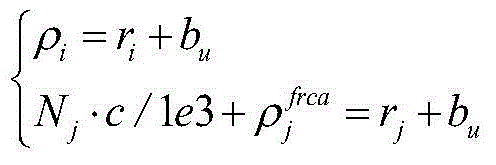Patents
Literature
116 results about "Time to first fix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
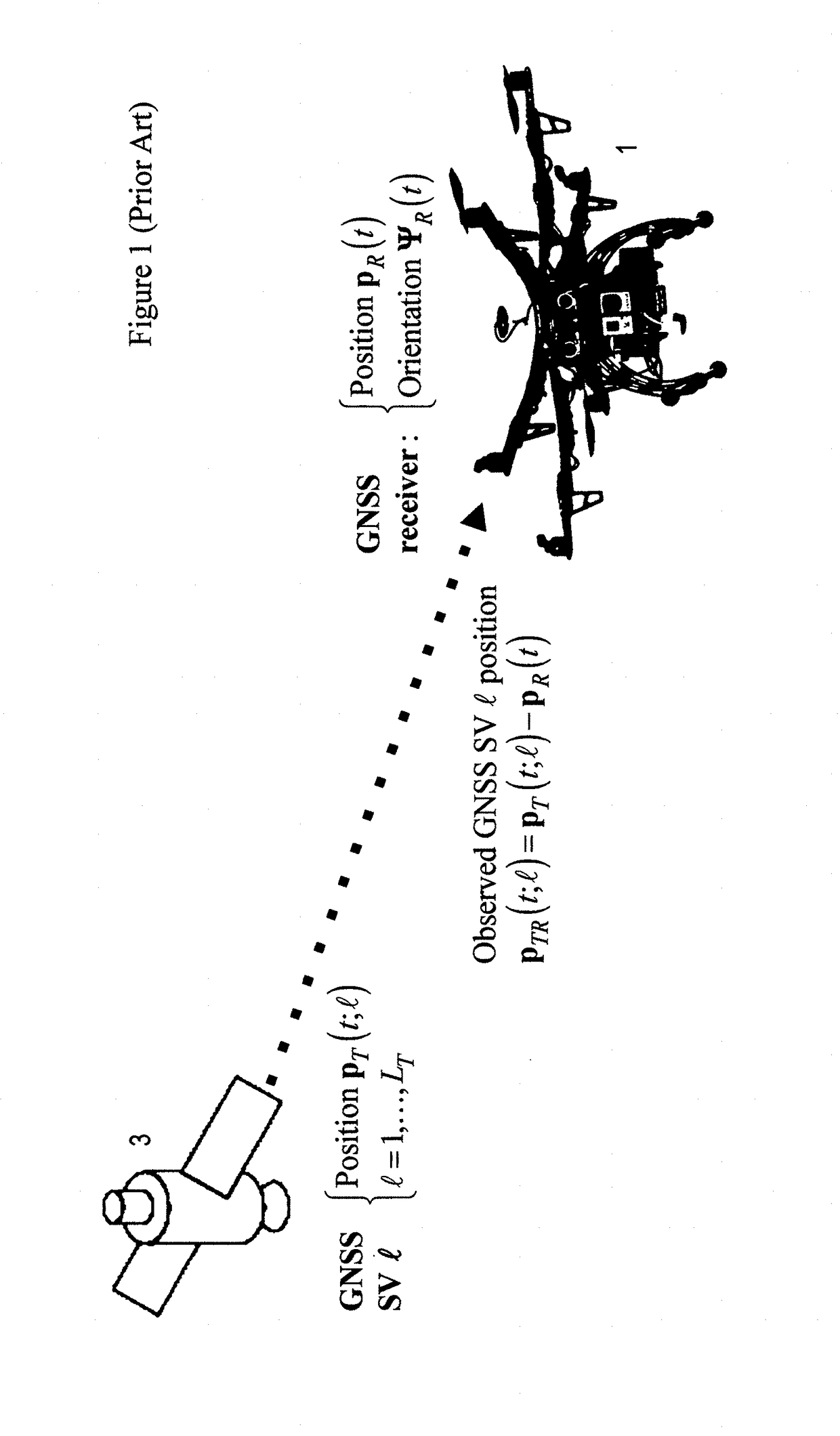
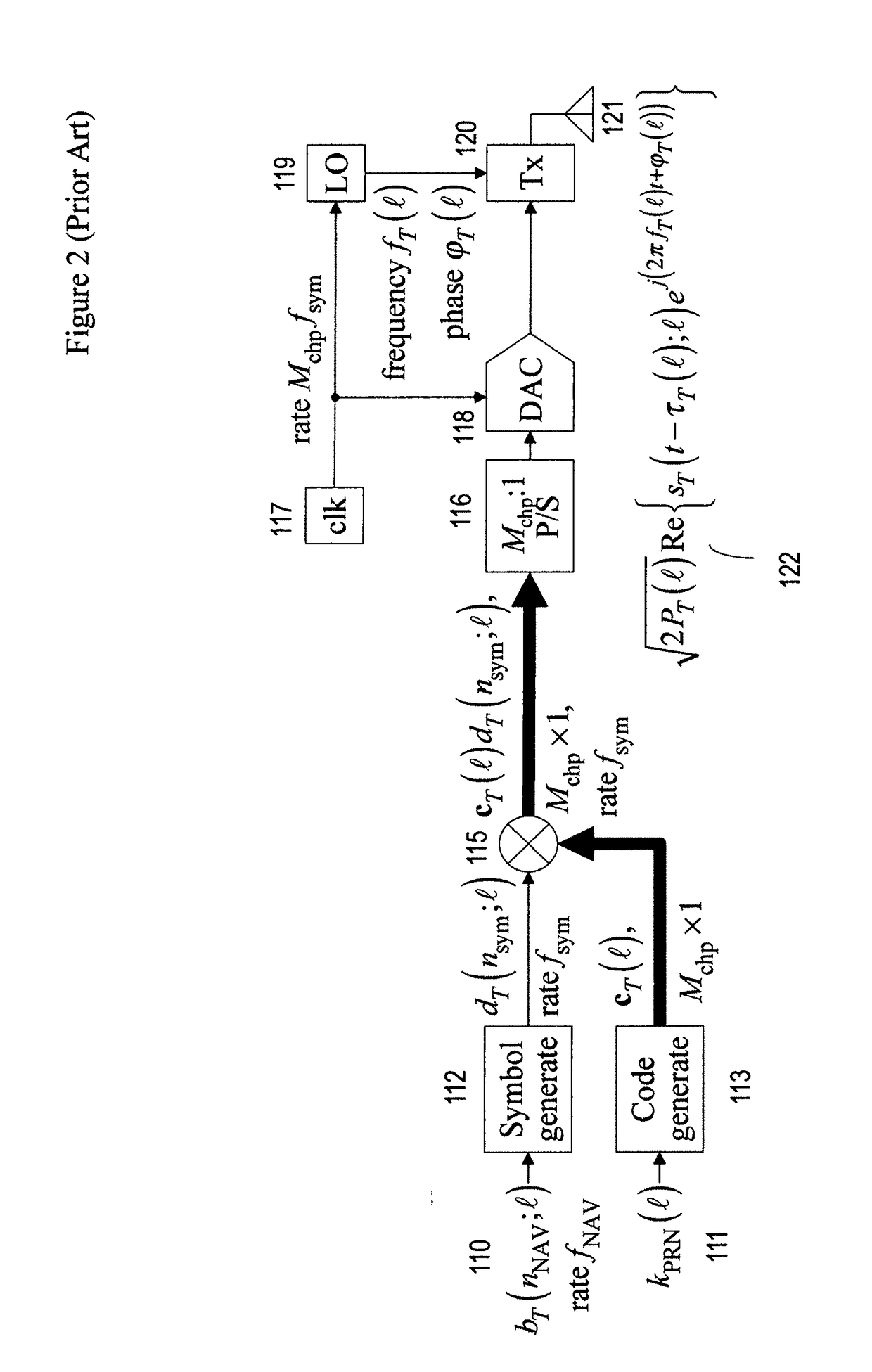
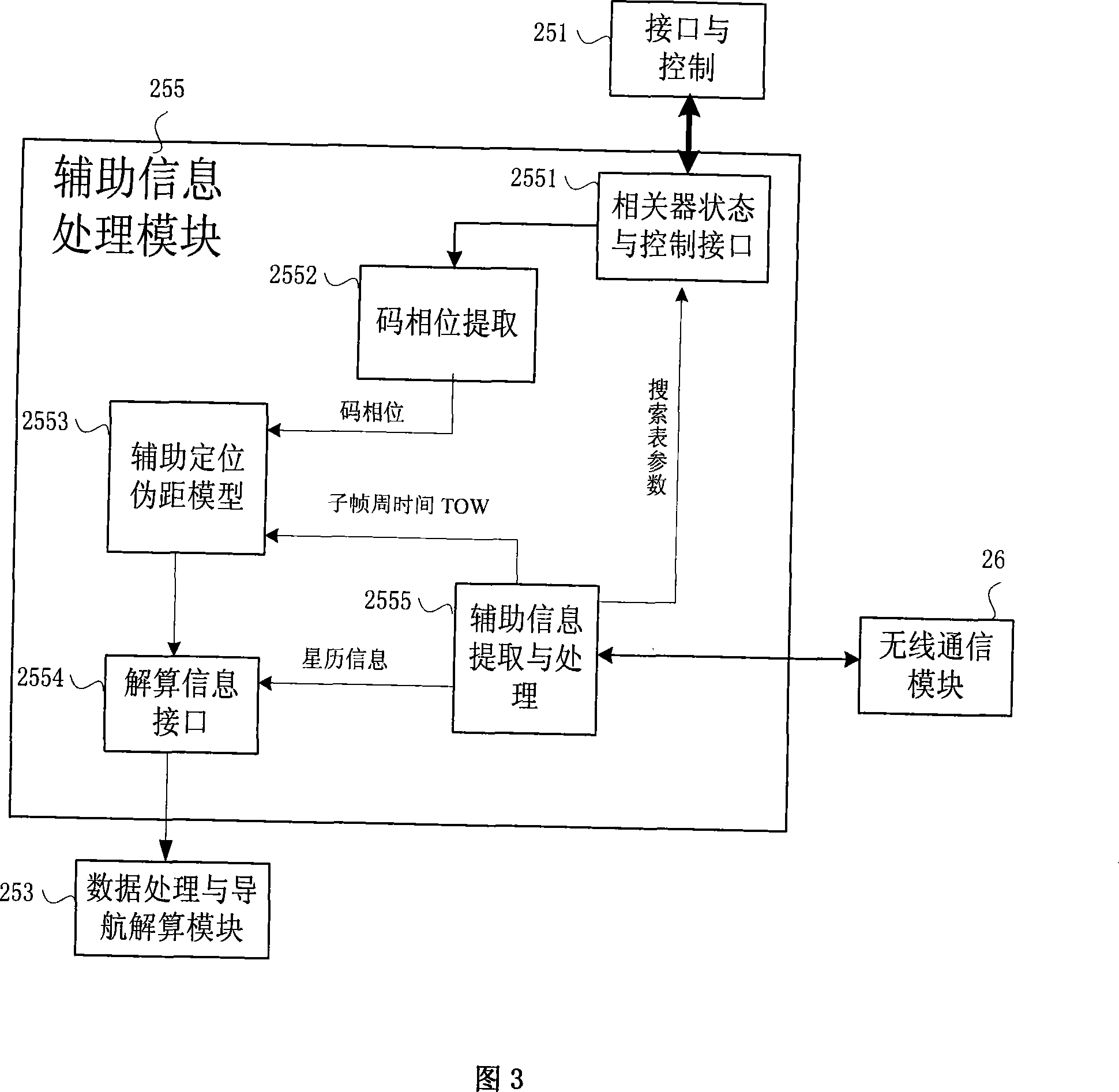
Time to first fix (TTFF) is a measure of the time required for a GPS navigation device to acquire satellite signals and navigation data, and calculate a position solution (called a fix).
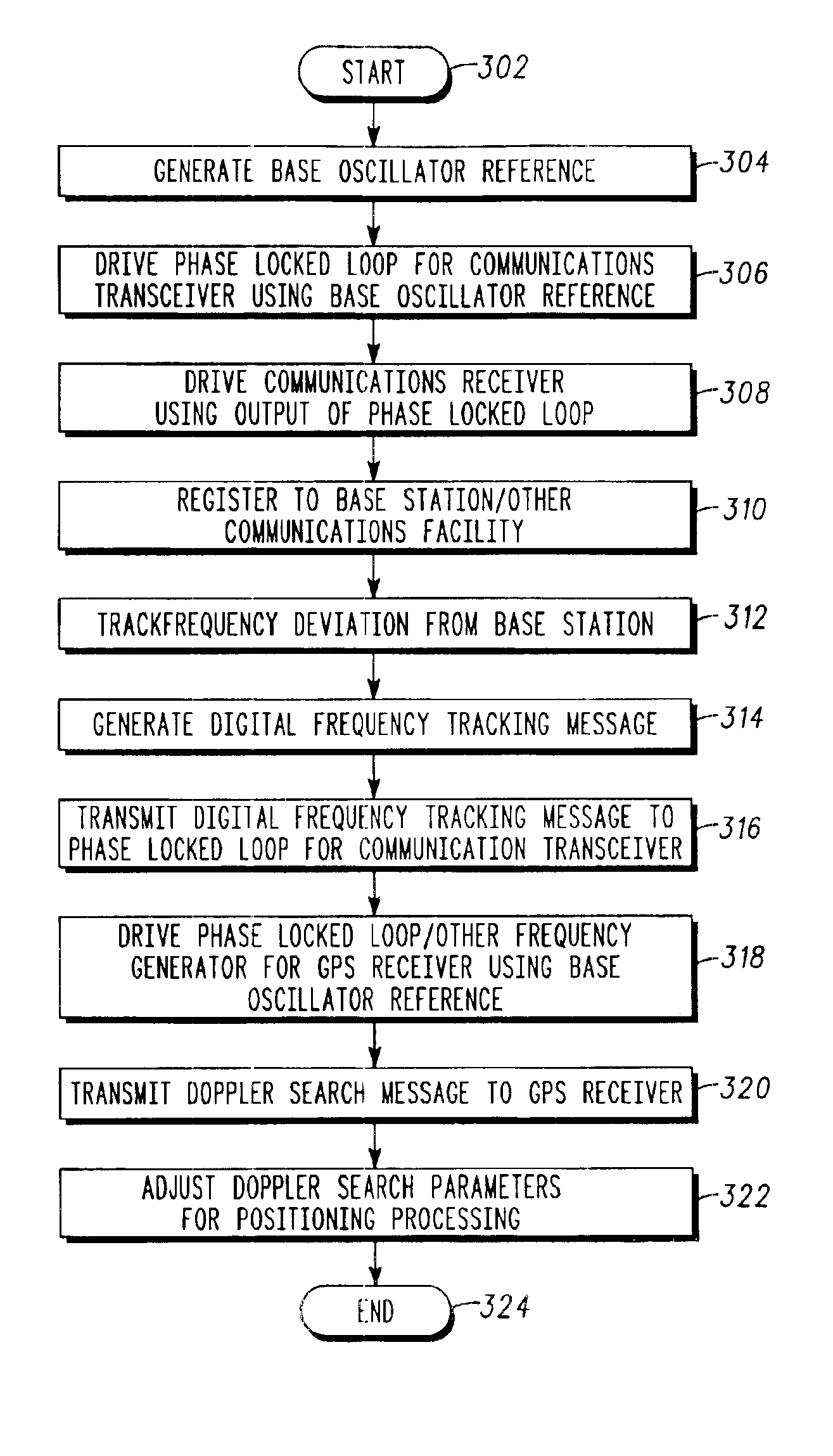
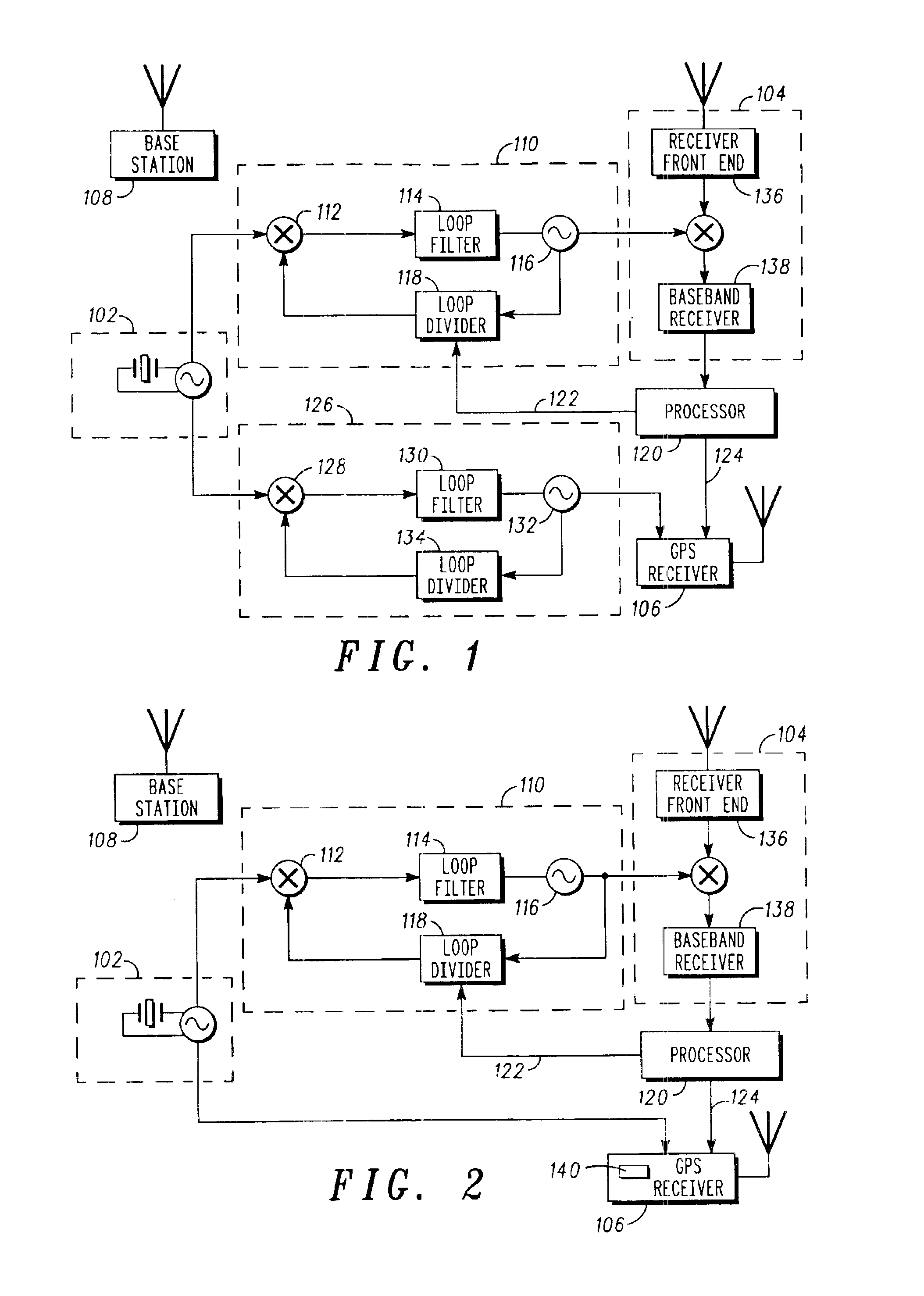
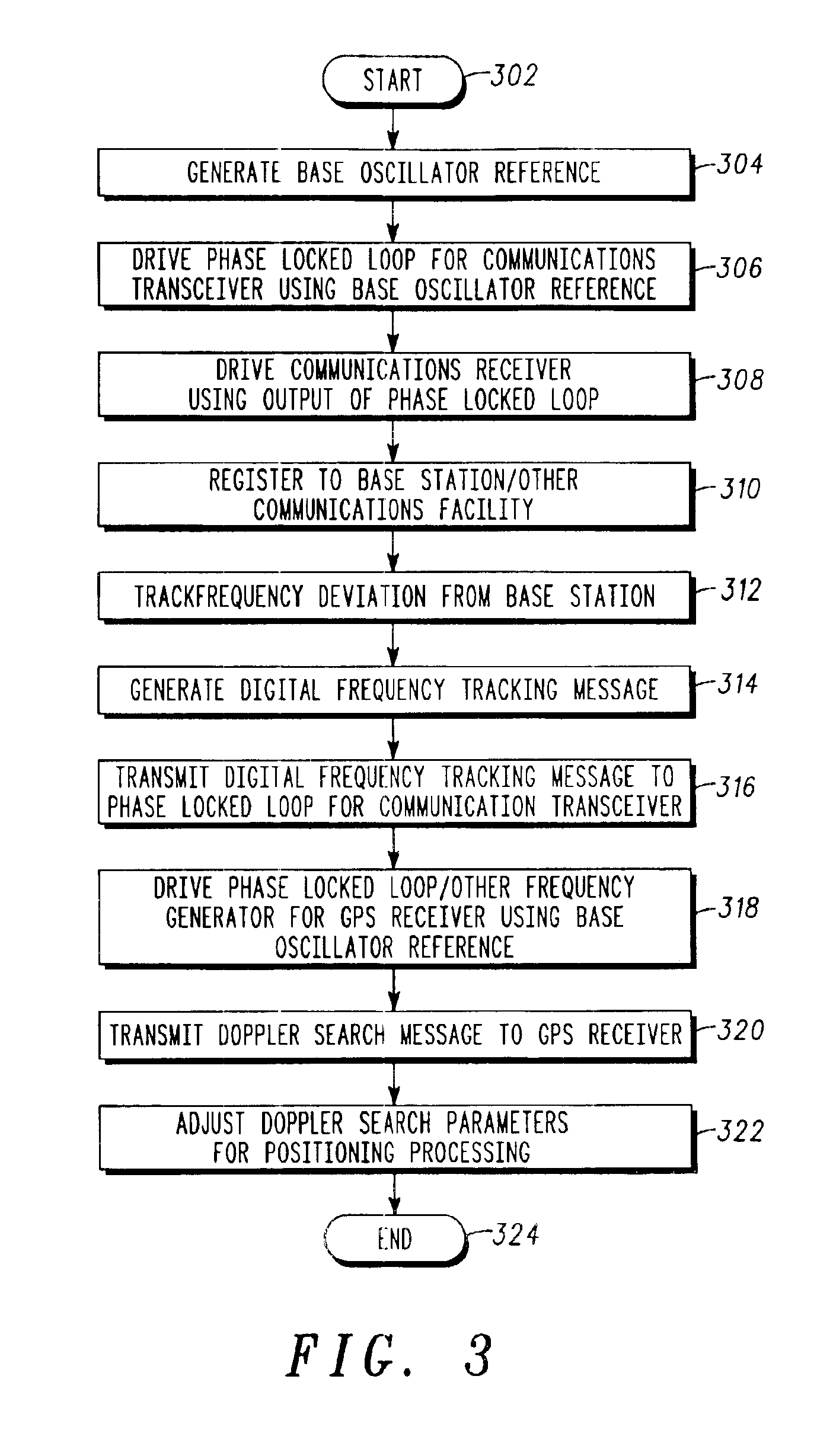
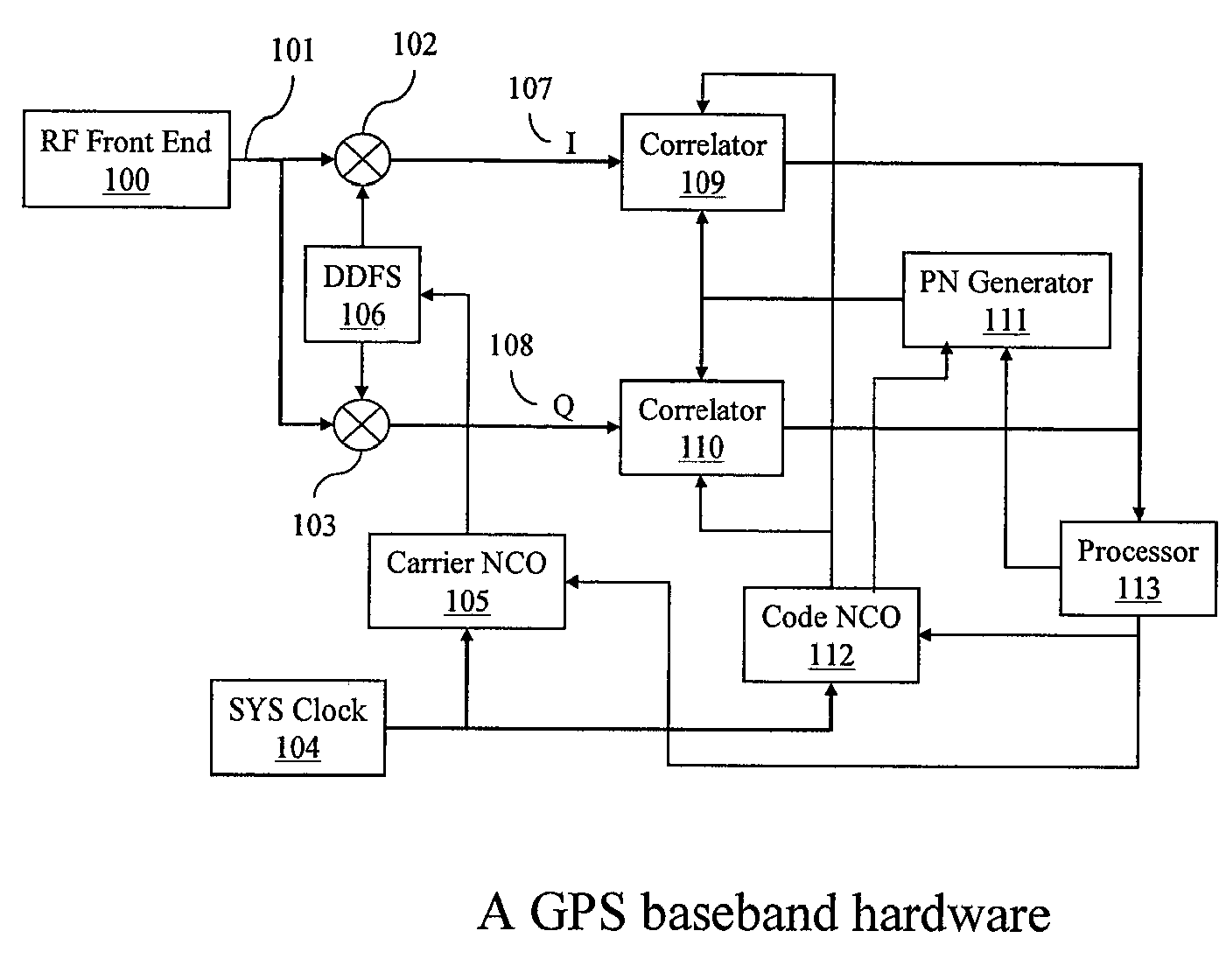
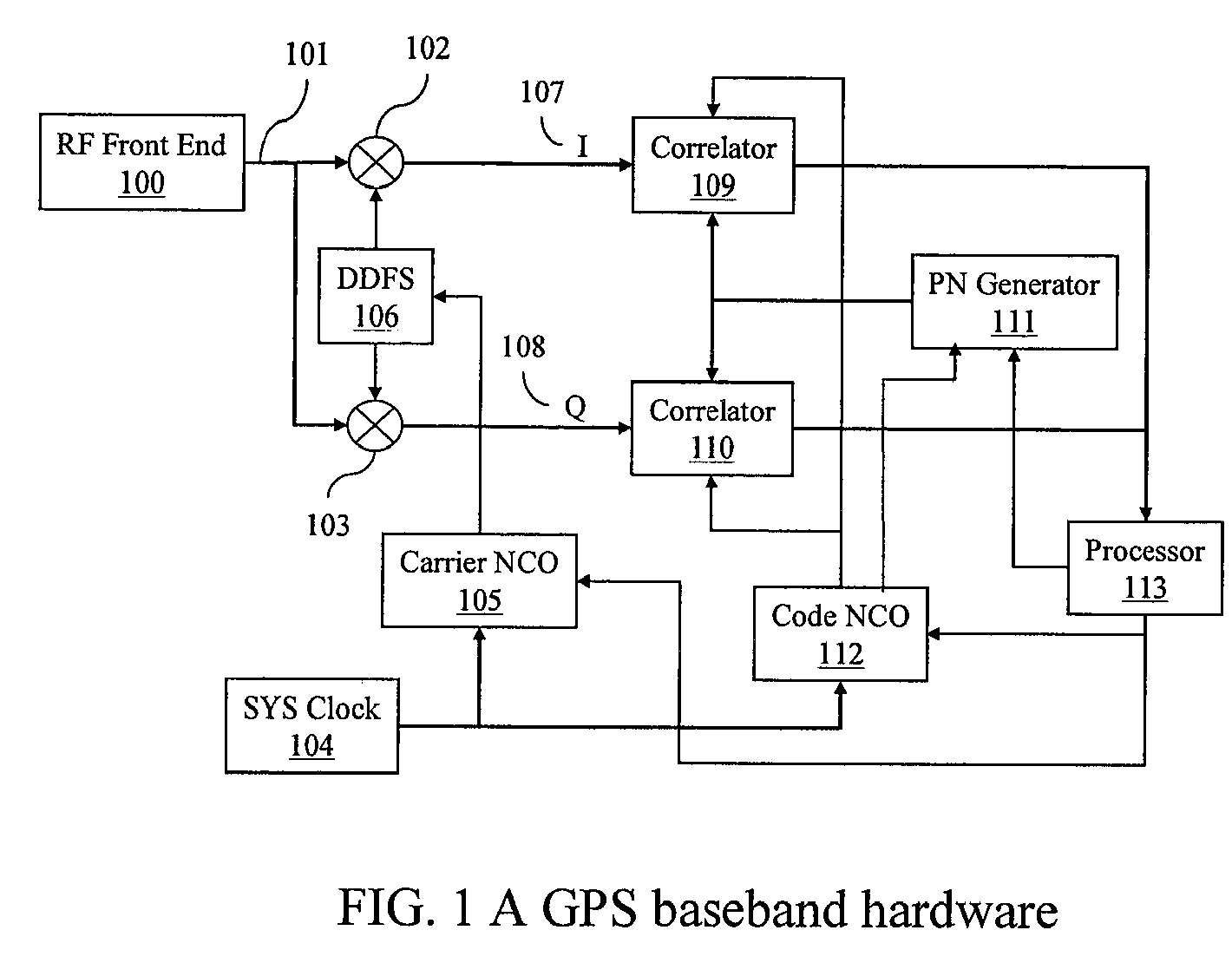
System and method for frequency management in a communications positioning device
InactiveUS6867734B2High positioning accuracySufficient GPS performanceSynchronisation arrangementPulse automatic controlTime to first fixTransceiver
A frequency management scheme for a hybrid communications / positioning device, such as a cellular / GPS or other combined device, generates a local clock signal for the communications portion of the device, using a crystal oscillator or other part. The oscillator output may be delivered to a phase locked loop to drive a high-frequency clock for the cellular or other communications portion of the hybrid device. A processor may determine frequency error between the phase locked loop and base station or other reference, to derive a digital frequency tracking message. A Doppler search or other logical control message may likewise be communicated from the processor to a GPS or other positioning receiver. The GPS receiver circuitry may consequently adjust Doppler center, window width or other parameters to enhance time to first fix or other performance. The architecture eliminates the need for a second crystal or other direct oscillator in the GPS receiver portion of the hybrid device, while still maintaining GPS performance. The architecture of the design also eliminates the need for frequency correcting elements in the crystal oscillator or other base reference oscillator or clock. The invention can furthermore be used in any system, radio, modem, transceiver, or receiver that has two or more receivers that share one reference or base oscillator or clock.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
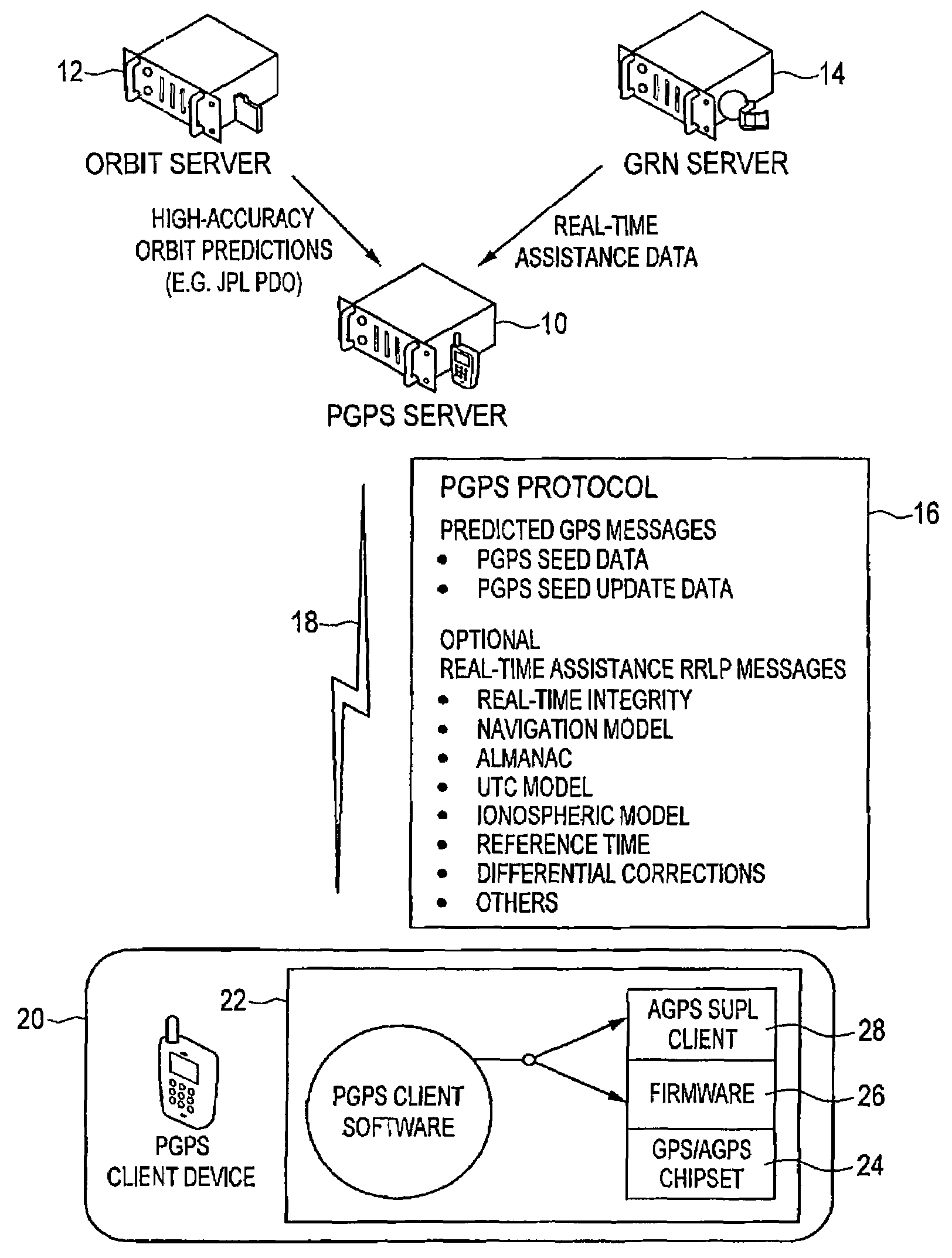
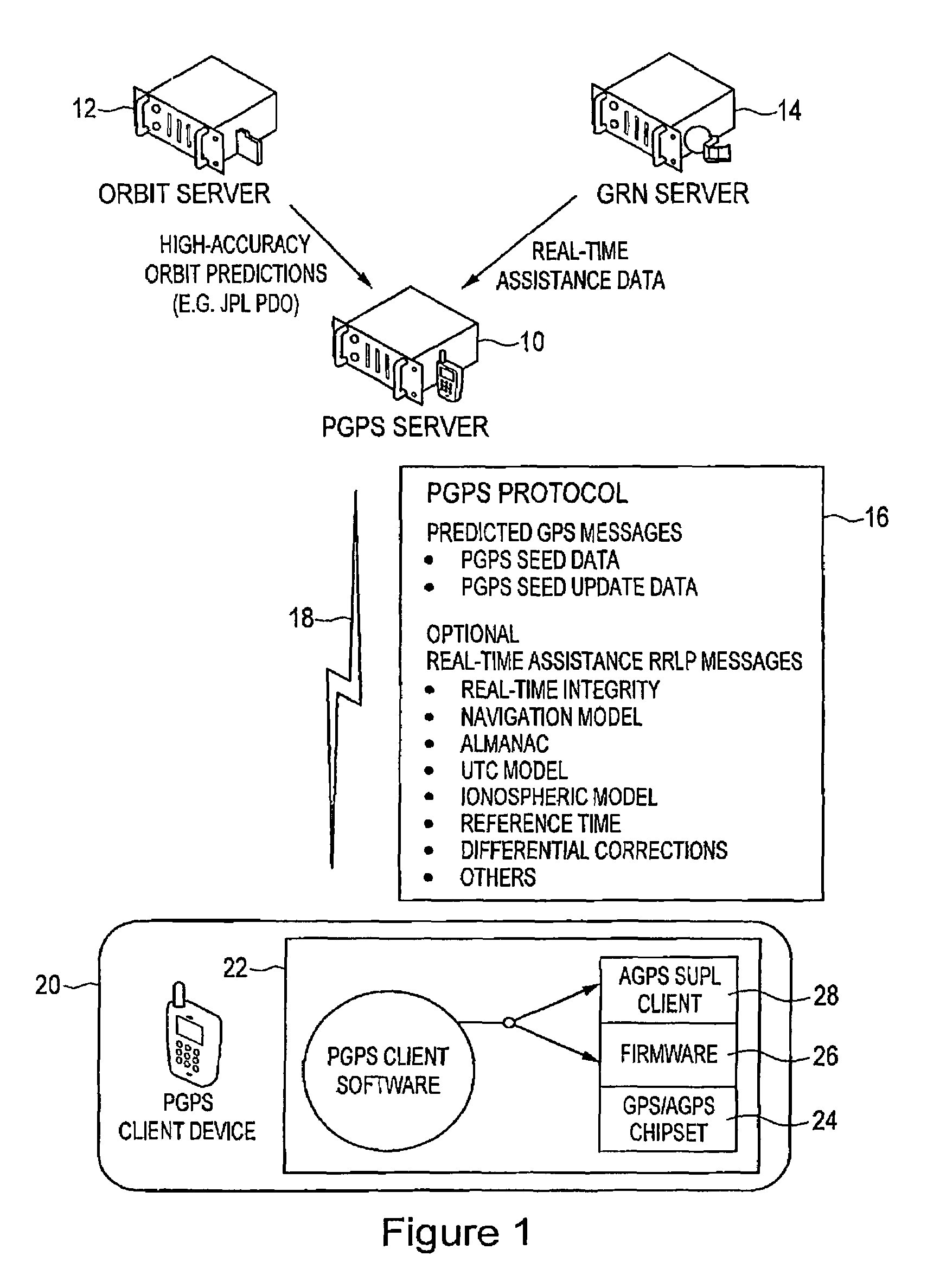
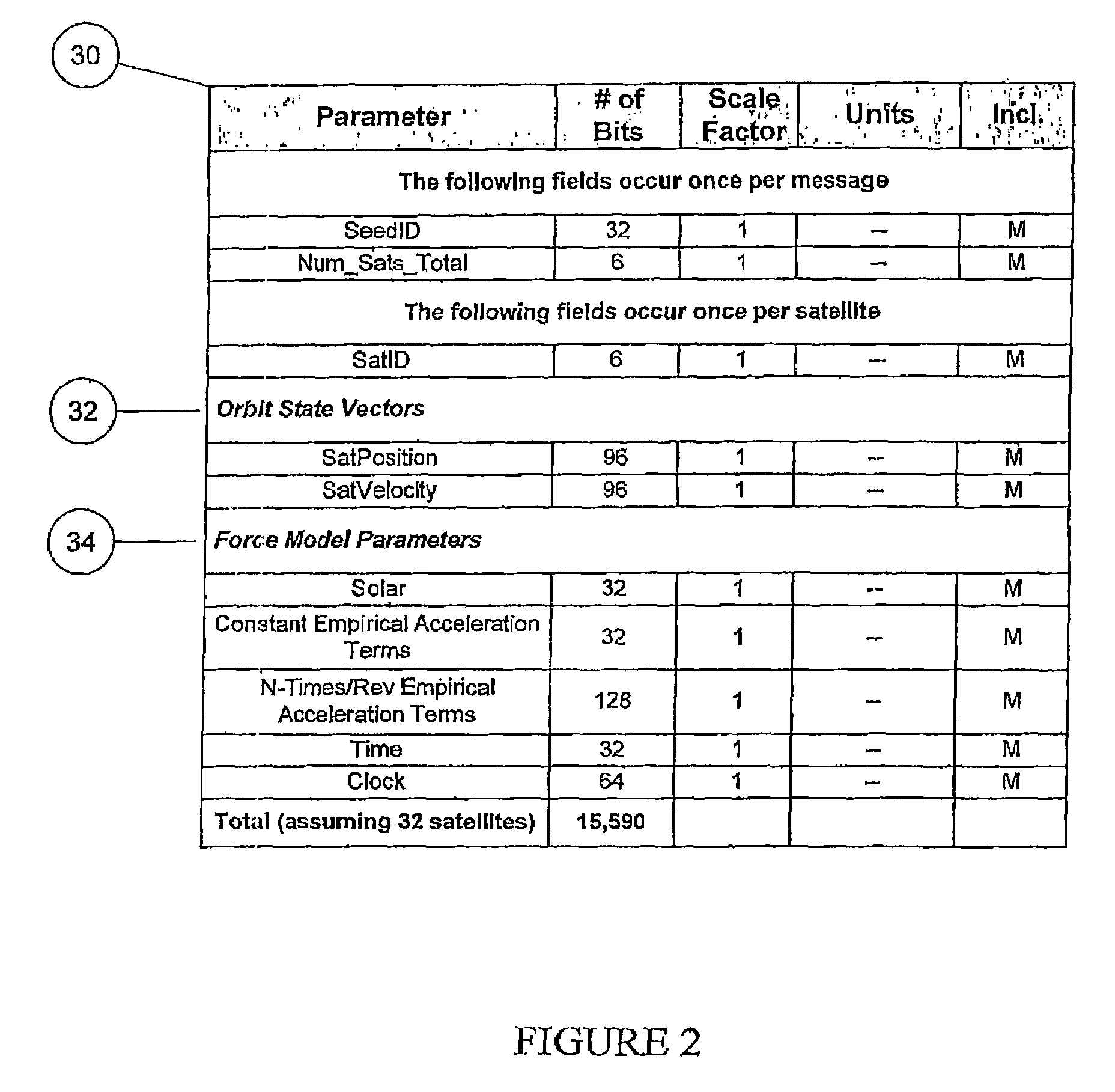
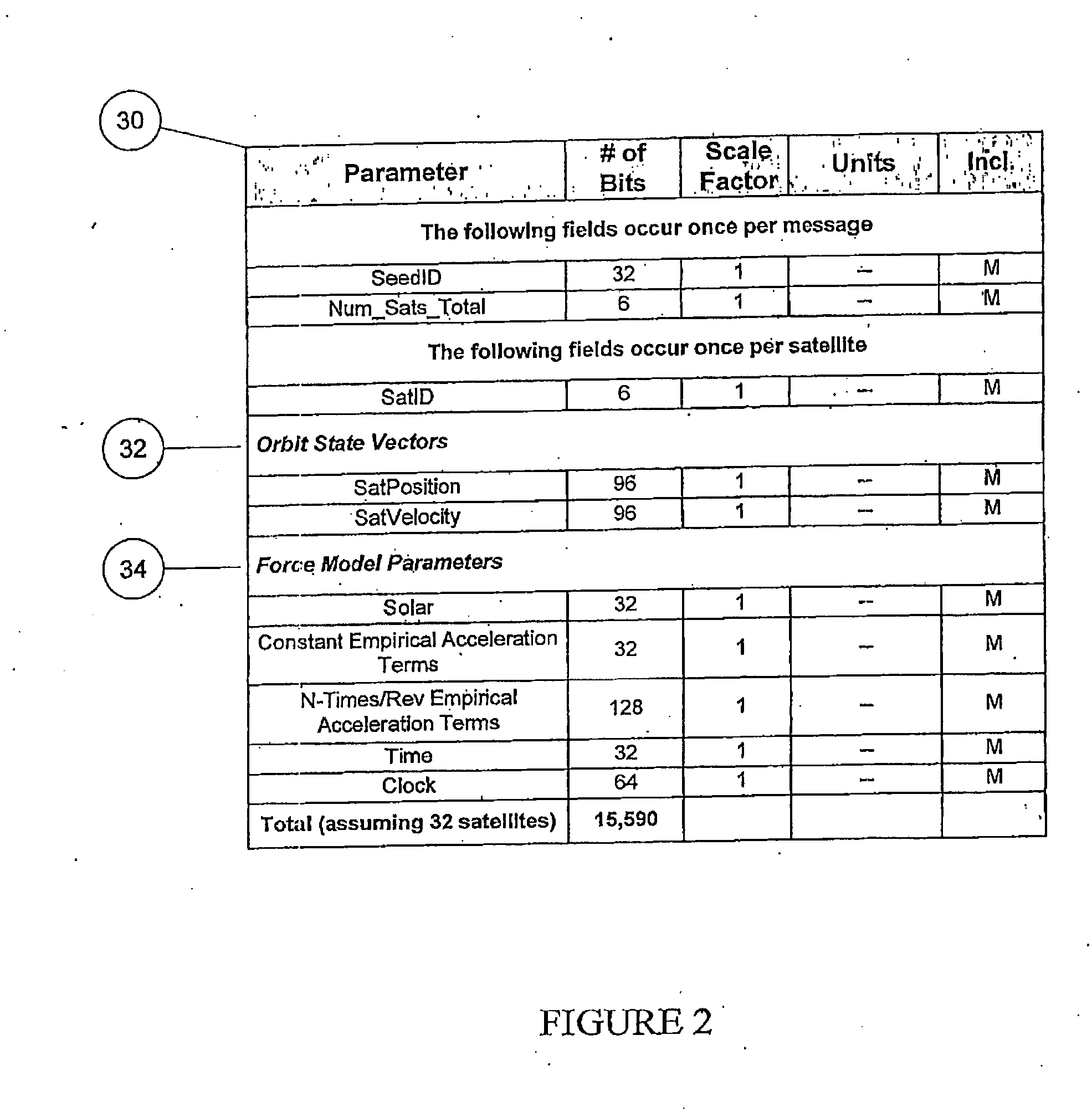
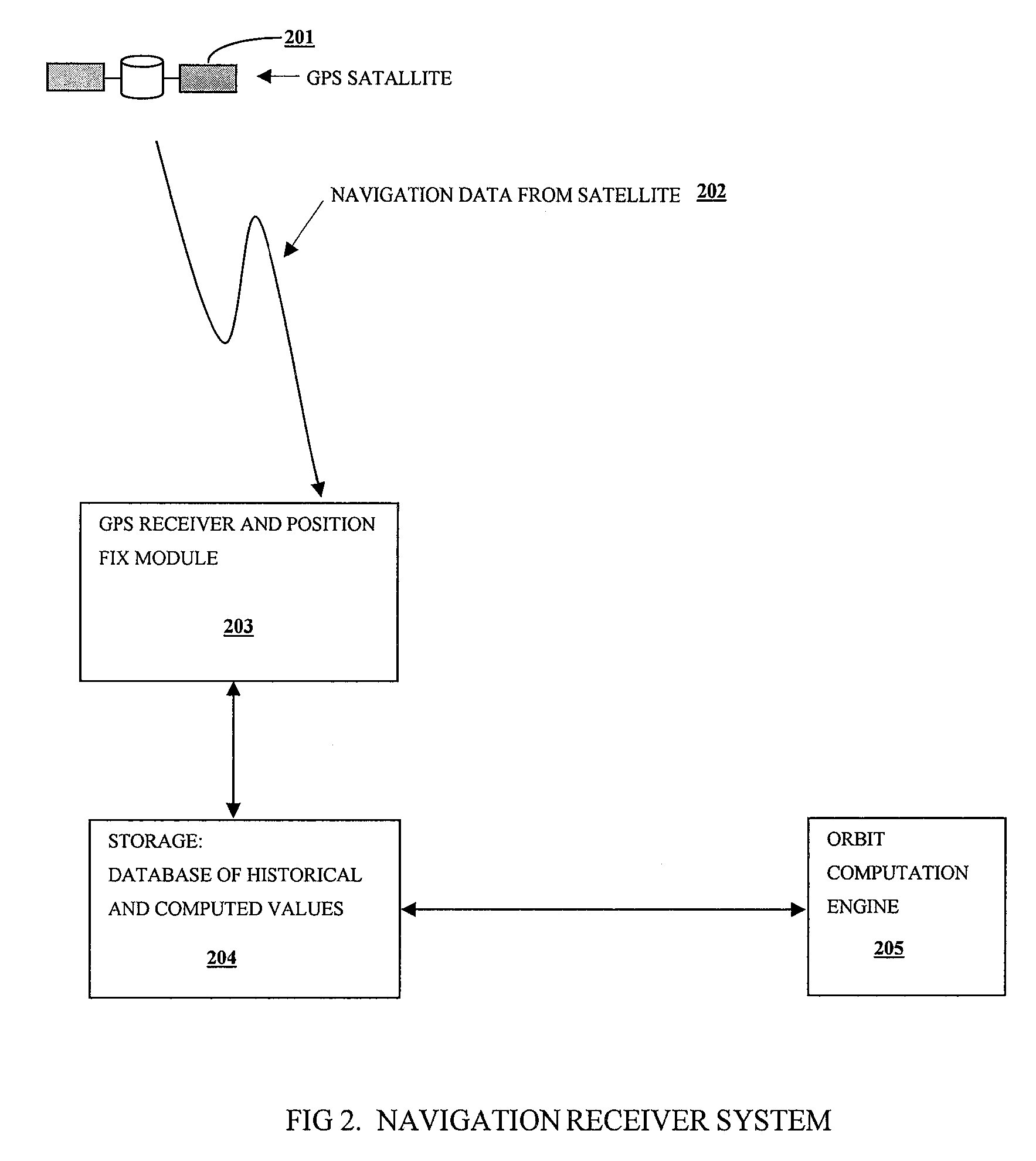
Distributed orbit modeling and propagation method for a predicted and real-time assisted GPS system
ActiveUS7612712B2Easy to integrateNavigational calculation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingData setTime to first fix
A distributed orbit and propagation method for use in a predicted GPS or GNSS system, which includes a predicted GPS server (PGPS Server), a source of high accuracy orbit predictions (Orbit Server), a global reference network (GRN Server) providing real-time GPS or GNSS assistance data to the PGPS Server, a predicted GPS client (PGPS Client) running on a device equipped with a GPS or AGPS chipset. In response to requests from the PGPS Client, the PGPS Server produces and disseminates an initial seed dataset consisting of current satellite orbit state vectors and orbit propagation model coefficients. This seed dataset enables the PGPS Client to locally predict and propagate satellite orbits to a desired future time. This predictive assistance in turn helps accelerate Time To First Fix (TTFF), optimize position solution calculations and improve the sensitivity of the GPS chip present on, or coupled with, the device. In contrast with other conventional predicted GPS systems that forward large volumes of predicted orbits, synthetic ephemeris or synthetic almanac data, this method optimally reduces data transfer requirements to the client, and enables the client to locally synthesize its own predicted assistance data as needed. This method also supports seamless notification of real-time satellite integrity events and seamless integration of predicted assistance data with industry standard real-time assistance data.
Owner:RX NETWORKS INC
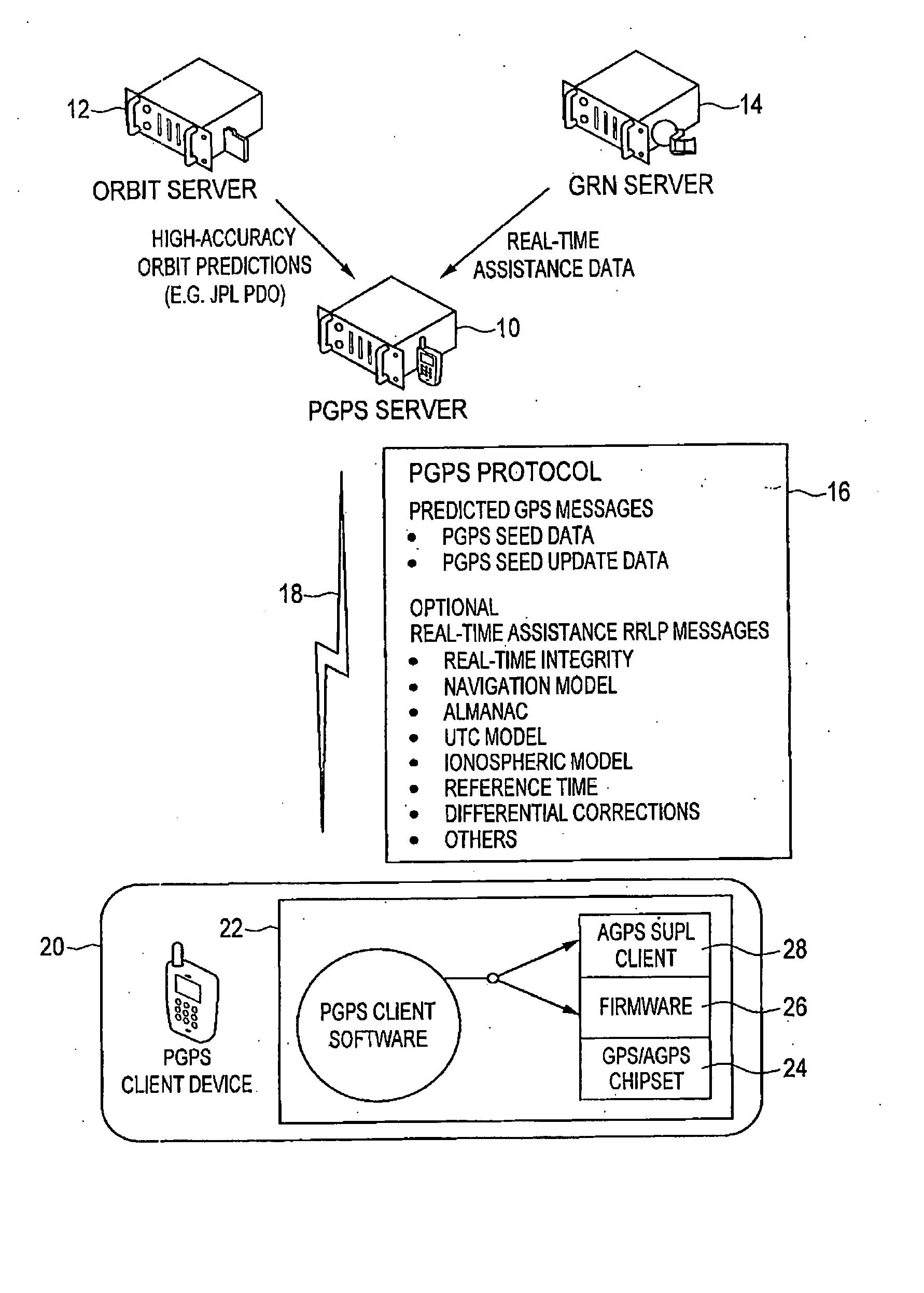
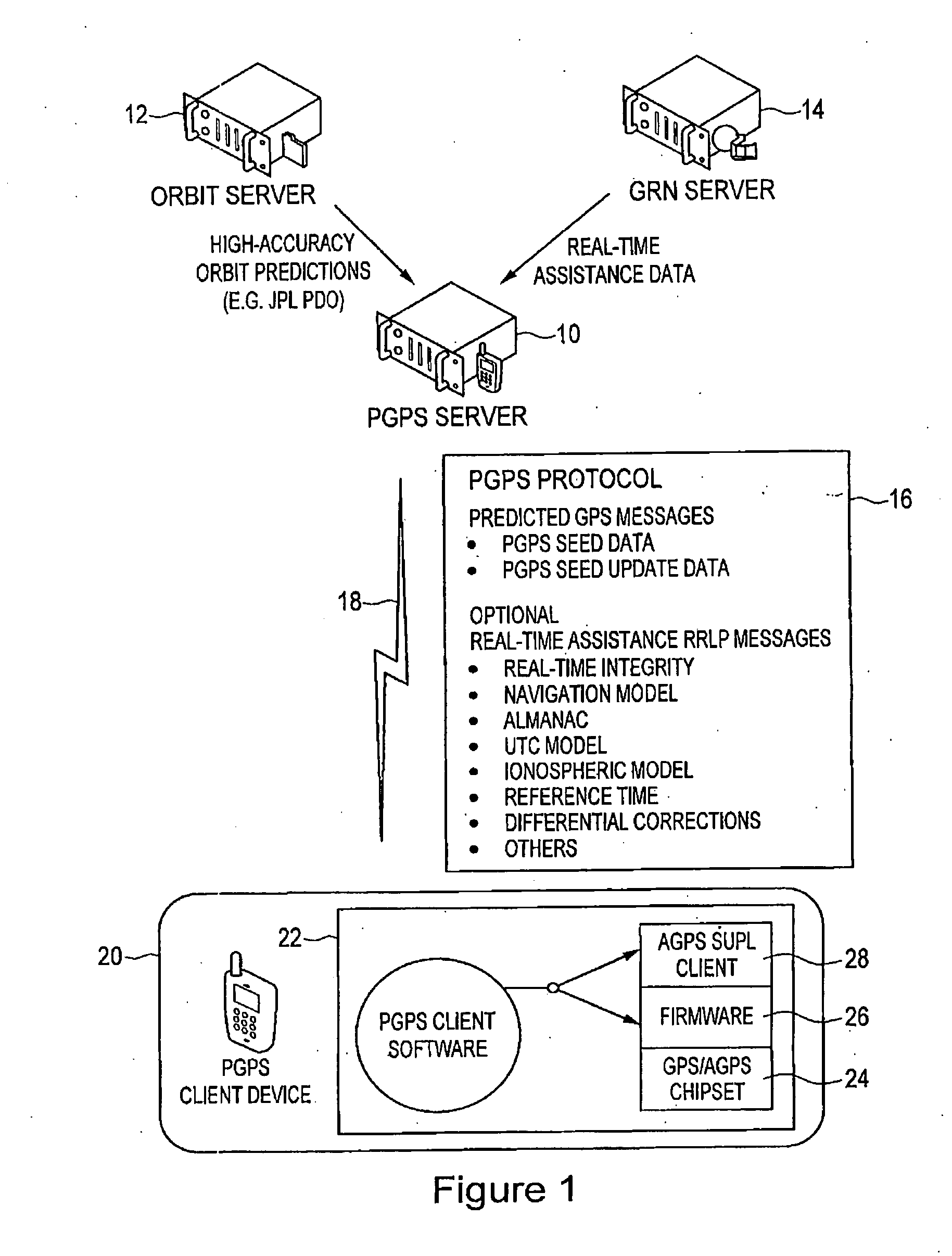
Distributed orbit modeling and propagation method for a predicted and real-time assisted GPS system
ActiveUS20080018527A1Easy to integrateNavigational calculation instrumentsRadio transmissionData setTime to first fix
A distributed orbit and propagation method for use in a predicted GPS or GNSS system, which includes a predicted GPS server (PGPS Server), a source of high accuracy orbit predictions (Orbit Server), a global reference network (GRN Server) providing real-time GPS or GNSS assistance data to the PGPS Server, a predicted GPS client (PGPS Client) running on a device equipped with a GPS or AGPS chipset. In response to requests from the PGPS Client, the PGPS Server produces and disseminates an initial seed dataset consisting of current satellite orbit state vectors and orbit propagation model coefficients. This seed dataset enables the PGPS Client to locally predict and propagate satellite orbits to a desired future time. This predictive assistance in turn helps accelerate Time To First Fix (TTFF), optimize position solution calculations and improve the sensitivity of the GPS chip present on, or coupled with, the device. In contrast with other conventional predicted GPS systems that forward large volumes of predicted orbits, synthetic ephemeris or synthetic almanac data, this method optimally reduces data transfer requirements to the client, and enables the client to locally synthesize its own predicted assistance data as needed. This method also supports seamless notification of real-time satellite integrity events and seamless integration of predicted assistance data with industry standard real-time assistance data.
Owner:RX NETWORKS INC
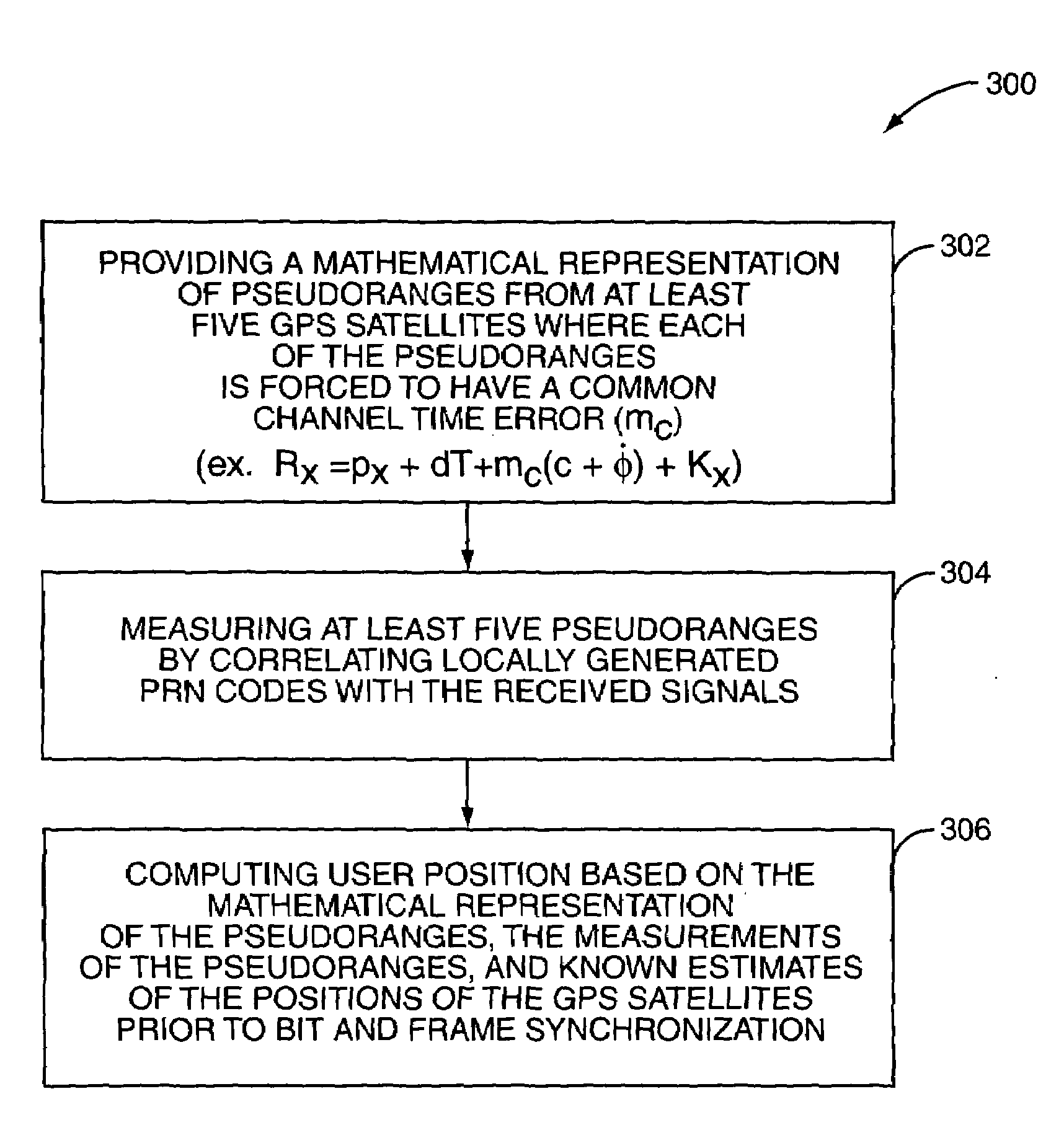
System and method for GPS navigation before signal bit synchronization
InactiveUS7064709B1Not substantially improve time-to-first-fixTime-to-first-fix is substantially reducedPosition fixationRadio transmissionTime errorTime to first fix
A system and method are provided for determining a position of a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver prior to bit and frame synchronization. As such, the time-to-first-fix is substantially reduced. More specifically, pseudoranges to five GPS satellites are measured by correlating locally generated Pseudo-Random Number (PRN) codes with signals received from the GPS satellites. After correlation, the pseudorange measurements are correct with an unknown integer number of milliseconds error, which is different for each of the pseudorange measurements. Using the measurements of the pseudoranges and a mathematical model where each of the pseudorange measurements is forced to have a common channel time error, the user position and the common channel time error are determined prior to bit and frame synchronization.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Subscriber unit, a cellular communication system and a method for determining a location therefor
InactiveUS20050280576A1Easy to updateImprove reliabilityDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationTime to first fixCellular communication systems
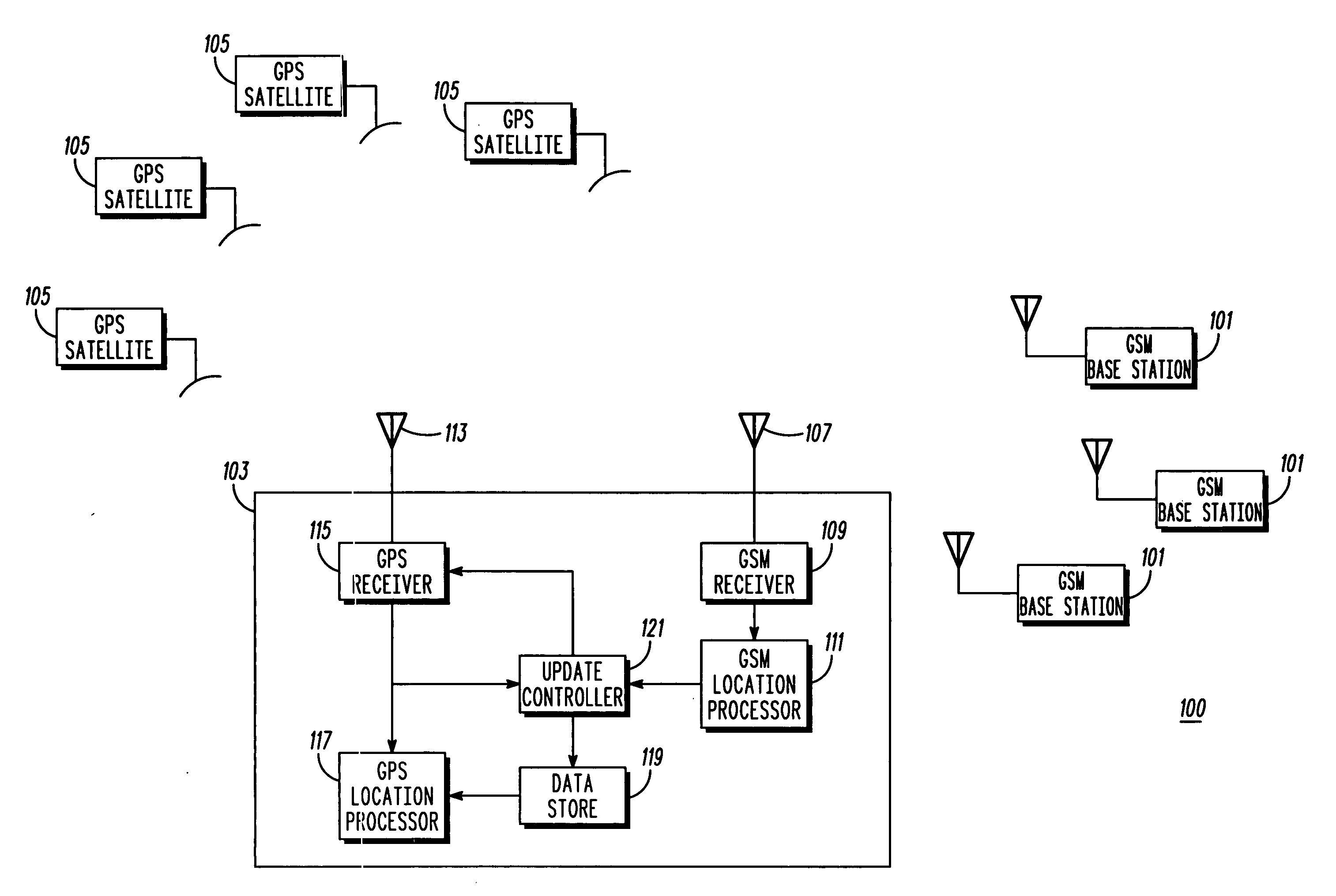
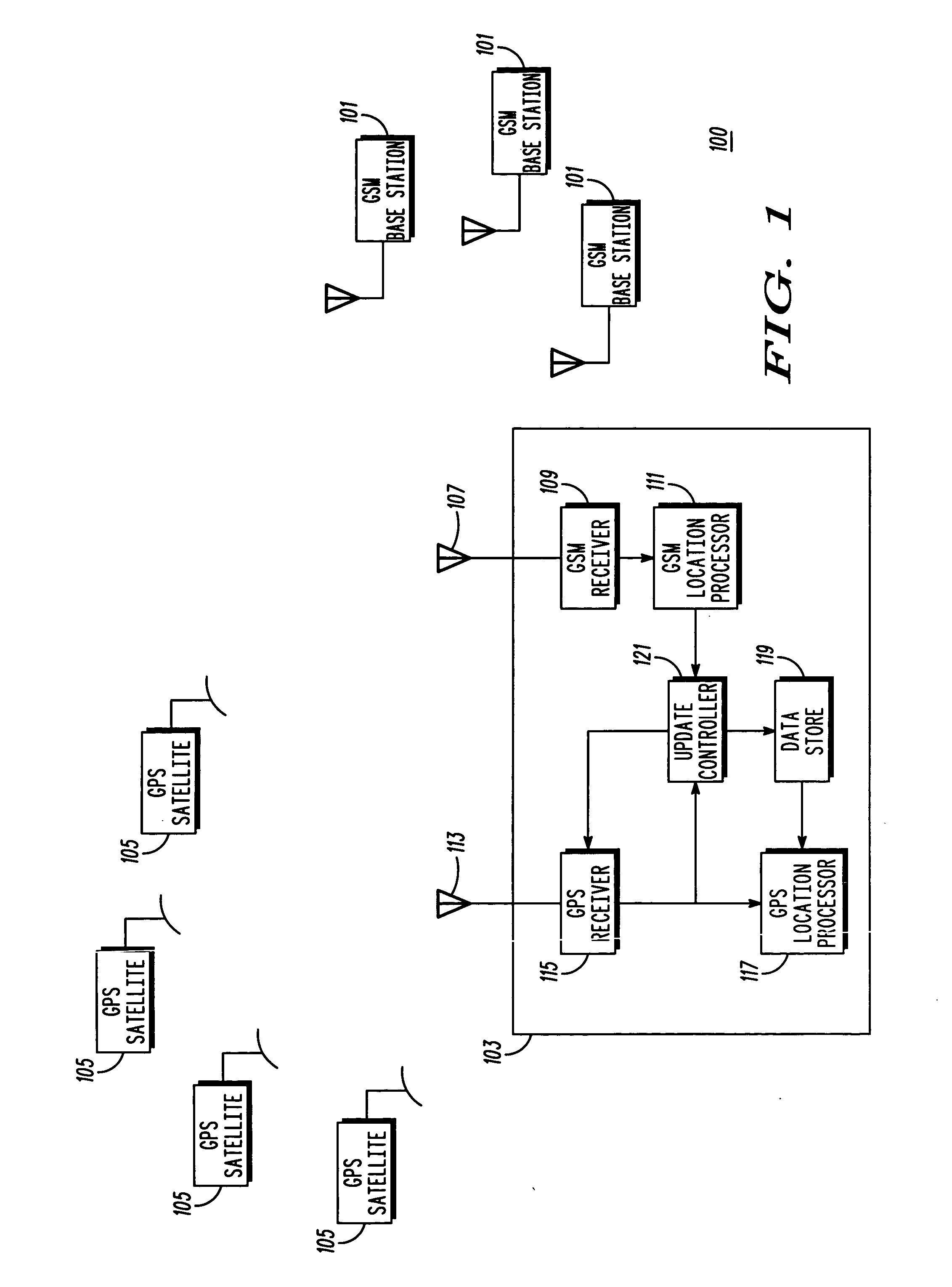
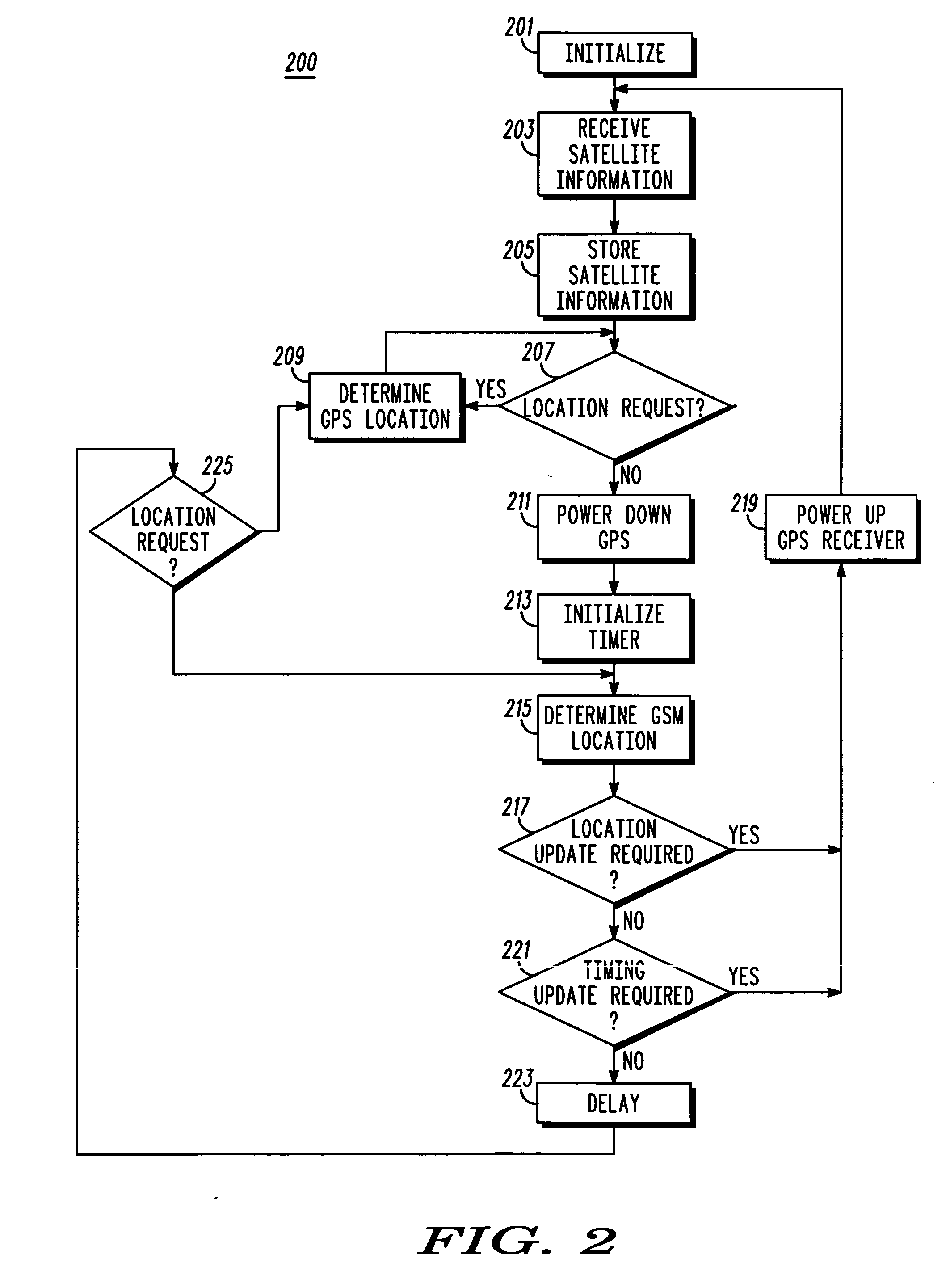
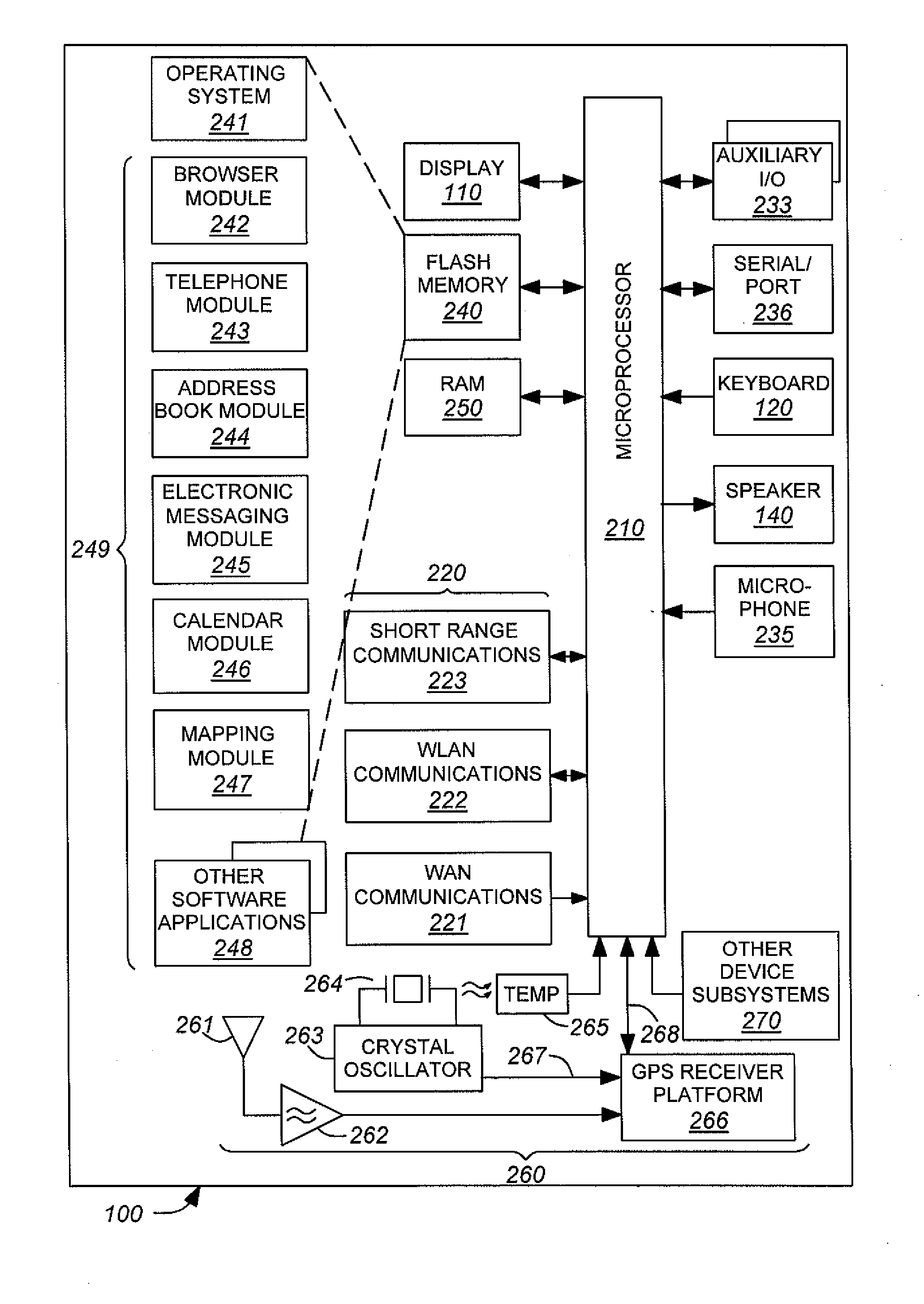
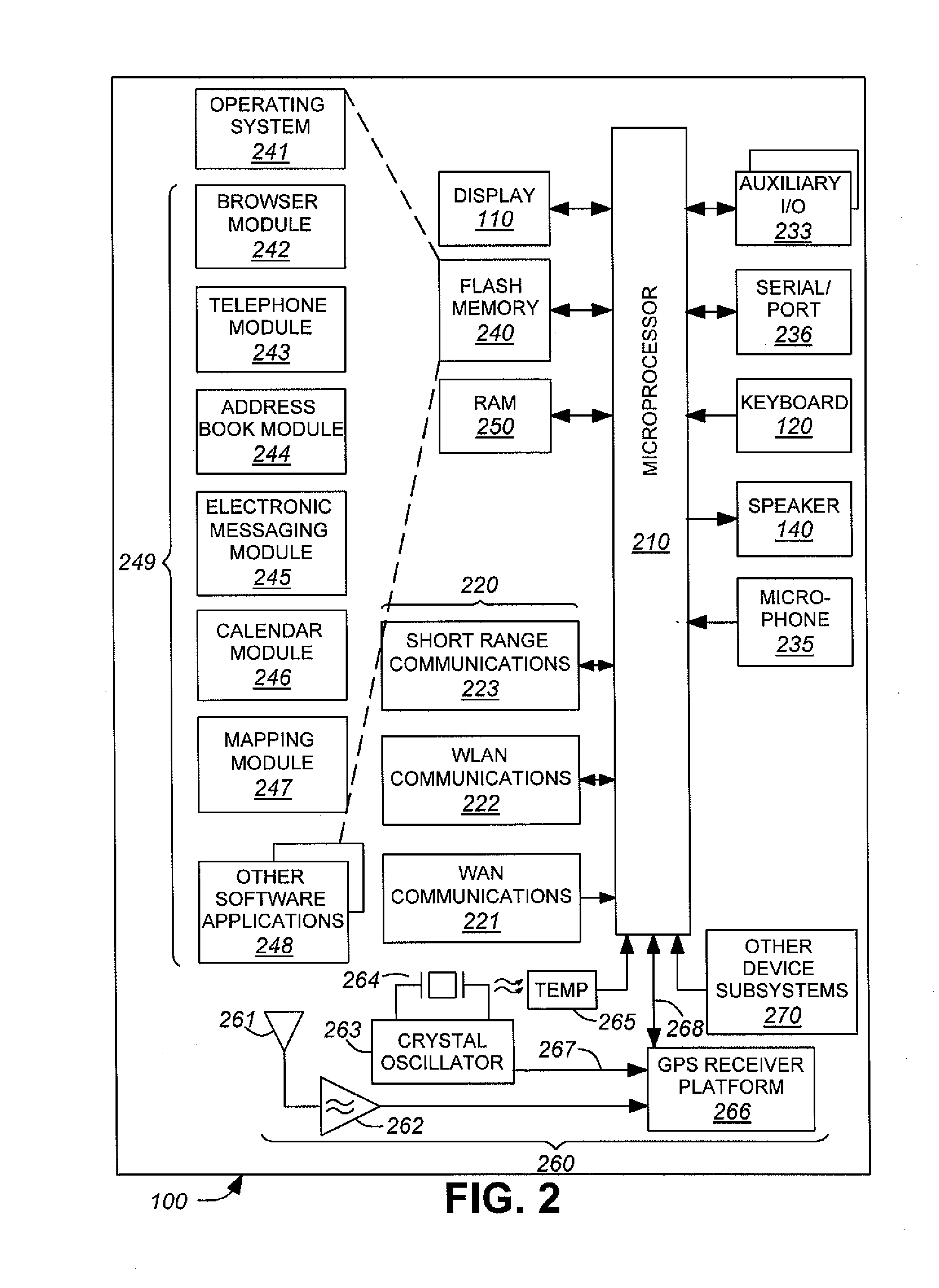
A subscriber unit (103) for a cellular communication system (100) comprises a first location processor (117) which determines a location estimate from signals transmitted from satellites (105) and from satellite information related to the satellites (105). The satellites (105) may be Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites. The subscriber unit (103) also comprises a receiver (115) which receives the satellite information, and further comprises a second location processor (111) which determines location estimates based on uplink or downlink transmissions in the cellular communication system (100). An update controller (121) determines an update time for the satellite information in response to the location estimates of the second location processor (111). Accordingly, the update operation may be optimised for the specific movement of the subscriber unit (103) without requiring satellite based location estimates. This may improve location determination accuracy, time to first fix and may reduce power consumption.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC +2
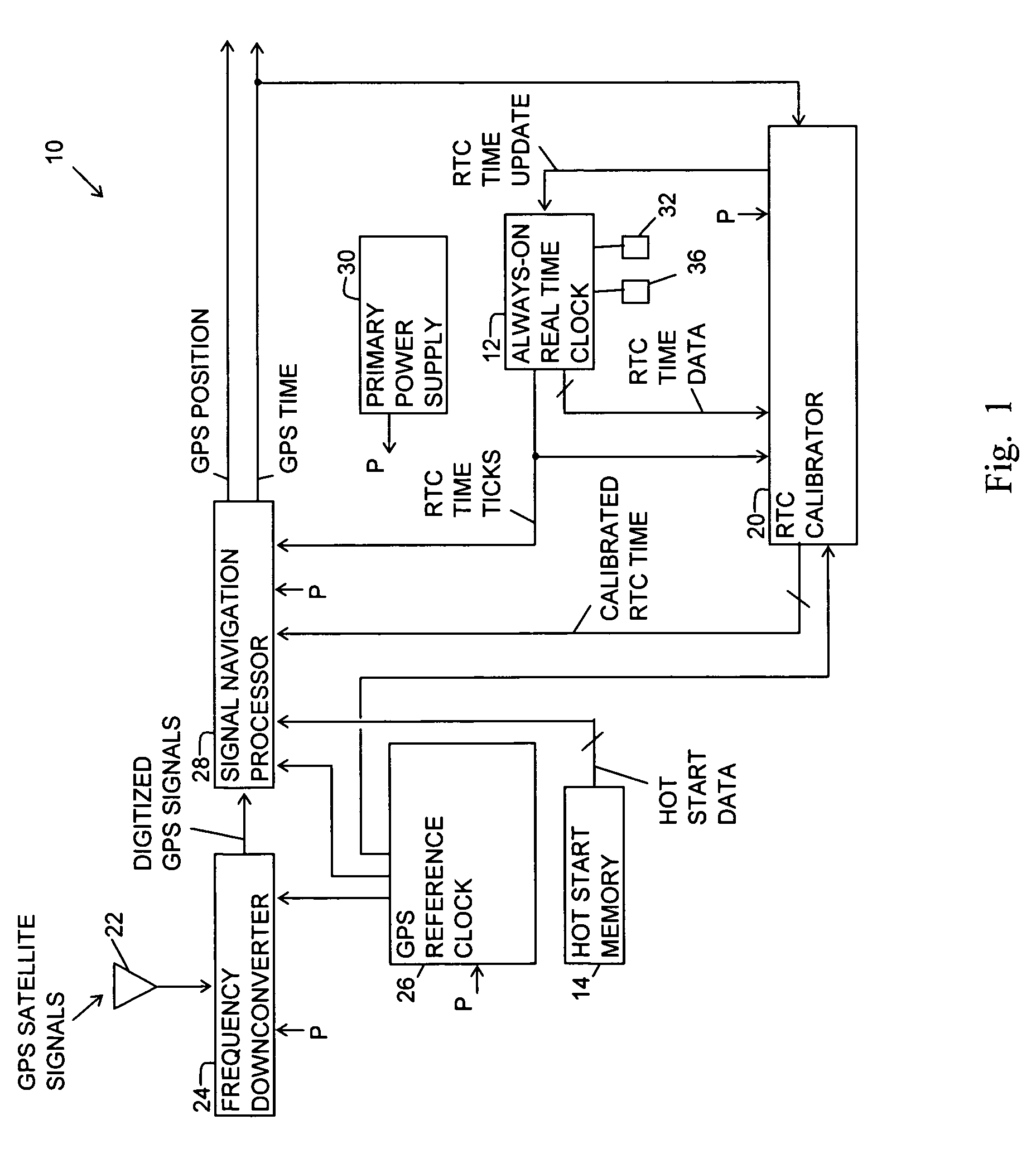
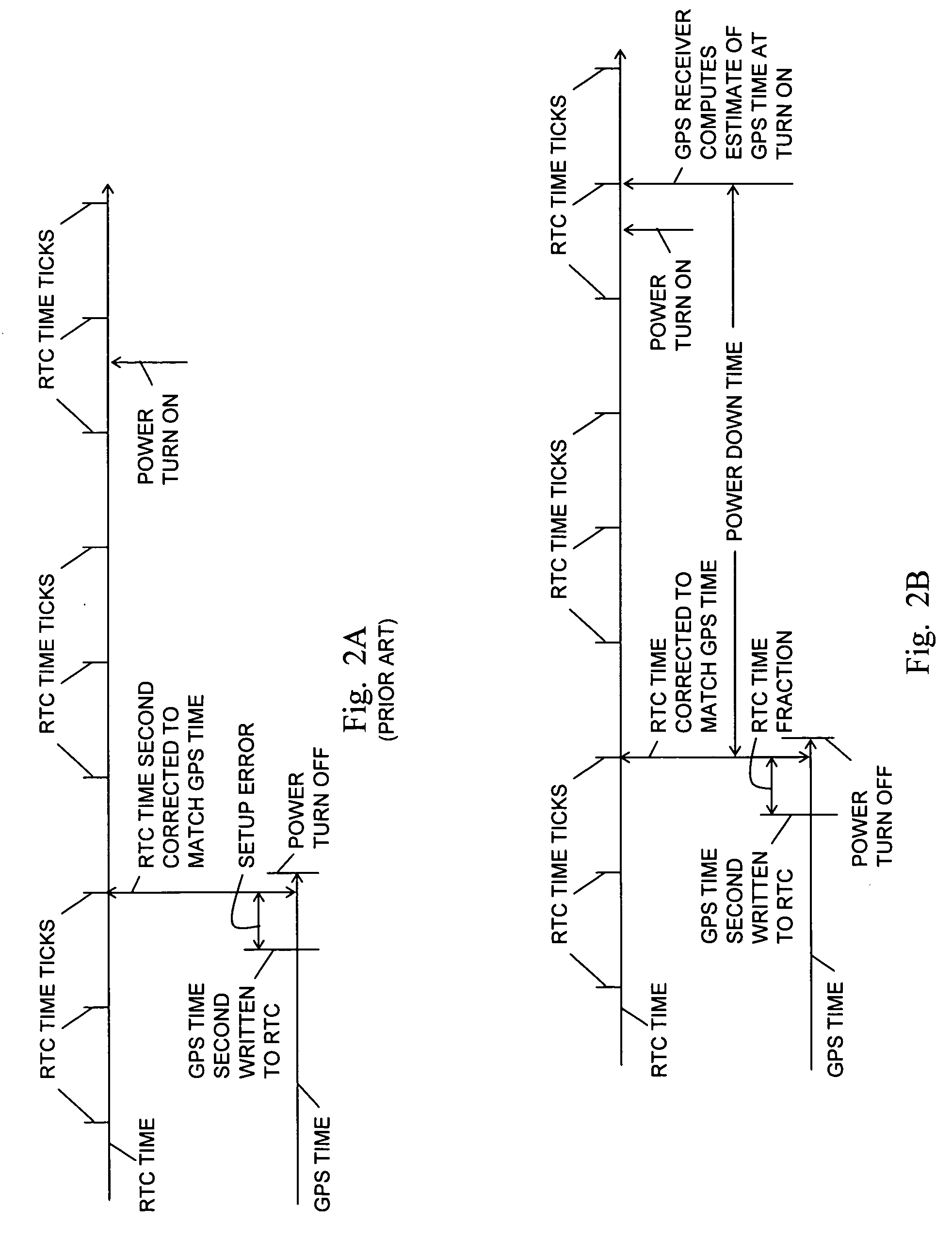
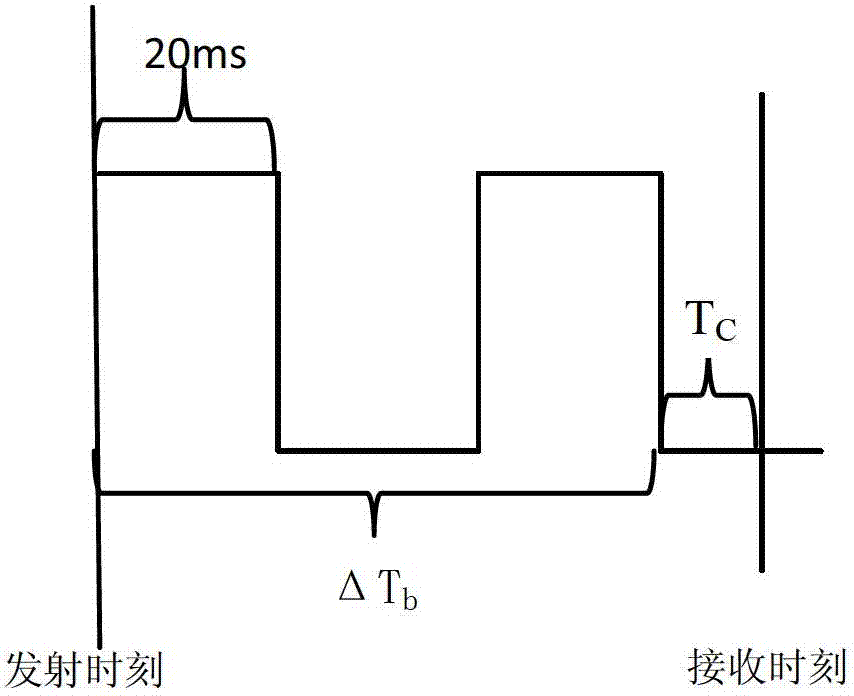
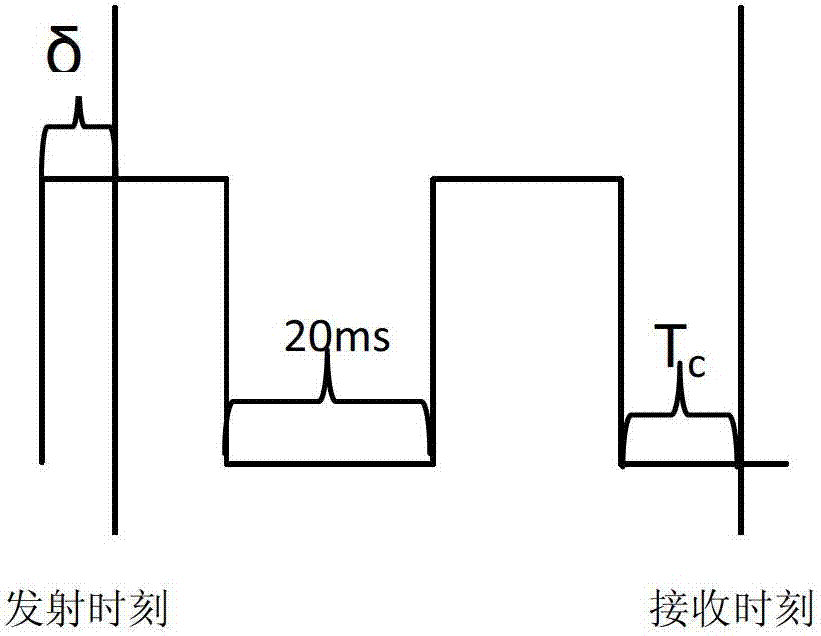
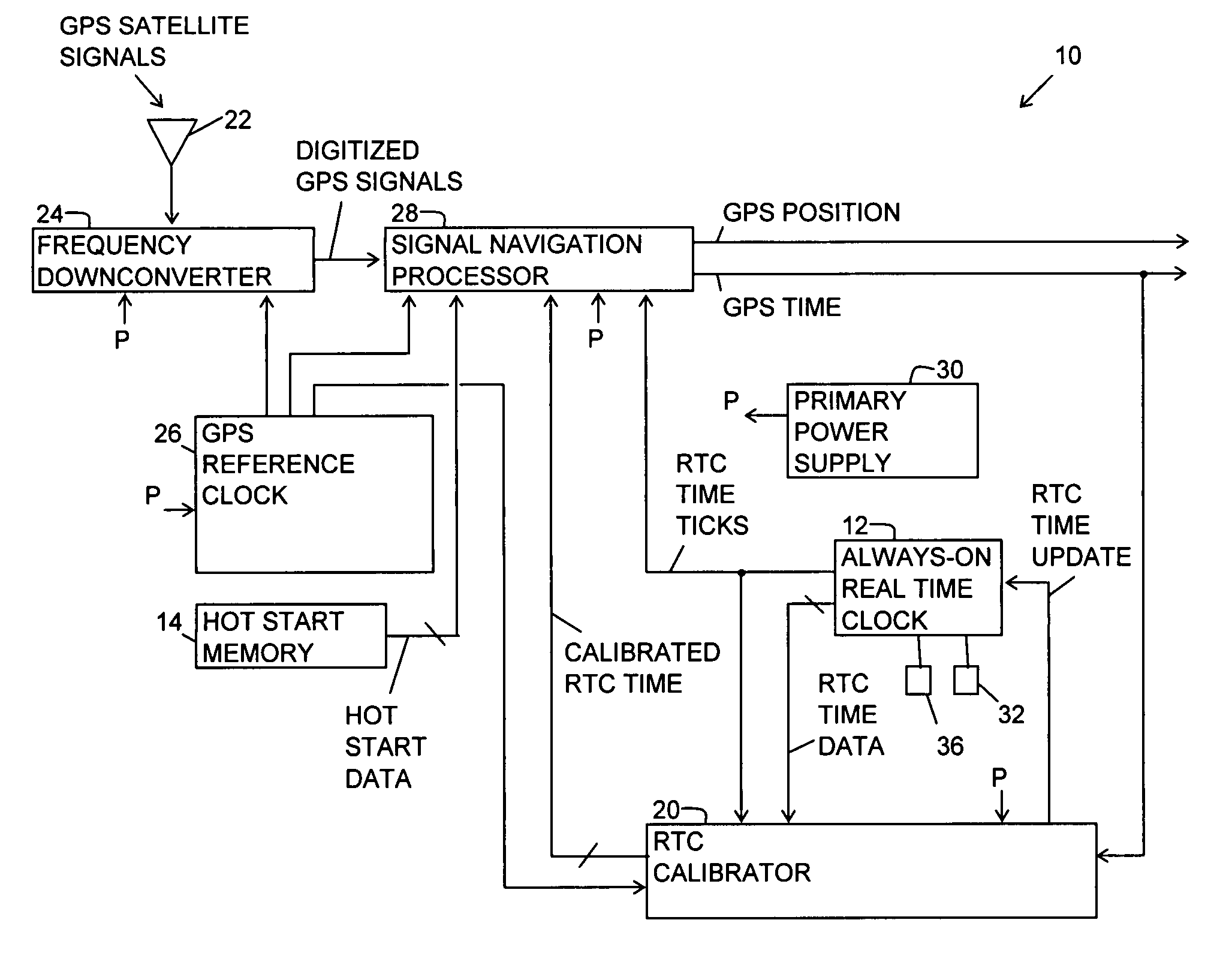
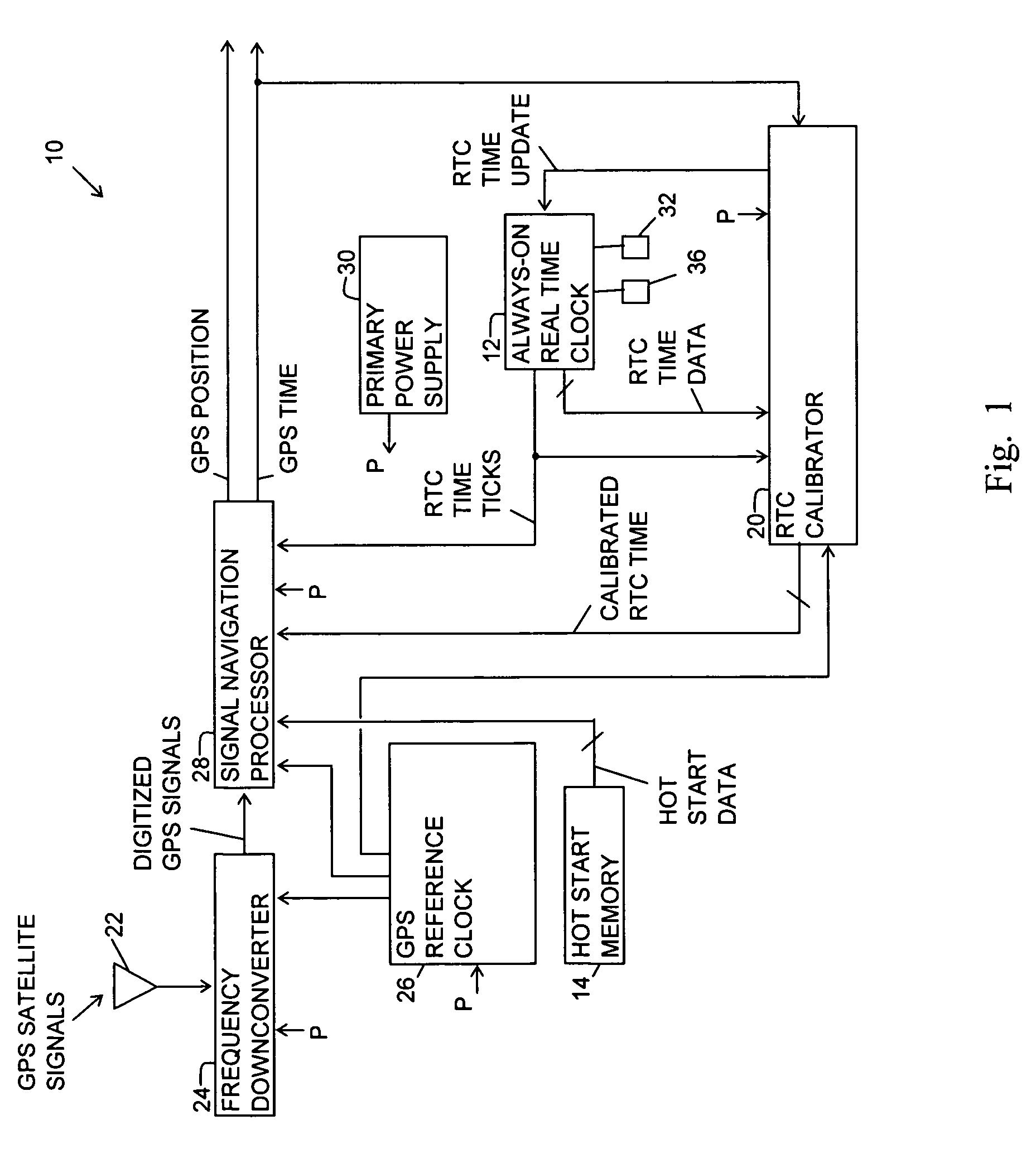
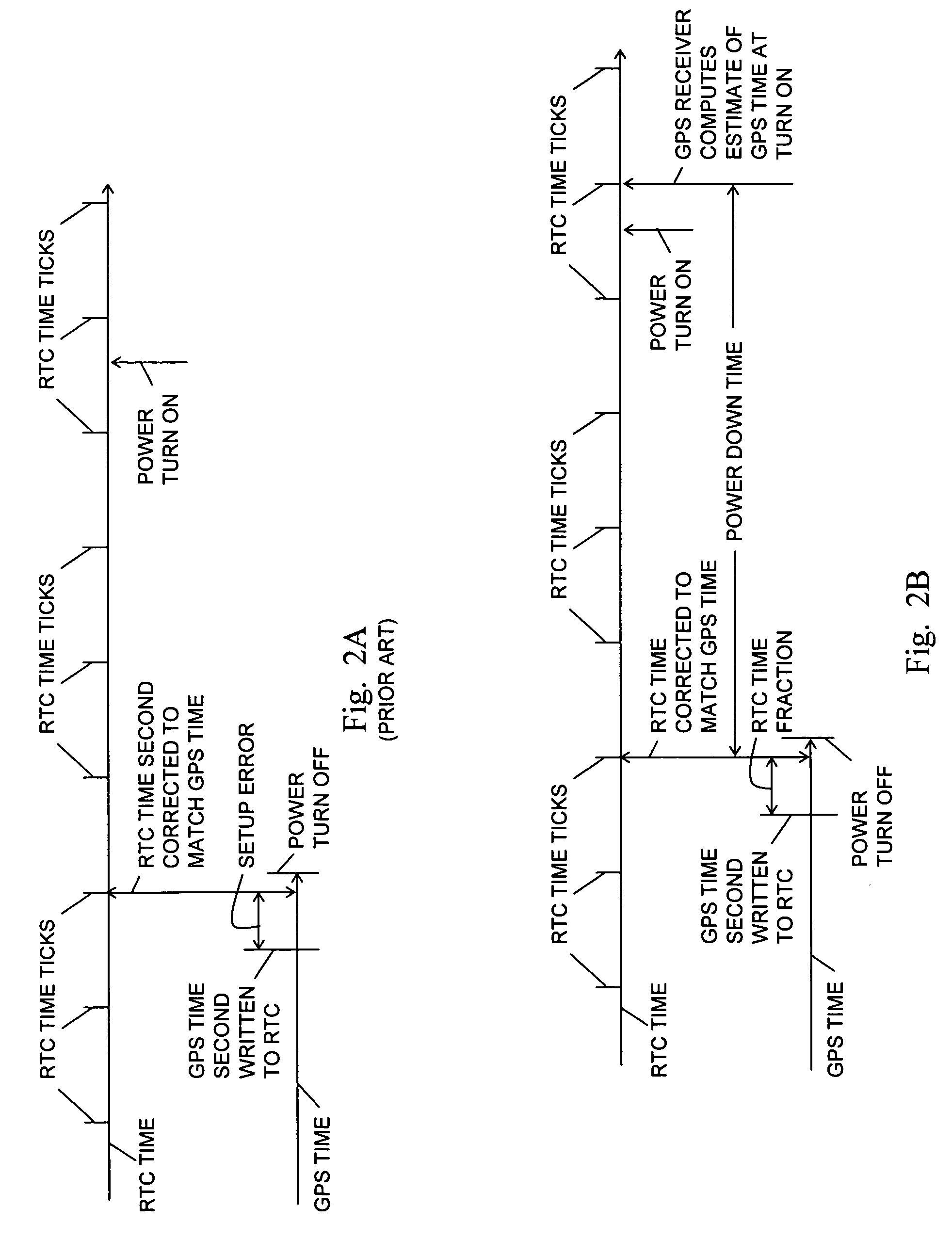
Fast time to first fix by calibration of a real time clock
ActiveUS20070268180A1Fast timeLow powerPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingReal-time clockImage resolution
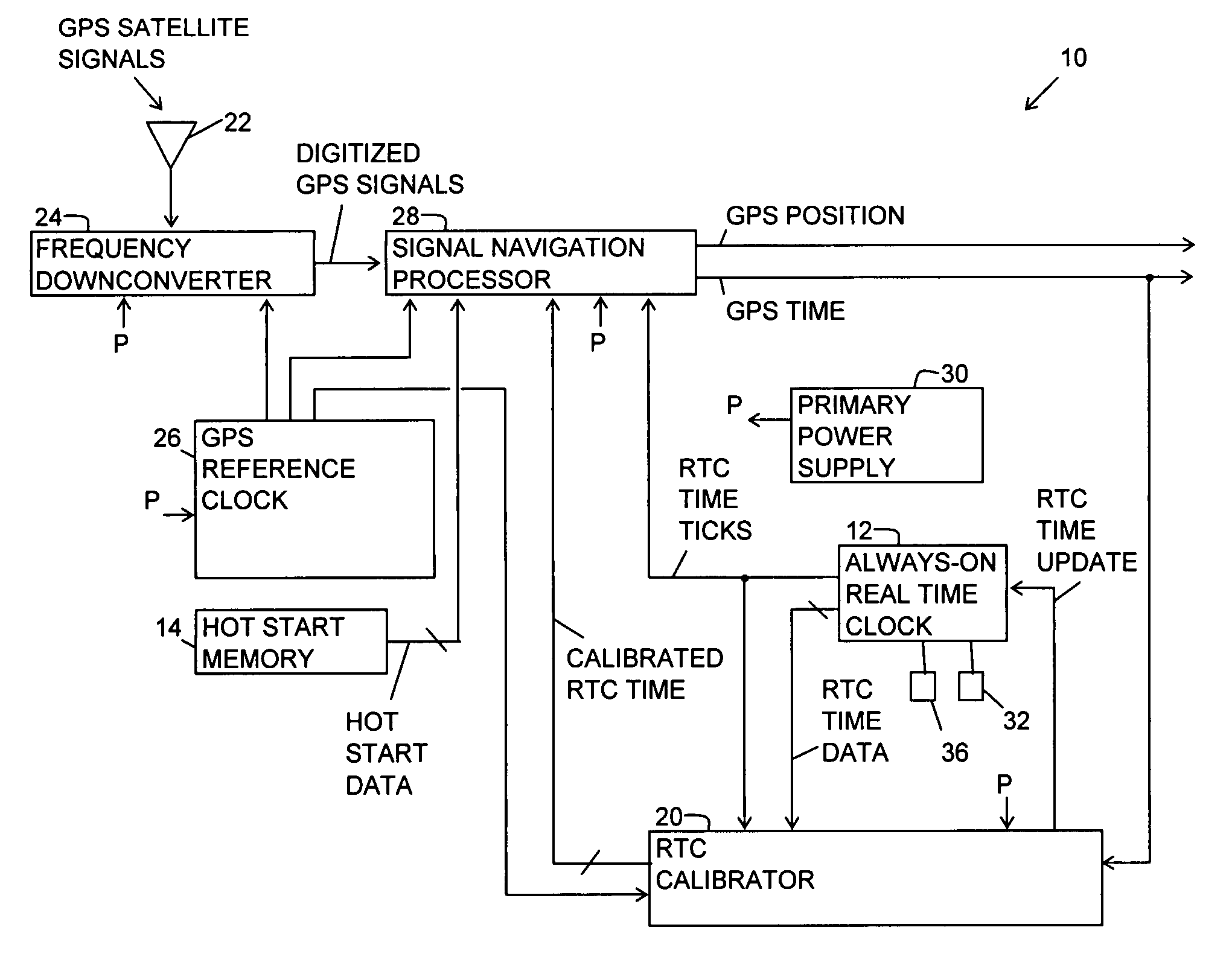
A generic navigation satellite system (GNSS) signal receiver having a fast time to first fix by calibrating a low power always-on real time clock (RTC). The receiver includes an RTC calibrator having a fraction calculator and a time expander. Before the receiver is powered off, the fraction calculator uses the fine resolution of GNSS time for determining a time fraction for RTC time. When the receiver is powered back on, the time expander uses an estimate of RTC time drift during the time that GNSS receiver had power off and the time fraction for calibrating and increasing the resolution of the RTC time for an RTC time tick. A signal navigation processor uses the calibrated RTC time for assisting a first fix with code phase search, integration time periods, resolution of epoch integer and / or location-in-space of GPS satellites.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
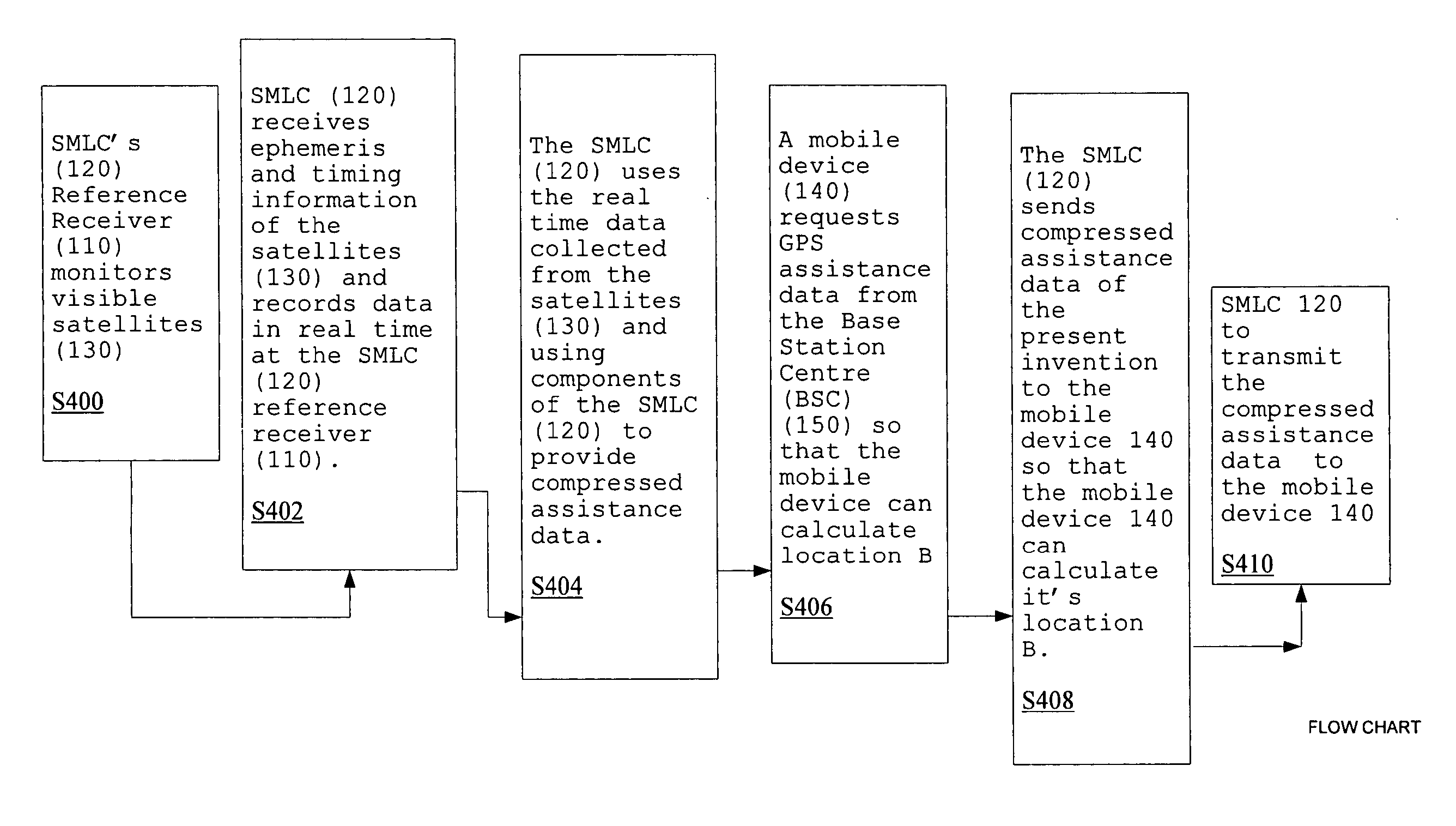
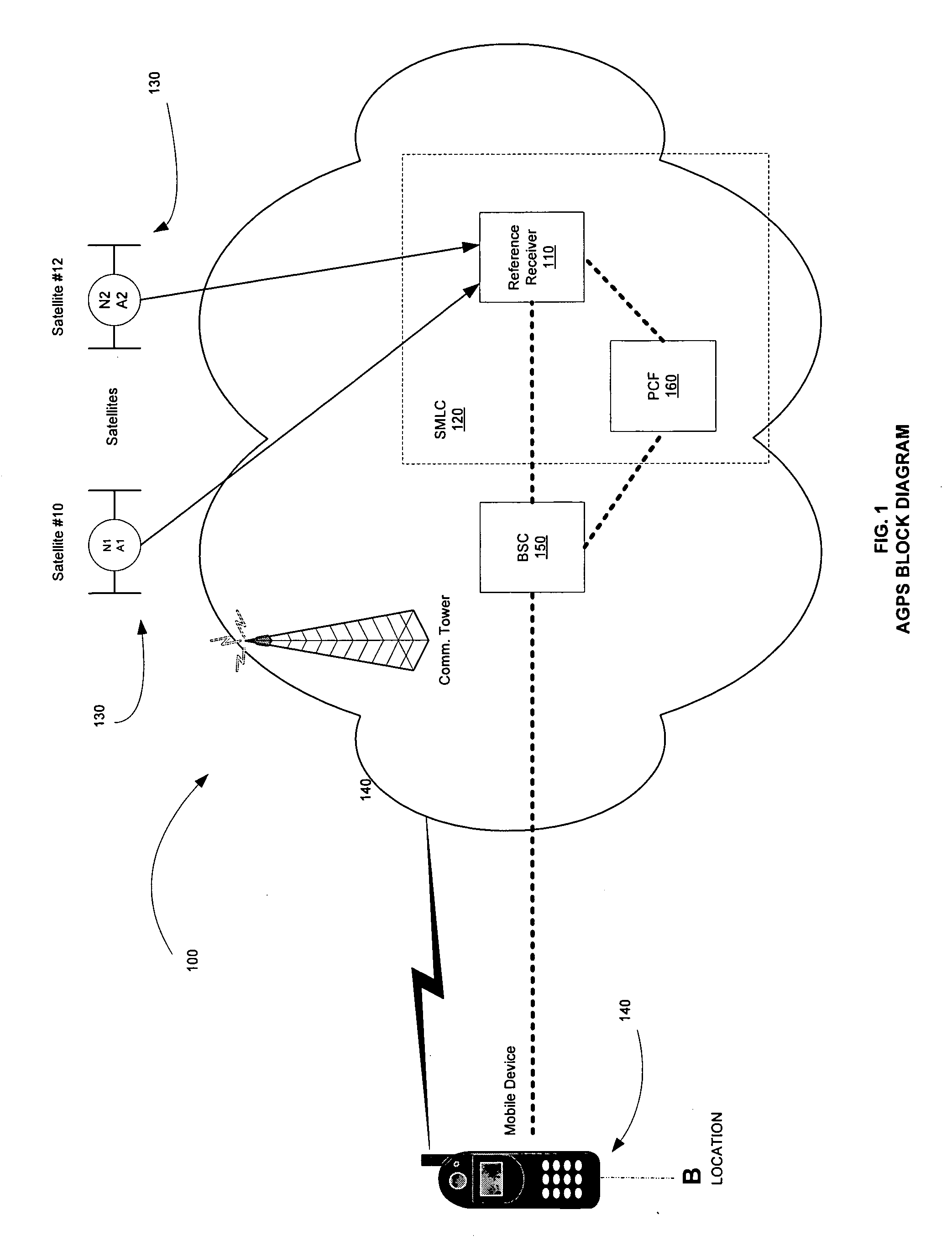
Method of compressing GPS assistance data to reduce the time for calculating a location of a mobile device
InactiveUS20070257838A1Eliminates long start timeHigh sensitivityPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingData informationTime to first fix
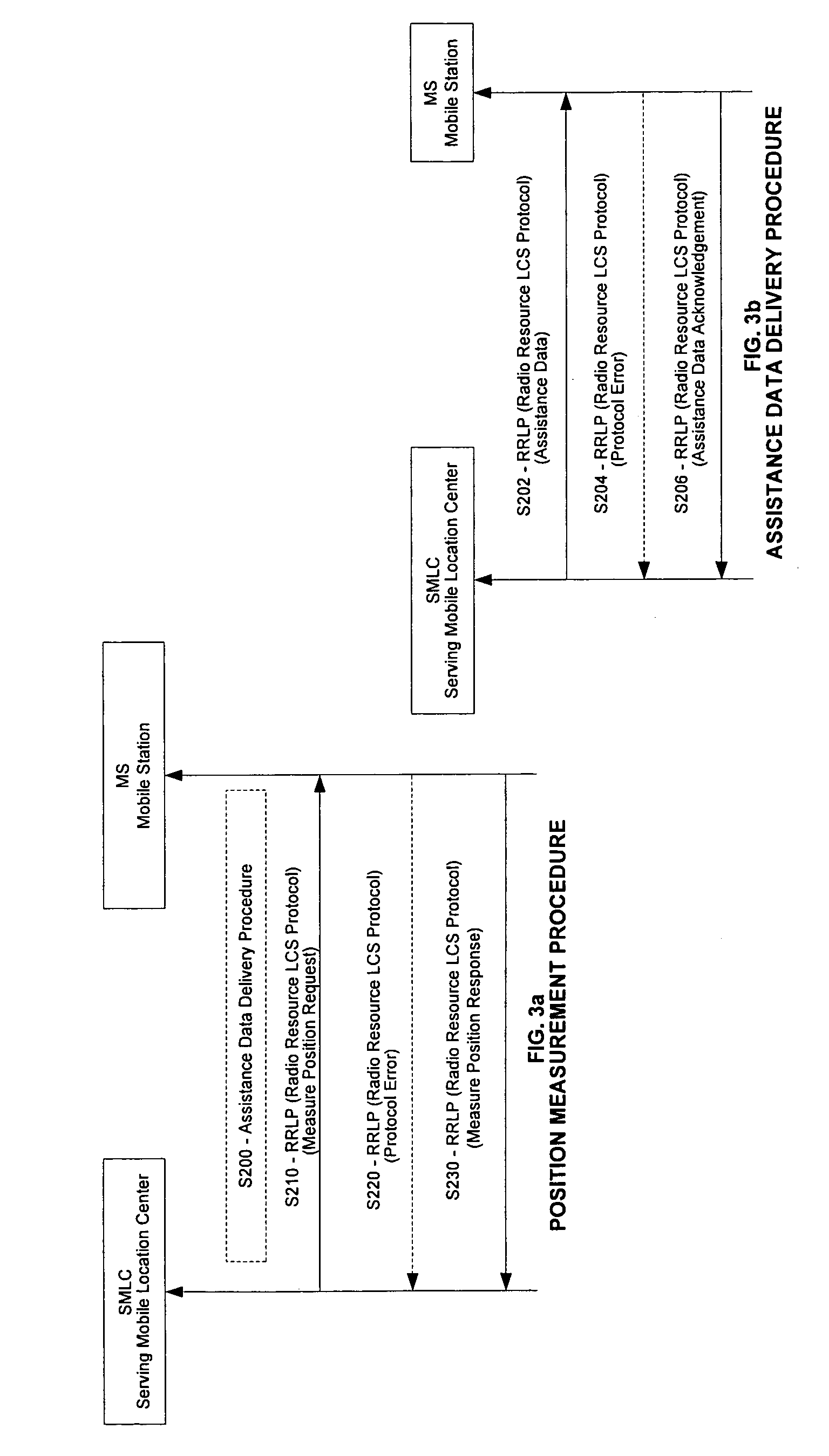
The invention relates to global positioning system (GPS) assistance data, and in particular, an embodiment in which a method of compressing GPS assistance data reduces the time to transmit data and also reduce time to calculate a location for a mobile device, such as a wireless telecommunications device. The method is especially-well suited for satellites have similar Almanac and / or Navigation Model information elements. The time for a Serving Mobile Location Centre (SMLC) to transmit the compressed assistance data to the mobile device is thus reduced. This eventually reduces the total time for a mobile device to calculate its location based on the assistance data information. Hence the time to first fix (TTFF) which is the time to calculate the first “fix” (also known as the first calculated location) is reduced.
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
Frequency aiding method and system for navigation satellite receiver with crystal oscillator frequency hysteresis
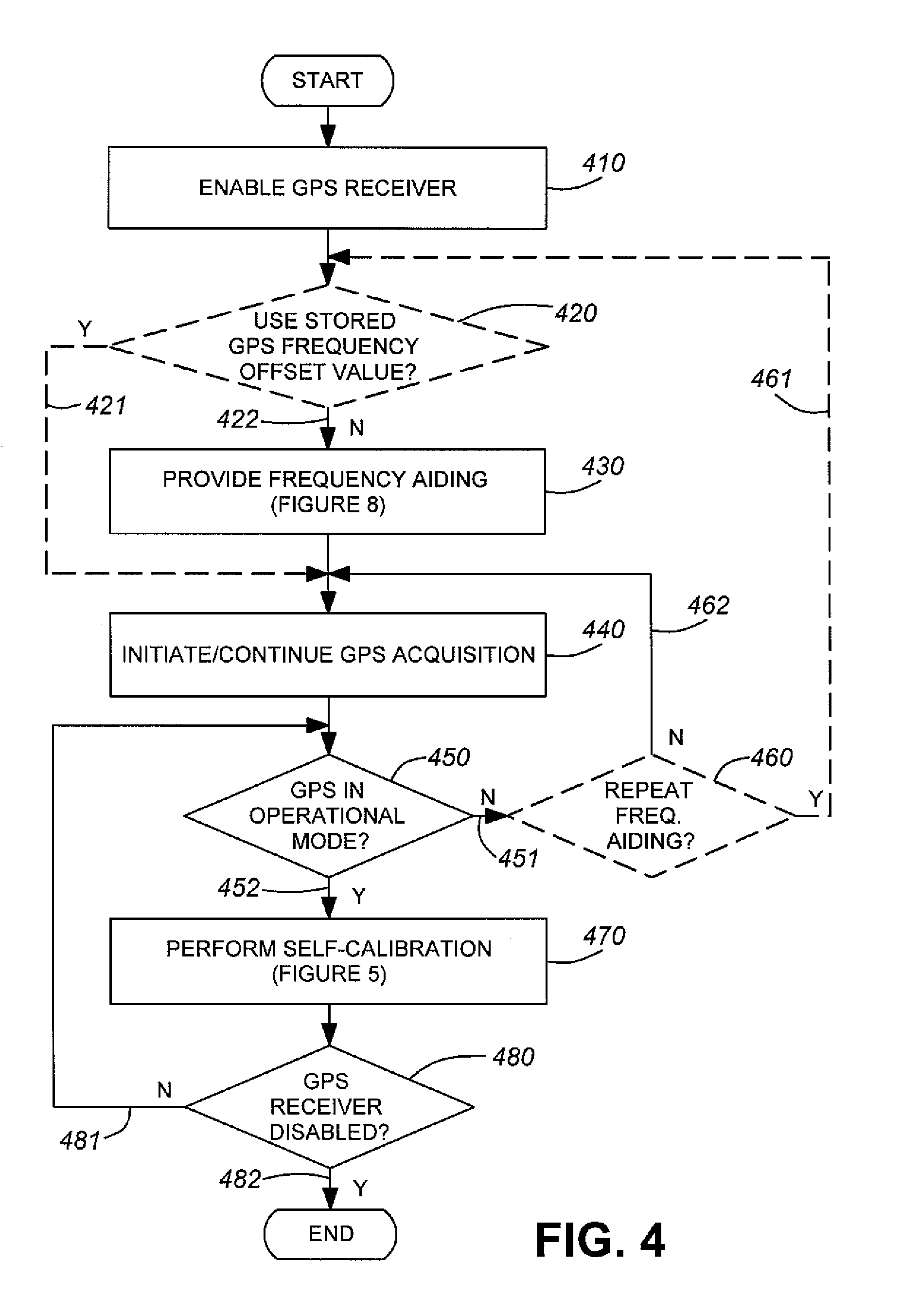
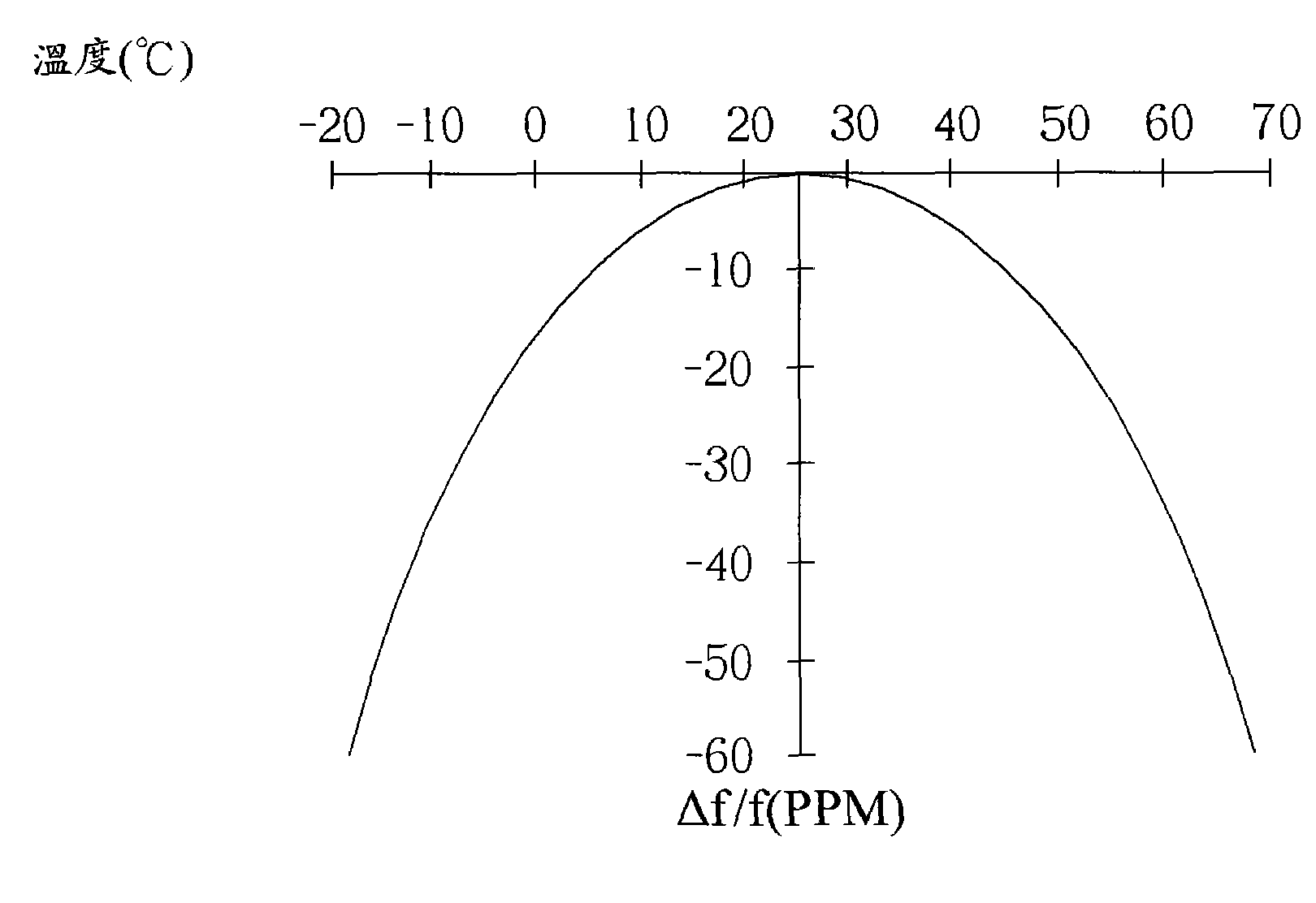
A method and apparatus for estimating oscillator signal variation due to temperature and for providing an estimated frequency to a GPS receiver in order to assist the GPS receiver to acquire the signals quickly is disclosed. A temperature sensor is closely thermally coupled with the crystal oscillator in the GPS receiver and during GPS tracking mode, when the error in the oscillator signal is known with precision, outer bounds of TCXO frequency at given temperatures are maintained, which may correspond to rising and falling temperature conditions. During acquisition mode, an estimated frequency value is provided to the GPS receiver based on a determined average of these bounds. Optionally, an uncertainty factor associated with the frequency estimated may also be provided. The two bounds take into account the hysteresis effects of the oscillator signal drift due to temperature so that a more accurate initial frequency estimate can be provided to the GPS receiver, thus reducing its average time to first fix.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus for self-calibration and adaptive temperature compensation in GPS receivers
InactiveUS7459984B2Quick initializationShort Time-To-First-Fix (TTFF)Radiation pyrometryTemperatue controlTime to first fixSelf adaptive
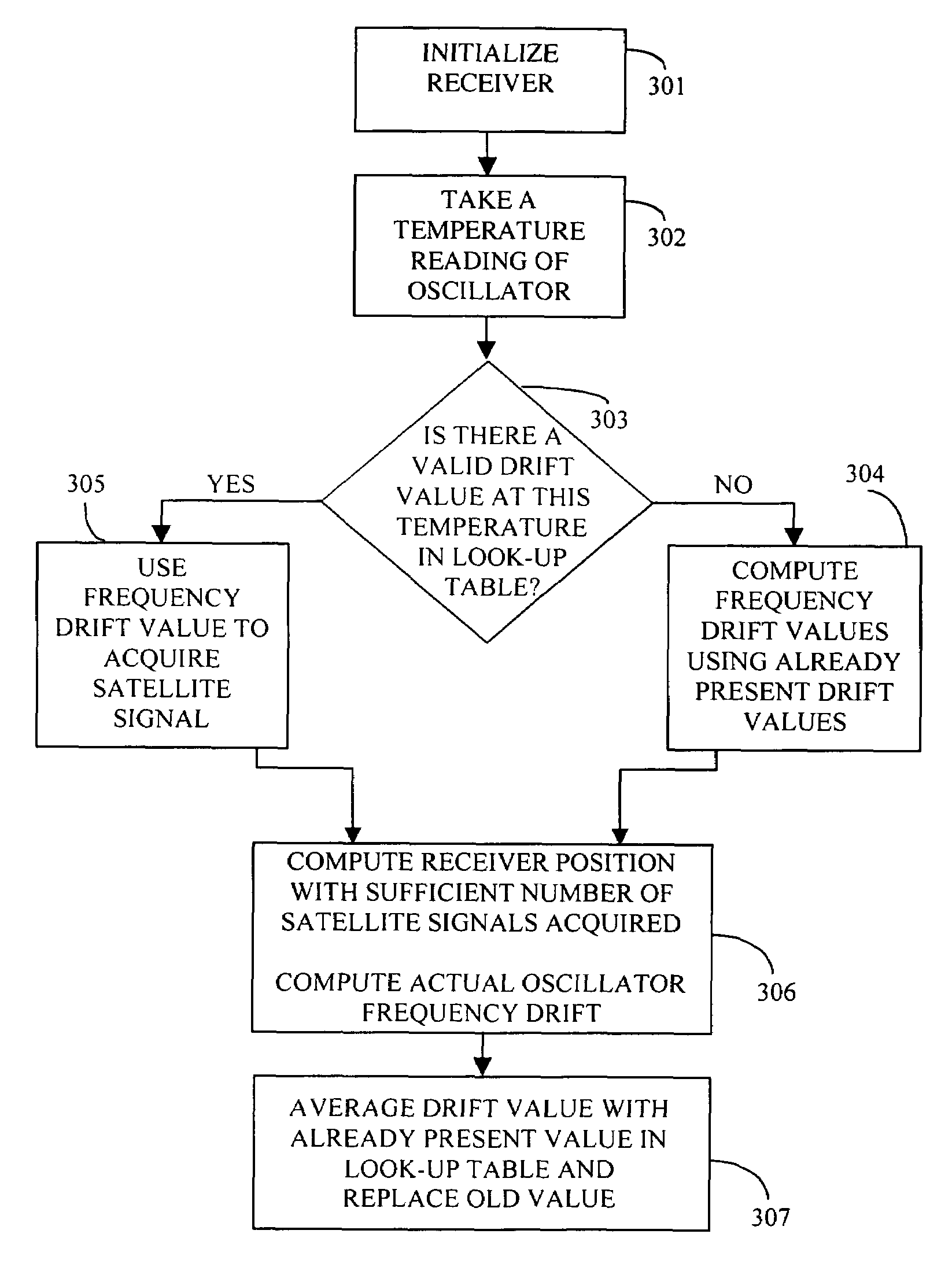
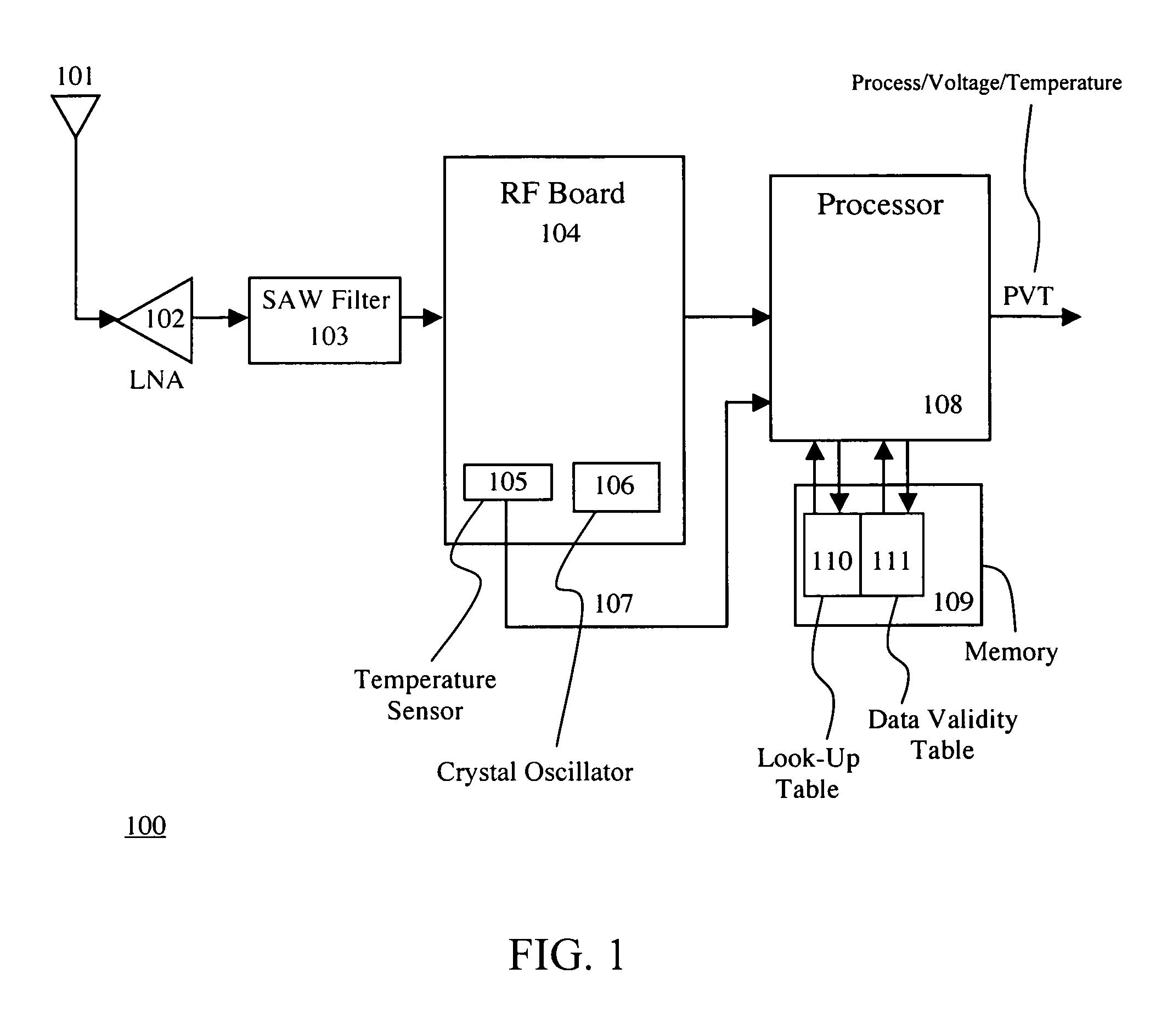
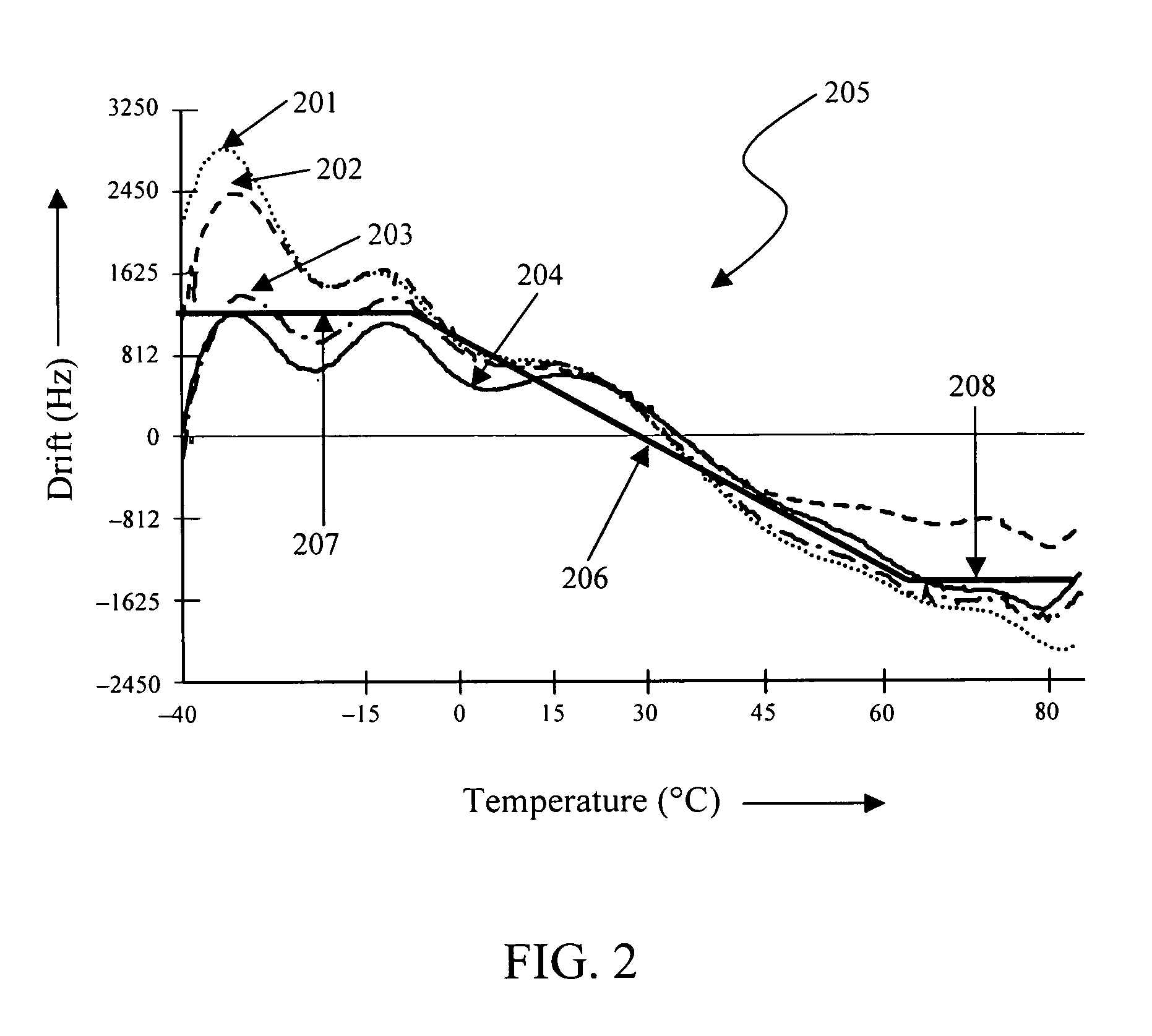
The invention provides a method and apparatus to optimally estimate and adaptively compensate the temperature-induced frequency drift of a crystal oscillator in a navigational signal receiver. A Read-Write memory encodes two tables, one for looking up frequency drift values versus temperature readings and another one for valid data confirmation on the first table. The initially empty look-up table is gradually populated with frequency drift values while the receiver computes the frequency drift along with its position. During initial start of the receiver or re-acquisition of satellite signals, the stored frequency drift value corresponding to the current temperature is used. If no valid frequency drift value is available, the frequency drift value is computed based on the existing frequency drift values in the table. This invention reduces the Time-To-First-Fix (TTFF) of the receiver and enables the receiver to self-calibrate, thus no additional factory calibration would be necessary.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Blind despreading of civil GNSS signals for resilient PNT applications
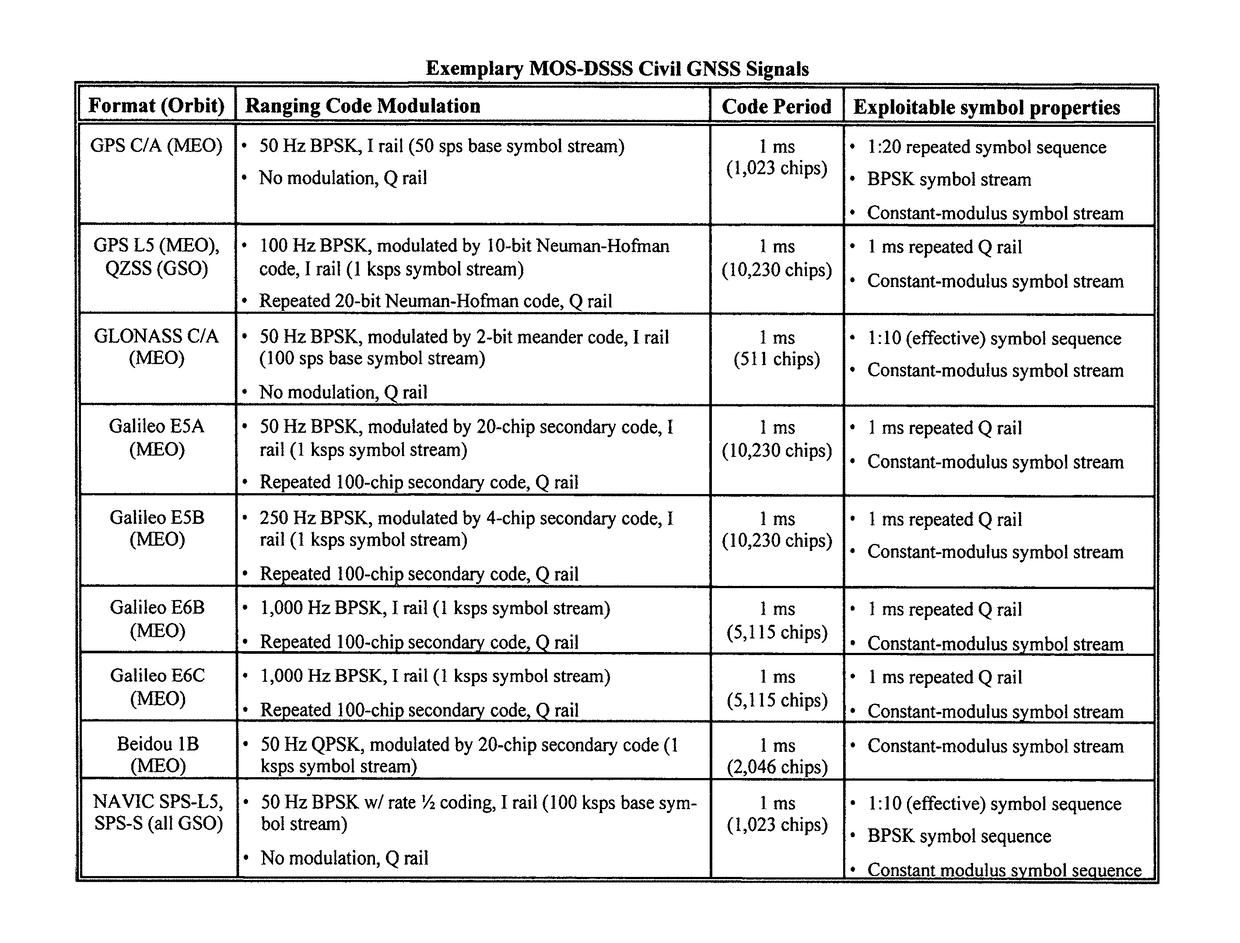
ActiveUS20170350985A1Reduce computing loadLow costSatellite radio beaconingTime to first fixDiversity scheme
A method, system and apparatus are claimed for receiving, blindly despreading, and determining geo-observables, of true civil Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) navigation signals generated by any of the set of satellite vehicles and ground beacons, amongst false echoes and malicious GNSS signals from spoofers and repeaters; for identifying malicious GNSS signals, and preventing those signals from corrupting or capturing Pointing, Navigation, and Timing tracking operations; and for geolocating malicious GNSS signals. The invention also provides time-to-first-fix over much smaller time intervals than existing GNSS methods and can operate both in the presence of signals with much wider disparity in received power than existing techniques, and in the presence of arbitrary multipath. Further embodiments employing spatial / polarization diverse receivers that remove non-GNSS jammers received by the system, as well as targeted GNSS spoofers that can otherwise emulate GNSS signals received at victim receivers, are also claimed.
Owner:AGEE BRIAN G
GPS receiver locating in doors and auxiliary satellite navigation positioning system
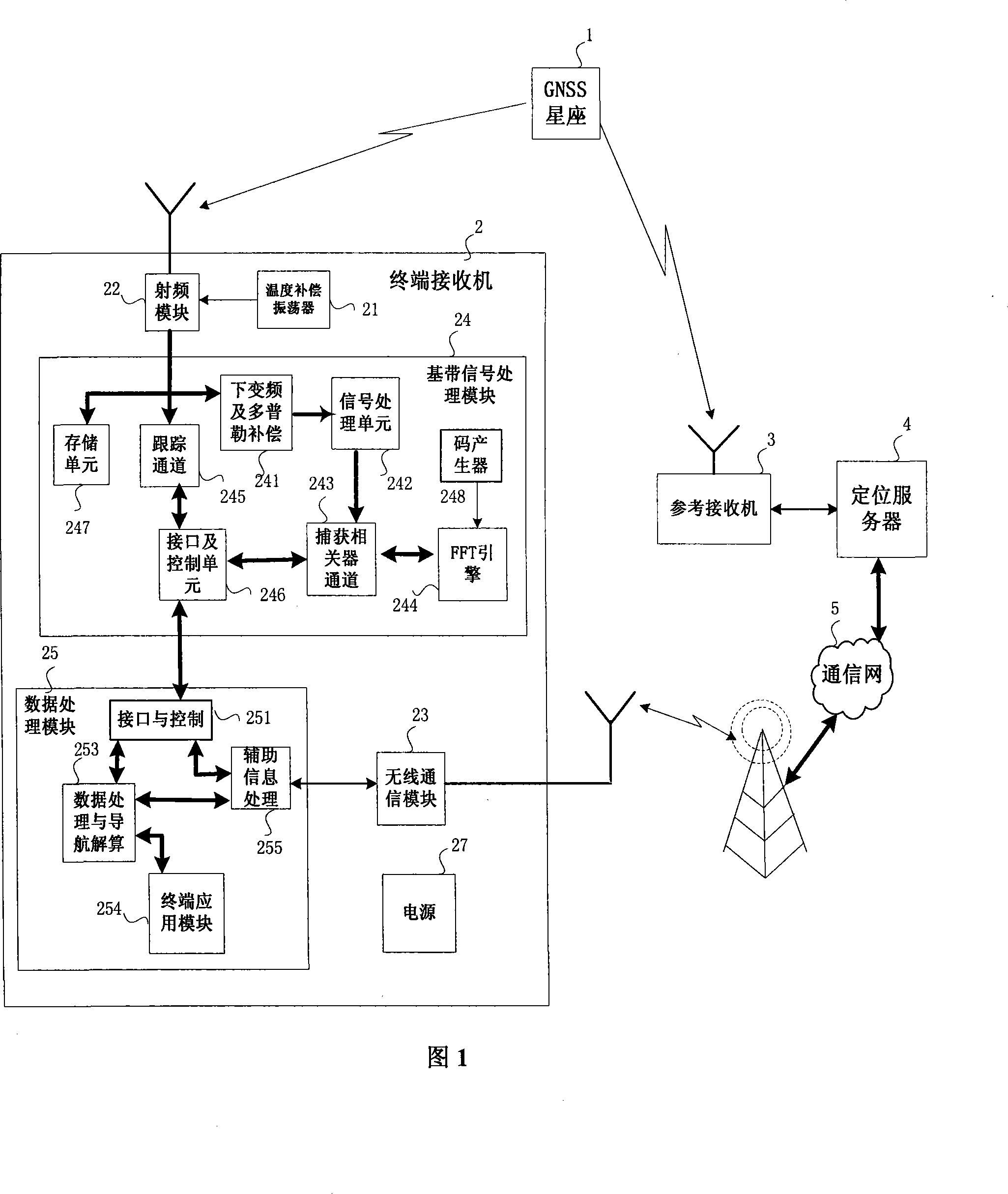
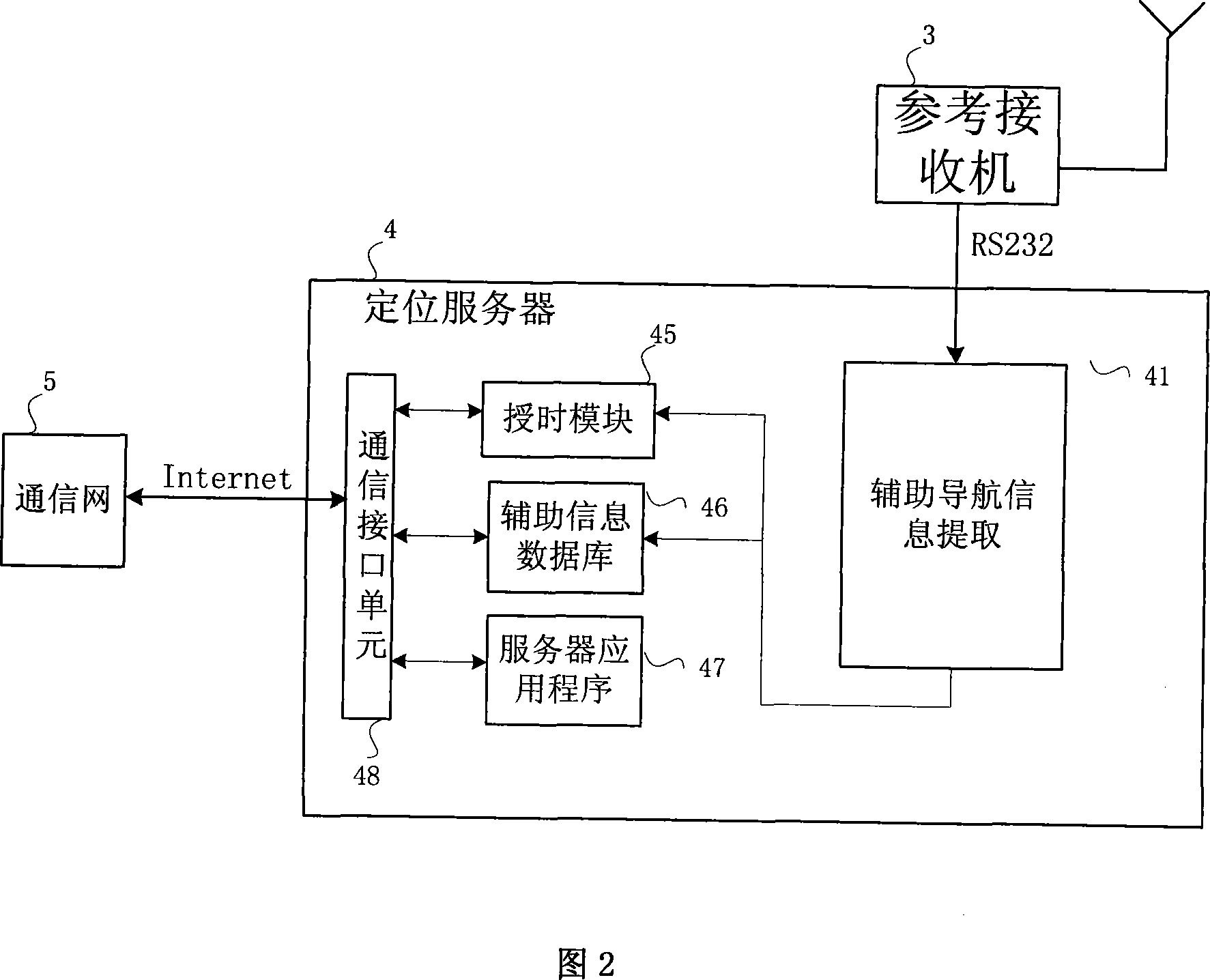
InactiveCN101206254AImprove sensitivity indexReduce time to first fixBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationTime to first fixHardware implementations
The invention relates to an auxiliary satellite navigation system and a global positioning system (GPS) receiver, in particular to a high-sensitivity navigation receiver mainly used indoors as well as an indoor positioning GPS receiver and an auxiliary satellite navigation positioning system adopting high-sensitivity satellite navigation positioning technology. The system at least comprises a terminal receiver, a reference receiver, a positioning server and a communication network; all devices are combined into an integral indoor positioning system; the entire system is divided into a high-sensitivity satellite navigation receiver and a network auxiliary system. Through adopting the positioning mode in which point positioning under weak signal condition is combined with continuous positioning under strong signal condition, the method mainly solves related technical problems such as the organic combination of integral hardware implementation. The invention has the advantages that: the system and the method improve the sensitivity index of a terminal user and reduce first positioning time; moreover, the designed navigation receiver can process indoor weak satellite signal, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI BEIGA NAVIGATION TECH CO LTD
Frequency aiding method and system for navigation satellite receiver with crystal oscillator frequency hysteresis
A method and apparatus for estimating oscillator signal variation due to temperature and for providing an estimated frequency to a GPS receiver in order to assist the GPS receiver to acquire the signals quickly is disclosed. A temperature sensor is closely thermally coupled with the crystal oscillator in the GPS receiver and during GPS tracking mode, when the error in the oscillator signal is known with precision, outer bounds of TCXO frequency at given temperatures are maintained, which may correspond to rising and falling temperature conditions. During acquisition mode, an estimated frequency value is provided to the GPS receiver based on a determined average of these bounds. Optionally, an uncertainty factor associated with the frequency estimated may also be provided. The two bounds take into account the hysteresis effects of the oscillator signal drift due to temperature so that a more accurate initial frequency estimate can be provided to the GPS receiver, thus reducing its average time to first fix.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus in standalone positioning without broadcast ephemeris
InactiveUS7564406B2High positioning accuracyBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingCommunications systemTime to first fix
The present invention provides methods and system for enabling a standalone navigation receiver capable of generating receiver specific predicted satellite orbits based on historical navigation data collected by and stored in the receiver. Thus, the navigation receiver is able to use the predicted satellite orbits to obtain better Time-To-First-Fix (TTFF) and position accuracy without the need of connecting to a remote server and the associated communications system. In an embodiment, a standalone navigation receiver having sufficient memory collects navigation data from navigation satellites and generates predicted satellite orbits using the collected navigation data. Under weak signal conditions when decoding of the navigation data is not possible, the receiver uses the predicted satellite orbits to predict the accurate satellite positions or the set of ephemeris and the associated pseudoranges. The predicted orbits may be accurate for several days without the reception of broadcast ephemeris.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
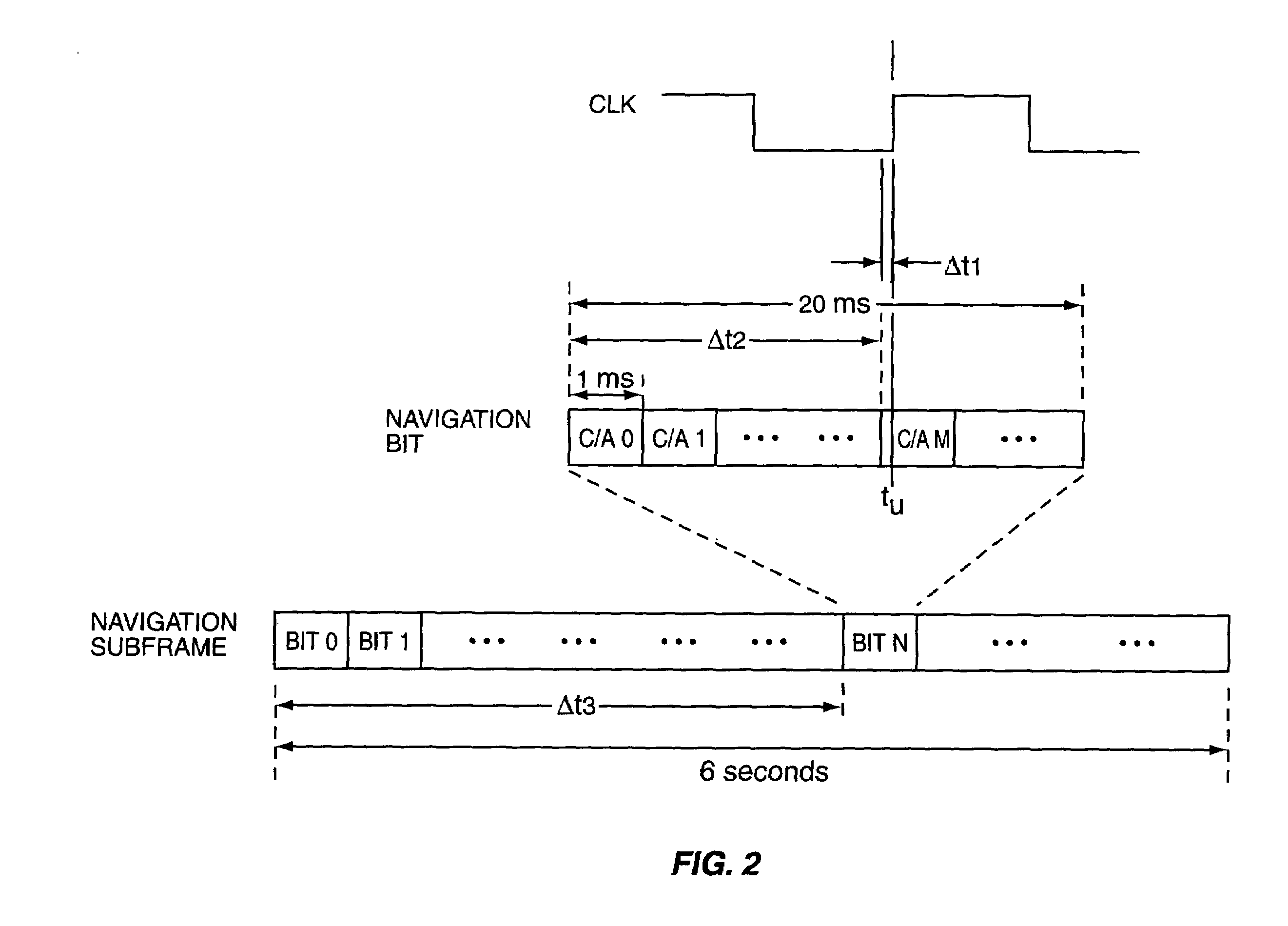
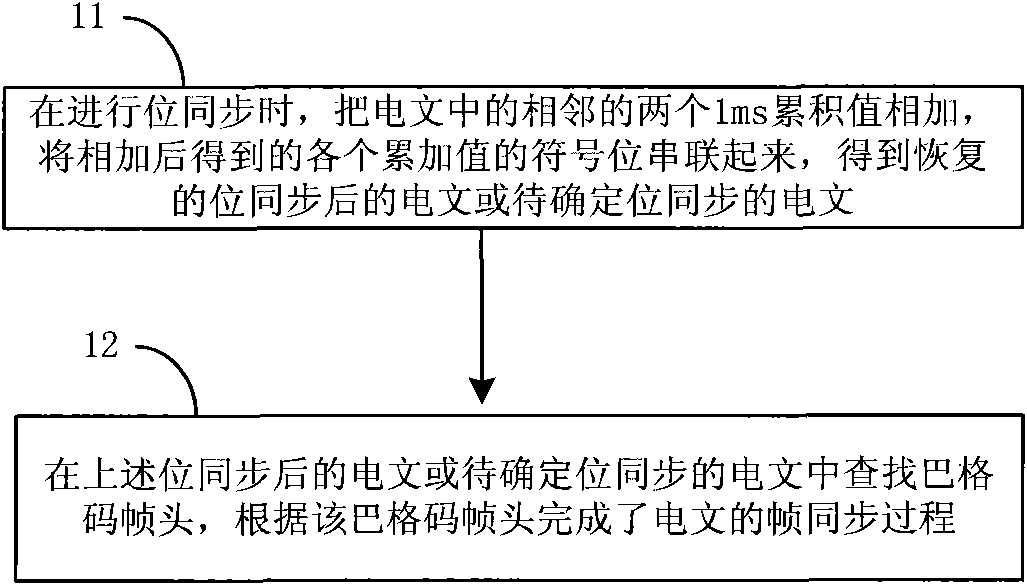
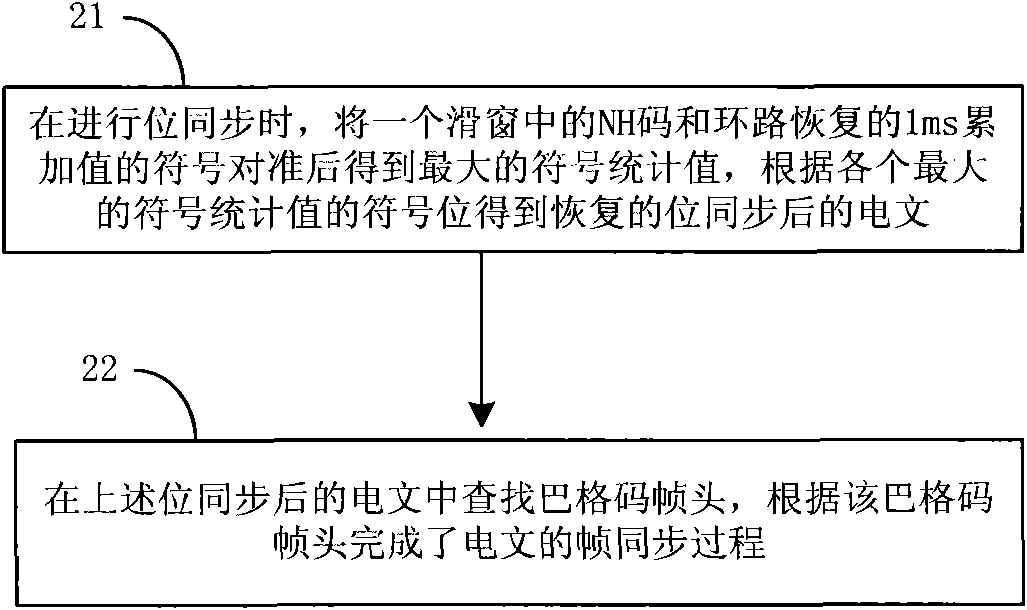
Method and device for achieving bit synchronization and frame synchronization of text of receiver
ActiveCN101594180AHigh speedReduce time to first fixPosition fixationRadio transmission for post communicationData synchronizationTime to first fix
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for achieving bit synchronization and frame synchronization of a text of a receiver. Aiming at a 500 bps text in a navigation digital receiver, the method mainly comprises the following steps: adding two adjacent 1 ms accumulated values in the text with a set time length in turn, and acquiring a text after the bit synchronization according to the accumulated value after the addition; and searching a trellis code frame header in the text after the bit synchronization according to the scheduled format information, and finishing the synchronization of the text for the bit synchronization to be determined according to the searched trellis code frame header. The method and the device can improve the speed of the bit synchronizationand the frame synchronization of navigation texts of 500 bps and 50 bps in the navigation digital receiver, save system resources, and improve the system reliability. Besides, the method and the device achieves the bit synchronization and the frame synchronization in an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), and can generate the satellite launch time more quickly and shorten the first-time positioning time of the navigation digital receiver.
Owner:华力智芯(成都)集成电路有限公司
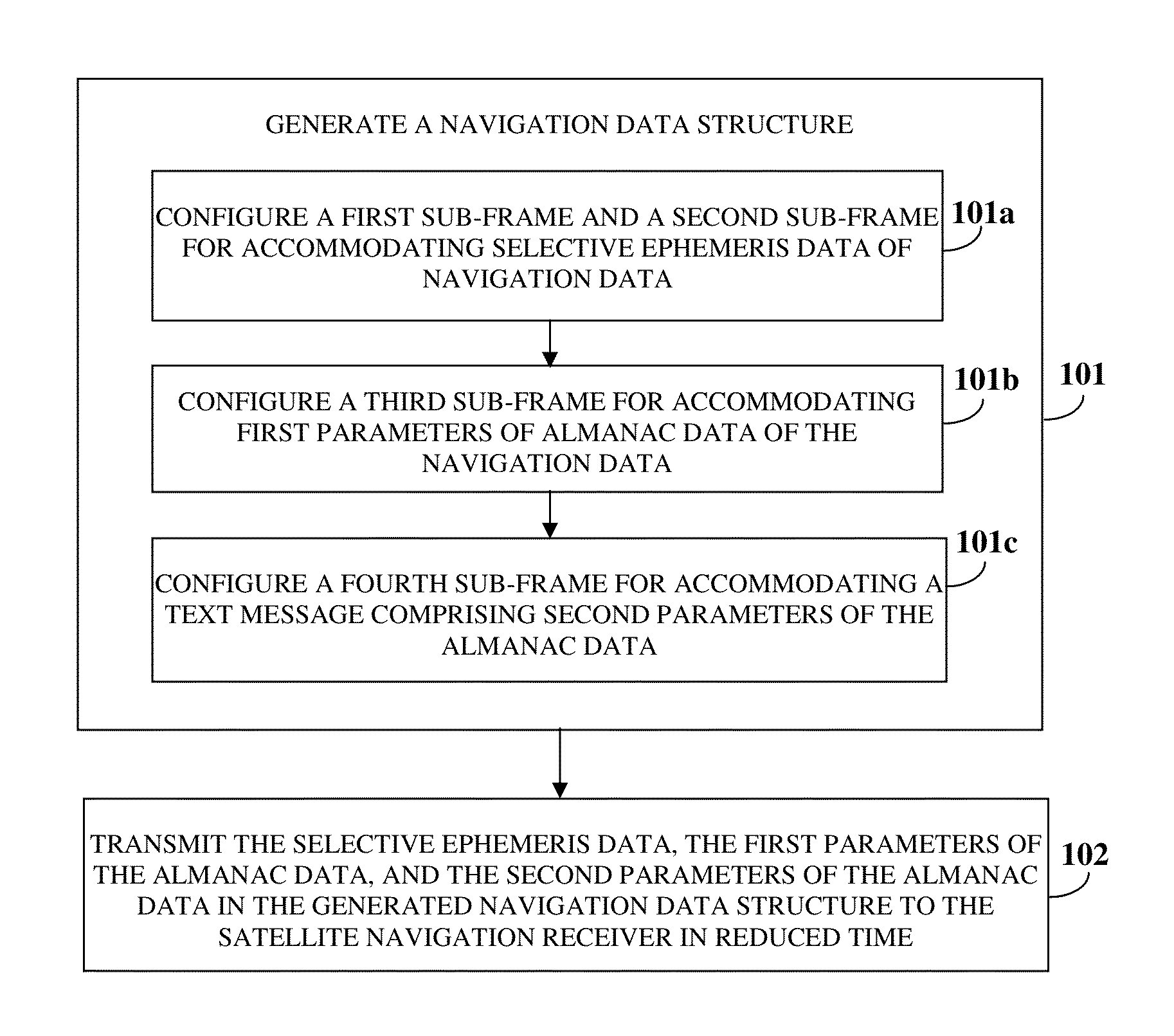
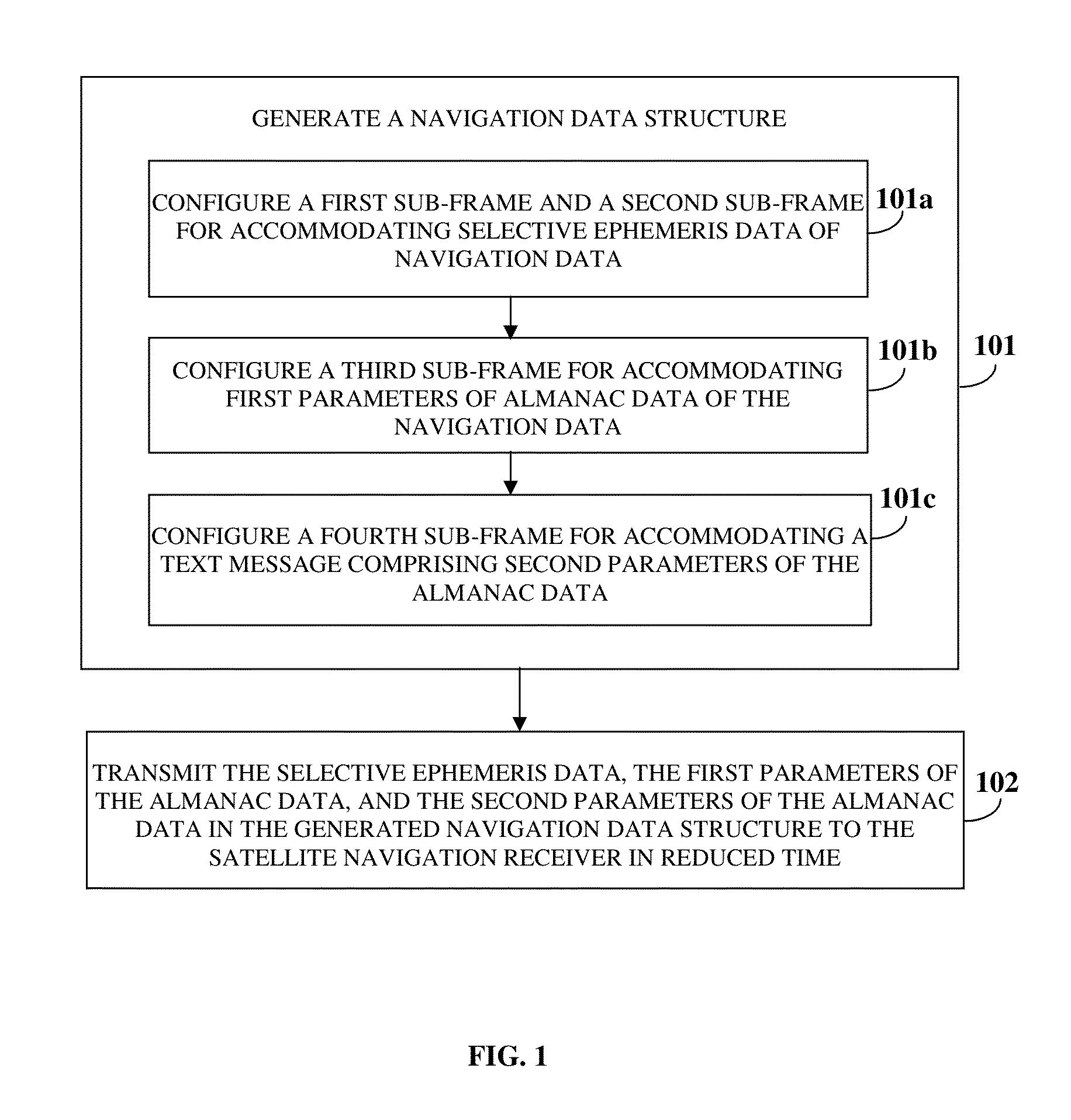
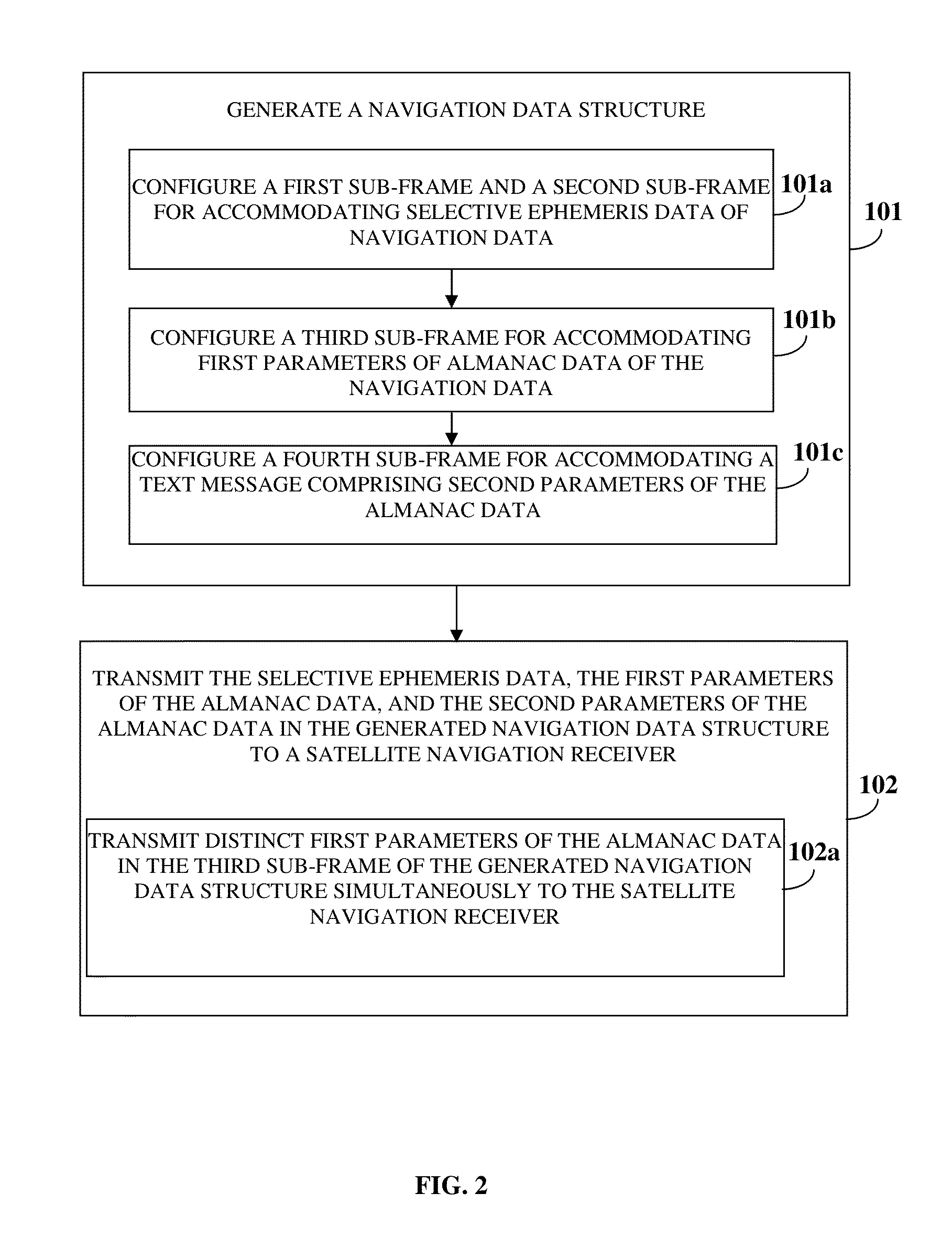
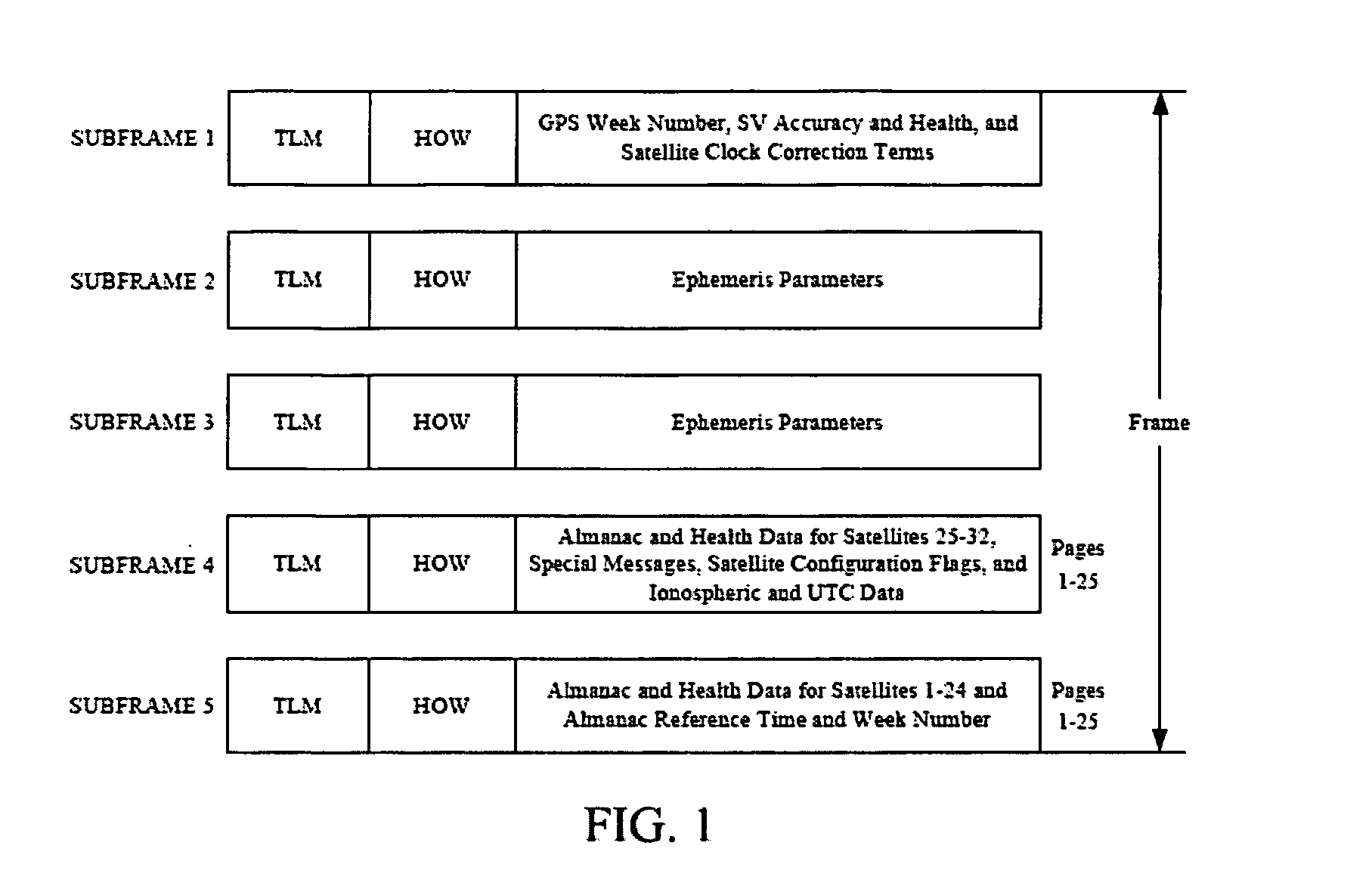
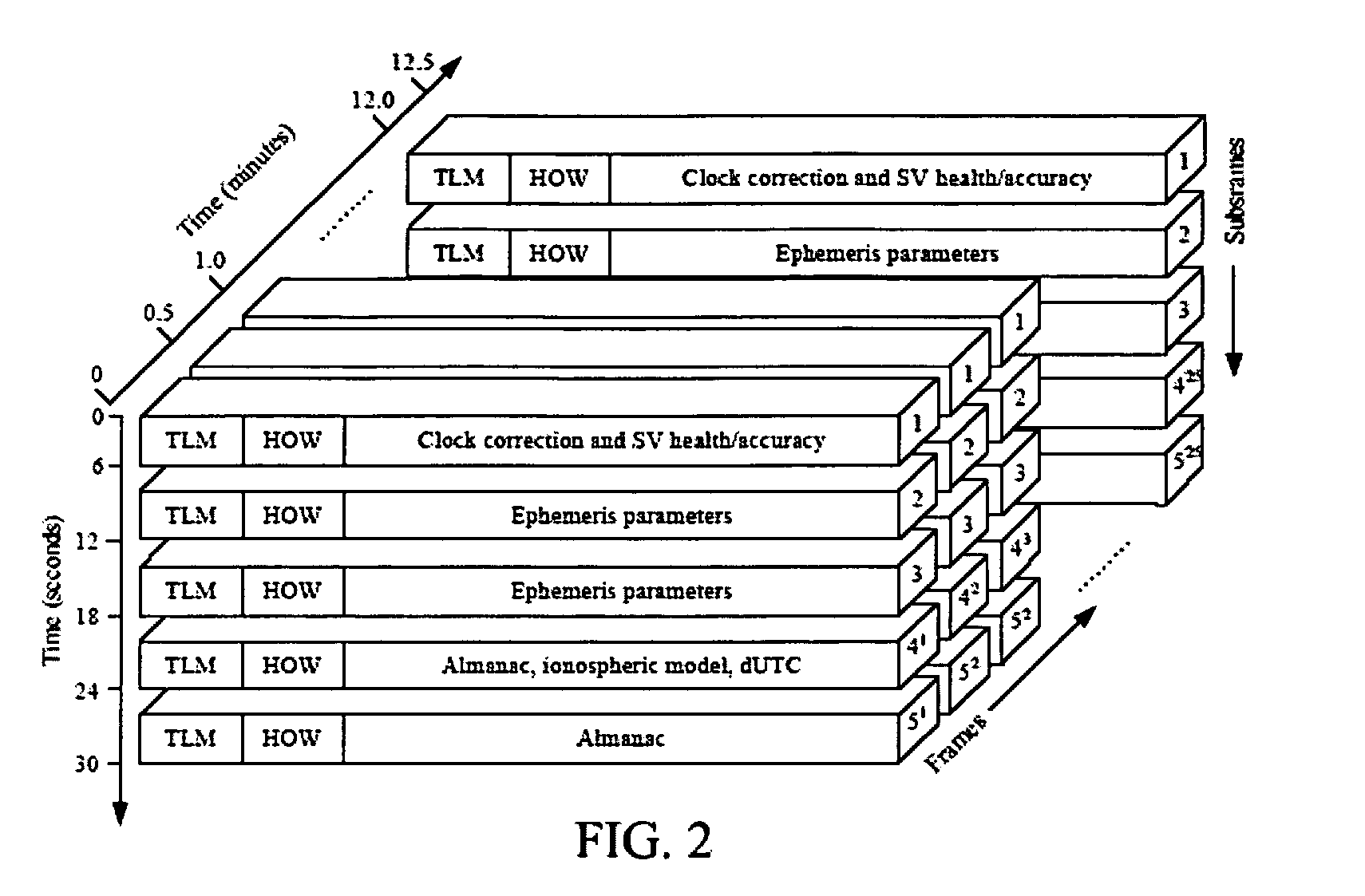
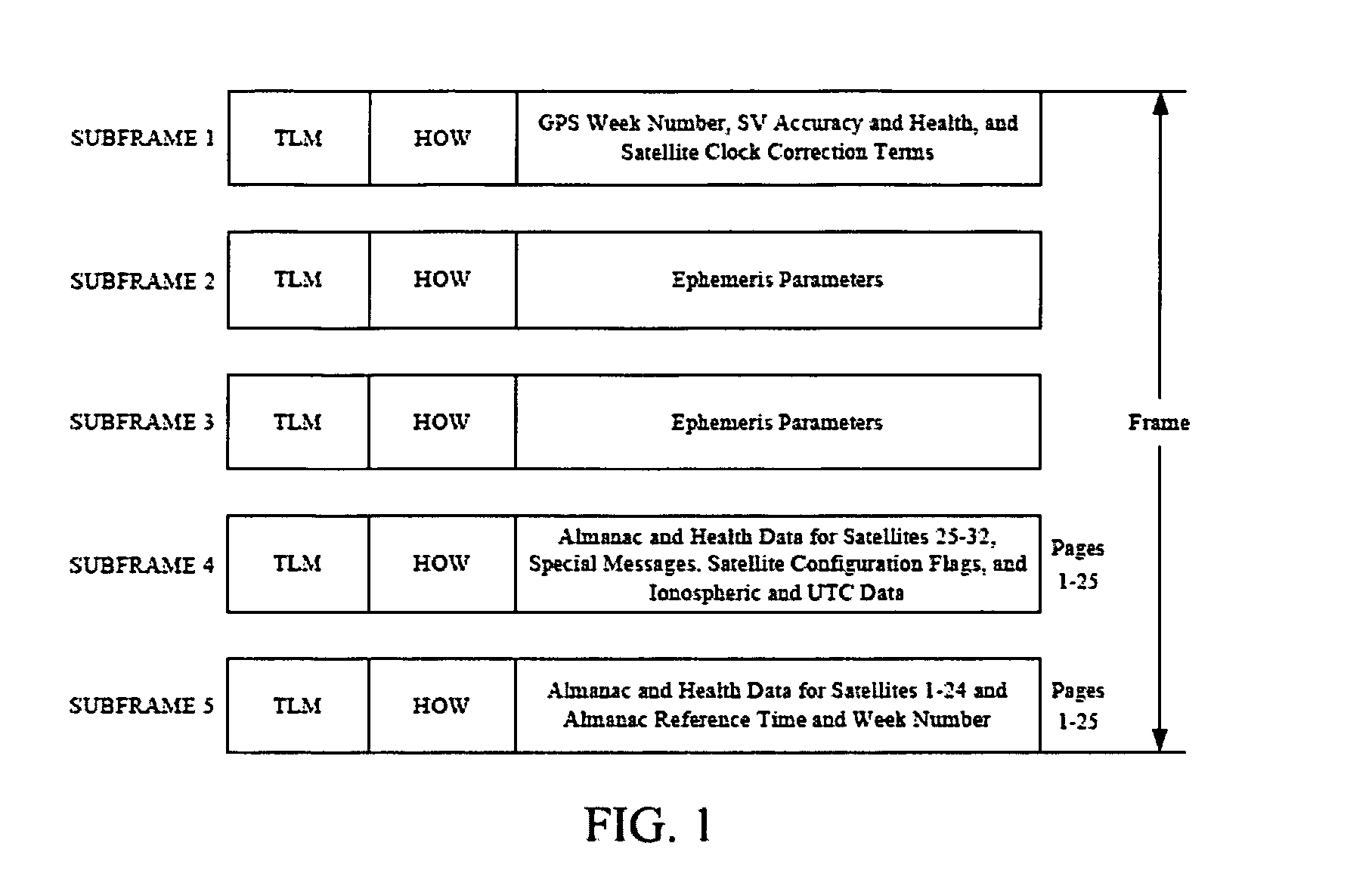
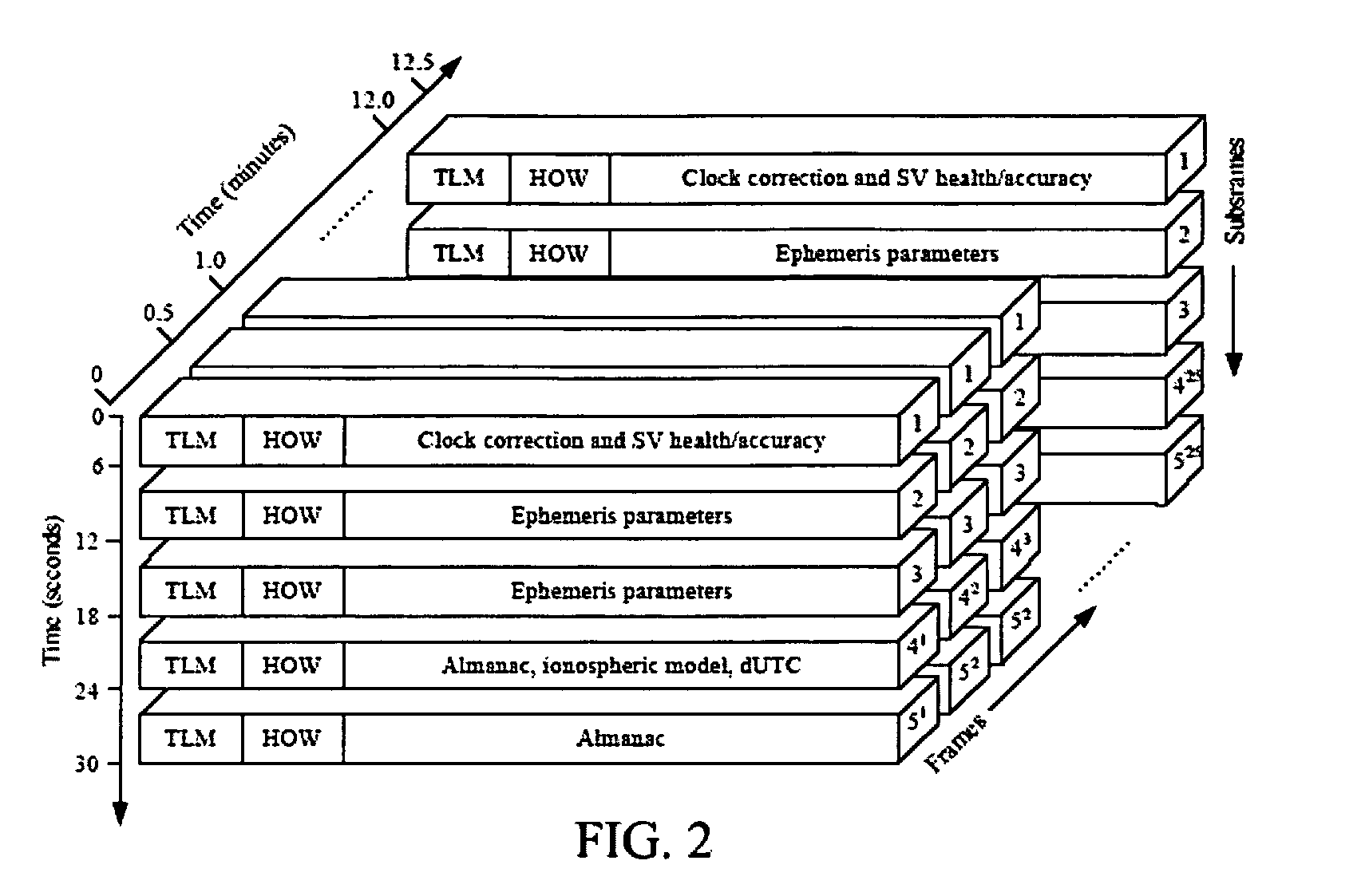
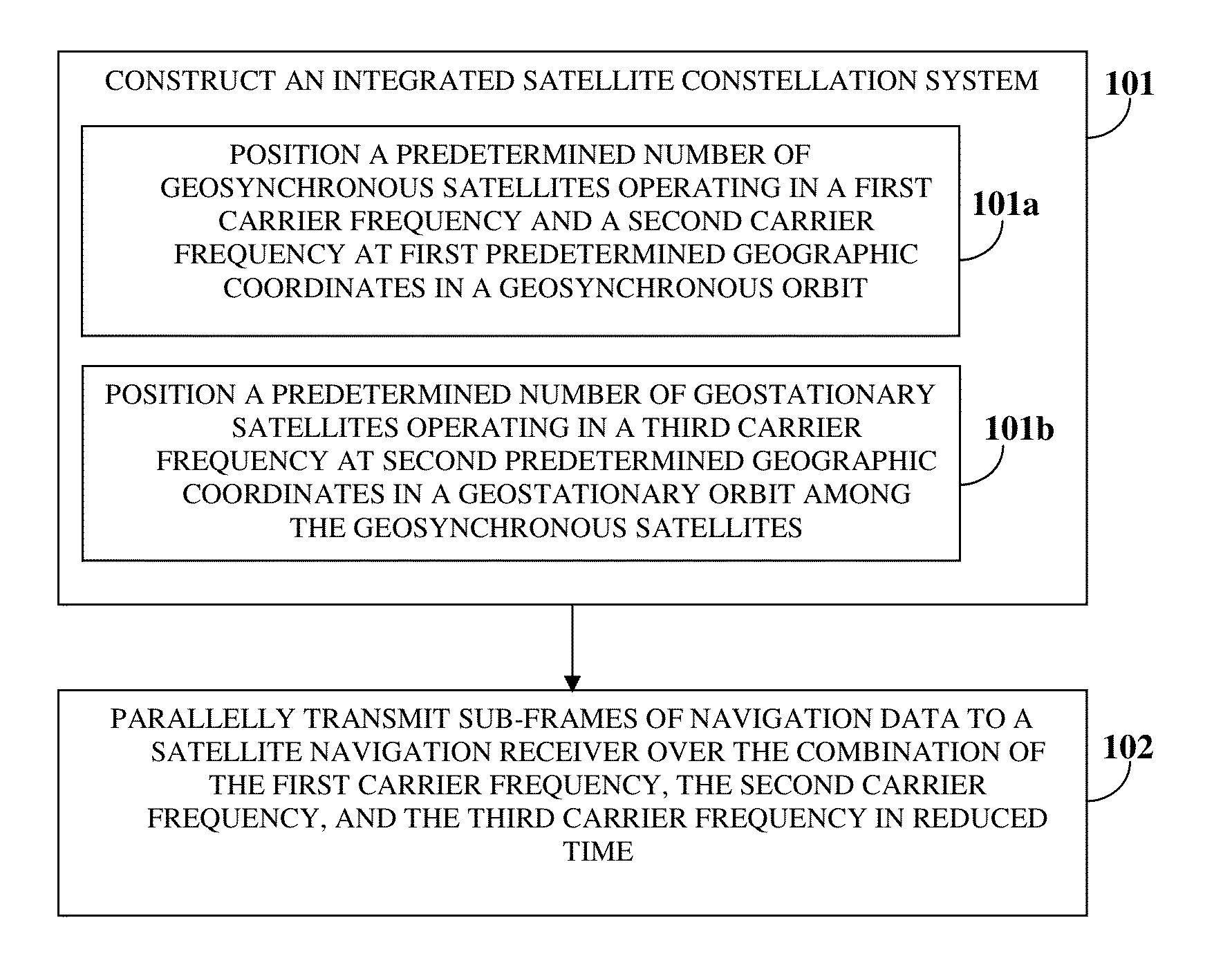
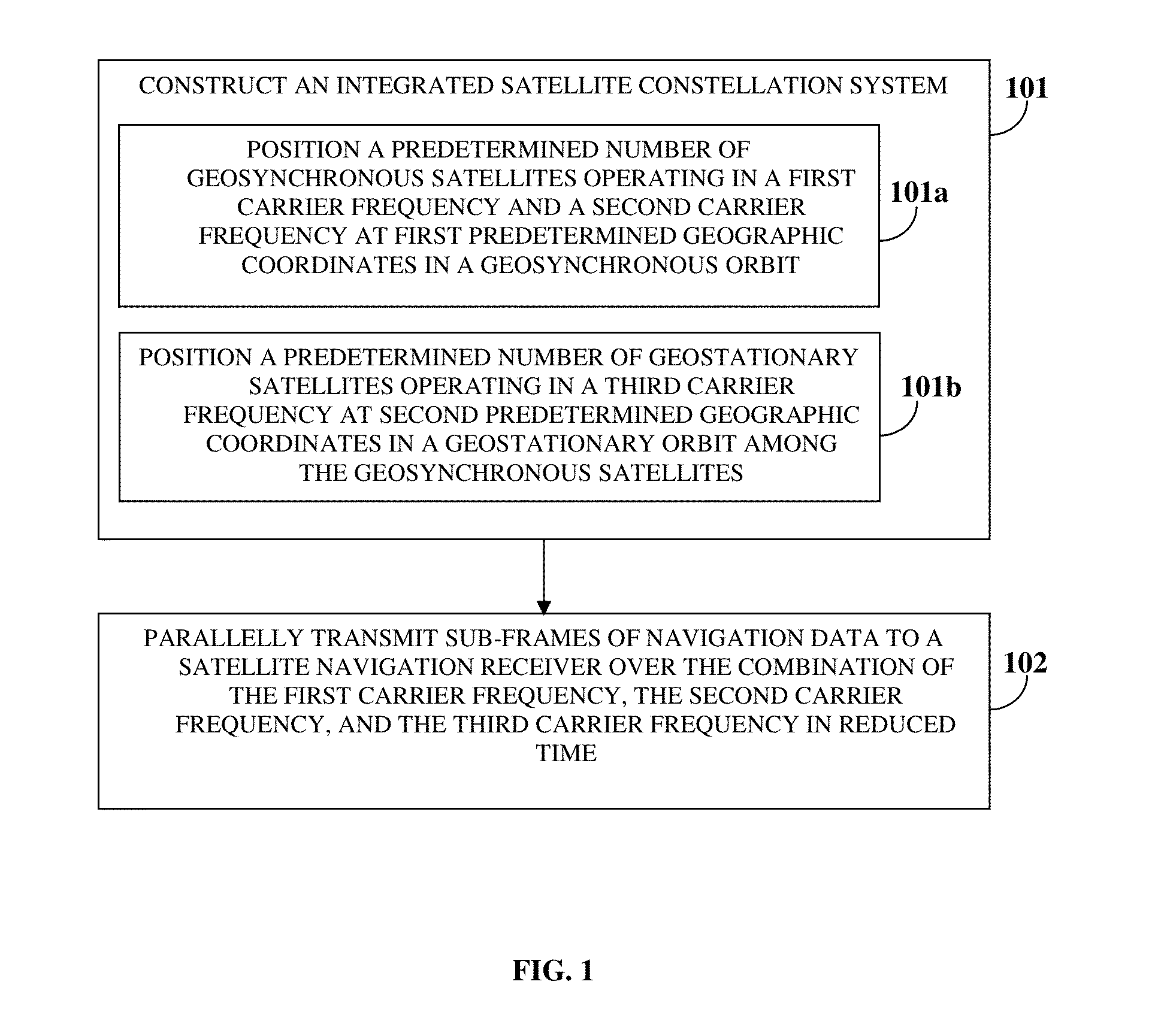
Navigation Data Structure Generation And Data Transmission For Optimal Time To First Fix
A method and system for transmitting navigation data to a satellite navigation receiver for reducing time to first fix is provided. A signal generation system generates a navigation data structure comprising a first sub-frame and a second sub-frame for accommodating selective ephemeris data, a third sub-frame for accommodating first parameters of almanac data, and a fourth sub-frame for accommodating a text message comprising second parameters of almanac data, and transmits the selective ephemeris data and the first and second parameters of almanac data to the satellite navigation receiver. The configuration of the navigation data structure enables the satellite navigation receiver to collect the navigation data in reduced time. Each satellite of a constellation simultaneously transmits distinct first parameters of the almanac data in the third sub-frame of the navigation data structure to the satellite navigation receiver, thereby allowing the satellite navigation receiver to receive collective almanac data in reduced time.
Owner:ACCORD SOFTWARE & SYST PVT
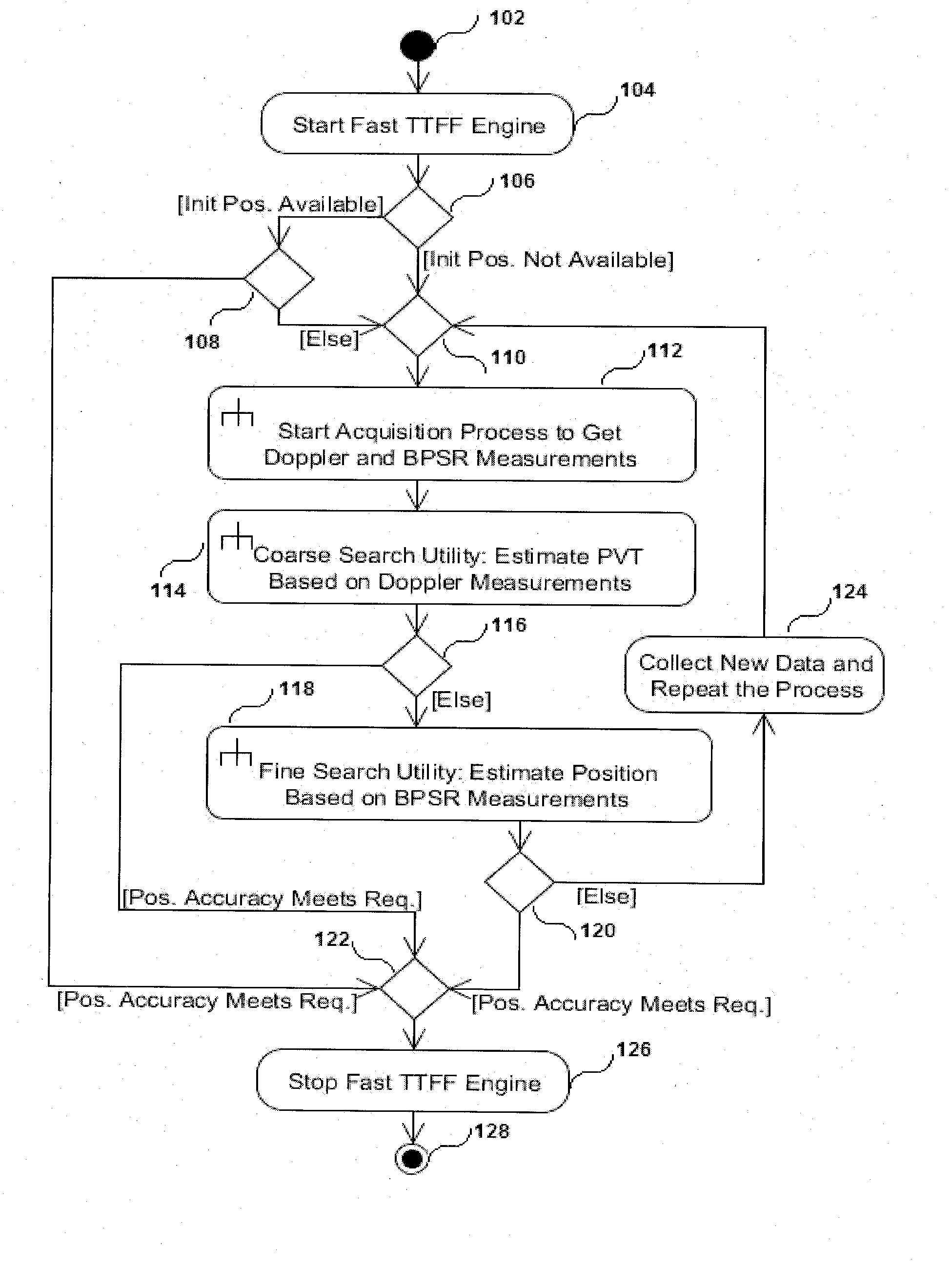
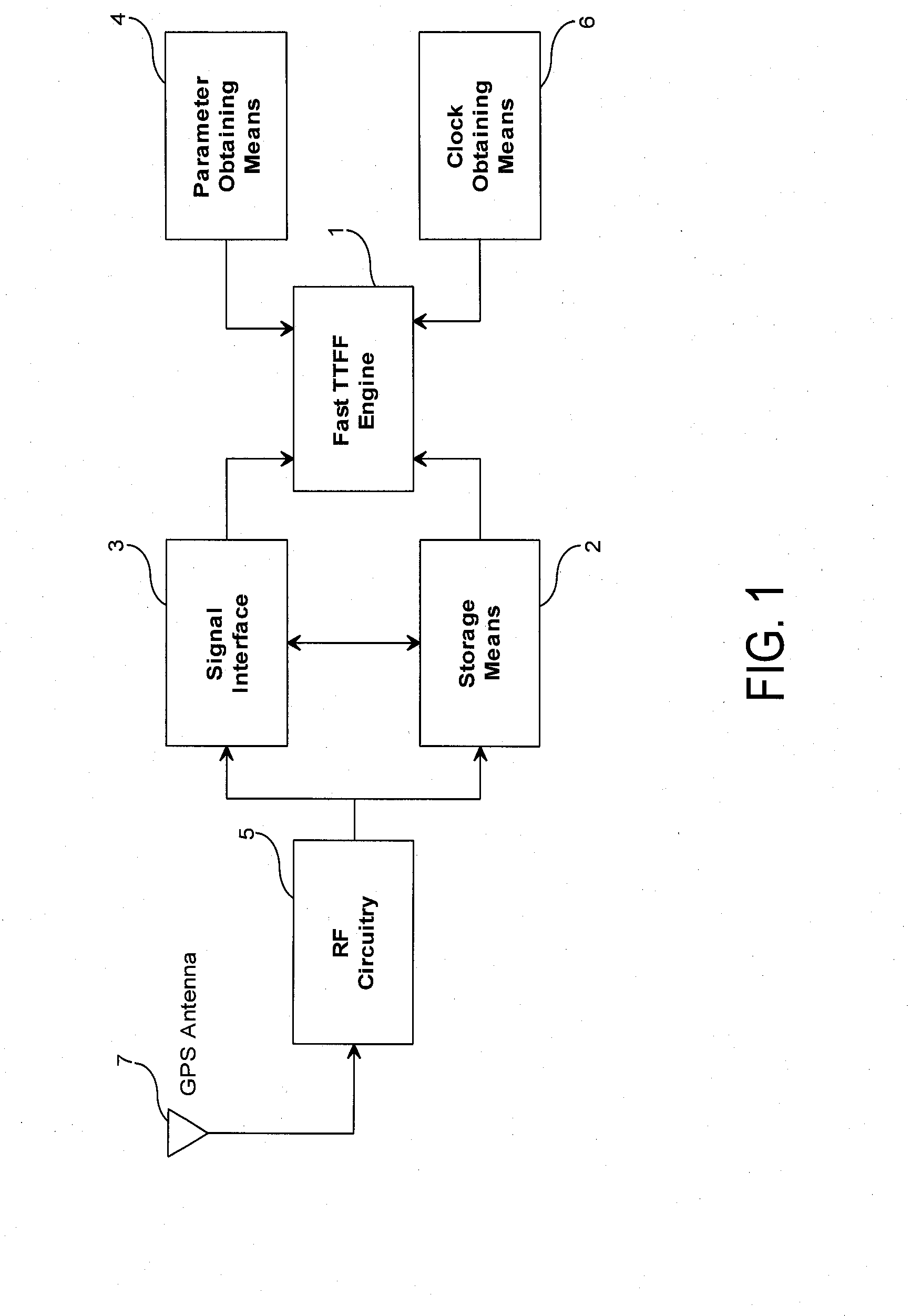
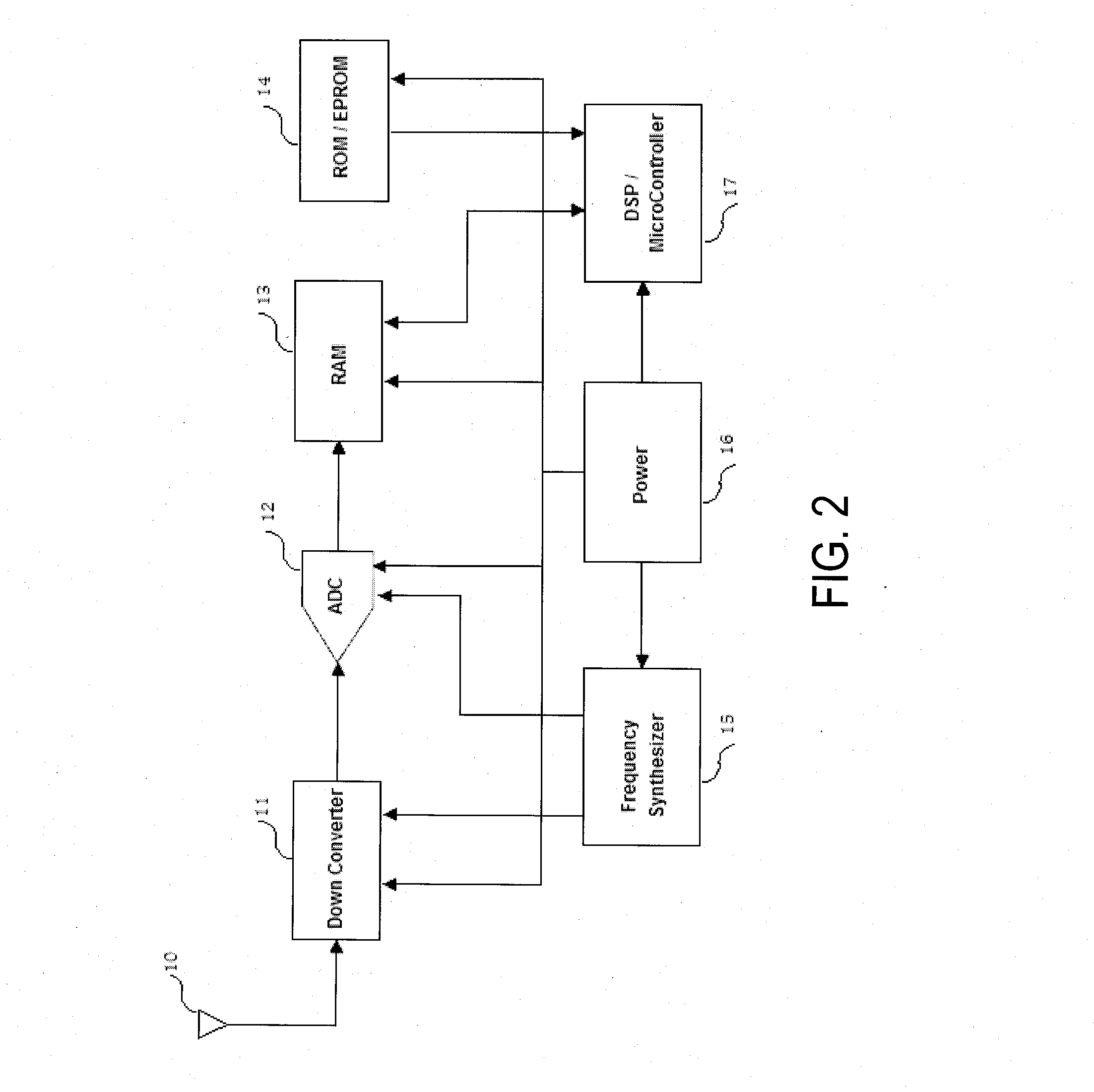
System, method and computer program for ultra fast time to first fix for a GNSS receiver
The present invention provides a system, method and computer program for a GNSS receiver that is operable to provide an ultra fast Time To First Fix (TTFF). The invention is implementable without requiring the decoding of a navigation message transmitted by GNSS satellite systems. The system of the present invention may comprise a parameter obtaining means, a clock obtaining means and a Fast TTFF engine. The parameter obtaining means may obtain satellite parameters of one or more GNSS satellites. The clock obtaining means may obtain a clock for estimating a GNSS time tag. The Fast TTFF engine may be linkable to a signal interface that is operable to provide I / Q samples from a GNSS antenna. The Fast TTFF engine may comprise a measurement generation utility, a coarse search utility and a fine search utility. The measurement generation utility may compute the Doppler frequency shift and the code phase of the one or more GNSS satellites based on the I / Q samples.
Owner:BASEBAND TECH
Beidou receiver and warm start method thereof
InactiveCN102778683AShorten the timeRapid positioningSatellite radio beaconingTime to first fixLeast squares
The invention discloses a Beidou receiver and a warm start method thereof. The warm start method of the Beidou receiver comprises the following steps of: obtaining the time T'r of a local receiving satellite signal; according to T'r, calculating a roughly-estimated satellite signal emission moment Tte; obtaining the coordinate of a satellite at the roughly-estimated satellite signal emission moment Tte; calculating the distance and the transmission time of the satellite to the last-time user positioning position; reconstructing a satellite signal emission moment T't with a error delta; according to the satellite signal emission moment T't, calculating the transmission time; comparing the transmission time with real satellite transmission time delta T to obtain the value of the error delta; regulating the error delta to add the error delta into the signal calculation of each satellite required by positioning; calculating a pseudorange; and carrying out a least square method to resolve a positioning result to finish the warm start. According to the warm start method of the Beidou receiver, which is disclosed by the invention, the first-time positioning time of the Beidou receiver can be improved, and a purpose of starting-up quick positioning is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
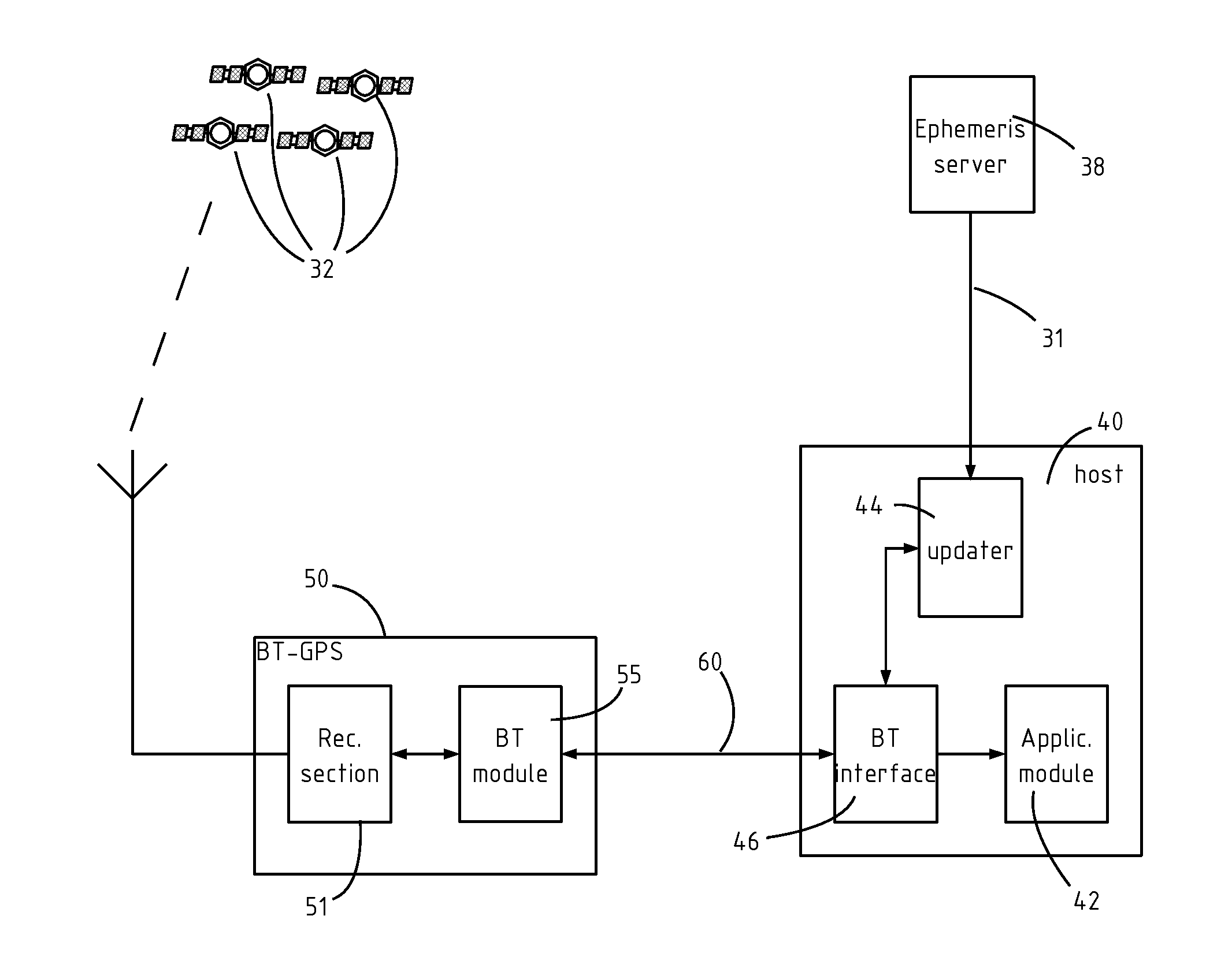
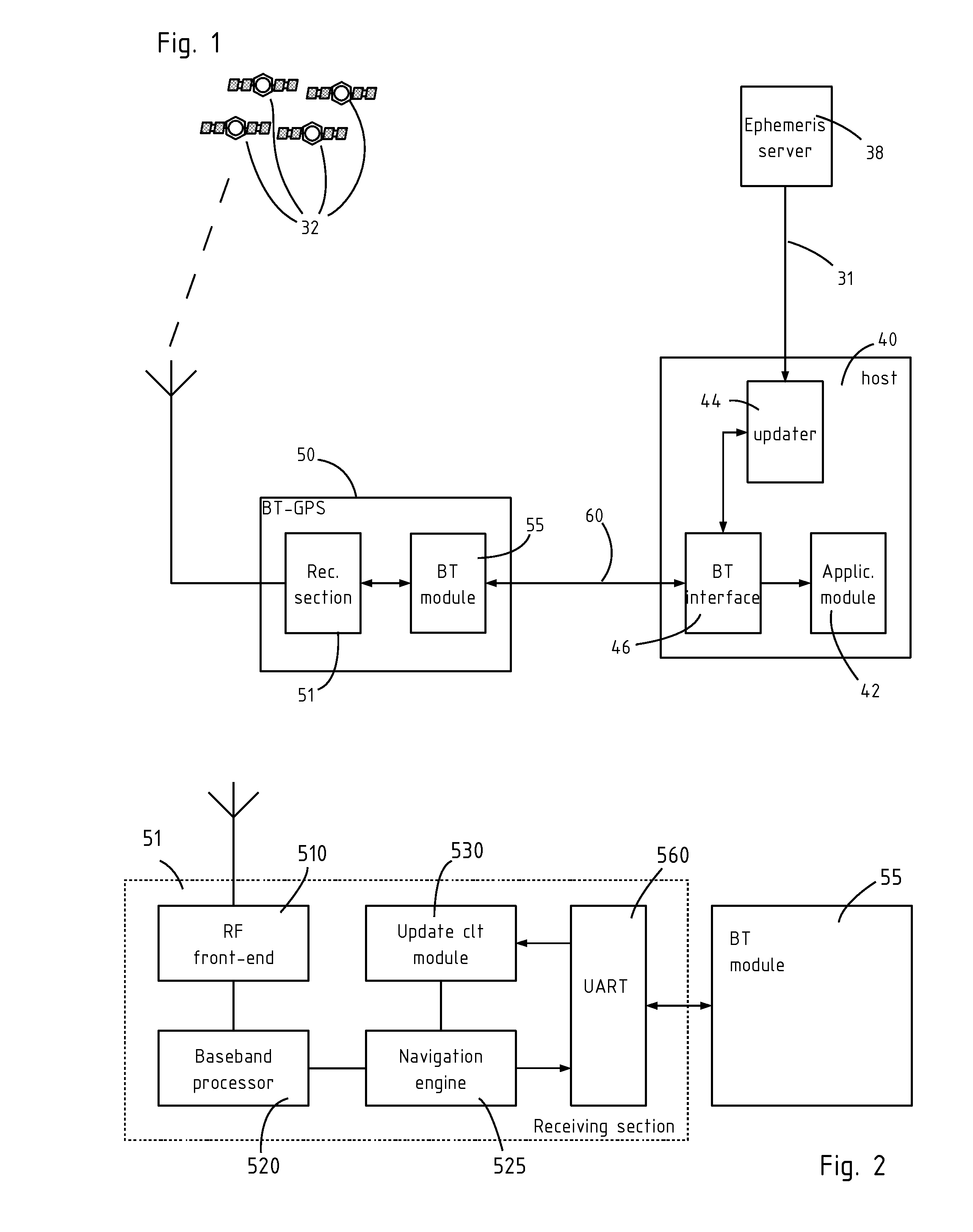
GNSS receiver with wireless interface
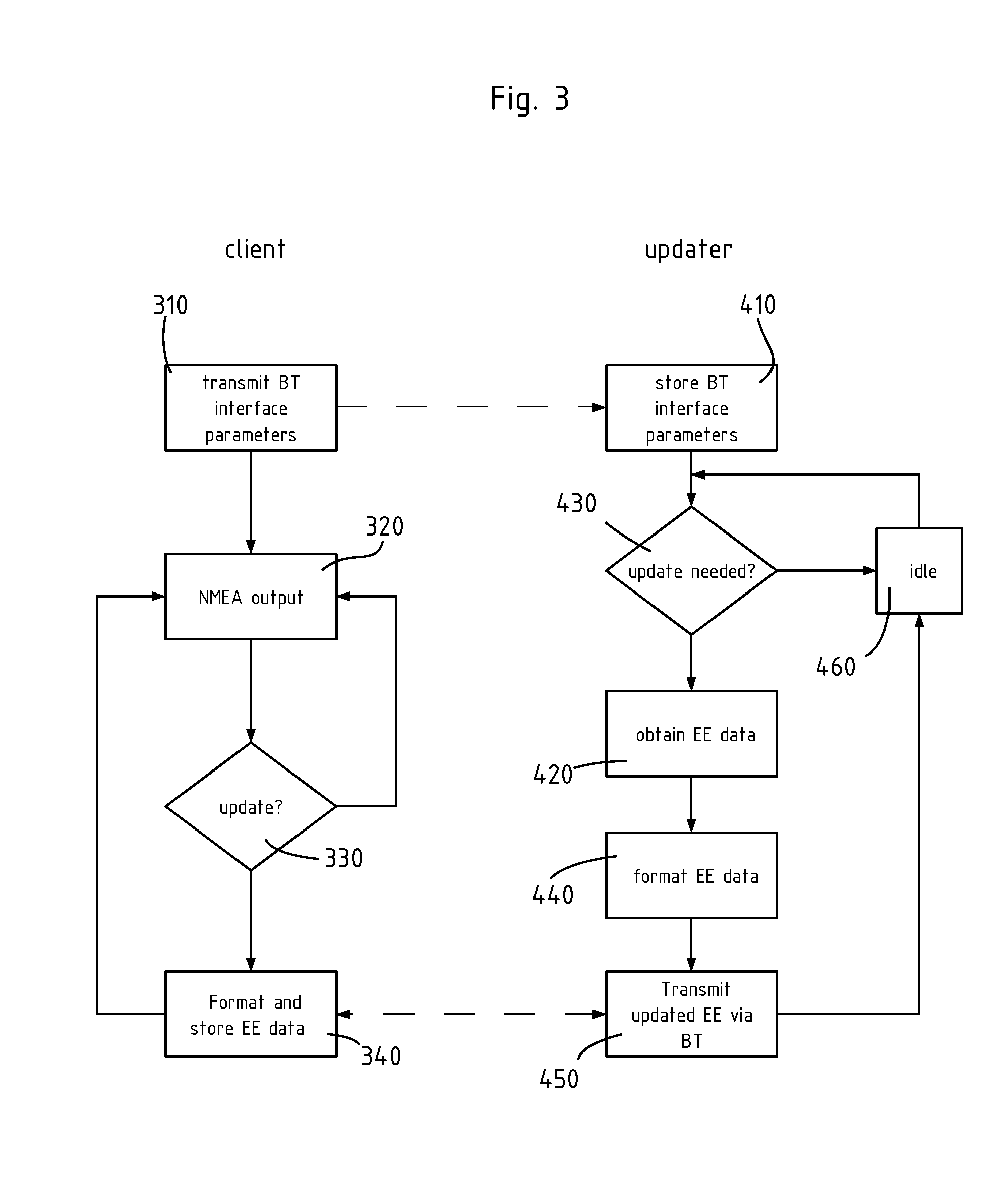
A wireless GNSS receiver, for example a Bluetooth® receiver, including a bidirectional link to the host, and an update client, for downloading extended ephemeris data from the host, by the Bluetooth® link. The invention reuses the protocol used for NMEA data transfer, in order to send the extended ephemeris data up to the receiver. Hence, the extended ephemeris data can be sent without having to instantiate any other type of connection to the receiver. The invention reduces the cost and complexity of BT-GPS receivers that want to make use of extended ephemeris technology in order to reduce the time to first fix of GPS receivers left off for more than four hours.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for updating global position system (GPS) ephemeris fast and reliably
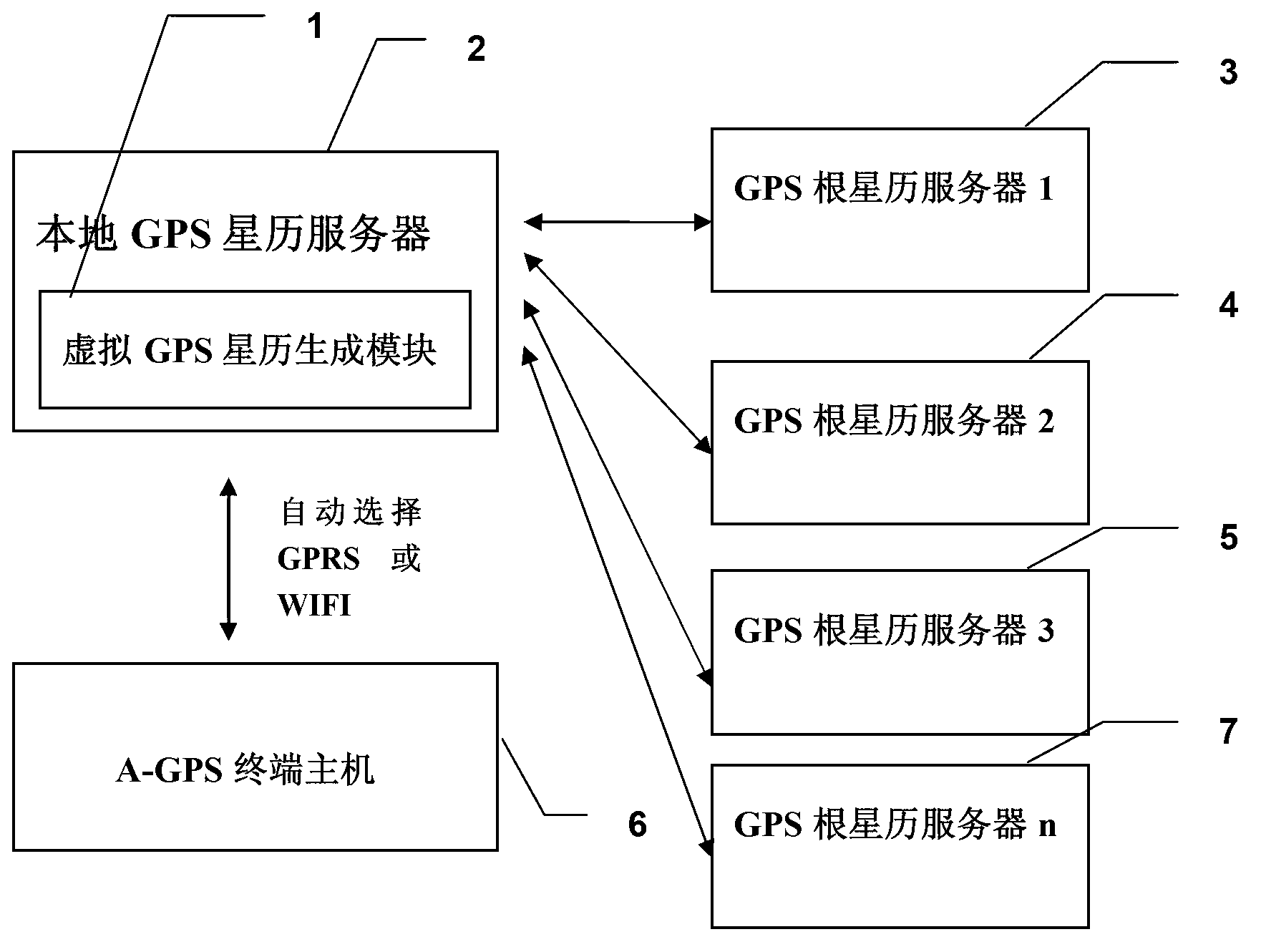
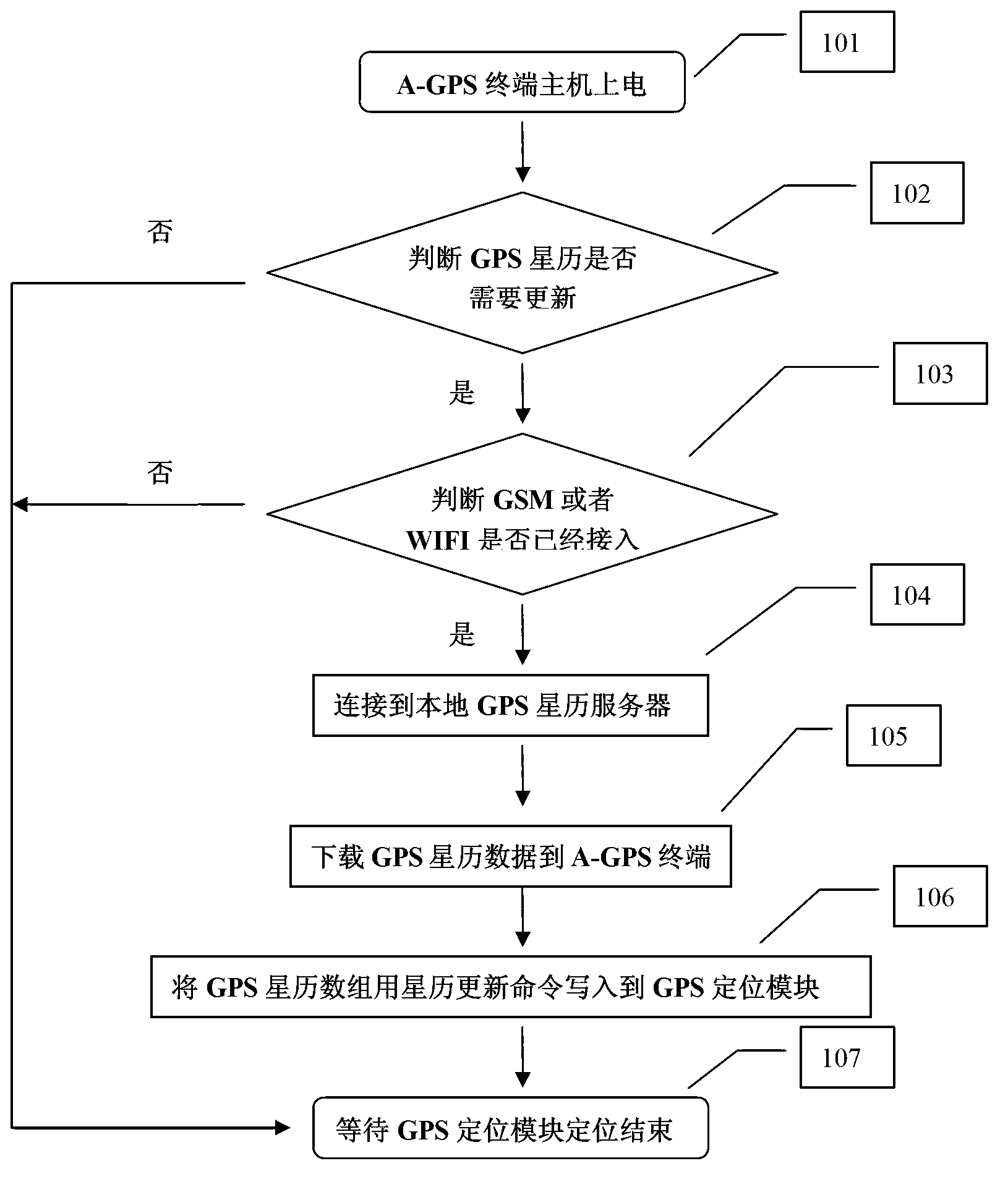
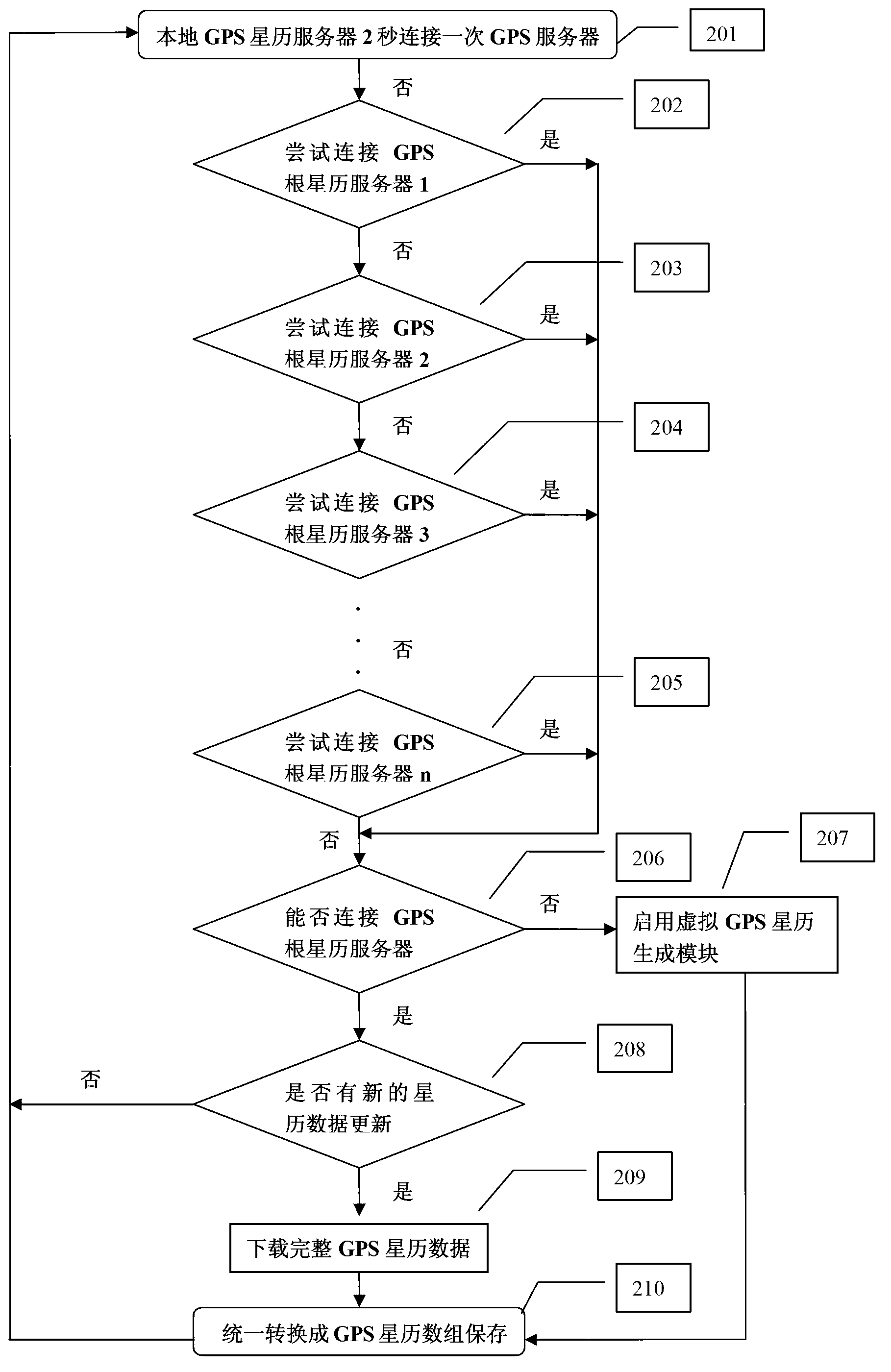
ActiveCN103197327AReduce TTFF timeRapid positioningSatellite radio beaconingTime to first fixEphemeris
The invention relates to a method and system for updating a global position system (GPS) ephemeris fast and reliably. According to the method and system for updating the GPS ephemeris fast and reliably, a local GPS ephemeris server is established, and a virtual GPS ephemeris generating module is arranged inside the local GPS ephemeris server. Normally the local GPS ephemeris server acquires ephemeris data from a GPS official ephemeris server. When the local GPS ephemeris server is disconnected with the GPS official ephemeris server, the virtual GPS ephemeris generating module starts to work to generate an accurate virtual ephemeris, and GPS ephemeris data in the local GPS ephemeris server are instantly switched into internal virtual GPS ephemeris data to guarantee continuity and reliability of the GPS ephemeris data. According to the method and system for updating the GPS ephemeris fast and reliably, the time to first fix (TTFF) of a host computer of each A-GPS terminal is shorten obviously, the TTFF of a positioning system of each A-GPS terminal can be shortened to less than 20 seconds after cold start, and therefore fast and reliable positioning is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fast time to first fix by calibration of a real time clock
A generic navigation satellite system (GNSS) signal receiver having a fast time to first fix by calibrating a low power always-on real time clock (RTC). The receiver includes an RTC calibrator having a fraction calculator. The RTC calibrator may also include a time expander. Before the receiver is powered off, the fraction calculator uses the fine resolution of GNSS time for determining a time fraction for RTC time. When the receiver is powered back on, the time expander uses an estimate of RTC time drift during the time that GNSS receiver had power off and the time fraction for calibrating and increasing the resolution of the RTC time for an RTC time tick. A signal navigation processor uses the calibrated RTC time for assisting a first fix with code phase search, integration time periods, resolution of epoch integer and / or location-in-space of GPS satellites.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
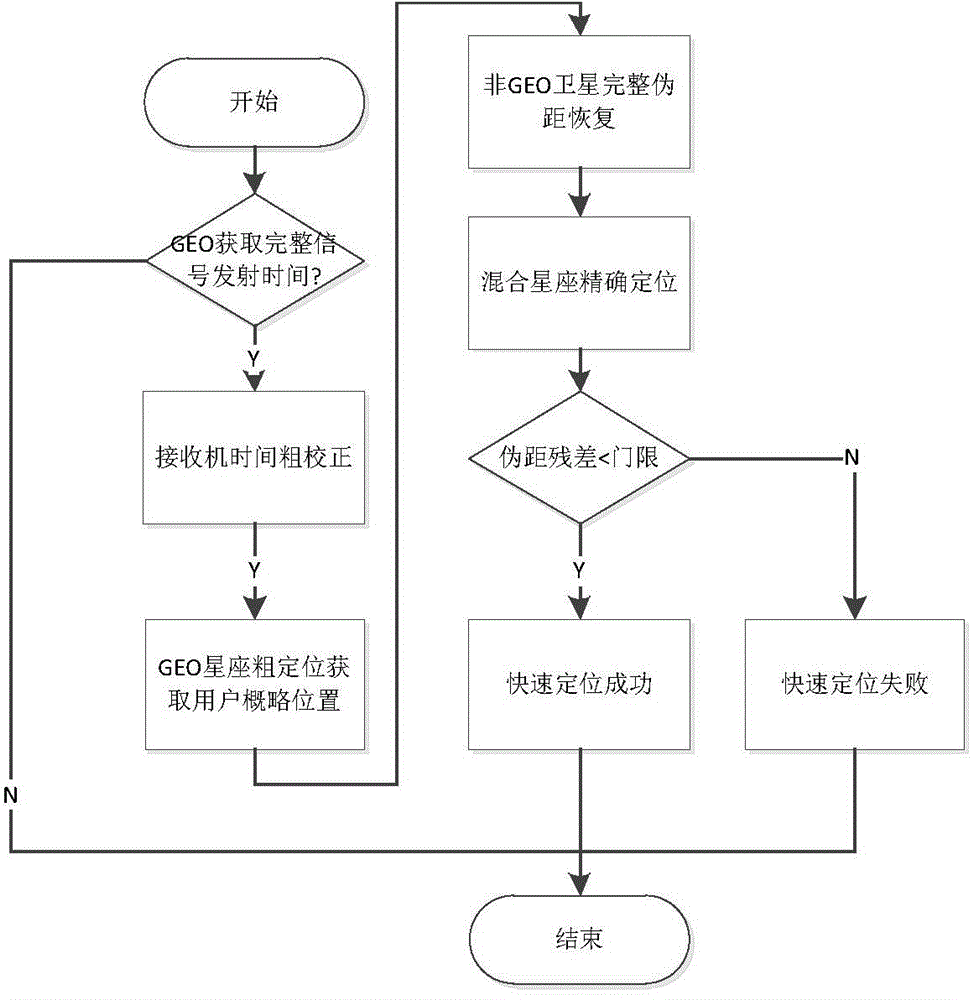
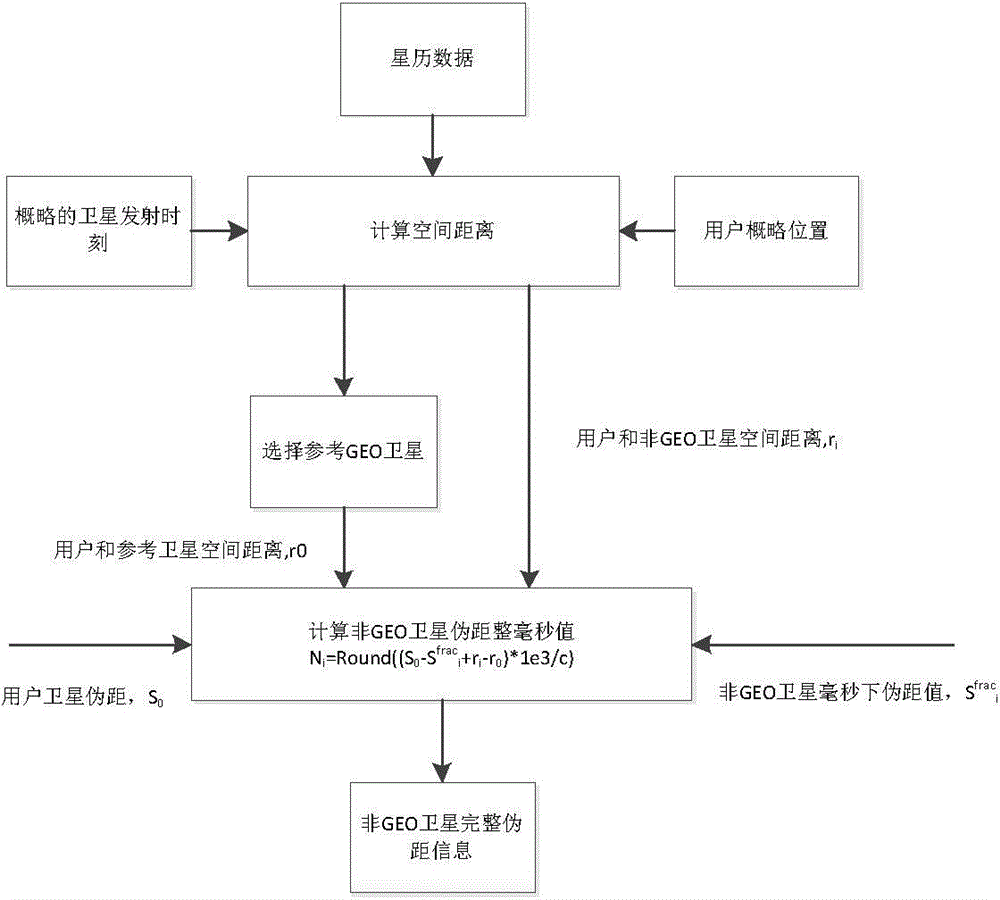
Quick locating method based on GEO constellation coarse location for Beidou receiver
The invention provides a quick locating method based on GEO constellation coarse location for a Beidou receiver by use of the characteristic that the GEO satellite in the hybrid constellation of the Beidou system is high in message rate, and solves the problem that when the outline coordinates of a receiver are unknown, the millisecond recovery algorithm for the traditional GNSS signal transmitting time cannot be applied due to a leap of calculated quantity. When the outline coordinates of the receiver are completely unknown, the GEO satellite of which the signal transmitting time is completely acquired is used at first for coarse location, then the millisecond integer time of the sending time of a non-GEO satellite is recovered according to the outline coordinates acquired by coarse location, and finally, all the visible satellites are utilized for accurate location. The quick locating method can achieve millisecond recovery of the non-GEO satellites which finish capture when the Beidou system only finishes frame alignment of GEO constellation, so that the time to first-time location of the receiver when the satellite ephemeris is known is earlier.
Owner:湖南中电星河电子有限公司
Systems and methods for generating a location of a mobile device using cell sector information
InactiveUS20110034178A1Well formedPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingTime to first fixMobile device
Systems and methods for generating a location of a mobile device using cell sector data are provided. A mobile device is in service connection with a base station, which has a corresponding service area. Upon entering the service area of another base station, the mobile device enters service connection with the second base station in a handoff event. The mobile device and / or the base station determines the location of each of the base stations, and estimates the approximate location of the mobile device based on the locations of the base stations. In one or more implementations, the estimated position can comprise a midpoint of a line joining the two base stations. The systems and methods can be implemented with a random location generator to improve accuracy. The approximate location of the mobile device can be inputted into a GPS-enabled device to reduce times to first fix.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method, system and device for position determination with predicted ephemeris
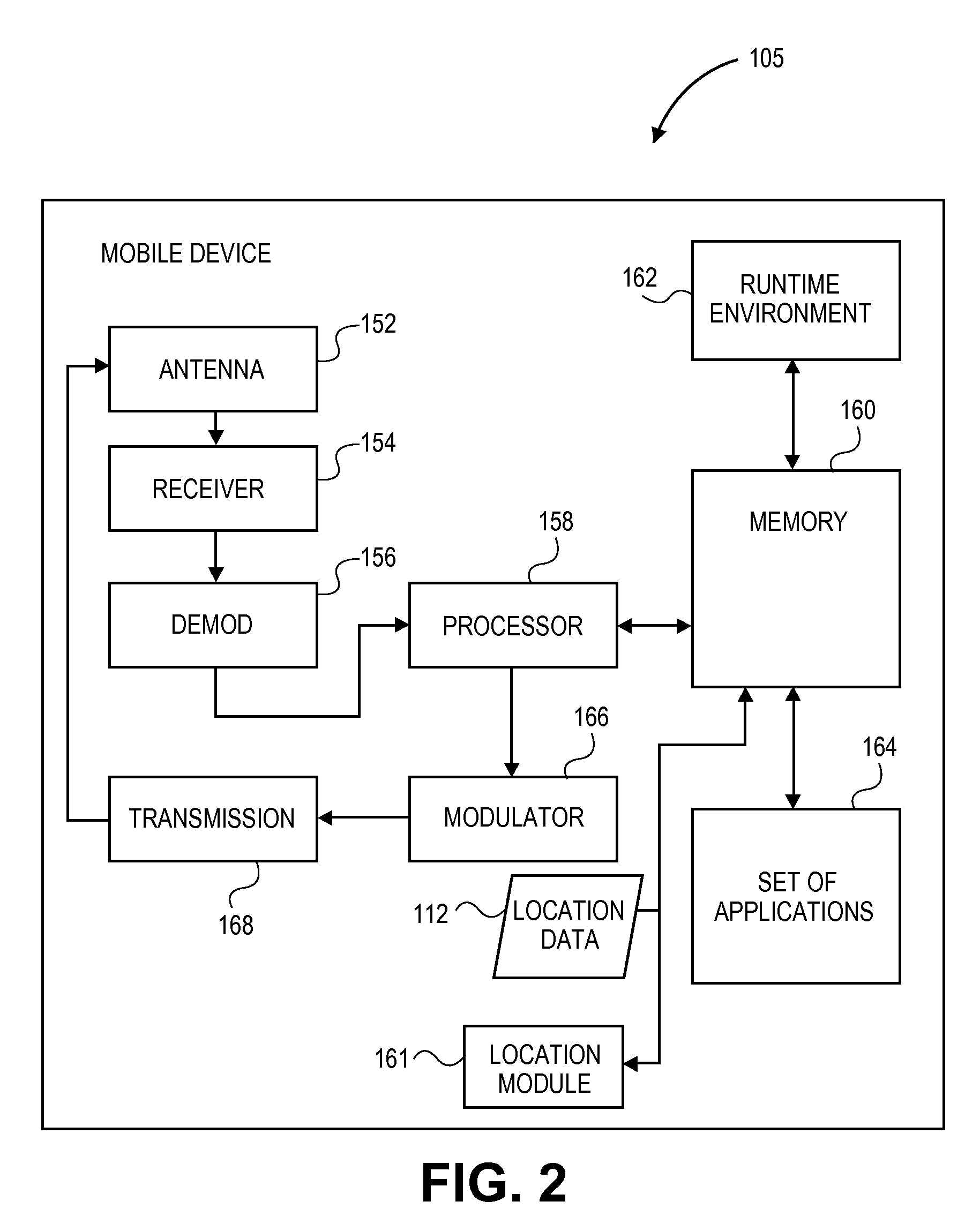
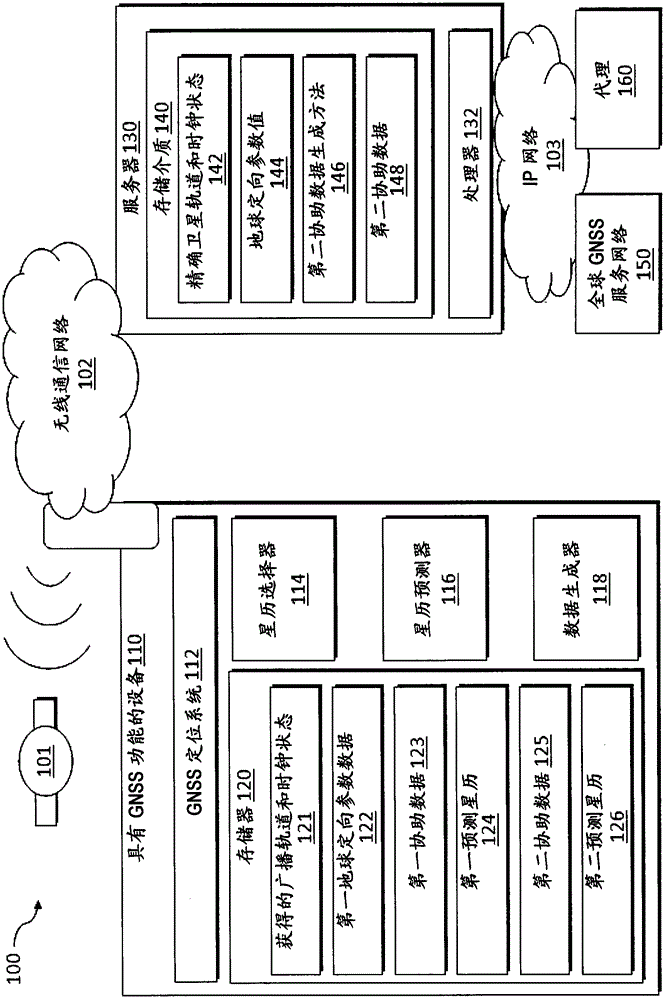
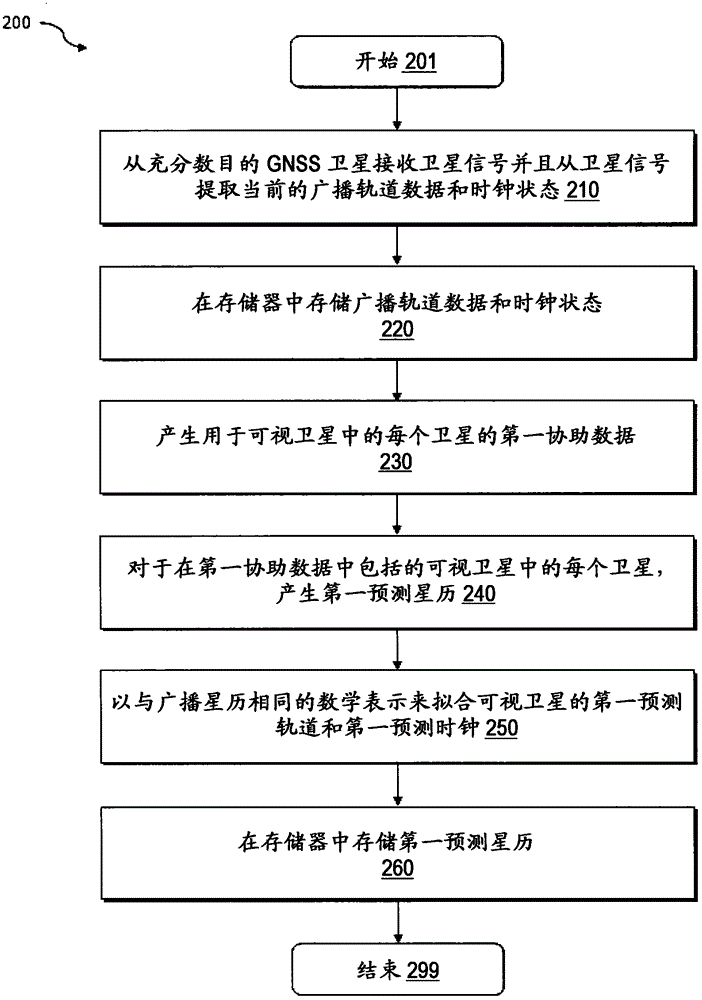
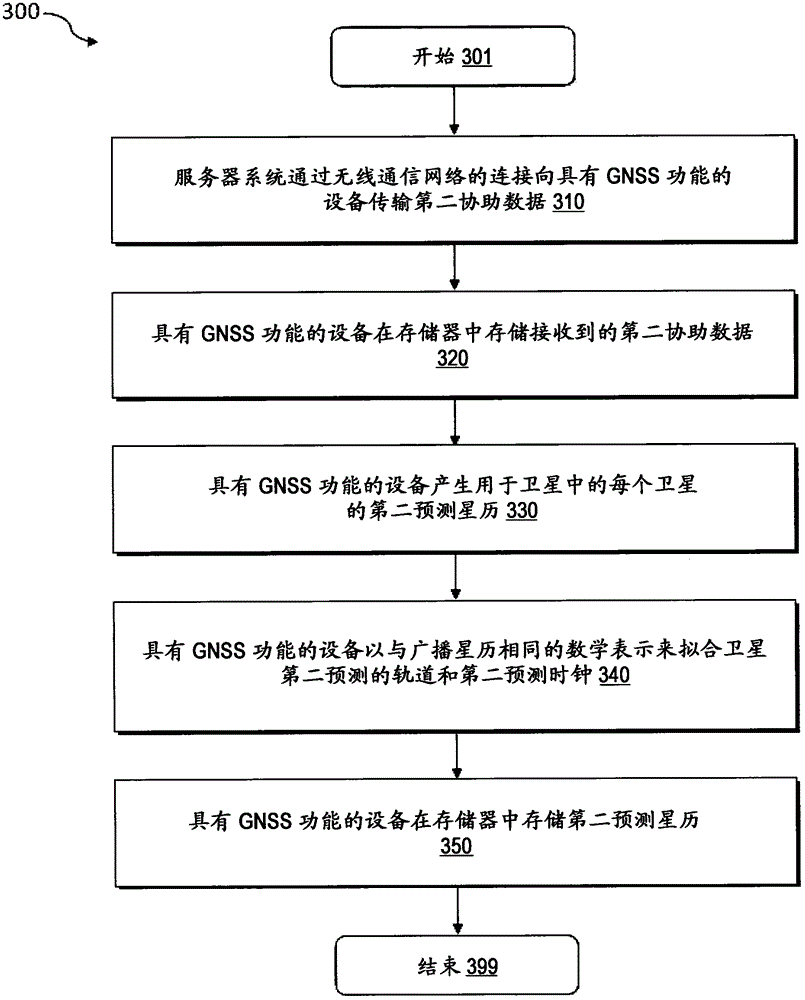
Method, system, and device are provided for position determination with the use of predicted ephemeris to reduce the time-to-first-fix. The method includes: in a device, receiving broadcast orbit data and clock states from a plurality of satellites to determine first assistance data for the plurality of satellites, and numerically predicting first ephemeris for the plurality of satellites using the first assistance data. The method also includes: in a server system, receiving precise orbit data and accurate satellite clock states from a global GNSS service network to determine second assistance data; in a device, receiving the second assistance data and numerically predicting second ephemeris using the second assistance data. The method further includes: in a device, receiving satellite signals from a plurality of satellites, checking the period of validity of the first predicted ephemeris and the second predicted ephemeris respectively to select a predicted ephemeris from both the first predicted ephemeris and the second predicted ephemeris.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
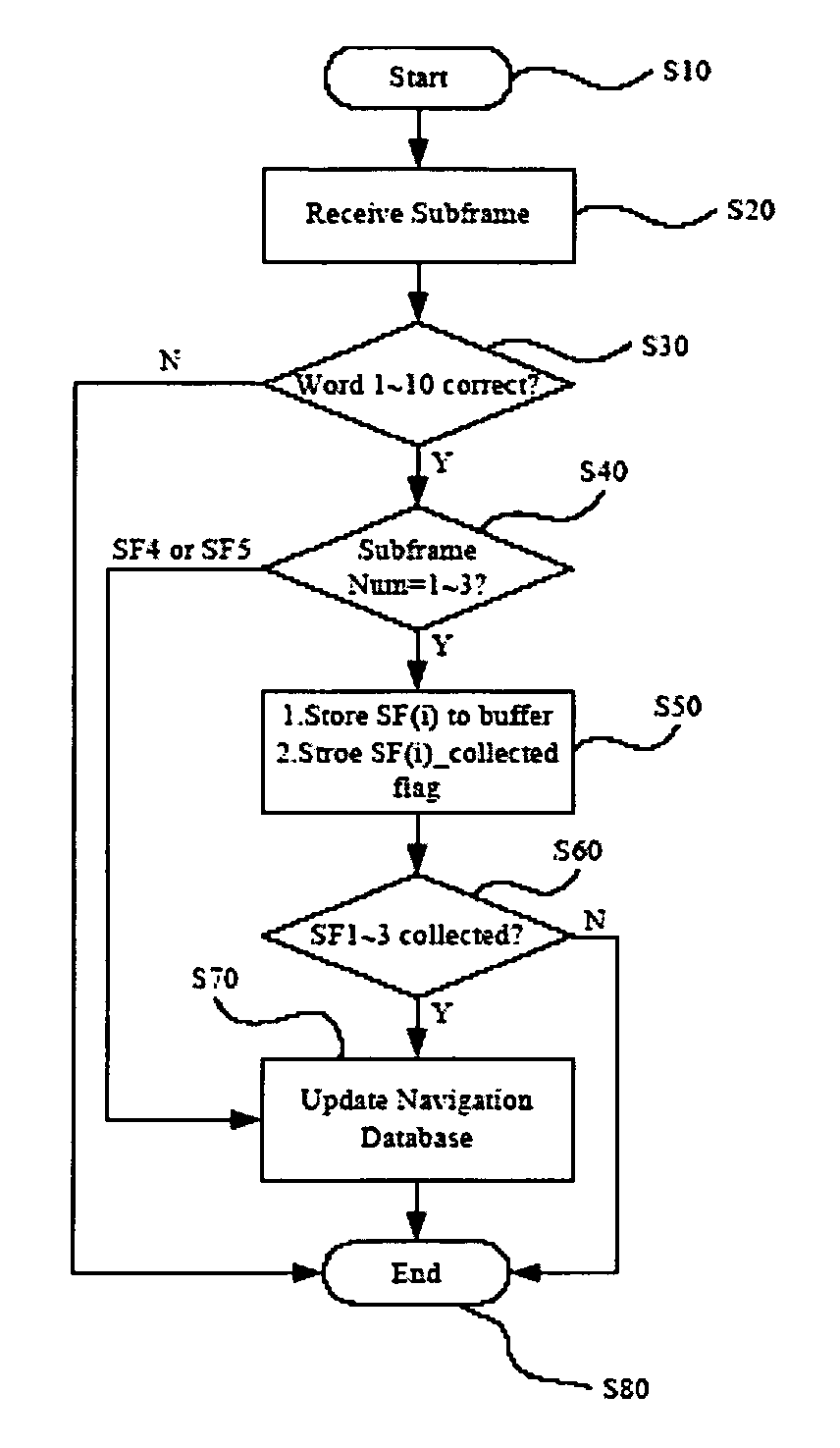
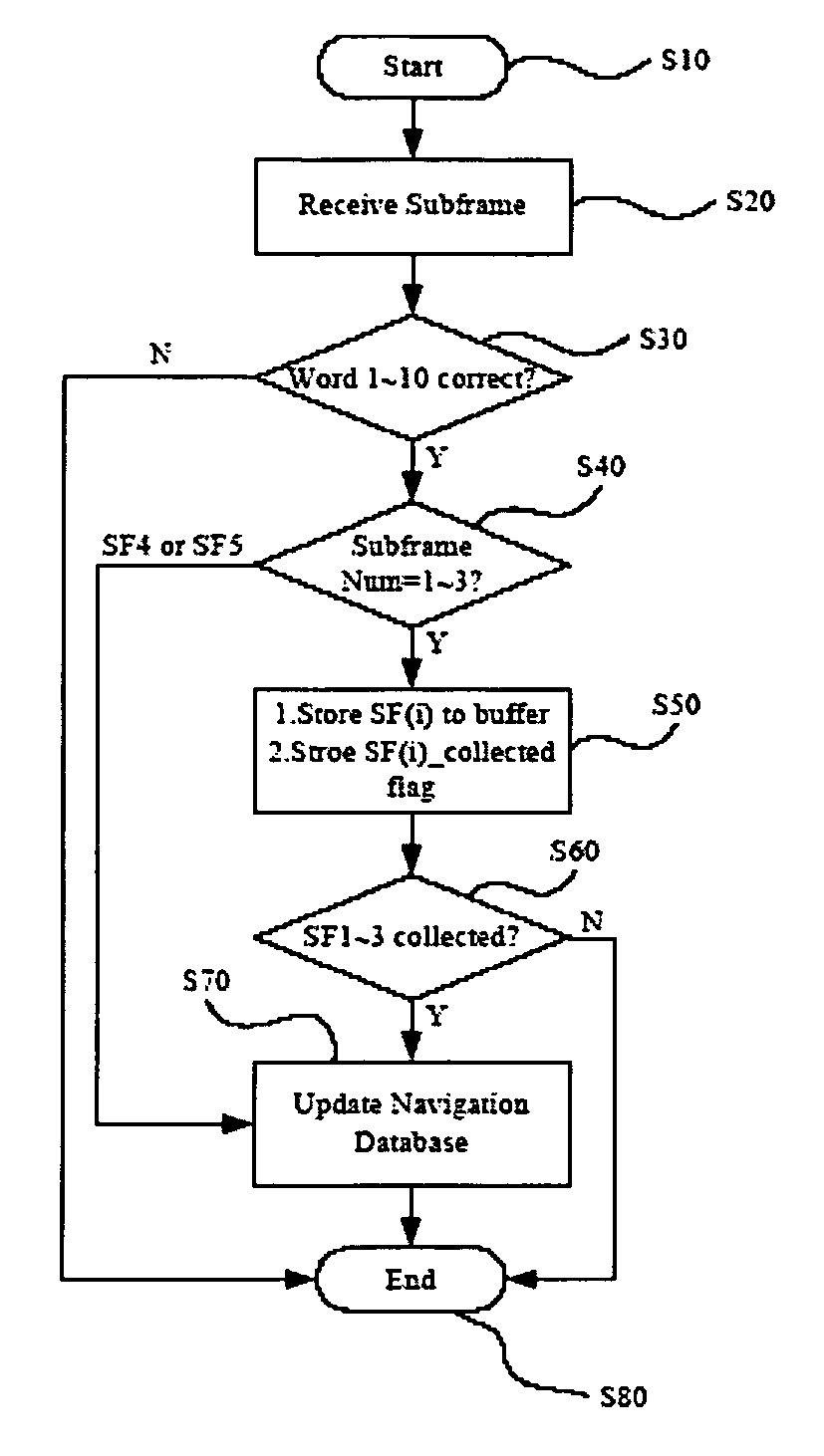
Method and apparatus for collecting subframes of satellite navigation data
ActiveUS20080165057A1Facilitate receiverShorten the timePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingTime to first fixSatellite
A method and apparatus for collecting subframes of navigation data of satellites are disclosed. In the method of the present invention, the subframe is divided into several sub-units, each sub-units includes one or more words. When a receiver receives a subframe with a subframe ID, the respective required sub-units of the subframe are checked. A dummy sub-unit is not necessary to be considered. Valid ones of the required sub-units are collected. If not all the required sub-units of the subframe have been collected, the absent sub-units are to be collected when the next subframe with the same subframe ID is received. Some protection schemes can be applied to raise the reliability of such sub-unit collection. Especially when the signal is weak or unstable, the present invention may significantly improve the TTFF (Time To First Fix) performance of the receiver.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method and apparatus for compensating clock bias
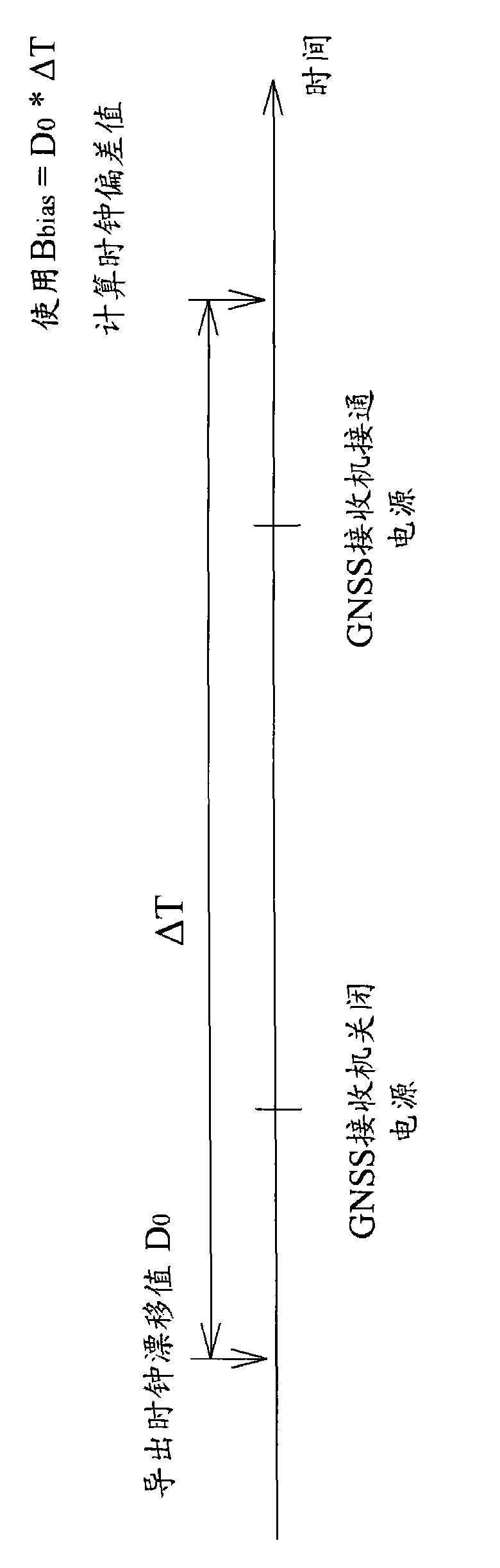
InactiveCN101655686AHelp syncReduce time to first fixPulse automatic controlBeacon systems using radio wavesTime informationClock drift
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for compensating clock bias, wherein the apparatus for compensating clock bias which is applied to a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver comprises a clock source for providing a reference time which has a clock bias to be compensated and a processing module which is coupled to the clock source for deriving at least one clock drifting value. The clock drifting value contains a first clock drifting value corresponding to a first time point. The clock bias is calculated according to the at least one clock drifting time and at leastone time section, wherein the at least one time section is a time period between the first time point and a special time point after the first time point. The method and the apparatus provided by theinvention can derive the time information and obviously decrease the first locating time.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method and apparatus for collecting subframes of satellite navigation data
ActiveUS7636060B2Facilitate receiverShorten the timeBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingTime to first fixMarine navigation
A method and apparatus for collecting subframes of navigation data of satellites are disclosed. In the method of the present invention, the subframe is divided into several sub-units, each sub-units includes one or more words. When a receiver receives a subframe with a subframe ID, the respective required sub-units of the subframe are checked. A dummy sub-unit is not necessary to be considered. Valid ones of the required sub-units are collected. If not all the required sub-units of the subframe have been collected, the absent sub-units are to be collected when the next subframe with the same subframe ID is received. Some protection schemes can be applied to raise the reliability of such sub-unit collection. Especially when the signal is weak or unstable, the present invention may significantly improve the TTFF (Time To First Fix) performance of the receiver.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Capturing method of satellite navigation signal in adjustable carrier wave doppler frequency searching range
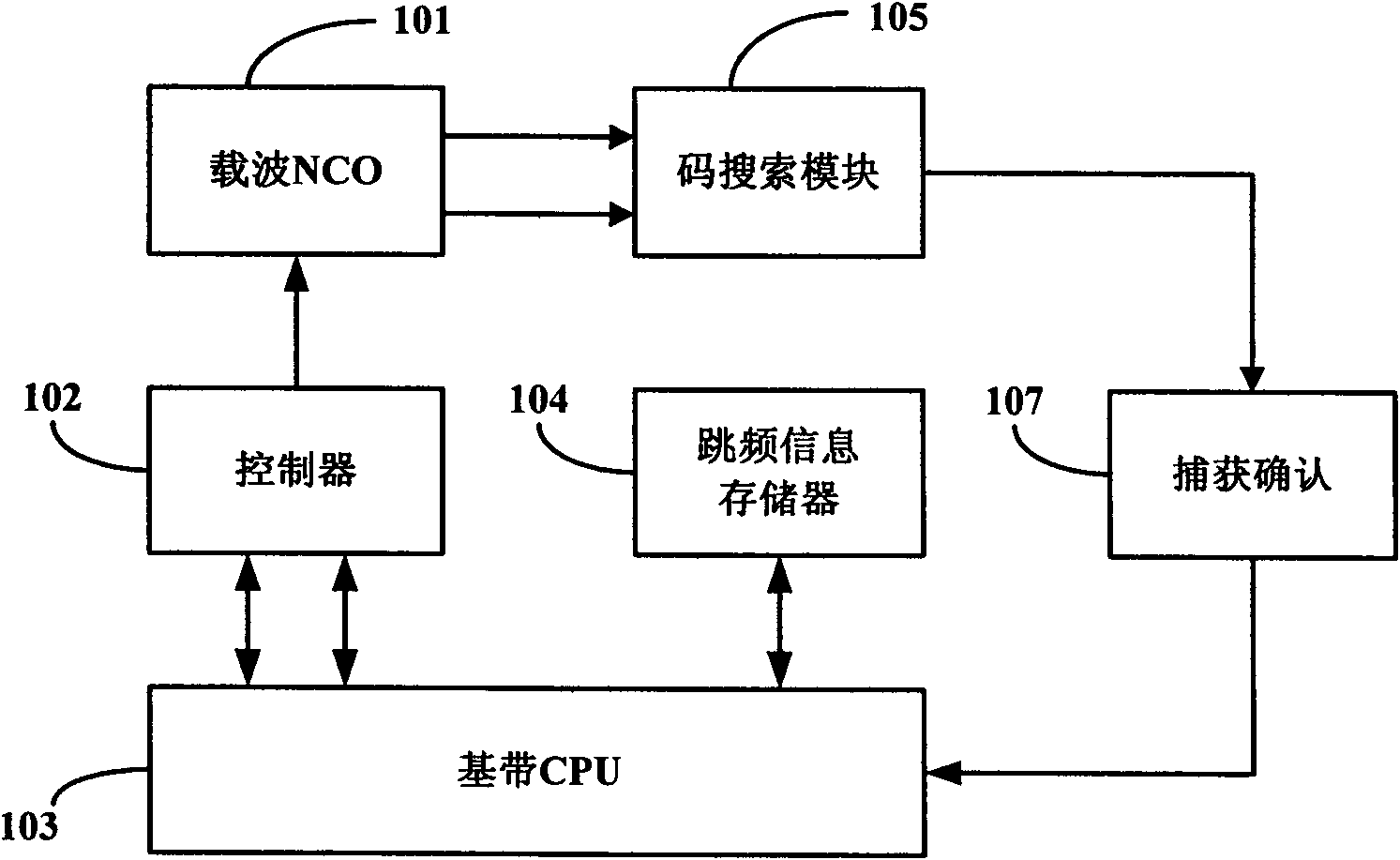
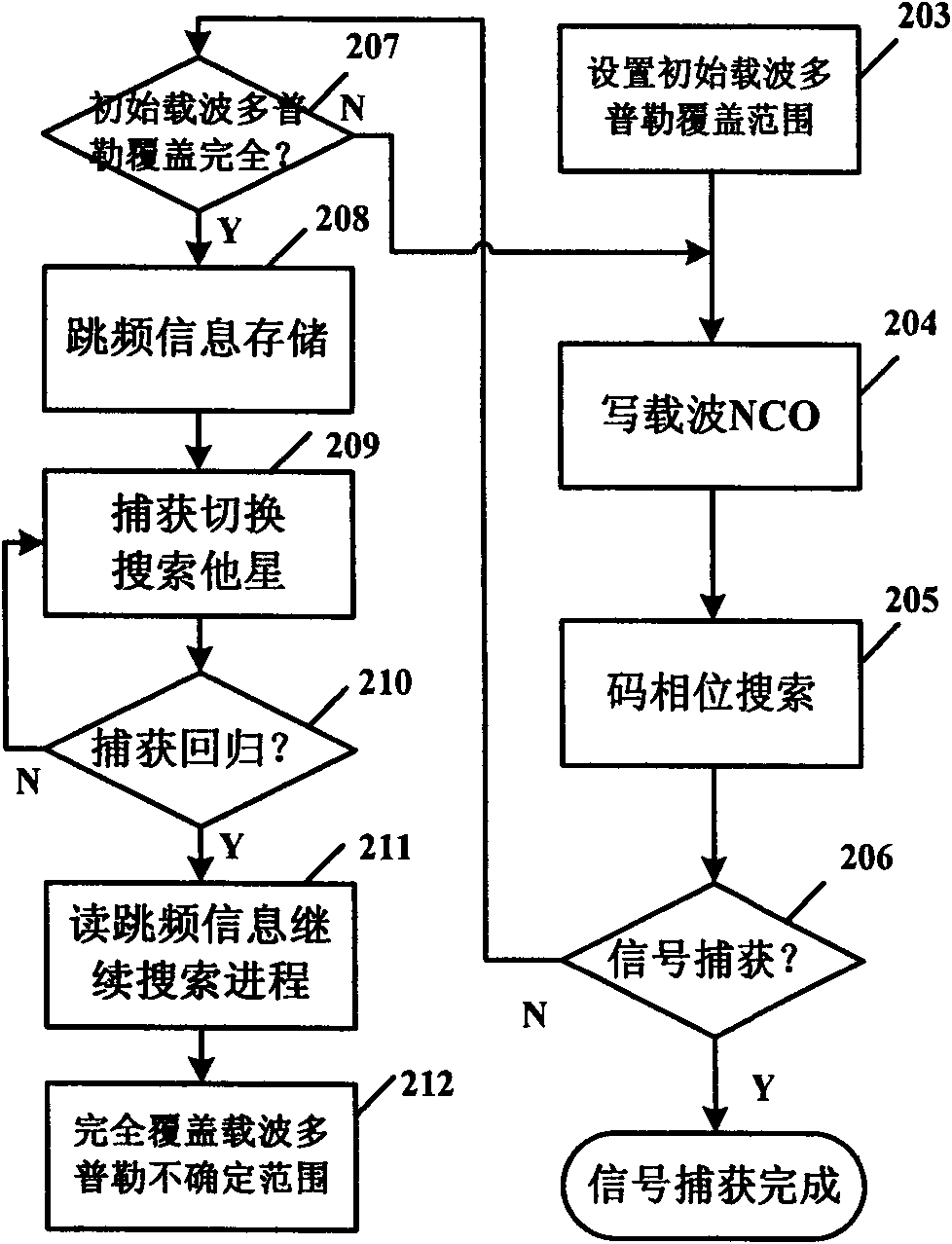
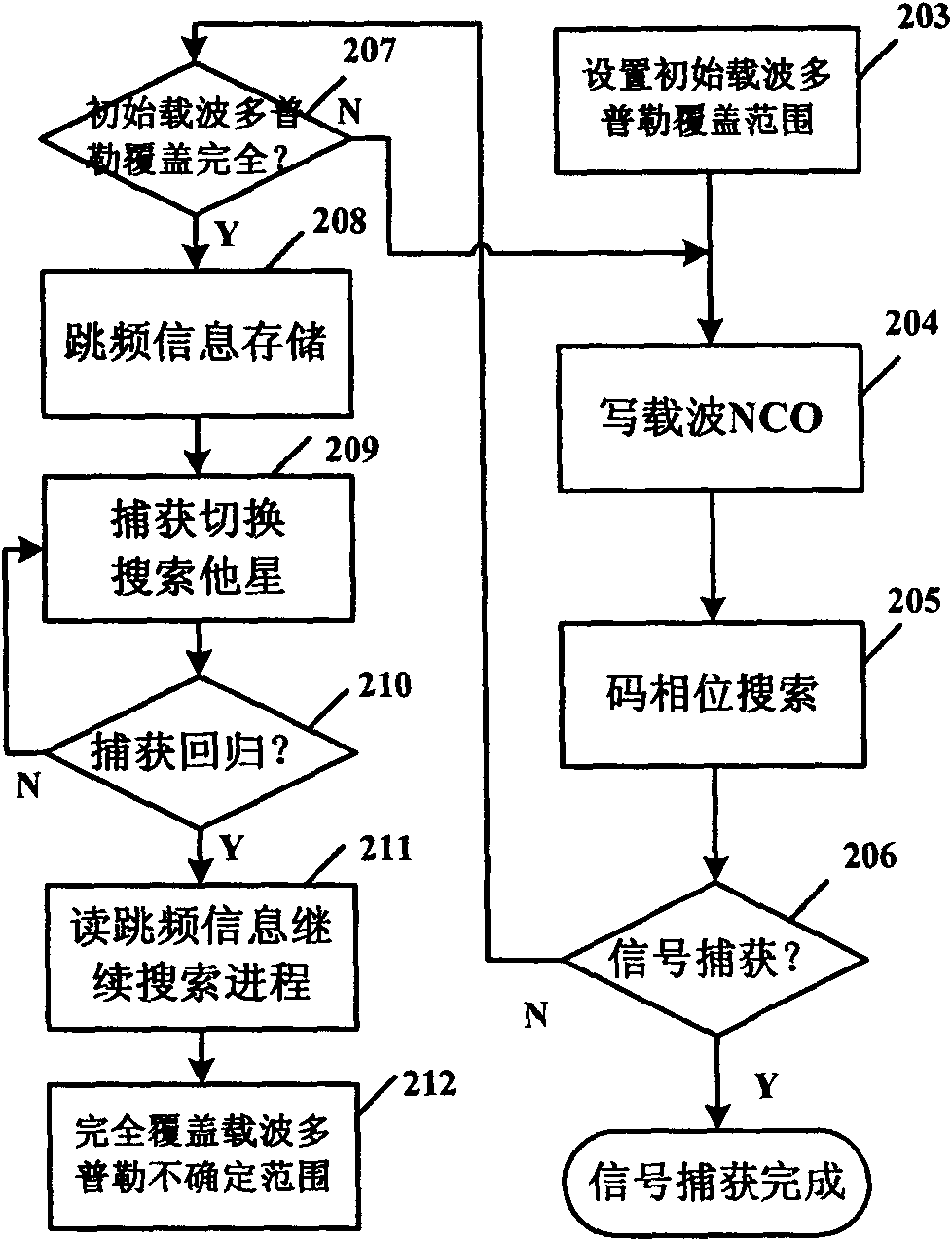
InactiveCN102426367AReduce search timeReduce time to first fixSatellite radio beaconingTime to first fixCarrier signal
The invention relates to a capturing method of a satellite navigation signal in an adjustable carrier wave doppler frequency searching range. The method comprises the following steps that: an initial carrier wave doppler covering range and a corresponded carrier frequency is generated; code phase searching is completed under the carrier wave frequency to obtain a corresponded capturing result; because the covering of the initial carrier wave doppler is complete, search frequency point information of the carrier wave doppler that is frequency hopping information is written into a frequency hopping information memory to complete storage of the frequency hopping information that can be used for subsequent continuous capturing; and other unresearched satellites are switched for continuous execution. According to the invention, searching of an undetermined range of a carrier wave frequency can be completed at the expense of few hardware costs and a fast speed; satellites can be searched ina short time as much as possible; and first positioning time of a receiver is improved.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Time To First Fix Optimization In A Satellite Navigation Receiver
ActiveUS20150077288A1Shorten the timeHigh data rateSatellite radio beaconingSynchronous orbitGeosynchronous satellite
A method and a system for reducing time to first fix (TTFF) in a satellite navigation receiver (SNR) includes constructing an integrated satellite constellation system (ISCS) for transmitting navigation signals over a combination of a first carrier frequency, a second carrier frequency, and a third carrier frequency. The ISCS includes a predetermined number of geosynchronous satellites positioned at first predetermined geographic coordinates in a geosynchronous orbit and a predetermined number of geostationary satellites positioned at second predetermined geographic coordinates in a geostationary orbit. The ISCS transmits navigation data to the SNR over the combination of the first carrier frequency, the second carrier frequency, and the third carrier frequency in reduced time, thereby reducing the TTFF in the SNR. The method and the system also reduce TTFF in a hot start mode and a snap start mode of the SNR by utilizing the third carrier frequency as a data channel.
Owner:ACCORD SOFTWARE & SYST PVT
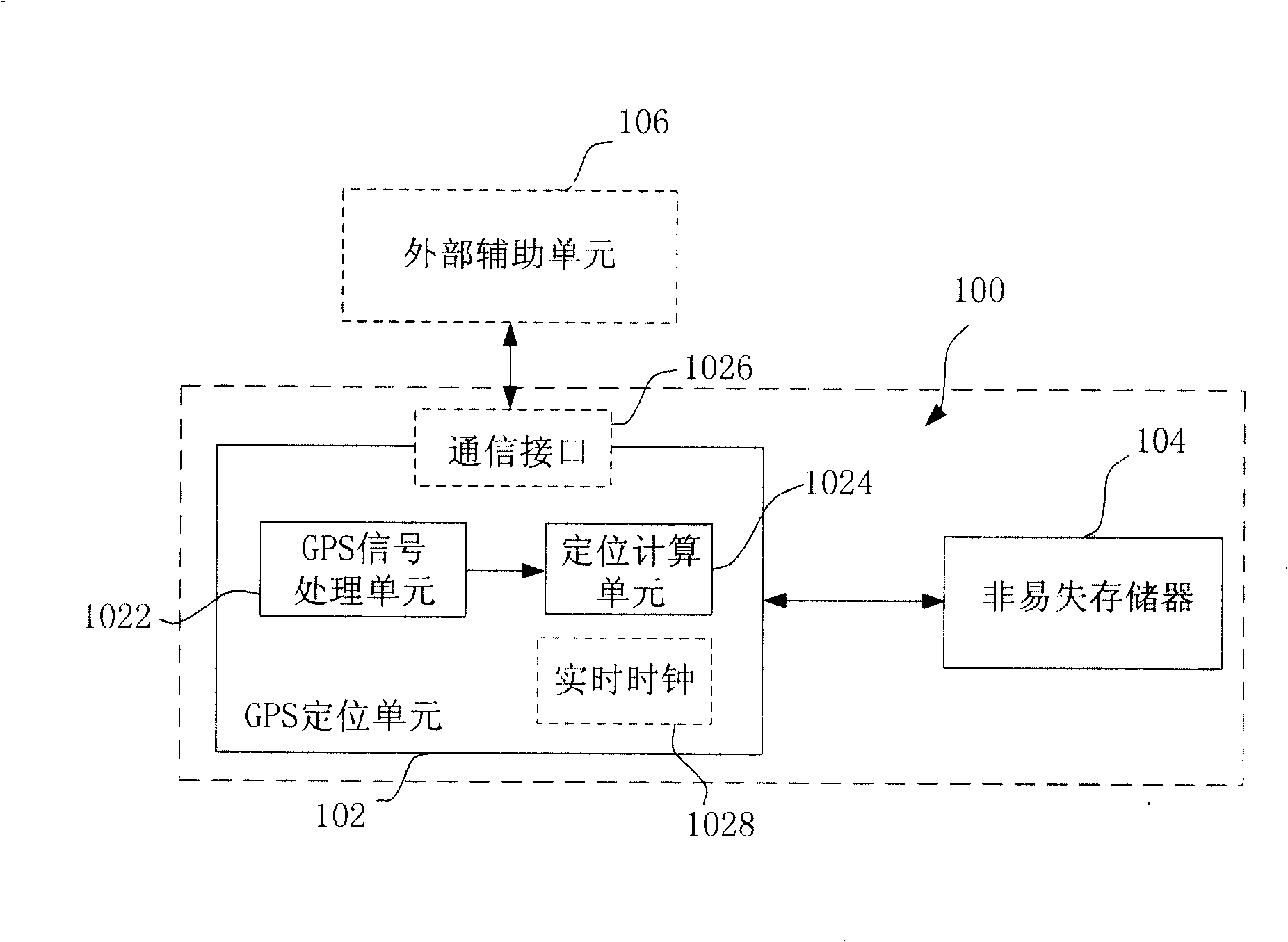
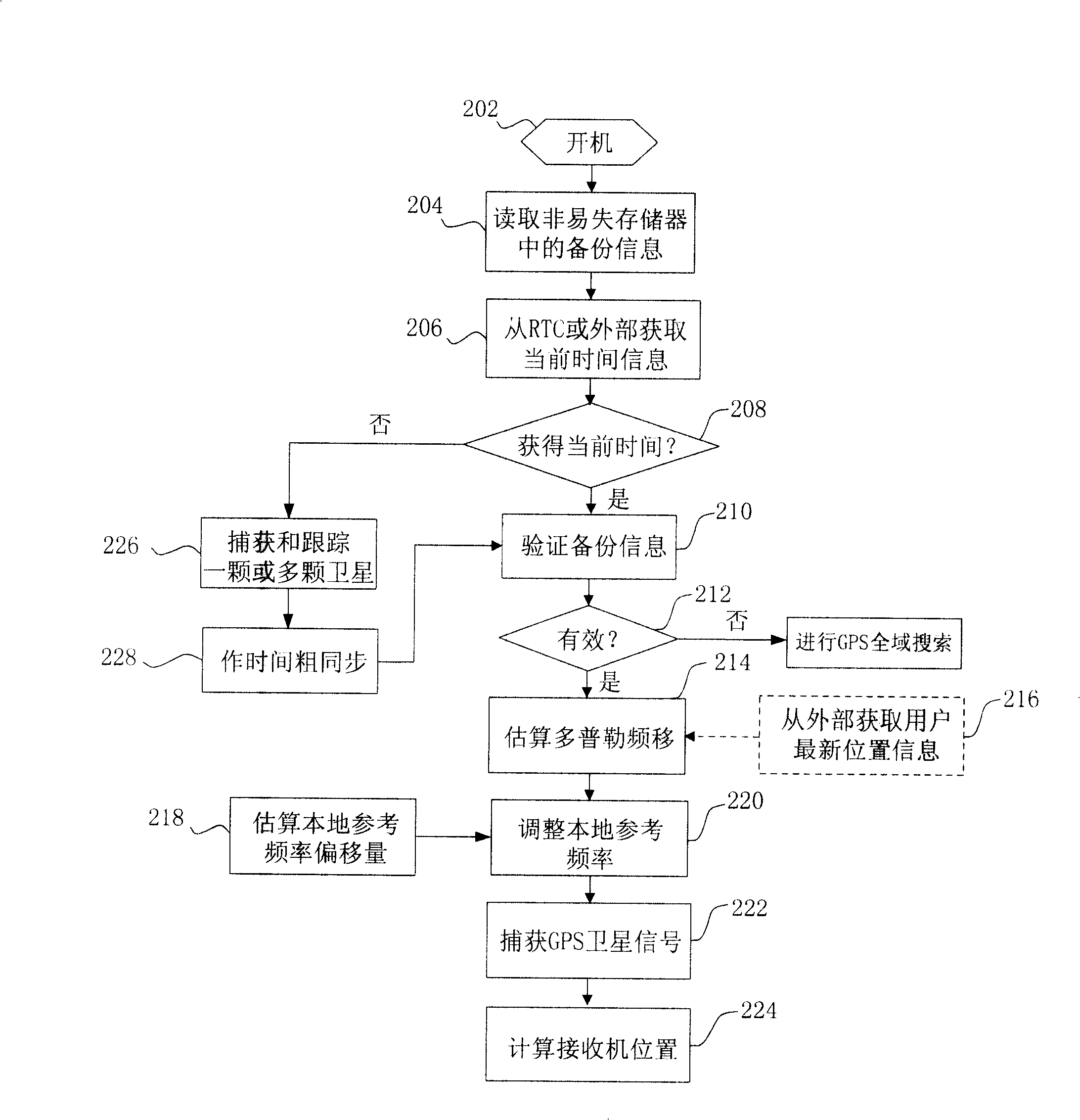
GPS receiver and method for reducing first positioning time after starting-up
ActiveCN101246208AShorten capture timeRapid positioningBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationElectrical batteryTime to first fix
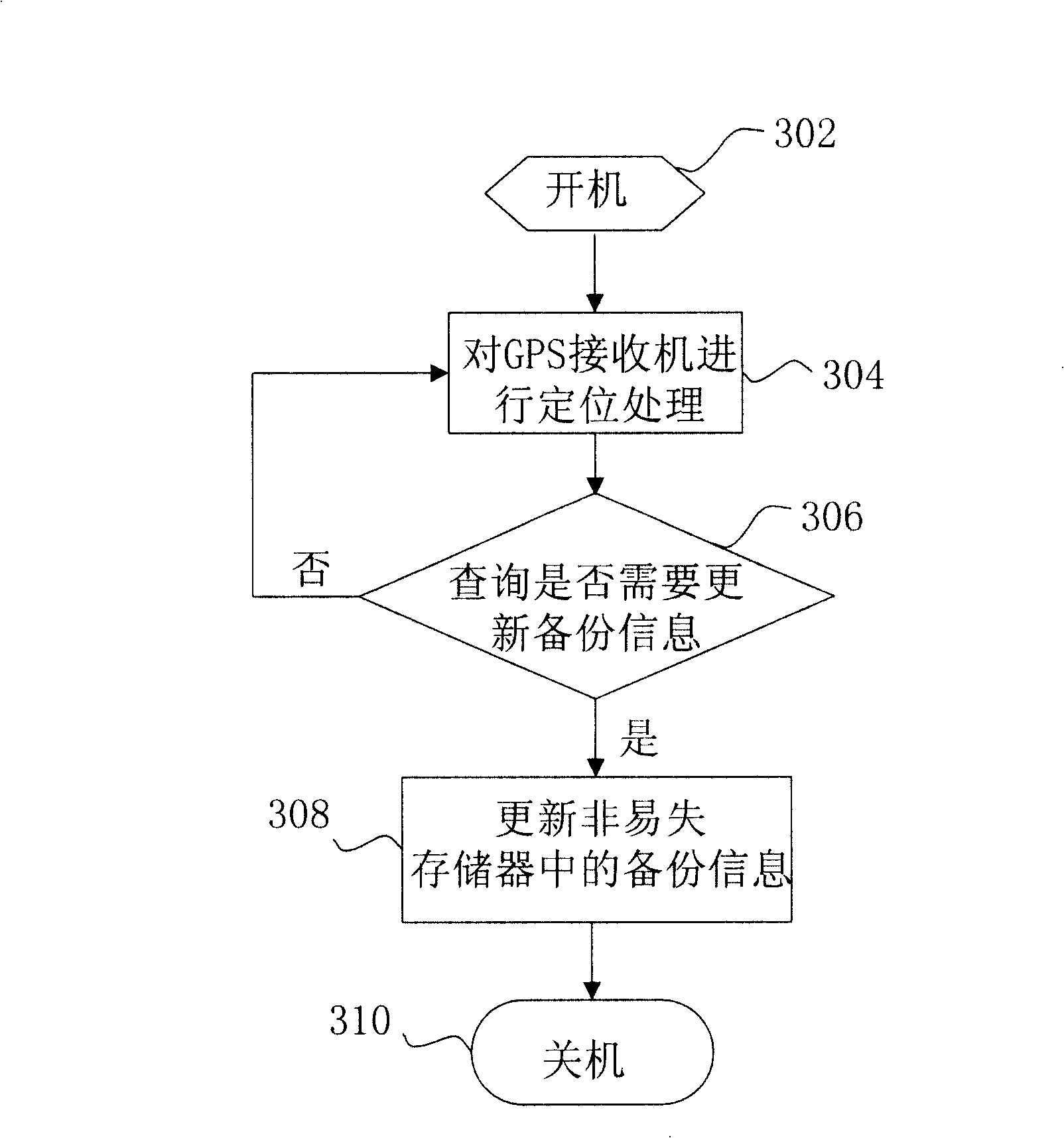
The invention discloses a GPS receiver which reduces first positioning time after starting up and the method thereof. The GPS receiver includes positioning unit and non-volatile storage which communicates with the positioning unit. The method which reduces the first positioning time of GPS receiver includes the following steps: reading backup information stored in the non-volatile storage; obtaining current time information; estimating the Doppler shift range; according to the range of Doppler shift, capturing GPS satellite; and calculating the position of the GPS receiver. Because of using the backup information in the non-volatile storage to estimate the range of Doppler shift, even if the system is at low battery condition or powered off, the backup information in the non-volatile storage is still valid, thereby the fast positioning after user turns on the GPS receiver is realized.
Owner:BEIJING BIG TOP MOMENT TECH CO LTD
Full-wave band GSM base station information acquisition system
InactiveCN103354648AQuick collectionComprehensive collectionWireless communicationFull waveTime to first fix
Disclosed in the invention is a full-wave band GSM base station information acquisition system. The method for implementing the system comprises the following steps: setting a starting mode of a global positioning system and obtaining first-time positioning time; setting interval time between scanning and searching; turning off a radio frequency switch to carry out full-waveband scanning; searching and obtaining base station signal information and base station information at a frequency point; newly adding or updating the base station signal information and base station information; uploading the base station signal information and base station information to a mobile detection terminal, carrying out querying and reporting to obtain and record base station positioning information of scanning each time; labeling the position of the base station at a map and drawing a distribution track and a zone of the base station; carrying out analyzing and classification on the base station information and the positioning information and storing the base station information; and analyzing the classified base station information for displaying. According to the information acquisition system provided by the invention, acquisition, analyzing, and classified displaying of base station information can be realized; and the precision is high and the real-time performance is excellent.
Owner:苏州翼凯通信科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com