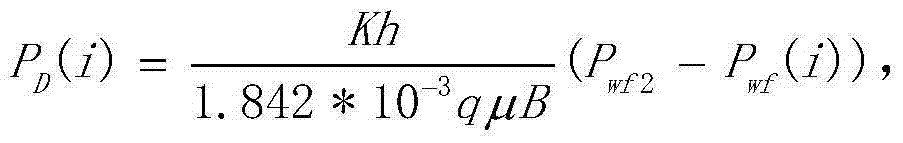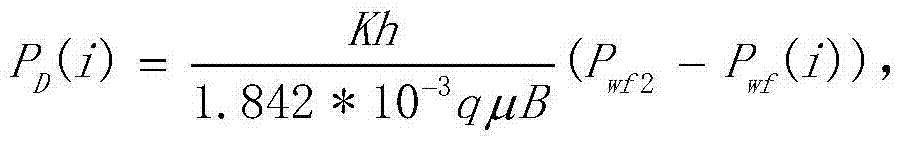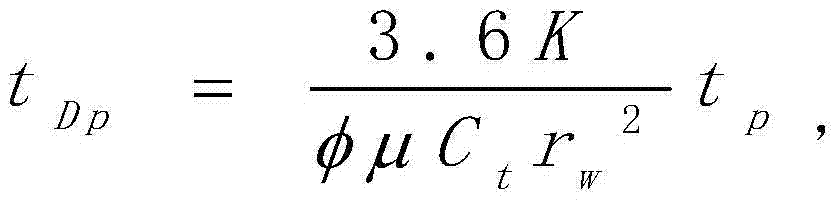Patents
Literature
313results about How to "Improve data utilization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
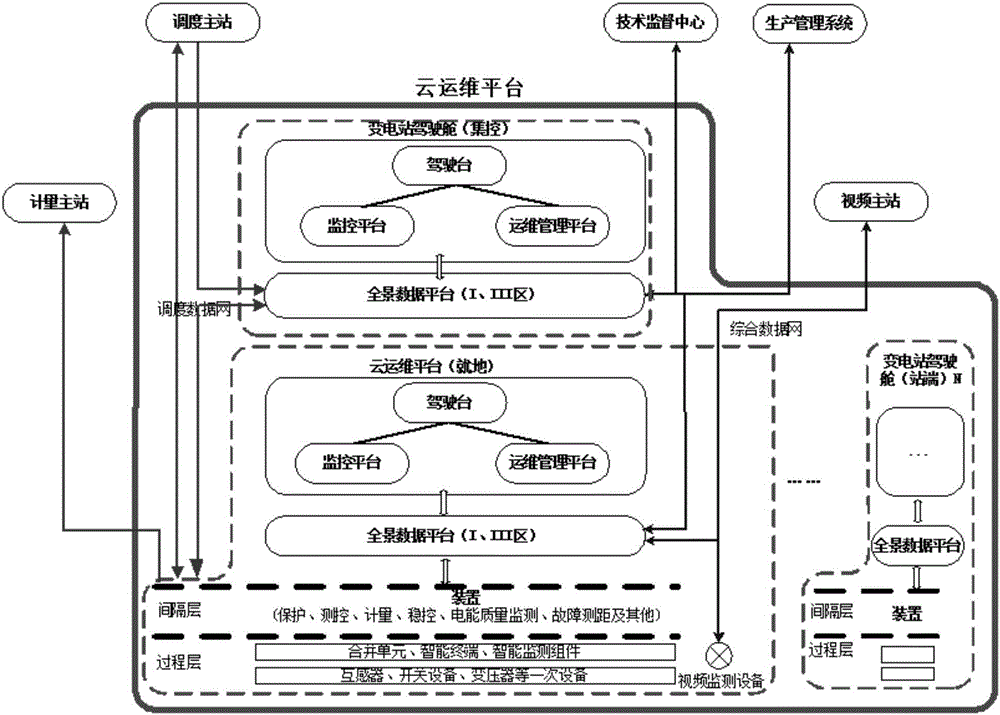
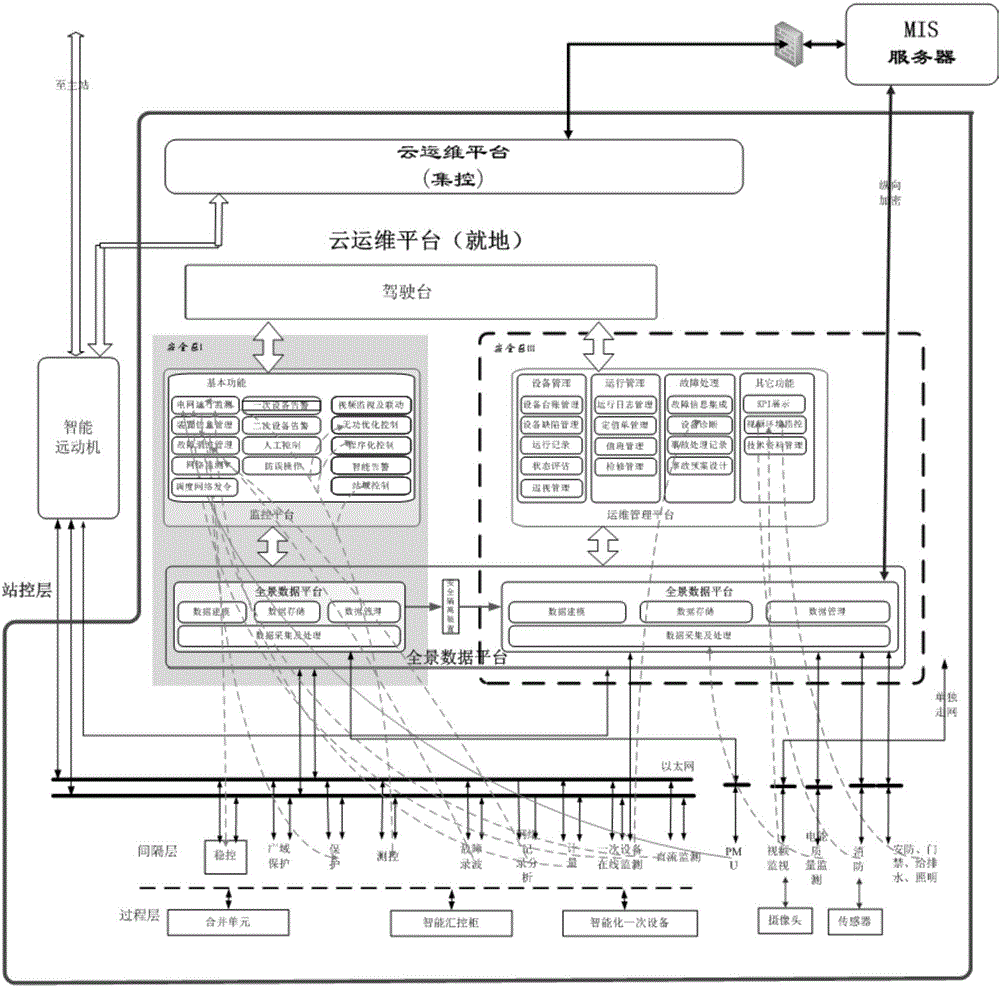
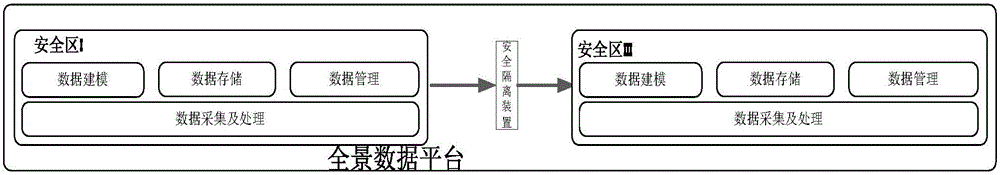
Substation secondary system operation and maintenance cloud platform
ActiveCN106709580AImprove data utilizationImprove interactivityData processing applicationsInformation technology support systemControl layerSynthetic data
The invention discloses a substation secondary system operation and maintenance cloud platform, comprising in-place layers and a centralized control layer, which are configured to read data from a production management system directly to realize equipment management, operation management, fault handling, duty management and maintenance management. The in-place layers and the centralized control layer exchange power grid operation data by means of a dispatching data network, and exchange operation and maintenance management data by means of an integrated data network; each in-place layer comprises a substation control layer, a spacing layer and a process layer; each process layer comprises all primary equipment of a substation, and transmits information of the primary equipment of the present layer to the substation control layer by means of corresponding detection equipment; and each spacing layer comprises all secondary equipment of the substation, and transmits information of the primary equipment of the present layer to the substation control layer by means of corresponding detection equipment. The substation secondary system operation and maintenance cloud platform integrates the cloud computing technology, the big data technology, the Internet of things technology and the mobile internet technology, unifies data interfaces and dispatching among different secondary operation and maintenance systems in safety regions, and realizes good management of operation and maintenance information.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
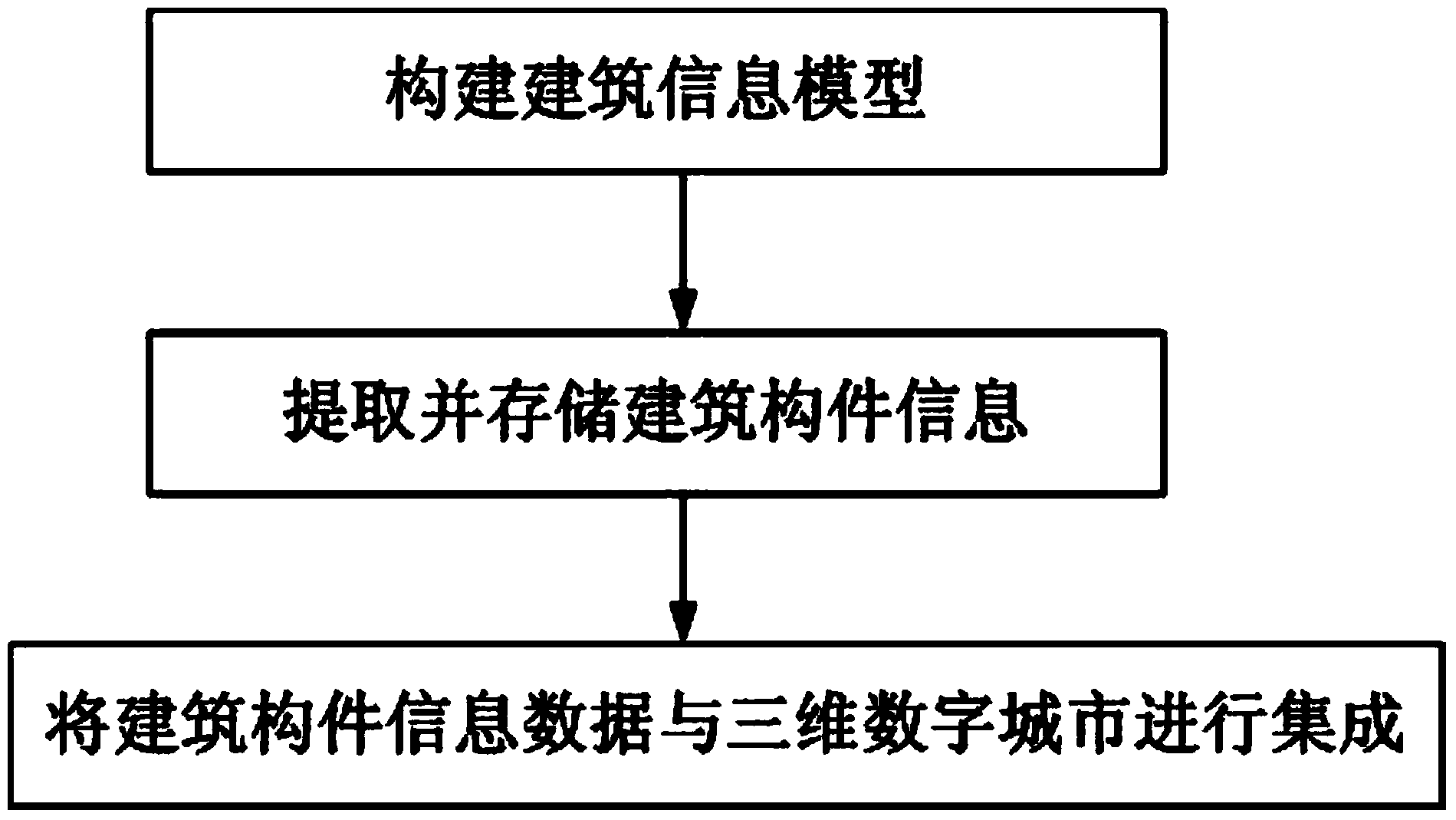
Large-scale building information model and three-dimensional digital city integration method
ActiveCN103942388ARealize integrated displayImprove data utilizationSpecial data processing applications3D modellingInformation repositorySpatial structure
The invention discloses a large-scale building information model and a three-dimensional digital city integration method, and belongs to the field of spatial information technology. Interactive construction is carried out on the building information model on the basis of construction drawings, then the building information model is converted into a building component information model through spatial and semantic information mapping, a building component information base is established, and integrated application of building component information is carried out in three-dimensional digital city scenes. A large-scale indoor spatial structure data source is provided for a three-dimensional digital city, and the utilization rate of data is improved; internal spatial structures of buildings and external environments are displayed integrally. The building component information model with consistent semantic and spatial information is established, various sensors in the buildings can be integrated, and useful supports are provided for smart city application.
Owner:CHONGQING SURVEY INST
Multiple video cameras synchronous quick calibration method in three-dimensional scanning system
A synchronous quick calibration method of a plurality of video cameras in a three-dimensional scanning system, which includes: (1) setting a regular truncated rectangular pyramid calibration object, setting eight calibration balls at the vertexes of the truncated rectangular pyramid, and respectively setting two reference calibration balls at the upper and lower planes; (2) using the video cameras to pick-up the calibration object, adopting the two-threshold segmentation method to respectively obtain the corresponding circles of the upper and lower planes, extracting centers of the circles, obtaining three groups of corresponding relationships between circle center points in the image and the centres of calibration ball in the space, solving the homography matrix to obtain the internal parameter matrix and external parameter matrix and obtaining the distortion coefficient, taking the solved video camera parameter as the initial values, and then using a non-linear optimization method to obtain the optimum solution of a single video camera parameter; (3) obtaining in sequence the external parameter matrix between a plurality of video cameras and a certain video camera in the space, using the polar curve geometric constraint relationship of the binocular stereo vision to establish an optimizing object function, and then adopting a non-linear optimization method to solve to get the optimum solution of the external parameter matrix between two video cameras.
Owner:NANTONG TONGYANG MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL MFR +1
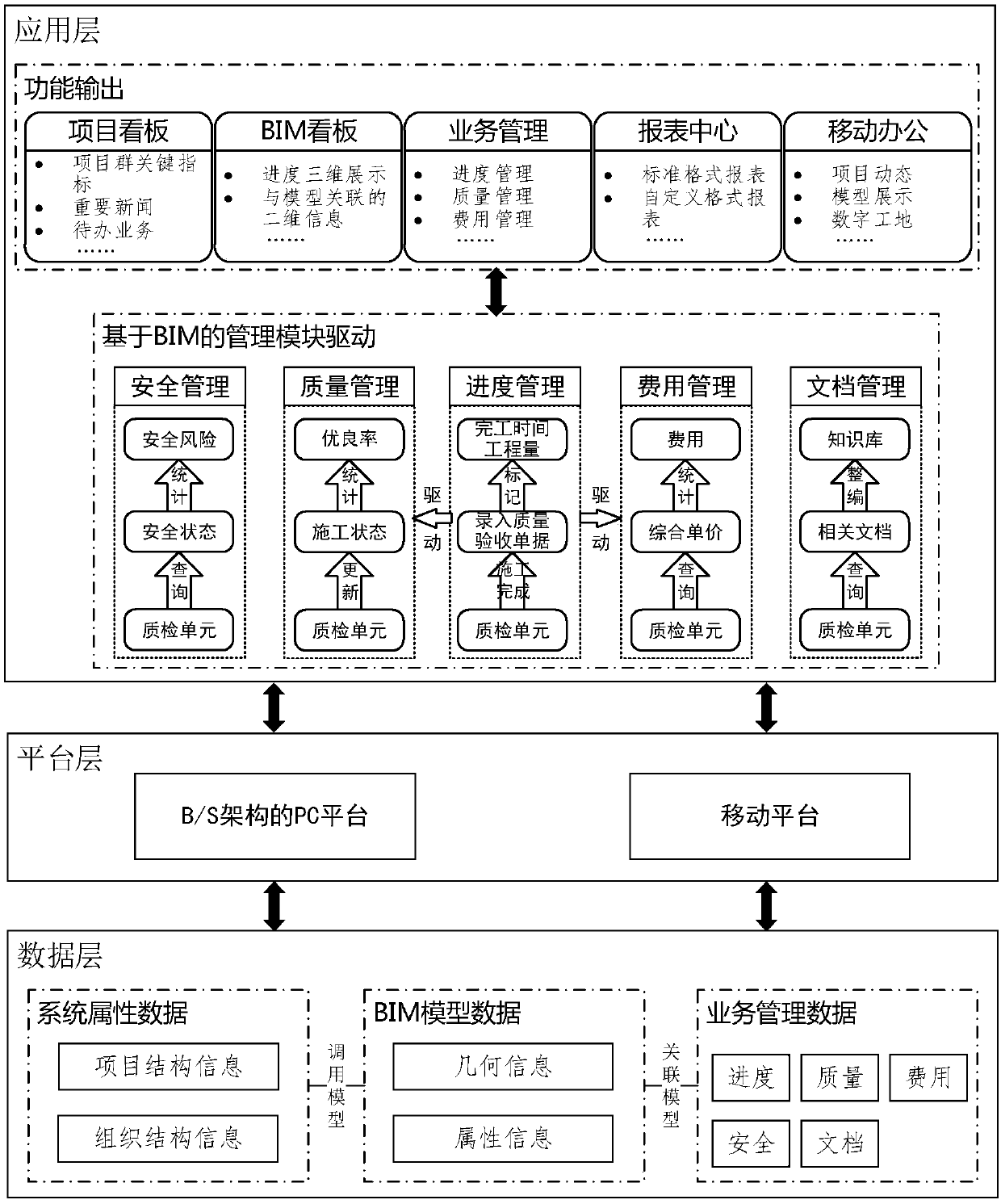
Digital management system and method for project construction processes
ActiveCN107622355AImprove acquisitionImprove circulation speedOffice automationResourcesBusiness managementProtocol Application
The invention discloses a digital management system for project construction processes. The system comprises a data layer, a platform layer and application layers, wherein the data layer comprises a BIM construction module which is created via a division principle of a construction quality management unit; the data layer comprises system attribute data, BIM model data and business management data;the platform layer consists of a B / S architecture-adopted PC platform and a mobile platform; the PC platform application layer consists of a project board module, a BIM board module, a business management module and a statement center module; a business management module comprises a progress management module, a quality management module, a safety management module, an expense management module and a document management module; and a mobile platform application layer is a mobile office layer which consists of a project dynamic module, a model display module and a digital construction site module. The system has the advantage of improving the management precision and efficiency of project construction processes.
Owner:CHANGJIANG SURVEY PLANNING DESIGN & RES
Data integration method and system of heterogeneous relational database based on XML (Extensive Makeup Language)
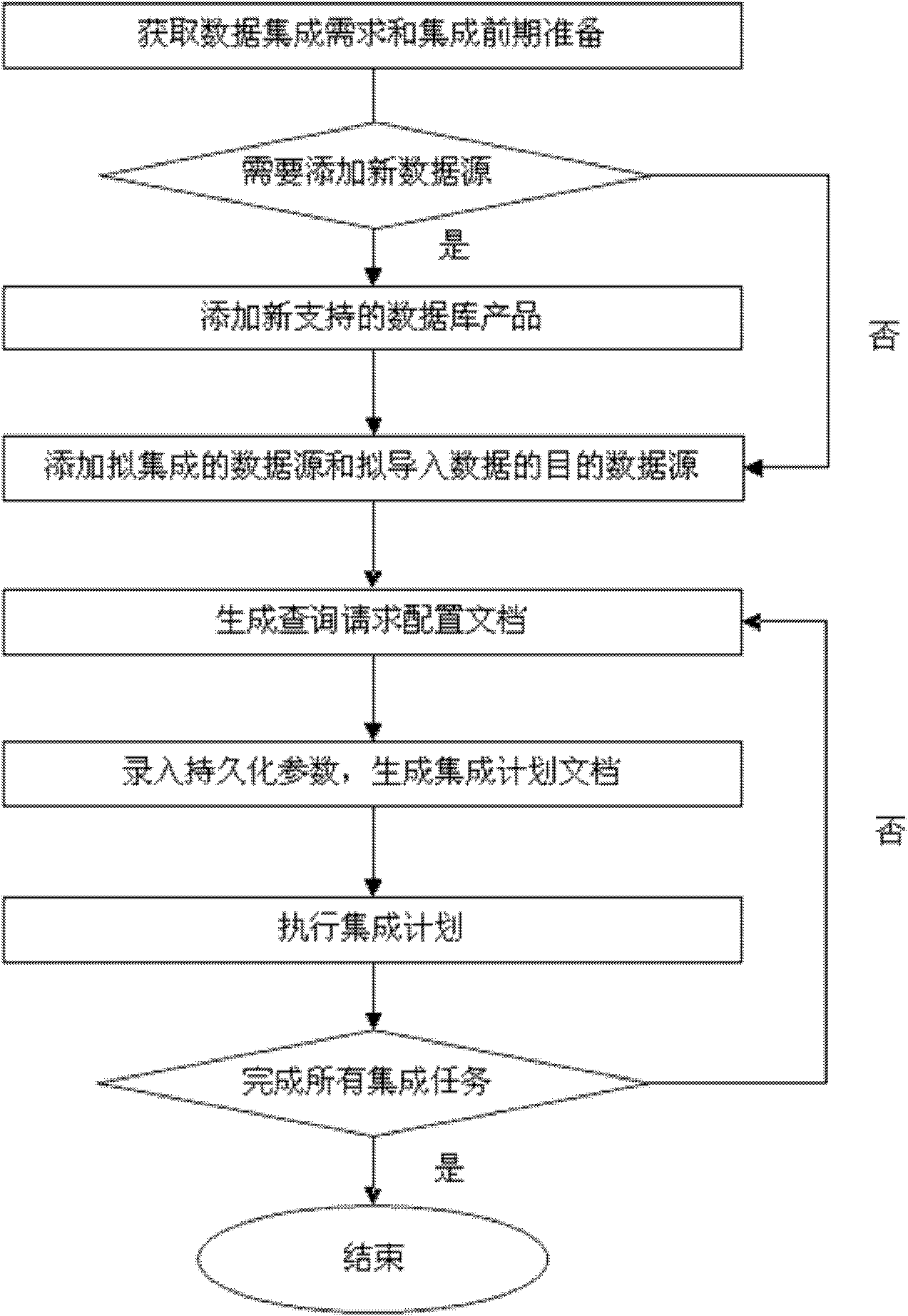
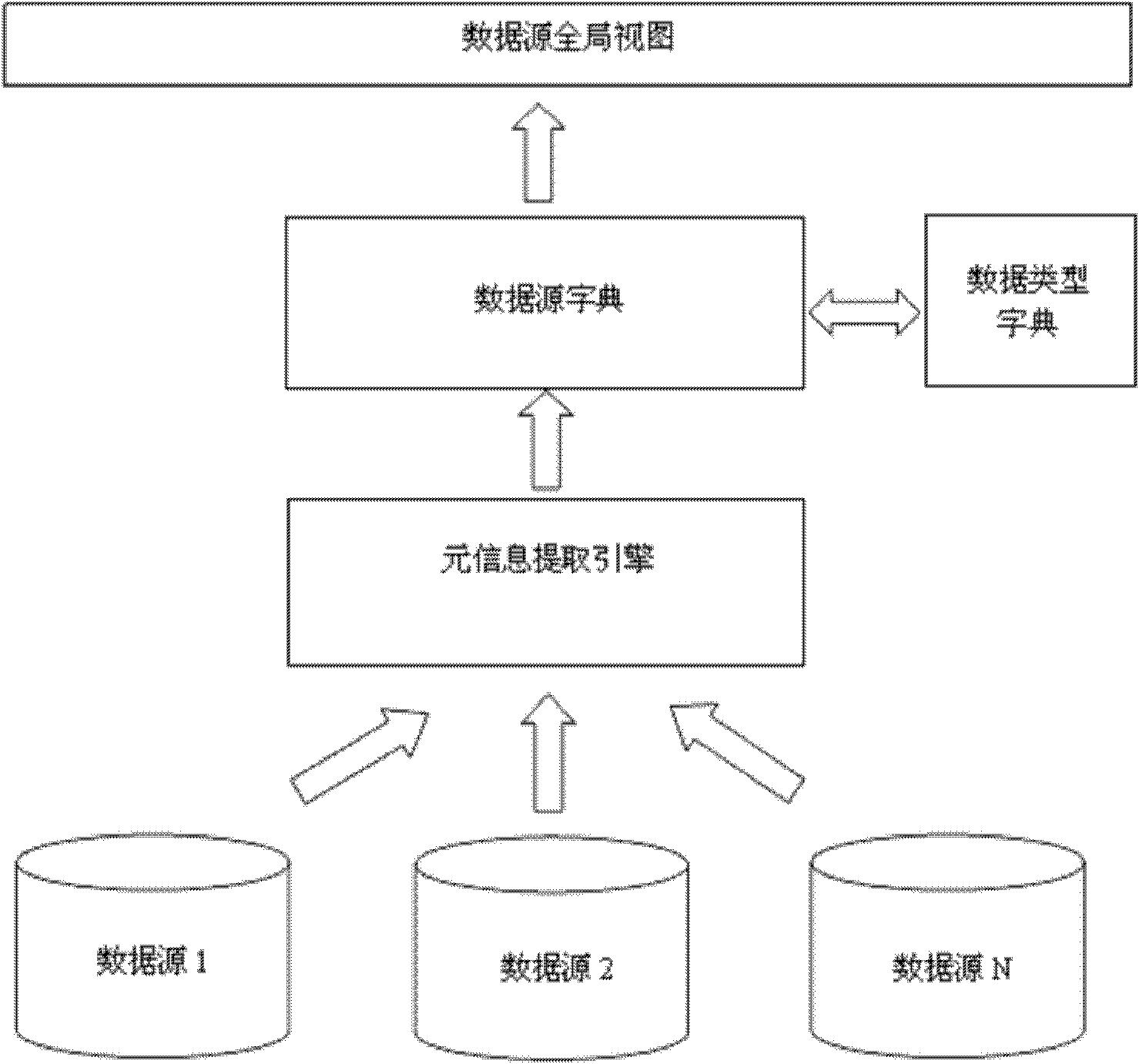
InactiveCN102081661ACutting costsEnsure consistencySpecial data processing applicationsData informationDecomposition
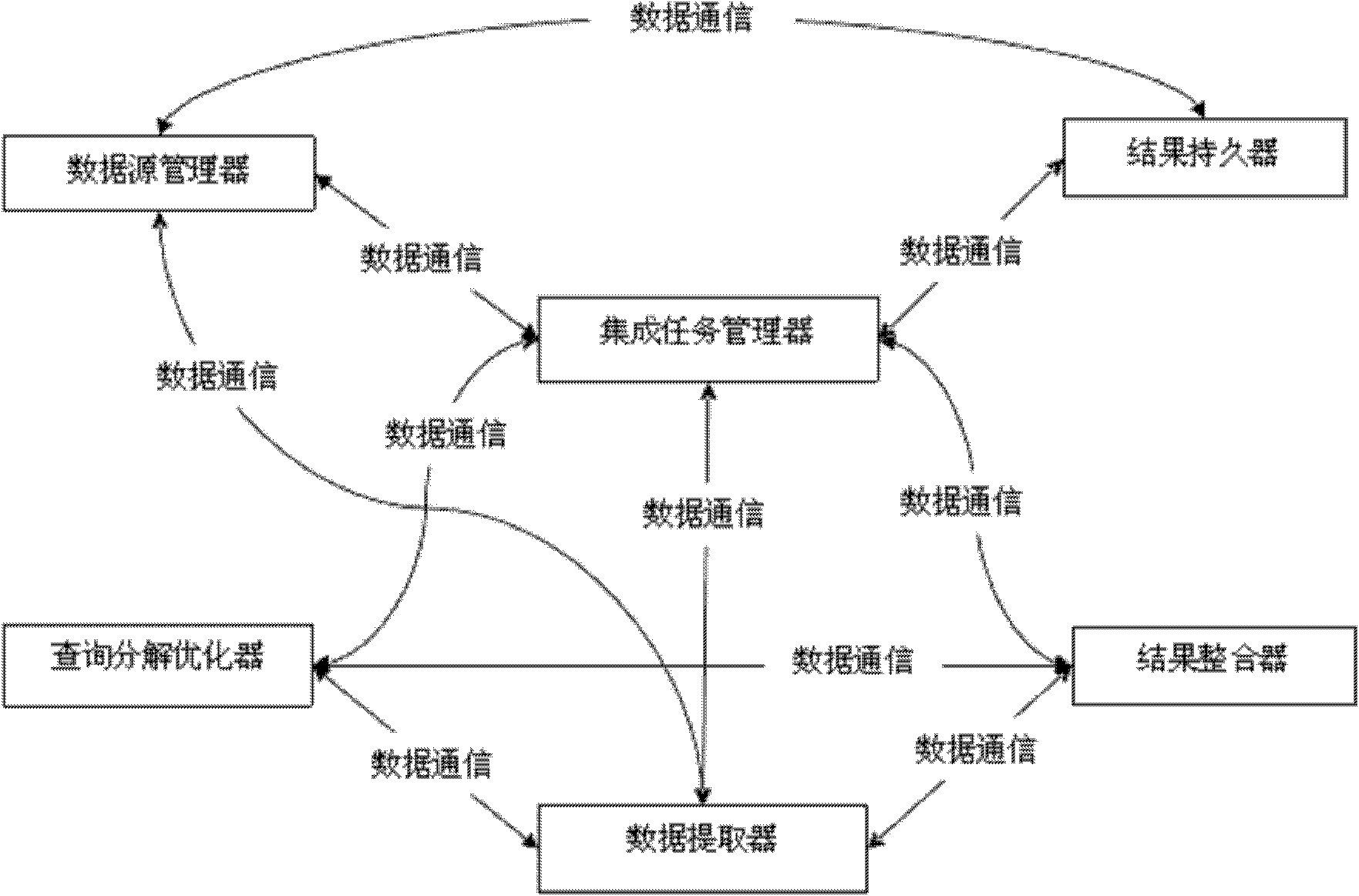
The invention discloses a data integration method and system of a heterogeneous relational database based on XML (Extensive Makeup Language), which aims to solve the problem that large amount of data information cannot be utilized efficiently. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring data integration requirement and integration pre-preparation; executing a database product which adds new support to the system if integration application involves in the new database product; adding a data source related to integration; generating a search request configuration file; entering persistent parameters on a persistent parameter configuration interface of the system; selecting an integration plan file on an integration plan executing interface of the system and executing the integration plan; waiting processing of a software system and repeating the steps 4 to 6 till all integration tasks are completed. The data integration system of the heterogeneous relational database based on XML is a functional module structure consisting of an integration task manager, a data source manager, a query decomposition optimizer, a data extractor, a result aggregator and a result persister.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Radar echo extrapolation method based on dynamic convolution neural network
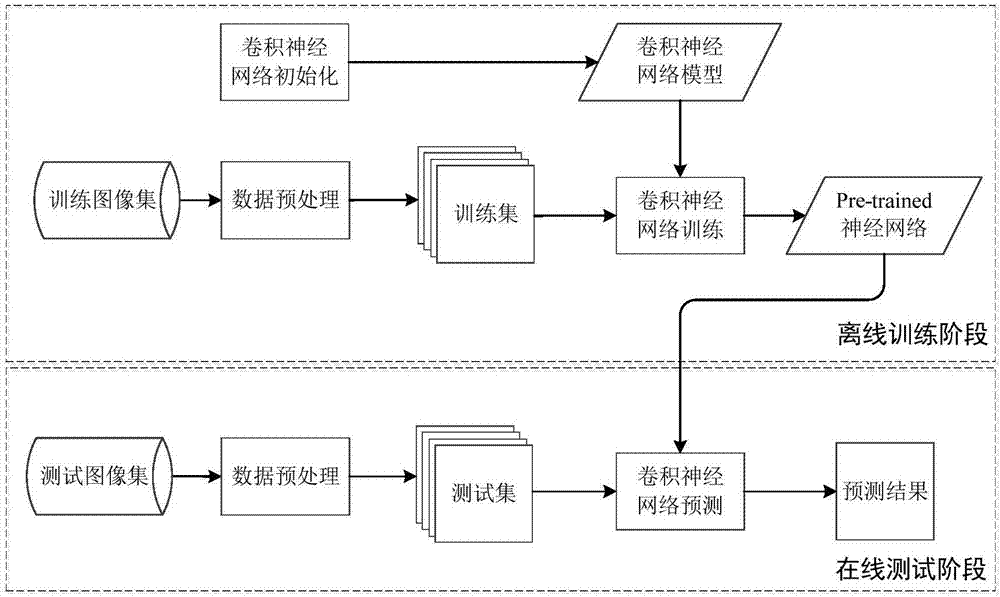
ActiveCN106886023AIncrease profitImprove data utilizationNeural architecturesICT adaptationTest sampleForward propagation
The invention discloses a radar echo extrapolation method based on a dynamic convolution neural network. The method comprises a step of offline convolutional neural network training which comprises the steps of carrying out data preprocessing on a given training image set to obtain a training sample set, initializing a dynamic convolution neural network model, training a dynamic convolution neural network by using the training sample set, calculating an output value through network forward propagation, and updating network parameters through backward propagation such that the dynamic convolution neural network converges. The method also comprises a step of online radar echo extrapolation which comprises the steps of converting a test image set into a test sample set through data preprocessing, testing the trained dynamic convolution neural network by using the test sample set, and carrying out convolution of a laster radar echo image inputted into an image sequence and a probability vector obtained in the network forward propagation to obtain a predicted radar echo extrapolation image.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
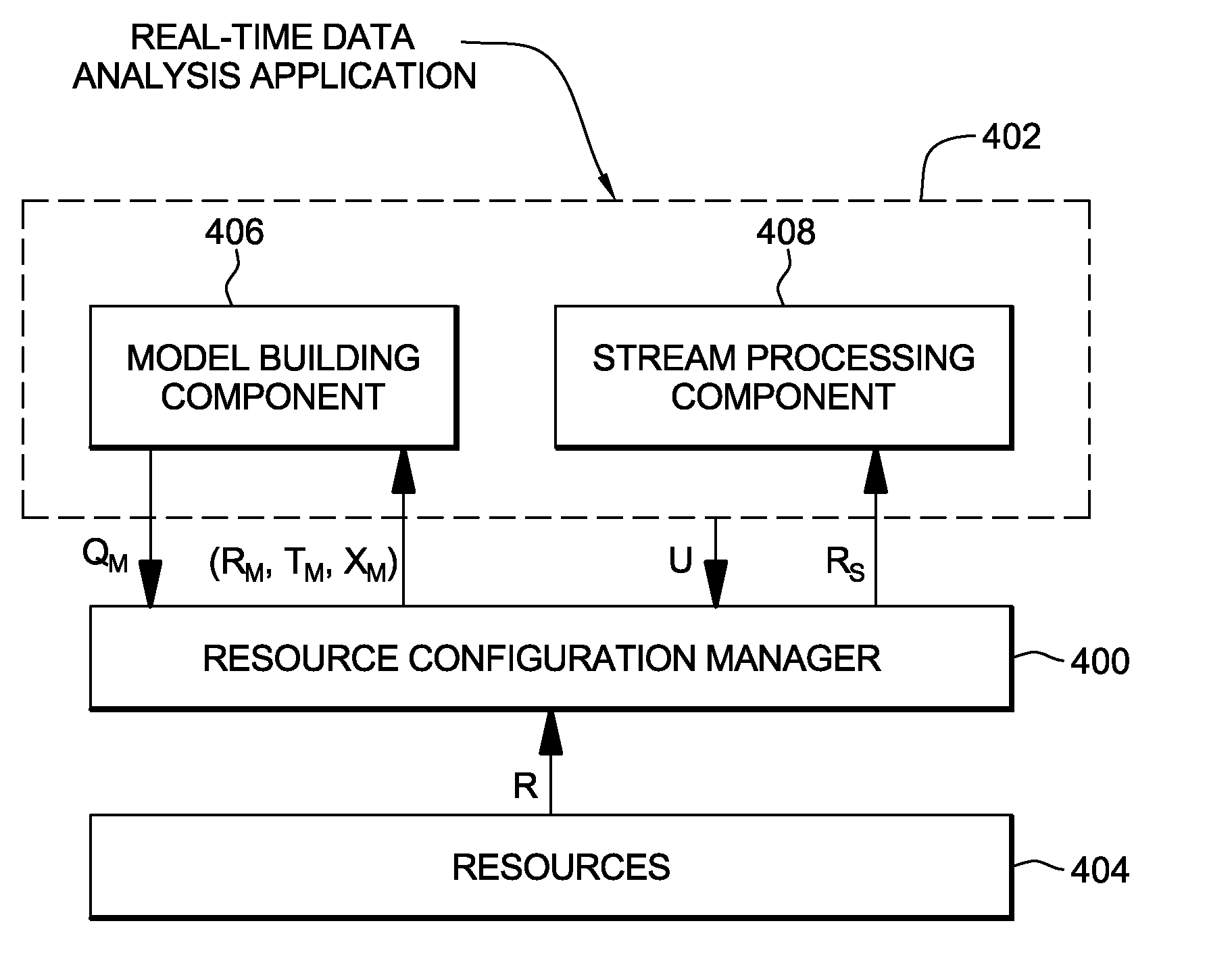
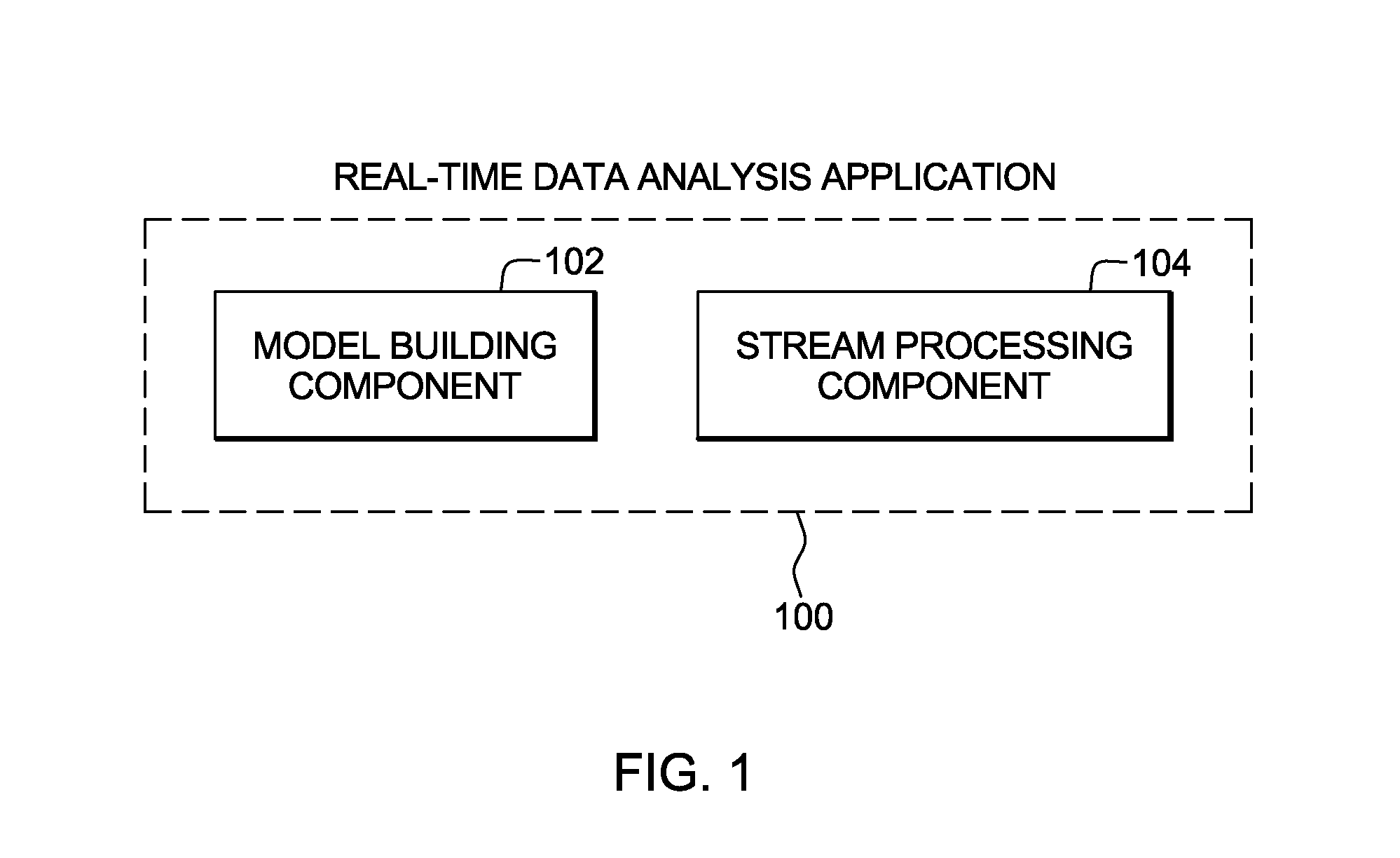
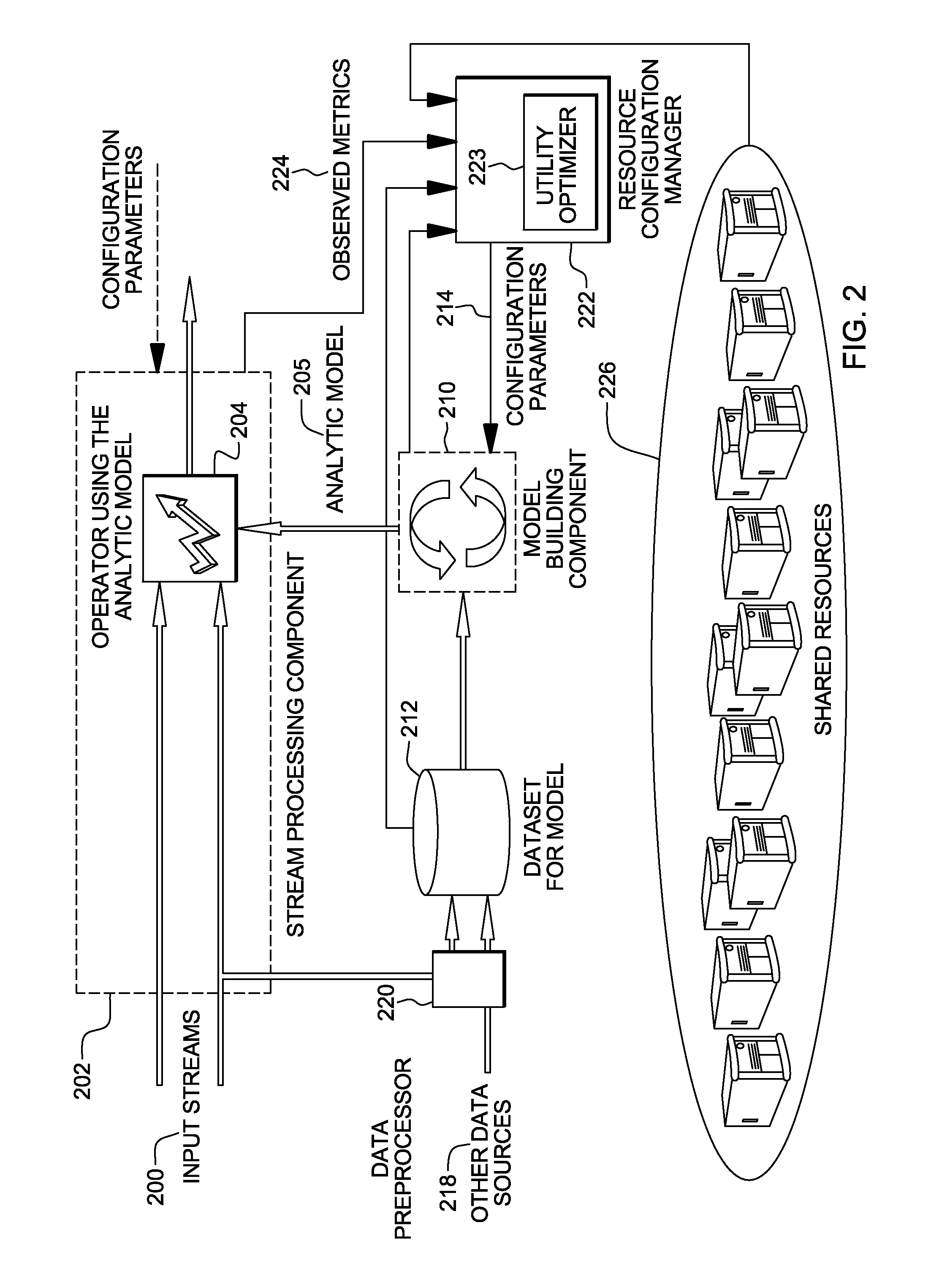
Managing model building components of data analysis applications
InactiveUS20110225584A1Improve data utilizationIncrease profitResource allocationError detection/correctionConfiguration interactionResource allocation
Data analysis applications include model building components and stream processing components. To increase utility of the data analysis application, in one embodiment, the model building component of the data analysis application is managed. Management includes resource allocation and / or configuration adaptation of the model building component, as examples.
Owner:IBM CORP
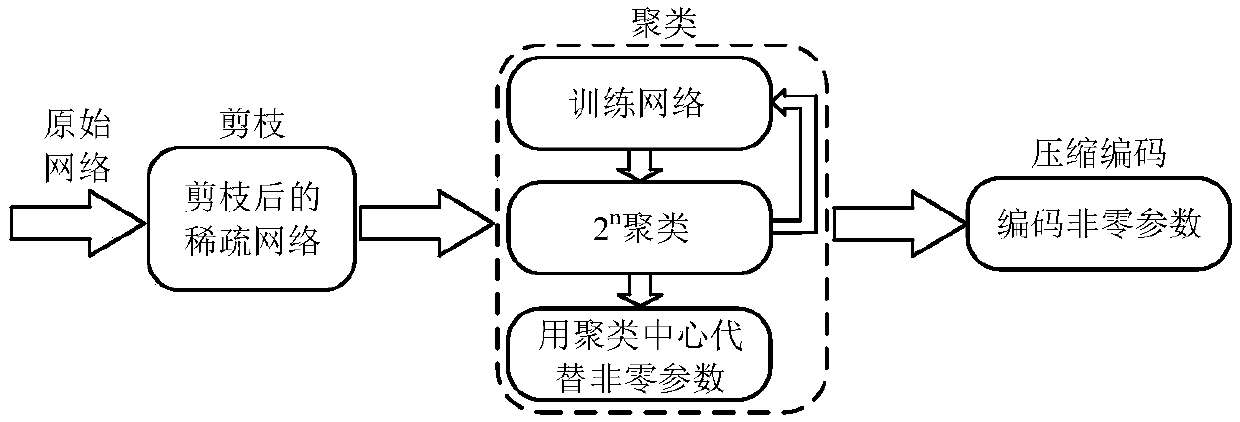
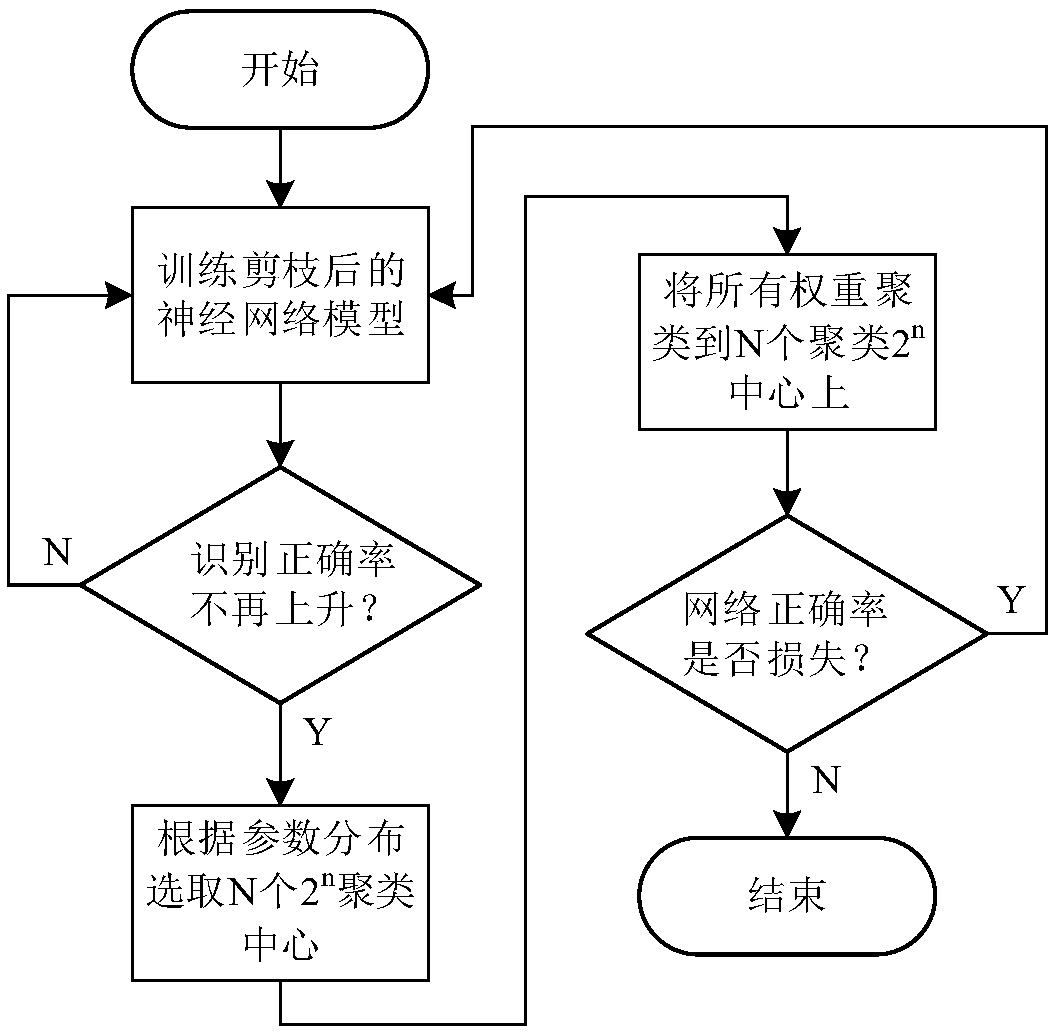
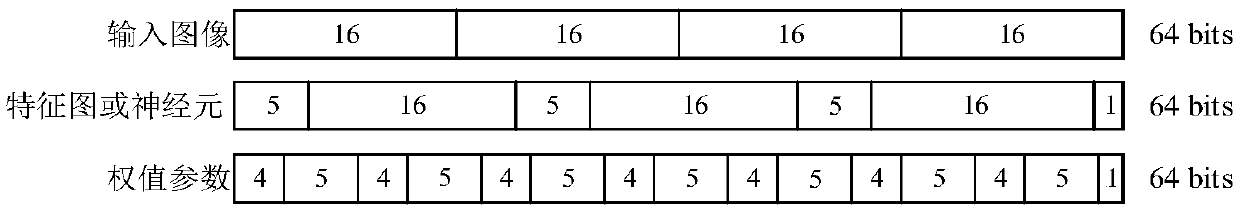
A sparse convolutional neural network accelerator and an implementation method
ActiveCN109635944ASimplify complexitySave storage resourcesNeural architecturesPhysical realisationEngineeringNeuron
The invention relates to a sparse convolutional neural network accelerator and a realization method, and the method comprises the steps: reading the connection weight of a sparse network in an off-chip DRAM into a weight input buffer area, decoding the connection weight through a weight decoding unit, and storing the connection weight in a weight on-chip global buffer area; Reading neurons into aneuron input buffer area, decoding the read neurons through a neuron decoding unit, and storing the decoded neurons in a neuron on-chip global buffer area; Determining a calculation mode of the PE calculation unit array according to the configuration parameters of the current layer of the neural network, and sending neurons and connection weights which are arranged after decoding to a PE calculation unit; Calculating the product of the neuron and the connection weight; In the accelerator, the multipliers in the PE units are all replaced by the shifters, and all basic modules can be configuredaccording to network calculation and hardware resources, so that the accelerator has the advantages of high speed, low power consumption, small resource occupation and high data utilization rate.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
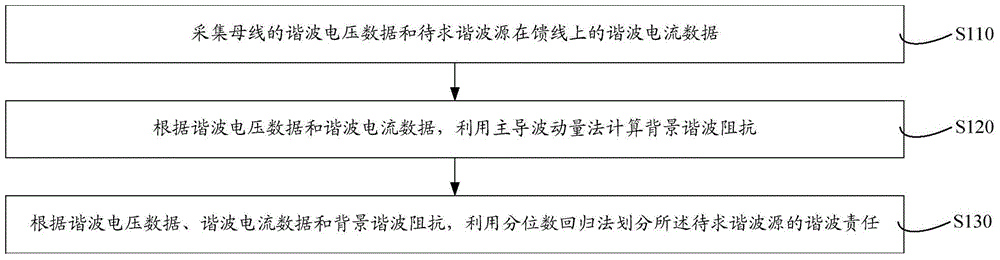
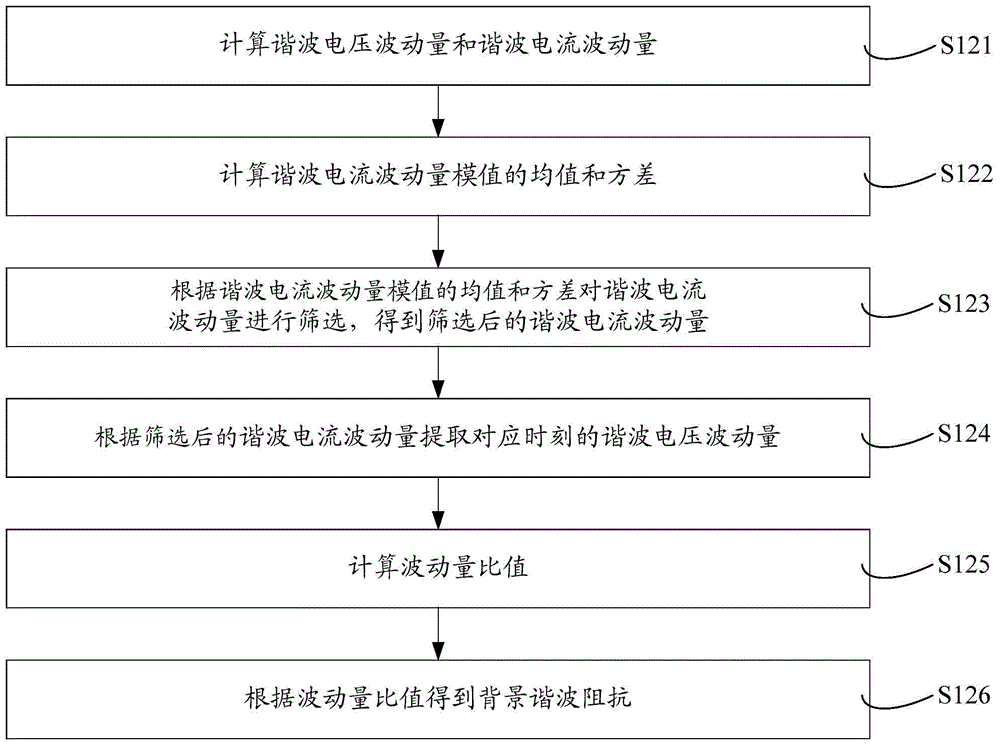
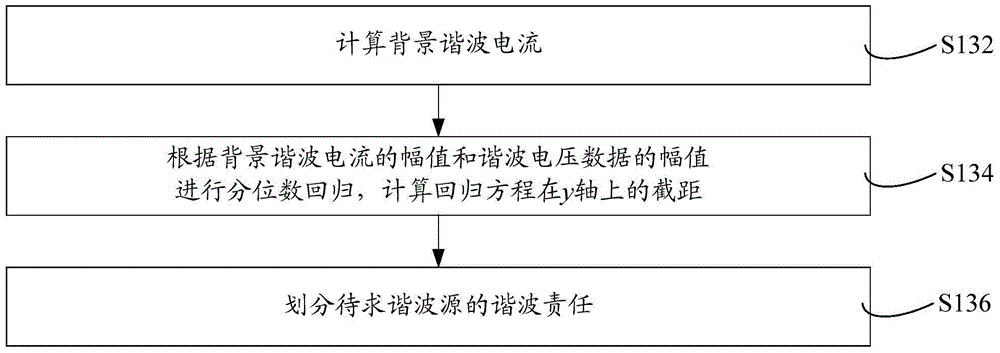
Harmonic contribution division method and harmonic contribution division system
ActiveCN104698273AAccurate calculationInhibition effectSpectral/fourier analysisQuantile regressionMomentum
The invention relates to a harmonic contribution division method and a harmonic contribution division system. The harmonic contribution division method comprises the following steps of acquiring harmonic voltage data of a bus and harmonic current data of a harmonic source to be calculated on a feeder line; calculating background harmonic impedance by using a leading fluctuation quantity method according to the harmonic voltage data and the harmonic current data; and dividing harmonic contributions of the harmonic source to be calculated by using a quantile regression method according to the harmonic voltage data, the harmonic current data and the background harmonic impedance. The background harmonic impedance is estimated by the leading fluctuation quantity method, fluctuation quantity with a leading function is screened out to calculate the background harmonic impedance, influences of background harmonic and measurement noise fluctuation on a background harmonic impedance estimation result are restrained effectively, and the background harmonic impedance is calculated accurately; and the background harmonic current is calculated according to the background harmonic impedance, and quantile regression is performed to obtain the harmonic contributions of the harmonic source. Calculation deviation caused by background harmonic fluctuation can be reduced, division accuracy is improved, and the stability and the data utilization rate are high.
Owner:GUANGZHOU POWER SUPPLY CO LTD +1
Well-testing interpretation model used for analyzing series structure of multiple fracture-cave units and methods
ActiveCN107563027AMonitor production statusReduce excavationSpecial data processing applicationsBorehole/well accessoriesCarbonate rockKarst
The invention discloses a well-testing interpretation model used for analyzing a series structure of multiple fracture-cave units and methods. The model includes: merging fracture-karst-cave reservoirbodies in fracture-cave-type oil reservoirs into the fracture-cave units; merging fracture-corrosion-hole reservoir bodies in the fracture-cave-type oil reservoirs into the fracture-cave units; for carbonate-rock fracture-cave-type oil reservoirs, using the fracture-cave units and fracture-hole units to approximate radial sector structure bodies; and regarding connection areas between sectors aspressure conducting areas with no pressure dropping, namely being equal to boundary pressure of the preceding sector by pressure of an outflow end of the subsequent sector, and being equal to a boundary inflow amount of the preceding sector by an outflow amount of the subsequent sector. One of the methods includes applying the model to analysis and interpretation technology of the fracture-cave-type oil reservoirs. According to the well-testing technology solution used for analyzing the fracture-cave-type oil reservoirs provided by the invention, a well-testing technology blank of the fracture-cave-type oil reservoirs is filled, a utilization rate of well-testing data is increased, and a well-testing analysis means is provided for knowing and evaluating fracture-cave-type oil reservoir structures.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
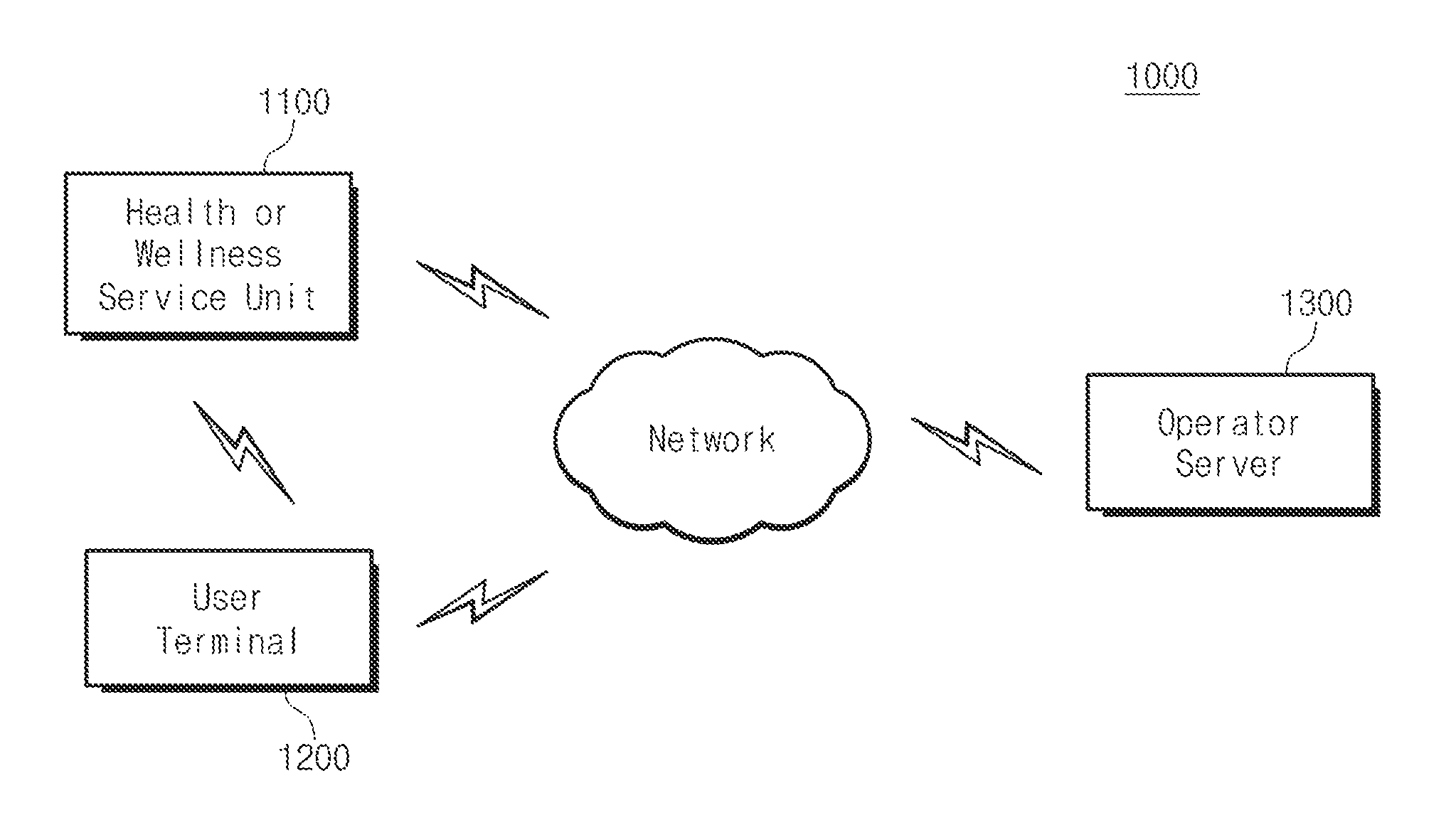
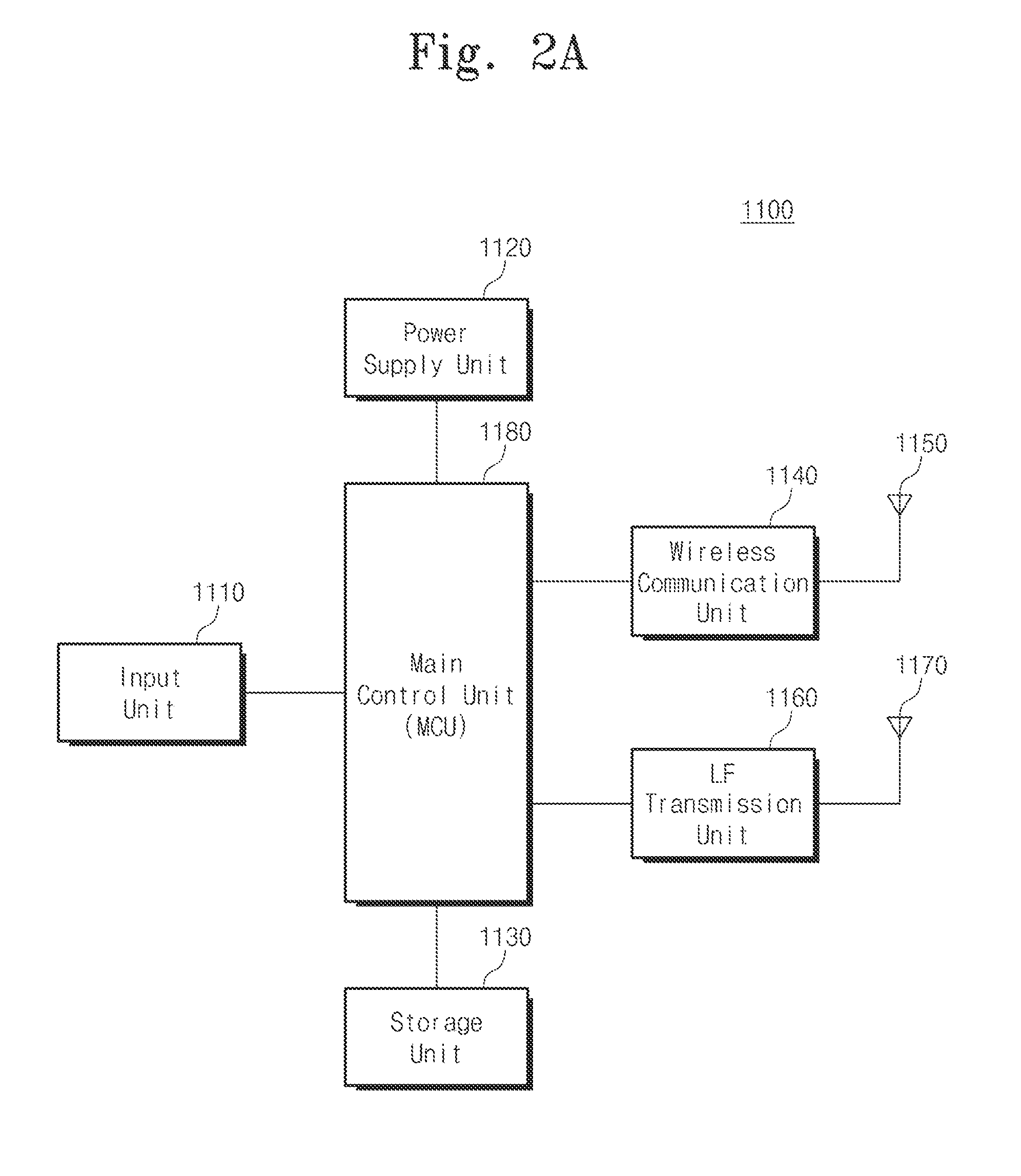
Self-direct m2m (machine-to-machine) comunication based user's daily activity logging and analyzing system with wearable and personal mobile devices
ActiveUS20160183029A1Raise data utilizationQuickly copePower managementTelemedicineLoggingMachine to machine
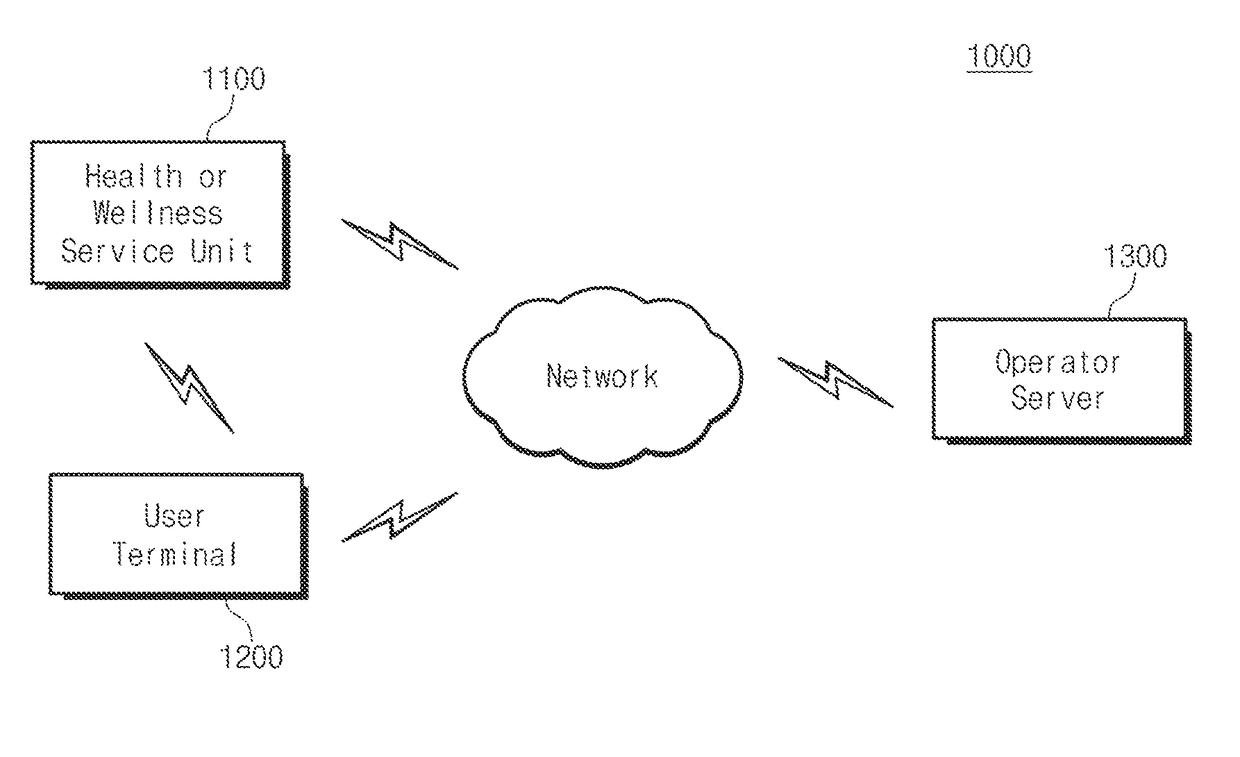
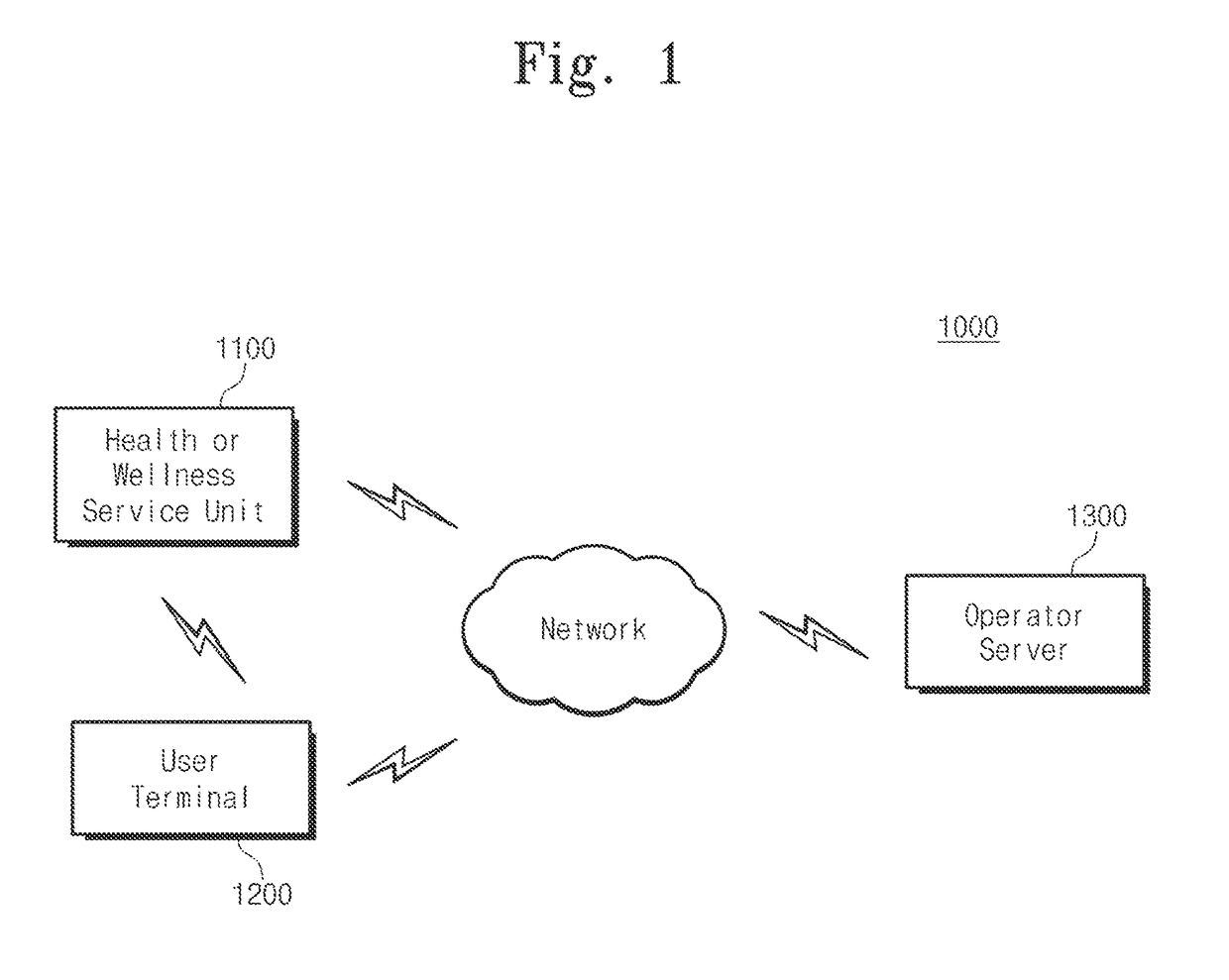
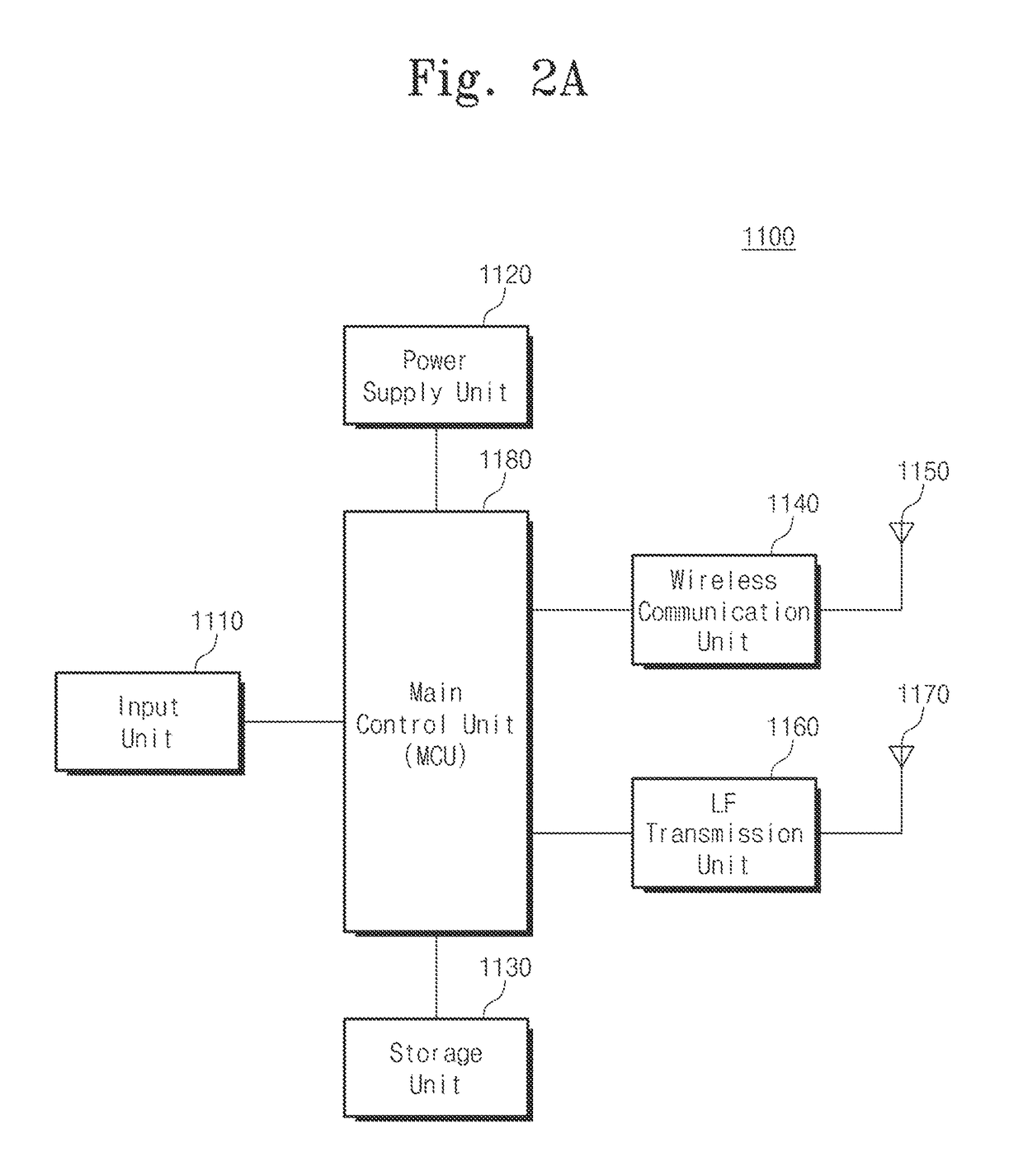
The present invention relates to a heath care system having proximity-based neighbor device wake-up and automatic user identification function, a method for automatic logging of user's daily activity history, and a method for managing a user activity pattern, and the system comprises: a health or wellness service unit; and an user terminal. The health or wellness service unit transmits a wake-up signal for changing a state of the user terminal from a sleep state into a wake-up state, a low frequency (LF) signal for identifying a physical distance and direction between the health or wellness service unit and the user terminal, and a measured biological signal of a measuring object. The user terminal receives the biological signal, the wake-up signal, and the LF signal through bidirectional wireless communication with the health or wellness service unit, and transmits a terminal identification (ID) and a received signal strength indication (RSSI) corresponding to the received LF signal.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
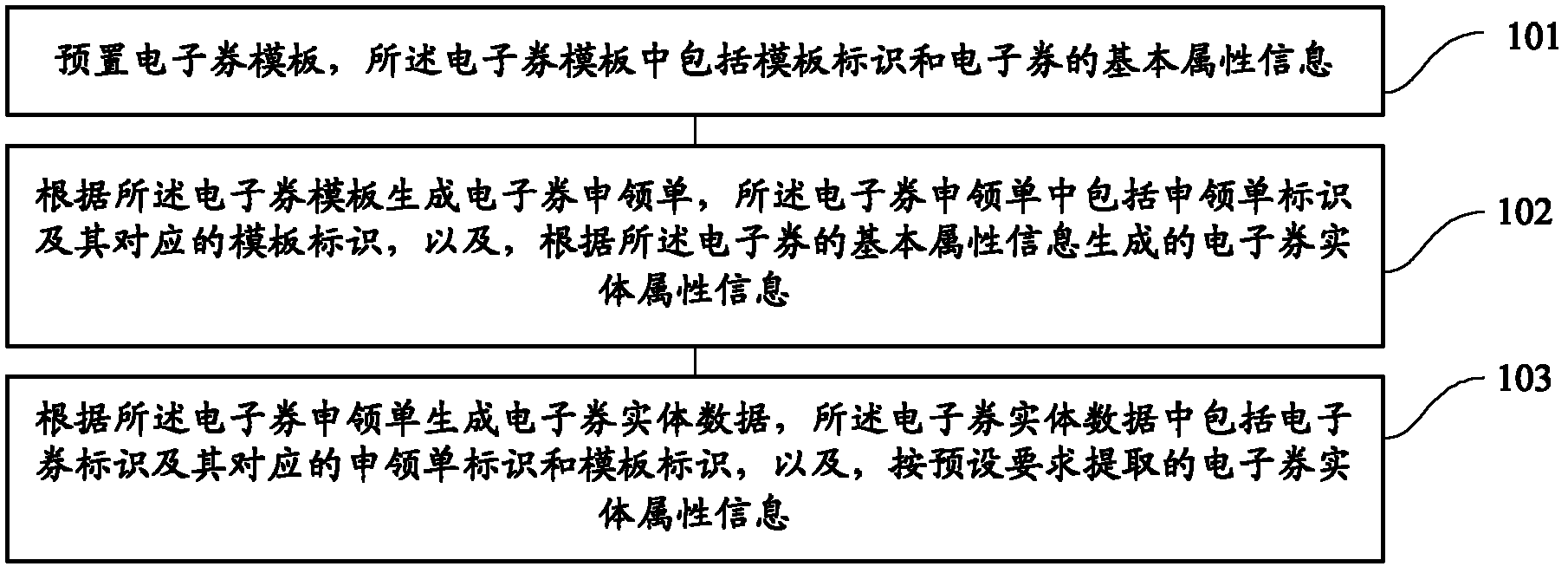
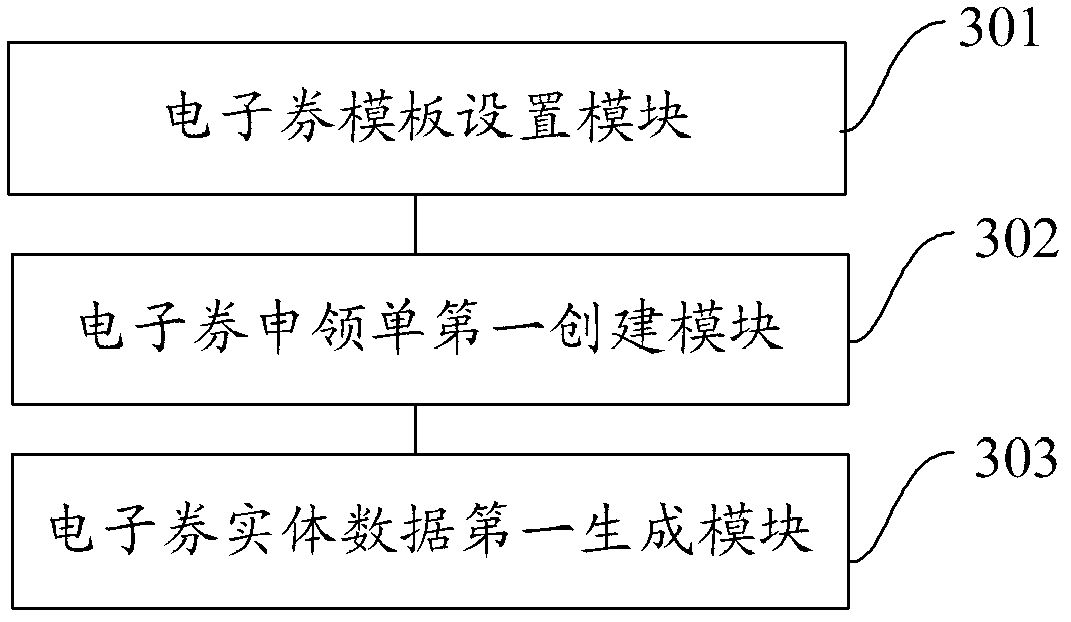
Electronic coupon data generation method and electronic coupon data generation device
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
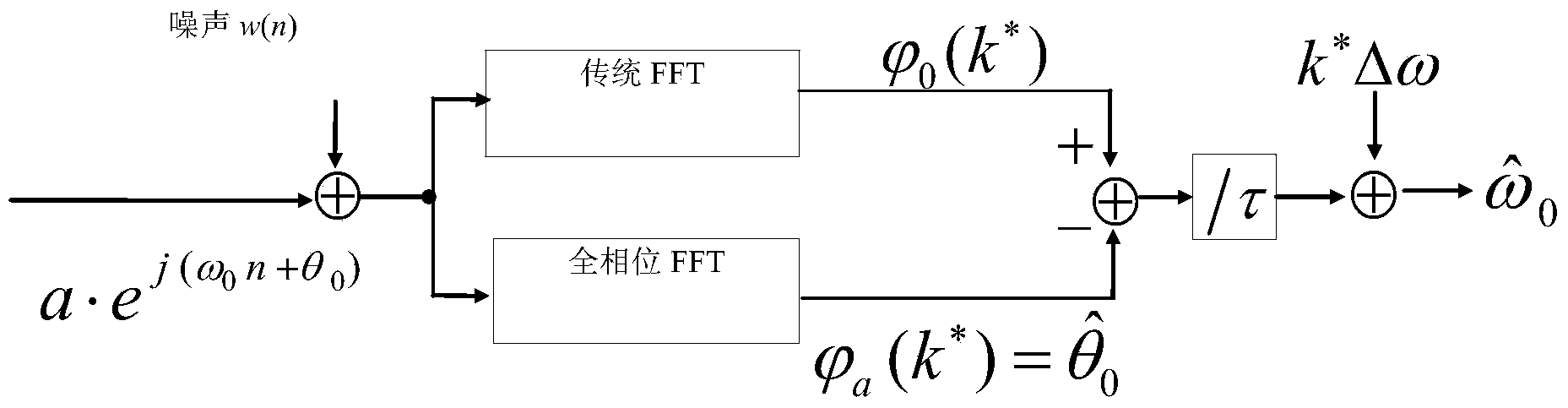
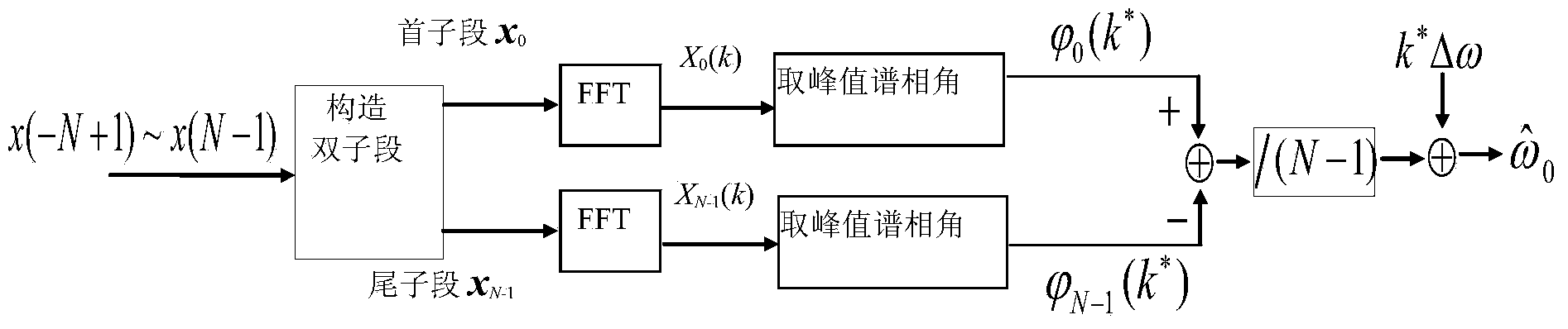
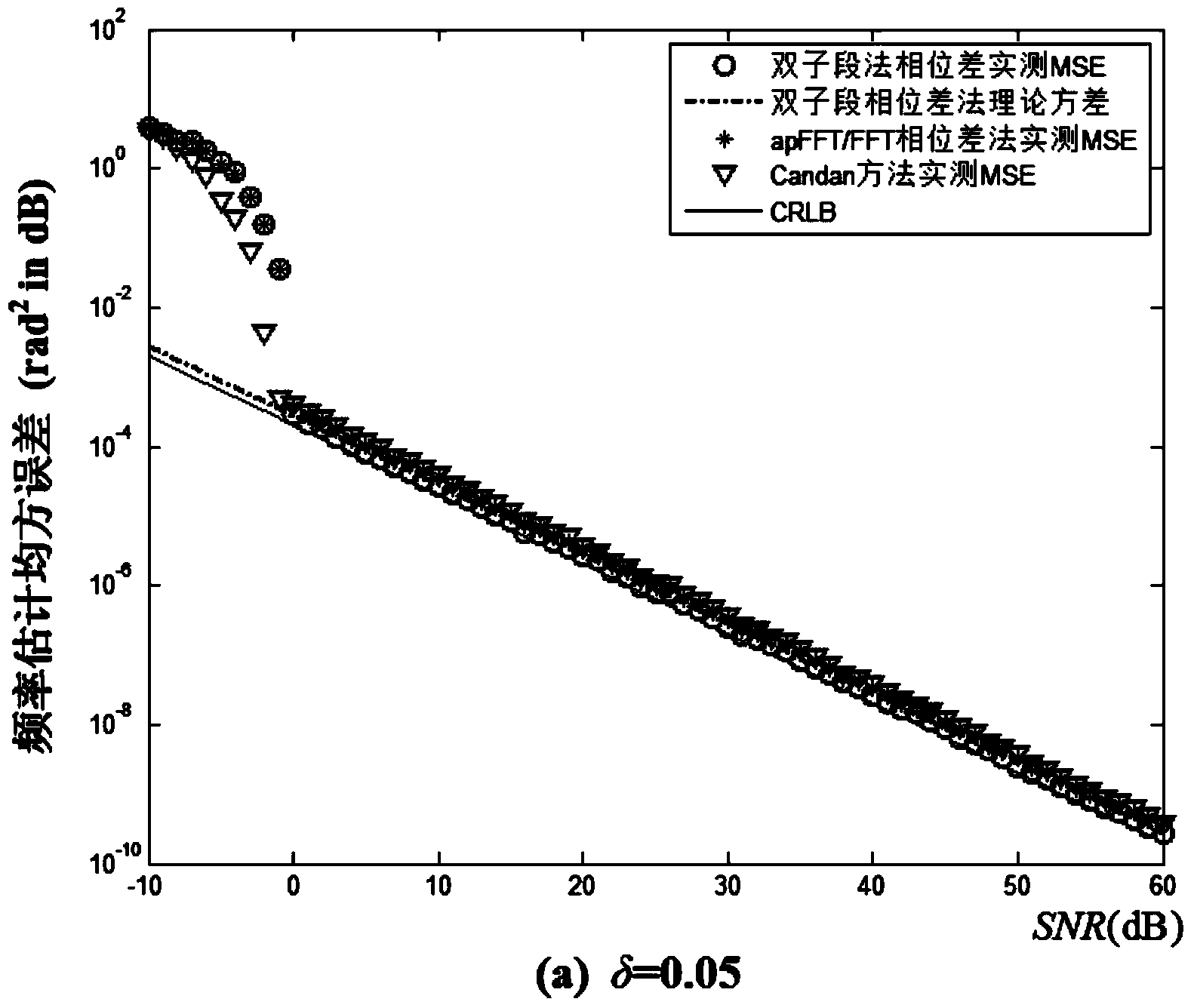
Double-subsegment phase difference frequency estimation method and device adopted by method
InactiveCN104076200AAchieve high-precision frequency measurementPromote engineering applicationFrequency measurement arrangementMean squareResource consumption
The invention discloses a double-subsegment phase difference frequency estimation method and a device adopted by the method. The method comprises the steps of taking first subsegments and tail subsegments in 2N-1 samples x(-N+1)-x(N-1) to form double subsegments; respectively performing FFT transformation on x0 and xN-1 to obtain corresponding peak value spectrums; performing simple linear treatment on a peak value spectrum phase (shown in description) difference value to obtain a frequency estimation result. The device comprises an analog-digital converter, a DSP device and a driving and displaying module, wherein signals x(t) to be detected are sampled through the analog-digital converter to obtain a sample sequence x(n), the sample sequence is fed into the DSP device in a parallel digital input mode, and parameter estimation of the signals is achieved through internal algorithm processing of the DSP device. Finally, the frequency estimation result and theoretical mean square errors of frequency estimation are displayed through the driving and displaying module. The double-subsegment phase difference frequency estimation method and the device are small in computation amount, and the estimation method is simple, high in efficiency and low in resource consumption, and the hardware cost is greatly saved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
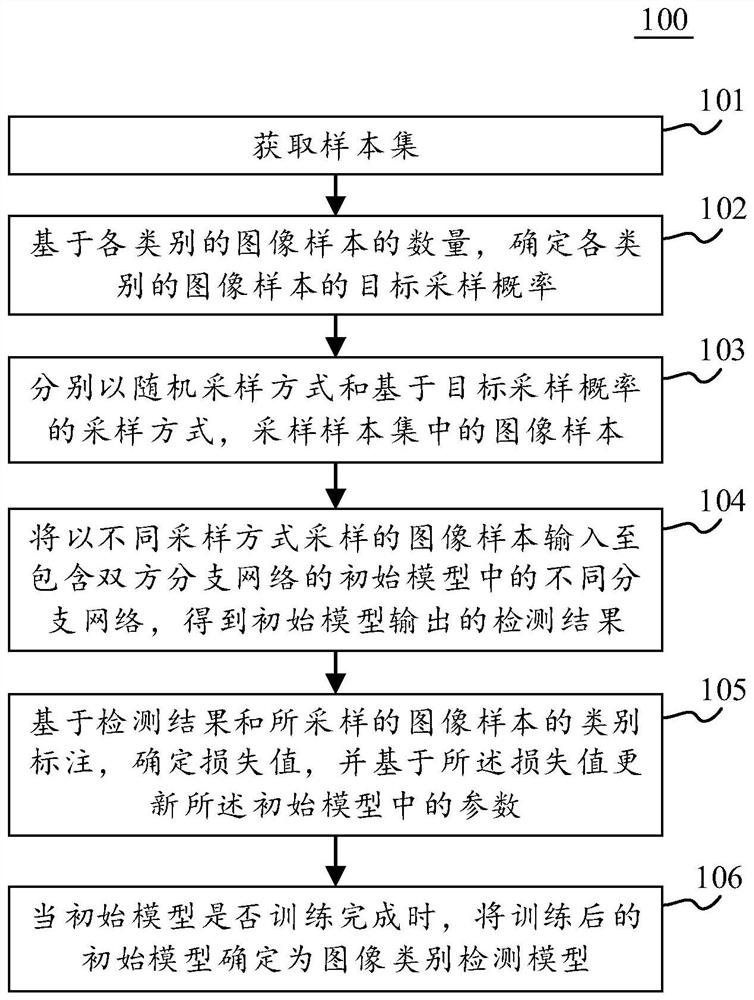
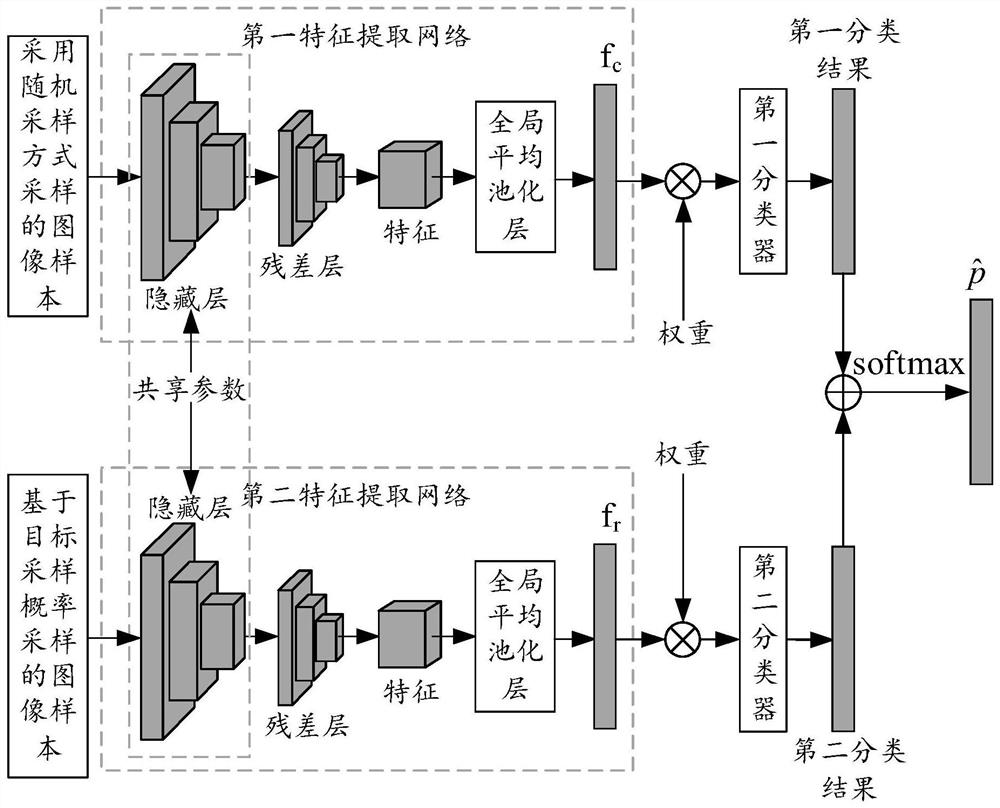
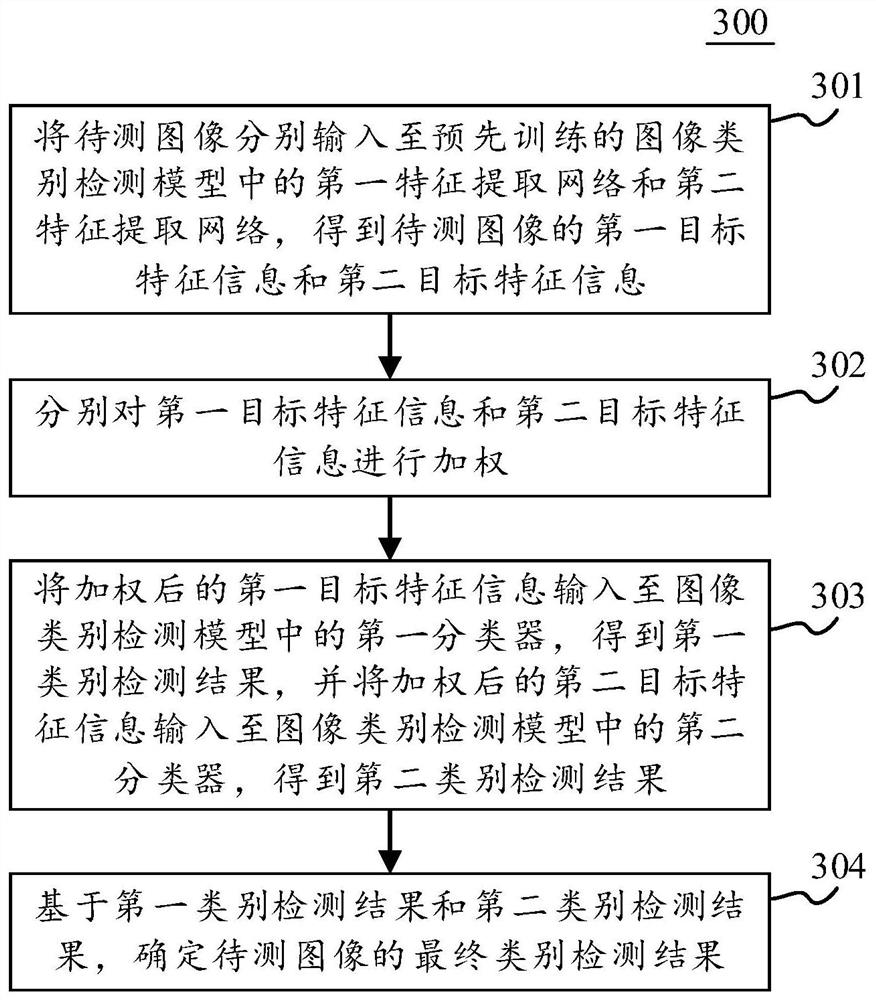
Model training method and device, image category detection method and device and electronic equipment
PendingCN111860573AImprove data utilizationImprove detection accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringSample image
The embodiment of the invention discloses a model training method and device, an image category detection method and device and electronic equipment. An embodiment of the method comprises the steps ofobtaining a sample set; determining a target sampling probability of each category of image samples based on the number of each category of image samples, and enabling the number of each category ofimage samples to be inversely proportional to the target sampling probability; using a random sampling mode and a sampling mode based on a target sampling probability respectively for sampling image samples in the sample set, taking the image samples sampled in different sampling modes as inputs of different branch networks in the initial model containing the double-branch network, and training the initial model based on annotation information of the sampled image samples to obtain an image category detection model. According to the embodiment, the data utilization rate in the model training process is improved, so that the model fully learns the characteristics of various types of image samples, and the detection precision of the image type detection model is improved.
Owner:MEGVII BEIJINGTECH CO LTD
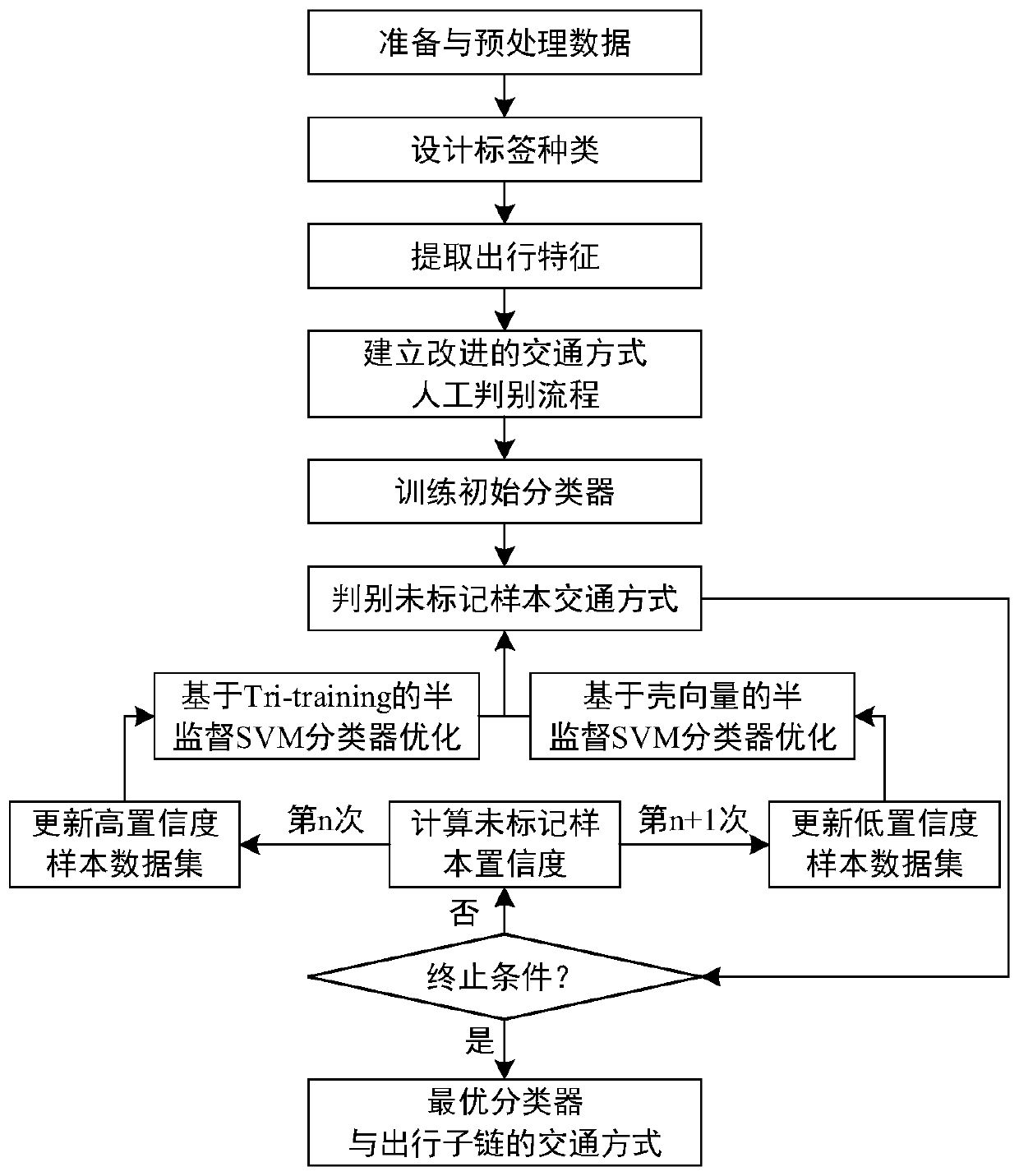
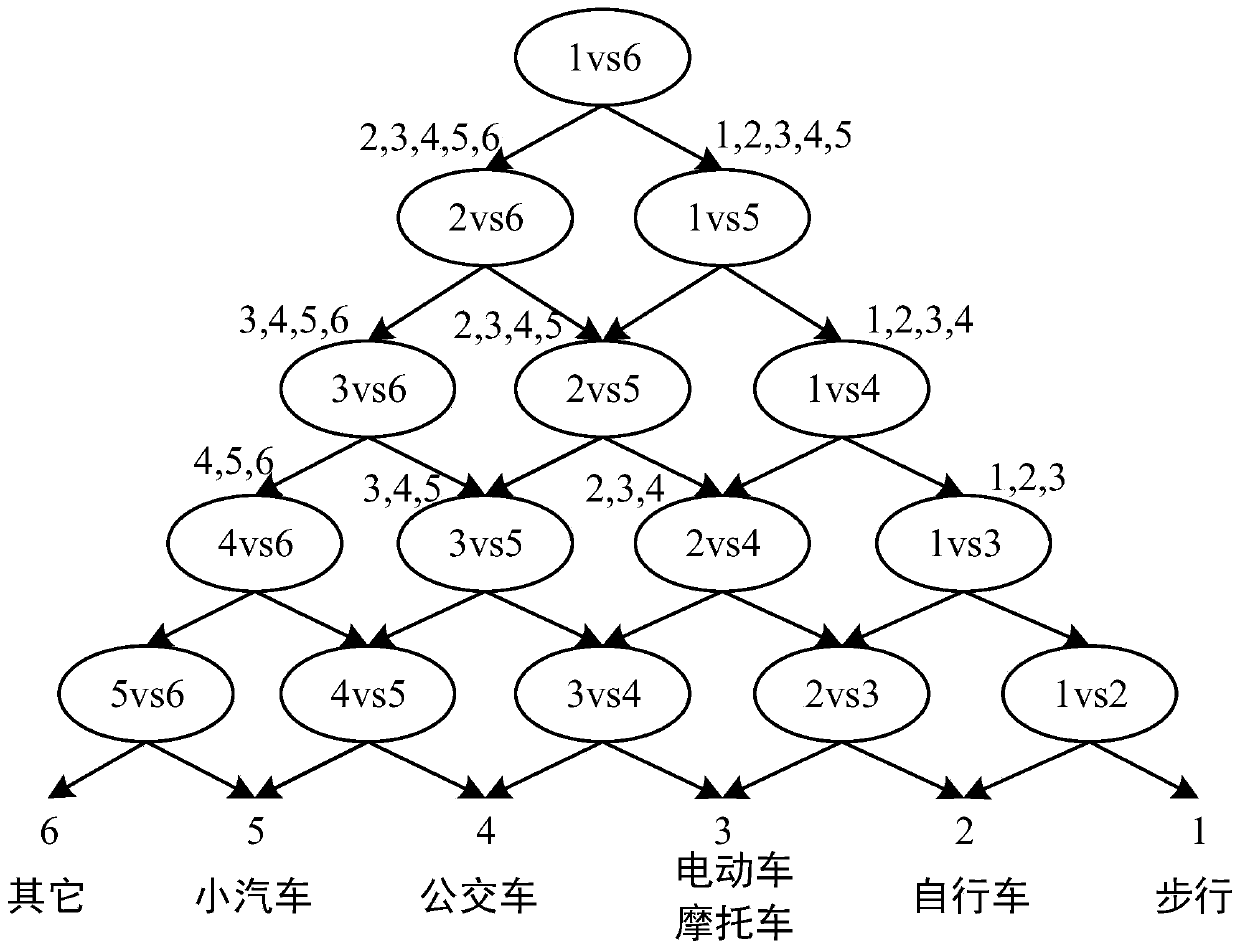
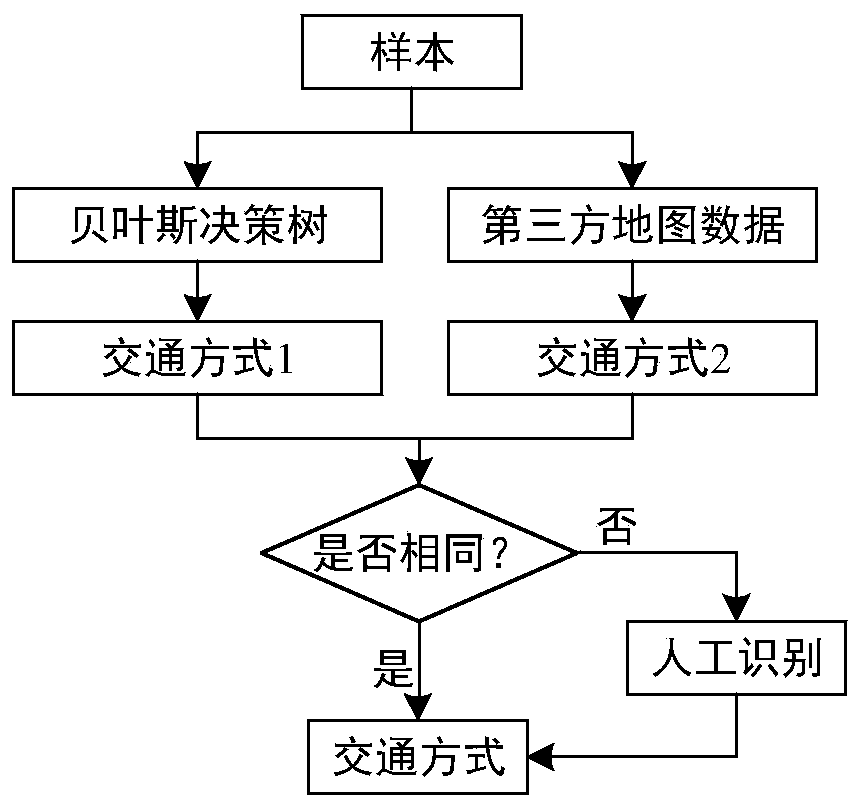
Traffic mode discrimination method of semi-supervised SVM based on mobile phone signaling data
InactiveCN109784416ALower acquisition costsLow costDetection of traffic movementCharacter and pattern recognitionData setSvm classifier
The invention relates to a computer identification technology, and specifically relates to a traffic mode discrimination method of semi-supervised SVM based on mobile phone signaling data. The methodcomprises: (1) preparing and preprocessing data; (2) designing label types; (3) extracting travel characteristics; (4) establishing an improved traffic mode manual identification process; (5) trainingan initial classifier; (6) judging the traffic mode of an unmarked sample; (7) judging whether the classifier meets a termination condition or not; (8) updating a high confidence coefficient sample data set; (9) optimizing a semi-supervised SVM classifier based on a Tri-training; (10) judging the traffic mode of an unmarked sample; (11) judging whether the classifier meets a termination condition; (12) updating a data set of a low-confidence sample; and (13) optimizing the shell vector-based semi-supervised SVM classifier. The information acquisition cost is reduced, the data utilization rateis improved, judgment is flexible and comprehensive, the precision is high, and the application scene is wider.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
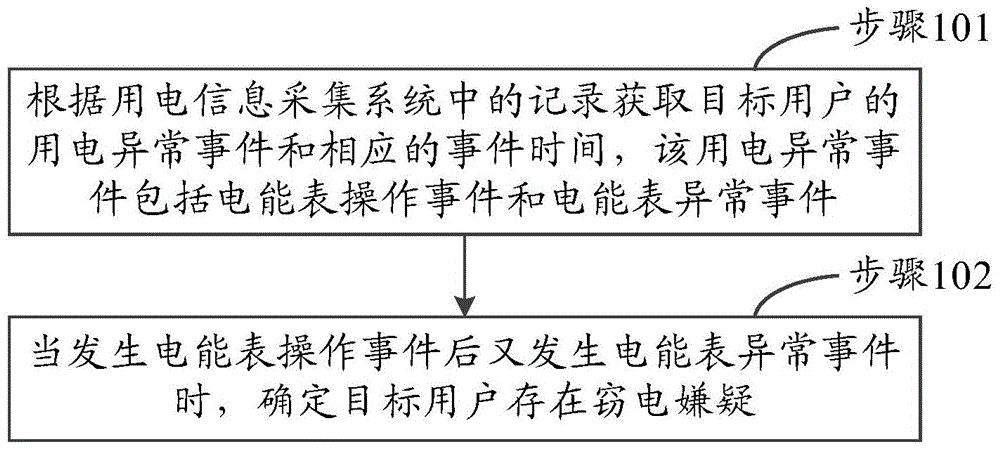
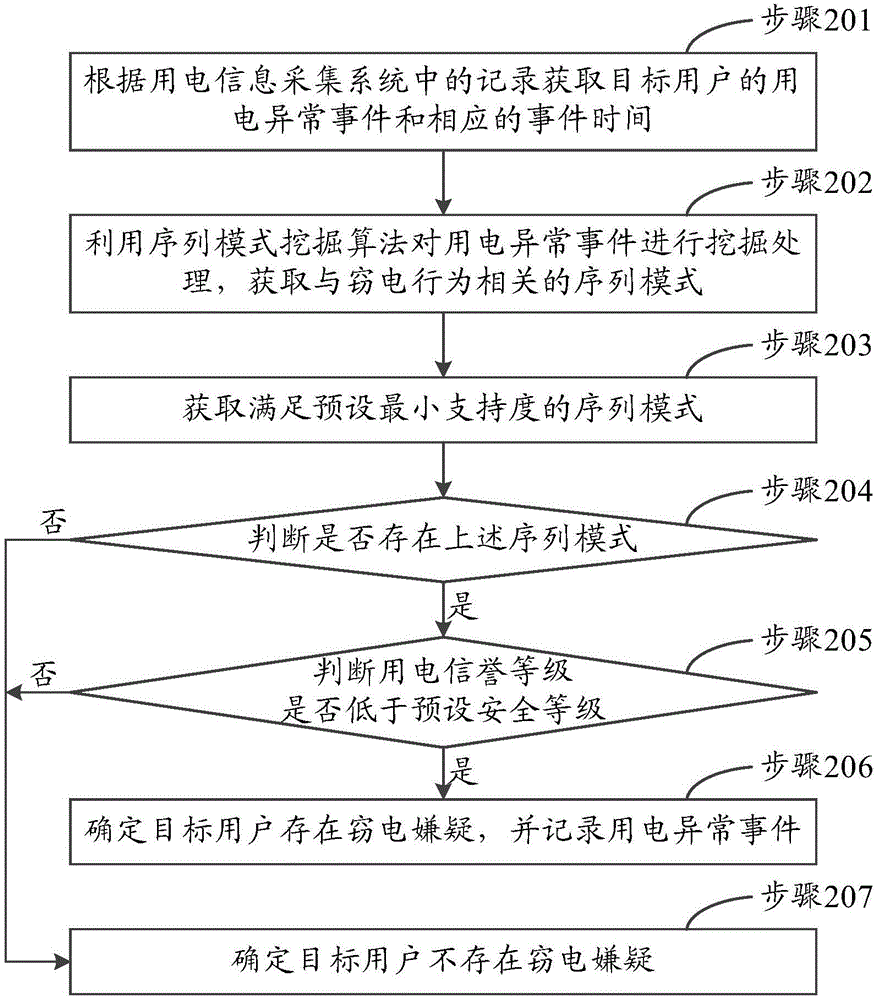
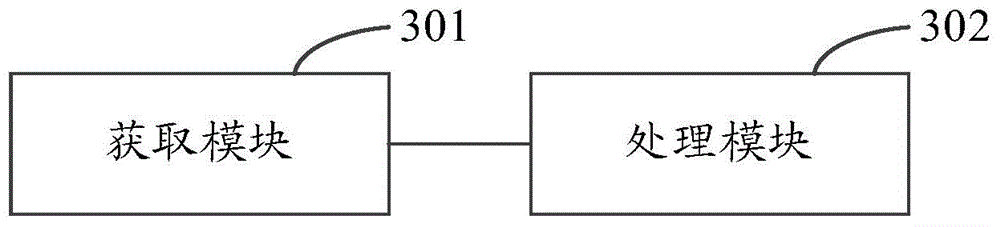
Power-stealing prevention analysis method and apparatus
ActiveCN104933272AImprove data utilizationElectricity credit rating is lowSpecial data processing applicationsTime integral measurementElectricity meterElectric energy
The invention discloses a power-stealing prevention analysis method and apparatus. The method includes acquiring the power consumption abnormal events and corresponding event time of a target user based on the records in a power consumption information acquisition system, wherein the power consumption abnormal events include electric energy meter operating events and electric energy meter abnormal events; and determining the target user being suspicious in power stealing when the electric energy meter operating events occur and then the electric energy meter abnormal events occur. According to the invention, some specified sequence modes related to the power-stealing events can be found out through the analysis of a lot of historical data in the power consumption information acquisition system, and whether the user is suspicious in power stealing can be determined. Therefore, the effectiveness and pertinency of the power-stealing prevention and checking of the power consumption information acquisition system can be improved, the effect of the power-stealing prevention of the power consumption information acquisition system can be fully achieved, and the data utilization rate is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
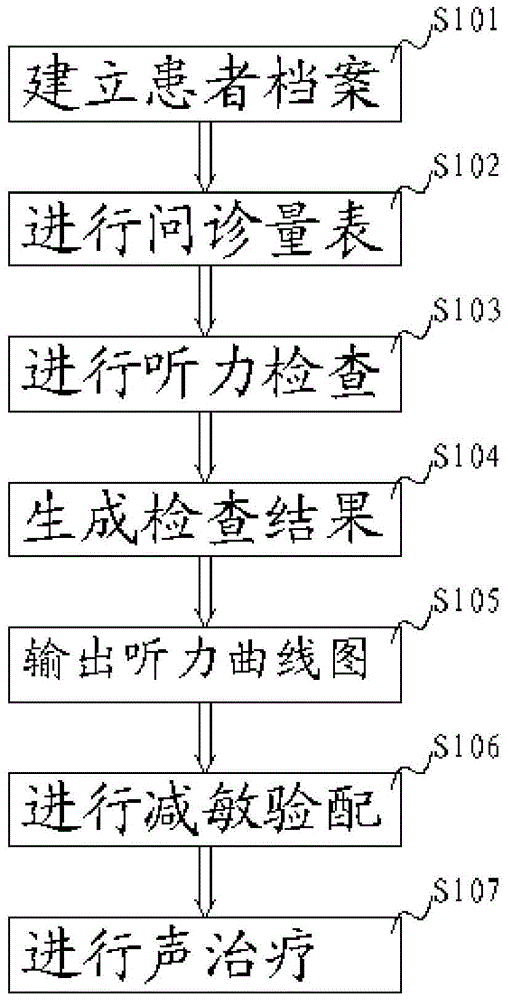
Tinnitus sound diagnosis and treatment method
InactiveCN105662426AImprove data utilizationImprove practicalityEar treatmentAudiometeringGraphicsTherapeutic Devices
The invention discloses a tinnitus sound diagnosis and treatment method. Tinnitus diagnosis and treatment methods, including S101: Establishing patient files; S102: Doctors conduct questionnaires on patients through questionnaires and assessment scales, and patients fill in the questionnaires and assessment scales by choosing, and doctors judge the overall situation of tinnitus of patients ; S103: The doctor checks the patient's auditory function; S104: Input and calculate the test data, establish a test result table and compare the data; S105: Output the test data, graphics, images and tinnitus test data, and choose whether to print; S106: According to Desensitization fitting is performed on the detected data. The desensitization fitting includes acoustic stimulation verification and therapeutic sound matching. The selected sounds form a formula, and the formula includes standard stimulation sounds, TRT sounds or background music and other sound types; S107: Combine the sound The treatment formula is output to the treatment device, and the patient is treated with sound through the treatment device.
Owner:FOSHAN BOZHI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for implementing orbit determination and time synchronization of Beidou satellite III
PendingCN110208831AGet rid of dependenceGood self-consistencySatellite radio beaconingData synchronizationSatellite orbit
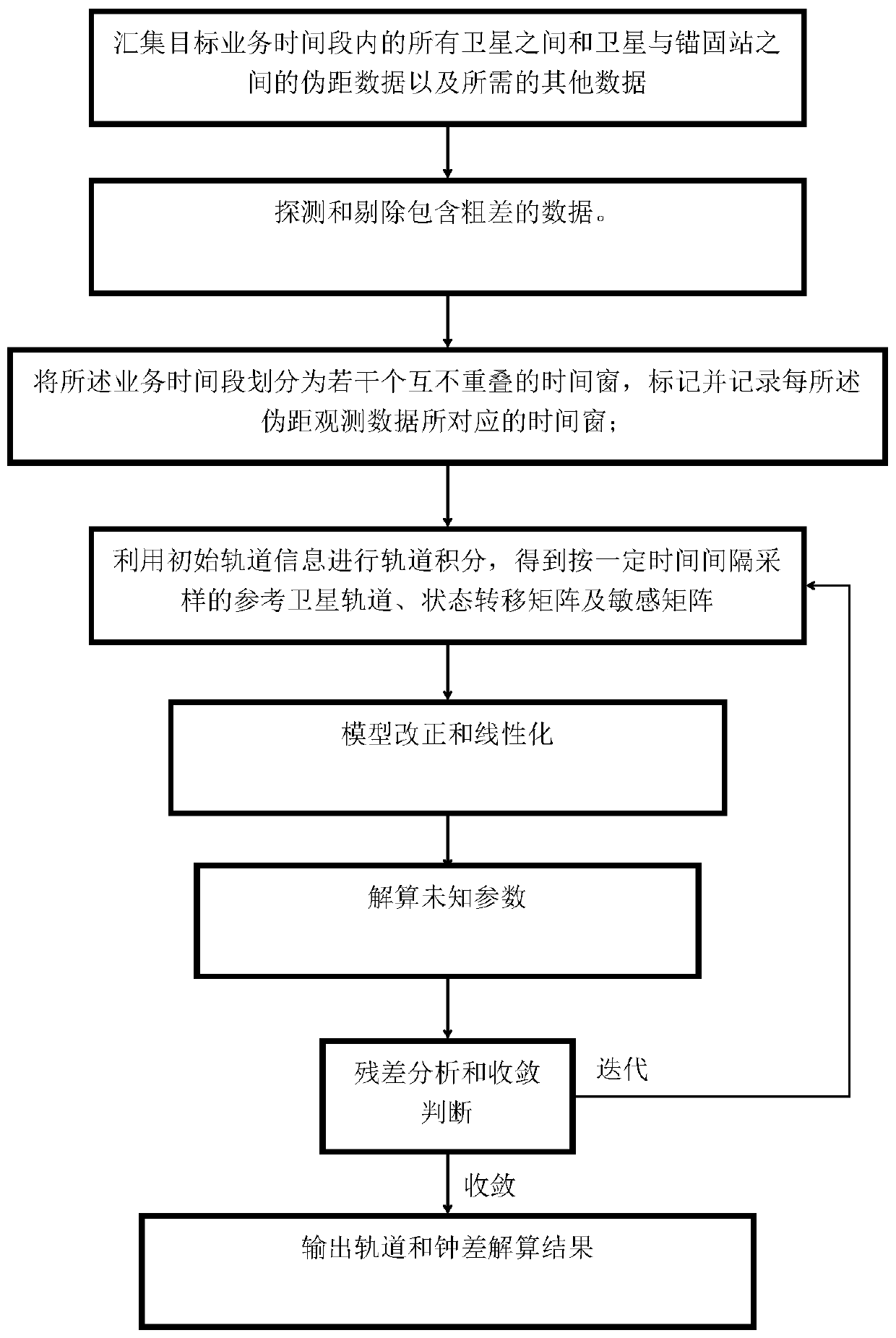
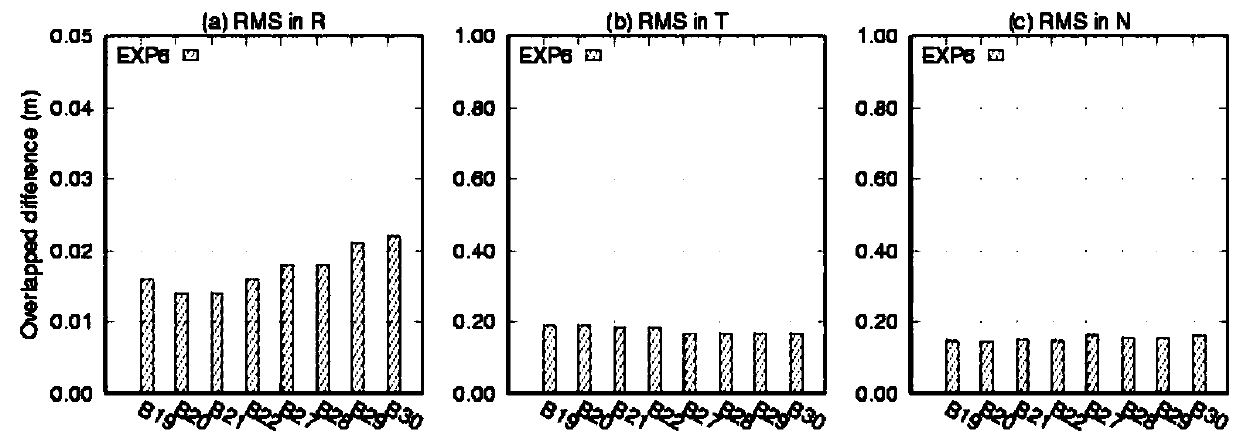
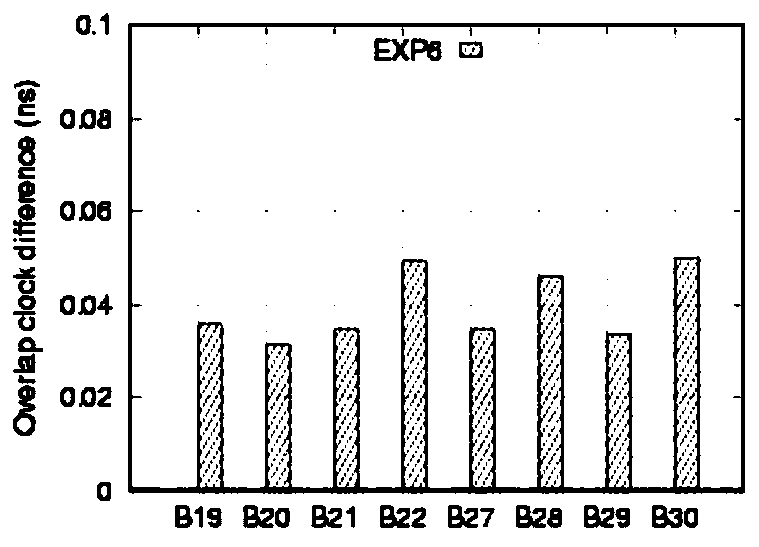
The invention discloses a method for implementing orbit determination and time synchronization of a Beidou satellite III by utilizing an inter-satellite link and an anchorage station, and belongs to the field of satellite navigation. According to the method, orbit determination and time synchronization are simultaneously implemented by utilizing data of the inter-satellite link and the anchorage station, a ground monitoring station is not required, and the Beidou satellite III can get rid of dependence on the monitoring station and implements autonomous navigation; in the data processing process, epoch naturalization does not need to be carried out, and thus, orbit information does not need to be predicted, and if satellite clock error non-zero-order item coefficients are simultaneously solved or ignored, clock error information also does not need to be predicted; only unidirectional pseudo-range data is required, bidirectional data pairing is not required, and a data utilization rateis high; and a satellite orbit and a clock error are simultaneously solved, statistical optimal solutions can be obtained, and the orbit and the clock error have better self-consistency.
Owner:中国人民解放军61540部队
Novel method for analyzing reservoir physical properties by using pressure drop section data in shale gas reservoir fracturing construction
InactiveCN104500016AAccurate results of reservoir physical propertiesImprove data utilizationFluid removalShale gasTrial and error
The invention discloses a novel method for analyzing reservoir physical properties by using pressure drop section data in shale gas reservoir fracturing construction. According to the method, change data of oil pressure and discharge capacity along with the construction time in the fracturing process is accurately read from a fracturing construction curve, and abnormal data with the fluctuation amplitude greater than 1 percent is removed; dimensionless pressure is defined, and the pressure drop section time is converted into a dimensionless form; and a theoretical dimensionless pressure value is calculated, the dimensionless pressure data is compared with the theoretical dimensionless pressure value, and if the error exceeds 1 percent, a trial and error method is used for re-adjusting the reservoir physical property permeability, the dimensionless storage coefficient, the single-well control radius and the dimensionless analytic parameter coefficient until the calculation precision is reached. The novel method has the beneficial effects that the pressure drop section data in the shale gas reservoir fracturing construction is used for analyzing the result accuracy of the reservoir physical properties, and the data utilization rate of the fracturing construction data is improved.
Owner:四川奥陶石油科技有限公司
Object-oriented data storage and retrieval system using index table
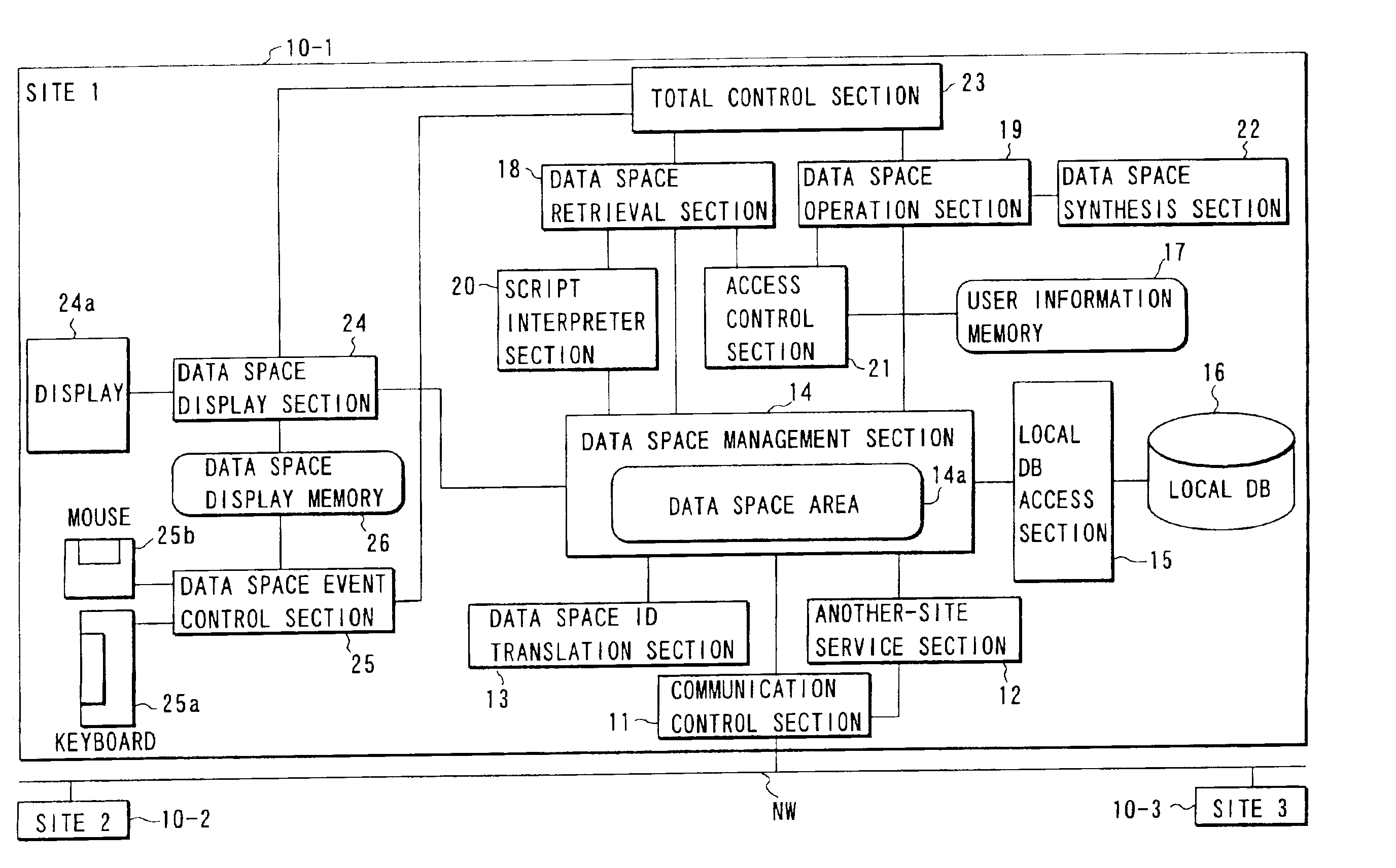
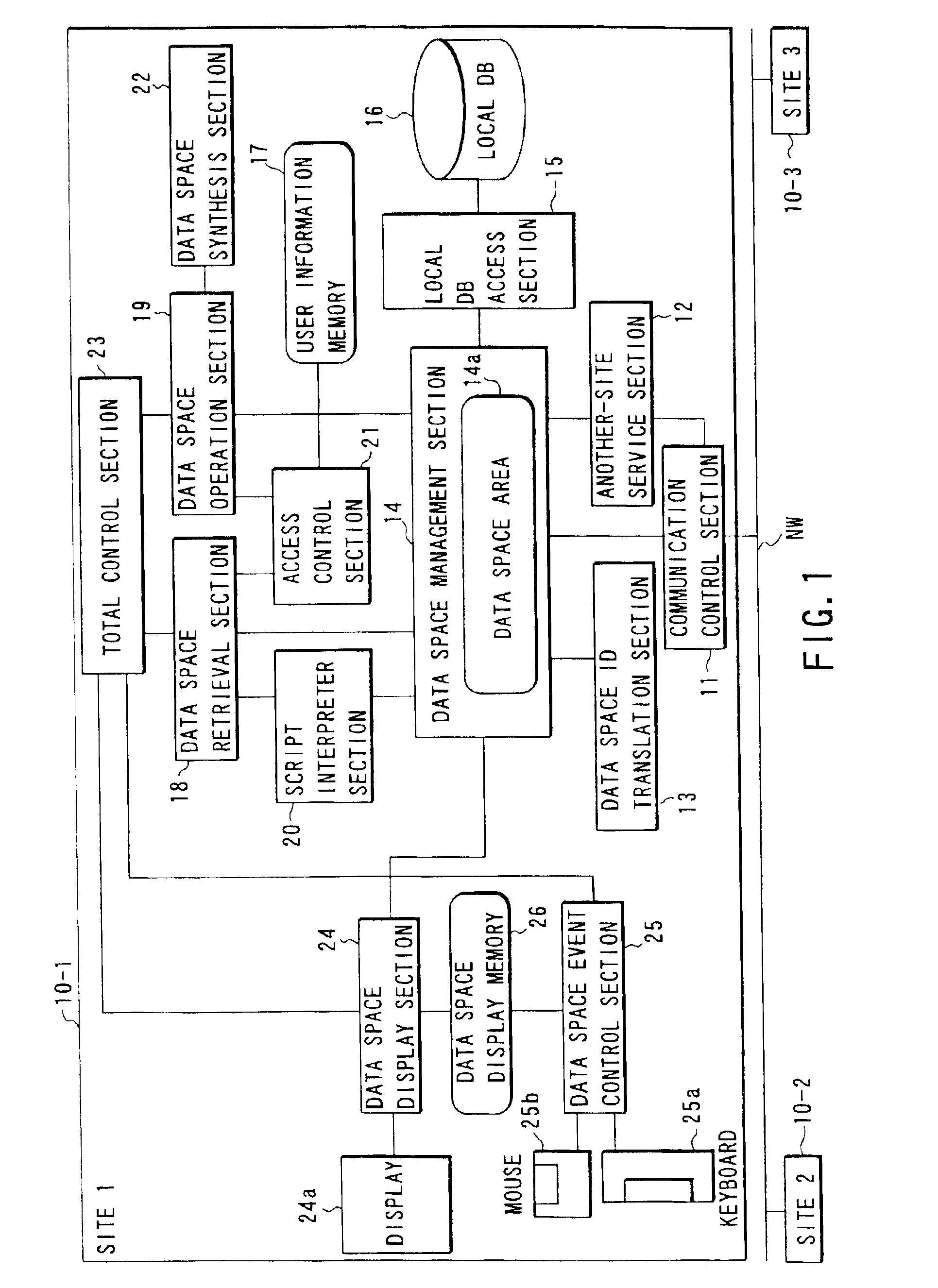
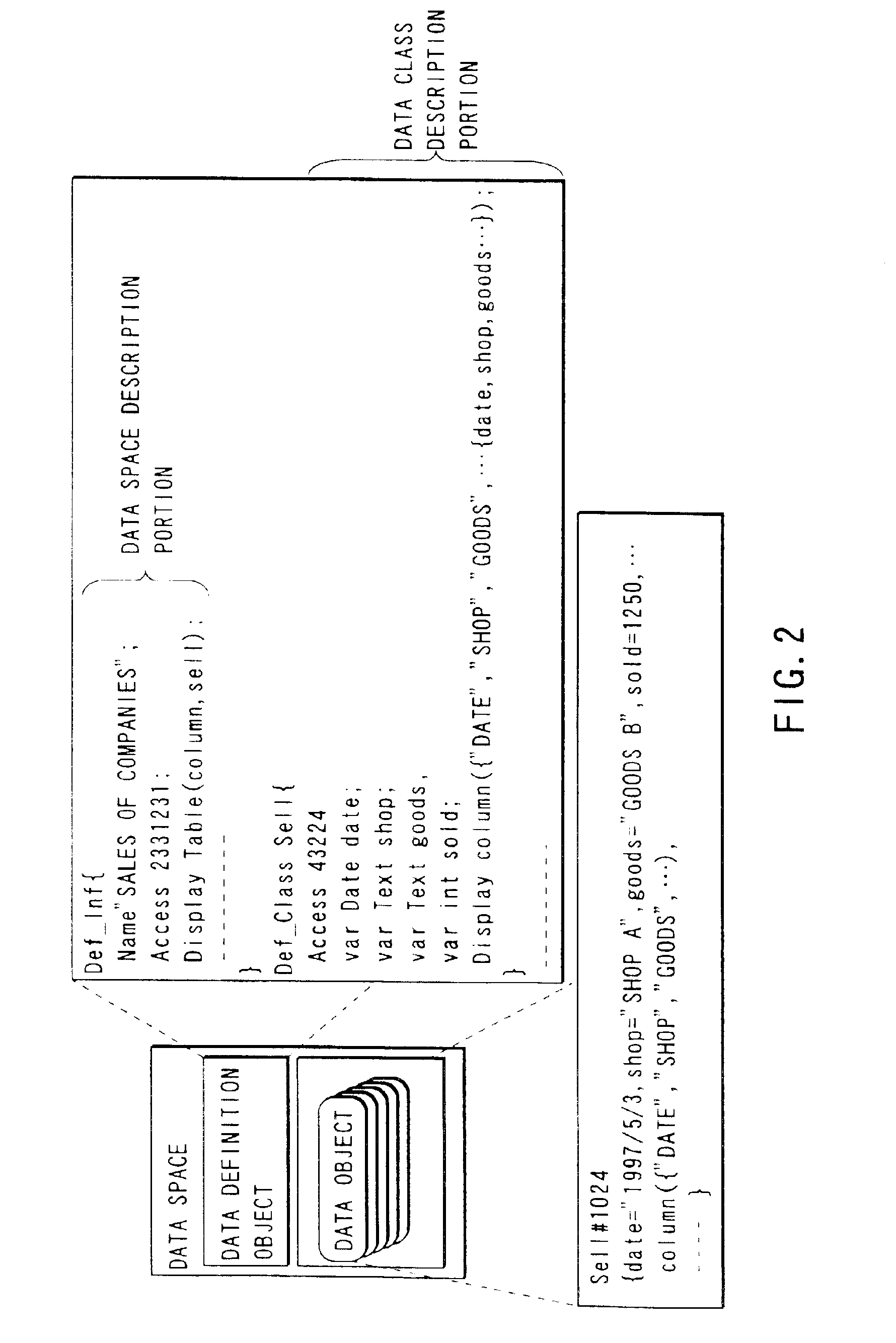
InactiveUS6857000B2Improve data utilizationFacilitating utilization of dataData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSystem usageData space
A data storage and retrieval system includes a data space area where a set of data belonging to a predetermined category and definition data describing definition of the structure and the presentation form of the data are stored, a data space retrieval section for retrieving data and definition data made to correspond to the data from the data space area, a data space operation section for rewriting the definition data made to correspond to the data retrieved by the retrieval section on the basis of another definition data stored in the data space area, and a display for displaying the data retrieved by the retrieval section on the basis of the definition data rewritten by the operation section.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Monitoring and managing system and monitoring and managing method for wind power storing station comprehensive information
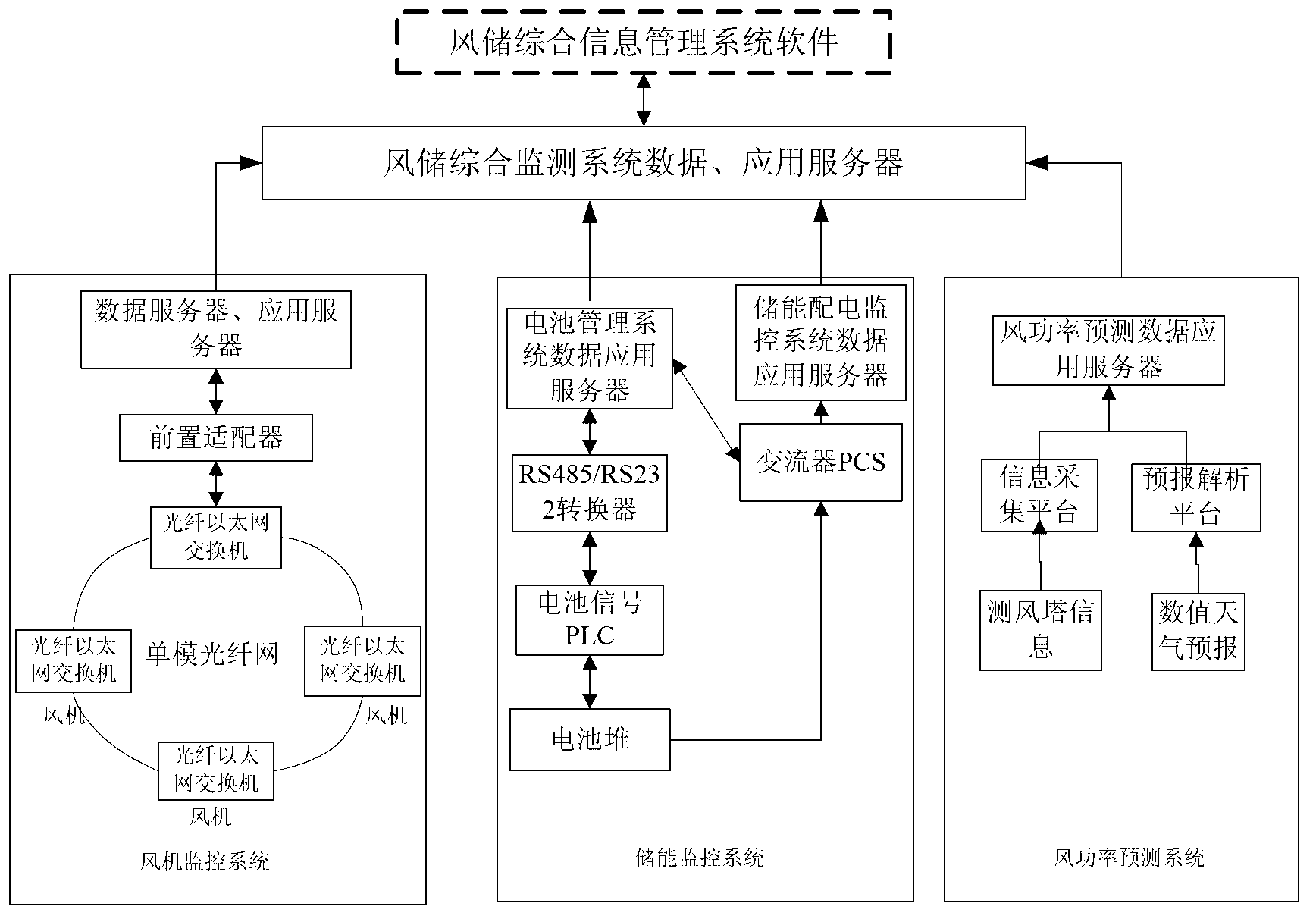
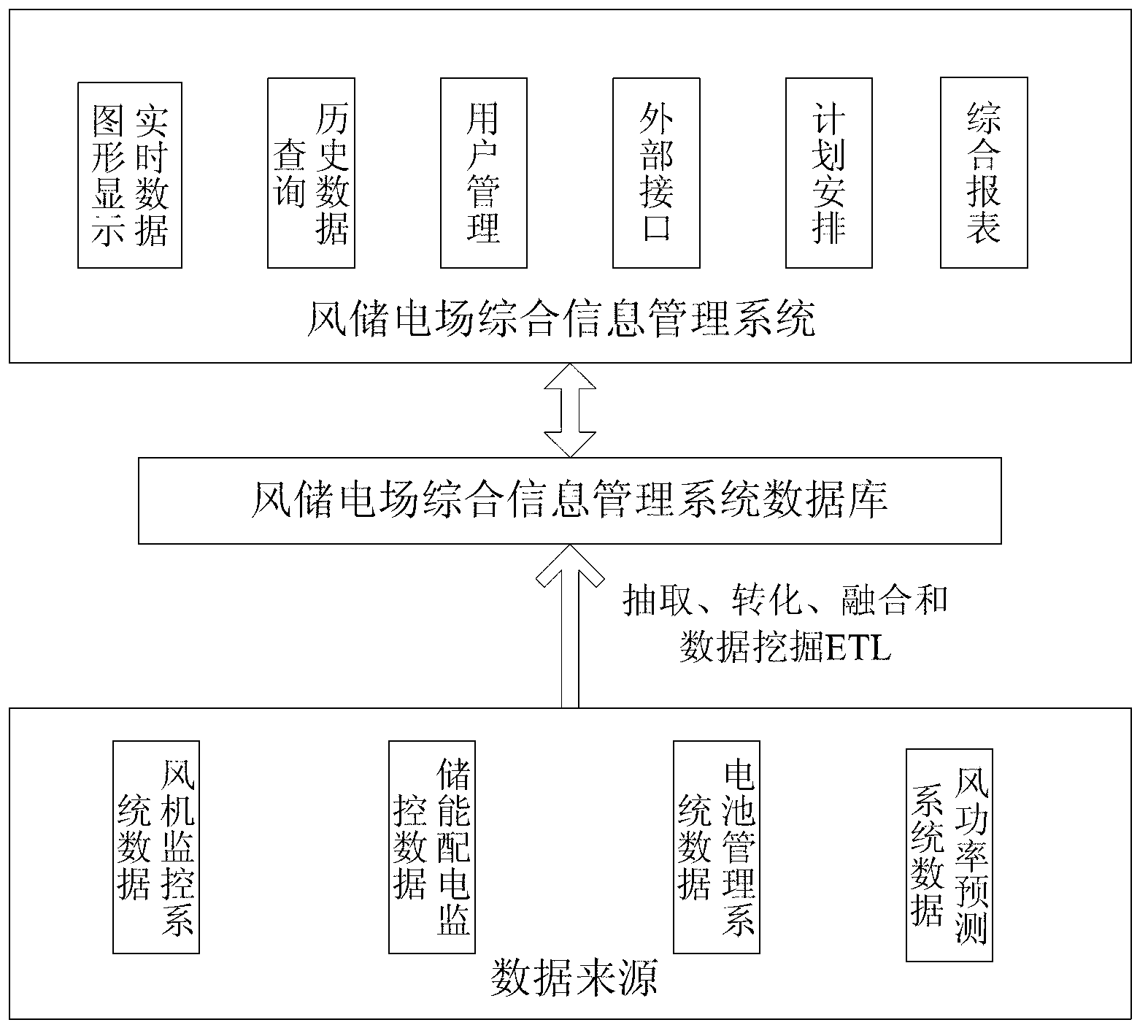
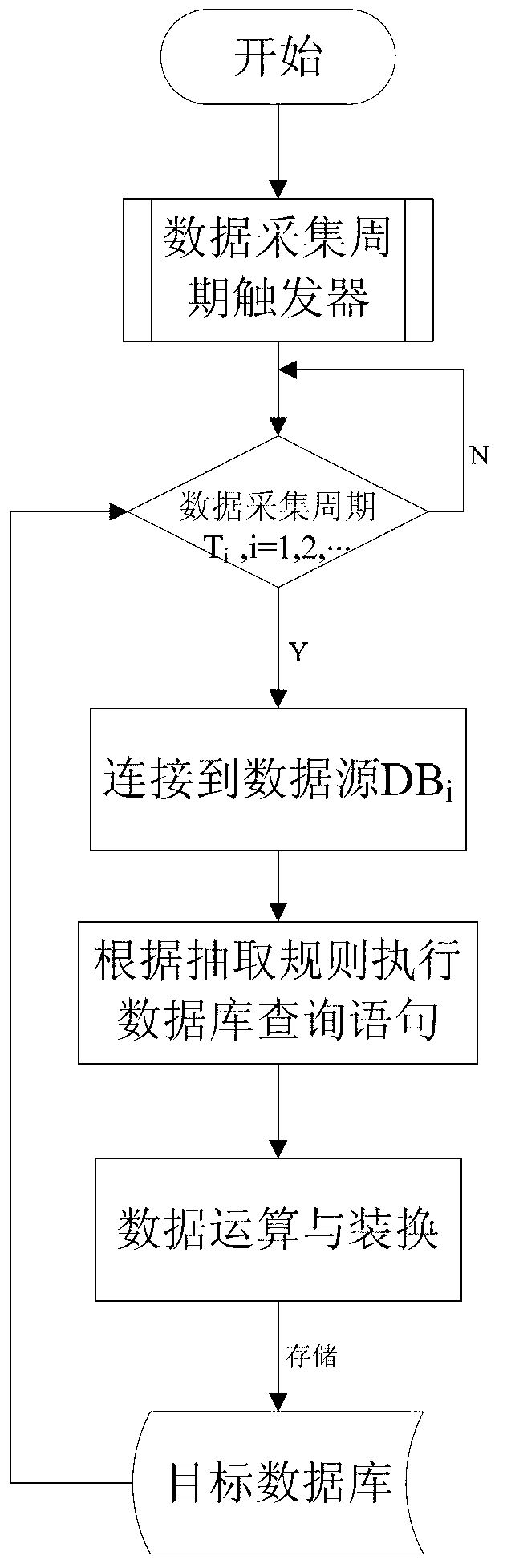
ActiveCN103310306AWell coordinatedImprove data utilizationTechnology managementResourcesElectrical batteryBattery management systems
The invention provides a monitoring and managing system for wind power storing station comprehensive information. The system comprises a wind turbine monitoring system, an energy-storing and power-distributing monitoring system, a wind power predicting system, a battery managing system and a wind storing comprehensive information system. The wind turbine monitoring system, the energy-storing and power-distributing monitoring system and the wind power predicting system are connected to the wind storing comprehensive information system. An energy-storing monitoring system part is composed of the battery managing system and the energy-storing and power-distributing monitoring system. Corresponding wind power data, data in the wind turbine monitoring system, data in an energy storing and converting system and data in the battery managing system are combined, and graphs, tables and other forms are utilized to provide overfull and direct display to operators and managers, display of wind storing comprehensive power generating performance is realized through deep extraction, excavation and analysis of the data, wind-storing coordinating operation is further optimized, and determine support is provided for superior scheduling and the managers.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Travelling information management system
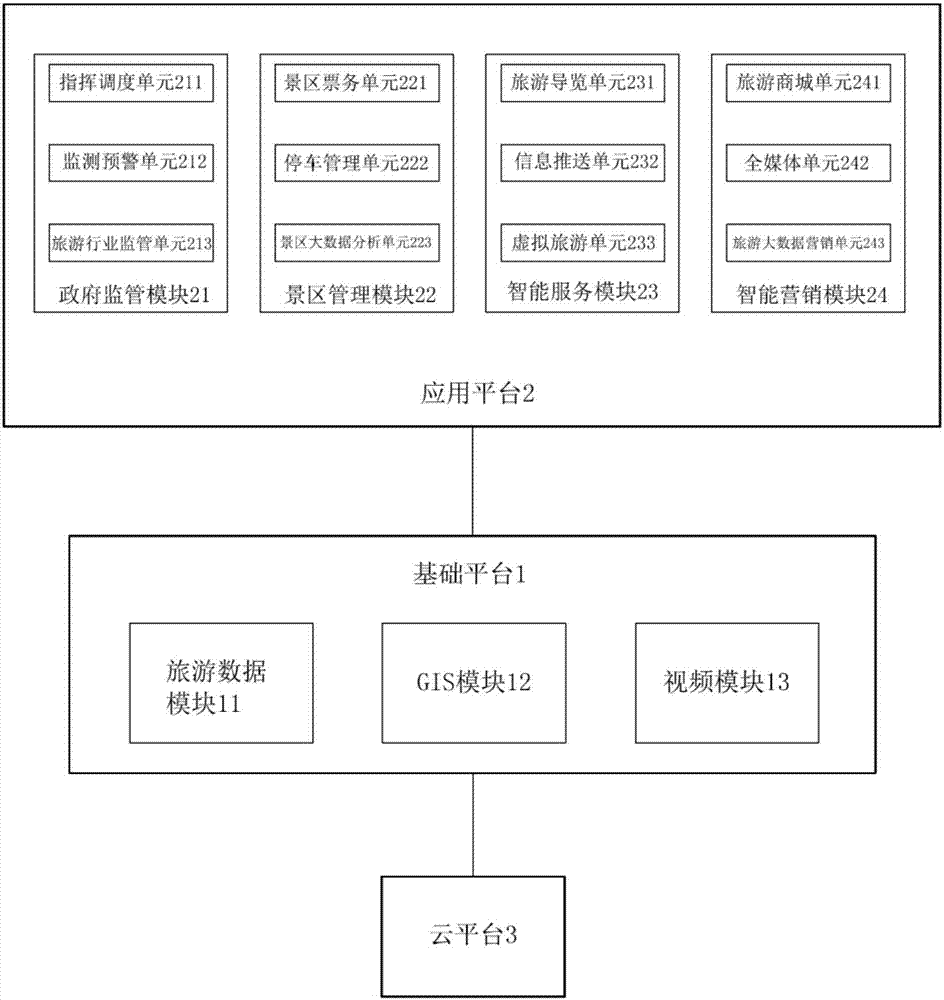
InactiveCN107491883AImprove data utilizationReduce operating costsResourcesData acquisitionManagement system
The invention relates to a travelling information management system which comprises a cloud platform, a basic platform and an application platform. The cloud platform utilizes cloud computing technology for constructing a basic operation environment for supporting operation of the basic platform and the application platform. The basic platform is used for performing data acquisition, processing an interface calling request which is transmitted from the application platform and performing comprehensive analysis processing. The application platform is used for transmitting the interface calling request for acquiring an analysis processing result of the basic platform. The application platform is further used for determining a corresponding management plan and supplying a traveling information service according to an analysis processing result which is fed back from the basic platform. Management plans in different angles are supplied according to different requirements. The travelling information management system has advantages of reducing system operation cost, facilitating dynamic expansion, simplifying maintenance, improving data utilization rate, etc.
Owner:中国东盟信息港股份有限公司
Processing system and method for three-value weight convolution network
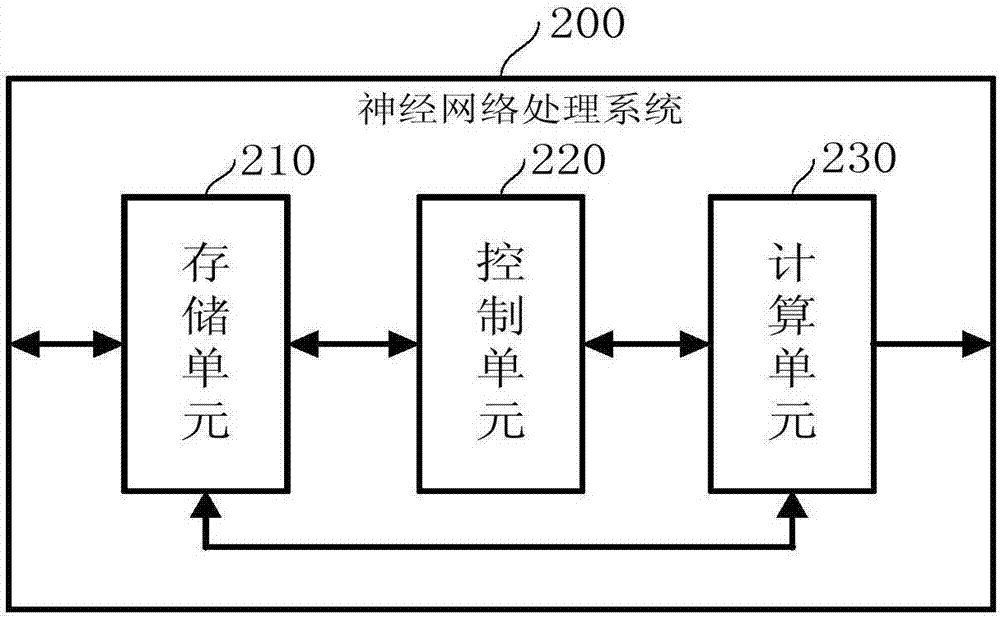
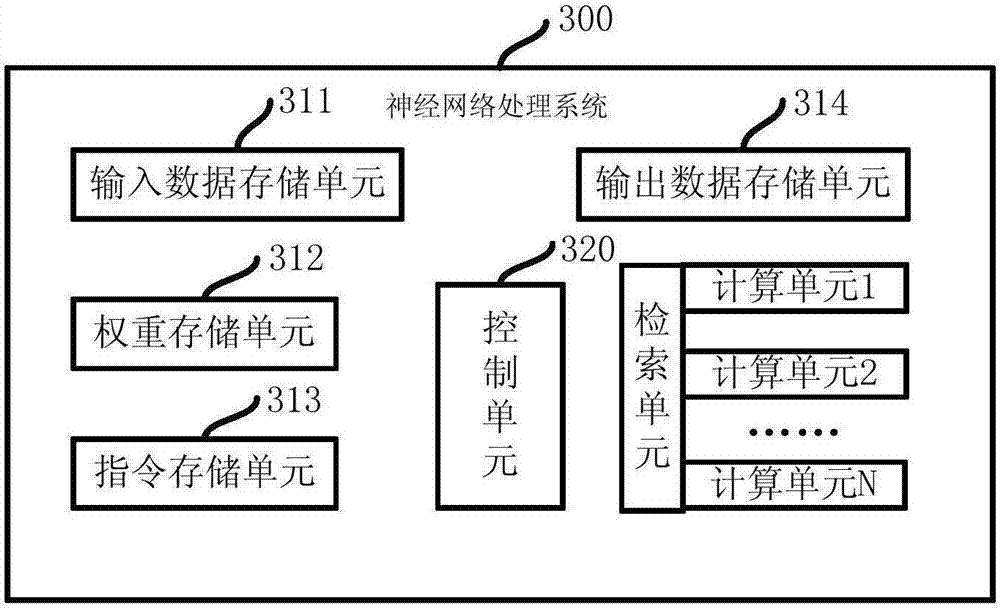
ActiveCN107256424AReduce overheadImprove data utilizationNeural learning methodsControl signalHandling system
The invention provides a processing system for three-value weight convolution network. The system comprises at least one storage unit which is used for storing data and an instruction; at least one control unit which is used for obtaining the instruction stored in the storage unit and transmitting a control signal; and at least one calculating unit which is used for obtaining a node value of one layer in a convolution neural network from the storage unit and the corresponding three-value weight data, and obtaining the node value of a next layer through the execution of addition and subtraction operations. The system reduces the data bit width in the calculation process of the convolution neural network, improves the convolution calculation speed, and reduces the storage capacity and work energy consumption.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-signal-source frequency and DOA joint detection method and device
ActiveCN107656237ALow costImplement samplingSpectral/fourier analysisRadio wave finder monitoring/testingChinese remainder theoremComputer science
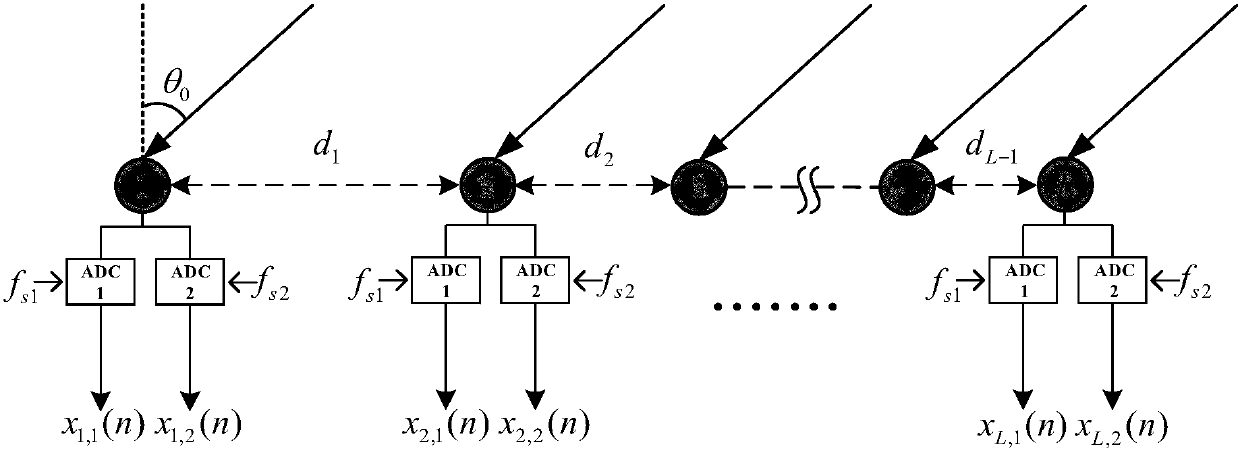
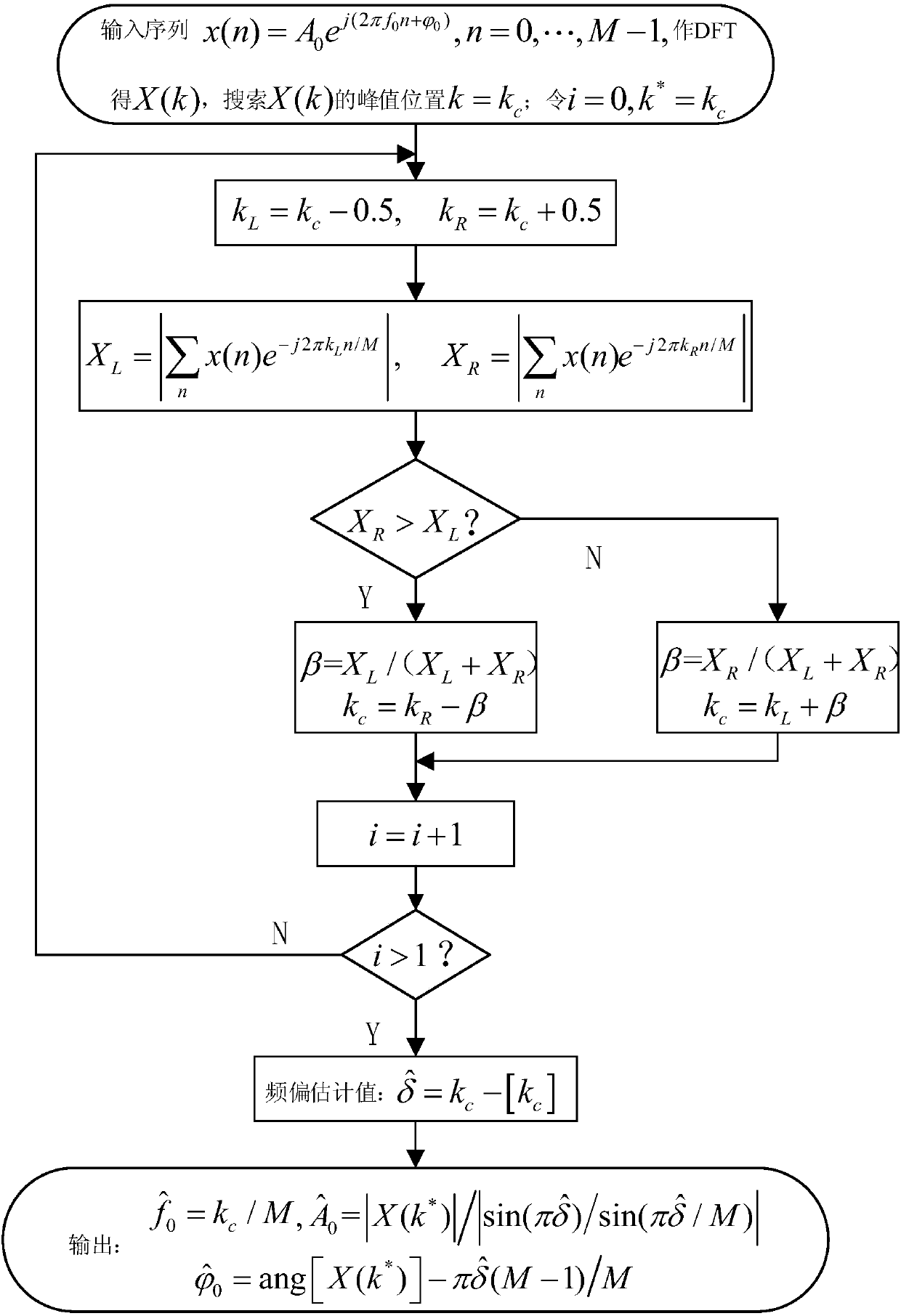
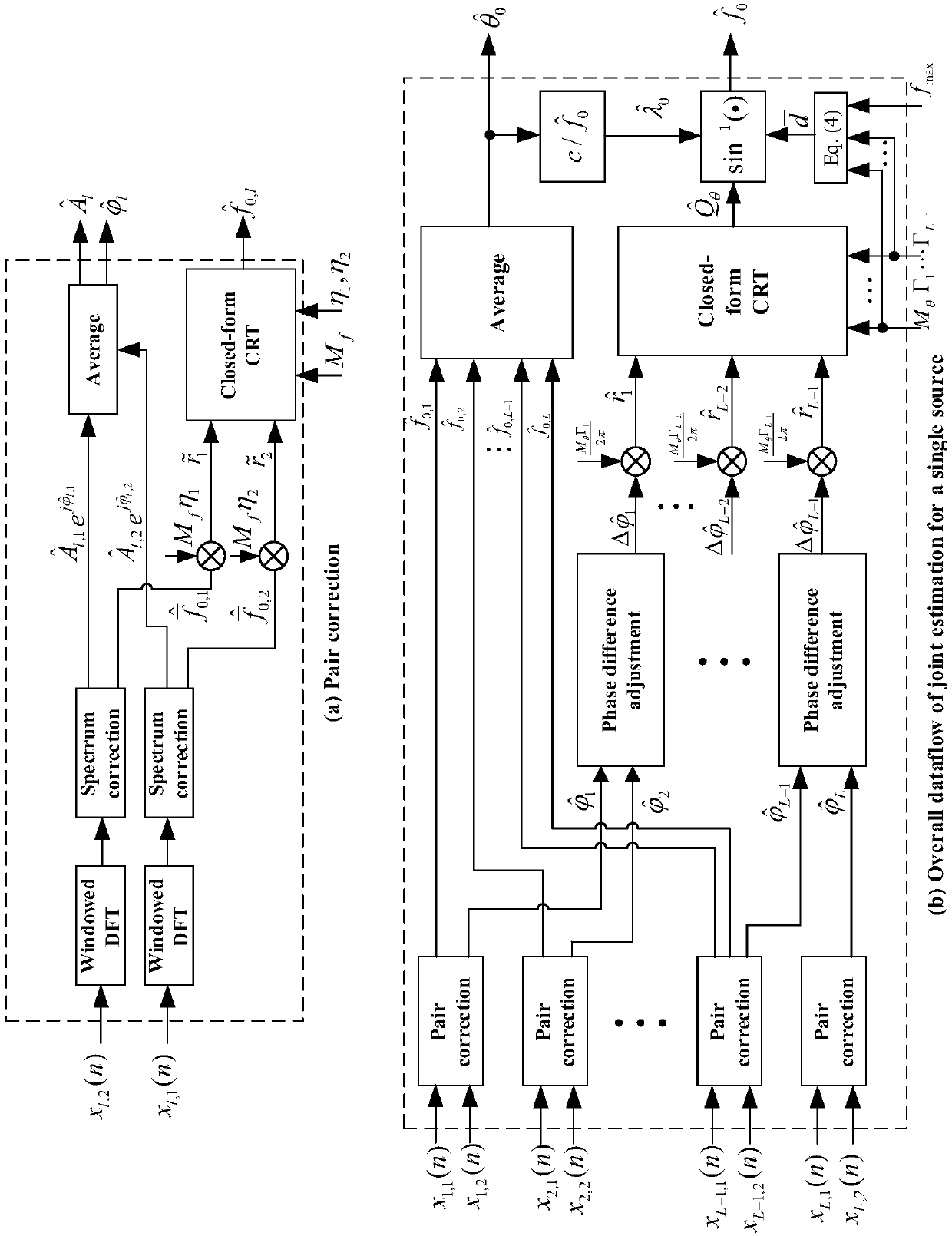
The invention discloses a multi-signal-source frequency and DOA joint detection method and a multi-signal-source frequency and DOA joint detection device. The multi-signal-source frequency and DOA joint detection method comprises the steps of: conducting Mf-point DFT on L paths of signal samples, correcting frequencies and phases of DFT results by using a Tsui spectrum corrector to obtain a parameter group of corrected D groups of frequencies, phases and amplitude values, and constructing D direction vectors by using the parameter group; grouping and matching the D direction vectors accordingto the minimum distance to obtain D pieces of signal source parameter matching information; constructing a frequency remainder group according to the D pieces of signal source parameter matching information, and substituting the frequency remainder group into a closed type robust Chinese remainder theorem (CRT) model for reconstruction, so as to obtain a frequency estimated value; and acquiring L-1 phase differences according to the D pieces of signal source parameter matching information, constructing a phase reminder group, substituting the phase remainder group and a reconstructed module value group into the closed type robust CRT model for reconstruction to obtain an intermediate parameter, and calculating to obtain a DOA estimated value. The multi-signal-source frequency and DOA jointdetection method and the multi-signal-source frequency and DOA joint detection device realize the high-precision frequency and DOA joint estimation of multiple pairs of targets.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Data storage system based on Hadoop architecture
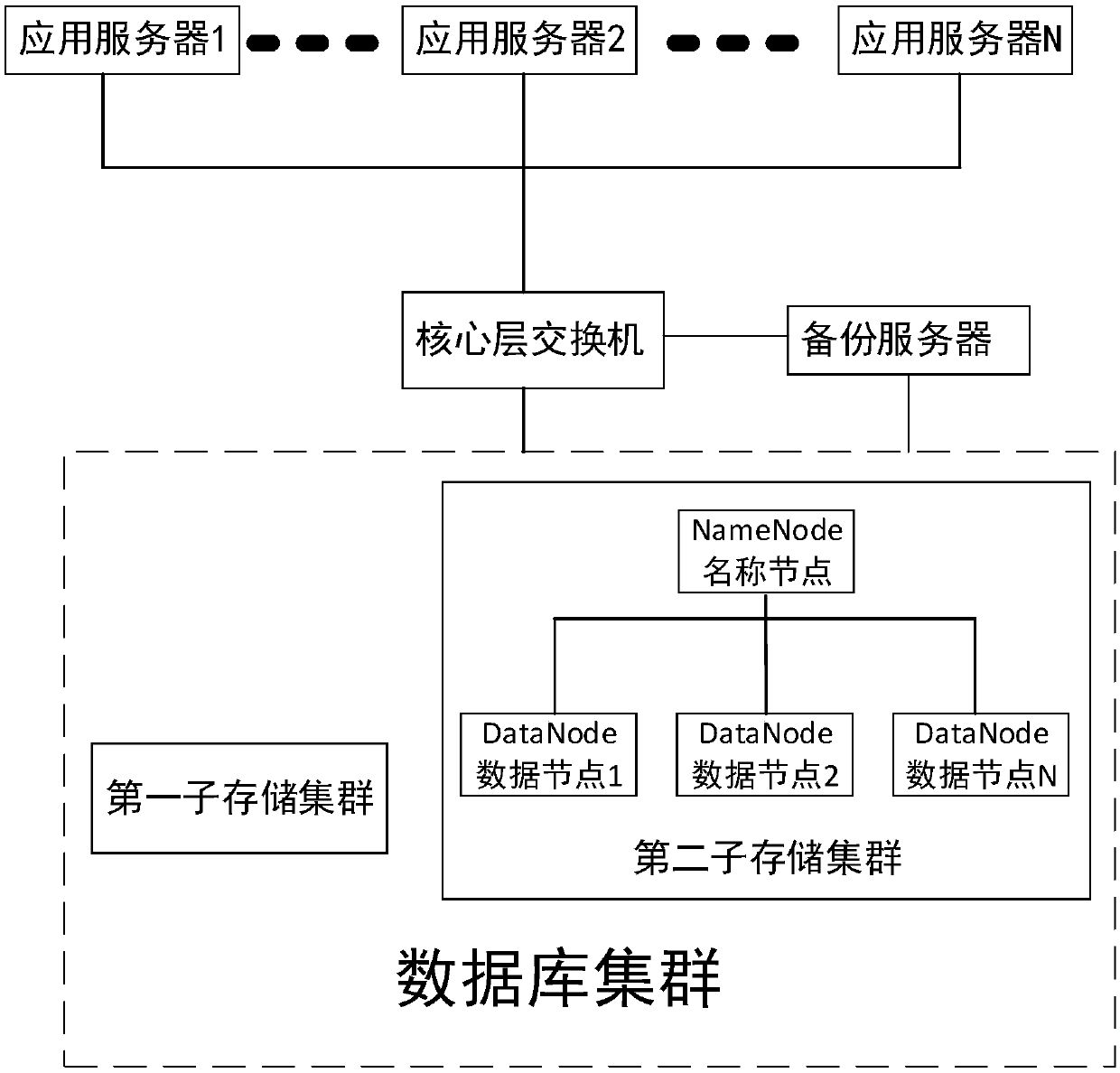
InactiveCN107800808AGuaranteed reliabilityImprove data utilizationTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsApplication serverReal-time data
The invention relates to a data storage system based on a Hadoop architecture. The storage system comprises at least one application server, a backup server, a database cluster and at least one core layer switch; the database cluster comprises a first sub-storage cluster and a second sub-storage cluster; basic data of structured data are stored in the first sub-storage cluster, and unstructured and semi-structured loose data are stored in the second sub-storage cluster; the application server, the backup server and the database cluster are respectively connected to the core layer switch; and the application server is connected with the backup server and the database cluster, and used for managing real time data of the backup server and the database cluster. The data storage system based onthe Hadoop architecture provided by the invention uses a distributed storage mode to store the data and uses redundant storage to ensure the reliability of the data. An HDFS (Hadoop Distributed FileSystem) module can reliably store massive files across machines, and stores various files as data block sequences of the same size.
Owner:GUANGDONG AOFEI DATA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
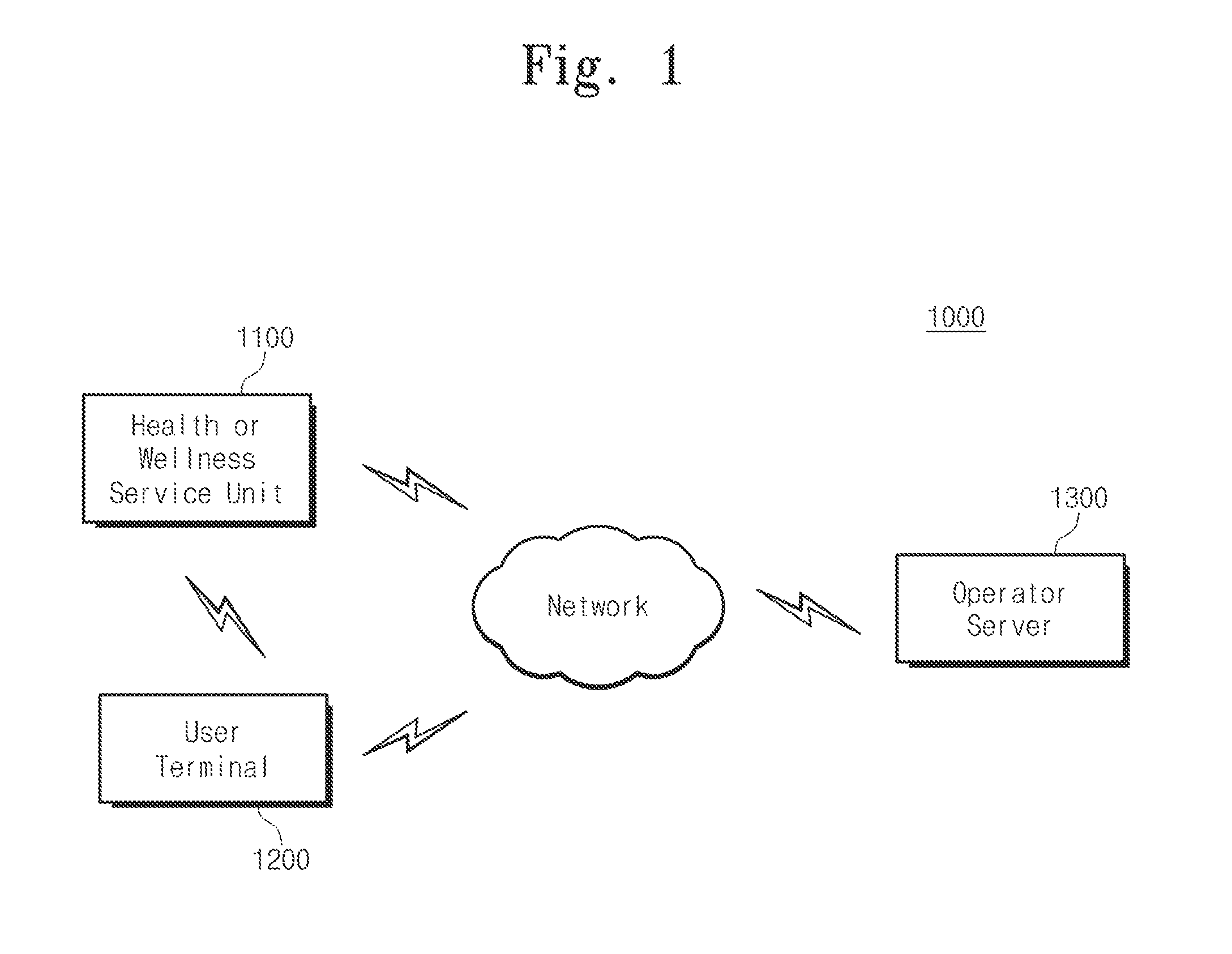
Self-direct M2M (machine-to-machine) communication based user's daily activity logging and analyzing system with wearable and personal mobile devices
ActiveUS9602952B2Respond quicklyImprove data utilizationPower managementData processing applicationsSleep stateReceived signal strength indication
The present invention relates to a heath care system having proximity-based neighbor device wake-up and automatic user identification function, a method for automatic logging of user's daily activity history, and a method for managing a user activity pattern, and the system comprises: a health or wellness service unit; and an user terminal. The health or wellness service unit transmits a wake-up signal for changing a state of the user terminal from a sleep state into a wake-up state, a low frequency (LF) signal for identifying a physical distance and direction between the health or wellness service unit and the user terminal, and a measured biological signal of a measuring object. The user terminal receives the biological signal, the wake-up signal, and the LF signal through bidirectional wireless communication with the health or wellness service unit, and transmits a terminal identification (ID) and a received signal strength indication (RSSI) corresponding to the received LF signal.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Production method of ammonium phosphate containing trace elements
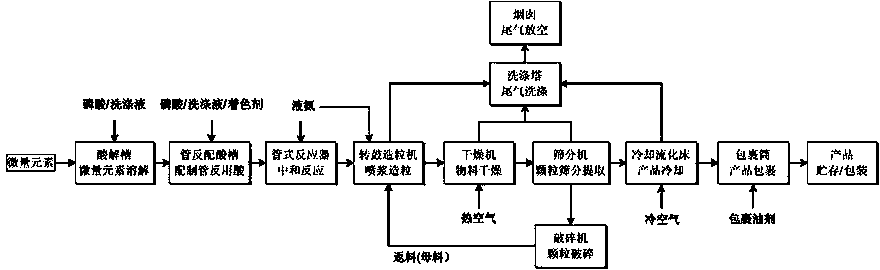
InactiveCN104193453AExcellent physical propertiesImprove data utilizationAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersFertilizerAcid preparations
The invention discloses a production method of ammonium phosphate containing trace elements. The production method is characterized by adopting a manner of dissolving by phosphoric acid and carrying out full ammonolysis reaction on oxides or salts containing trace elements in the ammonium phosphate production process, and specifically comprises the following steps: adding oxides or salts containing trace elements into an acidolysis tank; recovering a scrubbing solution, phosphoric acid and water from an ammonium phosphate scrubbing system and mixing and stirring; fully decomposing the oxides or salts containing trace elements to ions or complexes to form a phosphoric acid solution containing trace elements; conveying to an acid preparation tank of a tubular reactor by a feed pump; adding phosphoric acid, the scrubbing solution and process water to mix; quickly ammonifying in a tubular reactor and grouting and pelleting in a pelletizer; and then drying, sieving, cooling and wrapping to obtain an ammonium phosphate compound fertilizer containing trace elements. The ammonium phosphate compound fertilizer containing trace elements obtained by adopting the method has good solubility.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
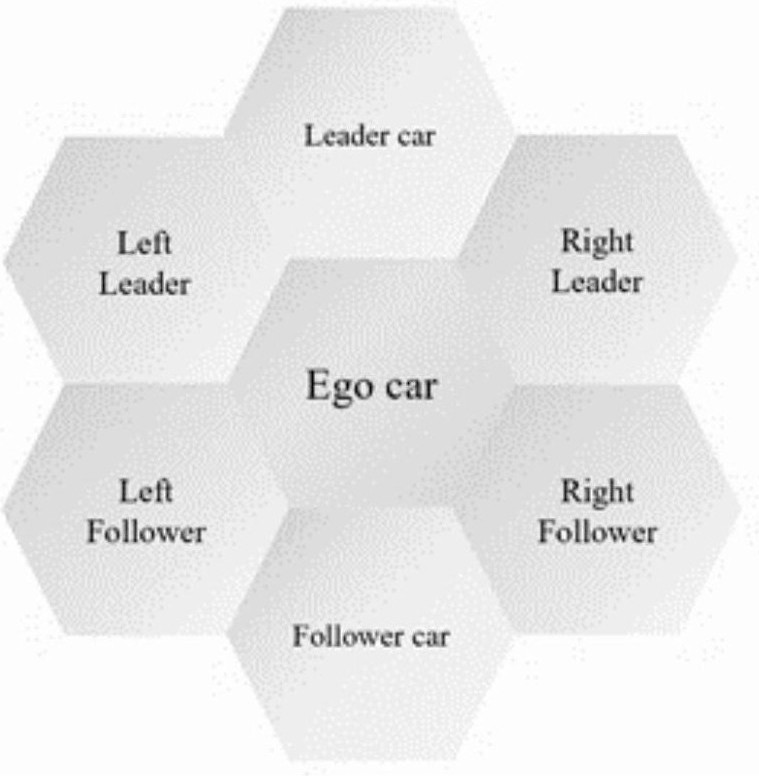
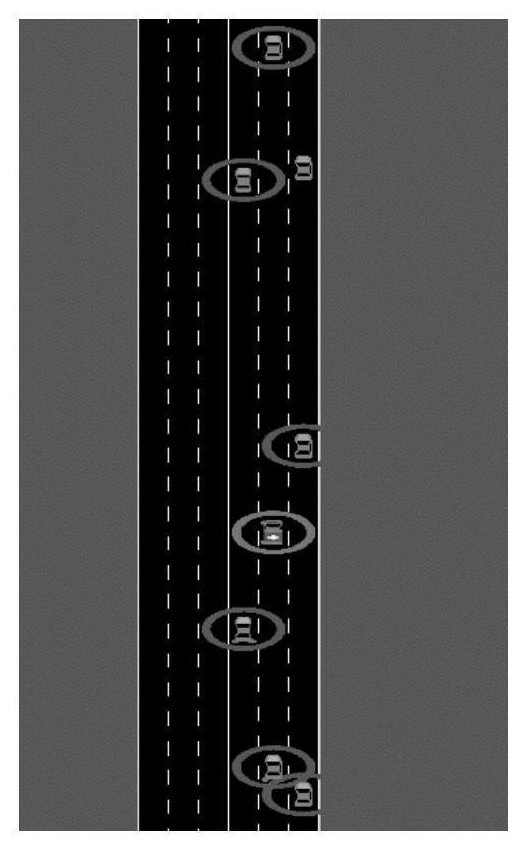
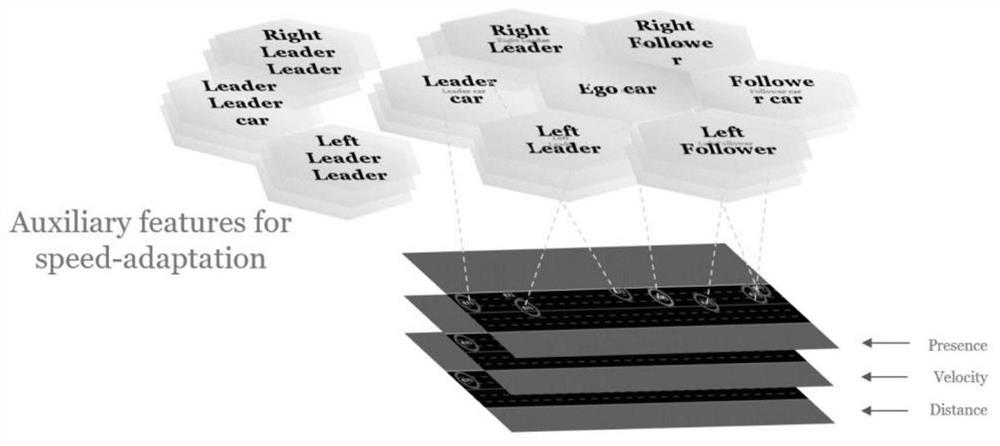
Emergency vehicle hybrid lane changing decision-making method based on reinforcement learning and avoidance strategies
ActiveCN112406867AImprove data utilizationImprove generalization abilityNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsAction selectionReal-time computing
The invention relates to an emergency vehicle hybrid lane changing decision-making method based on reinforcement learning and avoidance strategies. The method comprises the following steps: determining an optimized road section and execution strategies of ICCV and ICEV to be planned; initializing a DQN network of the ICEV to be planned; obtaining a state space of the DQN network based on the stateinformation of the ICEV to be planned, the six neighbor vehicles of the ICEV to be planned and the avoidance strategy execution condition of the preceding vehicle of the ICEV; obtaining an output value based on the state space of the DQN, and obtaining a preliminary decision and an action space based on the output value; establishing an action selection barrier, and verifying and selecting the obtained preliminary decision until the action finally selected from the output value or the action space meets the traffic rule and the road physical structure; defining a reward function for calculating a total reward corresponding to the action; and training the DQN network to obtain a trained DQN network. The method can be widely applied to the field of road lane changing decision control.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
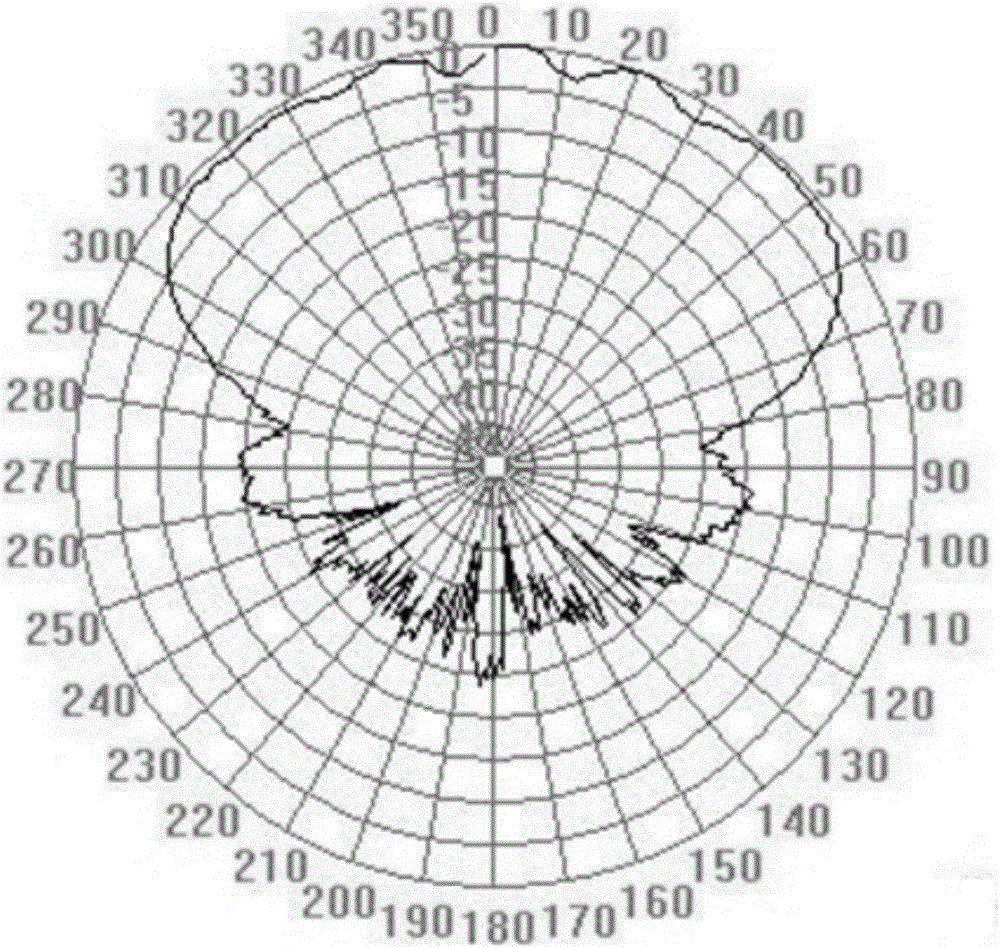
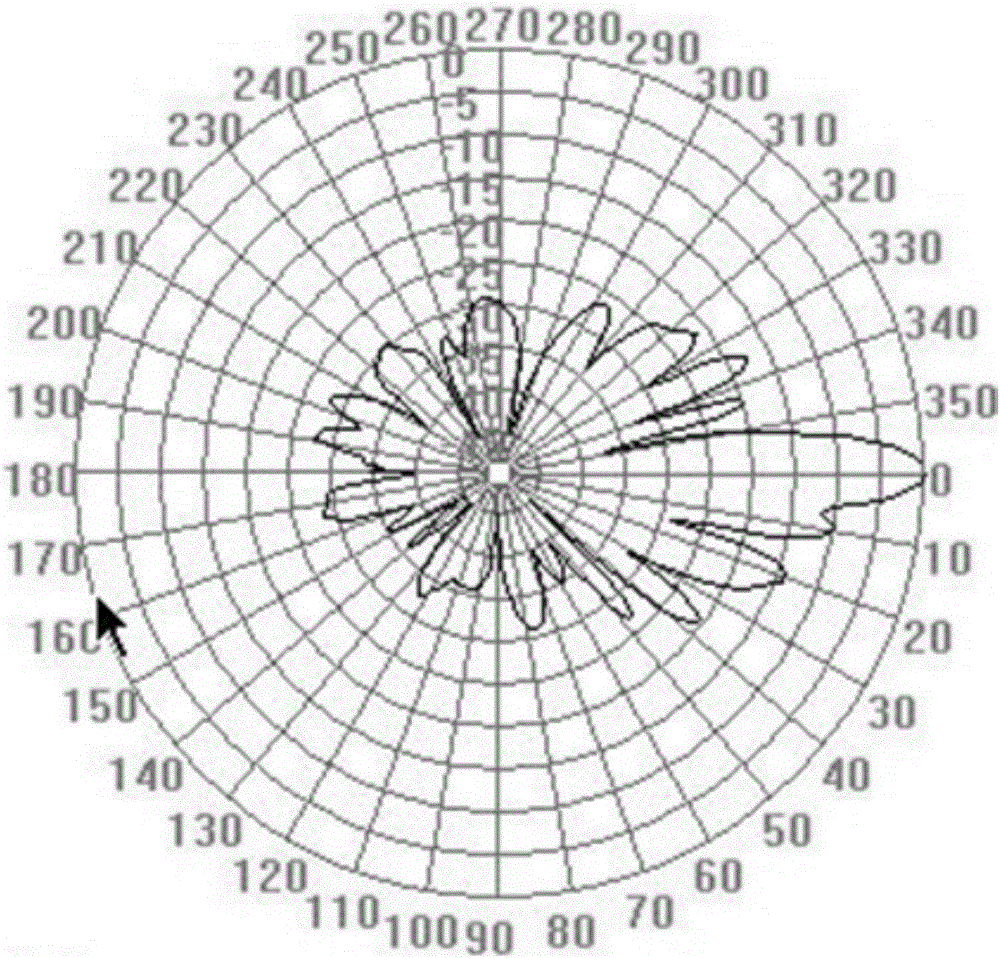
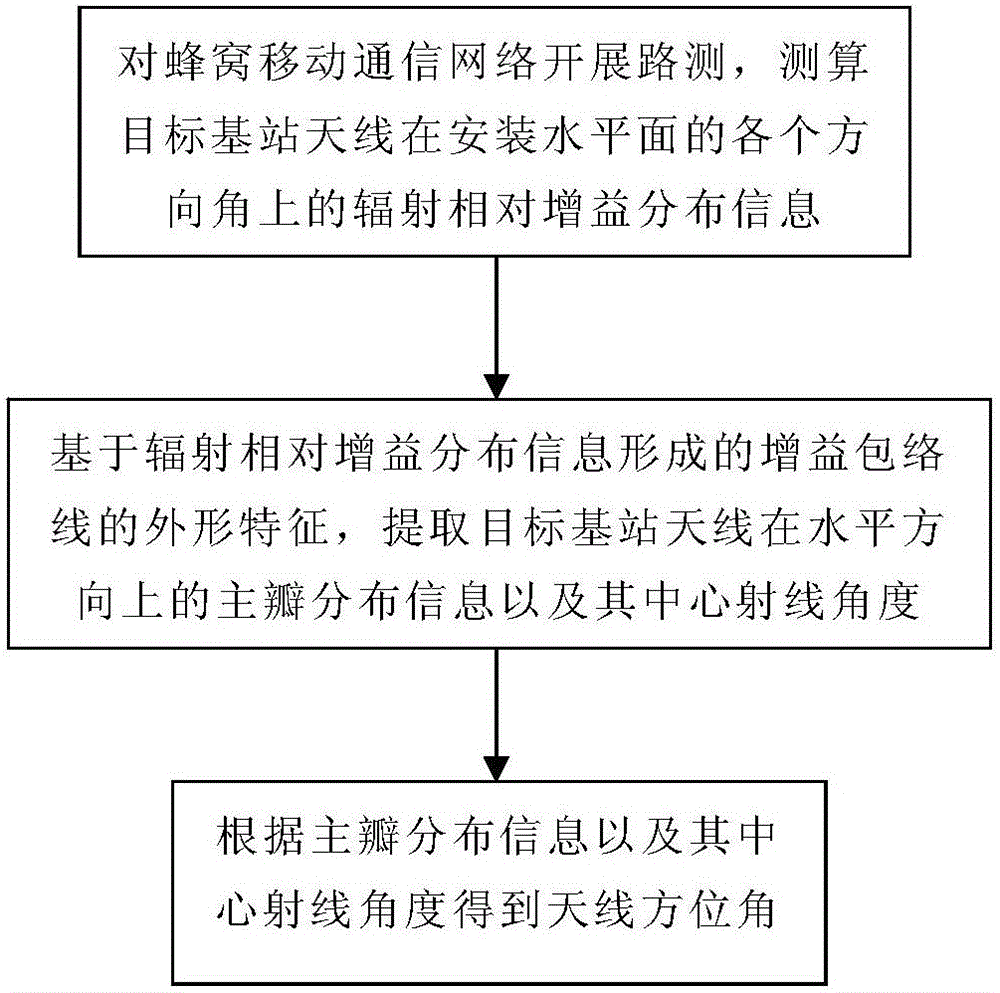
Method for measuring azimuth angle of mobile communication base station antenna
The invention discloses a method for measuring an azimuth angle of a mobile communication base station antenna, and includes the steps of: performing a drive test on a cellular mobile communication network, and measuring radiation relative gain distribution information of a target base station antenna at each azimuth angle of an installation horizontal plane; based on the shape characteristics of a gain envelope line formed by the radiation relative gain distribution information, extracting main lobe distribution of the target base station antenna in a horizontal direction and a central ray angle; and obtaining the azimuth angle of the antenna according to the main lobe distribution information and the central ray angle. According to the method for measuring the azimuth angle of the mobile communication base station antenna, people do not need to purchase or install special hardware by climbing up to a tower, and can complete measurement only by utilizing drive test data of an existing drive test terminal and sweep generator, the cost is low, and engineering implementation is easy; and a calculation result is high in degree of accuracy and stability, and a requirement for optimizing work of the cellular mobile communication network can be satisfied.
Owner:上海方库信息科技有限公司
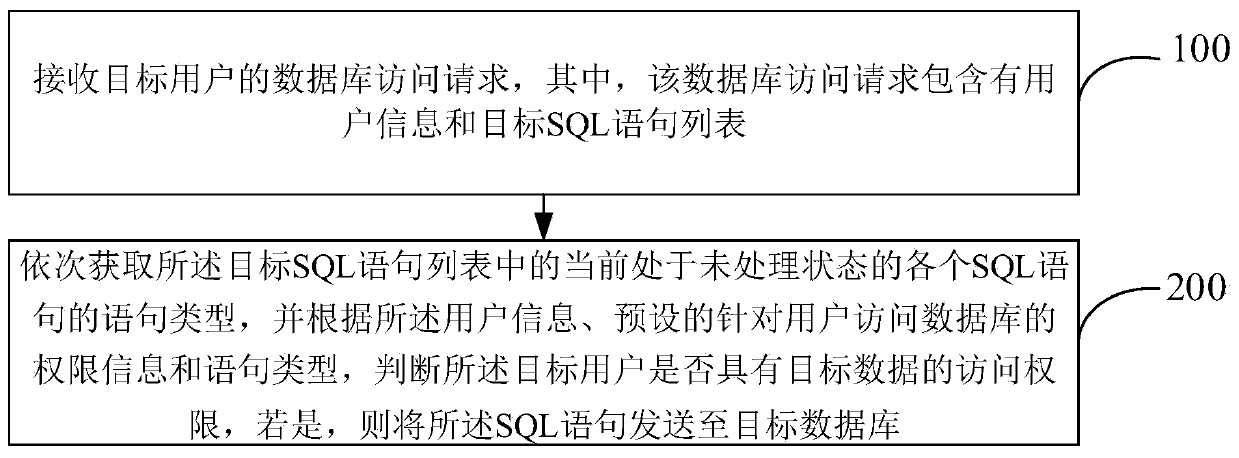
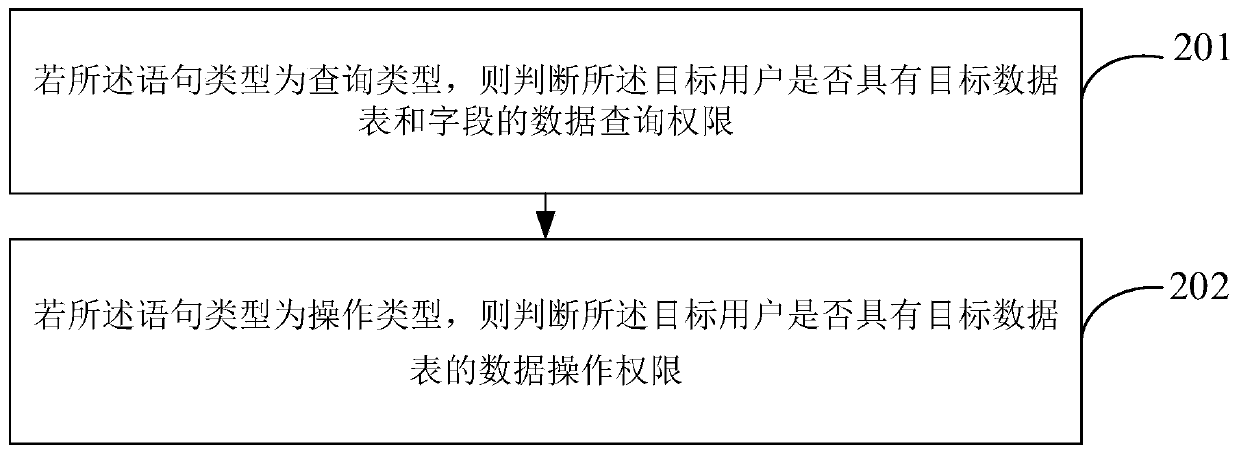
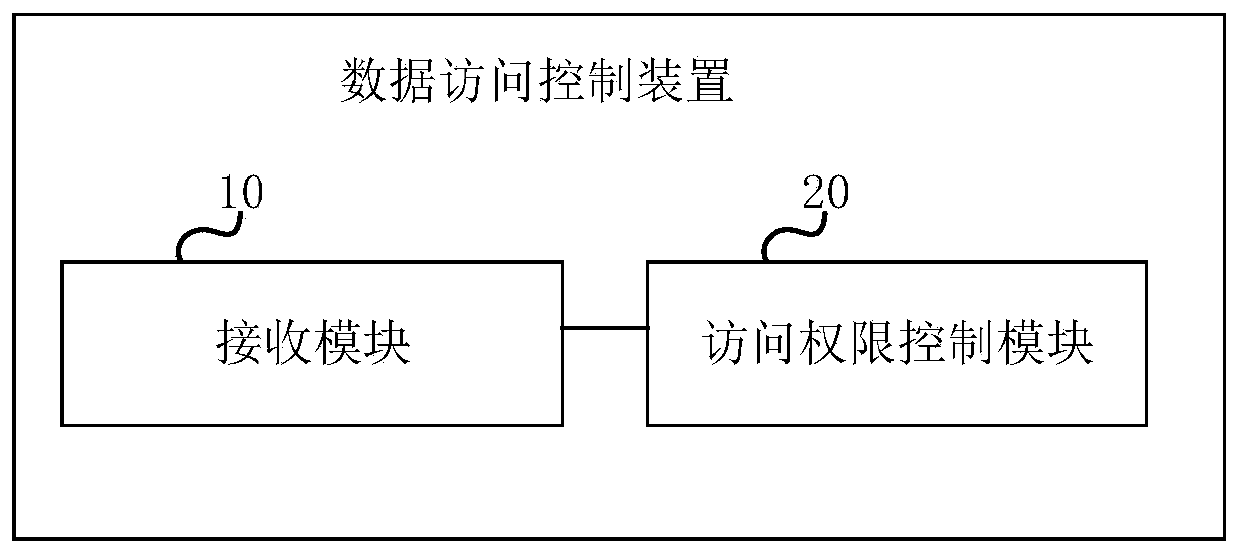
Data access control method and device
PendingCN111460506AImprove reliabilityIncrease flexibilityDigital data protectionEnergy efficient computingData access controlEngineering
The invention provides a data access control method and device. The method comprises the steps: receiving a database access request of a target user, the database access request comprising user information and a target SQL statement list; sequentially obtaining statement types of all SQL statements which are in an unprocessed state currently in the target SQL statement list, and judging whether the target user has the access permission of the target data or not according to the user information, preset permission information for the user to access the database and a statement type, If so, sending the SQL statement to the target database. According to the invention, the reliability and flexibility of data access control can be improved, and the universality of an application scene can be improved.
Owner:INDUSTRIAL AND COMMERCIAL BANK OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com