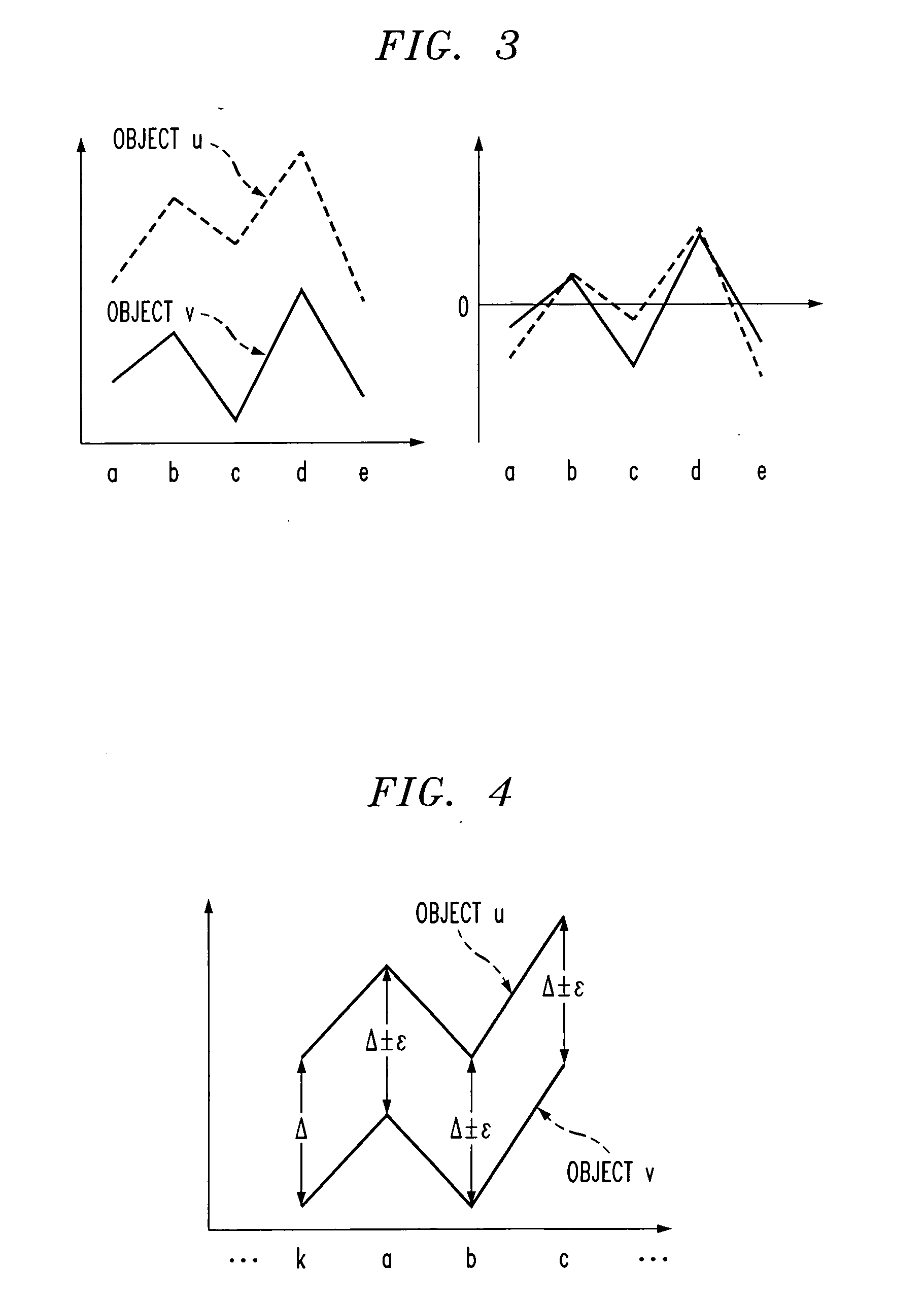Patents
Literature
354 results about "Multidimensional space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multidimensional Space. a space having more than three dimensions. Ordinary Euclidean space studied in elementary geometry is three dimensional, planes are two dimensional, and lines are one dimensional. The concept of a multidimensional space arose in the process of the generalization of the subject of geometry.
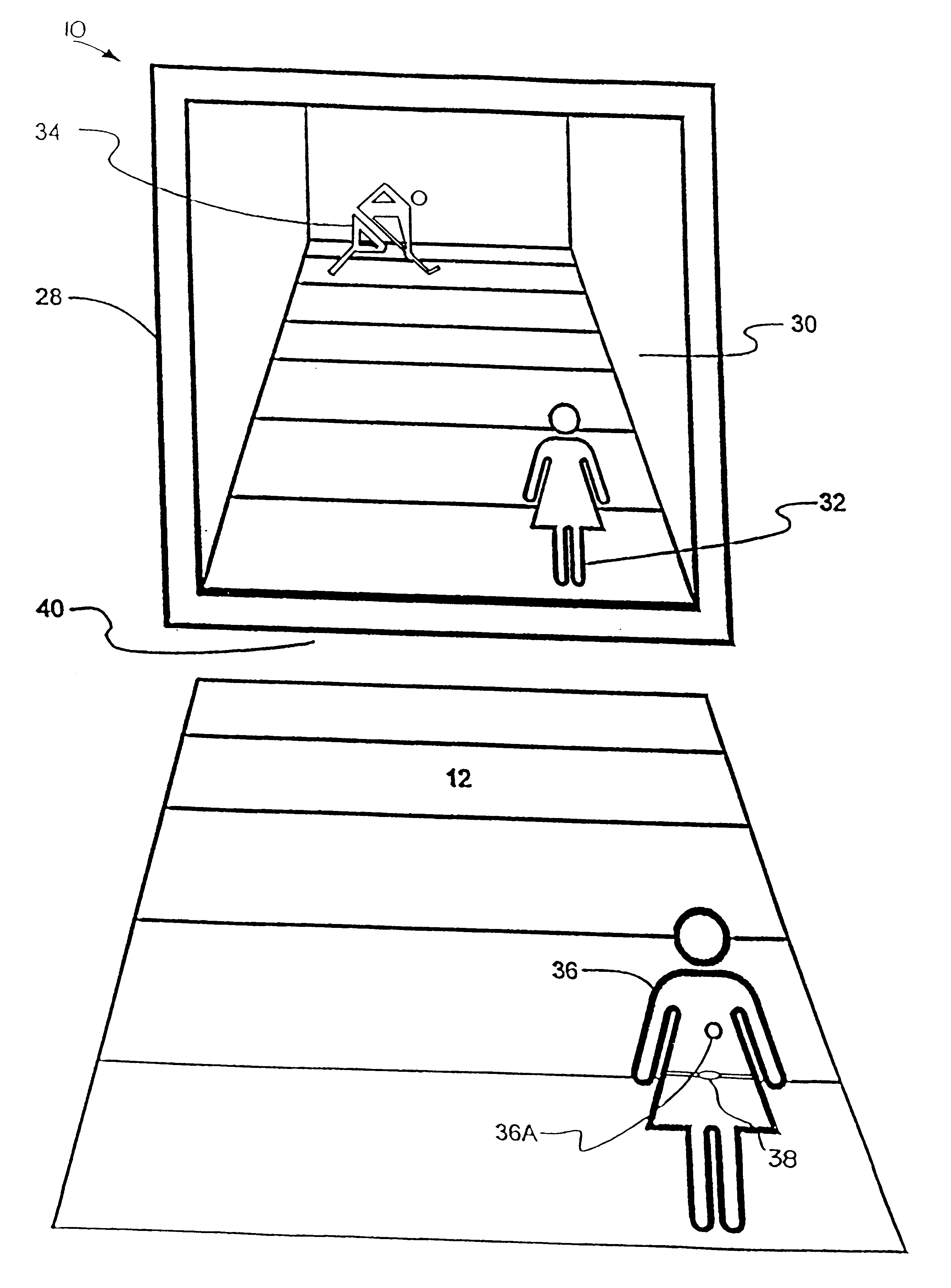
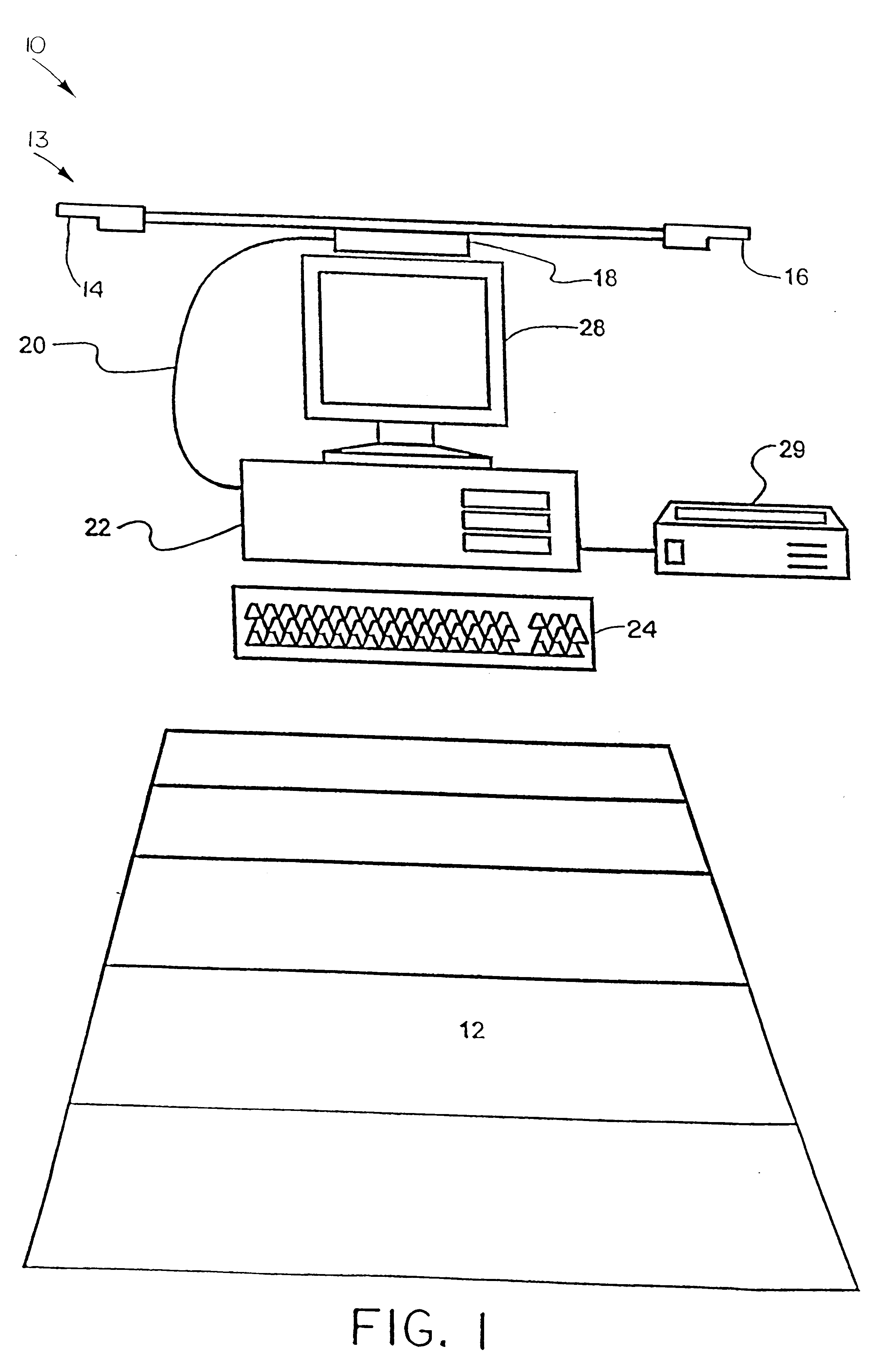
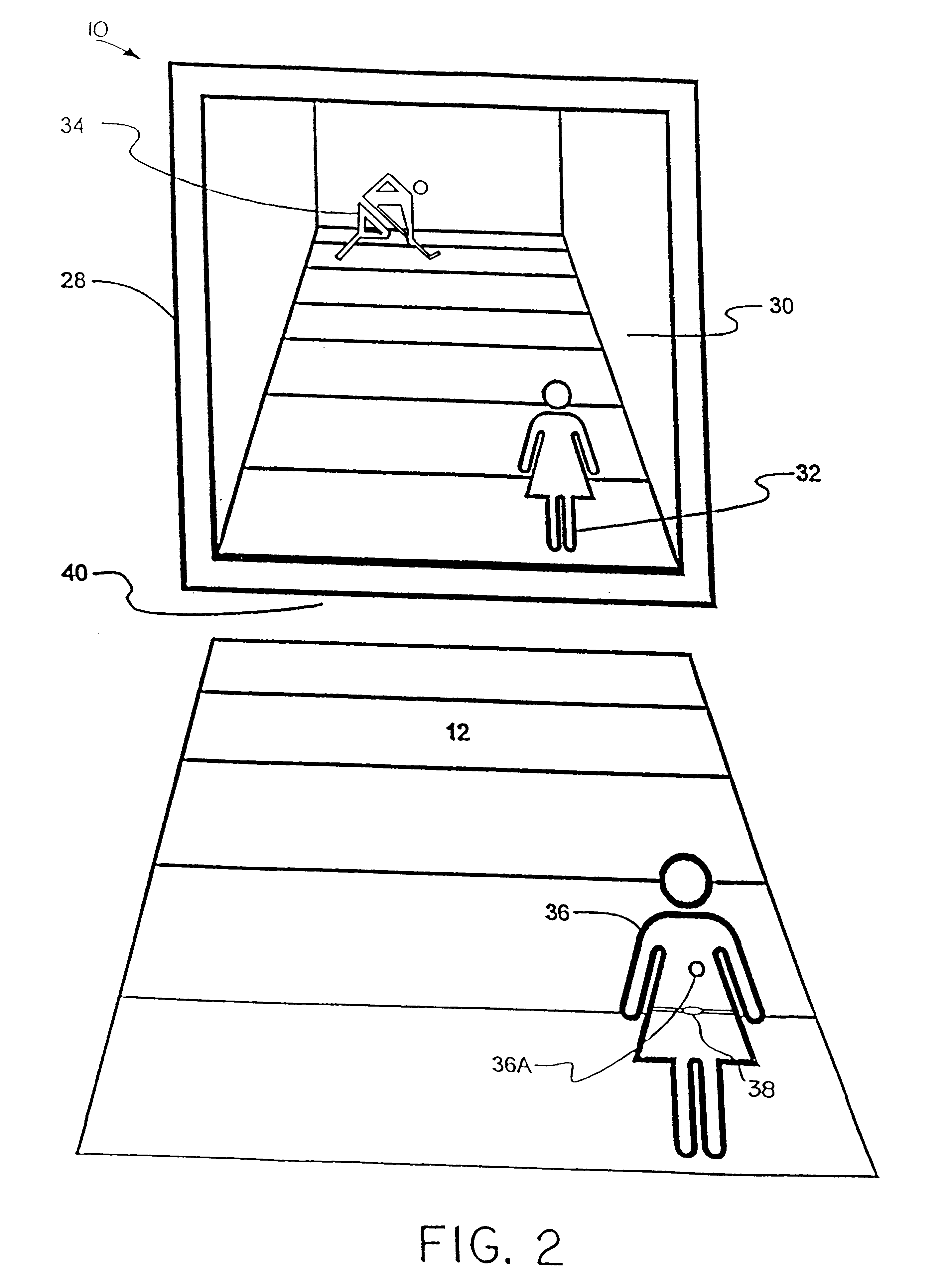
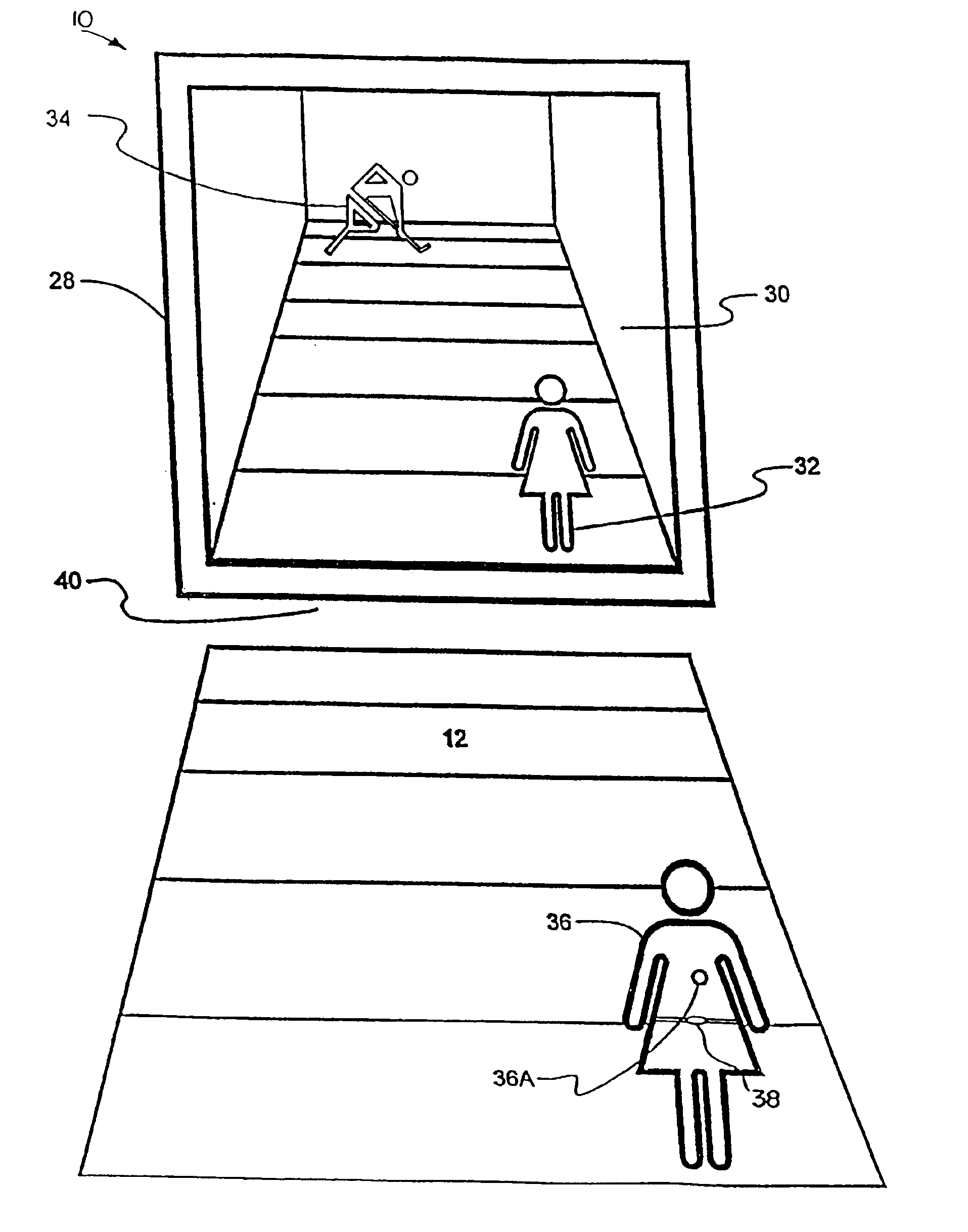
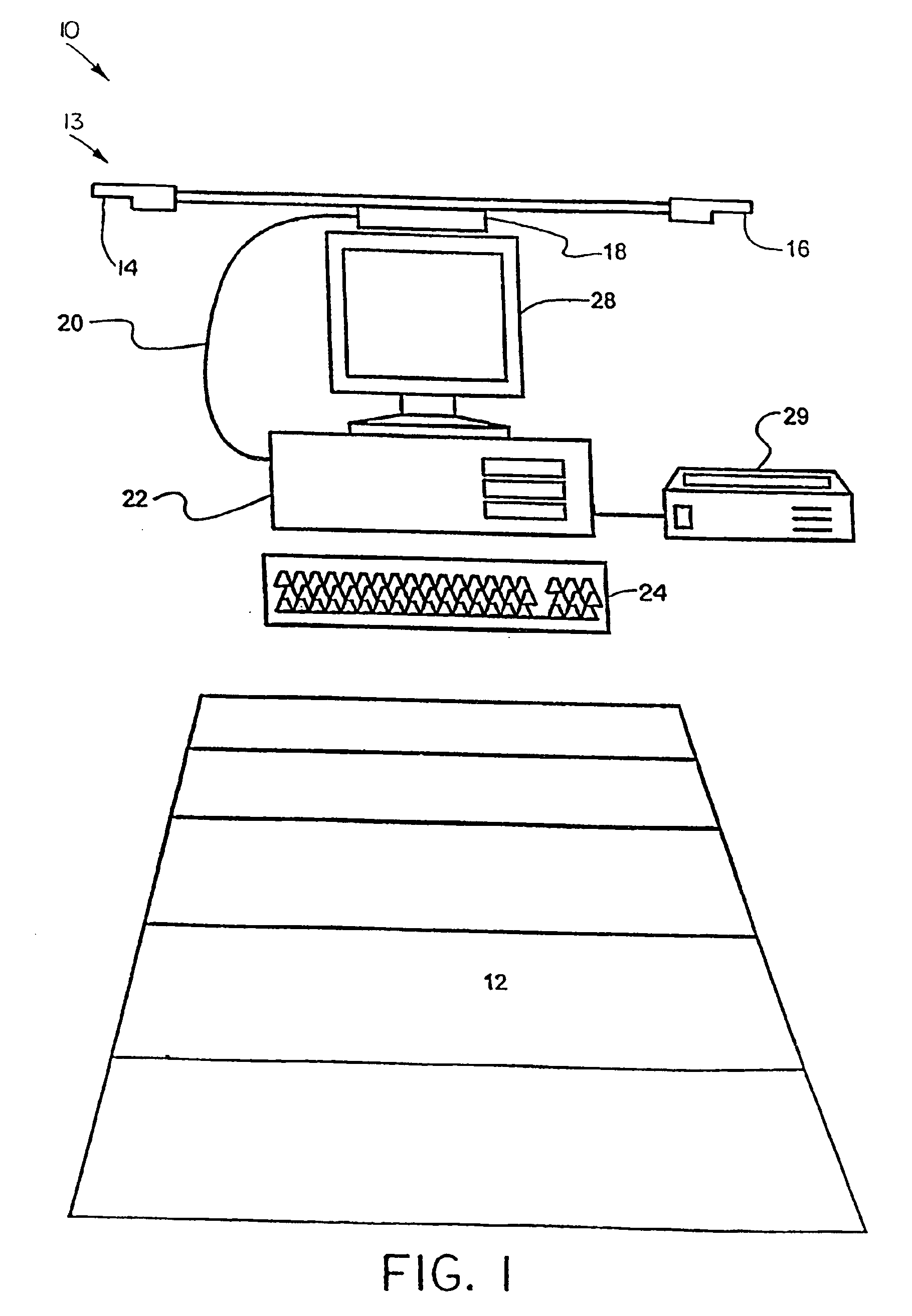
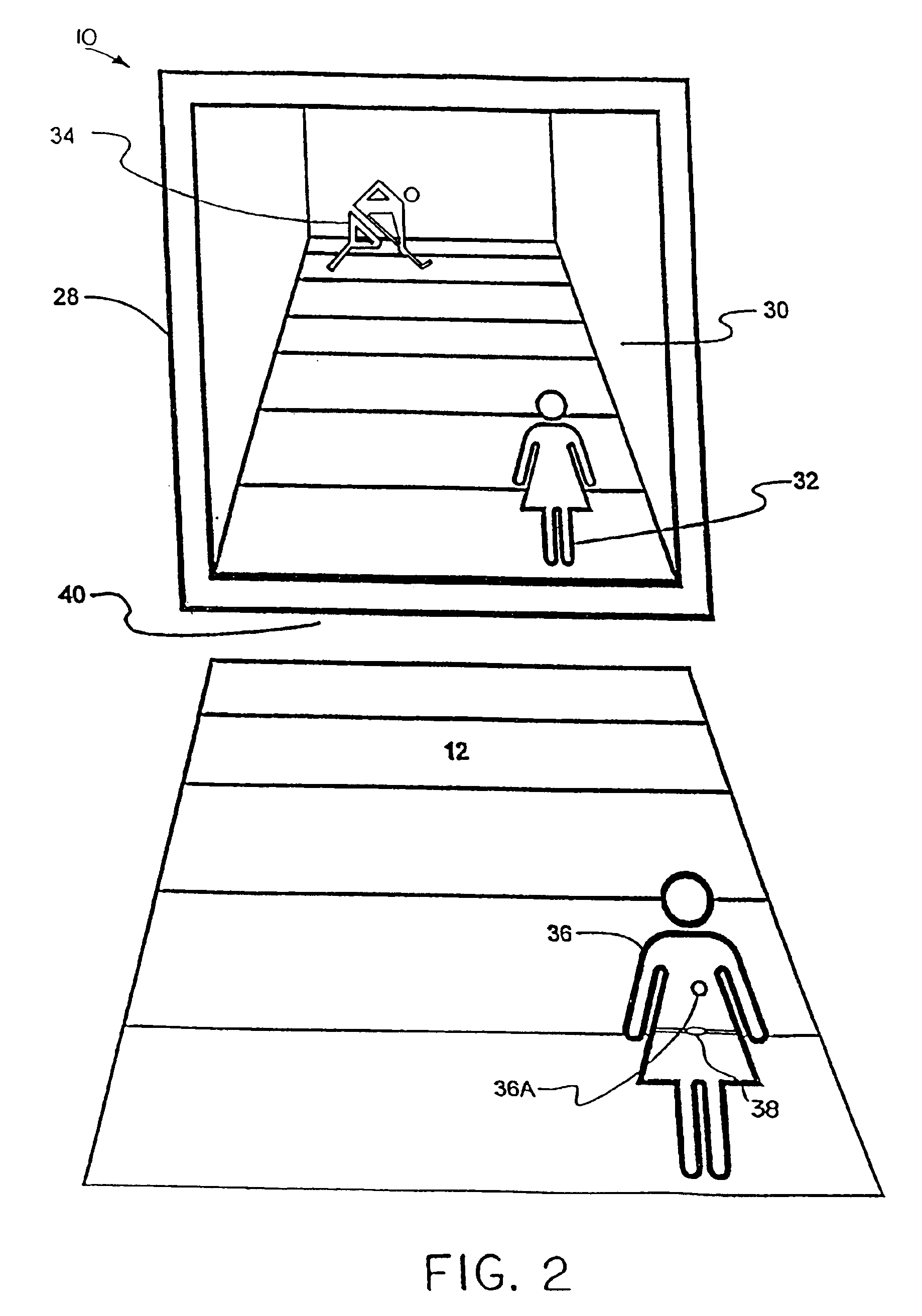
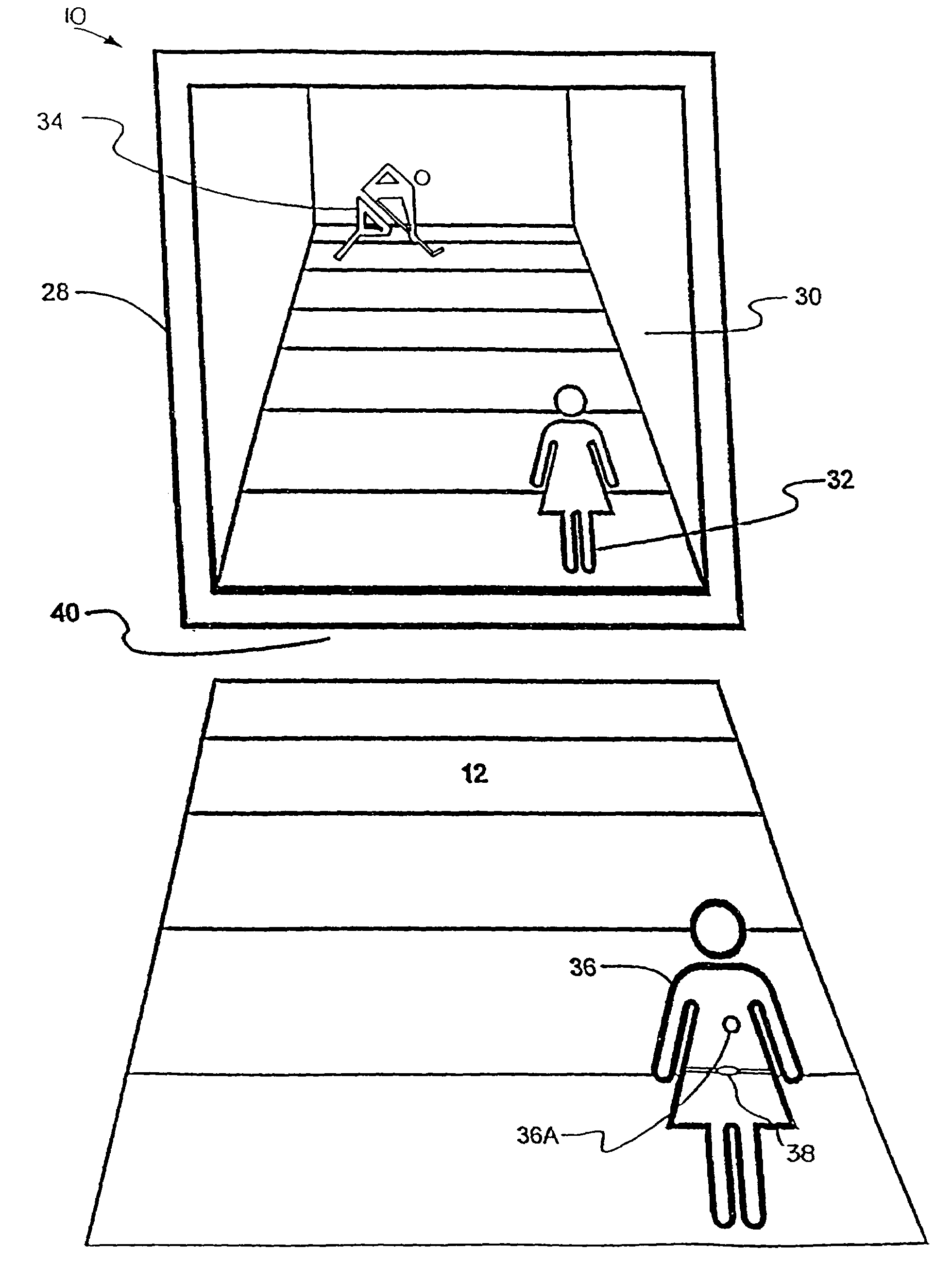
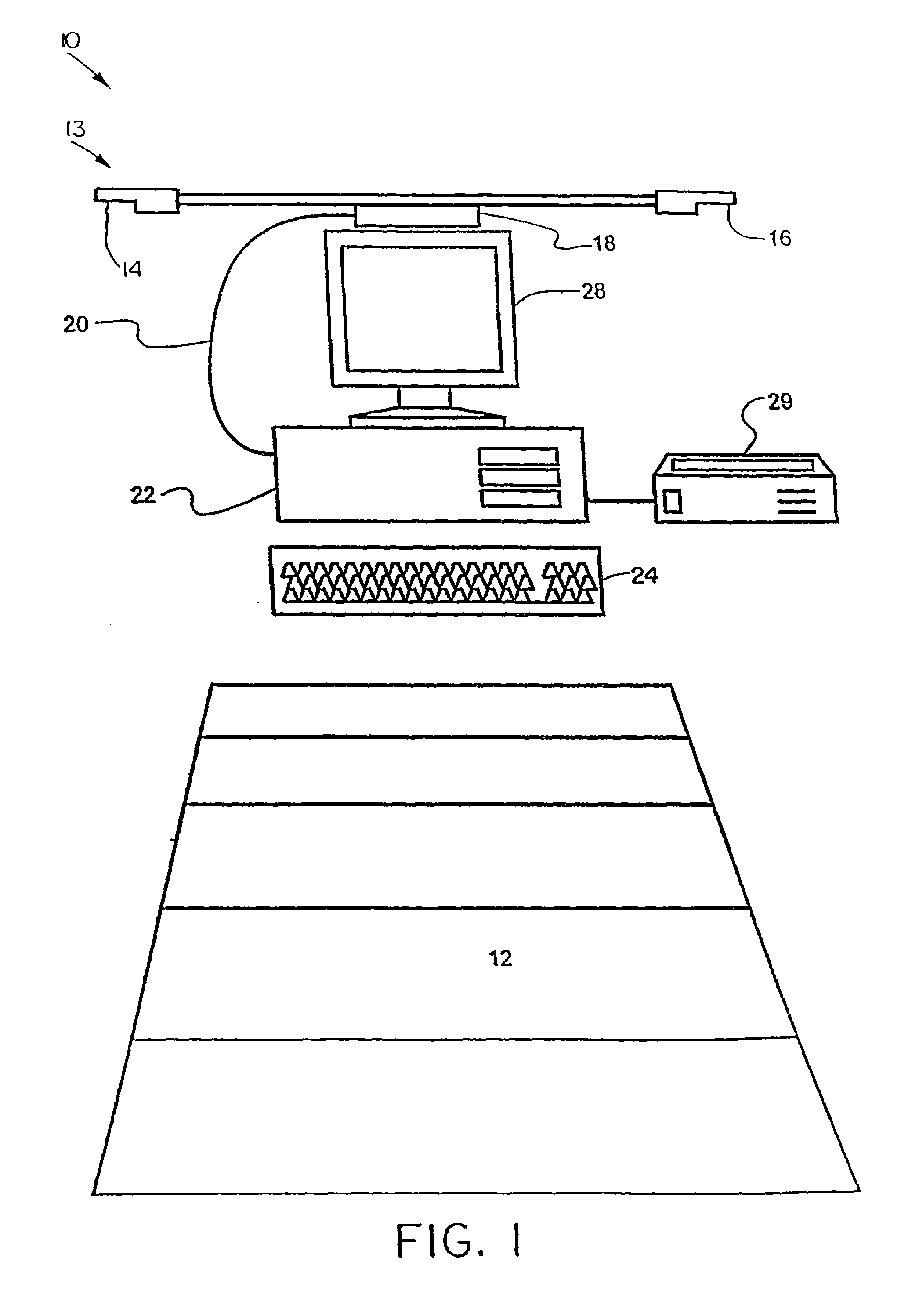
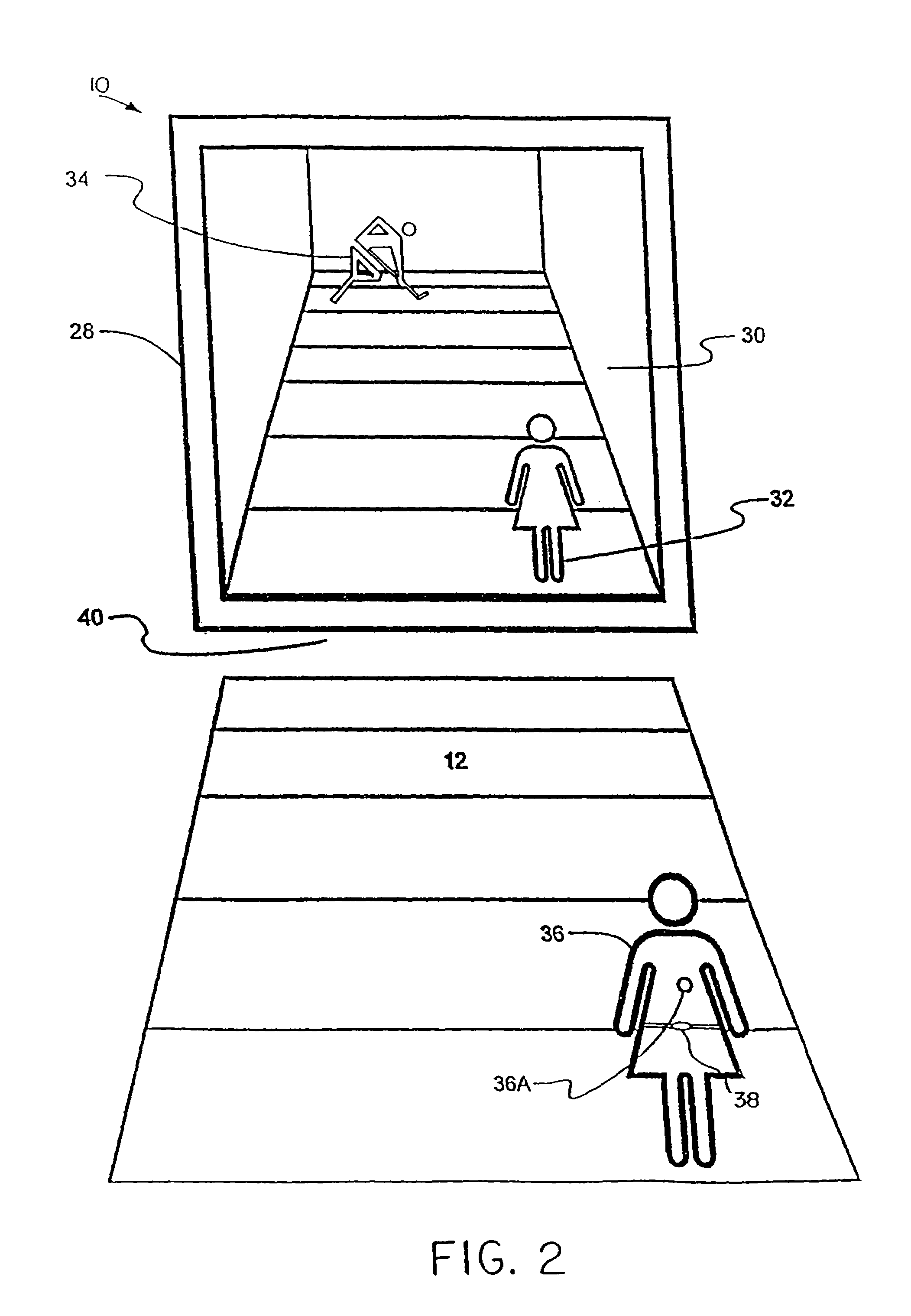
System and method for tracking and assessing movement skills in multidimensional space
InactiveUS6308565B1Improve athletic performanceImprove training performanceBall sportsDiagnostic recording/measuringMultidimensional scalingSkill sets
Accurate simulation of sport to quantify and train performance constructs by employing sensing electronics for determining, in essentially real time, the player's three dimensional positional changes in three or more degrees of freedom (three dimensions); and computer controlled sport specific cuing that evokes or prompts sport specific responses from the player that are measured to provide meaningful indicia of performance. The sport specific cuing is characterized as a virtual opponent that is responsive to, and interactive with, the player in real time. The virtual opponent continually delivers and / or responds to stimuli to create realistic movement challenges for the player.
Owner:IMPULSE TECH
System and method for tracking and assessing movement skills in multidimensional space
InactiveUS6876496B2Accurate modulationImprove performanceBall sportsDiagnostic recording/measuringMultidimensional scalingSkill sets
Accurate simulation of sport to quantify and train performance constructs by employing sensing electronics for determining, in essentially real time, the player's three dimensional positional changes in three or more degrees of freedom (three dimensions); and computer controlled sport specific cuing that evokes or prompts sport specific responses from the player that are measured to provide meaningful indicia of performance. The sport specific cuing is characterized as a virtual opponent that is responsive to, and interactive with, the player in real time. The virtual opponent continually delivers and / or responds to stimuli to create realistic movement challenges for the player.
Owner:IMPULSE TECH
System and method for tracking and assessing movement skills in multidimensional space
Accurate simulation of sport to quantify and train performance constructs by employing sensing electronics for determining, in essentially real time, the player's three dimensional positional changes in three or more degrees of freedom (three dimensions); and computer controlled sport specific cuing that evokes or prompts sport specific responses from the player that are measured to provide meaningful indicia of performance. The sport specific cuing is characterized as a virtual opponent that is responsive to, and interactive with, the player in real time. The virtual opponent continually delivers and / or responds to stimuli to create realistic movement challenges for the player.
Owner:IMPULSE TECH
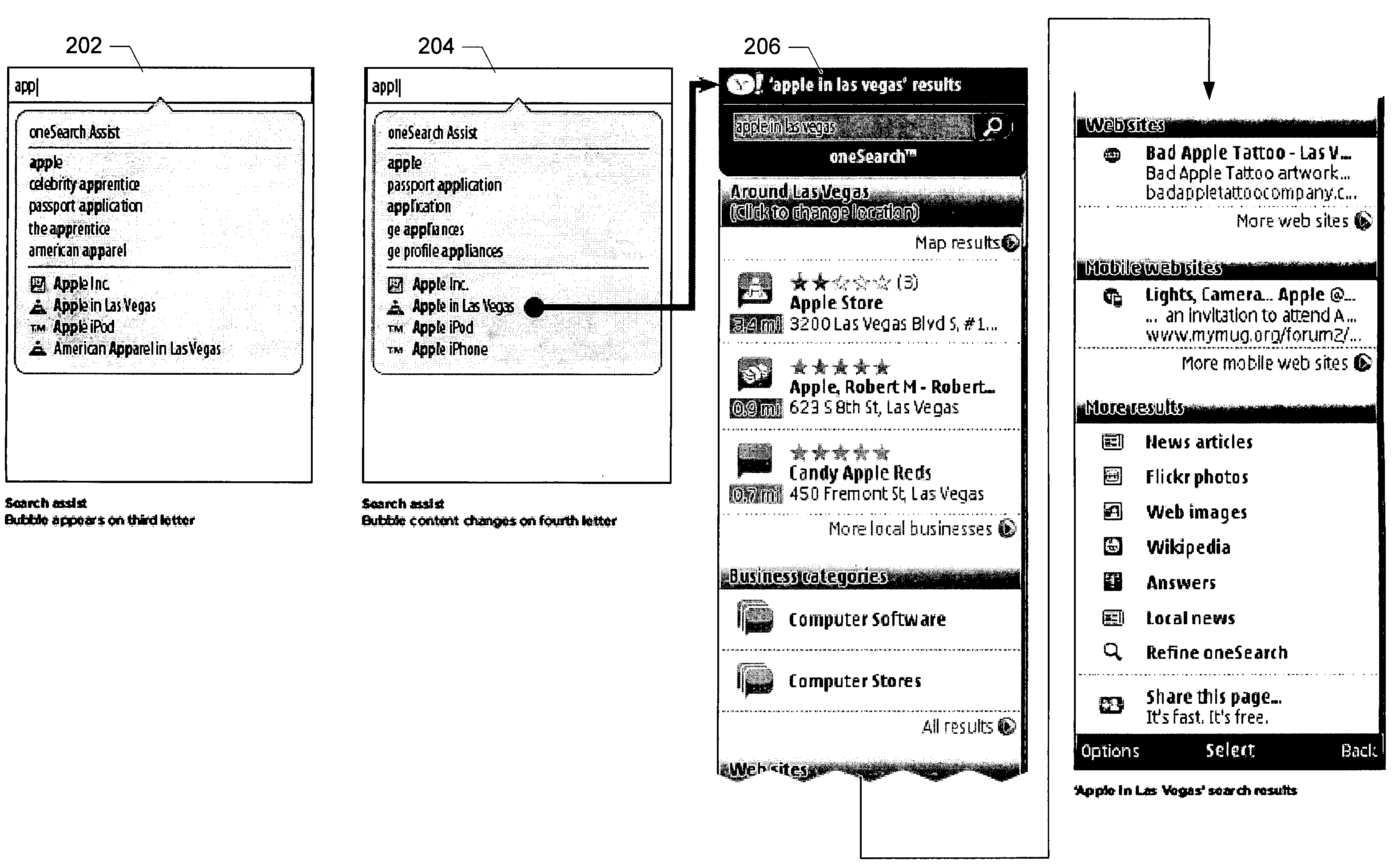
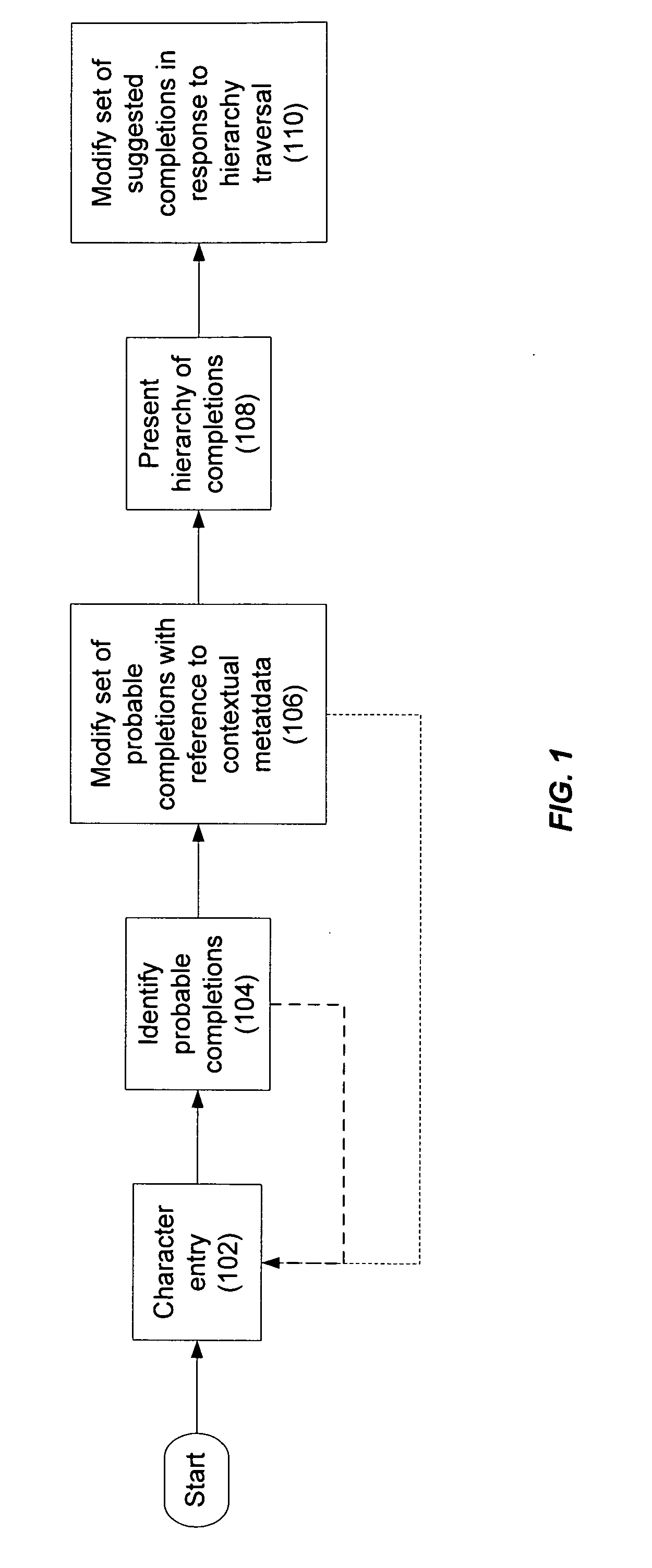
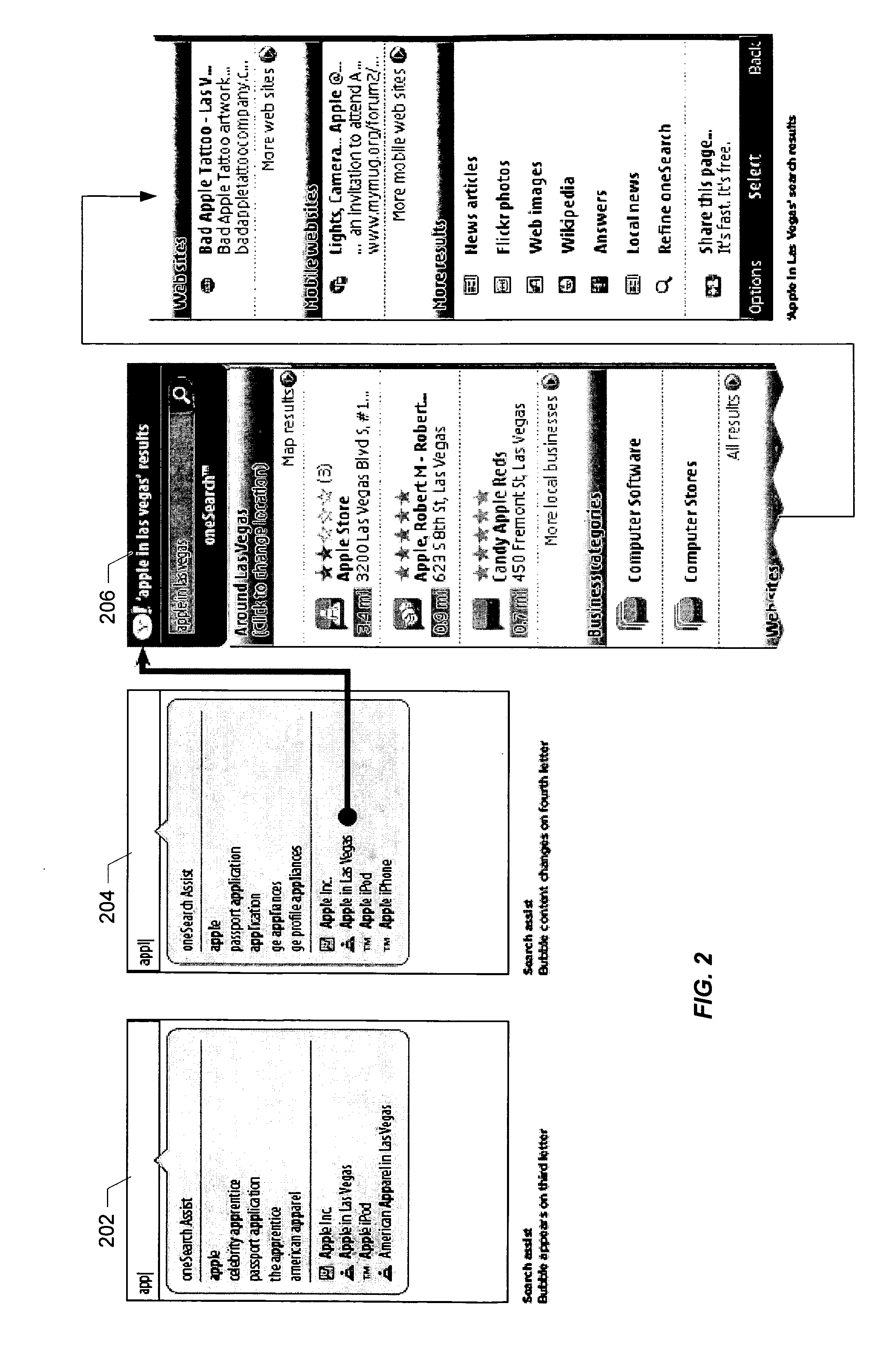
Techniques for input recogniton and completion
InactiveUS20090249198A1Entry of the partial input by the user is facilitatedSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSubject matterMulti dimensional
Methods and apparatus are described by which one or more input words may be predicted based on partial input from a user using a predictive model that employs contextual metadata which characterizes the user in a multi-dimensional space in which the dimensions are defined by one or more of a spatial aspect, a temporal aspect, a social aspect, or a topical aspect.
Owner:OATH INC
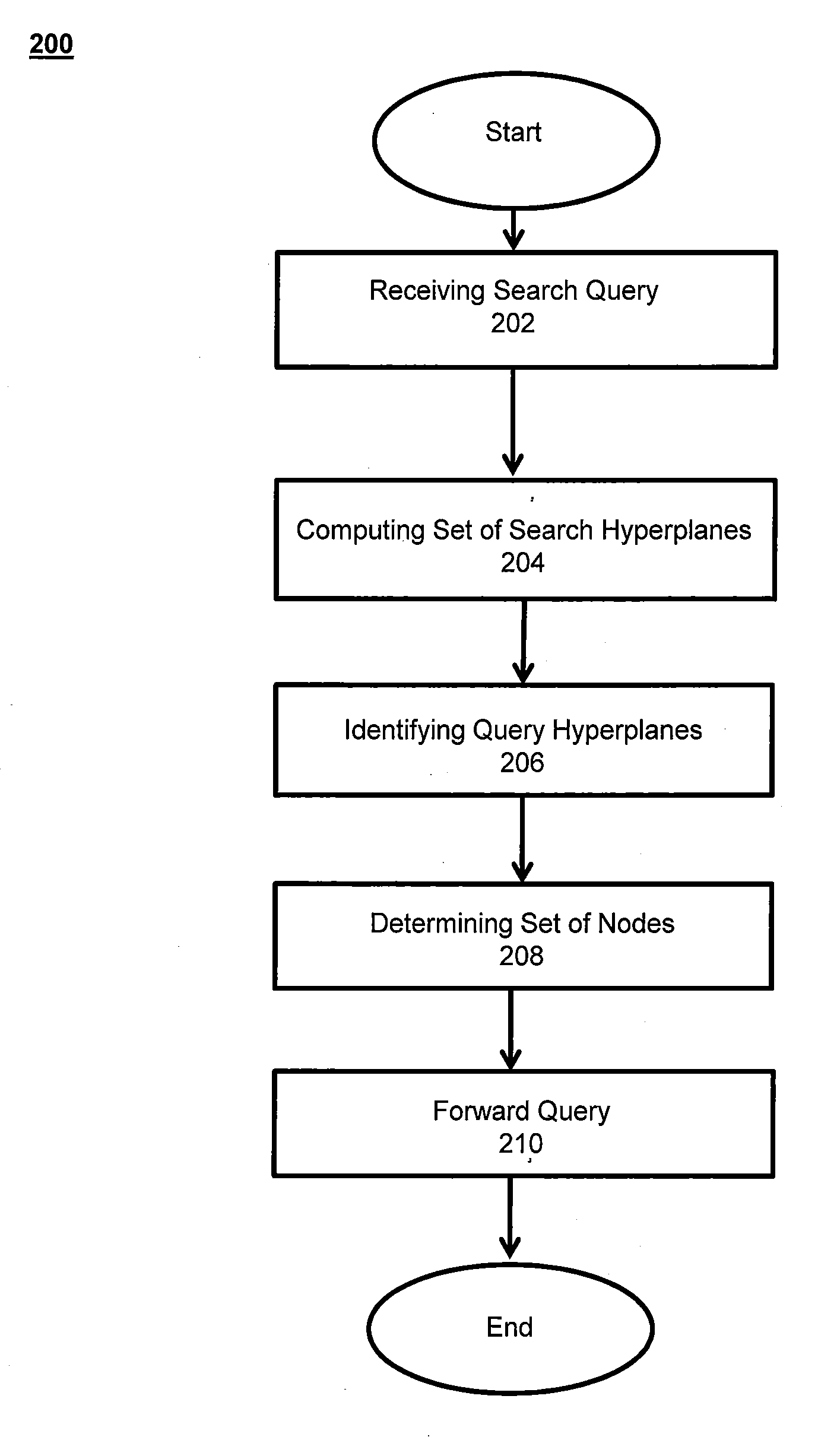
System and methods for mapping and searching objects in multidimensional space
ActiveUS20130138646A1Reduce in quantitySpeed up searchWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsData miningMultidimensional space
This invention relates to a system and methods for determining the placement of an object in a distributed key-value store by mapping the object to nodes in multidimensional hyperspace. A search function supports efficient object retrieval, even when the search query requests multiple objects and specifies them through non-primary keys. In response to a search query, the search is translated into hyperregions in the hyperspace to determine the set of nodes that hold the queried data object. The number of contacted nodes and the number of scanned objects are significantly reduced in comparison to prior art techniques.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
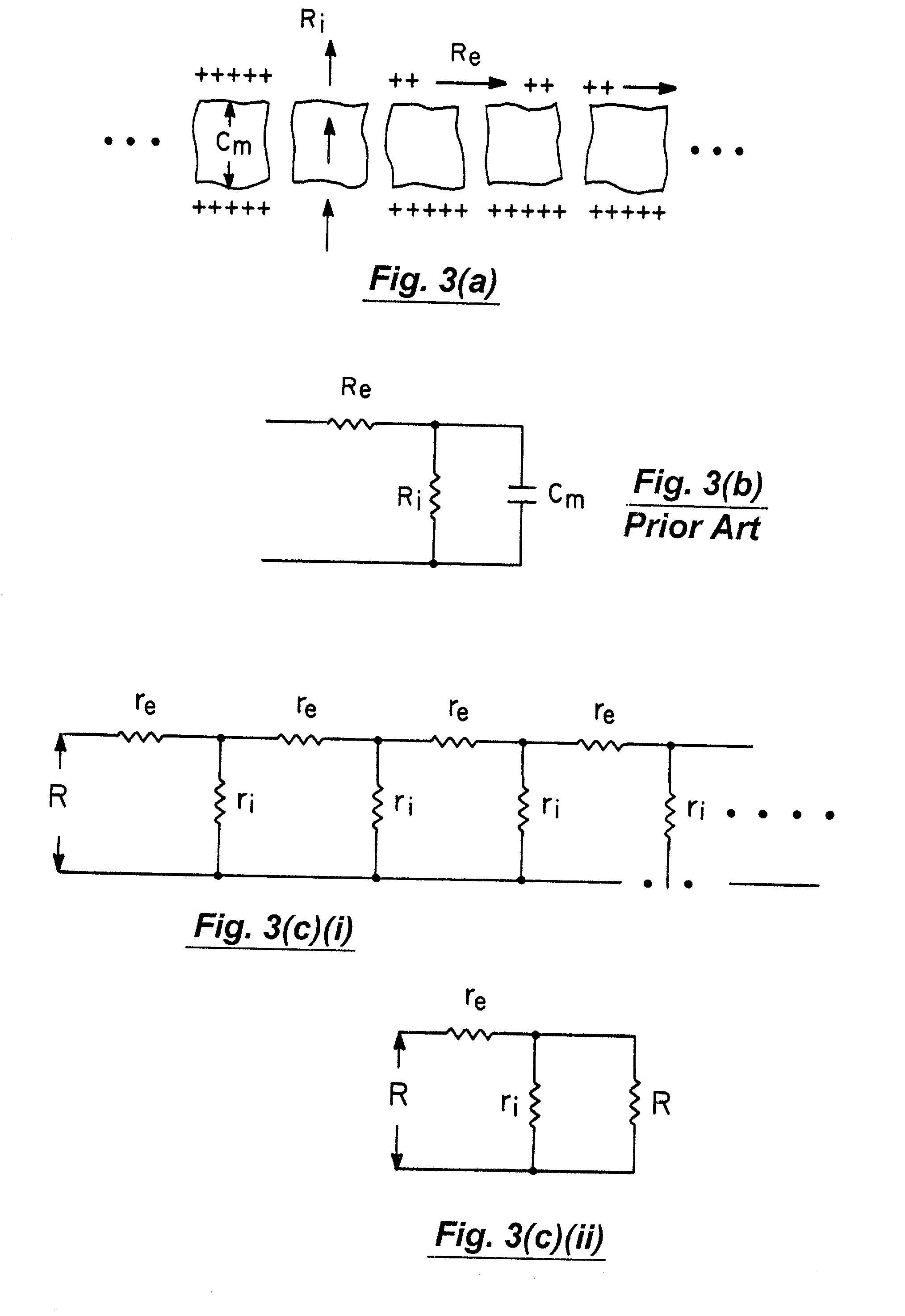
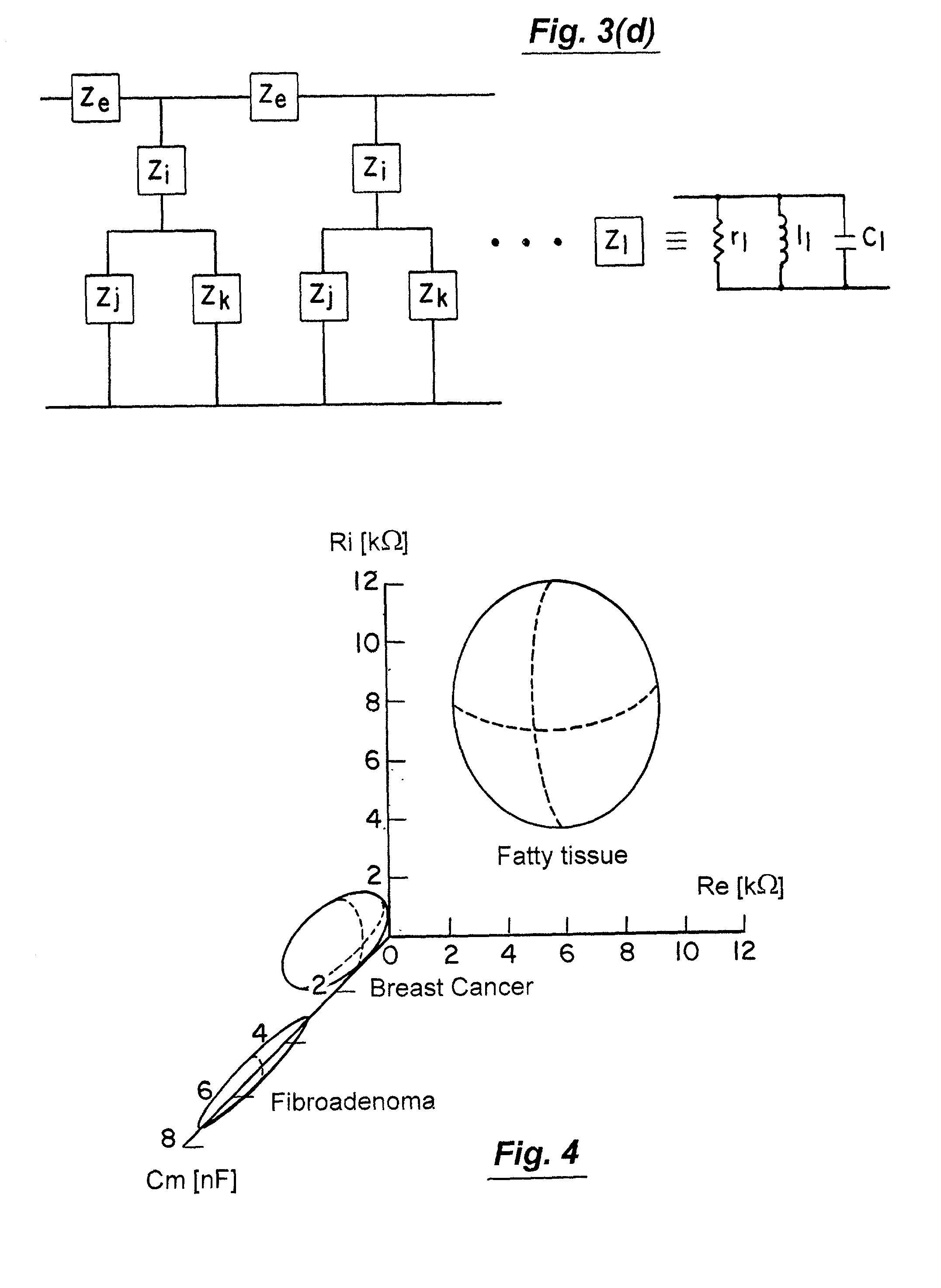
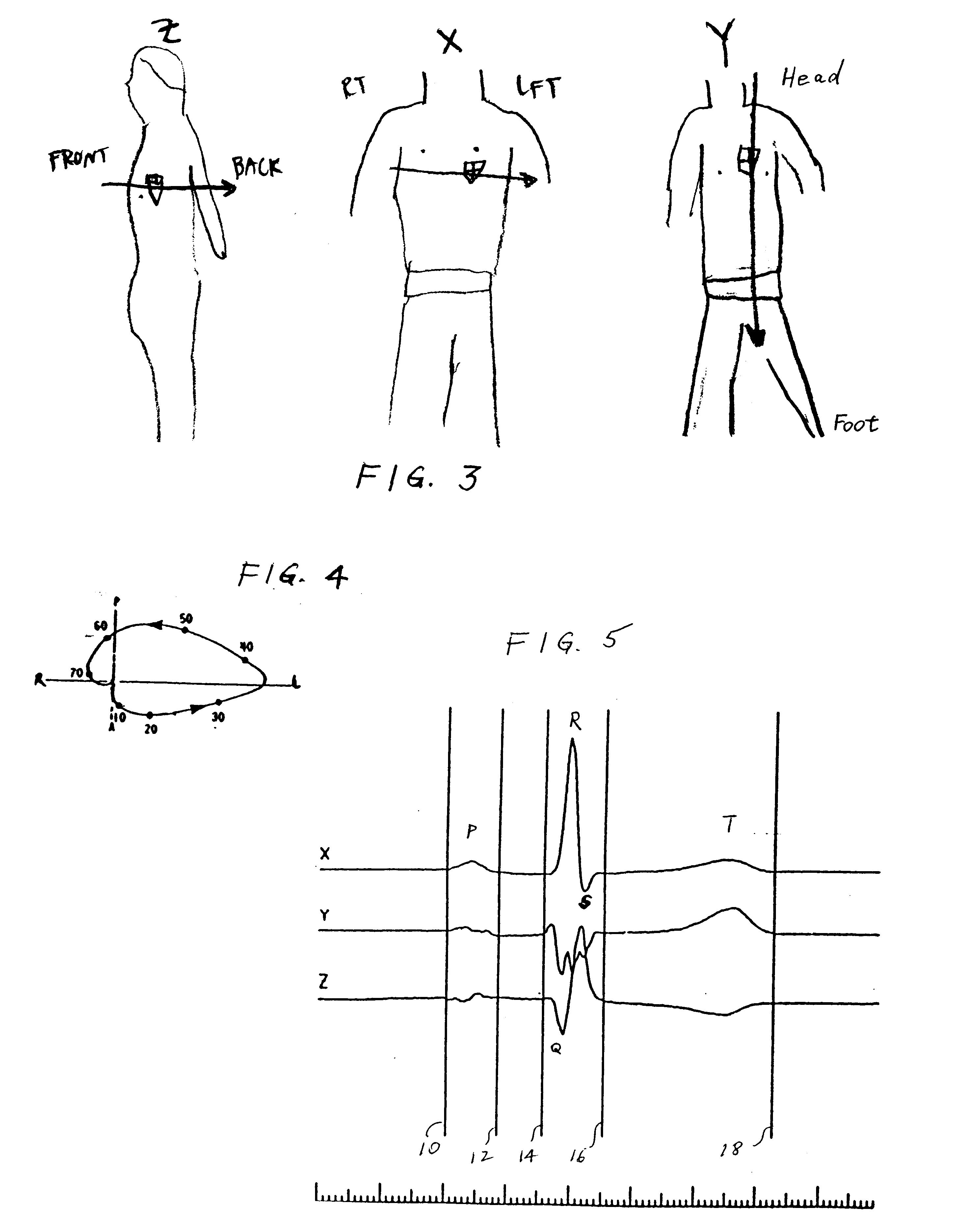
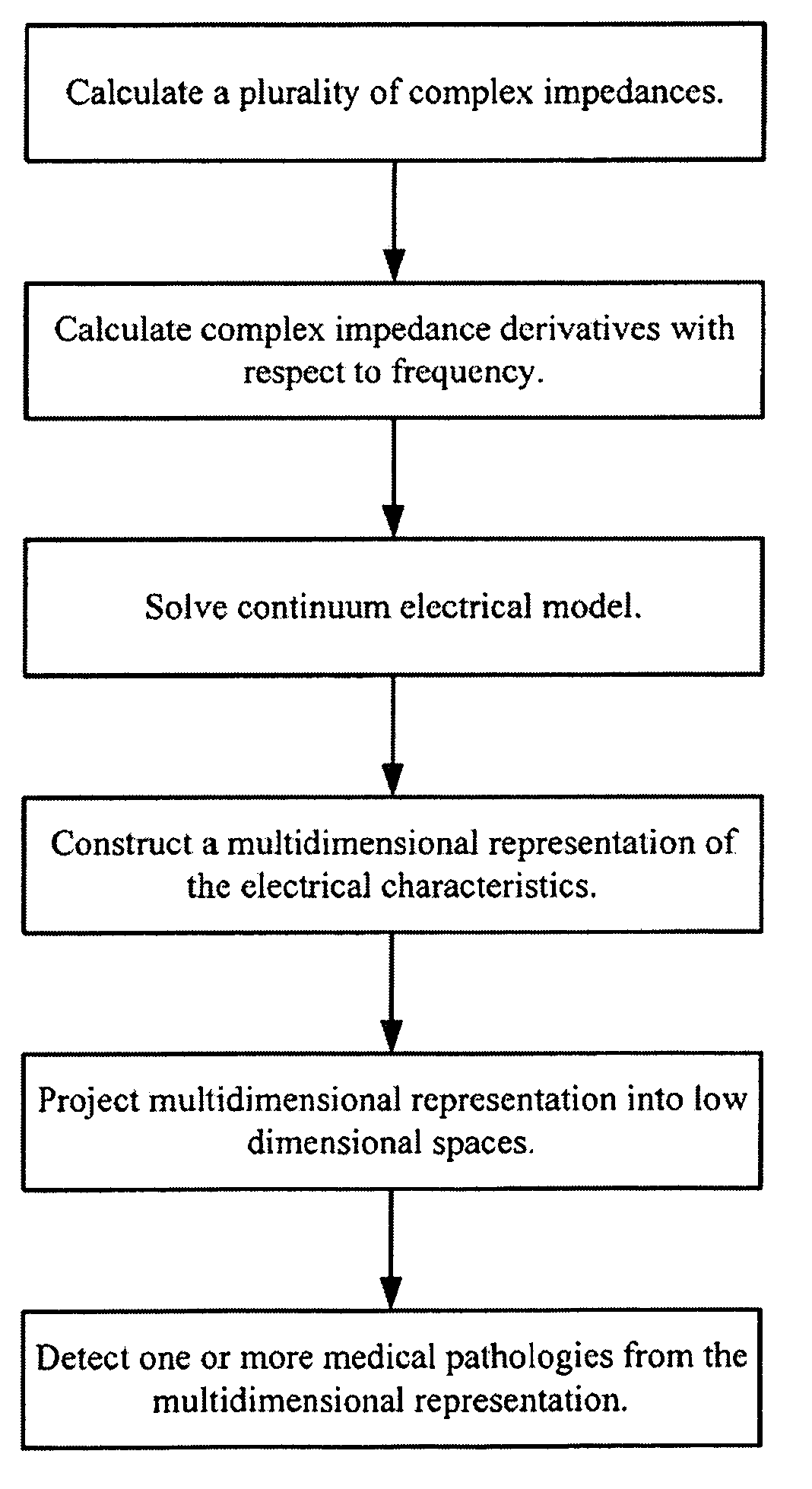
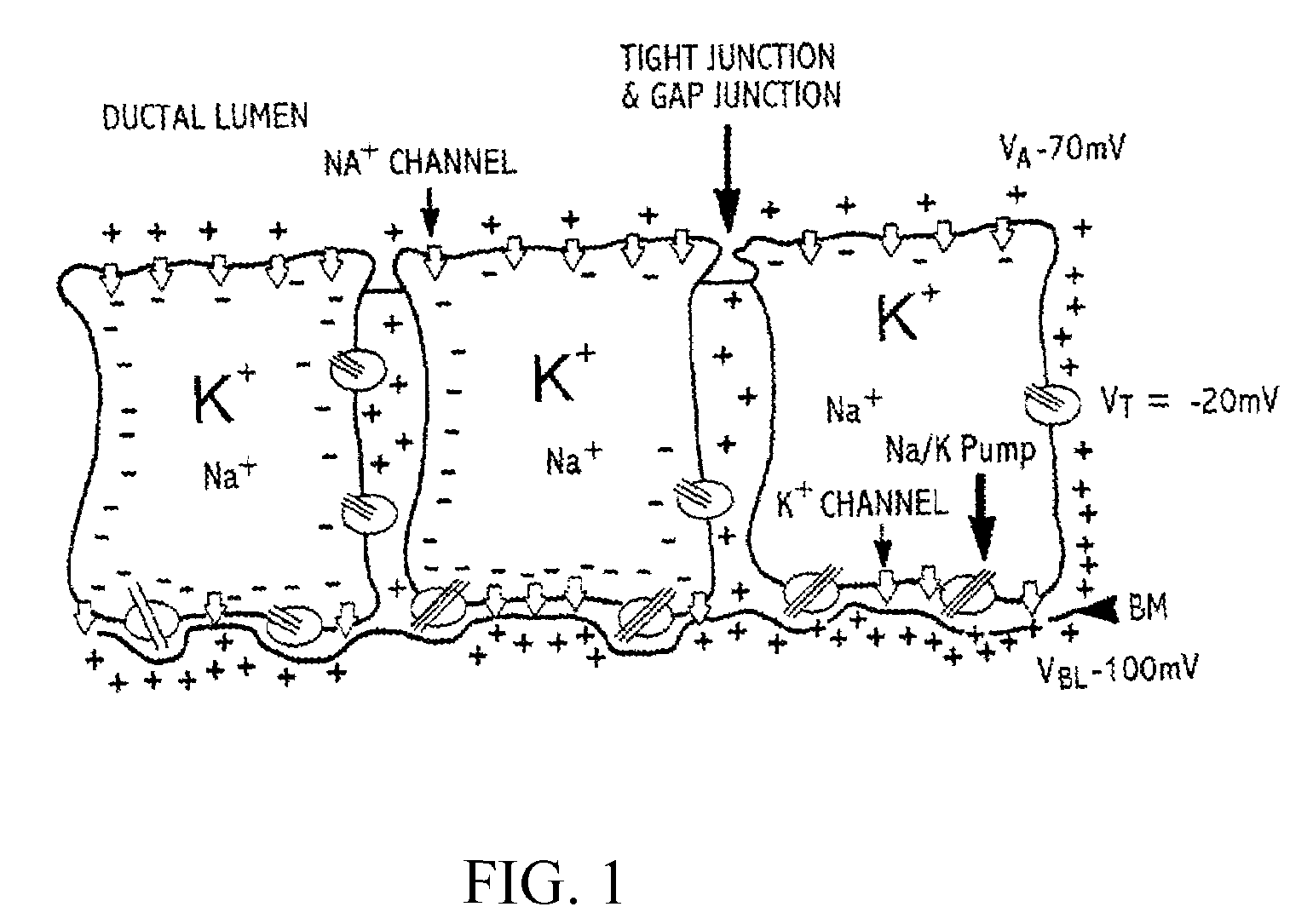
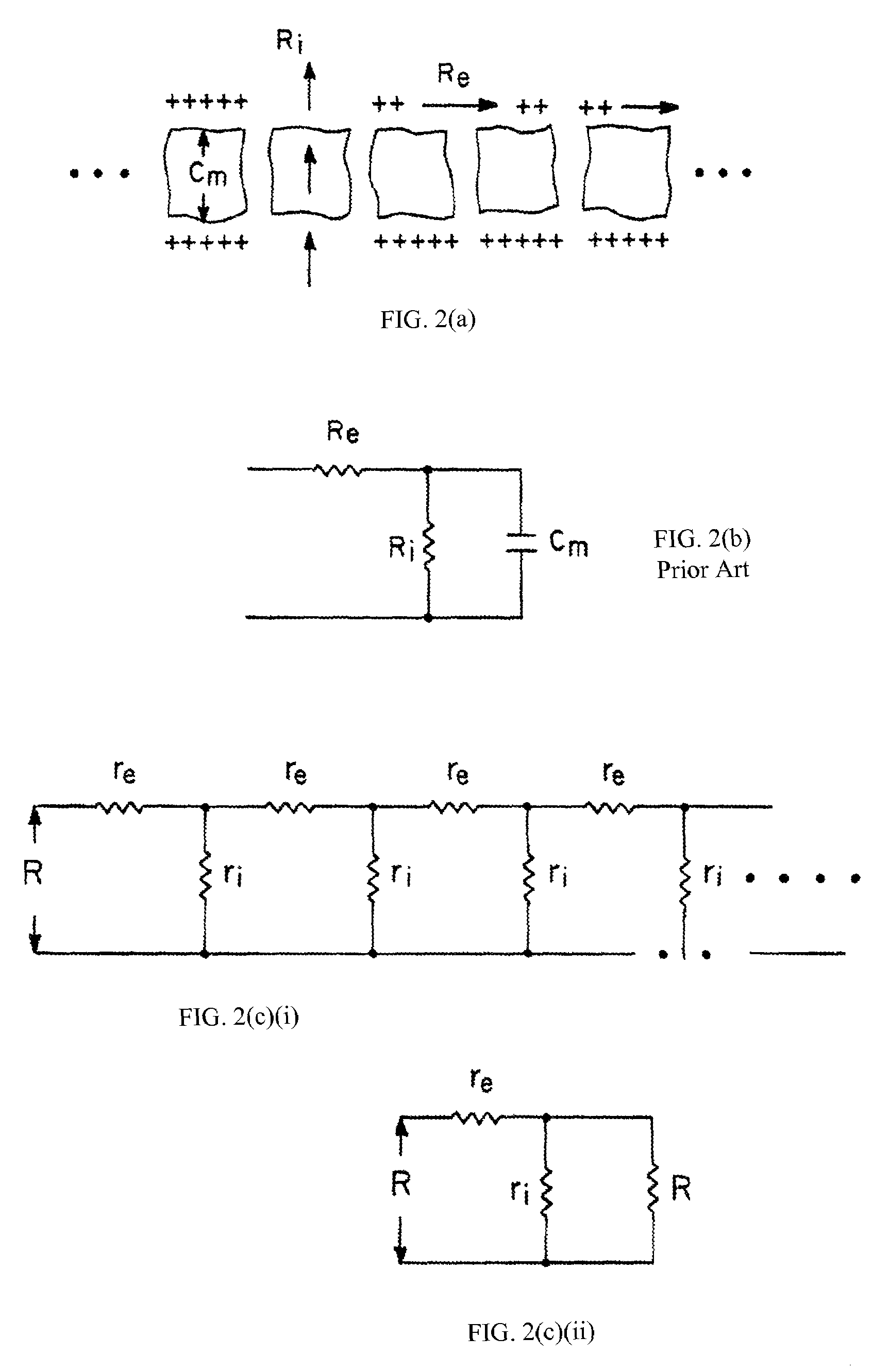
A method and apparatus that use complex impedance measurements of tissue in human or animal bodies for the detection and characterization of medical pathologies is disclosed. An analysis of the complex impedance measurements is performed by a trained evaluation system that uses a nonlinear continuum model to analyze the resistive, capacitive, and inductive measurements collected from a plurality of sensing electrodes. The analysis of the impedance measurements results in the construction of a multidimensional space that defines the tissue characteristics, which the trained evaluation system uses to detect and characterize pathologies. The method and apparatus are sufficiently general to be applied to various types of human and animal tissues for the analysis of various types of medical pathologies.
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
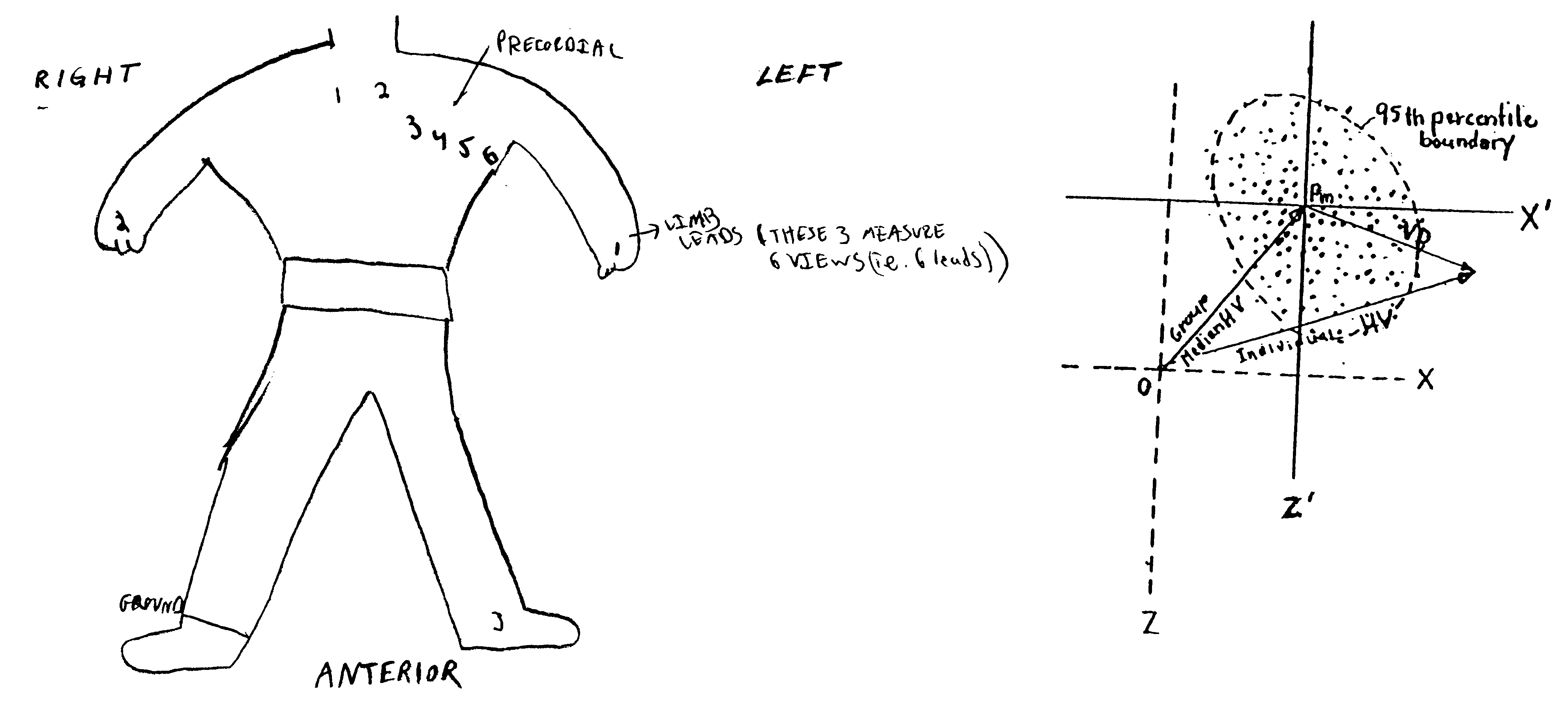
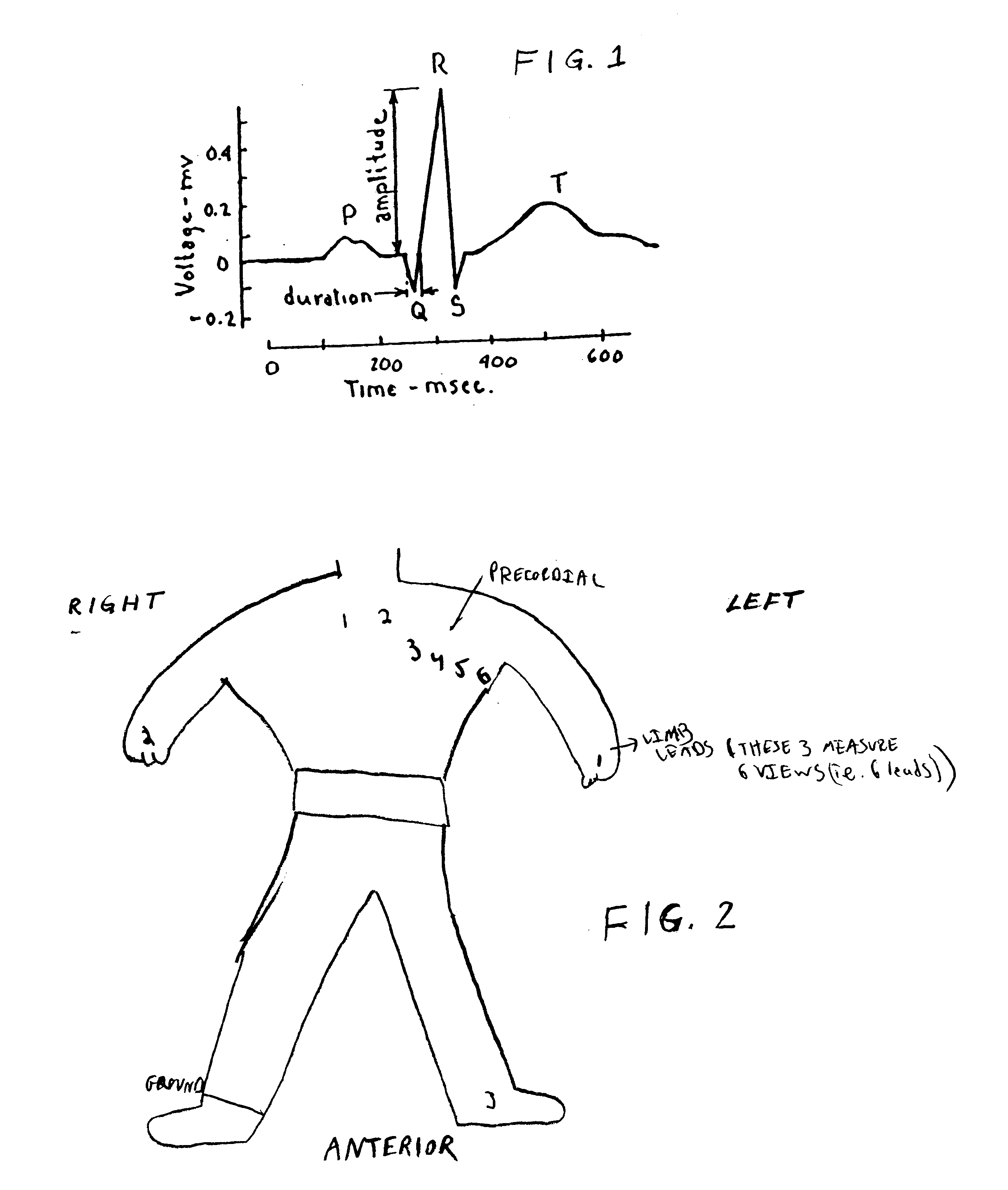
Method of analysis of the electrocardiogram
Owner:TOOLE J GERALD
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
Method of storing and retrieving multi-dimensional data using the hilbert curve
InactiveUS20030004938A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData spaceHilbert space
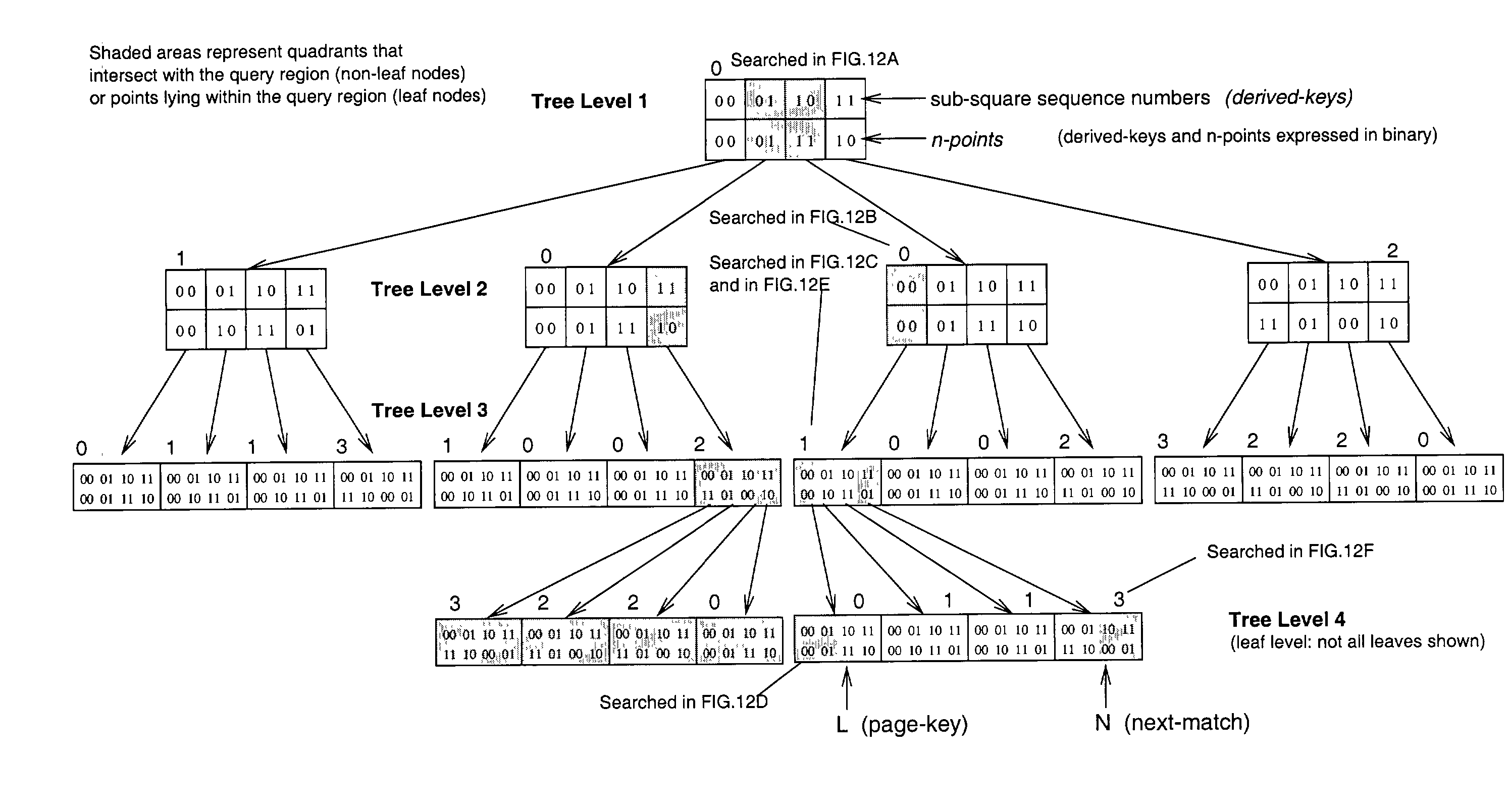
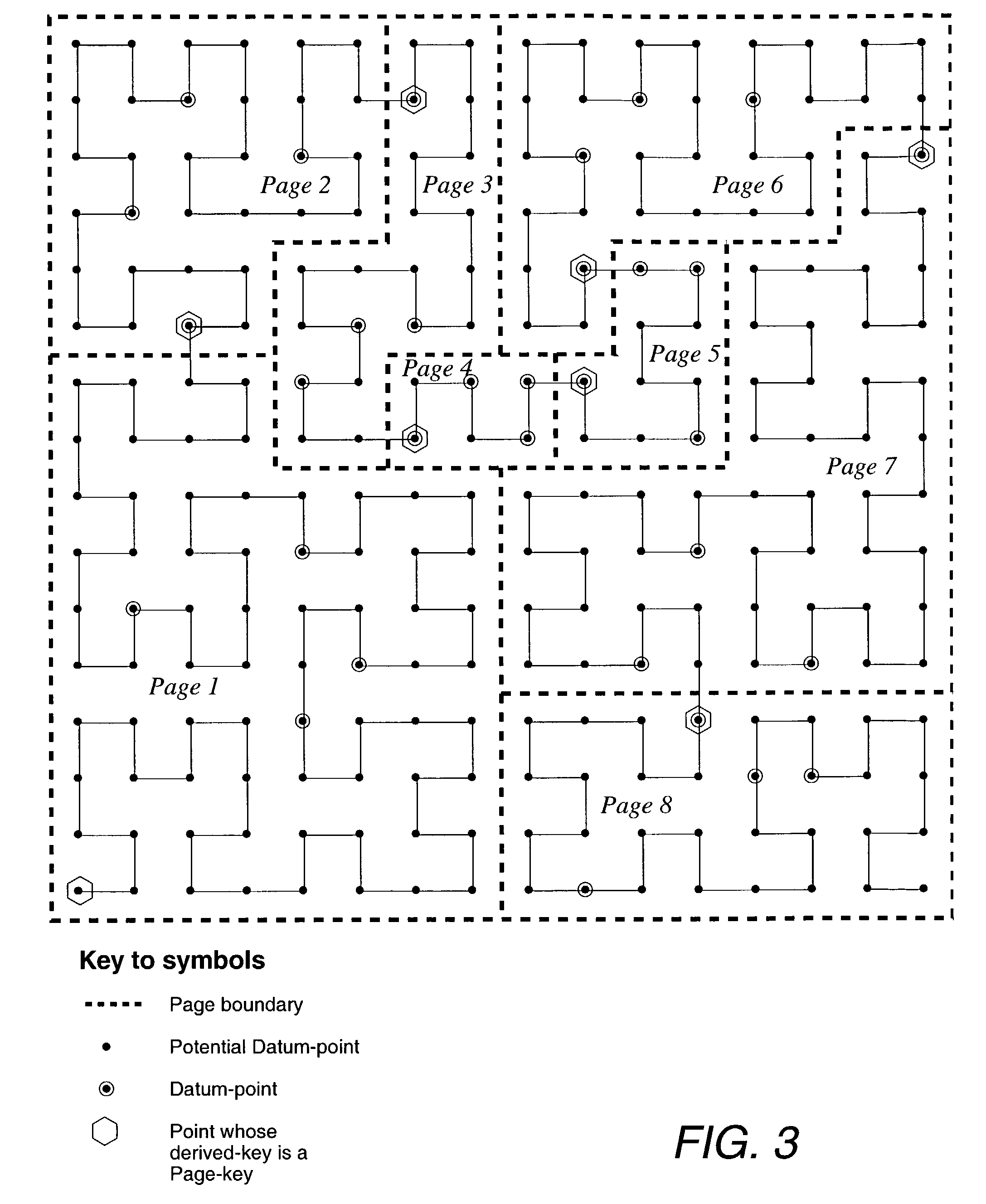
An improved method of partitioning and indexing multi-dimensional data that maps the data to one-dimensional values according to the sequence in which an approximation of a Hilbert space-filling curve passes through all of the points corresponding to potential multi-dimensional data in a data space. Data is partitioned into pages, each corresponding to a length of Hilbert curve. A page identifier is the sequence of the first point on its corresponding Hilbert curve section. The mapping orders data and also orders the data pages that contain data within a database. Mapping multi-dimensional data to one-dimensional values enables the data to be indexed using any one-dimensional index structure. The practical application of the indexing method is made viable and useful by the provision of a querying algorithm enabling data to be selectively retrieved in response to queries wherein all or some of the data that lies within a rectangular space within multi-dimensional space is required to be retrieved. The querying algorithm identifies pages whose corresponding curve sections intersect with a query region. The first intersecting page is found by calculating the lowest one-dimensional value corresponding to a possible multi-dimensional data value or point within the query region, and looking up in the index to find which page may contain this point. The next intersecting page, if it exists, is found by calculating the lowest one-dimensional value equal to or greater than the identifier of the next page to the one just identified. This new lowest one-dimensional, if found, is used to look up in the index and find the next page intersecting with the query region. Subsequent pages to be found, if any, are determined in a similar manner until no more are found. Pages found to intersect the query region can be searched for data lying within the query region.
Owner:LAWDER JONATHAN KEIR
Display method and apparatus for facilitating interaction with Web sites
The invention is a computer-implemented method and apparatus for organizing Web pages and other computer files relative to each other in a manner analogous to a three or four dimensional spatial relationship and displaying multiple Web pages simultaneously in multiple panels of a computer monitor in accordance with said spatial organization, whereby despite the organization, at least one of the Web pages or files can be made to stay in the same panel of the display while the user navigates through the virtual multidimensional space.
Owner:NOLEN JAMES A III
Multi-resolution graph-based clustering
InactiveUS6295504B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingCharacter and pattern recognitionReference sampleData set
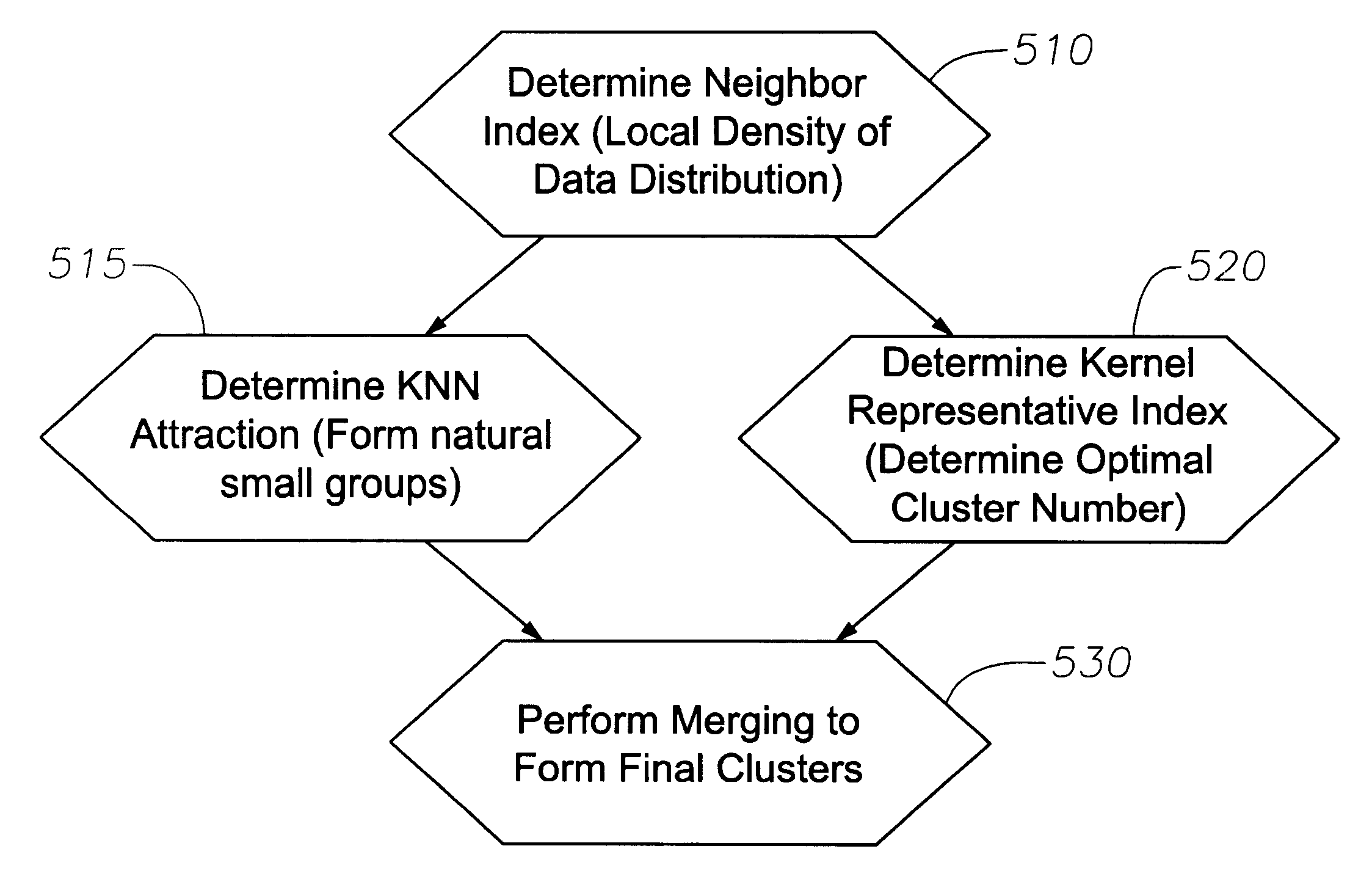
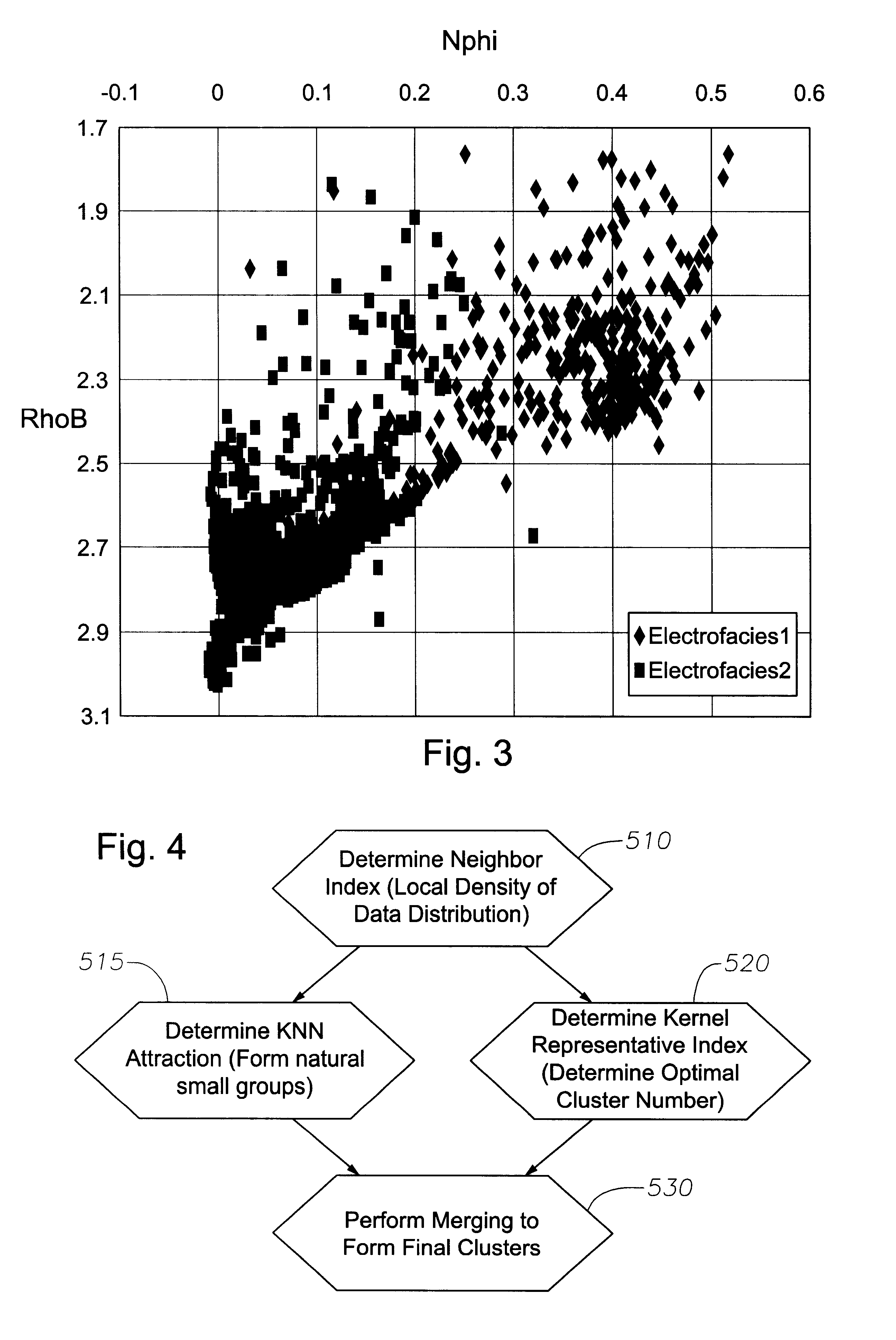
An apparatus and method for obtaining facies of geological formations for identifying mineral deposits is disclosed. Logging instruments are moved in a bore hole to produce log measurements at successive levels of the bore hole. The set of measurements at each such level of the bore hole interval is associated with reference sample points within a multidimensional space. The multidimensional scatter of sample points thus obtained is analyzed to determine a set of characteristic modes. The sample points associated with characteristic modes are grouped to identify clusters. A facies is designated for each of the clusters and a graphic representation of the succession of facies as a function of the depth is thus obtained. To identify the clusters, a "neighboring index" of each log measurement point in the data set is calculated. Next, small natural groups of points are formed based on the use of the neighboring index to determine a K-Nearest-Neighbor (KNN) attraction for each point. Independently of the natural group formation, an optimal number of clusters is calculated based on a Kernel Representative Index (KRI) and based on a user-specified resolution. Lastly, based on the data calculated from the prior steps, final clusters are formed by merging the smaller clusters.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Data replica selector
A method is provided for selecting a replication node from eligible nodes in a network. A multidimensional model is constructed that defines a multidimensional space and includes the eligible nodes, with each of the dimensions of the multidimensional model being a system characteristic. A data availability value is determined for each of the eligible nodes, and a cost of deploying is determined for each of at least two availability strategies to the eligible nodes. At least one of the eligible nodes is selected for replication of data that is stored on a source node in the network. The selecting step includes selecting the eligible node whose: data availability value is determined to be highest among the eligible nodes whose cost of deploying does not exceed a specified maximum, or cost of deploying is determined to be lowest among the eligible nodes whose data availability value does not exceed a specified minimum.
Owner:IBM CORP
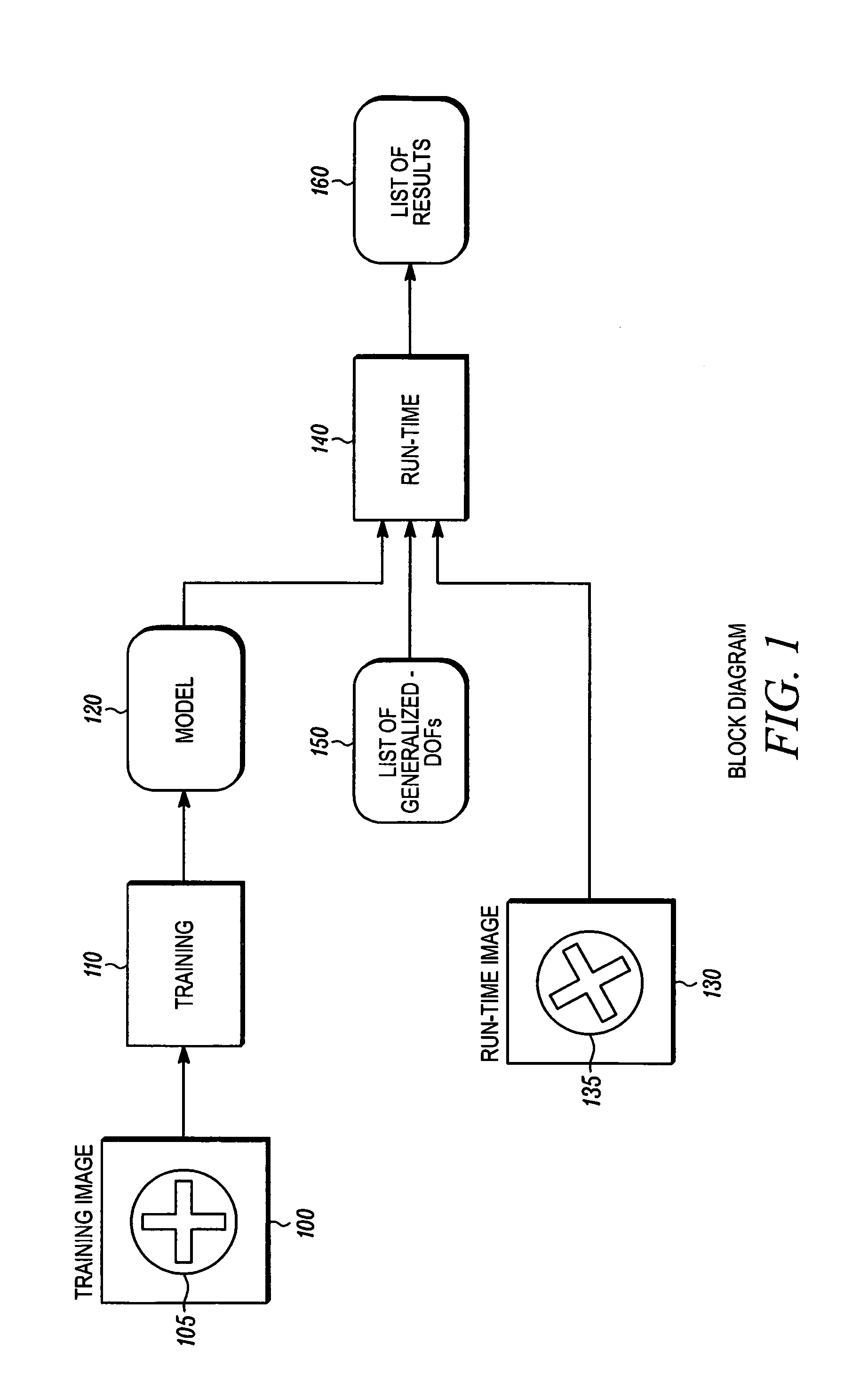
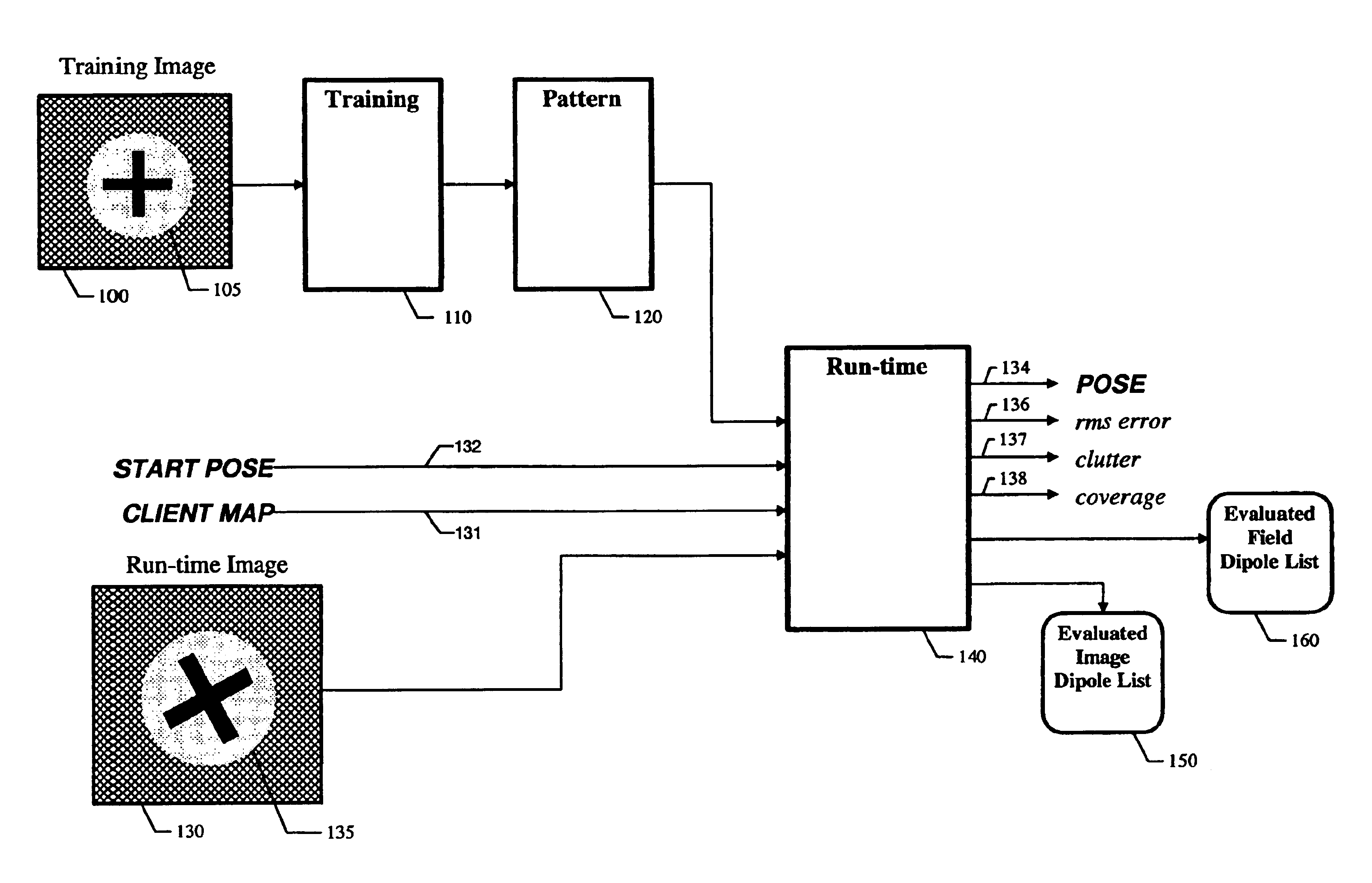
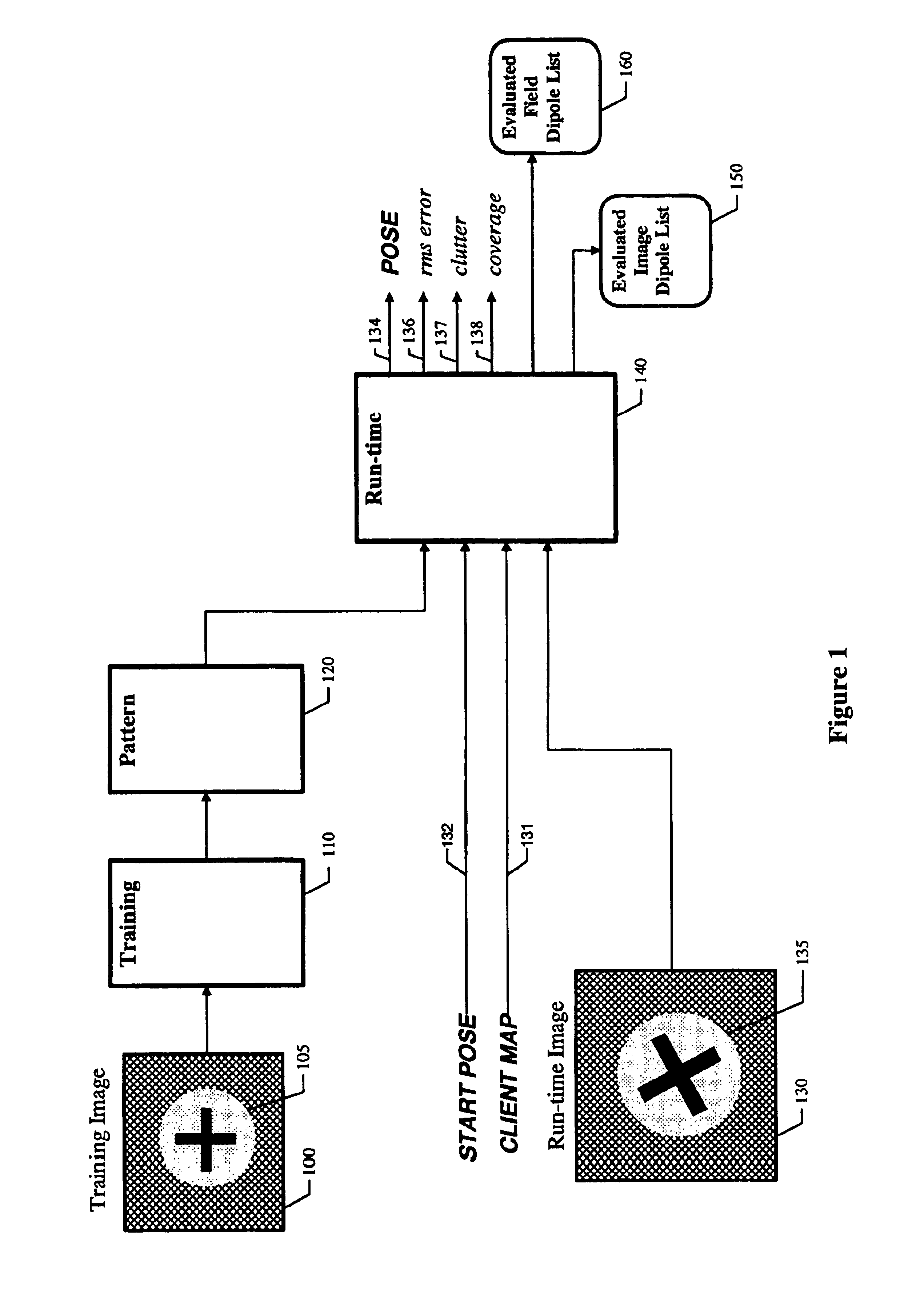
Method for fast, robust, multi-dimensional pattern recognition
InactiveUS7016539B1Pattern locating speedImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer vision
Disclosed is a method for determining the absence or presence of one or more instances of a predetermined pattern in an image, and for determining the location of each found instance within a multidimensional space. A model represents the pattern to be found, the model including a plurality of probes. Each probe represents a relative position at which a test is performed in an image at a given pose, each such test contributing evidence that the pattern exists at the pose. The method further includes a comparison of the model with a run-time image at each of a plurality of poses. A match score is computed at each pose to provide a match score surface. Then, the match score is compared with an accept threshold, and used to provide the location any instances of the pattern in the image.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
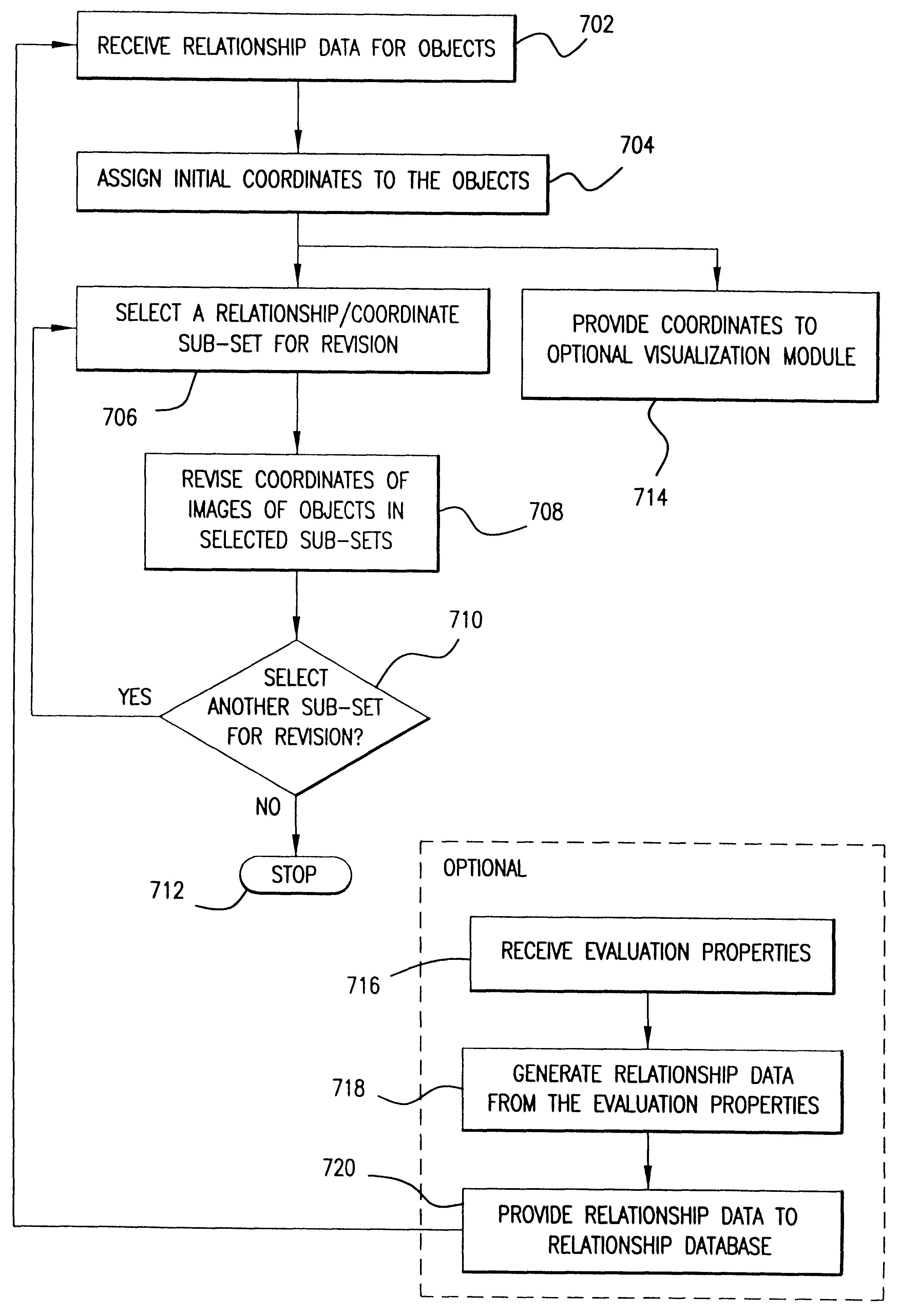
System, method, and computer program product for representing proximity data in a multi-dimensional space
A system, method and computer program product for representing precise or imprecise measurements of similarity / dissimilarity (relationships) between objects as distances between points in a multi-dimensional space that represents the objects. Self-organizing principles are used to iteratively refine an initial (random or partially ordered) configuration of points using stochastic relationship / distance errors. The data can be complete or incomplete (i.e. some relationships between objects may not be known), exact or inexact (i.e. some or all of the relationships may be given in terms of allowed ranges or limits), symmetric or asymmetric (i.e. the relationship of object A to object B may not be the same as the relationship of B to A) and may contain systematic or stochastic errors. The relationships between objects may be derived directly from observation, measurement, a priori knowledge, or intuition, or may be determined indirectly using any suitable technique for deriving proximity (relationship) data.
Owner:3 DIMENSIONAL PHARMA
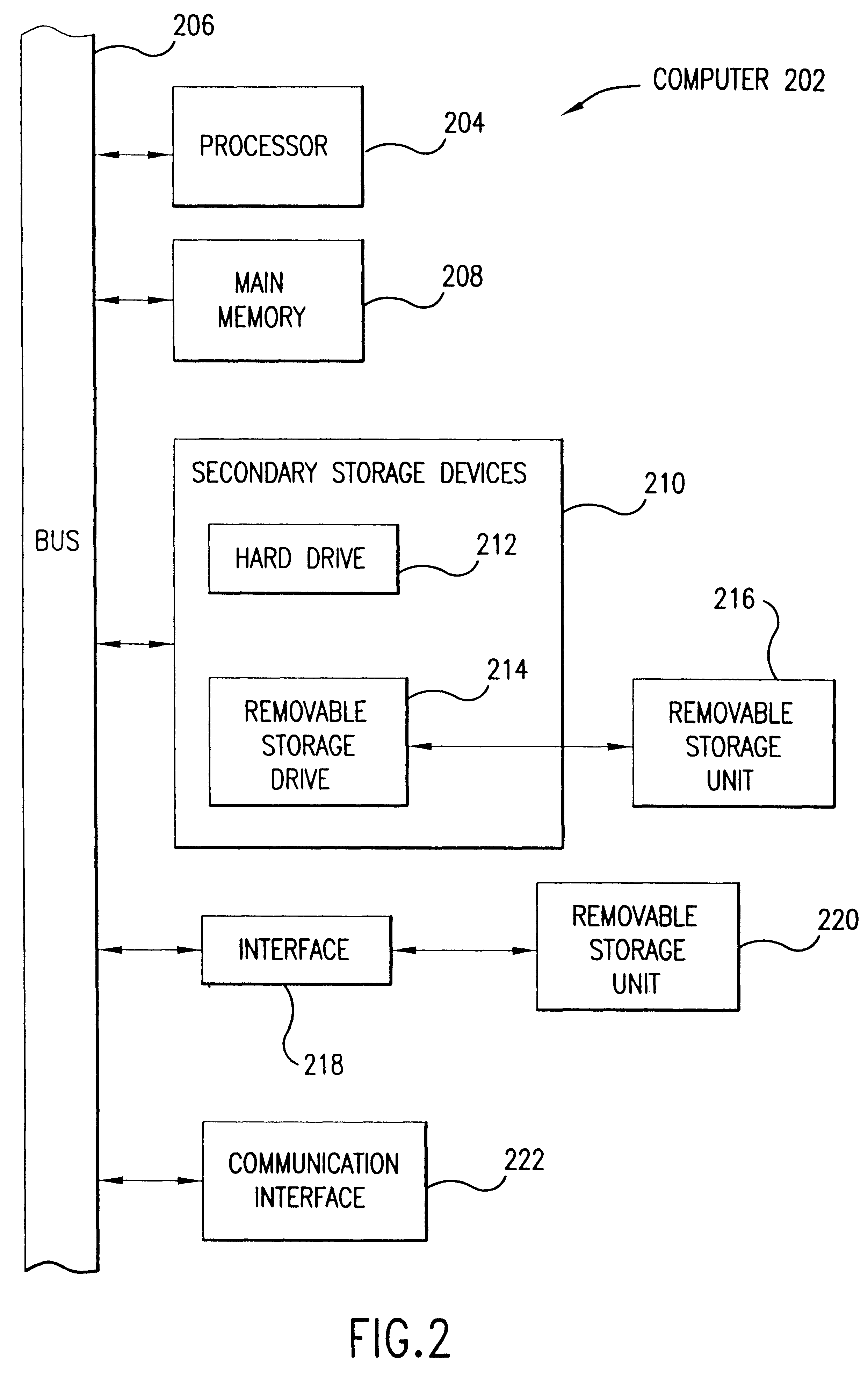
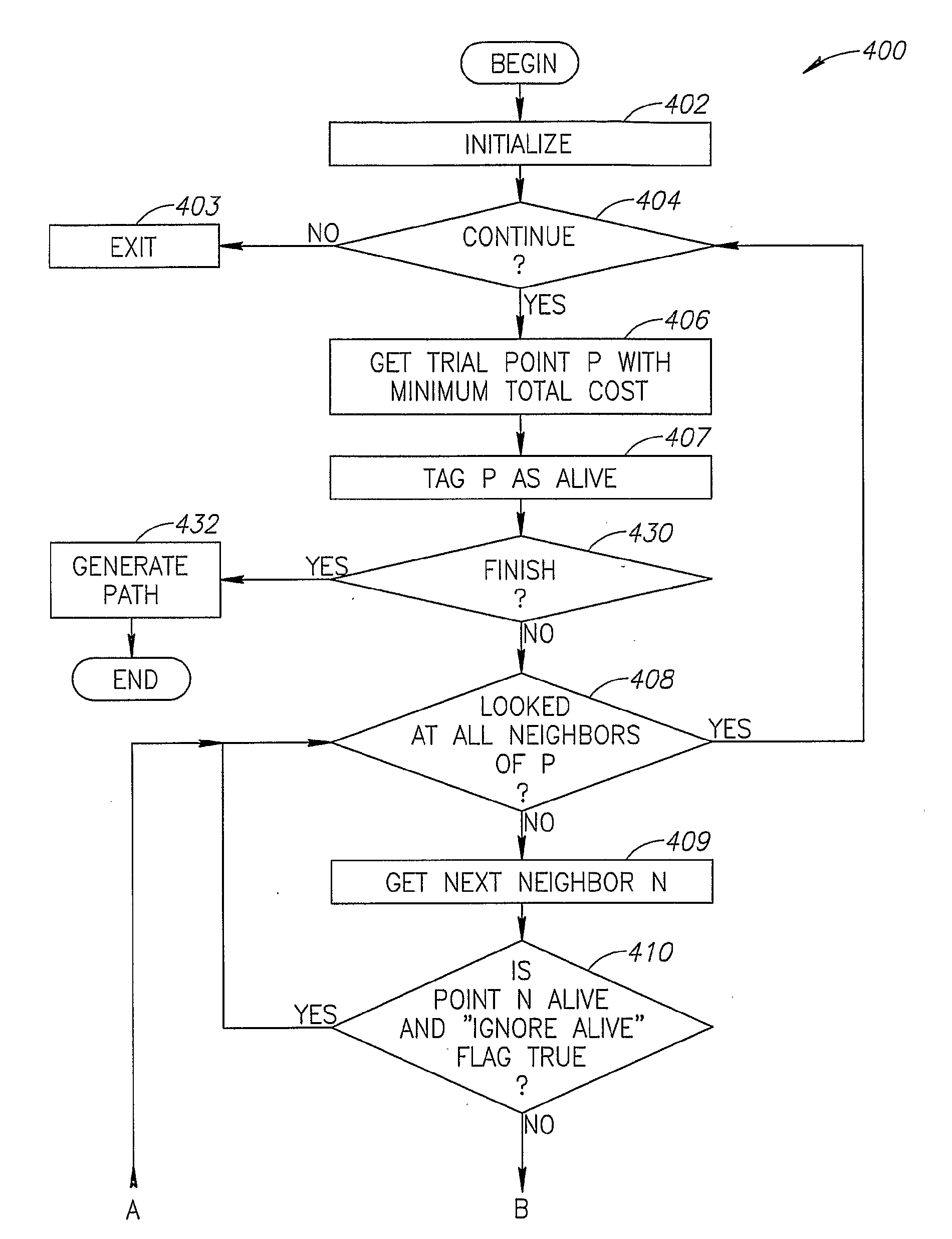
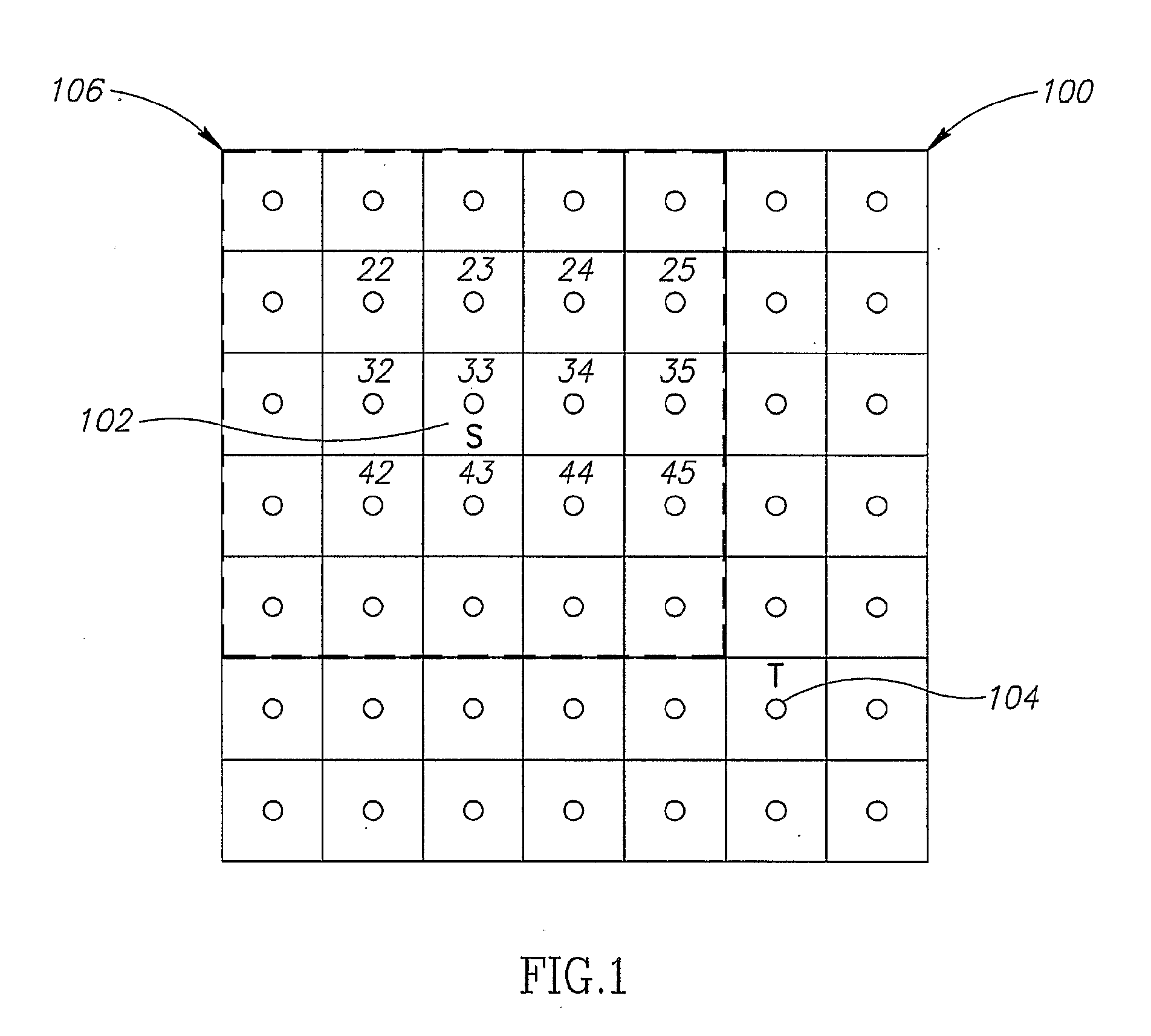
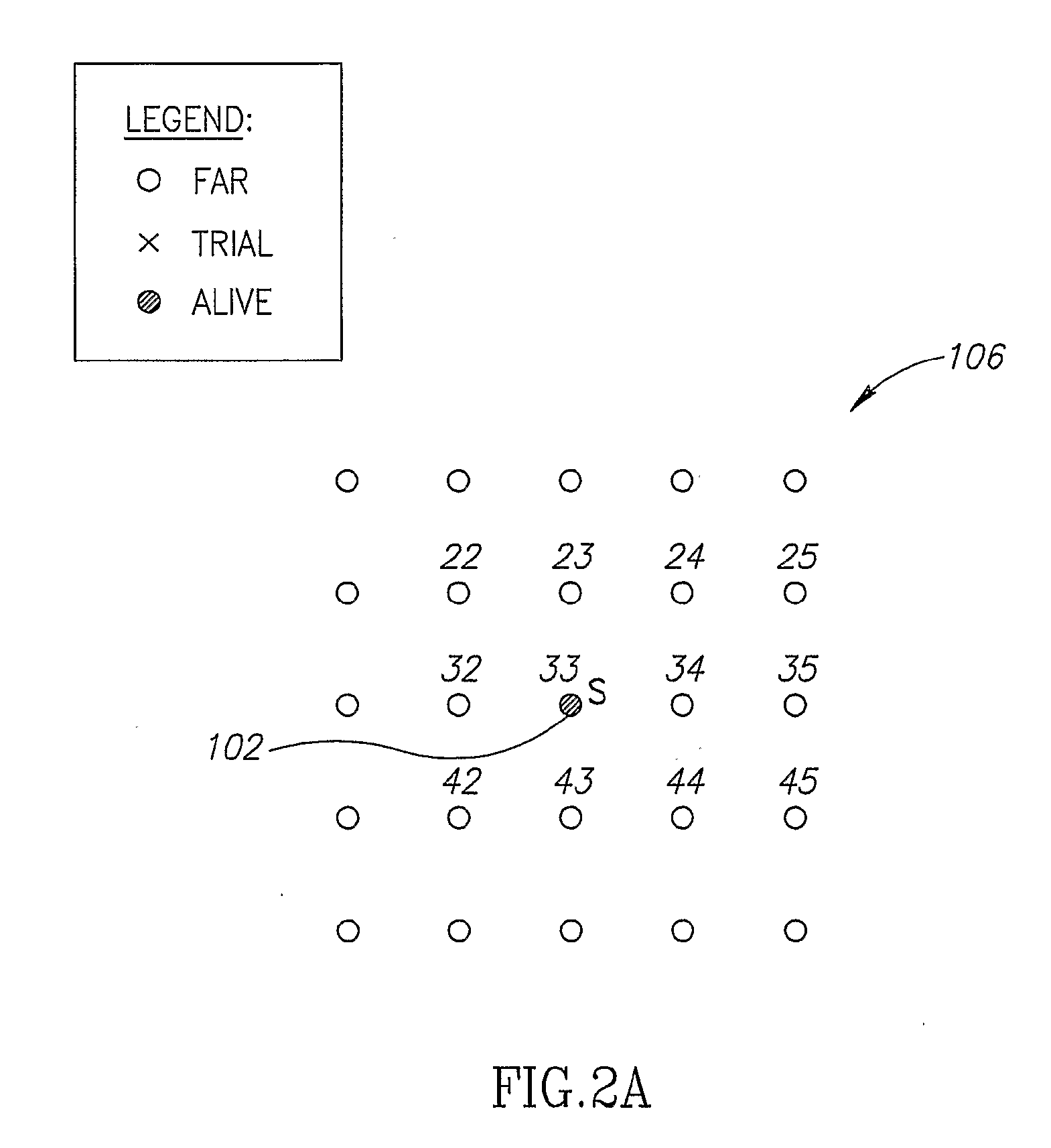
Targeted Marching
ActiveUS20080091340A1Minimize cost functionSmooth pathImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationPhysical spaceAlgorithm
A method of finding a path from a start point to a target point, in multi-dimensional space, including: (a) determining a plurality of points in a physical space, including a start point and an target point; (b) computing, using a cost function, for said points an accumulated path cost from the start point to a point; representing a minimal cost path from the start point to the point with respect to an optimization criteria; (c) computing for at least some of said points an estimated-cost-to-target from a point to the target point; and (d) after computing said costs, determining at least one of a minimal path or a minimal path cost of a path from the start point to the target point in the physical space, wherein the determination is based on said accumulated path costs, and is minimal with respect to the optimization criteria.
Owner:PHILIPS MEDICAL SYST TECH
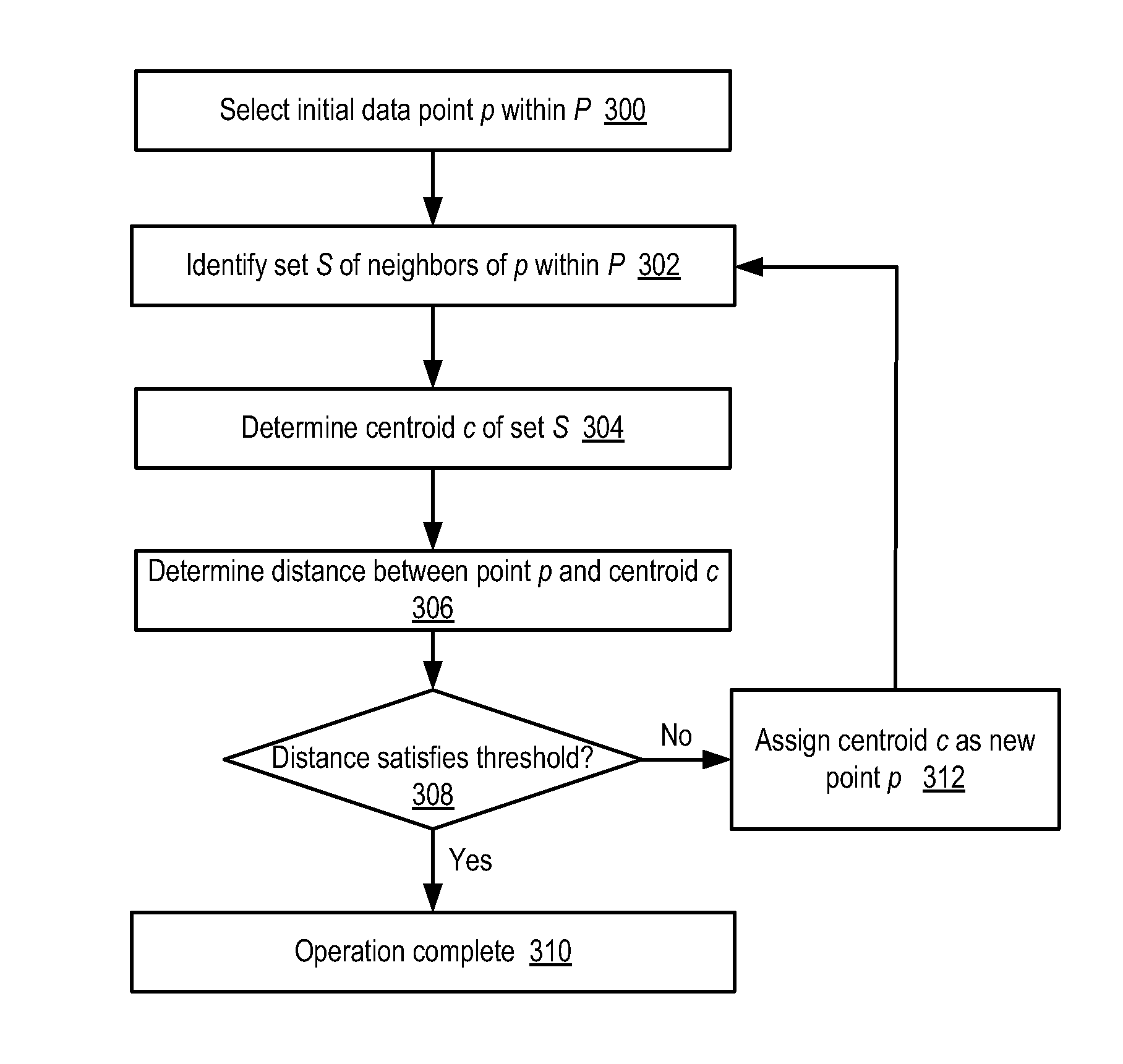
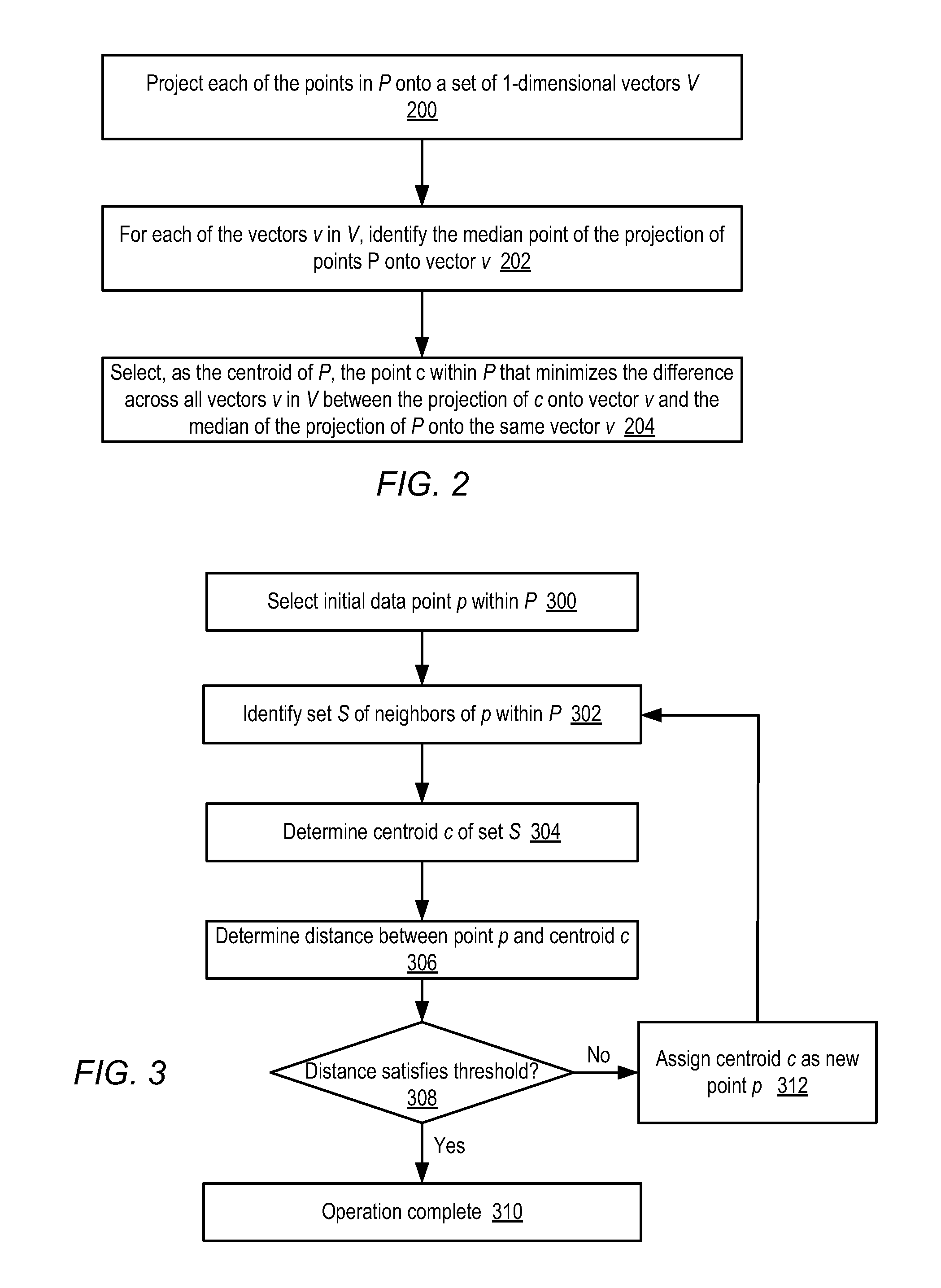
Clustering techniques for large, high-dimensionality data sets
ActiveUS8363961B1Digital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionHigh dimensionalityData set
A clustering method for high-dimensionality data includes identifying a set of nearest neighbors of a point in a multidimensional space and determining the centroid of the set of nearest neighbors, where the centroid is a member of the set of nearest neighbors. The method is then repeated using the neighbors identified around the computed centroid. In one embodiment, the method may terminate when the computed centroid becomes stationary over successive iterations. The resulting centroid may be returned as a mode of the data set. Points of the data set having common modes may be assigned to the same cluster.
Owner:ADOBE INC
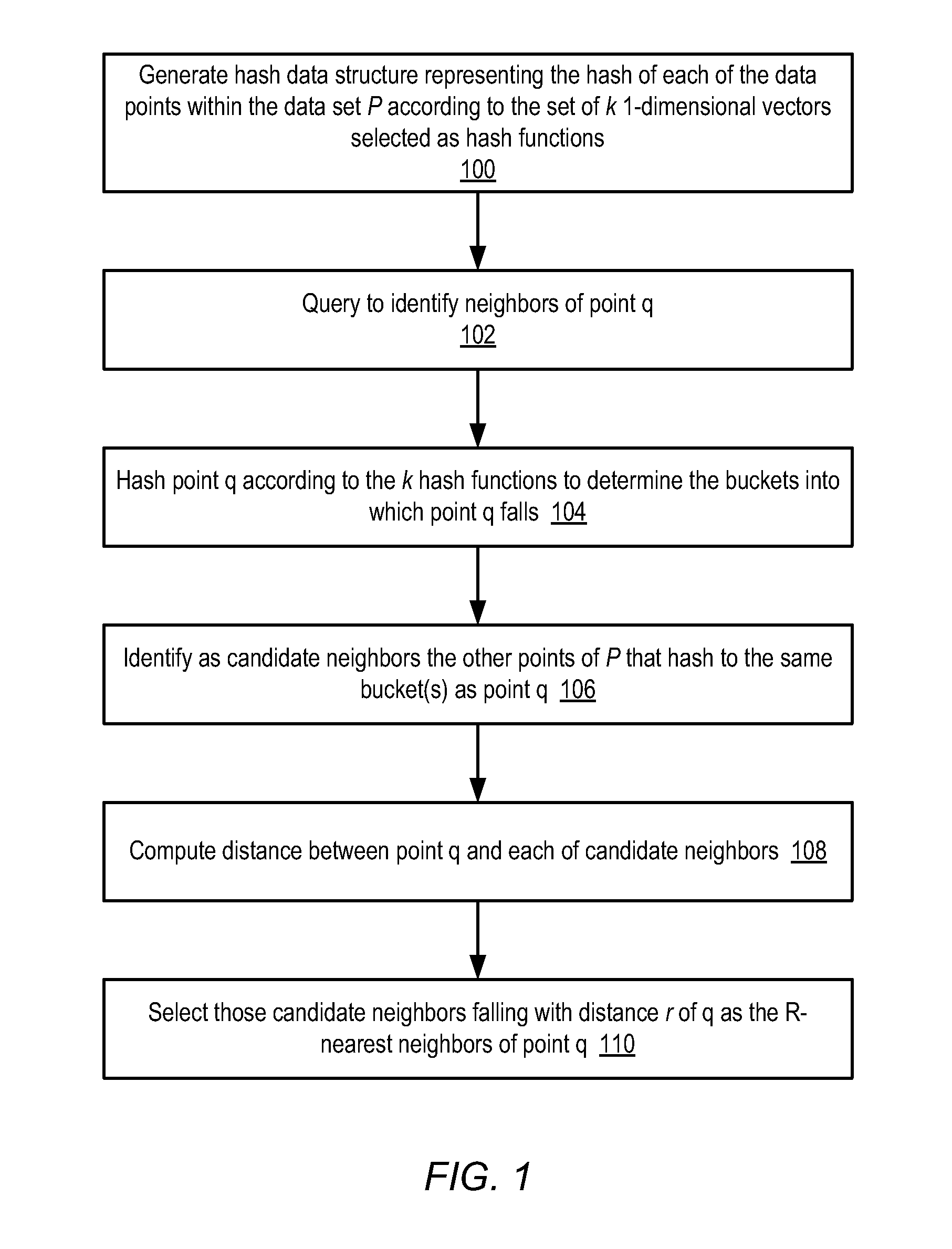
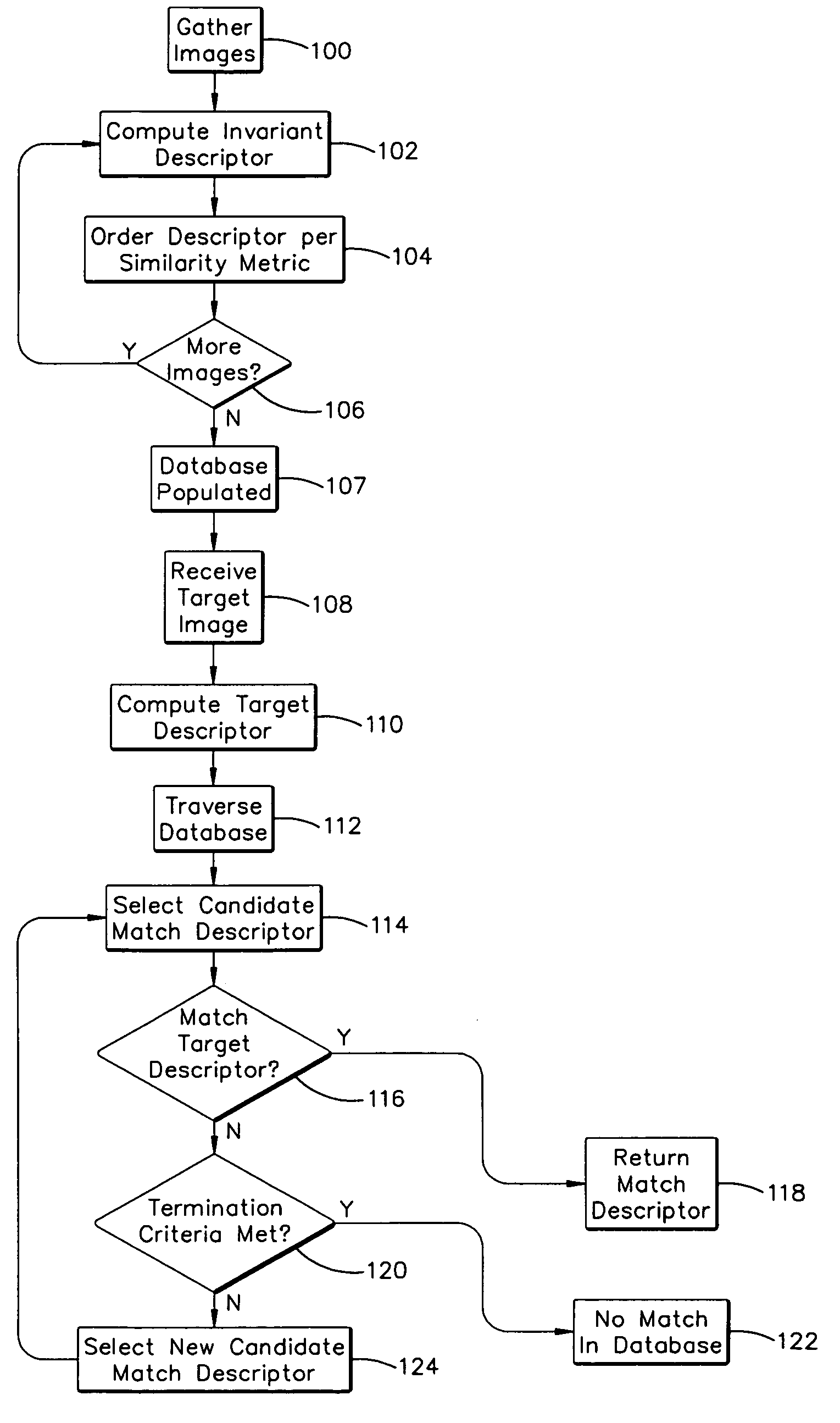
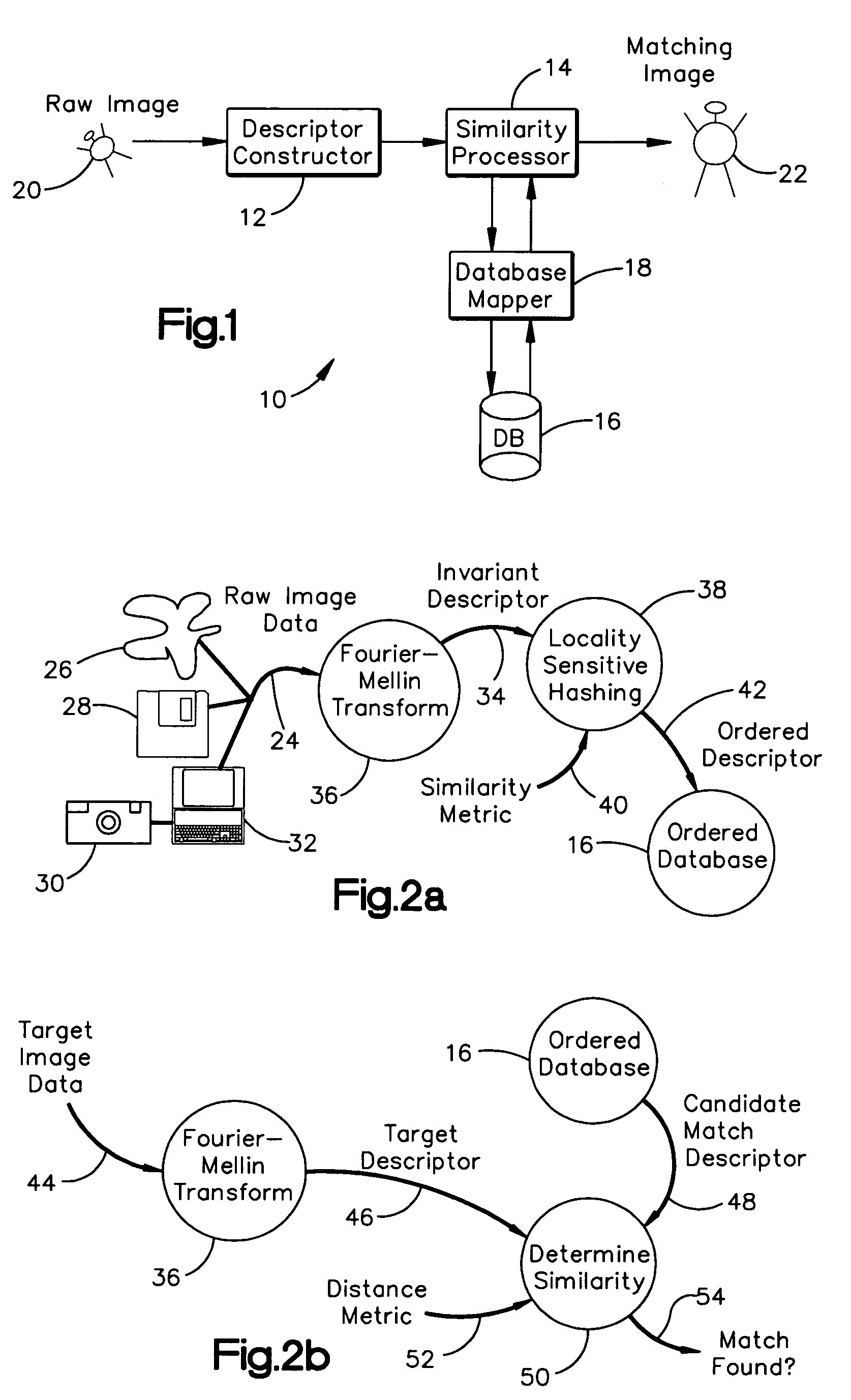
System and method for efficiently finding near-similar images in massive databases
Massive amounts of multimedia data are stored in databases supporting web pages and servers, including text, graphics, video and audio. Searching and finding matching multimedia images can be time and computationally intensive. A method for storing and retrieving image data includes computing a descriptor, such an a Fourier-Mellin Transform (FMT), corresponding to a multidimensional space indicative of each of the stored images and organizing each of the descriptors according to a set similarity metric. The set similarity metric is based on Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH), and orders descriptors near to other descriptors in the database. The set similarity metric employs set theory which allows distance between descriptors to be computed consistent with LSH. A target image for which a match is sought is then received, and a descriptor indicative of the target image is computed. The database is referenced, or mapped, to determine close matches in the database. Mapping includes selecting a candidate match descriptor from among the descriptors in the database and employing a distance metric derived from the similarity metric to determine if the candidate match descriptor is a match to the target descriptor.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
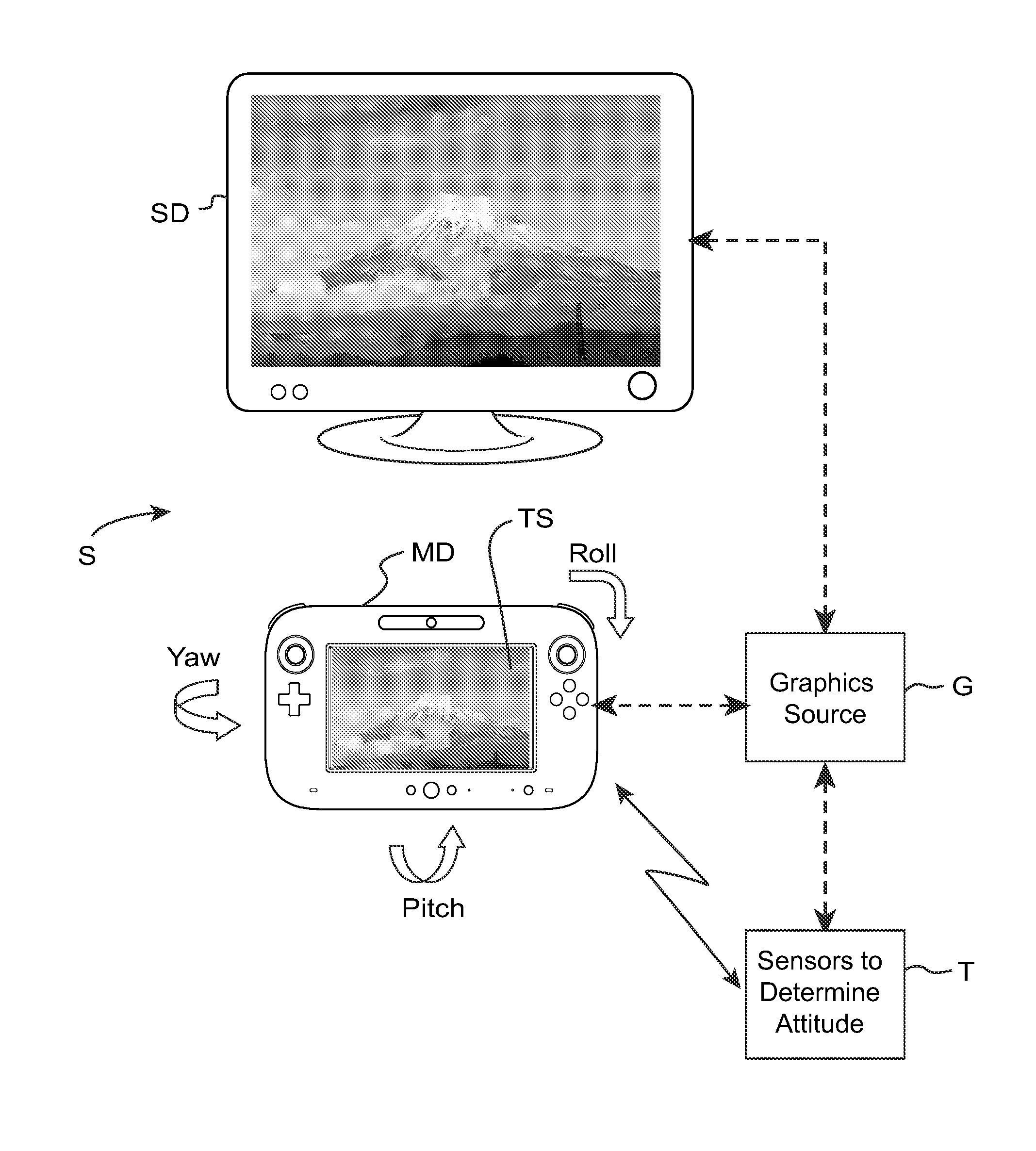
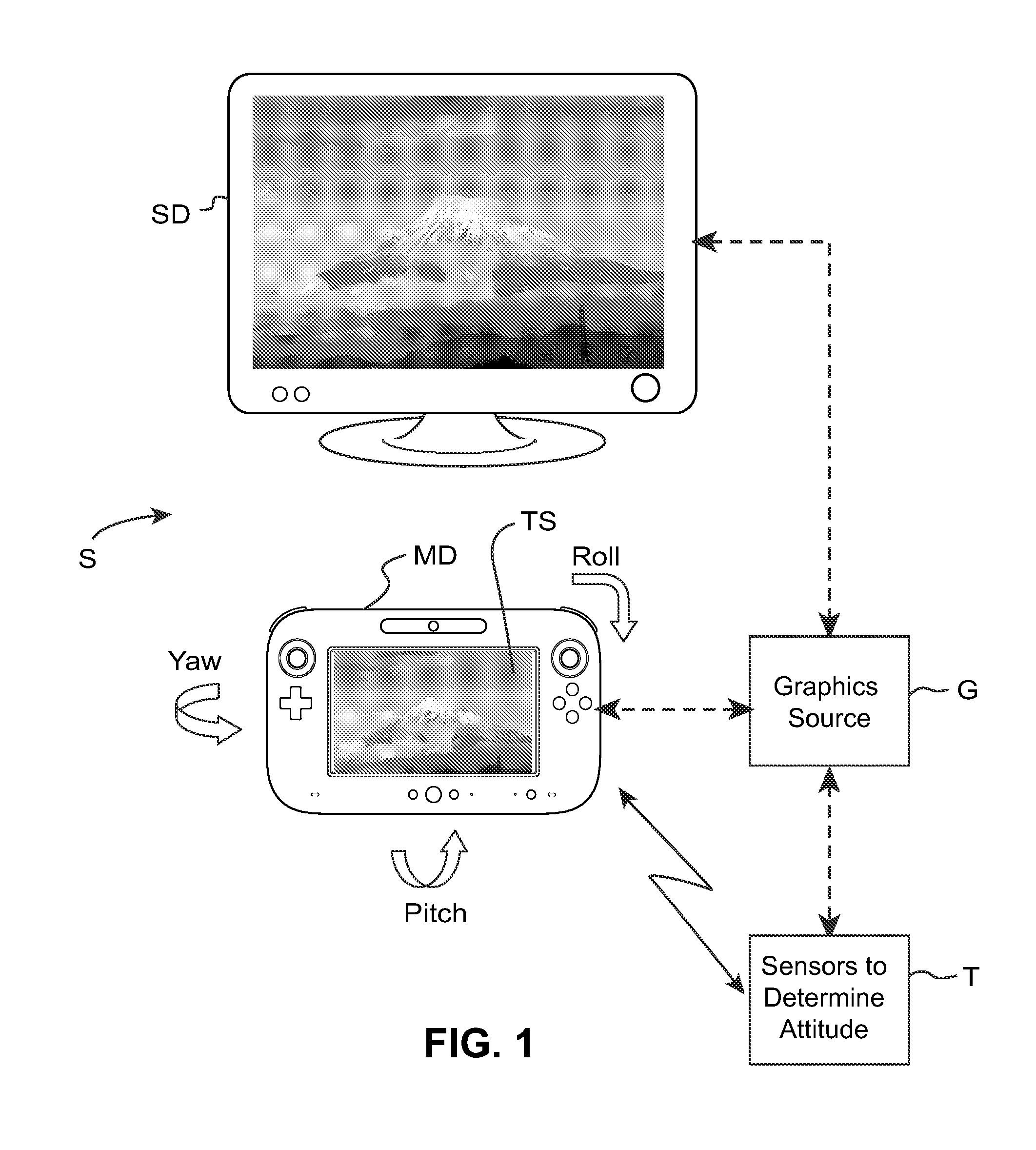
Spatially-correlated multi-display human-machine interface
ActiveUS20120026166A1Video gamesSelective content distributionVisual presentationSpatial correlation
A human-machine interface involves plural spatially-coherent visual presentation surfaces at least some of which are movable by a person. Plural windows or portholes into a virtual space, at least some of which are handheld and movable, are provided by using handheld and other display devices. Aspects of multi-dimensional spatiality of the moveable window (e.g., relative to another window) are determined and used to generate images. As one example, the moveable window can present a first person perspective “porthole” view into the virtual space, this porthole view changing based on aspects of the moveable window's spatiality in multi-dimensional space relative to a stationary window. A display can present an image of a virtual space, and an additional, moveable display can present an additional image of the same virtual space.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Method and device for perception of an object by its shape, its size and/or its orientation
InactiveUS7043465B2Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern perceptionComputer science
Owner:HLDG B E V +1
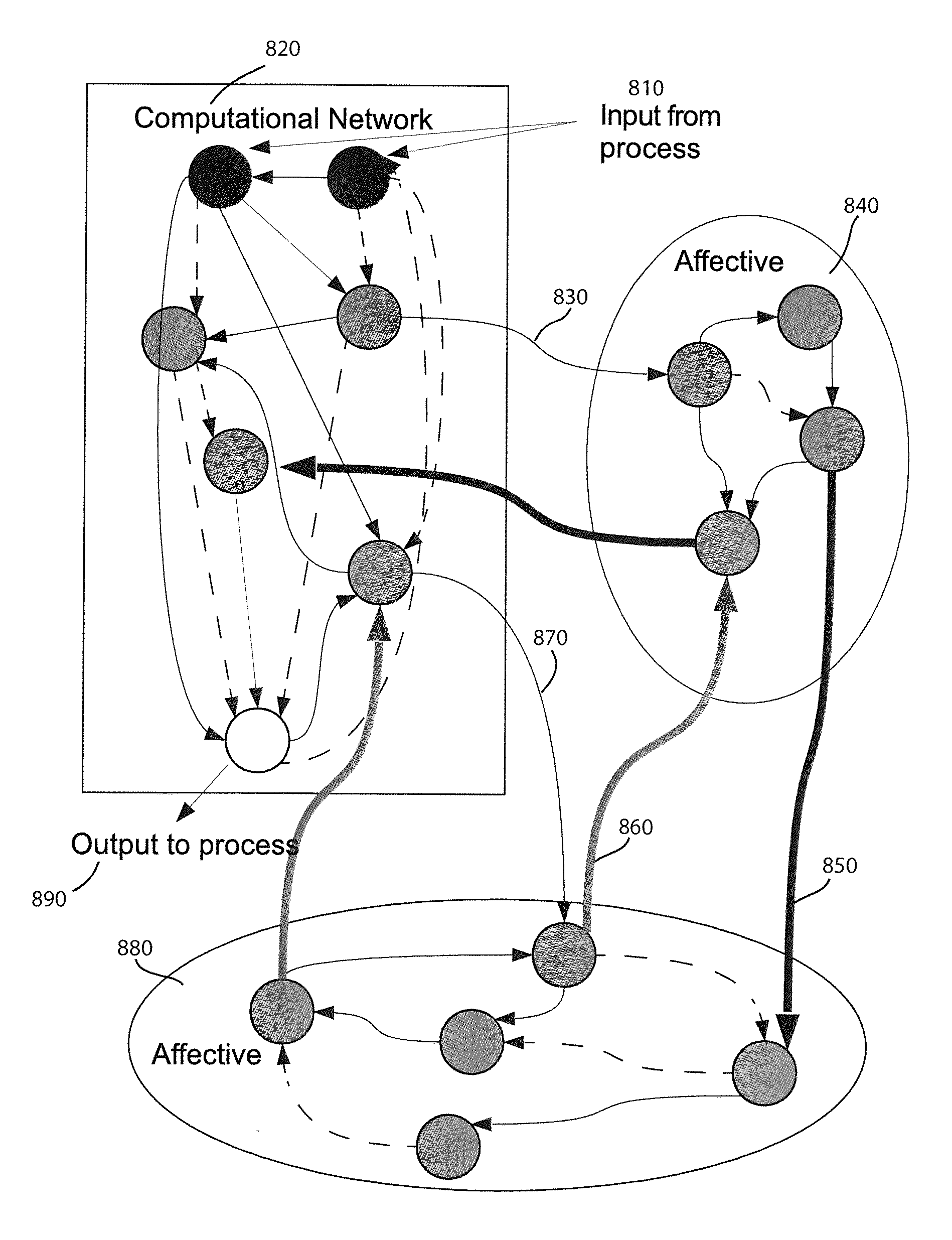
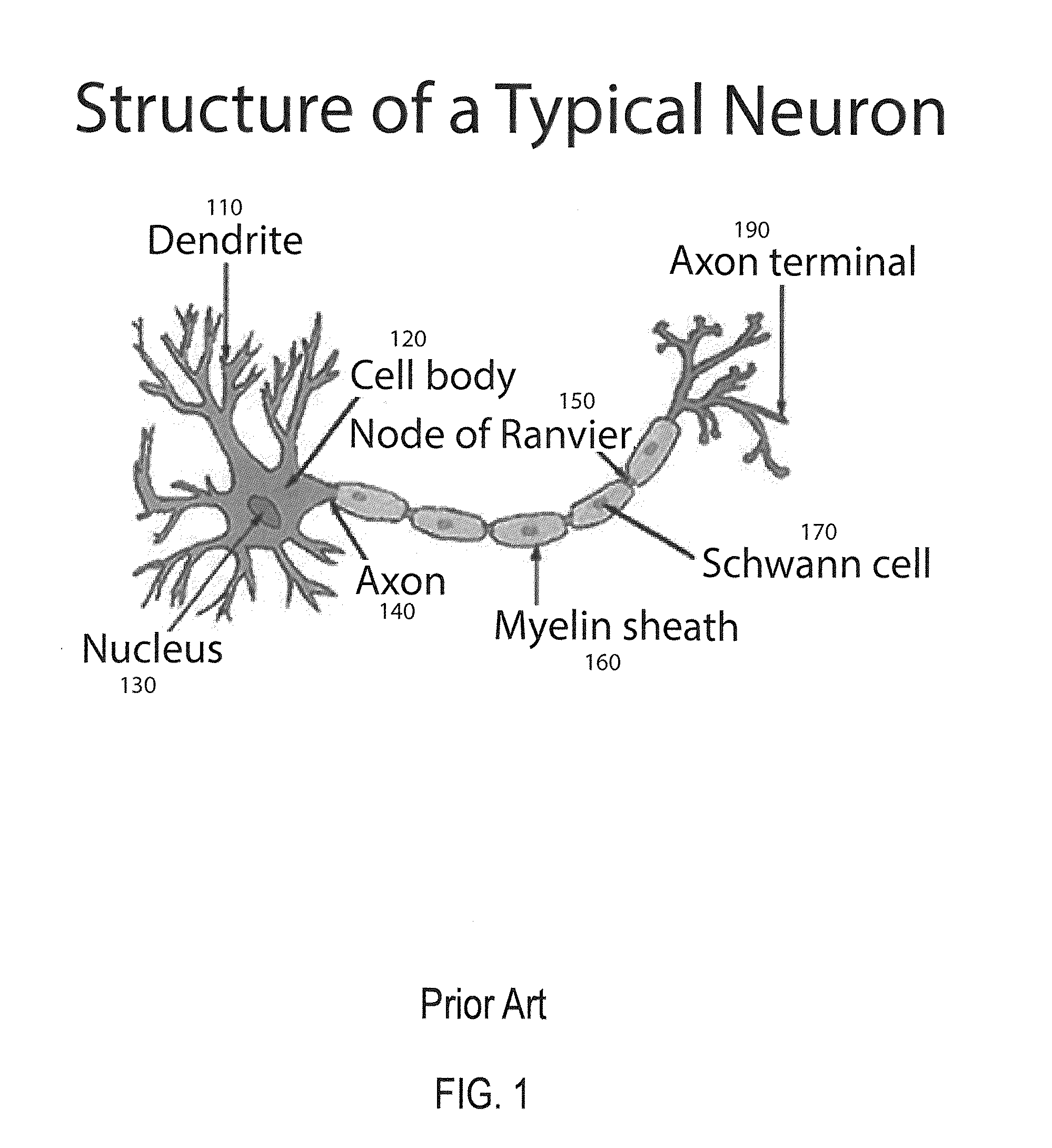
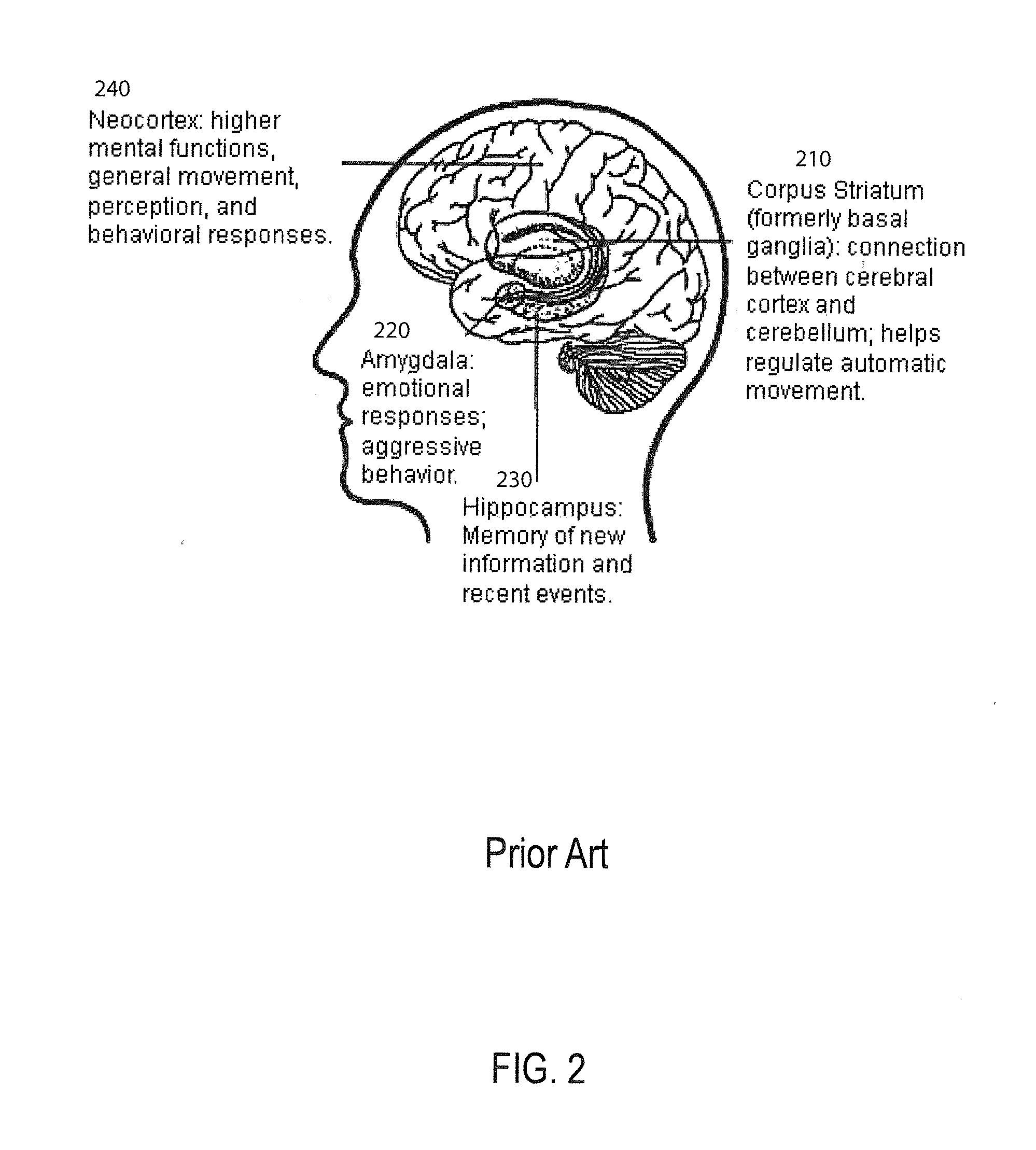
Method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network
ActiveUS20150106310A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsDigital dataComputational neuroscienceAnomaly detection
A method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired dynamic architecture (NIDA) for an artificial neural network is disclosed. The method comprises constructing, in one embodiment, an artificial neural network embodiment in a multi-dimensional space in memory such that a neuron is connected by a synapse to another neuron. The neuron and the synapse each have parameters and have features of long-term potentiation and long-term depression. Furthermore, crossover and mutation are employed to select children of parents. Through learning, an initial network may evolve into a different network when NIDA is applied to solve different problems of control, anomaly detection and classification over selected time units. The apparatus comprises in one embodiment a computational neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network with at least one affective network coupled to receive input data from an environment and to output data to the environment.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
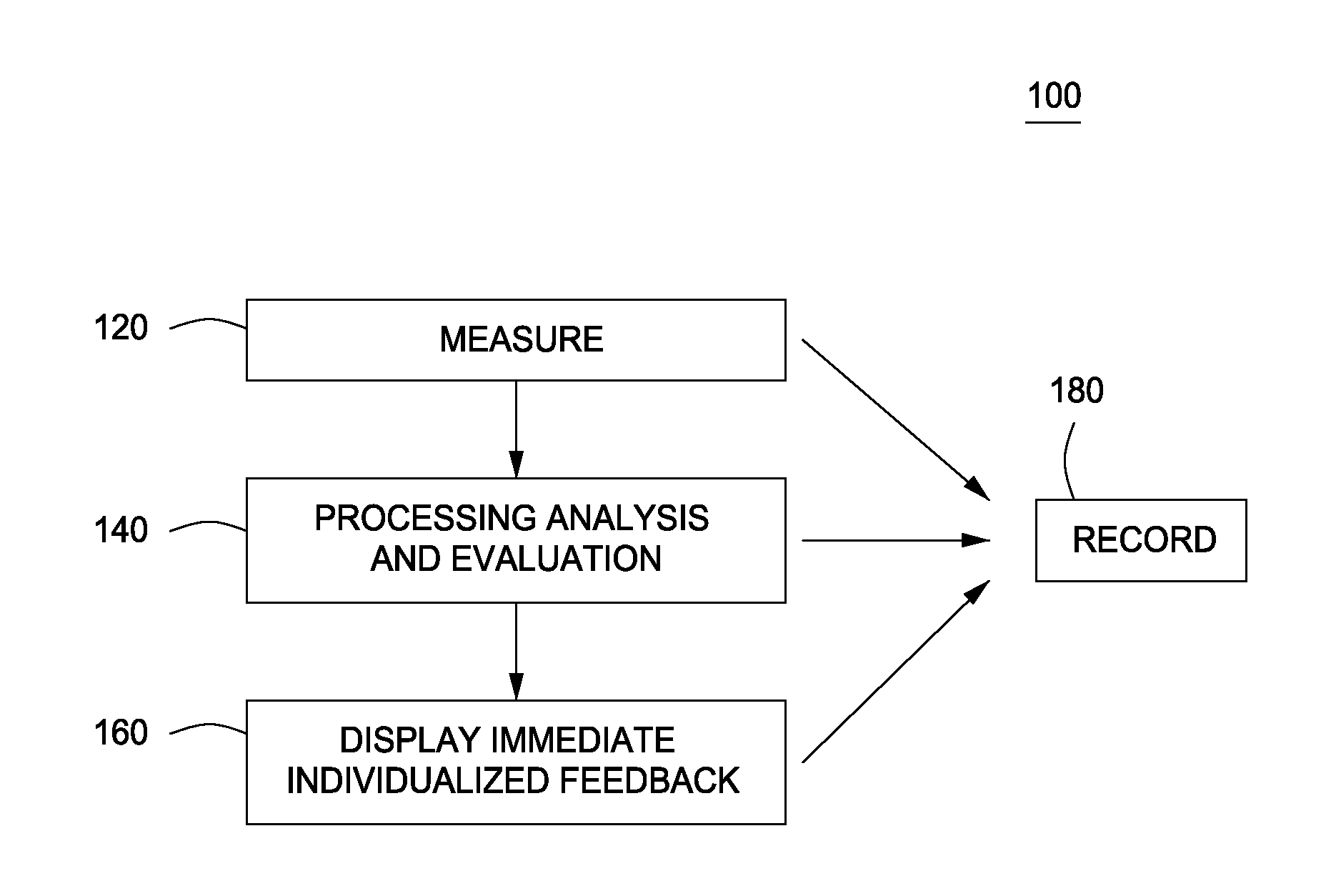
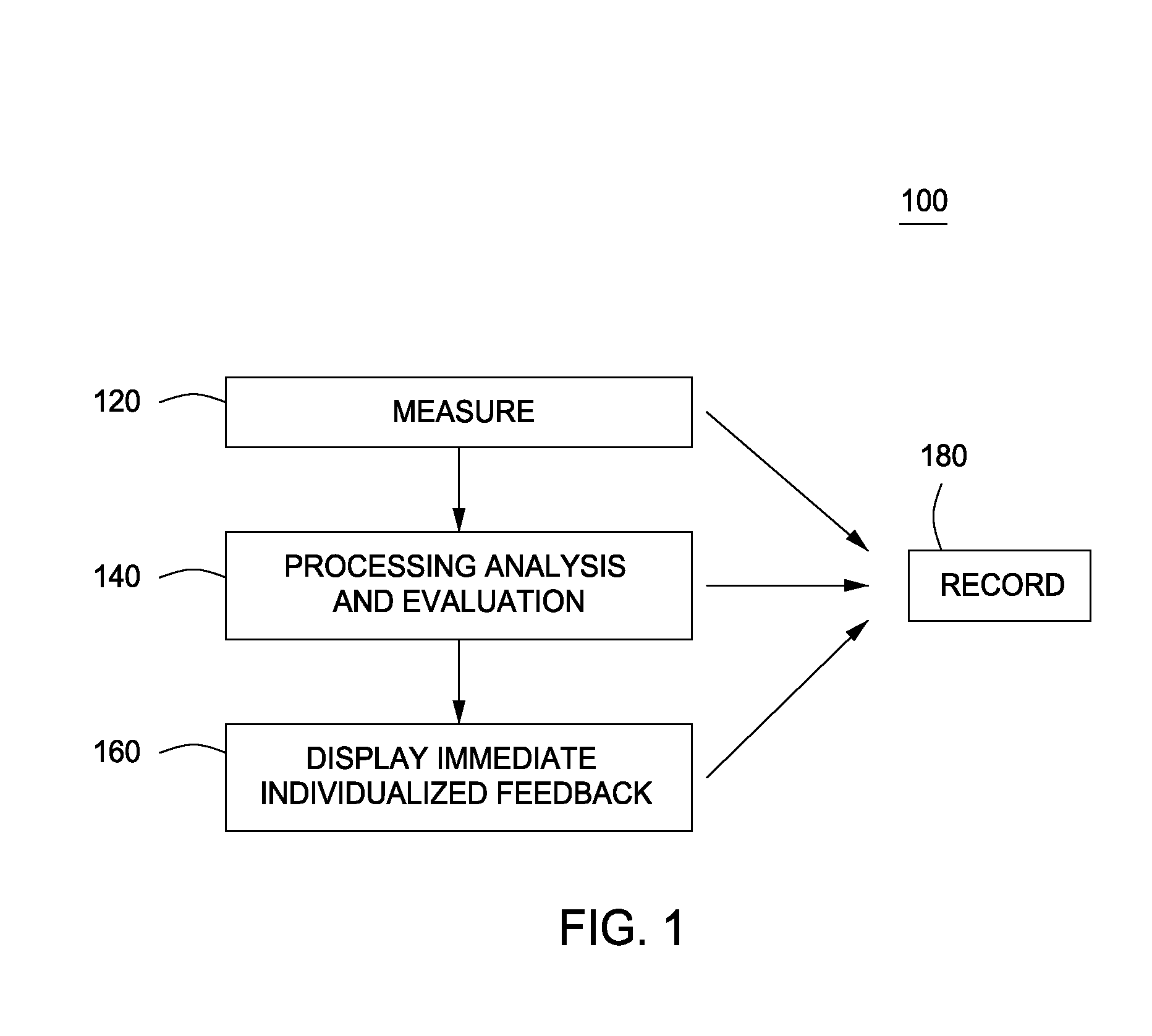
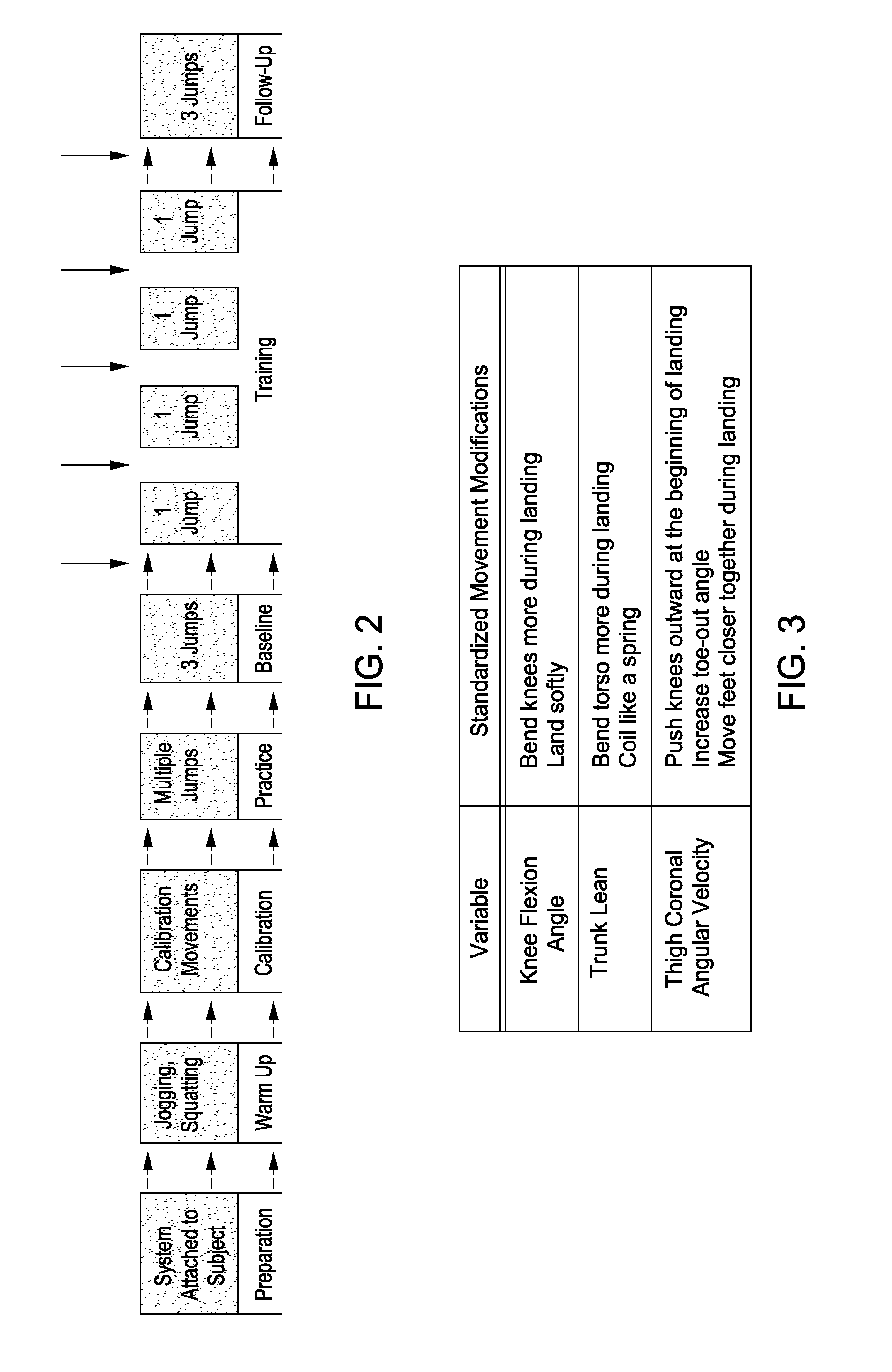
Systems and methods for measuring, analyzing, and providing feedback for movement in multidimensional space
InactiveUS20130244211A1Reduce harmImprove performancePhysical therapies and activitiesCosmonautic condition simulationsMultidimensional scalingMultidimensional space
The present invention provides systems and methods that measure and analyze a user's movement during a specific activity, then provide immediate, focused feedback as to how the user can modify the movement.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
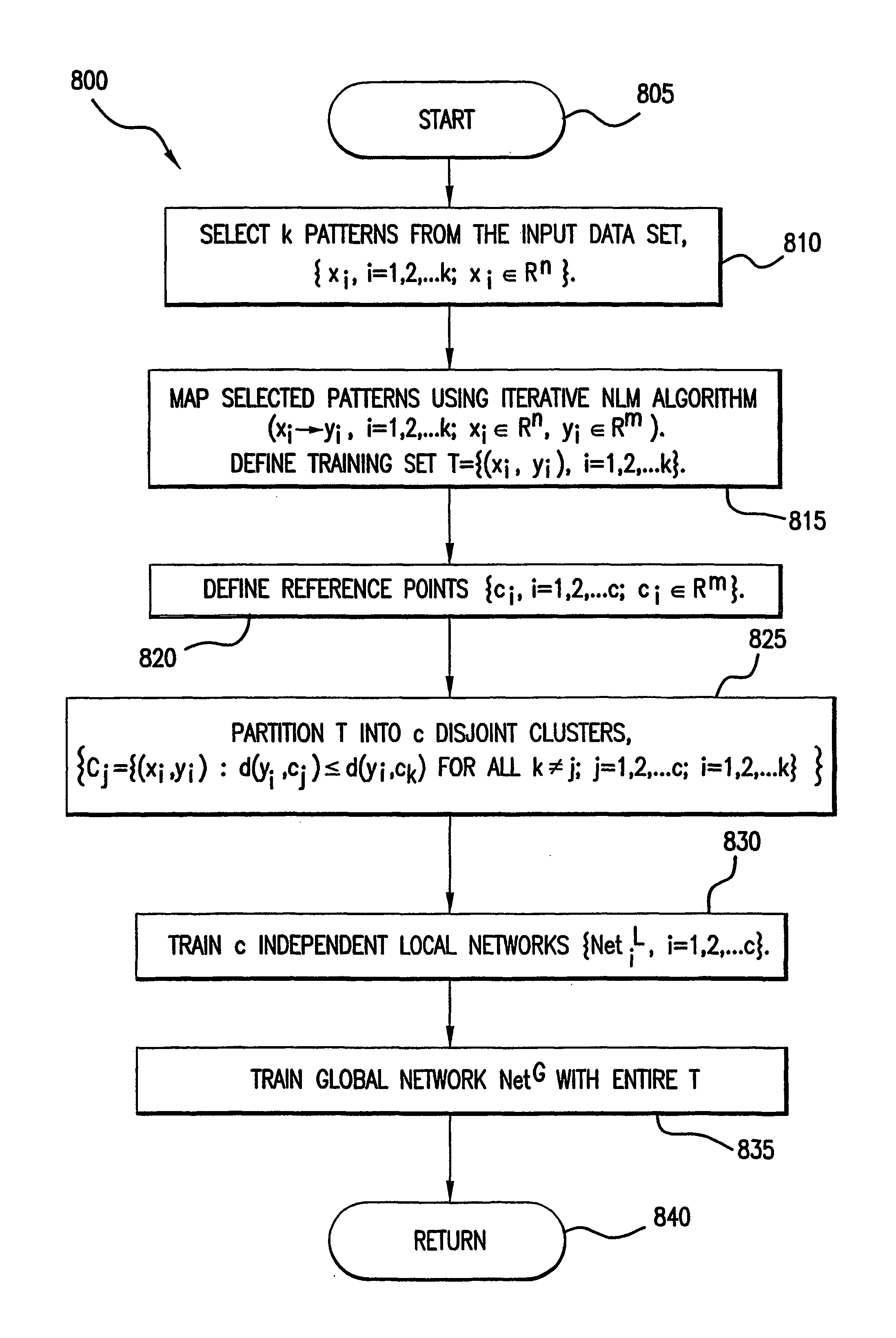
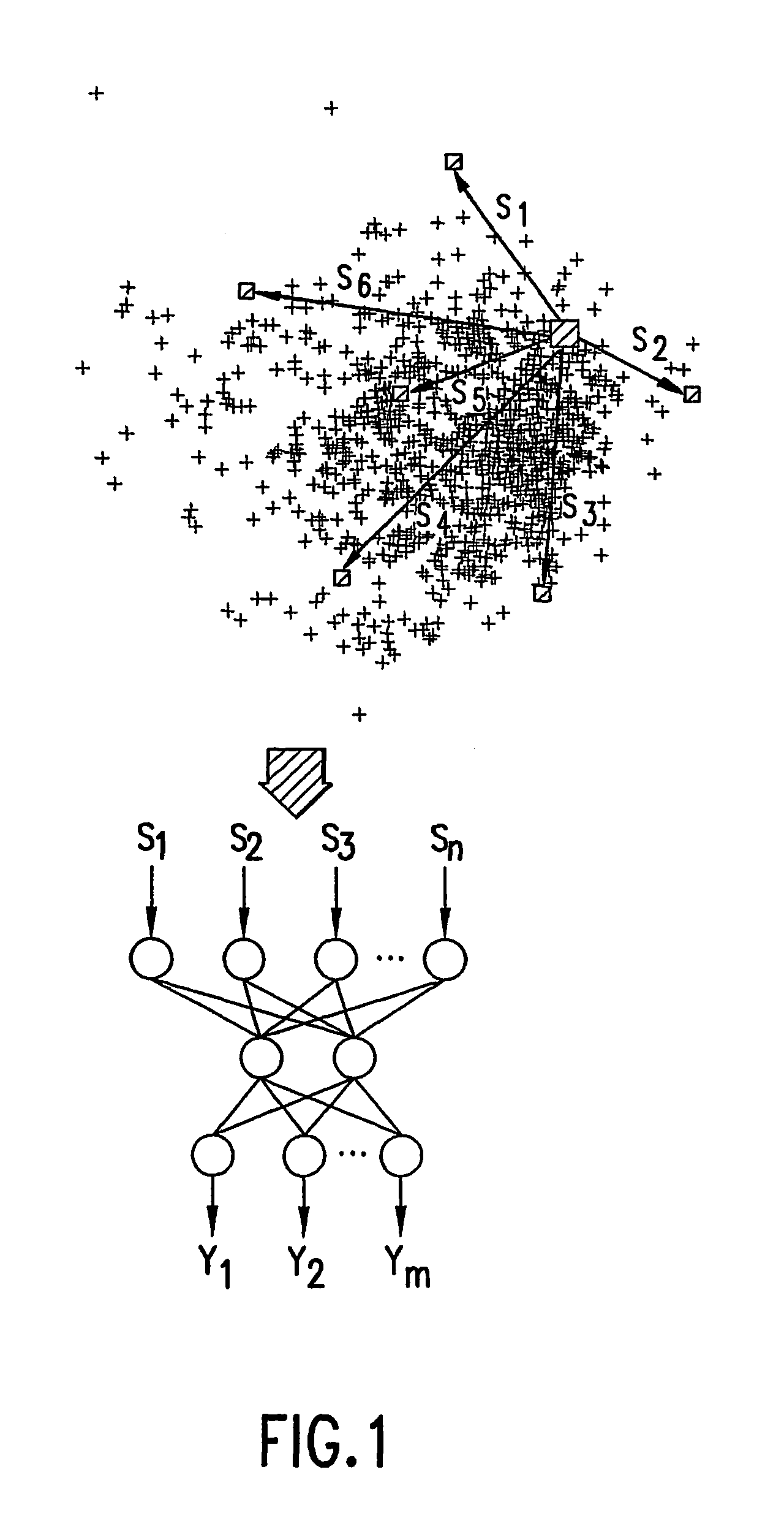
Method, system, and computer program product for representing object relationships in a multidimensional space
InactiveUS7139739B2Digital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsNerve networkMultidimensional scaling
A method, system, and computer product is presented for mapping a set of patterns into an m-dimensional space so as to preserve relationships that may exist between these patterns. A subset of the input patterns is chosen and mapped into the m-dimensional space using an iterative nonlinear mapping process based on subset refinements. A set of n attributes are determined for each pattern, and one or more neural networks or other supervised machine learning techniques are then trained in accordance with the mapping produced by the iterative process. Additional input patterns not in the subset are mapped into the m-dimensional space by determining their n input attributes and using the neural networks in a feed-forward (prediction) mode.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON PHARMA RES & DEV LLC
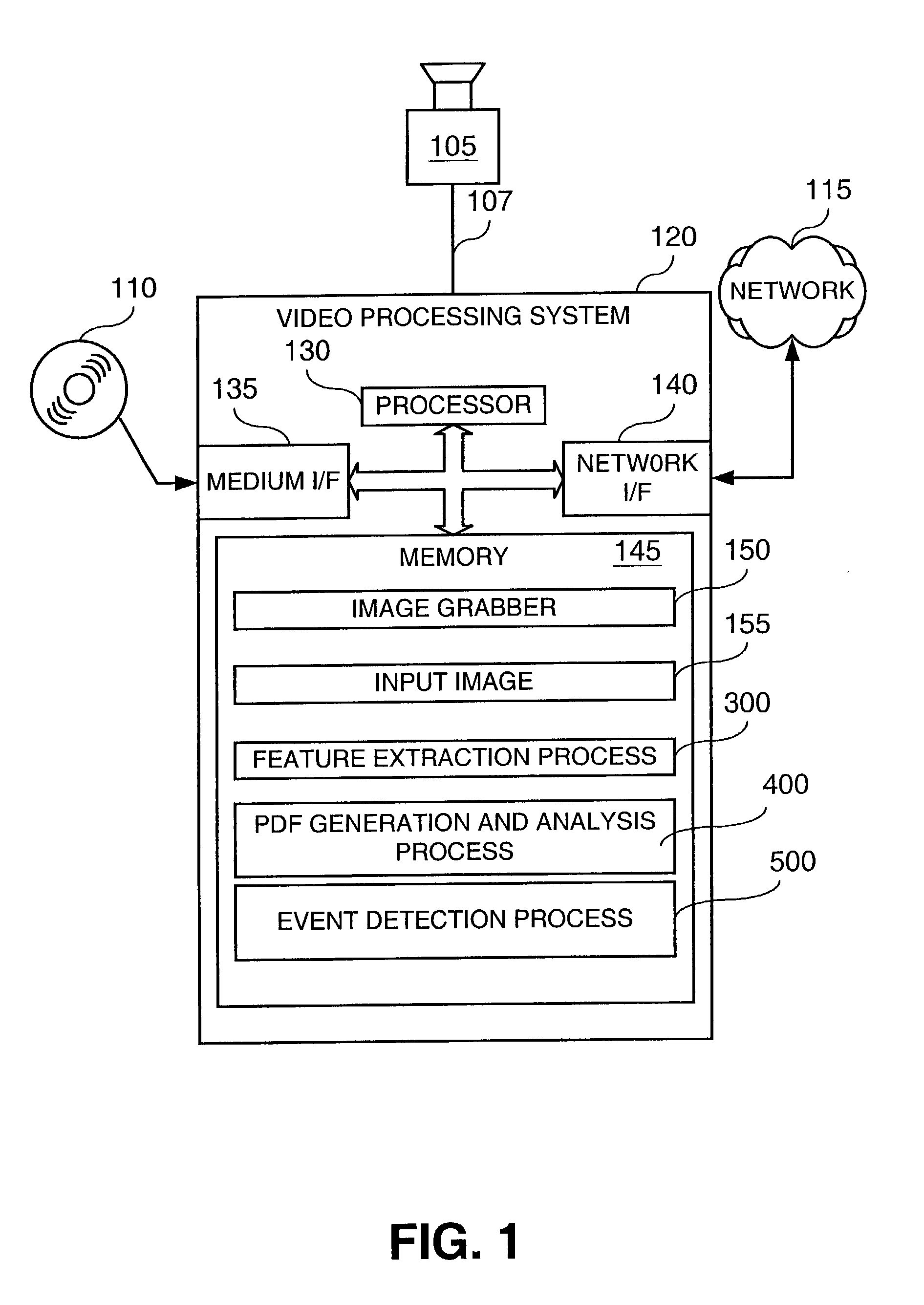
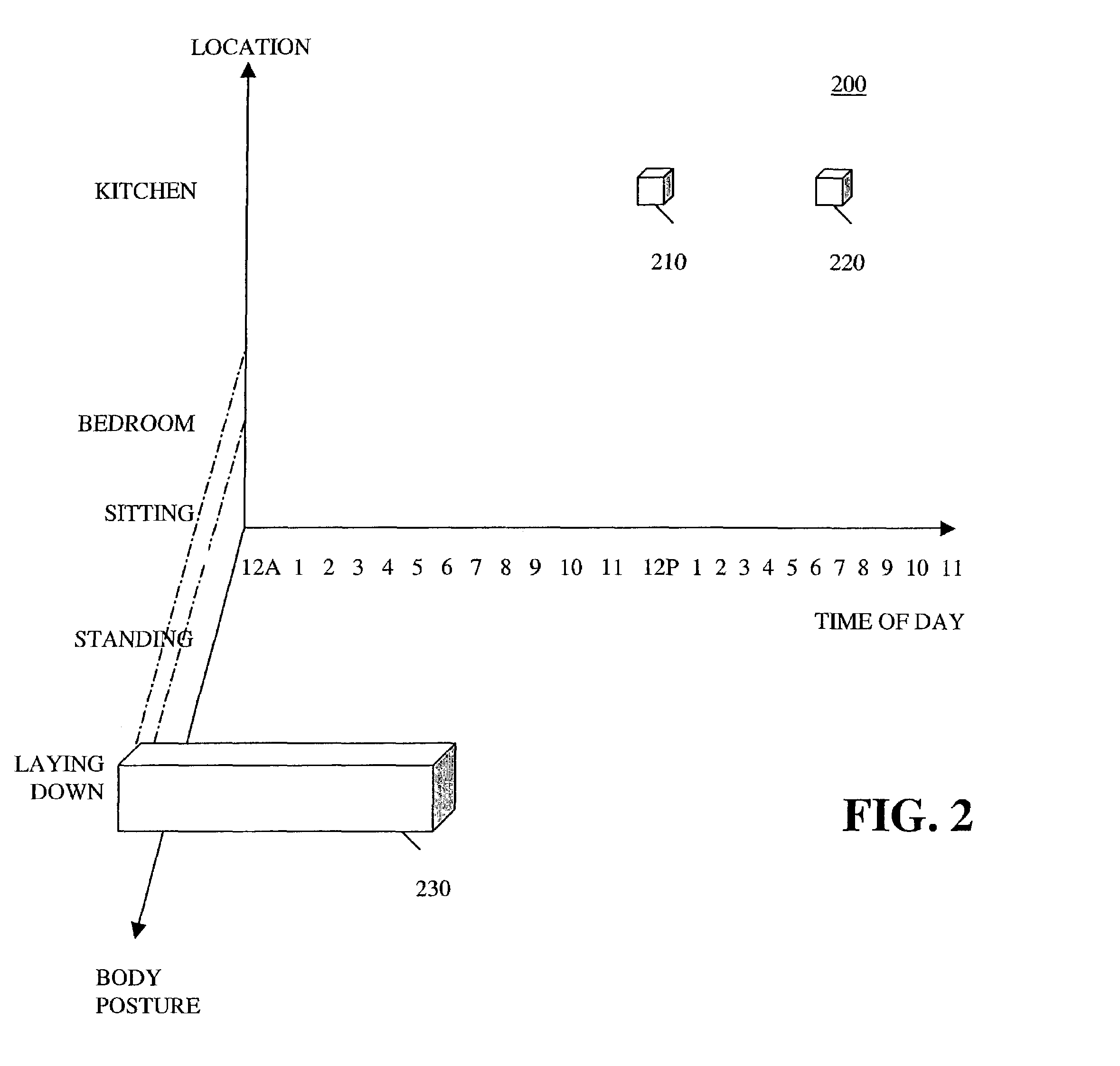
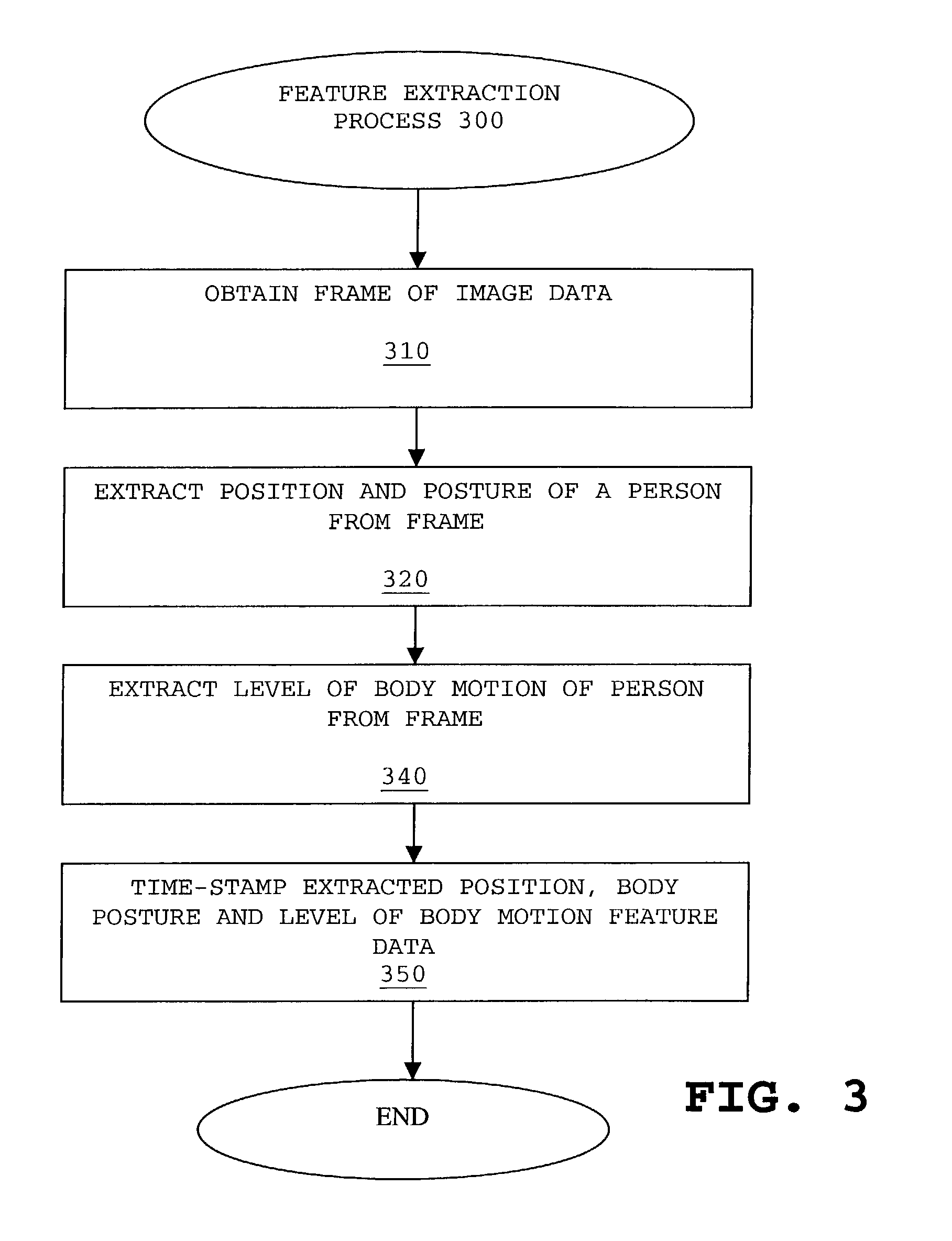
Method and apparatus for detecting an event based on patterns of behavior
A system and apparatus are disclosed for modeling patterns of behavior of humans or other animate objects and detecting a violation of a repetitive pattern of behavior. The behavior of one or more persons is observed over time and features of the behavior are recorded in a multi-dimensional space. Over time, the multi-dimensional data provides an indication of patterns of human behavior. Activities that are repetitive in terms of time, location and activity, such as sleeping and eating, would appear as a Gaussian distribution or cluster in the multi-dimensional data. Probability distribution functions can be analyzed using known Gaussian or clustering techniques to identify repetitive patterns of behavior and characteristics thereof, such as a mean and variance. Deviations from repetitive patterns of behavior can be detected and an alarm can be triggered, if appropriate.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
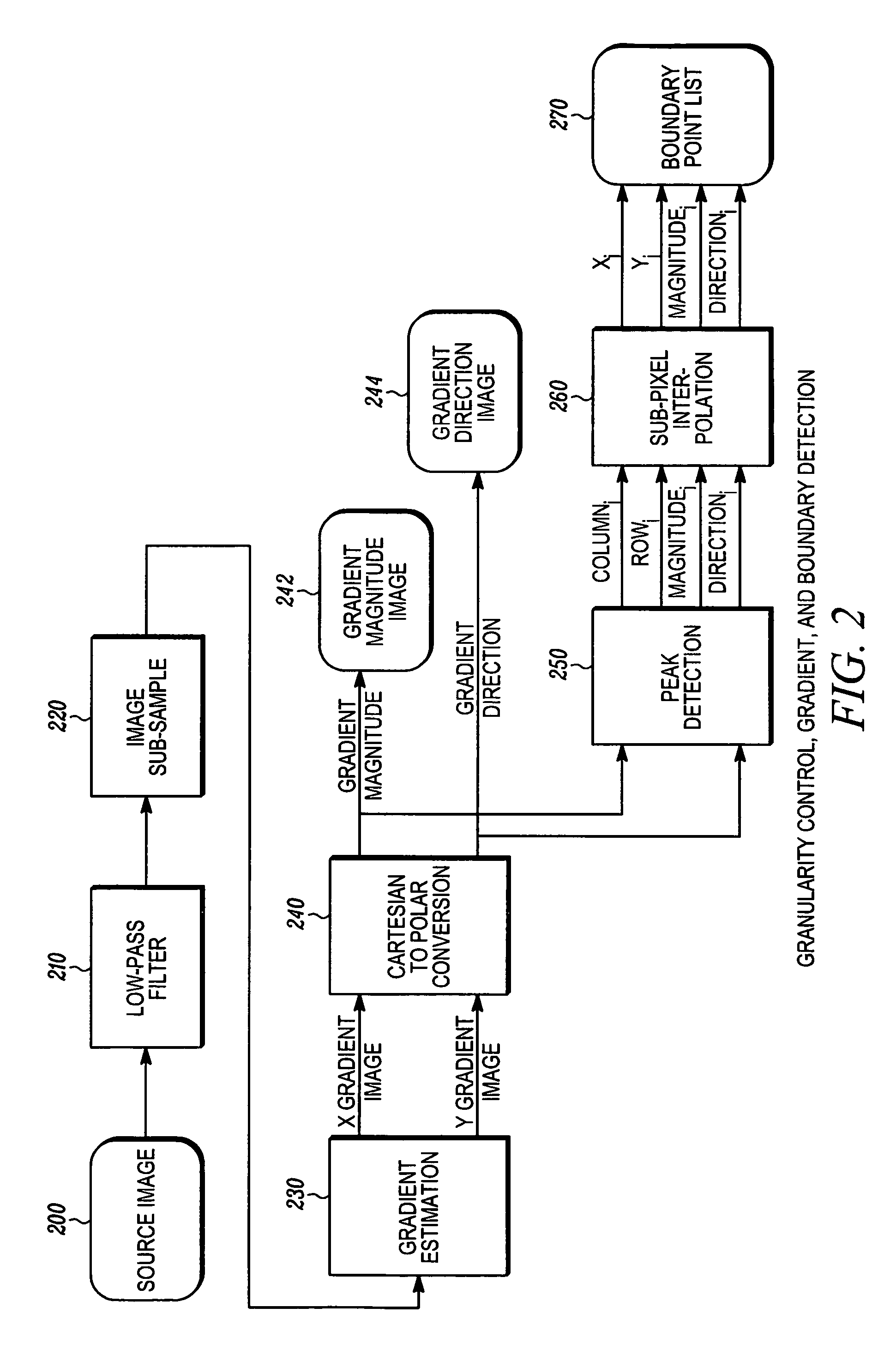
Fast high-accuracy multi-dimensional pattern localization
InactiveUS6856698B1Improve matchImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDegrees of freedomDigital image
A method and apparatus are provided for rapidly refining a given approximate location of a pattern to produce a more accurate location. The invention employs a multi-dimensional space that includes translation, orientation, and scale. The invention can serve as a replacement for the fine resolution phase of any coarse-fine system for pattern location. Patterns and images are represented by a feature-based description that can be translated, rotated, and scaled to arbitrary precision much faster than digital image re-sampling, and without pixel grid quantization errors. Thus, accuracy is not limited by the ability of a grid to represent small changes in position, orientation, or size (or other degrees of freedom). The invention determines an accurate object pose from an approximate starting pose in a small, fixed number of increments that is independent of the number of dimensions of the space, and independent of the distance between the starting and final poses, provided that the starting pose is within the “capture range” of the true pose. Thus, accuracy need not be sacrificed to keep execution time acceptable for practical applications. Specifying locations in four or more dimensions will often result in better matches between the pattern and image than two-dimensional location systems, thereby improving accuracy. Accuracy is not degraded if some portion of the object is missing or occluded, or if unexpected extra features are present.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
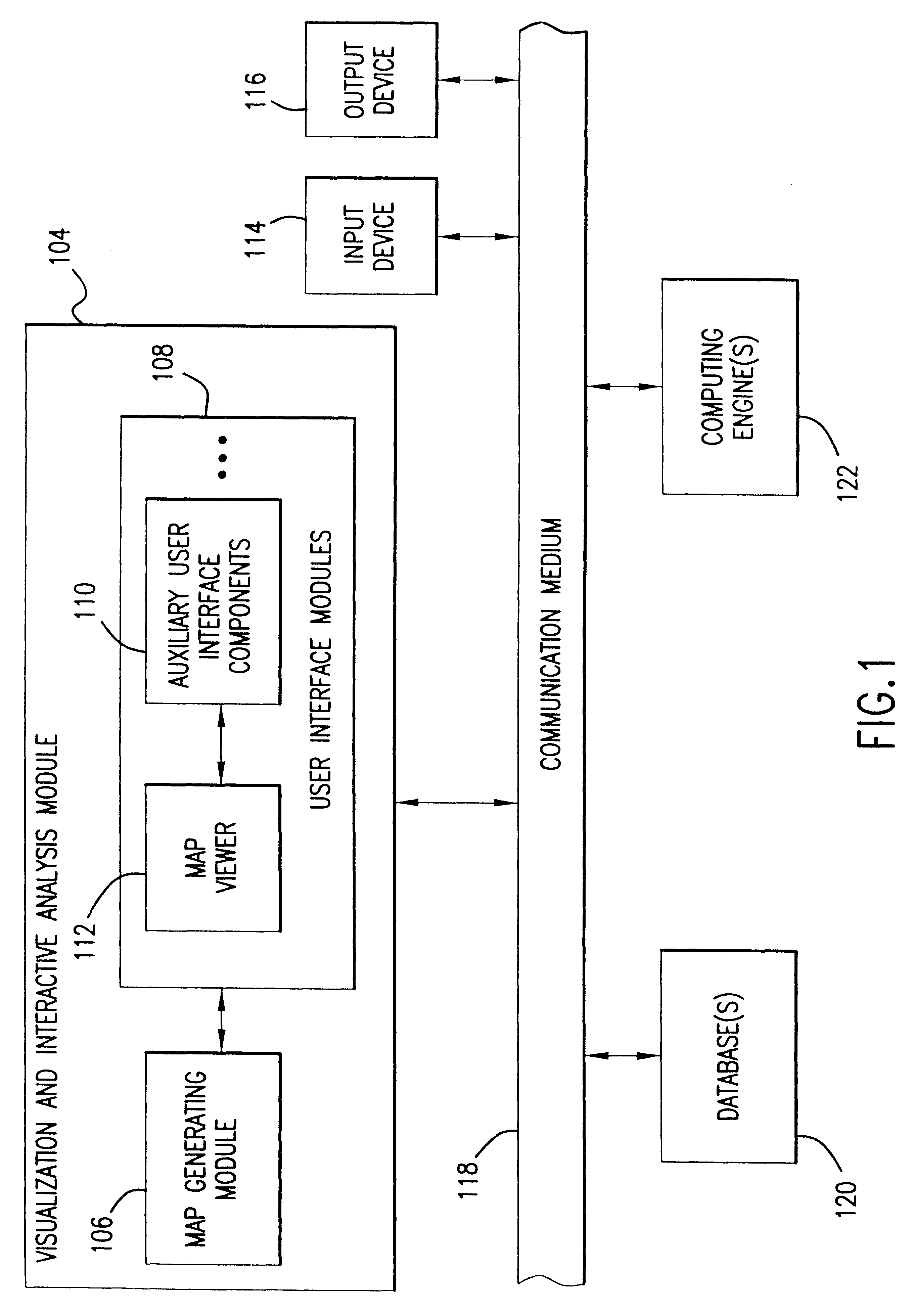
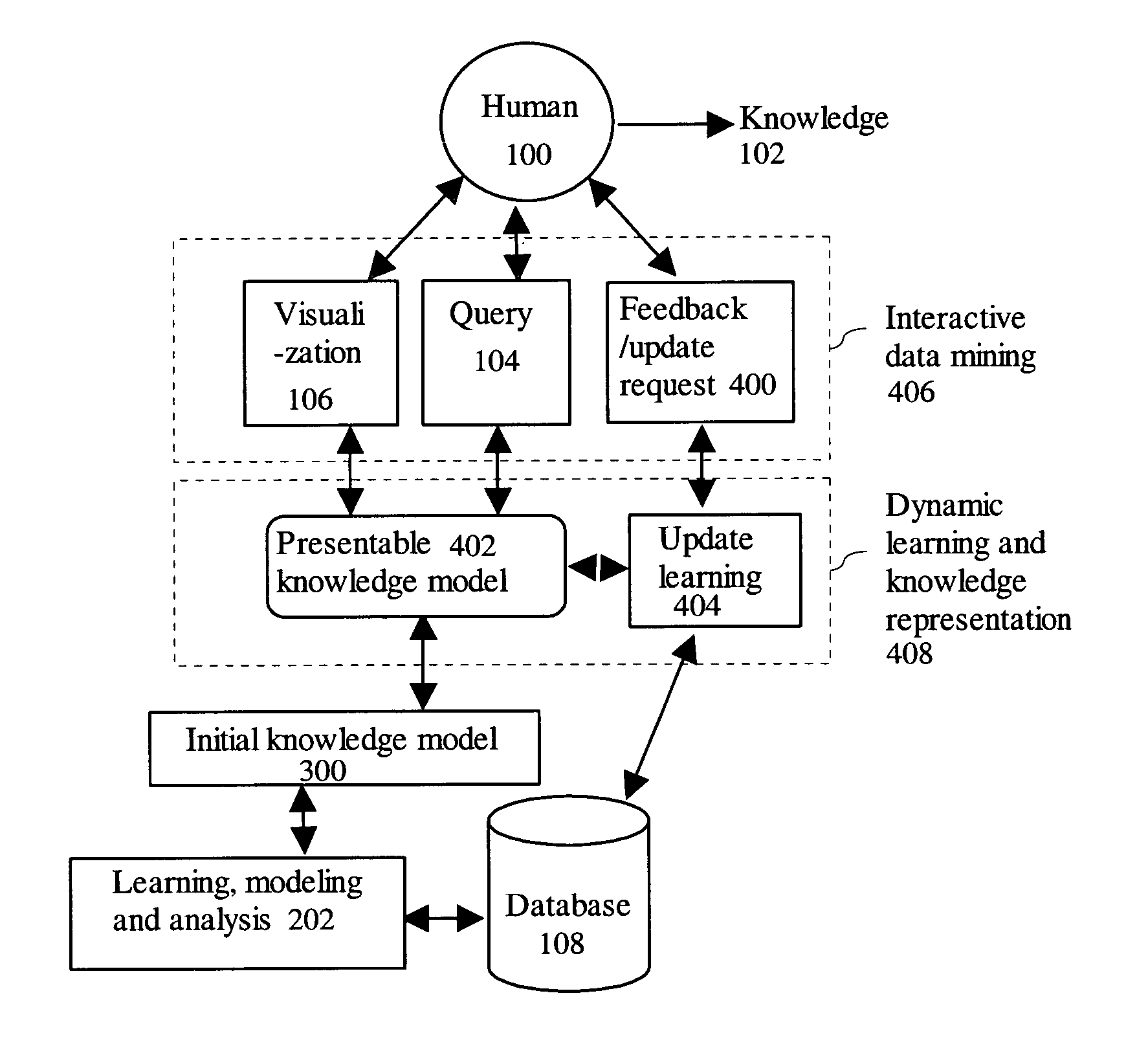
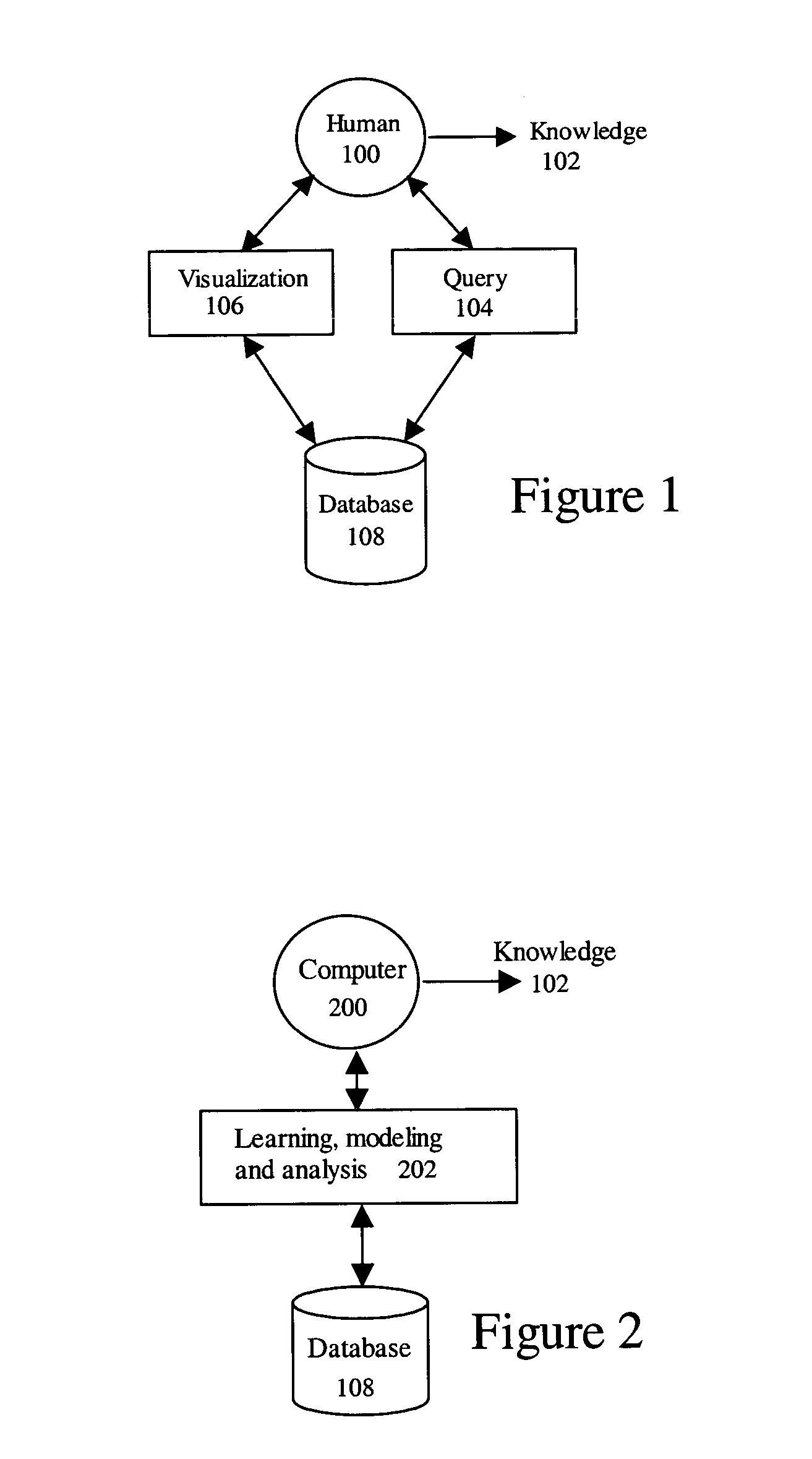
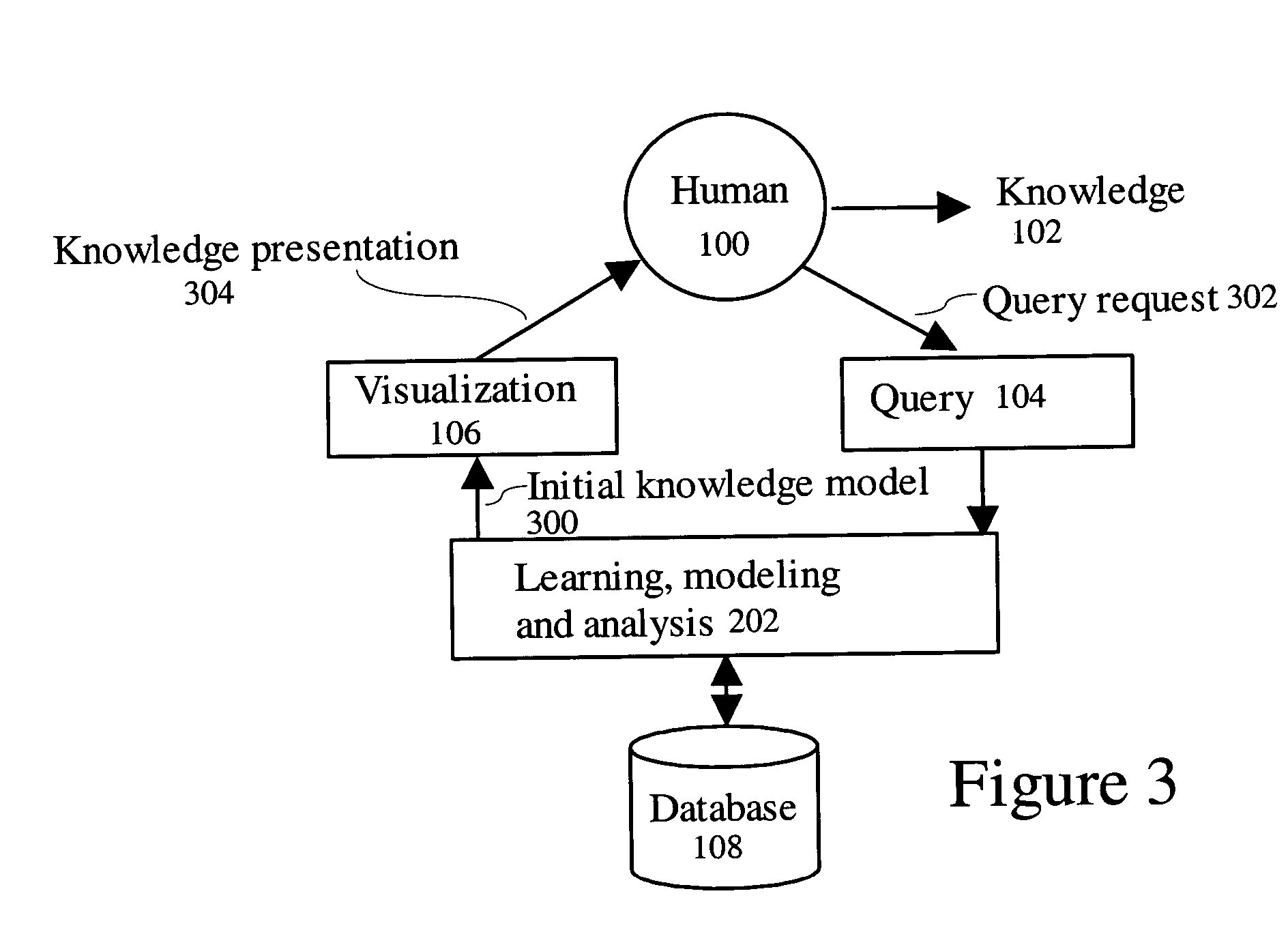
Dynamic learning and knowledge representation for data mining
ActiveUS7139764B2Effective visualizationEfficient confirmationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsPolygonal lineDynamic learning
An integrated human and computer interactive data mining method receives an input database. A learning, modeling, and analysis method uses the database to create an initial knowledge model. A query of the initial knowledge model is performed using a query request. The initial knowledge model is processed to create a knowledge presentation output for visualization. It further comprises a feedback and update request step that updates the initial knowledge model.A multiple level integrated human and computer interactive data mining method facilitates overview interactive data mining and dynamic learning and knowledge representation by using the initial knowledge model and the database to create and update a presentable knowledge model. It facilitates zoom and filter interactive data mining and dynamic learning and knowledge representation by using the presentable knowledge model and the database to create and update the presentable knowledge model. It further facilitates details-on-demand interactive data mining and dynamic learning and knowledge representation by using the presentable knowledge model and the database to create and update the presentable knowledge model.The integrated human and computer interactive data mining method allows rule viewing by a parallel coordinate visualization technique that maps a multiple dimensional space onto two display dimensions with data items presented as polygonal lines.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
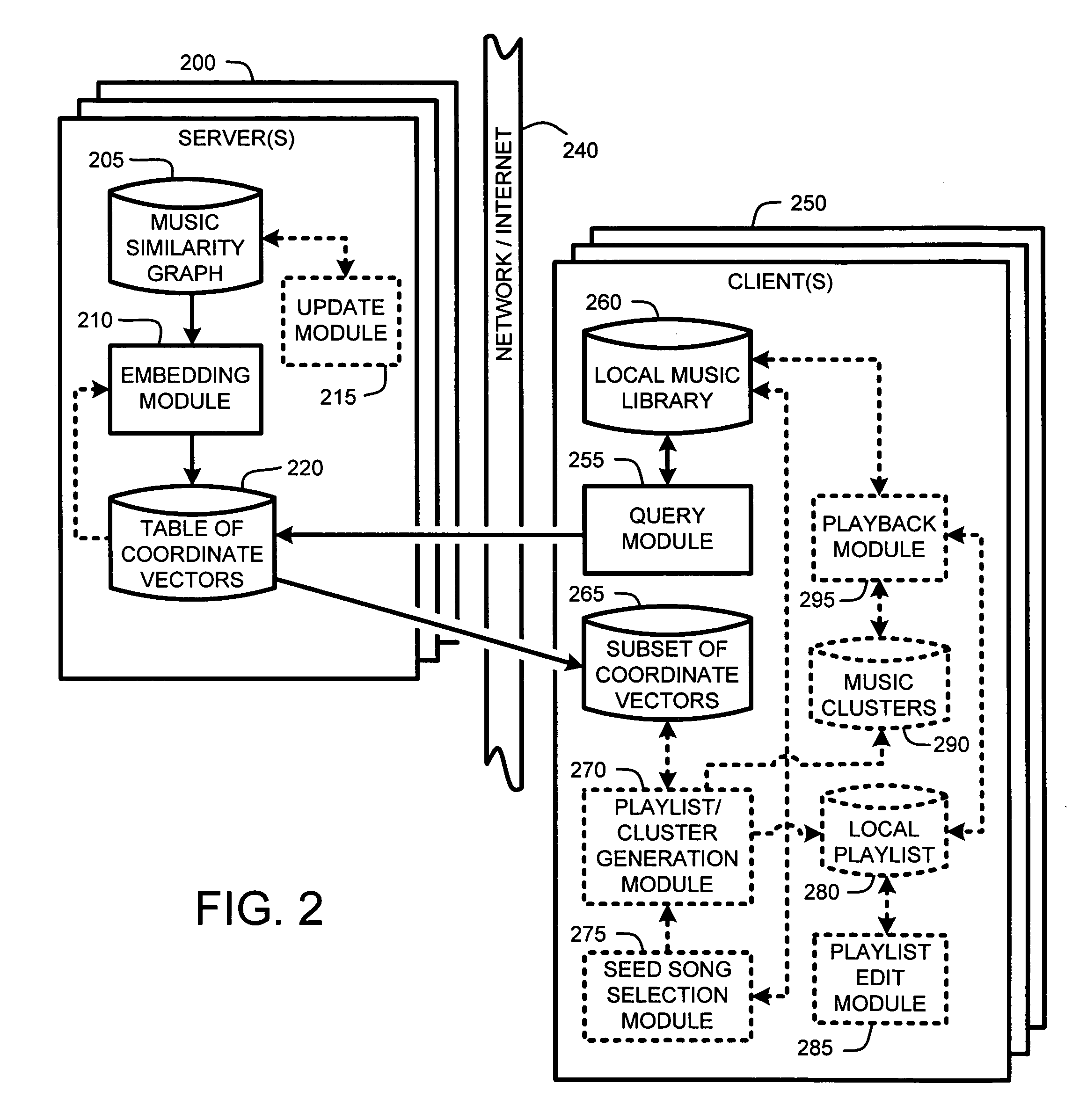
Client-based generation of music playlists from a server-provided subset of music similarity vectors
InactiveUS20060112082A1Easy to updateLimited amountMetadata audio data retrievalElectrophonic musical instrumentsPattern recognitionGraphics
A “Music Mapper” automatically constructs a set coordinate vectors for use in inferring similarity between various pieces of music. In particular, given a music similarity graph expressed as links between various artists, albums, songs, etc., the Music Mapper applies a recursive embedding process to embed each of the graphs music entries into a multi-dimensional space. This recursive embedding process also embeds new music items added to the music similarity graph without reembedding existing entries so long a convergent embedding solution is achieved. Given this embedding, coordinate vectors are then computed for each of the embedded musical items. The similarity between any two musical items is then determined as either a function of the distance between the two corresponding vectors. In various embodiments, this similarity is then used in constructing music playlists given one or more random or user selected seed songs or in a statistical music clustering process.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Navigation and viewing in a multidimensional space
InactiveUS20060080604A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer scienceMultidimensional space
Owner:ANDERSON THOMAS G
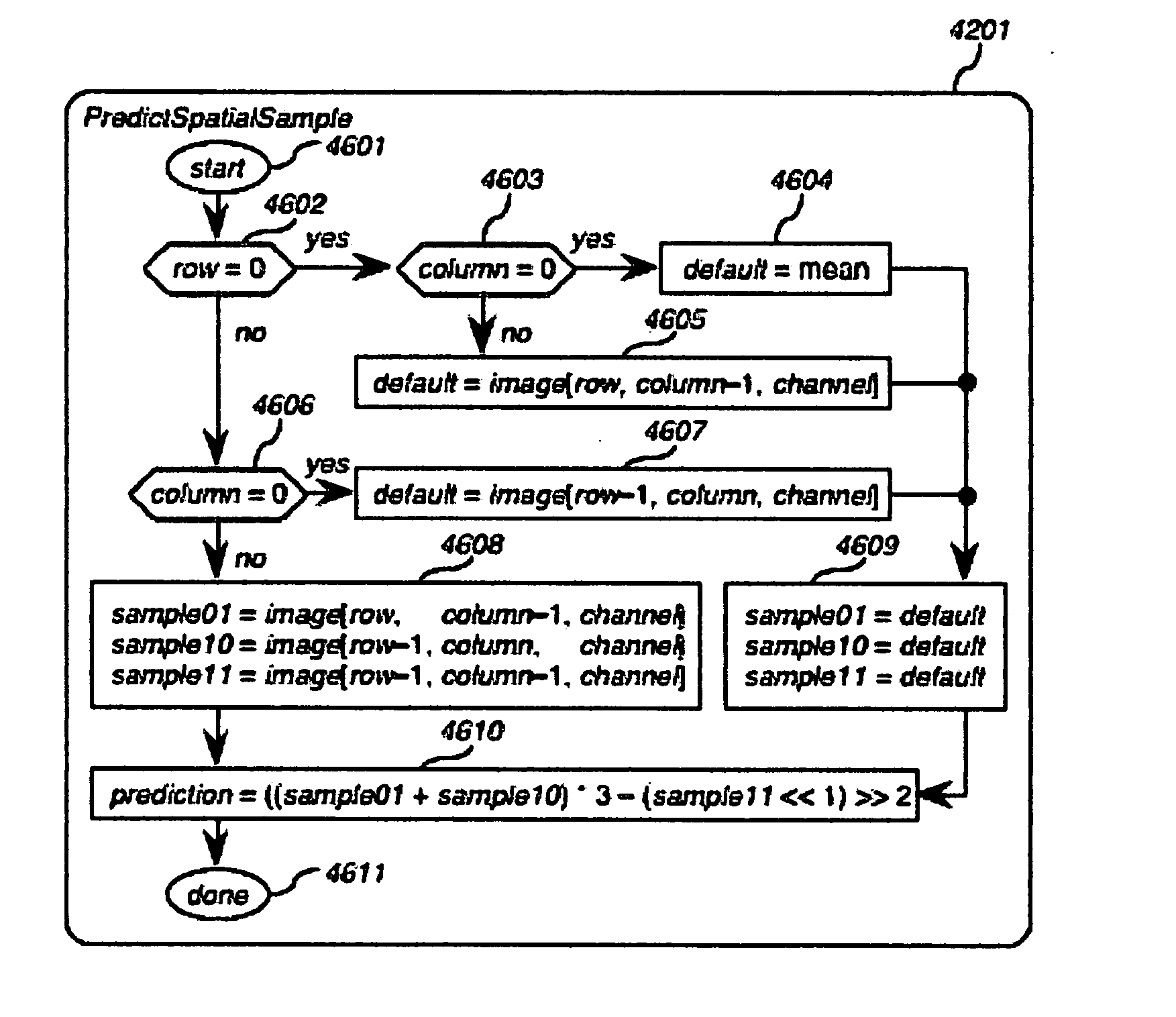
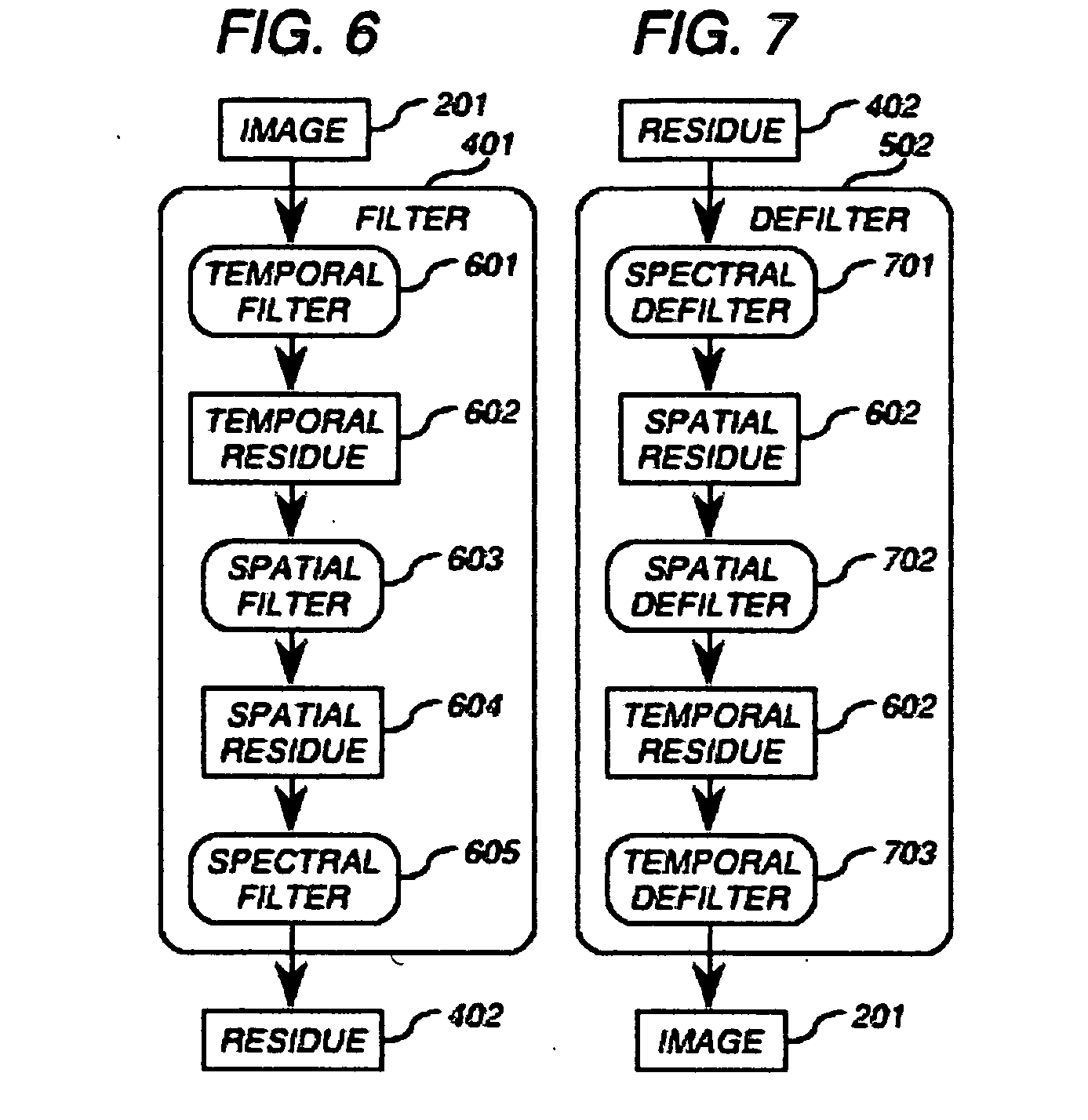
Method and apparatus for faster-than-real-time lossless compression and decompression of images
InactiveUS20080219575A1Maximize compression ratioMinimized on demandCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationFrequency spectrumContext independent
The present invention is a method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing data. In particular, the present invention provides for (de-)compressing naturalistic color-image and moving-image data, including high-precision and high-definition formats, with zero information loss, one-sample latency and in faster than real time on common computing platforms, resulting in doubled transmission, storage, and playback speed and doubled transmission bandwidth and storage capacity, and hence in doubled throughput for non-CPU-bound image-editing tasks in comparison with uncompressed formats. The present invention uses a nearly symmetrical compression-decompression scheme that provides temporal, spatial, and spectral compression, using a reversible condensing / decondensing filter, context reducer, and encoder / decoder. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the compression filter is implemented as a cascade of quasilinear feedforward filters, with temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral stages, where appropriate, in that order, whose support consists of adjacent causal samples of the respective image. The decompressor cascades quasilinear feedback inverse filters in the reverse order. The filters can be implemented with mere integer addition, subtraction, and either one-dimensional table lookup or constant multiplication and binary shifting, depending on the computing environment Tables permit the data precision to be constrained throughout to that of the image samples. The encoder uses a table of prefix codes roughly inversely proportional in length to their probability, while the decoder uses chunked decode tables for accelerated lookup. In the fastest and simplest mode, the code tables are context-independent. For greater power, at the cost of a reduction in speed, the code tables are based on the temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral adjacent causal residue samples, where contexts with similar probability distributions are incoherently collapsed by a context reducer using one-dimensional lookup tables followed by implicitly multidimensional lookup tables, to minimize the overall table size. The invention's minimal resource requirements makes it ideal for implementation in either hardware or software.
Owner:WITTENSTEIN ANDREAS
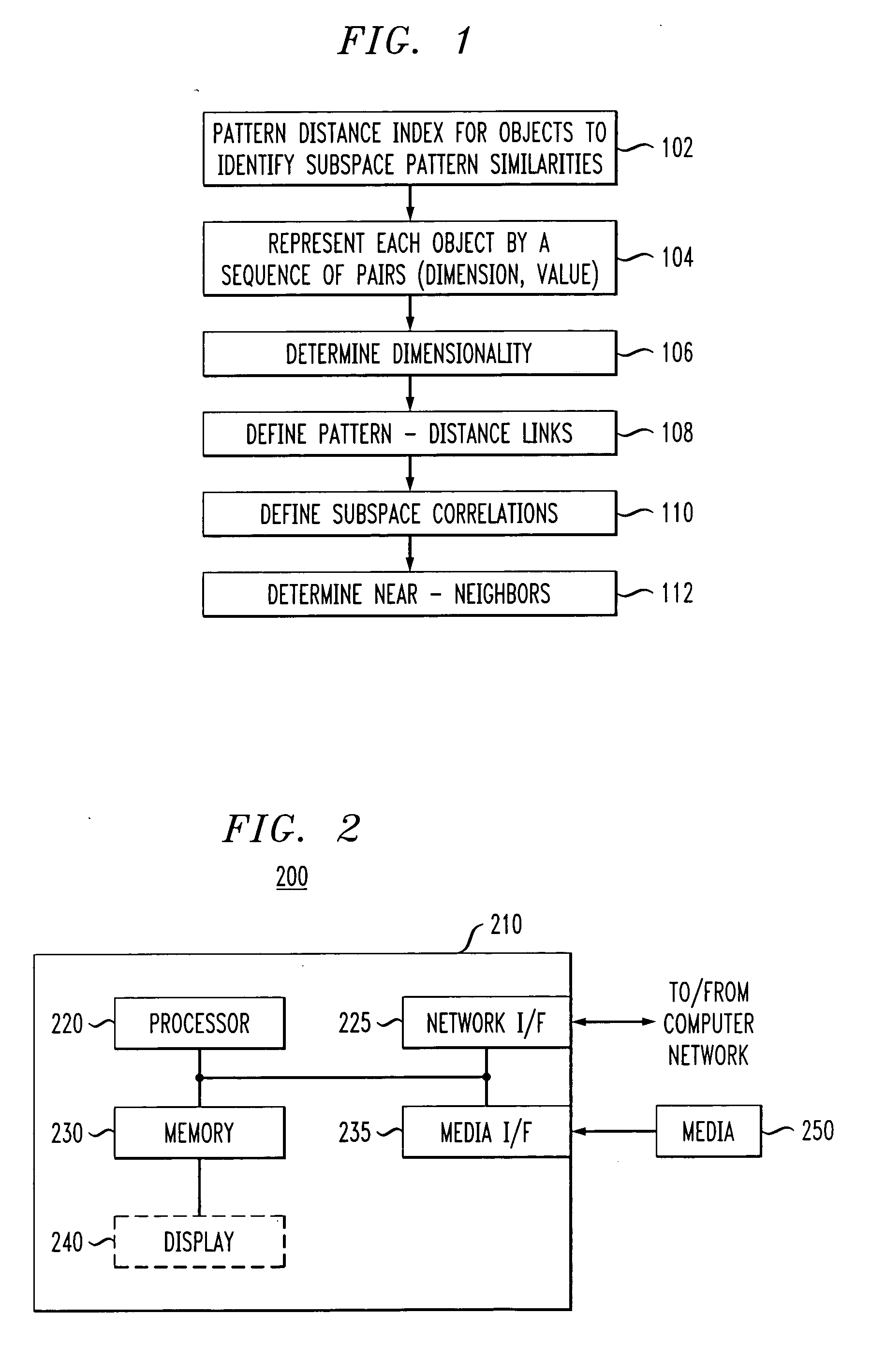
Near-neighbor search in pattern distance spaces
Owner:IBM CORP
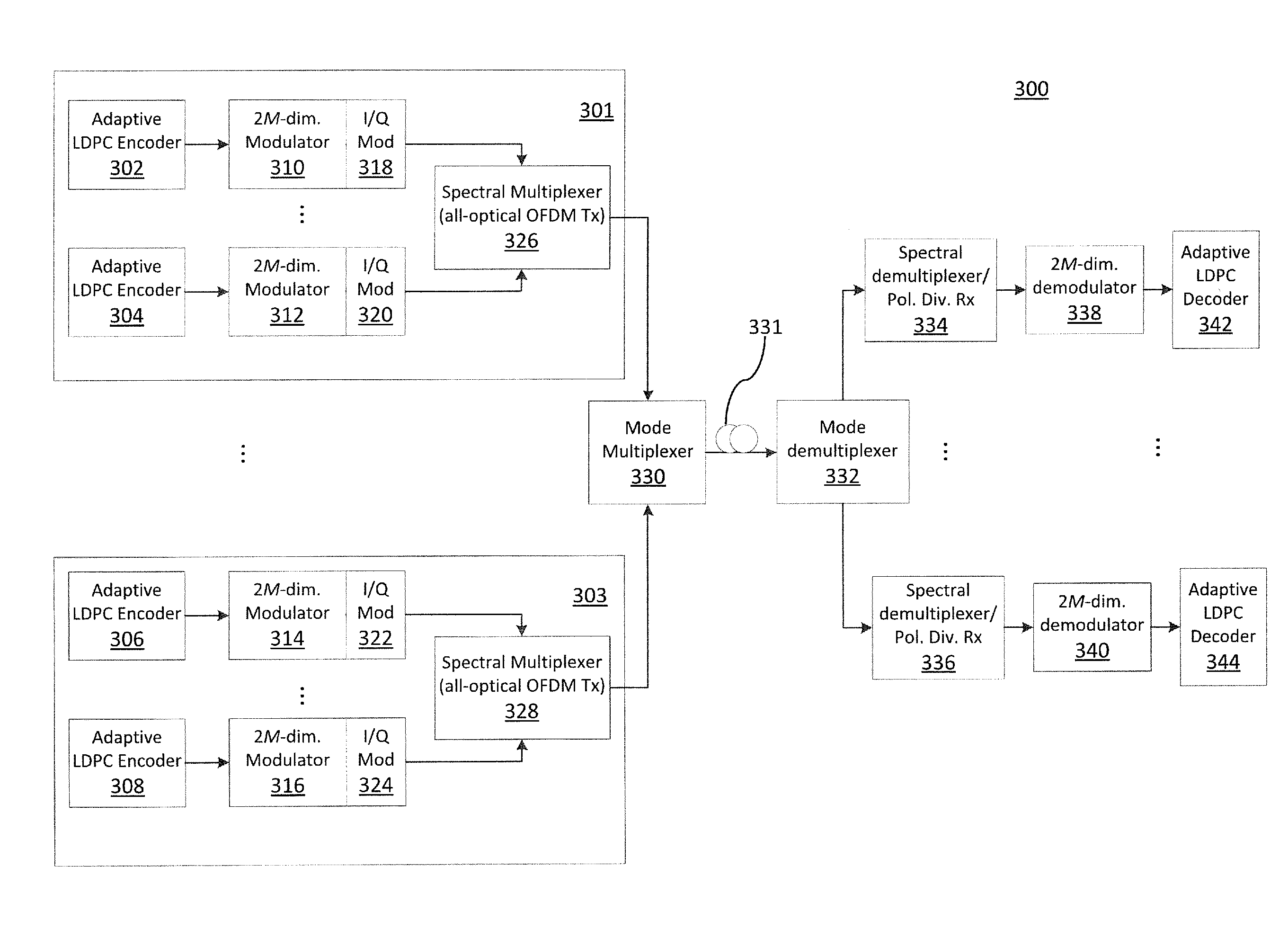
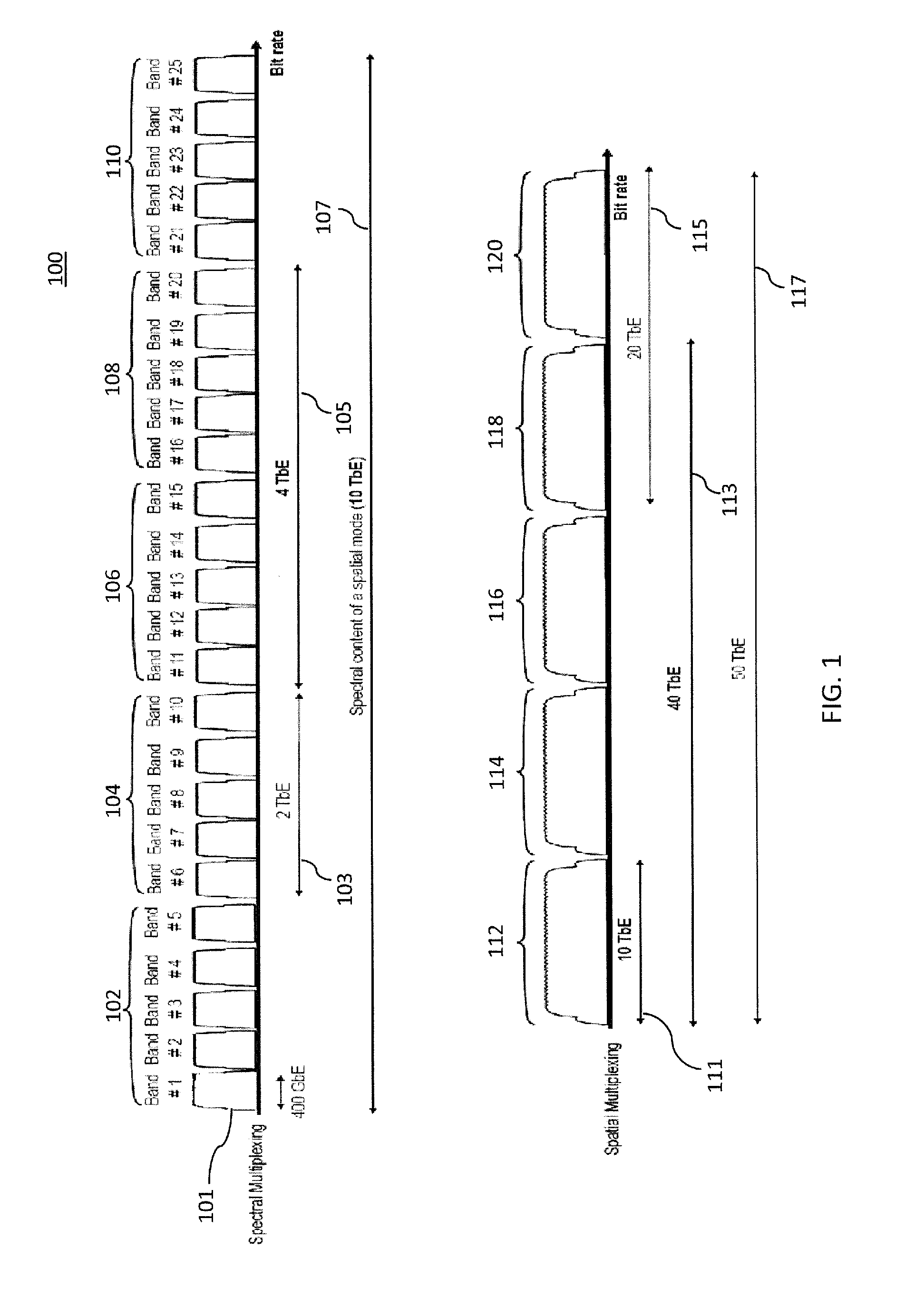
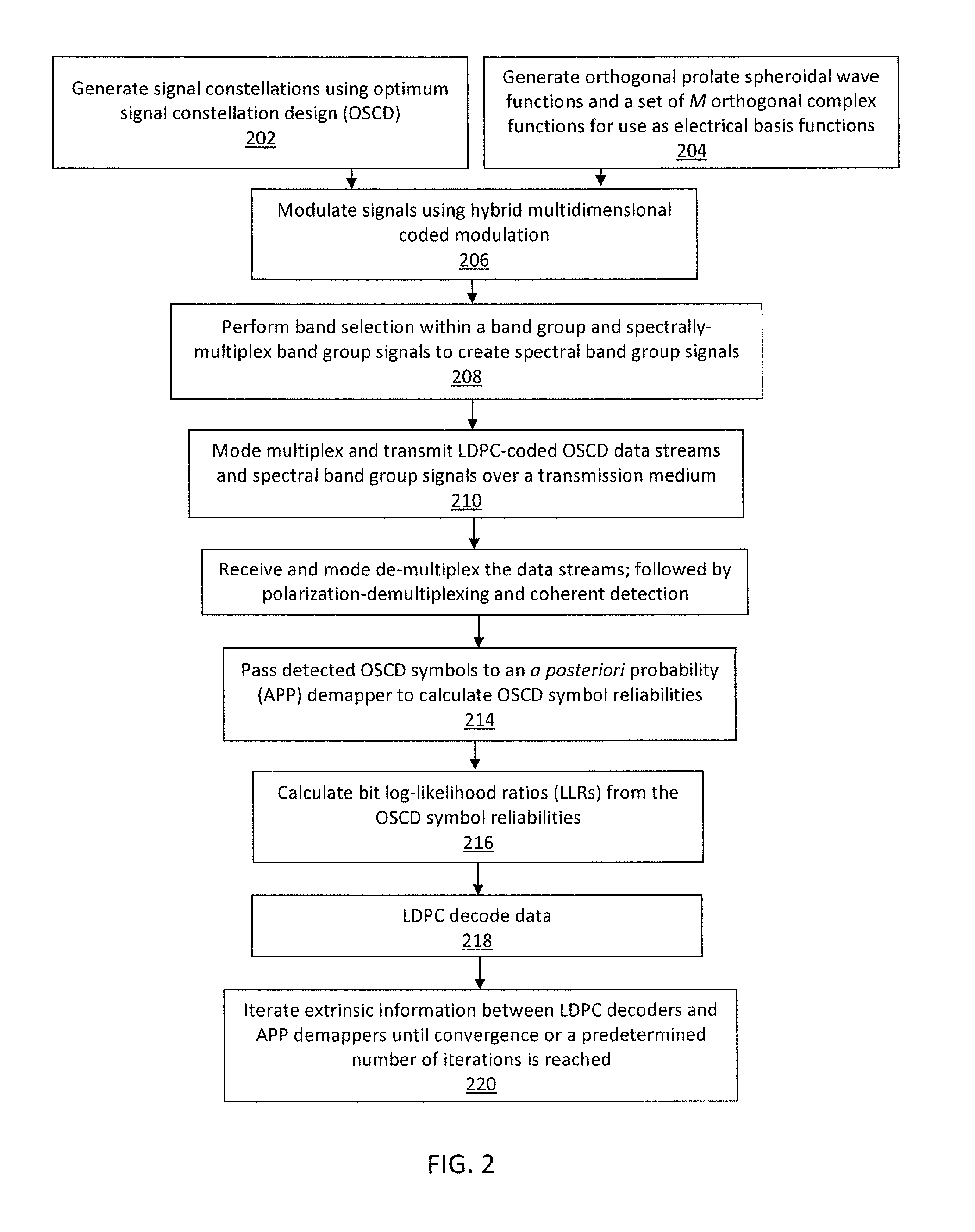
Ultra-high-speed optical transport based on adaptive ldpc-coded multidimensional spatial-spectral scheme and orthogonal prolate spheroidal wave functions
ActiveUS20140270759A1Polarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsSpectral bandsMultidimensional scaling
Systems and methods for transmitting data, including encoding one or more streams of input data using one or more adaptive Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) encoders, wherein the encoders generate one or more signal constellations; modulate one or more signals using hybrid multidimensional coded modulation; apply orthogonal prolate spheroidal wave functions as electrical basis functions; generate one or more spectral band group signals by selecting and combining two or more spectral band groups with center frequencies that are orthogonal to each other; and spectral-mode-multiplex and transmit the one or more adaptive LDPC-coded data streams including the one or more spectral band group signals combined into corresponding spatial modes over a transmission medium.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com