Patents
Literature
1802 results about "Grammaticality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
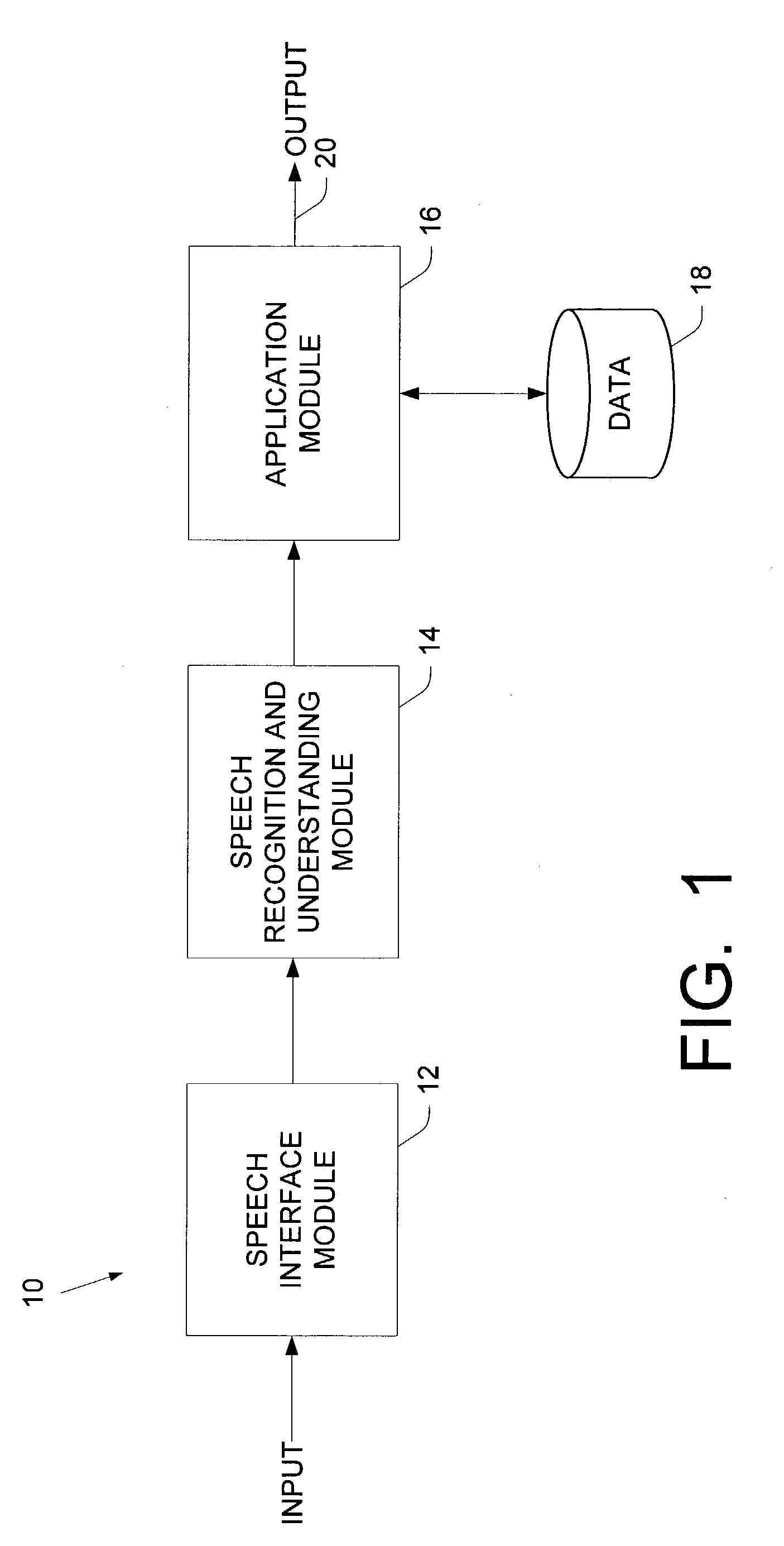
In linguistics, grammaticality is determined by the conformity to language usage as derived by the grammar of a particular speech variety. The notion of grammaticality rose alongside the theory of generative grammar, the goal of which is to formulate rules that define well-formed, grammatical, sentences. These rules of grammaticality also provide explanations of ill-formed, ungrammatical, sentences.
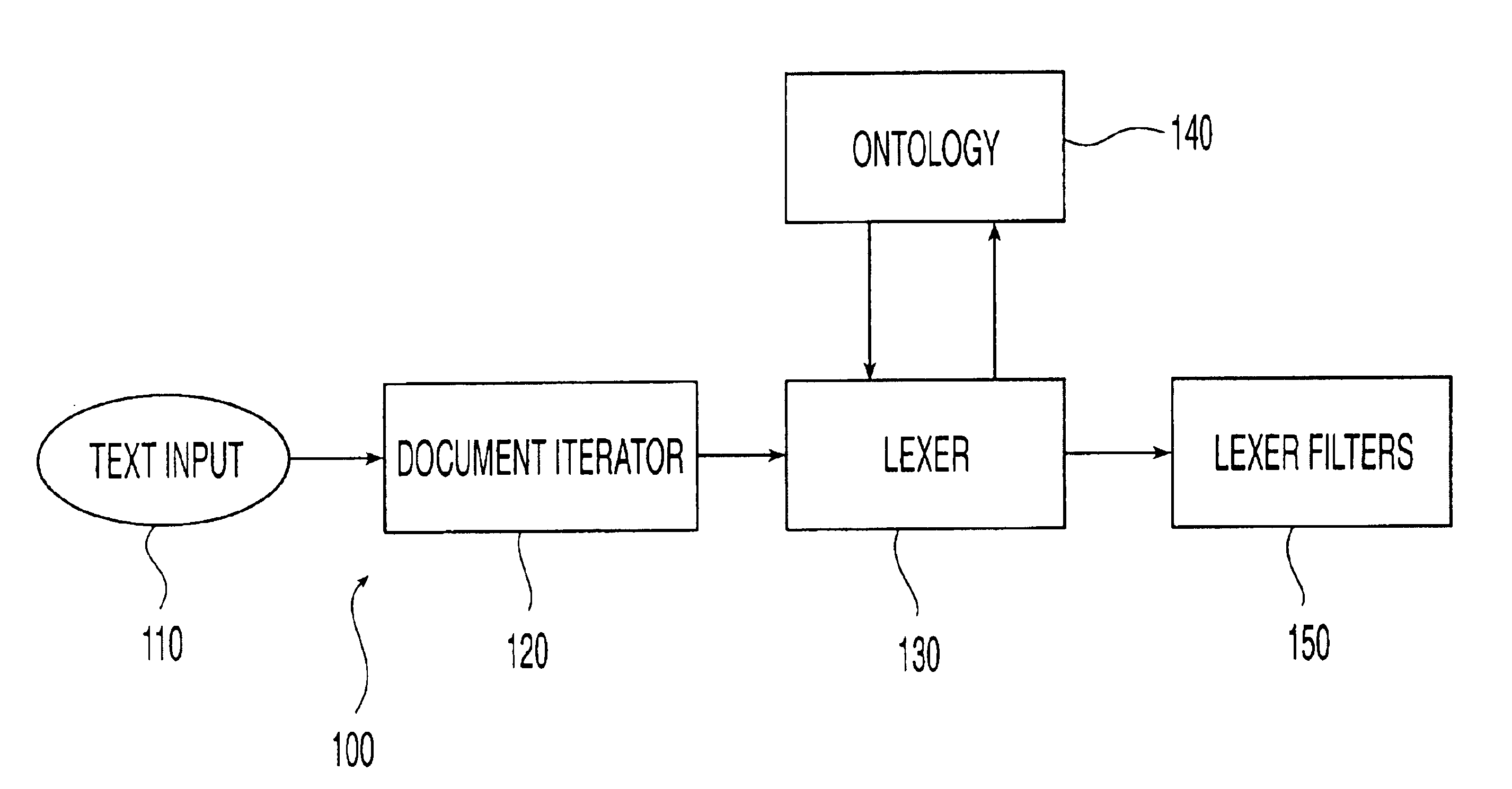
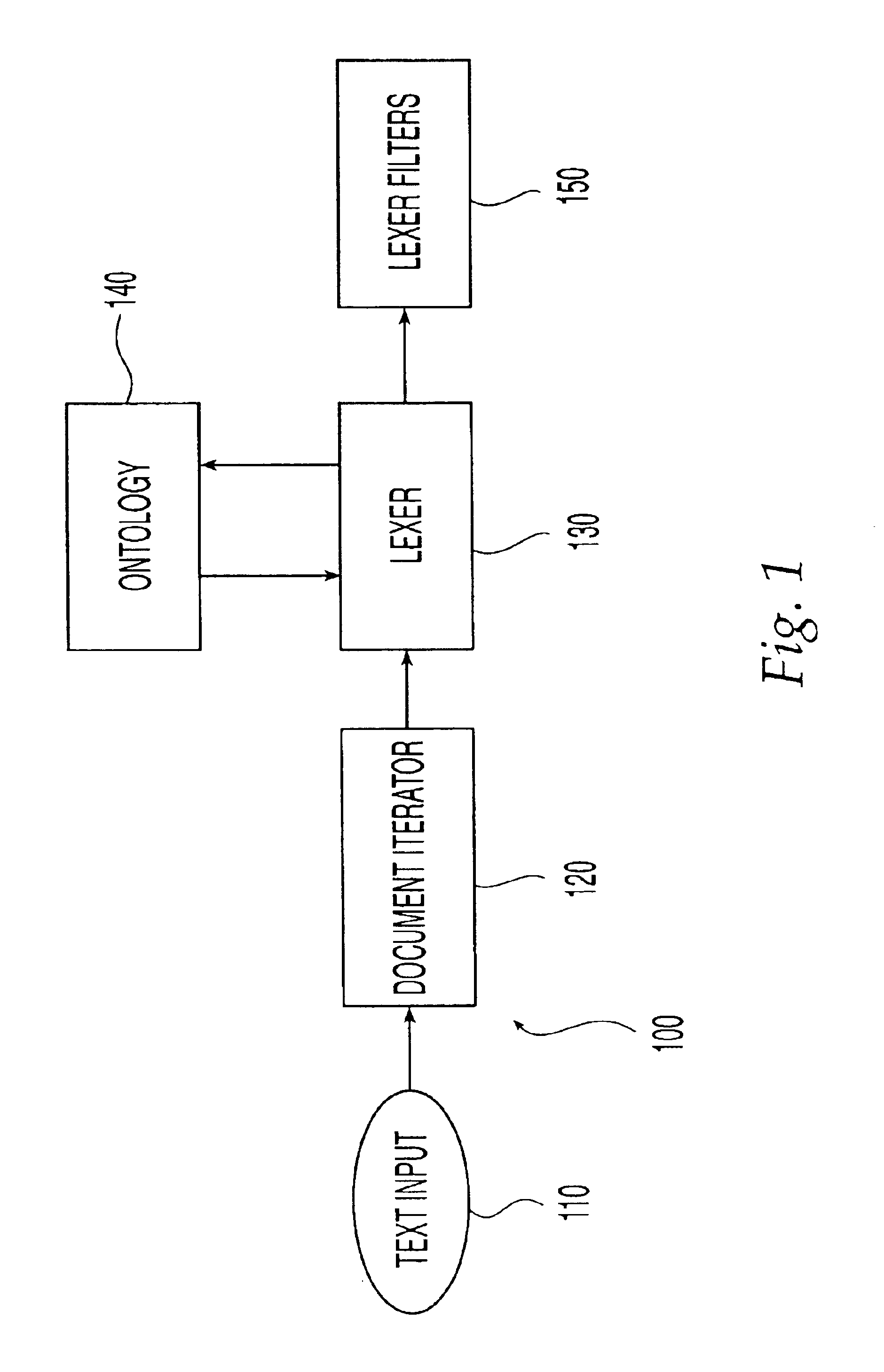
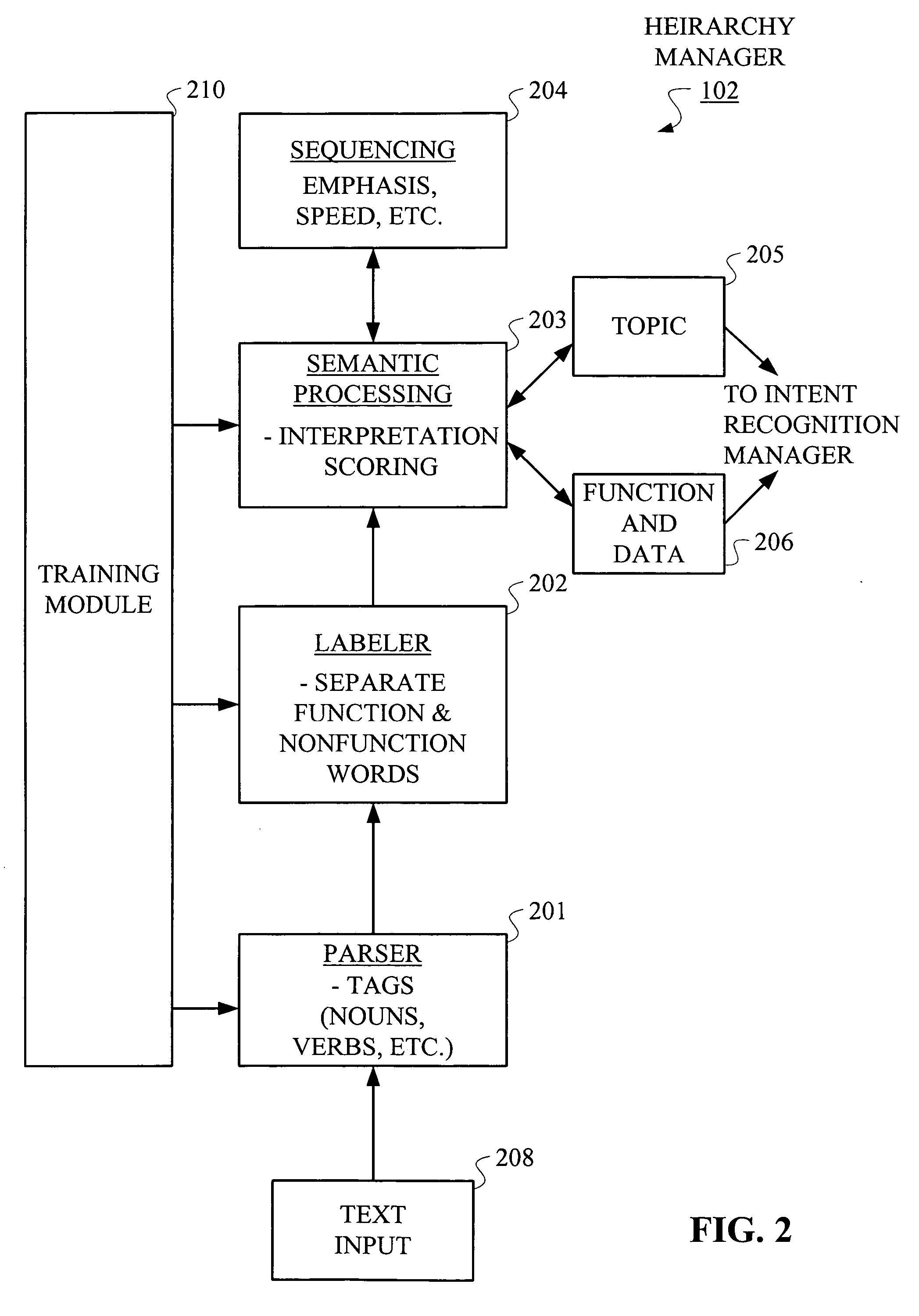
Ontology-based parser for natural language processing
ActiveUS7027974B1Maximum speedData processing applicationsNatural language data processingPart of speechNatural language programming
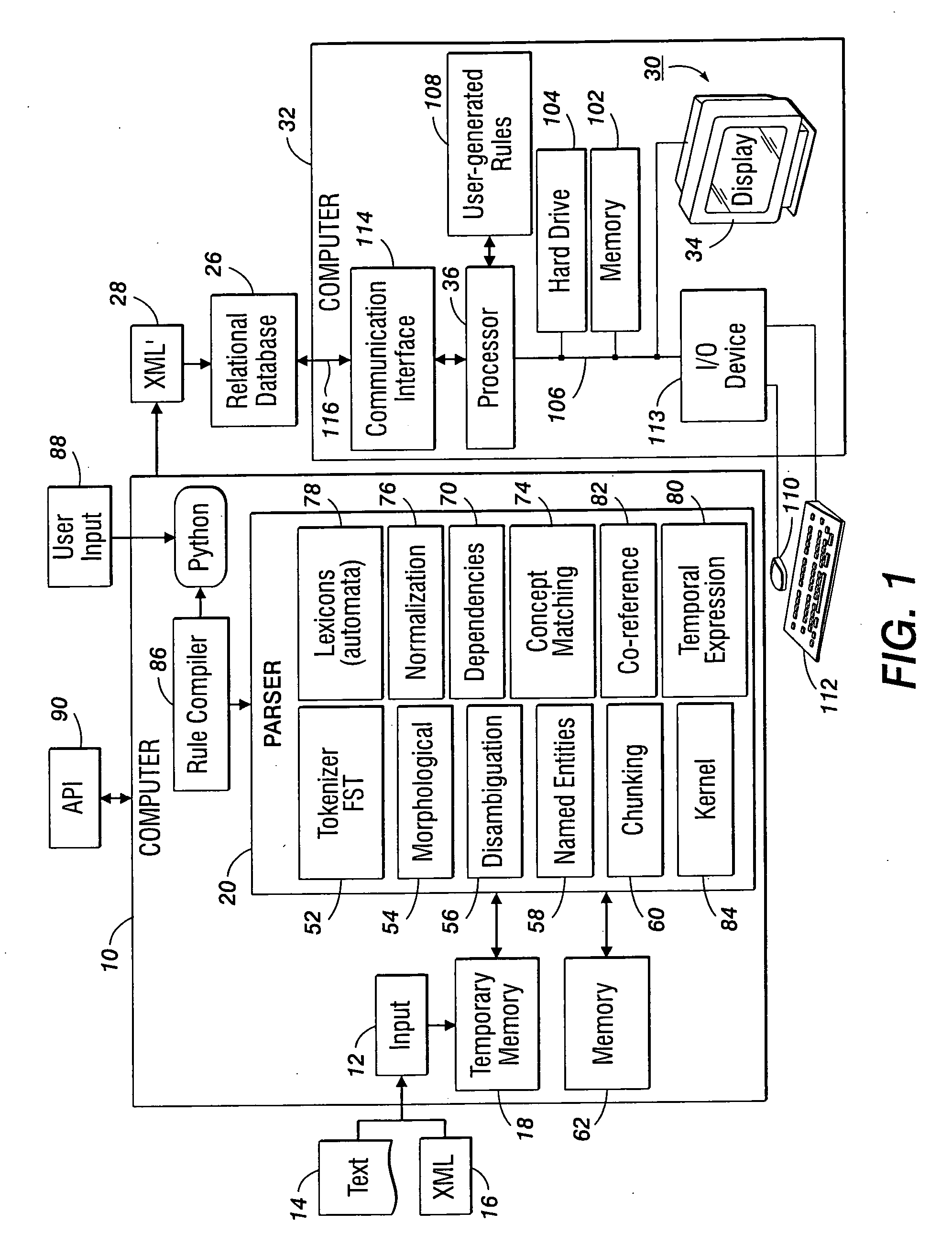
An ontology-based parser incorporates both a system and method for converting natural-language text into predicate-argument format that can be easily used by a variety of applications, including search engines, summarization applications, categorization applications, and word processors. The ontology-based parser contains functional components for receiving documents in a plurality of formats, tokenizing them into instances of concepts from an ontology, and assembling the resulting concepts into predicates. The ontological parser has two major functional elements, a sentence lexer and a parser. The sentence lexer takes a sentence and converts it into a sequence of ontological entities that are tagged with part-of-speech information. The parser converts the sequence of ontological entities into predicate structures using a two-stage process that analyzes the grammatical structure of the sentence, and then applies rules to it that bind arguments into predicates.
Owner:LEIDOS
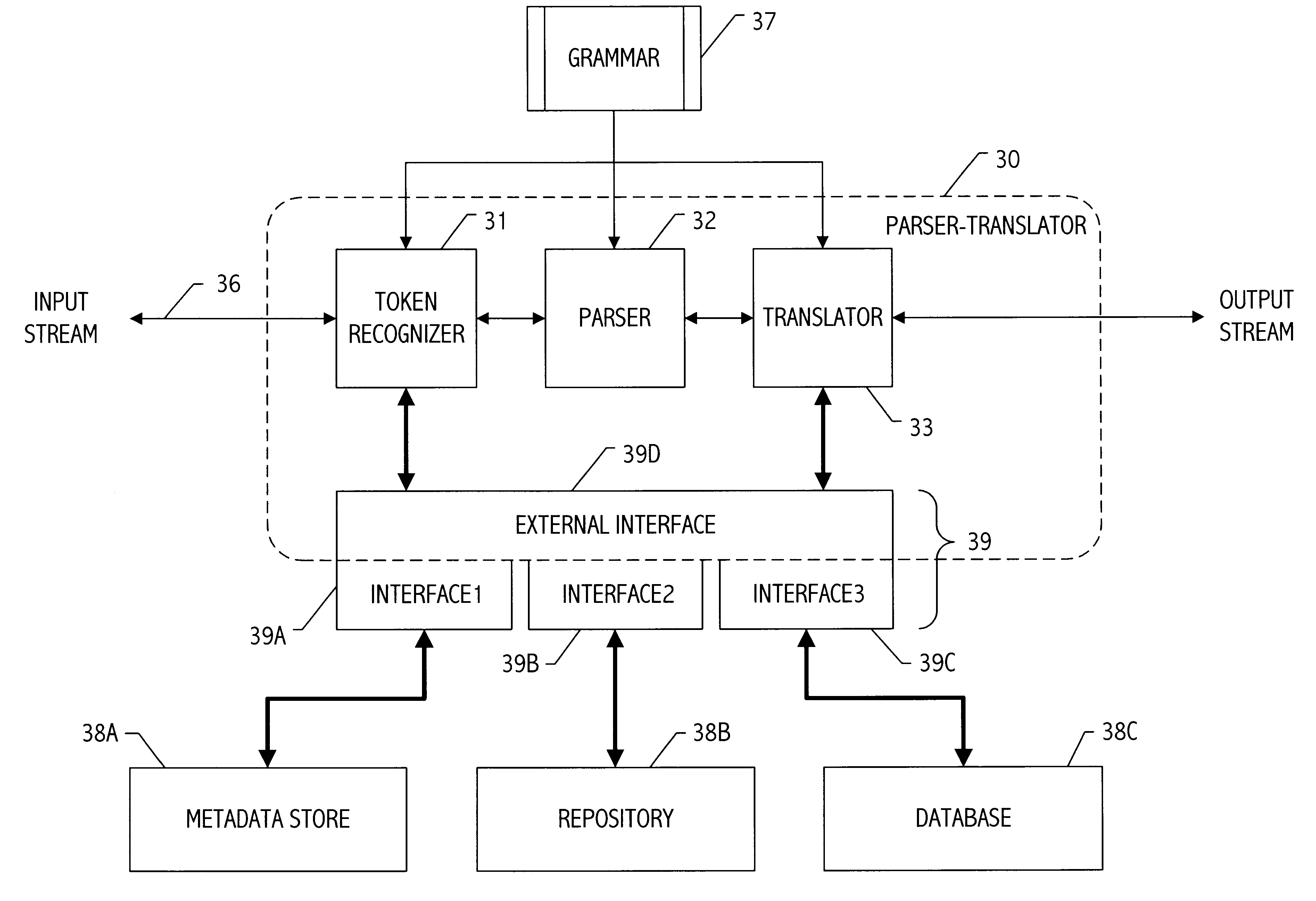
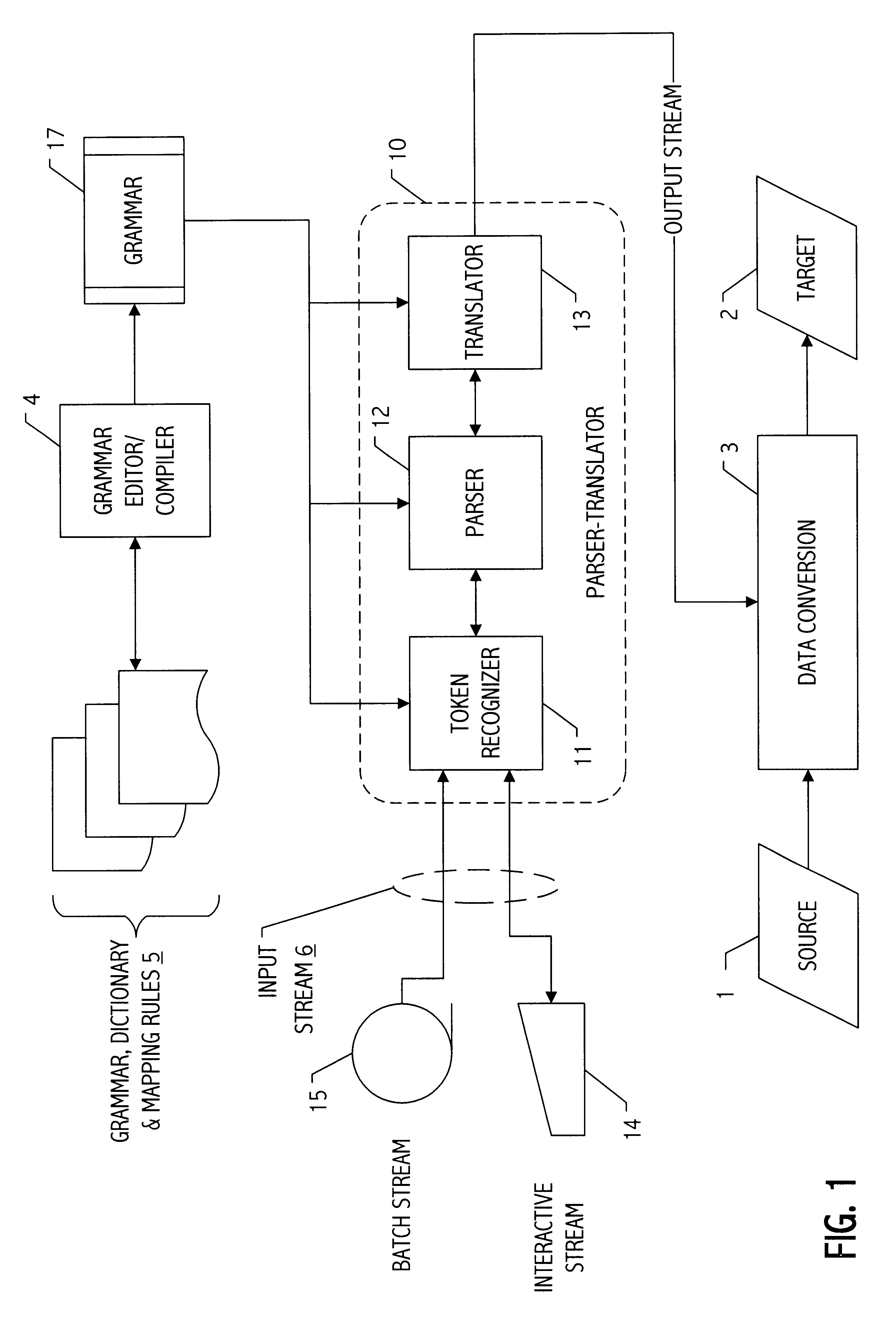
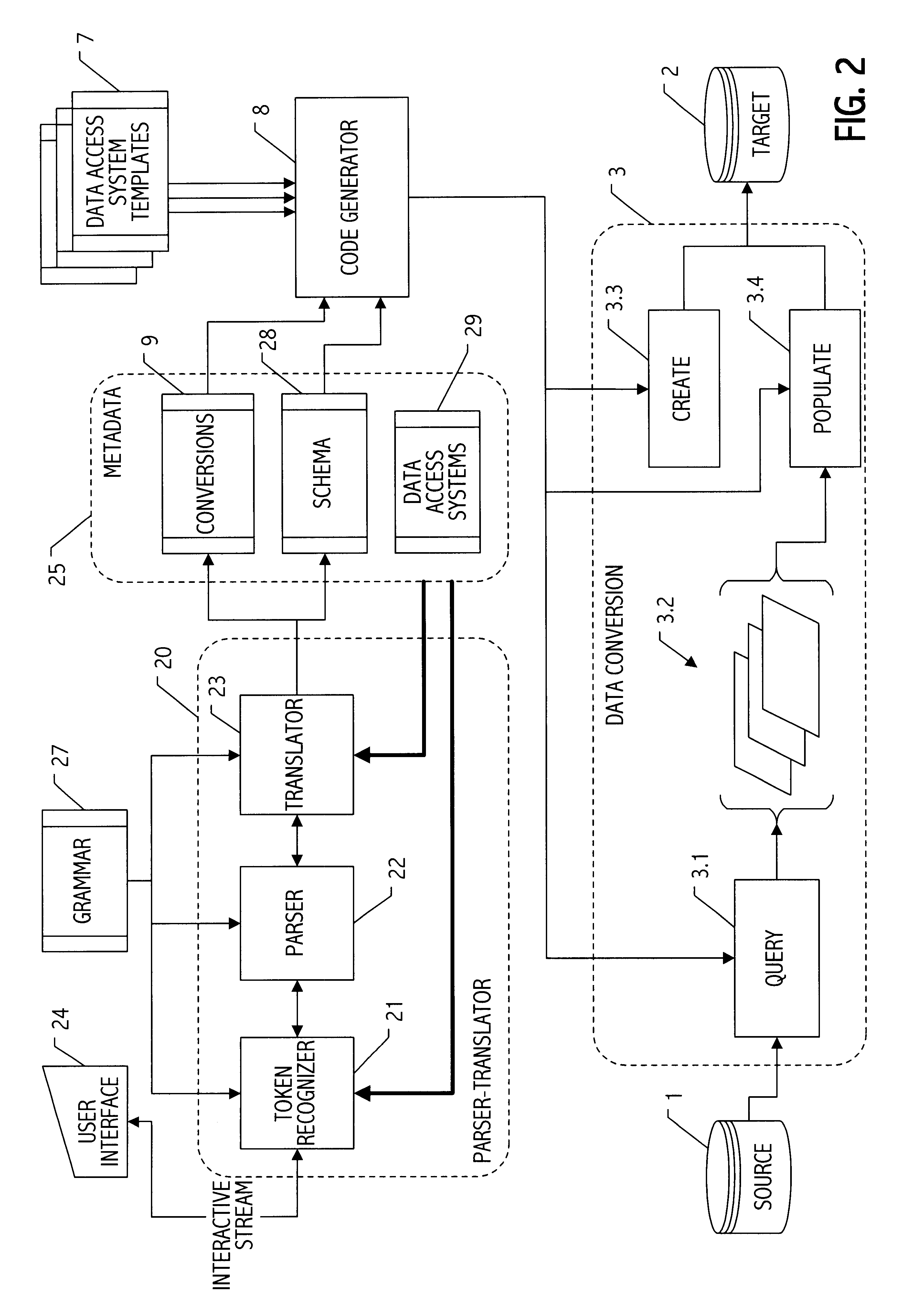
Parser translator system and method
A parser-translator technology allows a user to specify complex test and / or transformation statements in a high-level user language, to ensure that such test and / or transformation statements are well-formed in accordance with a grammar defining legal statements in the user language, and to translate statements defined by the user into logically and syntactically correct directives for performing the desired data transformations or operations. Using the parser-translator technology, a user can focus on the semantics of the desired operations and need not be concerned with the proper syntax of a language for a particular system. Instead, grammars (i.e., data) define the behavior of a parser-translator implementation by encoding the universe of statements (e.g., legal test and / or transformation statements) and by encoding translations appropriate to a particular data processing application (e.g., a data conversion program, etc.). Some parser-translator implementations described herein interface dynamically with other systems and / or repositories to query for information about objects, systems and states represented therein, and / or their respective interfaces. Some grammars described herein encode sensitivity to an external context. In this way, context-sensitive prompting and validation of correct specification of statements is provided. A combination of parser technology and dynamic querying of external system state allows users to build complex statements (e.g., using natural languages within a user interface environment) and to translate those complex statements into statements or directives appropriate to a particular data processing application.
Owner:VERSATA
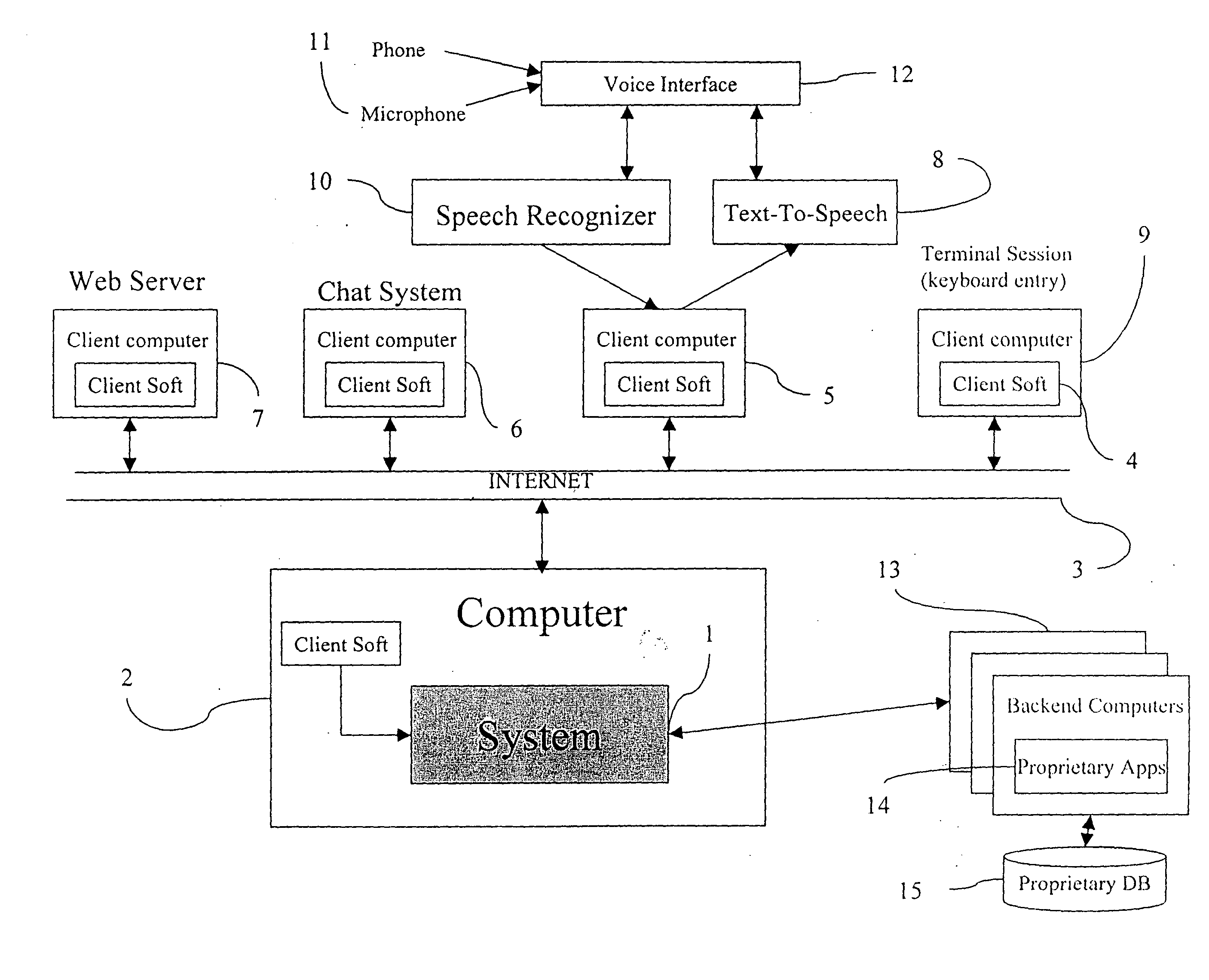
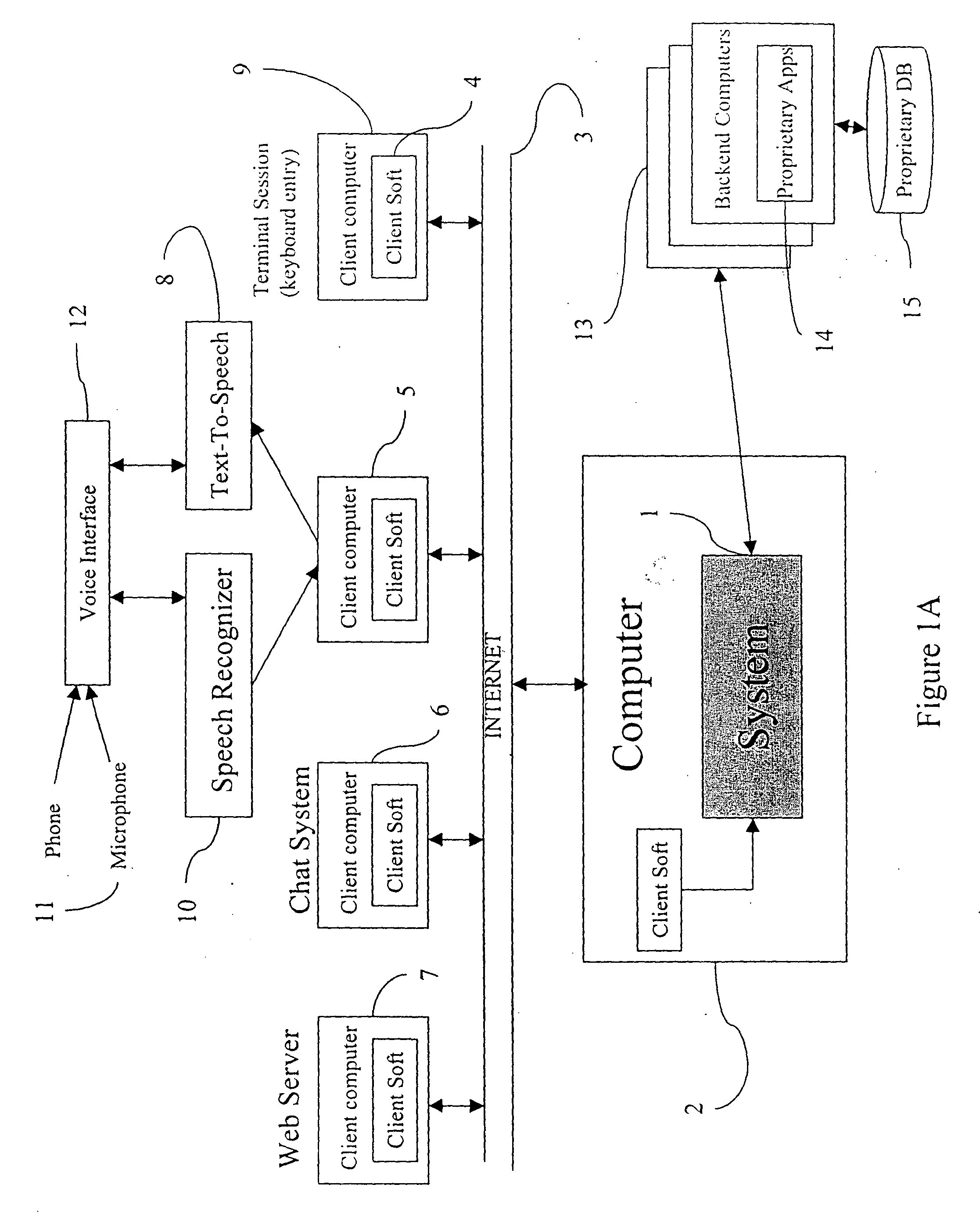
Intelligent home automation
InactiveUS20100332235A1Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageSpoken languageThe Internet
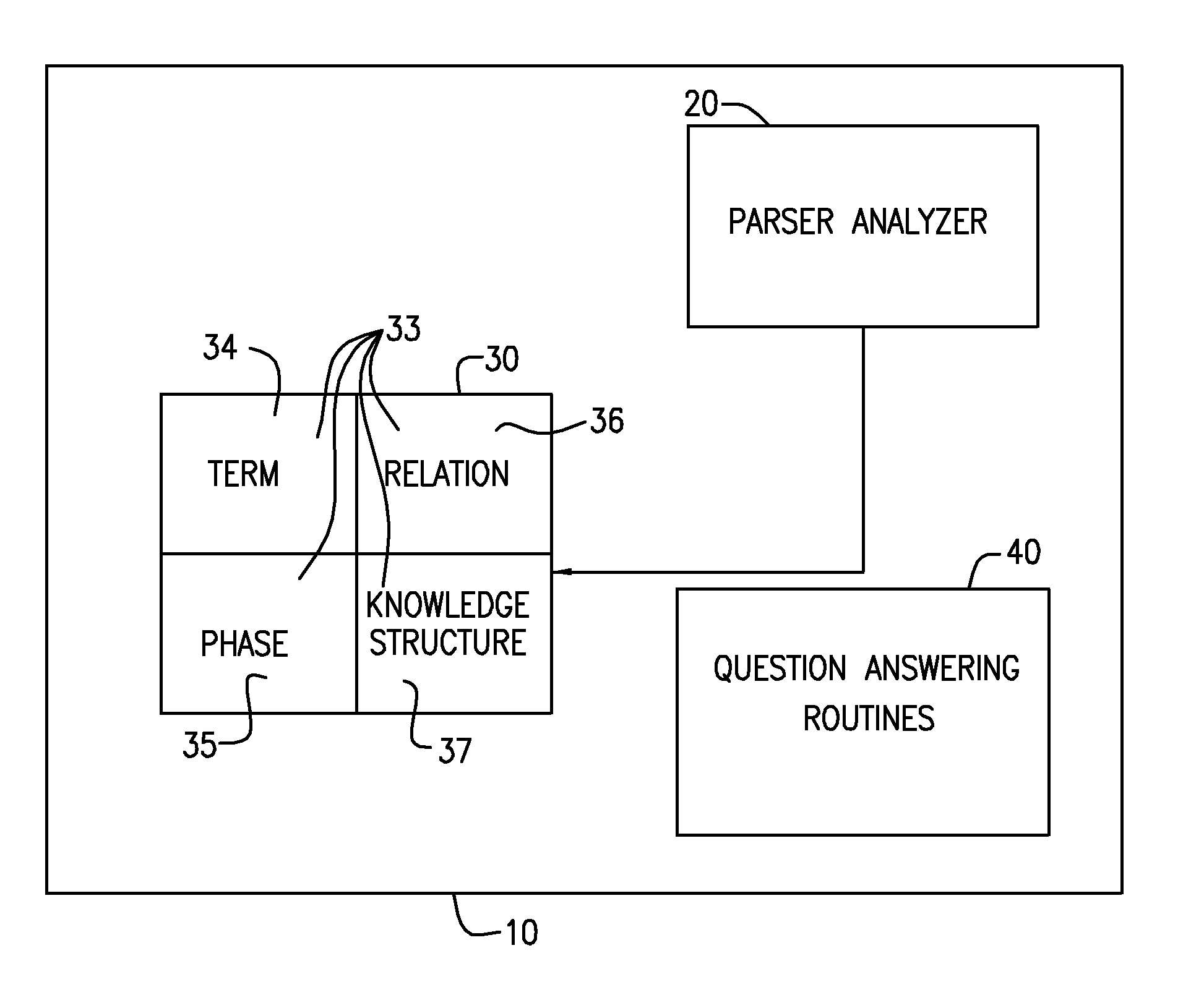
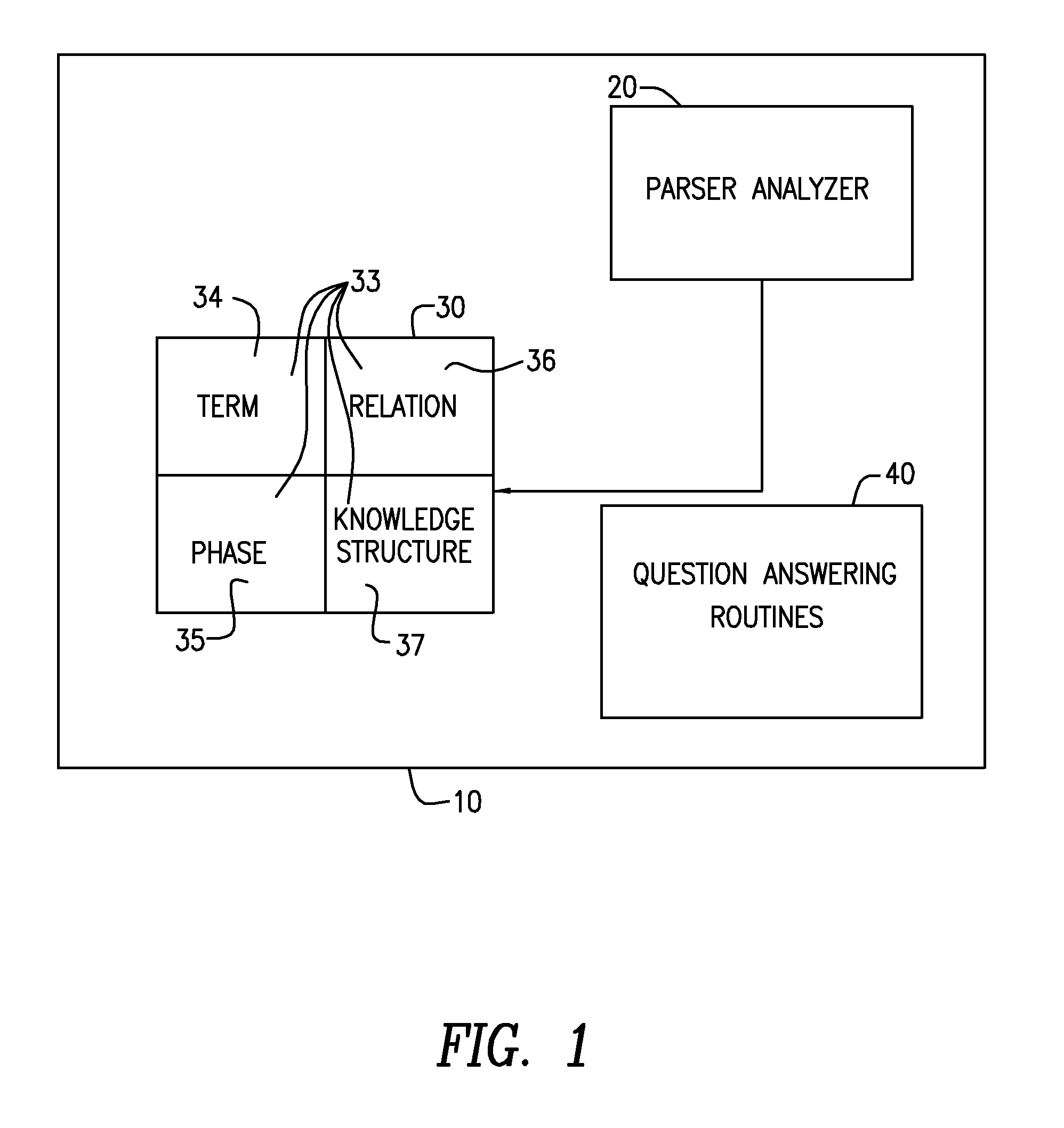
An intelligent home automation system answers questions of a user speaking “natural language” located in a home. The system is connected to, and may carry out the user's commands to control, any circuit, object, or system in the home. The system can answer questions by accessing the Internet. Using a transducer that “hears” human pulses, the system may be able to identify, announce and keep track of anyone entering or staying in the home or participating in a conversation, including announcing their identity in advance. The system may interrupt a conversation to implement specific commands and resume the conversation after implementation. The system may have extensible memory structures for term, phrase, relation and knowledge, question answering routines and a parser analyzer that uses transformational grammar and a modified three hypothesis analysis. The parser analyzer can be dormant unless spoken to. The system has emergency modes for prioritization of commands.
Owner:DAVID ABRAHAM BEN
Method and system for generating a document representation
ActiveUS20100228693A1Without structureHighly to changeDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisPart of speechGrammatical relation
A method, system and computer program product for generating a document representation are disclosed. The system includes a server and a client computer, and the method involves: receiving into memory a resource containing at least one sentence of text; producing a tree comprising tree elements indicating parts-of-speech and grammatical relations between the tree elements; producing semantic structures each having three tree elements to represent a simple clause (subject-predicate-object); and storing a semantic network of semantic structures and connections therebetween. The semantic network may be created from a user provided root concept. Output representations include concept maps, facts listings, text summaries, tag clouds, indices; and an annotated text. The system interactively modifies semantic networks in response to user feedback, and produces personal semantic networks and document use histories.
Owner:IFWE
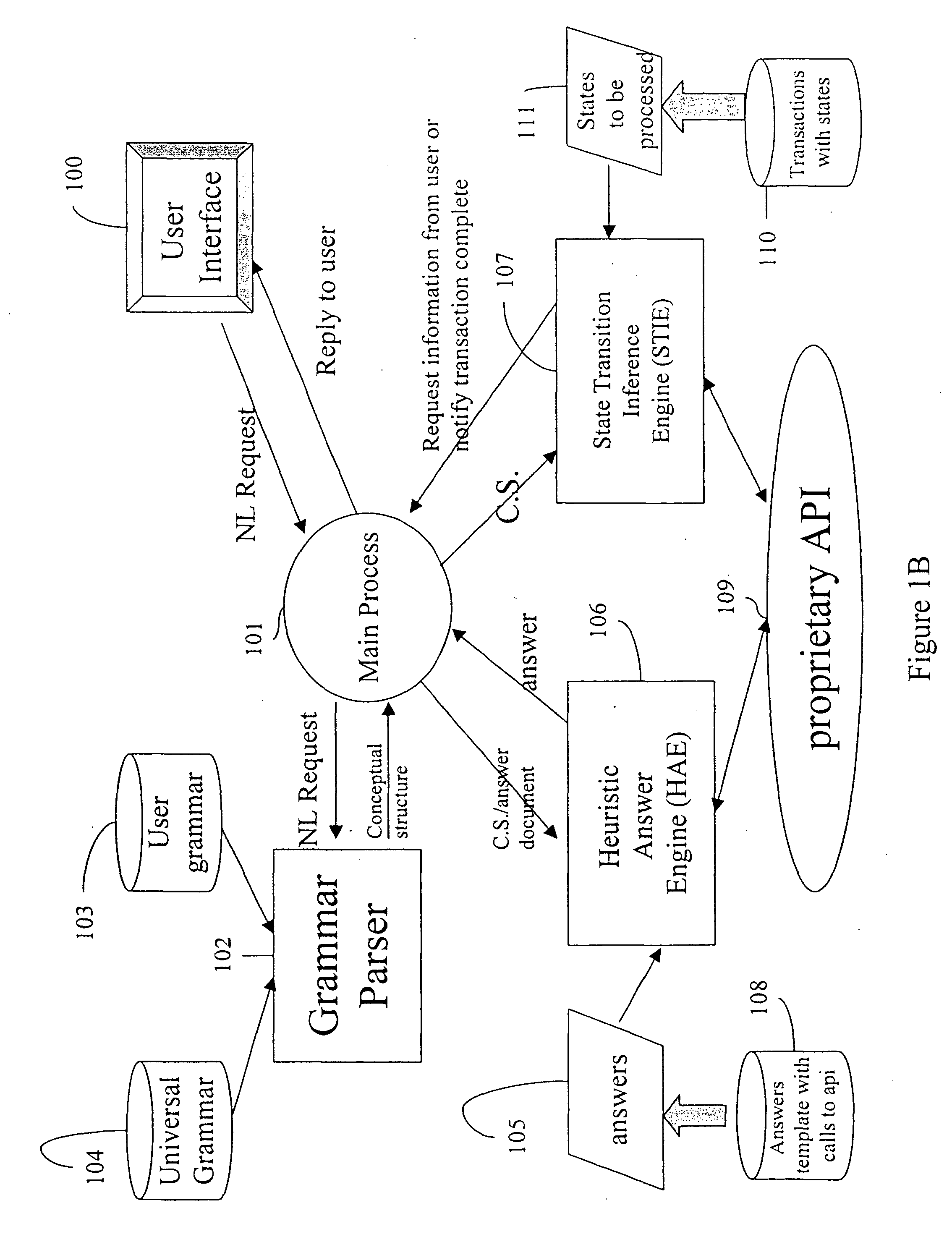
Method and system for interactive conversational dialogue for cognitively overloaded device users
ActiveUS7716056B2Easy and efficientAdapt quicklyNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionNatural language processingWave form
A system and method to interactively converse with a cognitively overloaded user of a device, includes maintaining a knowledge base of information regarding the device and a domain, organizing the information in at least one of a relational manner and an ontological manner, receiving speech from the user, converting the speech into a word sequence, recognizing a partial proper name in the word sequence, identifying meaning structures from the word sequence using a model of the domain information, adjusting a boundary of the partial proper names to enhance an accuracy of the meaning structures, interpreting the meaning structures in a context of the conversation with the cognitively overloaded user using the knowledge base, selecting a content for a response to the cognitively overloaded user, generating the response based on the selected content, the context of the conversation, and grammatical rules, and synthesizing speech wave forms for the response.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP +1
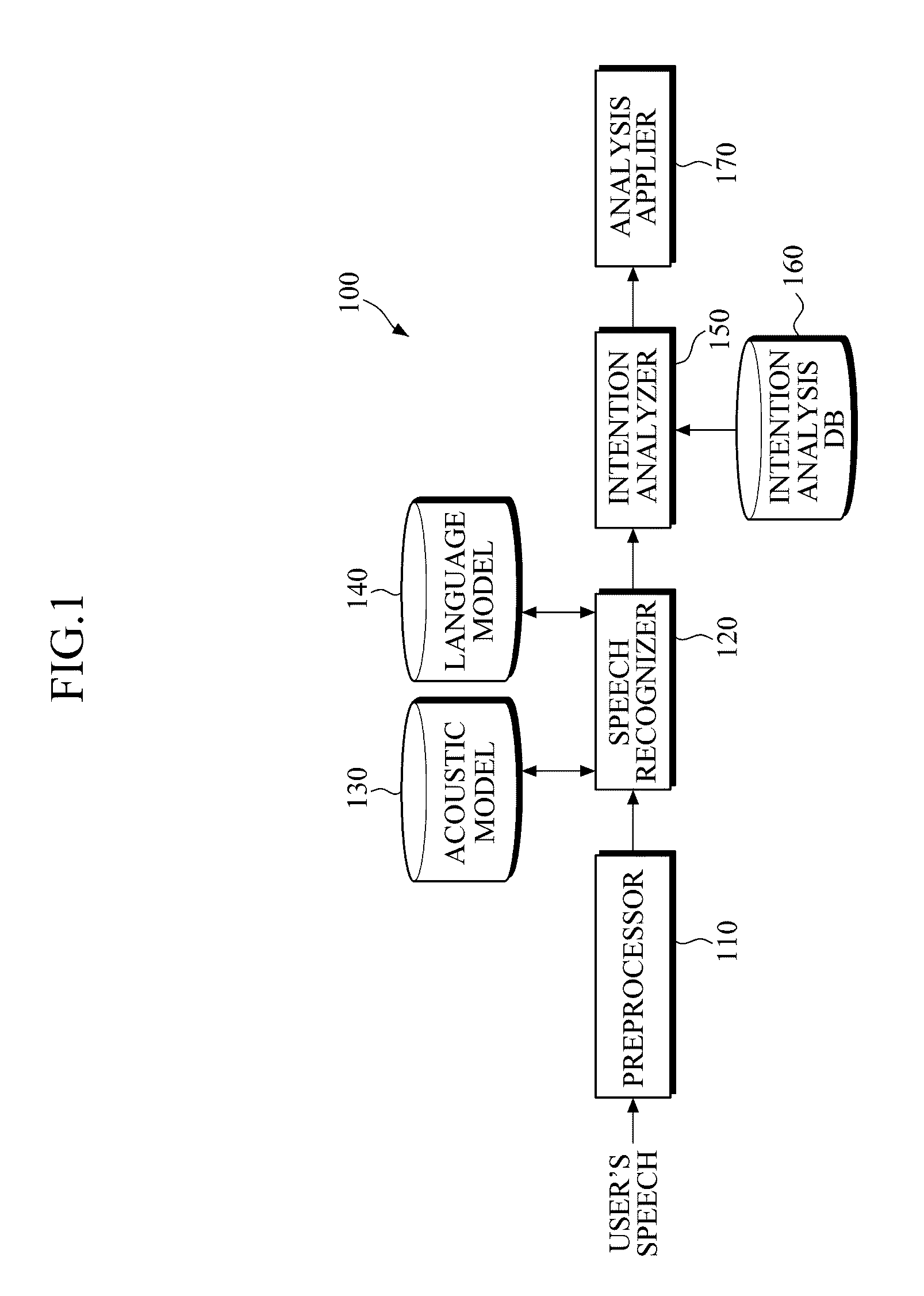
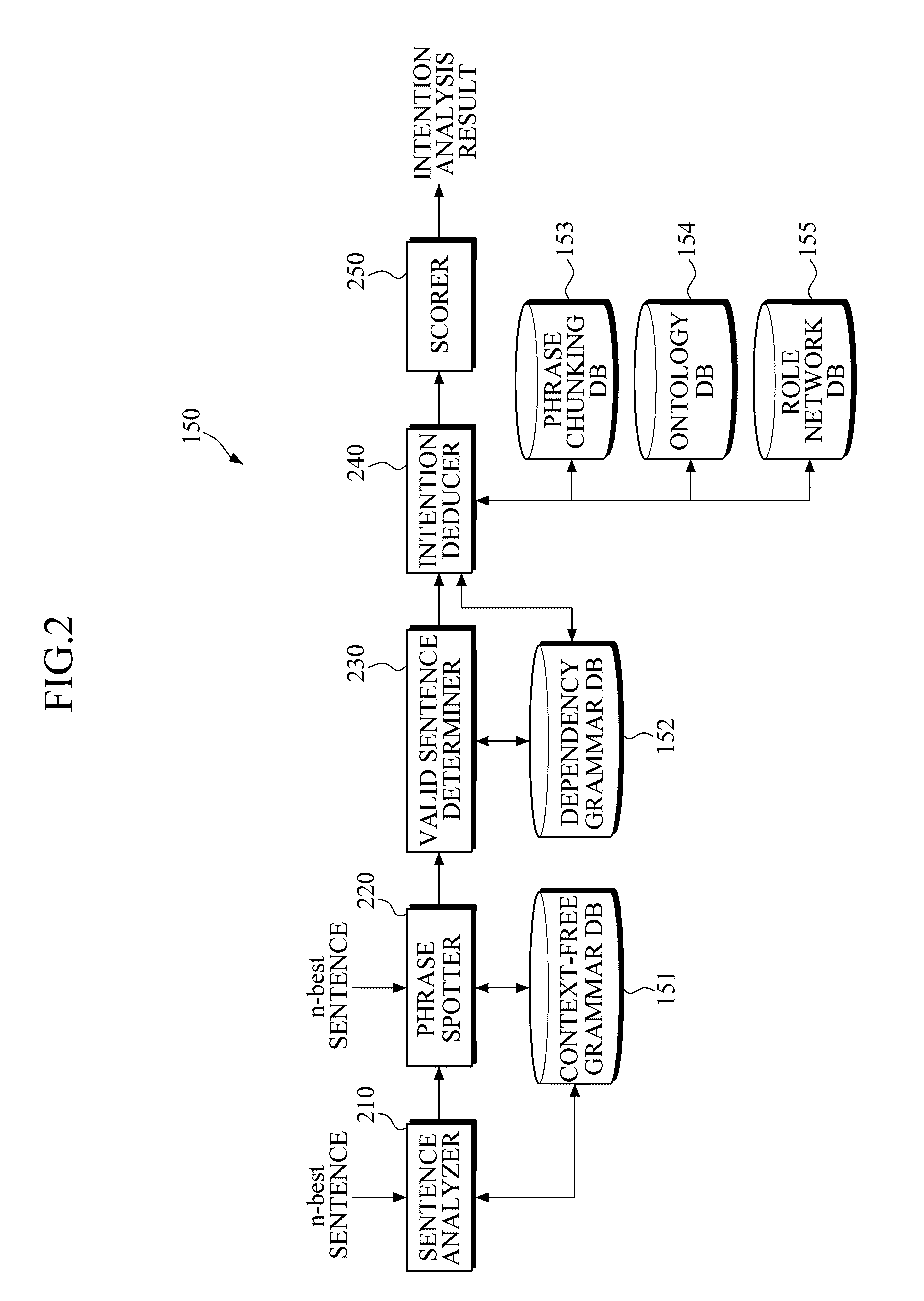
Apparatus and Method for Analyzing Intention
InactiveUS20110082688A1Natural language data processingSpeech recognitionSpeech soundSubvocal recognition
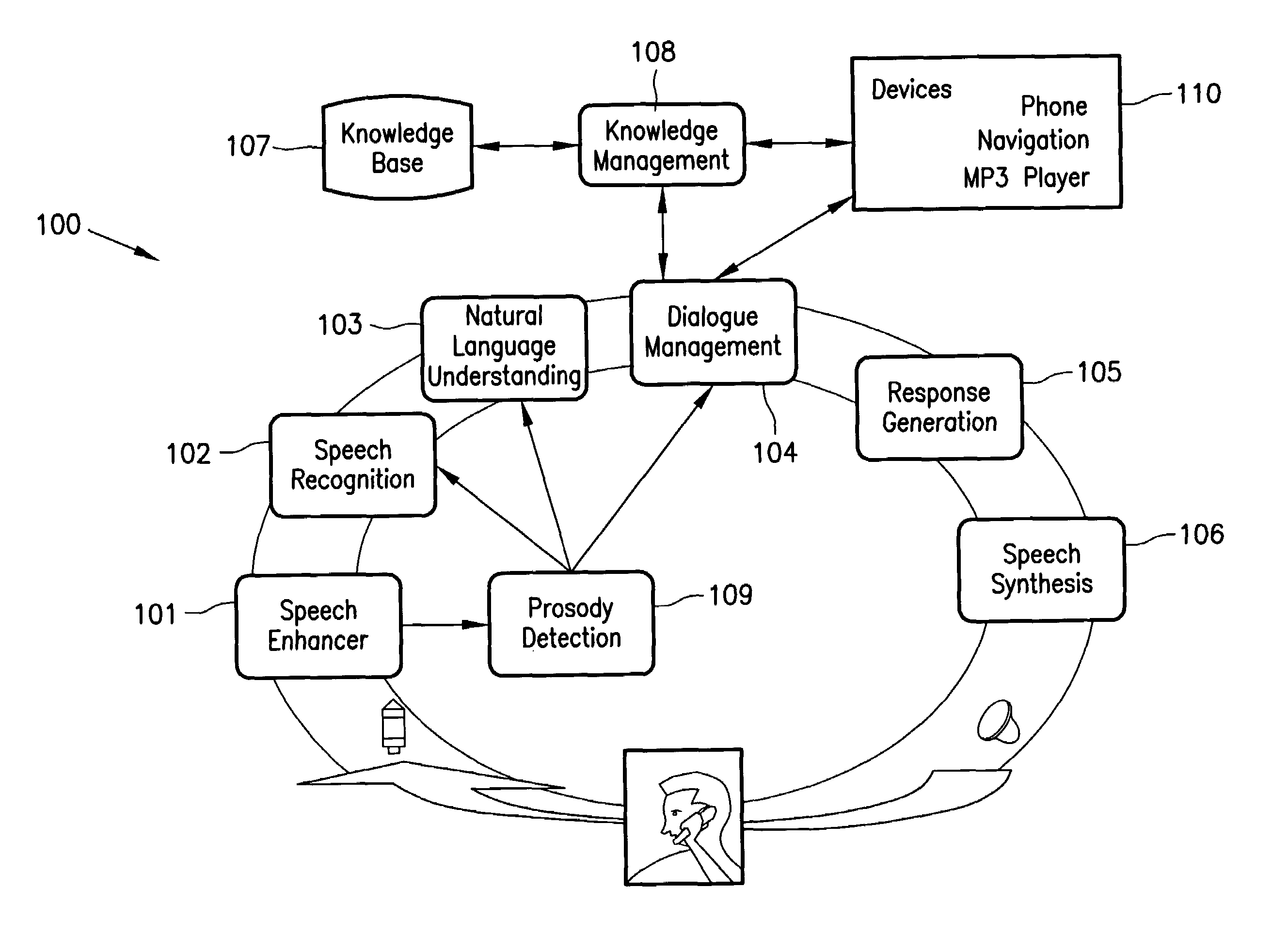
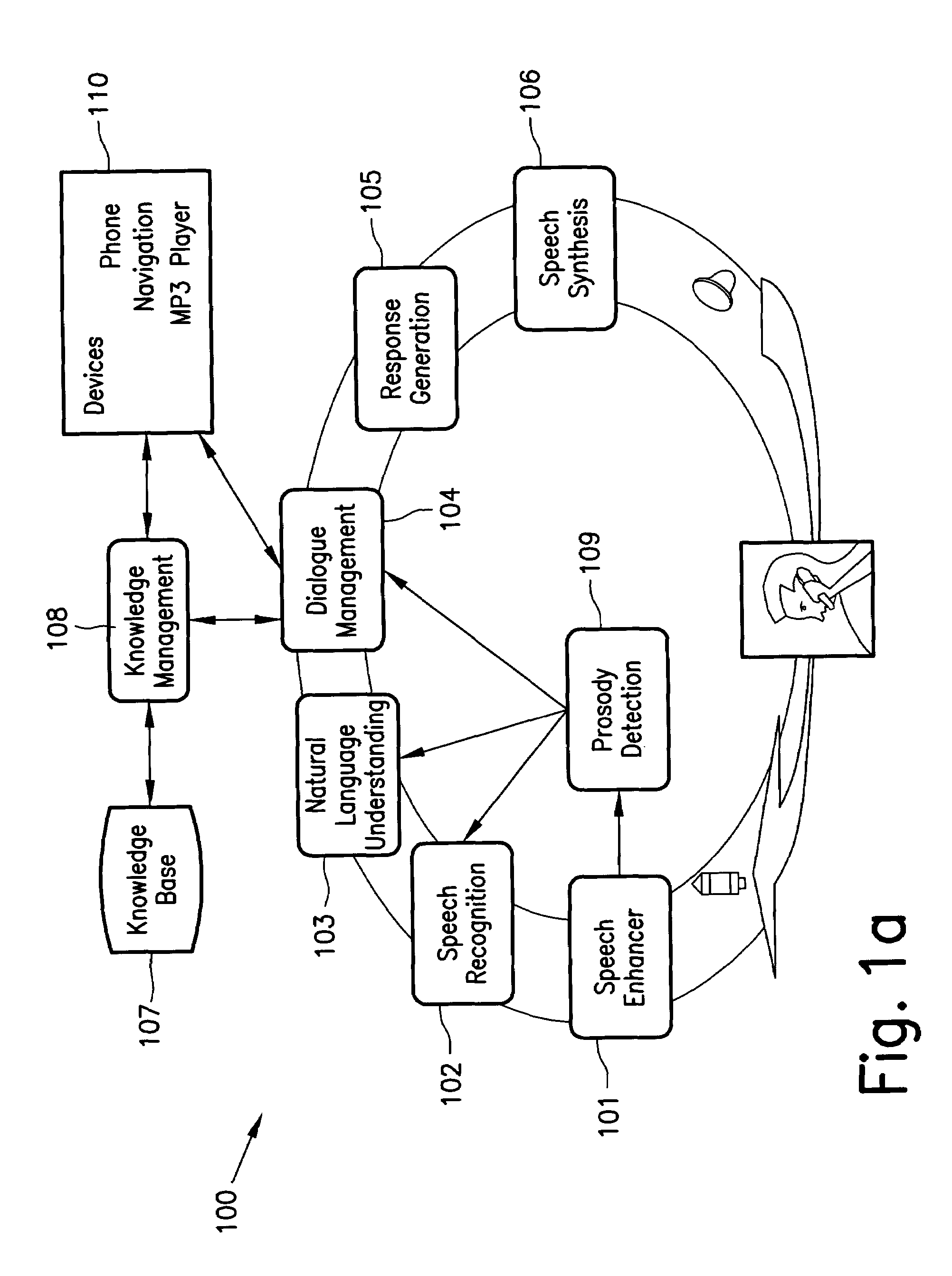
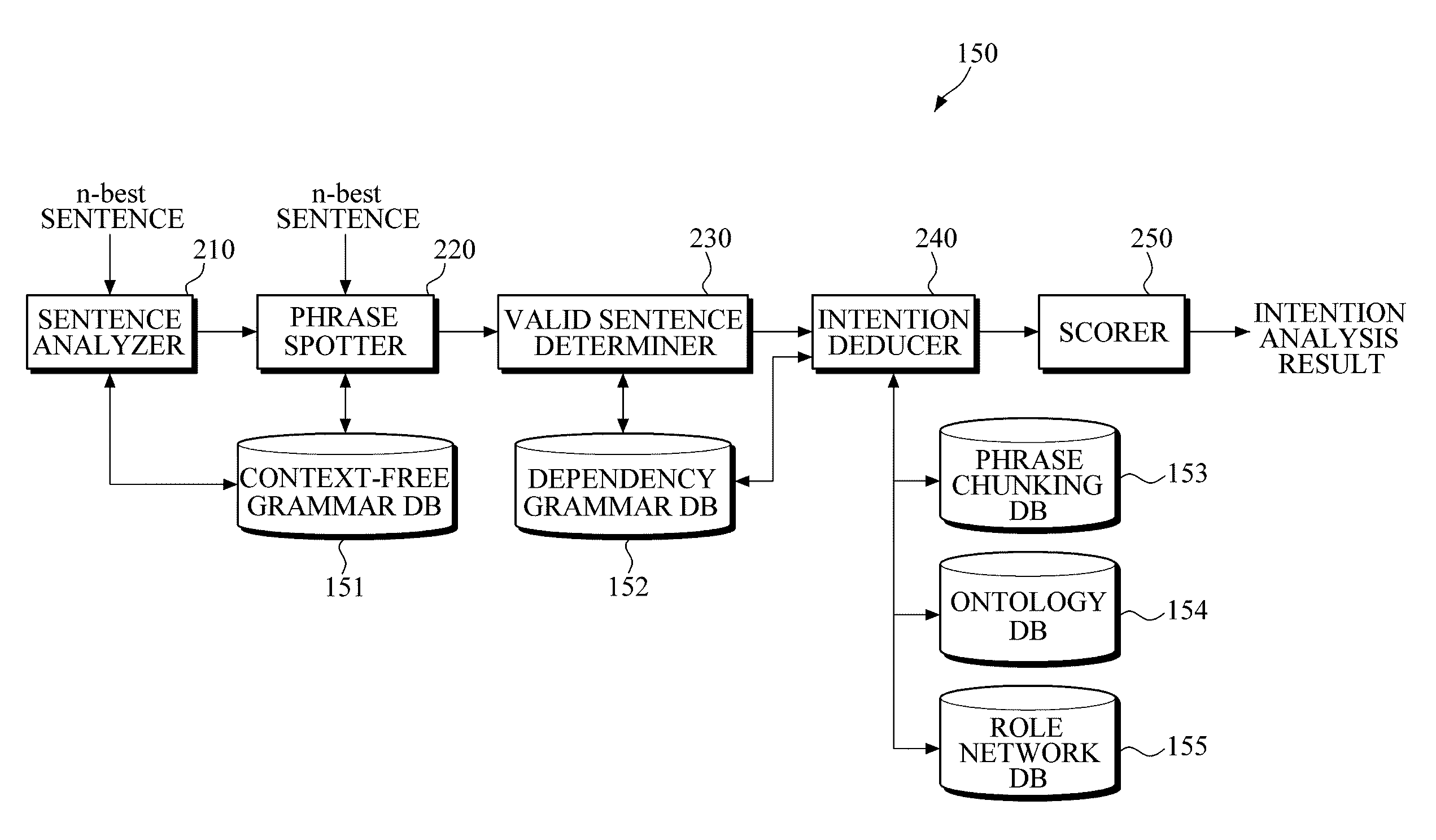
An apparatus and system for analyzing intention are provided. The apparatus for analyzing an intention applies a context-free grammar to each of one or more sentences in units of one or more phrases to perform phrase spotting on each sentence, thereby extending a recognition range for an out-of-grammar (OOG) expression. Meanwhile, the apparatus for analyzing an intention determines whether sentences that have undergone phrase spotting are grammatically valid by applying a dependency grammar to the sentences to filter an invalid sentence, and generates the intention analysis result of a valid sentence, thereby and grammatically and / or semantically verifying a sentence that has undergone speech recognition while extending a speech recognition range.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods for creating a phrase thesaurus
InactiveUS8374871B2Quick identificationMore complex and better performing systemsNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionHuman–robot interactionSpeech sound
The invention enables creation of grammar networks that can regulate, control, and define the content and scope of human-machine interaction in natural language voice user interfaces (NLVUI). More specifically, the invention concerns a phrase-based modeling of generic structures of verbal interaction and use of these models for the purpose of automating part of the design of such grammar networks.
Owner:NANT HLDG IP LLC
Process for automatic control of one or more devices by voice commands or by real-time voice dialog and apparatus for carrying out this process
InactiveUS6839670B1Reduce spendingSpeech recognitionElectric/fluid circuitAutomatic controlSpeech identification
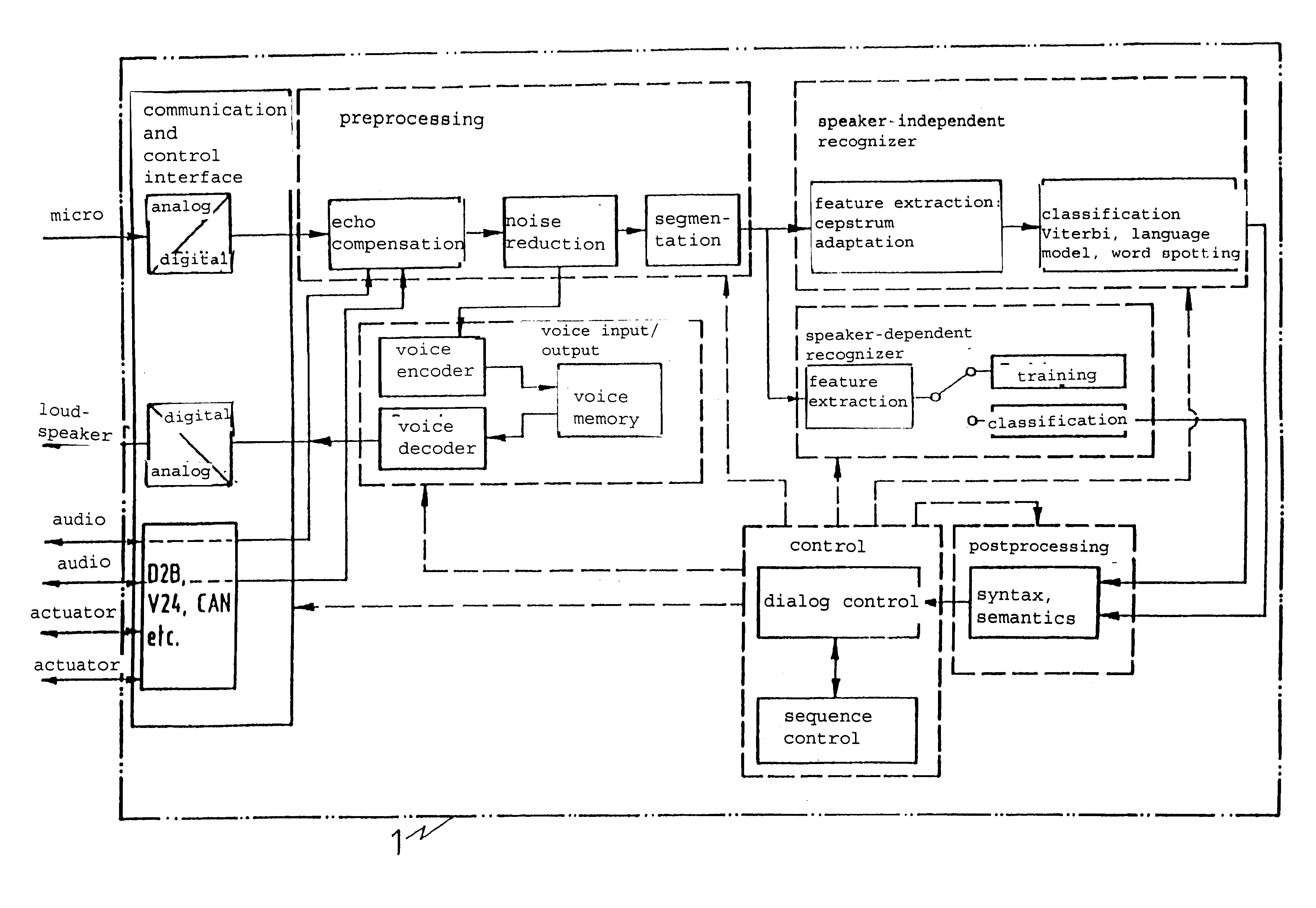
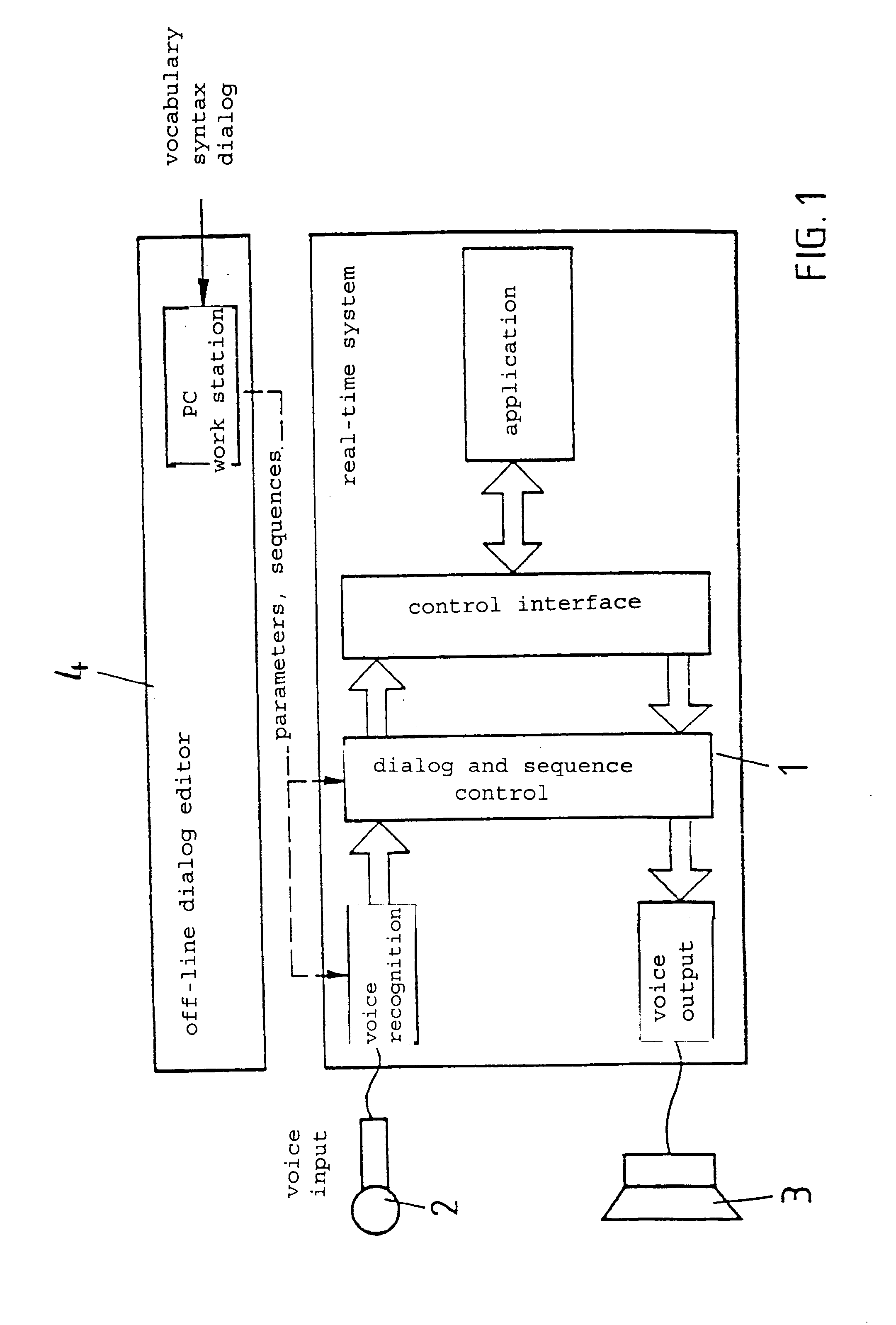
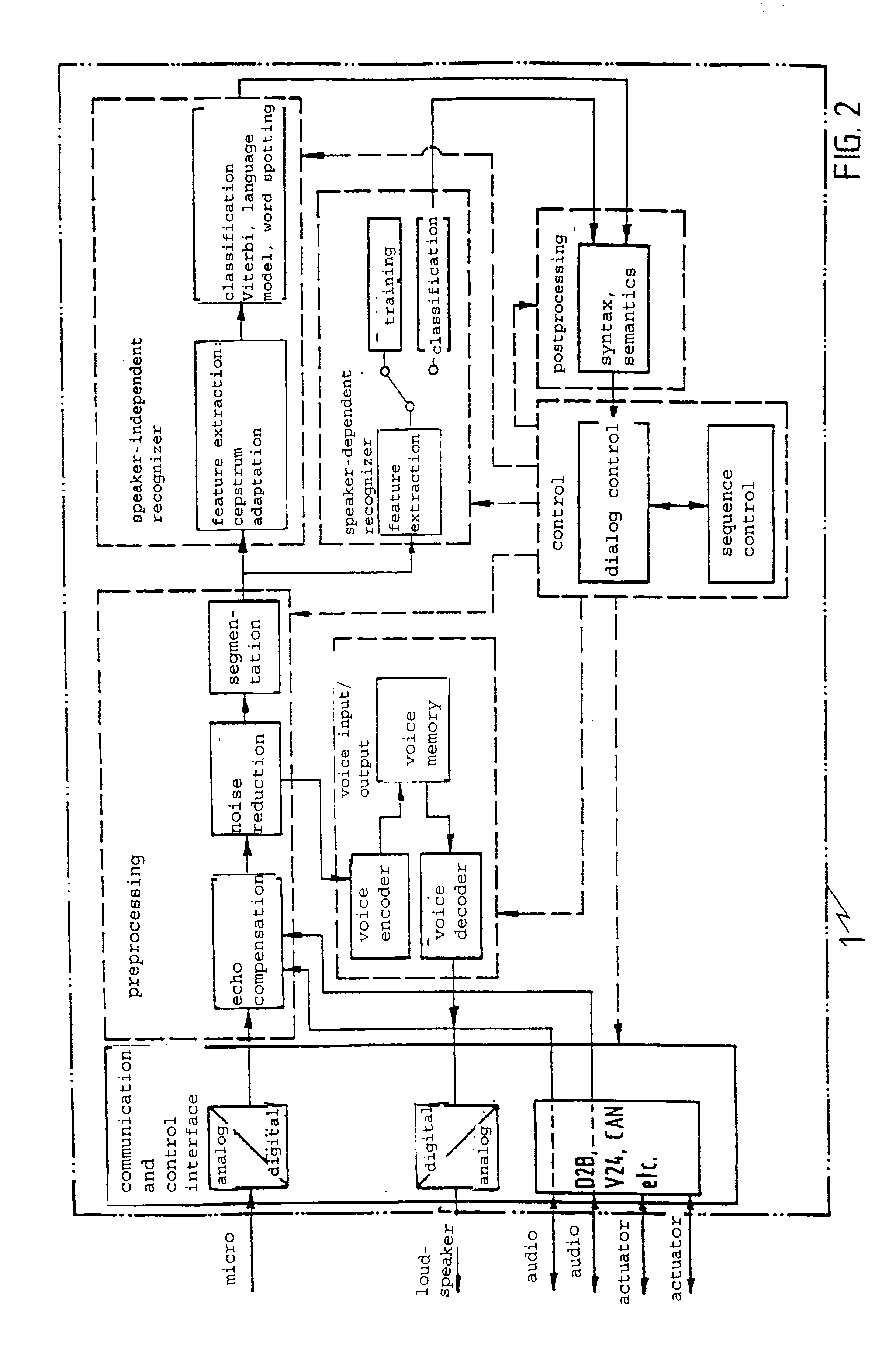
A speech dialog system wherein a process for automatic control of devices by speech dialog is used applying methods of speech input, speech signal processing and speech recognition, syntatical-grammatical postediting as well as dialog, executive sequencing and interface control, and which is characterized in that syntax and command structures are set during real-time dialog operation; preprocessing, recognition and dialog control are designed for operation in a noise-encumbered environment; no user training is required for recognition of general commands; training of individual users is necessary for recognition of special commands; the input of commands is done in linked form, the number of words used to form a command for speech input being variable; a real-time processing and execution of the speech dialog is established; and the speech input and output is done in the hands-free mode.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Linguistic user interface
ActiveUS20070179776A1Natural language data processingText database indexingNatural language processingUser input
A system for retrieval of text includes a processor which identifies grammar rules associated with text fragments of a text string that is retrieved from an associated storage medium, and retrieves text strings from the storage medium which satisfy the grammar rules. A display displays retrieved text strings. A user input device in communication with the processor enables a user to select text fragments of the displayed text strings for generating a query. The processor identifies grammar rules associated with the user-selected text fragments and retrieves text strings from the storage medium which satisfy the grammar rules.
Owner:MAJANDRO LLC
Method and apparatus for determining the meaning of natural language
InactiveUS7702500B2Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman languageGrammaticality
Owner:BLAEDOW KAREN R
Tagged markup language interface with document type definition to access data in object oriented database
InactiveUS6480860B1Data processing applicationsWebsite content managementExtensible markupDocument preparation
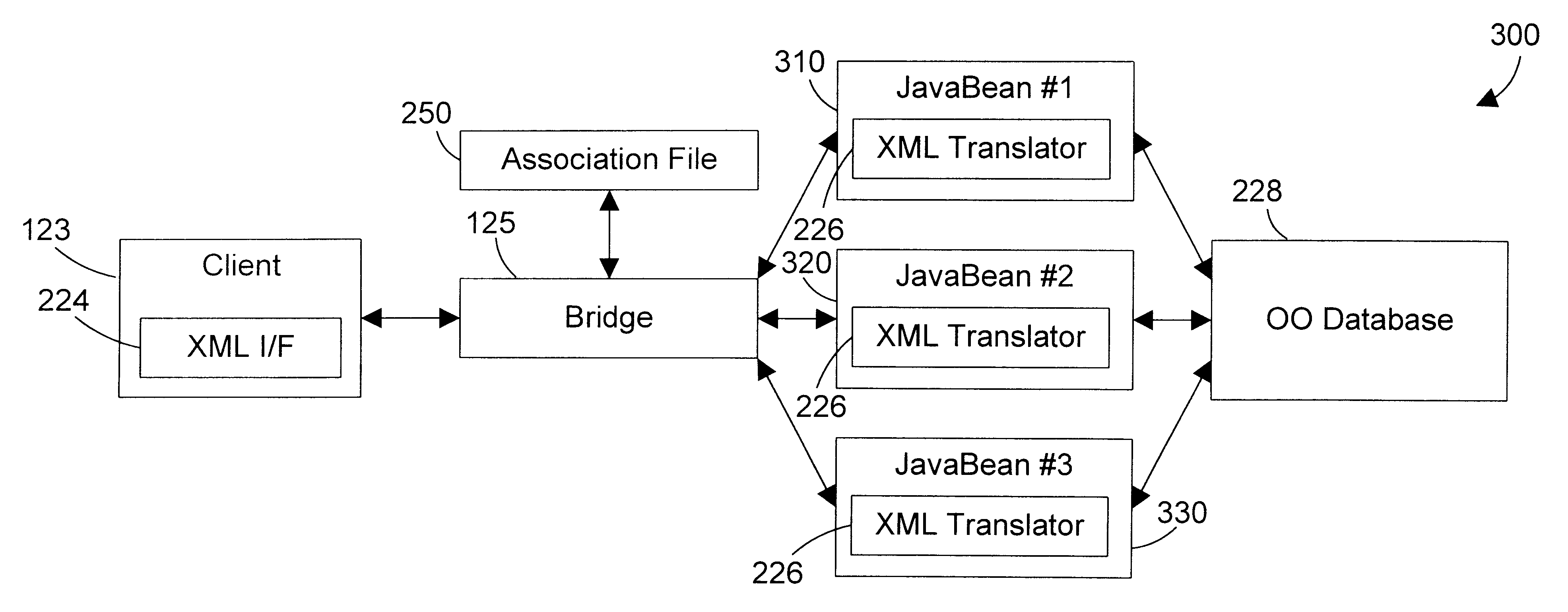
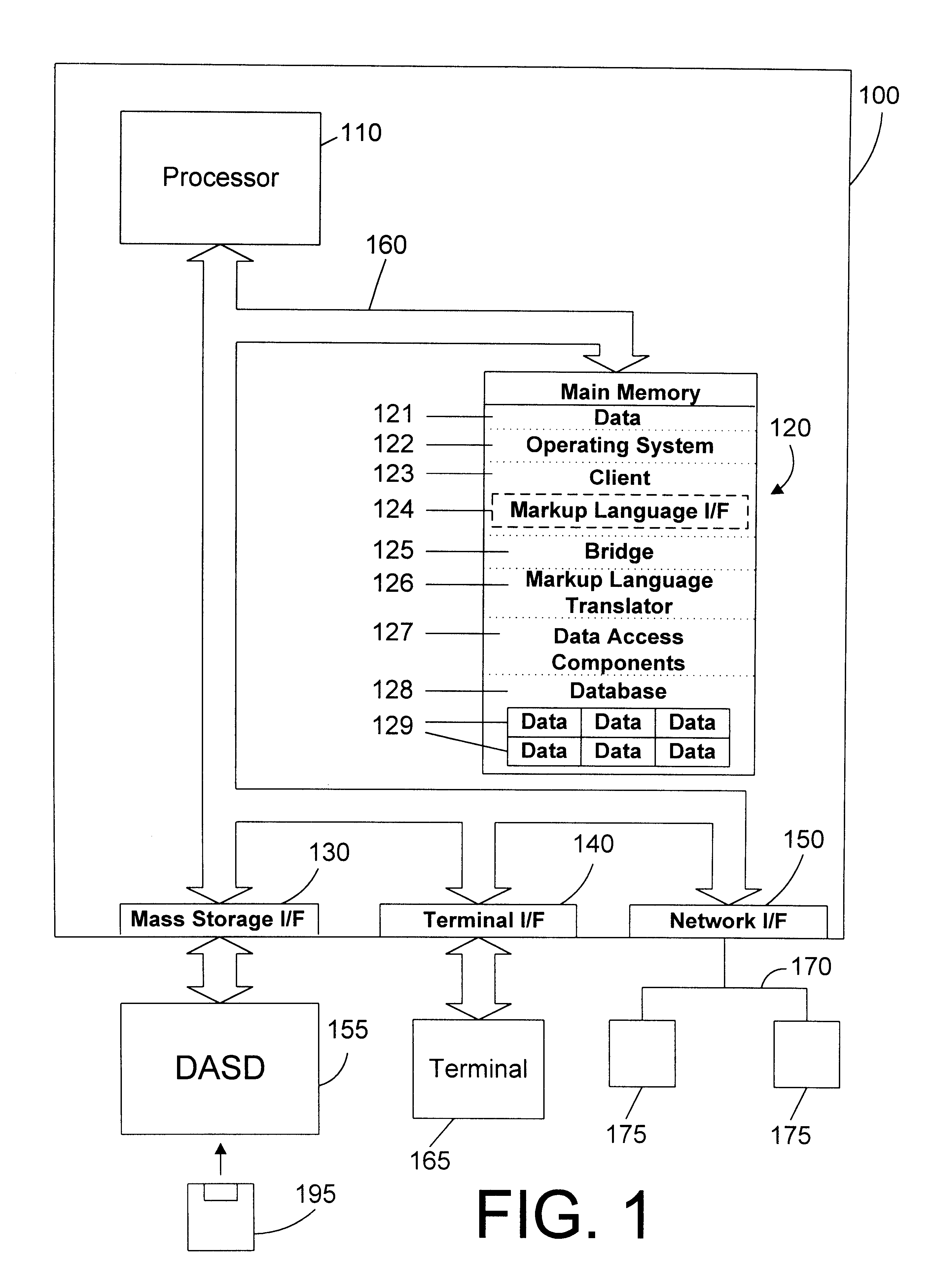
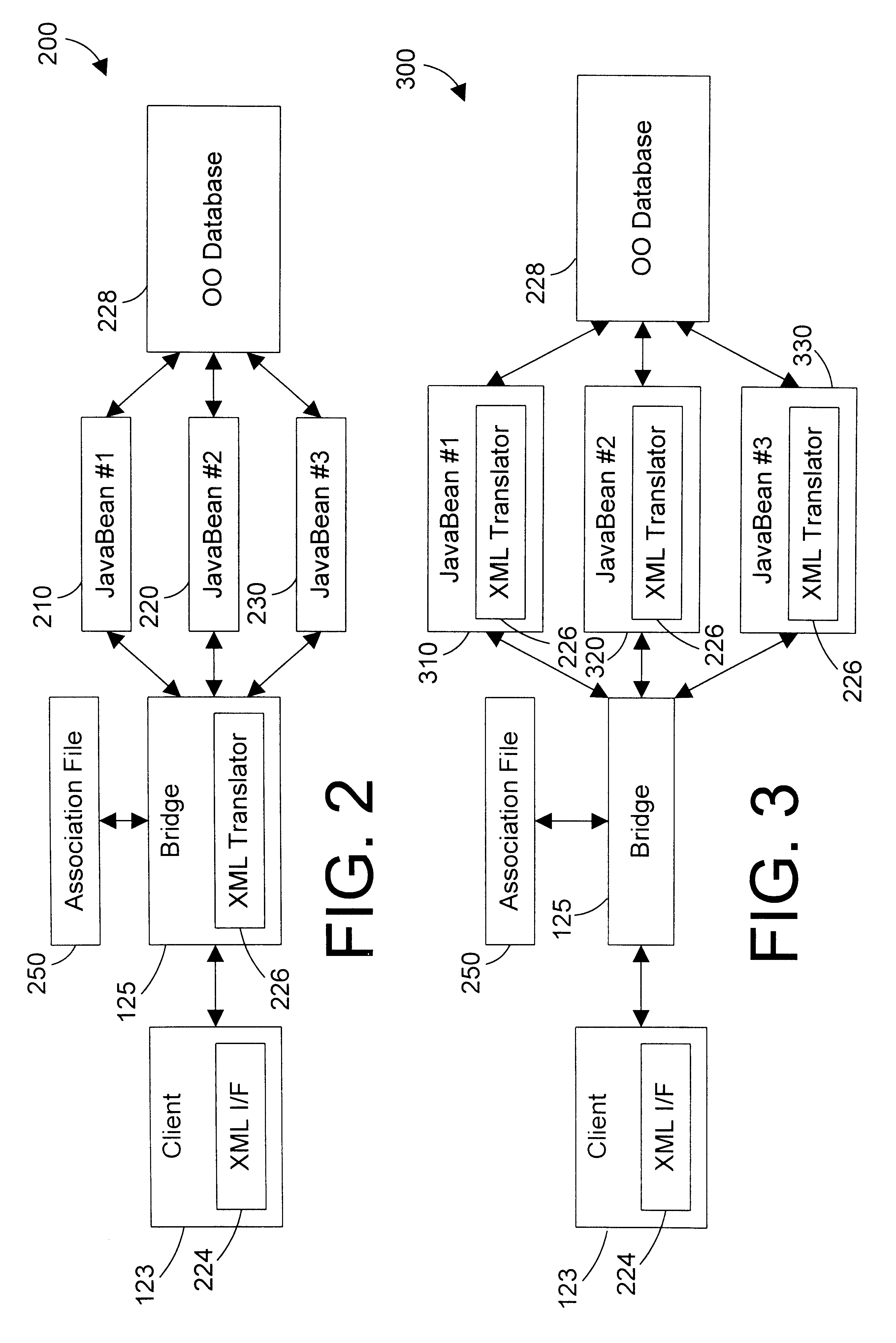
An apparatus and method defines a markup language for accessing data in a database. The markup language is preferably defined in extensible markup language (XML) by creating suitable document type definitions (DTDs), which define the grammar for accessing data in the database using the markup language. A bridge interprets the data request from the client in markup language format, a suitable database query for the database is formulated, and the data is then placed within a document for delivery in markup language format to the user. As new data types are added to the database, corresponding document type definitions (DTDs) may be dynamically generated, allowing a user to access new kinds of data in a database with a software tool that has a user-friendly graphical user interface without having to manually update the software tool for each new data type that is added to the database.
Owner:IBM CORP
Disambiguating a speech recognition grammar in a multimodal application
Disambiguating a speech recognition grammar in a multimodal application, the multimodal application including voice activated hyperlinks, the voice activated hyperlinks voice enabled by a speech recognition grammar characterized by ambiguous terminal grammar elements, including maintaining by the multimodal browser a record of visibility of each voice activated hyperlink, the record of visibility including current visibility and past visibility on a display of the multimodal device of each voice activated hyperlink, the record of visibility further including an ordinal indication, for each voice activated hyperlink scrolled off display, of the sequence in which each such voice activated hyperlink was scrolled off display; recognizing by the multimodal browser speech from a user matching an ambiguous terminal element of the speech recognition grammar; selecting by the multimodal browser a voice activated hyperlink for activation, the selecting carried out in dependence upon the recognized speech and the record of visibility.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
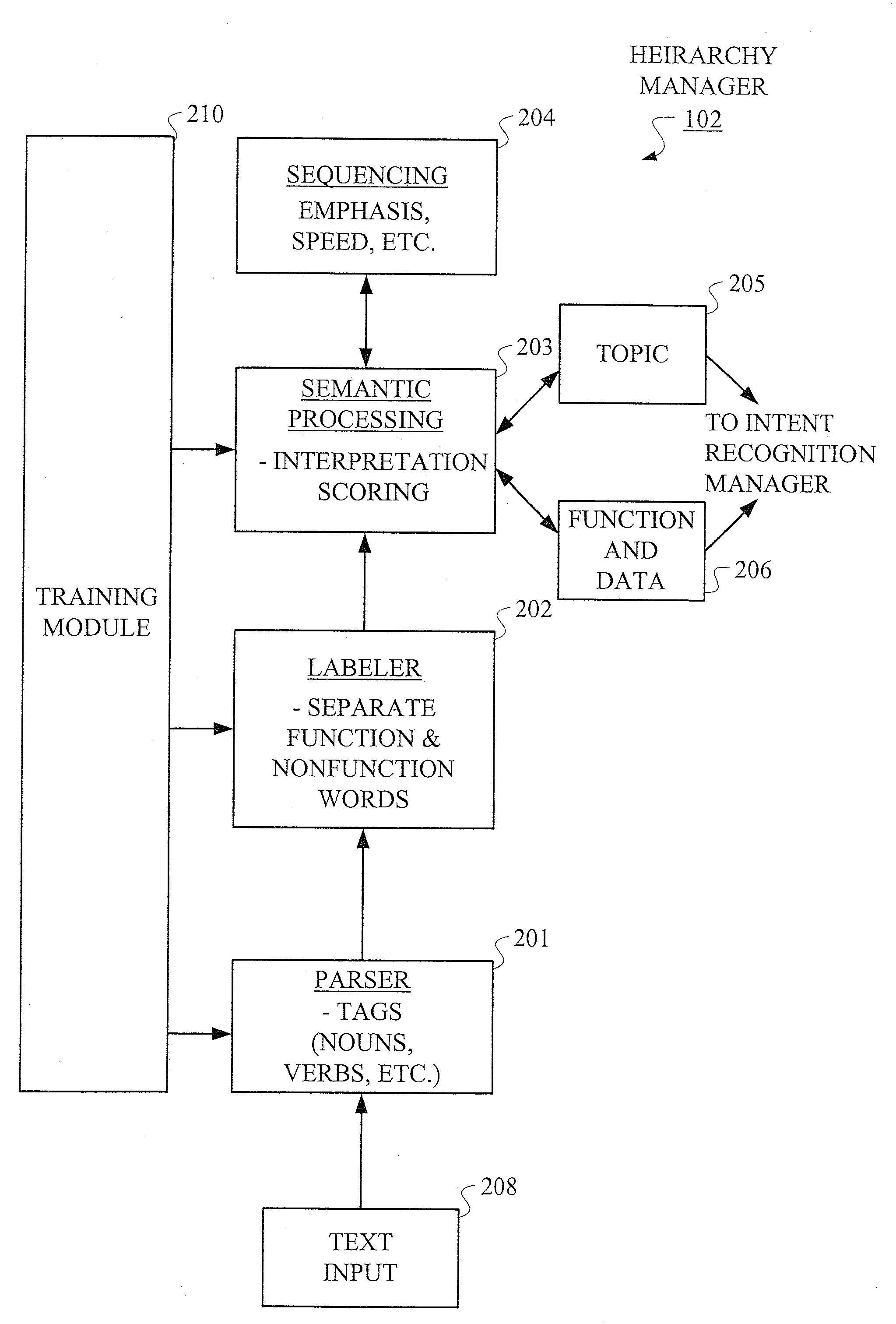
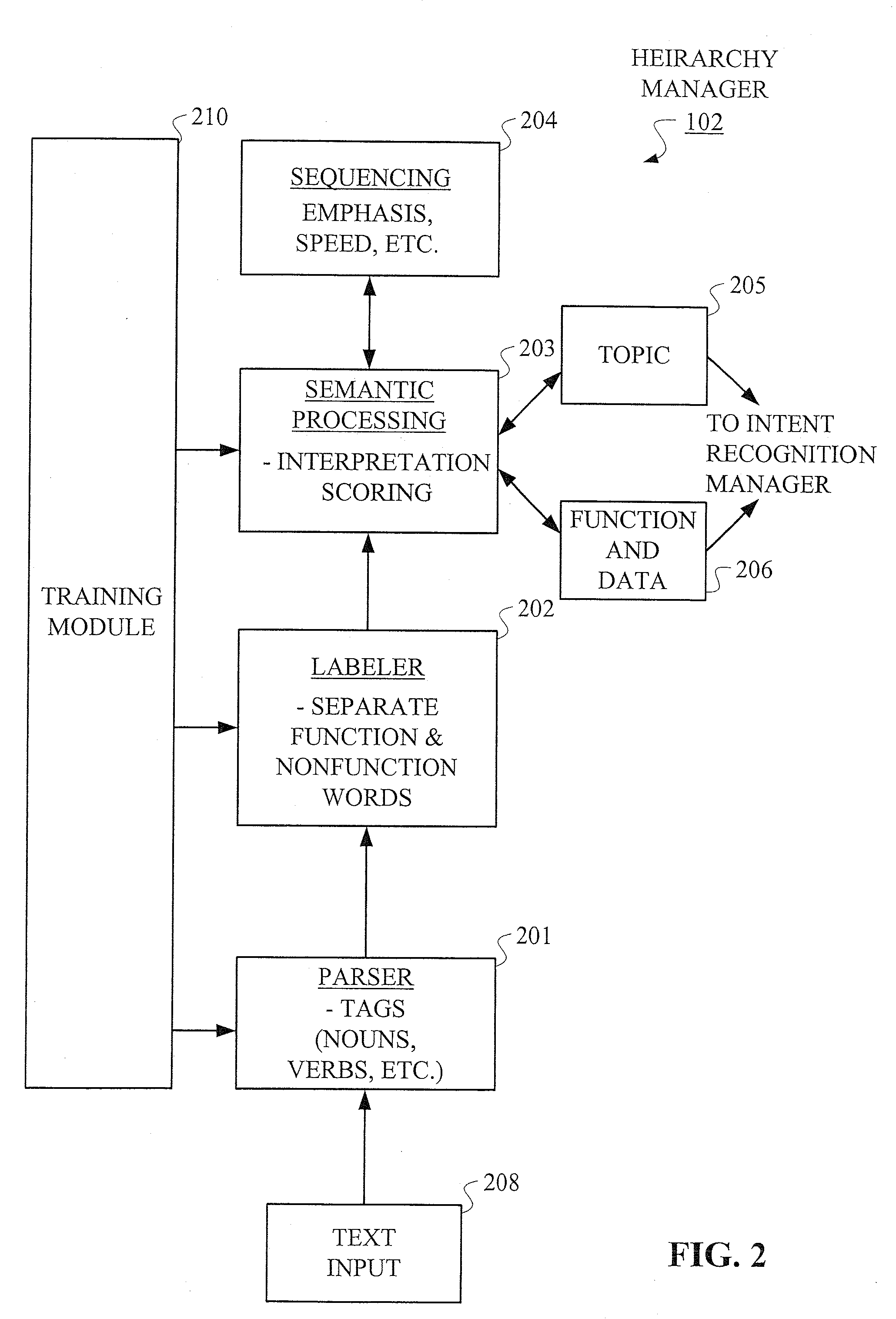
Hierarchical Methods and Apparatus for Extracting User Intent from Spoken Utterances
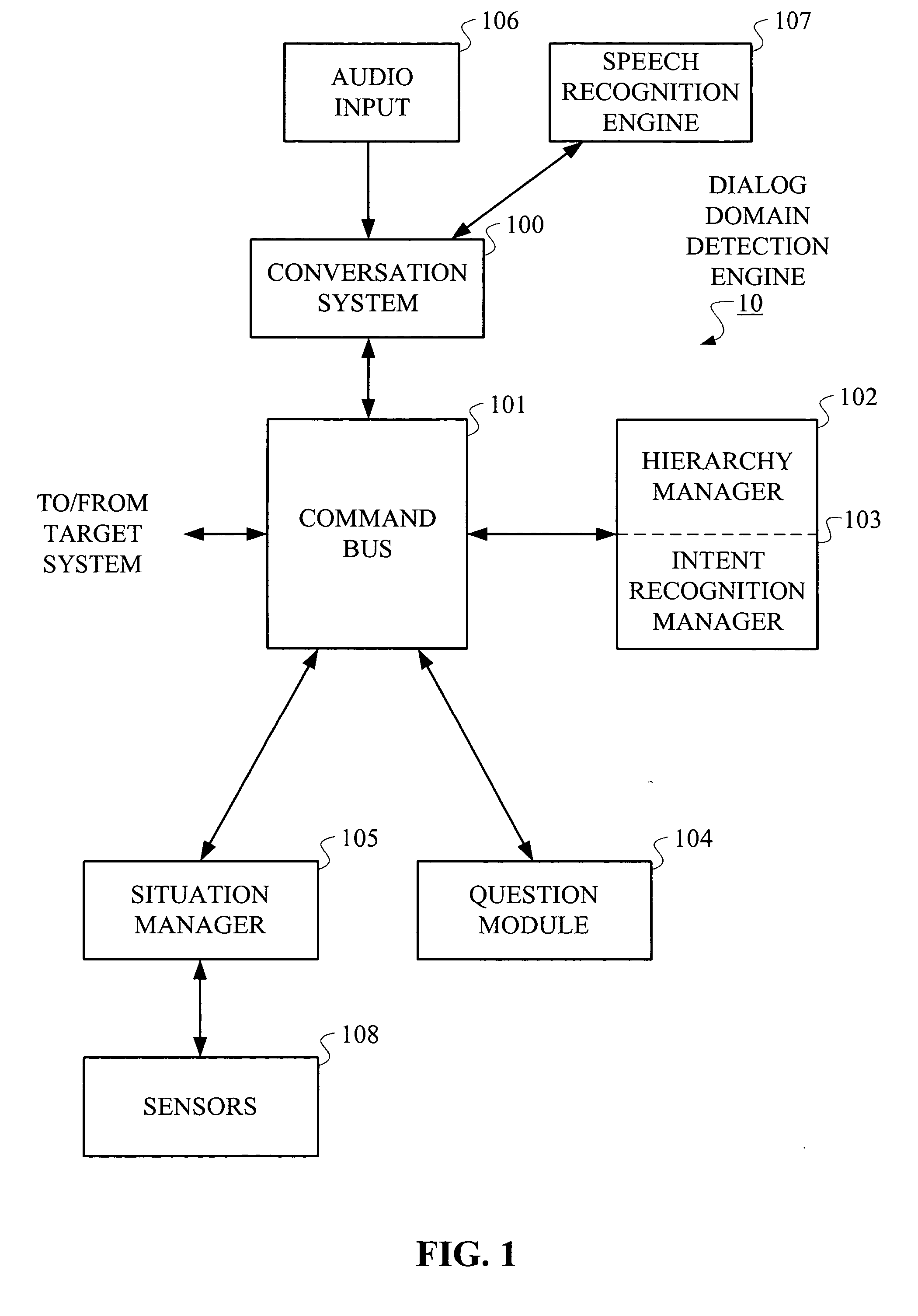
Improved techniques are disclosed for permitting a user to employ more human-based grammar (i.e., free form or conversational input) while addressing a target system via a voice system. For example, a technique for determining intent associated with a spoken utterance of a user comprises the following steps / operations. Decoded speech uttered by the user is obtained. An intent is then extracted from the decoded speech uttered by the user. The intent is extracted in an iterative manner such that a first class is determined after a first iteration and a sub-class of the first class is determined after a second iteration. The first class and the sub-class of the first class are hierarchically indicative of the intent of the user, e.g., a target and data that may be associated with the target. The multi-stage intent extraction approach may have more than two iterations. By way of example only, the user intent extracting step may further determine a sub-class of the sub-class of the first class after a third iteration, such that the first class, the sub-class of the first class, and the sub-class of the sub-class of the first class are hierarchically indicative of the intent of the user.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
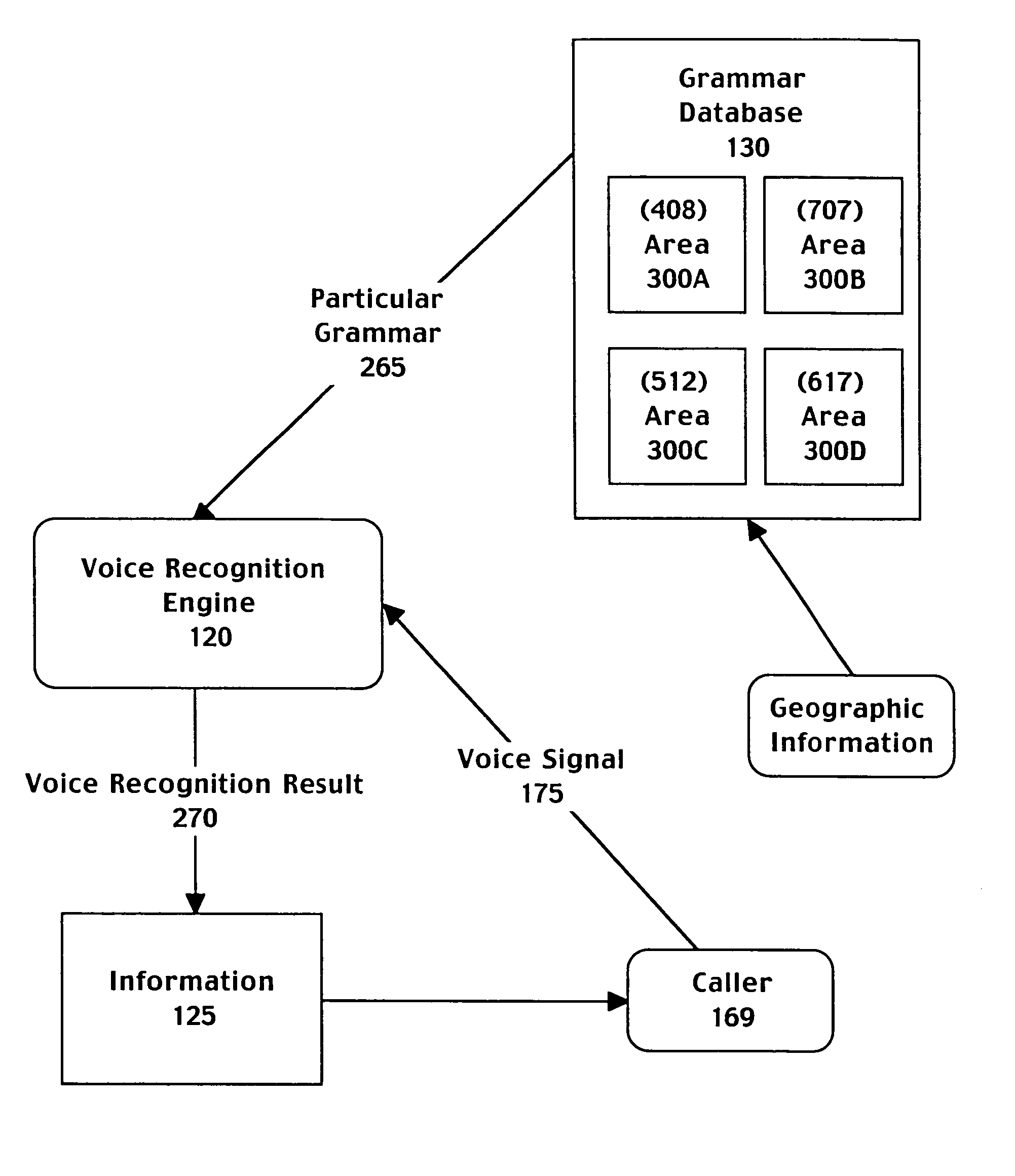
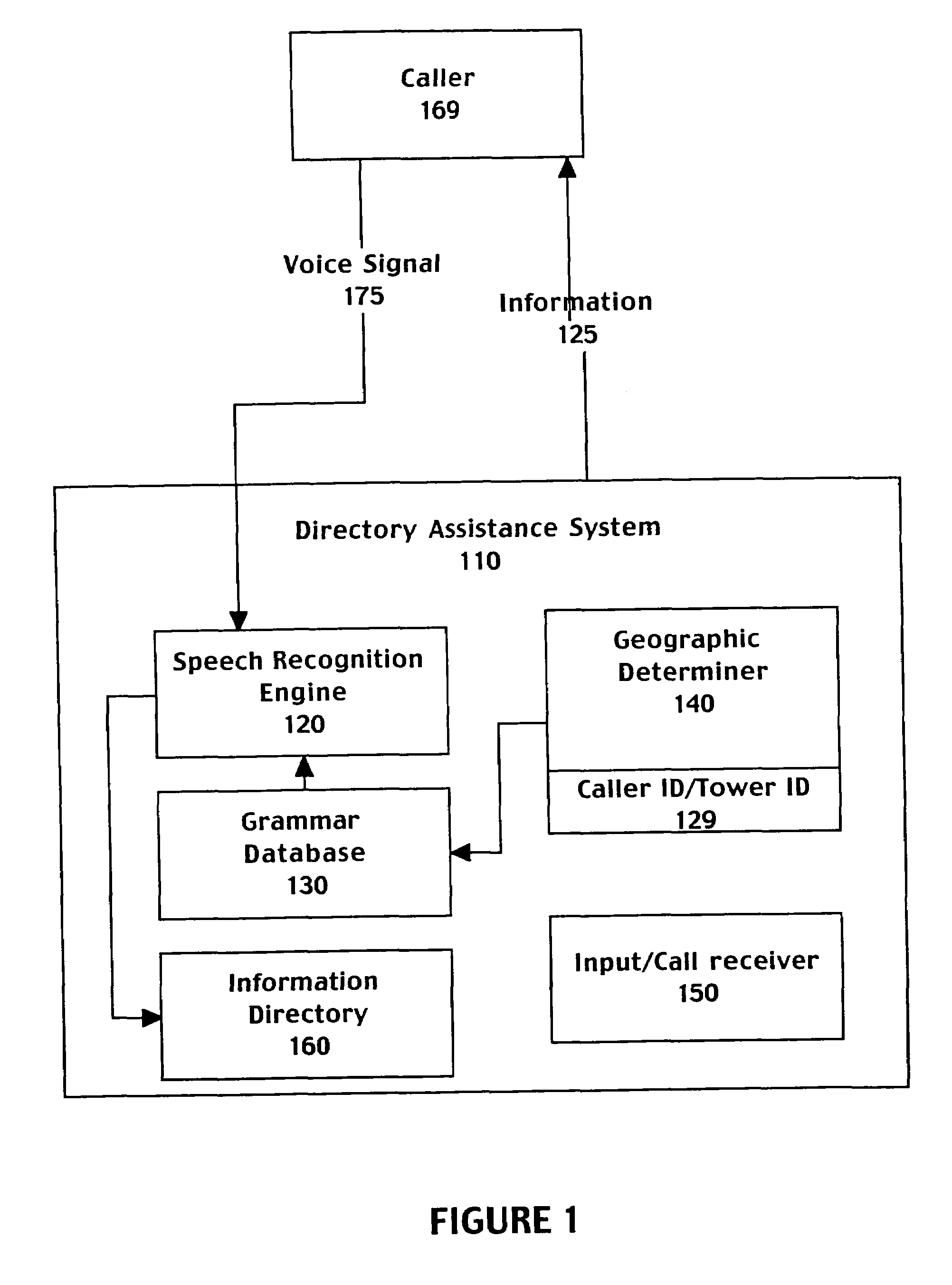
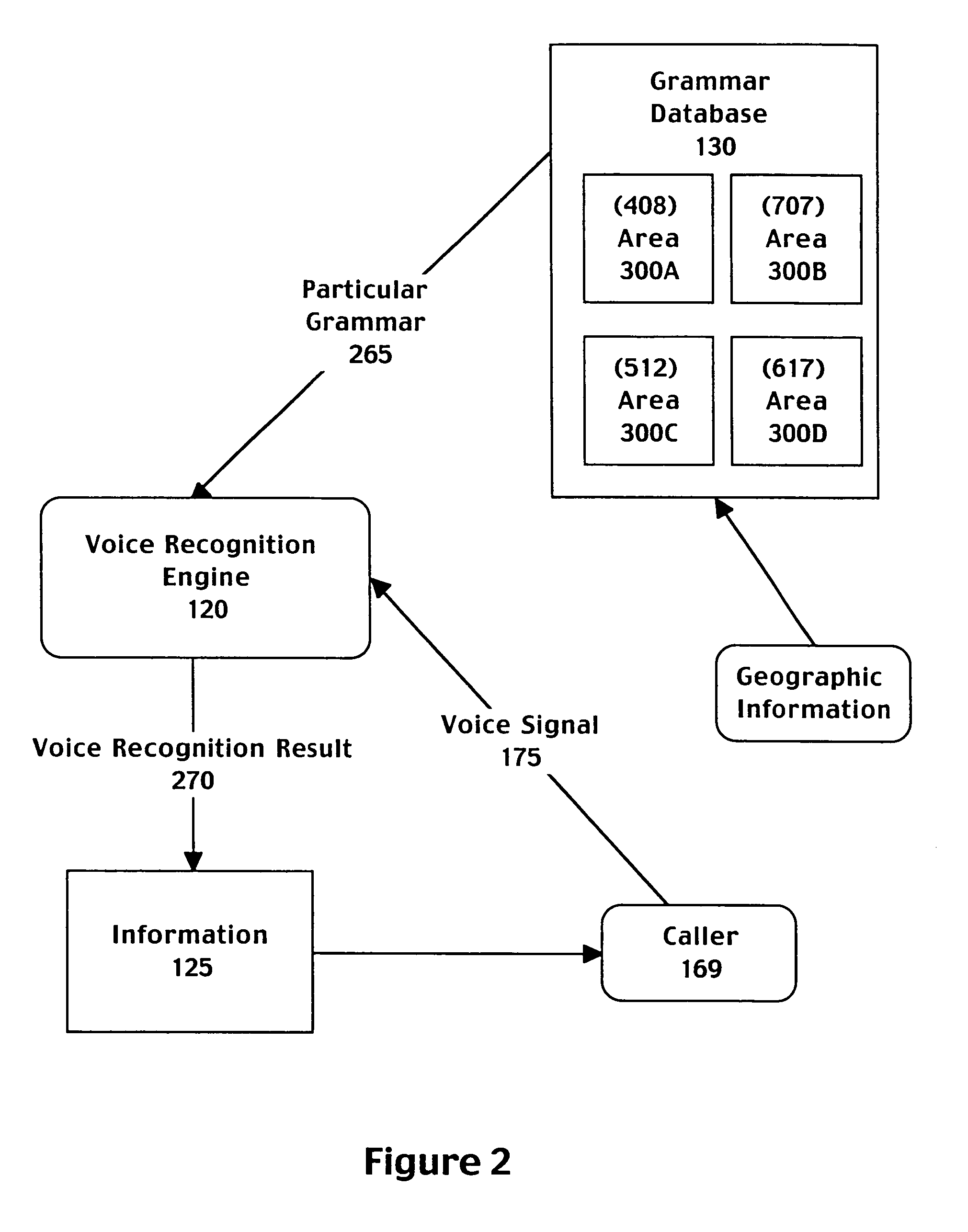
Method and system for selecting grammars based on geographic information associated with a caller
A computer implemented method for automatically processing a data request comprising accessing a voice signal from a caller, determining geographic information associated with the caller from telephone network information associated with a call made by the caller, and retrieving a speech recognition grammar customized to the geographic information associated with the caller. The method further includes recognizing the voice signal by matching the voice signal to an entry of the speech recognition grammar and providing a directory listing to the caller based on the entry of the speech recognition grammar. The selected grammar may be customized to bias speech recognition to more frequently recognize cities local to the geographic information.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
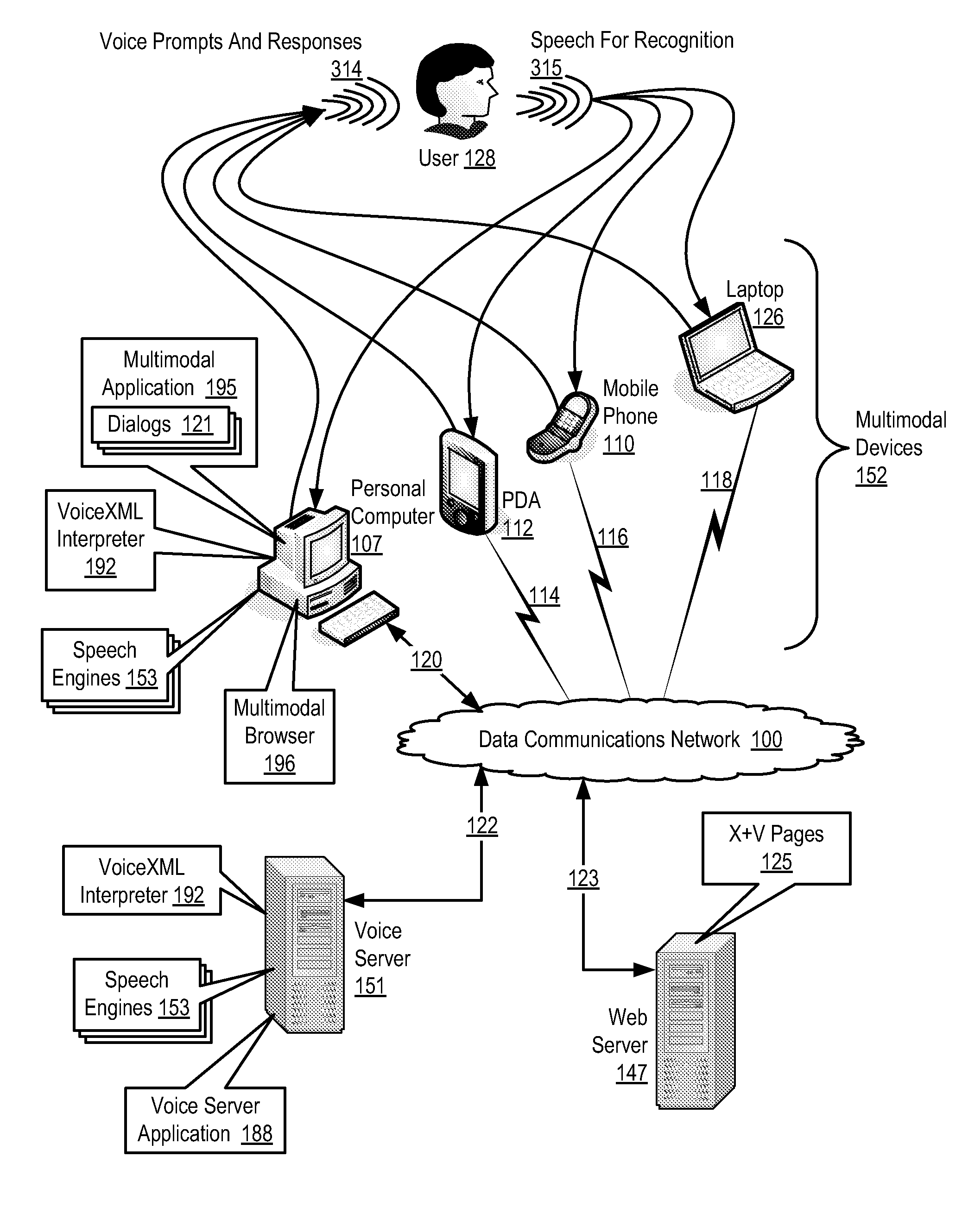
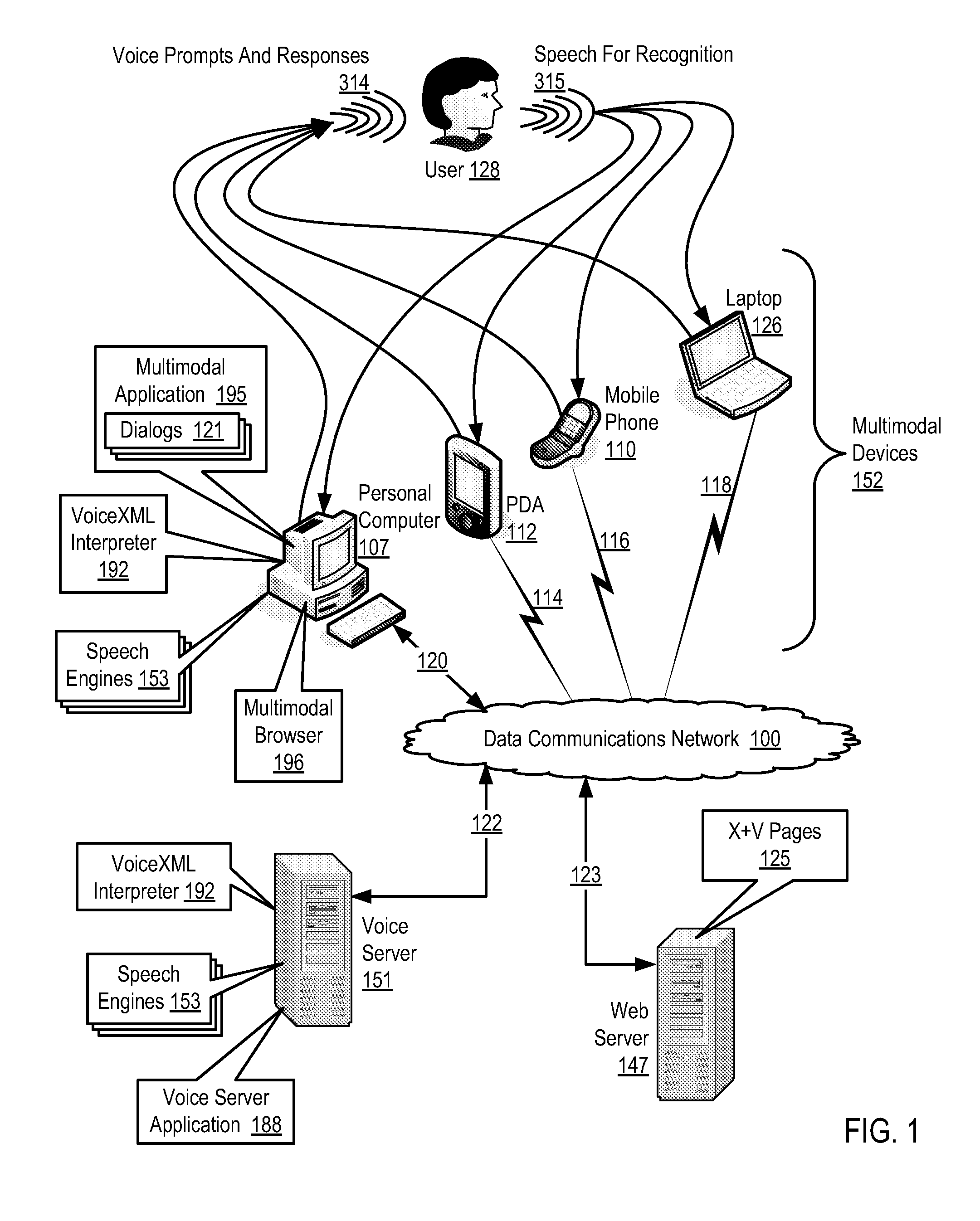
Supporting Multi-Lingual User Interaction With A Multimodal Application
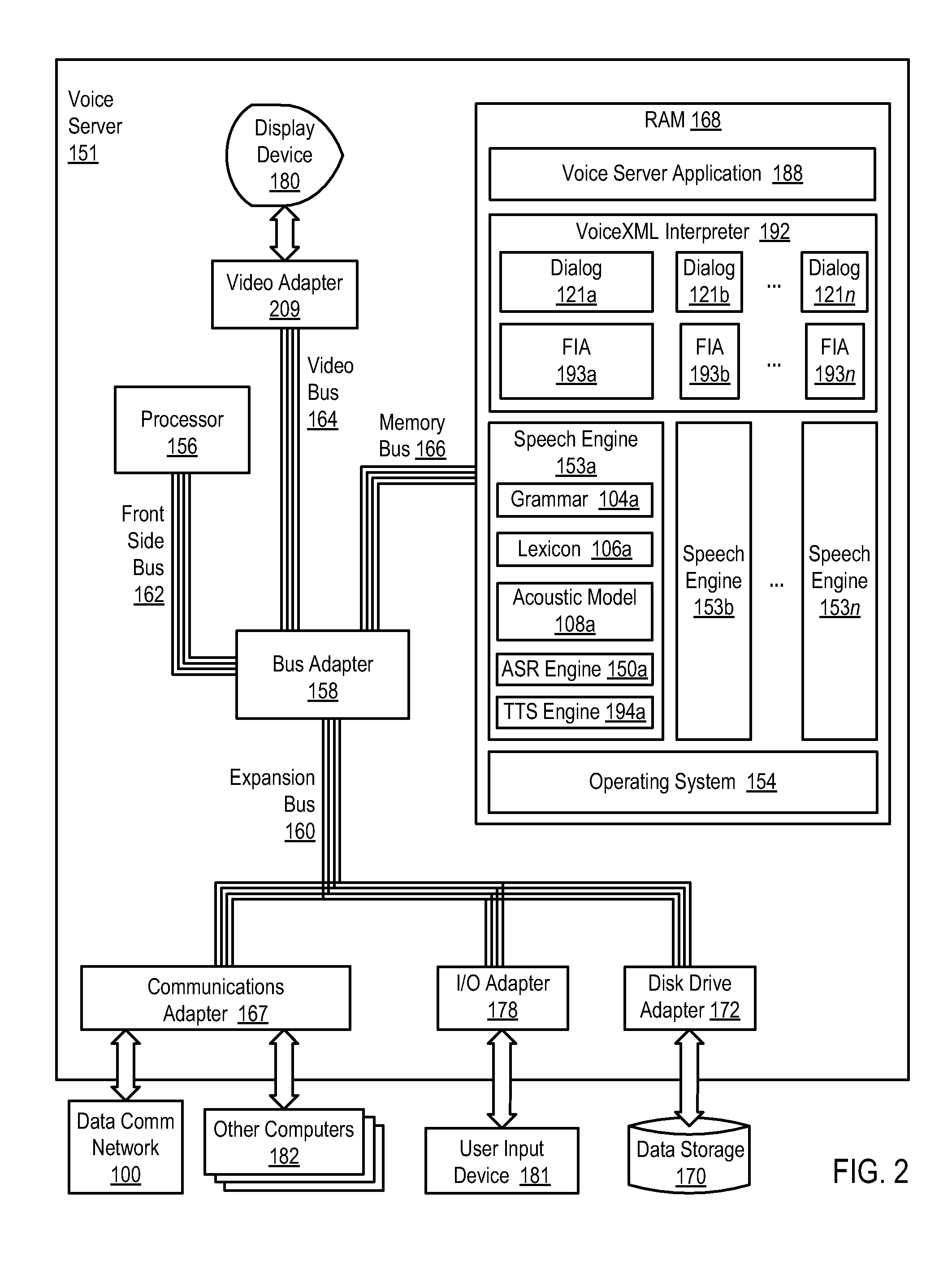
Methods, apparatus, and products are disclosed for supporting multi-lingual user interaction with a multimodal application, the application including a plurality of VoiceXML dialogs, each dialog characterized by a particular language, supporting multi-lingual user interaction implemented with a plurality of speech engines, each speech engine having a grammar and characterized by a language corresponding to one of the dialogs, with the application operating on a multimodal device supporting multiple modes of interaction including a voice mode and one or more non-voice modes, the application operatively coupled to the speech engines through a VoiceXML interpreter, the VoiceXML interpreter: receiving a voice utterance from a user; determining in parallel, using the speech engines, recognition results for each dialog in dependence upon the voice utterance and the grammar for each speech engine; administering the recognition results for the dialogs; and selecting a language for user interaction in dependence upon the administered recognition results.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Semantic object synchronous understanding implemented with speech application language tags
ActiveUS7200559B2Sound input/outputSpeech recognitionSpeech comprehensionApplication programming interface
A speech understanding system includes a language model comprising a combination of an N-gram language model and a context-free grammar language model. The language model stores information related to words and semantic information to be recognized. A module is adapted to receive input from a user and capture the input for processing. The module is further adapted to receive SALT application program interfaces pertaining to recognition of the input. The module is configured to process the SALT application program interfaces and the input to ascertain semantic information pertaining to a first portion of the input and output a semantic object comprising text and semantic information for the first portion by accessing the language model, wherein performing recognition and outputting the semantic object are performed while capturing continues for subsequent portions of the input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
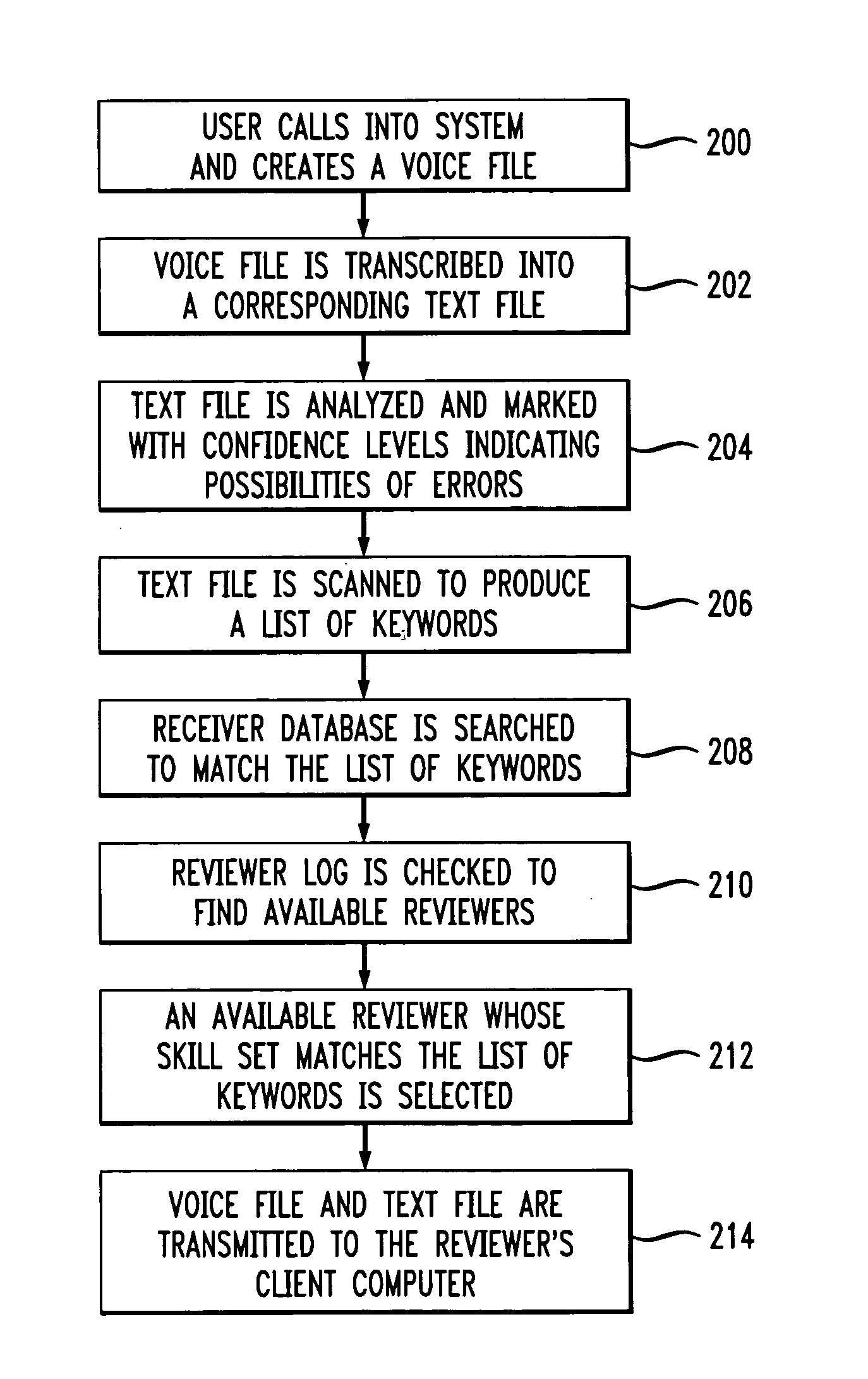
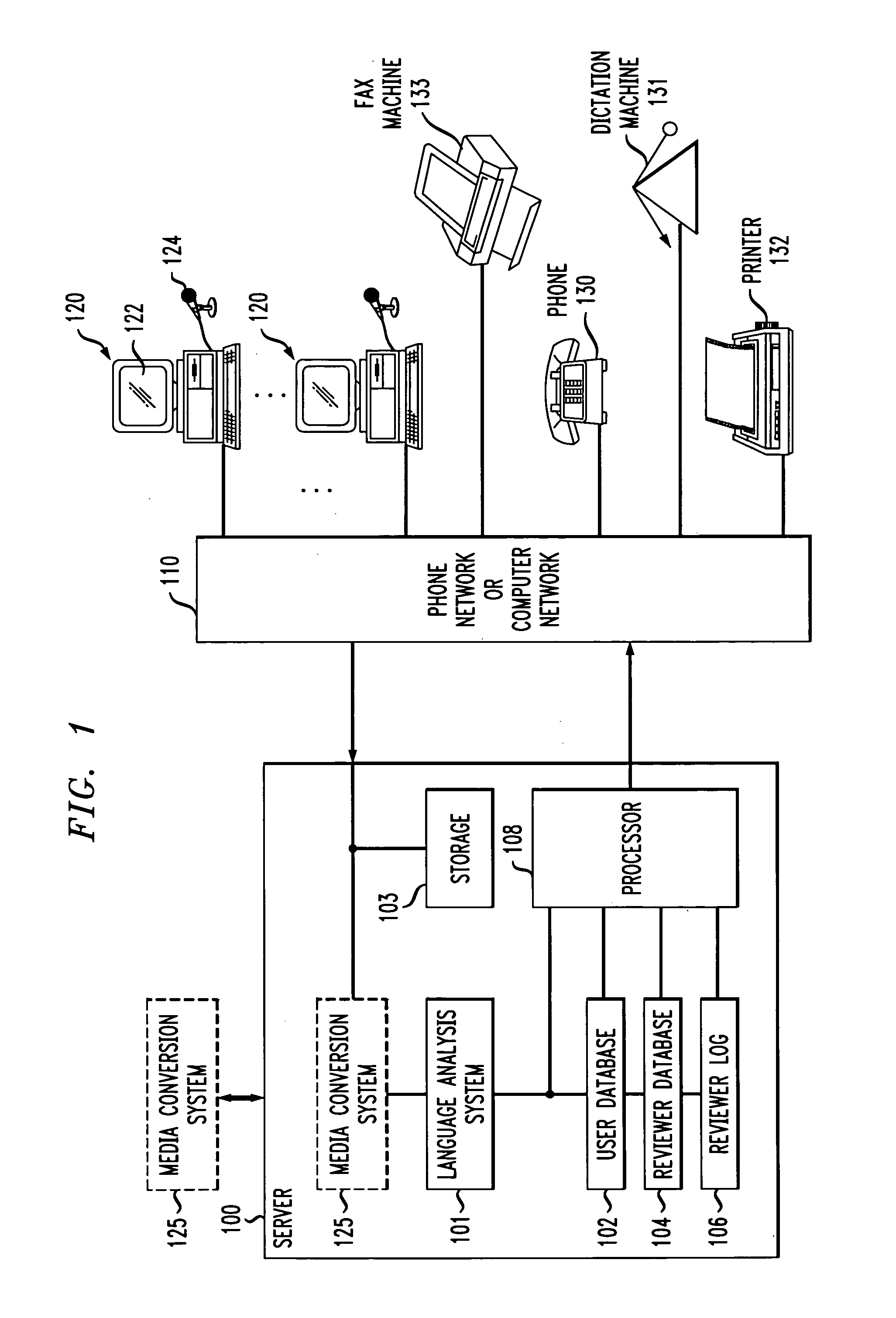
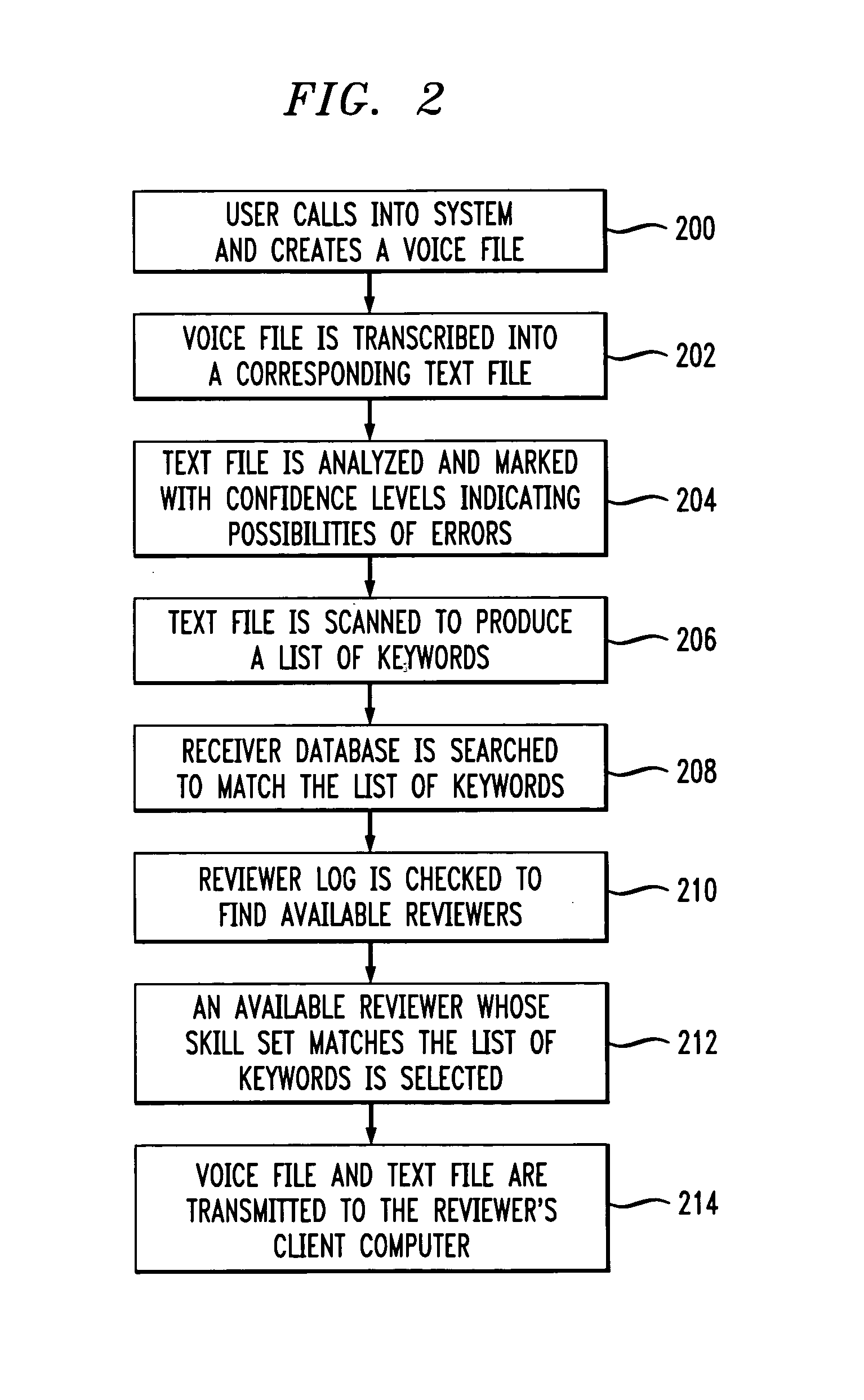
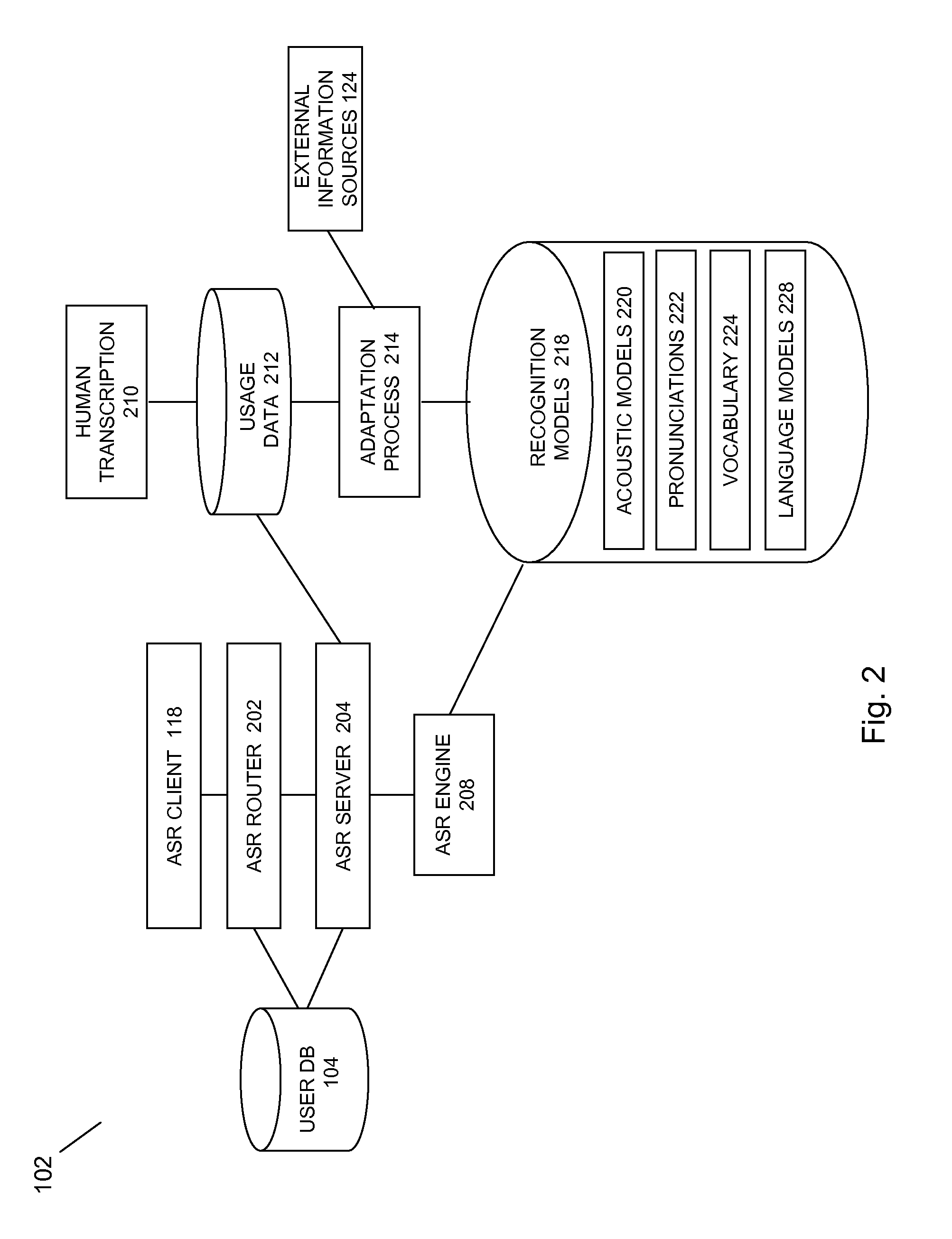
Method of and apparatus for improving productivity of human reviewers of automatically transcribed documents generated by media conversion systems
InactiveUS7236932B1Improve productivityPotential for errorSpeech recognitionDocumentation procedureFile system
An apparatus for improving productivity of human reviewers of transcribed documents generated by media conversion systems includes a server / client network of computers, memories and file systems. The server receives and stores voice files created by users of the system. The server is configured for coupling to a speech-to-text media conversion system to receive converted text files of the audio voice files. The server analyzes the converted text files and routes the converted files to the appropriate reviewers according to an adaptive algorithm. The converted files are displayed on the assigned reviewer's screen at the reviewer's workstation. To aid the reviewer in pinpointing potential errors, the workstation displays different segments of the converted files in different colors to reflect different confidence levels of transcription accuracy. Portions of the original voice message that correspond to the potential errors are played back for the reviewer. The reviewers' workstations also perform productivity enhancing functions such as spelling and grammar checking. After the reviewer has made all the necessary corrections, the reviewed files are transmitted back to the server to be stored and accessed by the users. A user database in the server is also updated to store recurrent user-specific errors corrected by the reviewer. A language analysis system is also disposed to adaptively correct user-specific errors in future reviews according to the information in the user database.
Owner:AVAYA INC
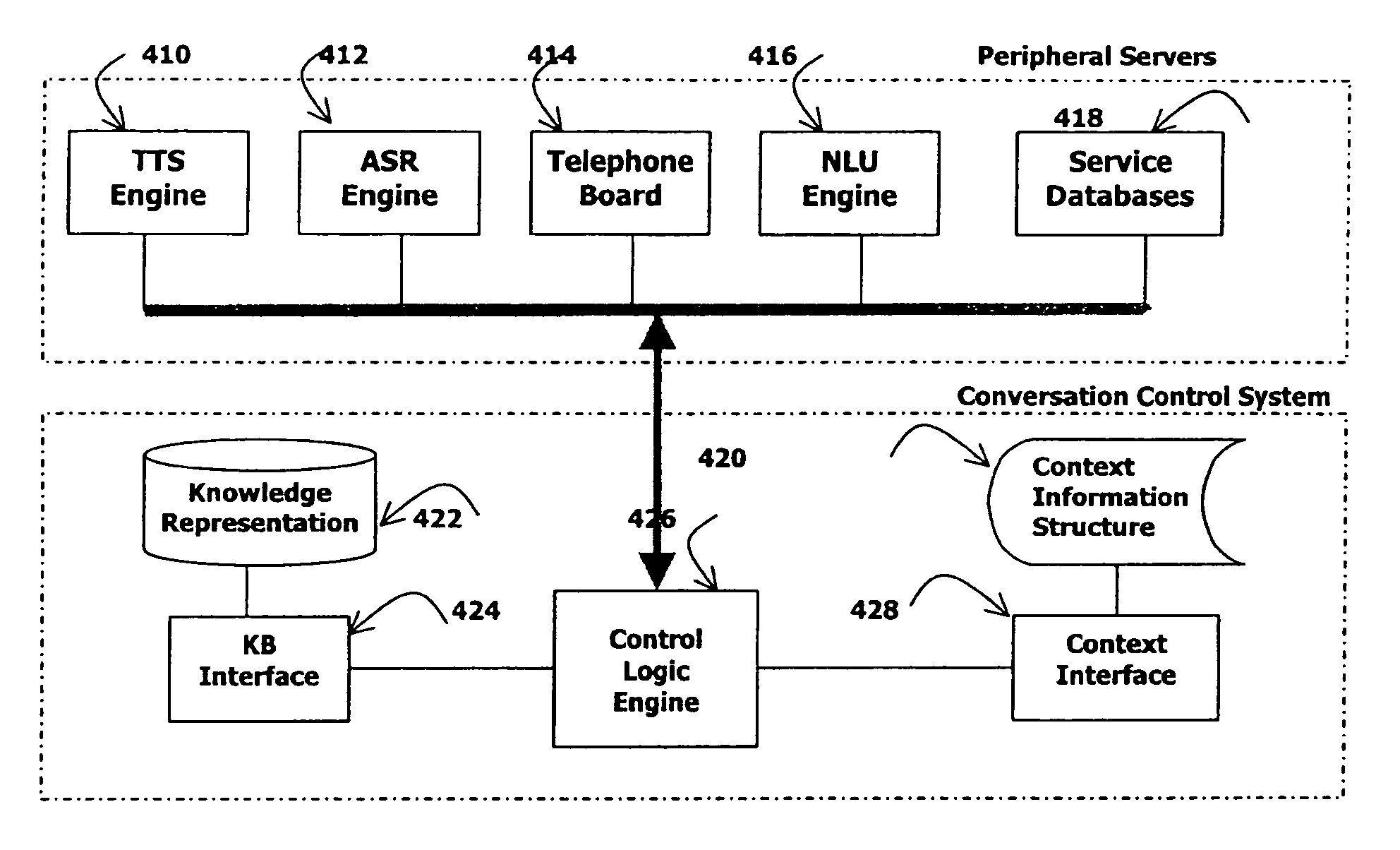
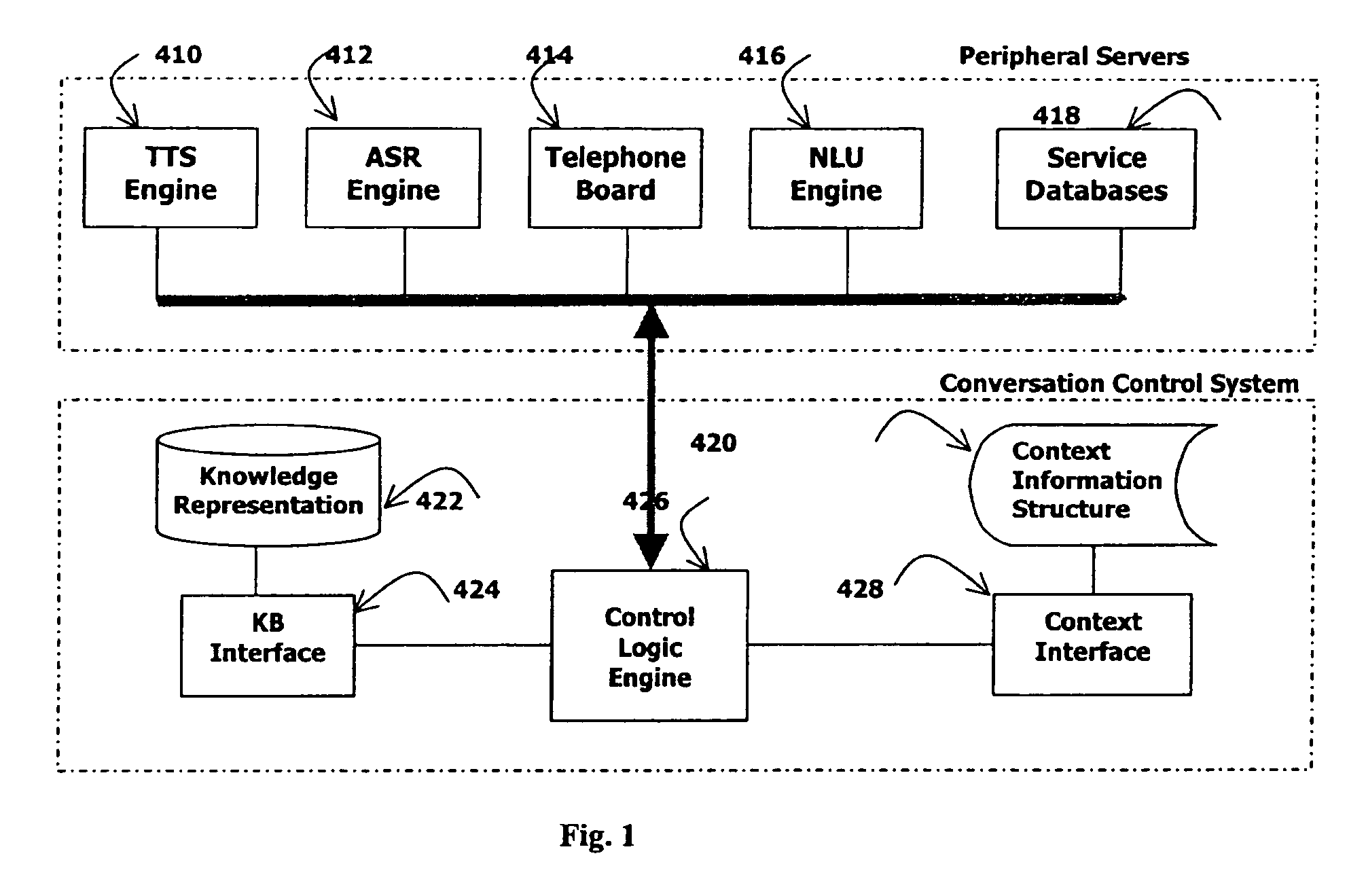
Knowledge-based flexible natural speech dialogue system
InactiveUS7386449B2Speech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHuman–computer interactionFixed position
A knowledge-based natural speech dialogue system includes: (i) a knowledge support system, (ii) a flexible dialogue control system, and (iii) a context information system. Flexibilities of the conversation structure, inherent in mixed-initiative mode for dealing with complex user request, are managed because the knowledge structures involved are represented by additional, powerful knowledge representation tools, and because the context information is retained by more specific data structures, which covers larger temporal scopes by the logic of the conversation, rather than by a fixed locality of the grammar flow. This system provides a simple yet reliable method to compensate for these factors to enable more powerful conversation engines with mixed-initiative capabilities.
Owner:VOICE ENABLING SYST TECH
Hierarchical methods and apparatus for extracting user intent from spoken utterances
Improved techniques are disclosed for permitting a user to employ more human-based grammar (i.e., free form or conversational input) while addressing a target system via a voice system. For example, a technique for determining intent associated with a spoken utterance of a user comprises the following steps / operations. Decoded speech uttered by the user is obtained. An intent is then extracted from the decoded speech uttered by the user. The intent is extracted in an iterative manner such that a first class is determined after a first iteration and a sub-class of the first class is determined after a second iteration. The first class and the sub-class of the first class are hierarchically indicative of the intent of the user, e.g., a target and data that may be associated with the target. The multi-stage intent extraction approach may have more than two iterations. By way of example only, the user intent extracting step may further determine a sub-class of the sub-class of the first class after a third iteration, such that the first class, the sub-class of the first class, and the sub-class of the sub-class of the first class are hierarchically indicative of the intent of the user.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Apparatus and methods for developing conversational applications
InactiveUS20040083092A1Improve speech recognition performanceQuick fixSemantic analysisSpeech recognitionState switchingApplication software
Owner:GYRUS LOGIC INC
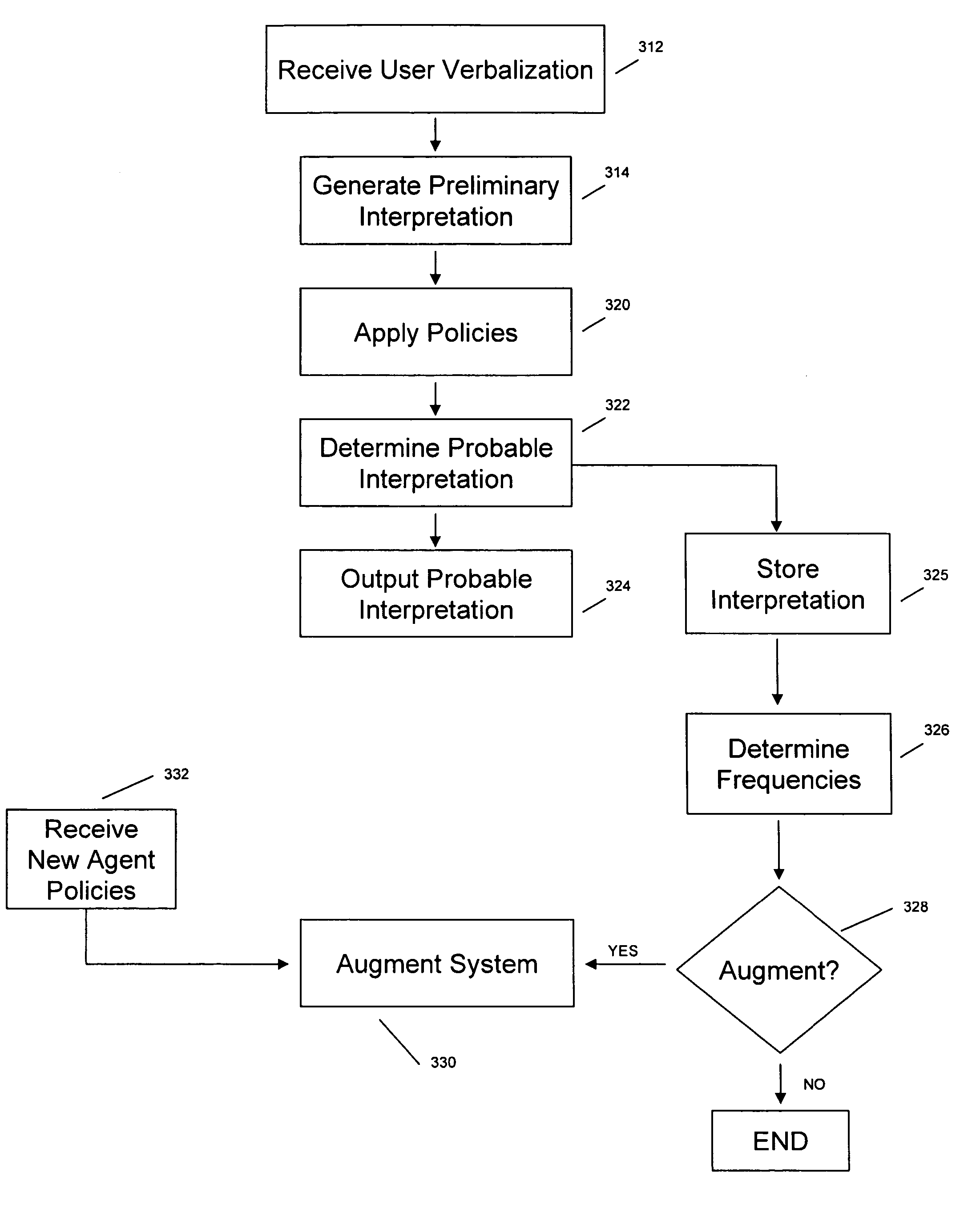
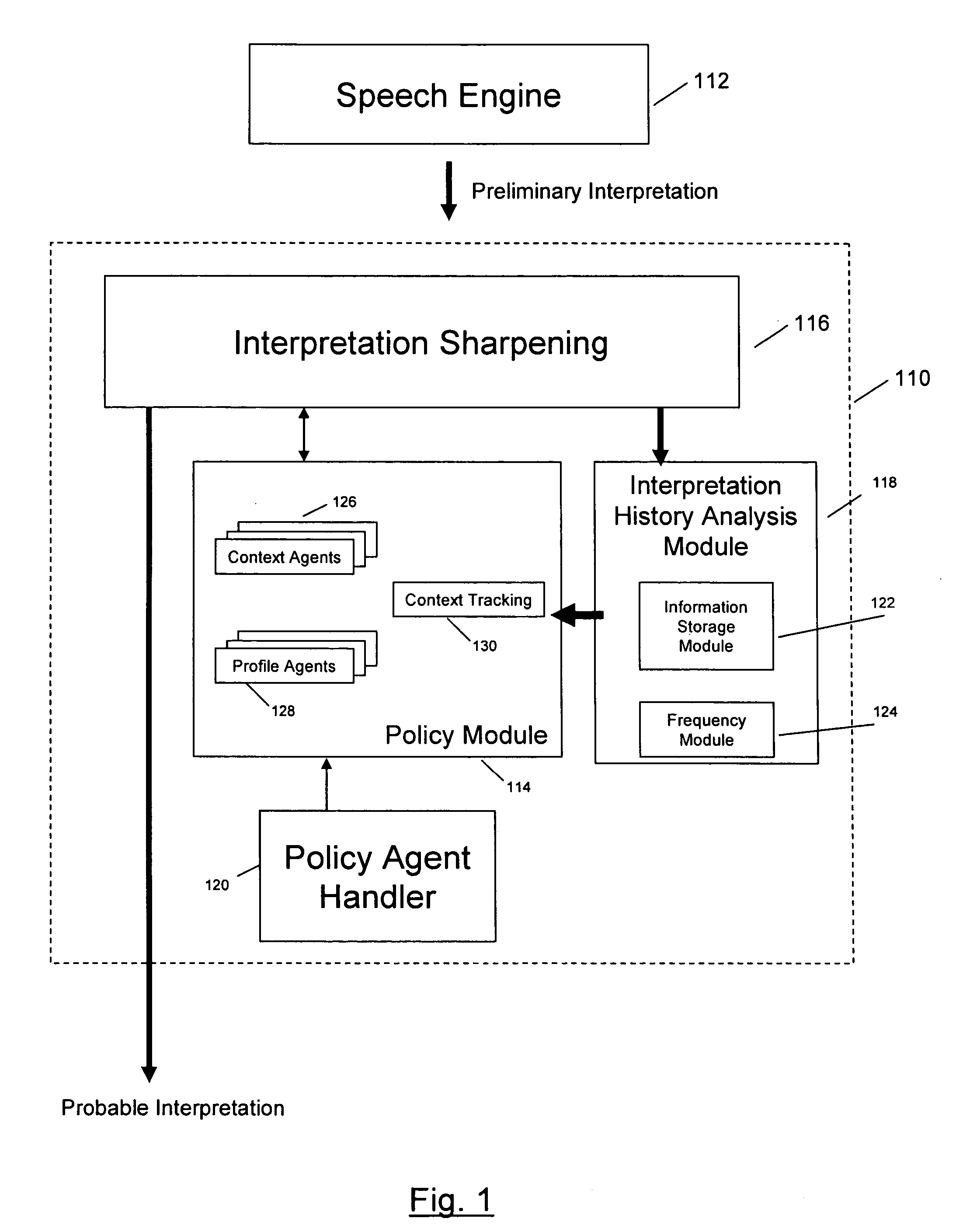
Dynamic speech sharpening
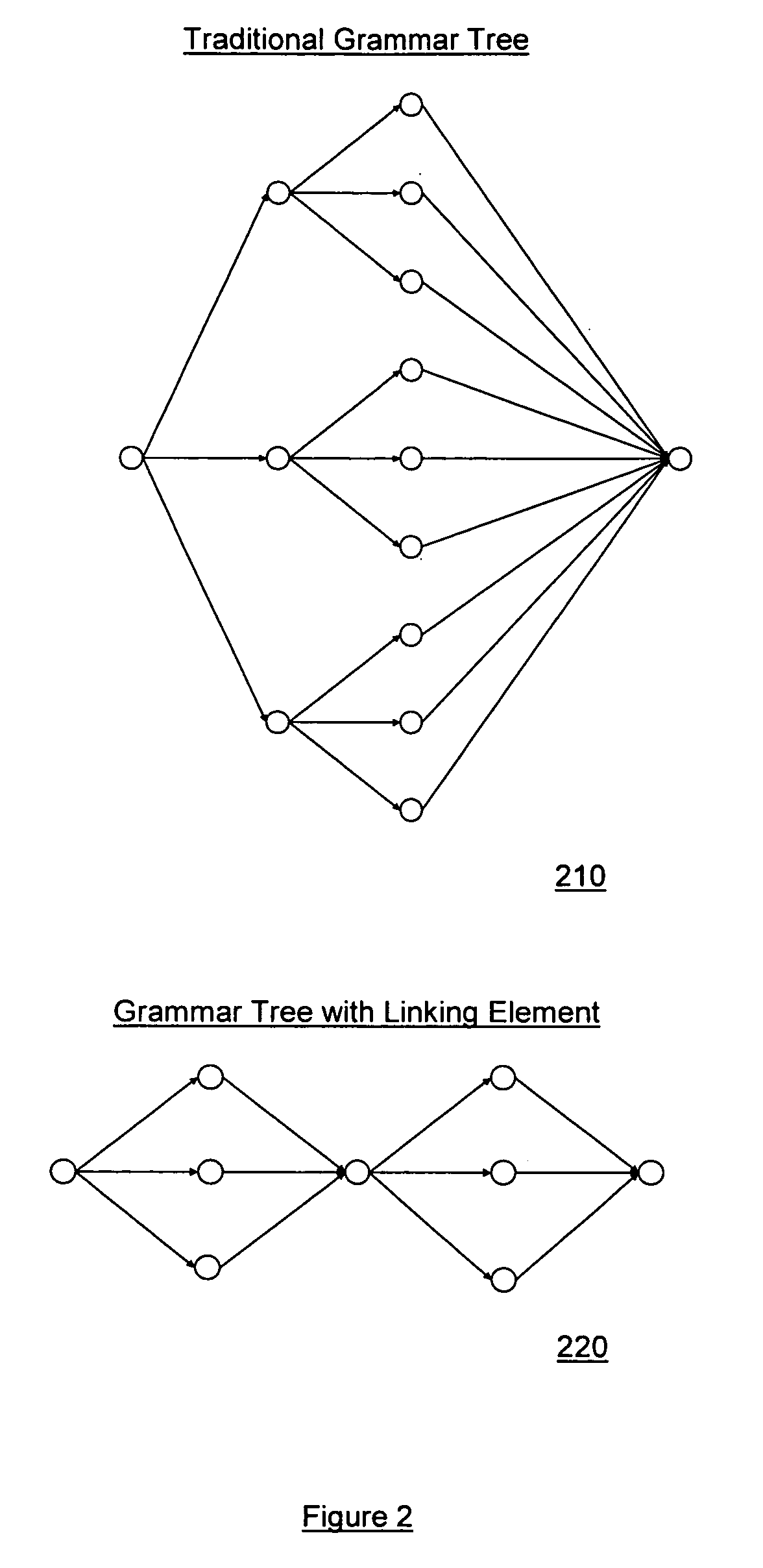
ActiveUS20070055525A1Enhancing automated speech interpretationImprove accuracySpeech recognitionSyllableContext based
An enhanced system for speech interpretation is provided. The system may include receiving a user verbalization and generating one or more preliminary interpretations of the verbalization by identifying one or more phonemes in the verbalization. An acoustic grammar may be used to map the phonemes to syllables or words, and the acoustic grammar may include one or more linking elements to reduce a search space associated with the grammar. The preliminary interpretations may be subject to various post-processing techniques to sharpen accuracy of the preliminary interpretation. A heuristic model may assign weights to various parameters based on a context, a user profile, or other domain knowledge. A probable interpretation may be identified based on a confidence score for each of a set of candidate interpretations generated by the heuristic model. The model may be augmented or updated based on various information associated with the interpretation of the verbalization.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
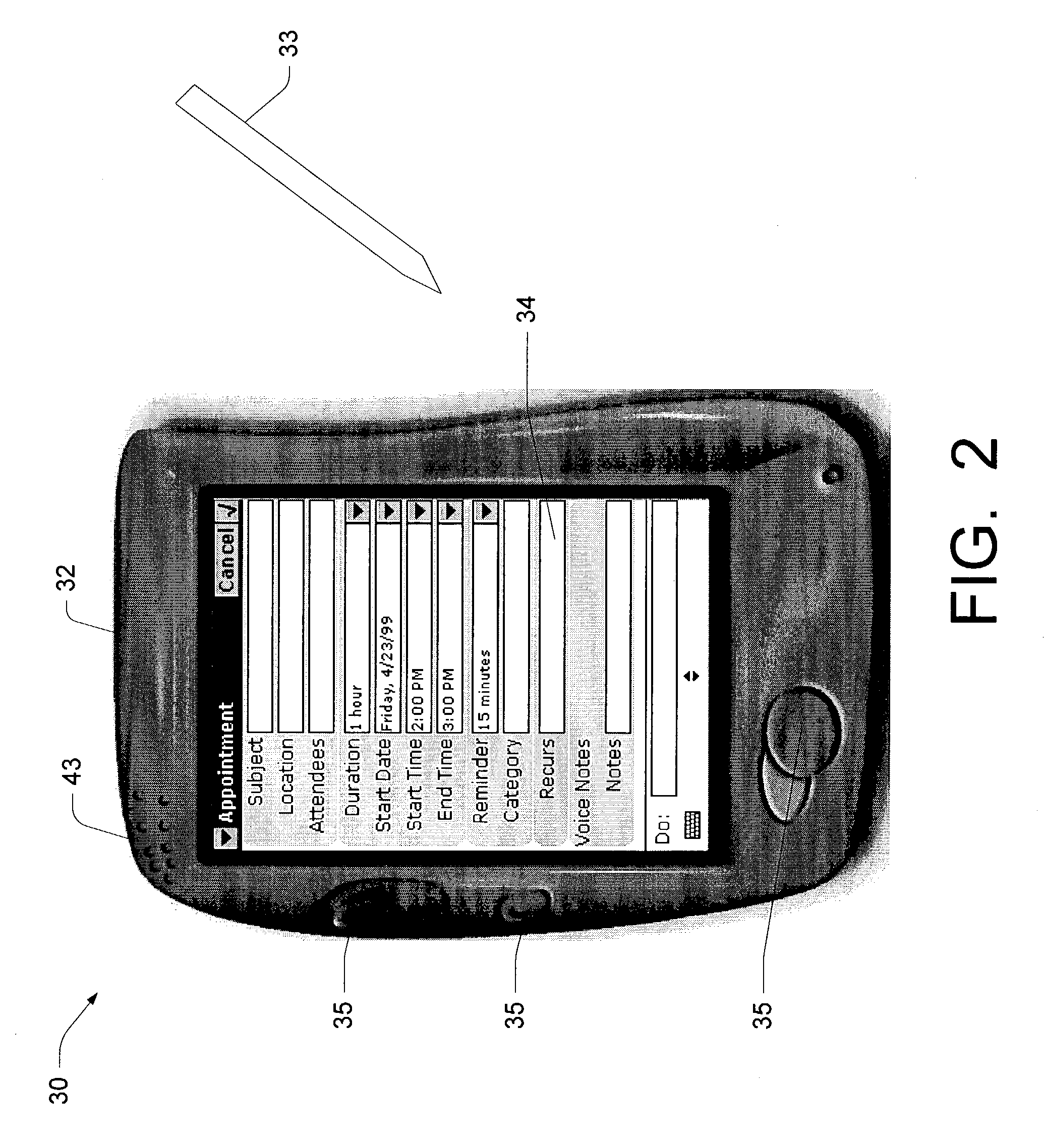
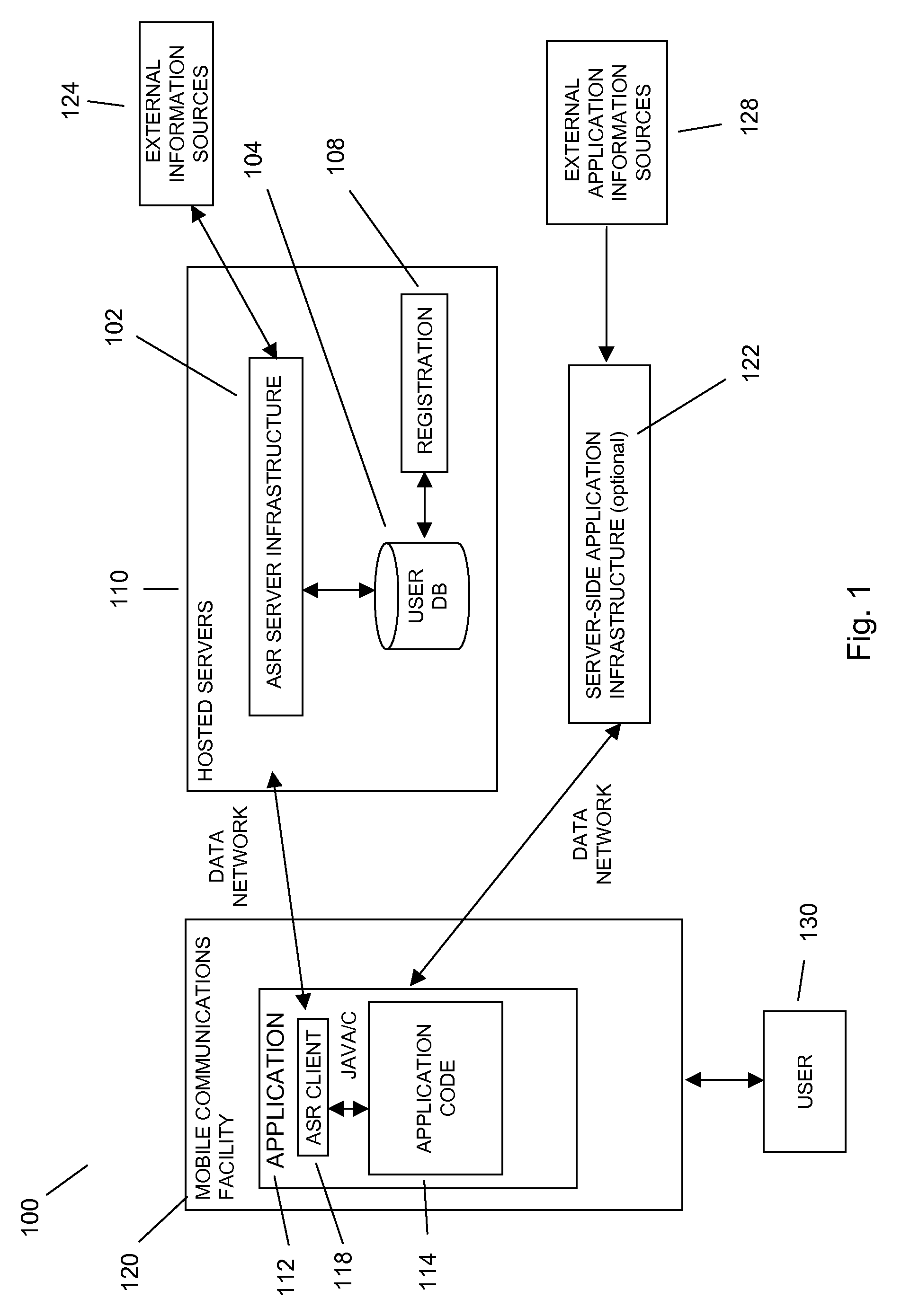
Application text entry in a mobile environment using a speech processing facility
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a mobile environment speech processing facility. The present invention may provide for the entering of text into a software application resident on a mobile communication facility, where recorded speech may be presented by the user using the mobile communications facility's resident capture facility. Transmission of the recording may be provided through a wireless communication facility to a speech recognition facility, and may be accompanied by information related to the software application. Results may be generated utilizing the speech recognition facility that may be independent of structured grammar, and may be based at least in part on the information relating to the software application and the recording. The results may then be transmitted to the mobile communications facility, where they may be loaded into the software application.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC +1
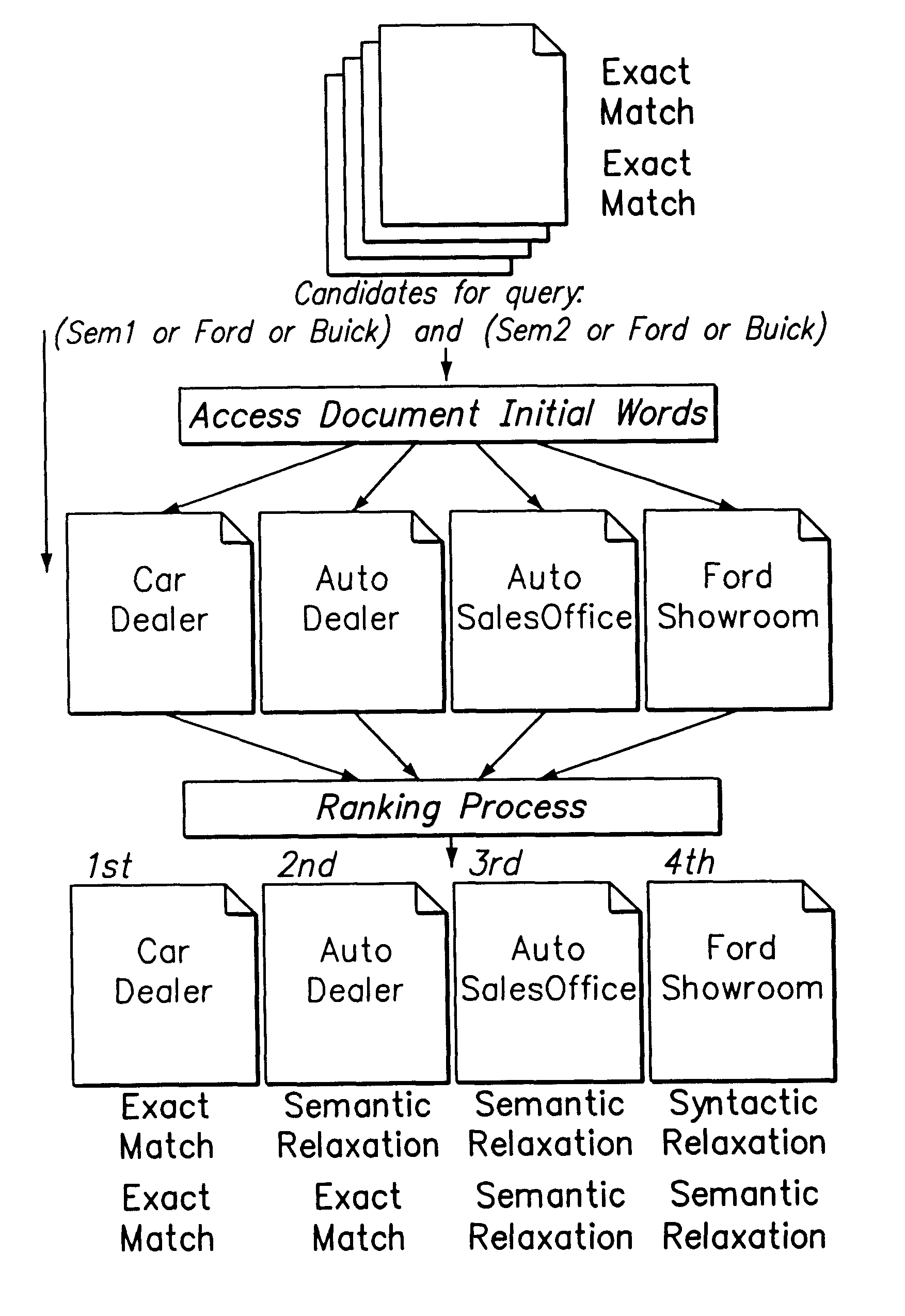
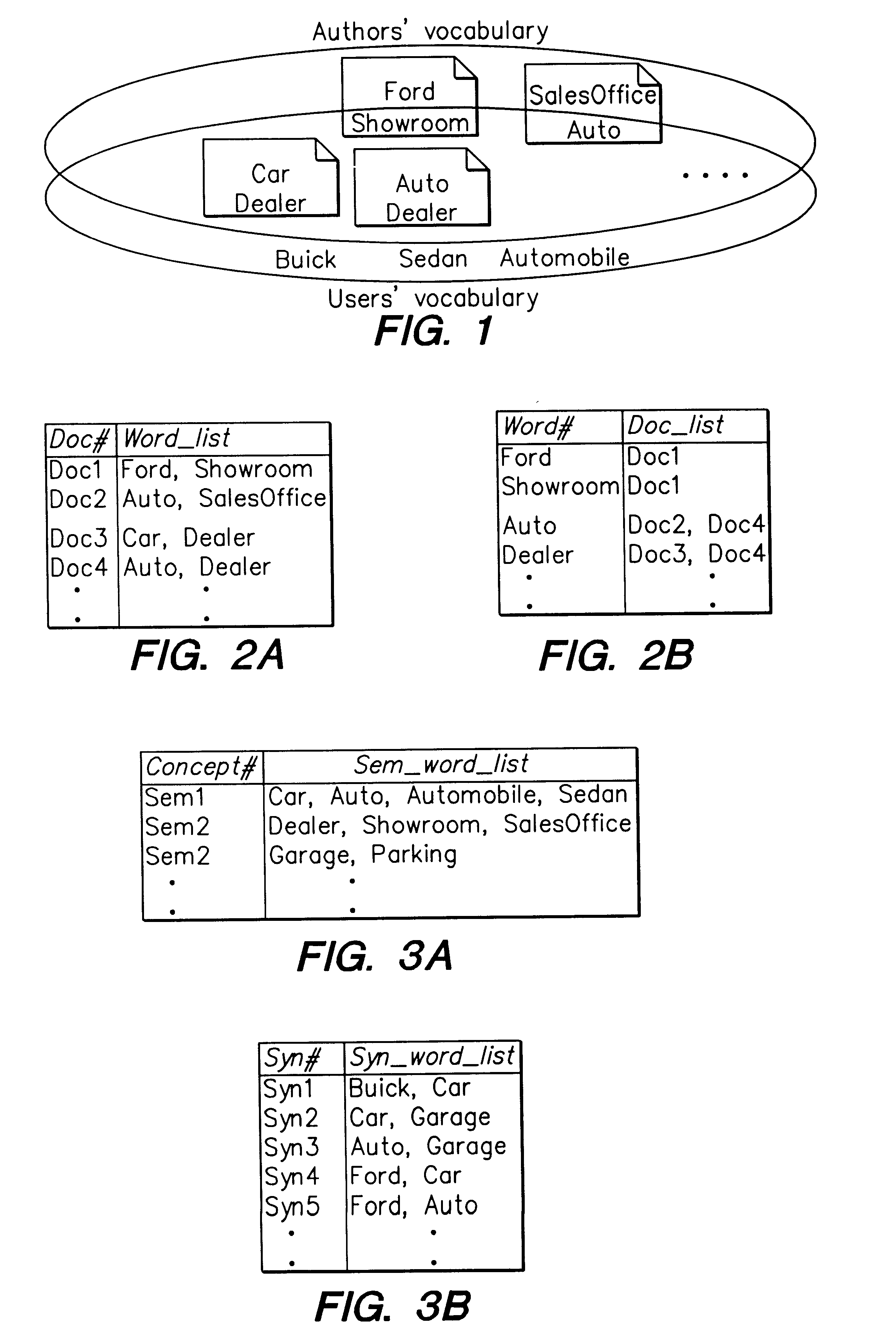
Supporting web-query expansion efficiently using multi-granularity indexing and query processing
A method and apparatus for efficient query expansion using reduced size indices and for progressive query processing. Queries are expanded conceptually, using semantically similar and syntactically related words to those specified by the user in the query to reduce the chances of missing relevant documents. The notion of a multi-granularity information and processing structure is used to support efficient query expansion, which involves an indexing phase, a query processing and a ranking phase. In the indexing phase, semantically similar words are grouped into a concept which results in a substantial index size reduction due to the coarser granularity of semantic concepts. During query processing, the words in a query are mapped into their corresponding semantic concepts and syntactic extensions, resulting in a logical expansion of the original query. Additionally, the processing overhead is avoided. The initial query words can then be used to rank the documents in the answer set on the basis of exact, semantic and syntactic matches and also to perform progressive query processing.
Owner:NEC CORP
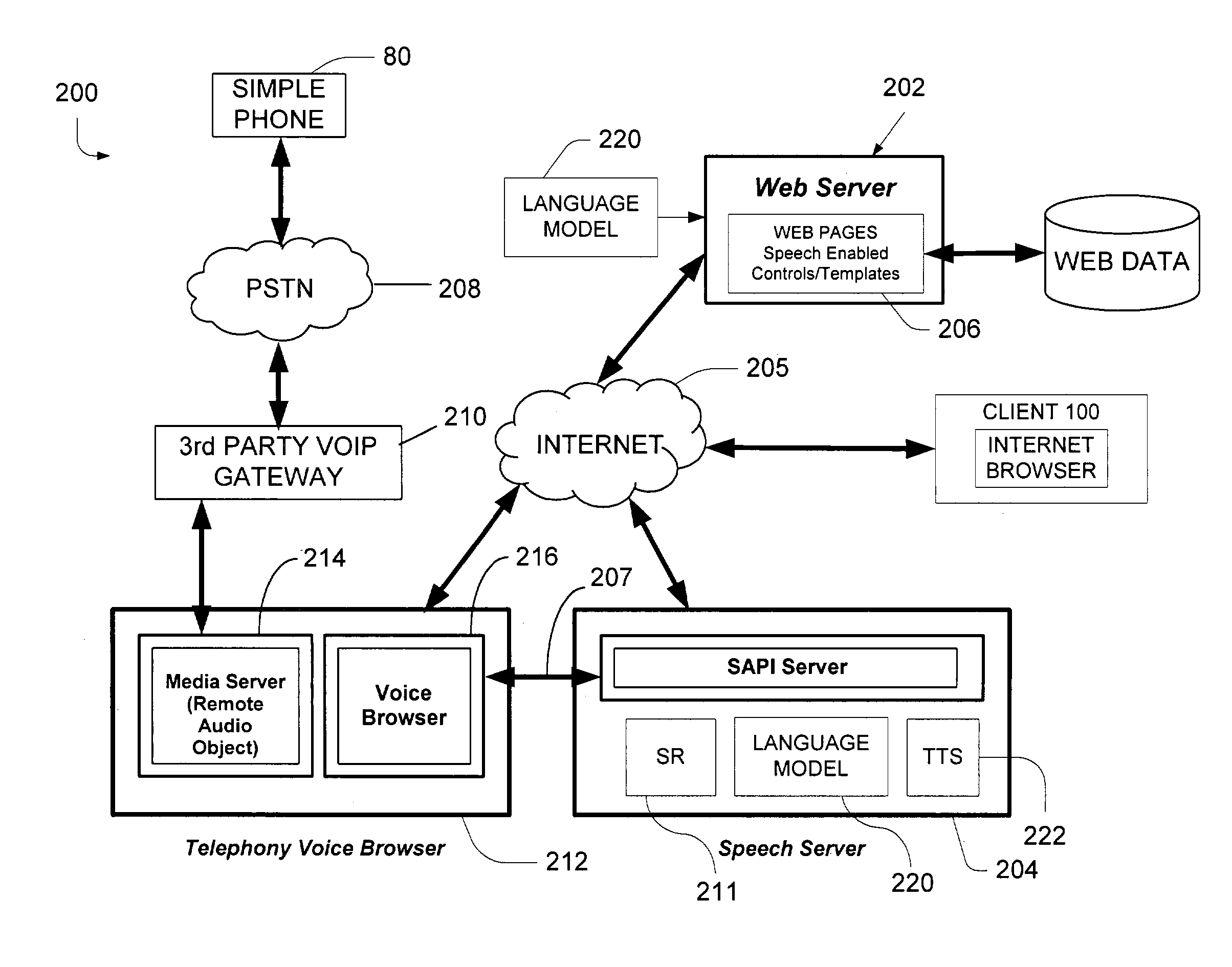
Dialog recognition and control in a voice browser
ActiveUS7003464B2Low costQuantity minimizationDevices with voice recognitionDigital computer detailsDocumentationSpeech sound
A voice browser dialog enabler for multimodal dialog uses a multimodal markup document with fields have markup-based forms associated with each field and defining fragments. A voice browser driver resides on a communication device and provides the fragments and identifiers that identify the fragments. A voice browser implementation resides on a remote voice server and receives the fragments from the driver and downloads a plurality of speech grammars. Input speech is matched against those speech grammars associated with the corresponding identifiers received in a recognition request from the voice browser driver.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
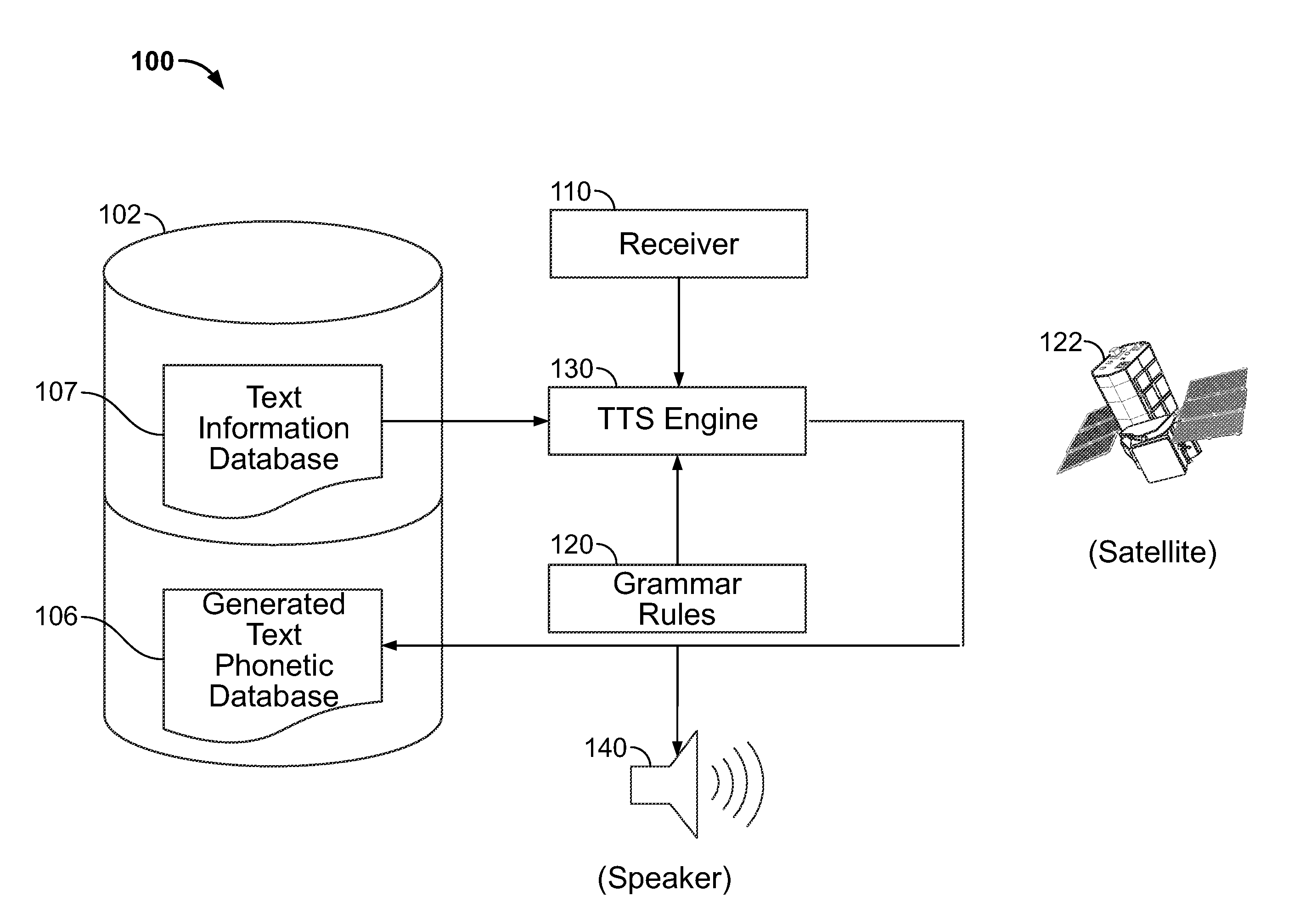
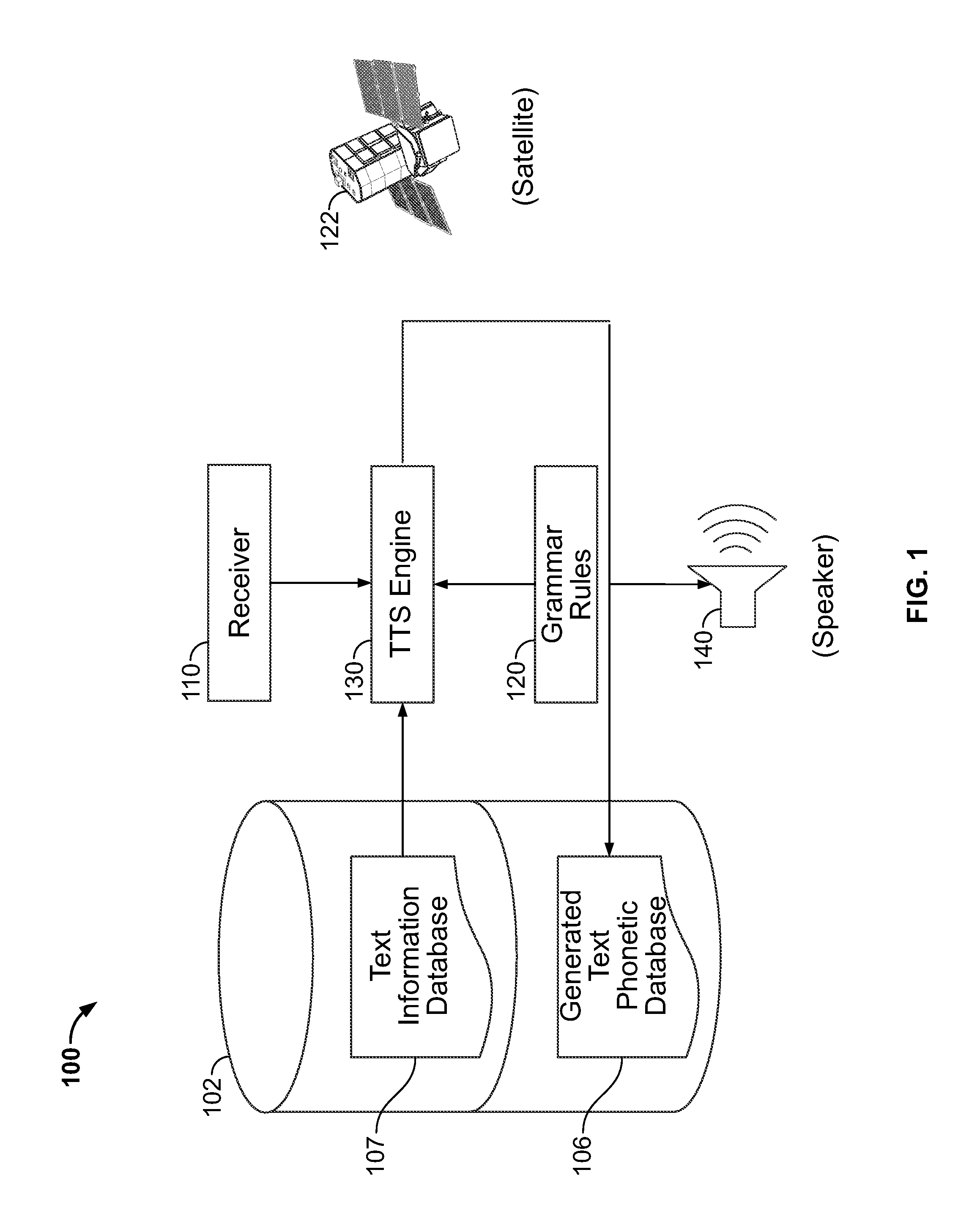
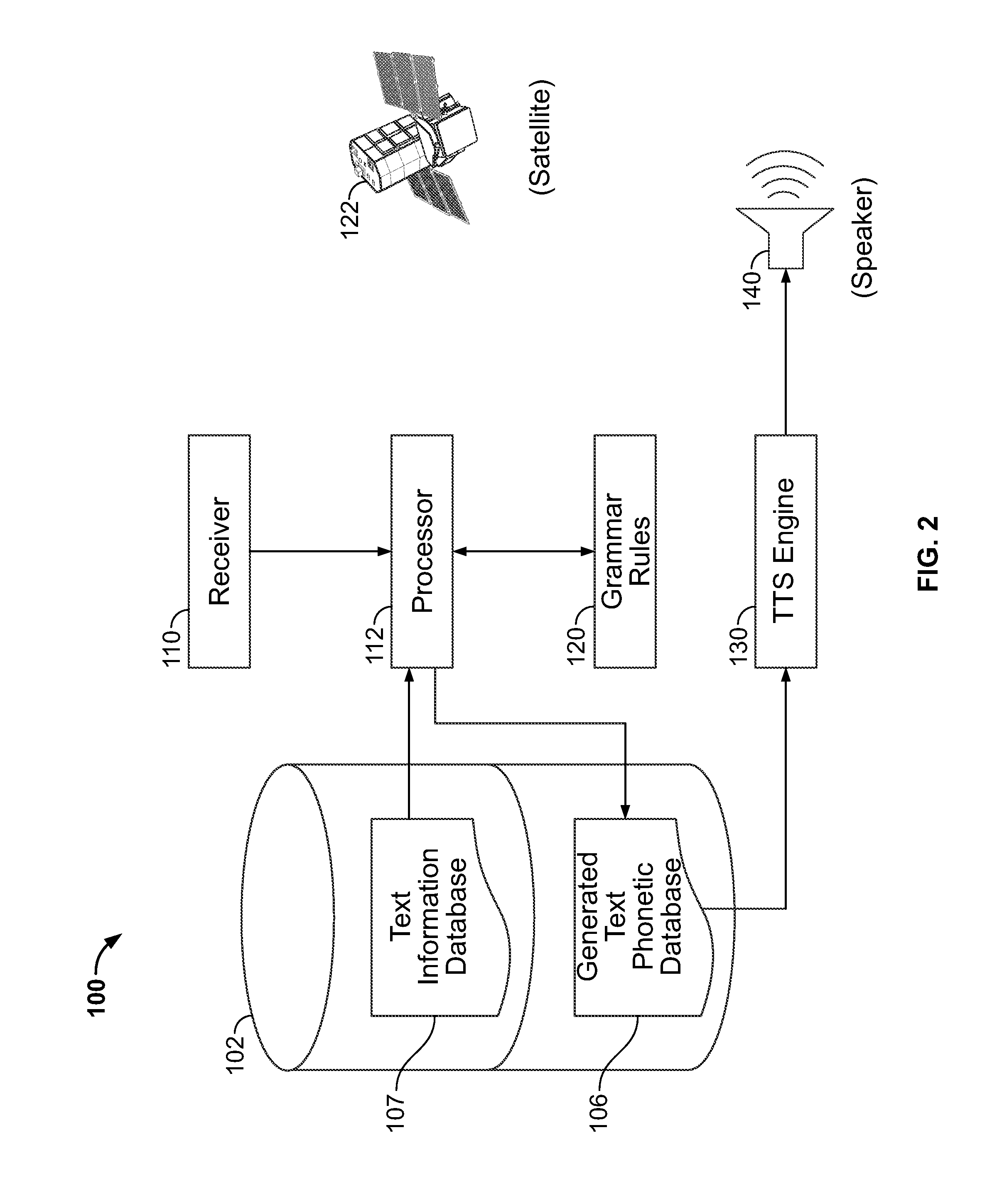
Text pre-processing for text-to-speech generation
A system and method are provided for improved speech synthesis, wherein text data is pre-processed according to updated grammar rules or a selected group of grammar rules. In one embodiment, the TTS system comprises a first memory adapted to store a text information database, a second memory adapted to store grammar rules, and a receiver adapted to receive update data regarding the grammar rules. The system also includes a TTS engine adapted to retrieve at least one text entry from the text information database, pre-process the at least one text entry by applying the updated grammar rules to the at least one text entry, and generate speech based at least in part on the least one pre-processed text entry.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
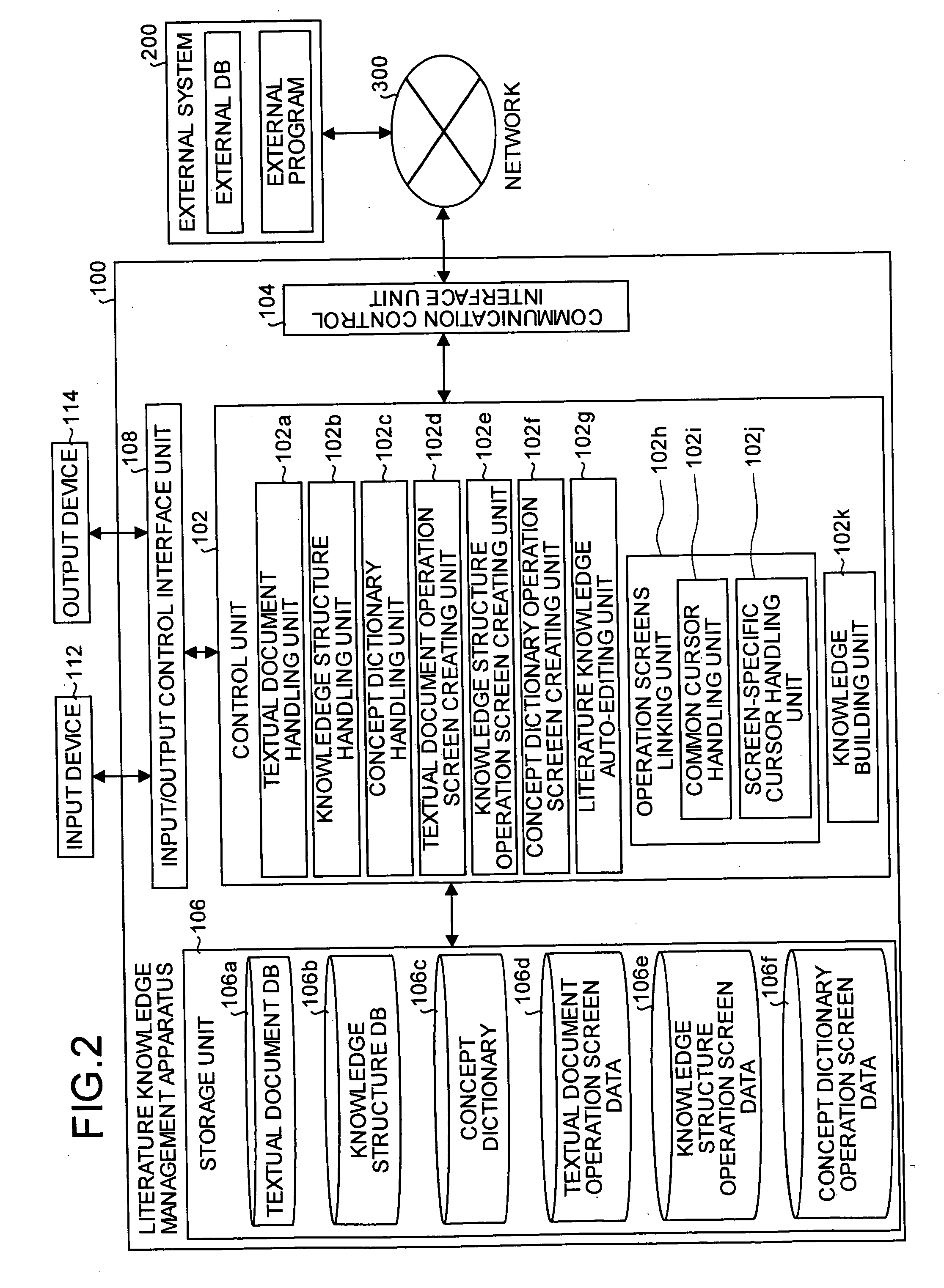
Document knowledge management apparatus and method
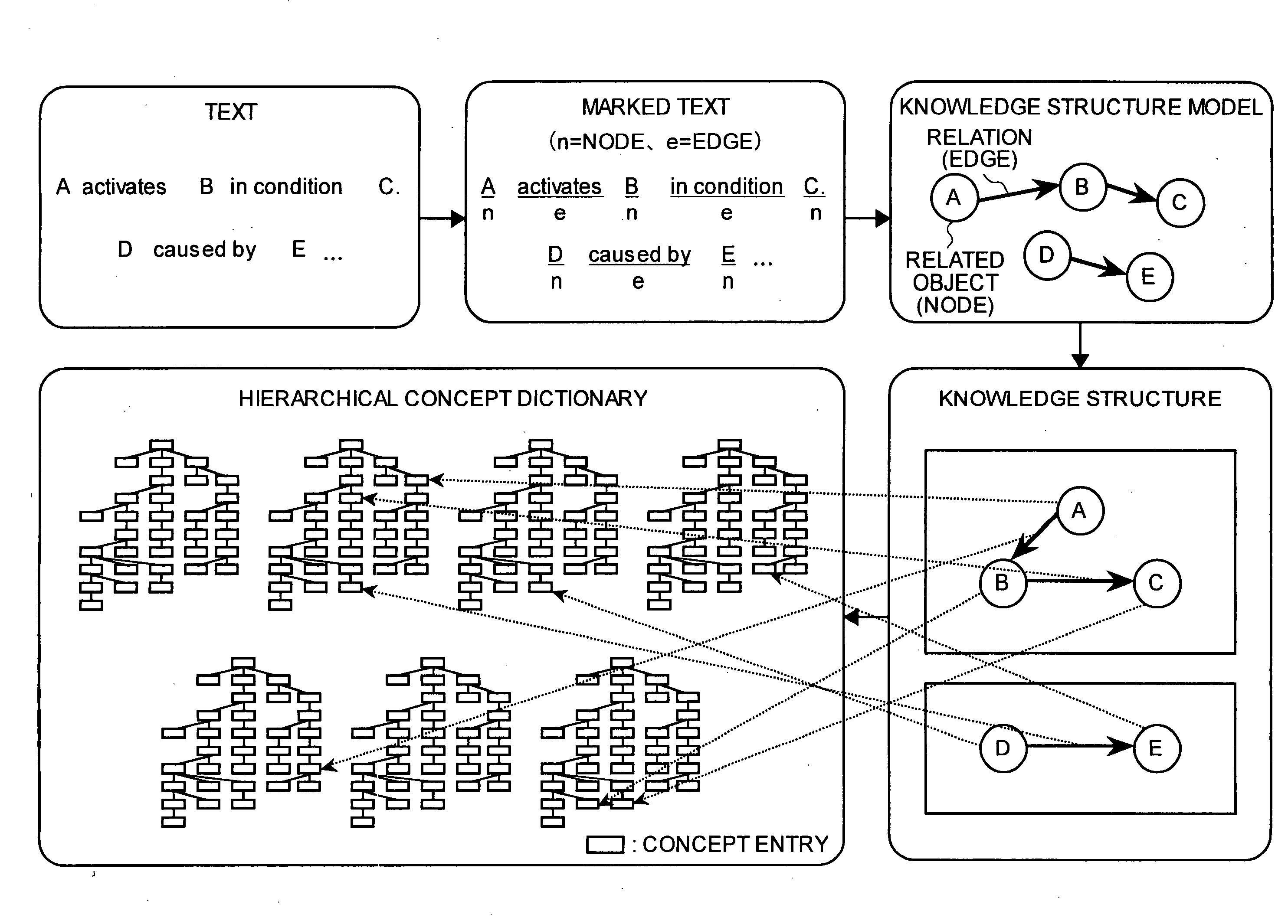
InactiveUS20050154690A1Efficient processingEasily correlatedDigital computer detailsUnstructured textual data retrievalPart of speechGraphics
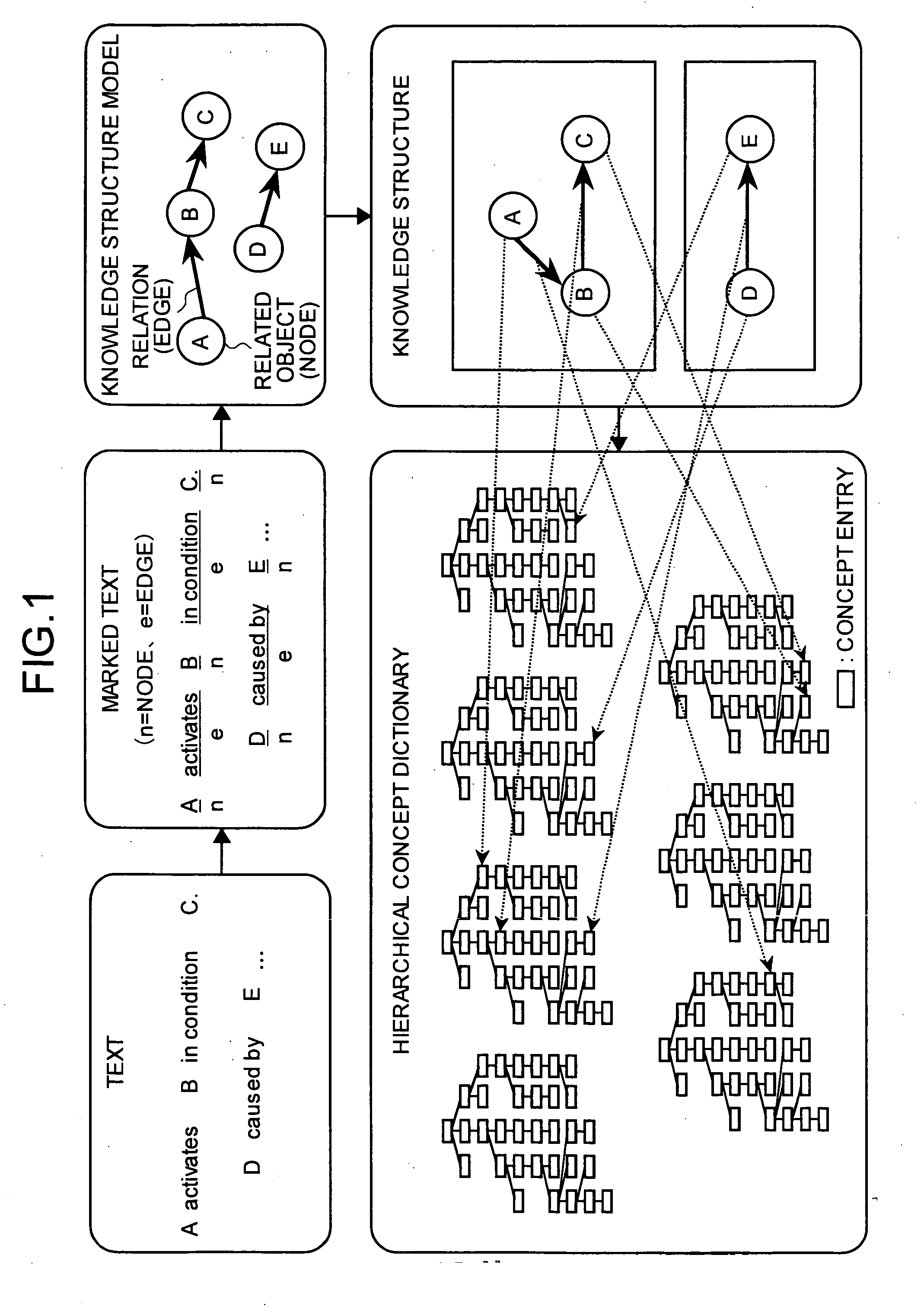
In the present invention, a textual document is syntactically analyzed and knowledge is constructed from a single word or plural words. The knowledge is then marked, from the broken down knowledge (represented by the underscores in FIG. 1) or from a part-of-speech, as a related object (node) or a relation (edge) (represented by ‘n’ or ‘e’ shown in FIG. 1). In other words, in the present invention a textual document is treated as knowledge constructed from a single word or plural words. The knowledge extracted from the textual document is structured to form a knowledge structure (such as a graph structure constituted from nodes and edges). At least one link can be established between each of the knowledge structure elements and a semantically closest concept entry in a hierarchical concept dictionary.
Owner:CELESTAR LEXICO SCI
Intelligent control with hierarchical stacked neural networks
ActiveUS8775341B1Increased complexityComplex mathematical operationDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisSemantic propertyNerve network
A system and method of detecting an aberrant message is provided. An ordered set of words within the message is detected. The set of words found within the message is linked to a corresponding set of expected words, the set of expected words having semantic attributes. A set of grammatical structures represented in the message is detected, based on the ordered set of words and the semantic attributes of the corresponding set of expected words. A cognitive noise vector comprising a quantitative measure of a deviation between grammatical structures represented in the message and an expected measure of grammatical structures for a message of the type is then determined. The cognitive noise vector may be processed by higher levels of the neural network and / or an external processor.
Owner:COMMONS MICHAEL LAMPORT
Phrase-based dialogue modeling with particular application to creating recognition grammars for voice-controlled user interfaces
InactiveUS20020128821A1Quick identificationLess timeNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionSpeech soundHuman system interaction
The invention enables creation of grammar networks that can regulate, control, and define the content and scope of human-machine interaction in natural language voice user interfaces (NLVUI). More specifically, the invention concerns a phrase-based modeling of generic structures of verbal interaction and use of these models for the purpose of automating part of the design of such grammar networks.
Owner:NANT HLDG IP LLC
Correcting substitution errors during automatic speech recognition
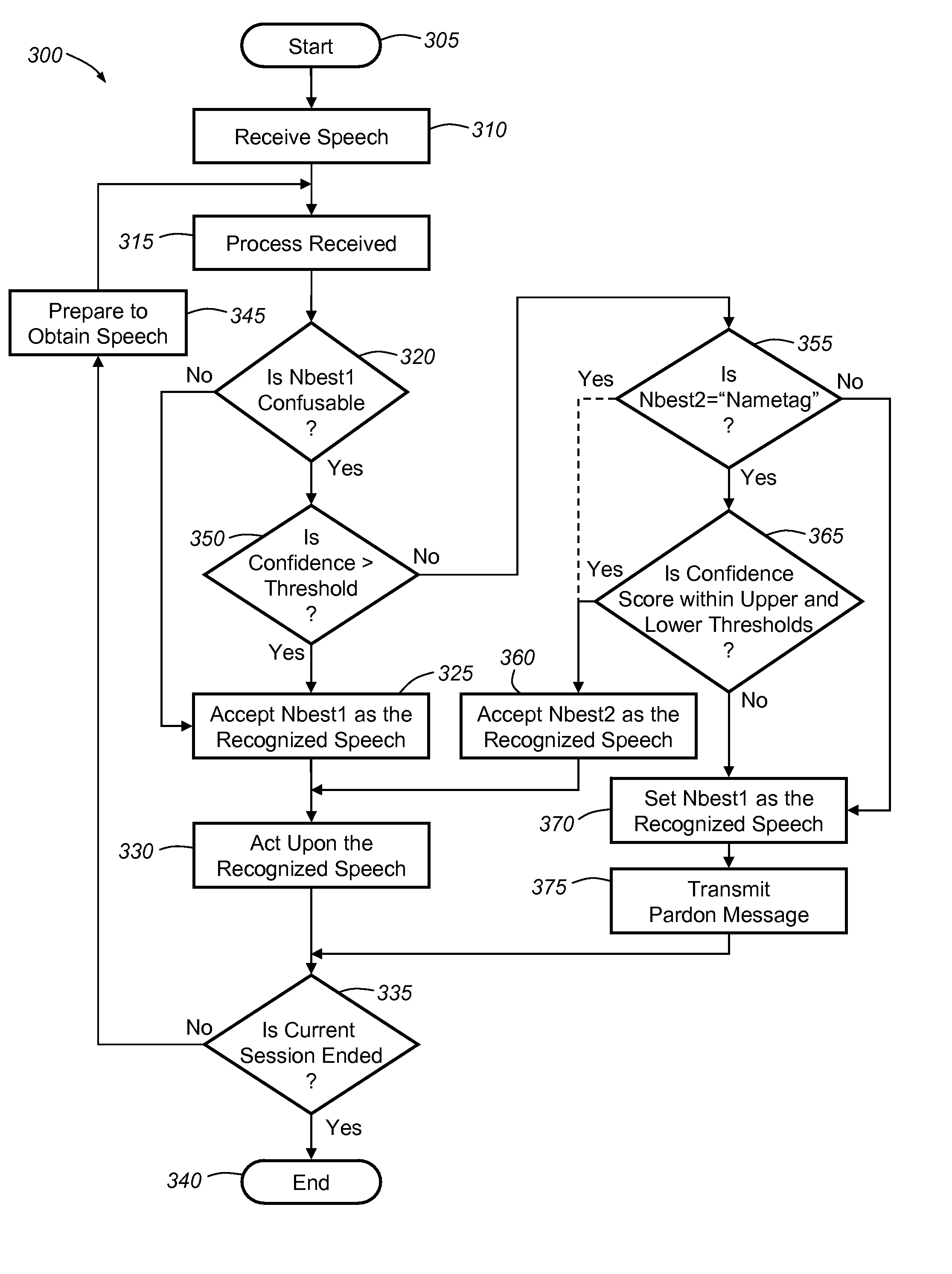
A speech recognition method includes the steps of receiving input speech containing vocabulary, processing the input speech with a grammar to obtain N-best hypotheses and associated parameter values, and determining whether a first-best hypothesis of the N-best hypotheses is confusable with any vocabulary within the grammar. The first-best hypothesis is accepted as recognized speech corresponding to the received input speech if the first-best hypothesis is not determined to be confusable with any vocabulary within the grammar. Where the first-best hypothesis is determined to be confusable, at least one parameter value of the first-best hypothesis can be compared to at least one threshold value. The first-best hypothesis can be accepted as recognized speech corresponding to the received input speech, if the parameter value of the first-best hypothesis is greater than the threshold value.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC
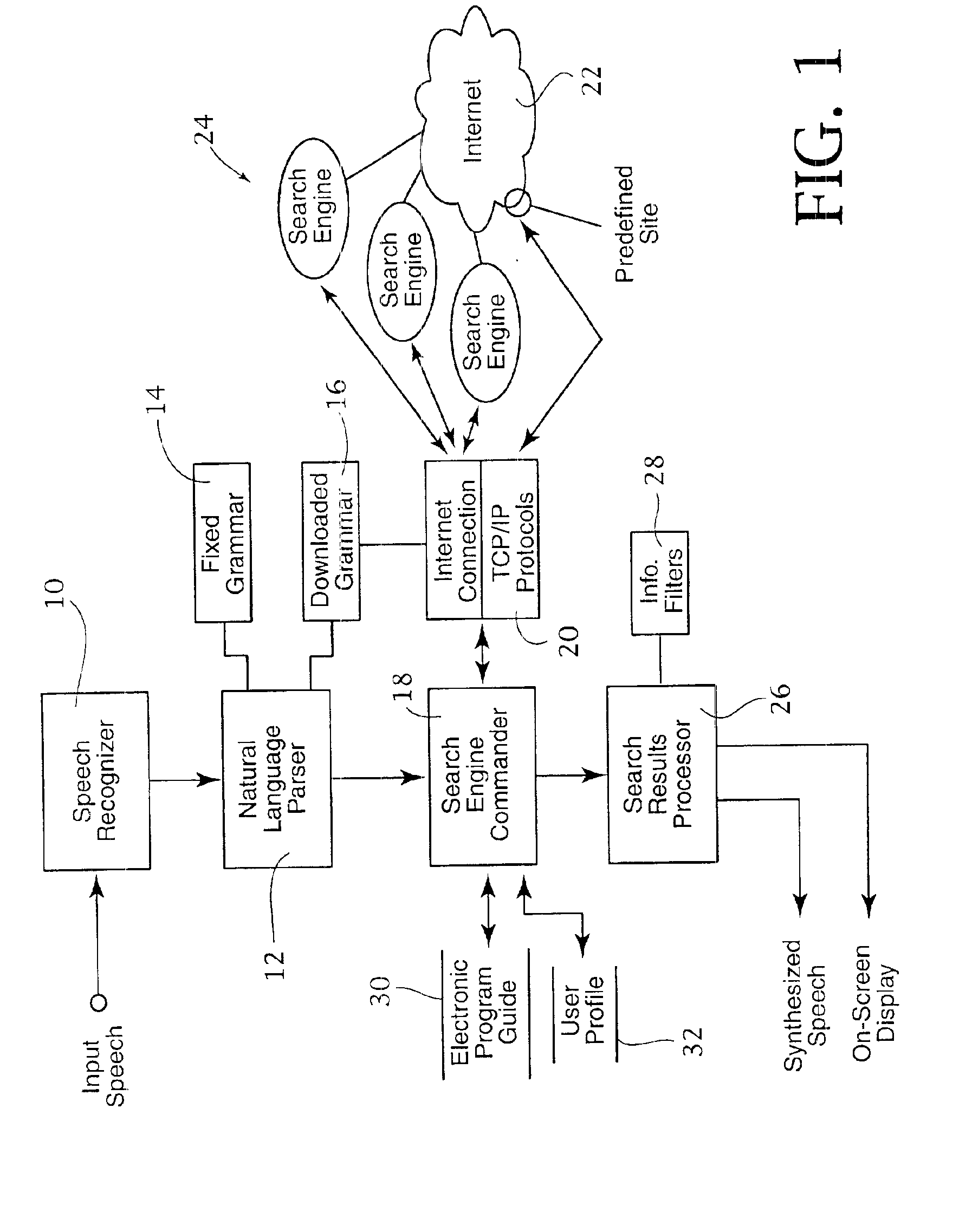
System and method for assessing TV-related information over the internet
InactiveUS6901366B1Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsData ingestionThe Internet
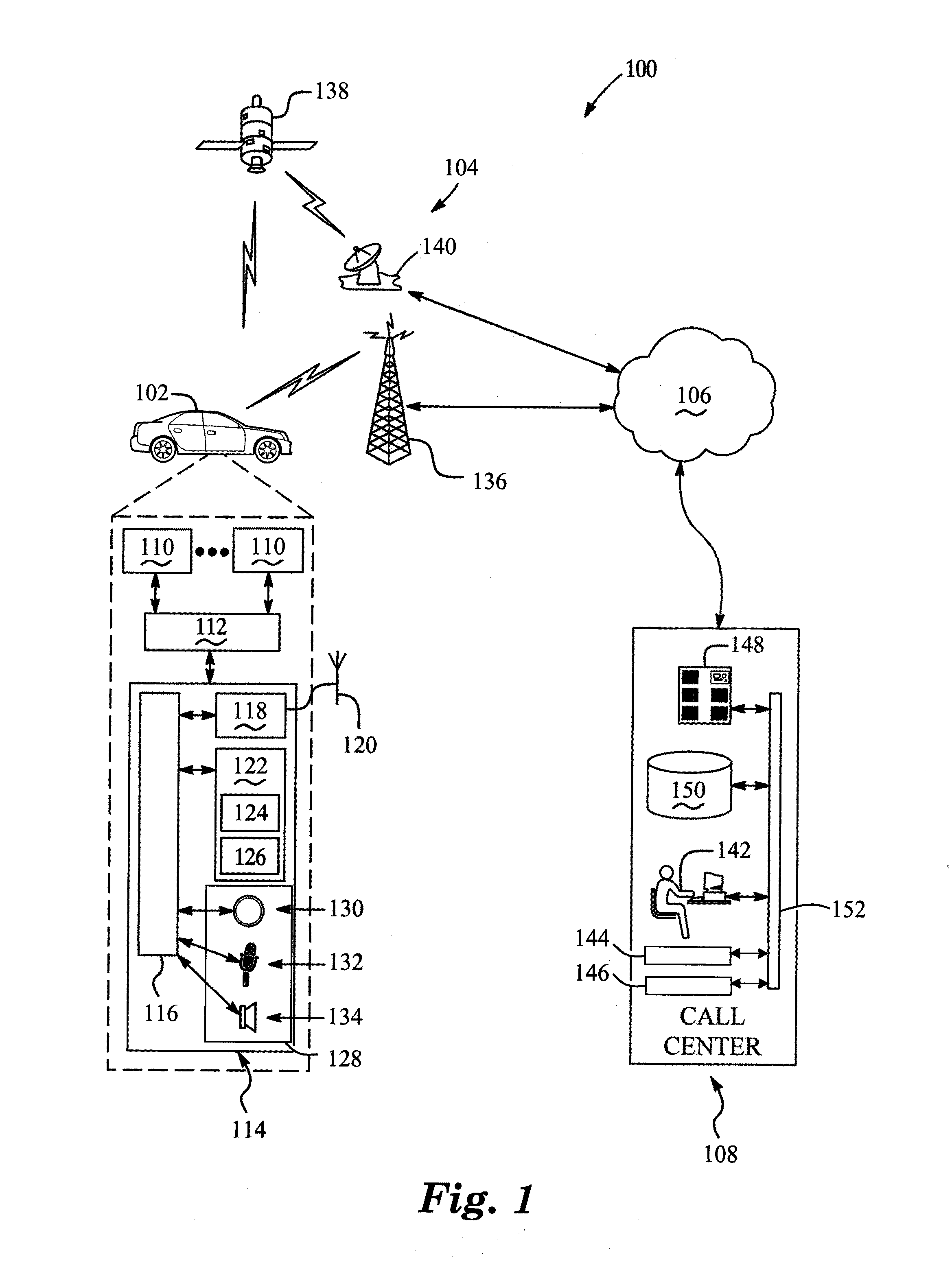
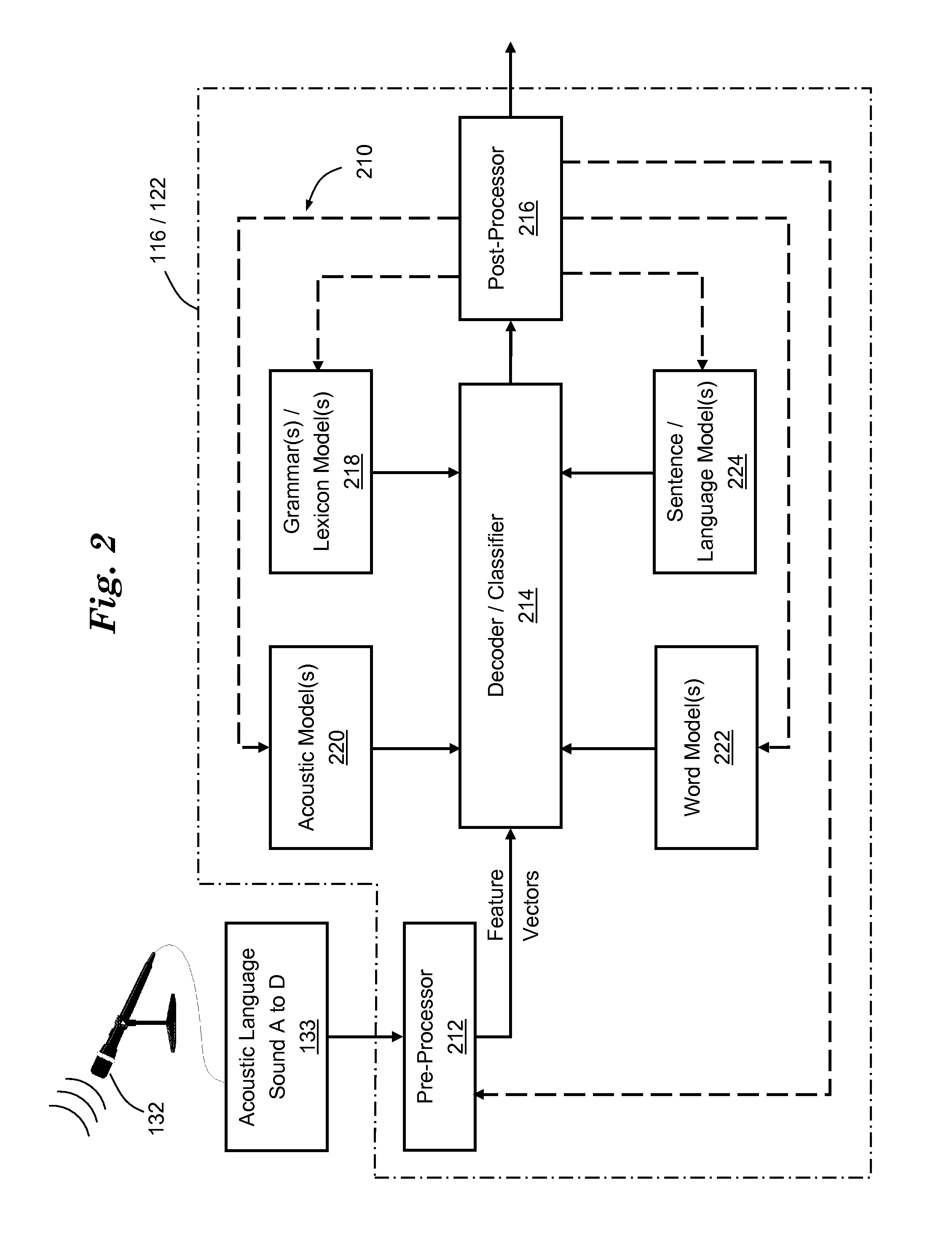
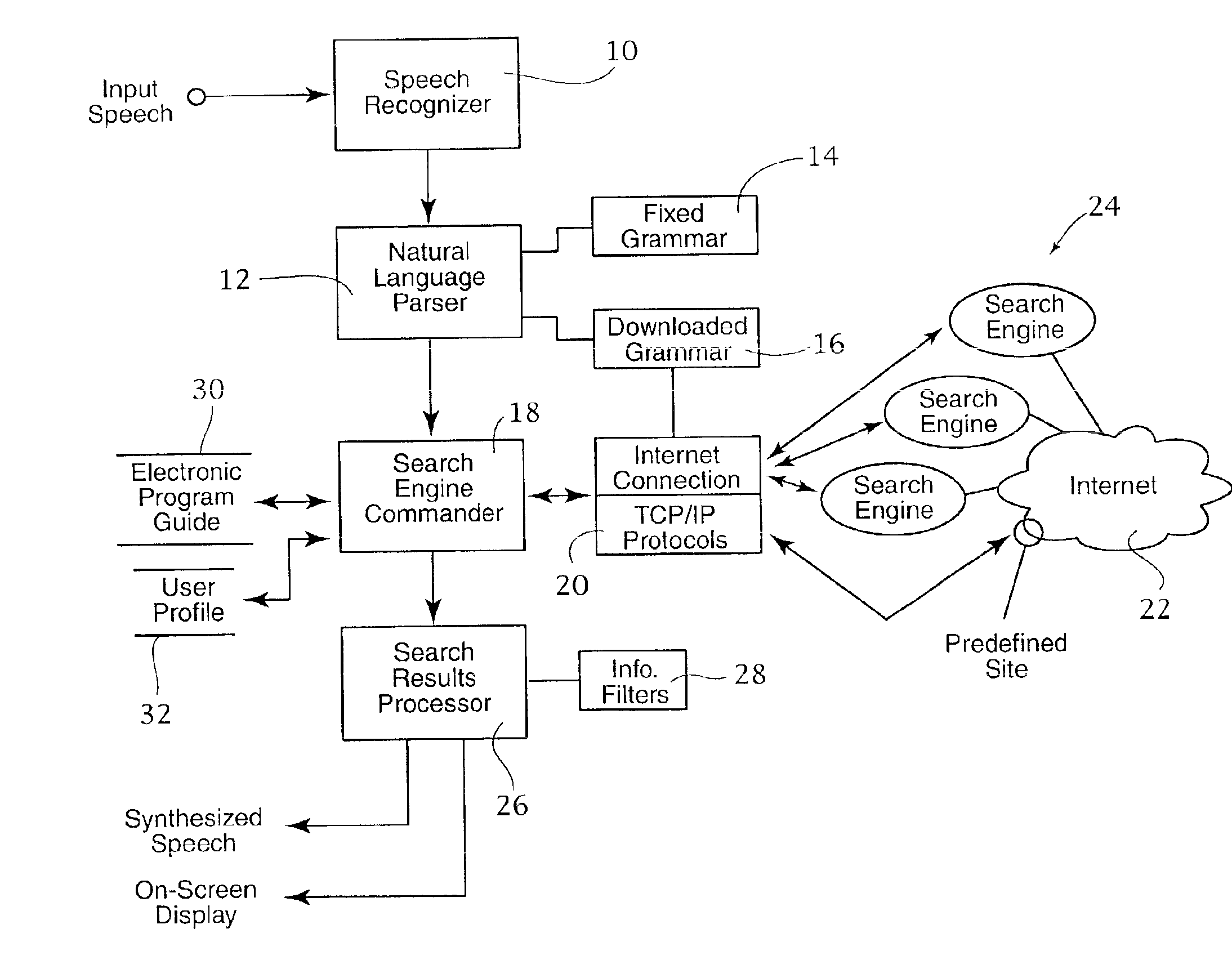
The system retrieves information from the internet using multiple search engines that are simultaneously launched by the search engine commander. The commander is responsive to a speech-enabled system including a speech recognizer and natural language parser. The user speaks to the system in natural language requests, and the parser extracts the semantic content from the user's speech, based on a set of goal oriented grammars. The preferred system includes a fixed grammar and an updatable or downloaded grammar, allowing the system to be used without extensive training and yet capable of being customized for a particular user's purposes. Results obtained from the search engines are filtered based on information extracted from an electronic program guide and from prestored user profile data. The results may be displayed on screen or through synthesized speech.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com