Patents
Literature
124results about How to "High result" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
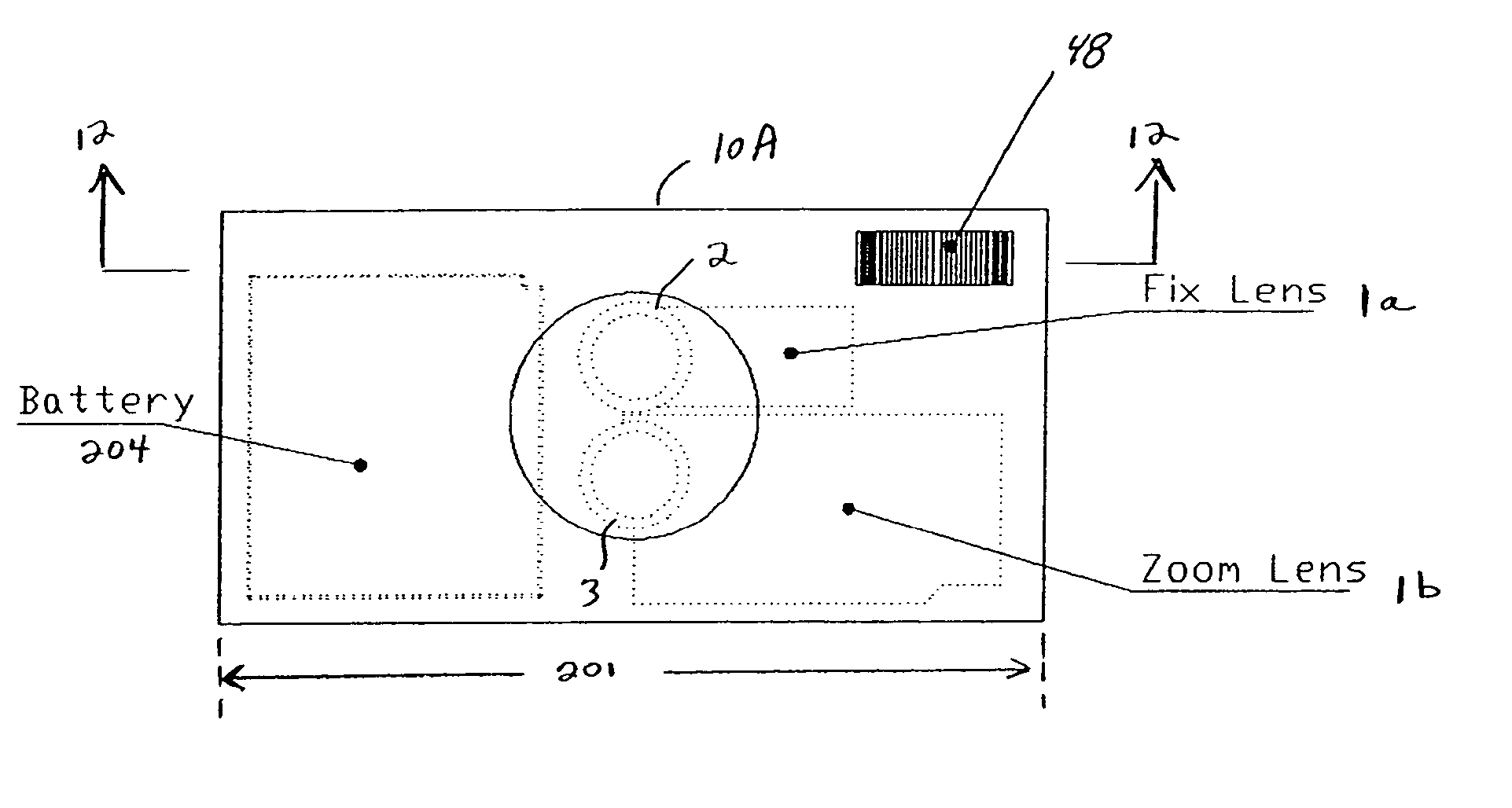
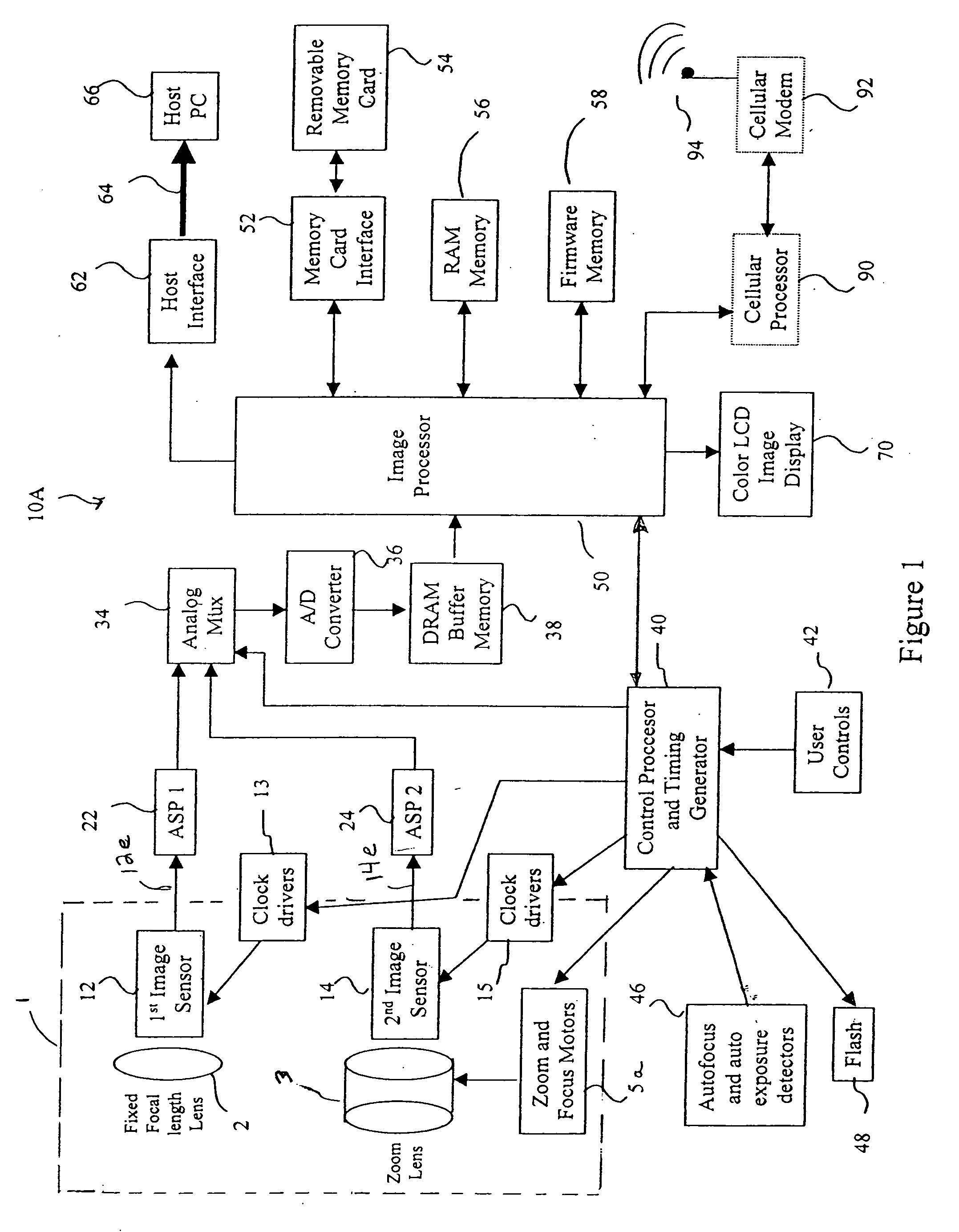
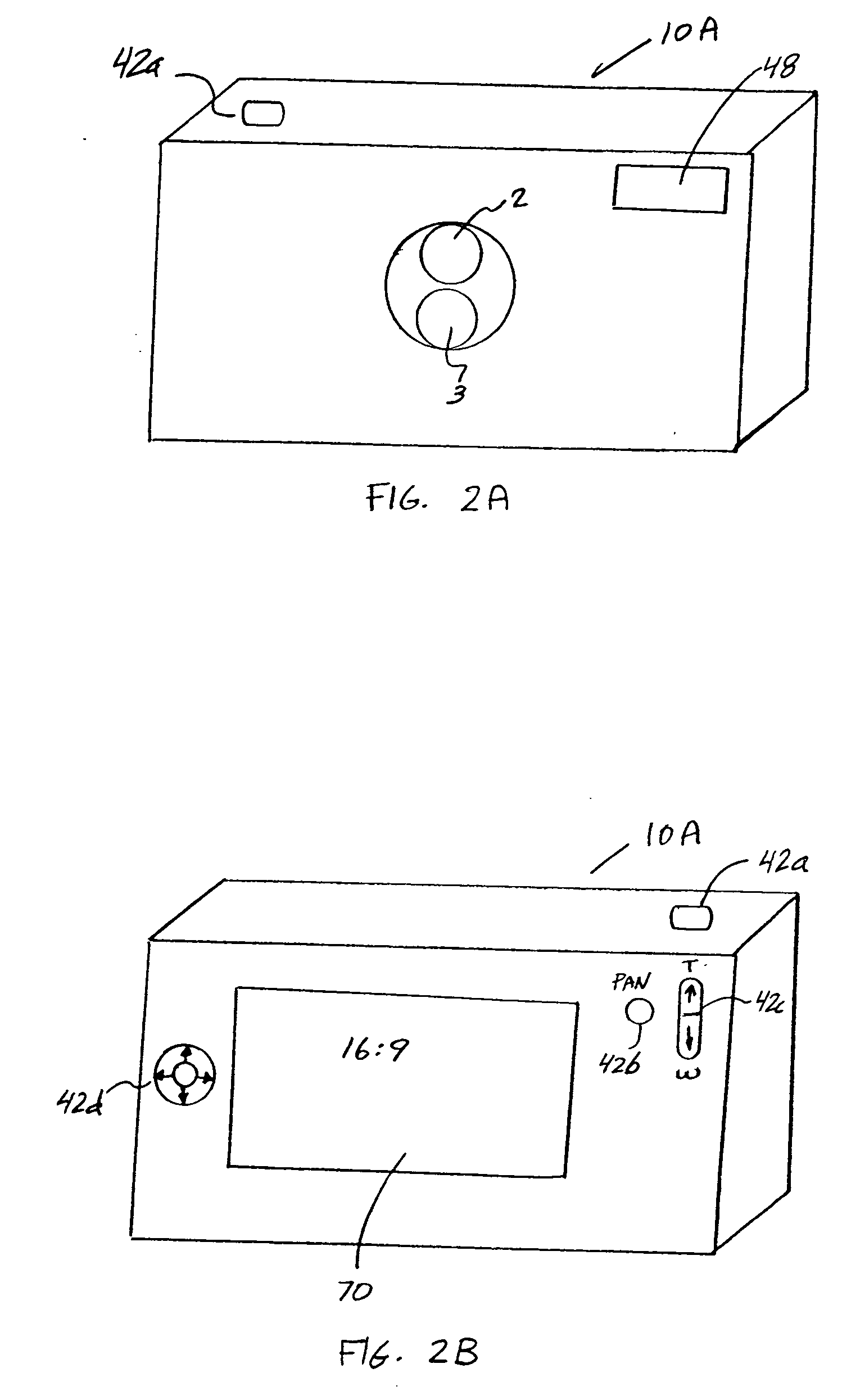
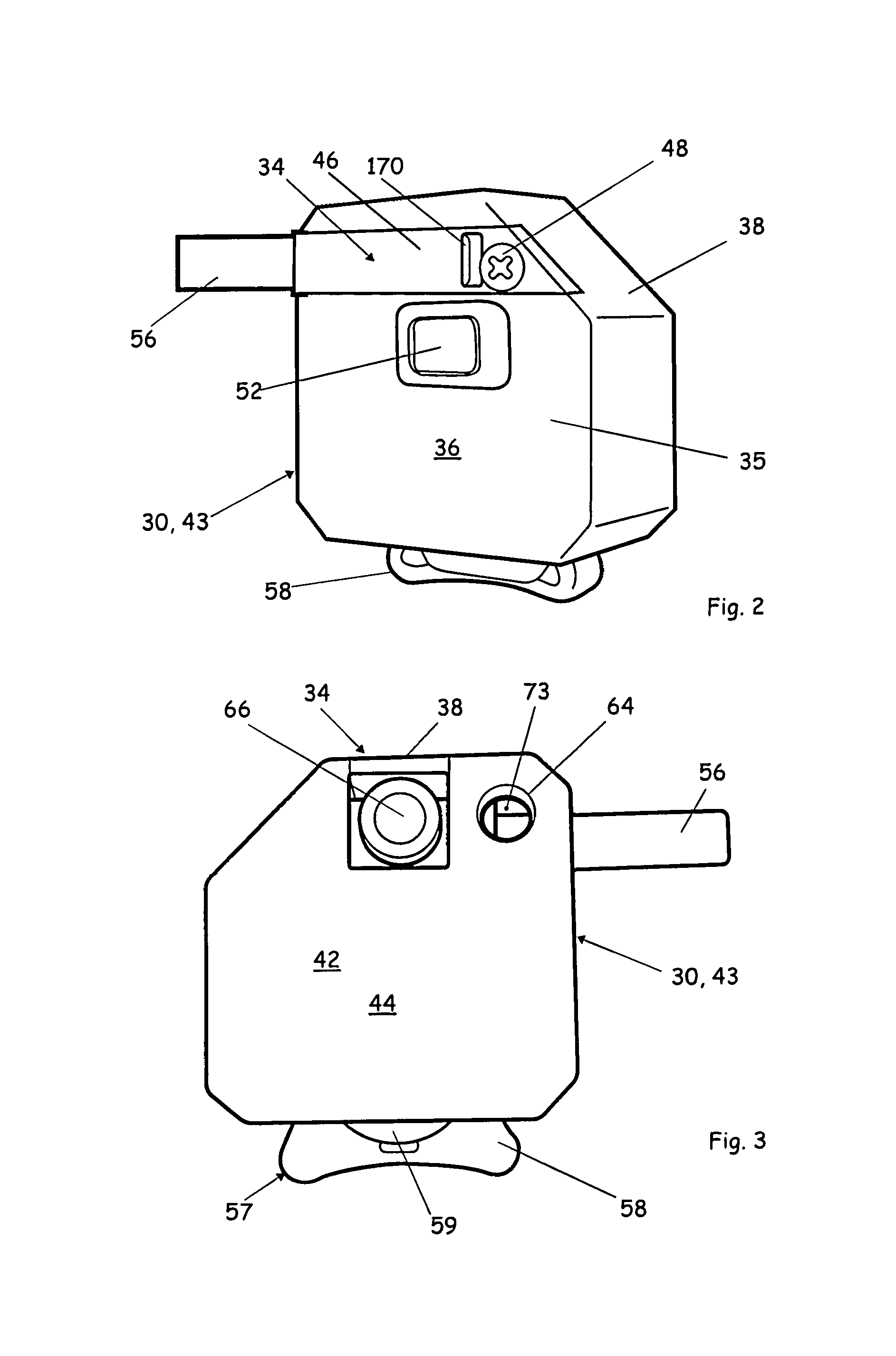
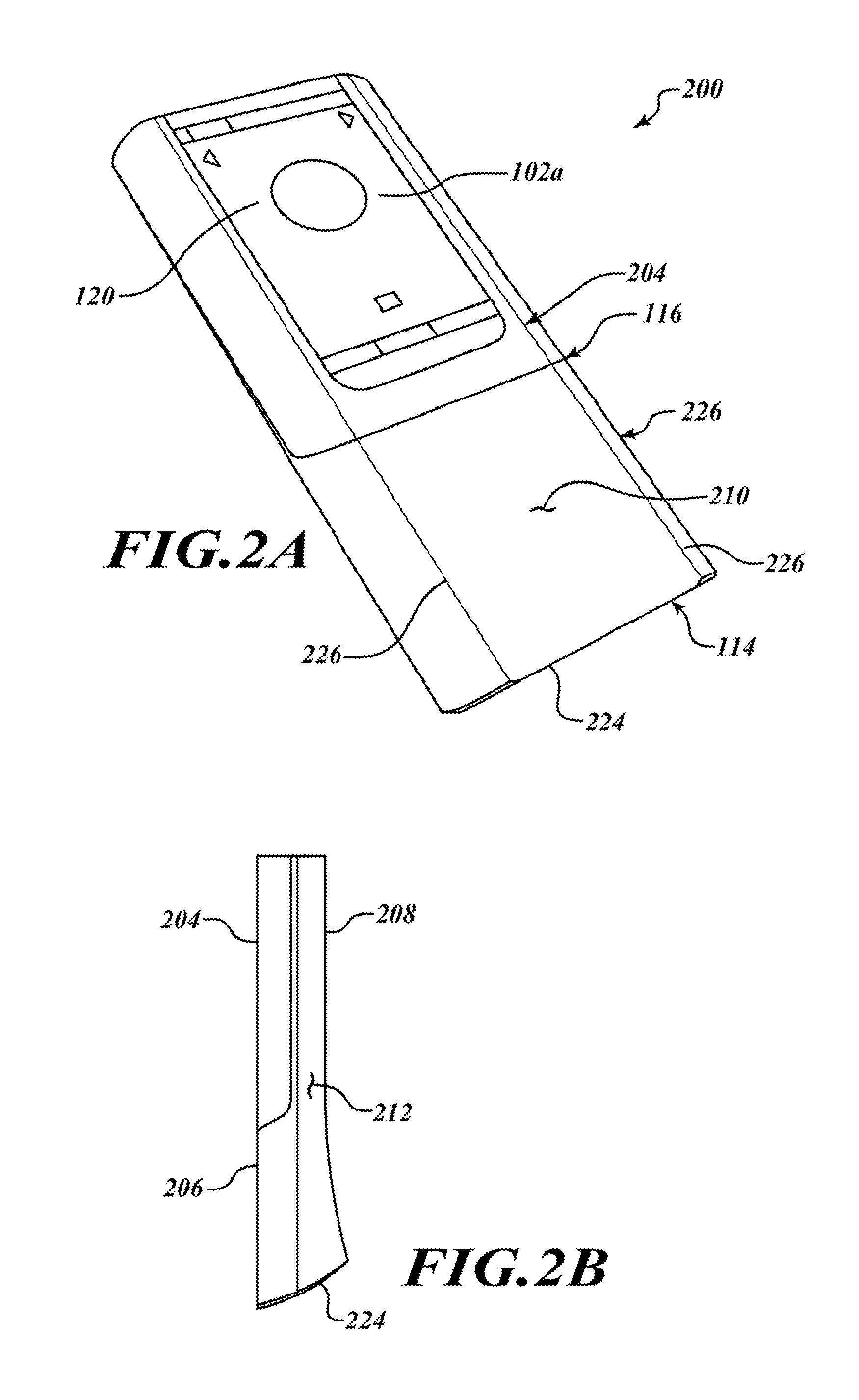
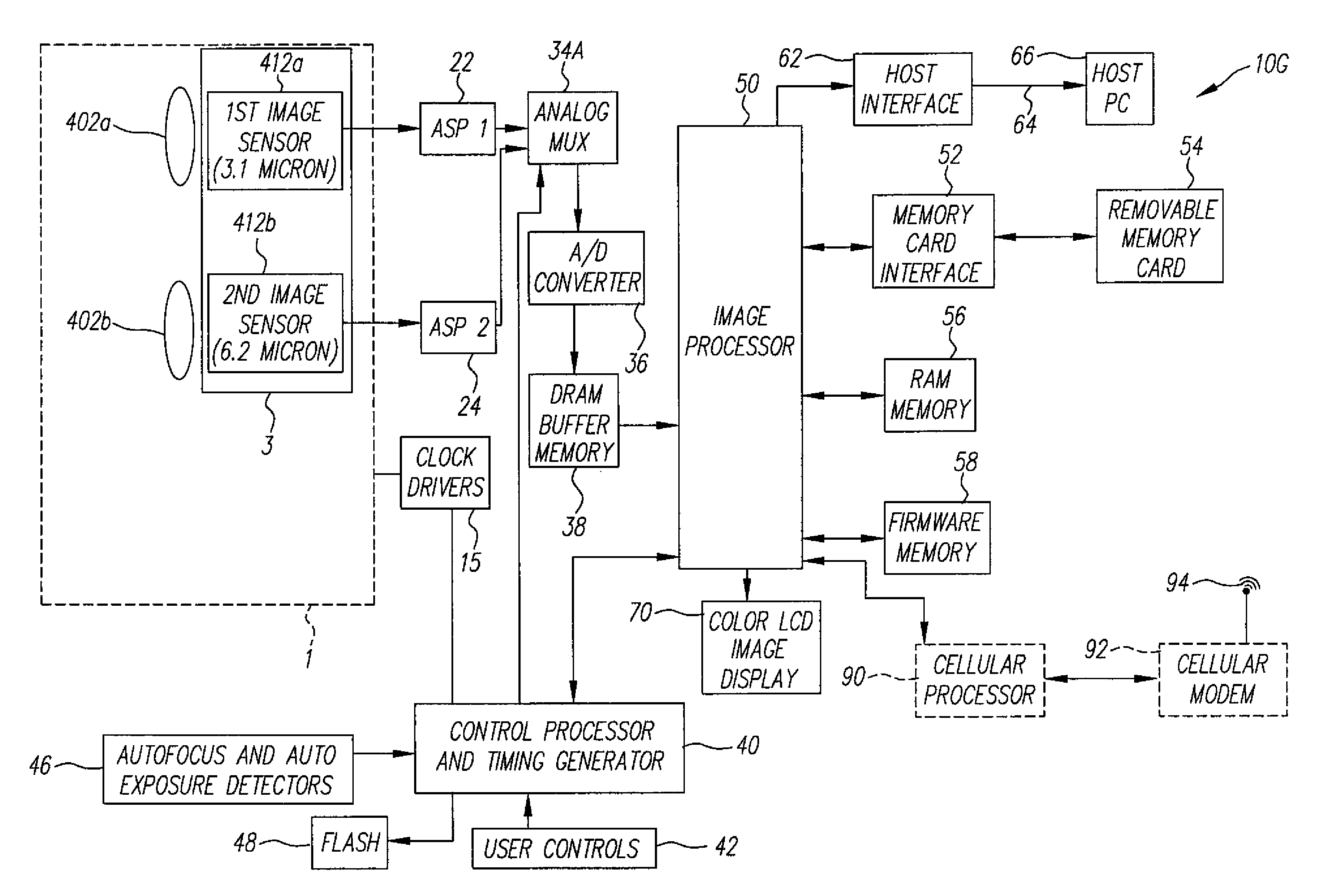
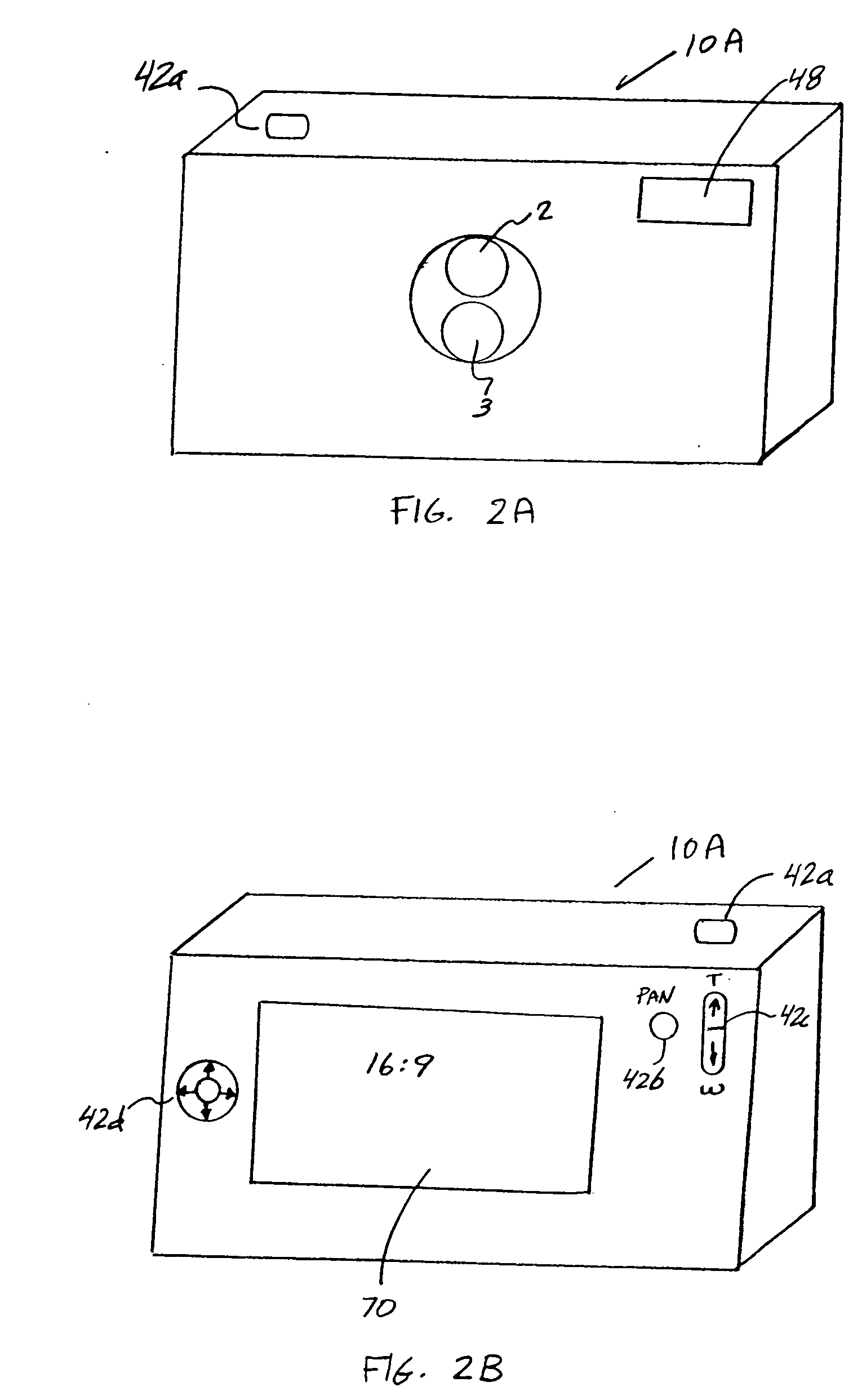
Camera phone using multiple lenses and image sensors to provide an extended zoom range
InactiveUS20060187338A1Low costHigh quality optical resultTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceCamera phoneTelephoto lens
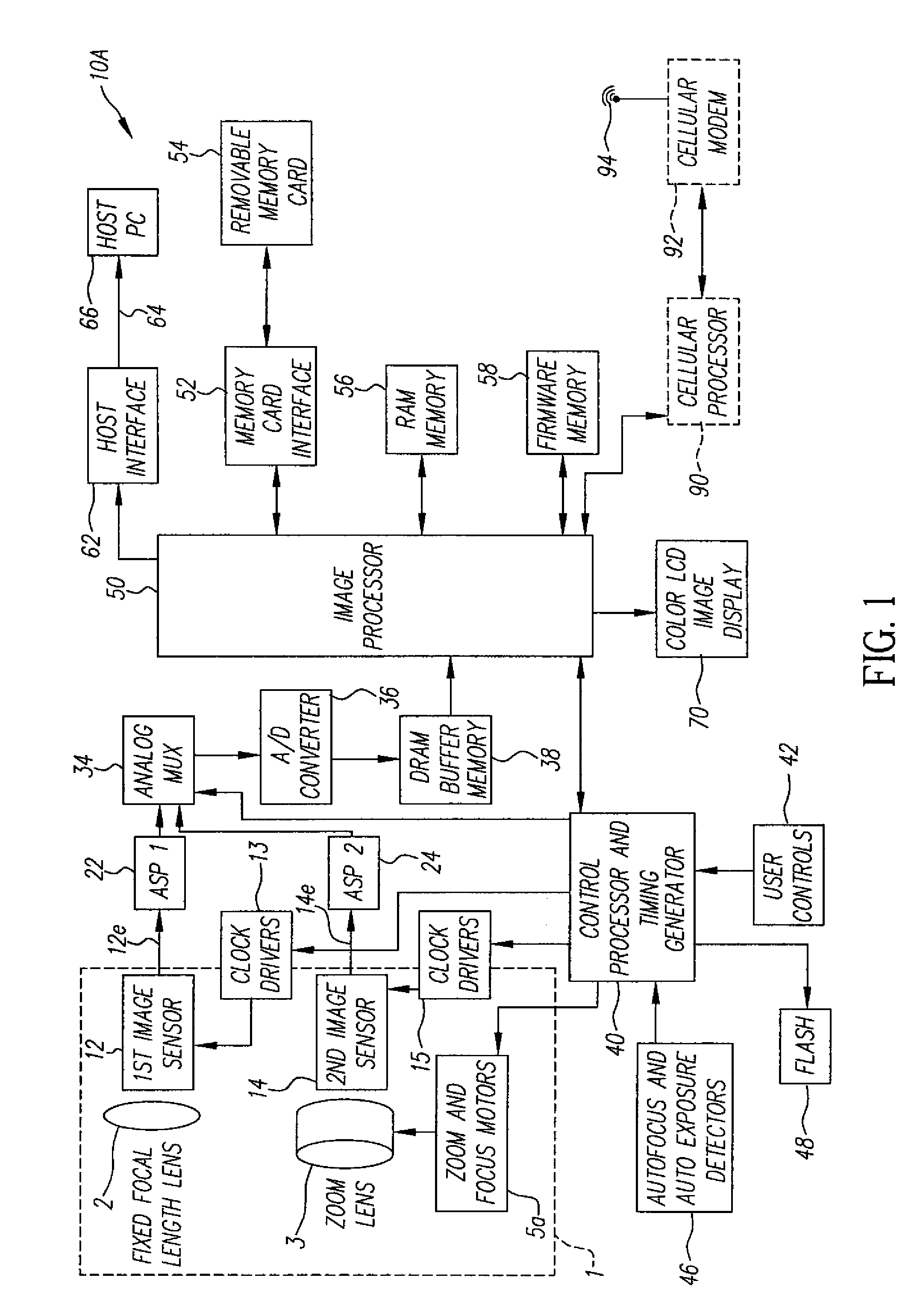
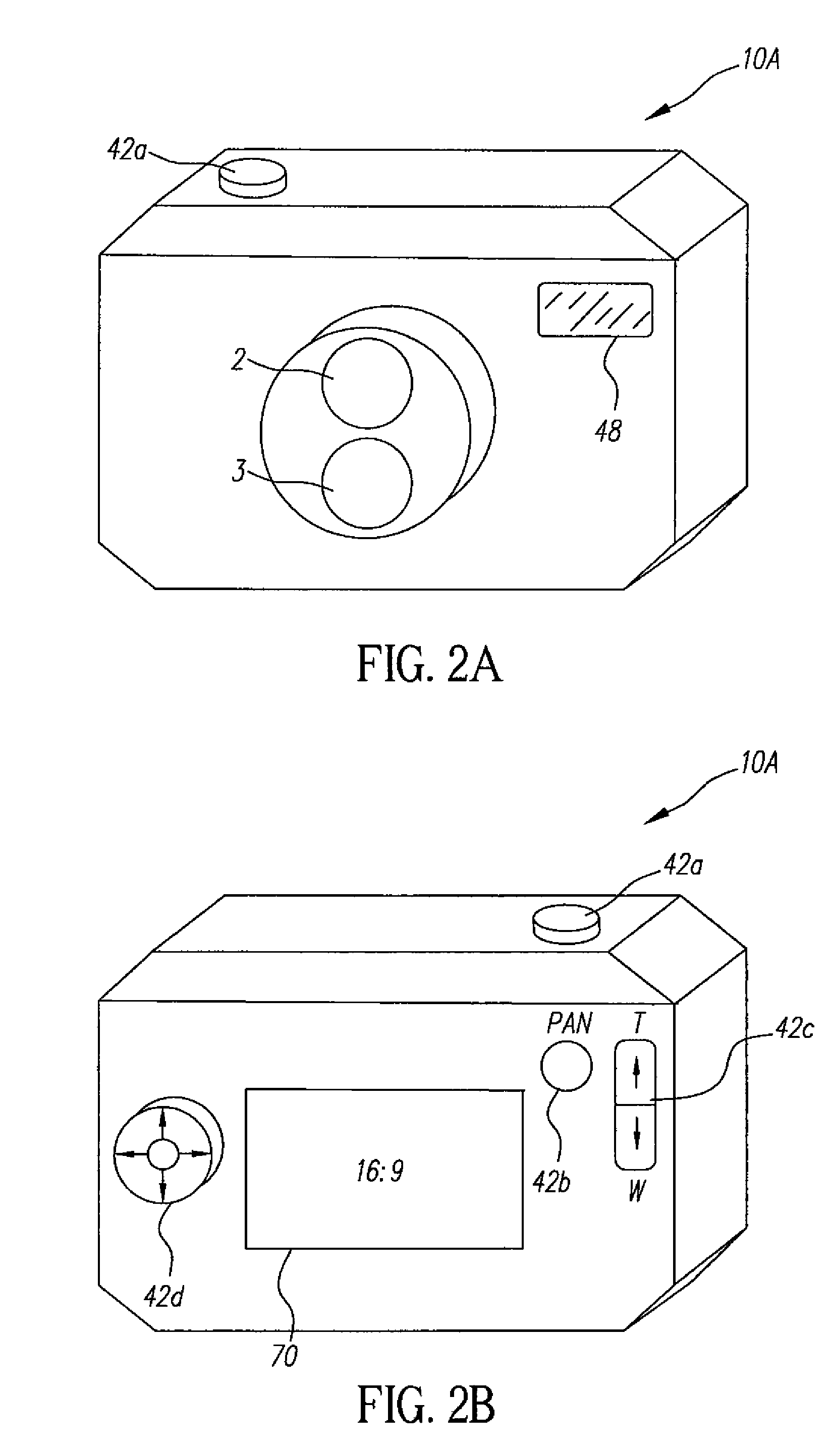
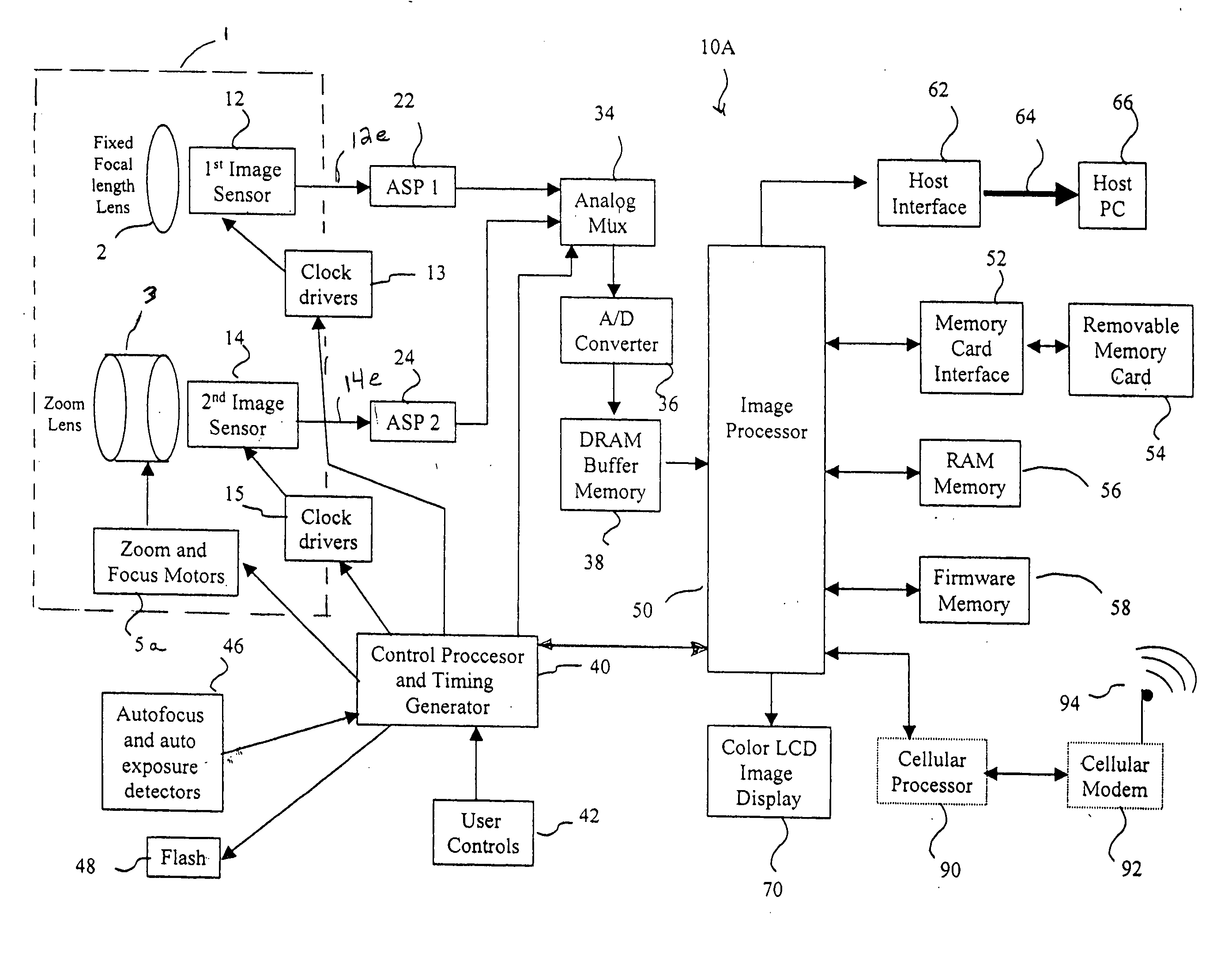
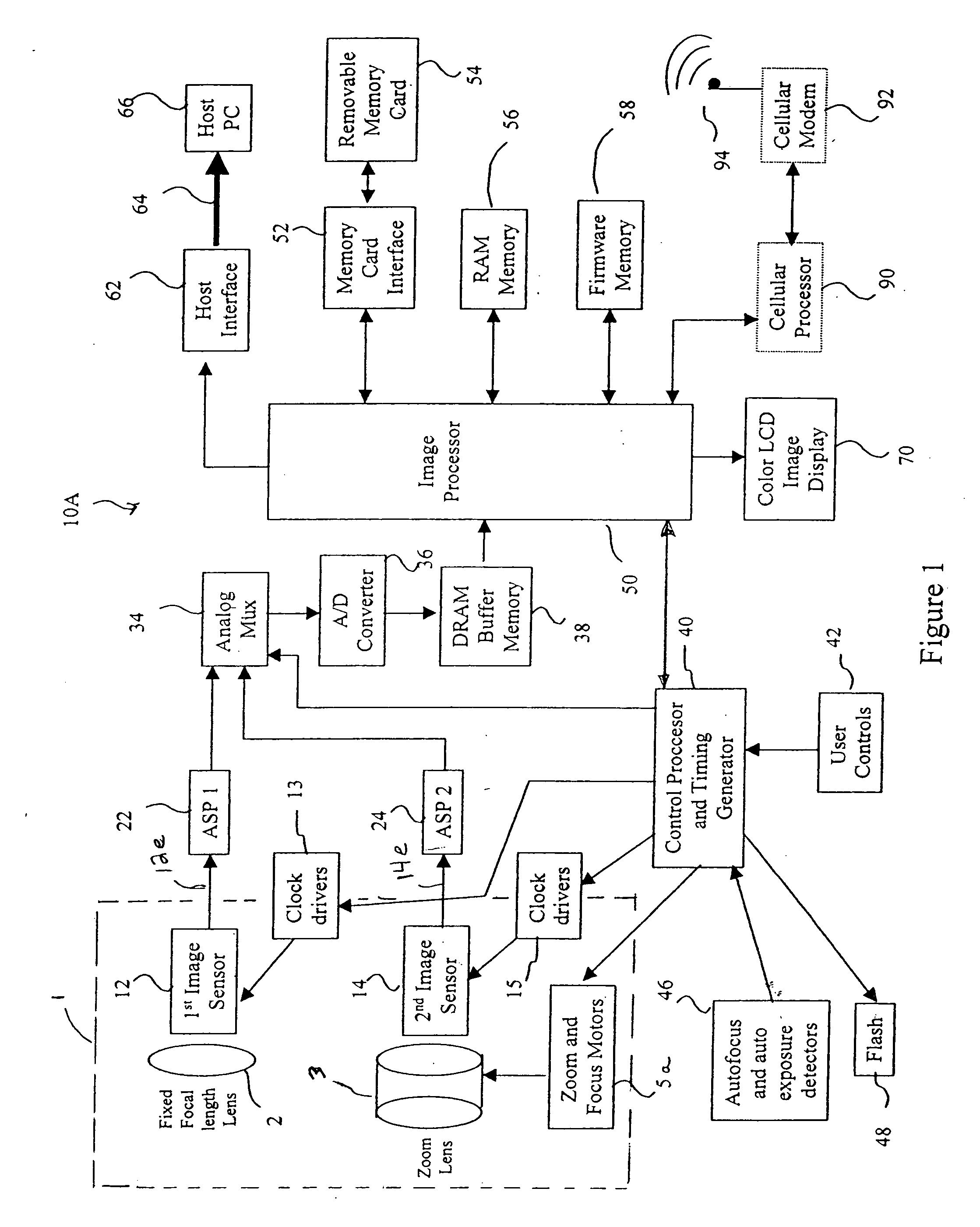
A camera phone includes a phone stage for generating voice signals, a first image sensor for generating a first sensor output, a first fixed focal length wide angle lens for forming a first image of the scene on the first image sensor, a second image sensor for generating a second sensor output, and a second fixed focal length telephoto lens pointing in the same direction as the first lens and forming a second image of the same scene on the second image sensor. A control element selects either the first sensor output from the first image sensor or the second sensor output from the second image sensor. A processing section produces the output image signals from the selected sensor output, and a cellular stage processes the image and voice signals for transmission over a cellular network.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
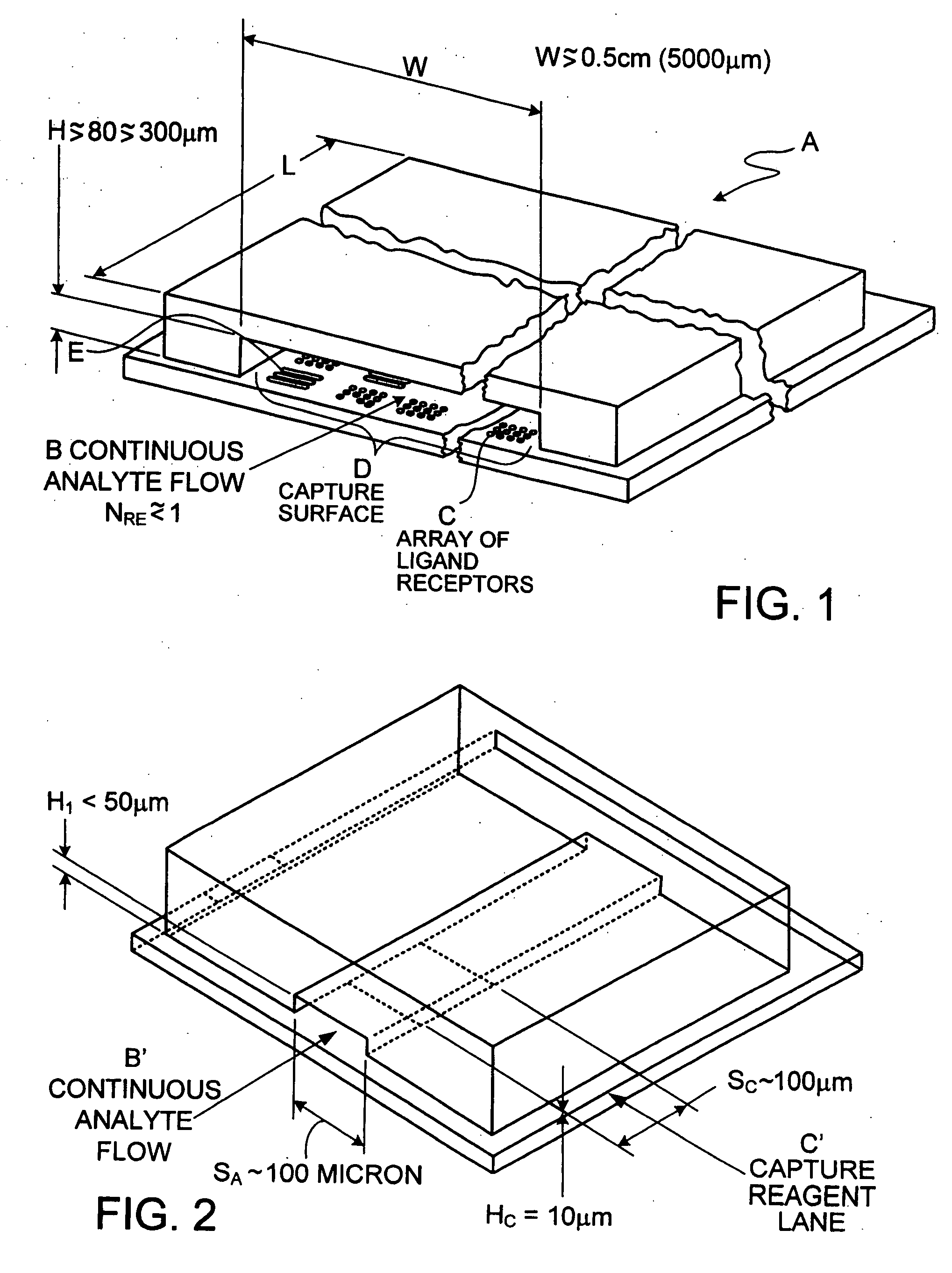
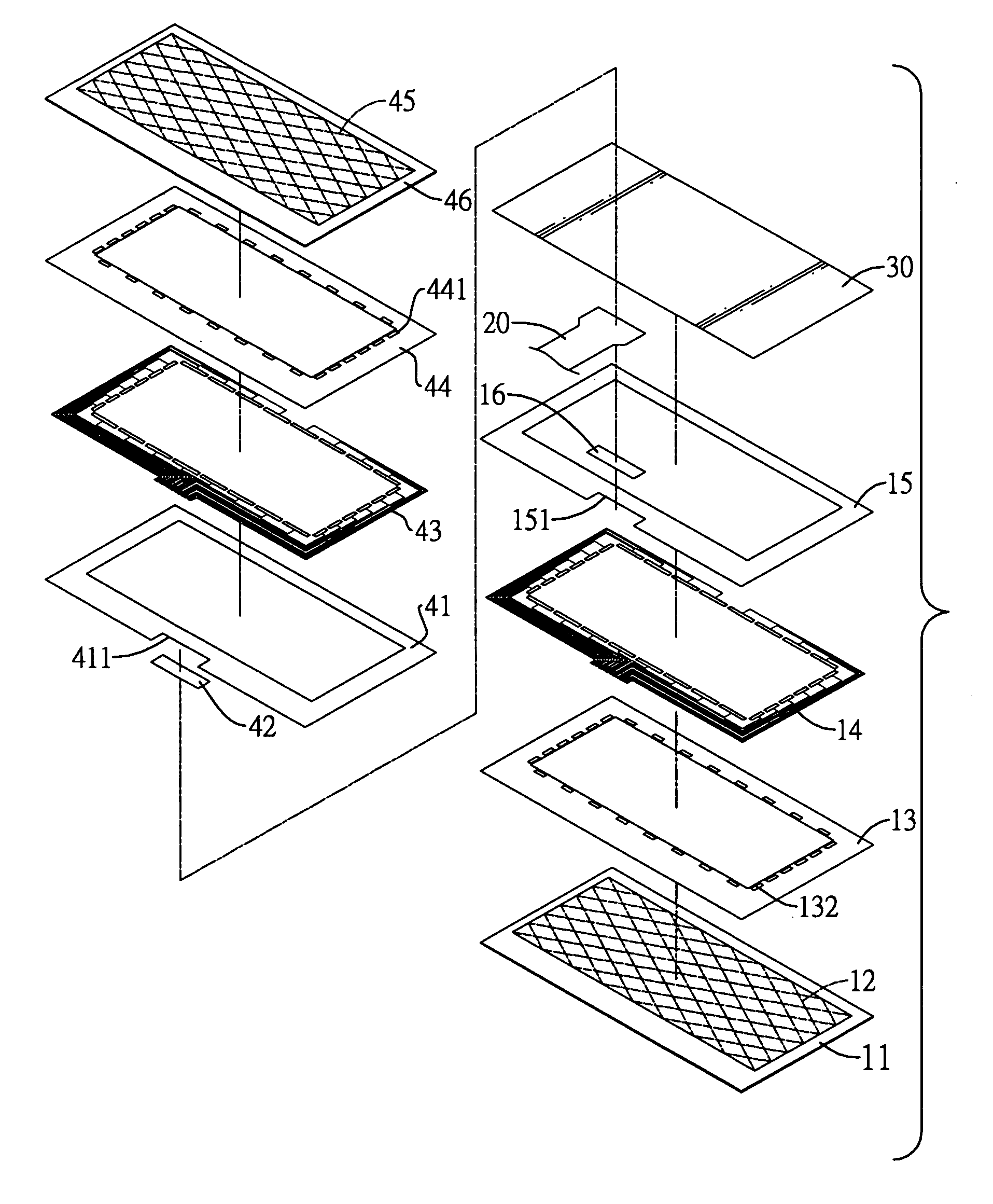
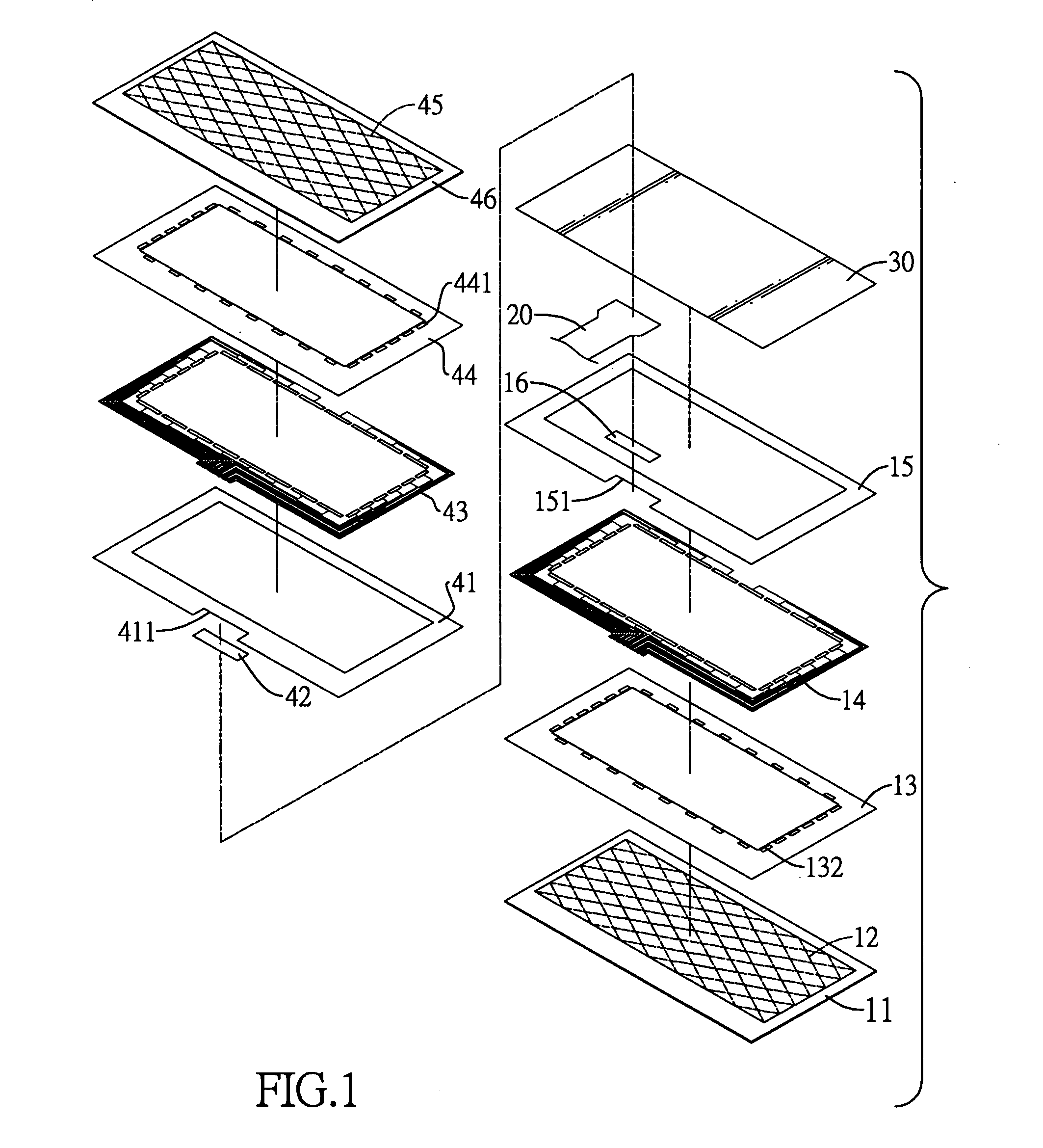
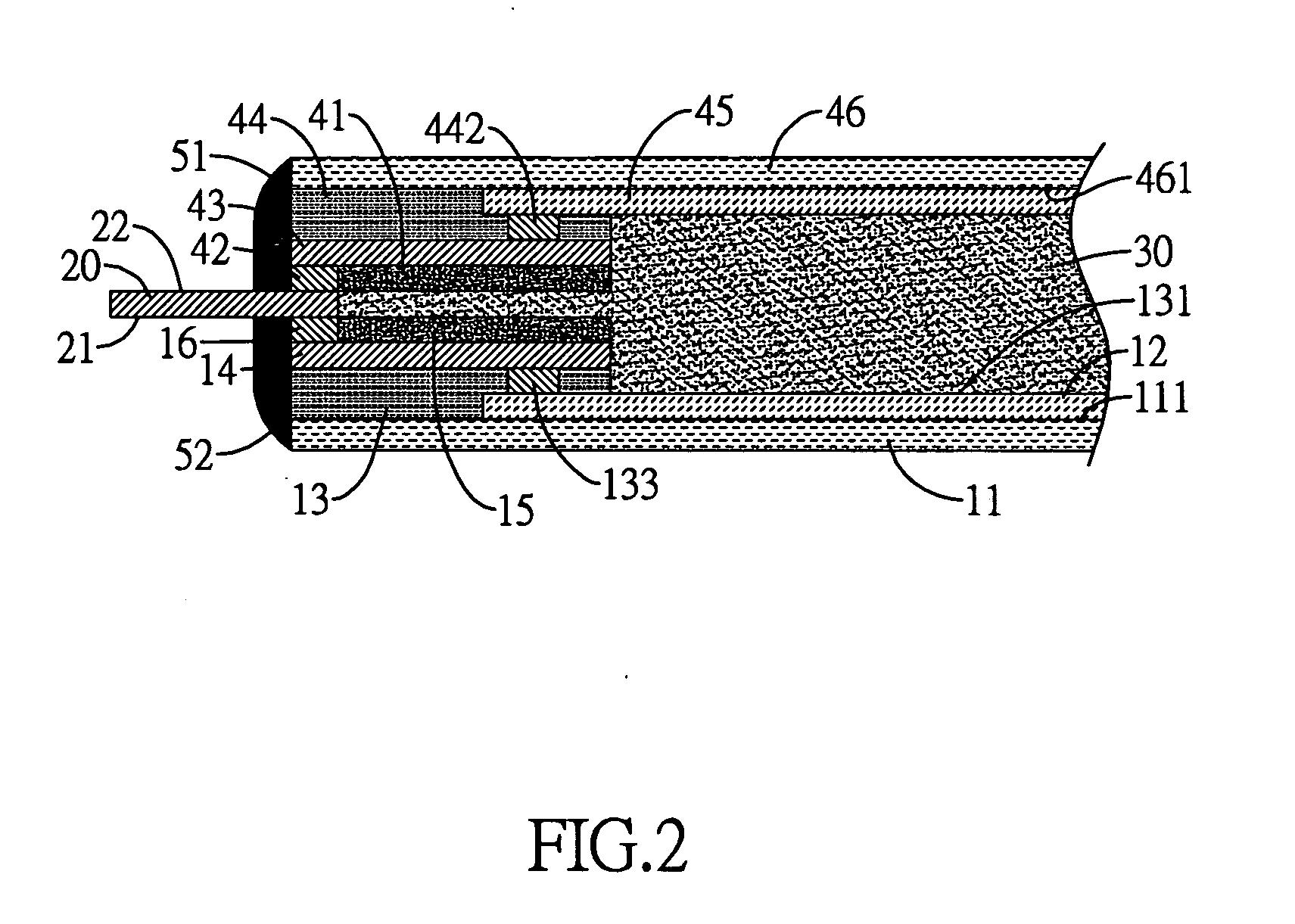
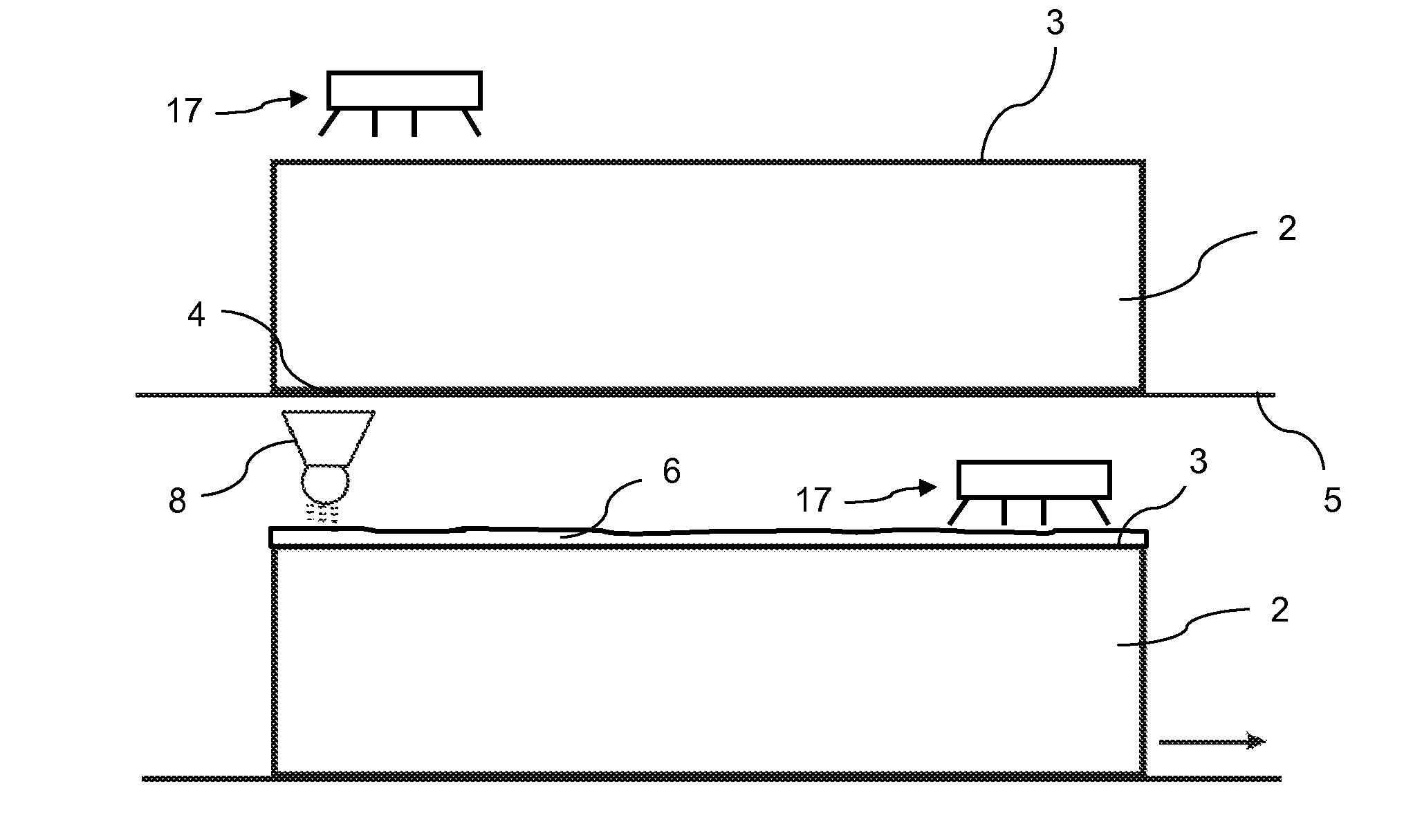
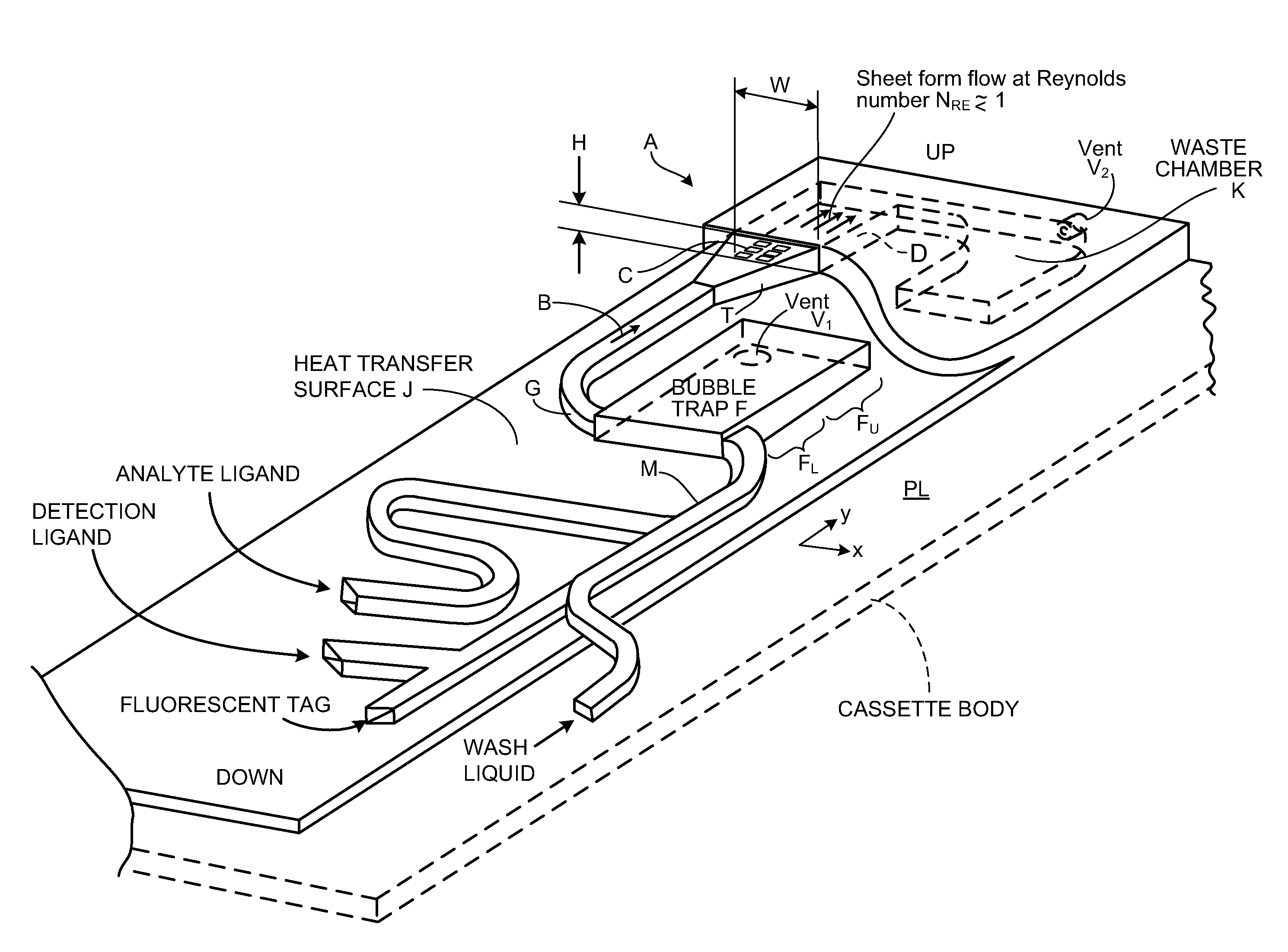
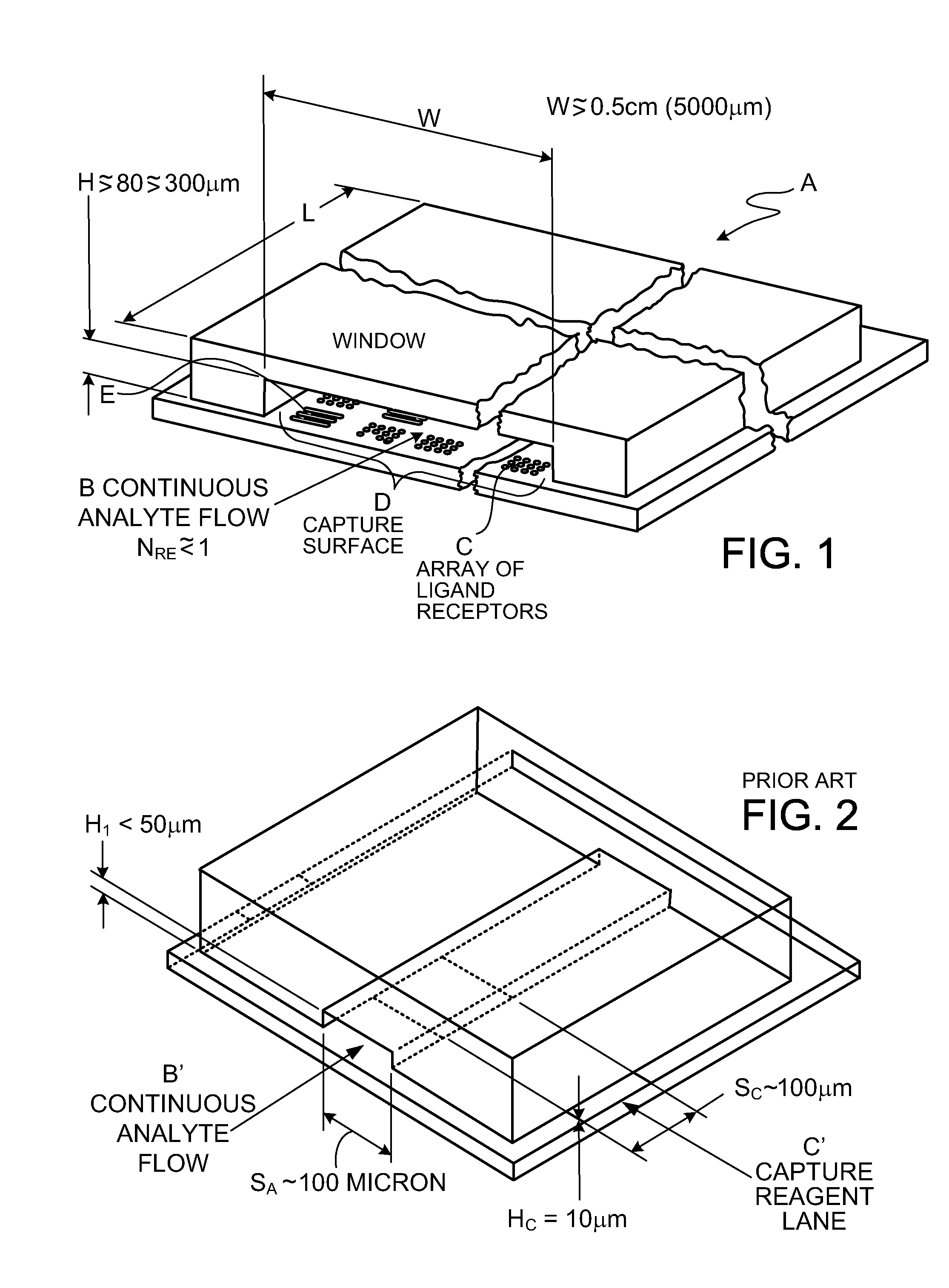
Assays based on liquid flow over arrays
InactiveUS20060275852A1Highly credible resultLow coefficient of variationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayAnalyte
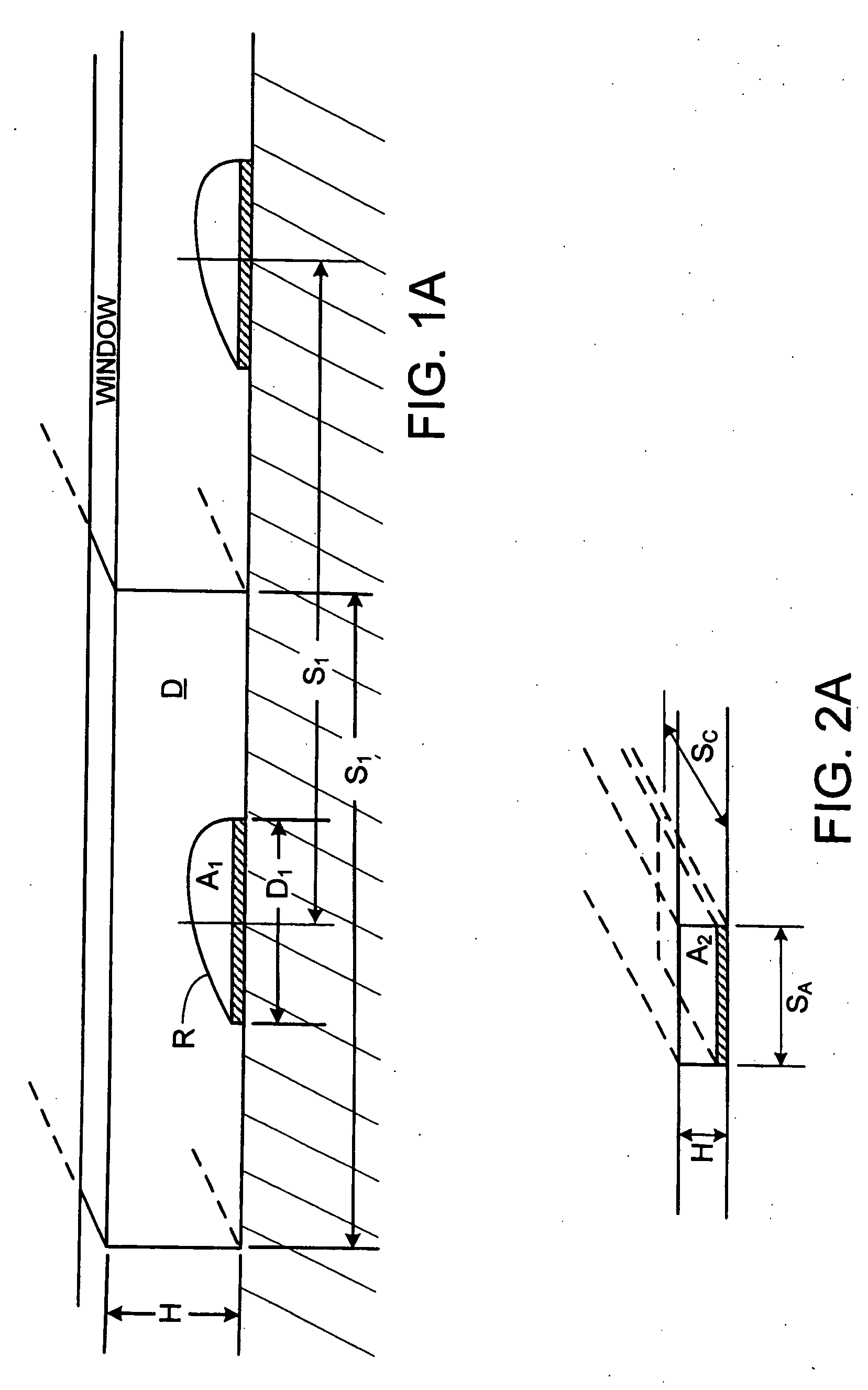
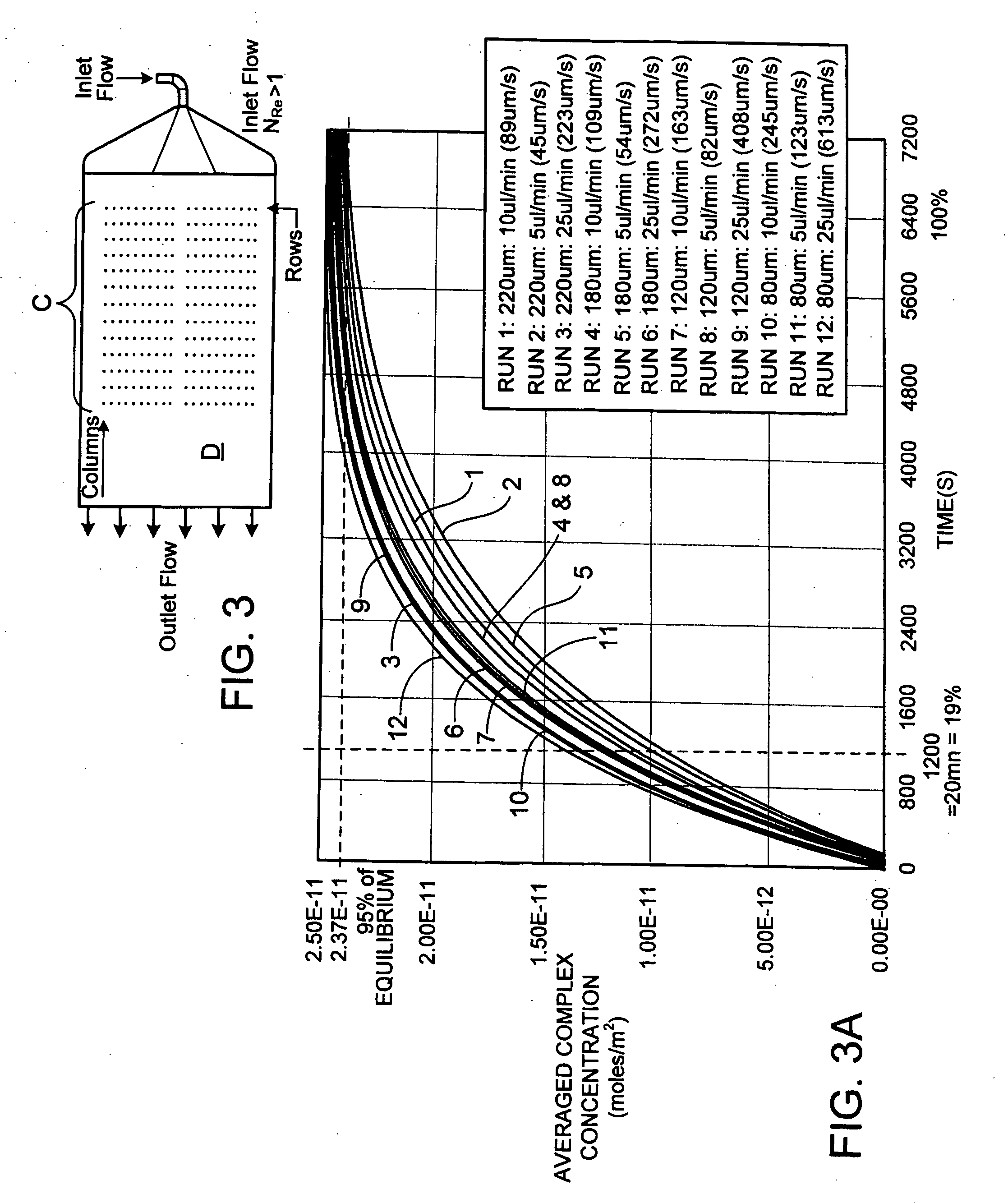
Cassette (50) performs assays, e.g. multiplexed protein biomarker assays. Wide, bubble-free, slow flows are produced from liquids stored on cassette (50), flowing over wide array (20) of ligand receptors on a capture surface. Flows of Reynolds Number less than about 1, preferably 1×10−1 to 5×10−3, are heated in region (34) preceding and including bubble removal system (128). Analyte is introduced through compressed septum (32). External actuations of displacement pumps (30, 37) and valves (137 A, B, and C) produce flows in response to flow-front optical sensors (150, 152). Elastic sheet provides pump and valve diaphragms and resilient expansion of mixing volume (131). Break-away cover portions are pistons. Heating is by conduction through cassette from external contact heater. Planar cassette body, when tilted from horizontal, enables upward flow from pumped storage (134, 135) to reaction (133) to waste (139), with buoyancy bubble removal before reaction. Reading of fluorescence is by external reader, employing calibration, control and reference features on capture surface. Extensive set of calibration features of differing intensities enables self-calibration.
Owner:AVANTRA BIOSCI CORP
Portable medical diagnostic systems and methods using a mobile device
ActiveUS20140072189A1High resultControl moreMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionAmbient lightingColor correction
A system and method for analysis of colorimetric test strip strips and disease management. The system can include an accessory that is operably coupled to a mobile device, the mobile device acquiring and / or analyzing images of the colorimetric test strips. The light box accessory can be detachably attached to the mobile device, or made to remain attached to the mobile device, but with the capability of having the light box accessory removed from the field of view of the camera for general photography purposes. In other embodiments, an image containing known calibration color(s) and reagent area(s) is obtained sans the light box for comparison with a previous calibration image to model changes in ambient lighting conditions and determine a color correction function. The correction can be applied to the detected reagent area color(s) for matching between the detected reagent area color(s) and reference color(s) on the reference chart. Optionally, the information can be processed and displayed to provide feedback, as well as transmitted to a health provider for analysis.
Owner:JANA CARE
Shuttering eyewear for use with stereoscopic liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20080062259A1Brighter and high resolution resultHigh resultSurgeryEndoscopesPolarizerOut of phase
An active eyewear method and system for viewing stereoscopic images is provided. The eyewear comprises polarization altering elements, such as twisted nematics or super twisted nematics, configured to receive light energy and rotate the polarization of light energy passing therethrough, and linear polarizers having polarization axes oriented in substantially identical orientations orthogonal to the first axis of polarization. The linear polarizers receive light energy from the polarization altering elements. The method comprises transmitting light energy through a sheet polarizer having an first axis of polarization, receiving the light energy with two polarization altering elements, each polarization altering operating out of phase with the other and in synchrony with a video field rate associated with the transmitting, and passing the light energy through two linear polarizers having substantially identical axes of polarization orthogonal to the first axis of polarization.
Owner:REAID INC
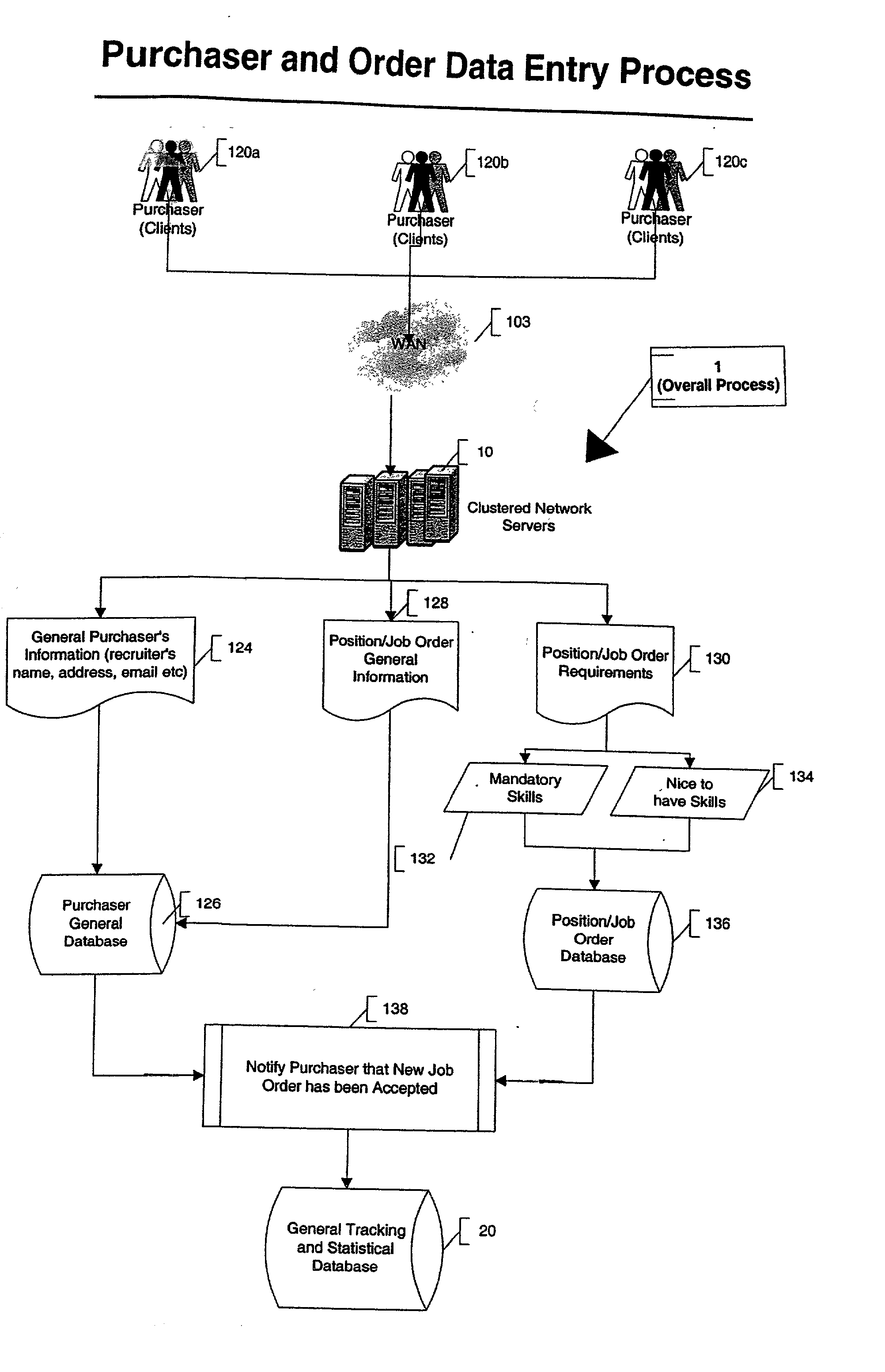
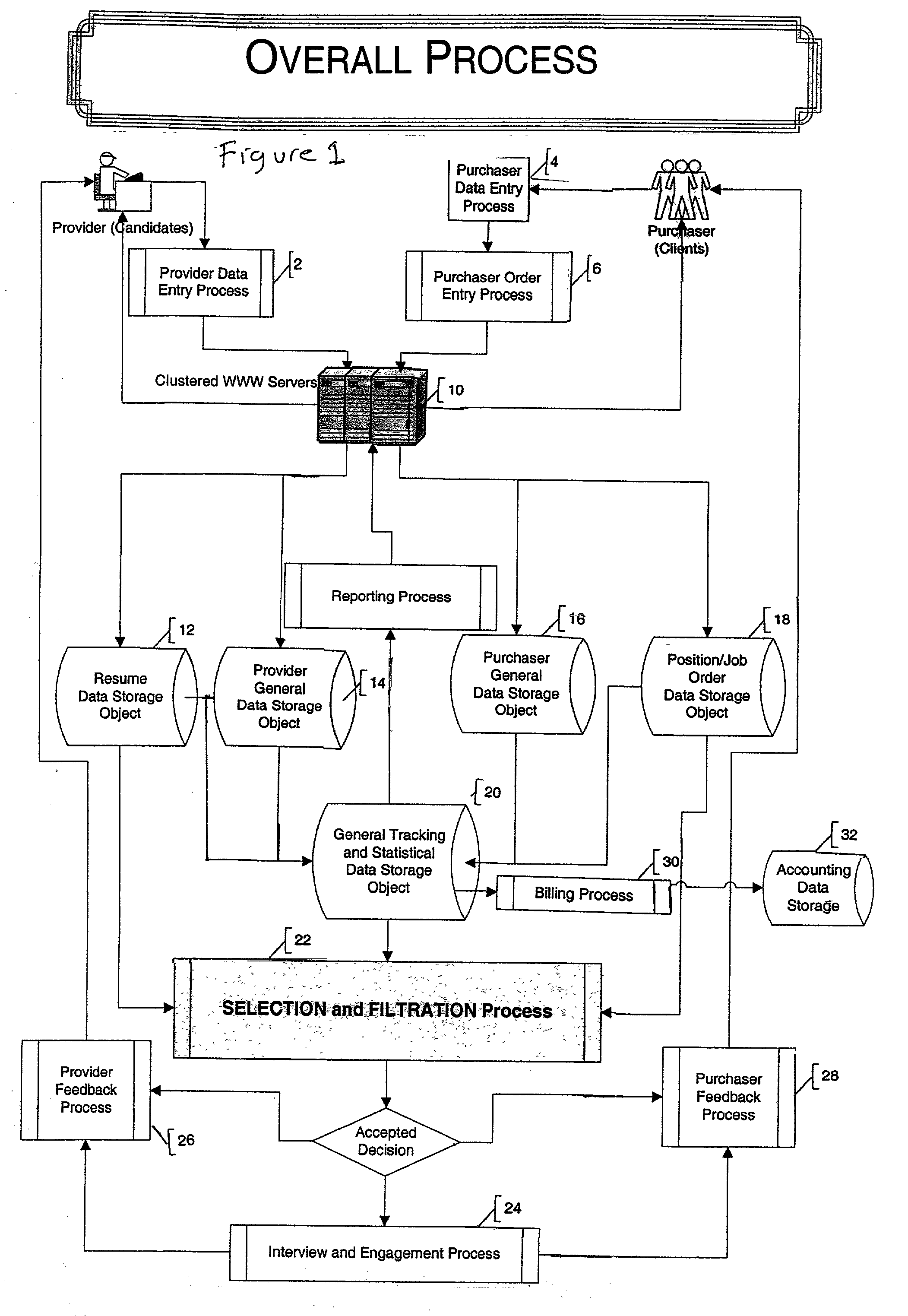
Automated system and method for managing a process for the shopping and selection of human entities
InactiveUS20030093322A1Avoids misunderstandHigh resultMarket predictionsOffice automationAutomated sequencingExpert system
This invention is a system and method for automatically managing a multi-step process in which human providers are selected for some purpose. Typical applications include the selection process associated with employment and dating services. The invention is directed to linking and coordinating the various steps of the selection process through automated sequencing, coordinating, tracking and status reporting processes. The interviewee answers questions that are printed, displayed, or spoken by an automated mechanism or questions are printed or displayed for use by a tester or interviewer. Answers can be written, spoken, or entered directly into a system by the interviewee. The invention provides a system and method for automatically scoring and ranking human providers with respect to selection criteria, making use of expert system concepts. Human shoppers are matched up and the usefulness of each match is scored on the basis of stated selection criteria of each human shopper.
Owner:INTRAGROUP
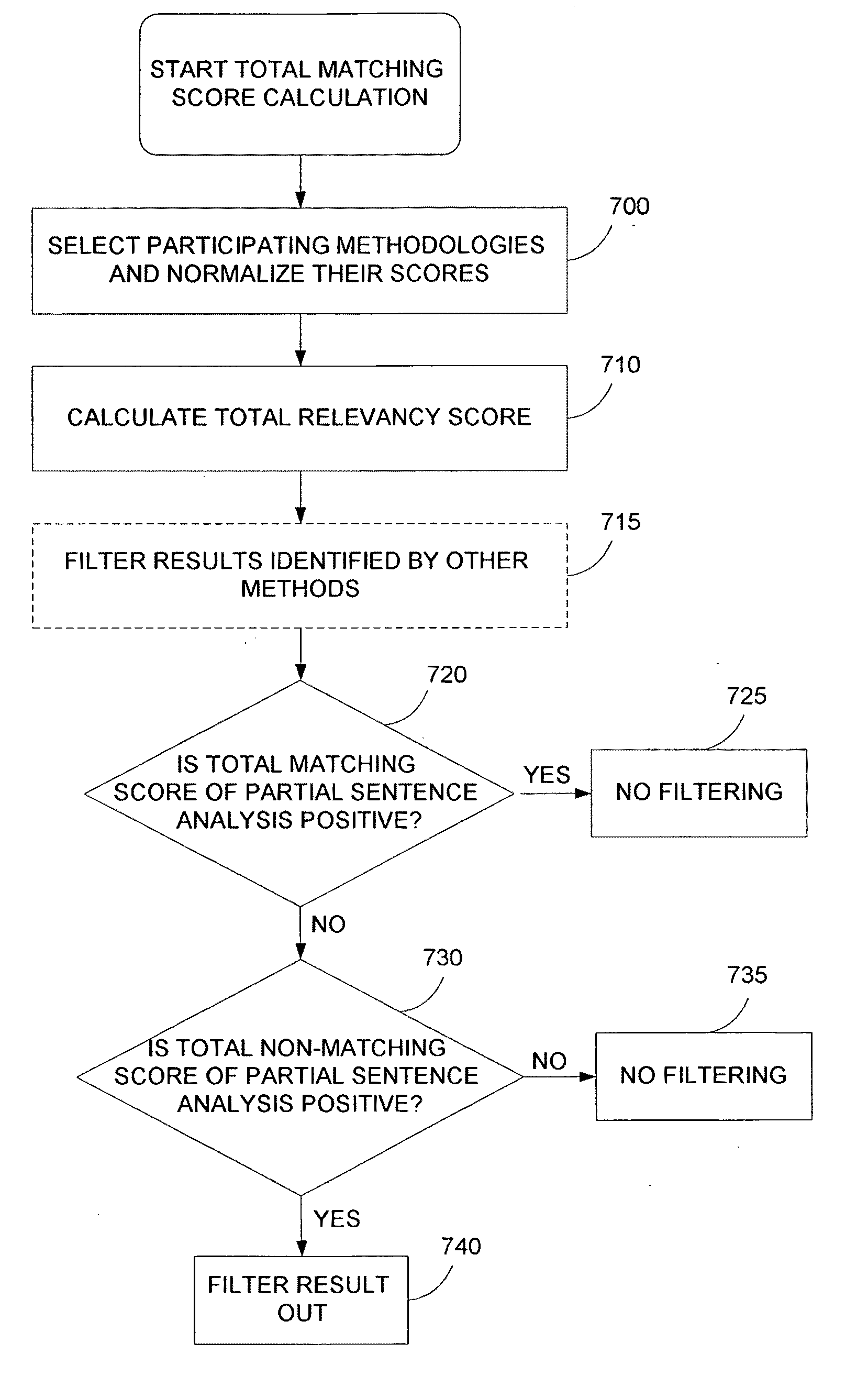
System and method for matching search requests and relevant data
InactiveUS20090254543A1High relevancy resultAccurately rankedDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsDocumentation procedureSentence analysis
A system and methods for matching between search requests and relevant data (web pages, online documents, essays, online text in general, images, video, footage etc.). The system comprises three components that can work separately or together and can be integrated with other search engine methods in order to further improve the relevancy of search results. The system can find similarity between different document and measure the distance (in similarity) between documents. The three components are: Context based understanding, comprising putting the documents in the context of aspects of the human knowledge external to the documents, Partial Sentence analysis and 100 percentage points to keyword / tag sets.
Owner:BER OFER +1
Sample collection and bioluminescent analysis system
ActiveUS20140004548A1Promote useReduce power consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhoton detectionPhoton counter
Methods and apparatus for evaluating the quality of an environment or process by measuring light emitted from a bioluminescent sample containing ATP, ADP, or alkaline phosphatase. The apparatus comprises a sample collection and analysis system used to collect a sample, mix reagents, react the sample, and collect it in a measurement chamber. The system includes an instrument having a photon detection assembly for use with the sample testing device and one or more probe assemblies that optically cooperate with the instrument. The instrument includes a dark chamber with a reflective interior surface which may be concave or preferably spherical, and a photon detection sensor such as a multi-pixel photon counter sensor. A substantially transparent portion of the probe assembly, and liquid contained therein, focus bioluminescence toward the photon detection sensor.
Owner:BIOCONTROL SYST
Capacitive touch panel
ActiveUS20120007824A1High yieldSuitable for manufactureElectronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingProduction rateFlexible circuits
A capacitive touch panel sequentially has a first glass substrate, a lower touch sensitive layer, a lower insulation ink layer, a lower conductor layer, a lower insulation layer, a lower conductive adhesive layer, a flexible circuit board, a transparent insulation adhesive layer, an upper insulation layer, an upper conductive adhesive layer, an upper conductor layer, an upper insulation ink layer, an upper touch sensitive layer and a second glass substrate. The aforementioned structure allows fabrication of the capacitive touch panel to be separated into a lower panel fabrication process and an upper panel fabrication process. The two independent fabrication processes prevent the capacitive touch panel from being damaged in one of the processes when the process is completed so as to increase the yield in production and further facilitate producing large-size touch panel.
Owner:TPK HLDG
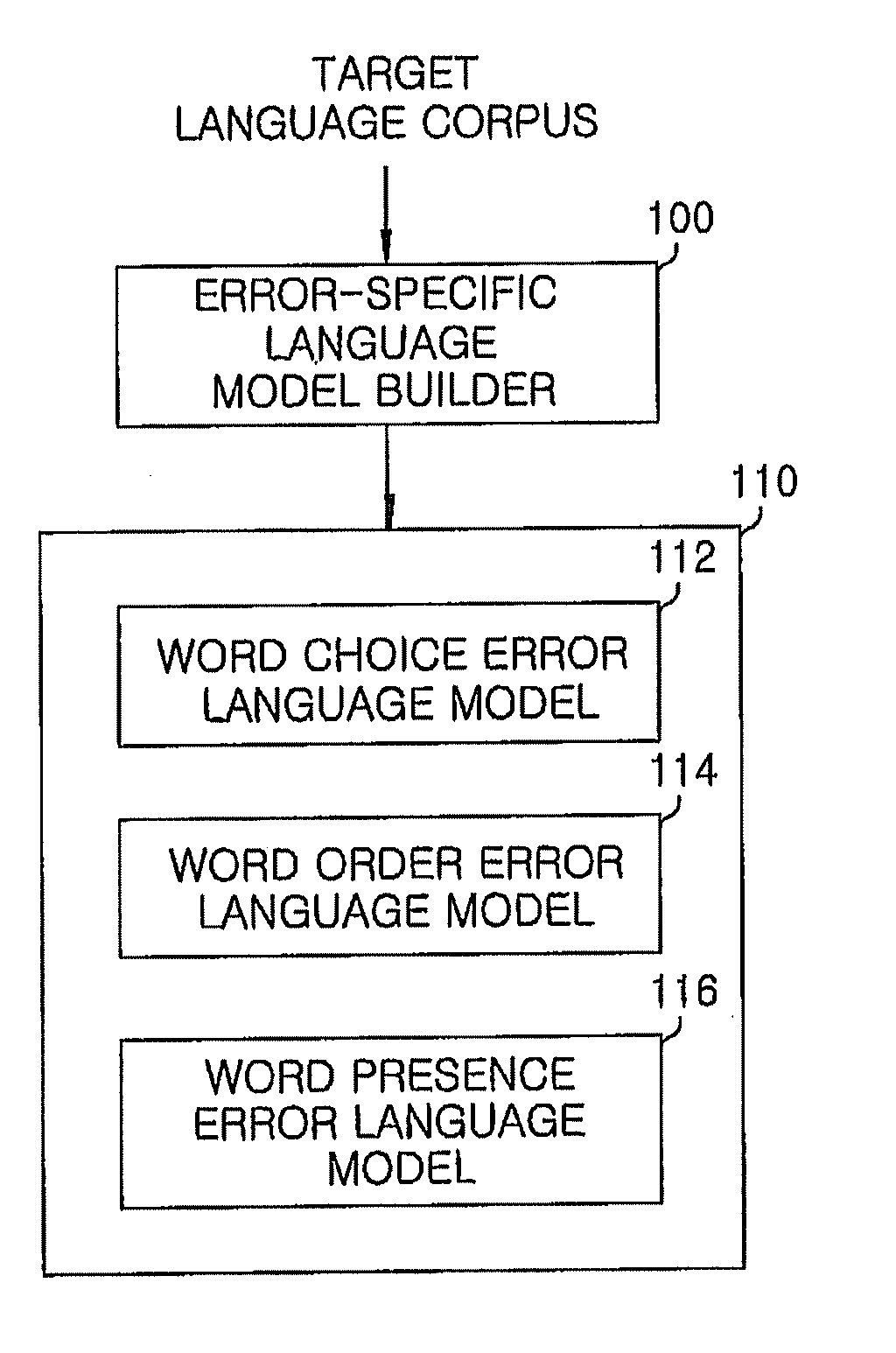
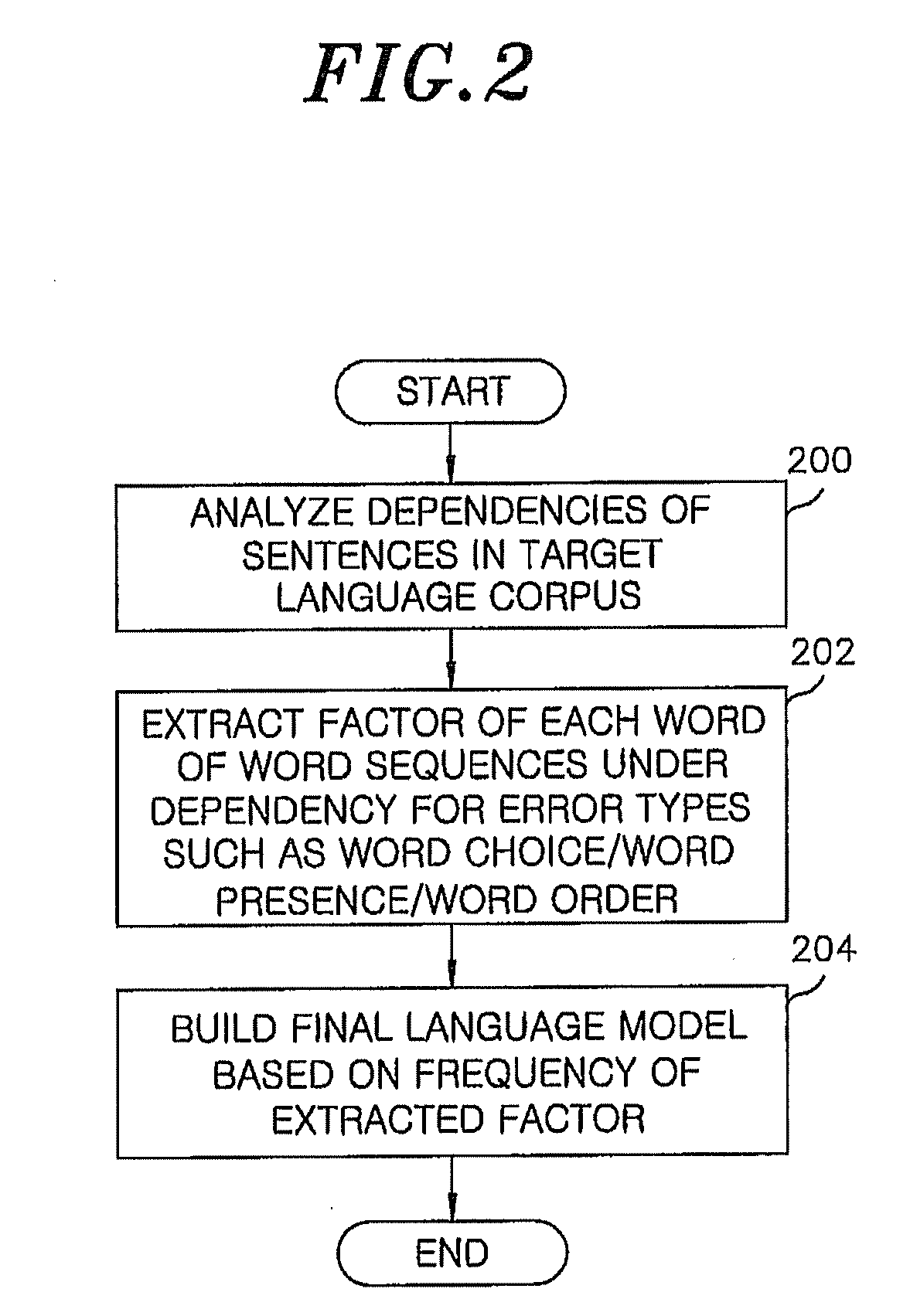
Post-editing apparatus and method for correcting translation errors
ActiveUS20100138210A1Improve translation performanceHigh resultNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsTranslation errorTranslation system
A post-editing apparatus for correcting translation errors, includes: a translation error search unit for estimating translation errors using an error-specific language model suitable for a type of error desired to be estimated from translation result obtained using a translation system, and determining an order of correction of the translation errors; and a corrected word candidate generator for sequentially generating error-corrected word candidates for respective estimated translation errors on a basis of analysis of an original text of the translation system. The post-editing apparatus further includes a corrected word selector for selecting a final corrected word from among the error-corrected word candidates by using the error-specific language model suitable for the type of error desired to be corrected, and incorporating the final corrected word in the translation result, thus correcting the translation errors.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Camera phone using multiple lenses and image sensors to provide an extended zoom range
InactiveUS7561191B2Increase the zoom rangeIncreasing size and costTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceCamera phoneTelephoto lens
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
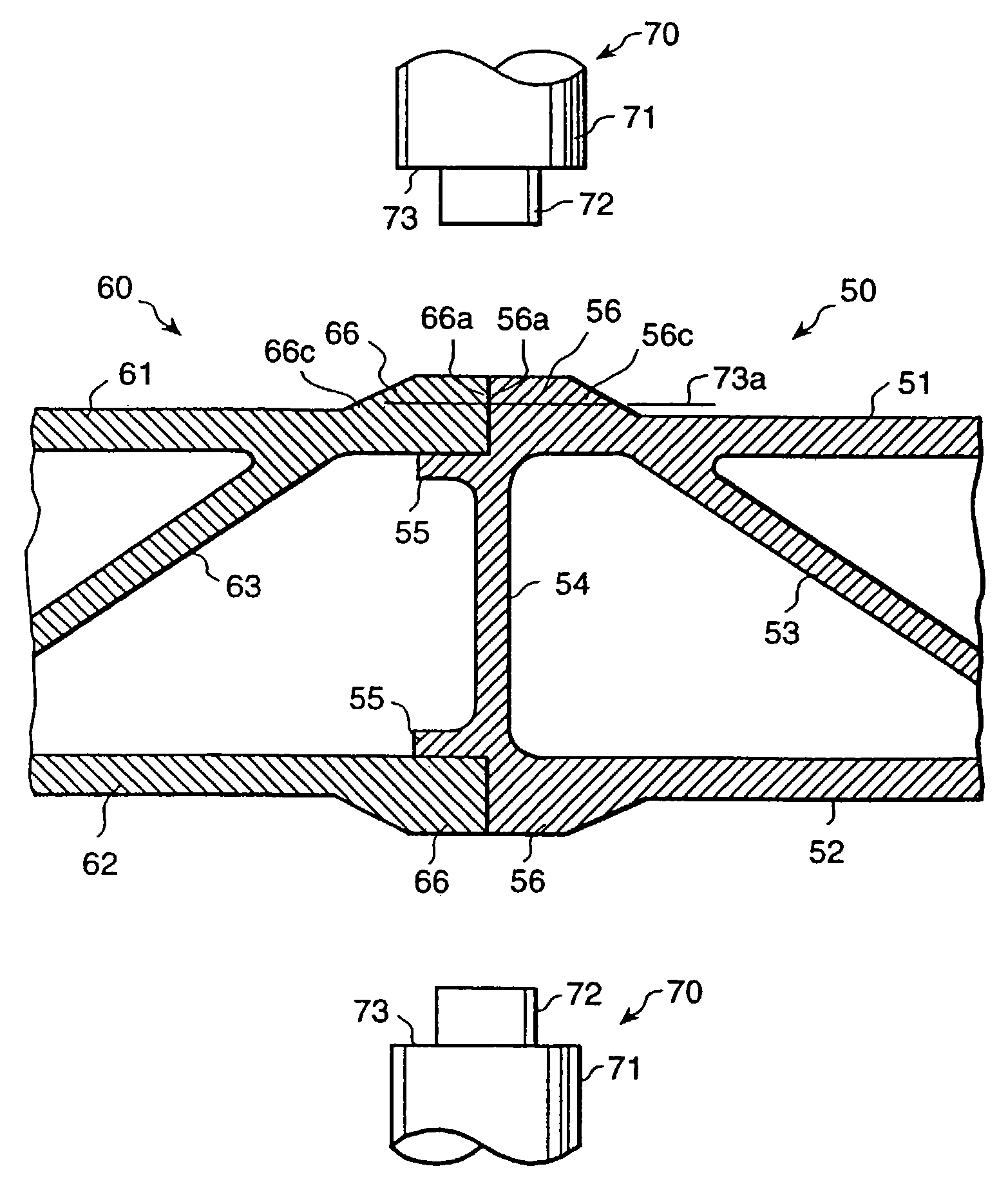
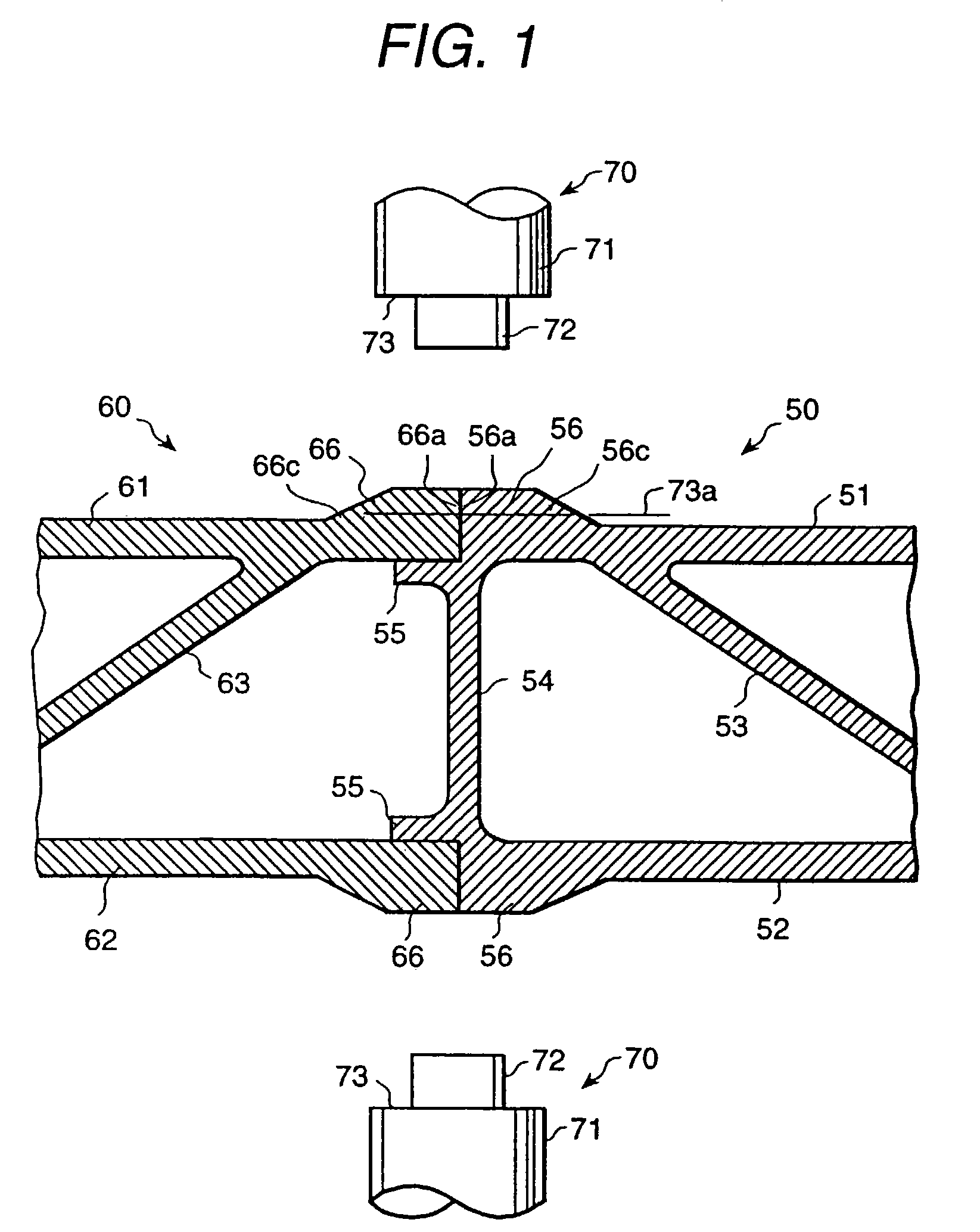
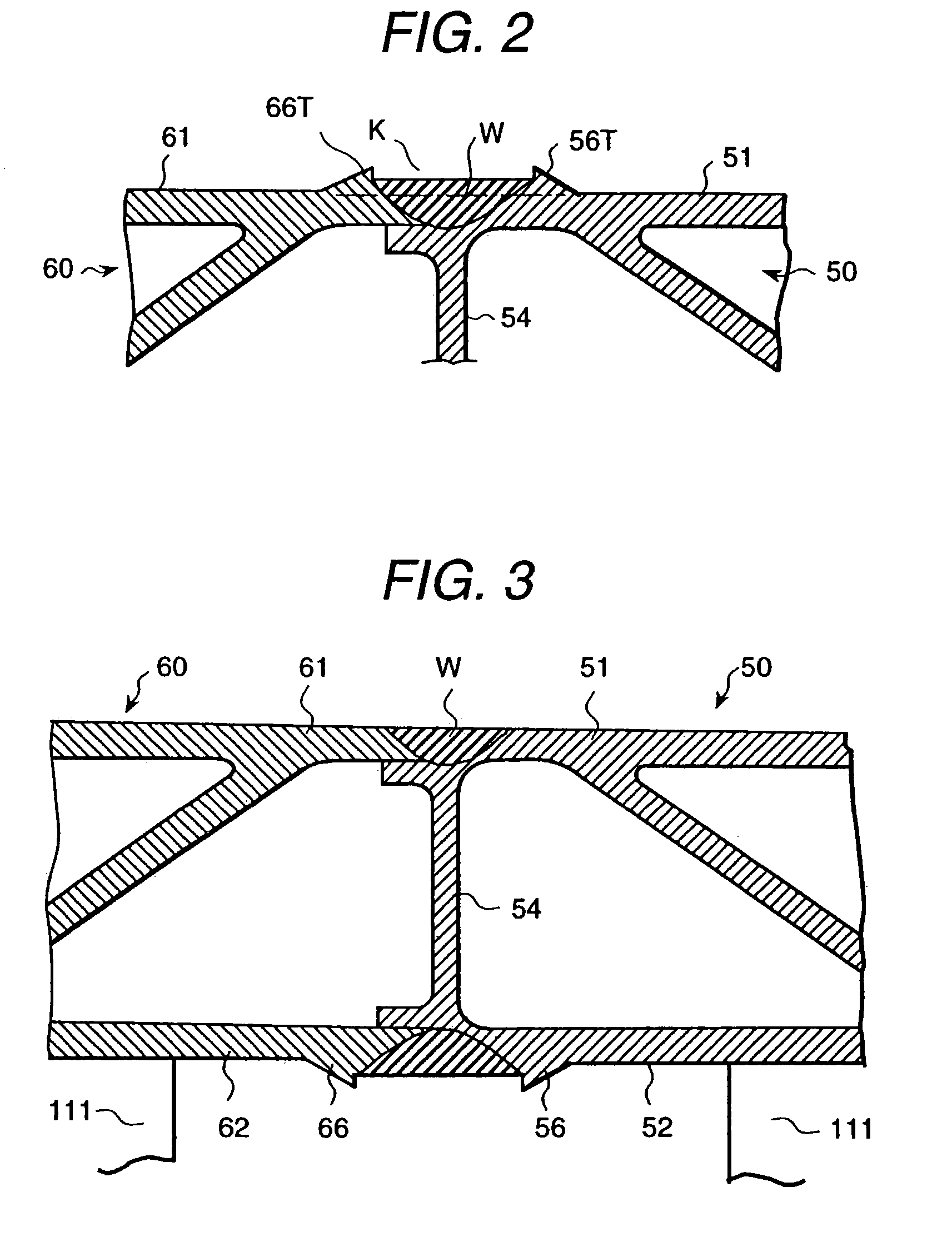
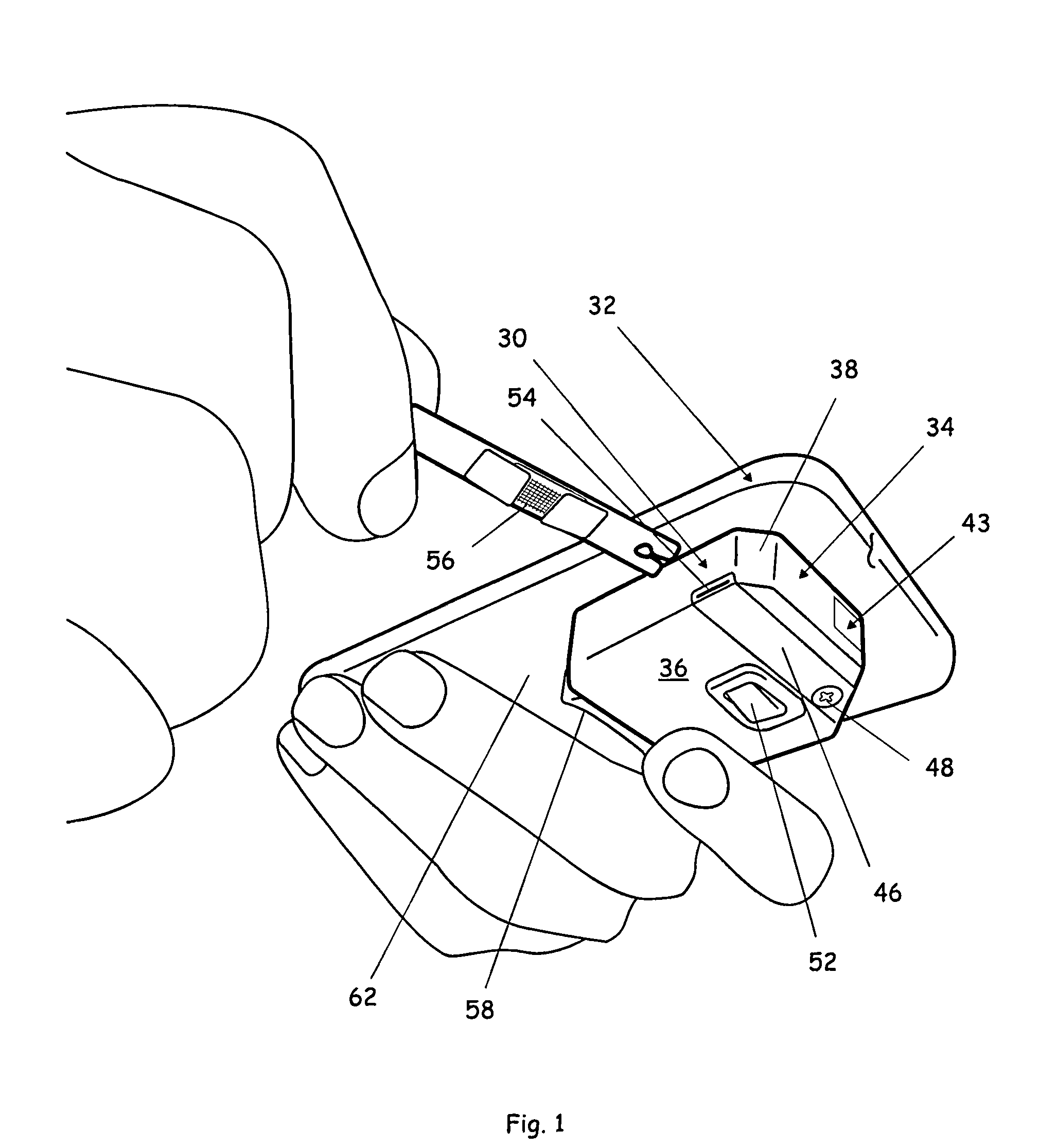
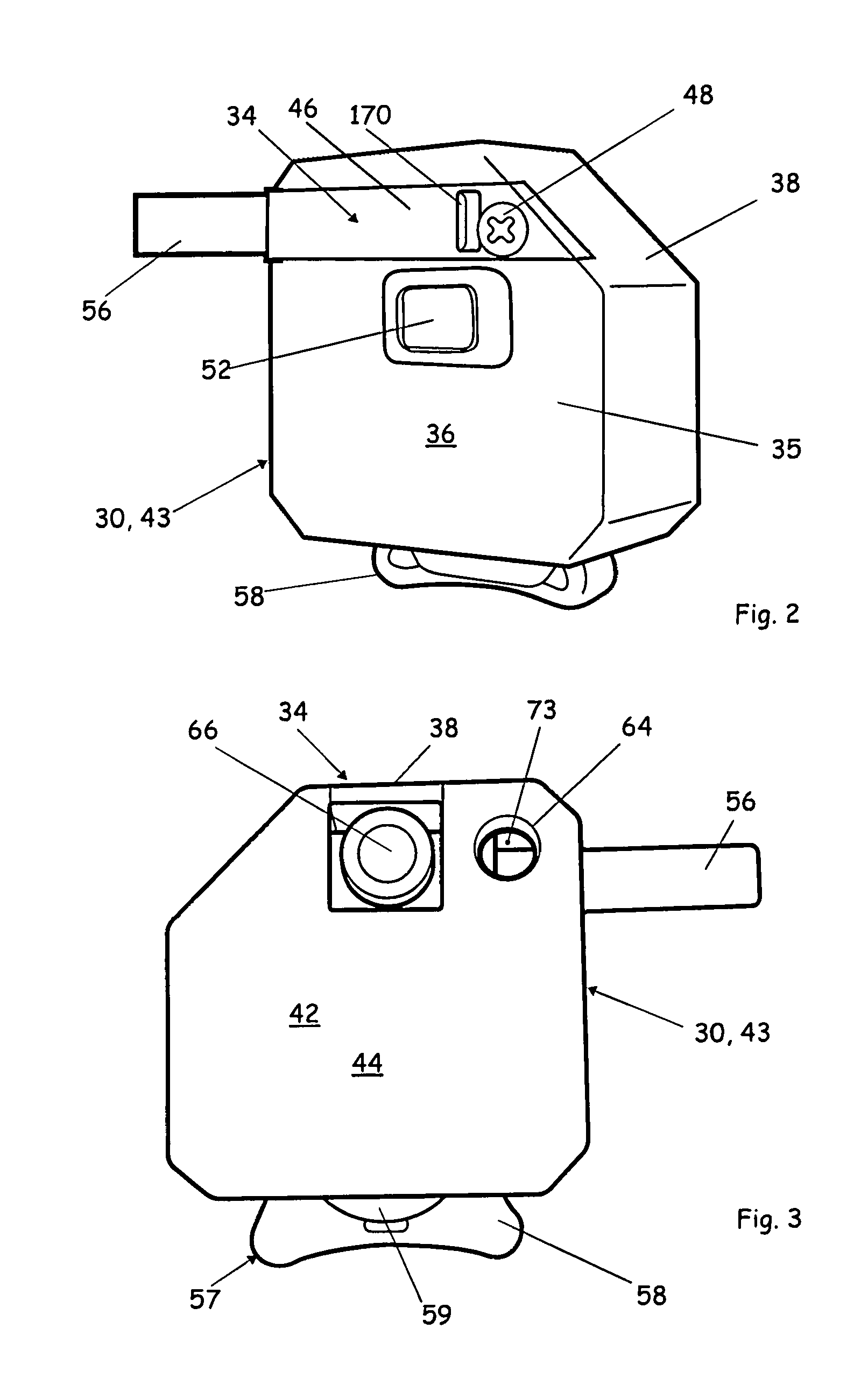
Compact image capture assembly using multiple lenses and image sensors to provide an extended zoom range
ActiveUS20060187311A1Low costHigh quality optical resultTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensImage capture
An optical image capture assembly for use in an electronic camera includes a first image sensor for generating a first sensor output; a first lens for forming a first image of the scene on the first image sensor; a second image sensor for generating a second sensor output; and a zoom lens for forming a second image of the scene on the second image sensor. The camera is contained within an enclosure and, in one variation of the assembly, either the first lens or the zoom lens (or both) forms its image through a folded optical system in which an optical path between the lens and its respective image sensor is folded at an angle in order to conserve space within the enclosure.
Owner:APPLE INC
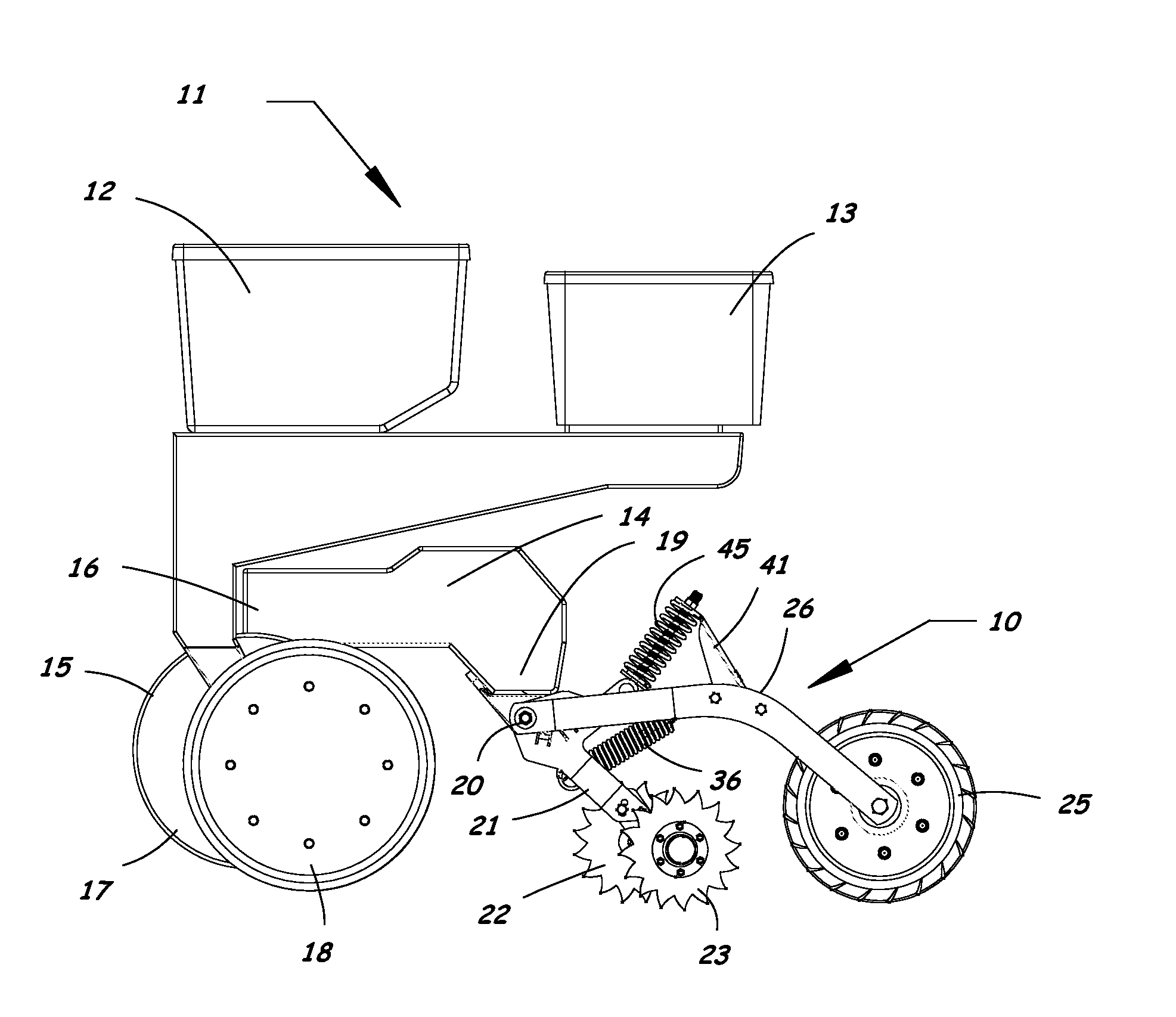
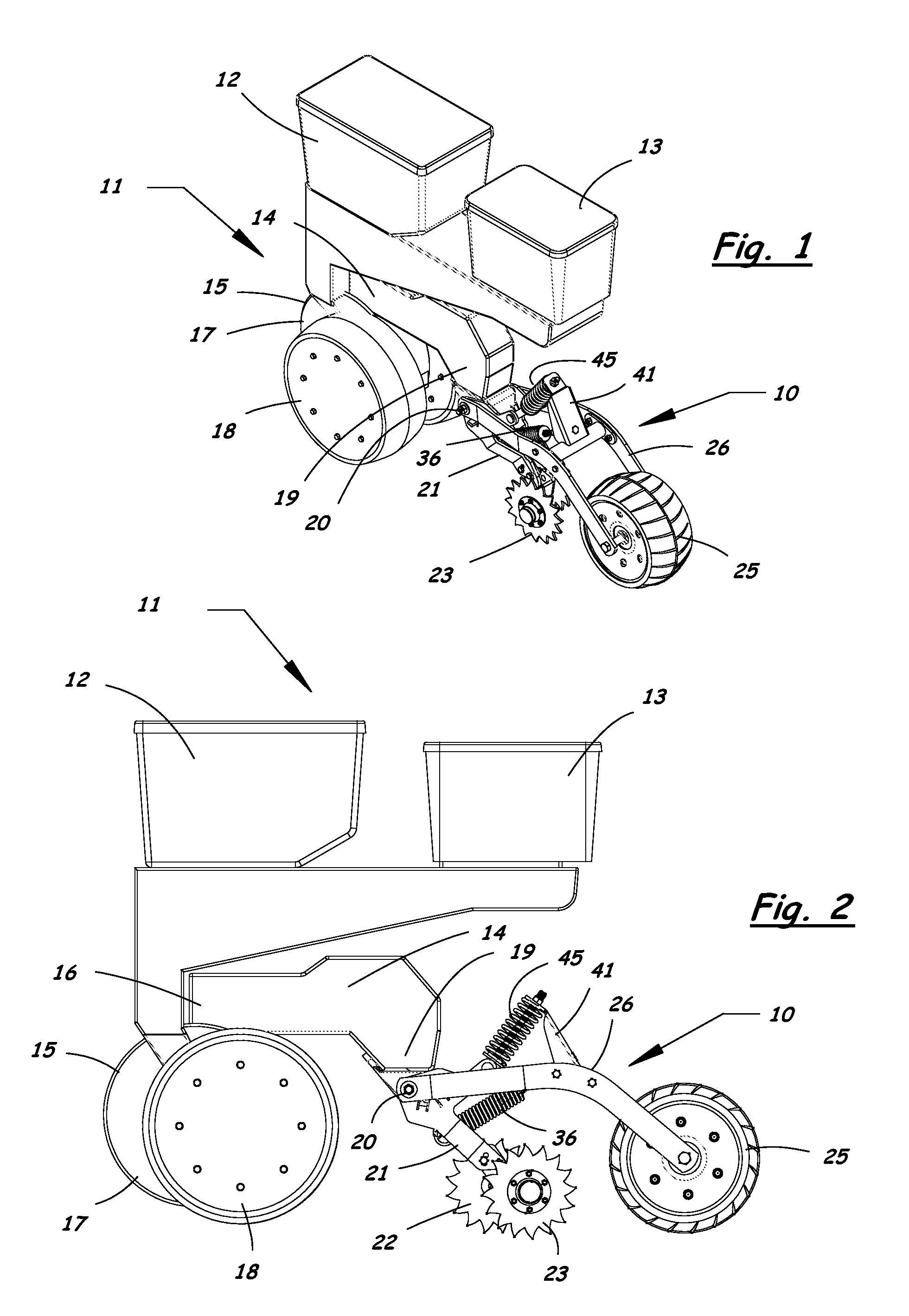
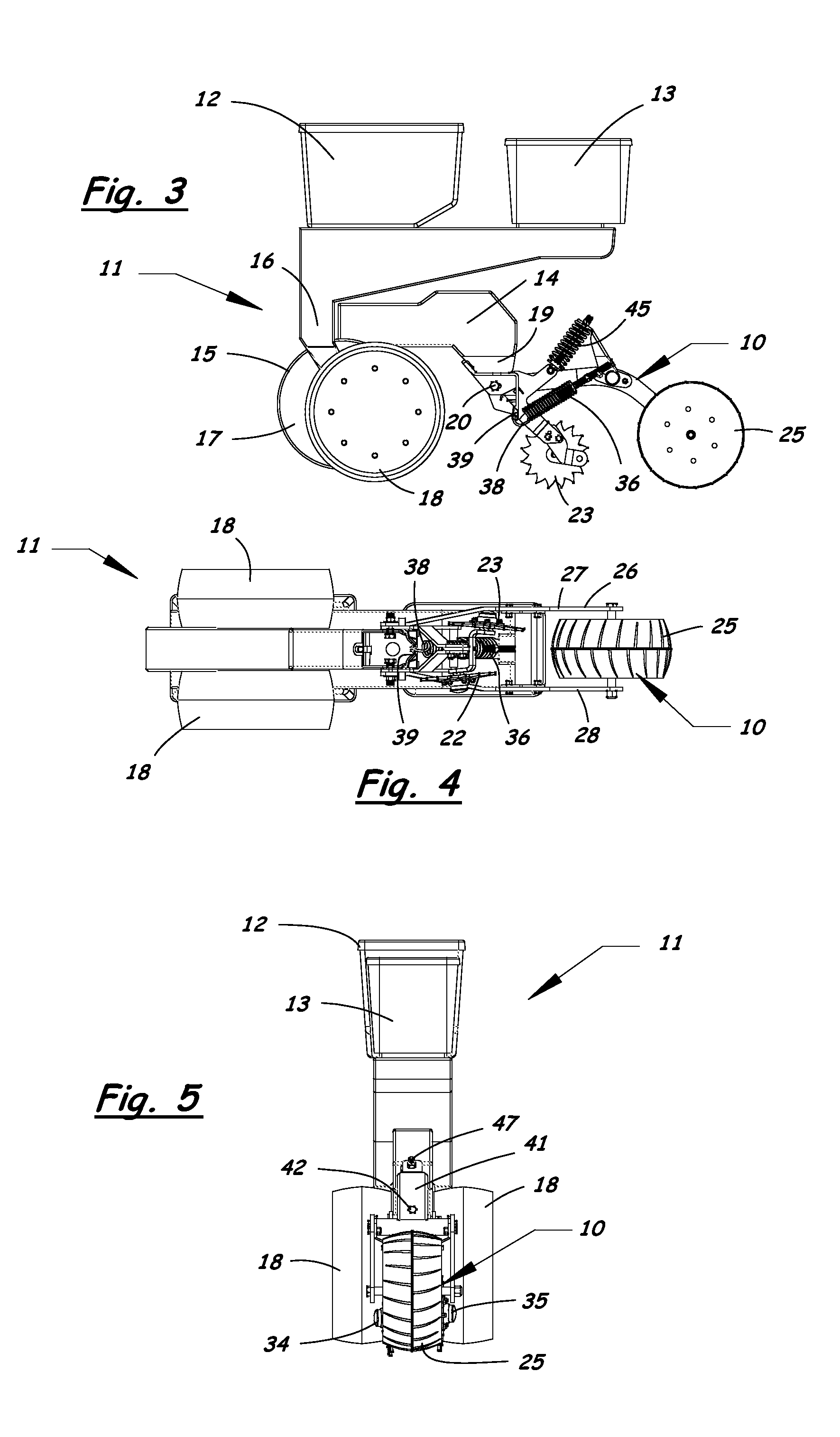
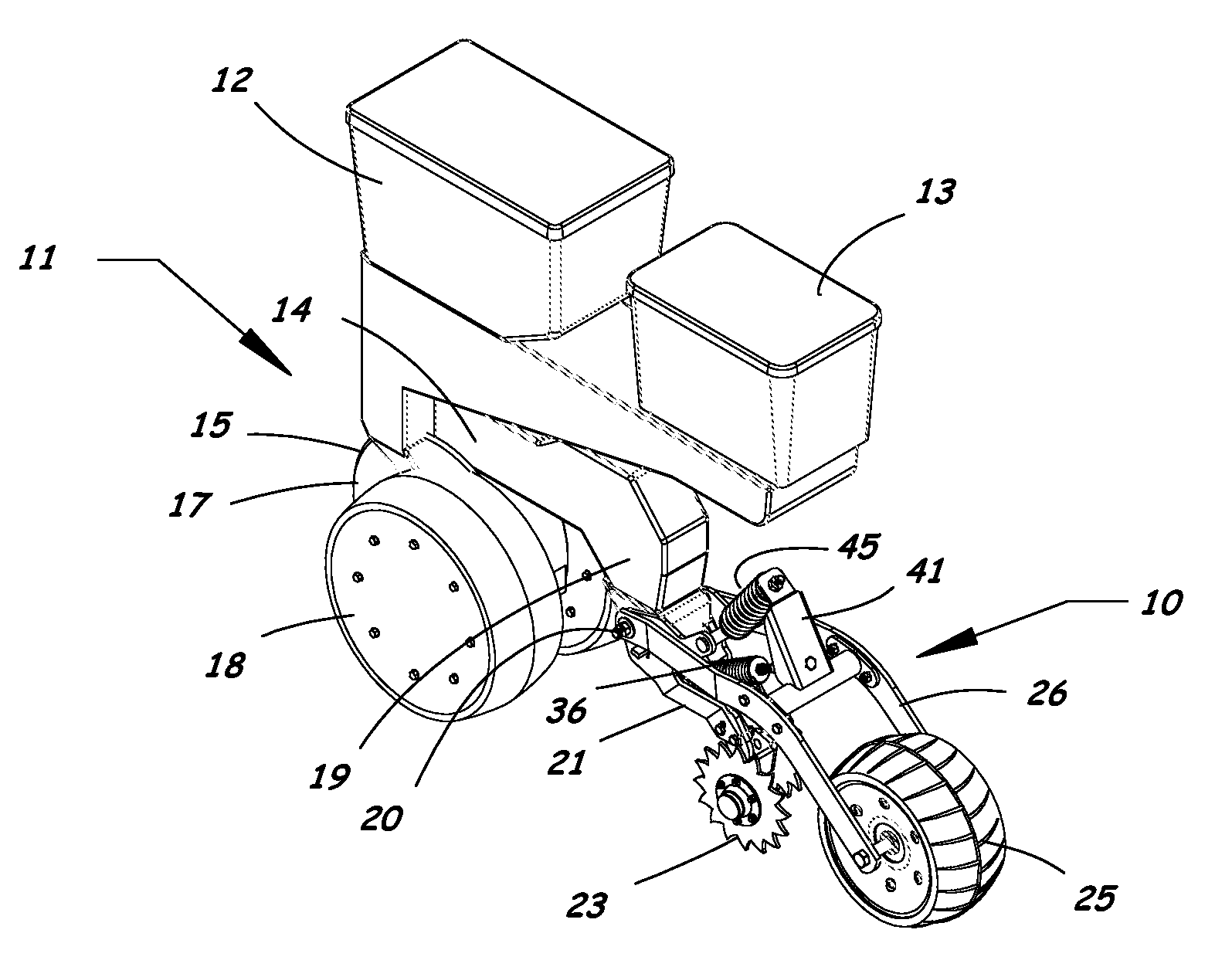
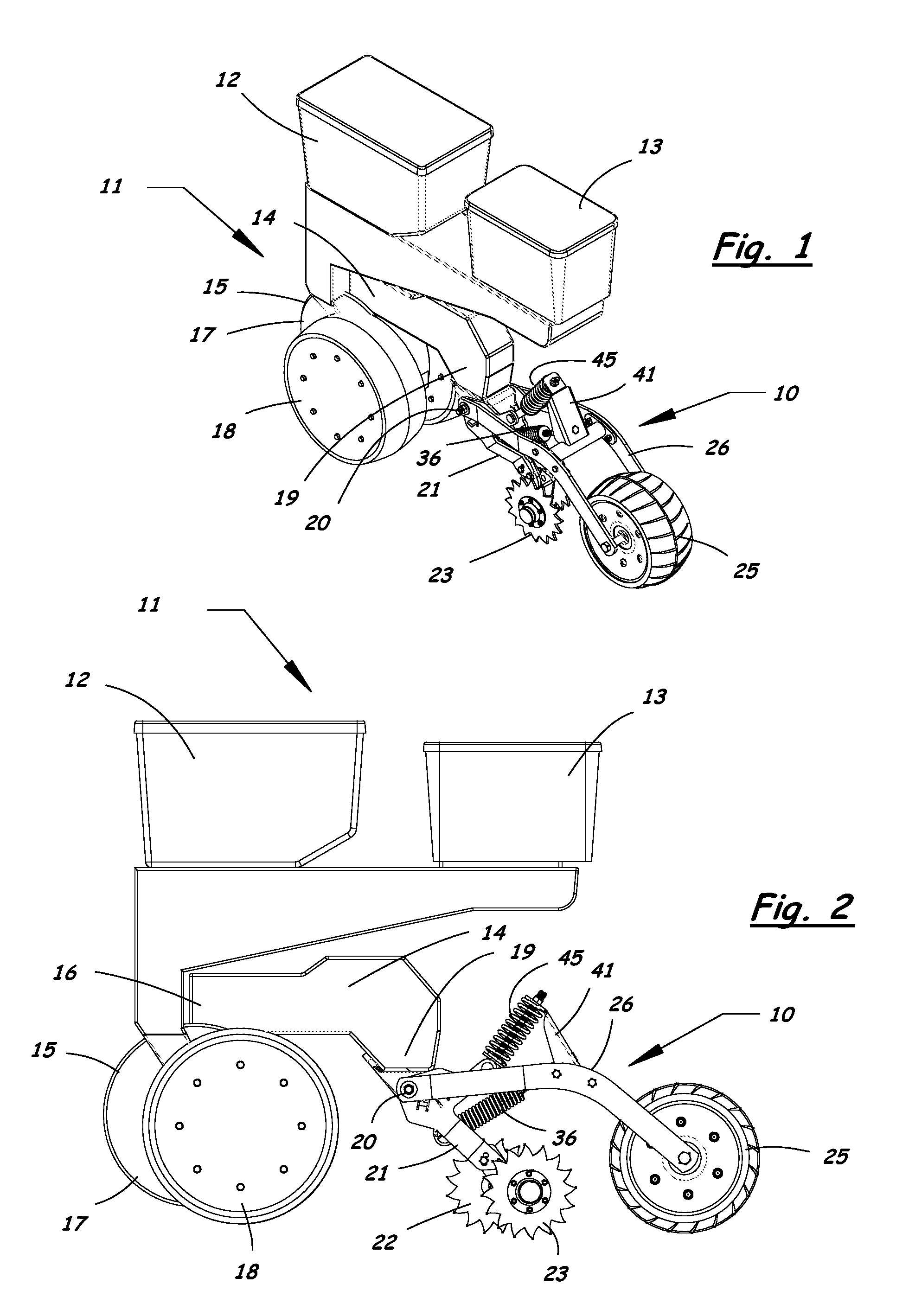
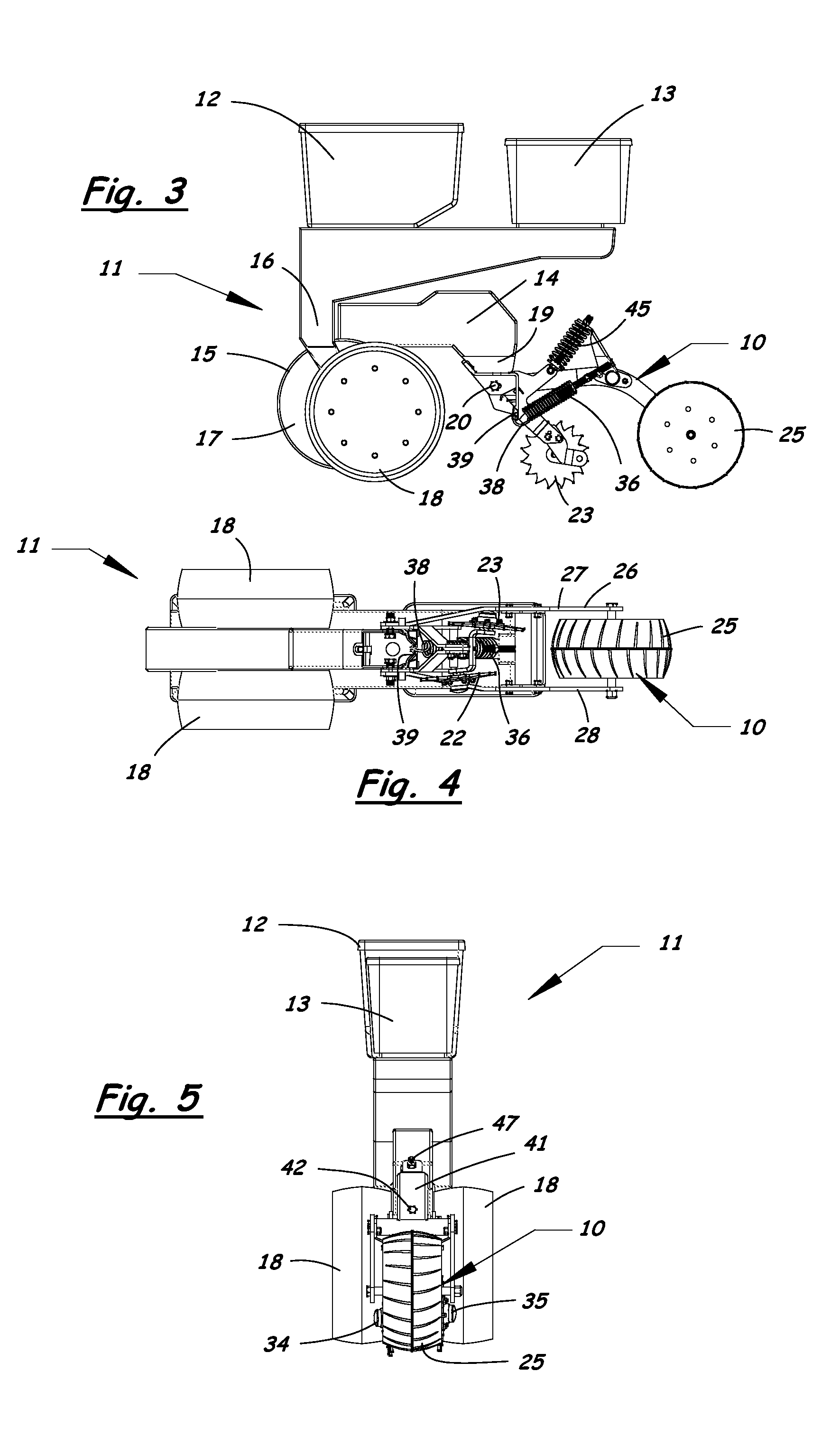
Furrow closing assembly and method
Agricultural planter row units feature soil finishing assemblies for closing a seed groove after seed is placed in the soil. An adjustable furrow closing assembly enhances upper seed groove coverage and closure with soil resulting in sustained relative humidity levels and optimum seed-to-soil contact for faster seed germination. The furrow closing assembly includes a closing wheel assembly having at least one closing wheel and a press wheel assembly having a press wheel following behind the closing wheels. The closing wheels and press wheel are attached to the planter row unit in a manner allowing the press wheel to move vertically relative to the closing wheels. Adjustable down-force systems are provided to vary the down force applied to the closing wheels and the press wheel to maintain optimum soil contact in irregular terrain and in varying soil densities and conditions to provide optimum soil coverage and compaction of the seed bed.
Owner:AG FOCUS LLC
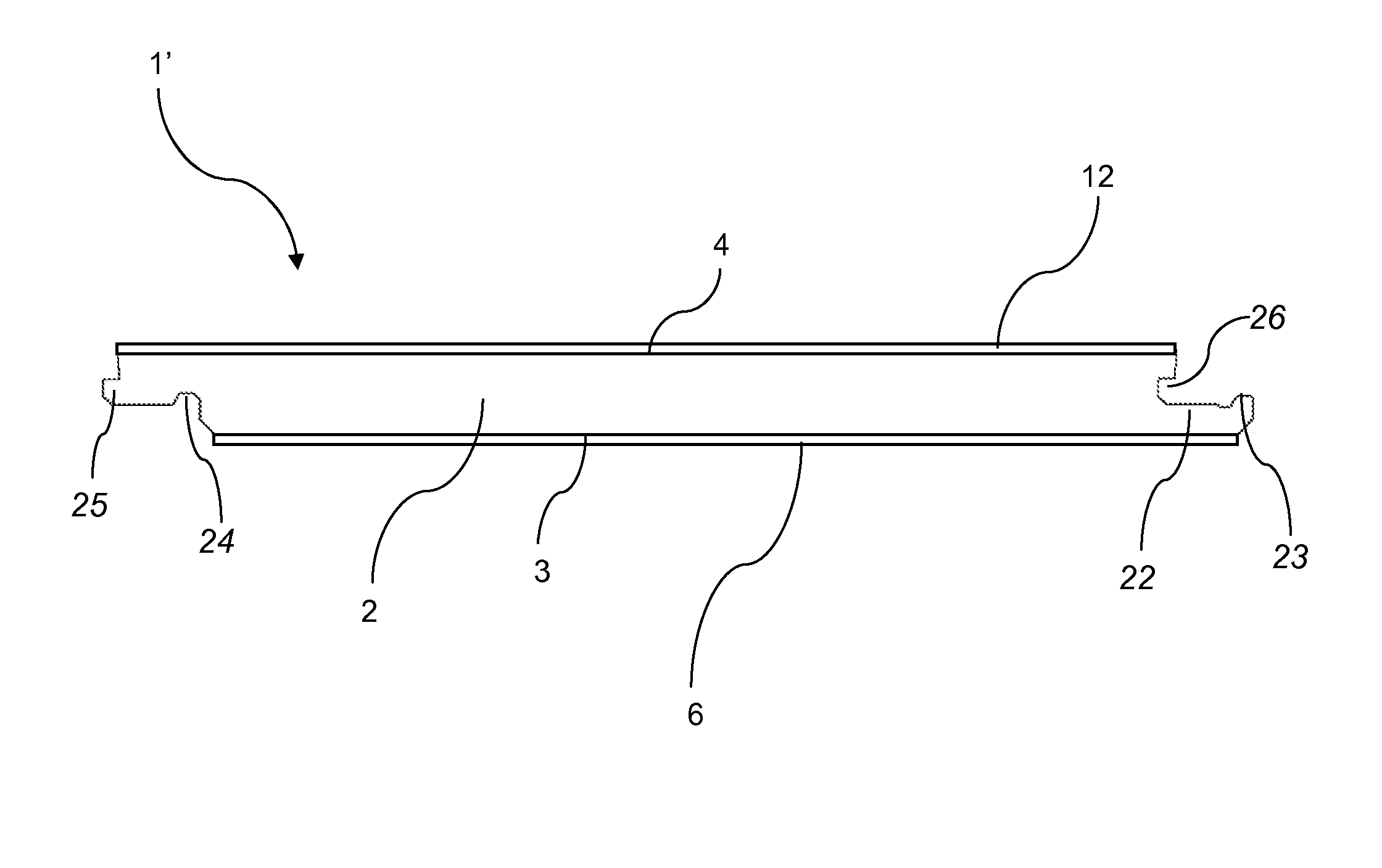
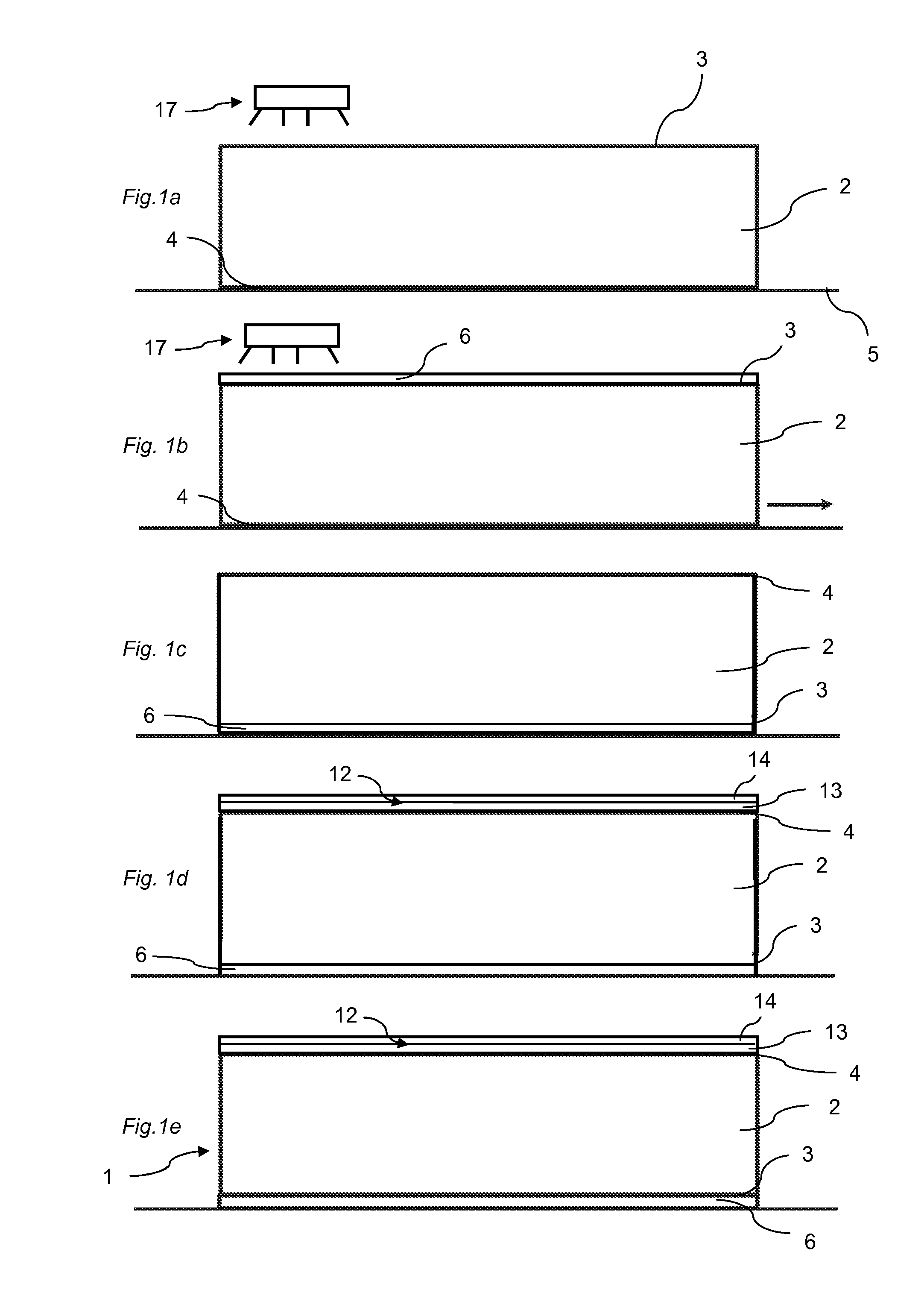
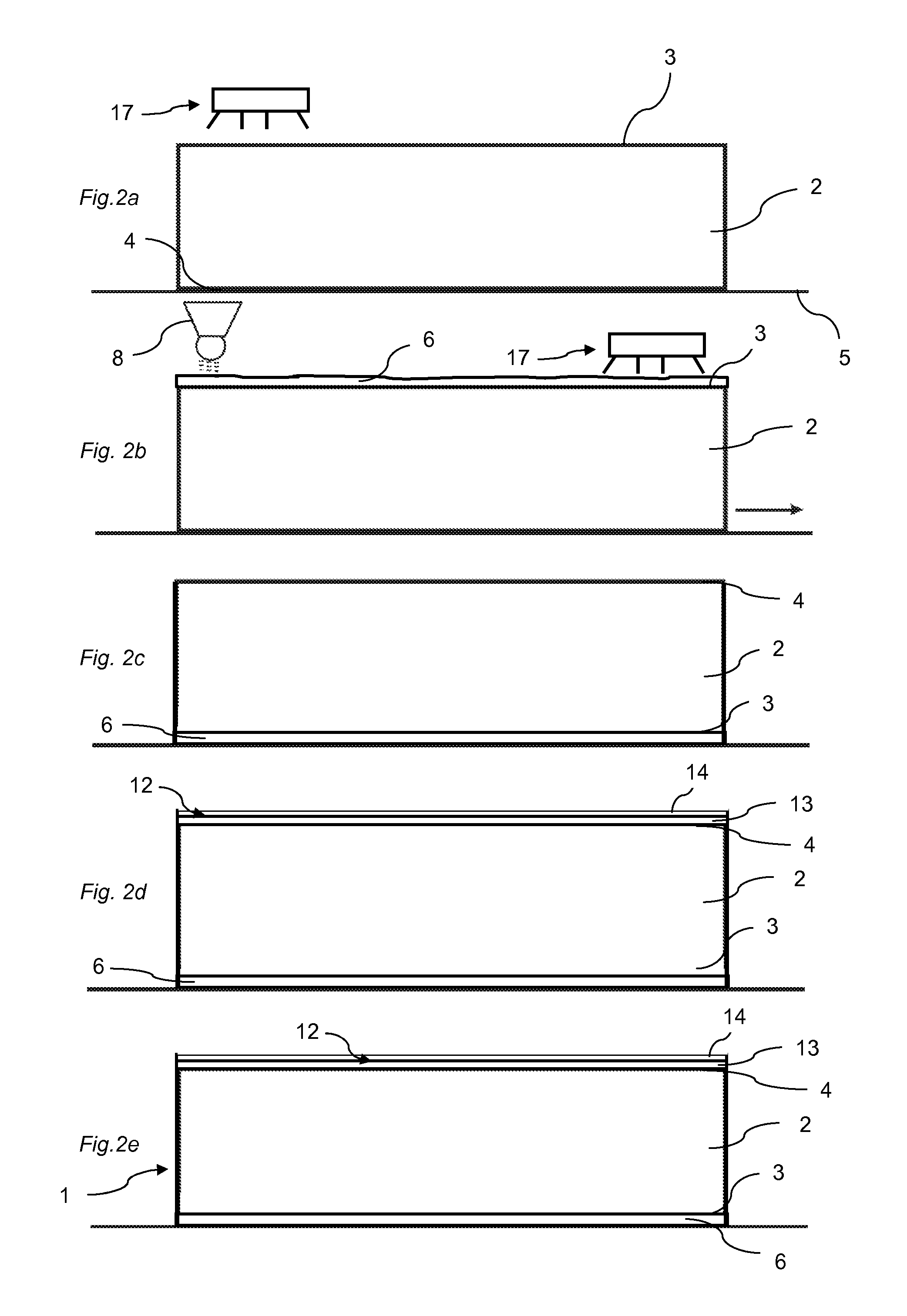
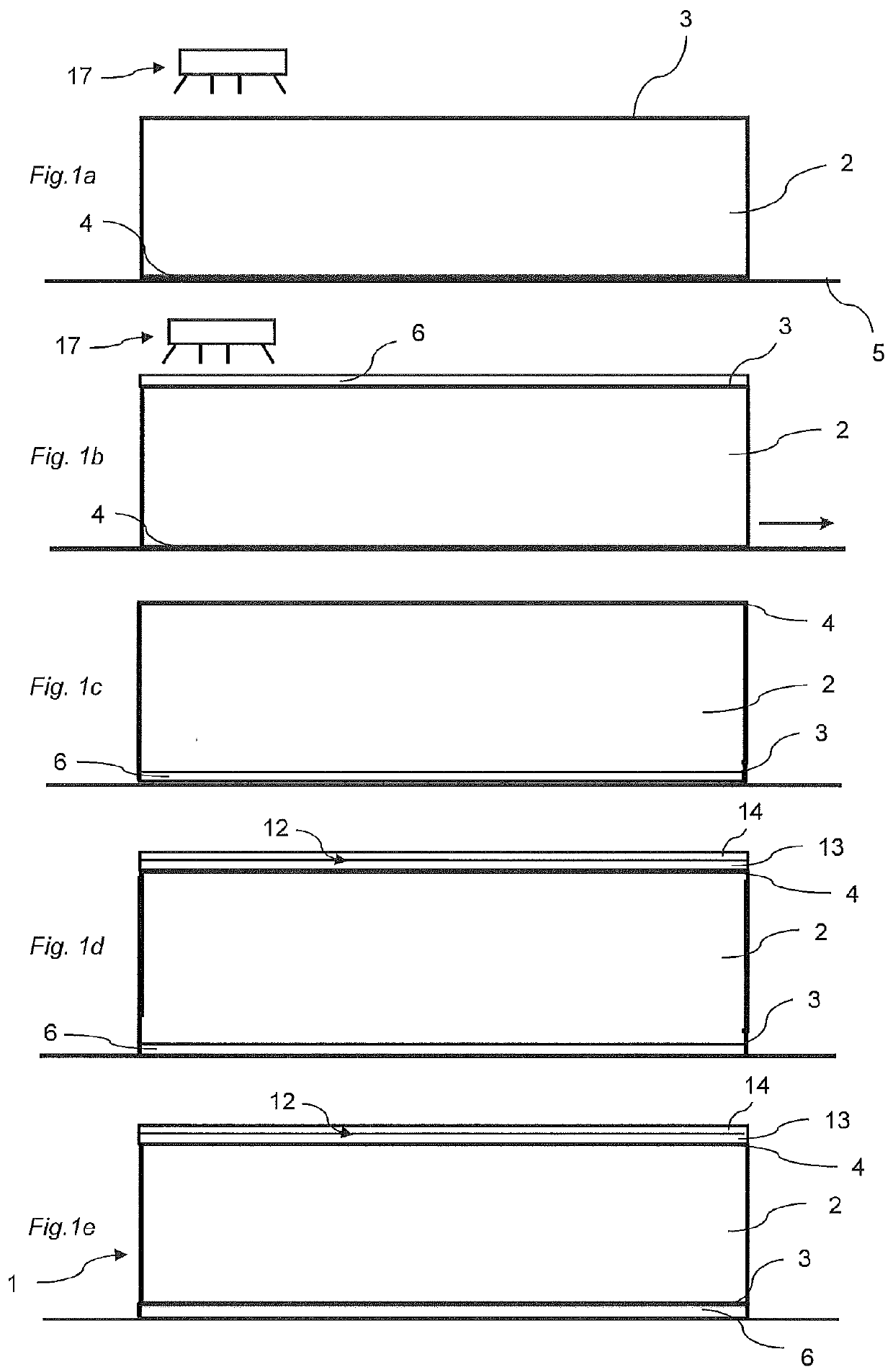
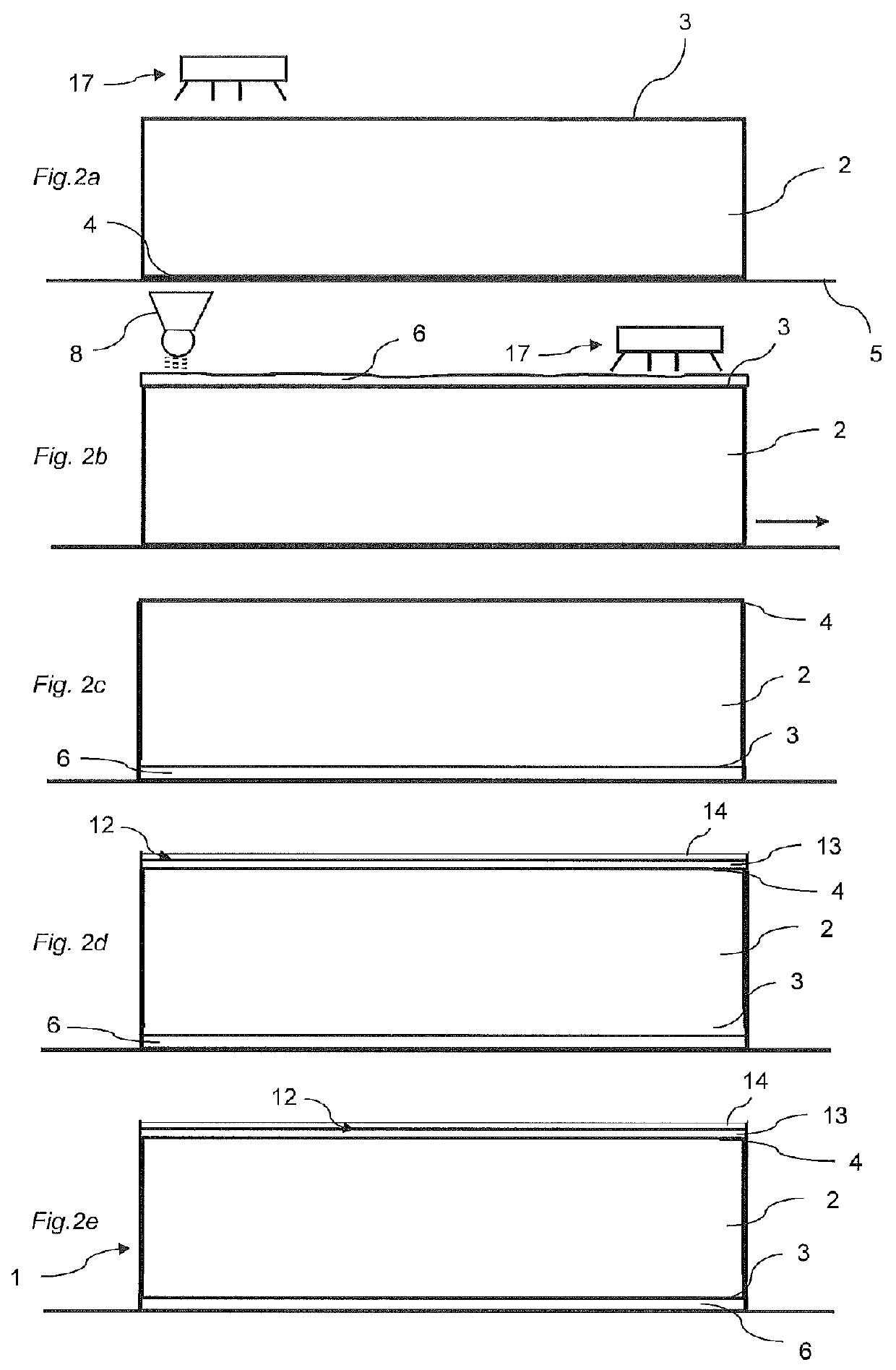
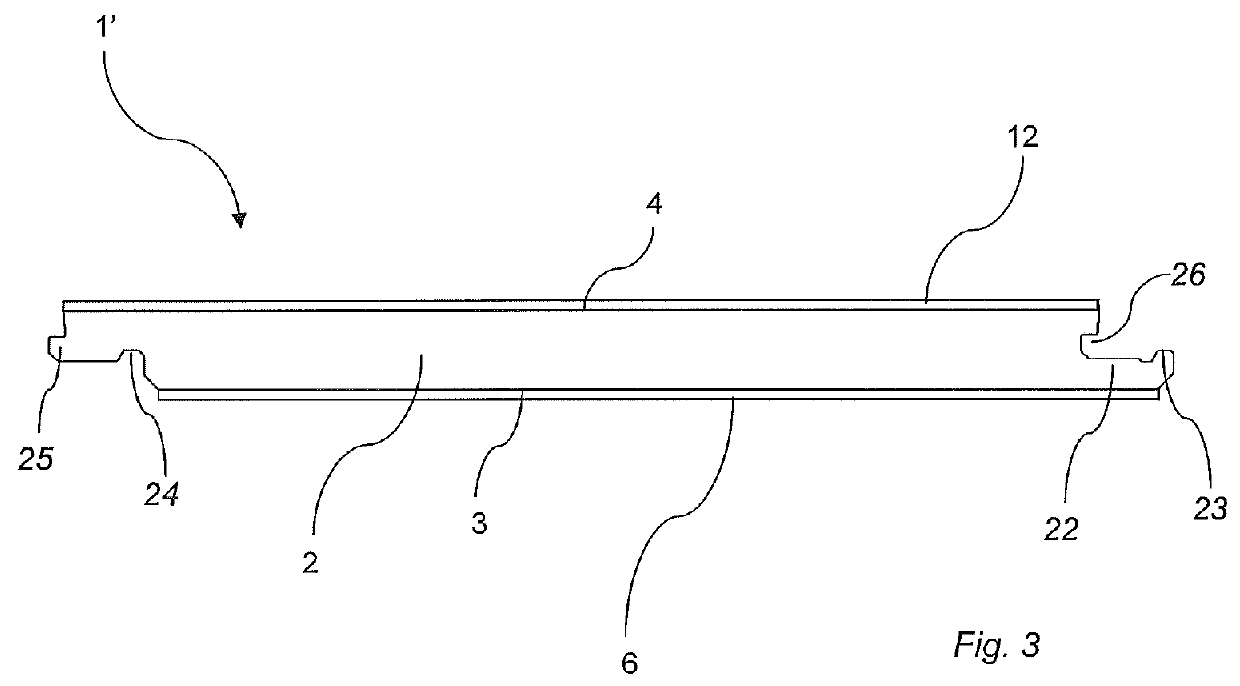
Method of producing a building panel and a building panel
ActiveUS20140199558A1Large shrinking forceReduce the amount requiredConstruction materialSynthetic resin layered productsSurface layerEngineering
A method of producing a building panel (1), including: providing a core (2), applying a balancing layer (6) having a first moisture content on a first surface (3) of the core (2), the balancing layer (6) comprising a sheet impregnated with a thermosetting binder, applying a surface layer (12) having a second moisture content on a second surface (4) of the core (2), the surface layer (12) comprising a thermosetting binder, adjusting the first moisture content of the balancing layer (6) such that the first moisture content of the balancing layer (6) is higher than the second moisture content of the surface layer (12) prior to curing, and curing the surface layer (12) and the balancing layer (6) by applying heat and pressure. Also, a semi-finished product adapted to be cured for forming a building panel (1).
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Furrow closing assembly and method
Agricultural planter row units feature soil finishing assemblies for closing a seed groove after seed is placed in the soil. An adjustable furrow closing assembly enhances upper seed groove coverage and closure with soil resulting in sustained relative humidity levels and optimum seed-to-soil contact for faster seed germination. The furrow closing assembly includes a closing wheel assembly having at least one closing wheel and a press wheel assembly having a press wheel following behind the closing wheels. The closing wheels and press wheel are attached to the planter row unit in a manner allowing the press wheel to move vertically relative to the closing wheels. Adjustable down-force systems are provided to vary the down force applied to the closing wheels and the press wheel to maintain optimum soil contact in irregular terrain and in varying soil densities and conditions to provide optimum soil coverage and compaction of the seed bed.
Owner:AG FOCUS LLC
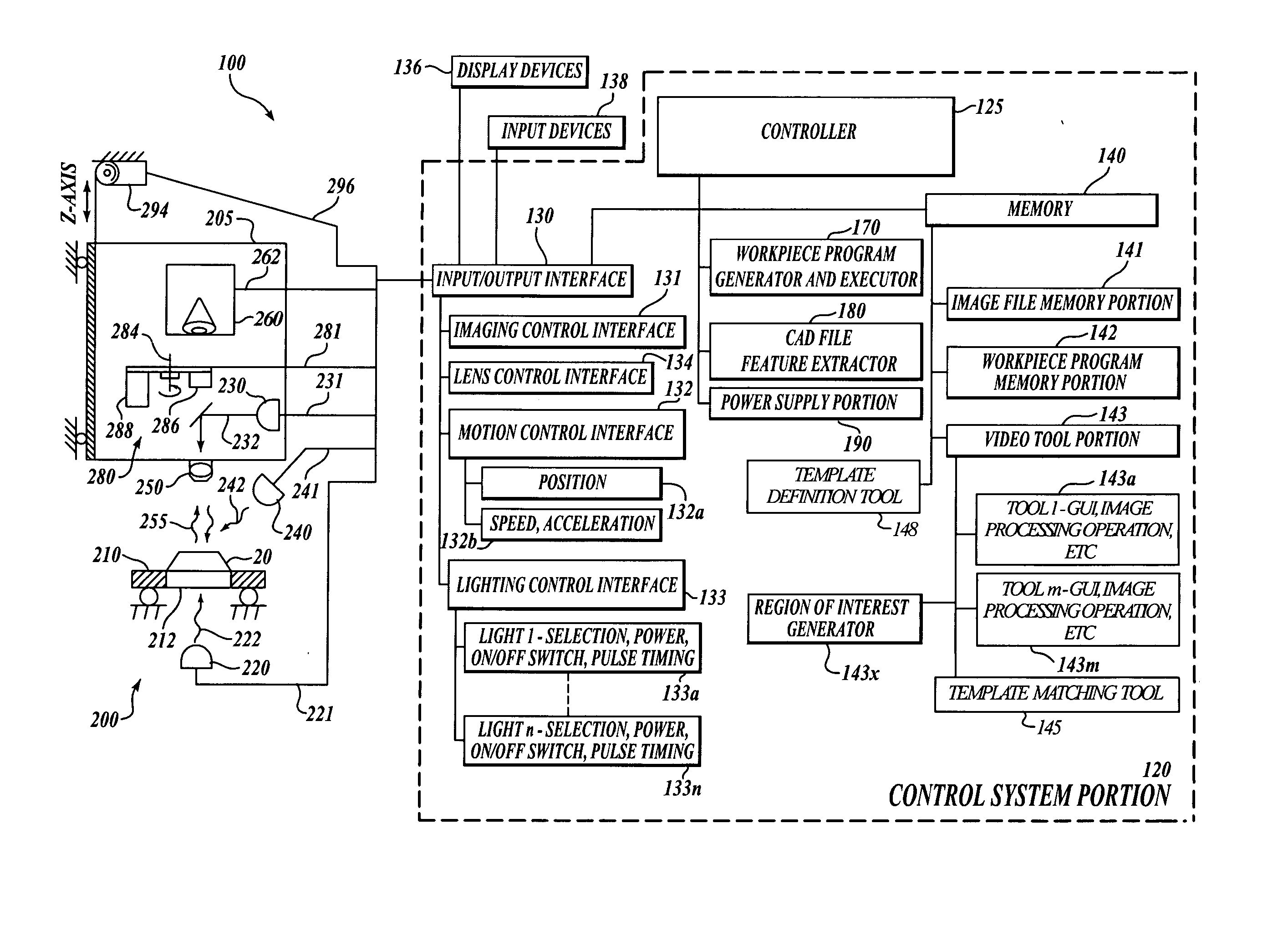
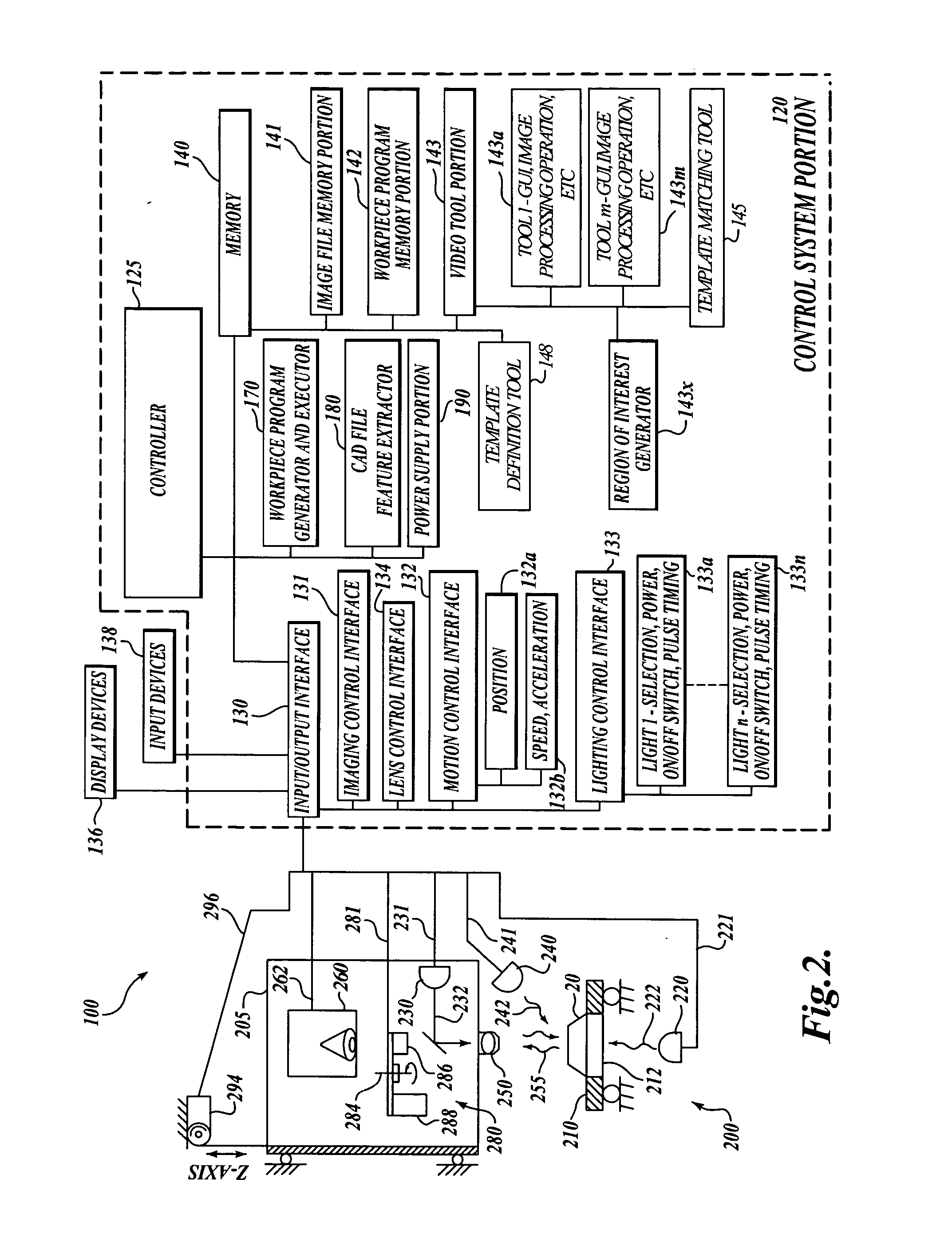
System and method for fast template matching by adaptive template decomposition
InactiveUS20070014467A1High accuracy template position resultReduced and approximately optimum processing timeCharacter and pattern recognitionTemplate matchingGeneral purpose
A fast template matching method by adaptive template decomposition is provided. The template decomposition technique subdivides a template into a number of horizontal and / or vertical subdivisions and one-dimensional characterizations are determined for the subdivisions. The template decomposition may be adapted during learn mode operations of a general-purpose precision machine vision inspection system, with the support of corresponding user interfaces. The matching results for one or more template decomposition configurations may be evaluated by a user, or by an automatic decomposition configuration evaluation routine, to determine a configuration that provides a desirable trade-off between speed and matching position accuracy. Automatic workpiece inspection instructions may implement the configuration to repeatedly provide optimum speed versus accuracy trade-offs during run mode operations of the inspection system.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Method of producing a building panel and a building panel
ActiveUS20160031189A1Low costReduce the amount requiredSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsSurface layerWork in process
A method of producing a building panel, including: providing a core, applying a balancing layer having a first moisture content on a first surface of the core, the balancing layer comprising a sheet impregnated with a thermosetting binder, applying a surface layer having a second moisture content on a second surface of the core, the surface layer comprising a thermosetting binder, adjusting the first moisture content of the balancing layer such that the first moisture content of the balancing layer is higher than the second moisture content of the surface layer prior to curing, and curing the surface layer and the balancing layer by applying heat and pressure. Also, a semi-finished product adapted to be cured for forming a building panel.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Friction stir welding method, frame members used therein, and product formed thereby
InactiveUS7036707B2High resultEasy to deleteWelding/cutting auxillary devicesStructural elementsEngineeringFriction stir welding
Disclosed is a friction stir welding technique which avoids occurrence of a dent, in a joining region, extending to a level beneath the joined surfaces. At end portions of the frame members to be joined, at the joining region, thickened parts which project toward the rotary body joining tool are provided. Two adjoining thickened parts, of adjacent members to be joined, can form a trapezoid shape. The rotary body joining tool has a small-diameter tip portion and a larger diameter portion. The rotary body joining tool is inserted in the thickened parts. In a state where the rotary body joining tool has been inserted small-diameter tip end first, to a level where the larger diameter portion of the rotary body joining tool overlaps the thickened part but does not extend below the upper surface of the non-thickened surfaces of the members joined, the rotary body is rotated and moved along the joining region. Even when a gap exists between two thickened parts, a desirable joining can be carried out. After the joining, the remaining parts of the thickened parts can be machined so as to form a smooth surface.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method of producing a building panel and a building panel
ActiveUS9181698B2Low costImprove balanceConstruction materialLamination ancillary operationsSurface layerEngineering
A method of producing a building panel (1), including: providing a core (2), applying a balancing layer (6) having a first moisture content on a first surface (3) of the core (2), the balancing layer (6) comprising a sheet impregnated with a thermosetting binder, applying a surface layer (12) having a second moisture content on a second surface (4) of the core (2), the surface layer (12) comprising a thermosetting binder, adjusting the first moisture content of the balancing layer (6) such that the first moisture content of the balancing layer (6) is higher than the second moisture content of the surface layer (12) prior to curing, and curing the surface layer (12) and the balancing layer (6) by applying heat and pressure. Also, a semi-finished product adapted to be cured for forming a building panel (1).
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
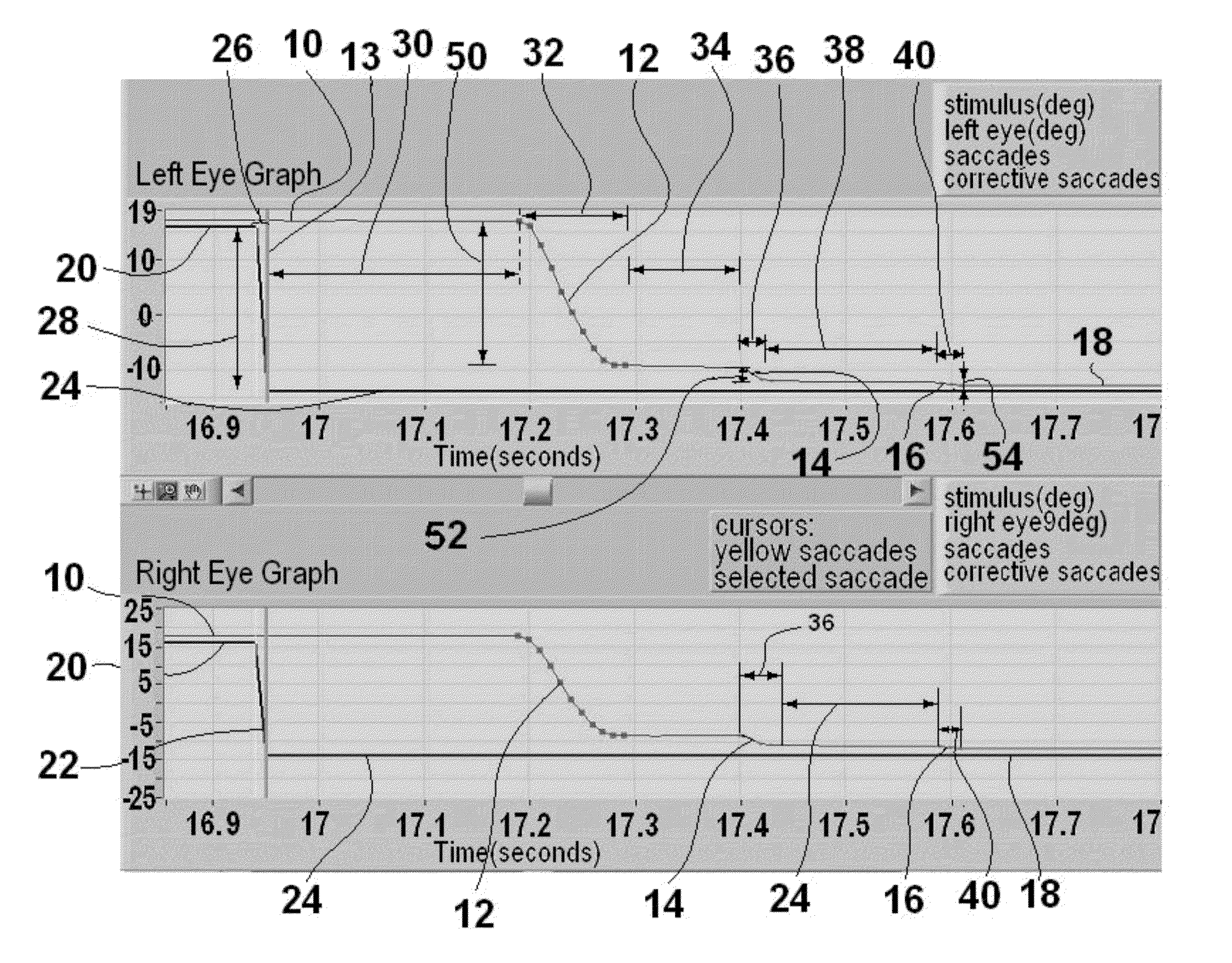
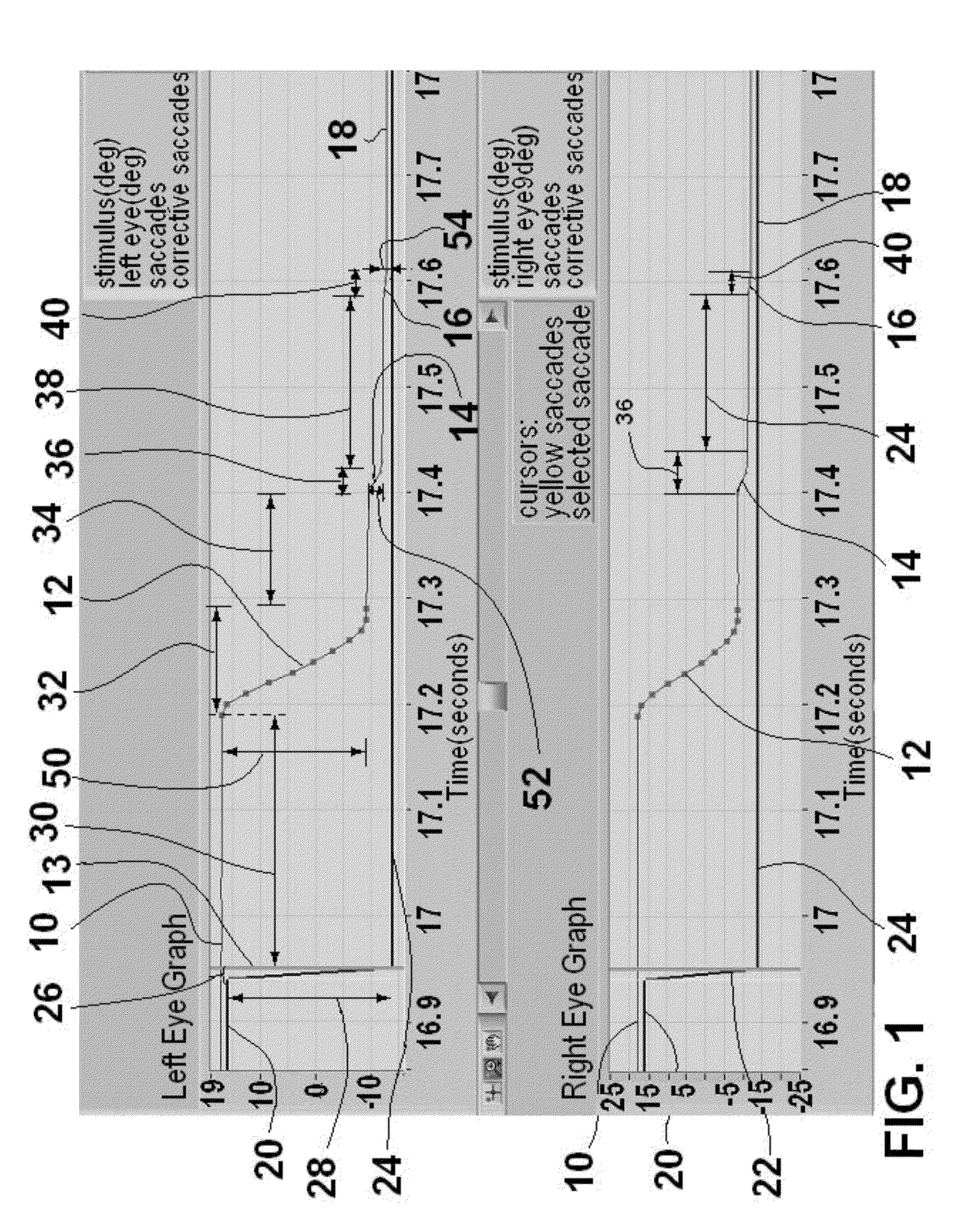
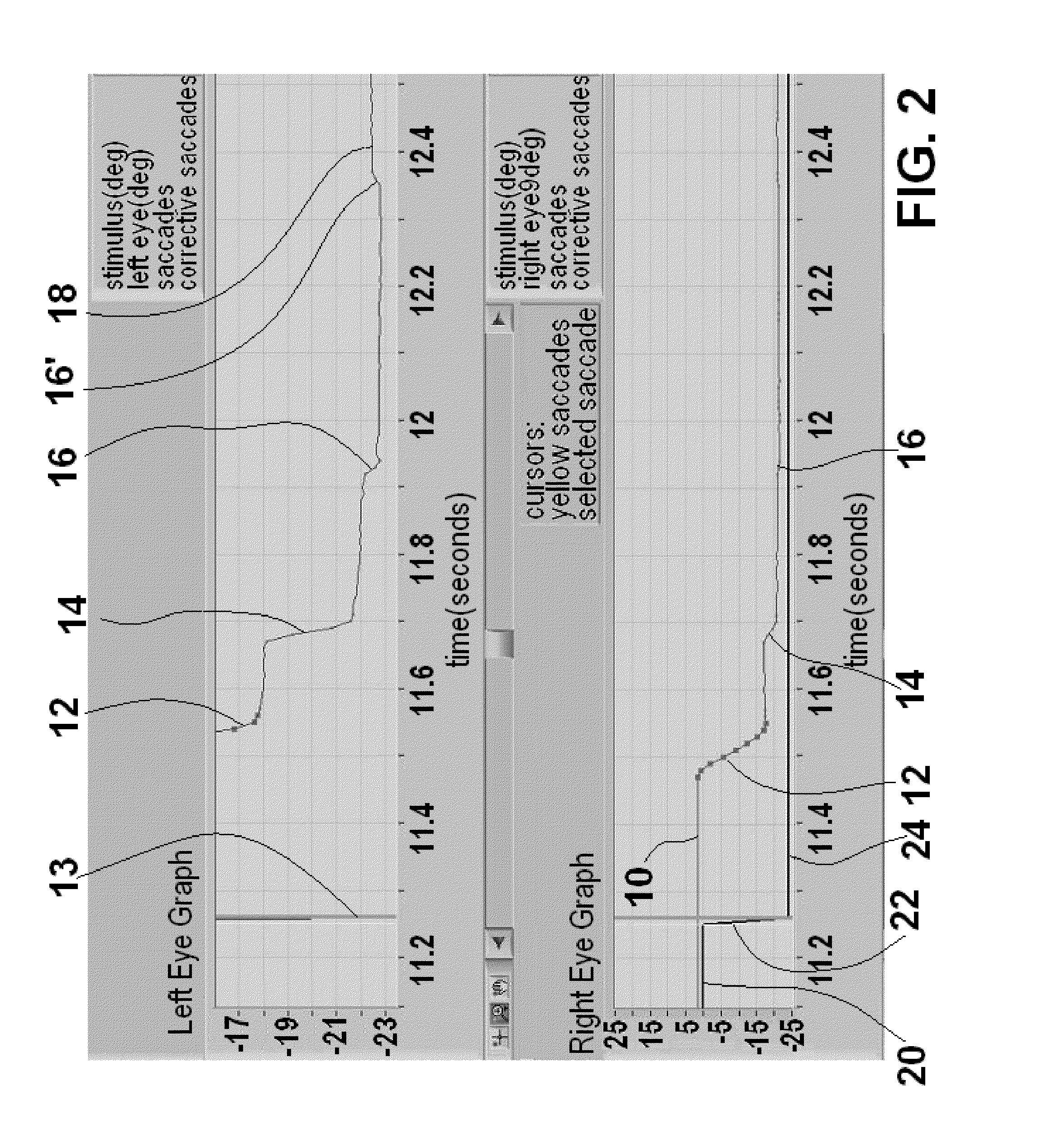
Method and apparatus for corrective secondary saccades analysis with video oculography system
ActiveUS20120081666A1High resultAid in diagnosisHealth-index calculationMedical automated diagnosisVogSaccade
A video oculography system for calculation and display of Corrective Secondary Saccades Analysis is disclosed. A method for Objective Diagnostics of at least one of traumatic brain injury, Internuclear Opthalmopligia, Ocular Lateral Pulsion, Progressive Supernuclear Palsy And Glissades comprises the steps of using a VOG system to calculate corrective saccades. The video oculography based system for the subject is configured to collect eye images of the patient in excess of 60 hz and configured to resolve eye movements smaller than at least 3 degrees of motion. The video oculography based system collects eye movement data wherein at least one fixation target is presented to the subject in a defined position configured to yield a voluntary saccadic eye response from at least one eye of the patient. The latency, amplitude, accuracy and velocity of each respective corrective saccade and totals latency and accuracy is calculated.
Owner:128 GAMMA LIQUIDATING TRUST +1
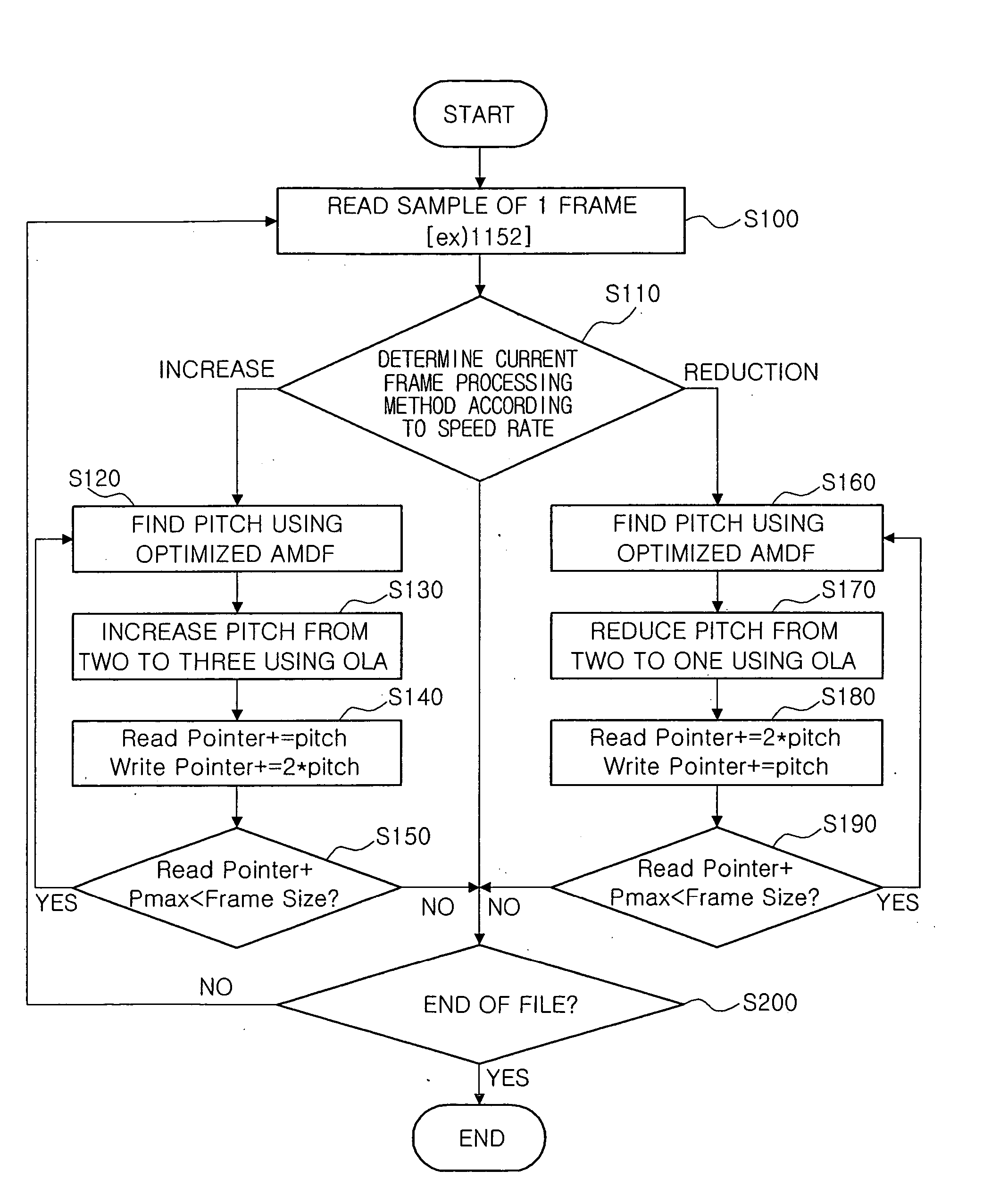
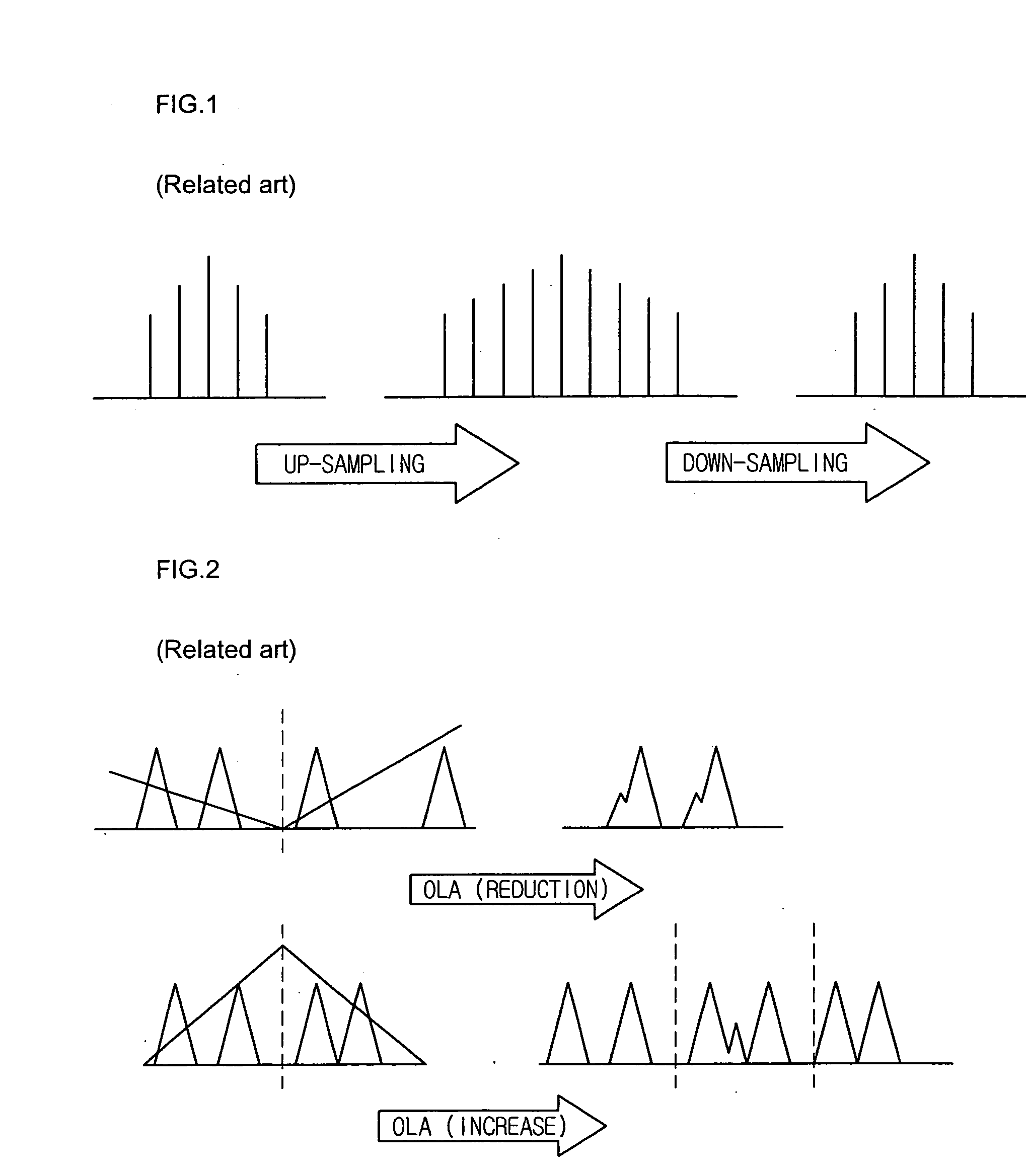
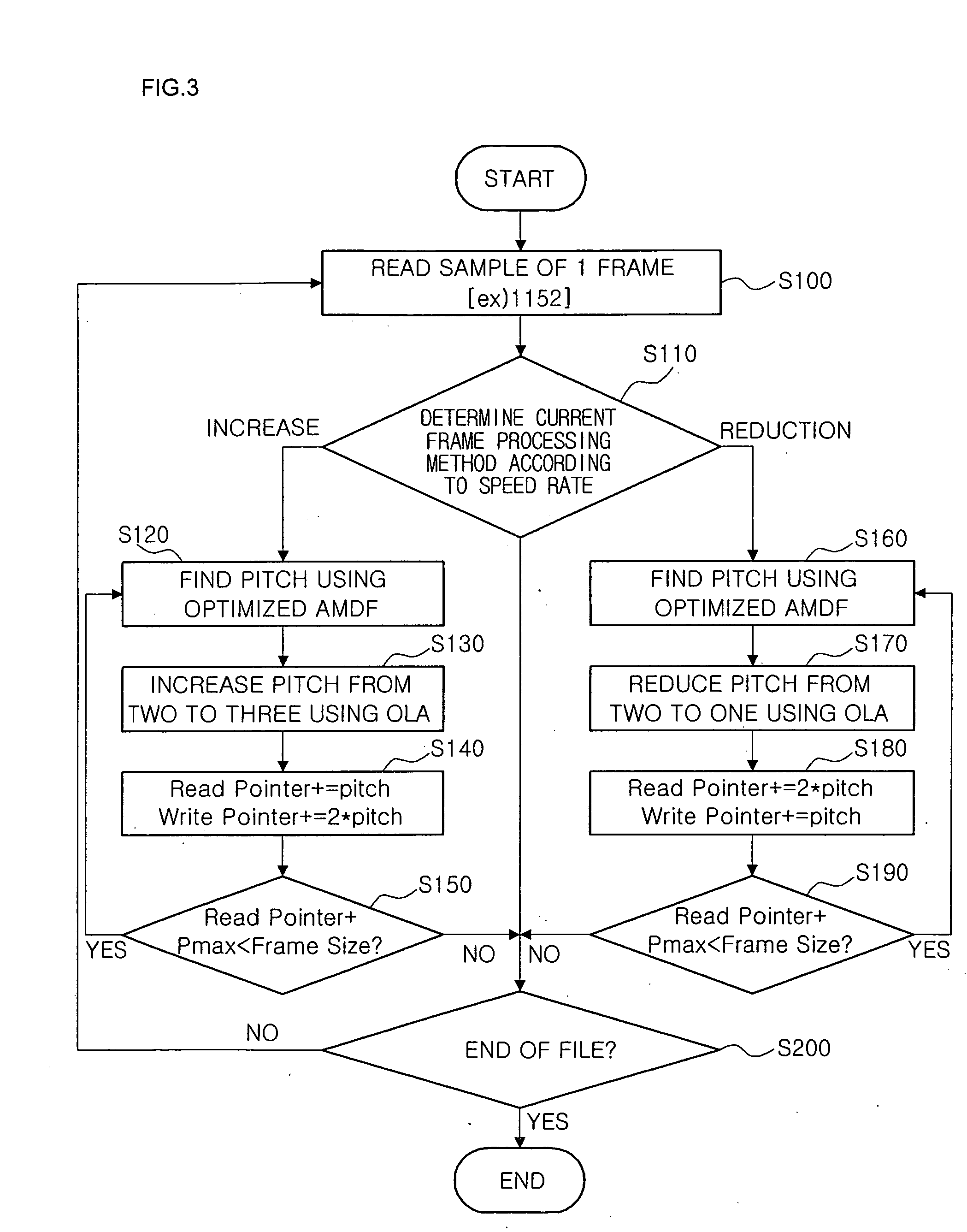
Method for controlling speed of audio signals
InactiveUS20060149535A1High quality TSM resultAccurate adjustmentSpeech analysisTime or data compression/expansionAudio signalAudio frequency
A method for controlling the speed of audio signals is provided. The method is based on a TSM that uses an optimized AMDF and an OLA. According to the method, the number of frame sets is differently set depending a TSM speed rate to set the interval of a speed rate, and the number of frame sets required for adjusting the speed rate is determined. Subsequently, a TSM process is performed only when the TSM process is required for the frame set determined to adjust the speed rate, and speed processing is performed such that an input frame becomes an output frame otherwise.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
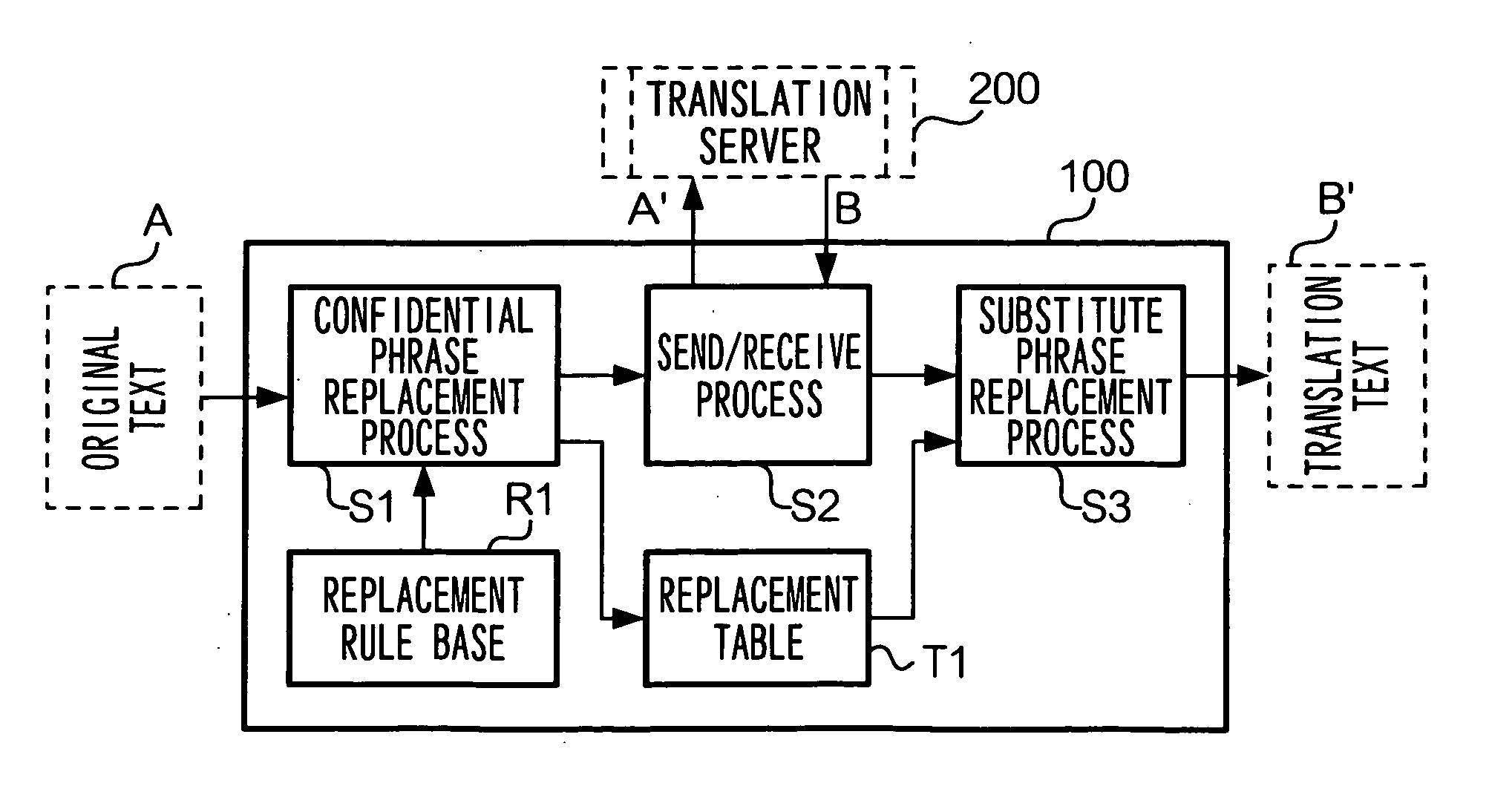
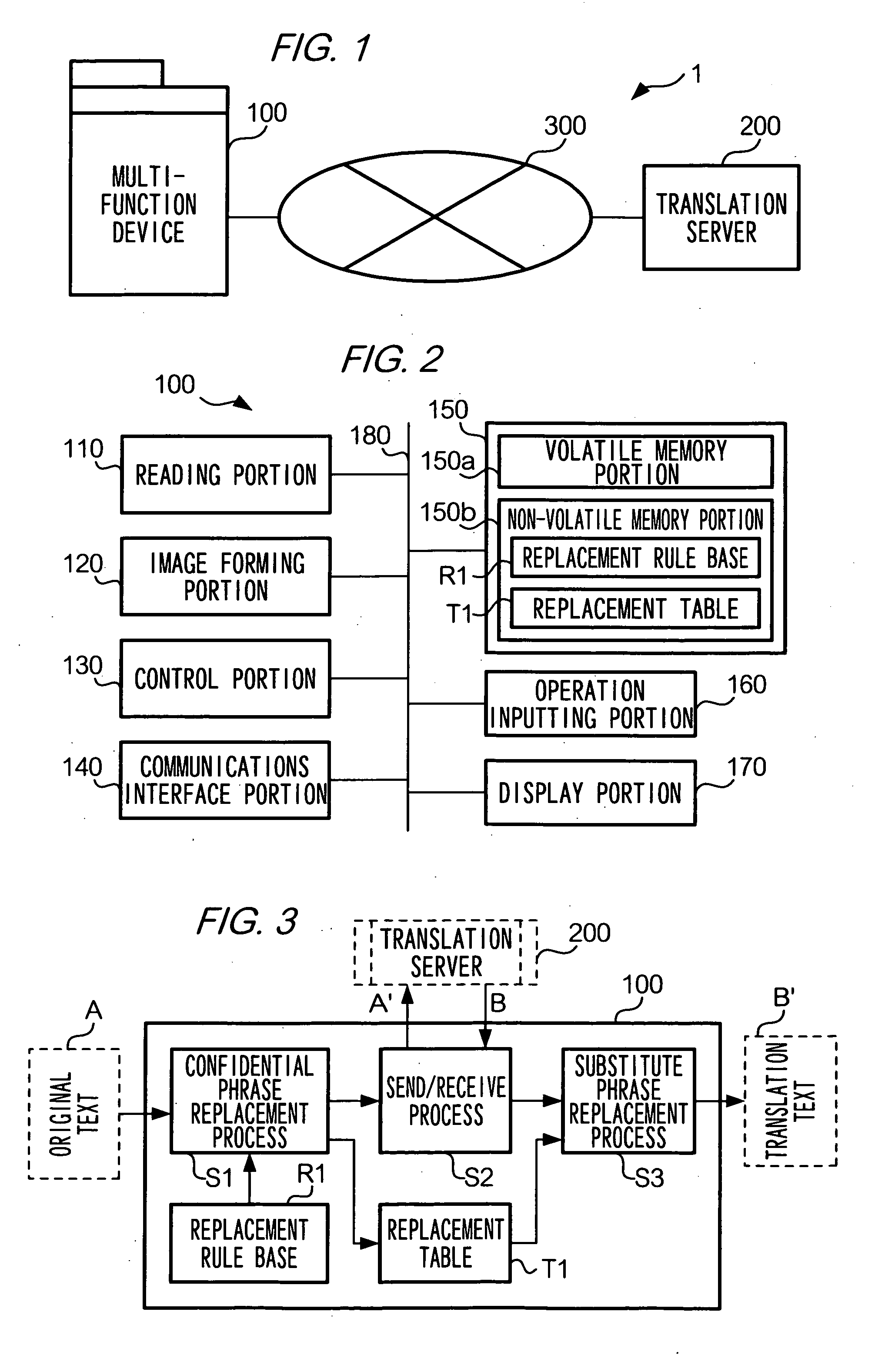
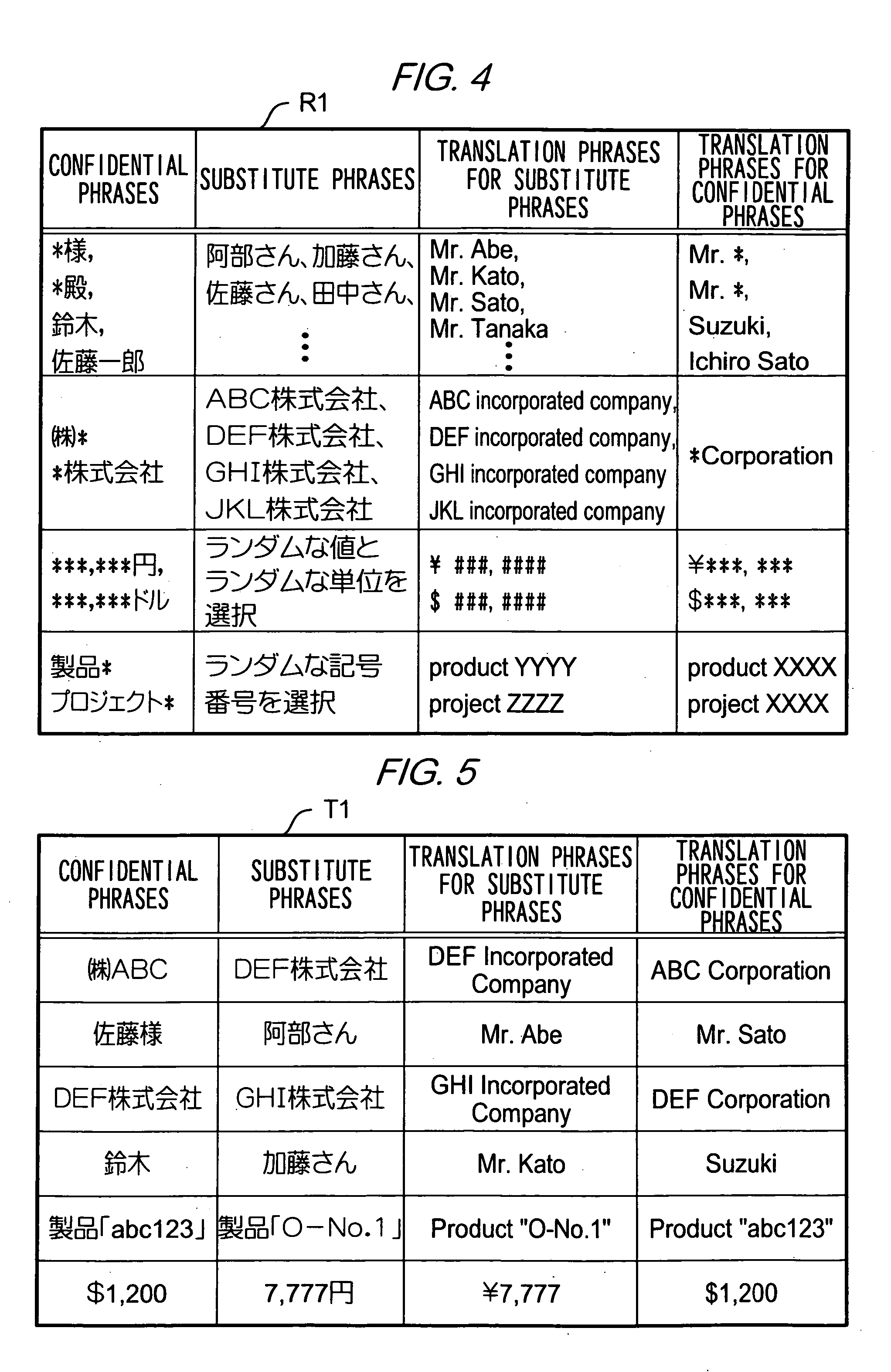
Translation requesting method, translation requesting terminal and computer readable recording medium
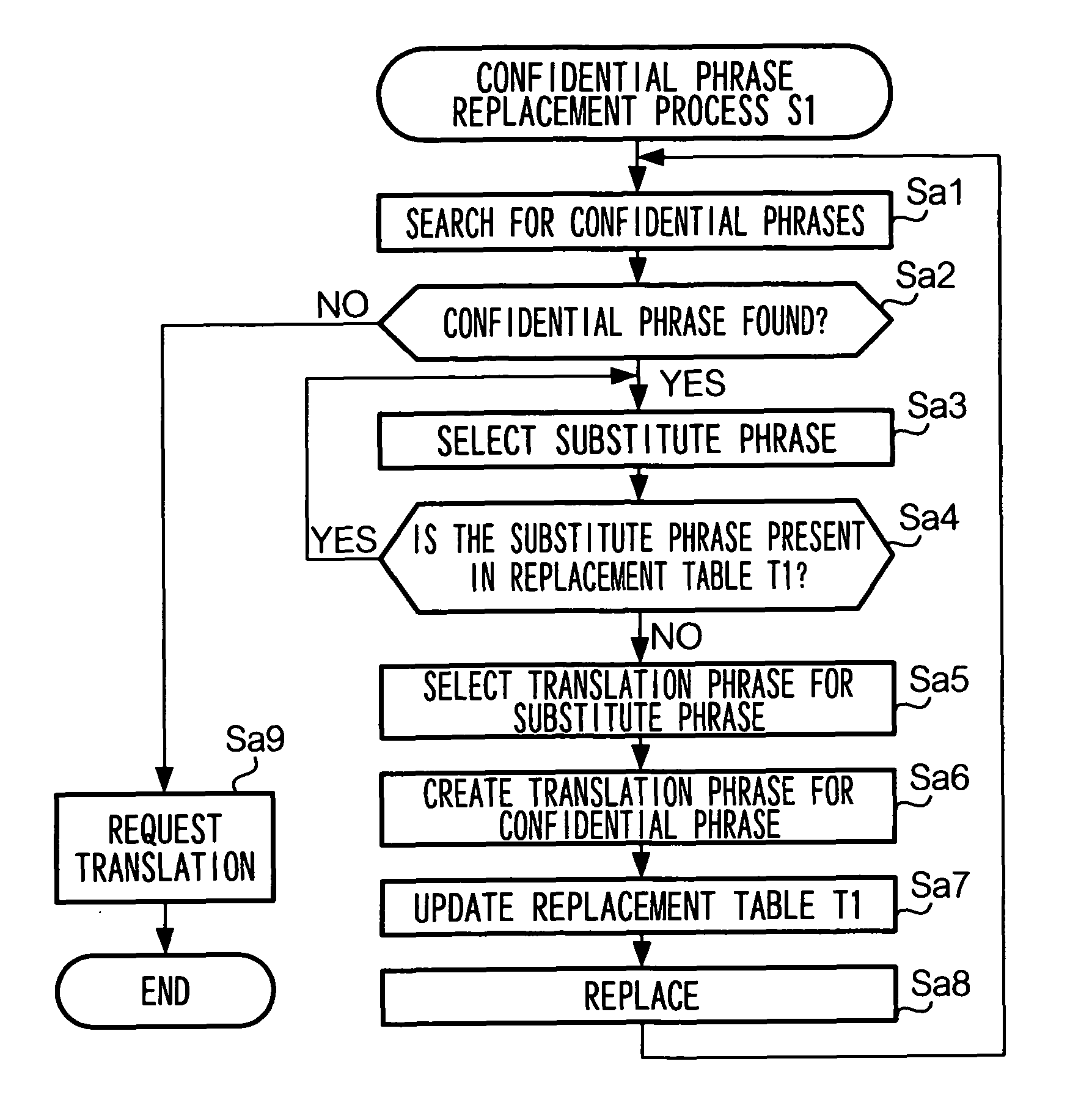
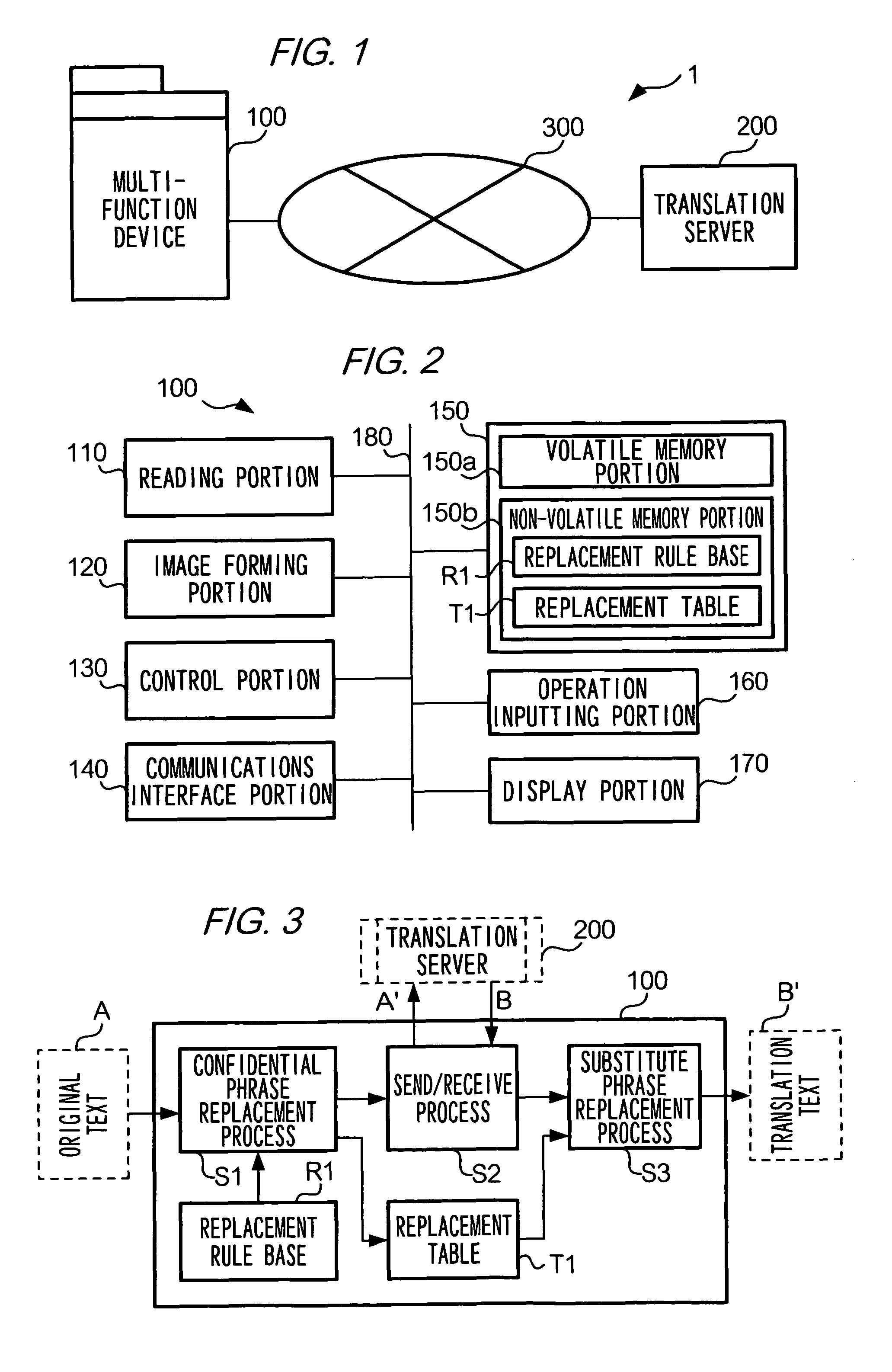
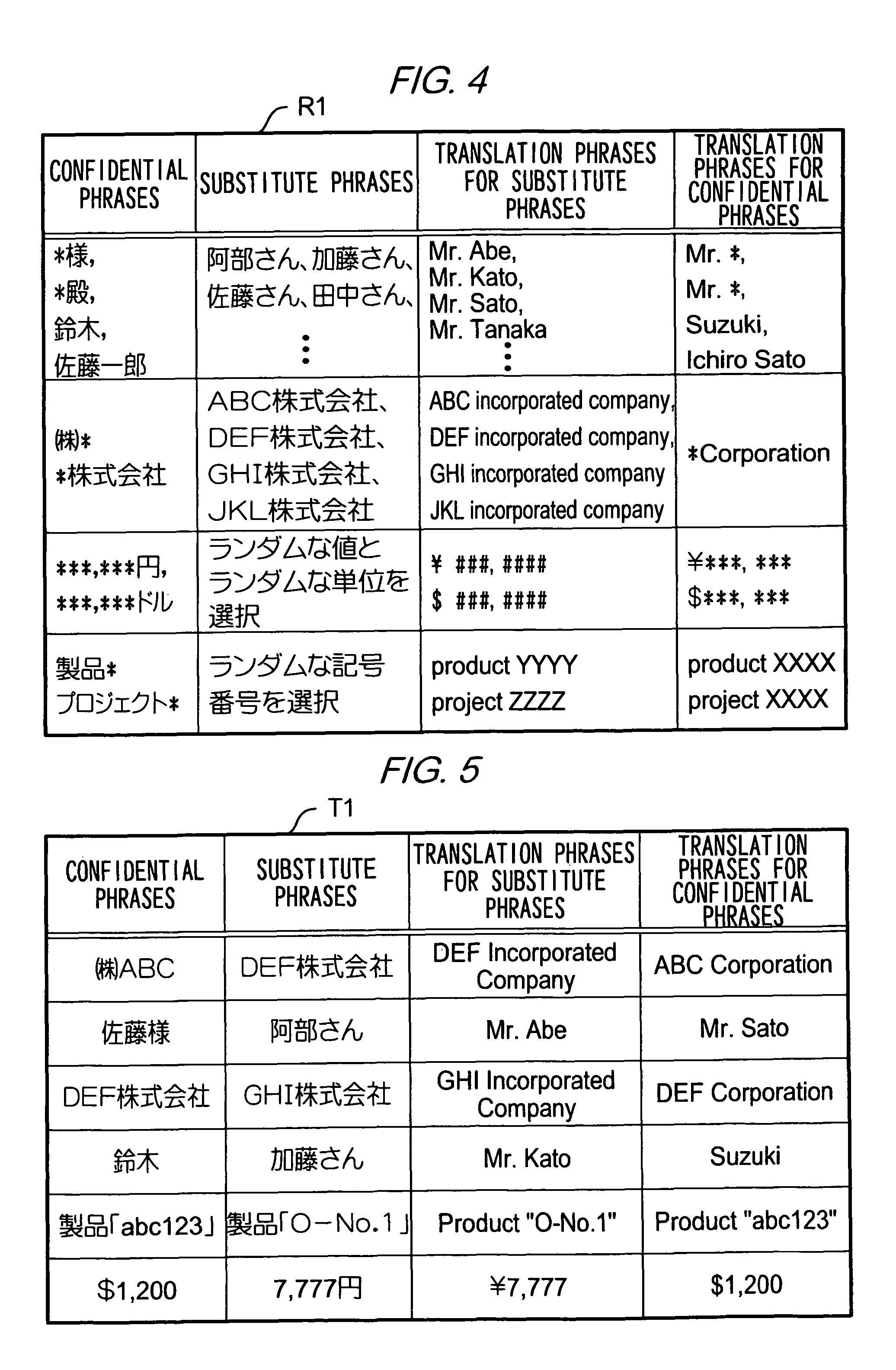
InactiveUS7801720B2High resultMaintain confidentialityNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic propertyRecording media
A translation requesting device has a first replacing unit, a translating unit and a second replacing unit. The first replacing unit replaces an original phrase to a substitute phrase. The translating unit translates the substitute phrase. The second replacing unit replaces the original phrase to a translation phrase based on the translated substitute phrase. The substitute phrase is decided to maintain semantic properties of the original phrase.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Portable medical diagnostic systems and methods using a mobile device
ActiveUS9241663B2Enhance the imageLow profileMaterial analysis by optical meansMachines/enginesAmbient lightingColor correction
A system and method for analysis of colorimetric test strip strips and disease management. The system can include an accessory that is operably coupled to a mobile device, the mobile device acquiring and / or analyzing images of the colorimetric test strips. The light box accessory can be detachably attached to the mobile device, or made to remain attached to the mobile device, but with the capability of having the light box accessory removed from the field of view of the camera for general photography purposes. In other embodiments, an image containing known calibration color(s) and reagent area(s) is obtained sans the light box for comparison with a previous calibration image to model changes in ambient lighting conditions and determine a color correction function. The correction can be applied to the detected reagent area color(s) for matching between the detected reagent area color(s) and reference color(s) on the reference chart. Optionally, the information can be processed and displayed to provide feedback, as well as transmitted to a health provider for analysis.
Owner:JANA CARE
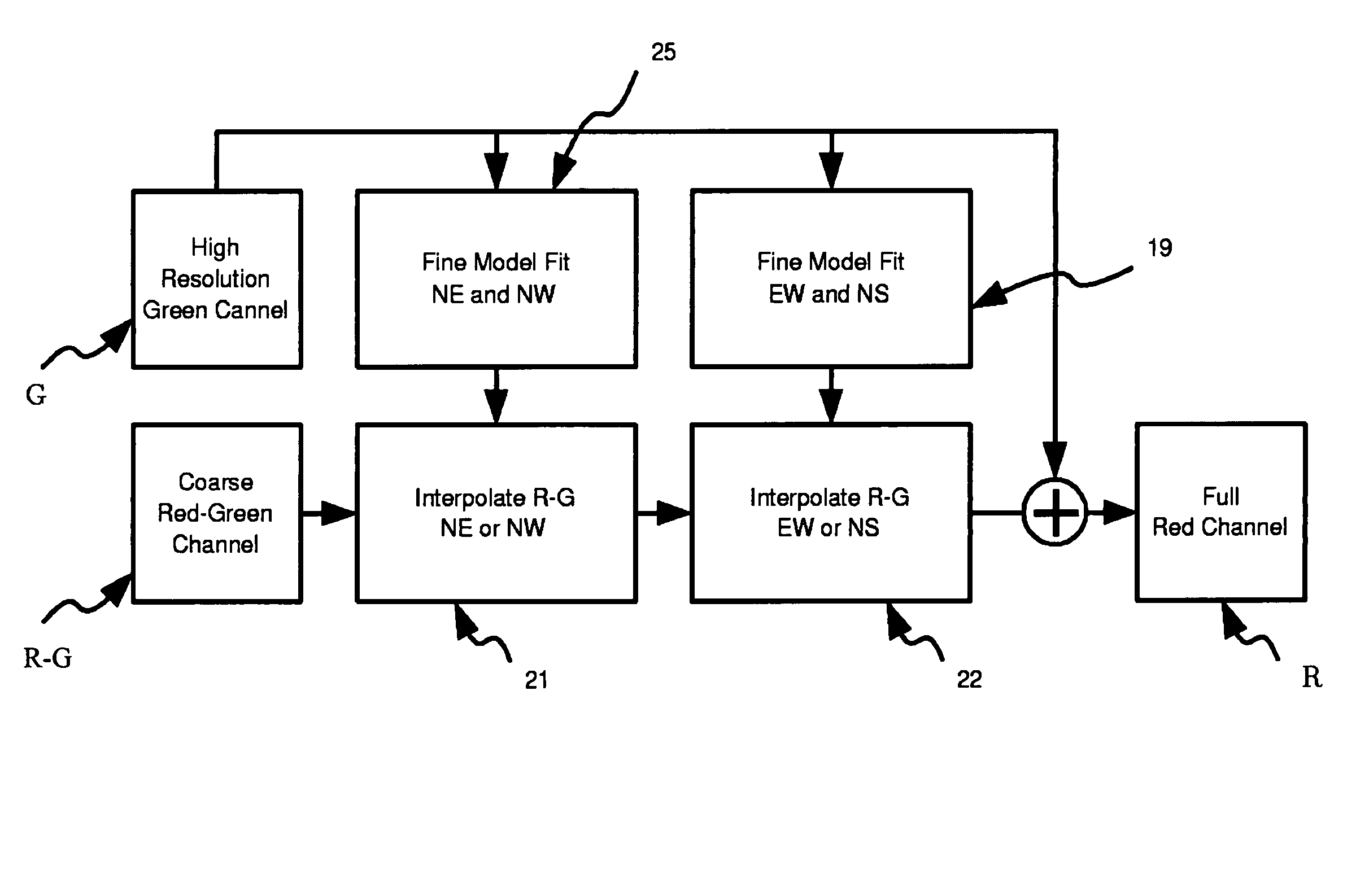
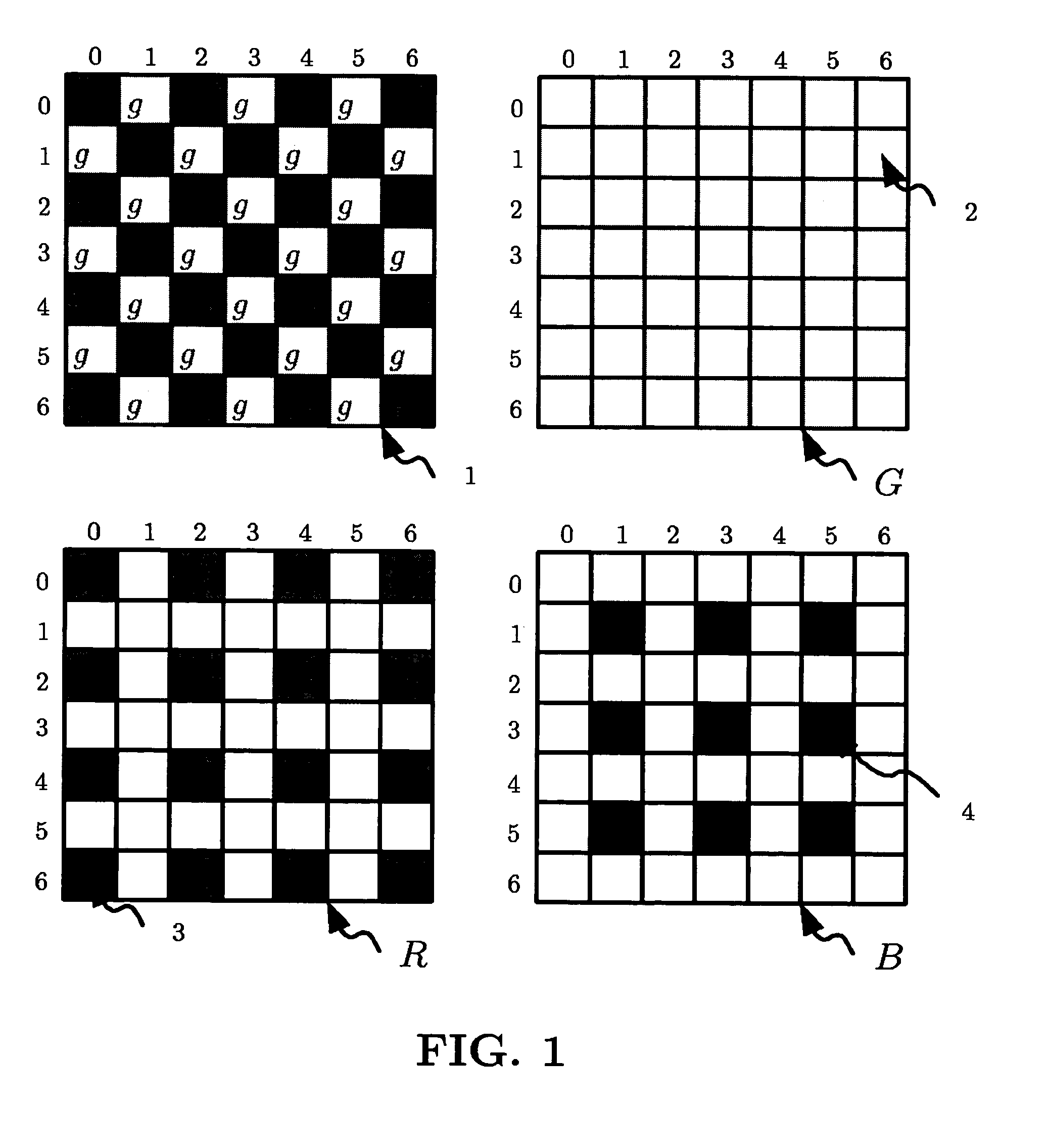
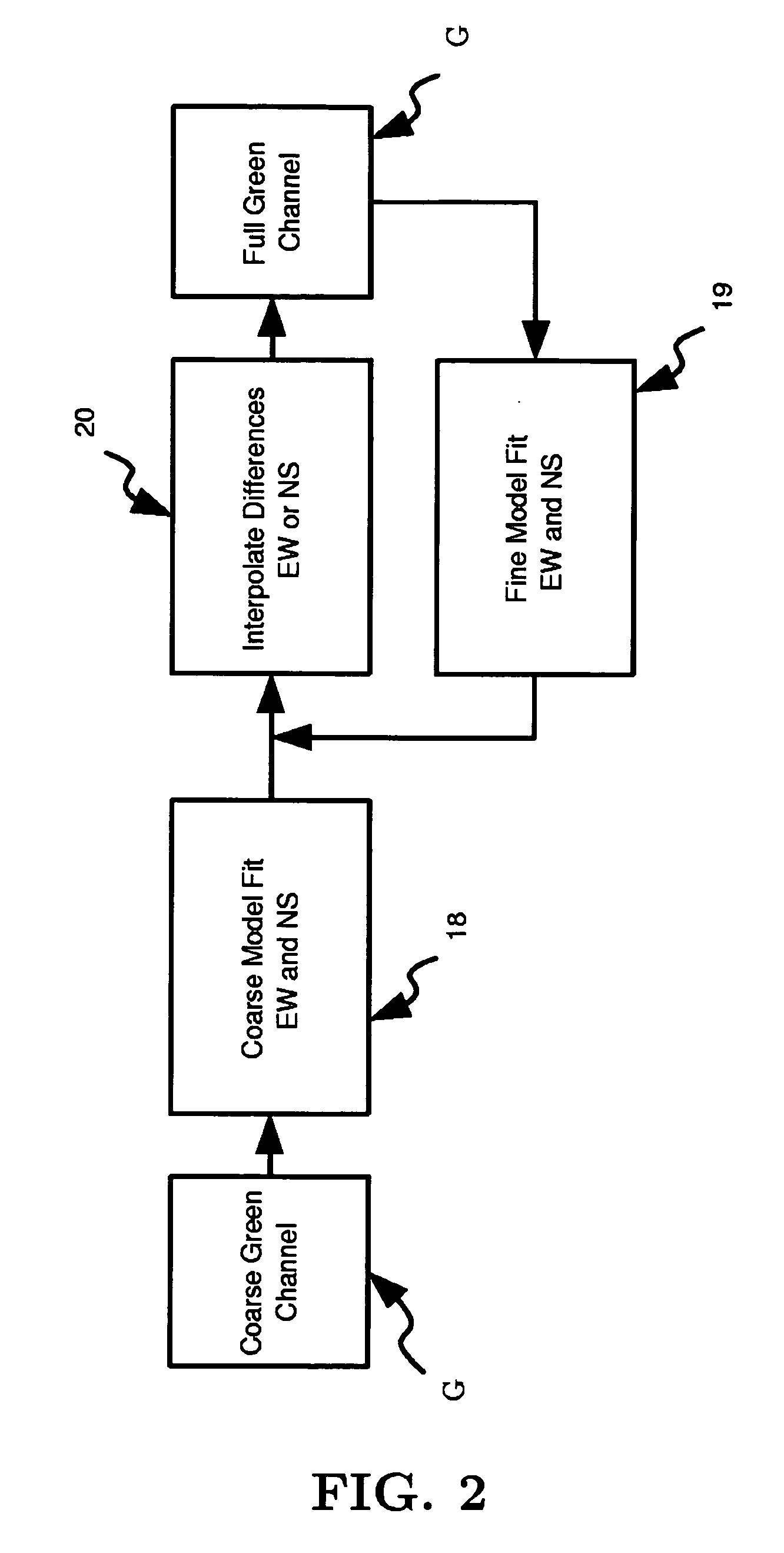
Fast edge directed demosaicing
ActiveUS20050146629A1High quality visual resultPromote reconstructionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor filter arrayErrors and residuals
An edge directed demosaicing algorithm for determining an edge direction from an input color filter array (CFA) sampled image is disclosed. Aspects of the present invention include calculating for a current missing green pixel, interpolation errors in an East-West (EW) direction at known neighboring green pixels, and averaging the EW interpolation errors to obtain an EW error. Interpolation errors are also calculated for the current missing green pixel in a North-South (NS) direction at known neighboring green pixels, and the NS interpolation errors are averaged to obtain a NS error. An EW or NS direction indicated by a minimum of the EW error and the NS error is then selected as the edge direction.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
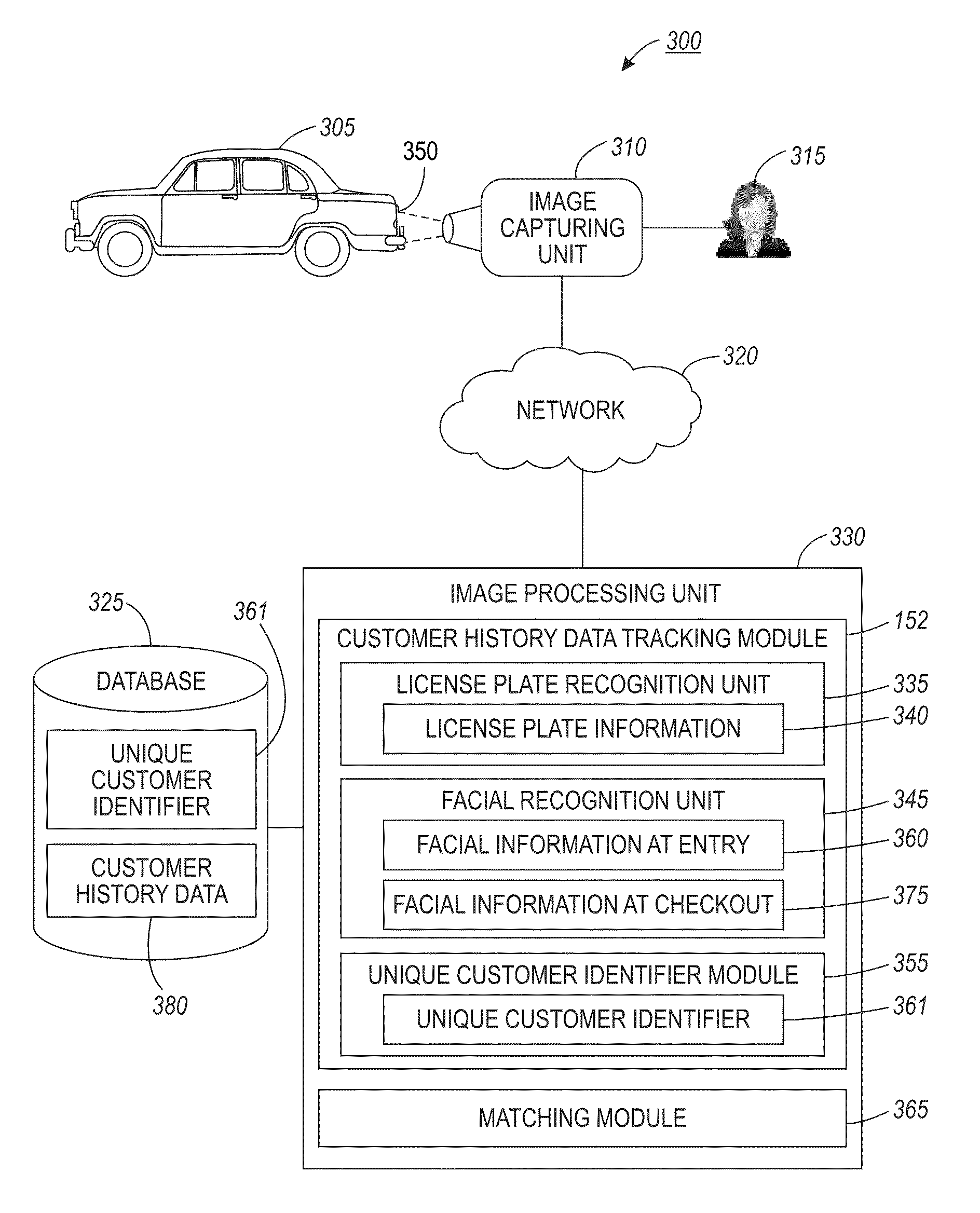
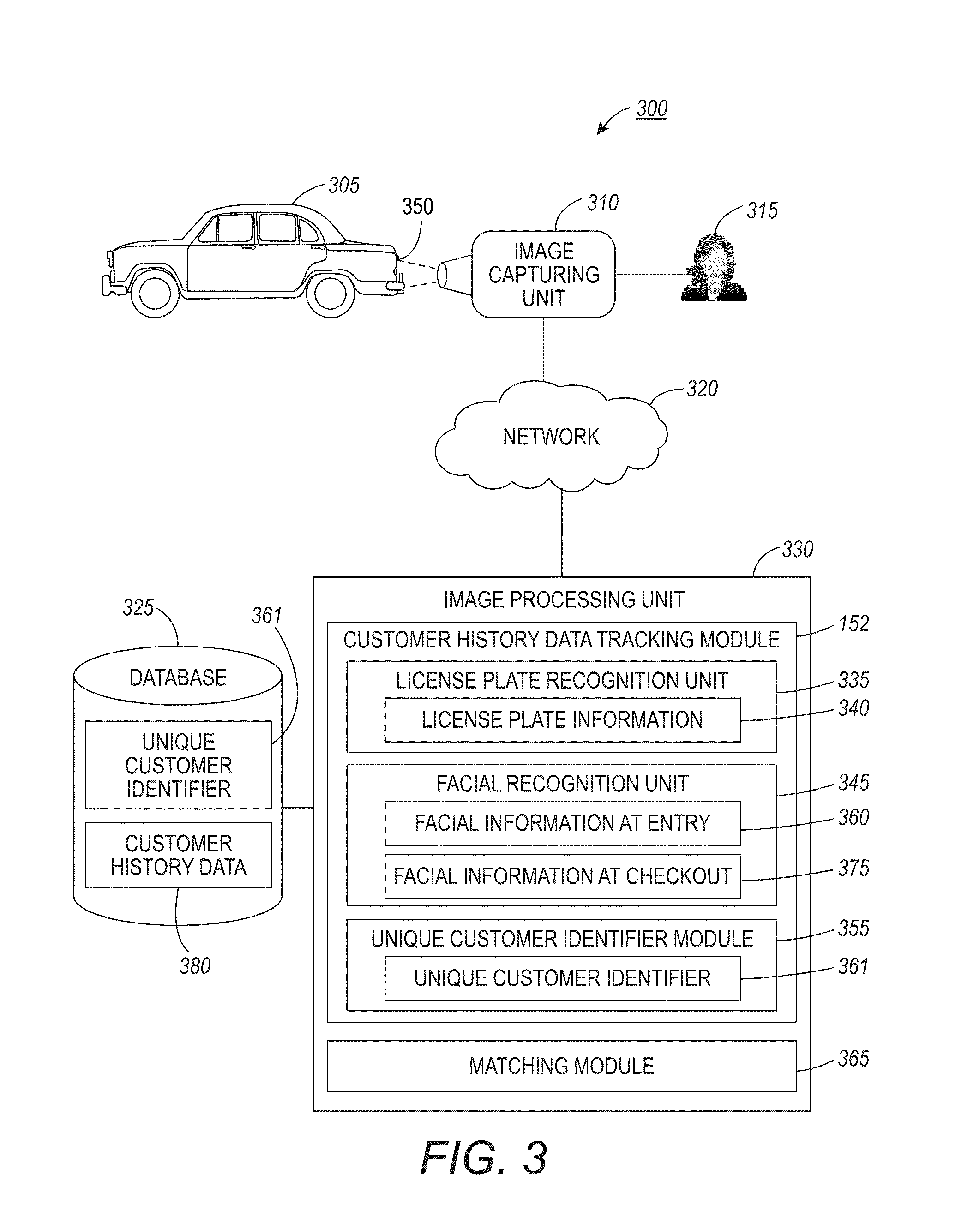
Methods, systems and processor-readable media for tracking history data utilizing vehicle and facial information
ActiveUS9008370B2Reduce difficultyLow yieldCharacter and pattern recognitionMarketingComputer visionCustomer order
A method and system for tracking a customer history data utilizing a combination of vehicle and facial information. A license plate image with respect to a customer vehicle can be captured and information with respect to the license plate obtained. The license plate information can be employed as an unique customer identifier with respect to customer history data, if the customer places an order (e.g., drive-through service). Facial images of the customer upon entry to a store and / or upon checkout can be captured and processed. The checkout image can be matched against a set of images in order to associate customer order information with customer history data identified from the license plate information for tracking an in-store order transaction.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
Translation requesting method, translation requesting terminal and computer readable recording medium
InactiveUS20060200339A1High resultMaintain confidentialityNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic propertyPaper document
As described above, the present invention also provides, in one aspect, a translation requesting device for translating a document having: a first replacing unit that replaces an original phrase to a substitute phrase; a translating unit that translates the substitute phrase; and a second replacing unit that replaces the original phrase to a translation phrase based on the translated substitute phrase, wherein the substitute phrase is decided to maintain semantic properties of the original phrase.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
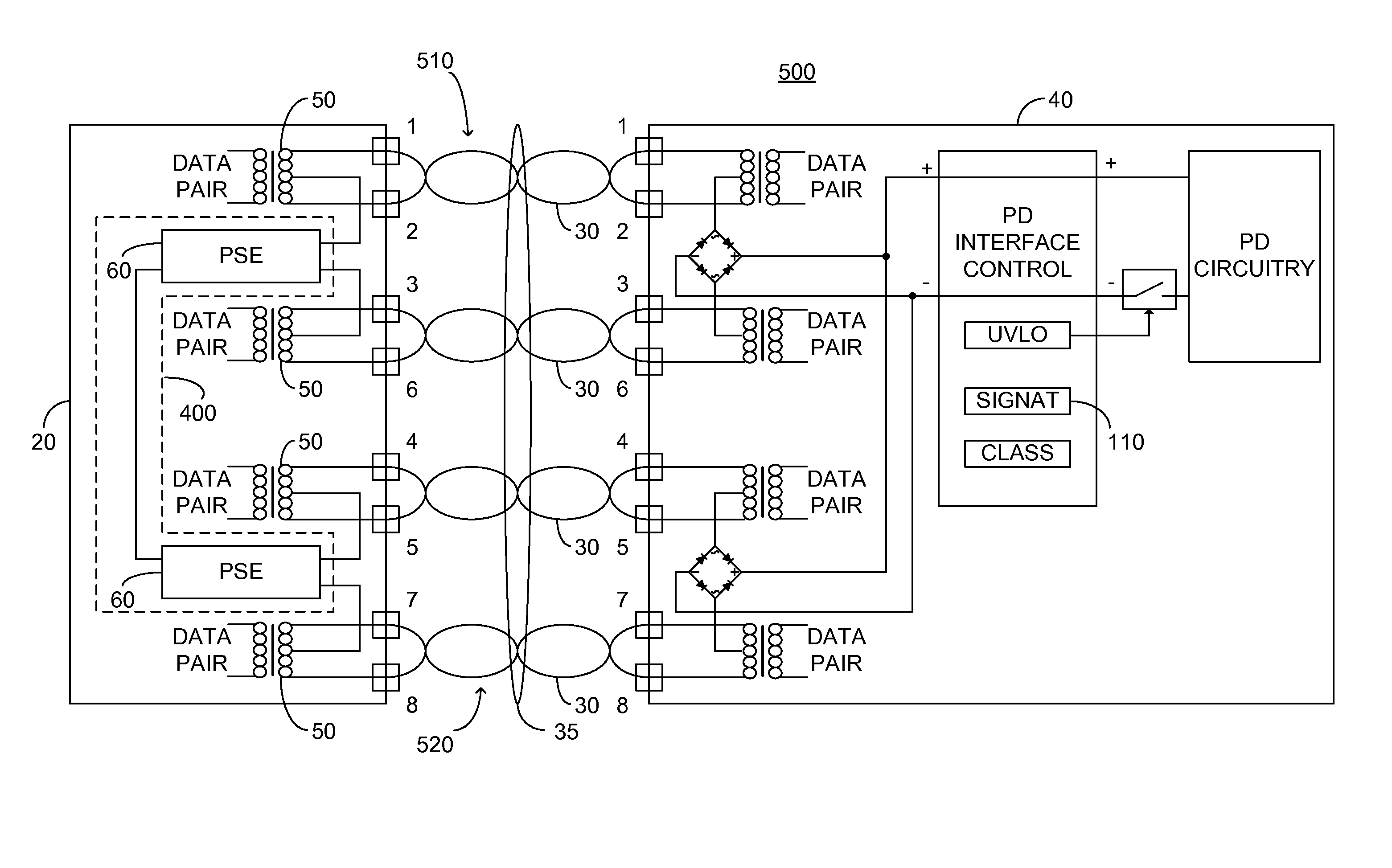
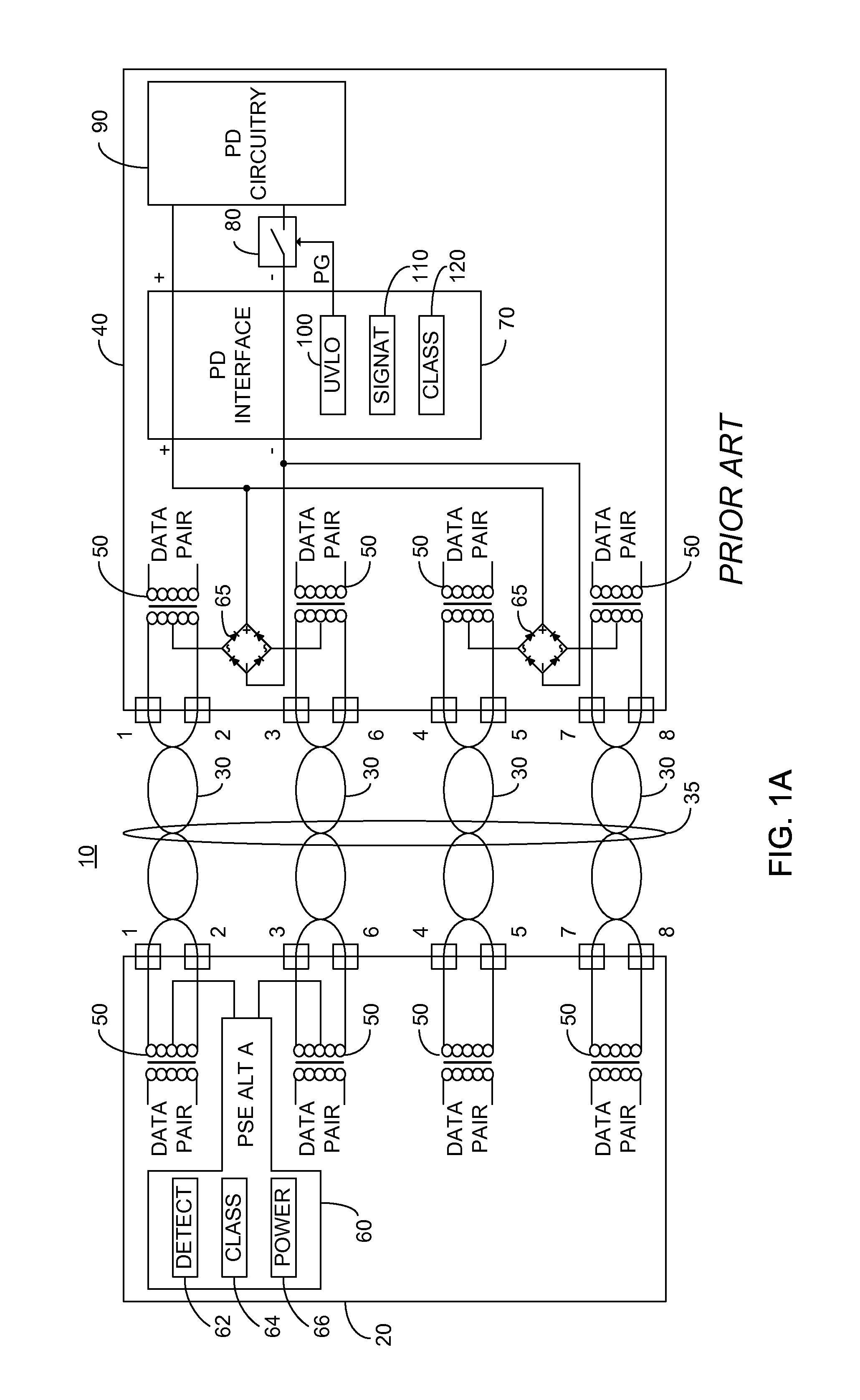
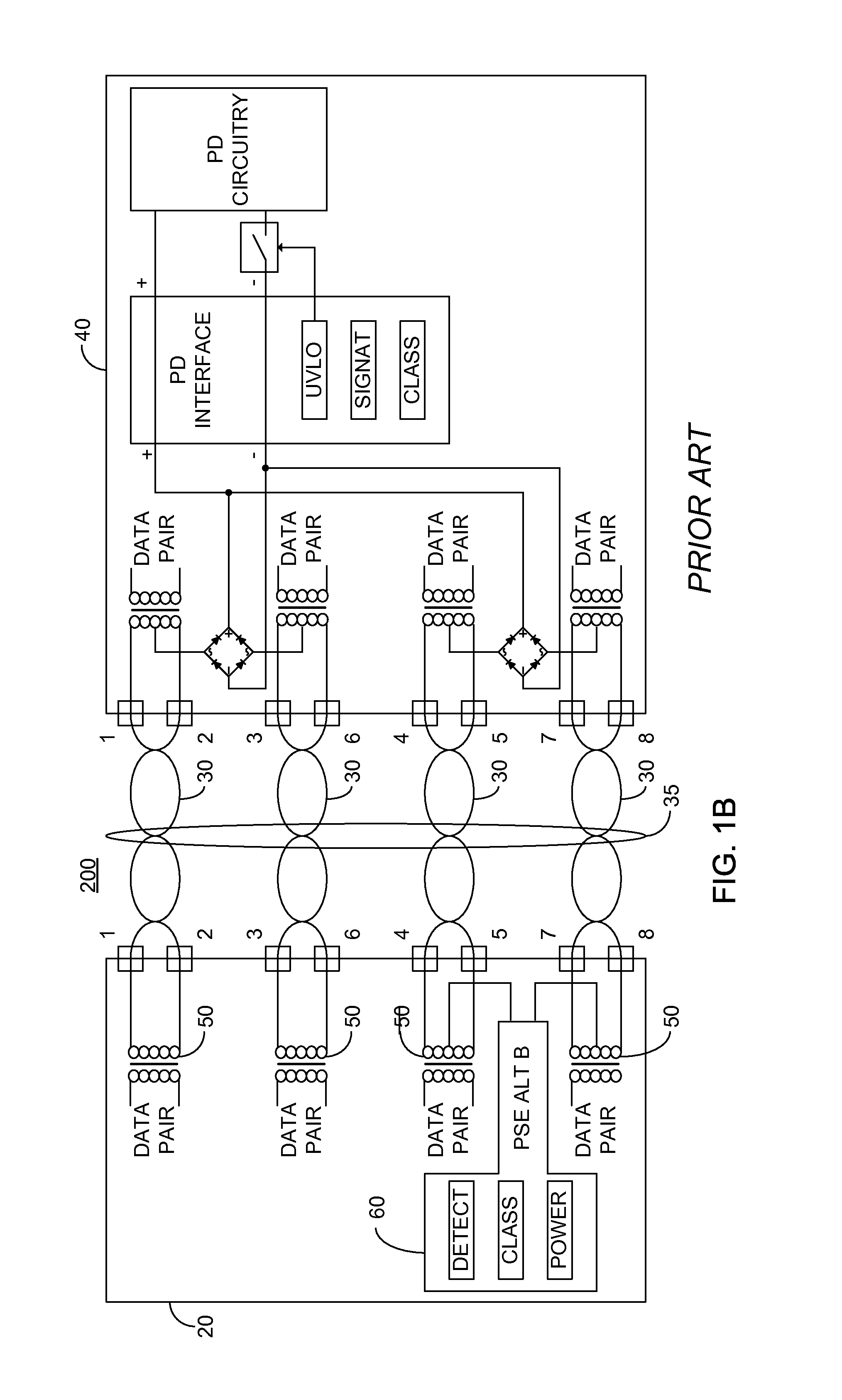
Detection for four pair powered devices
ActiveUS20130257161A1High impedance resultOvercome disadvantagesDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc network circuit arrangementsElectricityEngineering
Owner:MICROSEMI CORP ANALOG MIXED SIGNAL GRP LTD
Assays Based on Liquid Flow Over Arrays
InactiveUS20110319279A1Reduce solubilityEasy to usePeptide librariesHeating or cooling apparatusAnalyteFluorescence
Cassette (50) performs assays, e.g. multiplexed protein biomarker assays. Wide, bubble-free, slow flows are produced from liquids stored on cassette (50), flowing over wide array (20) of ligand receptors on a capture surface. Flows of Reynolds Number less than about 1, preferably 1×10−1 to 5×10−3, are heated in region (34) preceding and including bubble removal system (128). Analyte is introduced through compressed septum (32). External actuations of displacement pumps (30, 37) and valves (137 A, B, and C) produce flows in response to flow-front optical sensors (150, 152). Elastic sheet provides pump and valve diaphragms and resilient expansion of mixing volume (131). Break-away cover portions are pistons. Heating is by conduction through cassette from external contact heater. Planar cassette body, when tilted from horizontal, enables upward flow from pumped storage (134, 135) to reaction (133) to waste (139), with buoyancy bubble removal before reaction. Reading of fluorescence is by external reader, employing calibration, control and reference features on capture surface. Extensive set of calibration features of differing intensities enables self-calibration.
Owner:COURTAGEN LIFE SCI
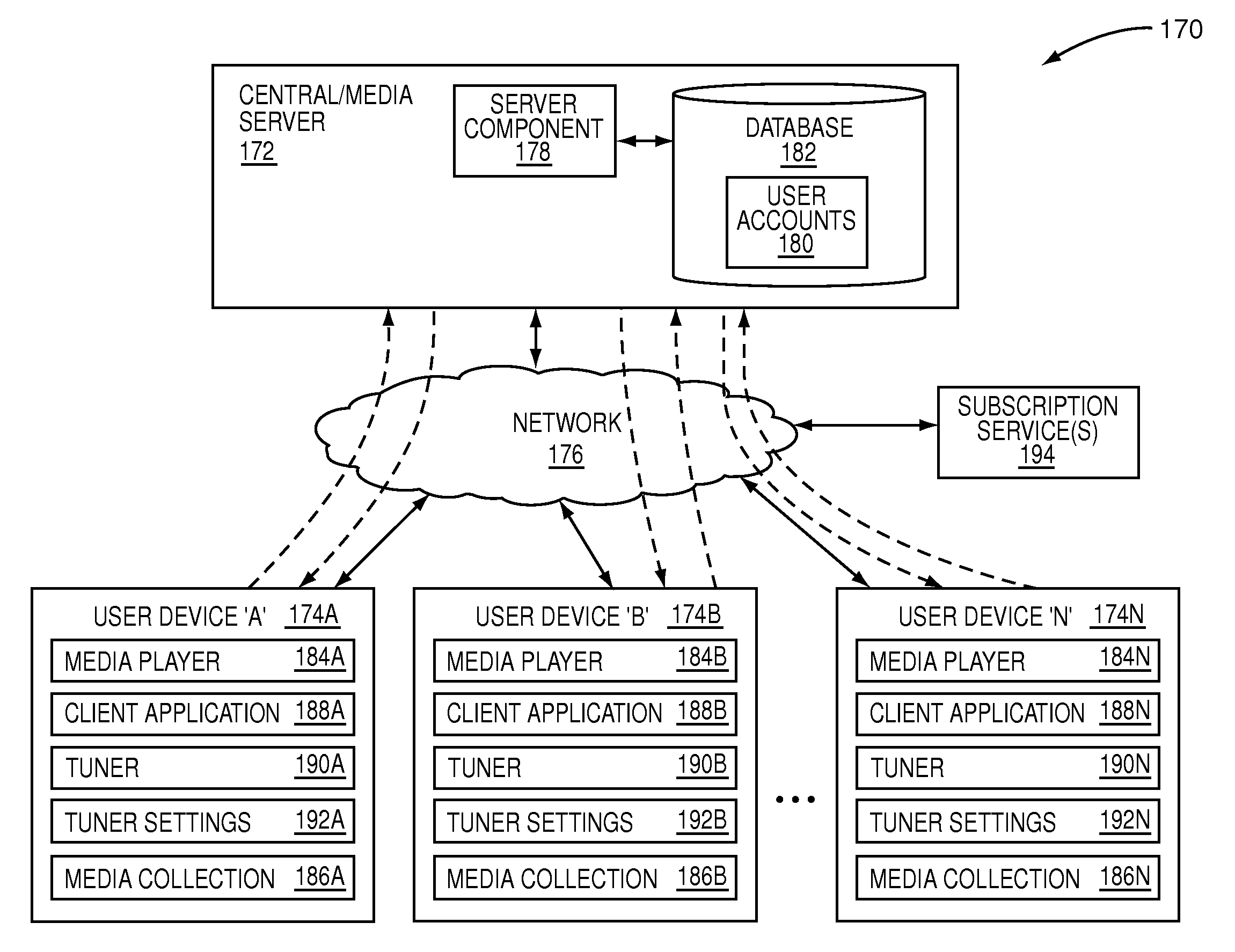
System and method for generating dynamically filtered content results, including for audio and/or video channels
InactiveUS20090164448A1Generate efficientlyHighly relevantMetadata audio data retrievalMetadata video data retrievalAudio frequencyInformation retrieval
A system and method for allowing a user to more effectively generate focused content results, including audio and / or video content. Content is dynamically filtered to generate content results in response to initial filtering settings or characteristics. The content results are provided to a user. Once the user finds and selects a content result of interest, additional filtering characteristics associated with the selected result are provided to the user as a suggestion for additional filtering. In this manner, the user is made aware of additional filtering settings or characteristics that can be used to focus the search results. Subsequent filter settings and filtering operations can be based on characteristics of previous relevant results in an iterative and dynamic manner. Focused results are more likely produced, because additional filtering settings are provided and adjusted according to characteristics of results deemed relevant by the user.
Owner:CONCERT TECH
Apparatus and method for correcting susceptibility artefacts in a magnetic resonance image
InactiveUS20150362575A1Efficient computational implementationSuitable for useImage enhancementImage analysisDisjoint-setImage registration
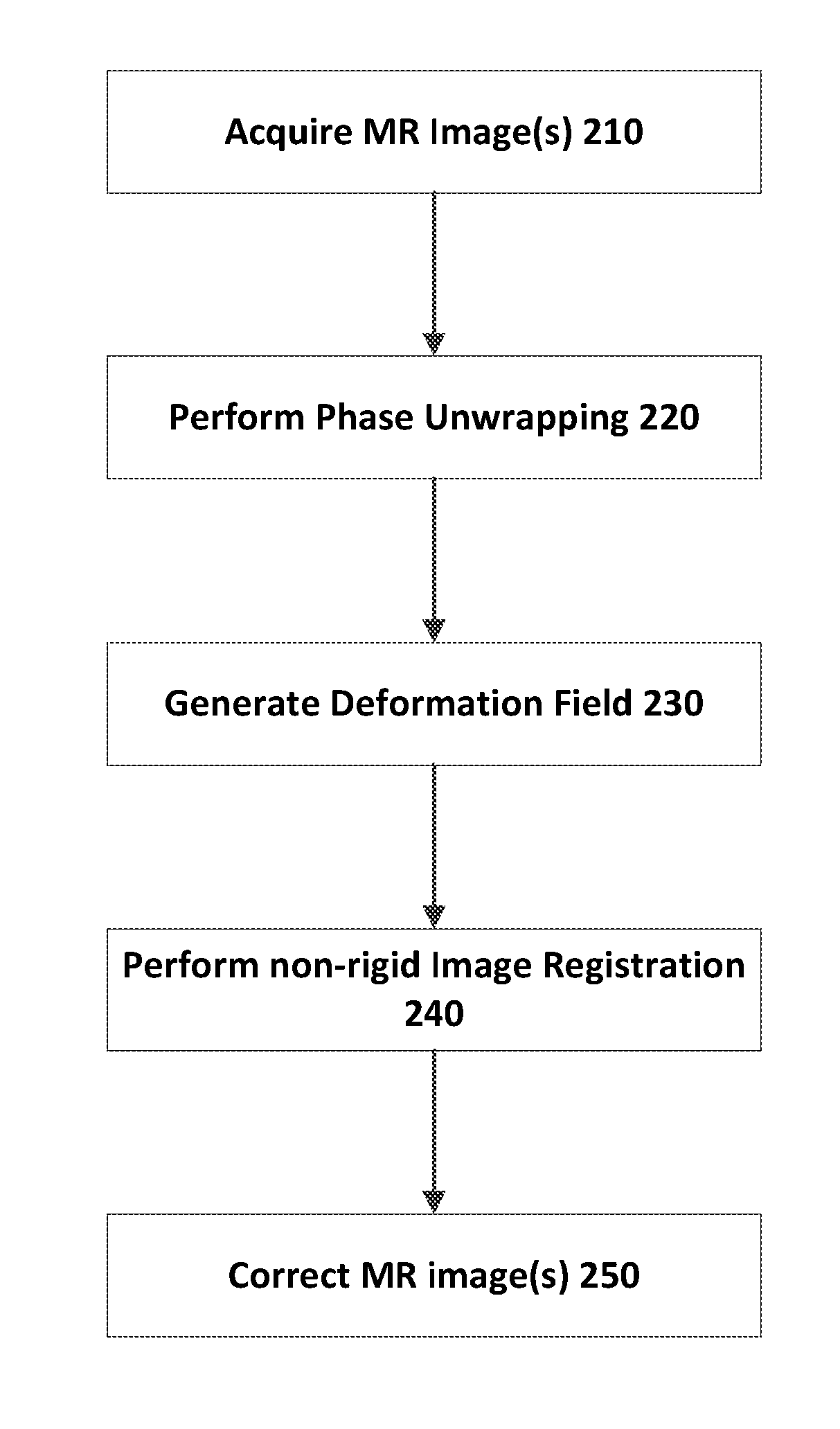
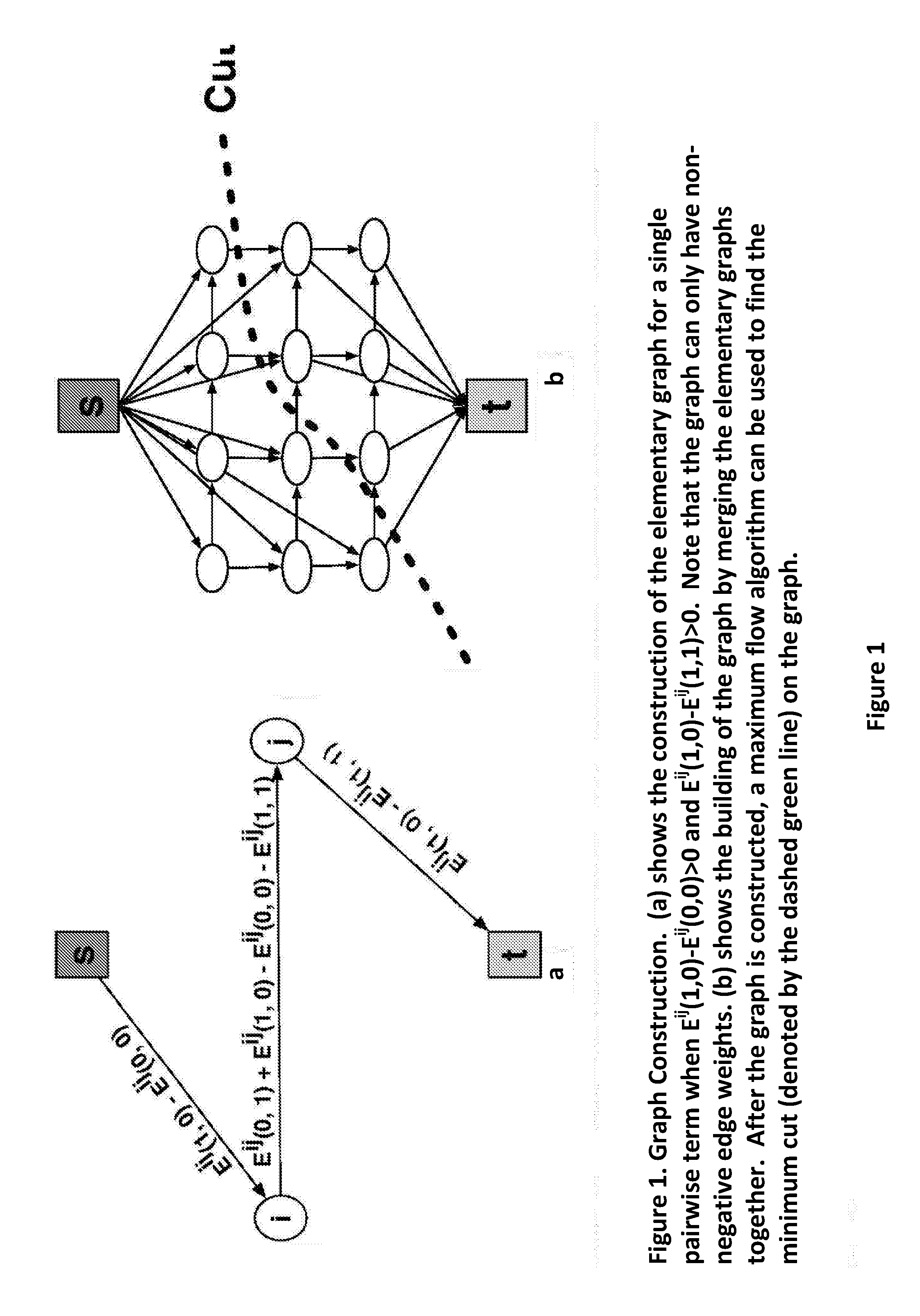
An apparatus and method are provided for performing phase unwrapping for an acquired magnetic resonance (MR) image. The method includes modelling the MR phase in the MR image using a Markov random field (MRF) in which the true phase φ(t) and the wrapped phase φ(w) are modelled as random variables such that at voxel i of said MR image φ(t)(i)=φ(w)(i)+2πn(i), where n(i) is an unknown integer that needs to be estimated for each voxel i. The method further includes constructing a graph consisting of a set of vertices V and edges E and two special terminal vertices representing a source s and sink t, where there is a one-to-one correspondence between cuts on the graph and configurations of the MRF, a cut representing a partition of the vertices V into disjoint sets S and T such that sεS and tεT. The method further includes finding the minimum energy configuration, E(n(i)|φ(w)) of the MRF on the basis that the total cost of a given cut represents the energy of the corresponding MRF configuration, where the cost of a cut is the sum of all edges going from S to T across the cut boundary. The method further includes using the values of n(i) in the minimum energy configuration to perform the phase unwrapping from φ(w) to φ(t) for the MR image. A confidence may be computed for each voxel using dynamic graph cuts. The unwrapped phase from two MR images acquired at different times may be used to estimate a field map from the phase difference between the two MR images. The field map may be converted into a deformation field which is then used to initialise a non-rigid image registration of the acquired MR image against a reference image. The deformation field of the non-rigid registration is controlled to be smoother where the confidence is high.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
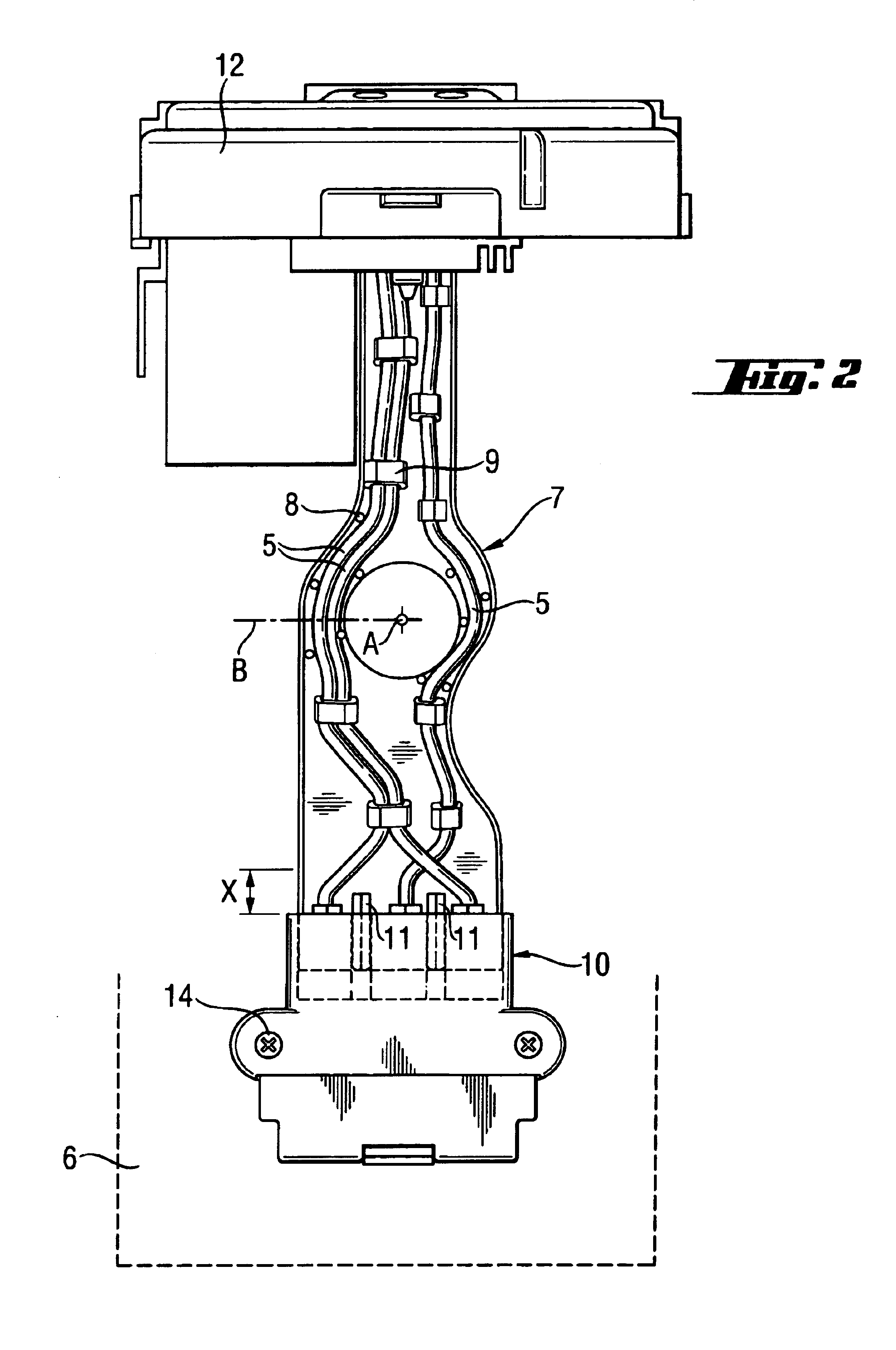
Electrical hand tool machine with vibration damped striking mechanism
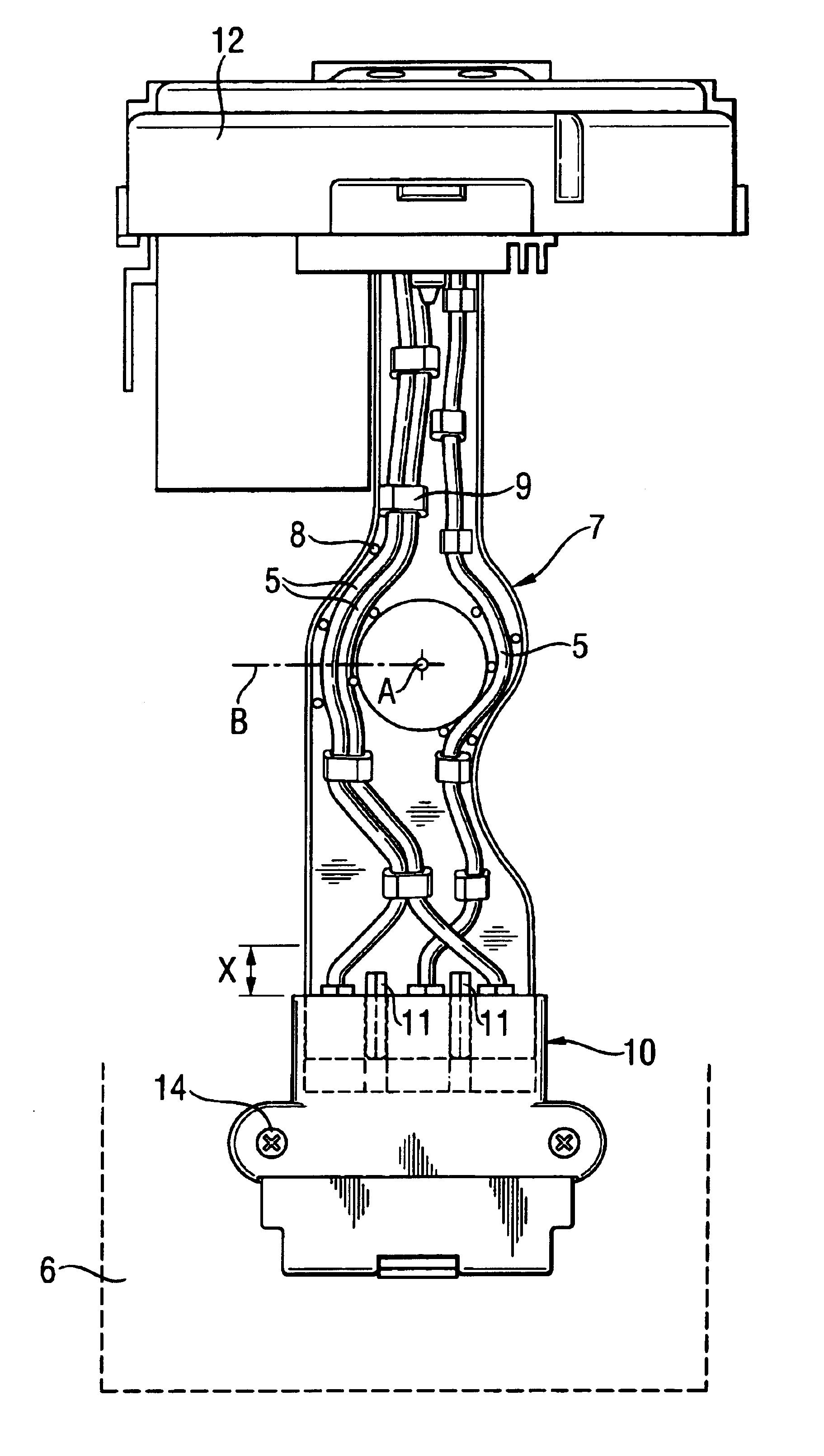
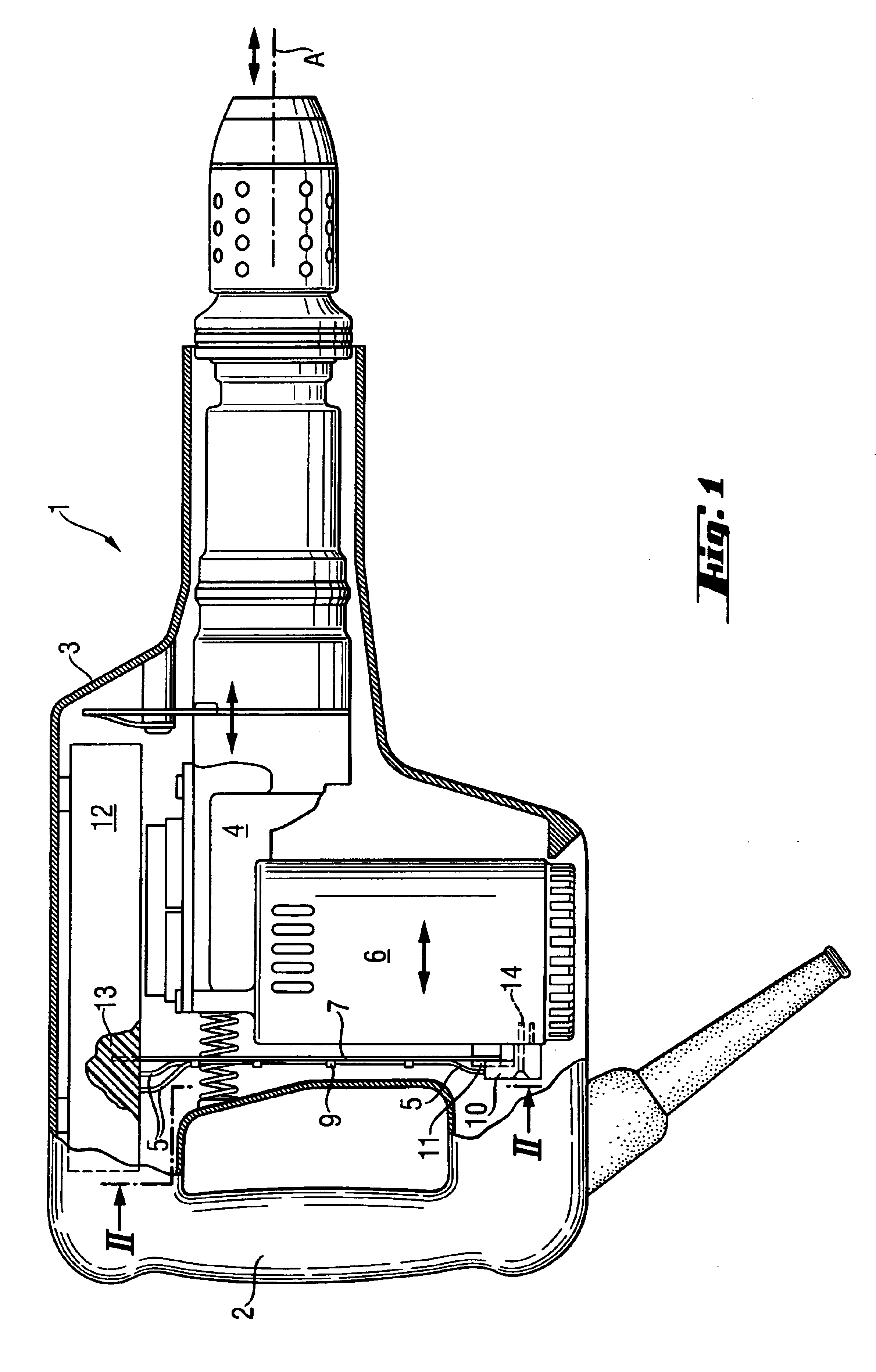
A partially percussive electrical hand tool machine (1) having a portable housing (3), a striking mechanism module (4) connected, in a vibration-damped manner, to the housing (3) and having electrical lines (5) for electrical connection of the relatively moveable striking mechanism module (4) to the housing (3). The electrical lines (5) are non-vibrationally attached in a bending flexible wiring bridge (7) arranged transverse to the striking axis (A).
Owner:HILTI AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com