Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Maximum accuracy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
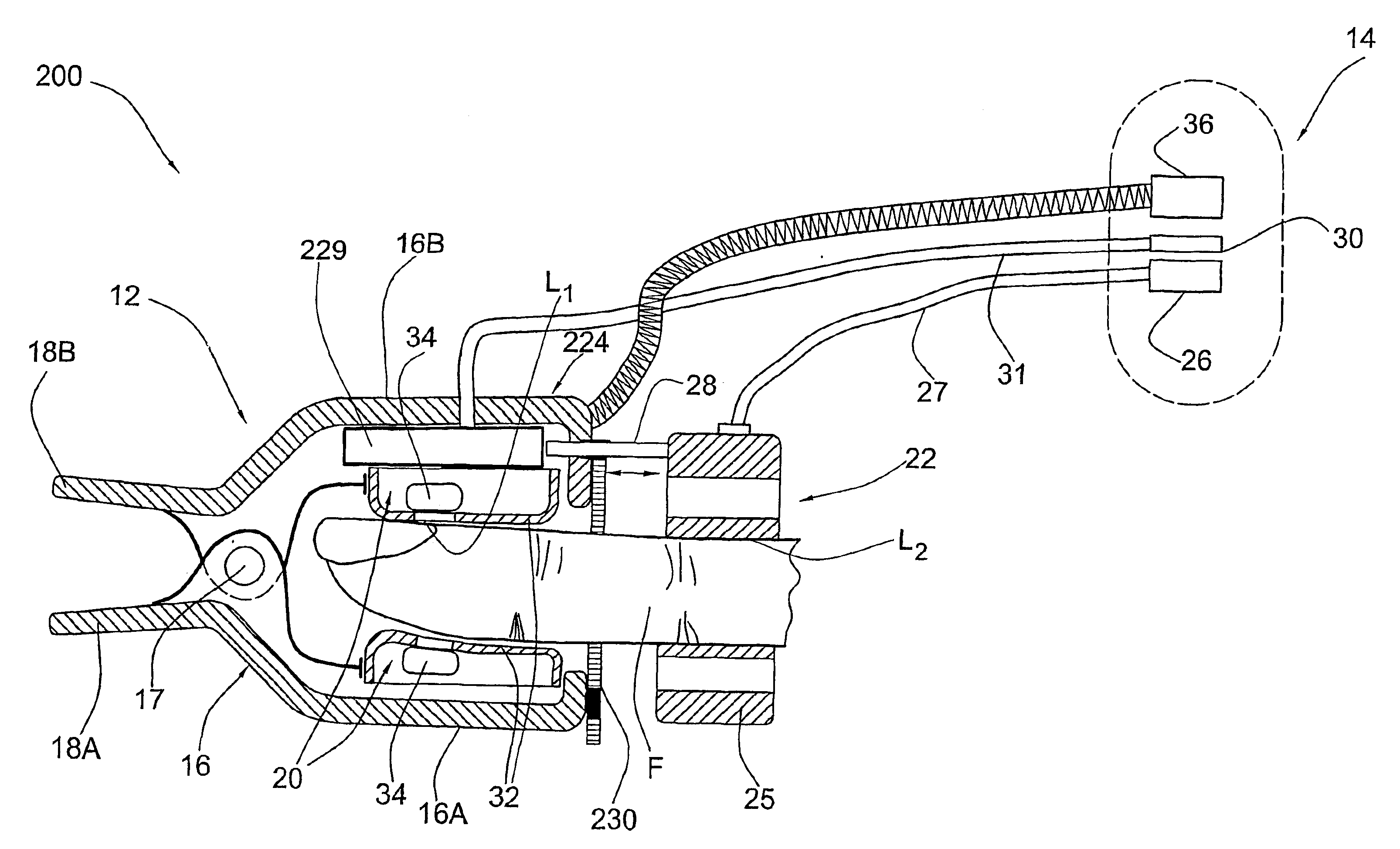
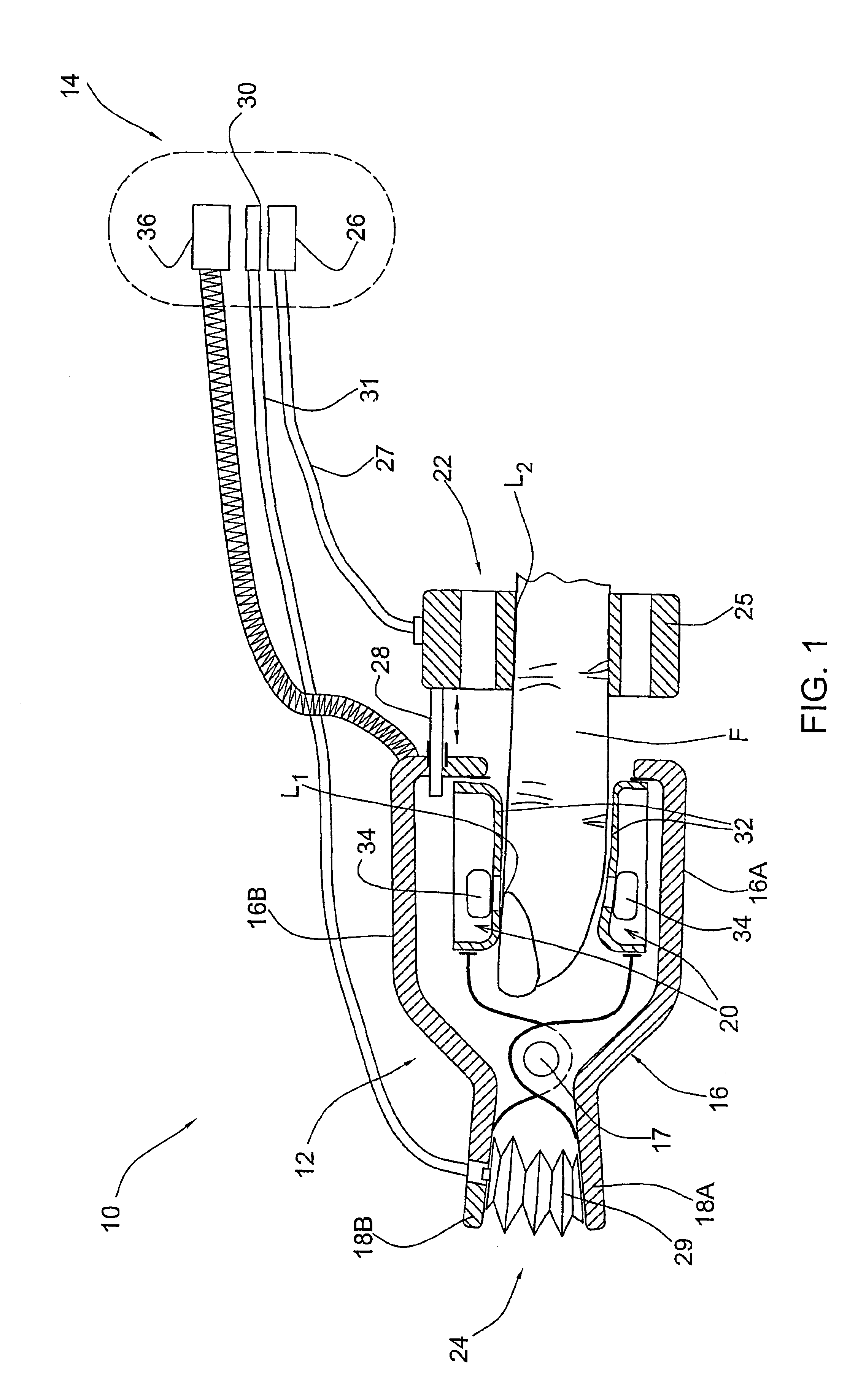
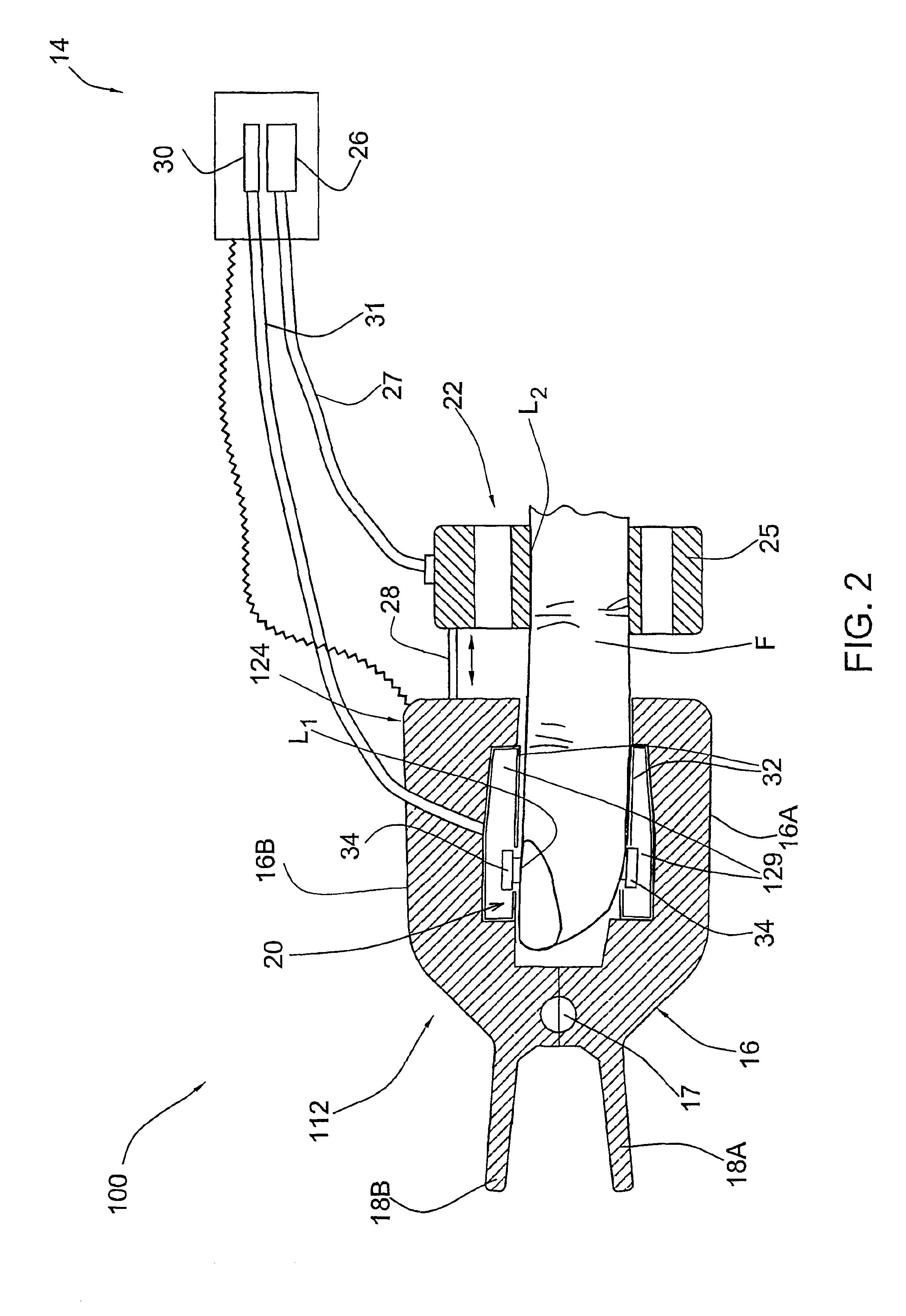
Probe for use in non-invasive measurements of blood related parameters
InactiveUS6983178B2Improve non-invasive measurementMaximum accuracyDiagnostics using pressureEvaluation of blood vesselsOptical measurementsNon invasive
A probe device for use in non-invasive optical measurements of at least one parameter of the patient's blood. The probe device comprises a finger holder in the form of a clip member that secures a fingertip between its clamping legs. The probe device supports a measuring unit for applying optical measurements to a measurement location on the finger and carries a pressurizing assembly operable for applying controllably variable, substantially under-systolic pressure to the finger in the vicinity of the measurement location. Several measurement sessions are performed at the measurement location with at least two different 3 wavelength of incident light to detect light response of the medium and generate measured data indicative thereof, and the pressure applied to the vicinity of the measurement location is simultaneously varied during measurements. The light response of the medium corresponding to different wavelength of the incident light and different pressure values during measurements. The light response of the medium corresponding to different wavelength of the incident light and different pressure values is analyzed, and an optimal pressure value is determined, so as to utilize the corresponding light response of the medium for deriving therefrom the at least on blood parameter.
Owner:ORSENSE LTD
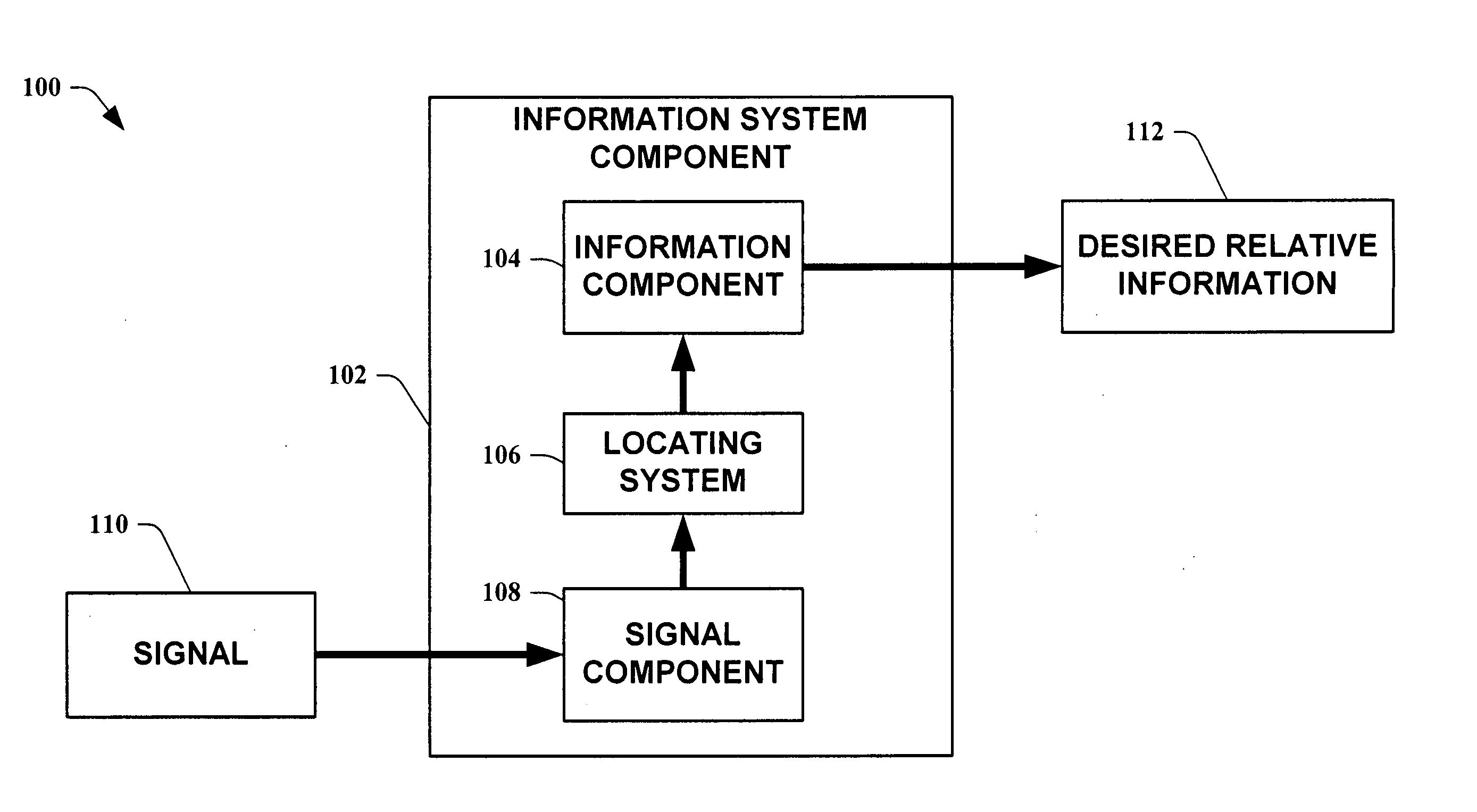
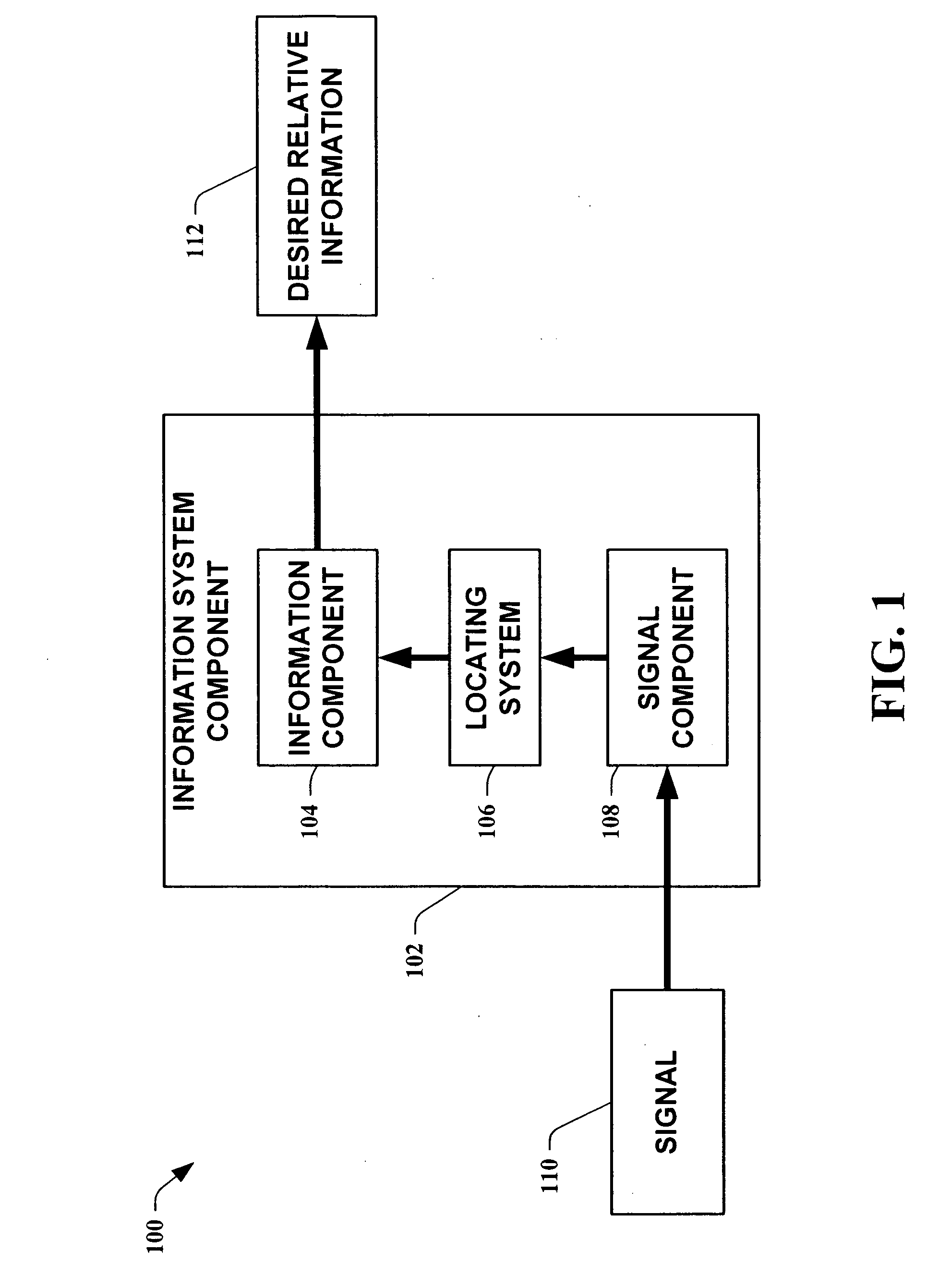
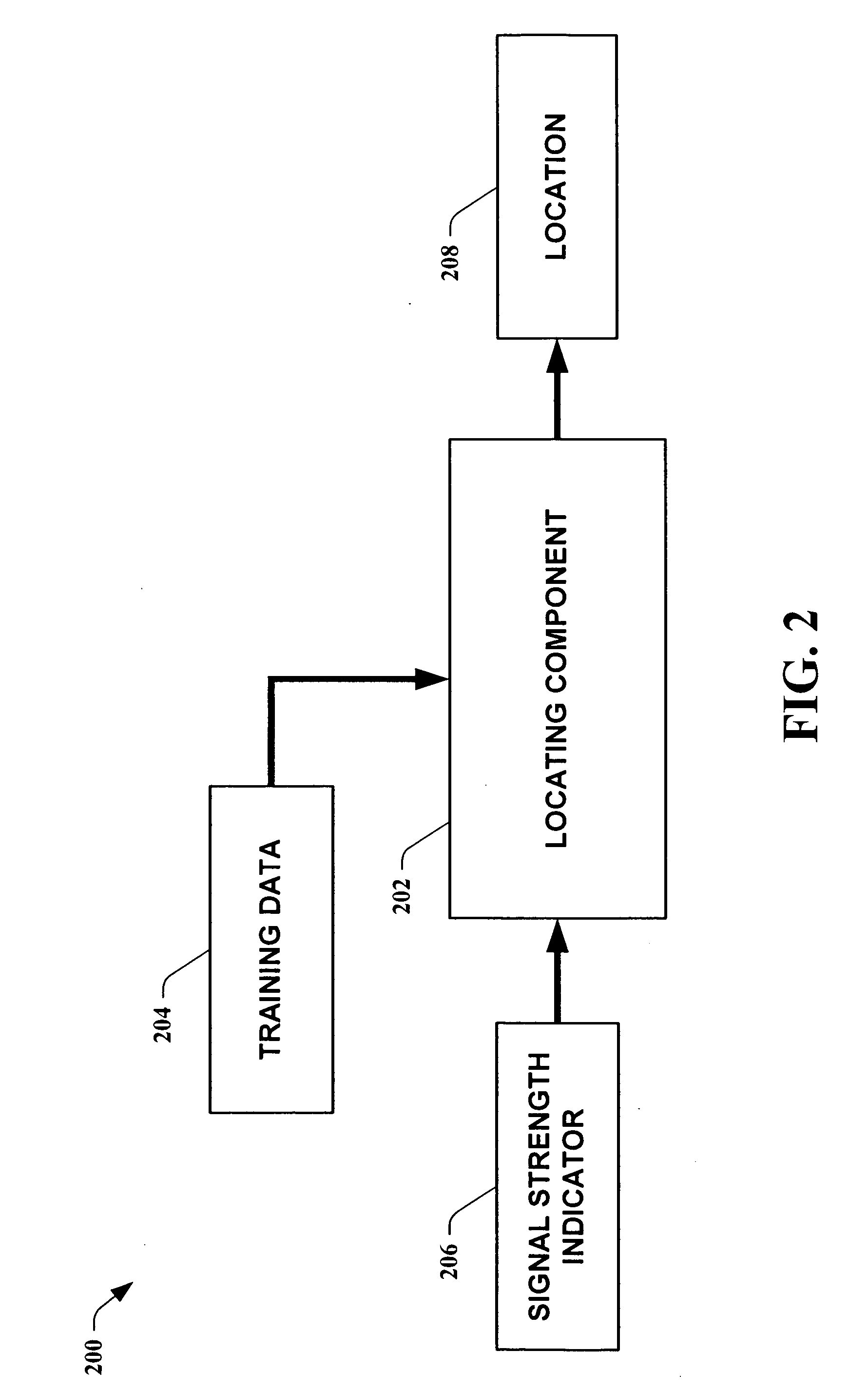
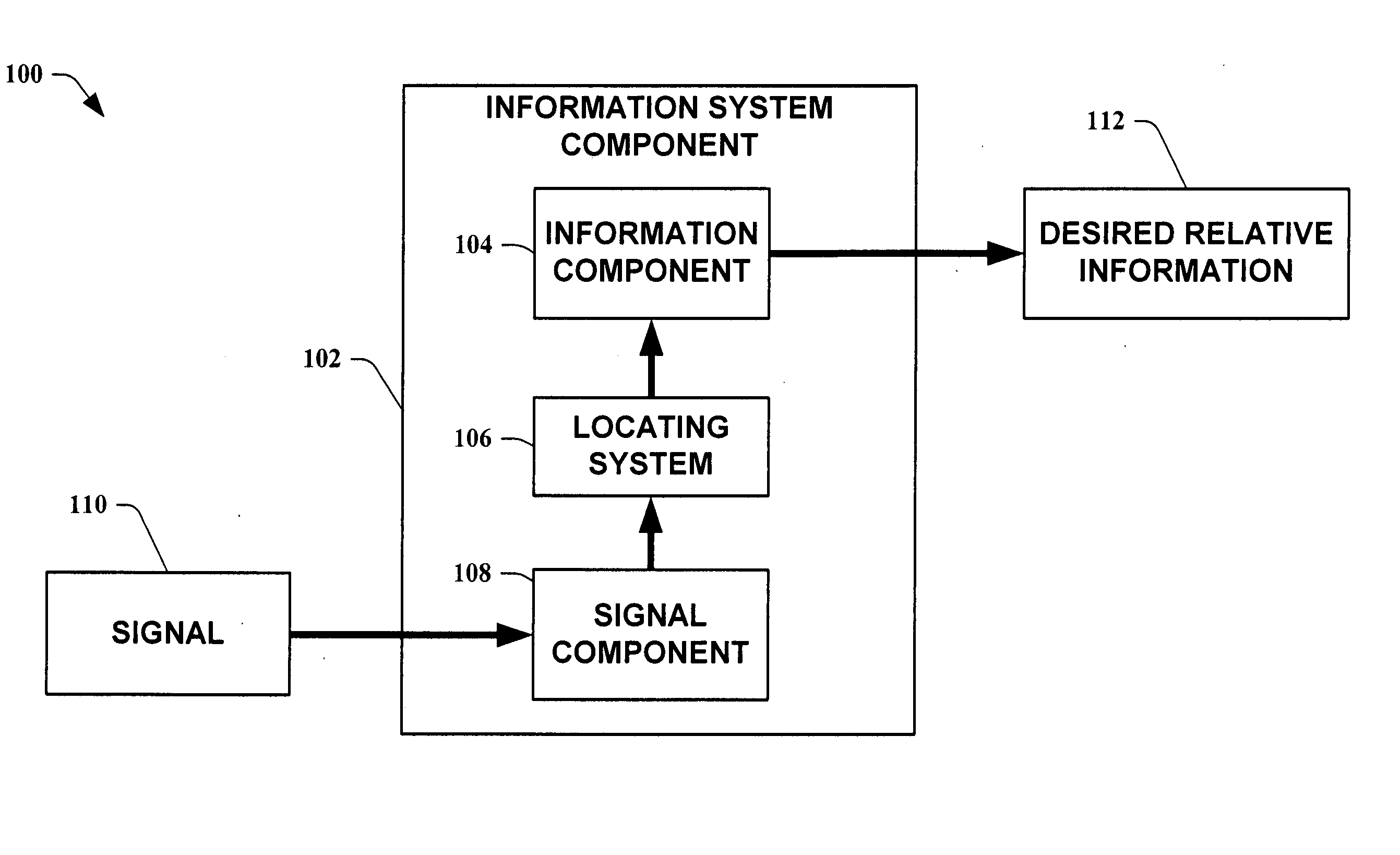
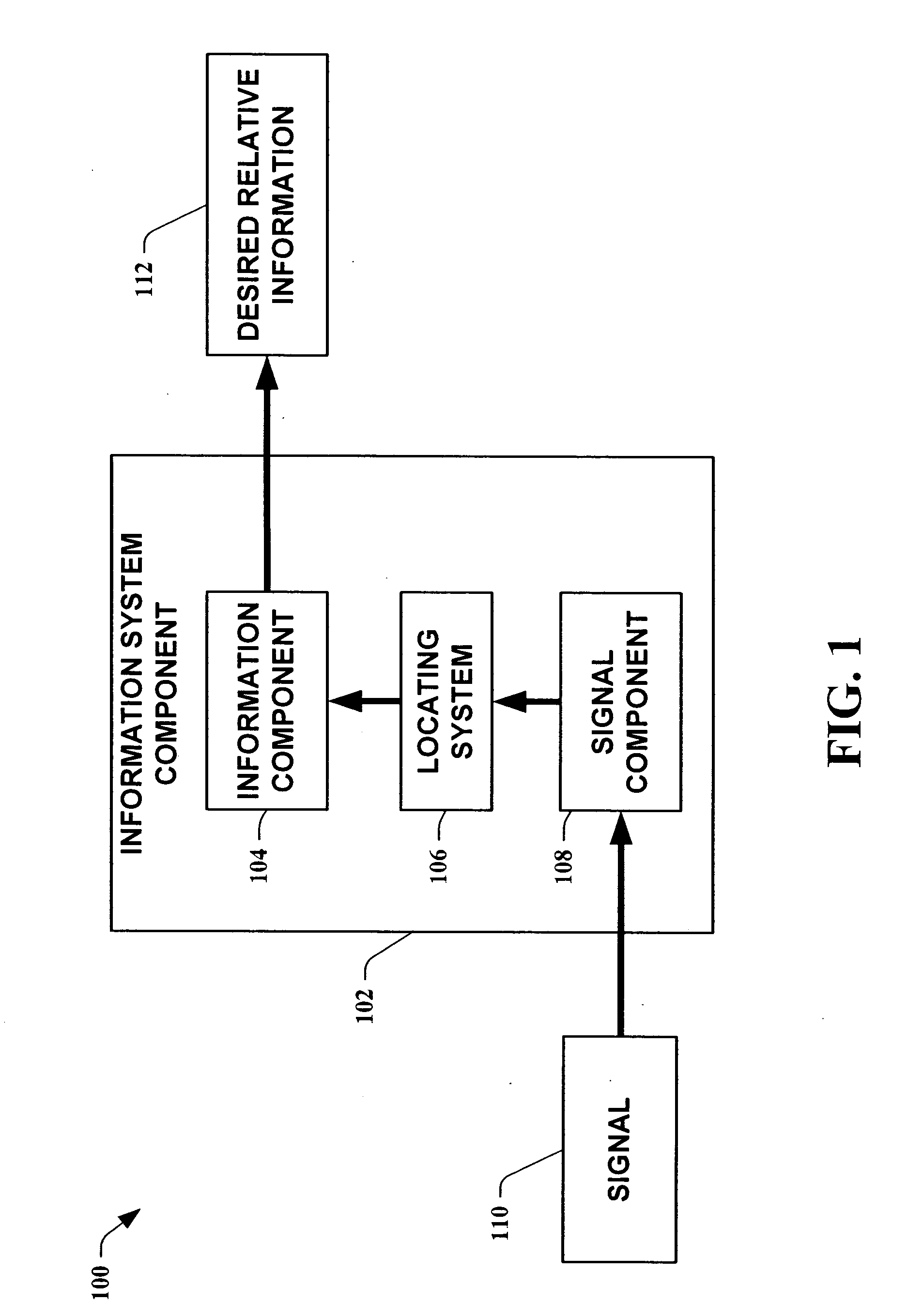
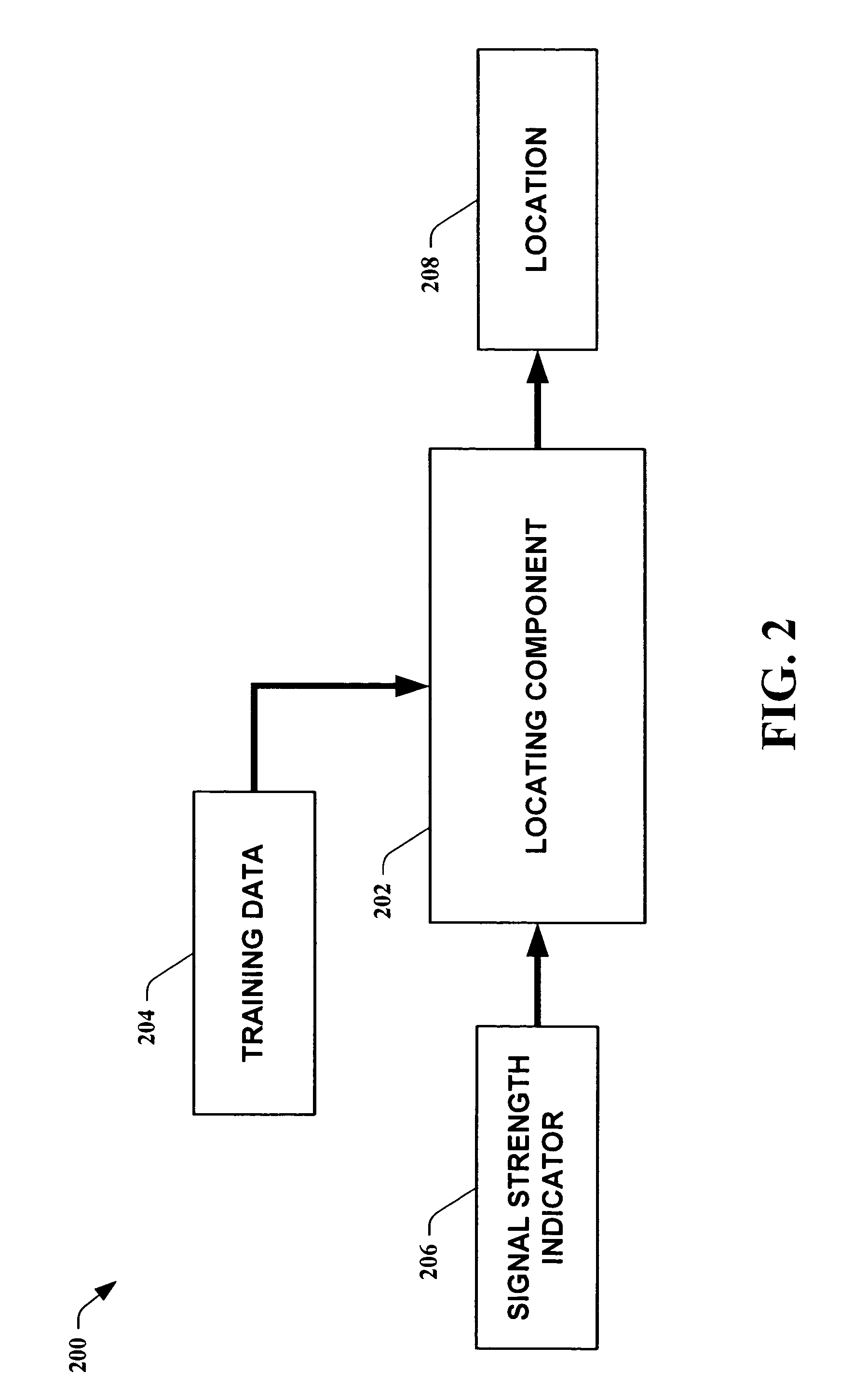
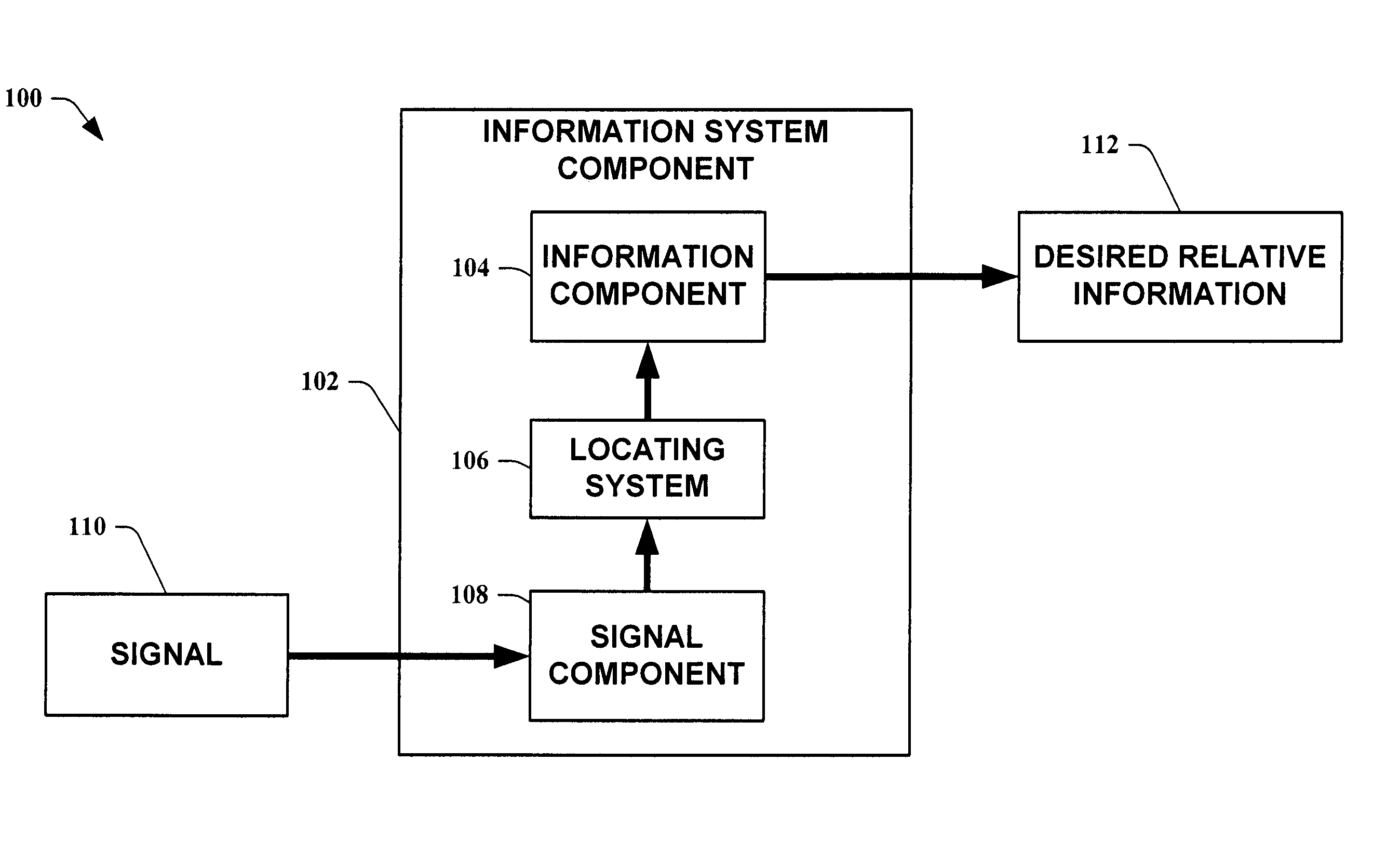
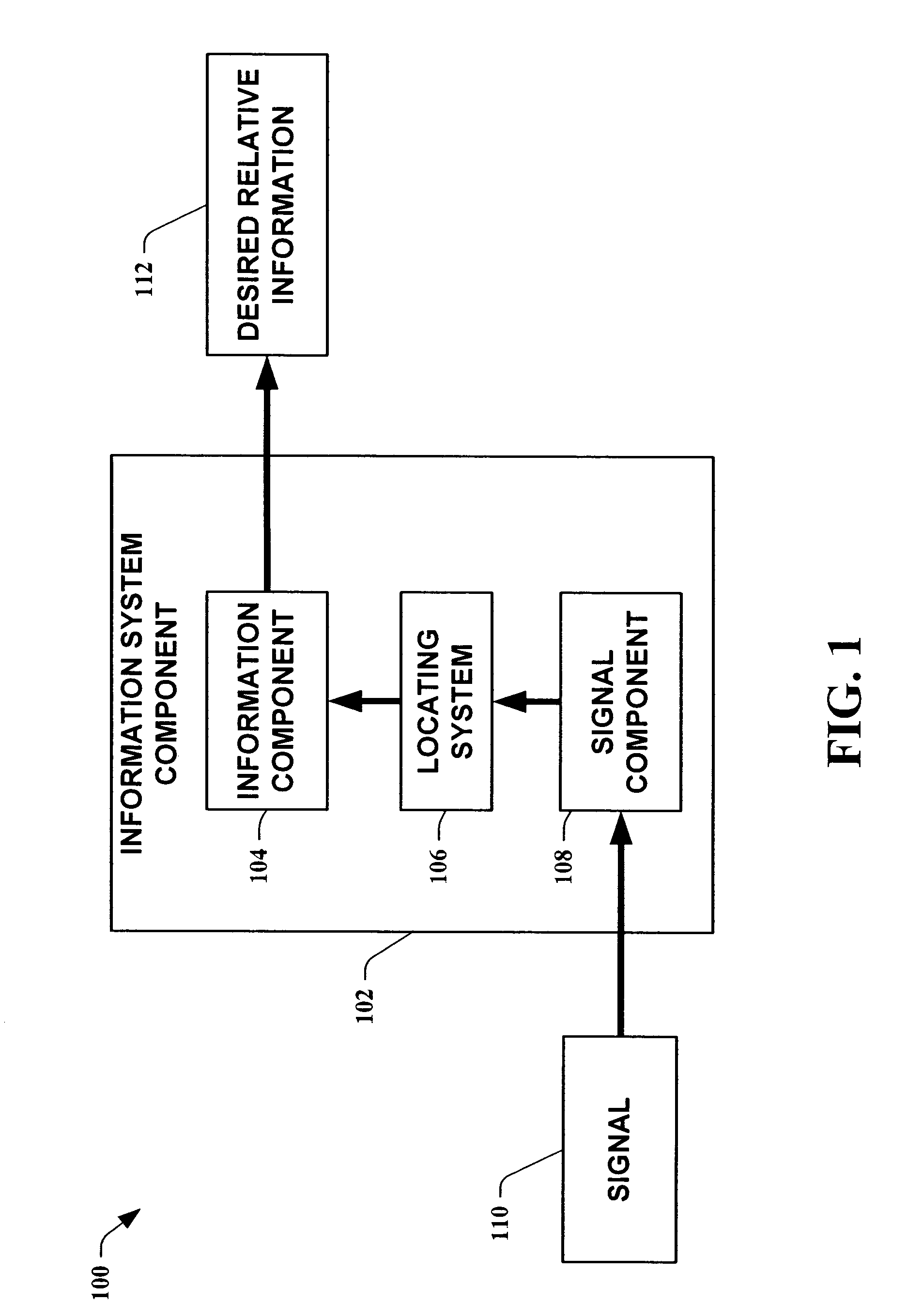
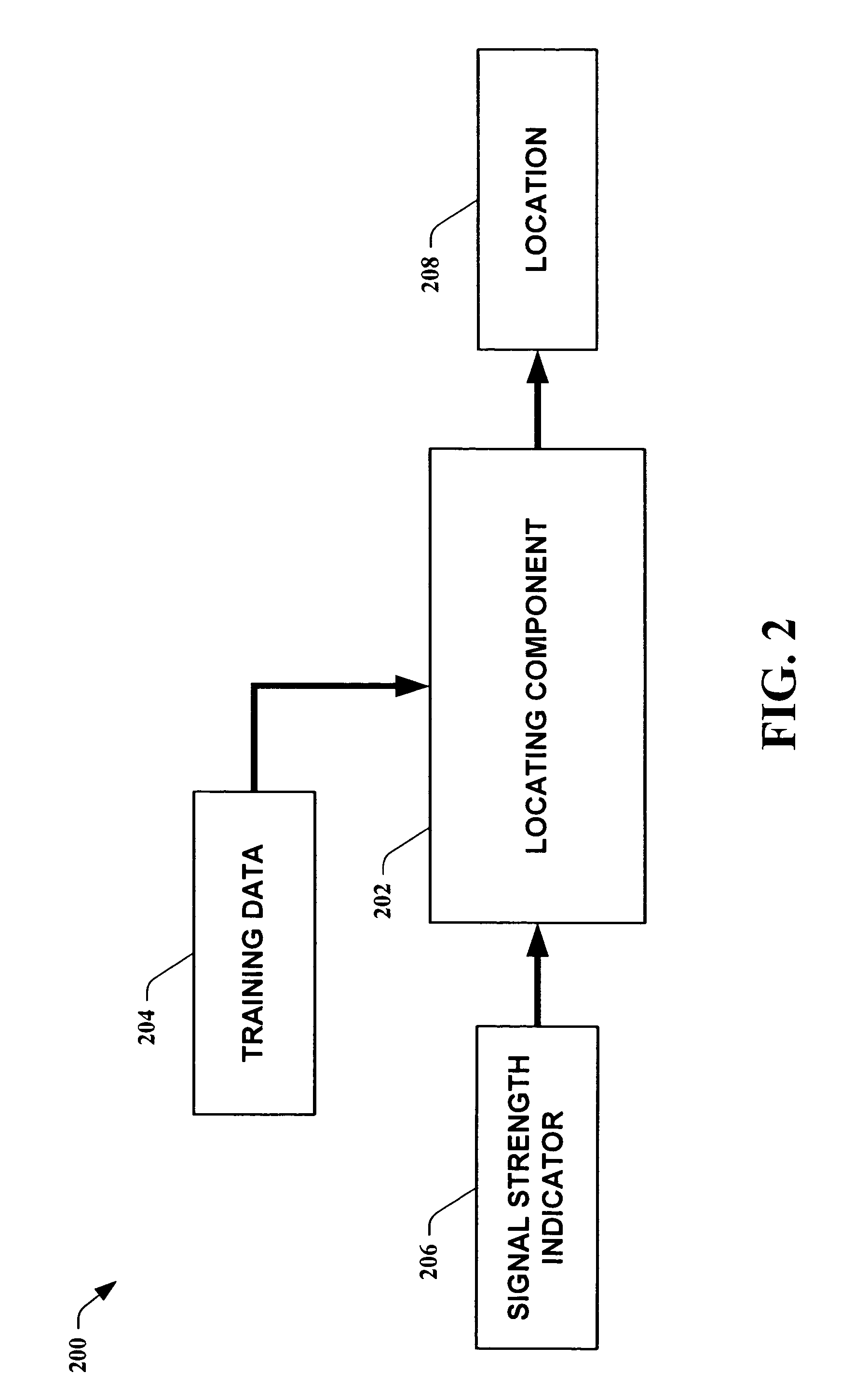
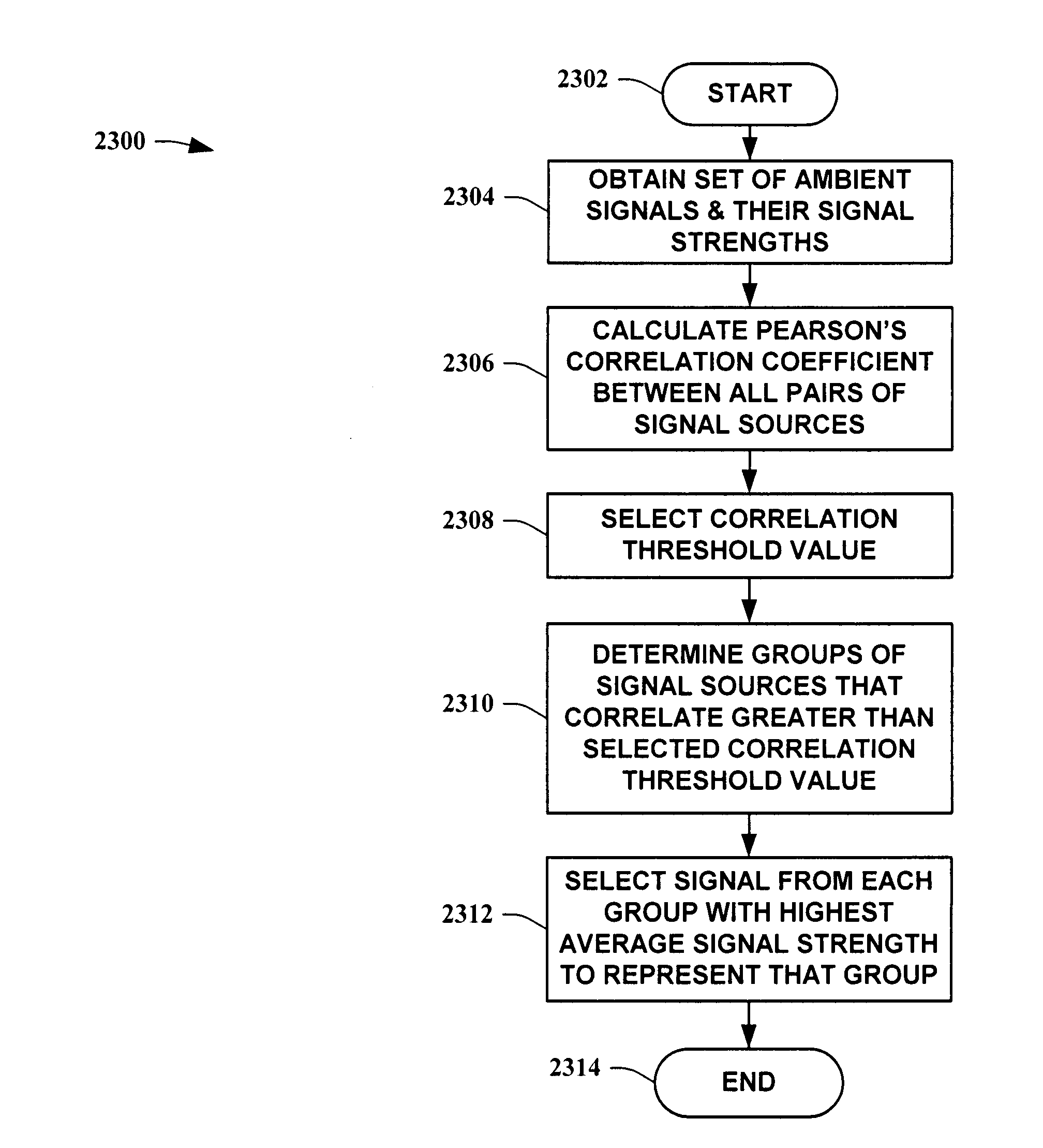
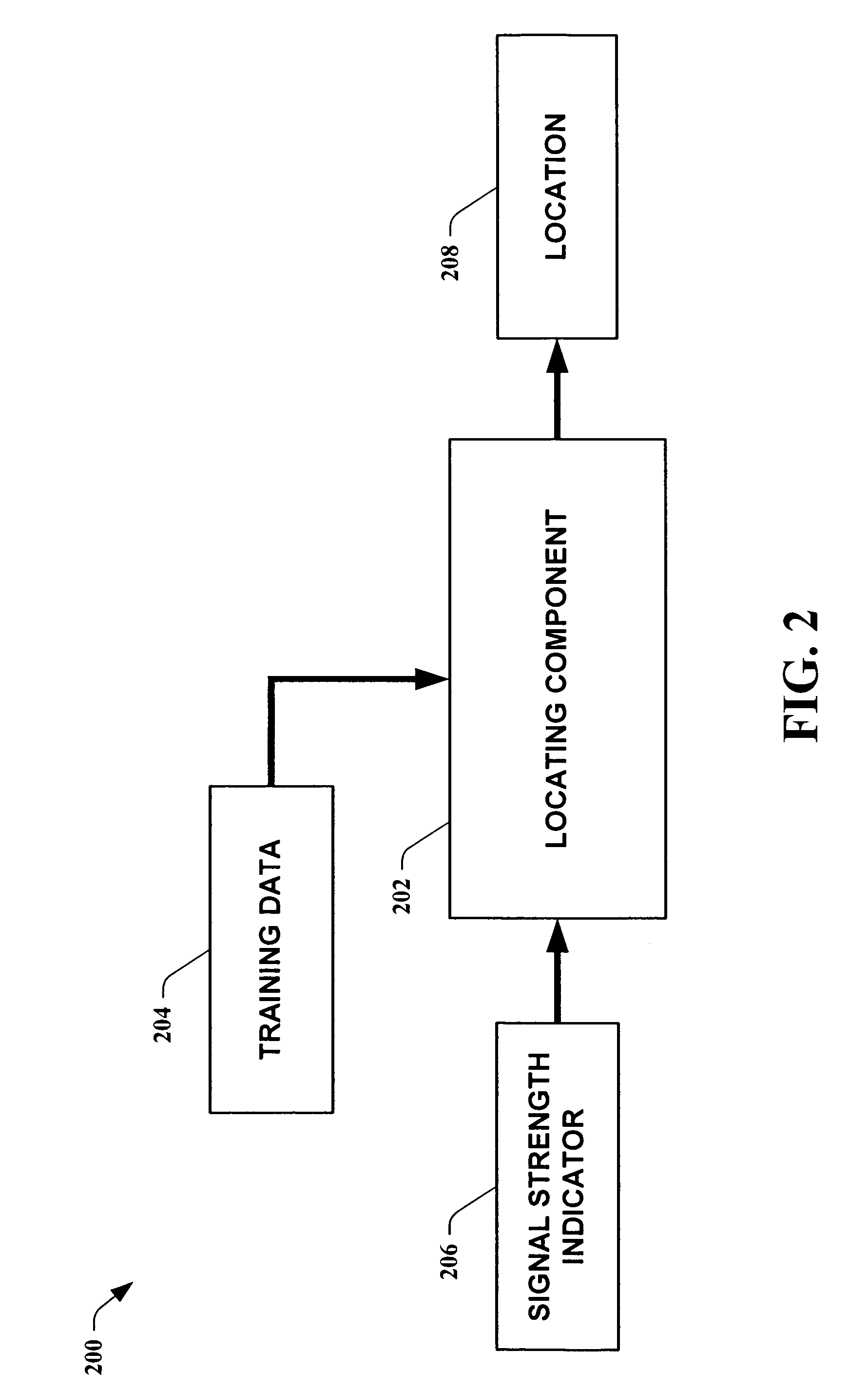
Methods for determining the approximate location of a device from ambient signals
InactiveUS20050020278A1Facilitates approximationSubstantial accuracy in determining locationRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationAlgorithmLocation Equipment
The present invention leverages changes in the sensed strength of radio signals at different locations to determine a device's location. In one instance of the invention, inference procedures are used to process ambient commercial radio signals, to estimate a location or a probability distribution over the locations of a device. In an instance of the invention, learning and inference methods are applied to rank vector of signal strength vectors. Moving to such rank orderings leads to methods that bypass consideration of absolute signal strengths in location calculations. The invention facilitates approximations for locating a device by providing a method that does not require a substantial number of available ambient signal strengths while still providing useful location inferences in determining locations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
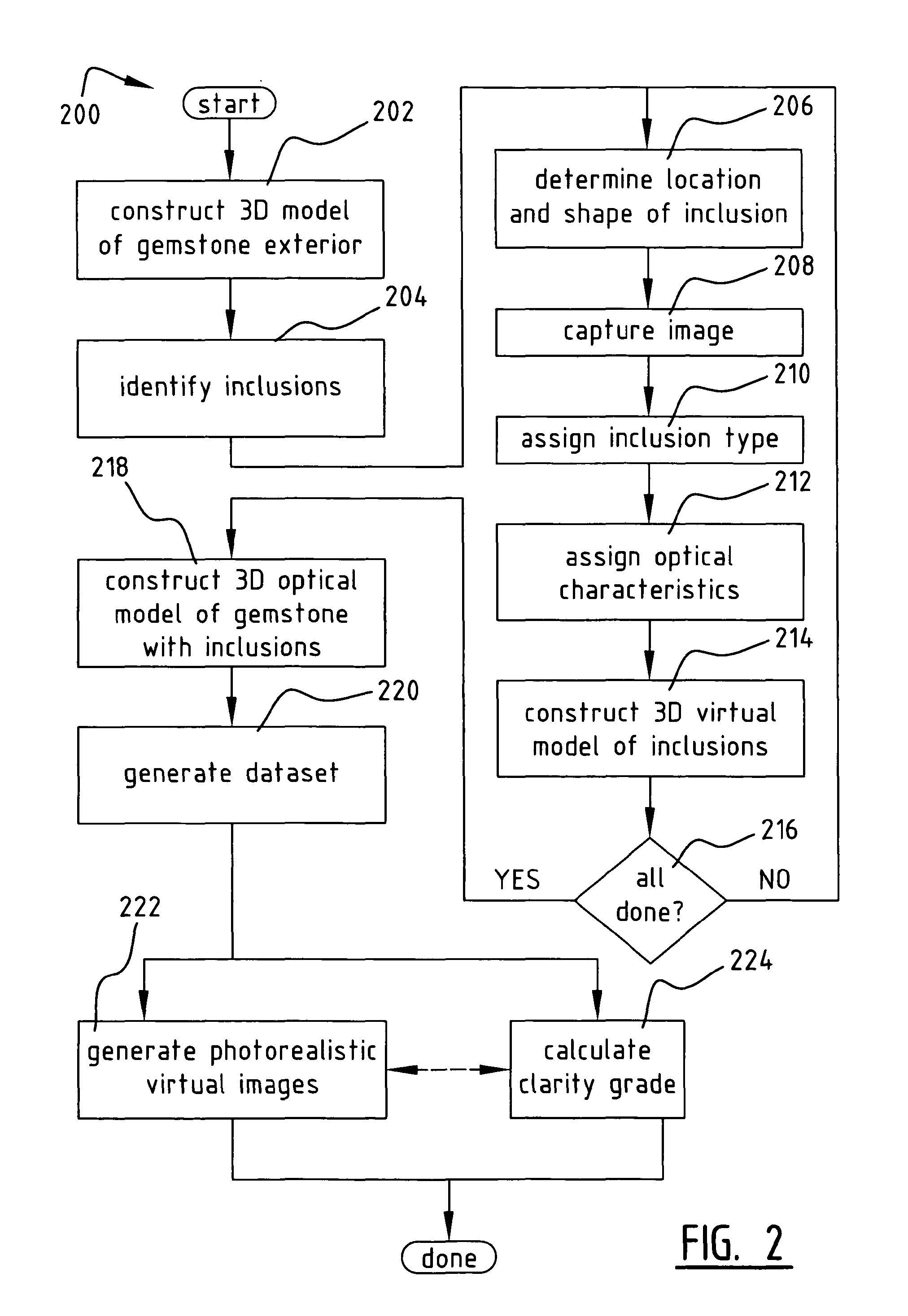
Method and System for Improved Optical Modeling of Gemstones
ActiveUS20100250201A1Reduce deficiencyImproved virtual optical modelingInvestigating jewelsOptically investigating flaws/contamination3d shapesOptical property
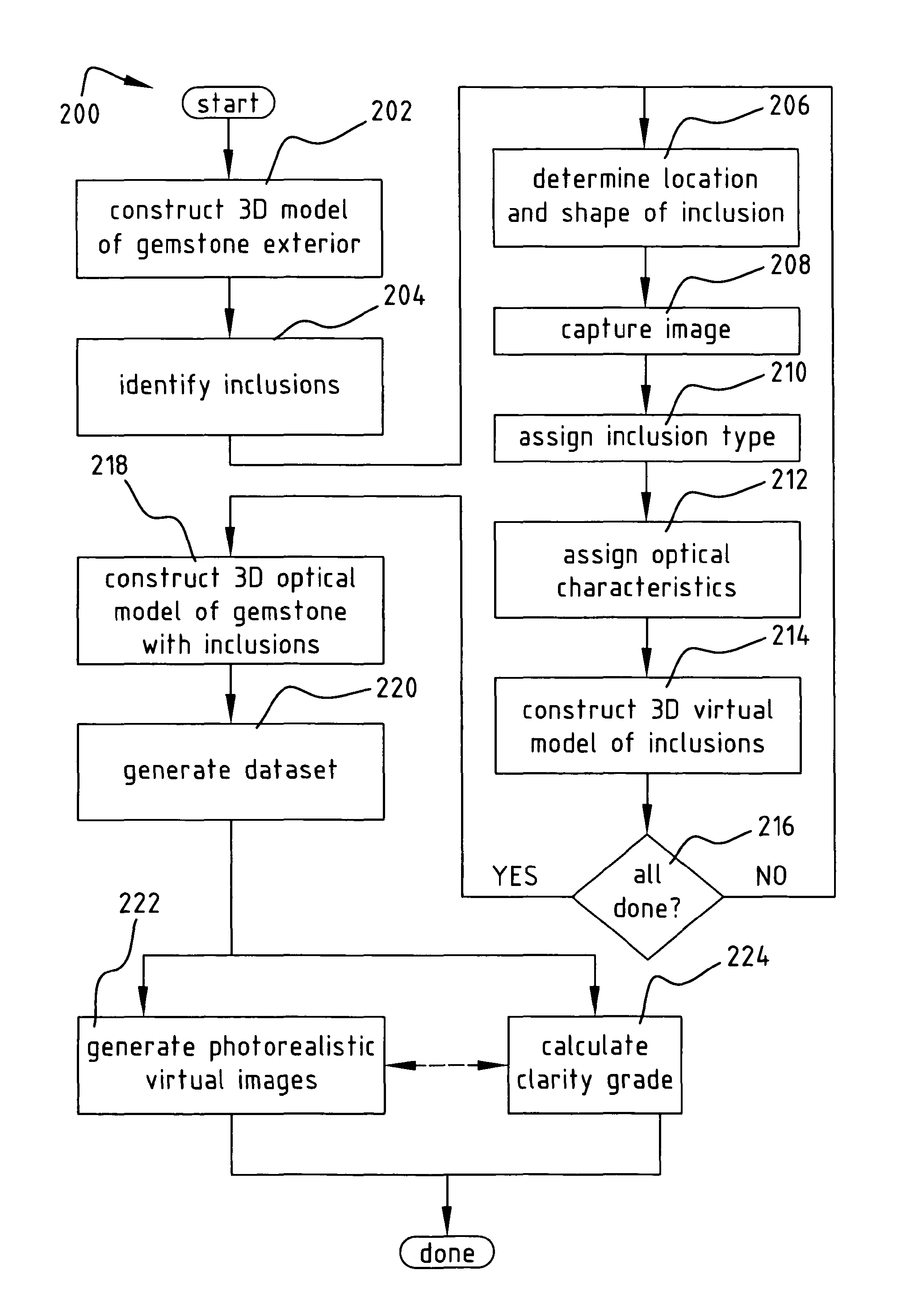
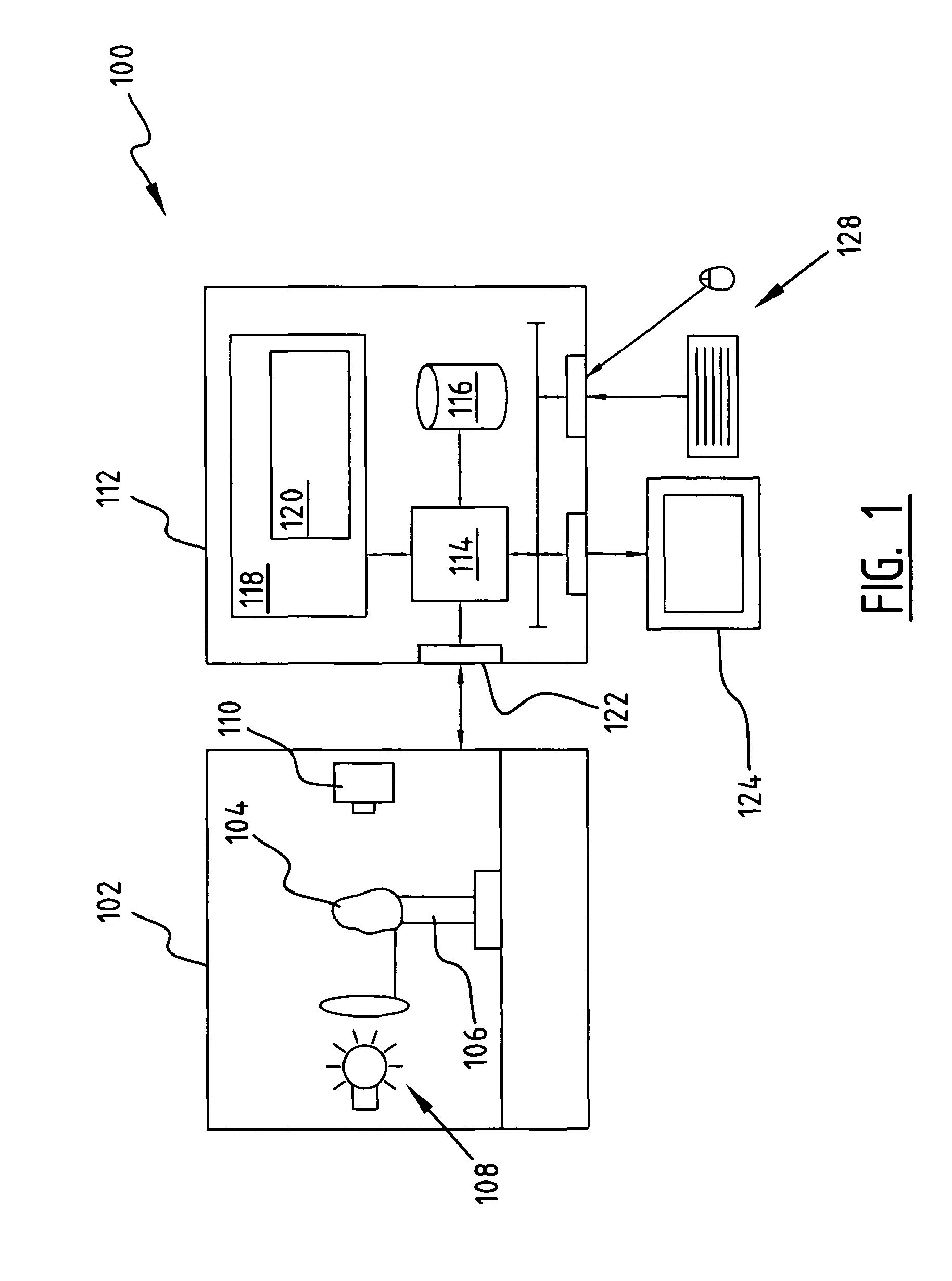
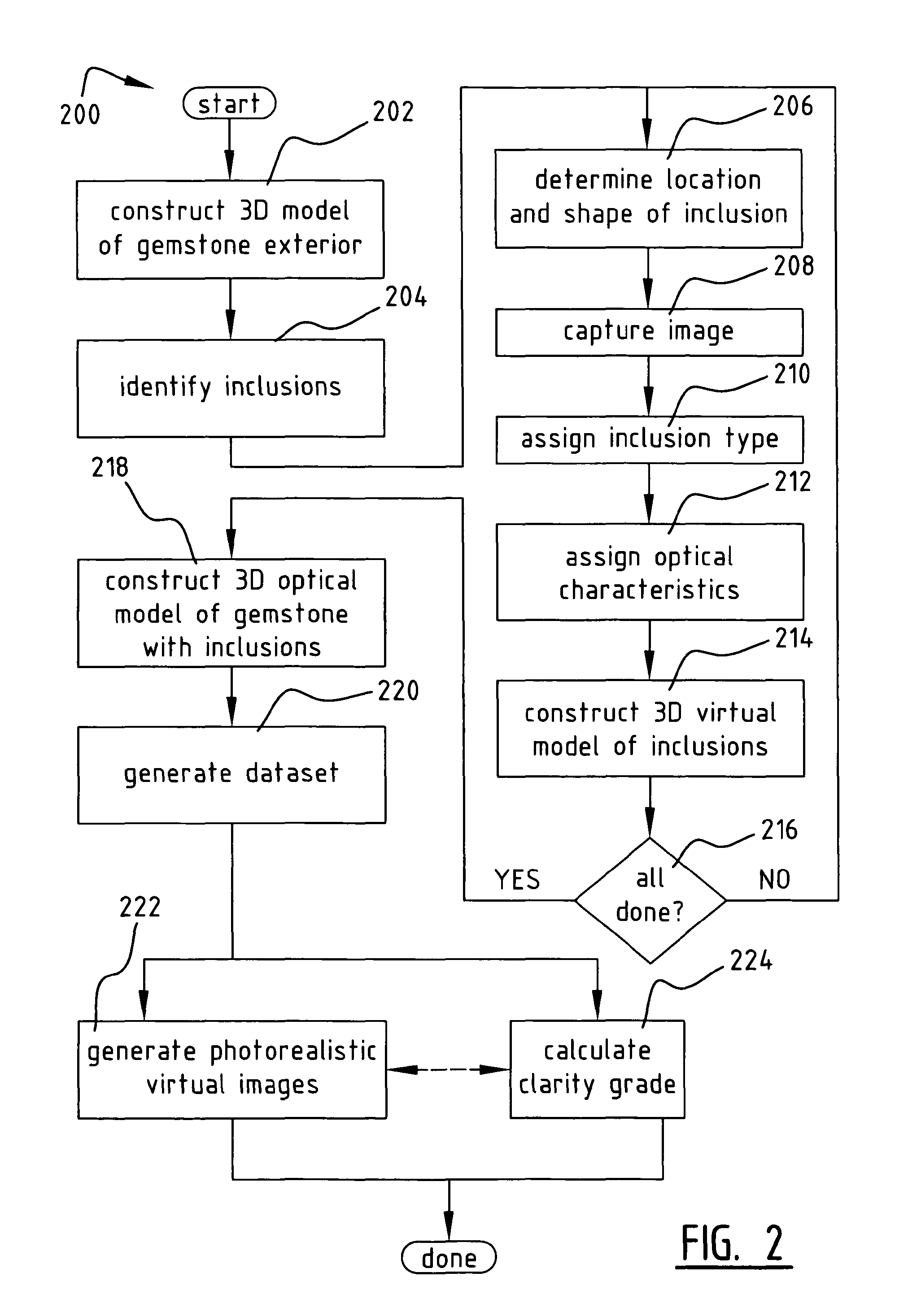
A method of constructing a virtual model of a gemstone including the steps of performing measurements of the gemstone to construct a three-dimensional (3D) model of an exterior surface of the gemstone; identifying one or more visible inclusions within an interior volume of the gemstone; for each identified inclusion, performing the steps of determining a location and 3D shape of the inclusion within the interior volume of the gemstone; capturing at least one image of the inclusion; using the at least one image to determine relevant optical characteristics of the inclusion; and constructing a 3D virtual model of the inclusion, said model including the 3D shape of the inclusion and optical properties of the inclusion based upon said optical characteristics; constructing a 3D virtual model of the gemstone which includes the 3D virtual model of the exterior surface of the gemstone and the 3D virtual models of the one or more visible inclusions within the interior volume of the gemstone; and generating a dataset representing said 3D virtual model, wherein said dataset may be used in subsequent computer analysis to provide a user with information relating to a visual characteristic of the gemstone.
Owner:IDEAL SCOPE
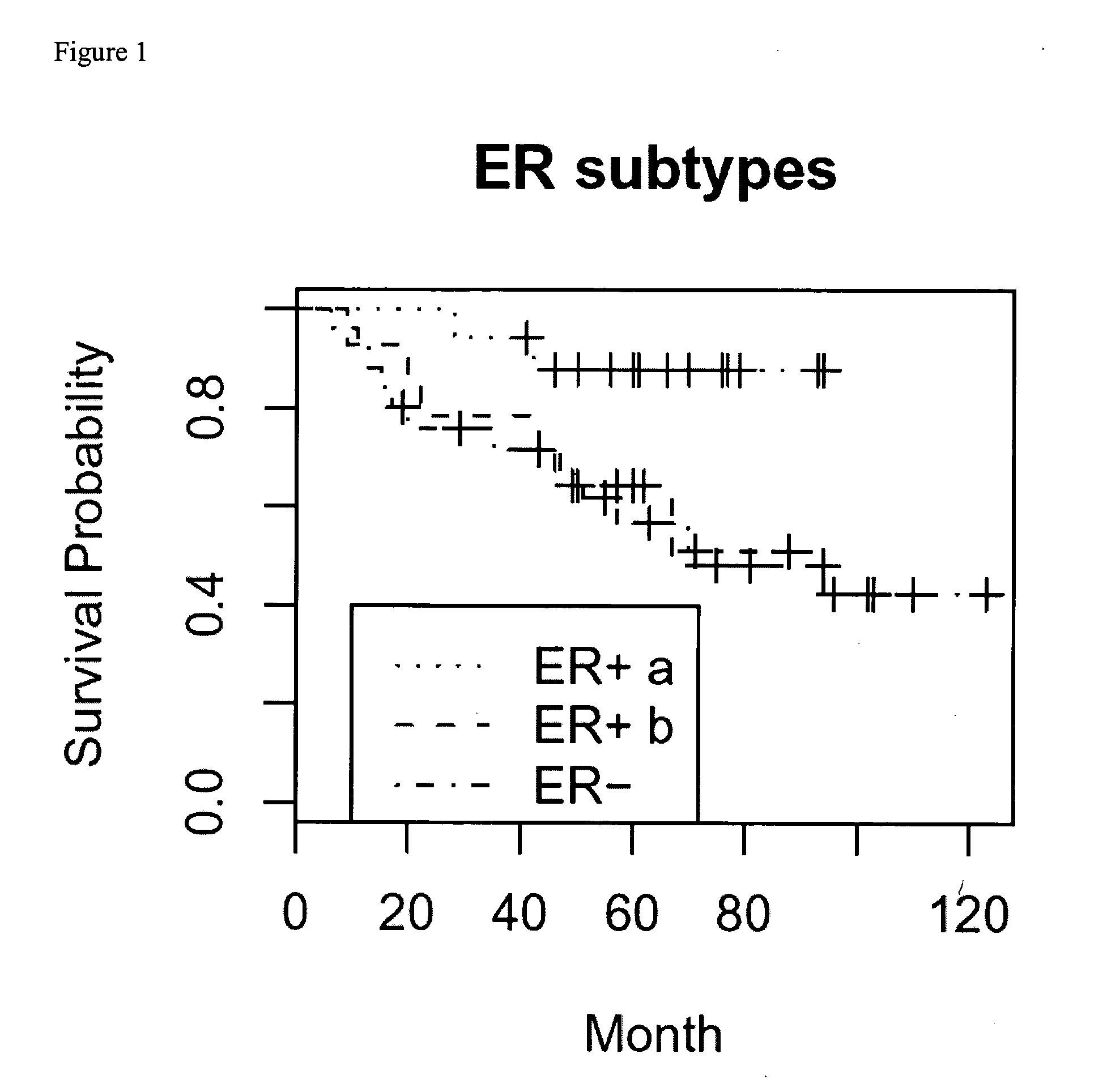
Signatures of ER status in breast cancer
InactiveUS20050208500A1Reduce severityReduce chanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPopulationExpression protein
The invention relates to the identification and use of gene expression profiles, or patterns, suitable for identification of populations that are positive and negative for estrogen receptor expression. The gene expression profiles may be embodied in nucleic acid expression, protein expression, or other expression formats, and may be used in the study and / or diagnosis of cells and tissue in breast cancer as well as for the study and / or determination of prognosis of a patient, including breast cancer survival.
Owner:ACTURUS BIOSCI INC +1
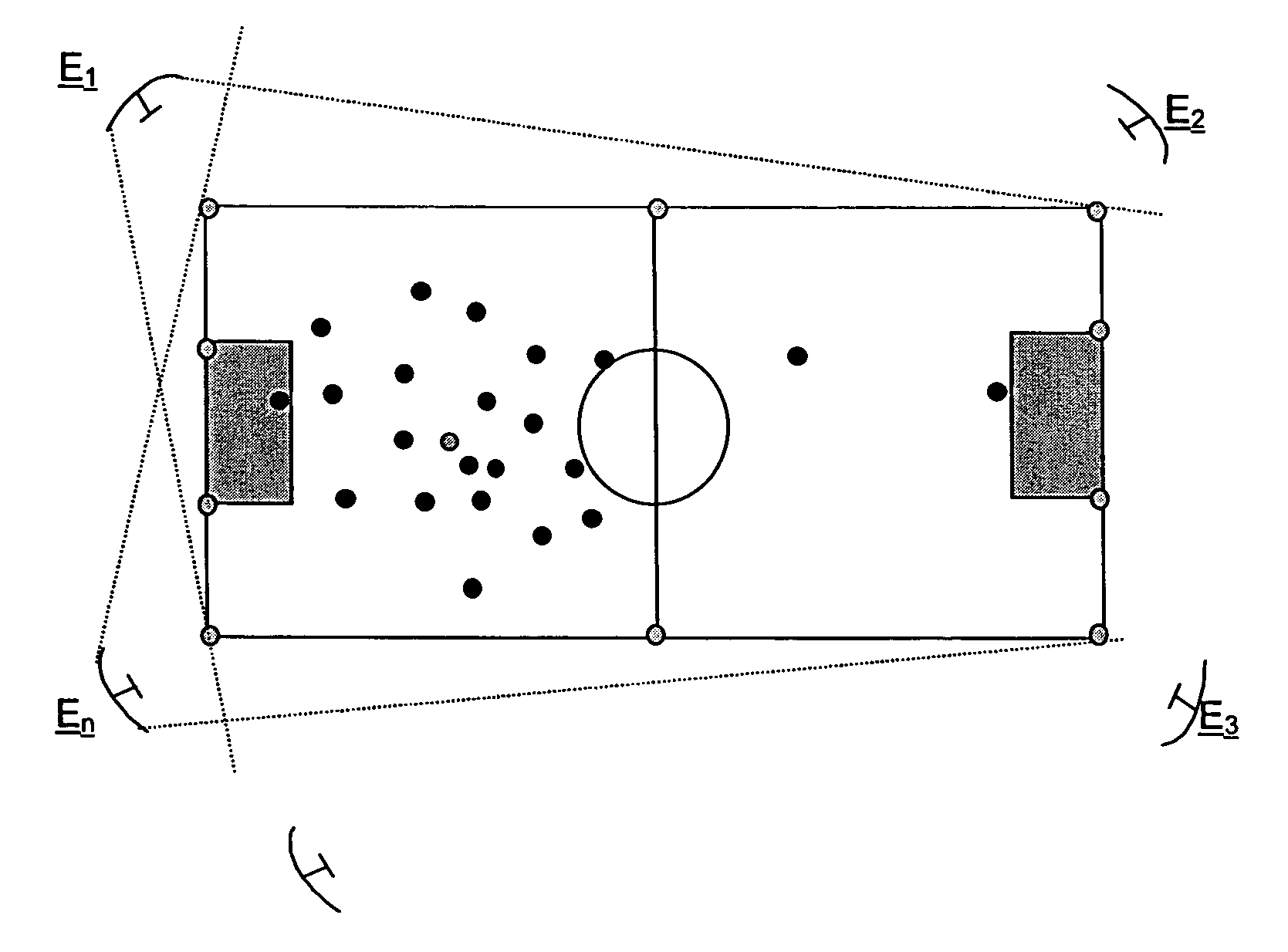
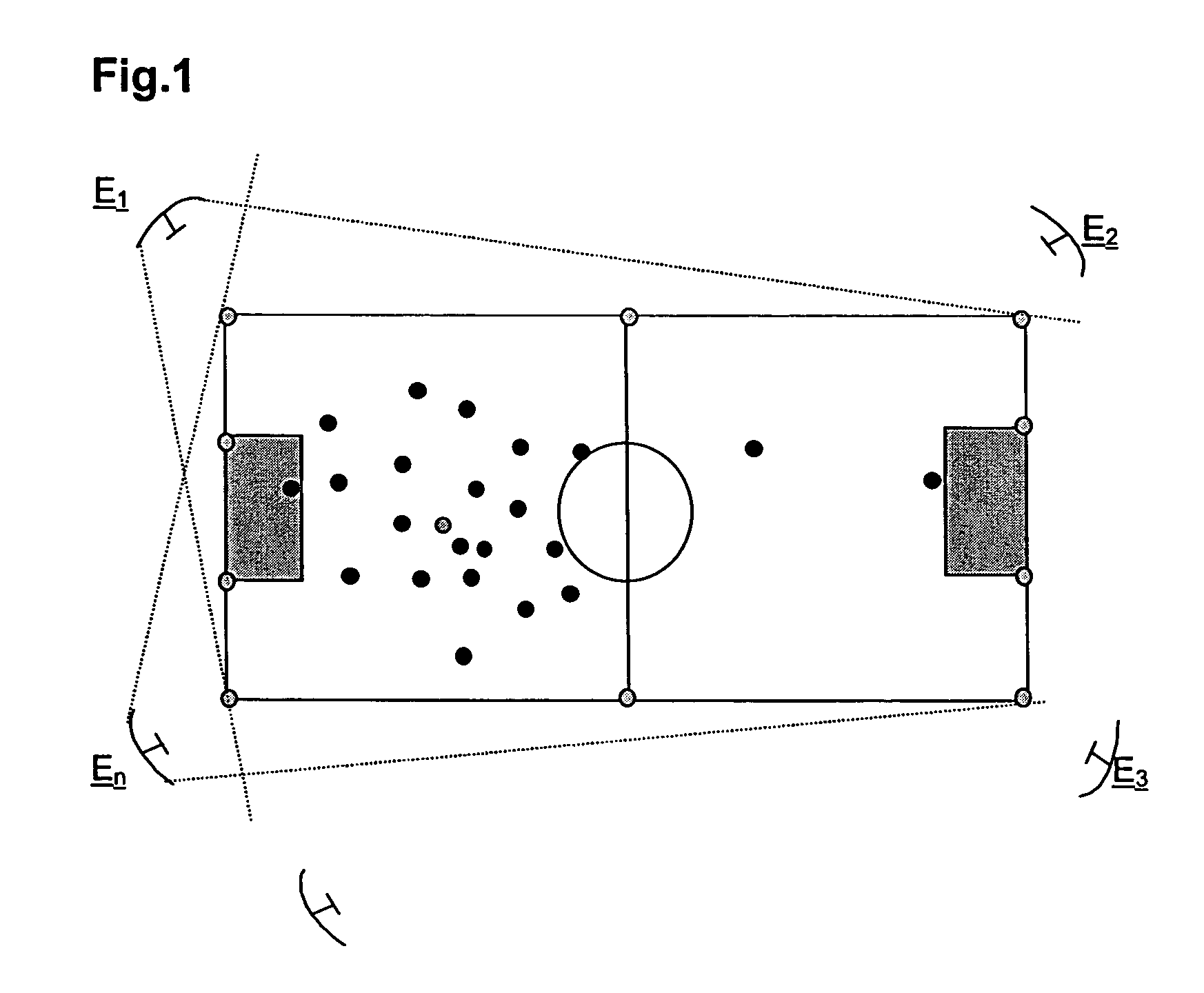
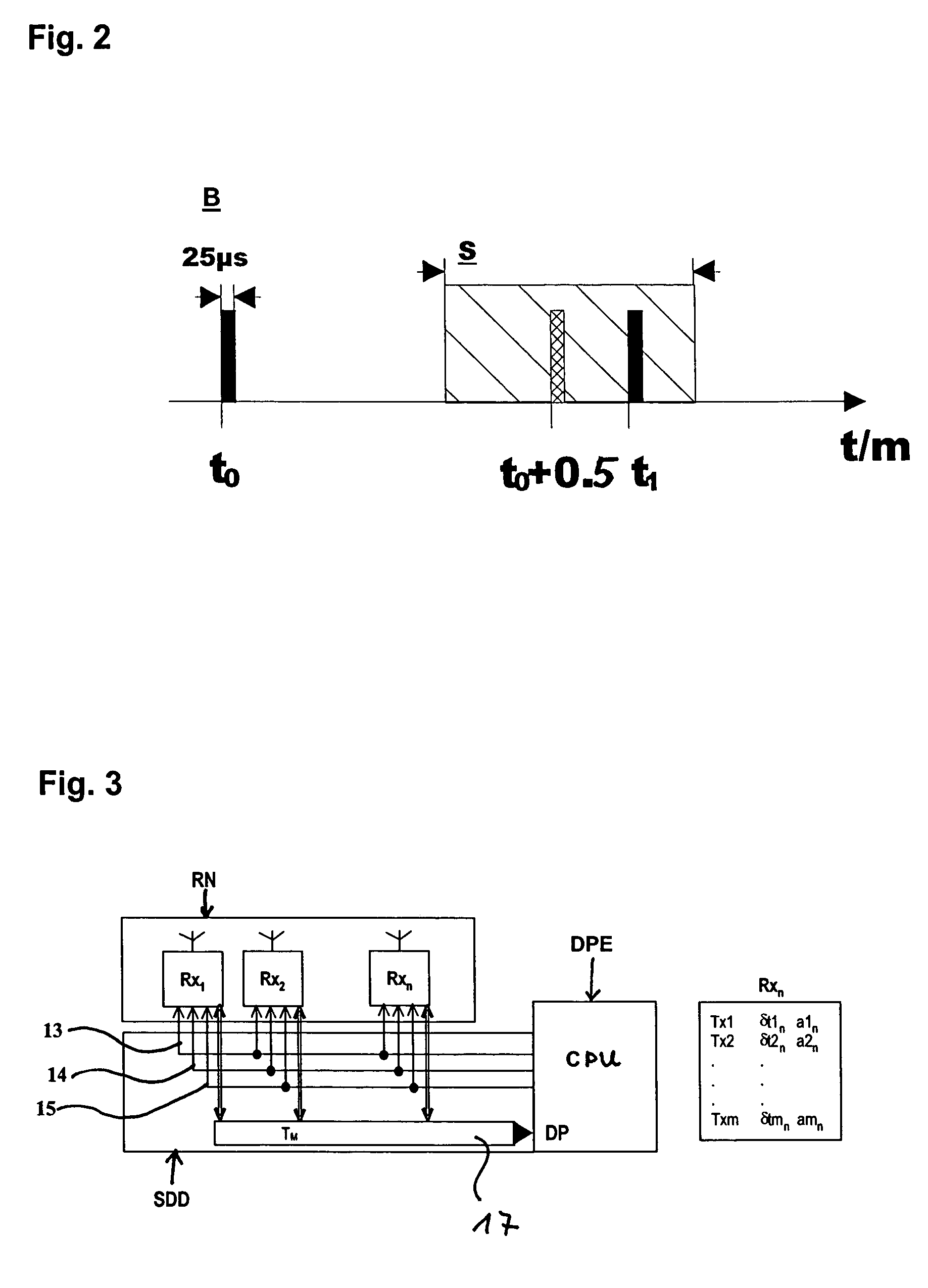
Method for the continuous real time tracking of the position of at least one mobile object as well as an associated device
ActiveUS7139582B2Reduce cross-correlationMaximize accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesGymnastic exercisingBurst transmissionTemporal resolution
In a method for the continuous real time tracking of the position of at least one mobile object in a defined multidimensional space, at least one mobile transmitter module is attached to at least one mobile object and the signals from the at least one module are received by a stationary receiving and signal processing network and then centrally processed. The signals emitted by each transmitter module are electromagnetic waves sent within a frequency band range using time division multiplexing techniques. Due to the fact that the frequency band is used as a single channel for the purpose of maximizing the accuracy with which a position is detected, and due also to the fact that the communication process between the transmitters and the receivers is based on the principle of pseudo-random time division multiplexing using burst transmissions of low cross correlation with non synchronized pseudo-random patterns, there is created a method for the continuous tracking of the position of one or more mobile objects at any time and in any place which is of very high positional resolution and has a temporal resolution of just a few milliseconds.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
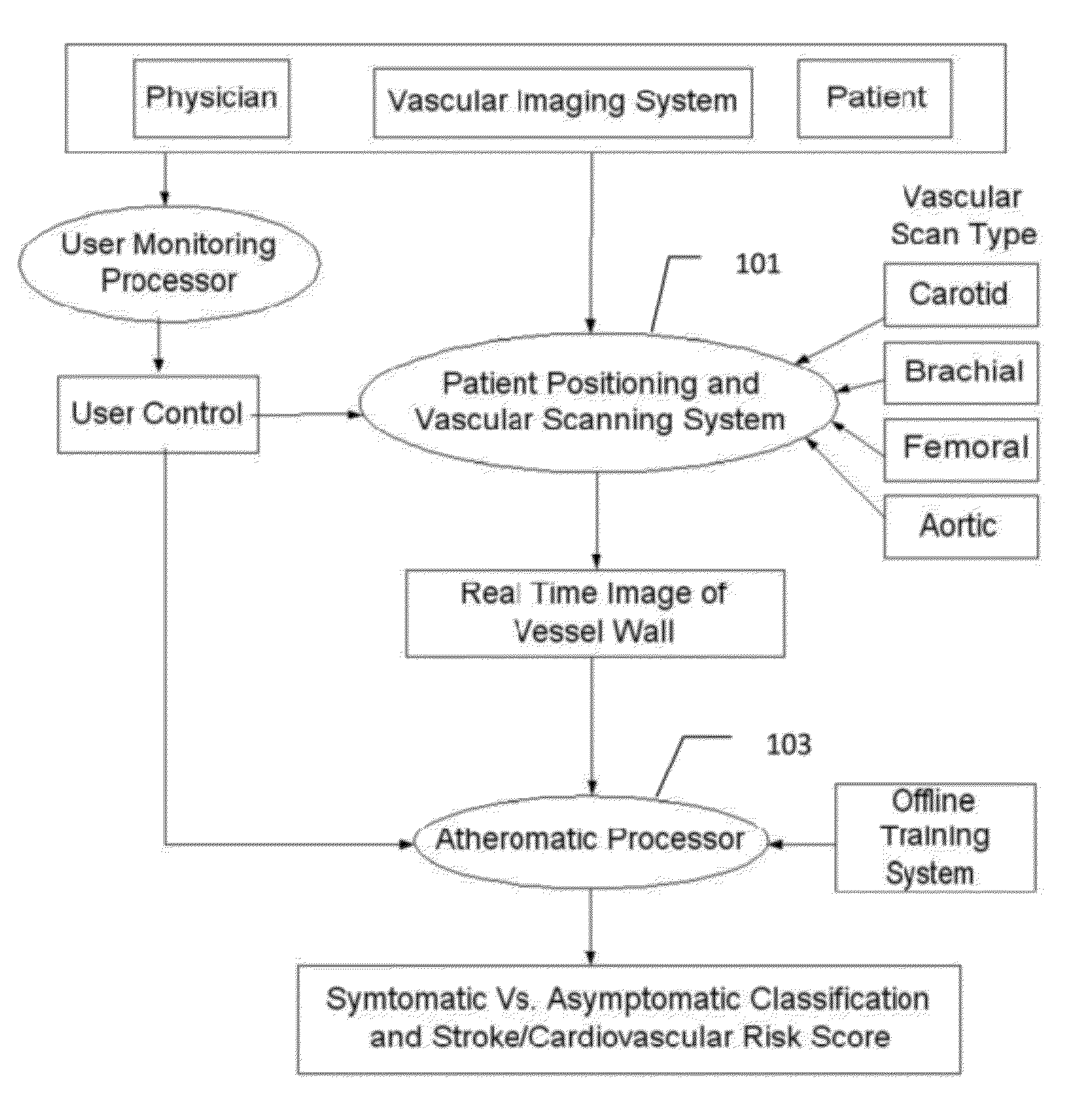
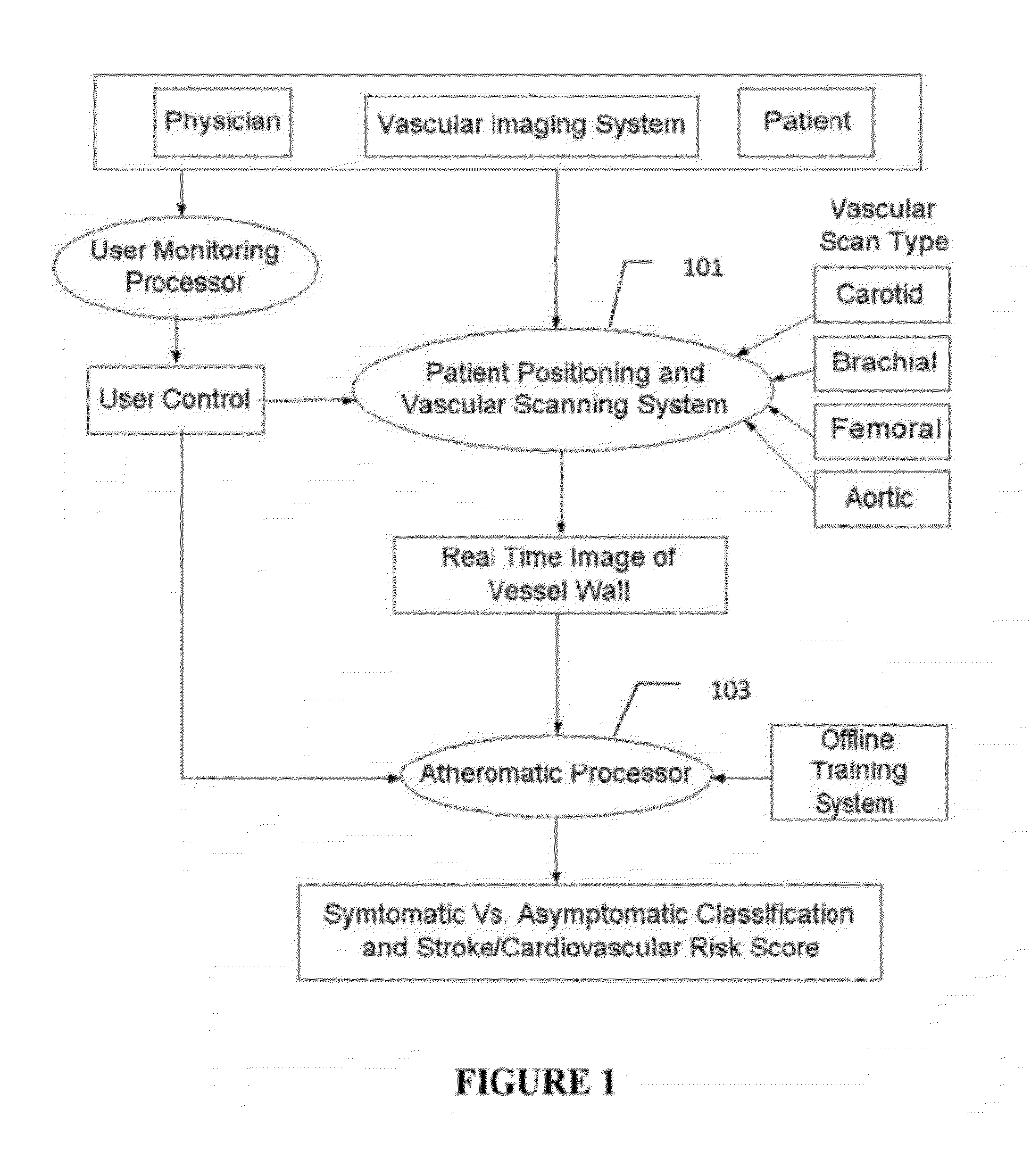
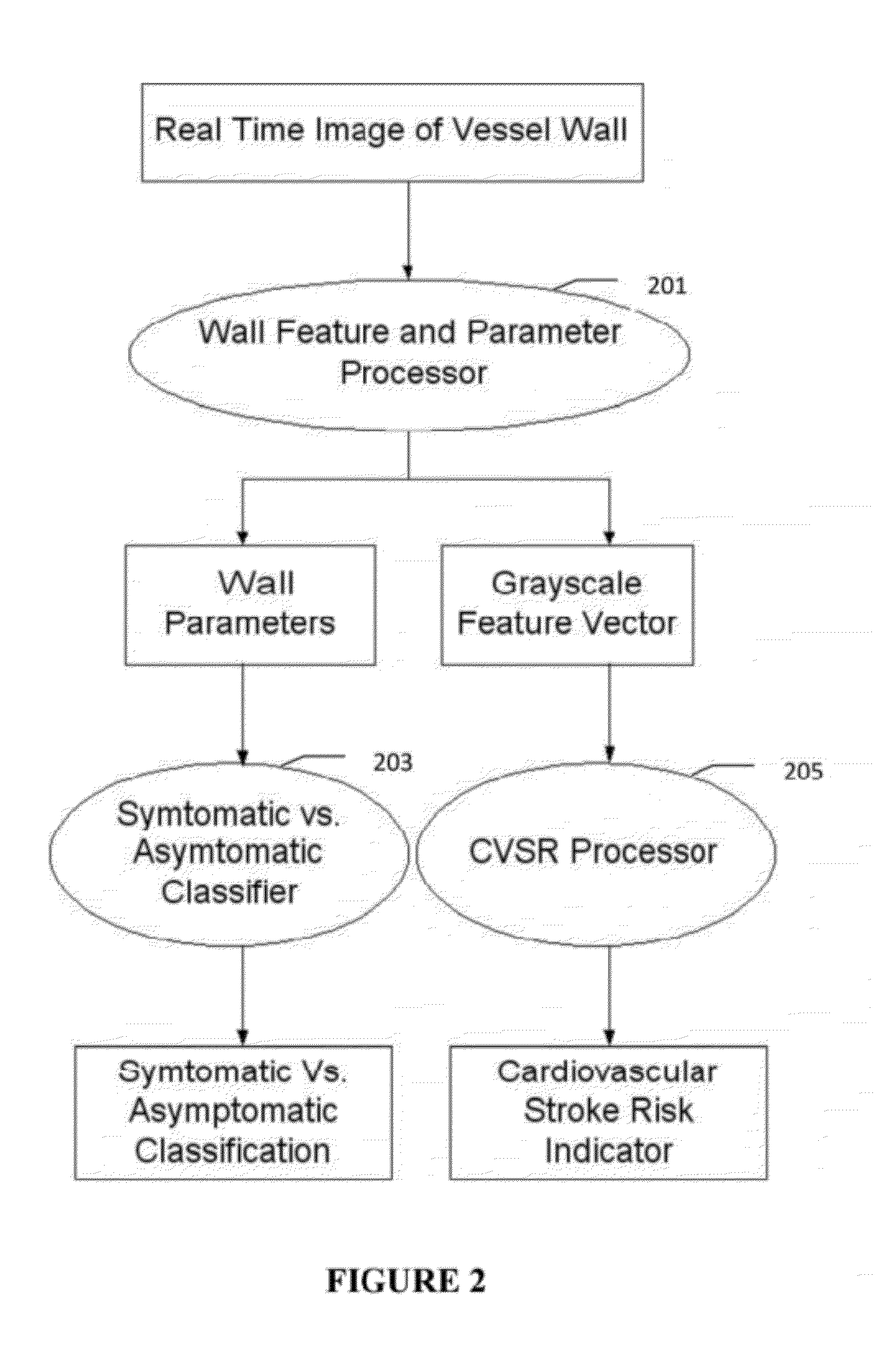
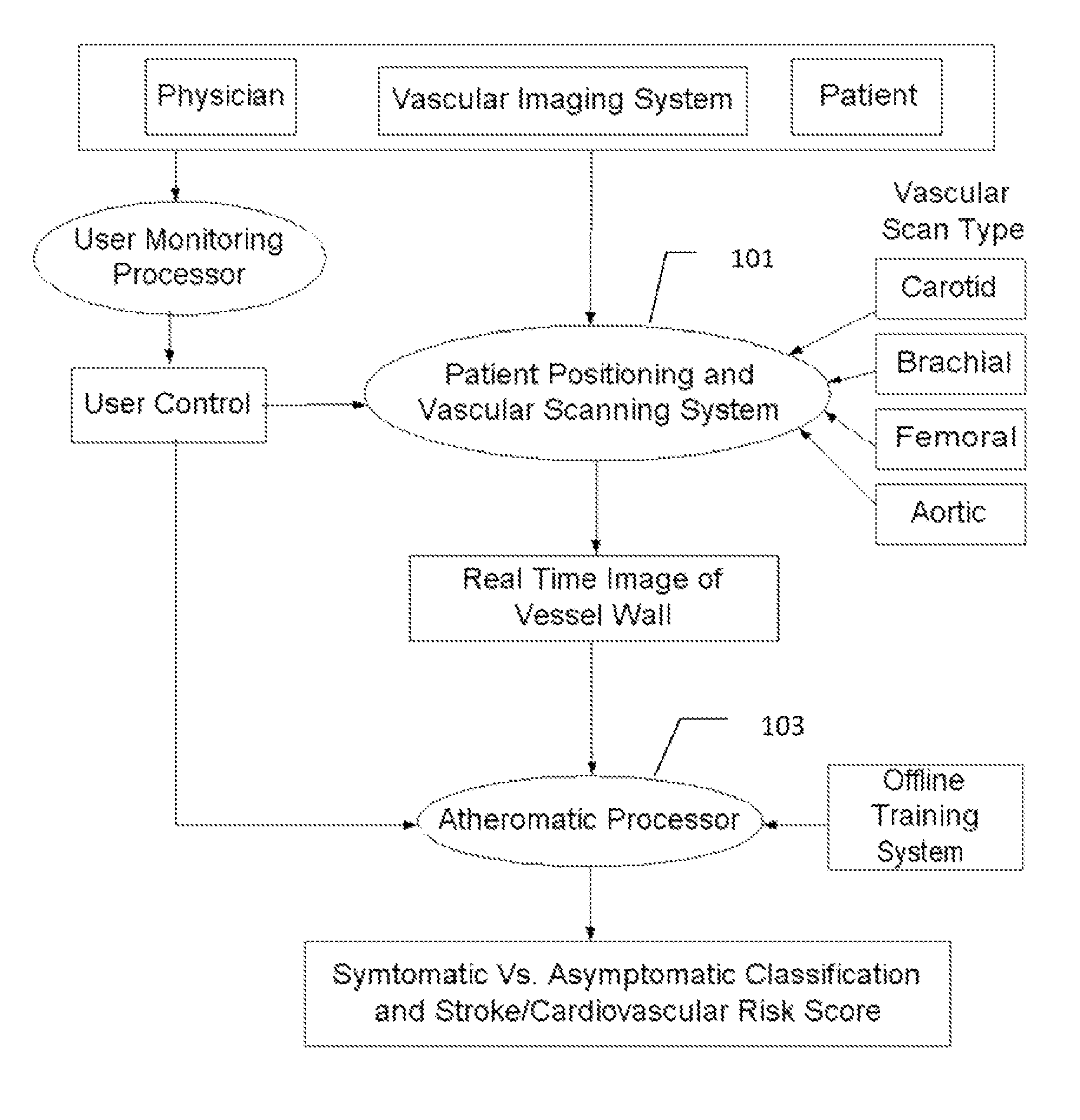
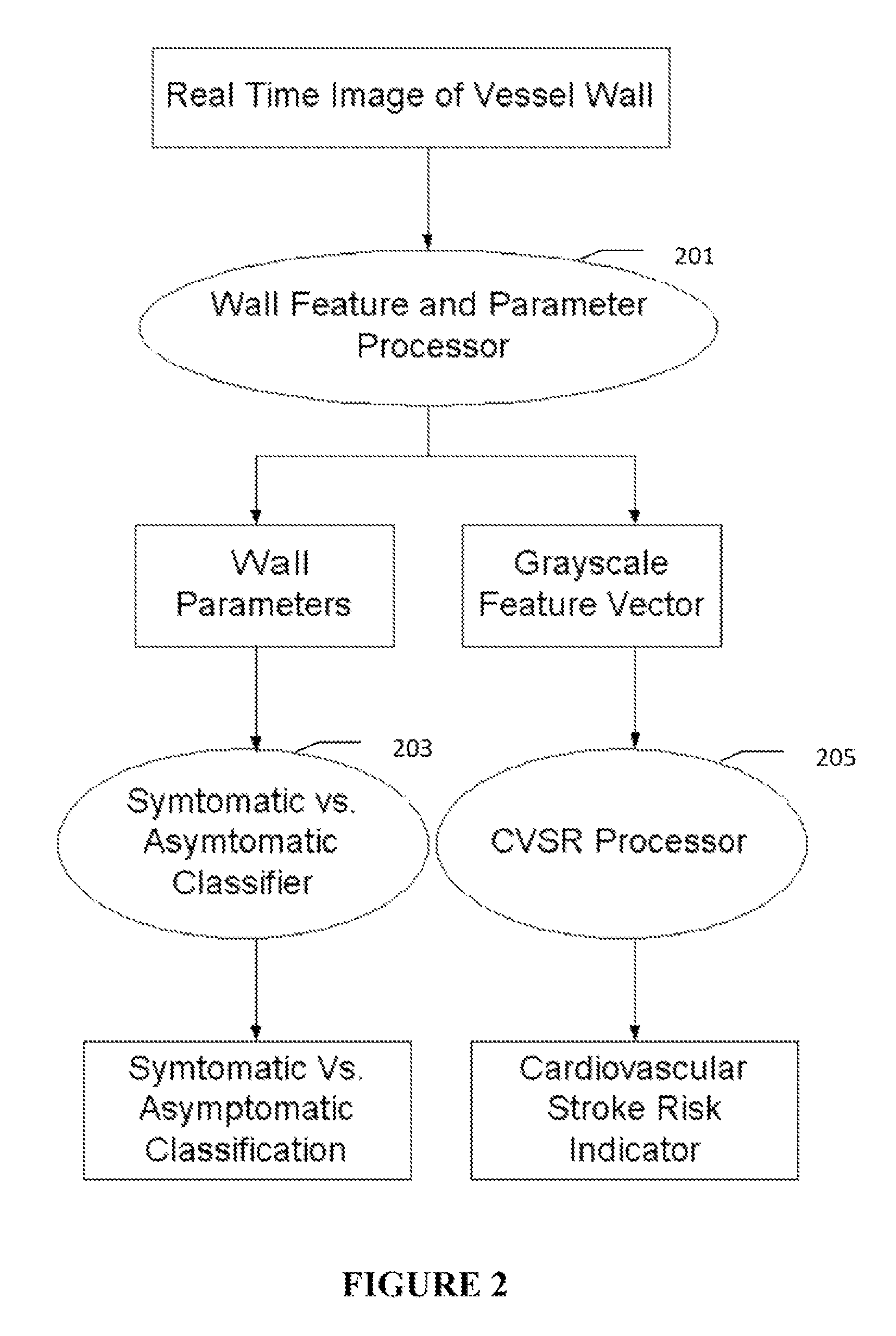
Imaging Based Symptomatic Classification Using a Combination of Trace Transform, Fuzzy Technique and Multitude of Features
InactiveUS20120078099A1Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsGray levelRadiology
A statistical (a) Computer Aided Diagnostic (CAD) technique is described for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification of carotid ultrasound images and (b) presents a cardiovascular risk score computation. We demonstrate this for longitudinal Ultrasound, CT, MR modalities and extendable to 3D carotid Ultrasound. The on-line system consists of Atherosclerotic Wall Region estimation using AtheroEdge™ for longitudinal Ultrasound or Athero-CTView™ for CT or Athero-MRView from MR. This greyscale Wall Region is then fed to a feature extraction processor which uses the combination: (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability. Another combination uses: (a) Local Binary Pattern; (b) Law's Mask Energy and (c) Wall Variability. Another combination uses: (a) Trace Transform; (b) Fuzzy Grayscale Level Co-occurrence Matrix and (c) Wall Variability. The output of the Feature Processor is fed to the Classifier which is trained off-line.
Owner:ATHEROPOINT
Systems for determining the approximate location of a device from ambient signals
InactiveUS20050020277A1Facilitates approximationSubstantial accuracy in determining locationInstruments for road network navigationDirection finders using radio wavesAlgorithmLocation Equipment
The present invention leverages changes in the sensed strength of radio signals at different locations to determine a device's location. In one instance of the present invention, inference procedures are used to process ambient commercial radio signals, to estimate a location or a probability distribution over the locations of a device. In another instance of the present invention, a system utilizes learning and inference methods that are applied to rank vector of signal strength vectors. Moving to such rank orderings leads to systems that bypass consideration of absolute signal strengths in location calculations. The present invention facilitates approximations for locating a device by providing a system that does not require a substantial number of available ambient signal strengths while still providing useful location inferences in determining locations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
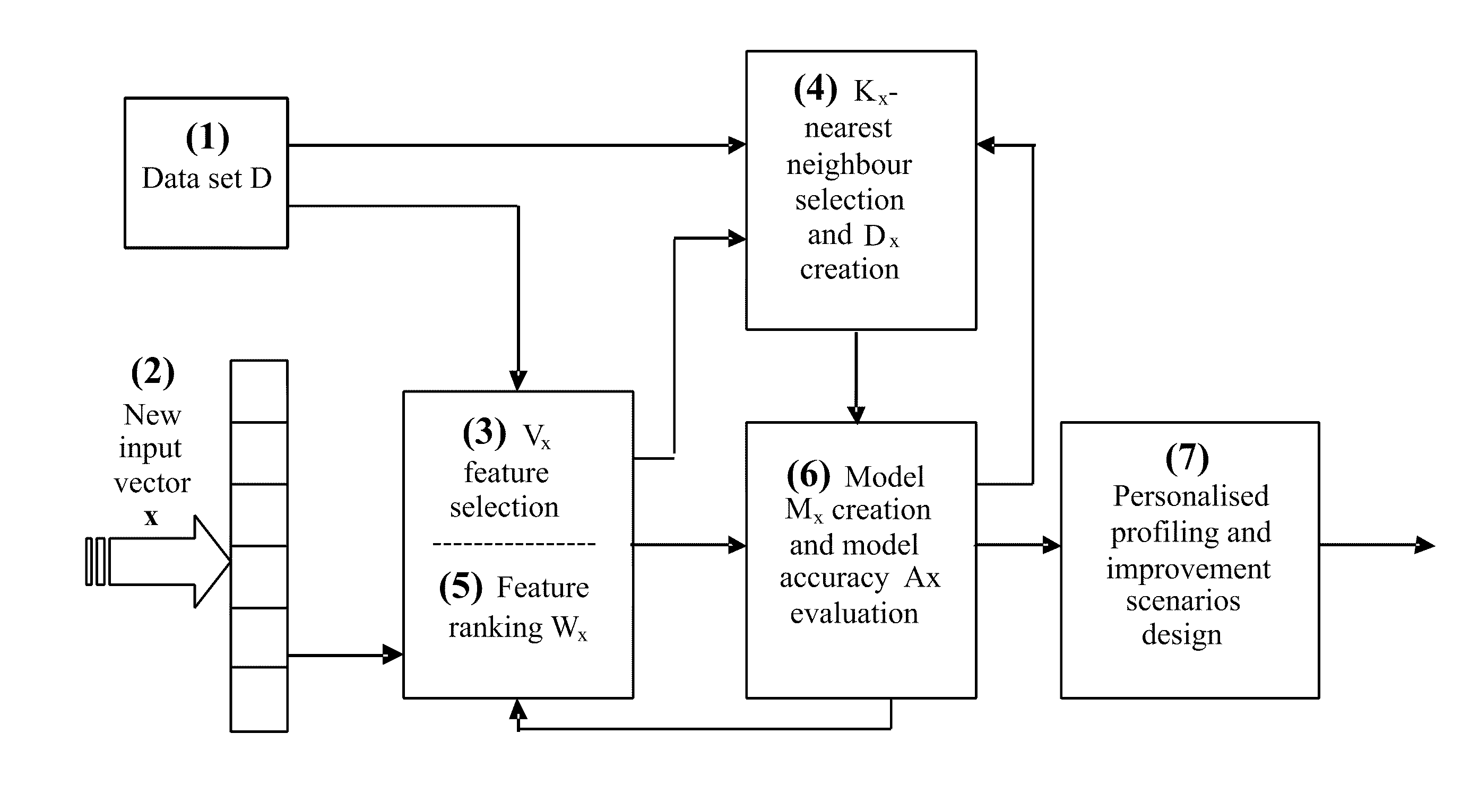
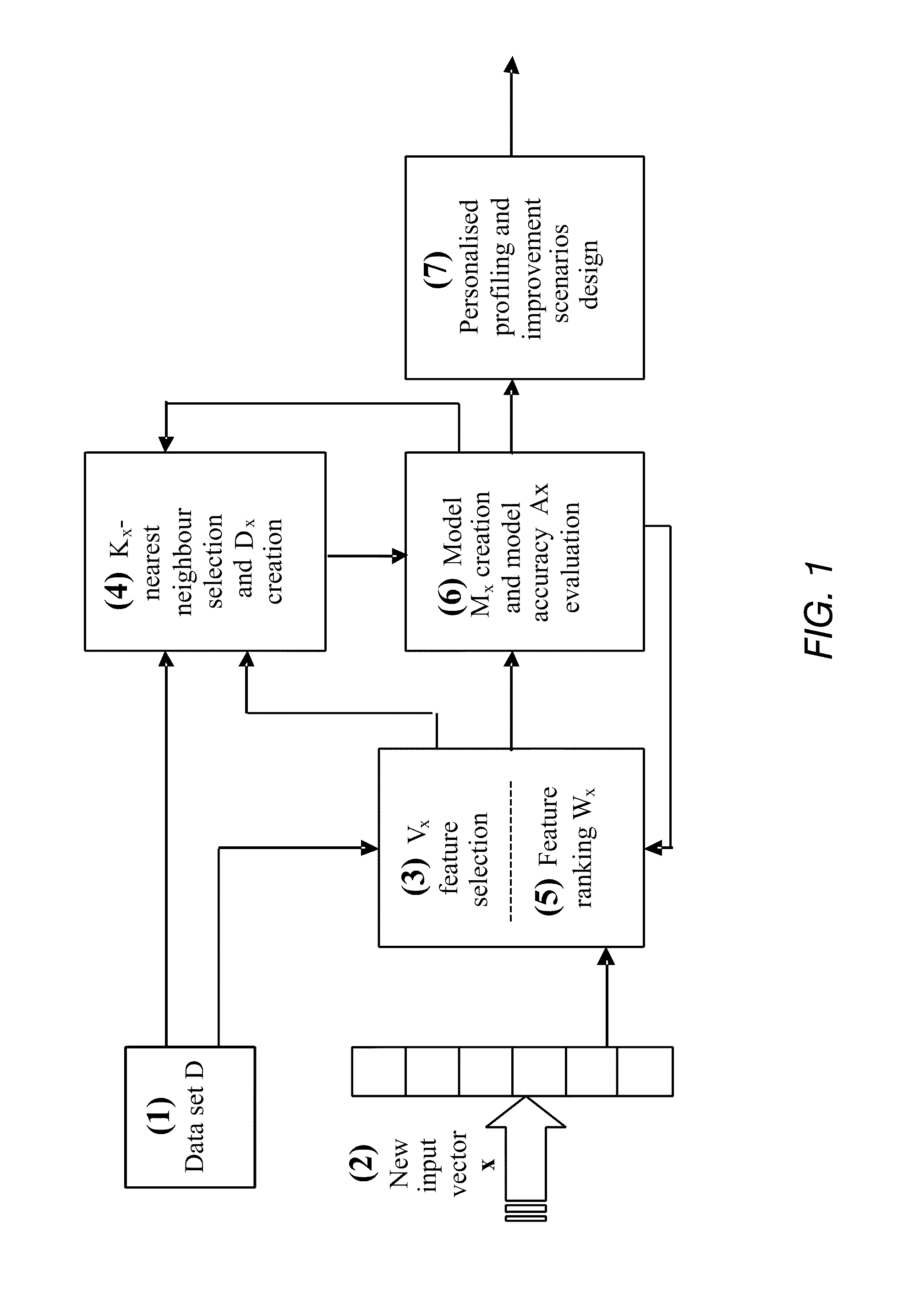
Data analysis and predictive systems and related methodologies
ActiveUS20110307228A1Maximum accuracyEasily realizedBiostatisticsForecastingData setVariable features
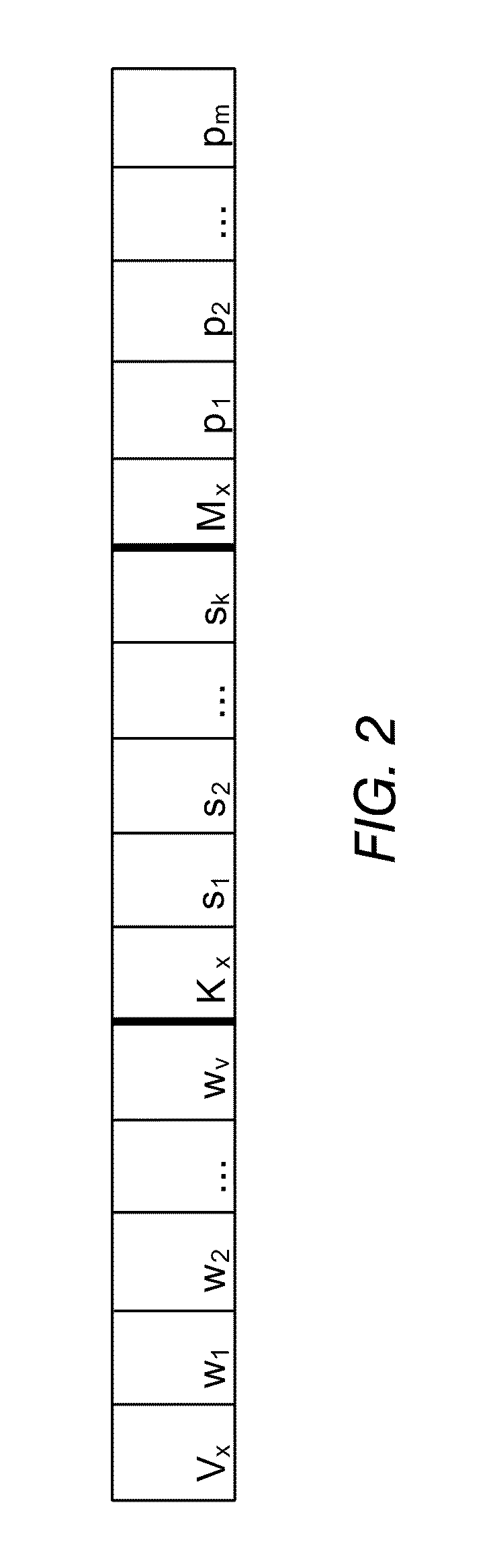
A method of optimising a model Mx suitable for use in data analysis and determining a prognostic outcome specific to a particular subject (input vector x), the subject comprising a number of variable features in relation to a scenario of interest for which there is a global dataset D of samples also having the same features relating to the scenario, and for which the outcome is known is disclosed. In one implementation, the method includes: (a) determining what number and a subset Vx of variable features will be used in assessing the outcome for the input vector x; (b) determining what number Kx of samples from within the global data set D will form a neighbourhood about x; (c) selecting suitable Kx samples from the global data set which have the variable features that most closely accord to the variable features of the particular subject x to form the neighbourhood Dx; (d) ranking the Vx variable features within the neighbourhood Dx in order of importance to the outcome of vector x and obtaining a weight vector Wx for all variable features Vx; (e) creating a prognostic model Mx, having a set of model parameters Px and the other parameters from (a)-(d); (f) testing the accuracy of the model Mx at e) for each sample from Dx; (g) storing both the accuracy from (f), and the model parameters developed in (a) to (e); (h) repeating (a) and / or (b) whilst applying an optimisation procedure to optimise Vx and / or Kx, to determine their optimal values, before repeating (c)-(h) until maximum accuracy at (f) is achieved.
Owner:KASABOV NIKOLA KIRILOV
Method and System for Improved Optical Modeling of Gemstones
ActiveUS20140107986A1Reduce deficiencyImproved virtual optical modelingInvestigating jewelsOptically investigating flaws/contamination3d shapesOptical property
A method of constructing a virtual model of a gemstone including the steps of performing measurements of the gemstone to construct a three-dimensional (3D) model of an exterior surface of the gemstone; identifying one or more visible inclusions within an interior volume of the gemstone; for each identified inclusion, performing the steps of determining a location and 3D shape of the inclusion within the interior volume of the gemstone; capturing at least one image of the inclusion; using the at least one image to determine relevant optical characteristics of the inclusion; and constructing a 3D virtual model of the inclusion, said model including the 3D shape of the inclusion and optical properties of the inclusion based upon said optical characteristics; constructing a 3D virtual model of the gemstone which includes the 3D virtual model of the exterior surface of the gemstone and the 3D virtual models of the one or more visible inclusions within the interior volume of the gemstone; and generating a dataset representing said 3D virtual model, wherein said dataset may be used in subseguent computer analysis to provide a user with information relating to a visual characteristic of the gemstone.
Owner:IDEAL SCOPE
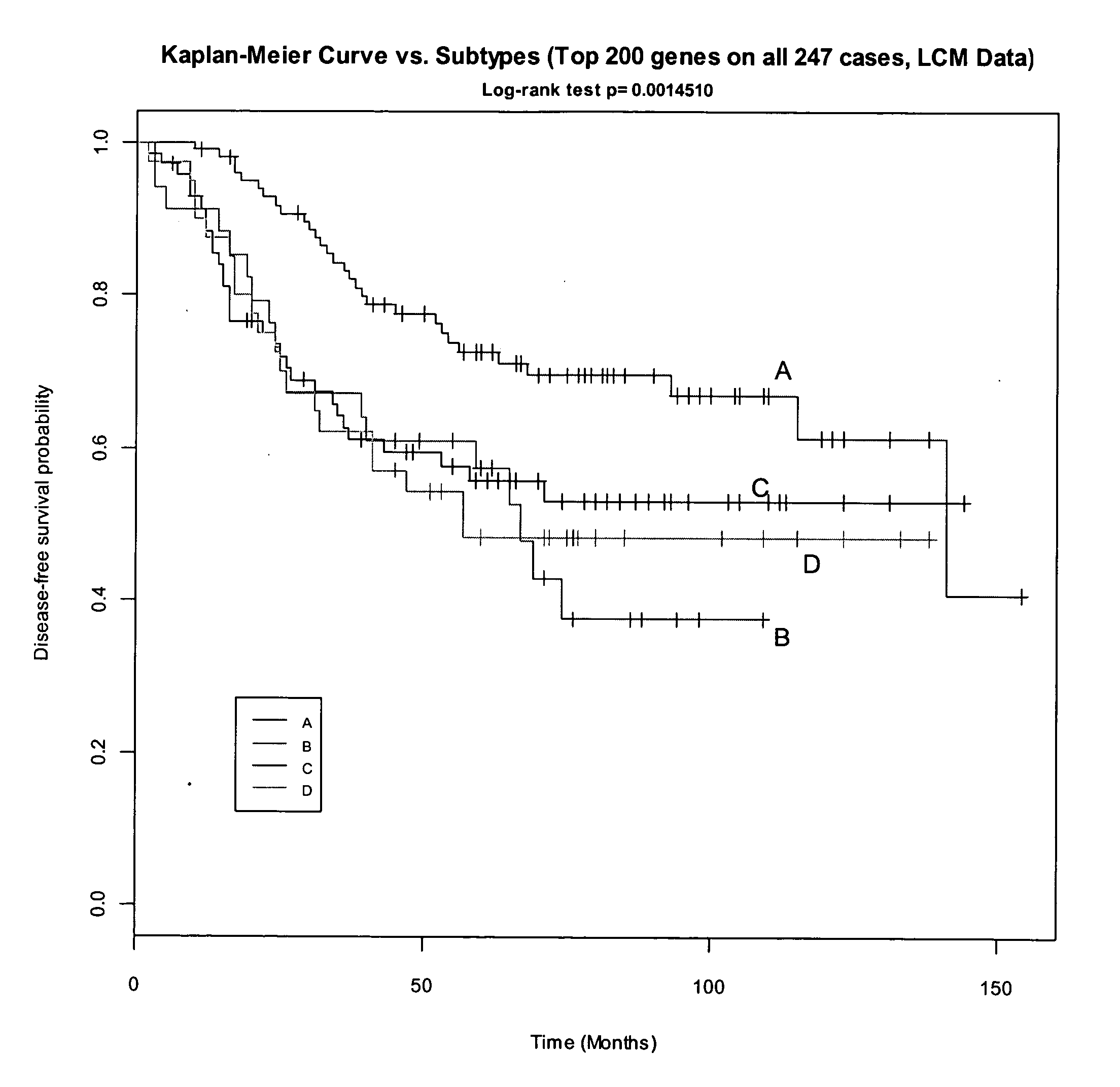
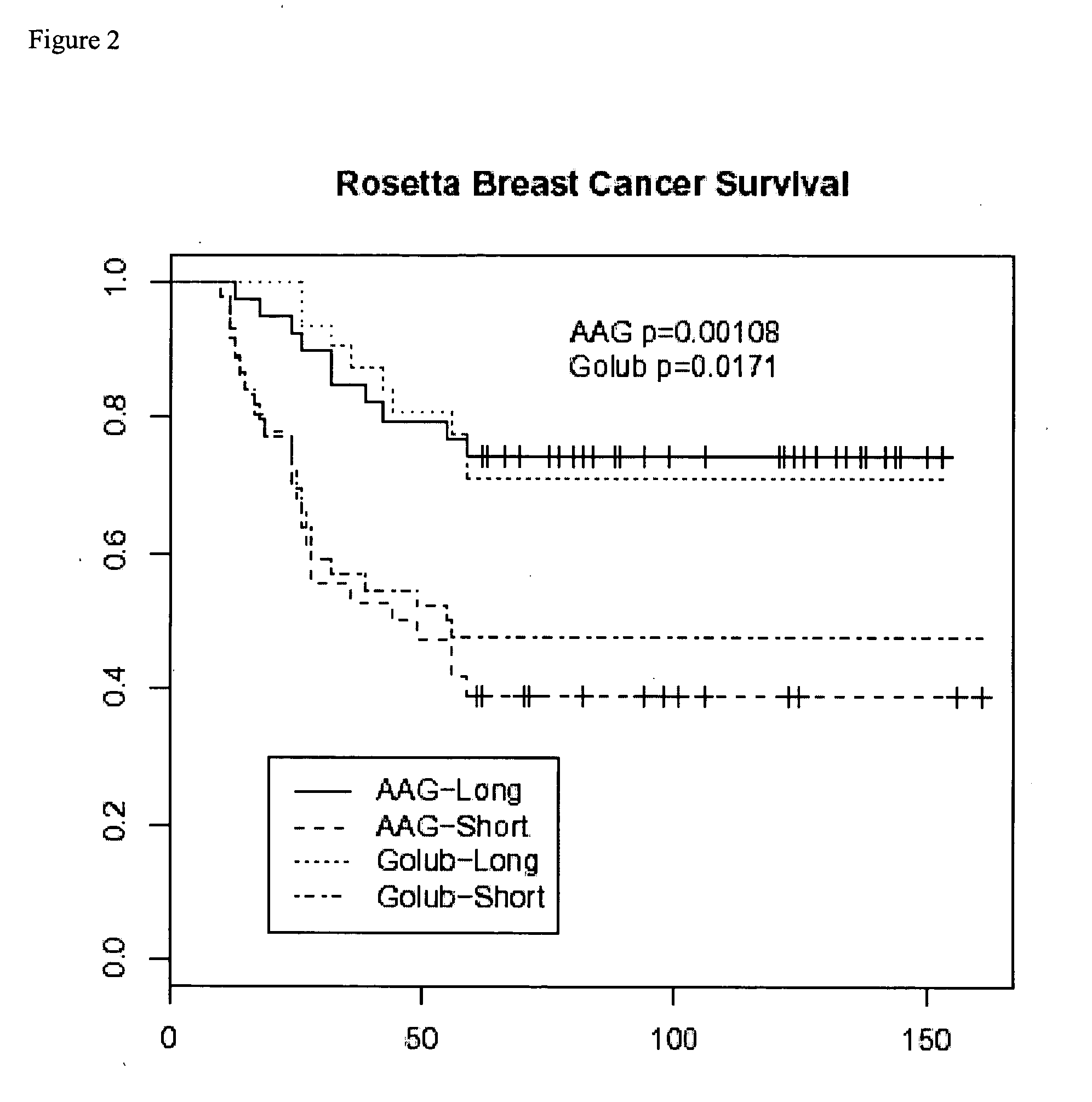
Breast cancer signatures
InactiveUS20050095607A1Reduce comparisonAffect analysisTumor rejection antigen precursorsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologySurvival outcome
The invention relates to the identification and use of gene expression profiles, or patterns, suitable for identification of breast cancer patient populations with different survival outcomes. The gene expression profiles may be embodied in nucleic acid expression, protein expression, or other expression formats, and may be used in the study and / or determination of the prognosis of a patient, including breast cancer survival.
Owner:ARCTURUS BIOSCI +1
Systems for determining the approximate location of a device from ambient signals
InactiveUS7738881B2Facilitates approximationMaximum accuracyInstruments for road network navigationDirection finders using radio wavesAlgorithmLocation Equipment
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
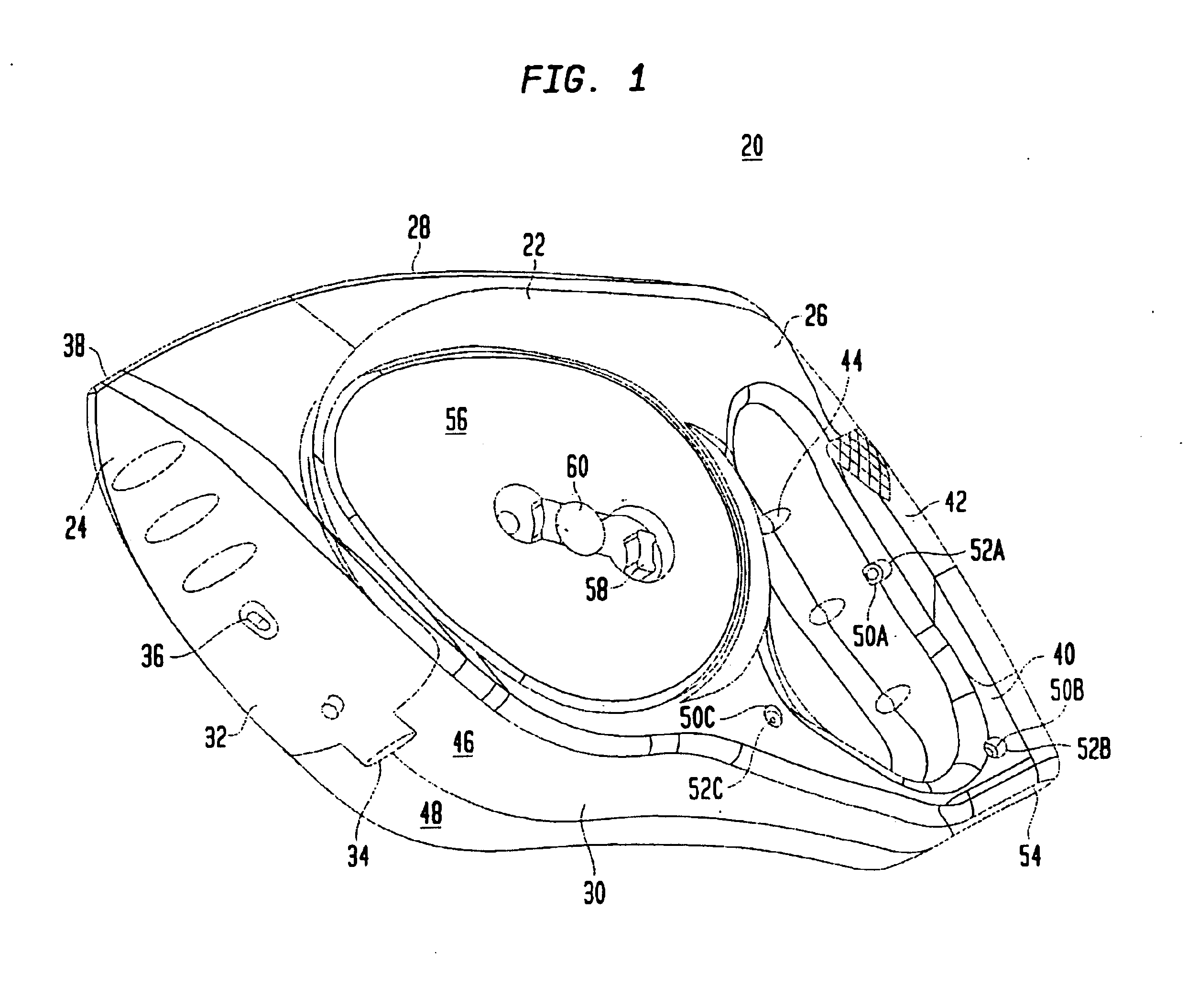
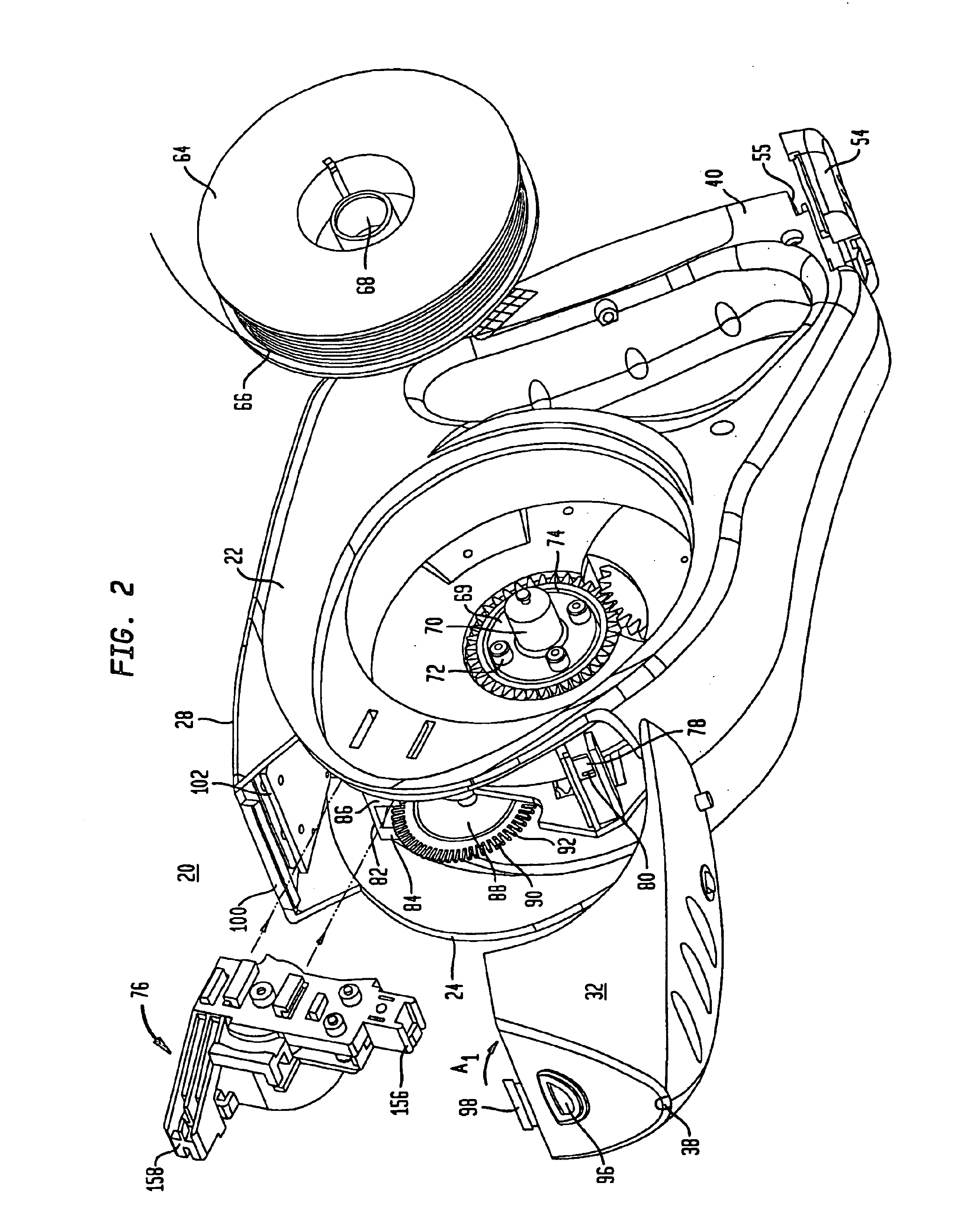
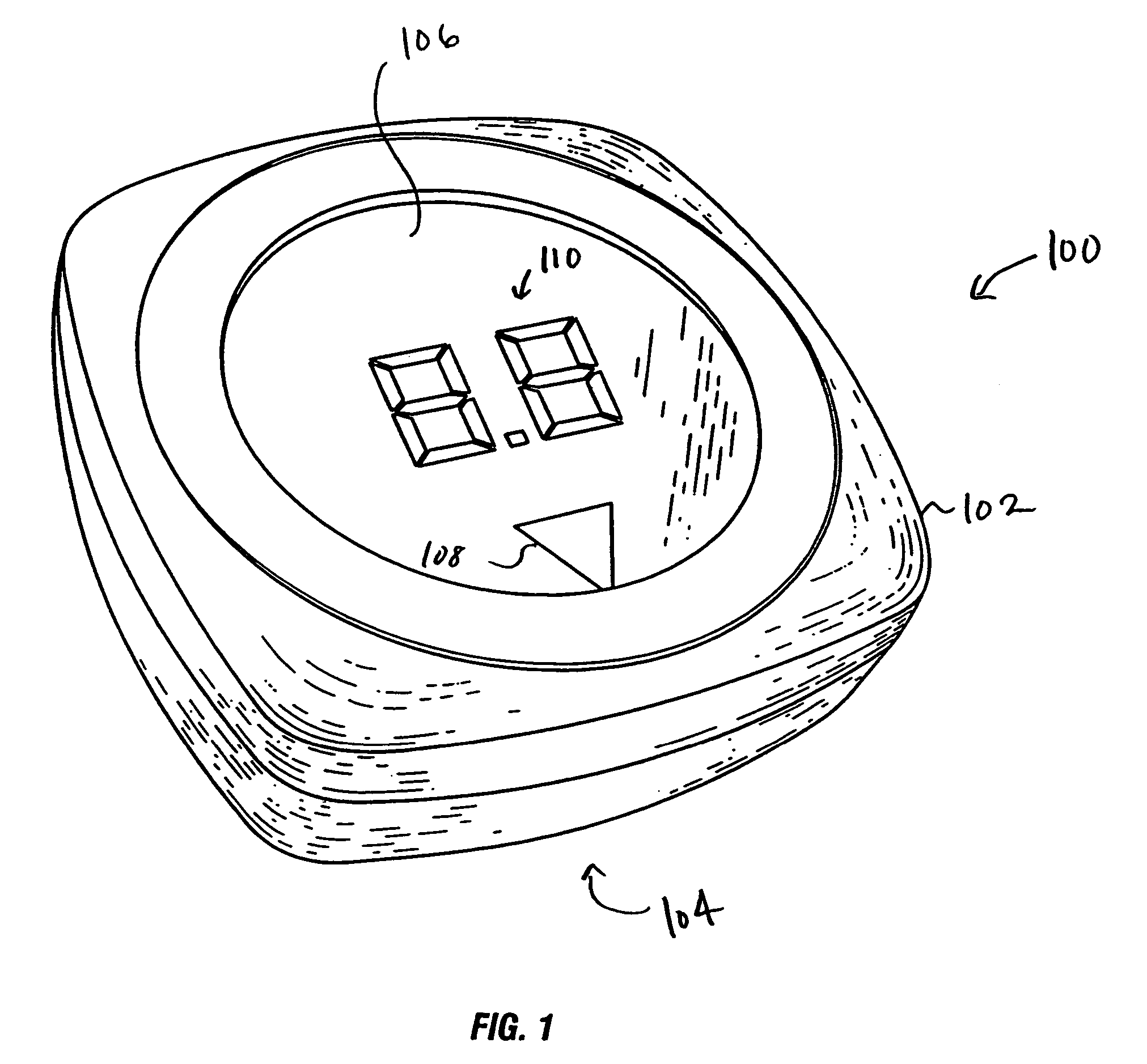
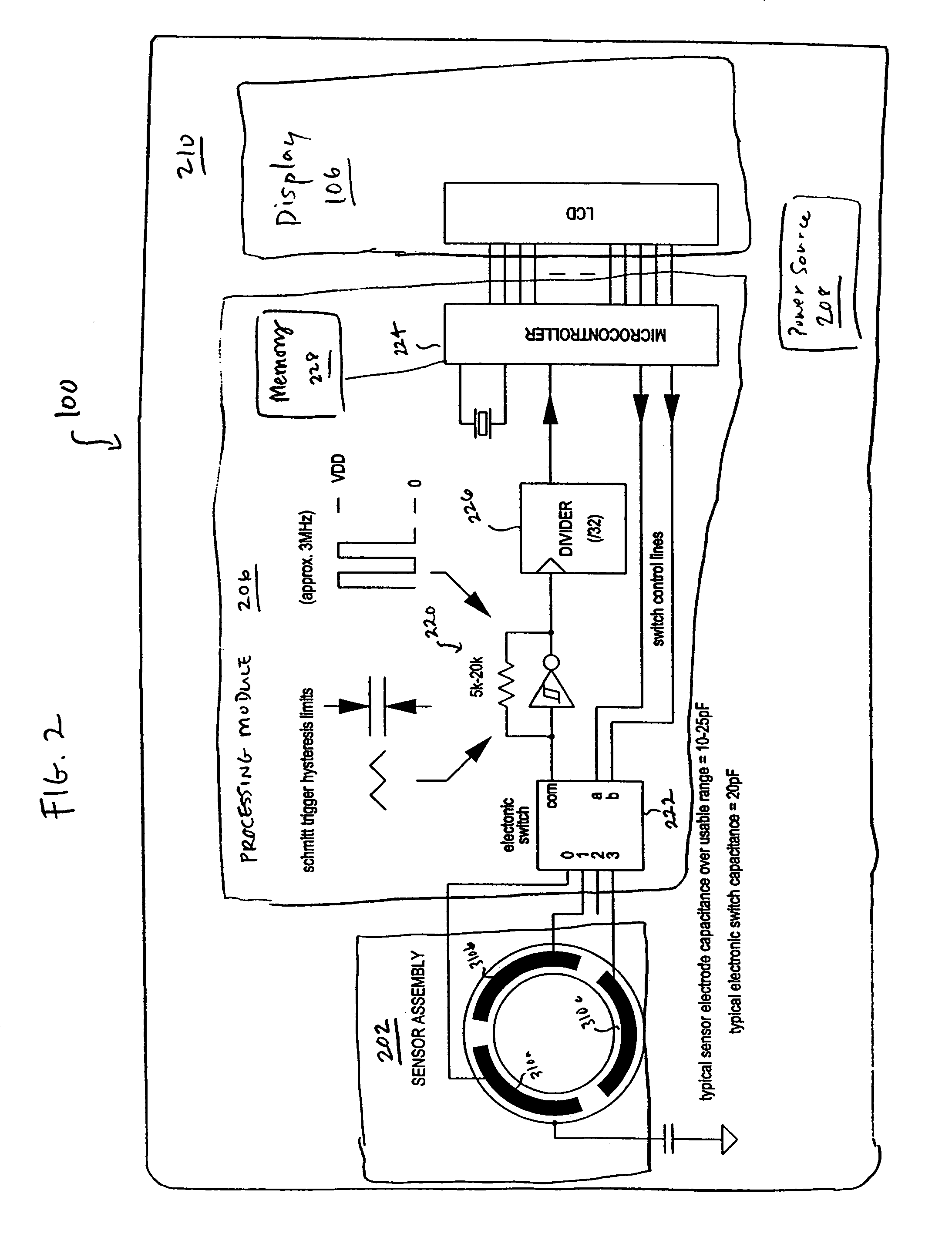
Digital measuring instrument having flexible measuring line
InactiveUS6868620B2Maximum accuracyMaximum precisionLength measurement chainsRulers for direct readingMeasuring instrumentEngineering
A digital measuring instrument includes a housing containing a measuring line, a rotatable drum engaging the line whereby movement of the line causes rotation of the drum, a storage spool mounted in the housing for storing the line, a crank assembly for rotating the storage spool for winding the measuring line about the storage spool, and a rotatable disc that rotates simultaneously with the measuring drum. The instrument includes an optical sensor in communication with the rotatable disk for compiling data related to rotation of the disk, and electronic circuitry in communication with the optical sensor for calculating a length of the line drawn from the housing. The housing has a well for receiving the storage spool and a side cover with a slideable lock for covering the well.
Owner:SOLAR WIDE INDAL
Methods for determining the approximate location of a device from ambient signals
InactiveUS7319877B2Facilitates approximationMaximum accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationAlgorithmLocation Equipment
The present invention leverages changes in the sensed strength of radio signals at different locations to determine a device's location. In one instance of the invention, inference procedures are used to process ambient commercial radio signals, to estimate a location or a probability distribution over the locations of a device. In an instance of the invention, learning and inference methods are applied to rank vector of signal strength vectors. Moving to such rank orderings leads to methods that bypass consideration of absolute signal strengths in location calculations. The invention facilitates approximations for locating a device by providing a method that does not require a substantial number of available ambient signal strengths while still providing useful location inferences in determining locations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Position-Determining and -Measuring System
InactiveUS20070292004A1Maximum accuracyEasy to adjustImage enhancementImage analysisDental ArticulatorsCoupling
The invention relates to a method for determining the position of at least one object (13, 22, 23), which is characterized in that images of at least one object (13, 22, 23) are captured by means of a single electronic camera (21). At least one optical auxiliary structure (1) is arranged on the object (13, 22, 23) to be measured or on other constructions that have a permanent spatial relationship to the object (13, 22, 23) to be measured. The measures / positions of the at least one object (13, 22, 23) in relation to the at least one reference position or a reference position which is simultaneously captured by the camera (21) are determined by evaluating the positions of the at least one auxiliary structure (1) in the captured images by means of a computer program. The invention also relates to a software and to an auxiliary transfer device which at one end comprises a coupling element (5) which allows a distinctly repositionable assembly on a face bow (20) comprising optical auxiliary structures (1) or on a device for the assembly (17) of at least one jaw model in an articulator (4) on a corresponding counterpart. The invention also relates to a device for the assembly of at least one jaw model in an articulator and to auxiliary devices for carrying out said method.
Owner:PETERS HEIKO
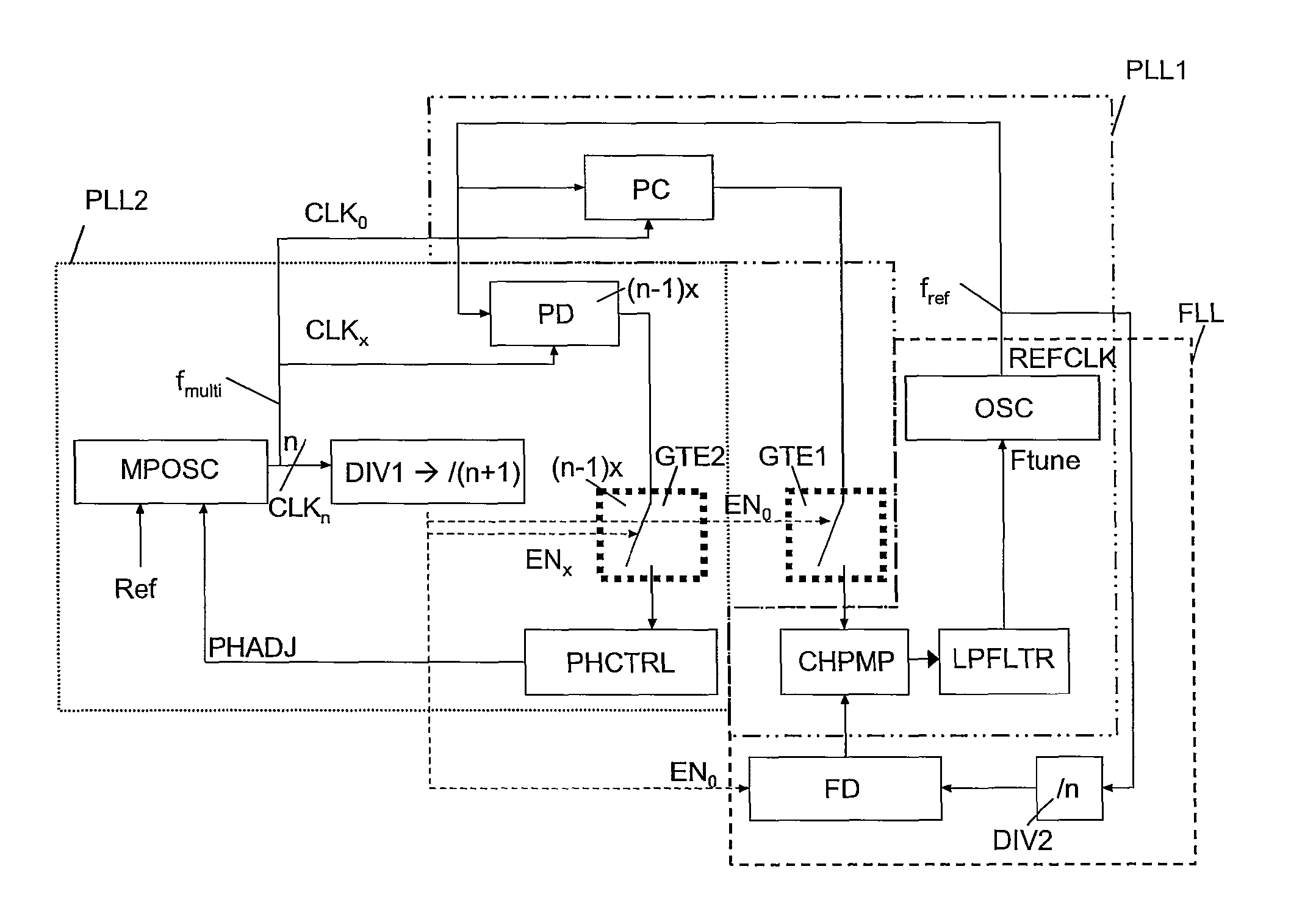
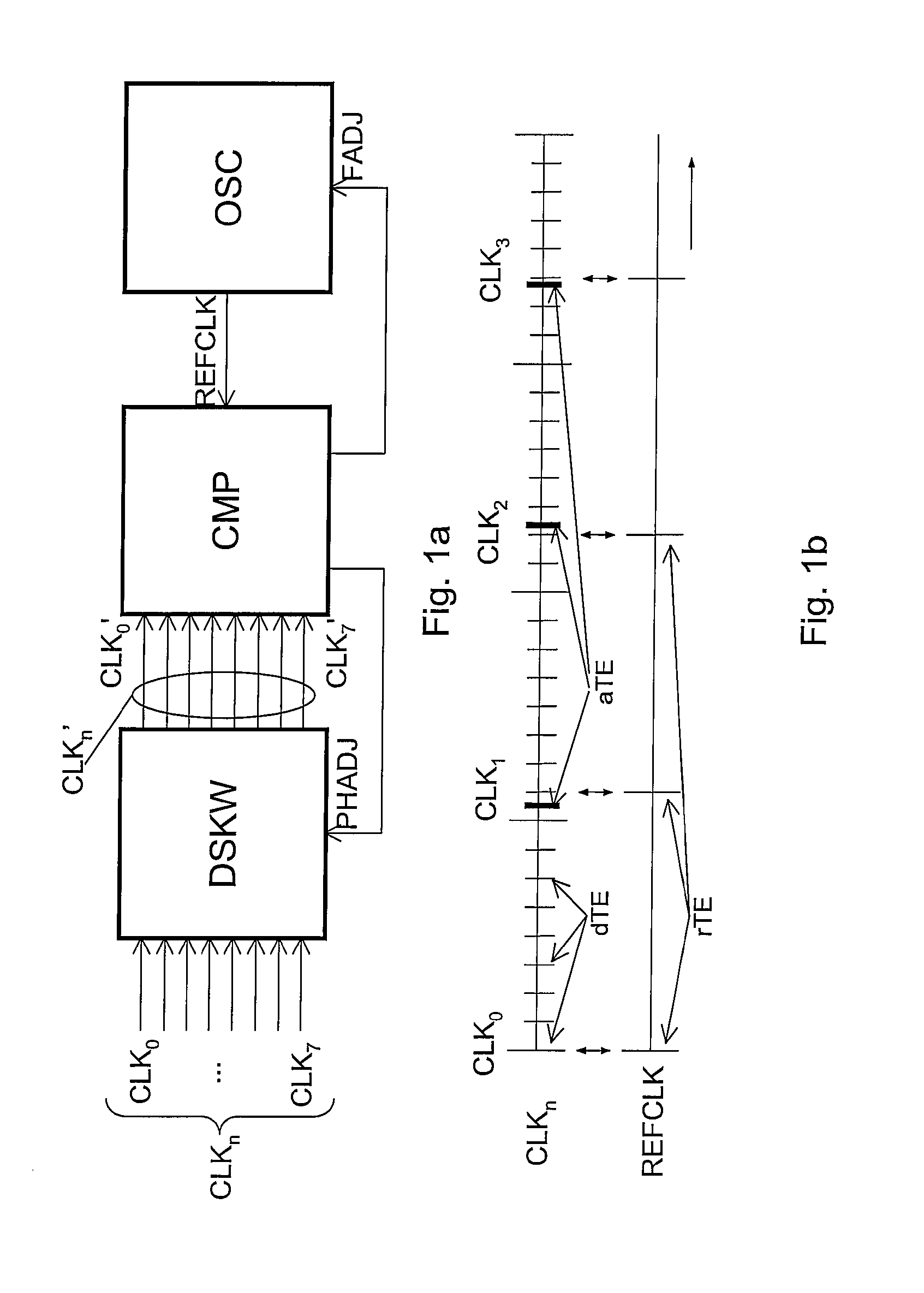
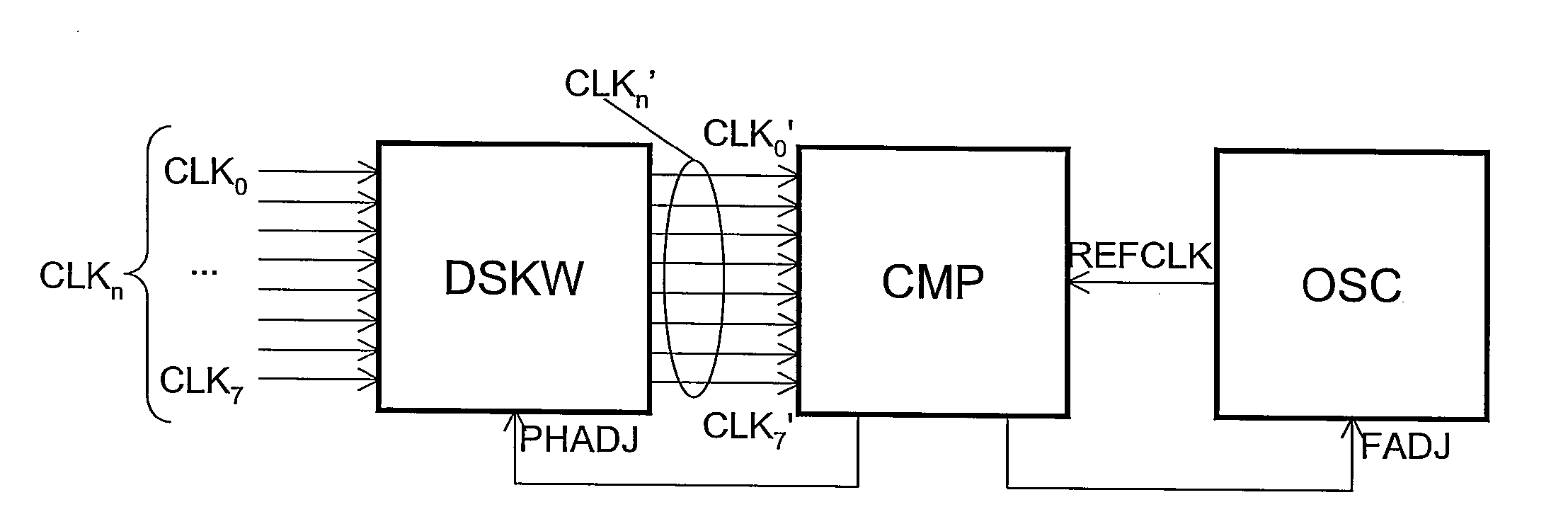
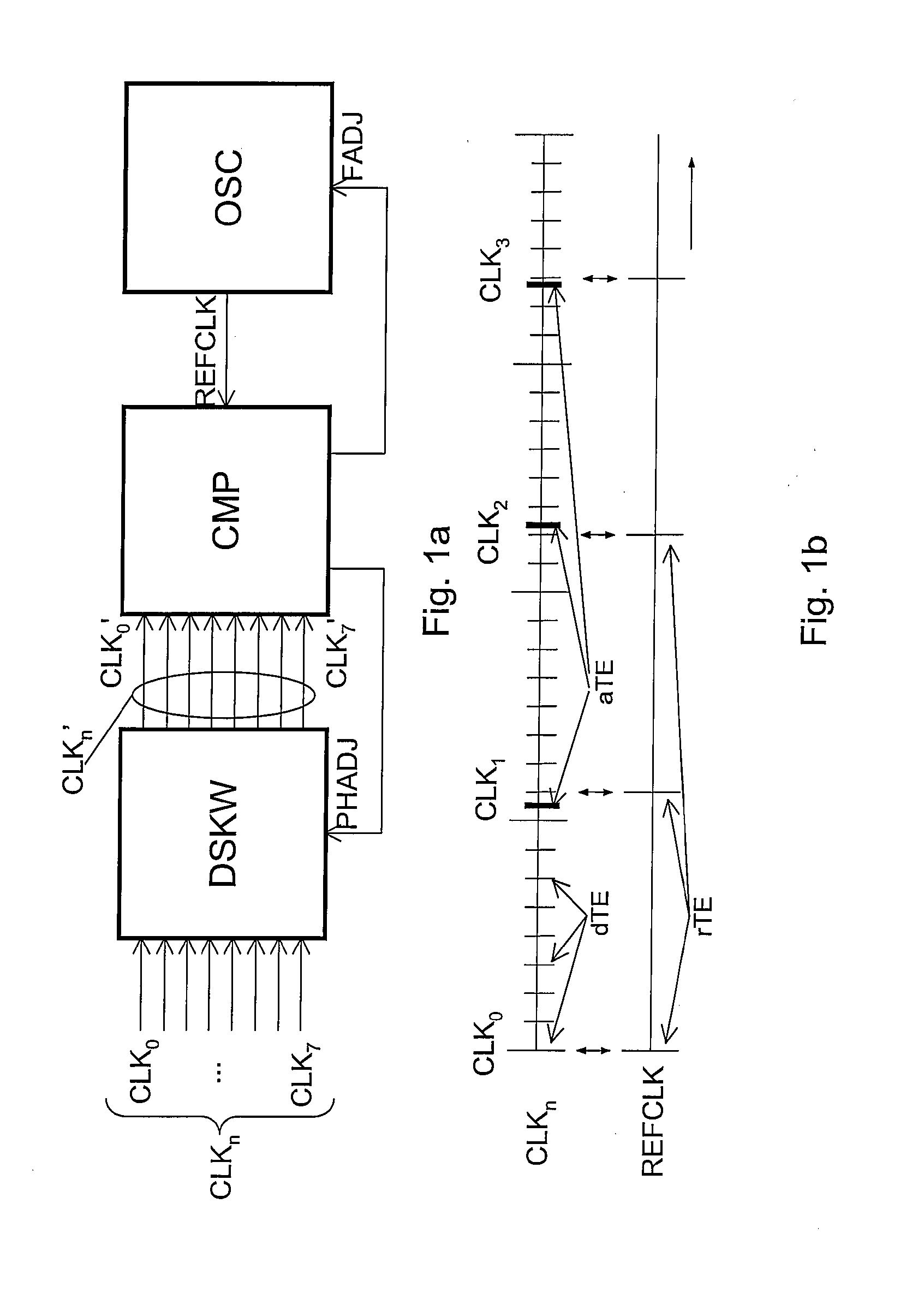
Multi-phase clock system
The invention relates to multi-phase clock system for receiving a plurality of clock signals (CLKo-n) comprising actual time events (aTE) defining different clock phases, the clock signals all having a same clock frequency but different clock phases, the system further arranged for receiving a reference clock signal (REFCLK) for providing reference time events (rTE) for the plurality of clock signals (CLKo-n), the reference clock signal (REFCLK) having a reference frequency different from the clock frequency, the reference frequency being selected such that each one of the subsequent reference time events (rTE) coincides with a desired time event (dTE) for a single one of the plurality of clock signals (CLKo-n).
Owner:NXP BV
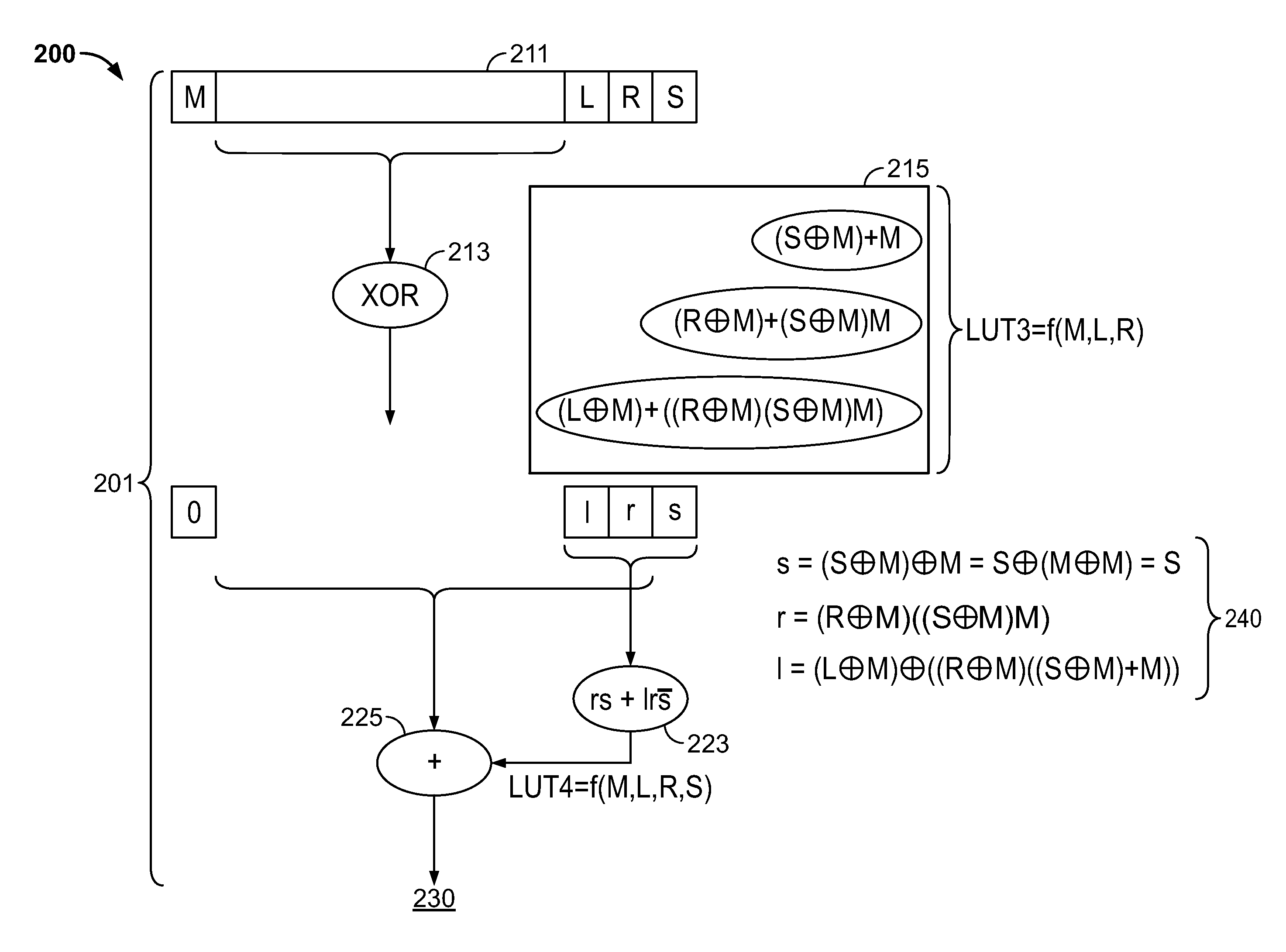
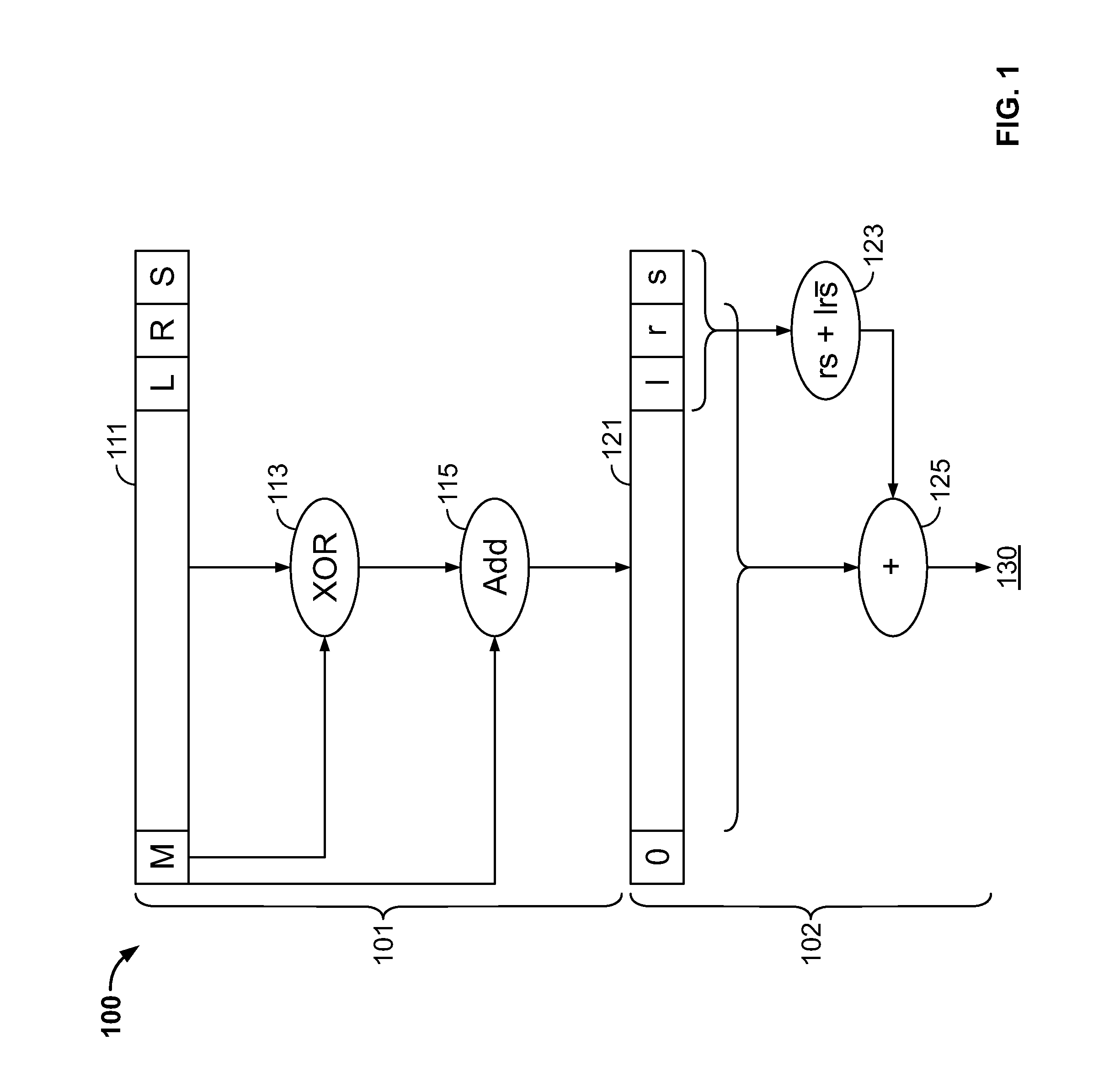
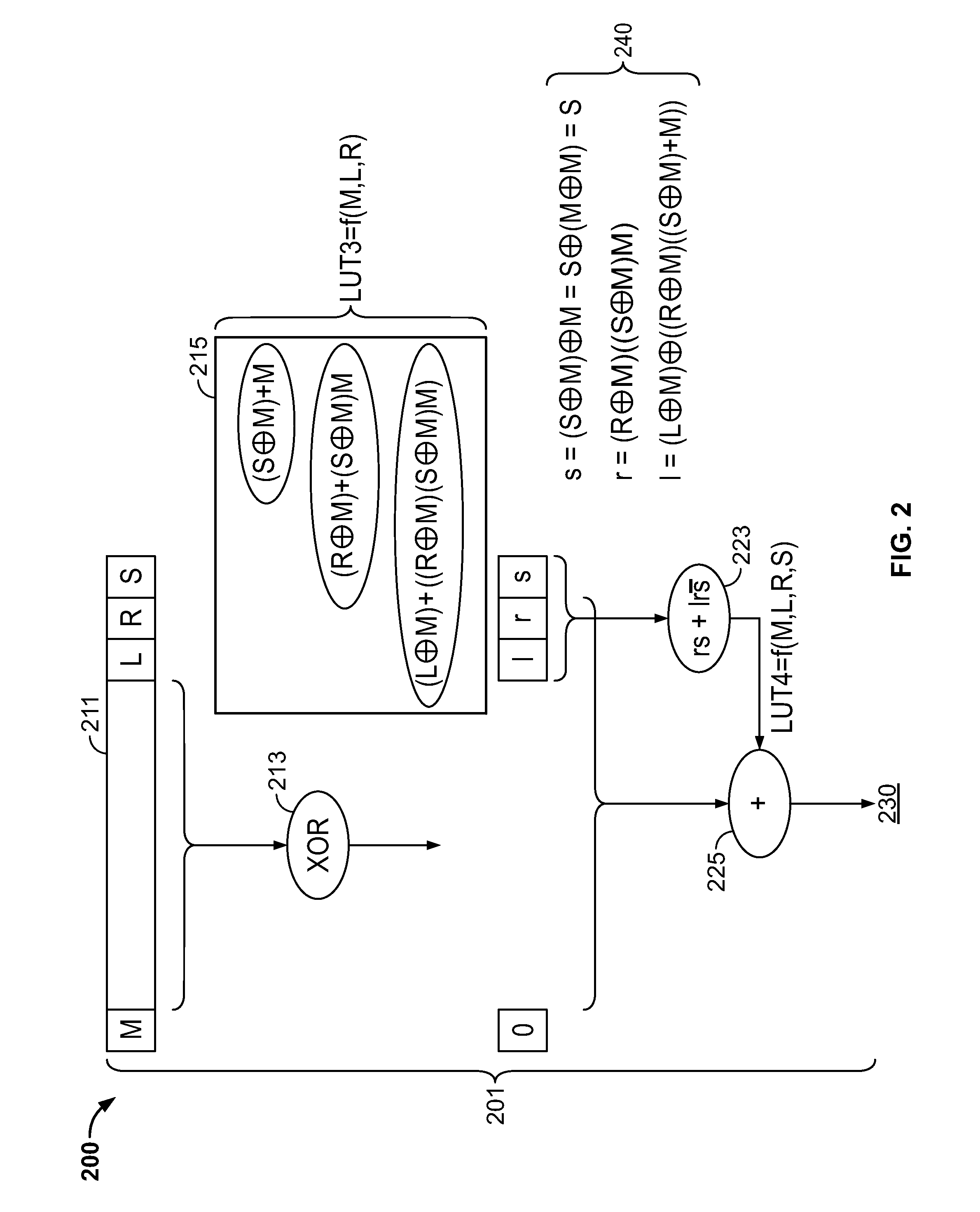
Fused floating point datapath with correct rounding
ActiveUS9348557B1Improve efficiencySmall area consumptionComputation using non-contact making devicesDatapath circuitsSign bit
In accordance with some embodiments, a floating point number datapath circuitry, e.g., within an integrated circuit programmable logic device is provided. The datapath circuitry may be used for computing a rounded absolute value of a mantissa of a floating point number. The floating point datapath circuitry may have only a single adder stage for computing a rounded absolute value of a mantissa of the floating point number based on one or more bits of an unrounded mantissa of the floating point number. The unrounded and rounded mantissas may include a sign bit, a sticky bit, a round bit, and / or a least significant bit, and / or other bits. The unrounded mantissa may be in a format that includes negative numbers (e.g., 2's complement) and the rounded mantissa may be in a format that may include a portion of the floating point number represented as a positive number, (e.g., signed magnitude).
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
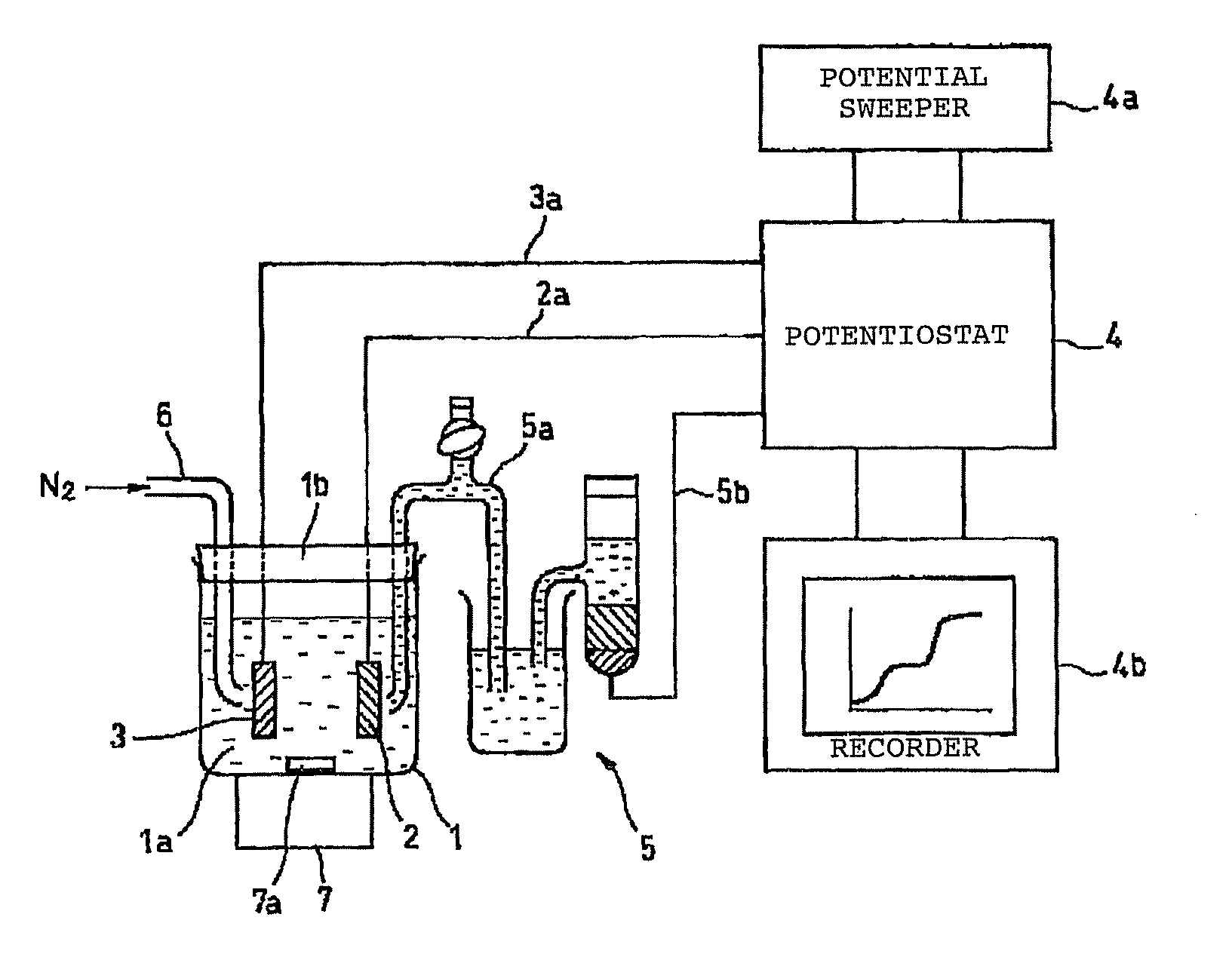
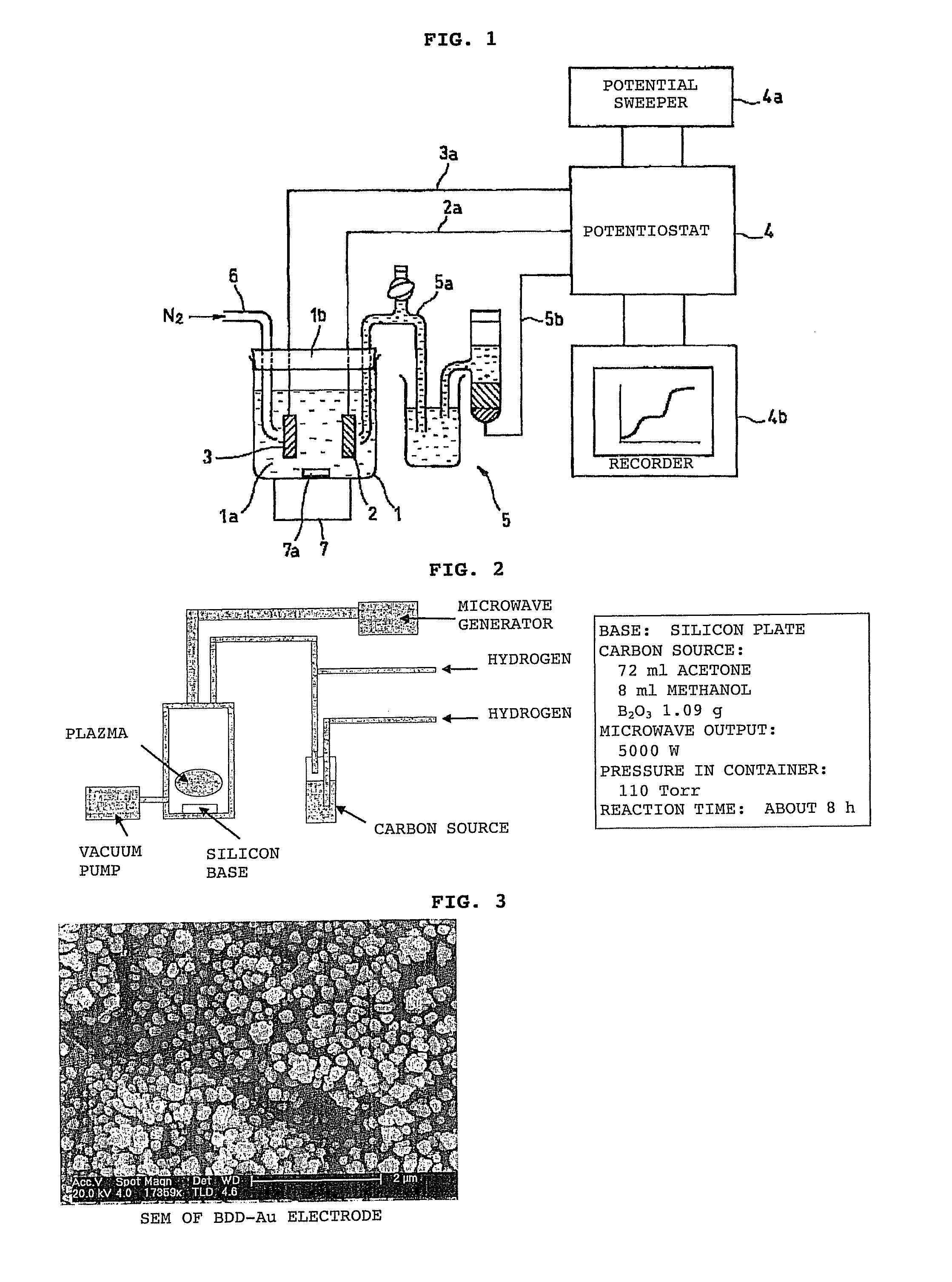
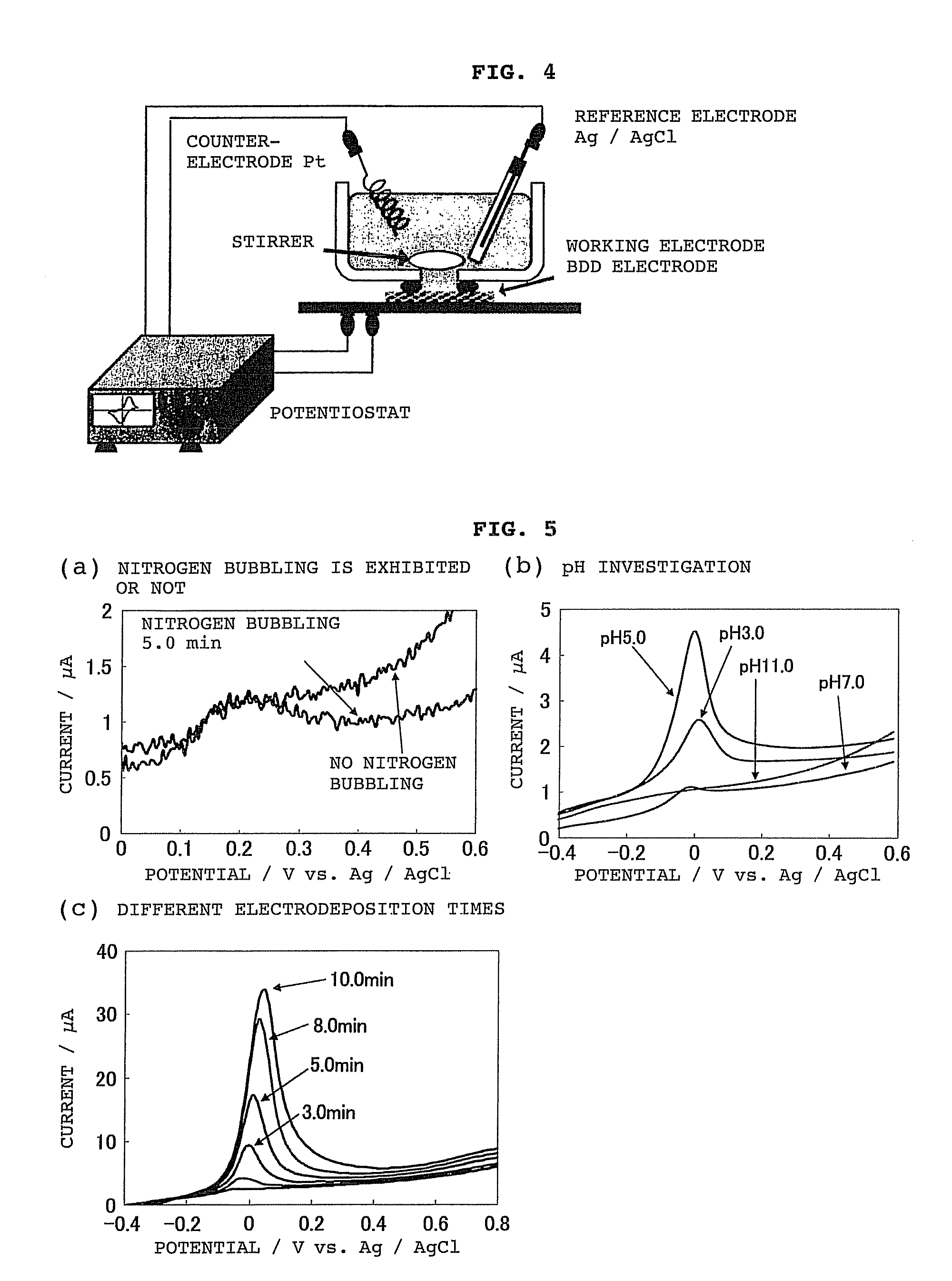
Electrochemical analysis method using boron-doped electroconductive diamond electrode
InactiveUS7883617B2Easy for quantitative analysisMaximum accuracyCellsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceElectrolytic agentPotential change
Owner:KEIO UNIV
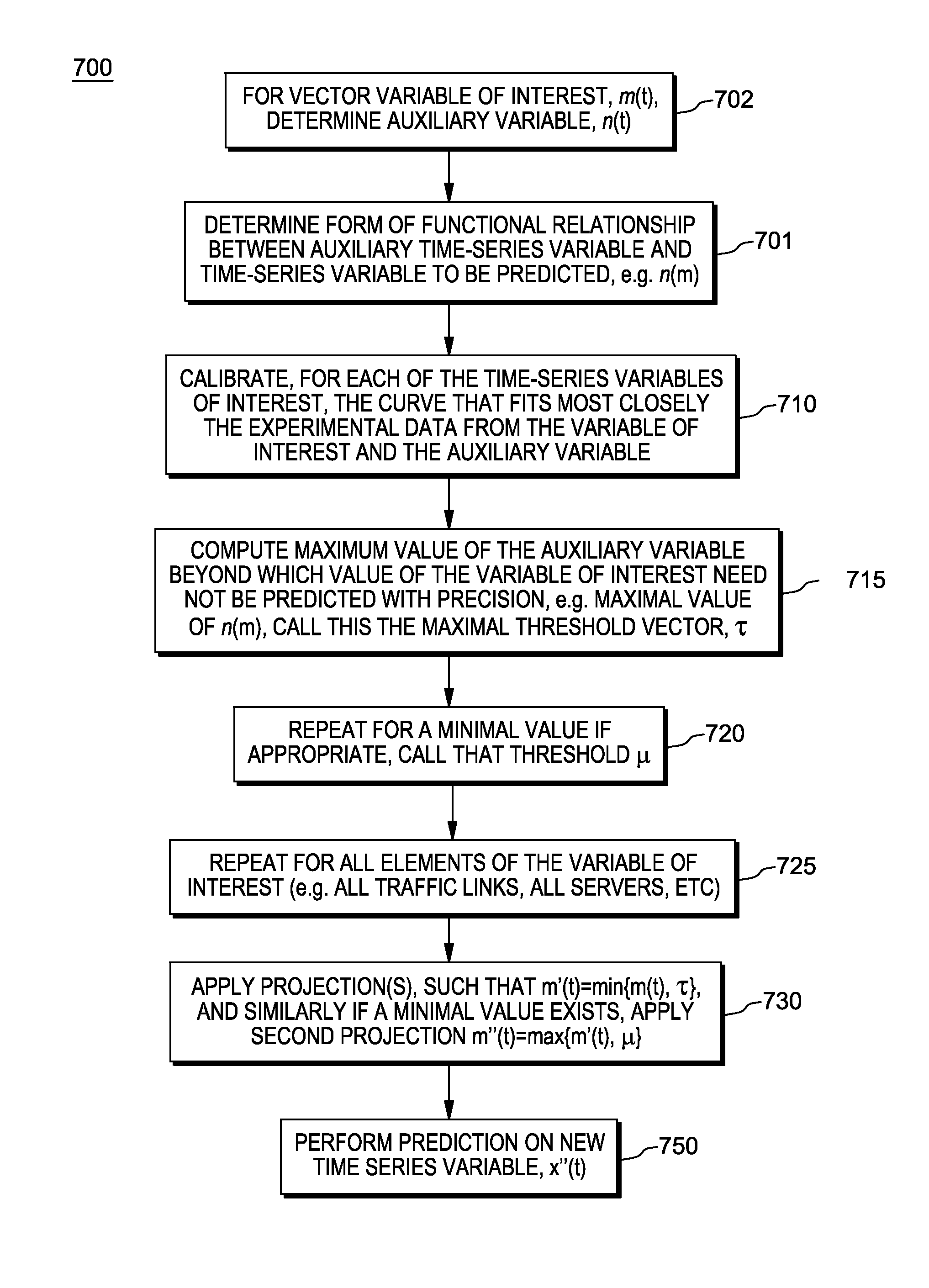
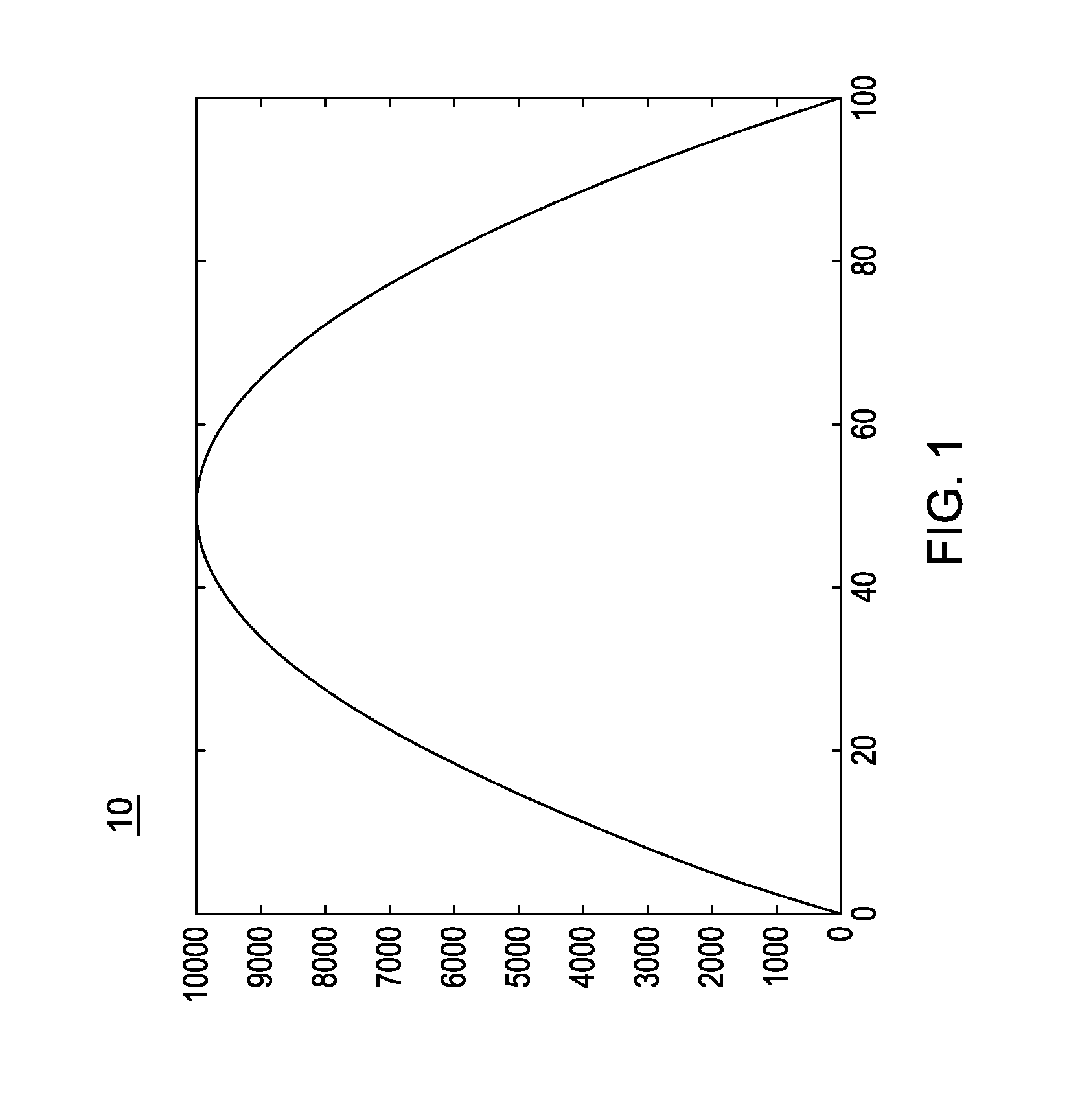
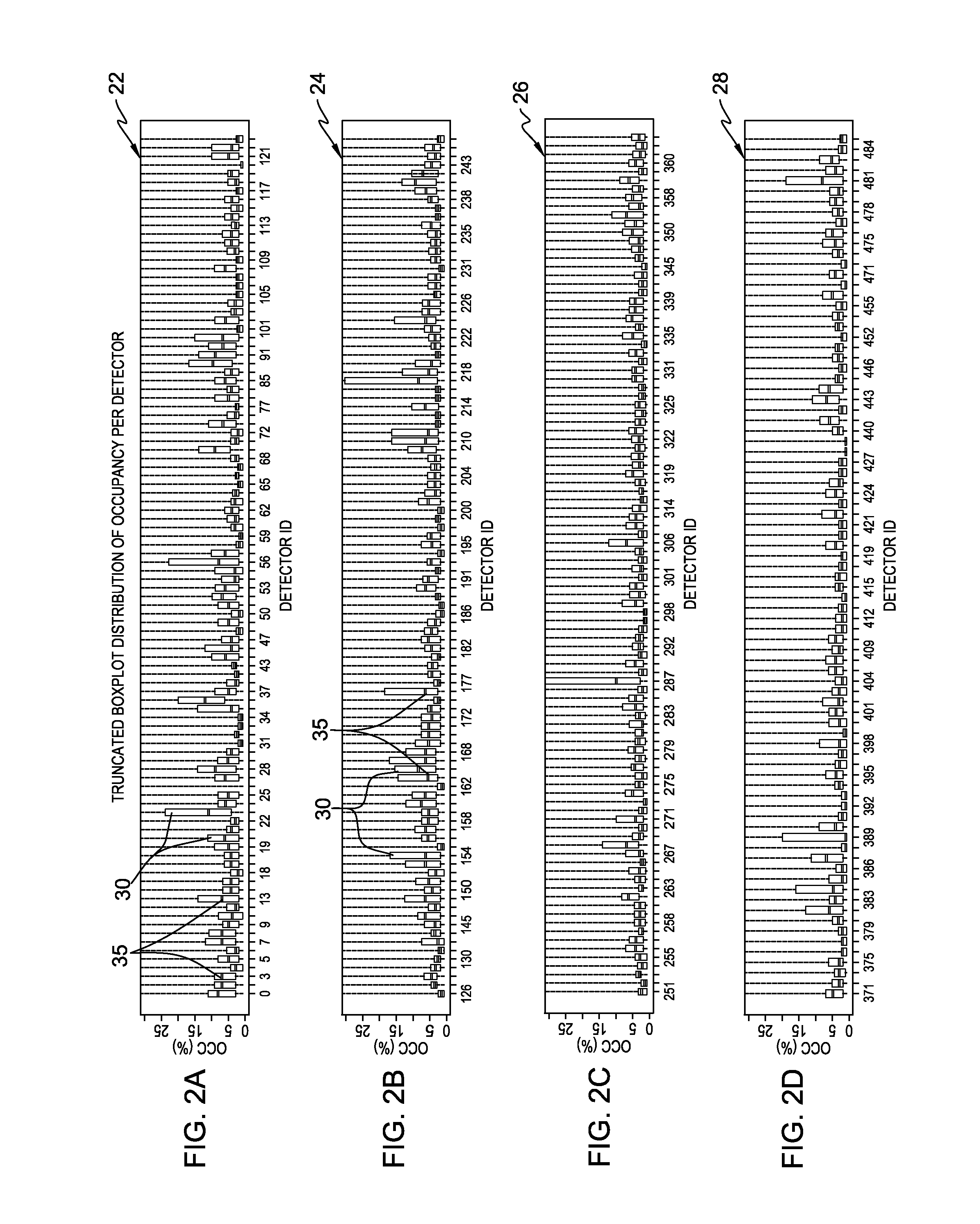
Performing-time-series based predictions with projection thresholds using secondary time-series-based information stream
InactiveUS20140309977A1Significant accuracy gainMaximum accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlDesign optimisation/simulationQuantile regressionPredictive modelling
A prediction modeling system and computer program product for implementing forecasting models that involve numerous measurement locations, e.g., urban occupancy traffic data. The system a data volatility reduction technique based on computing a congestion threshold for each prediction location, and using that threshold in a filtering scheme. Through the use of calibration, and by obtaining an extremal or other specified solution (e.g., maximization) of empirical volume-occupancy curves as a function of the occupancy level, significant accuracy gains are achieved and at virtually no loss of important information to the end user. The calibration use quantile regression to deal with the asymmetry and scatter of the empirical data. The argmax of each empirical function is used in a unidimensional projection to essentially filter all fully congested occupancy level and treat them as a single state.
Owner:IBM CORP
3-dimensional cable guide and cable based position transducer
ActiveUS7395609B2Minimal frictionReduce frictionAngles/taper measurementsMeasuring points markingTransducerEngineering
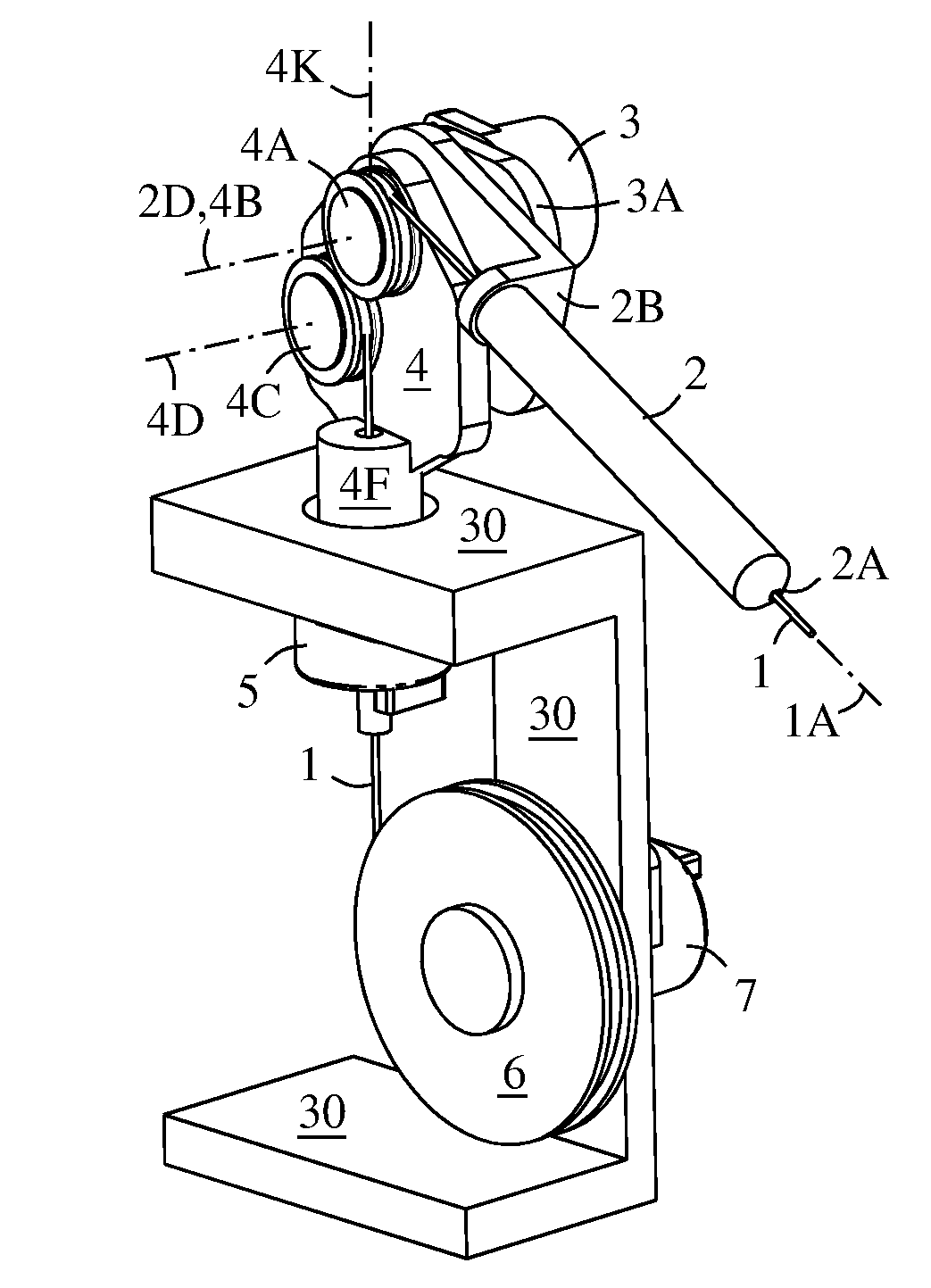
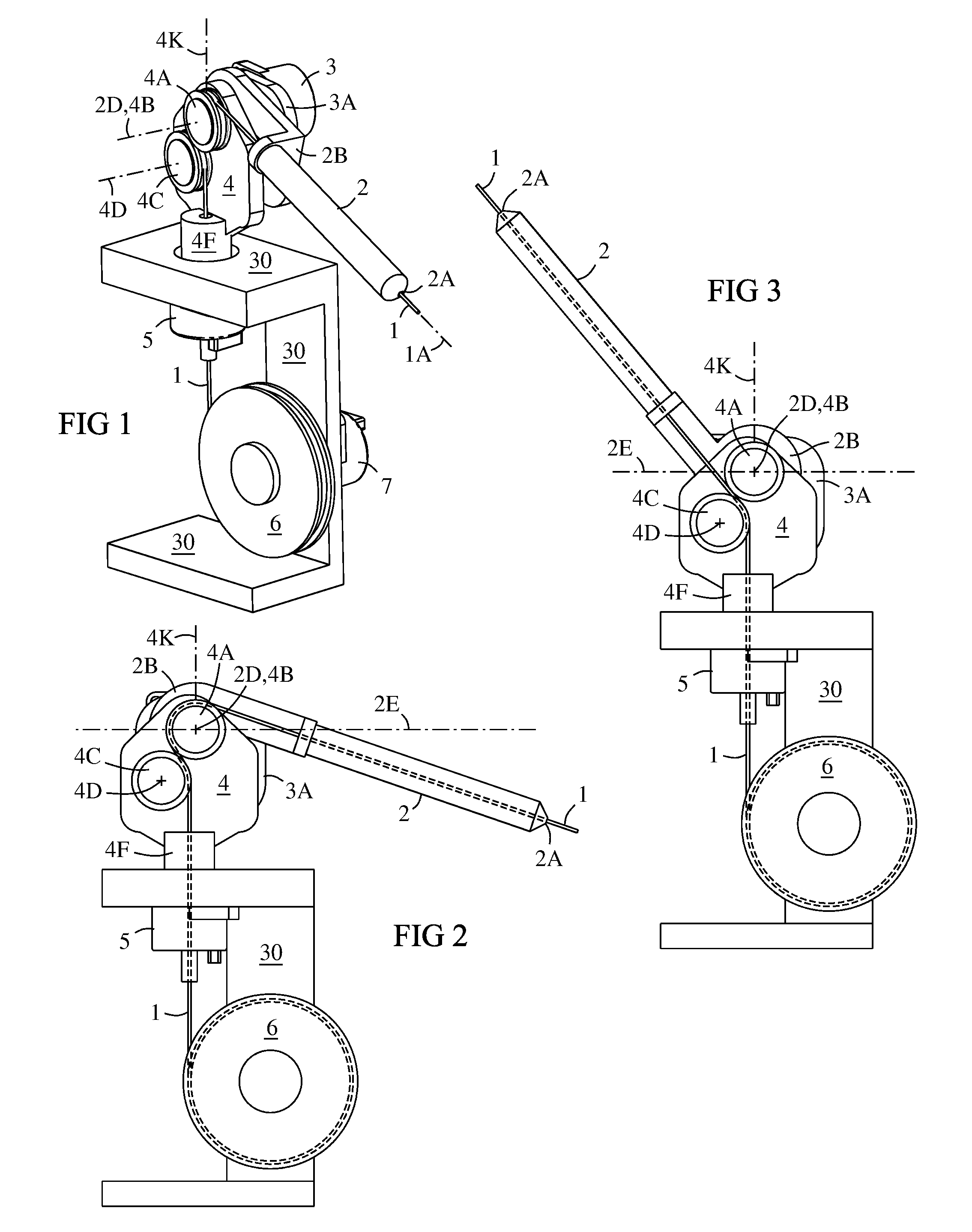
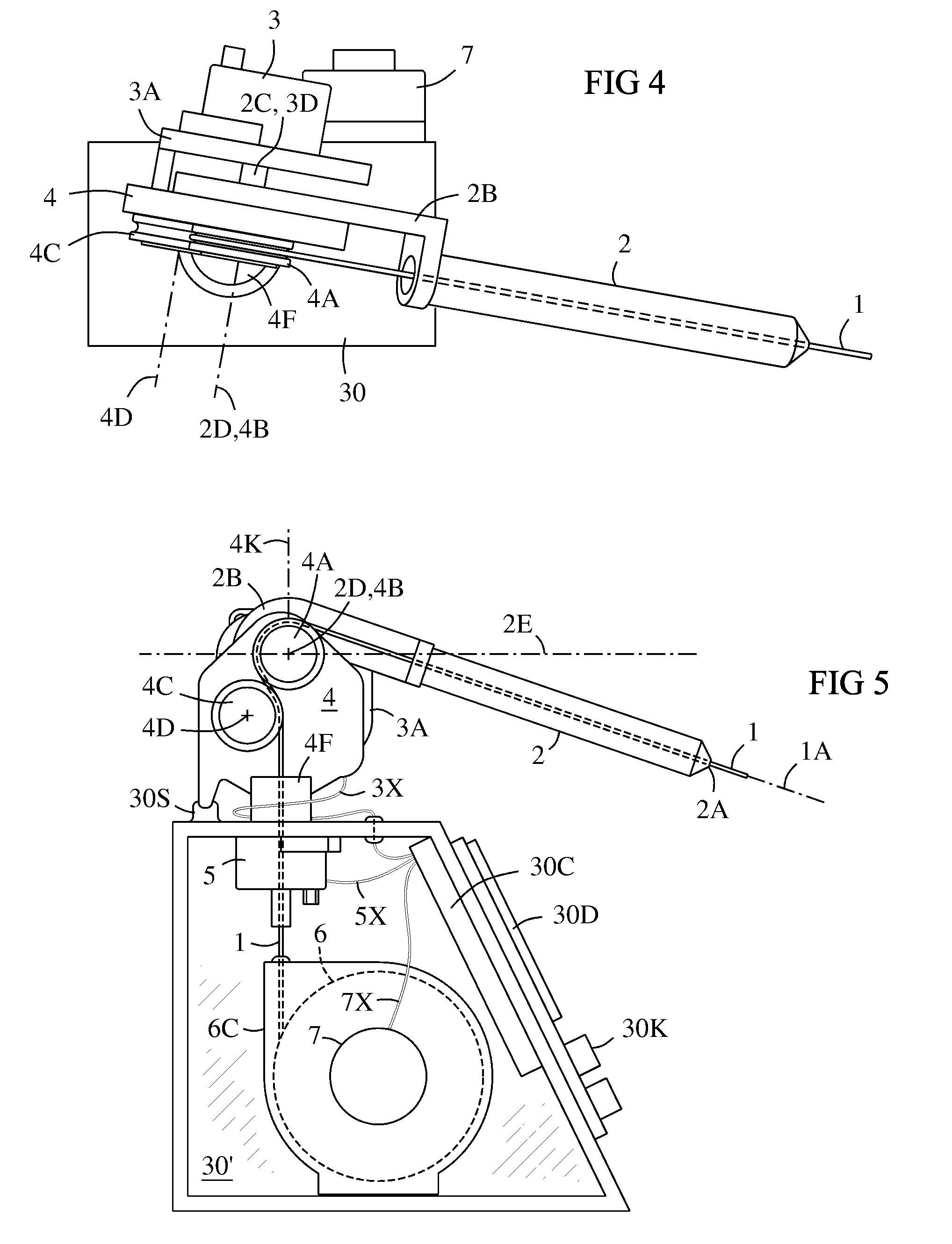
A pivoting cable extension arm (2) has a pivot sensor (3). The extension arm is mounted on a swivel frame (4) having a swivel sensor (5). The swivel frame has two tangent sheaves (4A, 4C) that allow a wide pivot range of the extension arm. A cable take-up drum (6) has a range sensor (7) for sensing the length of cable (1) extending from the drum. The three-sensors (3, 5, 7) provide data for computing 3D coordinates of the end of the cable (1) over a wide range of space surrounding the assembly. This allows an object to be measured and modeled in three dimensions by touching the cable end to points on the object and acquiring spatial coordinates of the points.
Owner:SPACEAGE CONTROL
Inclination sensor
InactiveUS7188426B2Readily and easily comprehend and useMaximum accuracyDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsLarge rangePhysics
An electronic inclination sensor is provided for the determination and display of surface inclination and the direction of such inclination. The information regarding the inclination and direction of inclination can be displayed such that an end user can readily and easily comprehend and use the information without additional interpretation. Further, when the inclination is displayed in decimal values, a large range of inclination angles can be displayed with significant accuracy.
Owner:EXELYS
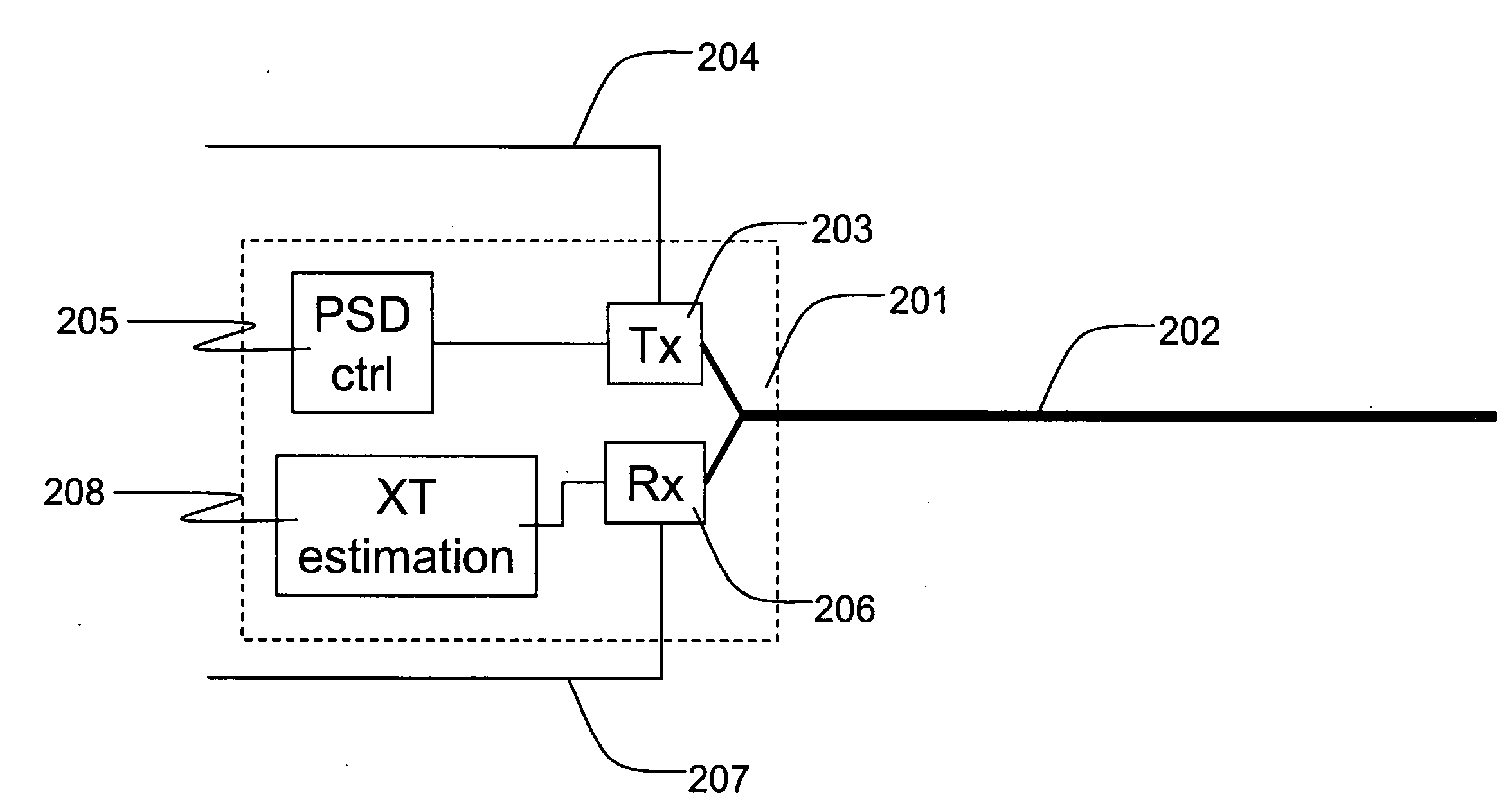
Device and associated method for measuring crosstalk
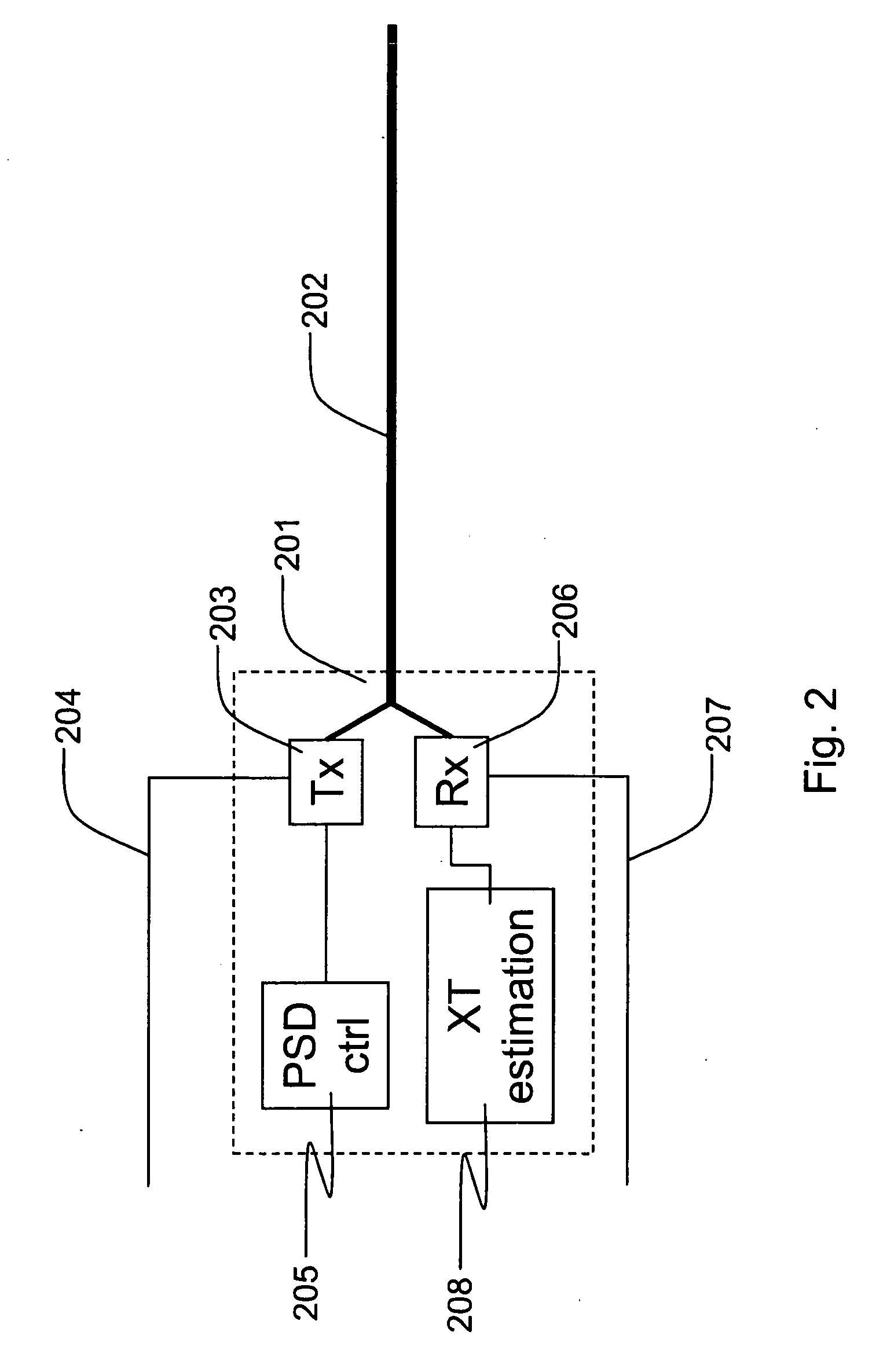
InactiveUS20090073868A1Reduce impactAvoid major impactFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsEngineeringSpectral density
The present invention relates to a crosstalk estimation device for estimating crosstalk between disturber communication lines and victim communication lines. The crosstalk estimation device is able to change the power spectral density PSD on the victim communication lines and / or the disturber communication lines. The crosstalk estimation device further receives measured changes in operational parameters on the victim communication lines and / or disturber communication lines in order to estimate the crosstalk induced in the victim communication lines and / or disturber communication lines.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and system for improved optical modeling of gemstones
ActiveUS8639479B2Reduce deficiencyImproved virtual optical modelingInvestigating jewelsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationGemstoneComputer science
Methods of constructing a virtual model of a gemstone are provided. Aspects of the methods include performing measurements of the gemstone to construct a three-dimensional (3D) model of an exterior surface of the gemstone; identifying one or more visible inclusions within an interior volume of the gemstone; capturing at least one image of the inclusion; using the at least one image to determine relevant optical characteristics of the inclusion; and constructing a 3D virtual model of the inclusion.
Owner:IDEAL SCOPE
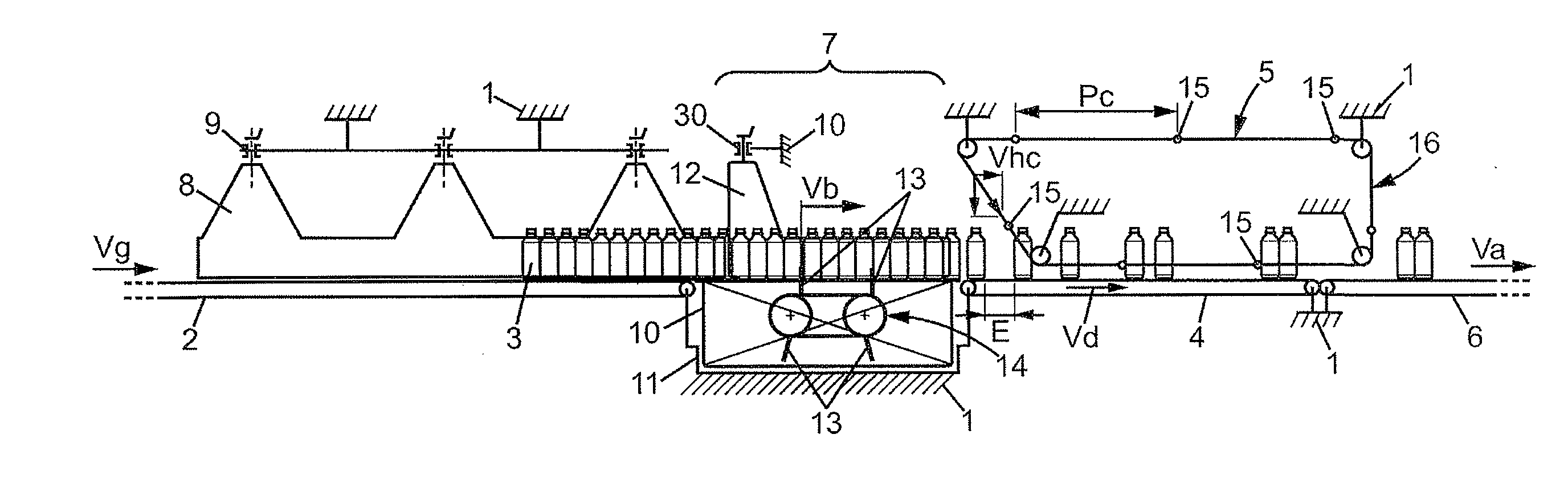
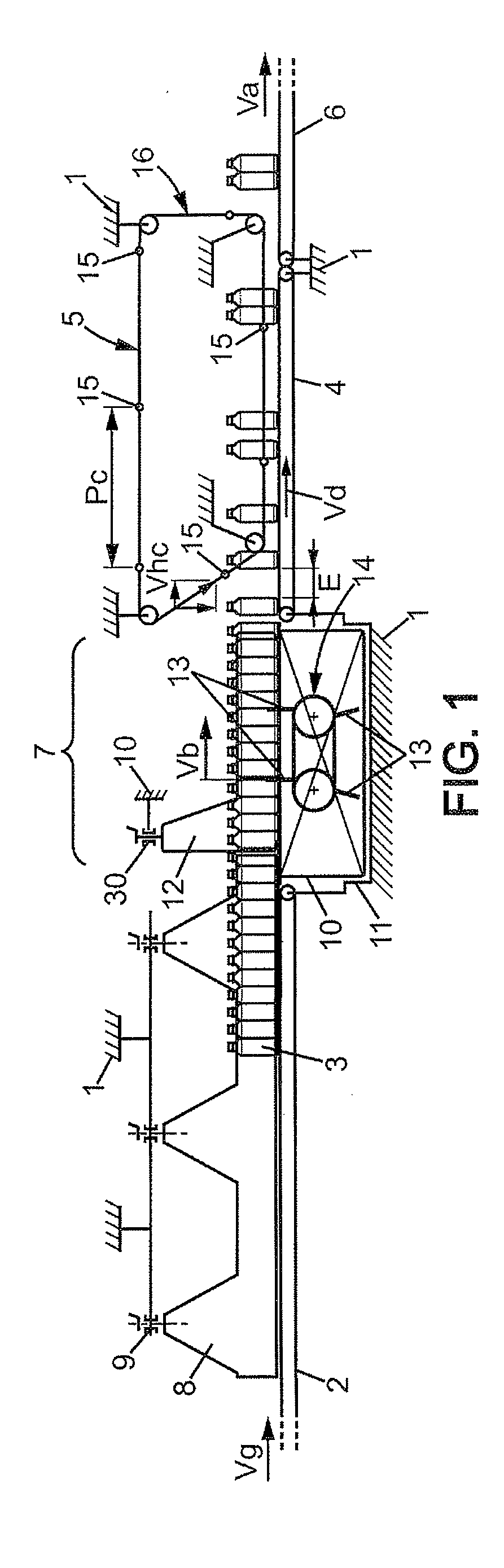
Plant for preparing batches of products, bottles or the like
The plant comprises: —an upstream conveyor (2), —a downstream conveyor (4), —a regulating device (7) comprising a system of retractable stops (13) which are inserted temporarily between two consecutive products in a single column, —and means for adjusting the speed of the different conveyors (2, 4), said plant additionally comprising means for adjusting the width of the passages of said adjusting device (7) in order to adapt the width of these passages to the dimensions of said products, and also comprising means for longitudinally adjusting the space between the consecutive rows of stops (13) which move along with the products.
Owner:C E R M E X CONSTR ETUD & RECH DE MATERIELS POUR LEMBALLAGE DEXPEDITION
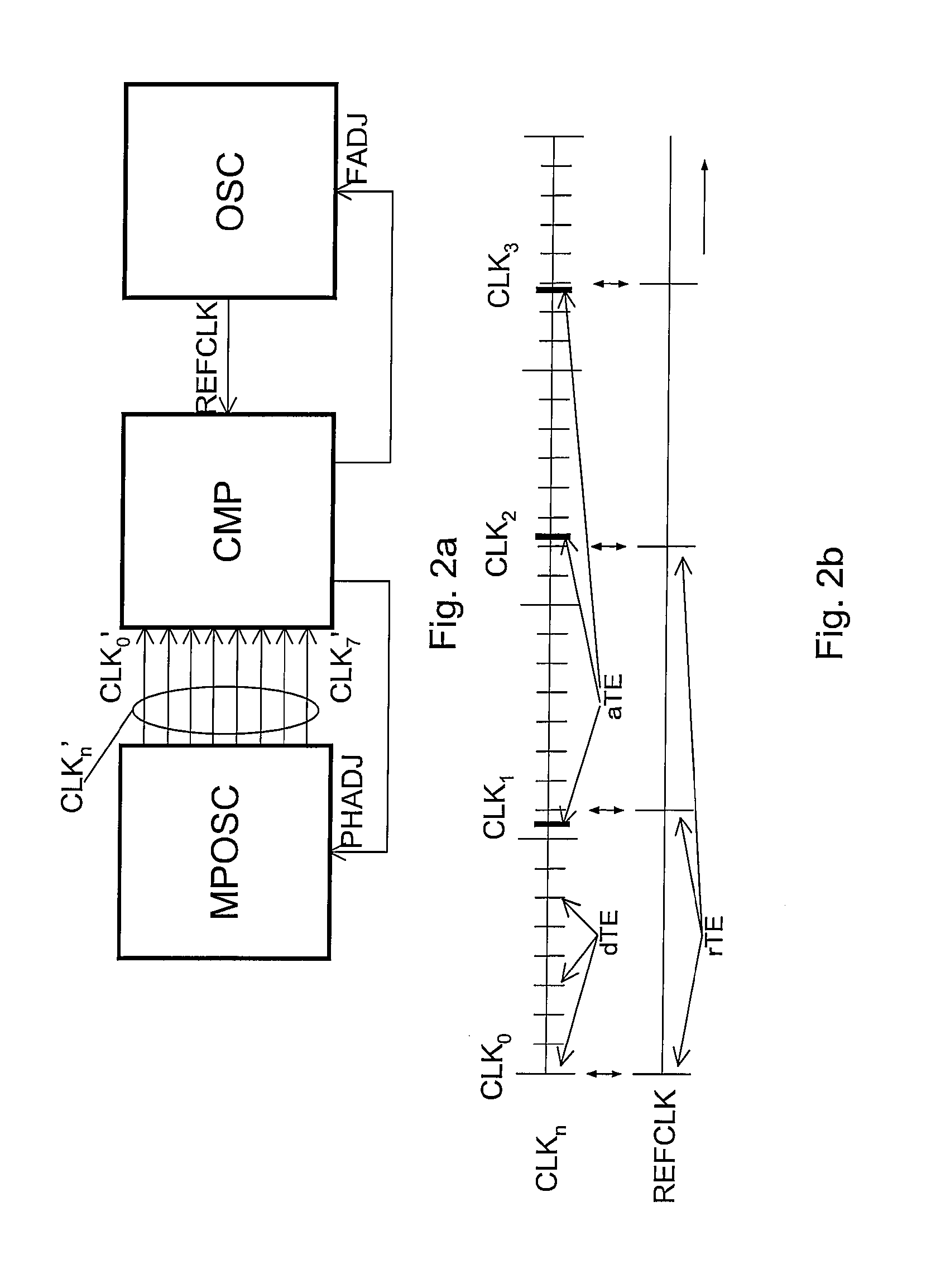
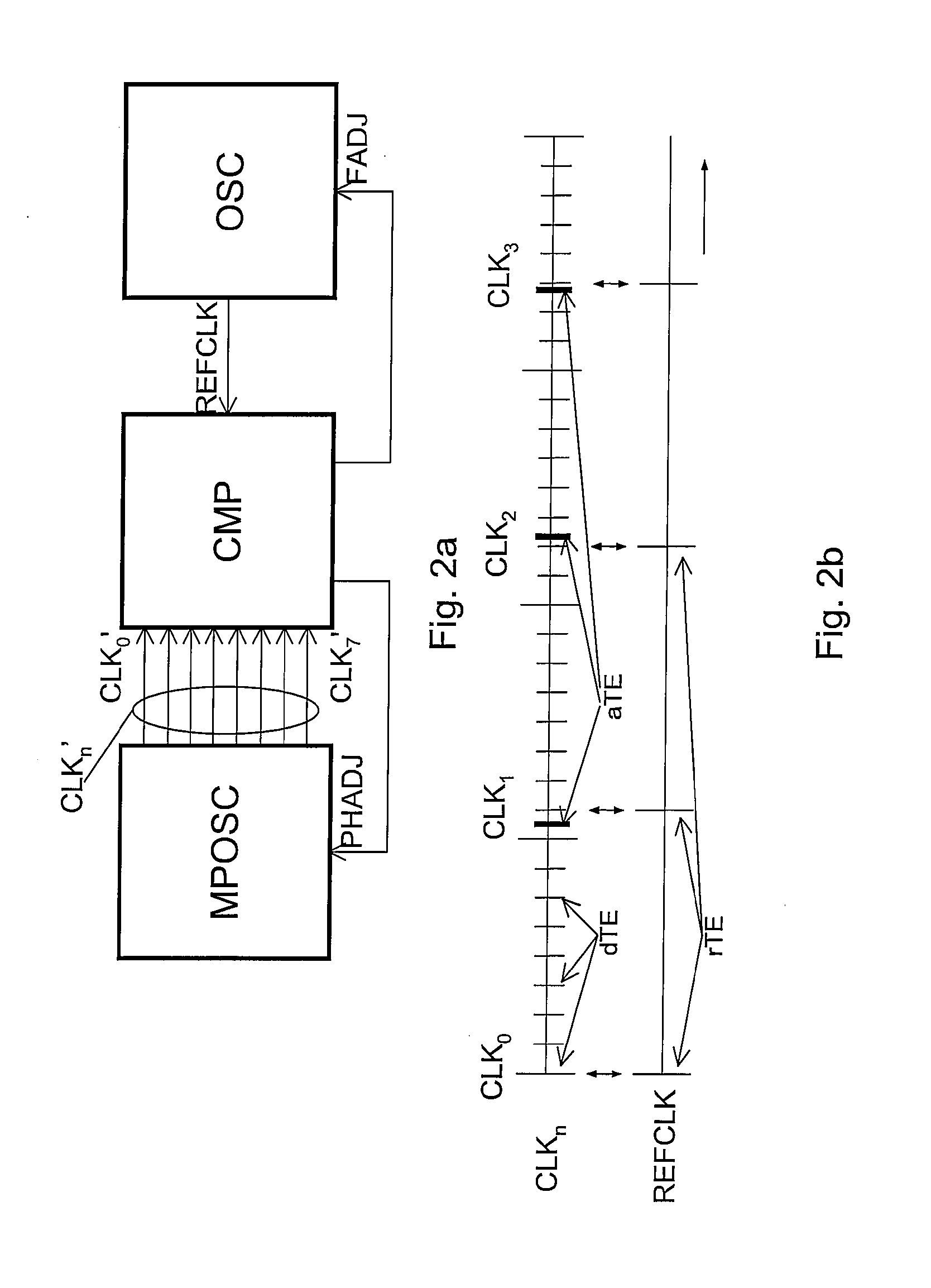
Multi-phase clock system
ActiveUS20100085093A1Reduce power consumptionMaximum accuracyPulse automatic controlTime-delay networksClock rateEngineering
The invention relates to multi-phase clock system for receiving a plurality of clock signals (CLKo-n) comprising actual time events (aTE) defining different clock phases, the clock signals all having a same clock frequency but different clock phases, the system further arranged for receiving a reference clock signal (REFCLK) for providing reference time events (rTE) for the plurality of clock signals (CLKo-n), the reference clock signal (REFCLK) having a reference frequency different from the clock frequency, the reference frequency being selected such that each one of the subsequent reference time events (rTE) coincides with a desired time event (dTE) for a single one of the plurality of clock signals (CLKo-n).
Owner:NXP BV
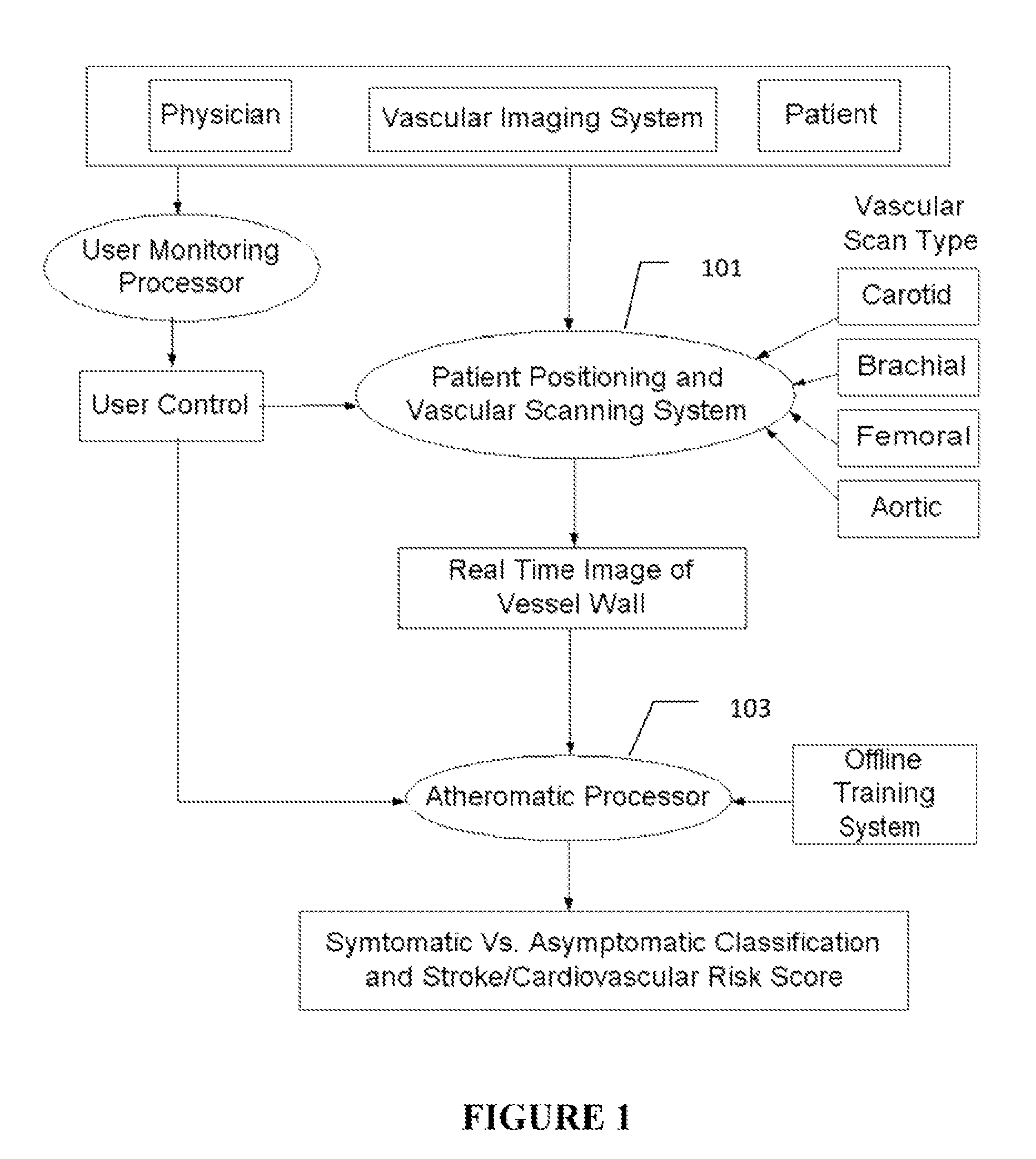
Imaging based symptomatic classification using a combination of trace transform, fuzzy technique and multitude of features
InactiveUS8532360B2Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsCarotid atherosclerosis2d ultrasound
Owner:ATHEROPOINT
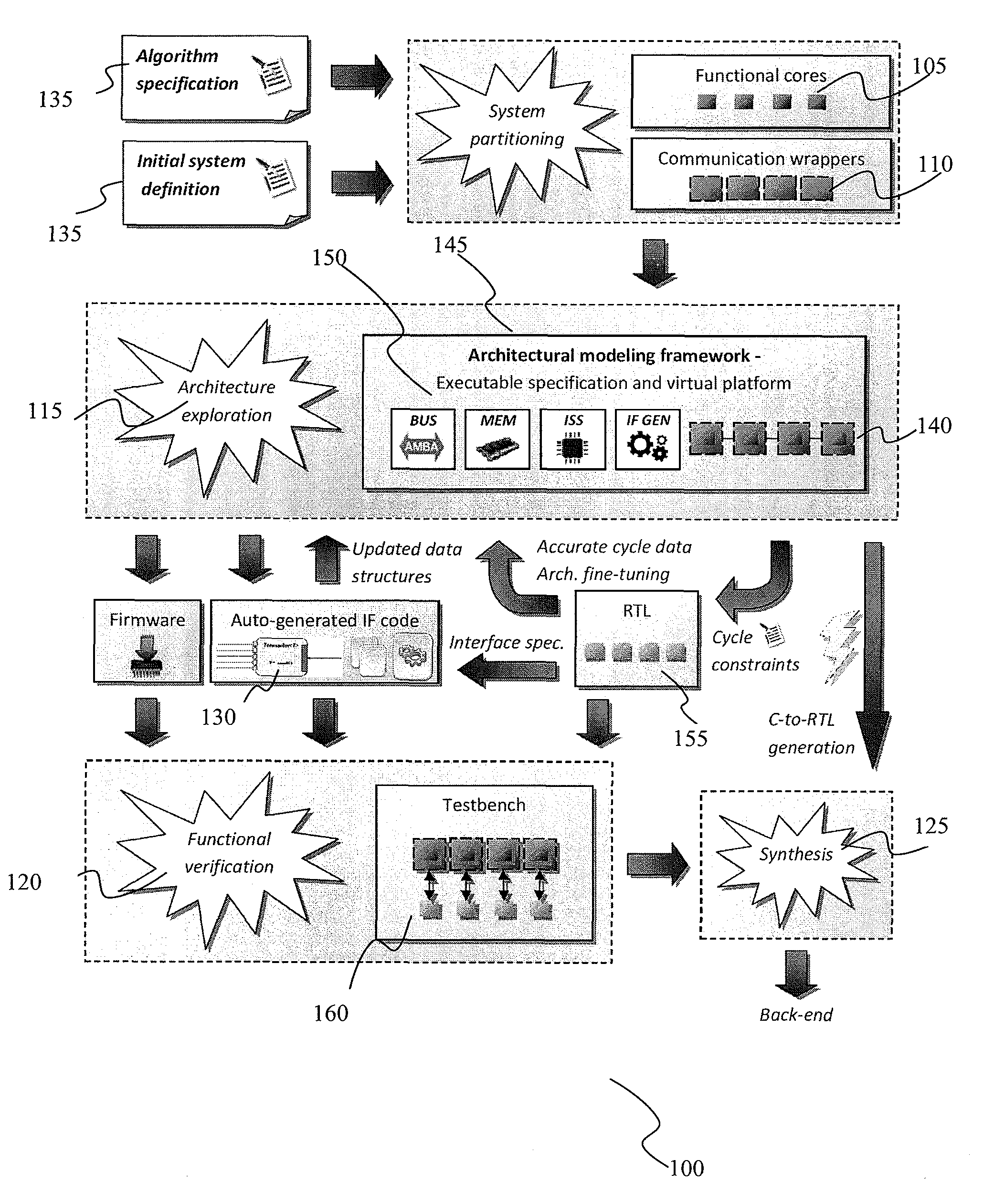
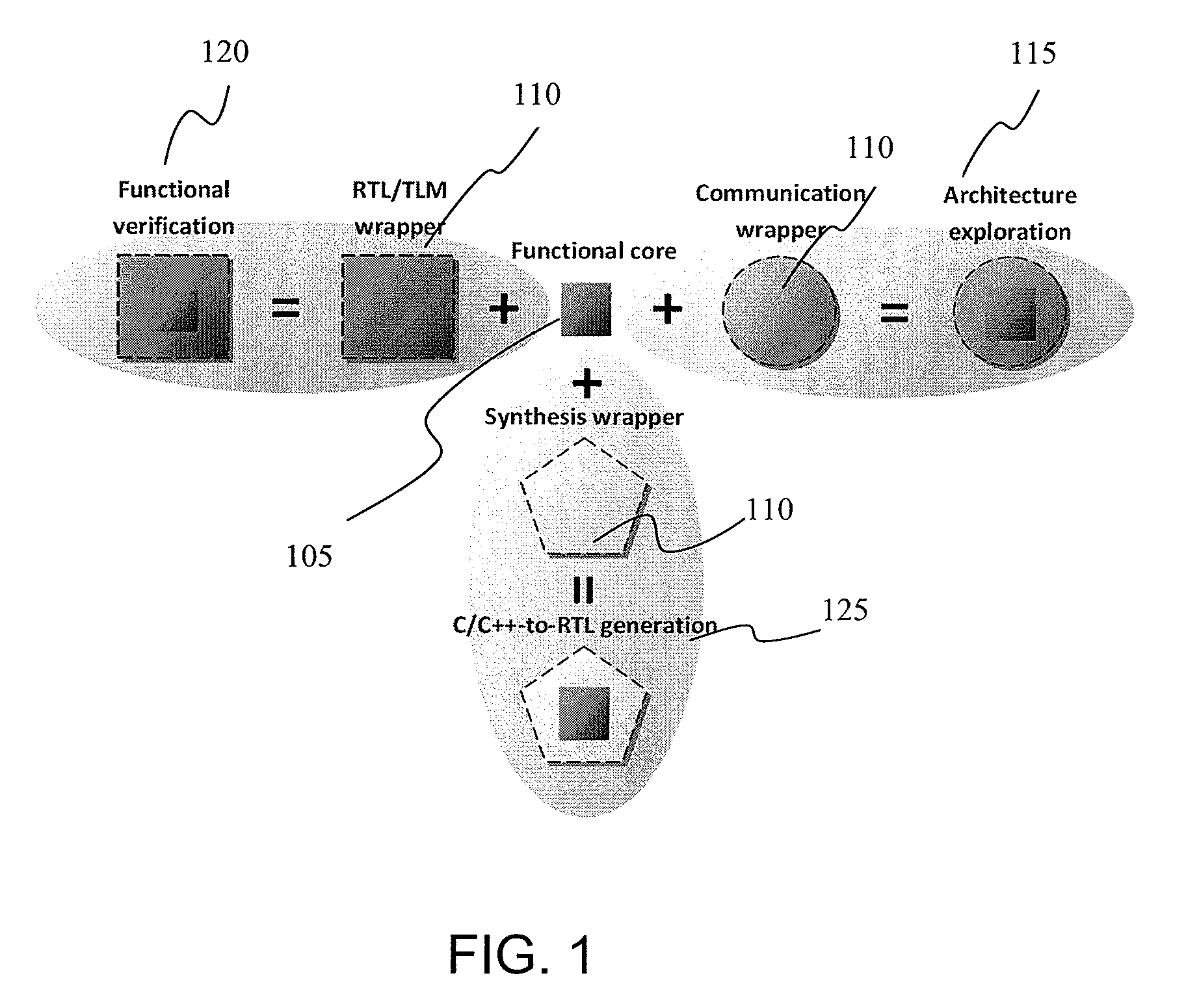
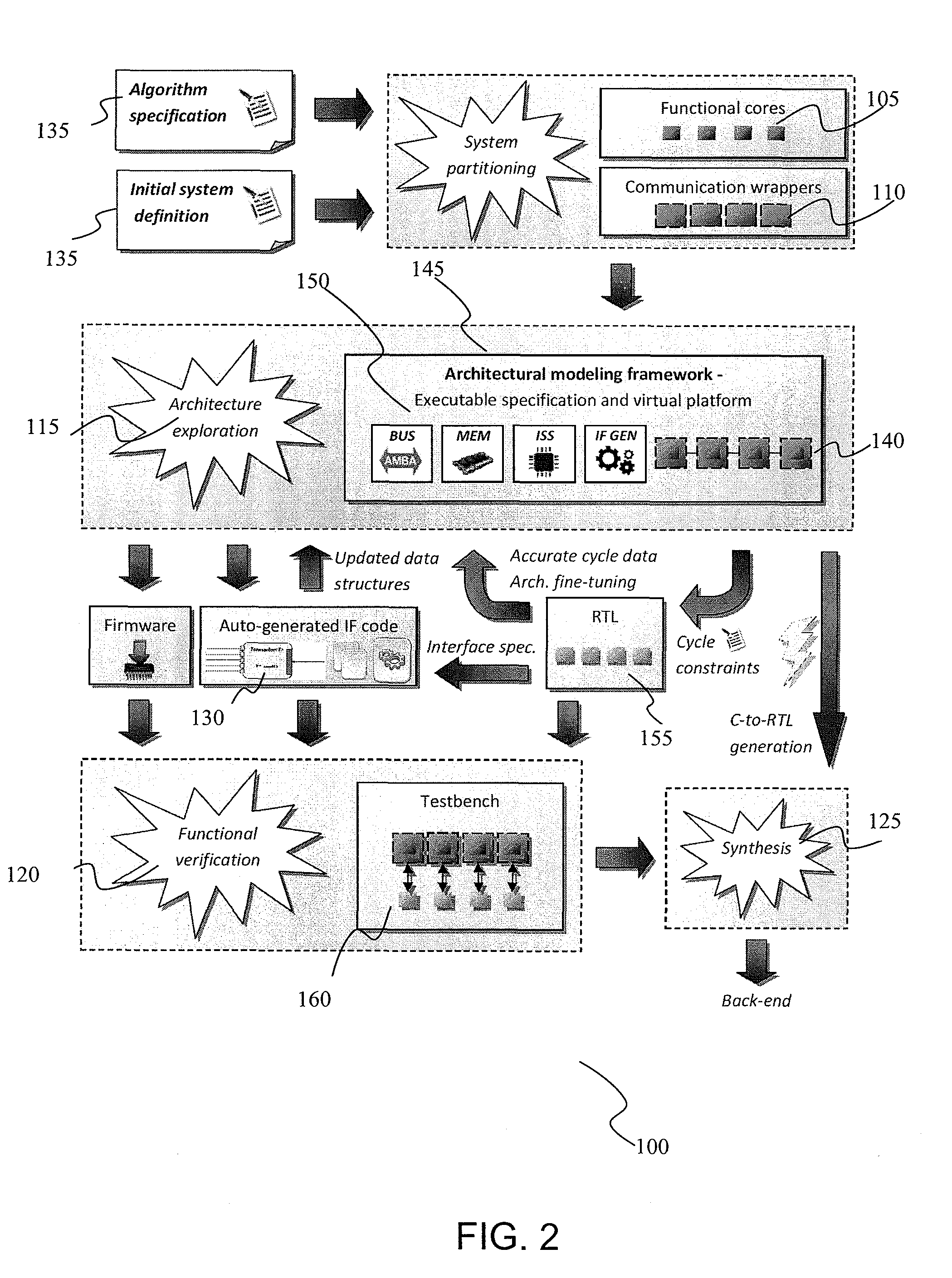
Integrated circuit modeling method and framework tool
ActiveUS8205174B2Improve usabilityMaximum accuracyDetecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designComputer architectureUser input
An integrated circuit modeling method 100 implementable on computer, which has an executable software model 145 having modules 140 of reusable functional cores 105 coded in a high level language and a virtual platform of the integrated circuit employable in an architecture exploration step 115. A modeling library of modules coded in high level languages and hardware level languages are provided and instantiated according to user input in a functional verification step 120 having a co-simulation environment, with interface code 170 between modules automatically generated by an interface generator 130 based on a two dimensional data array of hardware specification inputs 205, the interface code 170 further interfacing with wrappers engaged between high and hardware level language modules.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST CO LTD A LIMITED LIABILITY
Method of aligning hardpoints in aeronautical structures
ActiveUS20200130114A1Maximum accuracyIncrease the number ofFinal product manufactureAircraft assemblyPhysicsCorrection algorithm
The present disclosure relates to a method of assembling hardpoints in aeronautical structures, and more specifically, the disclosed method allows knowing the relative deviation of the hardpoints and of the positioning elements of the hardpoints with respect to a laser beam emitted by a laser collimator fixed to an adjustable support which can be adjusted in at least two directions in space, and by using a correction algorithm, it is possible to know the displacement necessary for locating the positioning elements such that they are aligned with respect to the hardpoints, the positioning elements in turn being moved as a result of the movement of the driven linear tables in one or in several iterative steps, at which time the position thereof is fixed and they are ready for the rest of the hardpoints to be assembled.
Owner:ACITURRI ENG S L U
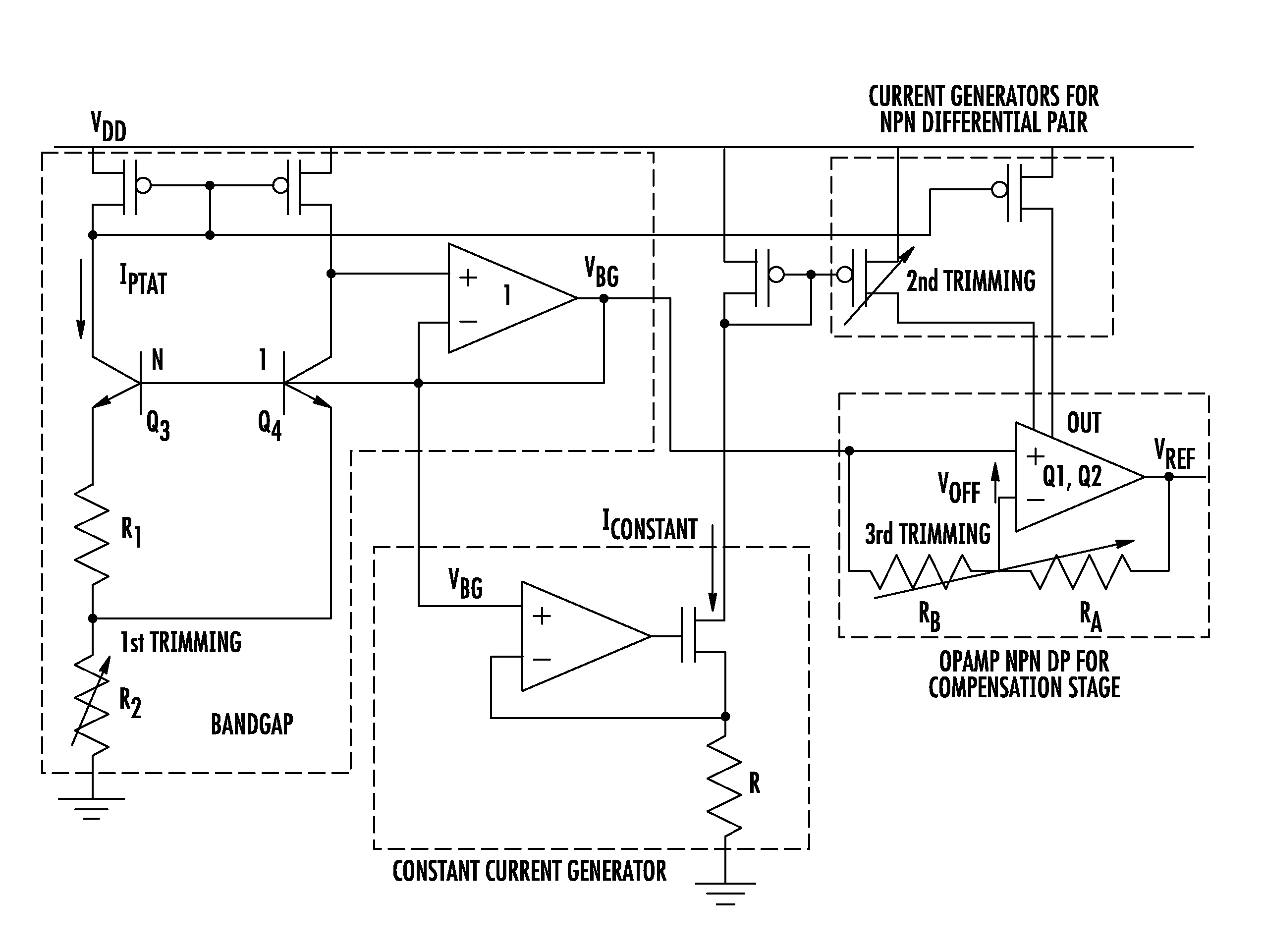
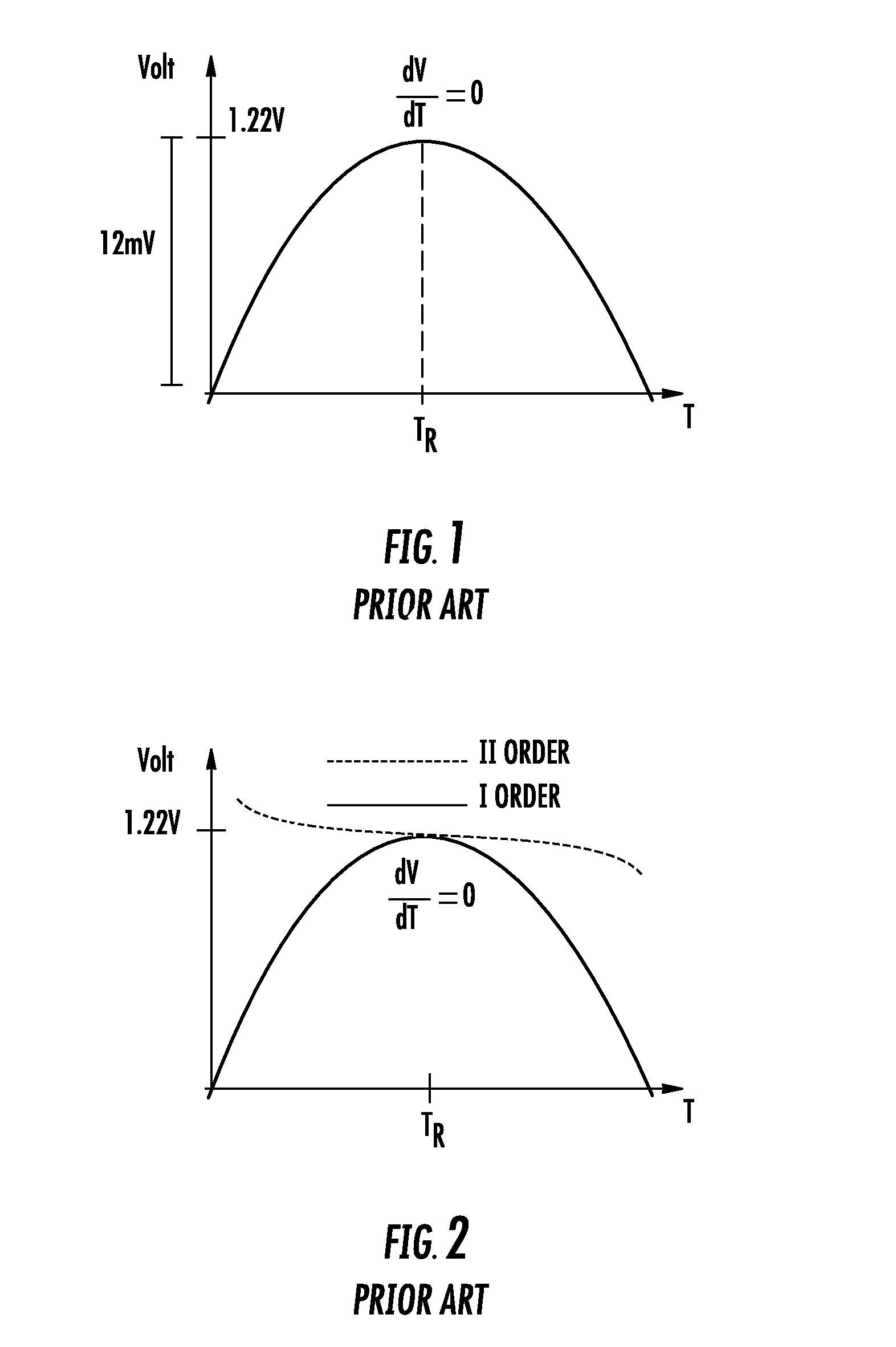
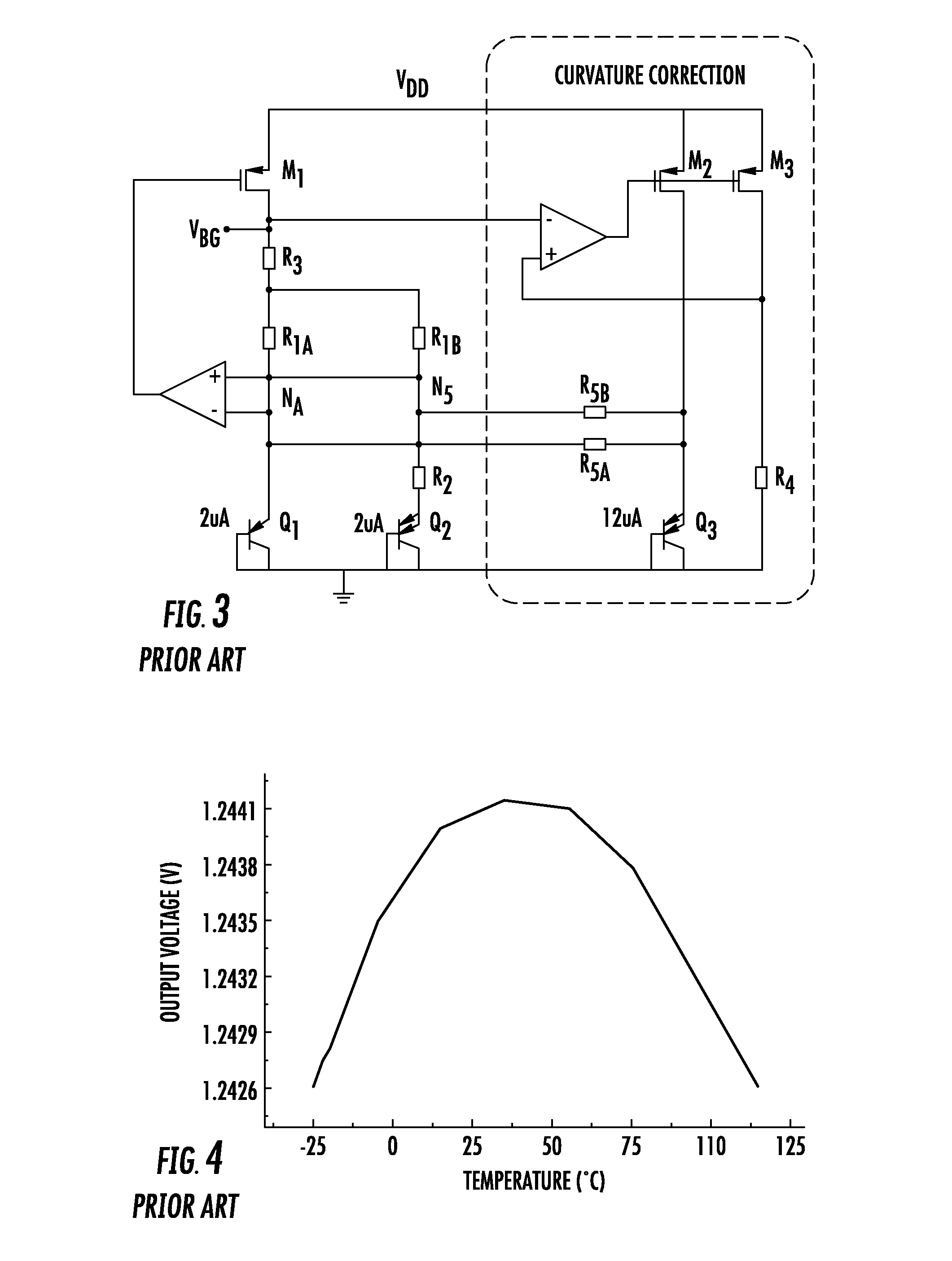
Band-gap voltage generator
A generator of a voltage logarithmically variable with temperature may include a differential amplifier having a pair of transistors, each coupled with a respective bias network adapted to bias in a conduction state the transistors first and second respectively with a constant current and with a current proportional to the working absolute temperature. The pair of transistors may generate between their control nodes the voltage logarithmically variable with temperature. The differential amplifier may have a common bias current generator coupled between the common terminal of the differential pair of transistors and a node at a reference potential, and a feedback line to provide a path for the current difference between the sum of currents flowing through the transistors of the differential pair and the common bias current.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
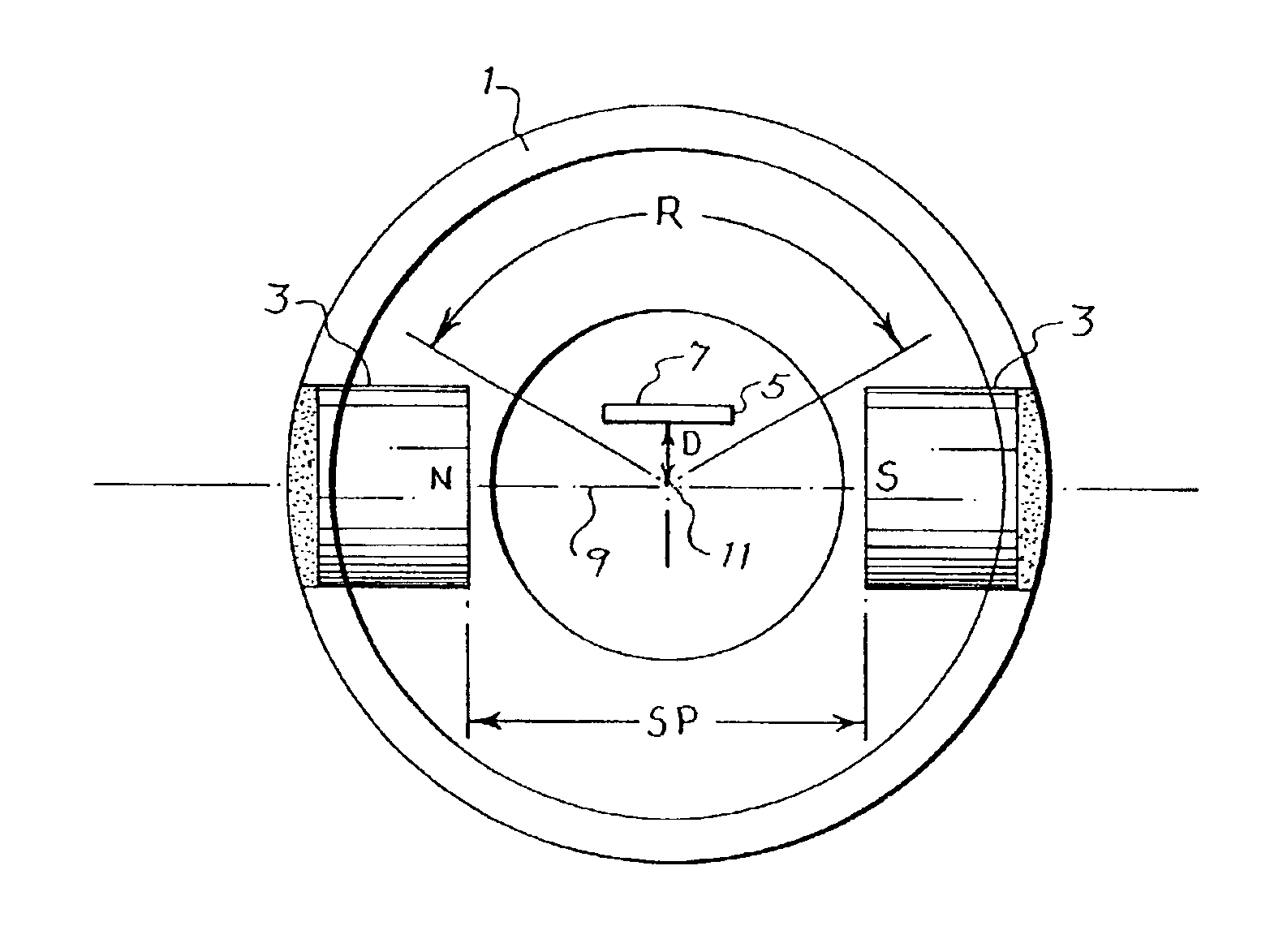
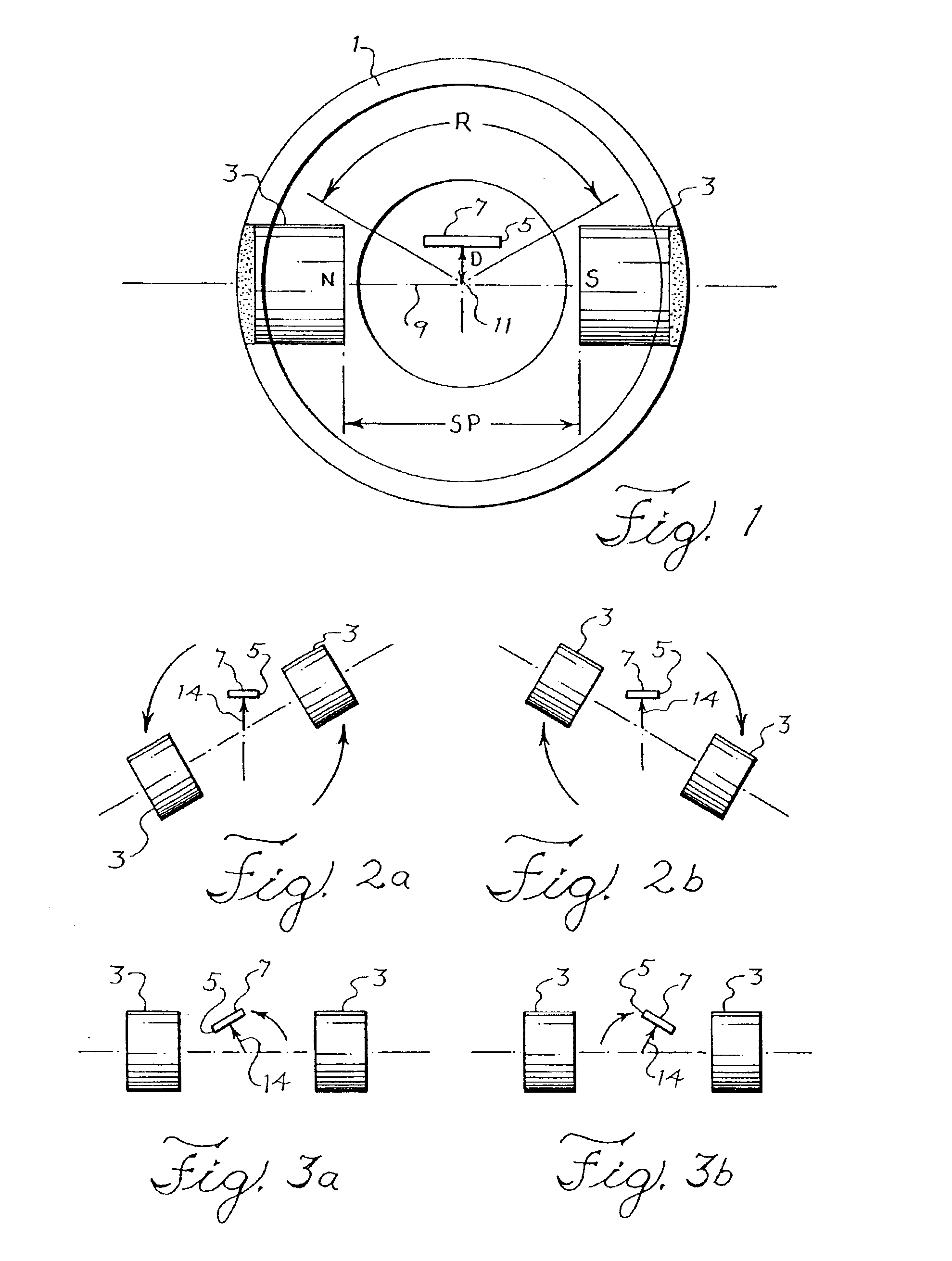
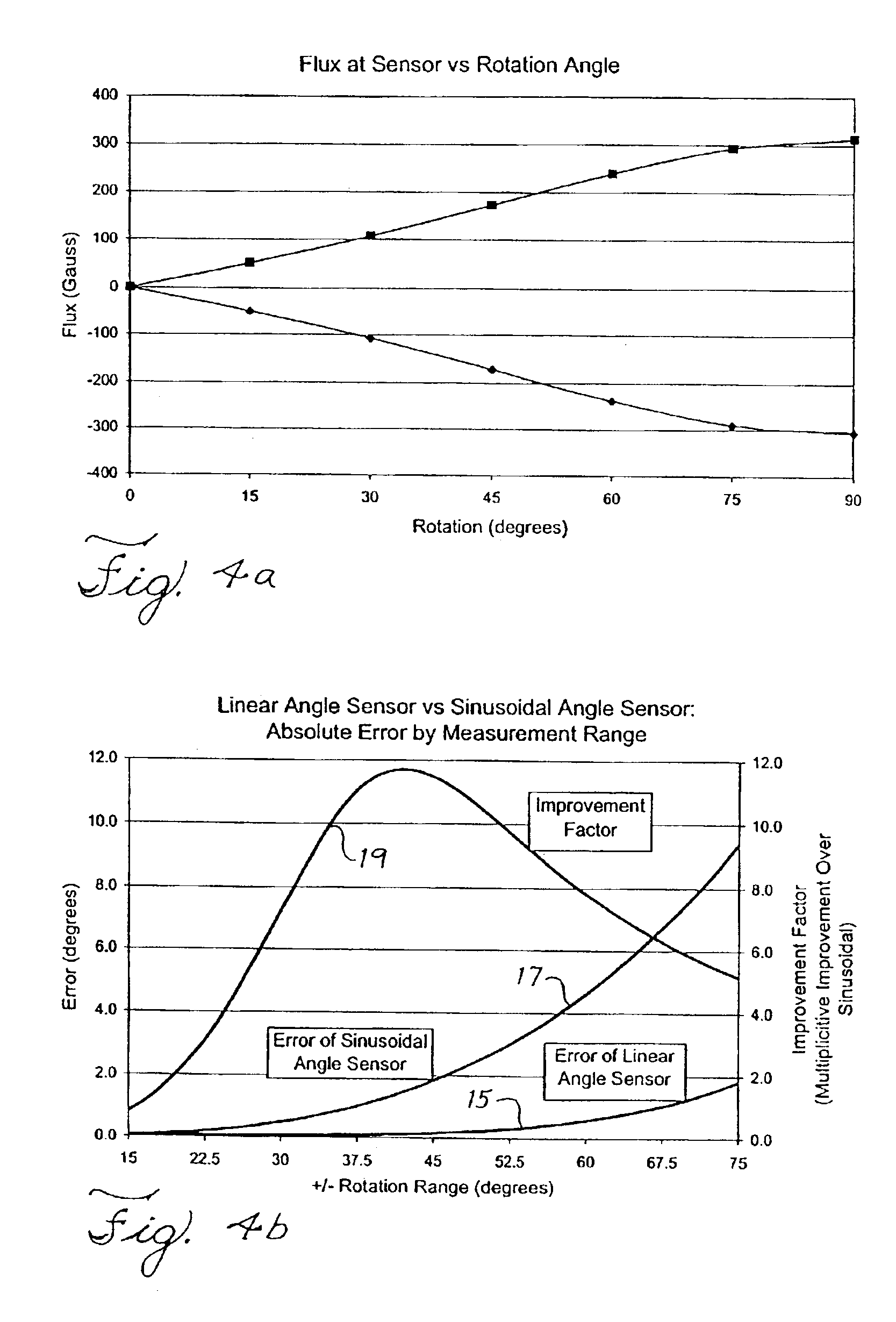
Angular position sensor
InactiveUS6960973B2Maximum accuracyAccurate detectionElectrical controlSolid-state devicesAngular distanceMagnetic flux
An angular position sensor employs a pair of magnets that are disposed on a rotating cylinder at opposite ends of a diameter of the cylinder. A hall-effect flux sensor is fixed within the cylinder and offset from a line of geometric and magnetic symmetry between the magnets. The offset sensor detects a linear change in flux of the magnets as the magnets rotate with the cylinder over a predetermined angular distance and thereby determines the angular position of the cylinder. The offset of the sensor is adjusted to reduce the sensing error.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
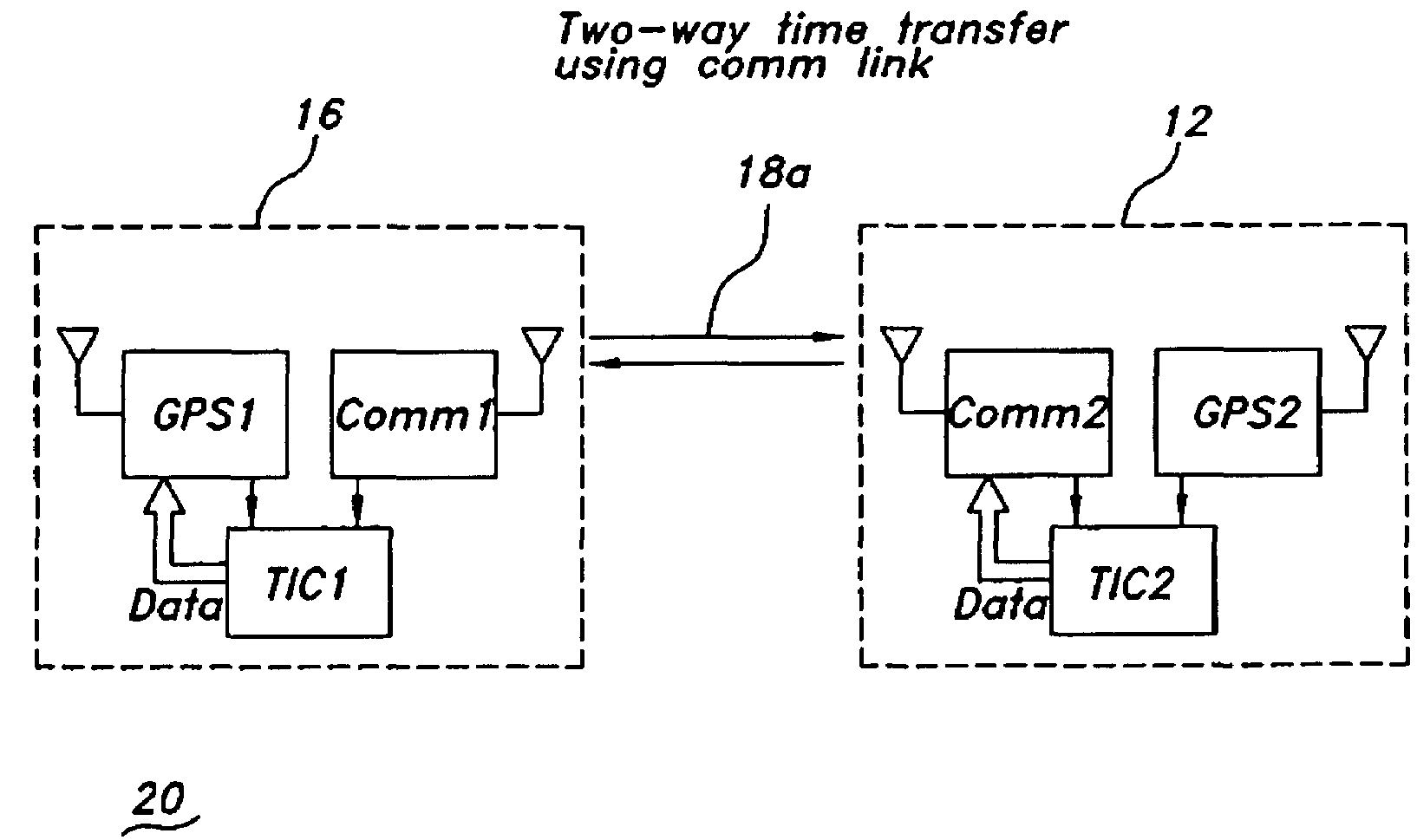
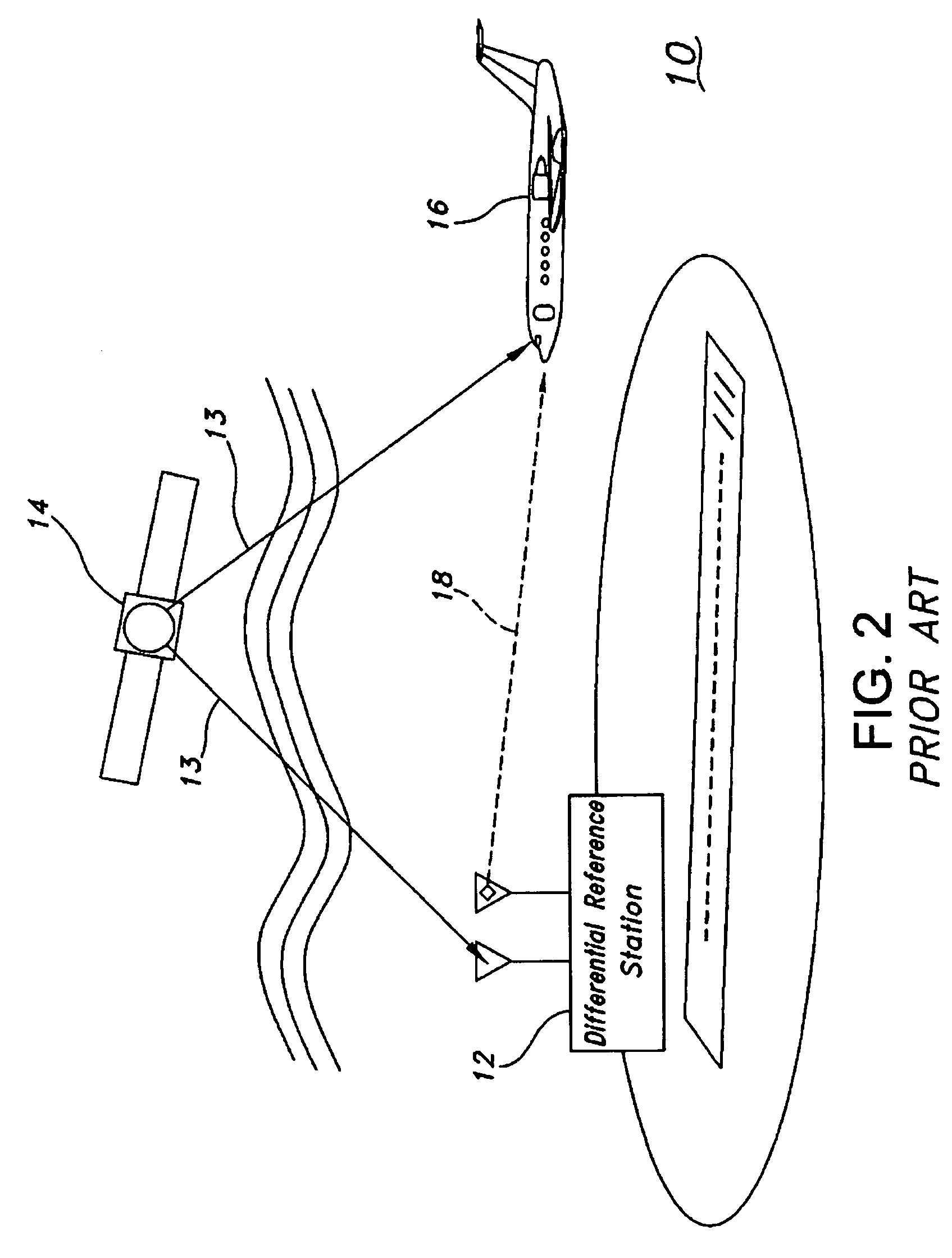
Communications link time transfer to improve navigation system accuracy
ActiveUS7679554B1Maximum accuracyPoor satellite geometriesPosition fixationBeacon systemsTelecommunications linkTime transfer
A method and apparatus for improving differential navigation accuracy uses time transfer over a two-way communications link. The communications link transmits an overall time offset between a differential reference station and a remote user. A differential navigation position solution is modified at the remote user with the overall time offset to improve the differential navigation accuracy. A first time offset between a first communications device and a first navigation receiver at the remote user is determined. A second time offset between the first communications device at the remote user and a second communications device at the differential reference station is determined. A third time offset between the second communications device and a second navigation receiver at the differential reference station is determined. An overall time offset from the first time offset, the second time offset, and the third time offset is computed and used to improve the differential navigation accuracy.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com