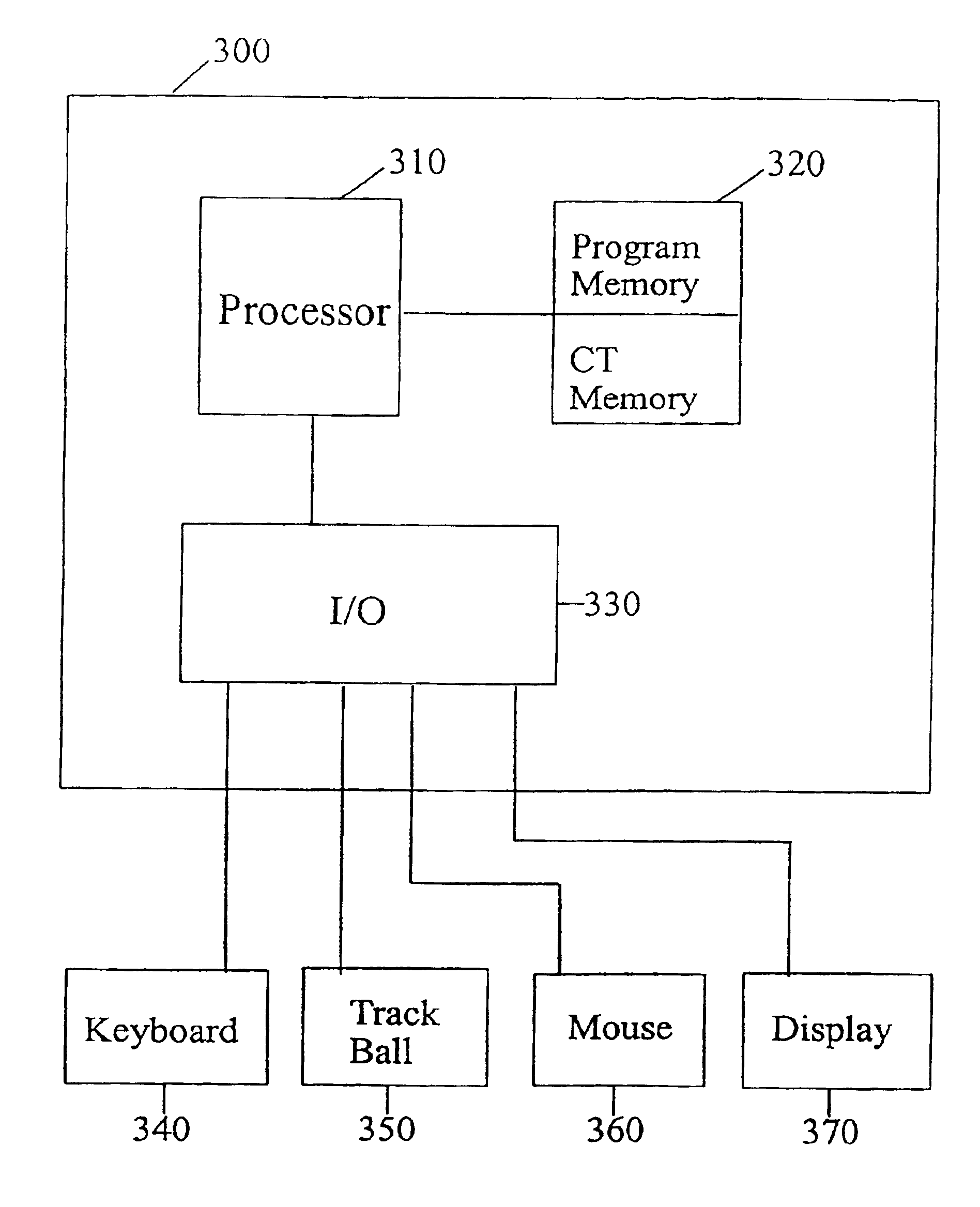
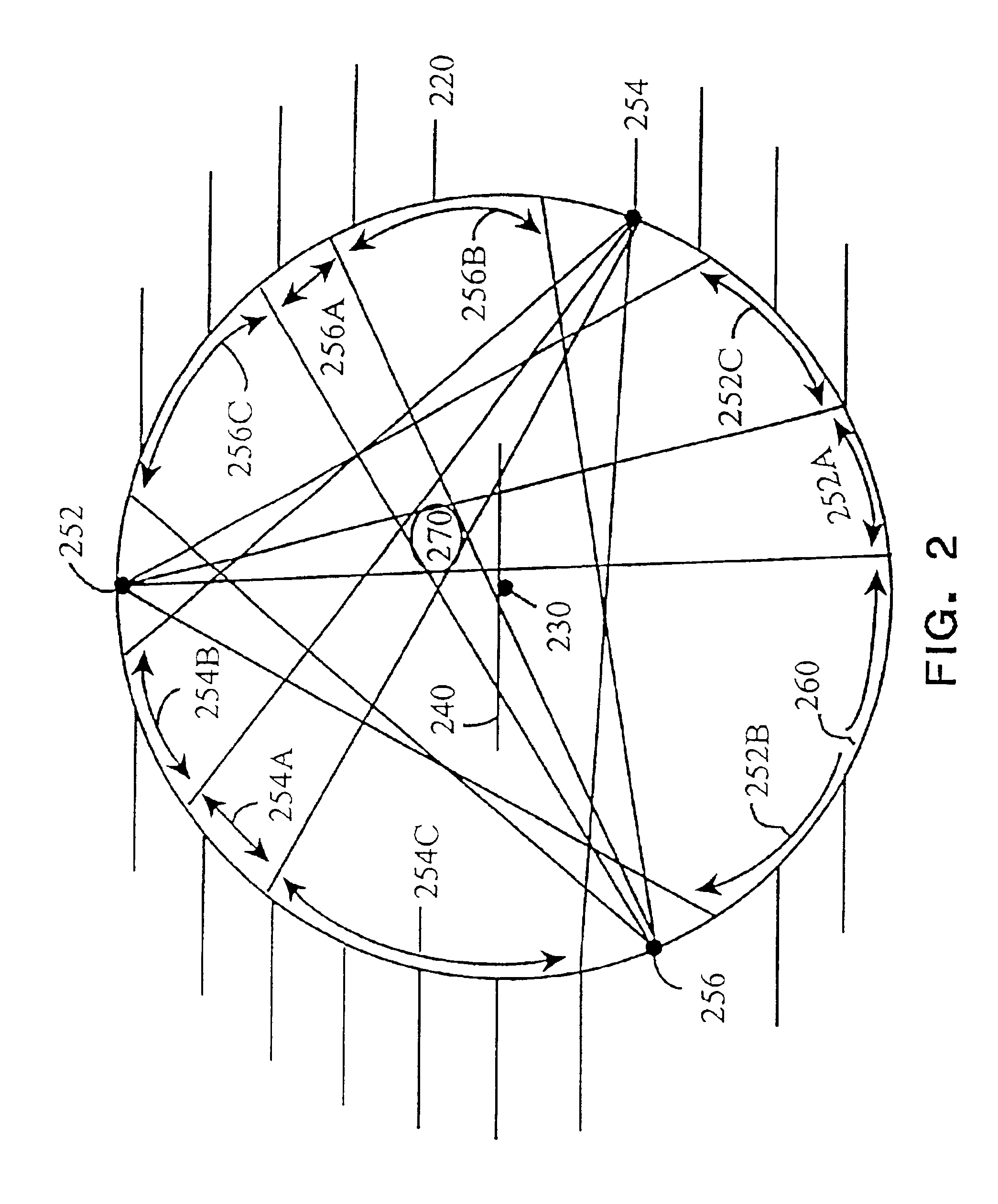
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Computer aided diagnostics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Graphical user interface for display of anatomical information
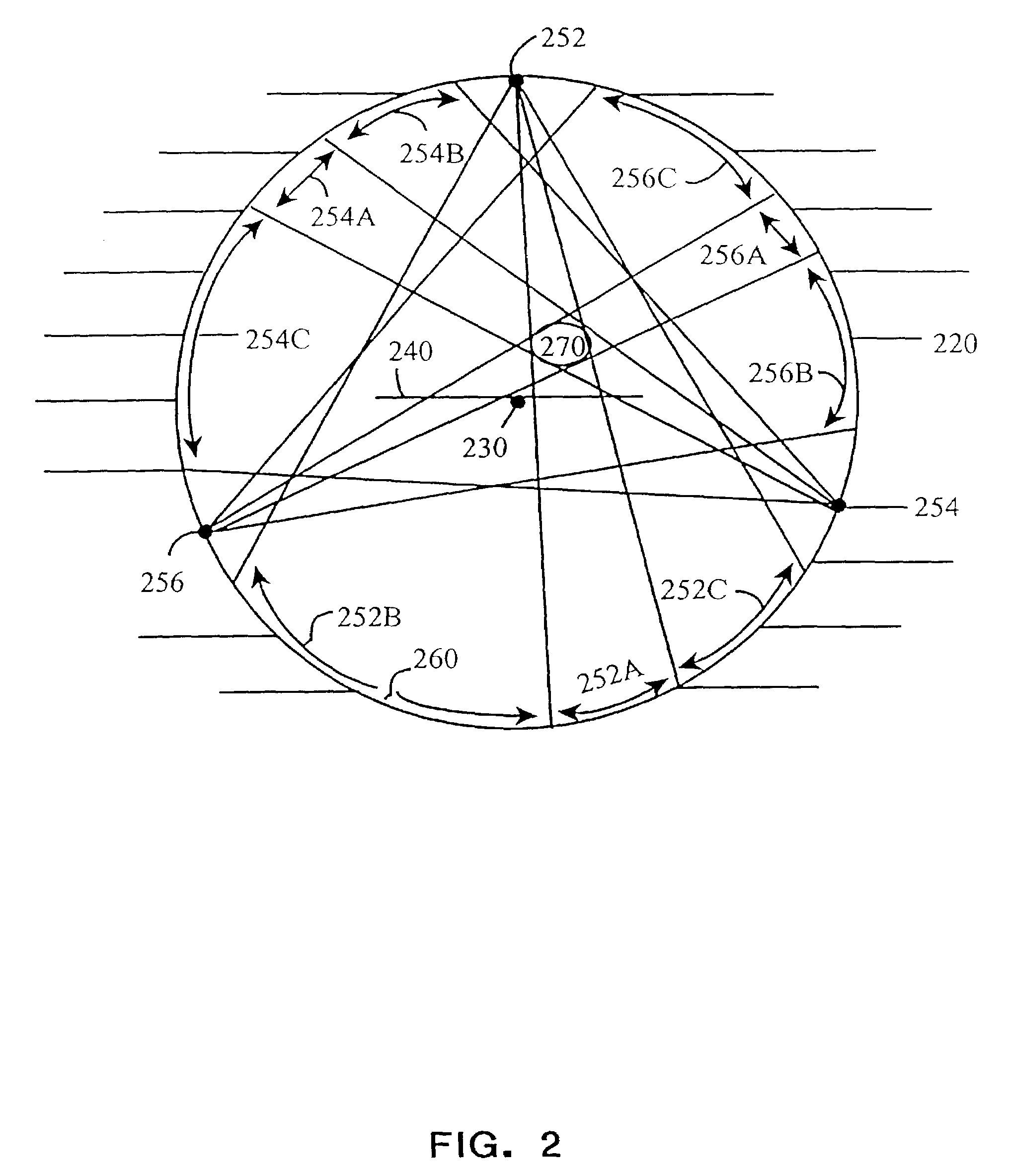
A computer-aided diagnostic method and system provide image annotation information that can include an assessment of the probability, likelihood or predictive value of detected or identified suspected abnormalities as an additional aid to the radiologist. More specifically, probability values, in numerical form and / or analog form, are added to the locational markers of the detected and suspected abnormalities. The task of a physician using such a system as disclosed is believed to be made easier by displaying markers representing different regions of interest.
Owner:MEVIS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS
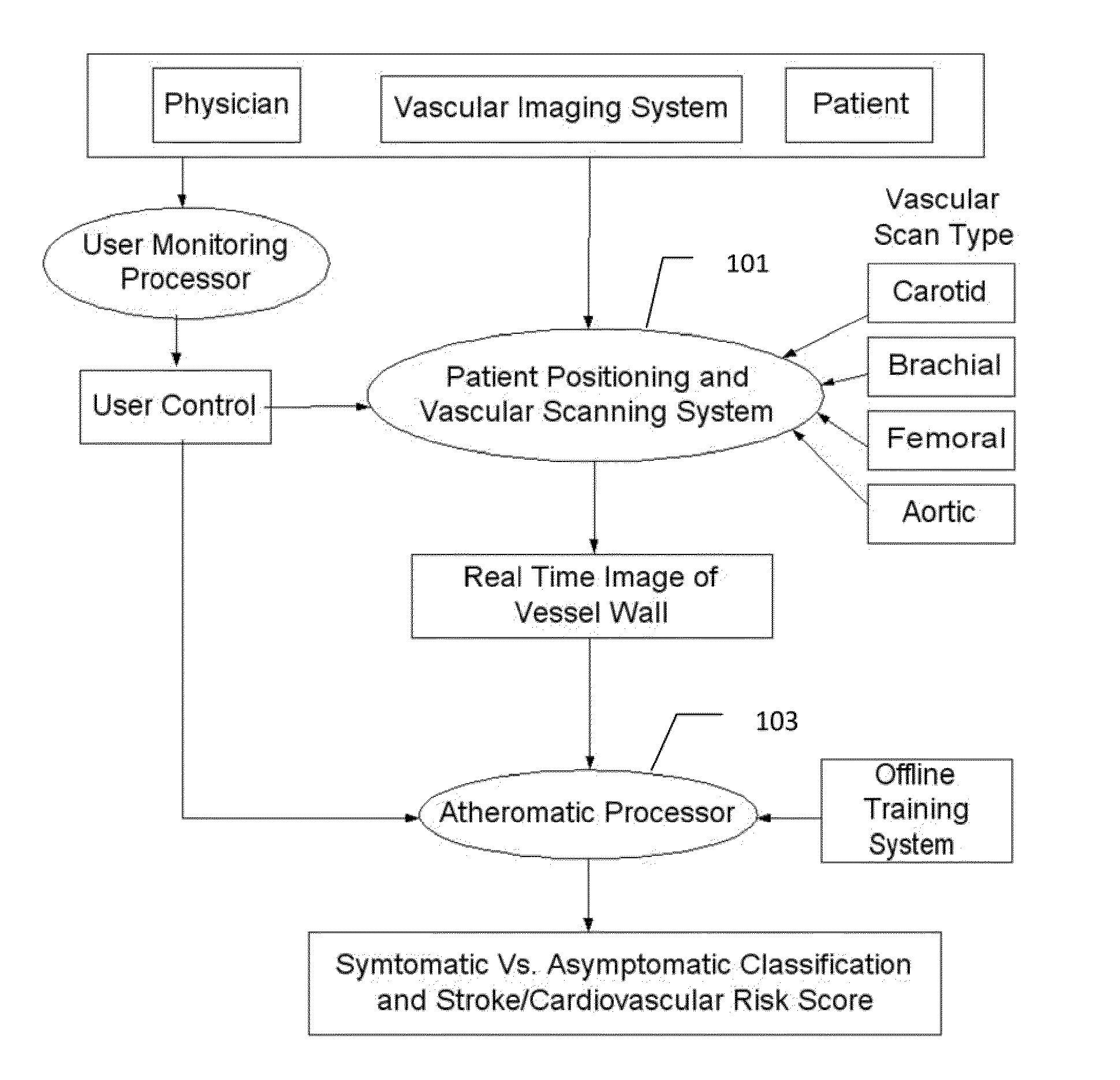
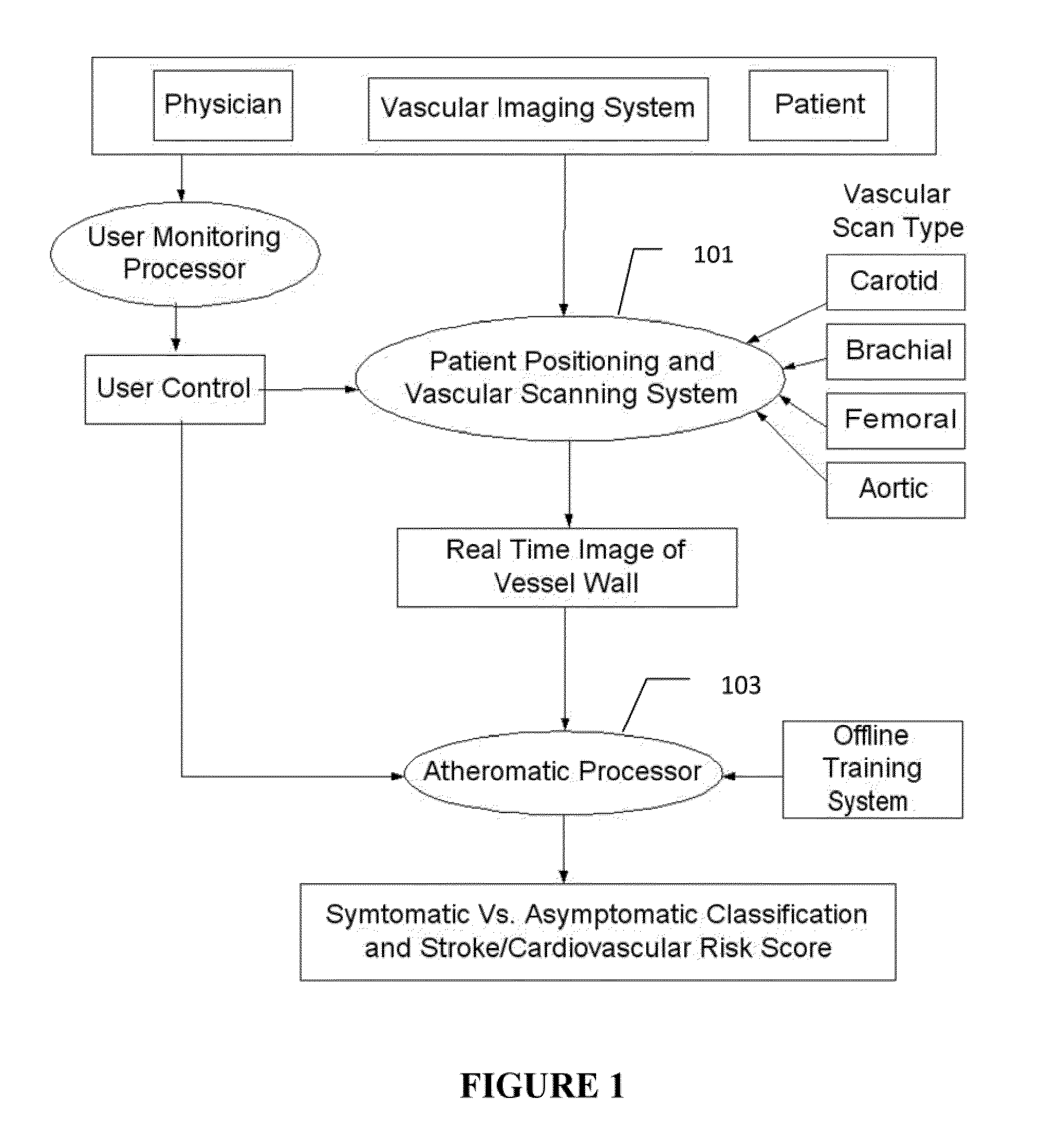
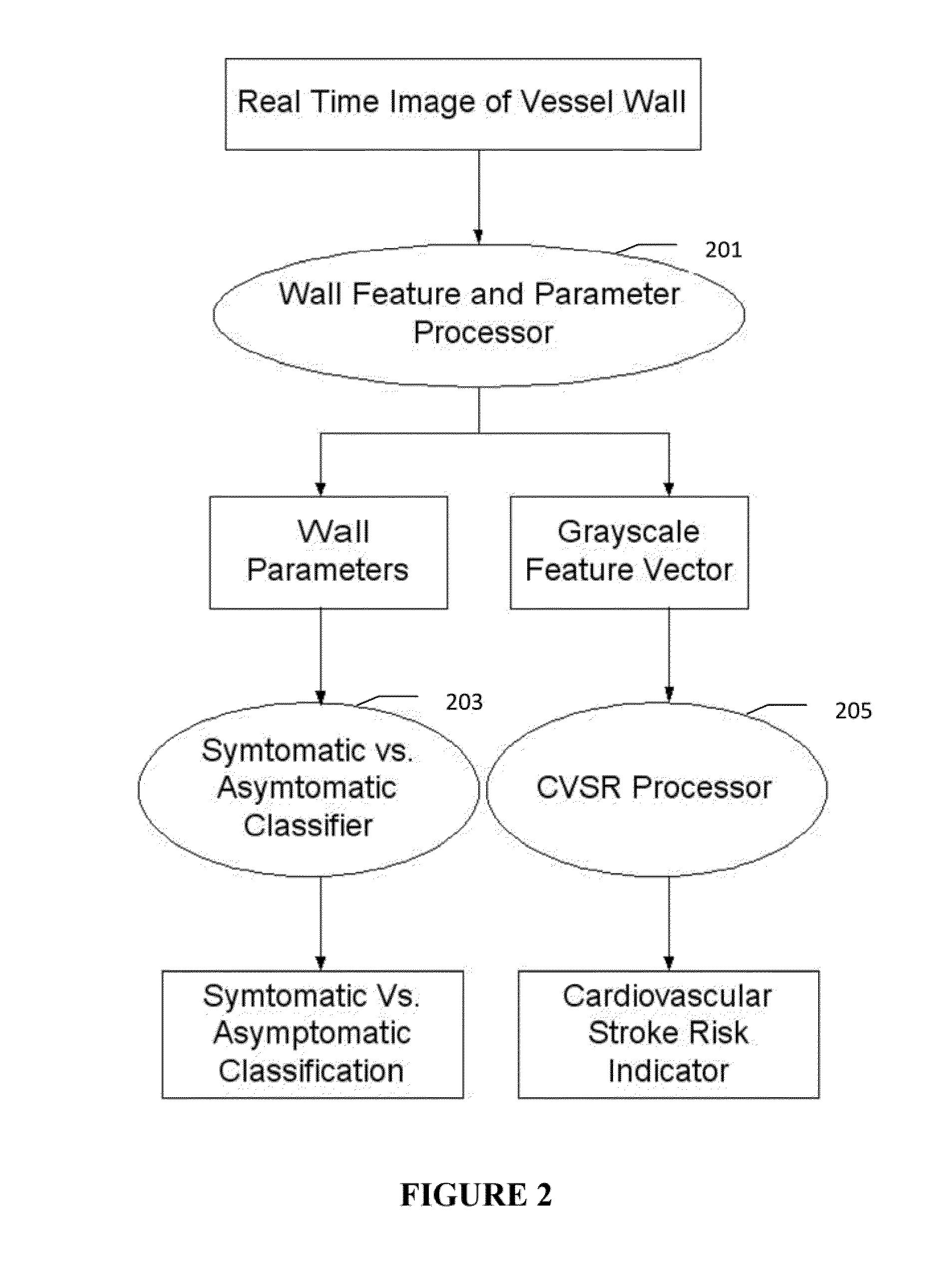
Imaging based symptomatic classification and cardiovascular stroke risk score estimation
InactiveUS20110257545A1Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementGround truthCross modality
Characterization of carotid atherosclerosis and classification of plaque into symptomatic or asymptomatic along with the risk score estimation are key steps necessary for allowing the vascular surgeons to decide if the patient has to definitely undergo risky treatment procedures that are needed to unblock the stenosis. This application describes a statistical (a) Computer Aided Diagnostic (CAD) technique for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification of carotid ultrasound images and (b) presents a cardiovascular stroke risk score computation. We demonstrate this for longitudinal Ultrasound, CT, MR modalities and extendable to 3D carotid Ultrasound. The on-line system consists of Atherosclerotic Wall Region estimation using AtheroEdge™ for longitudinal Ultrasound or Athero-CTView™ for CT or Athero-MRView from MR. This greyscale Wall Region is then fed to a feature extraction processor which computes: (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability. The output of the Feature Processor is fed to the Classifier which is trained off-line from the Database of similar Atherosclerotic Wall Region images. The off-line Classifier is trained from the significant features from (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability, selected using t-test. Symptomatic ground truth information about the training patients is drawn from cross modality imaging such as CT or MR or 3D ultrasound in the form of 0 or 1. Support Vector Machine (SVM) supervised classifier of varying kernel functions is used off-line for training. The Atheromatic™ system is also demonstrated for Radial Basis Probabilistic Neural Network (RBPNN), or Nearest Neighbor (KNN) classifier or Decision Trees (DT) Classifier for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification. The obtained training parameters are then used to evaluate the test set. The system also yields the cardiovascular stroke risk score value on the basis of the four set of wall features.
Owner:SURI JASJIT S
Graphical user interface for display of anatomical information
InactiveUS7072501B2Optimized for speedImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsGraphics
A computer-aided diagnostic method and system provide image annotation information that can include an assessment of the probability, likelihood or predictive value of detected or identified suspected abnormalities as an additional aid to the radiologist. More specifically, probability values, in numerical form and / or analog form, are added to the locational markers of the detected and suspected abnormalities. The task of a physician using such a system as disclosed is believed to be made easier by displaying markers representing different regions of interest.
Owner:MEVIS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS
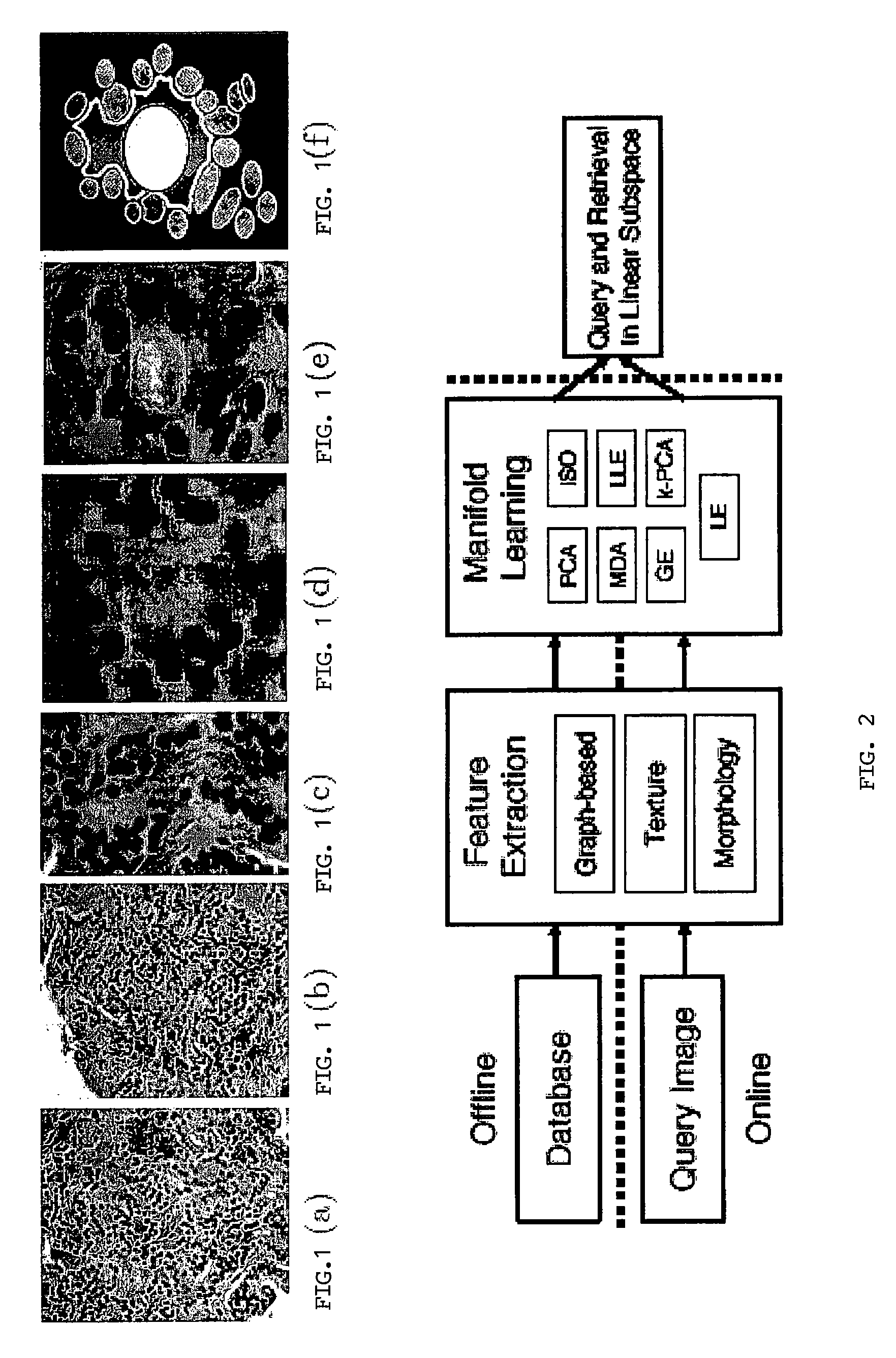
Malignancy diagnosis using content - based image retreival of tissue histopathology
ActiveUS20100098306A1Reduce dimensionalityHigh magnificationImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsImaging Feature
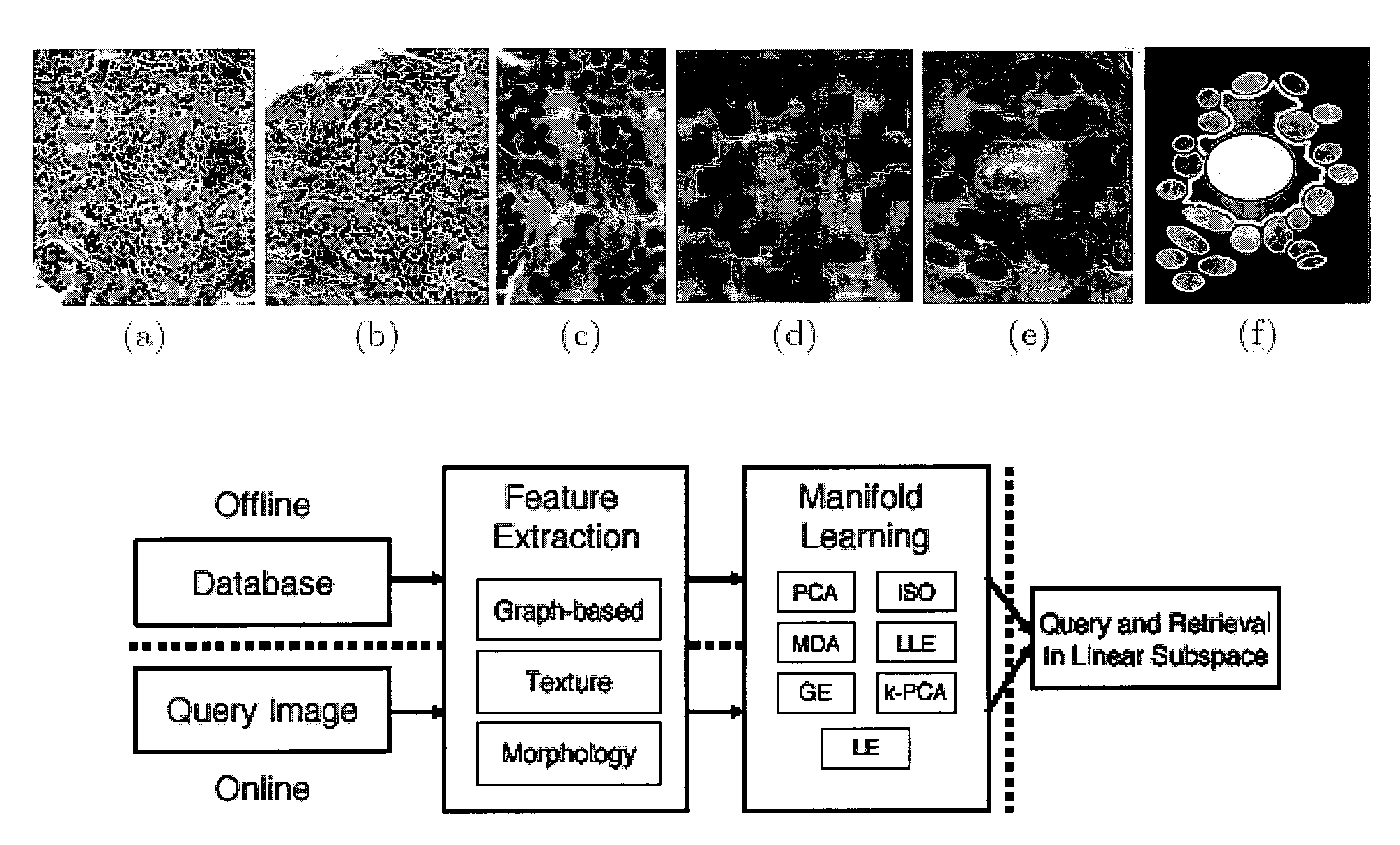
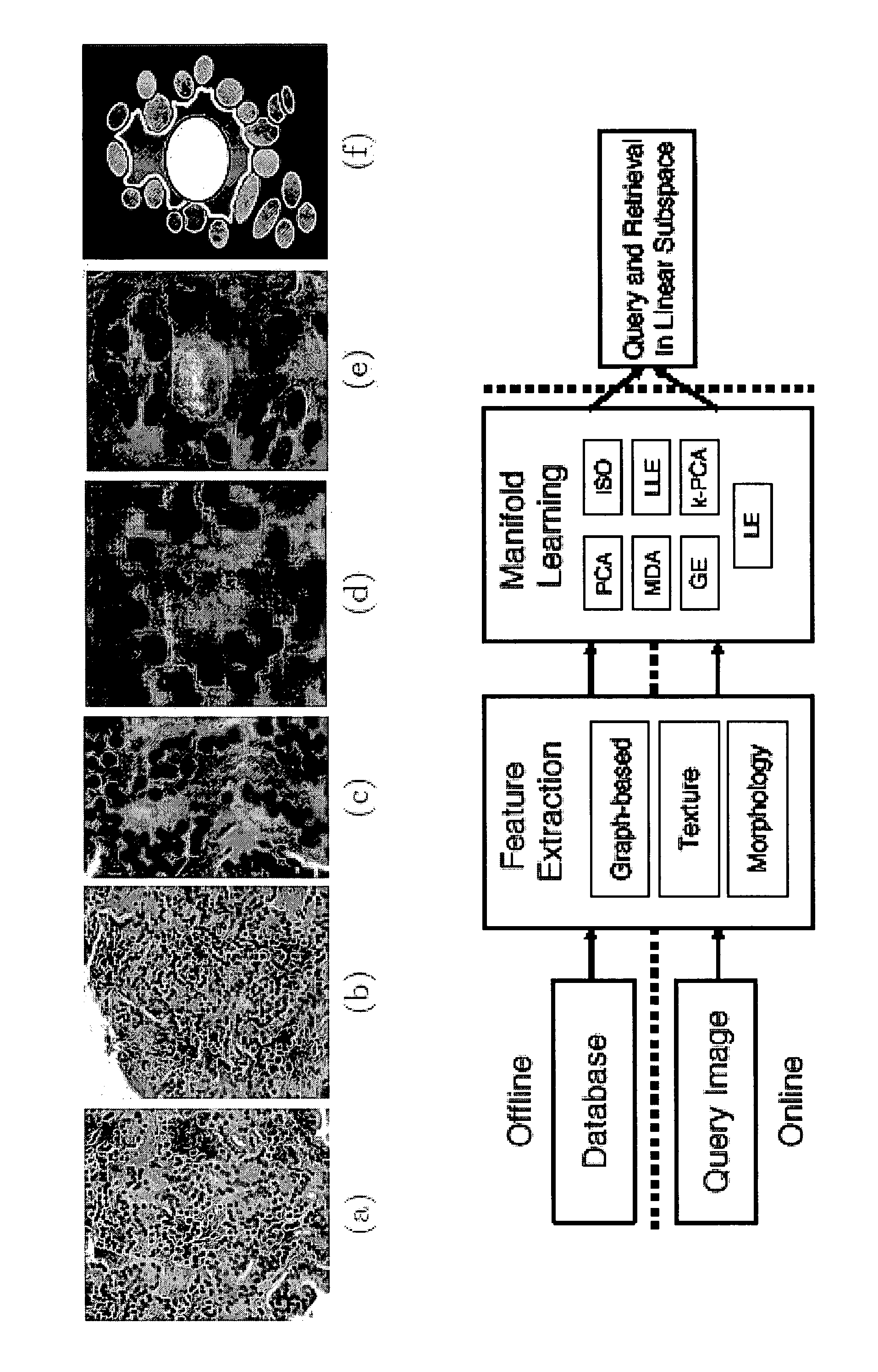
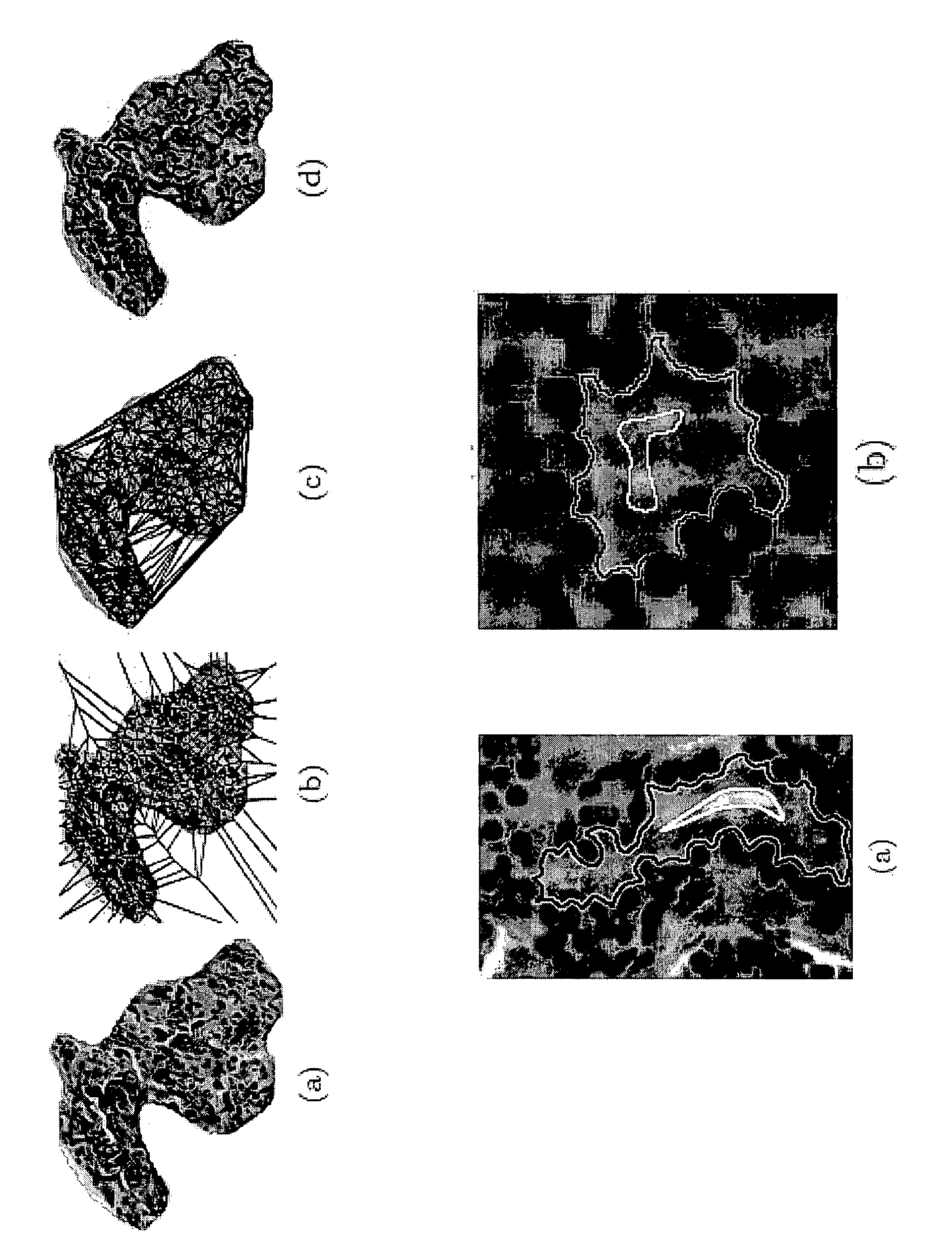
This invention relates to computer-aided diagnostics using content-based retrieval of histopathological image features. Specifically, the invention relates to the extraction of image features from a histopathological image based on predetermined criteria and their analysis for malignancy determination.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
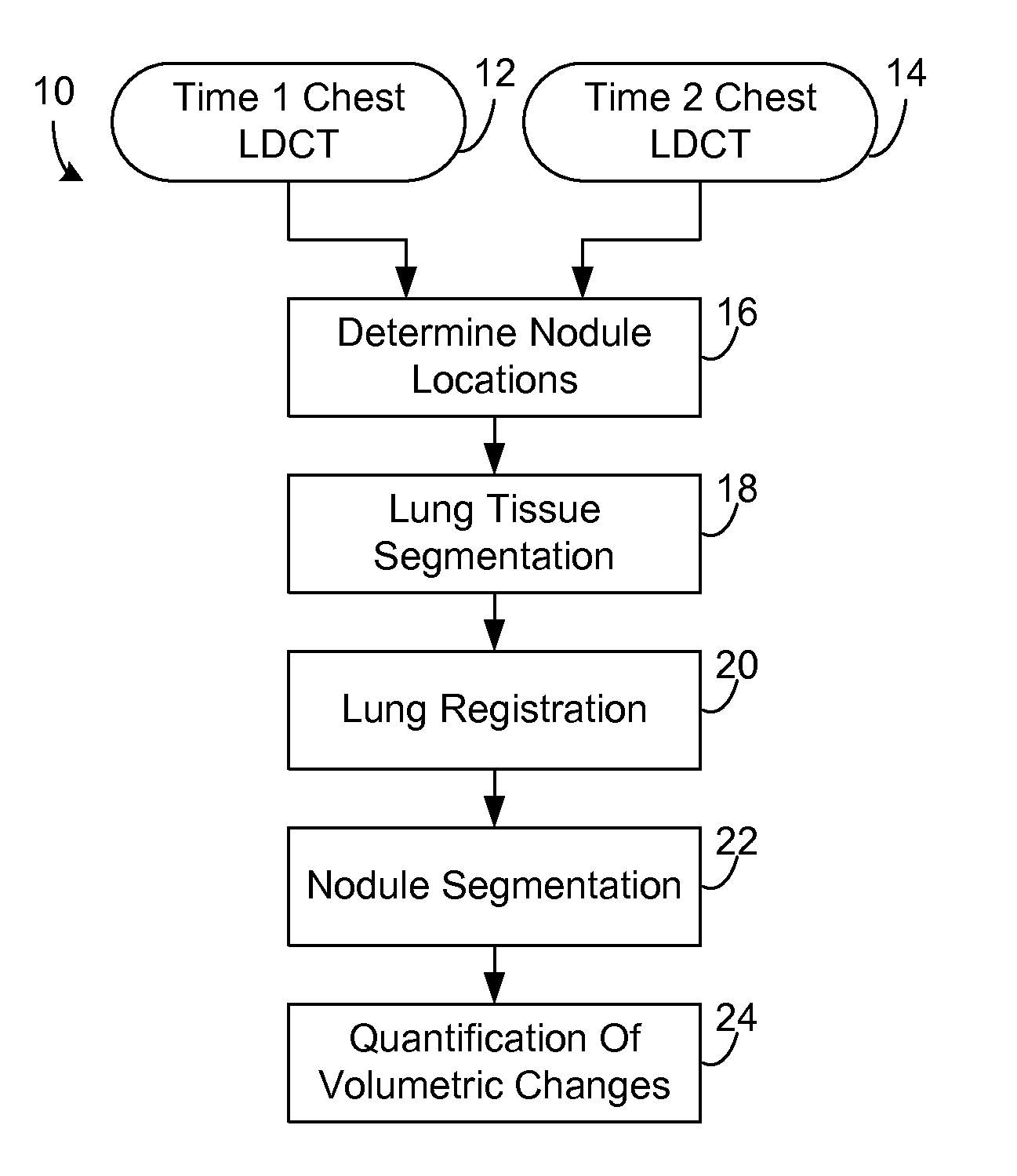
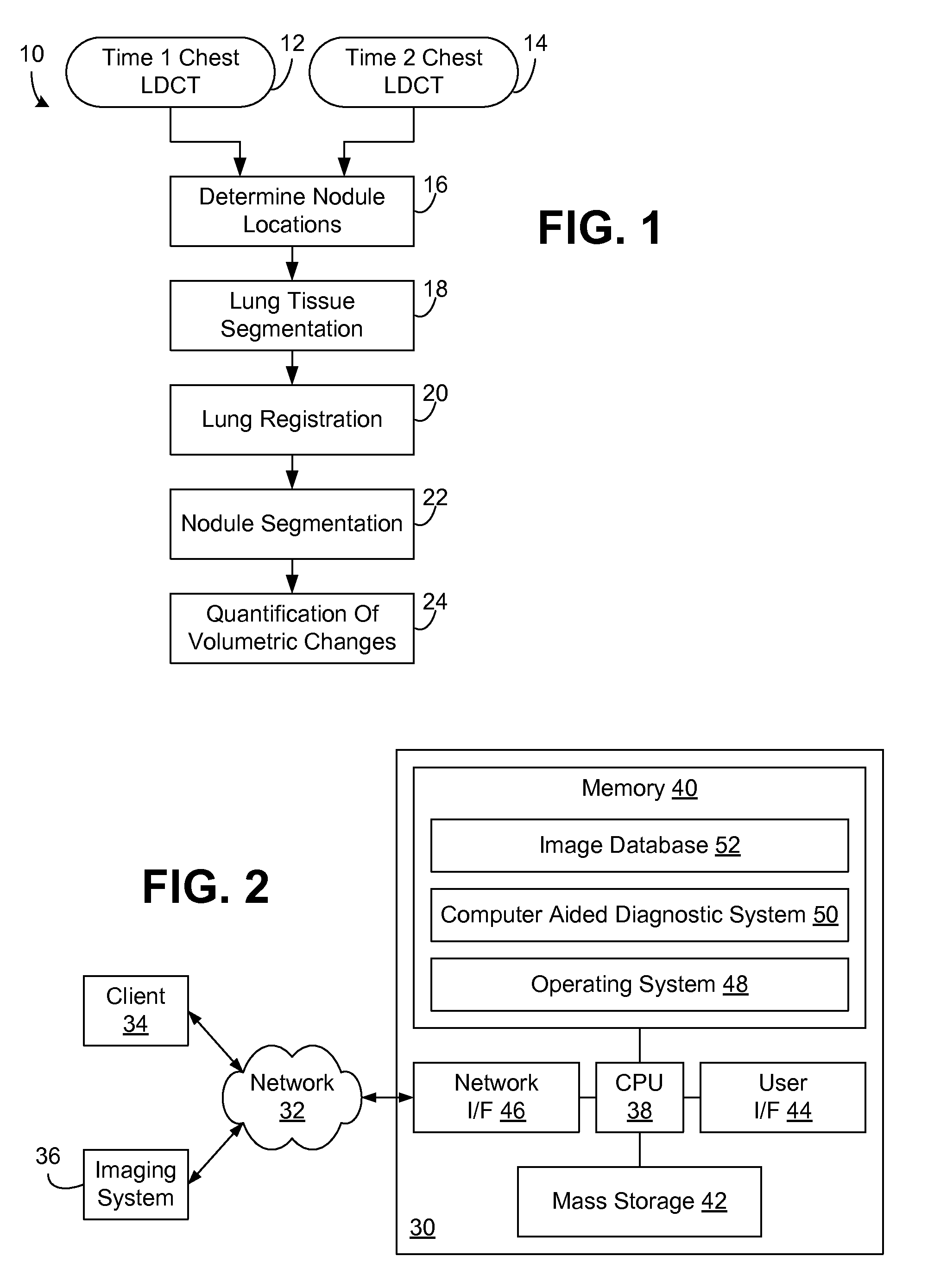
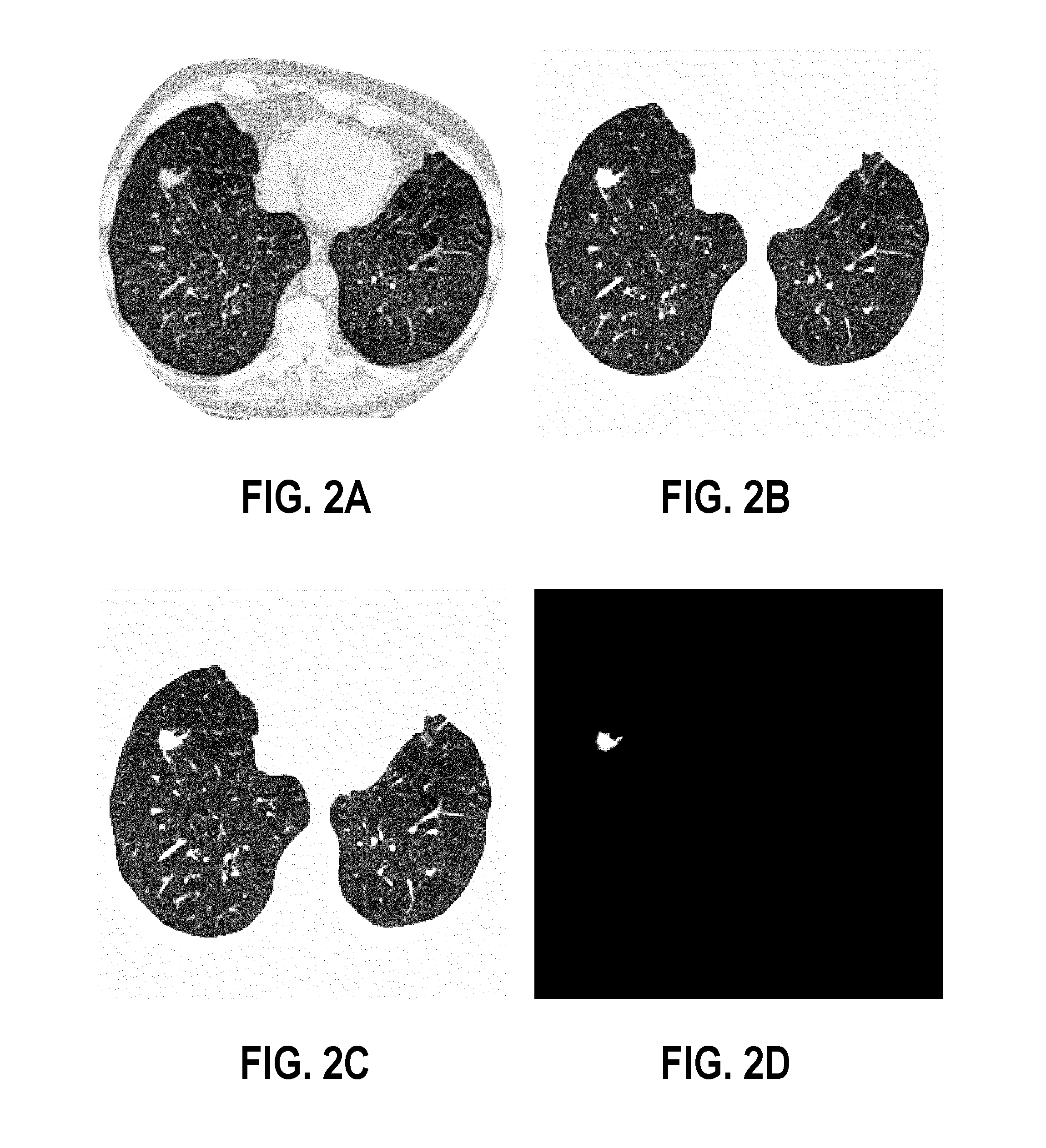
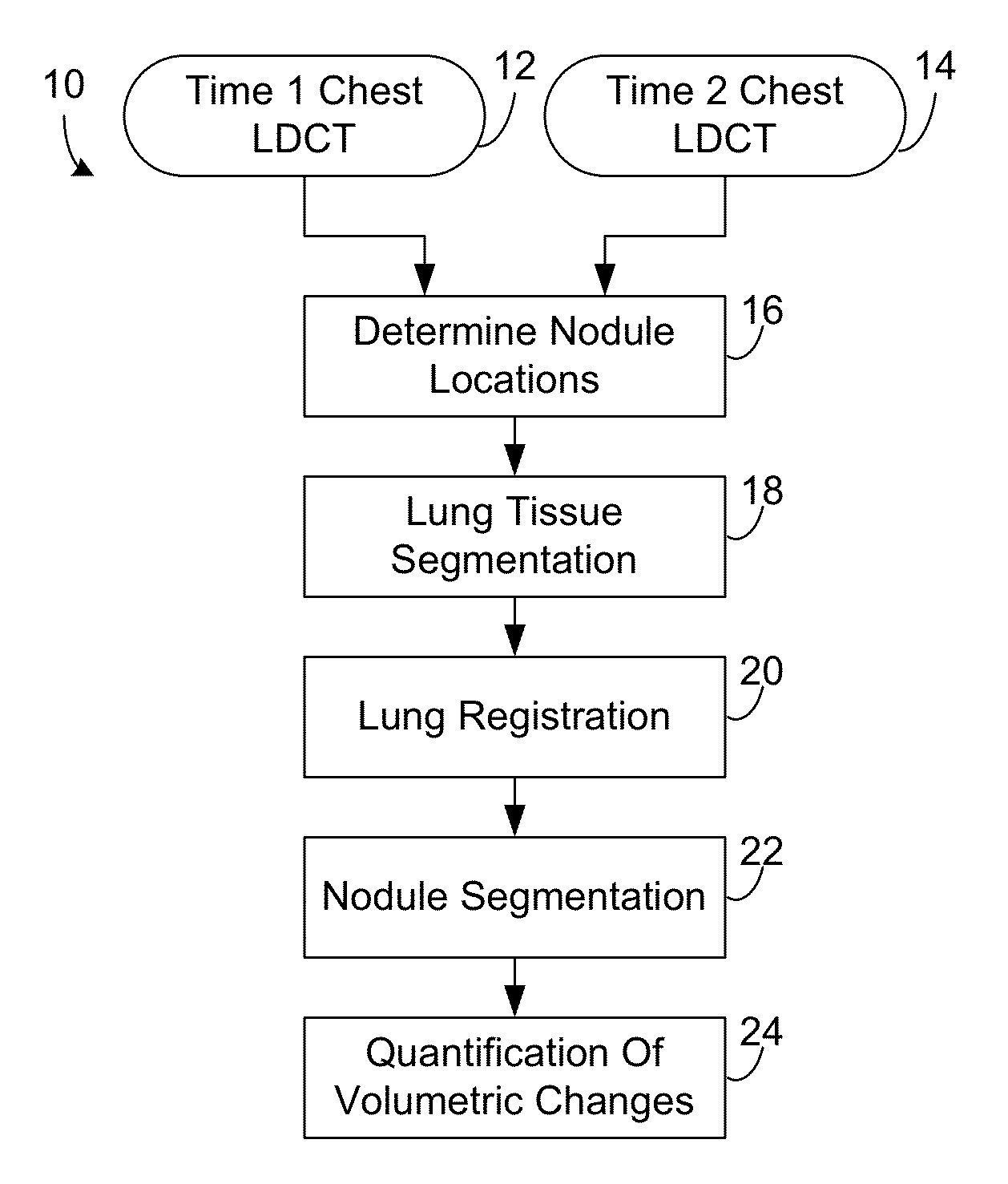
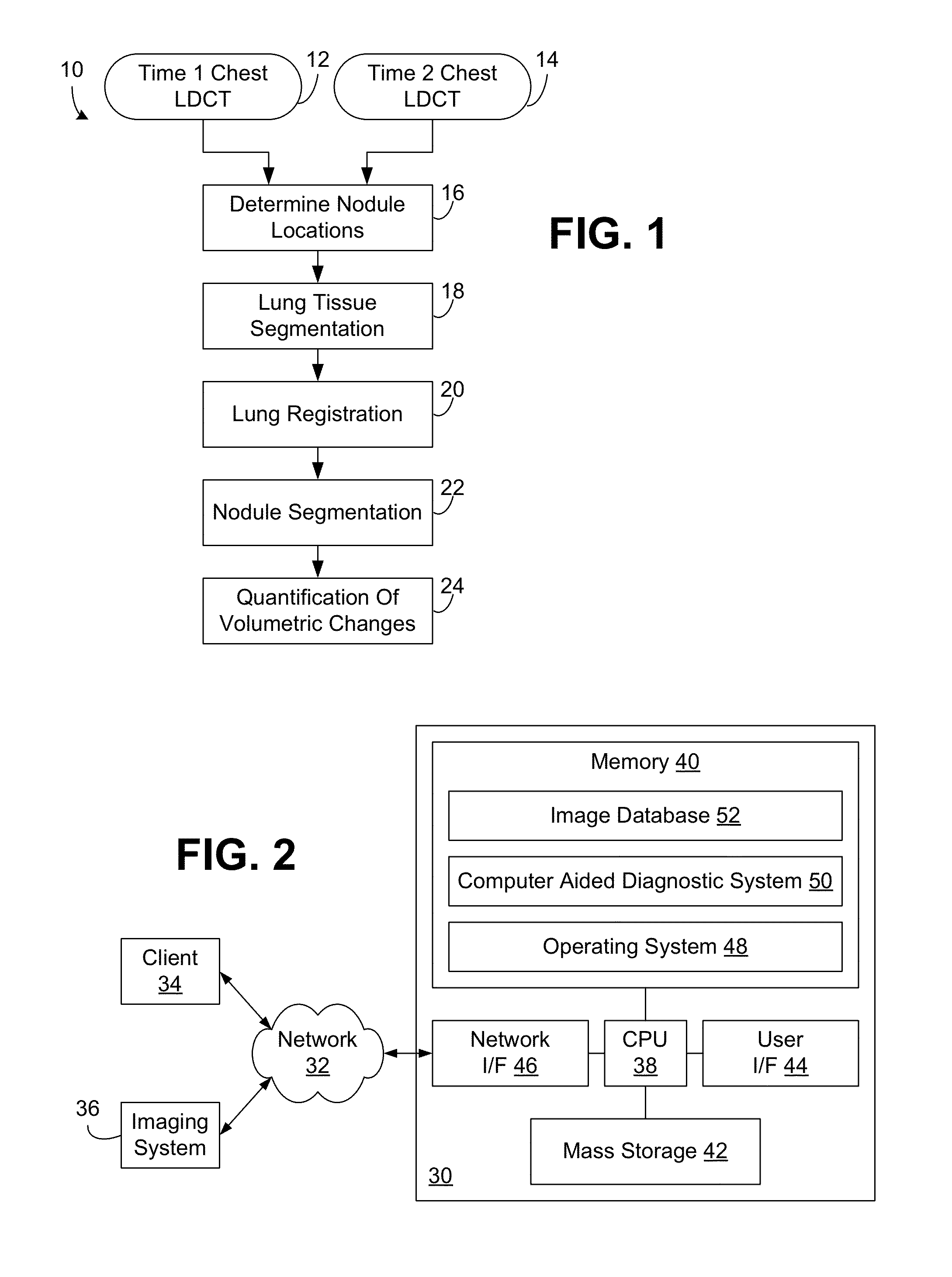
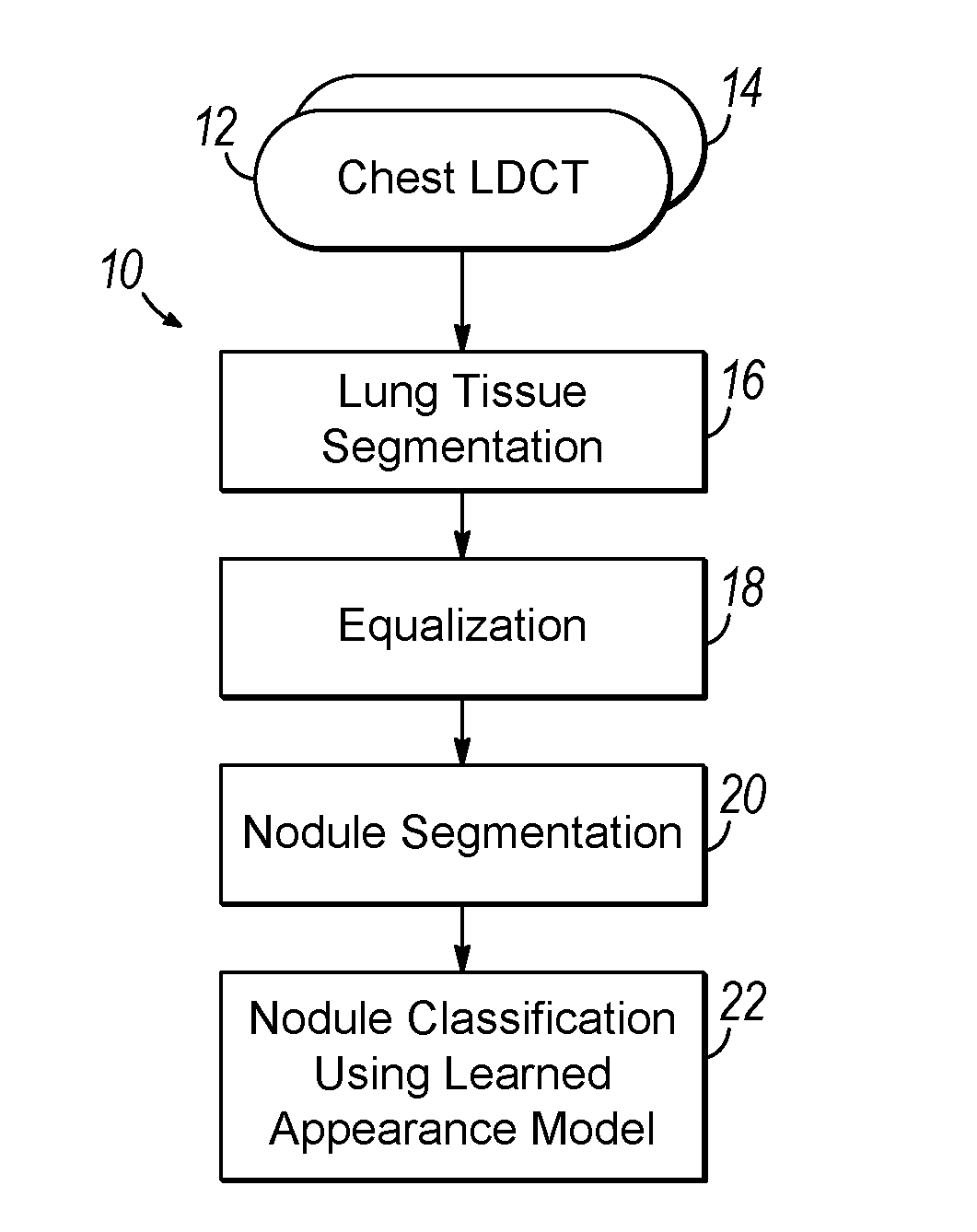
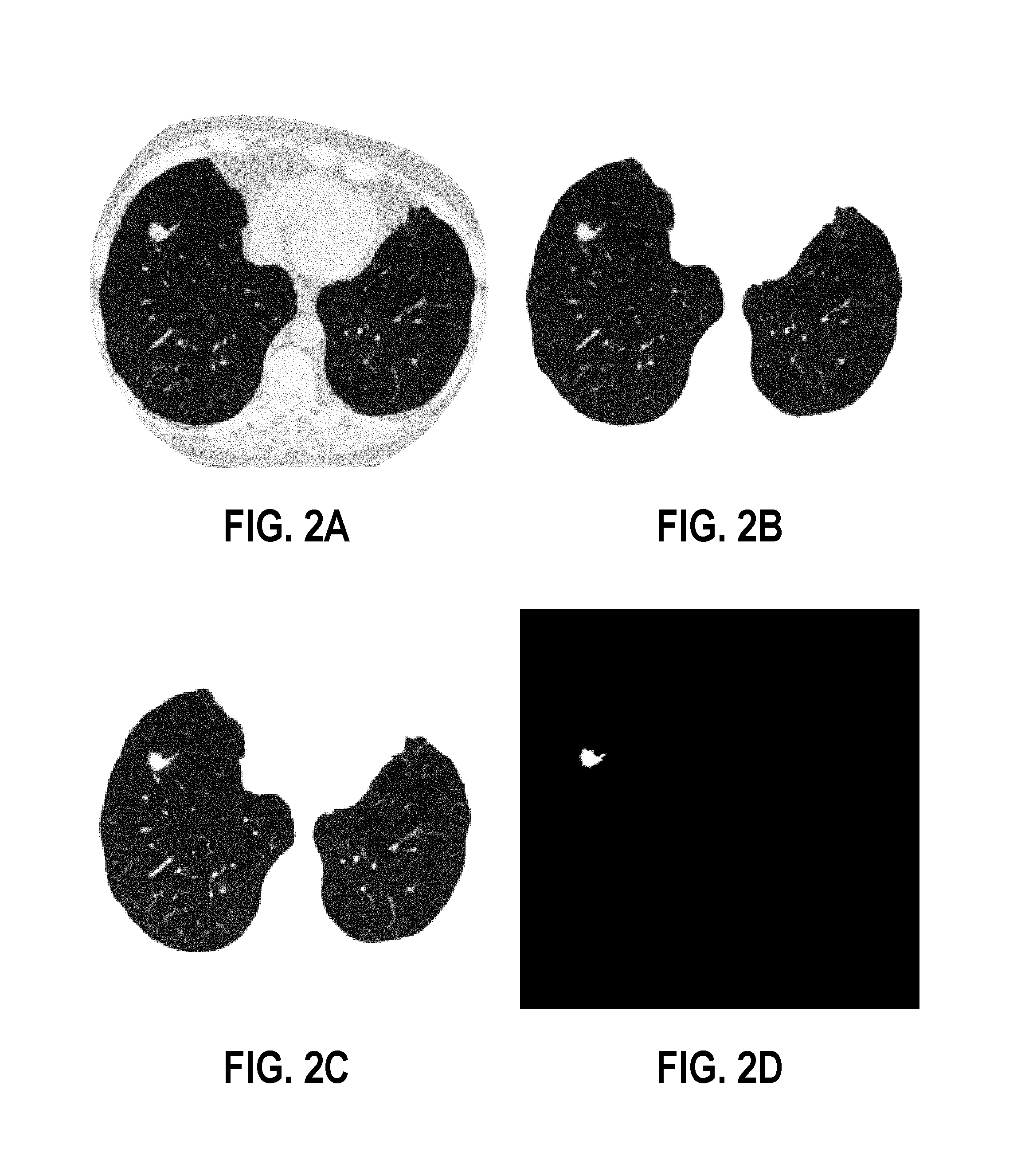
Computer aided diagnostic system incorporating lung segmentation and registration
ActiveUS20100111386A1Change in volume of a noduleImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleComputer aided diagnostics
A computer aided diagnostic system and automated method diagnose lung cancer through tracking of the growth rate of detected pulmonary nodules over time. The growth rate between first and second chest scans taken at first and second times is determined by segmenting out a nodule from its surrounding lung tissue and calculating the volume of the nodule only after the image data for lung tissue (which also includes image data for a nodule) has been segmented from the chest scans and the segmented lung tissue from the chest scans has been globally and locally aligned to compensate for positional variations in the chest scans as well as variations due to heartbeat and respiration during scanning. Segmentation may be performed using a segmentation technique that utilizes both intensity (color or grayscale) and spatial information, while registration may be performed using a registration technique that registers lung tissue represented in first and second data sets using both a global registration and a local registration to account for changes in a patient's orientation due in part to positional variances and variances due to heartbeat and / or respiration.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Graphical user interface for display of anatomical information
A computer-aided diagnostic method and system provide image annotation information that can include an assessment of the probability, likelihood or predictive value of detected or identified suspected abnormalities as an additional aid to the radiologist. More specifically, probability values, in numerical form and / or analog form, are added to the locational markers of the detected and suspected abnormalities. The task of a physician using such a system as disclosed is believed to be made easier by displaying markers representing different regions of interest.
Owner:MEVIS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS
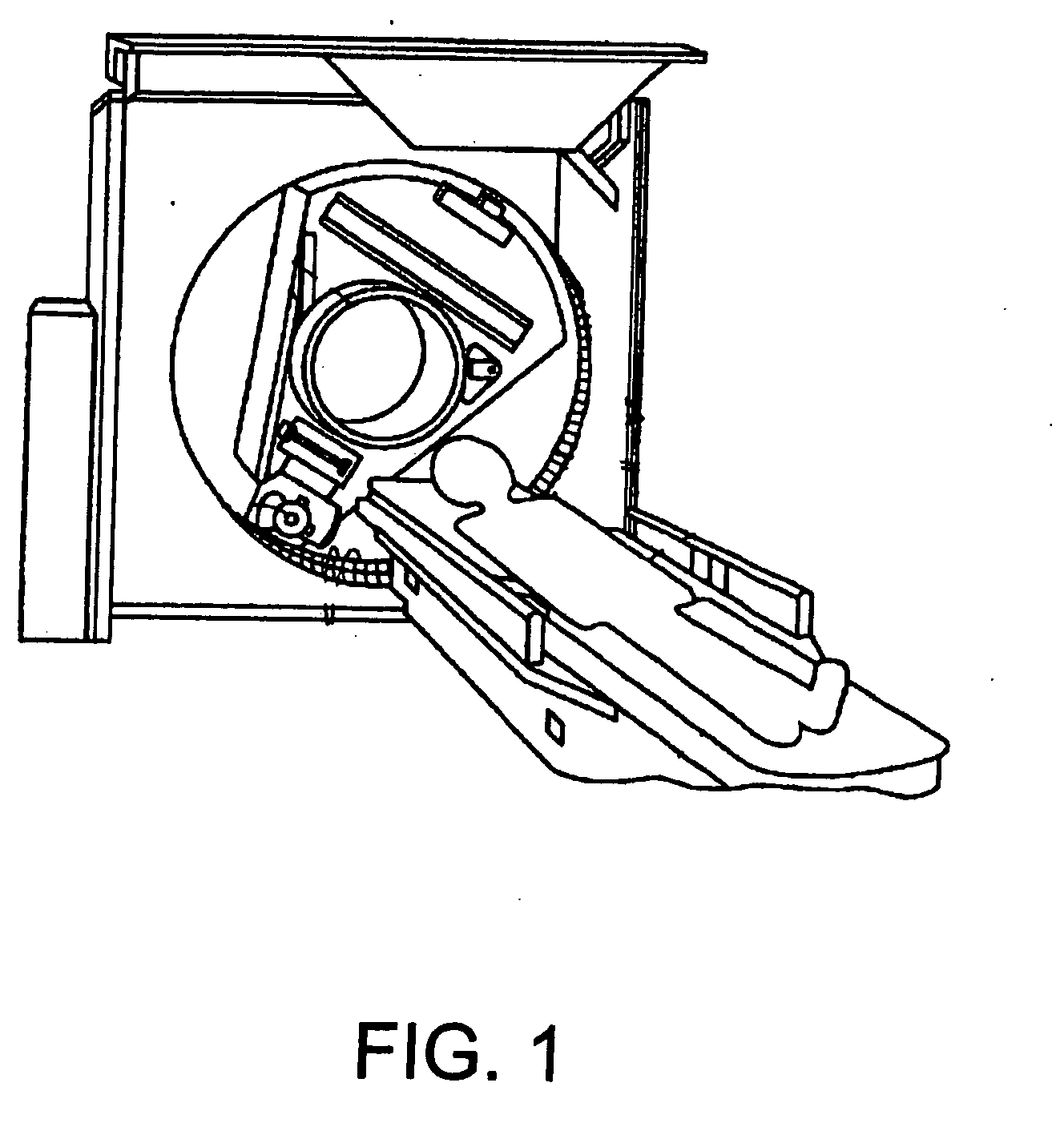
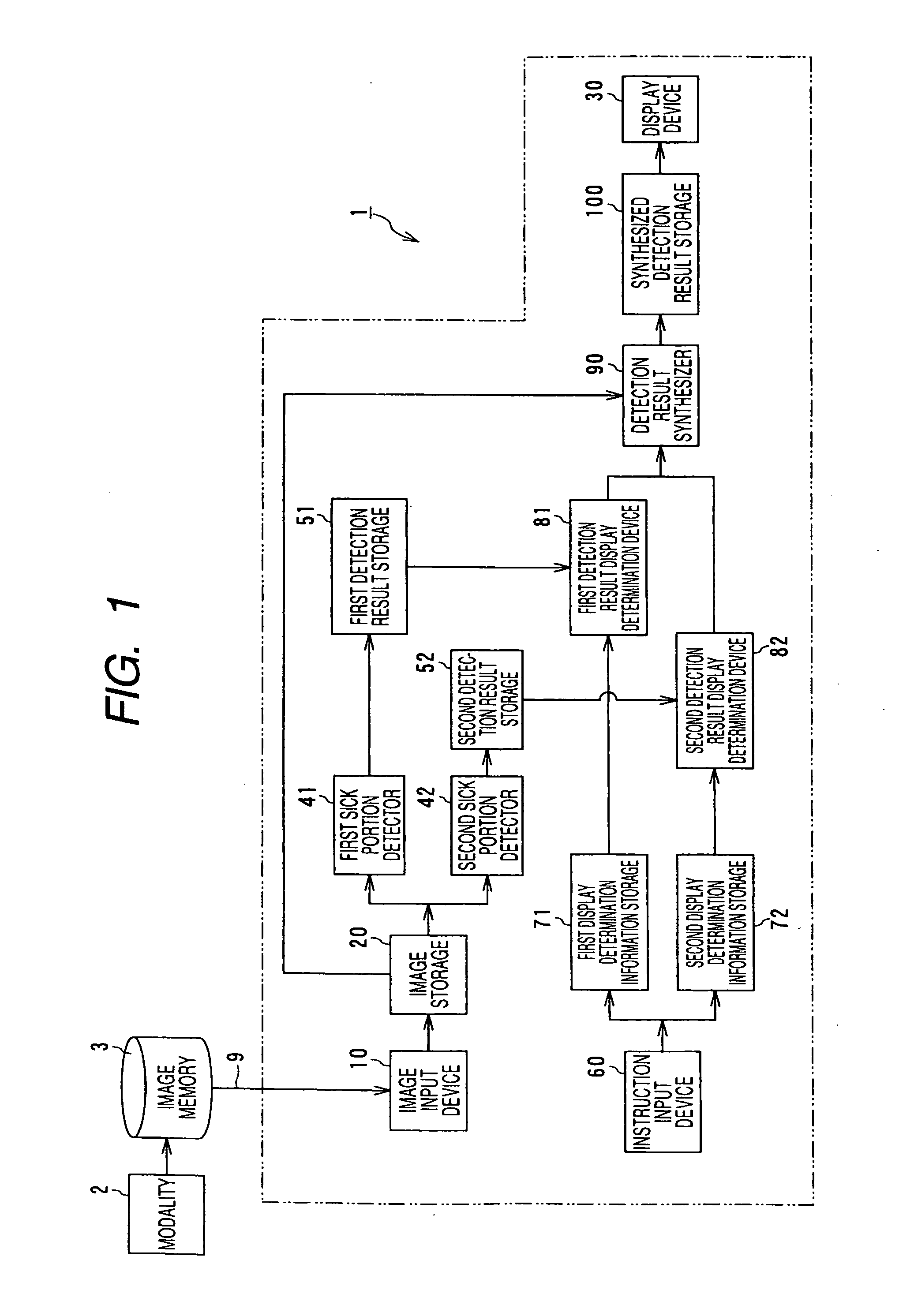
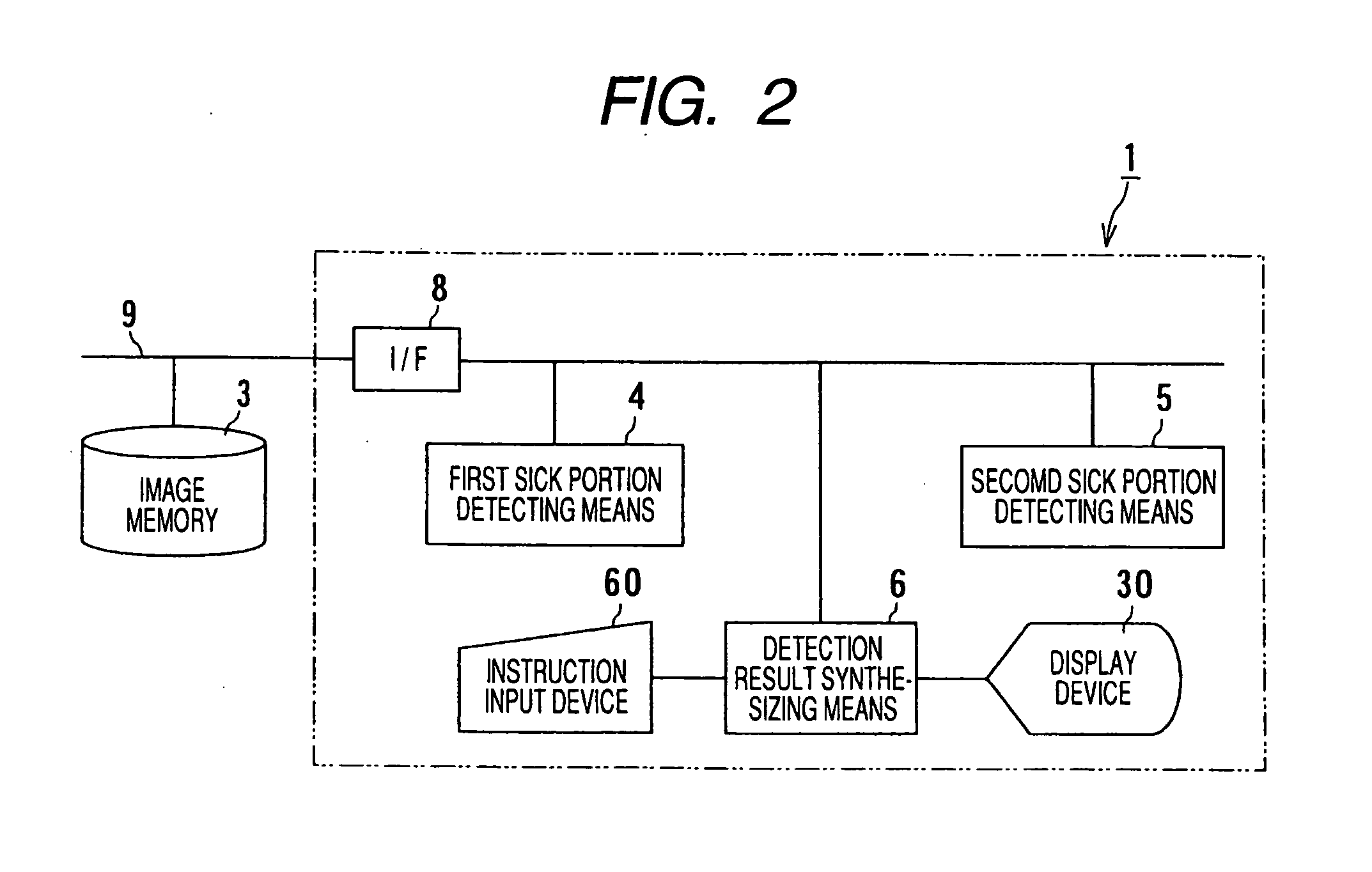
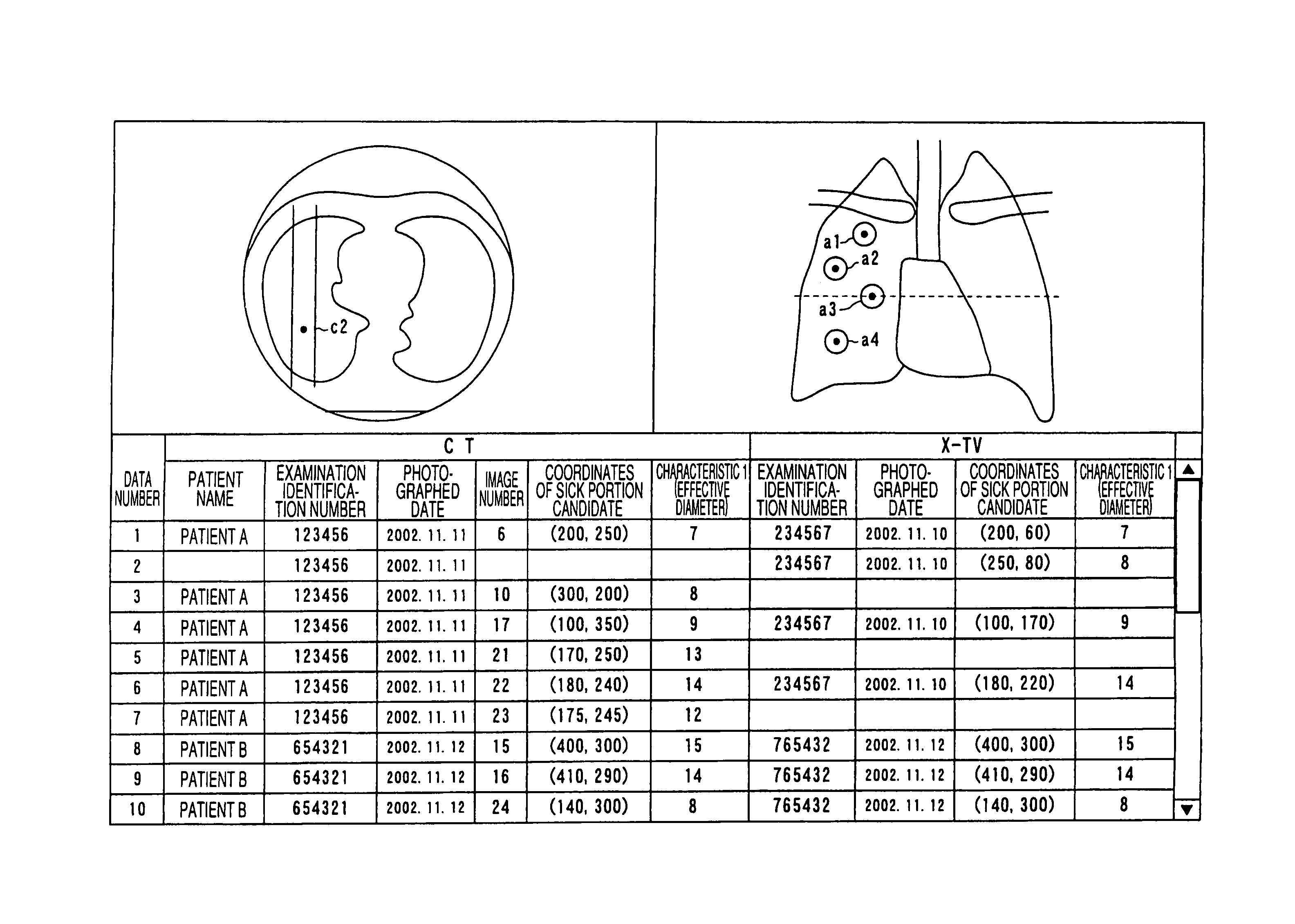
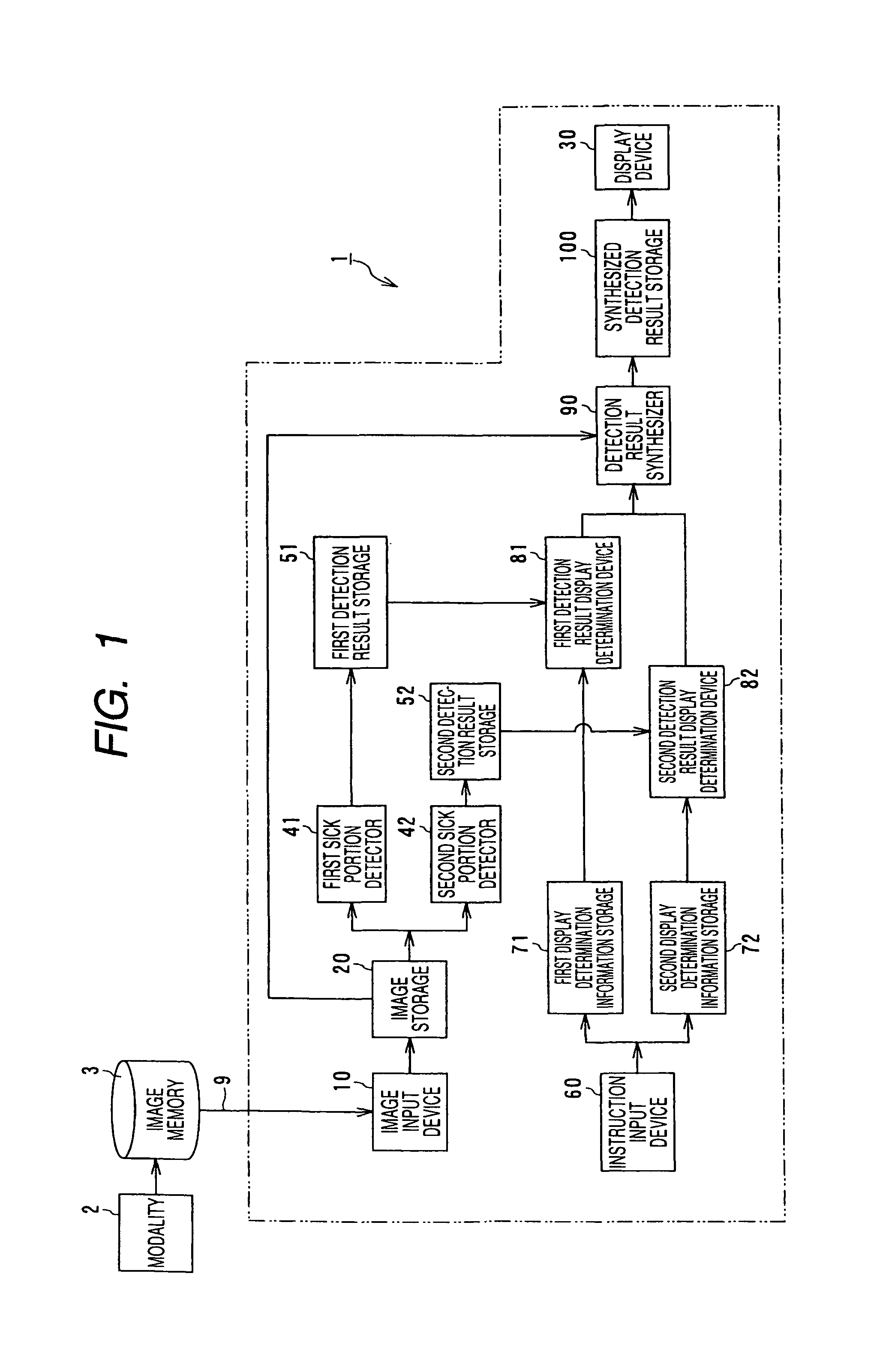
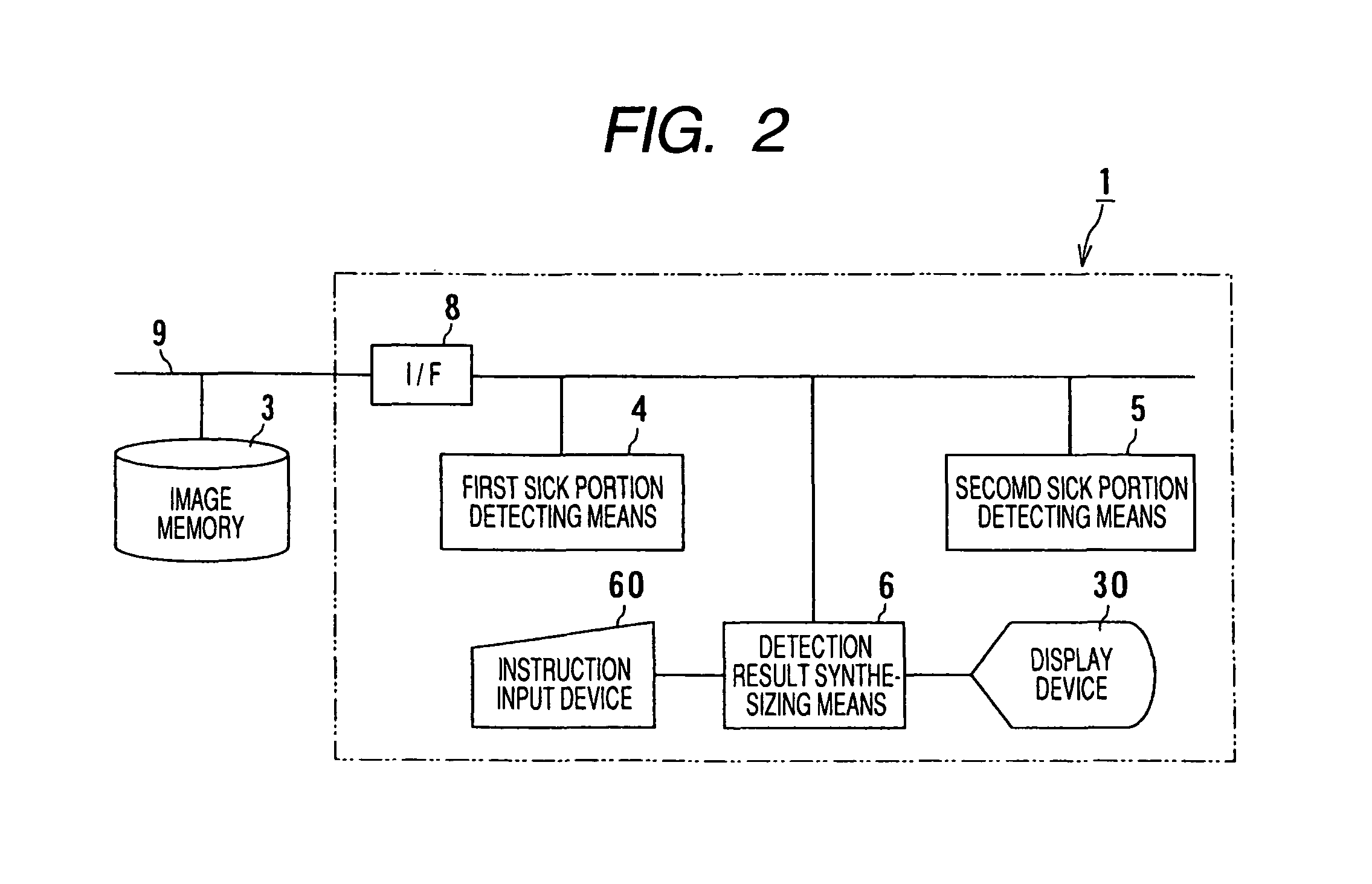
Computer-aided diagnostic apparatus
ActiveUS20060050943A1Easy to checkImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsImage detection
A computer aided diagnostic system according to the invention is characterized in that first sick portion detecting means for detecting a sick portion candidate based upon an image acquired by a first modality, second sick portion detecting means for detecting a sick portion candidate based upon an image related to the same region of interest of the same subject and acquired by a second modality different from the modality, detection result synthesizing means for comparing the results of detection by the first and second sick portion detecting means and correspondence displaying means for relating the position of the sick portion candidate detected by the first sick portion detecting means on an image analyzed by the second sick portion detecting means and displaying it and for relating the position of the sick portion candidate detected by the second sick portion detecting means on an image analyzed by the first sick portion detecting means and displaying it are provided. According to the above-mentioned configuration, the computer aided diagnostic system that enables a double check comparing images acquired by plural apparatuses can be provided.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
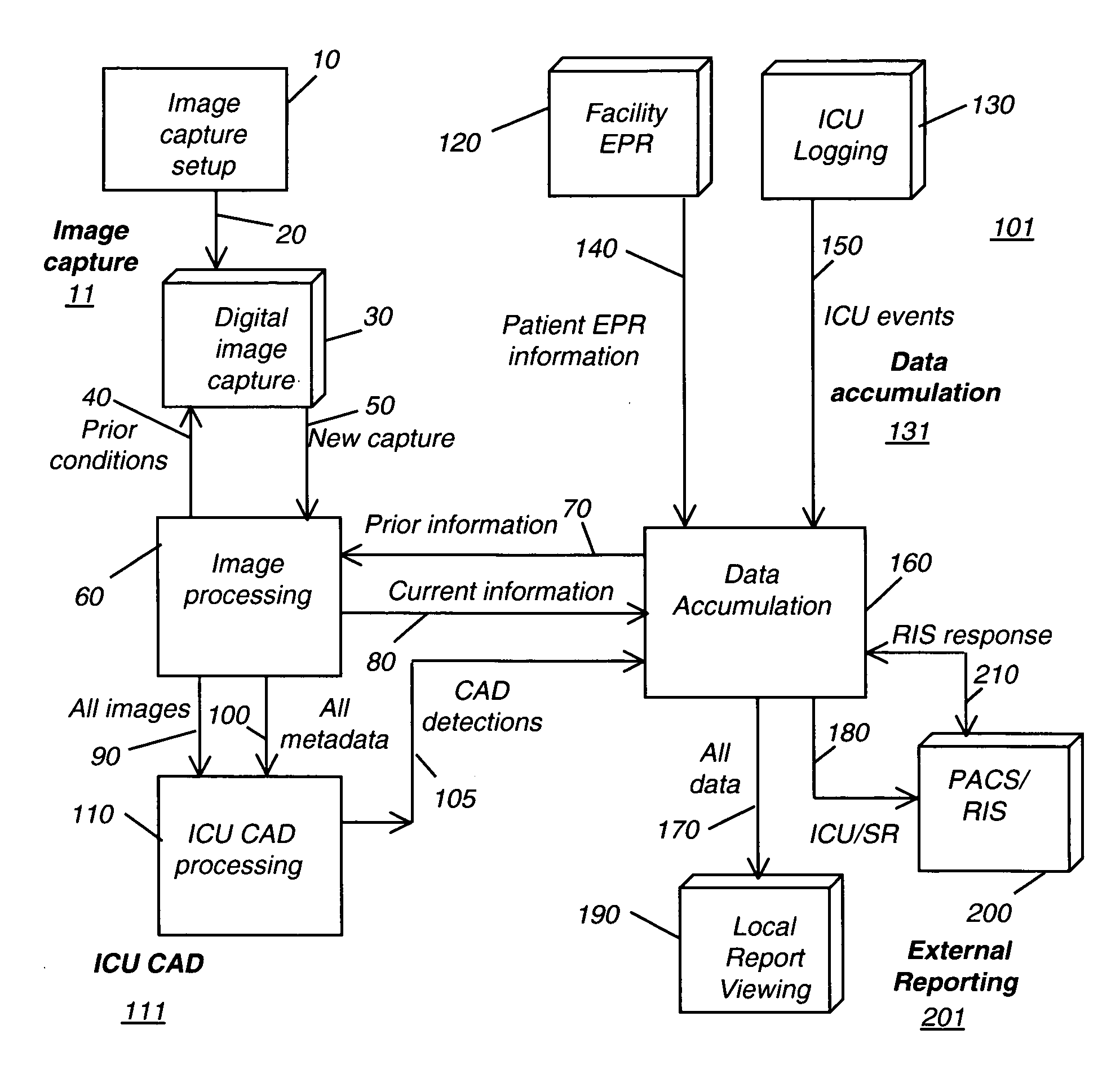
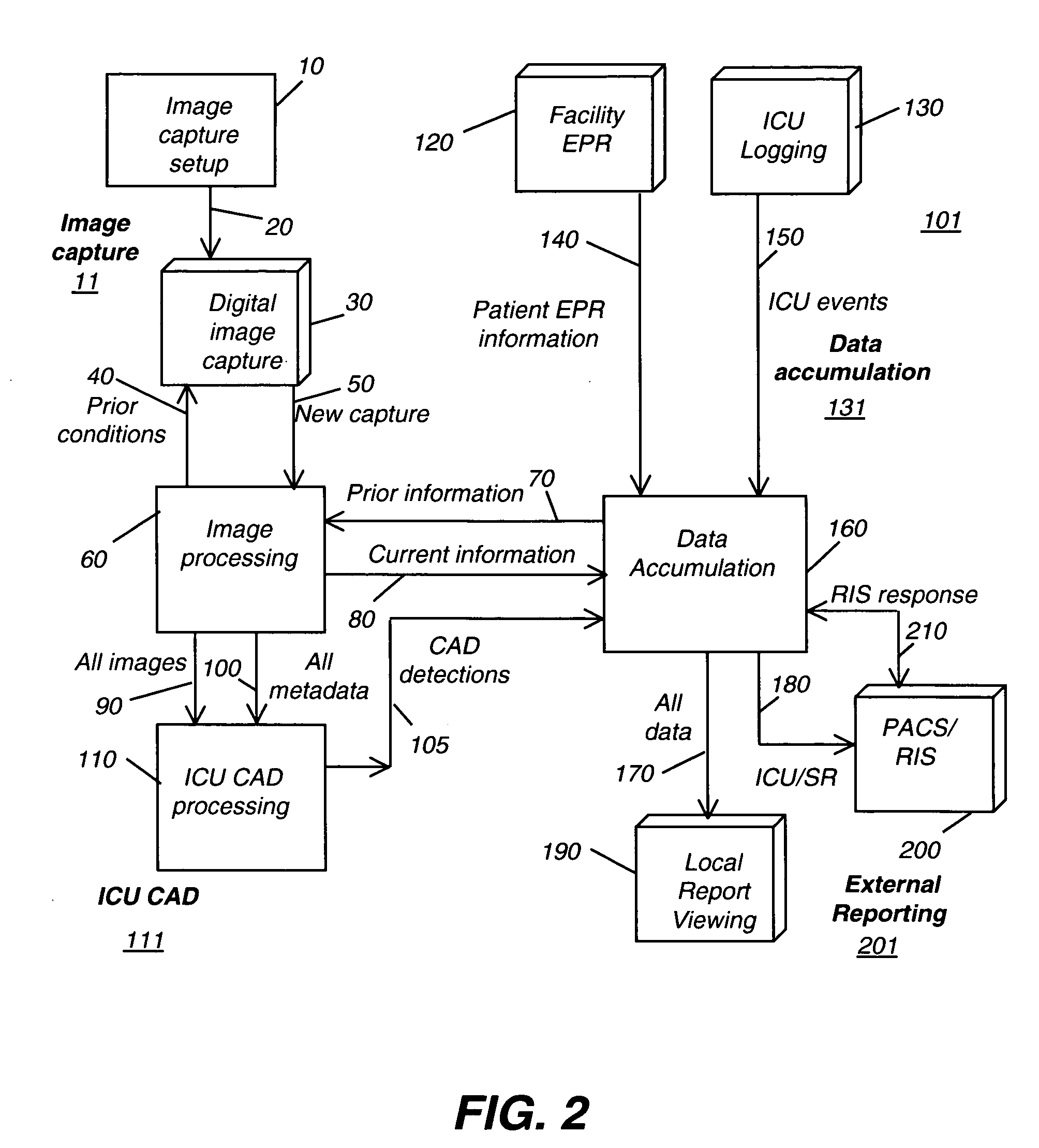
Medical information system for intensive care unit
InactiveUS20080077001A1Enabling useImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsMedical ward
A method for longitudinal tracking of a patient in a critical care facility. A first diagnostic image at a time t1 is obtained, taken using a first set of imaging parameters. At least a portion of the first set of imaging parameters is stored. A second diagnostic image is obtained at a time t2, later than time t1, using a second set of imaging parameters. At least a portion of the second set of imaging parameters is stored. First and second diagnostic images are of substantially the same body tissue. A region of interest is identified from either the first or second diagnostic image. A computer aided diagnostic process executes for a portion of the region of interest on each of the first and second diagnostic images. Results of the computer aided diagnostic process are compared.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
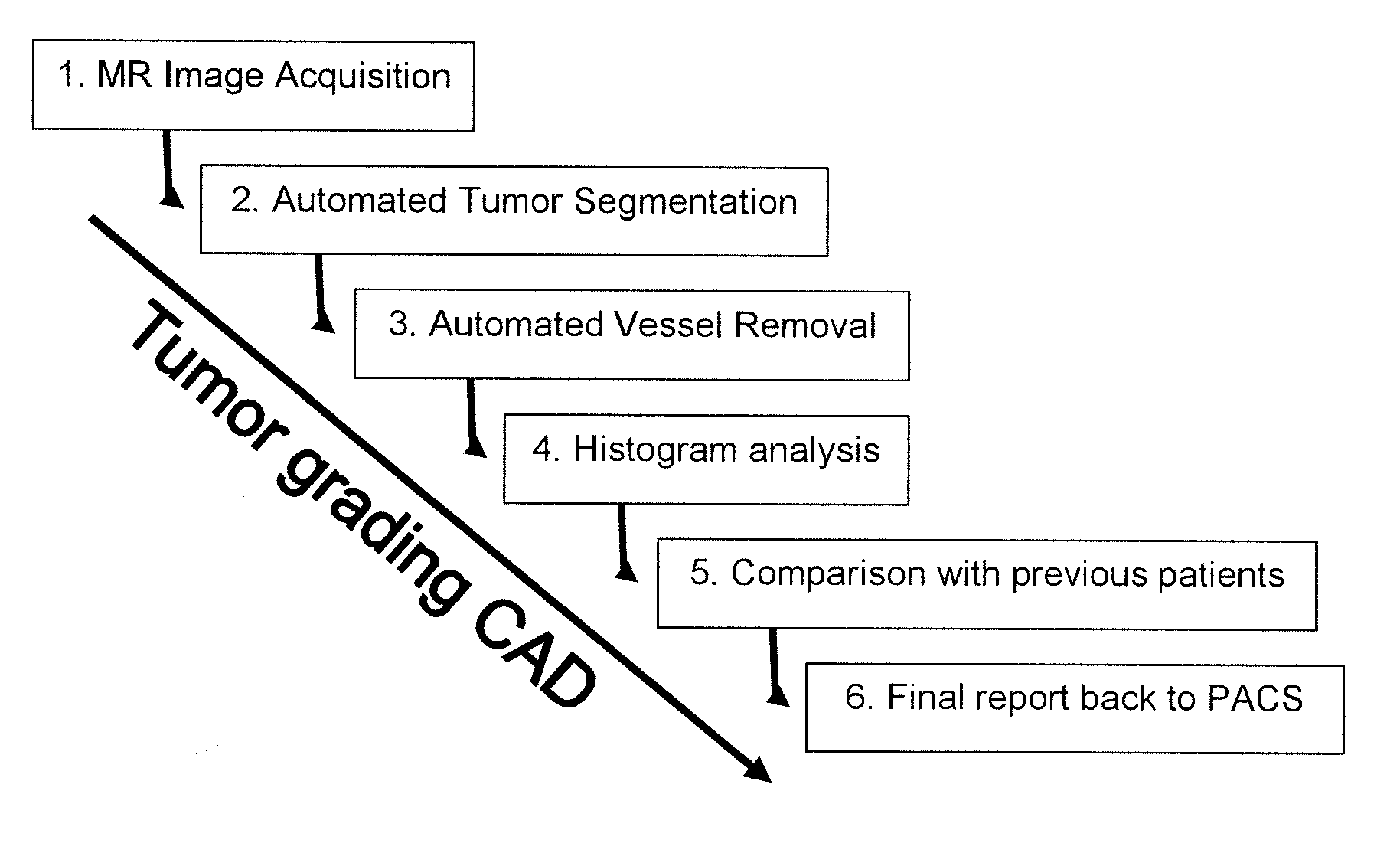
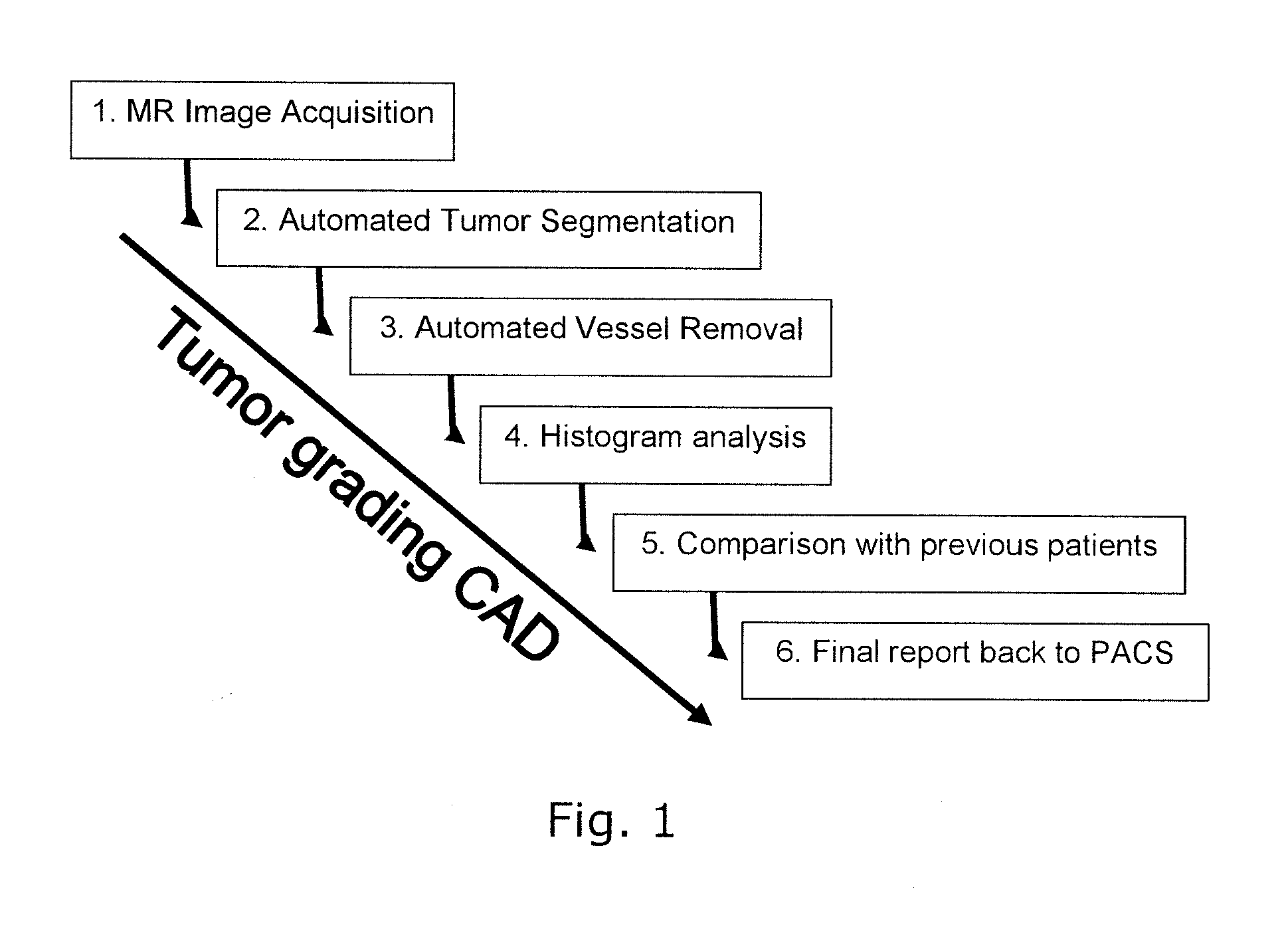
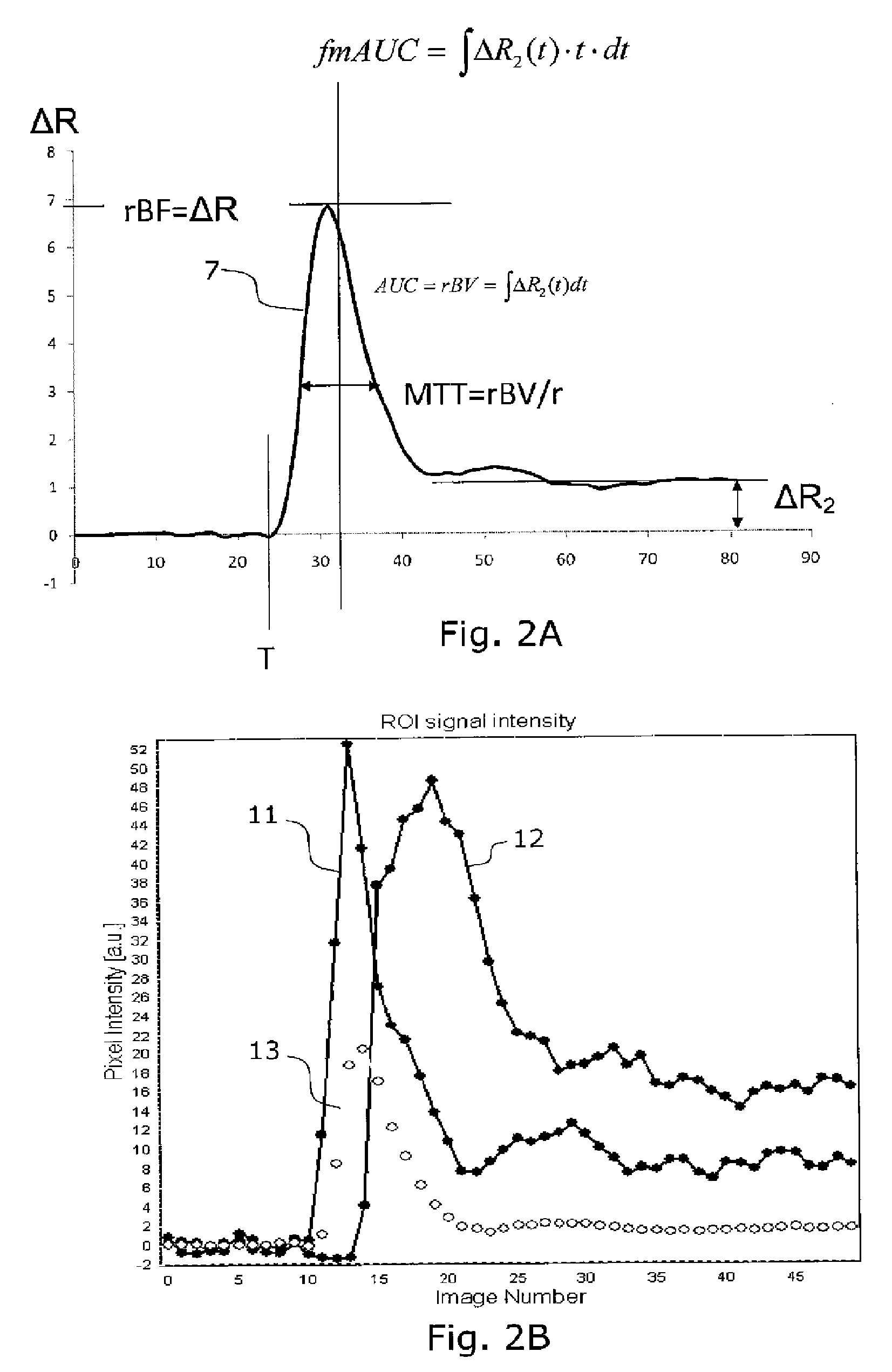
Vessel segmentation in dce mr imaging
ActiveUS20110170759A1Improve diagnostic accuracyMaximise variationImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsDynamic contrast
The invention relates to segmenting blood vessels in perfusion MR images, more particularly, the invention relates to automated vessel removal in identified tumor regions prior to tumor grading. Pixels from a perfusion related map from dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE) MR images are clustered into arterial pixels and venous pixels by e.g. a k-means class cluster analysis. The analysis applies parameters representing the degree to which the tissue entirely consists of blood (such as relative blood volume (rBV), peak enhancement (ΔR2max) and / or post first-pass enhancement level (ΔR2p)) and parameters representing contrast arrival time at the tissue (such as first moment of the area (fmAUC) and / or contrast arrival time (T0)). The artery and venous pixels are used to form a vessel mask. The invention also relates to a computer aided diagnostic (CAD) system for tumor grading, comprising automated tumor segmentation, vessel segmentation, and tumor grading.
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
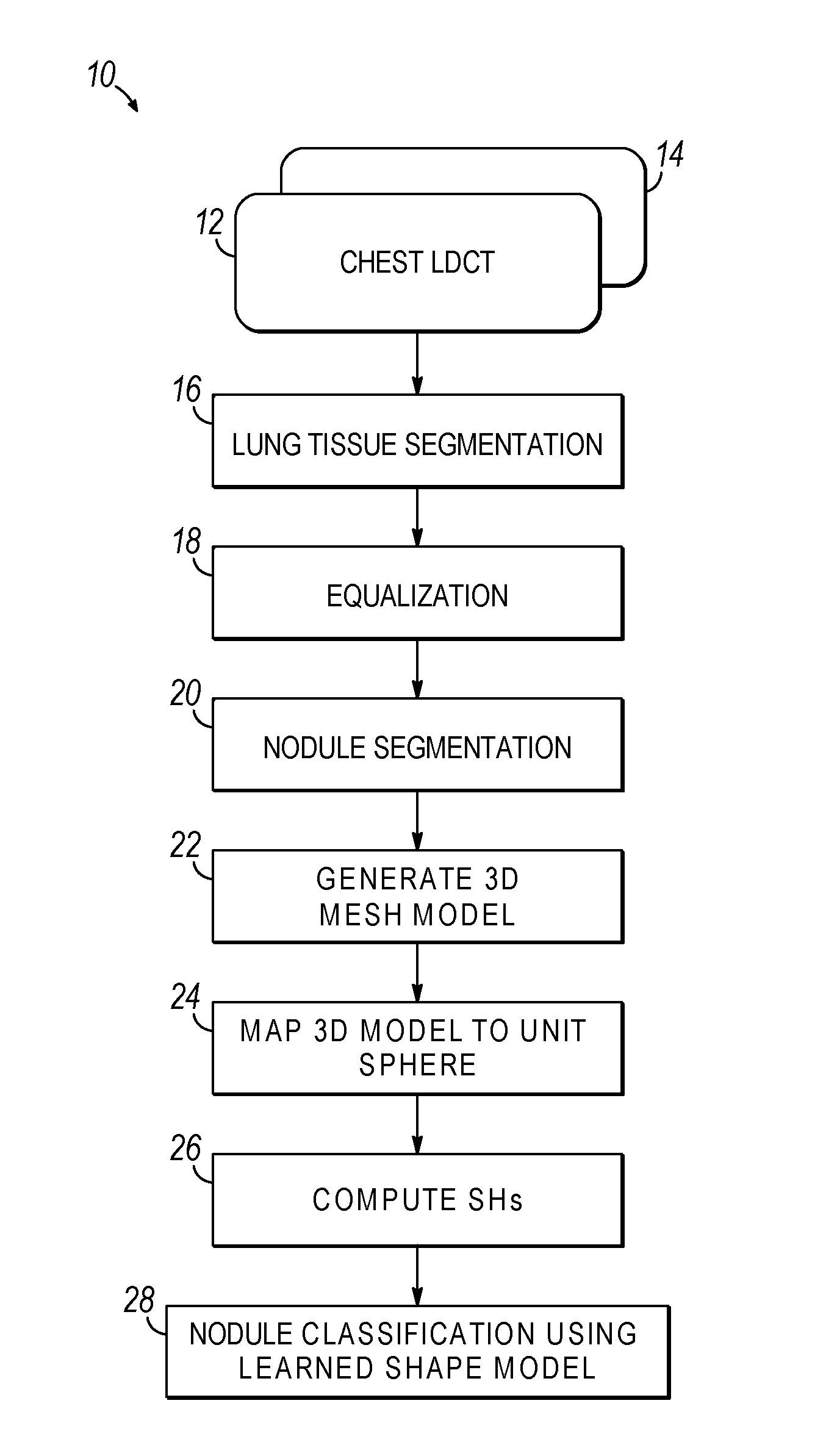
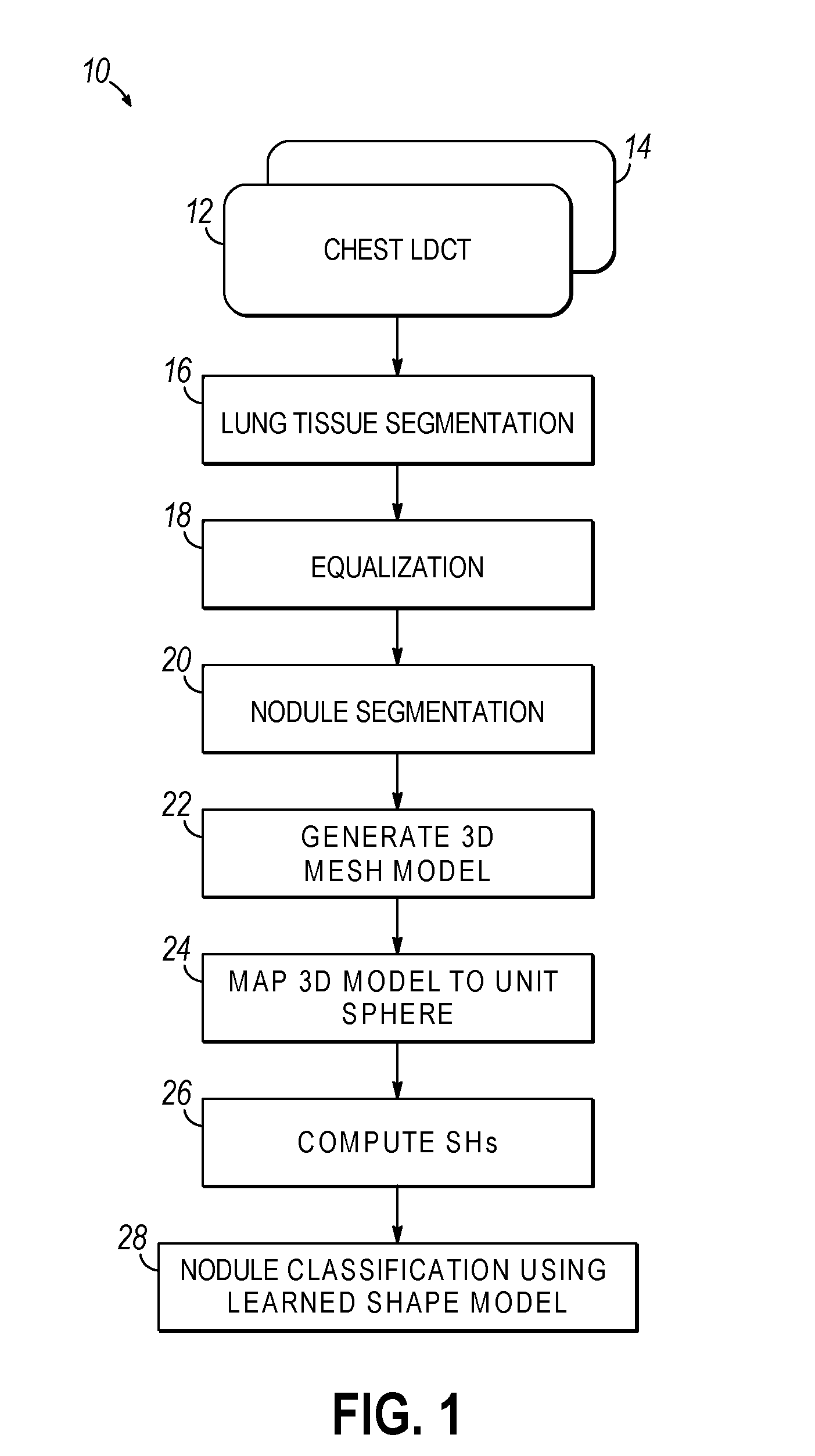
Computer aided diagnostic system incorporating shape analysis for diagnosing malignant lung nodules
A computer aided diagnostic system and automated method diagnose lung cancer through modeling and analyzing the shape of pulmonary nodules. A model used in such analysis describes the shape of pulmonary nodules in terms of spherical harmonics required to delineate a unit sphere corresponding to the pulmonary nodule to a model of the pulmonary nodule.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Computer aided diagnostic system incorporating lung segmentation and registration
ActiveUS8731255B2Change in volume of a noduleImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleComputer aided diagnostics
A computer aided diagnostic system and automated method diagnose lung cancer through tracking of the growth rate of detected pulmonary nodules over time. The growth rate between first and second chest scans taken at first and second times is determined by segmenting out a nodule from its surrounding lung tissue and calculating the volume of the nodule only after the image data for lung tissue (which also includes image data for a nodule) has been segmented from the chest scans and the segmented lung tissue from the chest scans has been globally and locally aligned to compensate for positional variations in the chest scans as well as variations due to heartbeat and respiration during scanning. Segmentation may be performed using a segmentation technique that utilizes both intensity (color or grayscale) and spatial information, while registration may be performed using a registration technique that registers lung tissue represented in first and second data sets using both a global registration and a local registration to account for changes in a patient's orientation due in part to positional variances and variances due to heartbeat and / or respiration.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Patient treatment systems and methods
PendingUS20180330059A1Medical data miningHealth-index calculationComputer aided diagnosticsPatient input
Presented are systems and methods for providing doctors and patients with treatment information based on computer-aided diagnoses that has been generated using patient input, electronic health care record information, and medical instrument input data. The treatment and / or diagnostic information may be shared with health care professionals and specialists, as needed.
Owner:ADVINOW INC
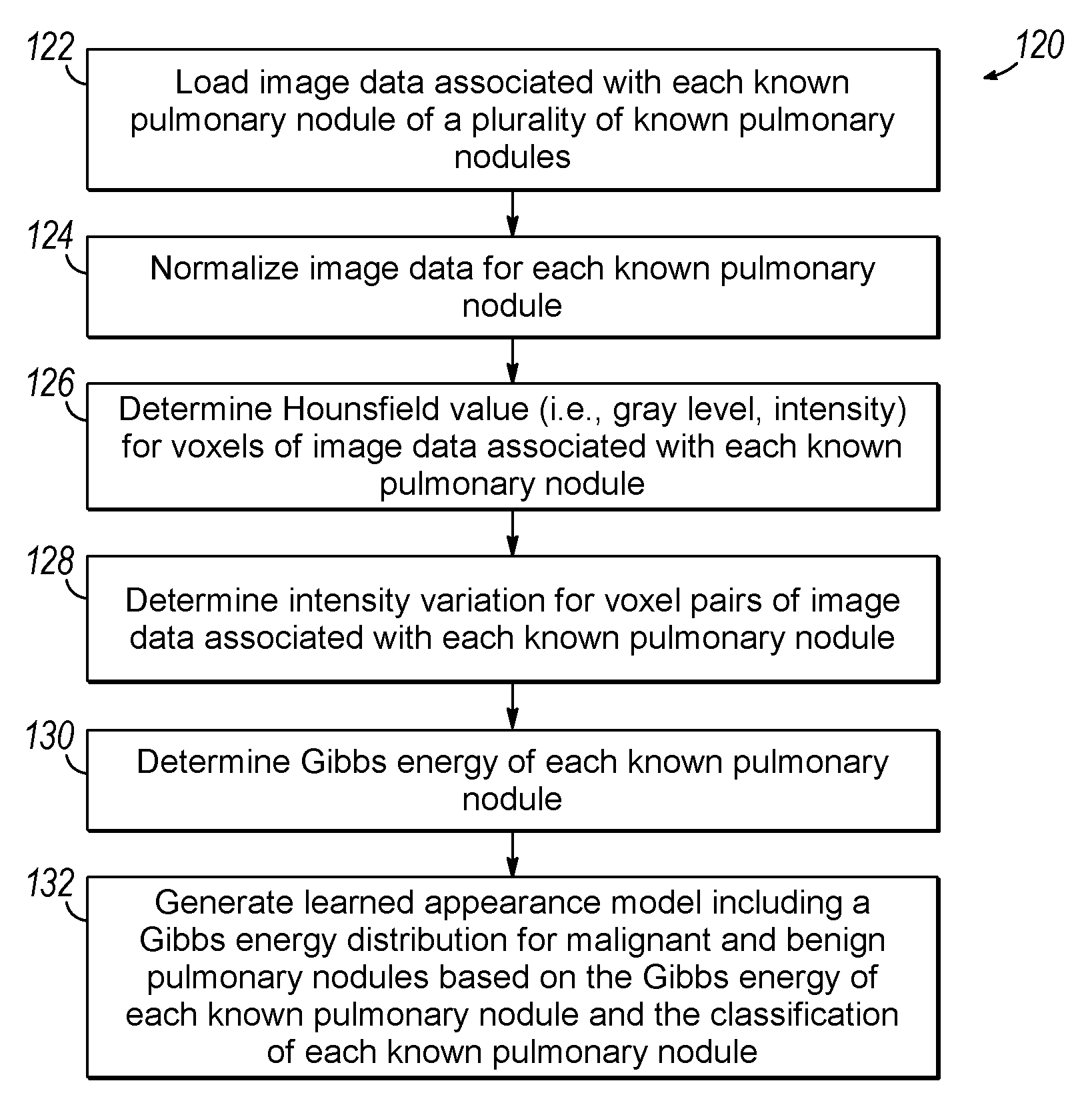
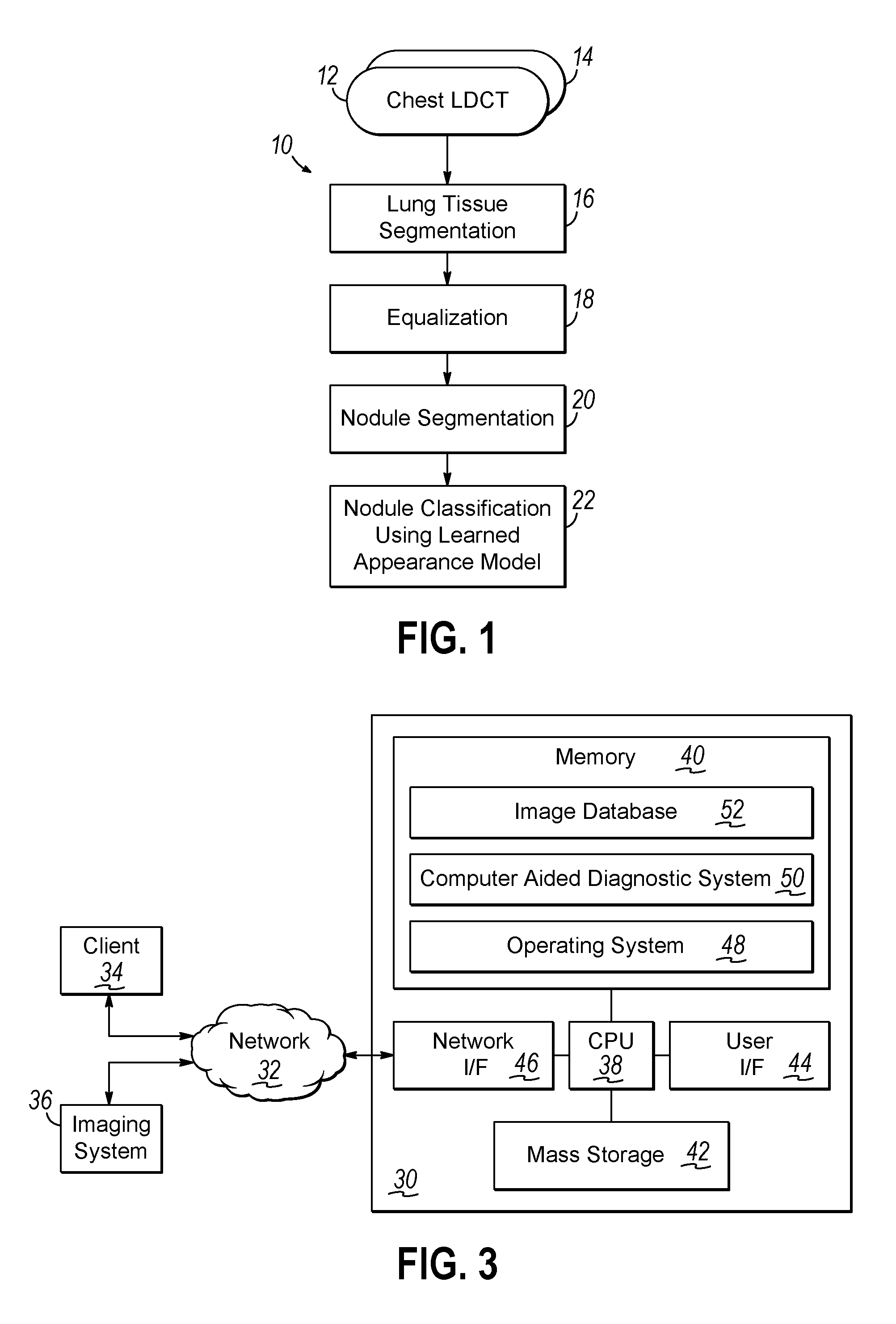
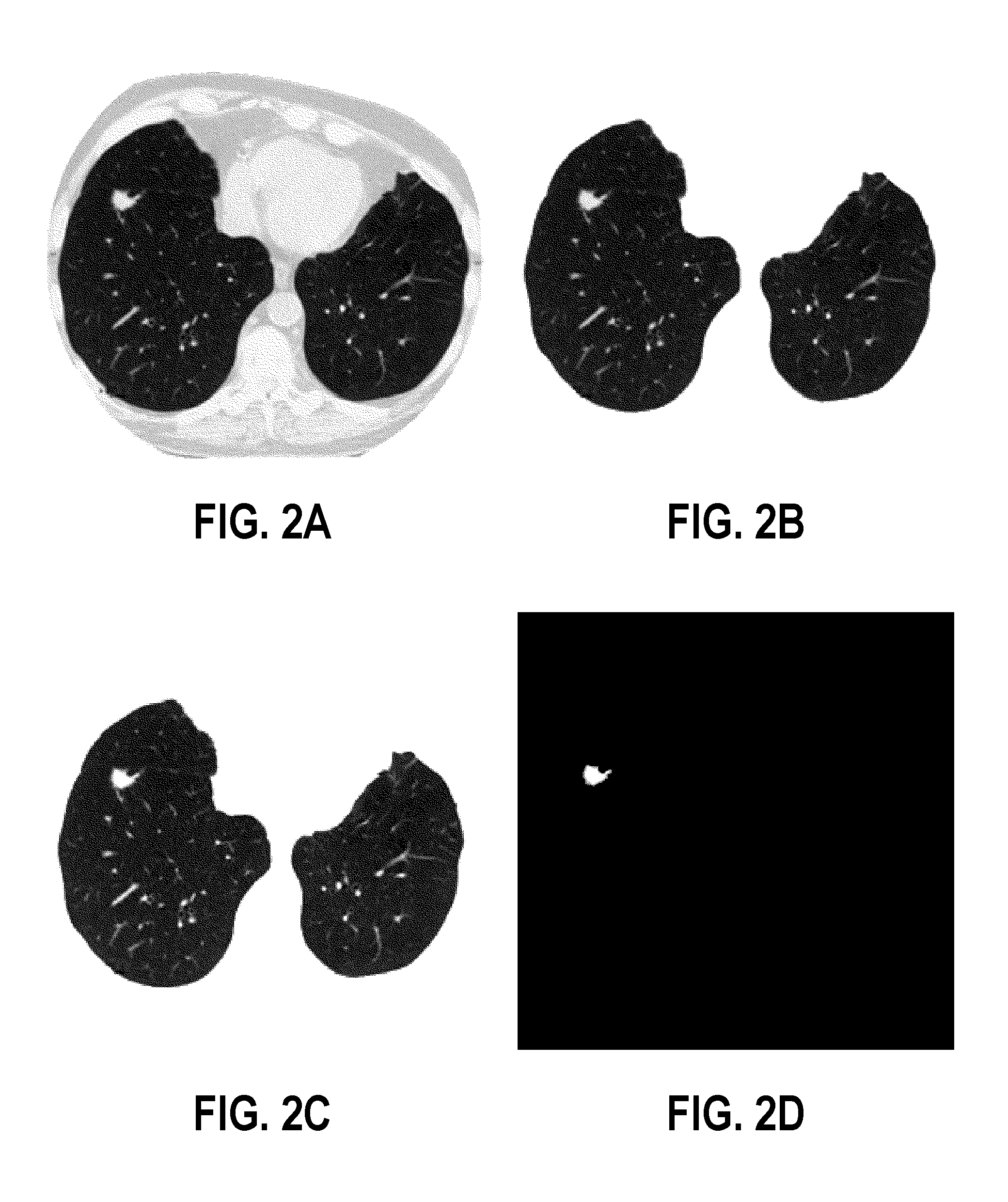
Computer aided diagnostic system incorporating appearance analysis for diagnosing malignant lung nodules
A computer aided diagnostic system and automated method diagnose lung cancer through modeling and analyzing the visual appearance of pulmonary nodules. A learned appearance model used in such analysis describes the appearance of pulmonary nodules in terms of voxel-wise conditional Gibbs energies for a generic rotation and translation invariant second-order Markov-Gibbs random field (MGRF) model of malignant nodules with analytically estimated characteristic voxel neighborhoods and potentials.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
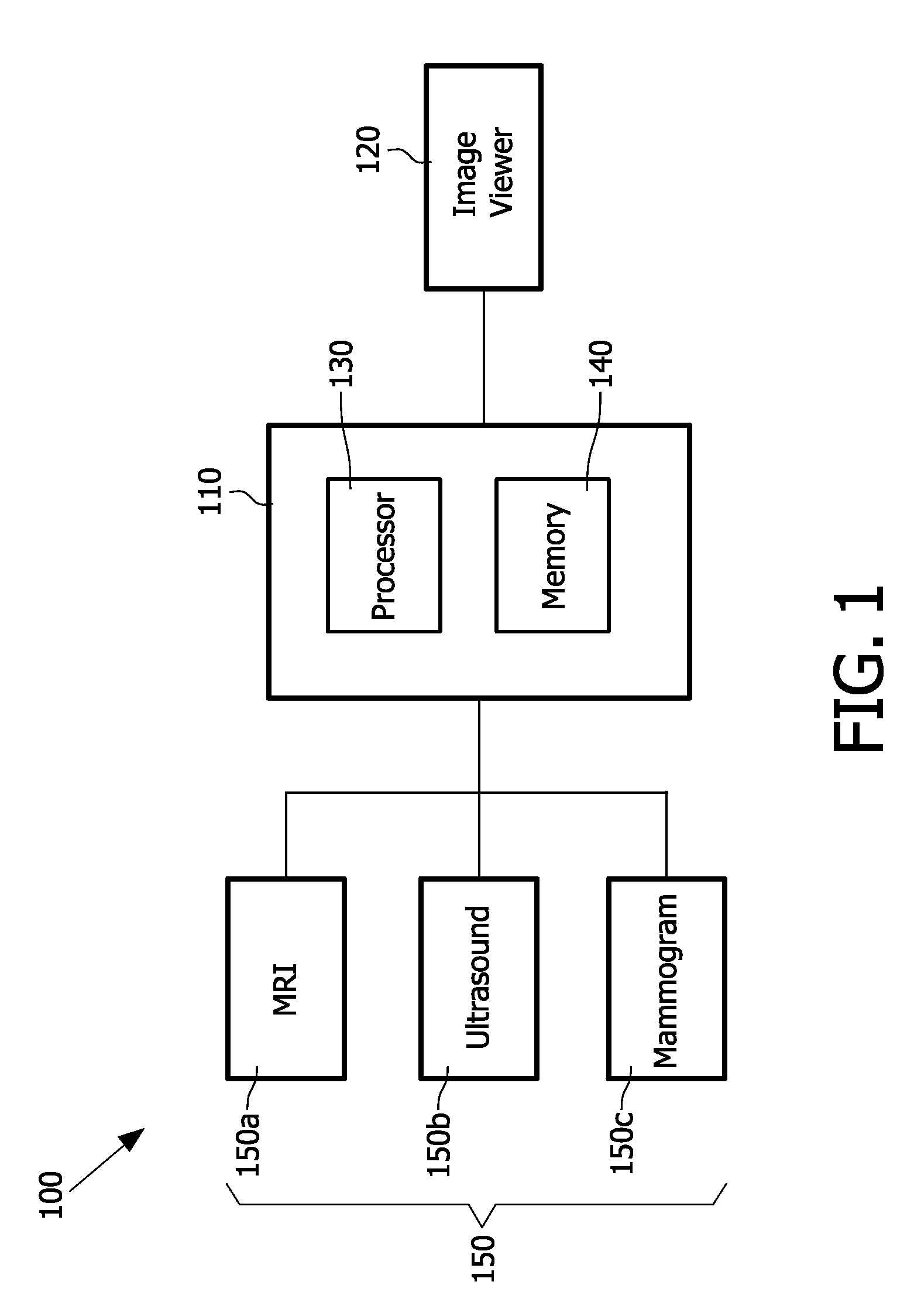
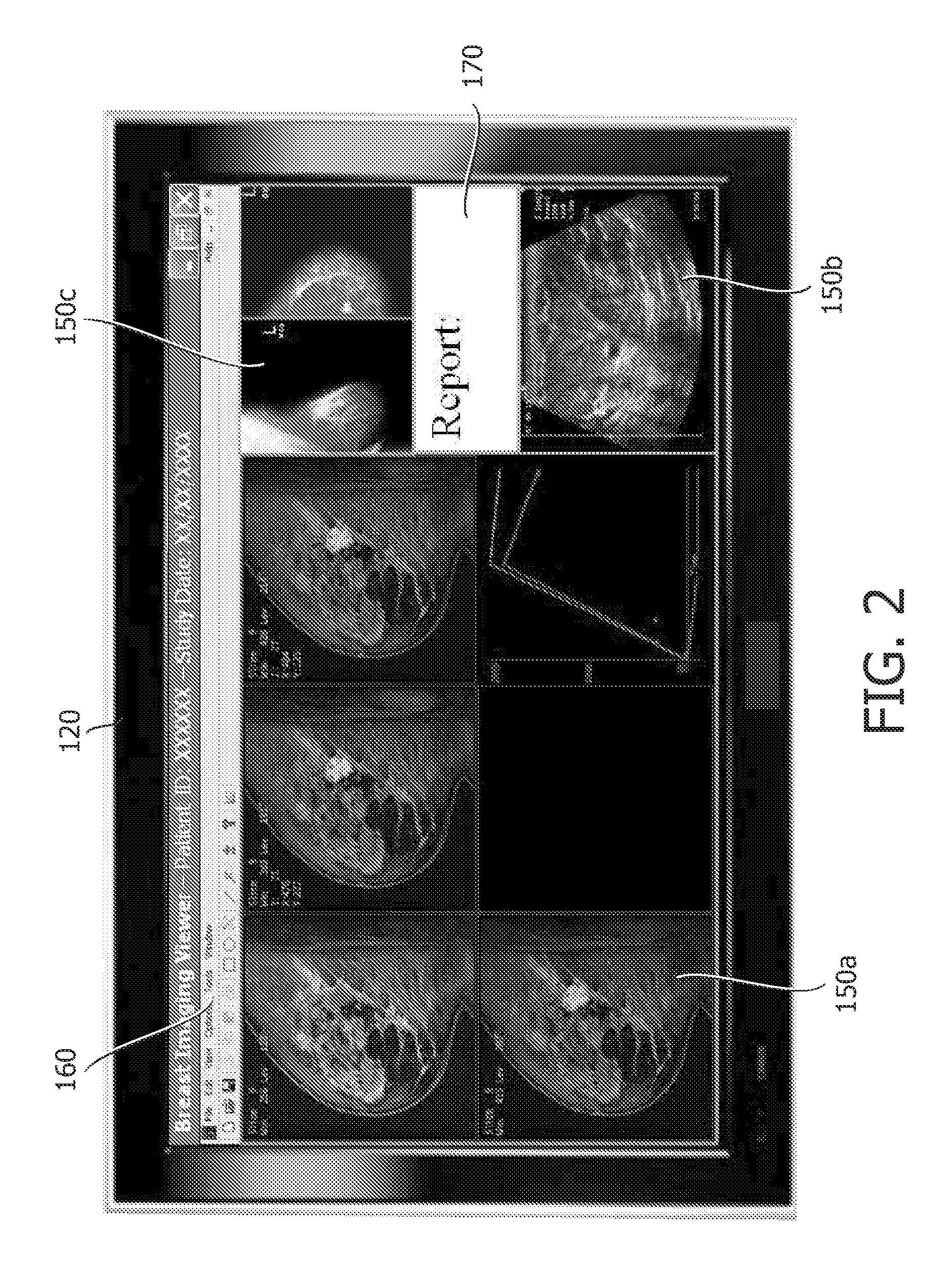
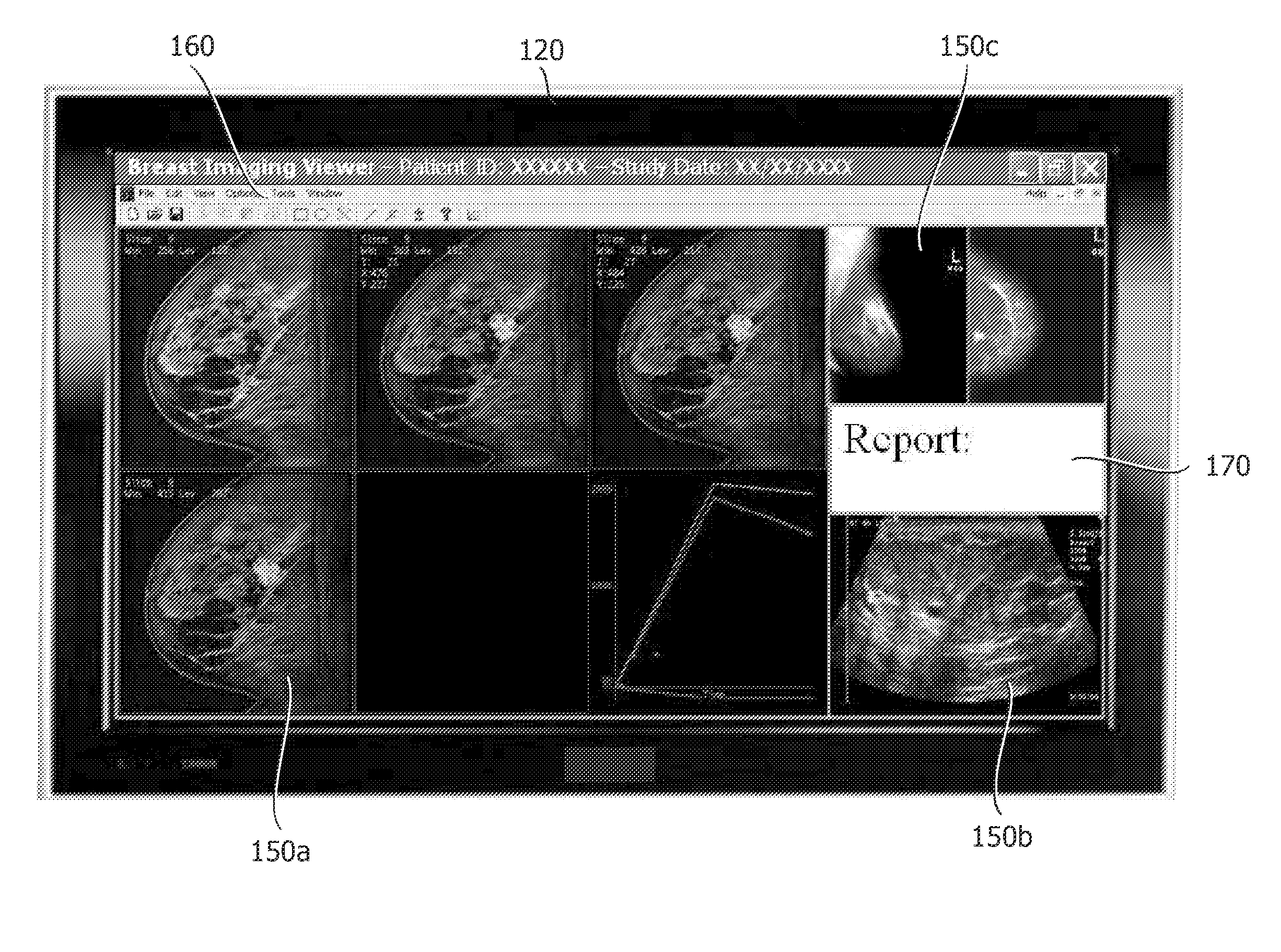
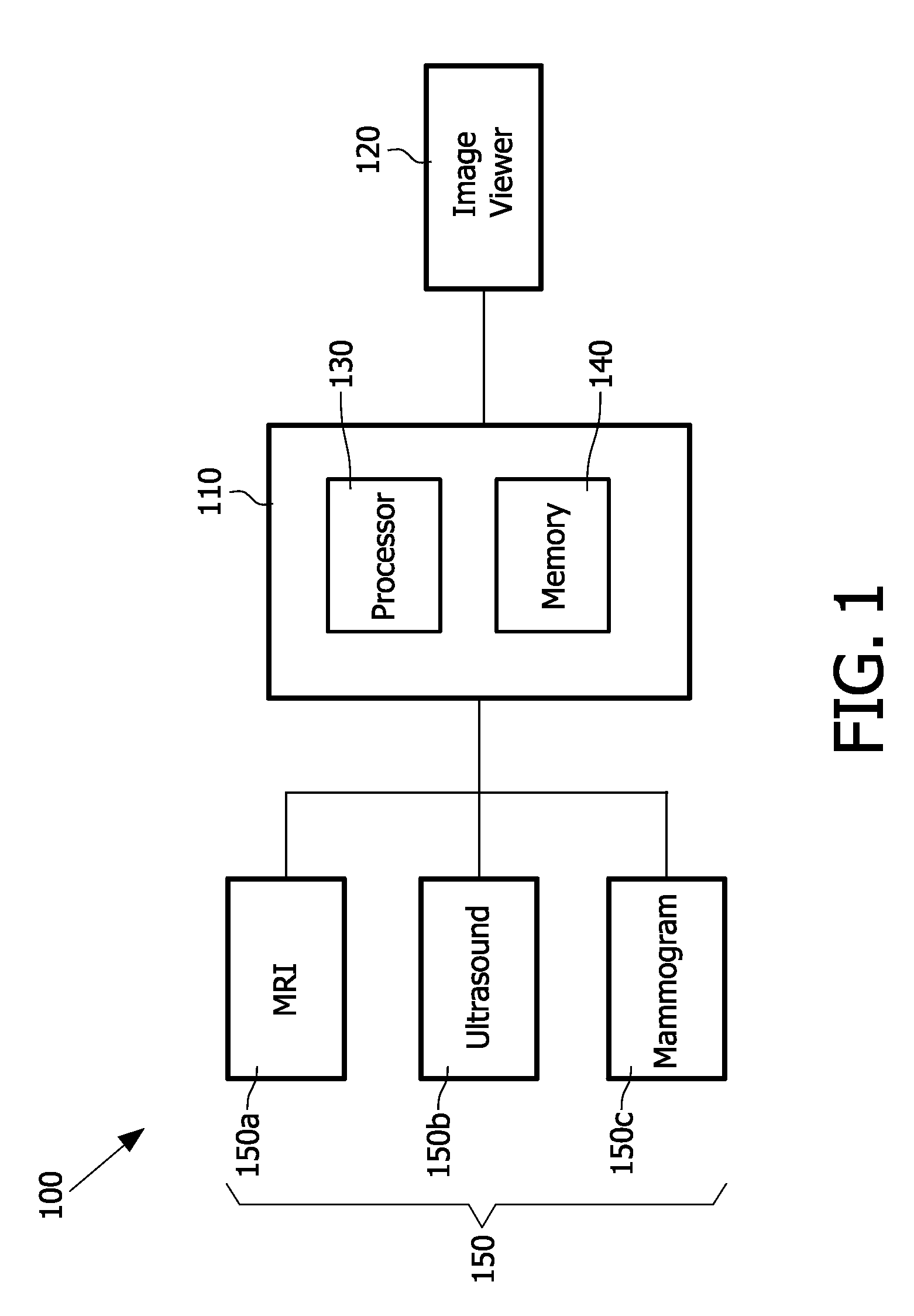
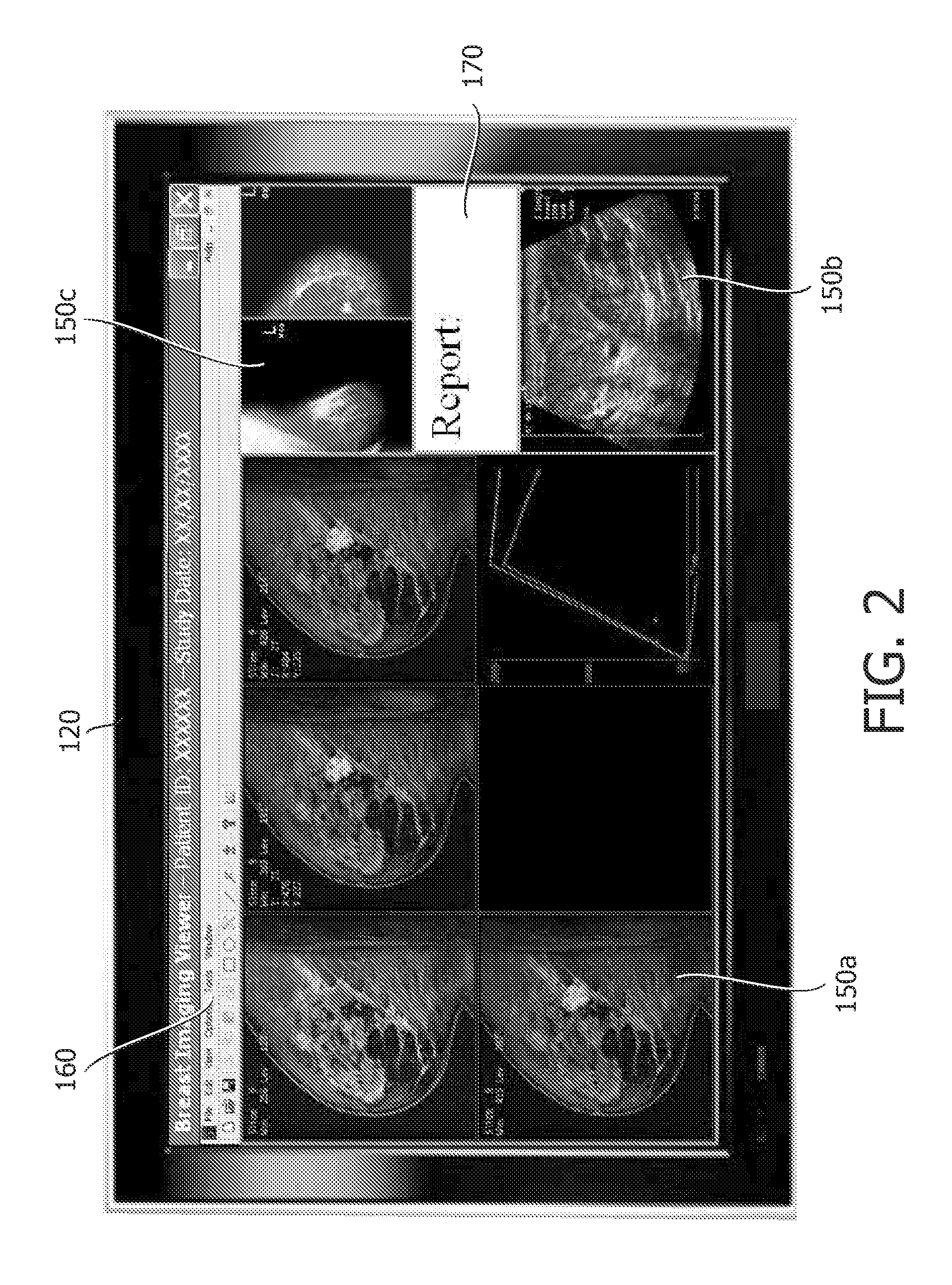
Multiple modality computer aided diagnostic system and method
ActiveUS20110087089A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsData processing applicationsComputer aided diagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology Modality
A diagnostic system having an image loader including a processor for processing multiple modality images, at least one of the multiple modality images being a mammogram image, the processing including generating diagnostic information based on a computer aided diagnostic tool and an image viewer simultaneously displaying the multiple modality images.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
Malignancy diagnosis using content-based image retreival of tissue histopathology
ActiveUS8280132B2Reduce dimensionalityHigh magnificationImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsImaging Feature
This invention relates to computer-aided diagnostics using content-based retrieval of histopathological image features. Specifically, the invention relates to the extraction of image features from a histopathological image based on predetermined criteria and their analysis for malignancy determination.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
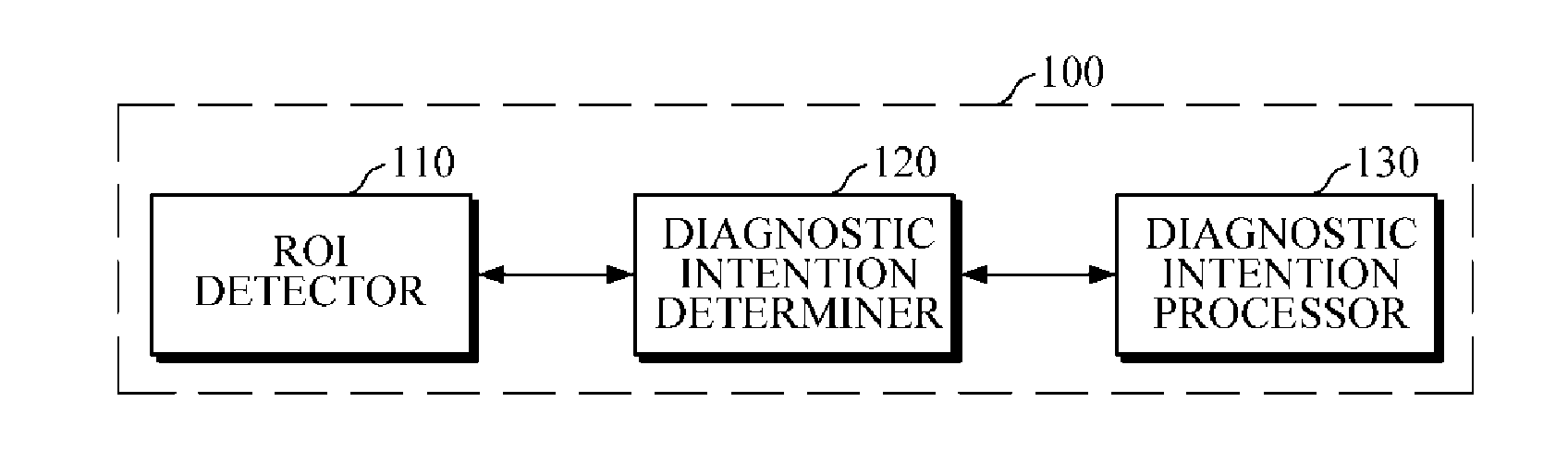
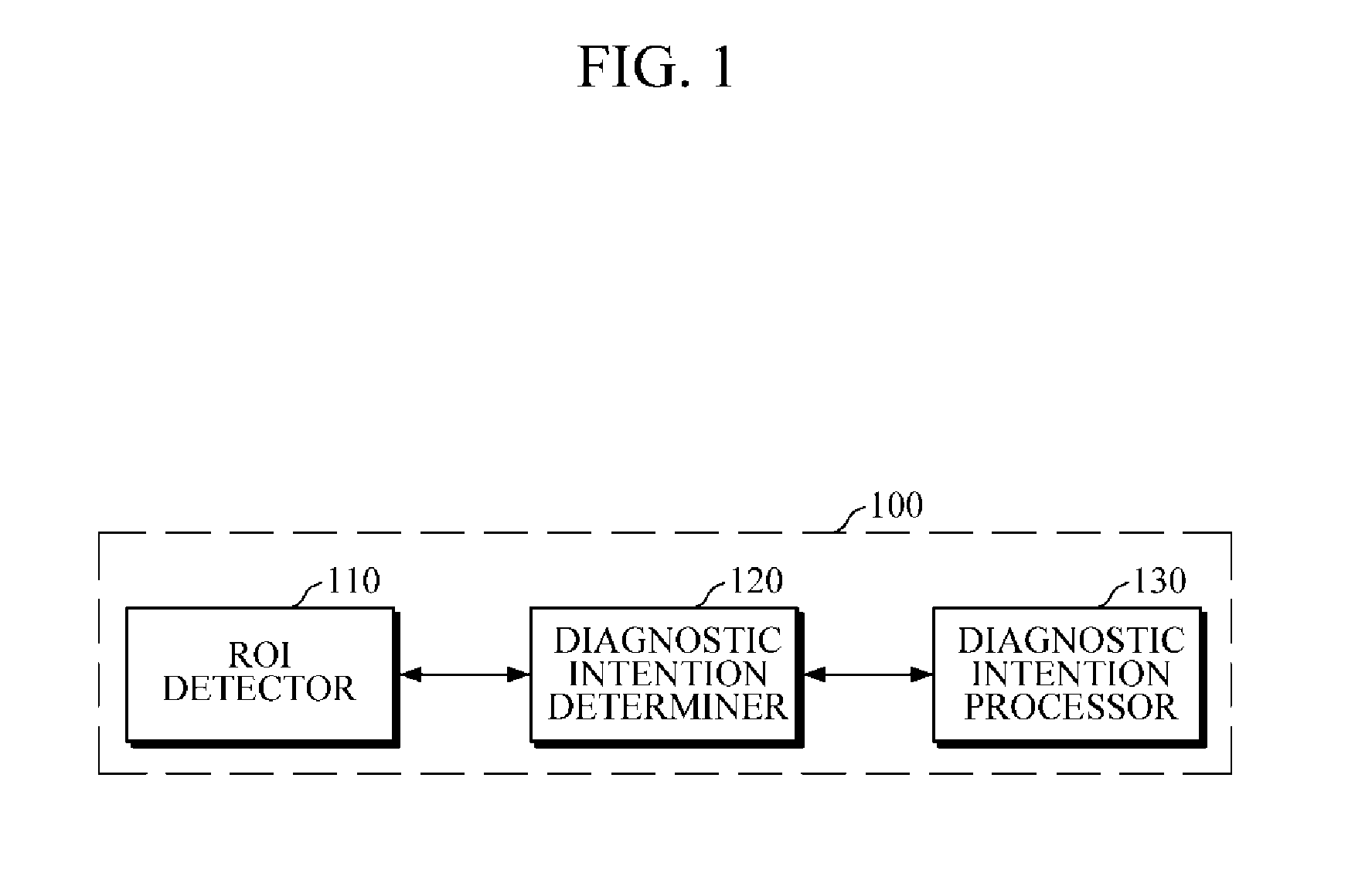
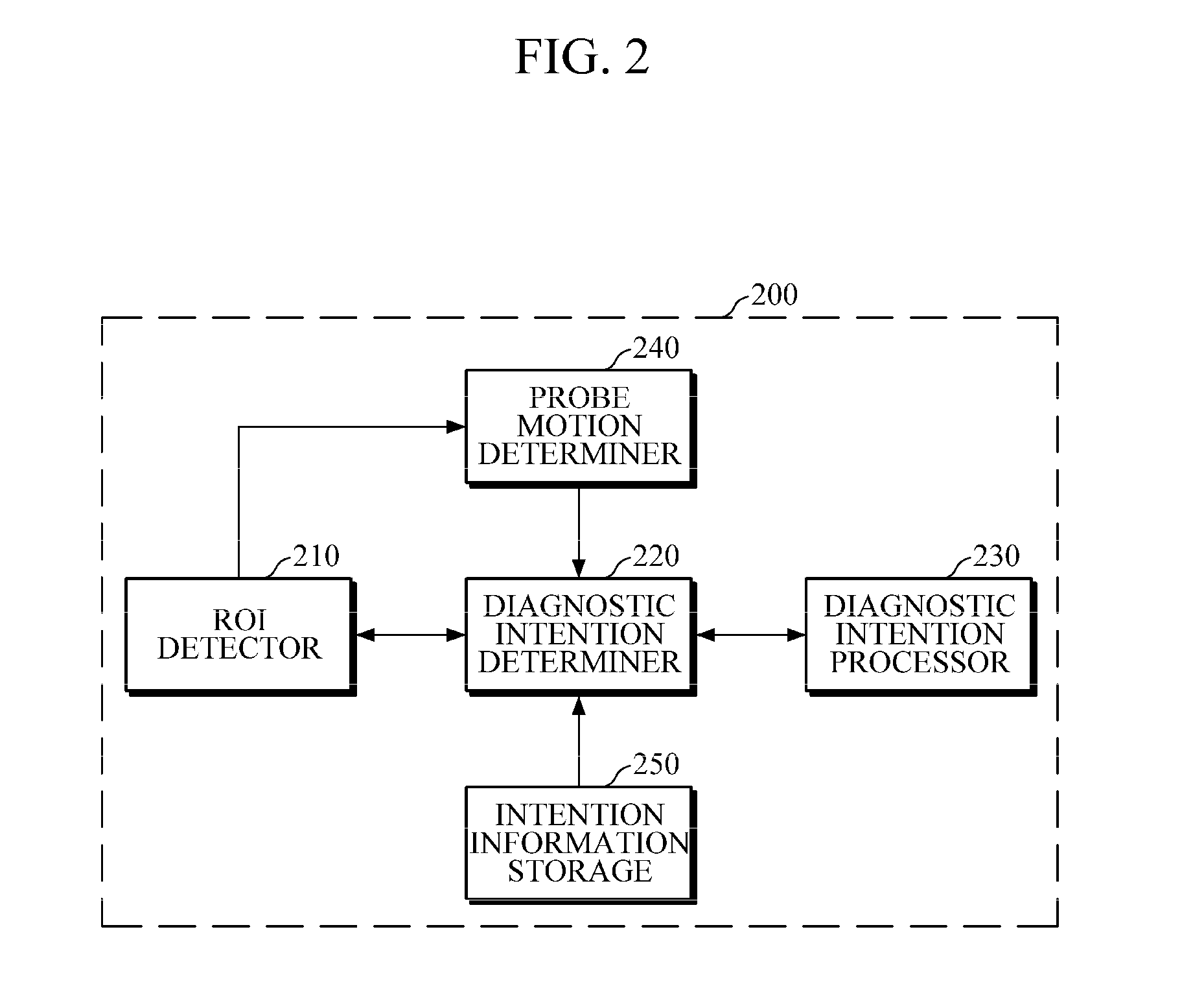
Computer-aided diagnostic apparatus and method based on diagnostic intention of user
ActiveUS20160155227A1Saving diagnostic informationImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsComputer-aided
A computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) apparatus and a CAD method based on the diagnostic intention of a user are provided. The CAD apparatus includes a region of interest (ROI) detector configured to detect an ROI from an image input from a probe, and a probe motion determiner configured to determine a motion of the probe in response to the ROI detector detecting the ROI. The CAD apparatus further includes a diagnostic intention determiner configured to determine a diagnostic intention of a user based on the determined motion of the probe, and a diagnostic intention processor configured to perform a diagnostic procedure based on the determined diagnostic intention of the user.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
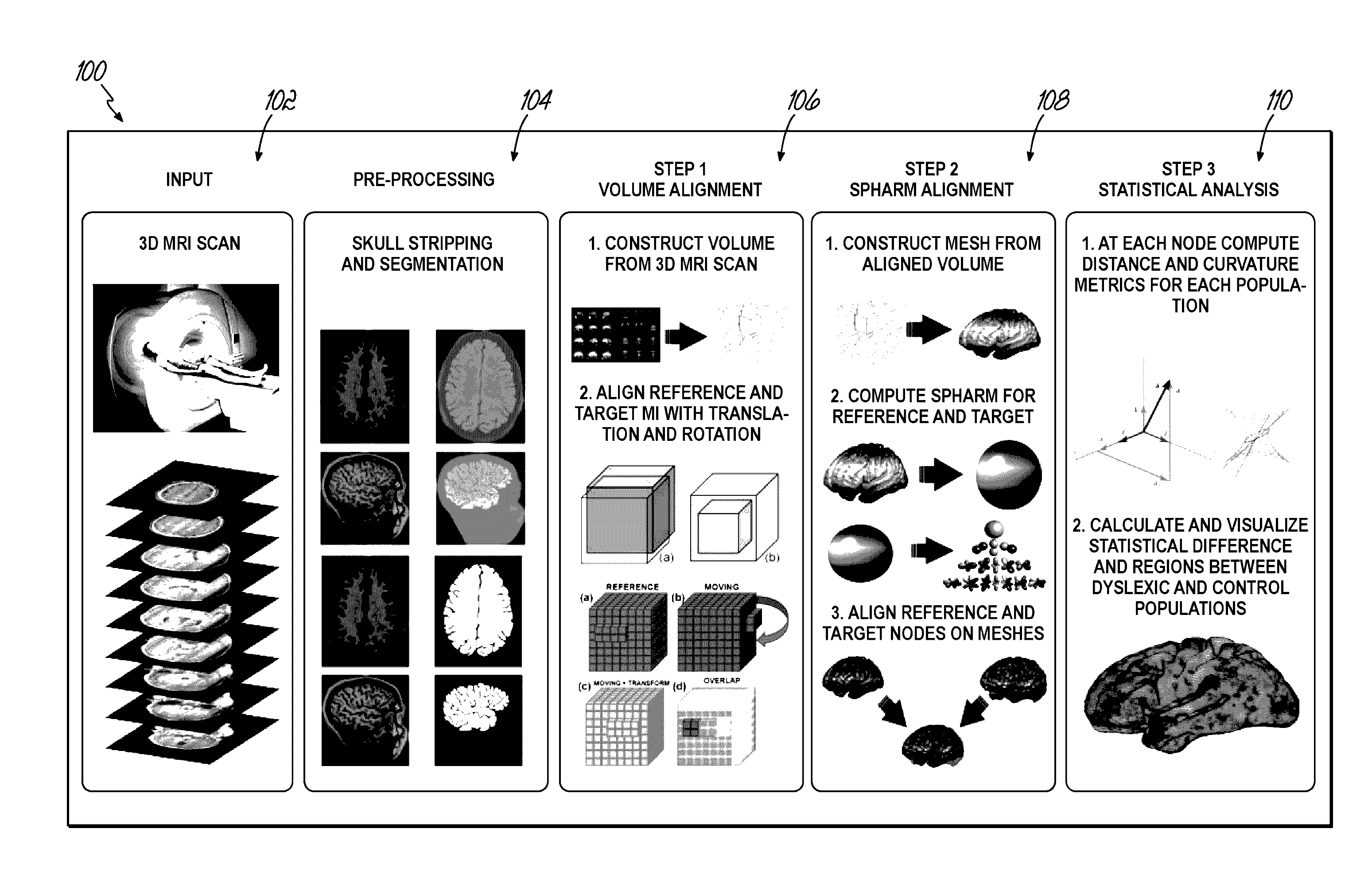
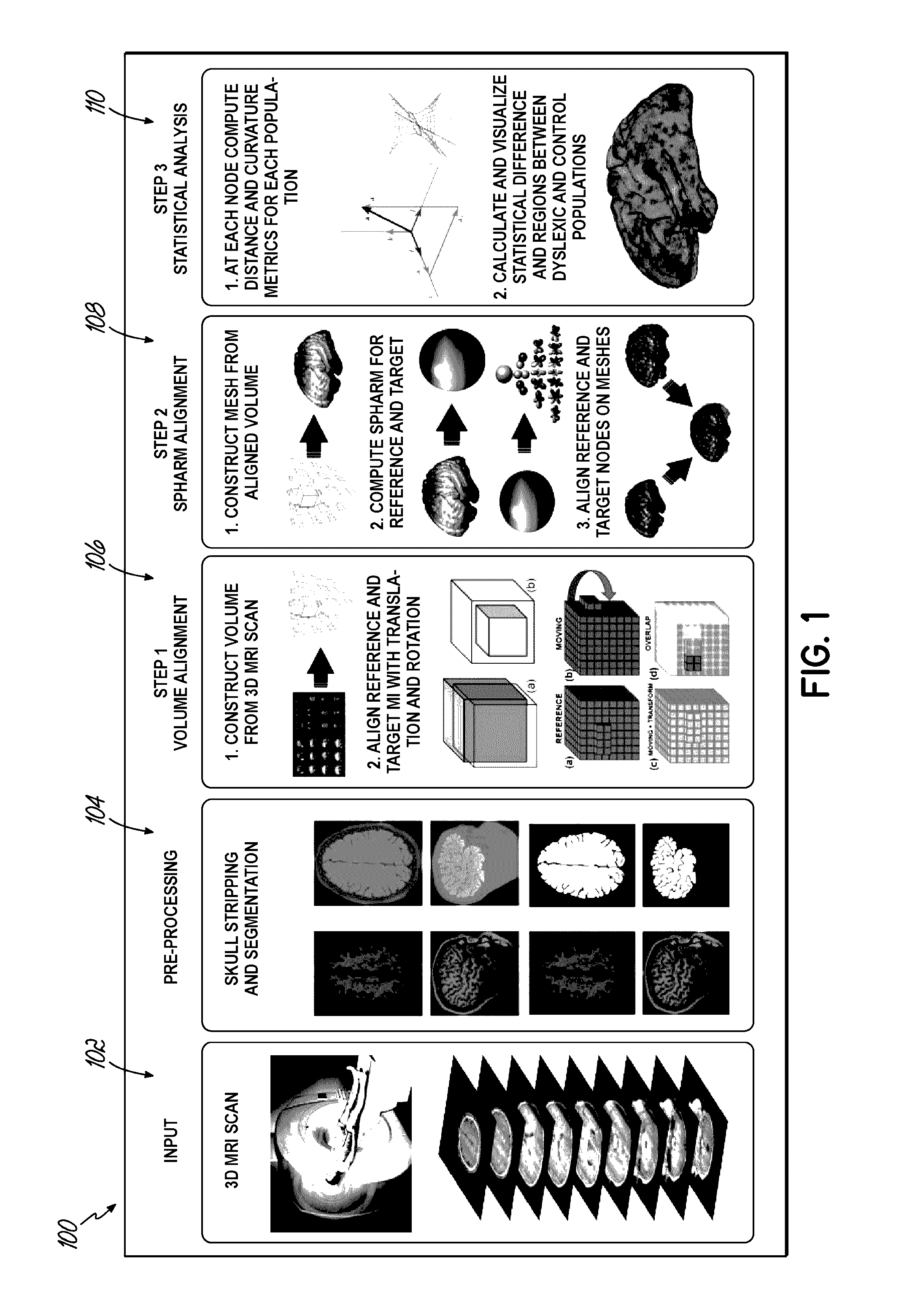
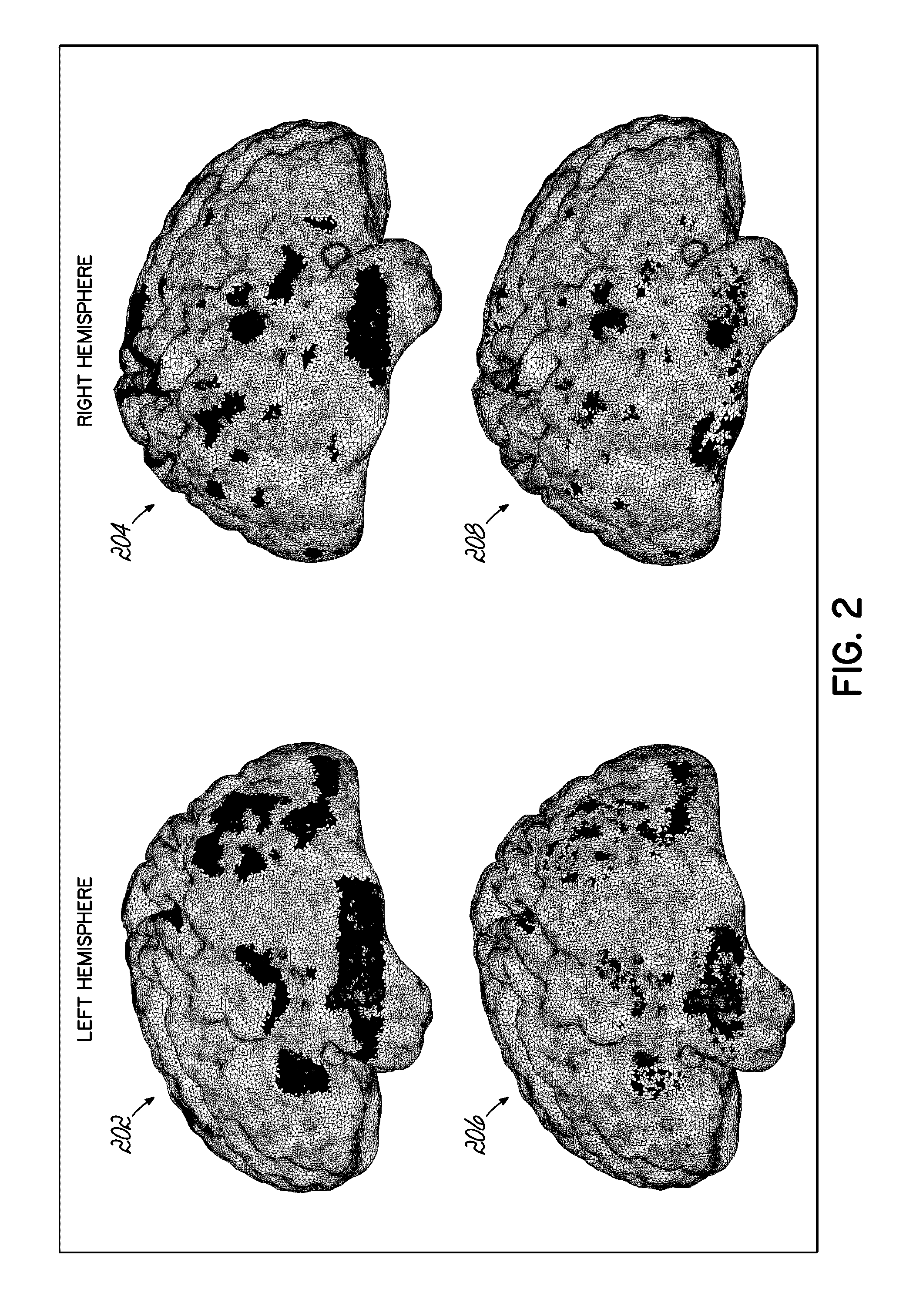
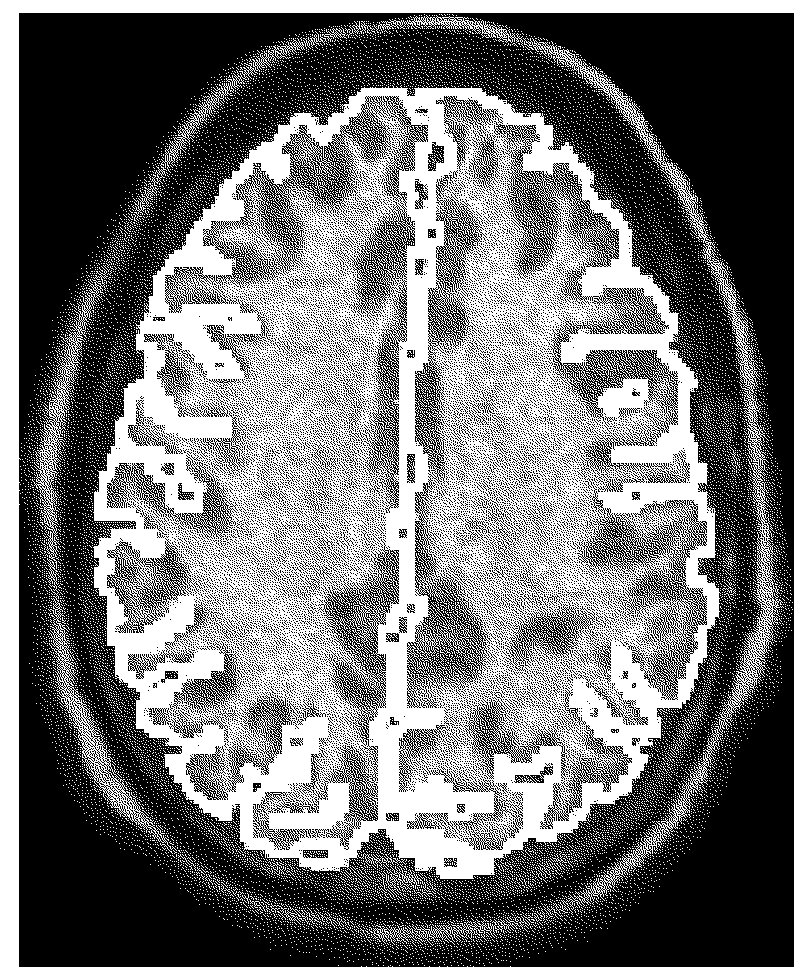
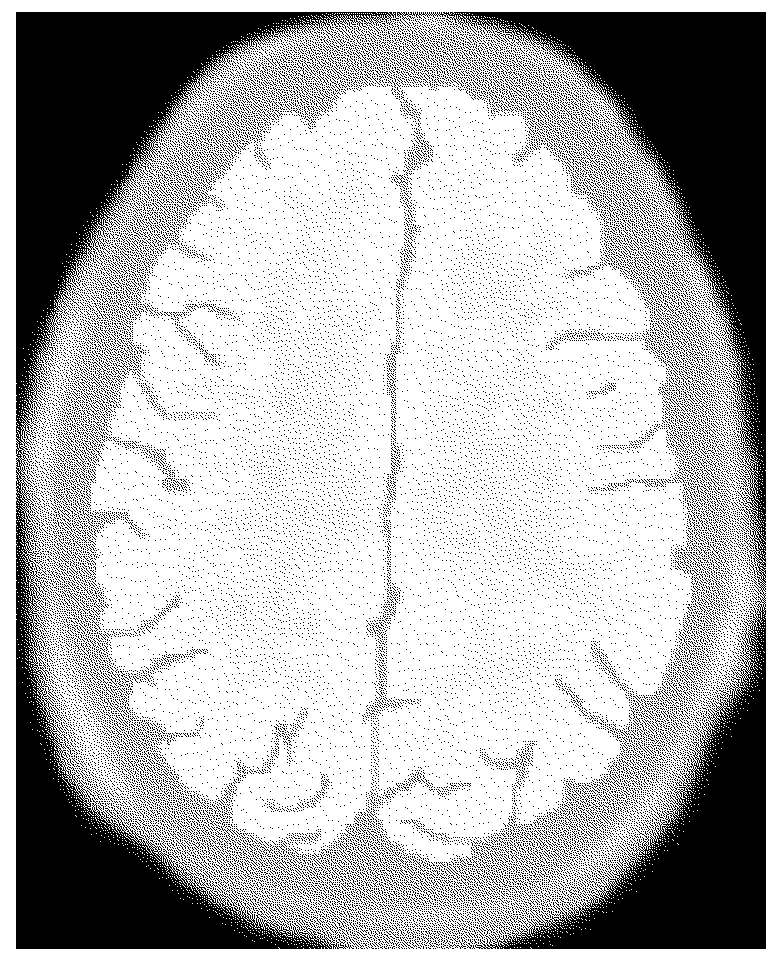
Computer aided diagnostic system incorporating 3D shape analysis of the brain for identifying developmental brain disorders
A computer aided diagnostic system and automated method classify a brain through modeling and analyzing the shape of a brain cortex, e.g., to detect a brain cortex that is indicative of a developmental disorder such as ADHD, autism or dyslexia. A model used in such analysis describes the shape of brain cortices in terms of spherical harmonics required to delineate a unit sphere corresponding to the brain cortex to a model of the brain cortex.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
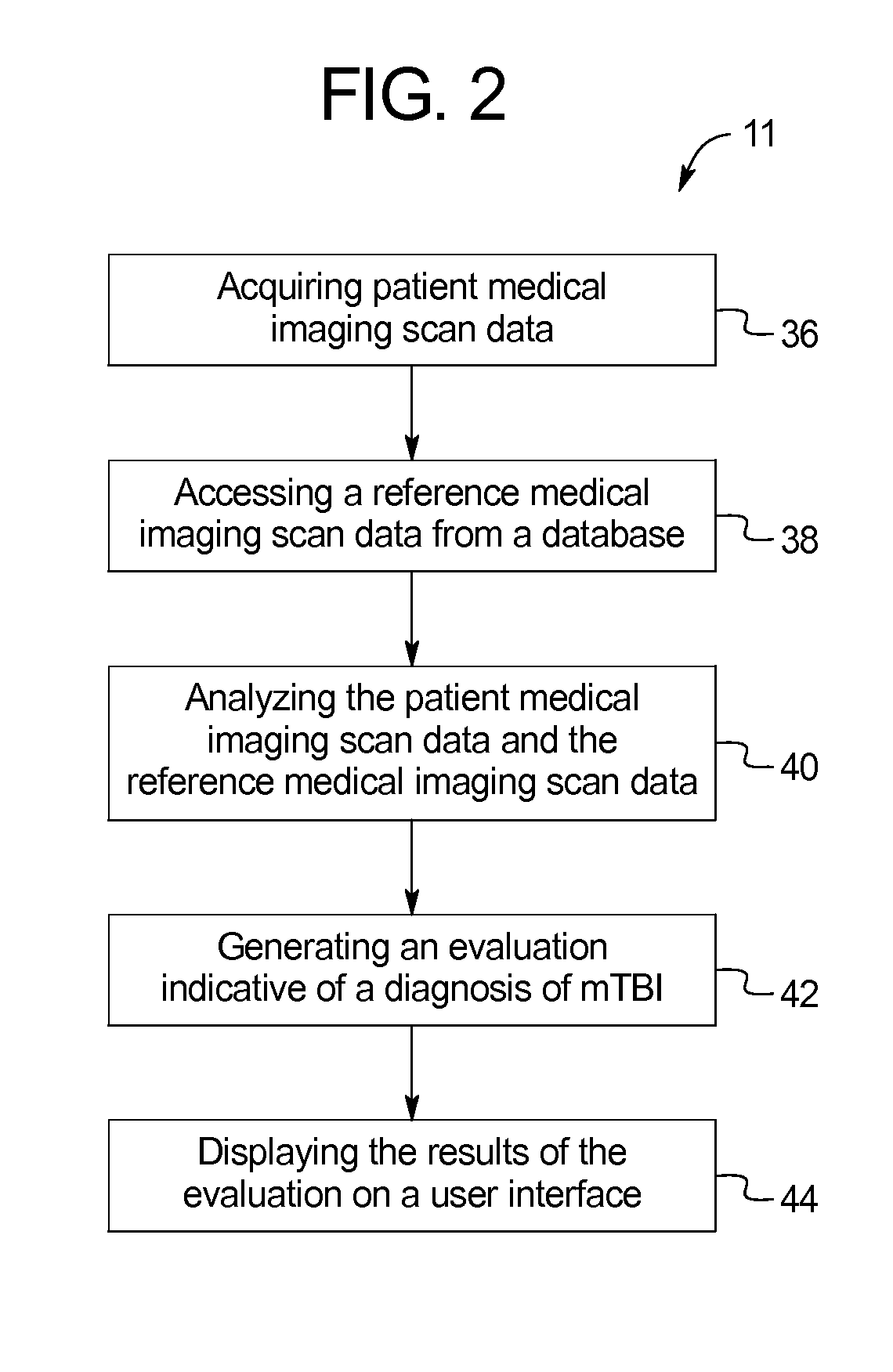
Systems and methods for evaluating a brain scan
ActiveUS20140270052A1Superior and objective evaluationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputer aided diagnosticsData set
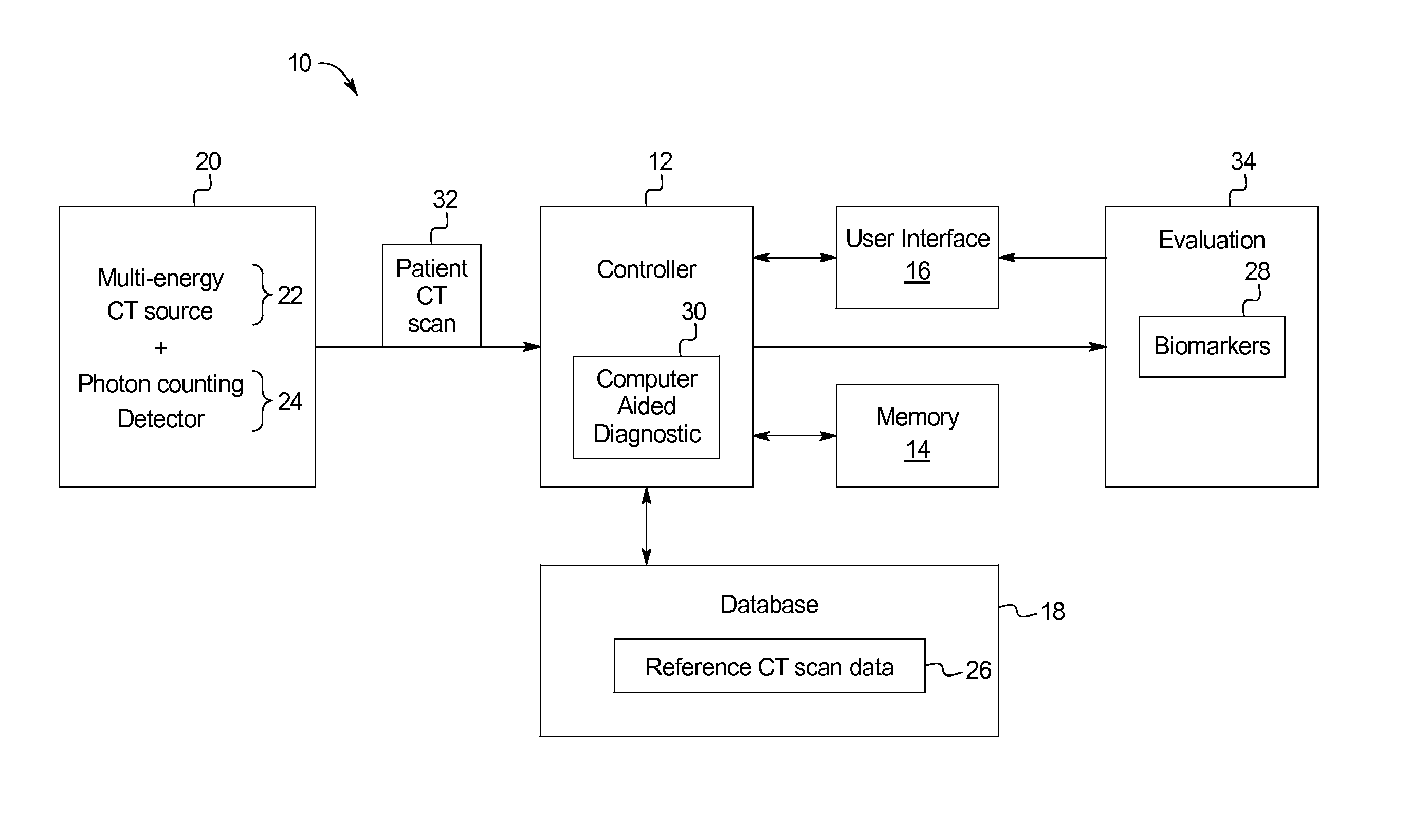
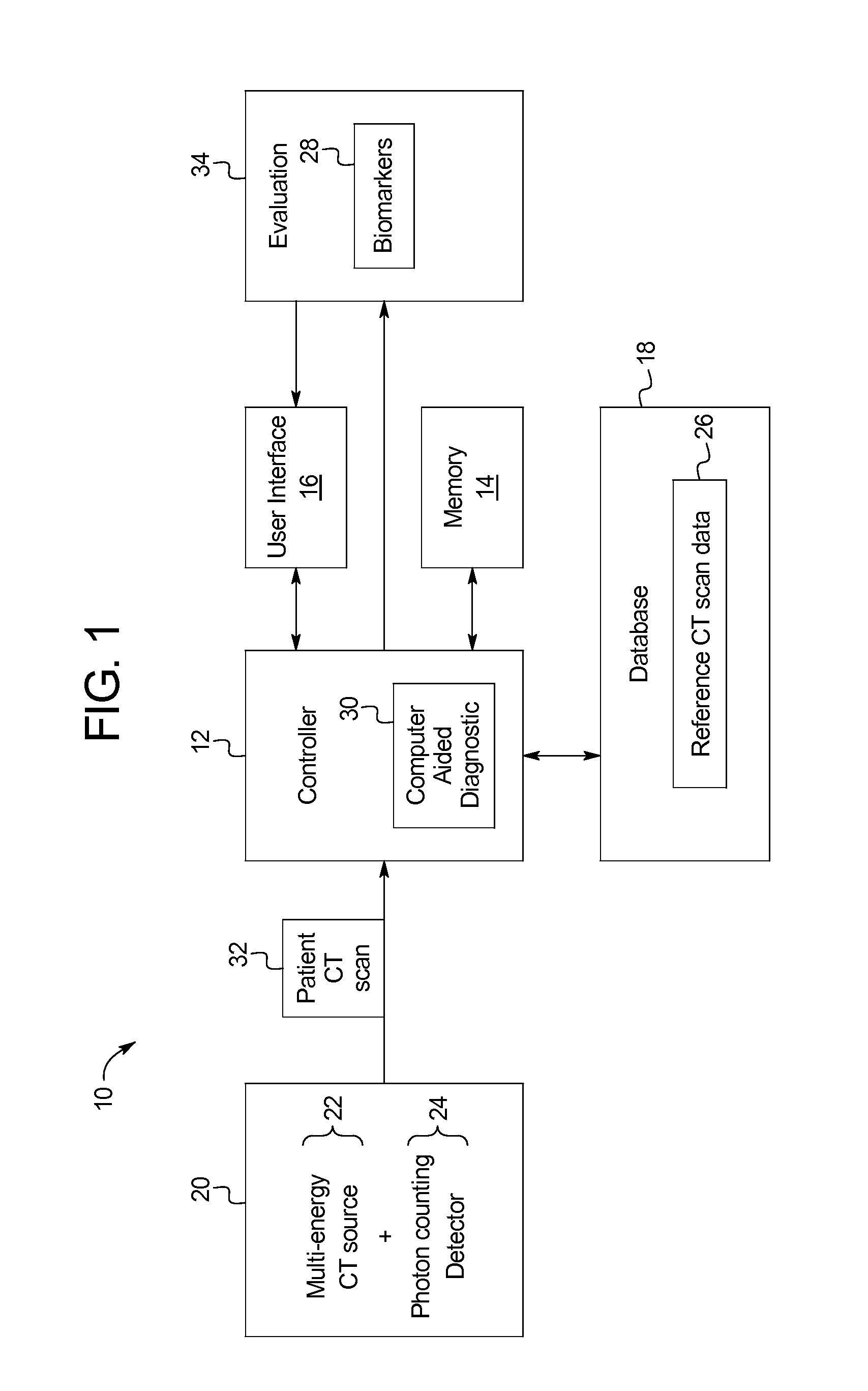
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for evaluating a brain scan using reference data. Specifically, the systems and methods include a computed tomography (CT) scanner for the purpose of diagnosing concussions or mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBI). The system includes a multi-energy x-ray source (i.e., spectral CT), a photon counting x-ray detector, and a content-aware computer aided diagnostic (CAD) algorithm designed to detect imperceptible changes indicative of structural and physiological damage caused by a concussive event by comparing raw volumetric datasets of baseline (healthy) reference scan data to patient scan data taken after a concussive event.
Owner:VESTEVICH JACQUELINE K
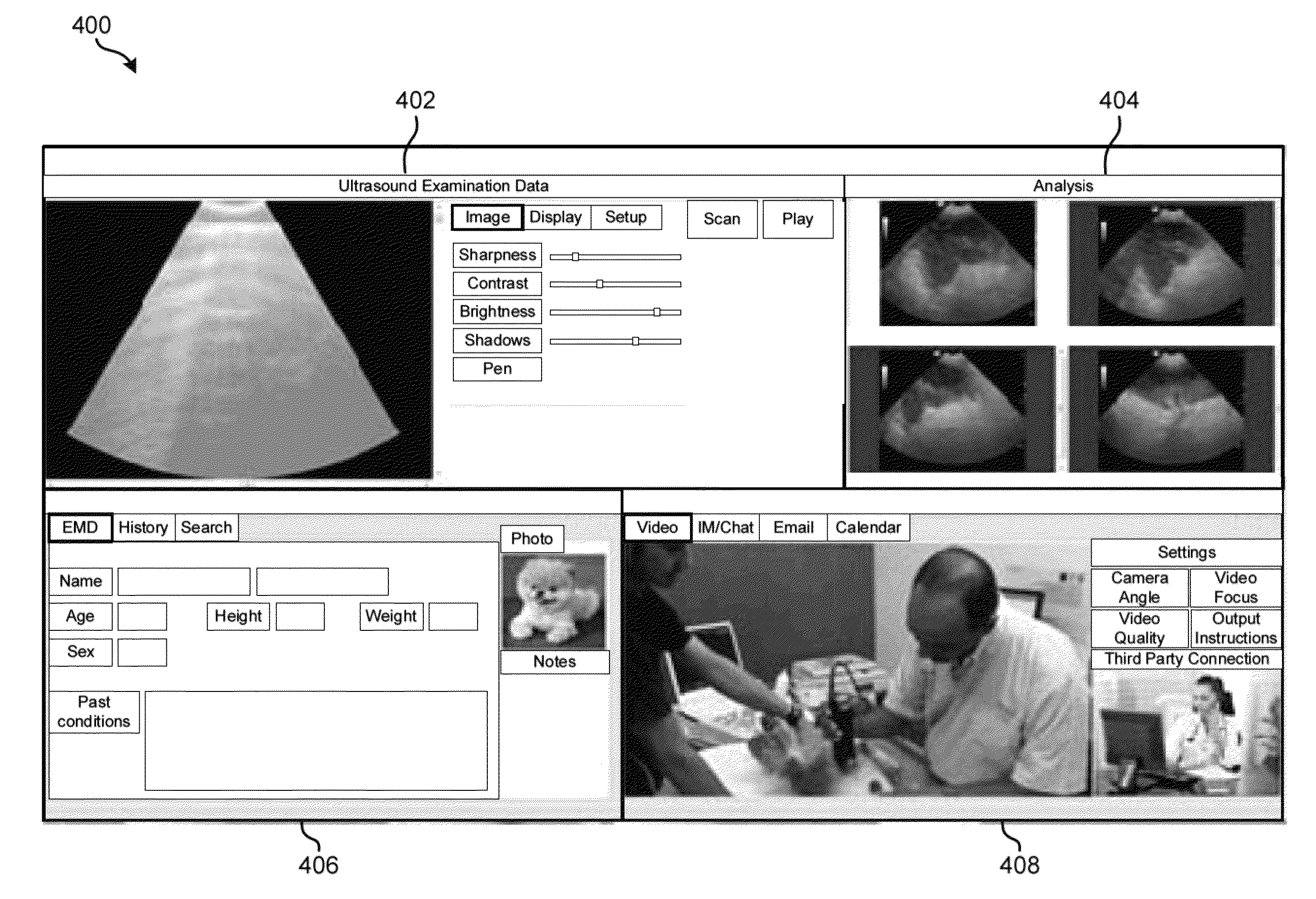
Multi-site video based computer aided diagnostic and analytical platform
ActiveUS9021358B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsMulti siteComputer aided diagnostics
In one embodiment, a method includes receiving a stream of biometric imaging data of a patient; receiving medical data about the patient; receiving a video stream depicting a source of the biometric imaging data; receiving supplemental information selected from a group consisting of: a second video stream depicting a human, one or more use cases corresponding to the biometric imaging data, an image of anatomy comparable to the biometric imaging data; and preparing for simultaneous output to a graphical user interface on a single display screen: the biometric imaging data, the medical data, the video stream depicting a source of the biometric imaging data, and the supplemental information. Each of the biometric imaging data, the medical data about the patient, the video stream depicting a source of the biometric imaging data, and the supplemental information is simultaneously output in a unique region of the graphical user interface.
Owner:EAGLEYEMED
Computer-aided diagnostic systems and methods for determining skin compositions based on traditional chinese medicinal (TCM) principles
ActiveUS20110238604A1Digital computer detailsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionSkin complexionComputer aided diagnostics
Computer-aided systems and methods are provided for determining the skin composition of a specific user according to Traditional Chinese Medicinal (TCM) principles by statistically analyzing biological and / or psychological information collected from such user, such as age, gender, bodily sensation, skin condition and complexion, sleep pattern, dietary habits, energy level, stress level, physical fitness and emotional wellness, so as to classify the skin composition of the user according to TCM principles but without employing a TCM practitioner. Preferably, the skin composition classification is indicative of Yin-Yang balance of the skin of the user or the lack thereof. The present systems and methods may further recommend to the user one or more topical skin care regimens and / or ingestible skin benefit products suitable for the skin composition of the specific user.
Owner:ELC MANAGEMENT LLC
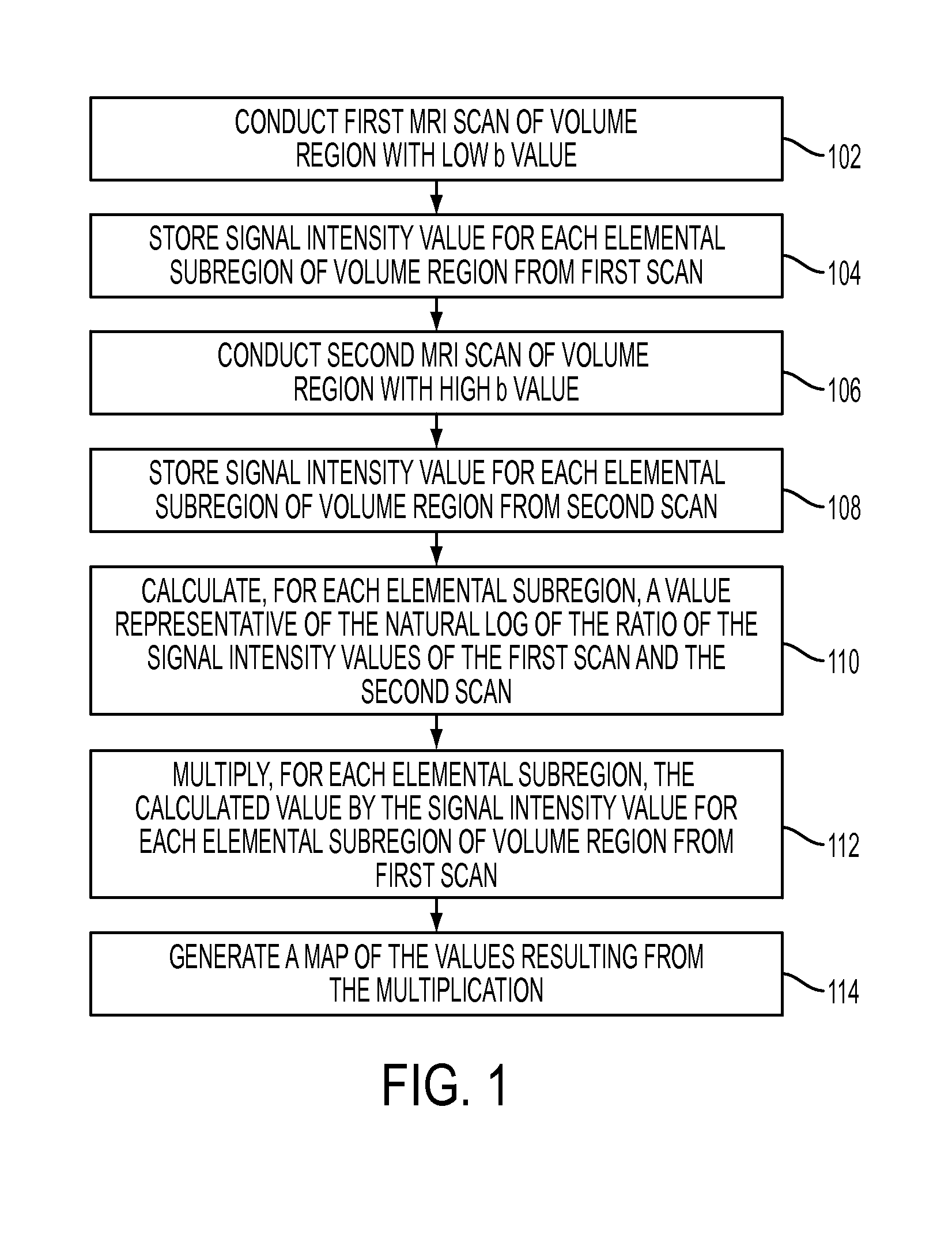
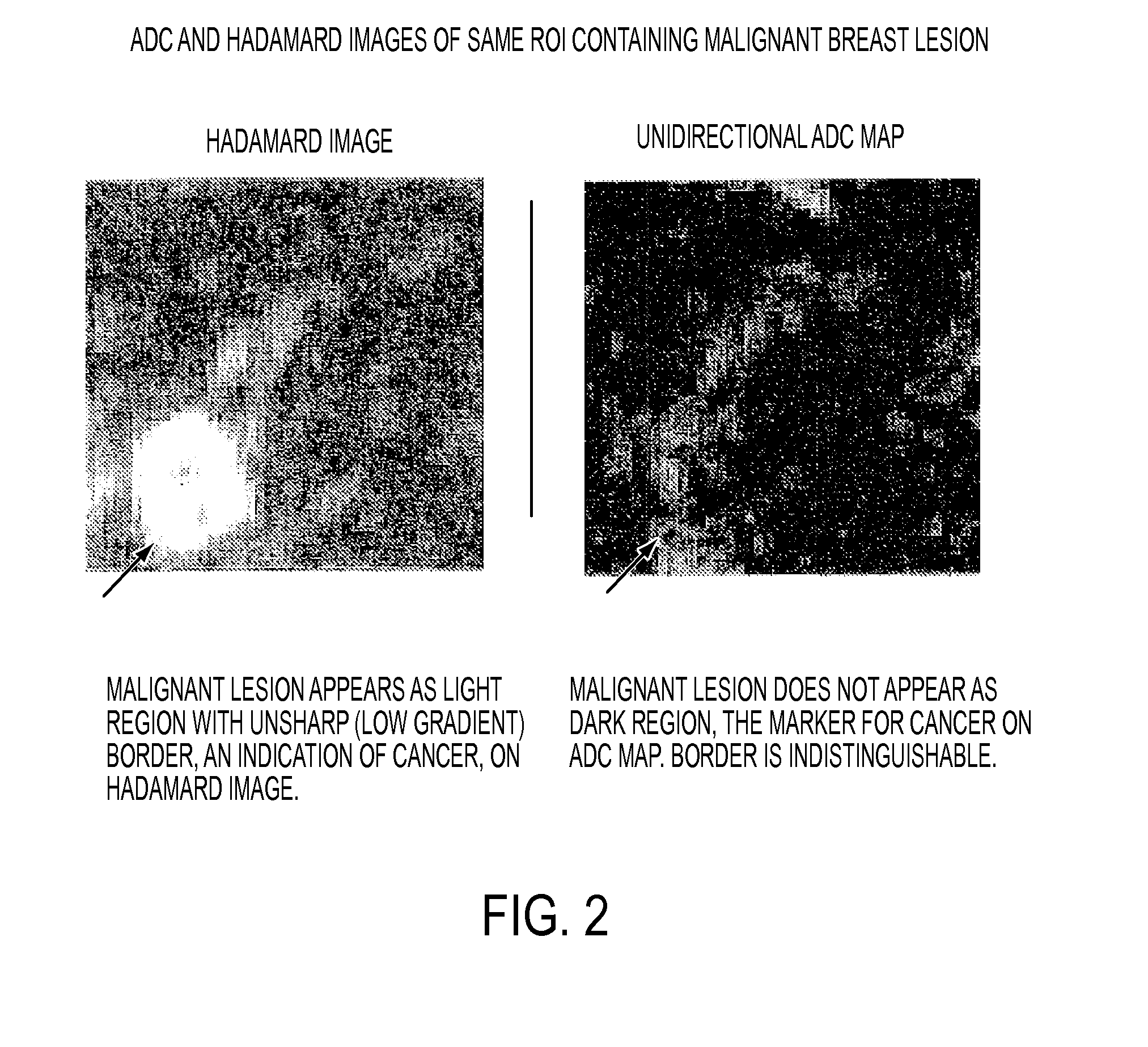
Computer aided diagnostic method and device
InactiveUS20150119697A1Medical automated diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer aided diagnosticsDiffusion
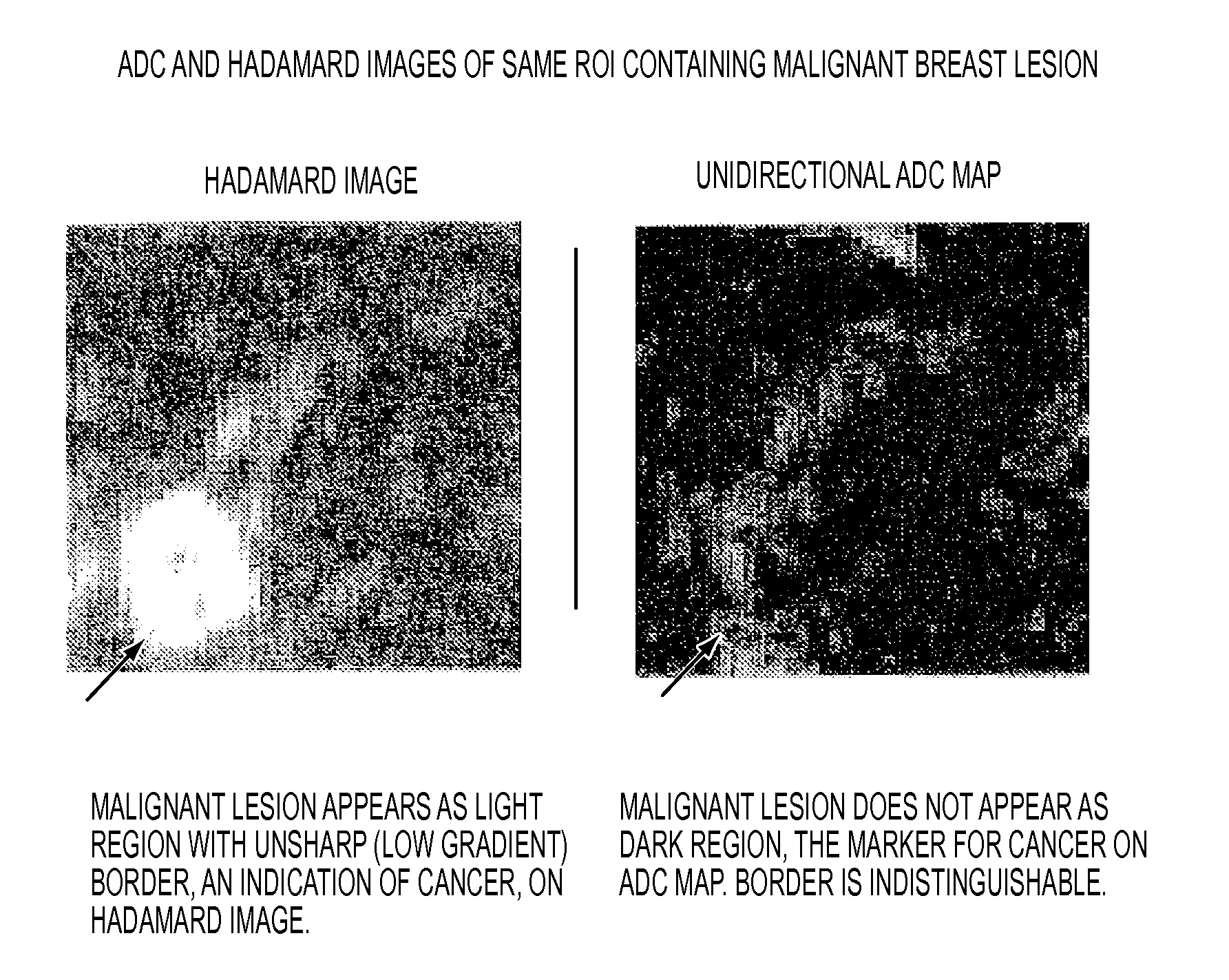
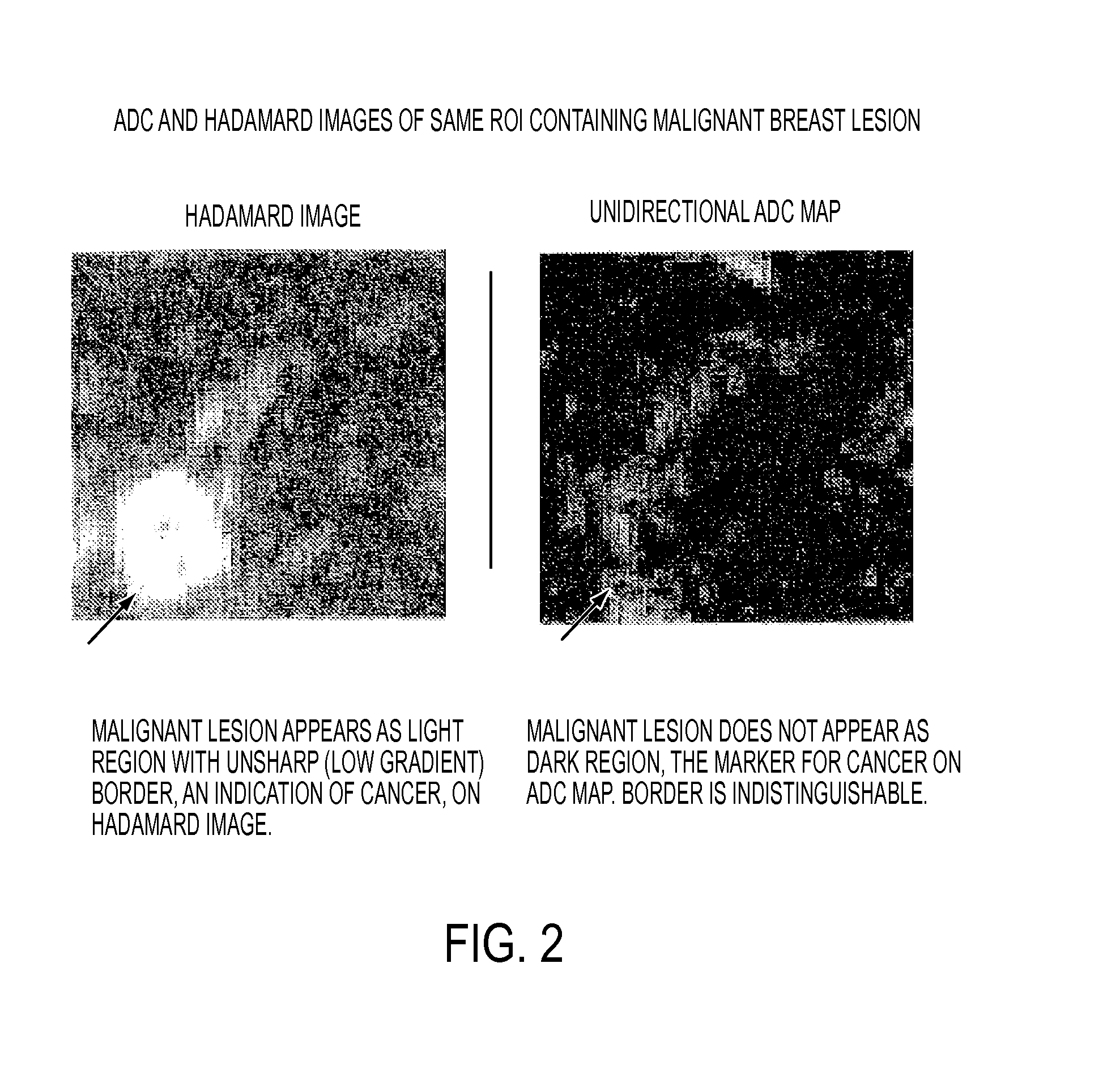
A method for characterizing regions on a map or image generated from diffusion image data of a region of a patient's body, including: loading into a data processing device image data achieved by calculation from MR diffusion imaging; providing a first threshold level to distinguish pixels with image data values that are above or below the values found that are not representative of pathological portions of the region; providing a second threshold level higher than the first threshold; deriving a measure related to the gradient pattern of those pixels that lie within a margin zone defined by those pixels that satisfy a criterion of the second threshold but do not satisfy a criterion of the first threshold and; outputting the measure related to the gradient as a parameter indicative of the likelihood that the pixels that are within the margin zone and / or a region of the body part are cancerous.
Owner:ALAN PENN & ASSOCIATES INC
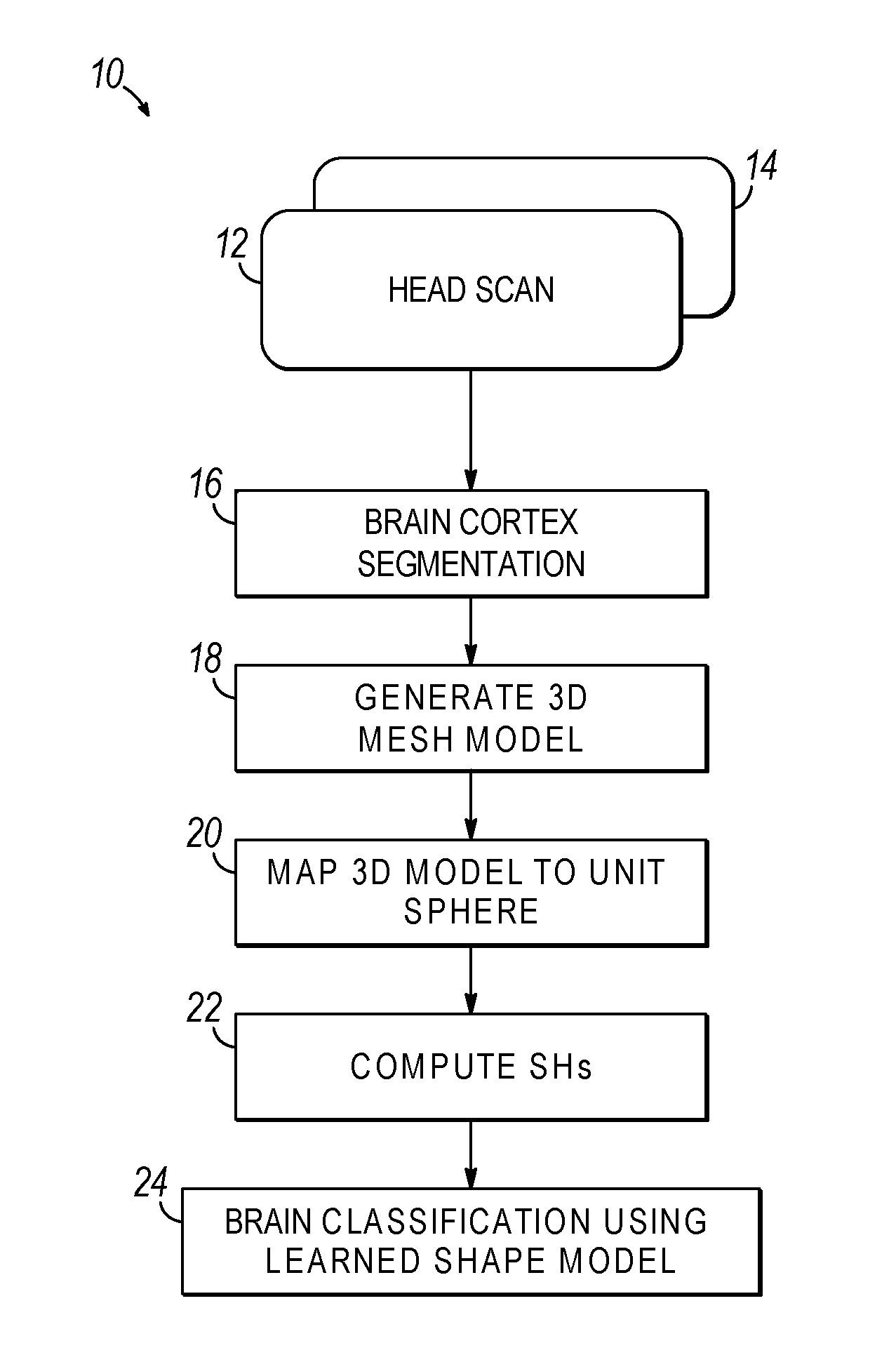
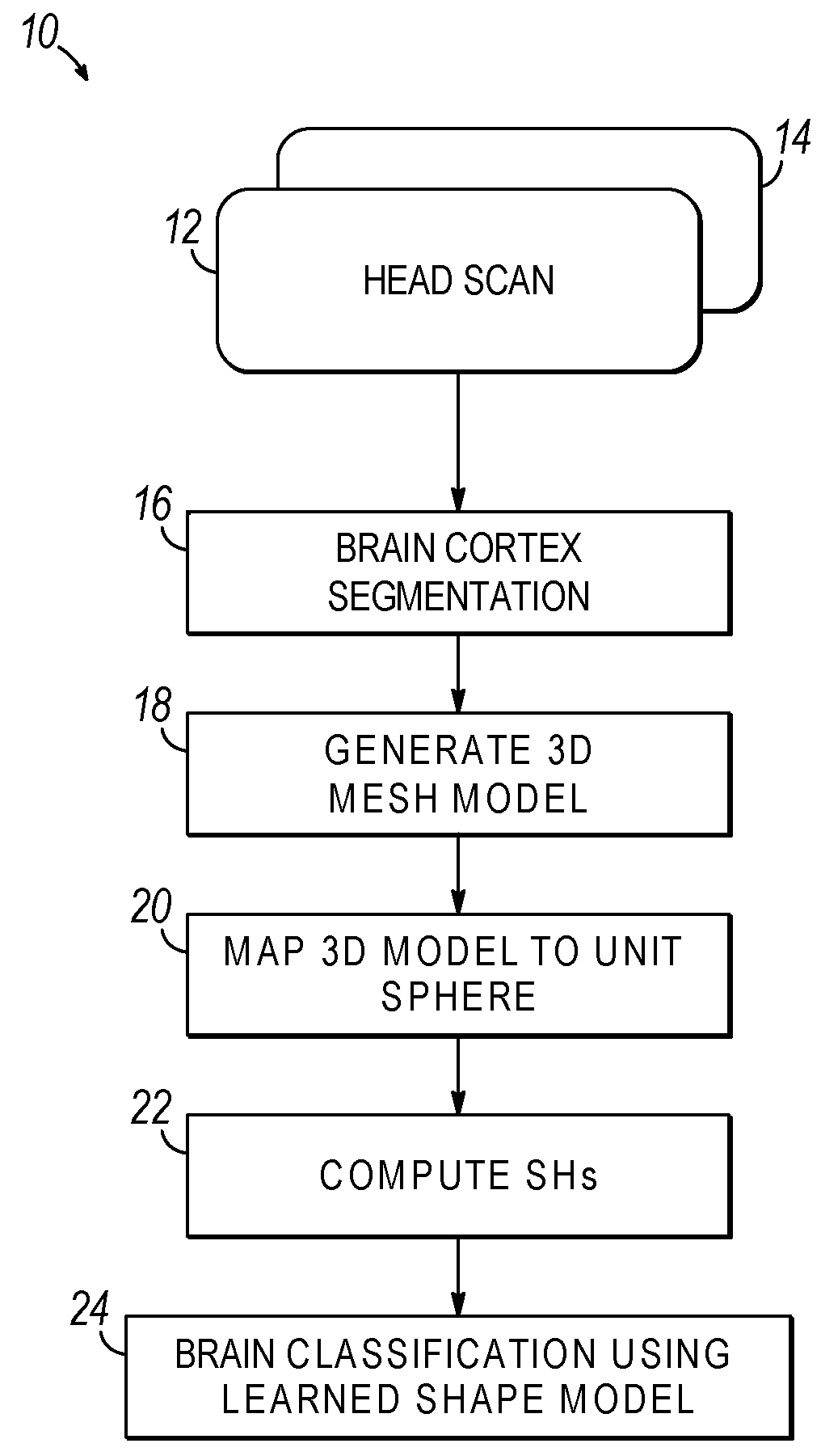
Computer aided diagnostic system for mapping of brain images
ActiveUS20170032520A1Overcomes drawbackImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsSpherical harmonics
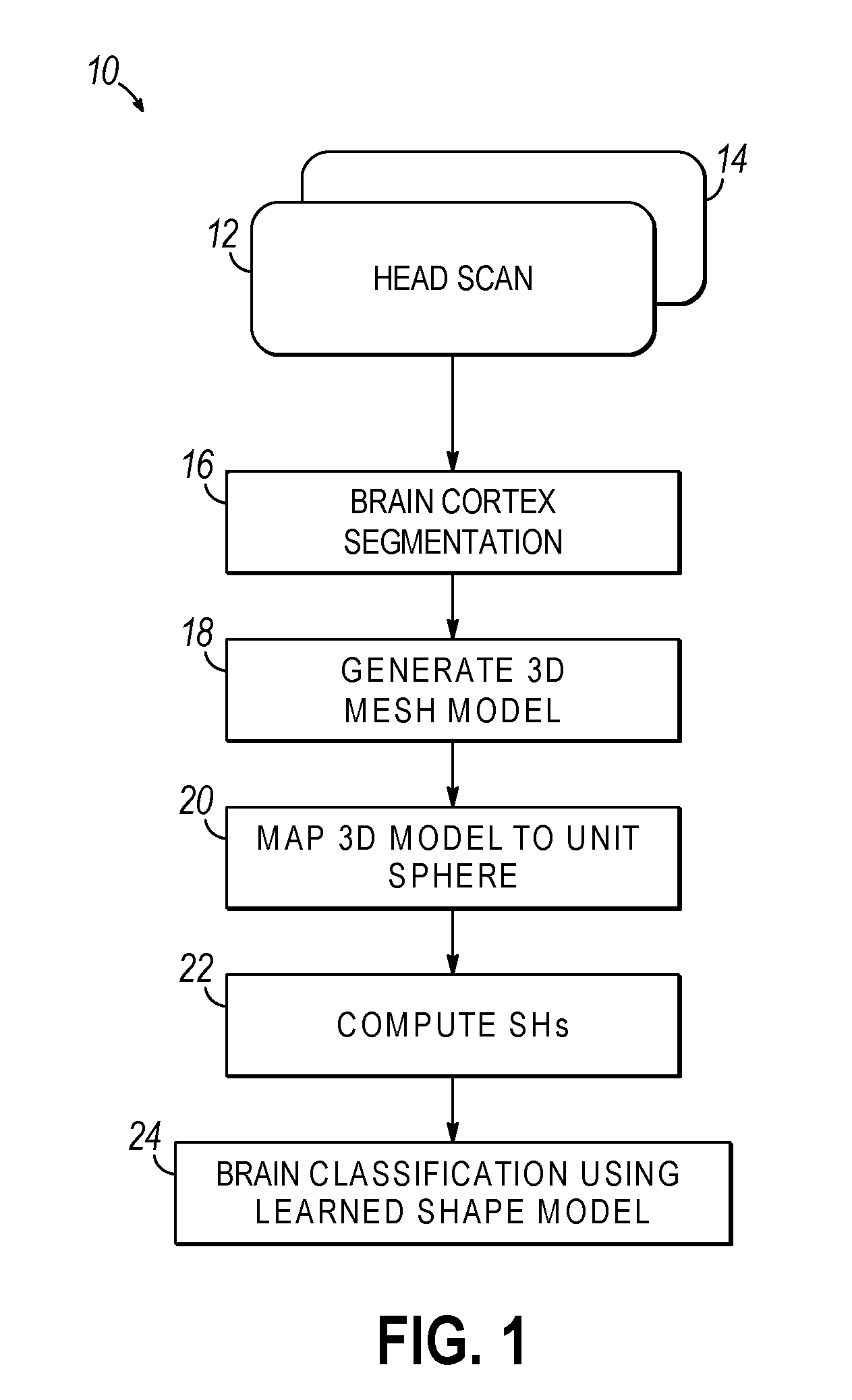
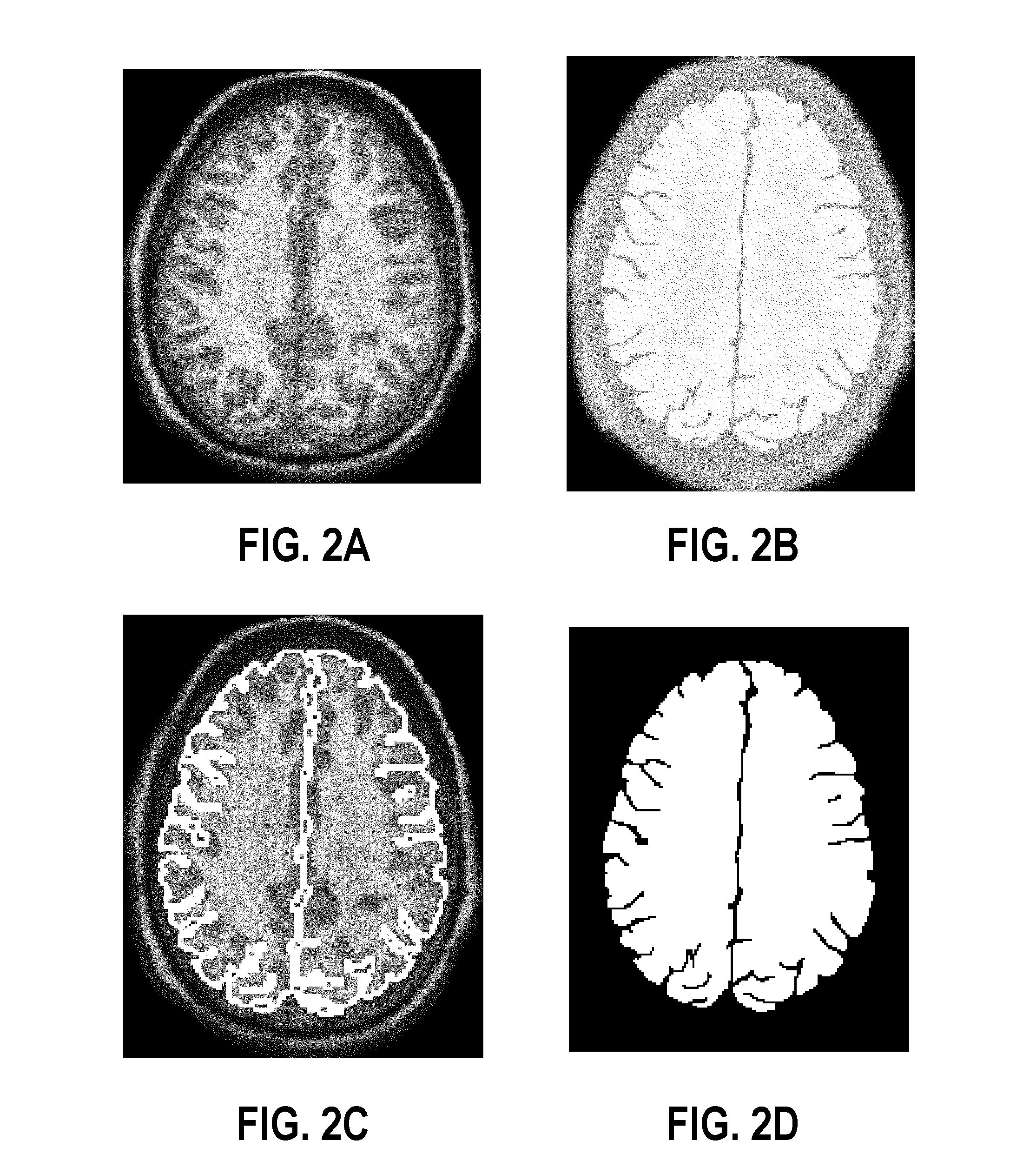
Systems, methods, and computer program products for classifying a brain are disclosed. An embodiment method includes processing image data to generate segmented image data of a brain cortex. The method further includes generating a statistical analysis of the brain based on a three dimensional (3D) model of the brain cortex generated from the segmented image data. The method further includes using the statistical analysis to classify the brain cortex and to identify the brain as being associated with a particular neurological condition. According to a further embodiment, generating the 3D model of the brain further includes registering a 3D volume associated with the model with a corresponding reference volume and generating a 3D mesh associated with the registered 3D volume. The method further includes generating the statistical analysis by analyzing individual mesh nodes of the registered 3D mesh based on a spherical harmonic shape analysis of the 3D model.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Computer aided diagnostic method and device
ActiveUS20130012805A1Better contrast resolutionSuppress artifactsMedical automated diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer aided diagnosticsMr diffusion
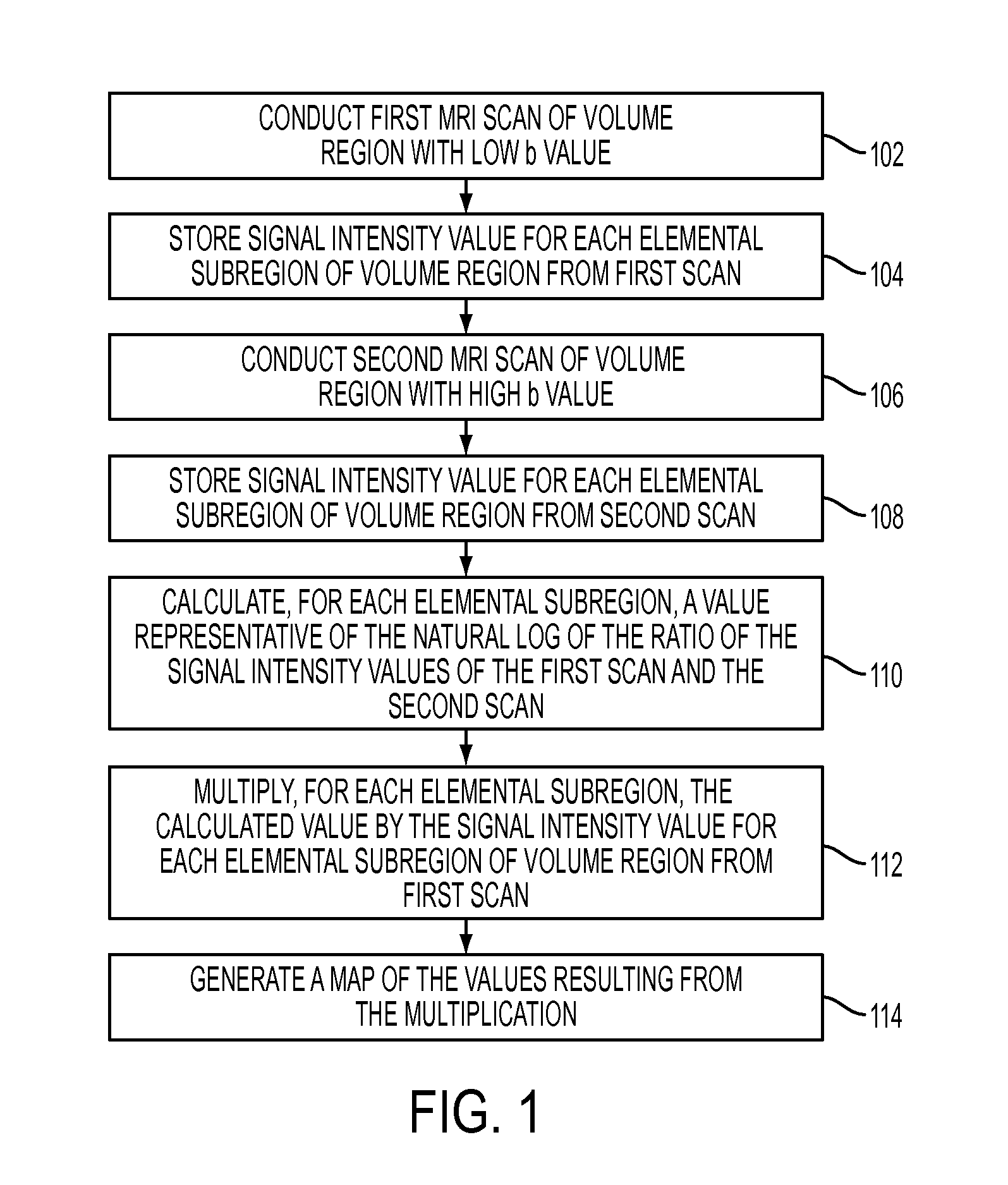
A method for generating a map of a region of a patient's body containing one or more lesions that provides information about MR diffusion properties and / or level of suspicion of malignancy. Performing at least one first scan of the region with an MRI apparatus set to a first b value to obtain a first matrix of pixel or voxel values, int(B1); performing at least one second scan of the region with the apparatus set to a second b value to obtain a second matrix of pixel or voxel intensity values, int(B2); deriving a first computed value that is a monotonic function of ln(int(B1) / int(B2); multiplying each computed value by a value proportional to int (B1) to obtain a second computed value; and producing a representation of all the second computed values that is indicative of the likelihood that one or more of the lesions are malignant.
Owner:PENN ALAN
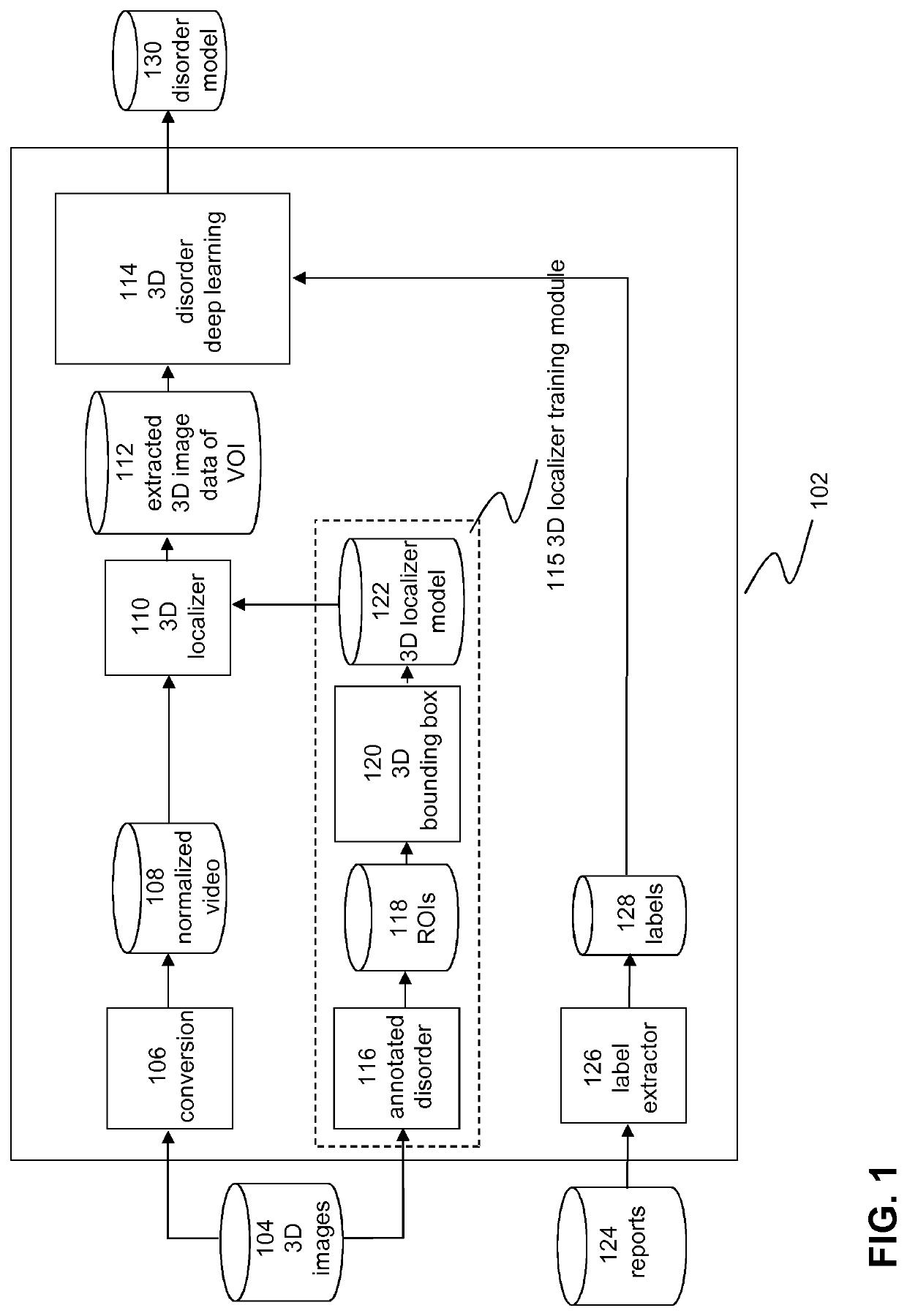
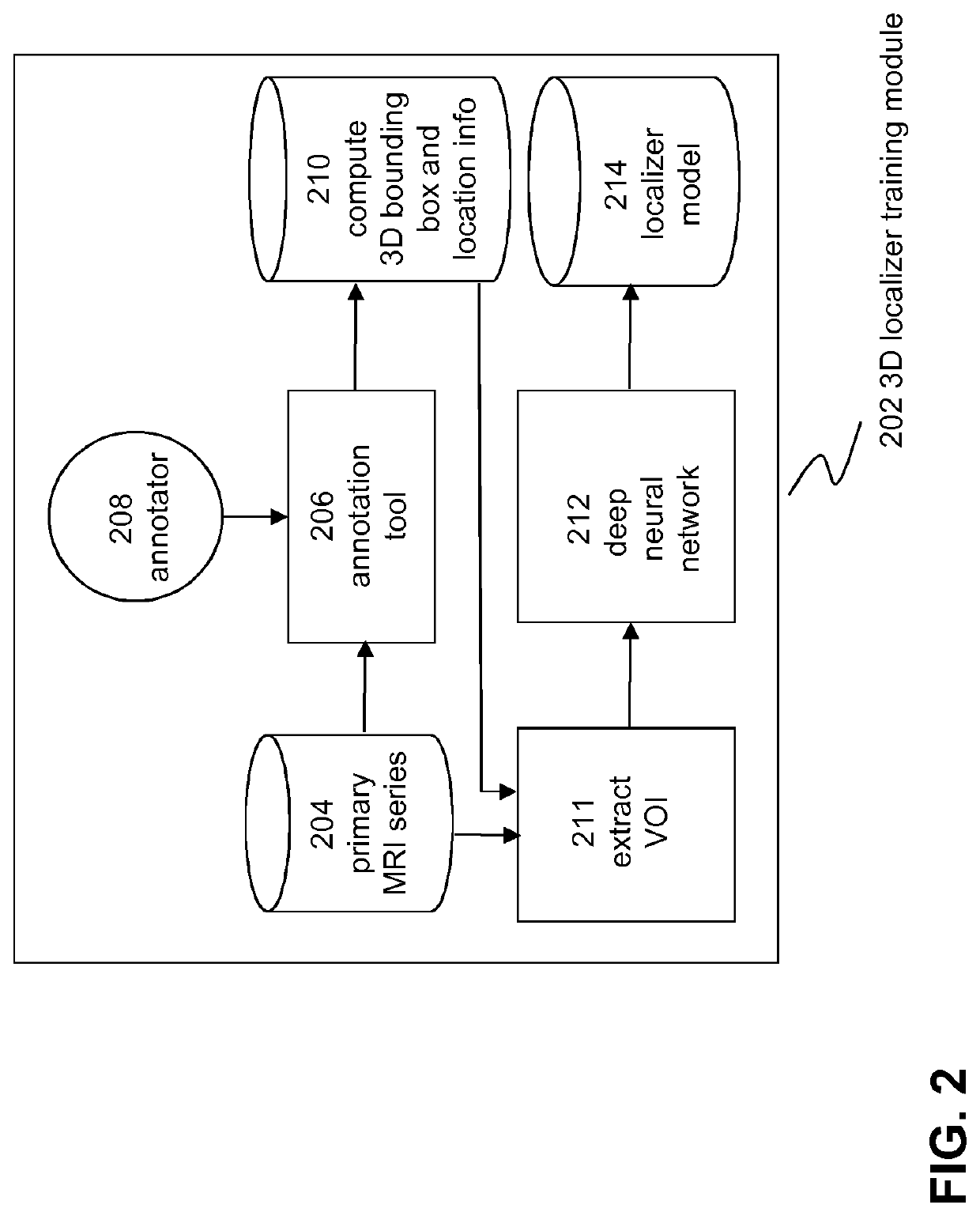
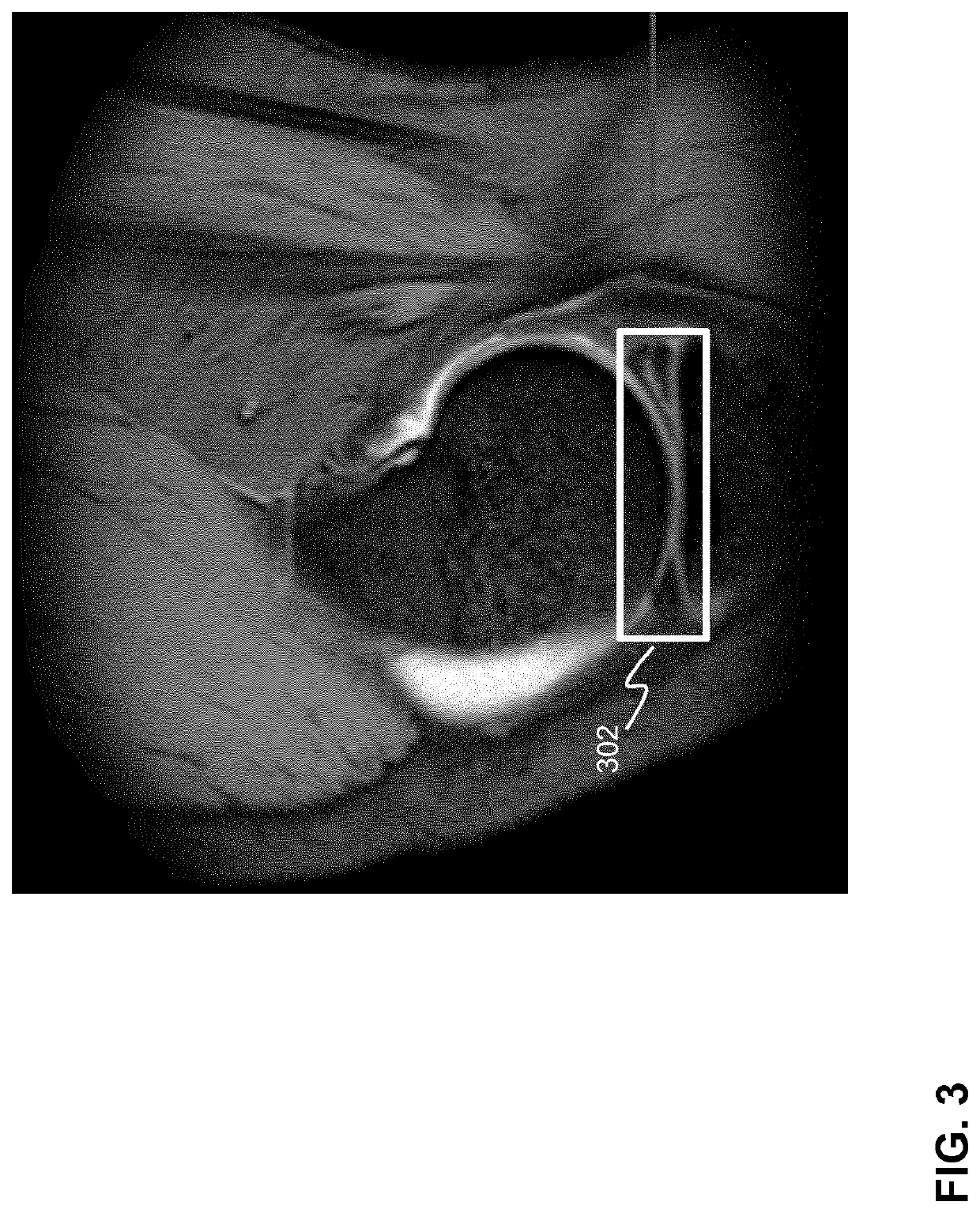
Computer-aided diagnostics using deep neural networks
PendingUS20200219609A1Improve performanceLower the volumeMedical automated diagnosisMedical imagesComputer aided diagnosticsVoxel
A computer-implemented method for determining a pathology in 3D image data is describe wherein the method may comprise:receiving at least a first 3D image of a body part, the 3D image comprising voxels associated with a predetermined image volume; a first 3D convolutional neural network determining a position of a volume of interest (VOI) in the image volume of the first 3D image, the VOI being associated with a pathology of the body part, the VOI defining a sub-volume of the image volume; determining first VOI voxels by selecting voxels of the first 3D image that have a position within the VOI as determined by the first 3D convolution neural network and providing the first VOI voxels to the input of a second 3D convolutional neural network; the second 3D convolutional ON neural network, determining a target label value on the basis of at least the first VOI voxels, the target label value being indicative of the presence or absence of a pathology in the VOI; and, generating a medical report by associating the target label value determined by the second 3D convolutional neural network with text and / or sentences representing a description of the pathology.
Owner:AIDENCE BV
Multiple modality computer aided diagnostic system and method
ActiveUS8452613B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsData processing applicationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputer aided diagnostics
A diagnostic system having an image loader including a processor for processing multiple modality images, at least one of the multiple modality images being a mammogram image, the processing including generating diagnostic information based on a computer aided diagnostic tool and an image viewer simultaneously displaying the multiple modality images.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
Computer-aided diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS9168007B2Easy to checkImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsImage detection
A computer aided diagnostic system according to the invention is characterized in that first sick portion detecting means for detecting a sick portion candidate based upon an image acquired by a first modality, second sick portion detecting means for detecting a sick portion candidate based upon an image related to the same region of interest of the same subject and acquired by a second modality different from the modality, detection result synthesizing means for comparing the results of detection by the first and second sick portion detecting means and correspondence displaying means for relating the position of the sick portion candidate detected by the first sick portion detecting means on an image analyzed by the second sick portion detecting means and displaying it and for relating the position of the sick portion candidate detected by the second sick portion detecting means on an image analyzed by the first sick portion detecting means and displaying it are provided. According to the above-mentioned configuration, the computer aided diagnostic system that enables a double check comparing images acquired by plural apparatuses can be provided.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Computer aided diagnostic system incorporating 3D shape analysis of the brain for identifying developmental brain disorders
A computer aided diagnostic system and automated method classify a brain through modeling and analyzing the shape of a brain cortex, e.g., to detect a brain cortex that is indicative of a developmental disorder such as ADHD, autism or dyslexia. A model used in such analysis describes the shape of brain cortices in terms of spherical harmonics required to delineate a unit sphere corresponding to the brain cortex to a model of the brain cortex.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Computer aided diagnostic system incorporating appearance analysis for diagnosing malignant lung nodules
A computer aided diagnostic system and automated method diagnose lung cancer through modeling and analyzing the visual appearance of pulmonary nodules. A learned appearance model used in such analysis describes the appearance of pulmonary nodules in terms of voxel-wise conditional Gibbs energies for a generic rotation and translation invariant second-order Markov-Gibbs random field (MGRF) model of malignant nodules with analytically estimated characteristic voxel neighborhoods and potentials.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
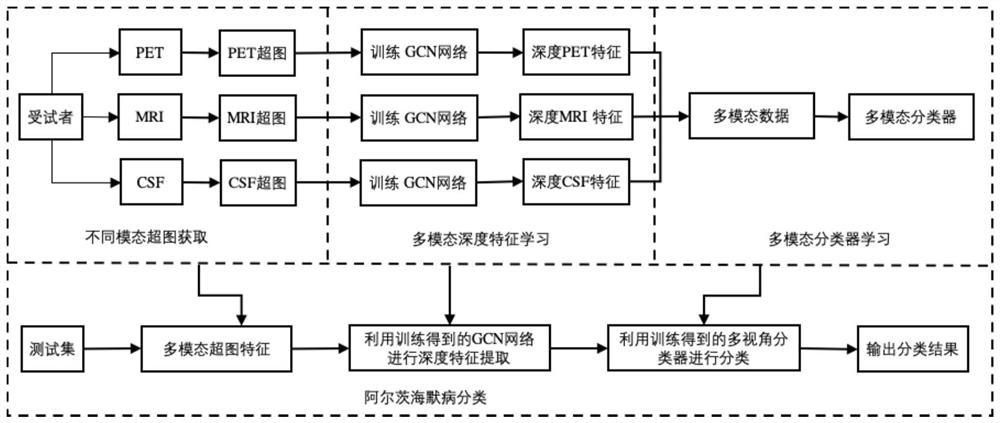
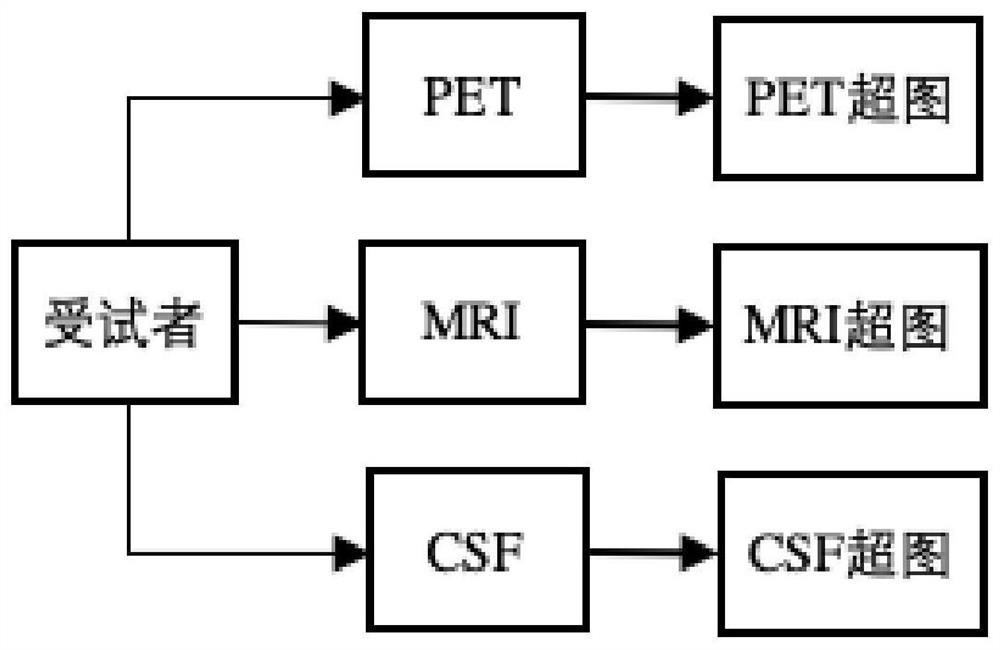
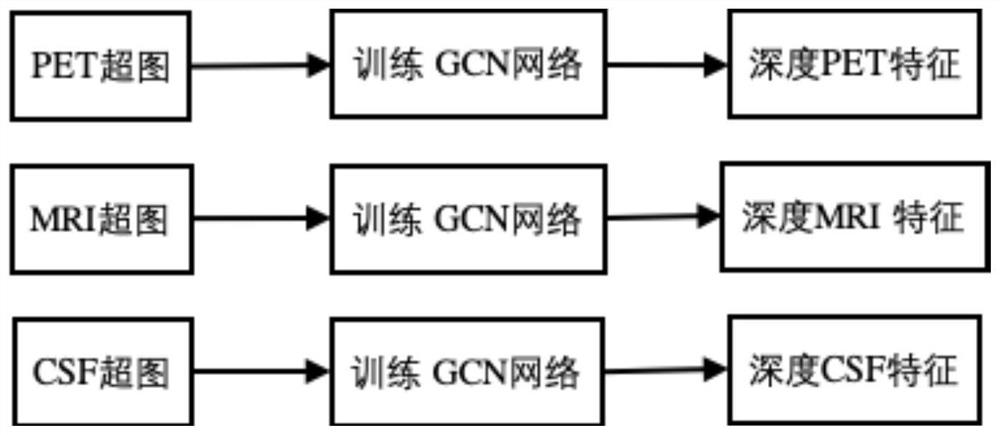
Alzheimer's disease classification method based on multi-modal hypergraph convolutional neural network
PendingCN112863664AReduce data dimensionalityImprove classification performanceMedical automated diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer aided diagnosticsClassification methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of intelligent medical computer-aided diagnosis application, and relates to an Alzheimer's disease classification method based on a multi-modal hypergraph convolutional neural network. The method comprises a training stage and a using stage, wherein the training stage comprises an initial multi-modal feature construction model, a deep multi-modal feature extraction model and final Alzheimer disease classification. The initial multi-modal construction model uses a K-nearest neighbor and hypergraph theory to construct a hypergraph for each modal, and the initial multi-modal construction model is obtained; in order to improve the effectiveness of the multi-modal features, based on the initial multi-modal hypergraph data, deep learning is carried out by using the hypergraph-based graph convolutional neural network to construct the deep multi-modal features, and compared with the original multi-modal features, the multi-modal features subjected to deep feature extraction have smaller data dimensions and a higher classification effect.
Owner:WUXI TAIHU UNIV +1
Computer-aided diagnostic systems and methods for determining skin compositions based on traditional chinese medicinal (TCM) principles
ActiveUS8489539B2Digital computer detailsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionSkin complexionComputer aided diagnostics
Computer-aided systems and methods are provided for determining the skin composition of a specific user according to Traditional Chinese Medicinal (TCM) principles by statistically analyzing biological and / or psychological information collected from such user, such as age, gender, bodily sensation, skin condition and complexion, sleep pattern, dietary habits, energy level, stress level, physical fitness and emotional wellness, so as to classify the skin composition of the user according to TCM principles but without employing a TCM practitioner. Preferably, the skin composition classification is indicative of Yin-Yang balance of the skin of the user or the lack thereof. The present systems and methods may further recommend to the user one or more topical skin care regimens and / or ingestible skin benefit products suitable for the skin composition of the specific user.
Owner:ELC MANAGEMENT LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com