Patents
Literature
563 results about "Mr images" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Digital topological analysis of trabecular bone MR images and prediction of osteoporosis fractures
The invention provides method, system and device for determining trabecular bone structure and strength by digital topological analysis, and offers, for the first time, a demonstration of superior associations between vertebral deformity and a number of architectural indices measured in the distal radius, thus permitting reliable and noninvasive detection and determination of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. A preferred embodiment provides imaging in three dimension of a region of trabecular bone, after which the 3D image is converted into a skeletonized surface representation. Digital topological analysis is applied to the converted image, and each image voxel is identified and classified as a curve, a surface, or a junction; and then associated with microarchitectural indices of trabecular bone to quantitatively characterize the trabecular bone network. The invention is applicable in vivo, particularly on human subjects, or ex vivo.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
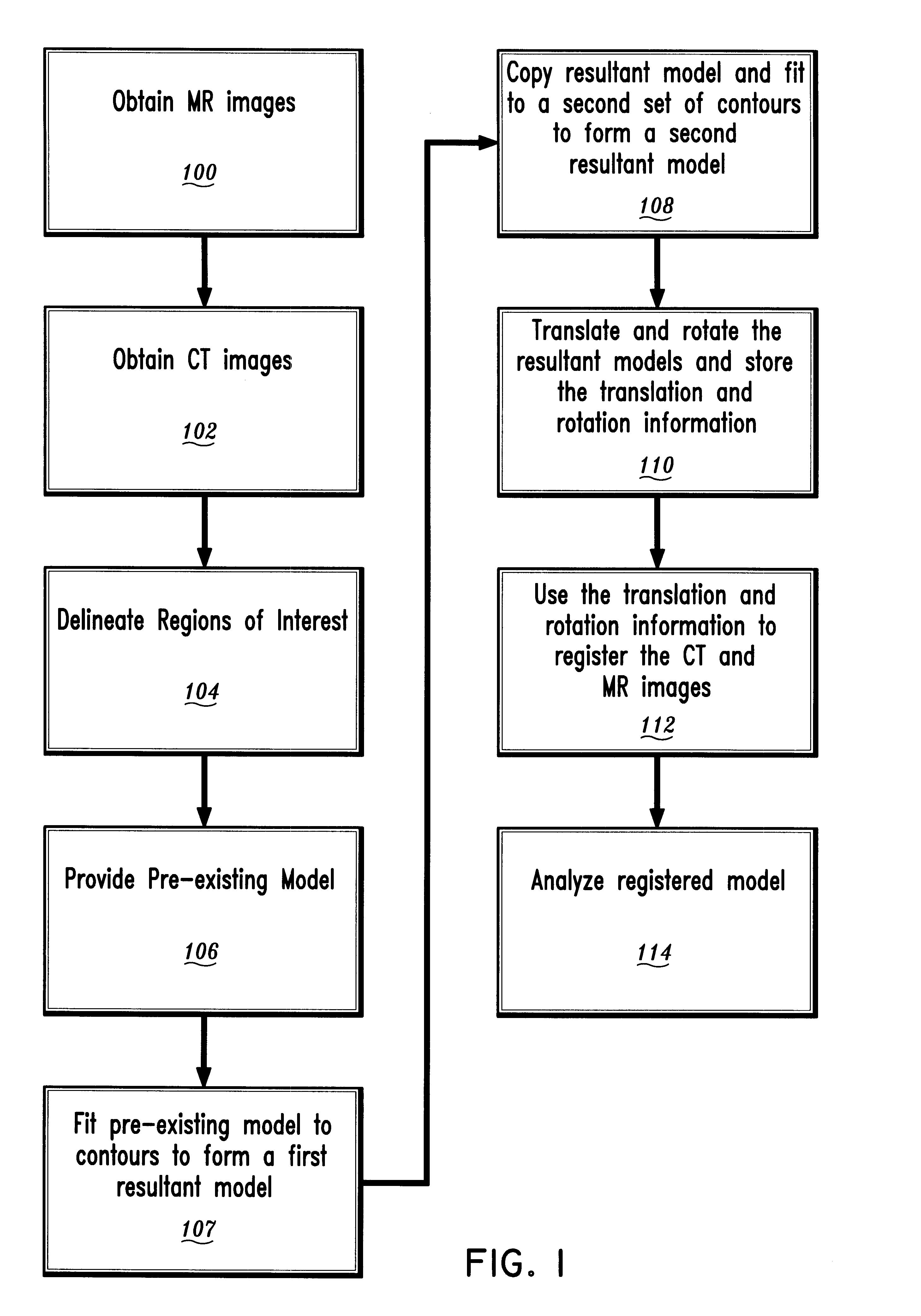
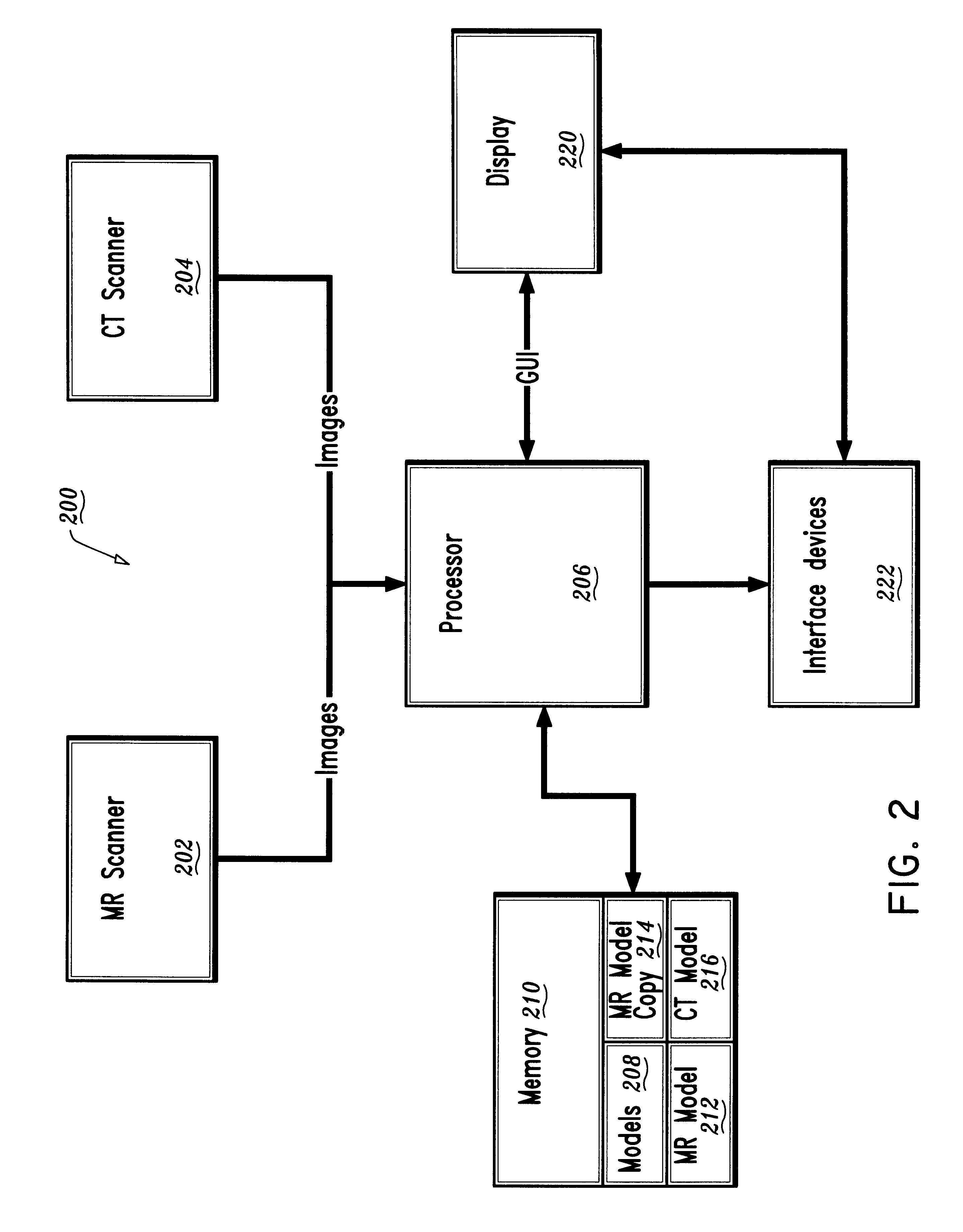
Model-based registration of cardiac CTA and MR acquisitions
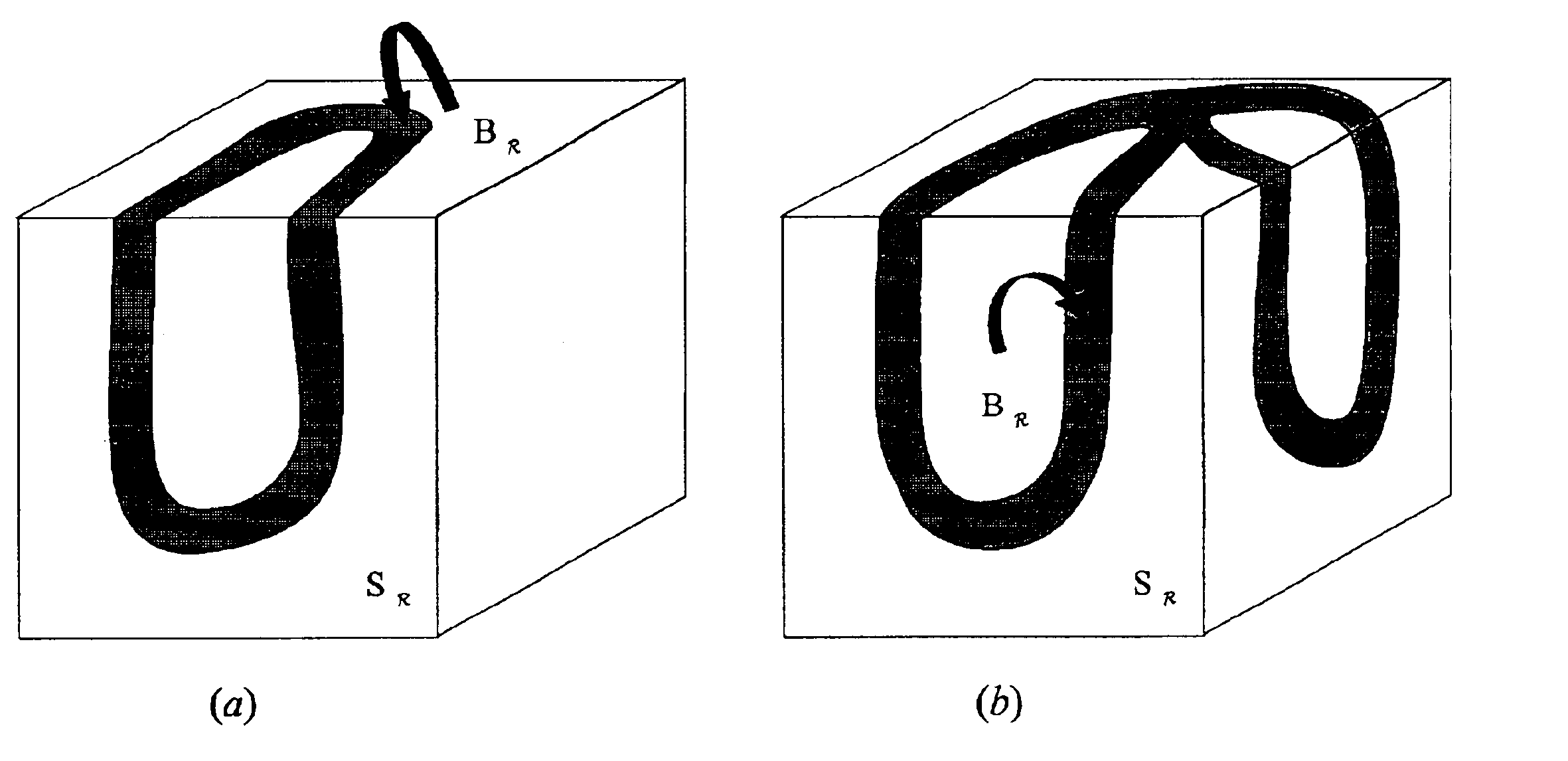
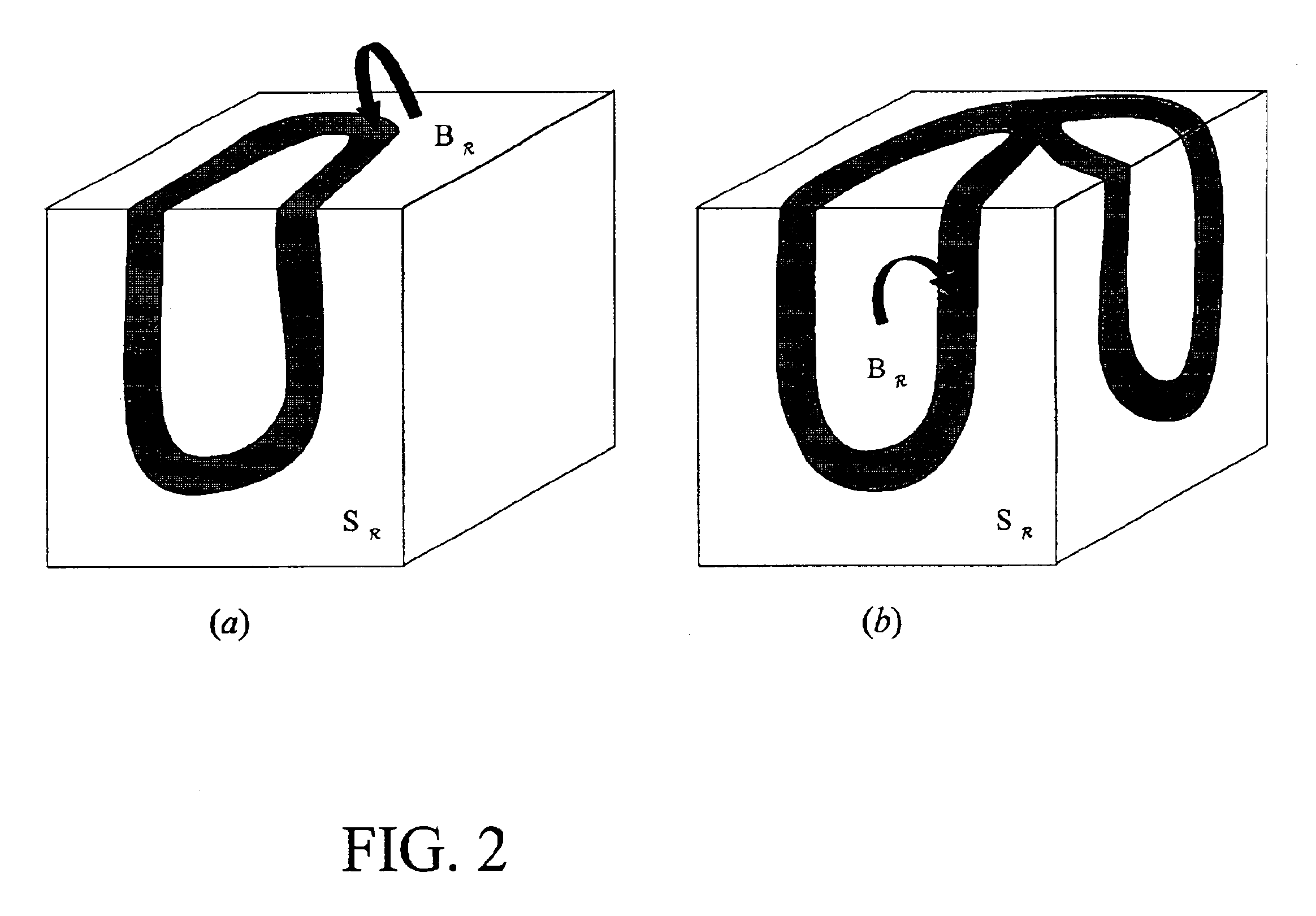
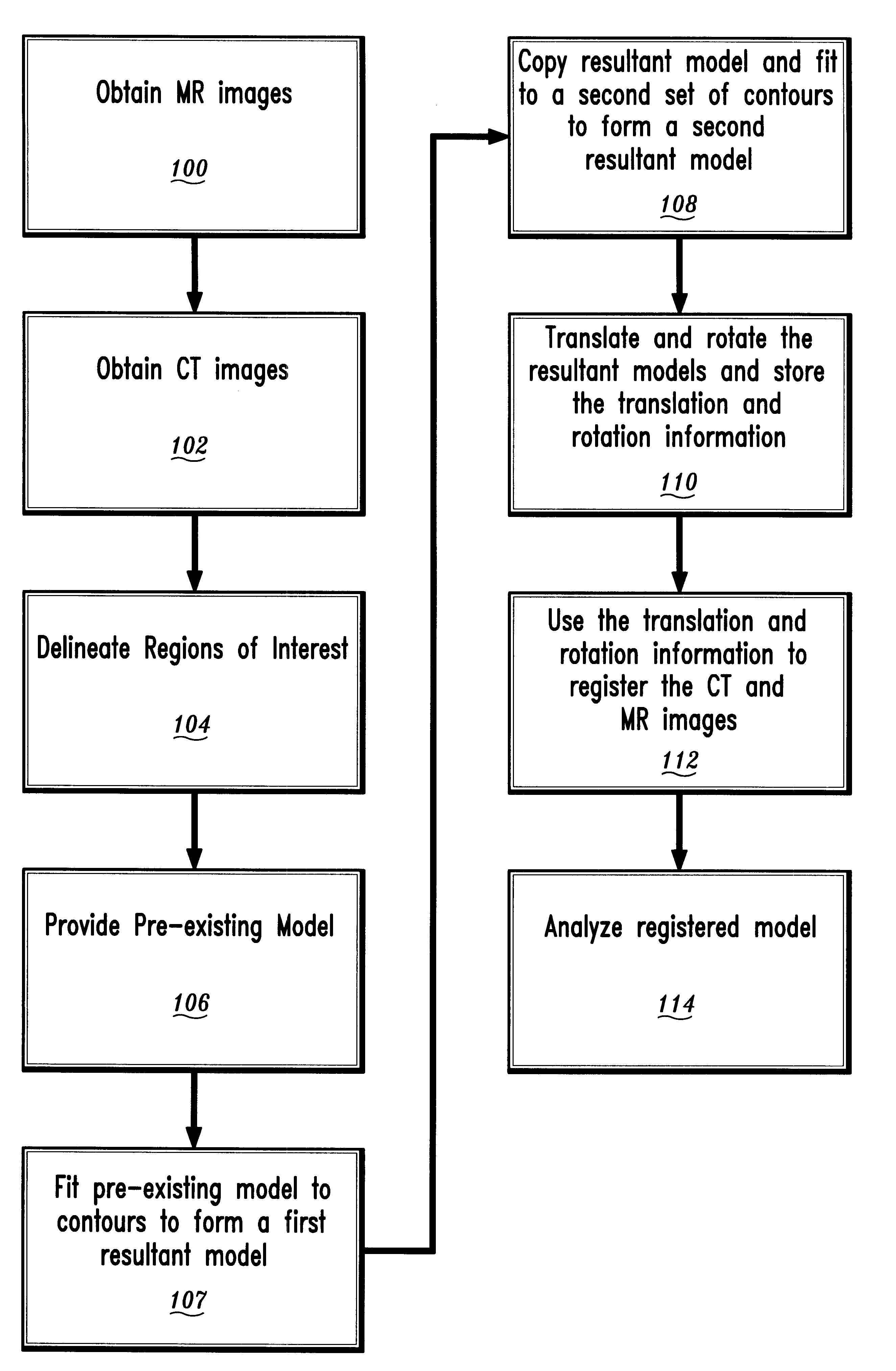
A method for registration of magnetic resonance (MR) and computed topography (CT) images, in accordance with the present invention includes providing MR images having a region of interest delineated by first contours and providing CT images having the region of interest delineated by second contours. A pre-existing model of the region of interest is also provided. The pre-existing model is fit to the first contours or the second contours to provide a first resultant model. The first resultant model is then copied to provide a copied model. The copied model is fit to the other of the first contours and the second contours to provide a second resultant model. By rotating and translating the first resultant model and the second resultant model, the first resultant model and the second resultant model are registered. The rotation and translation information are stored and applied to the images to provide registration between the MR images and the CT image
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
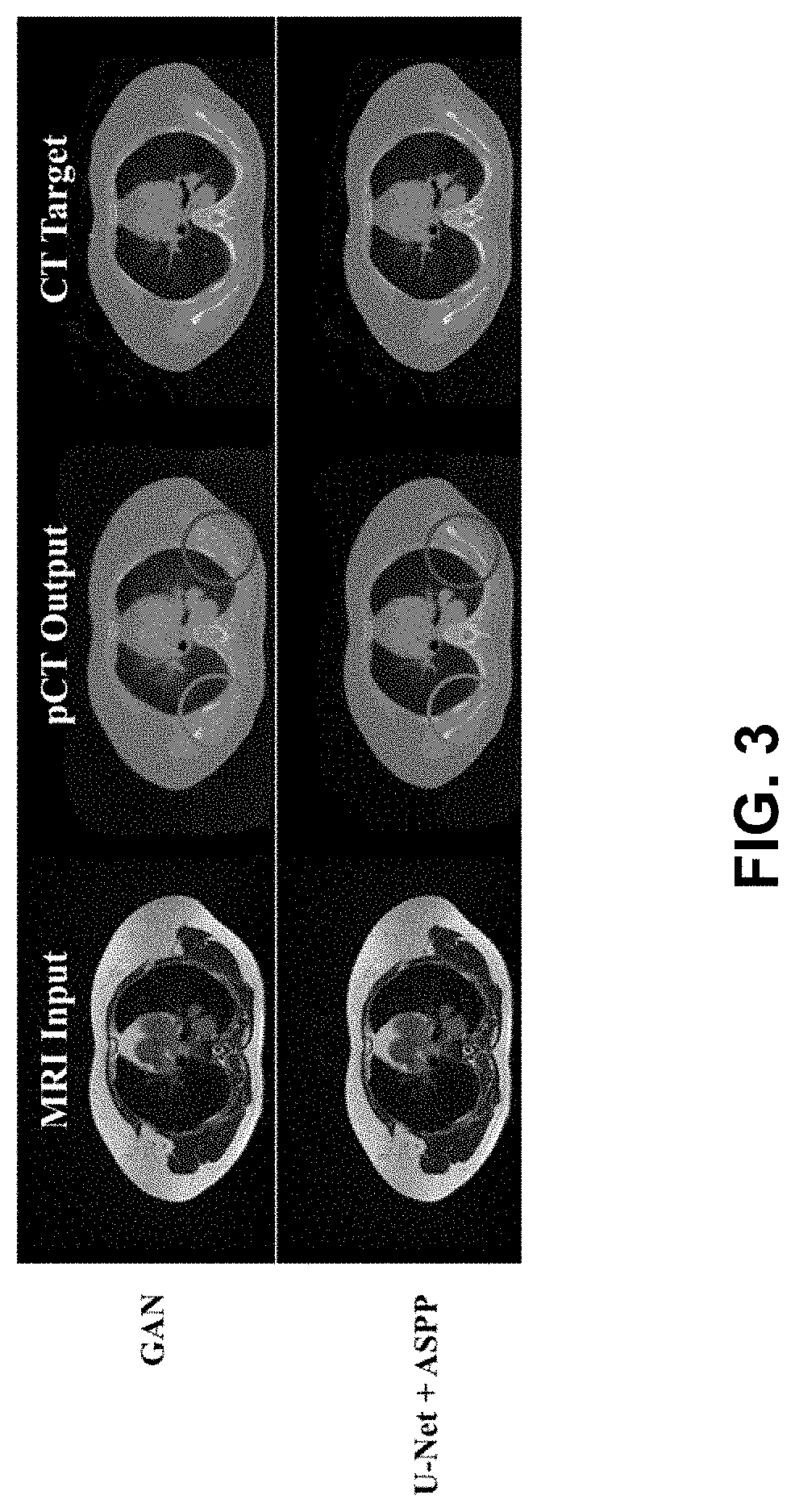
Ml-based methods for pseudo-ct and hr mr image estimation
The present disclosure describes a computer-implemented method of transforming a low-resolution MR image to a high-resolution MR image using a deep CNN-based MRI SR network and a computer-implemented method of transforming an MR image to a pseudo-CT (sCT) image using a deep CNN-based sCT network. The present disclosure further describes a MR image-guided radiation treatment system that includes a computing device to implement the MRI SR and CT networks and to produce a radiation plan based in the resulting high resolution MR images and sCT images.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
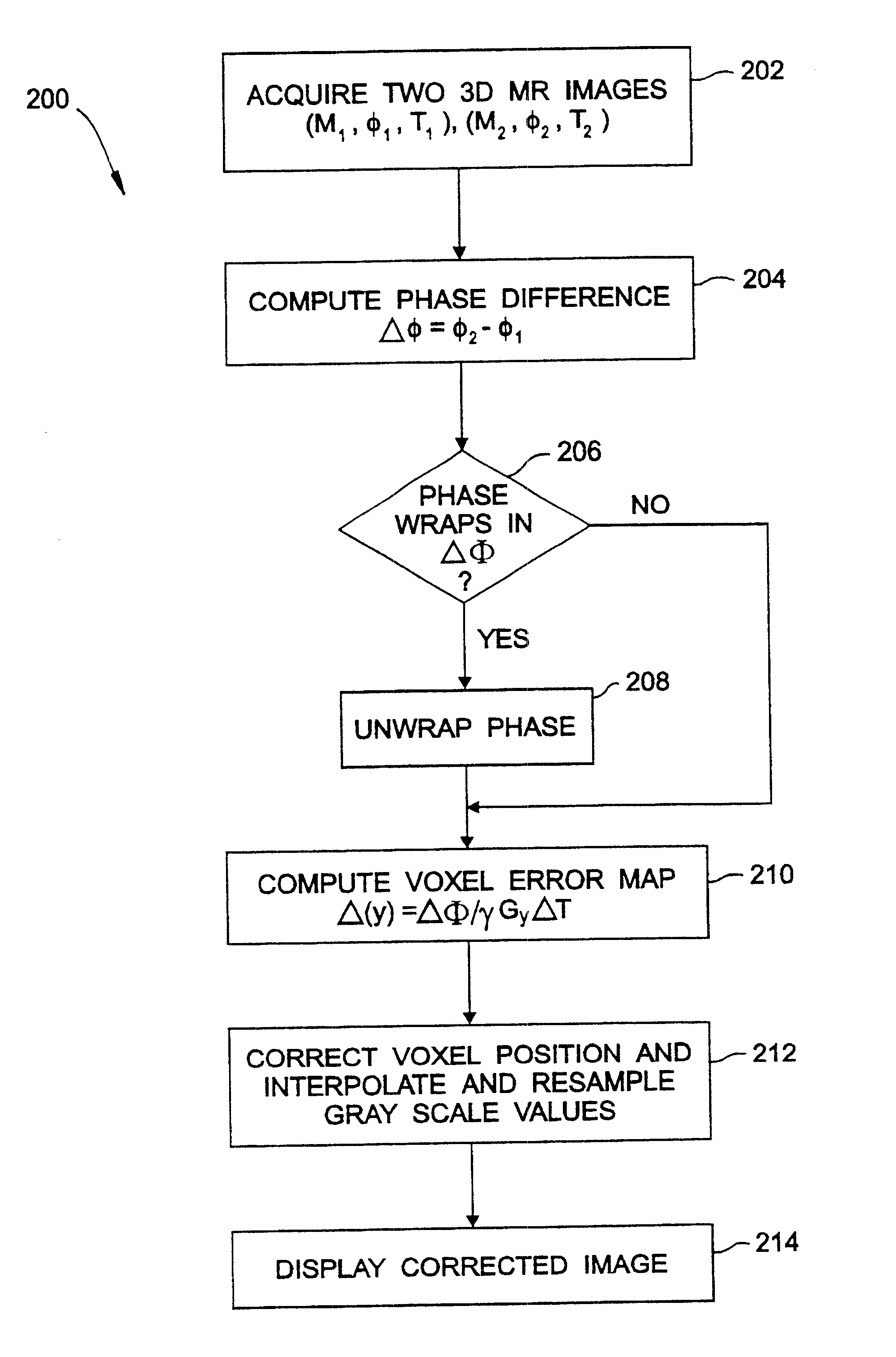
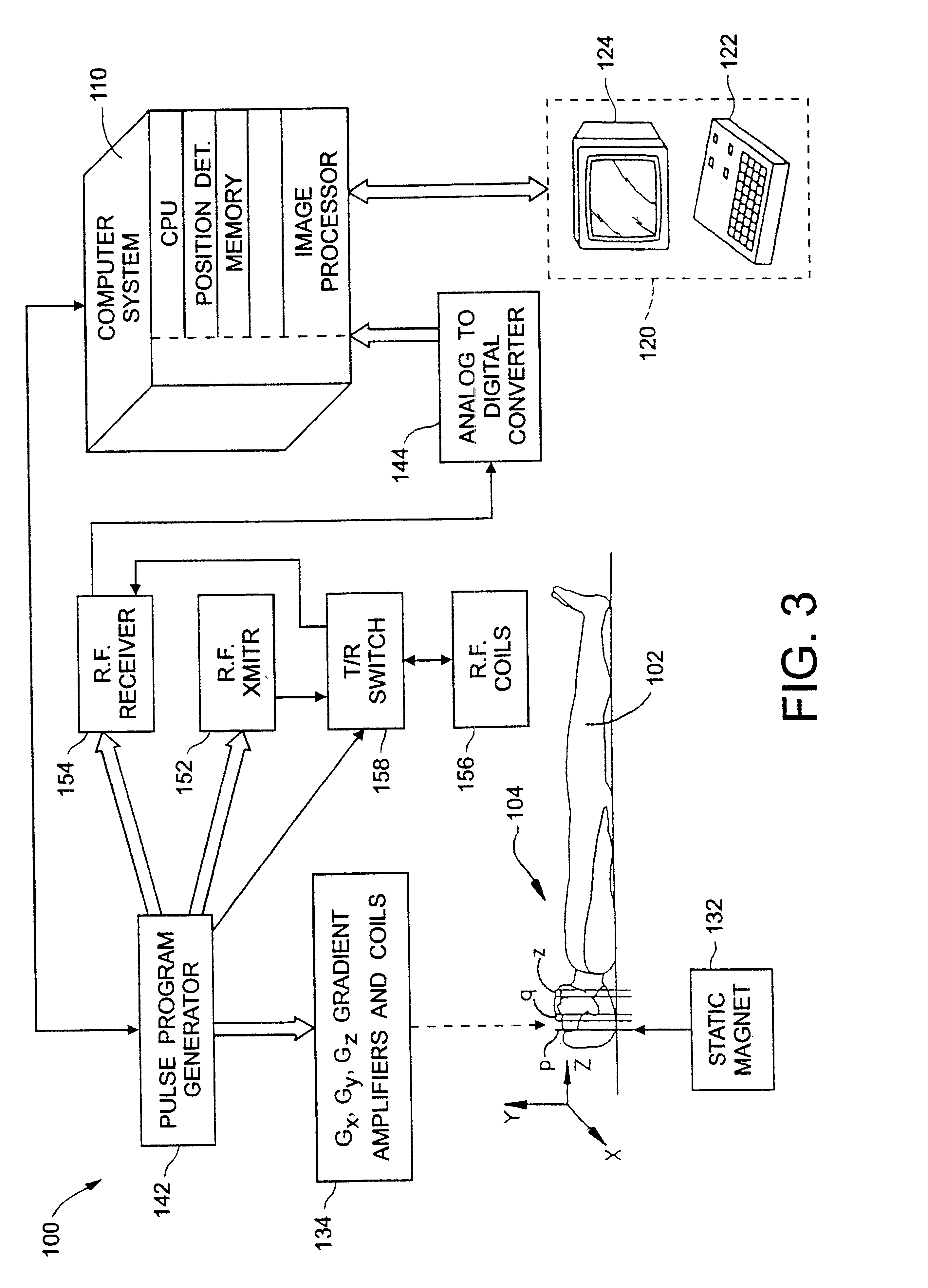
Geometric distortion correction in magnetic resonance imaging
A three dimensional (3D) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system (100) performs object-induced geometric distortion correction. The MRI system performs (202) a 3D MRI pulse sequence to acquire a first 3D MR image of an examination region containing at least a portion of a subject and performs (202) the 3D MRI pulse sequence a second time to acquire a second 3D MR image of the examination region A computer system (110) computes (210) a voxel error map based on a phase difference between the first and second 3D MR images and corrects (212) voxel positions in one of the 3D MR images in accordance with the voxel error map.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
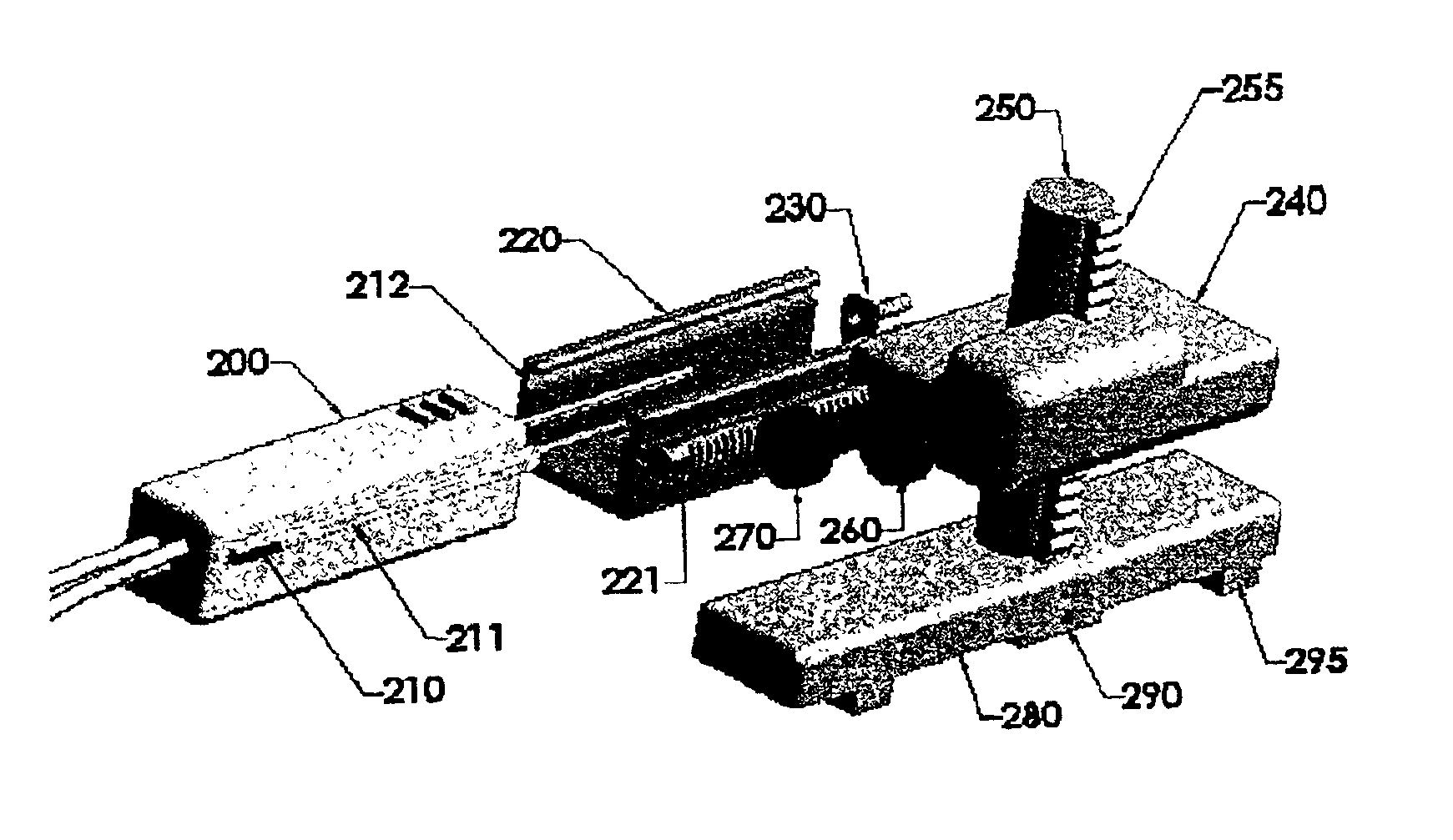
Breast biopsy and therapy system for magnetic resonance imagers
The present invention describes a device for performing breast biopsies and / or therapy within magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems. The apparatus includes a RF receiver antenna for magnetic resonance imaging of the breast. The RF coil includes openings in the front and side to provide access to the breast during the procedure. Compression plates are integrated into the breast coil which compress the breast either laterally or in the head / feet direction as required for optimal access to the breast. The apparatus includes a mechanical device for positioning interventional instruments in the breast such as biopsy or therapy instruments. The mechanical positioning devices position the instrument along the desired trajectory to the target site and insert the instrument into the breast while the patient remains inside the MRI scanner. Real time MR images may be acquired during instrument alignment and insertion to verify the trajectory. The mechanical positioning devices allow manipulation of instruments in any type of MRI scanner, including high field MRI systems with cylindrical magnets. The positioning devices provide a means to overcome limited access to the patient in MRI scanners. The positioning devices may be manually operated by means of gears, drive shafts, cables or other mechanical means. Or they may be electronically controlled by means of MR compatible motorized drive systems. The devices may be remotely controlled from outside the magnet for MRI systems that have limited access to the patient in the magnet. An interface between the electronically controlled drivers and the MRI scanner computer can provide robotic control of the instrument.
Owner:LAMPMAN DAVID A +1
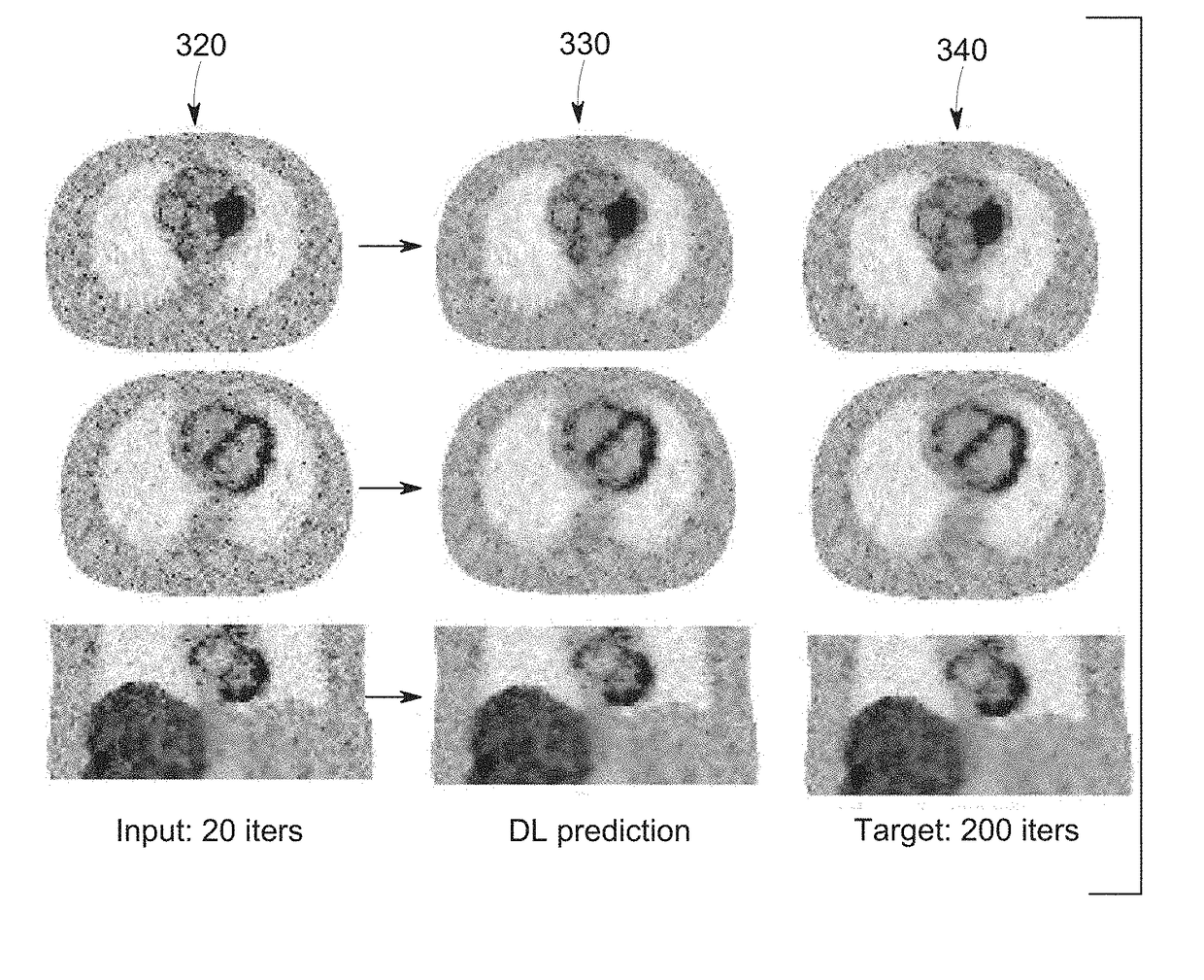
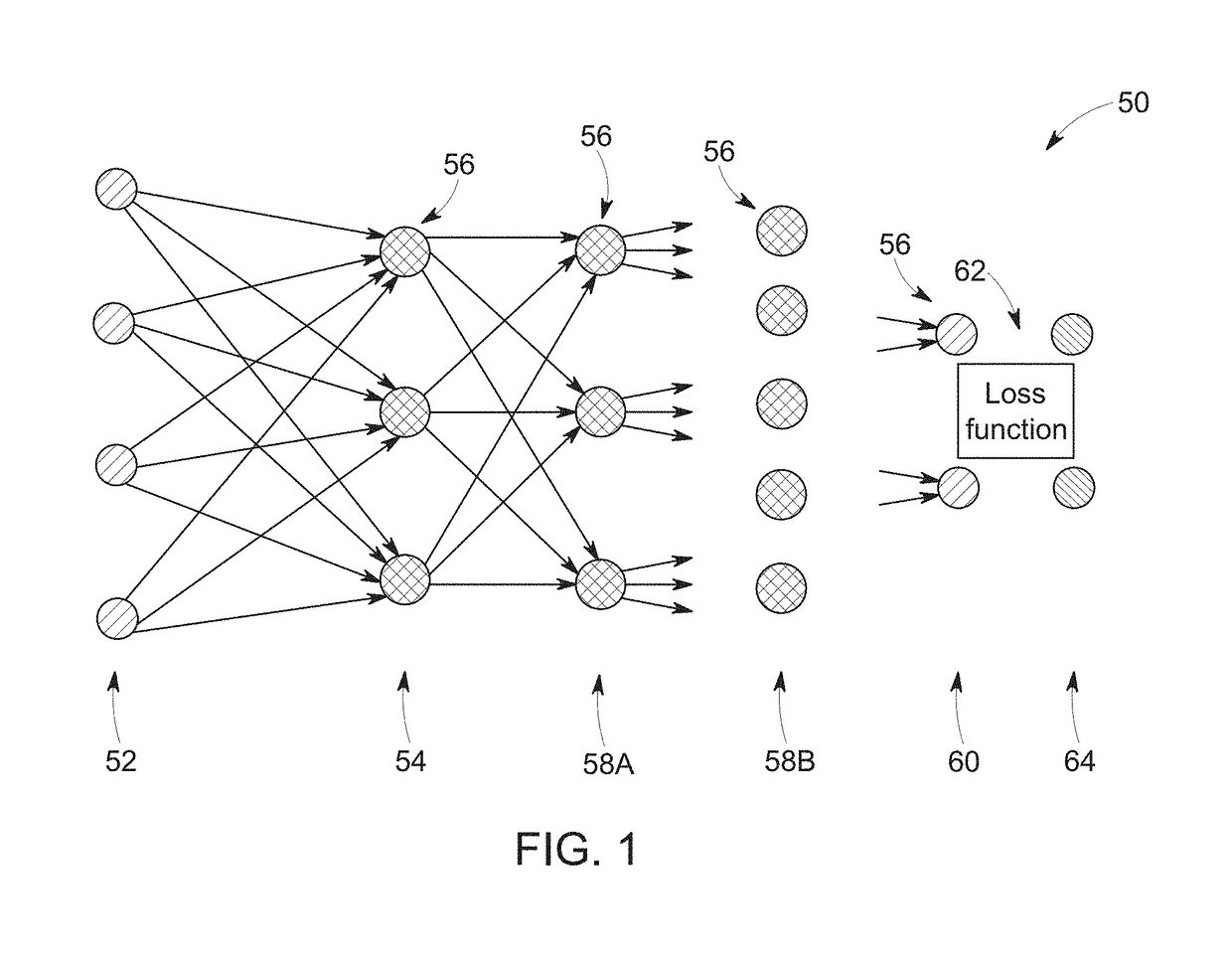
Deep learning based acceleration for iterative tomographic reconstruction
InactiveUS20180197317A1Reduce stepsImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionLearning basedTomographic reconstruction
The present discussion relates to the use of deep learning techniques to accelerate iterative reconstruction of images, such as CT, PET, and MR images. The present approach utilizes deep learning techniques so as to provide a better initialization to one or more steps of the numerical iterative reconstruction algorithm by learning a trajectory of convergence from estimates at different convergence status so that it can reach the maximum or minimum of a cost function faster.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
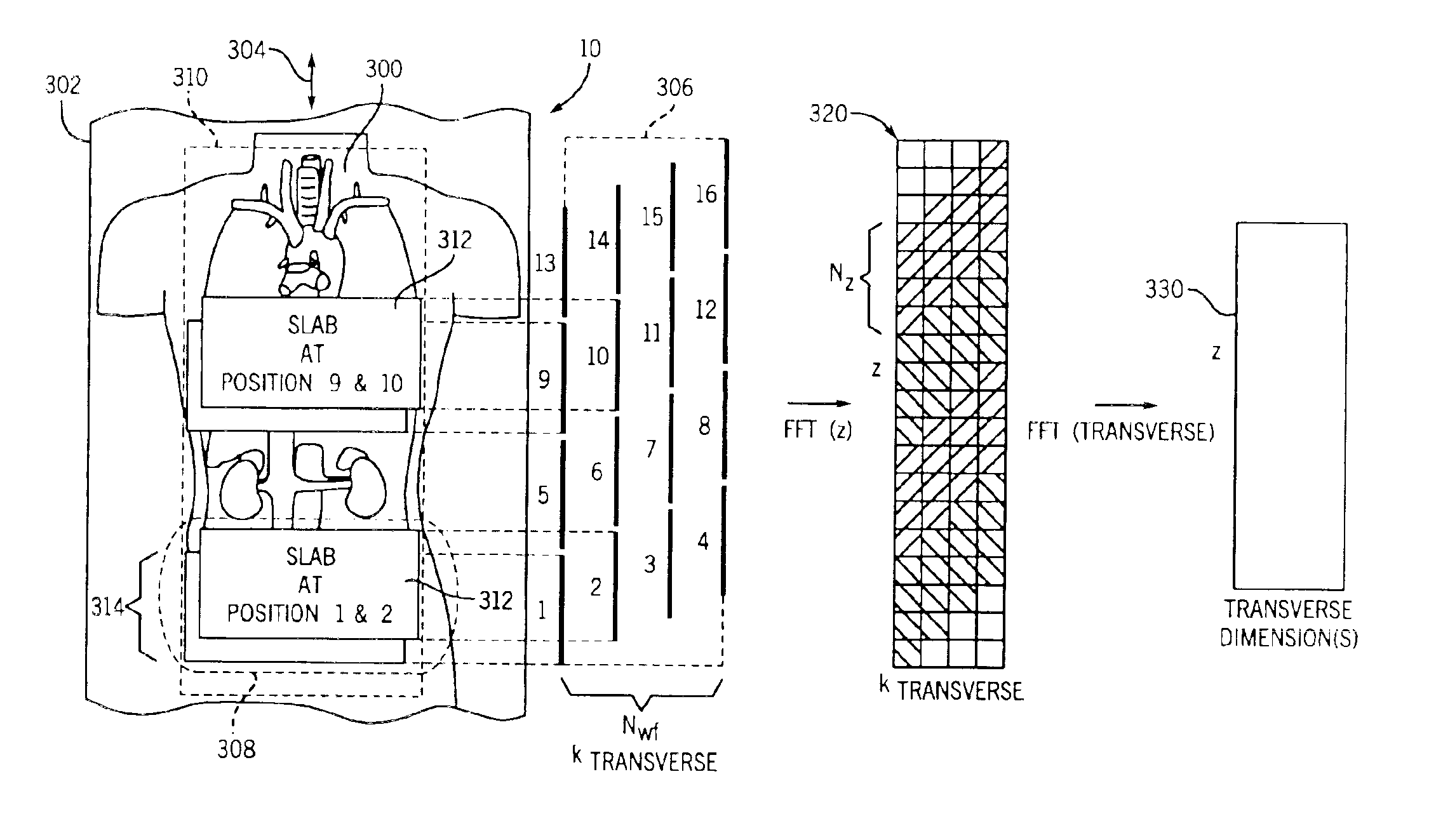
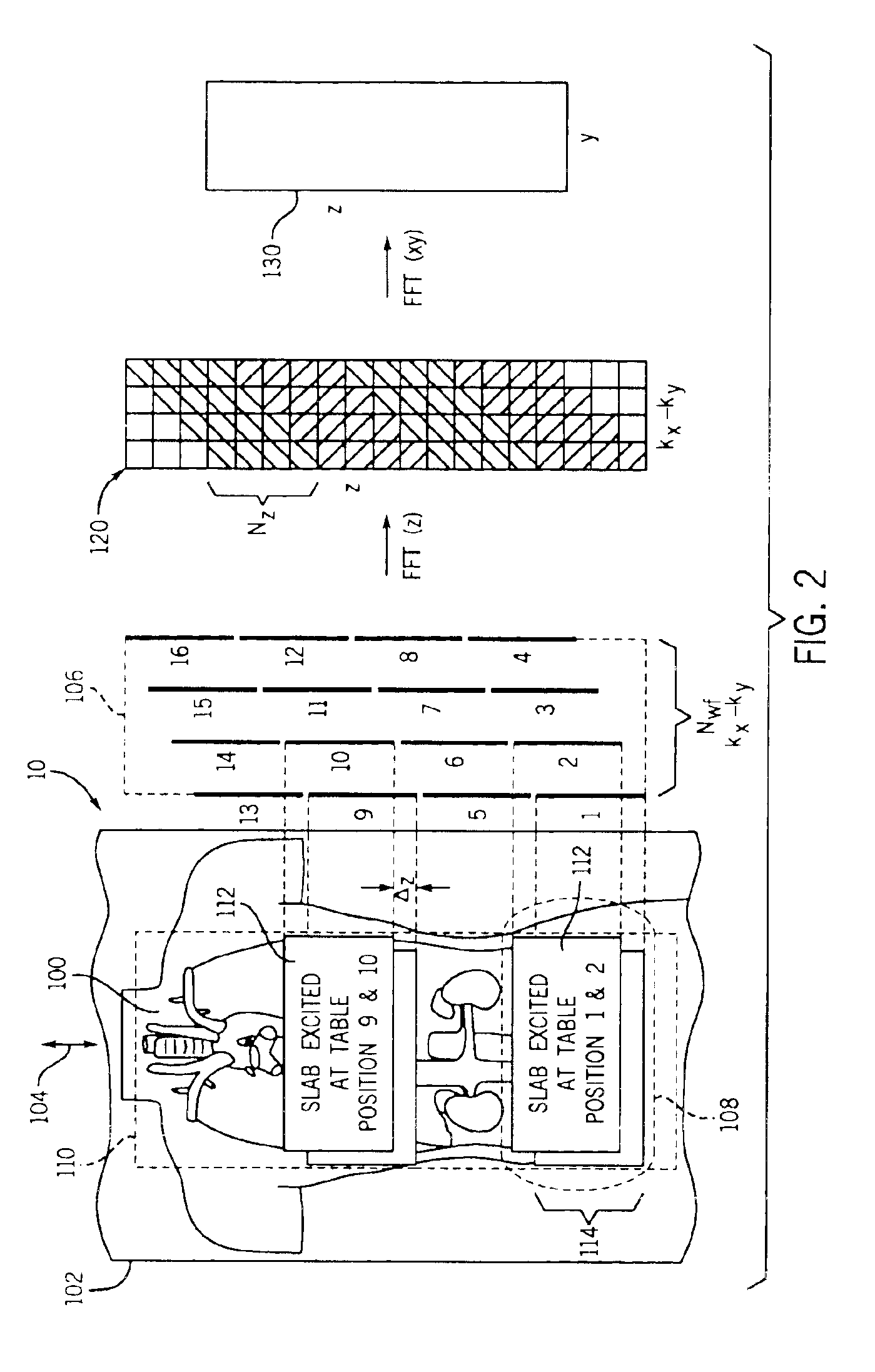
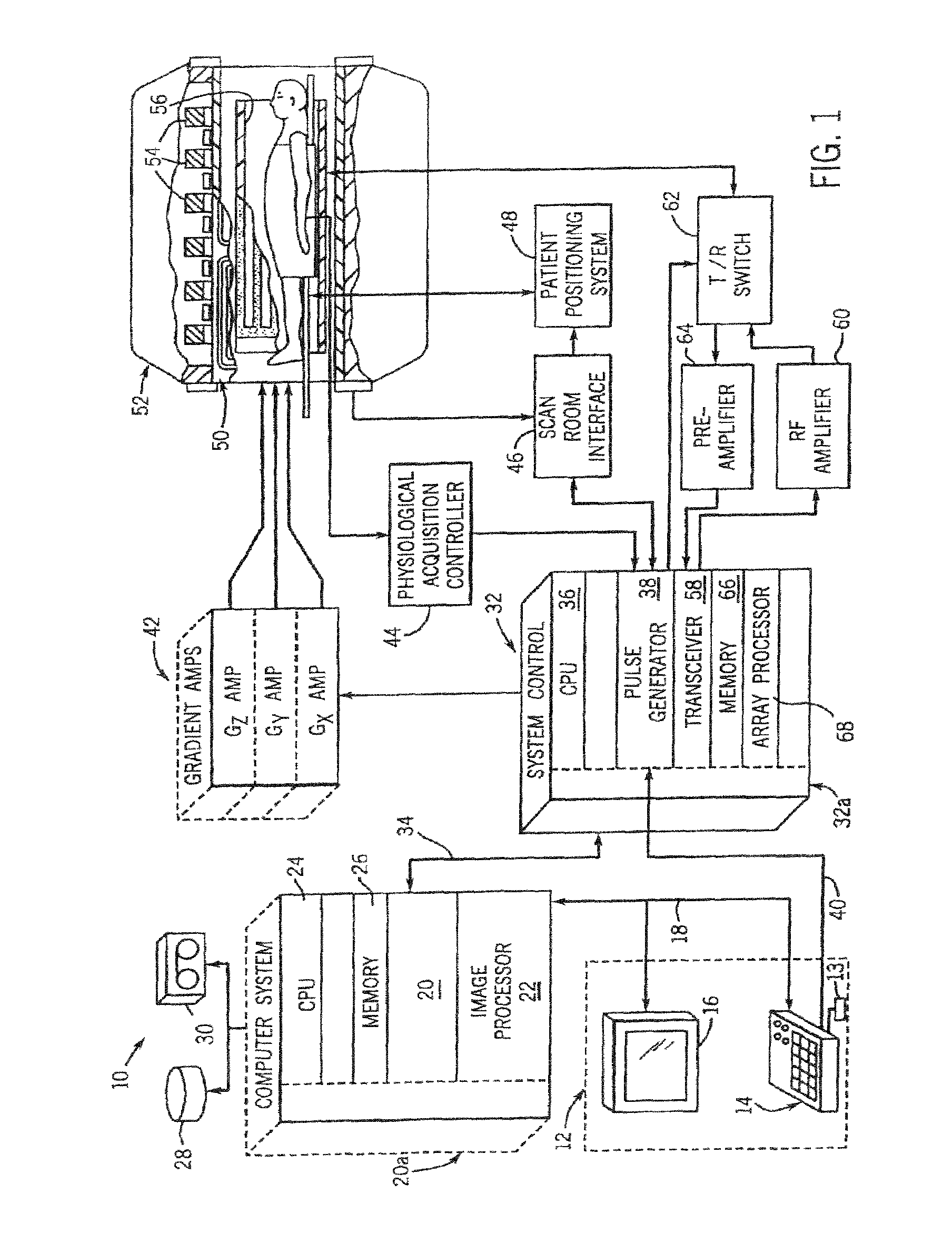
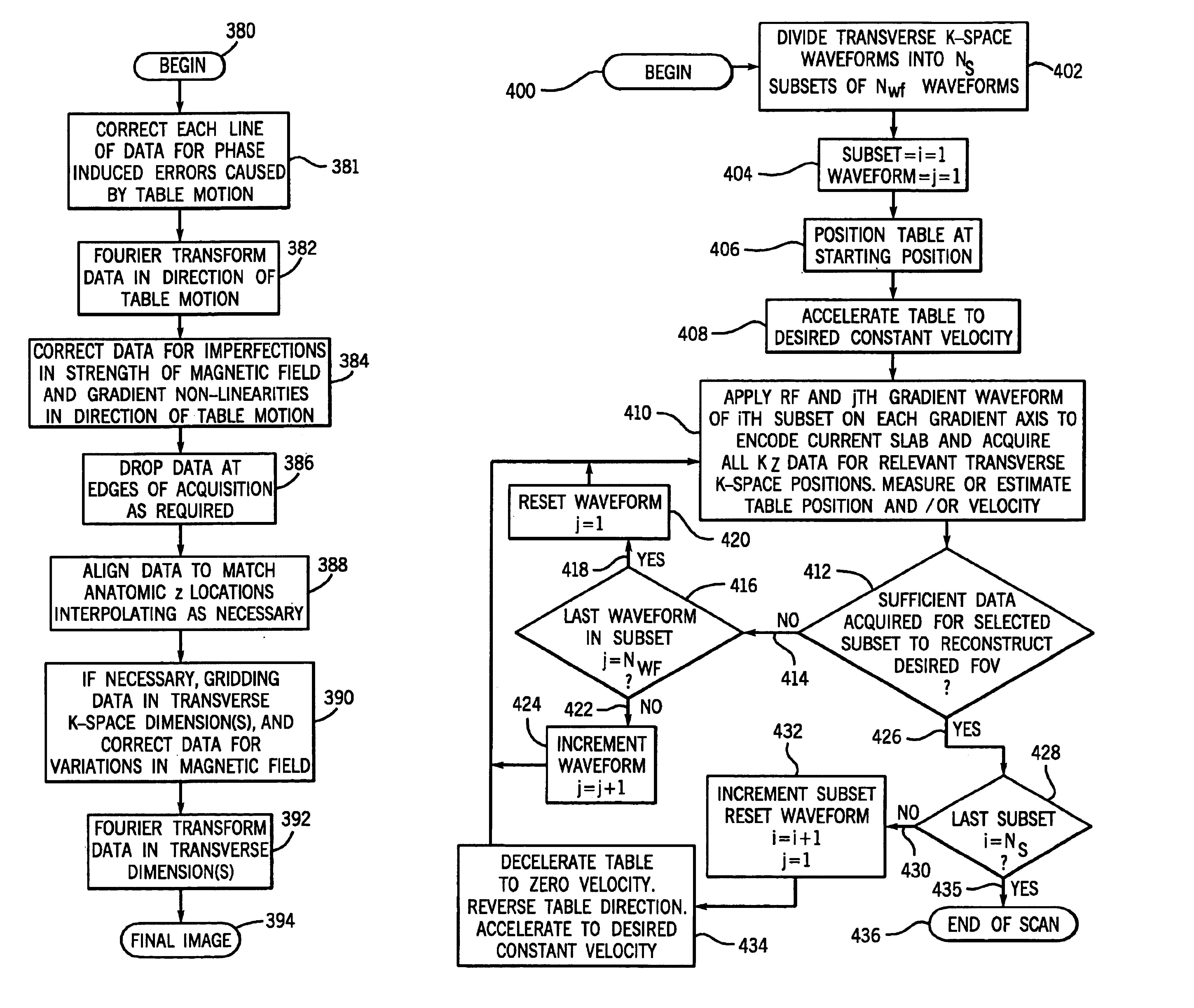
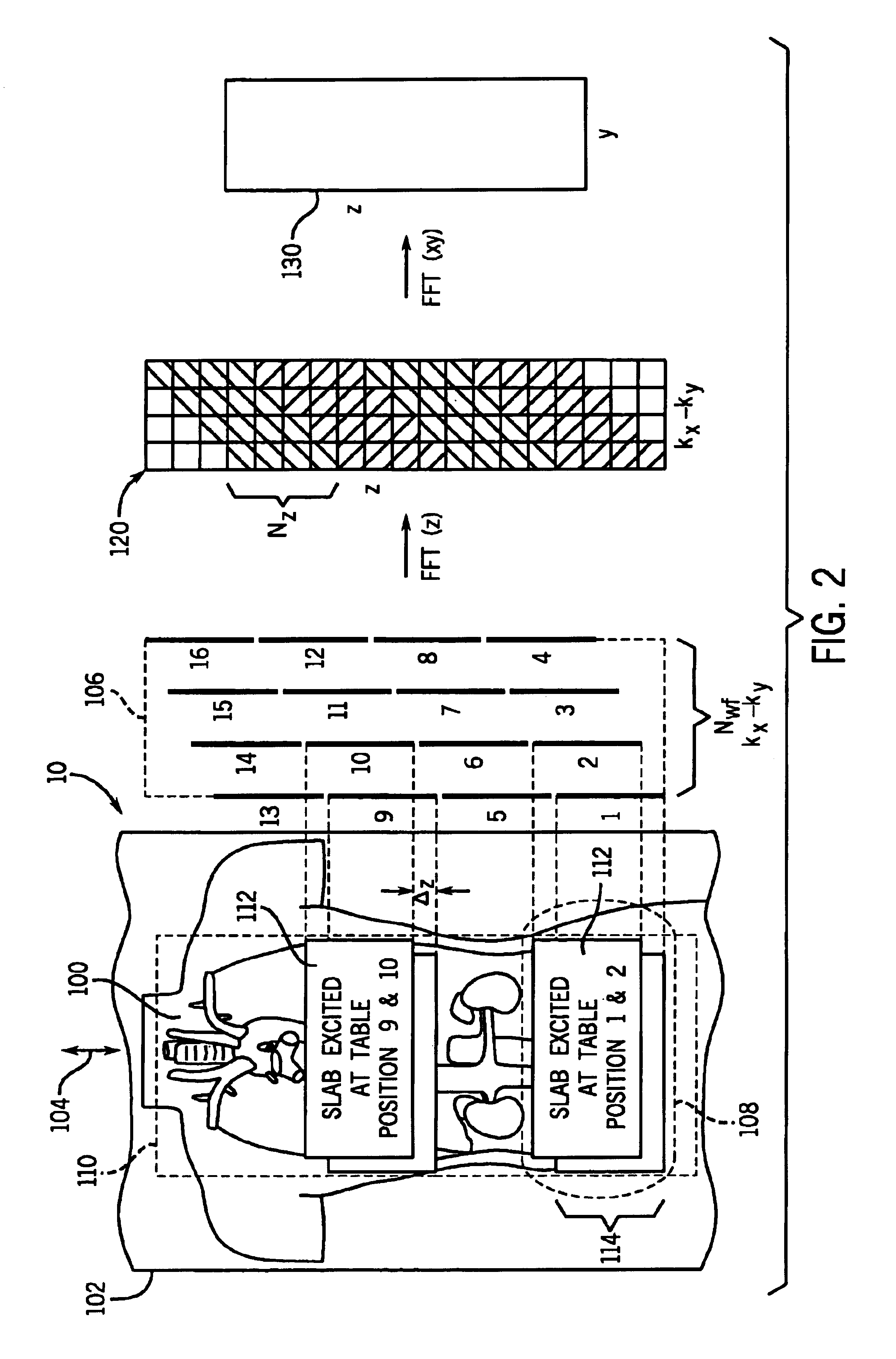
Moving table MRI with frequency-encoding in the z-direction
InactiveUS6897655B2Expand coverageShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLarge fovAcquisition time
A system and method are disclosed using continuous table motion while acquiring data to reconstruct MR images across a large FOV without significant slab-boundary artifacts that reduces acquisition time. At each table position, full z-encoding data are acquired for a subset of the transverse k-space data. The table is moved through a number of positions over the desired FOV and MR data are acquired over the plurality of table positions. Since full z-data are acquired for each slab, the data can be Fourier transformed in z, interpolated, sorted, and aligned to match anatomic z locations. The fully sampled and aligned data is then Fourier transformed in remaining dimension(s) to reconstruct the final image that is free of slab-boundary artifacts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
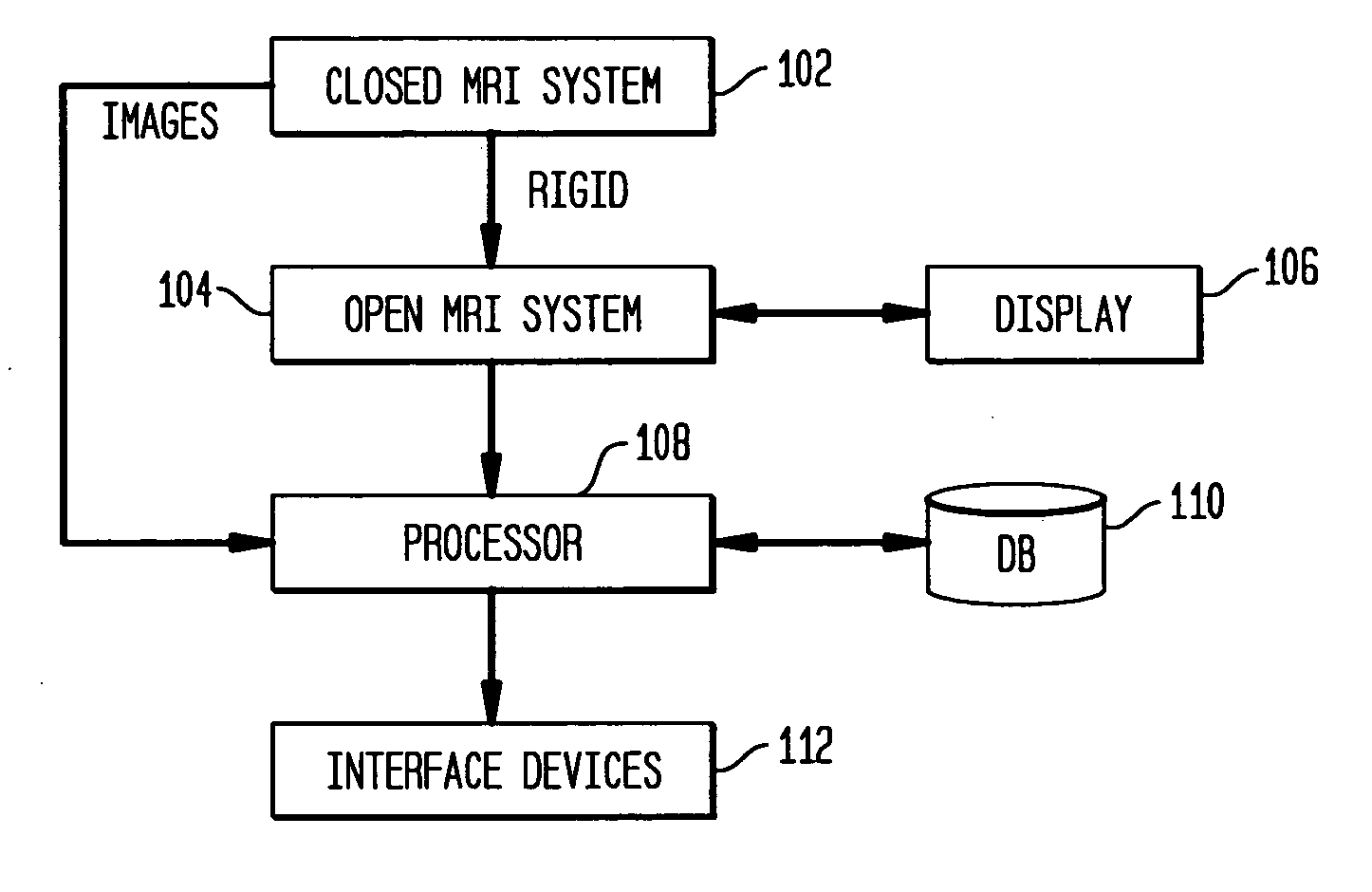
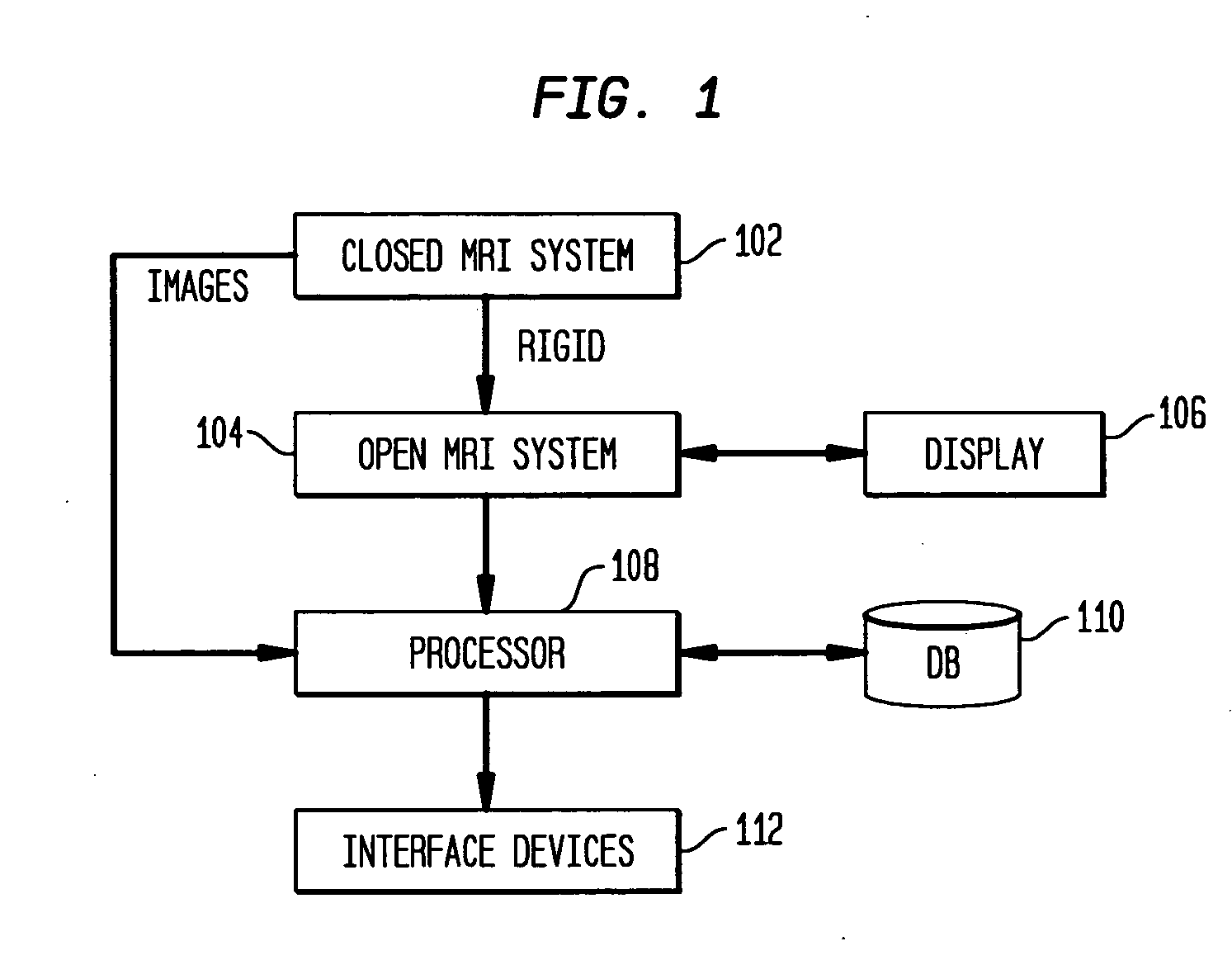
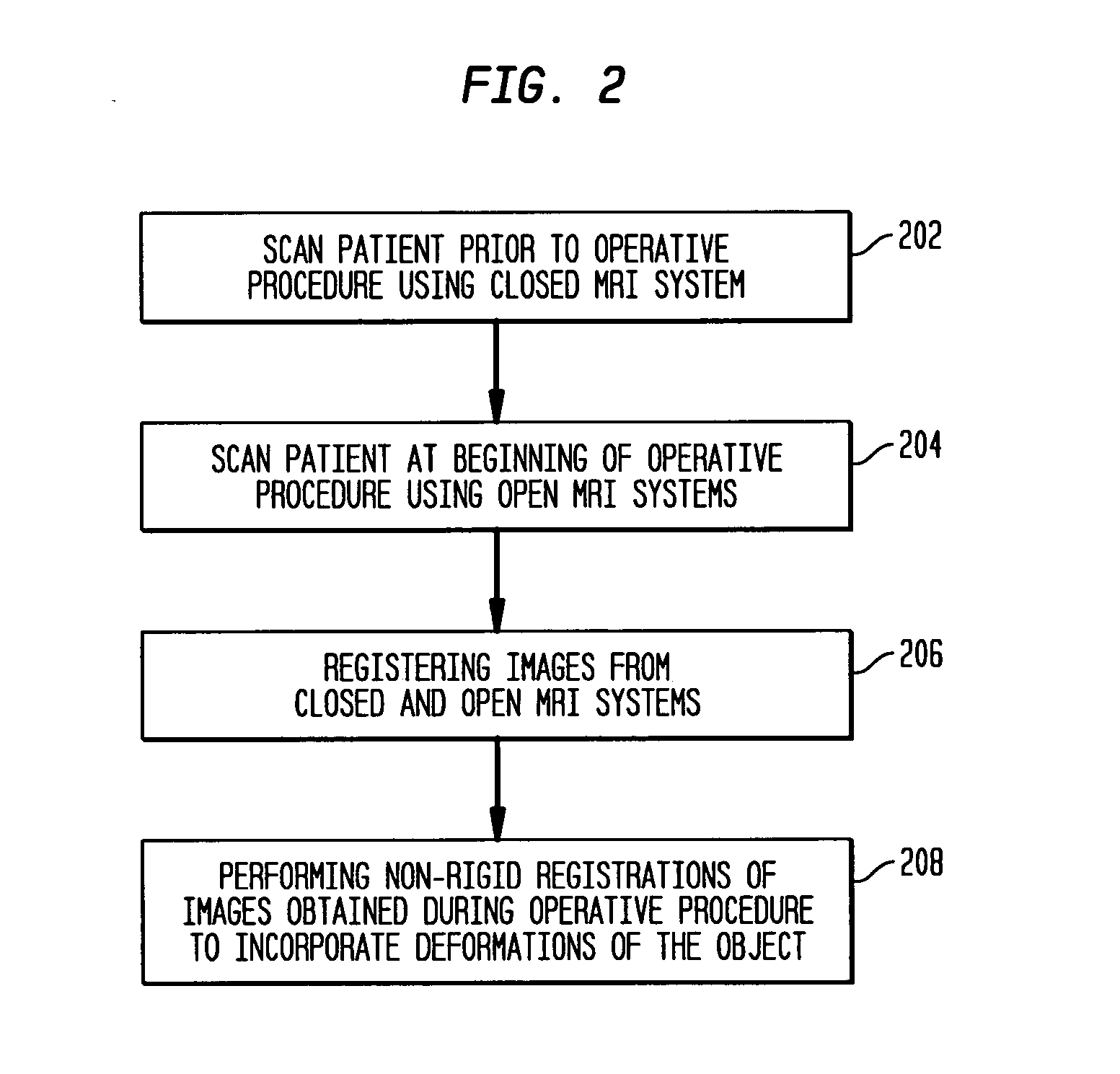
Method of registering pre-operative high field closed magnetic resonance images with intra-operative low field open interventional magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS20050245810A1Character and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceMri image
A system and method for registering pre-operative magnetic resonance (MR) images with intra-operative MR images is disclosed. A pre-operative MR image of an object is received. A set of intra-operative MR images of the object is received. The pre-operative MR image is rigidly registered with the initial intra-operative MR image. The subsequent set of intra-operative images is deformably registered. The pre-operative MR image undergoes both rigid and deformation transformation to match specification of each image with in intra-operative MR image set.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
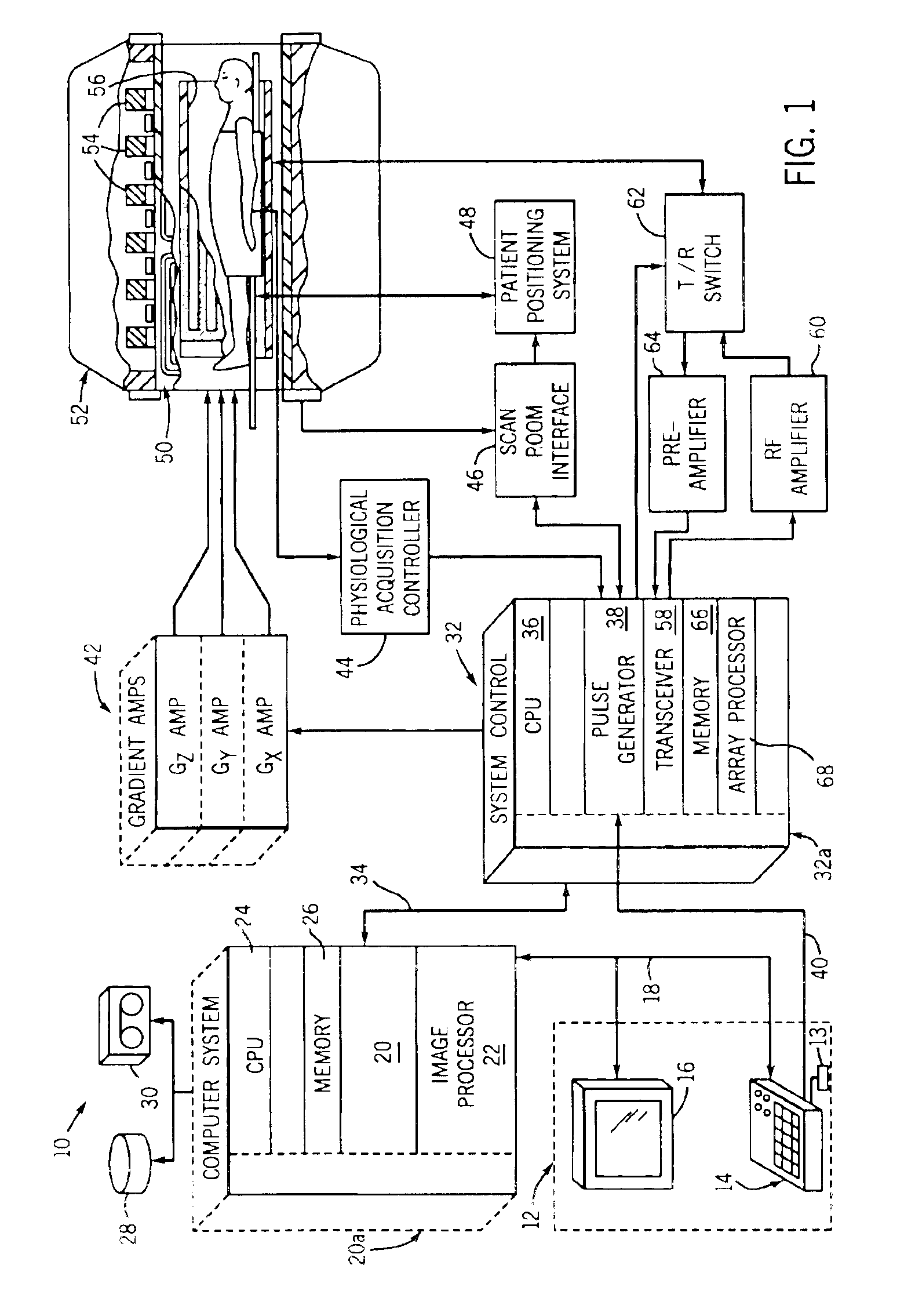
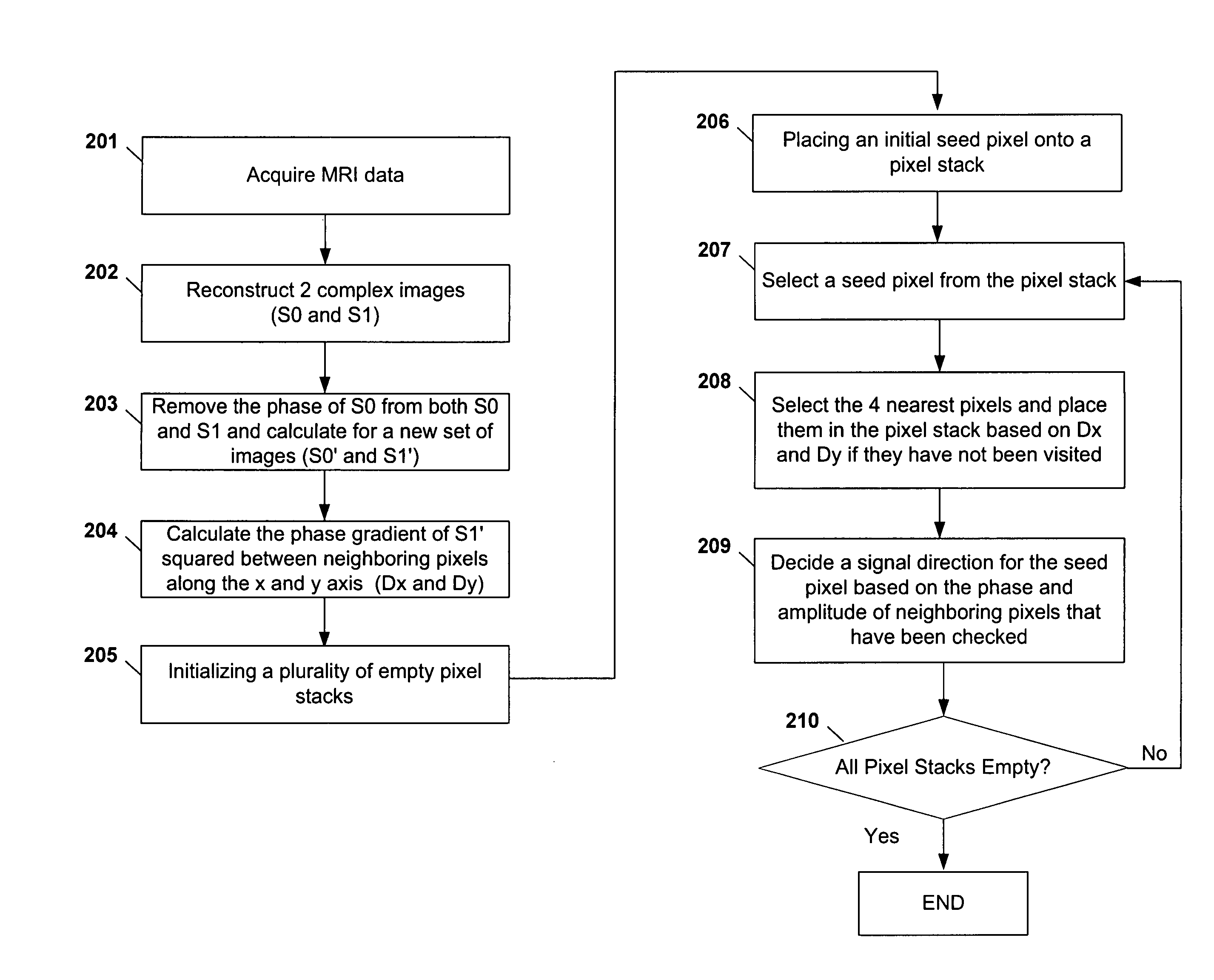
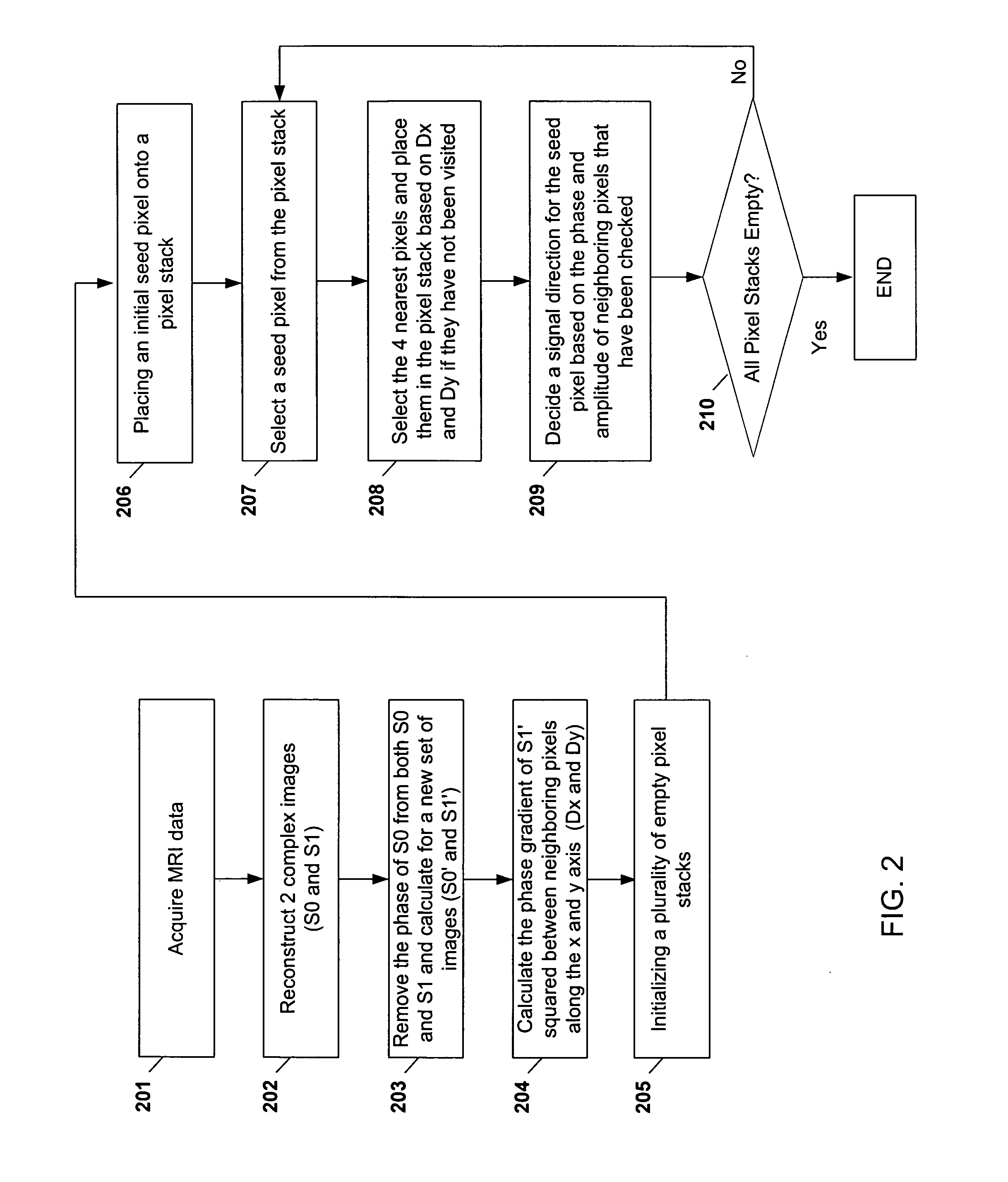
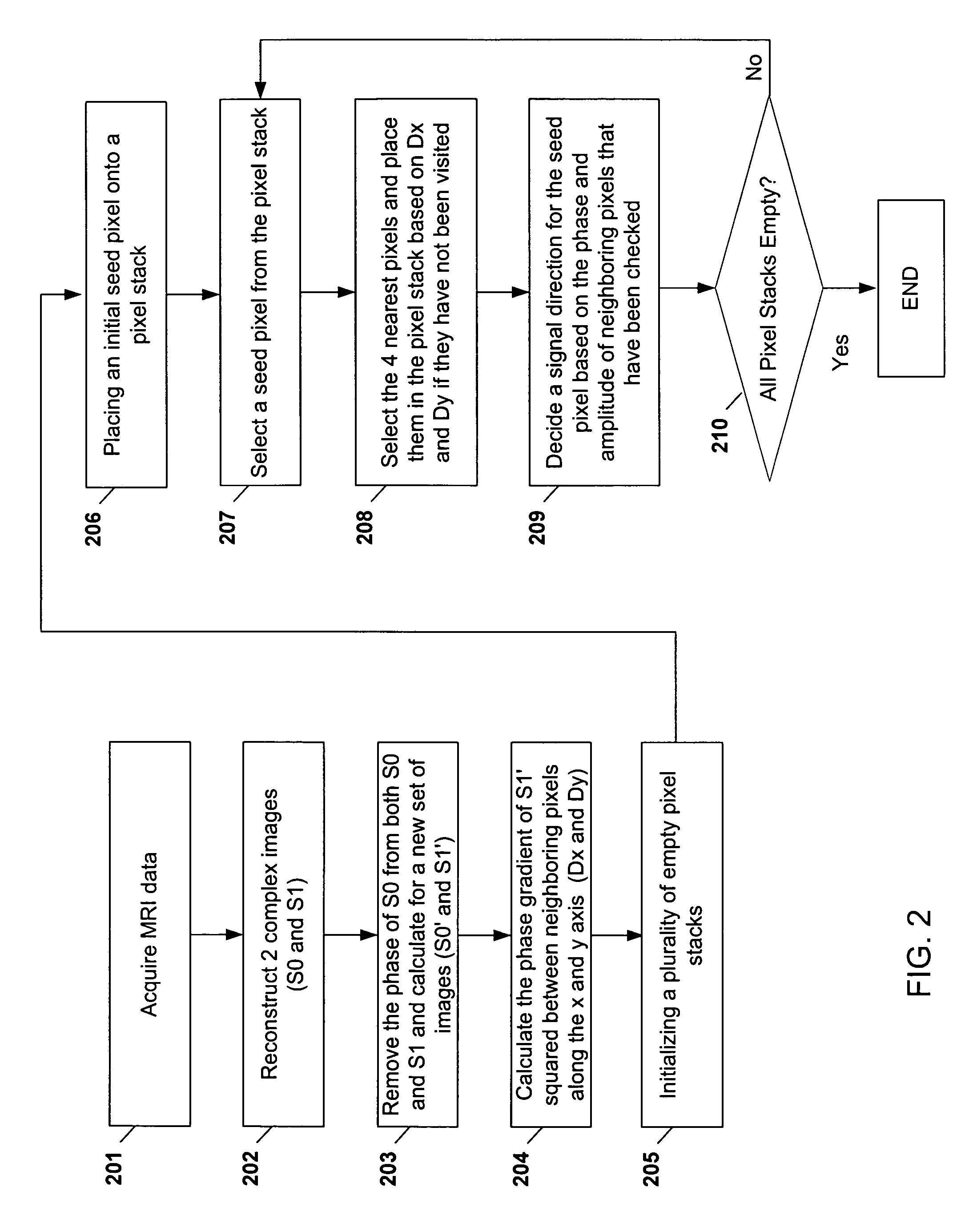
Method and apparatus for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20050165296A1Maintain consistencyAccurate identificationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correctionInversion recovery
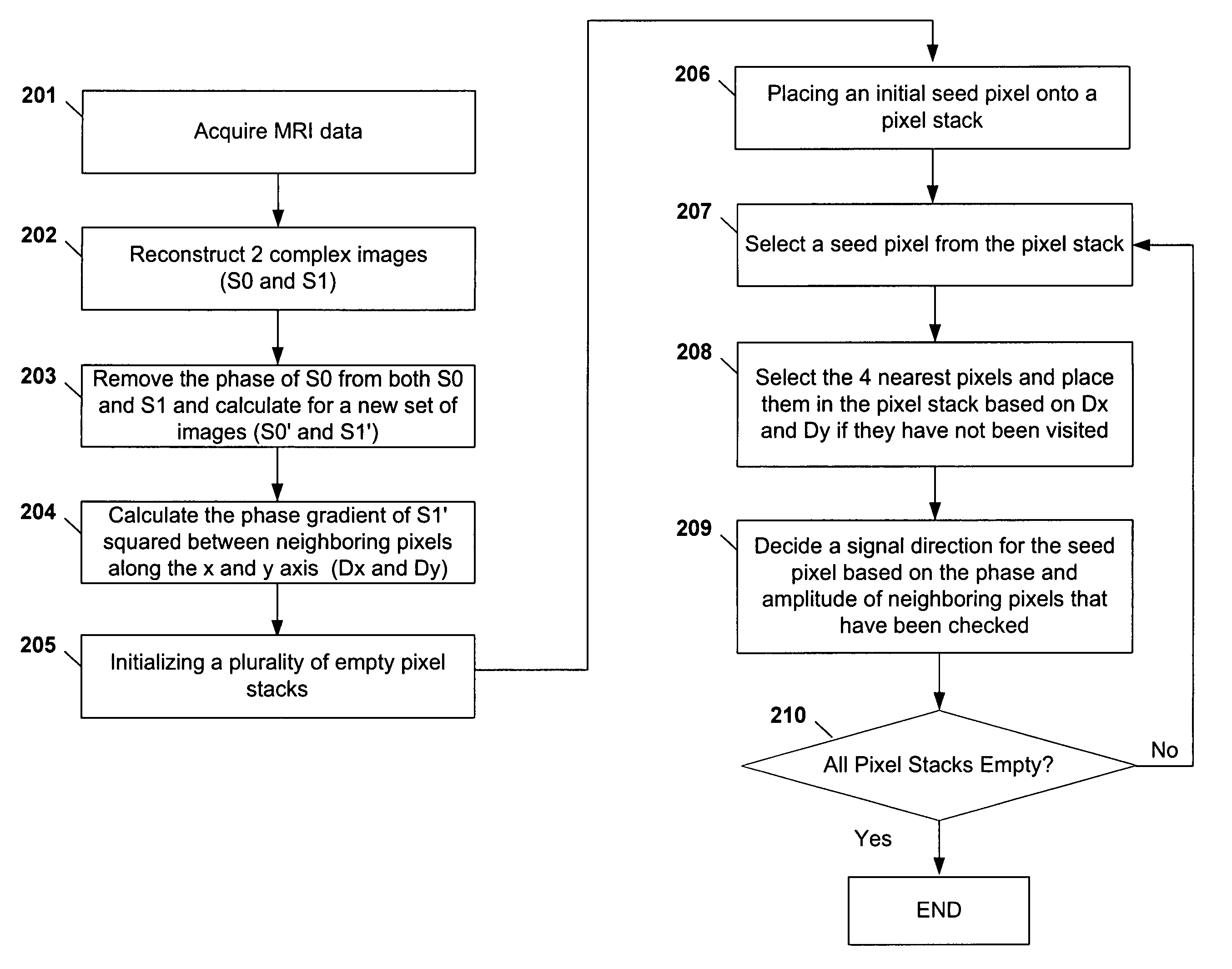
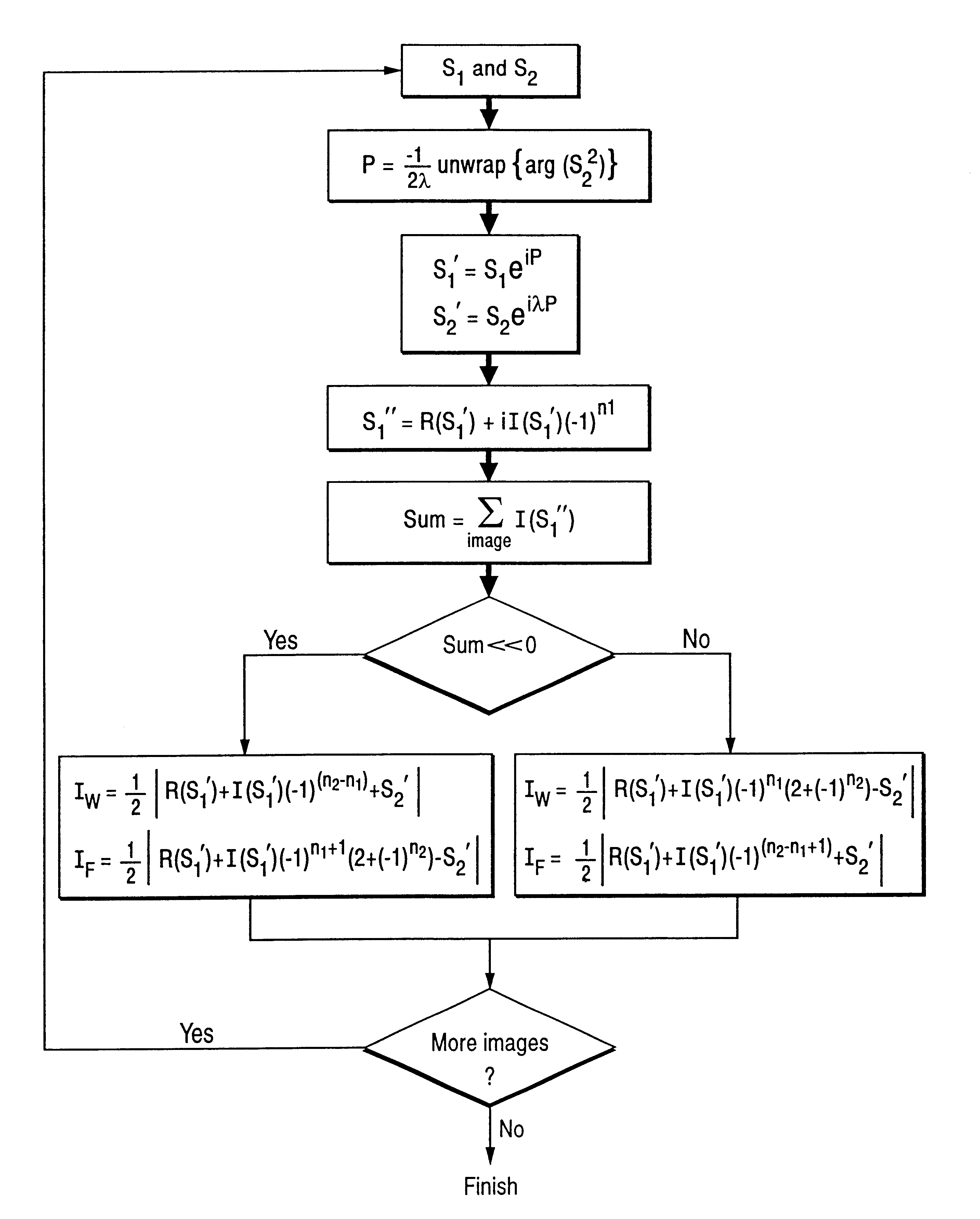
Systems and methods are described for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging using an efficient and robust phase correction algorithm. A method includes obtaining a plurality of MRI data signals, such as two-point Dixon data, one-point Dixon data, or inversion recovery prepared data. The method further includes implementing a phase-correction algorithm, that may use phase gradients between the neighboring pixels of an image. At each step of the region growing, the method uses both the amplitude and phase of pixels surrounding a seed pixel to determine the correct orientation of the signal for the seed pixel. The method also includes using correlative information between images from different coils to ensure coil-to-coil consistency, and using correlative information between two neighboring slices to ensure slice-to-slice consistency. A system includes a MRI scanner to obtain the data signals, a controller to reconstruct the images from the data signals and implement the phase-correction algorithm, and an output device to display phase sensitive MR images such as fat-only images and / or water-only images.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Image Guidance System for Deep Brain Stimulation
InactiveUS20090220136A1High precisionData thereby acquiredSurgical systems user interfaceCharacter and pattern recognitionImage guidanceMr images
This invention provides computerized image guidance systems for deep brain stimulation (DBS) surgery and related methods that improve accuracy of positioning of electrodes in the brains of subjects. Image guidance systems in accordance with the present invention incorporate advanced features such as capability of displaying, in any desired plane of view, a digitized three-dimensional neuroanatomical brain map that can be form fitted to a patient's medical images, such as brain MR images, and capability of displaying on the patient's medical images both the contours of anatomic structures from a digitized brain map, and digitized electrode recording data obtained intra-operatively.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Adjustable guide in computer assisted orthopaedic surgery
ActiveUS20120143198A1Easy to readEasy to adjustDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aidedNavigation system
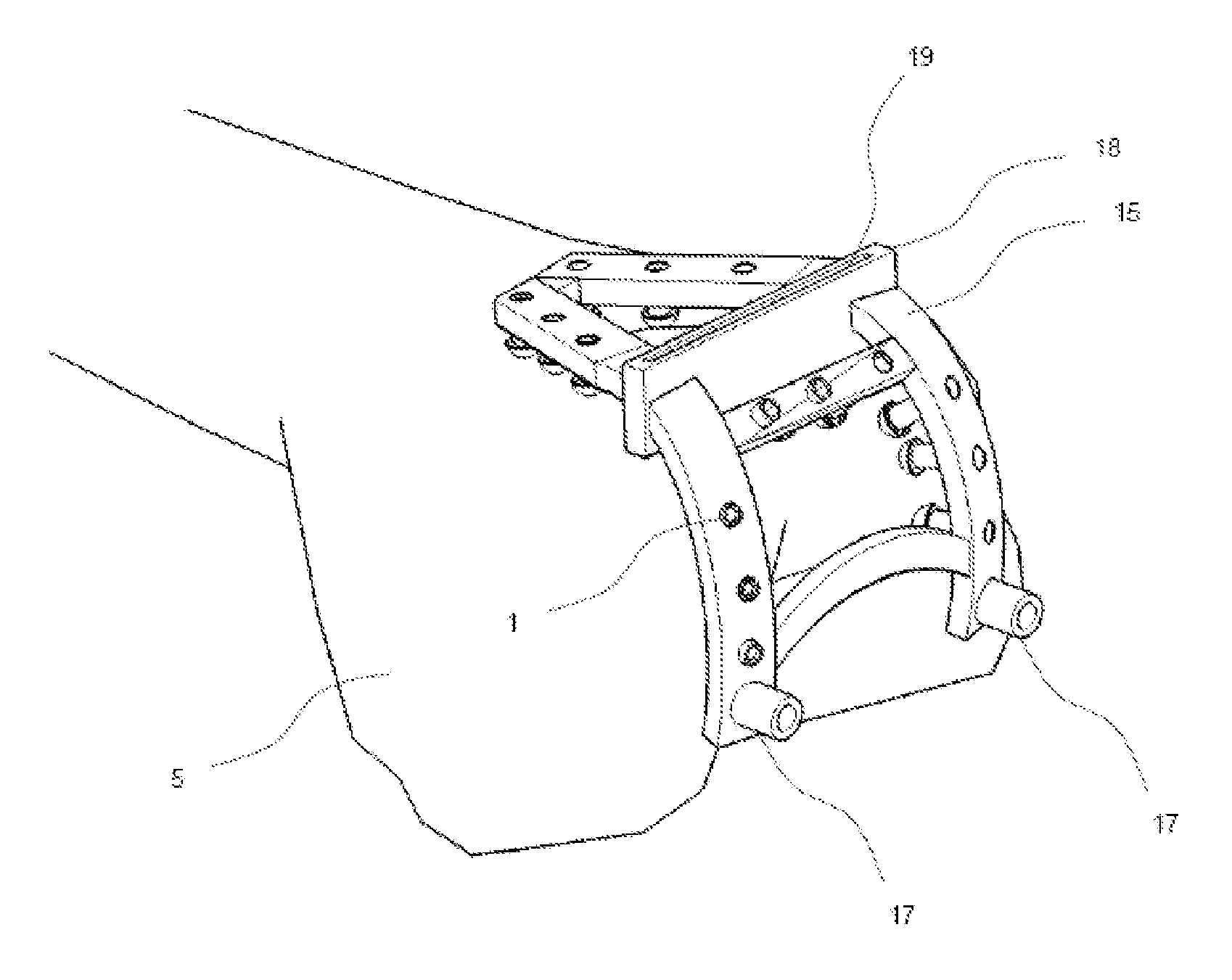
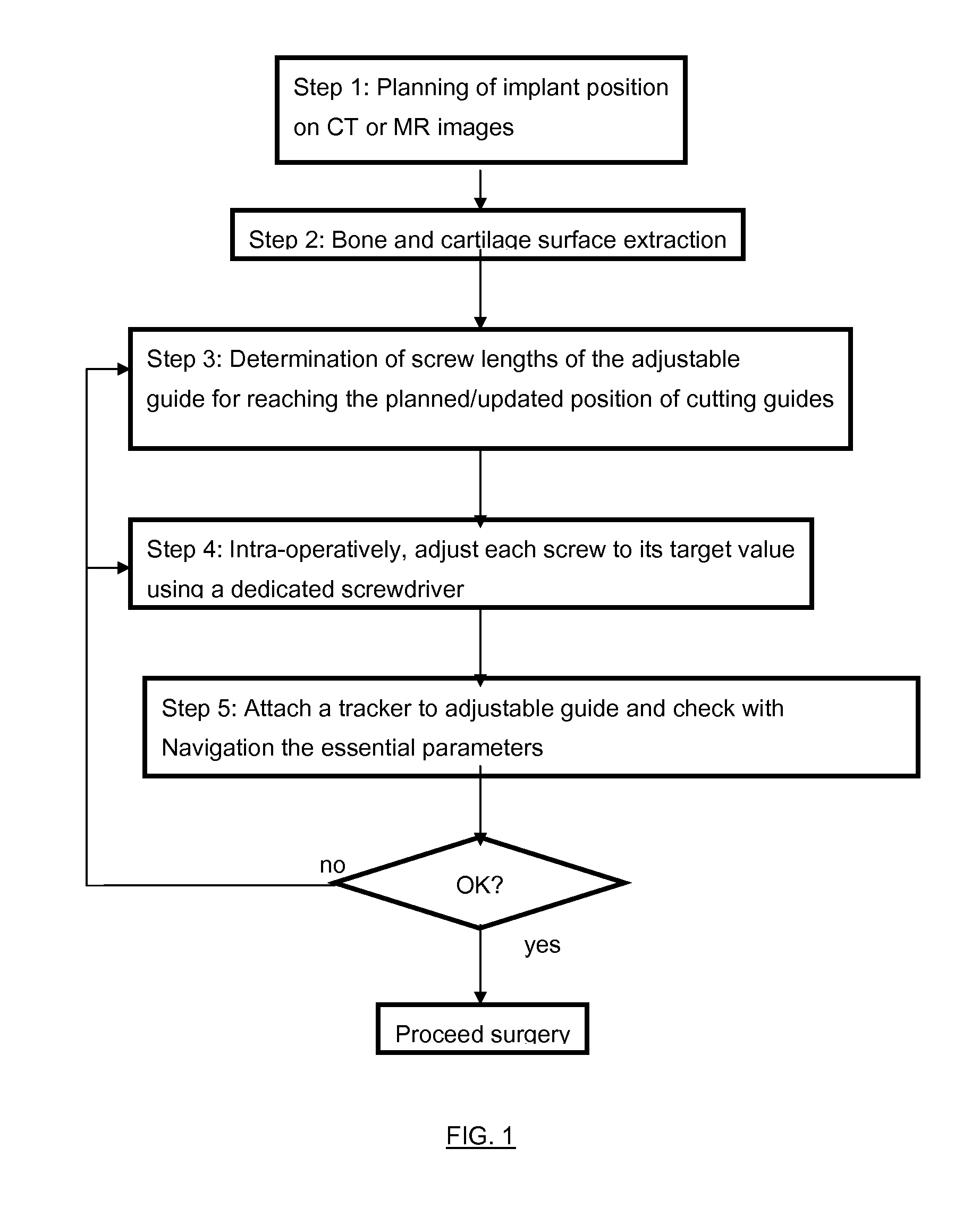
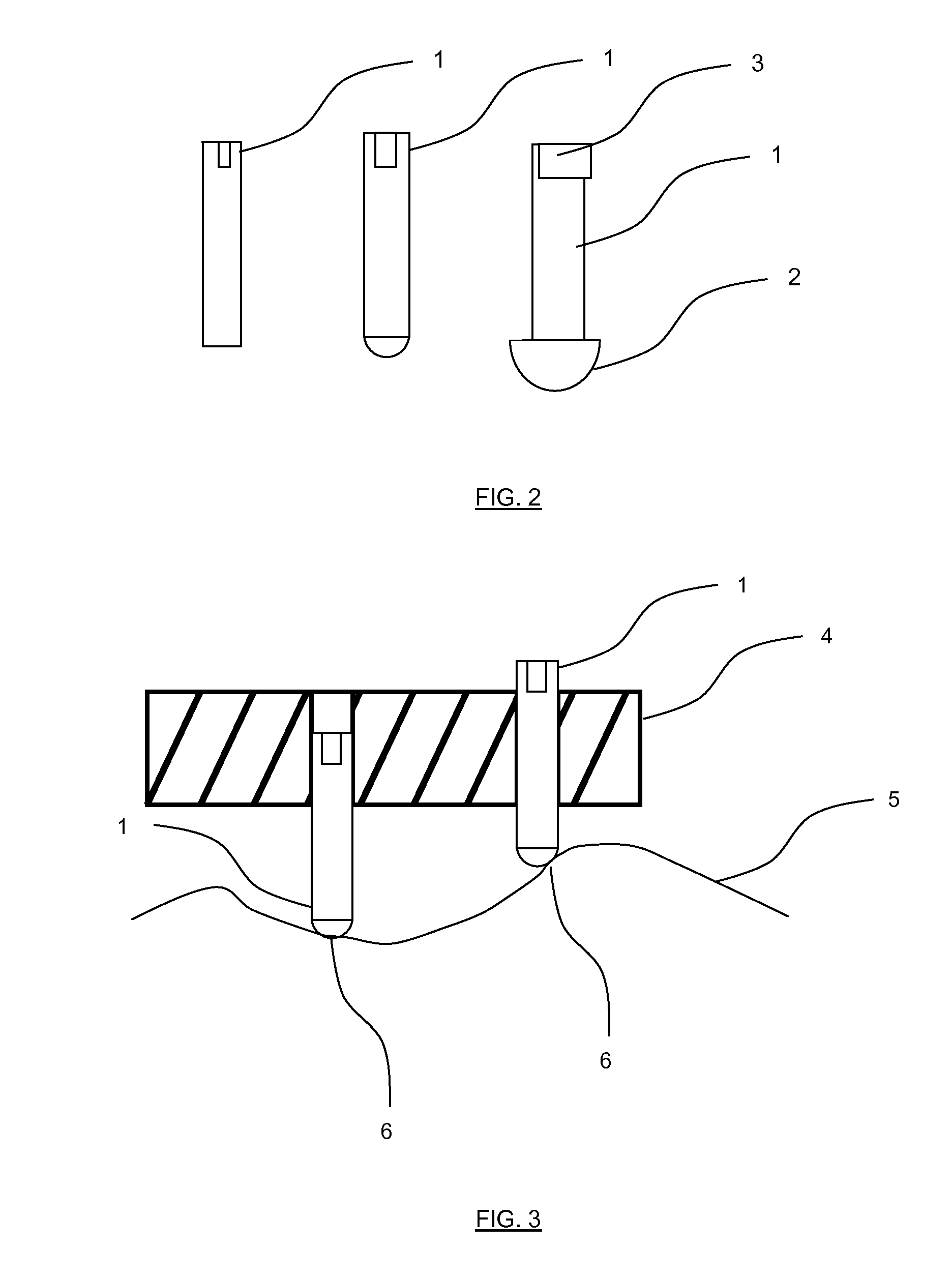
The present invention relates to a surgical navigation device, for the purpose of adjusting cutting planes to a desired position with respect to a bone of a patient, the device comprising:an adjustable guide (15) that contains several adjustable screws (1) that create contact points with the surface of the bone or cartilage such that the guide fits to the bone in a unique position calculated such that the holes and cutting blocks of the adjustable guide fit with the position planned on preoperative CT or MR images of the patient,a dedicated screwdriver (7) to adjust automatically the screws (1) to their target length,a navigation system used to check the correct position of the adjustable guide with respect to essential anatomical points and if necessary means to correct the positions of the adjustable screws.
Owner:BLUE ORTHO
Method and apparatus for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7227359B2Maintain consistencyAccurate identificationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correctionInversion recovery
Systems and methods are described for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging using an efficient and robust phase correction algorithm. A method includes obtaining a plurality of MRI data signals, such as two-point Dixon data, one-point Dixon data, or inversion recovery prepared data. The method further includes implementing a phase-correction algorithm, that may use phase gradients between the neighboring pixels of an image. At each step of the region growing, the method uses both the amplitude and phase of pixels surrounding a seed pixel to determine the correct orientation of the signal for the seed pixel. The method also includes using correlative information between images from different coils to ensure coil-to-coil consistency, and using correlative information between two neighboring slices to ensure slice-to-slice consistency. A system includes a MRI scanner to obtain the data signals, a controller to reconstruct the images from the data signals and implement the phase-correction algorithm, and an output device to display phase sensitive MR images such as fat-only images and / or water-only images.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
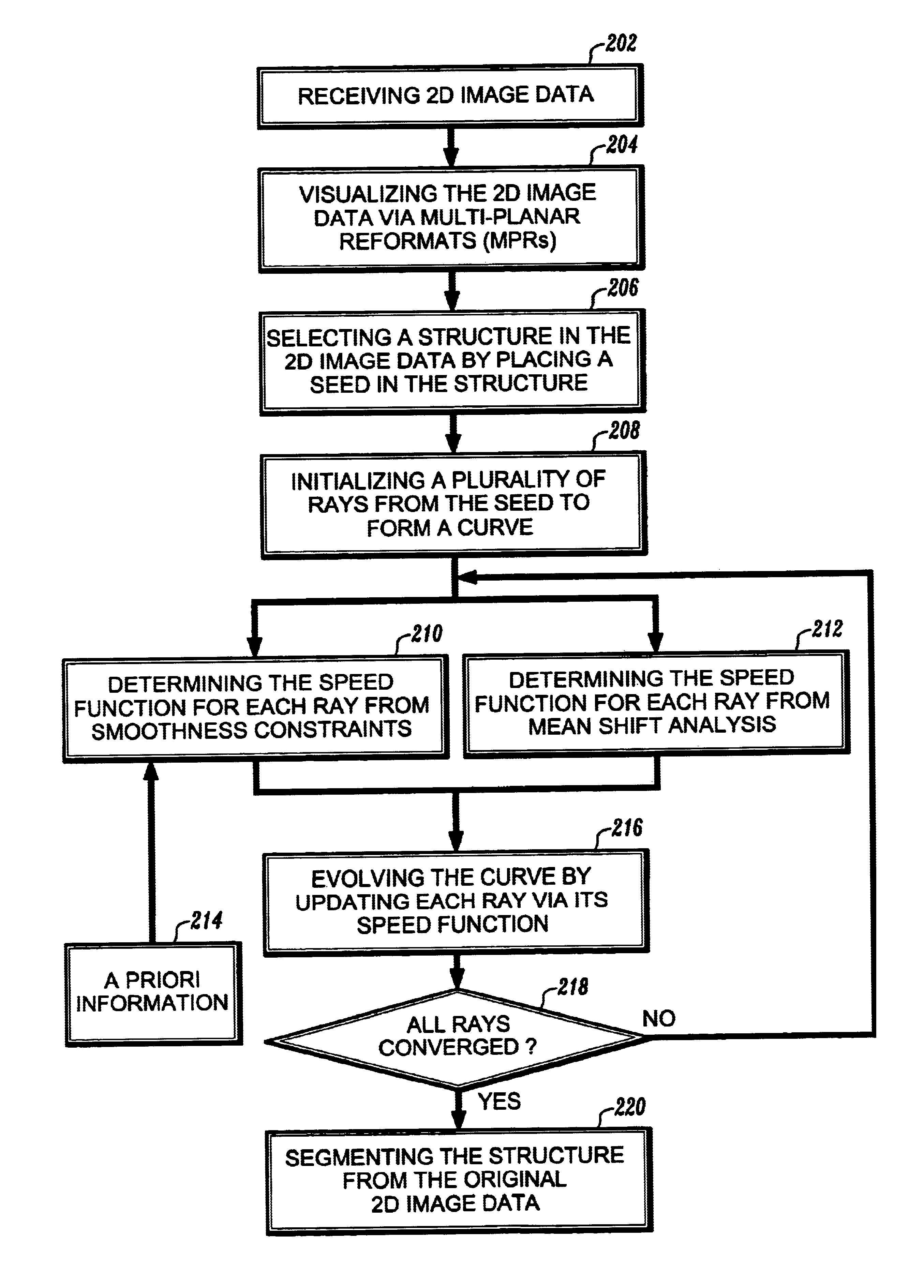
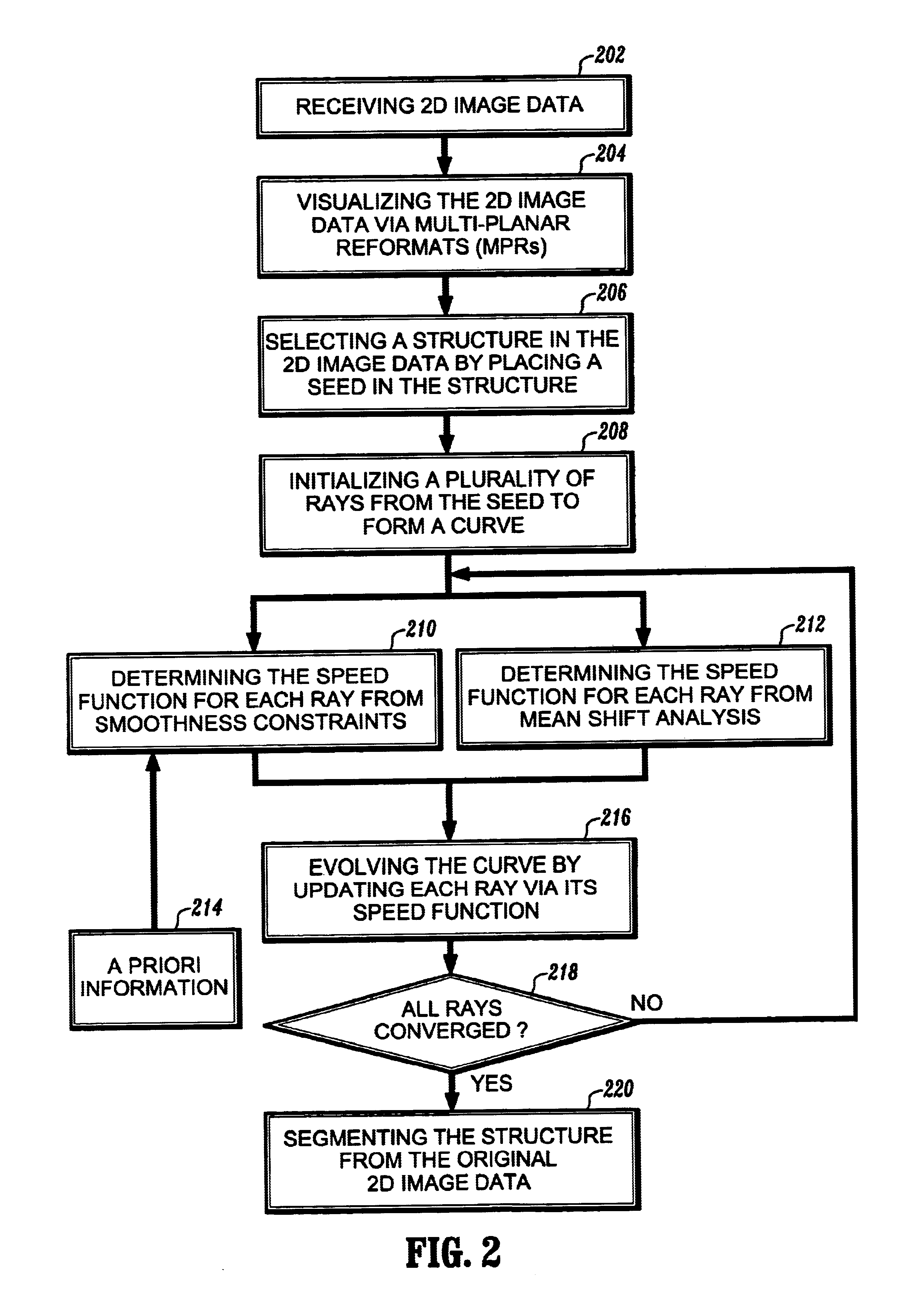
Vessel detection by mean shift based ray propagation
InactiveUS6947040B2Efficient and robustEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisMean-shiftDisplay device
A method for segmentation of 2D structures in CT and MR images is provided. The method is based on 2D ray propagation by mean-shift analysis with a smoothness constraint. Ray propagation is used to guide an evolving curve due to its computational efficiency and shape priors are incorporated for robust convergence. The method includes the steps of receiving 2D image data; visualizing the 2D image data on a display device; selecting a structure in the 2D image data by placing a seed in the structure; initializing a plurality of rays from the seed to form a curve; determining a speed function of each of the rays; evolving the curve by propagating the rays based on the speed function of each of the rays; converging the rays on a boundary of the structure; and segmenting the structure when all of the rays have converged on the structure's boundary.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
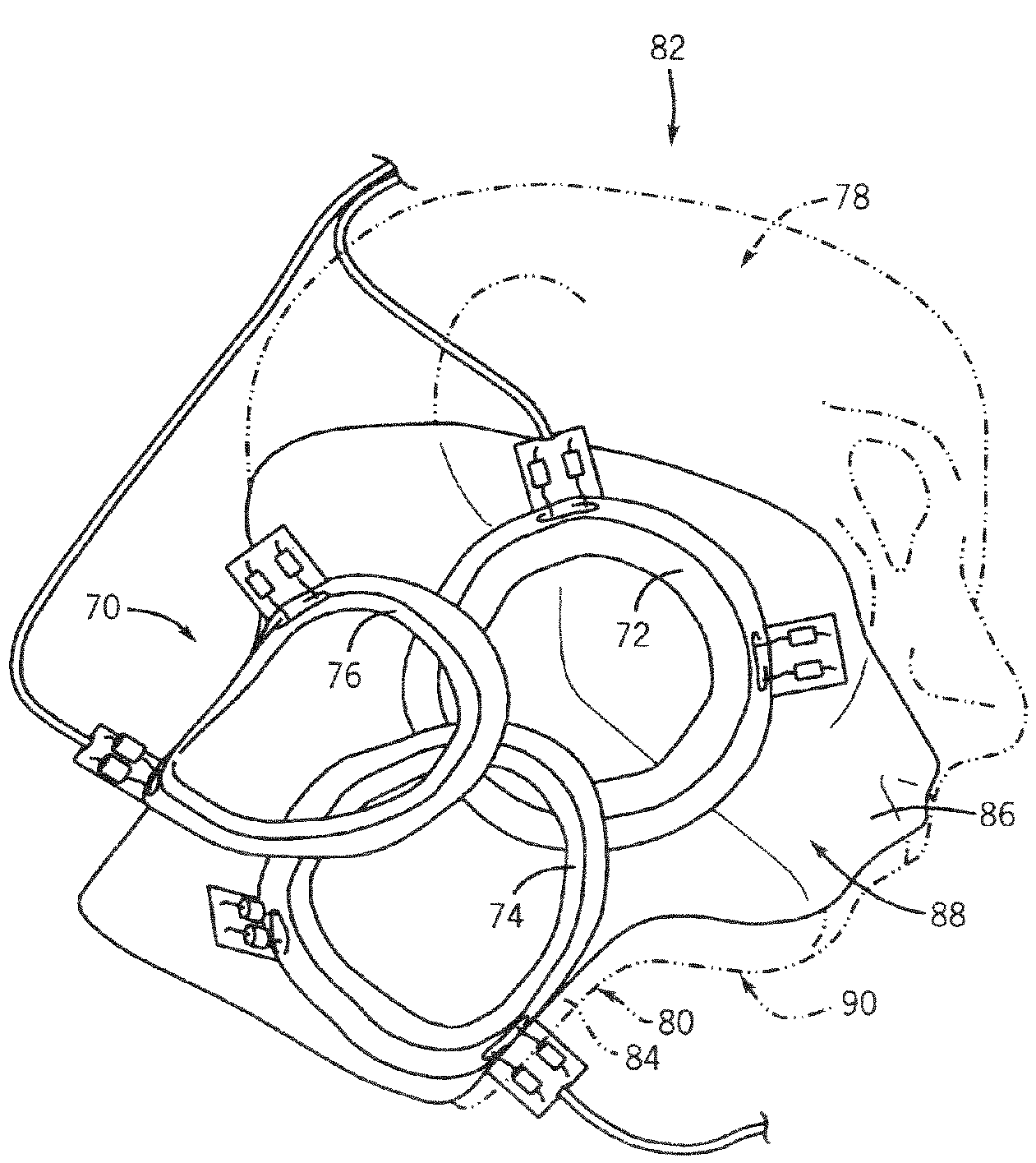
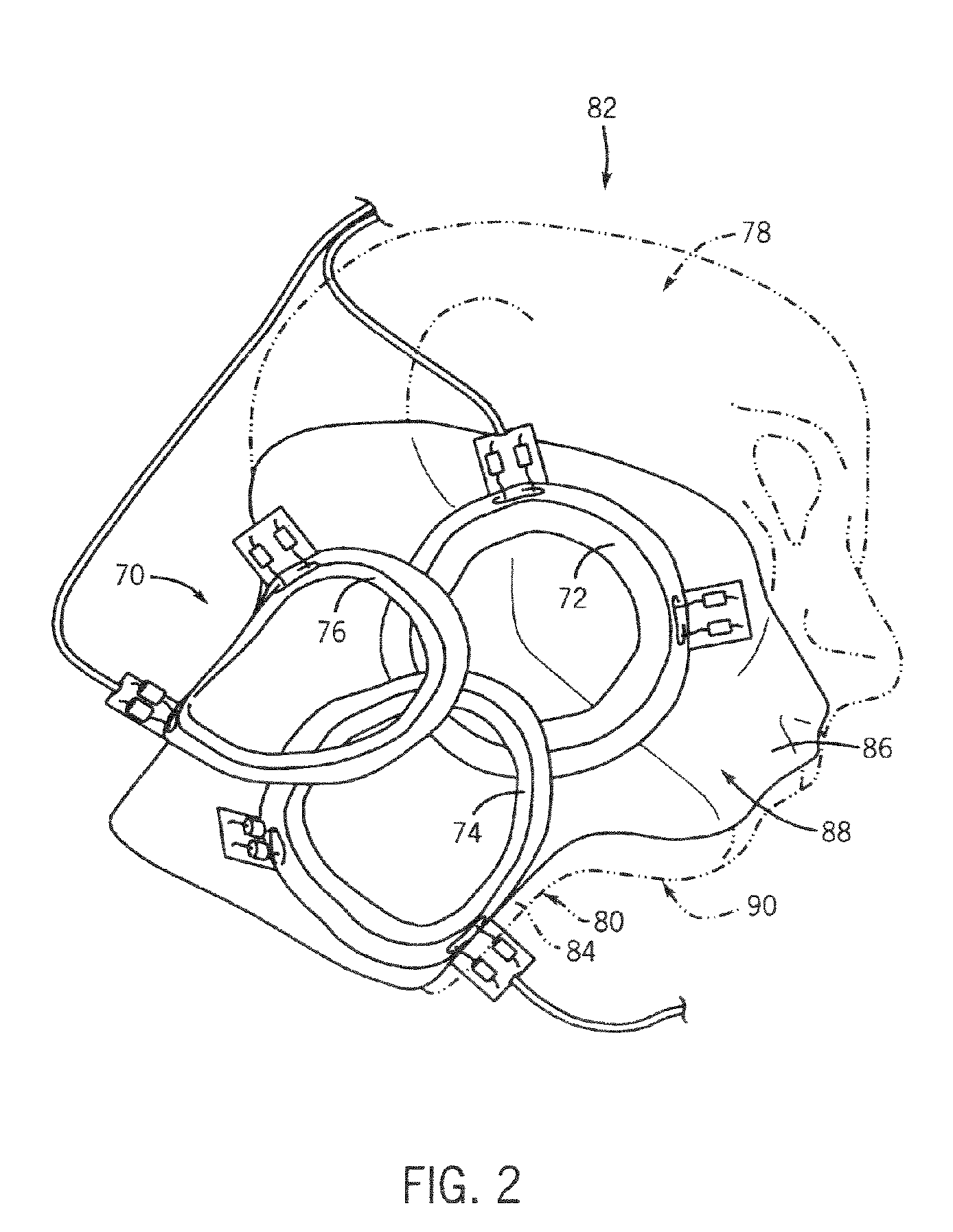
6-channel array coil for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7382132B1Easy to detectHigh resolutionMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionCoil arrayHigh resolution image
A method and apparatus for acquiring high resolution MR images of a carotid artery. A six-channel RF coil array has three RF coils placed in an overlapping pattern and positioned adjacent to a first region-of-interest (ROI) of an imaging patient. The six-channel RF coil also has three RF coils placed in an overlapping pattern and positioned adjacent to a second ROI of an imaging patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Moving table MRI with frequency-encoding in the z-direction
InactiveUS6891374B2Expand coverageShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLarge fovComplete data
A system and method are disclosed using continuous table motion while acquiring data to reconstruct MR images across a large FOV without significant slab-boundary artifacts that reduces acquisition time. At each table position, full z-encoding data are acquired for a subset of the transverse k-space data. The table is moved through a number of positions over the desired FOV and MR data are acquired over the plurality of table positions. Since full z-data are acquired for each slab, the data can be Fourier transformed in z, interpolated, sorted, and aligned to match anatomic z locations. The fully sampled and aligned data is then Fourier transformed in remaining dimension(s) to reconstruct the final image that is free of slab-boundary artifacts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
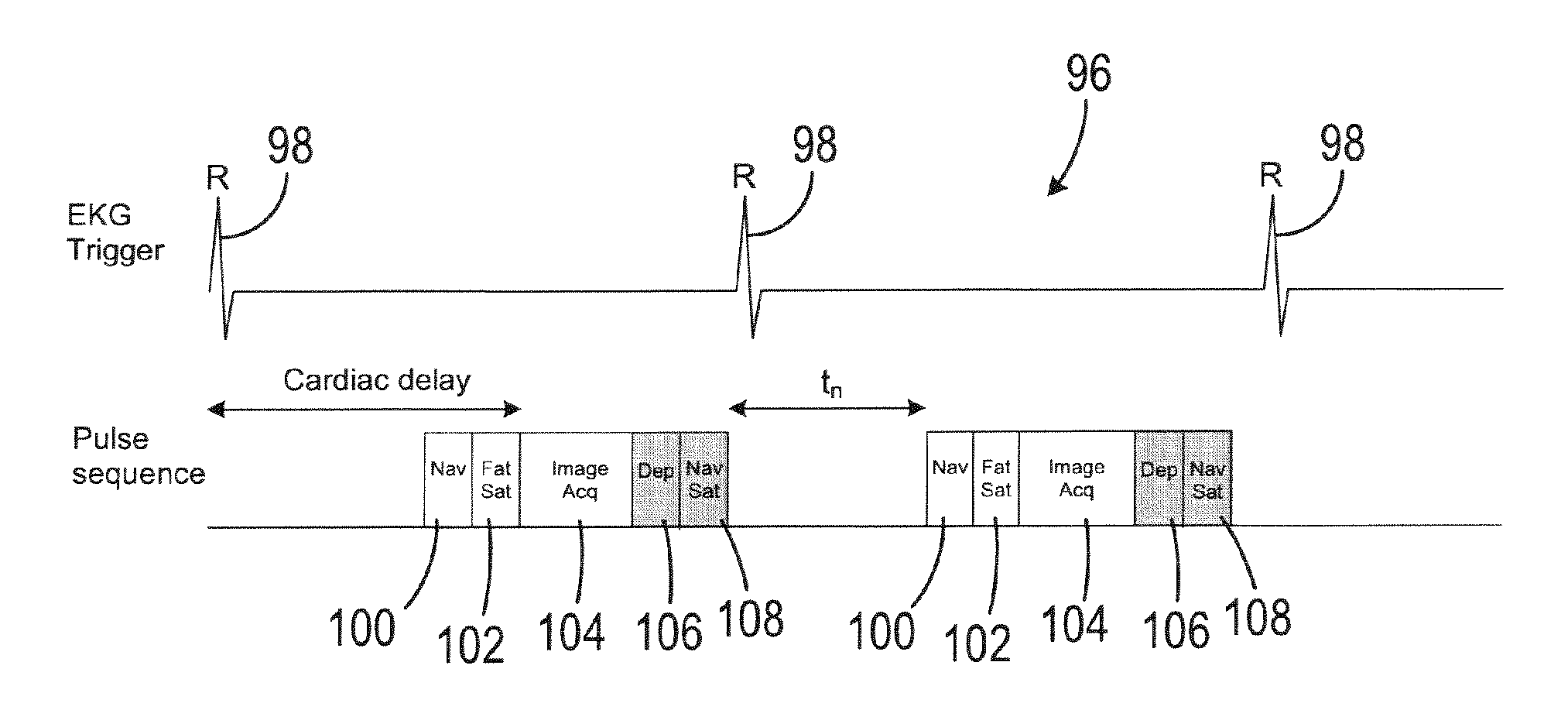
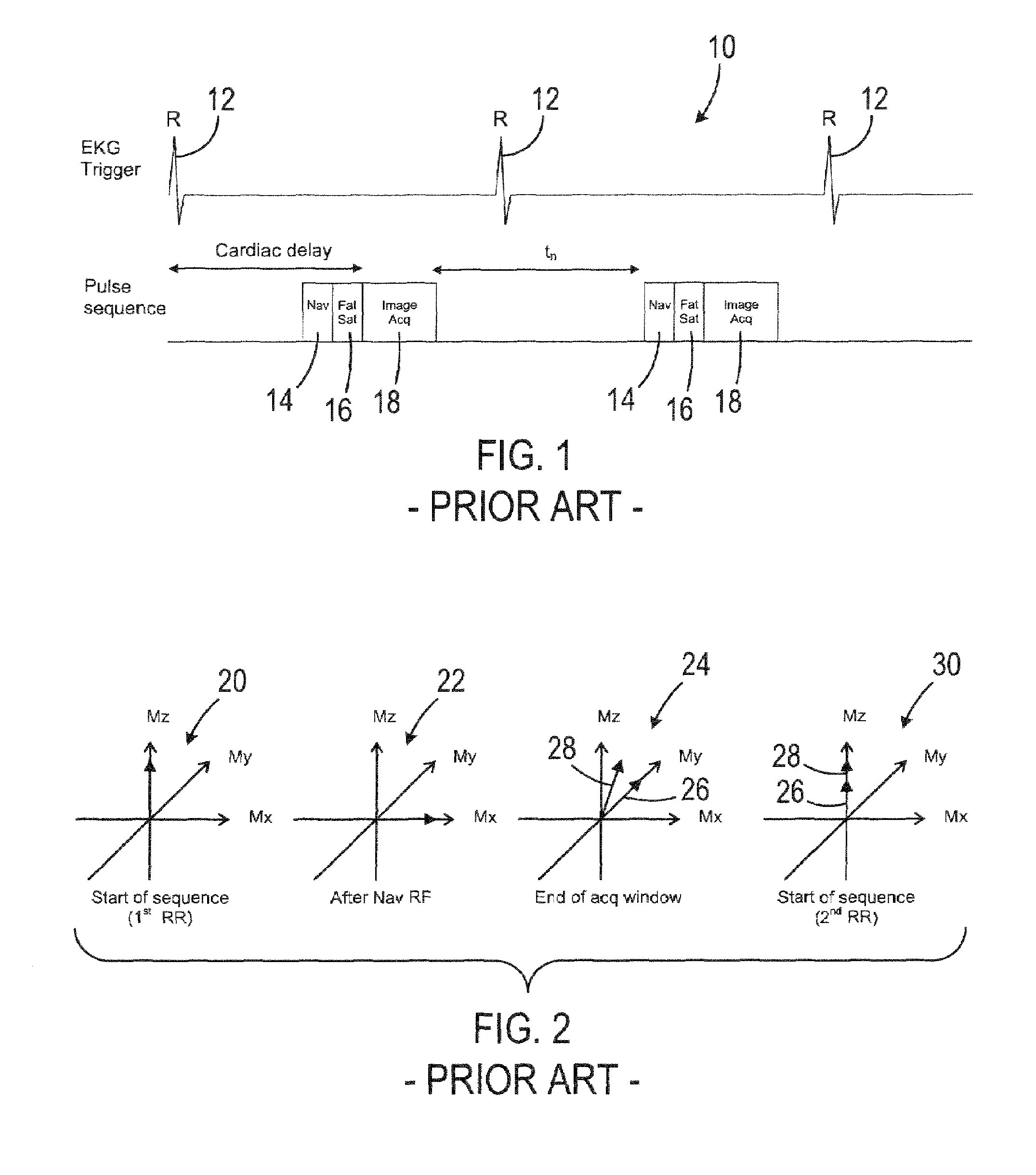
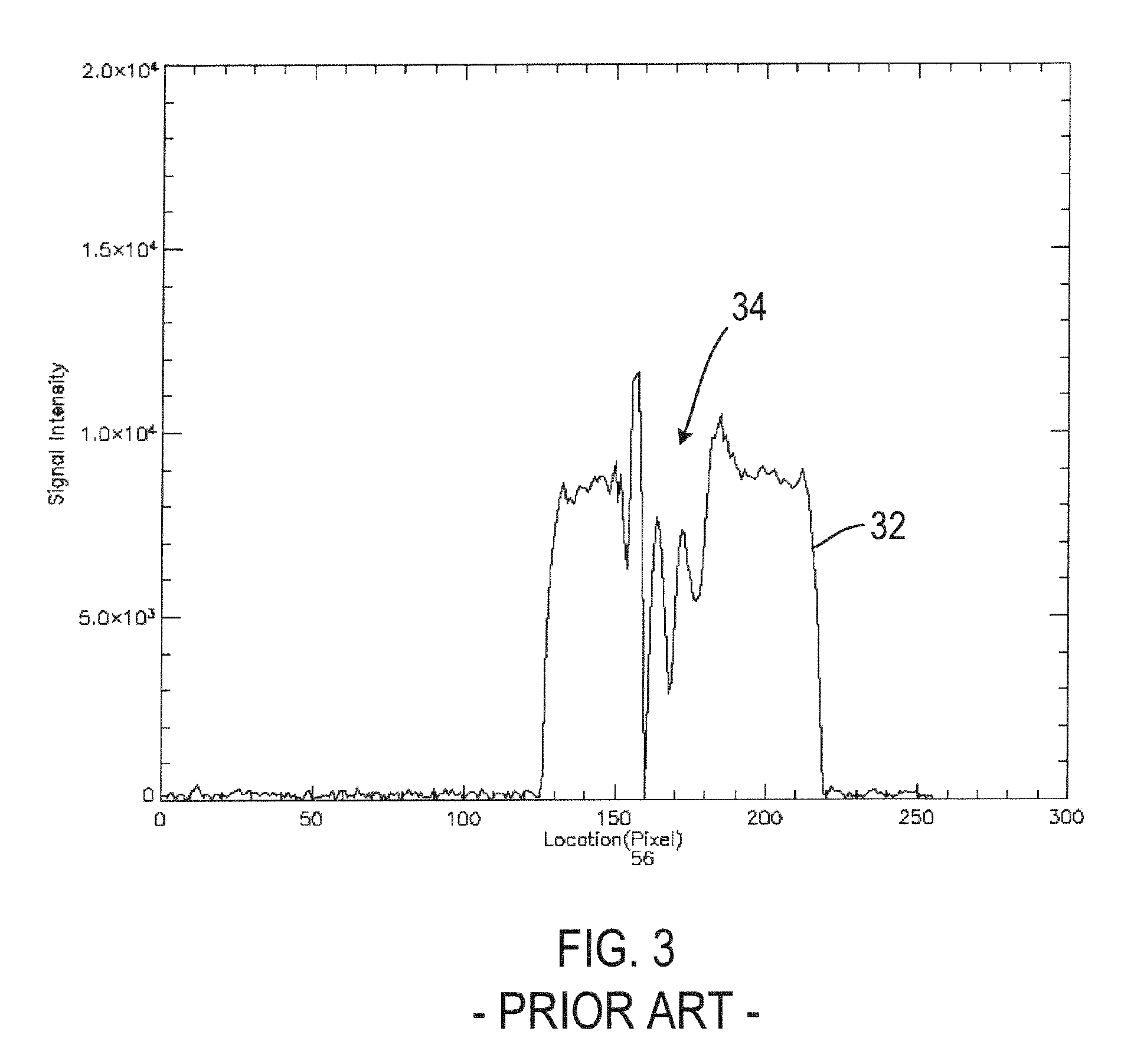
Method and apparatus for acquiring free-breathing MR images using navigator echo with saturation RF pulse
ActiveUS7689263B1Uniform recoveryOvercomes drawbackMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTransverse magnetizationSpins
A system and method of free-breathing MR imaging saturates an entire navigator profile at the end of an imaging segment of physiological motion cycle, e.g., heart cycle, thereby providing a uniform recovery of longitudinal magnetization for the next imaging cycle. Through use of at least one dephaser gradient following the image acquisition segment and a navigator RF saturation pulse, residual transverse magnetization is dephased and spins within a navigator tracker are saturated to ensure a uniform recovery of longitudinal magnetization for the next imaging period.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
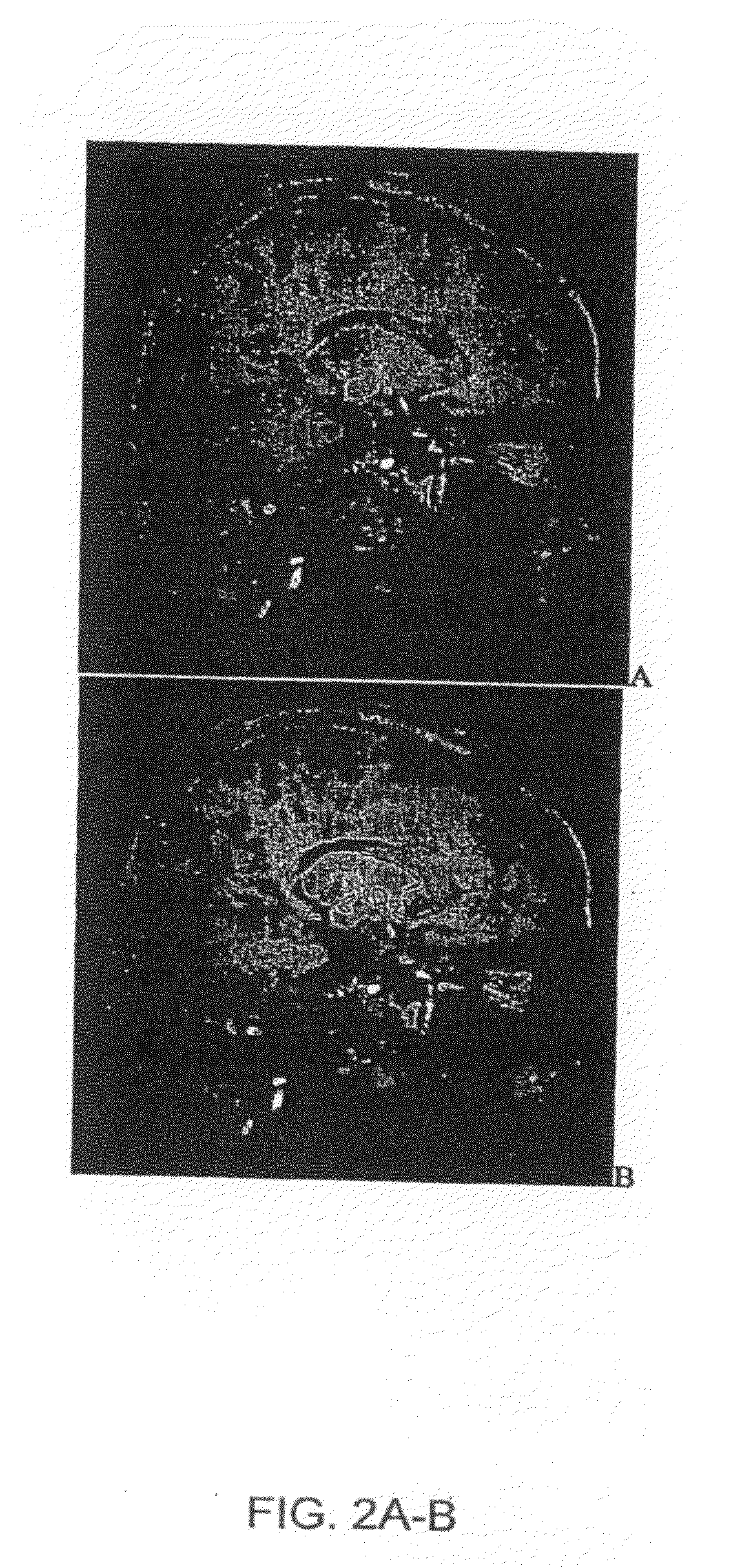
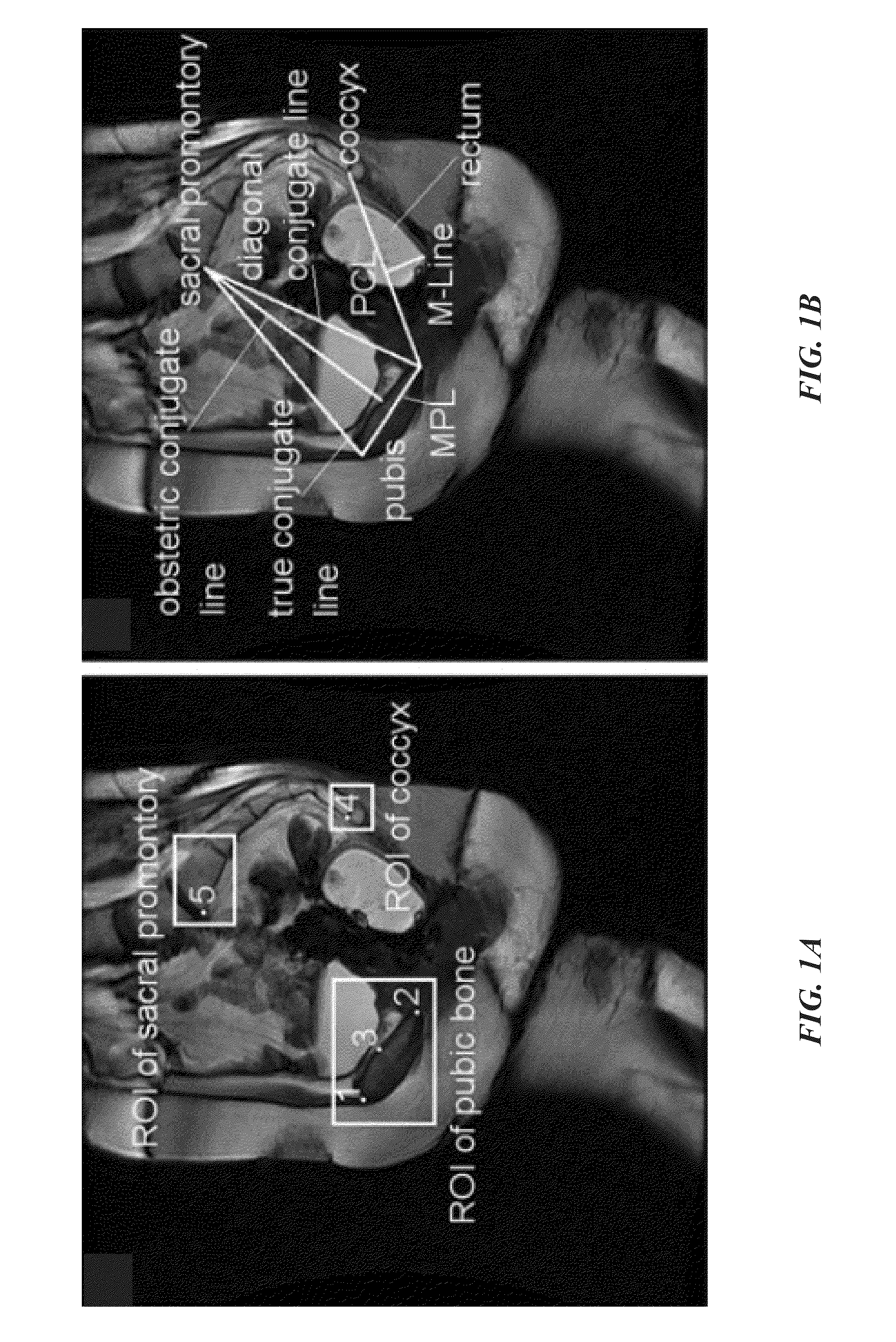
Image-based automated measurement model to predict pelvic organ prolapse
ActiveUS20160275678A1Reduce noiseImprove understandingImage enhancementImage analysisClinical informationPelvic diaphragm muscle
A system and methodology for the automated localization, extraction, and analysis of MRI-based features with clinical information to improve the diagnosis of pelvic organ prolapse (POP). The system can automatically identify reference points for pelvic floor measurements on MRI rapidly and consistent. It provides a prediction model that analyzes the correlation between current and new MRI-based features with clinical information to differentiate patients with and without POP. This system will enable the high throughput analysis of MR images for their correlation with clinical information to better detect POP. The presented system can also be applied to the automated localization and extraction of MRI features for the diagnosis of other diseases where clinical examination is not adequate.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
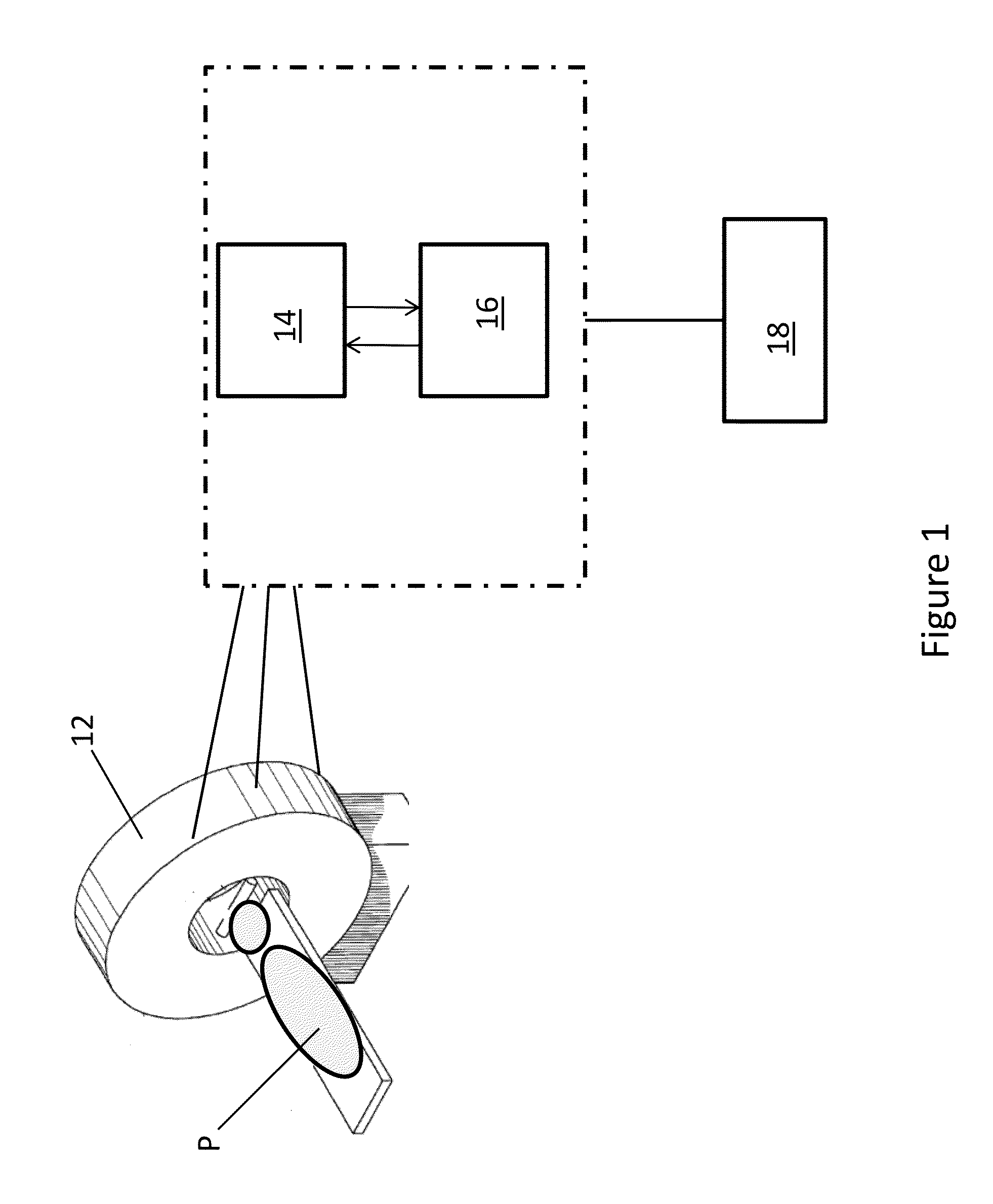
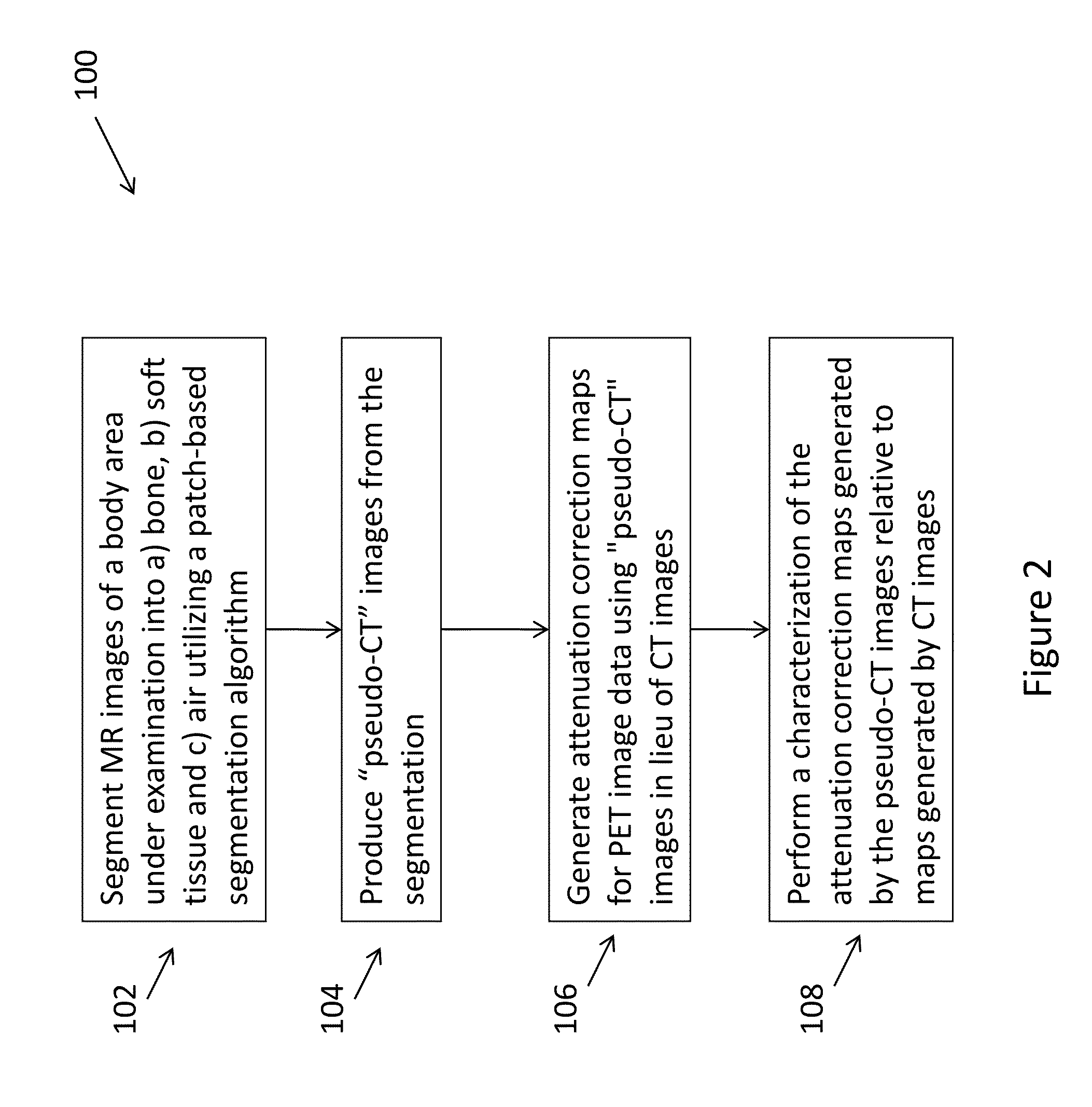
Method for creating attenuation correction maps for pet image reconstruction
A method (100) that generates attenuation correction maps for the reconstruction of PET data using MR images, such as, MR ultra-fast TE (UTE) images, Dixon MR images, as well as MR images obtained using other MR imaging methods.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for automated tracking of non-linear vessel movement using MR imaging
ActiveUS7209777B2Improve efficiencyEnhance the imageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLinear componentLinear motion
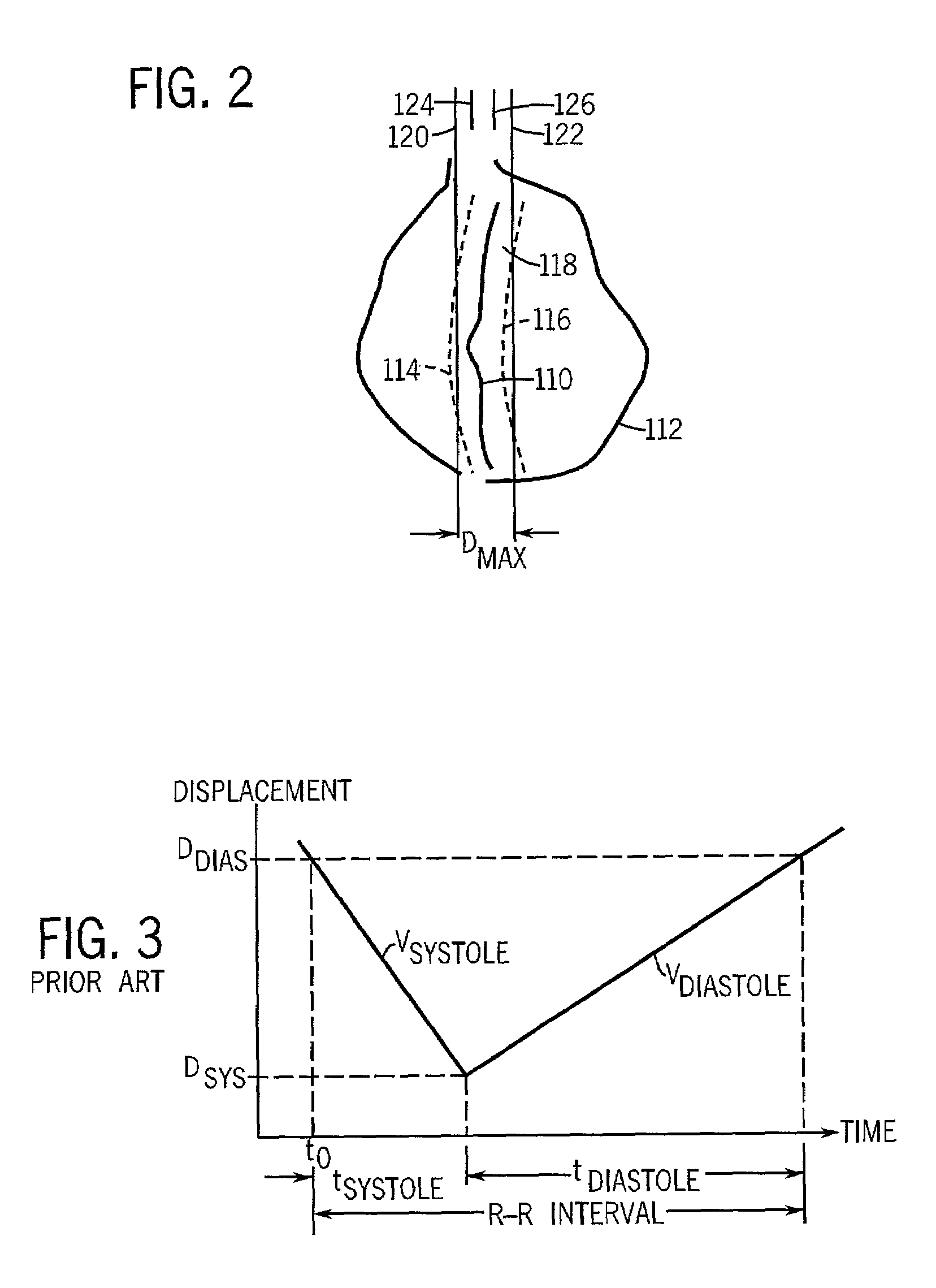
A system and method is disclosed for tracking a moving object using magnetic resonance imaging. The technique includes acquiring a scout image scan having a number of image frames and extracting non-linear motion parameters from the number of image frames of the scout image scan. The technique includes prospectively shifting slice location using the non-linear motion parameters between slice locations while acquiring a series of MR images. The system and method are particularly useful in tracking coronary artery movement during the cardiac cycle to acquire the non-linear components of coronary artery movement during a diastolic portion of the R—R interval.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Computerised Cortex Boundary Extraction From Mr Images
InactiveUS20080170791A1Improved and robust and accurateAccurate modelingImage enhancementImage analysisDigital dataData set
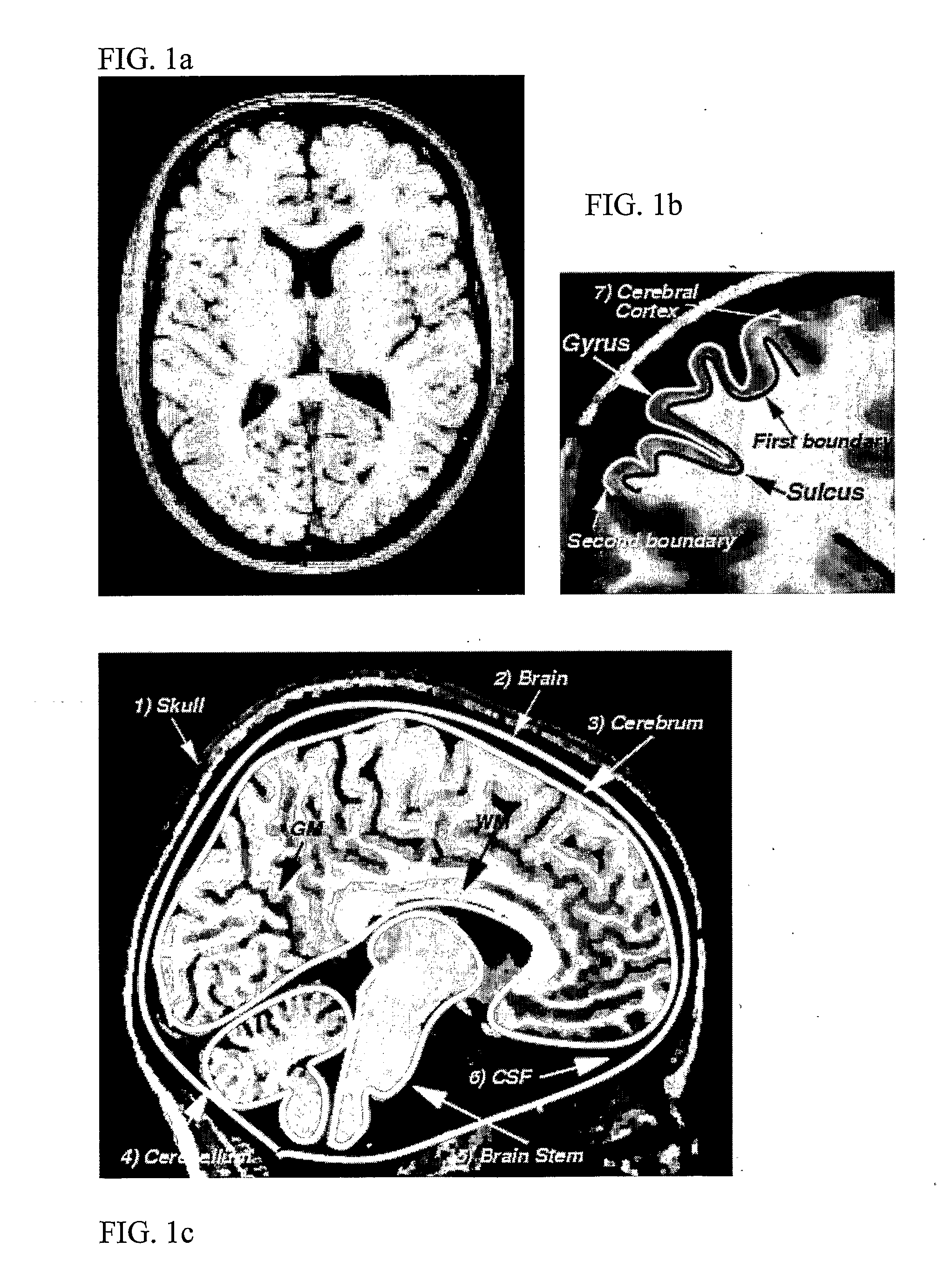
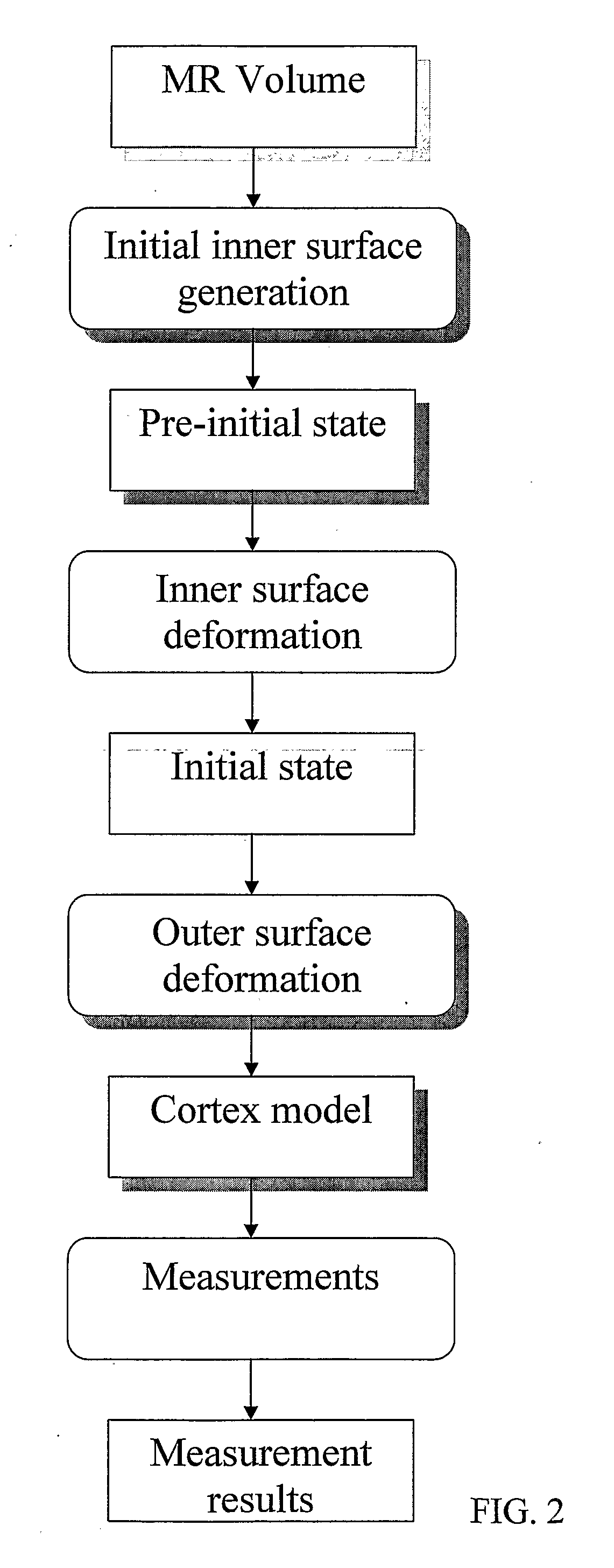
Method for processing digital images, such as magnetic resonance images of a brain. The images contain a first object, for example the cerebrum white matter, a second object, for example the cerebral cortex, and a third object, for example the cerebrospinal fluid. The method involves providing a digital dataset representing a deformable curve or surface that in an initial state approximates the boundary between the first object and the second object. Further, a vector force field is provided that for each point on the deformable curve or surface defines a direction from the point approximately towards the second boundary between the second and the third object, and this vector force field is applied for iteratively deforming the deformable curve or surface convergently towards the second boundary. In order to reconstruct a folded structure of the second object, for example the cortex, the vector force field also involves a normal vector field with a vector normal or approximately normal to the deformable curve or surface for each point on the deformable curve or surface.
Owner:AALBORG UNIV
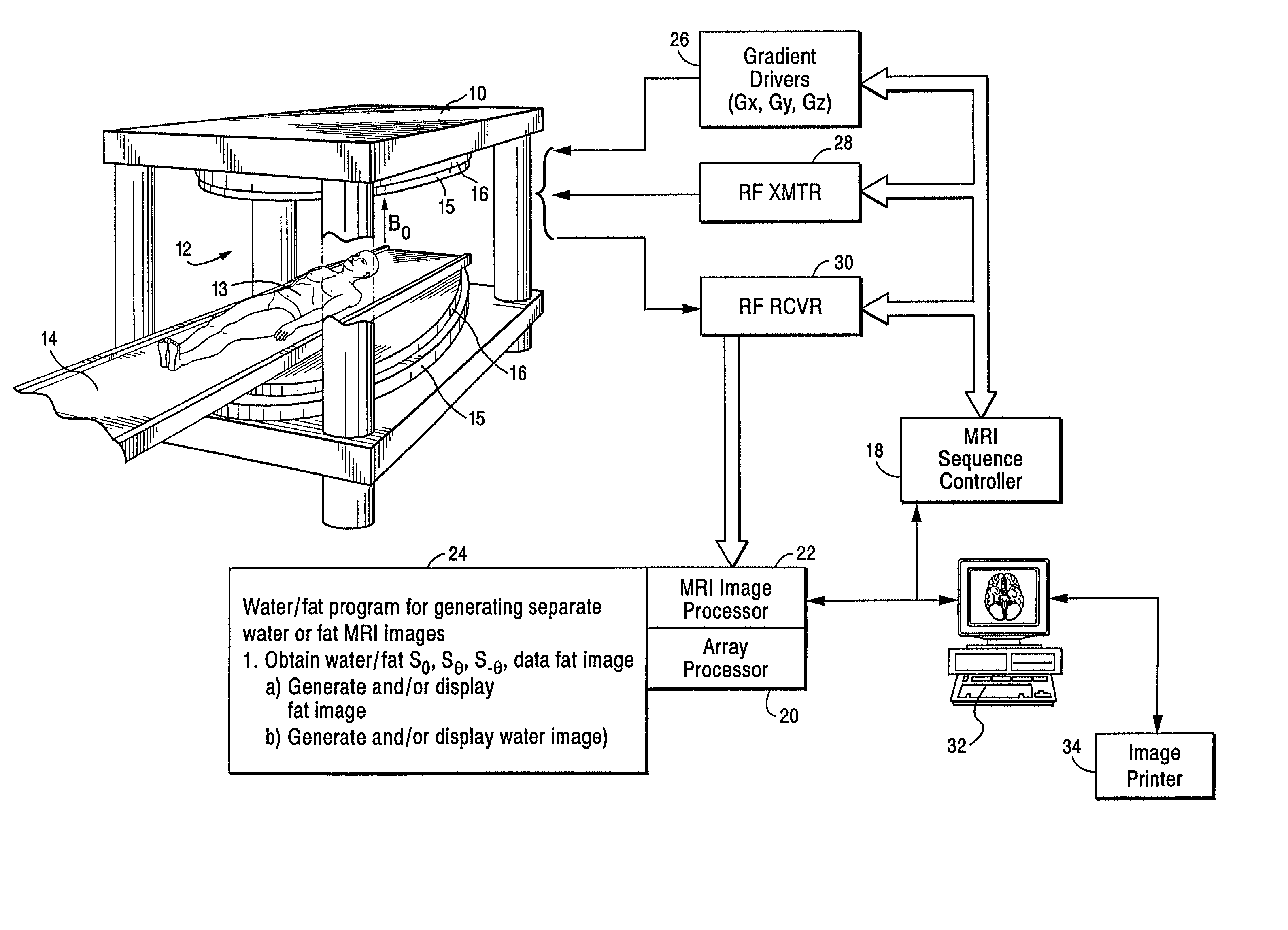
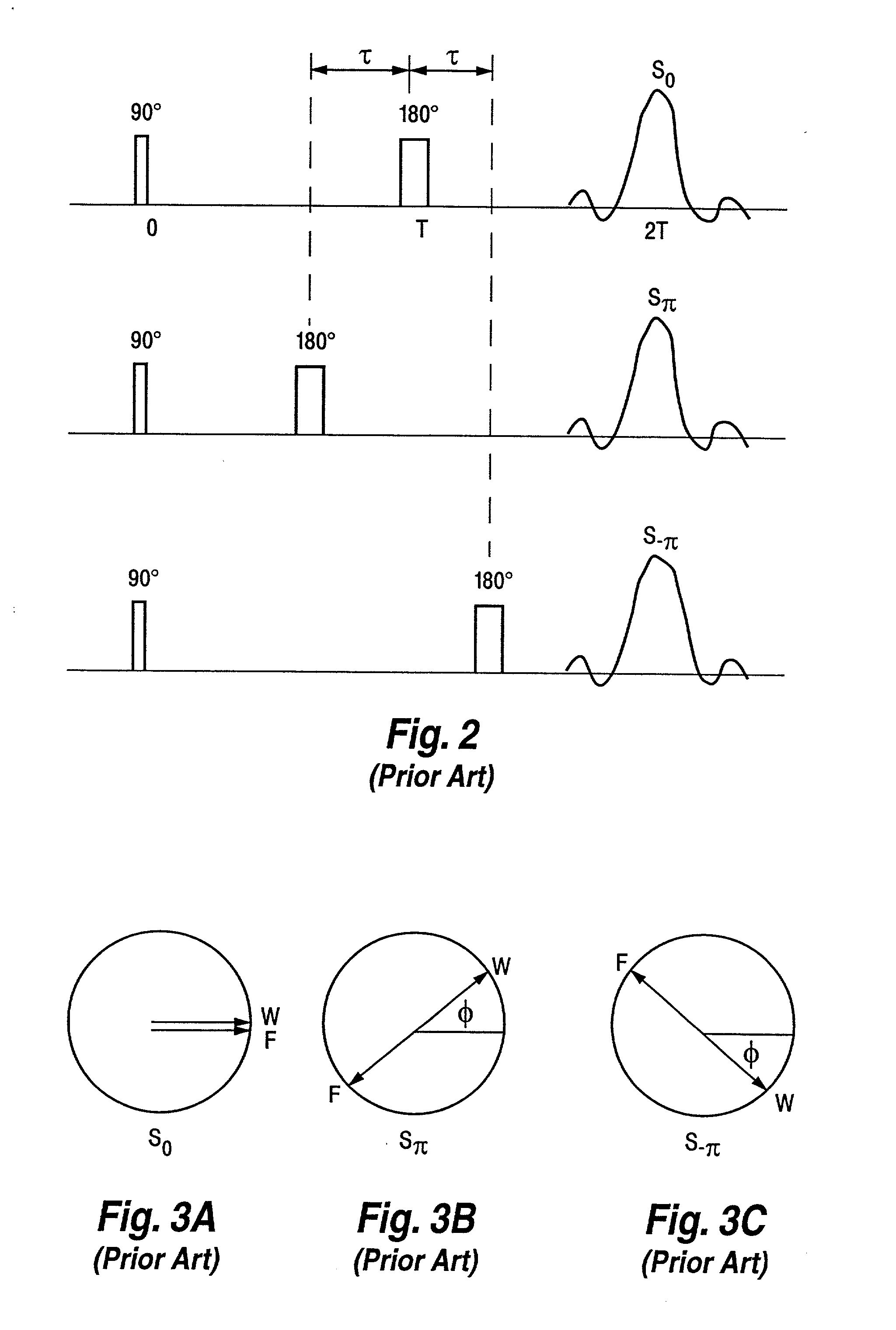
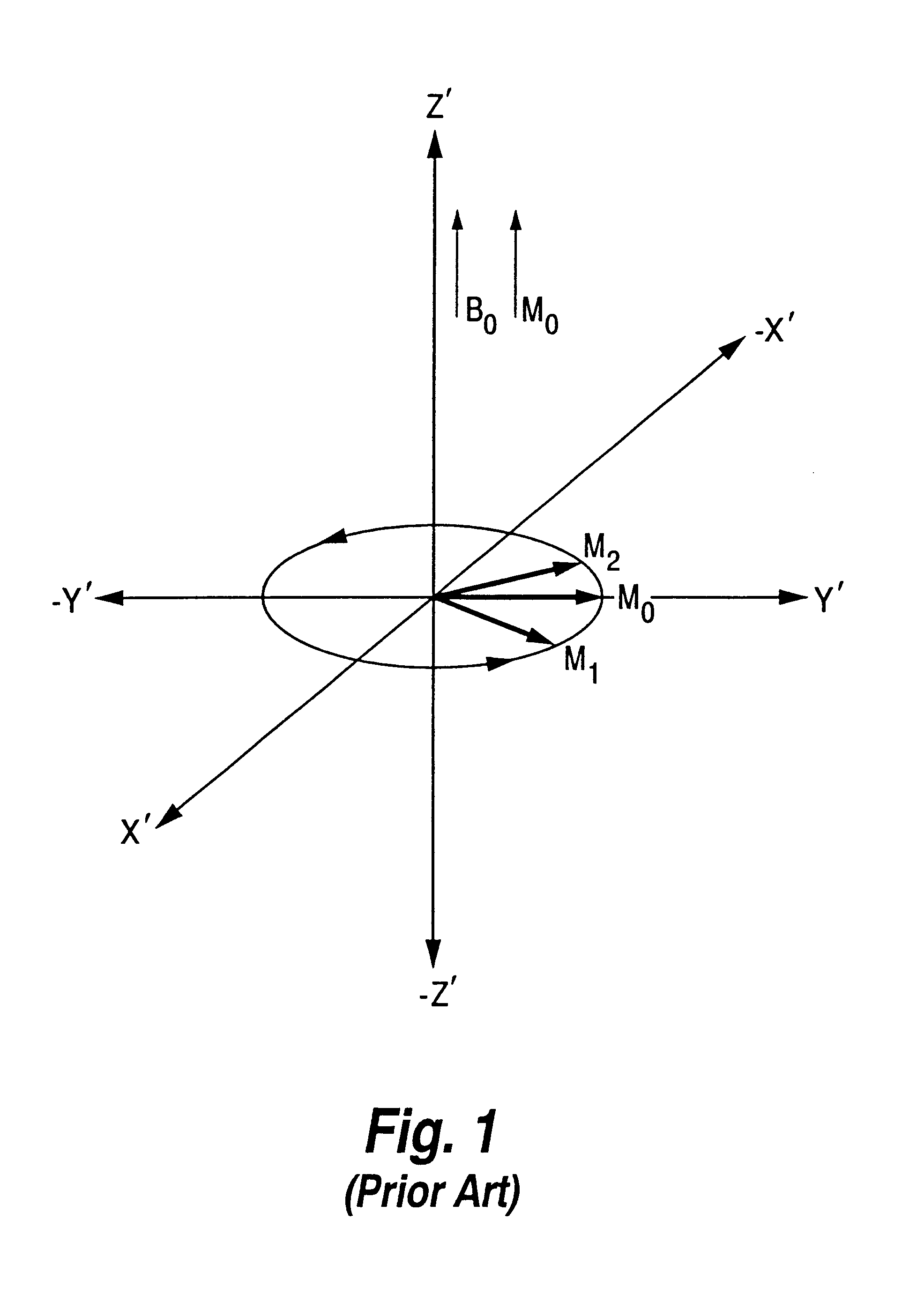
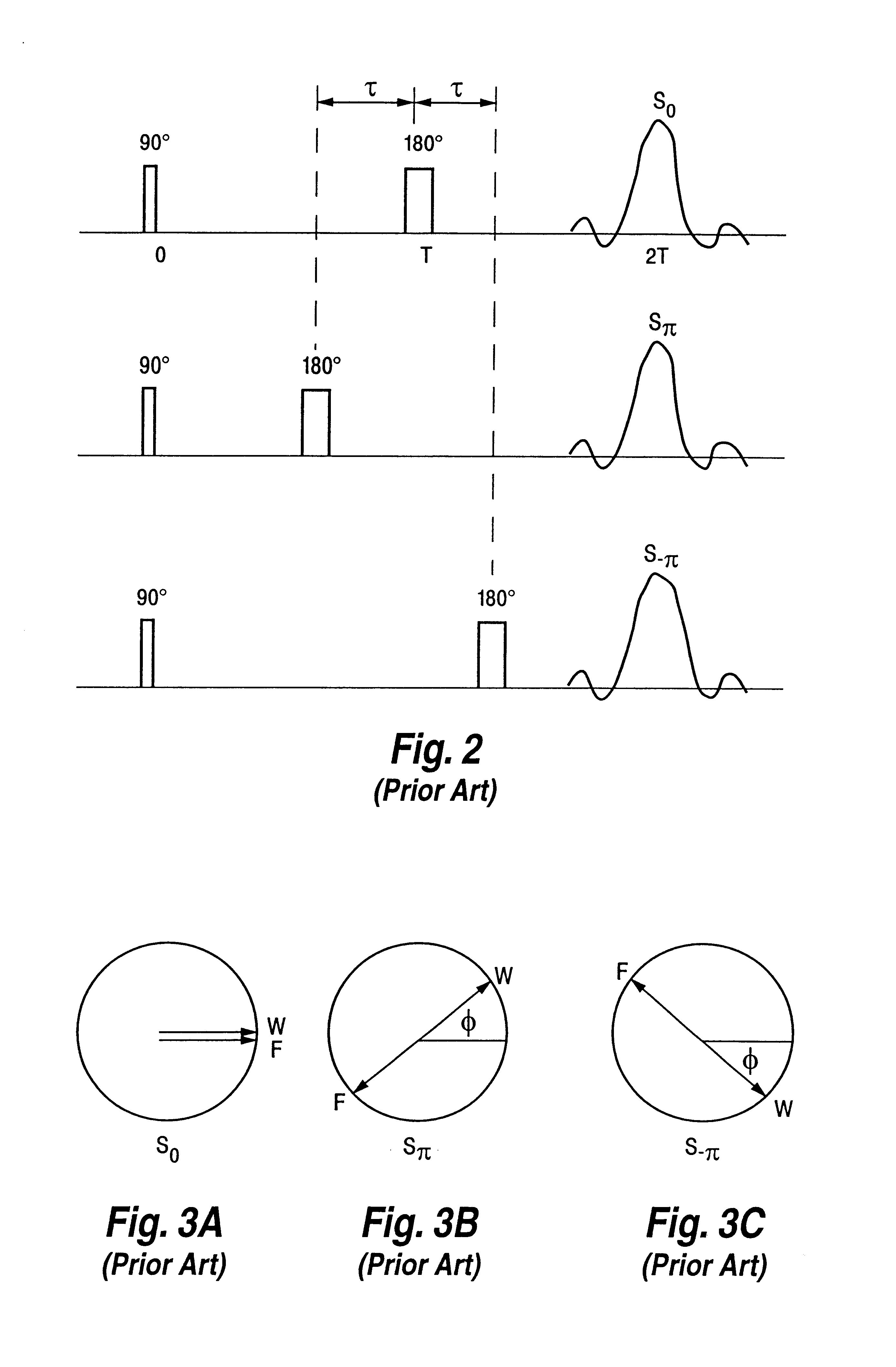
Separation and identification of water and fat MR images at mid-field strength with reduced T2/T2* weighting
InactiveUS20030060697A1Eliminate the effects ofCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringField strengthMr images
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method is disclosed for generating and identifying water and fat separated MR images. Image data is first acquired to obtain two echo images with the water and fat signals orthogonal in the first echo image, and parallel / anti-parallel in the second echo image. The effect of background field inhomogeneties are removed, and water and fat images are separated from each other. The separated water and fat images are identified according to the difference of their precessing frequencies.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
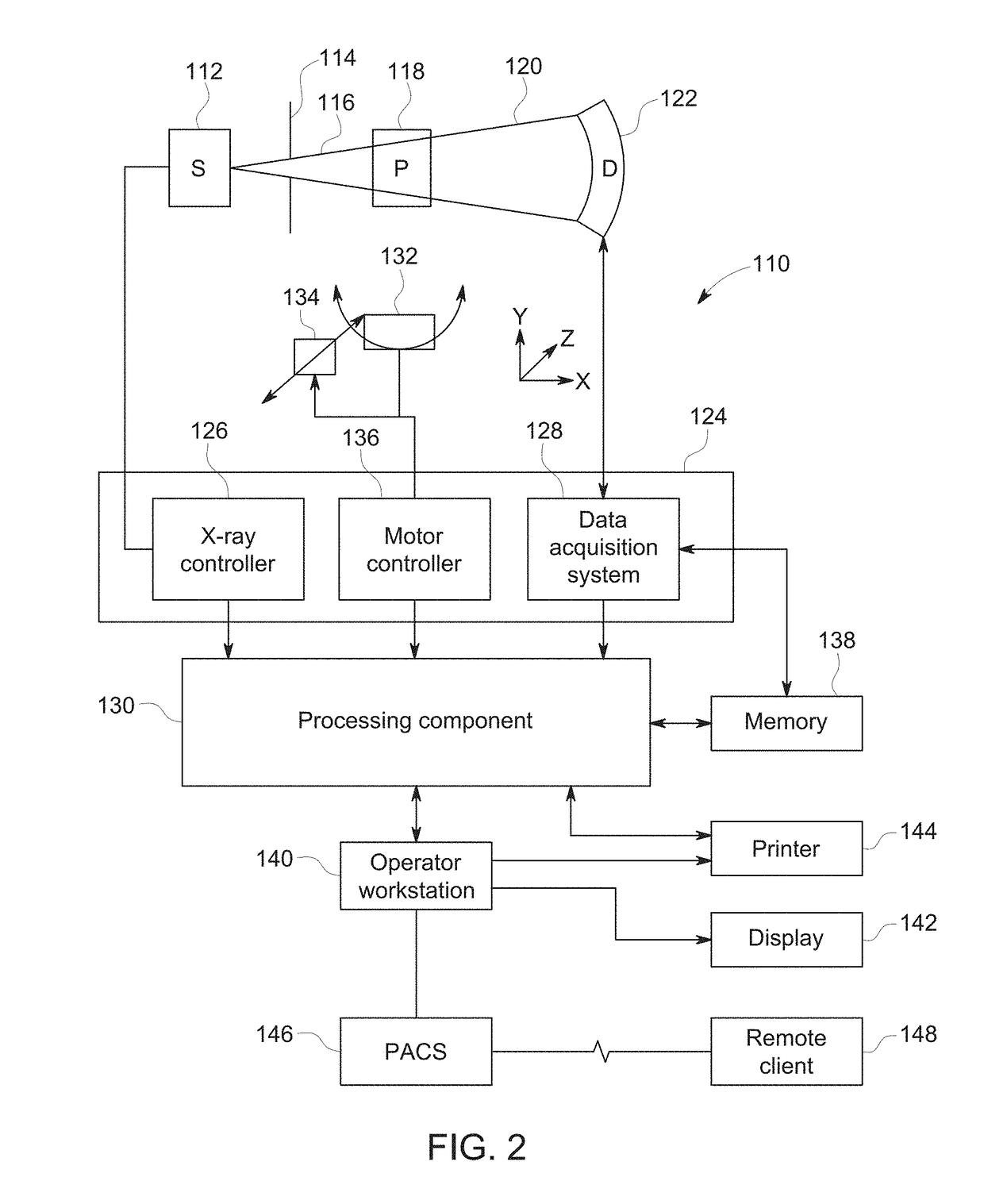
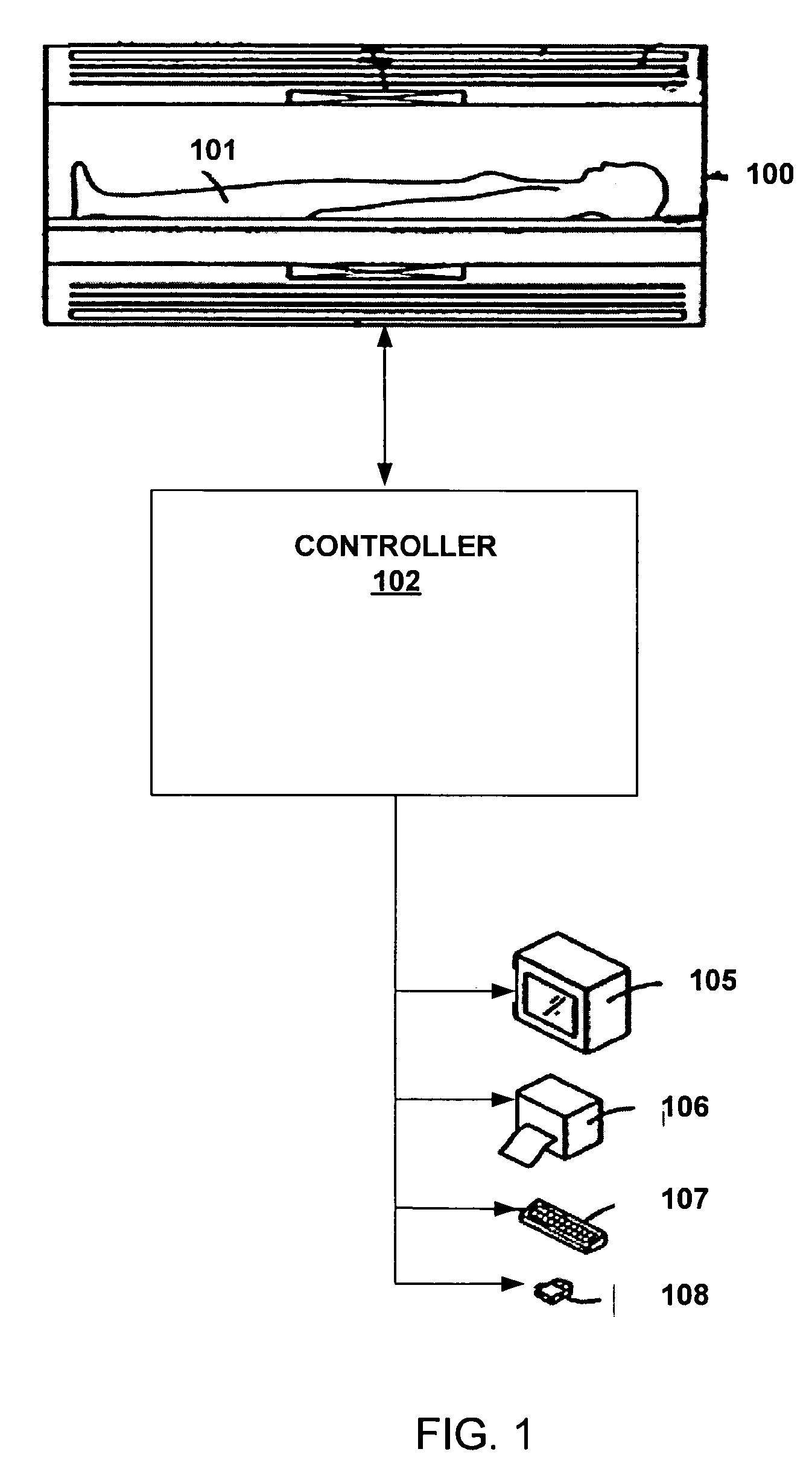
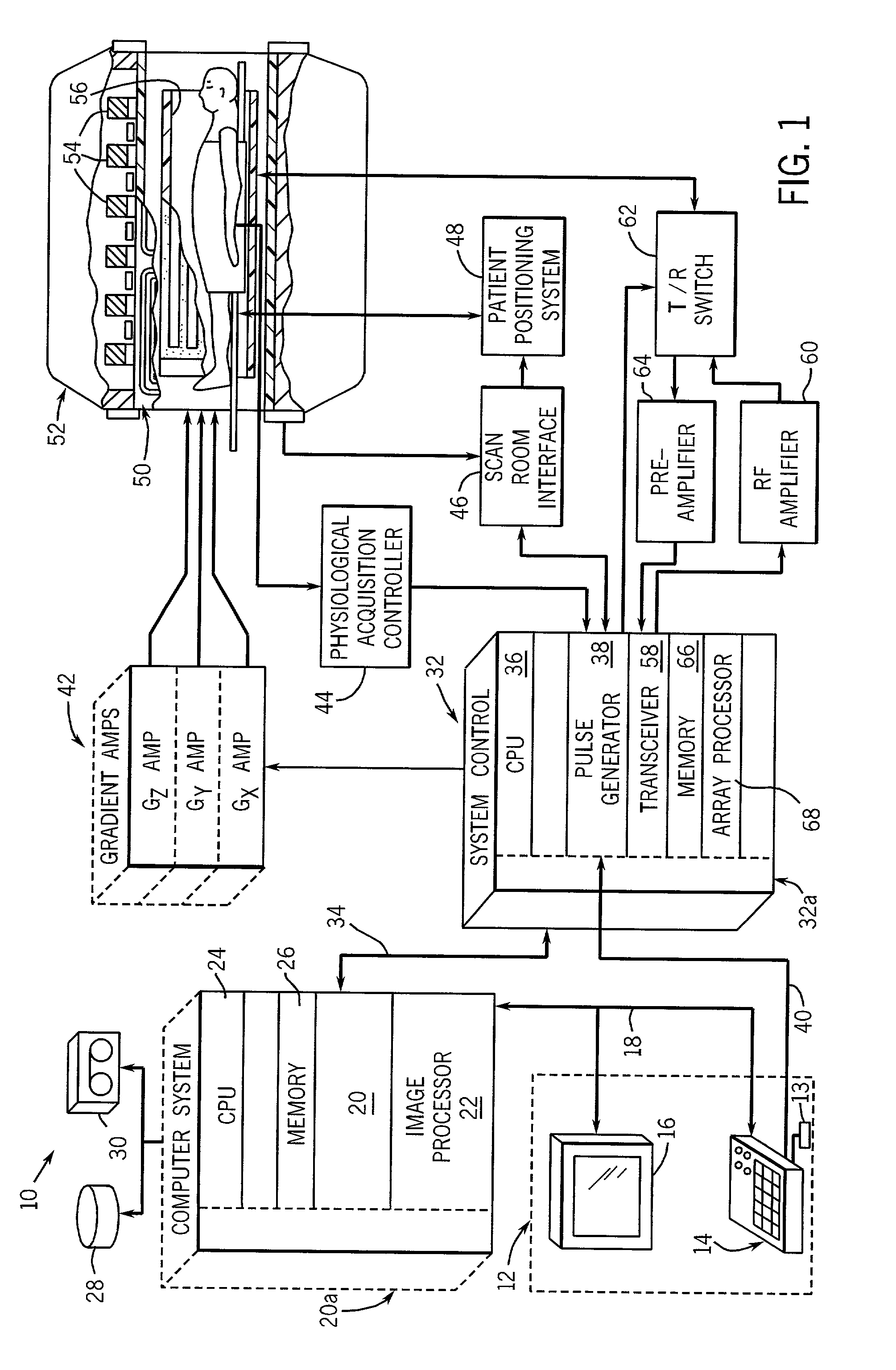
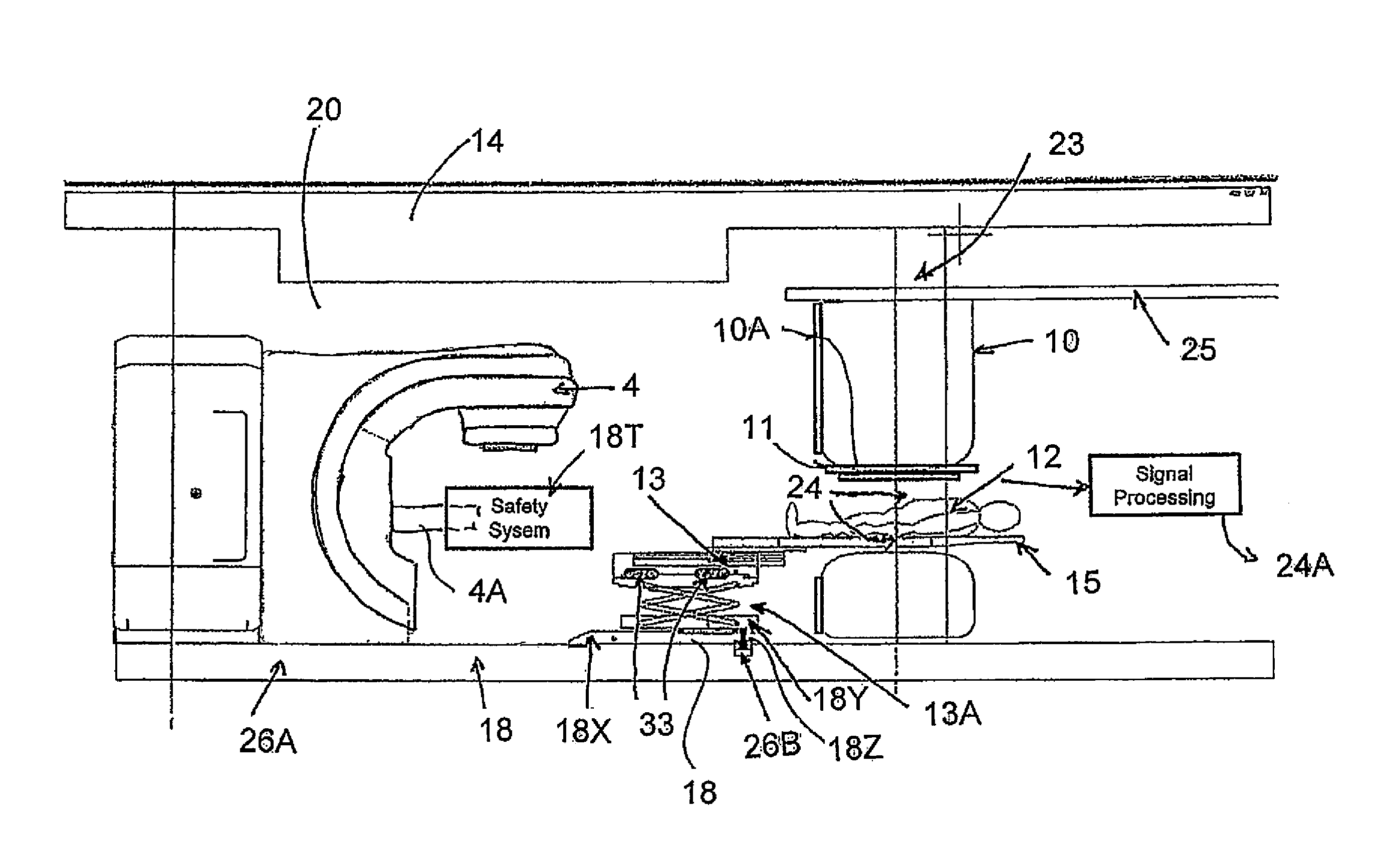
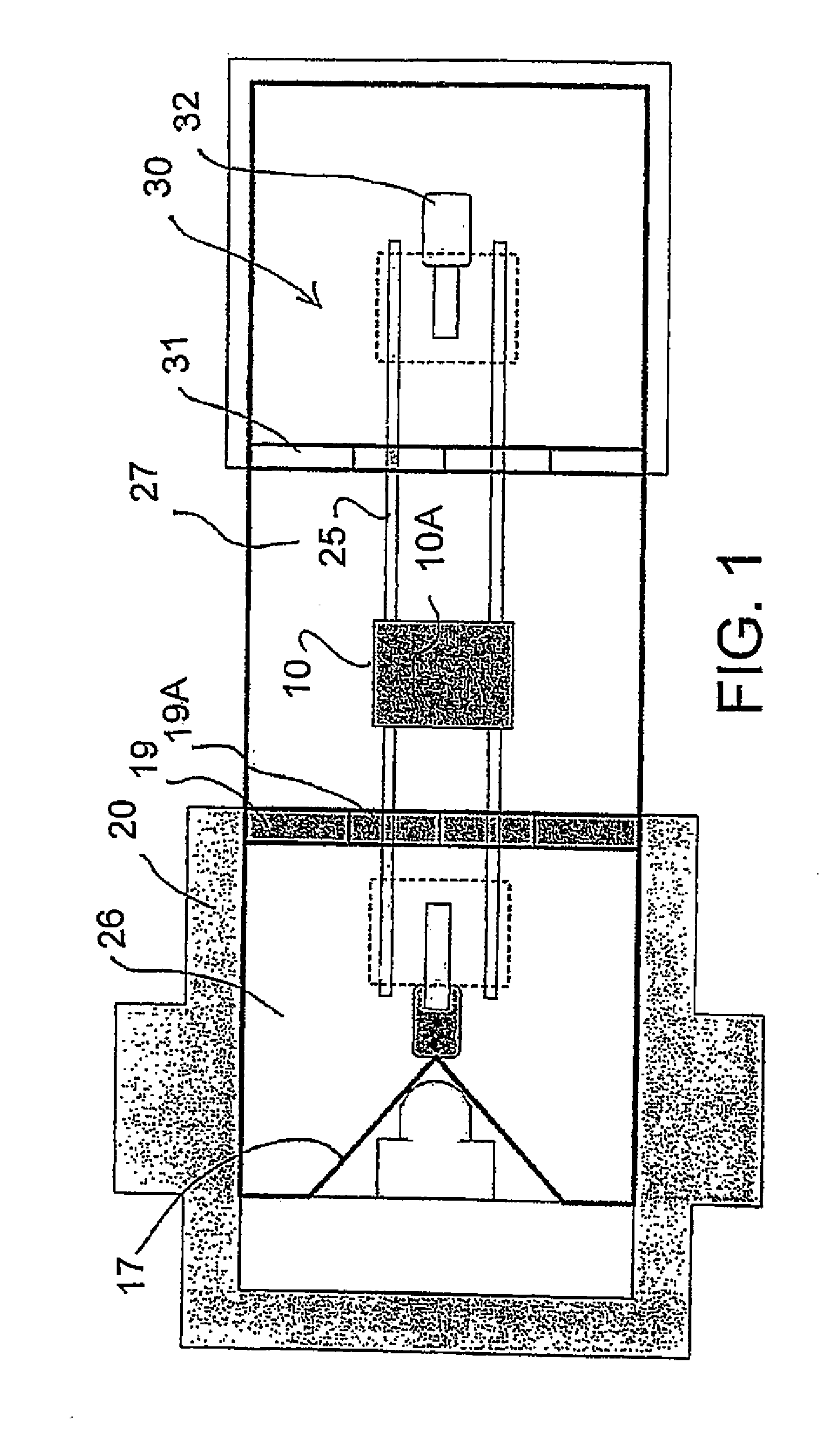
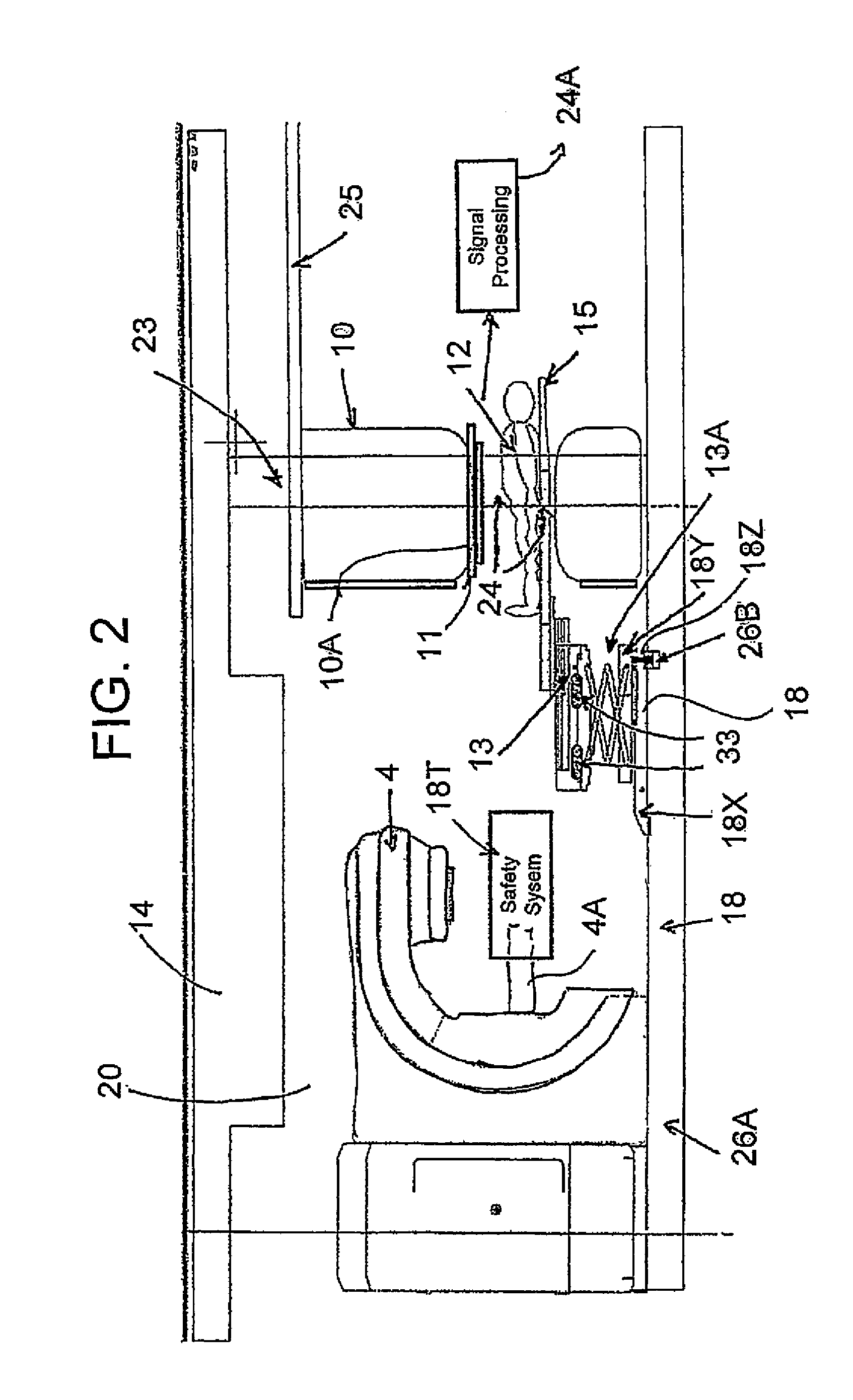
Patient Alignment in MRI Guided Radiation Therapy
InactiveUS20130235969A1Simple methodSharp contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMri guidedTransformation algorithm
Apparatus for radiation therapy combines a patient table, an MRI and a radiation treatment apparatus mounted in a common treatment room with the MR magnet movable through a radiation shielded door to an imaging position. An initial MR image and an initial X-ray image is used to generate an RT program for the patient to be carried out in a plurality of separate treatment steps. Before carrying out the procedure, a registration step is performed using a phantom by which X-ray images are registered relative to MR images to generate a transformation algorithm required to align the MR images of the part of the patient relative to the X-ray images. Prior to each separate treatment step a current MR image of the part of the patient is obtained and the transformation algorithm data is used from the current MR image is used in guiding the RT treatment step.
Owner:IMRIS
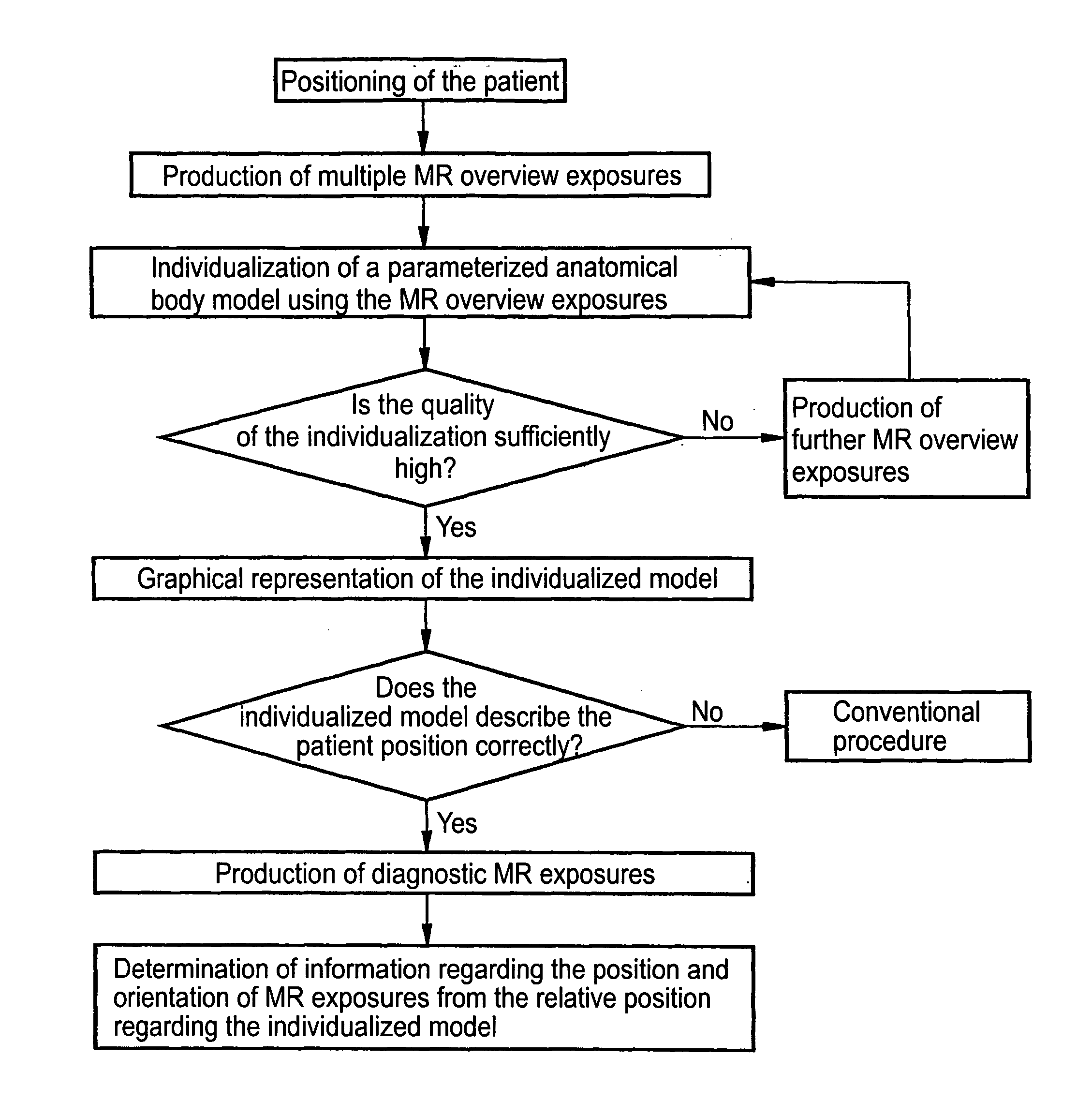
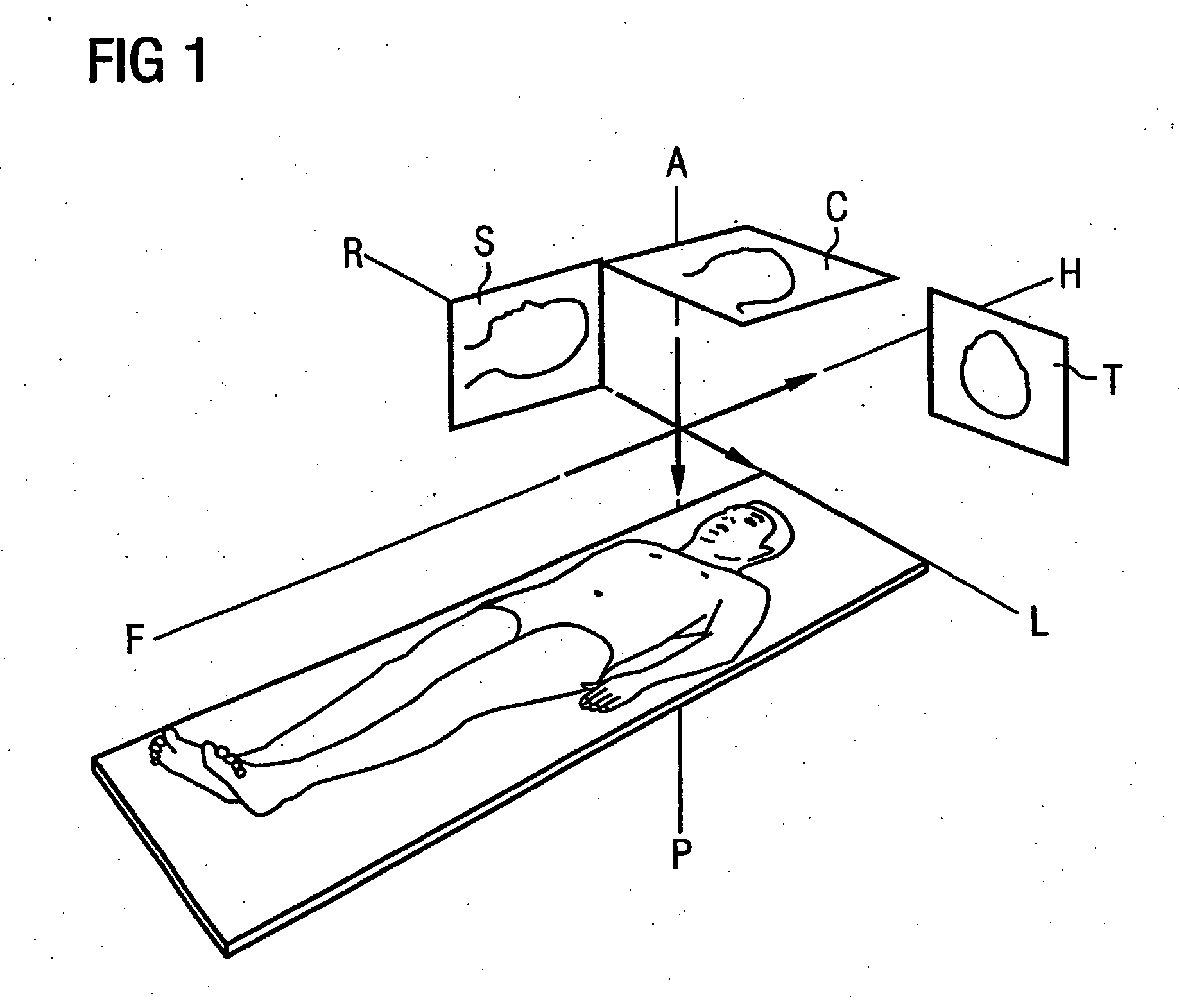
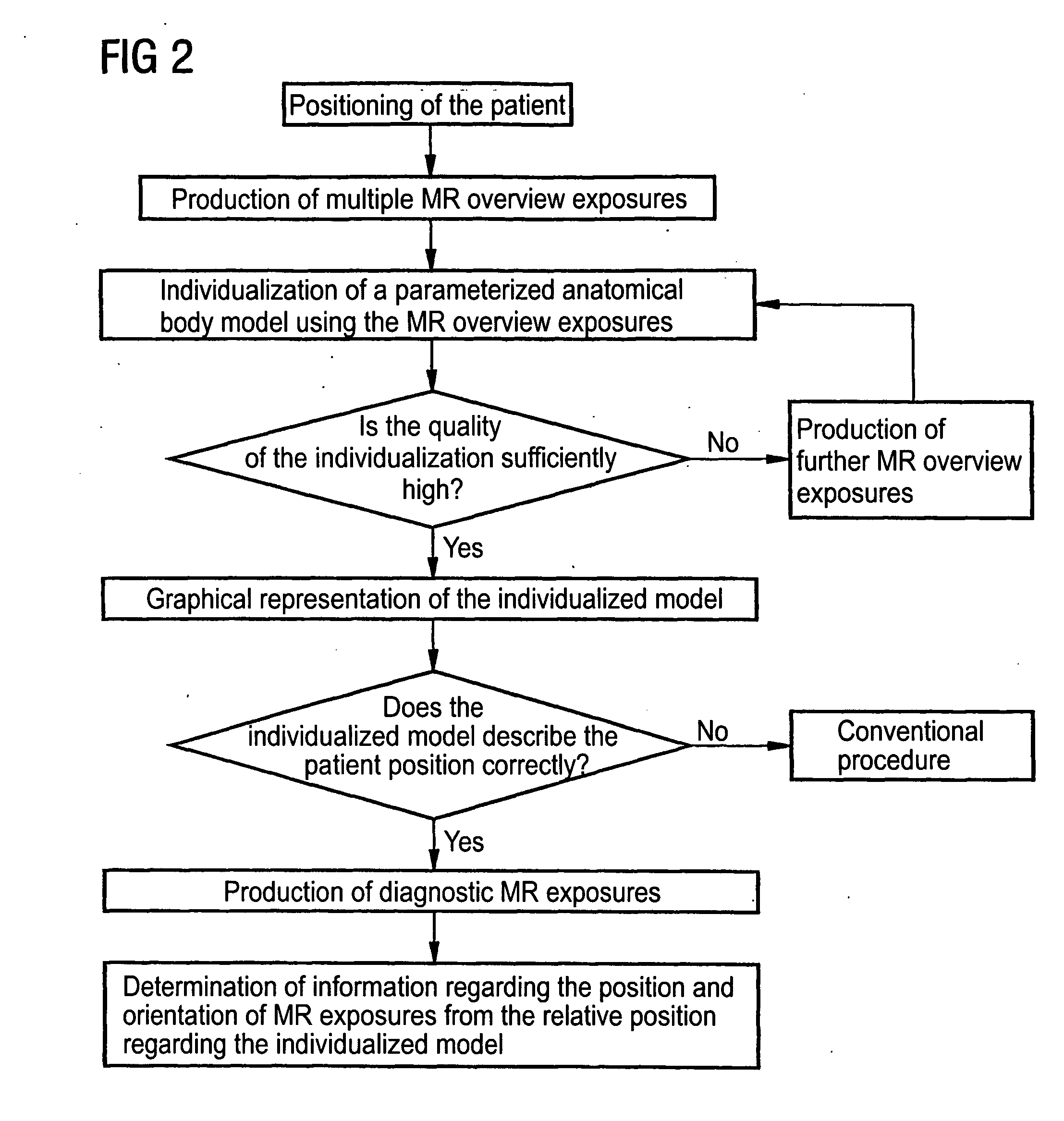
Determining patient-related information on the position and orientation of MR images by the individualisation of a body model
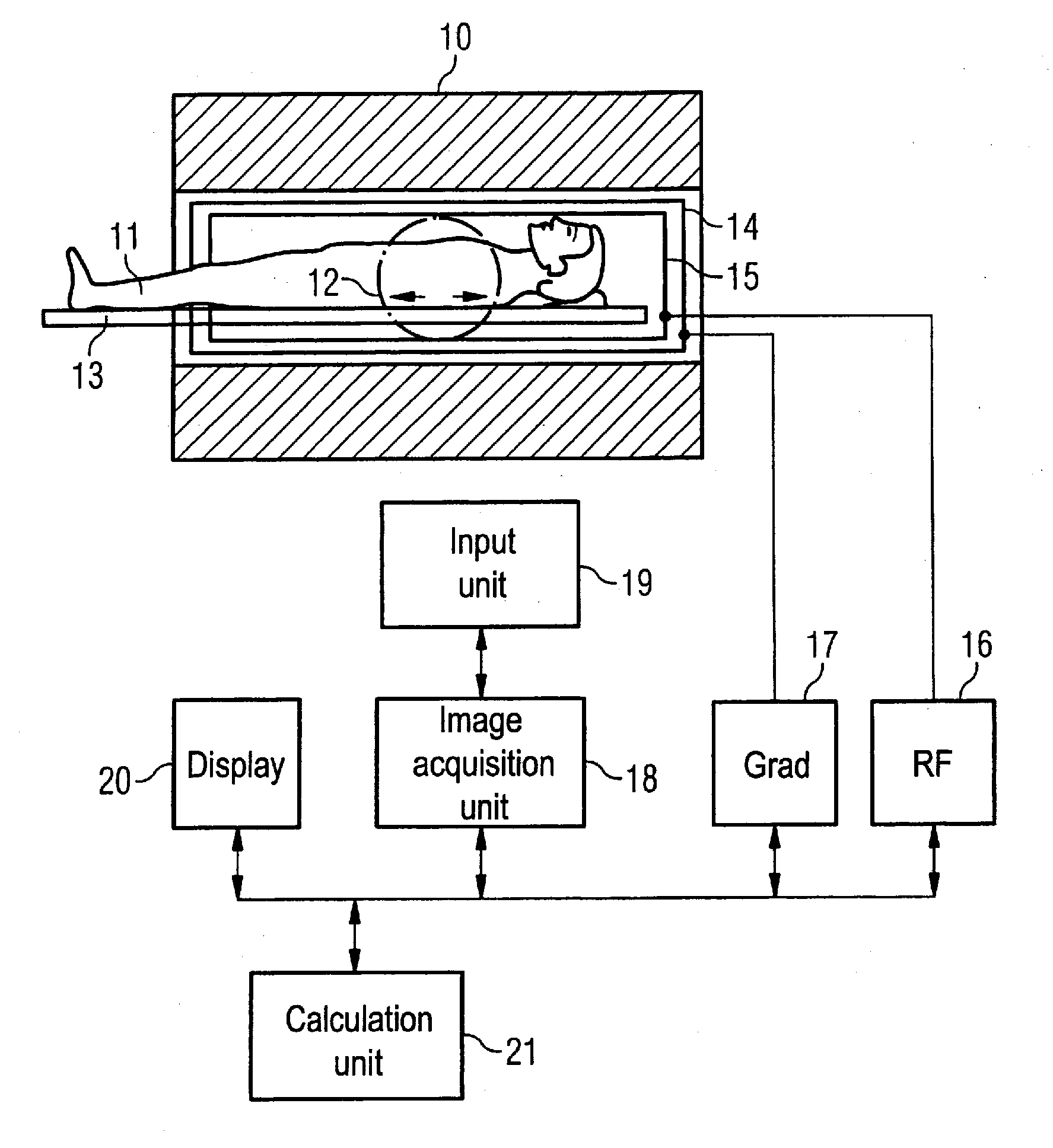
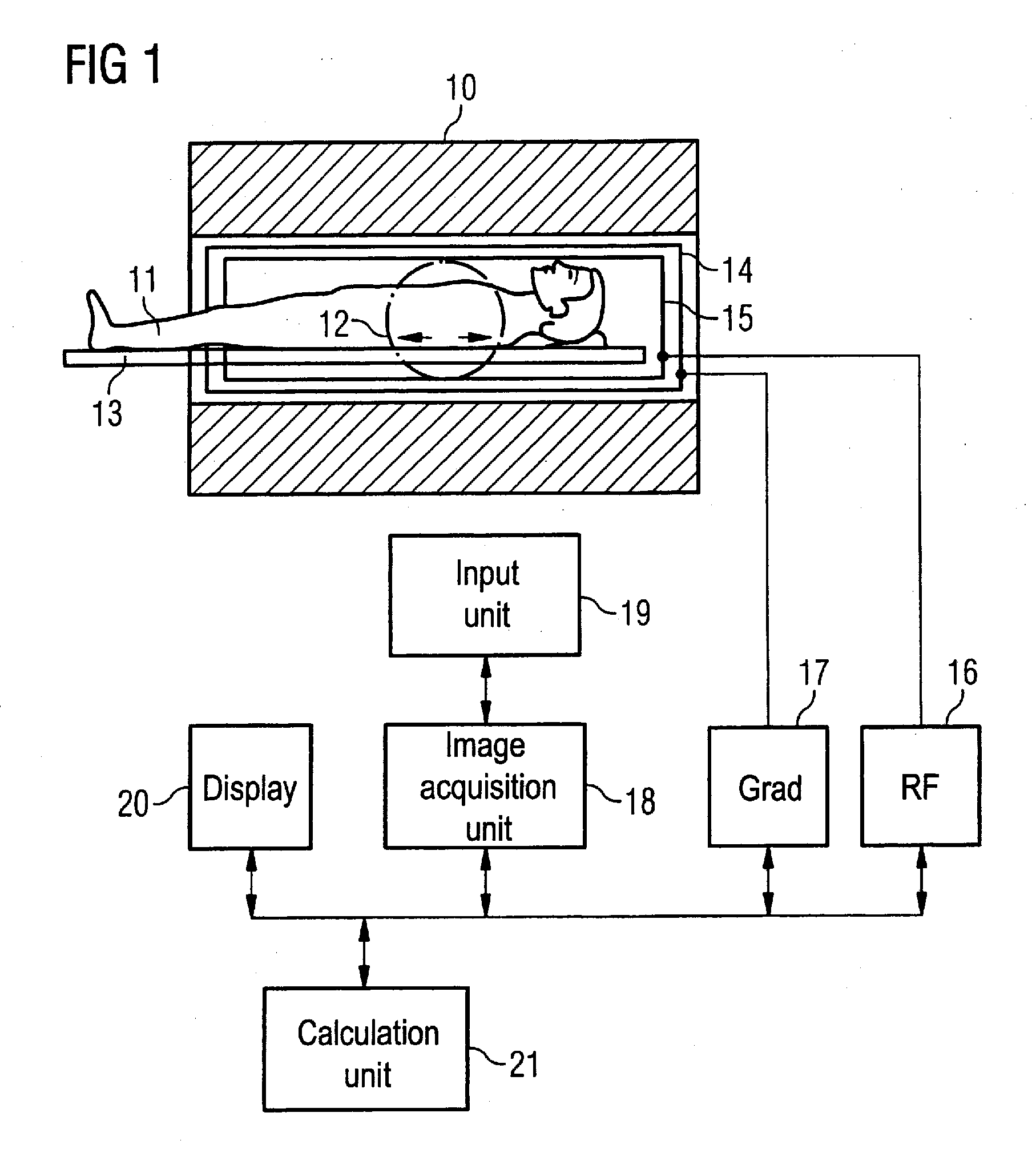
In a method for determination of patient-related information regarding the position and orientation of slice image exposures in magnetic resonance tomographic examinations, initial MR overview exposures (magnetic resonance overview exposures) of the body of the patient are produced. Using these initial MR overview exposures, a predetermined, parameterized anatomical body model (i.e. an anatomical body model) with specific variable model parameters is then individualized (customized). The determination of the patient-related information about the position and orientation of the subsequent (diagnostic) slice image exposures then ensues on the basis of the relative position of the slice image exposures with regard to the individualized body model. In the individualization, by variation of the model parameters the body model is adapted to specific structures determined from the initial MR overview exposures, which specific structures advantageously represent the body surface of the patient. The individualization process thereby corresponds to a mathematical optimization problem. Those values of the variable model parameters are determined that minimize a deviation measure of the model relative to the structures from the overview exposures.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
System and method to analyze blood parameters using magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20100030062A1Accurate measurementClear attributionMagnetic measurementsSensorsVascular compartmentCerebral metabolic rate
A system and method for accurately producing MR images of selected vascular compartments includes employing a control scan and a tag scan, each including velocity selective modules that suppress signal from blood flowing faster than a given cutoff velocity, to acquire control and tag sets of NMR data that may be subtracted to produce a compartment-specific MR image that is substantially free of information from stationary tissues and blood outside the selective vascular compartments. Accordingly, physiological parameters, such as oxygen saturation (SaO2), oxygen extraction fraction (OEF), and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2), can be generated from the compartment-specific images. Further still, kinetic curves of oxygen exchange can be created, thus providing detailed insight into oxygen exchange dynamics.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Vessel segmentation in dce mr imaging
ActiveUS20110170759A1Improve diagnostic accuracyMaximise variationImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsDynamic contrast
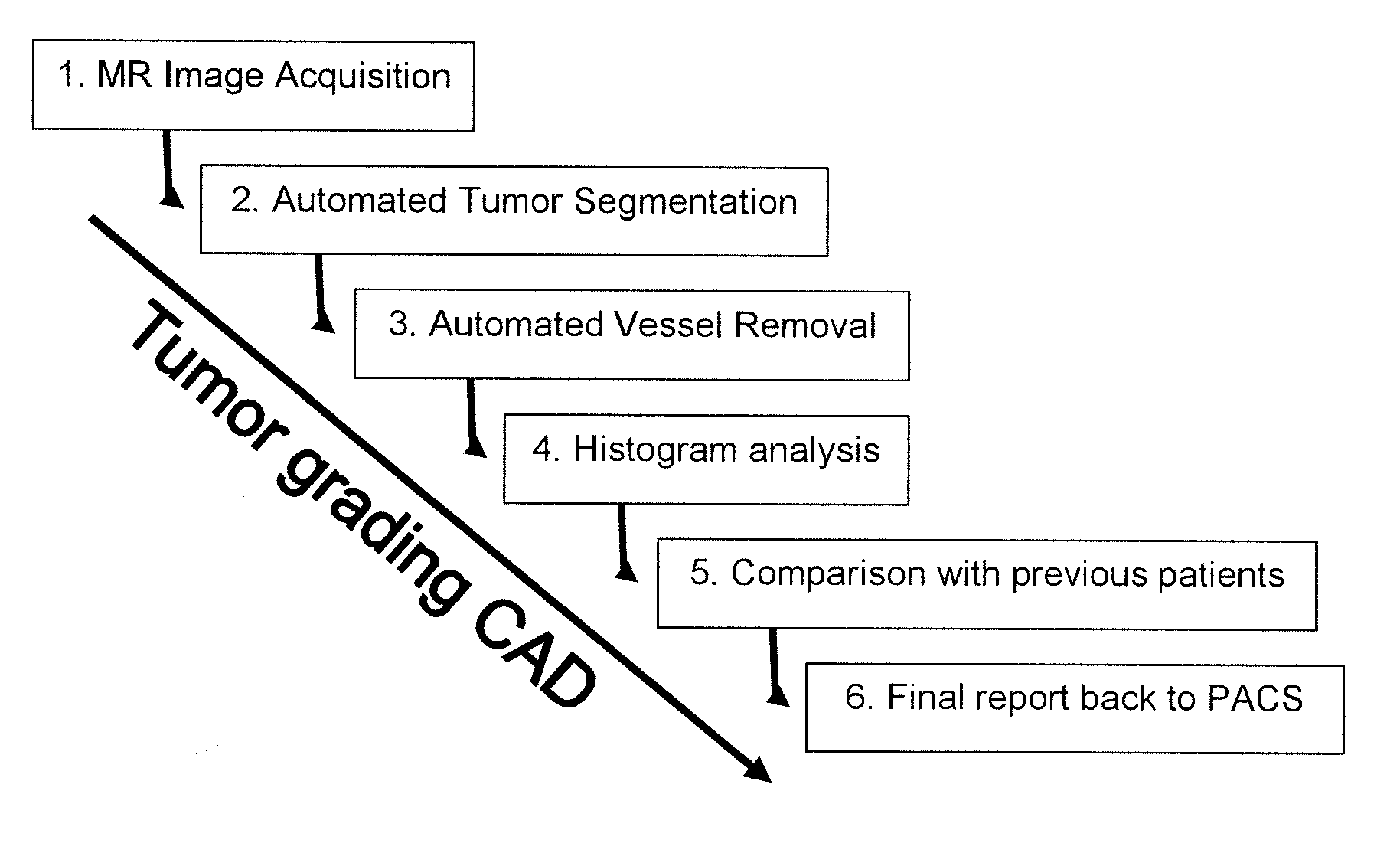
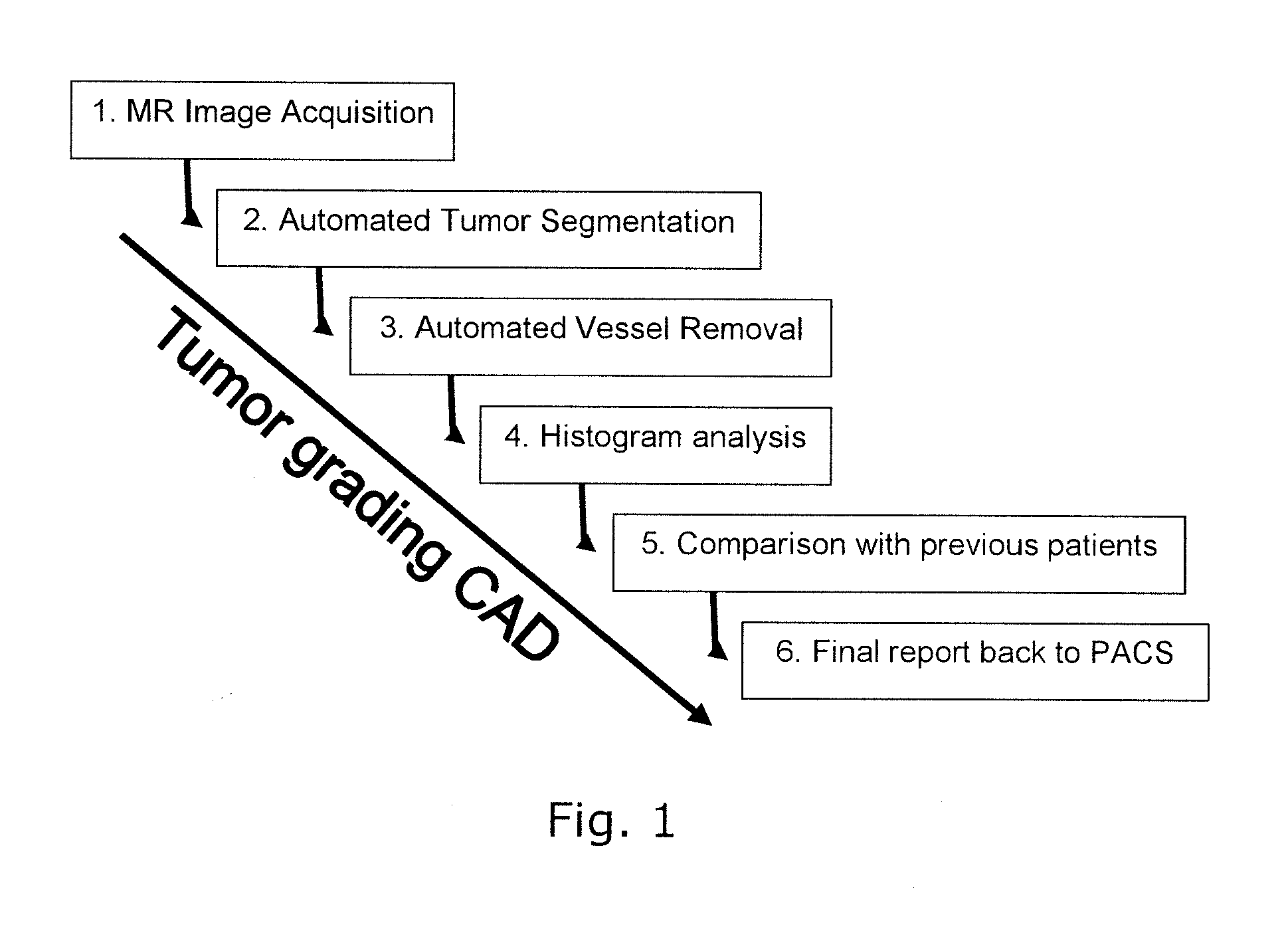
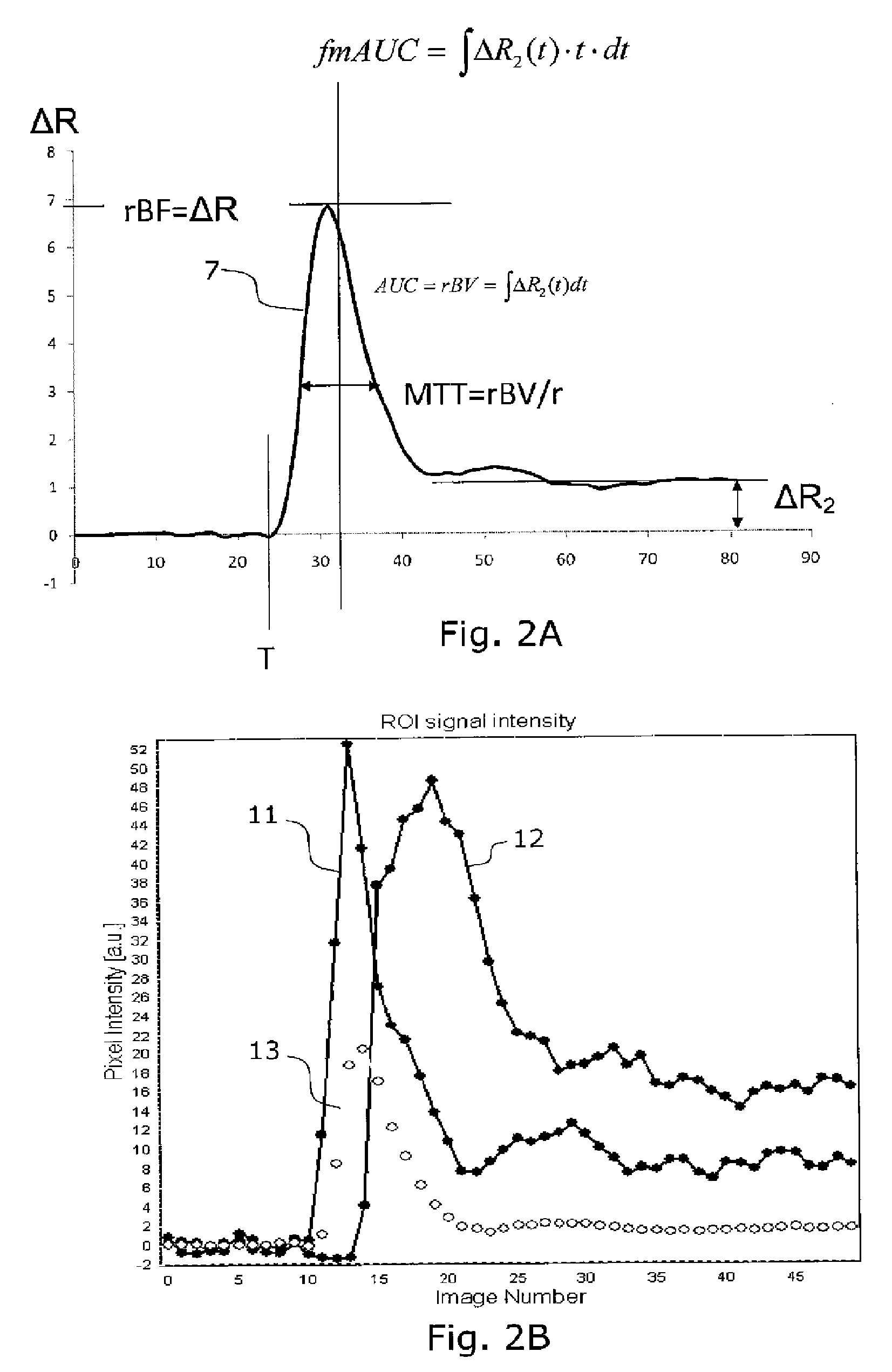
The invention relates to segmenting blood vessels in perfusion MR images, more particularly, the invention relates to automated vessel removal in identified tumor regions prior to tumor grading. Pixels from a perfusion related map from dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE) MR images are clustered into arterial pixels and venous pixels by e.g. a k-means class cluster analysis. The analysis applies parameters representing the degree to which the tissue entirely consists of blood (such as relative blood volume (rBV), peak enhancement (ΔR2max) and / or post first-pass enhancement level (ΔR2p)) and parameters representing contrast arrival time at the tissue (such as first moment of the area (fmAUC) and / or contrast arrival time (T0)). The artery and venous pixels are used to form a vessel mask. The invention also relates to a computer aided diagnostic (CAD) system for tumor grading, comprising automated tumor segmentation, vessel segmentation, and tumor grading.
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
Combined pet/mrt unit and method for simultaneously recording pet images and mr images
A combined PET / MRT unit is disclosed that includes a PET detector which is reduced by comparison with the prior art, and that consists, for example, of a PET detector with a polygonal arrangement of the detector elements or with a PET detector ring. The PET detector is reduced in an axial direction by comparison with the detectors of the prior art, as a result of which the costs for producing the expensive PET detectors are lowered. The reduction of the PET detector is possible because the MR measurement usually lasts longer than the PET measurement, and so a reduced PET detector can be used for the temporally sequential recording of a number of PET tomograms by mechanical displacement of the PET detector. Since the MR measurement lasts substantially longer, this mechanical displacement does not lead to a lengthening of the measuring time. The invention also relates to methods for simultaneously recording MR and PET tomograms in which the PET / MRT units according to the invention are used.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
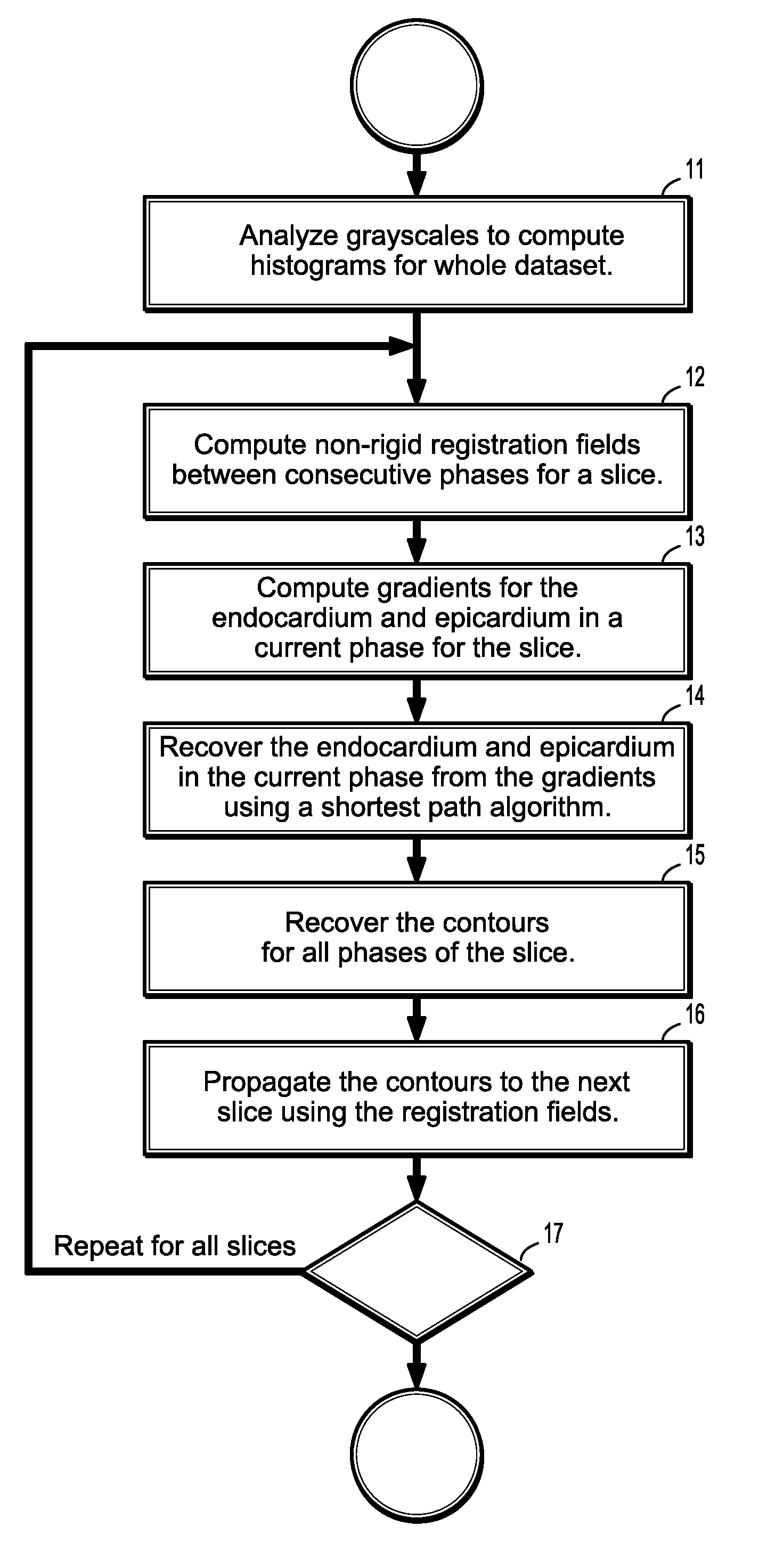
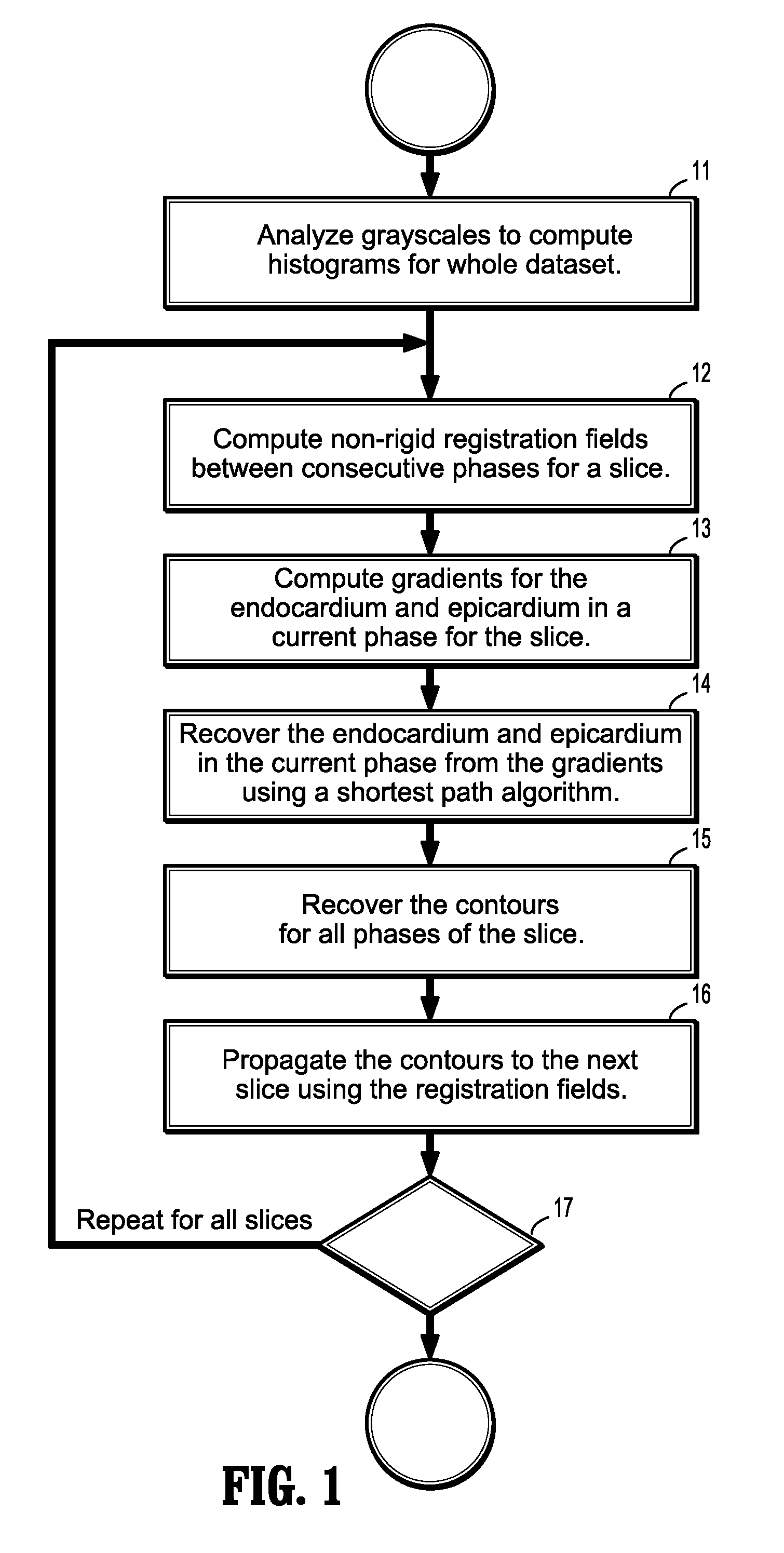
System and method for cardiac segmentation in mr-cine data using inverse consistent non-rigid registration
InactiveUS20110081066A1Guaranteed to be accurate and consistentImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageCardiac cycle
A method for cardiac segmentation in magnetic resonance (MR) cine data, includes providing a time series of 3D cardiac MR images acquired at a plurality of phases over at least one cardiac cycle, in which each 3D image includes a plurality of 2D slices, and a heart and blood pool has been detected in each image. Gray scales of each image are analyzed to compute histograms of the blood pool and myocardium. Non-rigid registration deformation fields are calculated to register a selected image slice with corresponding slices in each phase. Endocardium and epicardium gradients are calculated for one phase of the selected image slice. Contours for the endocardium and epicardium are computed from the gradients in the one phase, and the endocardium and epicardium contours are recovered in all phases of the selected image slice. The recovered endocardium and epicardium contours segment the heart in the selected image slice.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
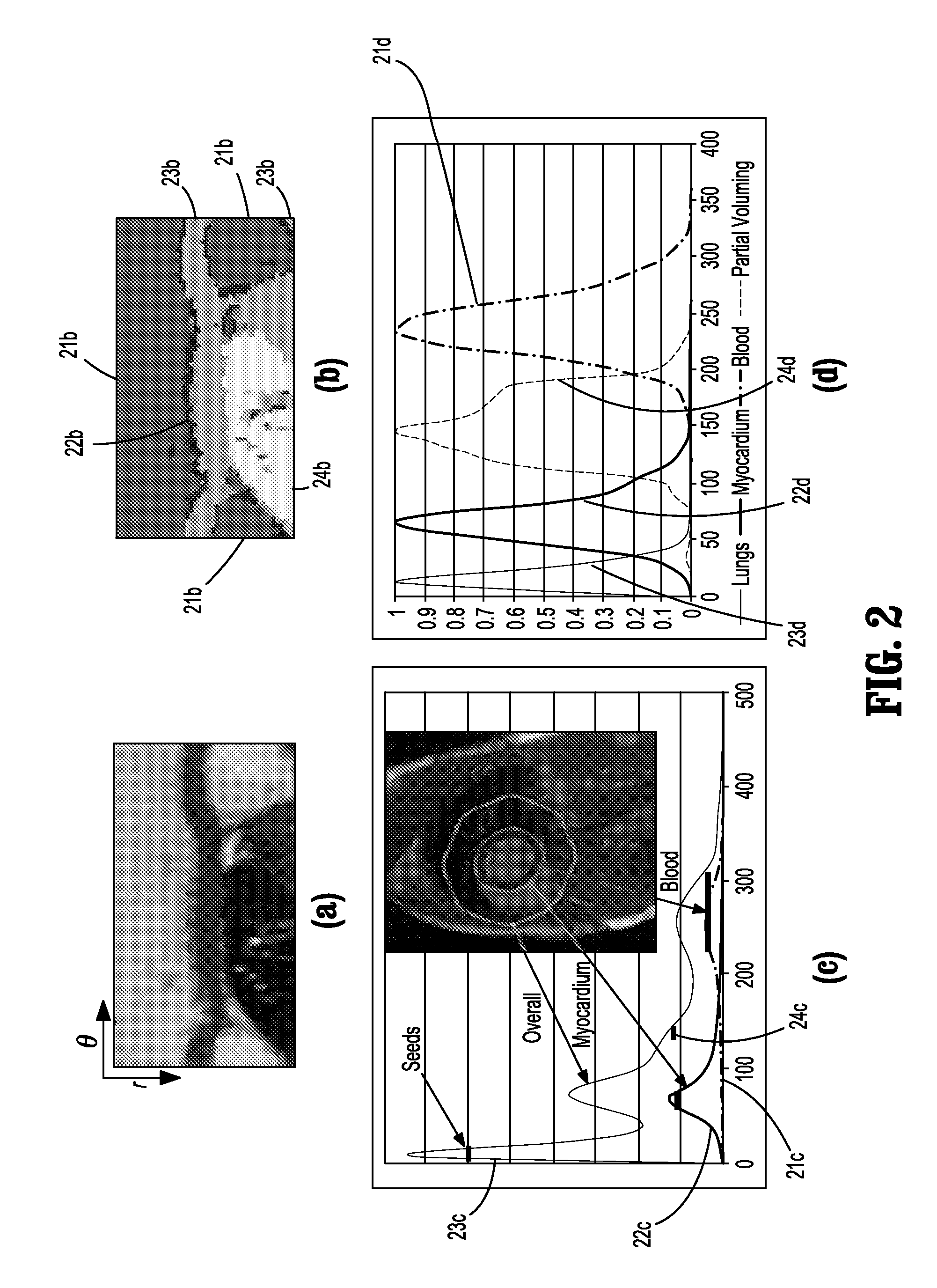
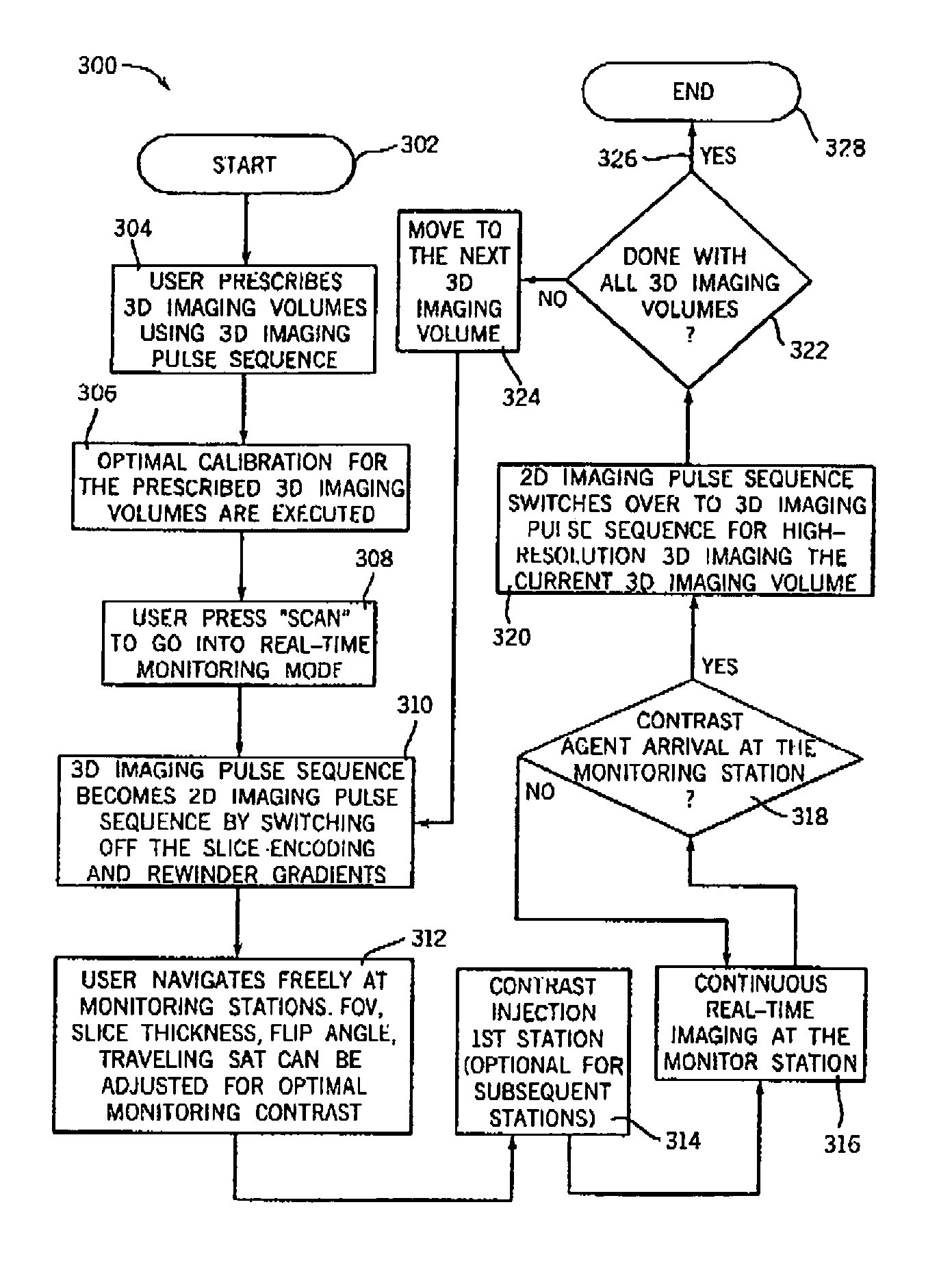
Real-time localization, monitoring, triggering and acquisition of 3D MRI
A technique embodied in a method and apparatus is disclosed for acquiring MR images in 2D and 3D using a common pulse sequence switchable in real-time. The technique includes identifying a 3D imaging volume and applying a 3D pulse sequence having the slice encoding and rewinder gradients disabled in one dimension. The technique then allows localizing and monitoring by acquiring 2D MR data. When it is desirable to enter a 3D imaging mode, the slice encoding and rewinder gradients are re-enabled in the common pulse sequence for acquisition of 3D MR data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and magnetic resonance system to optimize mr images
InactiveUS20090069668A1Simple procedureThe way is simple and fastImage enhancementImage analysisResonanceMri image
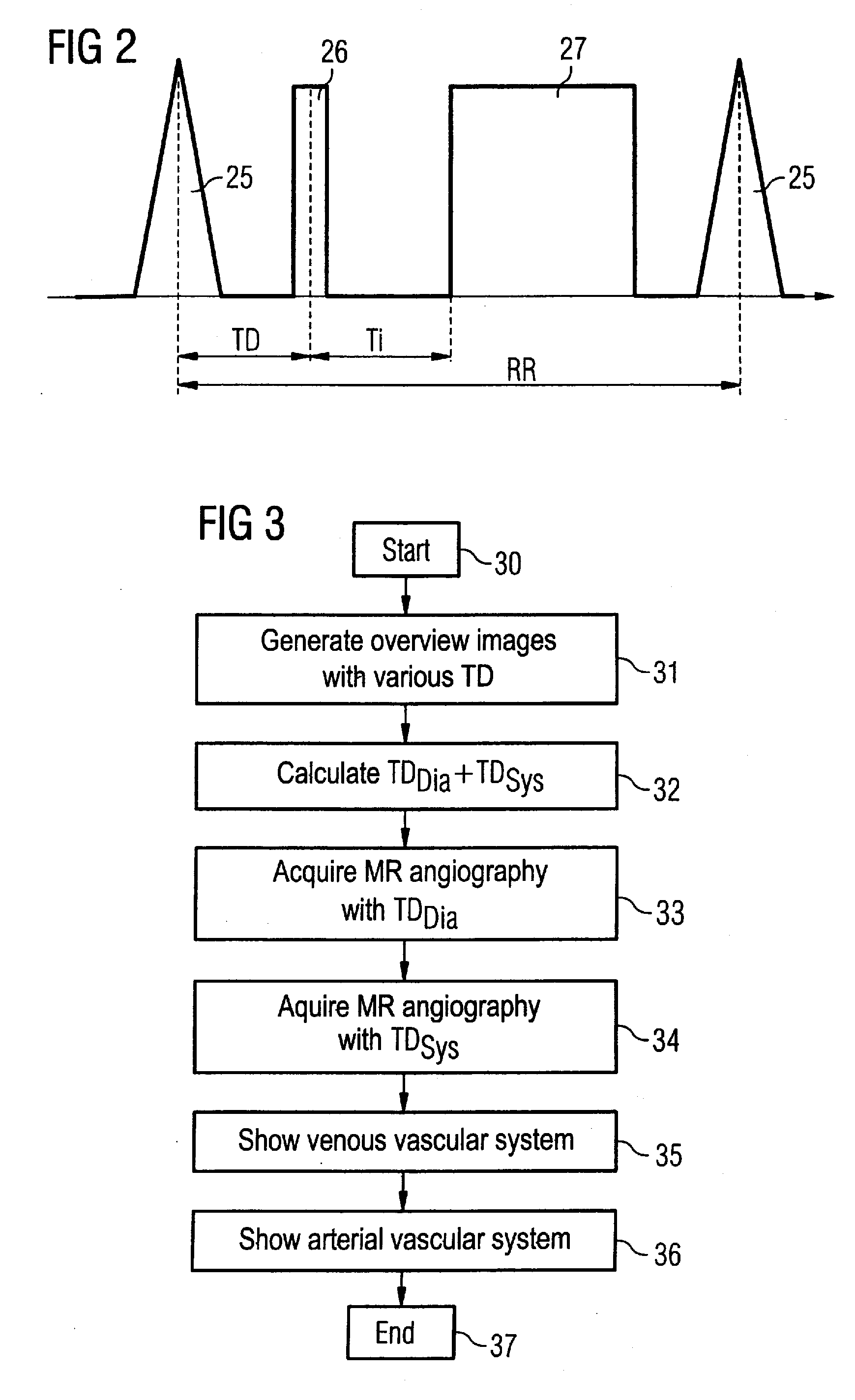
In a method and magnetic resonance MR system for the optimization of angiographic MR images of an examination subject, in which arteries can be presented separately from veins in the angiographic magnetic resonance images, multiple MR overview images are acquired, with at least one imaging parameter being varied in the acquisitions of the MR overview images, at least one optimized imaging parameter is automatically calculated using a quality criterion, and the optimized imaging parameter is provided for the acquisition of the angiographic magnetic resonance images in which arteries can be shown separately from the veins.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Separation and identification of water and fat MR images at mid-field strength with reduced T2/T2* weighting
InactiveUS6603990B2Reducing T.sub.2 and T.sub.2 * weightingCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringMr imagesMR - Magnetic resonance
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method is disclosed for generating and identifying water and fat separated MR images. Image data is first acquired to obtain two echo images with the water and fat signals orthogonal in the first echo image, and parallel / anti-parallel in the second echo image. The effect of background field inhomogeneties are removed, and water and fat images are separated from each other. The separated water and fat images are identified according to the difference of their precessing frequencies.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com