Patents
Literature
169 results about "R-tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
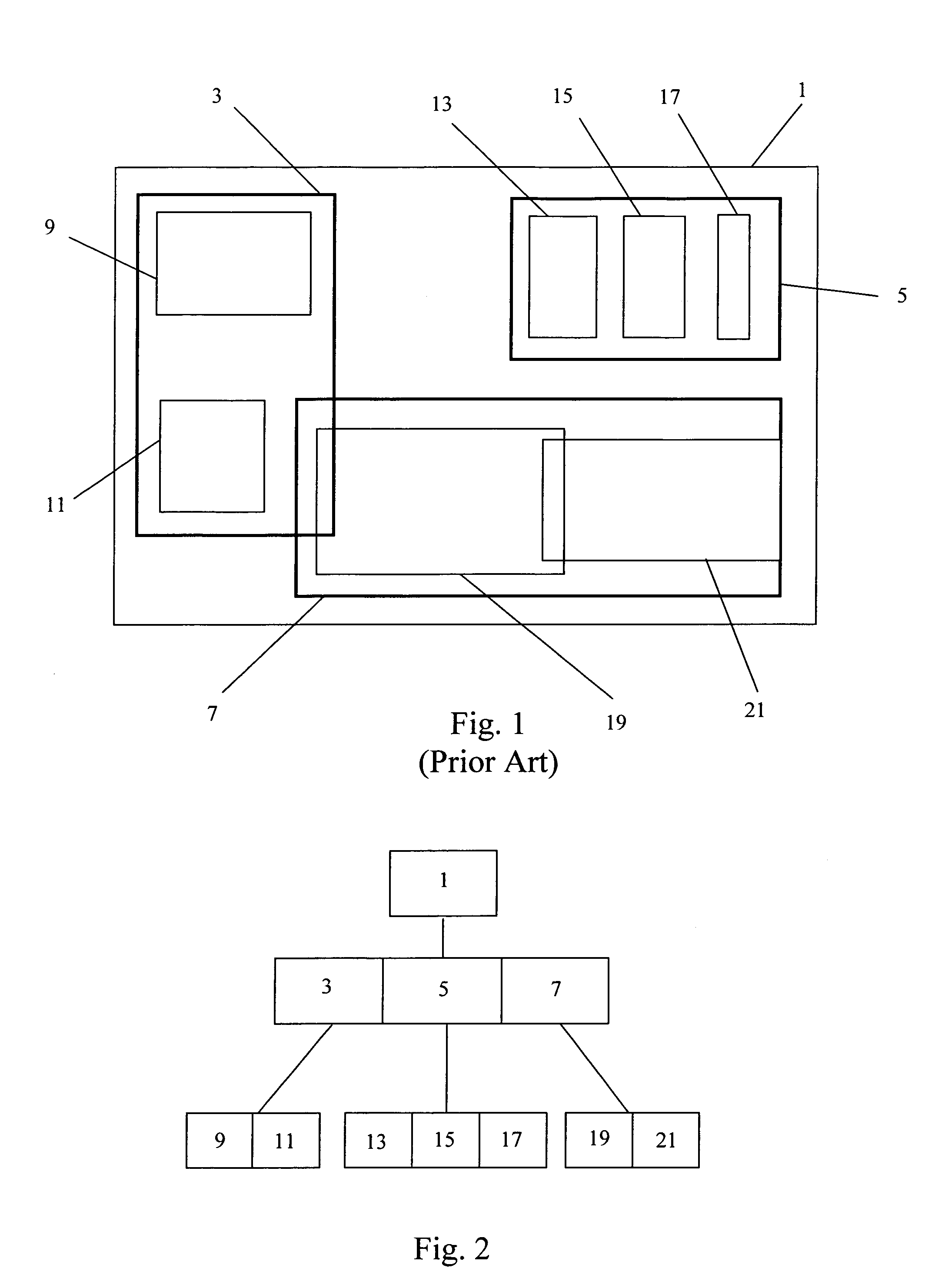
R-trees are tree data structures used for spatial access methods, i.e., for indexing multi-dimensional information such as geographical coordinates, rectangles or polygons. The R-tree was proposed by Antonin Guttman in 1984 and has found significant use in both theoretical and applied contexts. A common real-world usage for an R-tree might be to store spatial objects such as restaurant locations or the polygons that typical maps are made of: streets, buildings, outlines of lakes, coastlines, etc. and then find answers quickly to queries such as "Find all museums within 2 km of my current location", "retrieve all road segments within 2 km of my location" (to display them in a navigation system) or "find the nearest gas station" (although not taking roads into account). The R-tree can also accelerate nearest neighbor search for various distance metrics, including great-circle distance.
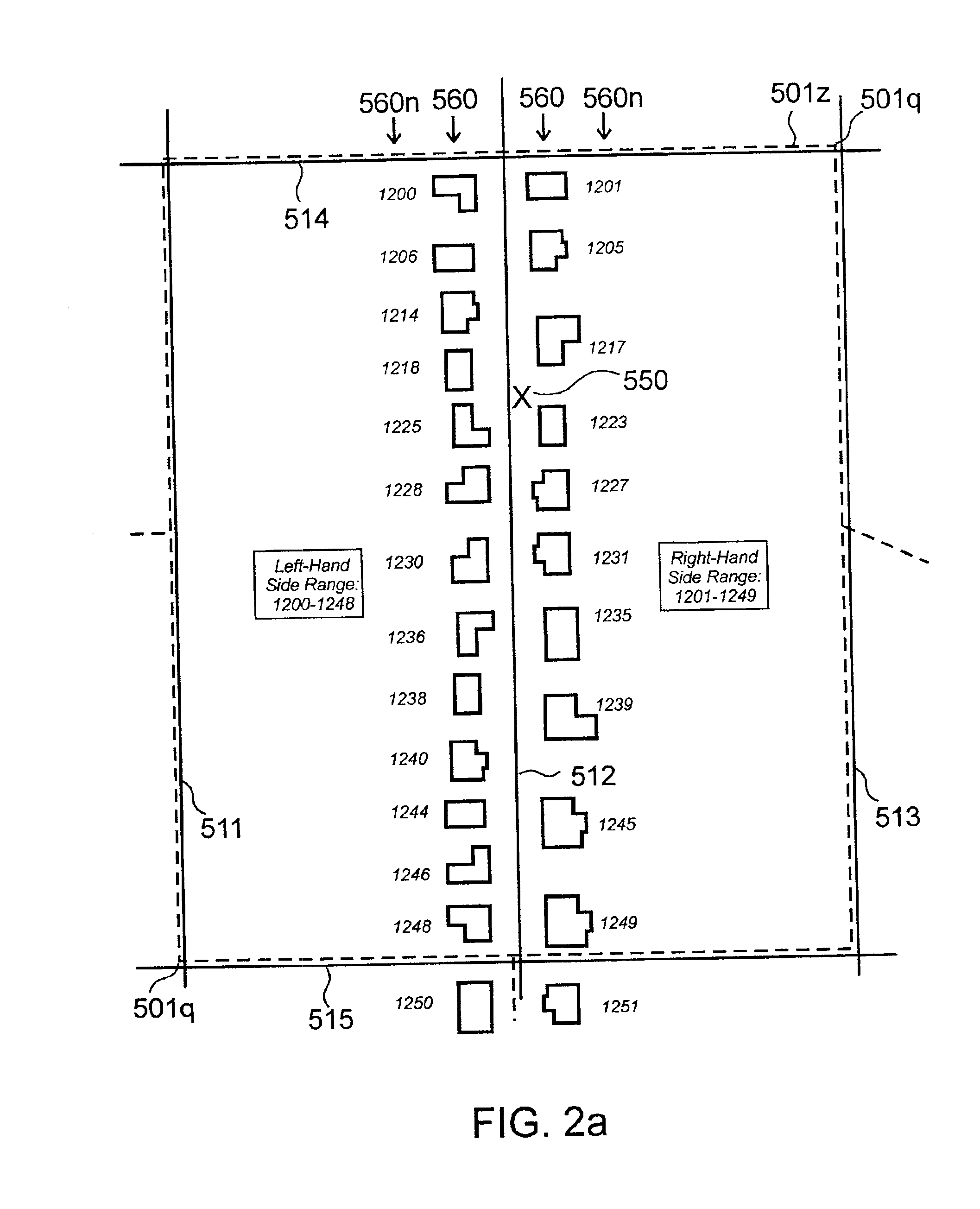
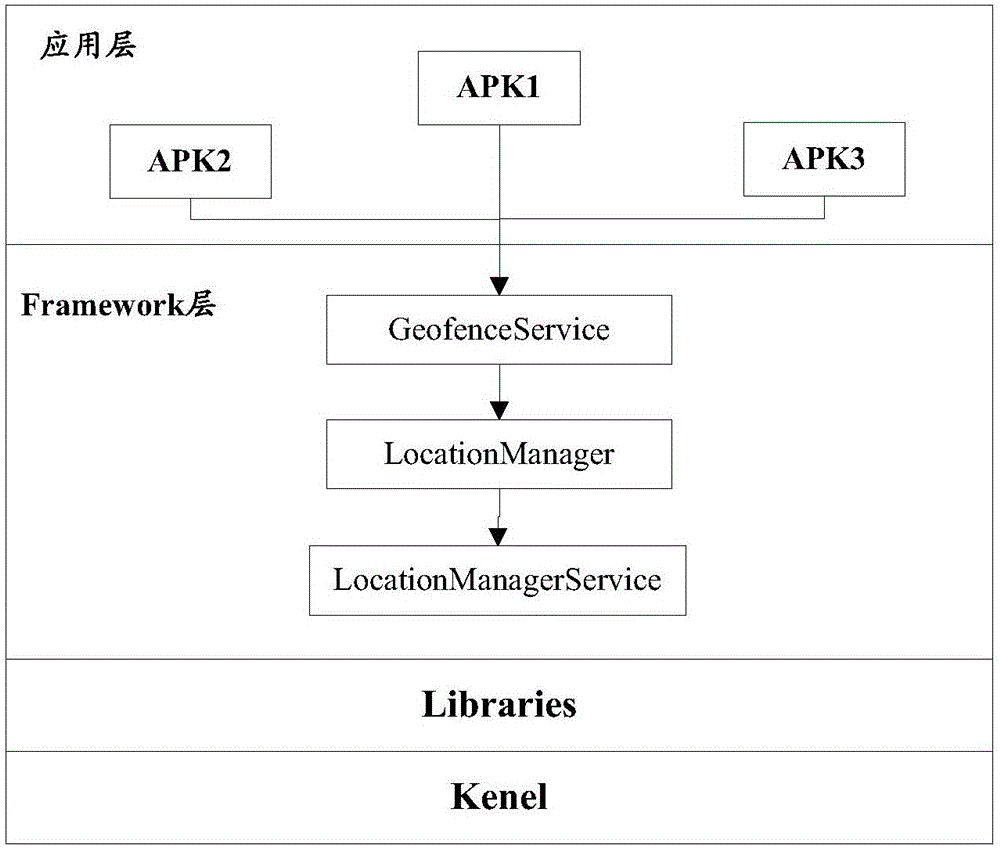
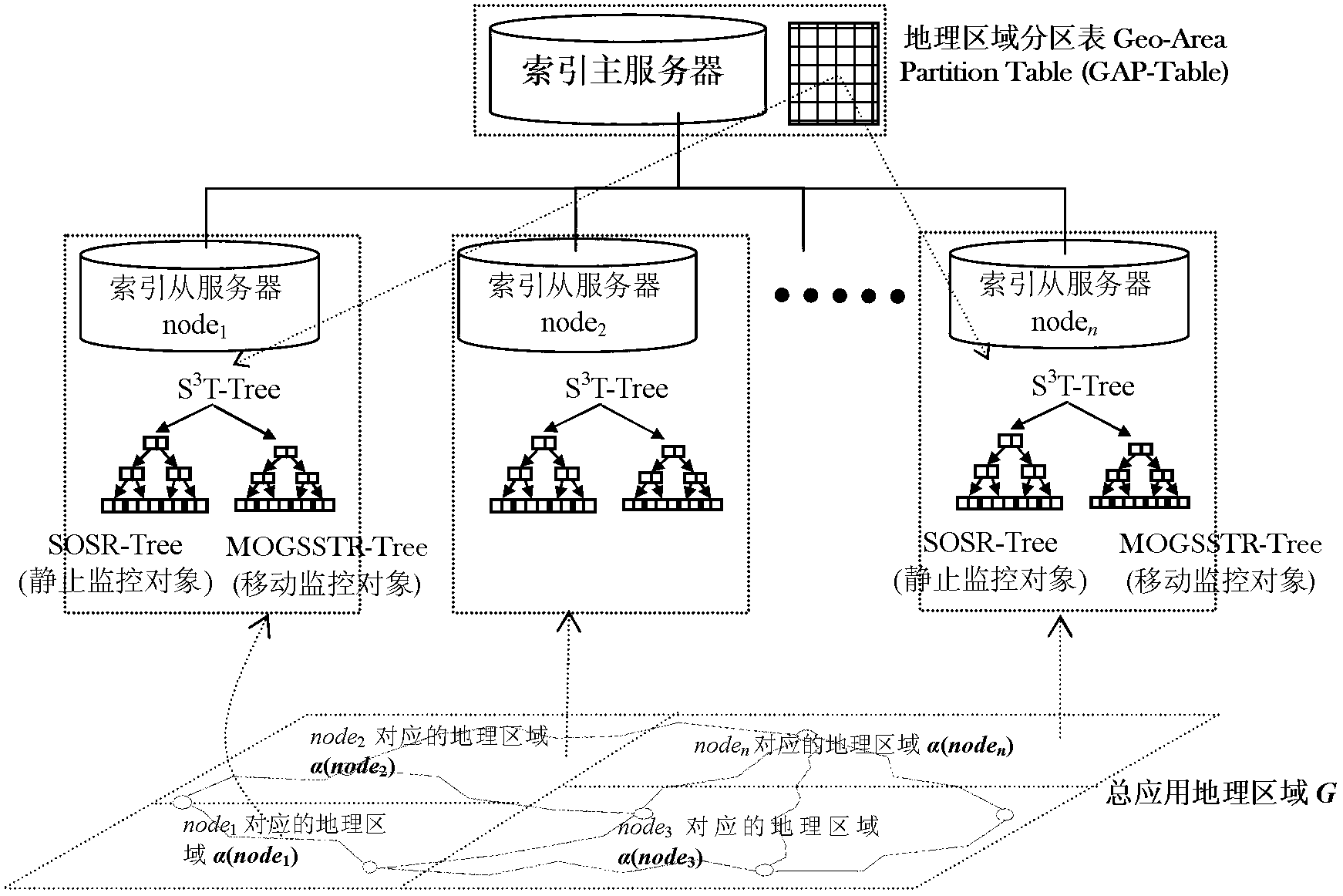
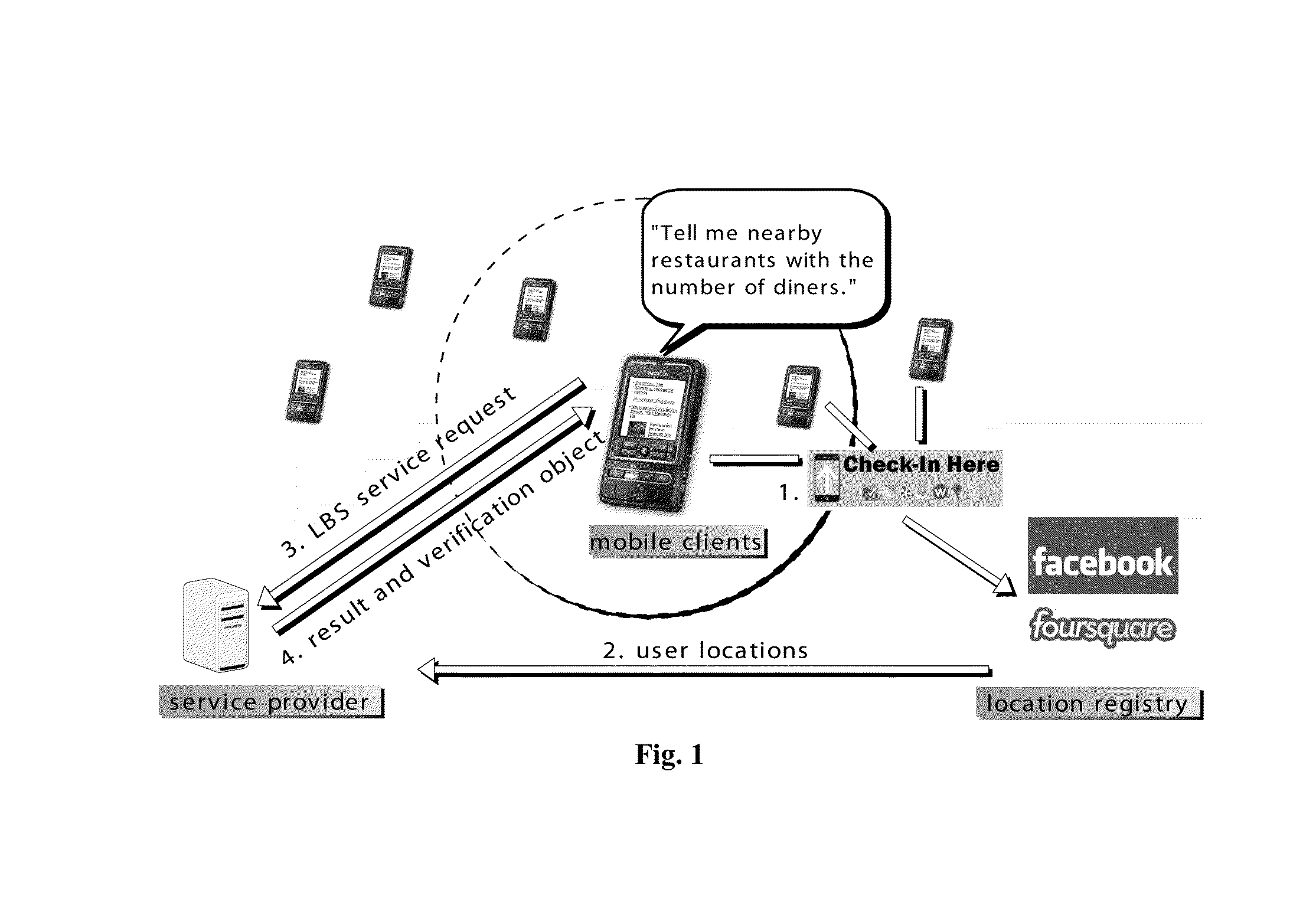
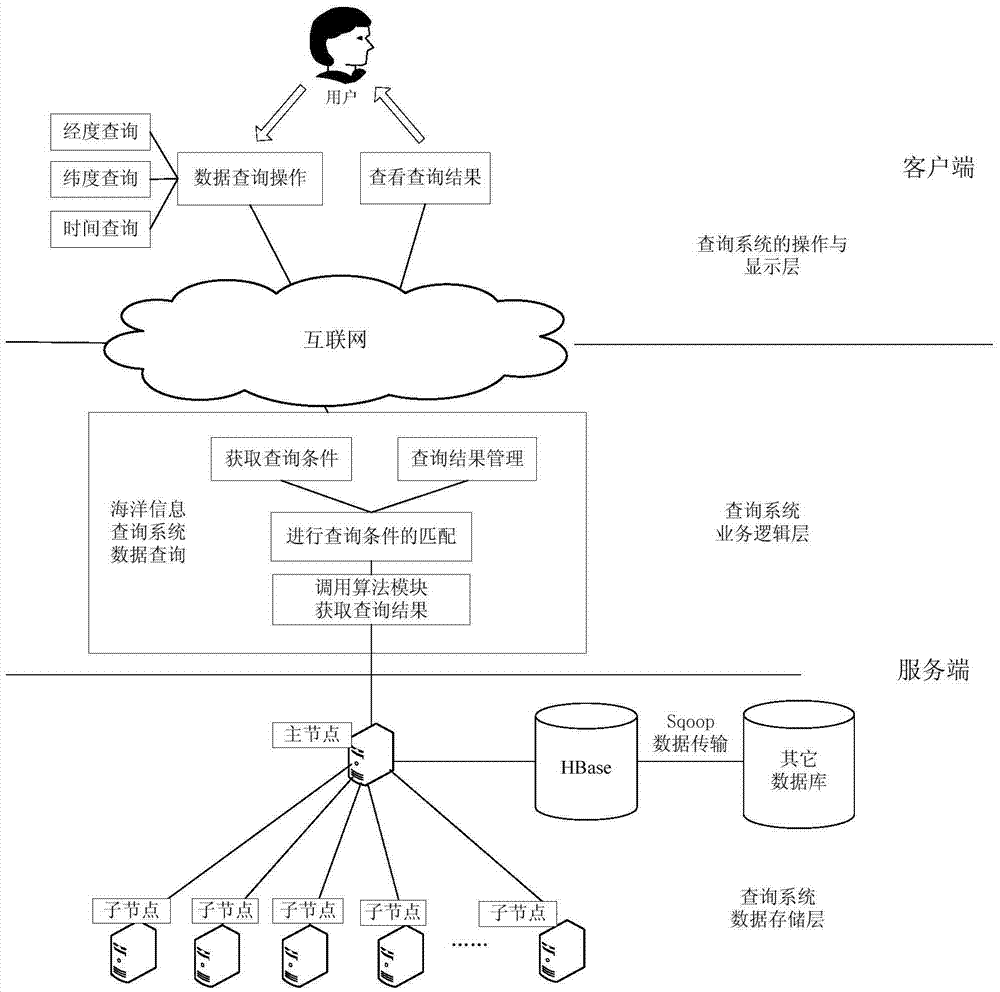
High-performance location management platform
An apparatus and method for rapid translation of geographic latitude and longitude into any of a number of application-specific location designations or location classifications, including street address, nearest intersection, PSAP (Public Safety Answering Point) zone, telephone rate zone, franchise zone, or other geographic, administrative, governmental or commercial division of territory. The speed of translation meets call-setup requirements for call-processing applications such as PSAP determination, and meets caller response expectations for caller queries such as the location of the nearest commercial establishment of a given type. To complete its translation process in a timely manner, a memory-stored spatial database is used to eliminate mass-storage accesses during operation, a spatial indexing scheme such as an R-tree over the spatial database is used to locate a caller within a specific rectangular area, and an optimized set of point-in-polygon algorithms is used to narrow the caller's location to a specific zone identified in the database. Additional validation processing is supplied to verify intersections or street addresses returned for a given latitude and longitude. Automatic conversion of latitude-longitude into coordinates in different map projection systems is provided. The memory-stored database is built in a compact and optimized form from a relational spatial database as required. The R-tree spatial indexing of the memory-stored database allows for substantially unlimited scalability of database size without degradation of response time. Maximum performance for database retrievals is assured by isolating the retrieval process from all updating and maintenance processes. Hot update of the in-memory database is provided without degradation of response time.
Owner:PRECISELY SOFTWARE INC +1
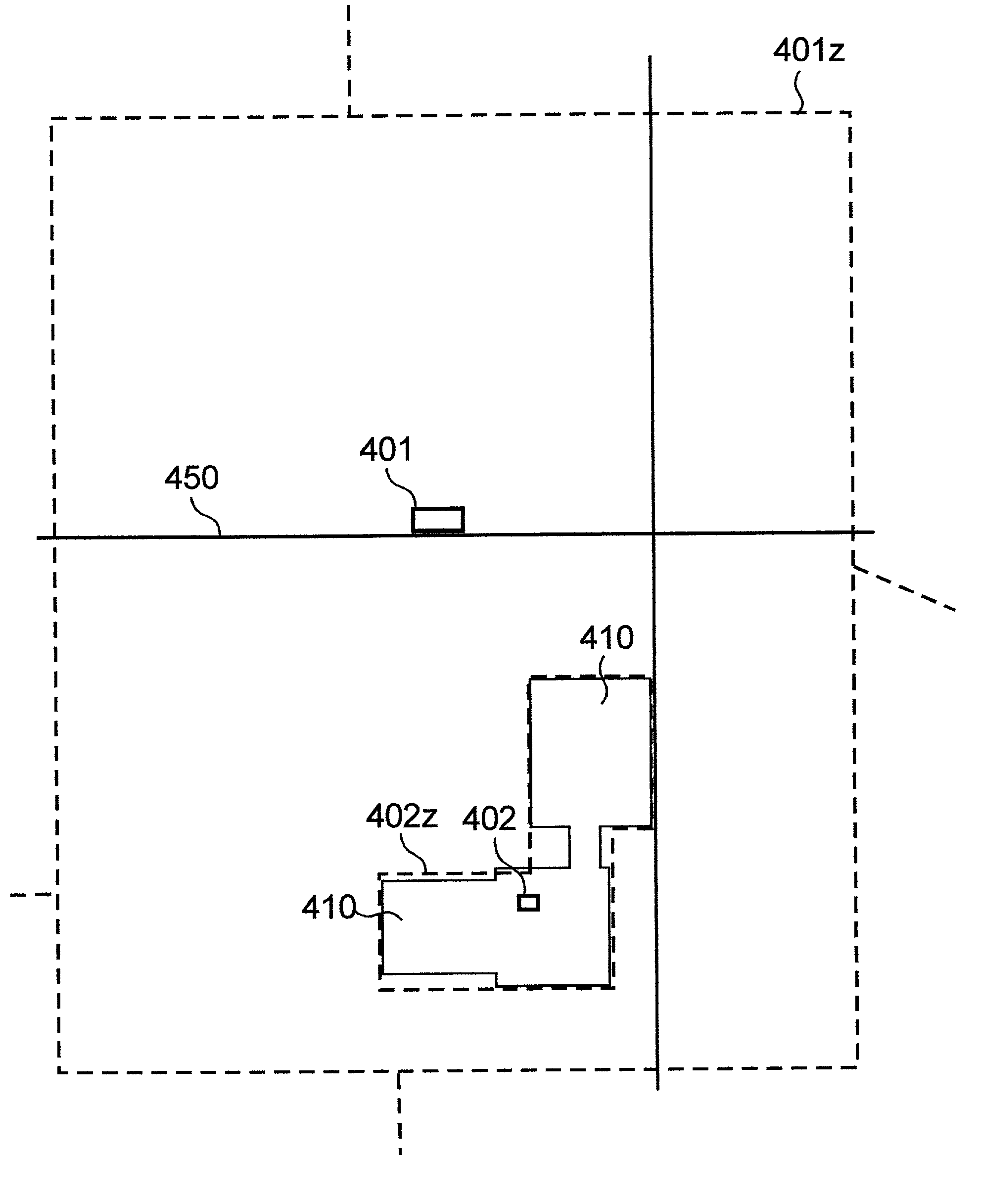
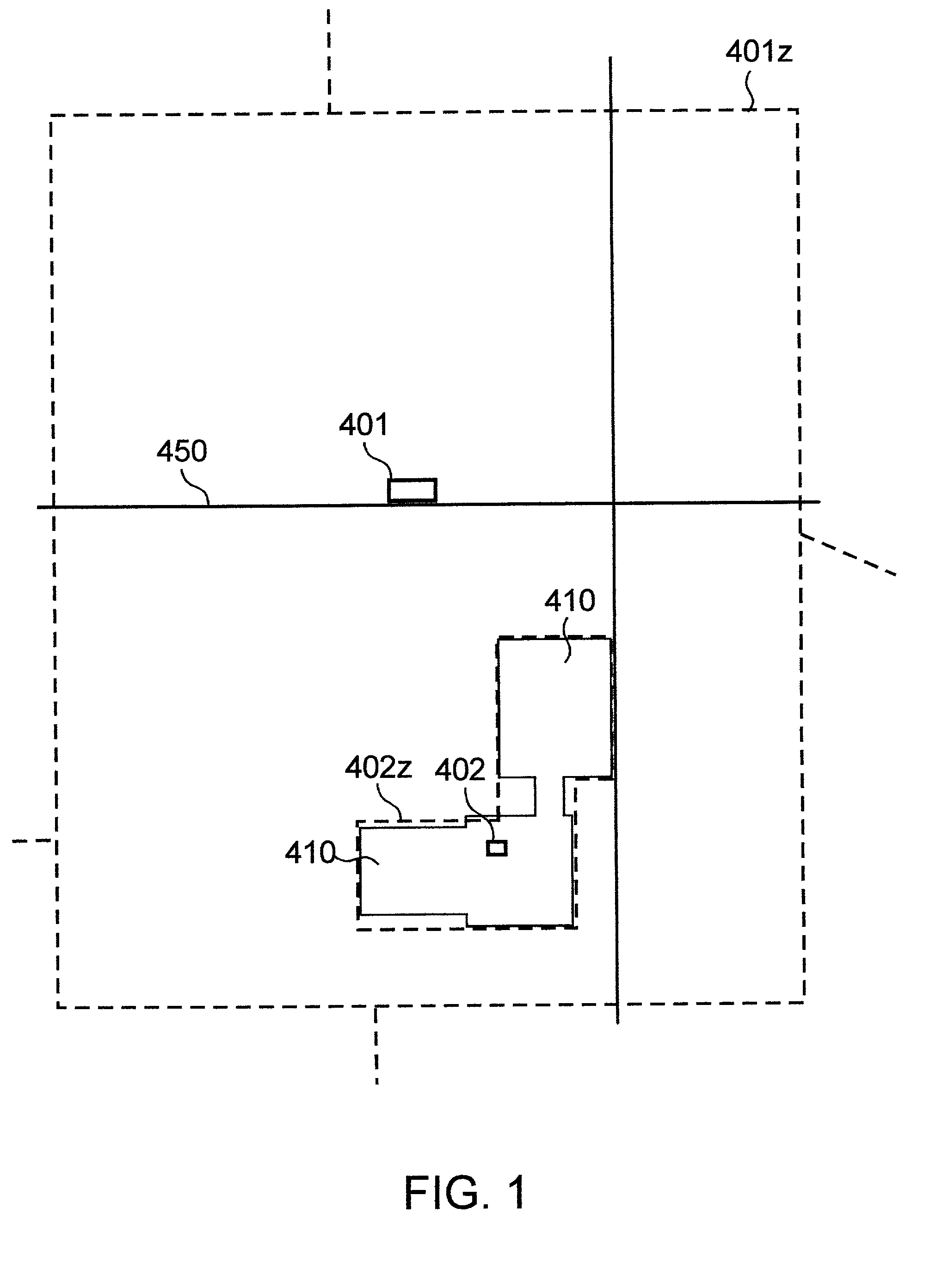
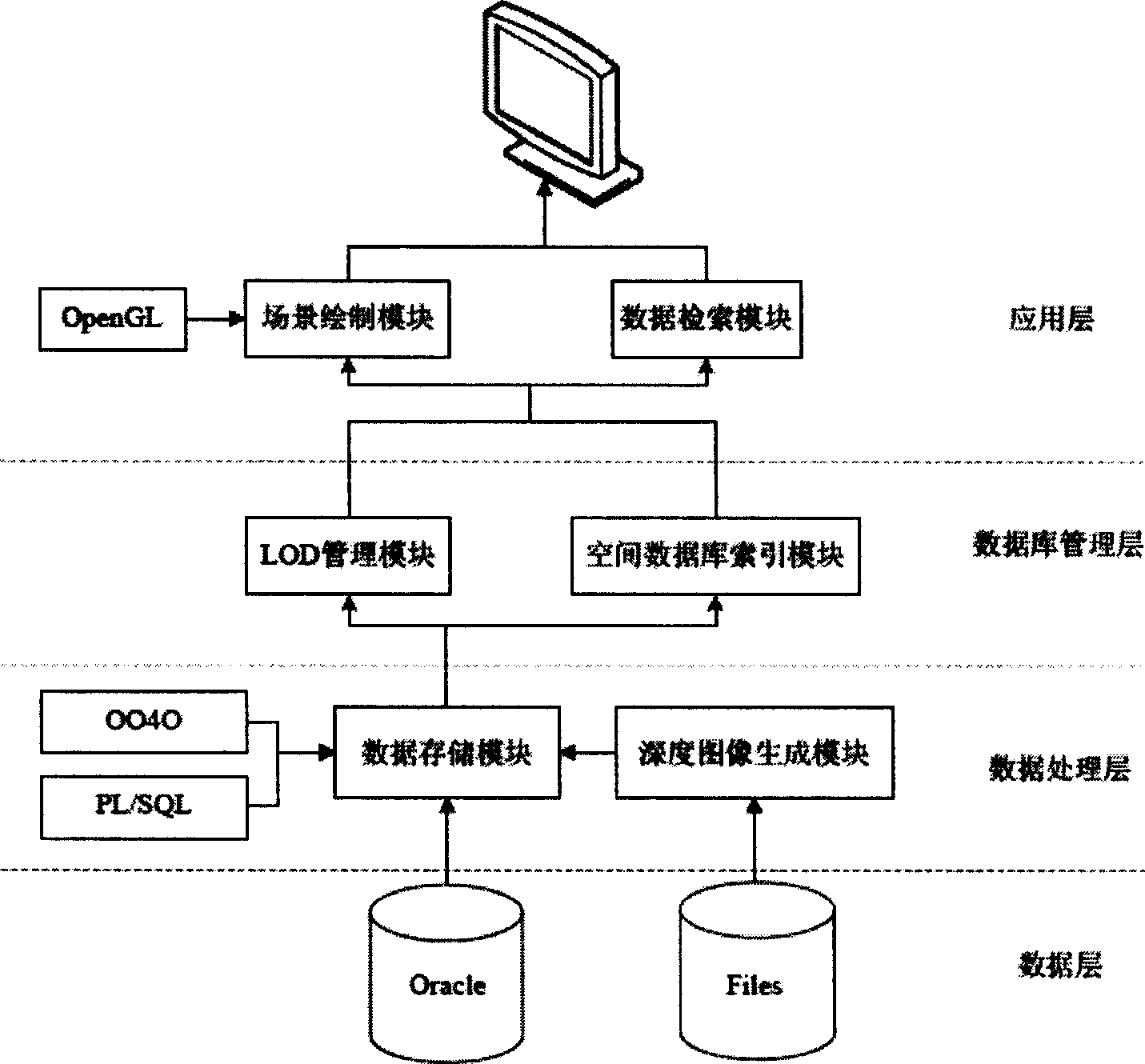
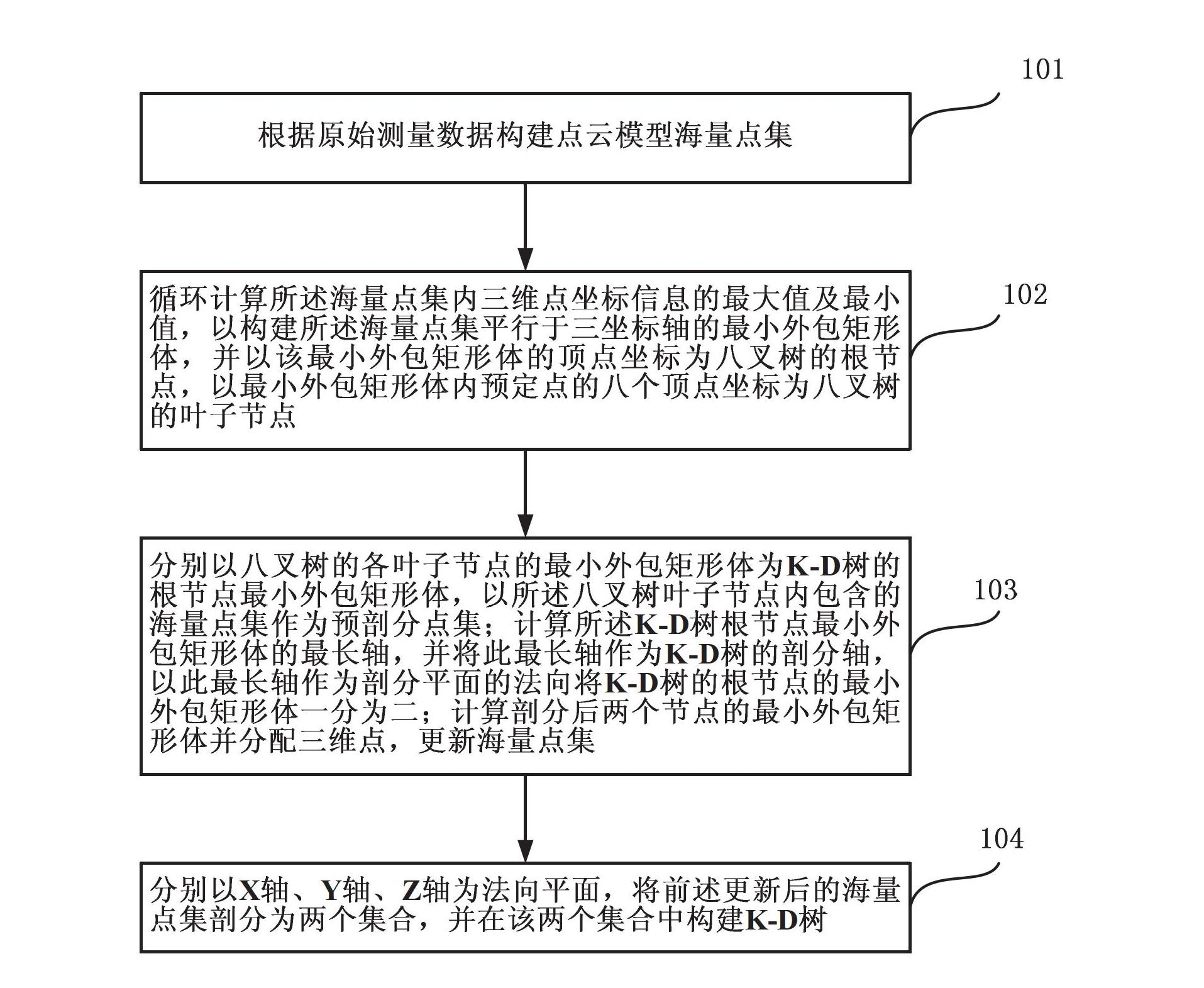
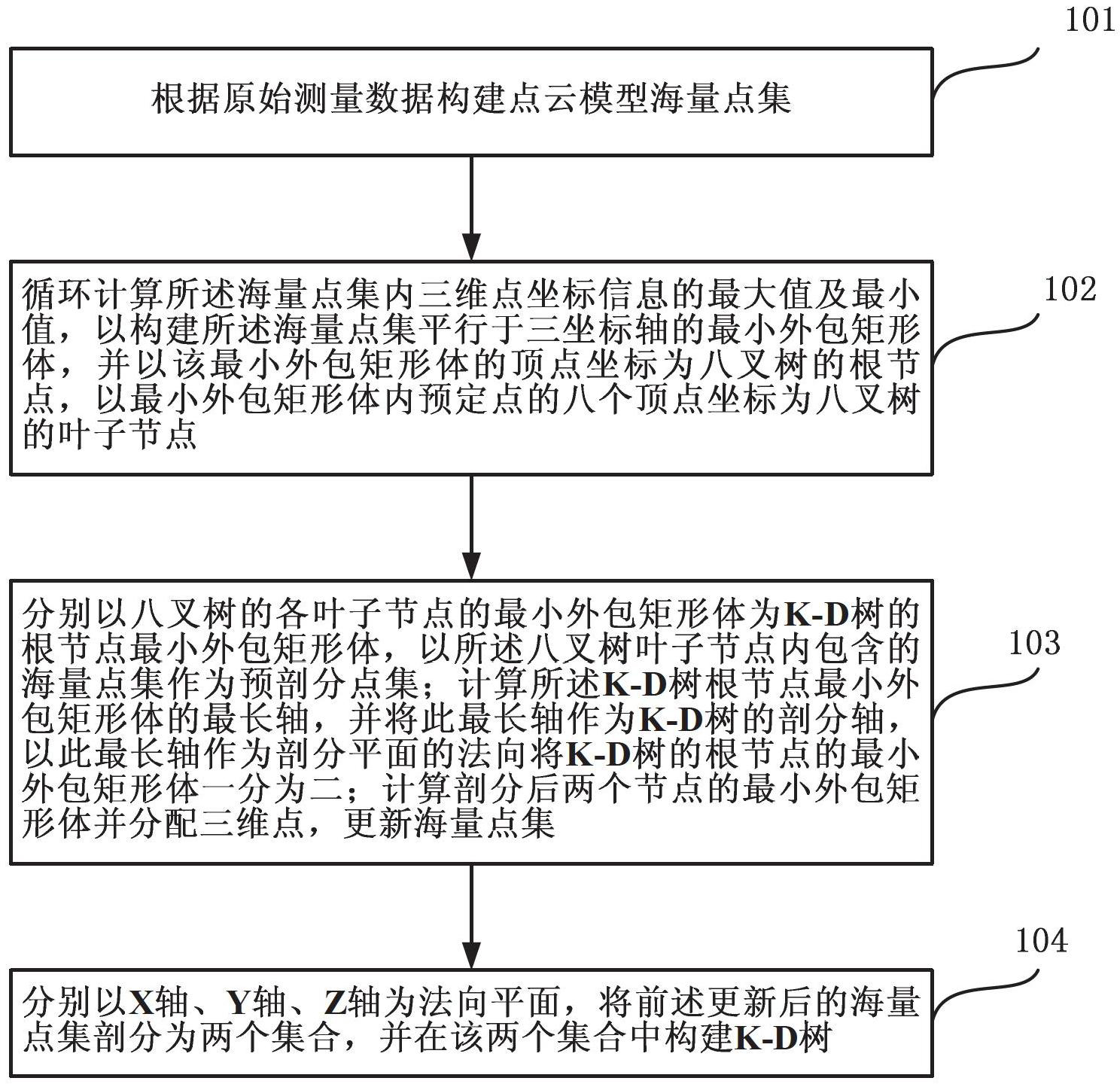
Range image-based 3D spatial data processing method and device
InactiveCN101533529AEfficient compressionMake up for lack of support2D-image generationSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum bounding boxR-tree
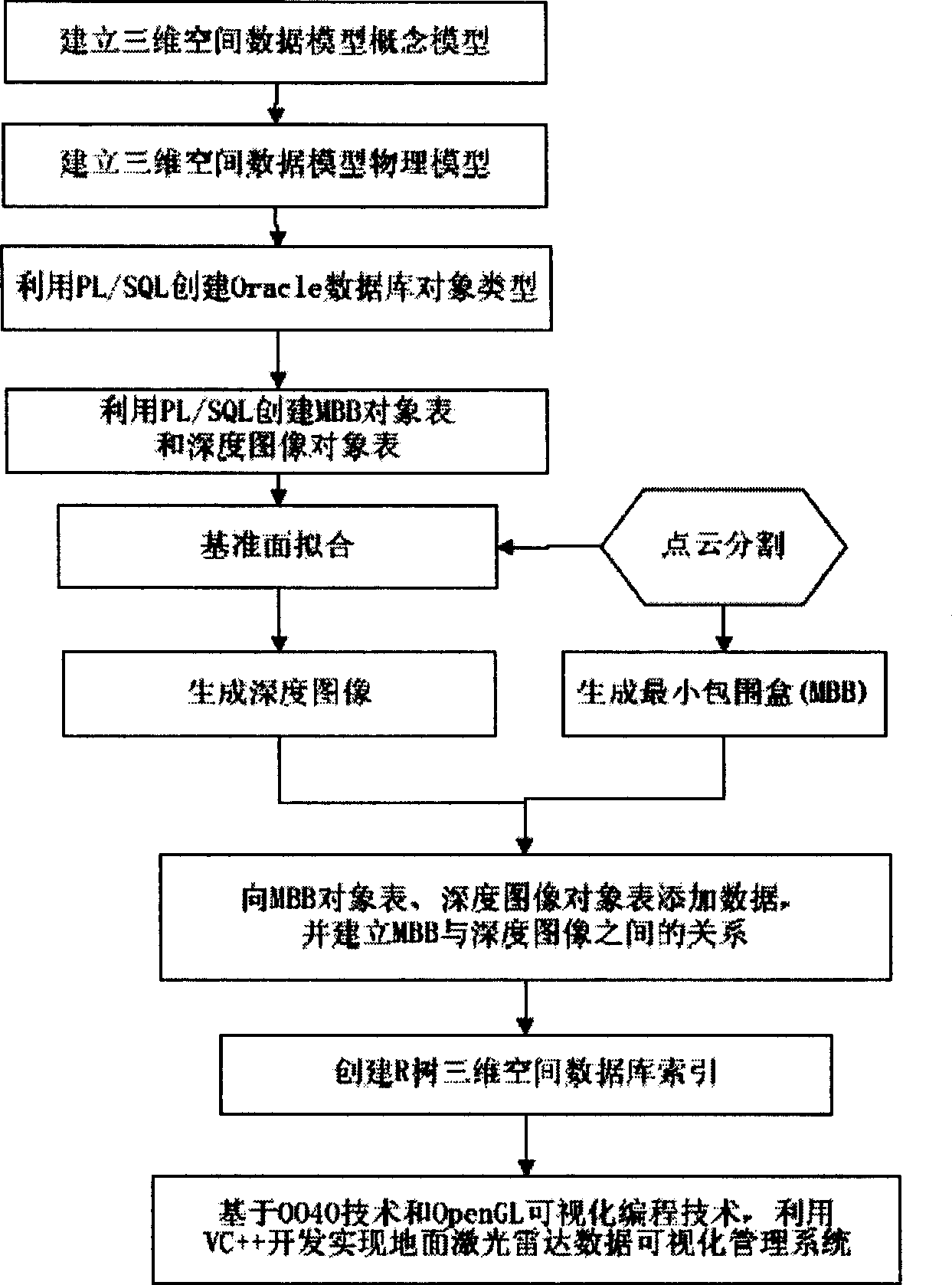
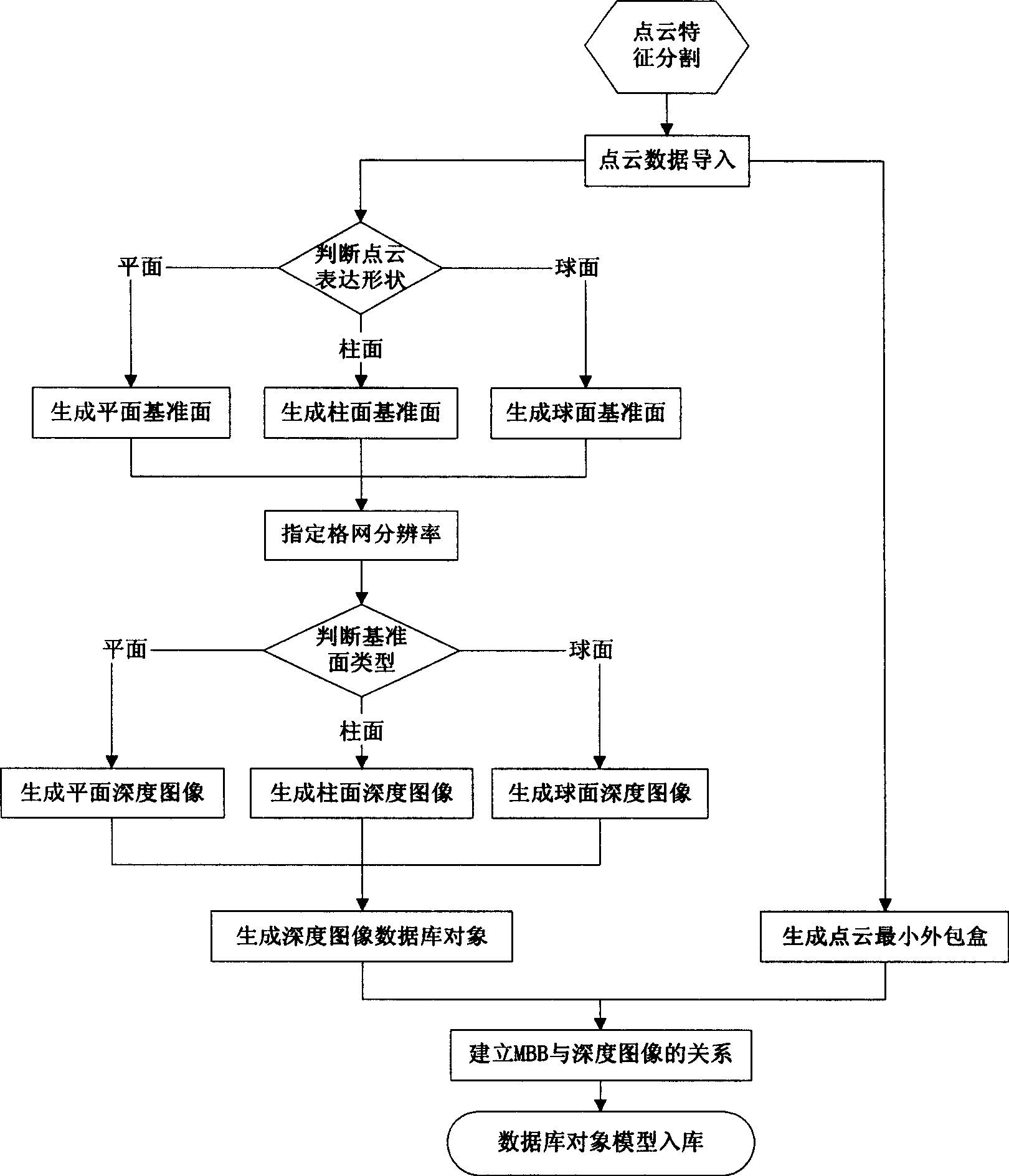
The invention relates to a range image-based 3D spatial data processing method and a device. In the method, ground laser radar is adopted to scan an object to obtain 3D point cloud data on the surface of the object; a database object table is established by a PL / SQL programming approach; a reference datum is fit according to point cloud which is segmented in advance to generate a minimum bounding box (MBB) of the point cloud and subsequently generate the range image according to the reference datum obtained by fitting. Later, data of the MBB and the range image are written into the database object table and the relation between the MBB and a range image object is established, subsequently, R tree 3D spatial database index is established for the database objects which enter the database, finally, visualization is realized based on Oracle Objects for OLE (OO4O) and OpenGL.
Owner:BEIJING UNIVERSITY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE
High-performance location management platform
InactiveUS6868410B2Quick translationEliminate mass-storage accessesData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsMass storageLongitude
An apparatus and method for rapid translation of geographic latitude and longitude into any of a number of application-specific location designations or location classifications, including street address, nearest intersection, PSAP (Public Safety Answering Point) zone, telephone rate zone, franchise zone, or other geographic, administrative, governmental or commercial division of territory. The speed of translation meets call-setup requirements for call-processing applications such as PSAP determination, and meets caller response expectations for caller queries such as the location of the nearest commercial establishment of a given type. To complete its translation process in a timely manner, a memory-stored spatial database is used to eliminate mass-storage accesses during operation, a spatial indexing scheme such as an R-tree over the spatial database is used to locate a caller within a specific rectangular area, and an optimized set of point-in-polygon algorithms is used to narrow the caller's location to a specific zone identified in the database. Additional validation processing is supplied to verify intersections or street addresses returned for a given latitude and longitude. Automatic conversion of latitude-longitude into coordinates in different map projection systems is provided.The memory-stored database is built in a compact and optimized form from a relational spatial database as required. The R-tree spatial indexing of the memory-stored database allows for substantially unlimited scalability of database size without degradation of response time. Maximum performance for database retrievals is assured by isolating the retrieval process from all updating and maintenance processes. Hot update of the in-memory database is provided without degradation of response time.
Owner:PRECISELY SOFTWARE INC +1
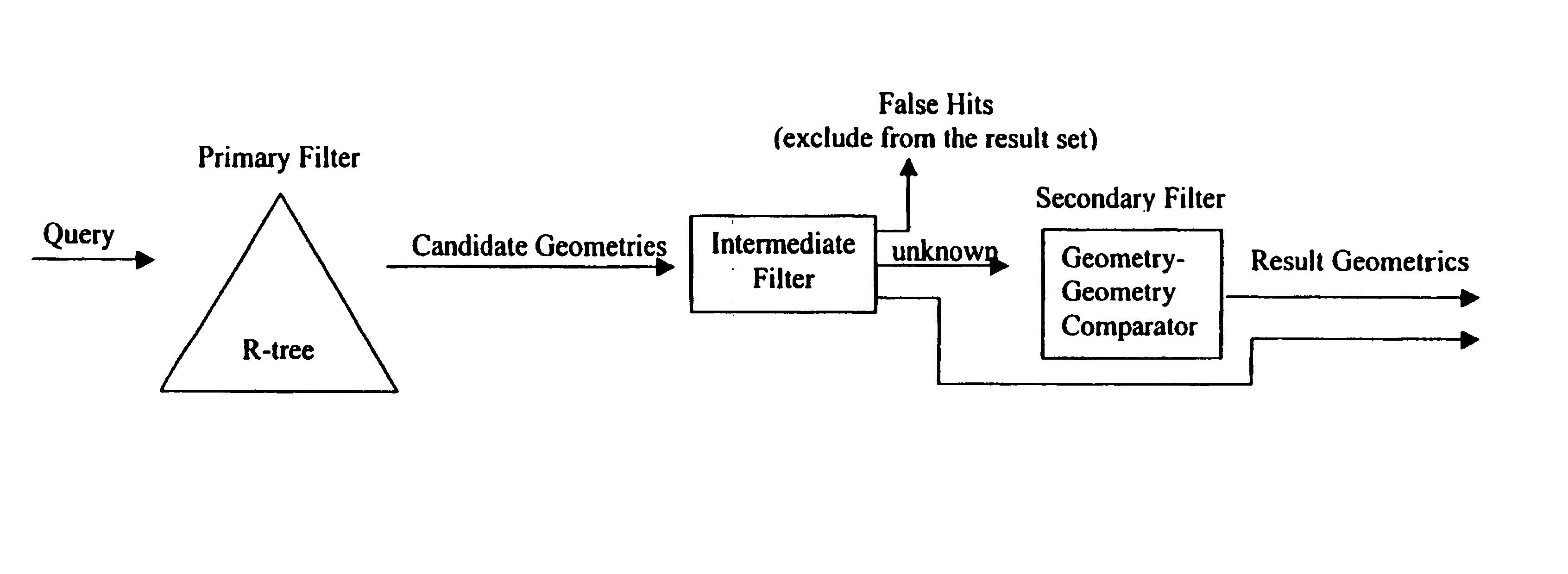
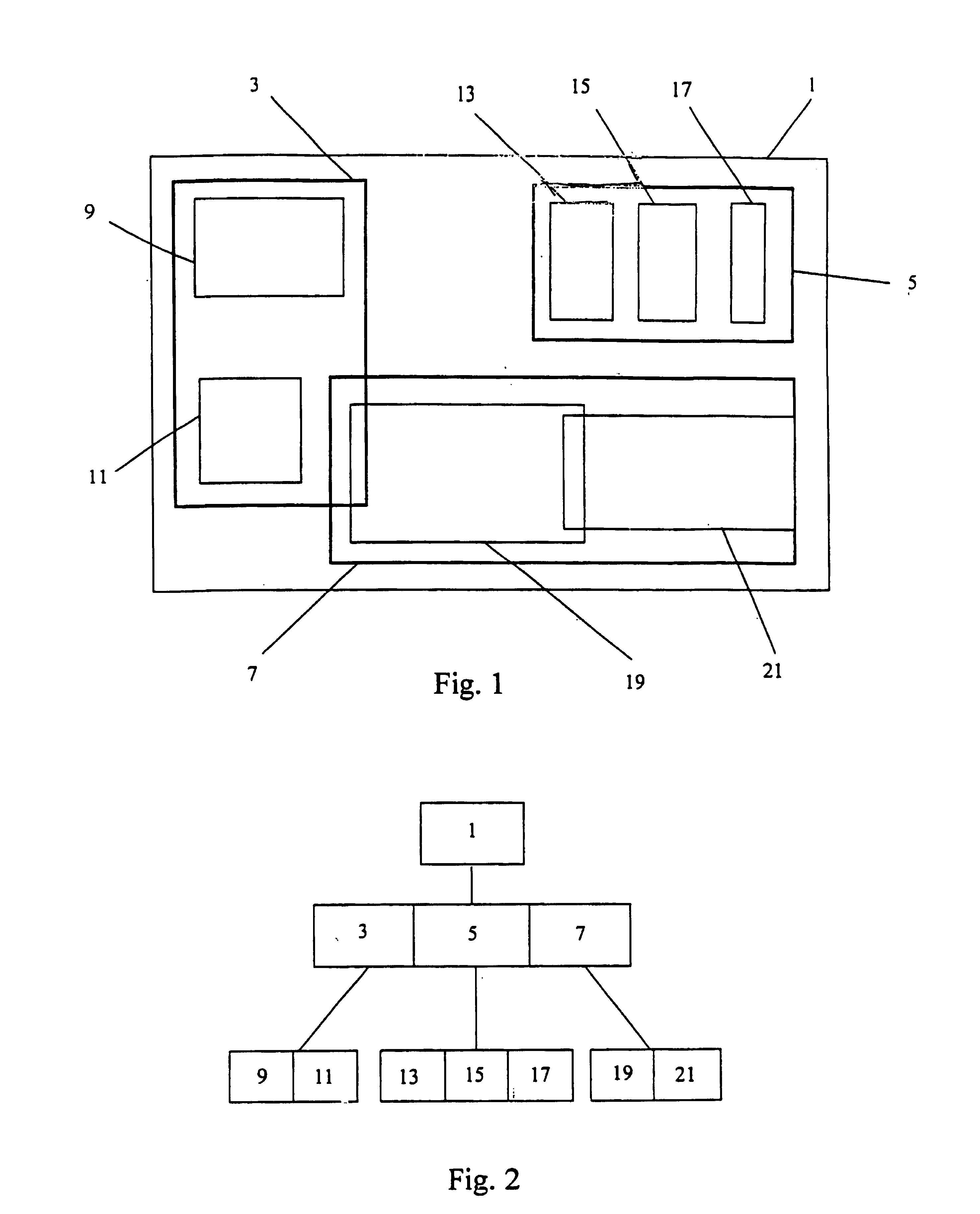
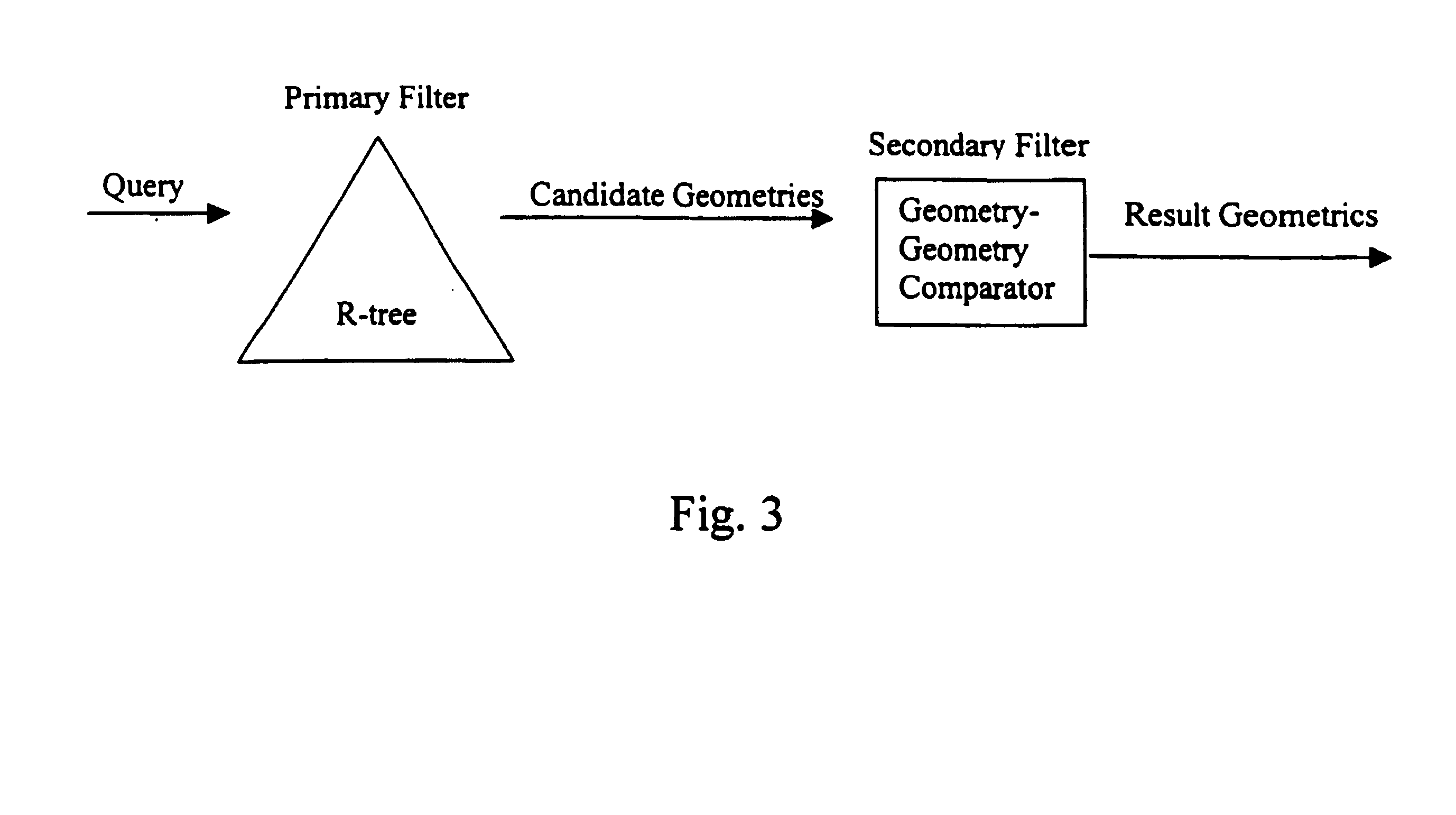
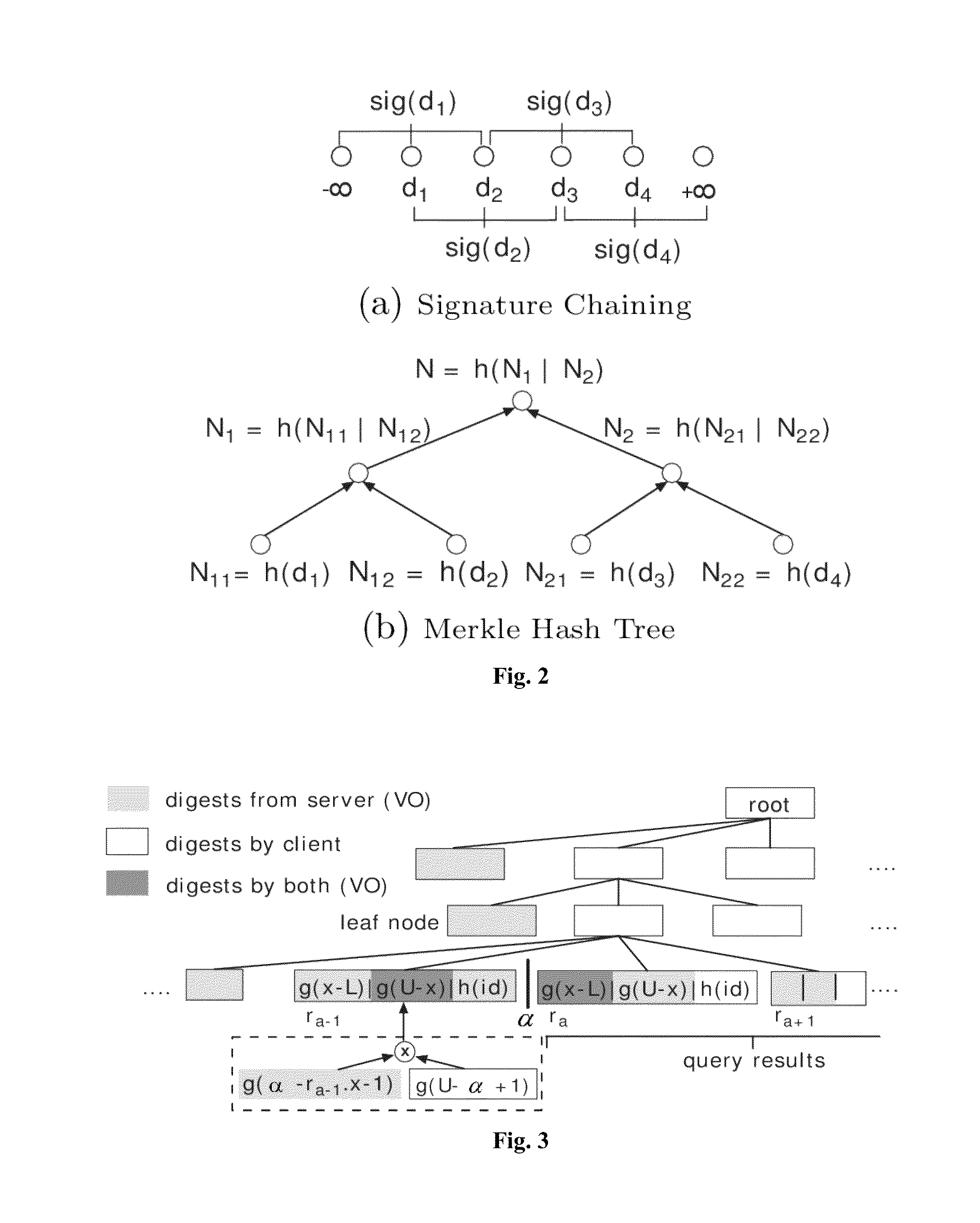
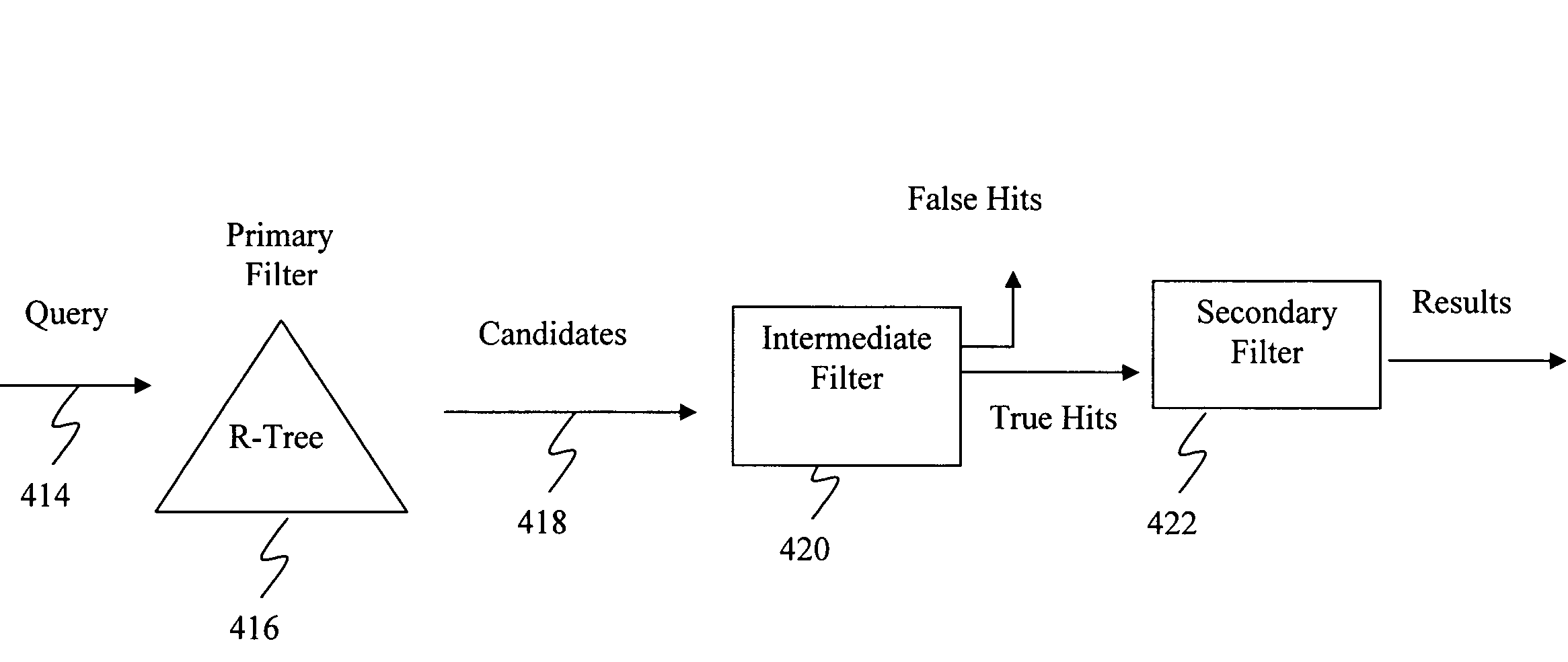
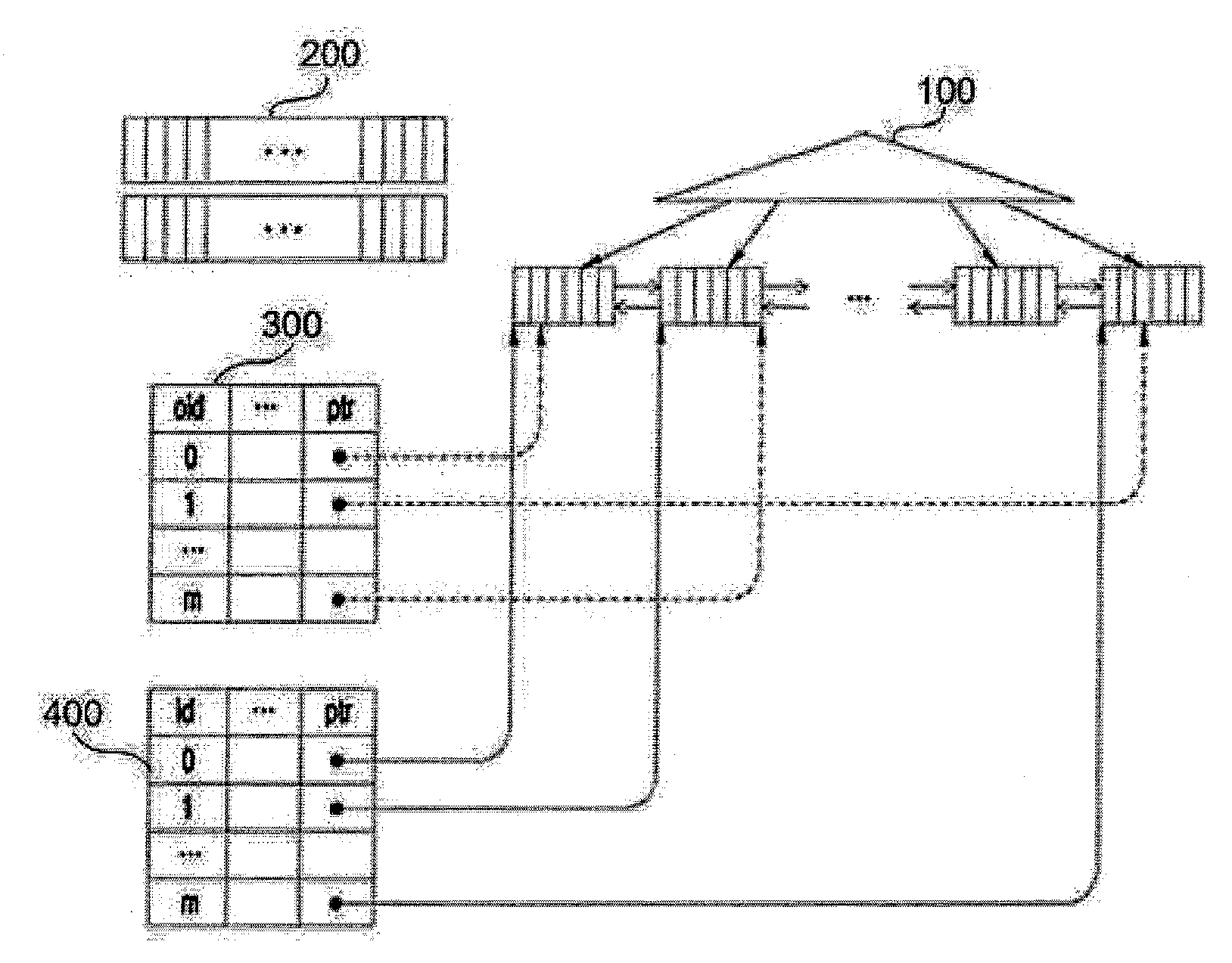
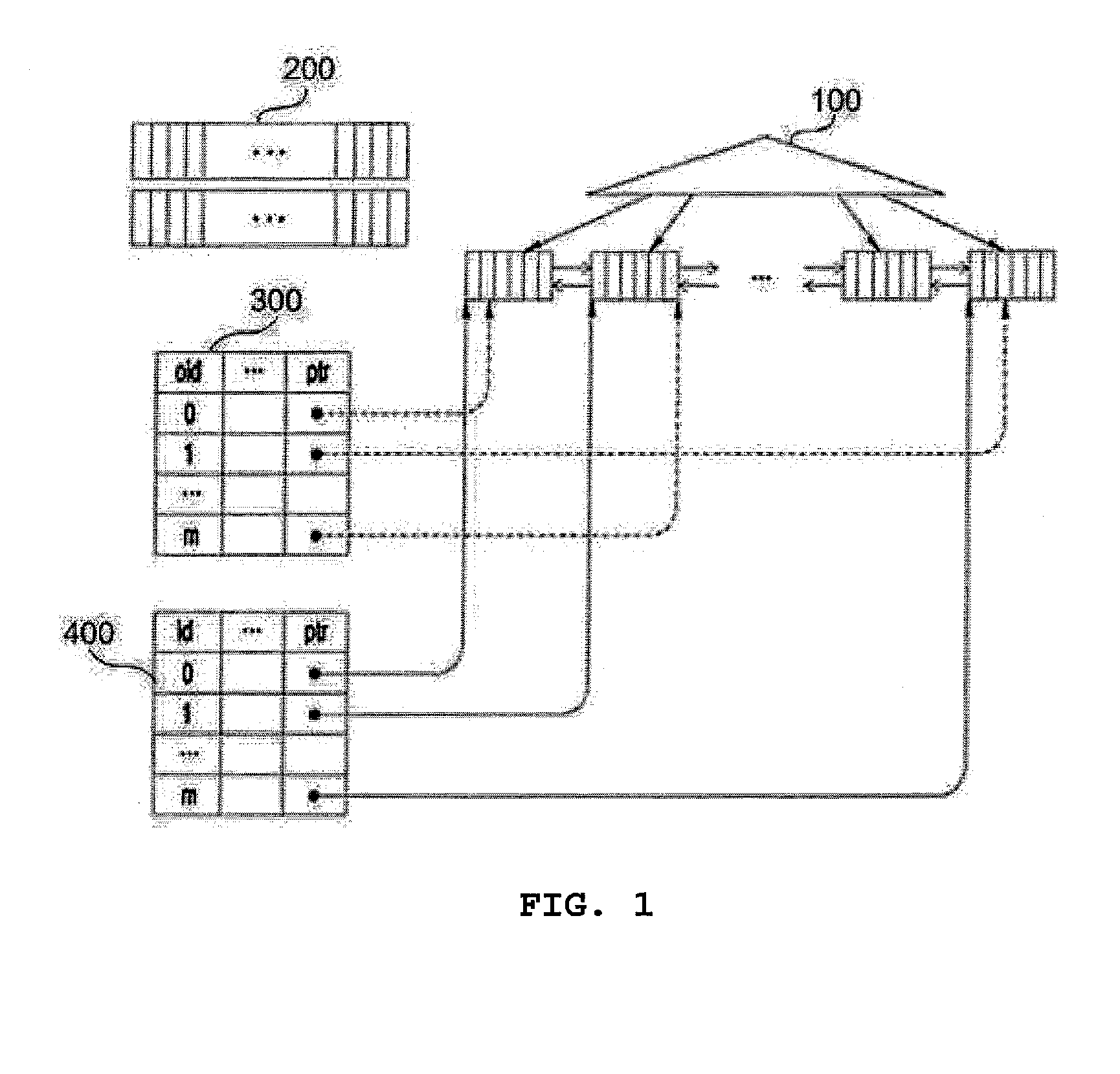
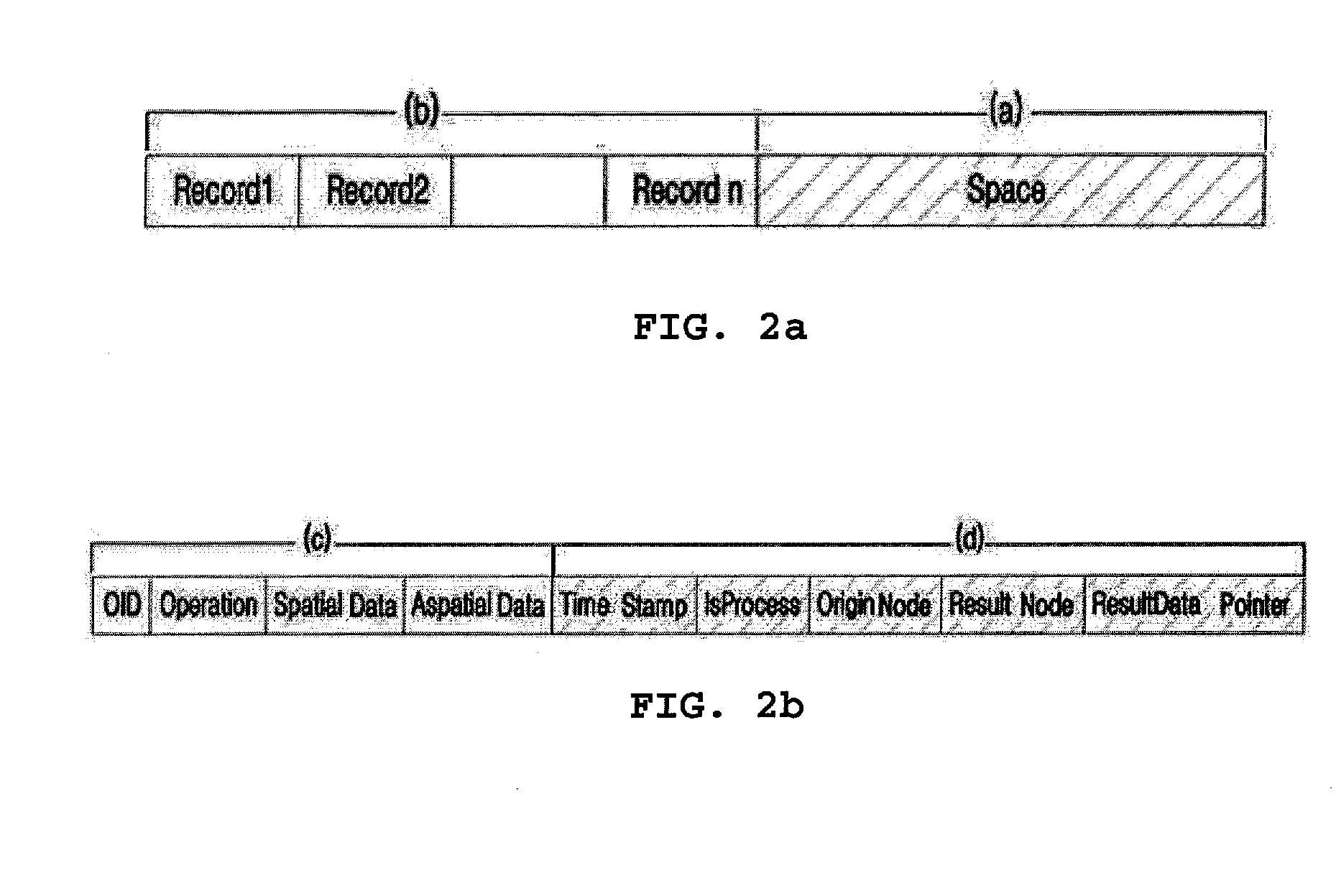
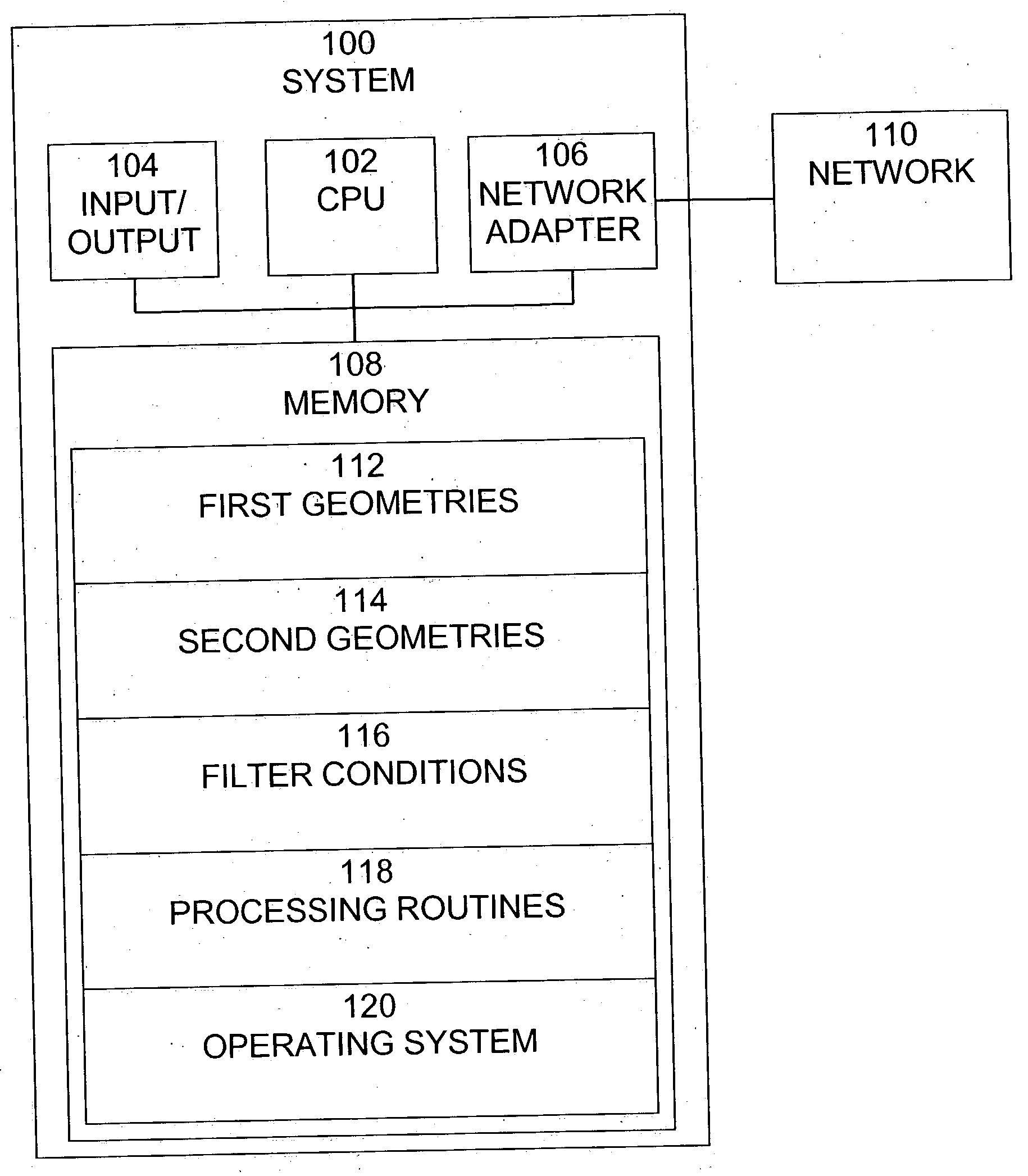
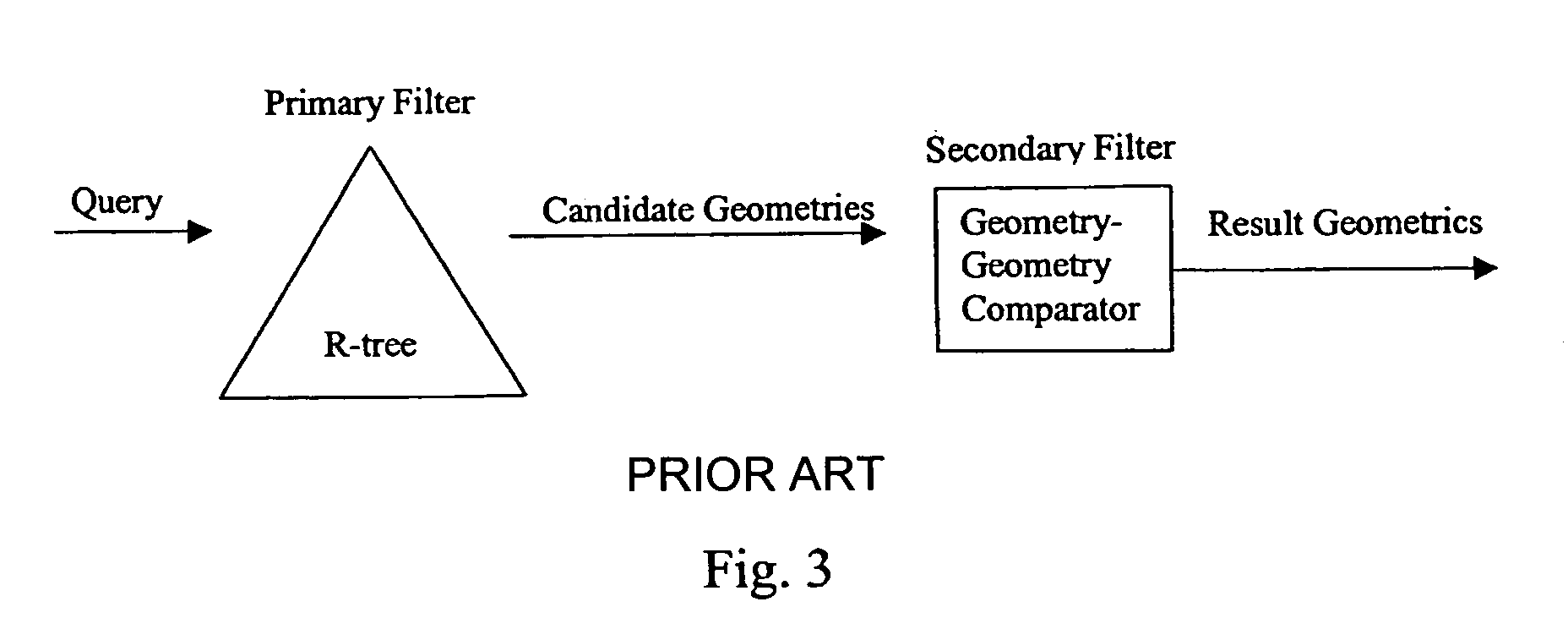
Query pruning using interior rectangles in an R-tree index
InactiveUS7080065B1Facilitating fast processing of queryLow costData processing applicationsGeographical information databasesR-treeComputer science
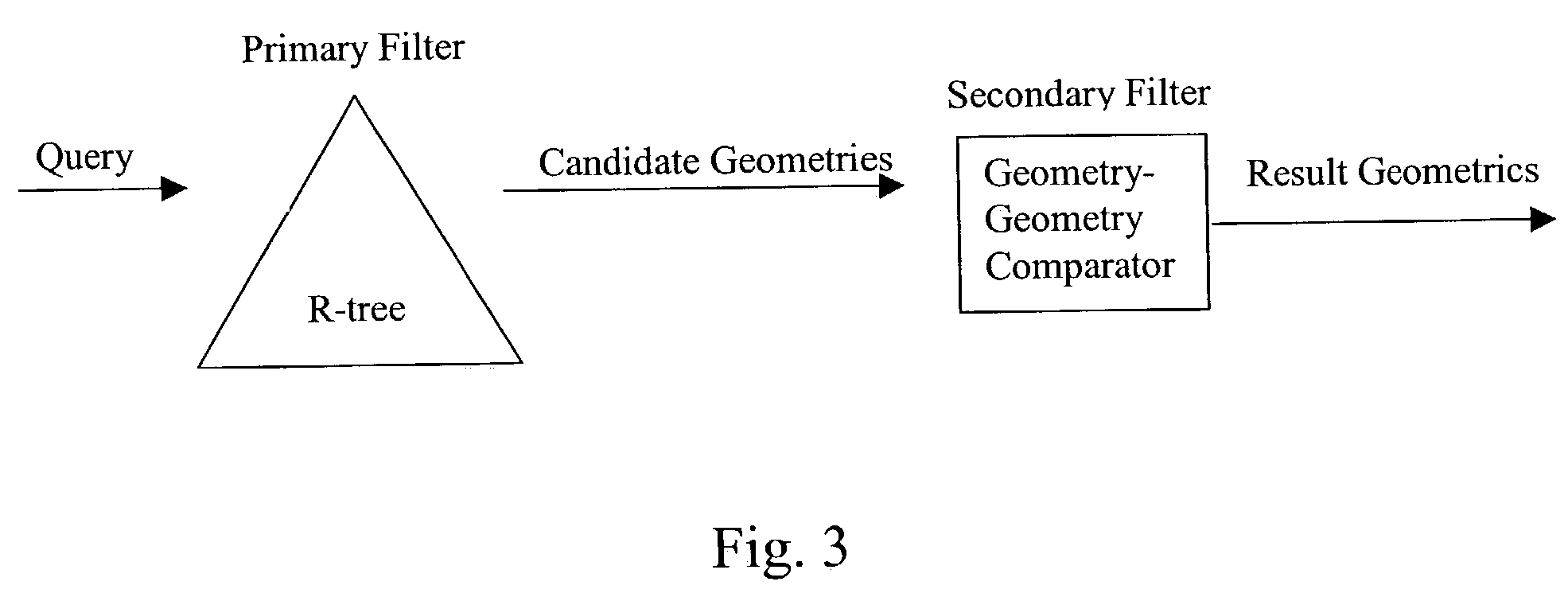
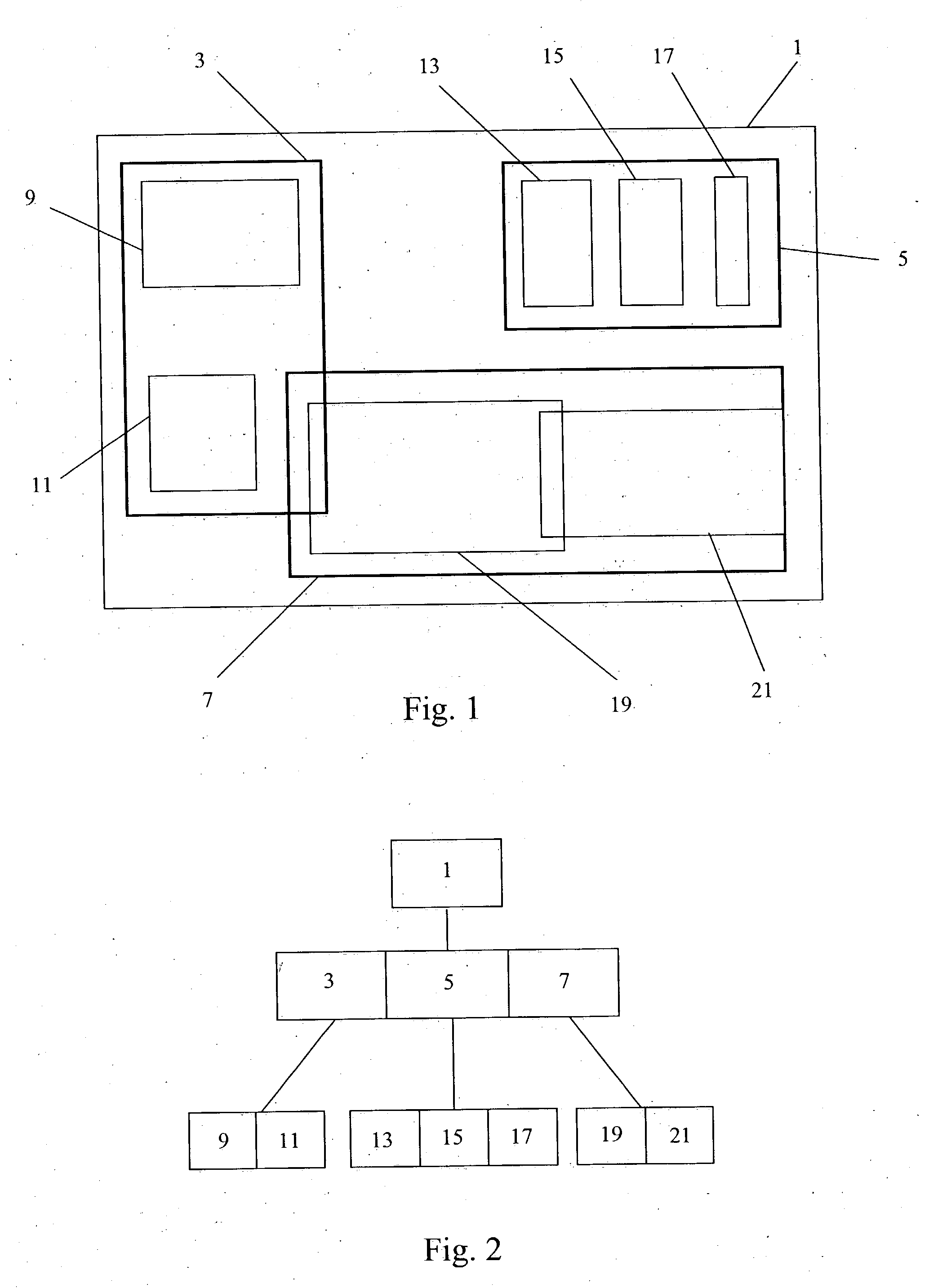
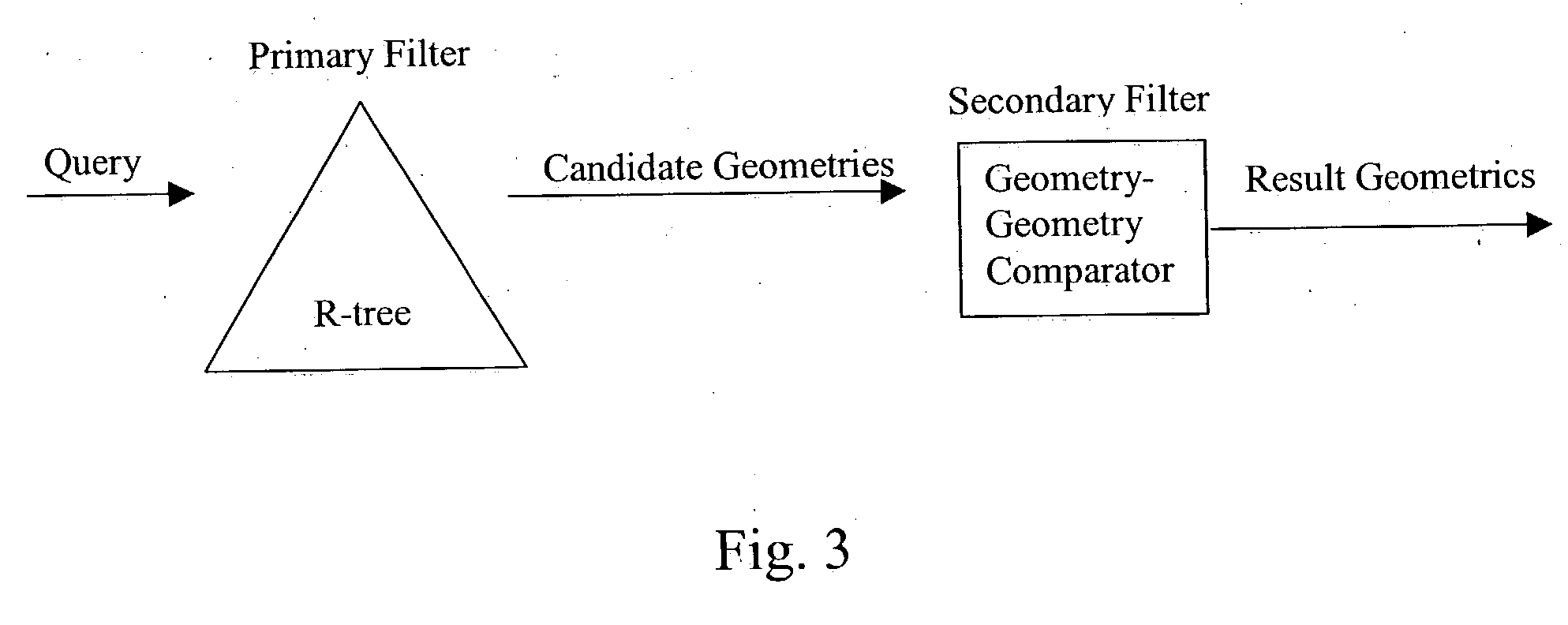
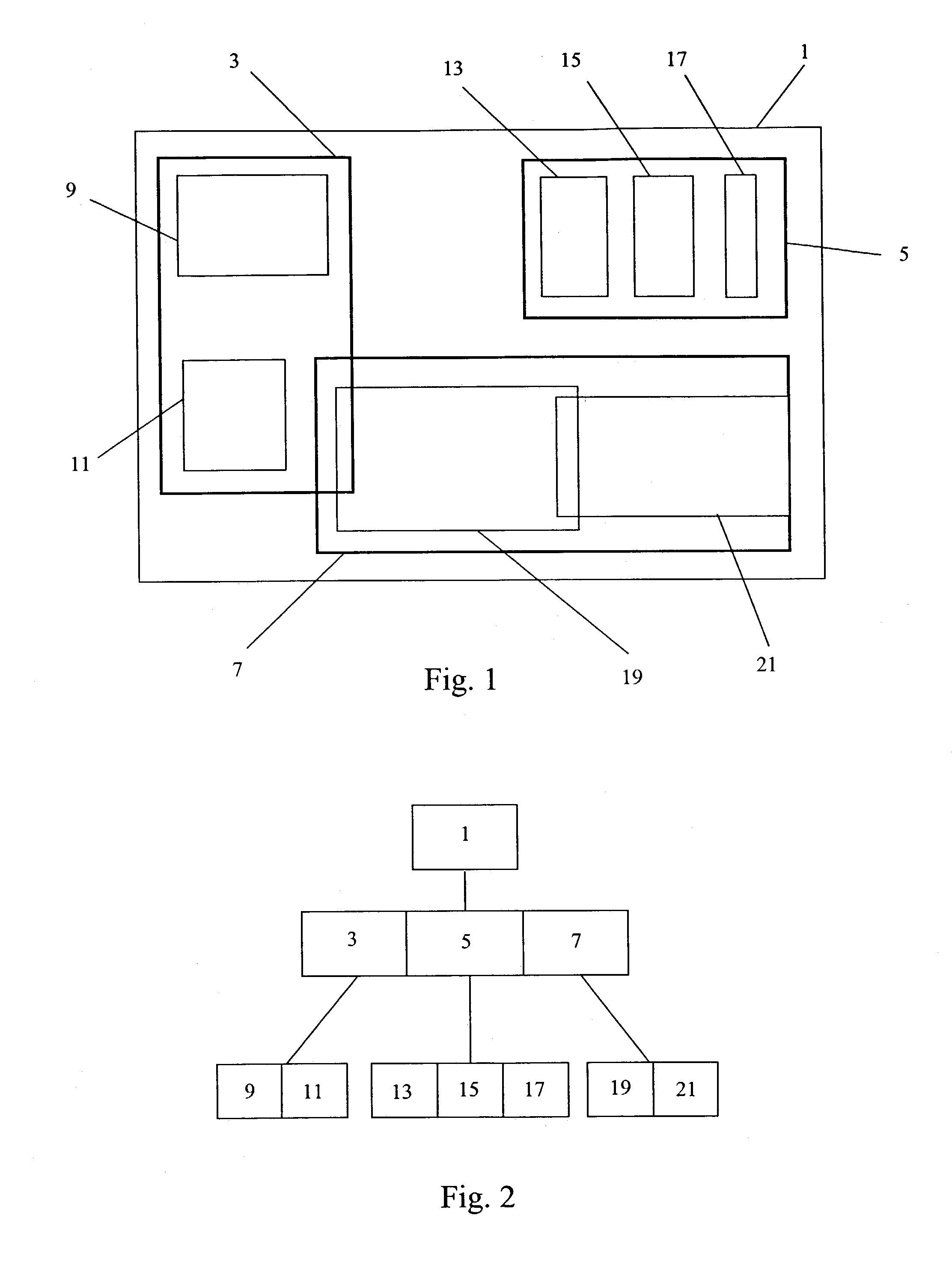
To determine relationships among objects represented in a database at least one interior rectangle lying entirely within a first geometric shape is define. A minimum bounding area for the first geometry and a minimum bounding area for a second geometry are defined and compared with one another to determine if the second geometry fulfills a primary filter condition of an interaction between the first and second geometries. Based on the fulfillment of the primary condition by the second geometry, it is determined whether an intermediate filter condition of interaction between the first and second geometries is fulfilled by analyzing the distribution of the second geometry with respect to at least one interior rectangle within the first geometry. It is determined whether the second geometry fulfills a secondary filter condition by comparing the second geometry with the first geometry if the second geometry fulfills the primary filter condition.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Rapid, spatial-data viewing and manipulating including data partition and indexing
ActiveUS20090060345A1Digital data processing detailsActive open surveying meansHigh densityCompositional data
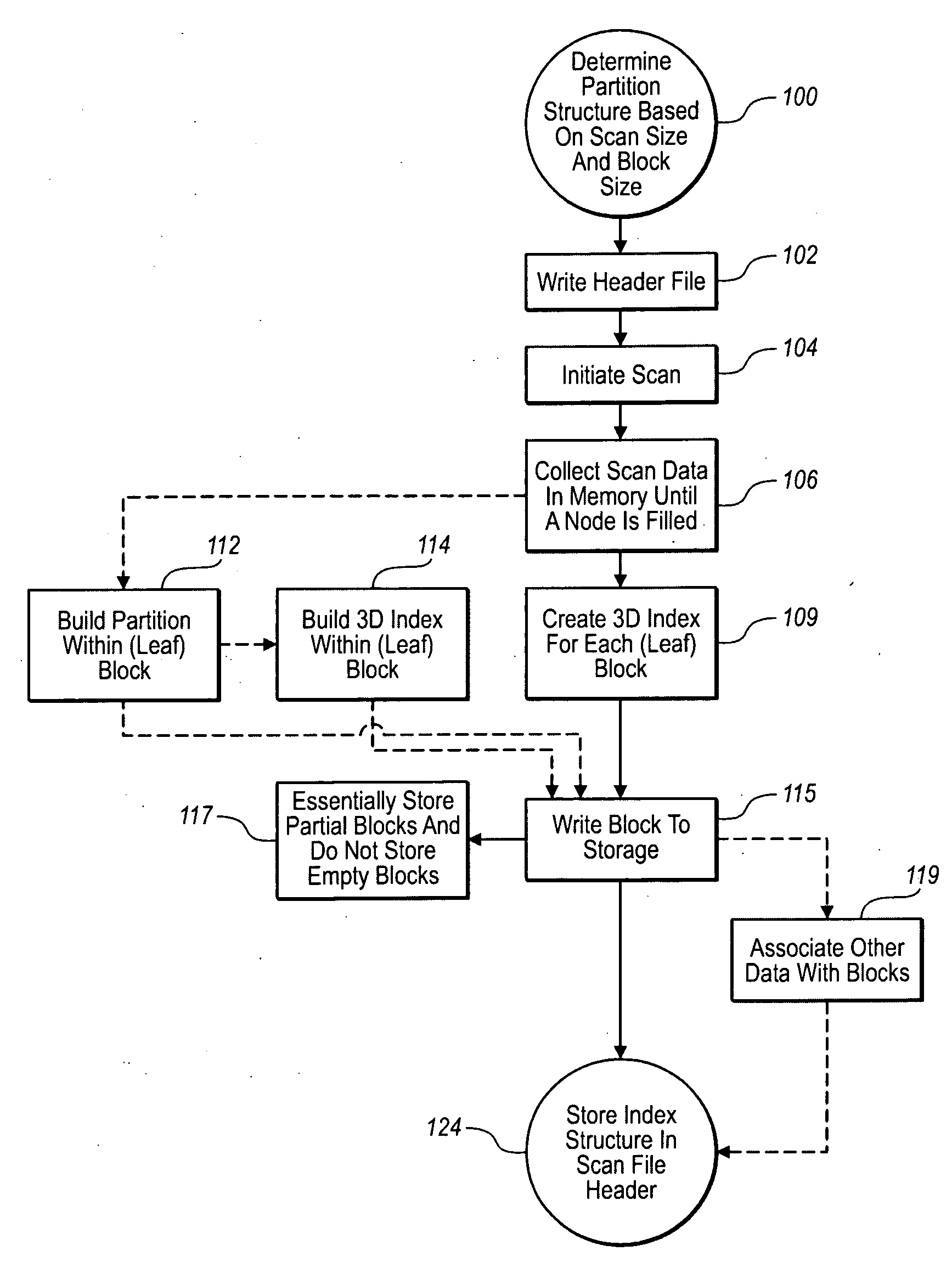
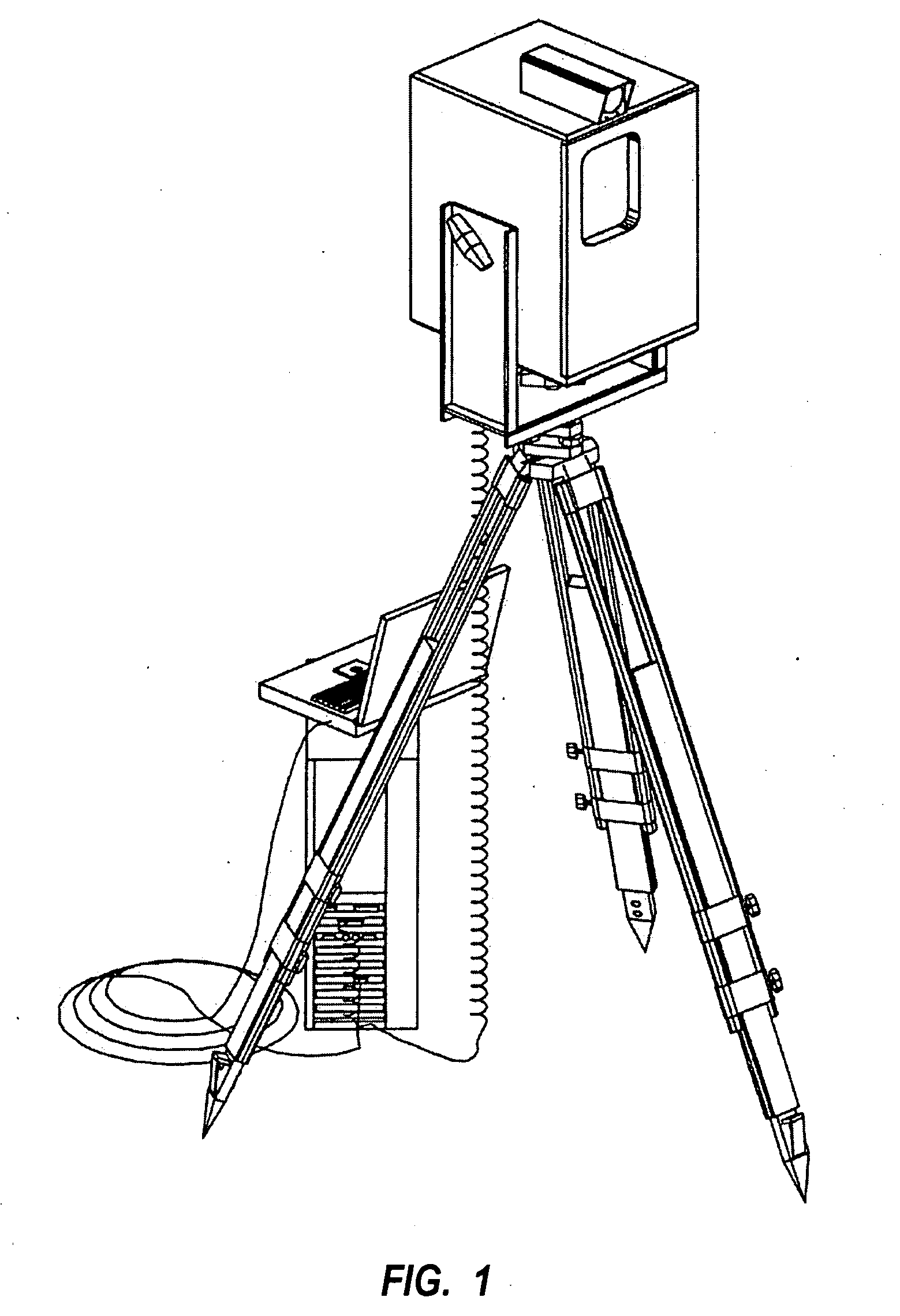
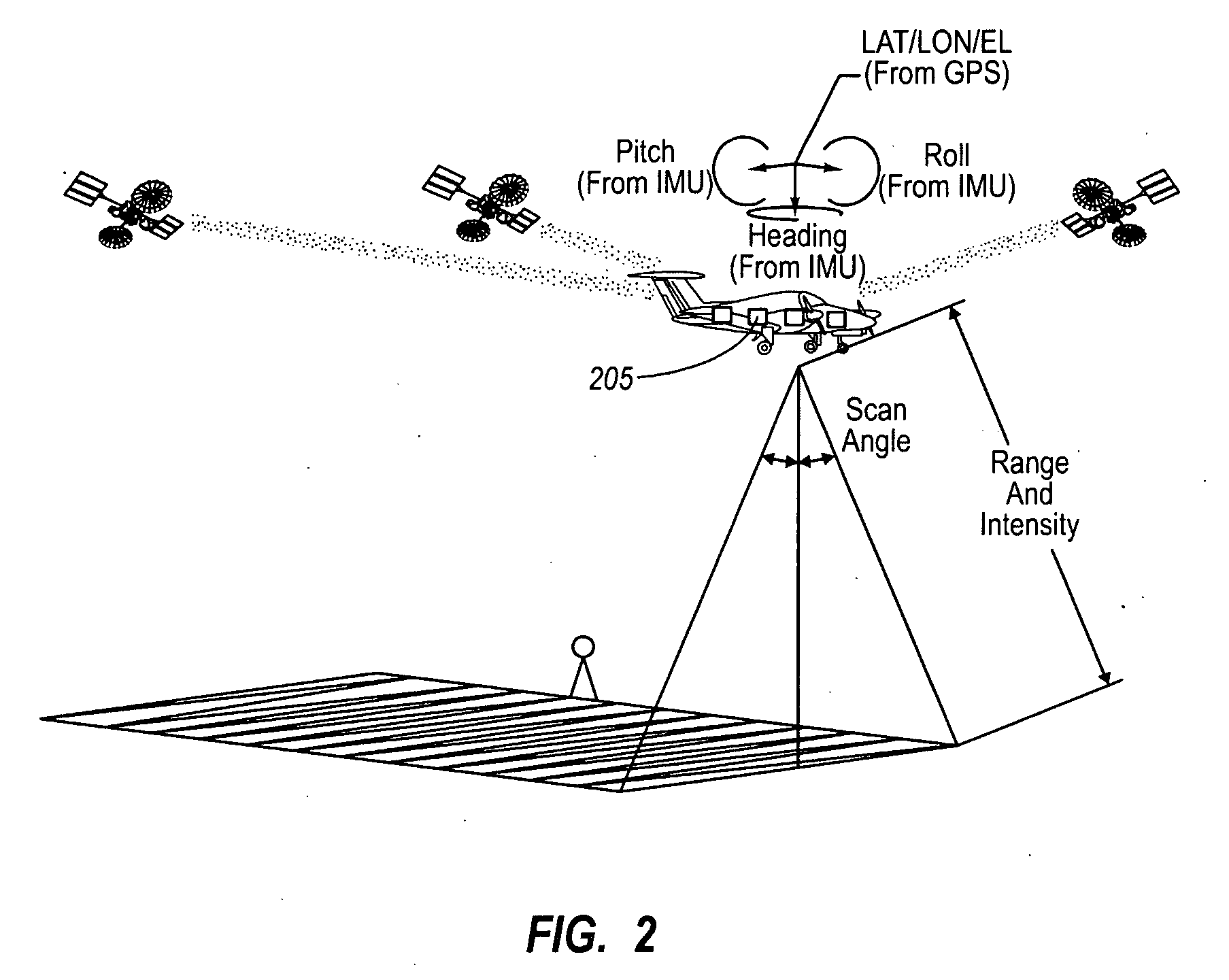
A high-density, distance-measuring laser system and an associated computer that processes the data collected by the laser system. The computer determines a data partition structure and stores that structure as a header file for the scan before data is collected. As the scan progresses, the computer collects data points until a predetermined threshold is met, at which point a block of data consisting of the data points up to the threshold is written to disk. The computer indexes each data block using all three coordinates of its constituent data points using, preferably, a flexible index, such as an R-tree. When a data block is completely filled, it is written to disk preferably with its index and, as a result, each data block is ready for access and manipulation virtually immediately after having been collected. Also, each data block can be independently manipulated and read from disk.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Uncertain space-time trajectory data range query method under road network environment
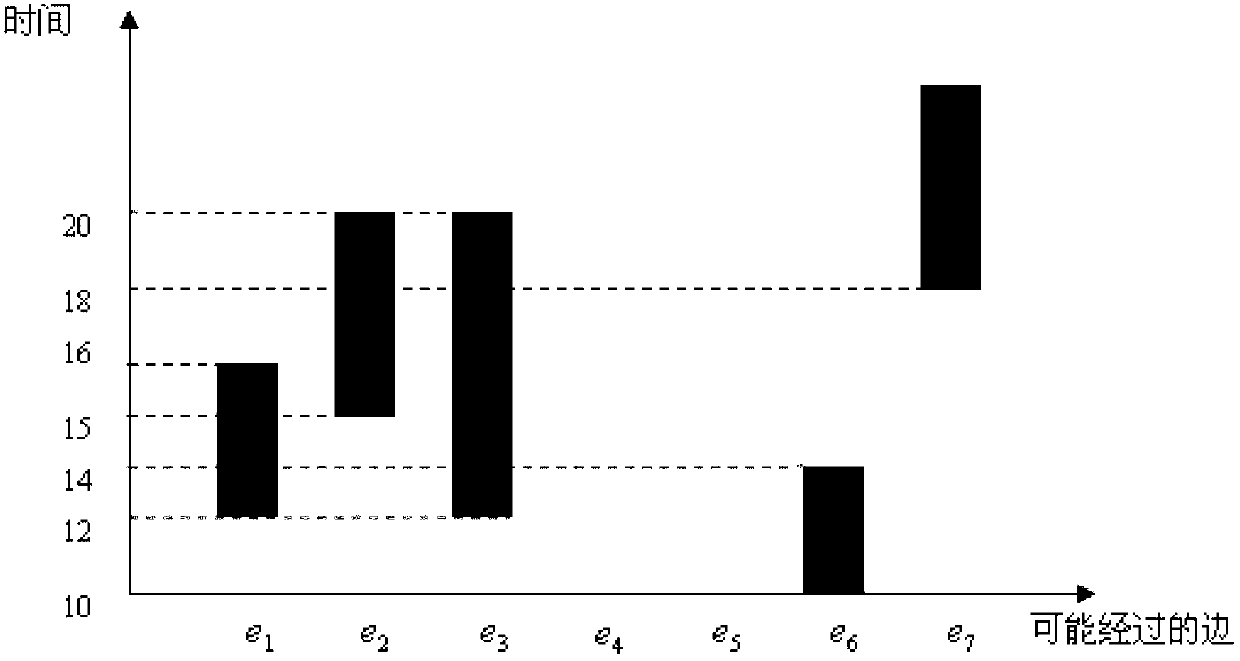
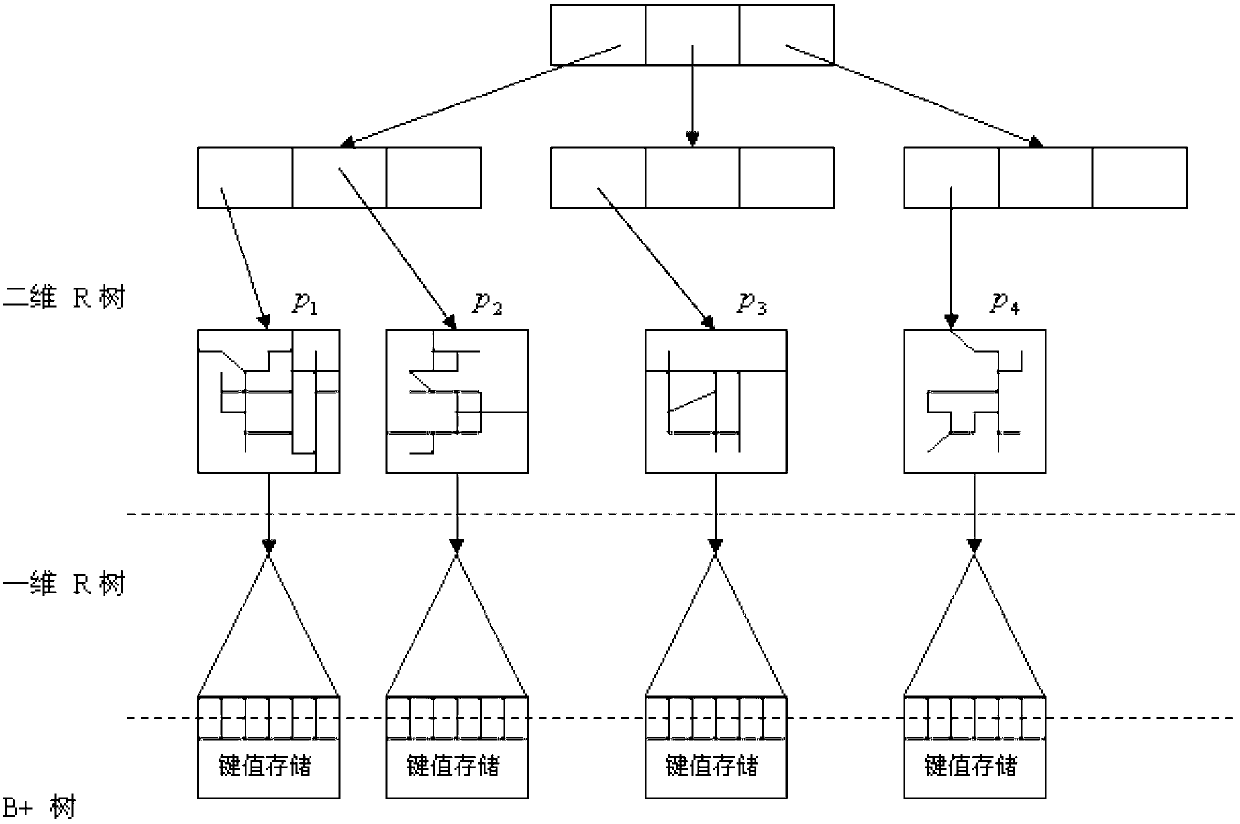
InactiveCN103106280AExtended processing timeImprove the efficiency of solving crimesSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmRoad networks
The invention discloses an uncertain space-time trajectory data range query method under road network environment. The process includes that firstly, a road network is divided into divided areas with the number of K; a hash table is established according to sides and divided corresponding relations; boundary points of the divided areas are calculated, and a two-dimensional space R tree index is established; the shortest path distance among the boundary points of each dividing is calculated; a one-dimensional R tree time quantum index is established for each dividing, and a B+ tree for storing trajectory data for each one-dimensional R tree is established; then, the earliest arrival time and the latest leaving time of a certain trajectory and an uncertain trajectory are calculated, and a unit segment assemble and divided beginning and ending time are inserted into time interval components; and finally, according to the dividing of a query point, distance information of a divided boundary point and the query point is calculated, and therefore a query result is obtained. According to the uncertain space-time trajectory data range query method under the road network environment, a small amount of input / output (I / O) operations and online calculation are only needed to be performed for a part of dividing, the query results can be obtained, and the query results are high in accuracy degree and fast in response speed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
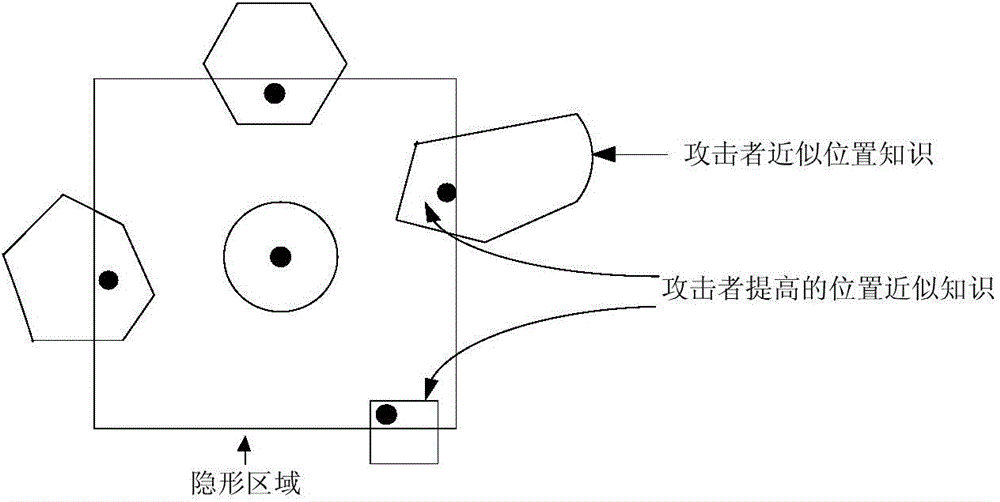
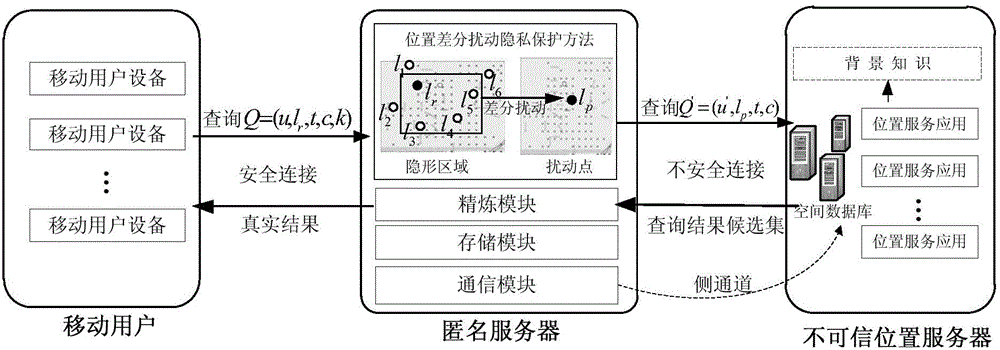
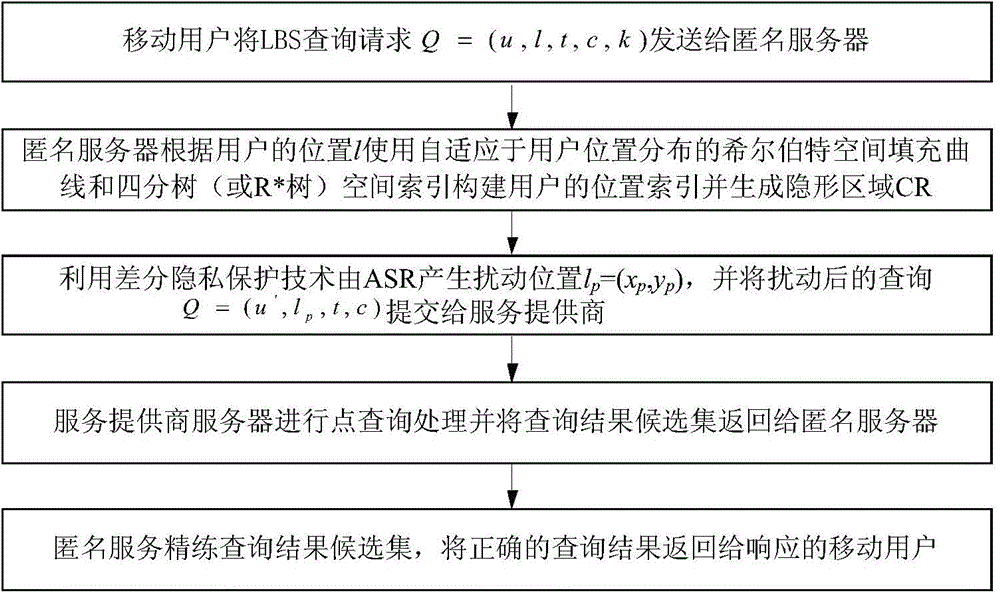
High-efficiency difference disturbance location privacy protection system and method
ActiveCN104394509AGenerate efficientlyGuaranteed correctnessTransmissionLocation information based serviceK-anonymitySide information
The invention discloses a high-efficiency difference disturbance location privacy protection system and a method, considering that the attacker has the challenge to the location privacy protection method based on the location disturbance and fuzzy technology about the background knowledge of the user side information, the difference privacy protection technology is guided to the location fuzzy privacy protection method, the Hilbert space filling curve capable of self-adaption transition on the user location according to the distributed change features in the geographic space of the mobile user and the current fashionable quadtree or R tree spatial index are used for forming the location index for all mobile users in the geographic space, and the K anonymity contact area satisfying the principle of reciprocity is effectively generated. Then, the difference privacy protection technology is used for generating the location disturbance point reasonable near user real location of k location points of the contact area as the query location of LBS user for requesting service from the LBS service provider, the problems and deficiencies of the existing method can be overcome.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
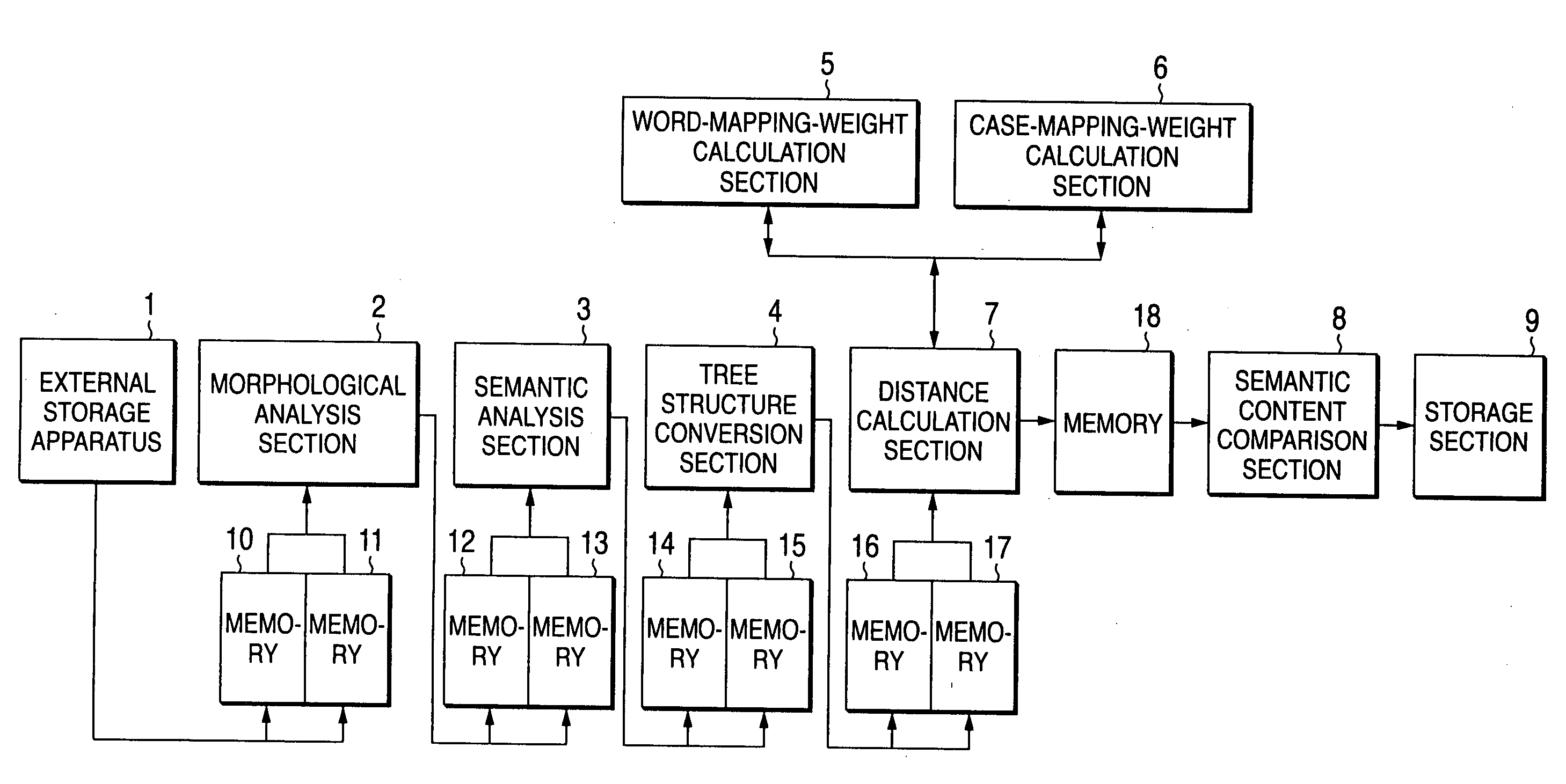
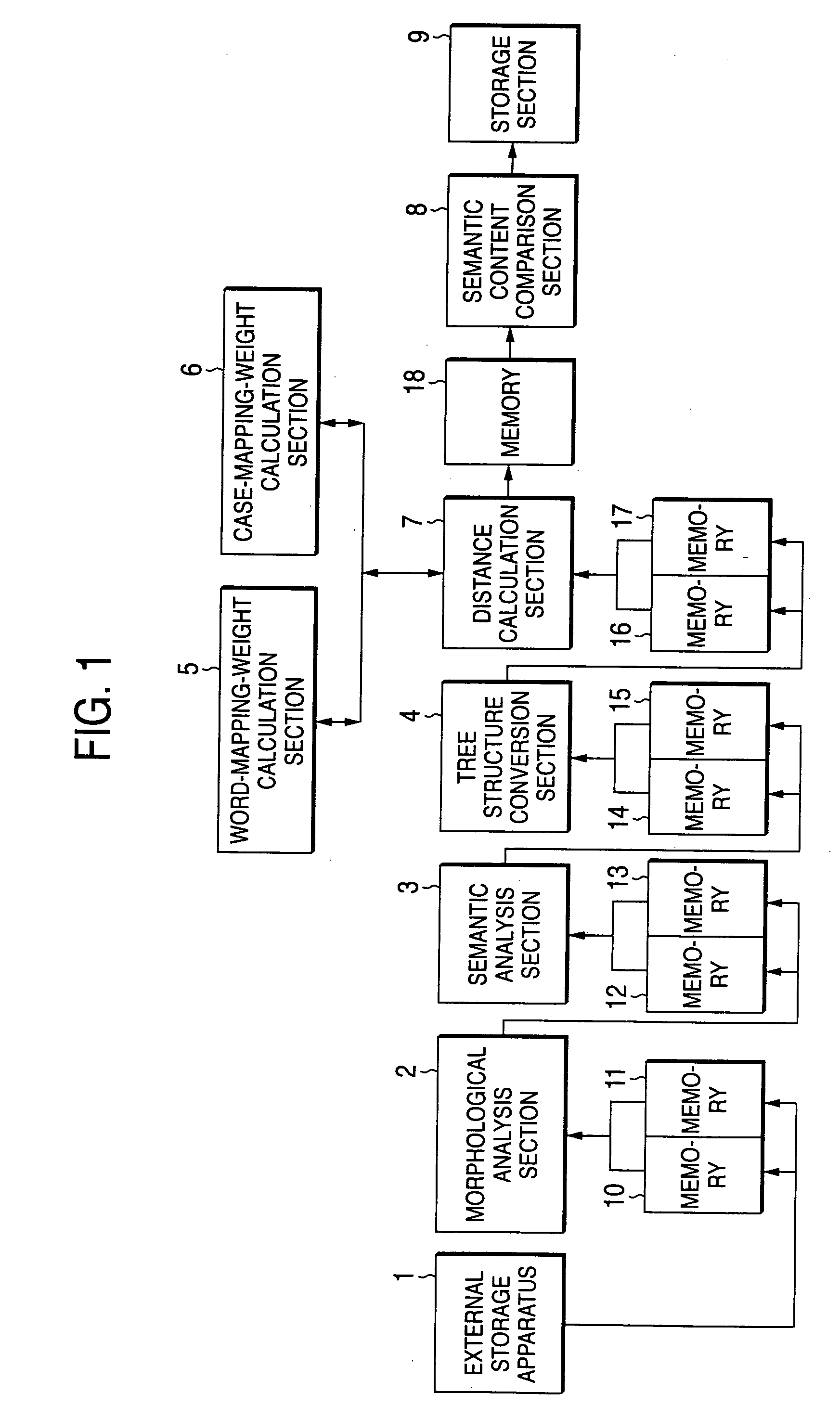
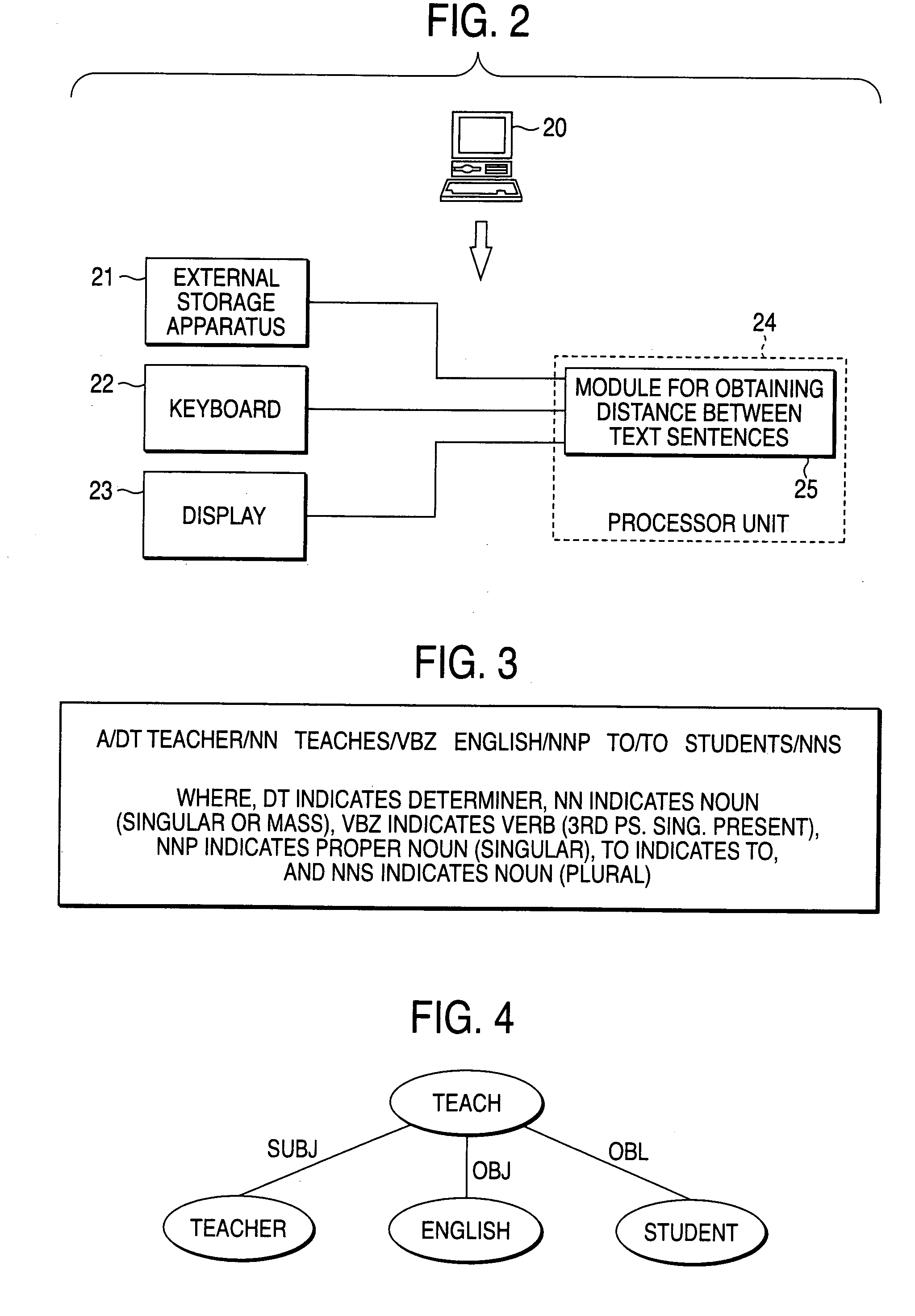
Text sentence comparing apparatus
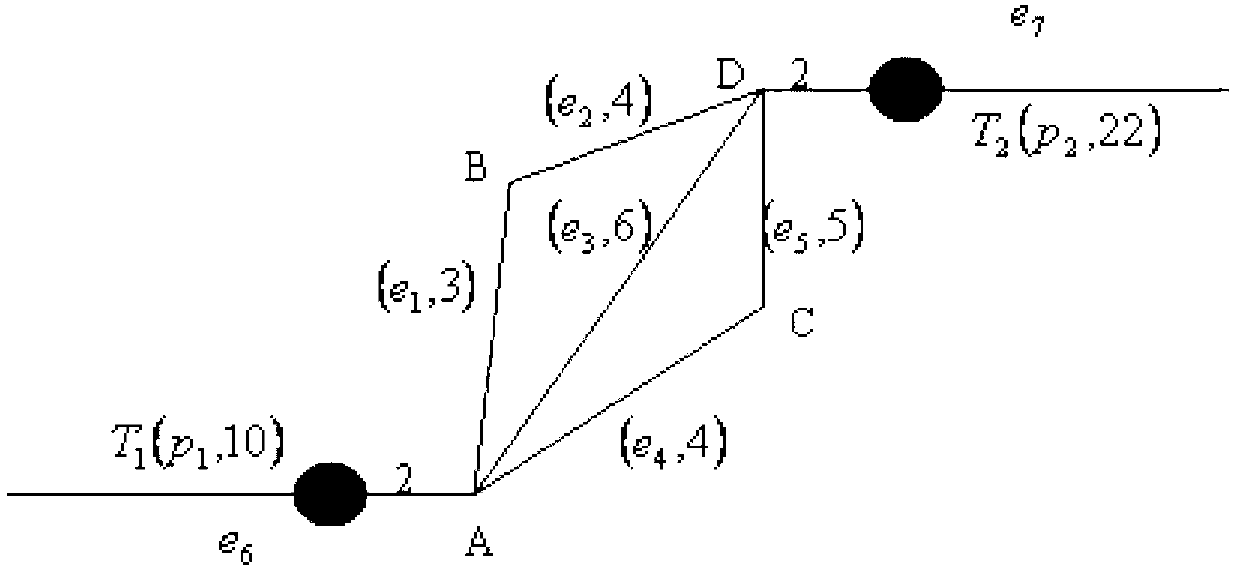
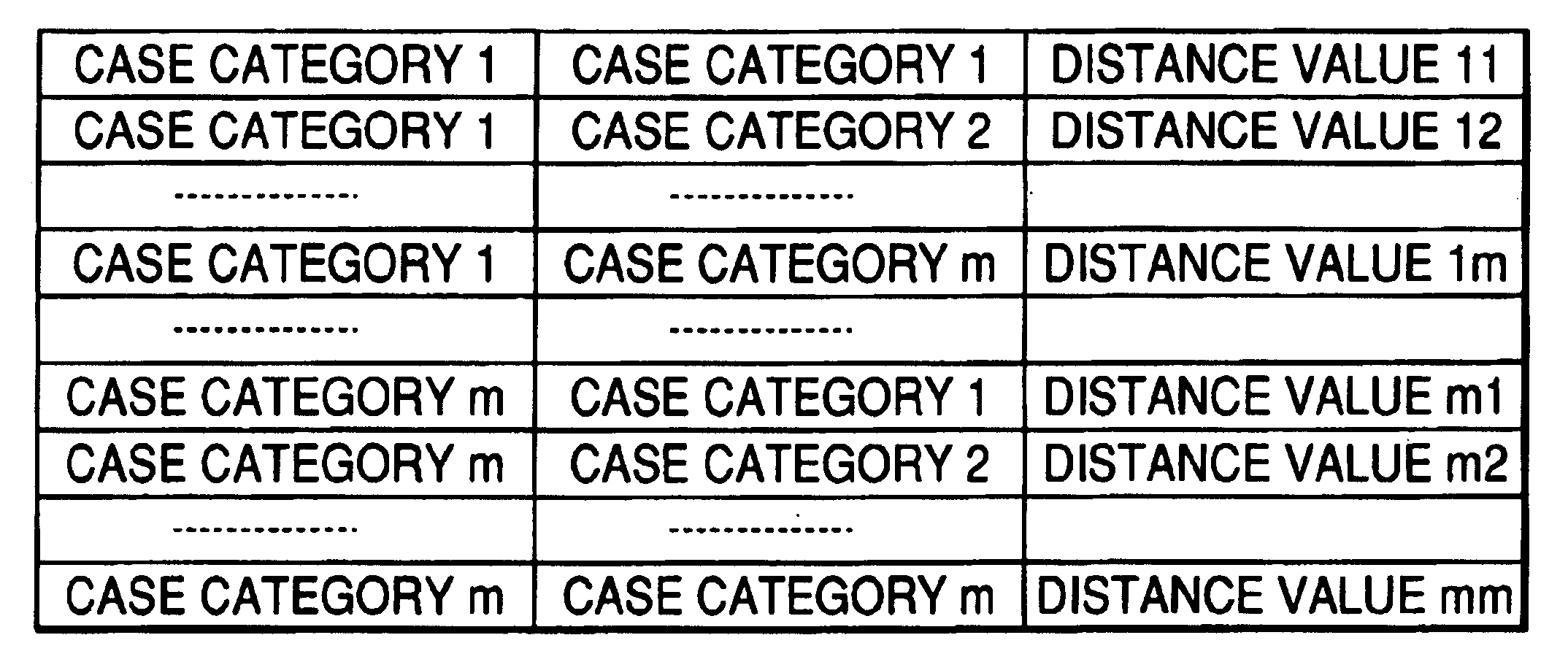
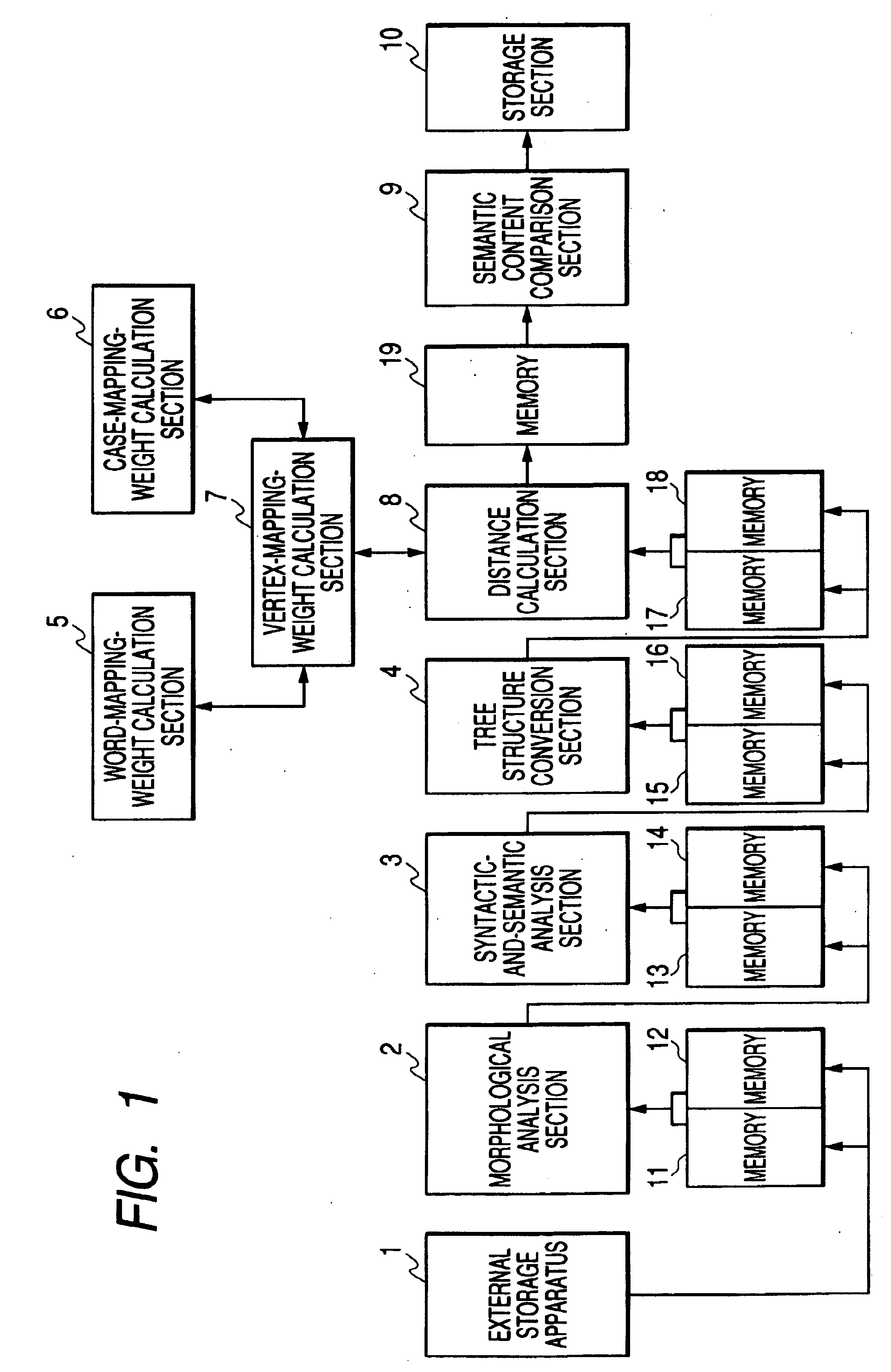
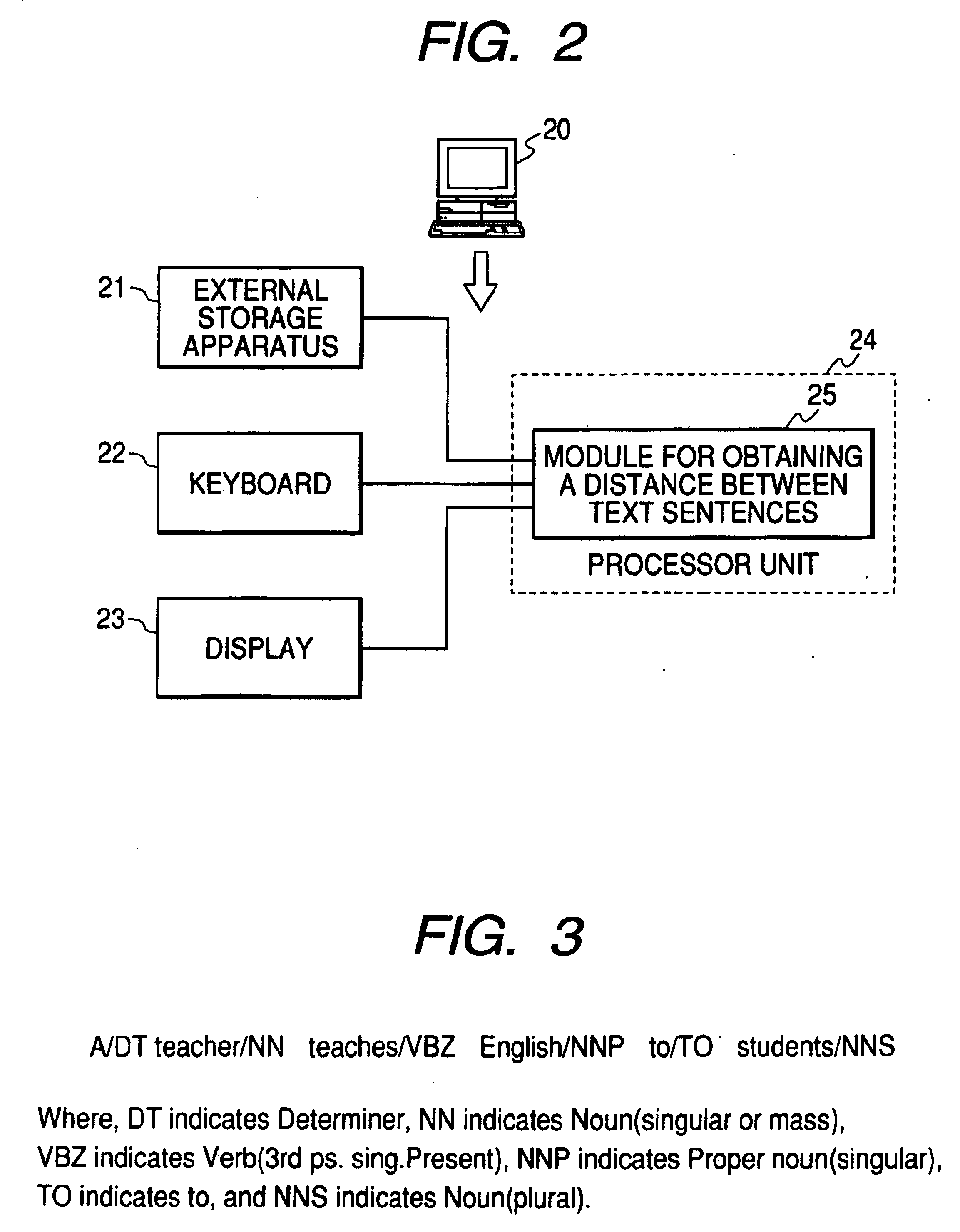
InactiveUS20040054521A1Improve accuracySemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmR-tree
A text sentence comparison method includes converting a first text sentence and a second text sentence into a first R tree (or a first RO tree) and a second R tree (or a second RO tree), respectively, calculating a distance between the first R tree and the second R tree (or a distance between the first RO tree and the second RO tree) on the basis of a distance between two R trees (or a distance between two RO trees), which is defined at least in accordance with a condition of a mapping between vertexes and edges of the two R trees (or the two RO trees), and calculating a distance between the first text sentence and the second text sentence on the basis of the calculated distance between the first R tree and the second R tree (or the calculated distance between the first RO tree and the second RO tree).
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
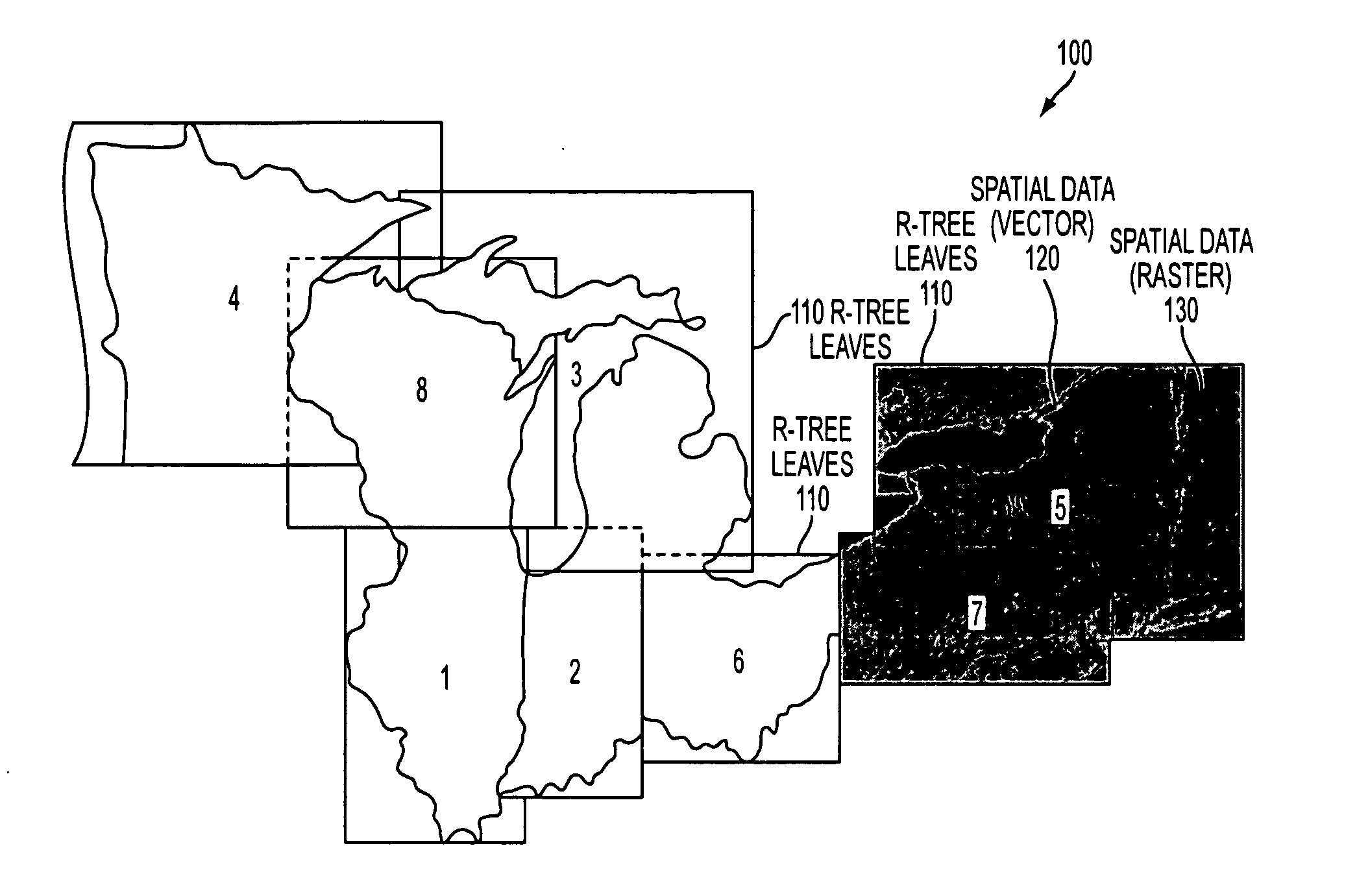
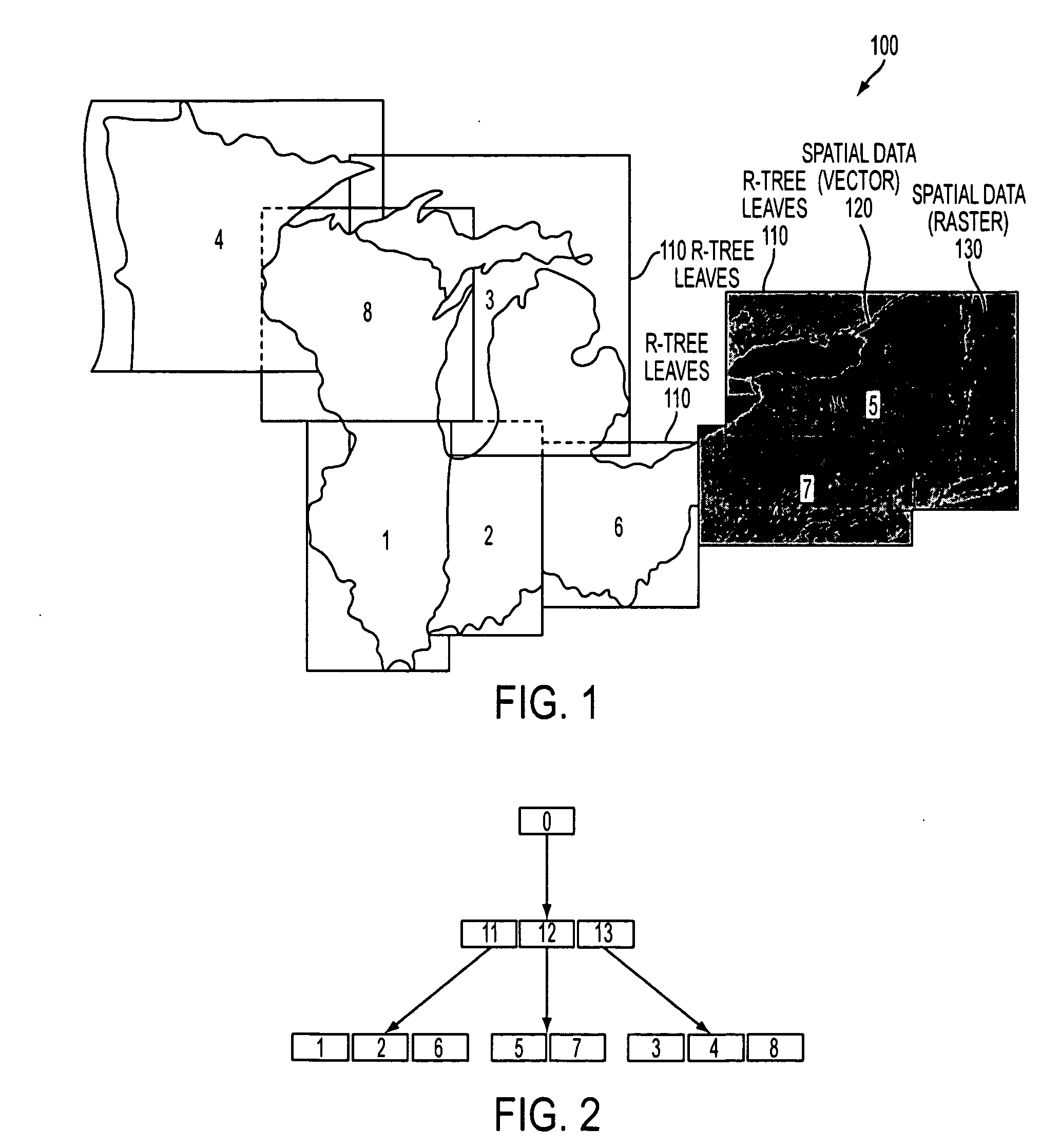
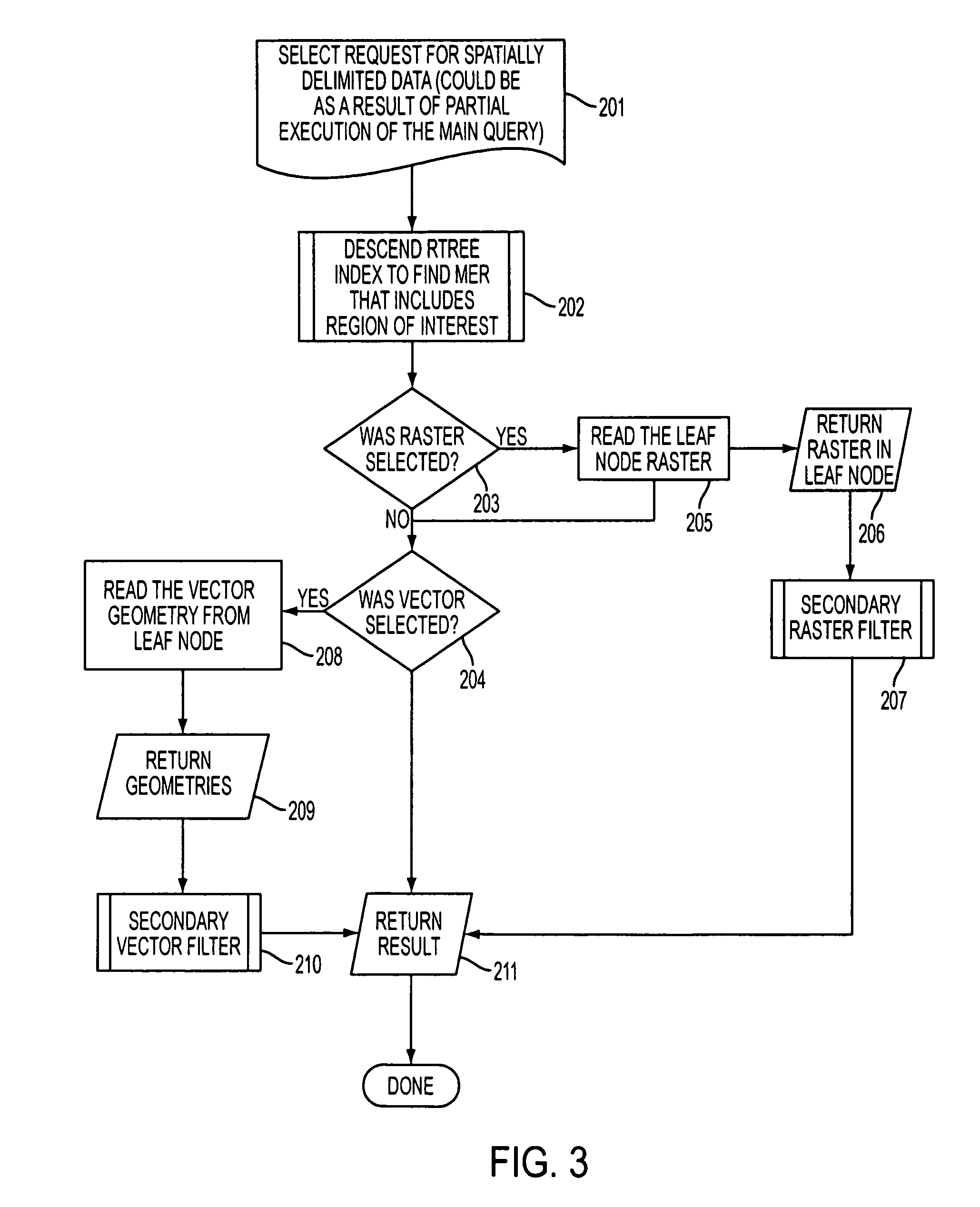
Method and apparatus for indexing, storing and retrieving raster (GRID) data in a combined raster vector system
InactiveUS20070253642A1Character and pattern recognitionGeographical information databasesVector systemR-tree
The invention relates to a method and apparatus that uses an R-tree's vector data as a mechanism for query and retrieval of raster data in conjunction with or instead of the vector data. The invention relates to a method of storing, indexing and retrieving raster data comprising: storing raster data, storing vector data, and indexing said raster data and said vector data with same index information.
Owner:MAPINFO
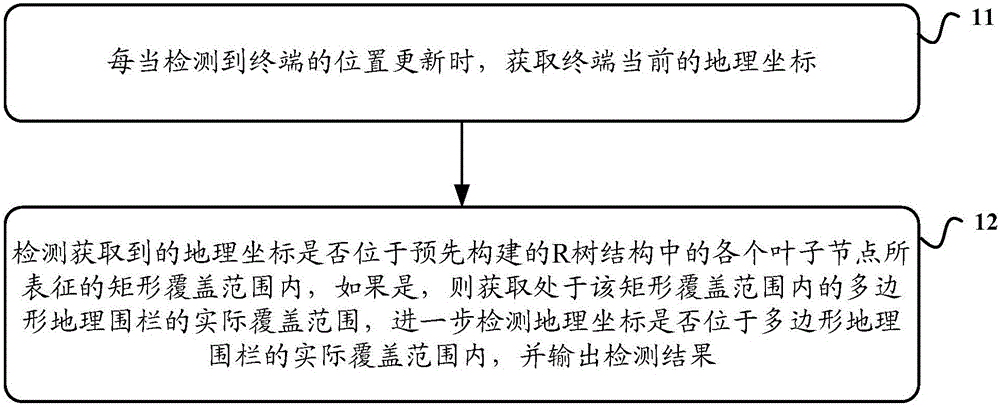
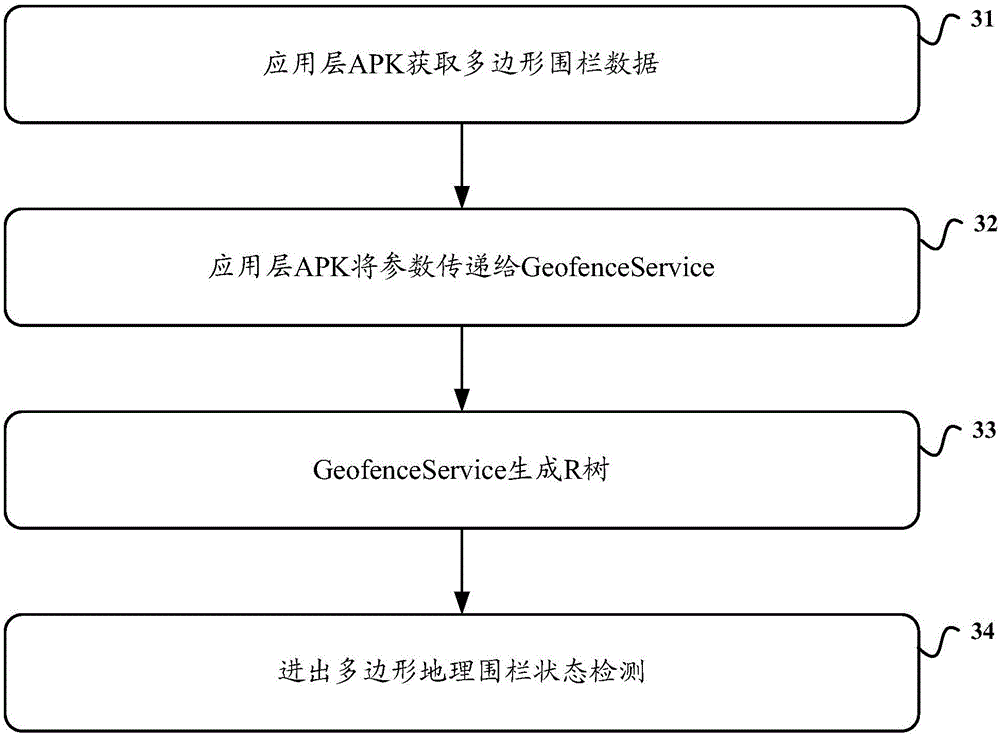
Position detecting method and device based on geo-fencing
InactiveCN105828292AHigh precisionSolve the problem that only circular geofences can be setLocation information based serviceNetwork planningLocation detectionAlgorithm
The embodiment of this invention discloses a position detecting method and device based on geo-fencing, relates to the field of position service, and is used for improving the accuracy of the position detection. the method includes the steps of when a position update of a terminal is detected, acquiring a current geographical coordinate of the terminal; detecting whether the acquired geographical coordinate is located in a rectangular coverage area represented by each leaf node in a pre-structured R-tree structure or not; if so, acquiring an actual coverage range of a polygonal geo-fence located in the rectangular coverage area; further detecting whether the geographical coordinate is located in the actual coverage range of the polygonal geo-fence or not, and outputting a detection result; and thus, the accuracy of the position detection is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MOBILE COMM TECH CO LTD
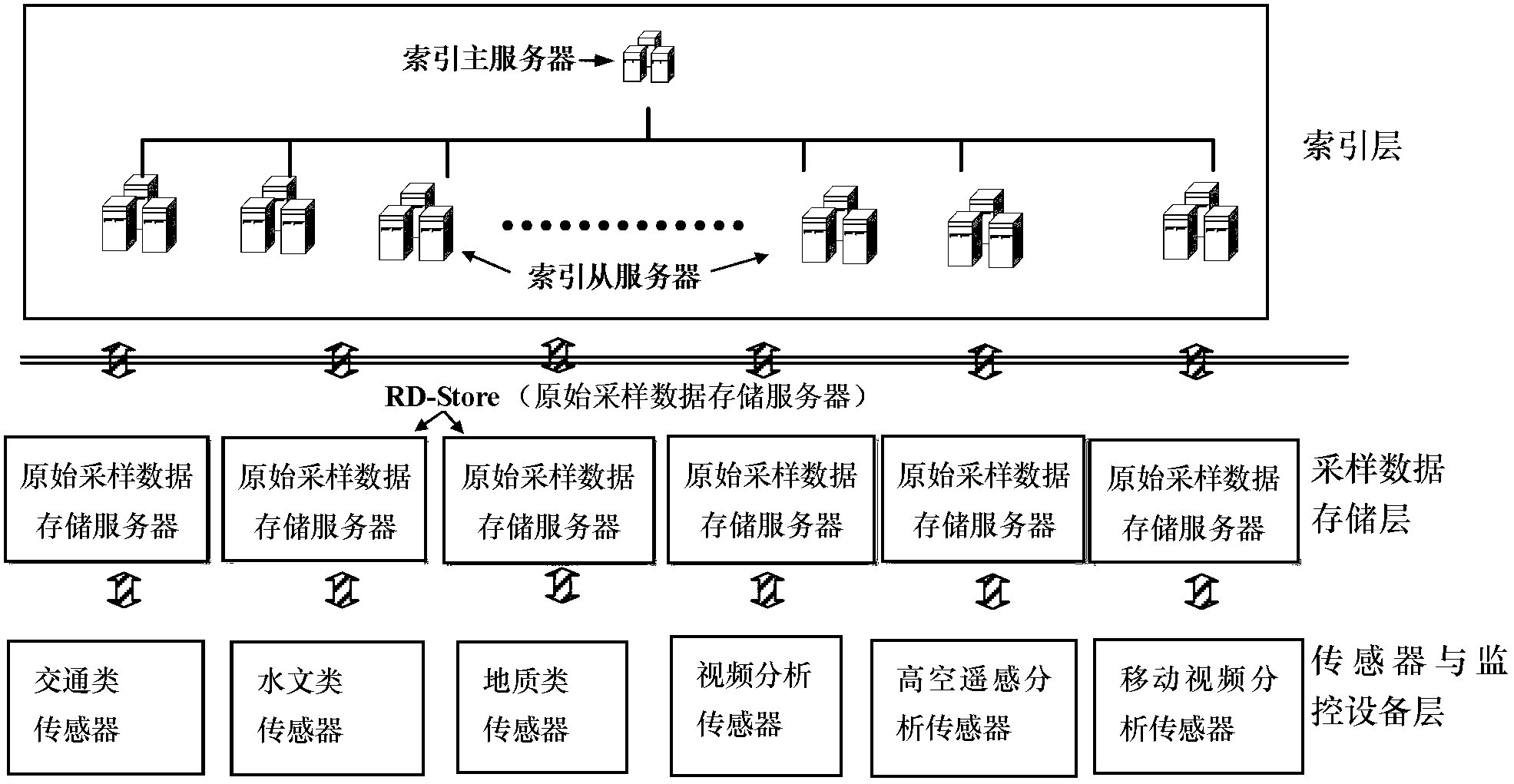
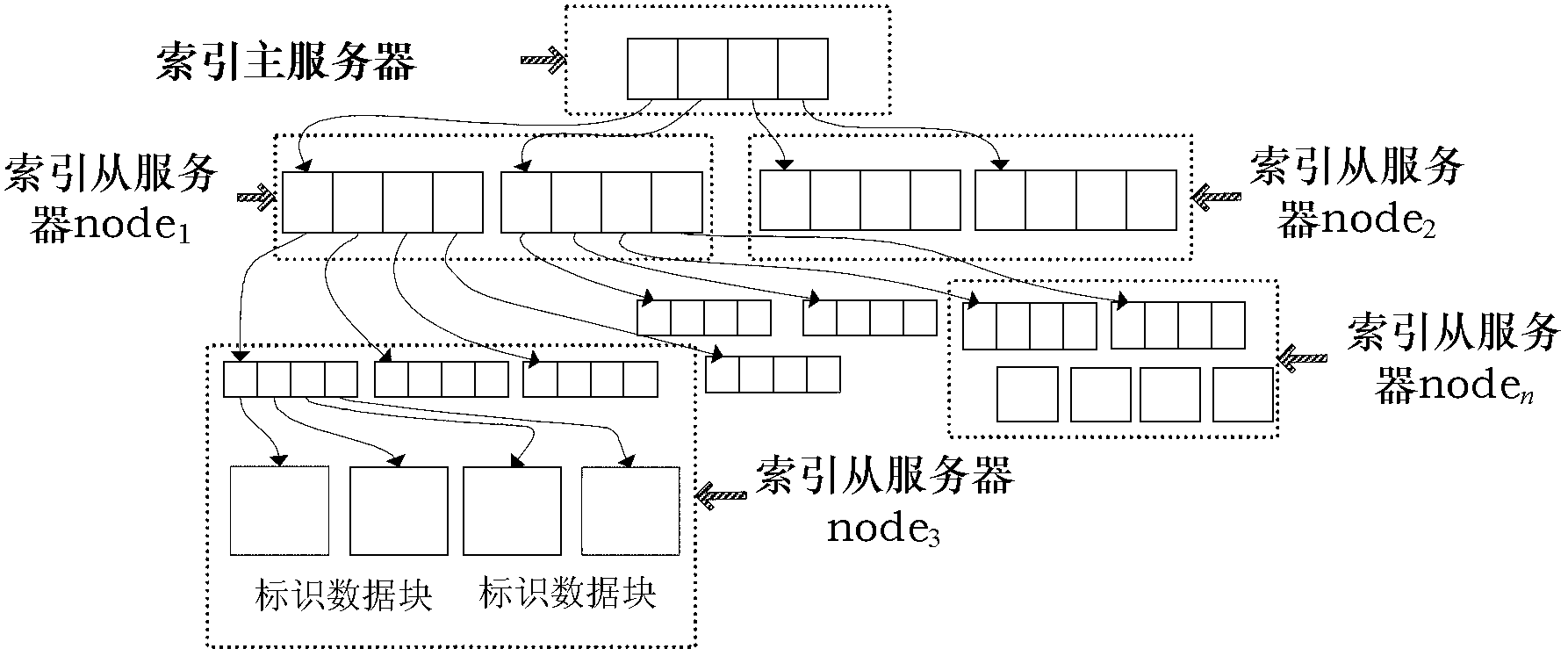
Data index building and query method for Internet of Things intellisense
The invention discloses a data index building and query method for Internet of Things intellisense. The method includes: firstly, sampling by a data monitoring unit, and storing data to a sample data storage server of the Internet of Things; secondly, allowing a sample data server to organize sampled values of one monitoring object according to a sampling time sequence to form a sampled value sequence of the monitoring object, and storing the sampled value sequence as an attribute value in data record of the monitoring object; and thirdly, building a tree index layer, and indexing the monitoring object data records stored by the sample data storage servers of the Internet of Things. The tree index layer comprises a plurality of index servers. A master node is named as an index master server, and other nodes are named as index slave servers. The tree index layer includes a full-text keyword B<+> tree index, an Internet of Things space-time R tree index, and a sample component symbolic keyword B<+> tree index. The data index building and query method for Internet of Things intellisense is applicable to real-time multimodal search of massive data of Internet of Things.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-dimensional space index method aiming at massive laser radar point cloud models
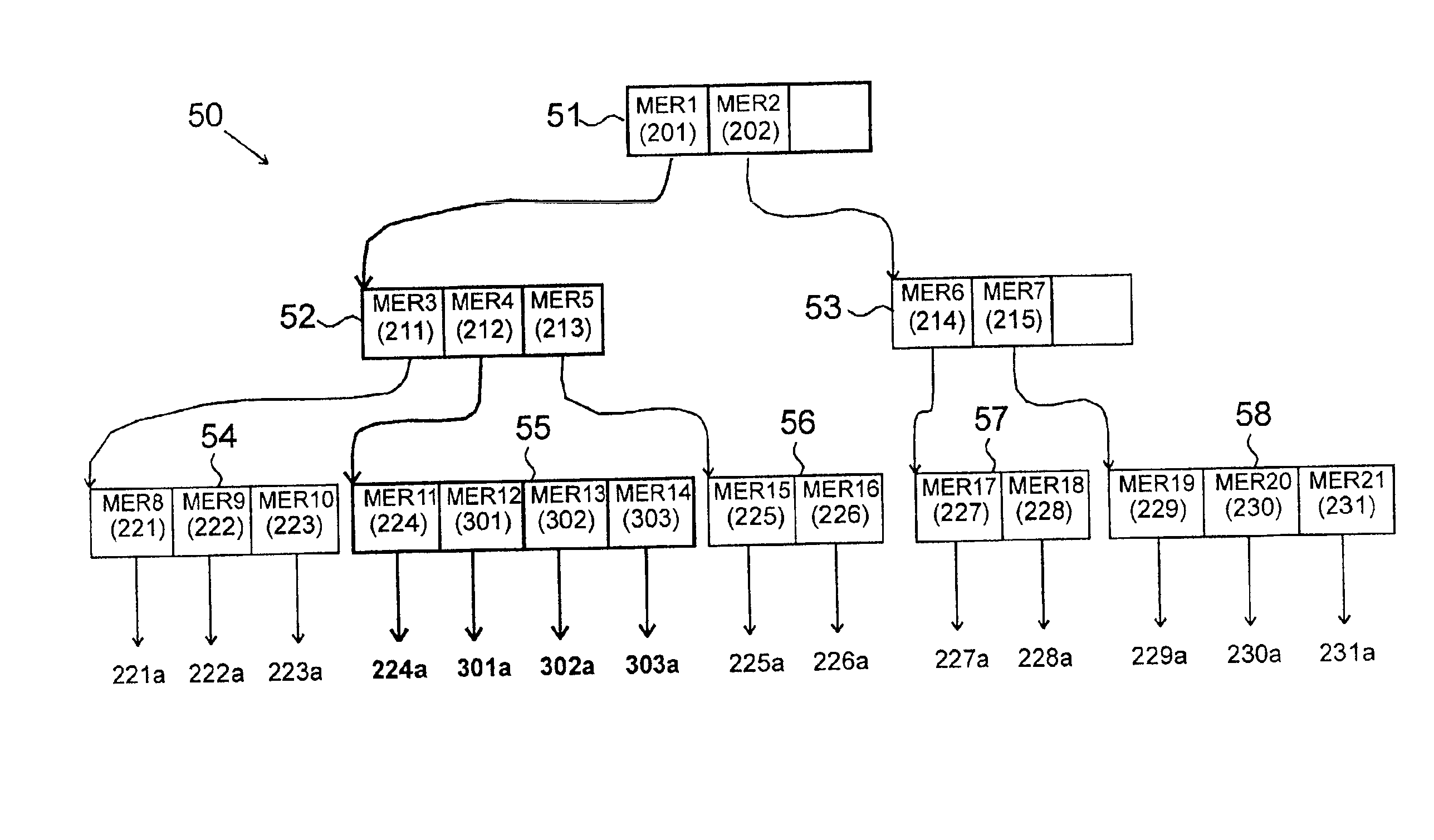
InactiveCN102682103AQuick searchEasy to handleSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum bounding rectangleR-tree
The invention discloses a three-dimensional space index method aiming at massive laser radar point cloud models. Aiming at characteristics of massive data and high spatial resolution of point cloud models, the method indexes data to a single three-dimensional space point by adopting a multi-level hybrid index strategy; aiming at an integrity characteristic of point cloud models, the method continuously subdivides massive cloud points from a minimum bounding rectangle (MBB) of an overall point cloud model by adopting a cotree index, and three-dimensional points in cotree index nodes are distributed uniformly in space; and aiming at a scattered characteristic and the data post-processing requirement of large-scale point cloud models, the method indexes a single three-dimensional space point by adopting a three-dimensional K-D tree, and the quick inquiry and processing of a single point coordinate and the attribute data of the single point coordinate can be achieved. On the basis of above integrated space index construction, the method adopts a three-dimensional R tree to manage the MBBs of a plurality of point cloud models in three-dimensional scenes, and a multi-level hybrid space index mode is formed finally.
Owner:北京建筑工程学院
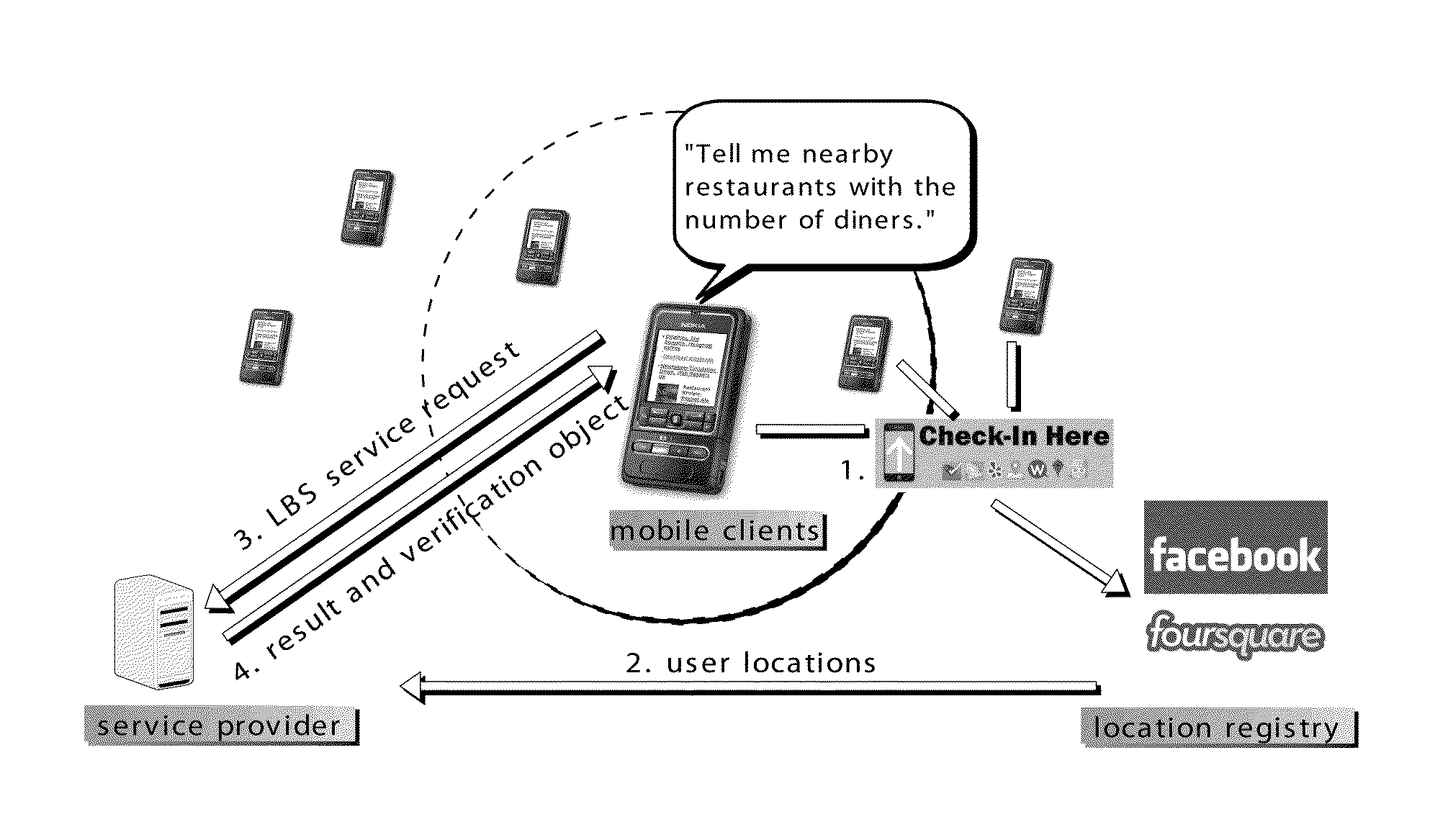
Method and Apparatus for Authenticating Location-based Services without Compromising Location Privacy
ActiveUS20140090023A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet privacyNear neighbor
A method and an apparatus for authenticating location-based services without compromising location privacy, which comprises a comprehensive solution that preserves unconditional location privacy when authenticating either range queries using three authentication schemes for R-tree and grid-file index, together with two optimization techniques, or k-nearest neighbor queries using two authentication schemes for R-tree and Voronoi Diagram index.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
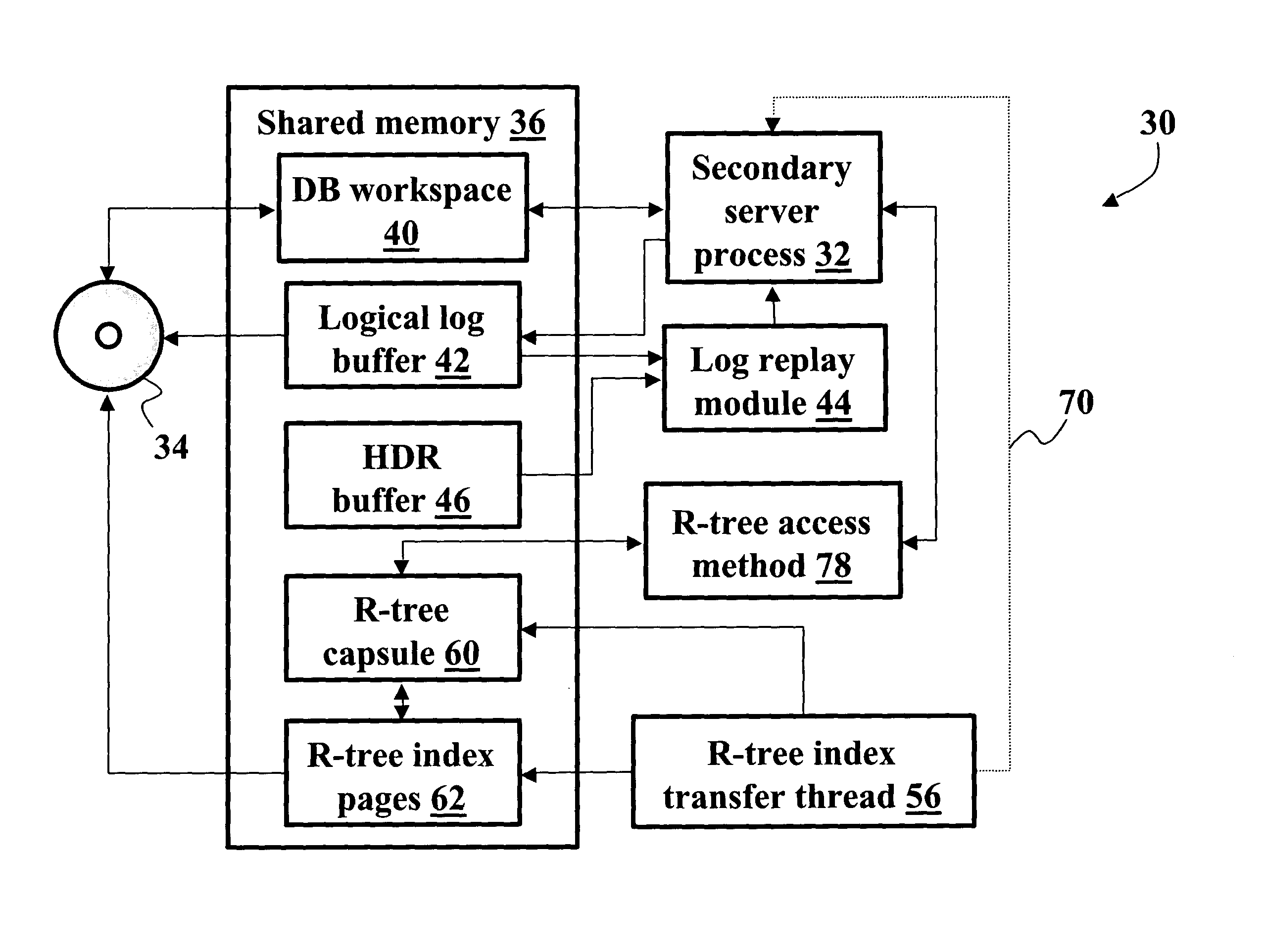
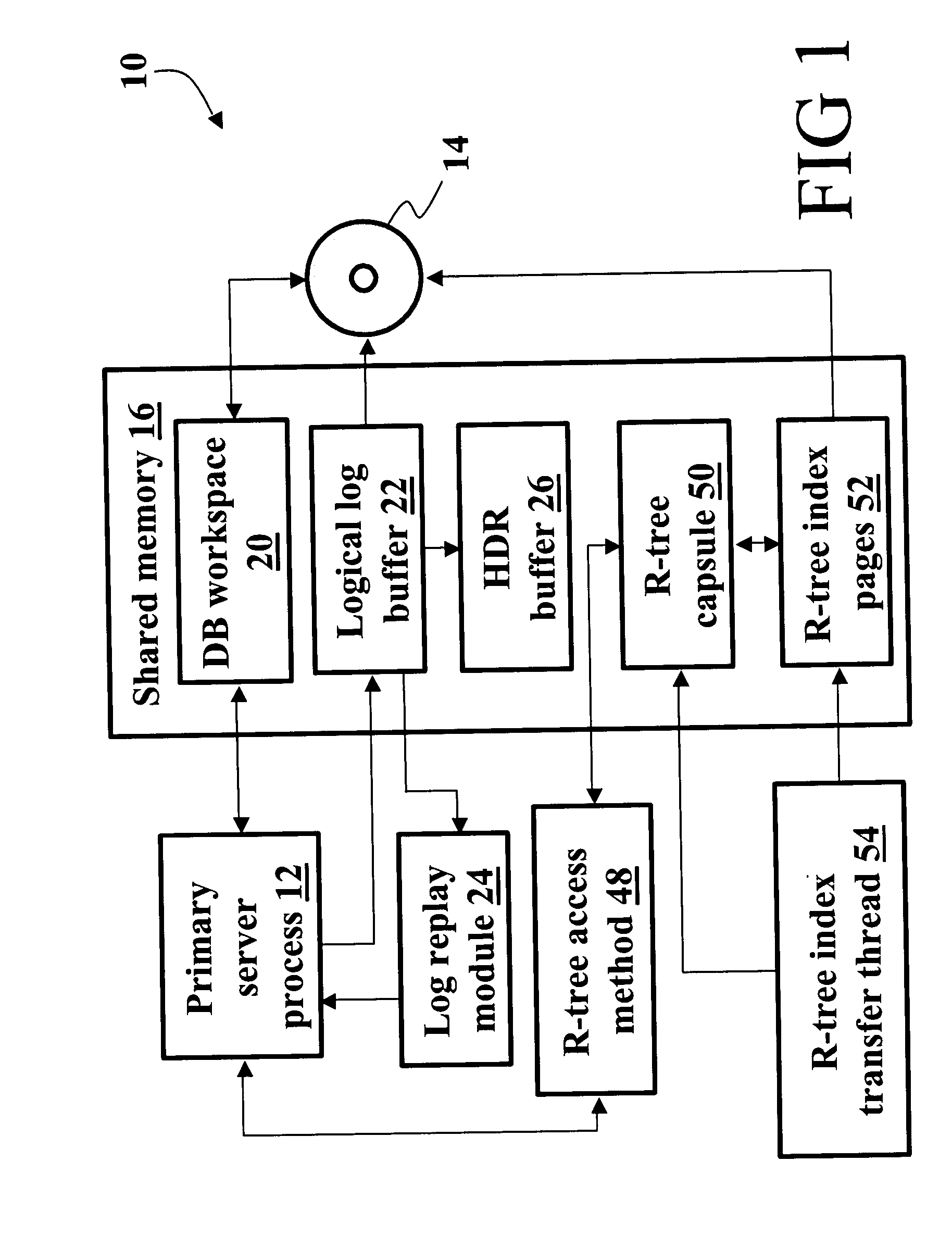
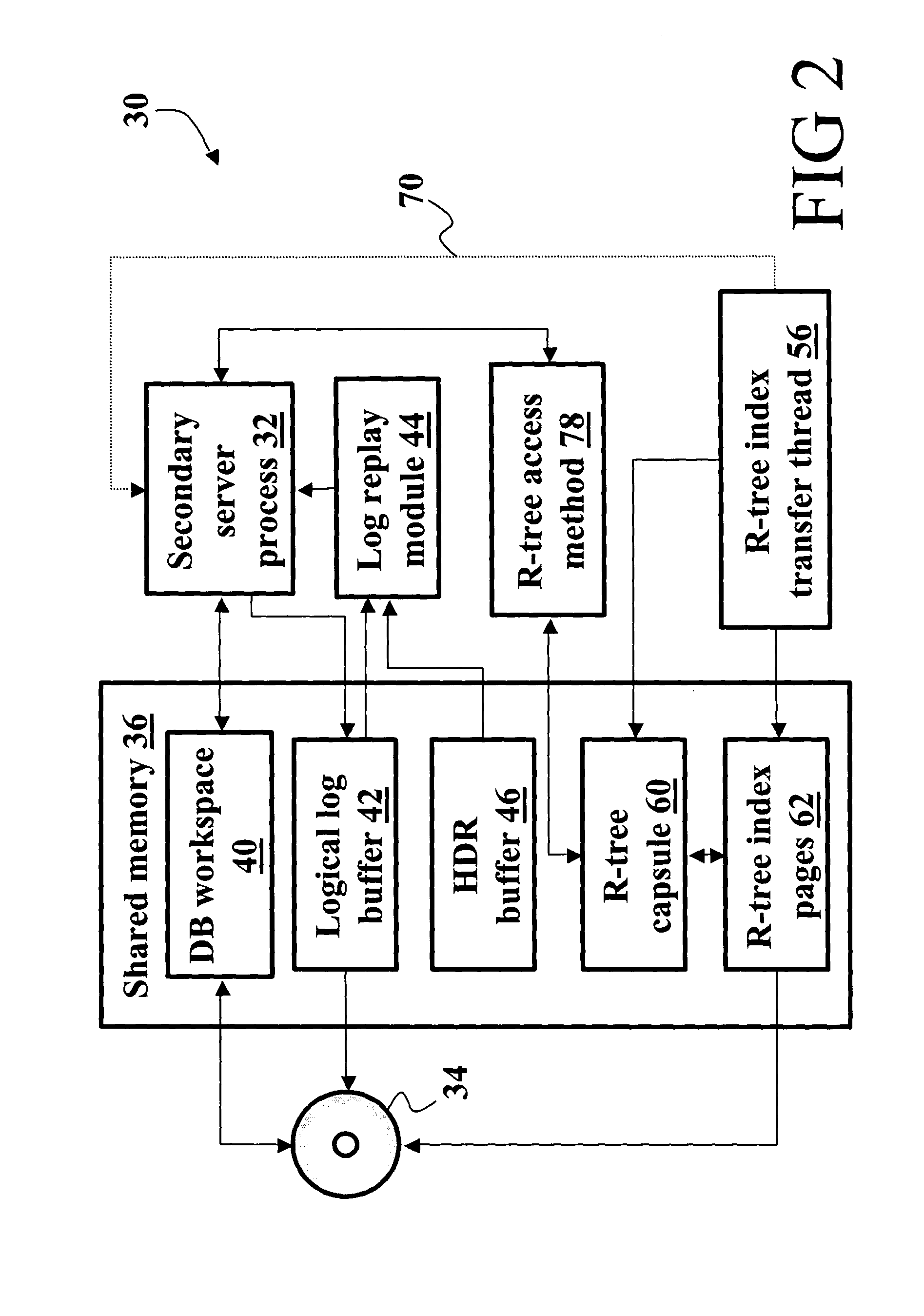
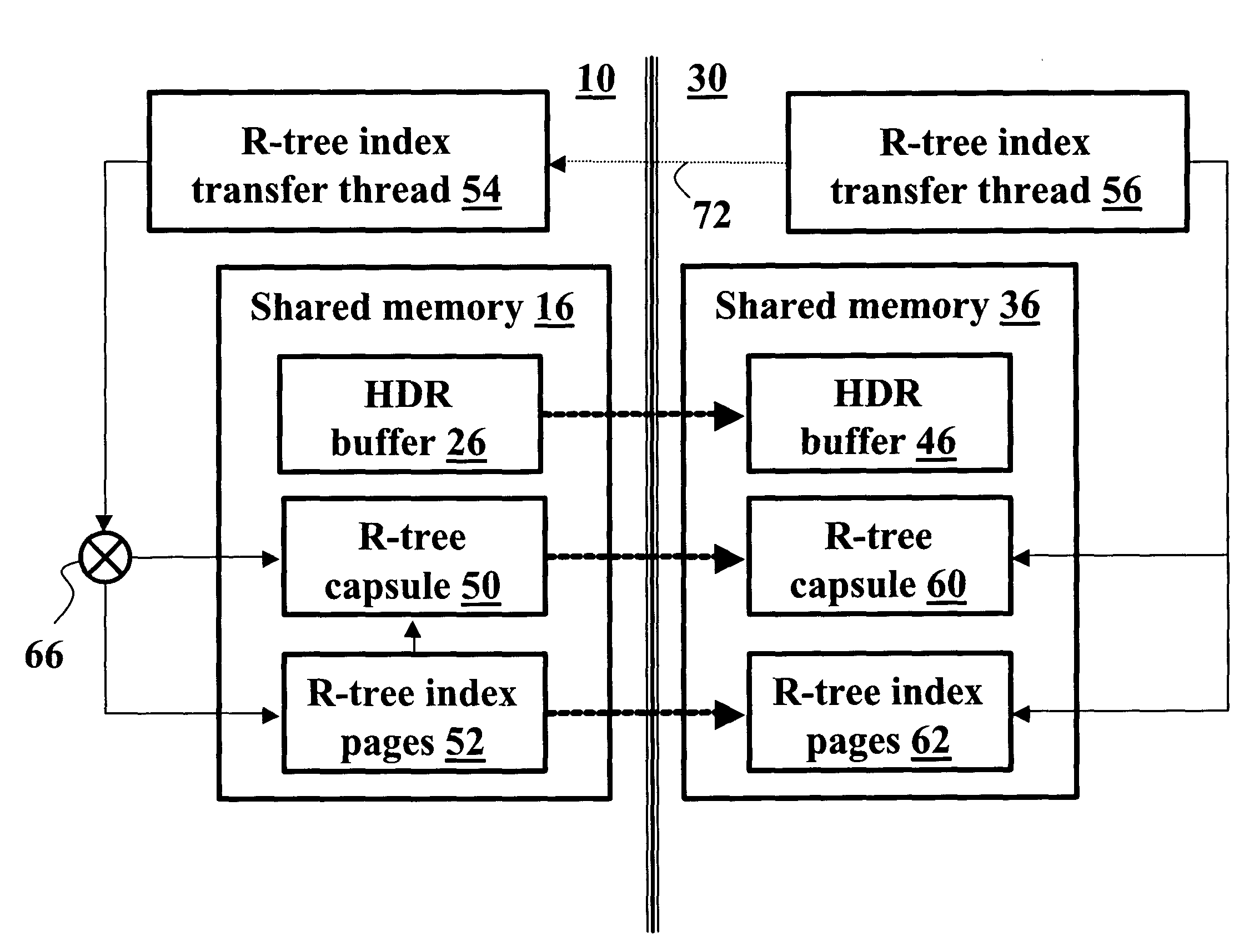
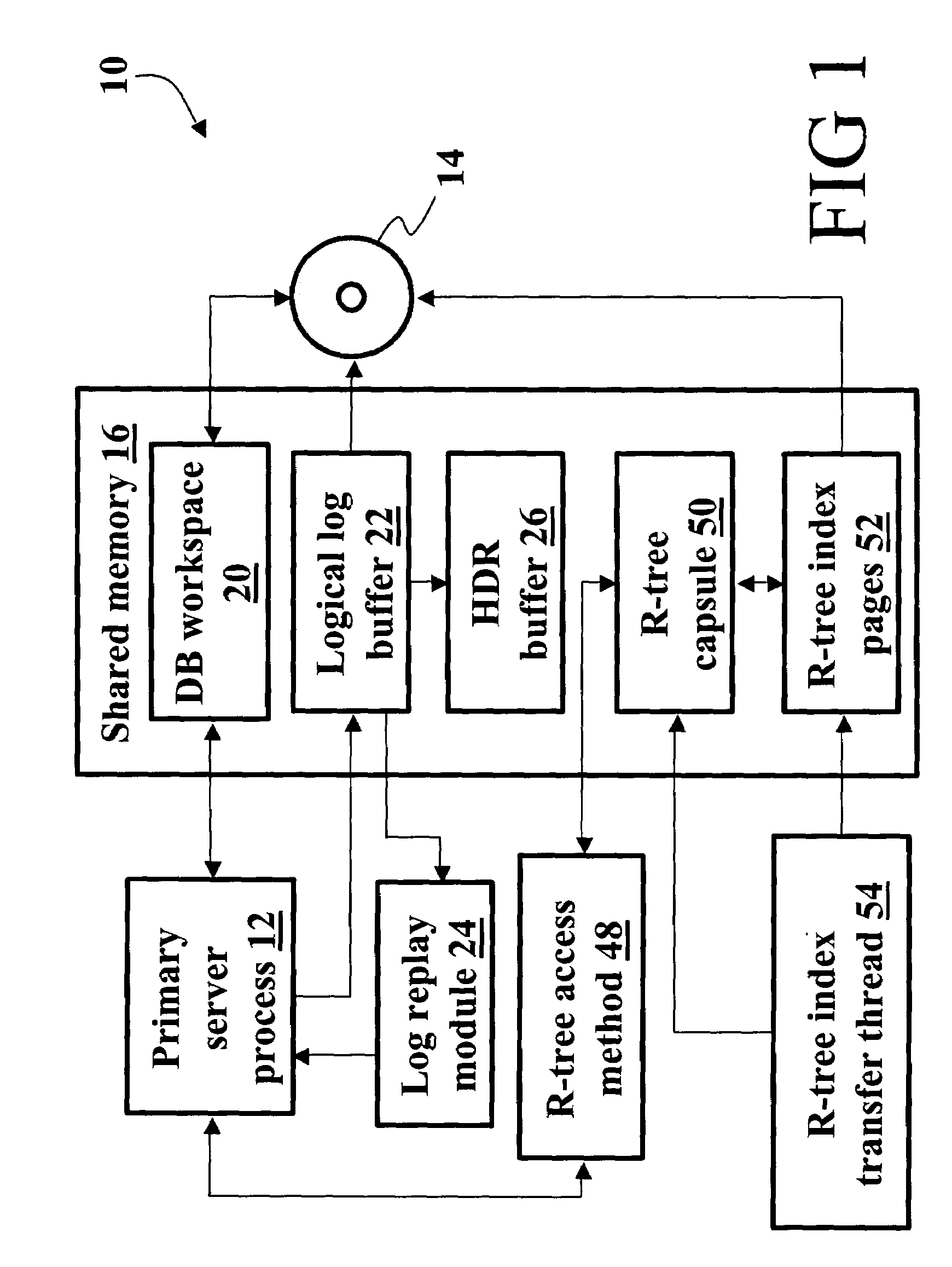
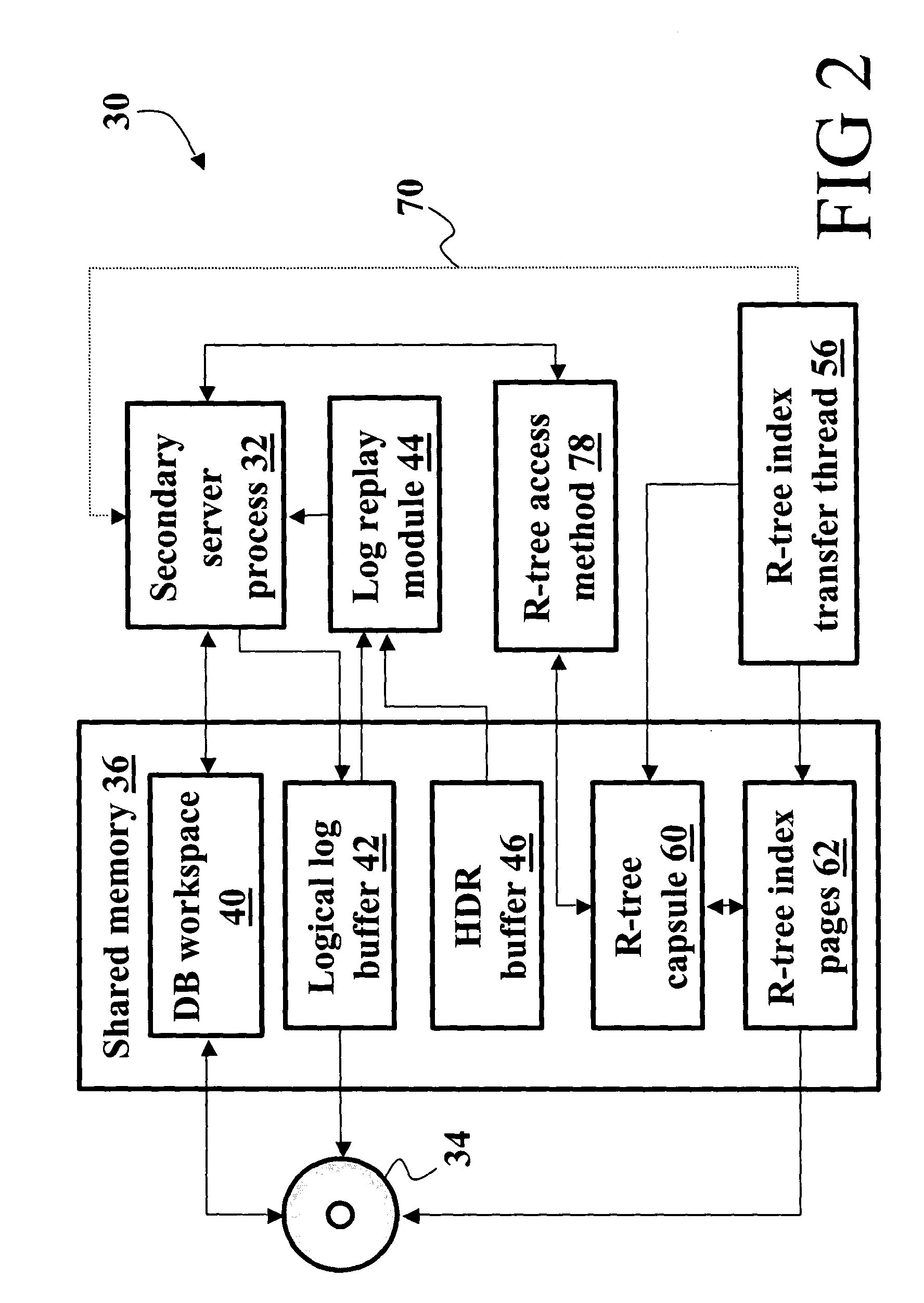
High availability data replication of an R-tree index
InactiveUS20050055445A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalHigh availabilityR-tree
In a database system having a primary server side (10) and a secondary server side (30), a high availability data replicator (26, 46) transfers log entries from the primary side (10) to the secondary side (30) and replays the transferred log entries to synchronize the secondary side (30) with the primary side (10). R-tree index transfer threads (54, 56) copy user-defined routines, the user defined index, and index databases deployed on the primary server side (10) to the secondary server side (30) and deploy the copied user-defined routines, reconstruct the user-defined index, and copy data pages on the secondary side (30) to make the user-defined index consistent and usable on the secondary side (30).
Owner:IBM CORP
Text sentence comparing apparatus
InactiveUS20040162806A1Improve accuracyDigital data processing detailsNatural language data processingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
A text sentence comparison method includes converting a first text sentence and a second text sentence into a first R tree (or a first RO tree) and a second R tree (or a second RO tree), respectively, calculating a distance between the first R tree and the second R tree (or a distance between the first RO tree and the second RO tree) on the basis of a distance between two R trees (or a distance between two RO trees), which is defined at least in accordance with a condition of a mapping between vertexes of the two R trees (or the two RO trees), and calculating a distance between the first text sentence and the second text sentence on the basis of the calculated distance between the first R tree and the second R tree (or the calculated distance between the first RO tree and the second RO tree).
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Rapid index method based on space-time data
InactiveCN101241511AImprove indexing speedSave storage spaceSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial partitionR-tree
The present invention provides a wireless communication computer field, in particular relating to a spatial-temporal data fast index method, it is a high effect indexing mechanism, storing different time stamp space-time state using overlapping indexed structure, if the adjacent time slices have identical R-tree index branch, only one version is kept, this reduces the storage space. At the same time, data on one time slice adopts blocking index mechanism based on the four-fork tree no longer finding whole index space, the whole space is divided into n=sumd-1i=0(2k)i sub-index spaces (d is depth of the four-fork tree, k is dimensionality of the index space), only need find one subspace therein, greatly reduces the index time. Utilizing the index method is used for high efficient location of multiple wireless move node and data monitor management.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Limited position-based region prewarning method
InactiveCN107154133AEfficient determinationAvoid catastrophic lossesMarine craft traffic controlAlarmsGeographic siteNODAL
The invention discloses a regional early warning method based on a limited location. According to the divided geographic location ranges of different danger levels, a plurality of electronic fences used to represent different danger levels are set up, and the electronic fences are polygonal; each electronic fence is established. The outermost minimum rectangle of the electronic fence; take each side of the electronic fence as a diagonal line, and establish the minimum outer rectangle for each edge, according to the smallest outer rectangle as the leaf node, the outermost smallest rectangle of the electronic fence as the root node and the preset R The tree construction rules establish an R tree; obtain the position of the target in real time, and use the ray algorithm based on the R tree index to judge whether the position of the target is located in a certain electronic fence area; according to the judgment that the target is in a certain electronic fence, In this way, the danger warning level of the target position is divided. Notifications are made through Beidou satellite signals, enabling relevant personnel to leave the dangerous area in time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Spatial index establishing method, spatial index use method and spatial index use device
ActiveCN103092853AHigh speedHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmDistribution characteristic
The invention discloses a spatial index establishing method, a spatial index use method and a spatial index use device. The spatial index establishing method includes using classes set in a classification database for classifying spatial objects in a spatial database; aiming at the spatial objects of each class and according to distribution of the spatial objects of the class in a spatial region, continuously dividing the spatial region by the aid of a quadtree mode until distribution of the spatial objects of the class in each divided sub-region satisfies set conditions; and establishing spatial indexes for the spatial objects of the class in each divided sub-region by the aid of an R-tree mode. Probability of interlapping of various spatial objects can be decreased by establishing the spatial indexes for the spatial objects of each class, and since spatial regions dense in spatial object distribution are divided into smaller regions according to distribution characteristics of all classes of spatial objects when the spatial indexes are established for each class of spatial objects, spatial overlapping probability is further decreased, and speed of using the established spatial indexes for searching is increased while accuracy of using the established spatial indexes for searching is improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Method for querying road network k aggregation nearest neighboring node based on Voronoi graph
InactiveCN102253961AReduce performanceSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceRoad networks
The invention belongs to the technical field of a spatial database and in particular relates to a method for querying a road network k aggregation nearest neighboring node (k-ANN) based on a Voronoi graph. The method comprises the following steps of: resolving a first nearest neighboring node (1-NN) of each query point through an R tree index; constructing a priority queue to store the 1-NN of all query points, wherein the weight is the current aggregation distance from each query point to a target node; extending a certain query point according to a certain sequence on the basis of a road network Voronoi graph, updating the aggregation distance of the next NN of the query point, inserting or updating and performing other kinds of operation on the priority queue until the target node at the head of the queue is extended by all the query points, then the target node is a first aggregation nearest neighboring node (1-ANN); and after the 1-ANN is deleted from the queue, acquiring a second aggregation nearest neighboring node (2-ANN) which accords with the conditions for the second time, and acquiring the k-ANN according to the characteristics. The method has excellent performance in the aspect of response time and page views of user query.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Query prunning using exterior tiles in an R-tree index
InactiveUS7219108B2The method is simple and fastReduce computing timeData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsTheoretical computer science
Determining relationships among objects represented in a database includes defining a plurality of tiles in the approximation of the first geometry by dividing the approximation of the first geometry in a first direction a plurality of times and dividing the approximation of the first geometry in a second direction perpendicular to the first direction a plurality of times. A second geometry is analyzed to determine if it fulfills a first filter condition with respect to any of the tiles defined in the approximation of the first geometry. If the second geometry fulfills the first filter condition with respect to any of the tiles defined in the first geometry carrying out a mathematical comparison of the first geometry and the second geometry.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Three-dimensional R-tree index expansion structure-based three-dimensional city model adaptive method
InactiveCN101996242AImplement Adaptive MethodsConvenient quantitative adjustmentSpecial data processing applicationsNODALLevel of detail
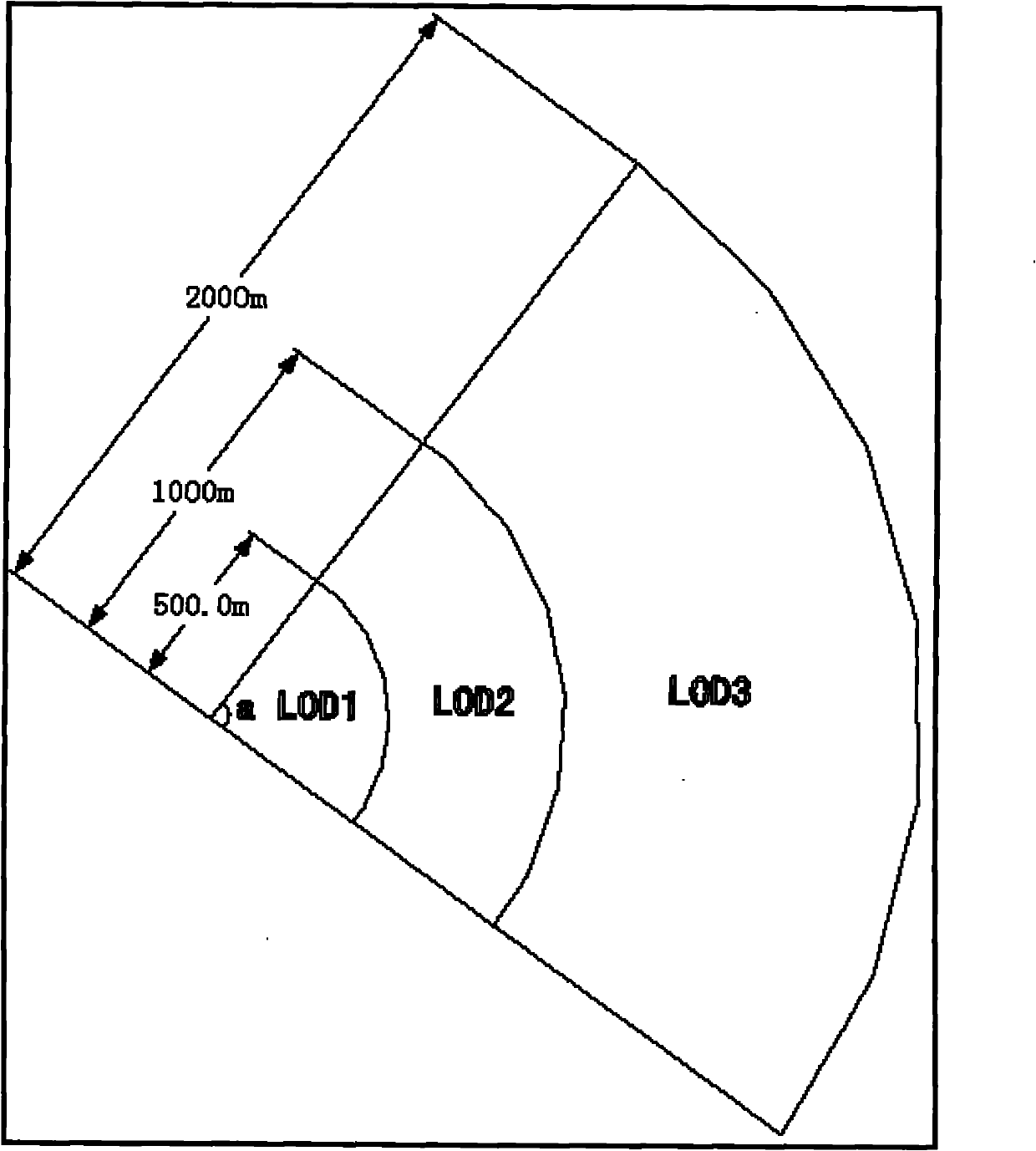
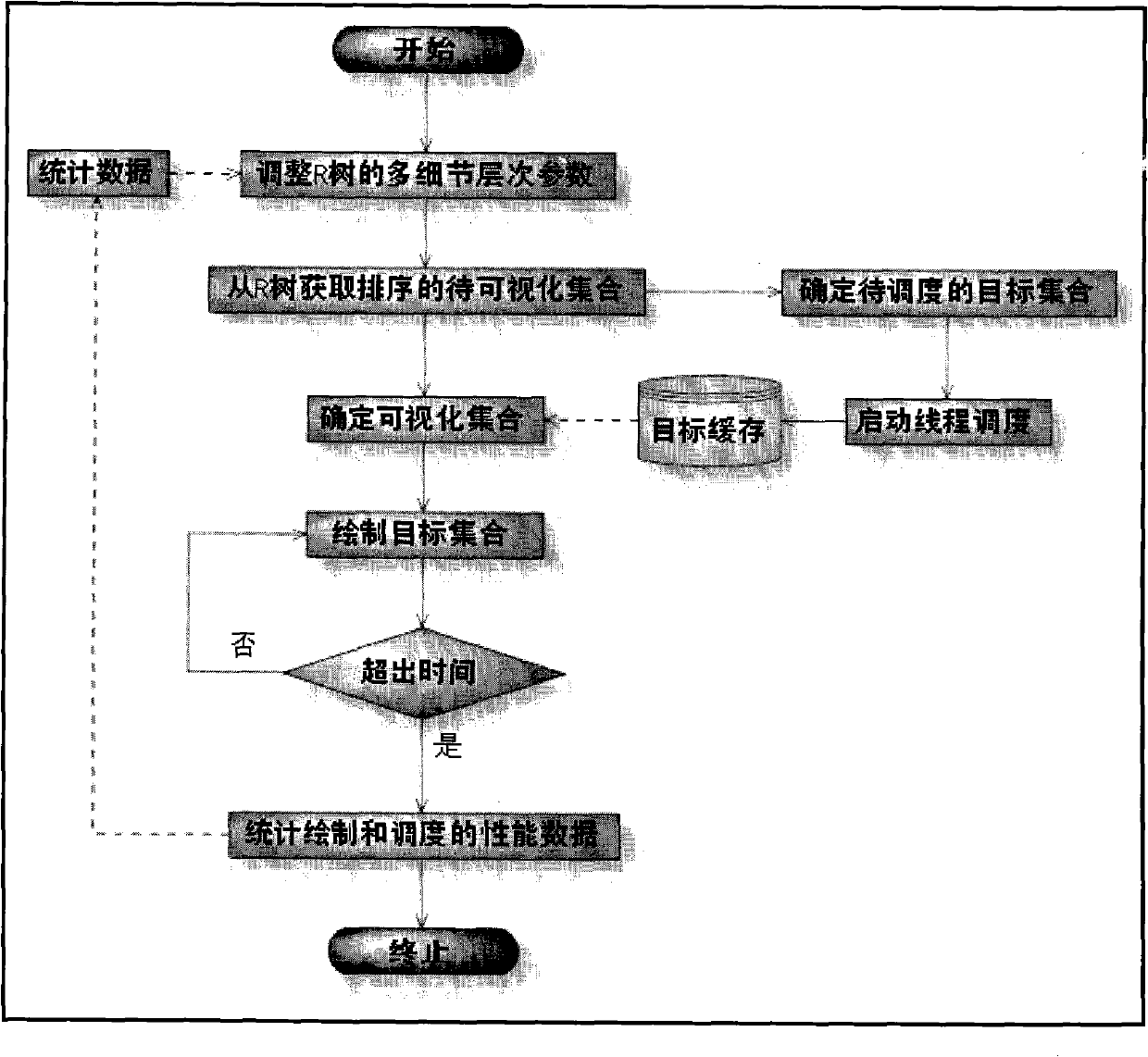
The invention relates to a three-dimensional R-tree index expansion structure-based three-dimensional city model adaptive method. The method comprises the following steps of: expanding a three-dimensional R-tree index expansion structure to ensure that an intermediate node can manage a target model; generating a multi-level of detail (LOD) target model from a leaf node layer to a root node layer, namely from bottom to top layer by layer, wherein different R-tree layers represent different LODs; a target in the leaf node layer is the highest LOD model; a father node of the leaf node layer is an LOD model of a second detail; and the LOD is gradually lowered upwards in turn, and the root node layer has the lowest LOD; defining multi-LOD definition parameters which comprise the number of layers, the farthest action range of the highest LOD, and the interlayer times; and in a real-time visual process, modifying the multi-LOD definition parameter in real time according to the current performance so as to quantitatively adjust the scene complexity of a three-dimensional city model.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Within-distance query pruning in an R-tree index
ActiveUS7239989B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationAlgorithmR-tree
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Lazy bulk insertion method for moving object indexing
InactiveUS20070233720A1Reduce the cost of updatesNone of such methods became significantDigital data processing detailsGeographical information databasesObject basedR-tree
The present invention relates to a lazy bulk insertion method for moving object indexing, which utilizes a hash-based data structure to overcome the disadvantages of an R-tree, and uses two buffers to simultaneously store operations in the buffers and process queries stored in the buffers, so that the overall update cost can be reduced. In the lazy bulk insertion method, a buffer is substituted and a state of the buffer is changed to a deactivated state if an input query cannot be stored in the buffer. Operations stored in the deactivated buffer are sequentially analyzed, information about objects corresponding to respective operations is obtained from a direct link to analyze the operations, and thus the operations are aligned on the basis of object IDs. Operations, aligned in ascending order of spatial objects, are identified depending on respective objects, effectiveness of the operations is determined, and thus the operations are realigned on the basis of terminal node IDs. The number of insert operations and the number of delete operations are counted for each terminal node, and variation in the number of empty spaces in the terminal node is obtained, thus splitting and merging of the terminal nodes is predicted. A processing sequence of queries is reorganized so as to reduce variation in the node on the basis of the predicted information.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
Within-distance query pruning in an R-tree index
ActiveUS20050015216A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationAlgorithmR-tree
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Delayed distance computations for nearest-neighbor queries in an R-tree index
ActiveUS7181467B2Data processing applicationsGeographical information databasesMinimum bounding rectangleTheoretical computer science
A method for locating neighboring data geometries of a query geometry. A minimum bounding rectangle of the query geometry is determined. A minimum bounding rectangle of each data geometry is determined. Candidate data geometries are identified by determining if a distance between the minimum bounding rectangle of the query geometry and the data geometry is less than a threshold distance. A distance between the query geometry and the candidate data geometry is mathematically calculated when a number of candidate data geometries equals a threshold number or when no more data geometries remain.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Database backup system using data and user-defined routines replicators for maintaining a copy of database on a secondary server
InactiveUS7330859B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDatabase backupHigh availability
In a database system having a primary server side (10) and a secondary server side (30), a high availability data replicator (26, 46) transfers log entries from the primary side (10) to the secondary side (30) and replays the transferred log entries to synchronize the secondary side (30) with the primary side (10). R-tree index transfer threads (54, 56) copy user-defined routines, the user defined index, and index databases deployed on the primary server side (10) to the secondary server side (30) and deploy the copied user-defined routines, reconstruct the user-defined index, and copy data pages on the secondary side (30) to make the user-defined index consistent and usable on the secondary side (30).
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Quick query method of position information on the basis of space index technology
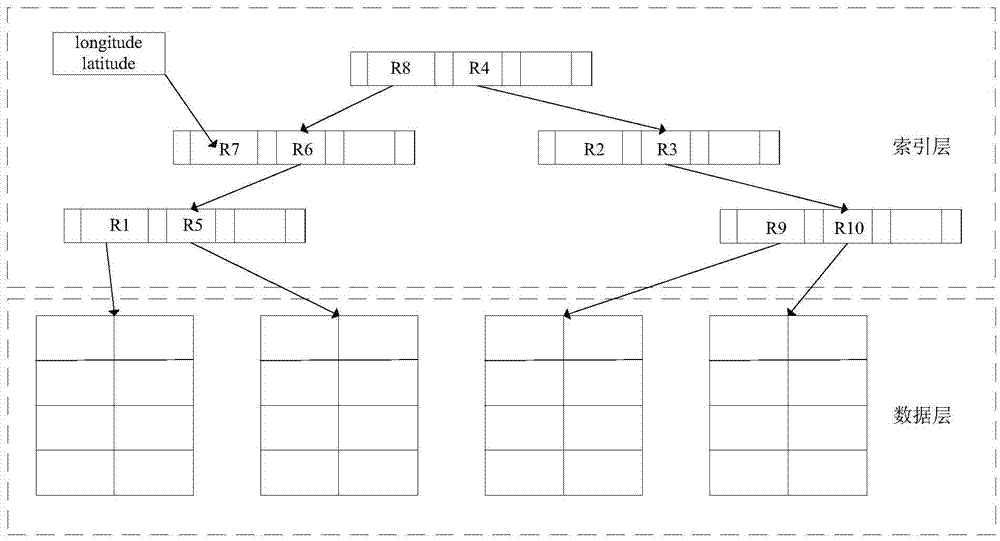
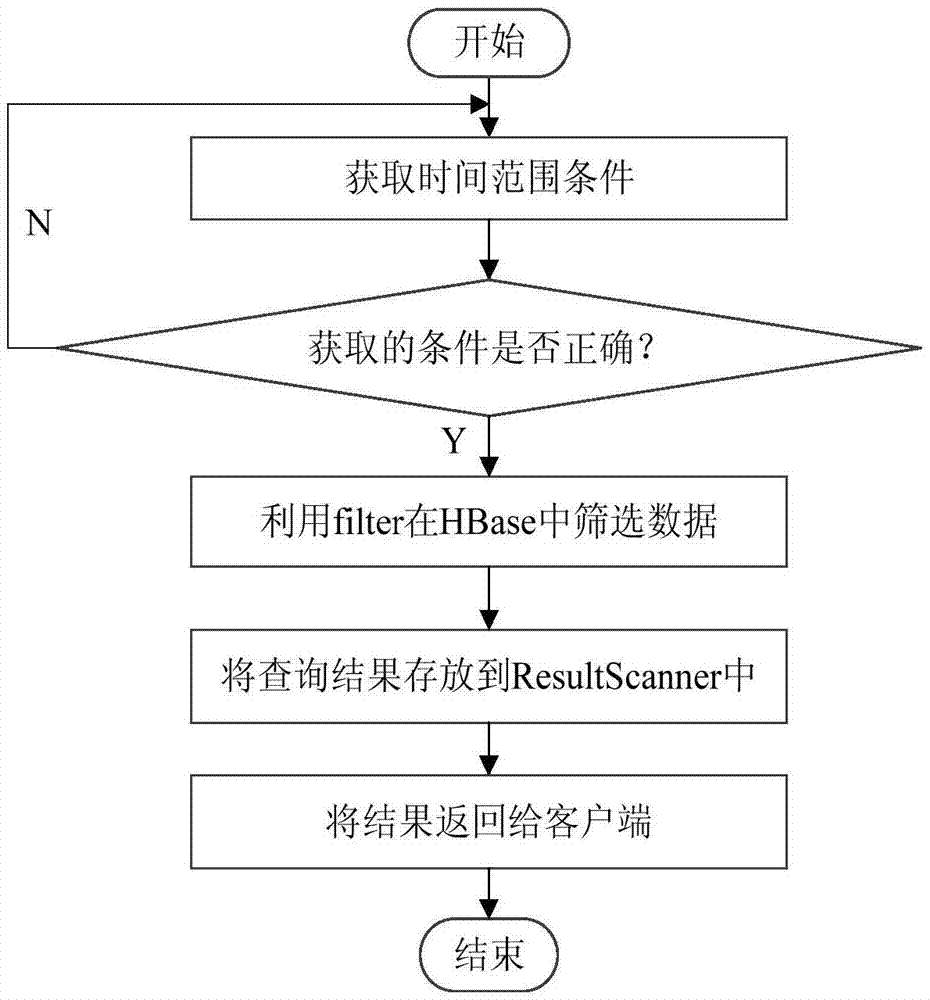
ActiveCN106933833AQuick searchAchieve parallelizationData processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationUser inputR-tree
The invention relates to a quick query method of position information on the basis of a space index technology. The method comprises the following steps that: according to target space coordinate information to be queried, establishing an R tree space index, establishing R tree node mapping on an HBase database, and forming a space index database; according to a minimum boundary rectangle formed by user input coordinate information, carrying out query in the space index database; and returning a query result to the user. By use of the method, an R tree space index technology can be adopted to realize the quick query of a space coordinate. A bottom layer adopts the HBase database as a storage medium, the parallelization of a query task can be realized, and query performance is improved. Information including oil spill and the like can be accurately positioned. In addition, compared with a traditional method, the quick query method is characterized in that query performance is obviously improved, and is suitable for system development which aims at oil field or ocean data coordinate information query.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
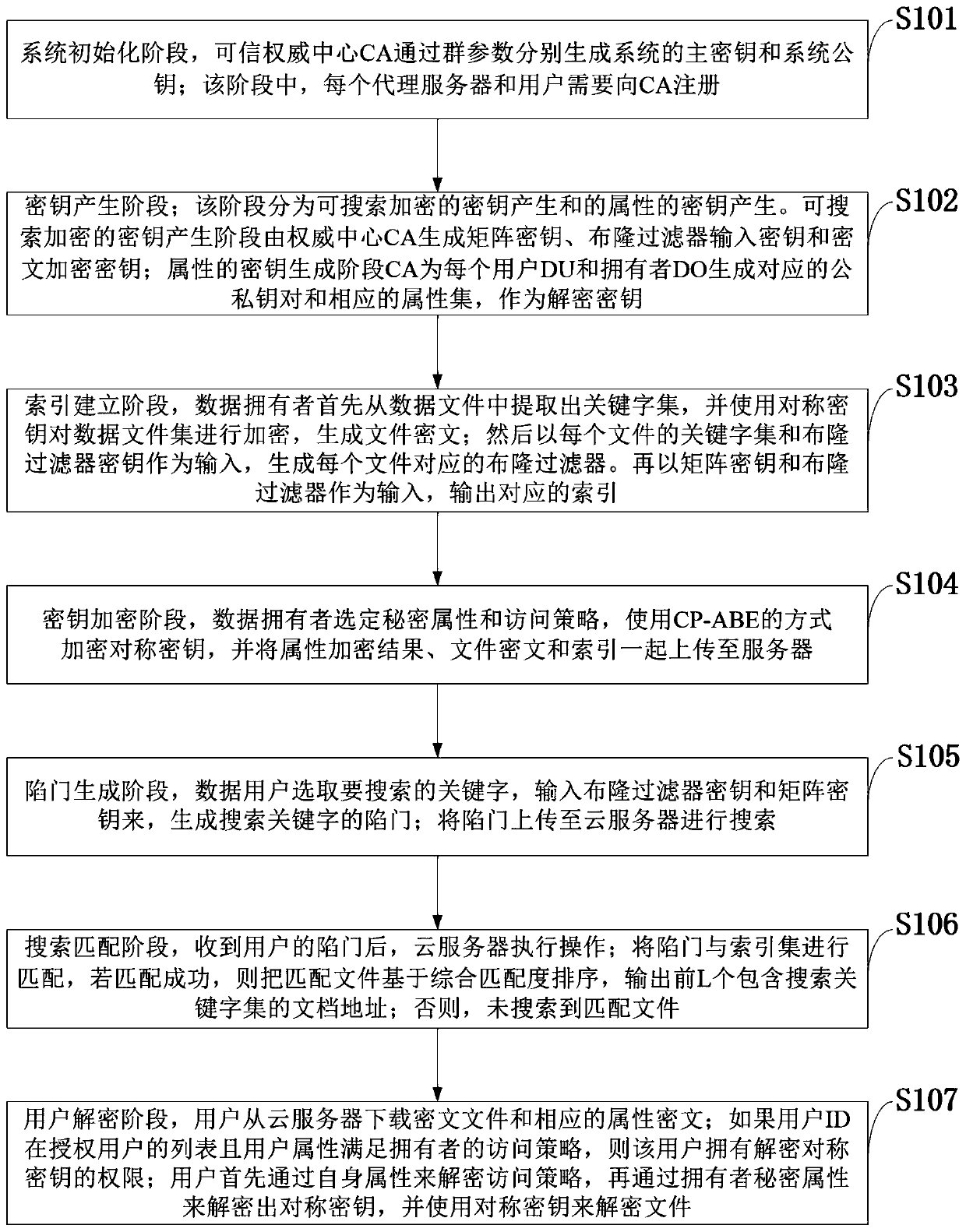
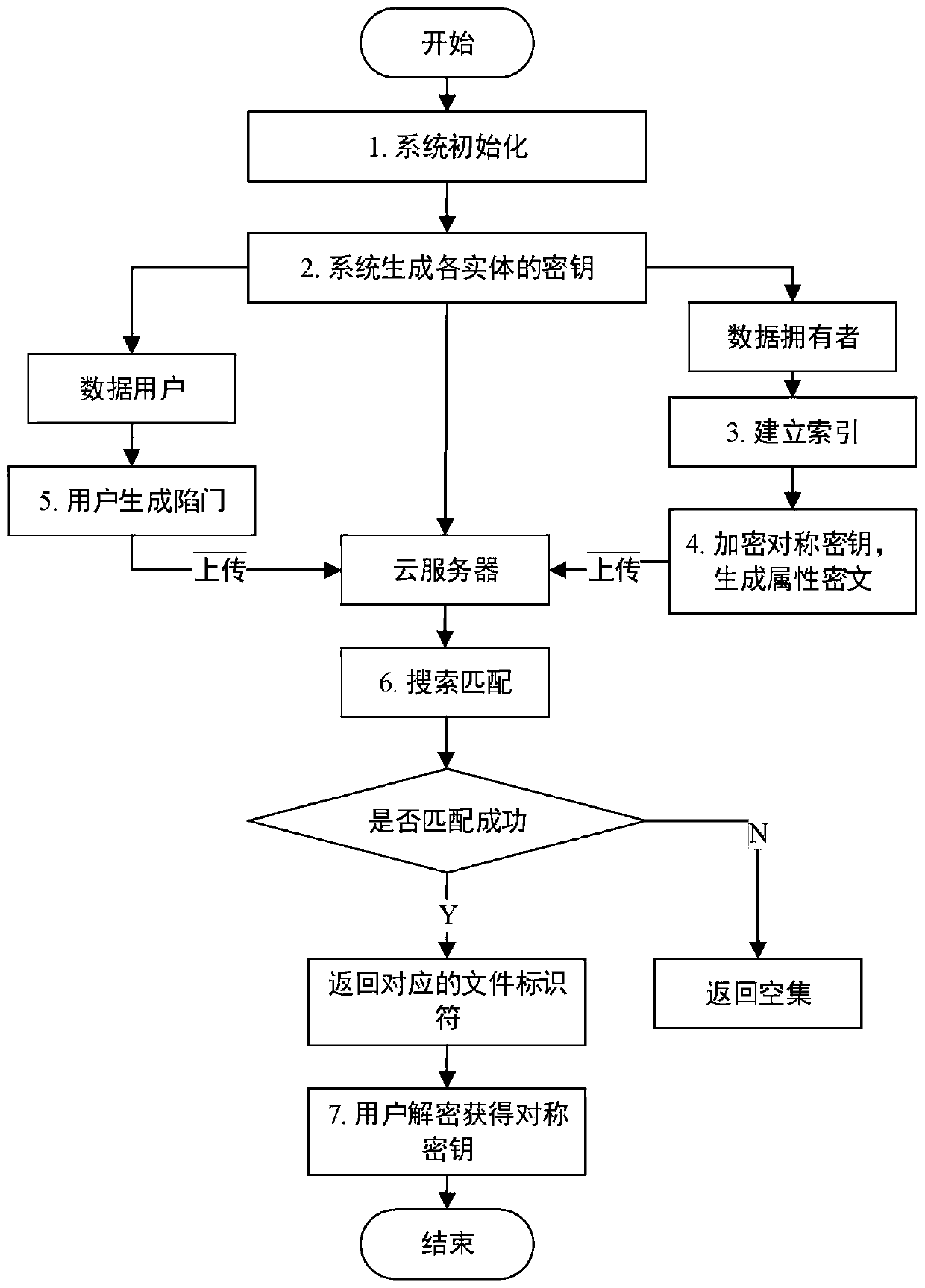
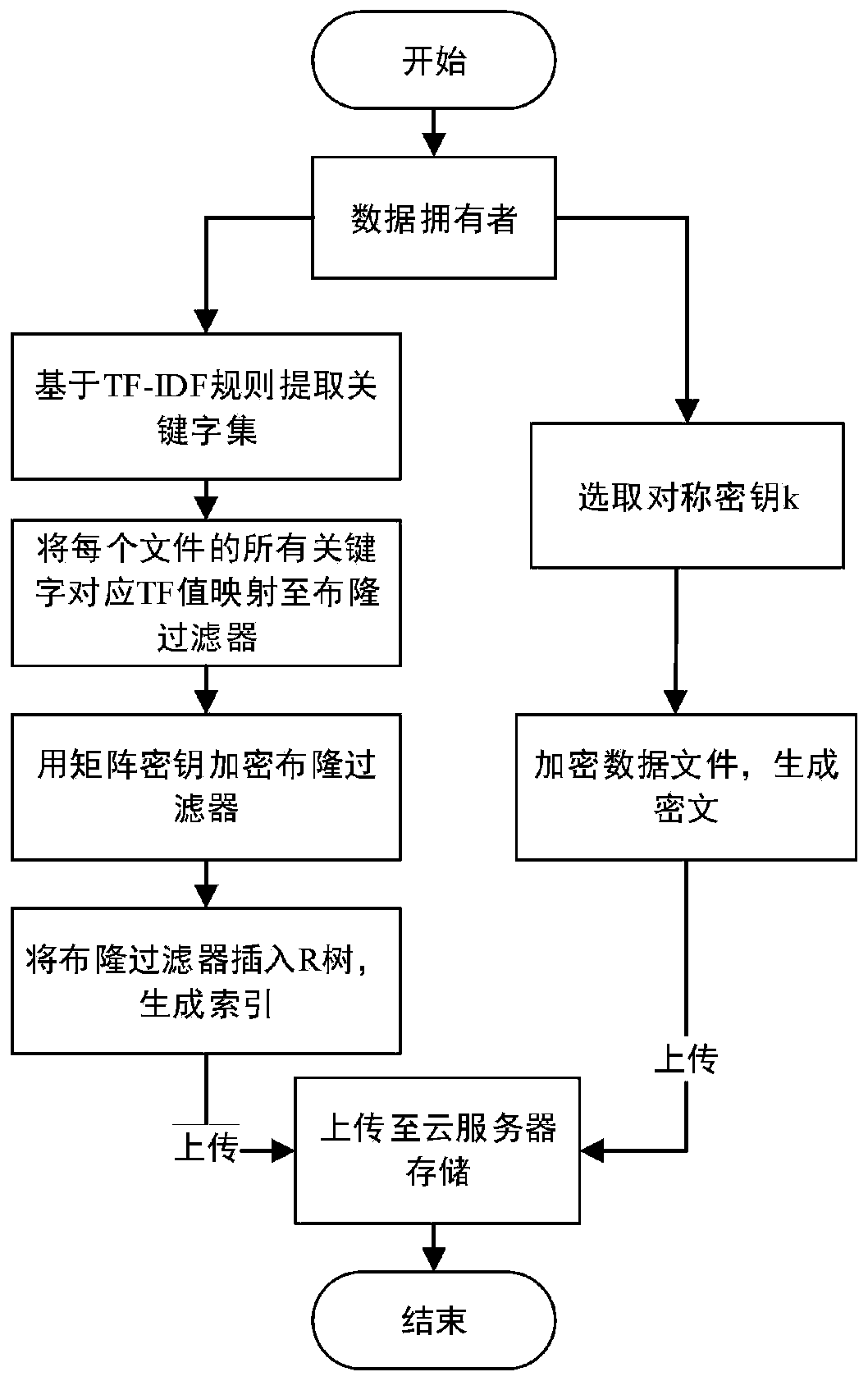
Efficient ciphertext retrieval method based on CP-ABE automatic correction and cloud computing service system
ActiveCN110138561AAvoid Frequency Guessing AttacksReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationGeneration processAccess structure
The invention belongs to the technical field of cloud computing private protection, and discloses an efficient ciphertext retrieval method based on CP-ABE automatic correction and a cloud computing service system. The method comprises the steps of storing an encrypted Bloom filter and a corresponding ciphertext file ID set in a leaf node of the R tree by combining the R tree and the Bloom filter as index structures; using the cloud server to perform the matrix positioning on the R tree according to the search trap door, and then match the encrypted Bloom filters in the leaf nodes; sorting thefiles according to the inner product result of the Bloom filter; introducing a random number in the trap door generation process, wherein different trap doors can be generated even if according to thesame keyword; performing the co-encryption by using the access structure and the owner secret attribute. According to the method, a symmetric key with a small CP-ABE encryption volume is used, so that the fine-grained access control is realized; a multi-agent server is introduced to realize the decentralization, and the collusion between the proxy servers is prevented.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
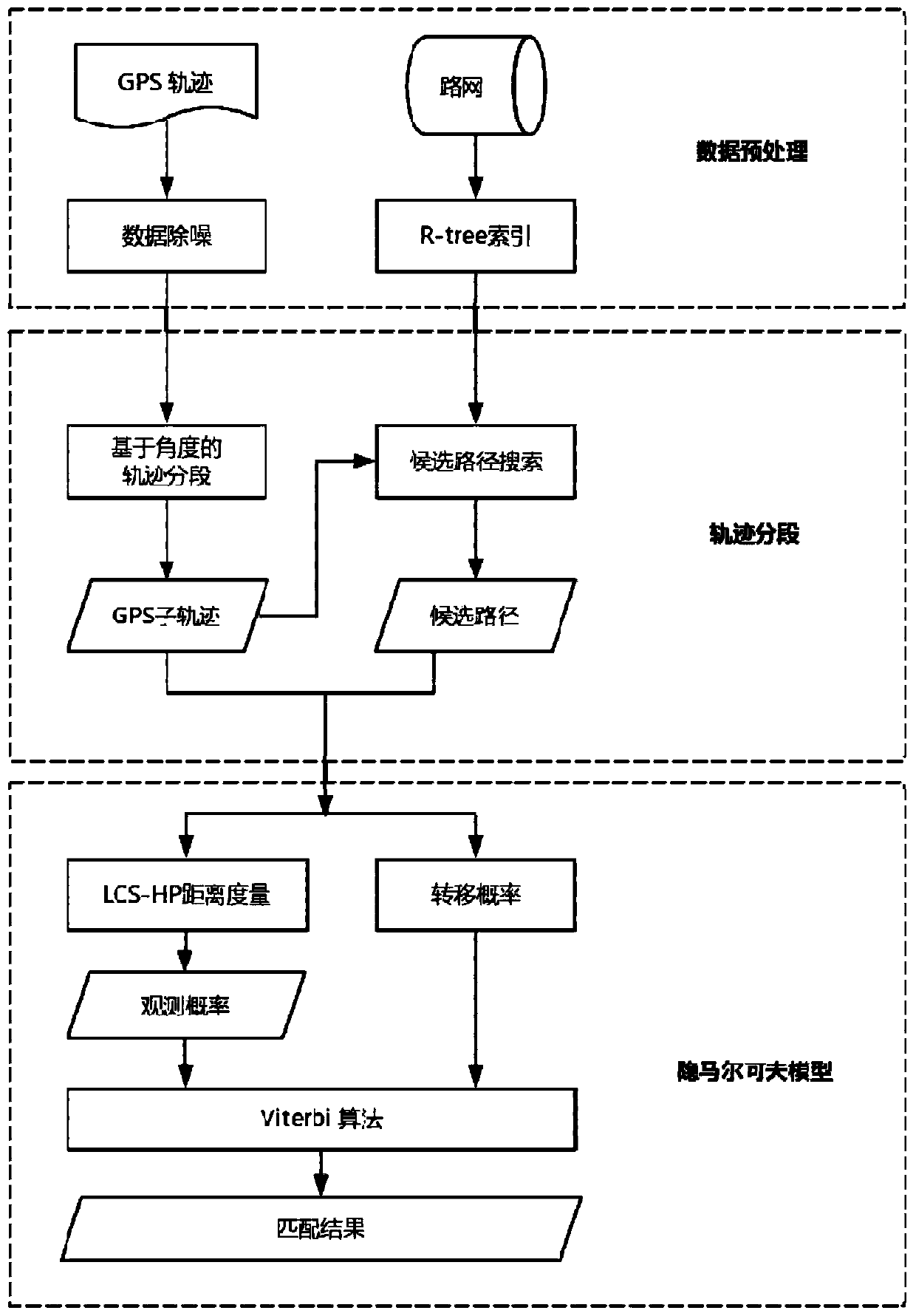
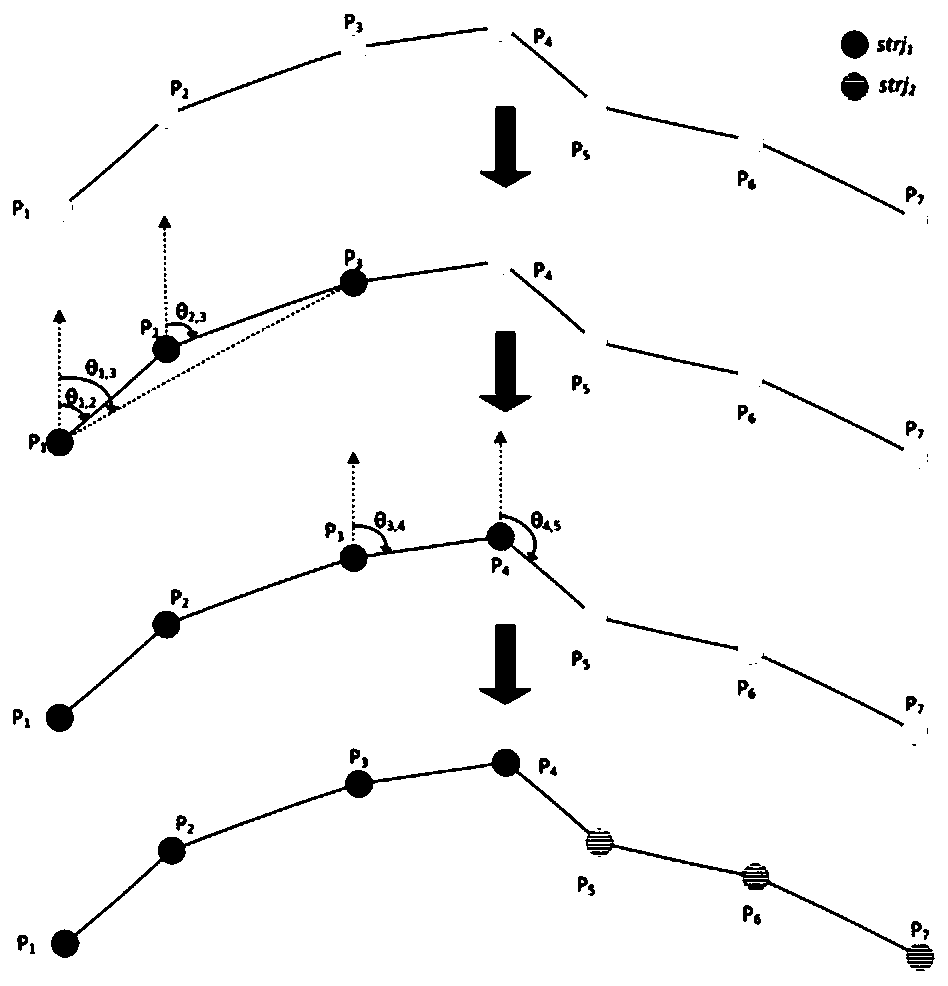
Segmentation-based hidden Markov model map matching method
ActiveCN110095127ASolve the problem of sensitivity to observational errorsSolve efficiency problemsInstruments for road network navigationHide markov modelHigh probability
The invention discloses a segmentation-based hidden Markov model map matching method. The method comprises the following steps: step one, carrying out noise processing on a GPS trajectory and establishing a R-tree spatial index on a road network; step two, carrying out segmentation on the GPS trajectory based on an angle and searching a candidate path set corresponding to the segmented sub-trajectory segments; and step three, selecting a path with the highest probability corresponding to the trajectory as a matching result by using a hidden Markov model. Therefore, a problem of low efficiencyof the GPS trajectory point-by-point map matching method is solved; and the accuracy of map matching is improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Storage and management method for vector big data in water conservancy space
ActiveCN110059067AEasy to classifyGood for index buildingGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsData setDistributed memory
Owner:NANJING NARI WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com