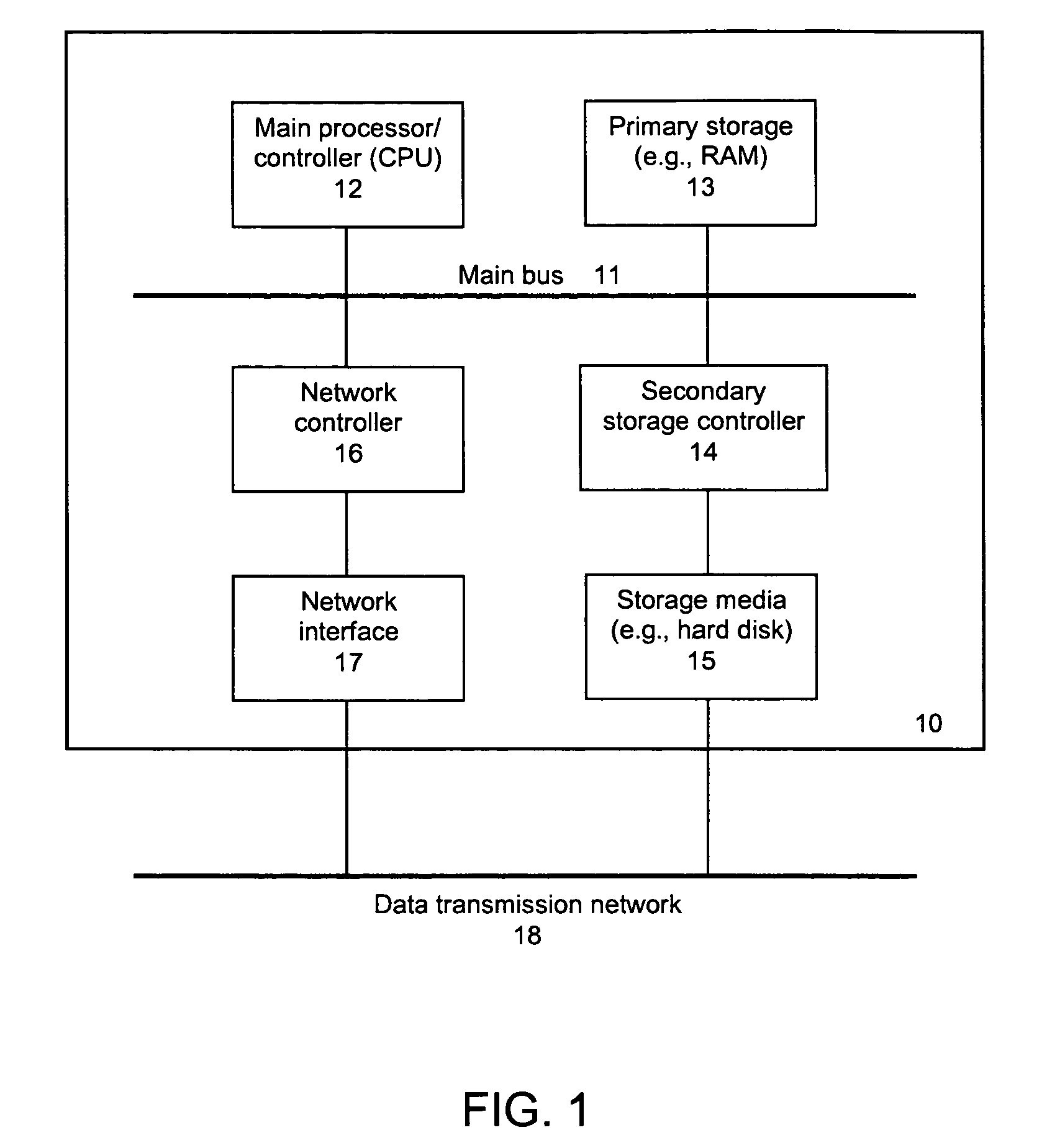
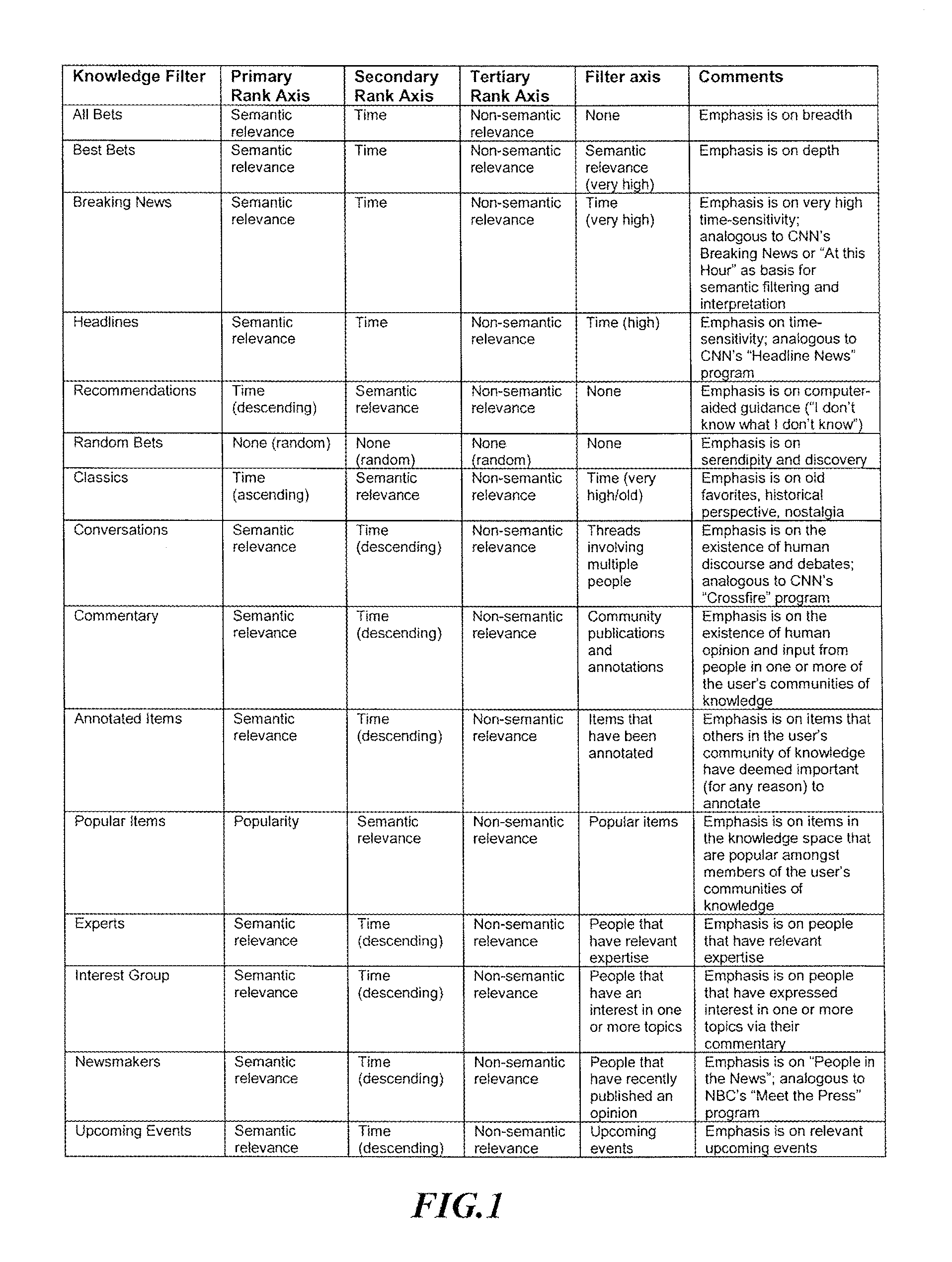
Patents
Literature
84 results about "Semantic property" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semantic properties or meaning properties are those aspects of a linguistic unit, such as a morpheme, word, or sentence, that contribute to the meaning of that unit. Basic semantic properties include being meaningful or meaningless – for example, whether a given word is part of a language's lexicon with a generally understood meaning; polysemy, having multiple, typically related, meanings; ambiguity, having meanings which aren't necessarily related; and anomaly, where the elements of a unit are semantically incompatible with each other, although possibly grammatically sound. Beyond the expression itself, there are higher-level semantic relations that describe the relationship between units: these include synonymy, antonymy, and hyponymy.
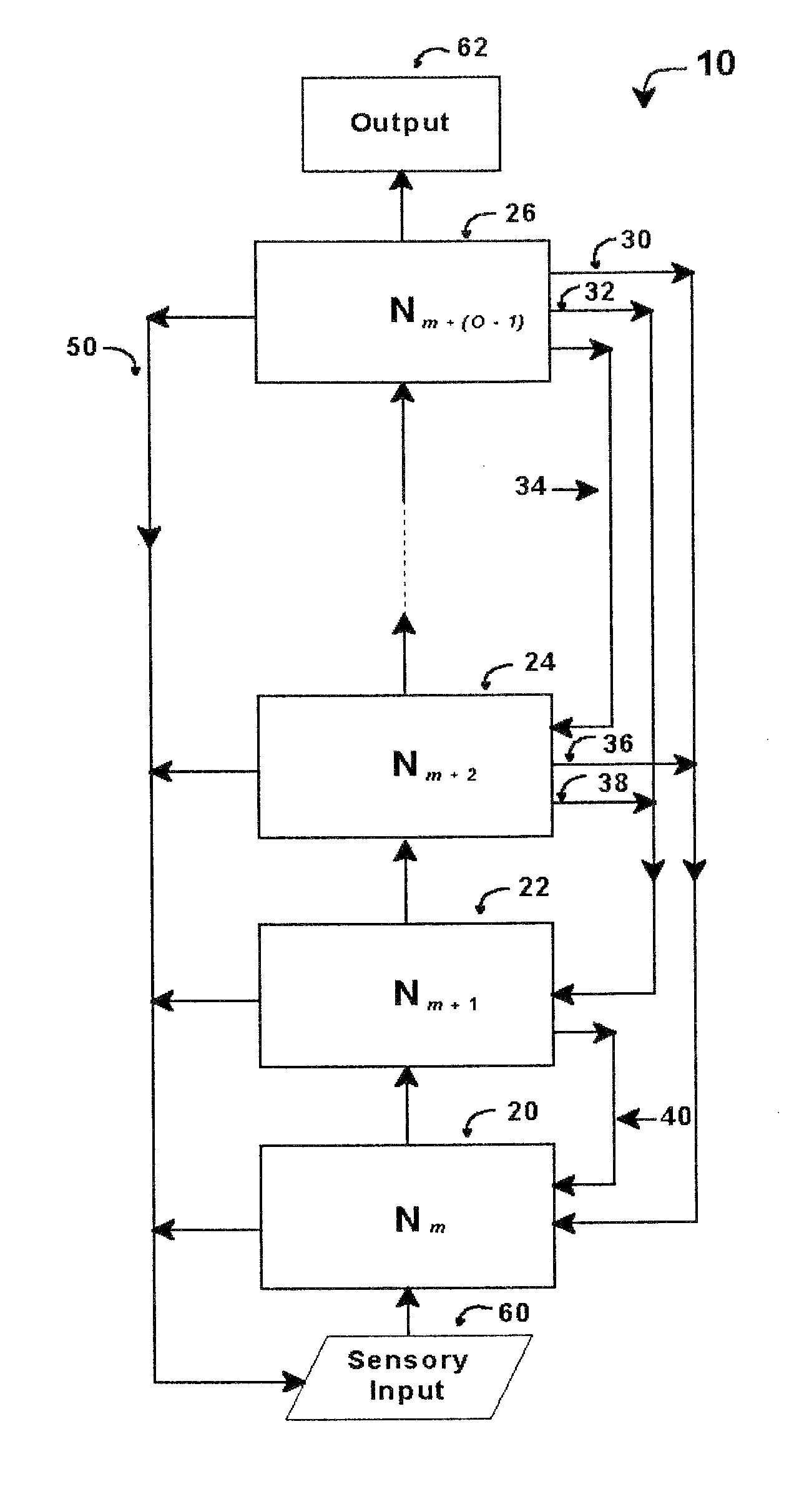
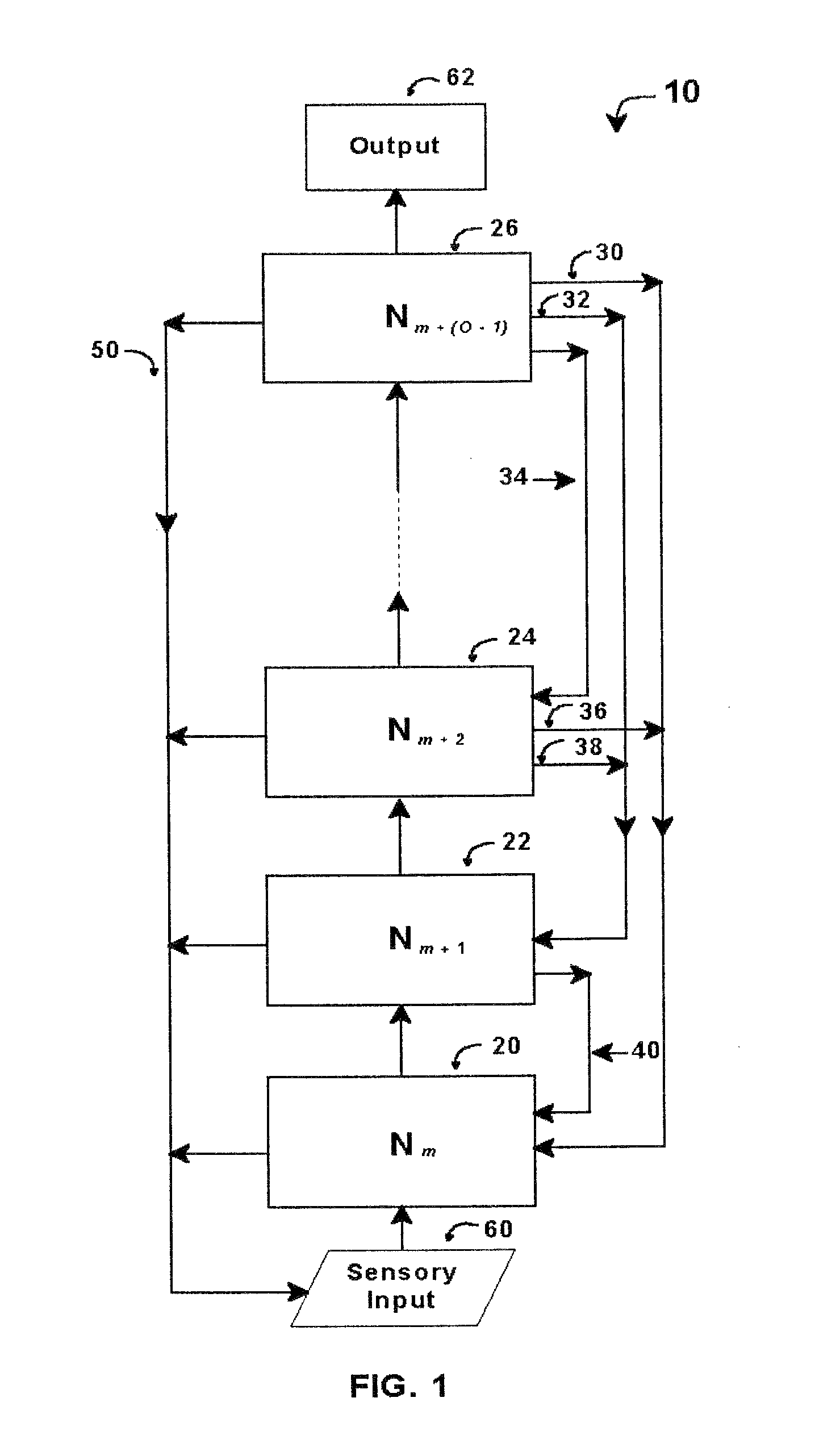
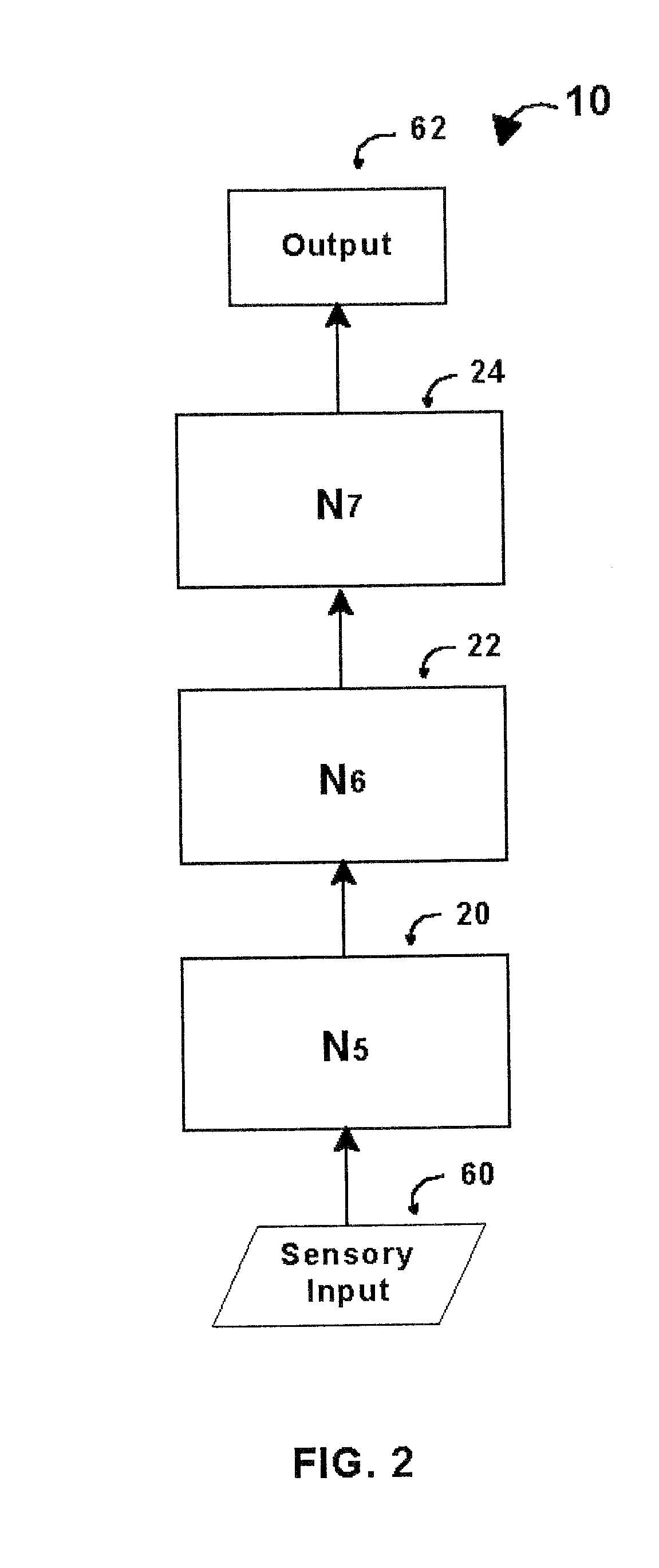
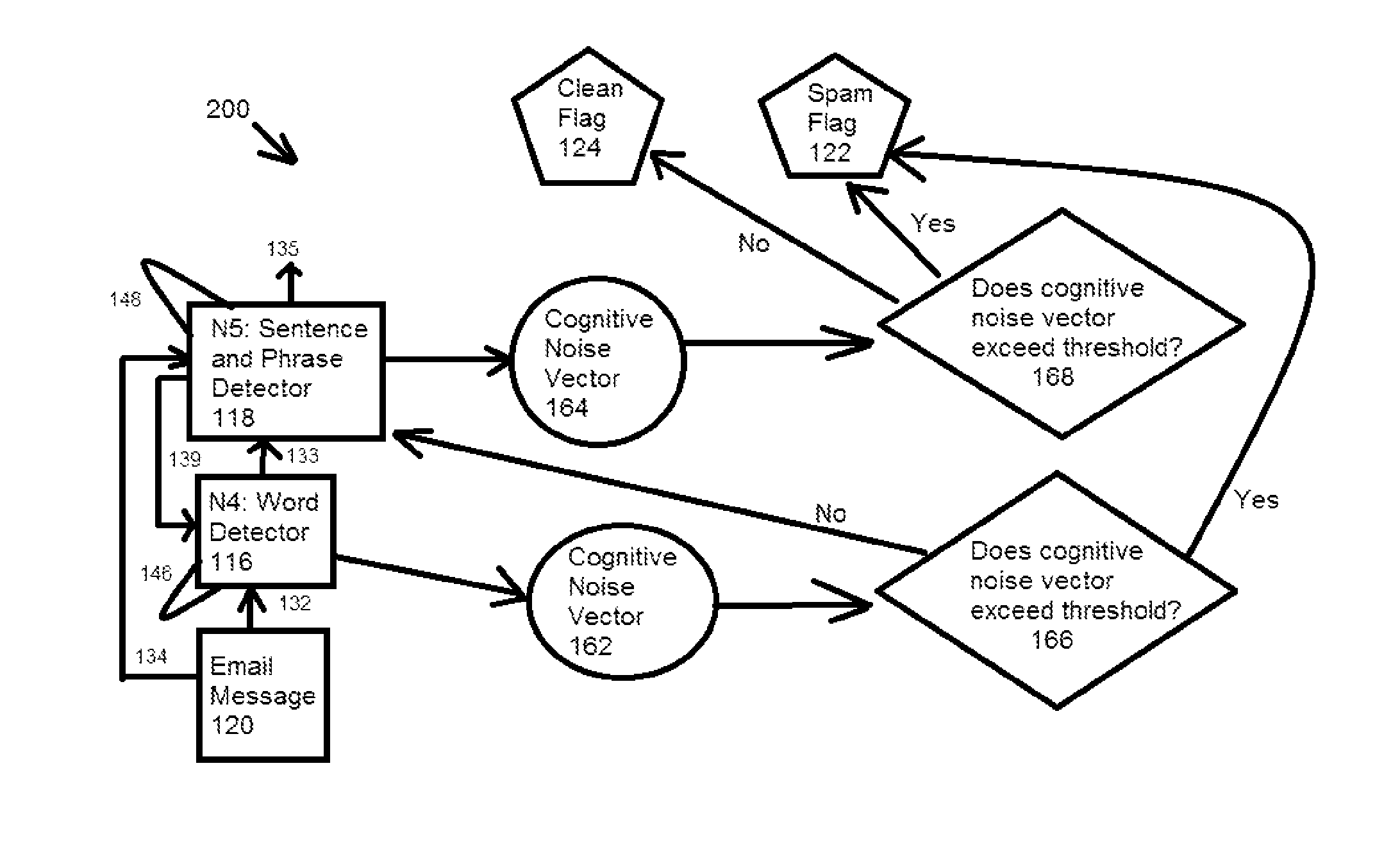
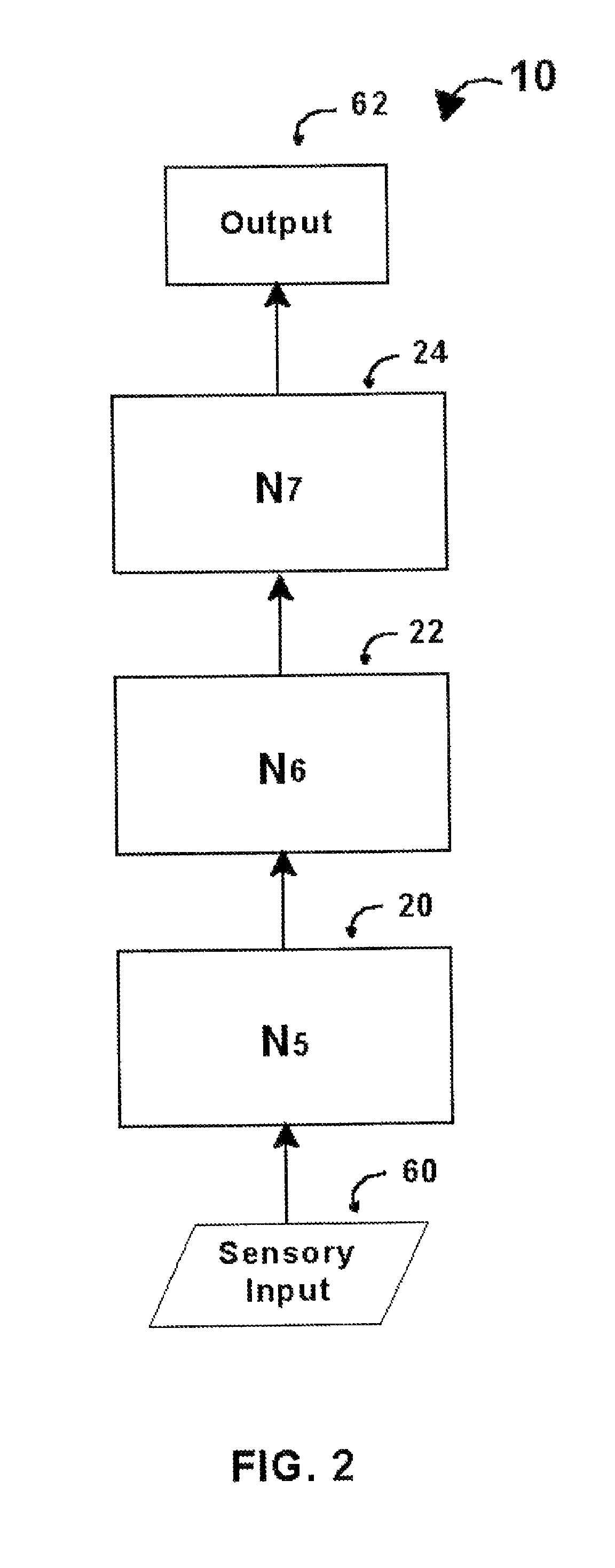
Intelligent control with hierarchical stacked neural networks
ActiveUS8775341B1Increased complexityComplex mathematical operationDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisSemantic propertyNerve network
A system and method of detecting an aberrant message is provided. An ordered set of words within the message is detected. The set of words found within the message is linked to a corresponding set of expected words, the set of expected words having semantic attributes. A set of grammatical structures represented in the message is detected, based on the ordered set of words and the semantic attributes of the corresponding set of expected words. A cognitive noise vector comprising a quantitative measure of a deviation between grammatical structures represented in the message and an expected measure of grammatical structures for a message of the type is then determined. The cognitive noise vector may be processed by higher levels of the neural network and / or an external processor.
Owner:COMMONS MICHAEL LAMPORT
Context-aware semantic virtual community for communication, information and knowledge management
InactiveUS20100100546A1Improved organizational information sharingIncrease searchDigital data processing detailsMultimedia data retrievalManagement toolApplication software
A method for creation of a semantic information management environment, said method comprised of steps of: providing said semantic information environment consisting of an architecture partitioned according to the classification of the use of natural language by information scale, dynamical properties, or semantic classifications; detection, classification, and storage of semantic and contextual information detected and stored by recording of observed contextual parameters associated with events in said semantic information management environment; said interactions including the use of information management or electronic communication applications embedded or linked to said architecture, or separate from said architecture; said observations including the use of natural language as parameters that have specific semantic properties; detection, classification and storage of use of natural language in said semantic information environment; representation of semantic processes containing said detected, classified, and stored contextual information and natural language use in said semantic information environment; said representations of semantic processes used to link and associate natural language use with objects, entities, facts, communication, information, and digital files in said semantic information environment; providing said users of said semantic information environment with information and knowledge management tools, reports, representations, and interfaces that utilize said semantic process representations.
Owner:KOHLER STEVEN FORREST
Multimedia archive description scheme
InactiveUS6941325B1Multimedia data indexingDrawing from basic elementsSemantic propertyDescription scheme
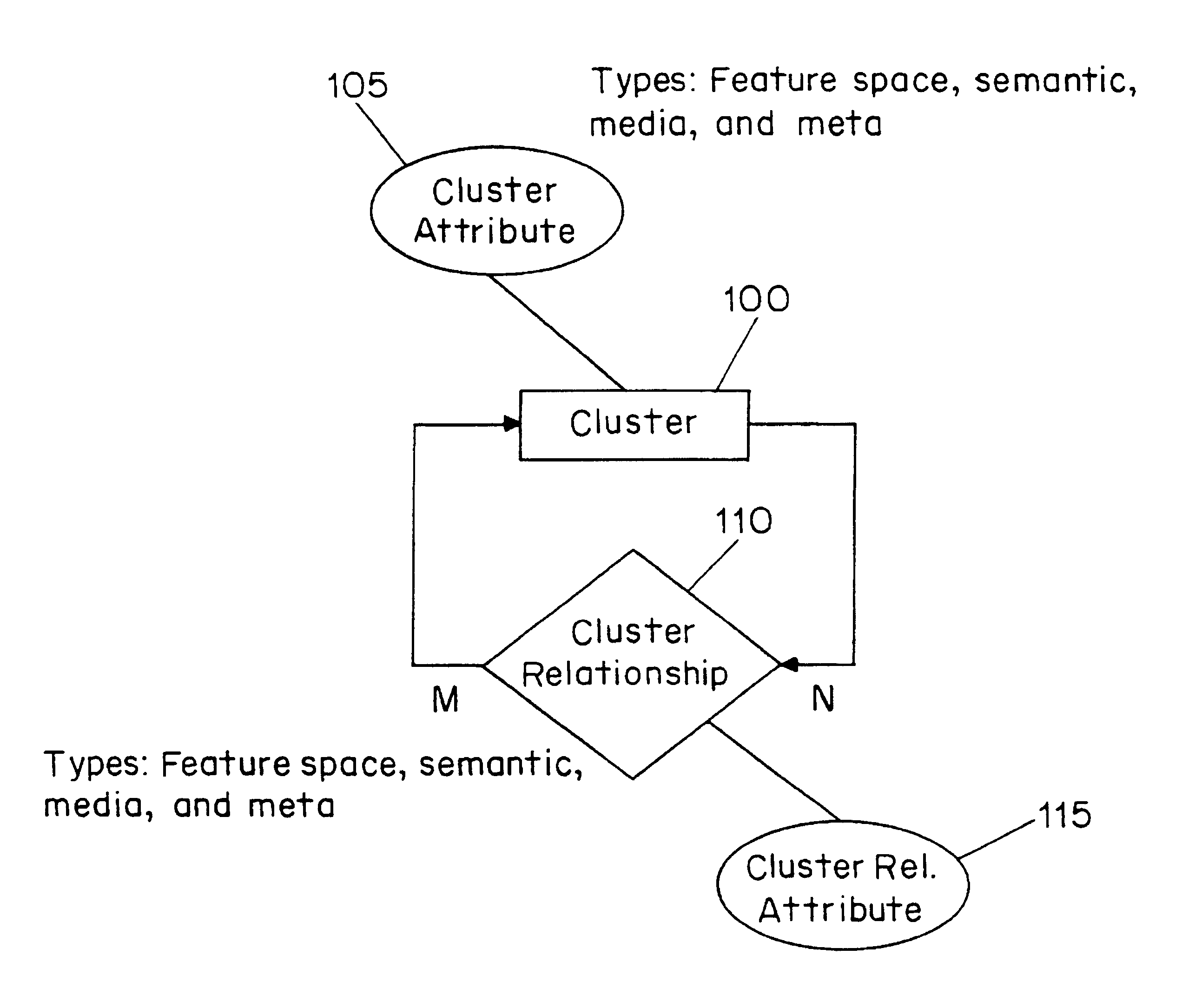
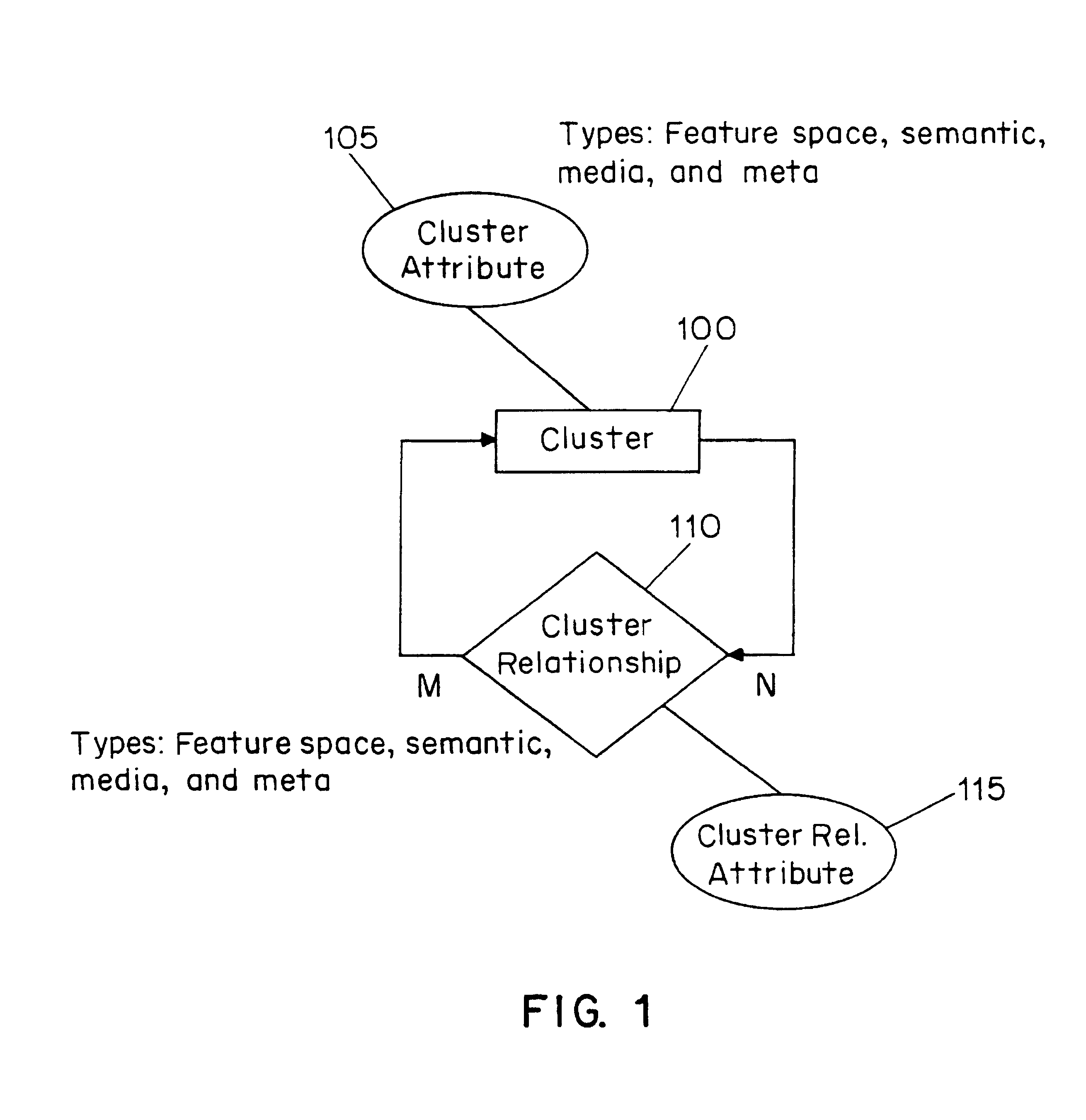
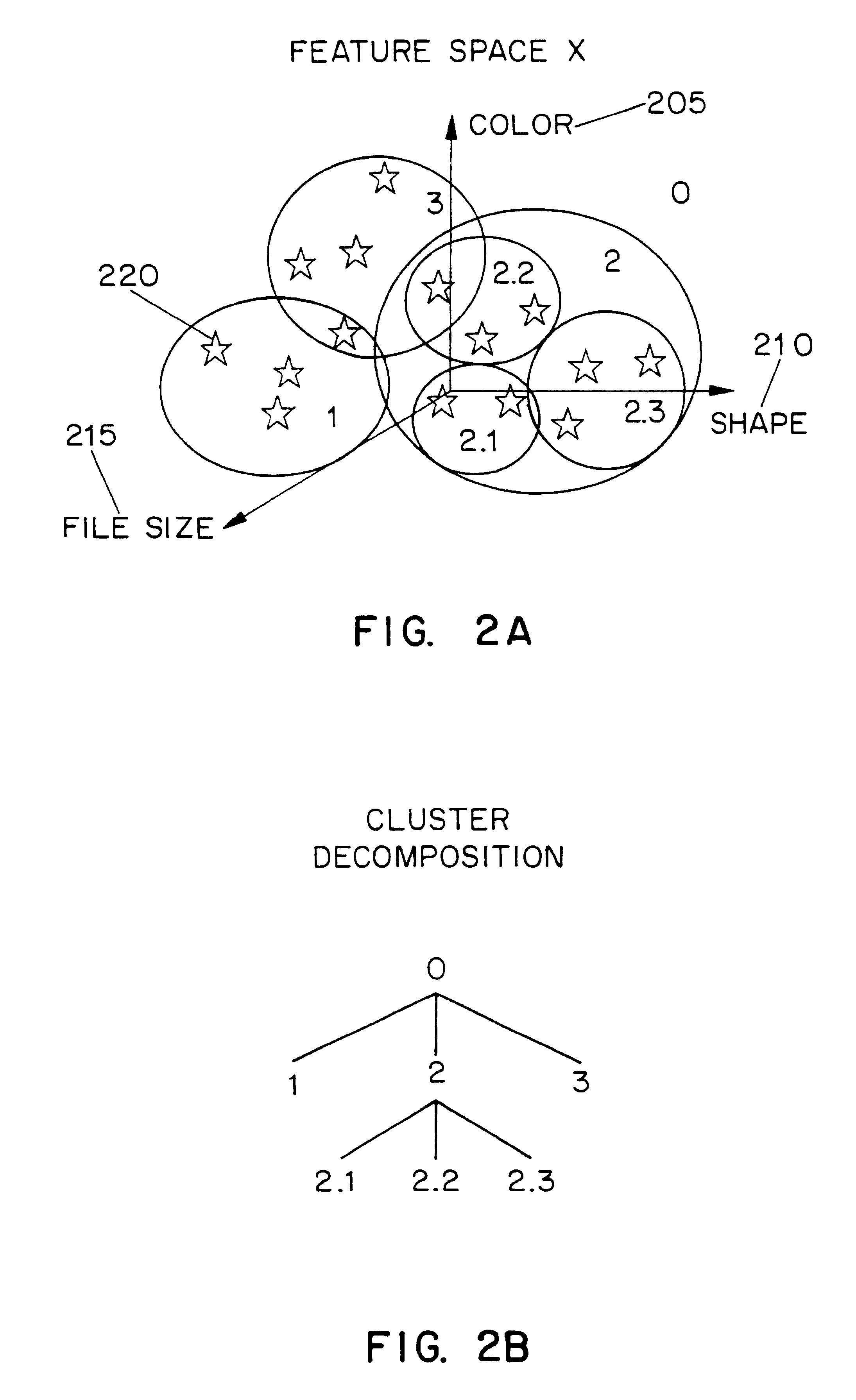
A multimedia archive description scheme is provided for characterizing a multimedia archive having records and associated record descriptions. The multimedia archive description scheme provides a data structure which relates records by similarity measures. The principle data structure in the multimedia archive description scheme is a cluster. A cluster includes one or more attributes of the records in the archive and can include one or more cluster relationships. Cluster attributes can include feature space attributes, semantic attributes, media attributes and meta attributes of the records in the archive. The cluster relationships can relate records to clusters or clusters to clusters. Cluster relationships can include feature space (syntactic) relationships, semantic relationships, media relationships and meta relationships. The multimedia archive description scheme provides an efficient form for describing a collection of records.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Methods and systems for automatically summarizing semantic properties from documents with freeform textual annotations
InactiveUS20100153318A1Improve food qualityImprove abilitiesDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingSemantic propertyText annotation
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
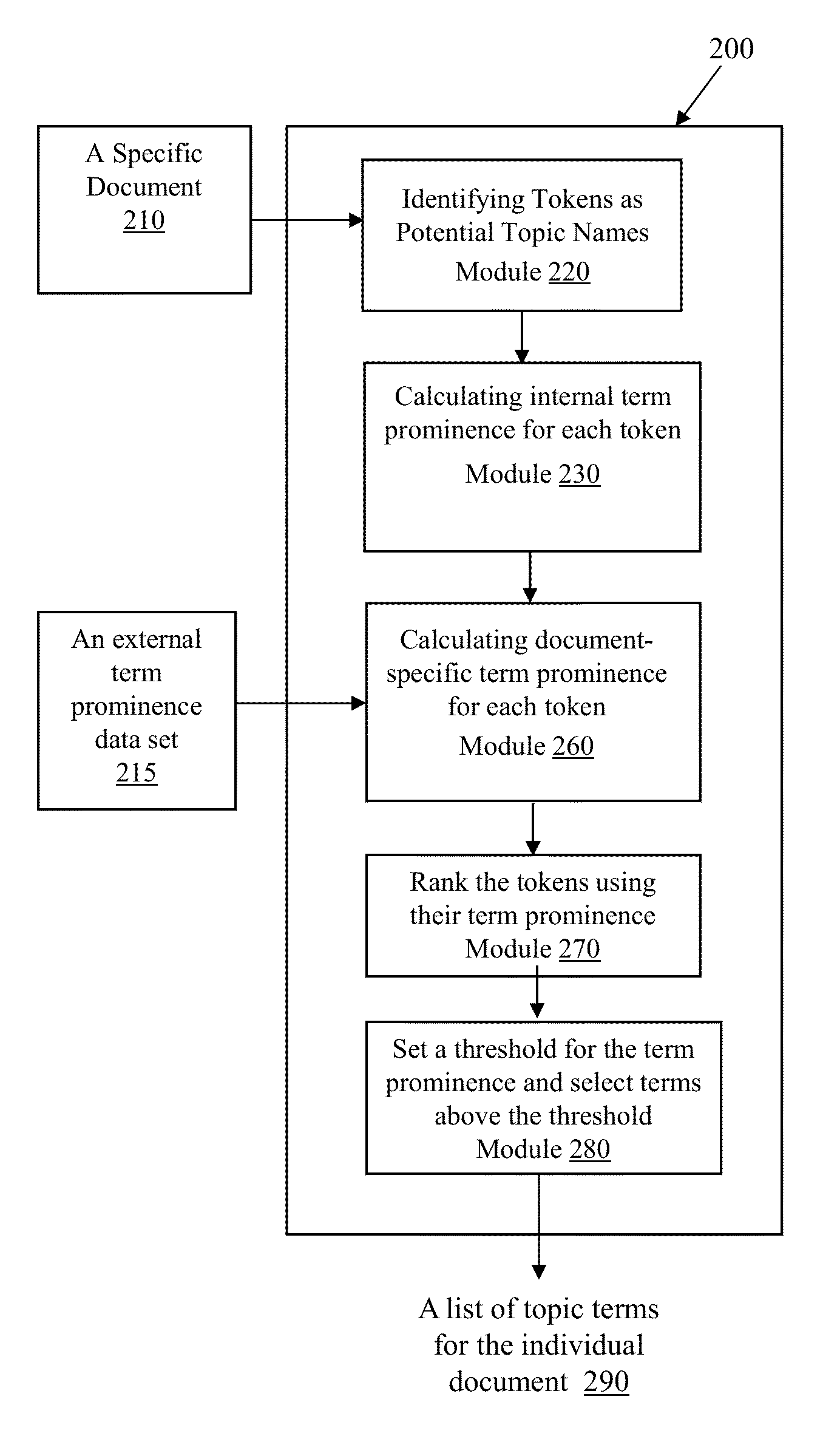
Automated topic discovery in documents and content categorization
ActiveUS9047283B1Easy to findEfficient and accurate and scalableWeb data indexingSemantic analysisSemantic propertyPart of speech
A computer-assisted method for discovering topics and categorizing contents in a document includes the steps of calculating an importance score for a term based on grammatical roles, parts of speech, and semantic attributes, selecting terms based on the importance score values of the respective terms, and outputting terms comprising the selected term to represent topics in the document, and building a category structure based on the selected terms.
Owner:LINFO IP LLC
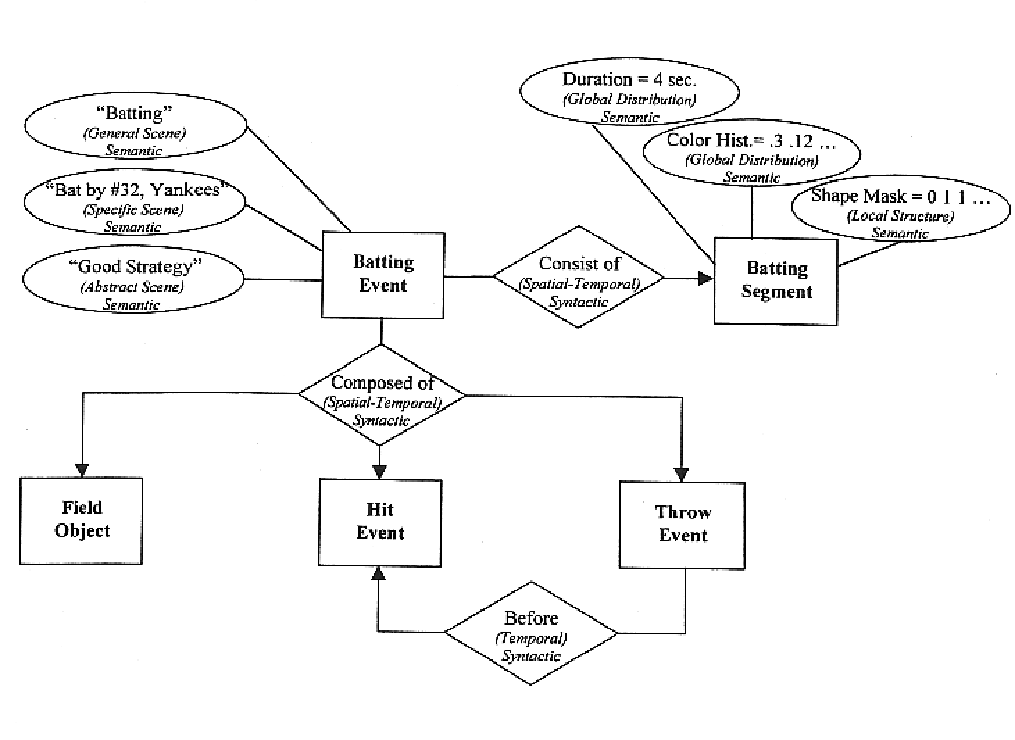
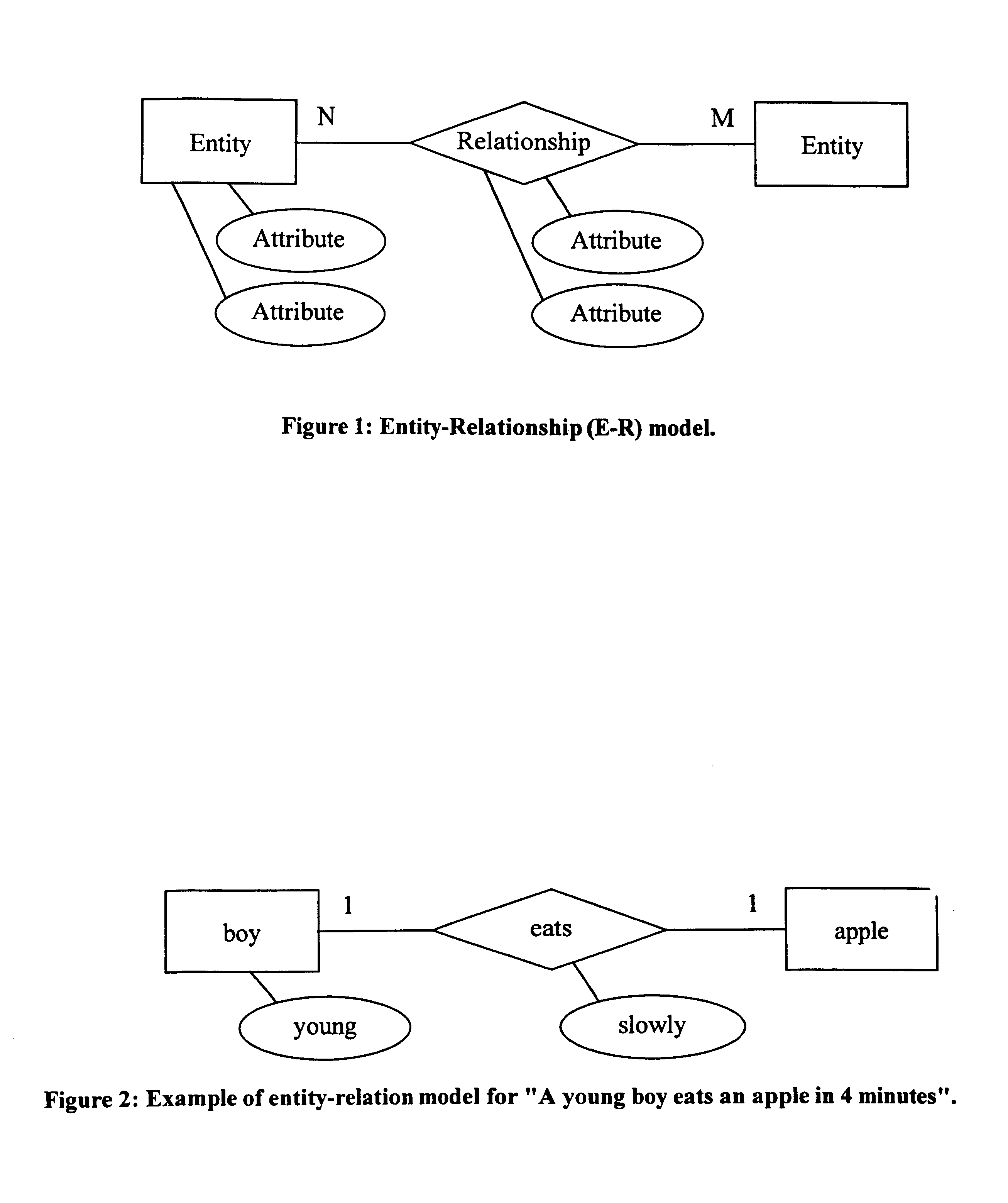
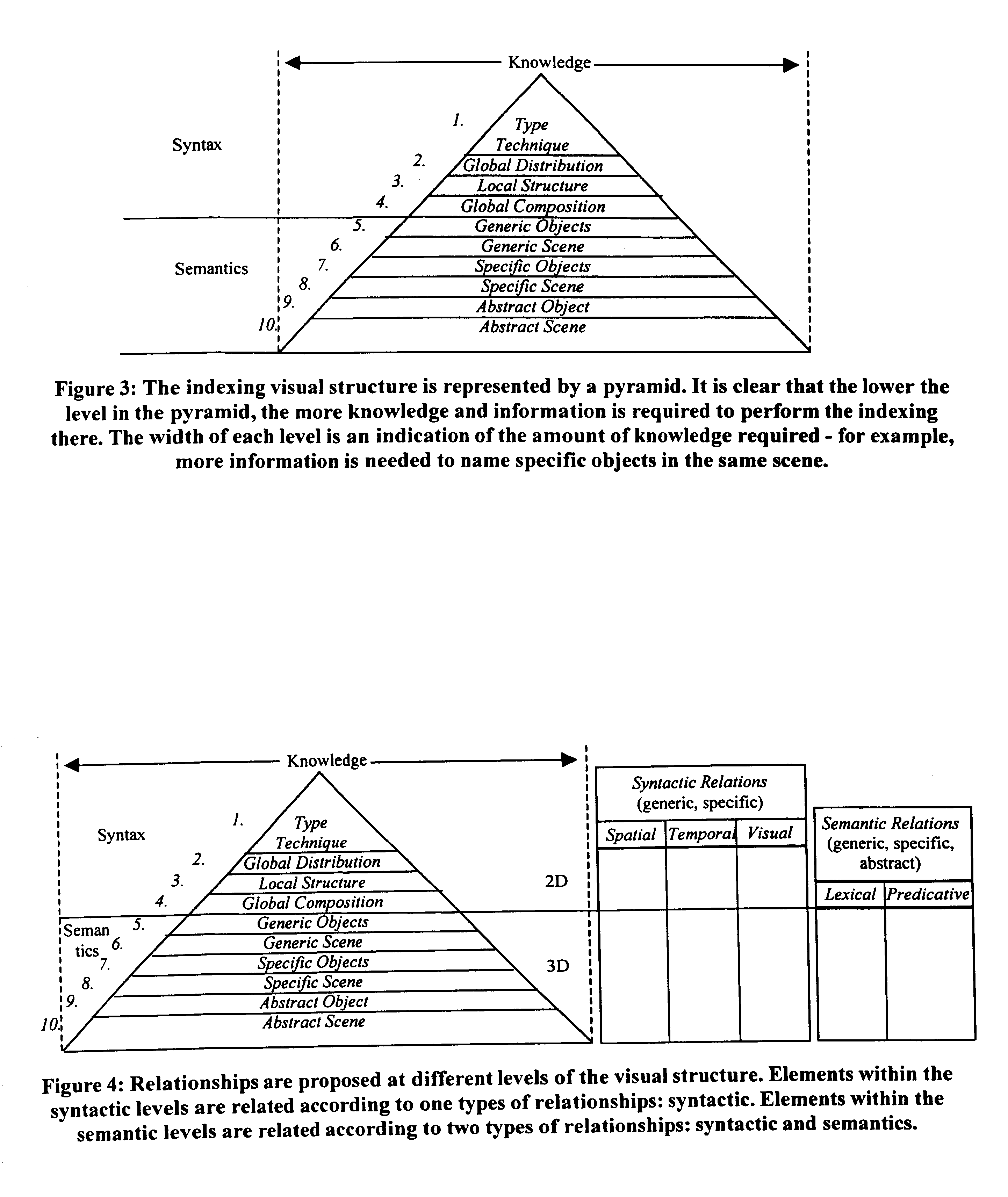
Fundamental entity-relationship models for the generic audio visual data signal description
InactiveUS6847980B1Enhanced content-sensitive general searchVideo data indexingData processing applicationsSemantic propertyData signal
An invention for generating standard description records from multimedia information. The invention utilizes fundamental entity-relation models for the Generic AV DS that classify the entities, the entity attributes, and the relationships in relevant types to describe visual data. It also involves classification of entity attributes into syntactic and semantic attributes. Syntactic attributes can be categorized into different levels: type / technique, global distribution, local structure, and global composition. Semantic attributes can be likewise discretely categorized: generic object, generic scene, specific object, specific scene, abstract object, and abstract scene. The invention further classifies entity relationships into syntactic / semantic categories. Syntactic relationship categories include spatial, temporal, and visual categories. Semantic relationship categories include lexical and predicative categories. Spatial and temporal relationships can be topological or directional; visual relationships can be global, local, or composition; lexical relationships can be synonymy, antonymy, hyponymy / hypernymy, or meronymy / holonymy; and predicative relationships can be actions (events) or states.
Owner:NAT SCI FOUND NSF
Intelligent control with hierarchical stacked neural networks
ActiveUS9053431B1Increased complexityComplex mathematical operationDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisSemantic propertyNerve network
Owner:COMMONS MICHAEL LAMPORT
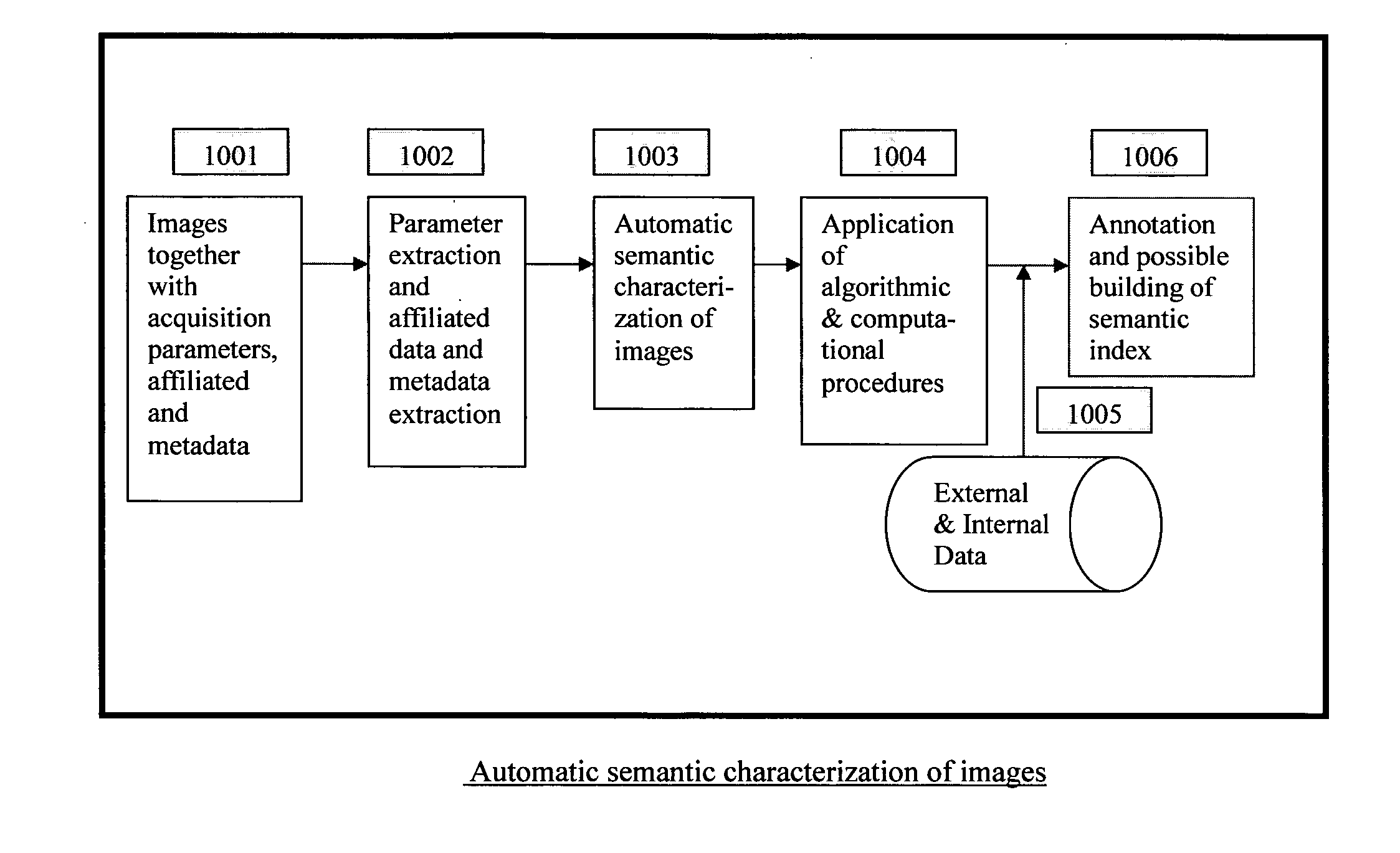
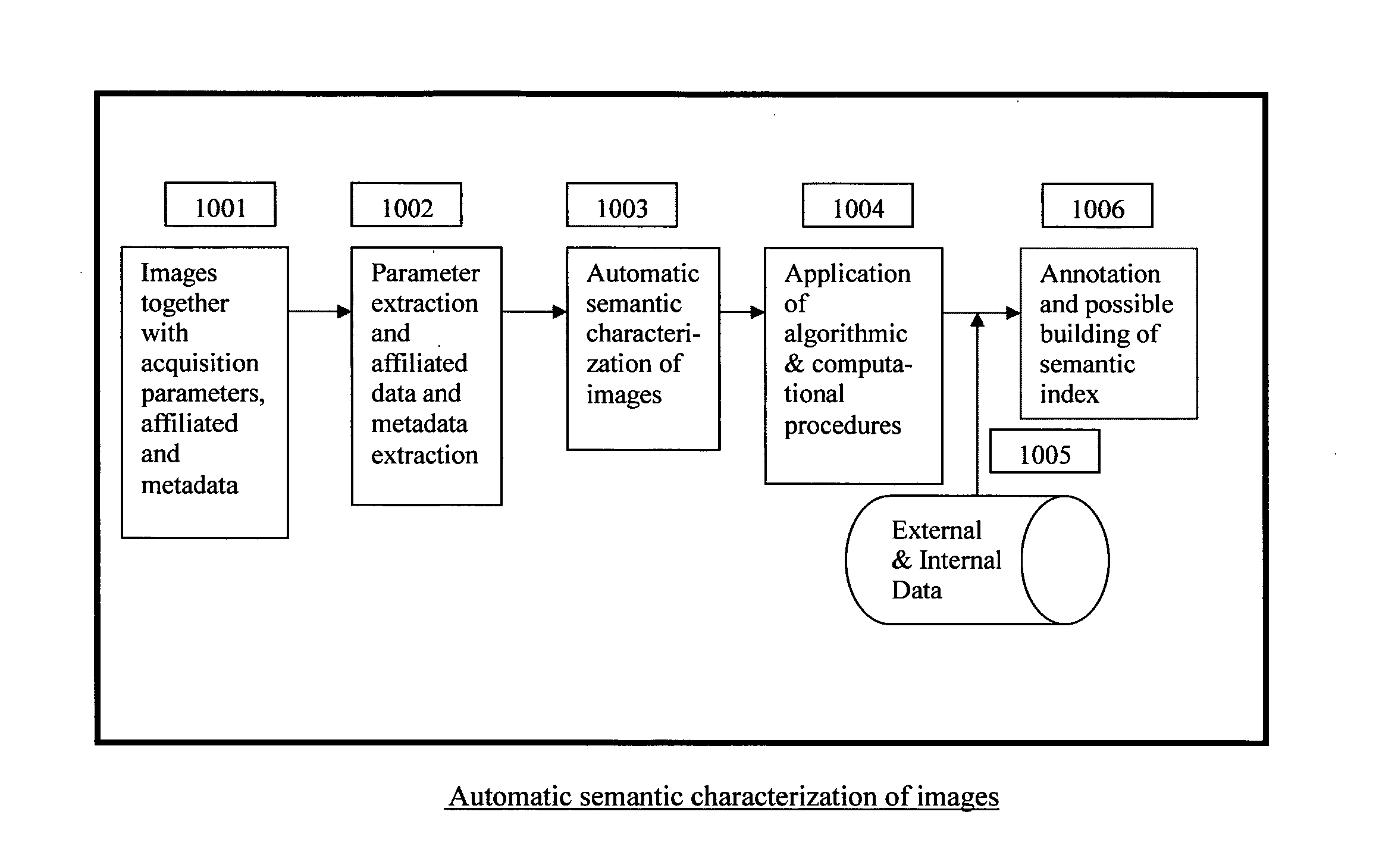
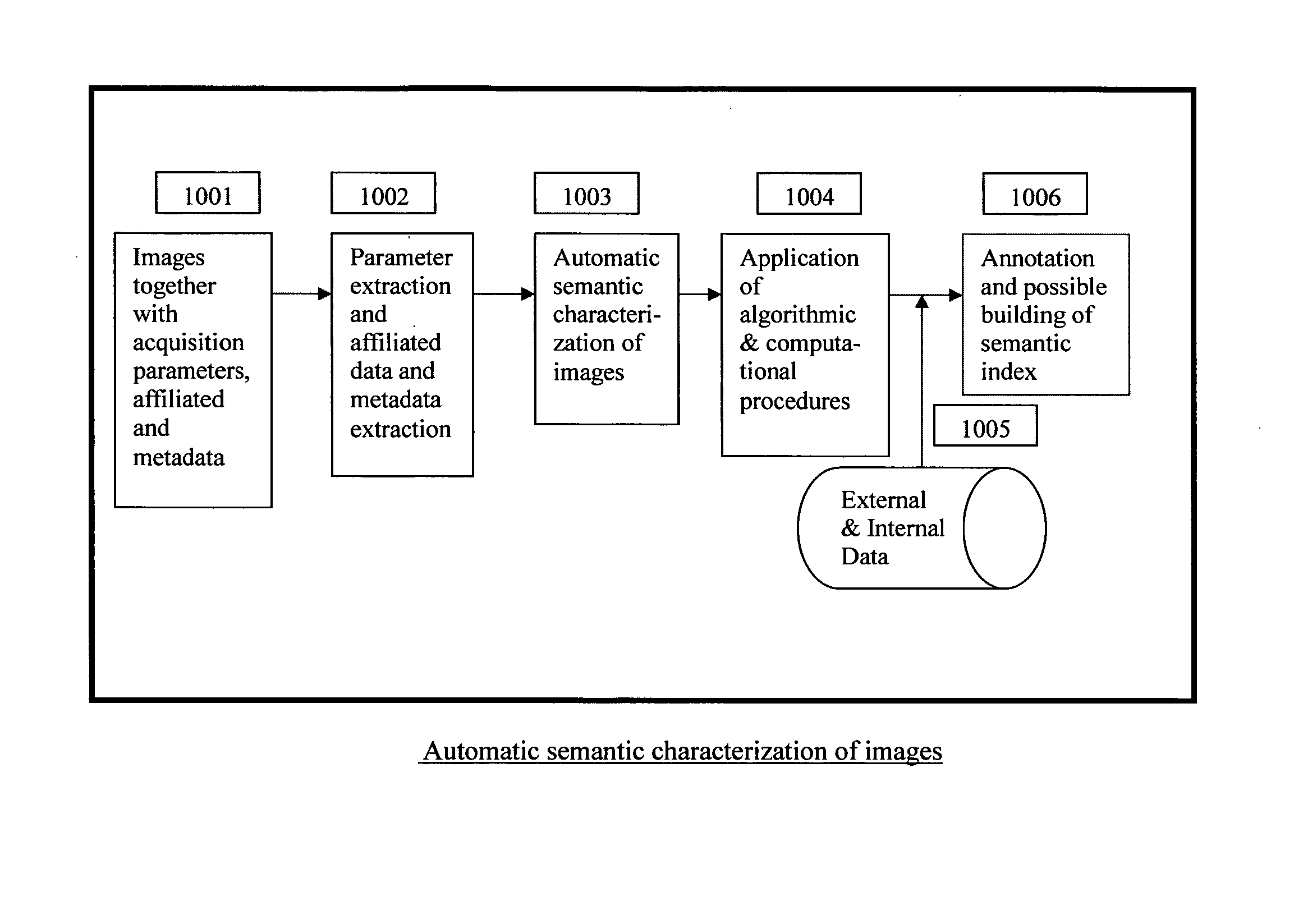
Automatic and Semi-automatic Image Classification, Annotation and Tagging Through the Use of Image Acquisition Parameters and Metadata
ActiveUS20110317885A1Improve accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMetadata still image retrievalTimestampSemi automatic
A method for characterizing image contents automatically or semi-automatically using image acquisition parameters and metadata is presented. The method establishes probabilistic and deterministic relationships between different types of metadata and the semantic attributes and contents of images. It furnishes a mechanism that enables the automatic and semi-automatic classification, annotation, tagging, indexing, searching, identification or retrieval of images based on their contents, semantic properties and metadata characteristics. The method uses, but is not limited to, image capture metadata such as focal length, exposure time, relative aperture, flash information, ISO setting, angle of view, subject distance, timestamp, GPS information as well as other forms of metadata, including but not limited to, captions, keywords, headings, tags, comments, remarks, titles which may be automatically, semi-automatically, or manually generated. The present invention can be applied to image databases, web searching, personal search, community search, broad-based or vertical search engines for internet, intranet, extranet or other usages.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
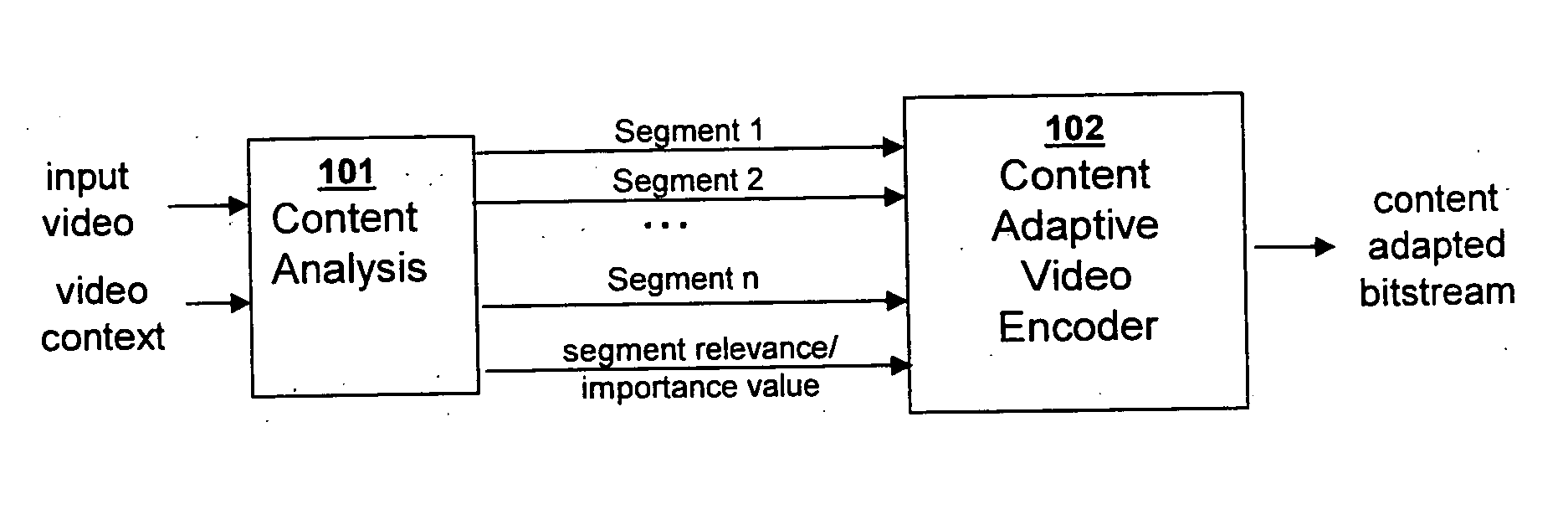
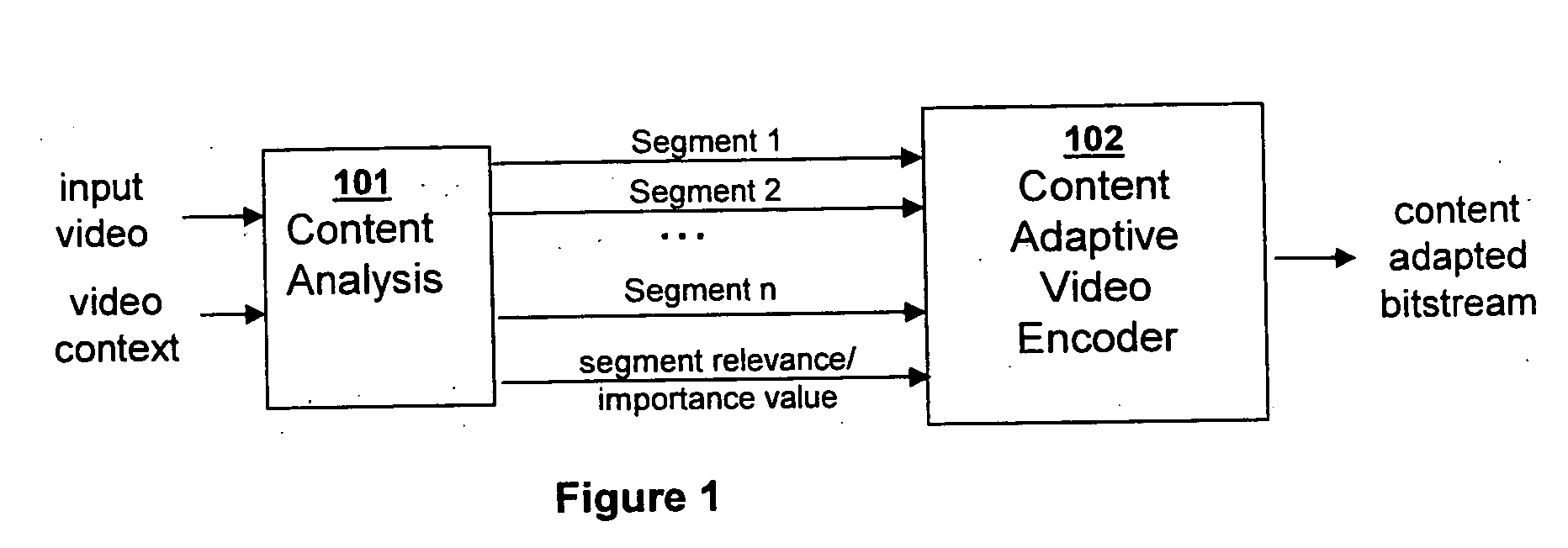
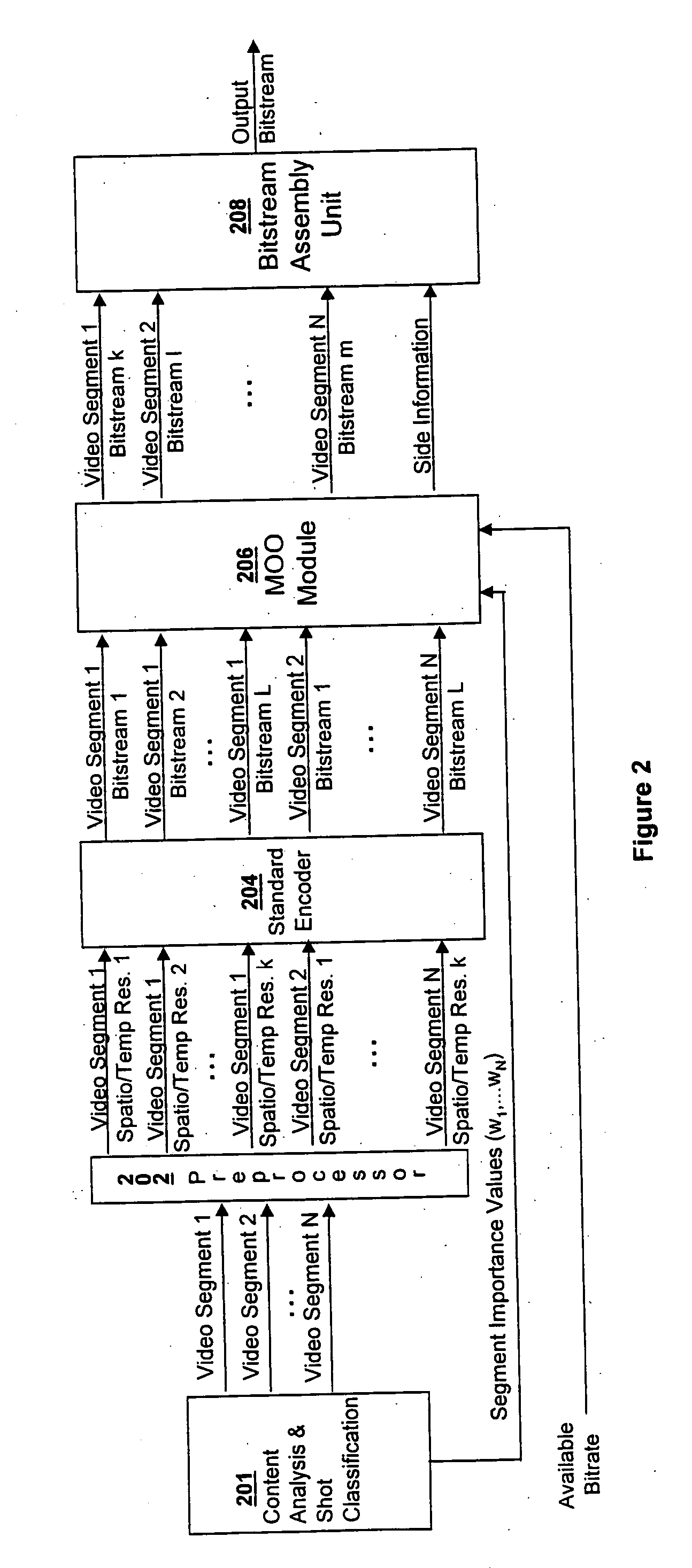
Video coding and adaptation by semantics-driven resolution control for transport and storage
InactiveUS20060188014A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSemantic propertyTemporal resolution
A method and system for modifying the spatial and / or temporal resolution and / or signal to noise ratio of temporal and / or spatial segments of compressed video based on semantic properties of the video content to adapt the compressed video size for transport and storage applications.
Owner:ARGELA TECH +1
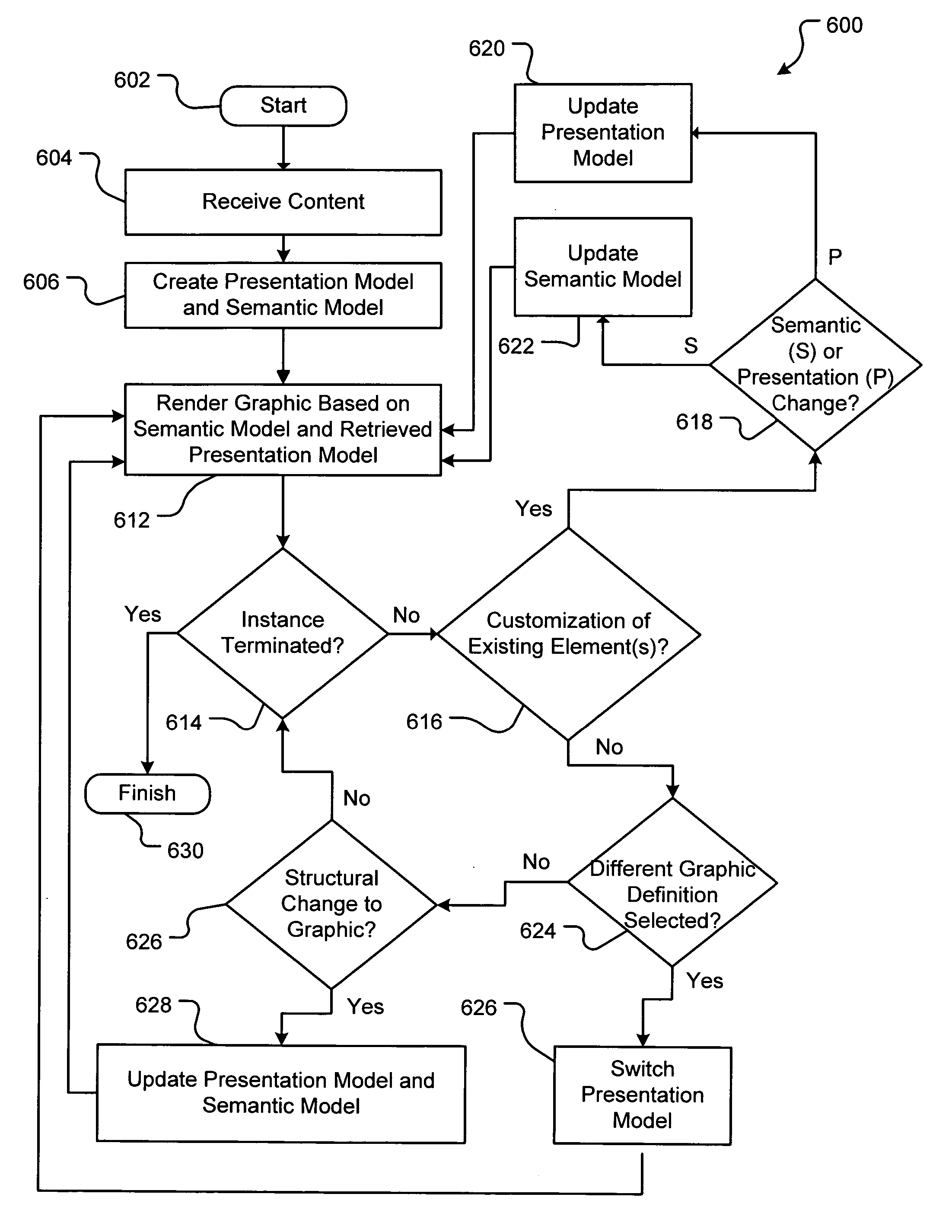
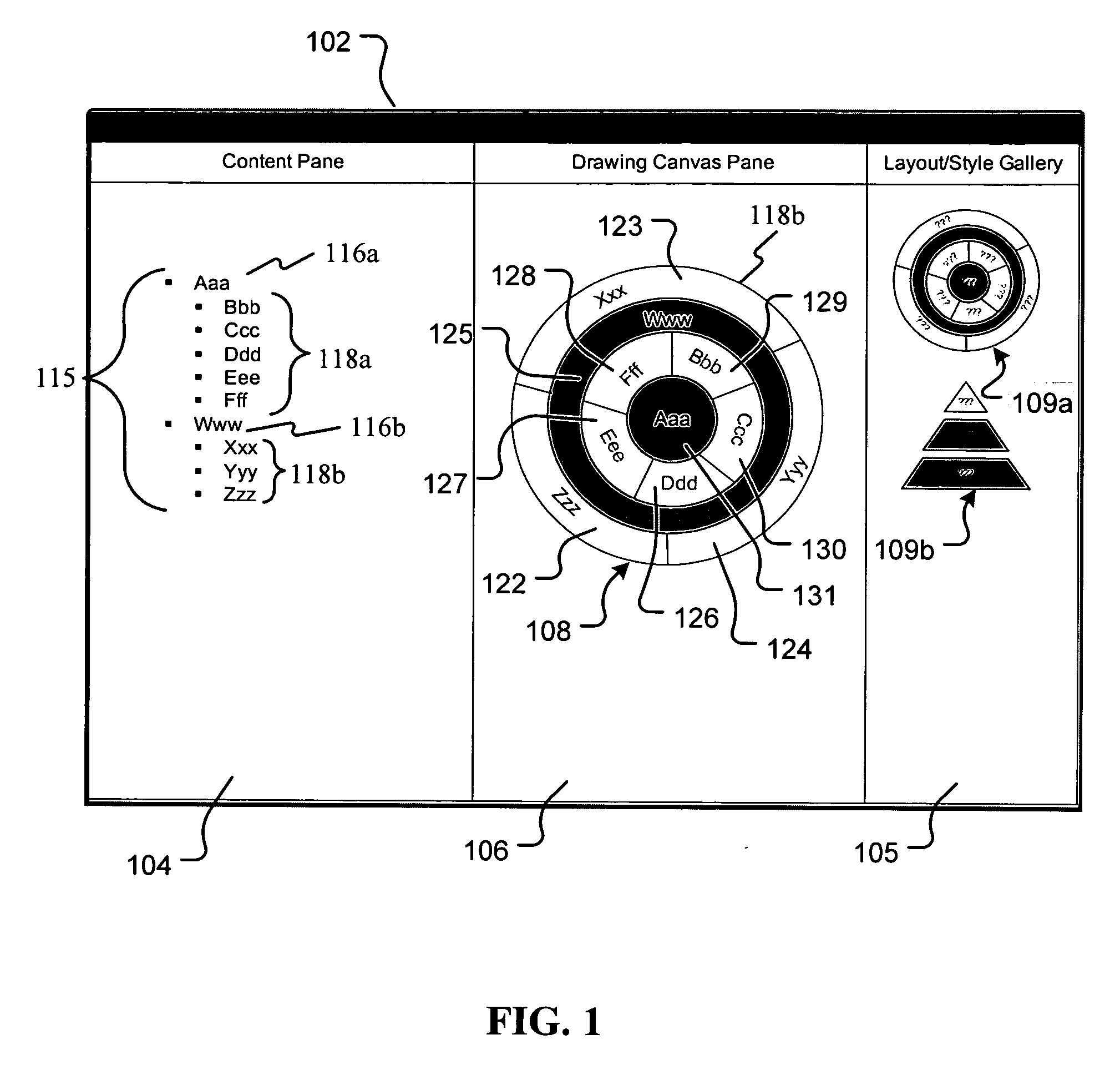
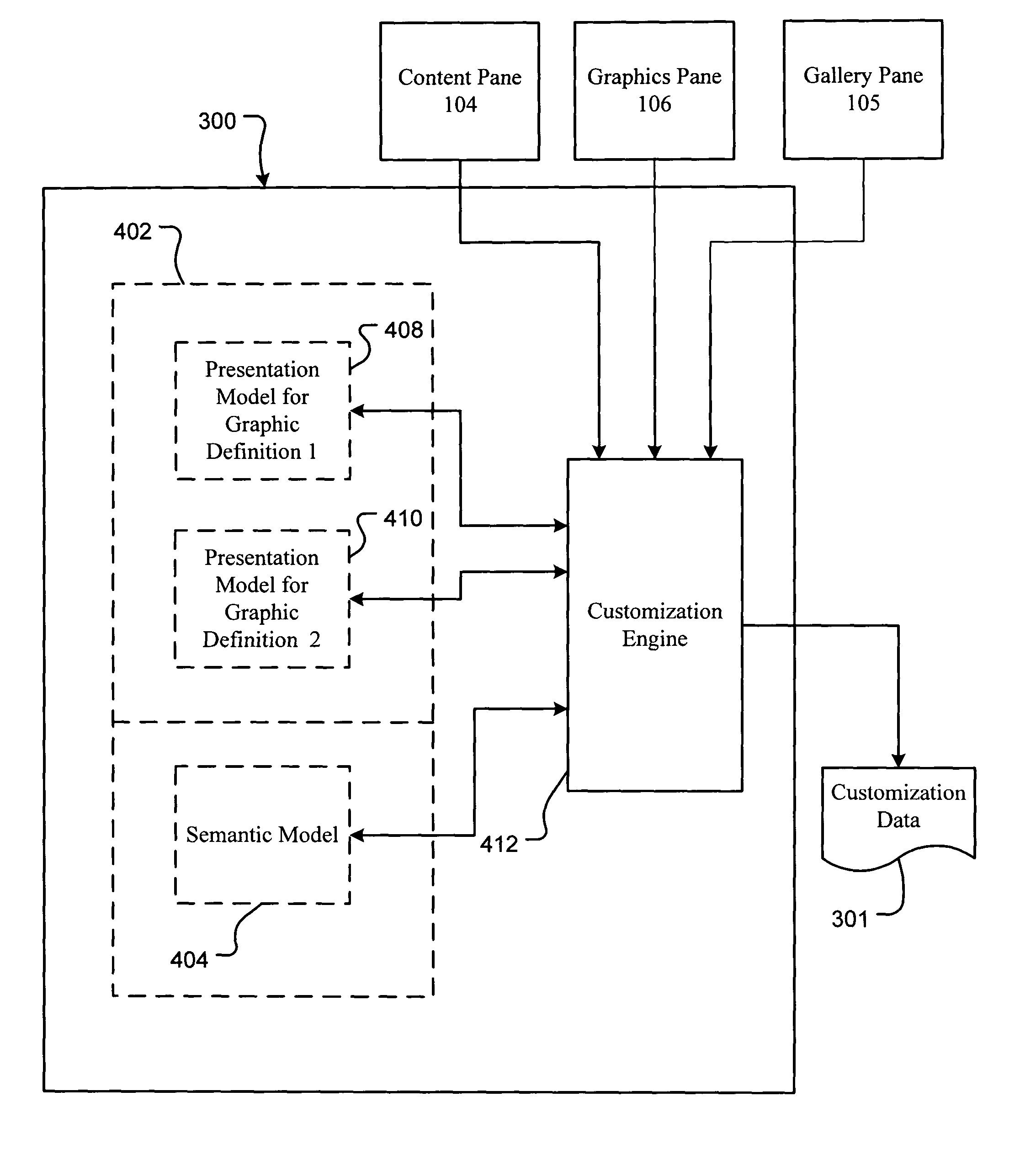
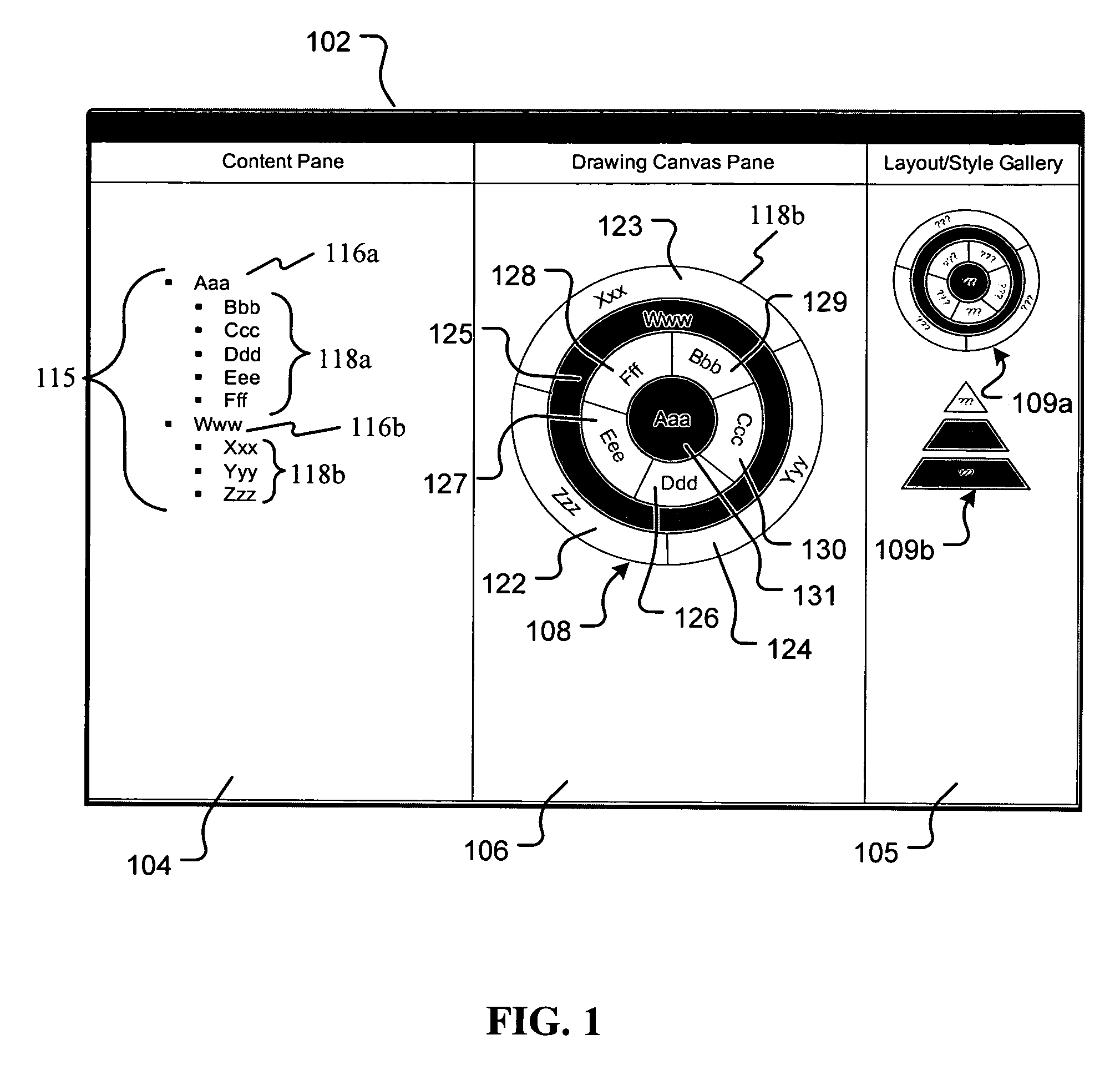
Maintaining graphical presentations based on user customizations
A method and system for rendering graphics based on user customizations in a computer graphics application are disclosed. The customizations relate to various properties of one or more graphical elements in the graphic. Such properties include positioning, size, formatting and other visual attributes associated with the graphical elements. These properties may be defined as either semantic properties or presentation properties. Semantic properties are persistent across all graphic definitions. Presentation properties are specific to the graphic definition to which each particular graphic belongs. Thus, a customization to a semantic property of a displayed graphic is preserved in memory for application not only to the currently displayed graphic, but also to all other graphic definitions that may be displayed in the future. In contrast, a customization to a presentation property is only preserved for the currently displayed graphic, and thus not preserved for all other graphic definitions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Automatic composition of services through semantic attribute matching
ActiveUS20060136428A1Maximizing numberDatabase management systemsDigital data processing detailsSemantic propertyComposite pattern
A method of automatically matching schemas begins by extracting schemas from sources and targets. Then, source and target attributes are extracted from the schemas. Each source schema will have multiple source attributes and each target schema will also have multiple target attributes. The source attributes and the target attributes are presented as nodes in a bipartite graph. This bipartite graph has edges between nodes that are related to each other. A plurality of similarity scores are defined between each set of related nodes. Each of the similarity scores is based on a different context-specific cue of the attributes that the nodes represent. These context-specific cues can comprise lexical name, semantic name, type, structure, functional mappings, etc. An overall weight is computed for each edge in the bipartite graph by combining the similarity scores of each set of nodes that form an edge. In addition, an optimal matching of the schemas is assembled, so as to indicate the level of similarity between each of the source and target schemas. The optimal matching selects pairs of nodes between source and target schemas that maximizes the number of nodes matched as well as the overall score of match for the nodes selected.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
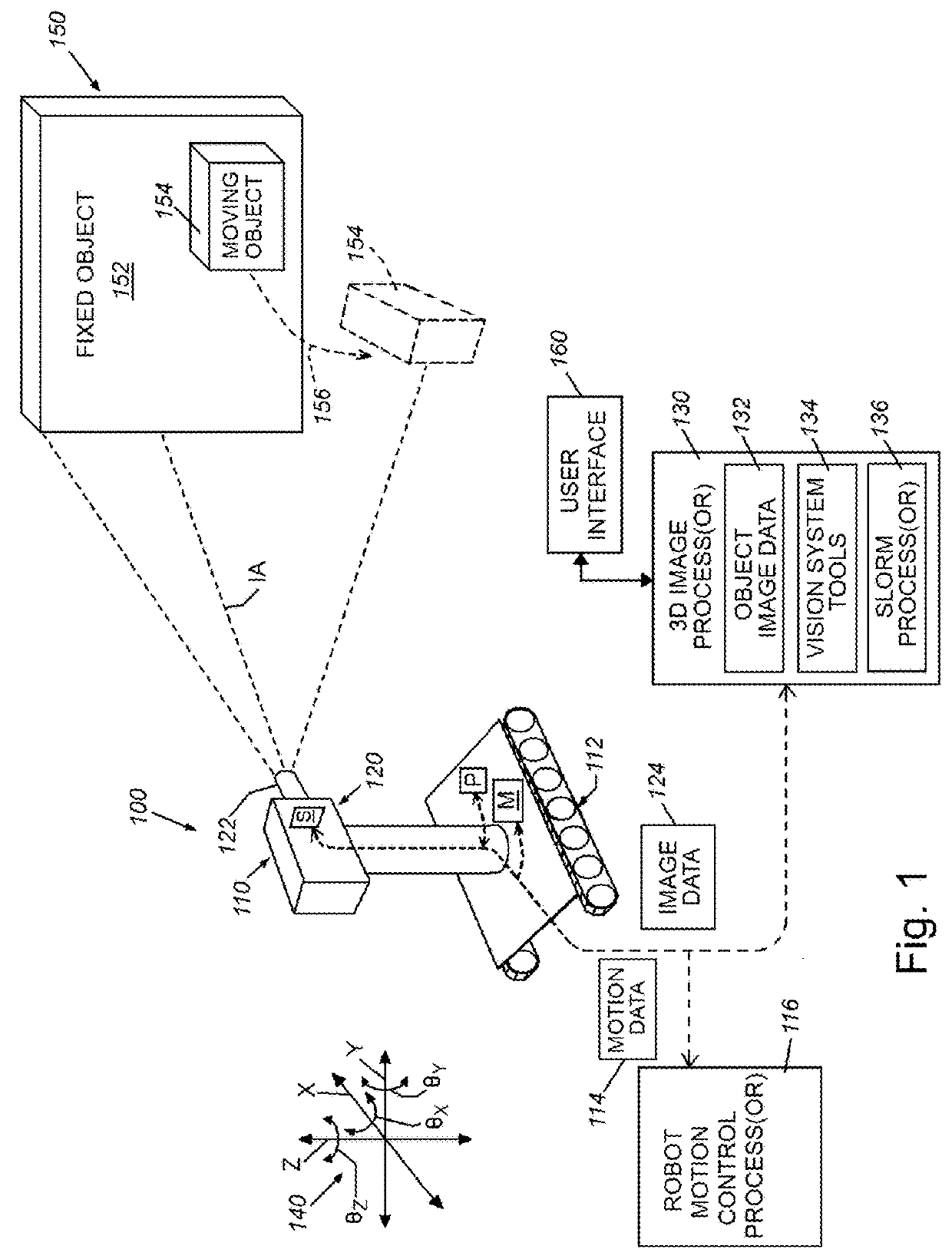
System and method for semantic simultaneous localization and mapping of static and dynamic objects
InactiveUS20180161986A1Enhanced freedom in manipulationOvercome disadvantagesProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage analysisSemantic propertyObject registration
A system for Semantic Simultaneous Tracking, Object Registration, and 3D Mapping (STORM) can maintain a world map made of static and dynamic objects rather than 3D clouds of points, and can learn in real time semantic properties of objects, such as their mobility in a certain environment. This semantic information can be used by a robot to improve its navigation and localization capabilities by relying more on static objects than on movable objects for estimating location and orientation.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
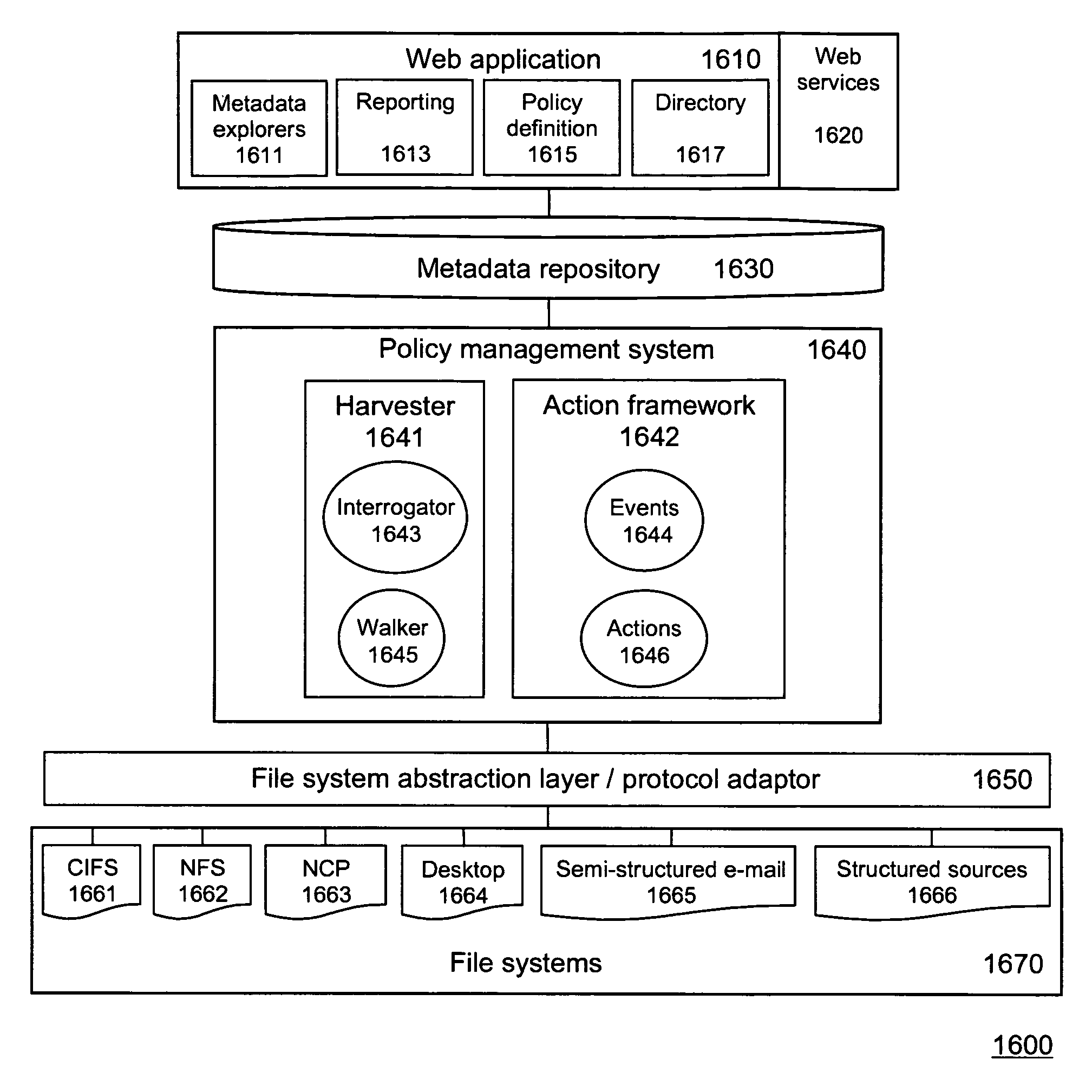
Method and apparatus for harvesting file system metadata
InactiveUS7801894B1Higher semantic levelEfficient storageDigital data processing detailsFile access structuresSemantic propertyDocumentation procedure
A harvester is disclosed for harvesting metadata of managed objects (files and directories) across file systems which are generally not interoperable in an enterprise environment. Harvested metadata may include 1) file system attributes such as size, owner, recency; 2) content-specific attributes such as the presence or absence of various keywords (or combinations of keywords) within documents as well as concepts comprised of natural language entities; 3) synthetic attributes such as mathematical checksums or hashes of file contents; and 4) high-level semantic attributes that serve to classify and categorize files and documents. The classification itself can trigger an action in compliance with a policy rule. Harvested metadata are stored in a metadata repository to facilitate the automated or semi-automated application of policies.
Owner:IBM CORP
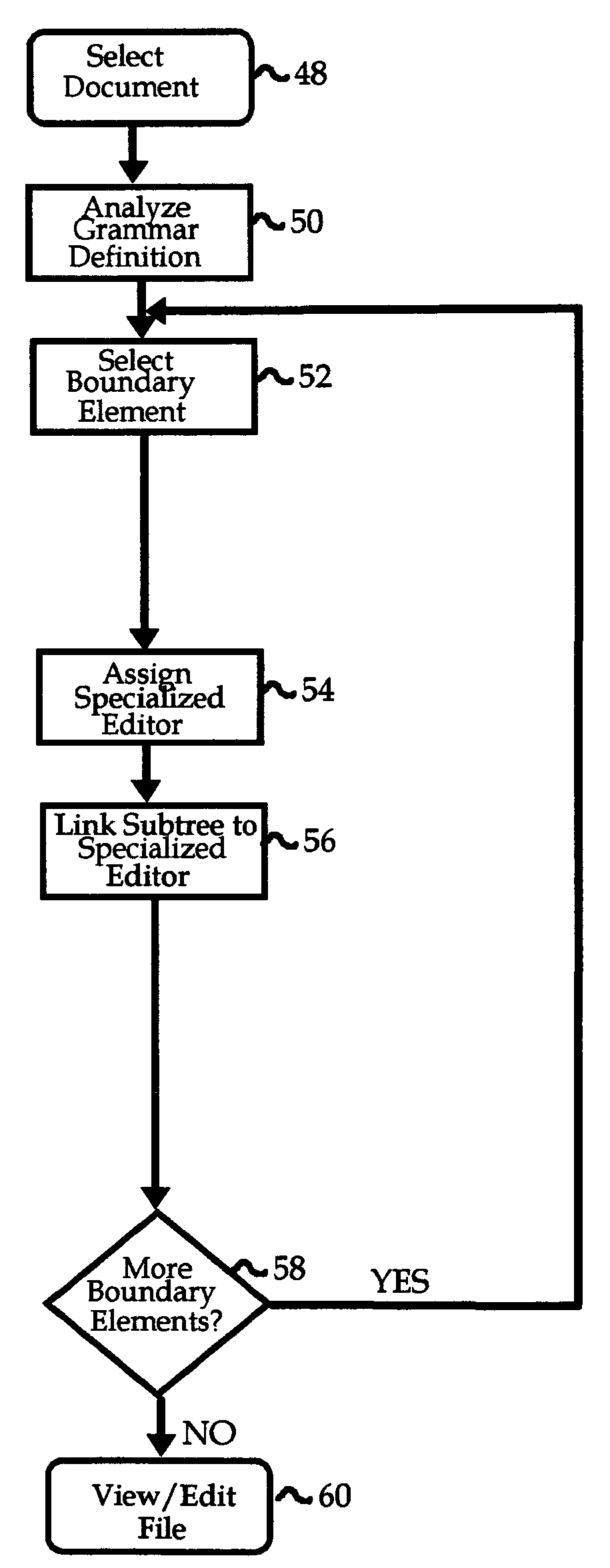
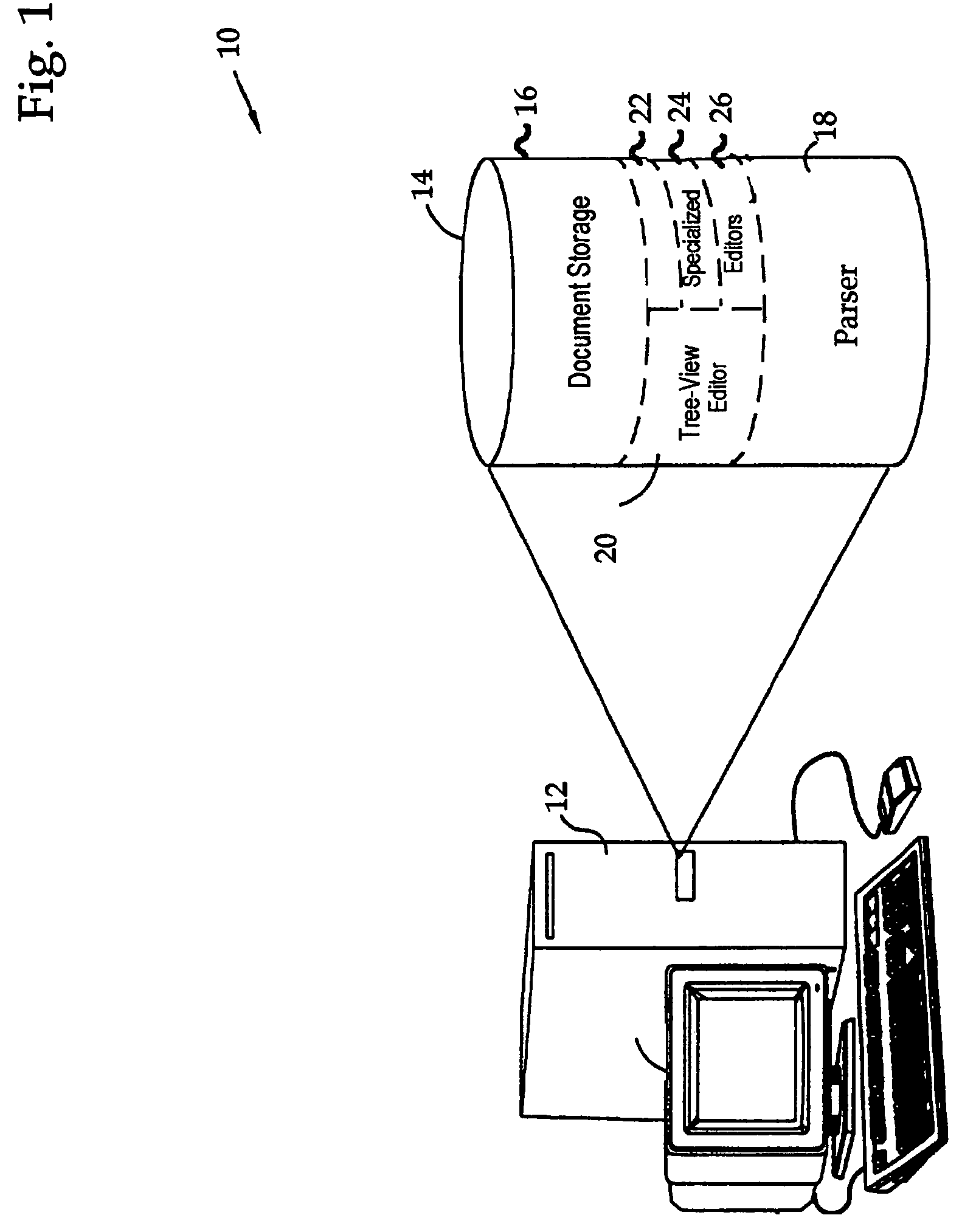
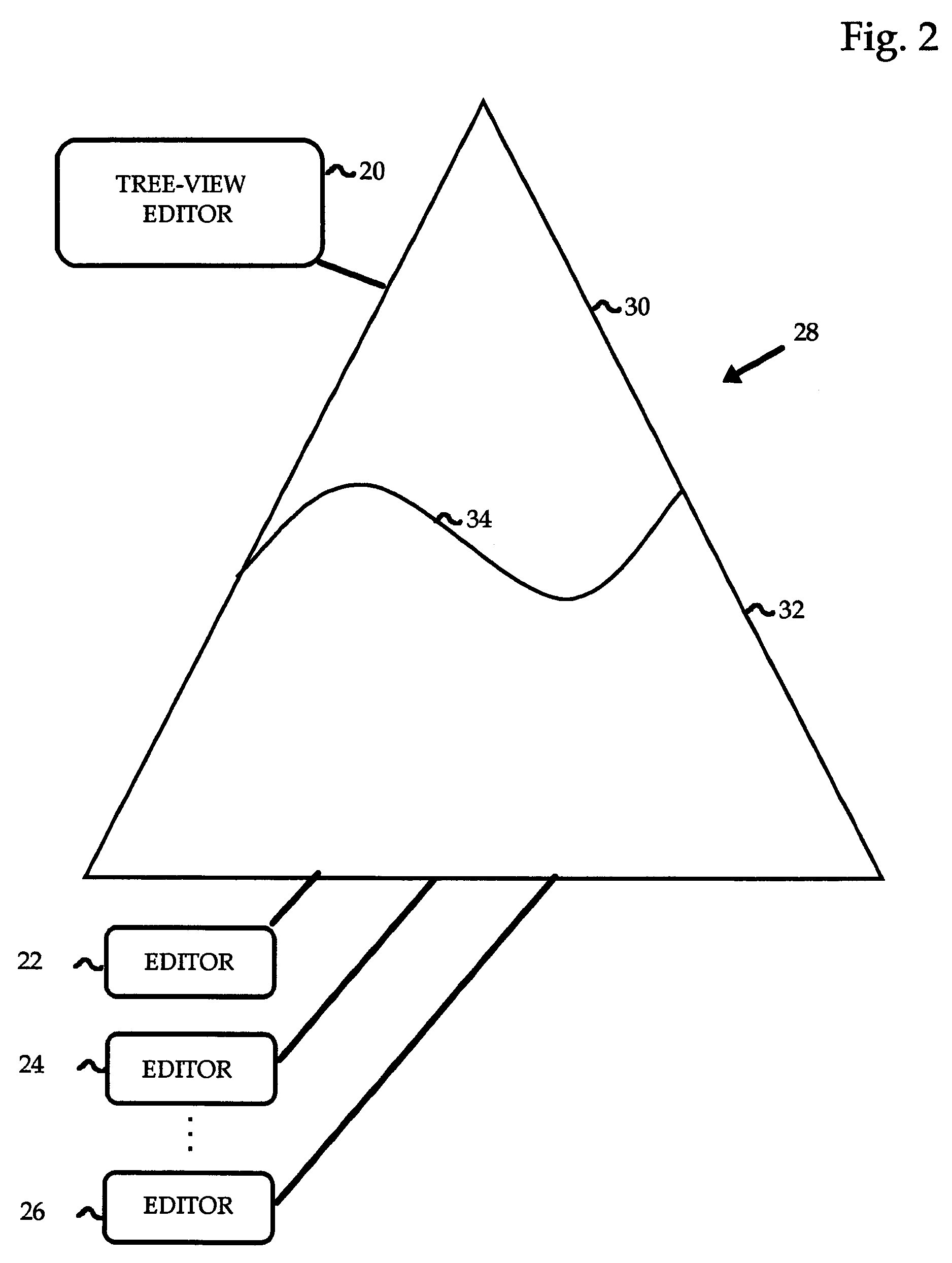
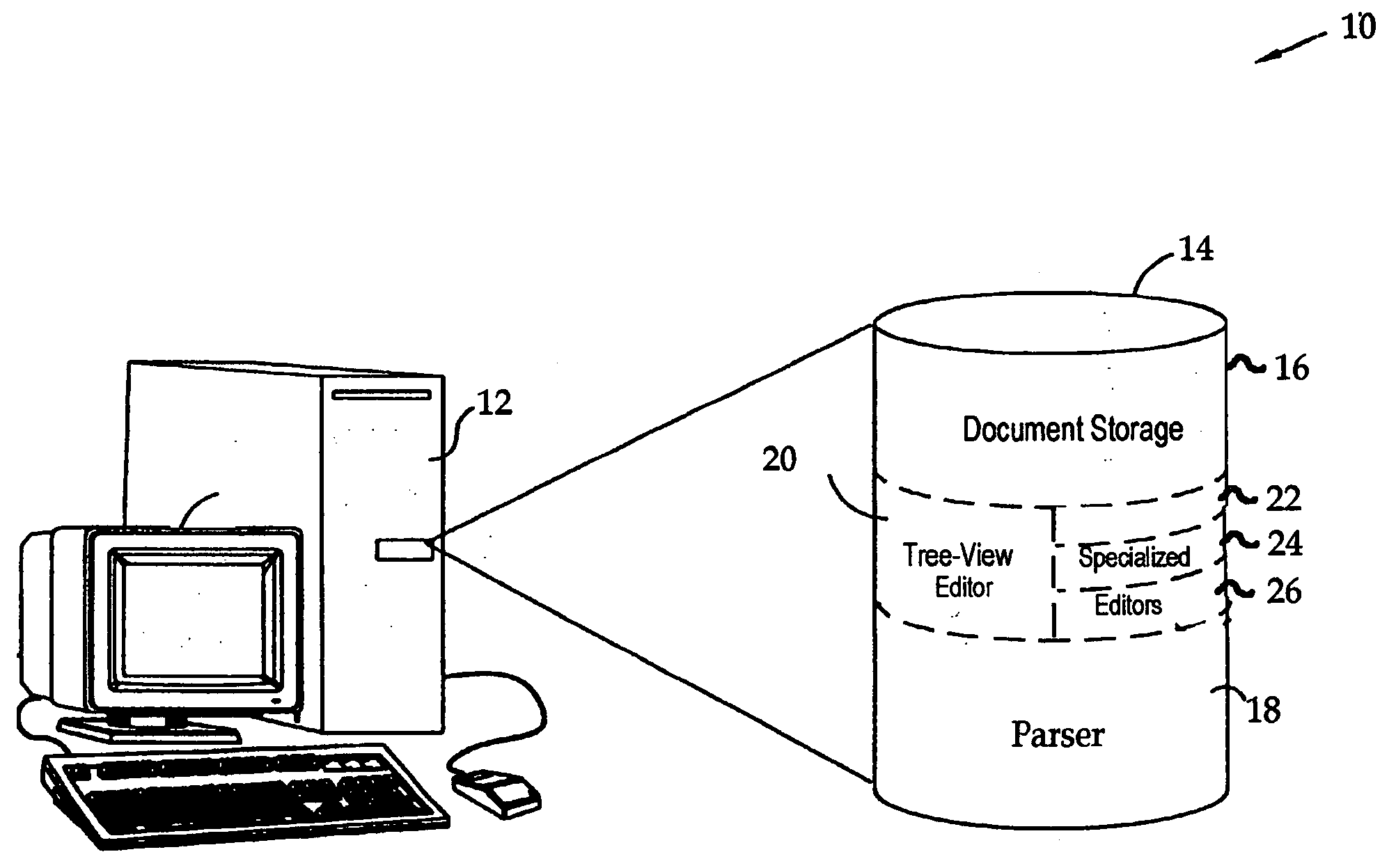
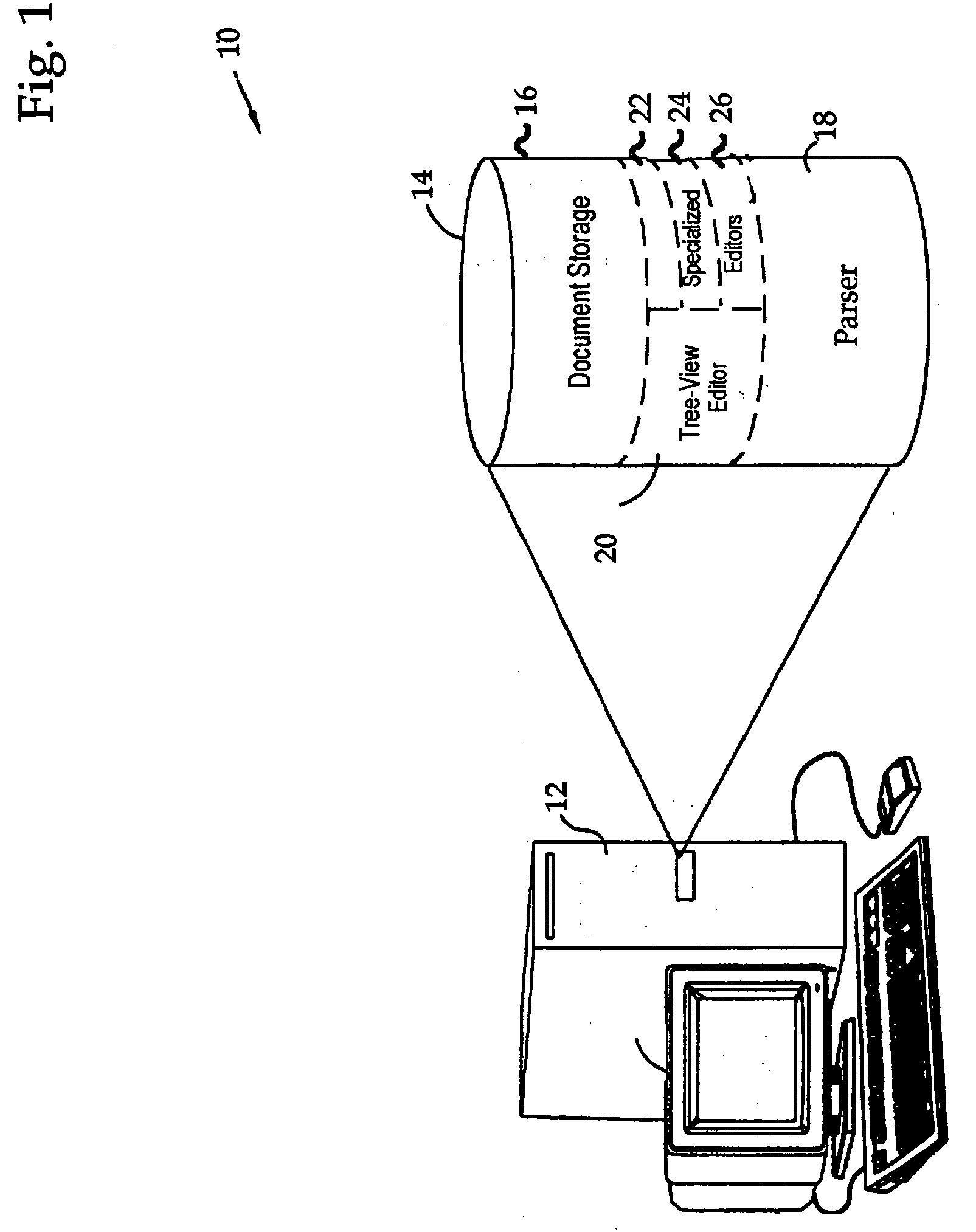
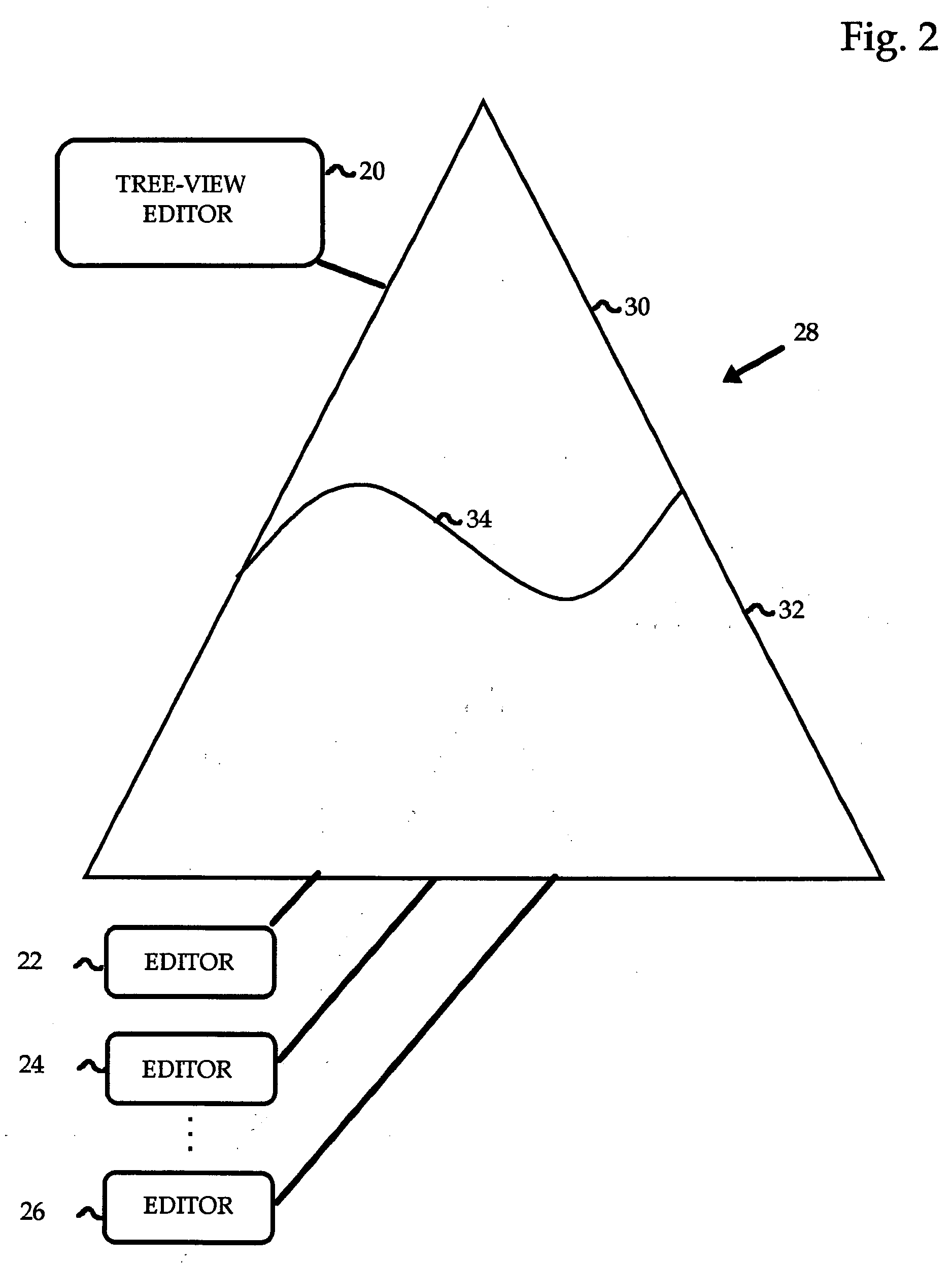
Viewing and editing markup language files with complex semantics
ActiveUS7412649B2Visual/graphical programmingSpecific program execution arrangementsSemantic treeSemantic property
The semantic hierarchy of a document written in a markup language is represented by a hierarchy of elements, which are viewed and edited using a tree view editor. Each element is represented as a node of a semantic tree, to which may be attached a special purpose editor, capable of editing the semantic properties of that particular element. Such special purpose editors handle the single element to which they are attached and may handle a hierarchy of elements that share common properties in the subtree headed by the single element. They offer a visualization of the elements to which they are attached that is not necessarily hierarchical in form.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
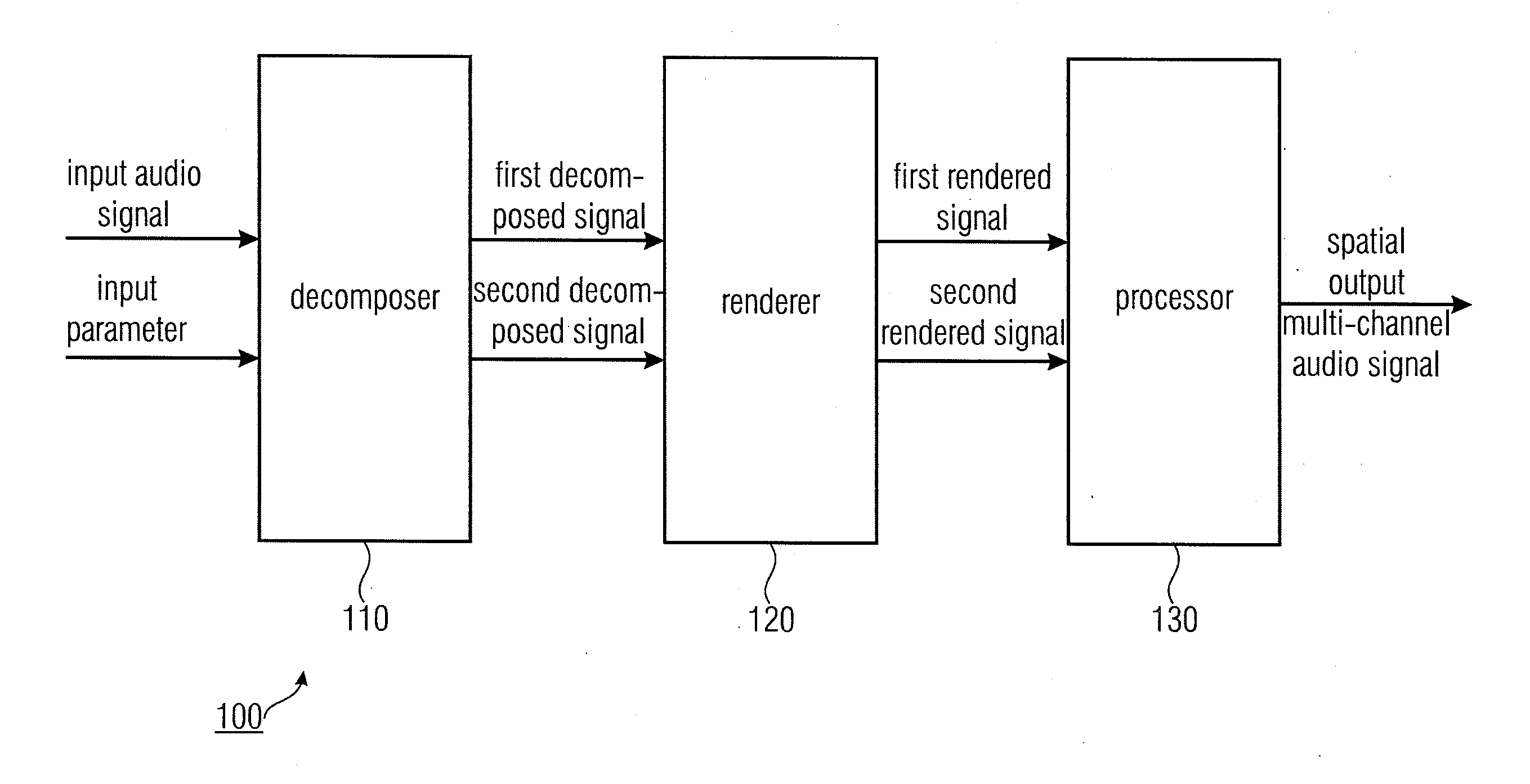
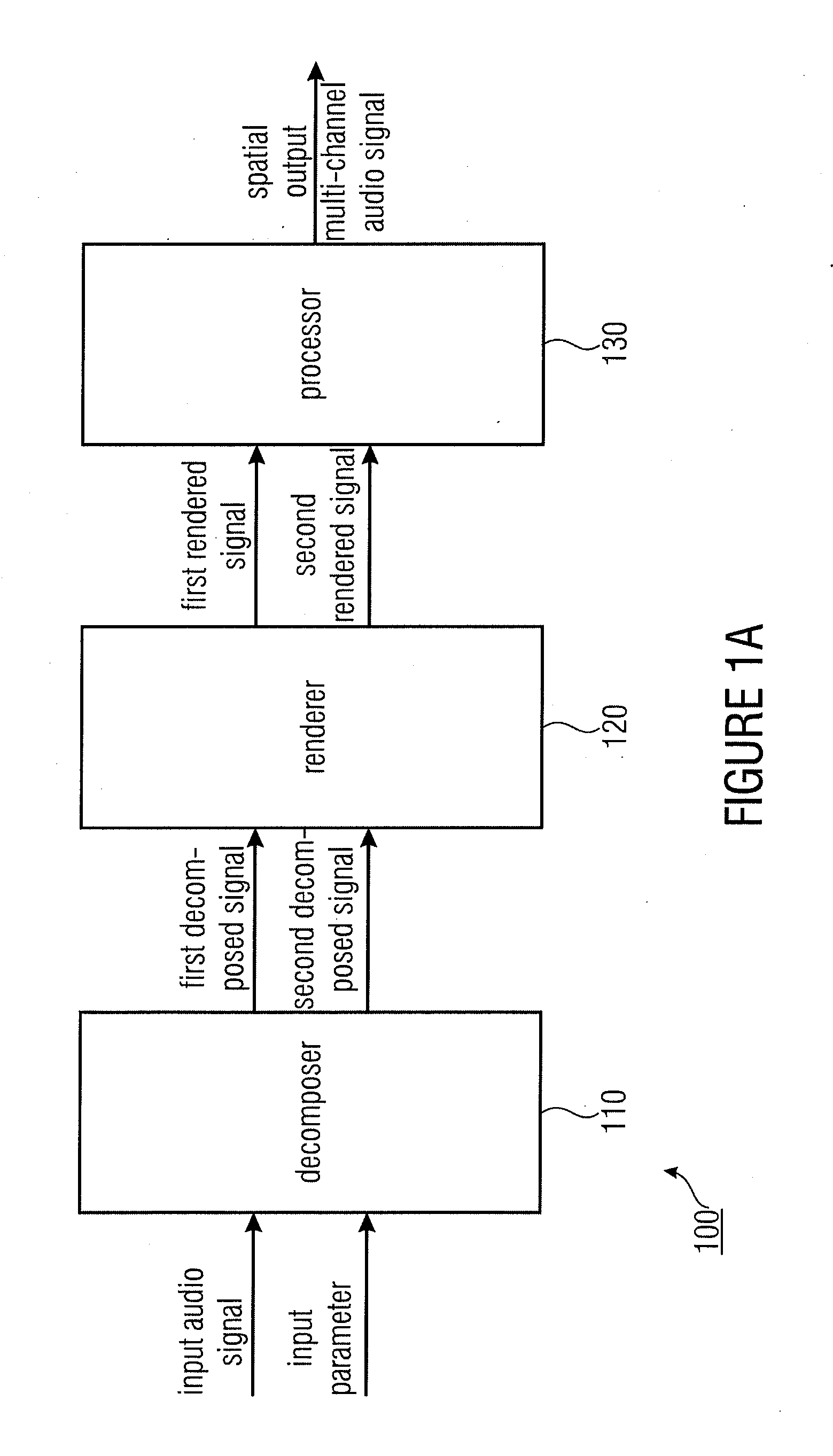
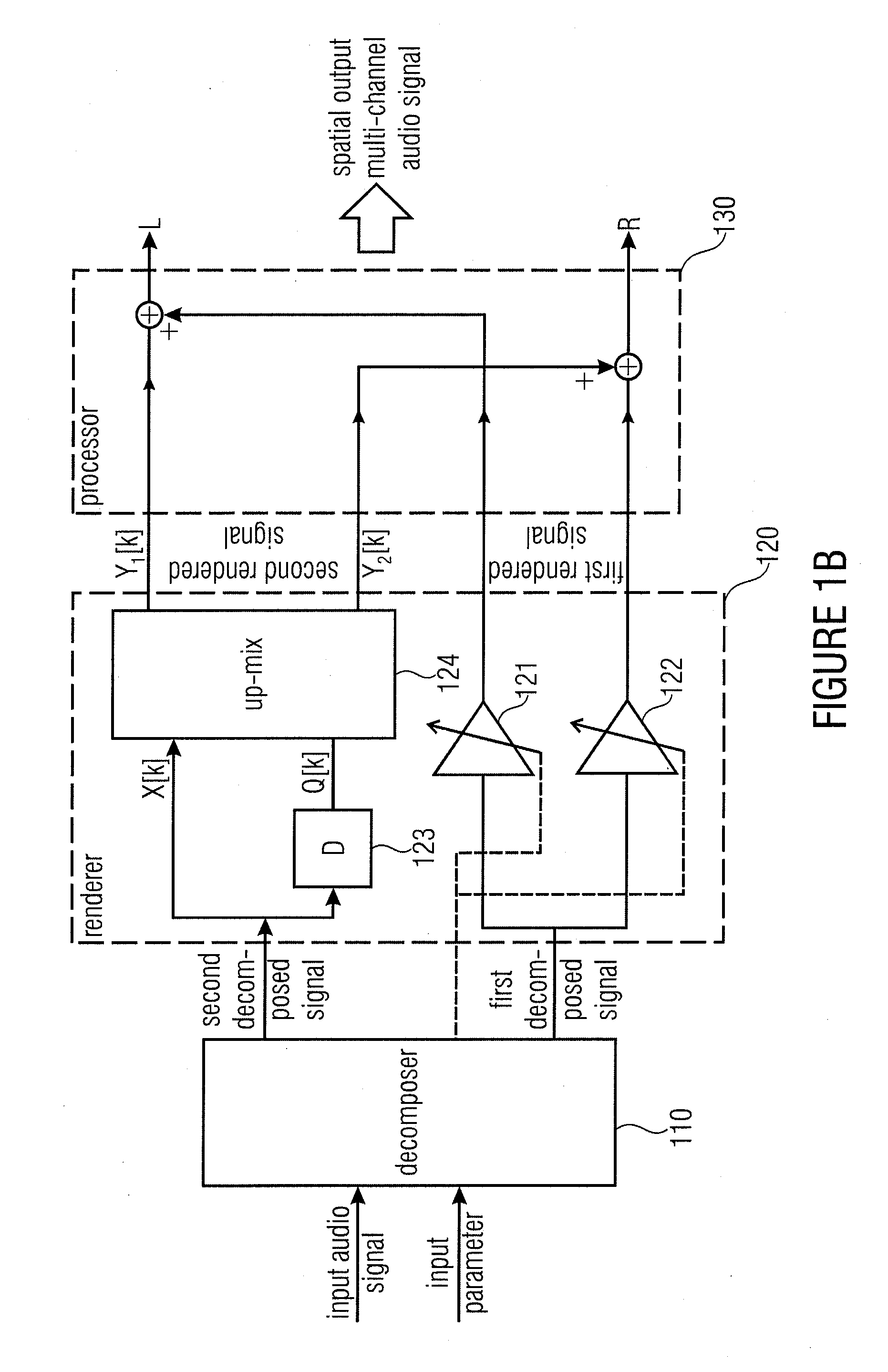
Apparatus for determining a spatial output multi-channel audio signal
ActiveUS20110200196A1Better perceptual qualityReduce computing costStereophonic systemsStereophonic arrangmentsSemantic propertyVocal tract
An apparatus for determining a spatial output multi-channel audio signal based on an input audio signal and an input parameter. The apparatus includes a decomposer for decomposing the input audio signal based on the input parameter to obtain a first decomposed signal and a second decomposed signal different from each other. Furthermore, the apparatus includes a renderer for rendering the first decomposed signal to obtain a first rendered signal having a first semantic property and for rendering the second decomposed signal to obtain a second rendered signal having a second semantic property being different from the first semantic property. The apparatus comprises a processor for processing the first rendered signal and the second rendered signal to obtain the spatial output multi-channel audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Robot distributed type representation intelligent semantic map establishment method
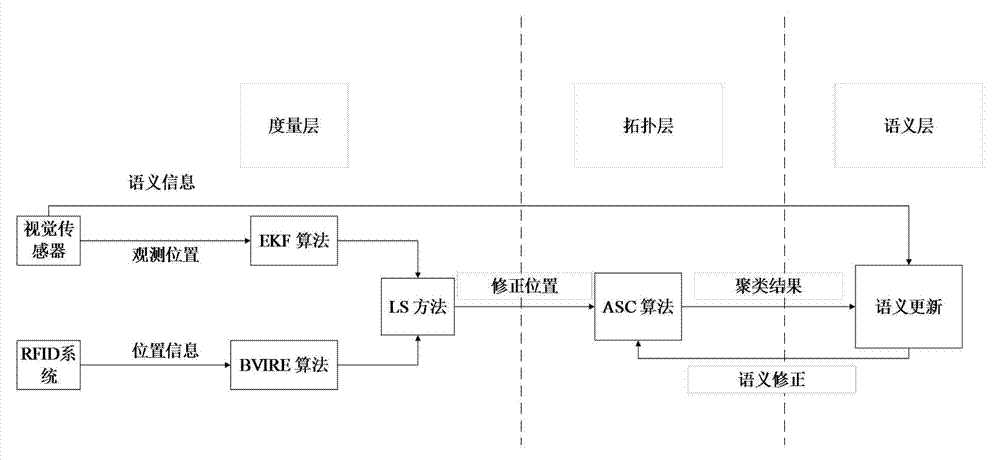
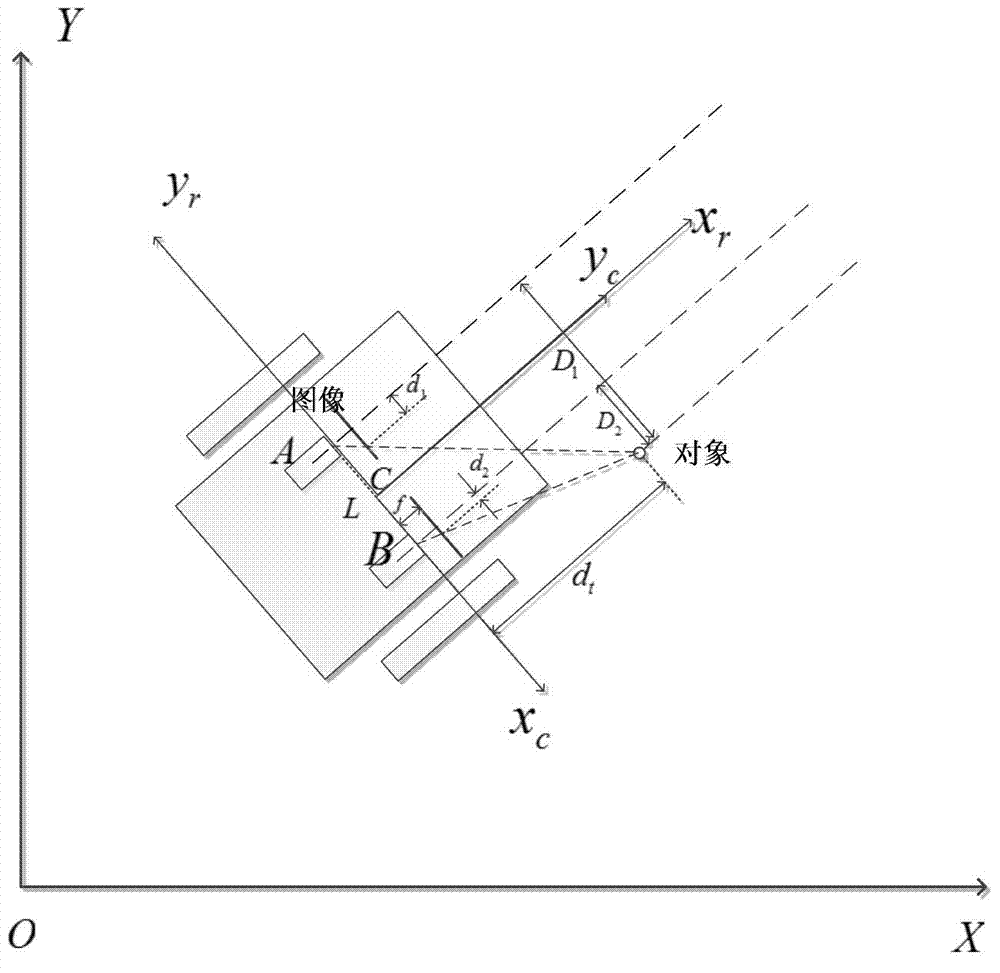
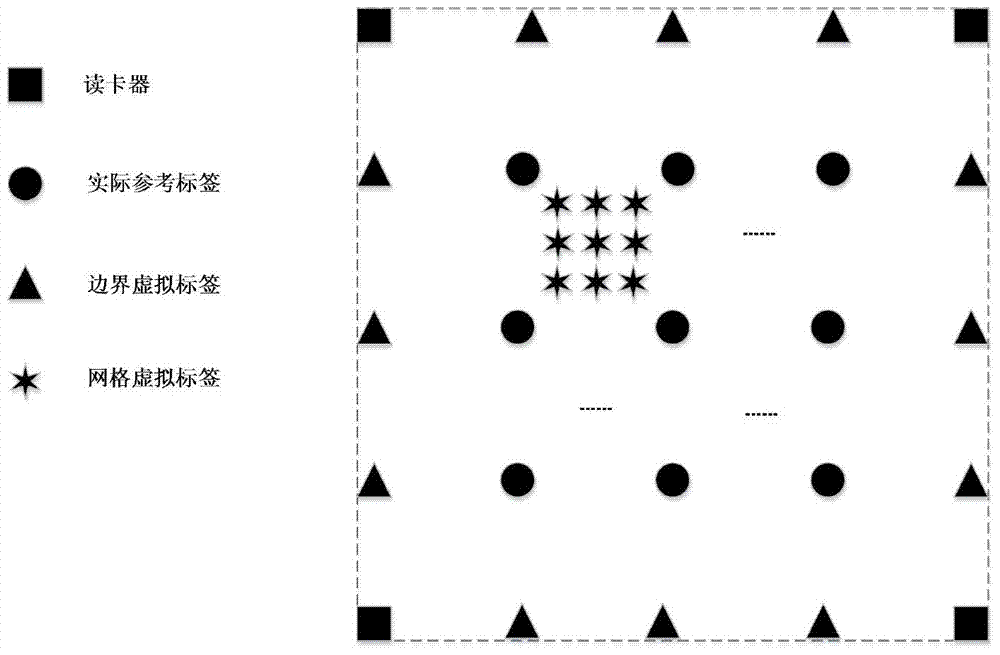
InactiveCN104330090AAddress limitationsHigh precisionInstruments for road network navigationVehicle position/course/altitude controlVisual positioningVisual perception
The invention discloses a robot distributed type representation intelligent semantic map establishment method which comprises the steps of firstly, traversing an indoor environment by a robot, and respectively positioning the robot and an artificial landmark with a quick identification code by a visual positioning method based on an extended kalman filtering algorithm and a radio frequency identification system based on a boundary virtual label algorithm, and constructing a measuring layer; then optimizing coordinates of a sampling point by a least square method, classifying positioning results by an adaptive spectral clustering method, and constructing a topological layer; and finally, updating the semantic property of a map according to QR code semantic information quickly identified by a camera, and constructing a semantic layer. When a state of an object in the indoor environment is detected, due to the adoption of the artificial landmark with a QR code, the efficiency of semantic map establishing is greatly improved, and the establishing difficulty is reduced; meanwhile, with the adoption of a method combining the QR code and an RFID technology, the precision of robot positioning and the map establishing reliability are improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Information nervous system
InactiveUS20080147788A1Web data indexingMultiple digital computer combinationsSemantic propertyNervous system
A system includes a server programmable to maintain semantic information and / or a client providing a user interface for a user to communicate with the server. In an embodiment, the processor of the server operates to secure information from information sources, semantically ascertain one or more semantic properties of the information, and / or respond to user queries based upon one or more of the semantic properties.
Owner:OMOIGUI NOSA
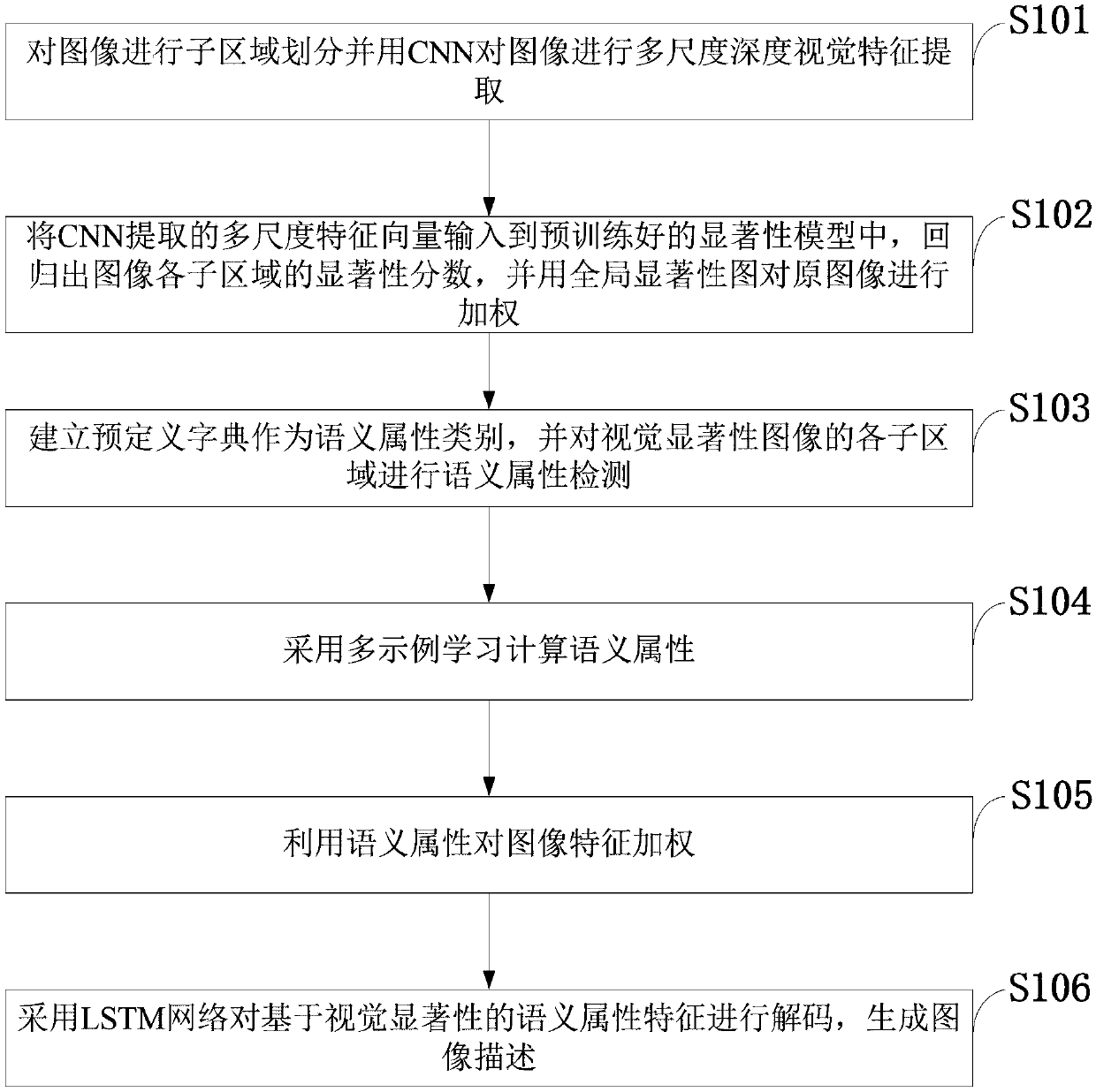
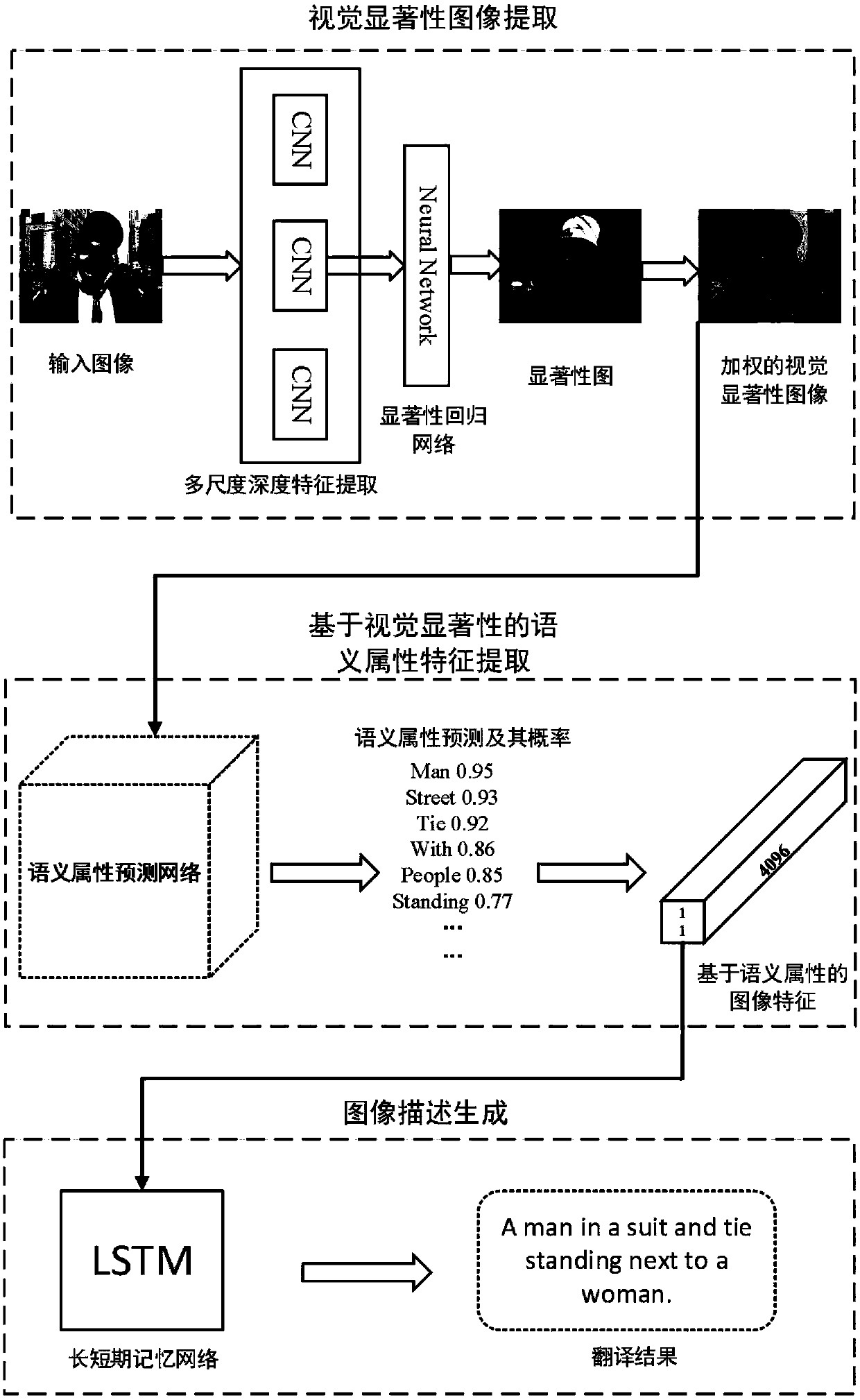
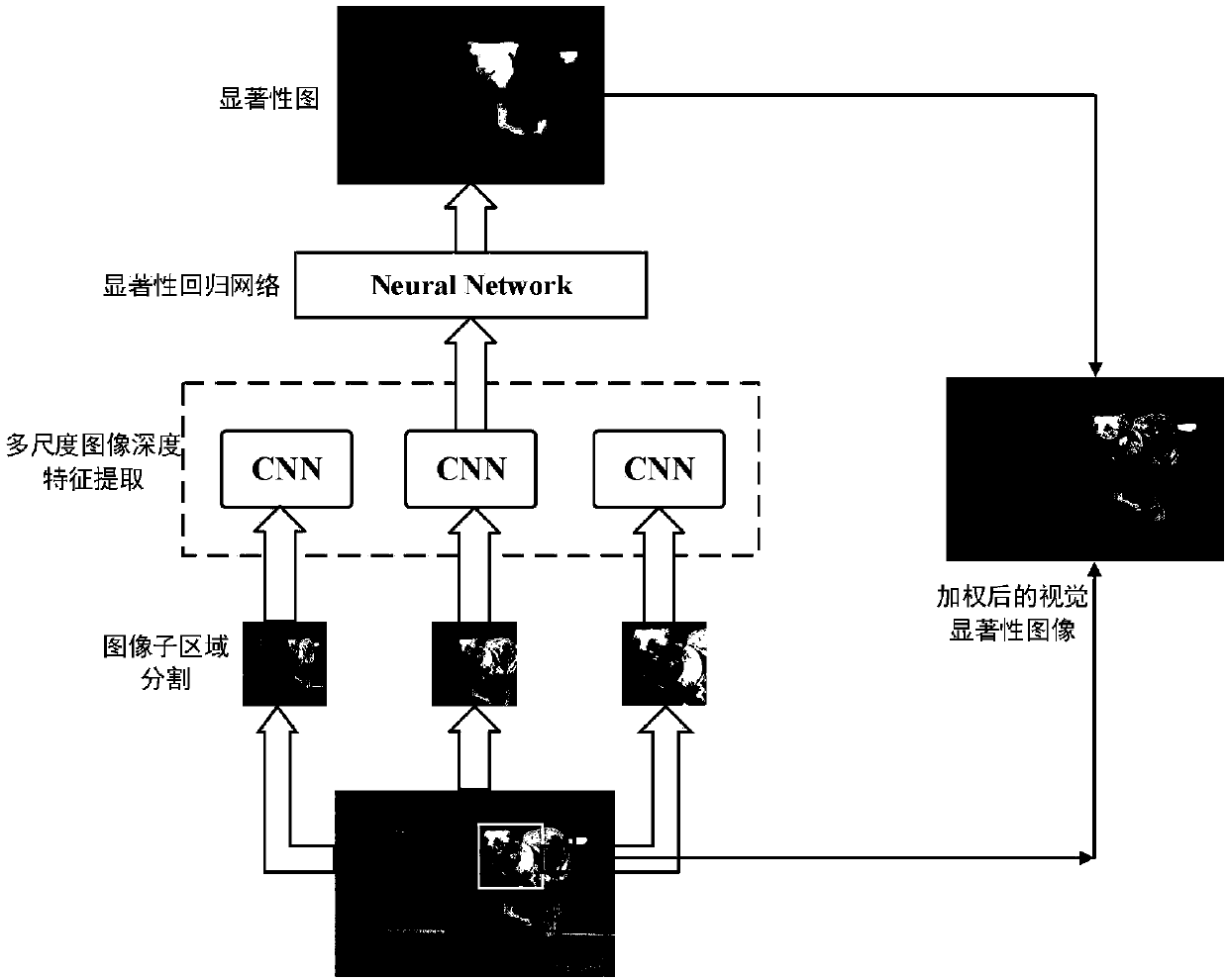
Visual salience and semantic attribute based cross-modal image natural language description method
ActiveCN107688821AIncrease the importanceReduce contributionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsSemantic propertyVision based
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer vision and natural language processing, and discloses a visual salience and semantic attribute based cross-modal image natural language description method. The method comprises the steps that multiscale deep visual features of all regions are extracted by adopting a convolutional neural network; by means of a pre-trained significance model,an image significance graph is returned, and an original image is weighted; a predefined dictionary is built to serve as a semantic attribute category, and semantic attribute detection is conducted ona visual significance image; semantic attributes are calculated through multi-instance learning; image features are weighted through the semantic attributes; visual-salience-based semantic attributefeatures are decoded through a long short-term memory network, and image description is generated. The method has the advantage of being high in accuracy and can be used for image retrieval under complex scenes, multi-objective image semantic understanding and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Forming coloring books from digital images
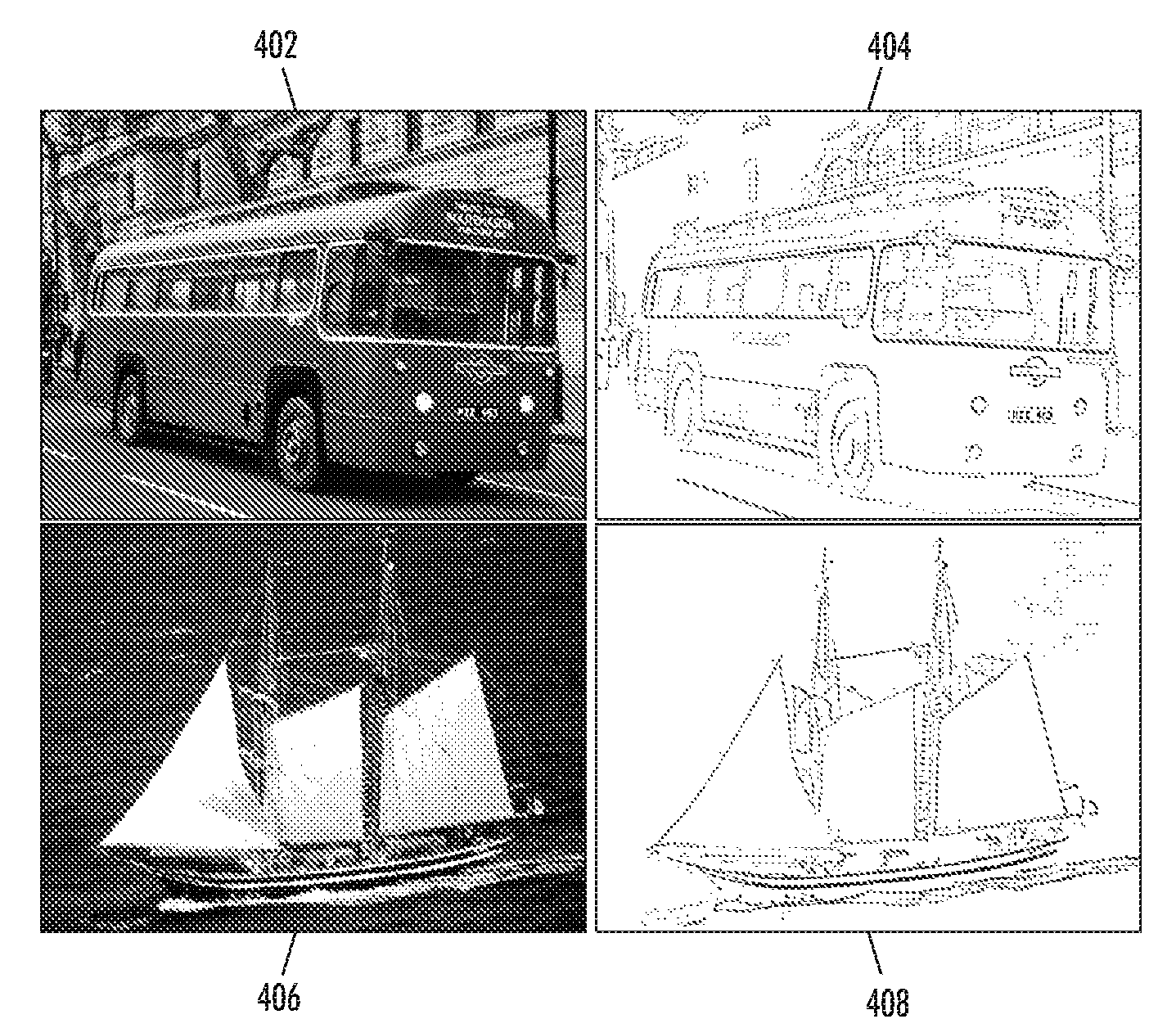
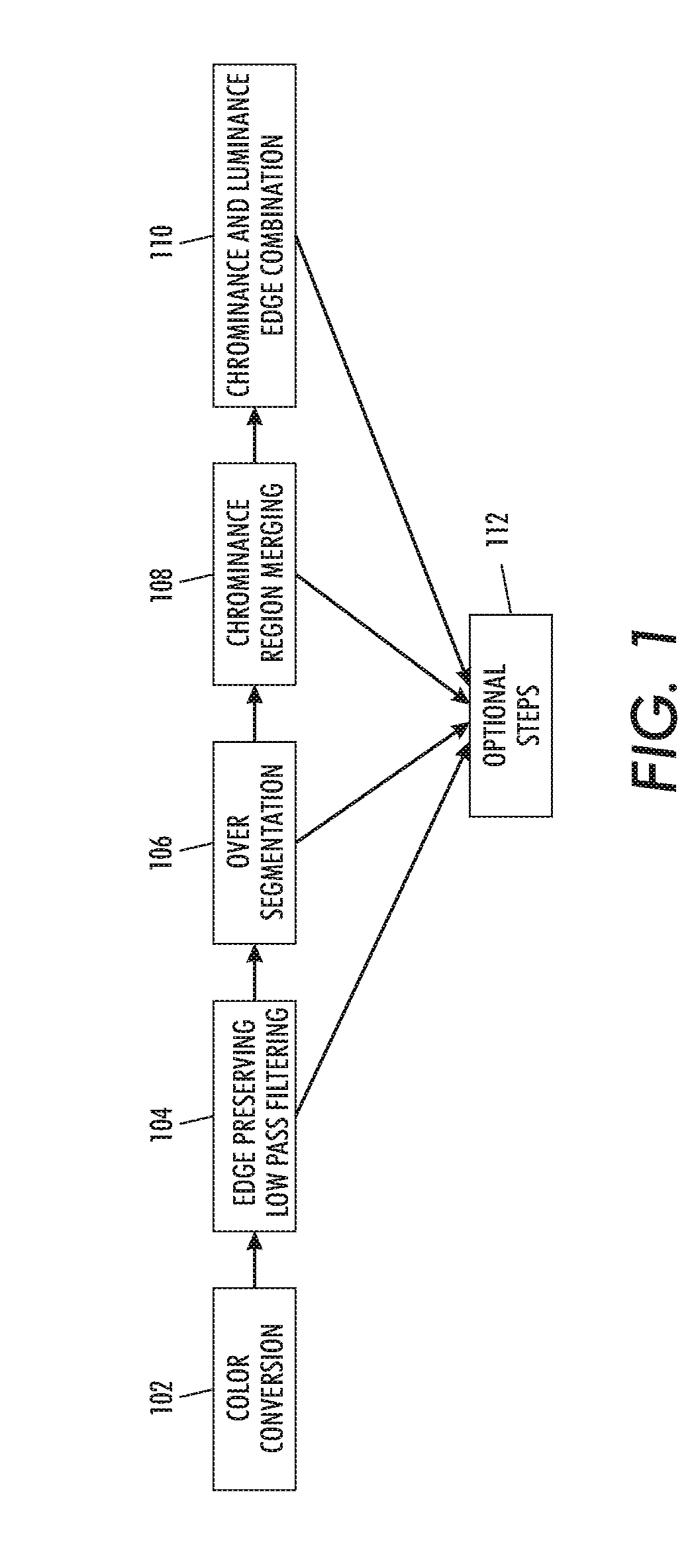
InactiveUS20080284791A1Improve performanceDifferent in contentImage analysis2D-image generationColor imageSemantic property
Embodiments herein include a method, service, apparatus, etc., that automatically generates a coloring book image that includes line drawings defining a small number of color coherent, clearly discriminated, closed regions while preserving the basic semantic properties of the original image. These regions hence can be filled in with colored inks, crayons, paints, etc. The method inputs a color image that can be a photograph, scanned image, etc. The method begins by transforming the color image into a chrominance-luminance space and then performs low pass filtering on the color image that preserves the chrominance edges of the features within the color image. Next, the method segments the color image into the features based on locations of the chrominance edges of the features. Then, the method can merge selected features into other features. After performing any merging, the method identifies the remaining chrominance edges of the features within the image and adds lines along the remaining chrominance edges to form outlines of the features. Then, the method automatically filters out all other data from the image to leave only the outlines and produce a revised image consisting of just the outlines. The revised image of just outlines is then output to the user.
Owner:XEROX CORP
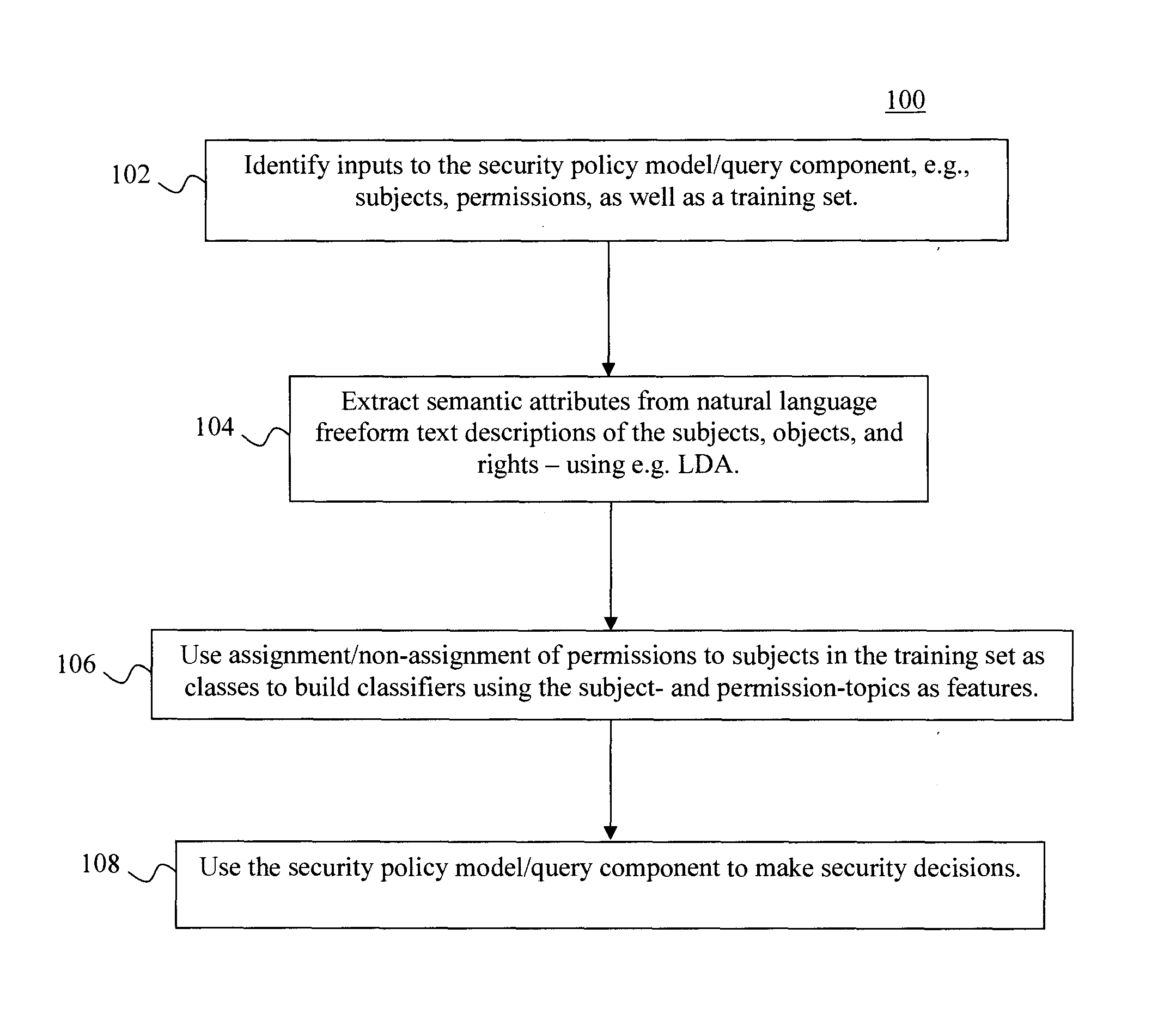
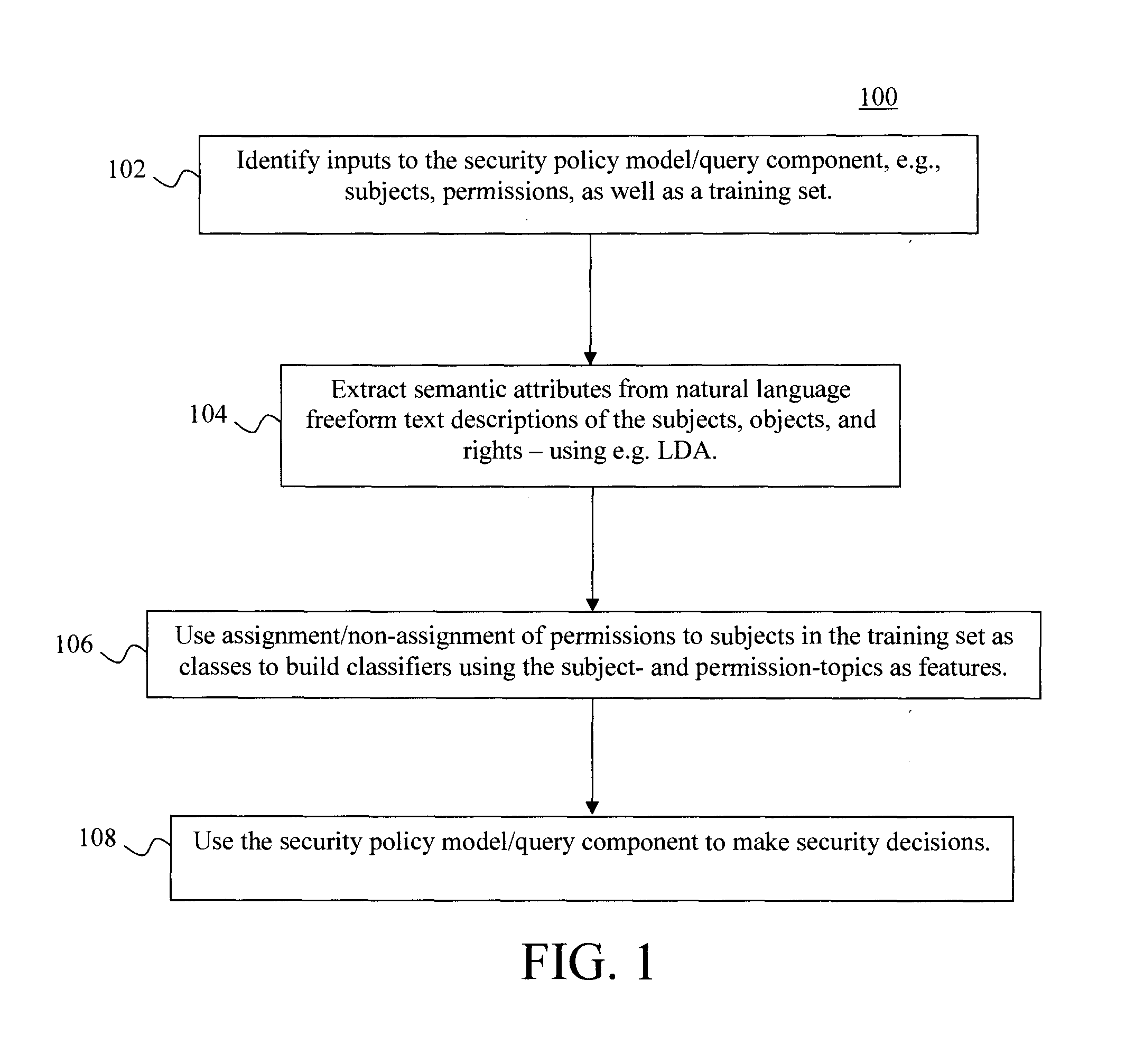
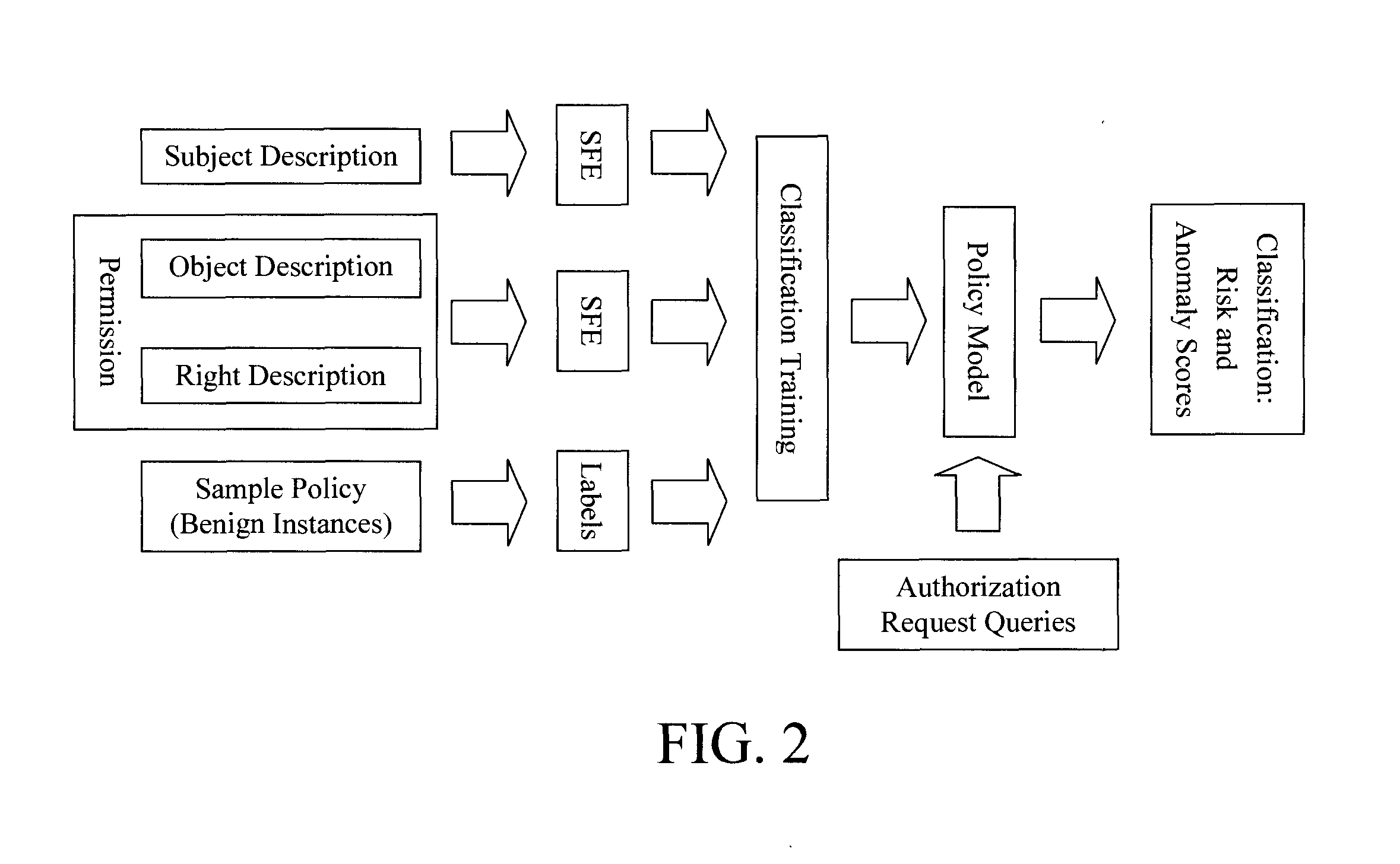
Inferring Security Policies from Semantic Attributes
Techniques for inferring security policies from semantic attributes are provided. In one aspect, a method for building a query component executable by a processor is provided. The method includes the steps of: (a) providing subjects and permissions related to making a security policy decision, as well as a training set of permission-to-subject assignments, as inputs to the security policy query component; (b) extracting semantic attributes from natural language freeform text descriptions of the subjects and the permissions; and (c) using machine learning to build the security policy query component based on the permission-to-subject assignments in the training set and the semantic attributes extracted in step (b).
Owner:IBM CORP
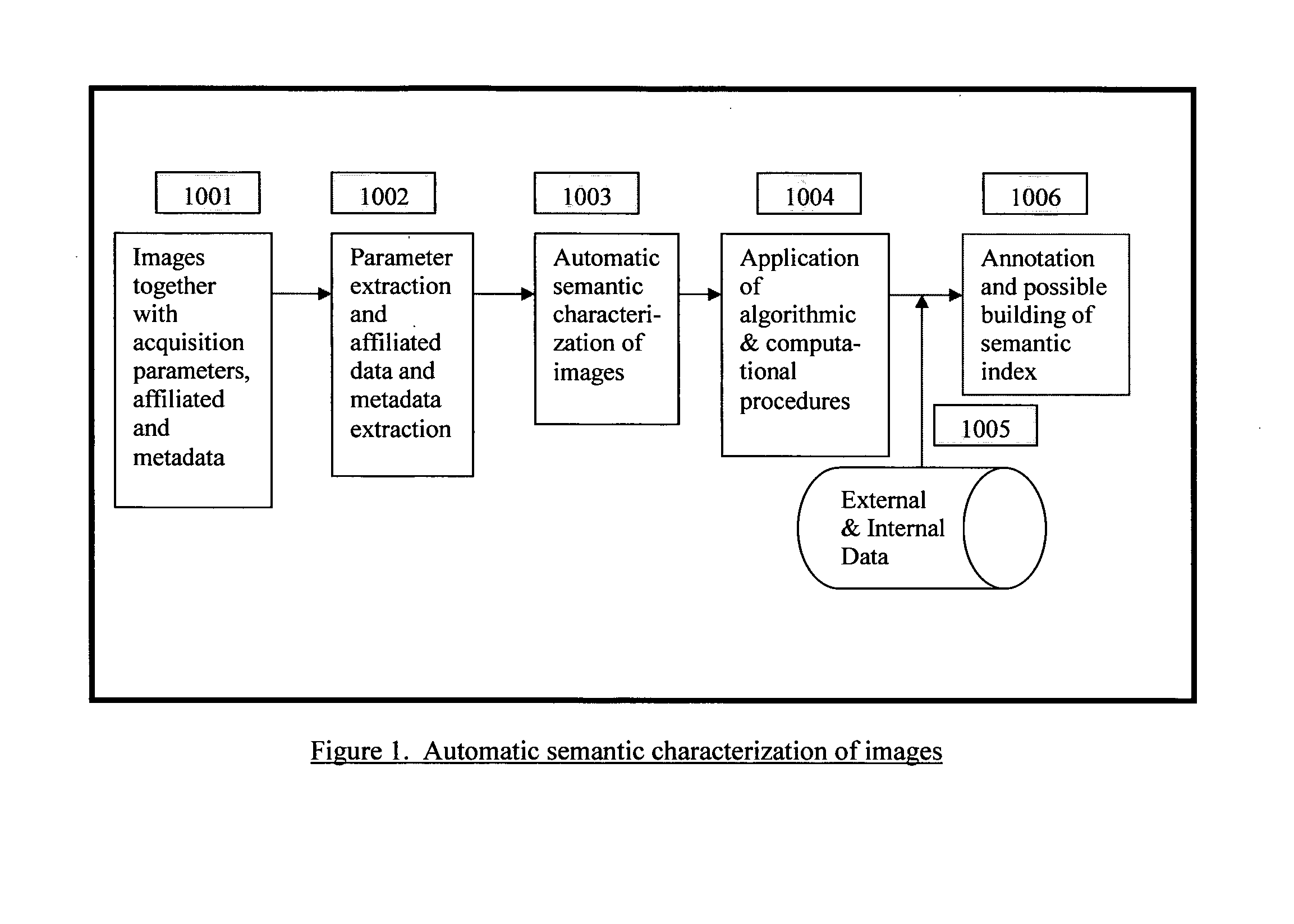
Automatic and semi-automatic image classification, annotation and tagging through the use of image acquisition parameters and metadata
ActiveUS8520909B2Improve accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMetadata still image retrievalTimestampSemi automatic
A method for characterizing image contents automatically or semi-automatically using image acquisition parameters and metadata is presented. The method establishes probabilistic and deterministic relationships between different types of metadata and the semantic attributes and contents of images. It furnishes a mechanism that enables the automatic and semi-automatic classification, annotation, tagging, indexing, searching, identification or retrieval of images based on their contents, semantic properties and metadata characteristics. The method uses, but is not limited to, image capture metadata such as focal length, exposure time, relative aperture, flash information, ISO setting, angle of view, subject distance, timestamp, GPS information as well as other forms of metadata, including but not limited to, captions, keywords, headings, tags, comments, remarks, titles which may be automatically, semi-automatically, or manually generated. The present invention can be applied to image databases, web searching, personal search, community search, broad-based or vertical search engines for internet, intranet, extranet or other usages.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
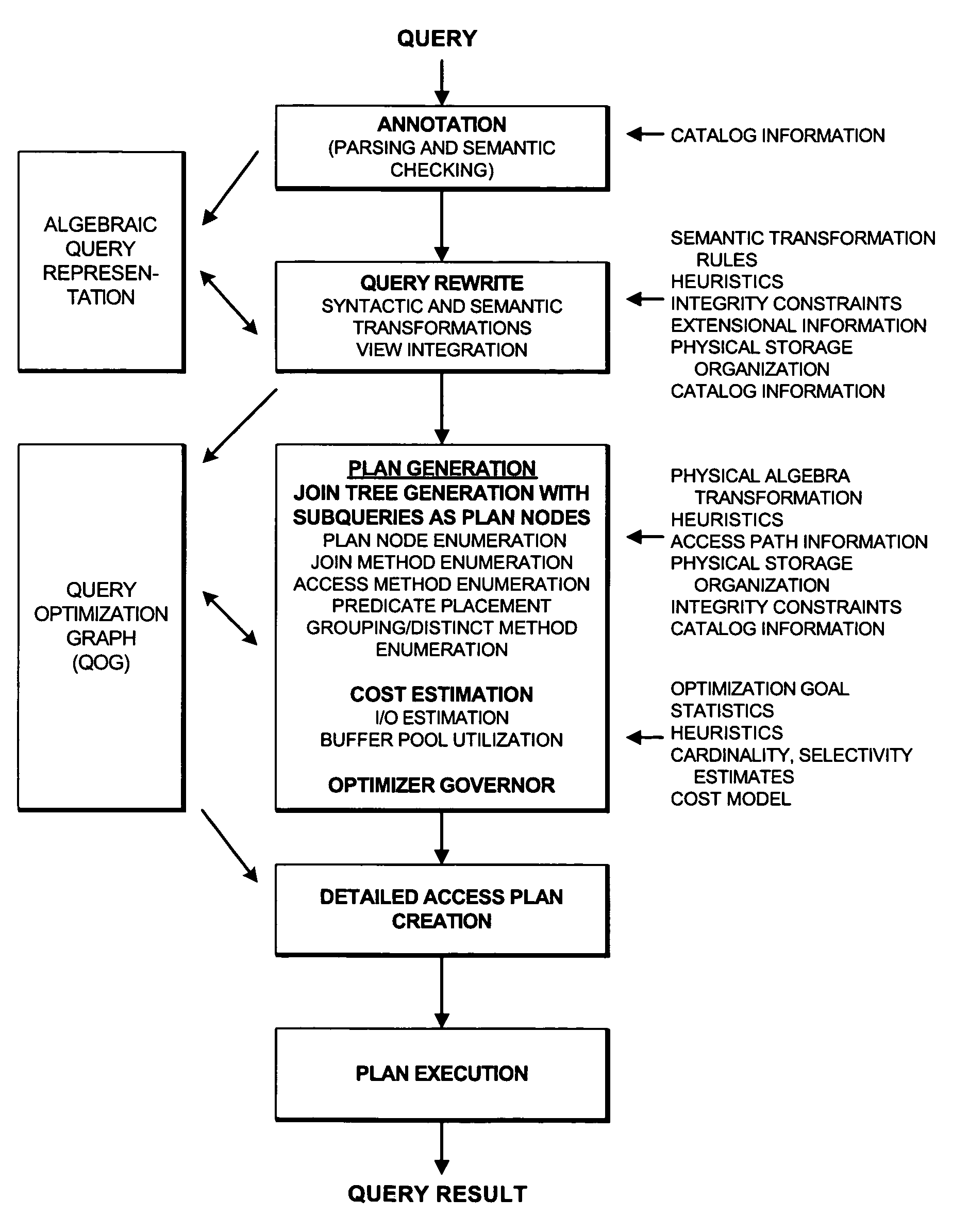
System and methodology for cost-based subquery optimization using a left-deep tree join enumeration algorithm
ActiveUS7617179B2Low cost of executionEasily considerData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalSemantic propertyDatabase query
A system providing methodology for cost-based enumeration of subqueries using a left-deep tree join enumeration algorithm is described. In one embodiment, for example, in a database system, a method of the present invention is described for optimizing a database query, the method comprises steps of: receiving a database query including at least one subquery; building a query optimization graph for each query block of the database query, the query optimization graph including plan nodes representing subqueries of each query block; generating a set of access methods and join methods for each plan node, including generating at least one access method for a subquery quantifier based on subquery type and semantic properties of the database query; determining an optimal access plan for each query block based upon selecting access methods, join methods, and join order for plan nodes of the query optimization graph having favorable execution costs; and constructing a detailed access plan for execution of the database query based upon the optimal access plan determined for each query block.
Owner:SAP AG
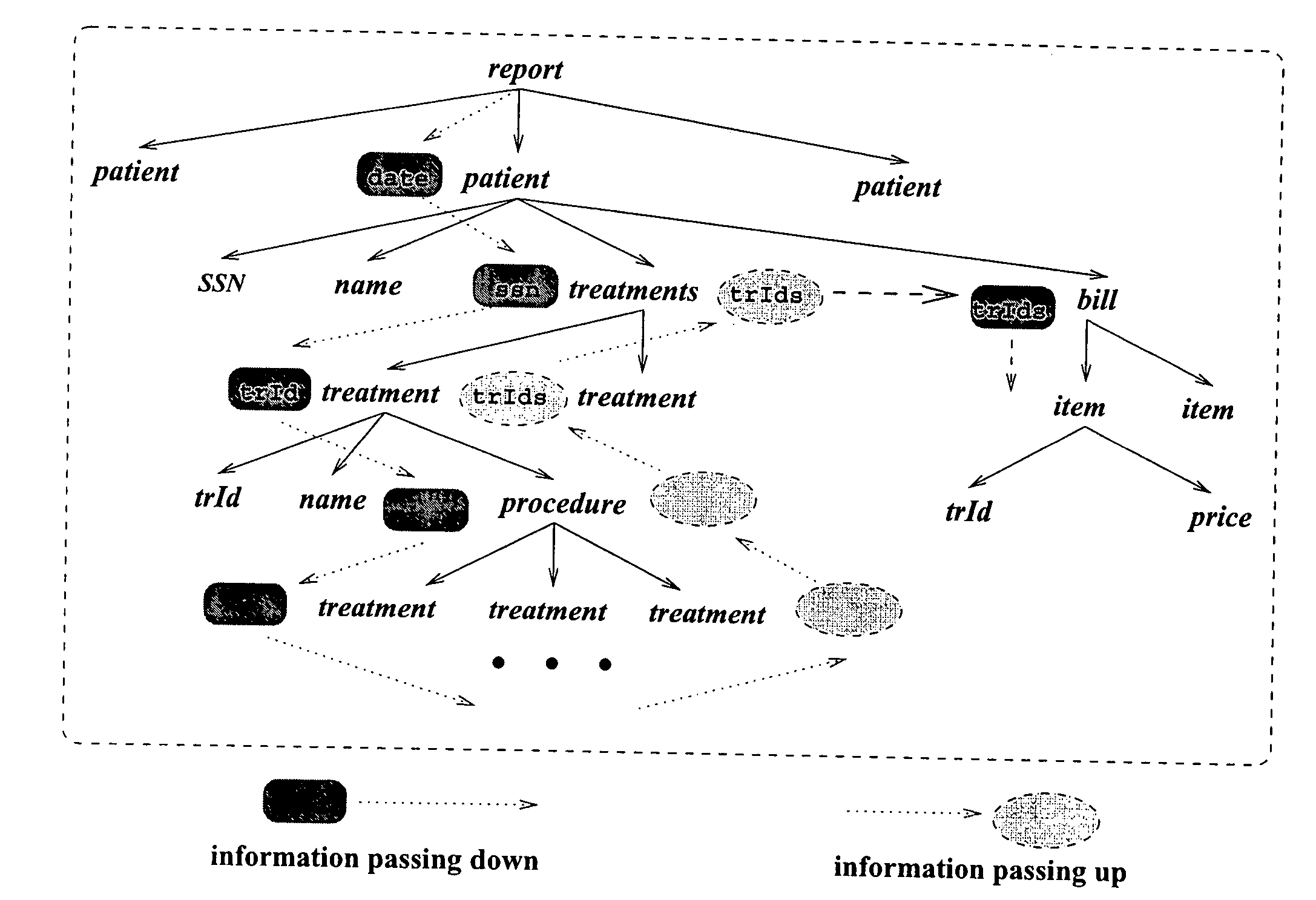
System and method for XML data integration
InactiveUS20050278368A1Effective evaluationNatural language data processingSemi-structured data mapping/conversionSemantic propertyData source
A framework is provided for integrating data from multiple relational sources into an XML document that both conforms to a given DTD and satisfies predefined XML constraints. The framework is based on a specification language, designated Attribute Integration Grammar (AIG), that extends a DTD by (1) associating element types with semantic attributes, (2) computing these attributes via parameterized SQL queries over multiple data sources, and (3) incorporating XML keys and inclusion constraints. The AIG uniquely operates on semantic attributes and their dependency relations for controlling context-dependent, DTD-directed construction of XML documents, and, as well as checks XML constraints in parallel with document-generation.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
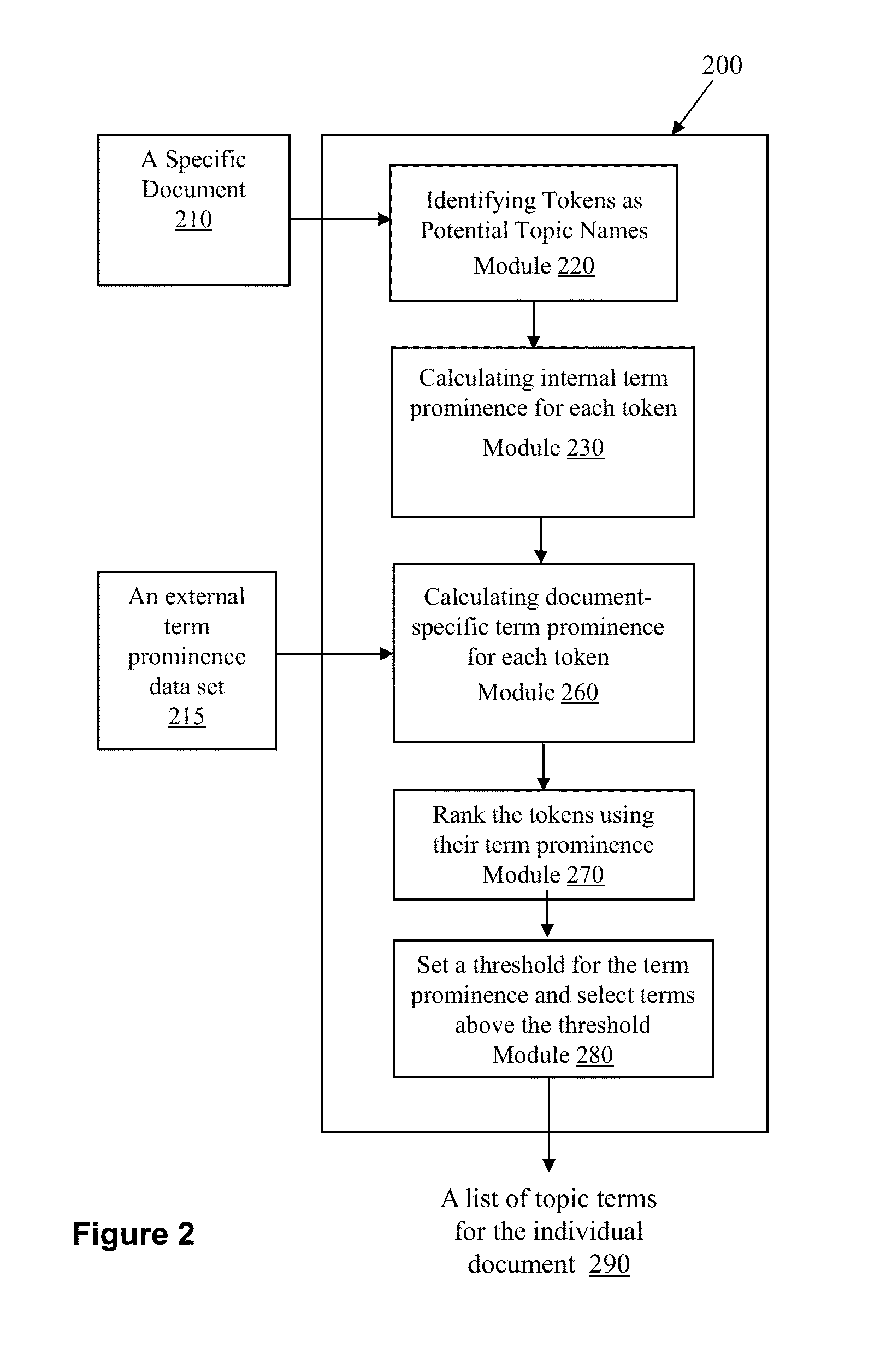
Text processing system and methods for automated topic discovery, content tagging, categorization, and search
InactiveUS9483532B1Easy to findEfficient and accurate and scalableWeb data indexingSemantic analysisSemantic propertyPart of speech
A computer system and methods are disclosed for automatically discovering topics and building a hierarchical topic structure, and for tagging and categorizing contents in a document or other natural language contents. The disclosed methods include steps for obtaining terms that best represent the topics in a text content, and building a hierarchical representation of topics of different levels or topic-comment relationships, and folder-subfolder structures. The methods further include obtaining, identifying, and selecting terms representing different degrees of informational importance based on the grammatical roles, parts of speech, and semantic attributes associated with the terms, using the terms to represent topics in the document, to automatically tag the document, to rank search results, and to build a category structure based on the selected terms.
Owner:LINFO IP LLC
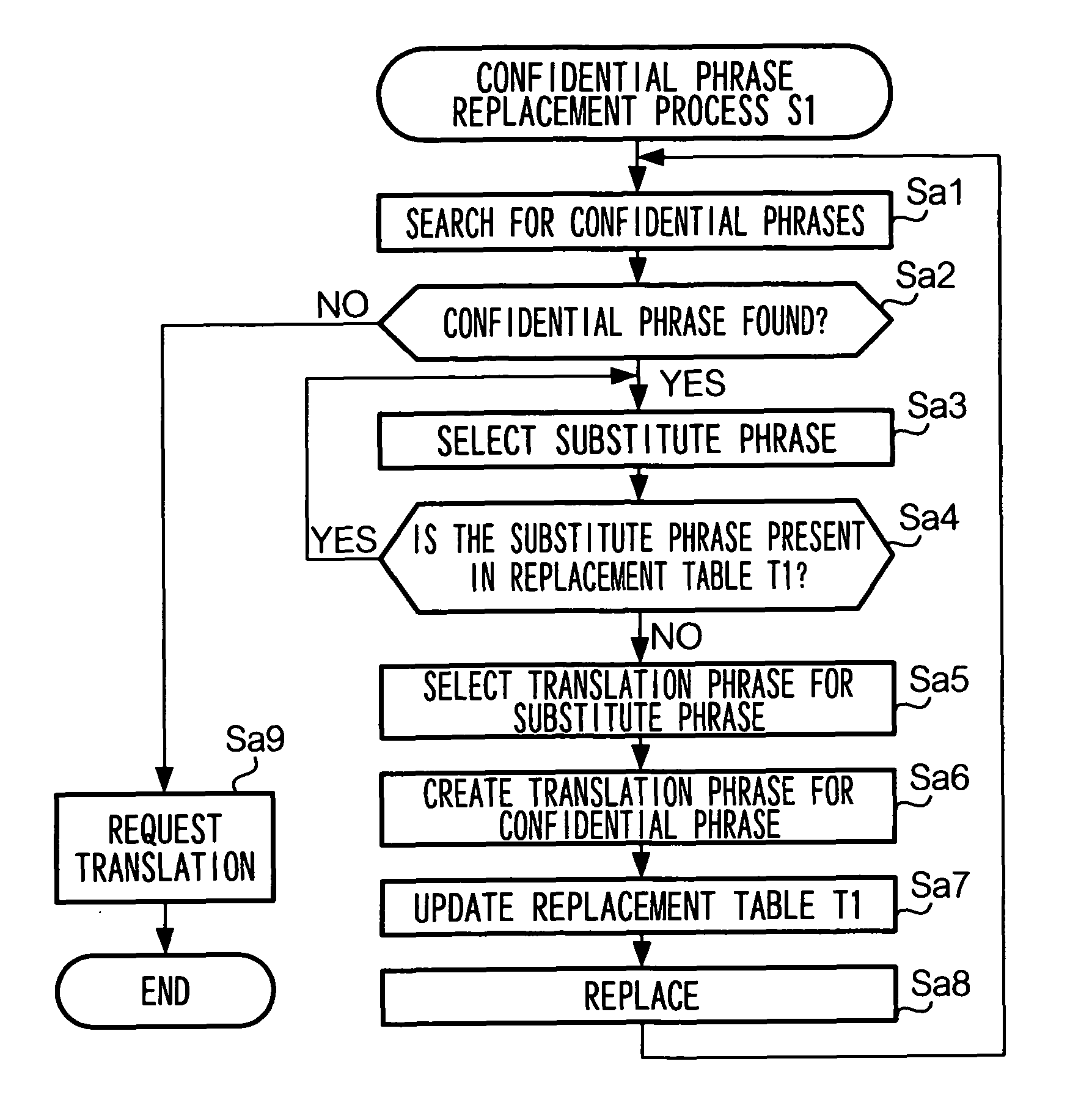
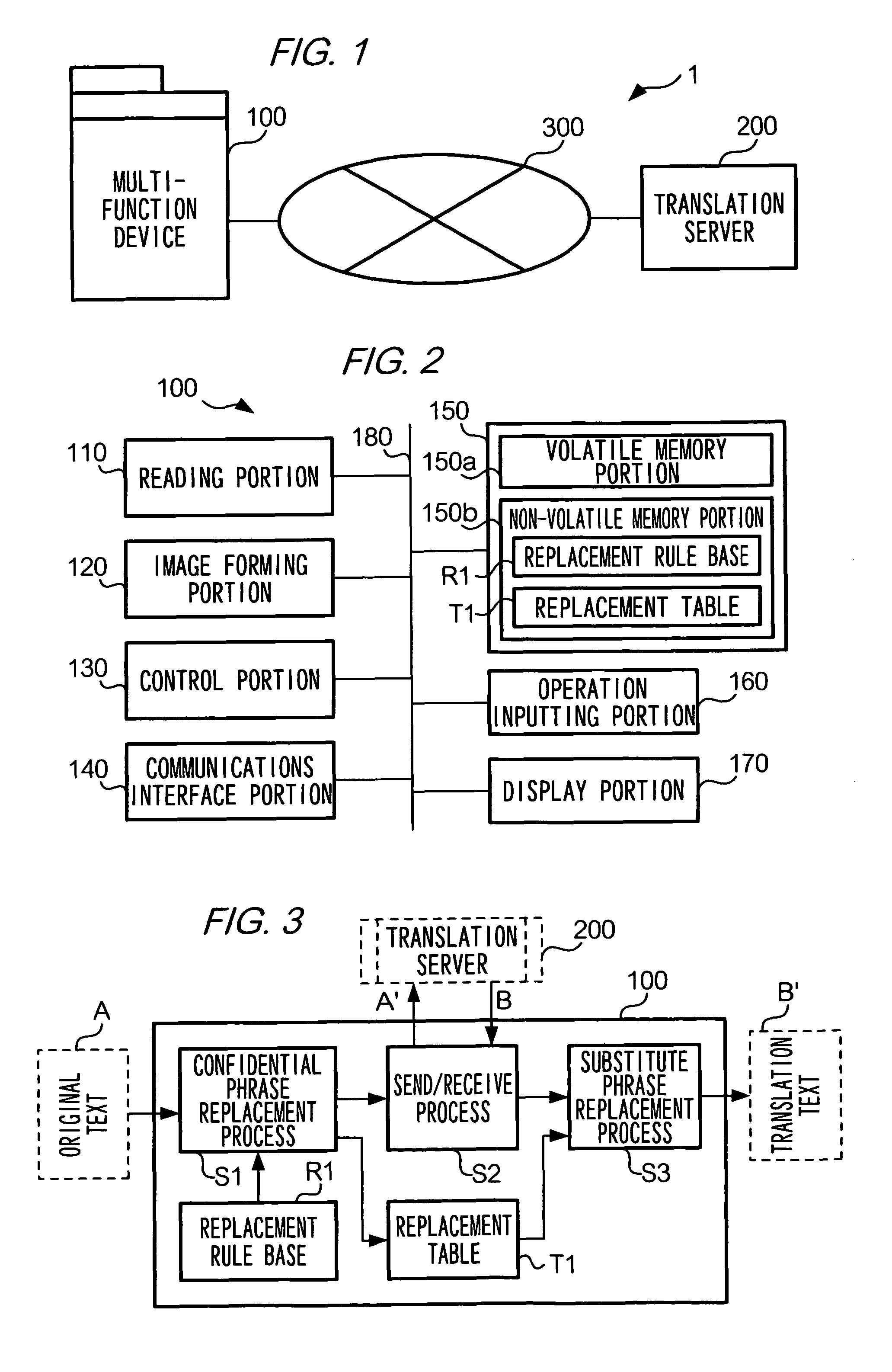
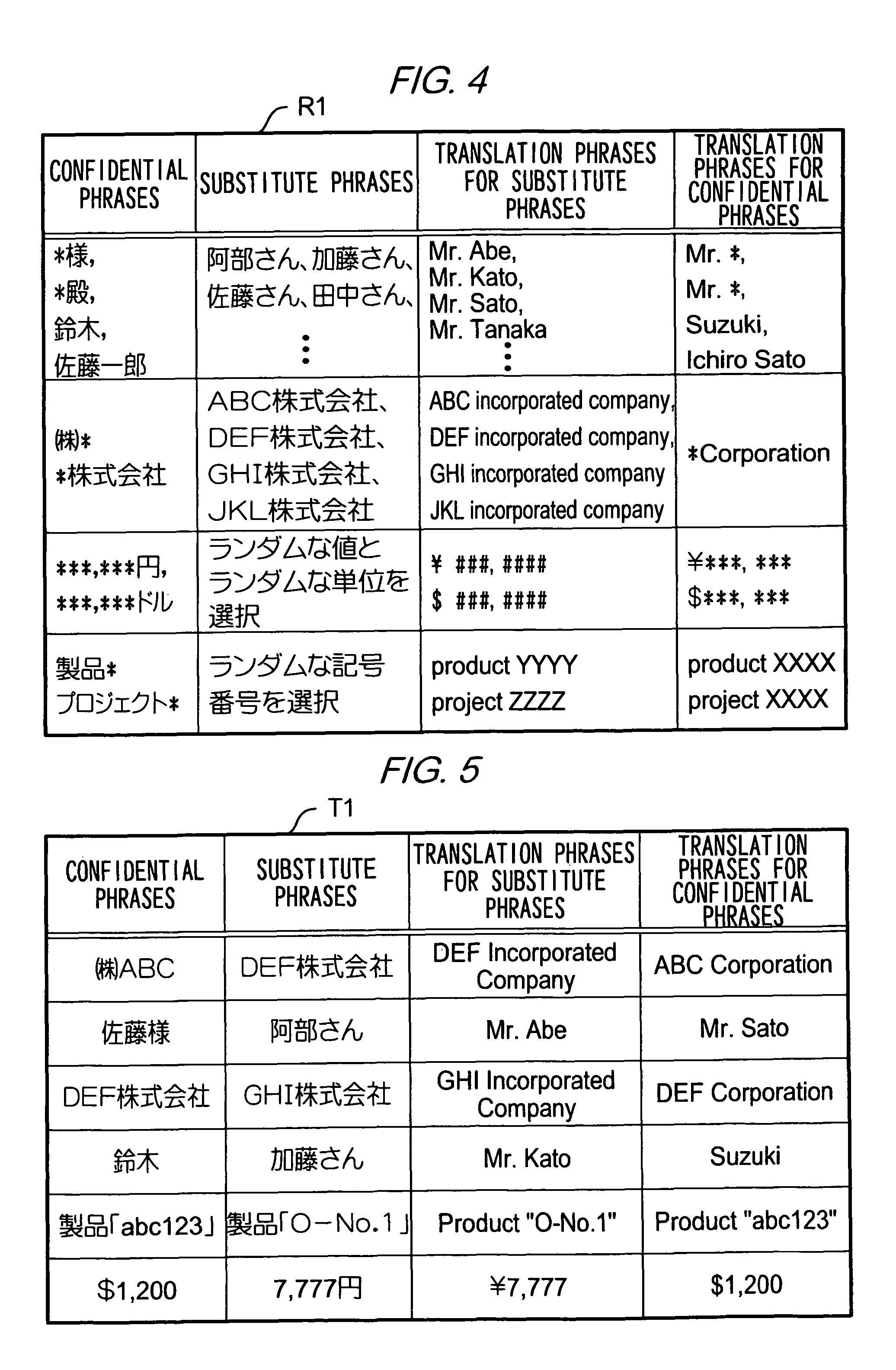
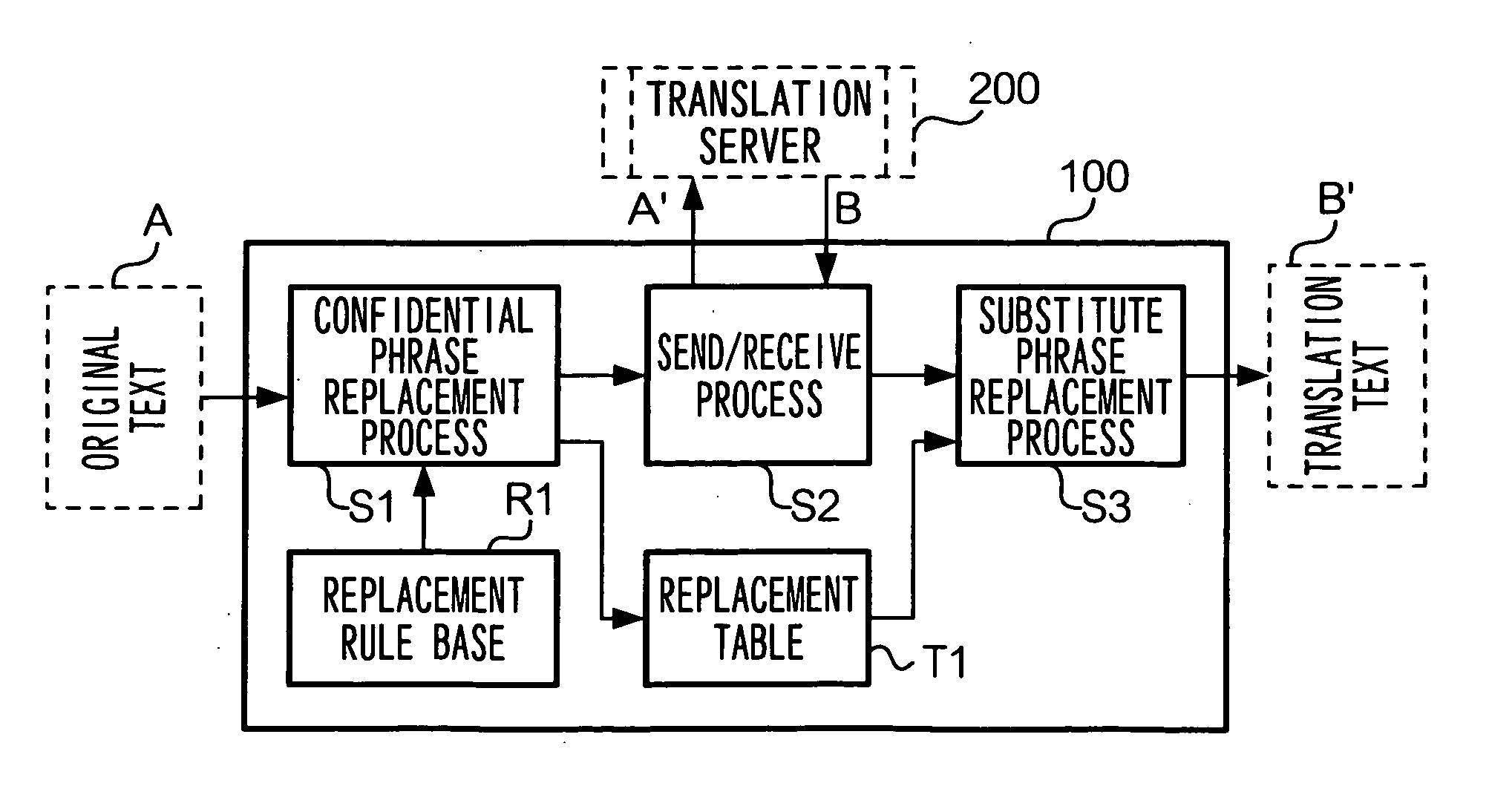
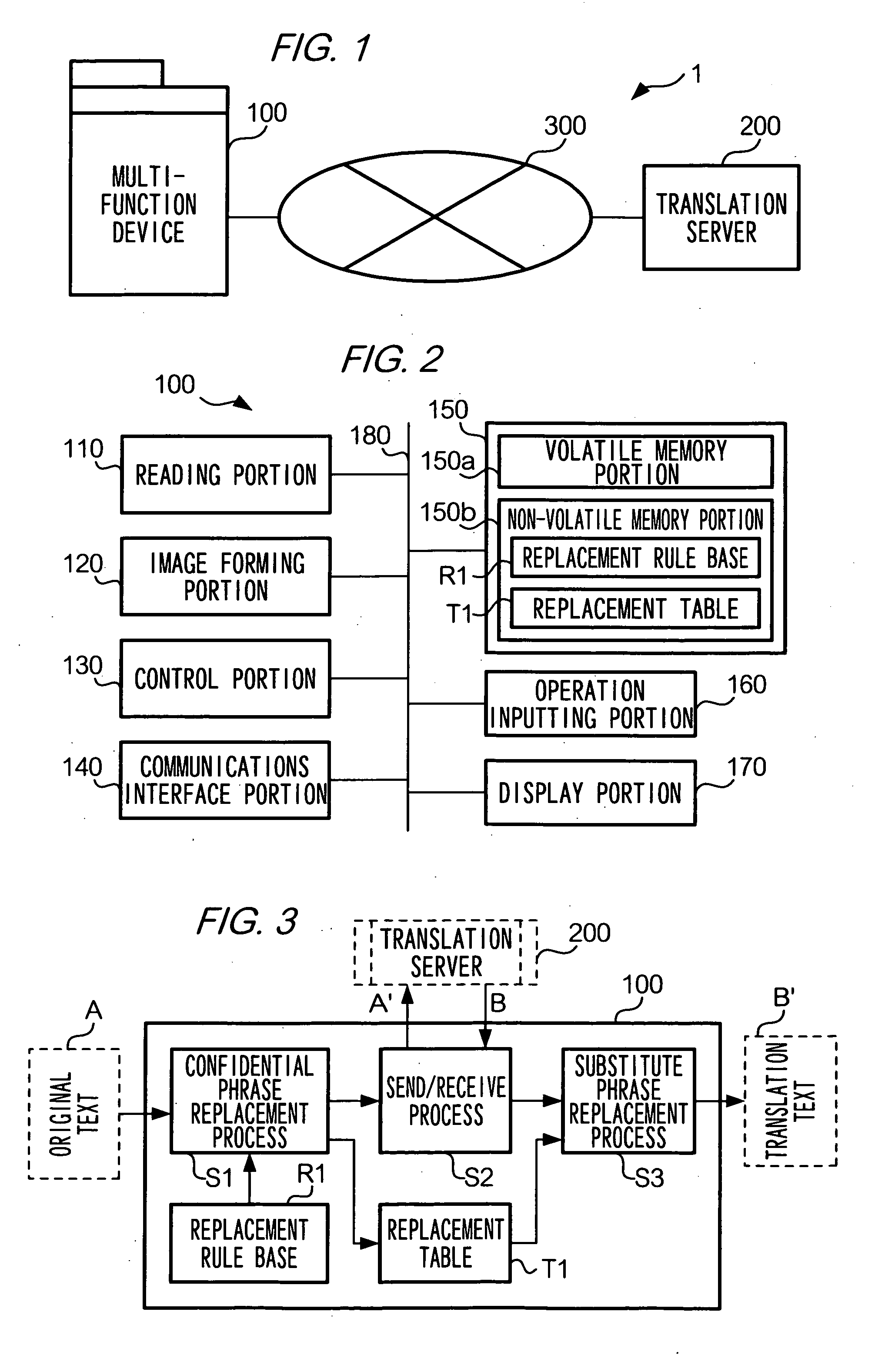
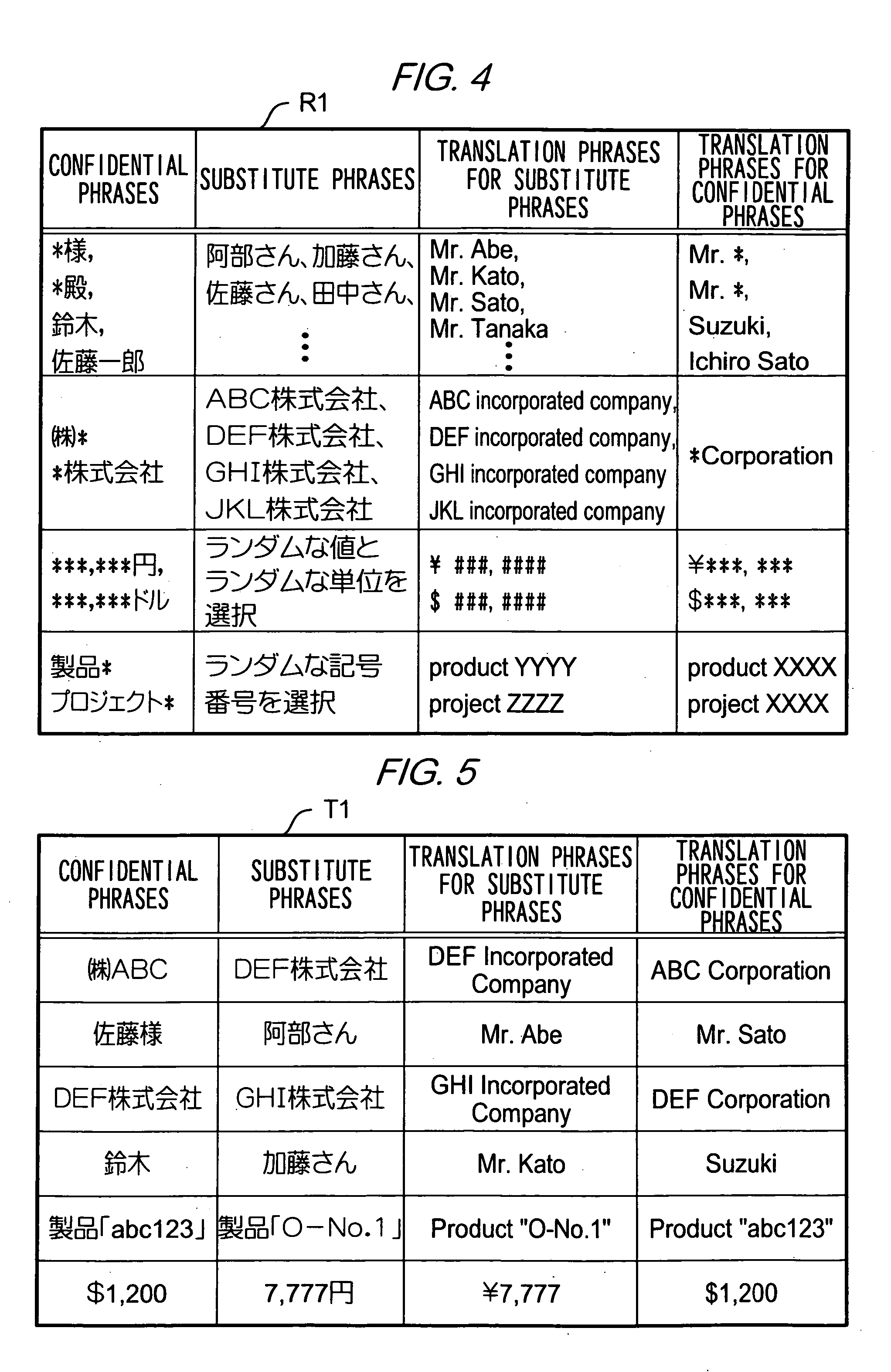
Translation requesting method, translation requesting terminal and computer readable recording medium
InactiveUS7801720B2High resultMaintain confidentialityNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic propertyRecording media
A translation requesting device has a first replacing unit, a translating unit and a second replacing unit. The first replacing unit replaces an original phrase to a substitute phrase. The translating unit translates the substitute phrase. The second replacing unit replaces the original phrase to a translation phrase based on the translated substitute phrase. The substitute phrase is decided to maintain semantic properties of the original phrase.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Translation requesting method, translation requesting terminal and computer readable recording medium
InactiveUS20060200339A1High resultMaintain confidentialityNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic propertyPaper document
As described above, the present invention also provides, in one aspect, a translation requesting device for translating a document having: a first replacing unit that replaces an original phrase to a substitute phrase; a translating unit that translates the substitute phrase; and a second replacing unit that replaces the original phrase to a translation phrase based on the translated substitute phrase, wherein the substitute phrase is decided to maintain semantic properties of the original phrase.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
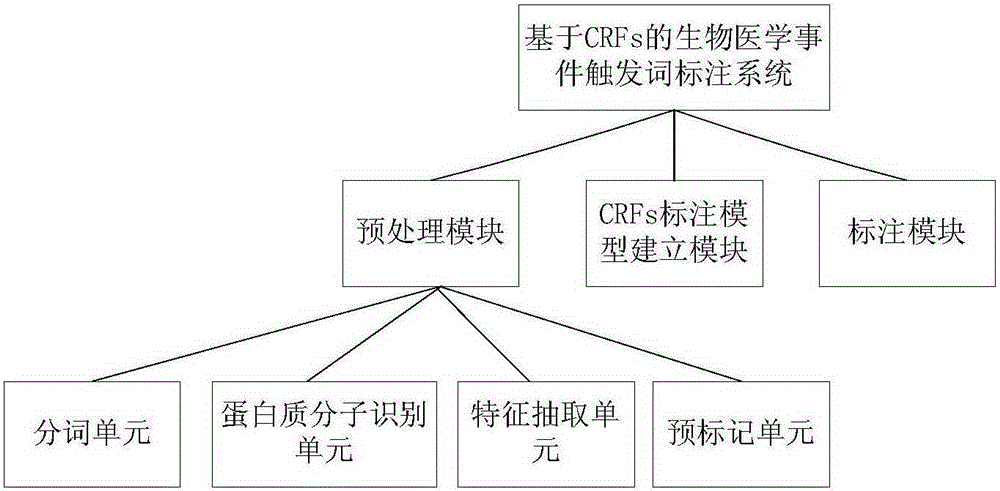
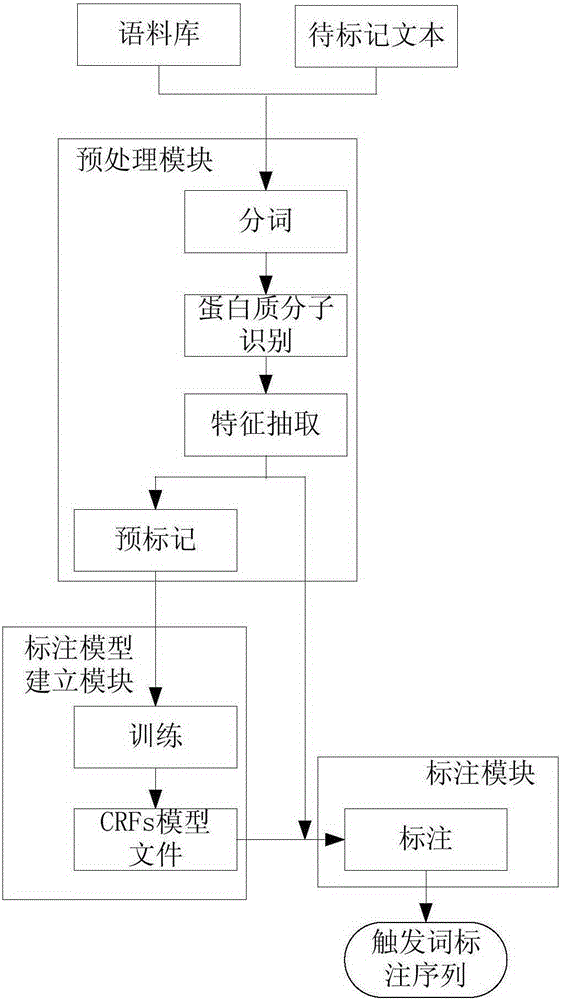
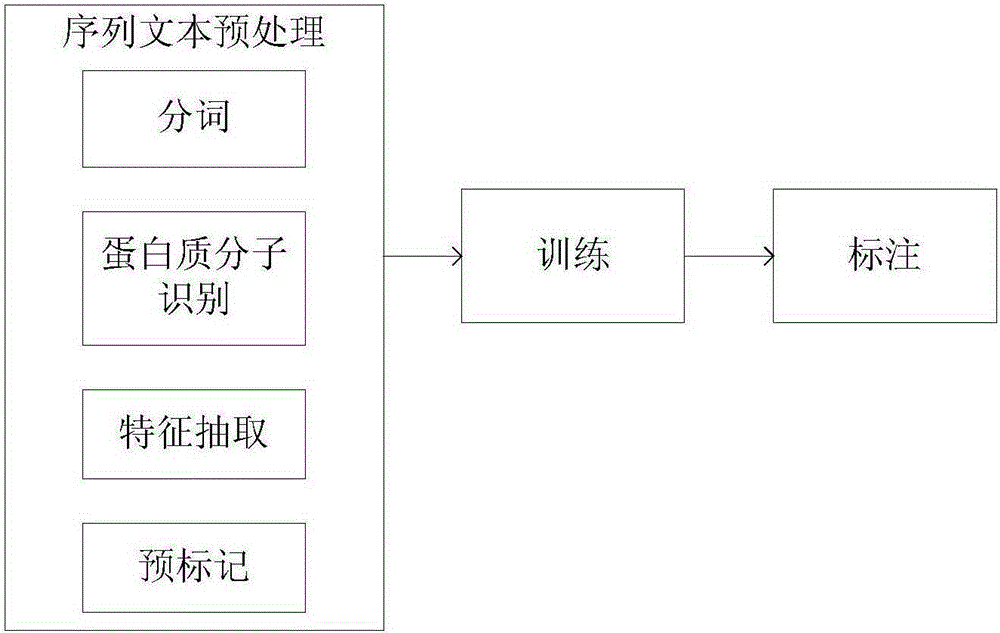
Trigger word tagging system and method for biomedical events
ActiveCN105260361ARealize the joint probabilityImprove recallSpecial data processing applicationsNatural language processingSemantic property
The invention discloses a trigger word tagging system and method for biomedical events. The trigger word tagging system comprises a pretreatment module, a tagging model building module and a tagging module, wherein the pretreatment module is used for acquiring a training sample and a testing sample and comprises a word segmentation unit, a protein molecule identification unit, a feature extraction unit and a pre-tagging unit; the word segmentation unit is used for acquiring the word sequence of an original text; the protein molecule identification unit is used for identifying protein molecules and replacing with a standard mode to bring more convenience for feature extraction and trigger word tagging; the feature extraction unit is used for extracting the word forms, the word characteristics and other syntactic properties and semantic properties, and finally pre-tags the word sequence as a training and testing sample set; the tagging model building module is used for building a feature template, generating characteristic functions, and estimating weights corresponding to the characteristic functions to obtain a CRFs trigger word tagging model; the tagging module is used for trigger word tagging of an unknown test sequence and displays the result on a GUI interface.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Maintaining graphical presentations based on user customizations
A method and system for rendering graphics based on user customizations in a computer graphics application are disclosed. The customizations relate to various properties of one or more graphical elements in the graphic. Such properties include positioning, size, formatting and other visual attributes associated with the graphical elements. These properties may be defined as either semantic properties or presentation properties. Semantic properties are persistent across all graphic definitions. Presentation properties are specific to the graphic definition to which each particular graphic belongs. Thus, a customization to a semantic property of a displayed graphic is preserved in memory for application not only to the currently displayed graphic, but also to all other graphic definitions that may be displayed in the future. In contrast, a customization to a presentation property is only preserved for the currently displayed graphic, and thus not preserved for all other graphic definitions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
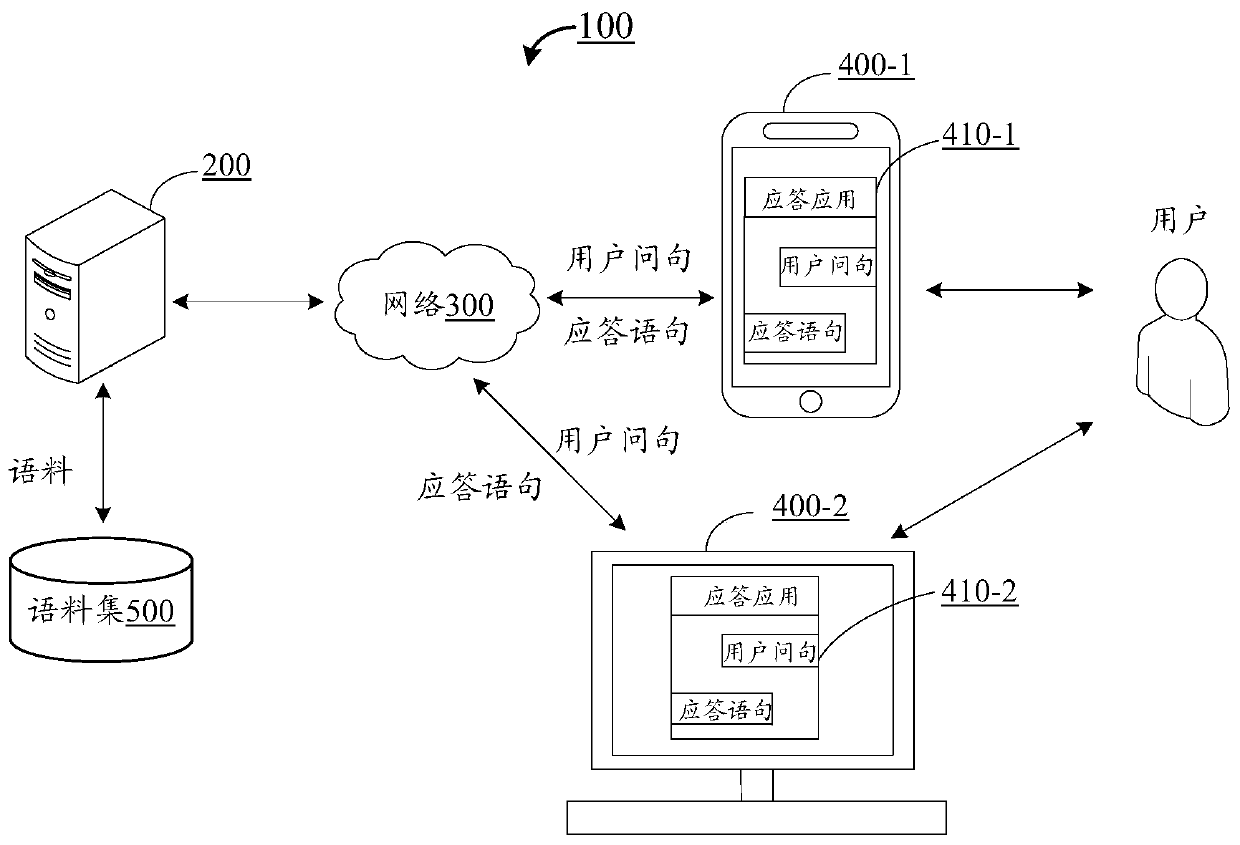
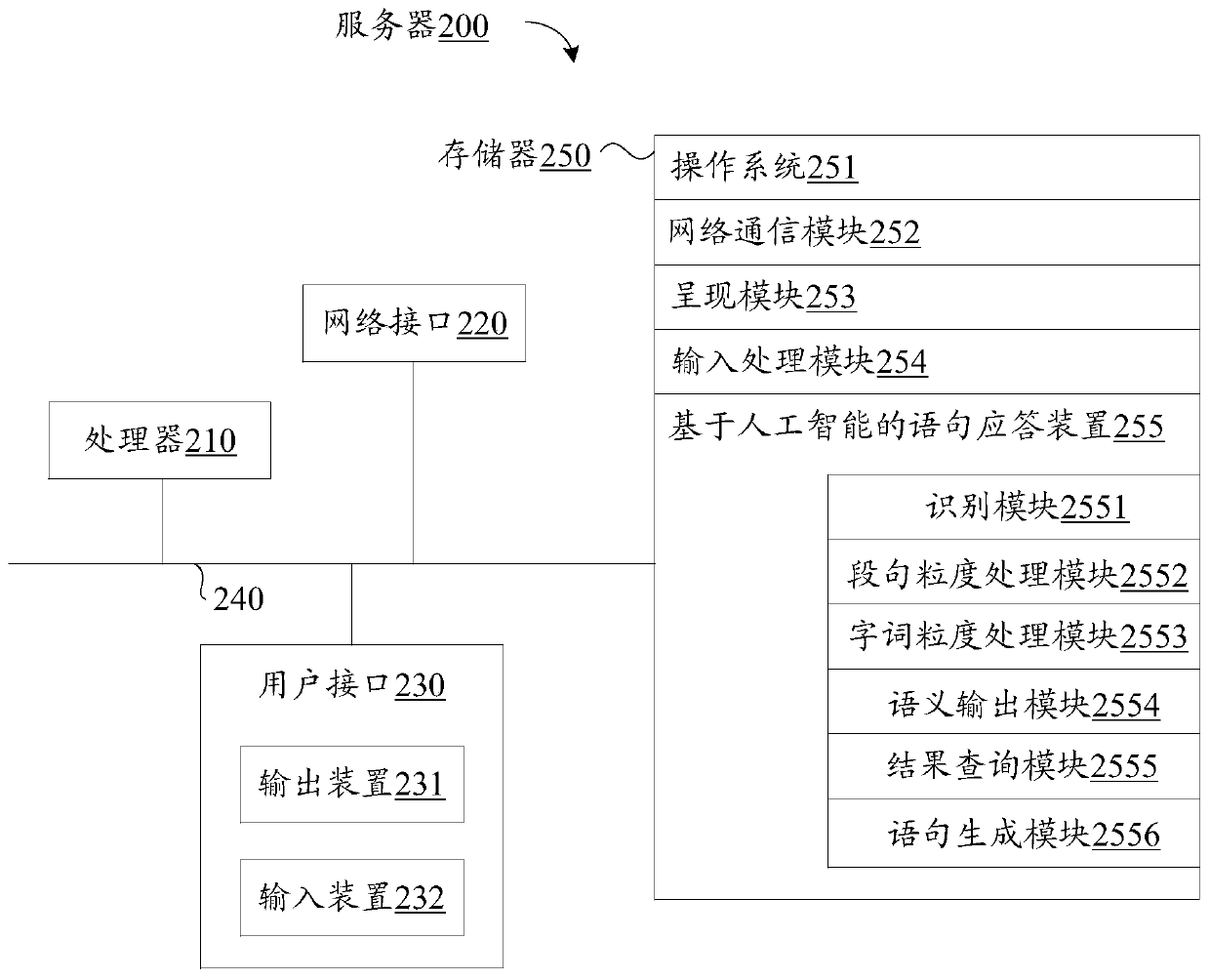
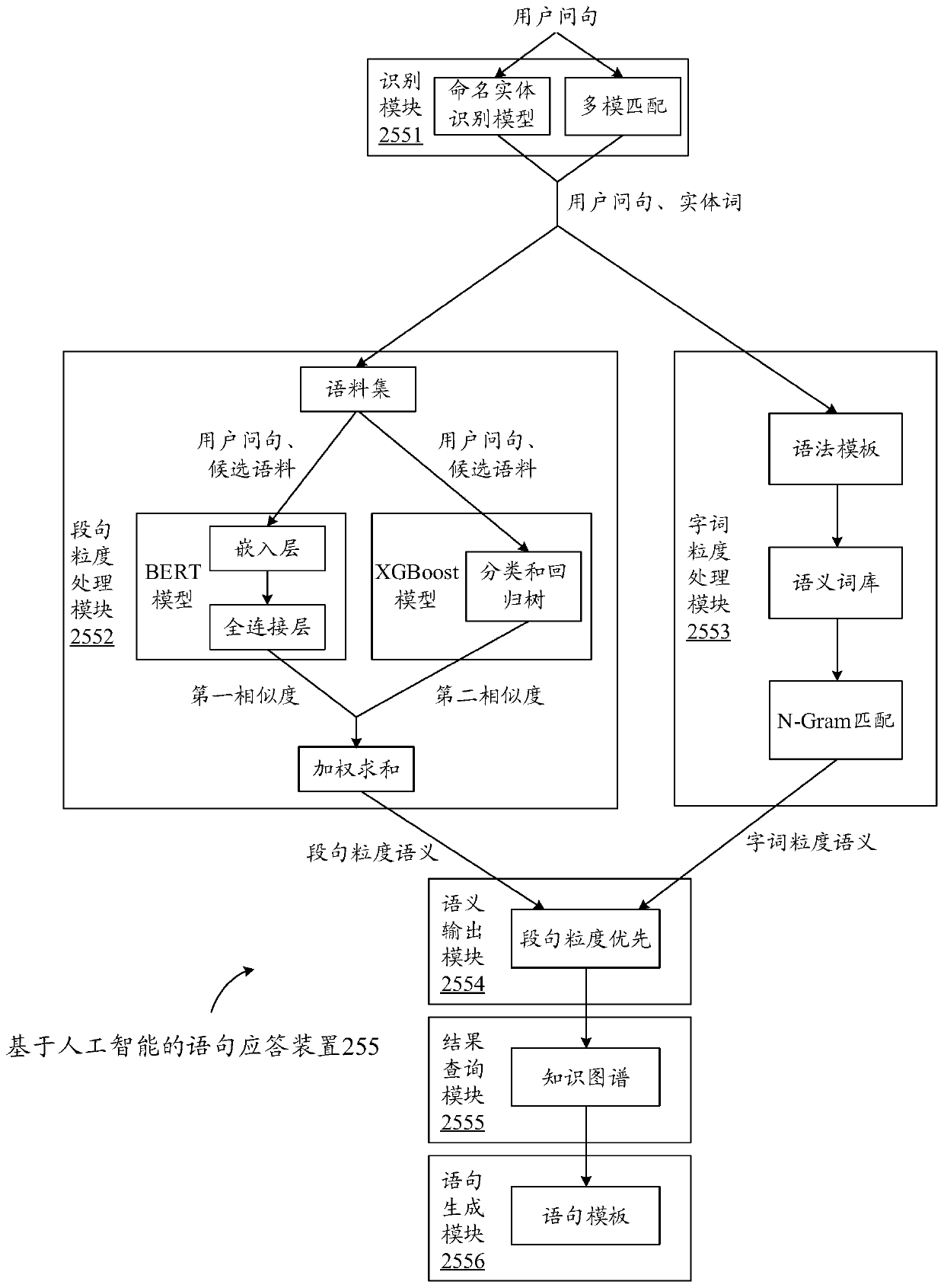
Statement response method and device based on artificial intelligence and electronic equipment
ActiveCN110489538AImprove applicabilityImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionText database queryingSemantic propertyAlgorithm
The invention provides a statement response method and device based on artificial intelligence, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The statement response method based on artificial intelligence comprises: obtaining a user question, and identifying entity words in the user question; determining a target corpus in a corpus set according to the user question, and determining semantics of thetarget corpus as segment sentence granularity semantics of the user question; determining semantic attributes corresponding to the entity words, and arranging the entity words according to progressiverelationships corresponding to the semantic attributes to obtain word granularity semantics of the user question; determining output semantics of the user question according to the segment sentence granularity semantics and the word granularity semantics; querying in a set knowledge graph according to the output semantics to obtain a semantic result; and generating a response statement accordingto the semantic result. Through the double-granularity mechanism, the semantic generalization ability can be improved, the applicability to different user questions is improved, and correct response is realized.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Viewing and editing markup language files with complex semantics
ActiveUS20060168562A1Visual/graphical programmingSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic propertySingle element
The semantic hierarchy of a document written in a markup language is represented by a hierarchy of elements, which are viewed and edited using a tree to which may be attached a special purpose editor, capable of editing the semantic properties of that particular element. Such special purpose editors handle the single element to which they are attached and may handle a hierarchy of elements that share common properties in the subtree headed by the single element. They offer a visualization of the elements to which they are attached that is not necessarily hierarchical in form.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com