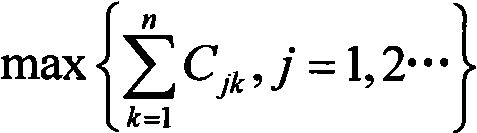Patents
Literature
4547 results about "Semantic information" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semantic information(Noun) (Research) the part of a message that is stored in the semantic memory system and can be tested with traditional verbal methods.
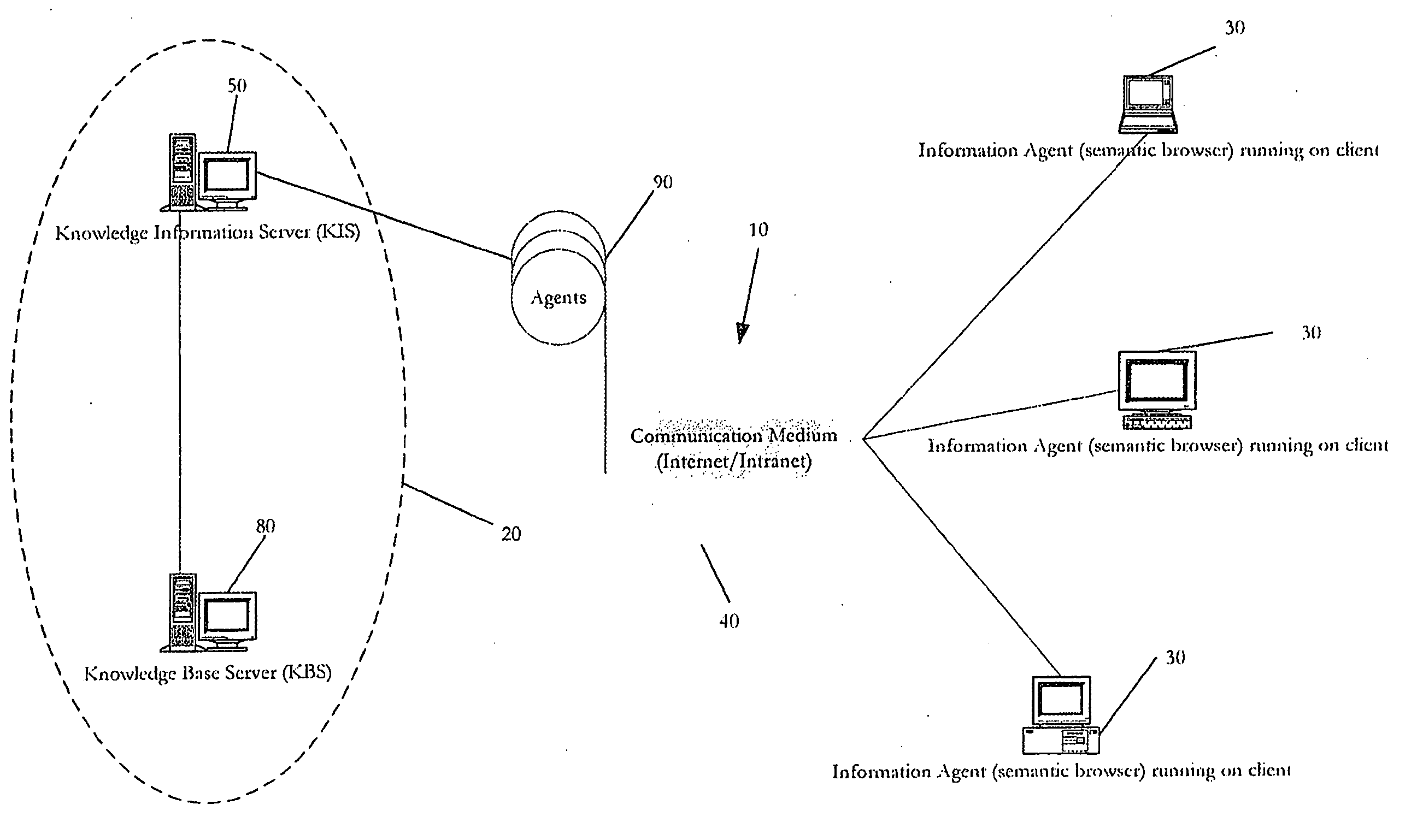
System and method for knowledge retrieval, management, delivery and presentation
InactiveUS20070038610A1Efficient queryWebsite content managementSpecial data processing applicationsAction CodeActive agent
The present invention is directed to an integrated implementation framework and resulting medium for knowledge retrieval, management, delivery and presentation. The system includes a first server component that is responsible for adding and maintaining domain-specific semantic information and a second server component that hosts semantic and other knowledge for use by the first server component that work together to provide context and time-sensitive semantic information retrieval services to clients operating a presentation platform via a communication medium. Within the system, all objects or events in a given hierarchy are active Agents semantically related to each other and representing queries (comprised of underlying action code) that return data objects for presentation to the client according to a predetermined and customizable theme or “Skin.” This system provides various means for the client to customize and “blend” Agents and the underlying related queries to optimize the presentation of the resulting information.
Owner:OMOIGUI NOSA
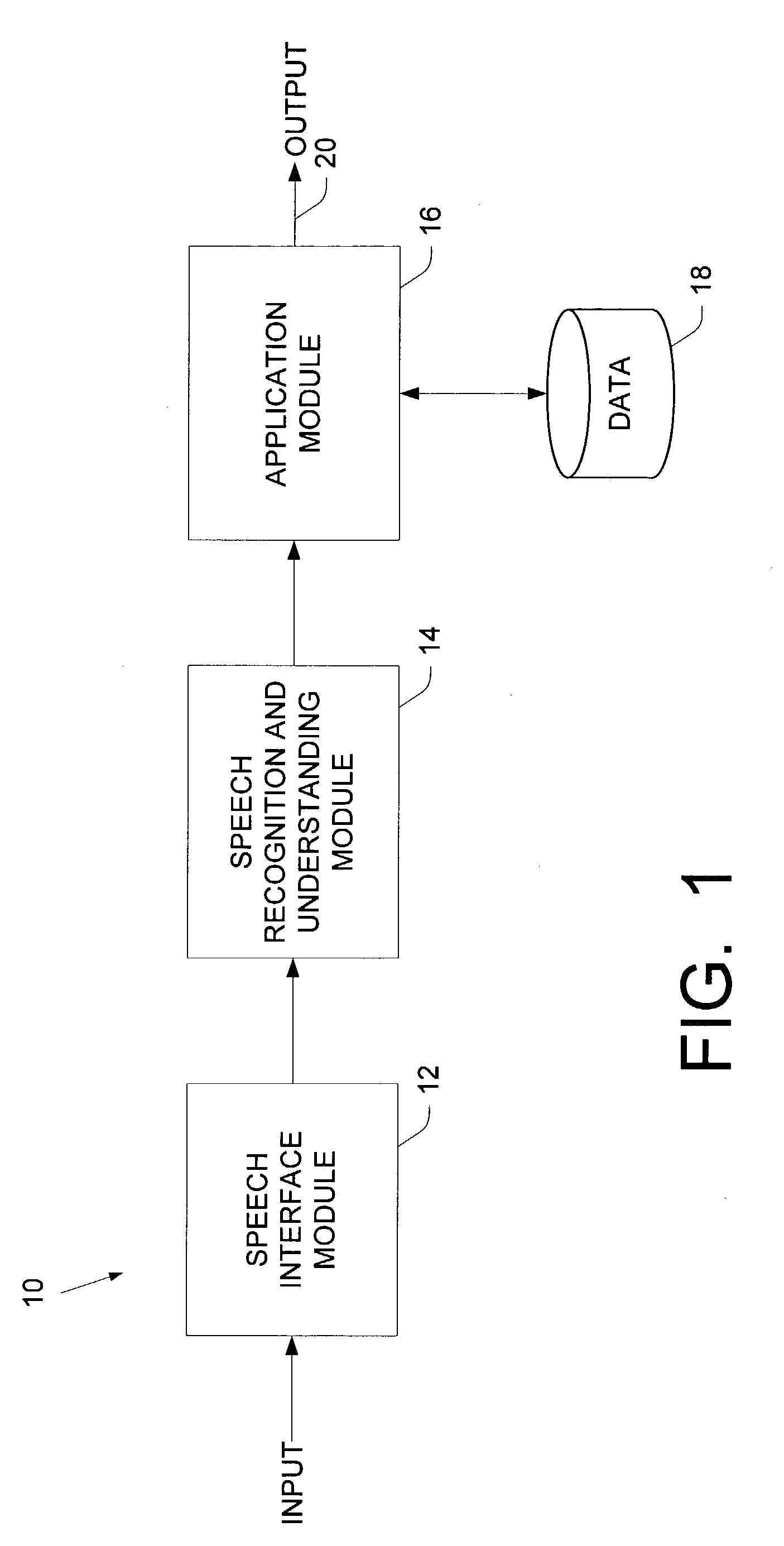
Semantic object synchronous understanding implemented with speech application language tags
ActiveUS7200559B2Sound input/outputSpeech recognitionSpeech comprehensionApplication programming interface
A speech understanding system includes a language model comprising a combination of an N-gram language model and a context-free grammar language model. The language model stores information related to words and semantic information to be recognized. A module is adapted to receive input from a user and capture the input for processing. The module is further adapted to receive SALT application program interfaces pertaining to recognition of the input. The module is configured to process the SALT application program interfaces and the input to ascertain semantic information pertaining to a first portion of the input and output a semantic object comprising text and semantic information for the first portion by accessing the language model, wherein performing recognition and outputting the semantic object are performed while capturing continues for subsequent portions of the input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
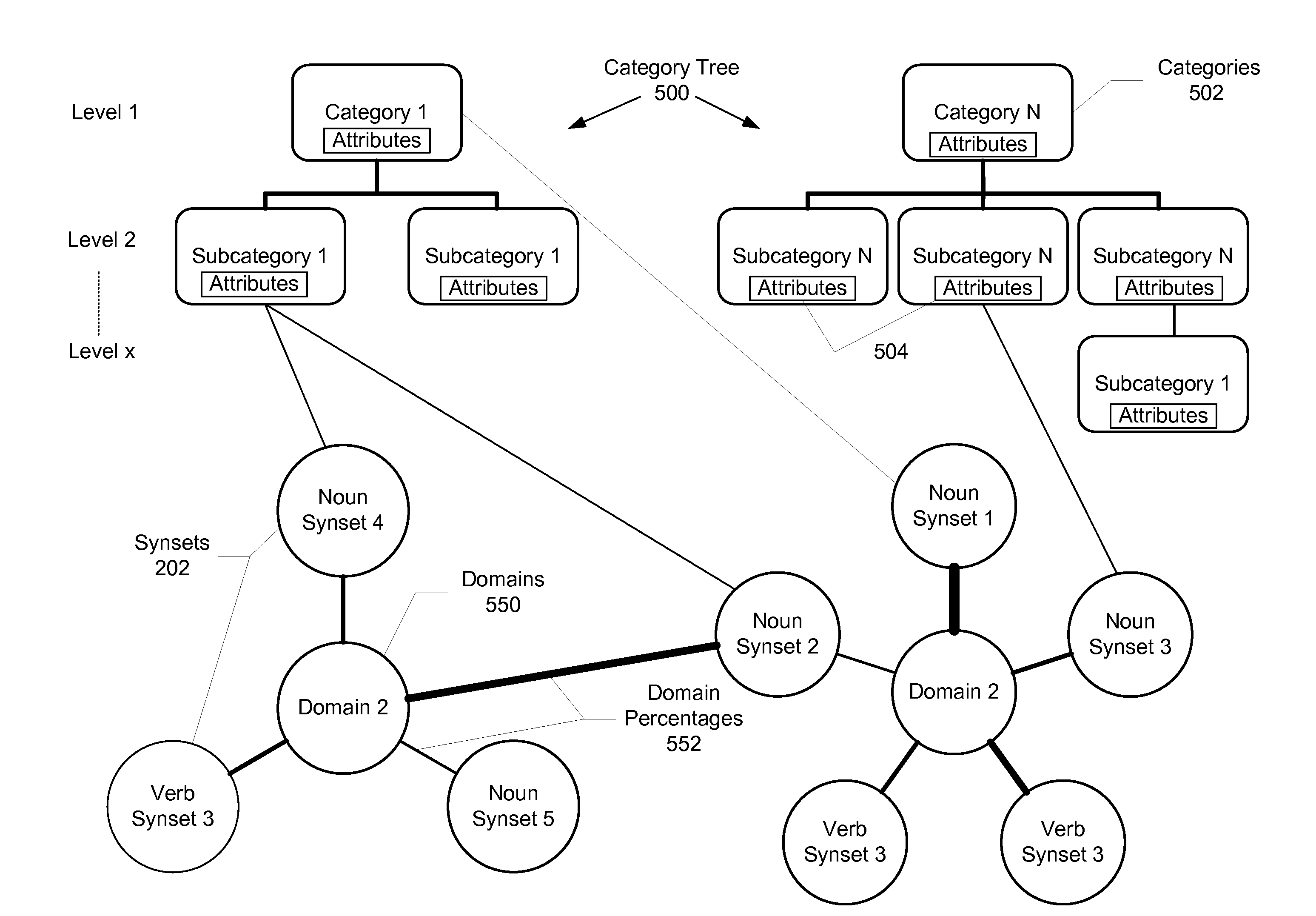
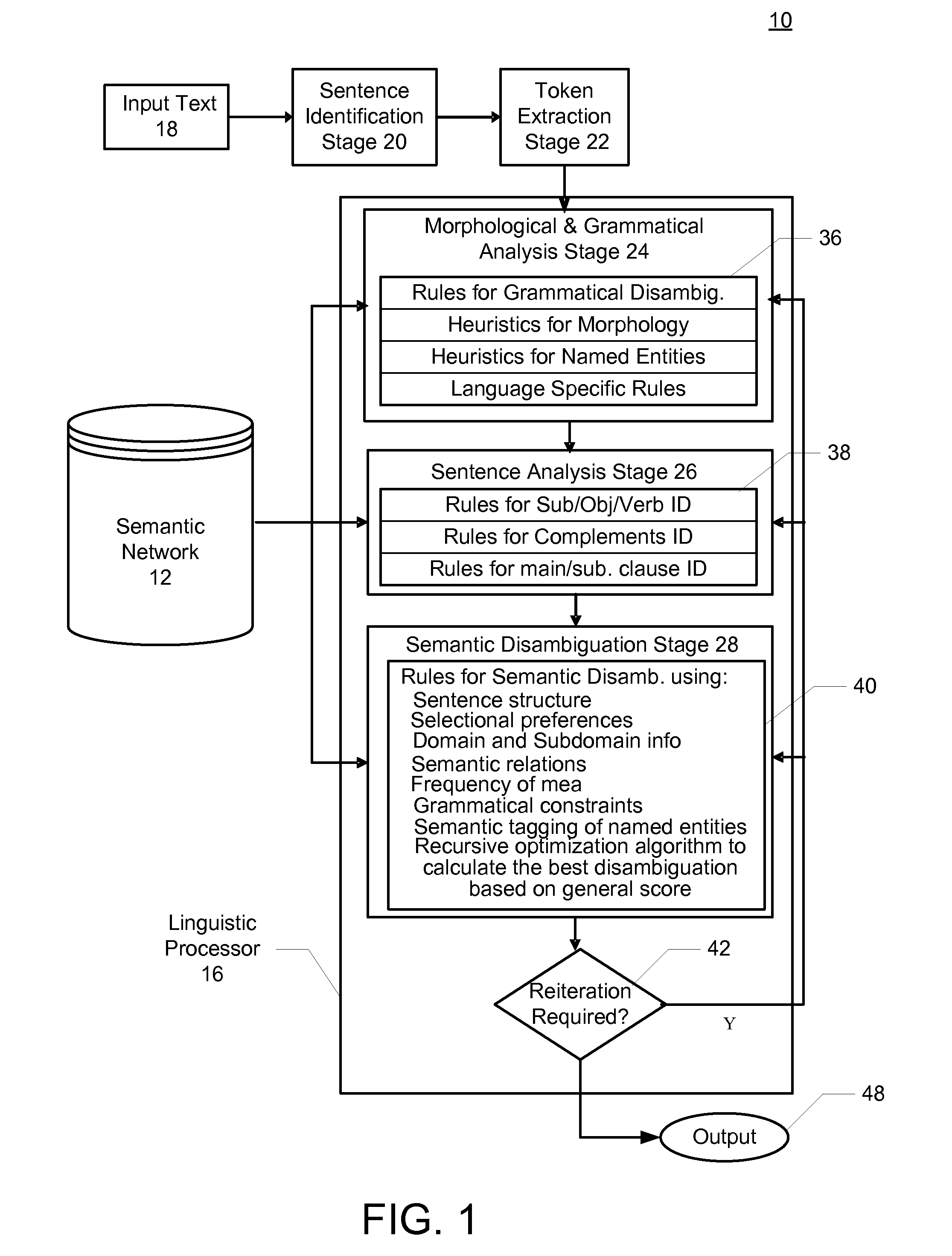
Method and system for automatically extracting relations between concepts included in text
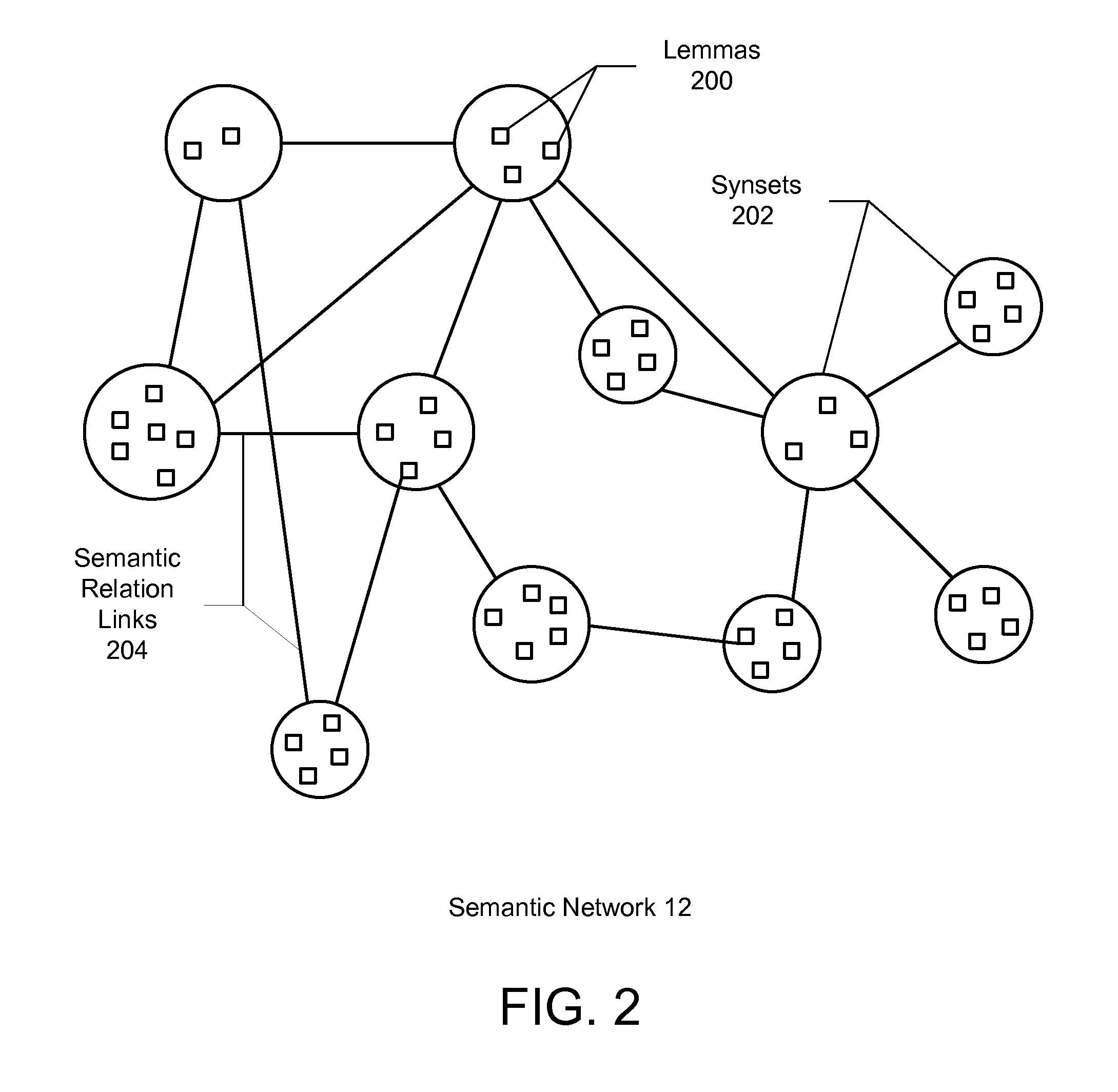
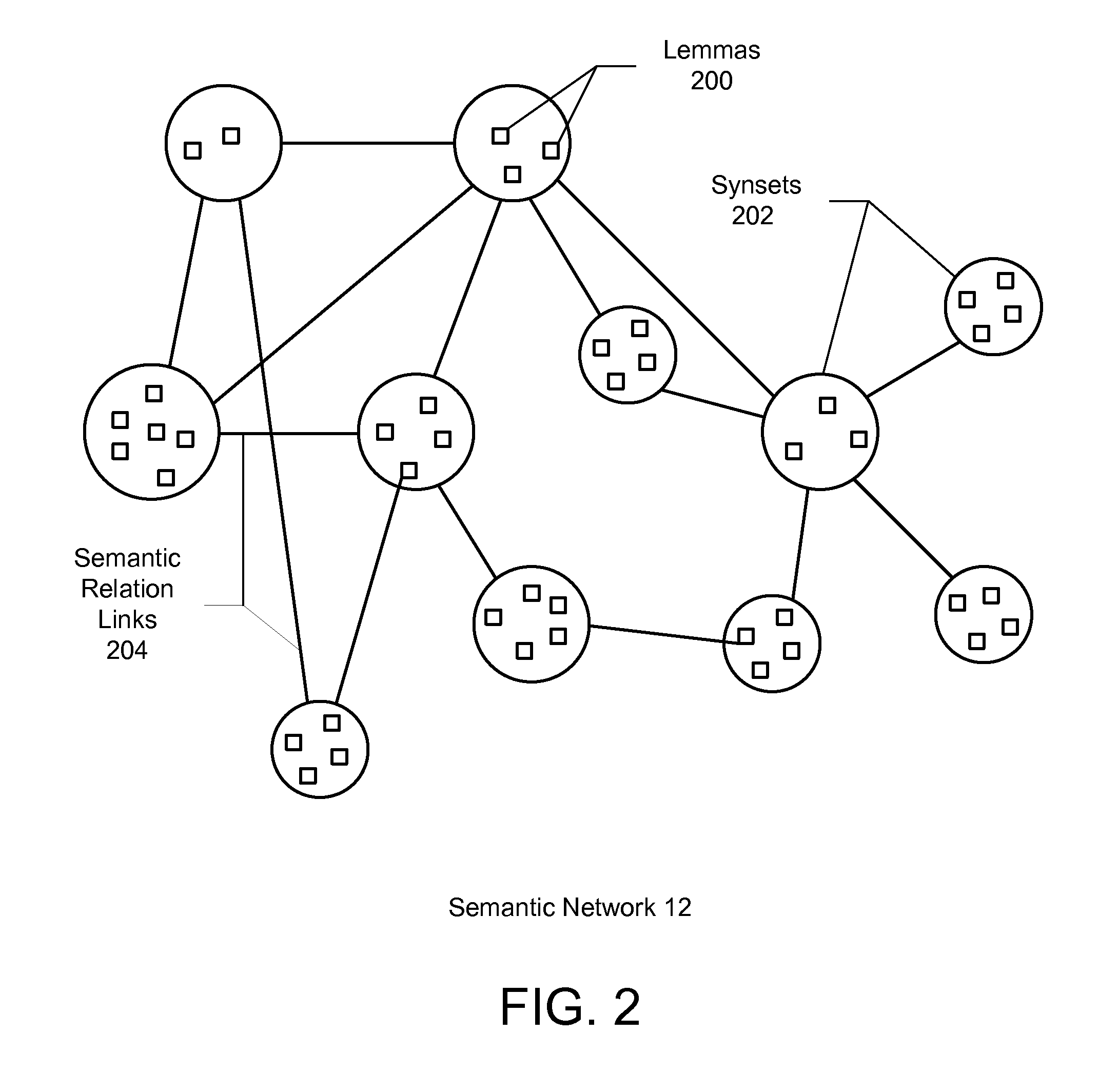
ActiveUS7899666B2Complete understandingSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic networkHuman language
A method and system for automatically extracting relations between concepts included in electronic text is described. Aspects the exemplary embodiment include a semantic network comprising a plurality of lemmas that are grouped into synsets representing concepts, each of the synsets having a corresponding sense, and a plurality of links connected between the synsets that represent semantic relations between the synsets. The semantic network further includes semantic information comprising at least one of: 1) an expanded set of semantic relation links representing: hierarchical semantic relations, synset / corpus semantic relations verb / subject semantic relations, verb / direct object semantic relations, and fine grain / coarse grain semantic relationship; 2) a hierarchical category tree having a plurality of categories, wherein each of the categories contains a group of one or more synsets and a set of attributes, wherein the set of attributes of each of the categories are associated with each of the synsets in the respective category; and 3) a plurality of domains, wherein one or more of the domains is associated with at least a portion of the synsets, wherein each domain adds information regarding a linguistic context in which the corresponding synset is used in a language. A linguistic engine uses the semantic network to performing semantic disambiguation on the electronic text using one or more of the expanded set of semantic relation links, the hierarchical category tree, and the plurality of domains to assign a respective one of the senses to elements in the electronic text independently from contextual reference.
Owner:EXPERT AI SPA
Method and system for mapping enterprise data assets to a semantic information model
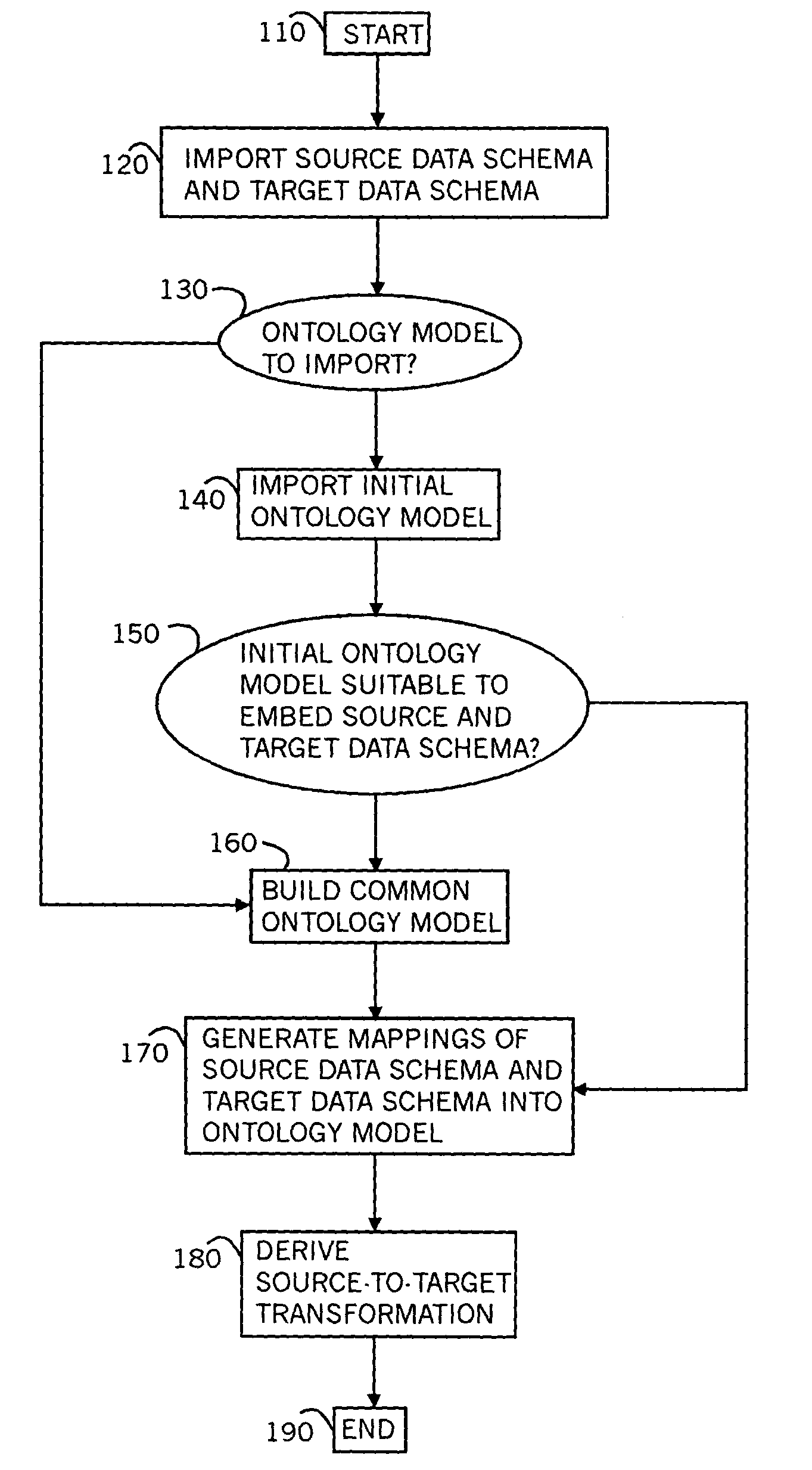
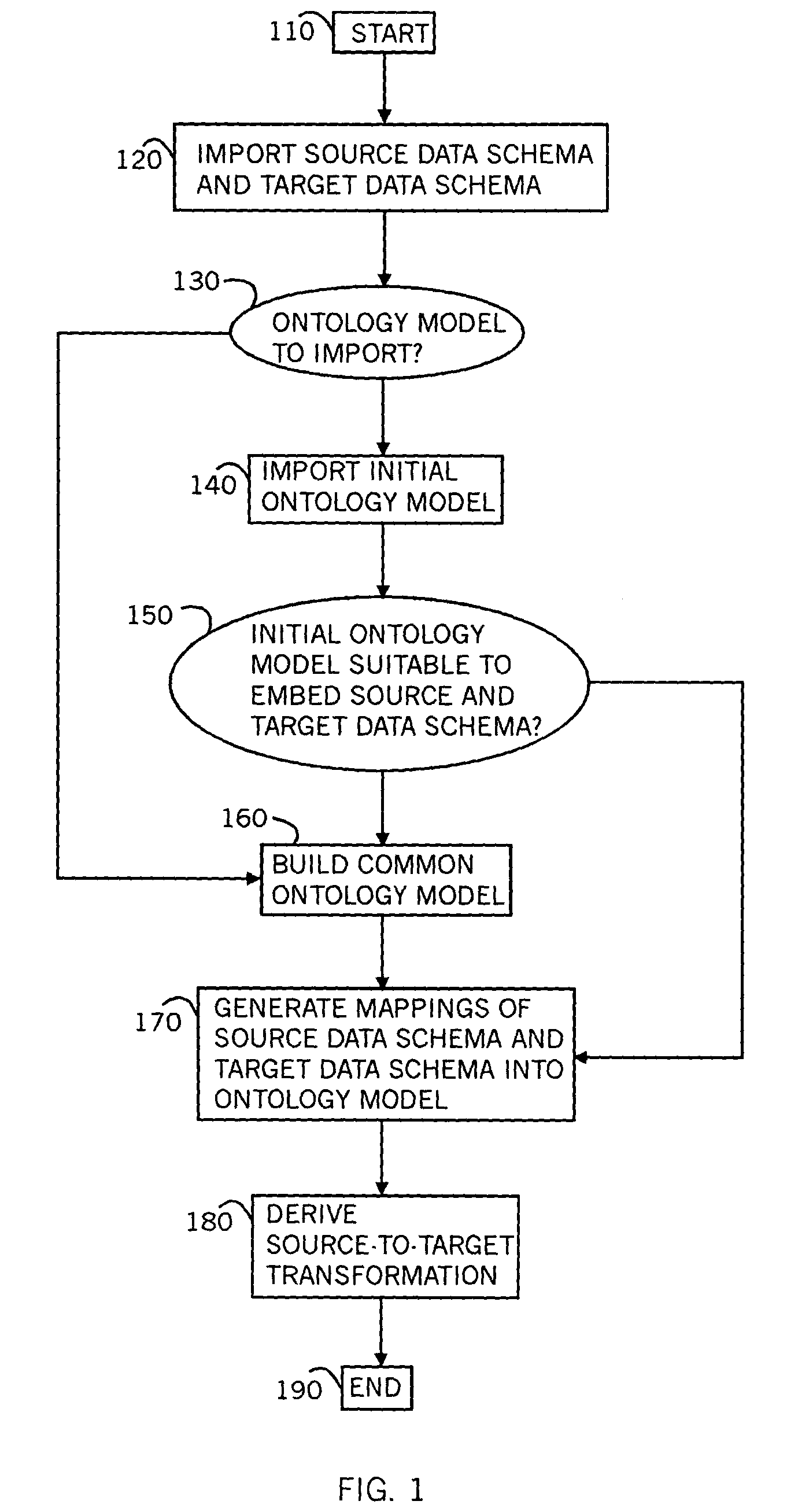
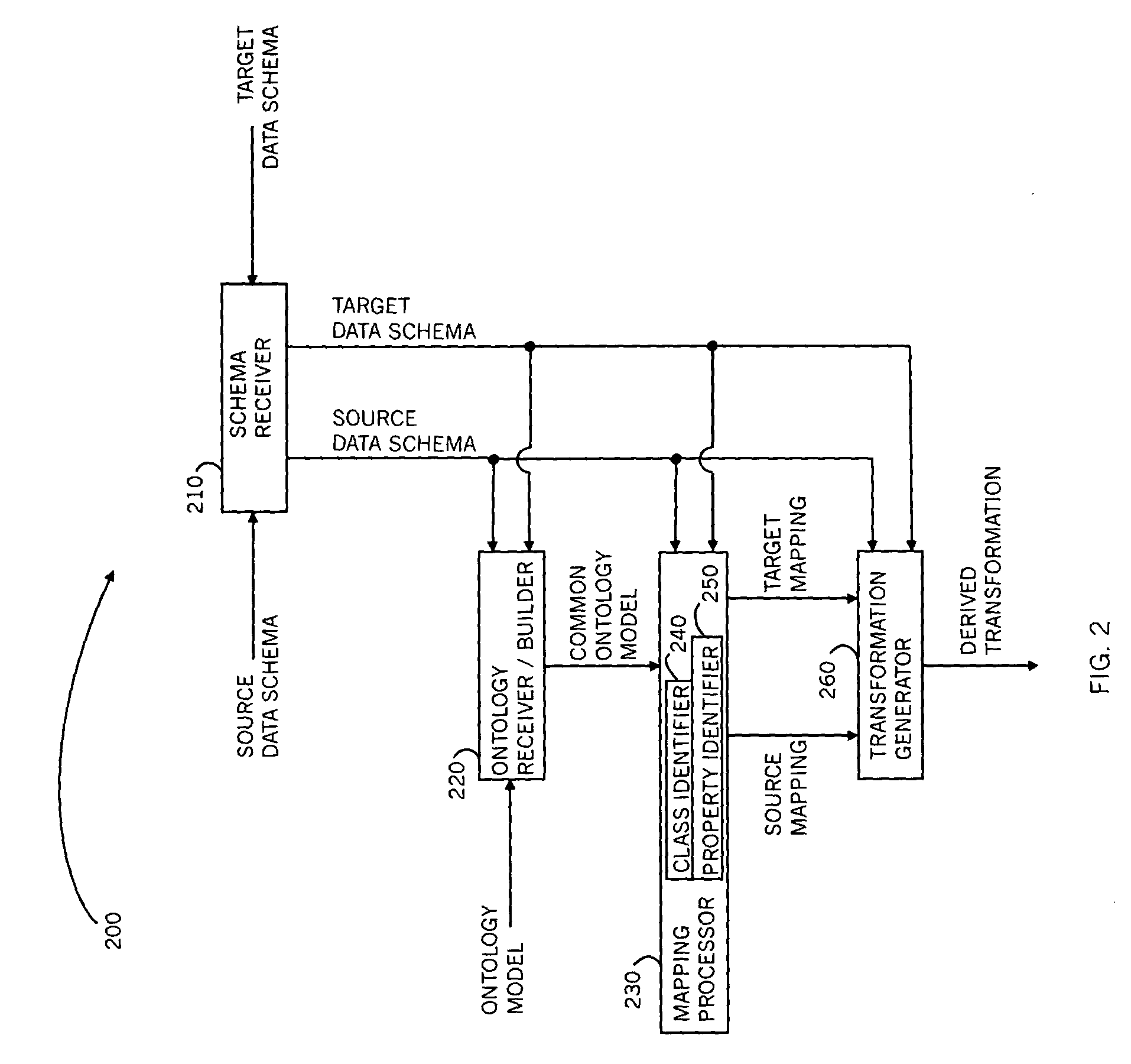
A method for mapping data schemas into an ontology model, including providing an ontology model including classes and properties of classes, providing a data schema, identifying a primary data construct within the data schema, identifying a secondary data construct within the primary data construct, mapping the primary data construct to a corresponding class of the ontology model, and mapping the secondary data construct to a property of the corresponding class of the ontology model. A system and a computer readable storage medium are also described and claimed.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for knowledge retrieval, management, delivery and presentation
InactiveUS20080162498A1Website content managementSpecial data processing applicationsAction CodeActive agent
The present invention is directed to an integrated implementation framework and resulting medium for knowledge retrieval, management, delivery and presentation. The system includes a first server component that is responsible for adding and maintaining domain-specific semantic information and a second server component that hosts semantic and other knowledge for use by the first server component that work together to provide context and time-sensitive semantic information retrieval services to clients operating a presentation platform via a communication medium. Within the system, all objects or events in a given hierarchy are active Agents semantically related to each other and representing queries (comprised of underlying action code) that return data objects for presentation to the client according to a predetermined and customizable theme or “Skin.” This system provides various means for the client to customize and “blend” Agents and the underlying related queries to optimize the presentation of the resulting information.
Owner:OMOIGUI NOSA
Recording audio metadata for stored images
InactiveUS20090150147A1Improve understandingImprove viewing experienceRecord information storageUsing detectable carrier informationDisplay deviceAudio signal flow
A method of processing audio signals recorded during display of image data from a media file on a display device to produce semantic understanding data and associating such data with the original media file, includes: separating a desired audio signal from the aggregate mixture of audio signals; analyzing the separated signal for purposes of gaining semantic understanding; and associating the semantic information obtained from the audio signals recorded during image display with the original media file.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method and system for automatically extracting relations between concepts included in text
ActiveUS20080275694A1Complete understandingSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic networkSemantic information
A method and system for automatically extracting relations between concepts included in electronic text is described. Aspects the exemplary embodiment include a semantic network comprising a plurality of lemmas that are grouped into synsets representing concepts, each of the synsets having a corresponding sense, and a plurality of links connected between the synsets that represent semantic relations between the synsets. The semantic network further includes semantic information comprising at least one of: 1) an expanded set of semantic relation links representing: hierarchical semantic relations, synset / corpus semantic relations verb / subject semantic relations, verb / direct object semantic relations, and fine grain / coarse grain semantic relationship; 2) a hierarchical category tree having a plurality of categories, wherein each of the categories contains a group of one or more synsets and a set of attributes, wherein the set of attributes of each of the categories are associated with each of the synsets in the respective category; and 3) a plurality of domains, wherein one or more of the domains is associated with at least a portion of the synsets, wherein each domain adds information regarding a linguistic context in which the corresponding synset is used in a language. A linguistic engine uses the semantic network to performing semantic disambiguation on the electronic text using one or more of the expanded set of semantic relation links, the hierarchical category tree, and the plurality of domains to assign a respective one of the senses to elements in the electronic text independently from contextual reference.
Owner:EXPERT AI SPA
Part-of-speech tagging using latent analogy
Methods and apparatuses to assign part-of-speech tags to words are described. An input sequence of words is received. A global fabric of a corpus having training sequences of words may be analyzed in a vector space. A global semantic information associated with the input sequence of words may be extracted based on the analyzing. A part-of-speech tag may be assigned to a word of the input sequence based on POS tags from pertinent words in relevant training sequences identified using the global semantic information. The input sequence may be mapped into a vector space. A neighborhood associated with the input sequence may be formed in the vector space wherein the neighborhood represents one or more training sequences that are globally relevant to the input sequence.
Owner:APPLE INC
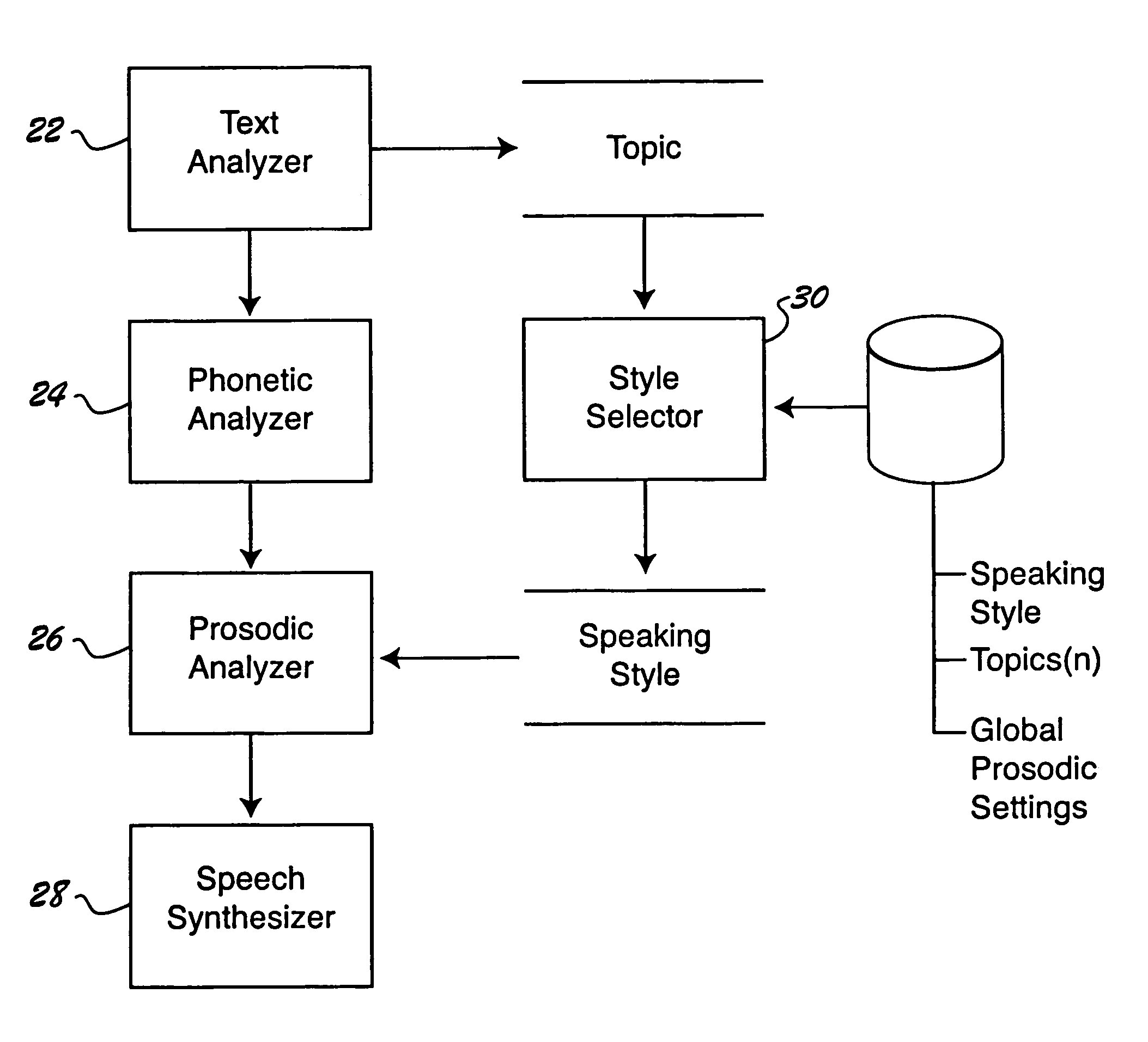
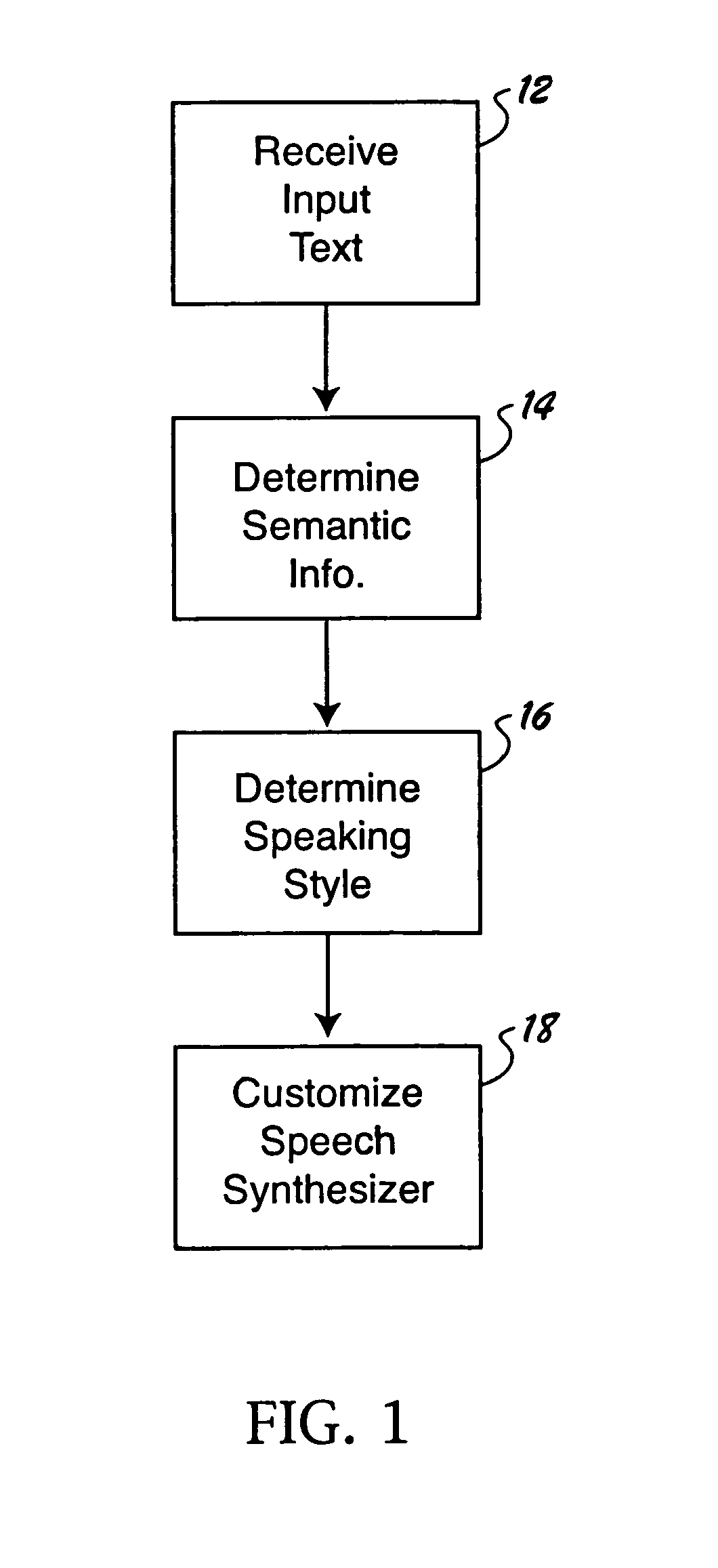
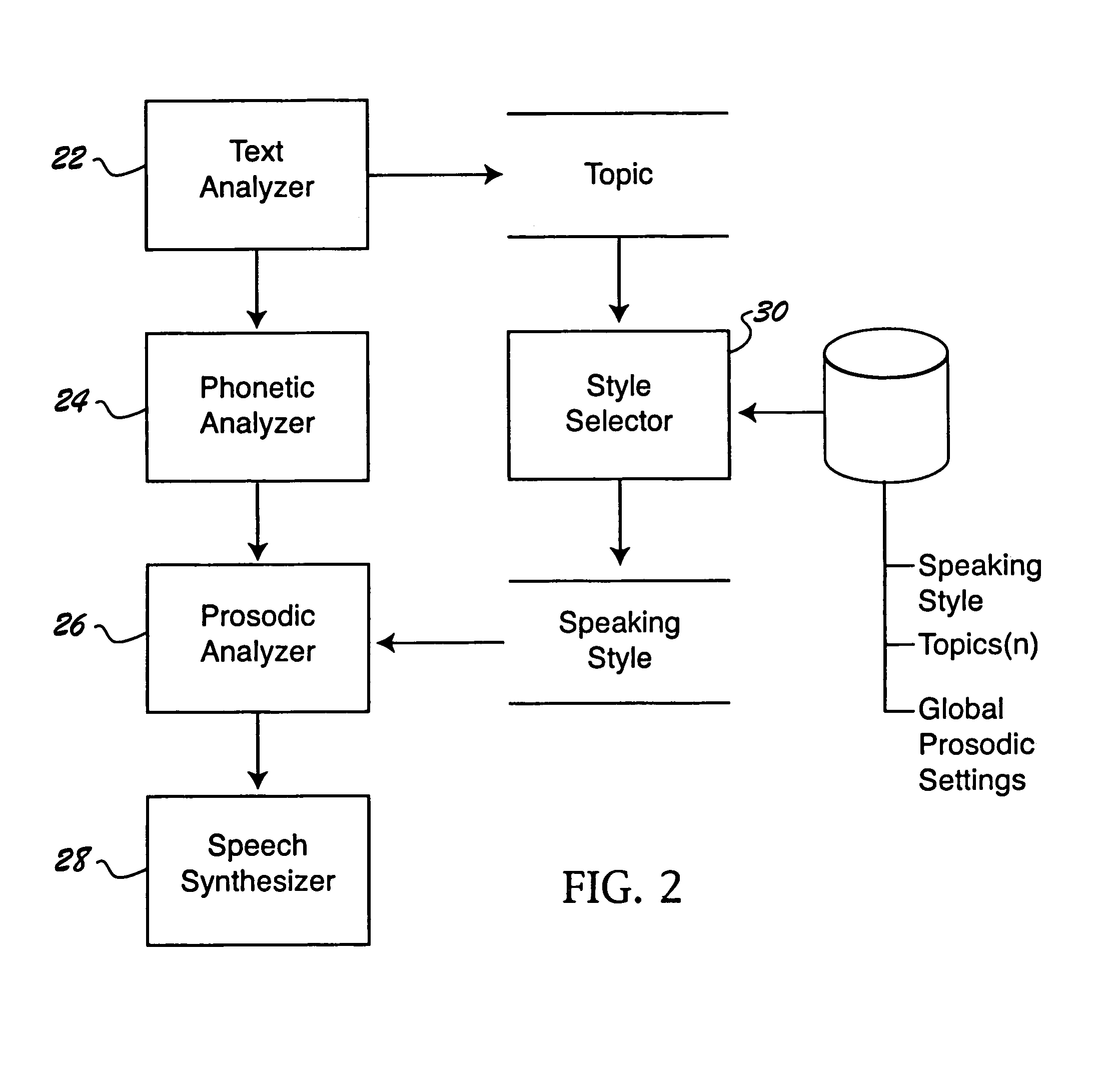
Customizing the speaking style of a speech synthesizer based on semantic analysis
A method is provided for customizing the speaking style of a speech synthesizer. The method includes: receiving input text; determining semantic information for the input text; determining a speaking style for rendering the input text based on the semantic information; and customizing the audible speech output of the speech synthesizer based on the identified speaking style.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
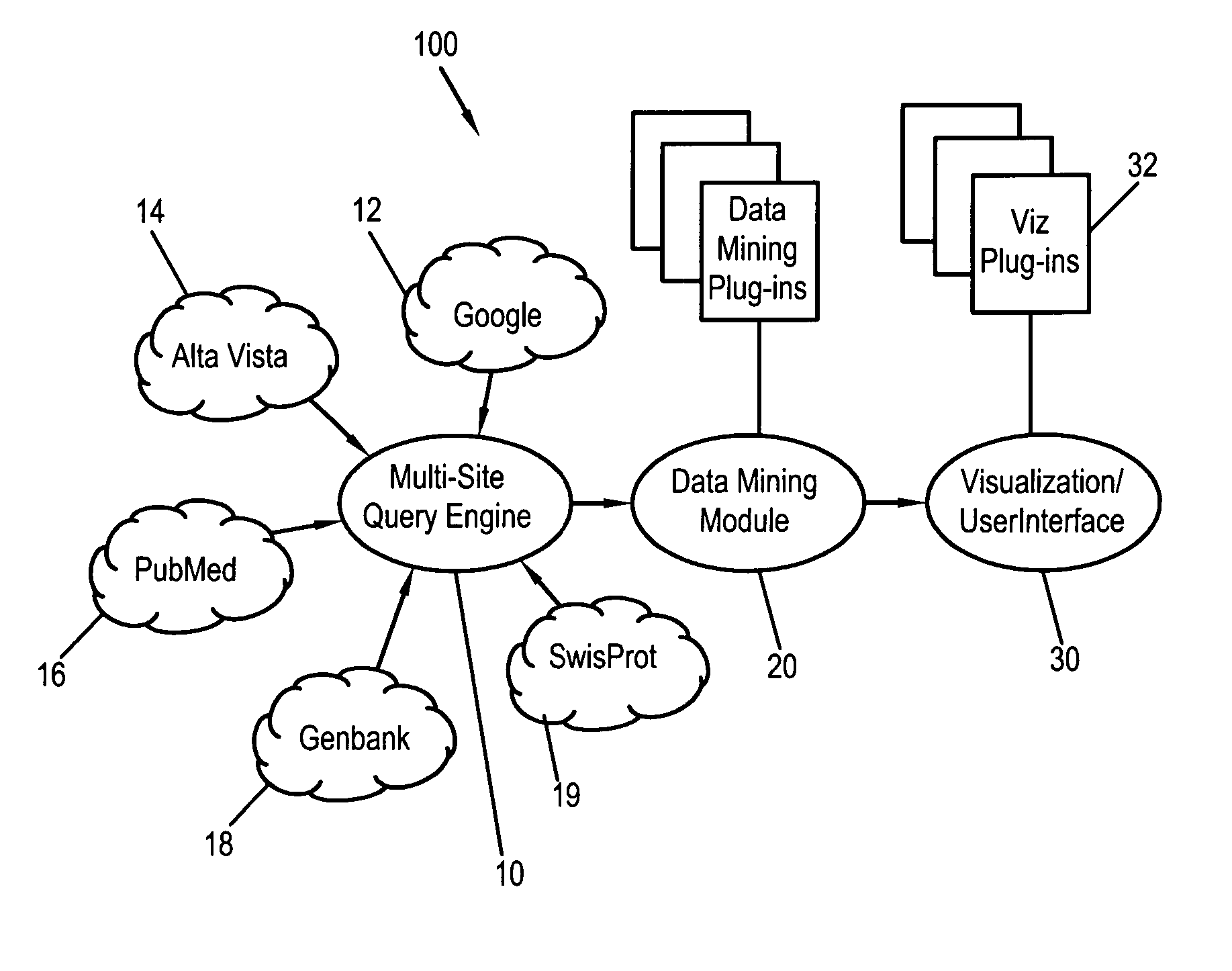
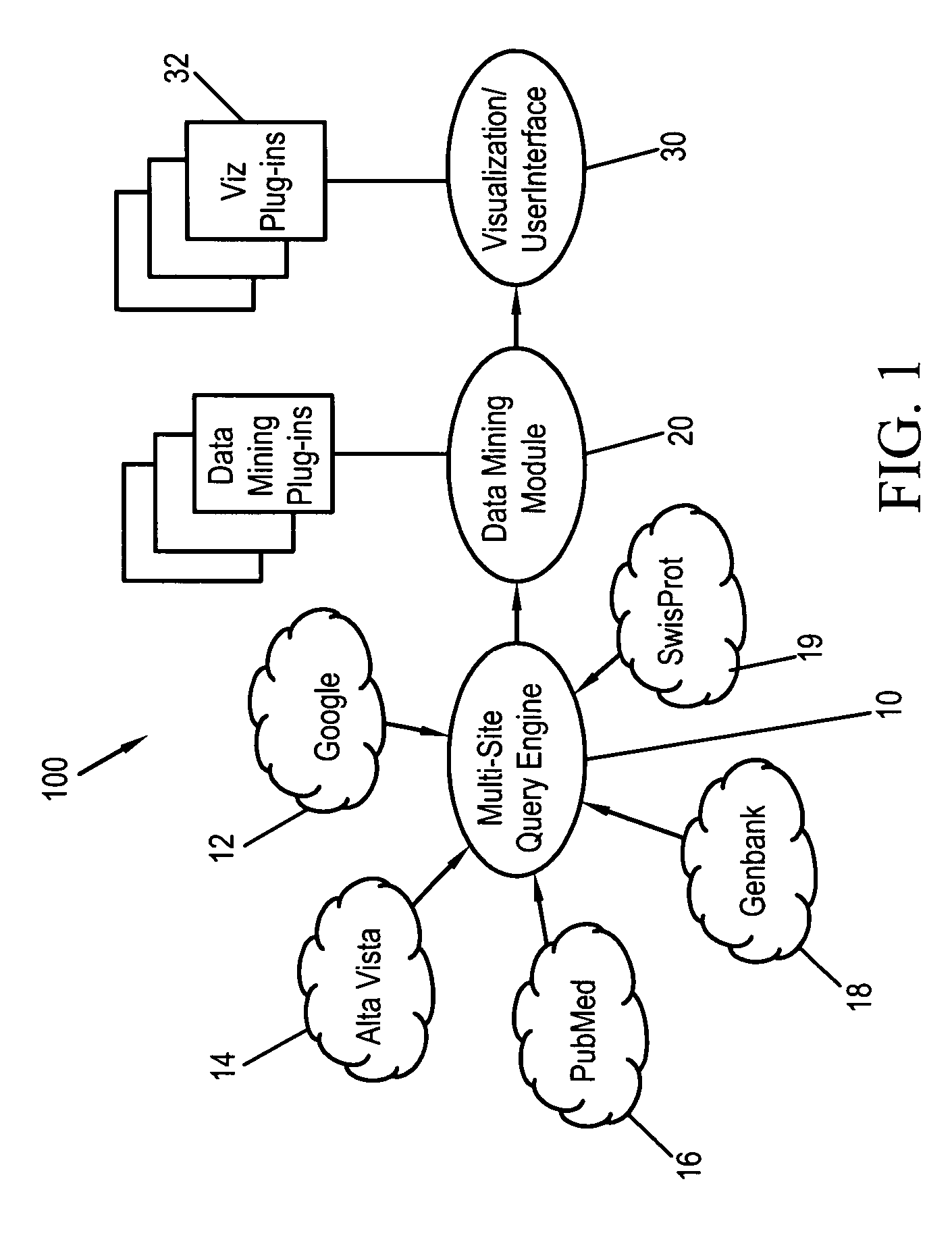
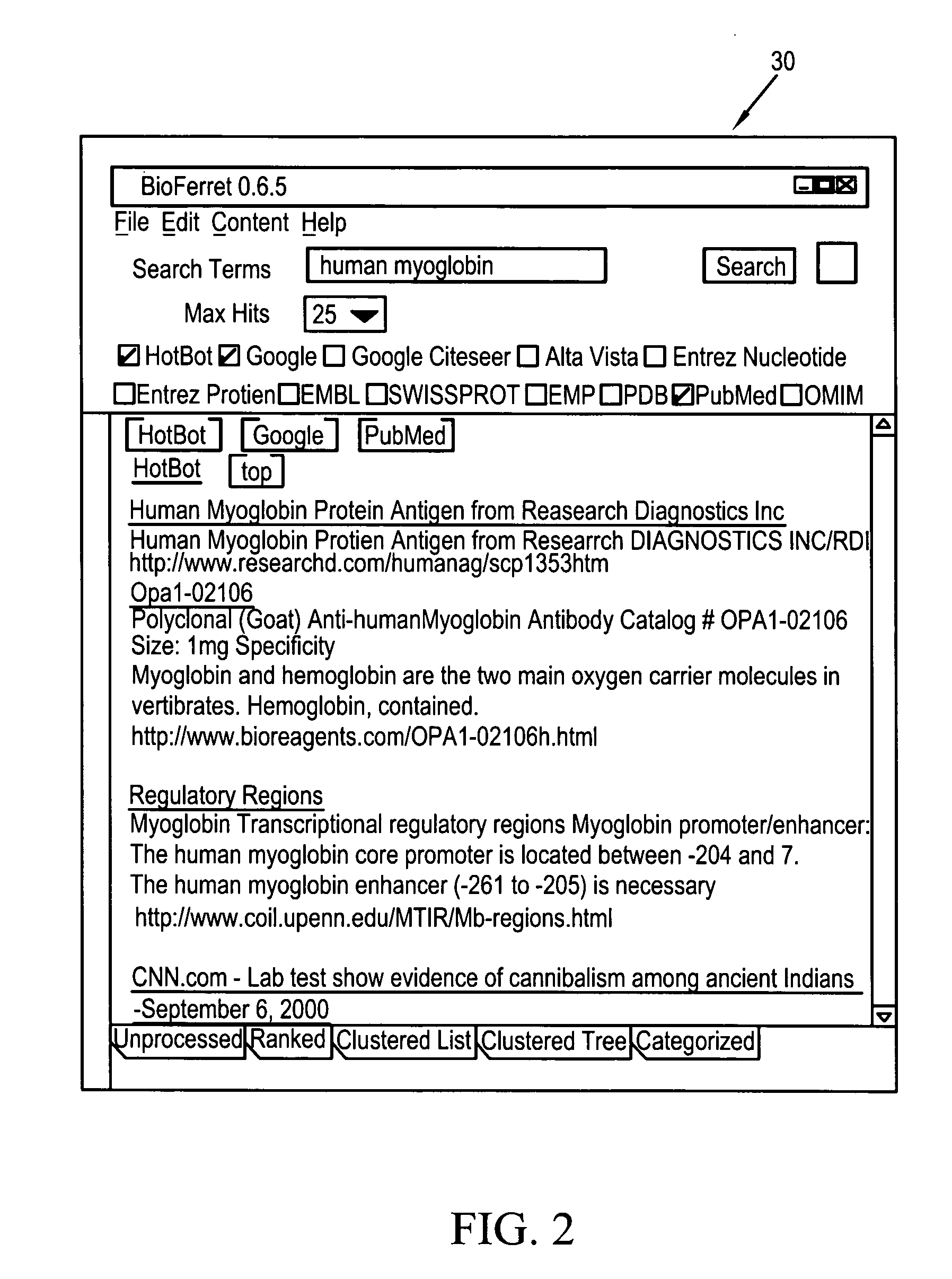
Systems, methods and computer readable media for performing a domain-specific metasearch, and visualizing search results therefrom
Systems, methods and computer readable media for performing a domain-specific metasearch, and obtaining search results therefrom. A metasearch engine capable of accessing generic, web-based search engines and domain-relevant search engines is provided to receive one or more queries inputted by a user, and to search for documents on at least one the generic, web-based search engines and domain-relevant search engines which are relevant to the queries. Raw data search results are fetched in the form of text documents. Relevant data including semantic information are extracted from the raw data search results, and converted to a local format. The relevant data having been converted to the local format may be visualized as a network visualization. Additionally or alternatively, the raw data search results may be ranked and / or filtered based on the linking of the relevant data. Visualization of the raw data having been ranked and / or filtered may be performed in addition to, or alternative to visualization of the network.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
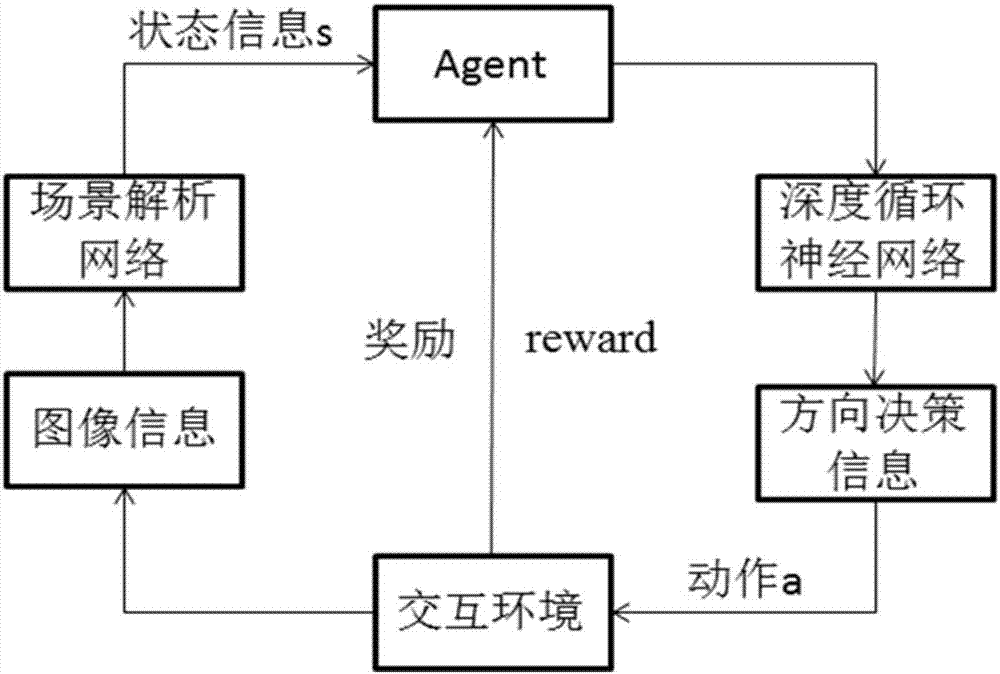
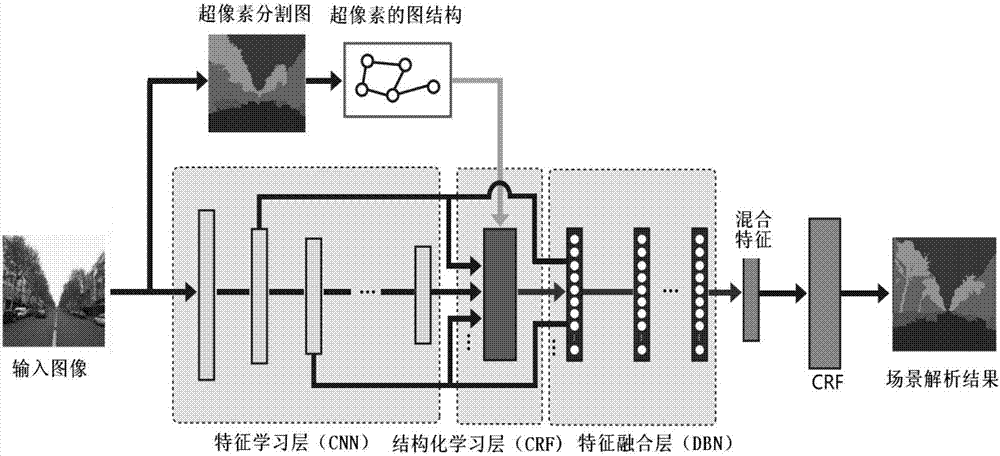
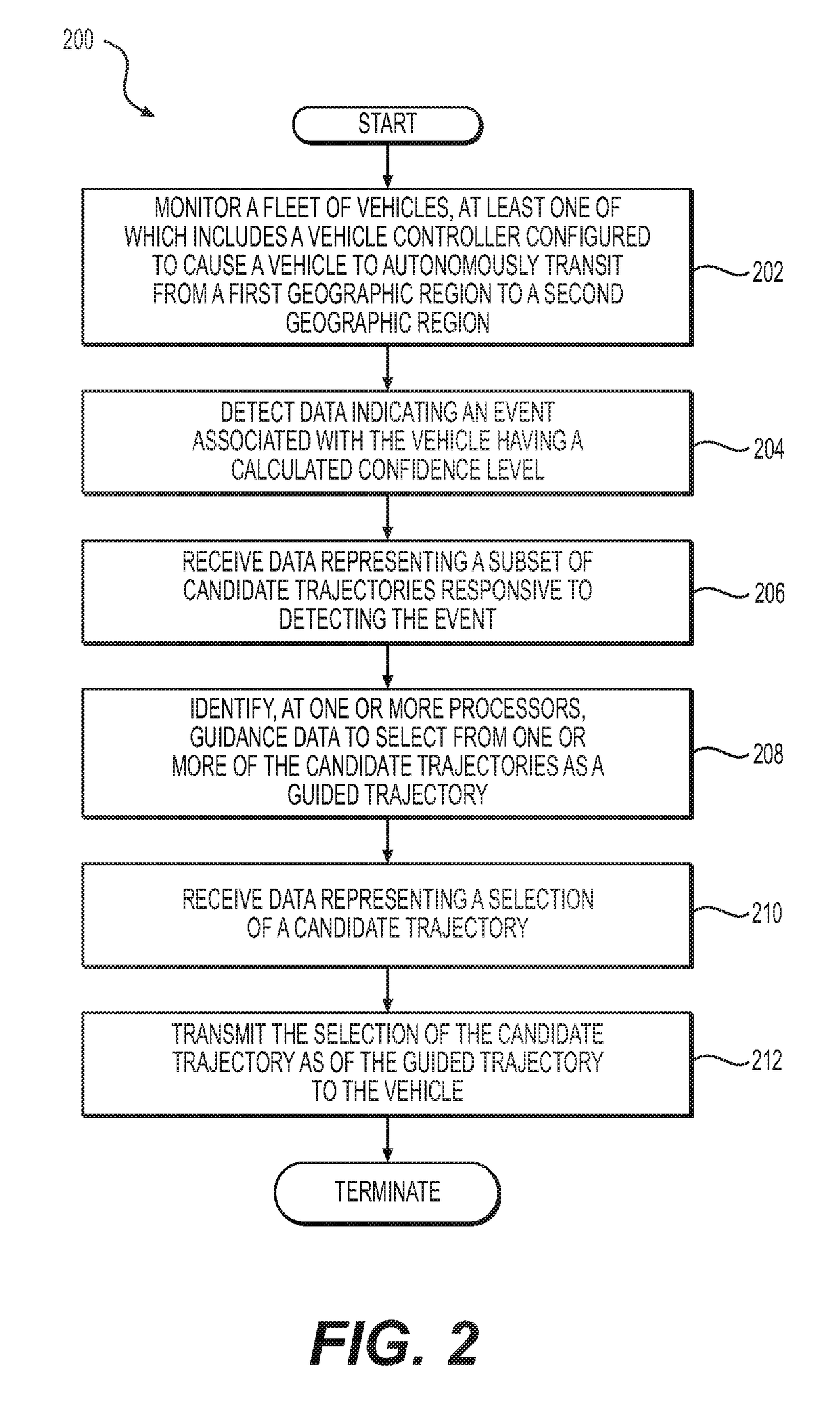
Deep and reinforcement learning-based real-time online path planning method of
ActiveCN106970615AReasonable method designAccurate path planningPosition/course control in two dimensionsPlanning approachStudy methods
The present invention provides a deep and reinforcement learning-based real-time online path planning method. According to the method, the high-level semantic information of an image is obtained through using a deep learning method, the path planning of the end-to-end real-time scenes of an environment can be completed through using a reinforcement learning method. In a training process, image information collected in the environment is brought into a scene analysis network as a current state, so that an analytical result can be obtained; the analytical result is inputted into a designed deep cyclic neural network; and the decision-making action of each step of an intelligent body in a specific scene can be obtained through training, so that an optimal complete path can be obtained. In an actual application process, image information collected by a camera is inputted into a trained deep and reinforcement learning network, so that the direction information of the walking of the intelligent body can be obtained. With the method of the invention, obtained image information can be utilized to the greatest extent under a premise that the robustness of the method is ensured and the method slightly depends on the environment, and real-time scene walking information path planning can be realized.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method and apparatus for category-based photo clustering in digital photo album
InactiveUS20060074771A1Character and pattern recognitionMetadata still image retrievalComputer visionComputer science
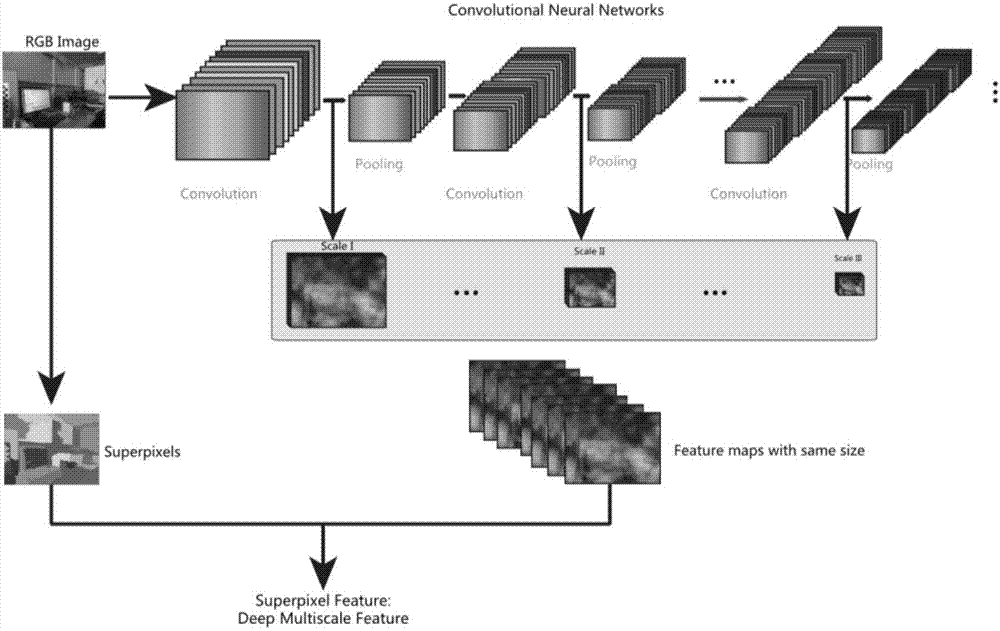
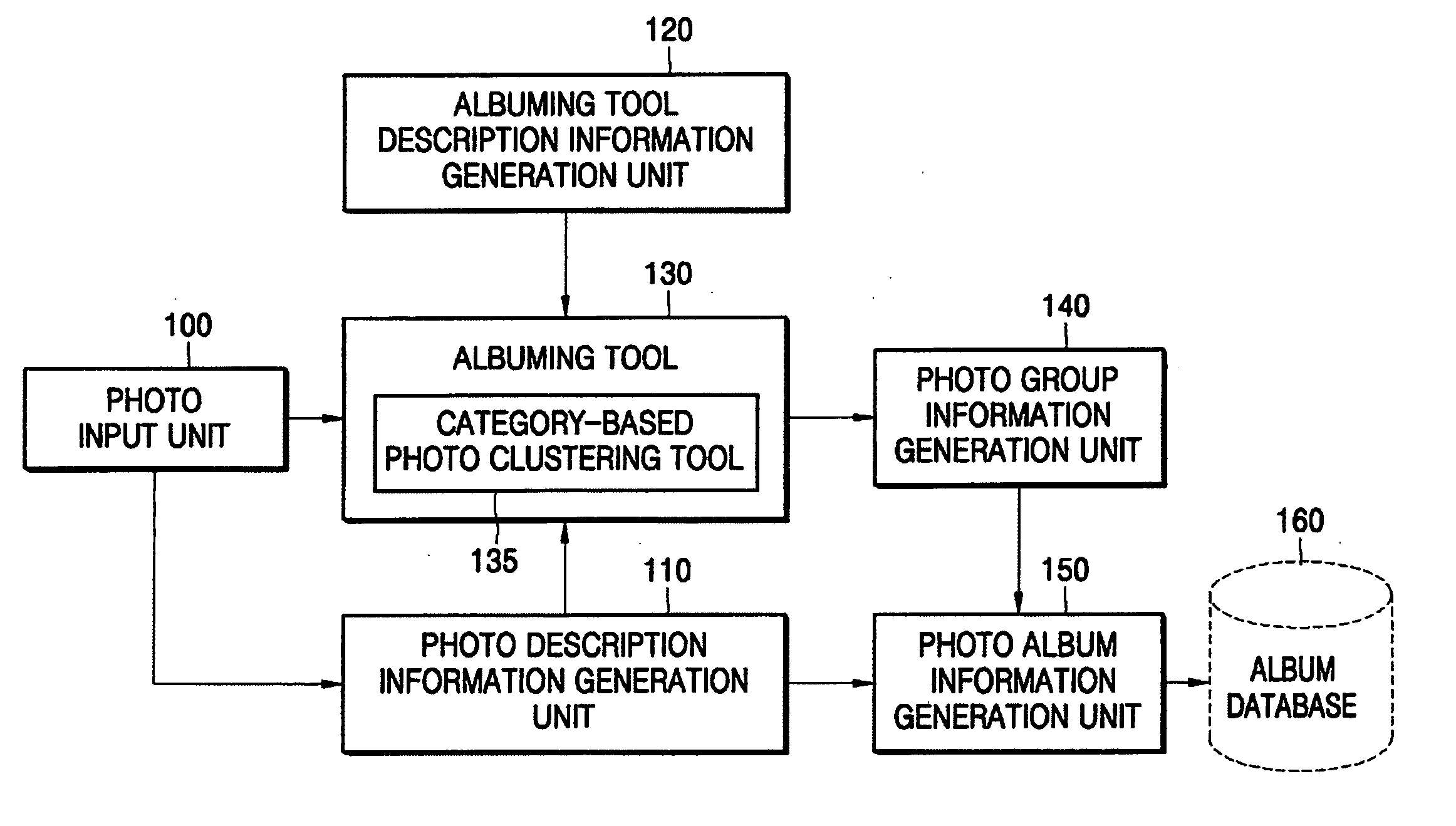
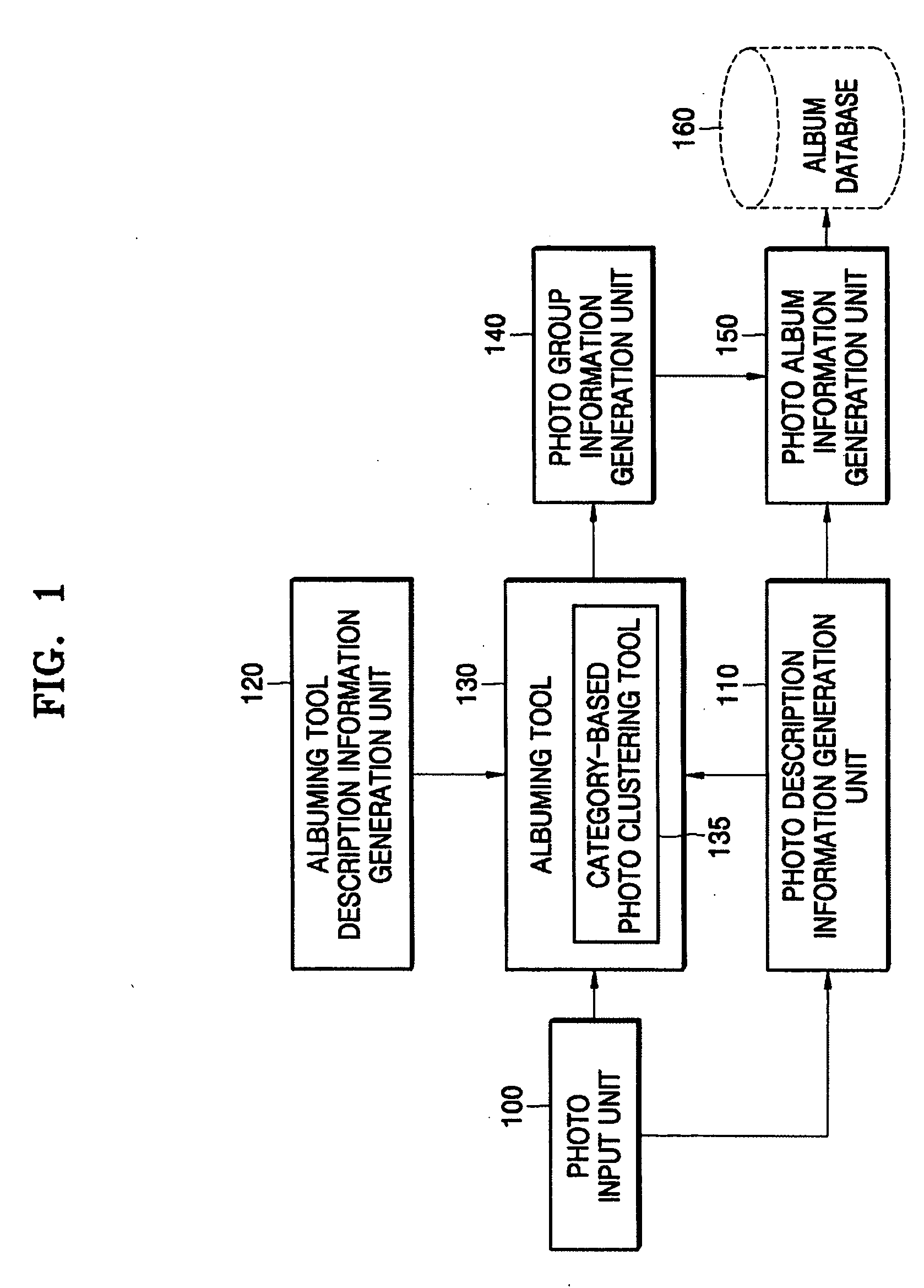
A method of category-based clustering of a digital photo album and a system thereof, the method includes: generating photo information by extracting at least one of camera information of a camera used to take a photo, photographing information, and a content-based feature value including at least one of color, texture, and shape feature values, and a speech feature value; generating a predetermined parameter including at least one of user preference indicating the personal preference of the user, photo semantic information generated by using the content-based feature value of the photo, and photo syntactic information generated by at least one of the camera information, the photographing information, and interaction with the user; generating photo group information categorizing photos by using the photo information and the parameter; and generating a photo album by using the photo information and the photo group information. According to the method and system, by using together user preference and content-based feature value information, such as color, texture, and shape, from the contents of photos, as well as information that can be basically obtained from photos, such as camera information and file information stored in a camera, a large volume of photos are effectively categorized such that an album can be fast and effectively generated with photo data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
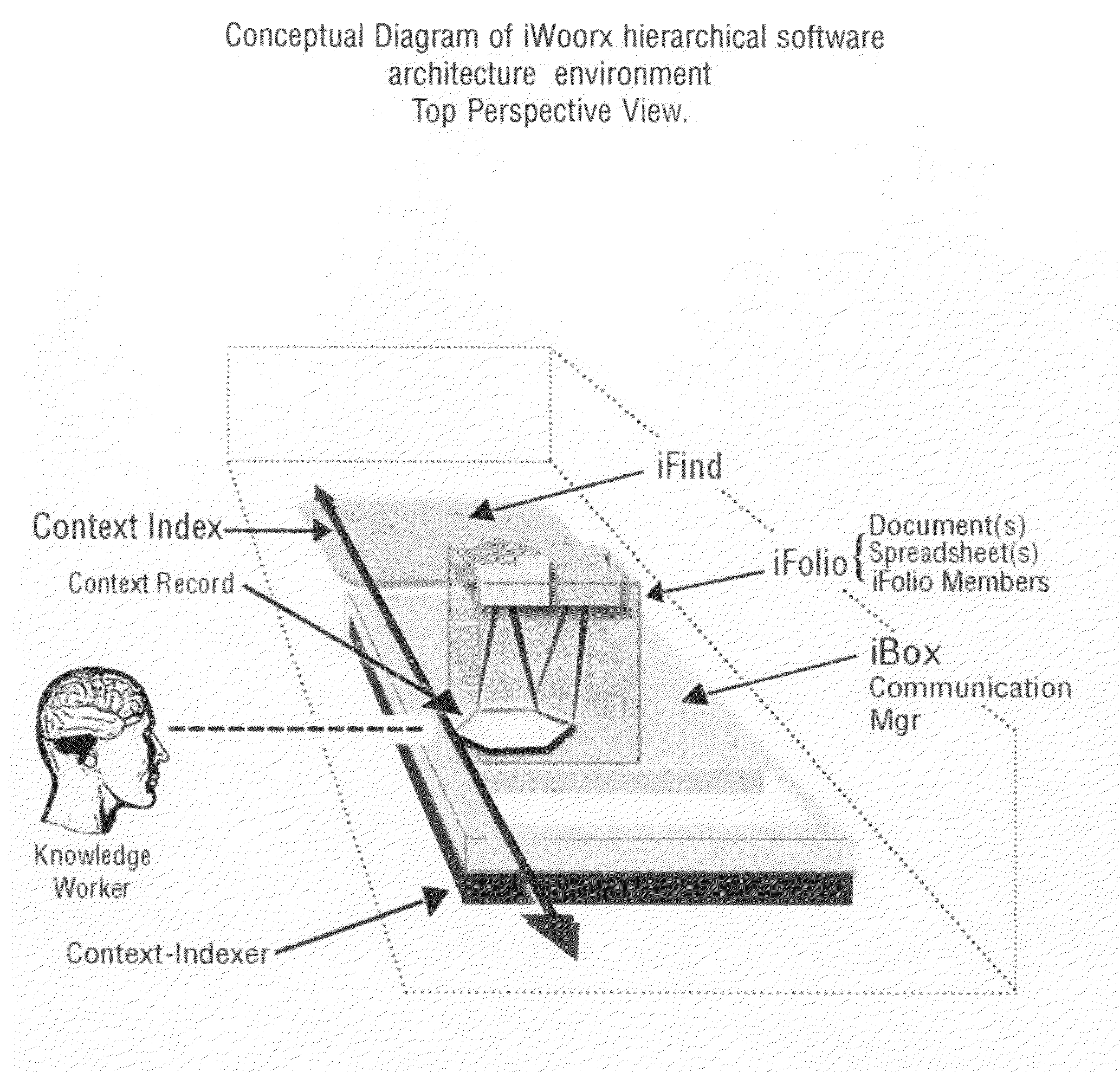
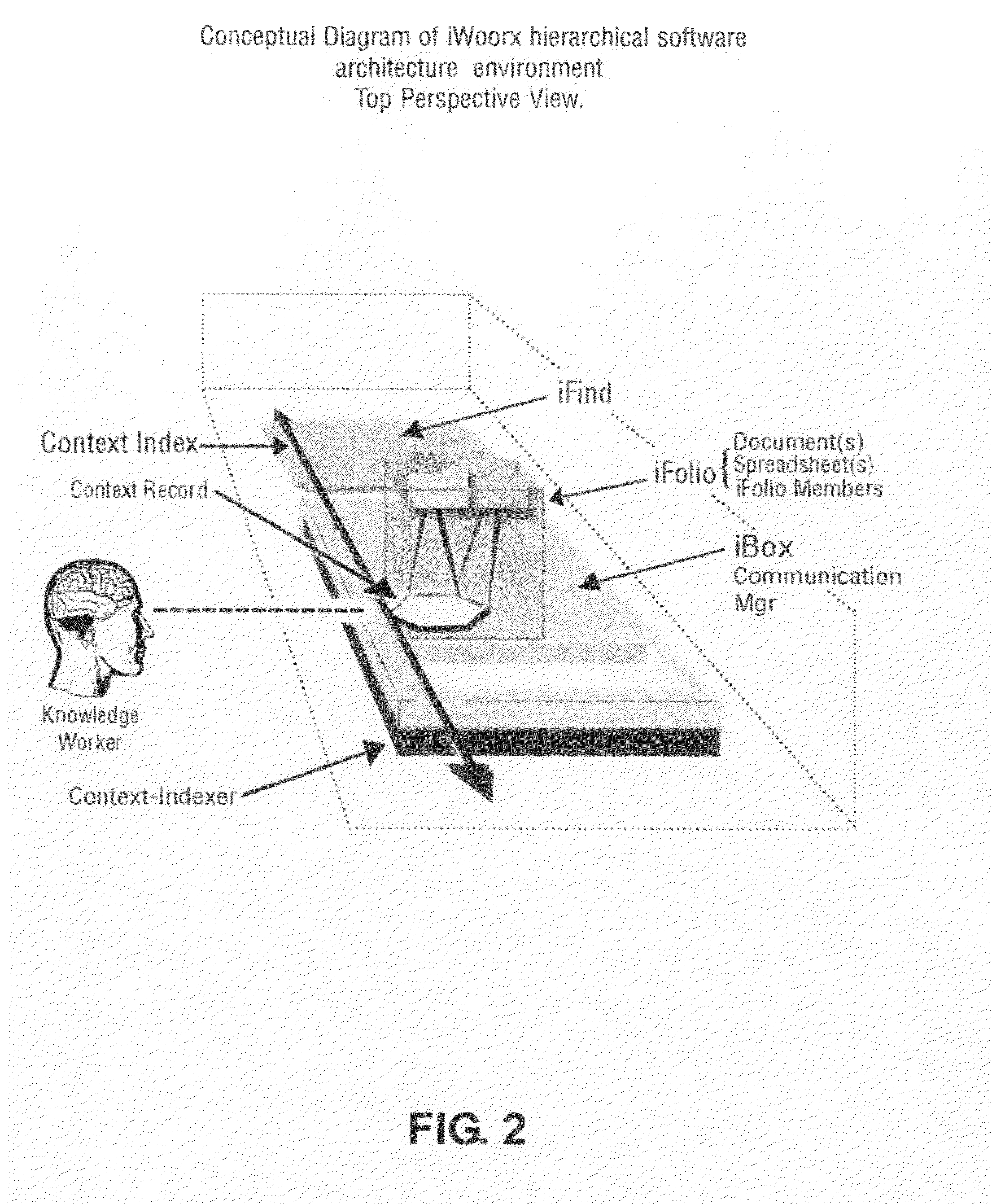
Context-aware semantic virtual community for communication, information and knowledge management
InactiveUS20100100546A1Improved organizational information sharingIncrease searchDigital data processing detailsMultimedia data retrievalManagement toolApplication software
A method for creation of a semantic information management environment, said method comprised of steps of: providing said semantic information environment consisting of an architecture partitioned according to the classification of the use of natural language by information scale, dynamical properties, or semantic classifications; detection, classification, and storage of semantic and contextual information detected and stored by recording of observed contextual parameters associated with events in said semantic information management environment; said interactions including the use of information management or electronic communication applications embedded or linked to said architecture, or separate from said architecture; said observations including the use of natural language as parameters that have specific semantic properties; detection, classification and storage of use of natural language in said semantic information environment; representation of semantic processes containing said detected, classified, and stored contextual information and natural language use in said semantic information environment; said representations of semantic processes used to link and associate natural language use with objects, entities, facts, communication, information, and digital files in said semantic information environment; providing said users of said semantic information environment with information and knowledge management tools, reports, representations, and interfaces that utilize said semantic process representations.
Owner:KOHLER STEVEN FORREST
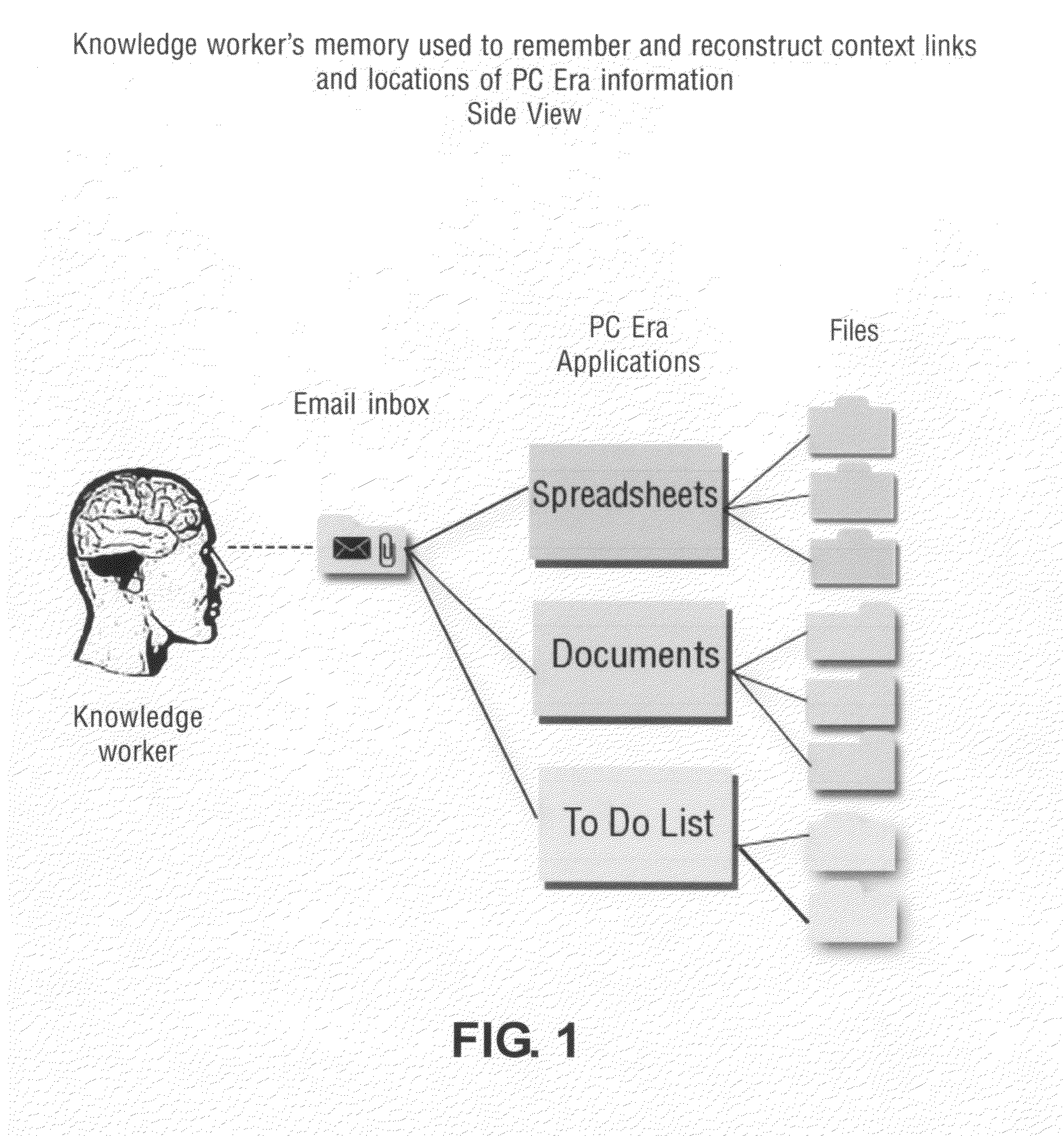
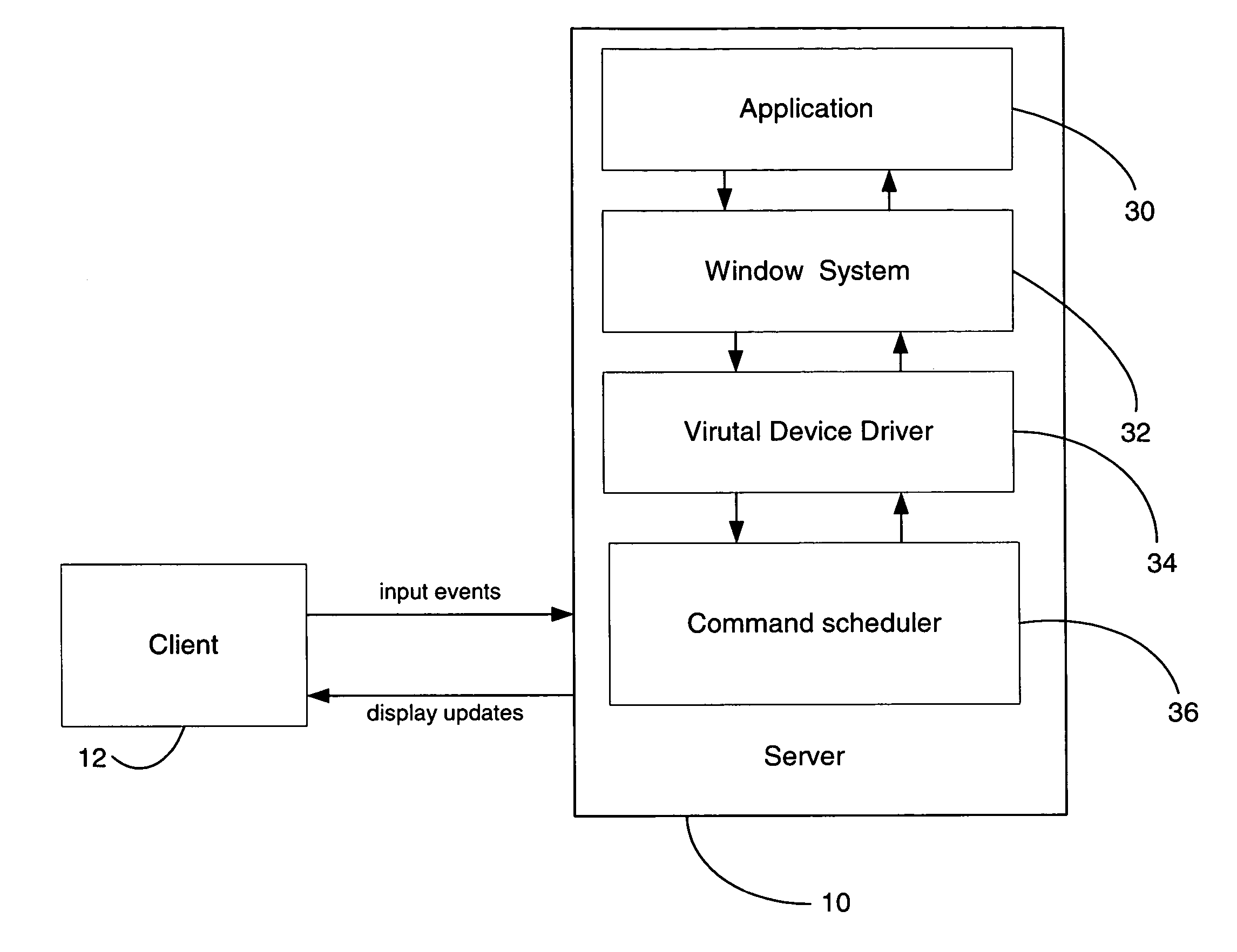
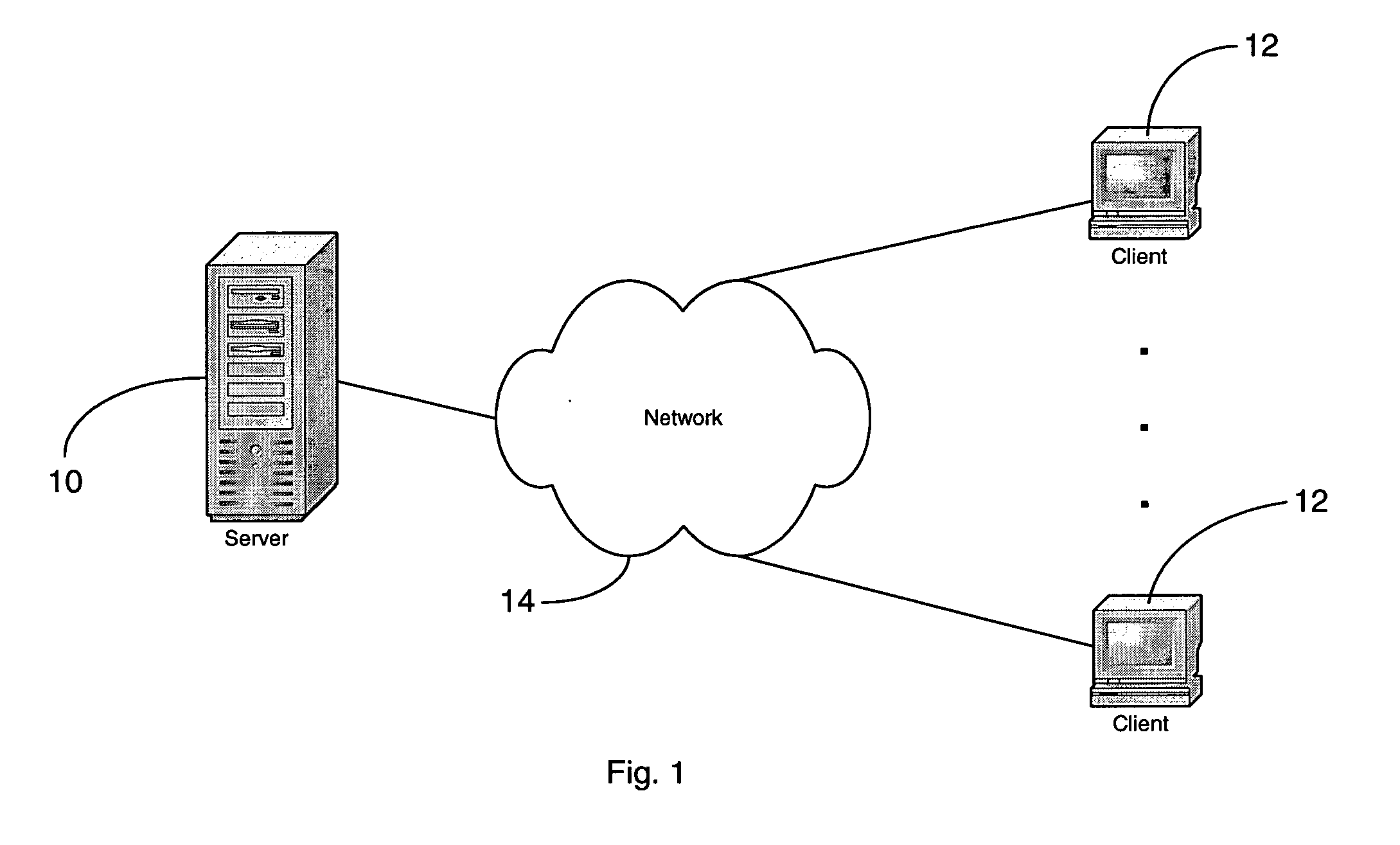
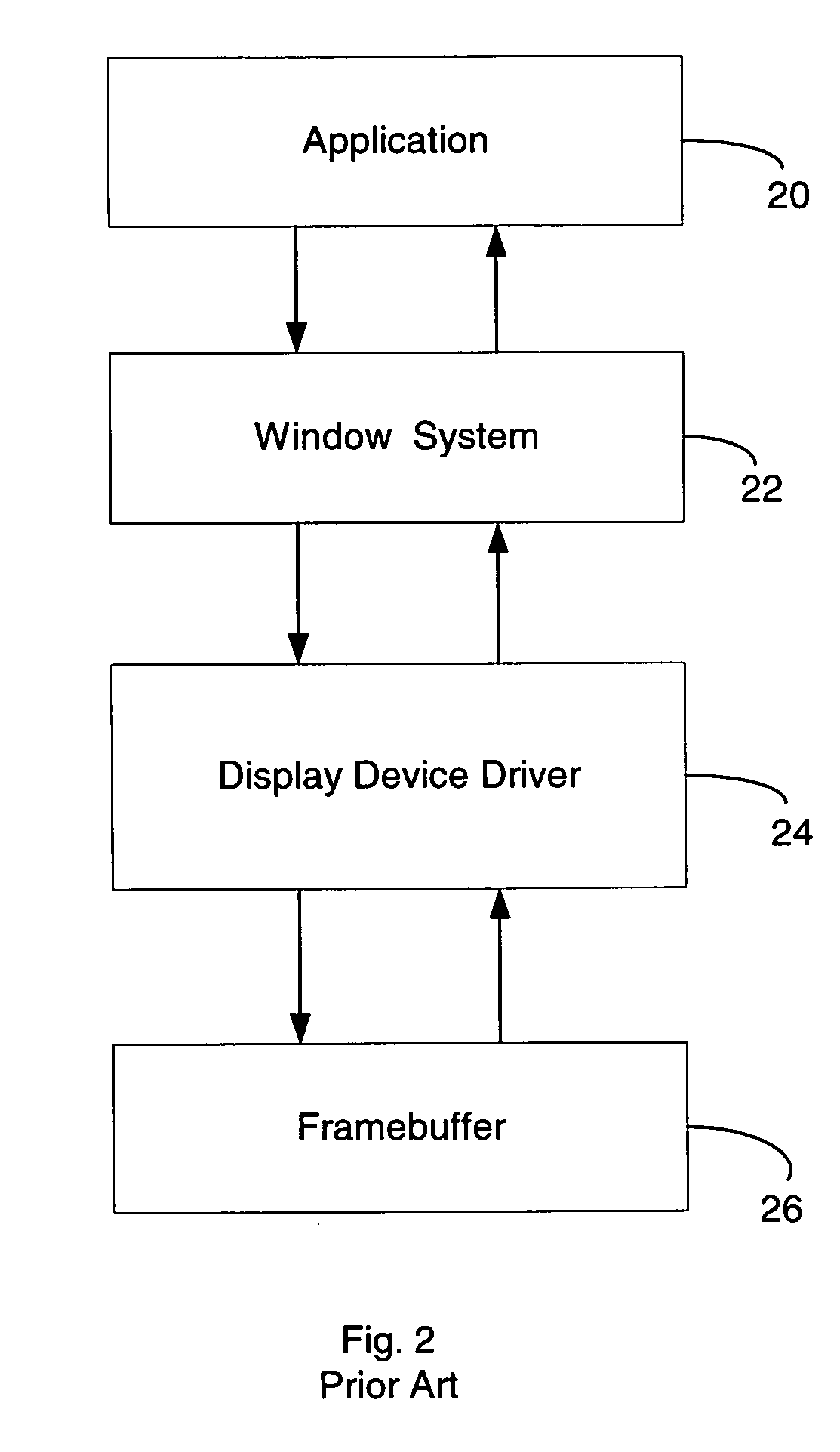
Thin-client network computing method and system
InactiveUS20060184614A1Multiple digital computer combinationsImage data processing detailsComputer hardwareUser input
A method and system are provided for executing an application remotely on a server computer for a client computer in a computer network. The server receives at user input from the client computer associated with the application, and executes the application. The server processes display commands of the application to generate display primitives, and translates the display primitives into lower level display commands defining display updates using semantic information of the display primitives. The lower level display commands are selected from a predetermined set of lower level display commands. The lower level display commands are aggregated and ordered into one or more command queues. Each command queue is associated with a given display region. The server computer transmits the lower level display commands in the one or more command queues over the network to the client computer. The client computer is capable of translating the lower level display commands into hardware calls for causing the client computer to display the display updates.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
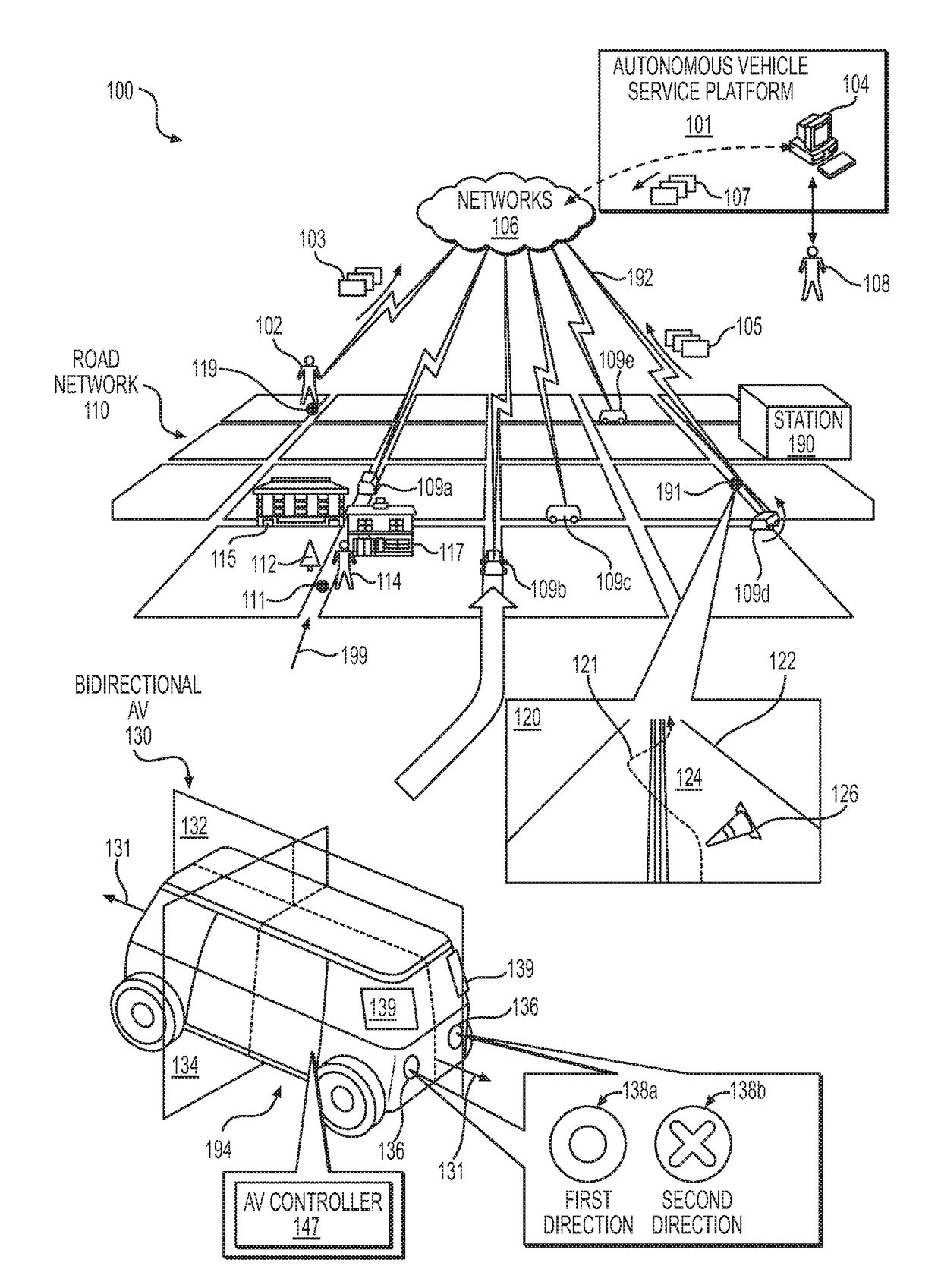
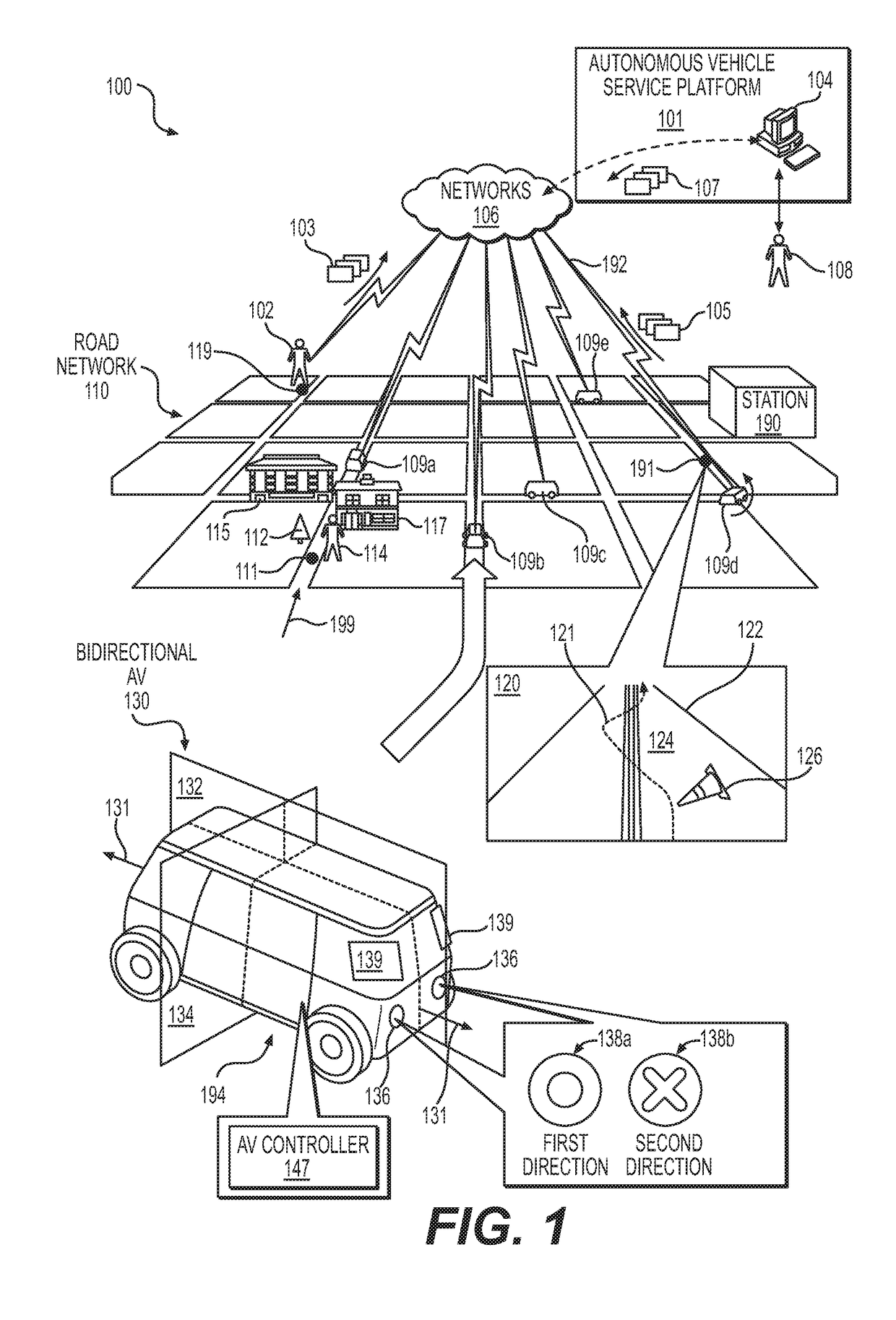
Automated extraction of semantic information to enhance incremental mapping modifications for robotic vehicles
ActiveUS20170316333A1Autonomous decision making processScene recognitionStatistical analysisHeat map
Systems, methods and apparatus may be configured to implement automatic semantic classification of a detected object(s) disposed in a region of an environment external to an autonomous vehicle. The automatic semantic classification may include analyzing over a time period, patterns in a predicted behavior of the detected object(s) to infer a semantic classification of the detected object(s). Analysis may include processing of sensor data from the autonomous vehicle to generate heat maps indicative of a location of the detected object(s) in the region during the time period. Probabilistic statistical analysis may be applied to the sensor data to determine a confidence level in the inferred semantic classification. The inferred semantic classification may be applied to the detected object(s) when the confidence level exceeds a predetermined threshold value (e.g., greater than 50%).
Owner:ZOOX INC
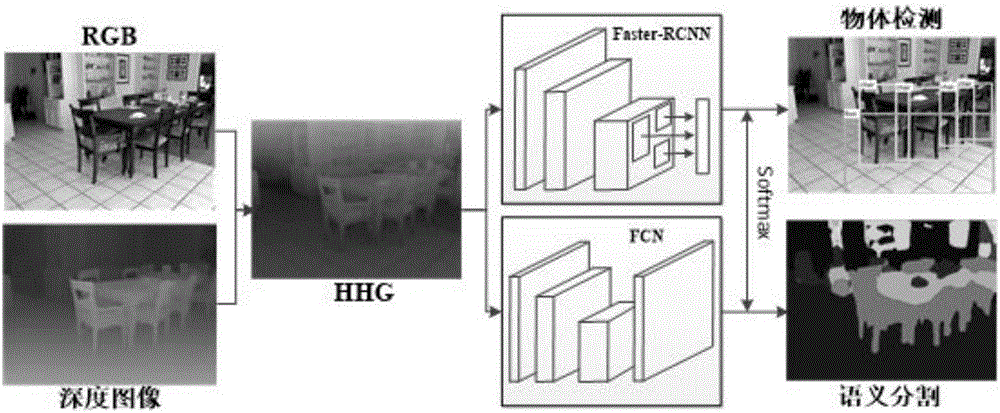
RGB-D image object detection and semantic segmentation method based on deep convolution network
ActiveCN106709568ACharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesMachine visionVisual perception
The invention discloses an RGB-D image object detection and semantic segmentation method based on a deep convolution network, which belongs to the field of depth learning and machine vision. According to the method provided by the technical scheme of the invention, Faster-RCNN is used to replace the original slow RCNN; Faster-RCNN uses GPU, which is fast in the aspect of feature extracting, and at the same time generates a regional scheme in the network; the whole training process is training from end to end; FCN is used to carry out RGB-D image semantic segmentation; FCN uses a GPU and the deep convolution network to rapidly extract the deep features of an image; deconvolution is used to fuse deep features and shallow features of the image convolution; and the local semantic information of the image is integrated into the global semantic information.
Owner:深圳市小枫科技有限公司
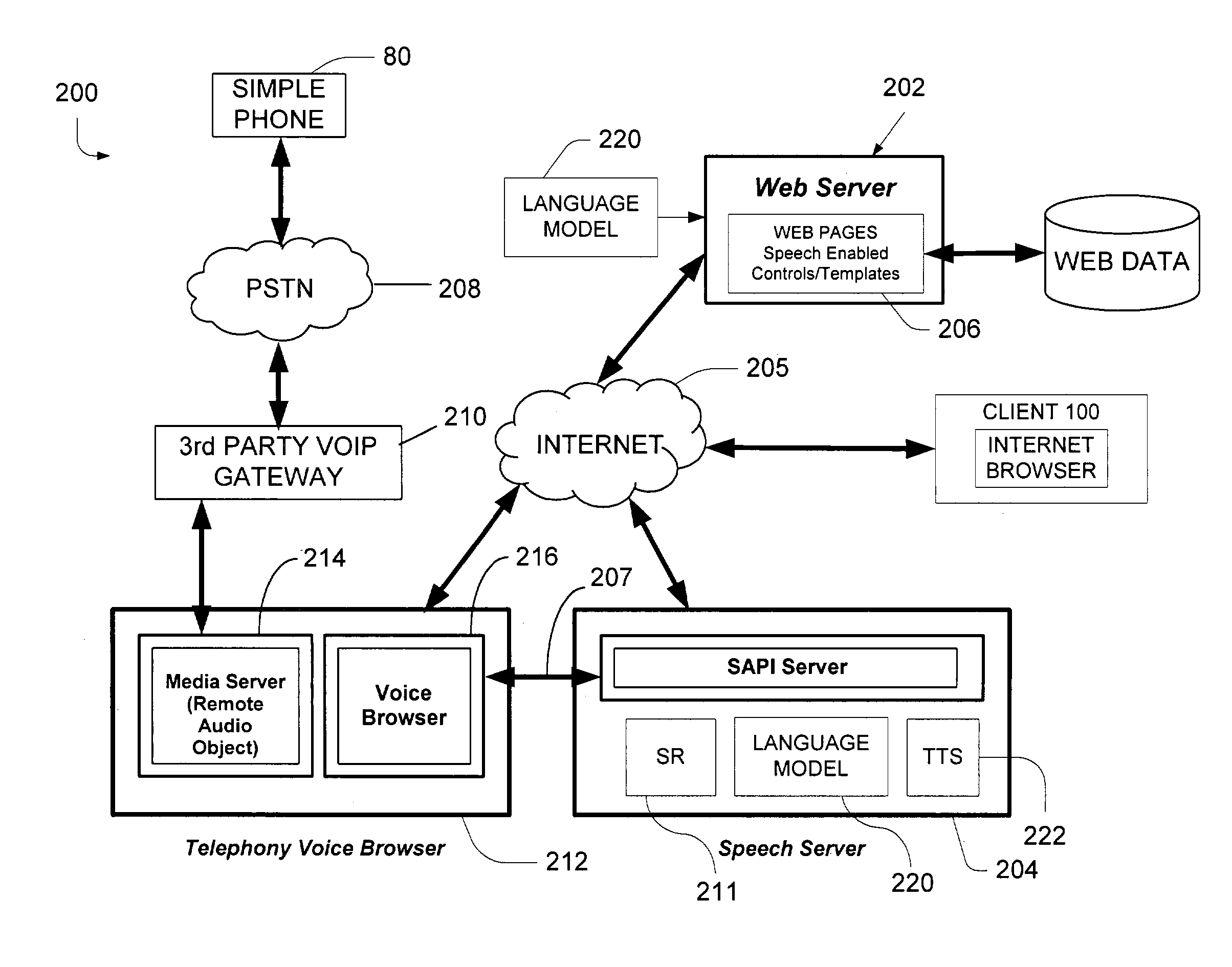
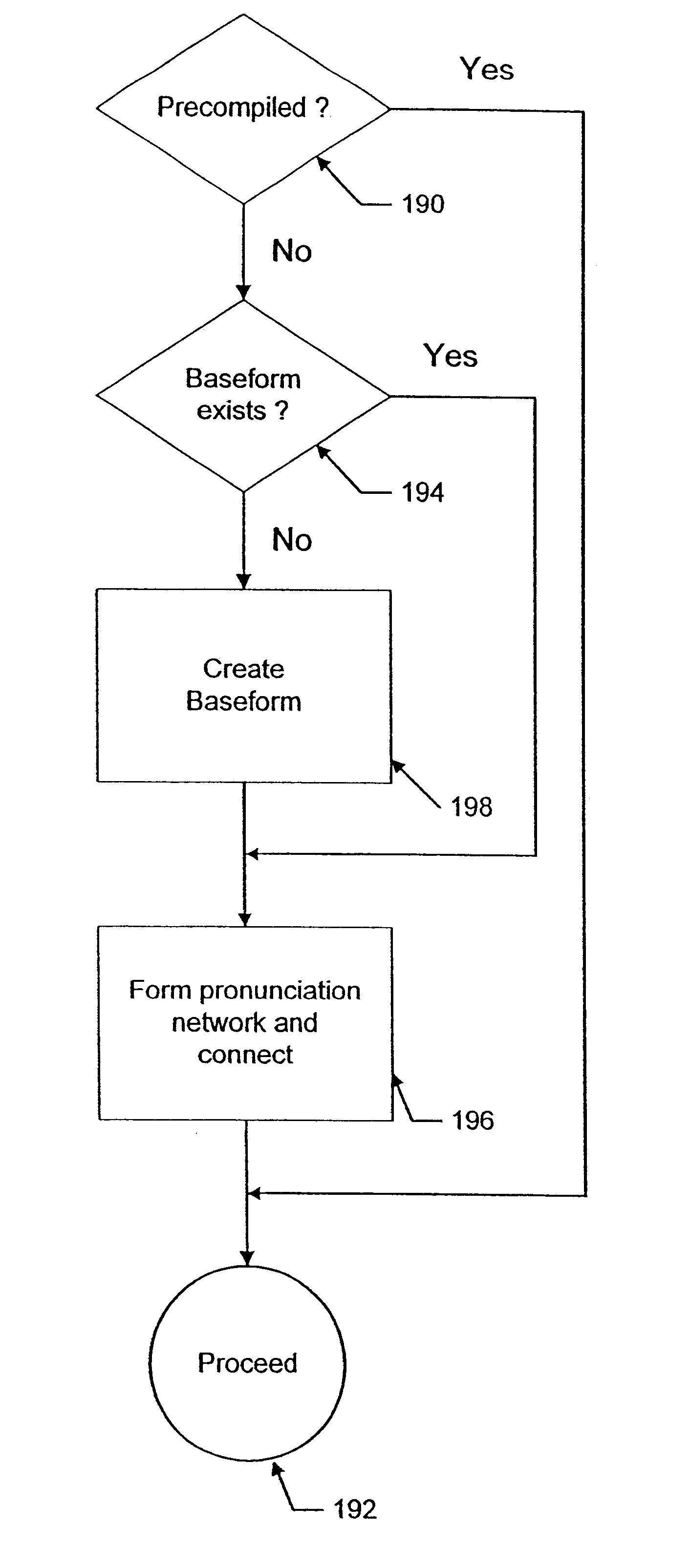
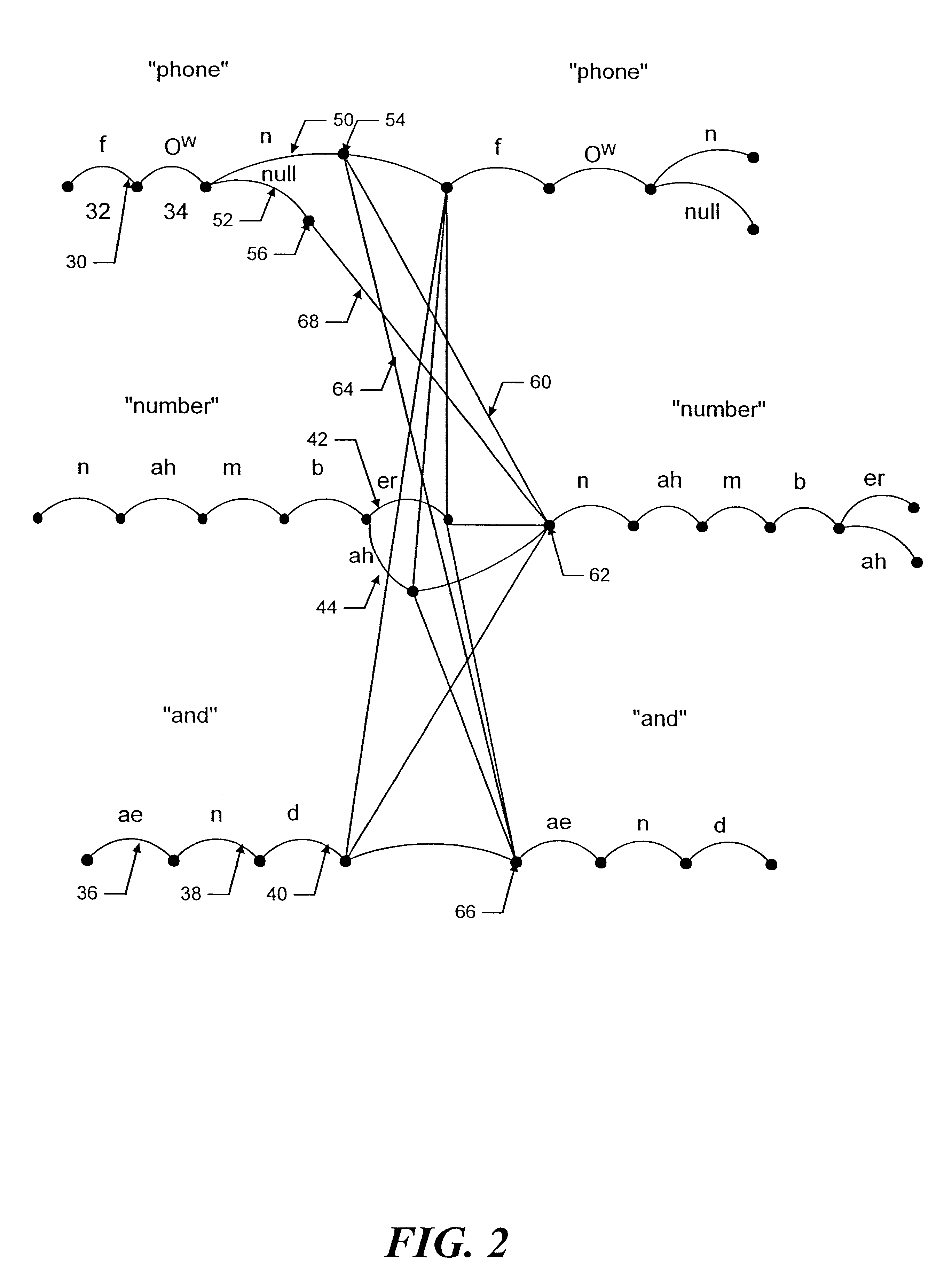
Method and apparatus for dynamic adaptation of a large vocabulary speech recognition system and for use of constraints from a database in a large vocabulary speech recognition system
InactiveUS6501833B2Facilitates rapid additionFast processingAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersPart of speechVocabulary speech recognition
The lexical network of a large-vocabulary speech recognition system is structured to effectuate the rapid and efficient addition of words to the system's active vocabulary. The lexical network is structured to include Phonetic Constraint Nodes, which organize the inter-word phonetic information in the network, and Word Class Nodes which organize the syntactic semantic information in the network. Network fragments, corresponding to phoneme pronunciations and labeled to specify permitted interconnections to each other and to phonetic constraint nodes, are precompiled to facilitate the rapid generation of pronunciations for new words and thereby enhance the rapid addition of words to the vocabulary even during speech recognition. Functions defined in accordance with linguistic constraints may be utilized during recognition. Different language models and different vocabularies for different portions of a discourse may also be invoked depending, in part, on the discourse history.
Owner:SPEECHWORKS INT
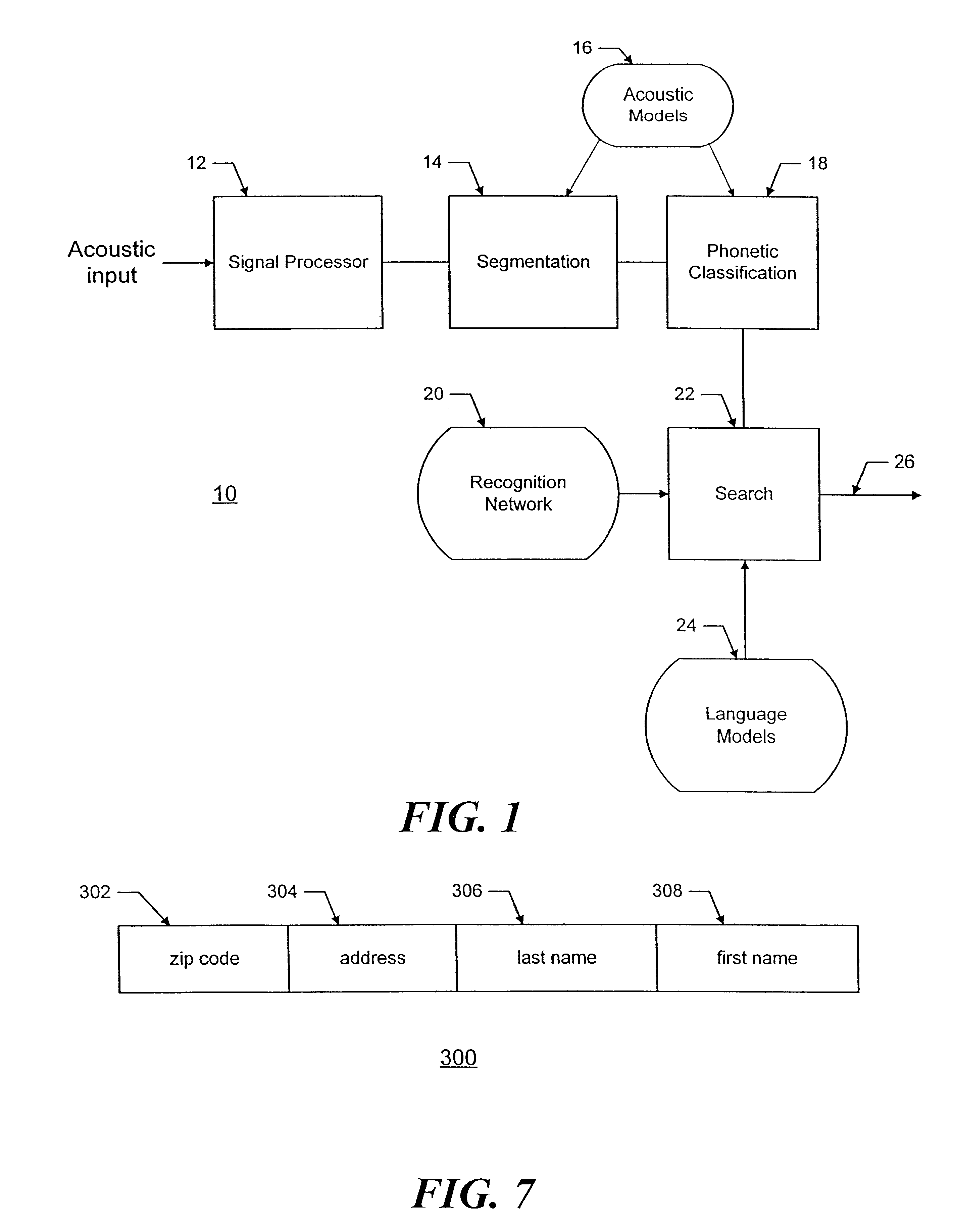
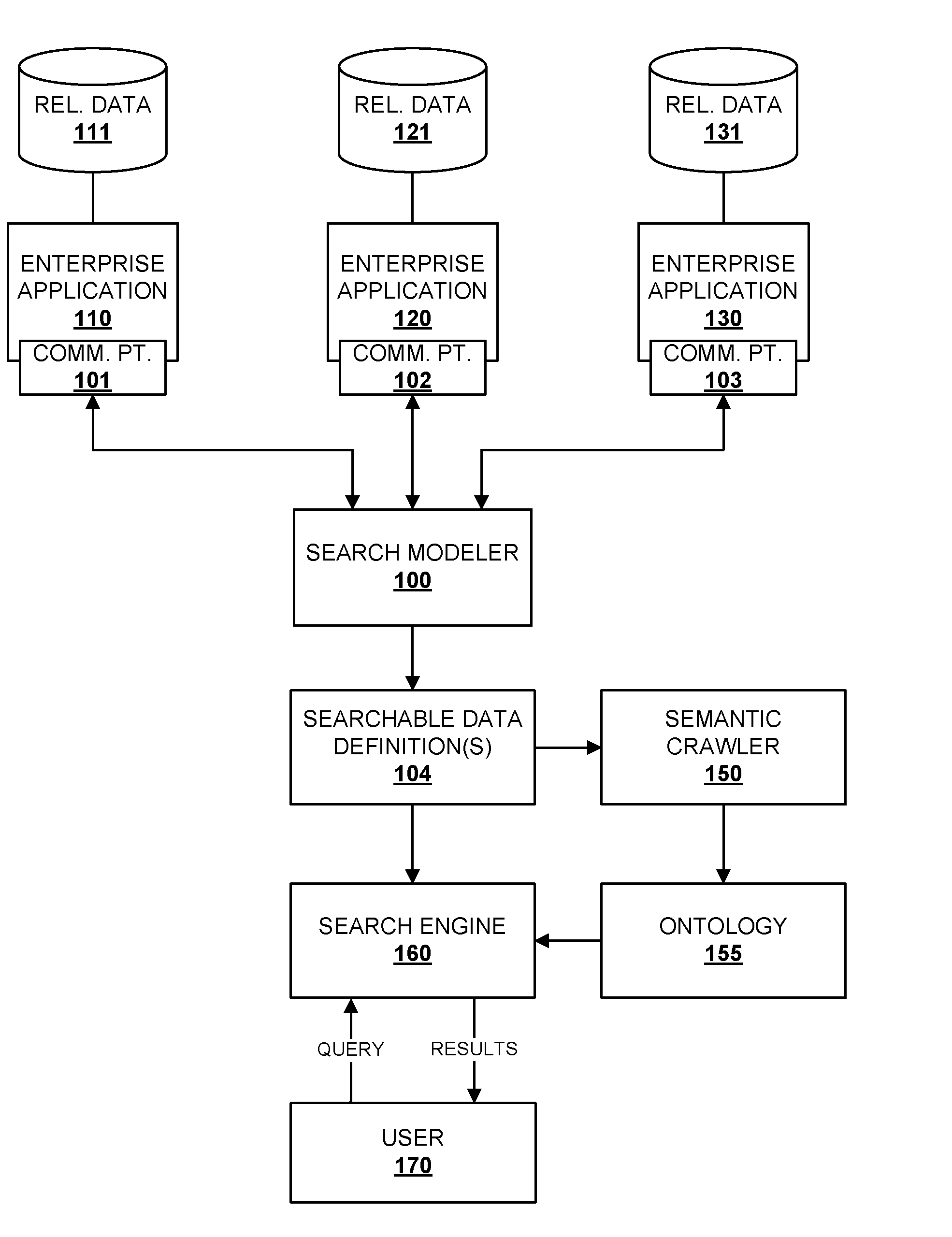
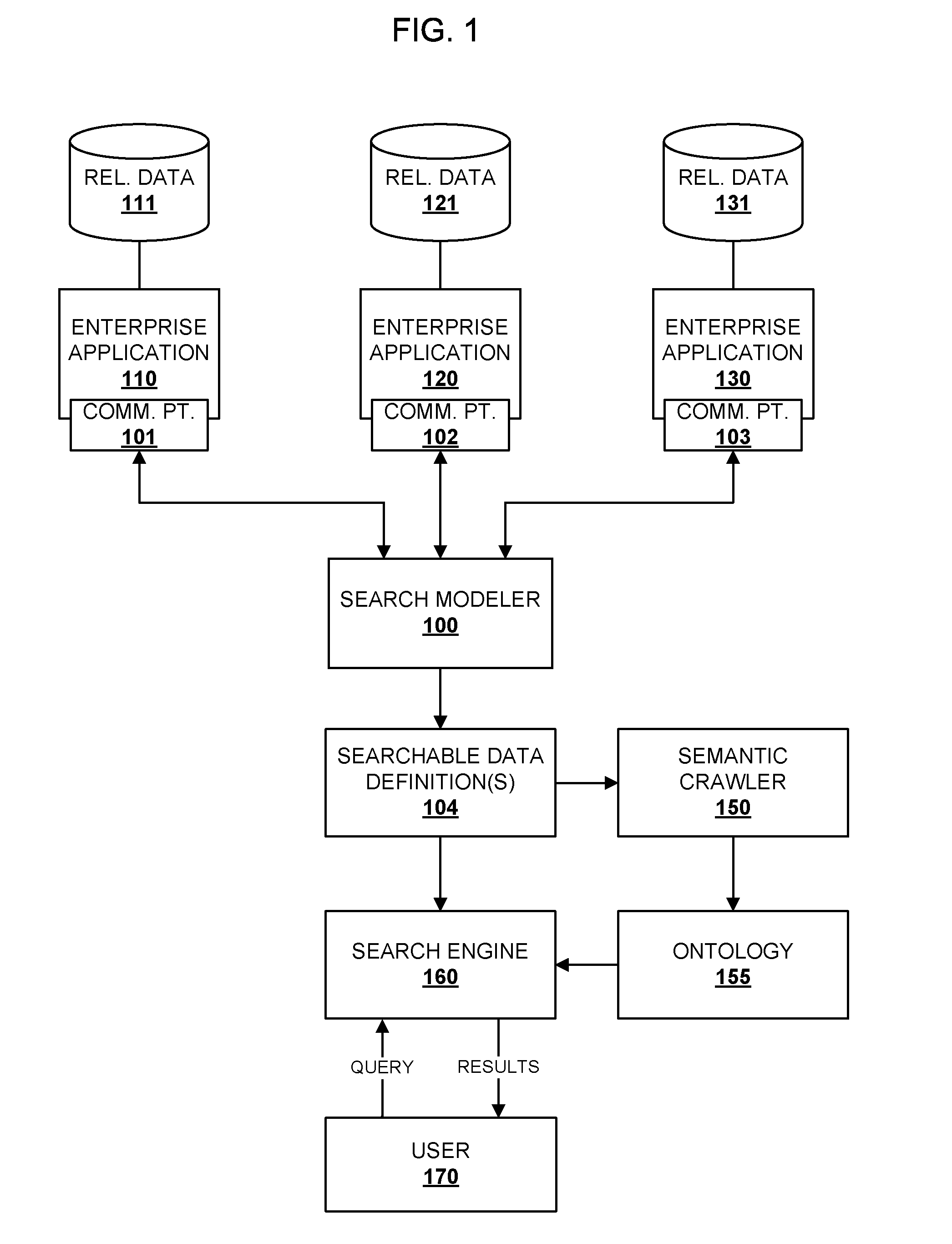
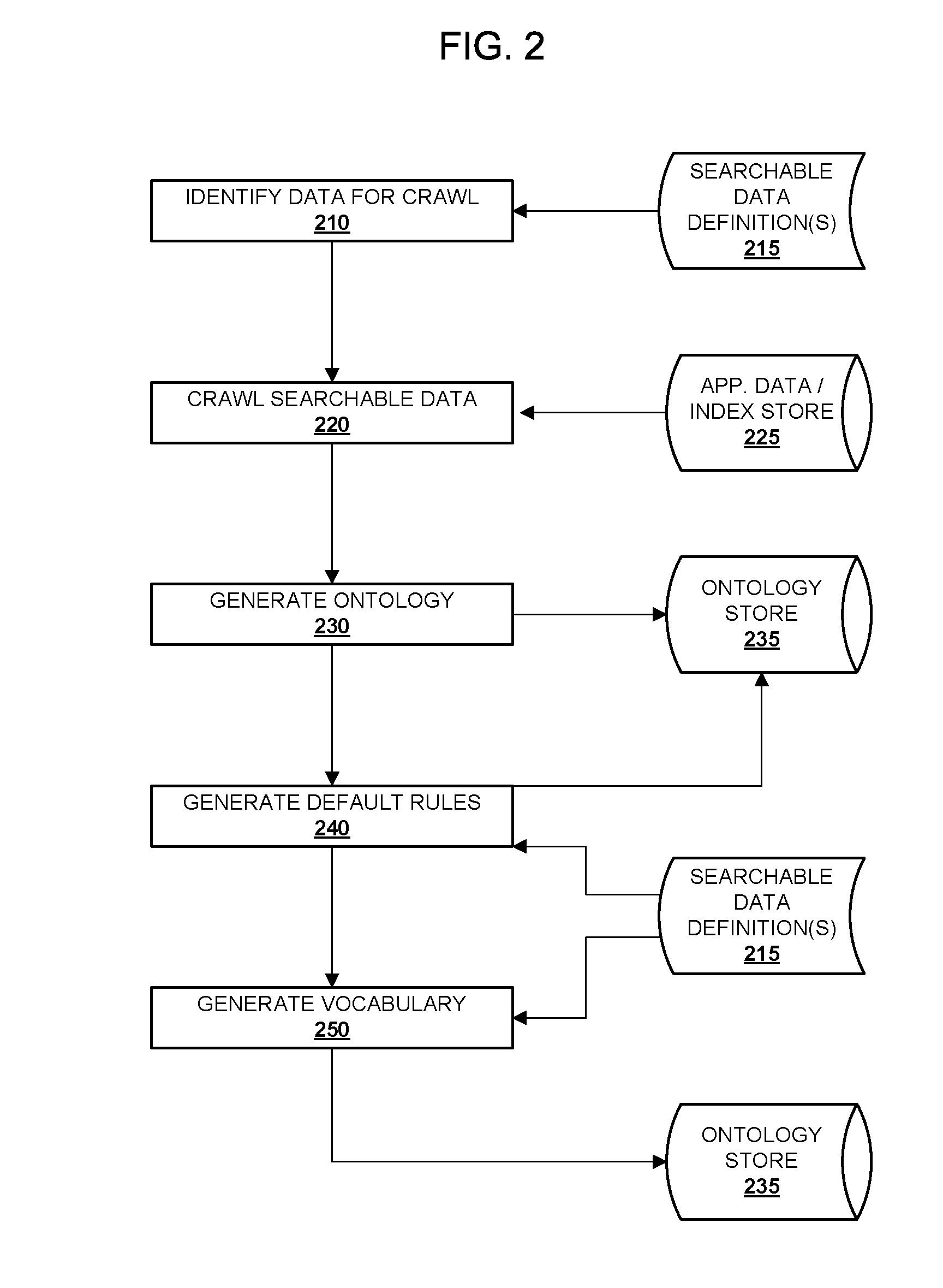
System and Method for Semantic Search in an Enterprise Application
ActiveUS20100070517A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsSemantic searchSemantic information
Embodiments of the present invention provide techniques for searching enterprise data using semantic information associated with enterprise applications. One or more searchable data definitions that describe searchable data associated with one or more enterprise applications may identify semantic relationships among searchable data in the application. An ontology for the application that describes semantic relationships among data associated with the application may be generated from the searchable data definitions. The ontology may be used to execute search queries and provide search results that include or result from semantic relationships among the searched data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
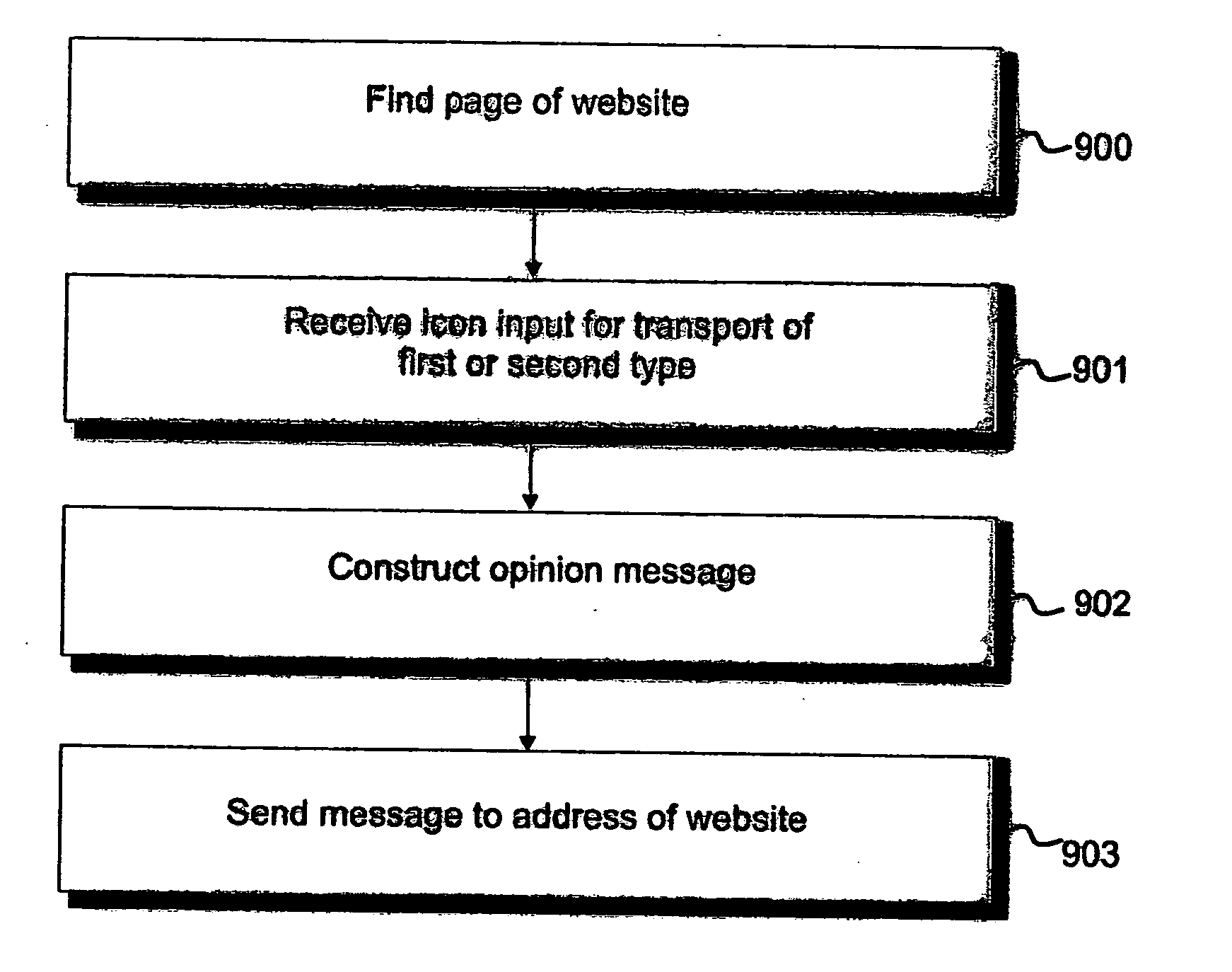
Obtaining user feedback on displayed items
User feedback regarding a displayed item, such as a web page, is obtained by providing a first and second transport-control elements, such as back buttons, that have the same effect for moving within or between displayable items but which have different associated semantic information. Upon activation of one of the transport-control elements, not only is the required movement effected, but data is output or stored indicative of the semantic information associated with the activated transport-control element. Thus, for example, the semantic information associated with one transport-control element can relate to a good user experience of the currently-displayed item whilst the semantic information associated with the other transport-control element can relate to a bad user experience of the displayed item. Related server arrangements and page and program code are also envisaged.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Multi-scale target detection method based on deep convolutional neural network
ActiveCN108564097AAccurate distinctionAccurate detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesNerve networkNetwork generation
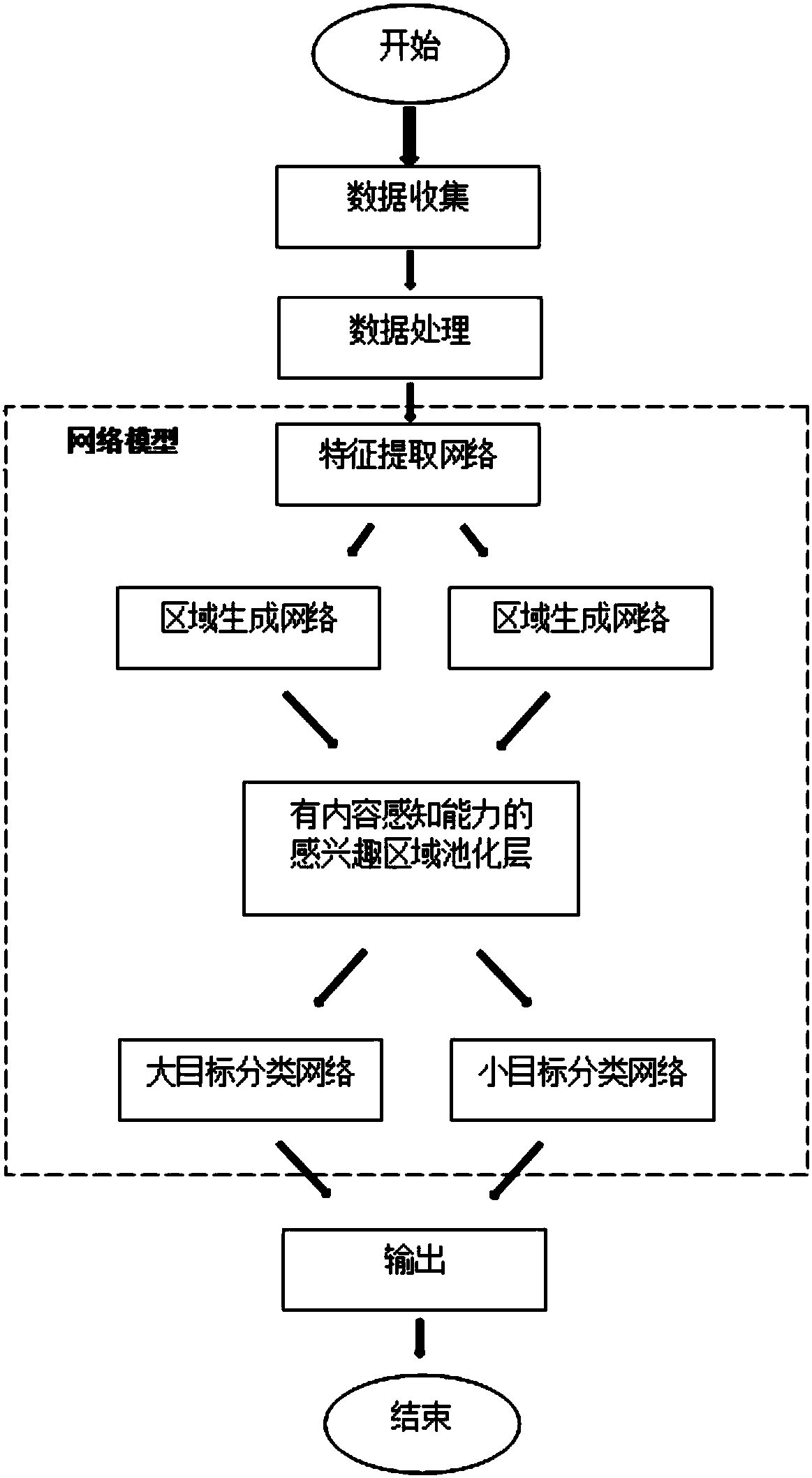
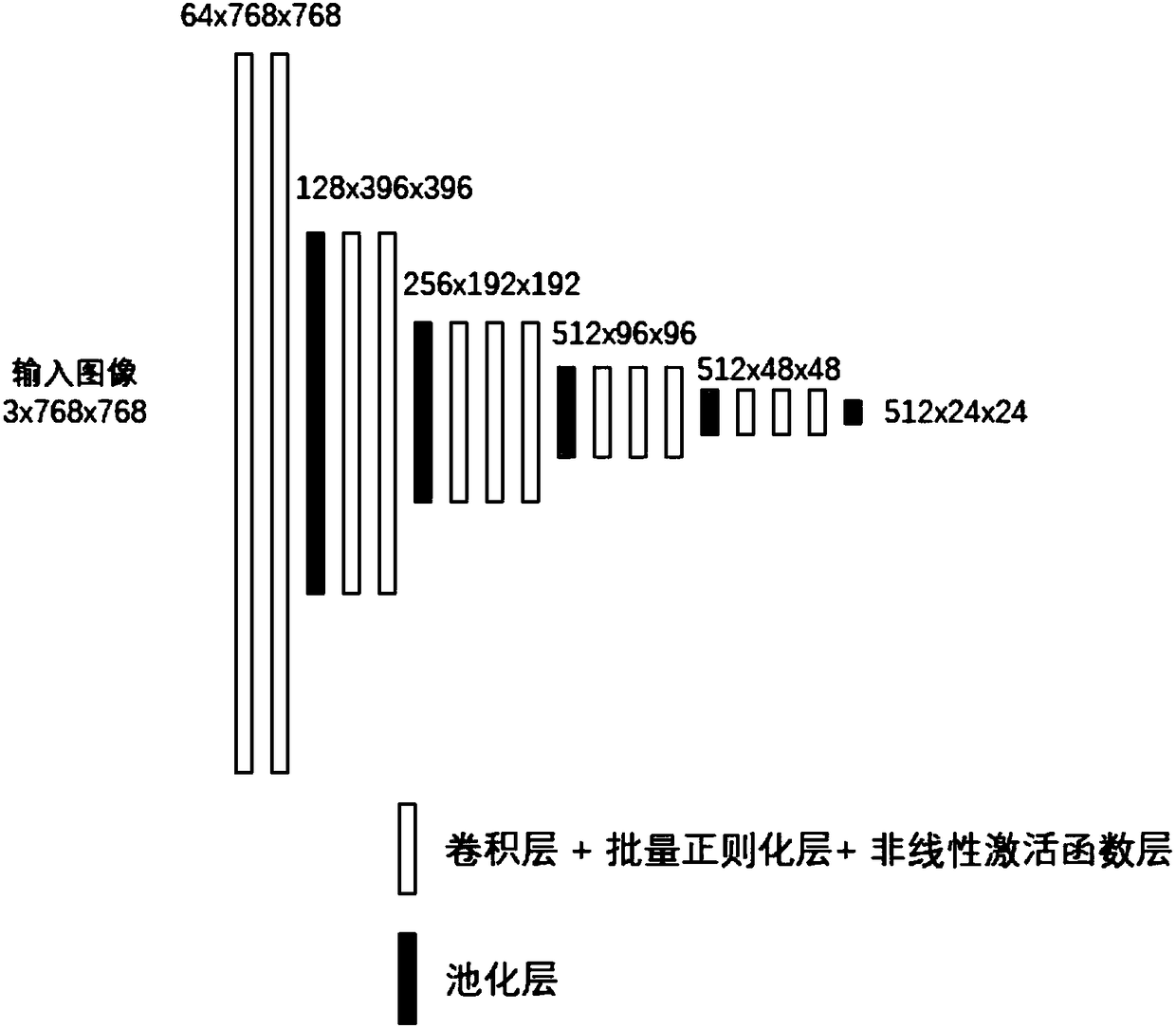
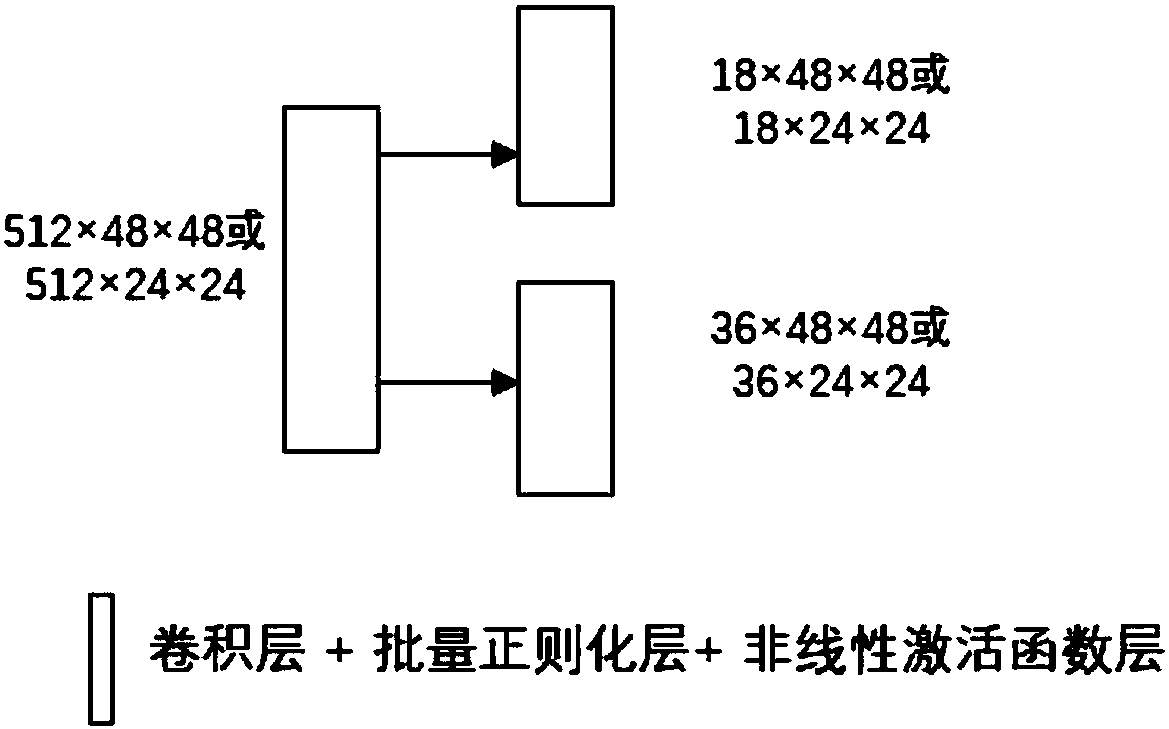
The invention discloses a multi-scale target detection method based on a deep convolutional neural network. The method comprises the steps of (1) data acquisition; (2) data processing; (3) model construction; (4) loss function definition; (5) model training; and (6) model verification. The method combines the ability of extracting image high-level semantic information of the deep convolutional neural network, the ability of generating candidate regions of region generation networks, the repair and mapping abilities of a content-aware region-of-interest pooling layer and the precise classification ability of multi-task classification networks, and therefore multi-scale target detection is completed more accurately and efficiently.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
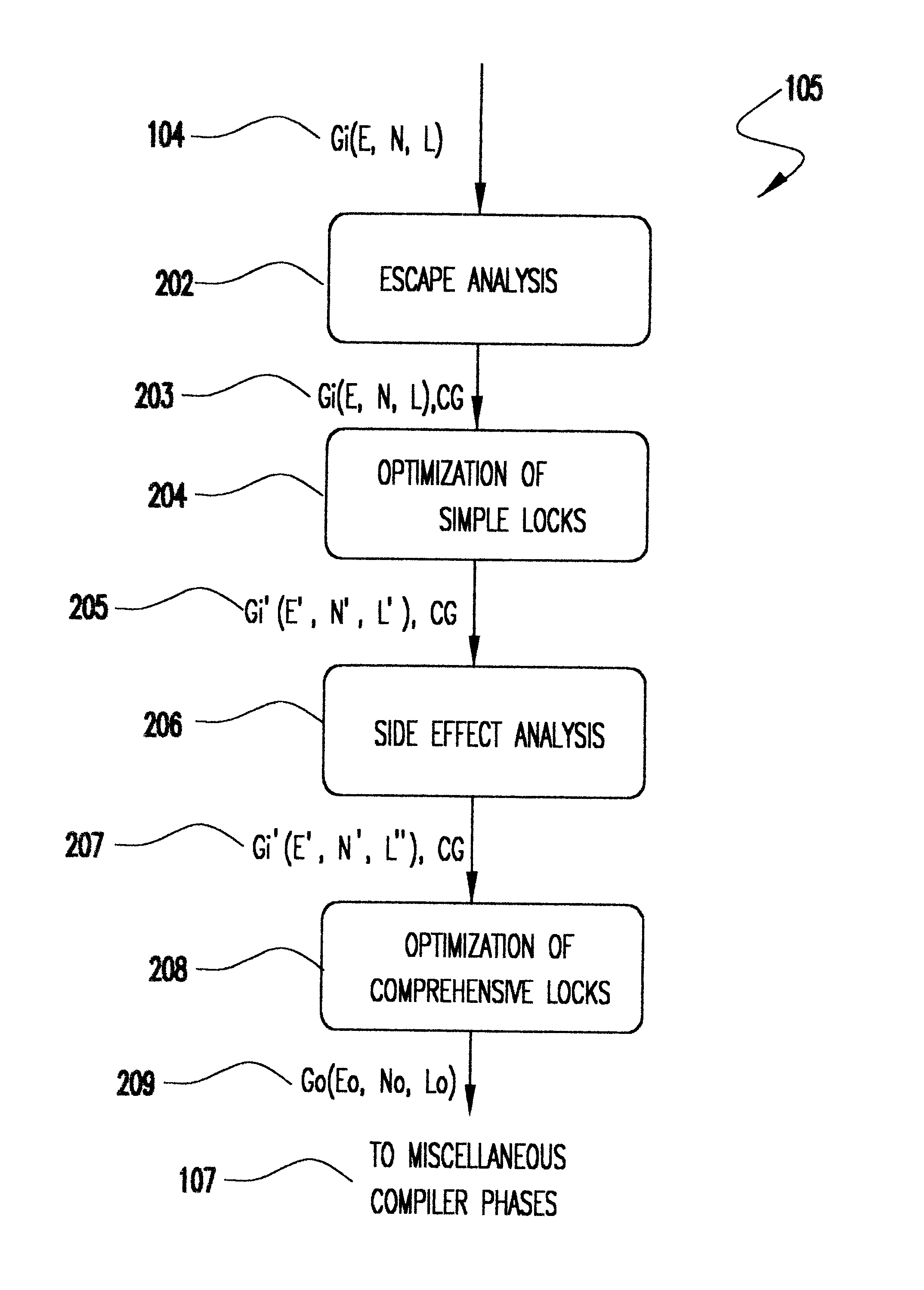
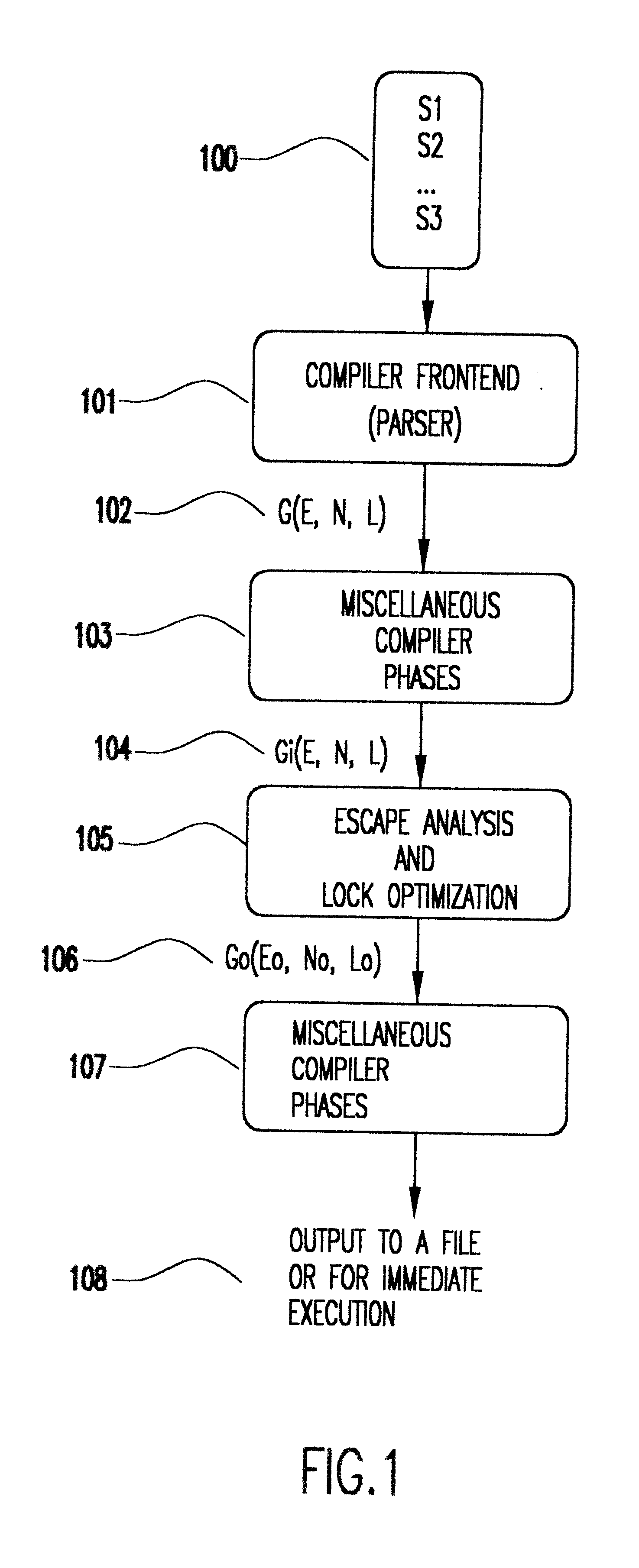
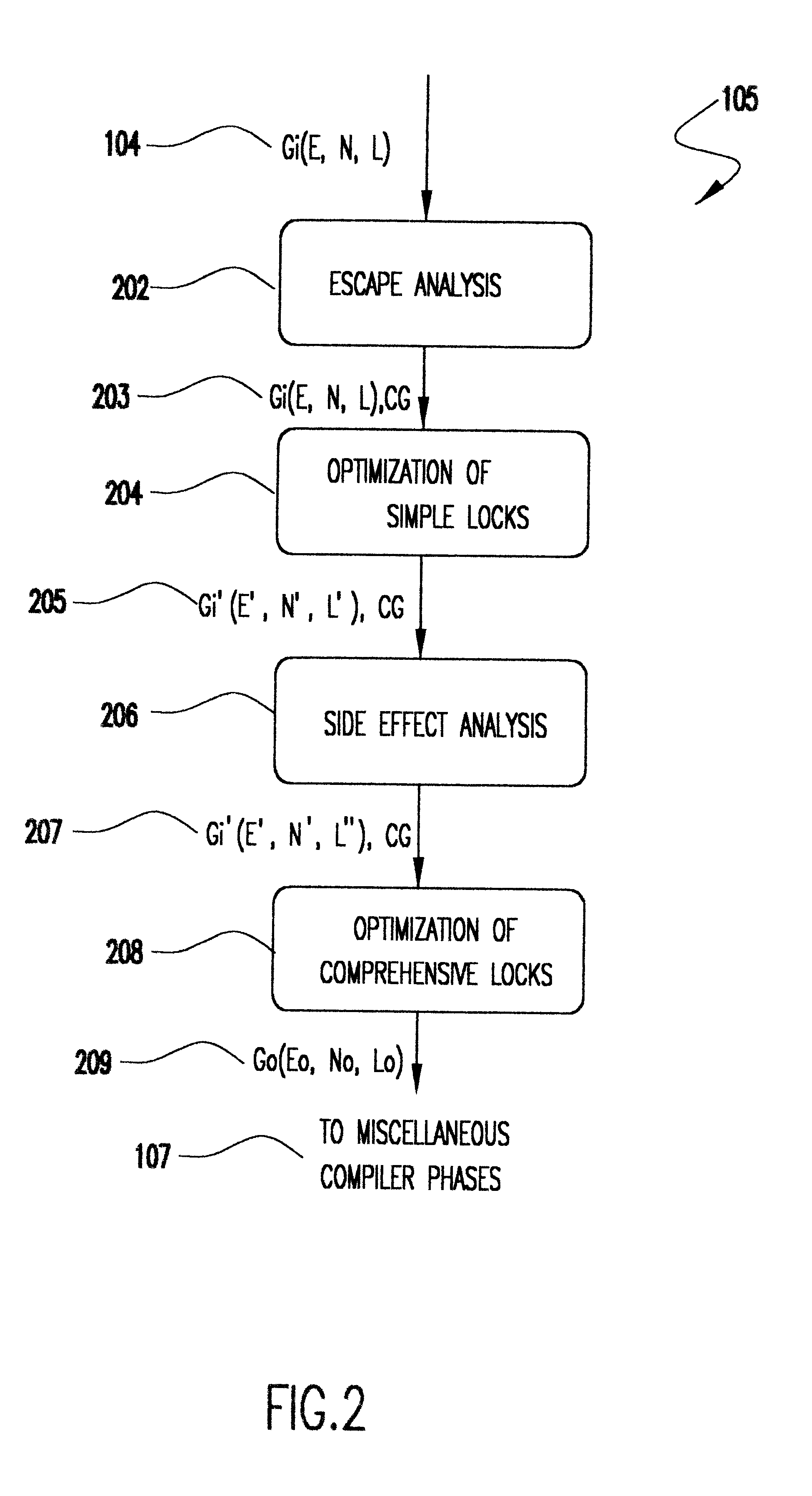
Method for optimizing locks in computer programs
InactiveUS6530079B1Easy to operateProgram synchronisationSoftware engineeringProgram planningSemantics
A method and several variants for using information about the scope of access of objects acted upon by mutual exclusion, or mutex, locks to transform a computer program by eliminating locking operations from the program or simplifying the locking operations, while strictly performing the semantics of the original program. In particular, if it can be determined by a compiler that the object locked can only be accessed by a single thread it is not necessary to perform the "acquire" or "release" part of the locking operation, and only its side effects must be performed. Likewise, if it can be determined that the side effects of a locking operation acting on a variable which is locked in multiple threads are not needed, then only the locking operation, and not the side effects, needs to be performed. This simplifies the locking operation, and leads to faster programs which use fewer computer processor resources to execute; and programs which perform fewer shared memory accesses, which in turn not only causes the optimized program, but also other programs executing on the same computing machine to execute faster. The method also describes how information about the semantics of the locking operation side effects and the information about the scope of access can also be used to eliminate performing the side effect parts of the locking operation, thereby completely eliminating the locking operation. The method also describes how to analyze the program to compute the necessary information about the scope of access. Variants of the method show how one or several of the features of the method may be performed.
Owner:IBM CORP
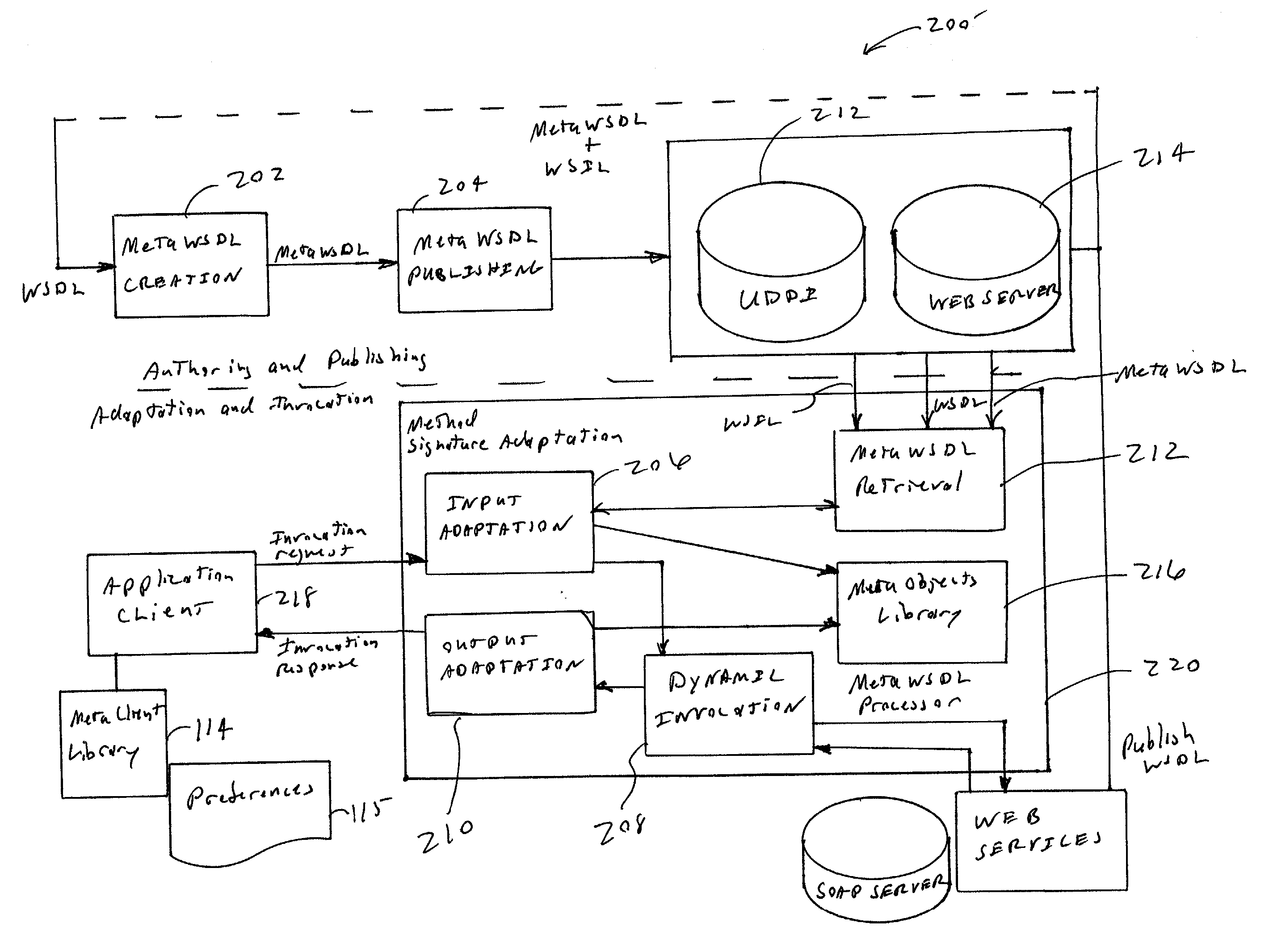
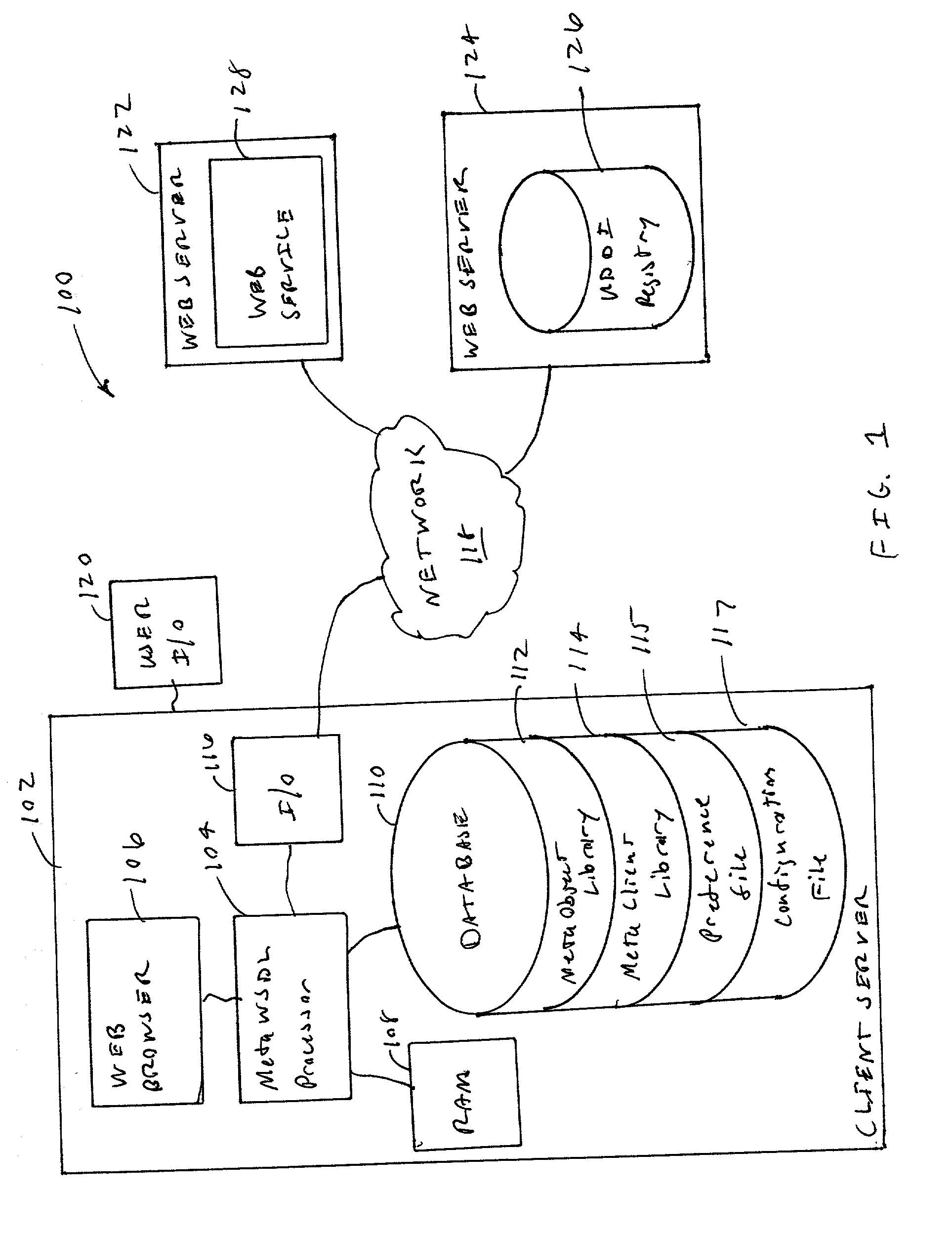
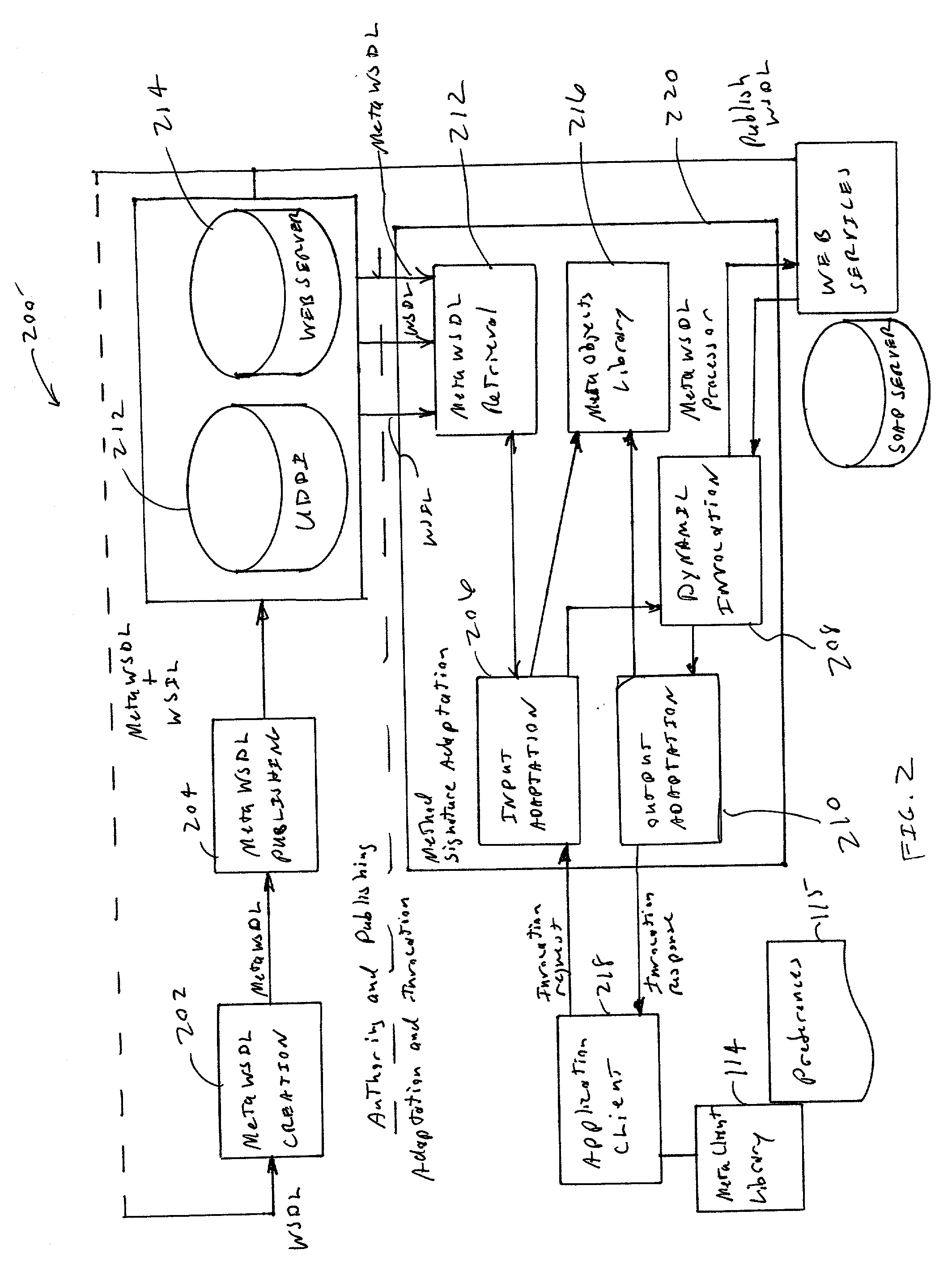
Method and apparatus of automatic method signature adaptation for dynamic web service invocation
InactiveUS20030217044A1Eliminate needPrecise constructionMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsWeb serviceSelf adaptive
A method (and apparatus) for adapting an input parameter,for dynamically invoke the target Web services, and for adapting output results, the method including: receiving an invocation request including an input parameter in a first format; retrieving MetaWSDL (Meta Web Service Description Language), wherein said MetaWSDL includes a universal XML (eXtended Markup Language) representation which includes semantic information of a Web service method signature; invoking a MetaWSDL processor to adapt the input parameter to a second format using the retrieved MetaWSDL; dynamically invoking the target Web services using the adapted parameter in the second format; and adapting the output result in a first format to a second format using the MetaWSDL.
Owner:IBM CORP
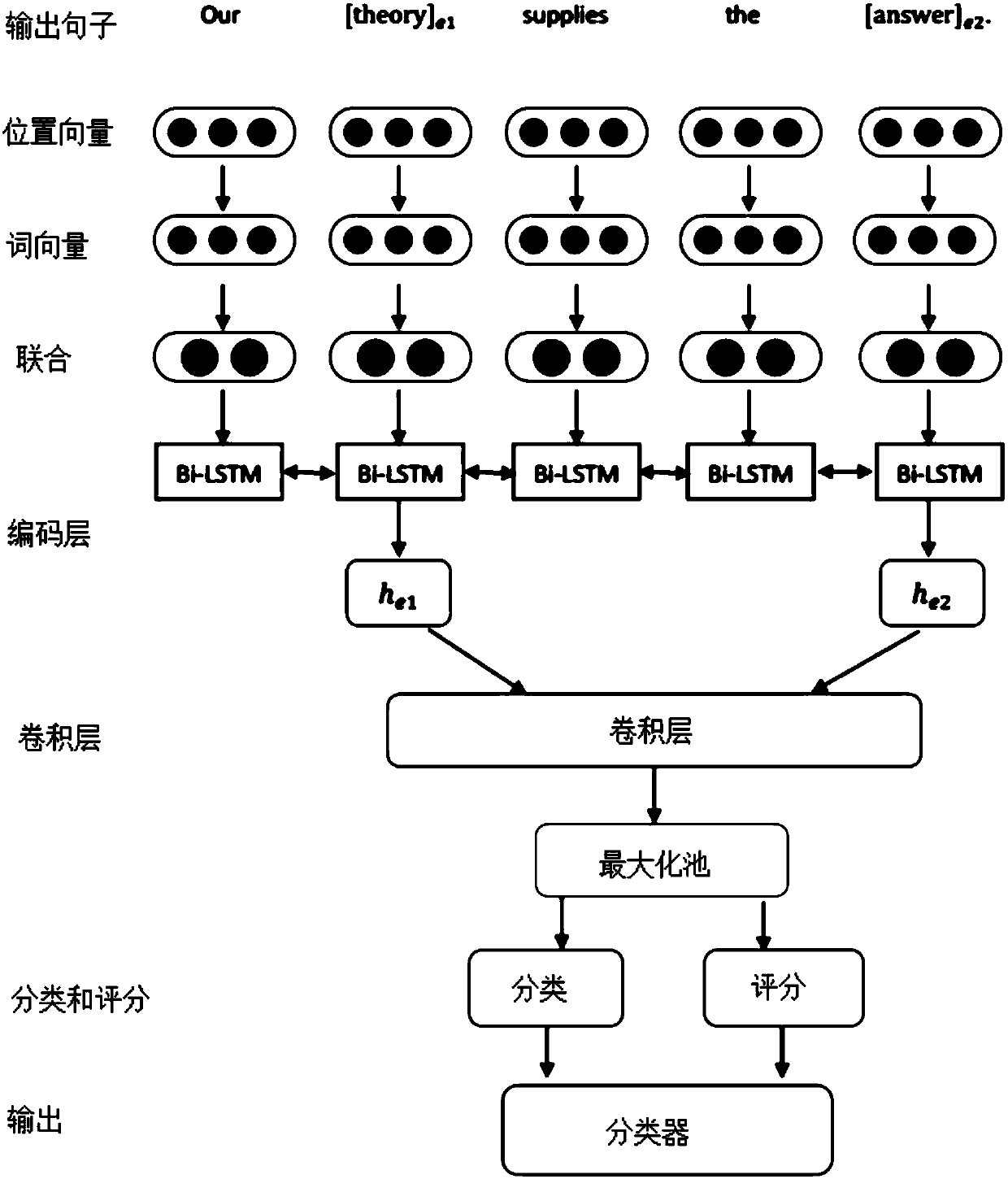
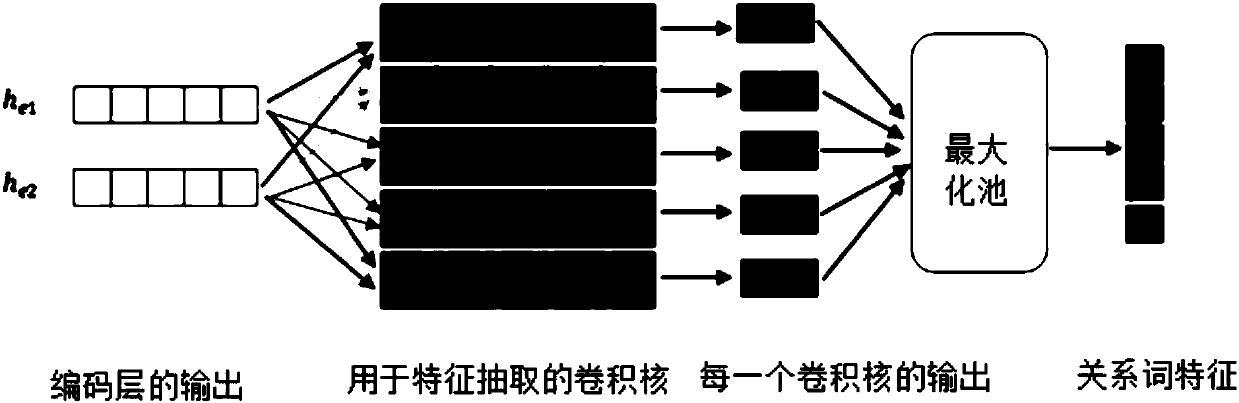
Method for relationship classification with LSTM and CNN joint model based on location
ActiveCN107832400AUniversalGood effectNatural language data processingNeural architecturesFeature vectorHigh dimensional
The invention relates to a method for relationship classification with an LSTM and CNN joint model based on location. The method includes the steps of (1) preprocessing data; (2) training word vectors; (3) extracting location vectors; acquiring the location vector feature and high-dimensional location feature vector of each word in a training set, cascading the word vector of each word with the high-dimensional location feature vector thereof to obtain a joint feature; (4) building a model for a specific task; encoding contextual information and semantic information of entities by use of bidirectional LSTM; outputting the vector of the location corresponding to the marked entities, inputting the output to CNN, outputting two entity nouns and their contextual information and relational wordinformation, and inputting the entity nouns and their contextual information and relational word information into a classifier for classification; (5) training the model by use of a loss function. The method does not need to manually extract any features, the joint model does not need to use additional natural language processing tools to preprocess the data, the algorithm is simple and clear, and the best effect at present is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Systems, methods, and computer readable media for visualization of semantic information and inference of temporal signals indicating salient associations between life science entities
ActiveUS20180082197A1Superior visualization systemSemantic analysisBiological modelsData scienceSemantic information
Disclosed systems, methods, and computer readable media can detect an association between semantic entities and generate semantic information between entities. For example, semantic entities and associated semantic collections present in knowledge bases can be identified. A time period can be determined and divided into time slices. For each time slice, word embeddings for the identified semantic entities can be generated; a first semantic association strength between a first semantic entity input and a second semantic entity input can be determined; and a second semantic association strength between the first semantic entity input and semantic entities associated with a semantic collection that is associated with the second semantic entity can be determined. An output can be provided based on the first and second semantic association strengths.
Owner:NFERENCE INC
Personalized and synergistic integration network multimedia search and enquiry method
InactiveCN101334796AImplement queryRealize automatic labelingSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationMultimedia search
The invention discloses a network multimedia searching and inquiry method integrating individualization and collaboration, which includes the following steps: (1) existing semantic information is adopted to automatically mark media object semanteme; (2) a user sub-file containing user information and personal preferences is established and a searching system sorts and optimizes the searched results according to the intention of the user; (3) the weight of each key phrase in the user sub-file is dynamically adjusted according to relevant feedbacks of the user so as to more accurately reflect the user intention; (4) a multi-layer sub-file mode respectively including the user sub-file, group sub-file and community sub-file is established and a succession and sharing mechanism is preserved between layers so as to both strive for sameness and allow the existence of difference and support a mass storage; (5) multi-modal information is converged and analyzed for multimedia semantic understanding so as to realize the cross-modal multimedia object searching. The invention can accurately learn about the intention of users and realize the high-accurate, individualized and cross-modal multimedia searching.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and system for cataloging news video
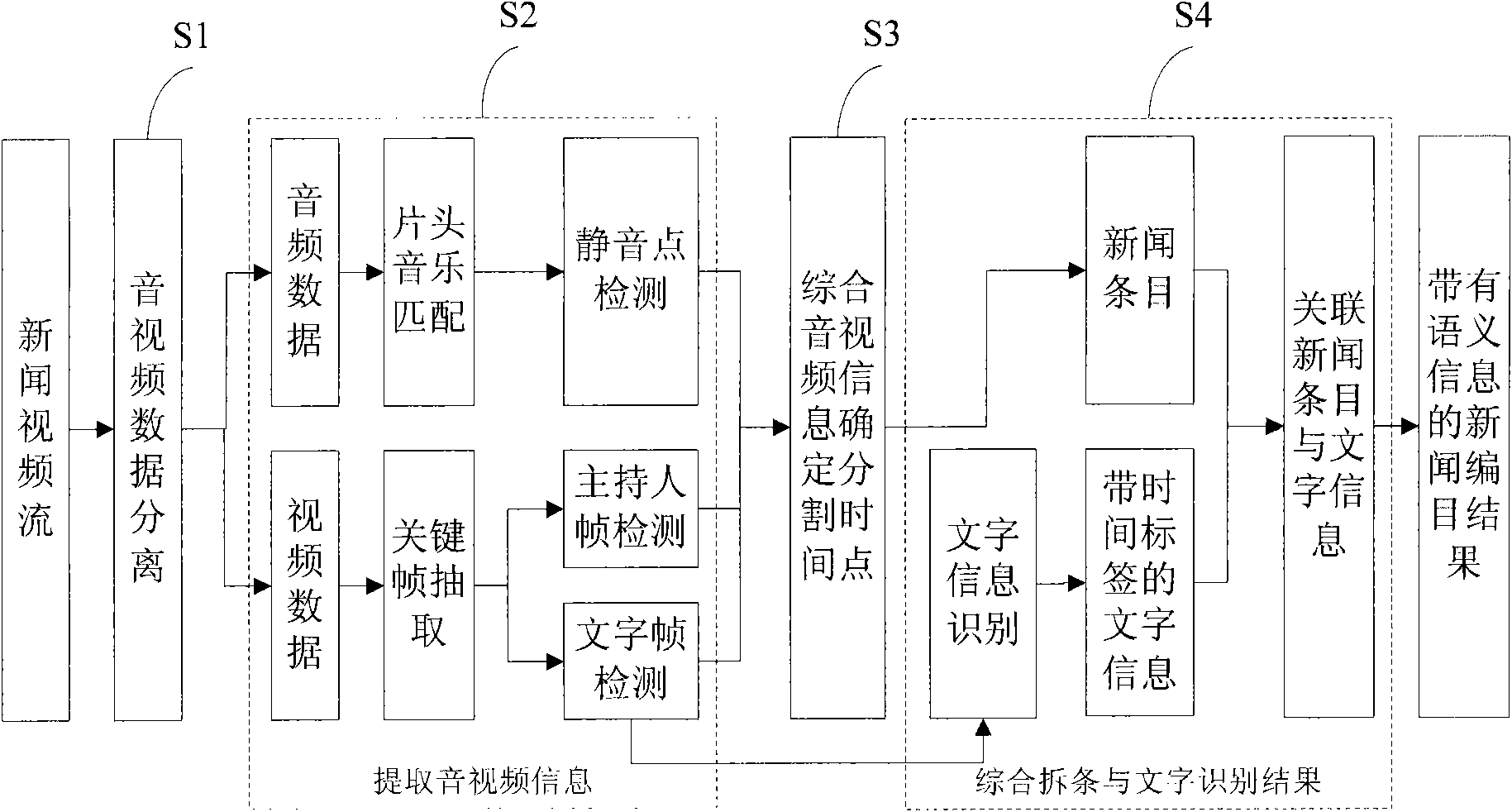
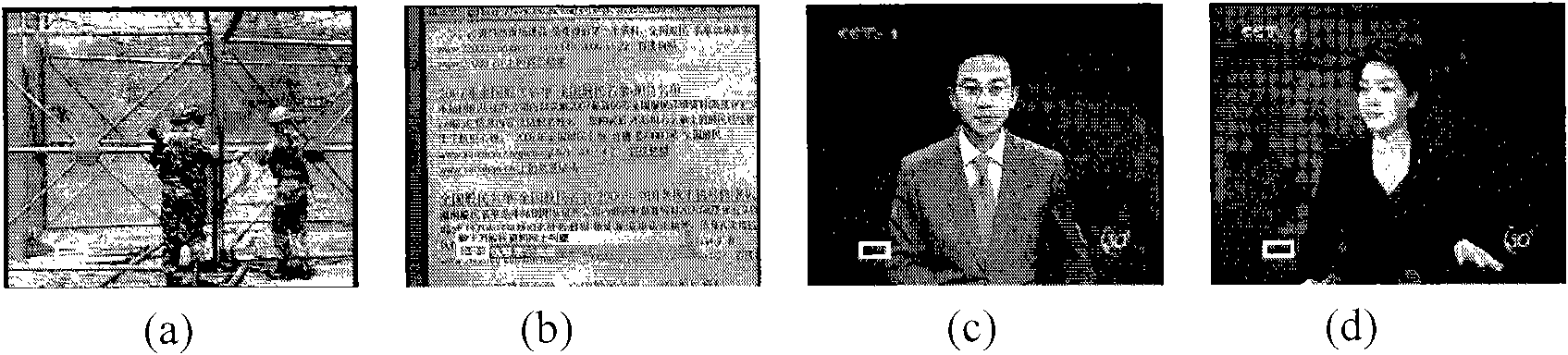
InactiveCN101616264AAutomatic catalog implementationSolve the problem of automatic semantic information annotationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer moduleCataloging
The invention relates to a method and a system for cataloging news video. The method realizes automatic cataloging of the news video based on caption bars, anchorman and audio mute point information in a news program, and comprises the following steps: carrying out audio-video separation of news video stream and head leader music matching of audio data to determine the effective time range of a news program in a file; determining an audio mute point, an anchorman frame and the emerging time of a caption frame within the effective time range, and carrying out comprehensive analysis processing to determine the division time point of news items; and identifying video caption information, associating the caption information with a division result, and taking the caption information after association as cataloging semantic information. The system comprises a bar removing module and an educing module connected with a news video bar-removing result database as well as a browse module, a play module and a correction module connected in parallel between a client and the news video bar-removing result database. The method and the system solve the problems of news automatic bar removing and news item automatic semantic information labeling and realize automatic cataloging of news programs, thereby having the advantages of high efficiency and low cost.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Information block extraction apparatus and method for Web pages
InactiveUS20050066269A1Improve performanceGuaranteed successDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisRepeat patternSemantic information
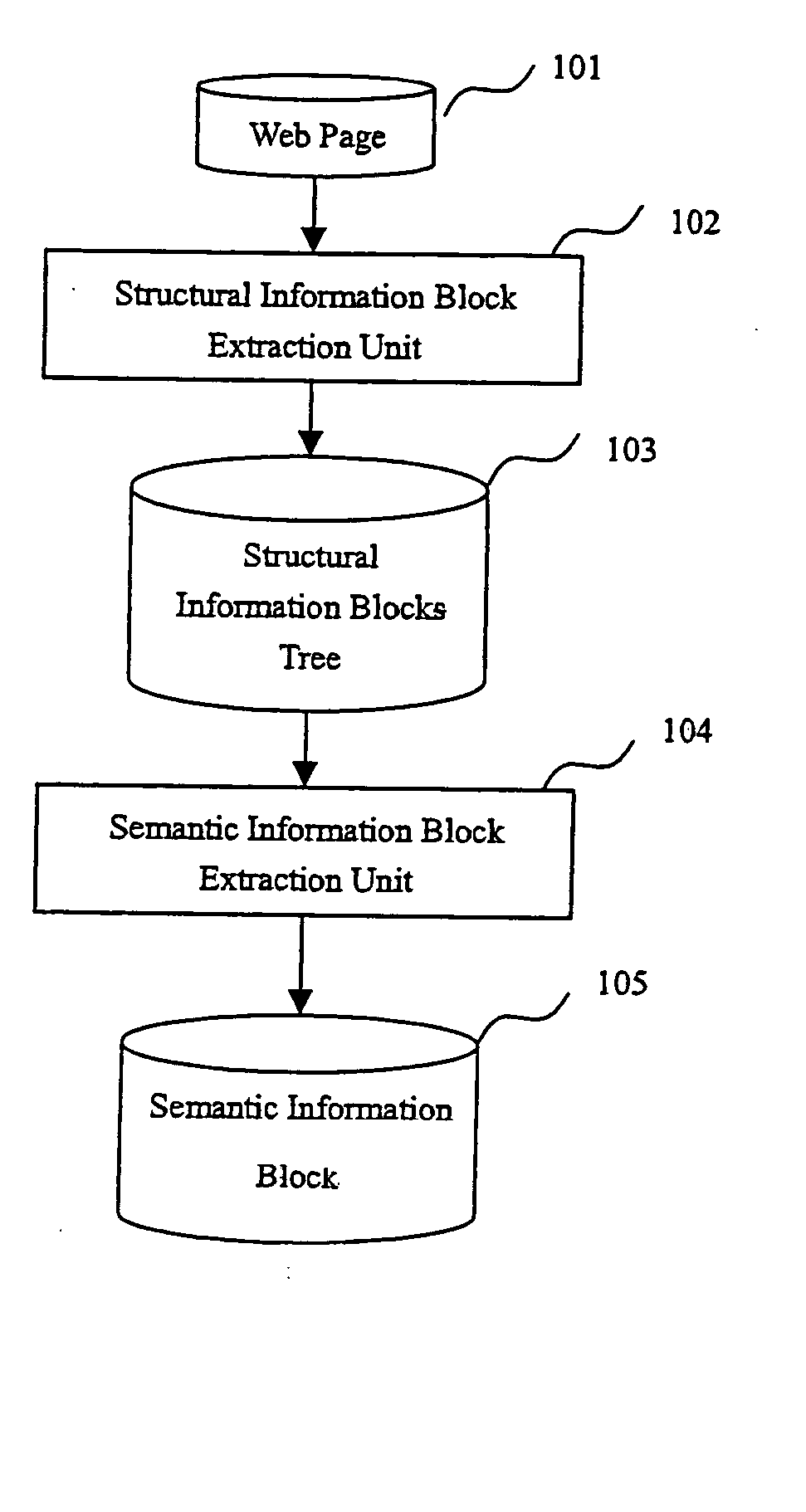
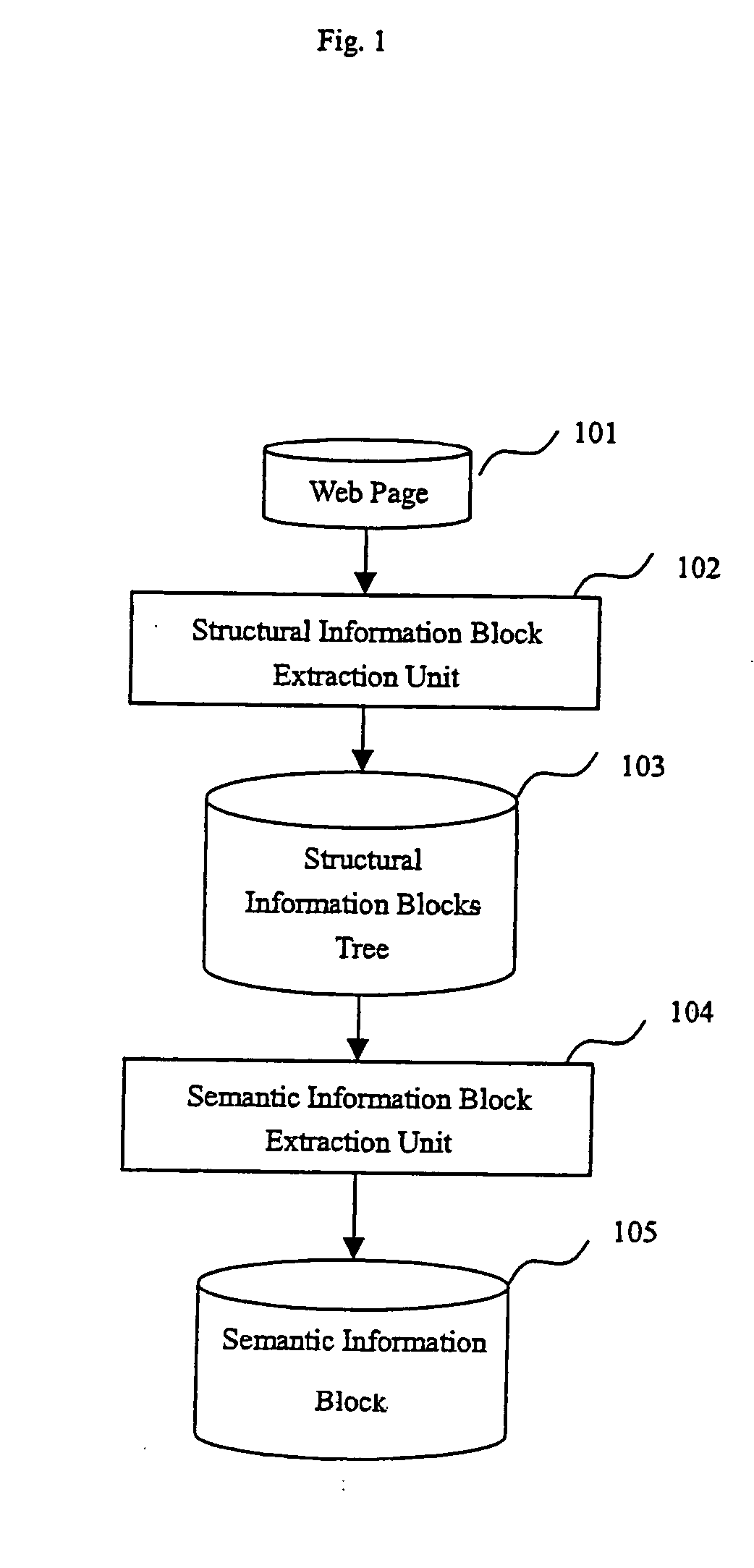
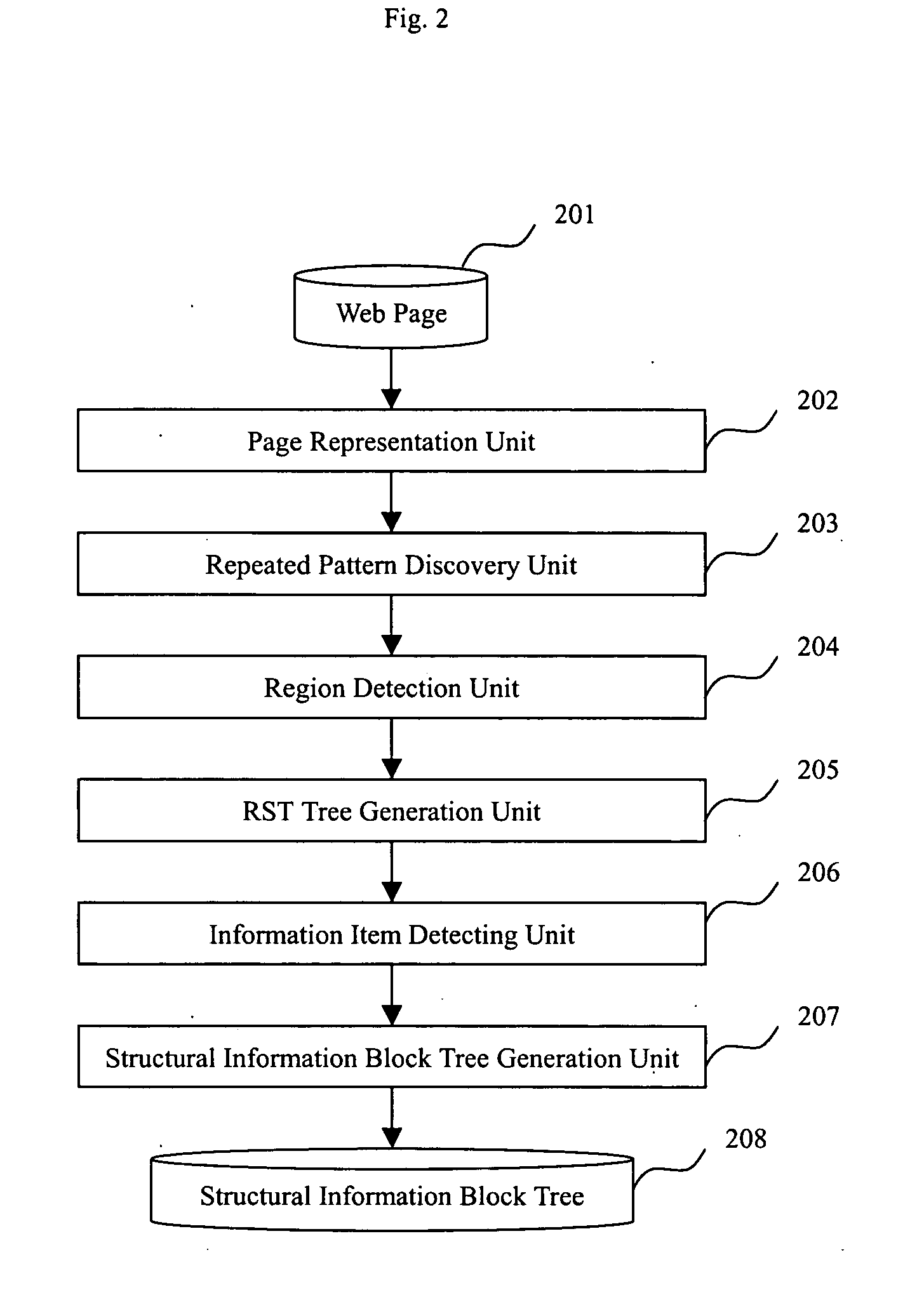
A method and apparatus for identifying coherent areas within a Web page. First, a Web page is parsed into an HTML DOM tree and an HTML tag token stream. Next, repeated-patterns are induced from the Web page. After filtering out improper repeated-patterns and generating corresponding instances of the repeated-patterns, the repeated-patterns are mapped back to corresponding regions in the Web page. Based on the mappings, a hierarchical RST tree containing information blocks is generated. Information items within the information blocks are detected then used to generate a hierarchical structural information block tree. Information blocks from the structural information block tree are then classified into text information blocks and link information blocks. Based on the classification and block semantic similarity, the bocks are clustered then grouped into semantic information blocks. The semantic information blocks contain main text information blocks and related link blocks which, if necessary, can be labeled.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
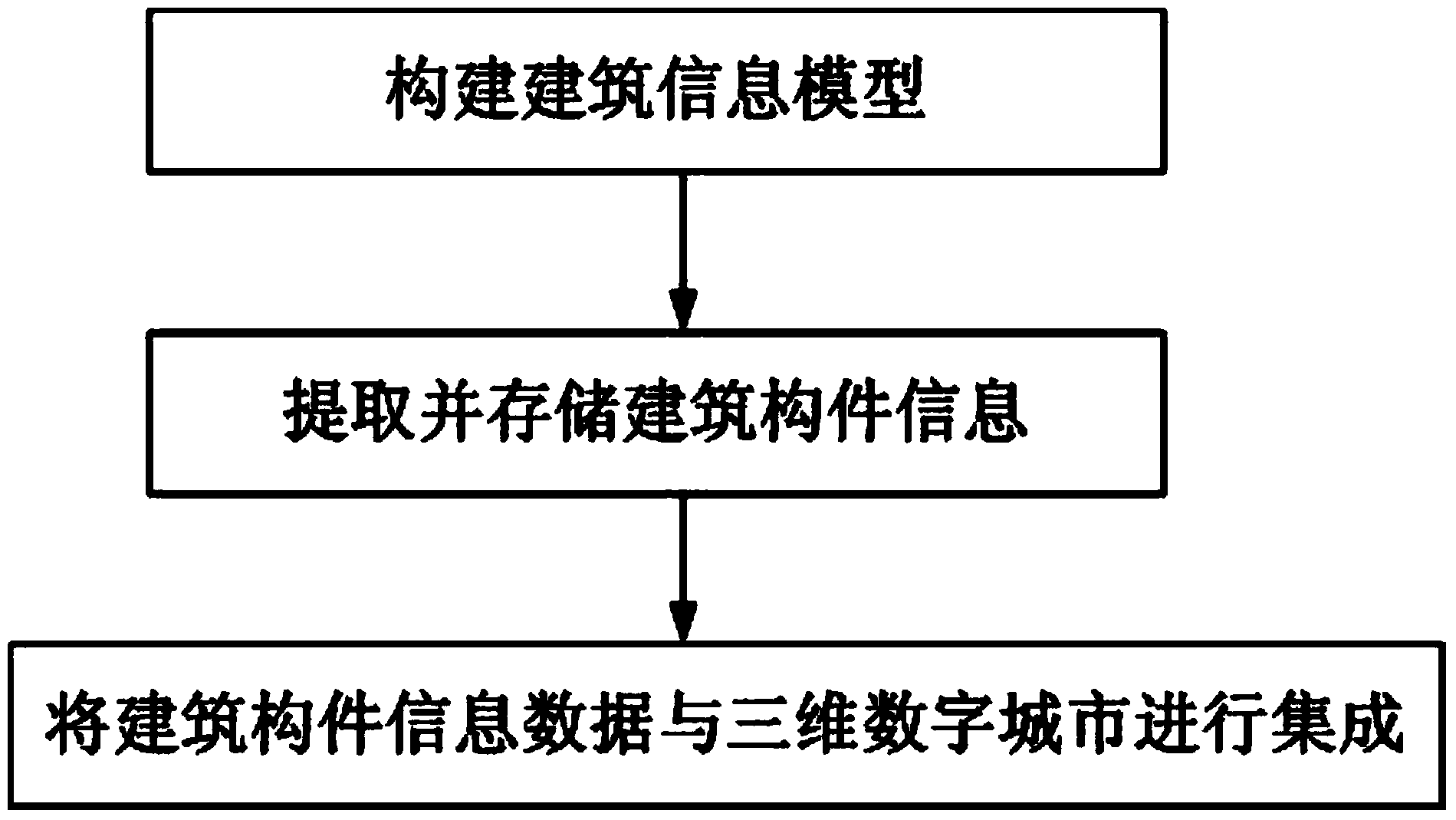
Large-scale building information model and three-dimensional digital city integration method
ActiveCN103942388ARealize integrated displayImprove data utilizationSpecial data processing applications3D modellingInformation repositorySpatial structure
The invention discloses a large-scale building information model and a three-dimensional digital city integration method, and belongs to the field of spatial information technology. Interactive construction is carried out on the building information model on the basis of construction drawings, then the building information model is converted into a building component information model through spatial and semantic information mapping, a building component information base is established, and integrated application of building component information is carried out in three-dimensional digital city scenes. A large-scale indoor spatial structure data source is provided for a three-dimensional digital city, and the utilization rate of data is improved; internal spatial structures of buildings and external environments are displayed integrally. The building component information model with consistent semantic and spatial information is established, various sensors in the buildings can be integrated, and useful supports are provided for smart city application.
Owner:CHONGQING SURVEY INST
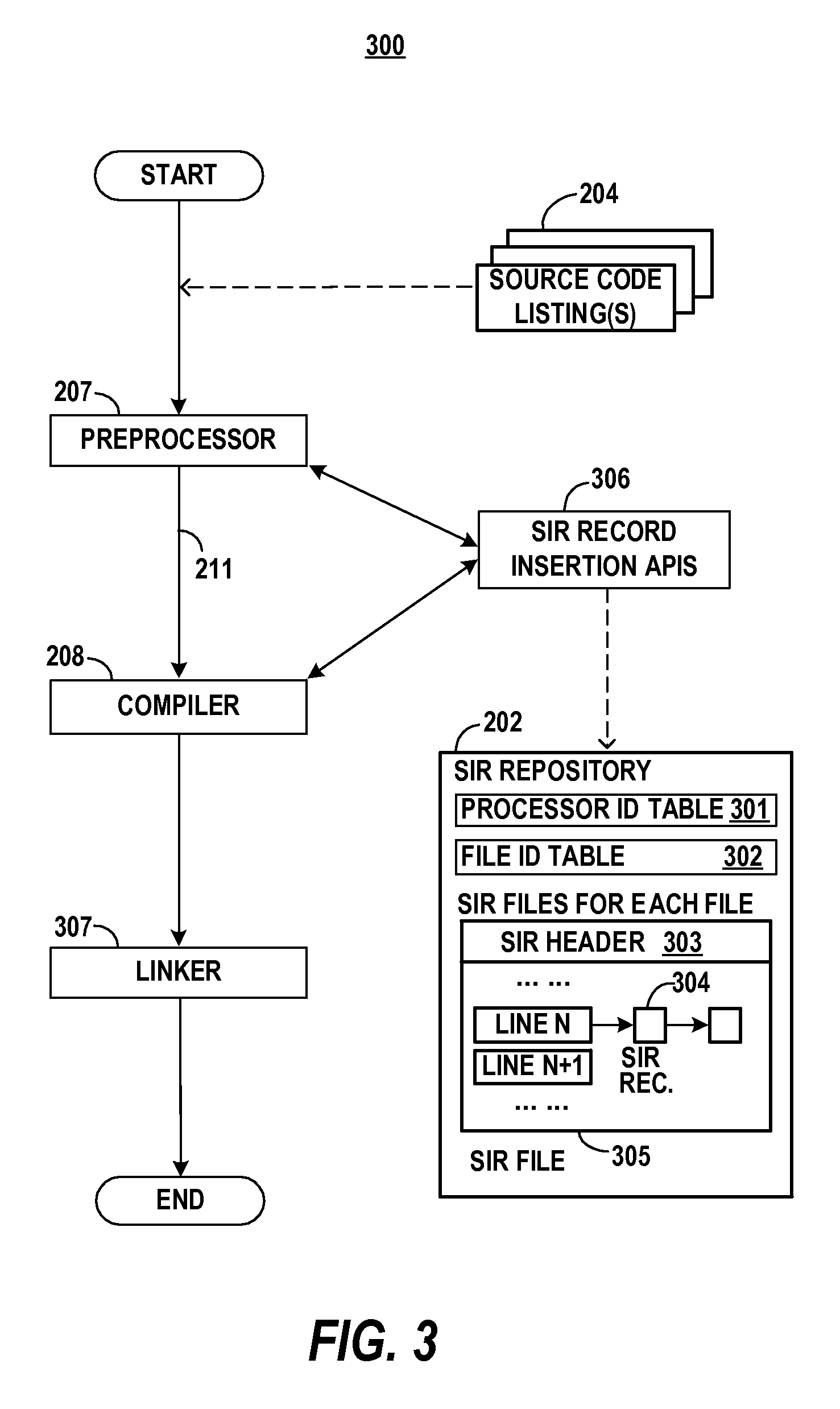
Method and System for presenting and analyzing software source code through intermediate representation
The present invention provides a method and system for producing intermediate representation of source code listings with possibly mixed syntaxes to assist software development applications in presenting and analyzing the source code listings through reading the intermediate representation. A source code processor calls Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to preserve source code information, which includes intermediate representation data sets and is preferably stored in a file-based repository. The source code processor is of a compiler, a preprocessor, a parser, or a comment document processor. The data sets capture lexical, syntax and semantic information of source code construct elements, and comprise of location, processor identification, construct category, and attribute data. A software development environment through a source code search engine is able to present source code construct elements, outlines, and symbol references from software packages over a plurality of distributed servers in a network such as the Internet.
Owner:ZHAO KAN
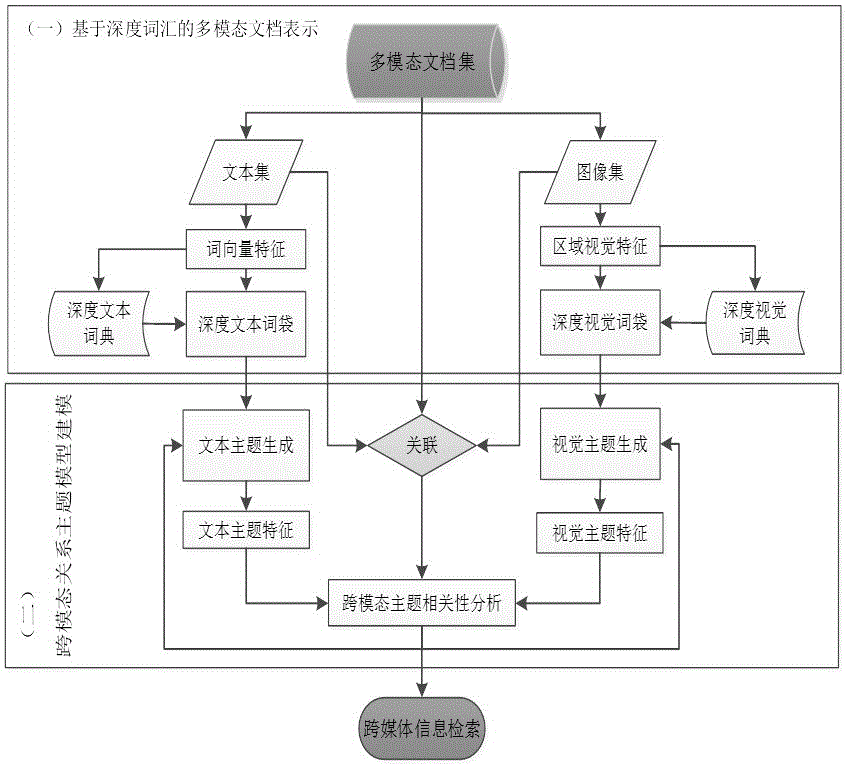
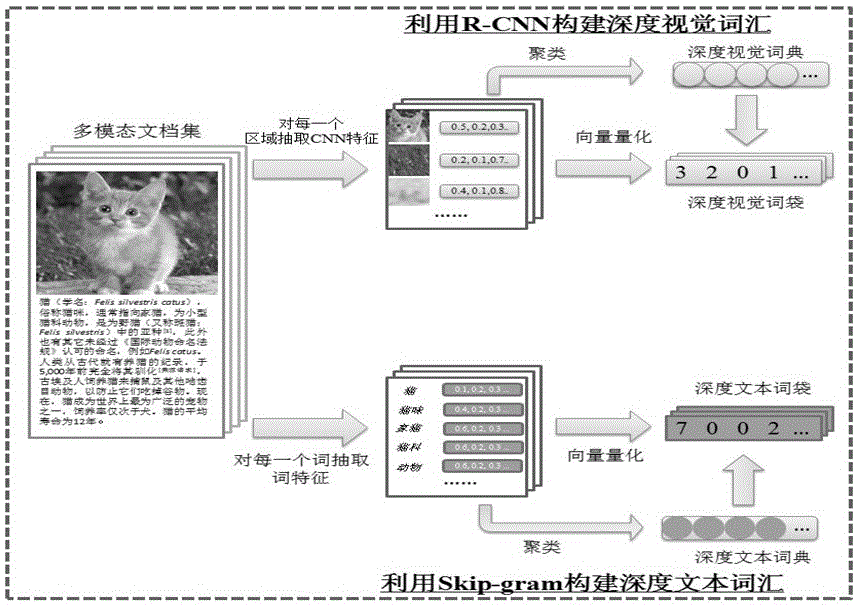
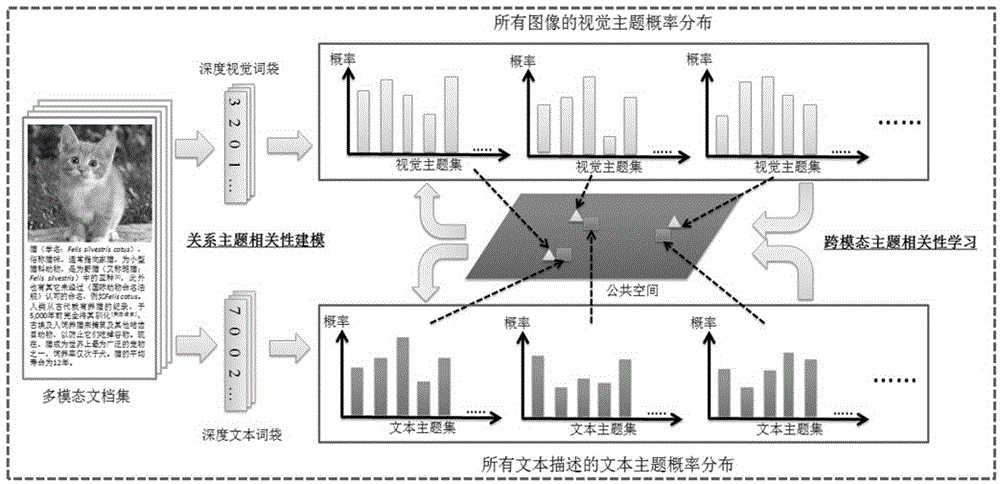
Cross-modal subject correlation modeling method based on deep learning
ActiveCN105760507AAlleviate the problemImprove retrieval efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsGeneration processDocumentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of cross-media correlation learning, and particularly relates to a cross-modal subject correction modeling method based on deep learning.The method includes two main algorithms of multi-modal file expression based on deep vocabularies and correlation subject model modeling fusing cross-modal subjection correction learning.A deep learning technology is utilized for constructing deep semantic vocabularies and deep vision vocabularies to describe a semantic description part and an image part in a multi-modal file.Based on multi-modal file expression, a cross-modal correlation subject model is constructed to model a whole multi-modal file set, so that the generation process of the multi-modal file and the correlation between different modals are described.The accuracy is high, and adaptability is high.The cross-modal subject correction modeling method has important meaning for efficient cross-media information retrieval in consideration of multi-modal semantic information on the basis of the large-scale multi-modal file (a text and an image), can improve retrieval correlation and promote user experience, and has great application value in the field of cross-media information retrieval.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com