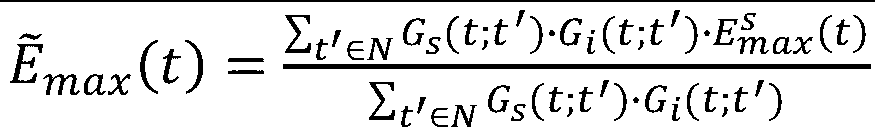Patents
Literature
90 results about "Hilbert curve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
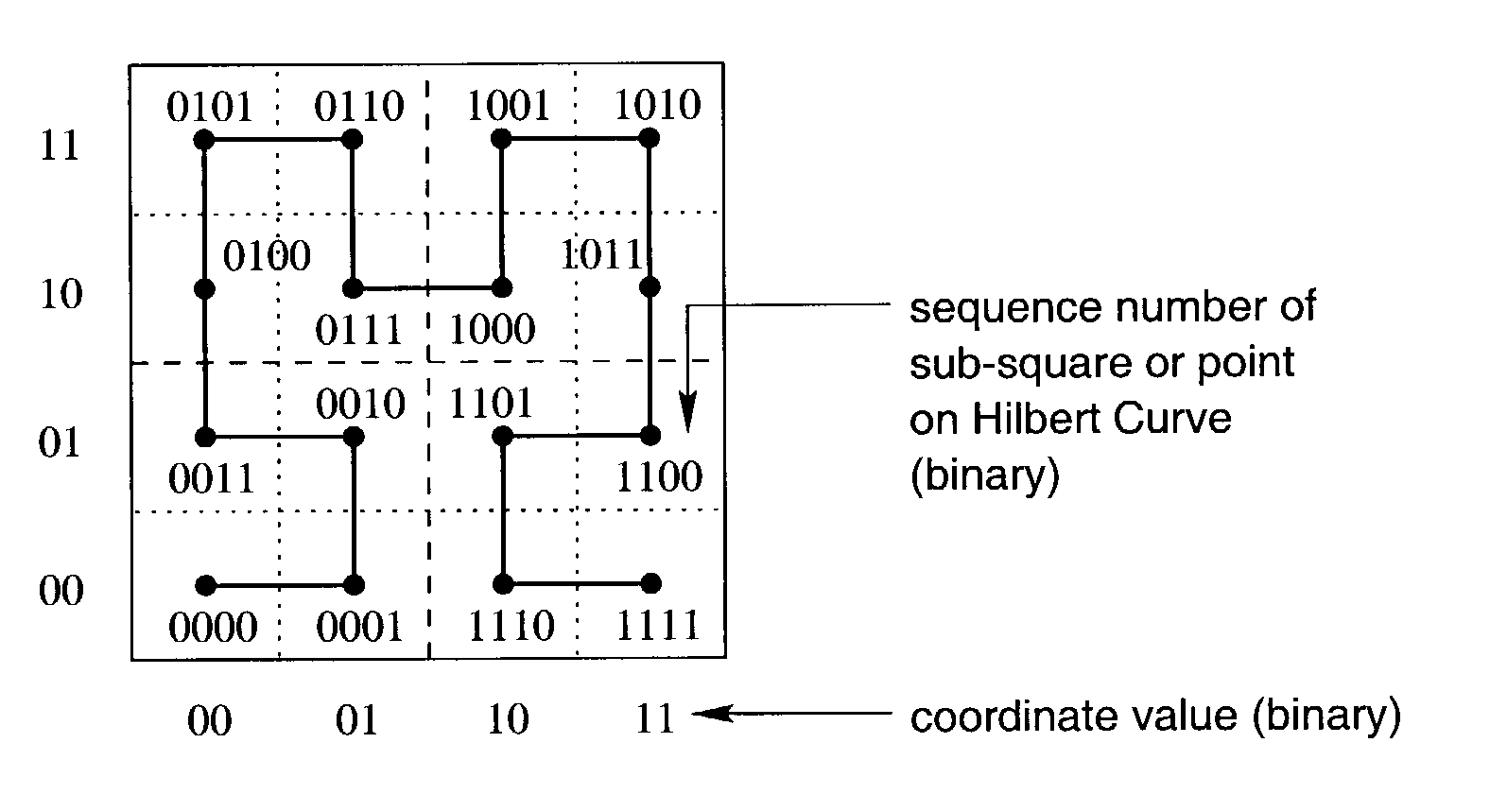
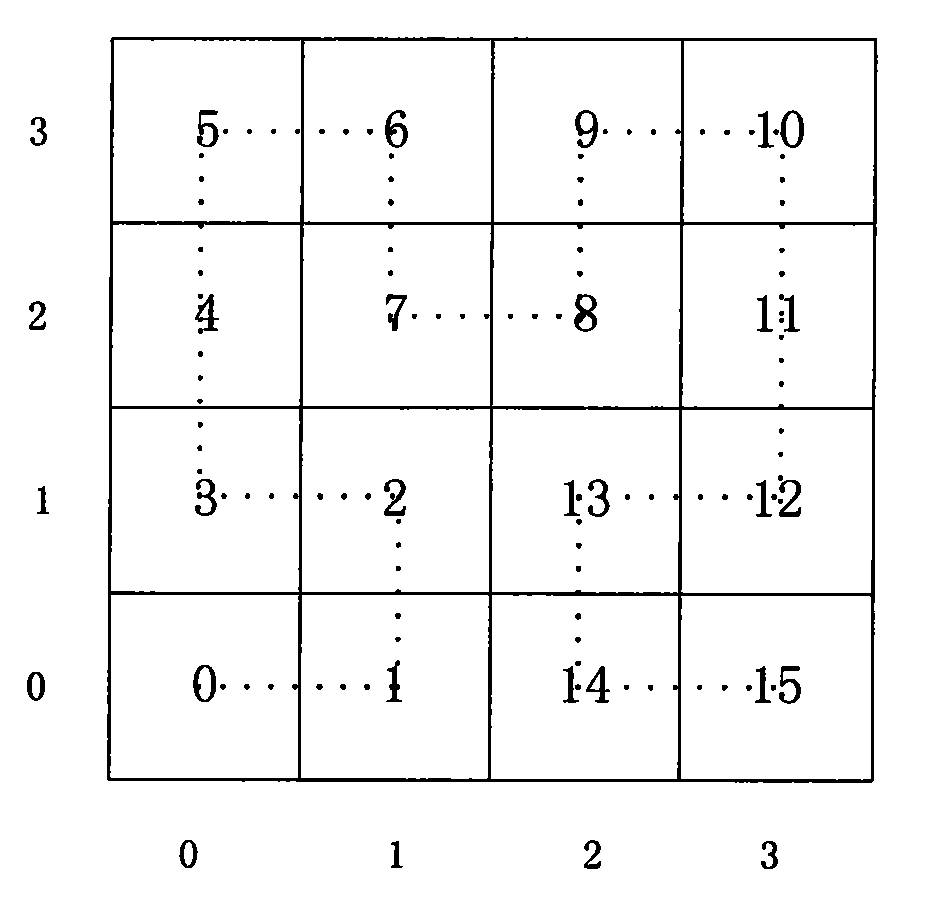
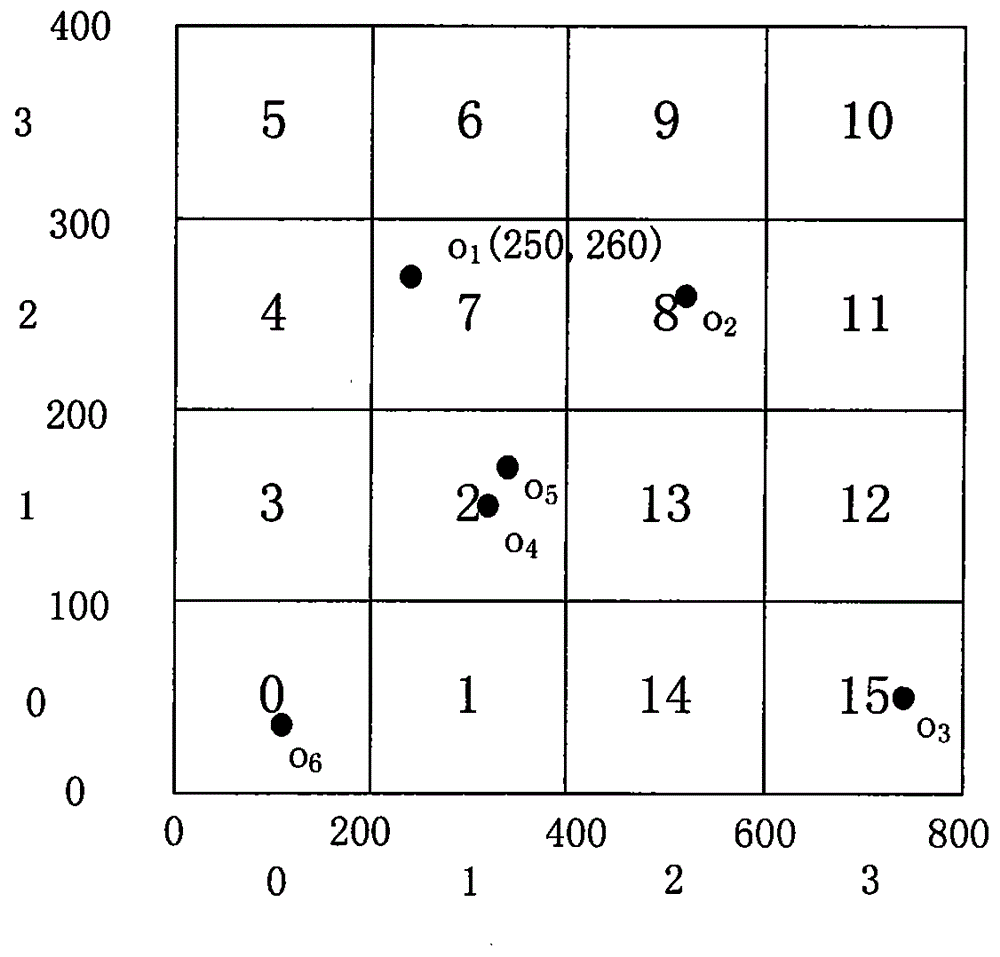
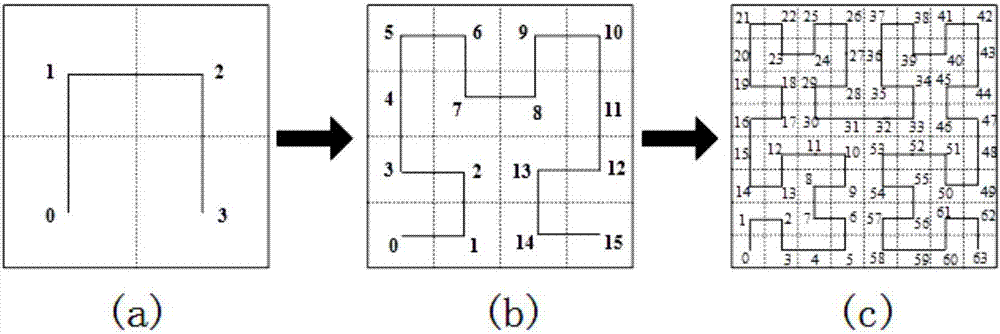
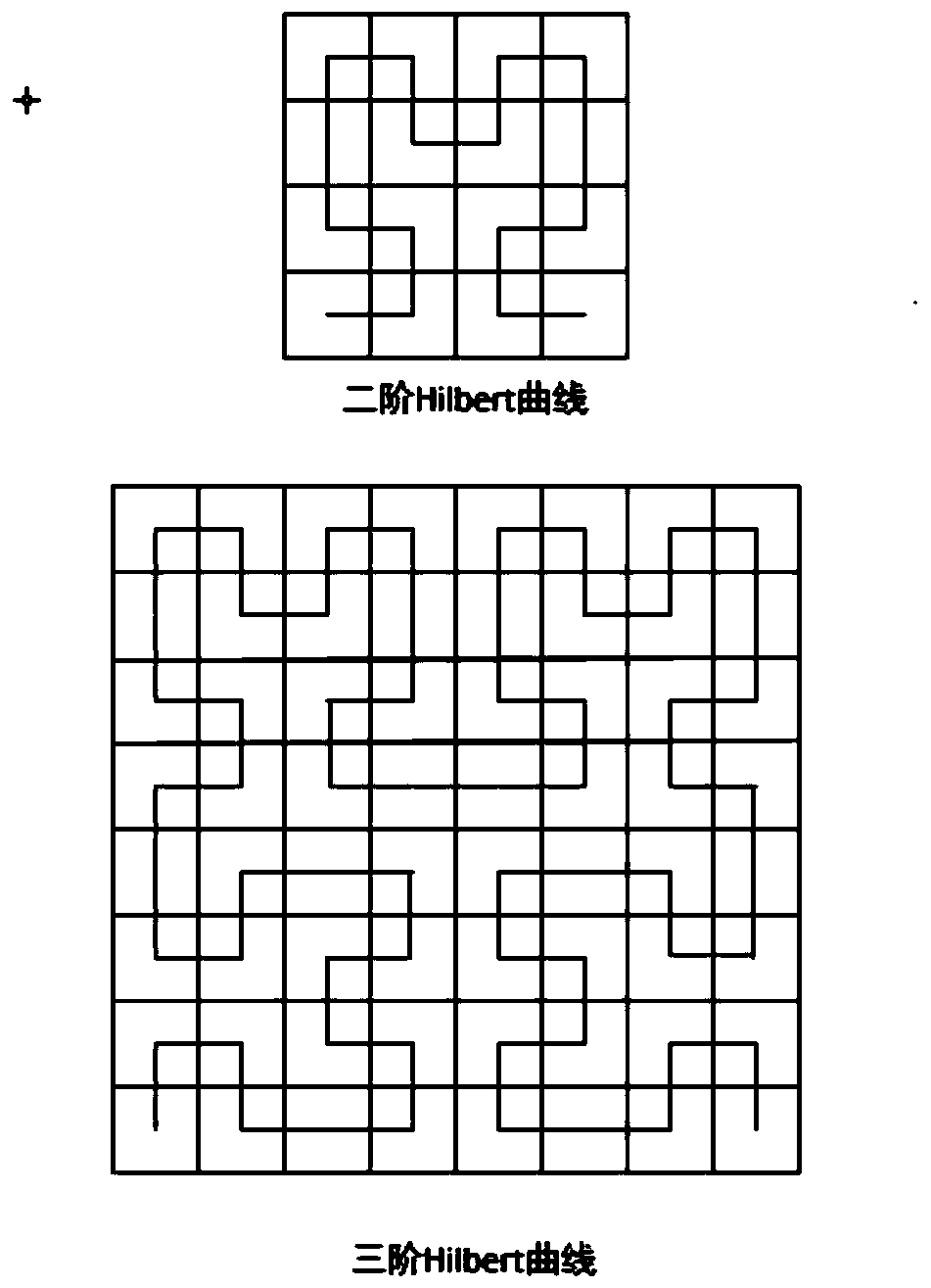
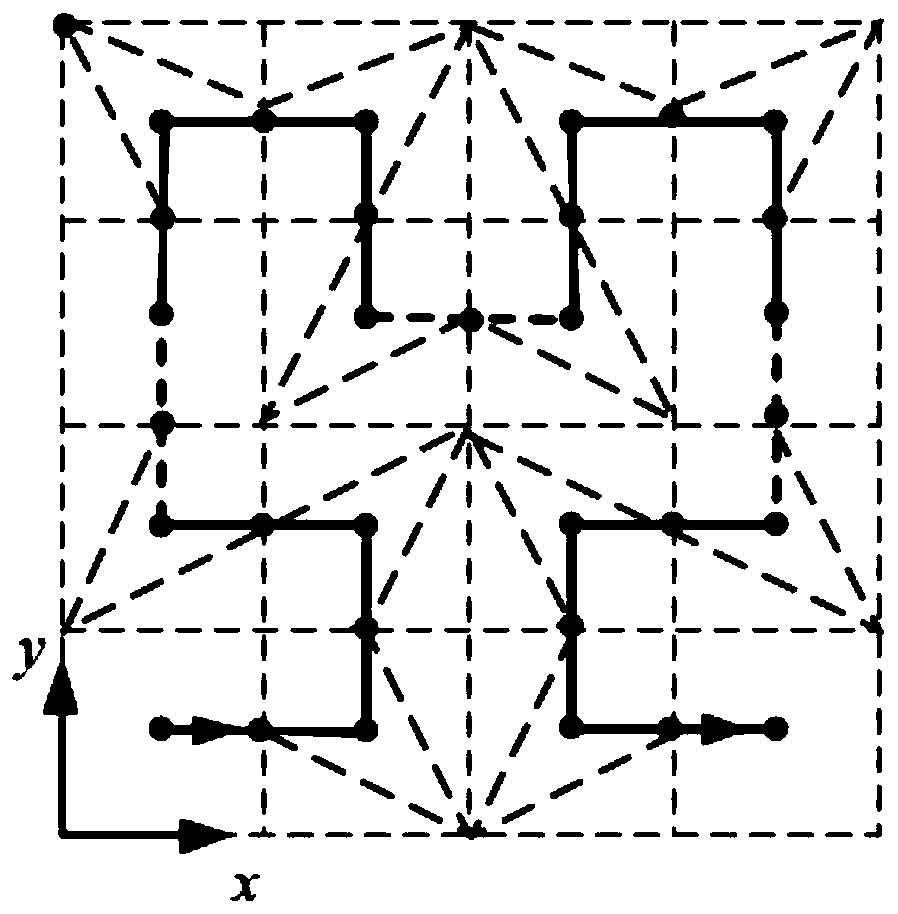
A Hilbert curve (also known as a Hilbert space-filling curve) is a continuous fractal space-filling curve first described by the German mathematician David Hilbert in 1891, as a variant of the space-filling Peano curves discovered by Giuseppe Peano in 1890. Because it is space-filling, its Hausdorff dimension is 2 (precisely, its image is the unit square, whose dimension is 2 in any definition of dimension; its graph is a compact set homeomorphic to the closed unit interval, with Hausdorff dimension 2).
Method of storing and retrieving multi-dimensional data using the hilbert curve
InactiveUS20030004938A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData spaceHilbert space
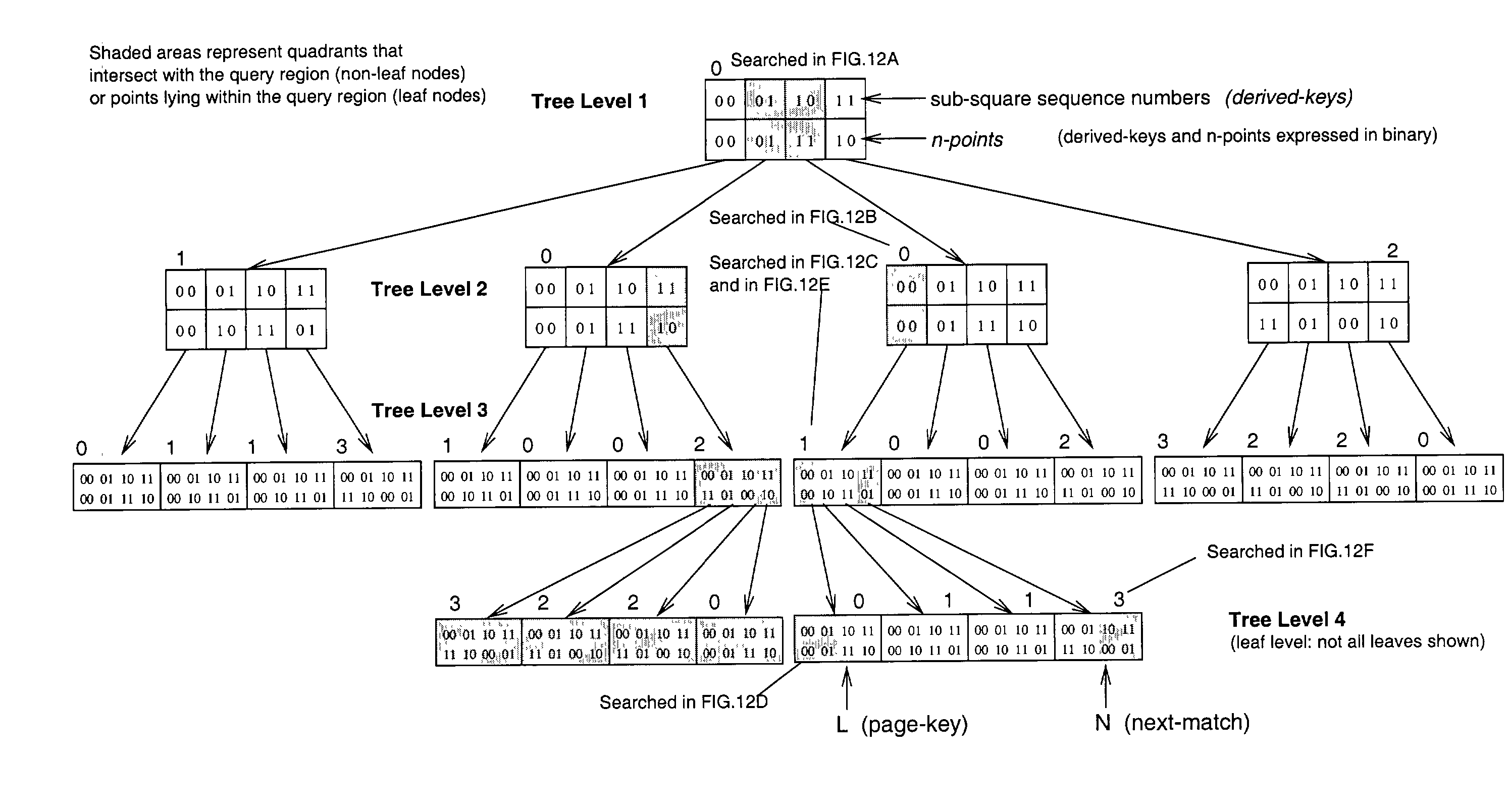
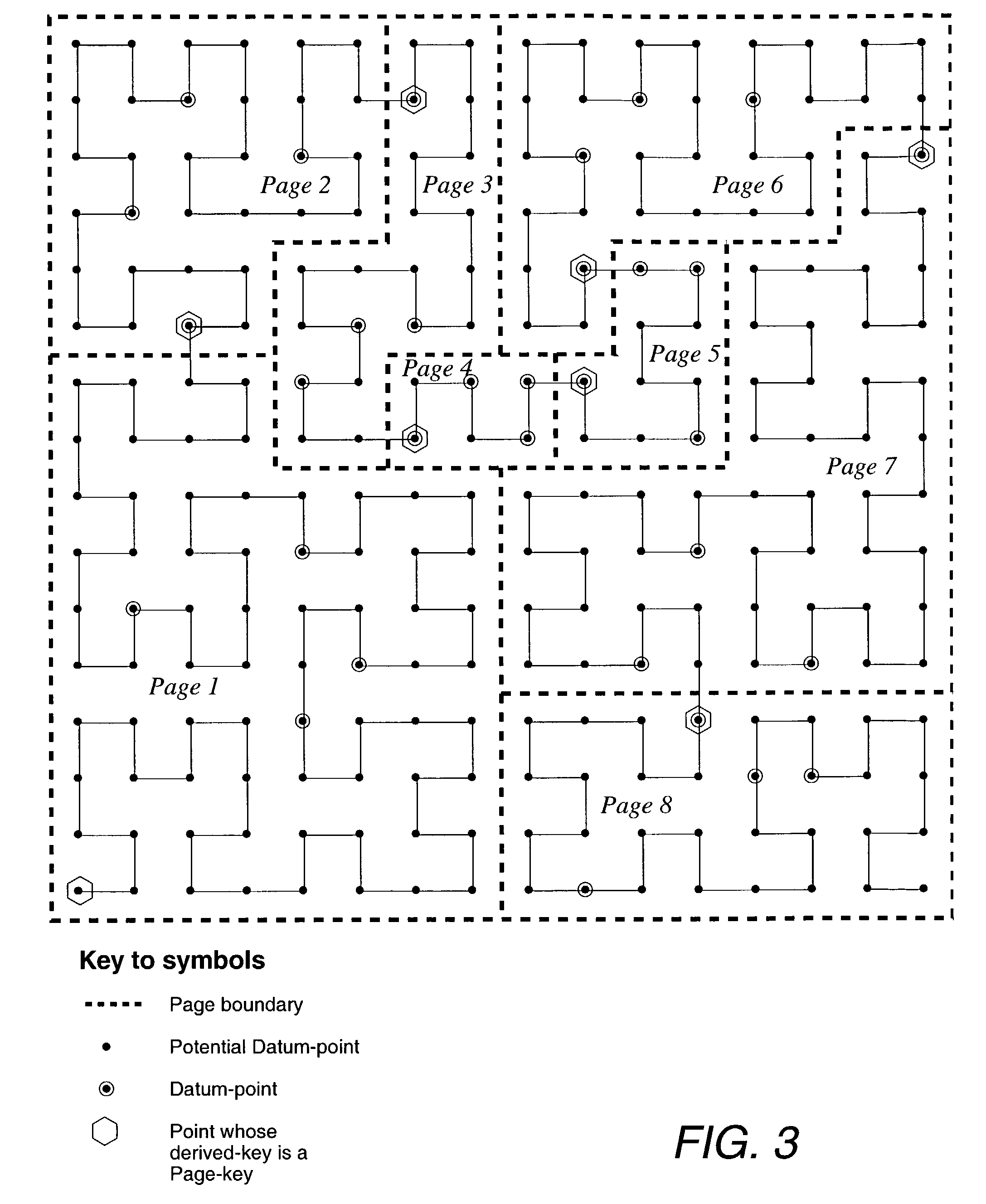
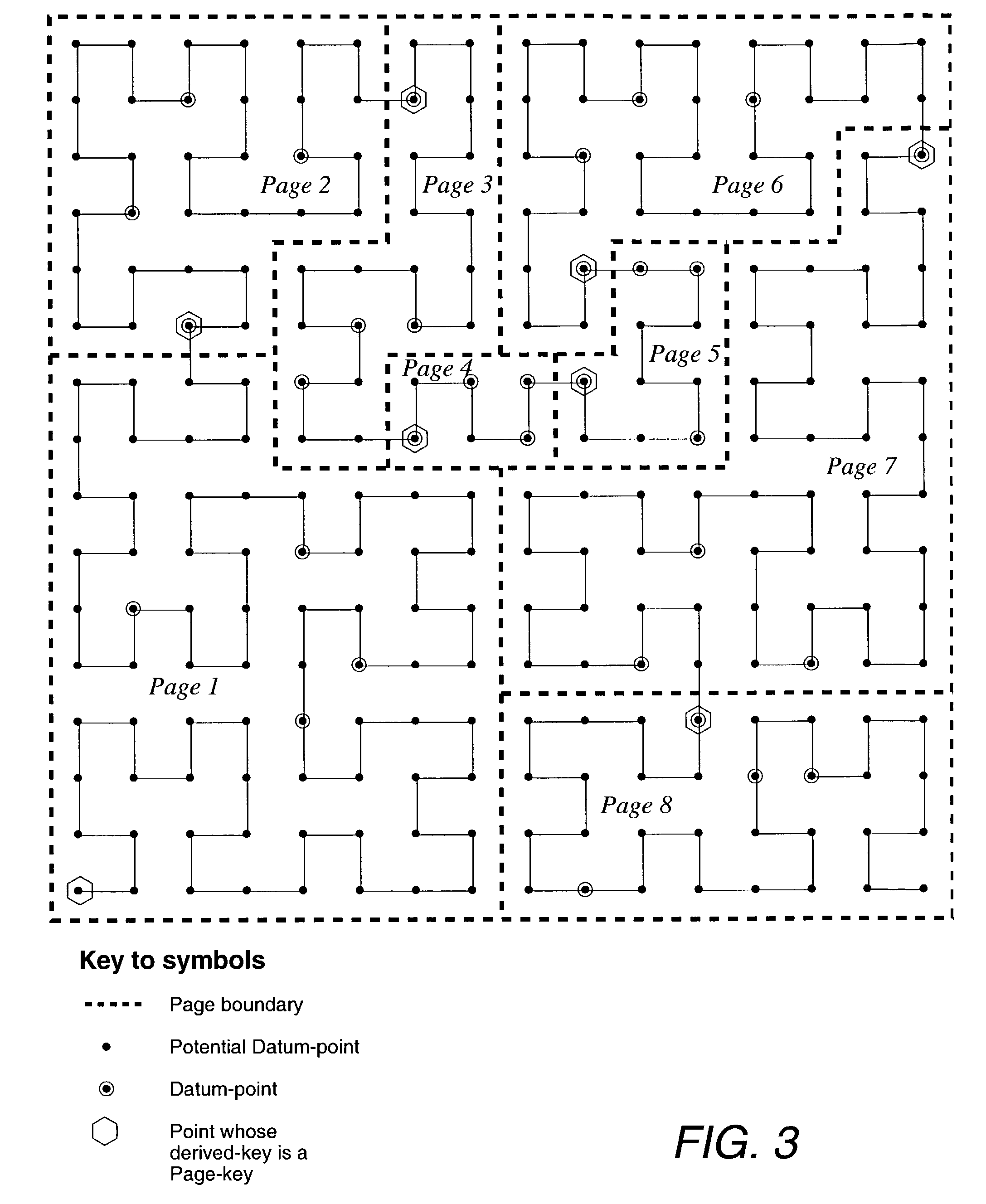
An improved method of partitioning and indexing multi-dimensional data that maps the data to one-dimensional values according to the sequence in which an approximation of a Hilbert space-filling curve passes through all of the points corresponding to potential multi-dimensional data in a data space. Data is partitioned into pages, each corresponding to a length of Hilbert curve. A page identifier is the sequence of the first point on its corresponding Hilbert curve section. The mapping orders data and also orders the data pages that contain data within a database. Mapping multi-dimensional data to one-dimensional values enables the data to be indexed using any one-dimensional index structure. The practical application of the indexing method is made viable and useful by the provision of a querying algorithm enabling data to be selectively retrieved in response to queries wherein all or some of the data that lies within a rectangular space within multi-dimensional space is required to be retrieved. The querying algorithm identifies pages whose corresponding curve sections intersect with a query region. The first intersecting page is found by calculating the lowest one-dimensional value corresponding to a possible multi-dimensional data value or point within the query region, and looking up in the index to find which page may contain this point. The next intersecting page, if it exists, is found by calculating the lowest one-dimensional value equal to or greater than the identifier of the next page to the one just identified. This new lowest one-dimensional, if found, is used to look up in the index and find the next page intersecting with the query region. Subsequent pages to be found, if any, are determined in a similar manner until no more are found. Pages found to intersect the query region can be searched for data lying within the query region.
Owner:LAWDER JONATHAN KEIR
Method of storing and retrieving multi-dimensional data using the hilbert curve
InactiveUS7167856B2Gain selective accessMinimizes numberData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData spaceHilbert space
Owner:LAWDER JONATHAN KEIR
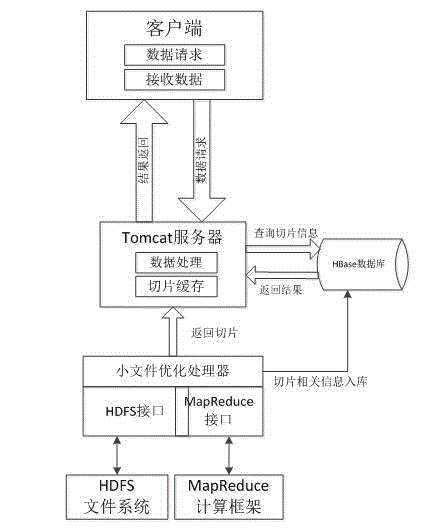
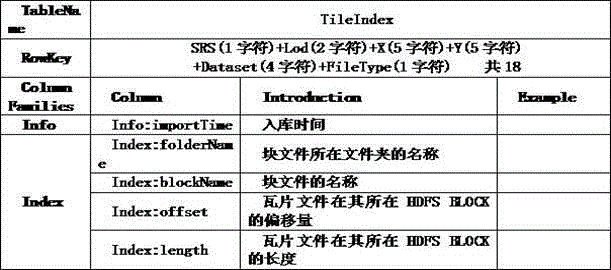
Mass small tile file storage management method based on hadoop
ActiveCN104820714AIncrease inbound storage speedEfficient storageGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsReal-time dataOriginal data
The invention provides a mass small tile file storage management method based on hadoop. According to the method, sequencing is carried out through a Hibert curve, and then, grid tile data is subjected to serialization compression storage by a Sequence File technology of the hadoop pre se; when tile compression blocks are generated, the multithreading parallel compression of a plurality of servers is realized, tile index information is generated, and the mass file library entering storage speed is accelerated; the regular naming of block file names is managed, and efficient storage, fast reading and high-performance grid data service can be provided for mass multi-source and multi-version grid small tiles; and ITMS (Improved Tile Map Service) is designed, and the problem of delay and bandwidth occupation caused by original data transmission and real-time data processing request responding, so that the project data retrieval and transmission requirements are met.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Spatio-temporal data indexing method in non-relational database
ActiveCN107423368AImprove storage efficiencyImprove query efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseDynamic network topology
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
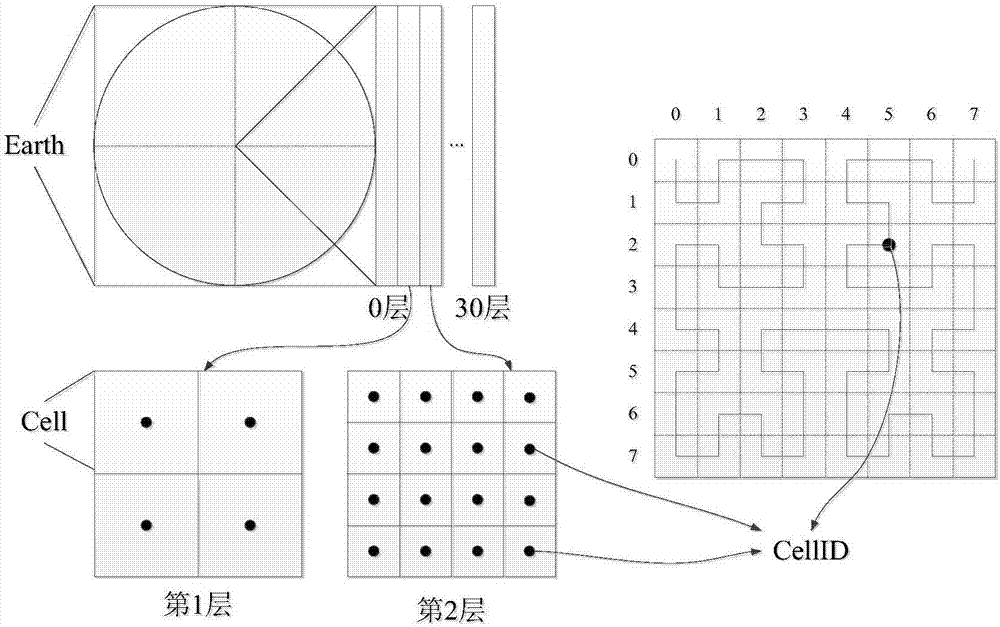
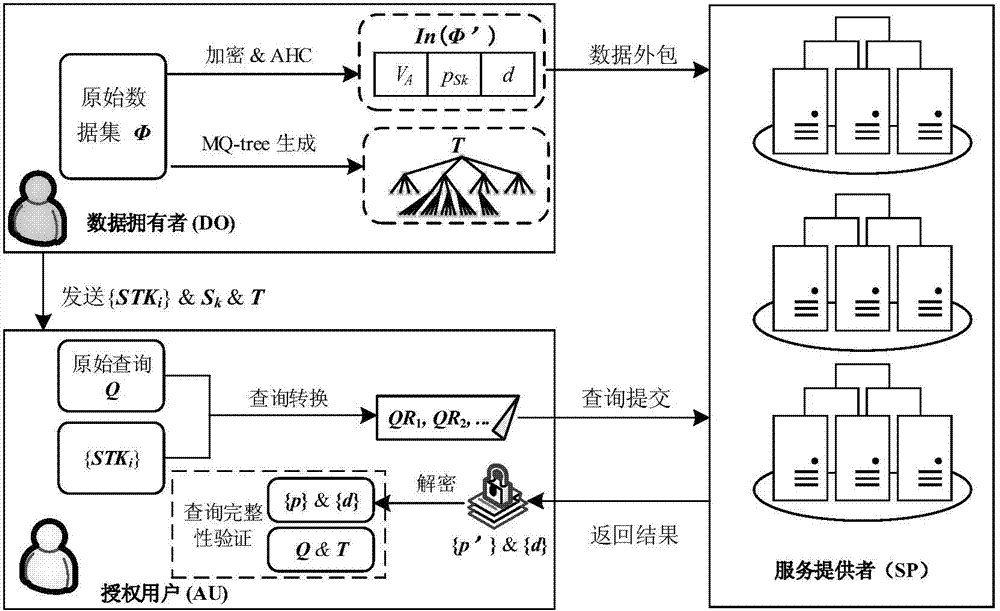
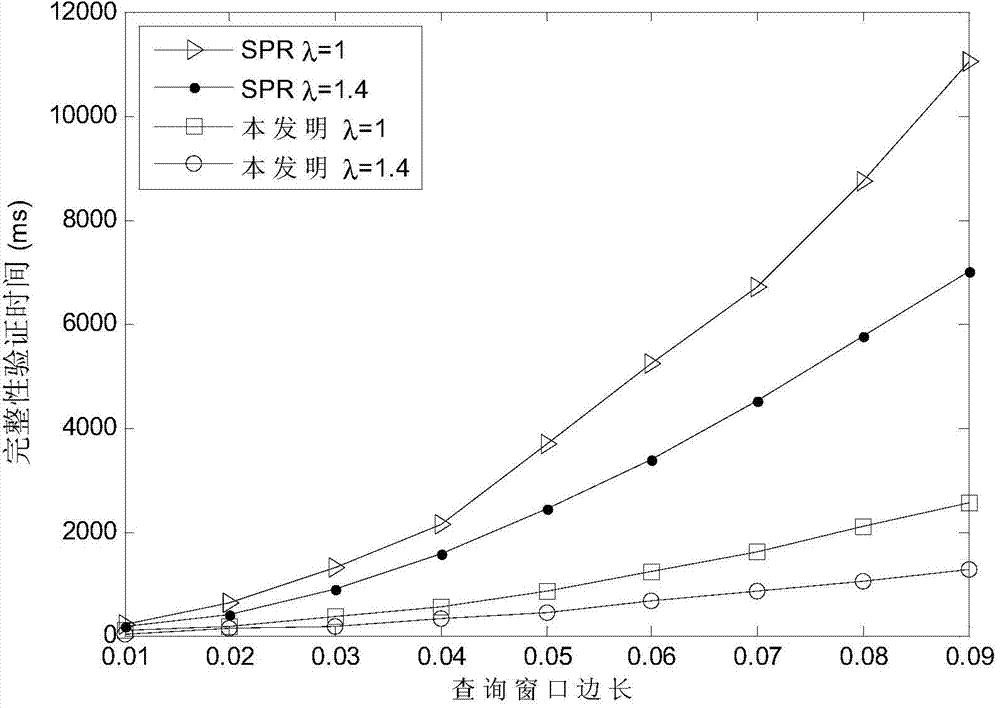
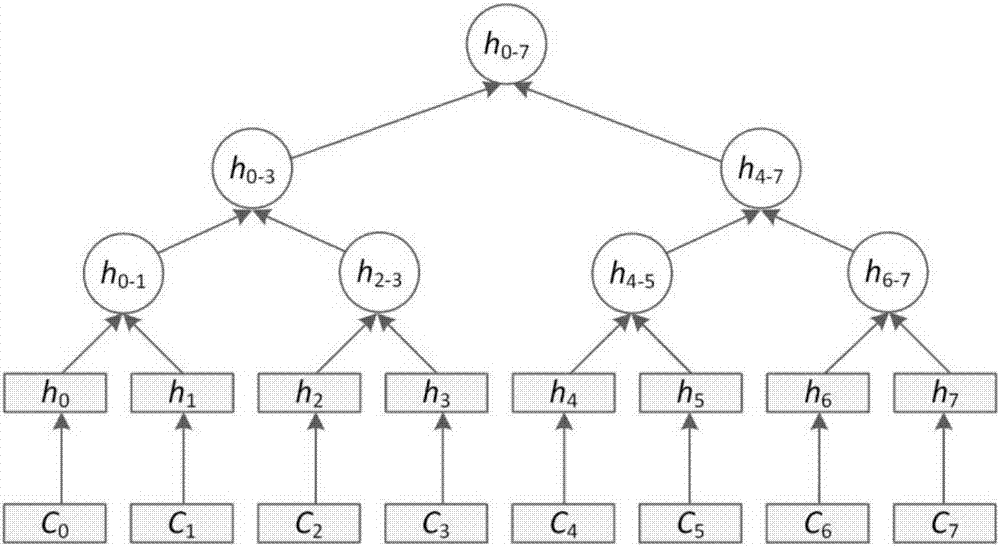
Merkle tree structure-based space inquiring integrity verification method
InactiveCN104750784AEasy to storeIncreased maintenance overheadSpecial data processing applicationsNODALTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a Merkle tree structure-based space inquiring integrity verification method. Based on an existing quadtree node generated by a self-adaption Hilbert curve, a Merkle tree structural construction method for supporting the inquiring integrity verification is provided, and an integrity verification method for range inquiring and KNN inquiring is provided, so that an integrity verification result provided by the Merkle tree structure-based space inquiring integrity verification method is free of phenomena of the misinformation and the false-information, and malevolence changing is difficult to carried out on a user inquired result by a service supplier. Under the mode of space data outsourcing service, the method can provide an efficient verification structural generating function, accurate range inquiring and a KNN inquiring integrity verification function for a user, and therefore the quality of space inquiring service can be guaranteed.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Video copying detection method based on robust hash
InactiveCN102393900AReduce computationShort timeCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsPattern recognitionTemporal information
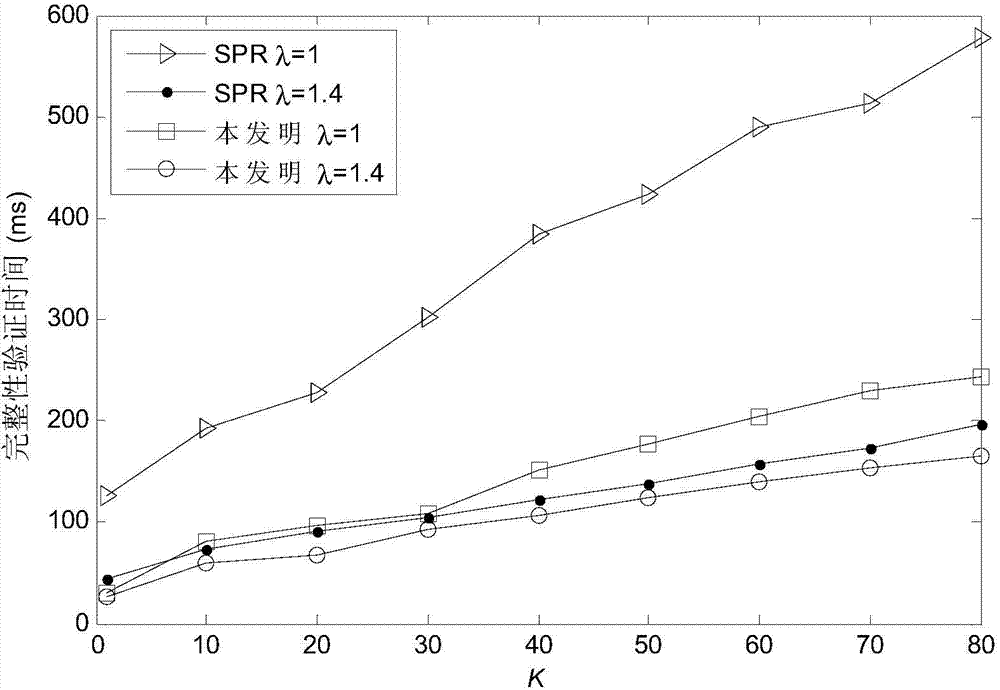
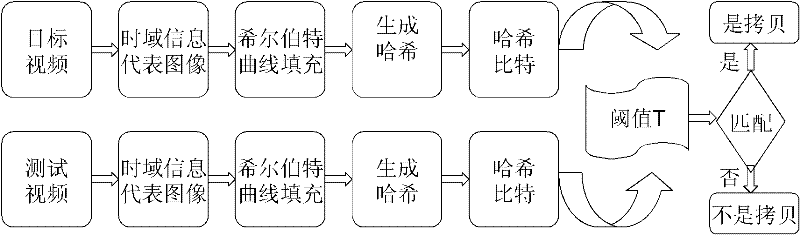
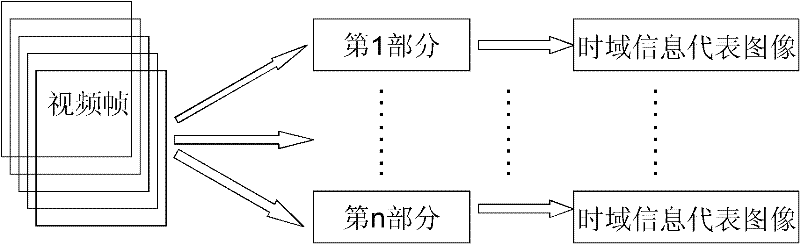
The invention discloses a video copying detection method based on robust hash. The advantages of spatial-temporal union information and a sequence characteristic in the aspect of reflecting video contents are used fully. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, dividing a video frame into parts which are overlapped with one another in 50 percent and generating a time domain information representative image by using the video frame of each part; secondly, filling the time domain information representative images by using a hilbert curve to further calculate a gray scale three-meanvalue of each block on the hilbert curve, and generating a hash fingerprint by comparing the three-mean values; and finally, performing hash matching according to the obtained hash fingerprint and judging whether the video is a copied video. An experimental result shows that the robustness and the discrimination of an extracted characteristic are greatly improved and developed.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
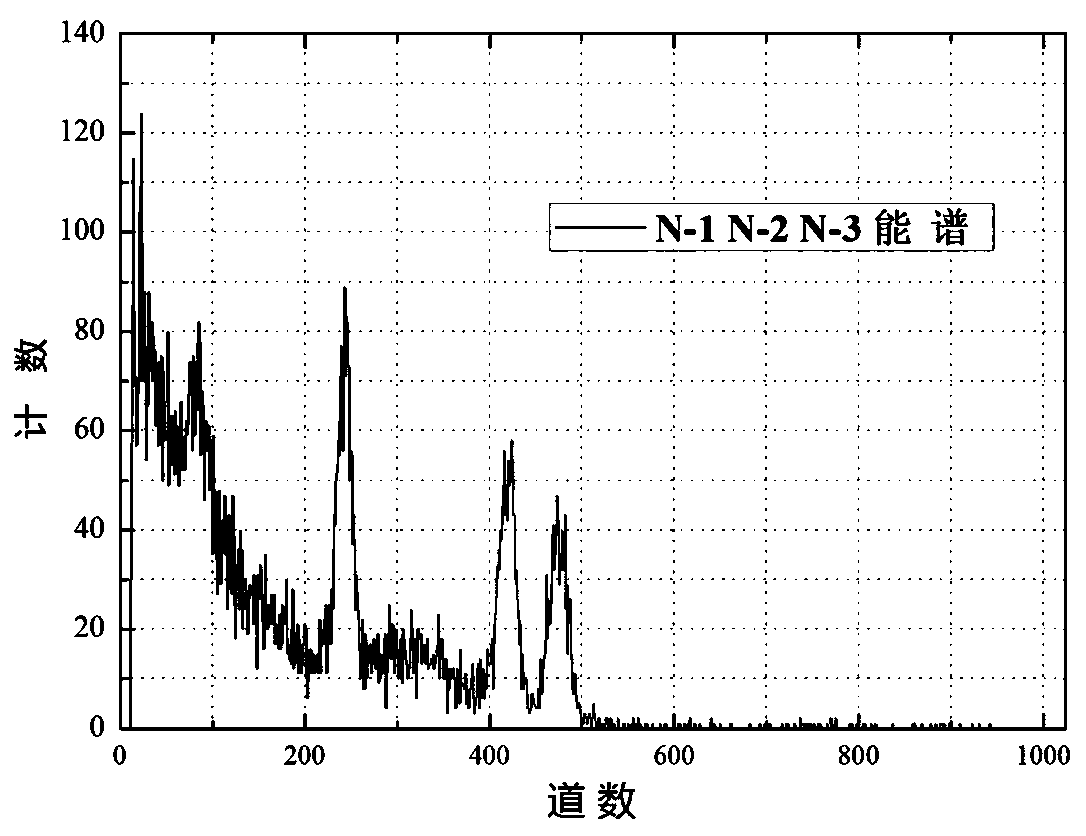
Energy spectrum analysis method based on Hilbert curve transformation and depth learning
ActiveCN109063741AImprove recognition rateImprove stabilityX-ray spectral distribution measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionAnalysis method
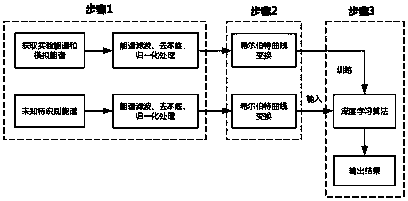
The invention discloses an energy spectrum analysis method based on Hilbert curve transformation and depth learning, belonging to the field of radiation environment monitoring and image recognition, which has the characteristics of high recognition rate, good stability and strong adaptability. The invention comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a detection energy spectrum and a simulation energy spectrum and performing pretreatment; (2) Transforming the traditional one-dimensional energy spectrum analysis into two-dimensional image recognition, training and testing the full spectrum input depth learning; (3) A depth learning algorithm for fast nuclide recognition is constructed, and the effect of the depth learning classifier is analyzed by determining the classification threshold and ROC curve.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
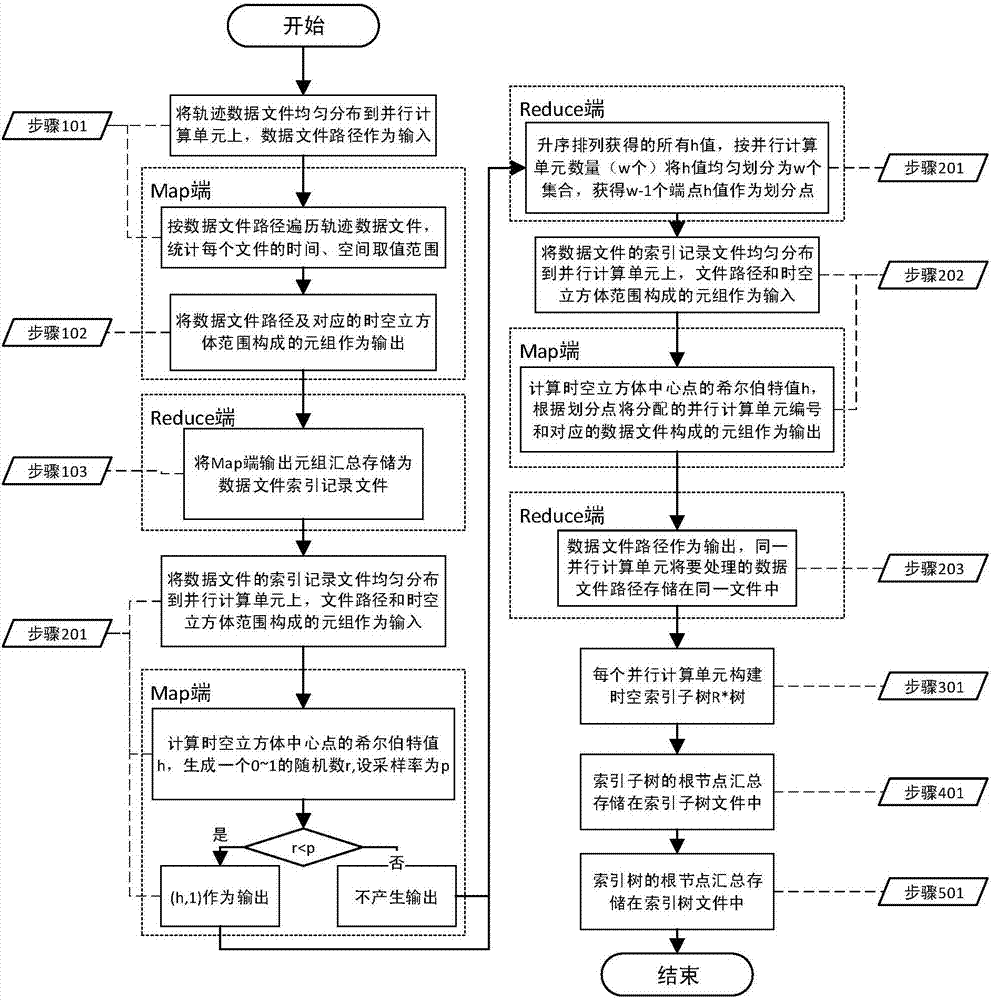
Spatial-temporal index constructing method oriented to massive track point data
ActiveCN107220285AReduce the chance of tiltingReduce storage consumptionSpecial data processing applicationsExtensibilityData file
The invention relates to a parallel spatial-temporal index constructing method oriented to massive track point data. According to the spatial-temporal index constructing method oriented to the massive track point data, with a track point data file being an index unit, the storage consumption of an index is lowered, so that an index structure has high expandability; meanwhile, by utilizing a Hilbert curve to divide a data file, compared with other modes from multi-dimension to one-dimension mapping, since the Hilbert curve has an excellent space filling characteristic, the dividing effect is better, and the probability of the occurrence of data skew can be lowered.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
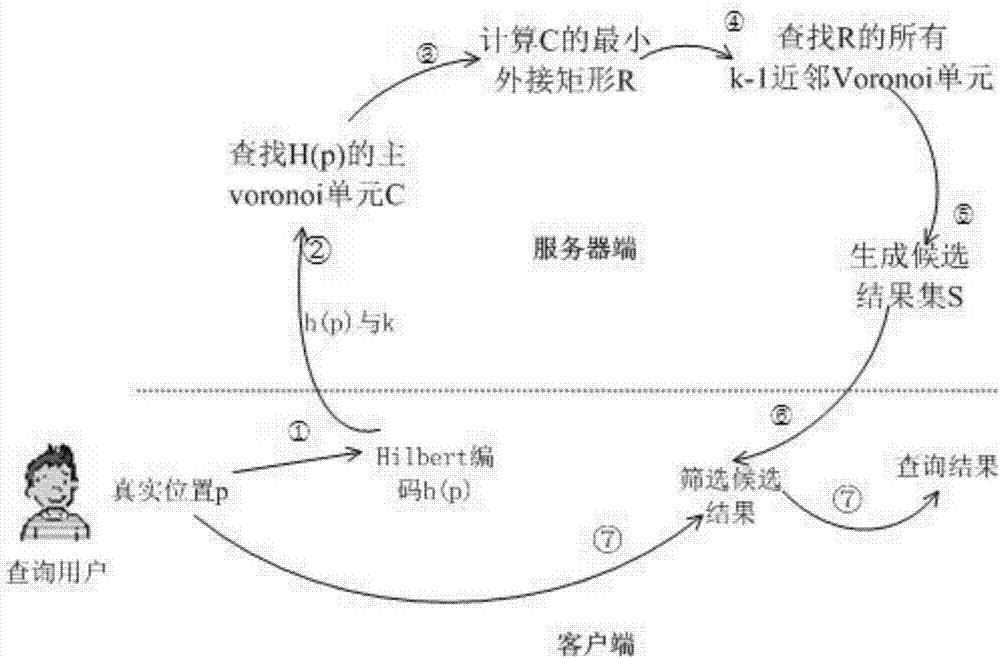
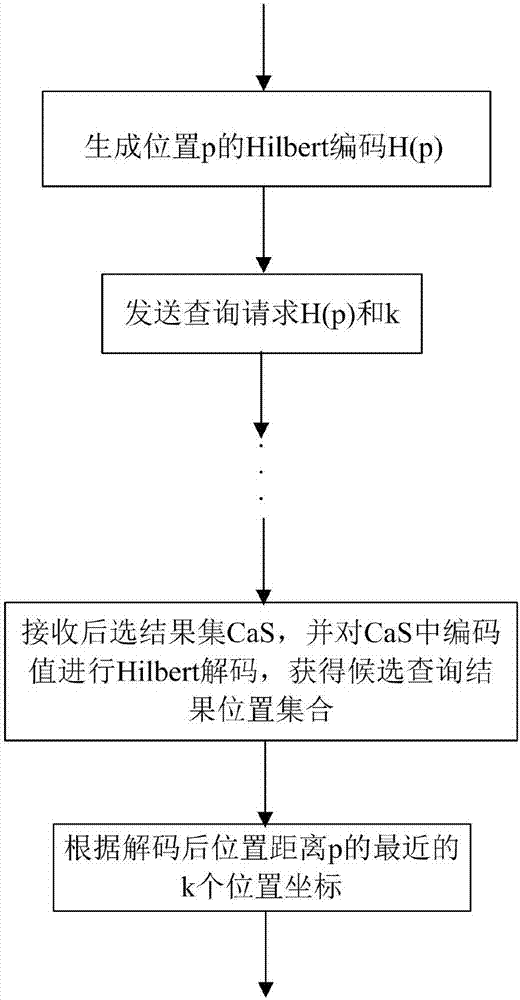
A privacy protection query method based on Voronoi polygons and Hilbert curve coding
ActiveCN107169372AImprove protectionImprove work efficiencyDigital data protectionSpecial data processing applicationsIndex mappingPrivacy protection
The invention relates to a privacy protection query method based on Voronoi polygons and Hilbert curve coding. The method comprises the steps that a server end performs Voronoi polygon partitioning on a plane where a target object is located, performs partitioning coding by using the Hilbert curve, and establishes a B+ tree index mapping the Hilbert cell coding and Voronoi polygons; a user submits a Hilbert curve coding value H (p) of a self-position p to the server via a client for k-neighbor query; the server end searches for a Voronoi polygon C corresponding to the H(p) on the query tree to generate the minimum enclosing rectangle R of C; the server end searches for k-1 neighbor Voronoi polygons of R, forms Hilbert curve coding values corresponding to the Voronoi polygons into a candidate query result set CaS and returns the result to the client; the user decodes the Hilbert curve coding values in the CaS to screen out the nearest neighbor target object. The method achieves k-neighbor query for protecting position privacy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Fast Delaunay triangulation method for arbitrarily-distributed large-scale point cloud data
ActiveCN105654552AReduce the search step sizeImprove network construction efficiency3D modellingComputational sciencePoint cloud
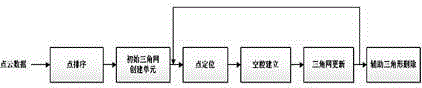
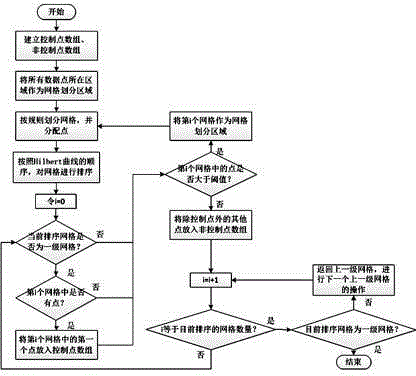
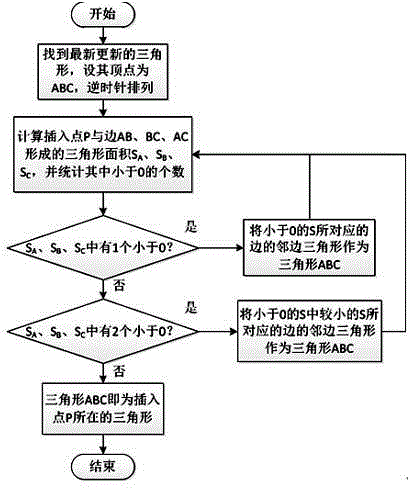
The invention provides a fast Delaunay triangulation method for arbitrarily-distributed large-scale point cloud data, comprising the following steps: dividing a multi-grid to create an initial triangulated network; inserting points one by one; updating the triangulated network; and deleting auxiliary triangles to complete Delaunay triangulation. Through multi-grid division and a sorting method through sequential grid traversing based on a Hilbert curve, the search step length in the point positioning process and the number of finally-deleted long-narrow triangles produced in the triangulation process are reduced. By adopting a new algorithm in the point positioning process, the process of solving the centers of gravity and intersecting edges of triangles is avoided, and the amount of calculation is reduced. The efficiency of Delaunay triangulation under the condition of a large amount of point cloud data and uneven distribution thereof is improved greatly.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
Multi-resolution image system
ActiveUS20170169544A1Geometric image transformationImage memory managementImage resolutionMulti resolution
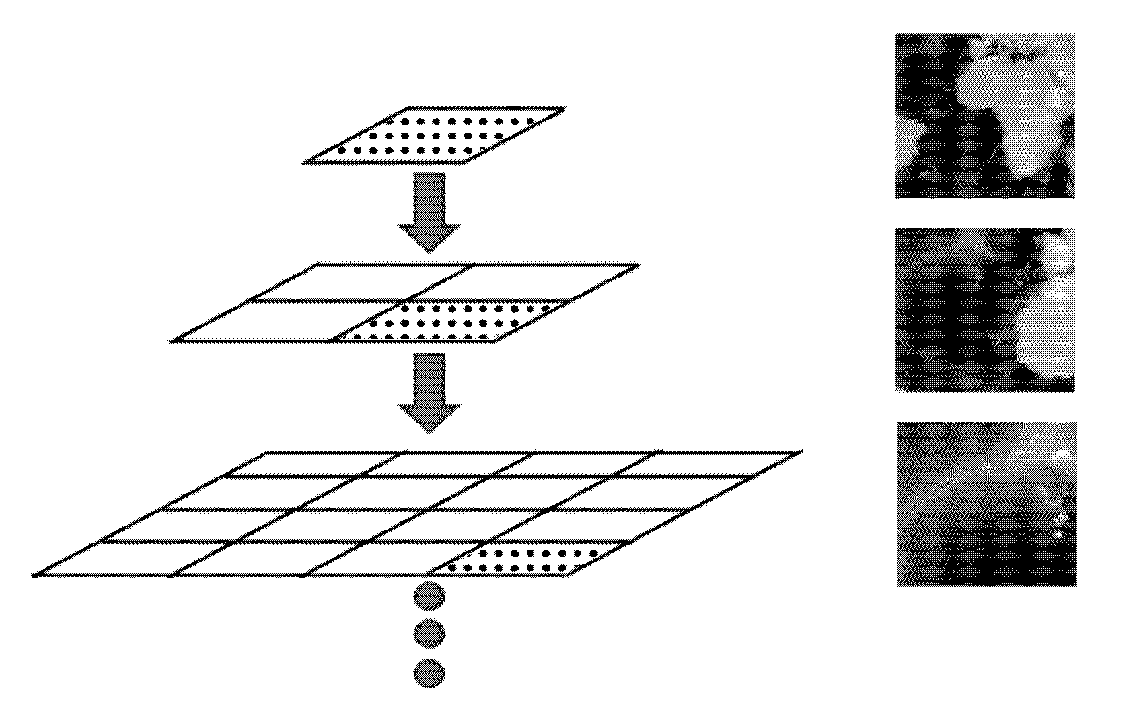
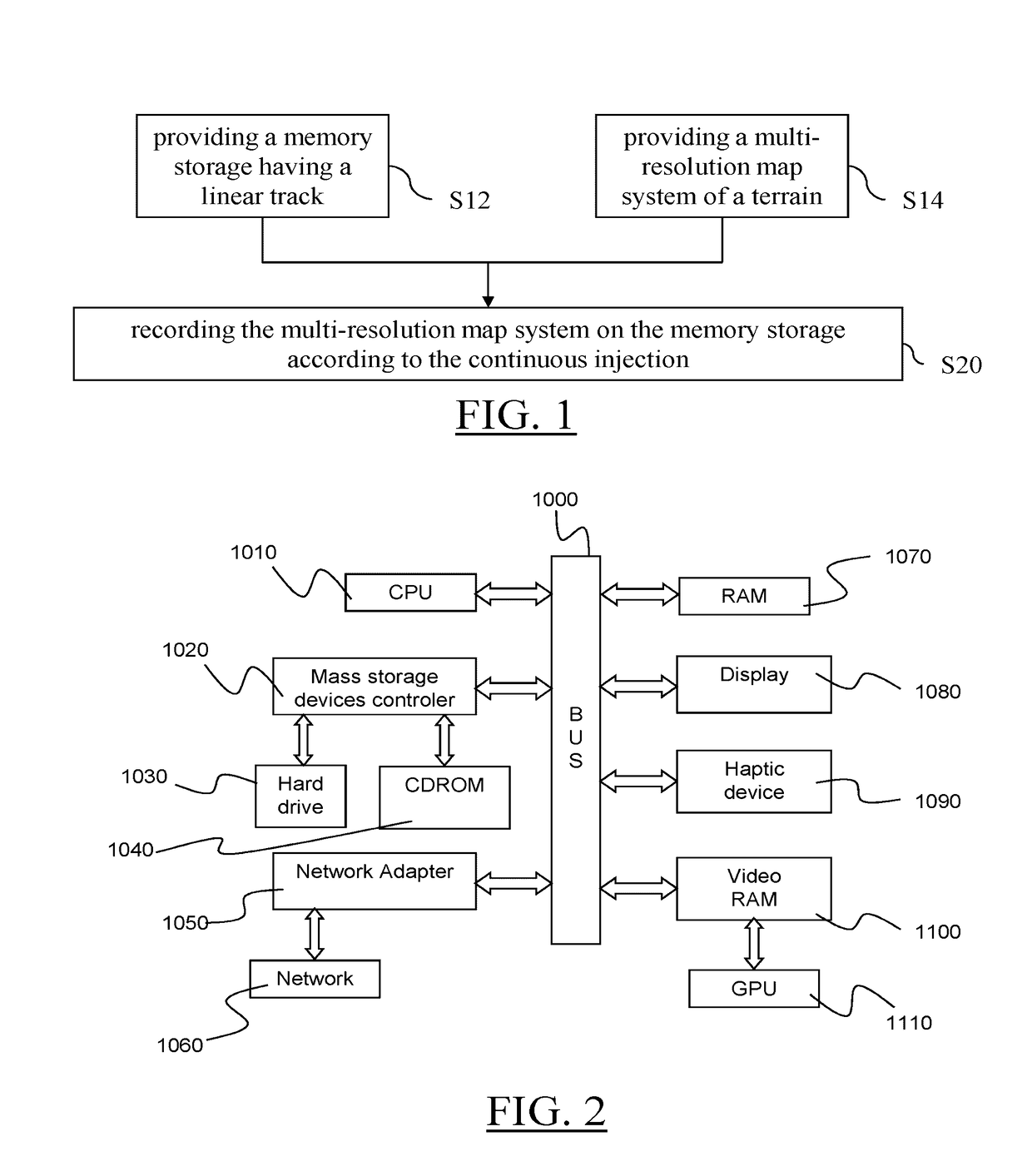
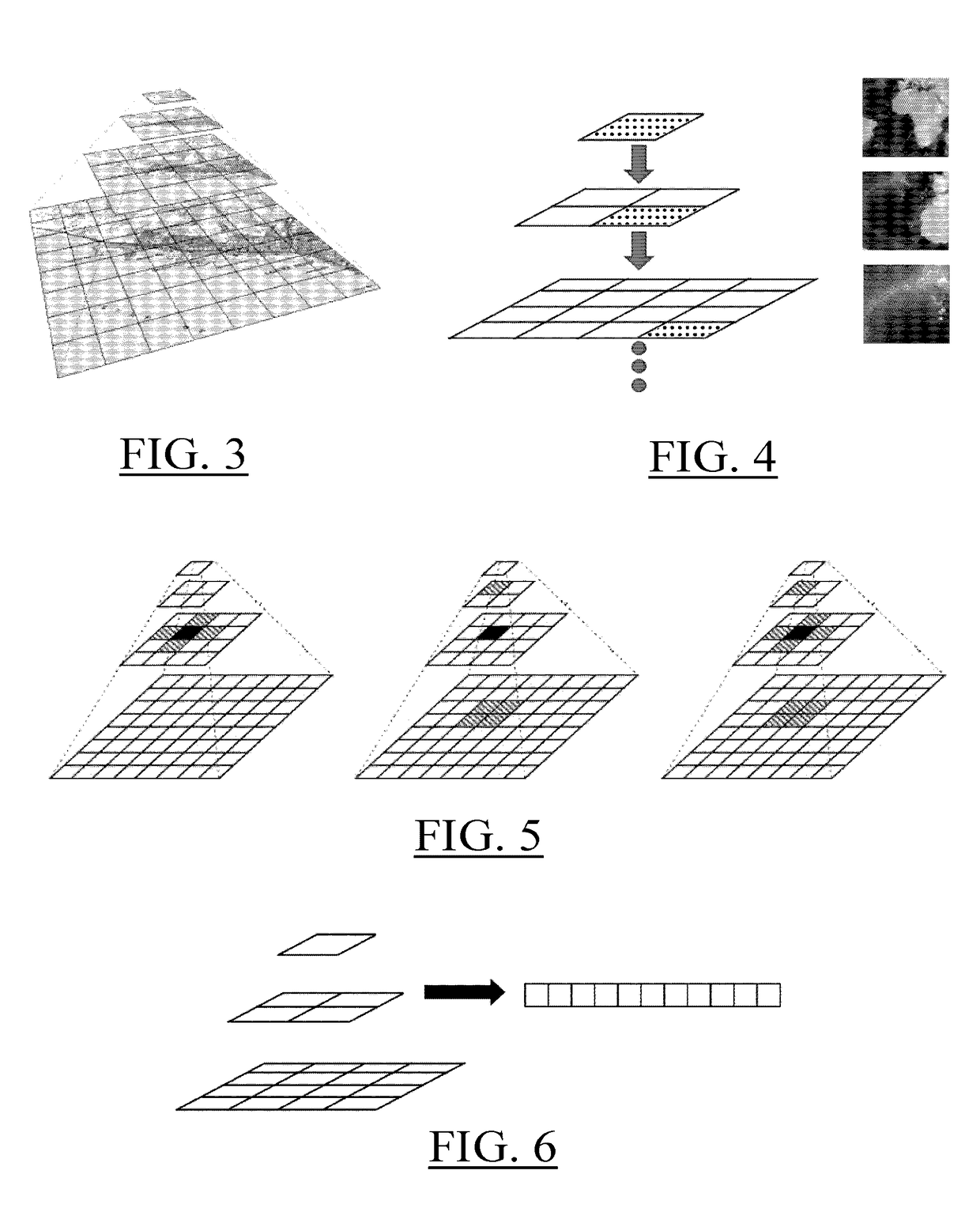
The invention notably relates to a memory storage having a linear track and having recorded thereon a multi-resolution image system of an object, the multi-resolution image system including a set of images, each image representing the object and having a respective resolution, wherein the recording is according to a continuous injection from a space-filling curve of the set of images to the linear track, the space-filling curve interlaces the different images, and the intersection between the space-filling curve and each image is on a Hilbert curve.The invention improves the way to record a multi-resolution image system of an object on a memory storage.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
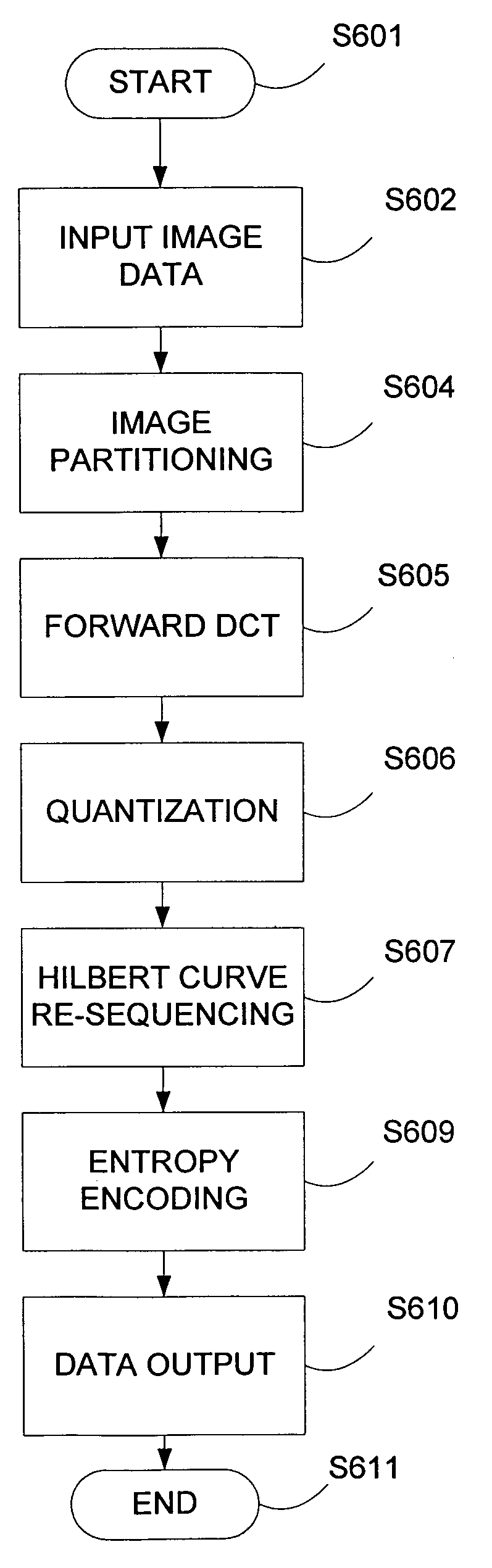
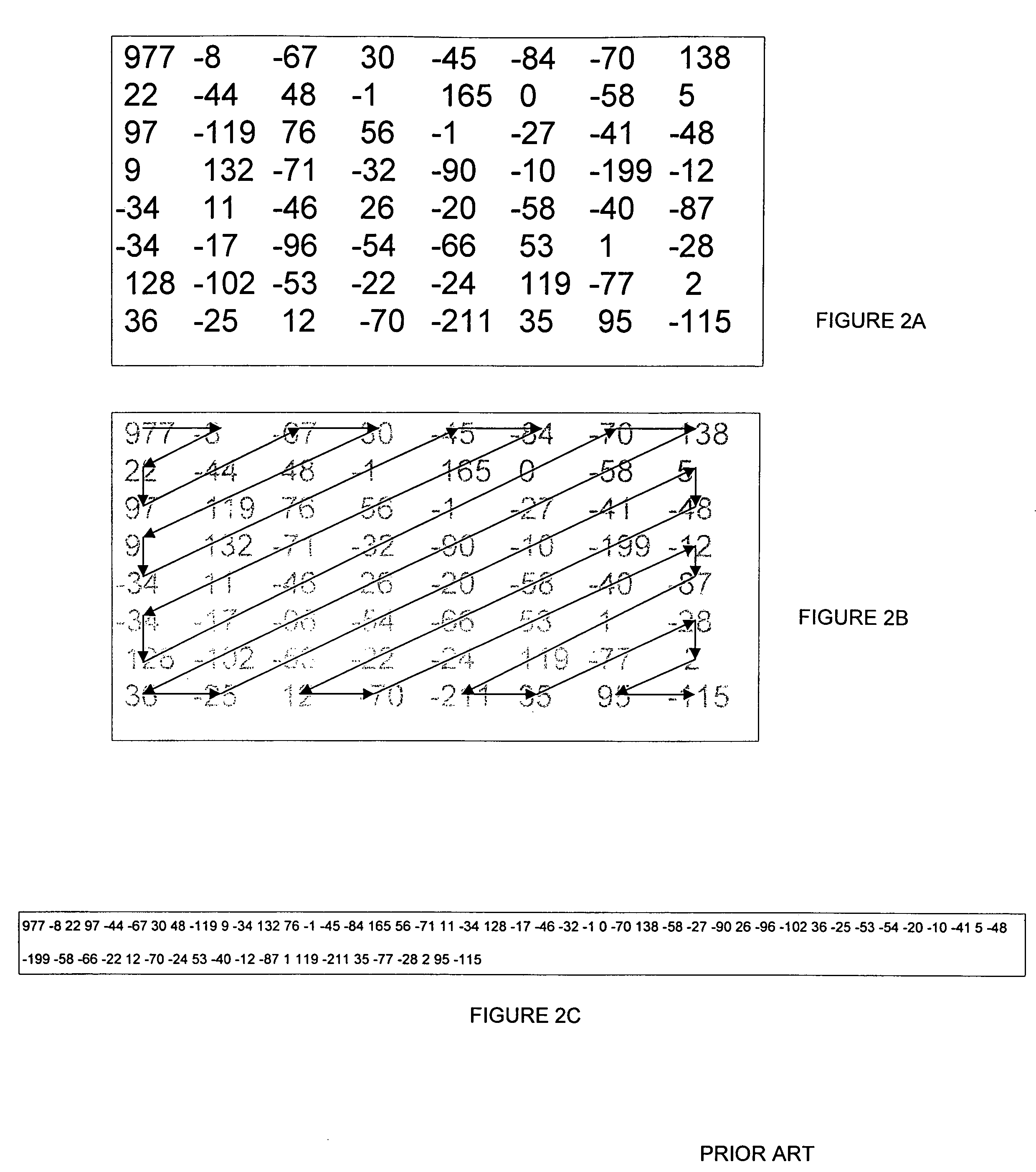
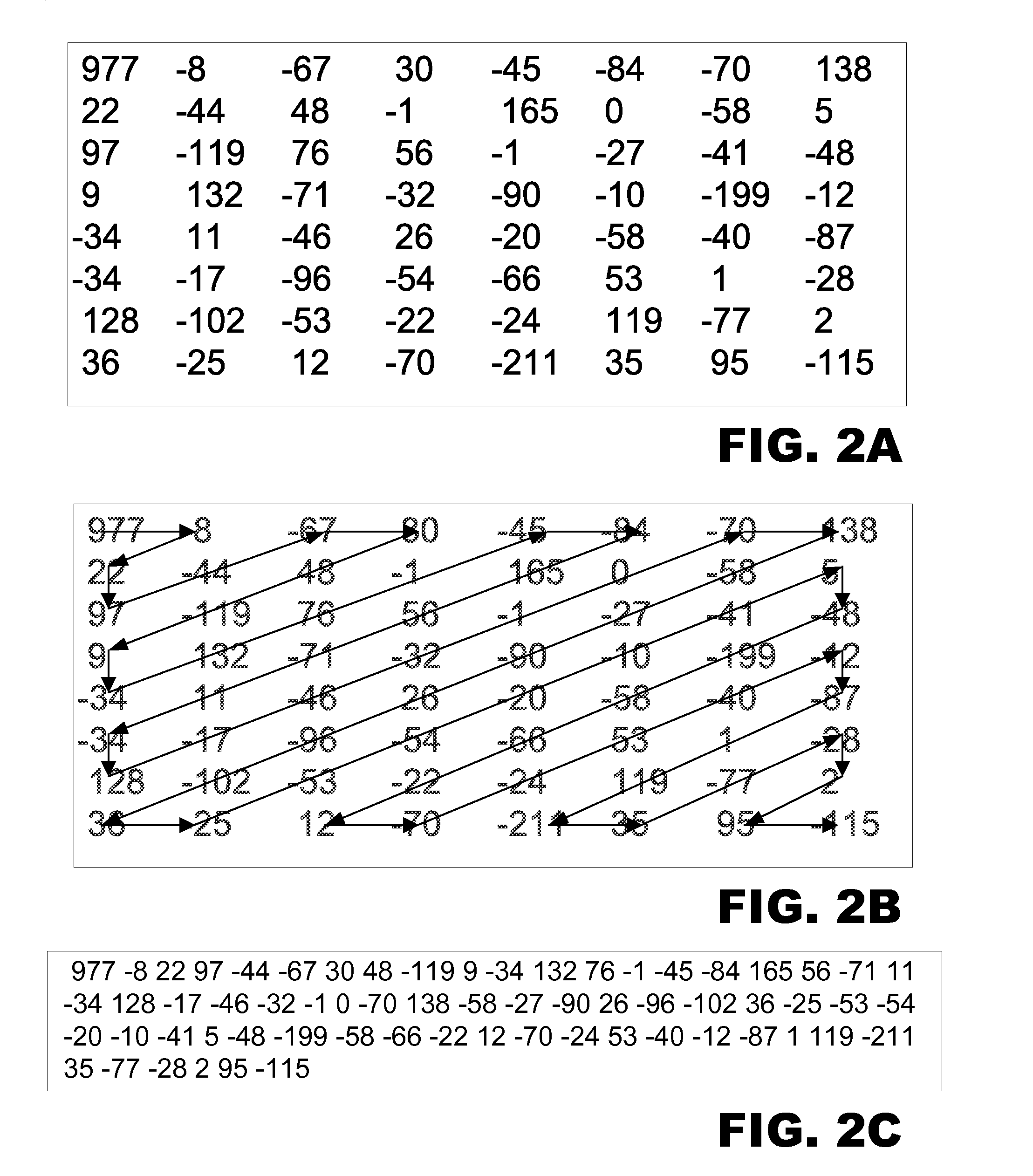
Enhanced image compression utilizing Hilbert curve scanning of quantized discrete cosine transform coefficients
ActiveUS7454055B1Improve image qualityReduce image quality degradationCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionJPEG
A method for compressing images, the method including the steps of partitioning image information for an image into partitioned information, transforming the partitioned information into transformed information using a discrete cosine transform (“DCT”), and quantizing the transformed information into quantized information. The method further includes the steps of sequencing the quantized information into sequenced information using a Hilbert curve scan, encoding the sequenced information into encoded information, and storing the encoded information. The DCT is a JPEG DCT.
Owner:OPEN INVENTION NEWTORK LLC
Enhanced Image Compression Utilizing Hilbert Curve Scanning of Quantized Discrete Cosine Transform Coefficients
InactiveUS20090067736A1Improve image qualityImprove overall utilizationCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionJPEG
A method for compressing images, the method including the steps of partitioning image information for an image into partitioned information, transforming the partitioned information into transformed information using a discrete cosine transform (“DCT”), and quantizing the transformed information into quantized information. The method further includes the steps of sequencing the quantized information into sequenced information using a Hilbert curve scan, encoding the sequenced information into encoded information, and storing the encoded information. The DCT is a JPEG DCT.
Owner:OPEN INVENTION NEWTORK LLC
Range query integrity verification method for outsourcing space database
ActiveCN103984728AImprove securityReduced chances of query analysisSpecial data processing applicationsValue setSpace object
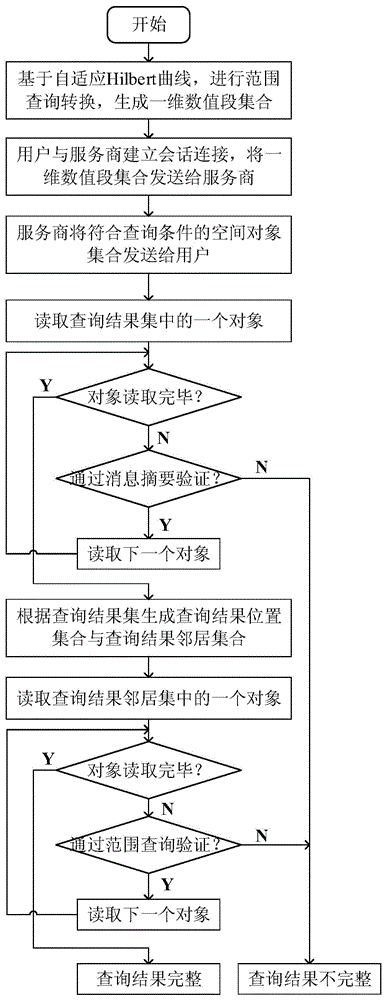
The invention discloses a range query integrity verification method for an outsourcing space database. The method comprises the steps of 1, querying the conversion based on the range of a self-adaptive Hilbert curve and generating a one-dimensional numerical value section set; 2, establishing conversation connection between a user and a service provider of the outsourcing space database by verification, and sending the one-dimensional numerical value section set to the service provider; 3, searching the space object sets, in accordance with the query conditions, in the database by the service provider according to the one dimensional numerical value set submitted by the user and returning the object set to the user; 4, receiving the query result set returned by the service provider and performing message extract verification on the query result set by the user; 5, verifying the integrity of the result set by the user according to the adjacent space object information in the query result. The method can provide efficient and safe range query integrity verification function for the user, so the behavior of the service provider for changing the query result is restrained, and the quality of the range query service is ensured.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Miniaturized antenna with reconfigurable frequency
InactiveCN109980368ASmall sizeAchieve the purpose of miniaturizationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric plateSwitching frequency
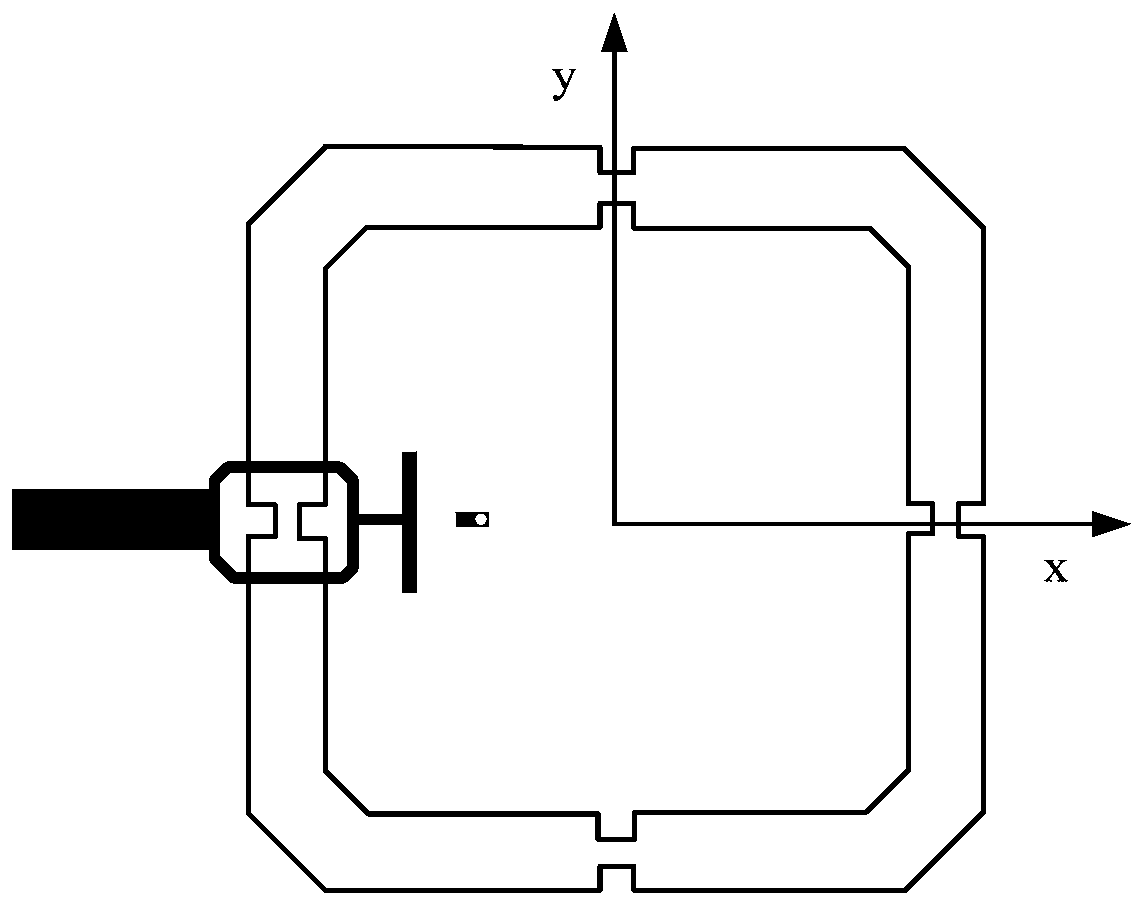
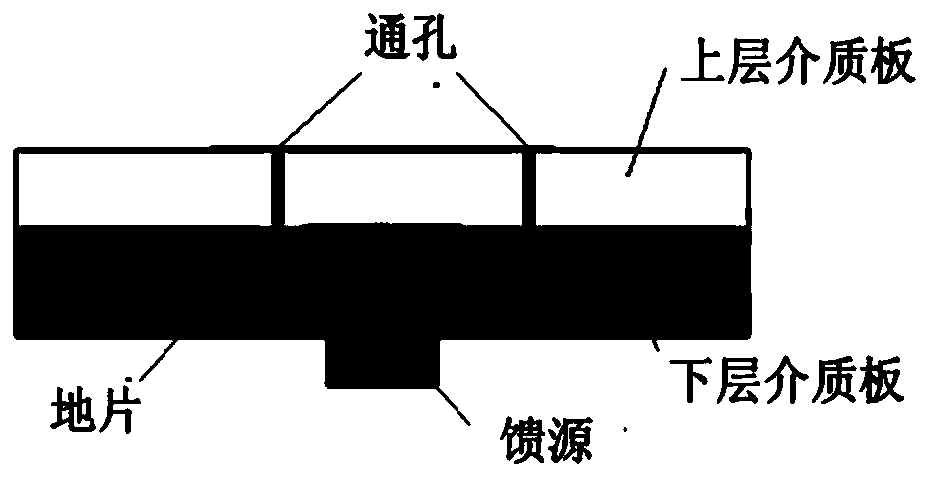
The invention discloses a miniaturized antenna with a reconfigurable frequency, which a ground piece, a first dielectric plate arranged on the ground piece, a coupling feeder arranged on the first dielectric plate, a second dielectric plate arranged on the coupling feeder and a radiation unit arranged on the second dielectric plate, wherein the ground piece is electrically connected with the radiation unit through first through holes passing through the first dielectric plate and the second dielectric plate; and the radiation unit is of a split ring resonator structure. In the invention, the antenna size is greatly reduced through adopting the split ring resonator structure as the radiation unit and adopting a Hilbert curve to carry out splitting on SRRs (Split Ring Resonators), thereby achieving the purpose of antenna miniaturization. Meanwhile, a plurality of metal through holes are arranged on the dielectric plates to connect the radiation unit and the ground piece, and the grounding of the radiation antenna at different positions is realized by using the on-off of a variable capacitance diode so as to achieve impedance transformation, so that the number of grounded diodes is changed to adjust the number of switching frequencies.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ELECTRONICS SYST ENG
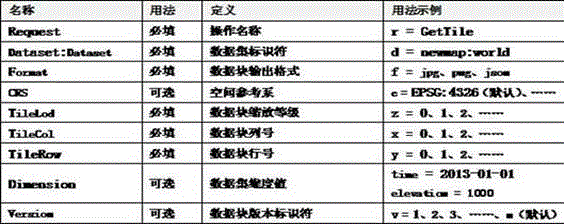
Method for configuring and querying an HBase multidimensional query system based on an Hilbert curve and an R-tree
ActiveCN104408039AQuick searchDatabase queryingSpecial data processing applicationsR-treeMultidimensional data
The invention discloses a method for configuring and querying an HBase multidimensional query system based on an Hilbert curve and an R-tree. The invention reduces multi-dimensional data to one-dimensional data by using a Hilbert curve on the one hand, and creating an R tree with respect to the multi-dimensional data on the HBase on the other hand. A correspondence is created between information of an identifier Hilbert ID of a mapped one-dimensional Hilbert curve and an original high-dimensional data ID. By the R-tree, query of high-dimensional data can be efficiently mapped to a set of one-dimensional Hilbert ID, so that quick query of multi-dimensional data on the HBase is realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Spatial data partitioning method in cloud environment
InactiveCN102902742AMeet the classification criteriaImprove real-time performanceSpecial data processing applicationsCluster algorithmComputation complexity
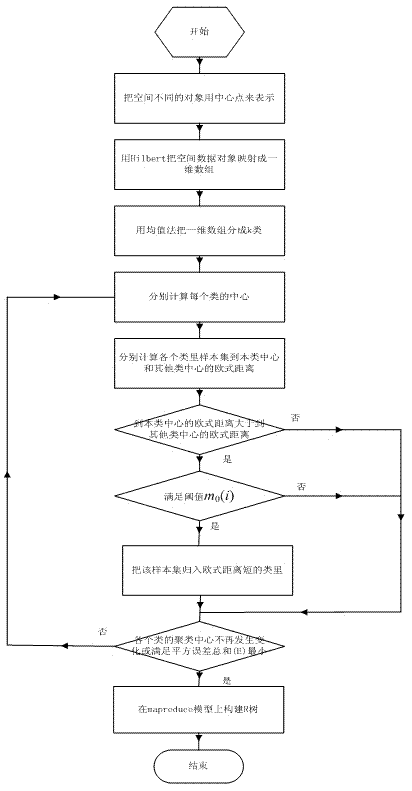
The invention discloses a spatial data partitioning method in a cloud environment, belonging to the technical field of computer networks. The method comprises the steps of firstly, uniformly partitioning a spatial data object by using a Hilbert curve coding method, and secondly partitioning adjacent spatial data objects into one type as far as possible by using an improved k-mean value clustering algorithm based on the first step. According to the spatial data partitioning method, the advantages of a conventional mean value method and a k-mean value clustering algorithm are synthesized, the standard in spatial data partitioning is met well, geographic spatial data can be uniformly distributed to map-reduce to be processed so as to establish an R-tree, so that the geographic spatial data index efficiency is improved. And moreover according to the method, the calculation complexity is low and the real-time capability of the algorithm is good.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
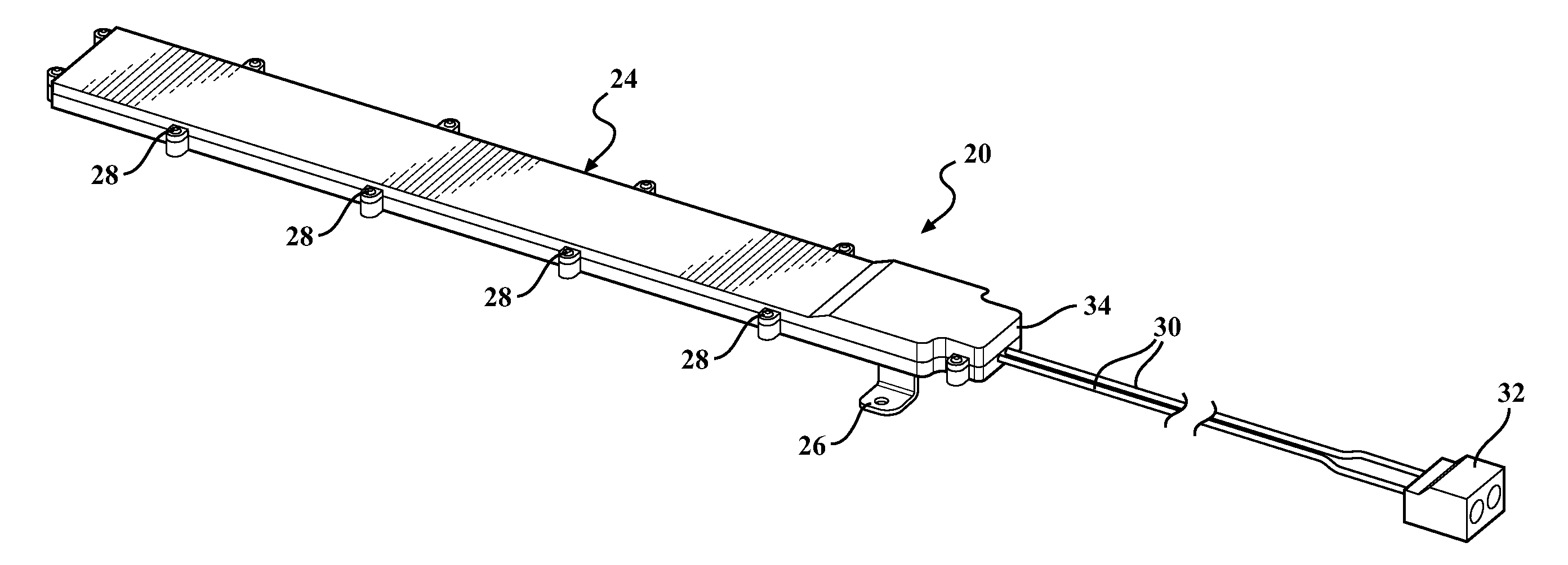
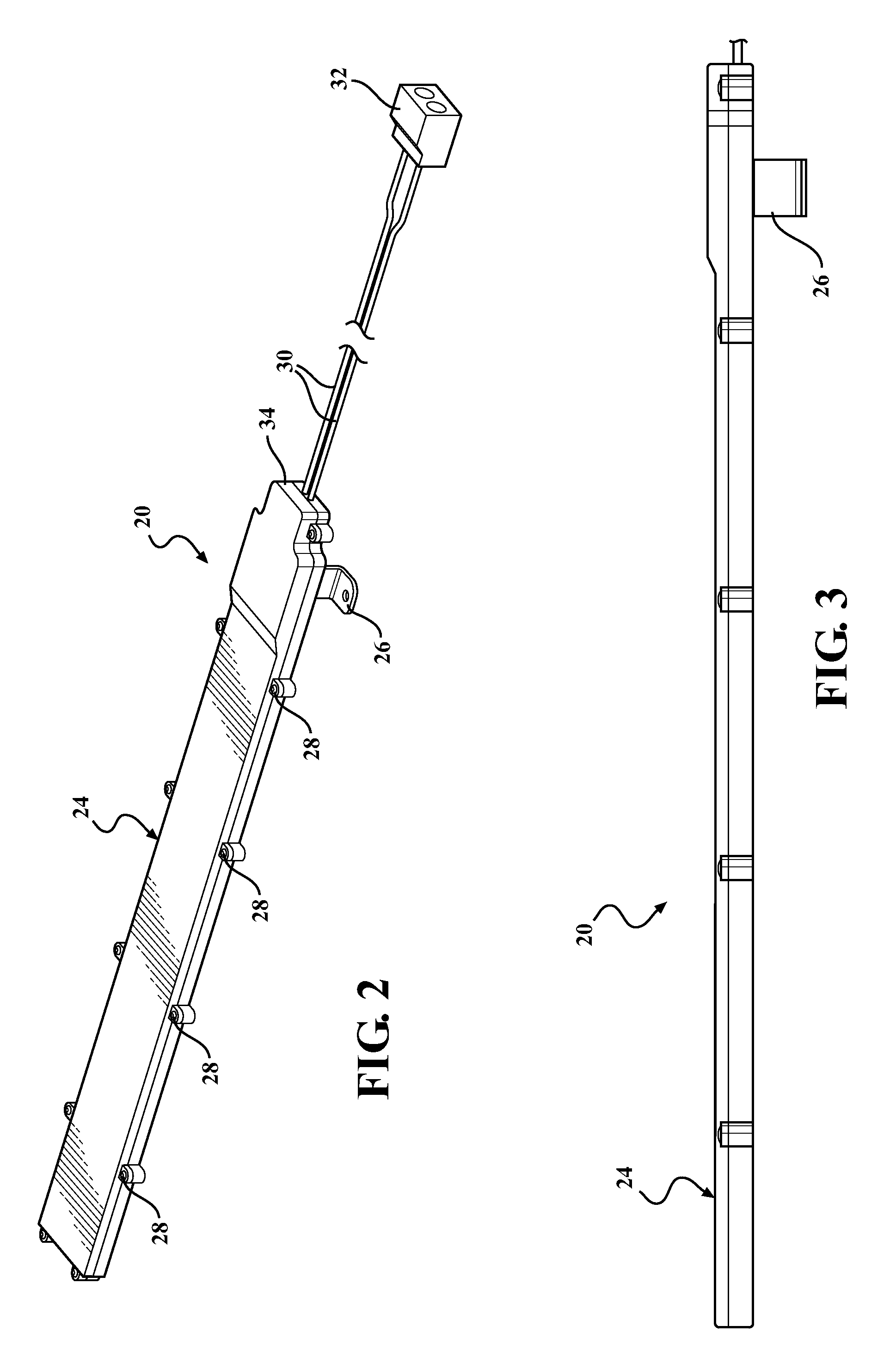
Antenna Assembly
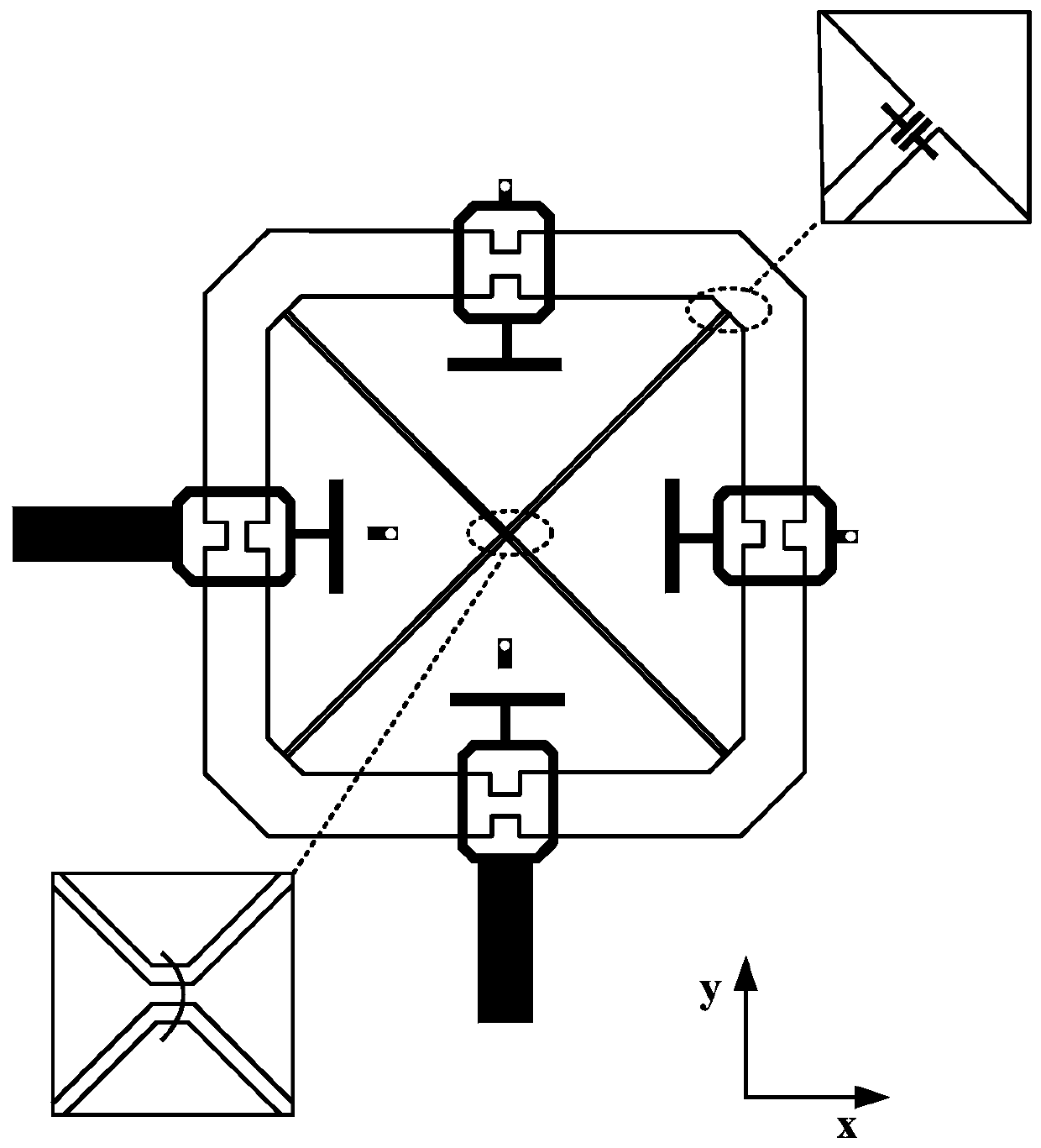
ActiveUS20120218155A1Beautiful appearanceImprove performanceAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesElongated active element feedField of viewPrinted circuit board
An antenna assembly for a vehicle including an environmentally sealed housing and a printed circuit board. The printed circuit board is at least partially disposed within the environmentally sealed housing and extends through a plurality of second order Hilbert Curves which are arranged in side-by-side relationship with one another. The antenna assembly is preferably disposed within a non-metallic structure of the vehicle, and therefore, the antenna assembly is hidden from view, thereby allowing the vehicle to have a more aesthetically pleasing external appearance. Additionally, the length of the trace is limited by the space inside of the non-metallic structure, and therefore, depending on the size of the non-metallic structure, a very long trace having a high performance could be printed on the printed circuit board.
Owner:HARADA IND OF AMERICA
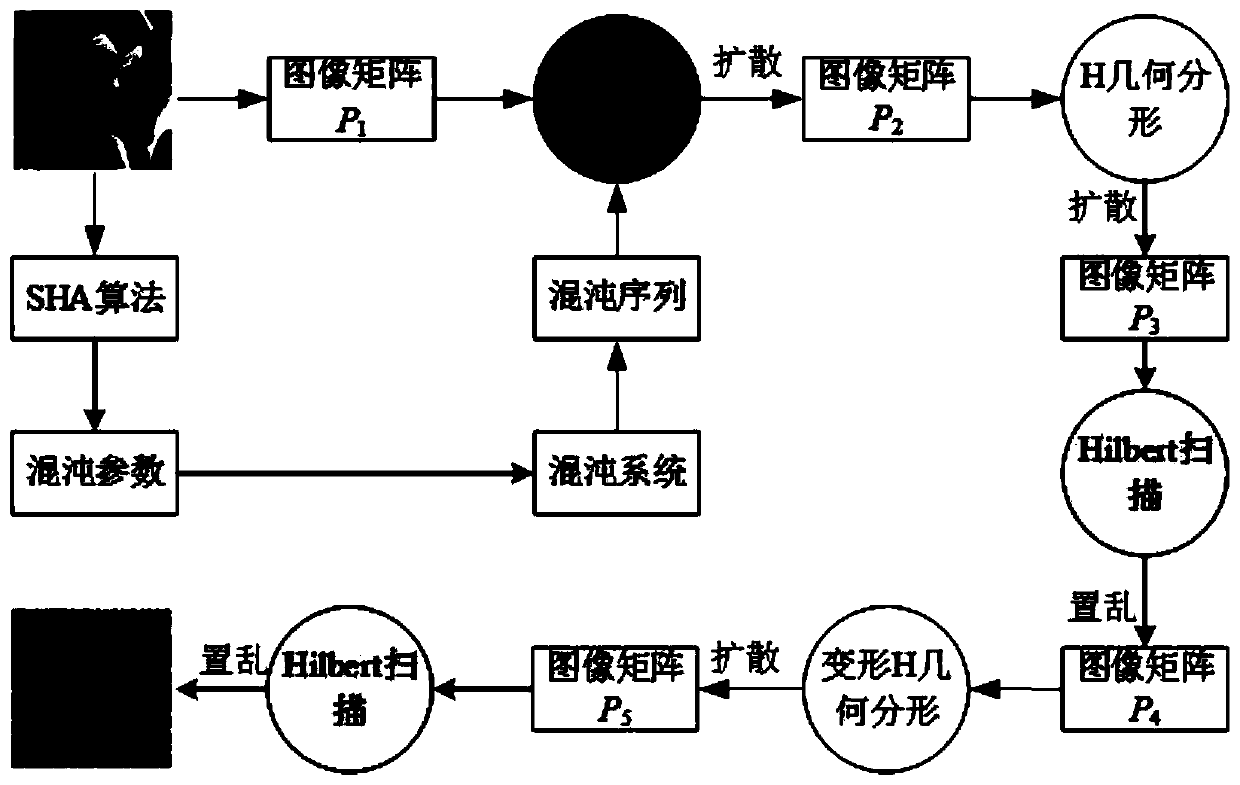
An image encryption method based on H geometric fractal and a Hilbert curve
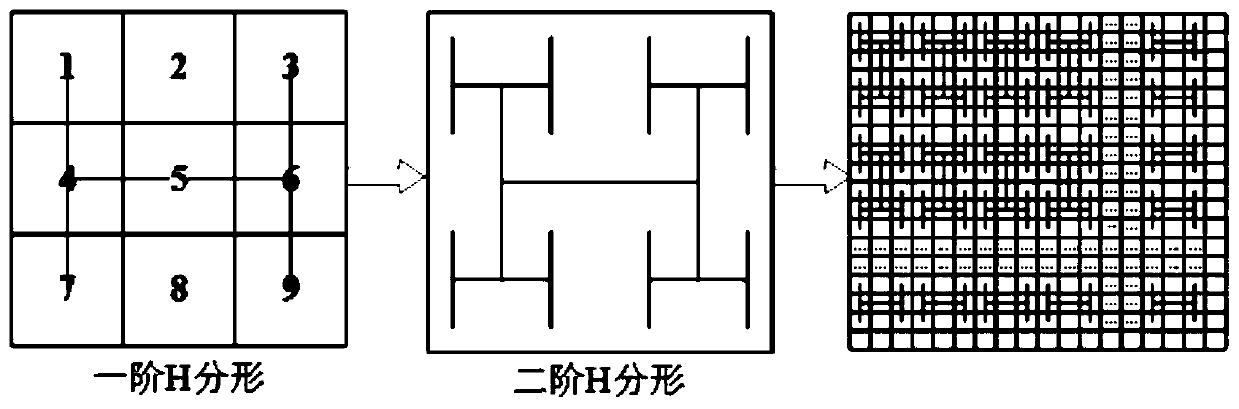
ActiveCN109903212AWide application of secure transmissionLarge key spaceImage data processing detailsDiffusionSecure transmission
The invention provides an image encryption method based on H geometric fractal and a Hilbert curve. The image encryption method comprises the following steps: calculating a hash value of the originalgray level image as an initial value of a chaotic system by using an SHA-3 algorithm, and carrying out bitwise ratio specificity or diffusion on image pixels by using a sequence generated by the chaotic system; And alternately carrying out diffusion operation and two-dimensional Hilbert scanning curve scrambling operation by using the second-order H fractal to obtain an encrypted image. Accordingto the invention, Hilbert curve scanning scrambling and H geometric fractal diffusion are adopted, and a chaotic system, DNA coding, a Hilbert scanning curve and H fractal are combined to realize tworounds of pixel position scrambling and pixel value diffusion; Experimental results and security analysis show that the method not only has enough key space to resist exhaustive attacks, but also canresist statistical attacks, differential attacks, data loss attacks and noise attacks, and is widely applicable to secure transmission of image information.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Fast image filtering method based on space filling curves and extreme points
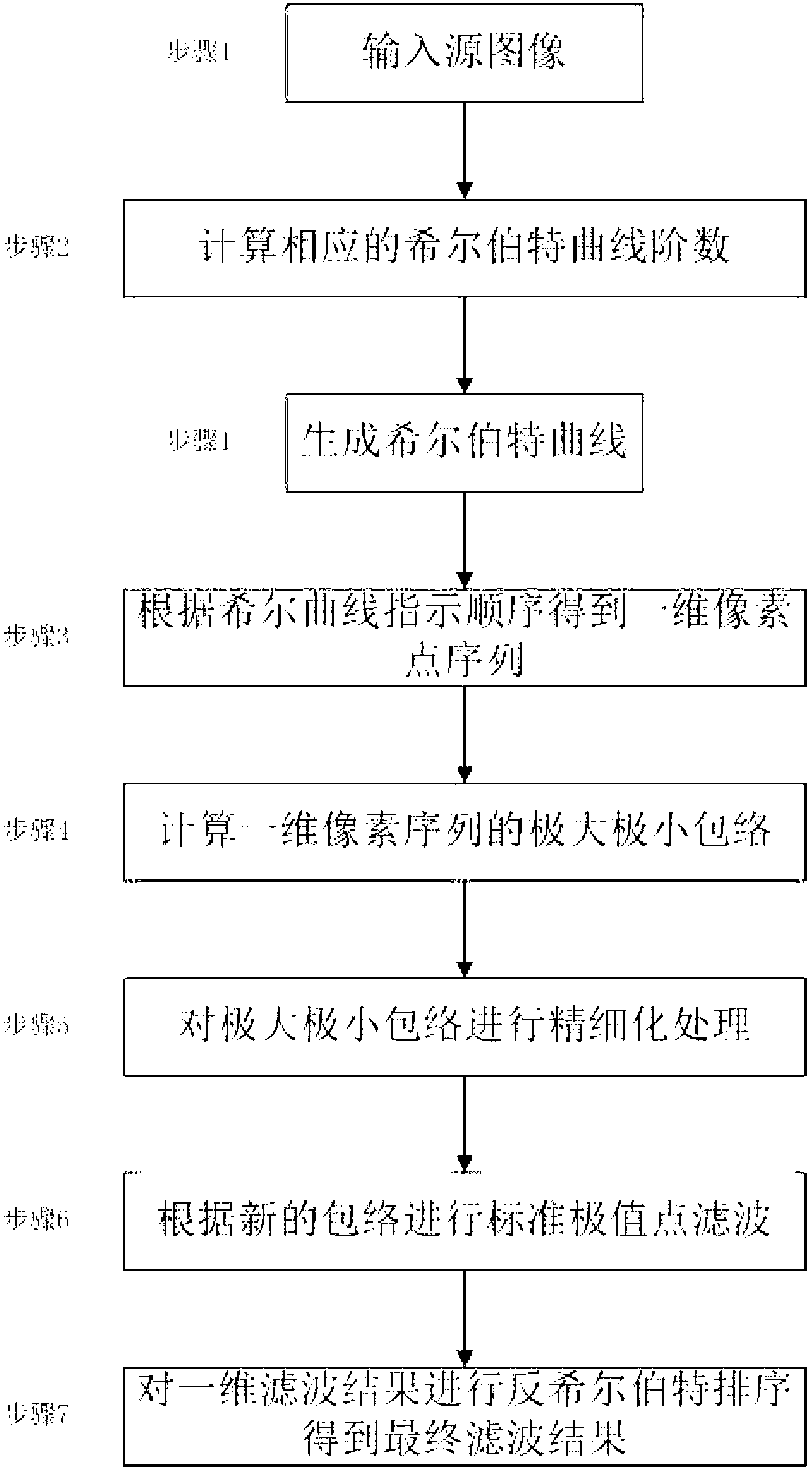
InactiveCN103218784AImprove filtering effectReduce interpolation errorImage enhancementPoint sequenceSource image
The invention relates to a fast image filtering method based on space filling curves and extreme points. The fast image filtering method based on the space filling curves and the extreme points comprises the following steps: a first step is that a source image to be filtered is input; a second step is that a Hilbert curve is generated; a third step is that pixel points in a two-dimensional image domain are subjected to sequencing according to an order indicated by the Hilbert curve, and a one-dimensional pixel point sequence is generated; a fourth step is that a maximum envelope and a minimum envelope of the one-dimensional pixel point sequence are calculated, and the obtained envelopes are subjected to fine processing; a fifth step is that the maximum envelope and the minimum envelope after the fine processing are used as input values, and an image base and image details after a smoothing filtering process are obtained through calculation of a mean value; and a sixth step is that one-dimensional filtering results of the image base and the image details are subjected to counter-Hilbert sequencing, an original two-dimensional image is divided into a smooth part and a detail part, and therefore filtering is finished. The fast image filtering method based on the space filling curves and the extreme points can extremely reduce interpolation errors and lower the complexity of the filtering, and can achieve a quasi-real-time effect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
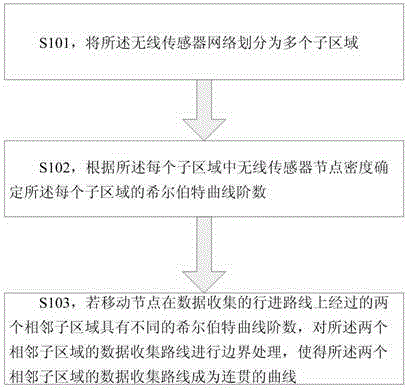
Data collection method
ActiveCN105959964AProlong survival timeReduce energy consumptionNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesWireless mesh networkWireless sensor networking
The invention discloses a data collection method. The method is applied to a wireless sensor network. According to the data collection method, data collection routes of a mobile node are planned based on a Hilbert curve. The method comprises the steps of dividing the wireless sensor network into multiple subareas; determining the Hilbert curve order of each subarea according to the density of wireless sensor network nodes in each subarea; carrying out boundary processing to the data collection routes of the two adjacent subareas if two adjacent subareas passed by the data collection advancing route of the mobile node have different Hilbert curve orders, thereby enabling the data collection routes of the two adjacent subareas to become a connected curve. According to the method, the data collection routes of the mobile node can be adjusted according to the density of the nodes, thereby adapting to a current network condition; and therefore, the node energy consumption is reduced, the network lifetime is improved, and the packet delivery rate is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
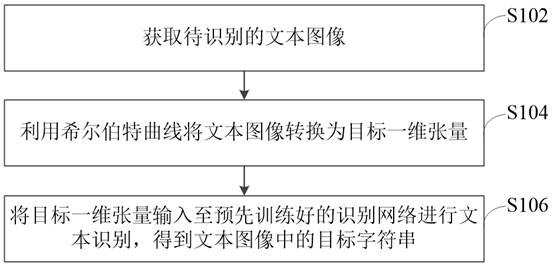
Text recognition method and device, equipment and medium
ActiveCN113343958AReduce identification costsImprove recognition efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesText recognitionRadiology
The invention relates to a text recognition method and device, equipment and a medium. The method comprises the steps that a to-be-recognized text image is acquired; the text image is converted into a target one-dimensional tensor through a Hilbert curve, and the target one-dimensional tensor is used for representing the sequence relation between pixels in the text image; and the target one-dimensional tensor is input into a pre-trained recognition network for text recognition to obtain a target character string in the text image. The text recognition cost can be reduced, the text recognition efficiency can be improved, and the text recognition difficulty can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING CENTURY TAL EDUCATION TECH CO LTD
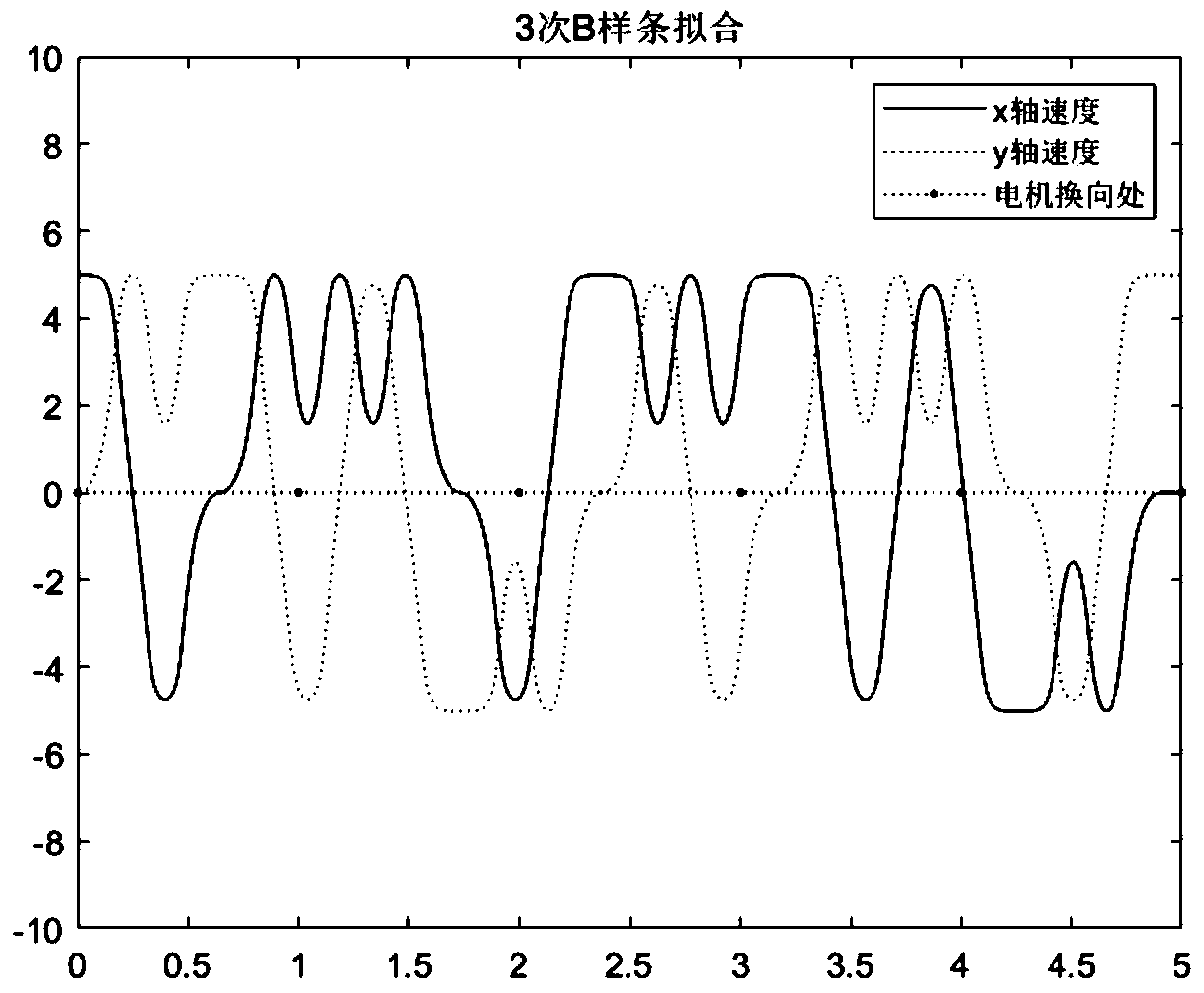
Improved 3D printing path filling method based on Hilbert curve
ActiveCN111002580AOptimize the number of starts and stopsOptimize the number of motor starts and stopsAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structures3d printComputer printing
An improved 3D printing path filling method based on a Hilbert curve comprises the following specific steps of (1) drawing the Hilbert curve, and storing coordinates of all control points of the Hilbert curve; (2) carrying out cubic B-spline curve fitting on the coordinates of the control points, carrying out interpolation smoothing on the fitted curve, and storing all control point coordinates ofthe smoothed curve; (3) drawing an optimized Hilbert curve by utilizing all the control points in the step (2), calculating the length of the curve, performing 3D simulation printing, and calculatingthe steering condition of the motor in each direction during printing; and (4) writing a method of fitting the Hilbert curve by using cubic B spline interpolation into 3D printing slicing software silicc3r, performing path filling and slicing processing on the model by using the silicc3r, finally exporting the model as a G-code code, and performing printing by using a 3D printer. According to theinvention, the condition of right-angle turning is reduced, and the starting and stopping times of the motor are reduced, so that an efficient 3D printing forming path is obtained.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
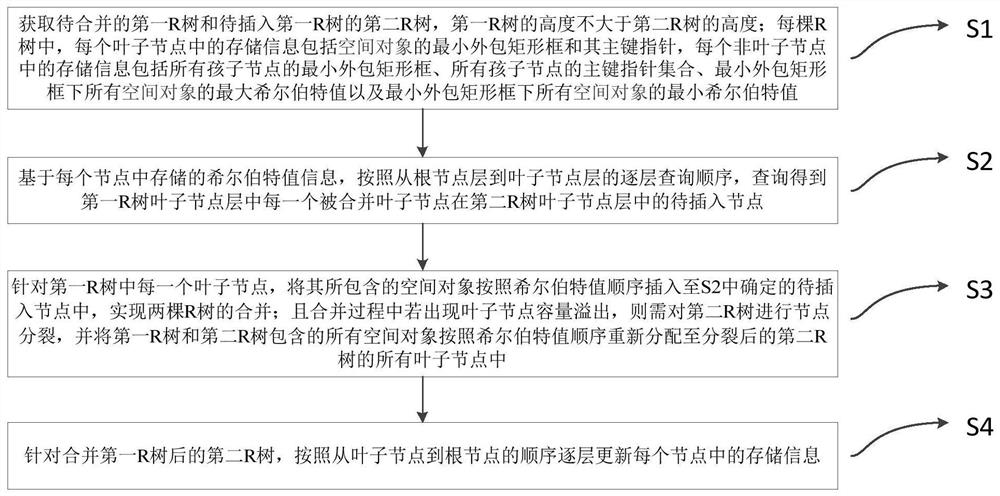
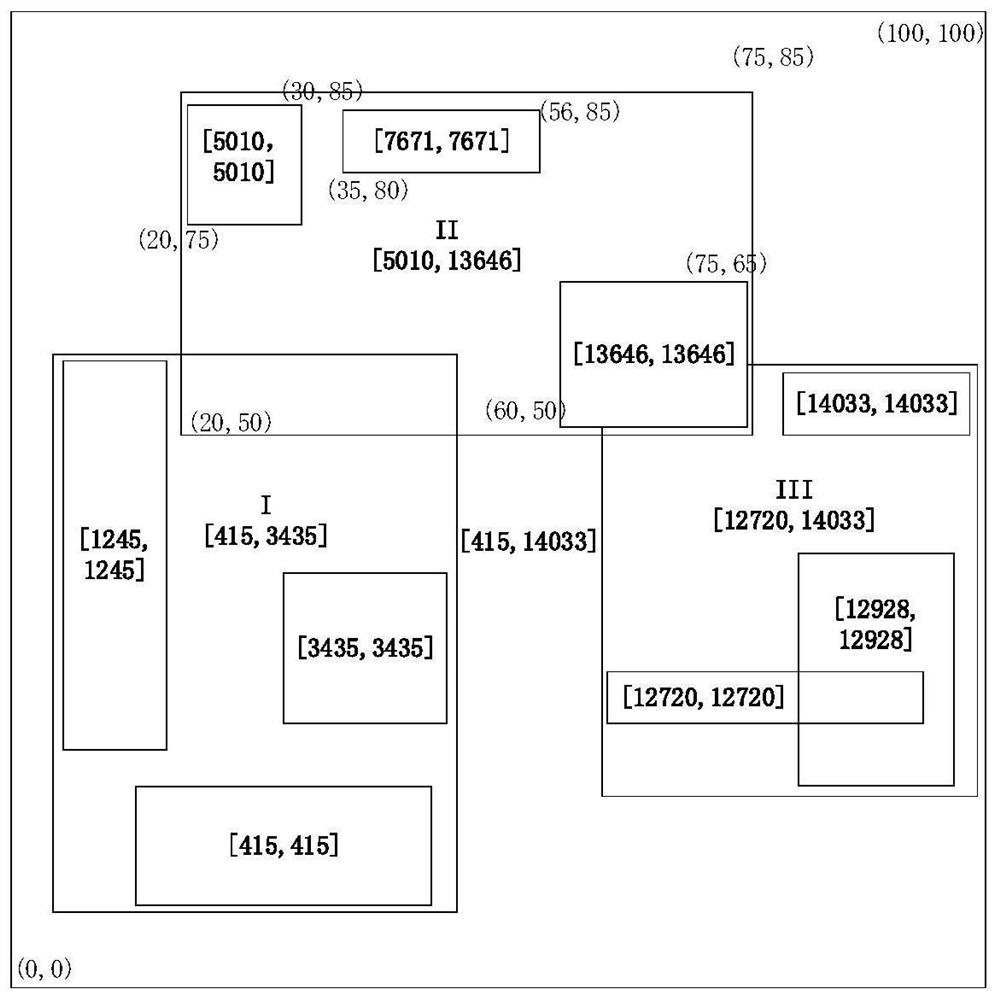
R-tree index merging updating method and device based on Hilbert curve and medium
ActiveCN112395288AQuick merge updateImprove merger efficiencyDatabase updatingSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceHilbert curve
The invention discloses an R-tree index merging updating method and device based on a Hilbert curve and a medium. The method comprises the steps of S1, acquiringa first R tree to be combined and a second R tree to be inserted into the first R tree, wherein the upper limit range and the lower limit range of Hilbert values of contained objects are stored in non-leaf nodes of the R trees; s2, querying a to-be-inserted node of each merged leaf node in the first R leaf sub-node layer in the second R leaf sub-node layer through a hierarchical query algorithm from top to bottom; s3, according to a hierarchical adjustment algorithm from bottom to top, for each leaf node in the first R tree, inserting space objects contained in the leaf node into the to-be-inserted nodes determined in the S2 according to a Hilbert value sequence, and realizing the combination of the two R trees; and S4, for the combined second R tree, updating the storage information in each node layer by layer according to a sequence from the leaf node to the root node. The method has important practical application value in the field of high-performance storage of geographic space-time big data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
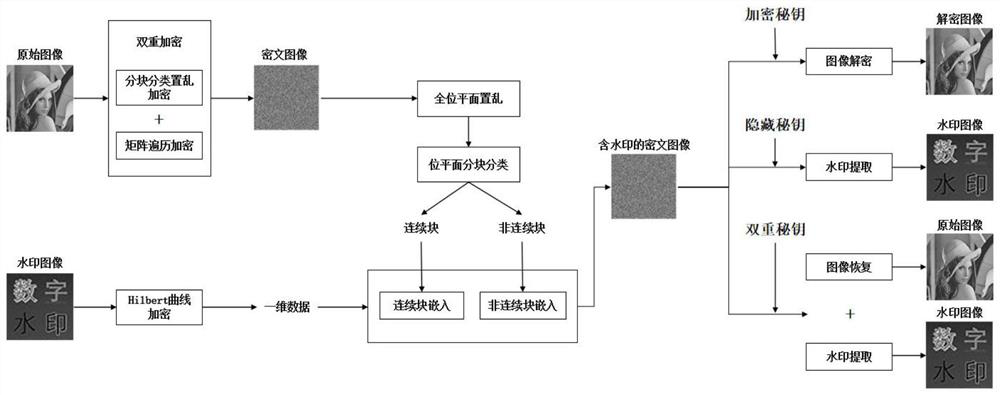
Separable ciphertext domain reversible data hiding method based on bit plane segmentation
ActiveCN114666453AImprove securityQuality improvementImage data processing detailsHigh level techniquesCiphertextTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a separable ciphertext domain reversible data hiding method based on bit plane segmentation, and the method comprises the steps: firstly providing a block classification scrambling algorithm and a traversal matrix encryption algorithm, and completing the encryption of an original image; secondly, realizing watermark image encryption by utilizing Hilbert curve encryption; in a ciphertext domain, an all-bit-plane scrambling technology is adopted, bit-plane rotation is firstly implemented, then the bit-plane rotation is partitioned and classified into continuous blocks and discontinuous blocks, and finally reversible data hiding is realized according to a pixel prediction method. Meanwhile, the secret keys can be separated, the hidden watermark can be extracted by the hidden secret key, the original image can be recovered by the encrypted secret key, and the watermark image can be extracted and the original image can be recovered by the double secret keys. According to the method, 100% reversibility is realized based on pixel prediction, the watermark image can be extracted without errors, the original image can be recovered 100%, and the method has the advantages of high safety, large capacity, high quality and good robustness.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
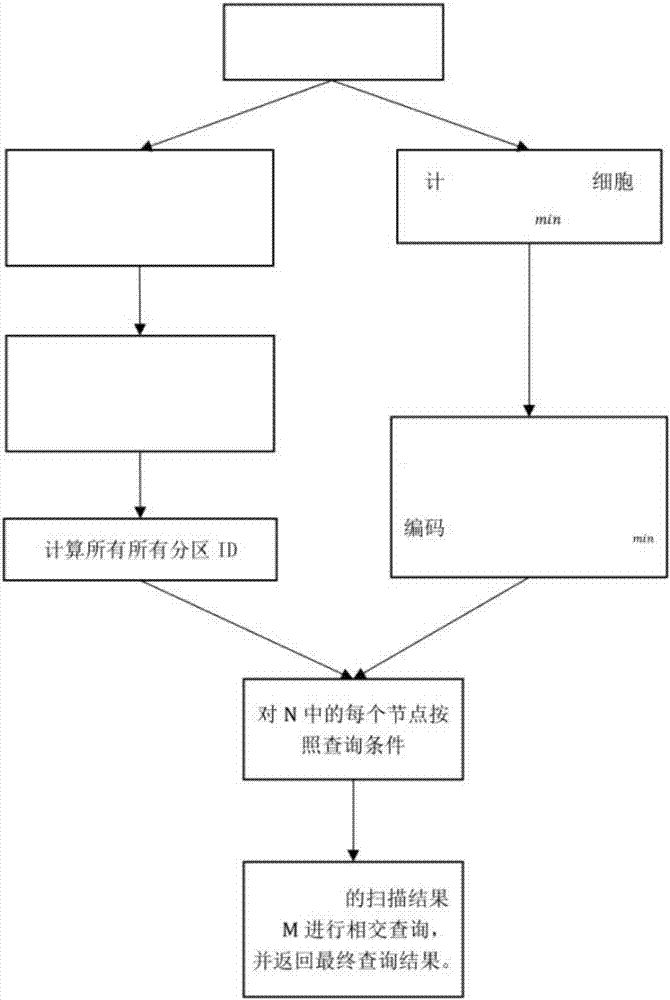
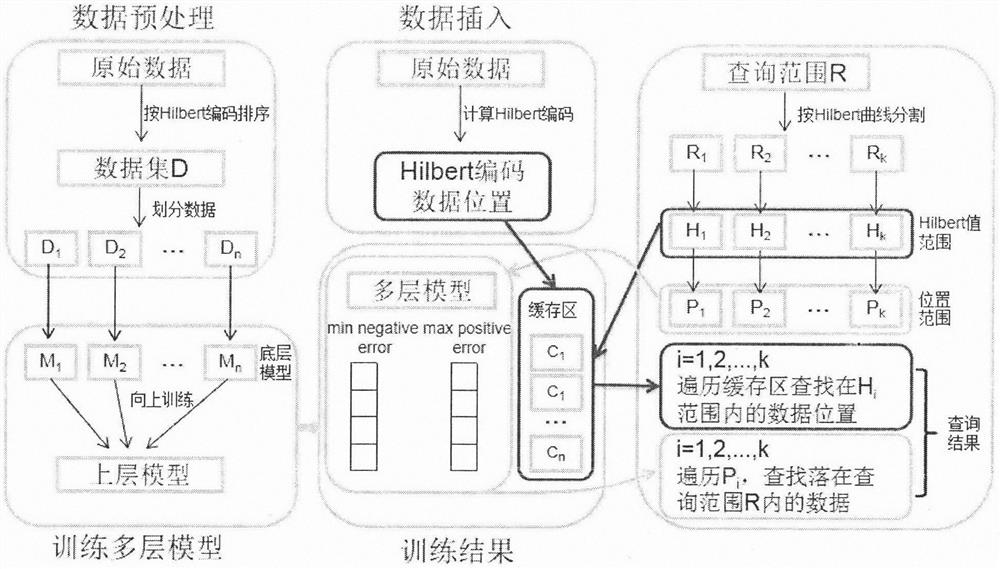
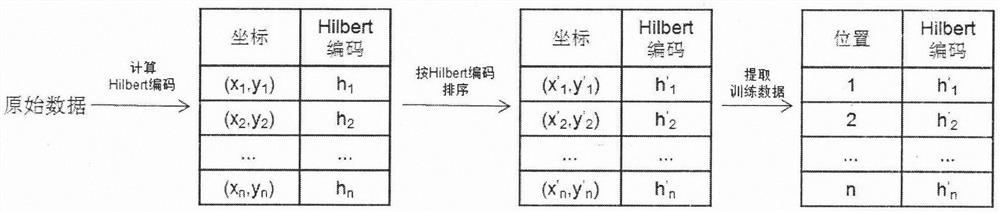
Spatial range query method based on extensible learning index
InactiveCN112035586AReduce space overheadImprove indexing efficiencyMachine learningGeographical information databasesTheoretical computer scienceLearning data
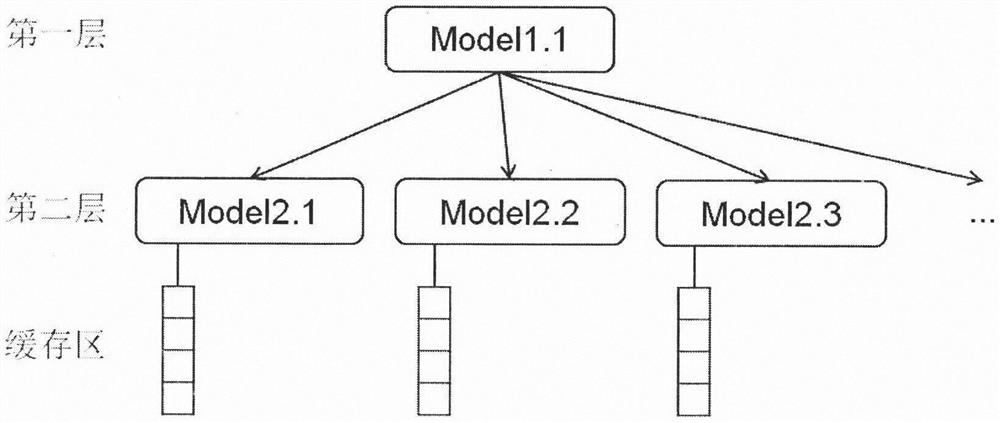
The invention discloses a spatial range query method based on an extensible learning index, and the method comprises the following steps: 1) performing data preprocessing: sorting spatial objects according to Hilbert coded values of coordinates, and extracting the Hilbert coded value of each piece of data and the position of the data as training data; 2) constructing an extensible multi-layer space learning index, training a multi-layer model, learning data distribution of a space object, and adding a cache region for data insertion and update operation; 3) performing a spatial range query operation based on the extensible multilayer learning index; after the data is sorted according to the Hilbert coding values, dividing the query range into a plurality of subareas according to the characteristics of the Hilbert curve; for each subarea, predicting the position of the data through the multi-layer learning index, traversing the corresponding cache region, and searching the data fallingin the query range. According to the method, machine learning and a space filling curve are fused into a space index, and an effective space range query method is designed according to a data distribution rule.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Secure location service scope query outsourcing method capable of implementing privacy protection
ActiveCN106899937AIntegrity guaranteedReduce overheadUser identity/authority verificationLocation information based serviceCiphertextPrivacy protection
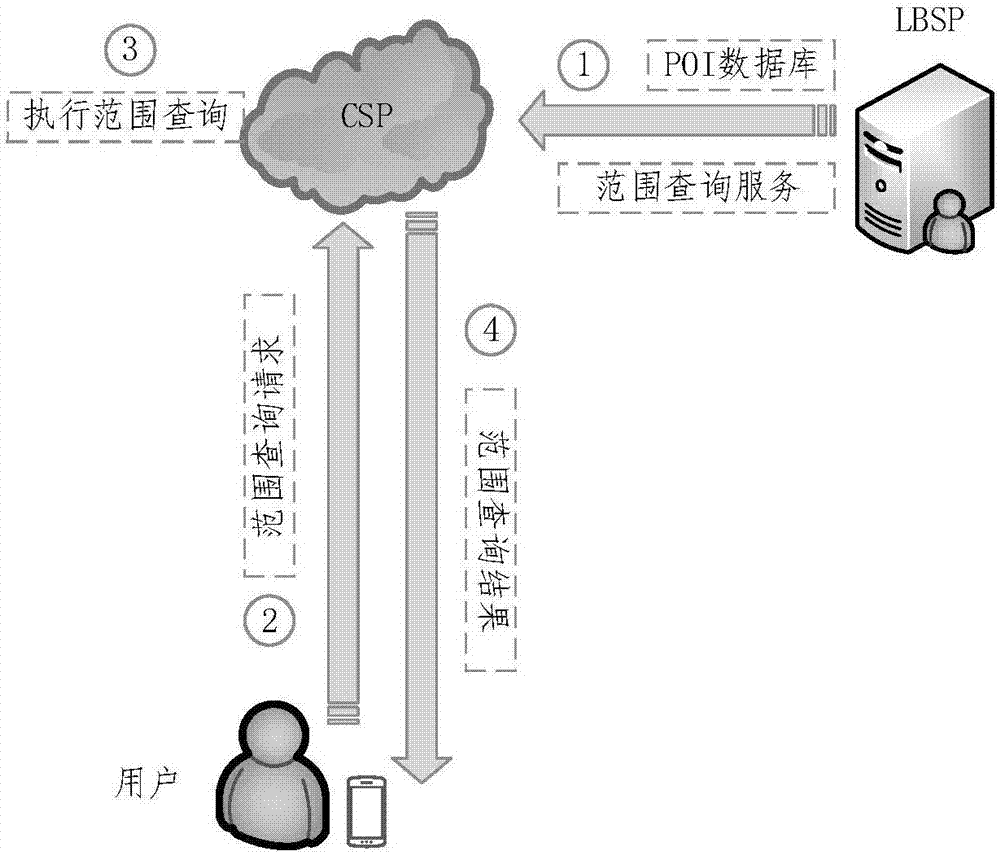
The invention discloses a secure location service scope query outsourcing method capable of implementing privacy protection. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, a location service provider preprocesses the POI data by using the Hilbert curve and the Merkle hash tree to obtain the POI data ciphertext set and the signature of the Merkle hash tree root, and sends the POI data ciphertext set and the signature to a cloud service provider; step 2, the location service provider preprocesses the user location information to obtain the Hilbert value range (i) Q ( / i) ' of the user location information, and sends the Hilbert value range (i) Q ( / i) ' to the cloud service provider; step 3, the cloud service provider implements one-to-one comparison on the Hilbert value range (i) Q ( / i) ' and the Hilbert value of each POI data ciphertext in the POI data ciphertext set, and returns the POI data ciphertext which has the same Hilbert value as the Hilbert value contained in the Hilbert value range (i) Q ( / i) ' to the user; and step 4, the user verifies the integrity and correctness of the returned POI data ciphertext. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the data privacy and the integrity of query results can be guaranteed, the computation and communication overheads can also be reduced, and thus the efficiency can be increased.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
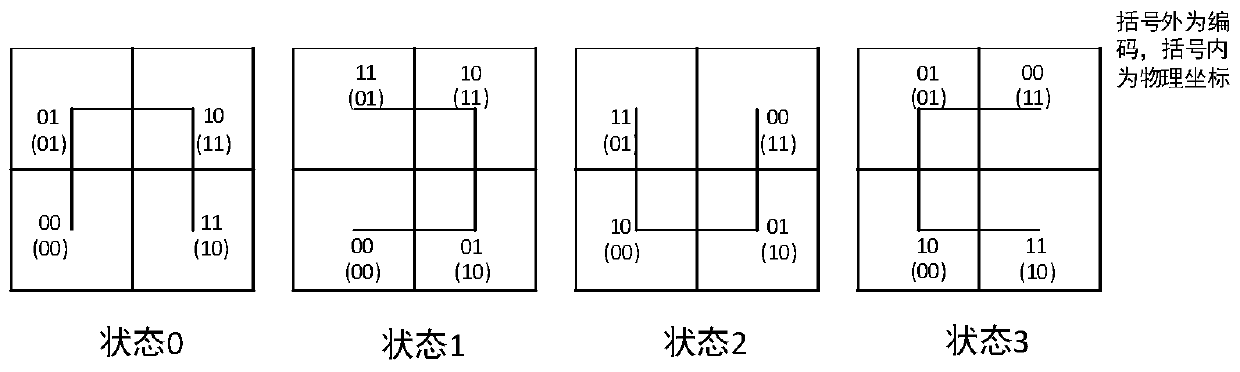
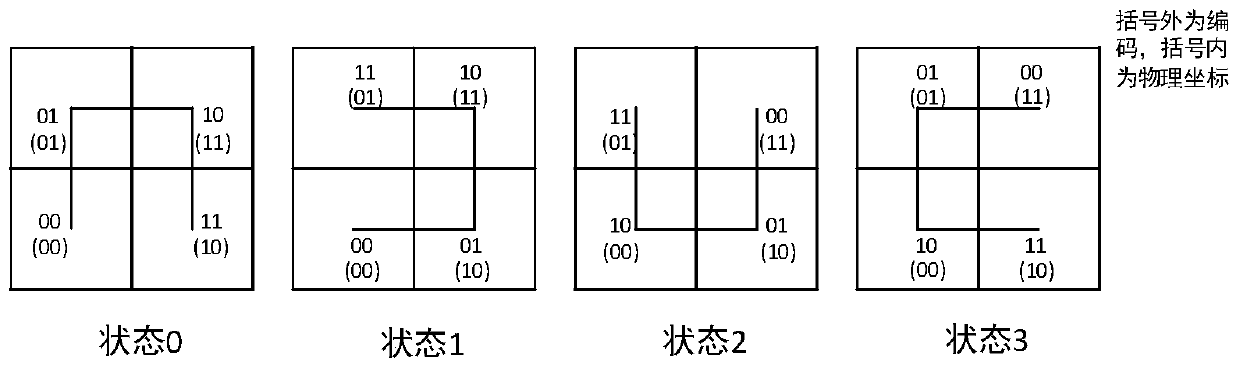
Hilbert curve encoding and decoding method based on state view
PendingCN110457317ASolve codingSolve decodingGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsDecoding methodsRound complexity
The invention relates to a Hilbert curve encoding and decoding method based on a state view, and belongs to the technical field of geographic information systems. The Hilbert curve encoding and decoding method comprises a stage of constructing a Hilbert curve state view: for a given state, respectively constructing two mapping tables of physical coordinates and coded values for coding, a mapping table of the physical coordinates and a next-order state, two reverse mapping tables of the coded values and the physical coordinates for decoding, and a reverse mapping table of the coded values and the next-order state; a Hilbert curve encoding stage: inquiring the state view from the bit, with the maximum incomplete value being 0, in binary representation of the input coordinates x and y, and calculating Hilbert encoding; and a the Hilbert decoding stage, inquiring a state view from the position which is not zero at most in the binary representation of the input Hilbert code, and calculatinga physical coordinate value. The Hilbert curve encoding and decoding method can reduce the complexity of Hilbert coding, and can better adapt to skew distribution of data.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
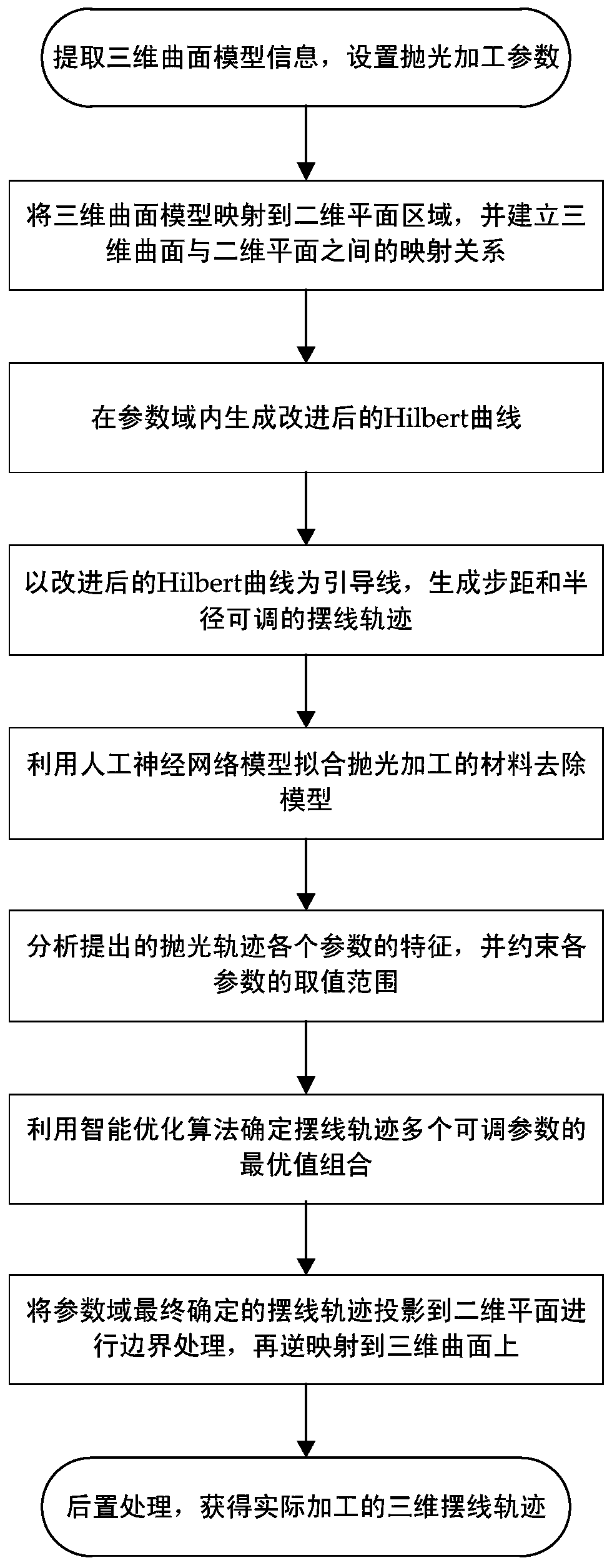
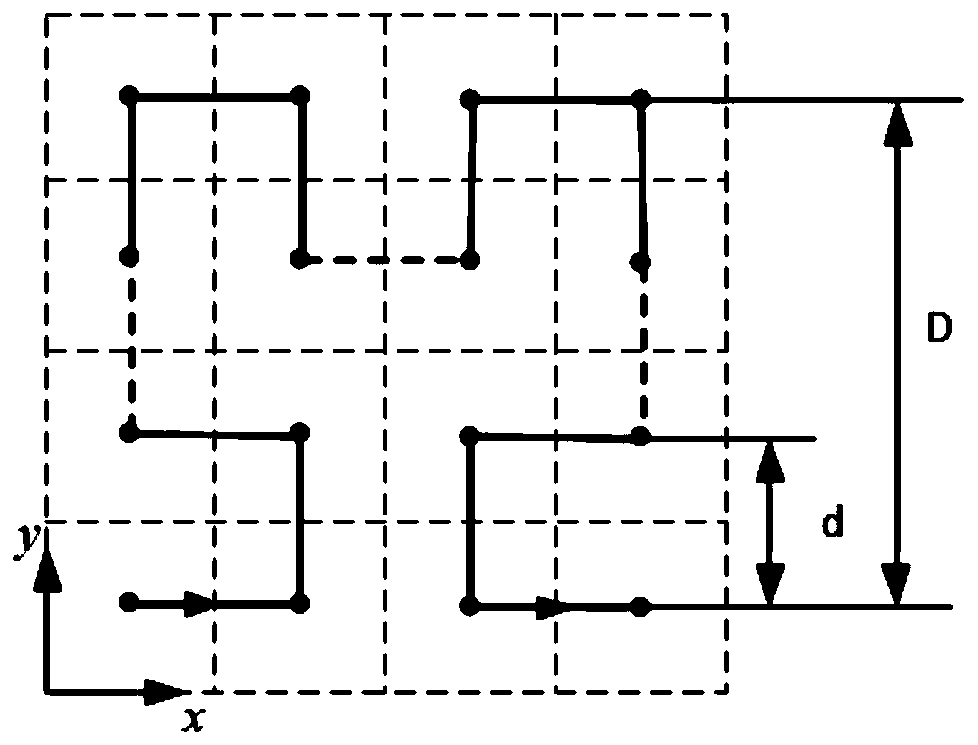
Three-dimensional cycloid-like intelligent polishing method guided by Hilbert curve
InactiveCN110532588AAchieve multi-directionalityEnsure polishing uniformityNeural learning methodsSpecial data processing applicationsMean squareMaterial removal
The invention discloses a three-dimensional cycloid-like intelligent polishing method guided by a Hilbert curve. The three-dimensional cycloid-like intelligent polishing method comprises the followingsteps: establishing a space mapping relationship between a three-dimensional curved surface and a two-dimensional plane of a workpiece; generating a standard Hilbert curve in the two-dimensional parameter domain, and performing deformation to obtain an improved Hilbert curve; taking the improved Hilbert curve as a guide line, and generating a cycloid track with adjustable step pitch and radius; fitting a polishing processing material removal calculation model by utilizing an artificial neural network, and predicting an average value and a mean square error of the material removal depth of each vertex of the three-dimensional grid curved surface; constraining the value range of each parameter of the polishing track; taking an average value and a mean square error of the material removal depth as optimization targets, and determining an optimal value combination of adjustable parameters in the cycloid trajectory by utilizing an intelligent optimization algorithm; projecting the cycloidtrajectory determined by the parameters to a two-dimensional plane, and reordering the disconnected trajectories on the boundary to form a complete cycloid trajectory; and inversely mapping the cycloid trajectory on the two-dimensional plane to the three-dimensional curved surface to obtain a final actually processed three-dimensional cycloid-like trajectory.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Hilbert encoding and decoding method under data skew distribution
ActiveCN110489605AReduce the number of iterationsAdapt to skewed situationsOther databases indexingEnergy efficient computingDecoding methodsTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a Hilbert encoding and decoding method under data skew distribution, and belongs to the technical field of image storage, spatial database indexing and the like. The method comprises the following steps: a Hilbert curve state view construction stage: constructing an encoding and decoding mapping table for realizing mapping between an encoding value and a coordinate and mapping to a next-order state; in the Hilbert encoding stage, the encoding process is divided into an immediate encoding stage and an order-by-order encoding stage, and Hilbert encoding is calculated; inthe decoding stage, the decoding process is divided into an immediate decoding stage and an order-by-order decoding stage, and corresponding physical coordinates are calculated; by introducing the immediate encoding stage and the immediate decoding stage, iterative table look-up operation on a specific sequence can be avoided, and high efficiency is achieved under the condition of specific data skew distribution.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com