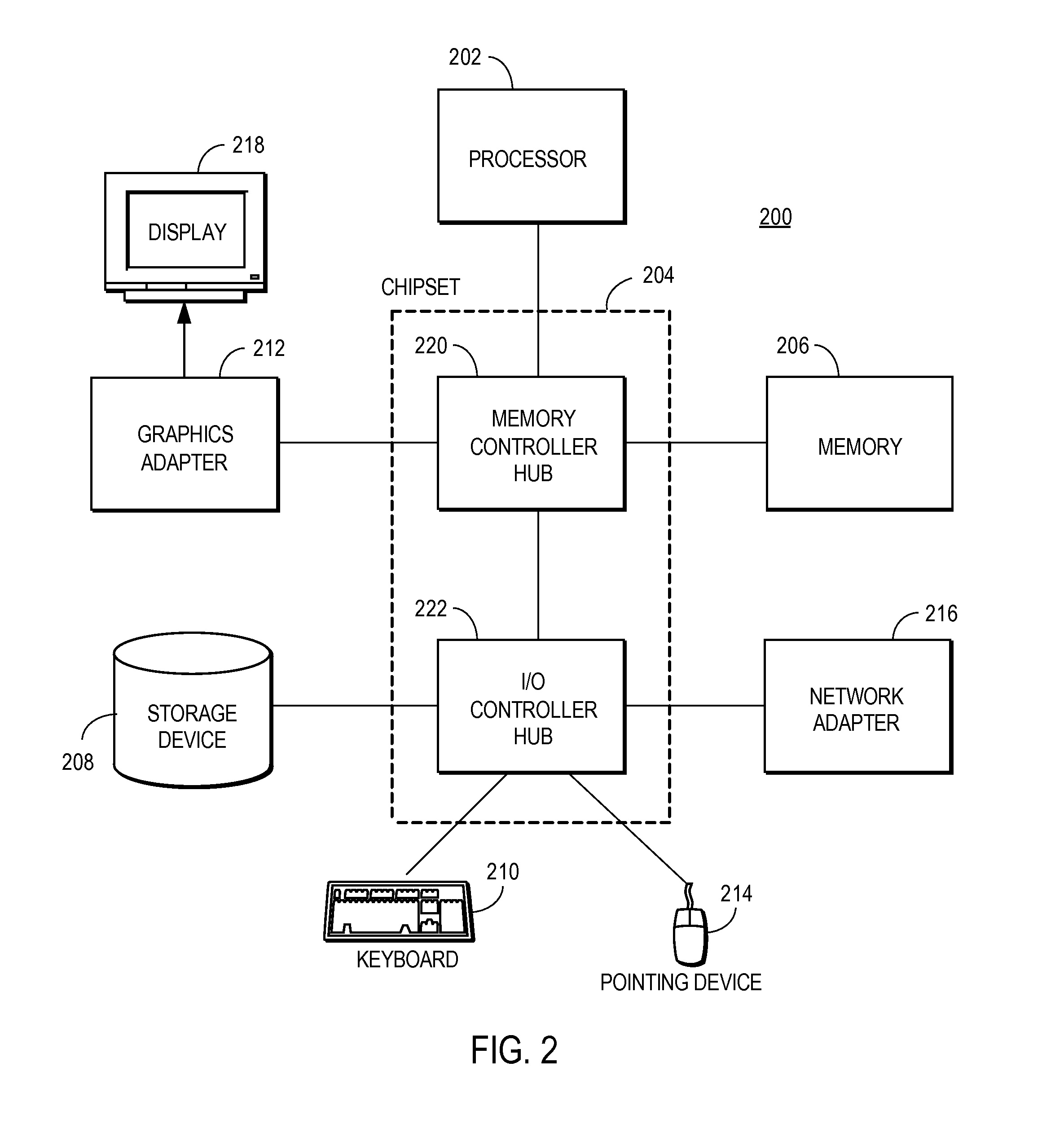
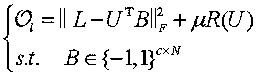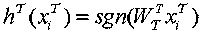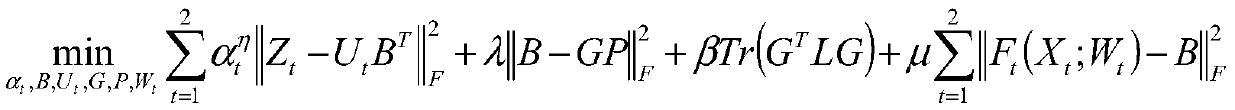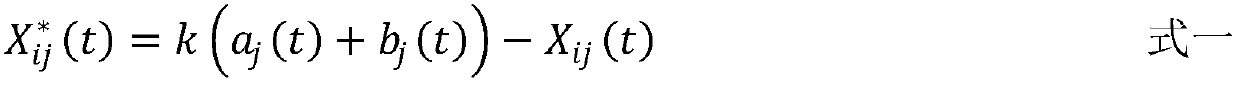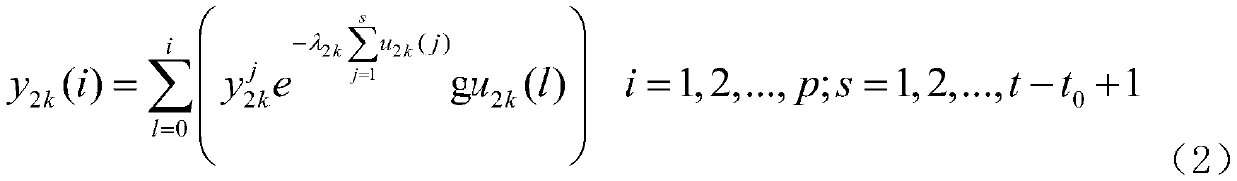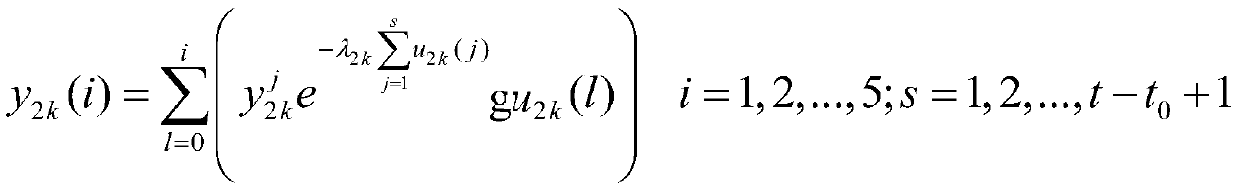Patents
Literature
74 results about "Discrete optimization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Discrete optimization is a branch of optimization in applied mathematics and computer science.
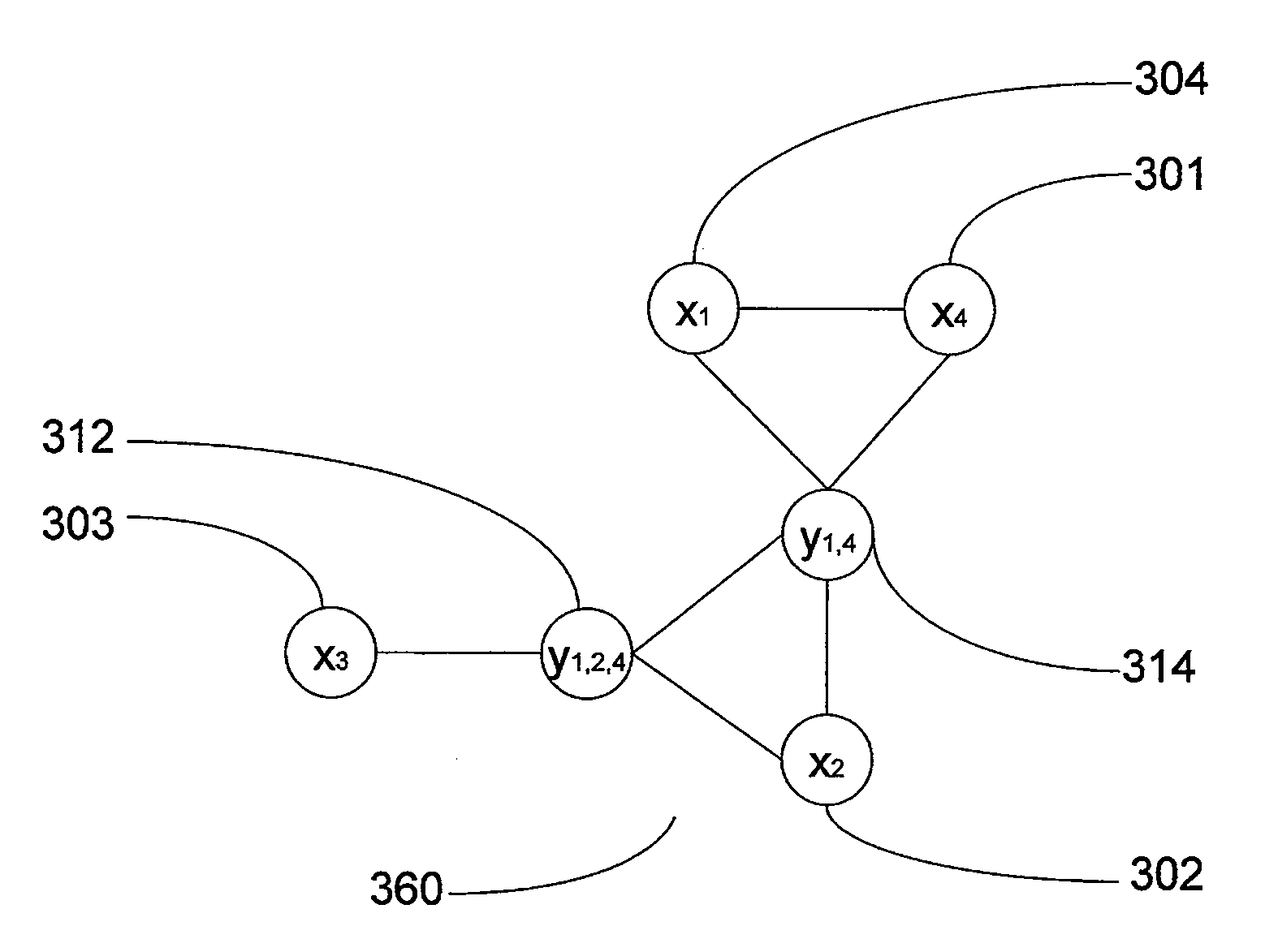
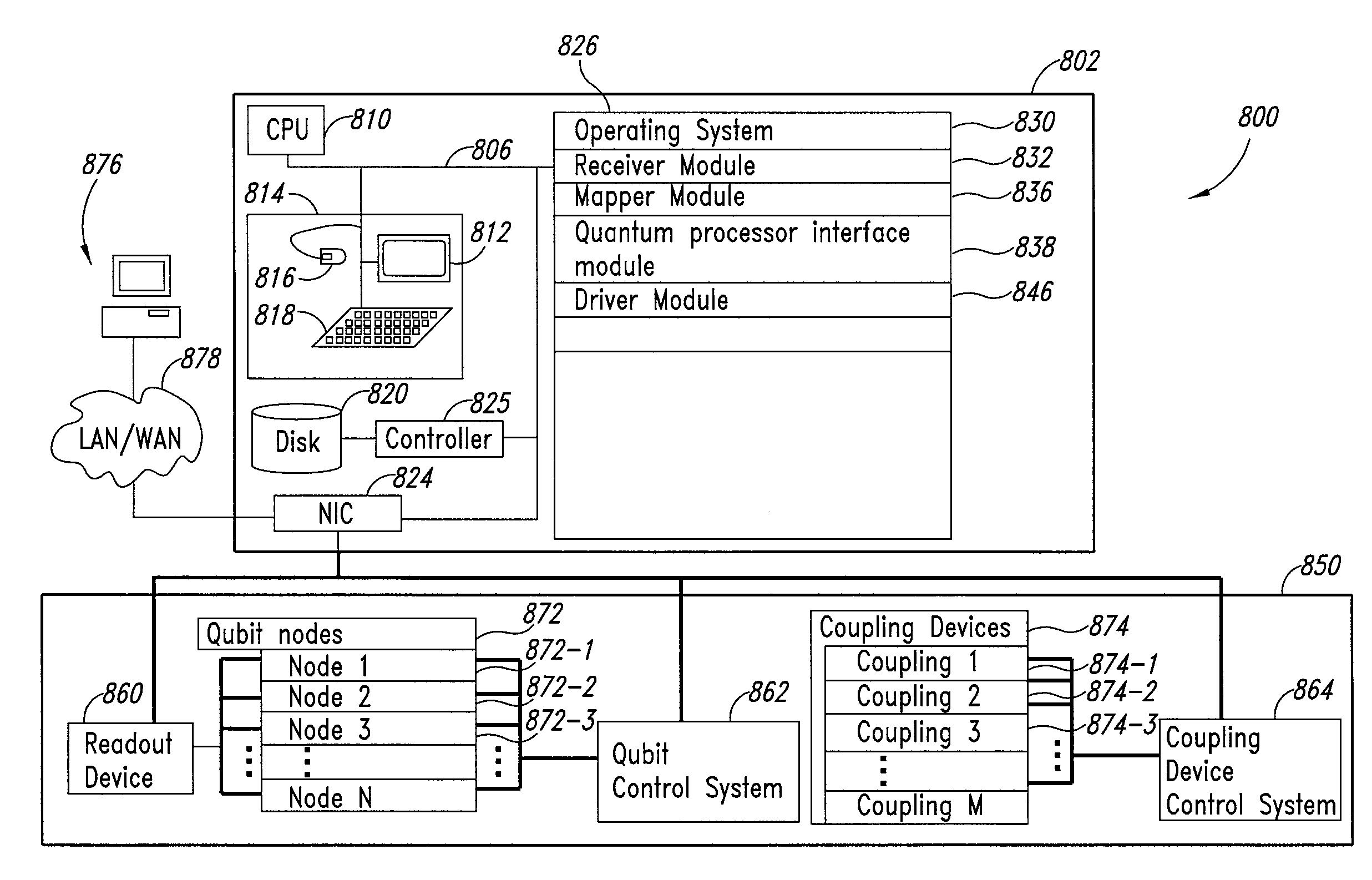
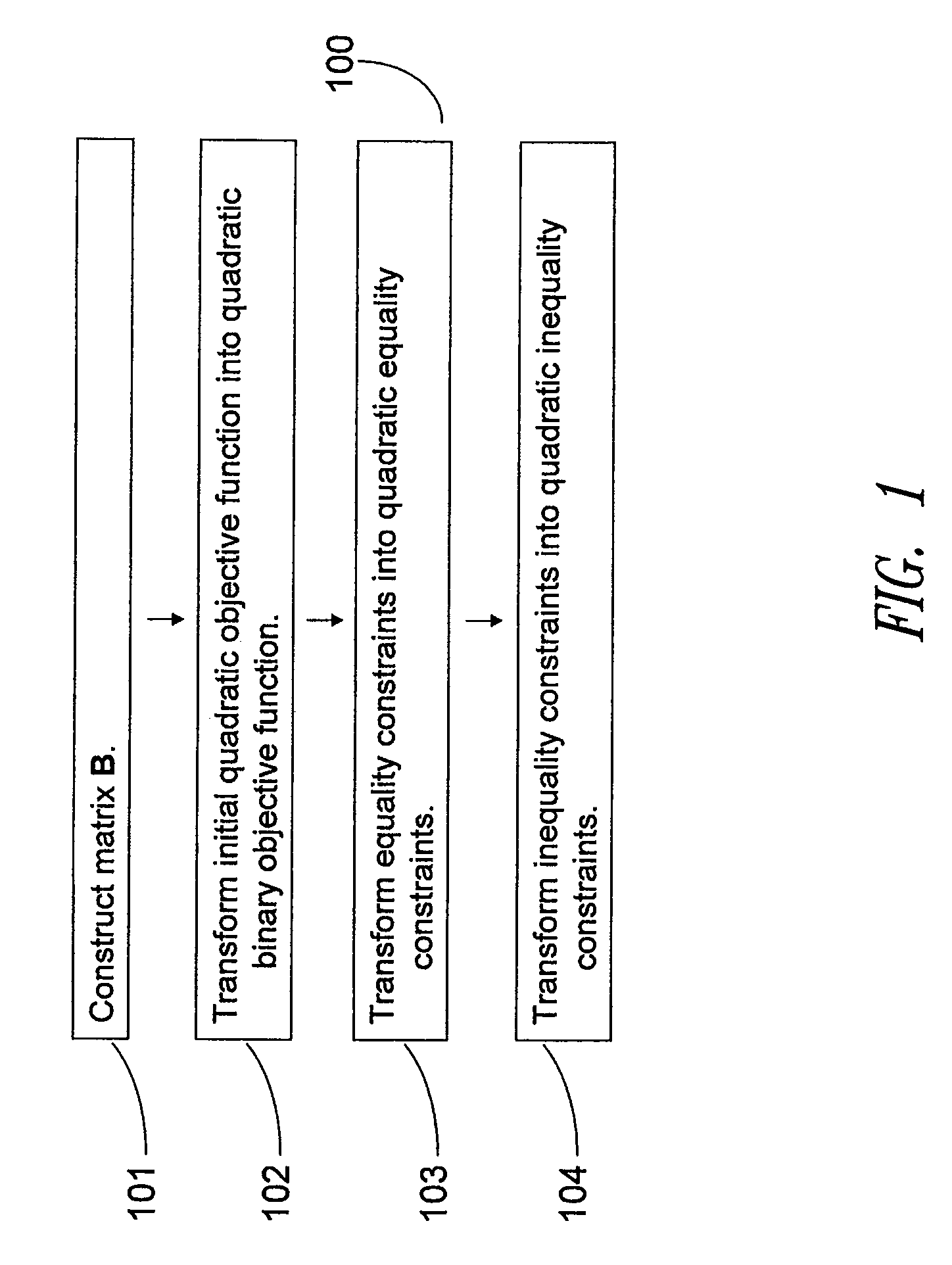
Method and system for solving integer programming and discrete optimization problems using analog processors
ActiveUS20080065573A1Improve legibilityDigital computer detailsChaos modelsAnalog processorDiscrete optimization
Discrete optimization problem are solved using an analog optimization device such as a quantum processor. Problems are solved using an objective function and at least one constraint corresponding to the discrete optimization problems. The objective function is converted into a first set of inputs and the at least one constraint is converted into a second set of inputs for the analog optimization device. A third set of inputs is generated which are indicative of at least one penalty coefficient. A final state of the analog optimization device corresponds to at least a portion of the solution to the discrete optimization problem.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
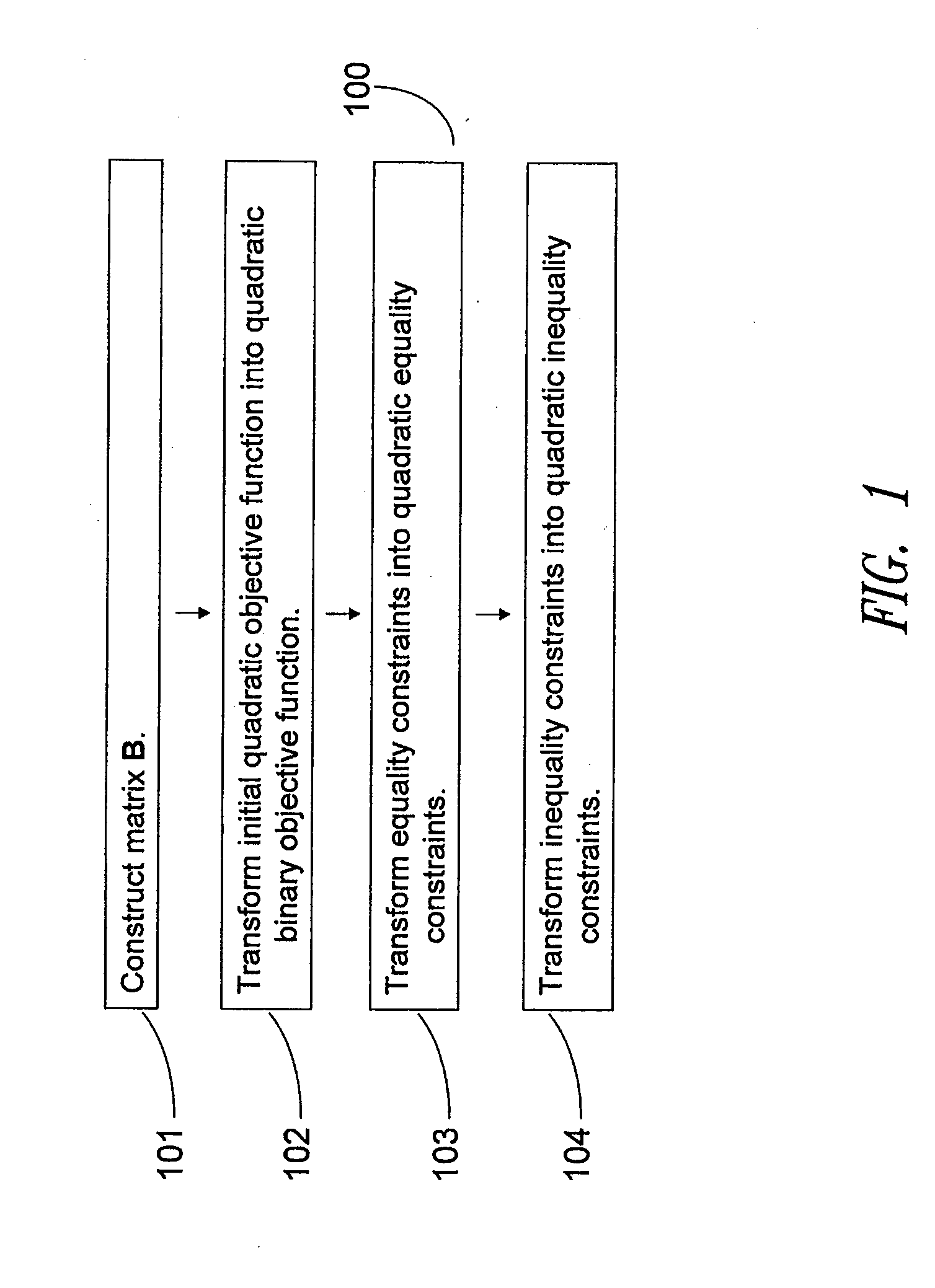
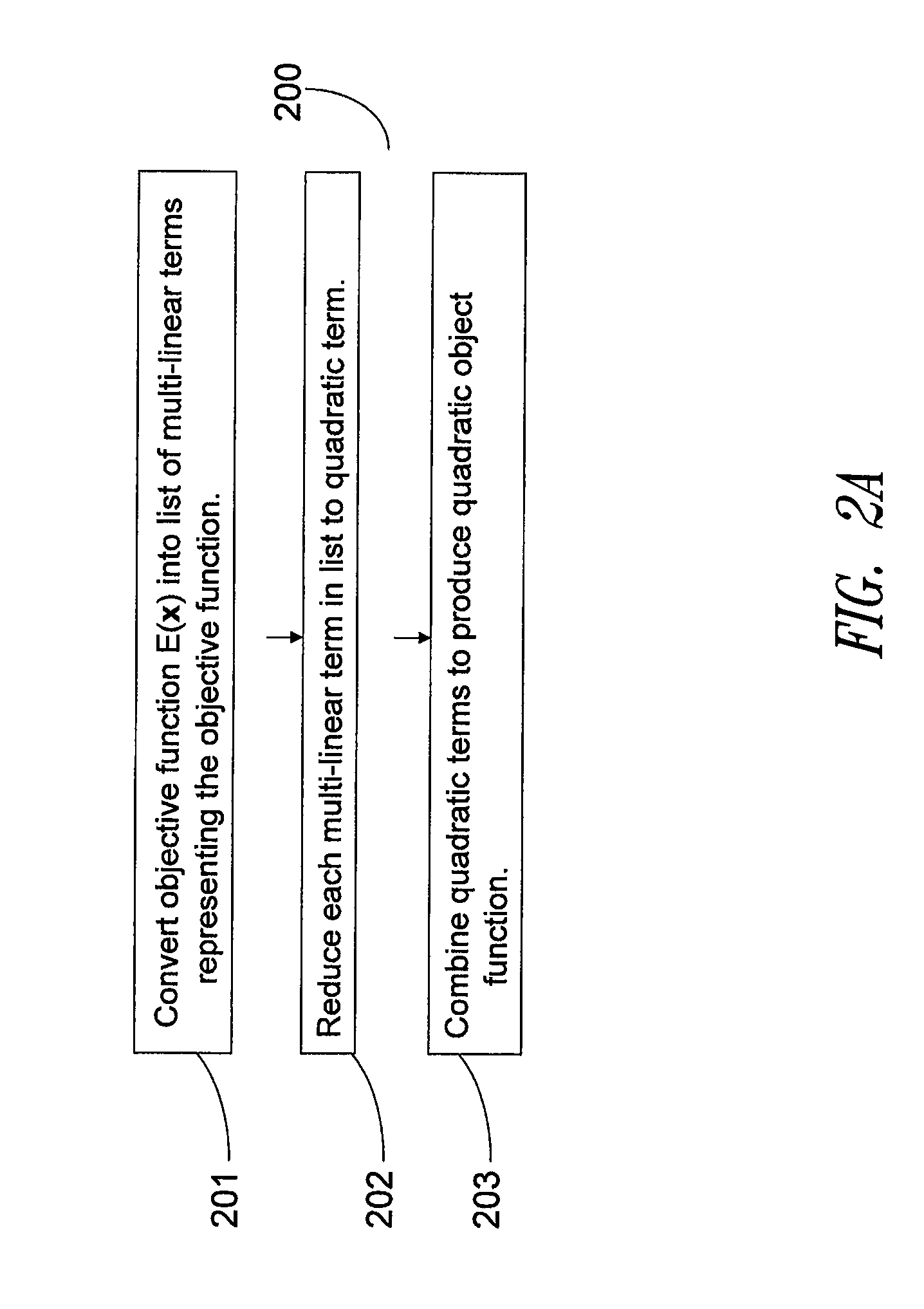
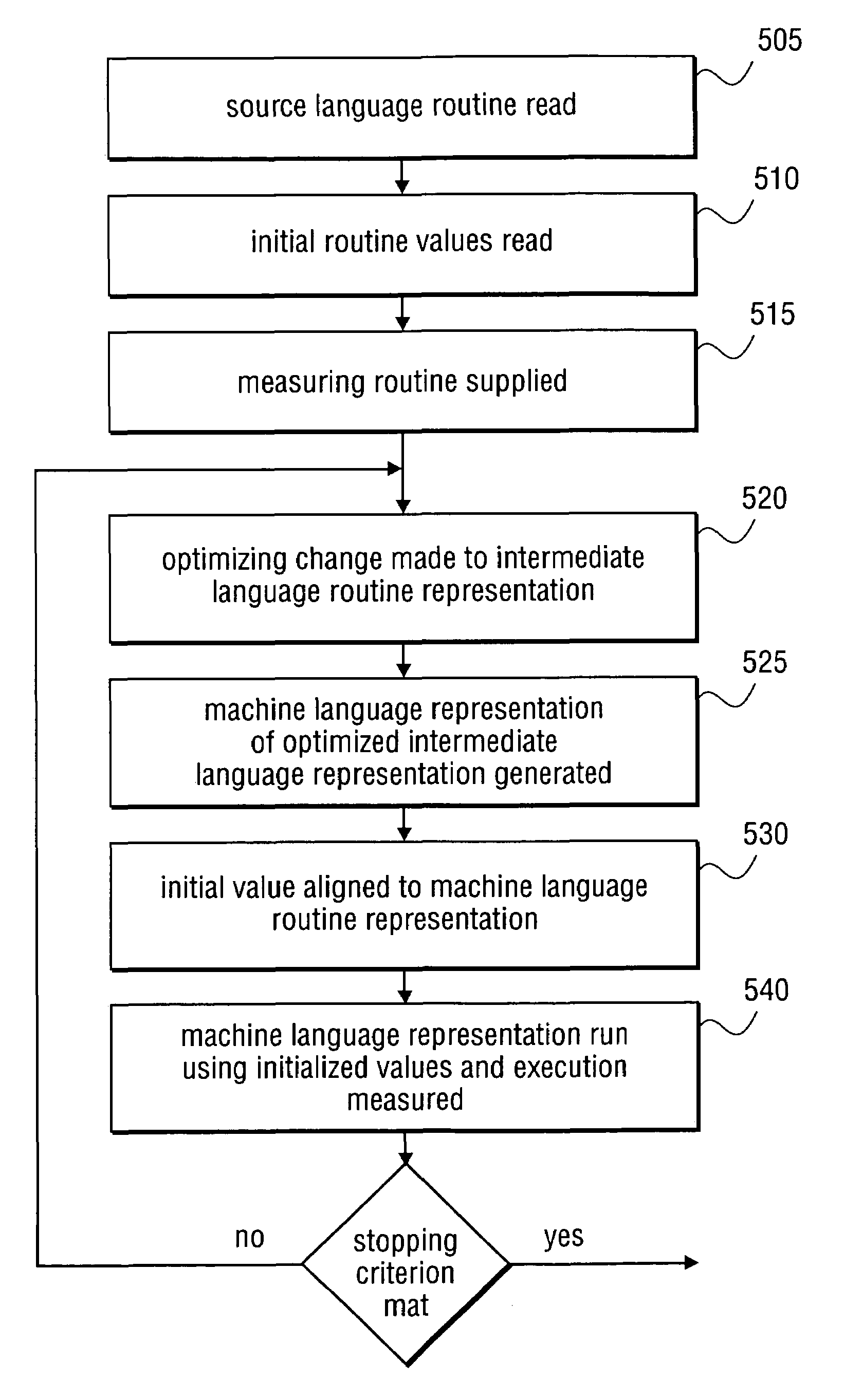
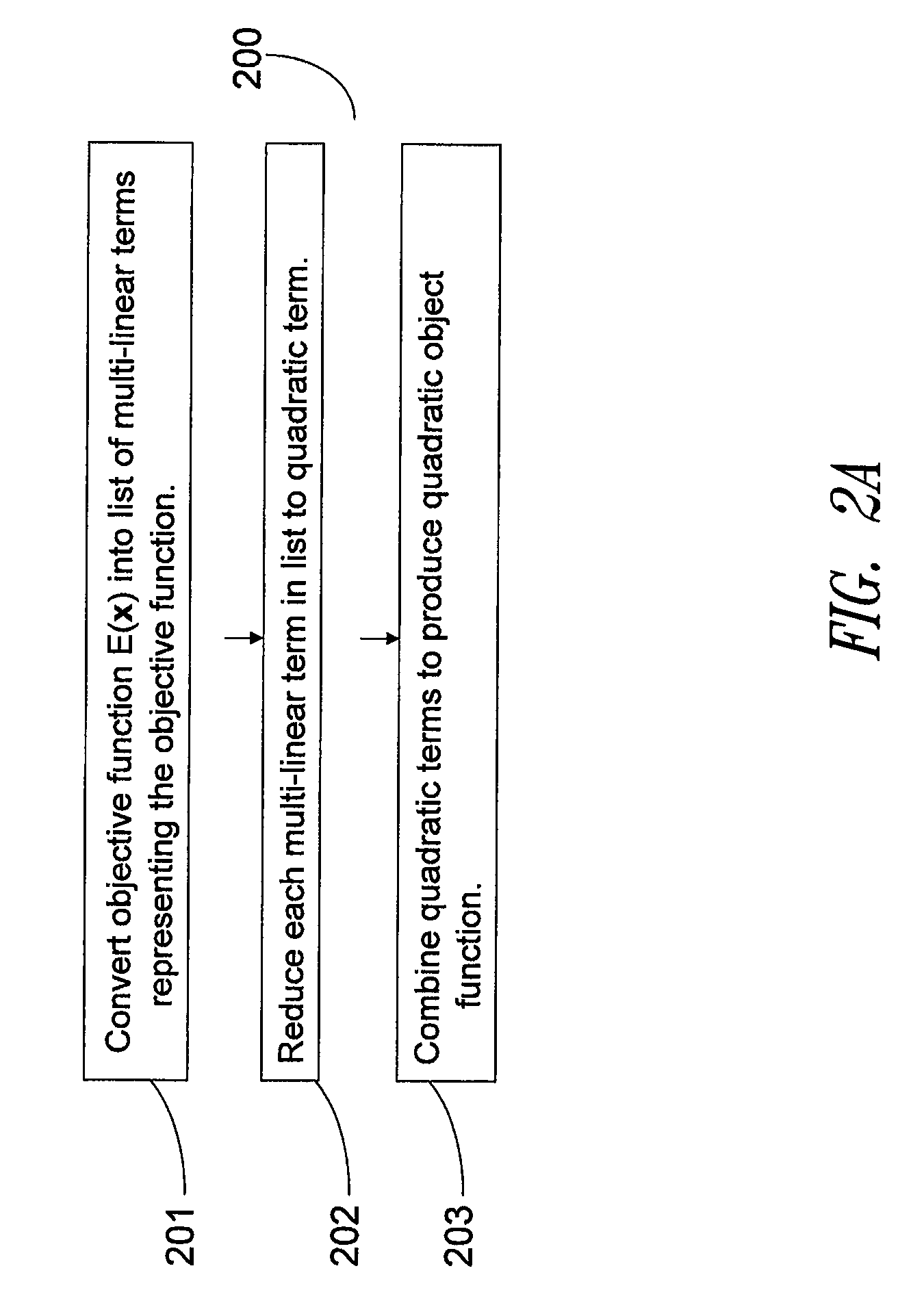
Iterative optimizing compiler
An optimizing compiler and method thereof performs a sequence of optimizing changes to an intermediate language representation of a routine, and measures an execution characteristic of each optimization, such as a timing of the machine language representation performed on an architecture similar to the target machine using a user selectable initialization state. The sequence of optimizations is selected according to a criterion that includes a lexicographic search and other methods. The pre-optimized code is also broken into segments wherein discrete optimizations are performed on each segment and measured using a user provided routine. The target routine is tested with the object code in main memory if not the cache if possible and optimizations are chosen only if they improve the target subroutine according to the user defined metric. After a stopping criterion is achieved, the most optimized code is selected.
Owner:INTEL CORP
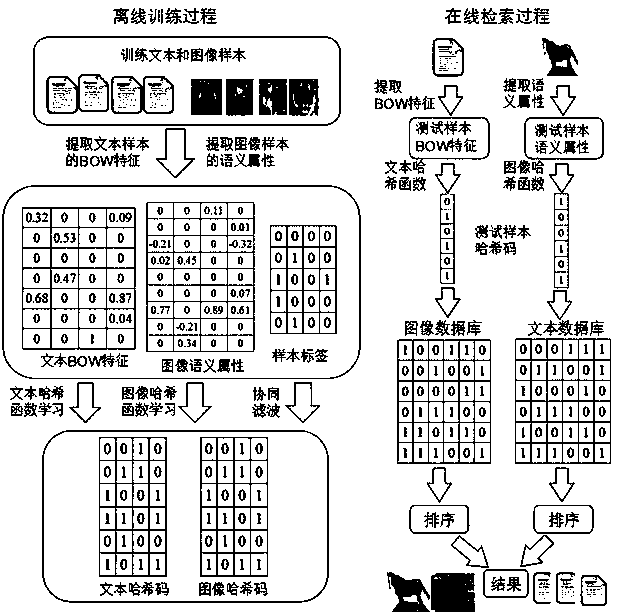
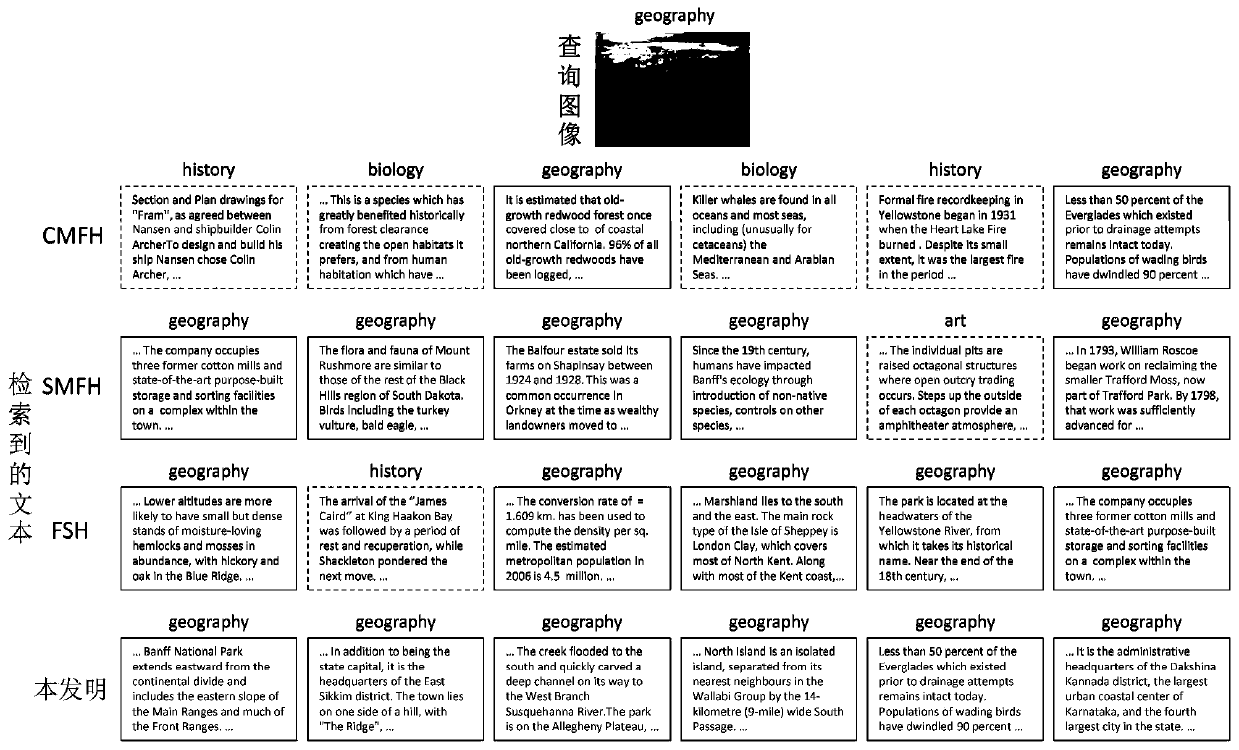
Discrete supervision cross-modal hashing retrieval method based on semantic alignment
ActiveCN107729513AImprove performanceBridging the Heterogeneous GapSpecial data processing applicationsHash functionSemantic alignment
The invention discloses a DSAH (discrete semantic alignment hashing) method based on semantic alignment for cross-modal retrieval. In the training process, a heterogeneous gap is reduced by the aid ofimage attributes and modal alignment semantic information. In order to reduce memory overhead and training time, a latent semantic space is learned by synergistic filtering, and the internal relationbetween a hash code and a label is directly built. Finally, in order to decrease quantization errors, a discrete optimization method is proposed to obtain a hash function with better performances. Inthe retrieval process, samples in a testing set are mapped to a binary space by the hash function, the Hamming distance between a binary code of a query sample and a heterogeneous sample to be retrieved is calculated, and front ranked samples are returned according to the sequence from small to large. Experimental results of two representative multi-modal data sets prove superior performances ofDSAH.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Method and system for solving integer programming and discrete optimization problems using analog processors
Discrete optimization problem are solved using an analog optimization device such as a quantum processor. Problems are solved using an objective function and at least one constraint corresponding to the discrete optimization problems. The objective function is converted into a first set of inputs and the at least one constraint is converted into a second set of inputs for the analog optimization device. A third set of inputs is generated which are indicative of at least one penalty coefficient. A final state of the analog optimization device corresponds to at least a portion of the solution to the discrete optimization problem.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
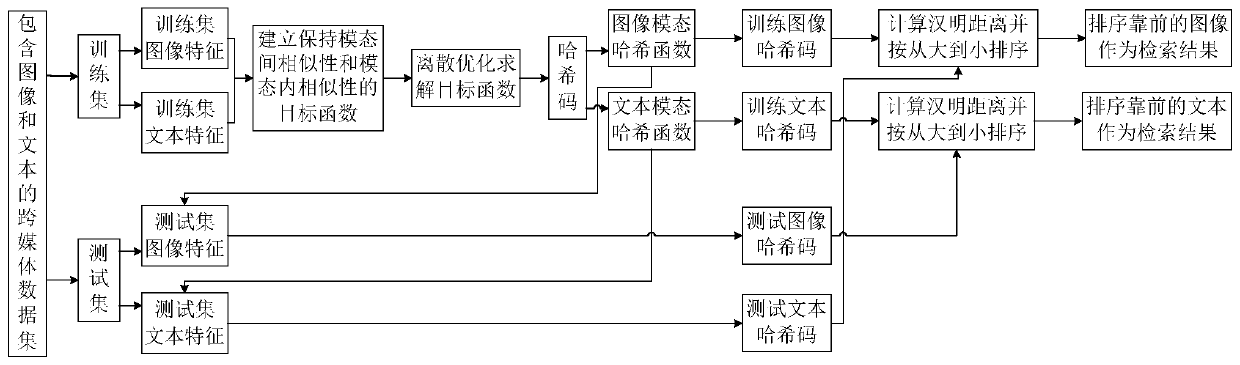
Cross-modal data discrete hash retrieval method based on similarity maintenance
ActiveCN110059198ATroubleshoot data retrieval issuesImprove accuracyMultimedia data indexingMultimedia data queryingModal testingCross modality
The invention discloses a cross-modal data discrete hash retrieval method based on similarity preservation. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a cross-modal retrieval data set composed of samples containing two modalities, and dividing the cross-modal retrieval data set into a training set and a test set; establishing an objective function for keeping similarity between modalities and similarity in modalities, and solving the objective function through a discrete optimization method to obtain a hash code matrix; learning a Hash function of each mode according to the Hashcode matrix; calculating Hash codes of all samples in the training set and the test set by using a Hash function; wherein one modal test set serves as a query set and the other modal training set serves as a retrieval set, calculating the Hamming distance between the Hash codes of the samples in the query set and the Hash codes of the samples in the retrieval set, wherein the sequence serves as aretrieval result. According to the method, the similarity between modalities and the similarity in the modalities can be effectively kept, the discrete characteristics of the Hash codes are considered, a discrete optimization method is adopted for solving the objective function, and therefore the cross-modality retrieval accuracy is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
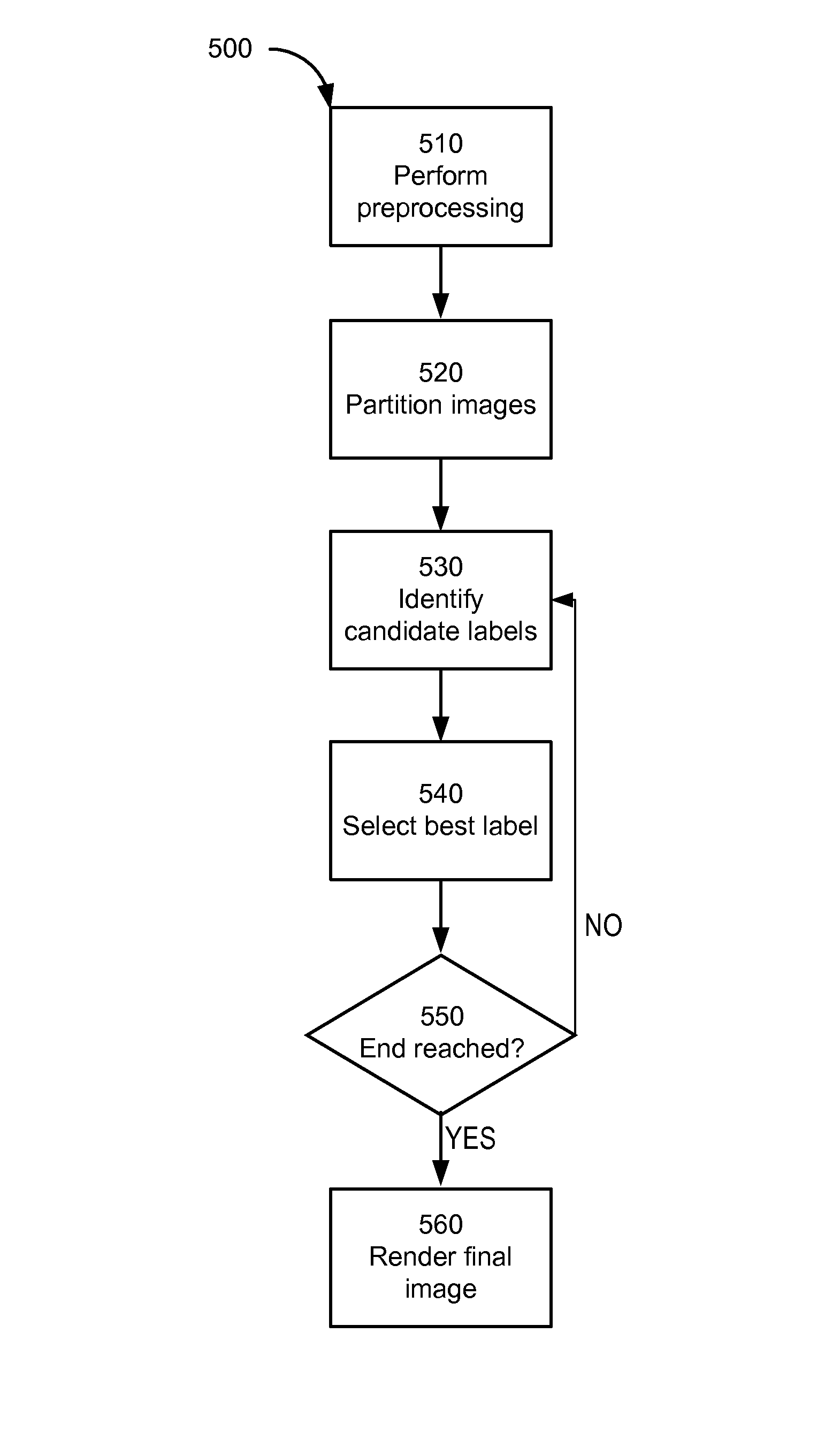
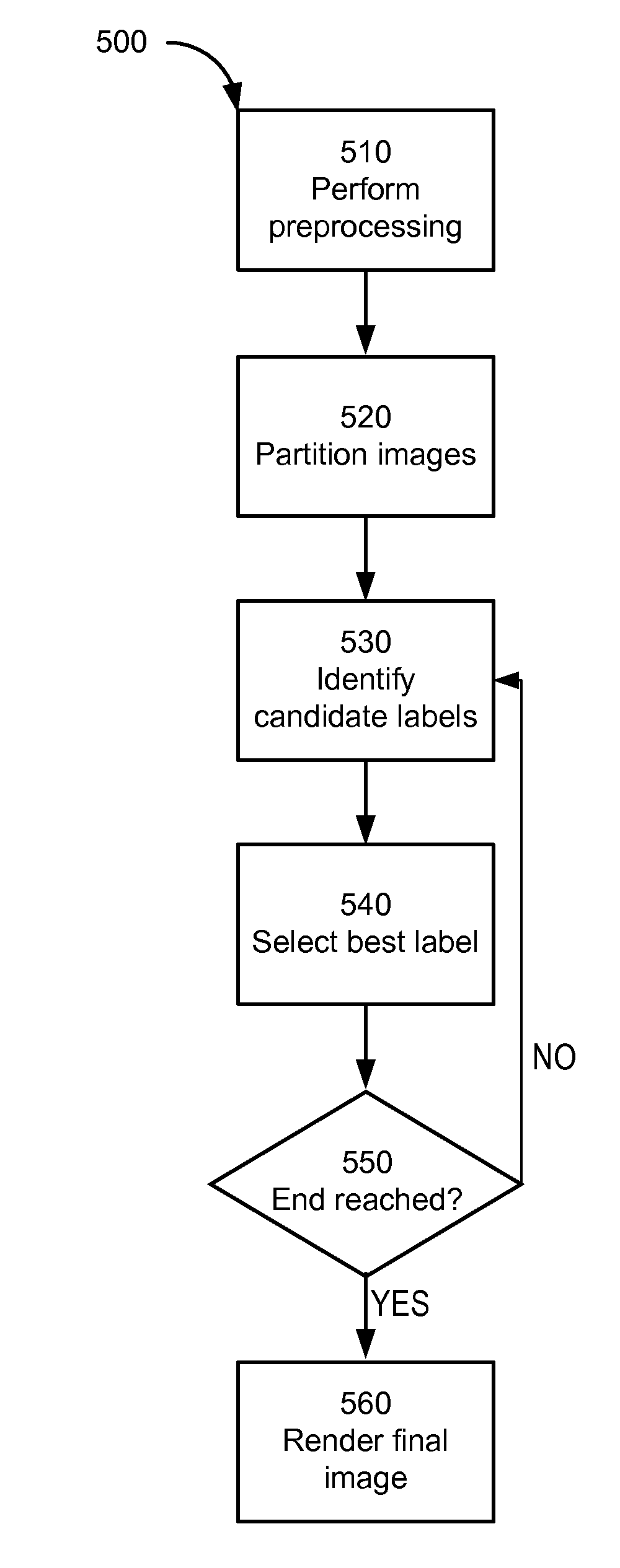
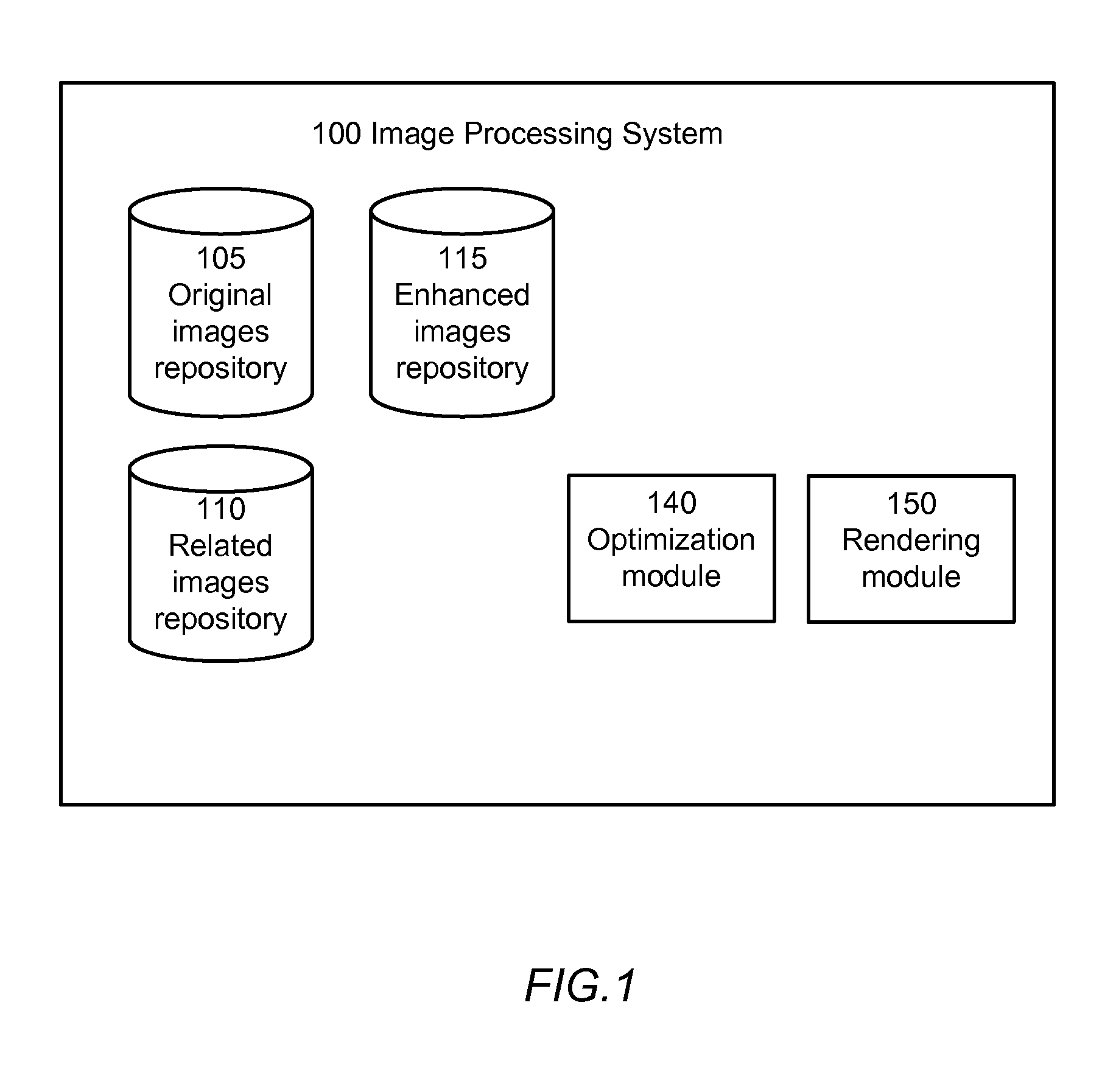
Image enhancement through discrete patch optimization
ActiveUS8396325B1Enhanced output imageEnhance the imageImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging processing
An image processing system enhances the resolution of an original image using higher-resolution image data from other images. The image processing system defines a plurality of overlapping partitions for the original image, each partition defining a set of non-overlapping site patches. During an optimization phase, the system identifies, for site patches of the original images, label patches within related images that are of most relevance. During a rendering phase independent of the optimization phase, an output image with enhanced resolution is synthesized by substituting, for site patches of the original image, the identified relevant label patches from the related images.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
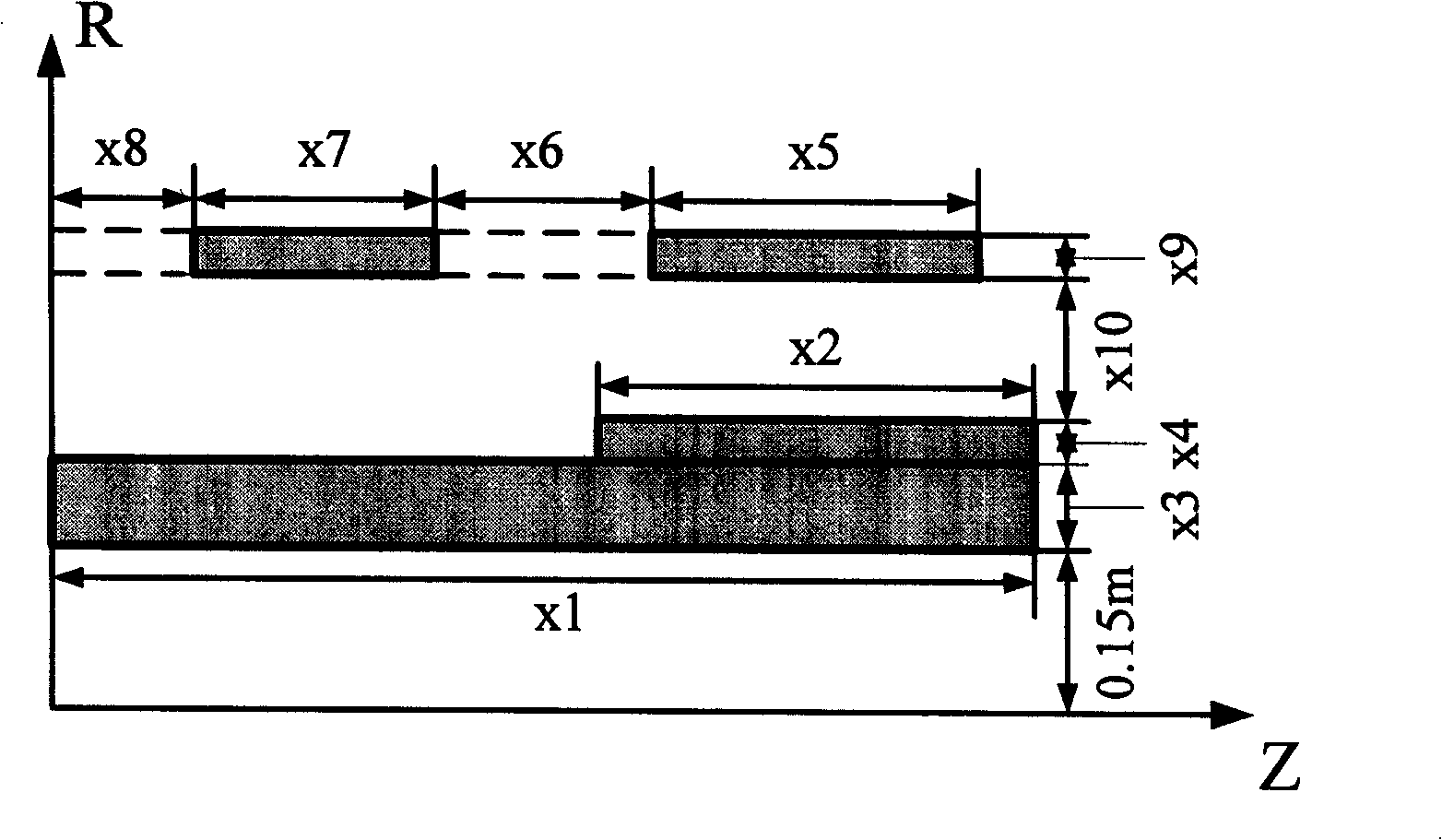
Discrete optimizing method for magnetic resonance image-forming superconducting magnet design
InactiveCN101339580AAvoid errorsStrong error robustnessSpecial data processing applicationsRoundingMagnetic field magnitude
The invention relates to an optimization design method for the discretization of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) superconducting magnets, which belongs to a superconducting magnet design technology and is characterized in that an objective function is set by a weighting method and indexes of magnetic field intensity, uniformity of magnetic field, stray field range, thread consumption, fabrication error, and the like are taken into comprehensive consideration. The use of discrete variables as optimization variables can avoid rounding and discretization errors occurring in common methods. By considering the robustness of errors in design objectives, the optimization design of the robustness is realized. The use of the design method for designing the superconducting magnets can take a plurality of design indexes into consideration in a synthesized manner, thus having the advantages of convenient processing and manufacturing and strong error robustness.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
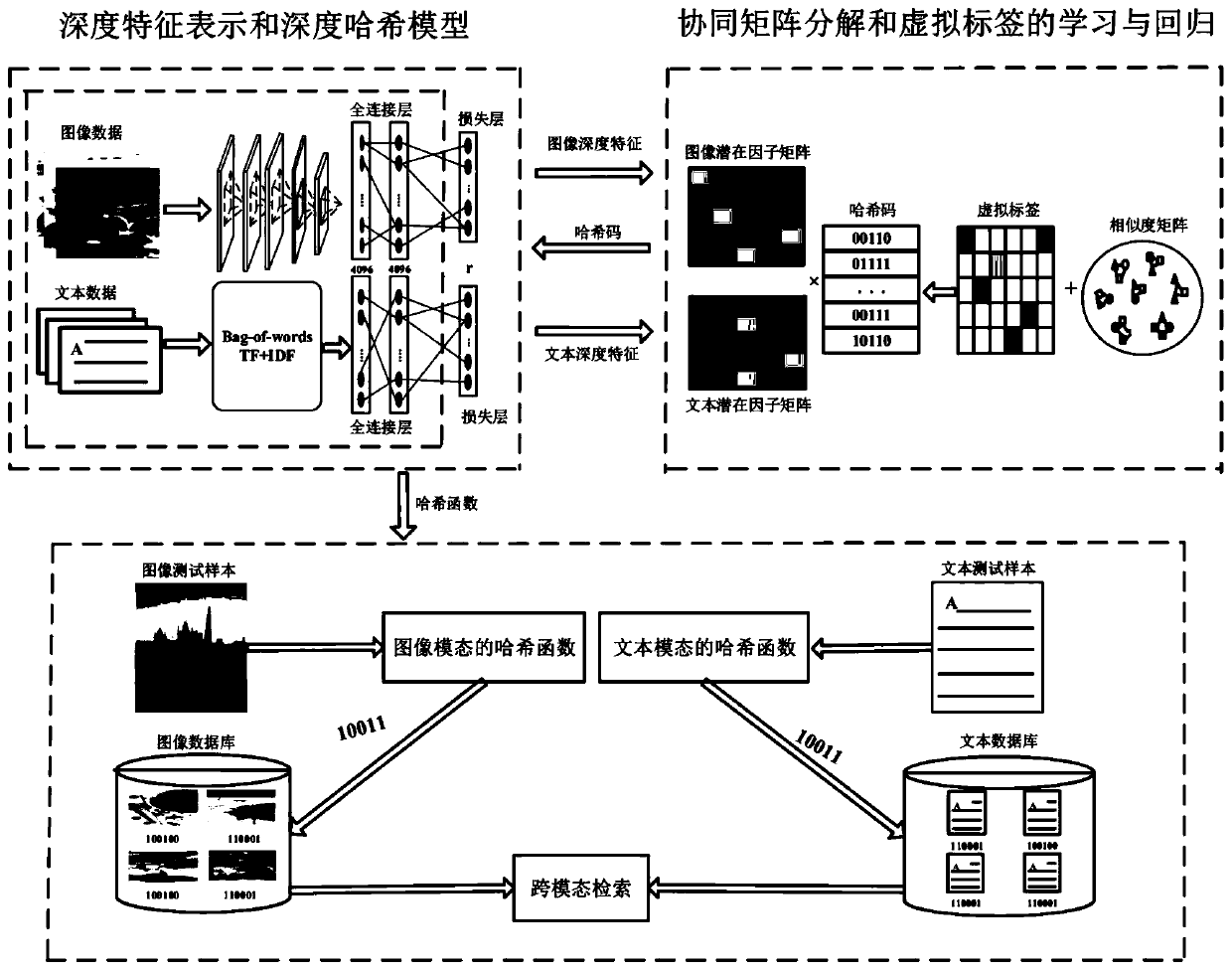
Unsupervised cross-modal hash retrieval method and system based on virtual label regression
ActiveCN110674323AGuaranteed Semantic ConsistencyEasy to learnCharacter and pattern recognitionStill image data indexingMatrix decompositionHash function
The invention provides an unsupervised cross-modal hash retrieval method and system based on virtual label regression, and the method comprises the steps: feature representation and hash function learning are integrated into a unified depth frame, and a shared hash code is learned through the cooperative matrix decomposition of multi-modal depth features, so as to guarantee that a plurality of modes share the same semanteme; on the basis, the concept of a virtual label is introduced, the virtual label is learned through non-negative spectrum analysis, and meanwhile, the learned virtual labelis returned to the hash code, so that the semantic consistency between the hash code and the virtual label is ensured; in the framework, collaborative matrix decomposition of the depth features and learning and regression of the virtual tags are beneficial to learning of depth feature representation and hash functions, and improved depth feature representation and hash models are beneficial to collaborative matrix decomposition and learning and regression of the virtual tags, and the collaborative matrix decomposition and the virtual tags promote each other; and meanwhile, through a new discrete optimization strategy, the deep hash function and the hash code are directly updated, the quantization error of a relaxation strategy in an existing method is effectively reduced, and the cross-modal retrieval performance is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
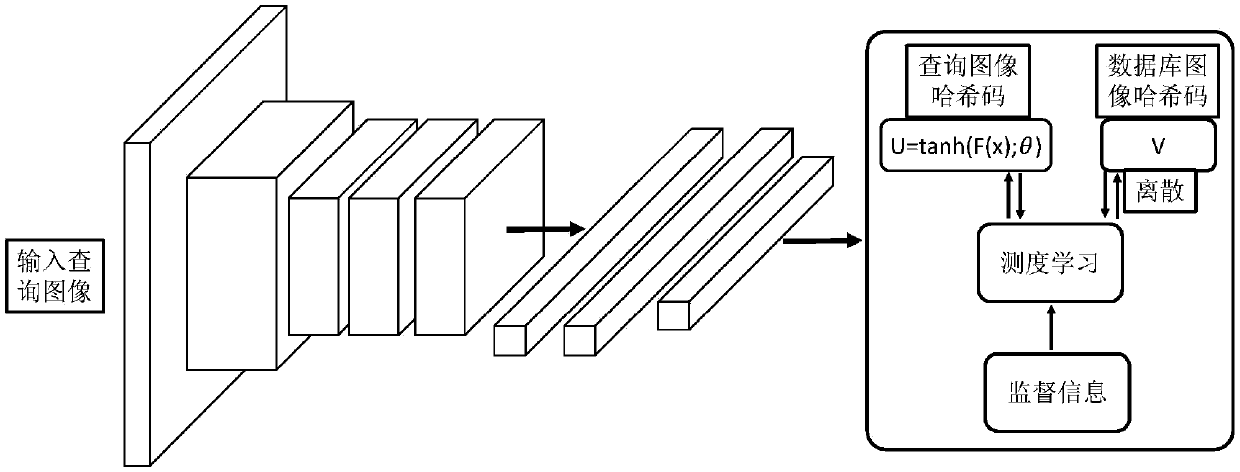
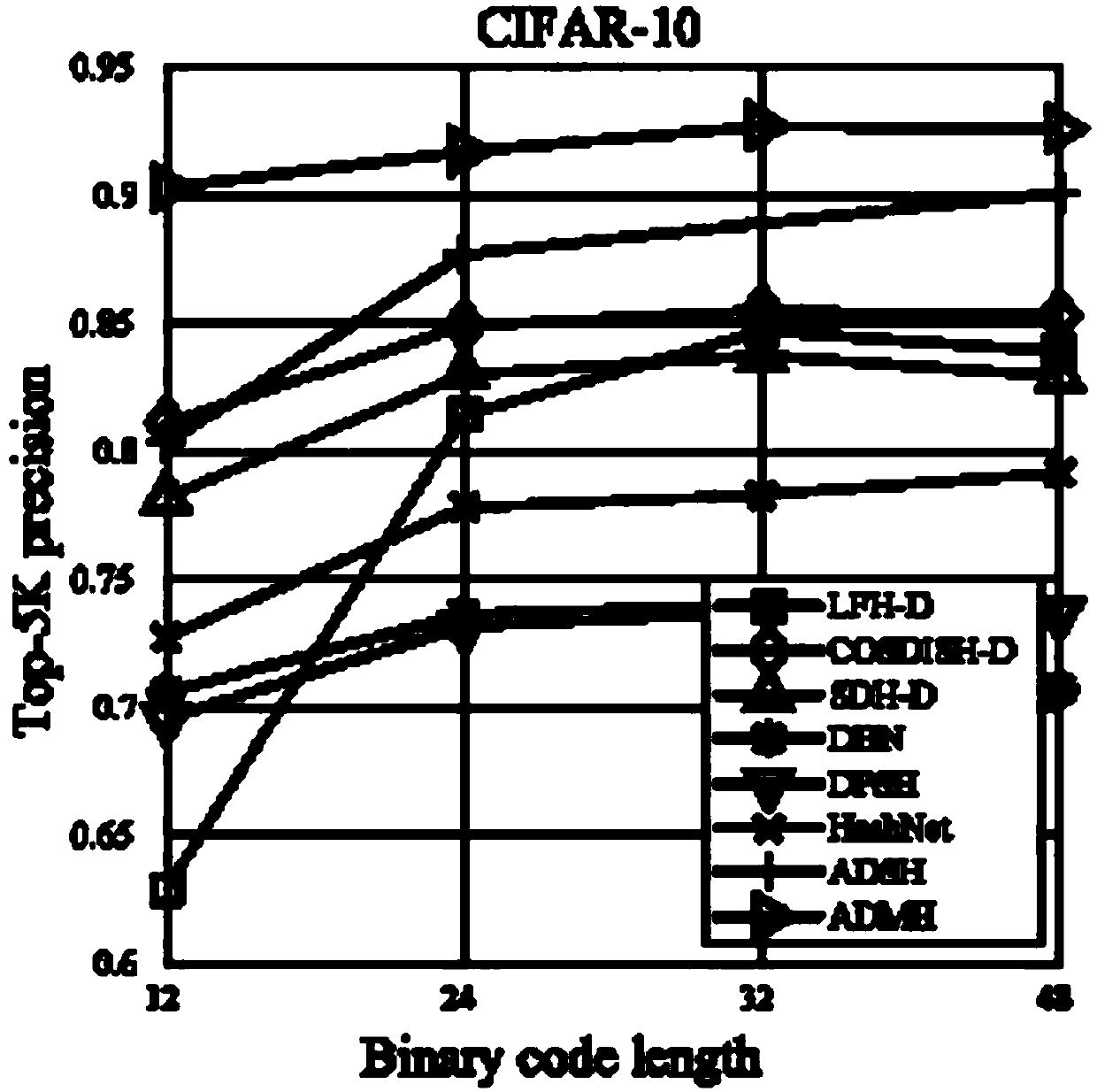
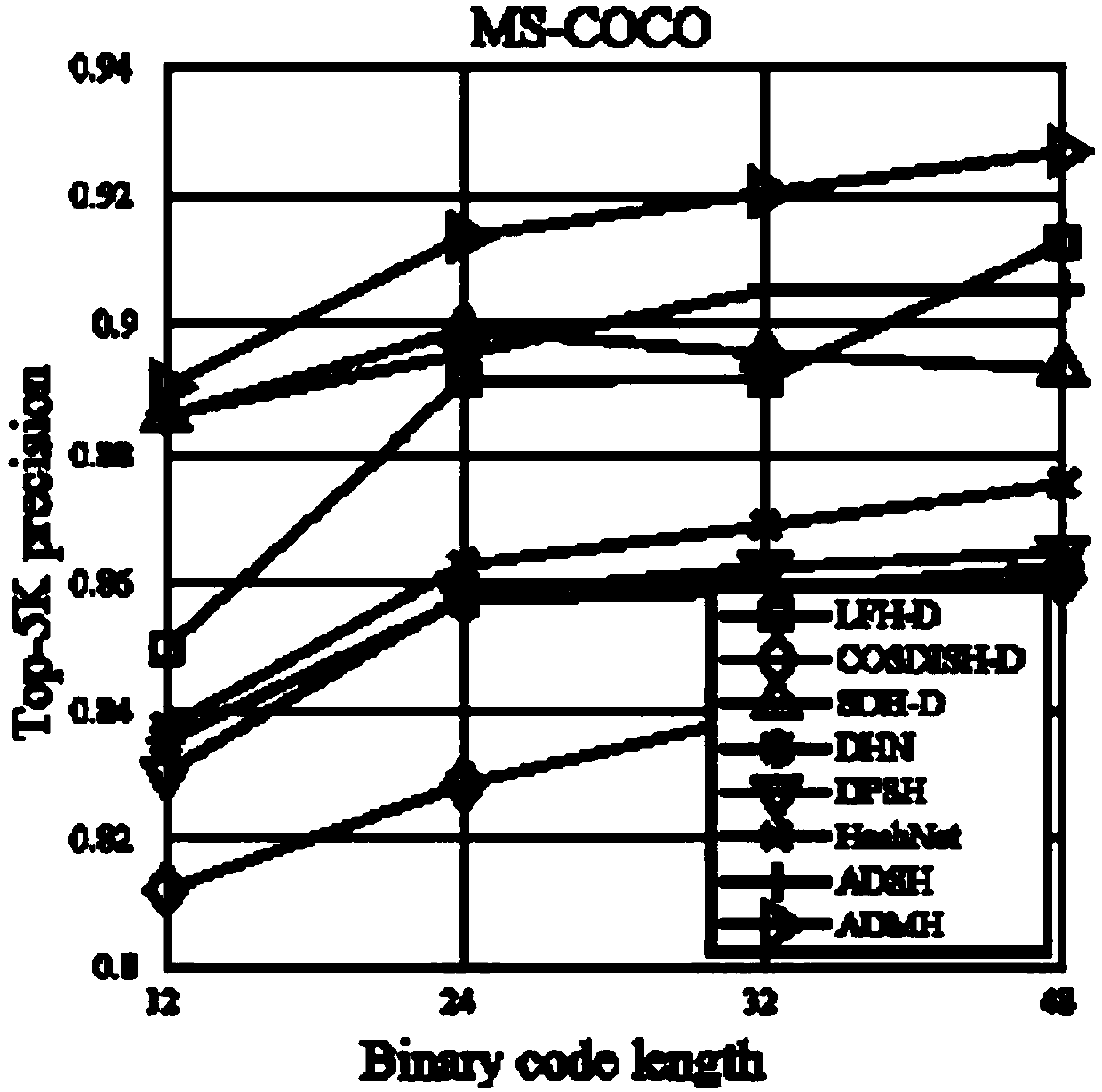
Fast Image Retrieval Method Based on Asymmetric Depth Discrete Hash, Retrieval Model and Model Construction Method
The invention provides a fast image retrieval method based on asymmetric depth discrete hash, a method for constructing a retrieval model and a retrieval model, wherein that scheme of the invention considers the compactness within a class and the separability between the hash codes of a query image and a database image, constructs a measure learning model, and simultaneously learn an approximate binary code of the query image and a discrete hash code of the database image through depth learning and discrete optimization; By constructing an asymmetric hash code learning framework, combining measure learning, depth learning and discrete optimization, a depth convolutional neural network is trained to learn discrete discriminant hash codes for database images and query images. So that the minimum Hamming distance between classes of hash codes is greater than the maximum Hamming distance within the class.
Owner:成都快眼科技有限公司
Discrete source mask optimization
ActiveUS20150378262A1Reduce computing costMinimize the possibilityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPupilComputer science
A method for improving a lithographic process for imaging a portion of a design layout onto a substrate using a lithographic projection apparatus, the method including: calculating a discrete pupil profile based on a desired pupil profile; selecting a discrete change to the discrete pupil profile; and applying the selected discrete change to the discrete pupil profile. The methods according to various embodiments disclosed herein may reduce the computational cost of discrete optimization from O(an) to O(n) wherein a is constant and n is the number of knobs that can generate discrete change in the pupil profile.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Fixed node discharge curve approximation and curved surface mesh generation optimizing technology
InactiveCN102831648AMaintain surface shapeAnti-aliased malformed mesh3D modellingEngineeringMesh optimization
The invention relates to a fixed node discharge curve approximation and curved surface mesh generation optimizing technology which obviously improves the quality of a curved surface mesh and can be applied to the boundary discrete optimization and visualization technology when generating a body-fitted mesh. The technology comprises the following steps of: (1.1) establishing a curved surface model by a computer according to the curved surface to be analyzed, and determining the curved surface boundary, shape, mesh number and mesh step; (1.2) projecting the curved surface to a plane, generating a two-dimensional body-fitted mesh according to the projection area, and projecting the body-fitted mesh to the original curved surface; (1.3) optimizing the boundary node of the curved surface mesh according to the length maximization rule; (1.4) optimizing the internal node of the curved surface mesh according to the area maximization rule; and (1.5) optimizing the mesh step according to the optimization algorithm defining the mesh step, and finally generating a high-quality curved surface mesh. The technology provided by the invention realizes the boundary discrete optimization in generation of a body-fitted mesh of a complicated boundary as well as the mesh optimization in the visualization technology.
Owner:邢学军
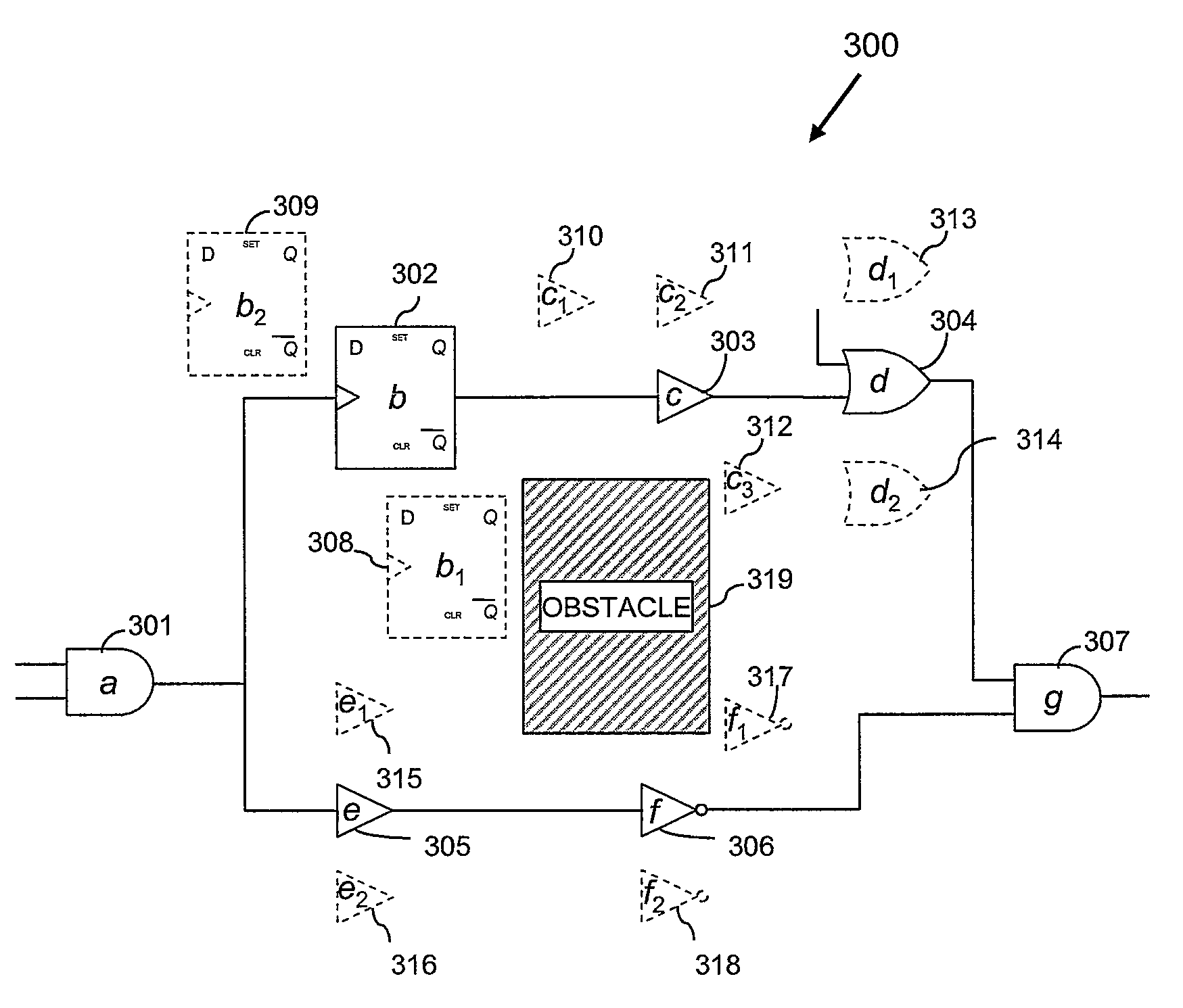
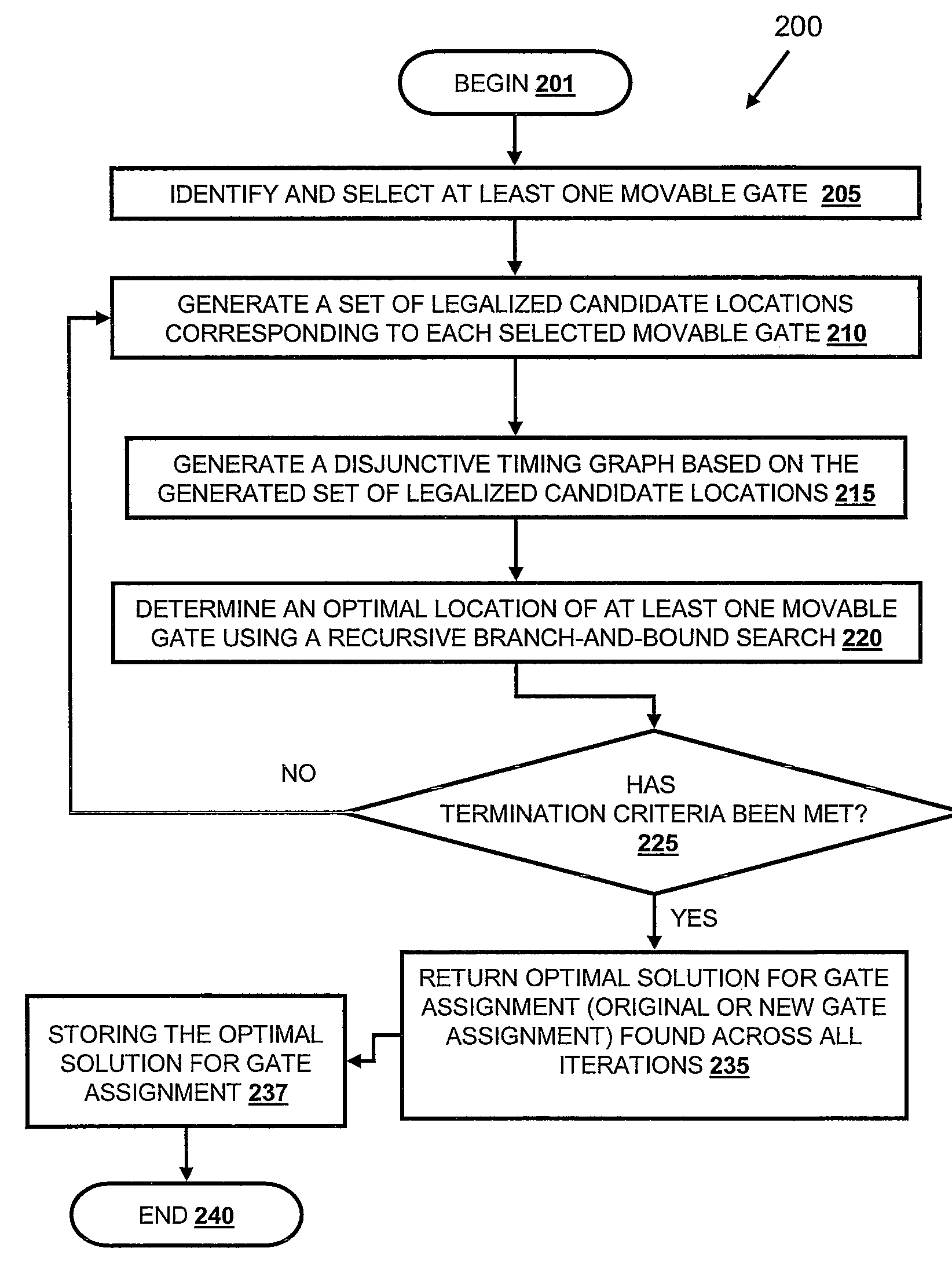
Incremental timing-driven, physical-synthesis using discrete optimization
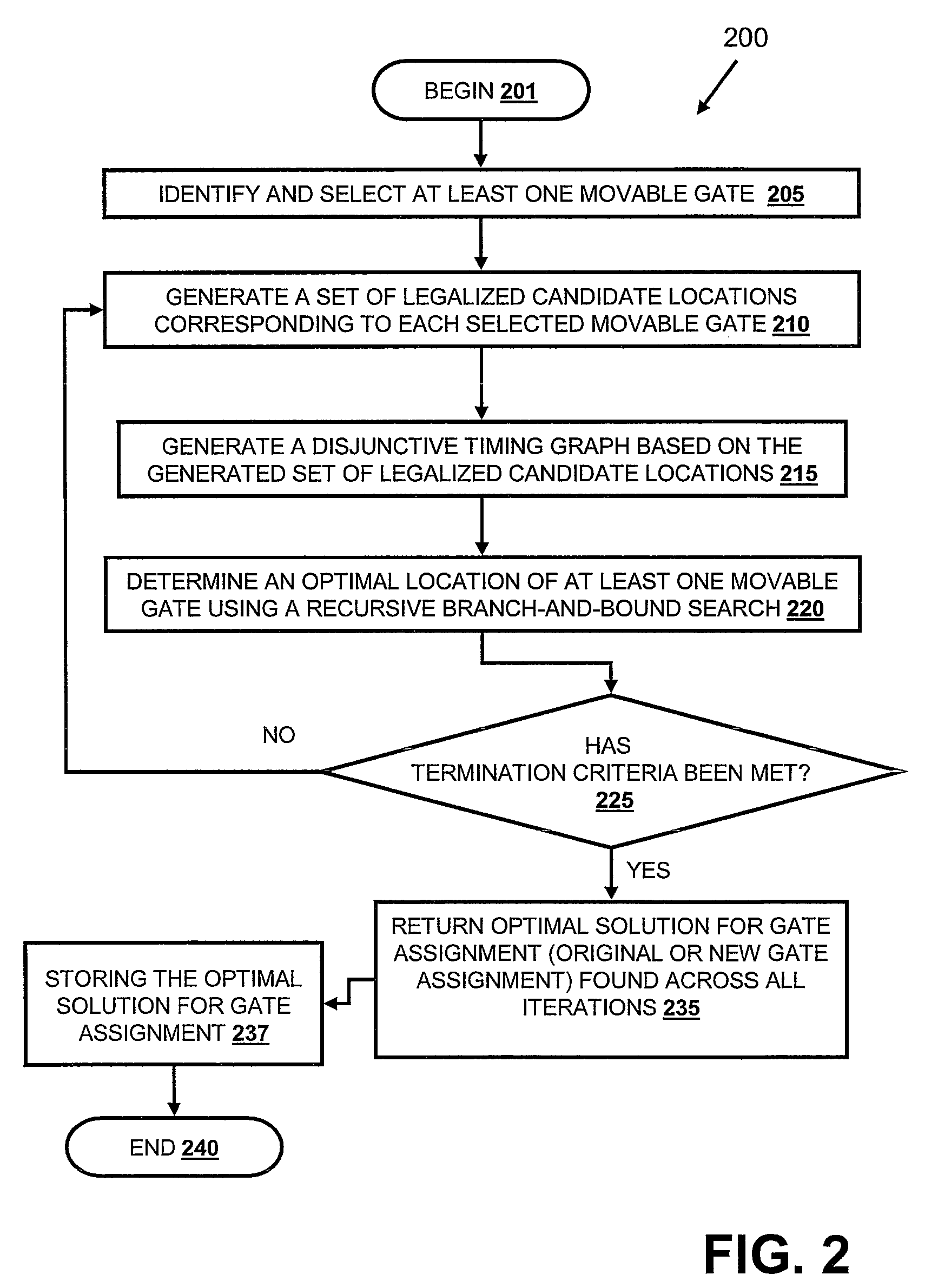
ActiveUS7707530B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designData processing systemSelection criterion
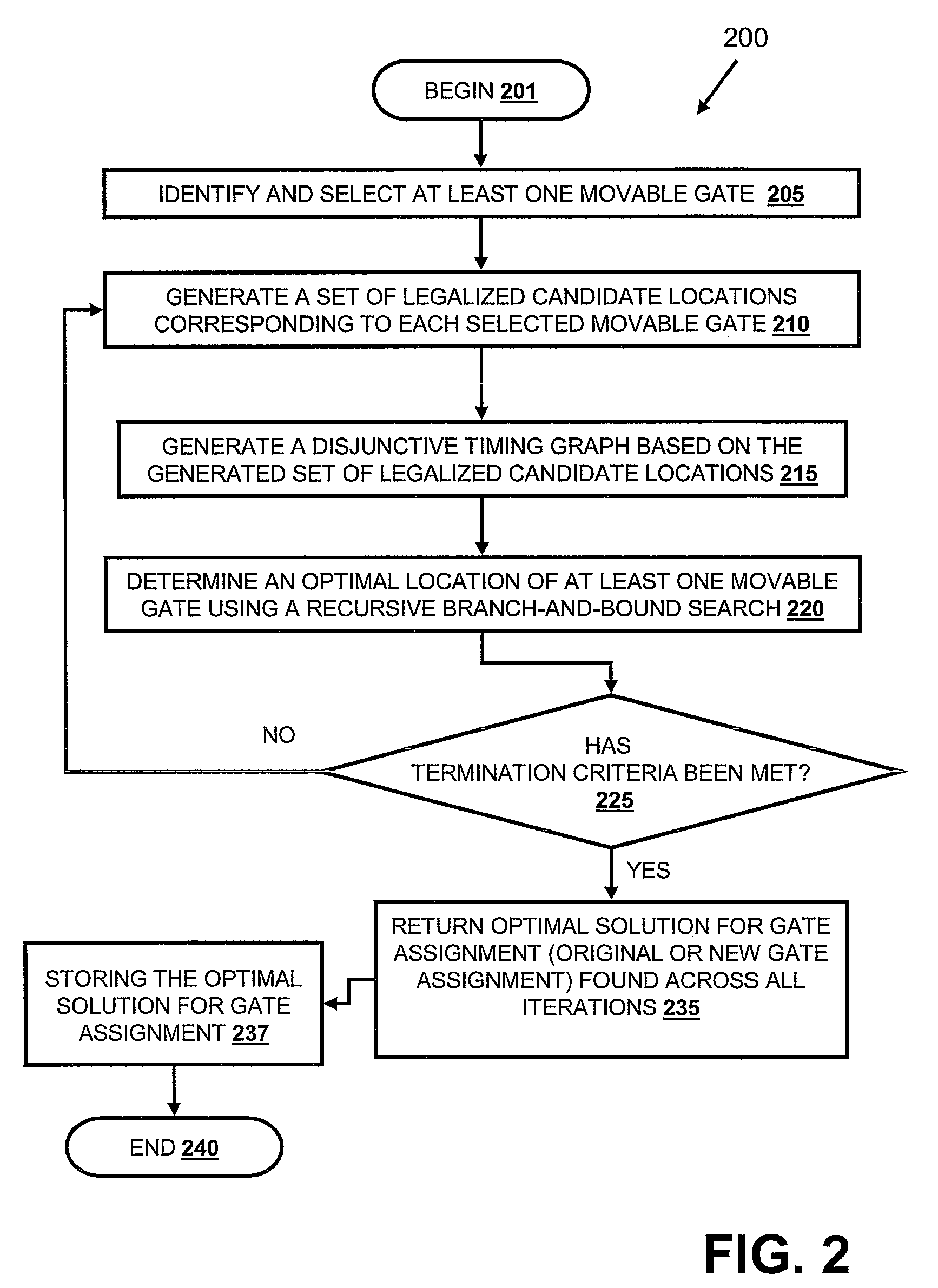
A method, data processing system and computer program product for optimizing the placement of logic gates of a subcircuit in a physical synthesis flow. A Path Smoothing utility identifies one or more movable gates based on at least one selection criteria. A set of legalized candidate locations corresponding to one or more identified movable gates is generated. A disjunctive timing graph based on the generated set of legalized candidate locations is then generated. An optimal location of one or more movable gate(s) is determined using a recursive branch-and-bound search and stored in the computing device.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Ship grid reconstruction method based on ring topology gauss dynamic particle swarm optimization algorithm
InactiveCN103345661AIncrease population diversityIncrease success rateForecastingBiological modelsReconstruction methodPower grid
The invention discloses a ship grid reconstruction method based on a ring topology gauss dynamic particle swarm optimization algorithm and belongs to the field of swam intelligent computing. The ship grid reconstruction problem essentially belongs to multi-target multi-variable dispersing, optimization and combination problems. The defects that in the prior art, computing time is long and an unsatisfied solution can be easily searched exist when the ship grid reconstruction problem is solved, and special requirements of ships for security and instantaneity are difficult to meet. The ring topology is introduced into a dispersed GDPS optimization algorithm, information communication among particles is made to be relatively slow, the influence on other particles is small when a few of particles drop in a local extreme value, and therefore searching for the globally optimal solution is more facilitated. Meanwhile, the ring topology is relatively simple, and the computing time can be obviously shortened. According to the method, population diversity can be kept in the whole searching process, and the globally optimal effect can be more rapidly and better obtained.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
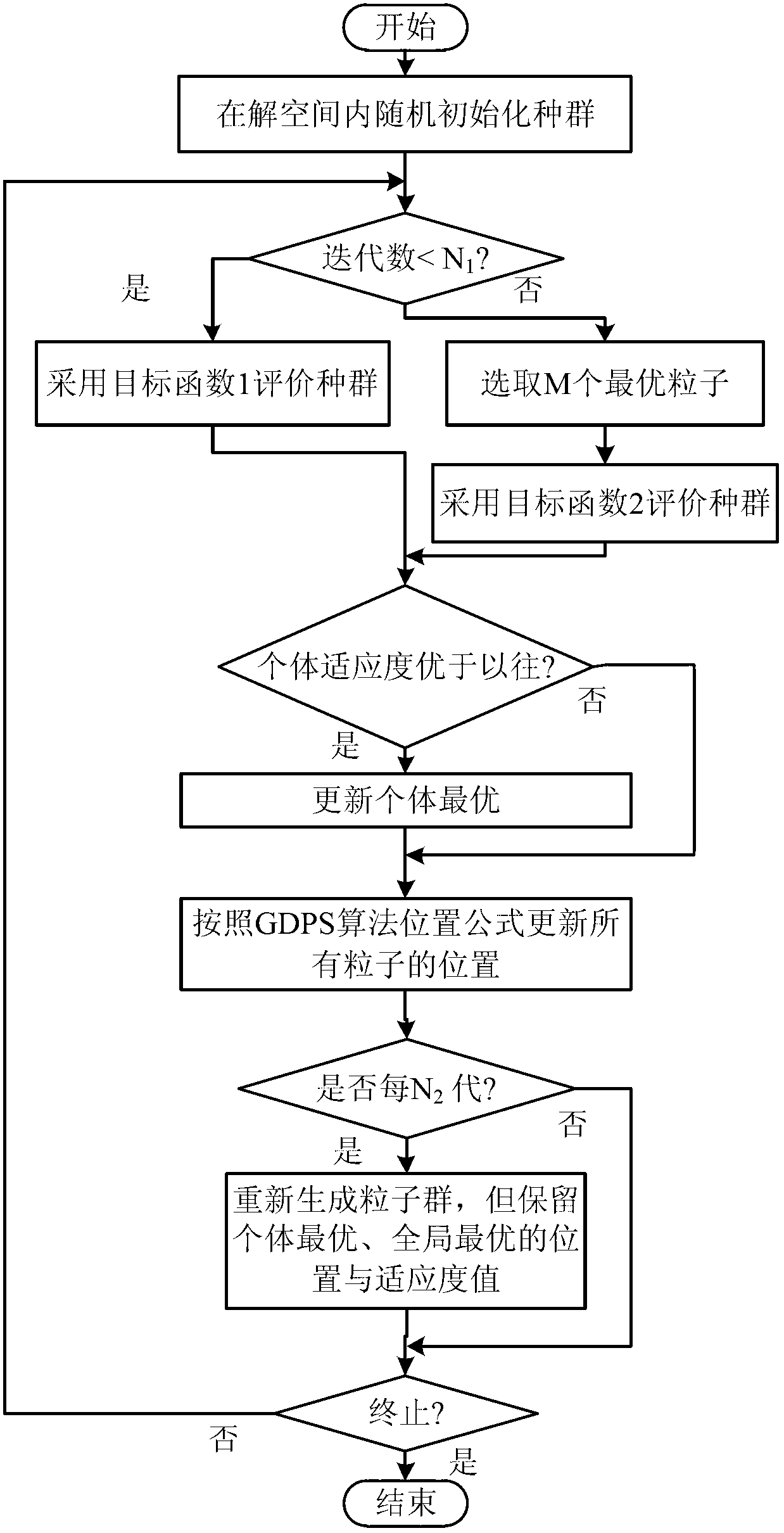
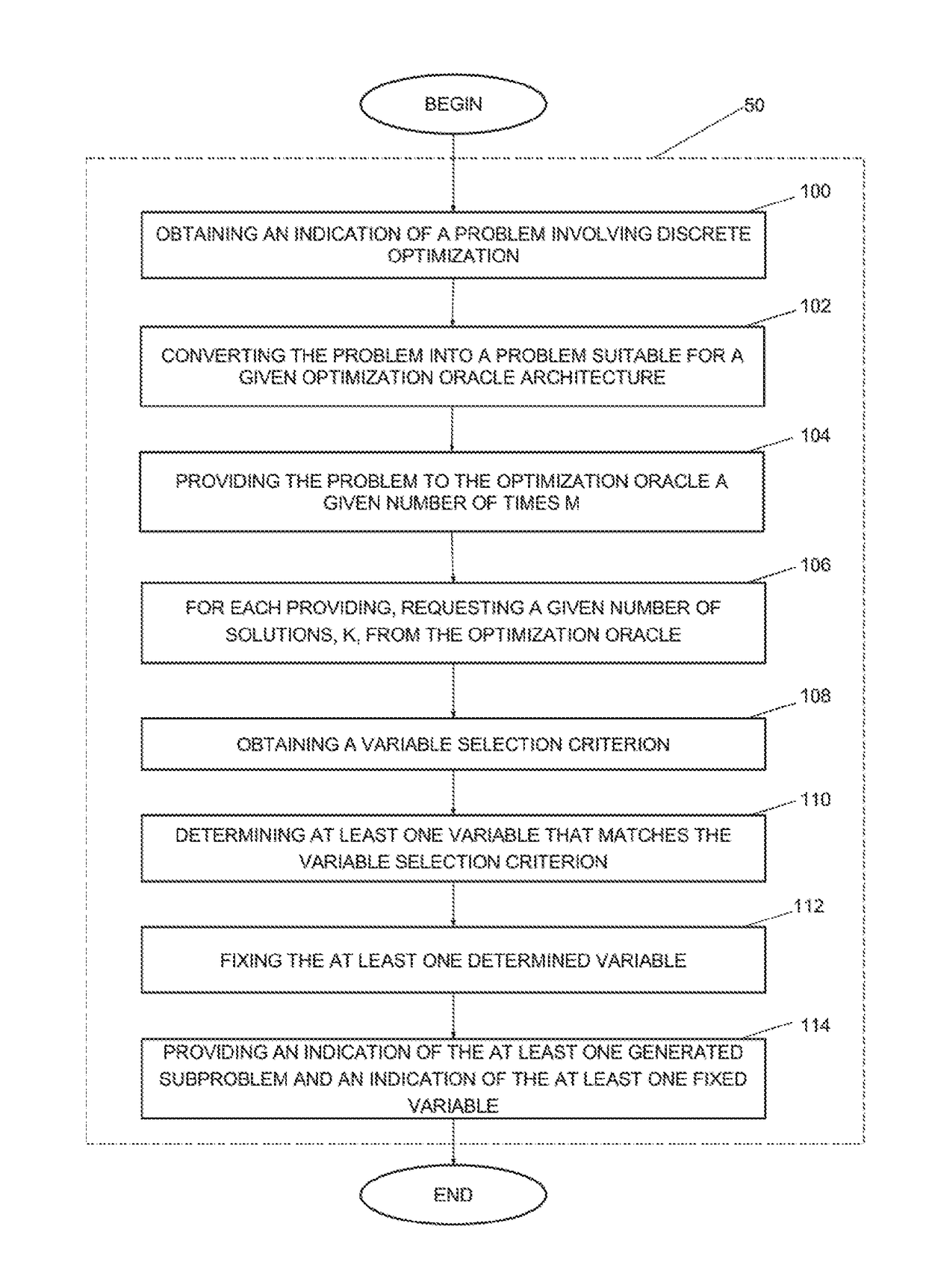
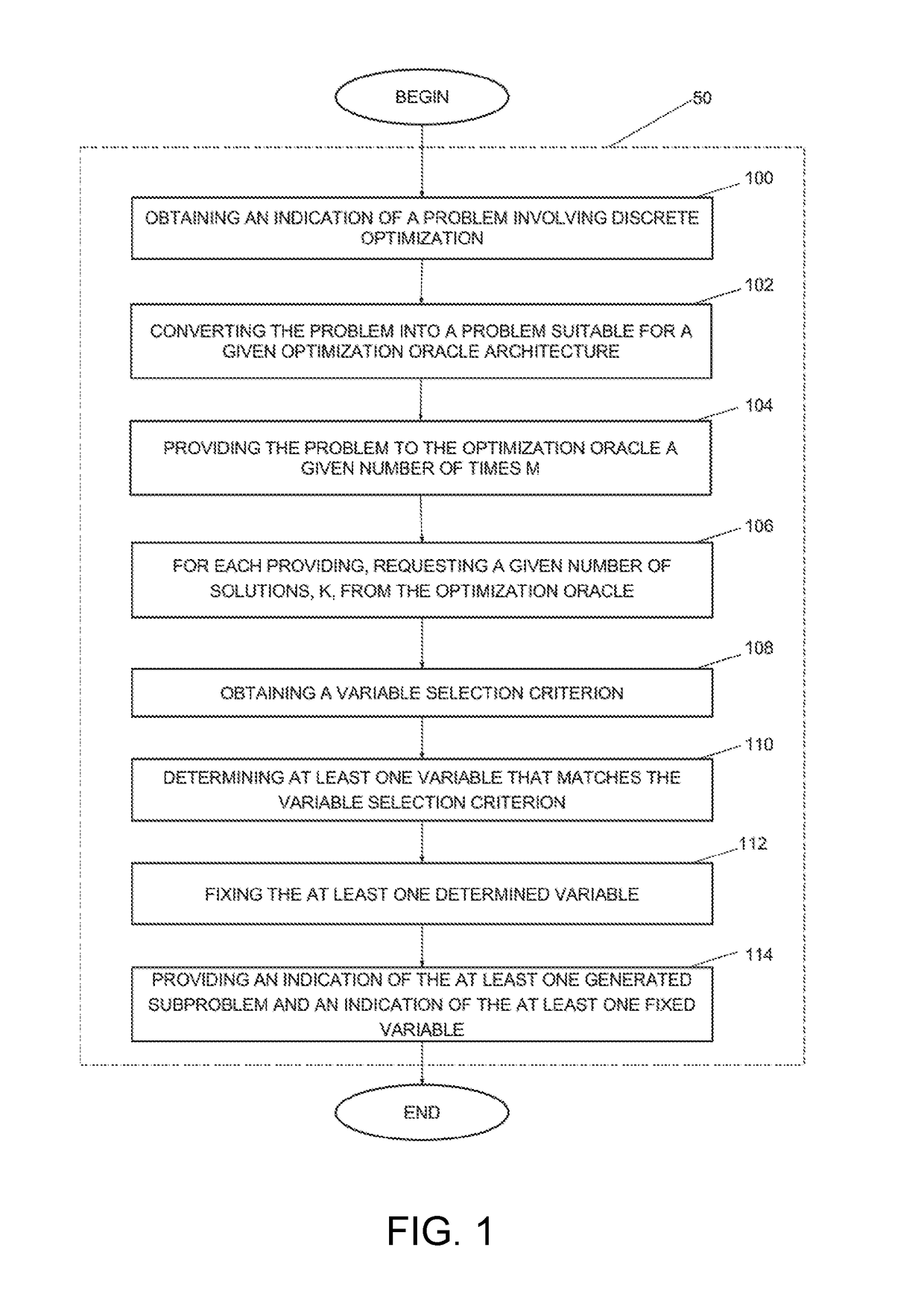
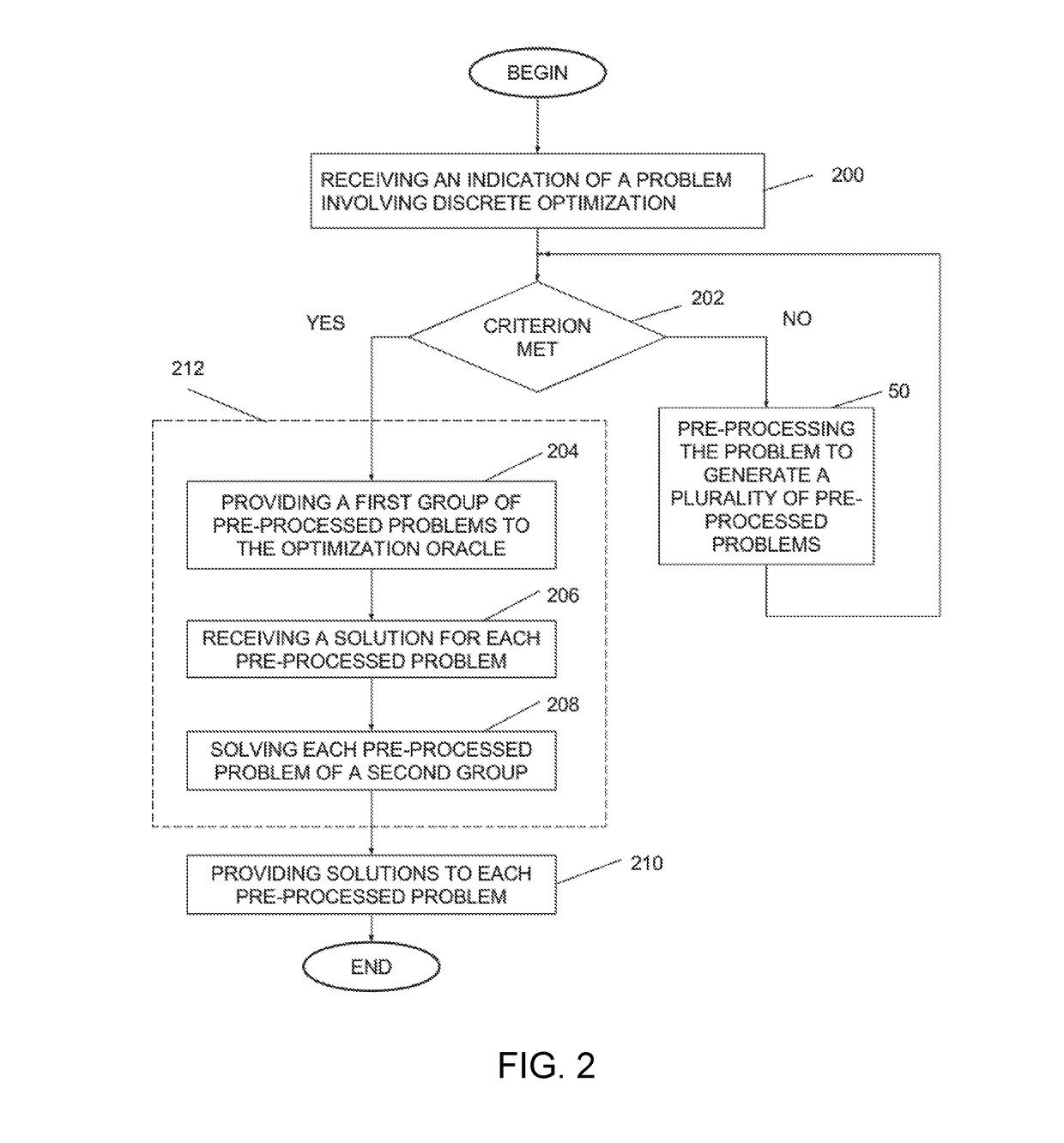
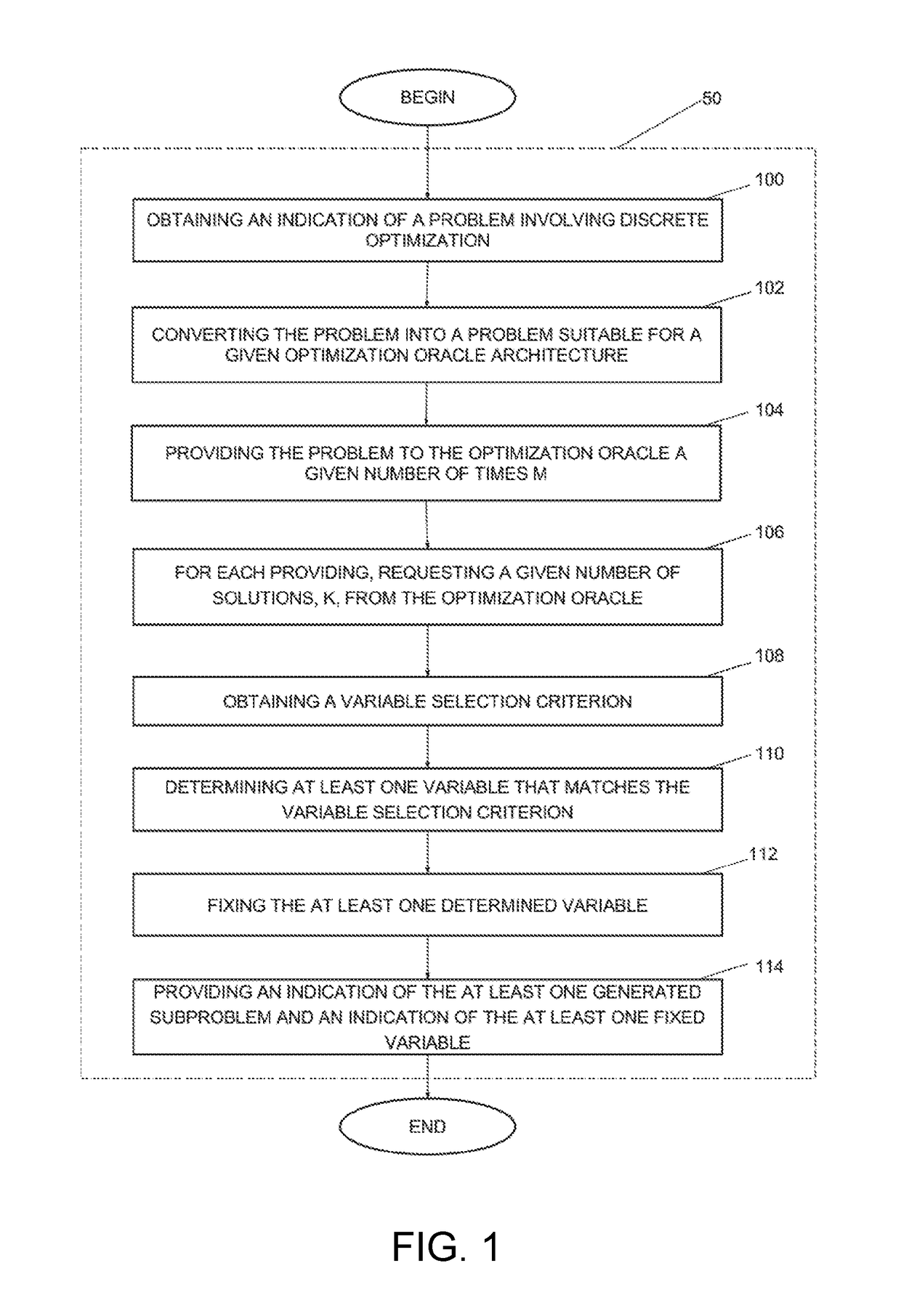
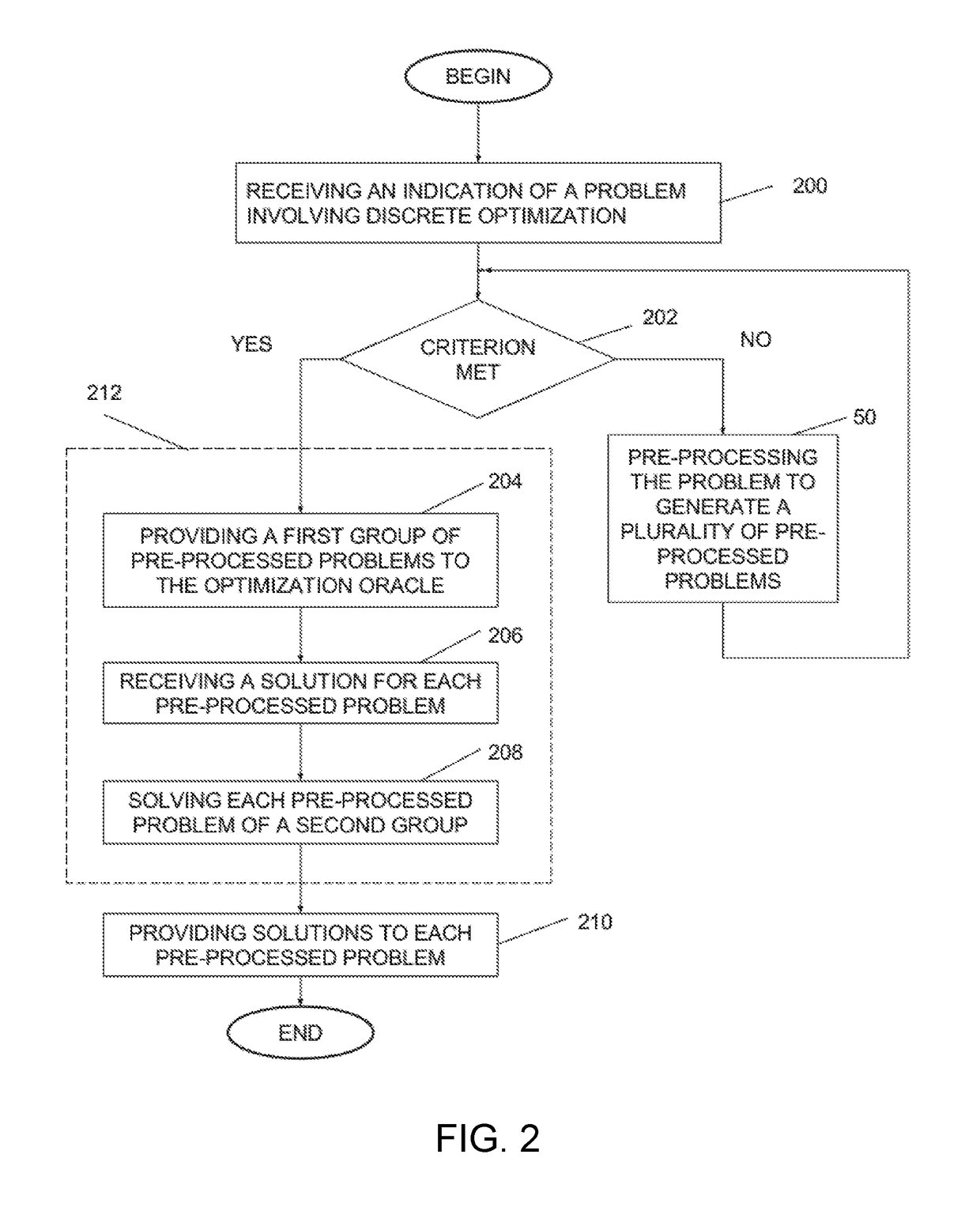
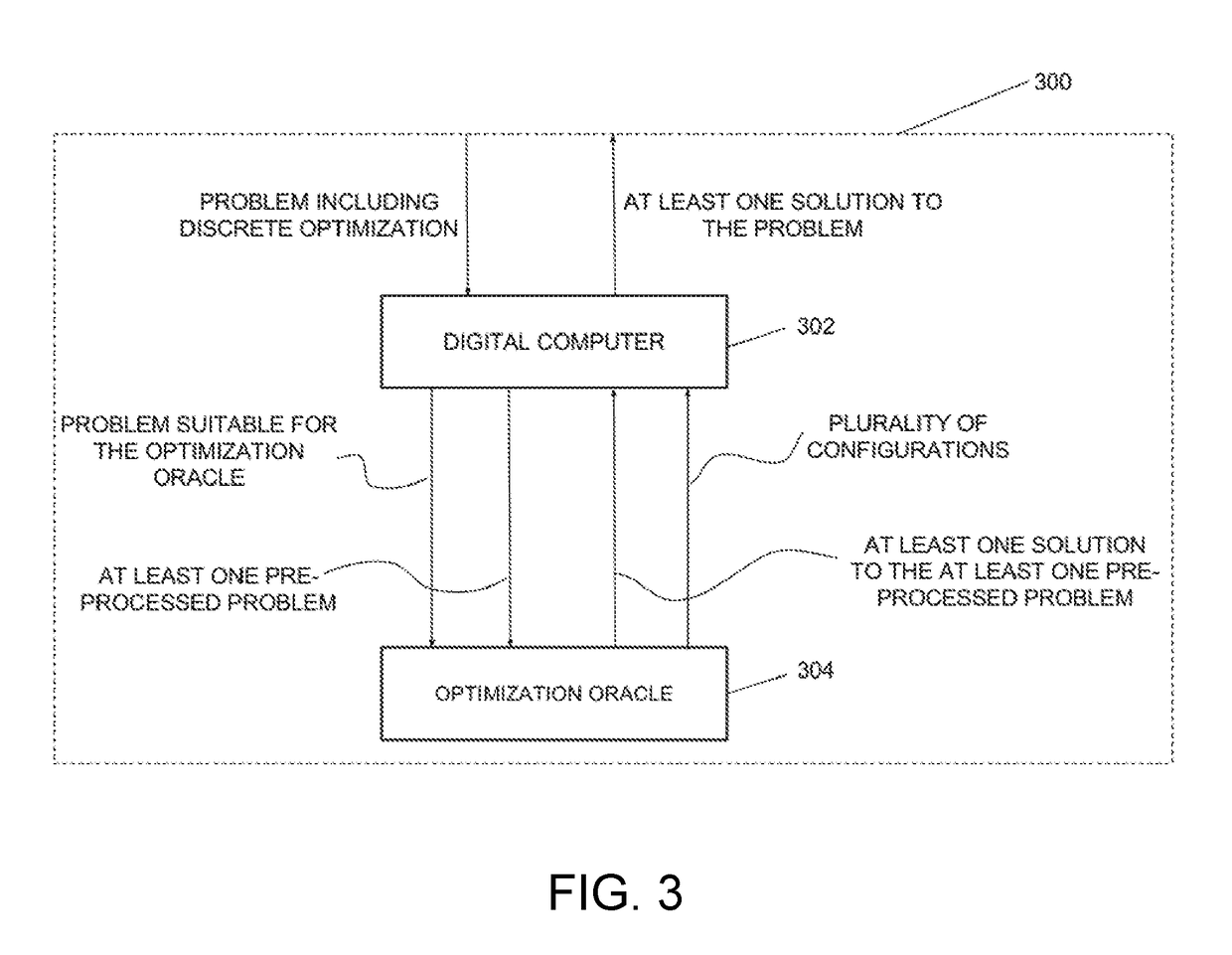
Method and system for decomposing a problem involving discrete optimization into a plurality of smaller subproblems and use of the method for solving the problem
ActiveUS20170255592A1Small sizeReduce decreaseQuantum computersKnowledge representationTheoretical computer scienceSelection criterion
A method is disclosed for preprocessing a problem involving discrete optimization over a plurality of variables, the method comprising obtaining an indication of a problem involving discrete optimization; converting the problem involving discrete optimization into a problem suitable for a given optimization oracle architecture of an optimization oracle; providing a given number of times M the problem suitable for the given optimization oracle architecture to the optimization oracle; for each providing of the problem, performing a given number K of calls to the optimization oracle; each call generating a given configuration; obtaining a variable selection criterion, the variable selection criterion for determining at least one variable of the plurality of generated configurations that can be fixed; determining at least one variable that matches the variable selection criterion and a corresponding value for each variable; fixing the at least one determined variable at the corresponding value in the problem involving discrete optimization to thereby preprocess the problem to generate at least one subproblem and providing an indication of the at least one generated subproblem and an indication of the at least one fixed variable.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method for Incremental, Timing-Driven, Physical-Synthesis Using Discrete Optimization
ActiveUS20090132981A1Easy to placeAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designData processing systemSelection criterion
A method, data processing system and computer program product for optimizing the placement of logic gates of a subcircuit in a physical synthesis flow. A Path Smoothing utility identifies one or more movable gates based on at least one selection criteria. A set of legalized candidate locations corresponding to one or more identified movable gates is generated. A disjunctive timing graph based on the generated set of legalized candidate locations is then generated. An optimal location of one or more movable gate(s) is determined using a recursive branch-and-bound search and stored in the computing device.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Aggregation node location method based on improved discrete difference algorithm
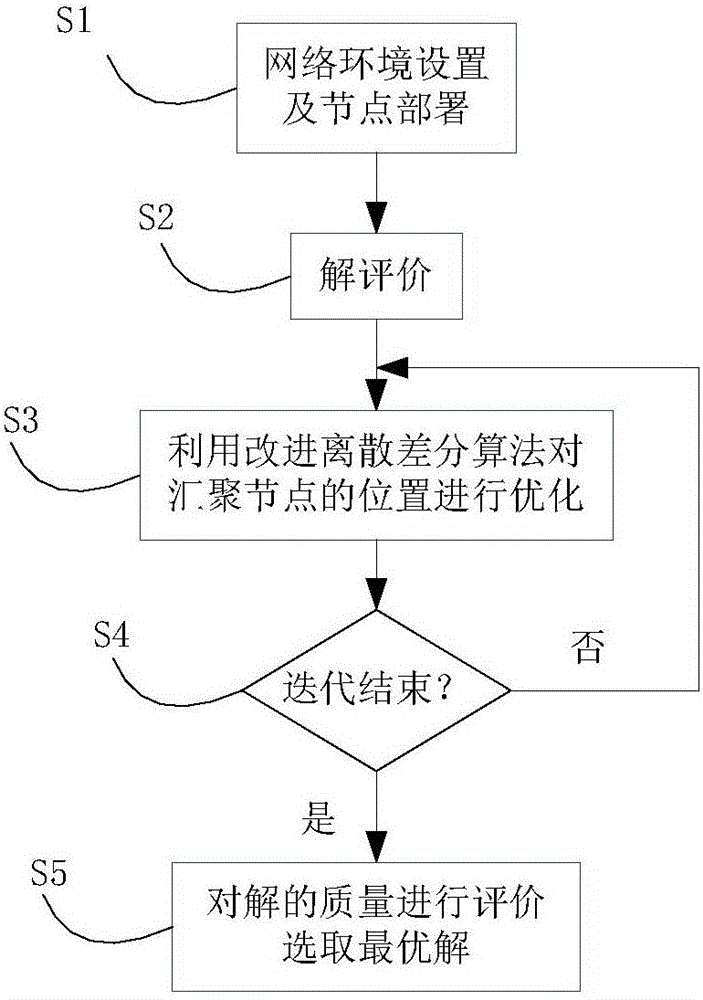
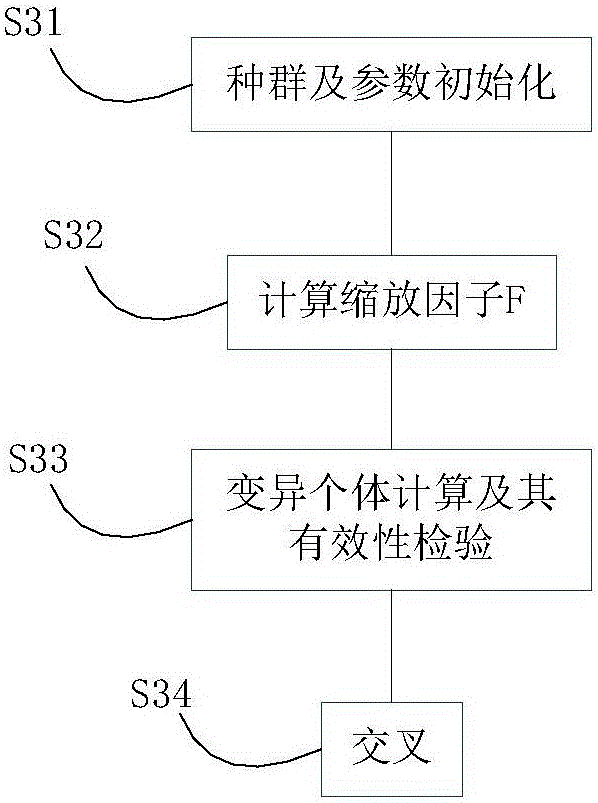
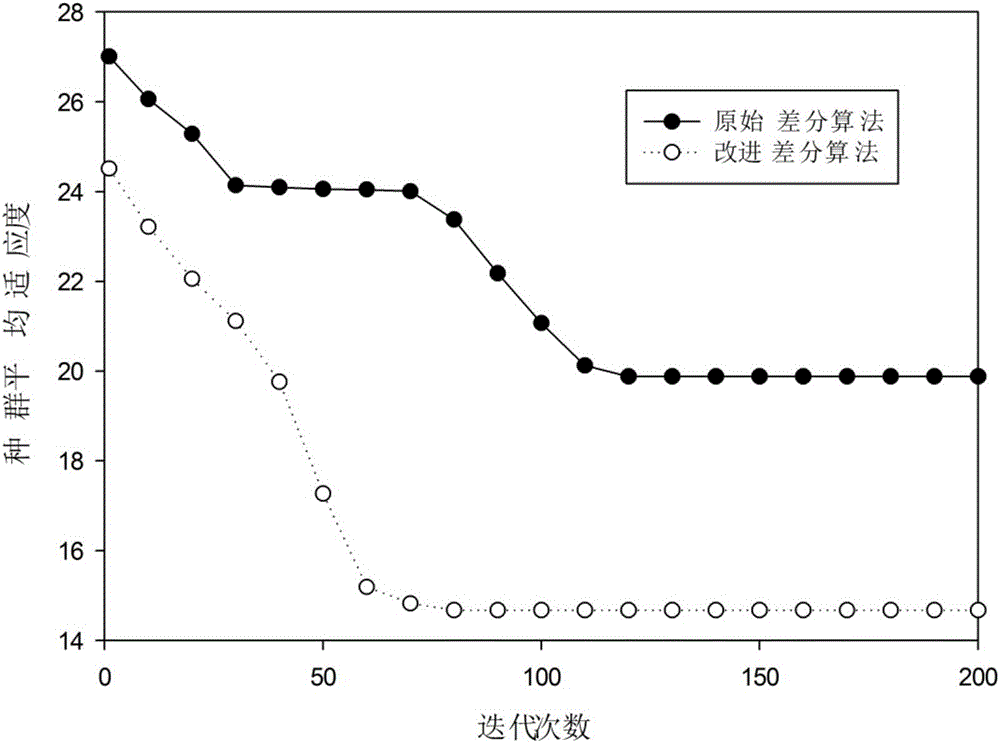
ActiveCN105959912AImprove reliabilityImprove service qualityNetwork topologiesLocation information based serviceLocal optimumDifferential algorithm
The present invention provides an aggregation node location method based on an improved discrete difference algorithm. The influence of the isomerism of nodes and the reliability of the routing path in real engineering on aggregation node location is fully considered, an adaptive zoom factor is introduced into the improved discrete difference algorithm to allow the algorithm to maintain high global search capability at the initial stage and maintain high global local search capability at the later period; an adaptive variation mechanism is introduced, an appropriate variation strategy is selected according the trend of the population evolution in the evolution process to maintain the diversity of the population and avoid falling into the local optimum so as to improve the global optimization capability of the discrete difference algorithm, rapidly converging the algorithm and solve the technical problems of the precocity convergence and falling into the local minimum of the original difference algorithm at the discrete variable optimization, and therefore the optimized aggregation node location disposition is obtained, the data communication reliability is enhanced, and the network service quality is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
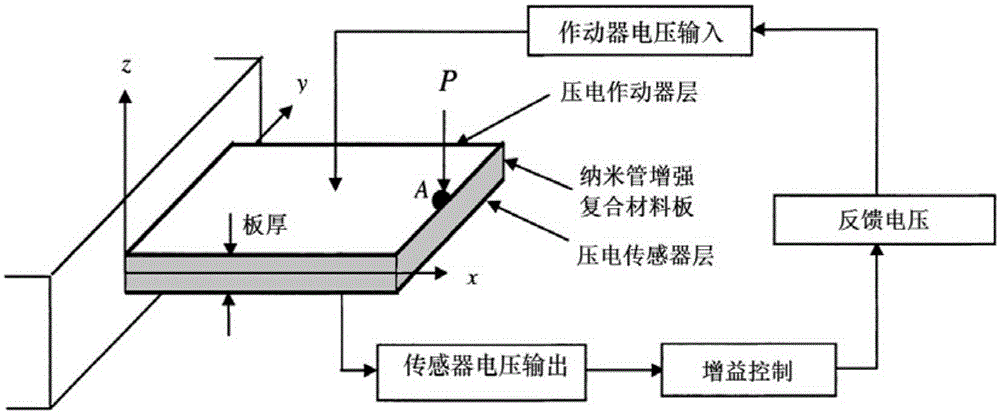
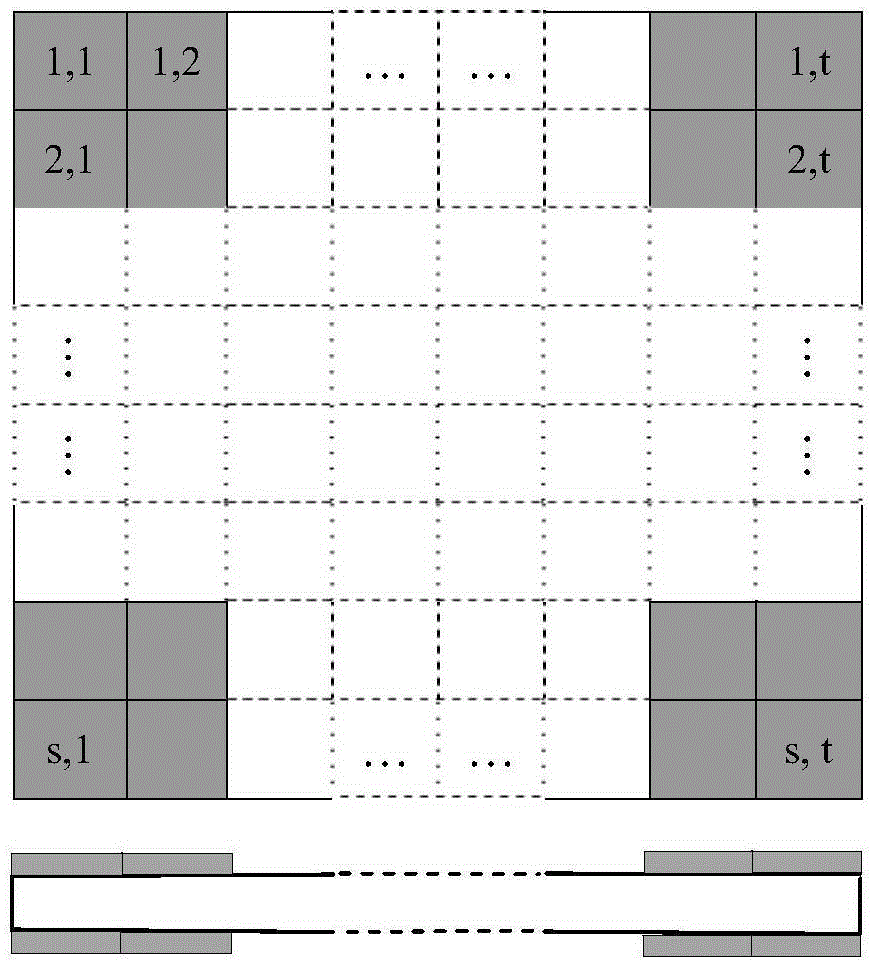
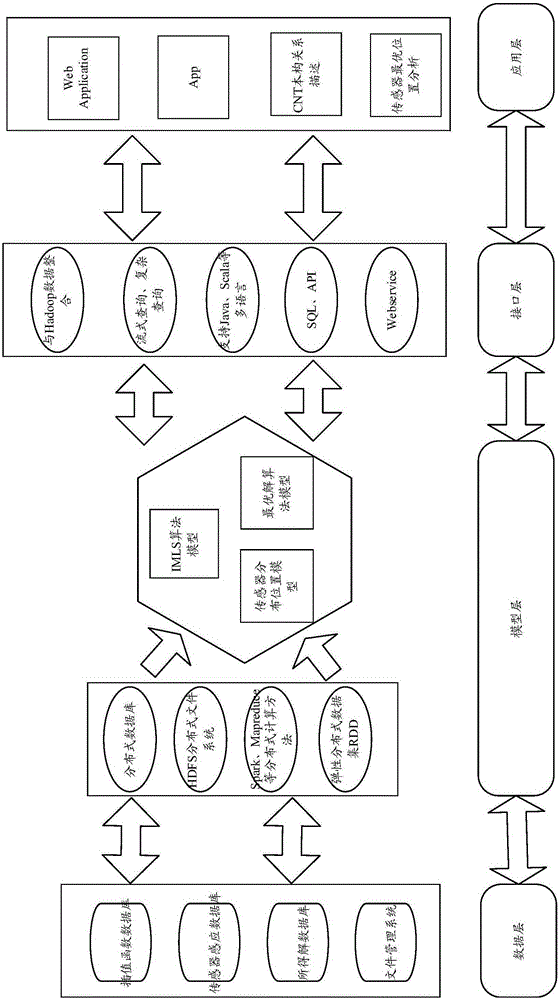
FG-CNT reinforced composite plate vibration control method based on Spark in ocean engineering
ActiveCN105184016AImprove bindingBroaden applicationSpecial data processing applicationsVibration controlEngineering
The invention relates to an FG-CNT reinforced composite plate vibration control method based on Spark in ocean engineering. The method comprises the steps that a latest meshless method IMLS-Ritz is adopted, and a shape function which is good in smoothness and continuous in derivative is fit through values of several unrelated nodes; meanwhile, constitutive relation description of a functionally grated CNT reinforced composite plate shell is improved, and therefore the problem that how to distribute sensors or actuators to the suitable positions of CNTs to reach the optimal position where numerical analysis can be performed on structural strain is solved; the optimal solution of the collocating positions of the actuators is searched through a discrete optimization algorithm, and a cloud computing platform based on the Spark is built for massive computing data. By means of the FG-CNT reinforced composite plate vibration control method based on the Spark in ocean engineering, the problem that in a finite element method, the solution is not convergent or errors are large is solved, the data storing quantity and computing quantity are significantly improved, the computing time is shortened, and the analysis efficiency is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
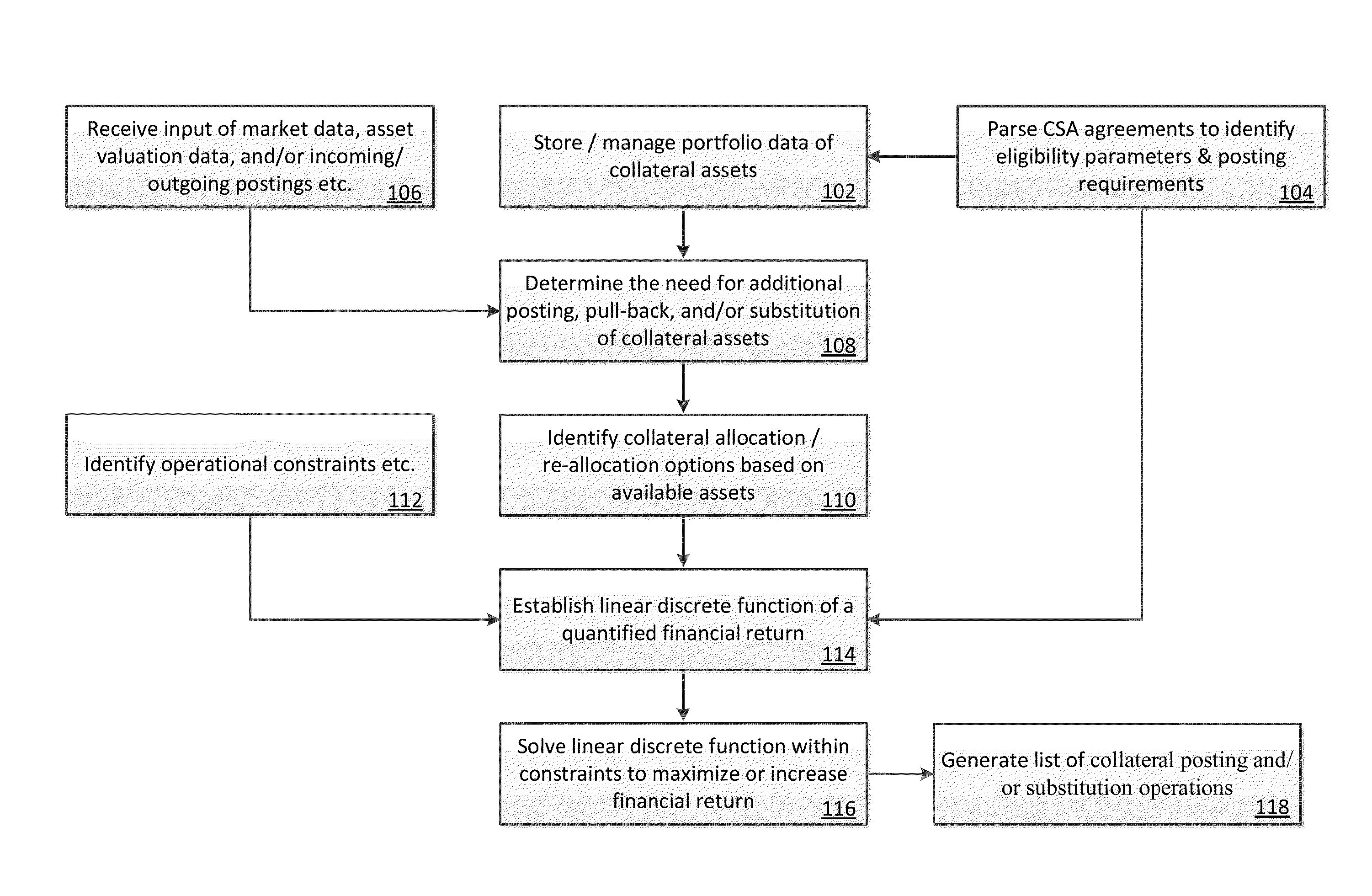
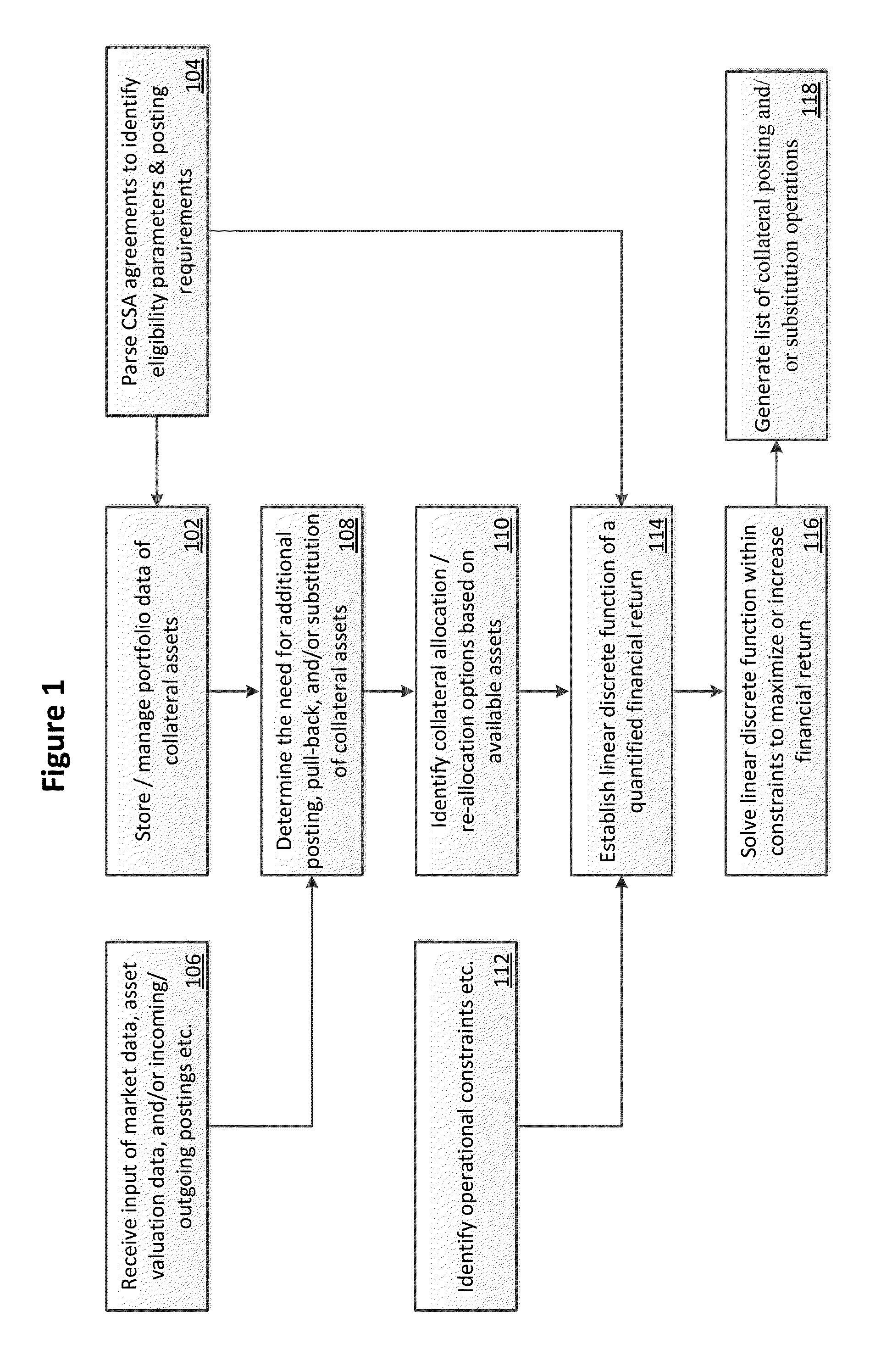
Systems and methods for collateral management
InactiveUS20150287140A1Automate the determinationEfficient and effectiveFinanceOperational costsCollateral management
Computer-based systems and methods have been developed wherein at least one embodiment is capable of automatically determining the optimal collateral holdings in compliance with Credit Support Annex (CSA) agreements, and dynamically reallocating the collateral holdings as time progresses, in order to maintain the optimality of the portfolio of holdings through Customer Service Representatives' (CSR) operations. The optimal allocation may be defined as one that minimizes the operational cost of satisfying CSA agreements via collateral postings. Data may be stored concerning attributes of the components of the holdings of the counterparties, available inventory of assets (securities and cash), current market factors (e.g., interest rates, LIBOR), which are constantly updated. A discrete optimization routine may be used to generate feasible global optimal solutions to allocate and / or reallocate the collateral postings satisfying the operational constraints.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Image enhancement through discrete patch optimization
ActiveUS8571349B1Enhance the imageImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging processing
An image processing system enhances the resolution of an original image using higher-resolution image data from other images. The image processing system defines a plurality of overlapping partitions for the original image, each partition defining a set of non-overlapping site patches. During an optimization phase, the system identifies, for site patches of the original images, label patches within related images that are of most relevance. During a rendering phase independent of the optimization phase, an output image with enhanced resolution is synthesized by substituting, for site patches of the original image, the identified relevant label patches from the related images.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
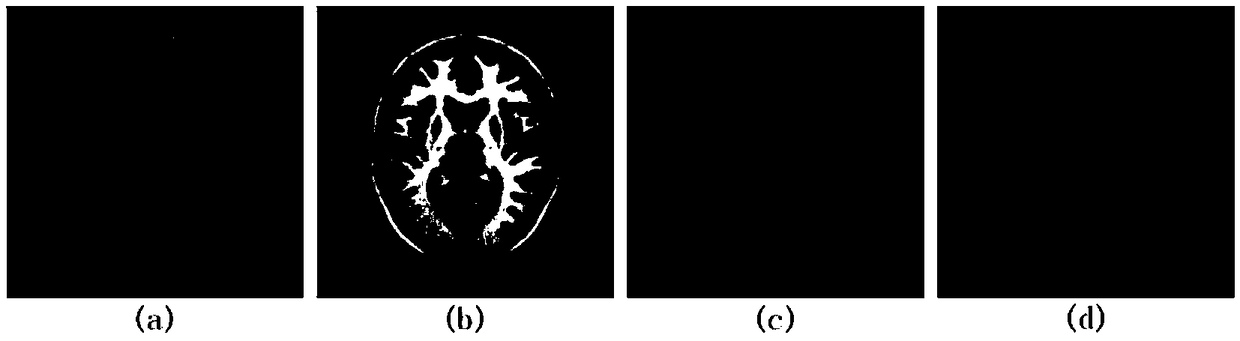
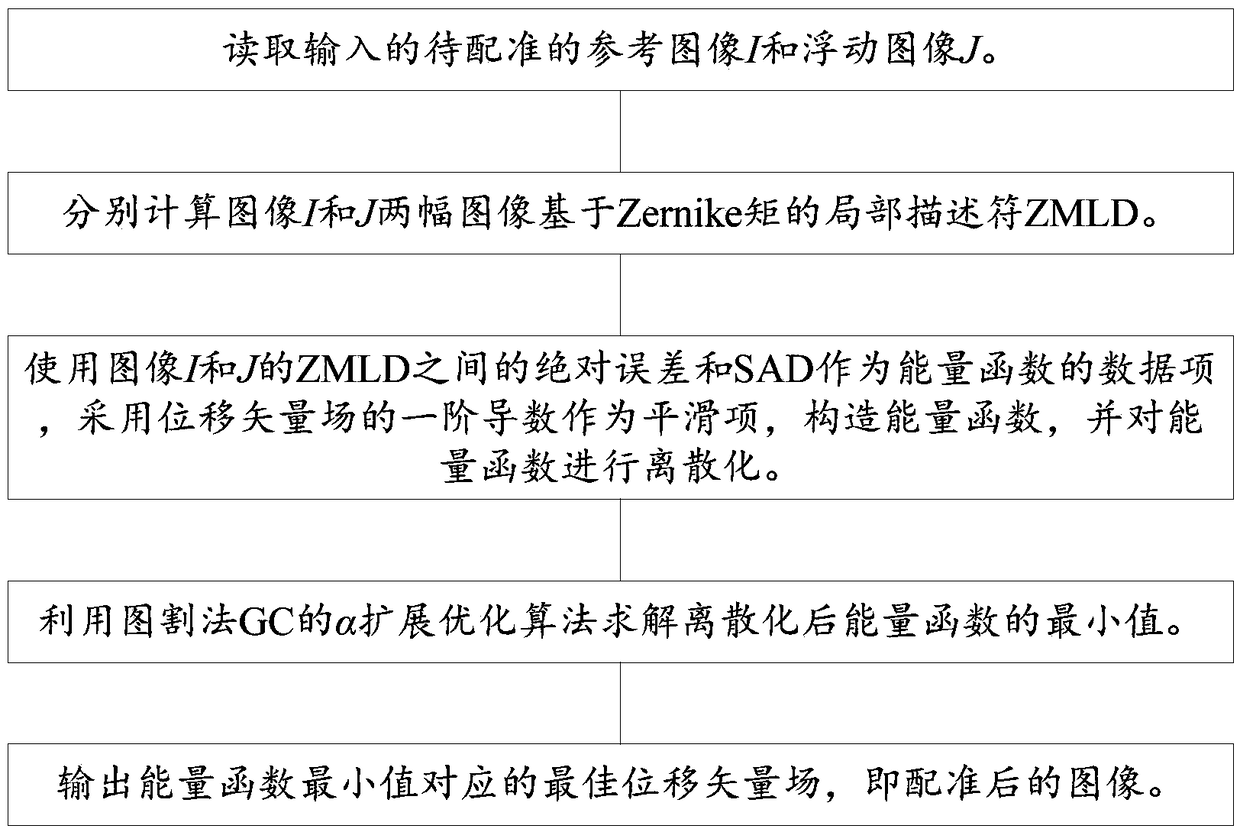
Non-rigid multi-modality medical image registration method based on discrete optimization of ZMLD (Zernike Moments based Local Descriptor) and GC (Graph Cuts)
InactiveCN108711168AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisEnergy functionalDiscretization
The invention discloses a non-rigid multi-modality medical image registration method based on discrete optimization of ZMLDs (Zernike Moments based Local Descriptor) and GCs (Graph Cuts) and relates to the technical field of medical image processing. The method mainly comprises the steps of respectively calculating the ZMLD of a reference image I and a floating Image J, constructing an energy function by using an absolute error between the ZMLDs of the images I and J and an SAD (Sum of absolute differences) as data items of the energy function and a first-order derivative of a displacement vector field as a smooth item; solving a minimum value of the discretized energy function by using an alpha expansion optimization algorithm of the GC, and outputting an optimal displacement vector fieldcorresponding to the minimum value of the energy function, that is, a registrated image. According to the non-rigid multi-modality medical image registration method based on the discrete optimizationof the ZMLD and the GC, the problems that intensity and edge and textural features of an image cannot be accurately and simultaneously extracted, and the continuous optimization calculation is relatively high in complexity and is prone to local optimum in an existing method when noise and intensity distortion of the image occurs in a non-rigid image are solved. Experiments show that the precisionand efficiency of the non-rigid multi-modality medical image registration are improved by using the method of the invention.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
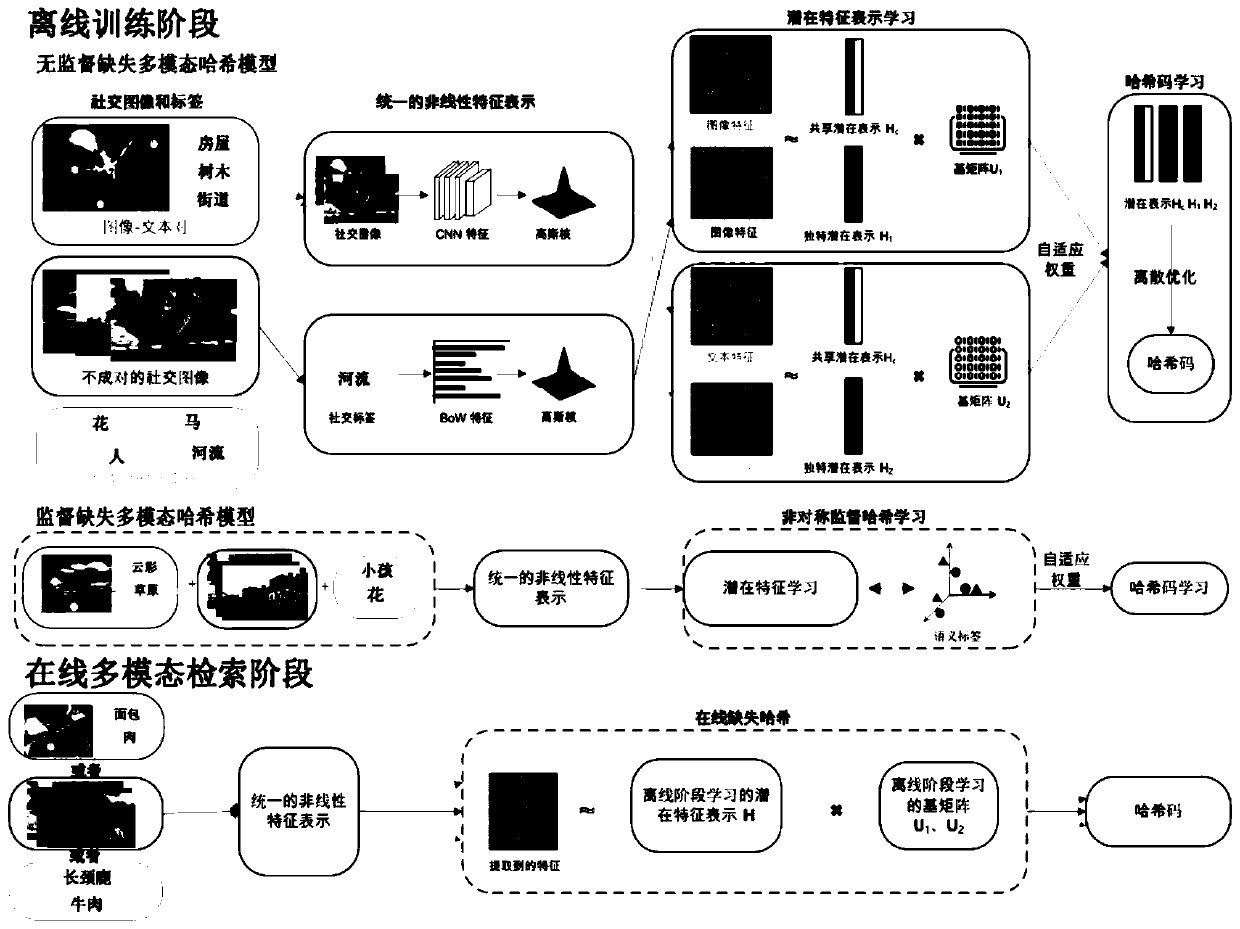
Social image retrieval method and system based on missing multi-modal hash
ActiveCN111090765ASolve the problem of inaccurate retrievalReduce quantization errorMetadata still image retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsMissing dataPaired Data
The invention provides a social image retrieval method and system based on missing multi-modal hash. A shared potential representation is learned for completely paired data; a unique potential representation is learned for missing data; the relations between different modes of images and labelsare explored, an online hash retrieval mode suitable for completely paired data and missing data at the same time is constructed, hash codes are directly solved by designing a new discrete optimization strategy, the quantization error of a relaxation strategy in the prior art is effectively reduced, andthe retrieval performance is improved; on the basis of an unsupervised missing multi-modal hash method, the invention is expanded to a supervised learning mode, an asymmetric hash learning method is used for guiding a projection learning process, the identification capability of hash codes is improved, the binary hash codes are directly solved, the speed is high, the operation is simple, and the learning efficiency is ensured.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHENGZHONG COMP NETWORK TECH CONSULTING
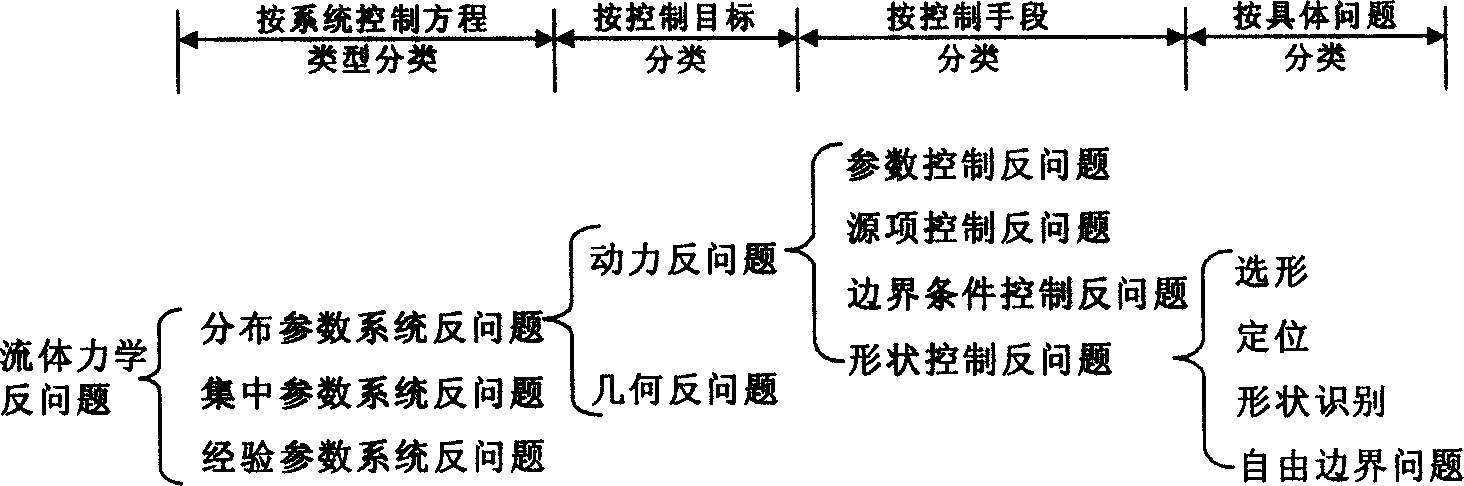
Study method of inverse problem on hydraulics for water resources and hydroelectric engineering
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
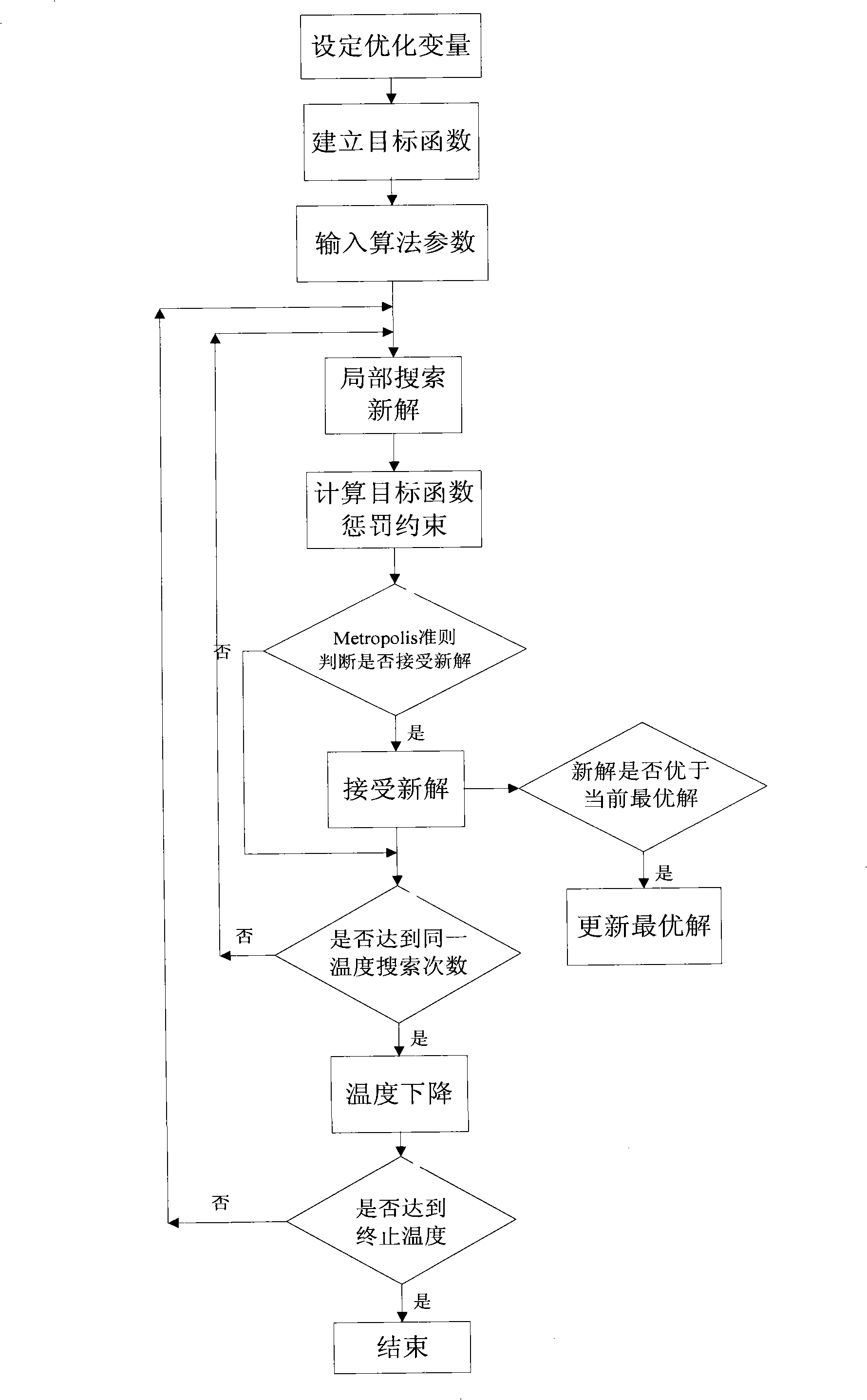
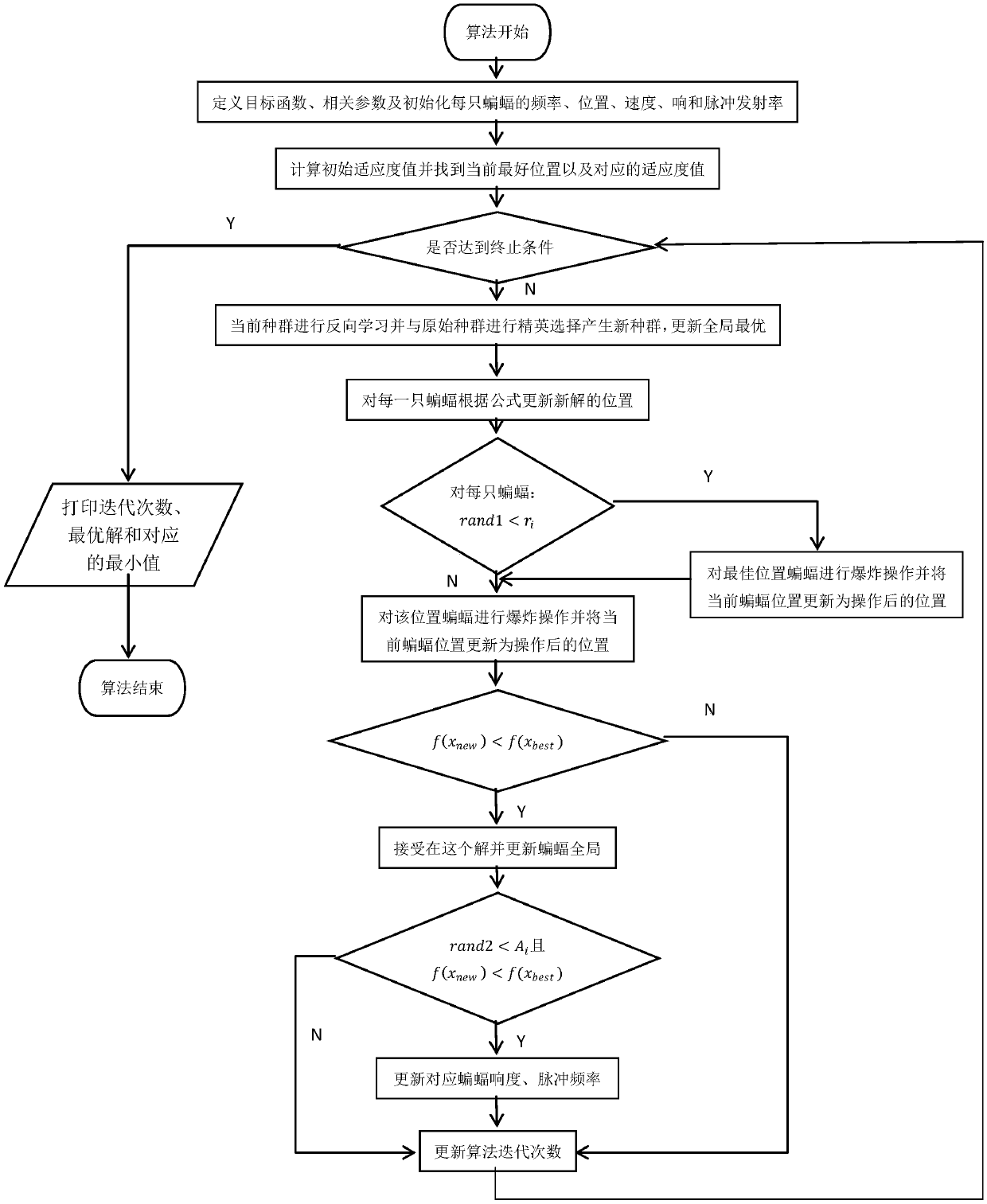
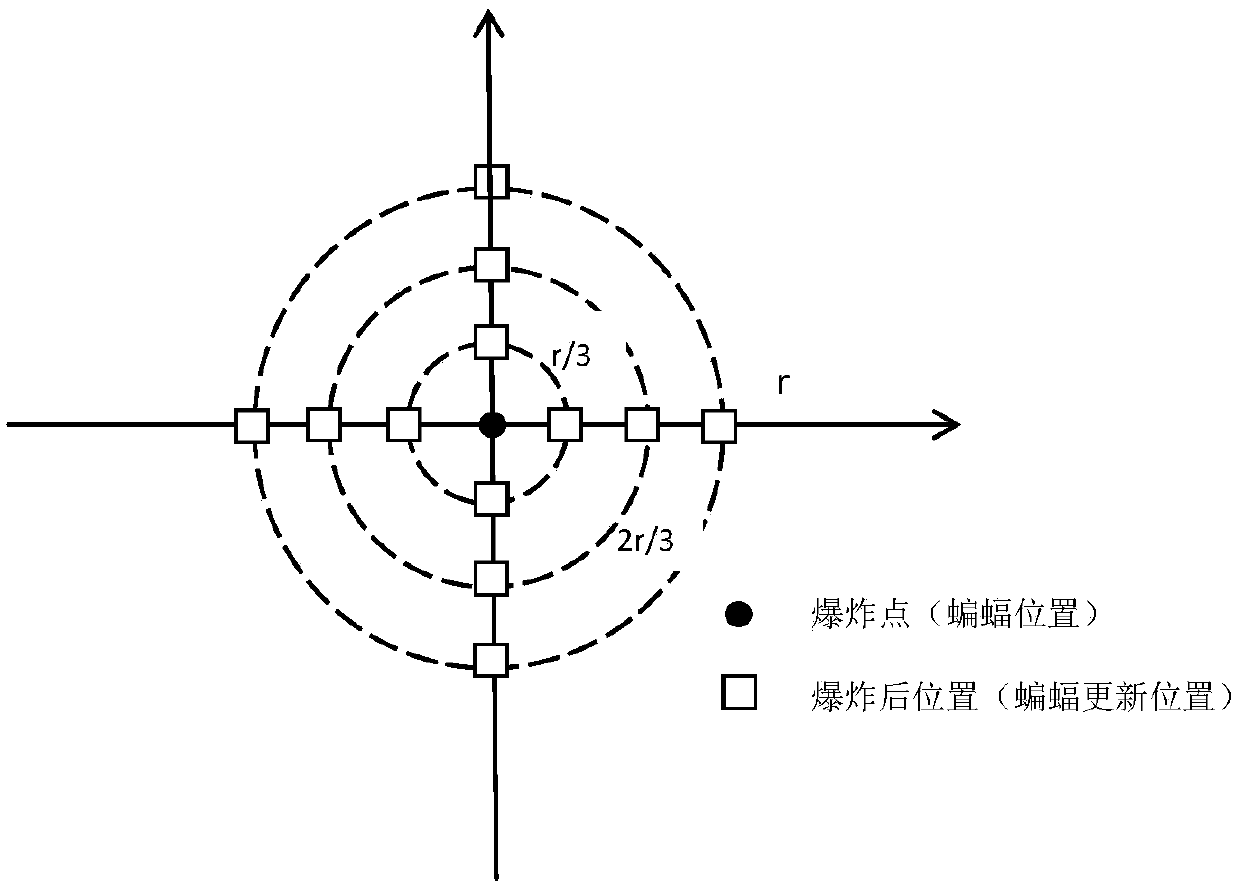
Single target optimization problem method integrating explosion strategy, opposition-based learning and bat algorithm and system
PendingCN108694438AImprove local exploration capabilitiesIncrease diversityArtificial lifeNeural learning methodsLocal optimumMicrochiroptera
The invention relates to a bat algorithm and a system, belonging to the field of data processing, and particularly relates to a single target optimization problem method integrating explosion strategy, opposition-based learning and bat algorithm and a system. In the optimization process, the opposition-based population of each bat in the bat algorithm is obtained by opposition-based learning, andthe elite selection is performed on the two populations, thus the diversity of the population is increased, and the global search ability is improved, the local optimal solution is avoided, the explosion strategy is added during the flight process, thus the local exploration ability of the algorithm is improved, and the optimal solution is more accurately searched. Through the simulation test of 12 typical test functions and knapsack problems, it is proved that DGOBA has higher efficiency for solving continuous and discrete optimization problems.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
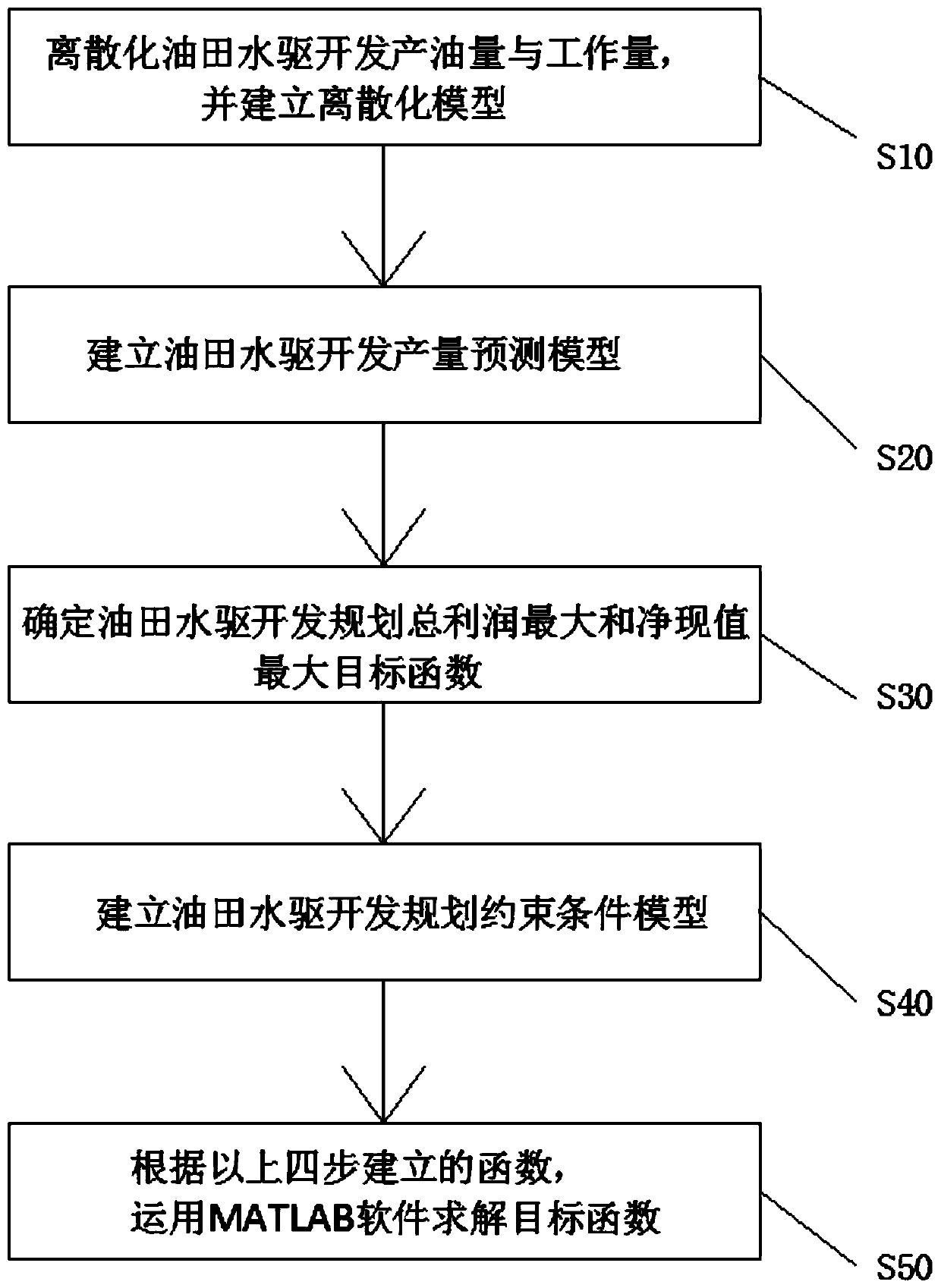
A discrete optimization method for water flooding oil field development planning
ActiveCN109816148AAvoid wastingReduce development costsClimate change adaptationForecastingWater floodingOil field
The invention discloses a discrete optimization method for water flooding oil field development planning. The method comprises the following steps that S10, the oil production amount and the workloadof water flooding oil field development are discretized; S20, a water flooding oilfield development yield prediction model is established; S30, a water flooding oil field development planning objective function is determined; S40, a water flooding oil field development planning constraint condition model is established; and S50, the objective function is solved by using MATLAB software according to the function established in the four steps. The invention provides a discrete optimization method for a water flooding oil field development plan, which is used for the water flooding oil field development plan, provides an optimal development mode for the water flooding oil field development, provides a basis for an oil field development plan manager to select a development plan scheme, avoidsthe waste of development resources, and saves the development cost. Therefore, a new discrete optimization method for the development planning of the water flooding oil field is formed, and objectivity, accuracy and practicability are achieved.
Owner:CHENGDU NORTH OIL EXPLORATION DEV TECH
Discrete optimization design method for connecting structures
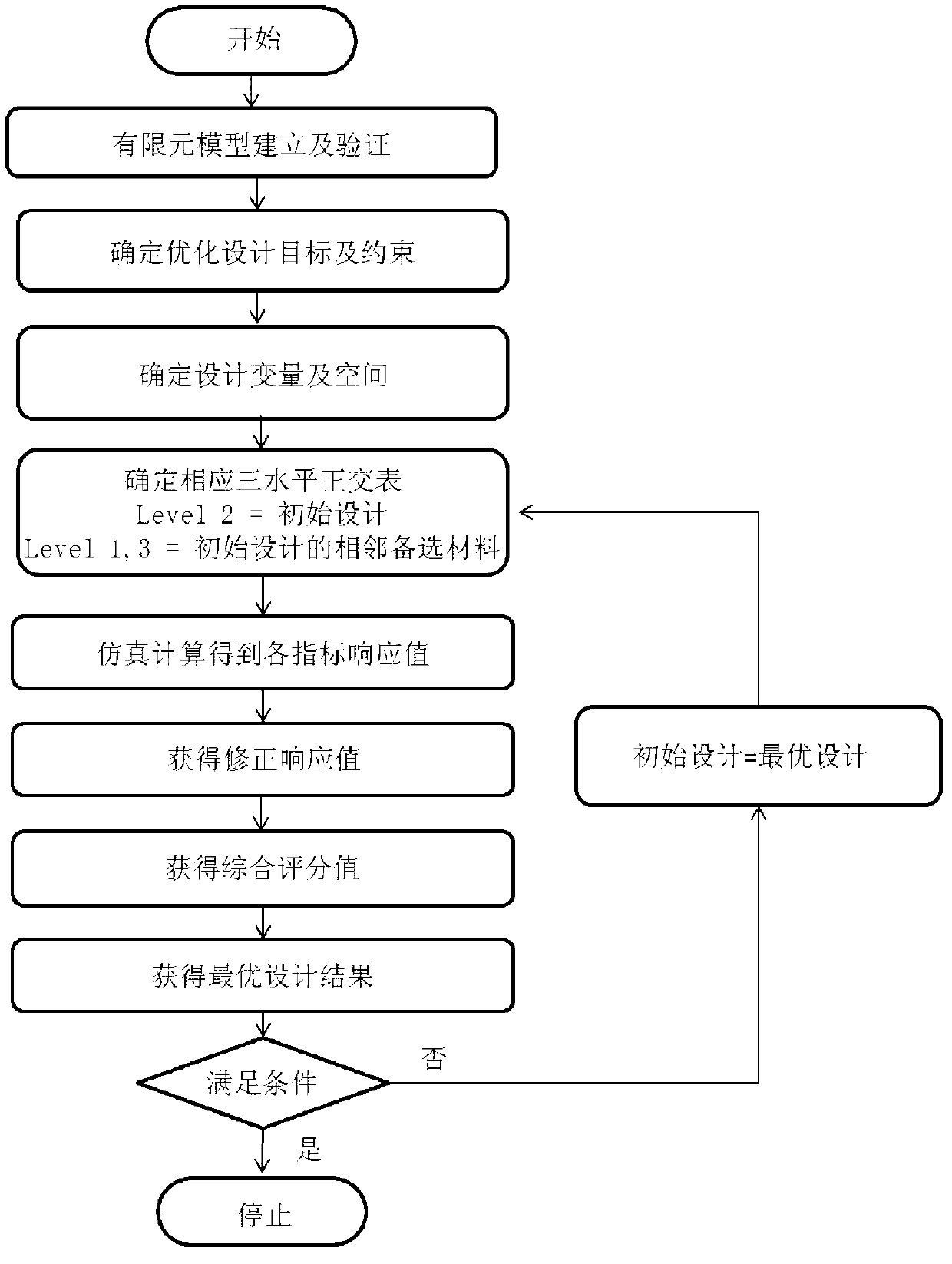
InactiveCN103218501AExcellent design resultReduce development costsSpecial data processing applicationsTarget ResponseThree level
The invention discloses a discrete optimization design method for connecting structures. The method mainly comprises the following steps: creating a collision finite element model; and then, determining an optimization target, constraint conditions and design variables to be optimized, and creating a three-level orthogonal table; obtaining target response values through numerical simulation calculation, and obtaining correction response values; and finally, reasonably selecting an optimal solution through a comprehensive evaluation value. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for solving the defects that the direct problem time dispatched by a genetic algorithm is overmuch, the response surface created by an approximation model method is a continuous space, the precision is low, and the like, and the discrete optimization design method is high in precision and efficiency and is particularly suitable for discrete optimization design problem of connecting structures with various variables and various levels. The method disclosed by the invention can be further used for reasonably guiding the design of the connecting structures to improve the performance of the connecting structures.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
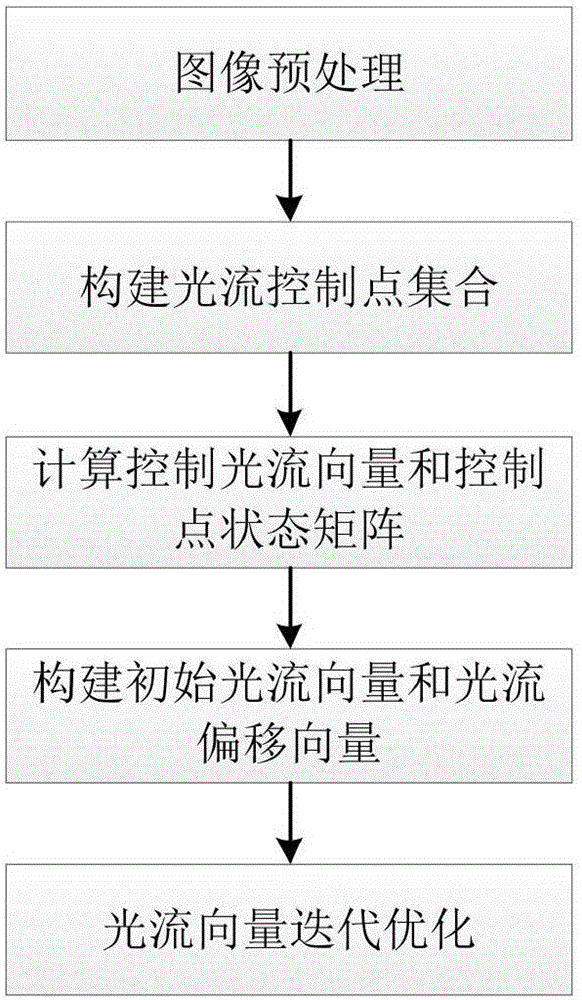
Method for estimating optical flow directed at large displacement
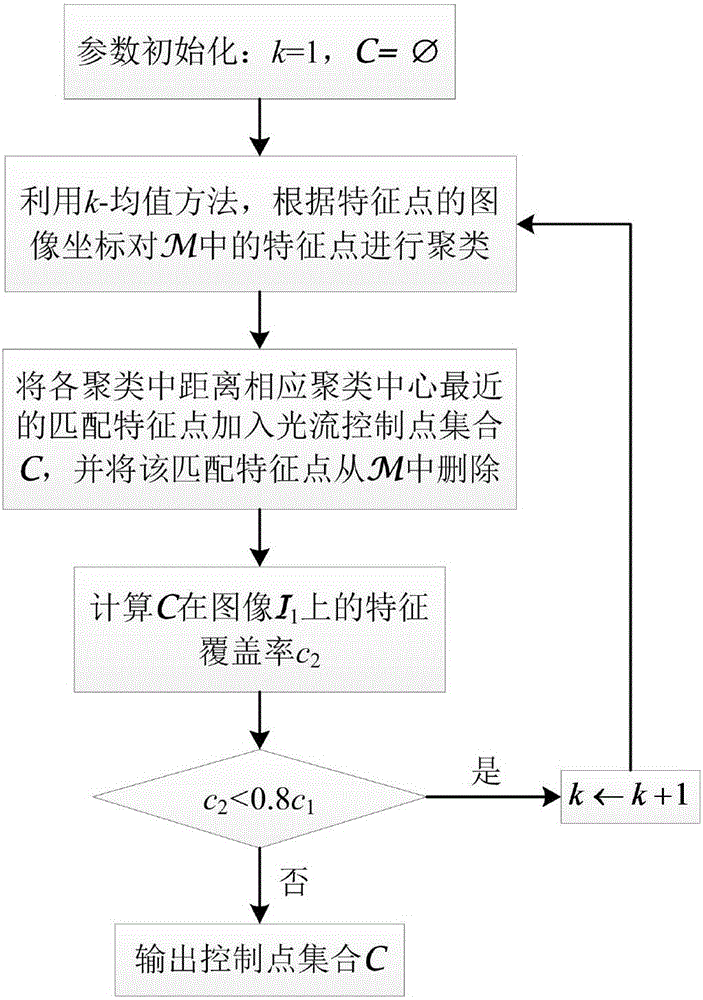
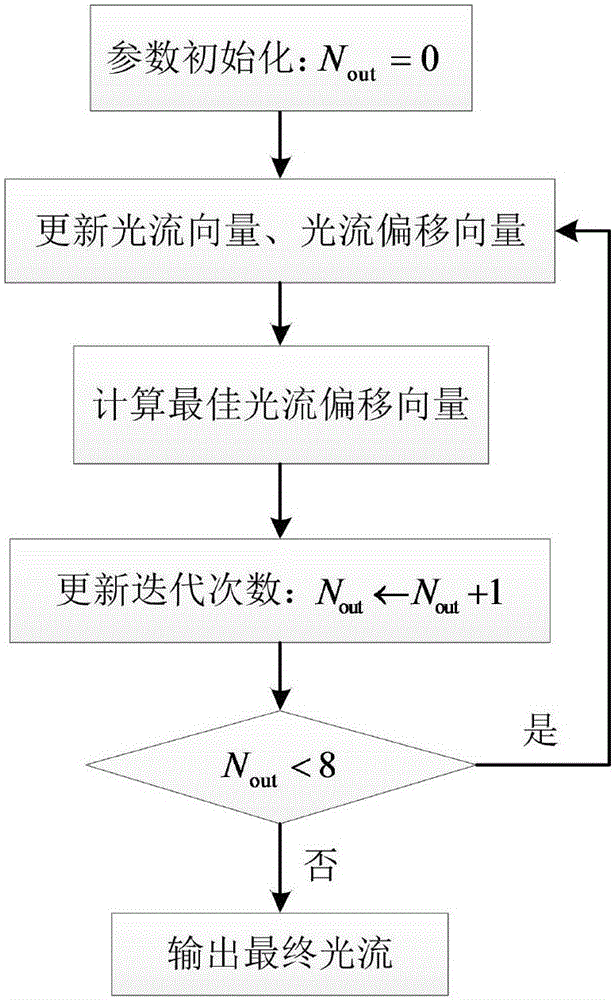
ActiveCN106600629AHigh precisionHigh Optical Flow Estimation ResultsImage analysisDiscrete optimizationComputer science
The invention discloses a method for estimating optical flow, directed at large-scale movement, aiming at computing dense pixel corresponding relationship among images containing large displacement and large-scale varying scenarios. The method includes the following steps: firstly, pre-processing input images; then constructing an optical flow control point set, and computing a control optical flow vector and a control point state matrix, and constructing an initial optical flow vector and an optical flow offset vector; and finally, realizing iterative optimization of the optical flow under the framework of discrete optimization. According to the invention, the method can effectively process large displacement and large-scale varying scenarios in the estimation of optical flow, noticeably increases the precision of optical flow estimation of large-scale movement, and has noticeable increase in computing efficiency compared with prior art.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and system for setting parameters of a discrete optimization problem embedded to an optimization solver and solving the embedded discrete optimization problem
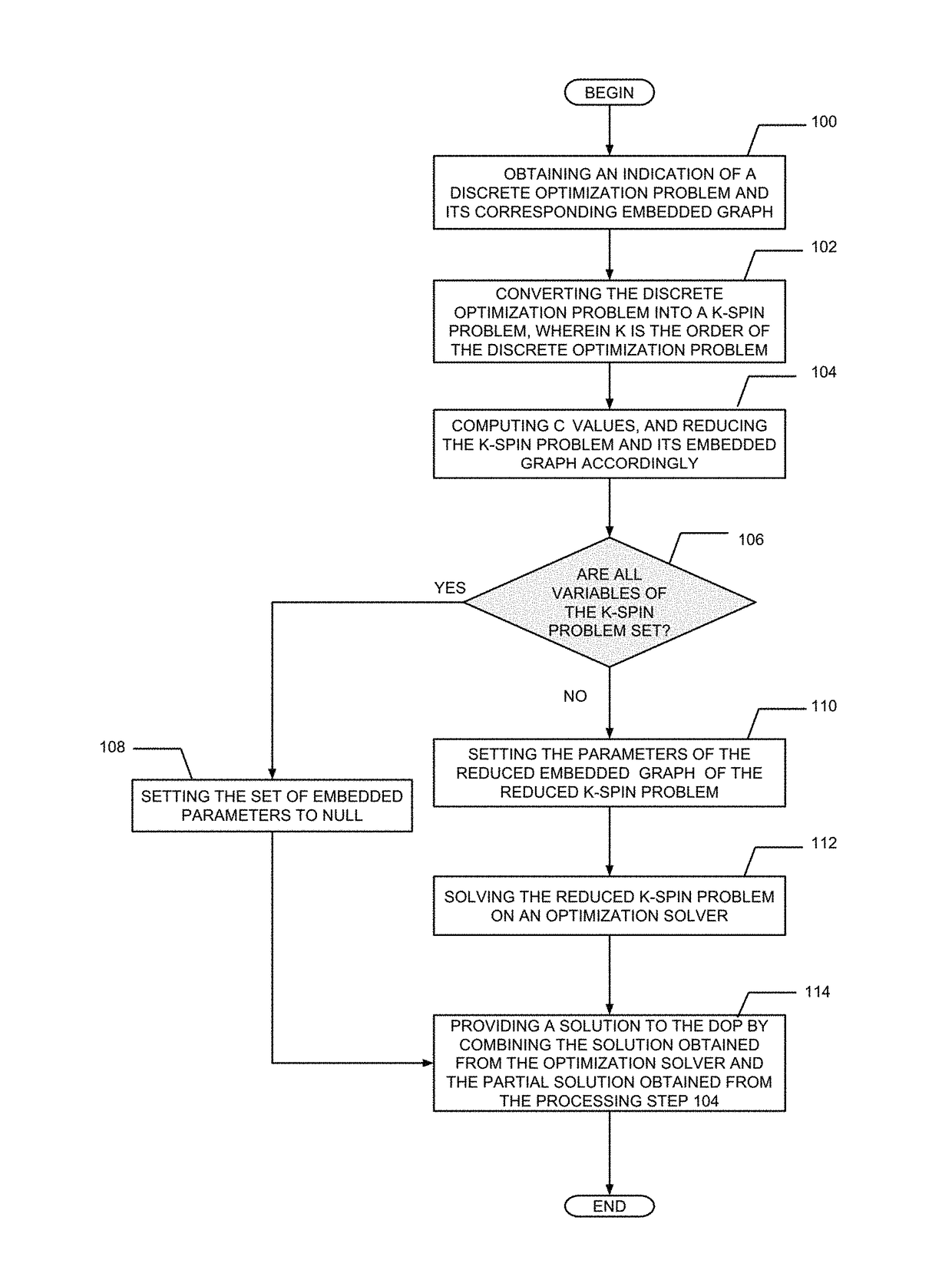
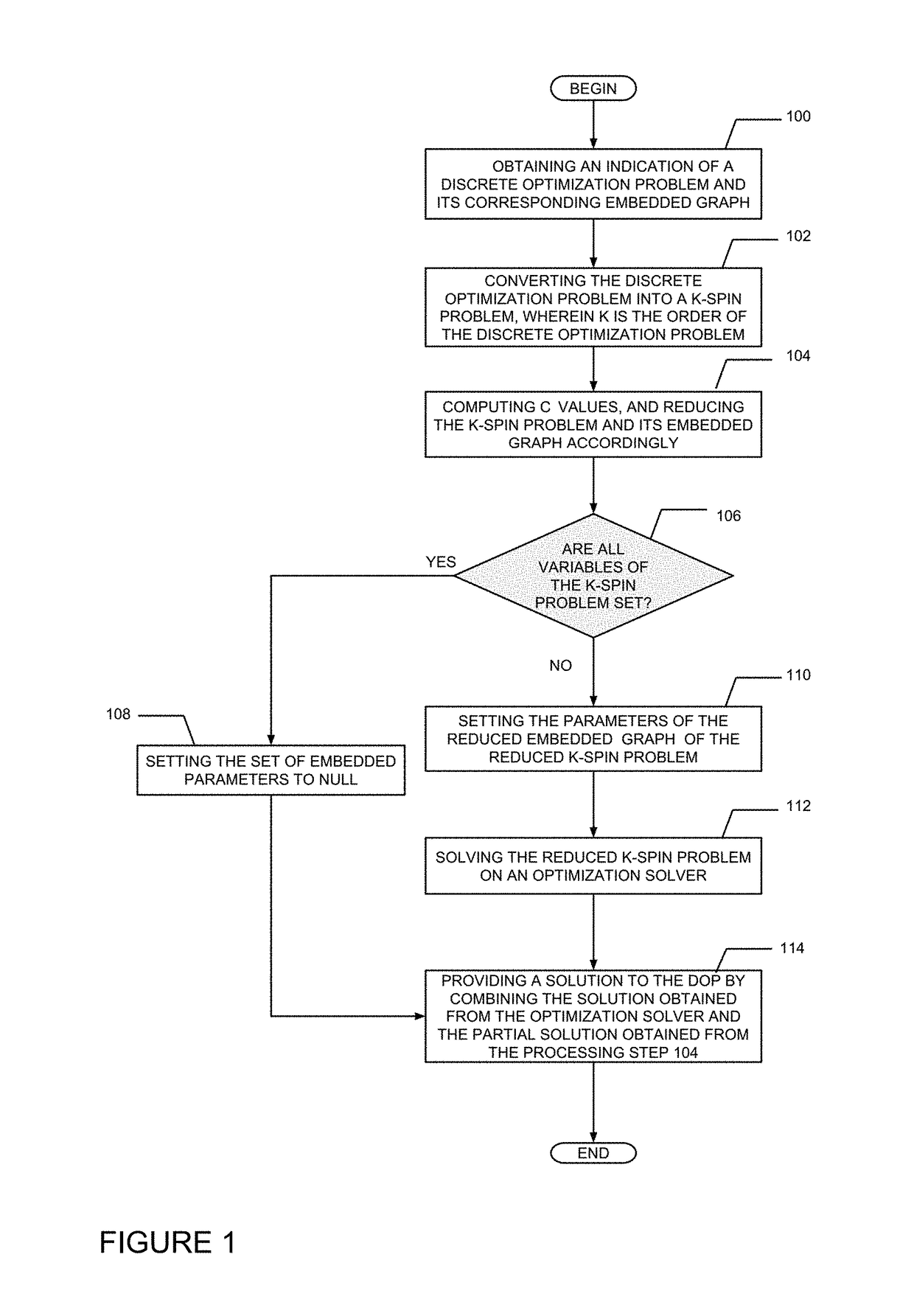
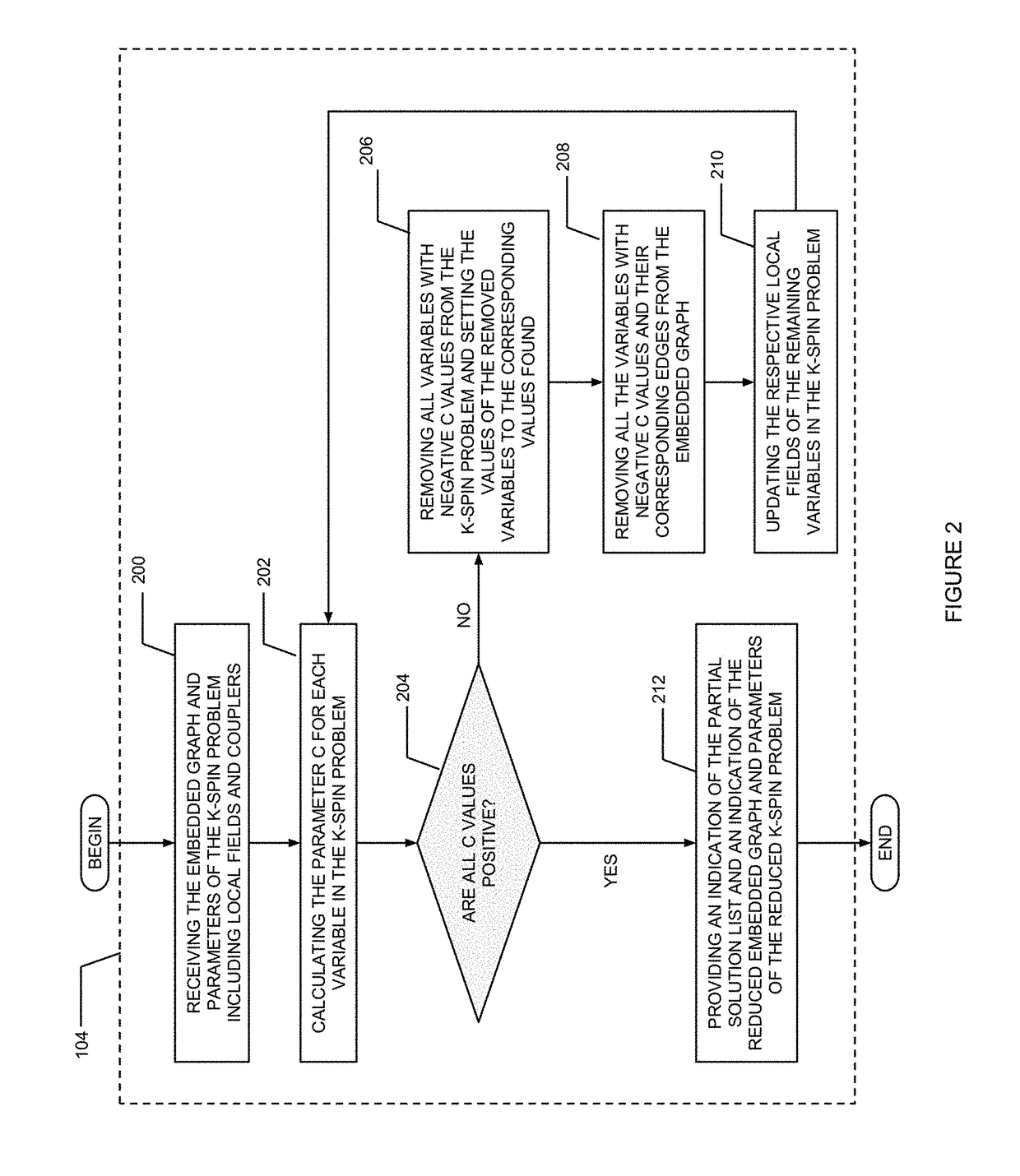
ActiveUS20180137083A1Reduce computing costProcessing problemInternal combustion piston enginesComplex mathematical operationsCouplingPartial solution
A method and system are disclosed for setting parameters of a discrete optimization problem embedded to an optimization solver and solving it. The method comprises converting the discrete optimization problem to a K-spin problem, wherein the K-spin problem is defined asminHK-spin=∑j=1Nhjsj+∑k=2K∑j1j2…jkJj1j2…jksj1sj2…sjkwherein parameter K is the order of the discrete optimization problem, wherein parameter J is a coupling value between two vertices and parameter h is a local field value; generating a reduced K-spin problem and a corresponding reduced embedded graph; setting the parameter J of each edge of the reduced embedded graph; setting the parameter h of each given vertex of the reduced embedded graph; setting the parameter J of each edge of the reduced embedded graph connecting two vertices representing the same corresponding variable in the reduced K-spin problem; solving the reduced K-spin problem and combining at least one solution obtained from the optimization solver with a partial solution list.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
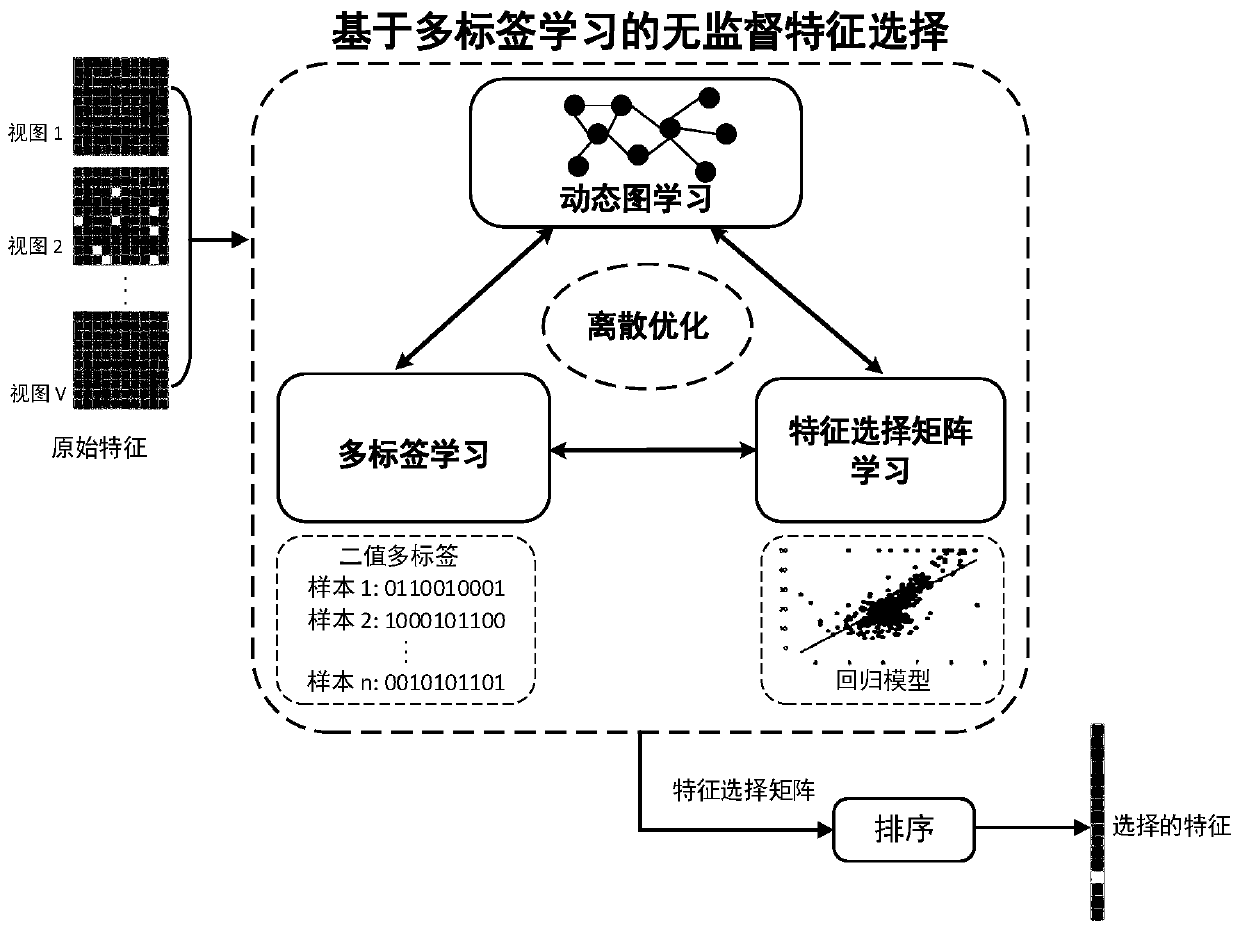
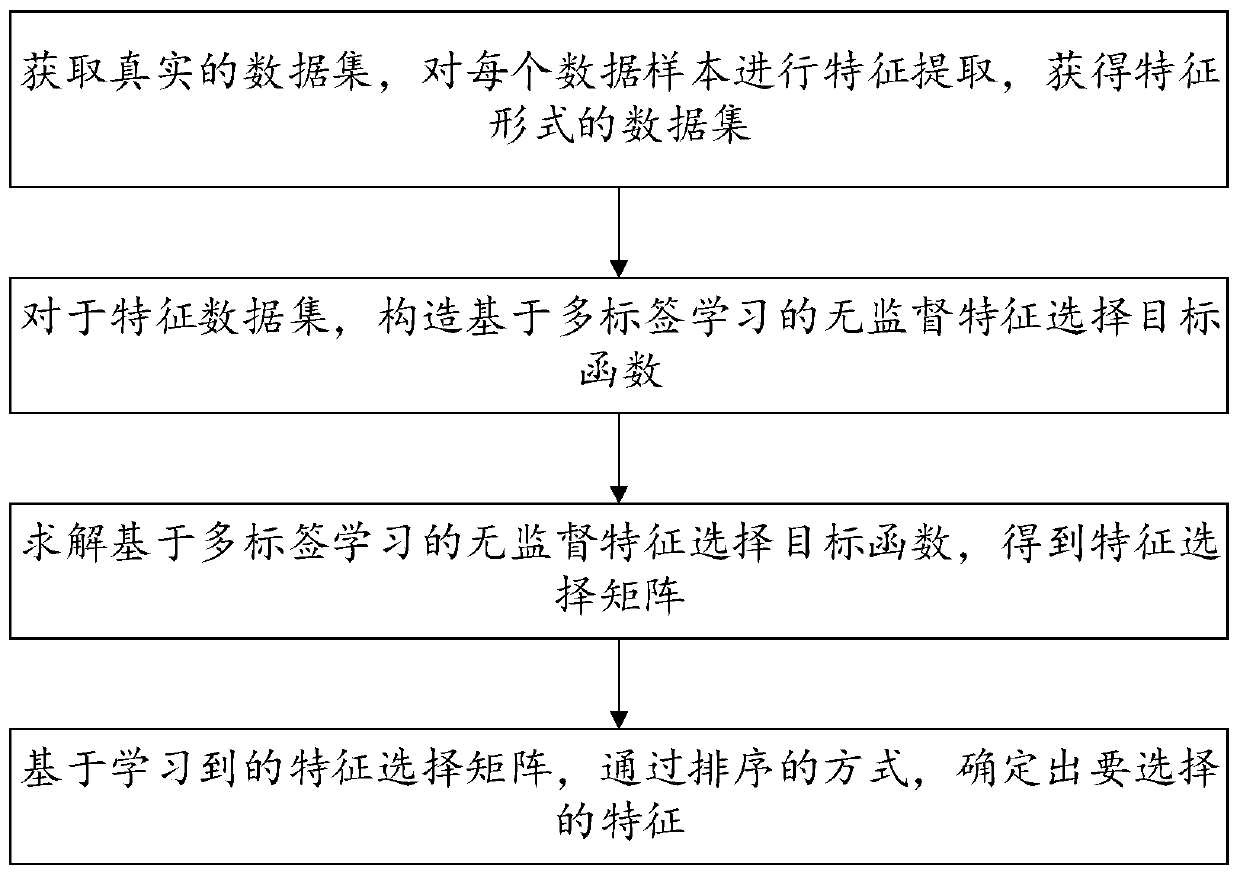
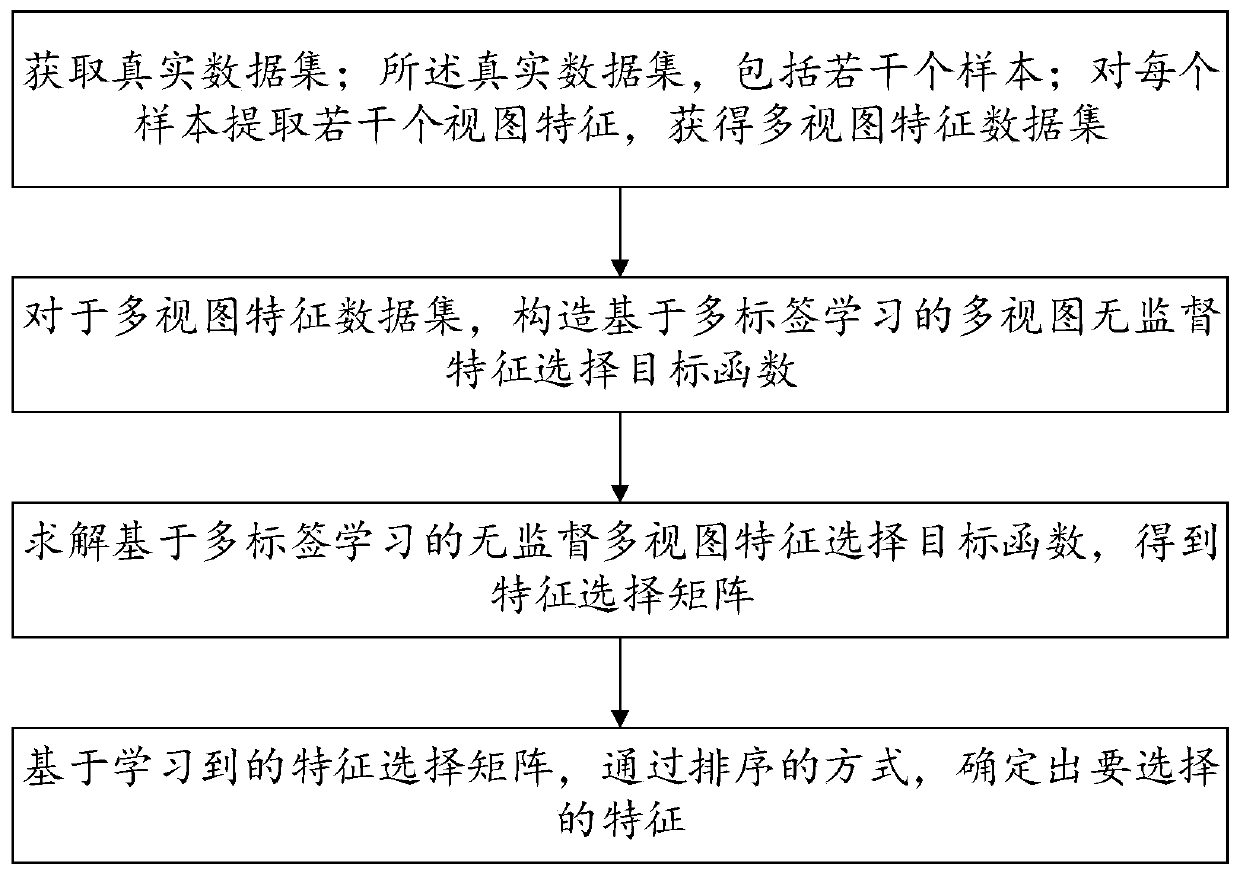
Unsupervised feature selection method and system based on multi-label learning
ActiveCN111027636ADiscriminatingChoose accuratelyCharacter and pattern recognitionAugmented lagrange multiplier methodData set
The invention provides an unsupervised feature selection method and system based on multi-label learning, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out feature extraction of each obtained data sample, obtaining a feature data set, learning a binary multi-label matrix and a feature selection matrix for the feature data set, and constructing an unsupervised feature selection target function basedon multi-label learning; solving an unsupervised feature selection target function based on multi-label learning by adopting a discrete optimization method based on an augmented Lagrange multiplier method to obtain a feature selection matrix; and sorting the feature selection matrix to determine selected target features. Learning multiple tags for semantic guidance and executing feature selection, and applying binary constraints in spectrum embedding to obtain multiple tags to guide a final feature selection process. In addition, a dynamic sample similarity graph is constructed in a self-adaptive mode to capture a data structure, so that the multi-label discrimination capability is enhanced.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Method and system for decomposing a problem involving discrete optimization into a plurality of smaller subproblems and use of the method for solving the problem
ActiveUS10152454B2Small sizeSpeed up the processQuantum computersKnowledge representationTheoretical computer scienceSelection criterion
A method is disclosed for preprocessing a problem involving discrete optimization over a plurality of variables, the method comprising obtaining an indication of a problem involving discrete optimization; converting the problem involving discrete optimization into a problem suitable for a given optimization oracle architecture of an optimization oracle; providing a given number of times M the problem suitable for the given optimization oracle architecture to the optimization oracle; for each providing of the problem, performing a given number K of calls to the optimization oracle; each call generating a given configuration; obtaining a variable selection criterion, the variable selection criterion for determining at least one variable of the plurality of generated configurations that can be fixed; determining at least one variable that matches the variable selection criterion and a corresponding value for each variable; fixing the at least one determined variable at the corresponding value in the problem involving discrete optimization to thereby preprocess the problem to generate at least one subproblem and providing an indication of the at least one generated subproblem and an indication of the at least one fixed variable.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
Discrete optimization method based on matrix workshop AGV scheduling
PendingCN113064392AReduce time complexityQuality improvementElectric/hybrid propulsionTotal factory controlAlgorithmDiscrete optimization
The invention relates to the technical field of workshop free guide trolley delivery scheduling, and particularly belongs to a discrete optimization method based on matrix workshop AGV scheduling. The method comprises the steps of 1, presetting related parameters of a discrete weed optimization algorithm, wherein the related parameters include an initial population number, a maximum population number, a minimum seed number and a maximum seed number; 2, initializing a population, specifically, generating a high-quality solution by using a neighborhood nearest distance heuristic algorithm, and generating other solutions by using a random generation method until the initial population number is reached; 3, optimizing the initialized population; and 4, outputting an optimal solution, specifically, judging whether a stop condition of calculating time of 5s is reached or not, and if not, returning to the step 3; and if the stop condition is reached, outputting the optimal solution in the current population. According to the invention, the scheduling scheme suitable for the actual production of the workshop can be obtained, and the scheduling management and optimization of the AGV are realized.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com