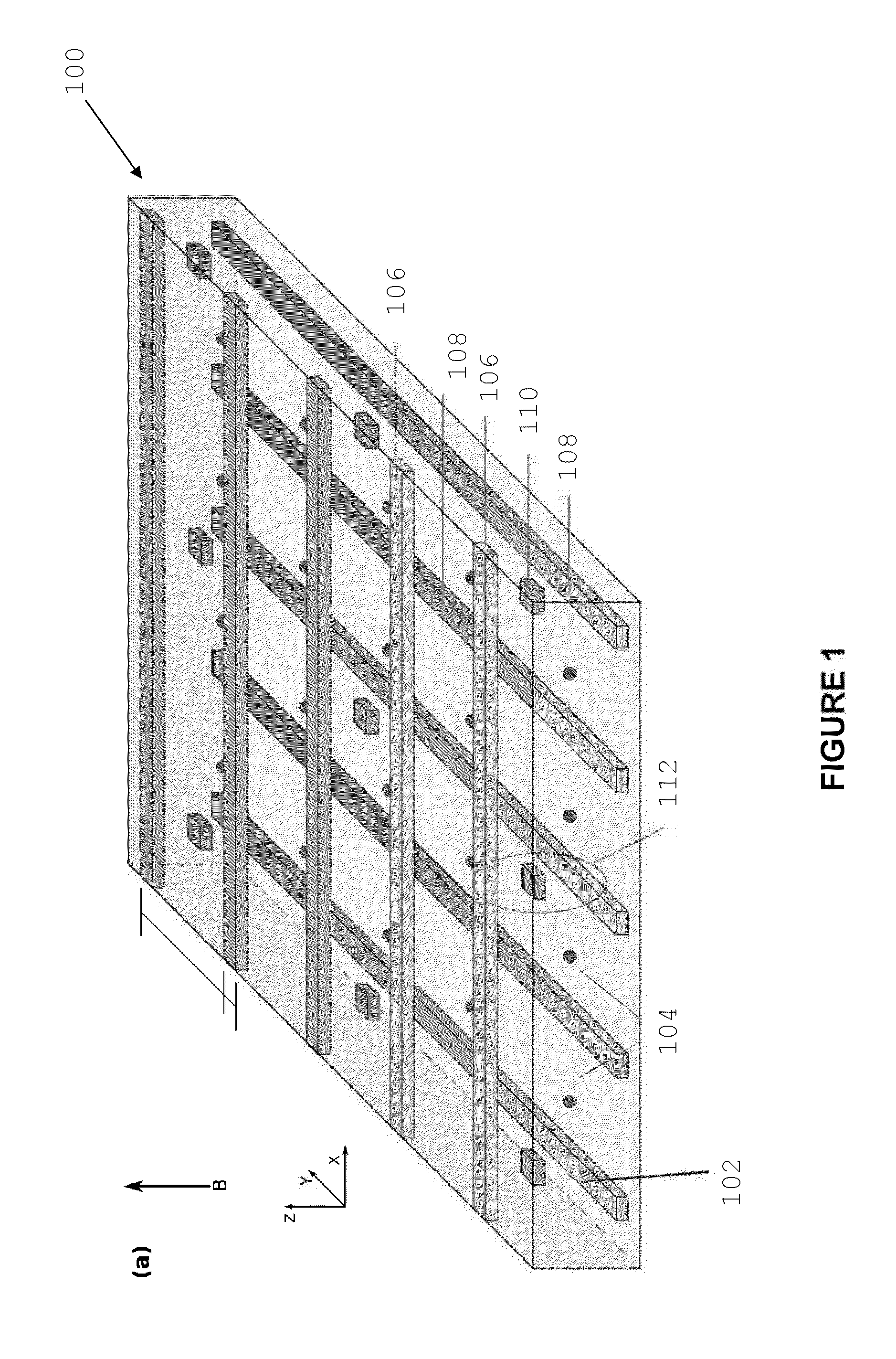
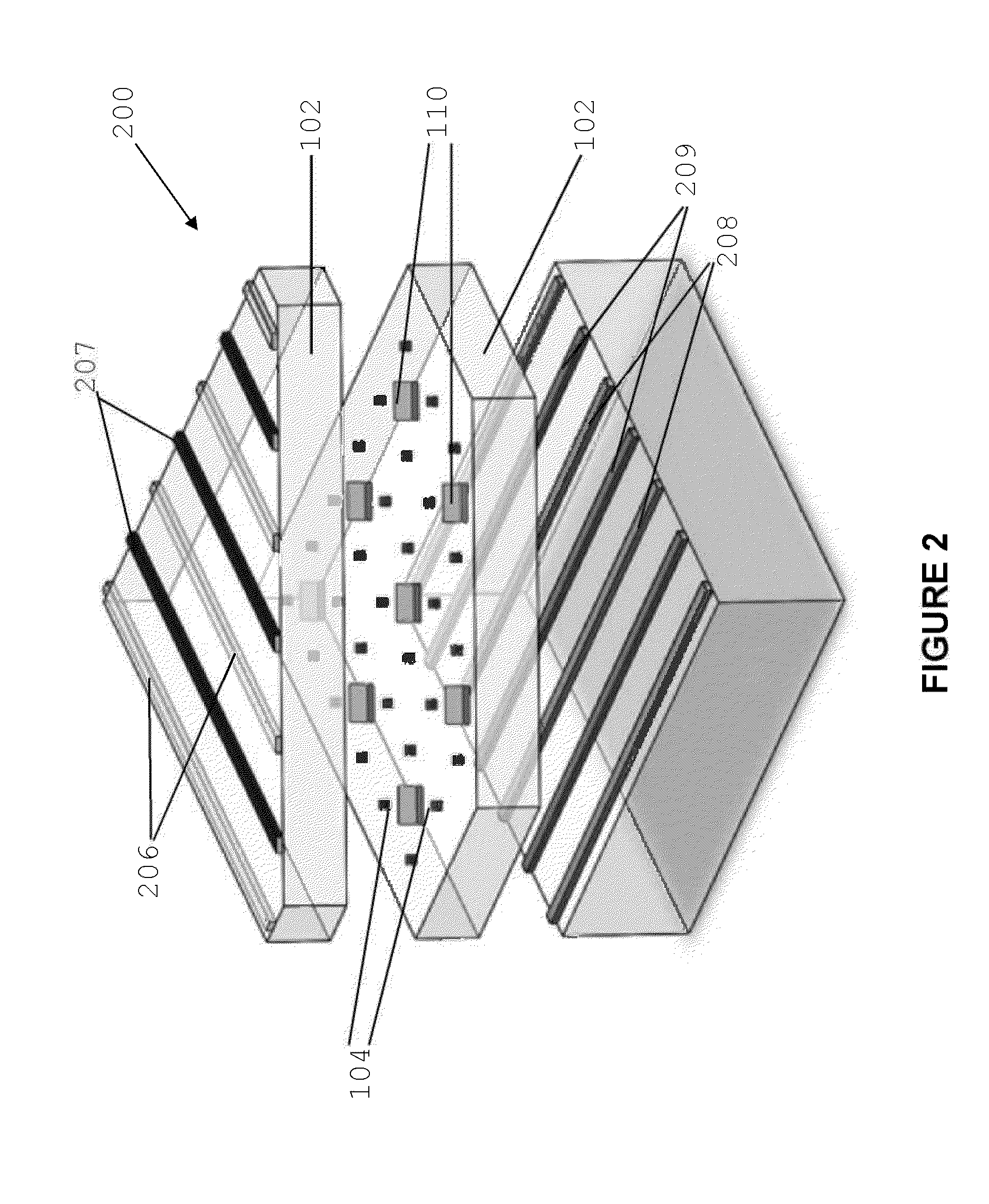
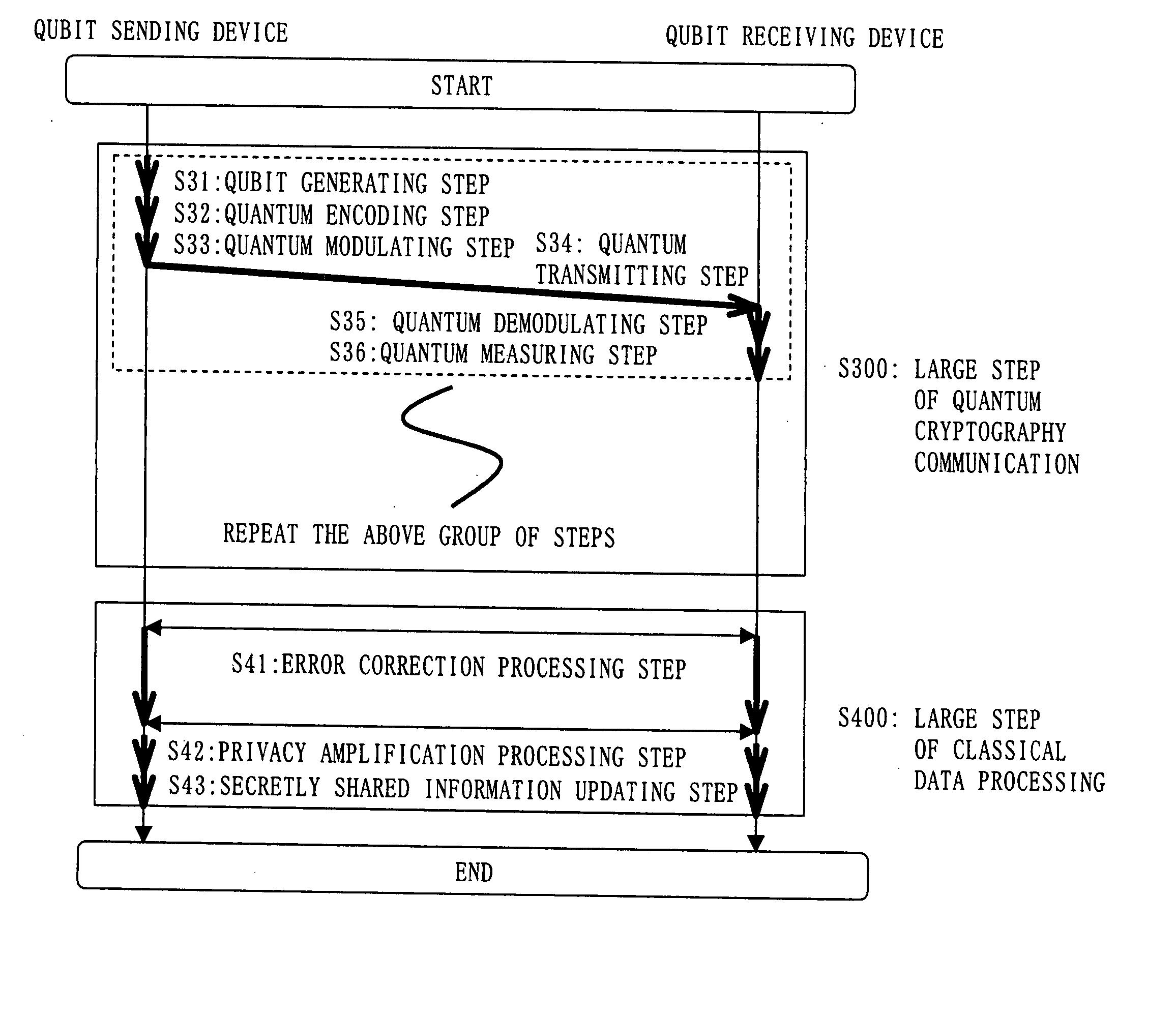
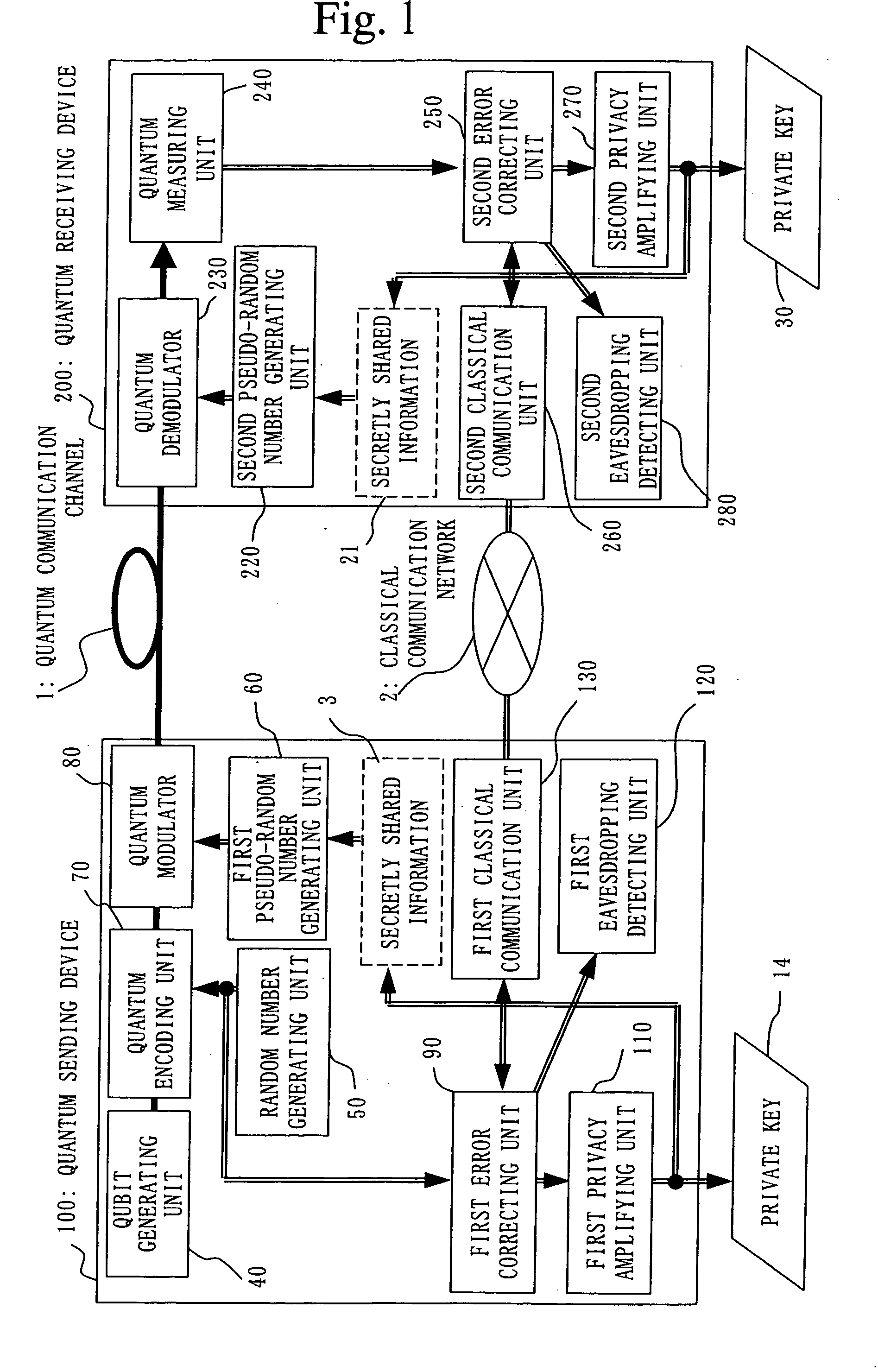
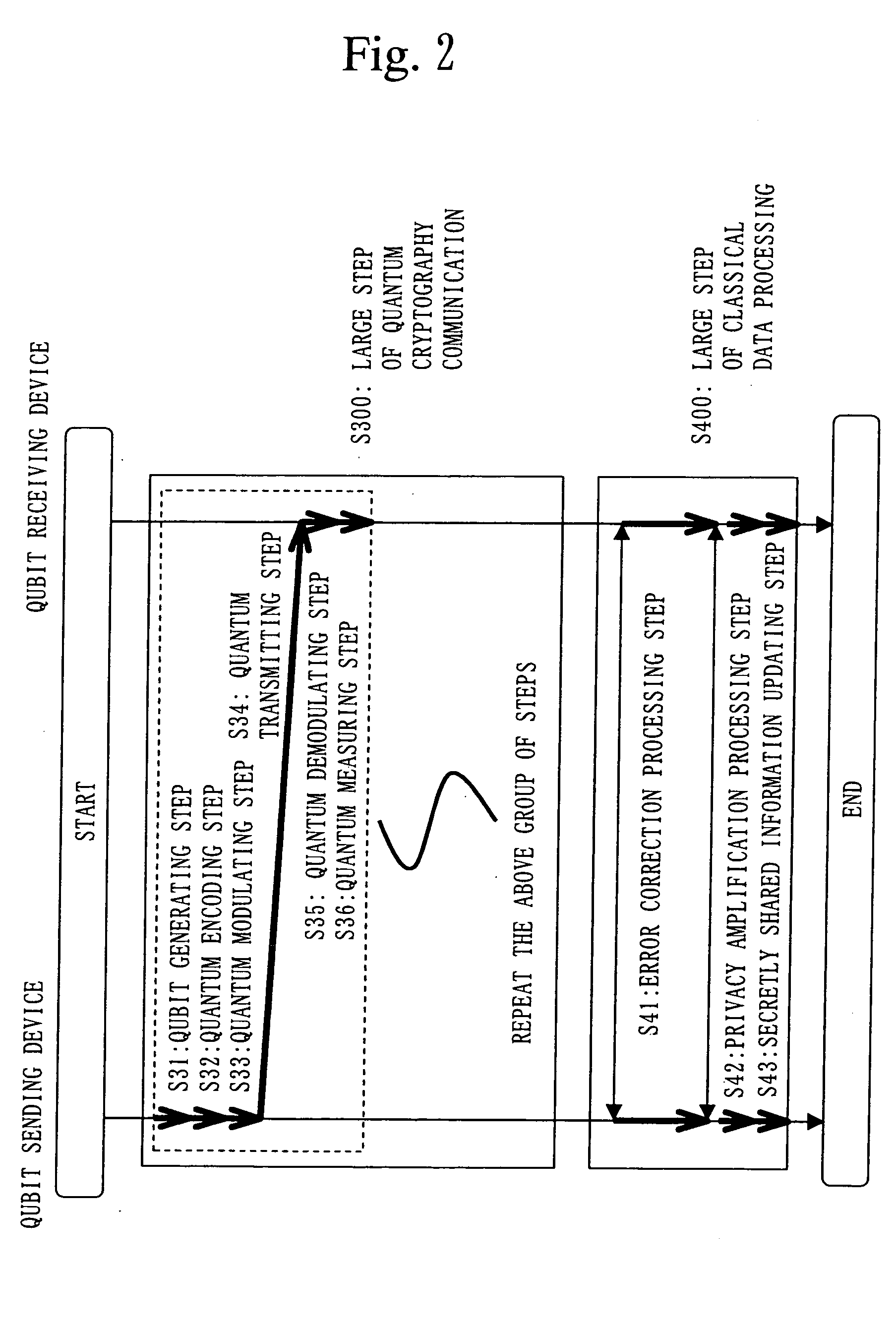
Crytographic communication apparatus
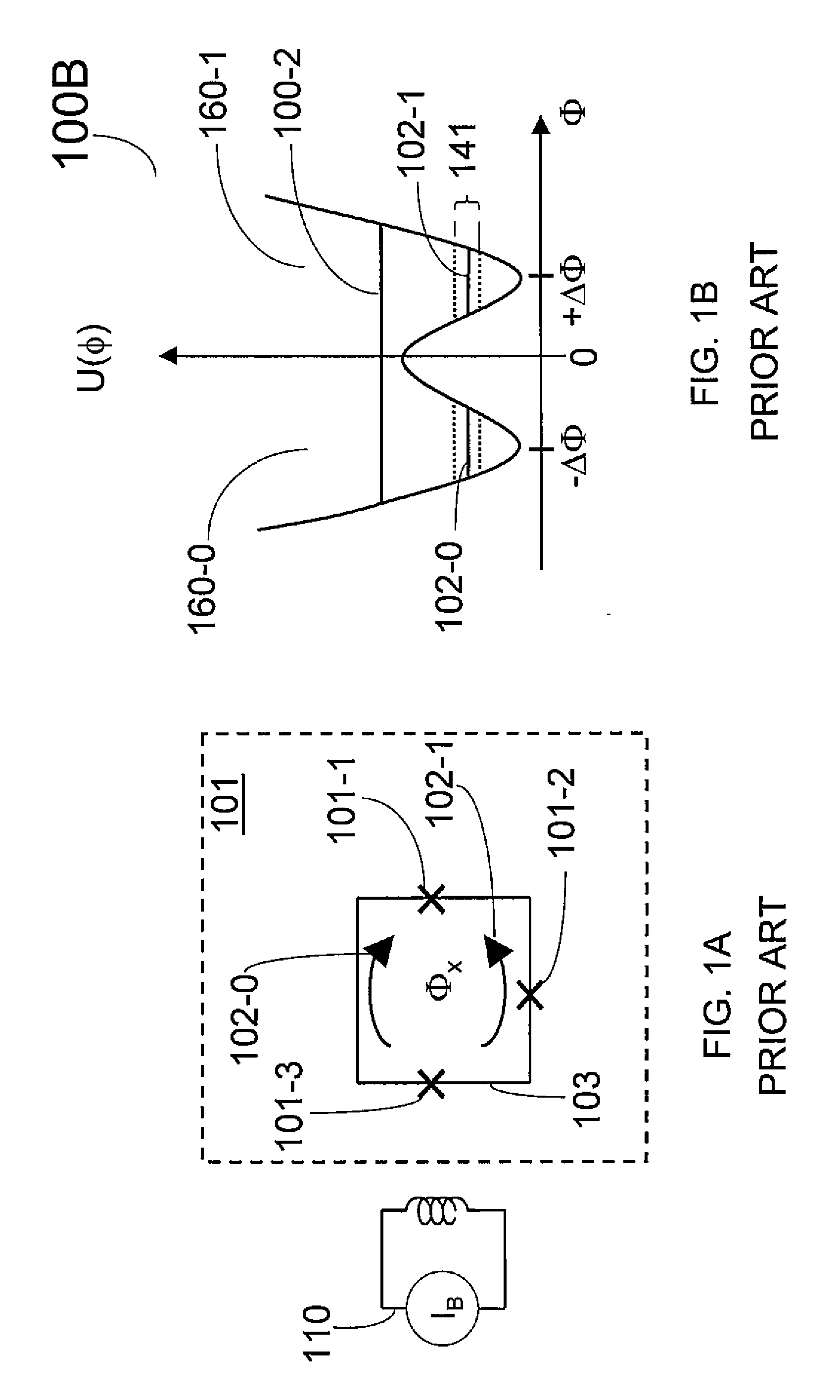
InactiveUS20050157875A1Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesPseudo random number generationQuantum electrodynamics
A qubit generating unit 40 generates a qubit having a predetermined quantum state. A qubit encoding unit 70 performs quantum encoding of the generated qubit. A first pseudo-random number generating unit 60 generates a first pseudo-random number from secretly shared information 3 which has been secretly shared with the quantum receiving device 200 in advance. A quantum modulator 80 performs quantum modulation of the qubit on which quantum encoding has been performed based on the first pseudo-random number and sends the modulated qubit to the quantum receiving device 200. A second pseudo-random number generating unit 220 generates a second pseudo-random number from secretly shared information 21 which has been secretly shared with the above quantum sending device 100 in advance synchronously with generation of the above first pseudo-random number. A qubit demodulator 230 performs quantum demodulation of the qubit which has been received from the quantum demodulator 80 based on the second pseudo-random number.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com