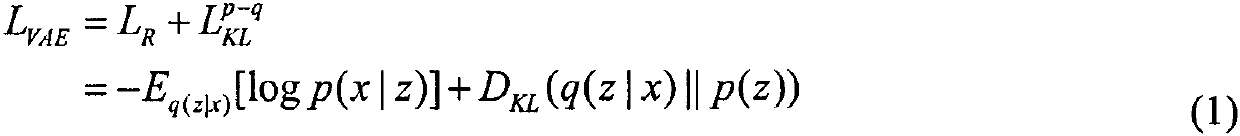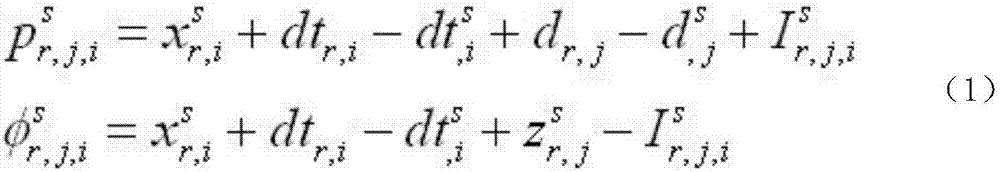Patents
Literature
1011 results about "Satellite orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electronic monitoring systems and methods
InactiveUS7123141B2Improve sanitationElectric signalling detailsBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalWeb browserGps receiver
Owner:CONTESTABILE ROBERT A
Electronic monitoring systems and methods
InactiveUS20050040944A1Unintended contactImprove sanitationElectric signalling detailsBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalWeb browserGps receiver
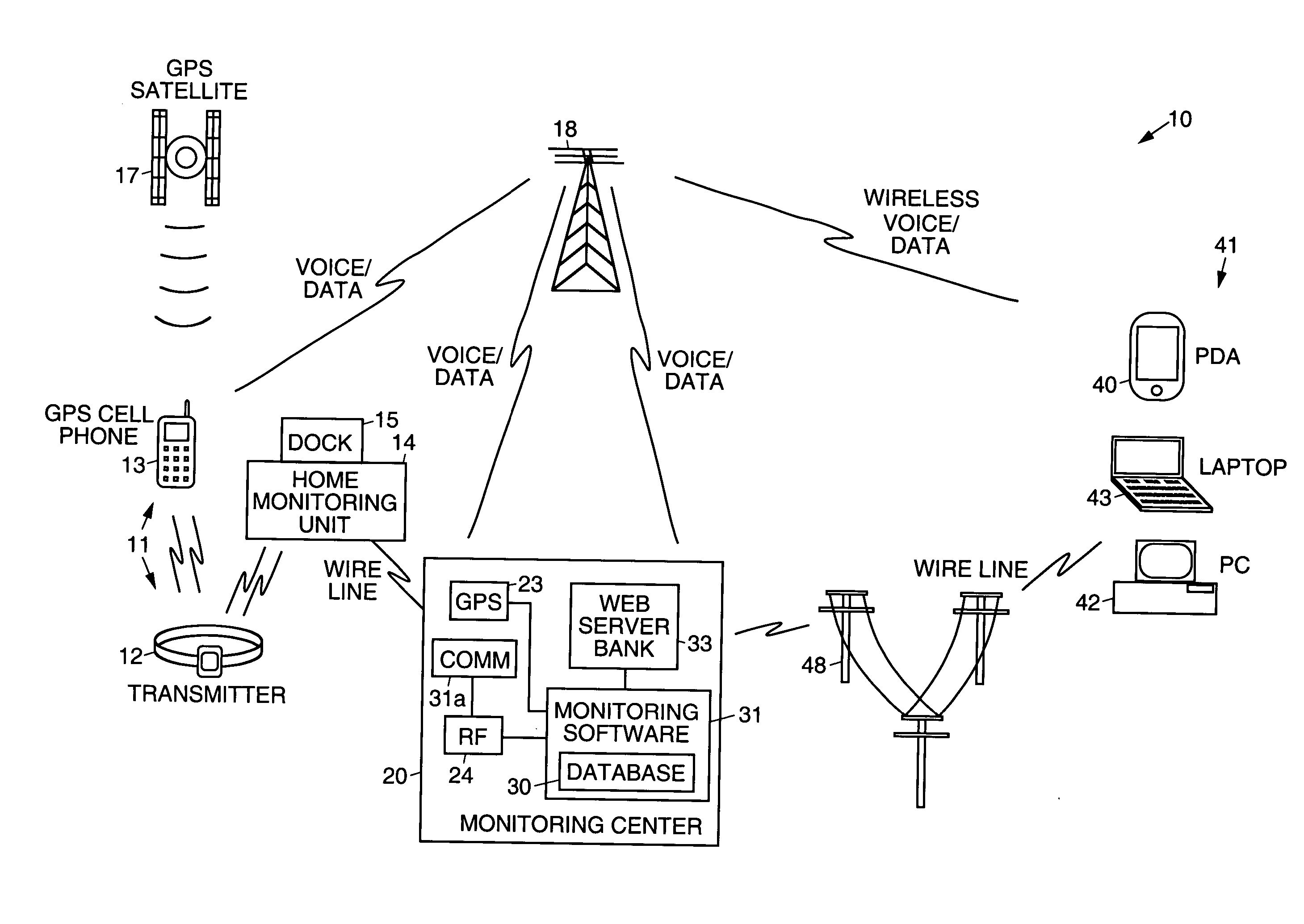
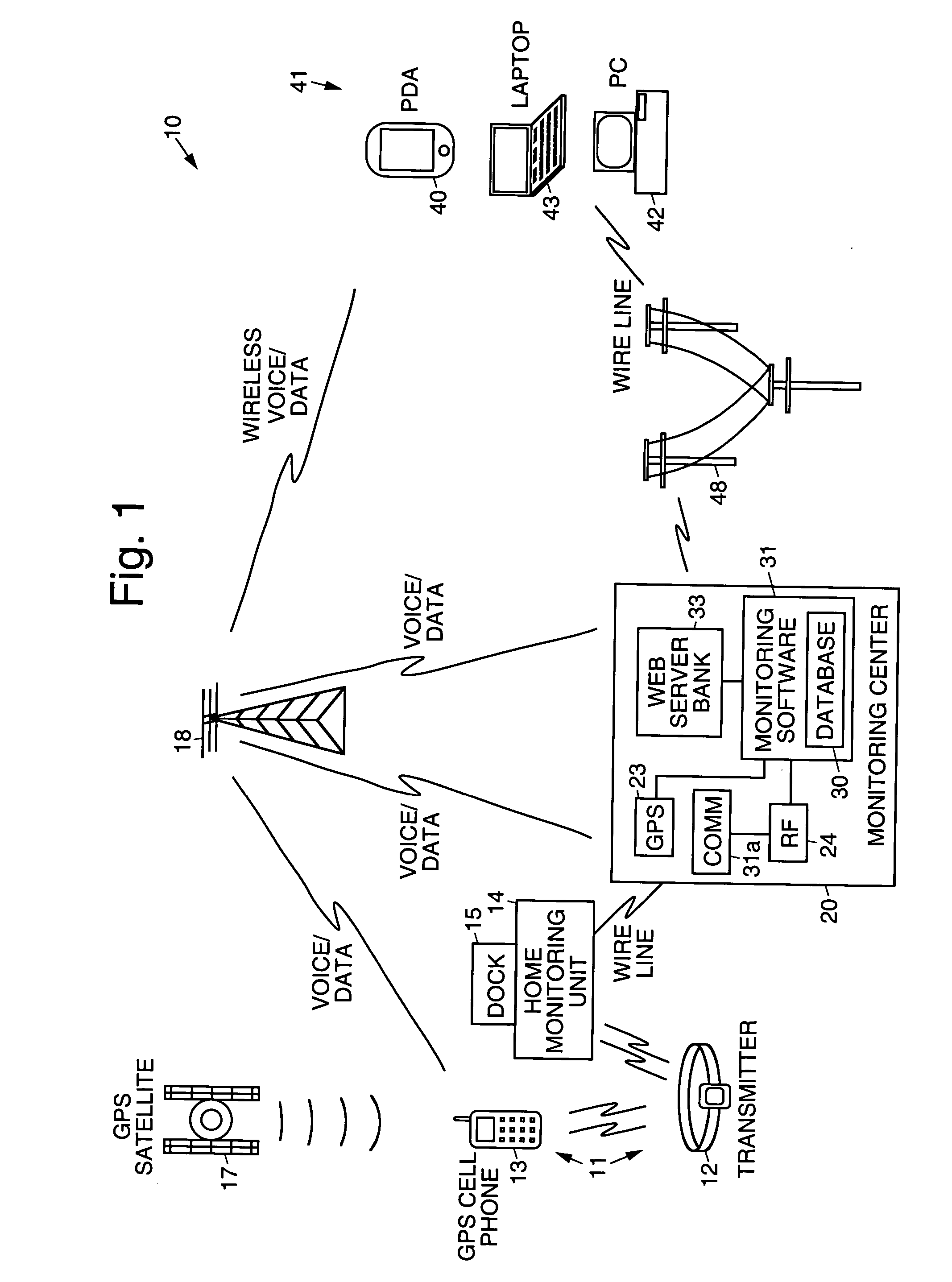
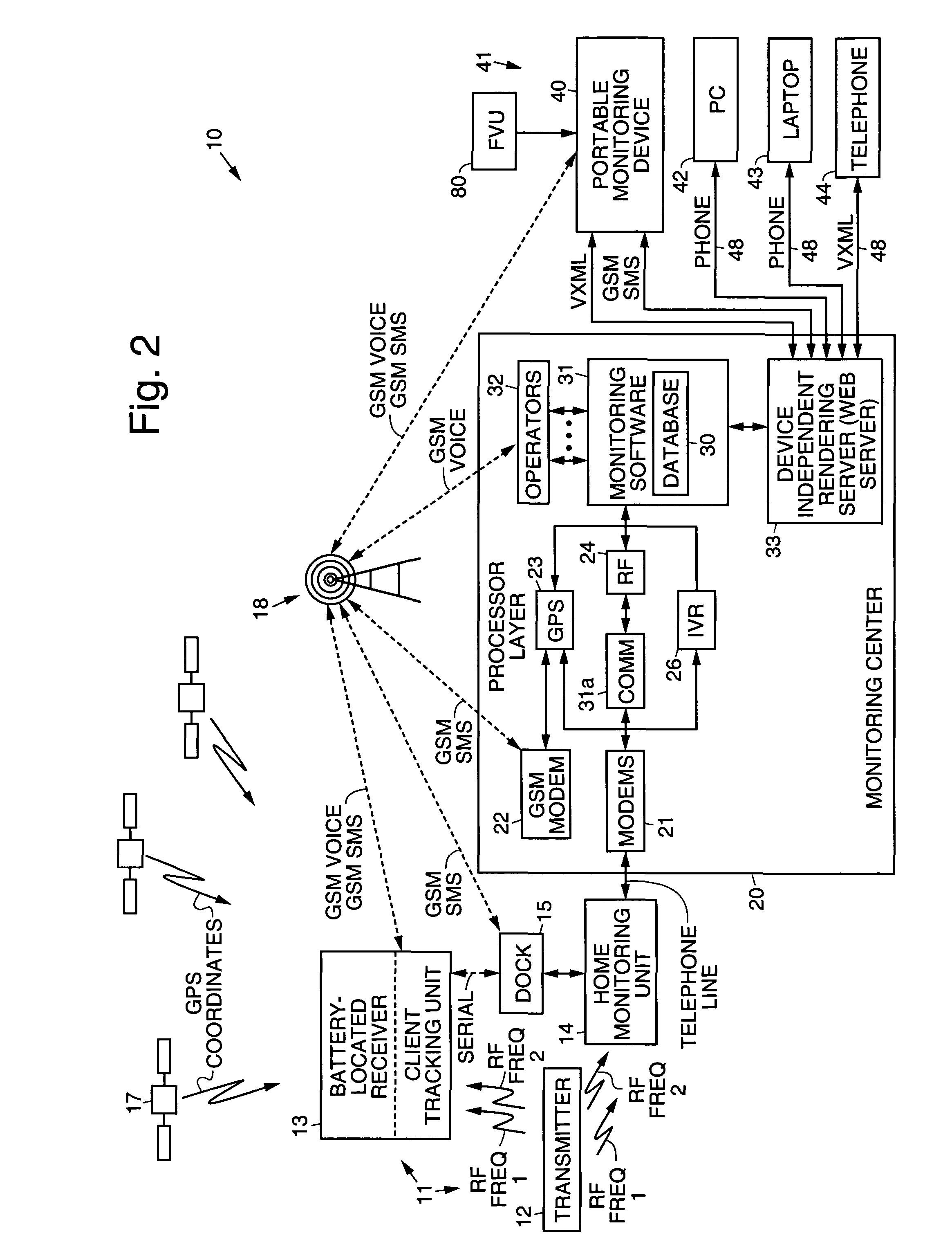
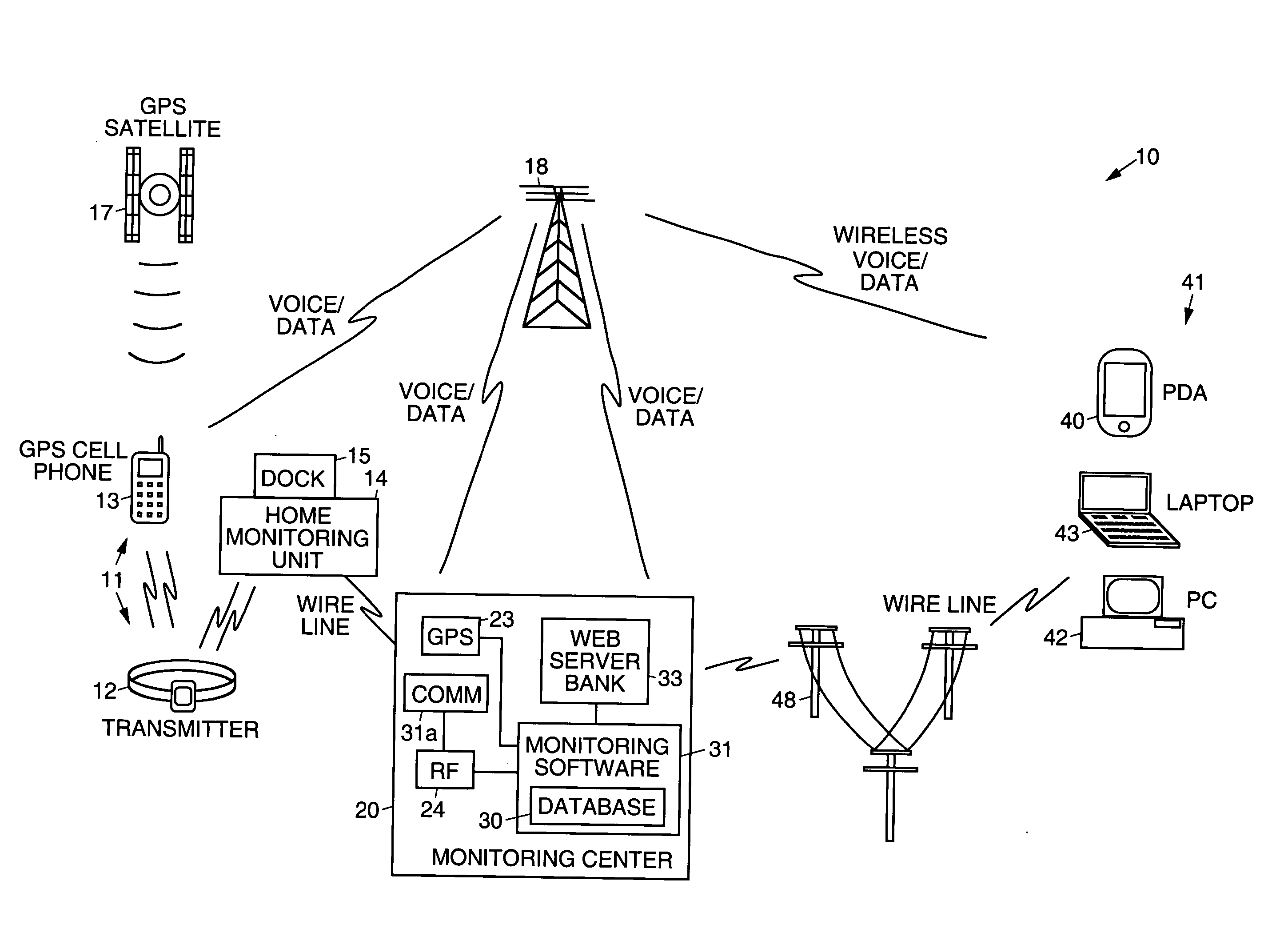
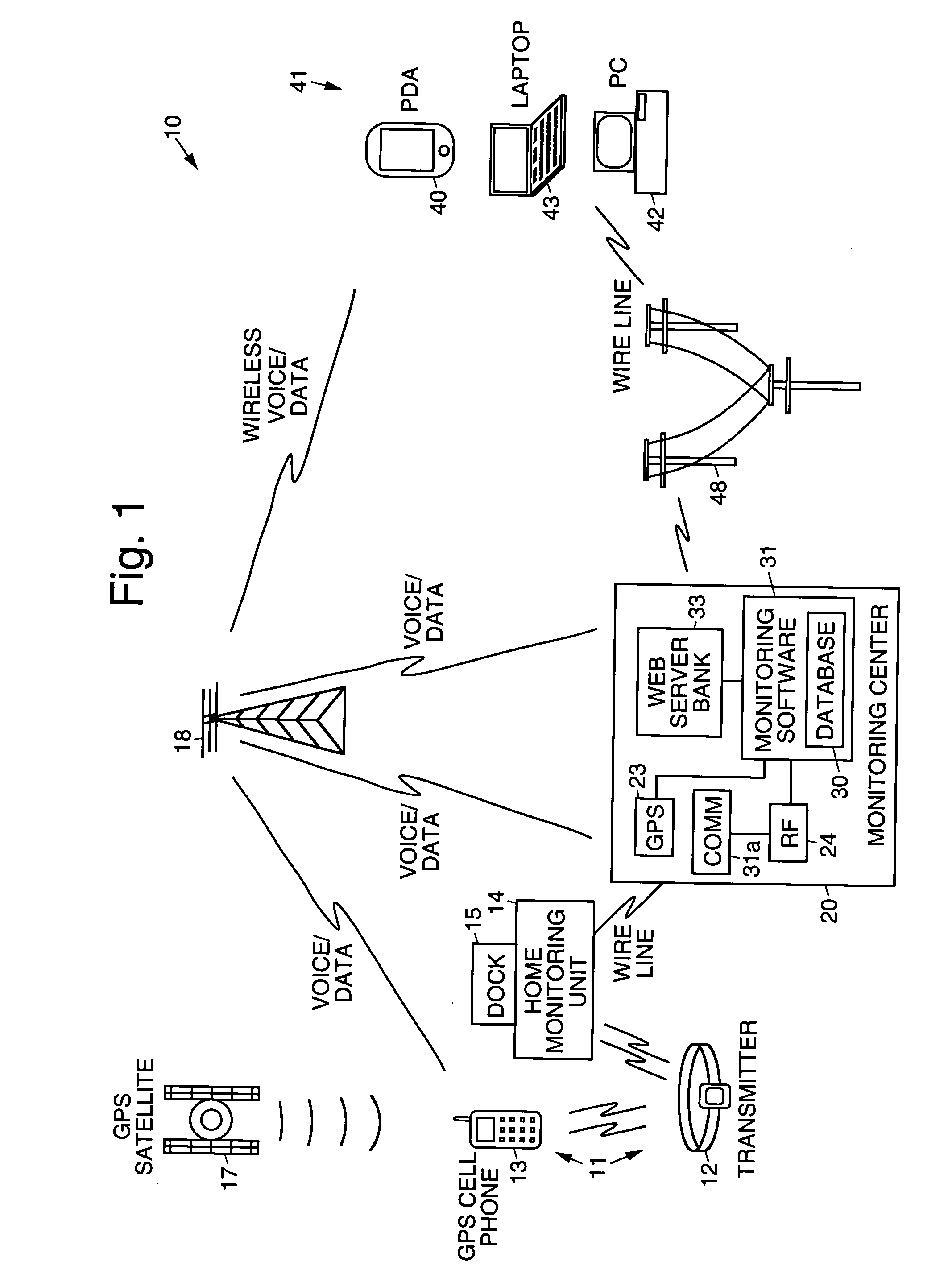
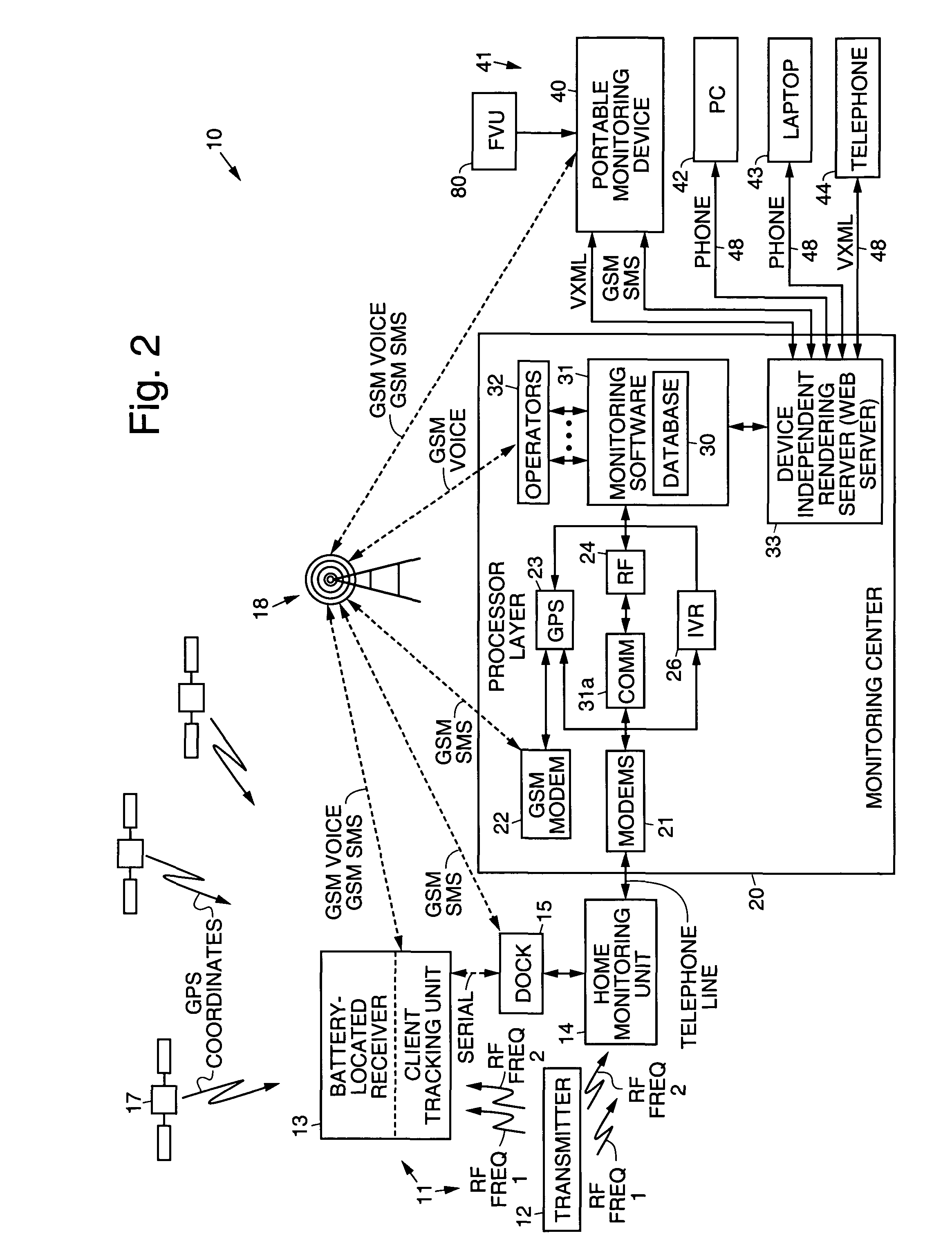
Electronic monitoring systems and methods that permit full-time tracking and management of, and communication with, monitored clients that carry a client tracking unit and wear a transmitter, by a monitoring individual that carries a wireless portable monitoring device. A central monitoring station having a central database is ported to a plurality of processor interfaces, including RF, GPS, and integrated voice, for example. The central database is wirelessly linked to the portable monitoring device, which is programmed to remotely track and manage clients by way of the respective interfaces. A monitoring unit is coupled to (or includes) a dock that docks the client tracking unit. The client tracking unit has a GPS receiver that receives position signals from satellites orbiting the Earth to permit tracking of the client. The client tracking unit has a battery that houses a receiver that receives signals transmitted by the transmitter and monitors transmitted signals to determine if an alarm event has occurred relating to the transmitter or location of the client. The portable monitoring device has cellular and web browser capabilities that provide access to the central monitoring station by way of a network, and permits retrieval and changing of information by the monitoring individual regarding monitored clients. Information regarding specific clients or a group of clients may be retrieved (optionally using voice commands) from the central monitoring station, modified by the monitoring individual, or selected clients may be directly communicated with using the voice capabilities of the portable monitoring device and client tracking unit.
Owner:CONTESTABILE ROBERT A
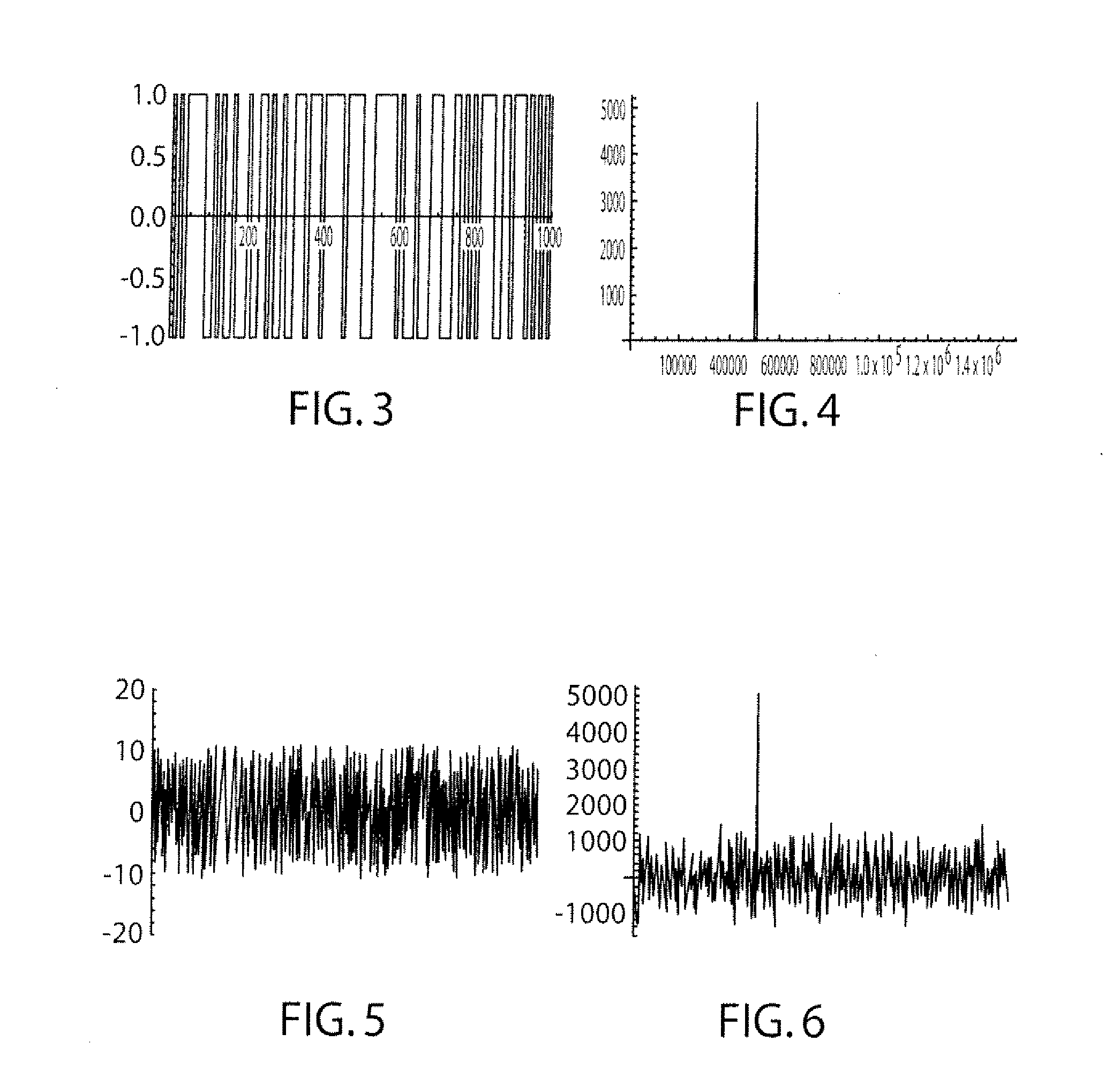
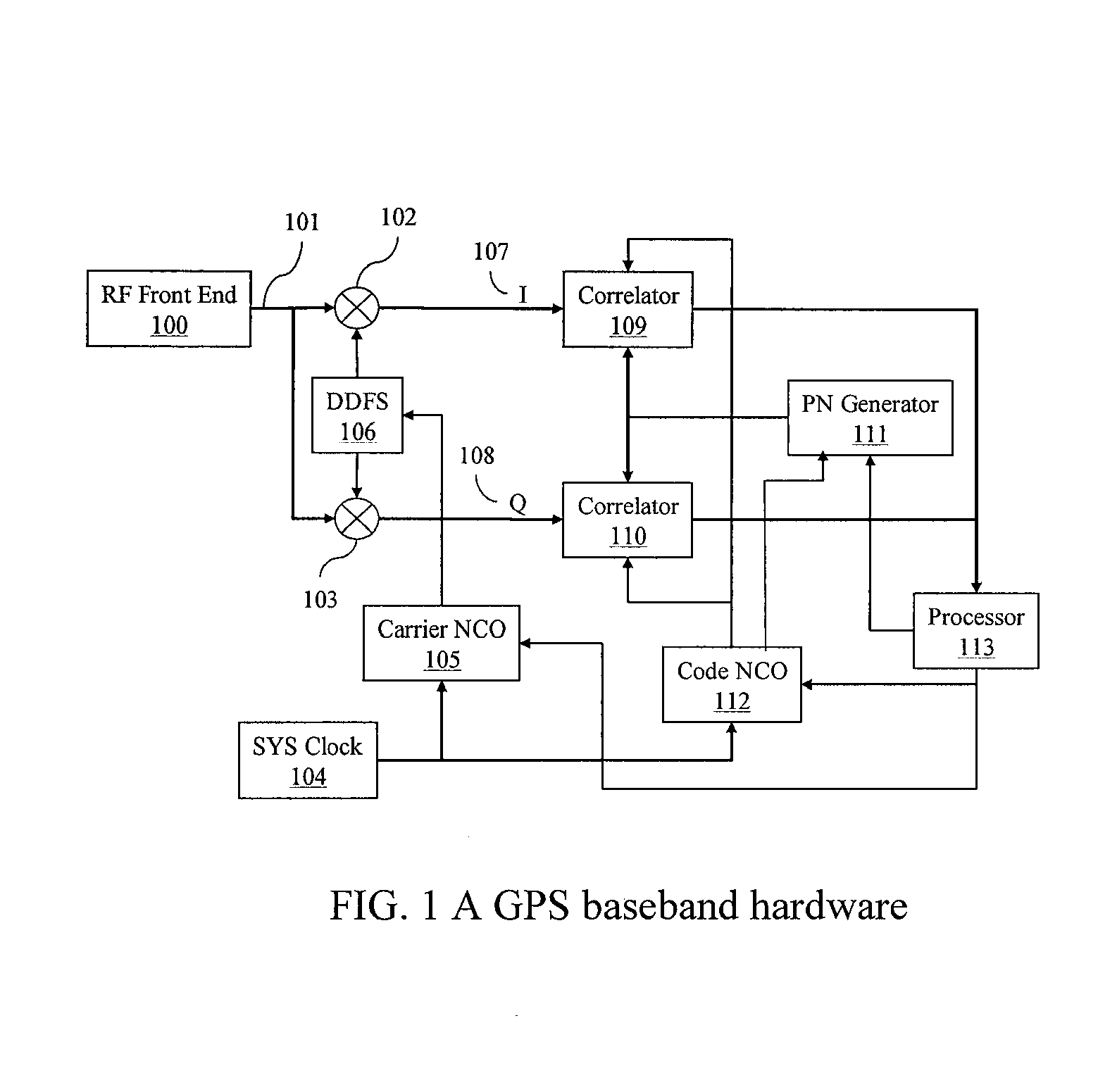
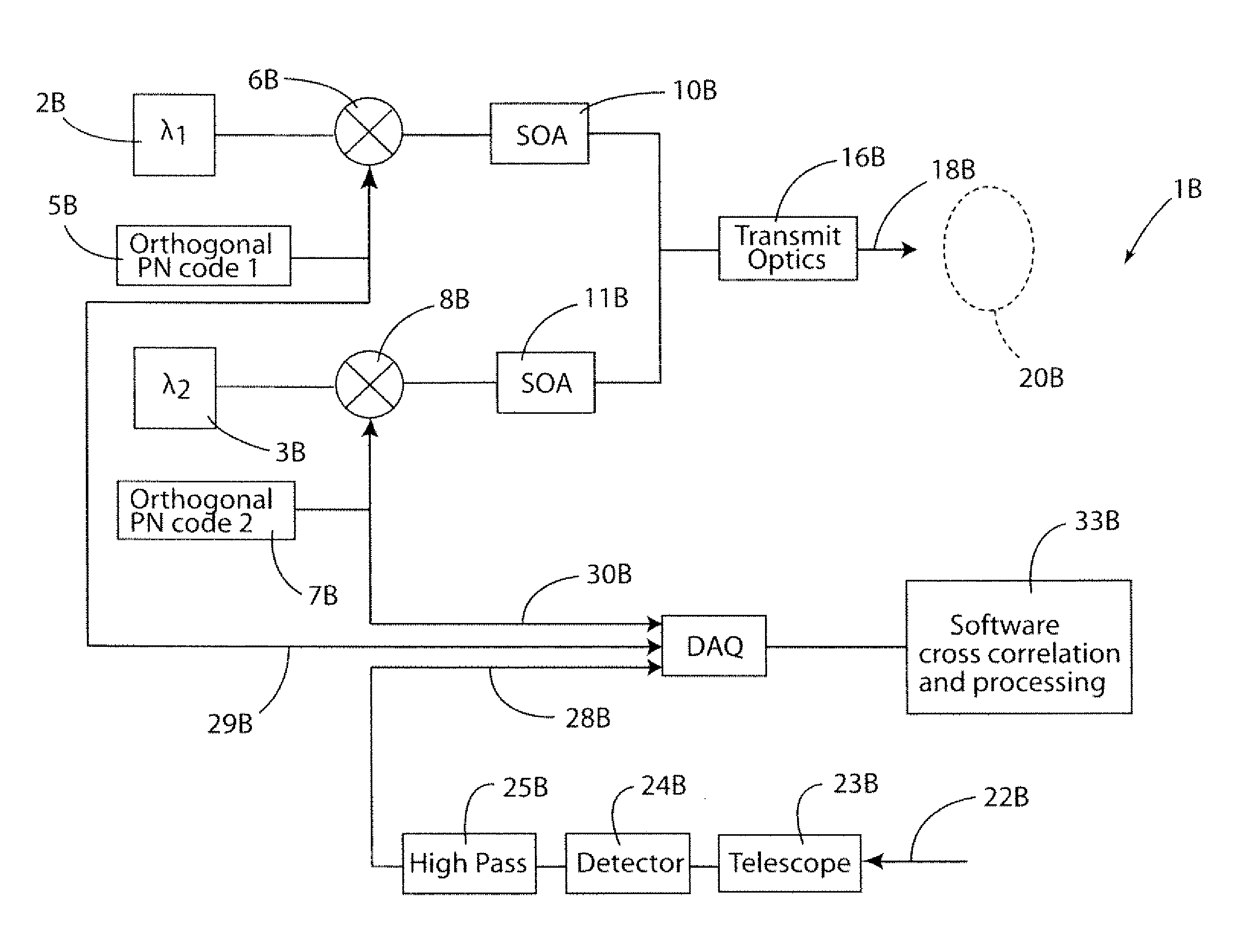
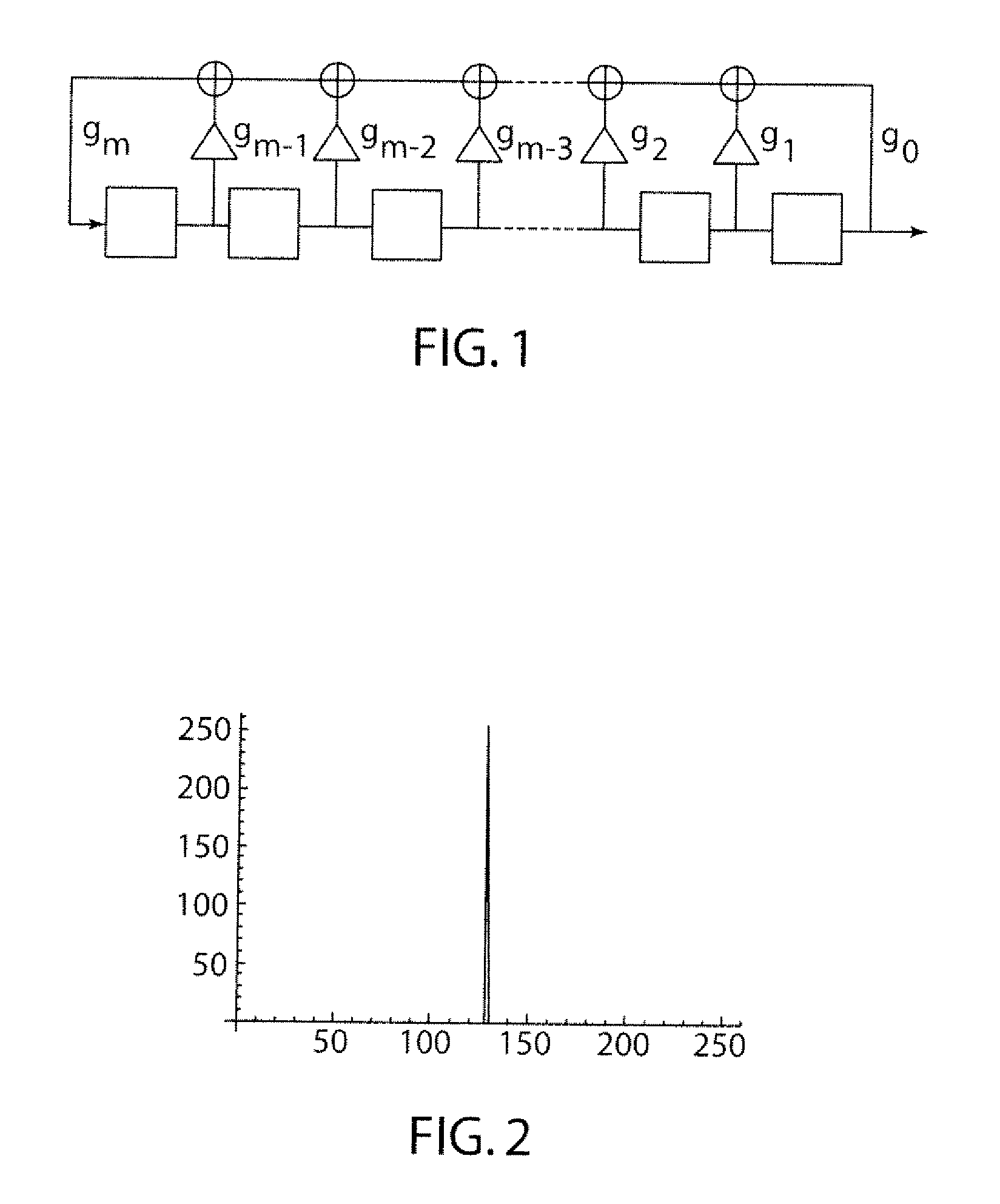
Time Shifted PN Codes for CW LIDAR, RADAR, and SONAR
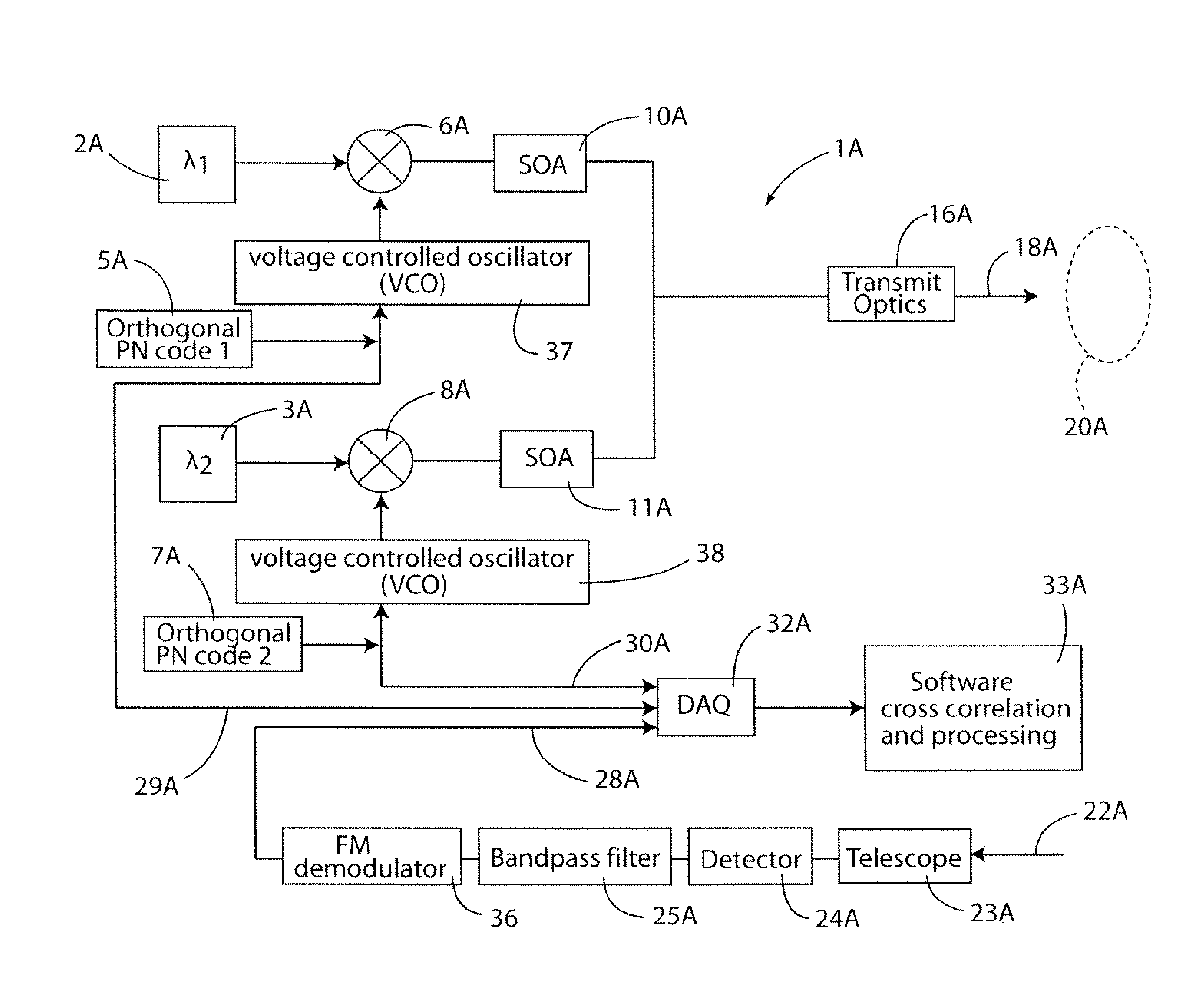
A continuous wave Light Detection and Ranging (CW LiDAR) system utilizes two or more laser frequencies and time or range shifted pseudorandom noise (PN) codes to discriminate between the laser frequencies. The performance of these codes can be improved by subtracting out the bias before processing. The CW LiDAR system may be mounted to an artificial satellite orbiting the earth, and the relative strength of the return signal for each frequency can be utilized to determine the concentration of selected gases or other substances in the atmosphere.
Owner:NASA
Method and apparatus for satellite orbital change using space debris
An apparatus for orbital change of a satellite incorporates a capture mechanism for space debris and a tether connecting the capture mechanism to a satellite. The tether is extendable to position the capture mechanism relative to the space debris. A controller is employed for timed release of the space debris by the capture mechanism for orbital change by the satellite.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
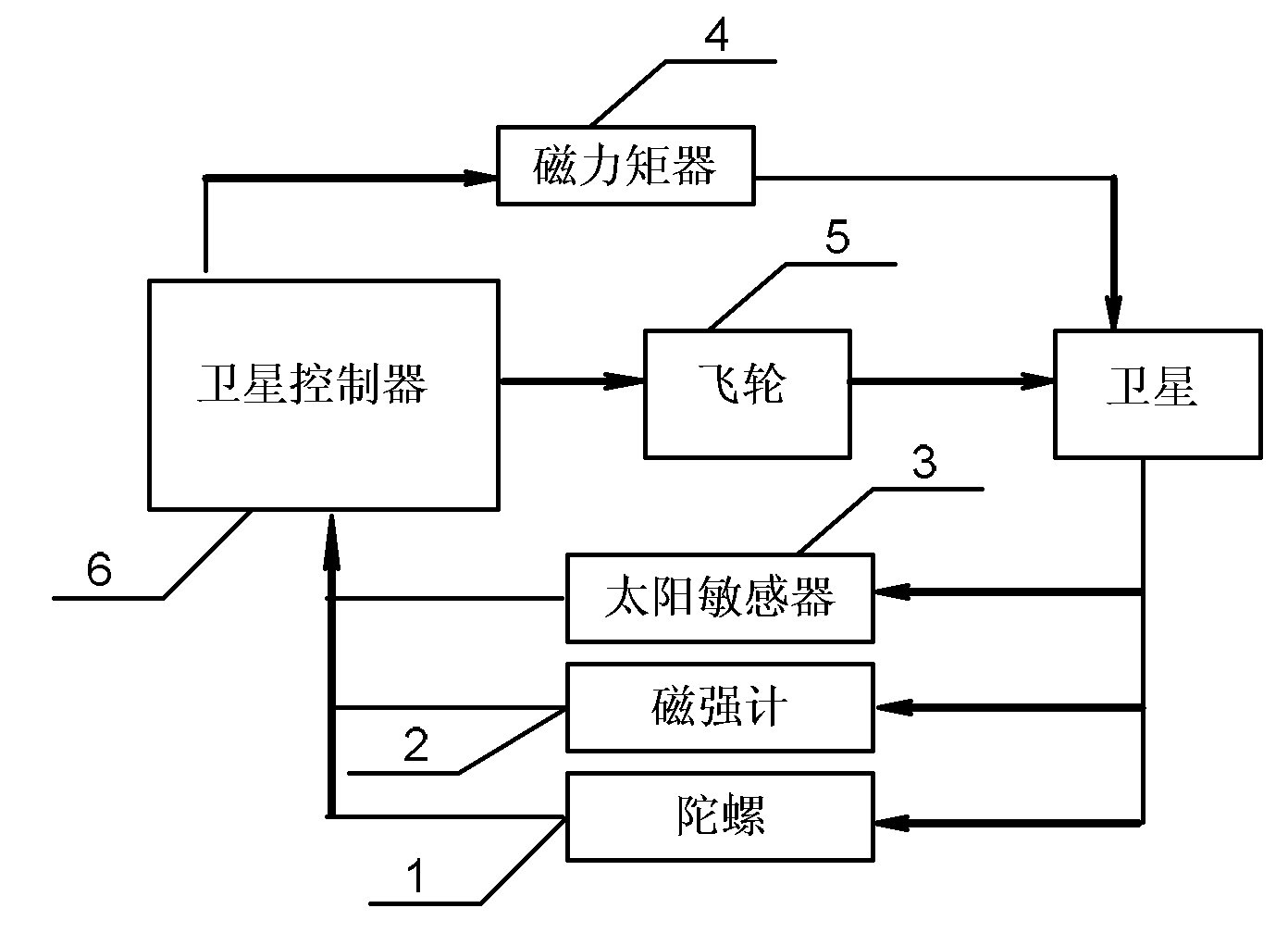
Satellite posture all-round controlling method based on magnetic moment device and flywheel
InactiveCN101934863ASimple configurationImprove securityCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusMagnetic tension forceControl system
The invention discloses a satellite posture all-round controlling method based on a magnetic moment device and a flywheel, relating to an all-round posture controlling method for completing a satellite orbit-injection phase by using the magnetic moment device and the flywheel. The invention solves the problems of low reliability and short service life of the traditional satellite posture all-round controlling technology. The satellite posture all-round controlling method comprises the following steps of: 1, setting controller parameters according to the requirement of a control system; 2, measuring a geomagnetic field intensity vector Bb, a satellite angular velocity vector Wb and a solar azimuth, and sending the measured data to a satellite controller; 3, calculating an expected control moment vector Tm and a control magnetic moment vector Mm, and sending the control magnetic moment vector Mm to the magnetic moment device; 4, acquiring an effective solar azimuth vector Alfa; 5, calculating a control input moment vector Tw and sending to the flywheel; and 6, jointly completing the satellite posture all-round control by the magnetic moment device according to the control magnetic moment vector Mm and the flywheel according to the control input moment vector Tw. The invention is suitable for the field of satellite posture control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
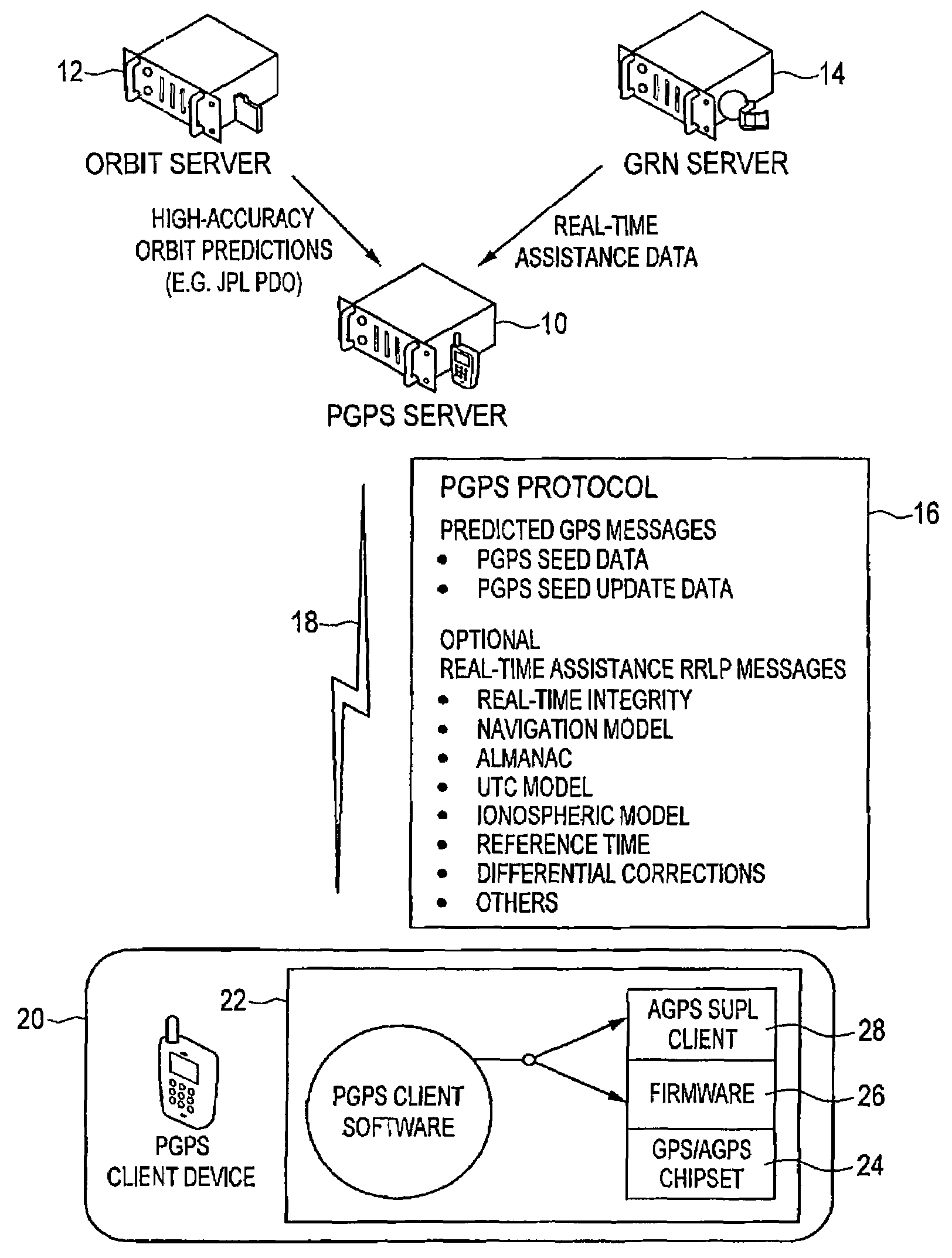
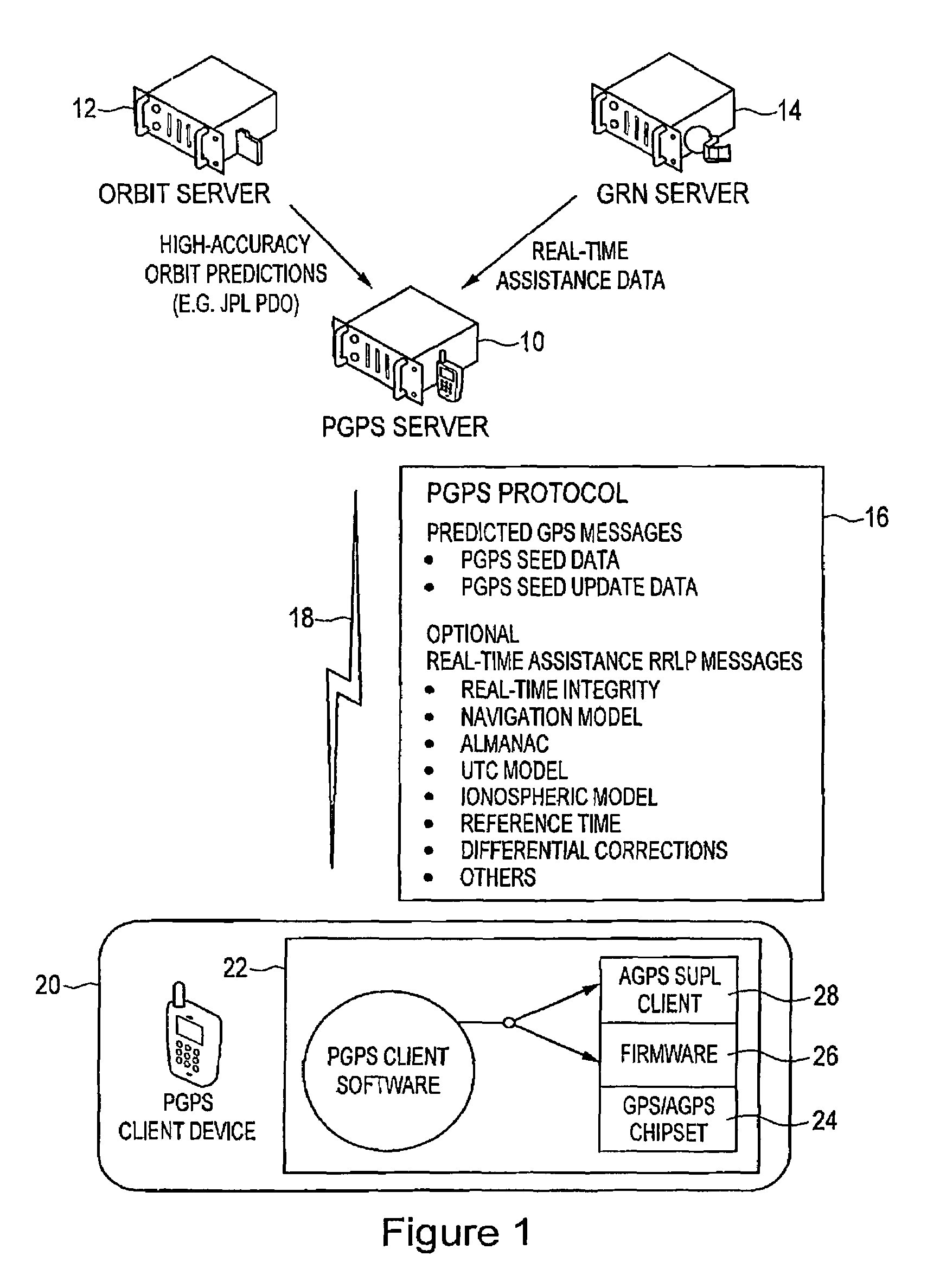
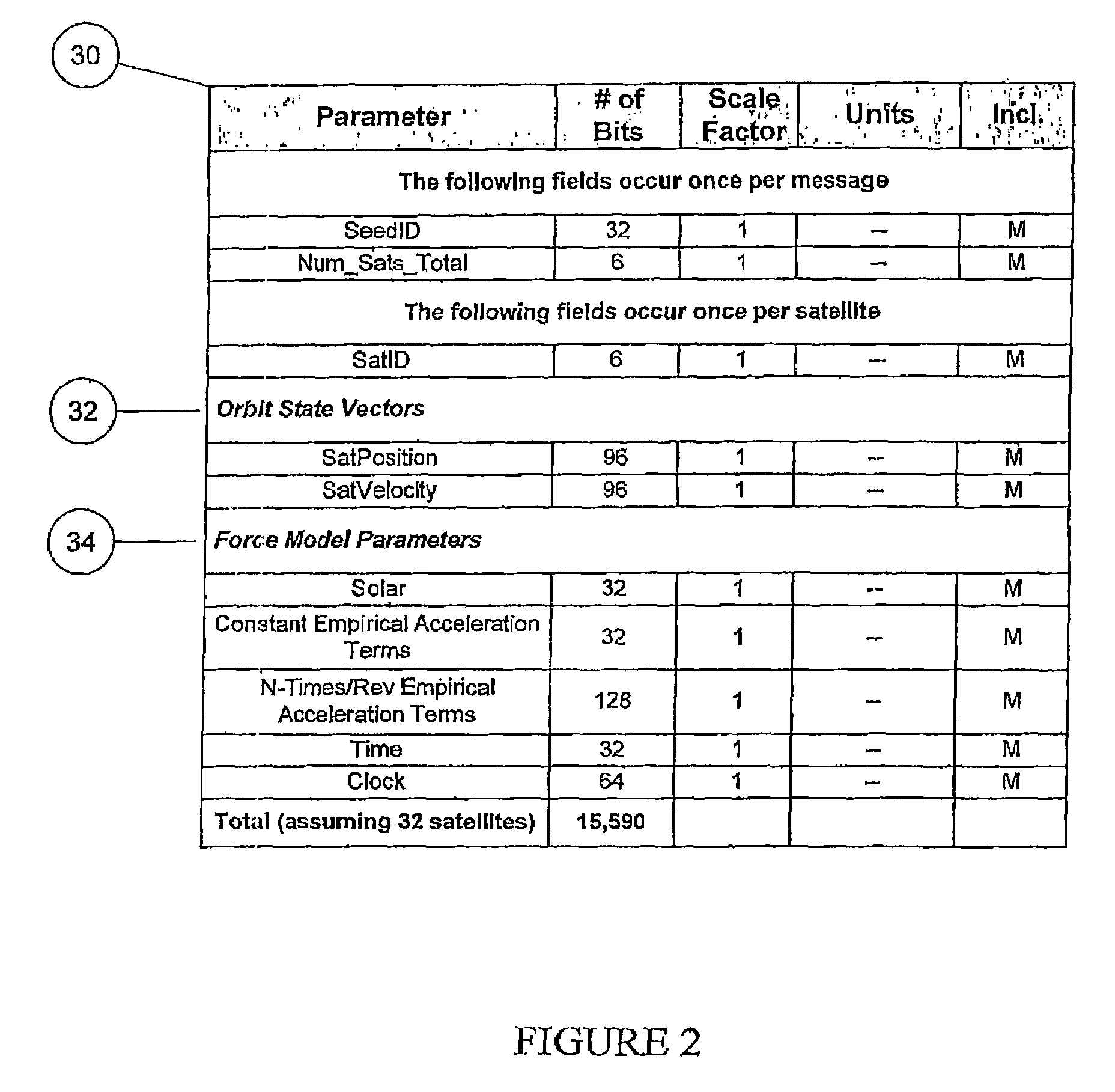
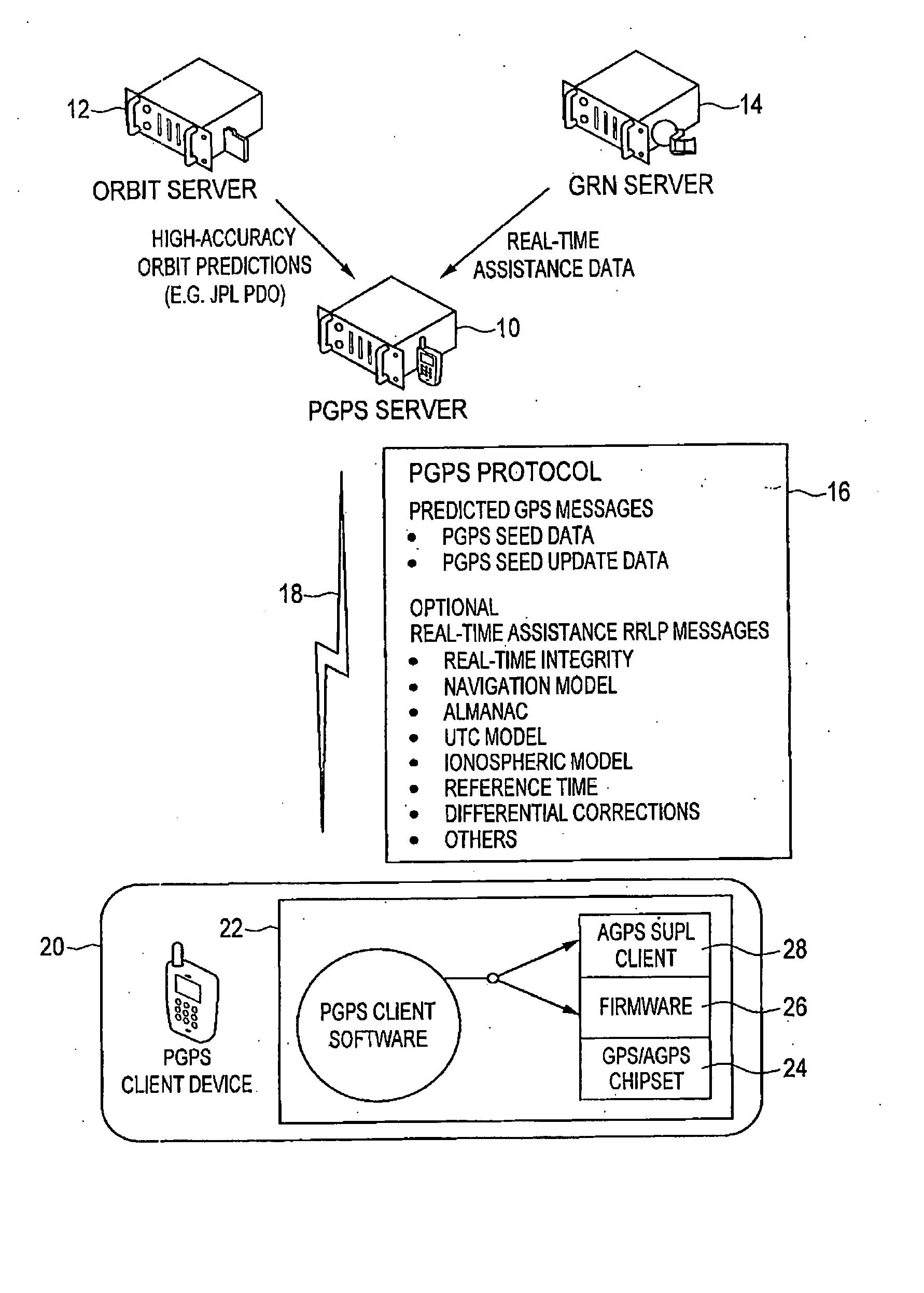
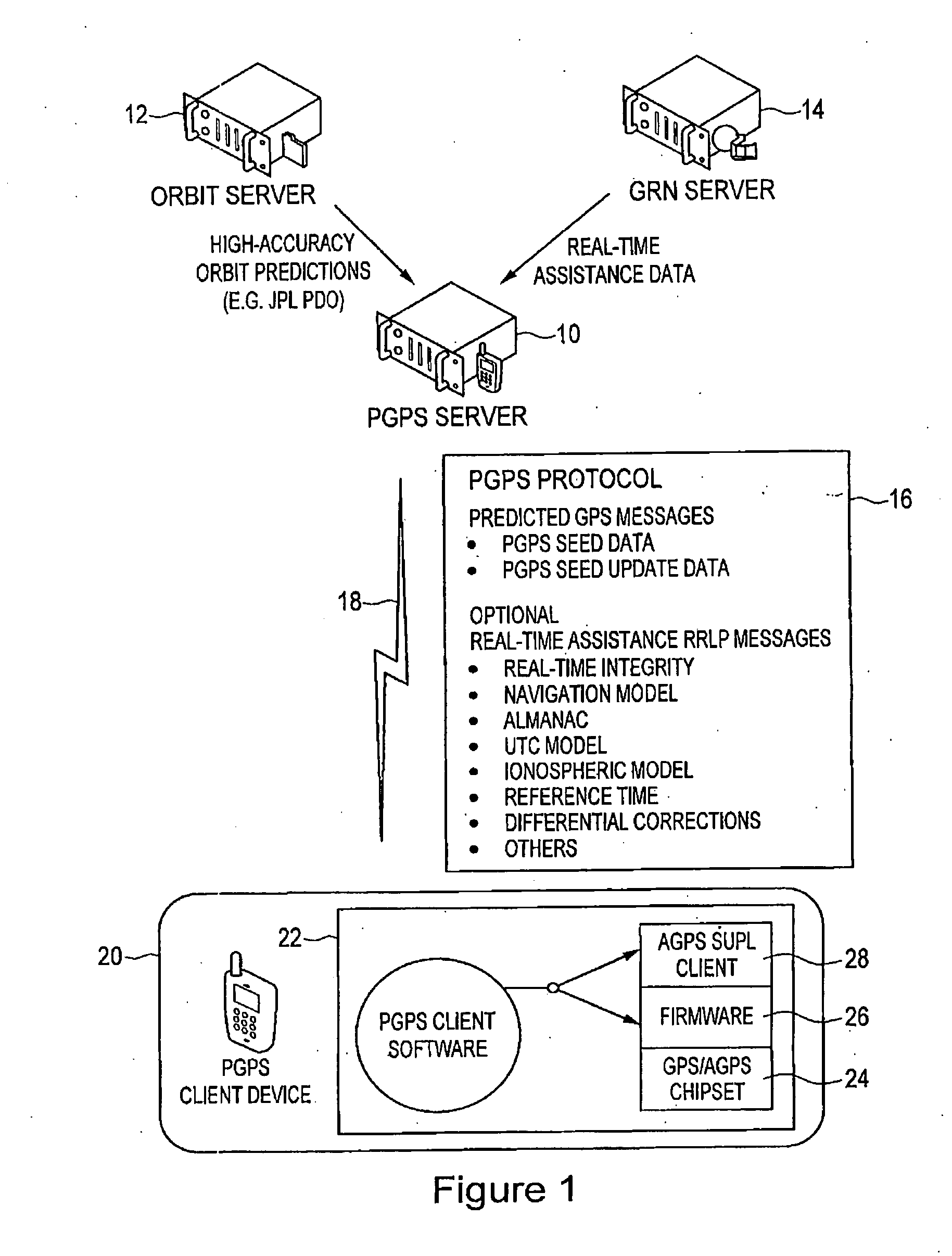
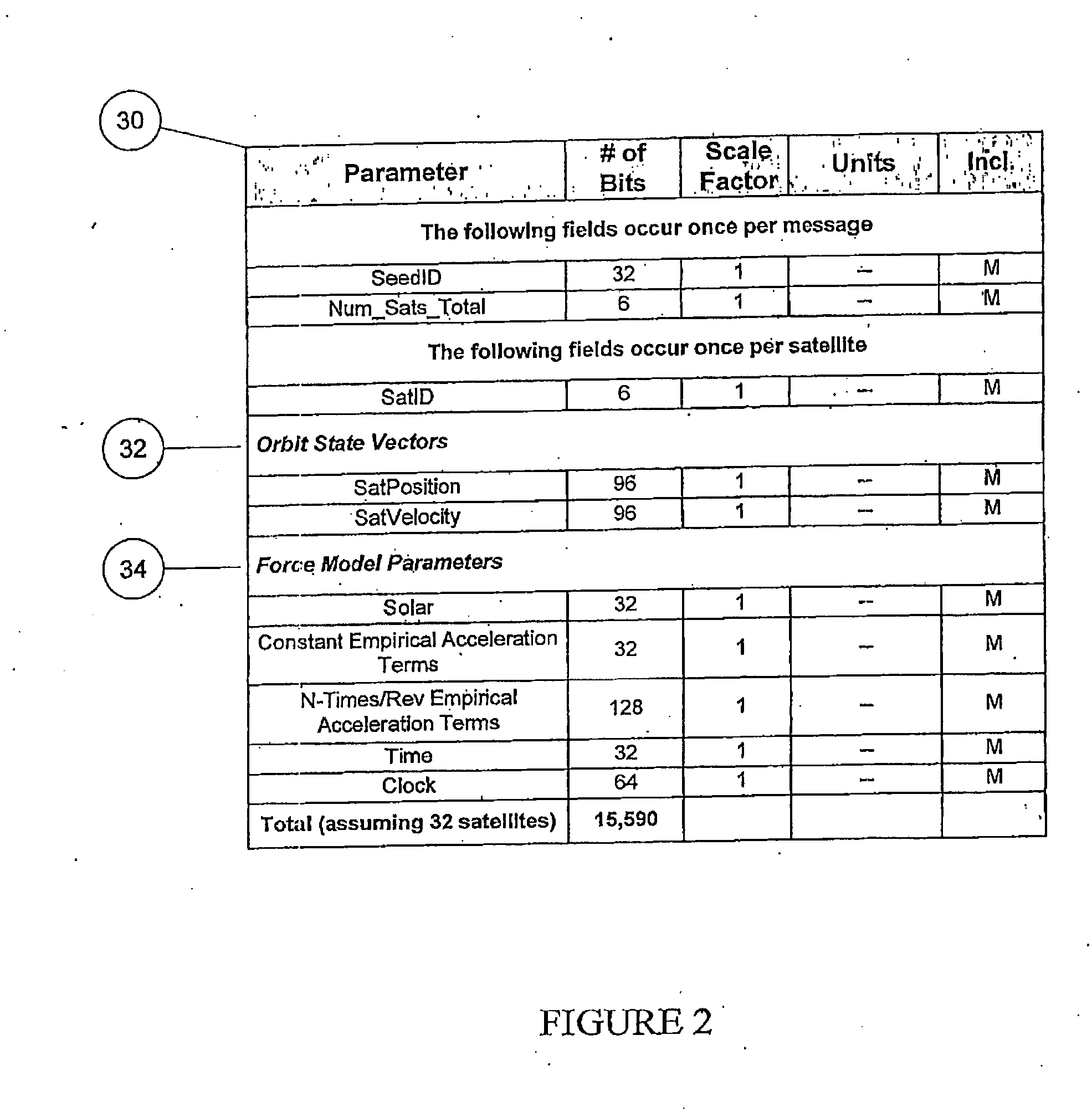
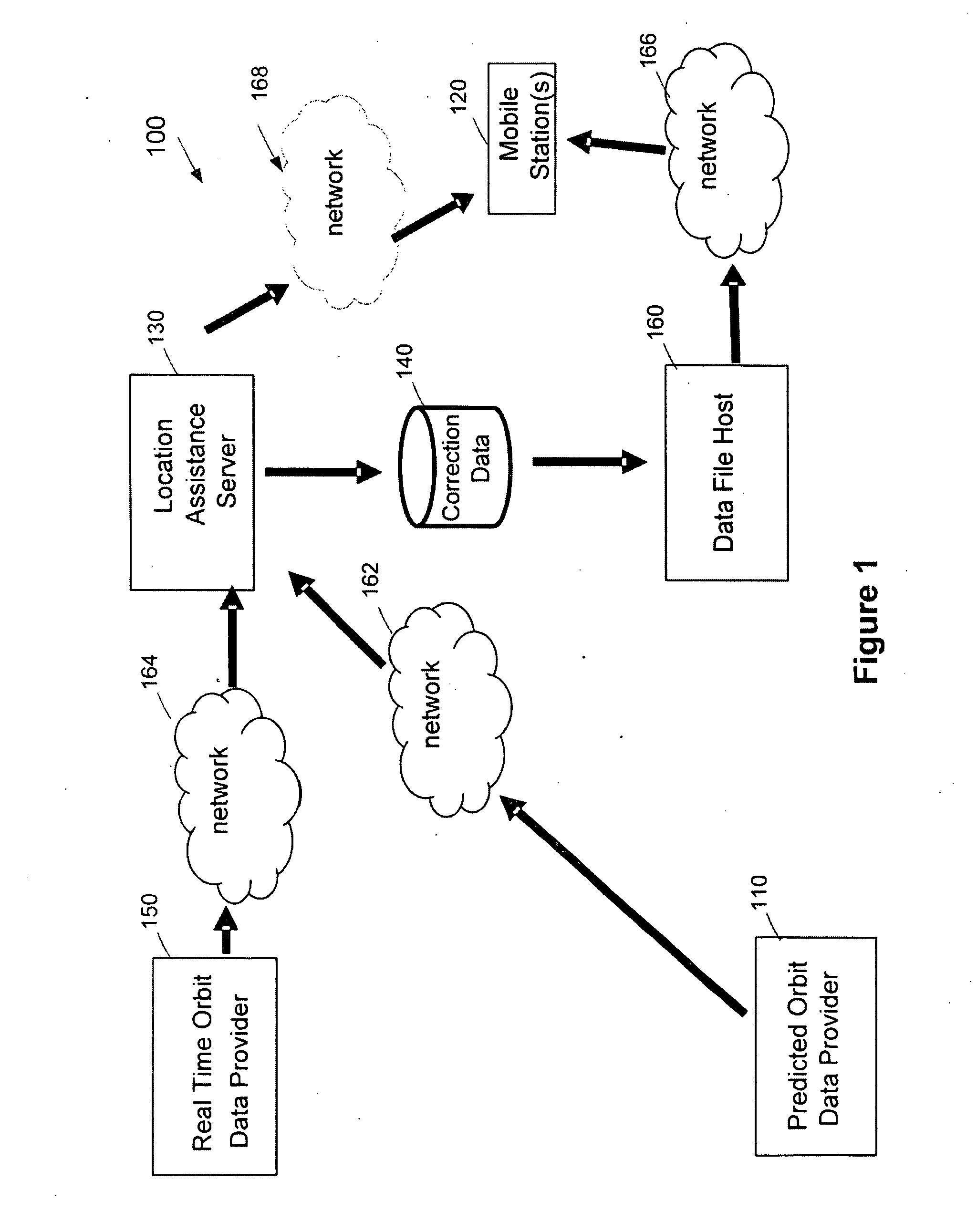
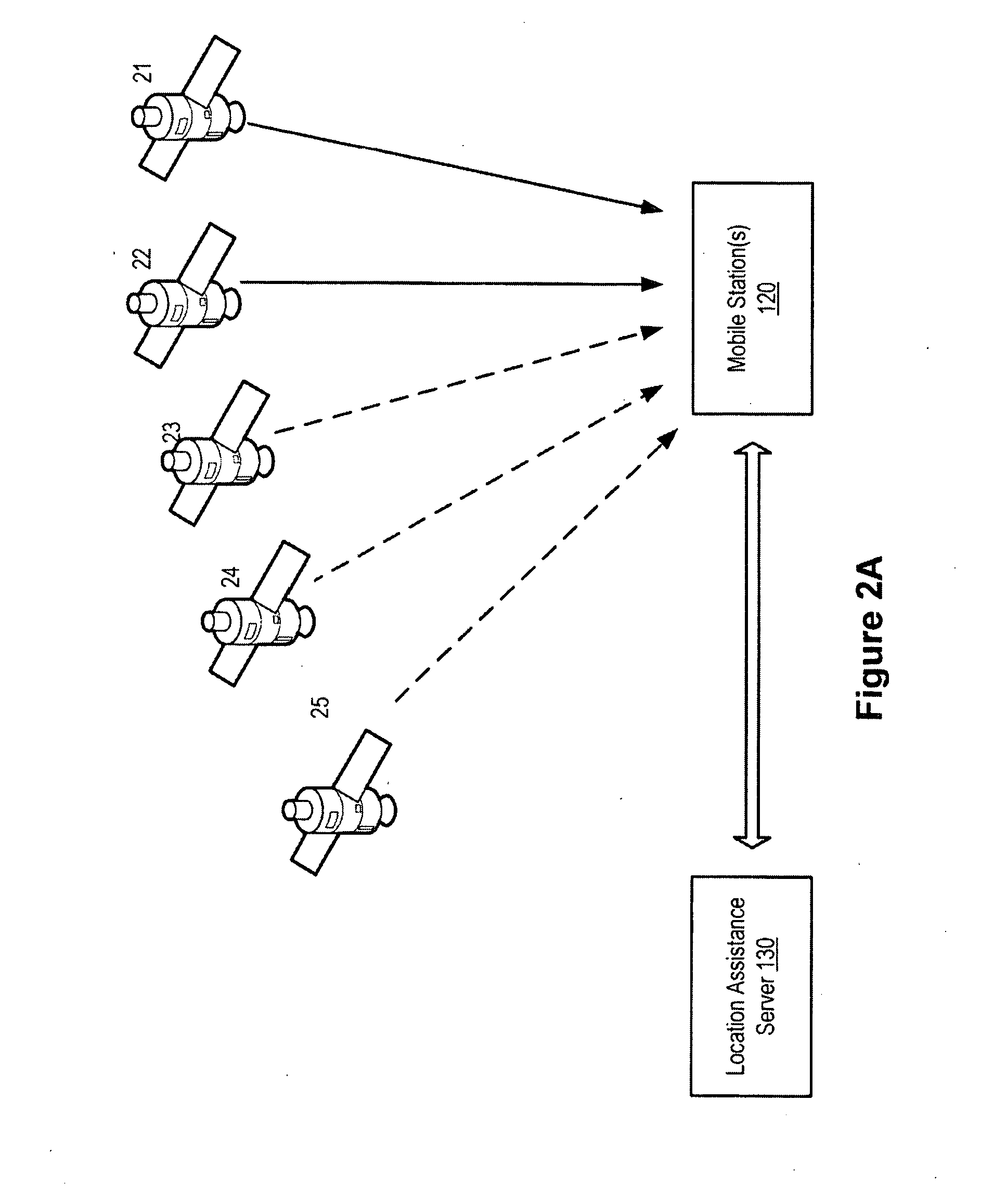
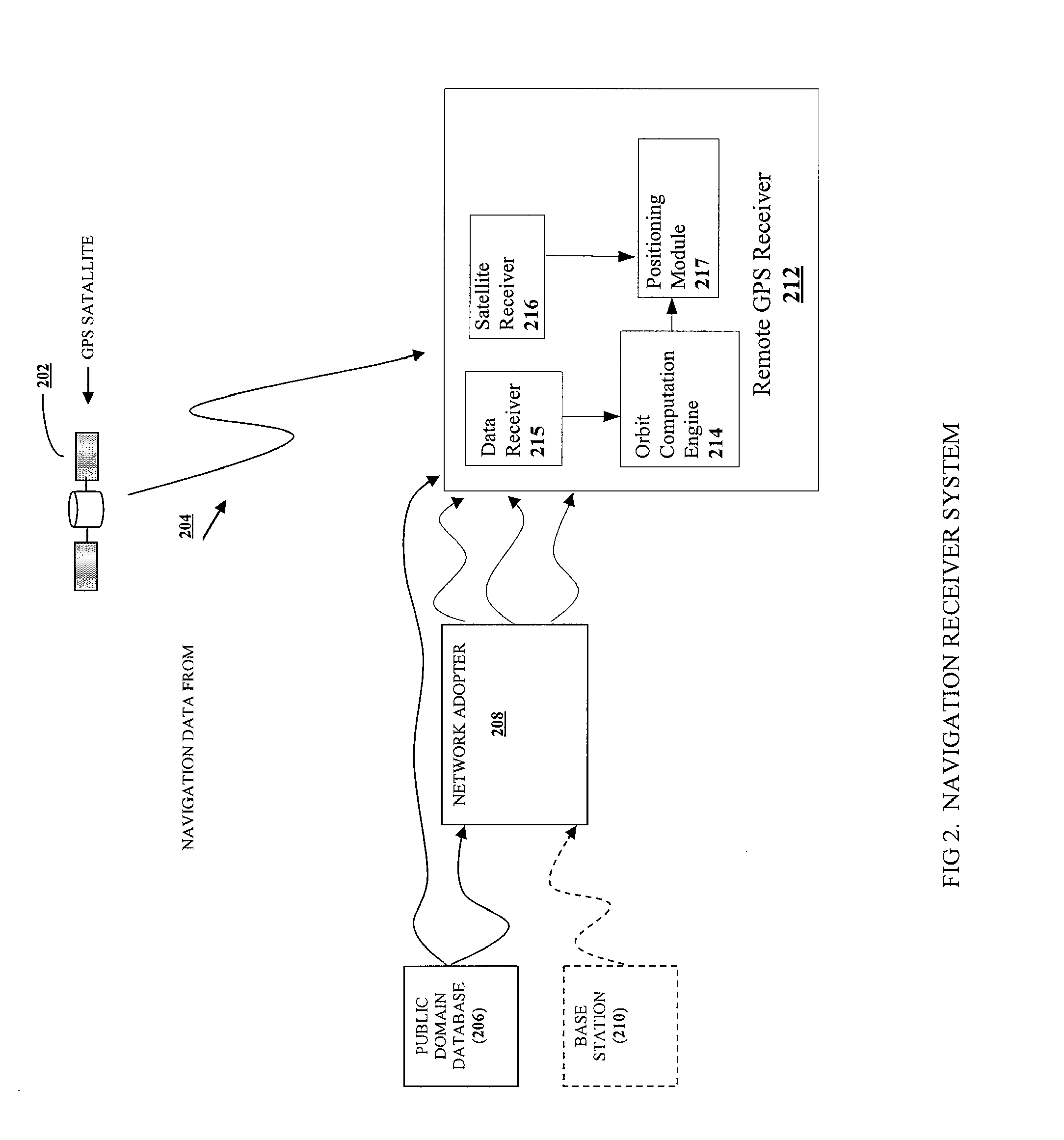
Distributed orbit modeling and propagation method for a predicted and real-time assisted GPS system
ActiveUS7612712B2Easy to integrateNavigational calculation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingData setTime to first fix
A distributed orbit and propagation method for use in a predicted GPS or GNSS system, which includes a predicted GPS server (PGPS Server), a source of high accuracy orbit predictions (Orbit Server), a global reference network (GRN Server) providing real-time GPS or GNSS assistance data to the PGPS Server, a predicted GPS client (PGPS Client) running on a device equipped with a GPS or AGPS chipset. In response to requests from the PGPS Client, the PGPS Server produces and disseminates an initial seed dataset consisting of current satellite orbit state vectors and orbit propagation model coefficients. This seed dataset enables the PGPS Client to locally predict and propagate satellite orbits to a desired future time. This predictive assistance in turn helps accelerate Time To First Fix (TTFF), optimize position solution calculations and improve the sensitivity of the GPS chip present on, or coupled with, the device. In contrast with other conventional predicted GPS systems that forward large volumes of predicted orbits, synthetic ephemeris or synthetic almanac data, this method optimally reduces data transfer requirements to the client, and enables the client to locally synthesize its own predicted assistance data as needed. This method also supports seamless notification of real-time satellite integrity events and seamless integration of predicted assistance data with industry standard real-time assistance data.
Owner:RX NETWORKS INC
Distributed orbit modeling and propagation method for a predicted and real-time assisted GPS system
ActiveUS20080018527A1Easy to integrateNavigational calculation instrumentsRadio transmissionData setTime to first fix
A distributed orbit and propagation method for use in a predicted GPS or GNSS system, which includes a predicted GPS server (PGPS Server), a source of high accuracy orbit predictions (Orbit Server), a global reference network (GRN Server) providing real-time GPS or GNSS assistance data to the PGPS Server, a predicted GPS client (PGPS Client) running on a device equipped with a GPS or AGPS chipset. In response to requests from the PGPS Client, the PGPS Server produces and disseminates an initial seed dataset consisting of current satellite orbit state vectors and orbit propagation model coefficients. This seed dataset enables the PGPS Client to locally predict and propagate satellite orbits to a desired future time. This predictive assistance in turn helps accelerate Time To First Fix (TTFF), optimize position solution calculations and improve the sensitivity of the GPS chip present on, or coupled with, the device. In contrast with other conventional predicted GPS systems that forward large volumes of predicted orbits, synthetic ephemeris or synthetic almanac data, this method optimally reduces data transfer requirements to the client, and enables the client to locally synthesize its own predicted assistance data as needed. This method also supports seamless notification of real-time satellite integrity events and seamless integration of predicted assistance data with industry standard real-time assistance data.
Owner:RX NETWORKS INC
Method for setting multilayer satellite network system route
InactiveCN101299713AImprove effectivenessReduce transmission delayStar/tree networksRadio transmissionQuality of serviceNetworked system
The present invention relates to a method for setting multilayer satellite network system route, including steps of: 1. setting parameters for the network initialization; 2. fixing a time, solving satellite orbit parameters in the interval of time, calculating the location coordinates of the satellite and the length of the link between stars, and establishing a network topological structure; 3. calculating the load of link between stars of the multi-layer satellite network; 4. calculating the process and exchange time delay on stars according to the queuing theory; 5. searching source satellite and object satellite of each satellite layer; 6. selecting the satellite layer for transporting services according to the communication service instruction requirement and network states, and searching an optimum route according to routing algorithm. Relative to traditional stationary orbit satellite, the present invention has small transmission delay, and high validity. The system has advantages of more flexible routing, effective guaranty of service quality, multiple replaceable chain circuits, stronger survivability, a capacity of processing and exchanging on star, optical or microwave links between stars, and capability of providing wideband synthetic service for users in global scope.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
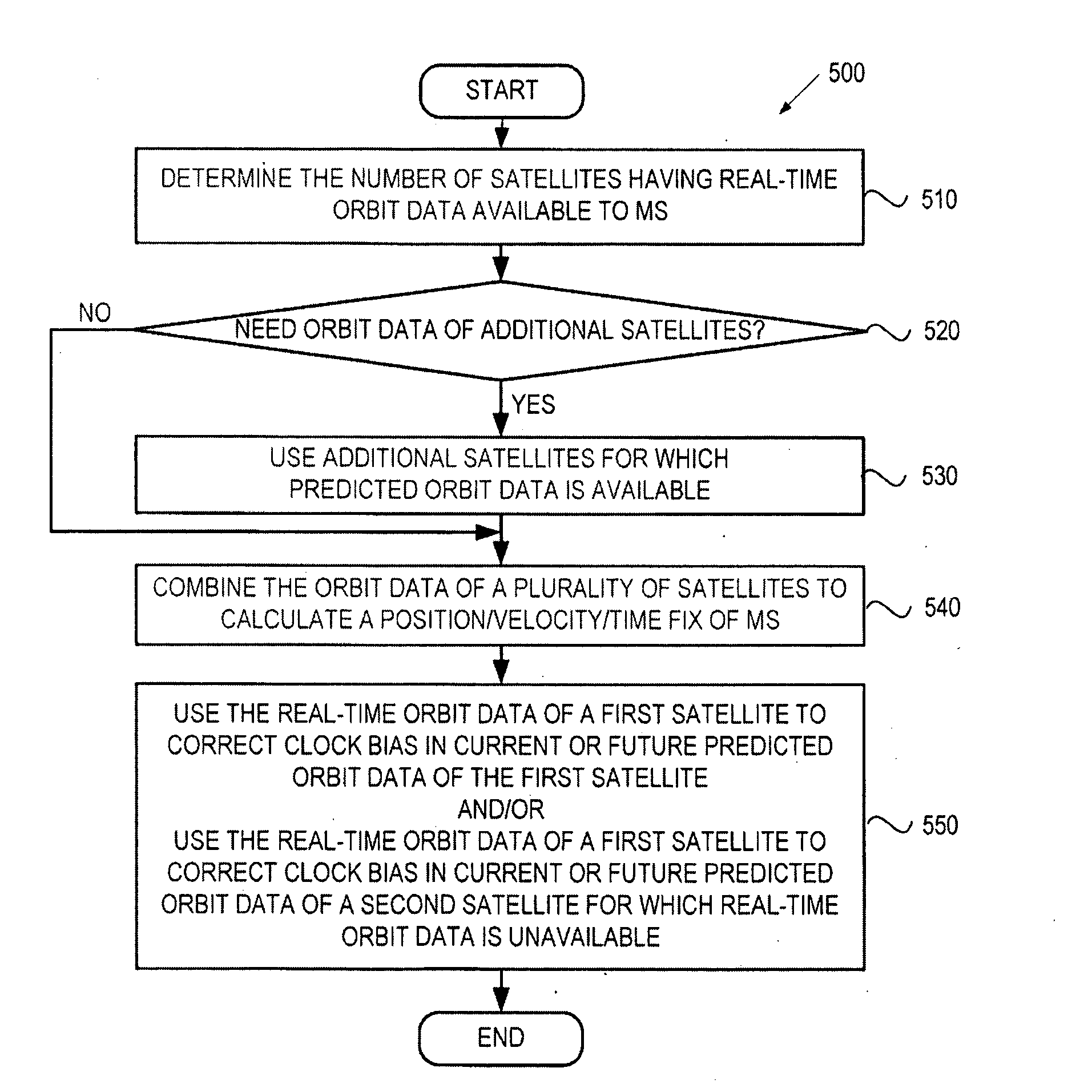
Method and apparatus for position determination with hybrid sps orbit data
InactiveUS20100194634A1Improves accuracy in fixImprove clock accuracyBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingMobile stationSatellite orbit
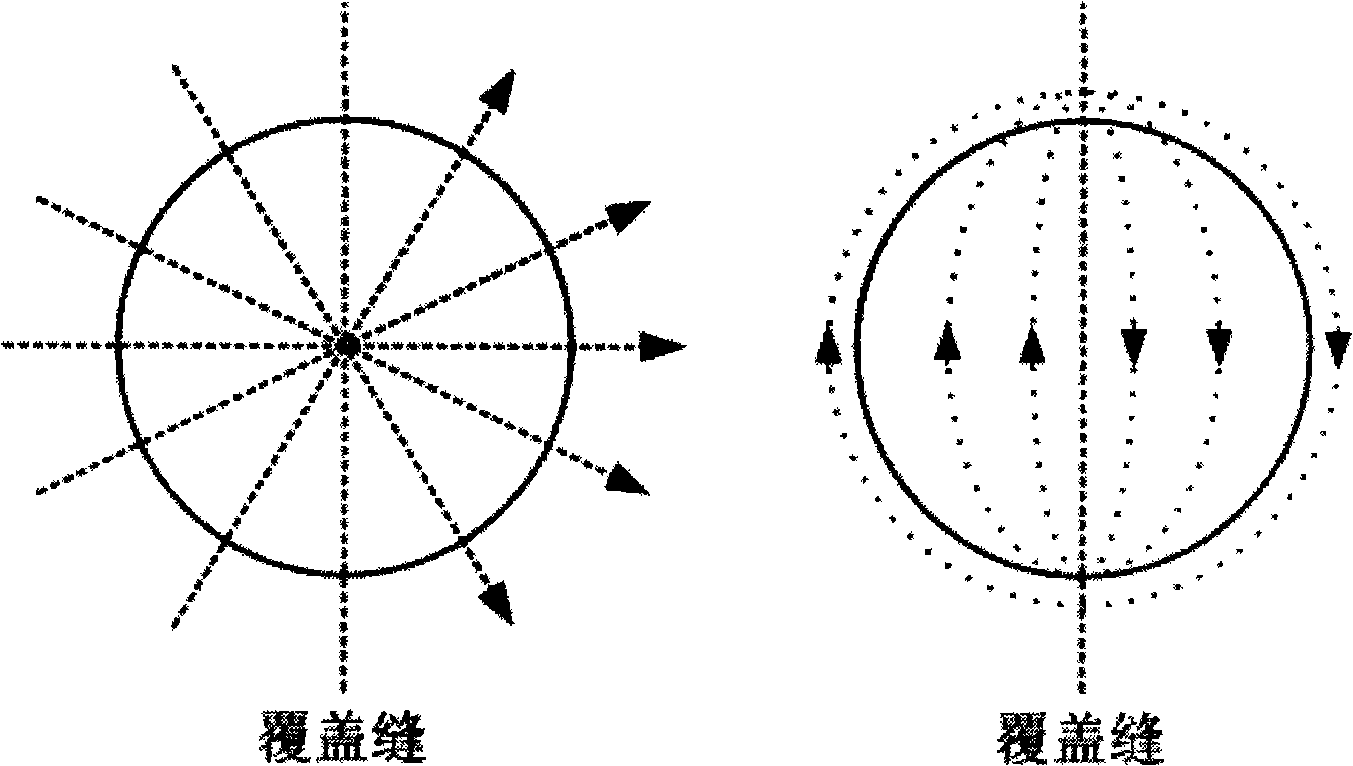
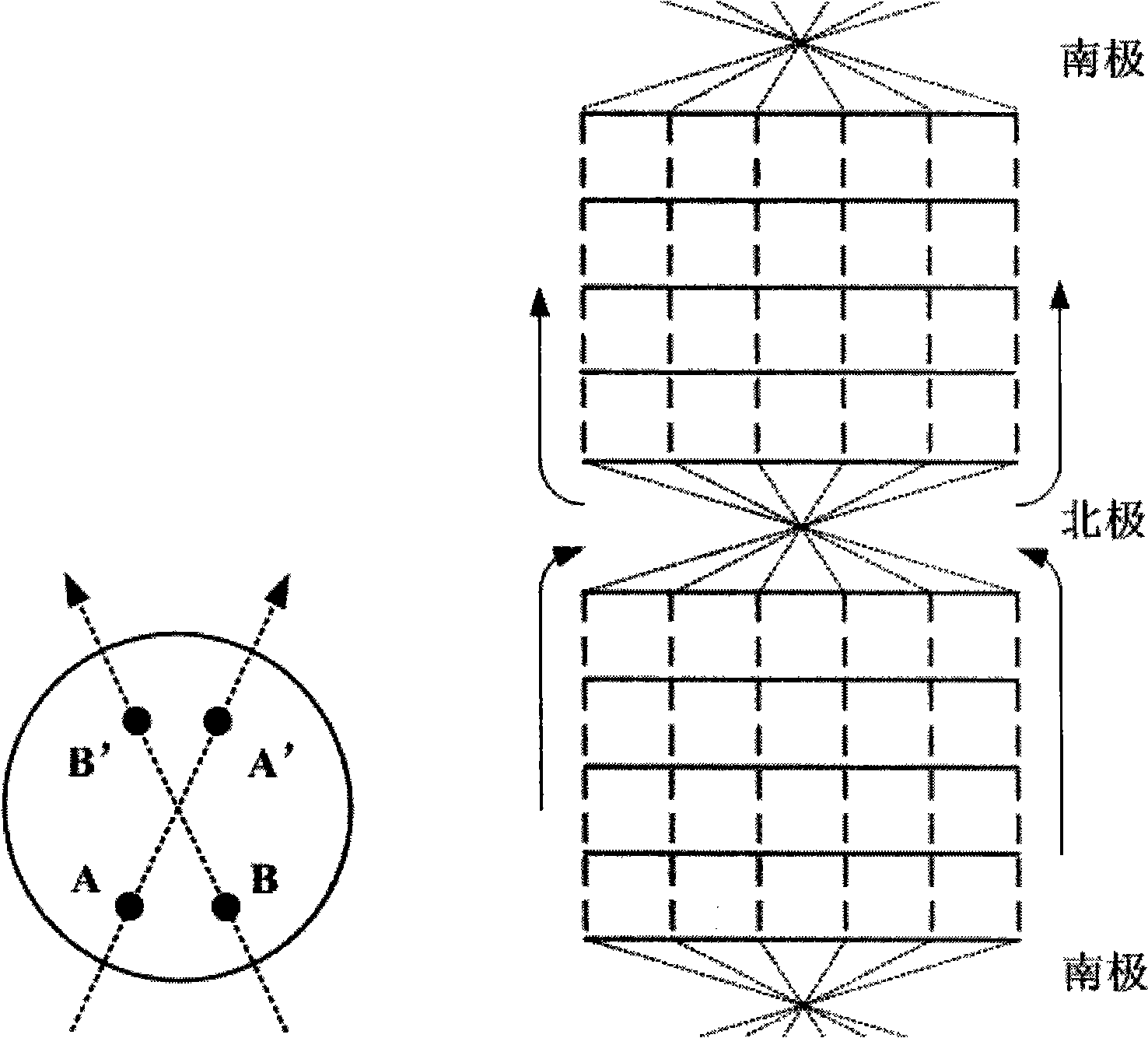
A method and system for a mobile station to determine its position (or velocity) and time using a hybrid combination of satellite orbit data. In one aspect, the mobile station combines predicted orbit data from one satellite and real-time orbit data from another satellite in the determination of a fix. The combination can be made to the satellites in the same or different satellite systems. The mobile station can use the real-time orbit data of a satellite at one time period and the predicted orbit data of the same satellite at another time period. In another aspect, the mobile station can use the real-time orbit data to correct the clock bias in the predicted orbit data. The correction to the clock bias can be made to the same satellite that provides the real-time orbit data, or to a different satellite in the same or in another satellite system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus in positioning without broadcast ephemeris
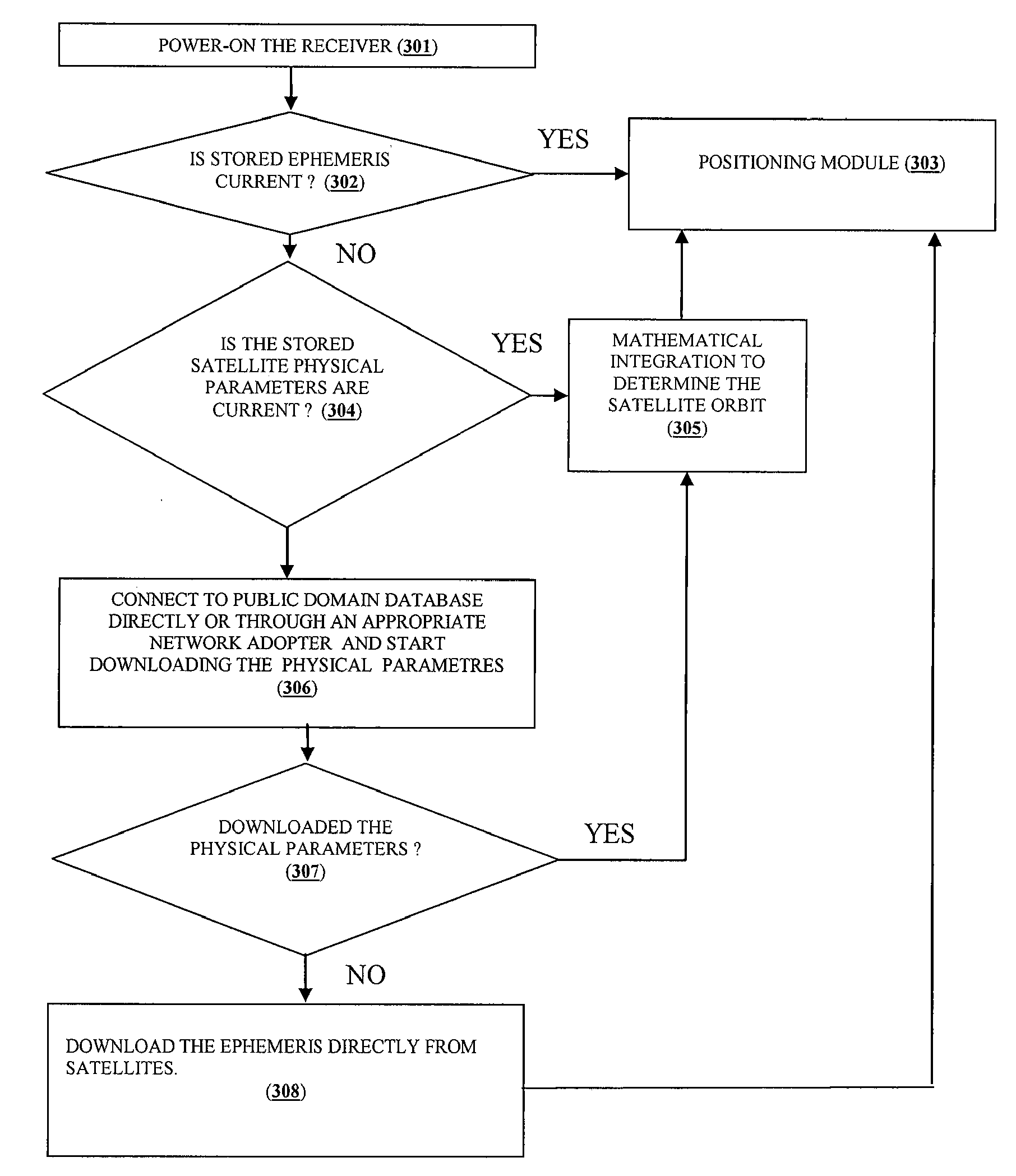
ActiveUS20080270026A1Reduce the amount of calculationGood receiver position accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationEphemerisSatellite orbit
Provided herein are methods and system for enabling a navigation receiver to generate receiver specific satellite orbital models based on relatively small sets of parameters obtained from a server. In an embodiment, a set of parameters for a satellite includes a force parameter (e.g., solar radiation pressure), initial condition parameters (e.g., satellite position and velocity at a time instance) and time correction coefficients, which the receiver uses in a numerical integration to predict the position of the satellite. The set of parameters needed for the integration is small compared to current methods which require transmission of a complete set of ephemeris and other parameters for each satellite. Since the set of parameters is relatively small, it requires less communication resources to transmit compared to current methods. Further, the integration based on the small set of parameters enables the receiver to predict satellite orbits with low computational load.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
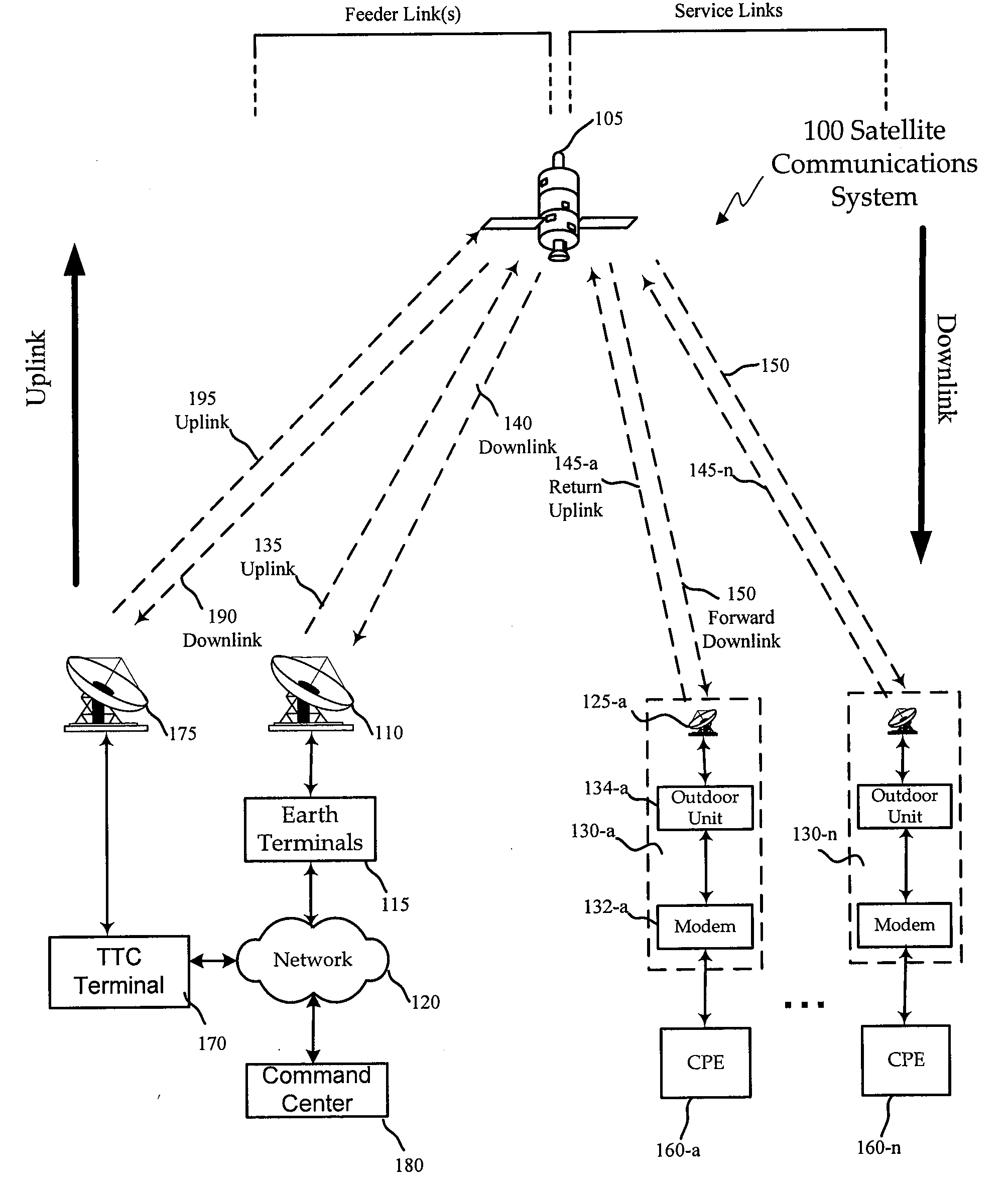
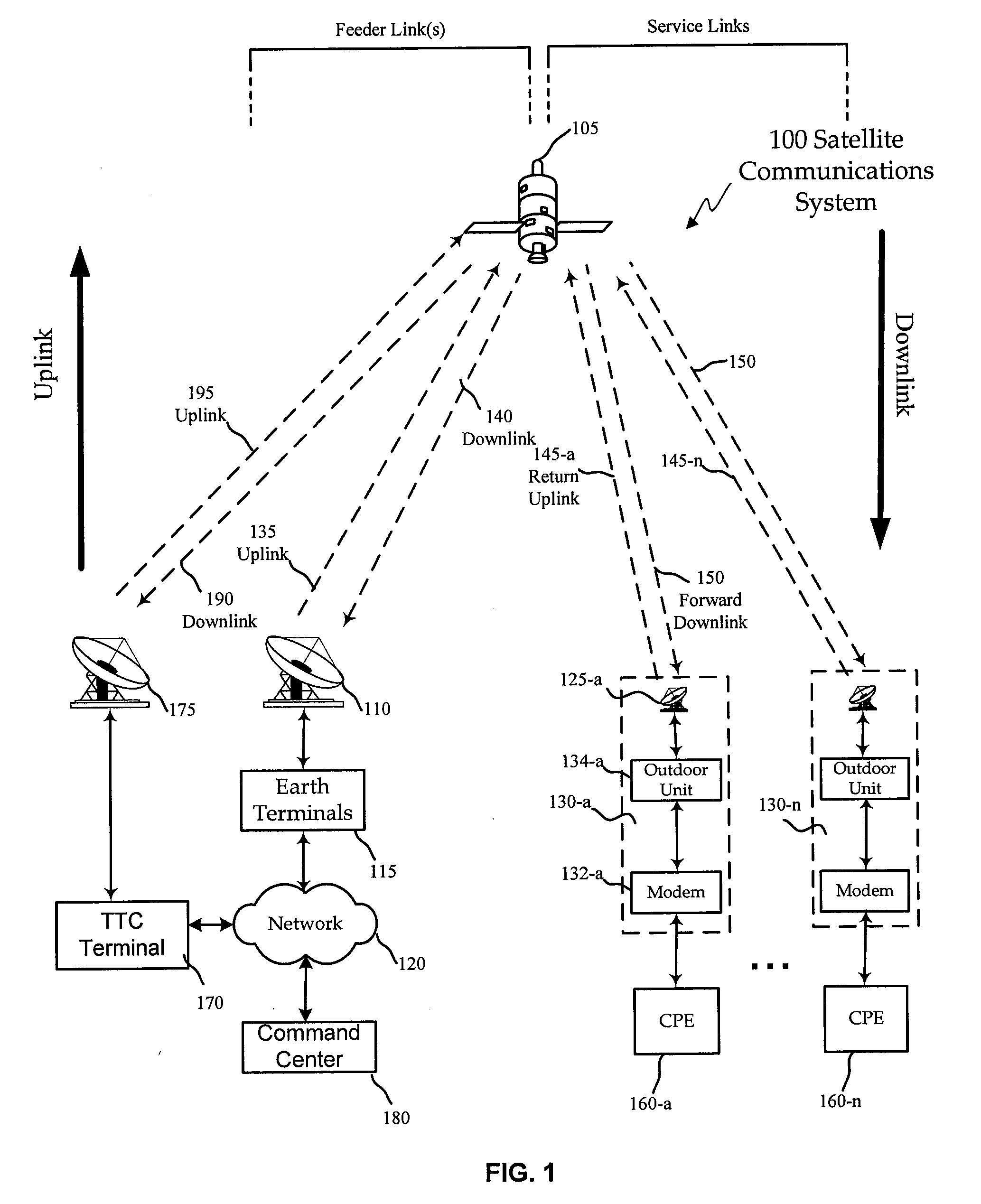
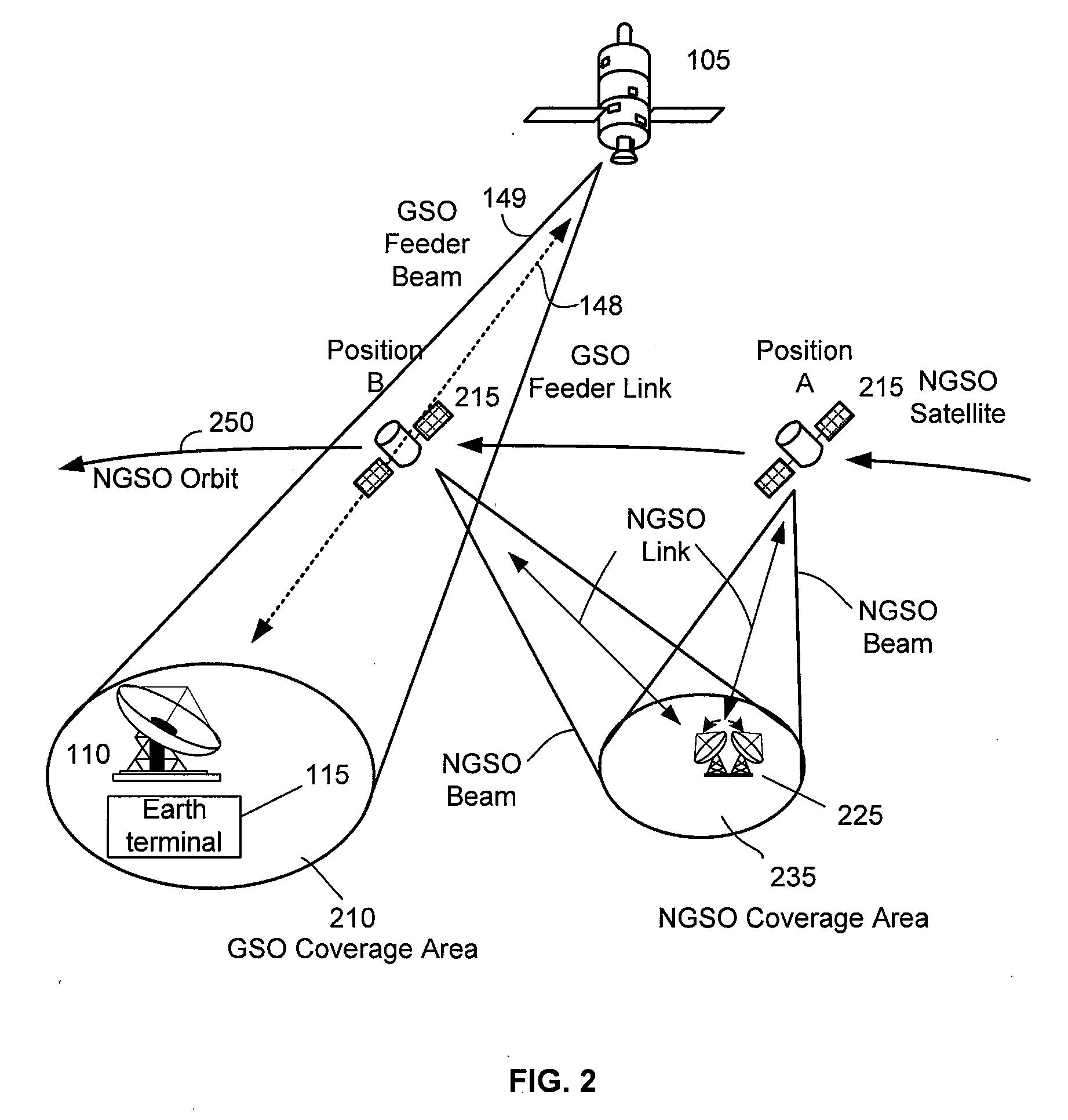
Non-interfering utilization of non-geostationary satellite frequency band for geostationary satellite communication
ActiveUS20090093213A1Guaranteed continuous useActive radio relay systemsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A method and system of utilizing non-geostationary satellite orbit (NGSO) frequency spectrum in a geostationary satellite orbit (GSO) satellite communication system in a non-interfering manner. The GSO satellite communication system comprises an Earth terminal to transmit signals to a GSO satellite using a GSO frequency spectrum, the Earth terminal further operable to transmit signals to the GSO satellite using an extended frequency spectrum, the extended frequency band including the GSO frequency spectrum and a non-geostationary (NGSO) frequency spectrum; a command center operative to instruct the Earth terminal to transmit signals to the GSO satellite using the GSO frequency spectrum, when an NGSO satellite is expected to be in-line with respect to the Earth terminal and the GSO satellite; and wherein the command center is further operative to instruct the Earth terminal to transmit signals to the GSO satellite using the extended frequency spectrum, when no NGSO satellite is expected to be in-line with respect to the Earth terminal and the GSO satellite.
Owner:VIASAT INC
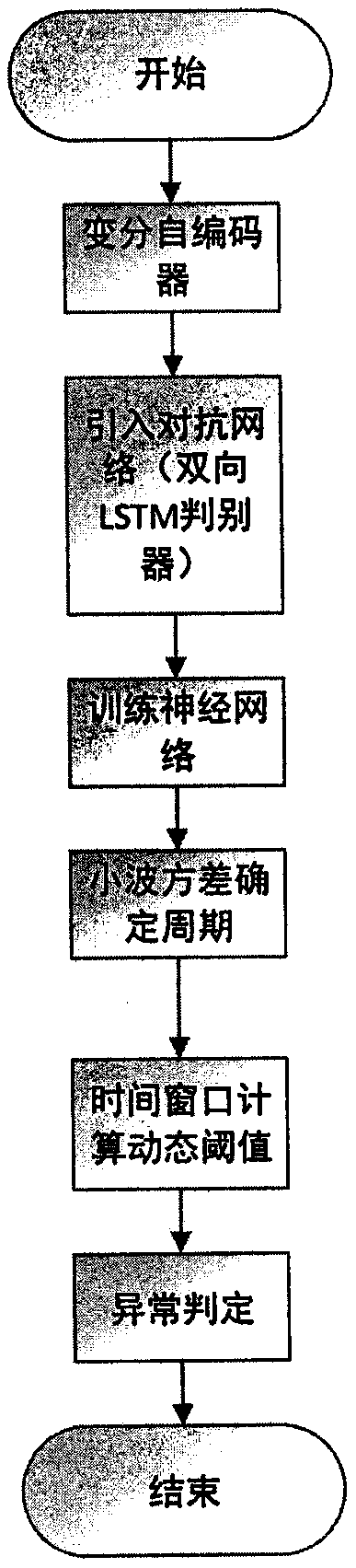
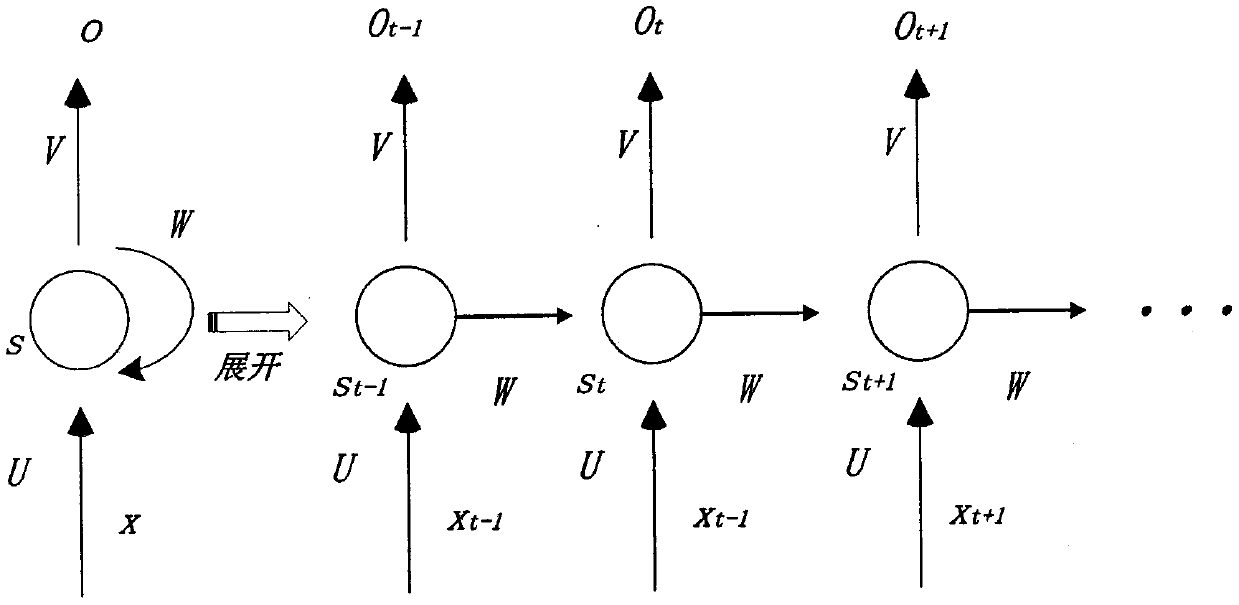
A satellite anomaly detection method of an adversarial network autoencoder
ActiveCN109948117AAnomaly detection decreasedImprove accuracyRadio transmissionNeural architecturesShort-term memoryOriginal data
The invention discloses an abnormity detection method for satellite telemetry data through an adversarial network autoencoder, and the method comprises the steps: breaking the limitation of a traditional empirical model, and employing a pure data driving model; on the basis of a variational autoencoder, introducing a confrontation network idea, using a bidirectional LSTM (Long Short Term Memory) (Long-short term memory network) as a discriminator, and judging whether satellite telemetry data is abnormal or not by using errors of reconstructed data and original data; aiming at the redundancy problem of a satellite sensor, the conventional situation is broken through, and a Markov distance is used for measuring a reconstruction error. In combination with periodicity of satellite orbit operation, a dynamic threshold determination method based on a periodic time window is provided. The method has the advantages that pure data driving is adopted, expert experience is not needed, and the method can be suitable for various occasions; By combining the respective advantages of the variational auto-encoder and the generative adversarial network, the proposed network has the characteristics of high training speed and relatively easy convergence; eliminating redundant data influence between satellite telemetry data by adopting a Mahalanobis distance. According to the periodicity of the satellite, the dynamic threshold method based on the periodic time window is provided, and the misjudgment rate is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Time shifted PN codes for CW LiDAR, radar, and sonar
A continuous wave Light Detection and Ranging (CW LiDAR) system utilizes two or more laser frequencies and time or range shifted pseudorandom noise (PN) codes to discriminate between the laser frequencies. The performance of these codes can be improved by subtracting out the bias before processing. The CW LiDAR system may be mounted to an artificial satellite orbiting the earth, and the relative strength of the return signal for each frequency can be utilized to determine the concentration of selected gases or other substances in the atmosphere.
Owner:NASA
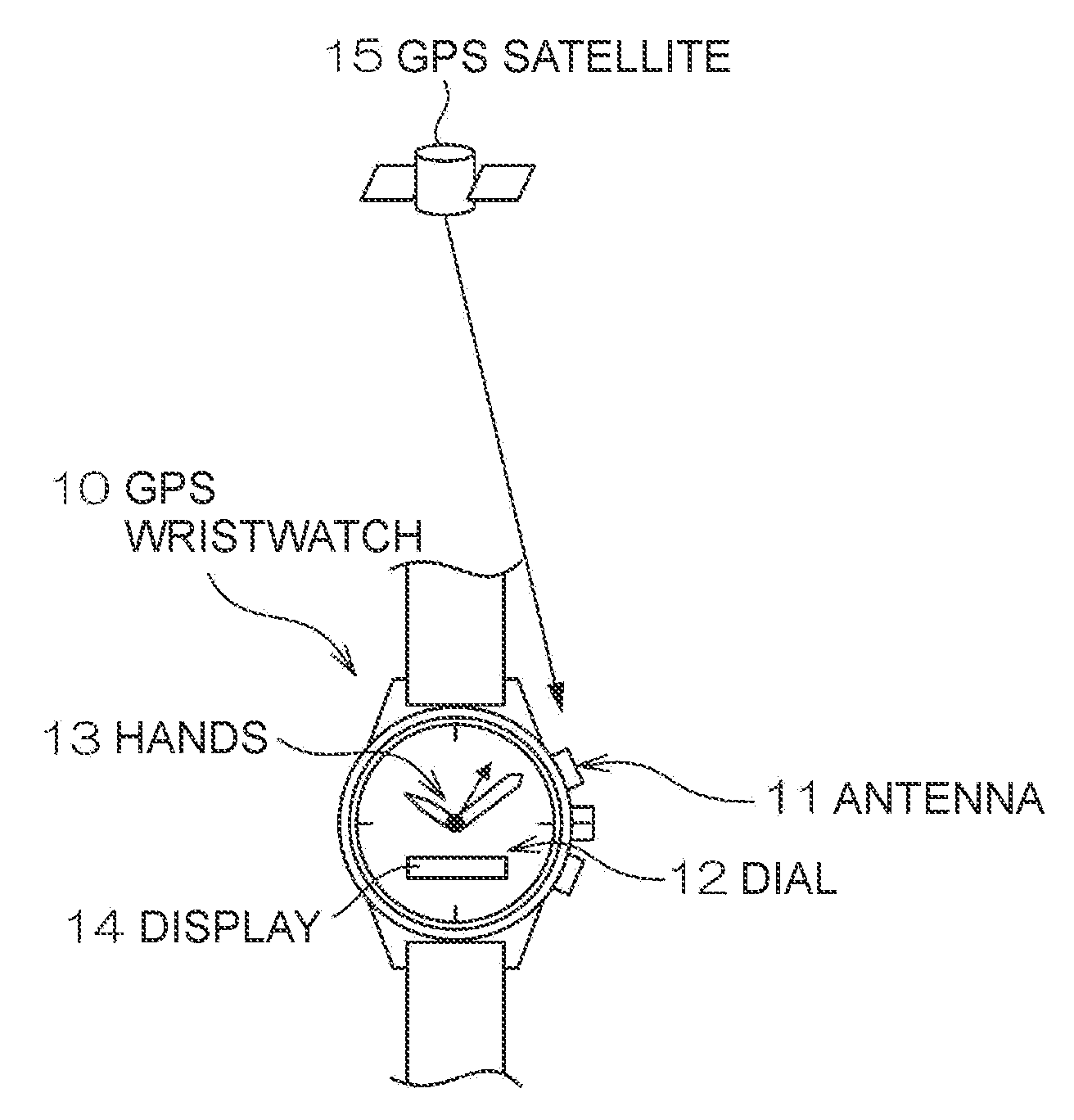
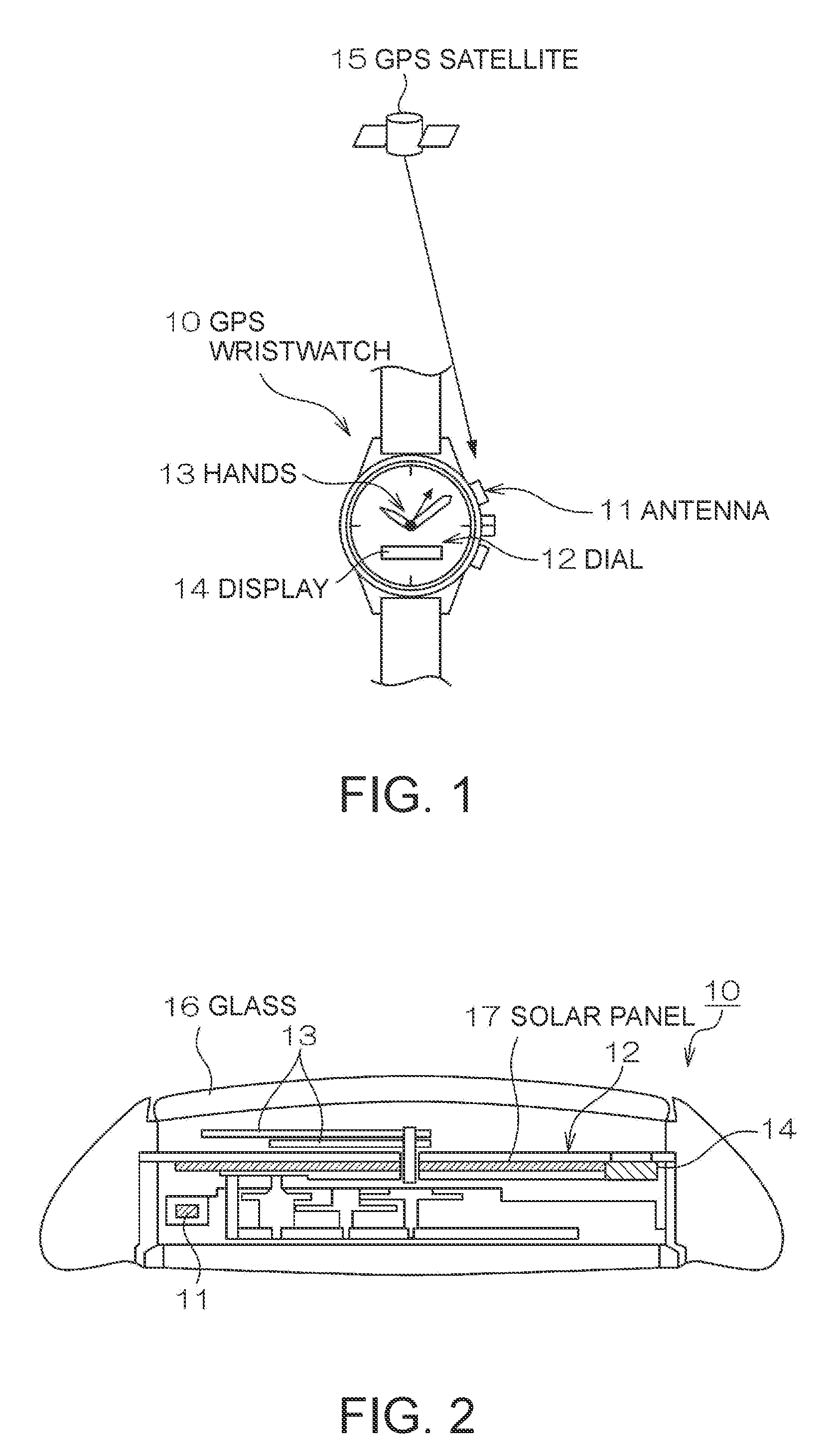
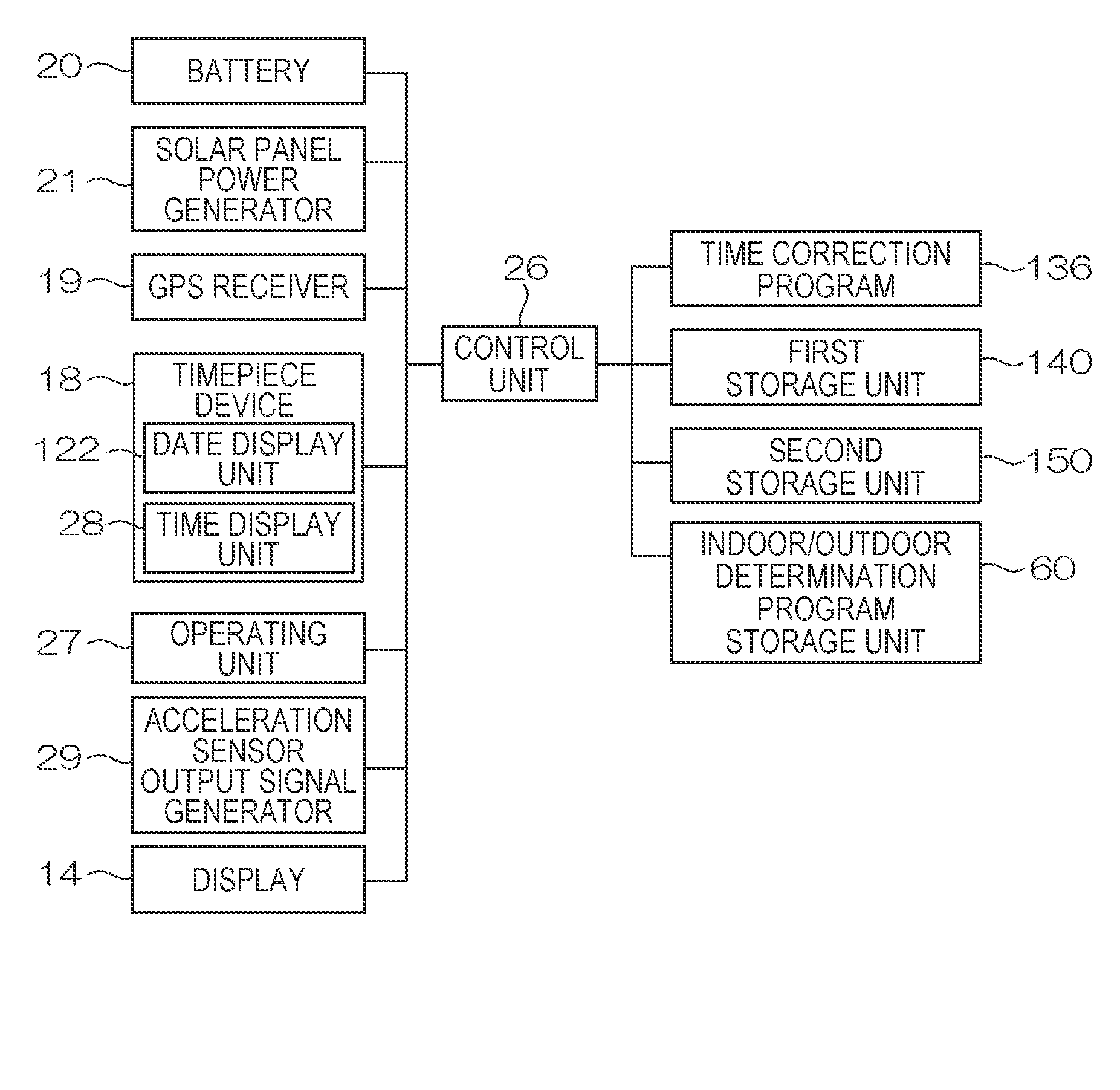
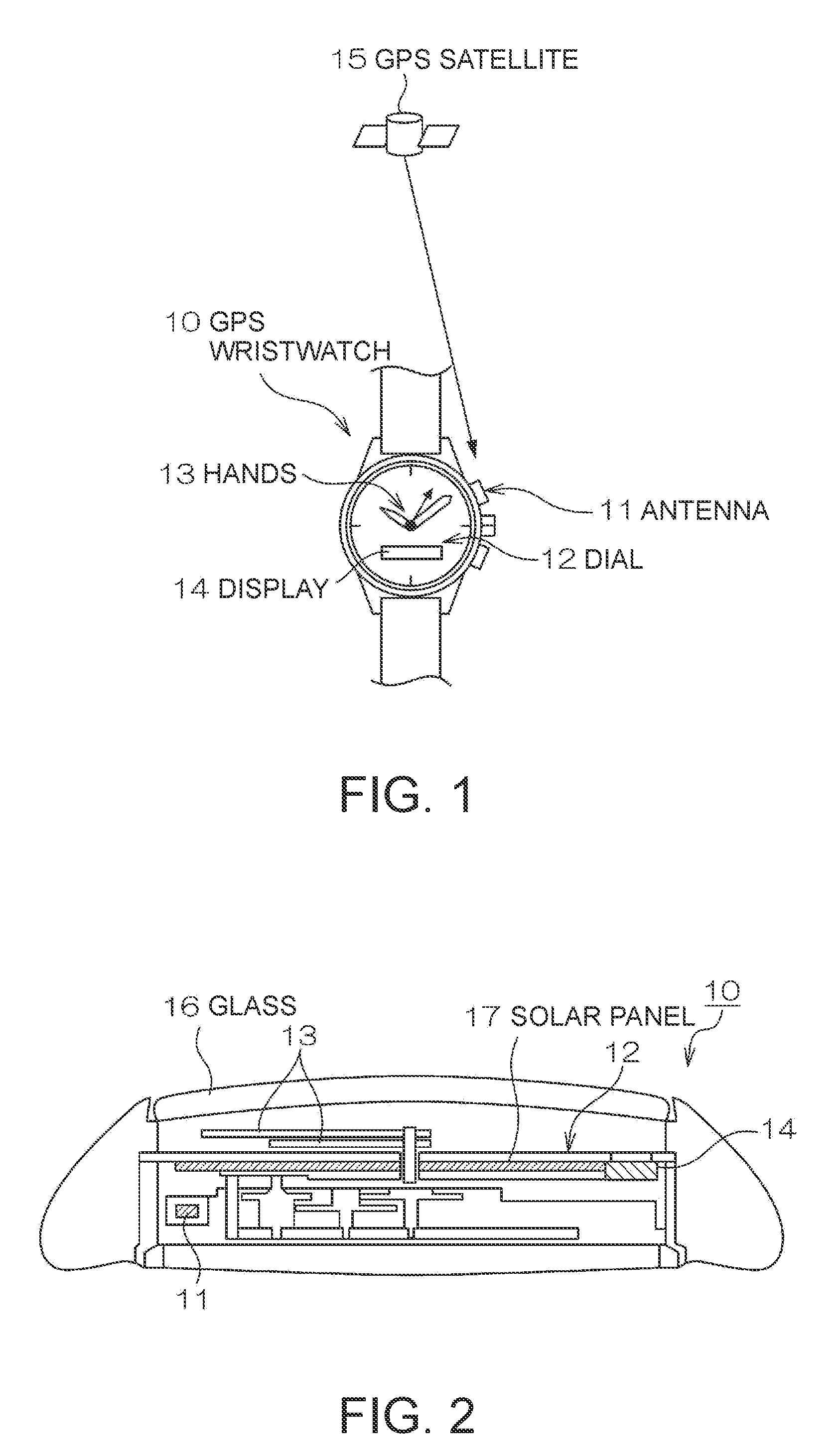
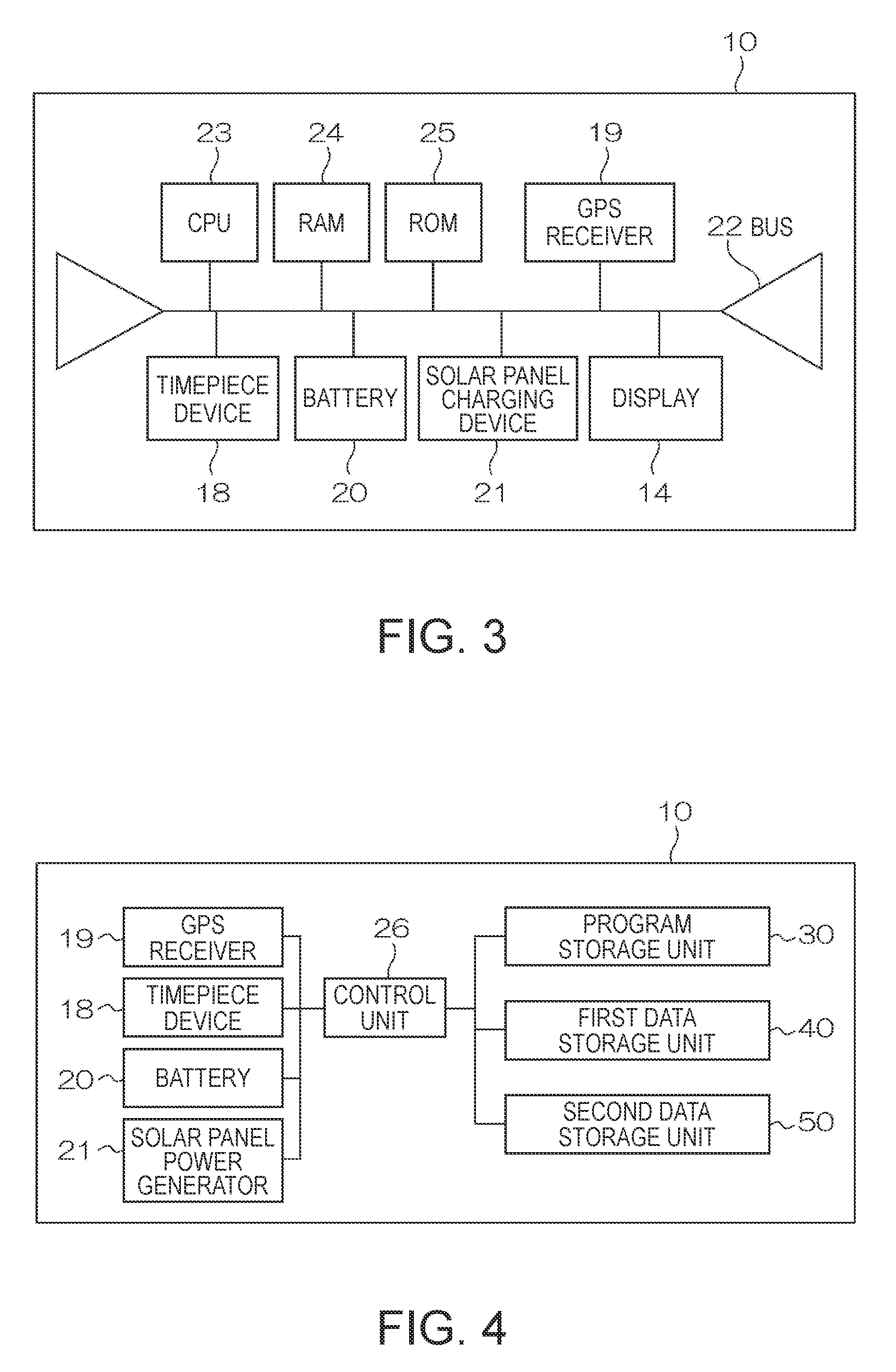
Electronic Device and Time Adjustment Method
InactiveUS20080030403A1Reduce consumptionThermometer detailsPV power plantsTime informationSatellite orbit
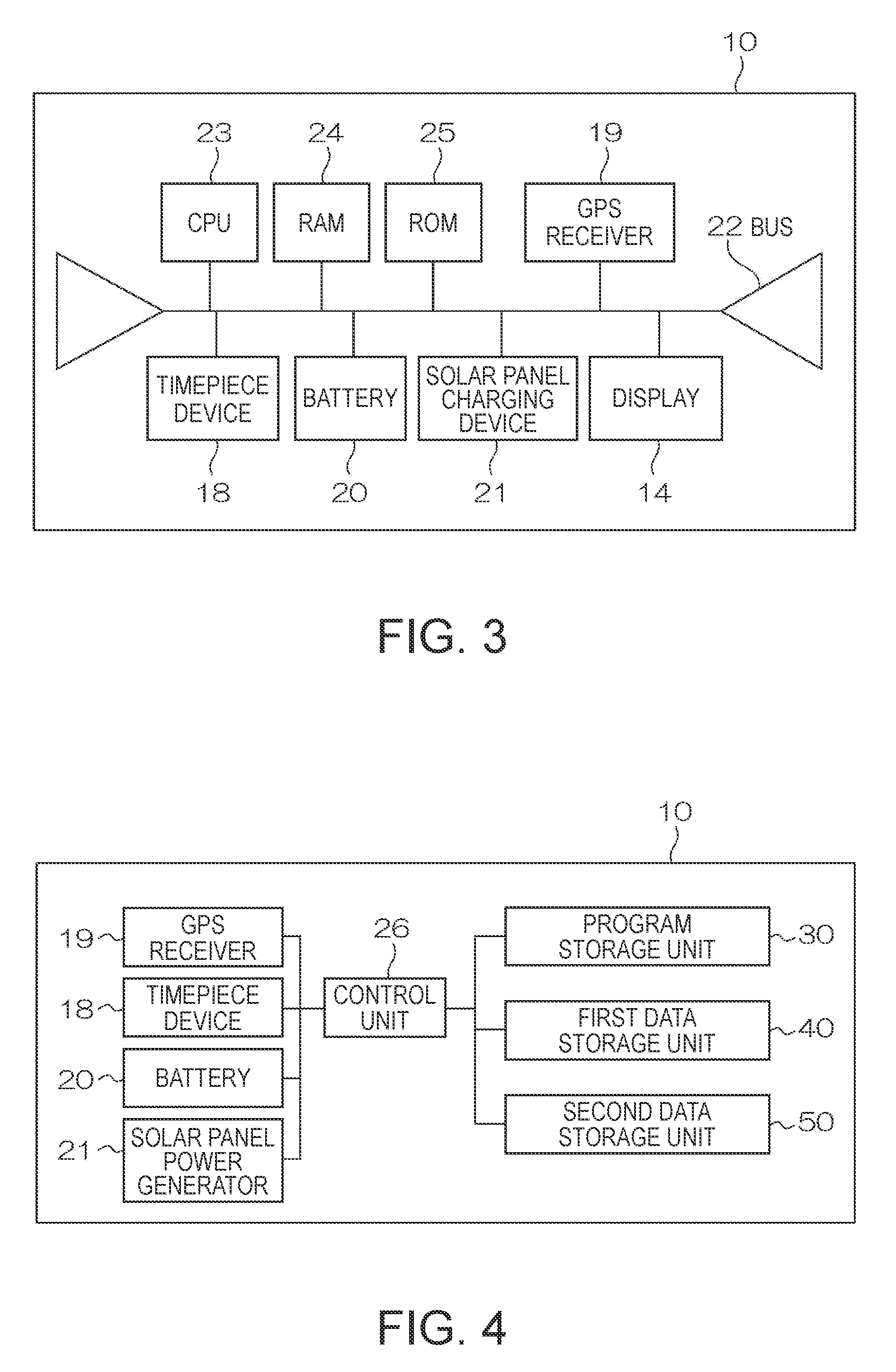
An electronic device having a reception unit that receives satellite signals from positioning information satellites orbiting the Earth; a time information generating unit that generates time information; a time correction information storage unit that stores time correction information for correcting the time information; a time correction information generating unit that generates the time correction information based on the satellite signals; an environmental information acquisition unit that gets information about the reception unit environment; a reception environment information generating unit that generates reception environment information for the reception unit based on the environment information; and a positioning information satellite selection unit that selects the positioning information satellite from which signals are to be received by the reception unit based on the reception environment information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
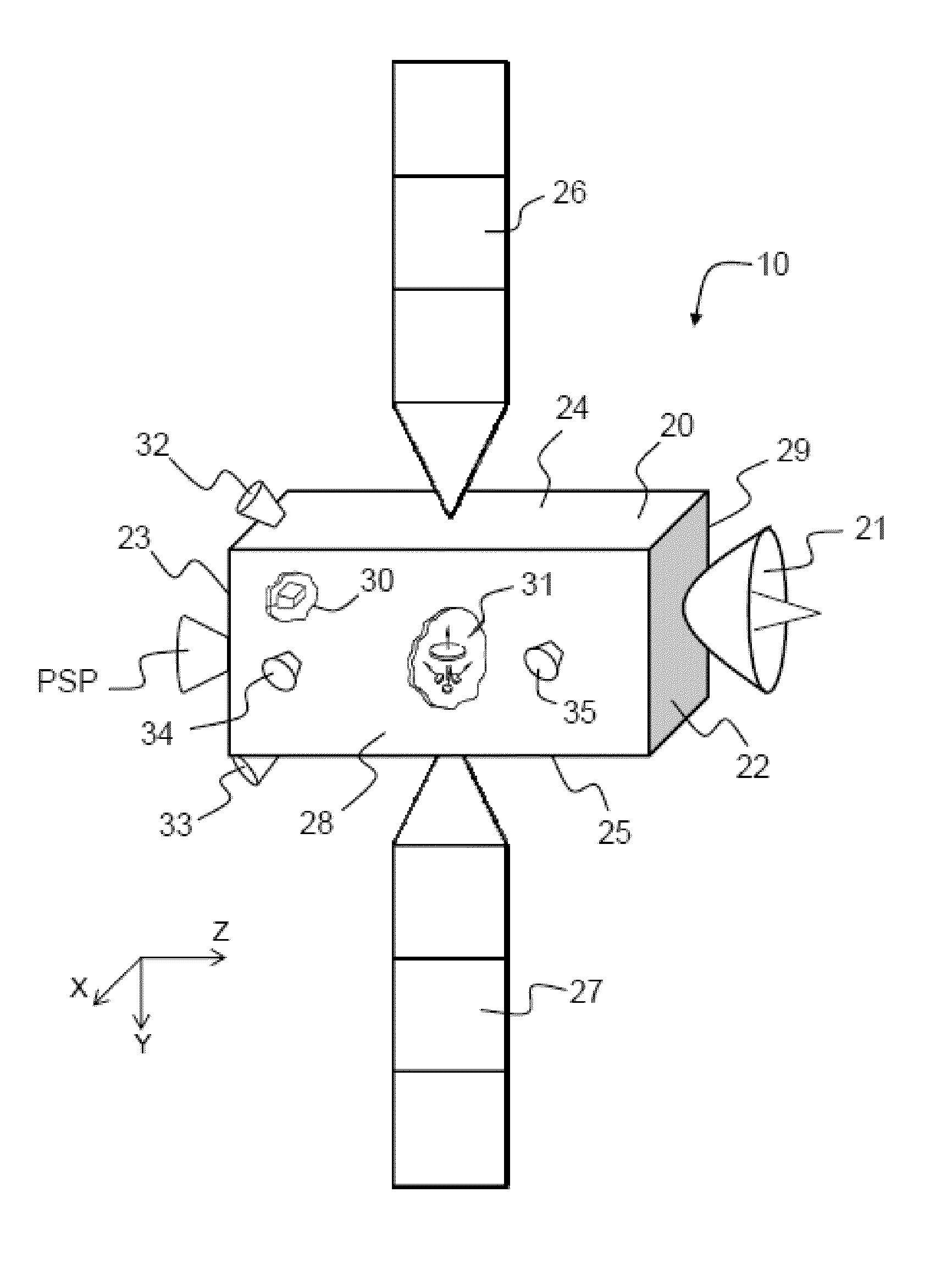
Propulsion System for Satellite Orbit Control and Attitude Control
A propulsion system for the orbit control of a satellite with terrestrial orbit having an angular momentum accumulation capacity comprises a propulsion unit able to deliver a force along an axis F having a component perpendicular to the orbit, and a motorized mechanism connected on the one hand to the propulsion unit and on the other hand to a structure of the satellite, the motorized mechanism being able to displace the propulsion unit along an axis V parallel to the velocity of the satellite, and able to orient the propulsion unit so as to make it possible to control: a component of the force along the axis V, for orbit control, an amplitude and a direction of couple in a plane perpendicular to the axis F, for control of the angular momentum.
Owner:THALES SA
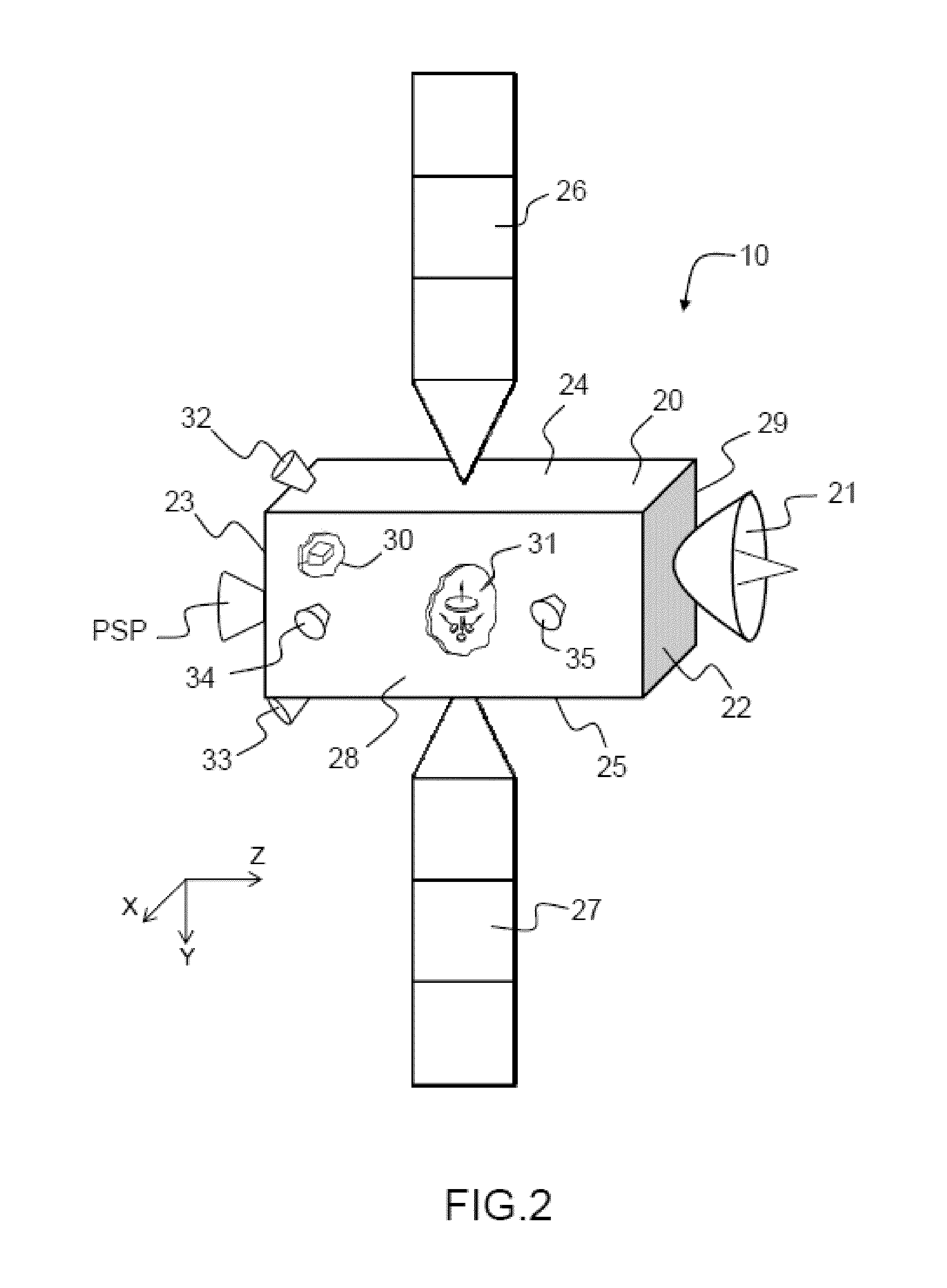
Propulsion system in two modules for satellite orbit control and attitude control
ActiveUS20140361123A1Cosmonautic propulsion system apparatusArtificial satellitesAttitude controlSatellite orbit
A propulsion system for the orbit control of a satellite in Earth orbit driven at a rate of displacement along an axis V tangential to the orbit comprises two propulsion modules, fixed to the satellite, and facing one another relative to the plane of the orbit, each of the propulsion modules comprising, in succession: a motorized rotation link about an axis parallel to the axis V; an offset arm; and a plate supporting two thrusters, suitable for delivering a thrust on an axis, arranged on the plate on either side of a plane P at right angles to the axis V passing through a centre of mass of the satellite; each of the two thrusters being oriented in such a way that the thrust axes of the two thrusters are parallel to one another and at right angles to the axis V.
Owner:THALES SA
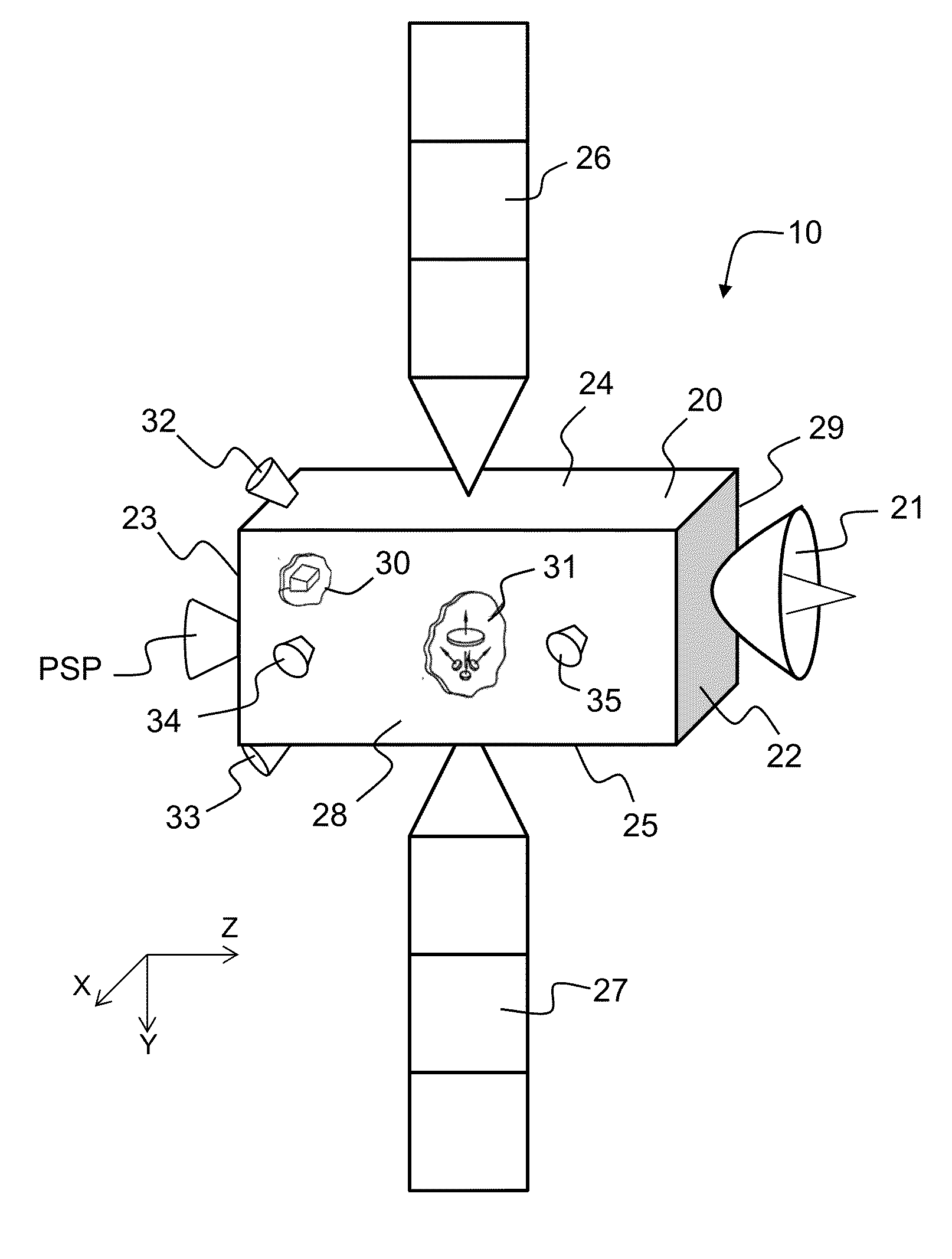
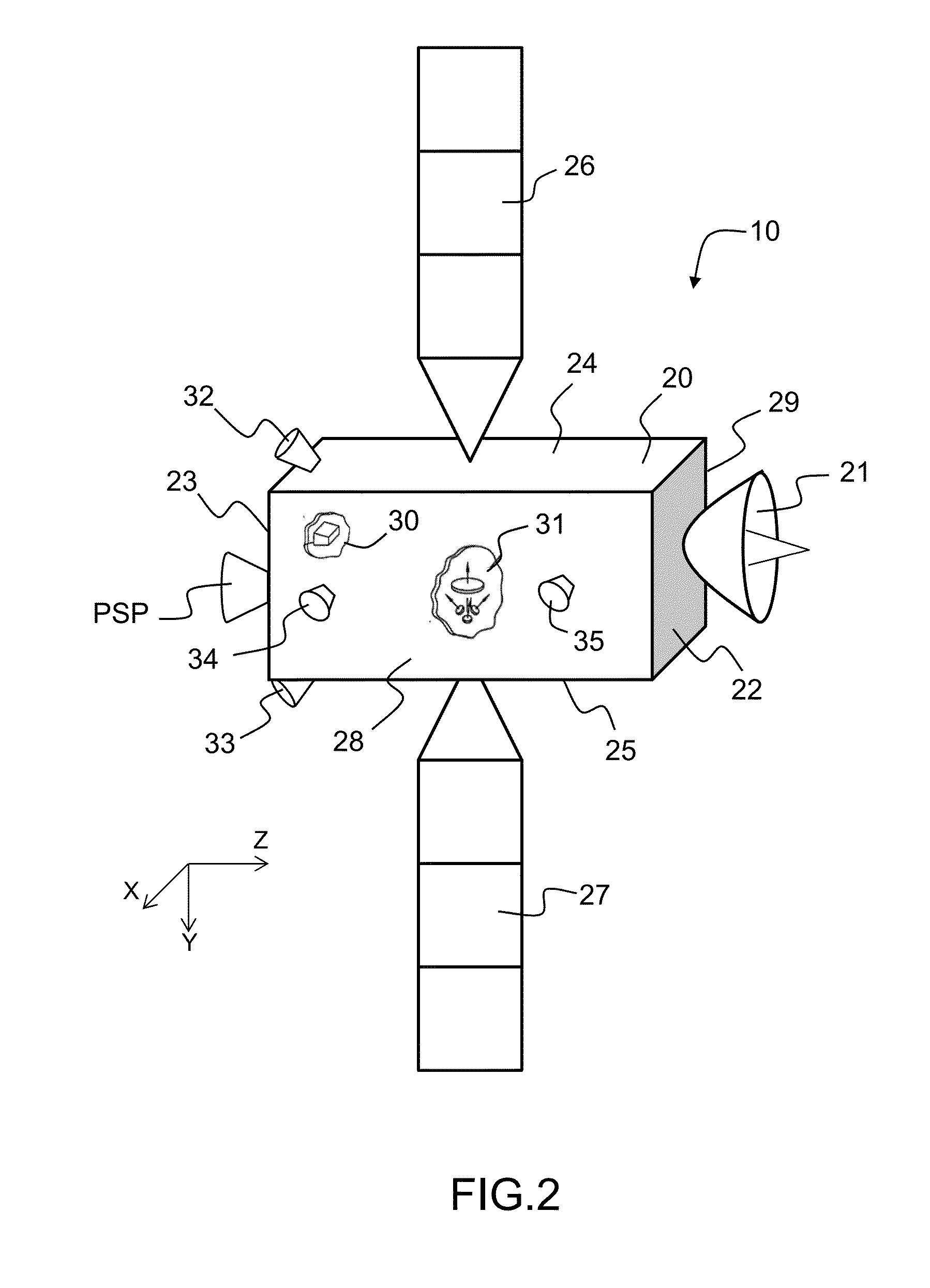
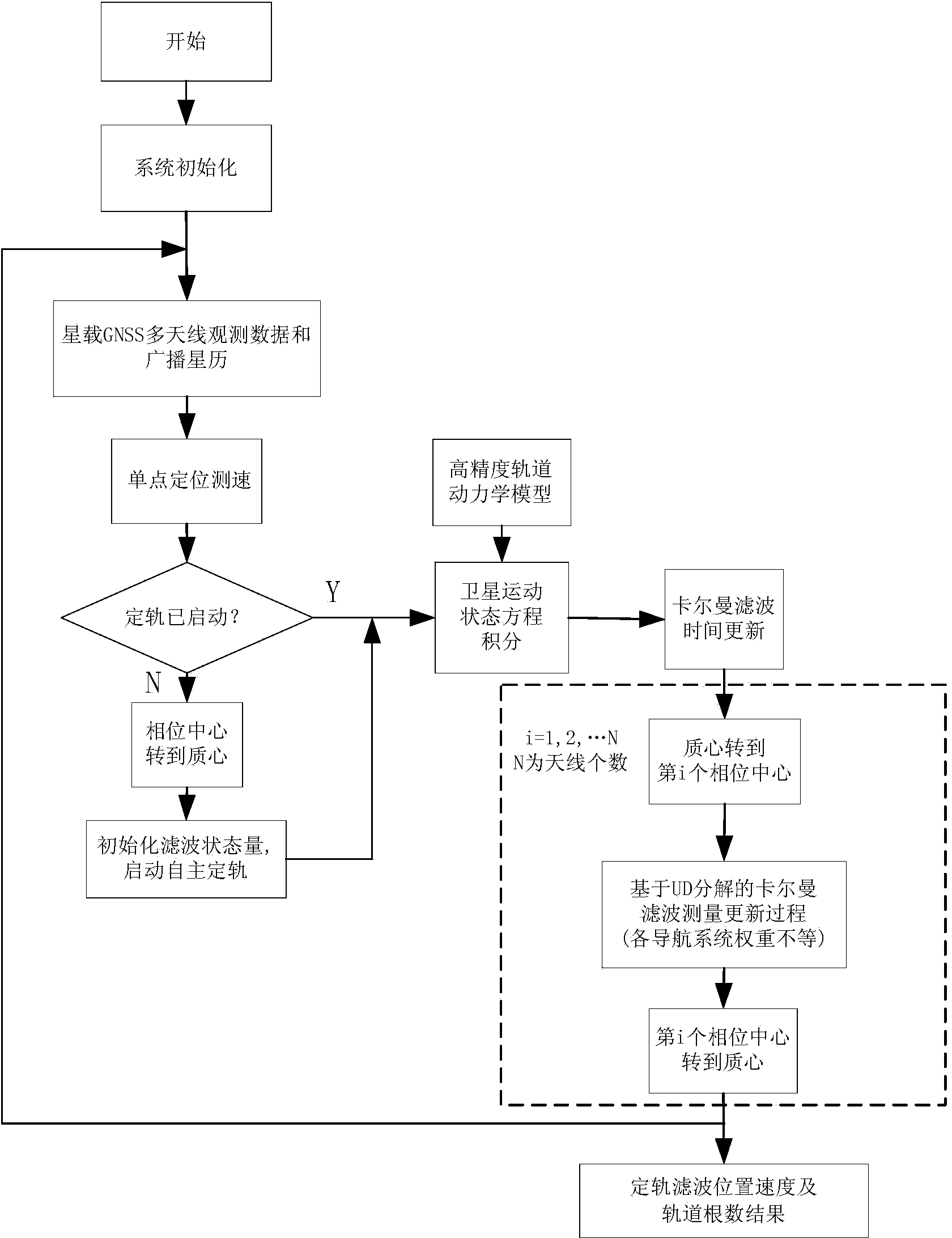
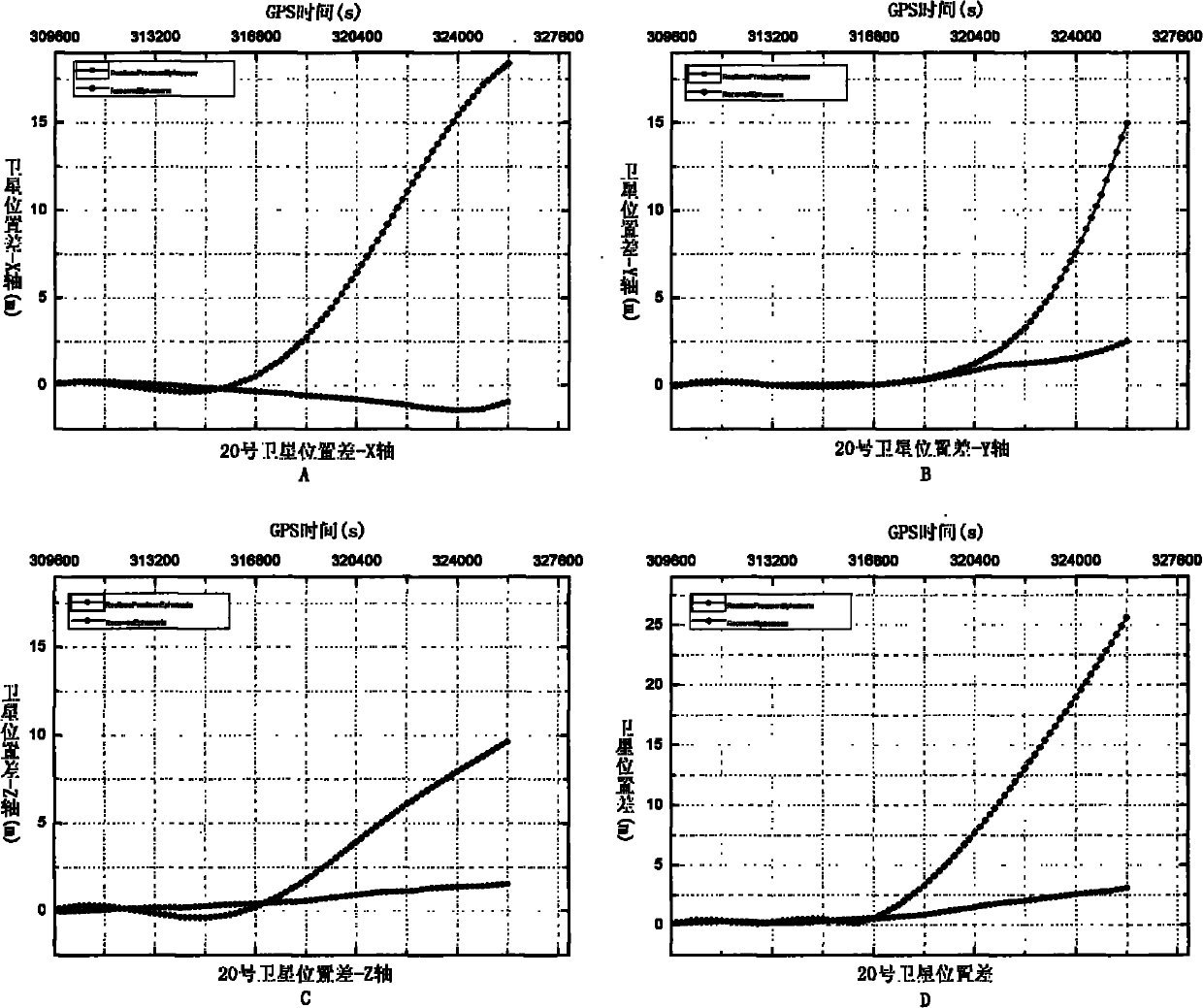
Satellite autonomous orbit determination method based on satellite-borne GNSS multiple antennas
ActiveCN103675861AExcellent data fusion resultsImprove the accuracy of orbit determinationInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteKaiman filter
A satellite autonomous orbit determination method based on satellite-borne GNSS multiple antennas. According to the method, a Kalman filter is extended; multiple GNSS antennas measured pseudorange observation values are made full use of to carry out real-time filtering correction of an orbit prediction value using a high precision mechanical model; and high precision satellite orbit information is obtained. According to the invention, the problems of the high precision orbit determination in a complex posture maneuver can be solved. In the invention, the orbit determination result is high in precision, good in stability, and highly real-time, can meet the orbit determination demand of the low orbit satellite and high precision satellite, can be widely applied to the high precision orbit determination of the space station, high resolution earth observation satellite and other space missions, and has a wide promotion and application prospect.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Image motion compensation method for space optical remote sensor
InactiveCN101825475ASolve the positioning problemImprove calculation accuracyPicture taking arrangementsImage motionSatellite orbit
The present invention provides an image motion compensation method for a space optical remote sensor, relating to an image motion compensation method and solving the problem that the current image motion velocity vector calculation method used in image motion compensation cannot satisfy complex imaging tasks and the calculation result is not accurate. The process of the image motion compensation method is as follows: creating five coordinate systems starting from ground targets to image points, transferring the coordinates for a plurality of times according to the rotation and translation principles among vectors, describing the positions of the targets and the image points in the camera coordinate systems, obtaining the image motion velocity vector calculation formula and the calculation method when the satellite forms images of the targets, then obtaining the image motion velocity vector used in the image motion compensation of the space optical remote sensor. The image motion compensation method overcomes the deficiency in the prior art, dependently calculates the target positions needed in the image motion velocity vector calculation and integrally considers the orbit and attitude parameters, besides. The image motion compensation method is suitable for complex imaging tasks and general satellite orbit, and is used in the fields such as atmospheric environment monitoring, resources exploration, disaster prevention and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
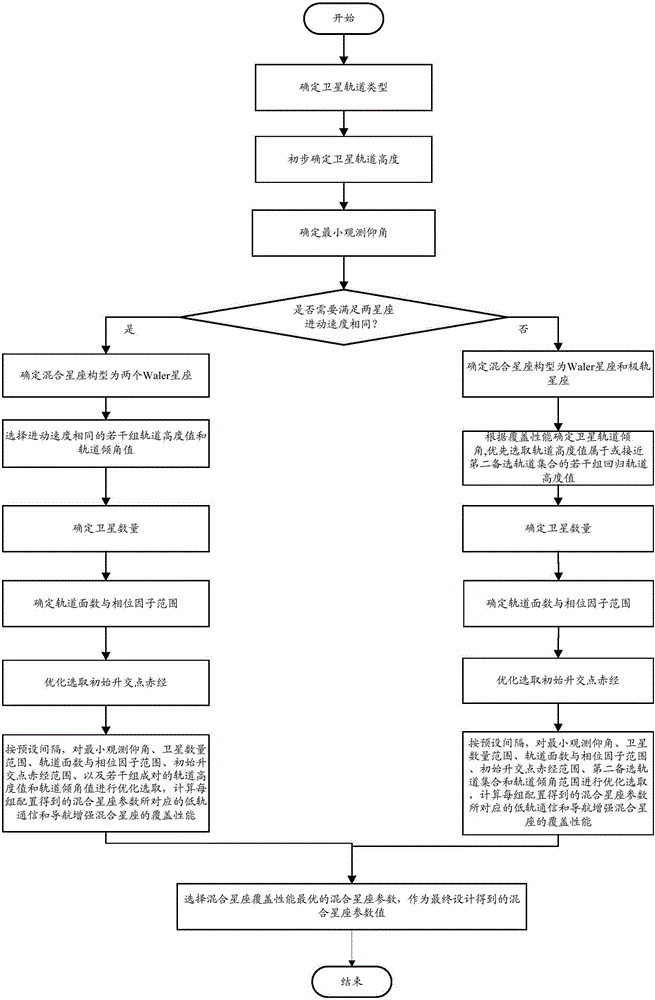
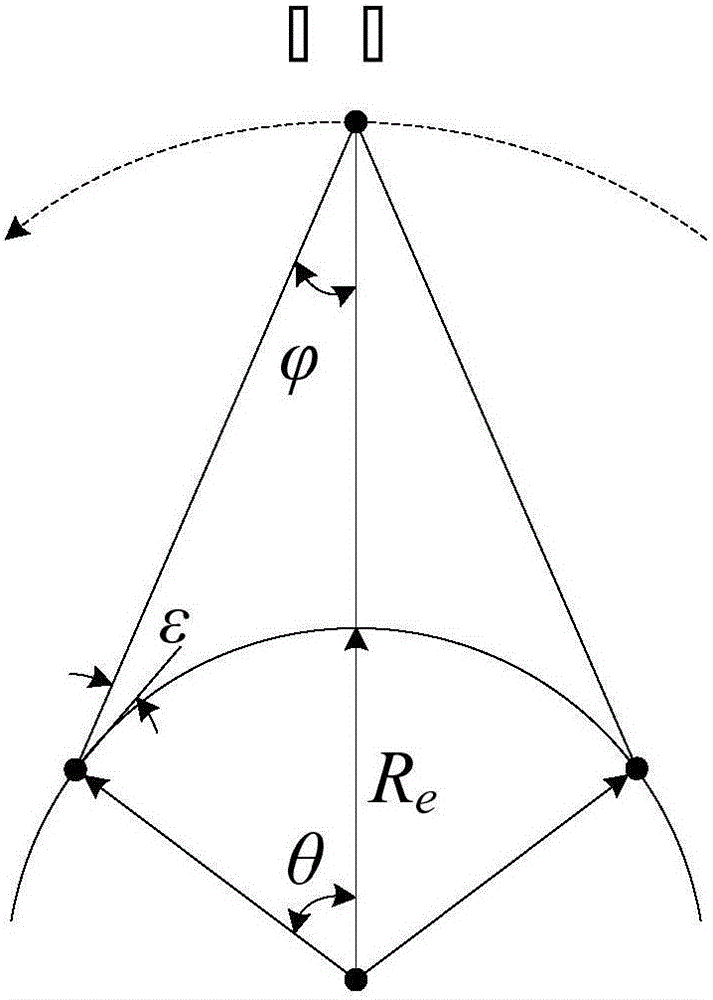
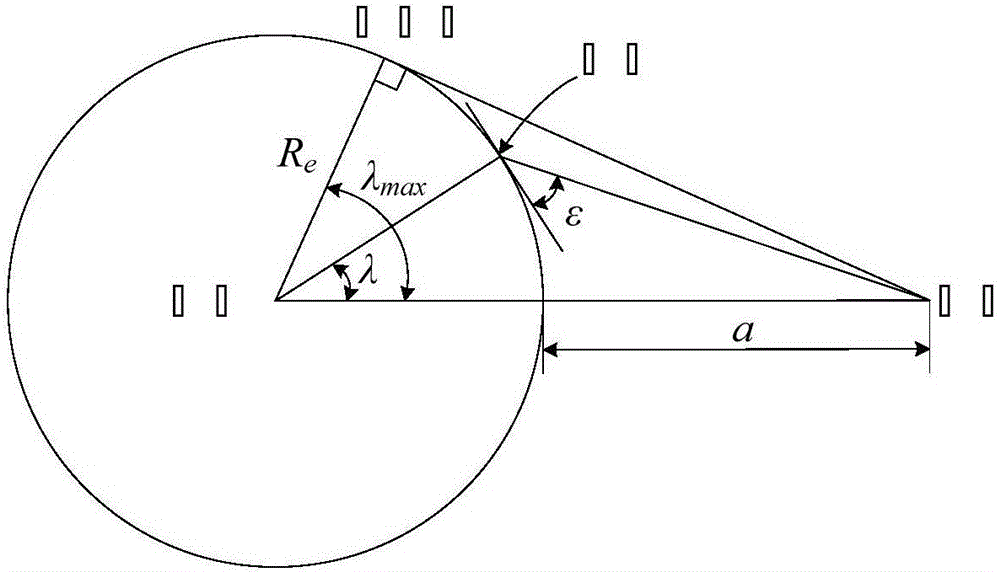
Optimization design method of low-orbit communication and navigation enhancement mixed constellation
ActiveCN106249253AImprove compatibilityFacilitate communicationRadio transmissionSatellite radio beaconingElevation angleIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
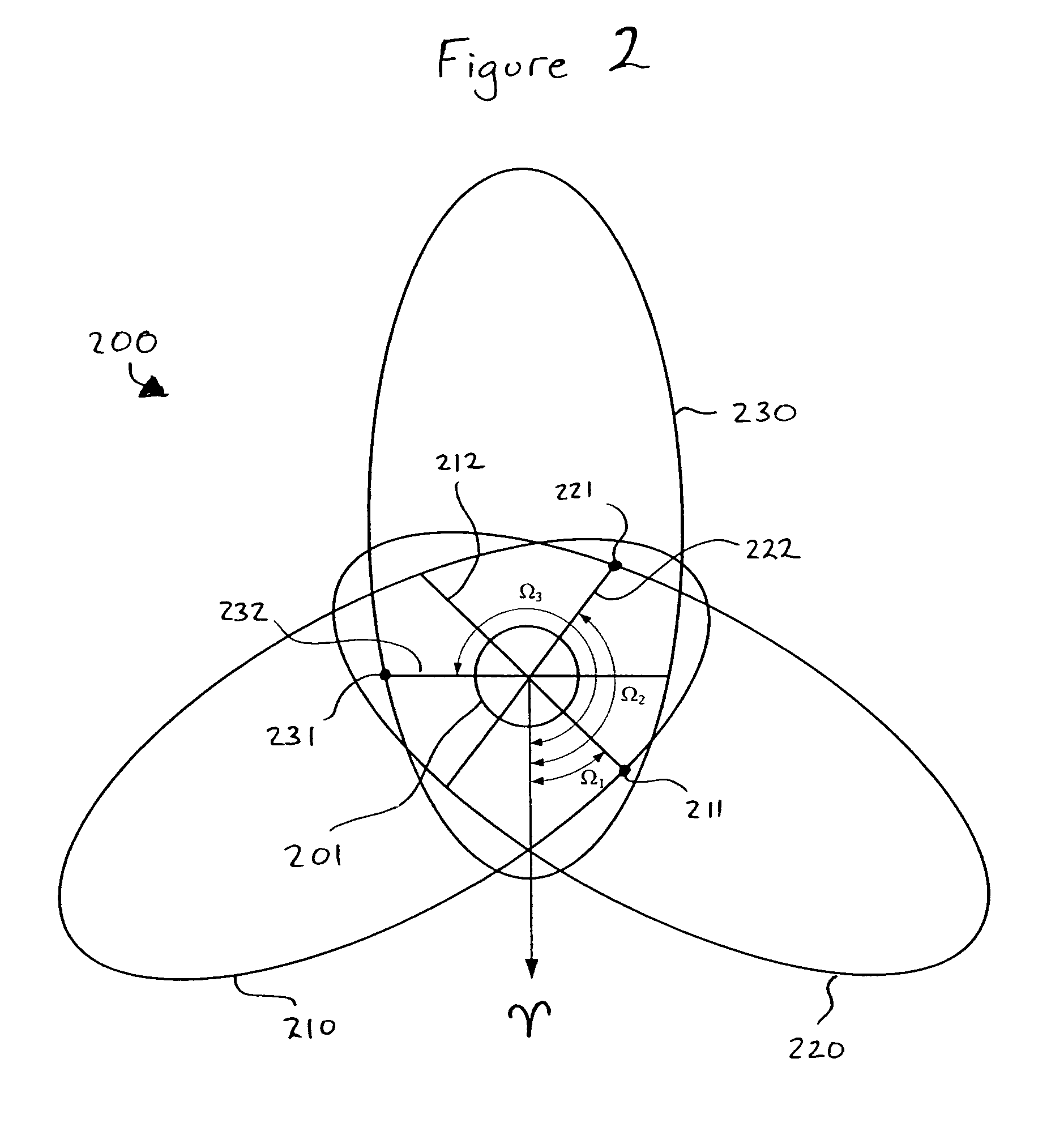
The invention provides an optimization design method of a low-orbit communication and navigation enhancement mixed constellation. The method comprises the following steps: determining a satellite orbit type; determining a satellite orbit height; determining a minimum observation elevation angle; selecting constellation configuration; determining an orbit inclination angle; determining a satellite quantity; determining an orbit surface quantity and a phase factor; selecting initial ascending node right ascension in an optimized mode; analyzing coverage performance of the low-orbit communication and navigation enhancement mixed constellation; and after traversing ends, comparing all mixed constellation parameters satisfying design requirements, and selecting an optimal solution. The method has the following advantages: through combination of factors needing to be considered for design of a communication and navigation enhancement constellation at each phase, the designed low-orbit communication and navigation enhancement mixed constellation can satisfy user demands, is excellent in constellation performance, is small in satellite quantity and quite good in compatible mutual operation capability between constellations.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
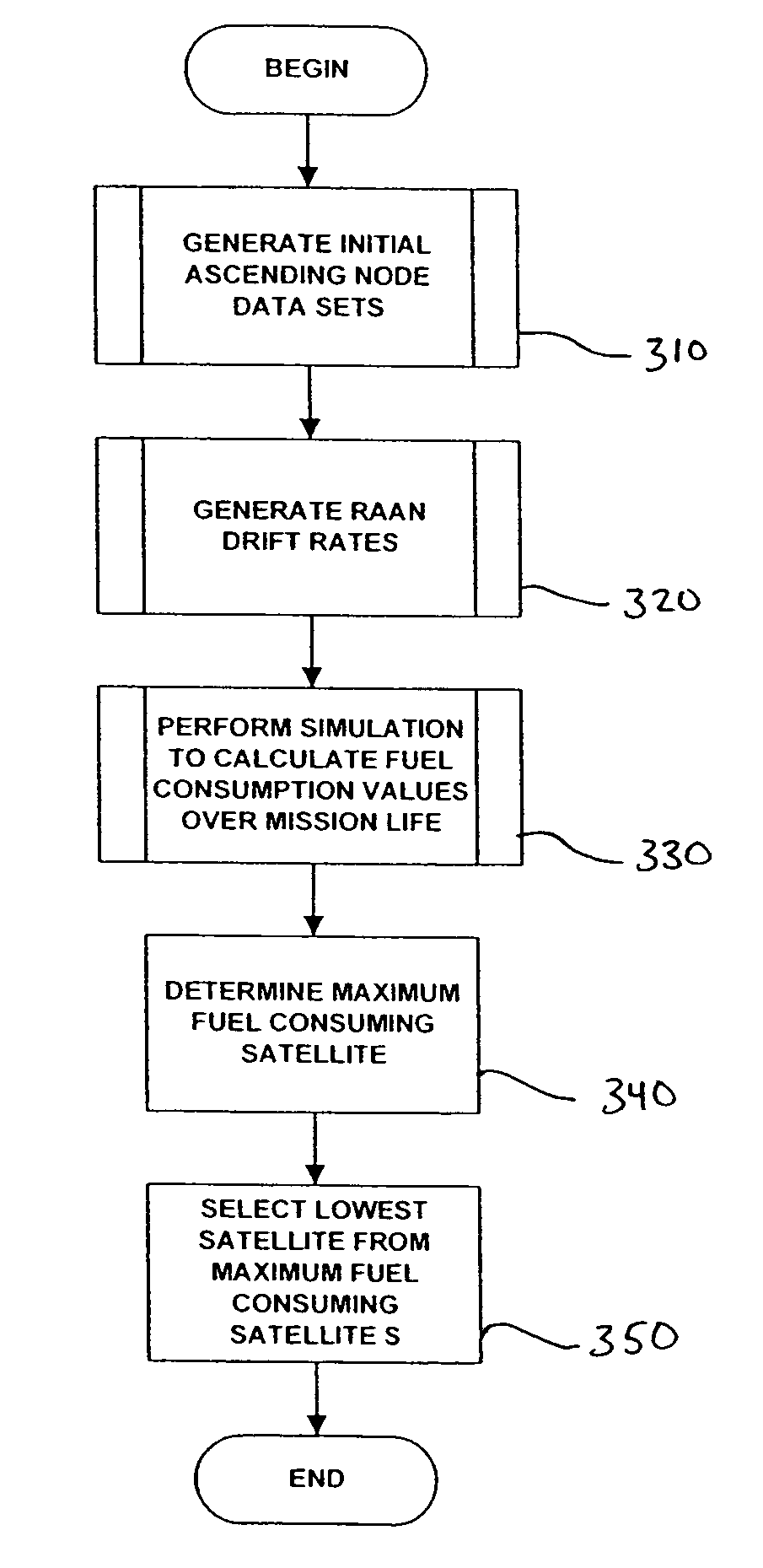
Stationkeeping optimization for inclined elliptical satellite orbit constellations
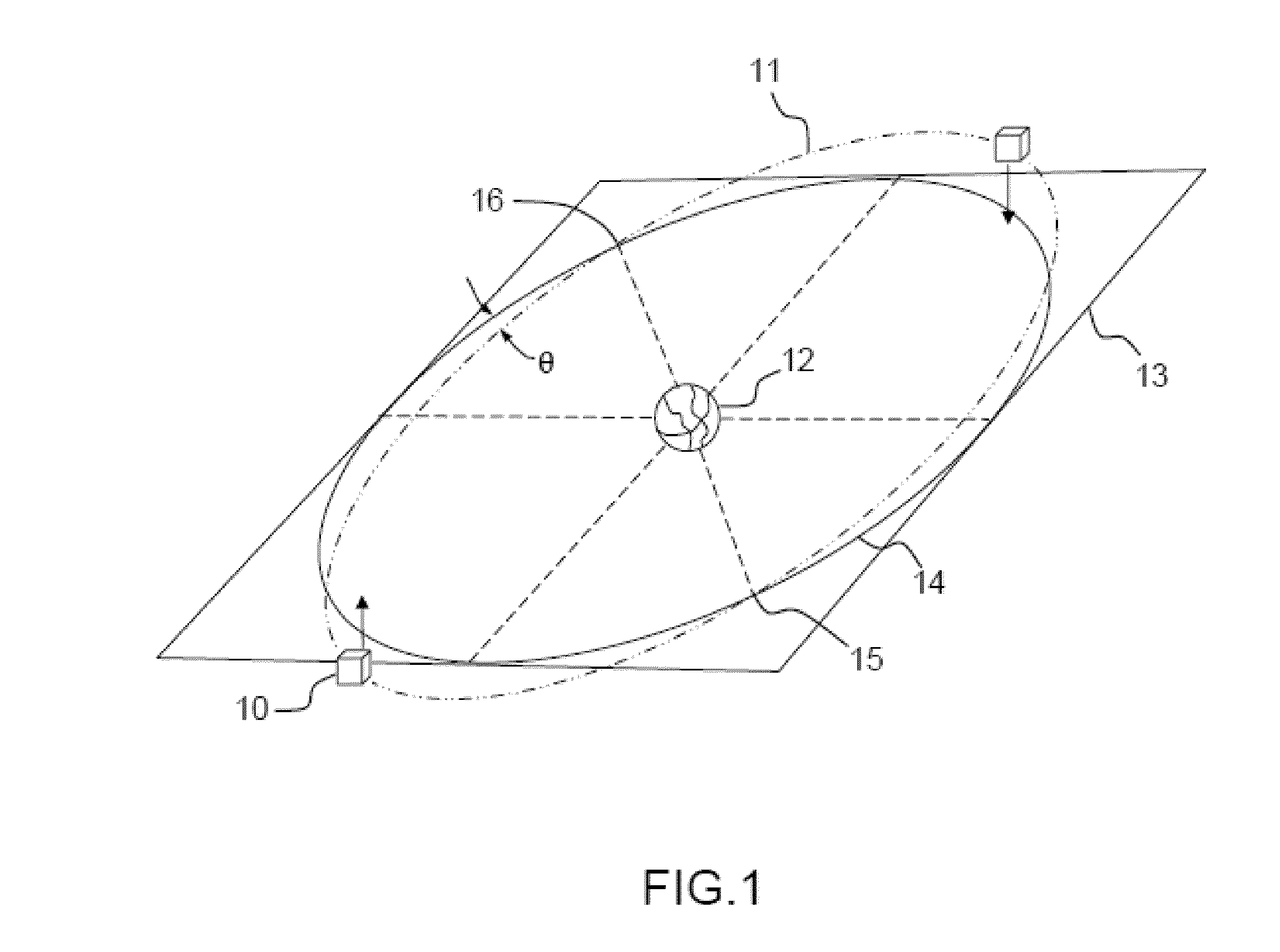
ActiveUS7720604B1Reduce fuel consumptionMinimum consumptionInstruments for comonautical navigationCosmonautic partsEllipseSatellite orbit
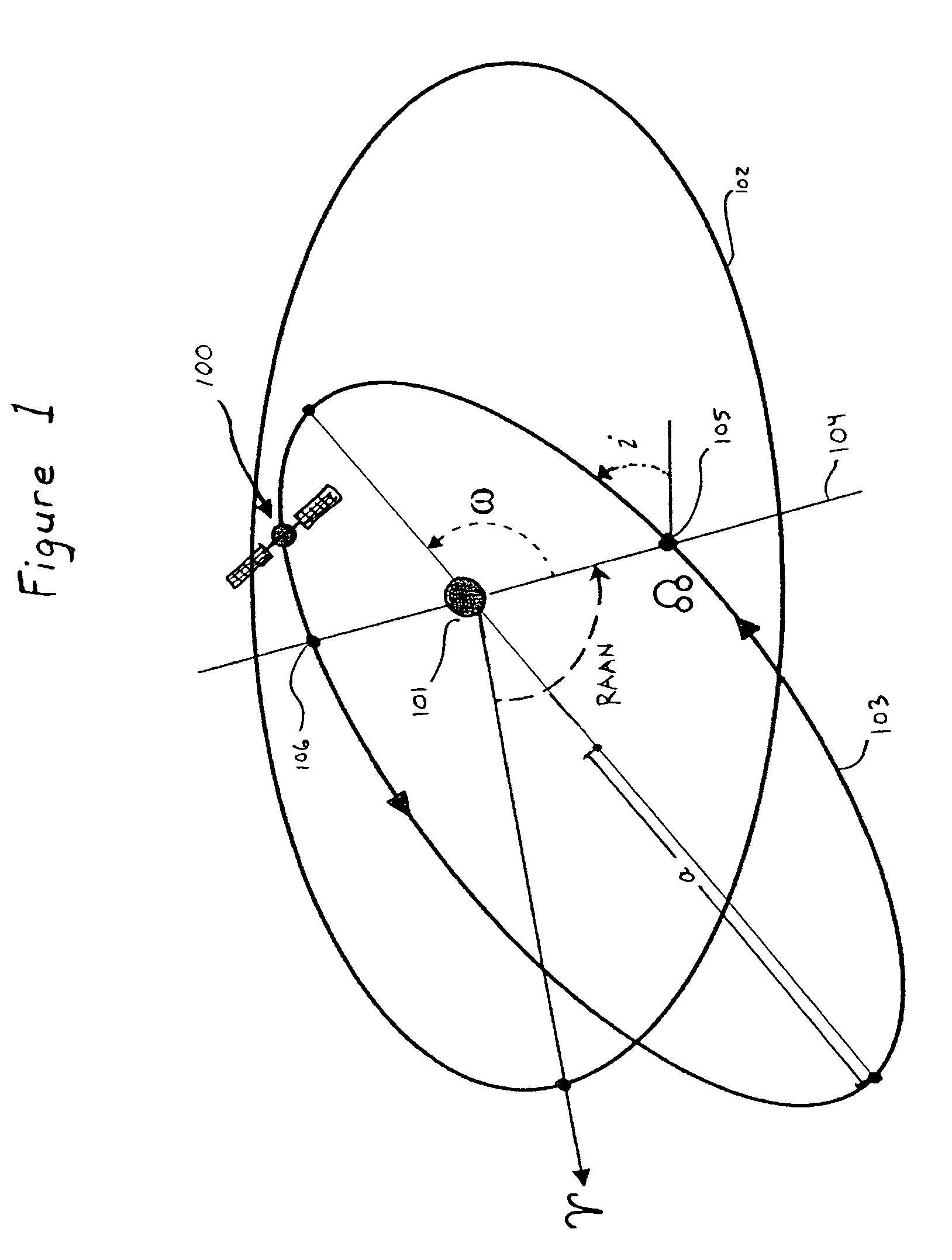
A satellite constellation optimized for stationkeeping fuel consumption is provided. The satellite constellation includes a plurality of satellites, each satellite having a corresponding inclined elliptical orbit, each orbit having an initial right ascension of ascending node (“RAAN”) value, a RAAN drift rate, a semi-major axis, an eccentricity, an argument of perigee and an inclination. Each satellite has a fuel consumption value required to maintain the RAAN drift rate, the semi-major axis, the eccentricity, the argument of perigee and the inclination of the corresponding orbit. The initial RAAN value and the RAAN drift rate for each orbit correspond to a minimized fuel consumption value for the satellite having the highest fuel consumption value. The initial RAAN value and RAAN drift rate may be determined by calculating, for each possible data combination of an initial RAAN value for each orbit and a RAAN drift rate for the constellation, a fuel consumption value for each satellite in the constellation, and selecting, from the fuel consumption values thus determined, the data combination corresponding to a lowest fuel consumption for a highest fuel-consuming satellite.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Around moon satellite dual spindle antenna direct land control method
ActiveCN101204994ARealize open-loop controlSimple calculationAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSpacecraft guiding apparatusEphemerisSatellite orbit
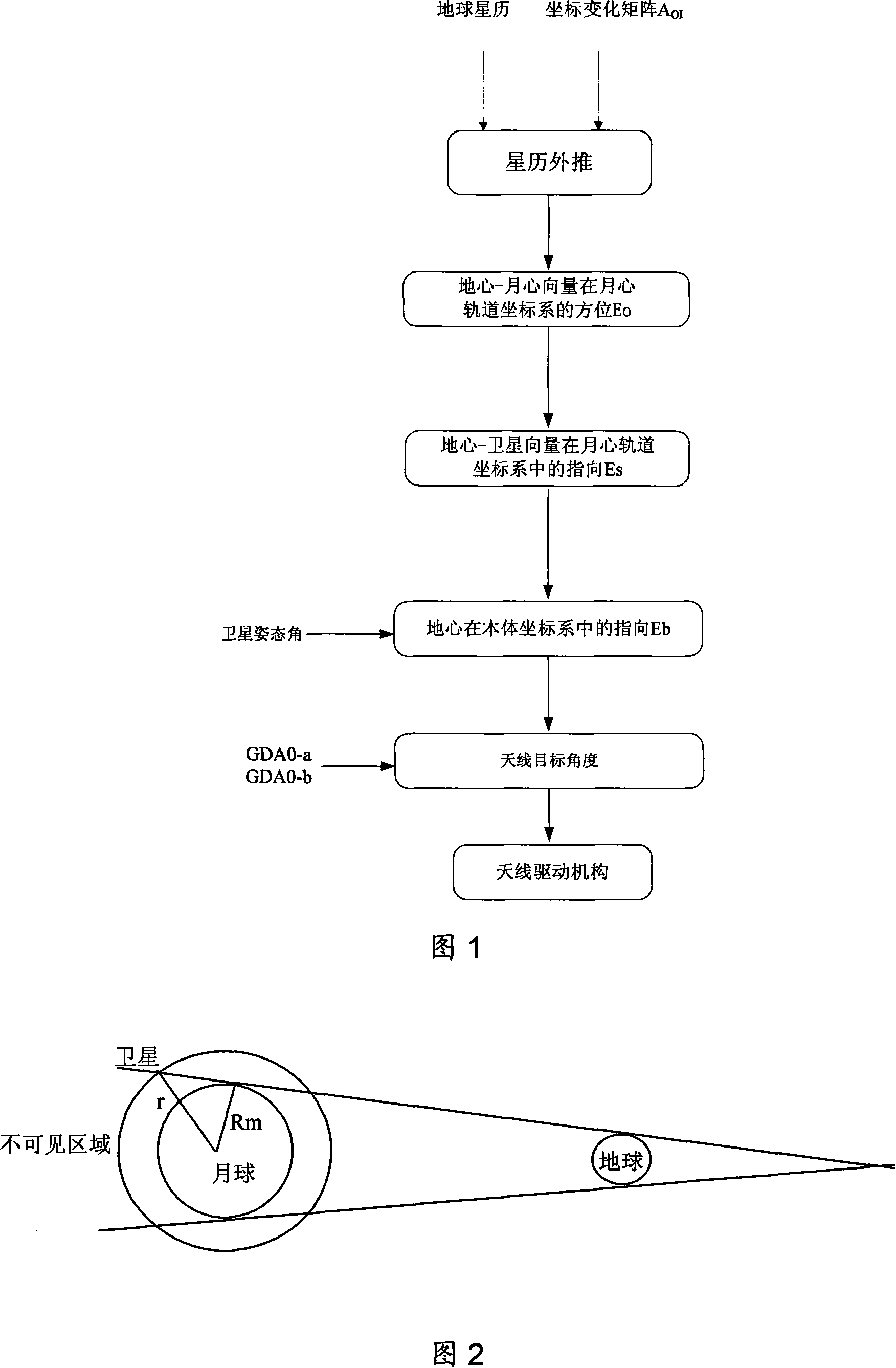
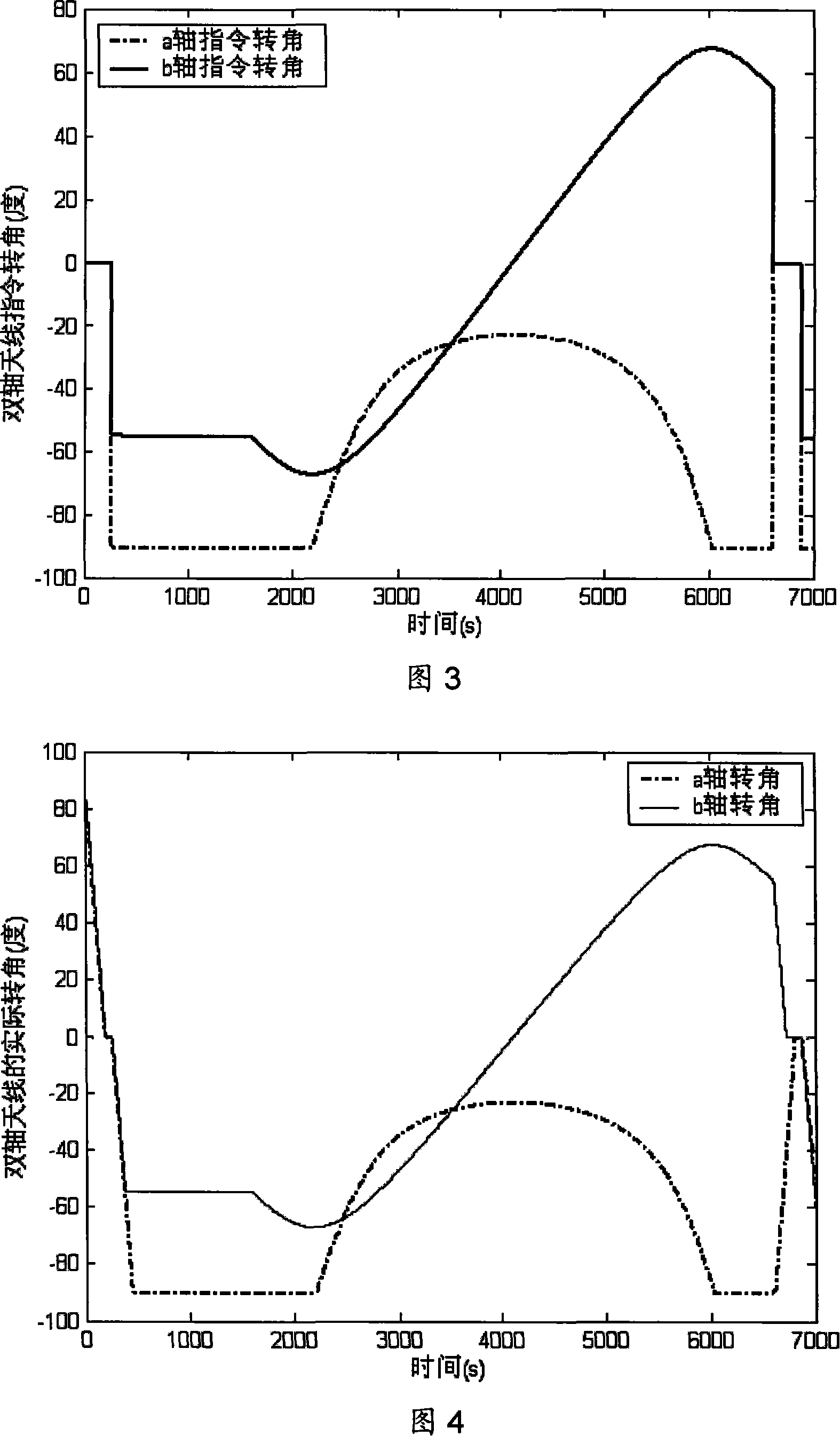
The invention discloses a method for controlling the pointing to the ground of the coaxial antenna of a lunar satellite. The method includes the following steps: first, according to earth ephemeris information transmitted from the ground to the satellite and a transformation matrix from an equatorial inertia system to a coordinate system of a satellite orbit, the ephemeris of the earth in the coordinate system in the satellite orbit in any moment is calculated ; second, according to the calculated ephemeris, visible earth region of the satellite is calculated and within the visible region, a pointing in the coordinate system of the satellite orbit of vector about the satellite pointing to geometer is calculated; the pointing in the coordinate system of the satellite orbit of vector about the satellite pointing to geometer is calculated in a compensated way to obtain the pointing in the coordinate system of the satellite body of vector about the satellite pointing to geometer; according to the pointing in the coordinate system of the satellite body of vector about the satellite pointing to geometer, an antenna target angle is calculated; a final instruction angle is obtained after an antenna zero deviation is compensated and the final instruction angle is sent to an antenna drive mechanism which can drive the antenna to point to the earth. The invention overcomes the defects of the prior art and adopts a tracking mode of a simple ring-opening program to meet the requirements for pointing accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Electronic device and time adjustment method
InactiveUS7616153B2Reduce consumptionThermometer detailsBeacon systems using radio wavesTime informationSatellite orbit
An electronic device having a reception unit that receives satellite signals from positioning information satellites orbiting the Earth; a time information generating unit that generates time information; a time correction information storage unit that stores time correction information for correcting the time information; a time correction information generating unit that generates the time correction information based on the satellite signals; an environmental information acquisition unit that gets information about the reception unit environment; a reception environment information generating unit that generates reception environment information for the reception unit based on the environment information; and a positioning information satellite selection unit that selects the positioning information satellite from which signals are to be received by the reception unit based on the reception environment information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
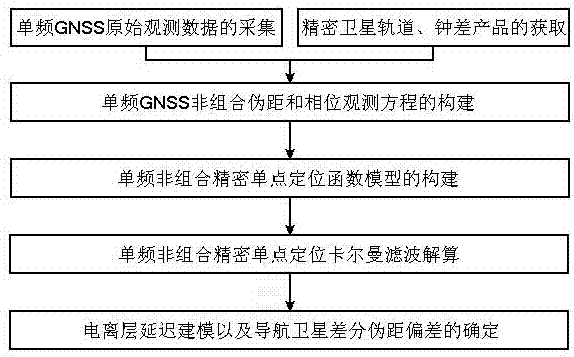
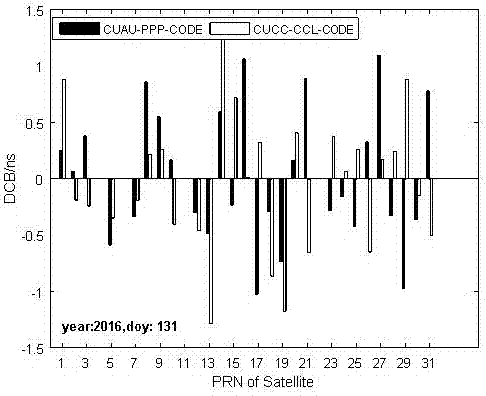
Method for determining satellite differential pseudo-range deviation based on single-frequency navigation satellite data
The invention discloses a method for determining the satellite differentia pseudo-range deviation based on single-frequency navigation satellite data, and relates to a satellite differential pseudo-range deviation determination and correction technology in satellite navigation applications. The method comprises the steps of A, acquiring single-frequency GNSS original observation data and obtaining precision satellite orbit and clock error products; B, building single-frequency GNSS non-combination pseudo-range and phase observation equations; C, building a single-frequency non-combination precision single-point positioning function model; D, solving single-frequency non-combination precision single-point positioning Kalman filtering; and E, performing ionospheric delay modeling and determining the navigation satellite differential pseudo-range deviation. Determination for navigation satellite differential pseudo-range deviation parameters is realized by using a single-frequency receiver, and the hardware cost of an existing navigation satellite differential pseudo-range deviation estimation method can be reduced by more than 90%. Meanwhile, the method is reasonable and simple in design and improves the efficiency. The design is not only low in cost, but also high in efficiency.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
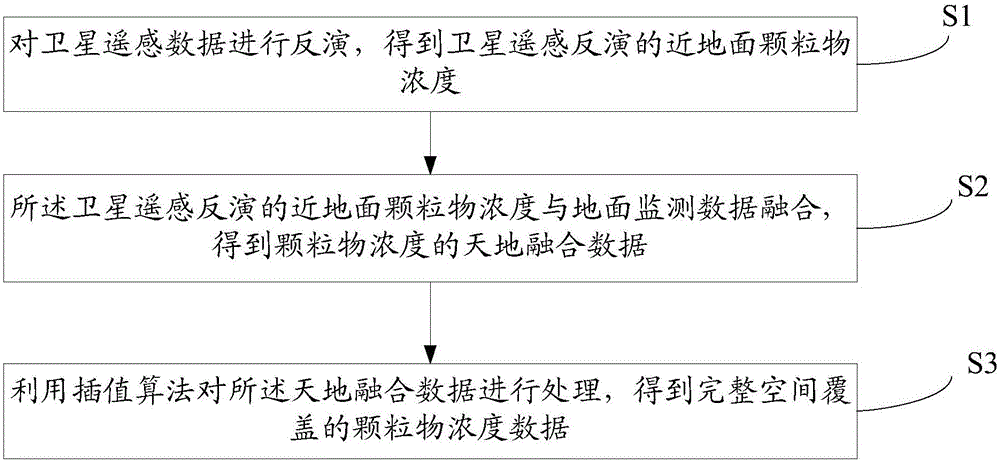
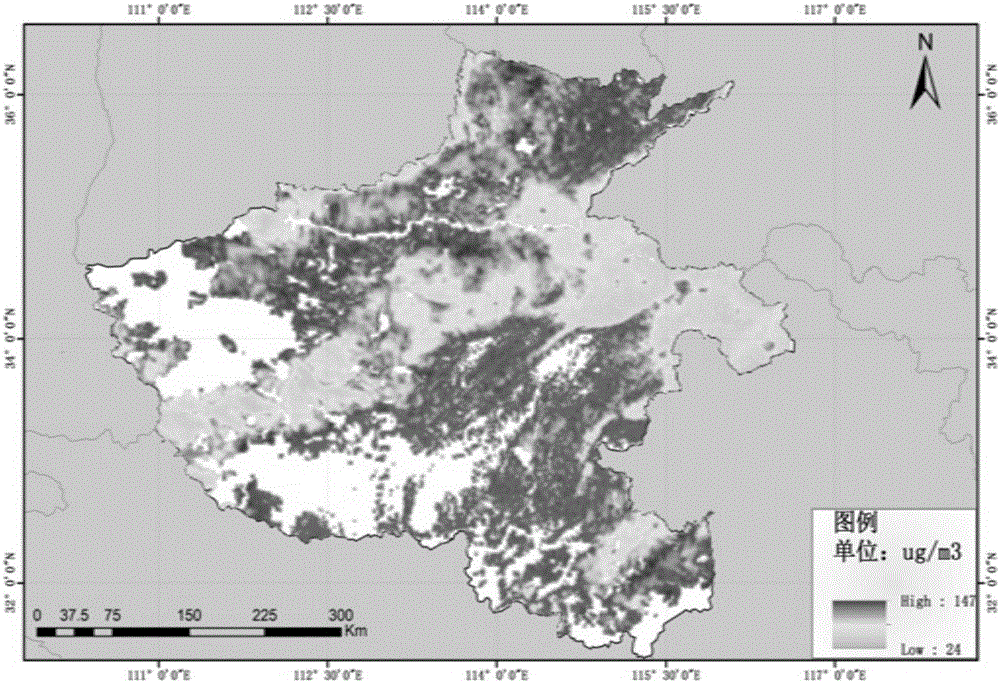
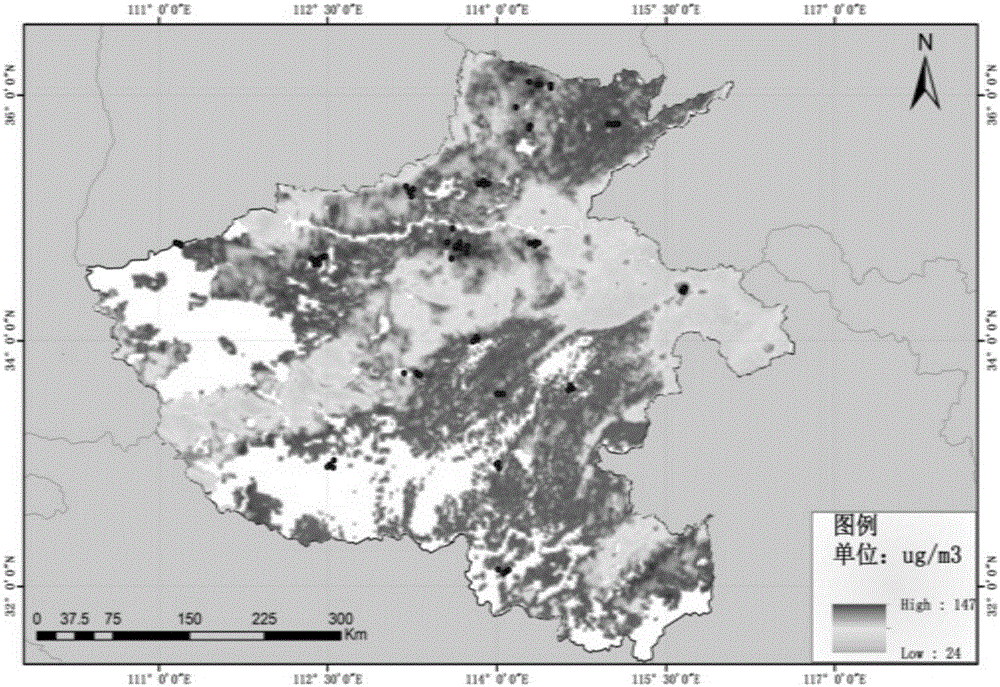
Data fusion-based atmospheric particulate matter remote sensing monitoring method
InactiveCN106124374ASolve the problem of missing concentration dataAvoid missingParticle suspension analysisElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite orbitAtmospherics
The invention discloses a data fusion-based atmosphere particulate matter remote sensing monitoring method, and relates to the technical field of air quality monitoring. According to the method, particulate matter concentration data of complete coverage space are obtained by fusing satellite remote sensing inversion data and ground surface monitoring data and performing interpolation operation on a fused result, so that the problem of particulate matter concentration data deficiency caused by weather, a satellite orbit interval, a cloud cover problem and the limitation of a dim target inversion algorithm is effectively solved, and the accuracy rate of air quality monitoring is greatly improved.
Owner:MAPUNI TECH CO LTD
Method for providing assistance data to mobile station of a satellite positioning system
ActiveUS20090303118A1Reduce shockIncrease autonomyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingEphemerisSatellite orbit
“Satellites of a satellite positioning system broadcast within the navigation signals ephemeris data having a certain period of validity. At a mobile station, ephemeris data are required for position-fixing. In assisted satellite positioning systems, acquisition of navigation signals emitted by the satellites is facilitated as assistance data are provided to the mobile station. At a server station, a request for assistance data issued by the mobile station is received, and the server station transmits ephemeris data as part of the assistance data to the mobile station in response to its request. Upon receiving the request for assistance data issued by the mobile station, the server station decides whether the mobile station could achieve a specified position fix accuracy if the mobile station was provided with the broadcast ephemeris data. In the positive, the server station transmits the broadcast ephemeris data to the mobile station. In the negative, the server station transmits, instead of broadcast ephemeris data, long-term ephemeris data to the mobile station as part of the assistance data requested. The long-term ephemeris data are derived from satellite orbit predictions and have a period of validity substantially increased with respect to the ephemeris data broadcast by the satellites.”
Owner:THE EURO UNION REPRESENTED BY THE EURO CO
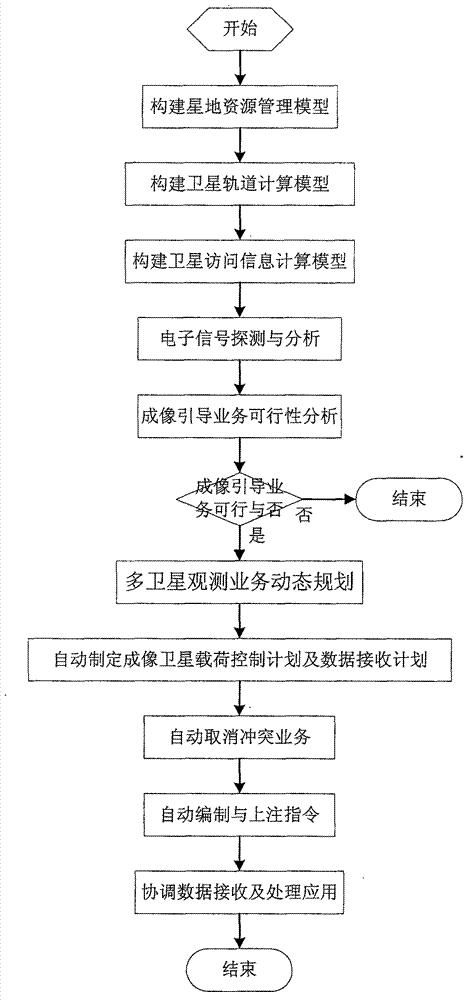
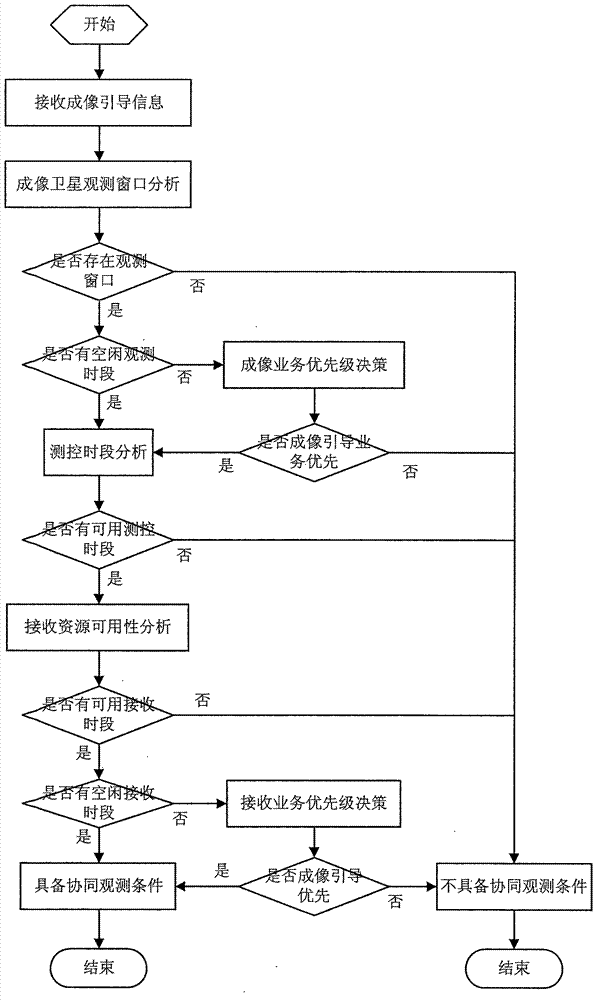
Multi-satellite cooperative observation business scheduling method
ActiveCN102780523AQuickly adjust the receiving service planning schemeIncrease catch rateRadio transmissionDynamic planningLand resources
The invention discloses a multi-satellite cooperative observation business scheduling method and relates to satellite observation business planning and scheduling technology in a satellite operation control field. The multi-satellite cooperative observation business scheduling method is based on a satellite operation control system, builds a star land resource management model, a satellite orbit calculation model and a satellite access information calculation model, adopts a satellite observation business dynamic planning algorithm to regulate satellite observation business rapidly and dynamically, adopts an automatic processing mechanism to make a satellite load control plan and a data receiving plan immediately, adopts a satellite actual load control instruction compilation business trigger mechanism to compile satellite actual load control instructions in real time, and schedules an electronic signal detection satellite and an imaging observation satellite to complete cooperative observation business. The multi-satellite cooperative observation business scheduling method has the advantages of being rapid in response speed, accurate in calculation method, high in automation and the like and is particularly suitable for a marine moving target multi-satellite cooperative observation field.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Data quality monitoring method for local enhancing system
ActiveCN101950025ARealize high precision interpolationHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingData integrityEphemeris
The invention discloses a data quality monitoring method for a local enhancing system, which mainly solves the problem that the satellite orbit position calculation accuracy by the traditional data quality monitoring method is relatively low. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, checking the data integrity and validity of a received broadcast ephemeris to acquire a group of accurate and valid ephemeris data; secondly, checking the consistency of the group of ephemeris data; thirdly, carrying out real-time precision ephemeris detection, new and old ephemeris detection and ephemeris-almanac detection on the broadcast ephemeris data with uniformity respectively; and finally, according to the data availability detection result, generating an available matrix and an available broadcast ephemeris group of the broadcast ephemeris. The method has the advantages of high satellite orbit position calculation accuracy and low ephemeris fault error detection probability and can effectively solve the problem of man-made interference on the broadcast ephemeris and almanac of a satellite navigation system.
Owner:中电科星河北斗技术西安有限公司
Propulsion system with four modules for satellite orbit control and attitude control
ActiveUS20140361124A1Cosmonautic propulsion system apparatusArtificial satellitesNatural satelliteAttitude control
A propulsion system for the orbital control of a satellite with terrestrial orbit travelling with a speed of displacement along an axis V tangential to the orbit comprises two propulsion assemblies, fixed to the satellite facing one another with respect to the plane of the orbit, each of the propulsion assemblies comprising two propulsion modules; each of the propulsion modules successively comprising: a motorized link for rotation about an axis parallel to the axis V, an offset arm, and a platen supporting a propulsion unit able to deliver a thrust oriented along an axis perpendicular to the axis V; the two propulsion modules of each propulsion assembly being linked to the satellite on either side and substantially at equal distances from a plane perpendicular to the axis V passing through a centre of mass of the satellite.
Owner:THALES SA
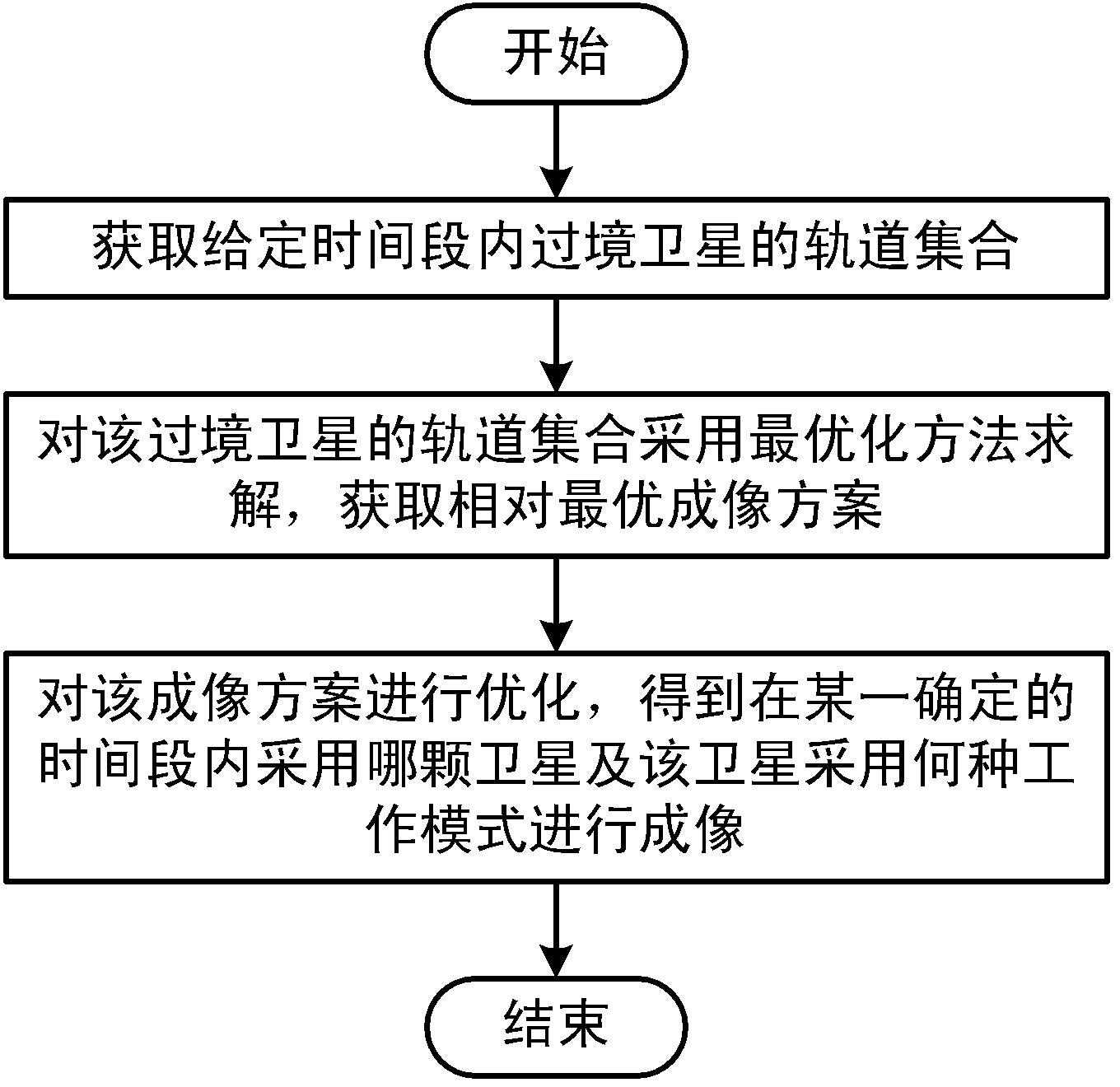
Method for realizing multi-satellite combined imaging
ActiveCN103294925AEasy accessShorten acquisition cycleSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataSatellite orbit
The invention discloses a method for realizing multi-satellite combined imaging. The method for realizing multi-satellite combined imaging includes the steps that an orbit rendezvous of transiting satellites in a given time quantum is obtained, the orbit rendezvous of the transiting satellites is solved in an optimization method to obtain a relatively optimum imaging scheme, and the imaging scheme is optimized to determine which satellite is adopted and what work mode is adopted by the satellite for imaging in a certain given time quantum. The method for realizing multi-satellite combined imaging combines the satellite orbit computing technology and the artificial intelligence technology, and includes the steps of rapid obtaining of the orbits of the transiting satellites, automatic selection of multi-target optimization algorithms, automatic optimization of an imaging coverage scheme, and the like. The method has the advantages of being high in degree of automation, efficient in algorithm and the like, and can be used for building a unified district observation platform for multi-satellite combined imaging. By means of the method for realizing multi-satellite combined imaging, a user can determine the optimum satellite resource from numerous satellite resources, and the cycle of obtaining satellite remote sensing data for the user is made to be as short as possible.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Area enhanced precision positioning service method suitable for large-scale users
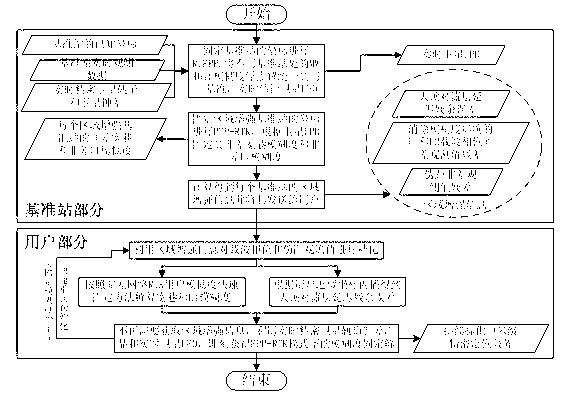
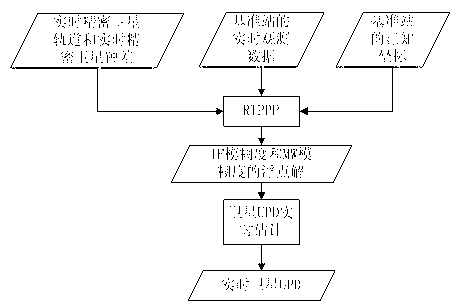
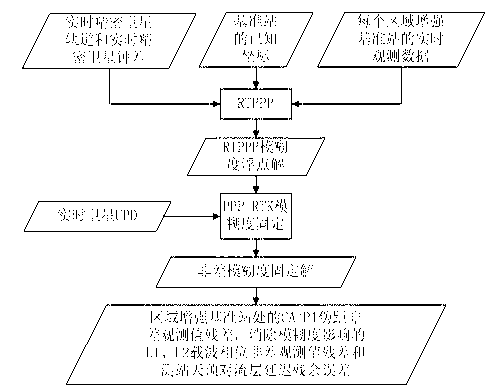
InactiveCN103344978ASolve the burden of real-time data communicationIncrease the number ofSatellite radio beaconingTroposphereReal-time data
The invention discloses an area enhanced precision positioning service method suitable for large-scale users. According to the technical scheme, the method includes the steps that after the users effectively fix wide-lane ambiguity and L1 ambiguity of at least four satellites in a zero difference network RTK processing mode, area enhanced information of surrounding base stations does not need to be acquired, at this moment ambiguity fixed results and zenith troposphere delay residual errors acquired by interpolation are used as known truth values, received satellite UPD information is combined, and an ambiguity fixed solution in a PP-RTK mode can be immediately acquired without initialization. Due to the fact that satellite UPD, real-time satellite orbits and real-time satellite clock errors are only related to the satellites, and short-term forecast lasting tens of seconds to a few minutes can be conducted, the information can be broadcasted to the users through the communication satellites in a broadcast mode, and then real-time data communication burdens among the users and the base stations can be greatly reduced. Once user ambiguity is firstly fixed, the number of the users simultaneously serviced by an area enhanced system is no longer restricted at this moment.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com