Patents
Literature
1087 results about "Database retrieval" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
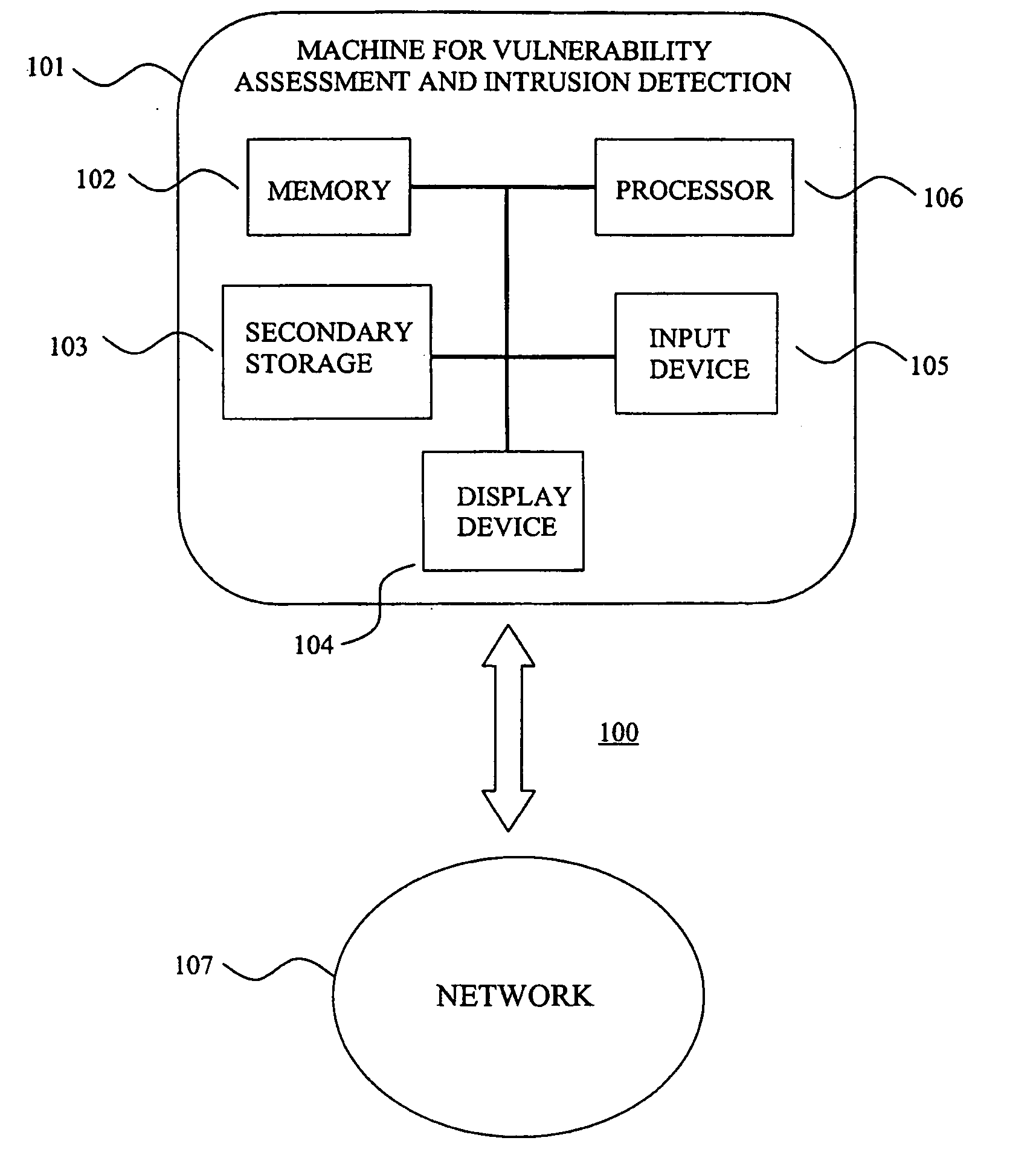
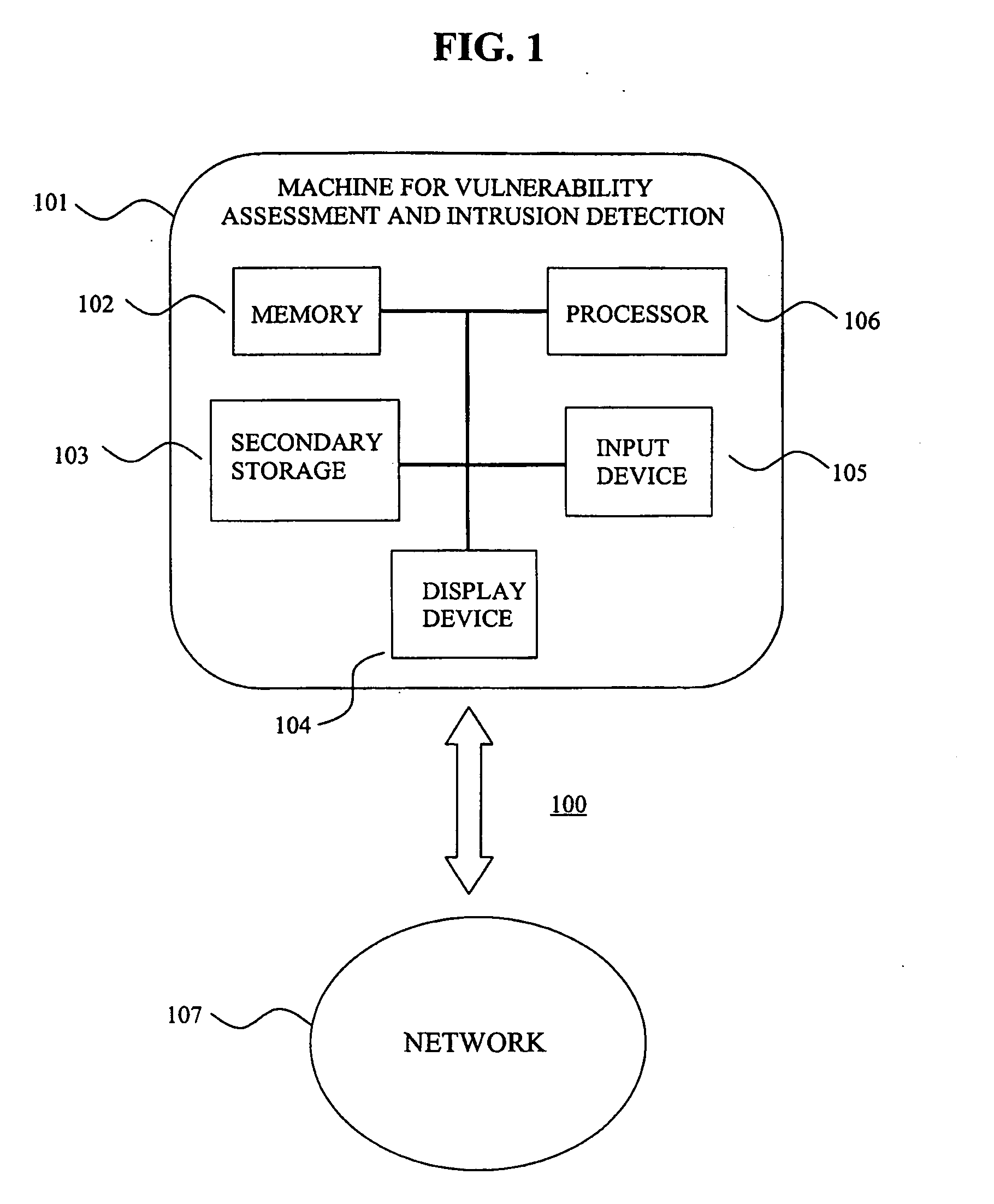
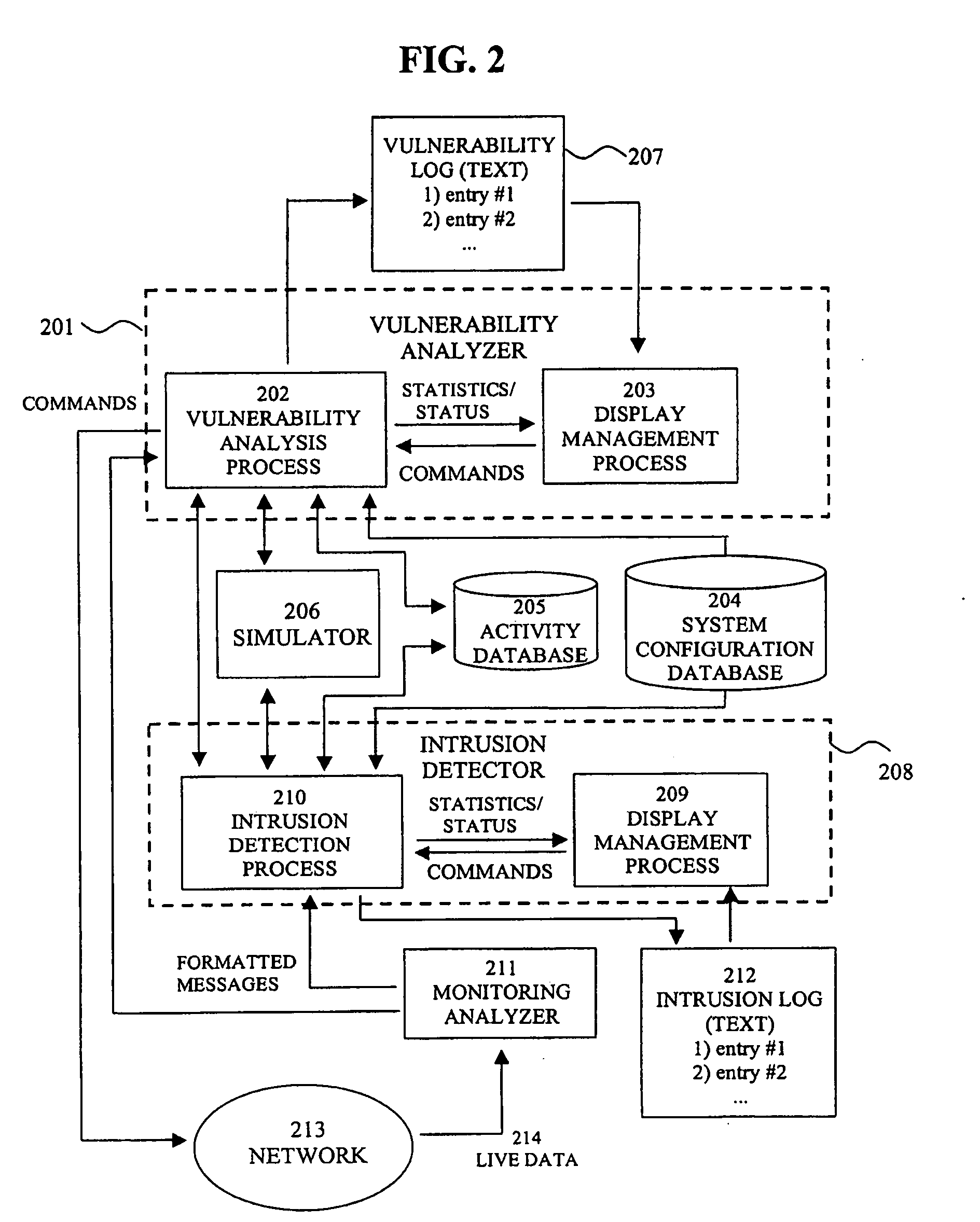
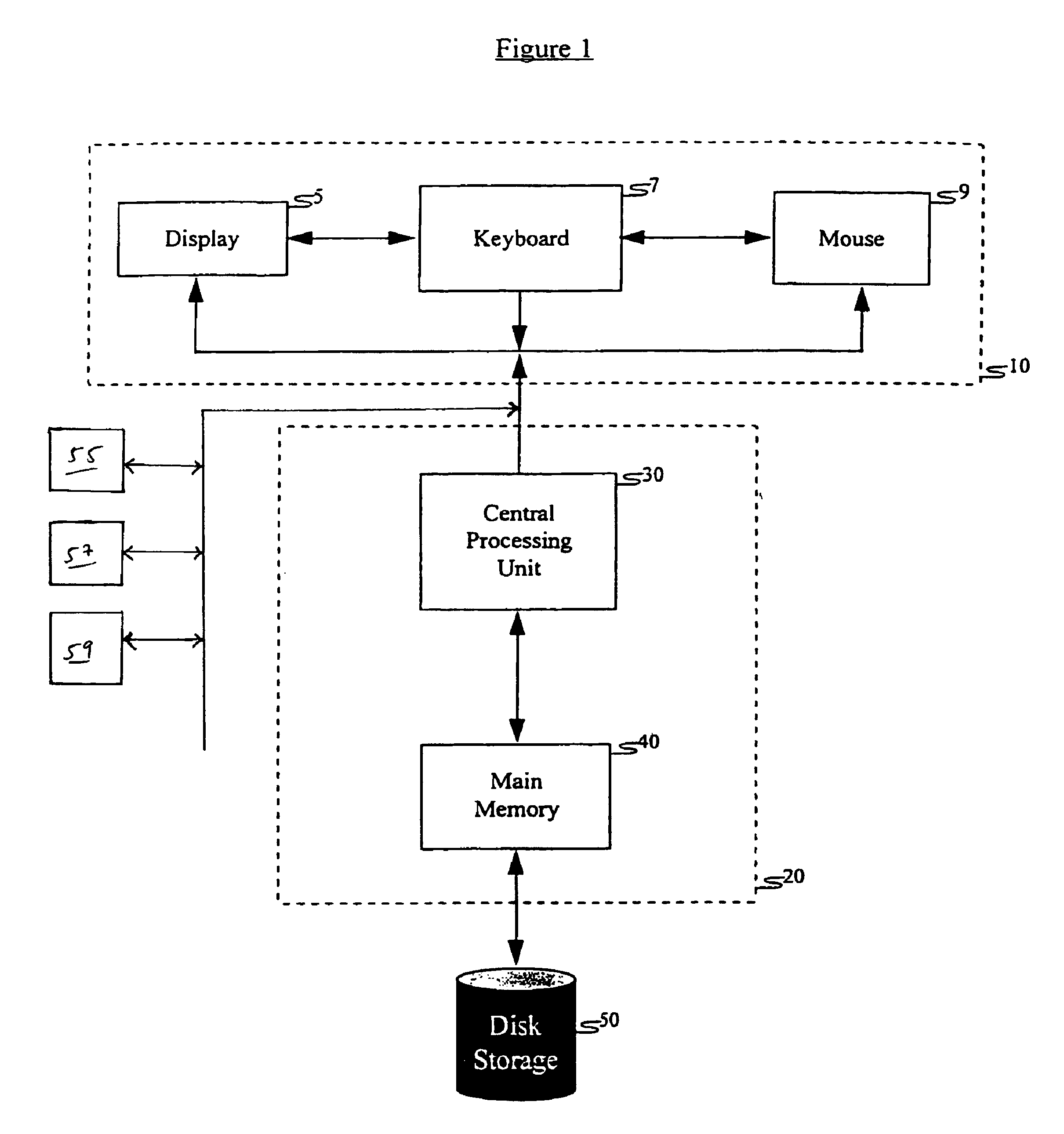
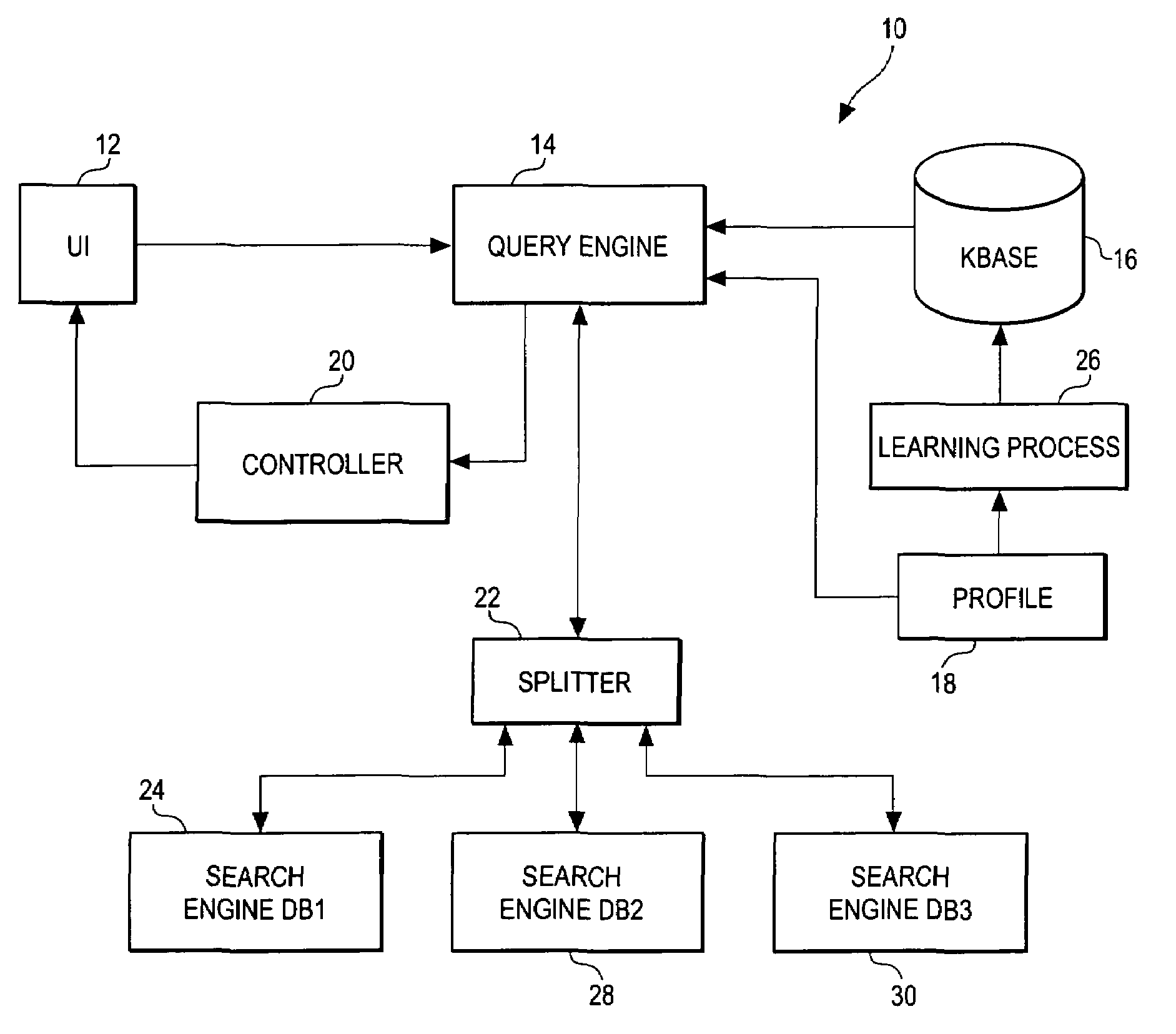
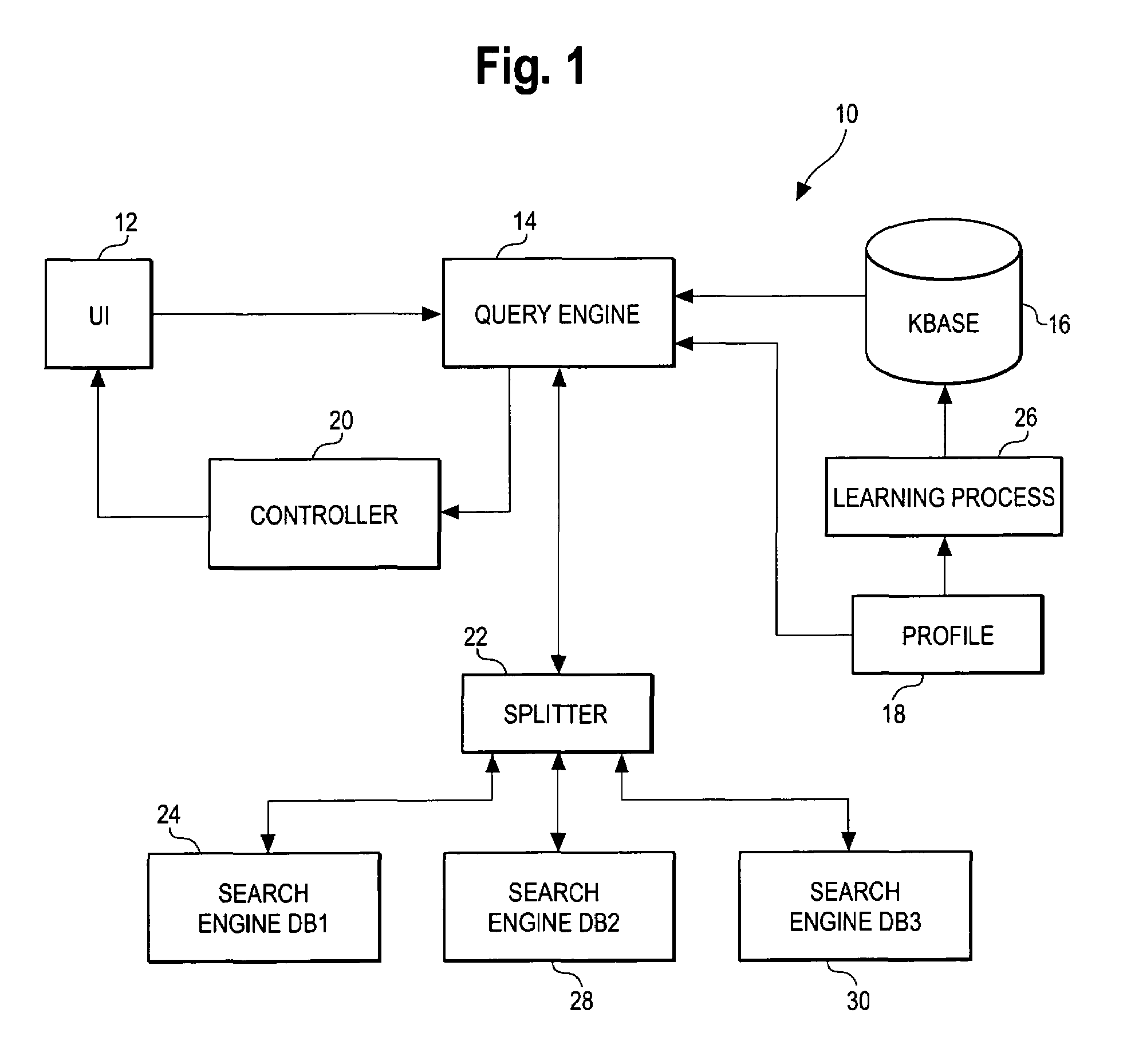
System for intrusion detection and vulnerability assessment in a computer network using simulation and machine learning
InactiveUS20060191010A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer configurationData transmission
The present invention provides a system and method for predicting and preventing unauthorized intrusion in a computer configuration. Preferably, the invention comprises a communication network to which at least two computing devices connect, wherein at least one of the computing devices is operable to receive data transmitted by the other computing device. The invention further comprises a database that is accessible over the network and operable to store information related to the network. A vulnerability assessment component is provided that is operable to execute a command over the communication network, and a data monitoring utility operates to monitor data transmitted over the communication network as the vulnerability assessment component executes commands. Also, an intrusion detection component is included that is operable to provide a simulated copy of the network, to generate a first data transmission on the simulated copy of the network that represents a second data transmission on the communication network, and to compare the first data transmission with a second data transmission. The vulnerability assessment component preferably interfaces with the intrusion detection component to define rules associated with the first and second data transmissions, to store the rules in the database, and to retrieve the rules from the database in order to predict and prevent unauthorized intrusion in the computer configuration.
Owner:PACE UNIVERSITY
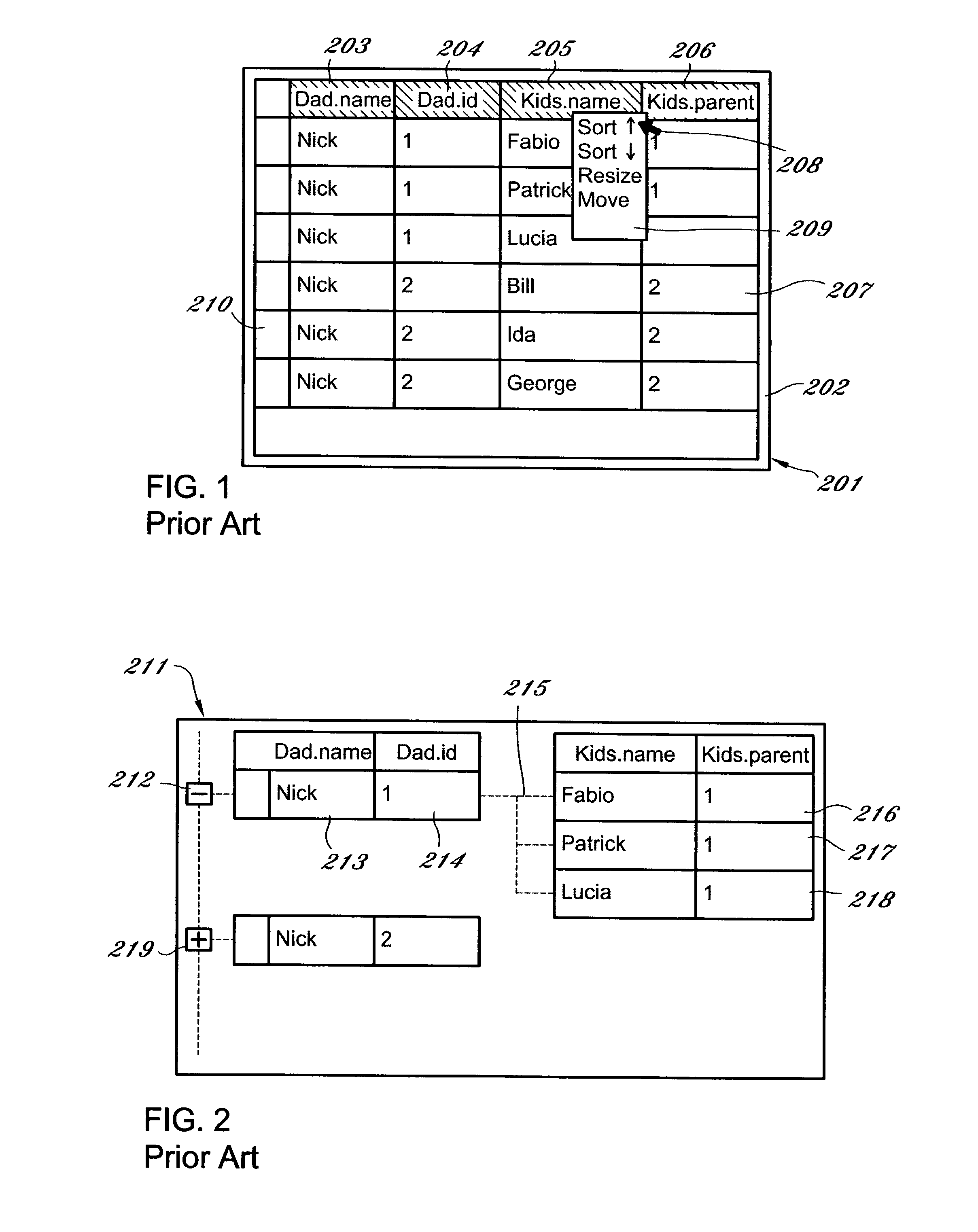
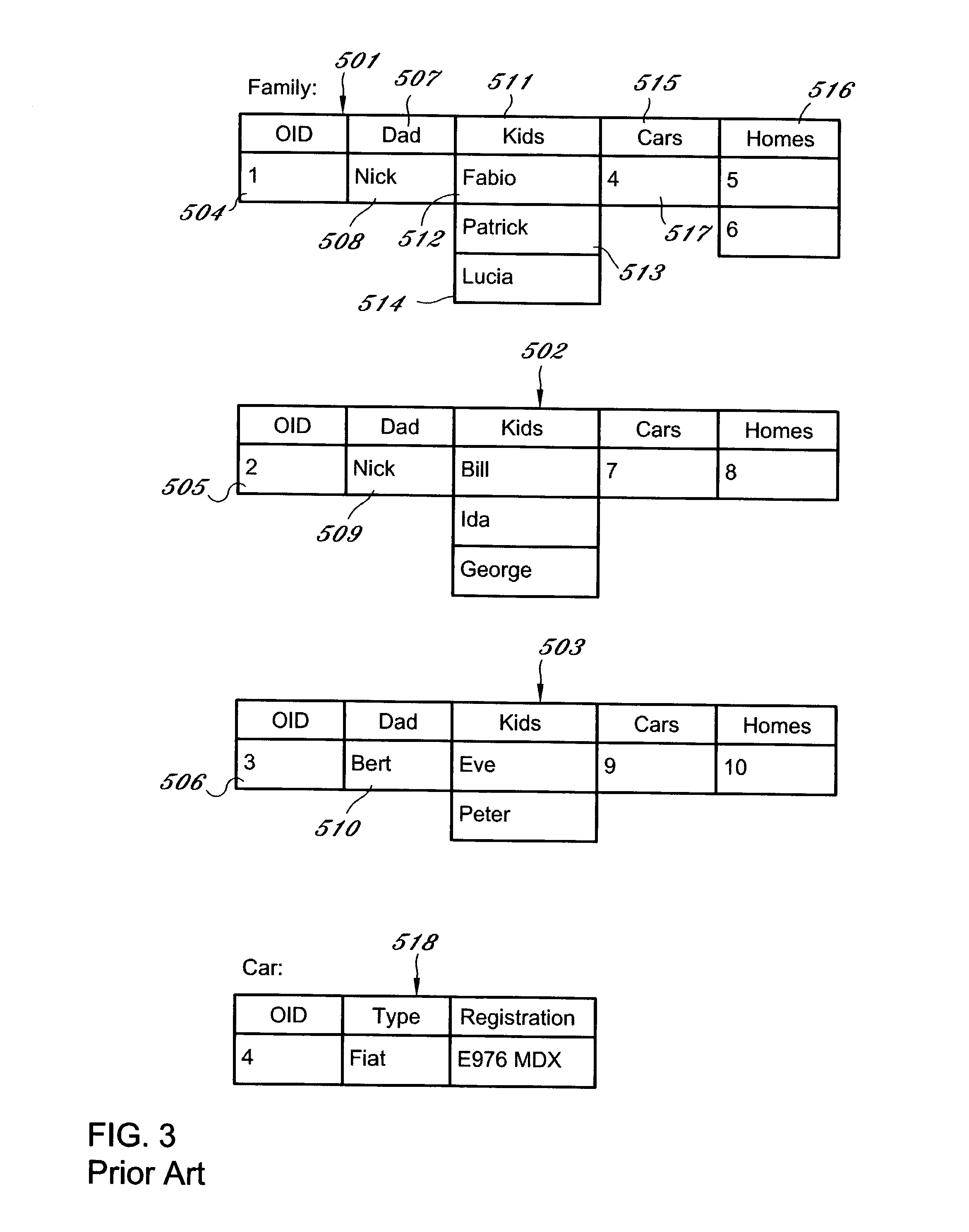
Representation of data records
ActiveUS7461077B1Easy to browseConsistent interfaceDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData sourceDisplay device
A computerized method for representing a data record comprising: querying a data source to obtain data selected from the group consisting of a data element in a record, and metadata concerning the record; presenting in a display a record handle for manipulation of the record; presenting in the display a data item wherein the data item is a list of data items or a reference to another record; and, optionally, presenting on the display the metadata above the data item. In some embodiments, the method includes the step of retrieving one or more heterogeneous records from a plurality of databases for display and manipulation. The invention is also a grid control programmed to implement a disclosed method and is a computer-readable medium having computer-executable instructions for performing a disclosed method. The invention links the grid control of the invention with automatic query generation using hierarchical data schema trees. Both the trees and the grid records represent relational foreign keys as extra reference columns. In the grid control, these reference columns are additional embedded record handles.
Owner:MUSICQUBED INNOVATIONS LLC
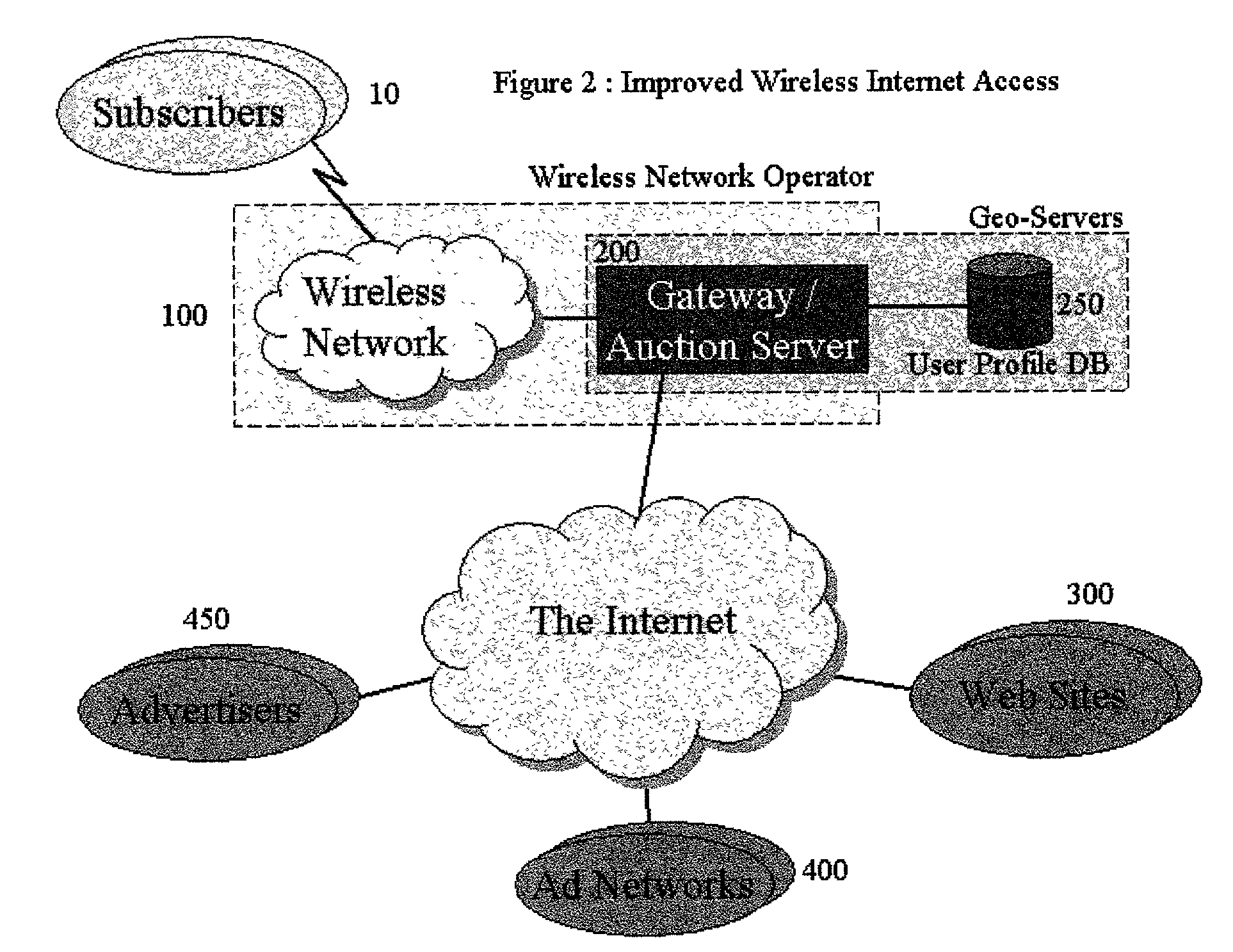
Method and apparatus for generating targeted impressions to internet clients
InactiveUS20020046104A1Saving in computing timeSave bandwidthMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsClient-sideDatabase retrieval
A method and system of using a server to facilitate a transaction between a subscriber and providers for a right to advertise to the subscriber is disclosed. The server is configured to have access to a profile database storing a set of information regarding the subscriber. The method comprises the steps of connecting the subscriber to the server, generating an identifier to specify the subscriber, retrieving from the profile database at least a set of information regarding the subscriber with the identifier, forwarding the retrieved information to the providers, receiving an offer from the providers, the offer being responsive to the information of the subscriber, accepting an offer from the providers based on given criteria, and forwarding the buyer's advertisement to the subscriber.
Owner:GEOMICRO
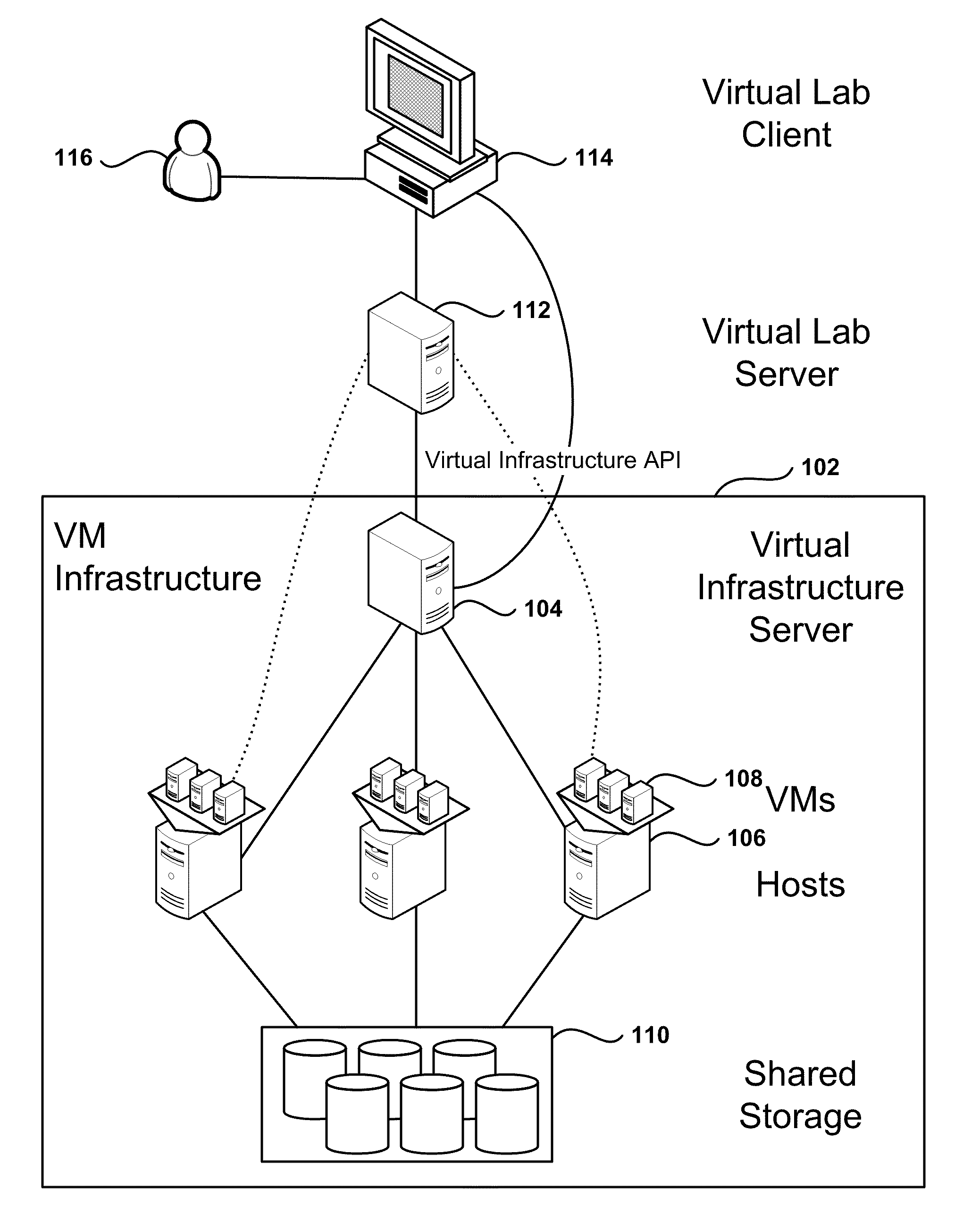
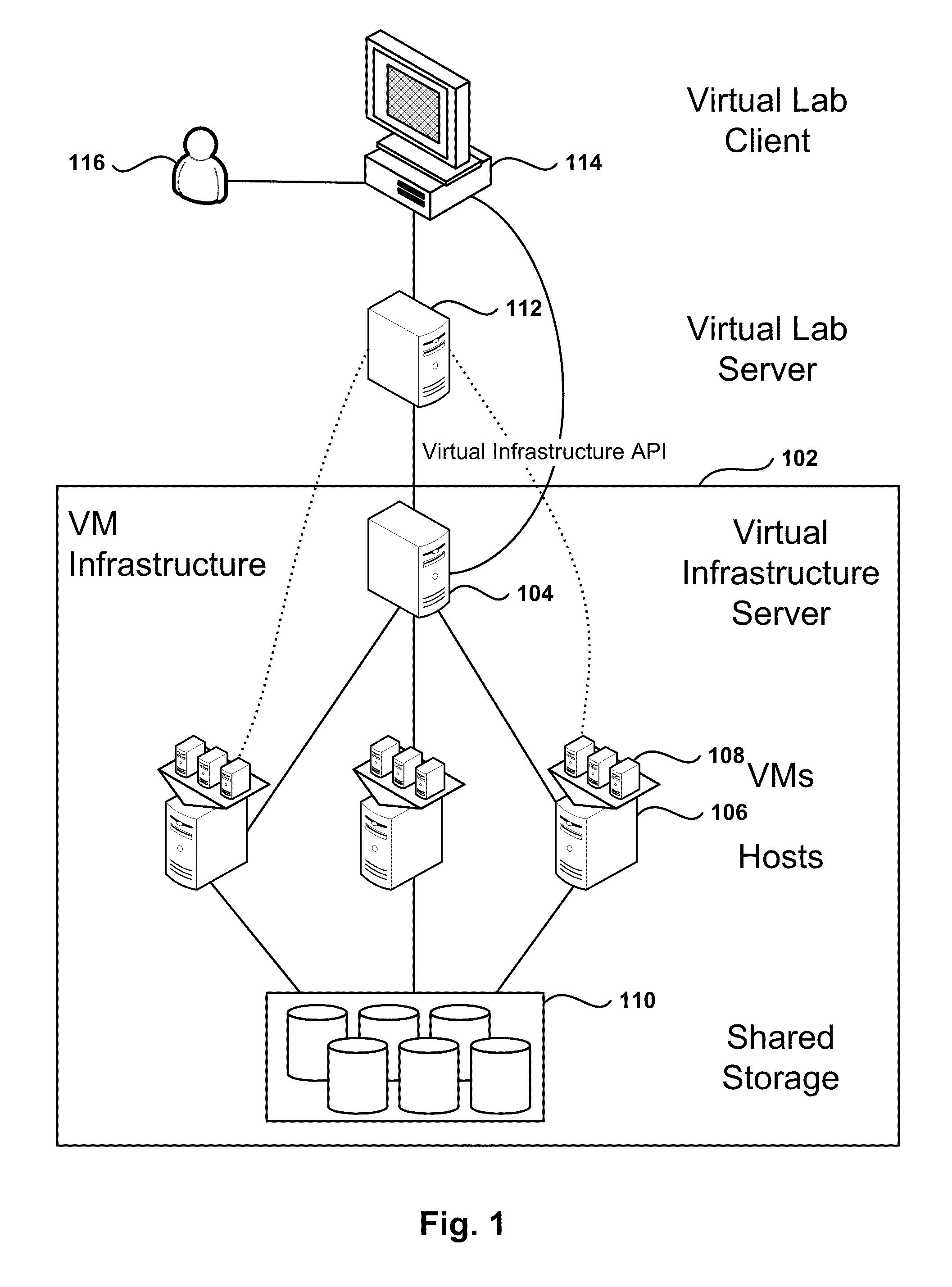
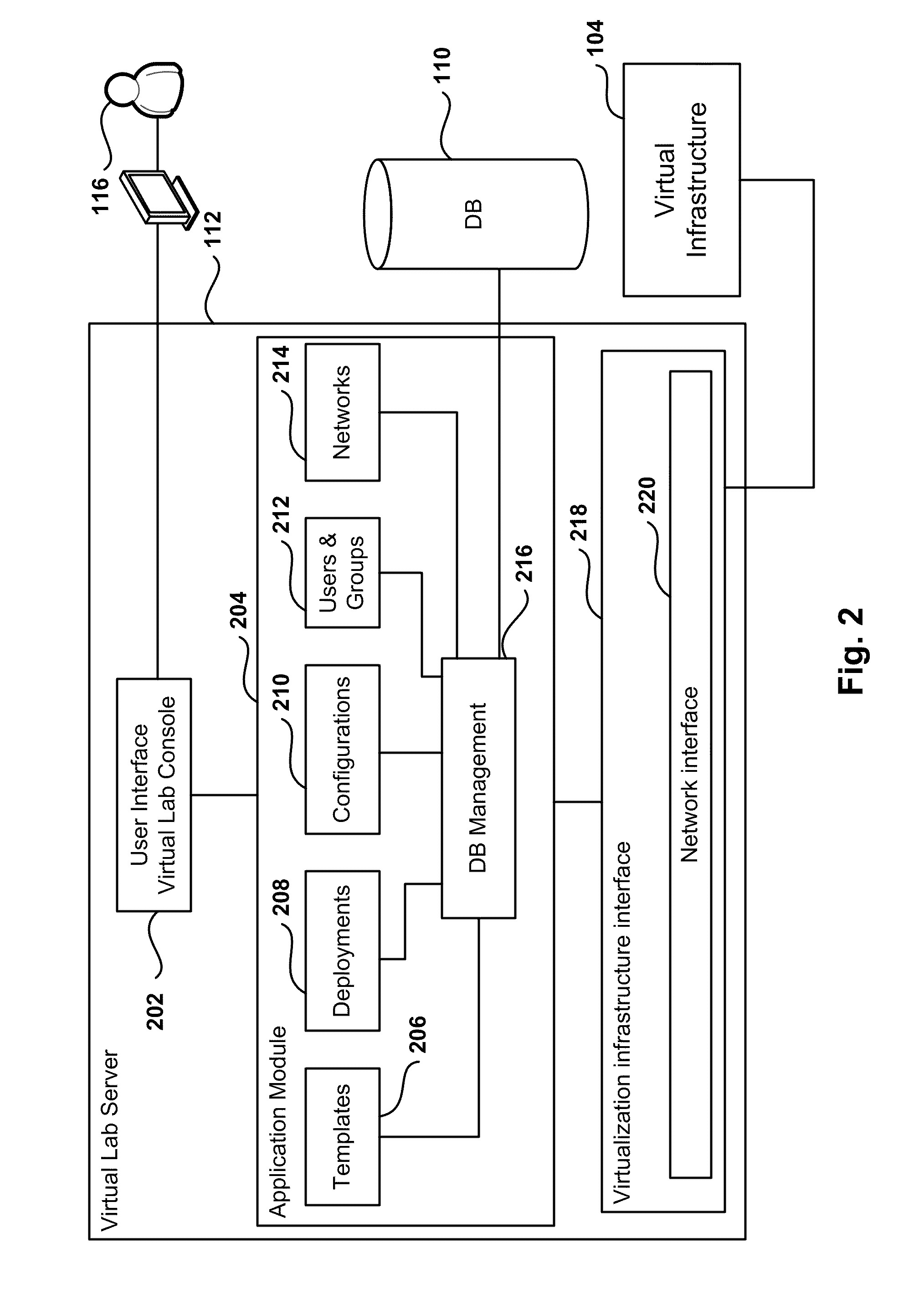
Automated Network Configuration of Virtual Machines in a Virtual Lab Environment
Methods, systems, and computer programs for creating virtual machines (VM) and associated networks in a virtual infrastructure are presented. The method defines virtual network templates in a database, where each virtual network template includes network specifications. A configuration of a virtual system is created, which includes VMs, virtual lab networks associated with virtual network templates, and connections from the VMs to the virtual lab networks. Further, the configuration is deployed in the virtual infrastructure resulting in a deployed configuration. The deployment of the configuration includes instantiating in the virtual infrastructure the VMs of the configuration, instantiating in the virtual infrastructure the virtual lab networks, retrieving information from the database, and creating and executing programming instructions for the VMs. The database information includes the network specifications from the virtual network templates associated with the virtual lab networks, and network resources for the virtual lab networks from a pool of available network resources. The programming instructions are created for the particular Guest Operating System (GOS) running in each VM based on the GOS and on the retrieved database information. When executed in the corresponding VM GOS, the programming instructions configure the VMs network interfaces with the corresponding network specifications.
Owner:NICIRA
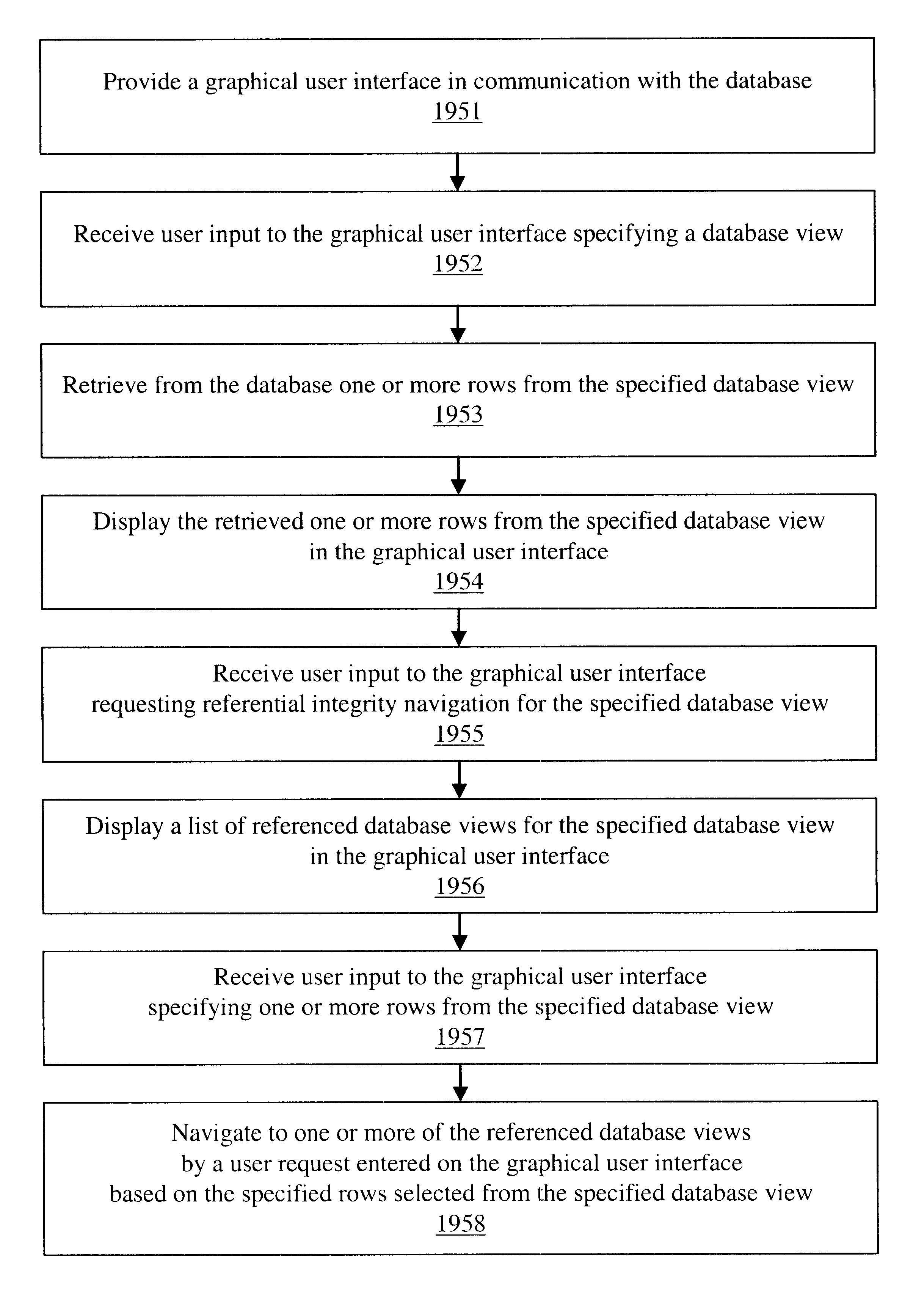
Navigation of view relationships in database system
InactiveUS6609122B1Maintaining correctness and consistency of dataData inconsistencyData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsOriginal dataApplication software
The invention is an improved system and method for browsing and editing data residing in database tables. The method of the present invention includes the steps of providing a graphical user interface in communication with a database, receiving user input to the graphical user interface, retrieving data from the database, displaying the retrieved data in the graphical user interface, and navigating to one or more referenced database tables or views by user request entered on the graphical user interface. The purpose of referential integrity is to prevent database users or applications from entering inconsistent data into a database. The goal of referential integrity navigation is to allow the user, having retrieved one or more rows of data, to navigate easily to the data in other tables that either refers to or is referred to by that data. These relationships are defined by referential integrity constraints, and the data thus retrieved by navigation is then available for all the operations possible on the original data, including data editing and further relational navigation. By storing a catalog of the relationships known to exist between Oracle's V$ views, the same form of navigation can be provided between these data sources.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
System and method for identifying infected networks and systems from unknown attacks
ActiveUS20150128274A1Fast transferMinimizing chanceMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer scienceData library
Systems and method of the present disclosure are directed to a network security monitor. The monitor can receive logs of a second computer network indicative of a status of the second computer network determined by a monitoring agent executing on the second computer network. The monitor can generate indexed logs from the logs based on log format. The monitor can retrieving a list of threat indicators from a database based on a schema from a plurality of threat indicators received from a plurality of heterogeneous repositories via the first computer network. The monitor can compare the list of threat indicators with the indexed logs. The monitor can generate a report based on the comparing to identify a threat.
Owner:CRYPTEIA NETWORKS
Multi-party conversation analyzer & logger
InactiveUS20140247926A1Combat useAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSpeech soundData library
In one aspect, the present invention facilitates the investigation of networks of criminals, by gathering associations between phone numbers, the names of persons reached at those phone numbers, and voice print data. In another aspect the invention automatically detects phone calls from a prison where the voiceprint of the person called matches the voiceprint of a past inmate. In another aspect the invention detects identity scams in prisons, by monitoring for known voice characteristics of likely imposters on phone calls made by prisoners. In another aspect, the invention automatically does speech-to-text conversion of phone numbers spoken within a predetermined time of detecting data indicative of a three-way call event while monitoring a phone call from a prison inmate. In another aspect, the invention automatically thwarts attempts of prison inmates to use re-dialing services. In another aspect, the invention automatically tags audio data retrieved from a database, by steganographically encoding into the audio data the identity of the official retrieving the audio data.
Owner:SECURUS TECH LLC
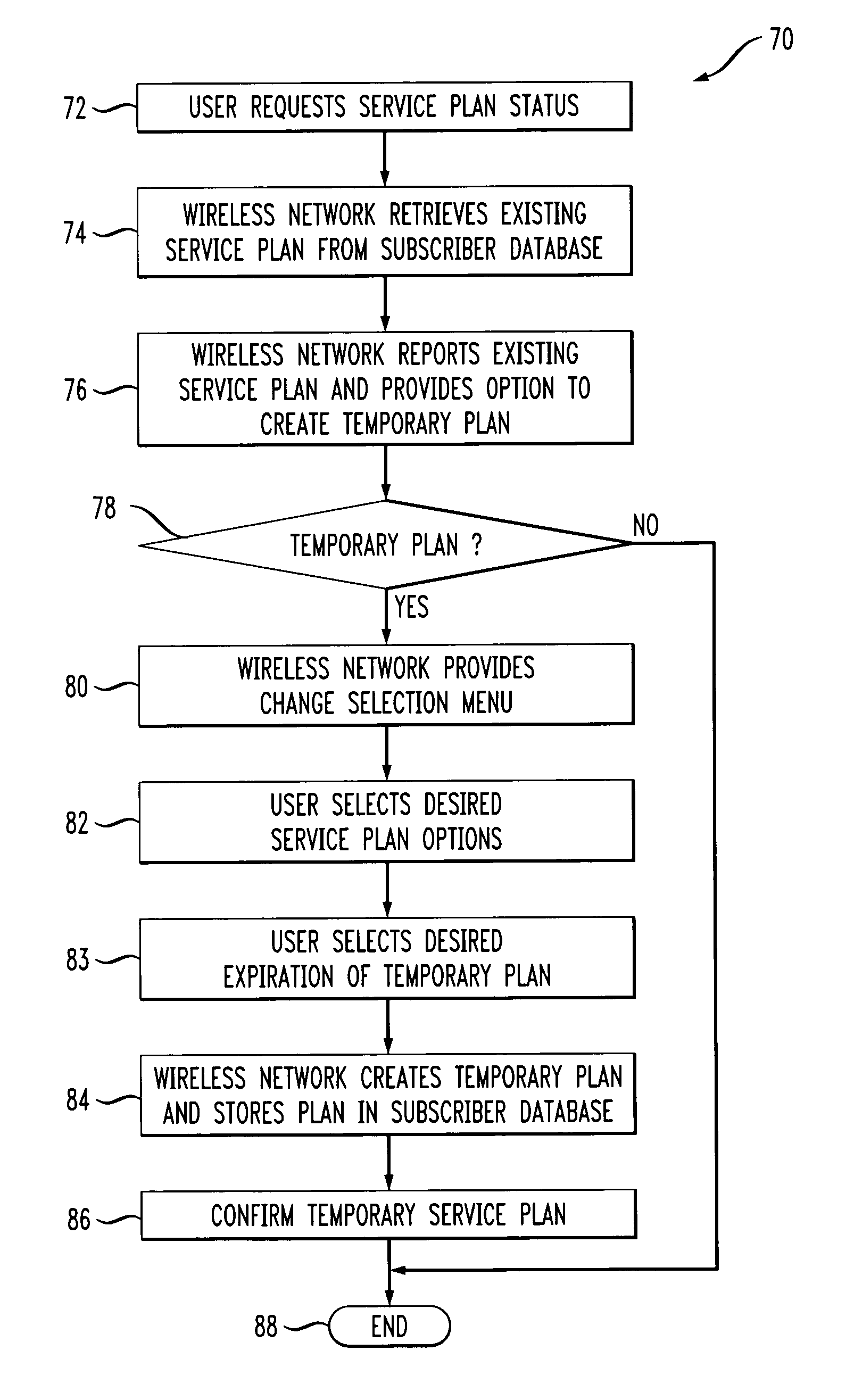
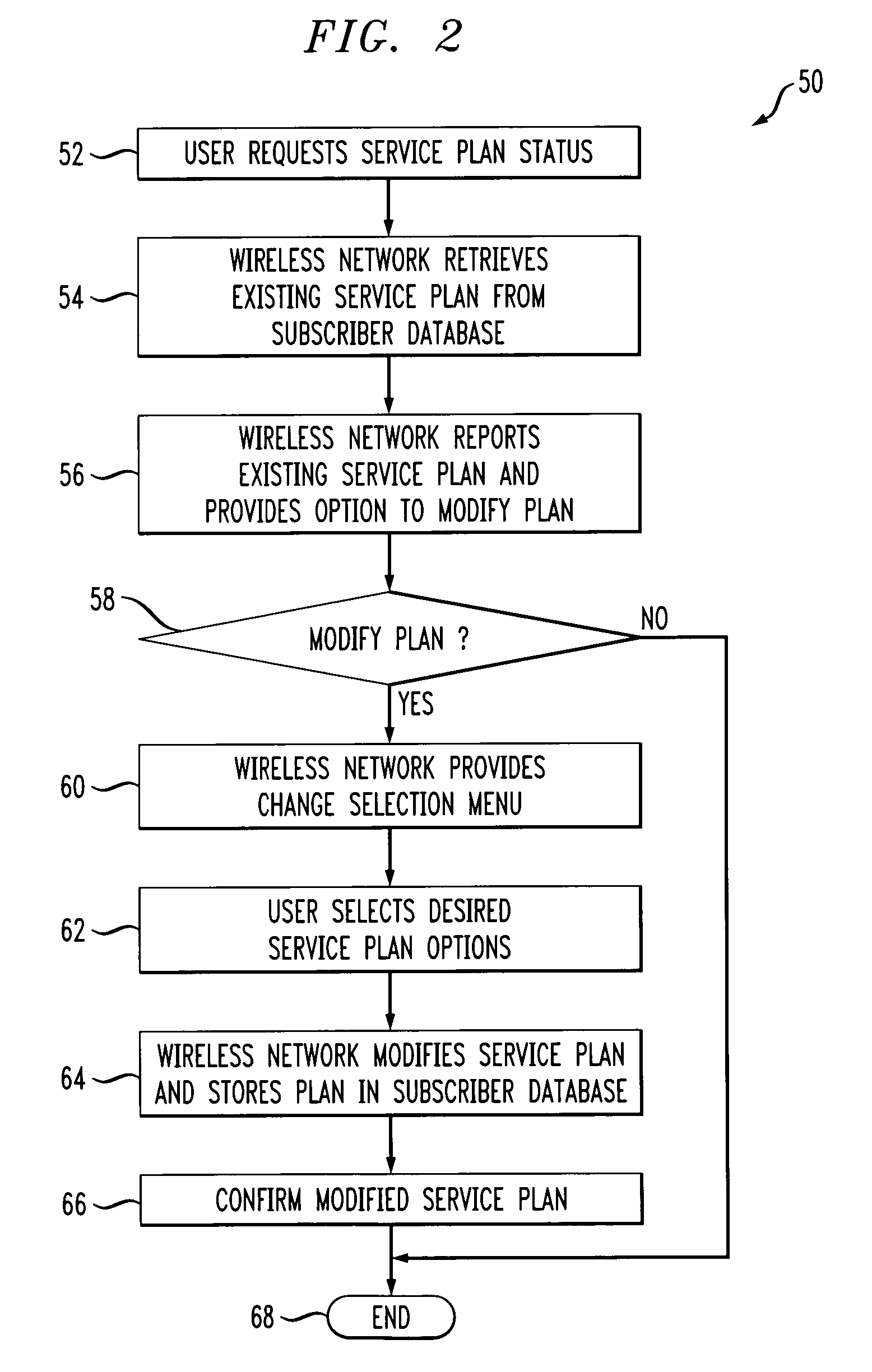
Method for changing mobile subscriber service plan
InactiveUS7236780B2Special service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsService planningProgram planning
A method for automating changes to a service plan between a mobile subscriber and a wireless service provider is provided. In one embodiment, the method creates a temporary service plan for the subscriber. This method includes: a) receiving a request to create the temporary plan, b) retrieving the subscriber's existing service plan from a subscriber database, c) providing a change selection menu to the user, d) modifying the existing service plan in conjunction with one or more user selections associated with the change selection menu to create the temporary plan, and e) storing the temporary plan in the subscriber database. In another embodiment, the method modifies the subscriber's existing service plan and the modified service plan supercedes the previous service plan. In another aspect, a method for processing a call from a mobile station associated with the subscriber when the temporary service plan is in effect is provided.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
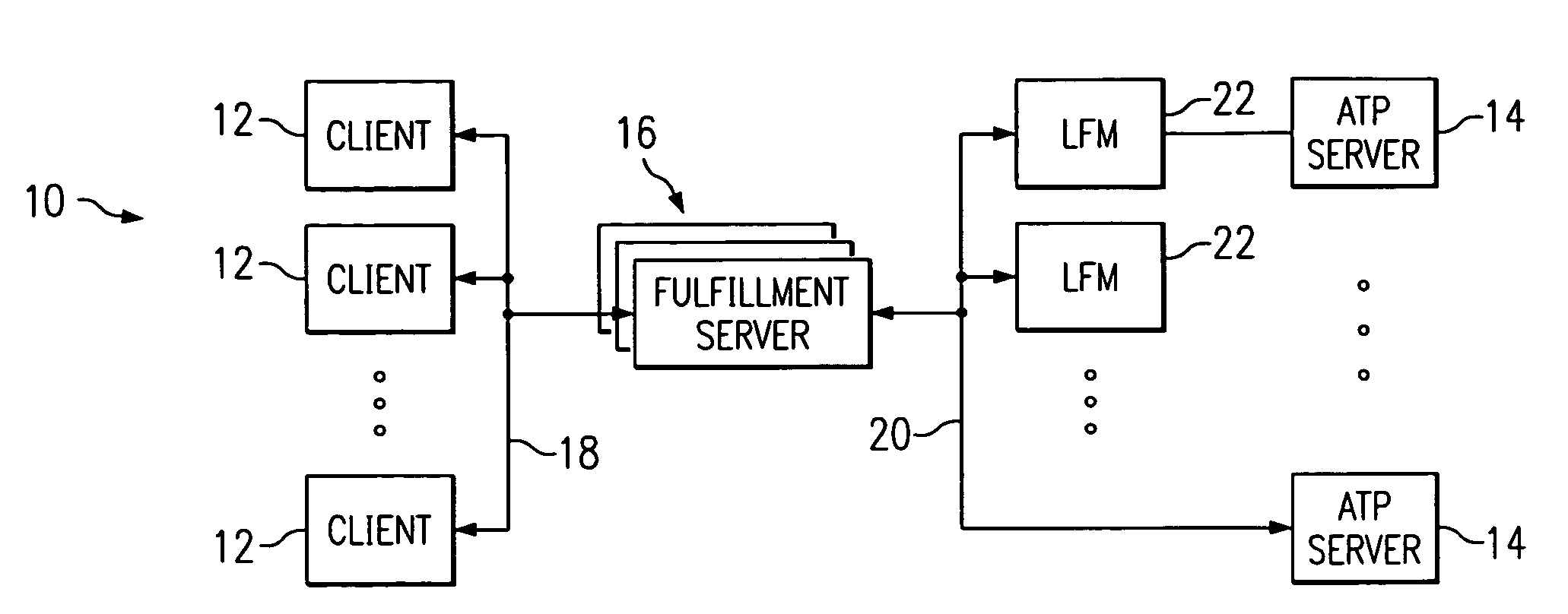
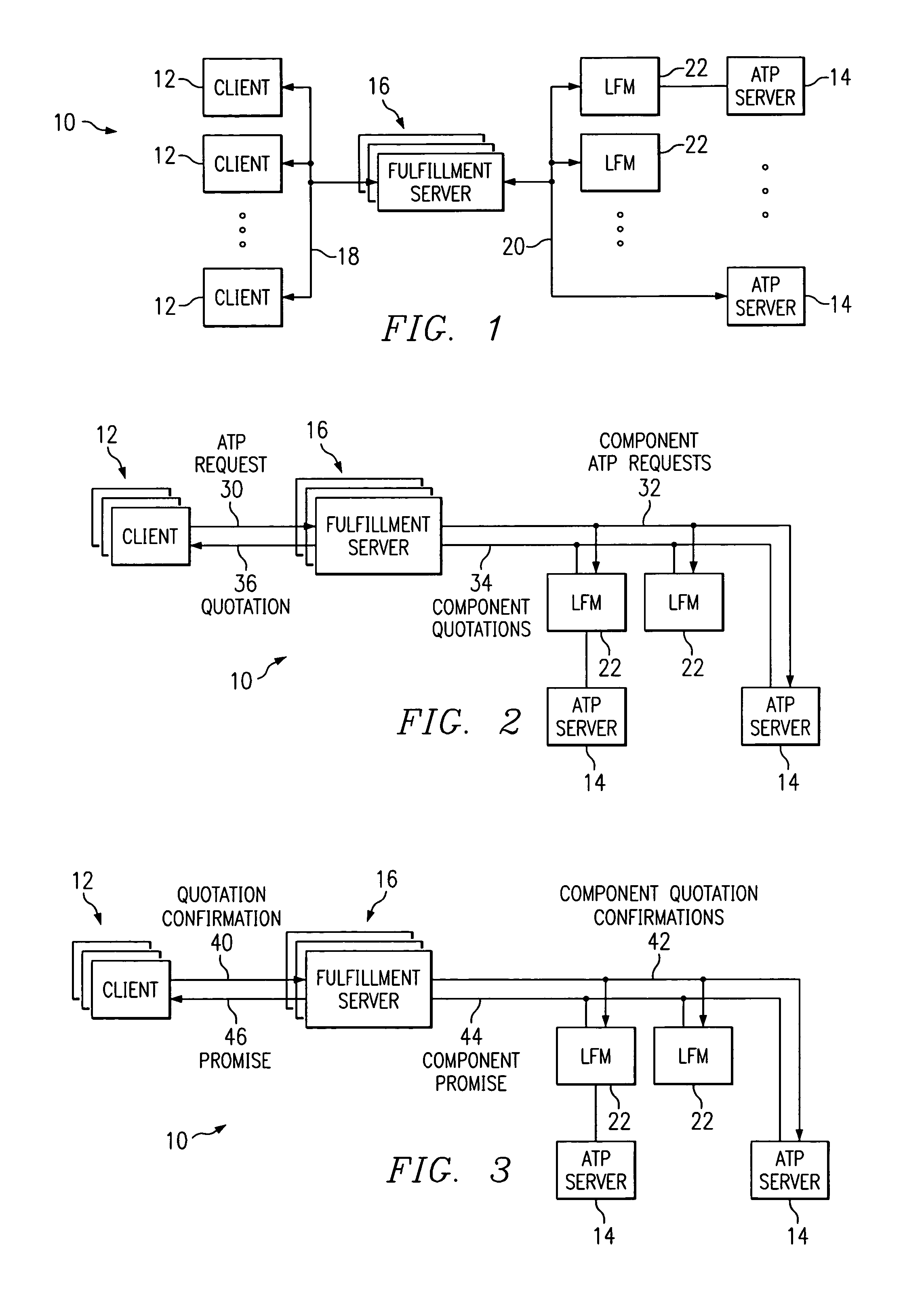
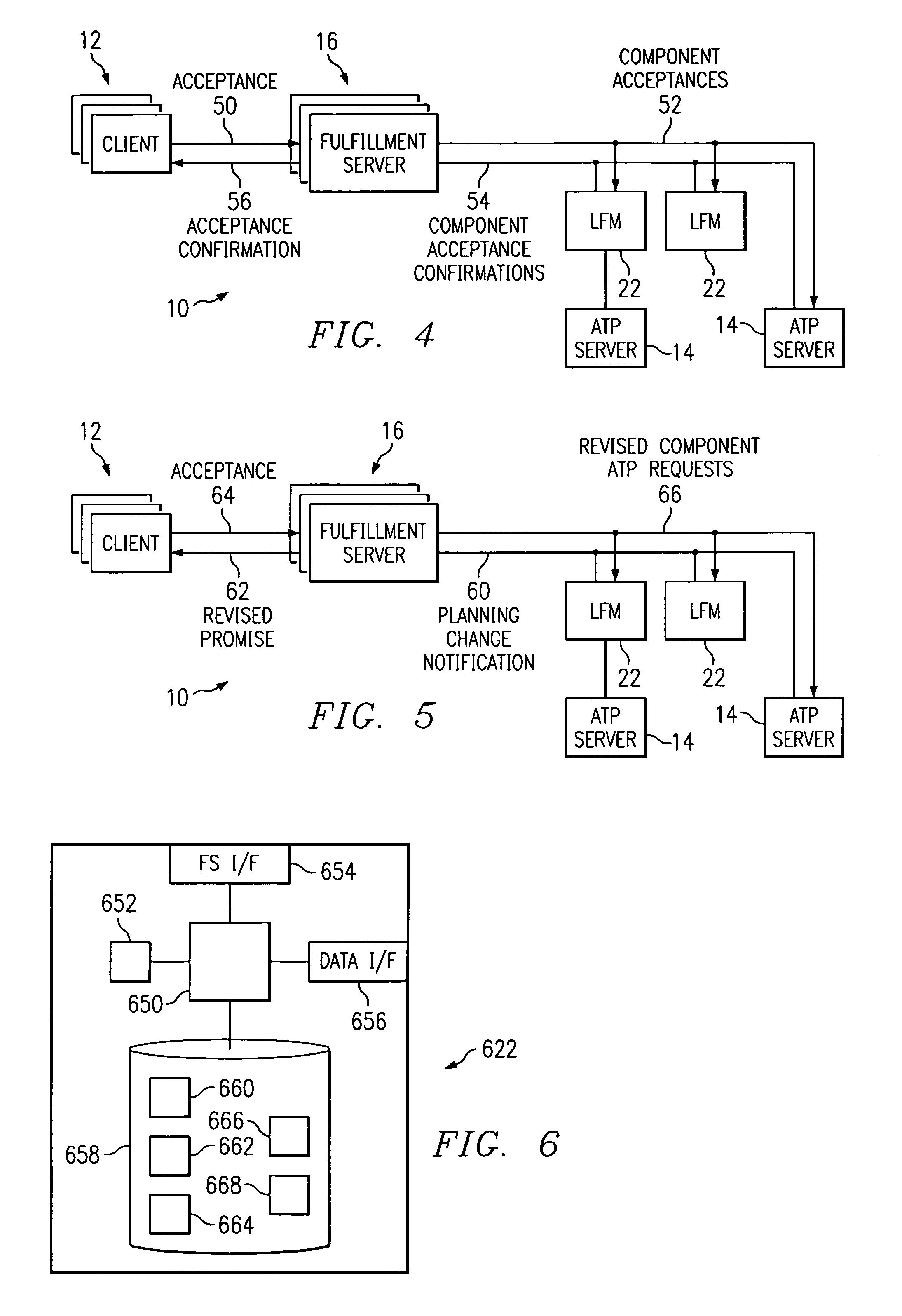
Fulfillment management system for managing ATP data in a distributed supply chain environment
ActiveUS7249044B2Disadvantages and and reduced eliminatedEnvironment reduced eliminatedMultiprogramming arrangementsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsLine itemComputer science
A fulfillment management system includes a database operable to store product availability information associated with at least one product. The fulfillment management system also includes one or more processors collectively operable to receive at least one component available-to-promise (ATP) request. Each component ATP request corresponds to a particular ATP request line-item for a desired product. The one or more processors are also operable to retrieve at least a portion of the product availability information associated with the desired product from the database for each component ATP request, determine an ATP response for each component ATP request using the retrieved product availability information, generate a component quotation for each component ATP request according to the corresponding ATP response, and communicate the component quotation for consolidation with other component quotations.
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
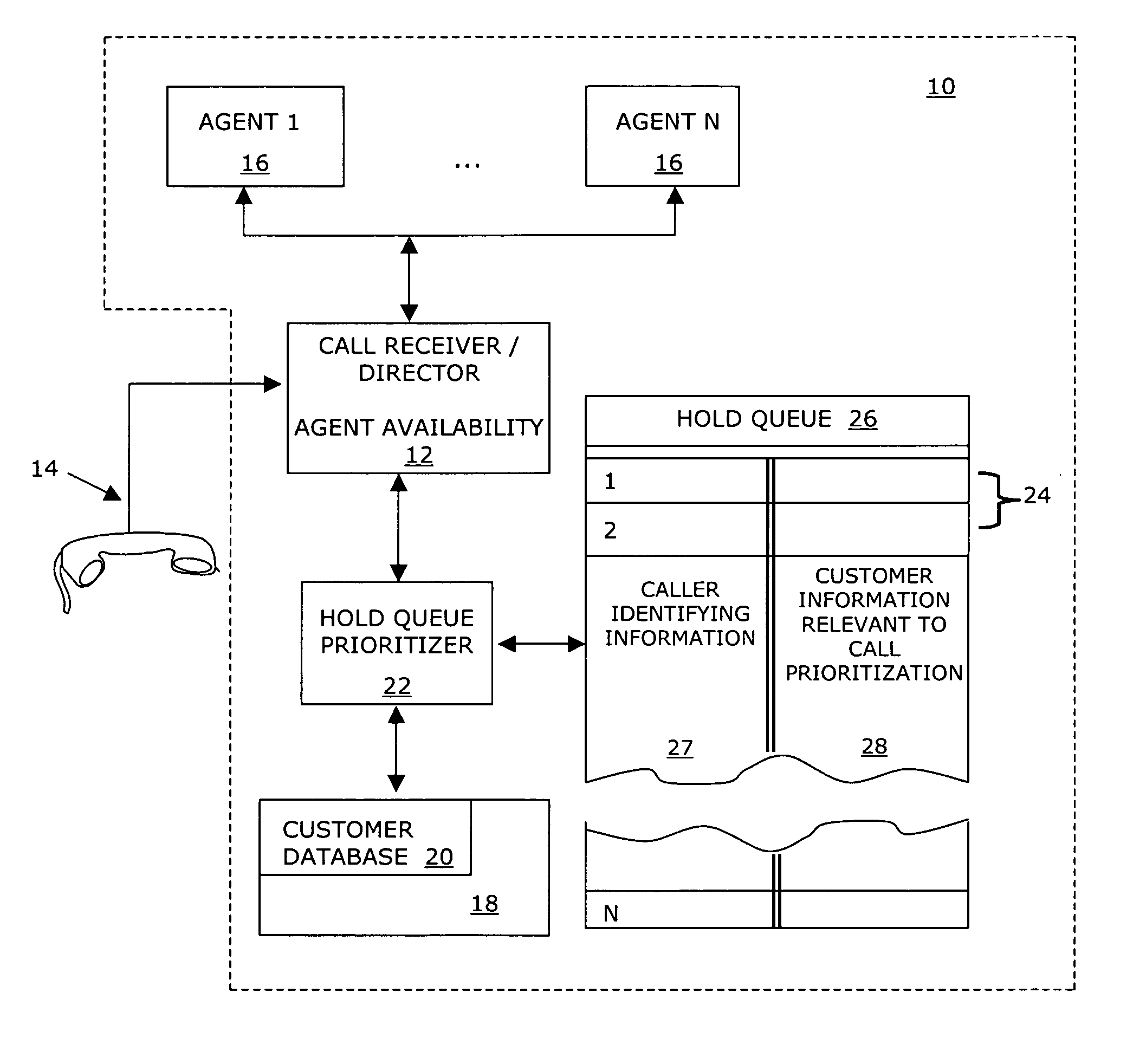
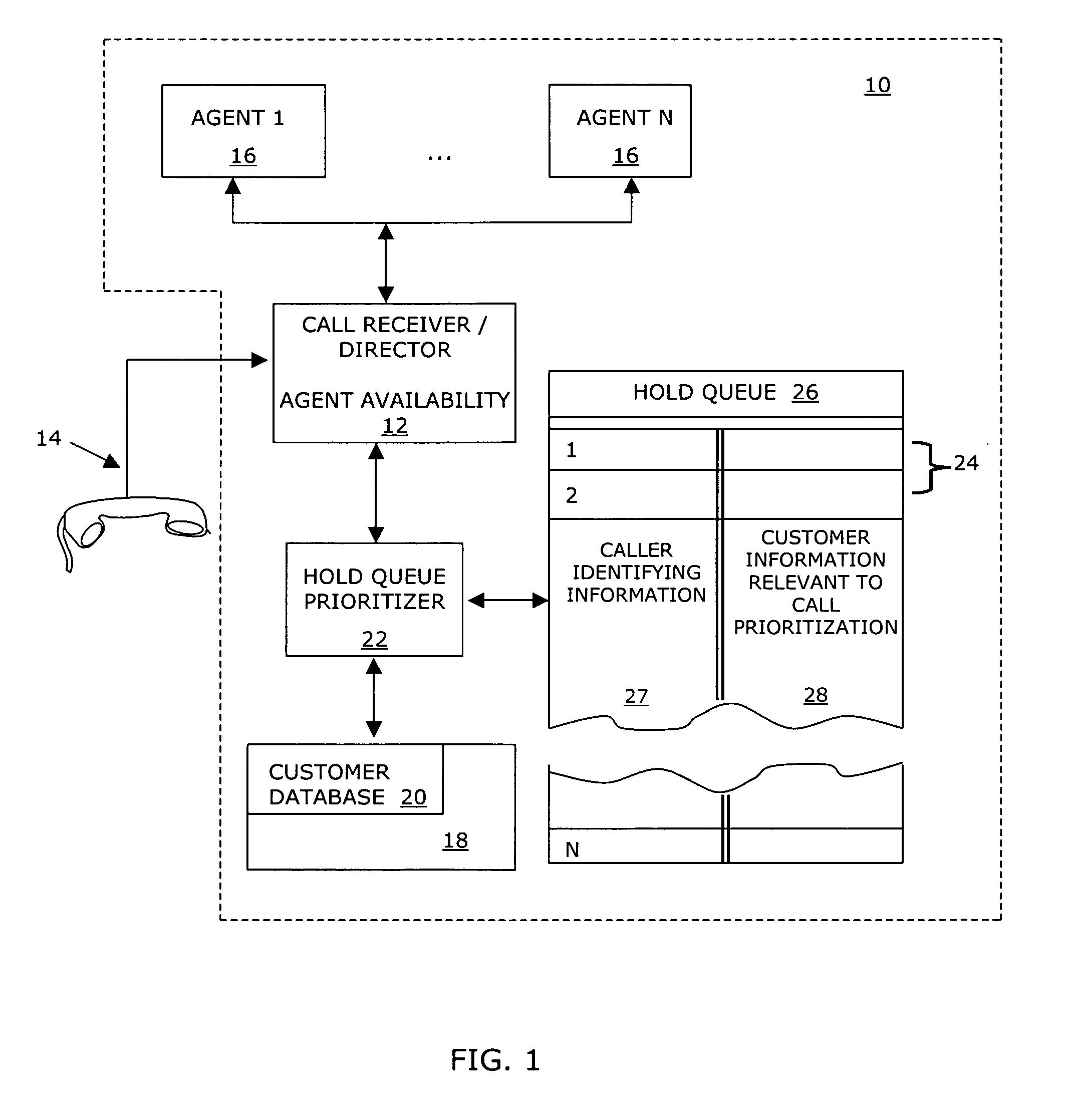
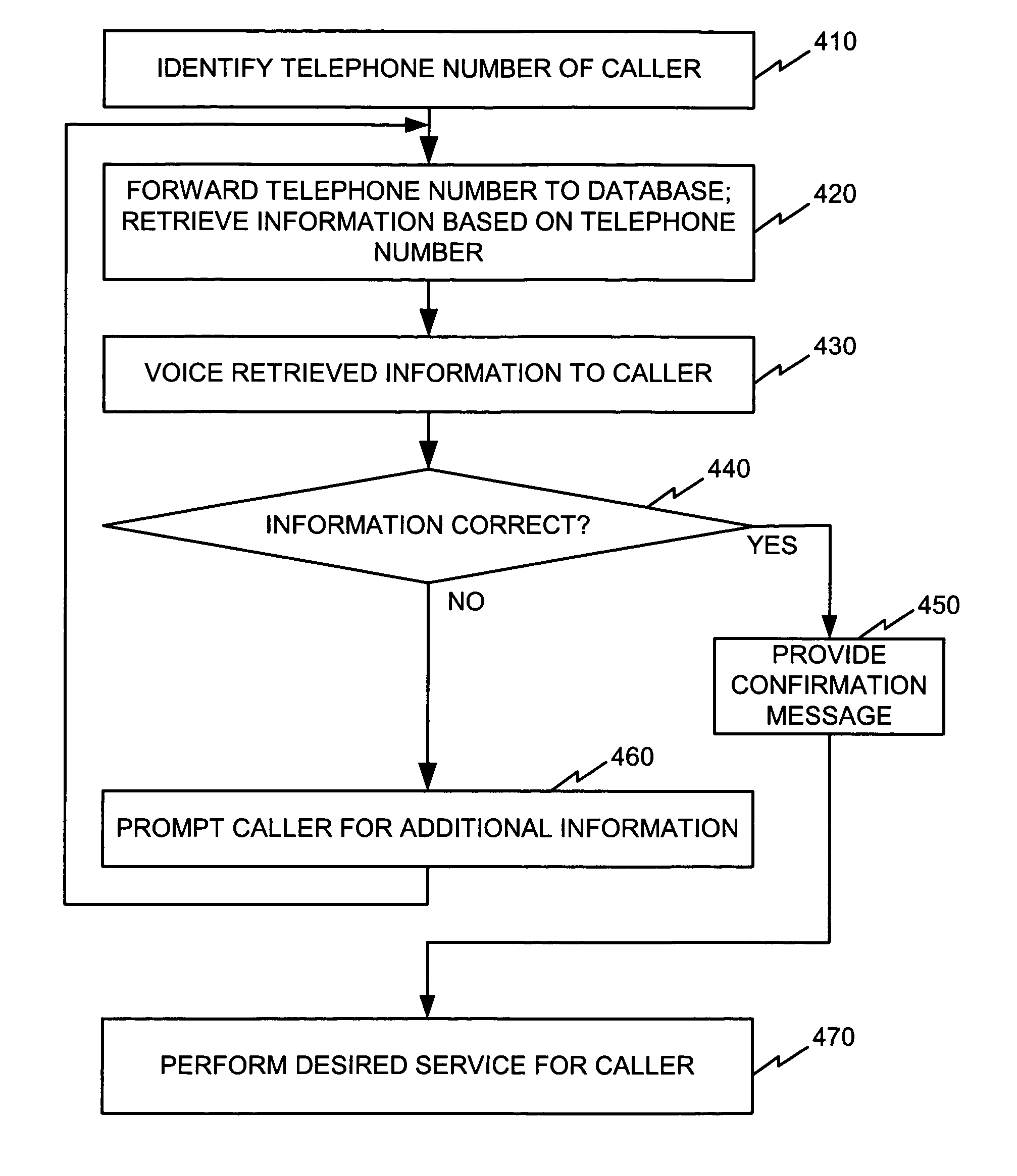
System and method for managing a hold queue based on customer information retrieved from a customer database
InactiveUS7068775B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCustomer informationDatabase retrieval
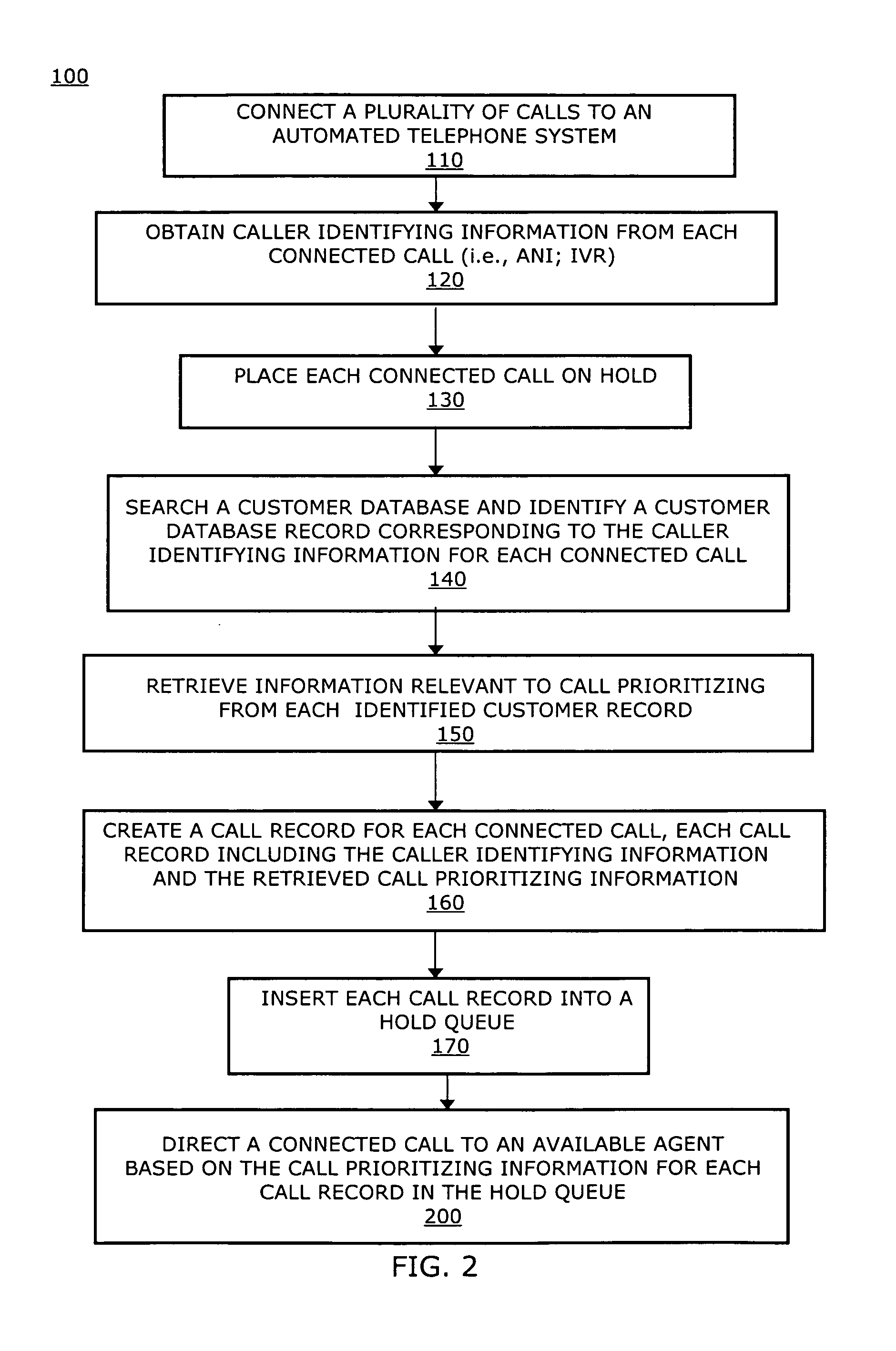
A system, including a method for prioritizing on hold calls connected to an automated telephone system is disclosed. The system and method utilizes customer information retrieved from a customer database as call prioritizing information for each connected call. The method begins by connecting a plurality of calls to the automated telephone system. Caller identifying information is obtained from each connected call and each connected call is placed on hold. Then, a customer database is searched and a customer database record is identified corresponding the obtained caller identifying information for each connected call. A call record for each connected call is created and inserted into the hold queue. Each call record includes the caller identifying information and call prioritizing information corresponding to the connected call. The connected calls are then directed to available agents based on the call prioritizing information stored in each call record in the hold queue.
Owner:WILMINGTON TRUST NAT ASSOC AS ADMINISTATIVE AGENT +1
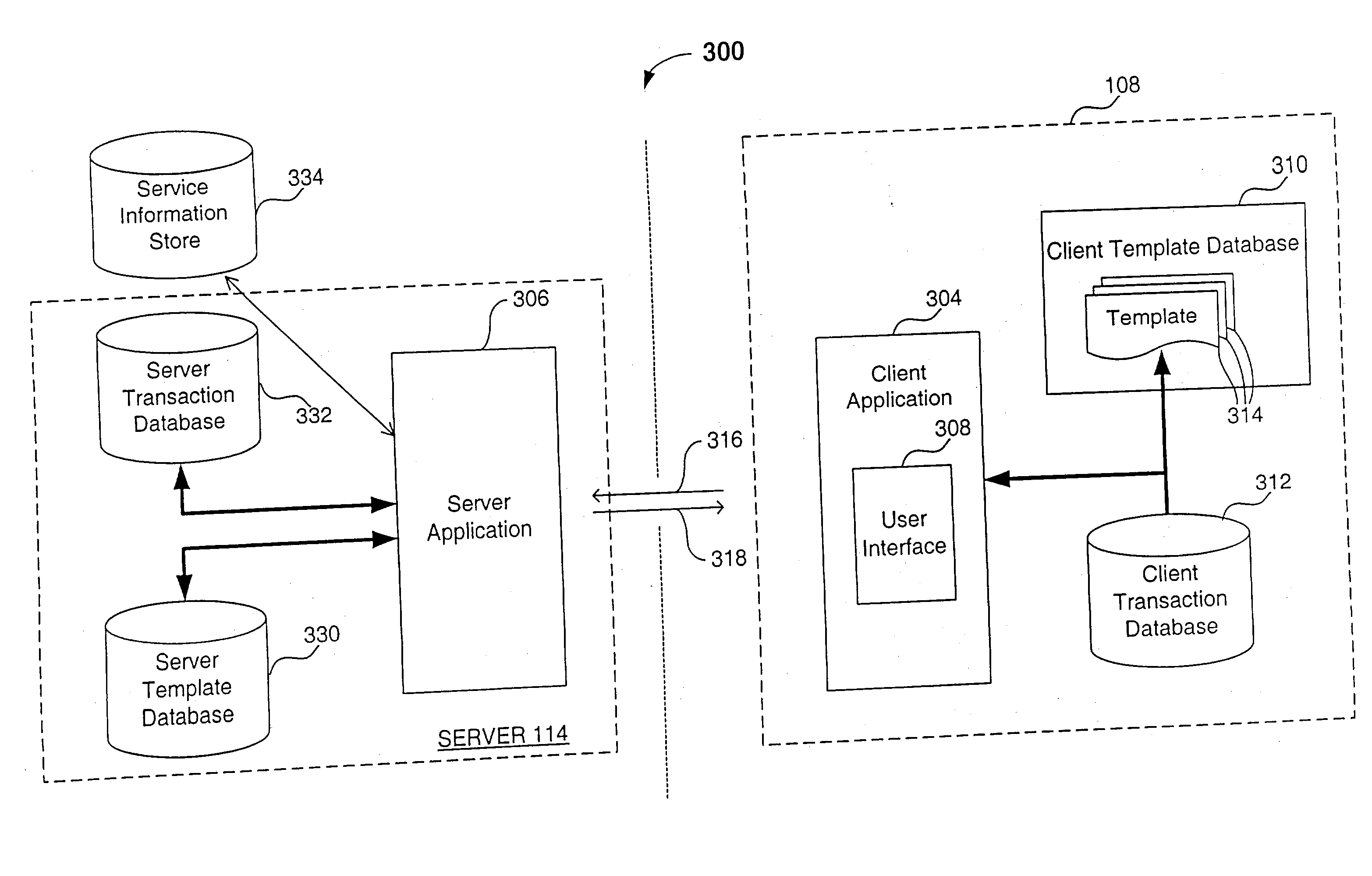
System, method and apparatus for utilizing transaction databases in a client - server environment
InactiveUS20030046291A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData fieldTransaction data
A system, method and apparatus for utilizing transaction databases in a client-server environment. The transaction databases can be used to receive and retain multiple server responses to consecutive client requests regardless of the temporal relationship between the multiple responses and consecutive requests. One method of the invention relates to how a client device displays information. This method is for use in a client-server system including one or more servers and a client device having a client transaction database, a client template database, and a user interface adapted to enable a user to enter requests. The method includes the steps of receiving a user request from the user via the user interface and retrieving a template from the client template database based on the user request. The template includes one or more data fields. The method also includes the step of retrieving information from the client transaction database based on the template, wherein the information relates to the one or more data fields of the template. A page is then displayed based on the template and the information relating to the one or more data fields.
Owner:FASCENDA ANTHONY C
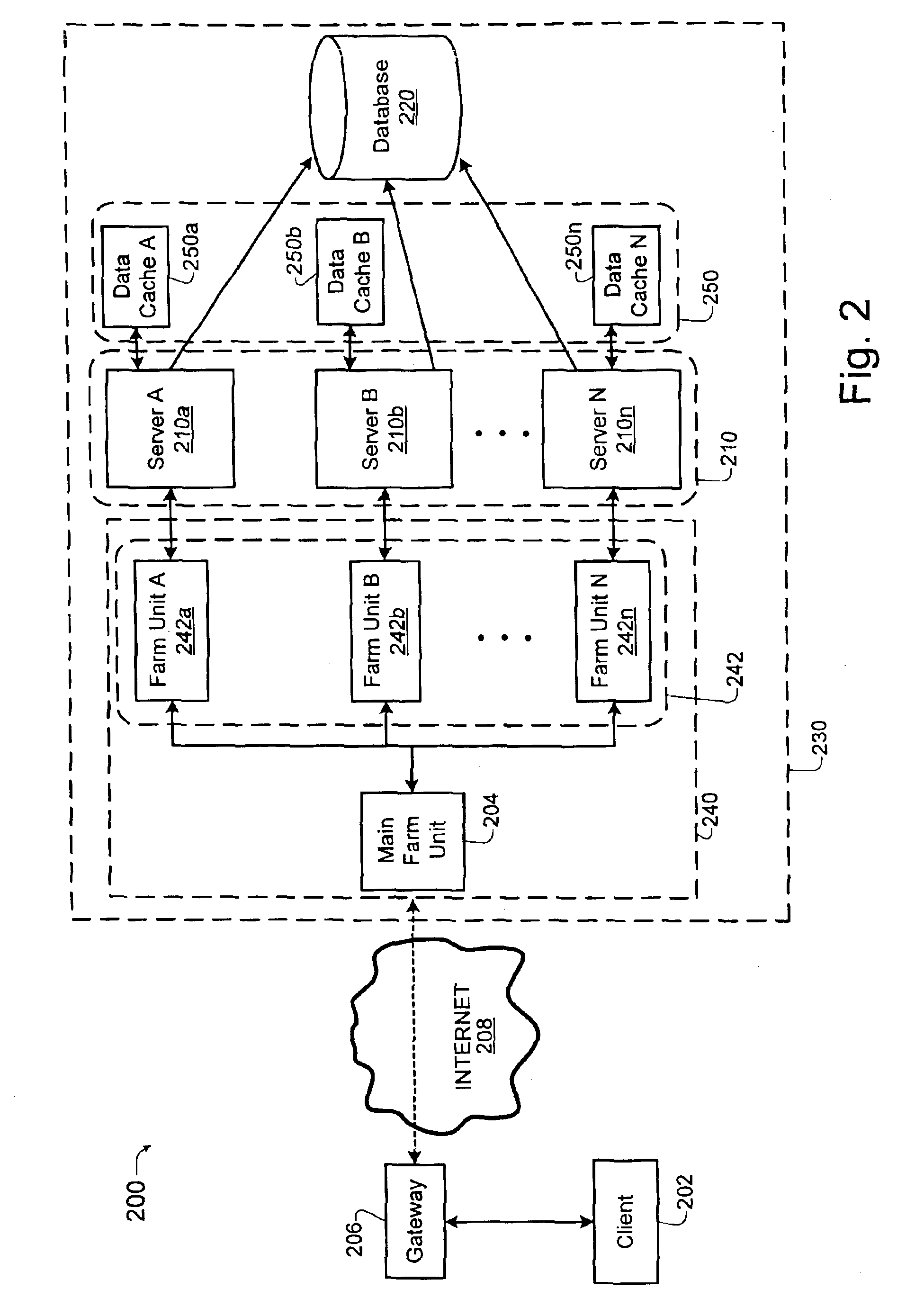
Load balancing technique implemented in a data network device utilizing a data cache
InactiveUS7197547B1Easy to useDigital data information retrievalMultiprogramming arrangementsE-commerceClient-side
A technique for implementing a load balanced server farm system is described which may be used for effecting electronic commerce over a data network. The system comprises a load balancing system and a plurality of servers in communication with the load balancing system. Each of the plurality of servers may include a respective data cache for storing state information relating to client session transactions conducted between the server and a particular client. The load balancing system is configured to select, using a load balancing protocol, an available first server from the plurality of servers to process an initial packet received from a source device such as, for example, a client machine of a customer. The load balancing system is also configured to route subsequent packets received from the source device to the first server. In this way, a “stickiness” scheme may be implemented in the server farm system whereby, once an electronic commerce session has been initiated between the first server and the source device, the first server may handle all subsequent requests from the source device in order to make optimal use of the state data stored in the first server's data cache. Before generating its response, the first server may verify that the state information relating to a specific client session stored in the data cache is up-to-date. If the first server determines that the state information stored in the data cache is not up-to-date, then the first server may be configured to retrieve the desired up-to-date state information from a database which is configured to store all state information relating to client sessions which have been initiated with the server farm system.
Owner:JUNE RAY
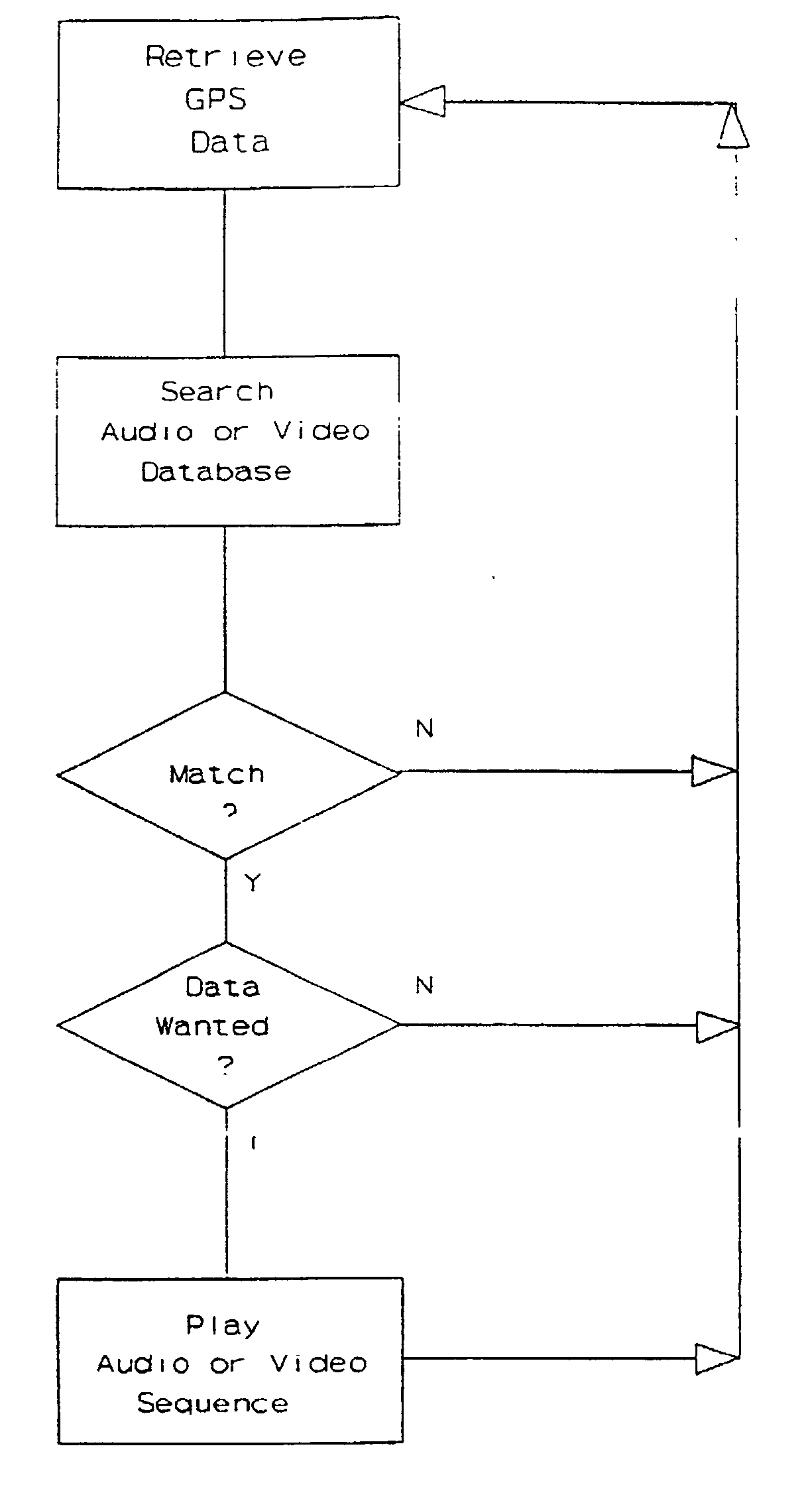
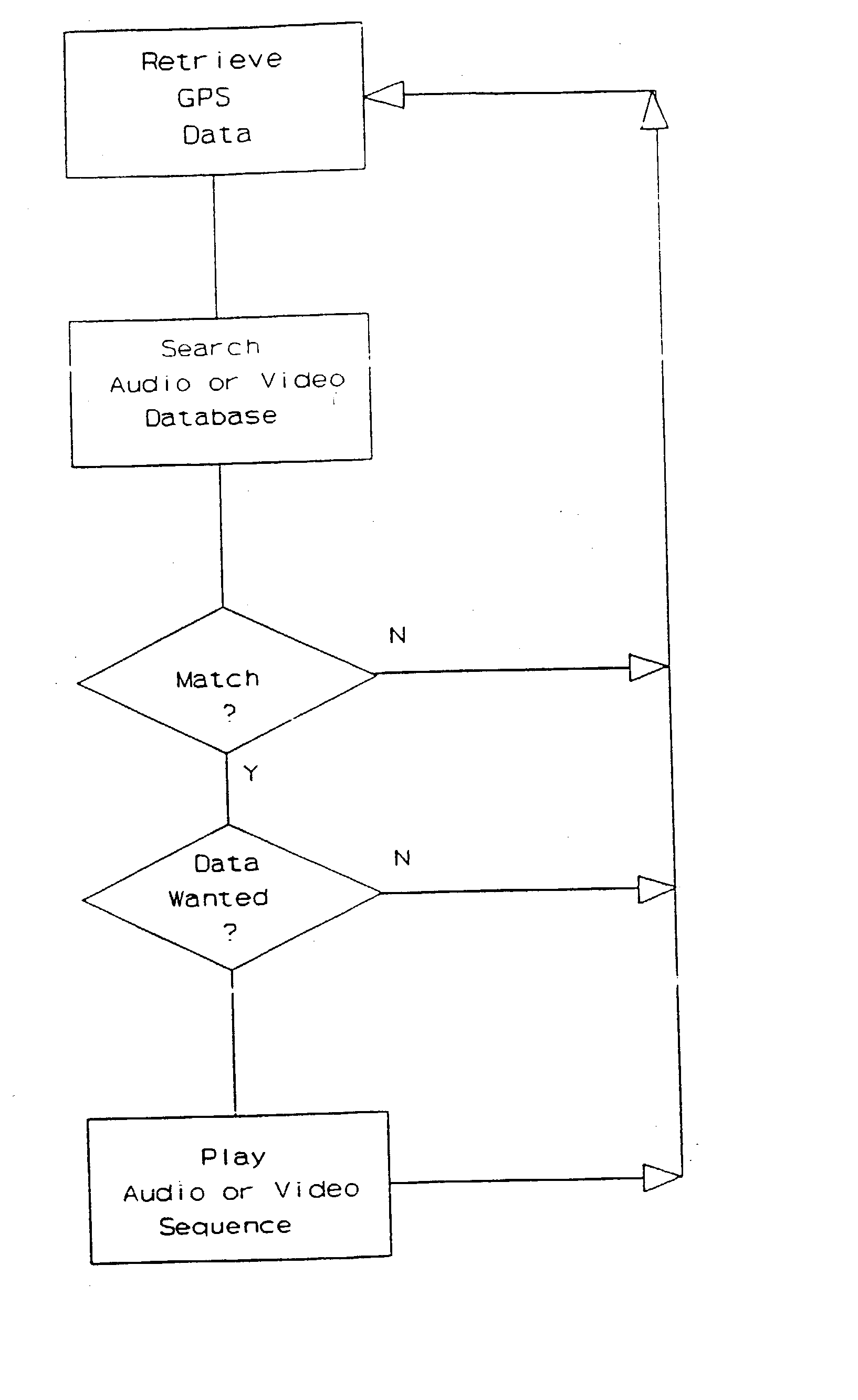
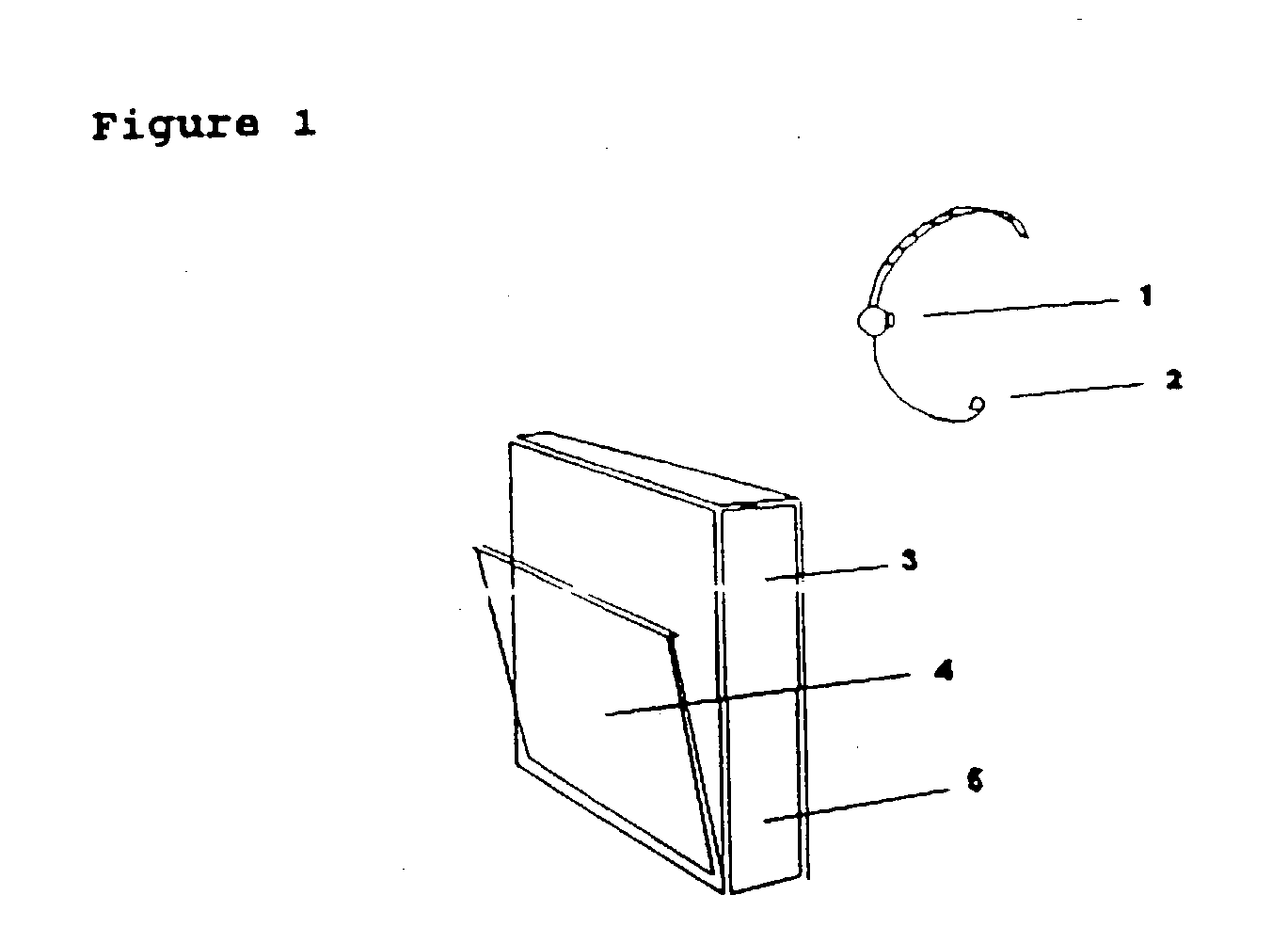
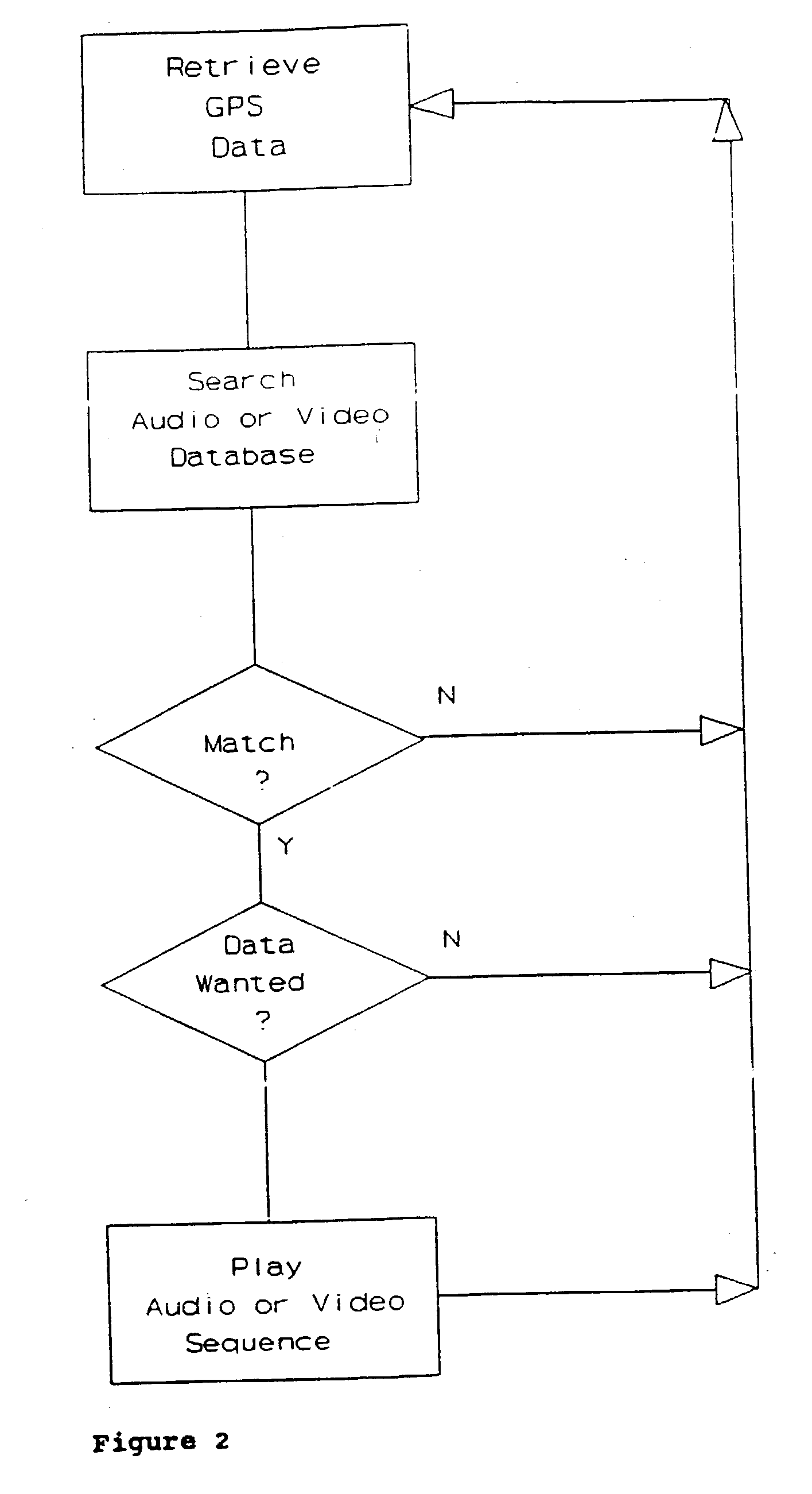
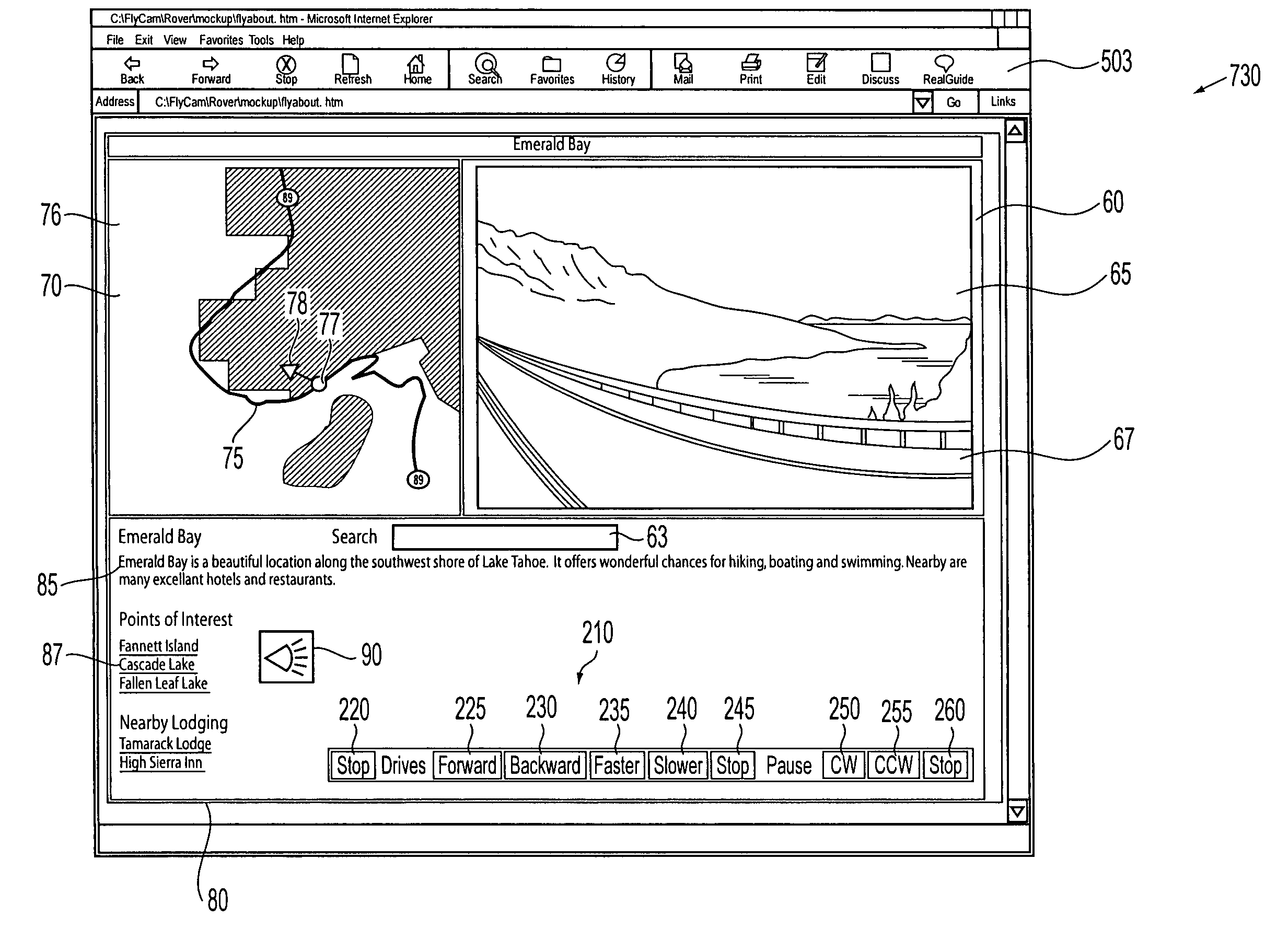
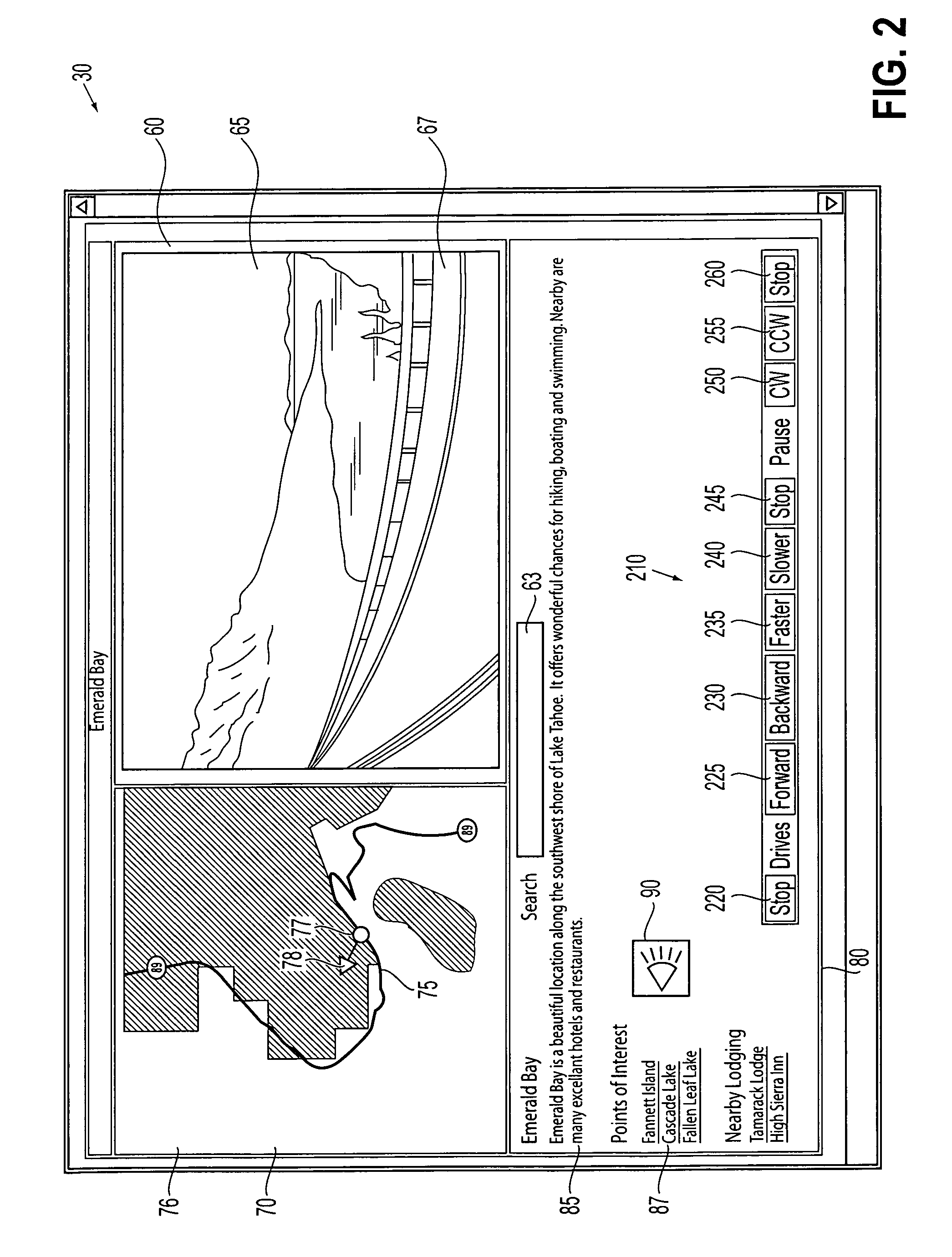
GPS explorer
InactiveUS20020167442A1Instruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsHands freeGlobal Positioning System
This is a portable information system which uses Global Positioning System (GPS) data as a key to automatically retrieve audiovisual data from a database. On a journey the system can automatically identify and describe places of specific interest to the user, landmarks and the history of nearby buildings, or locate hotels, hospitals, shops and products within a radius of the present position. Audible menus and voice command give hands-free and eyes-free control while driving, flying, sailing or walking.
Owner:TAYLOR WILLIAM MICHAEL FREDERICK
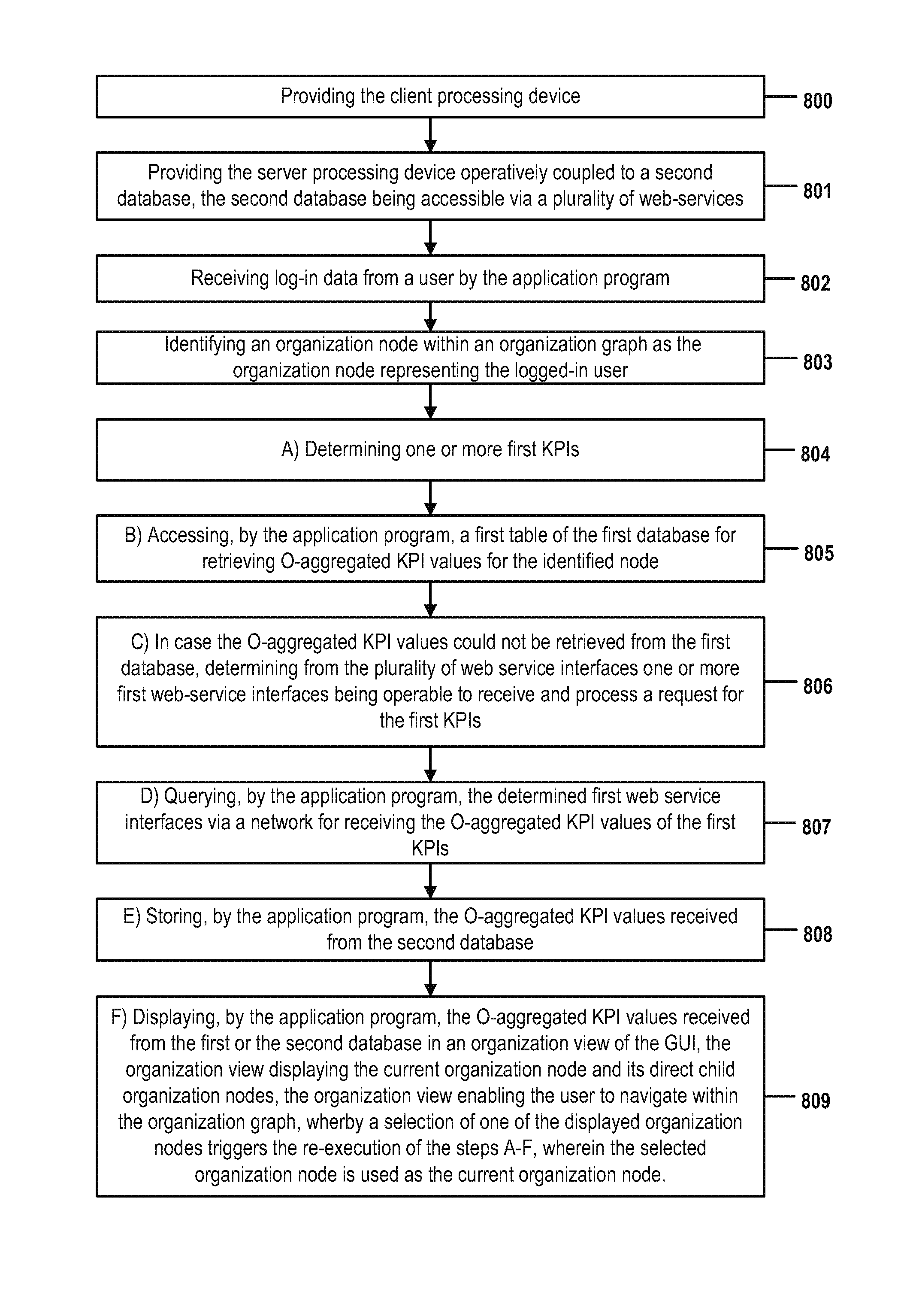
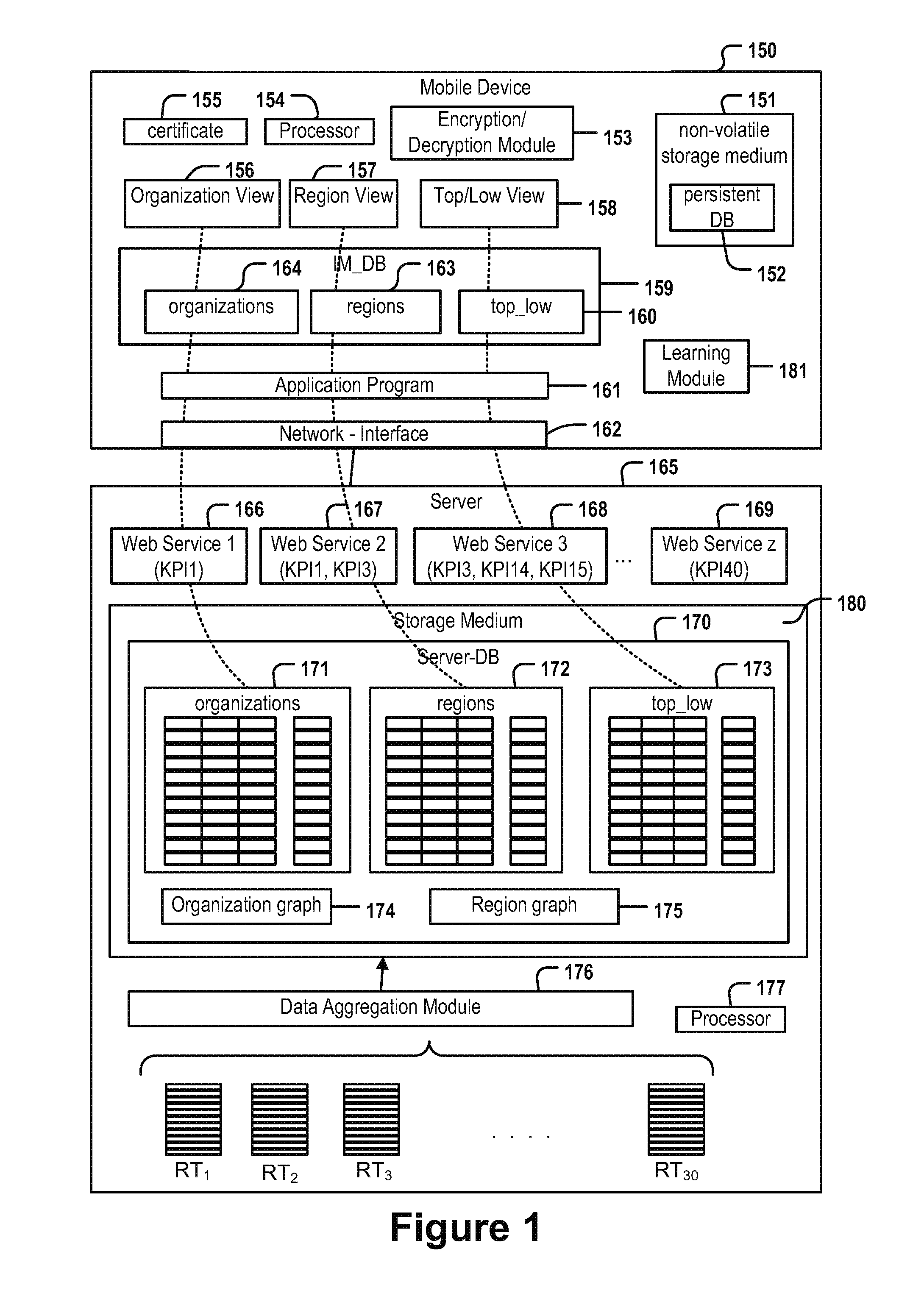
Computer-implemented method for specifying a processing operation
InactiveUS20120162265A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingSubject matterDatabase
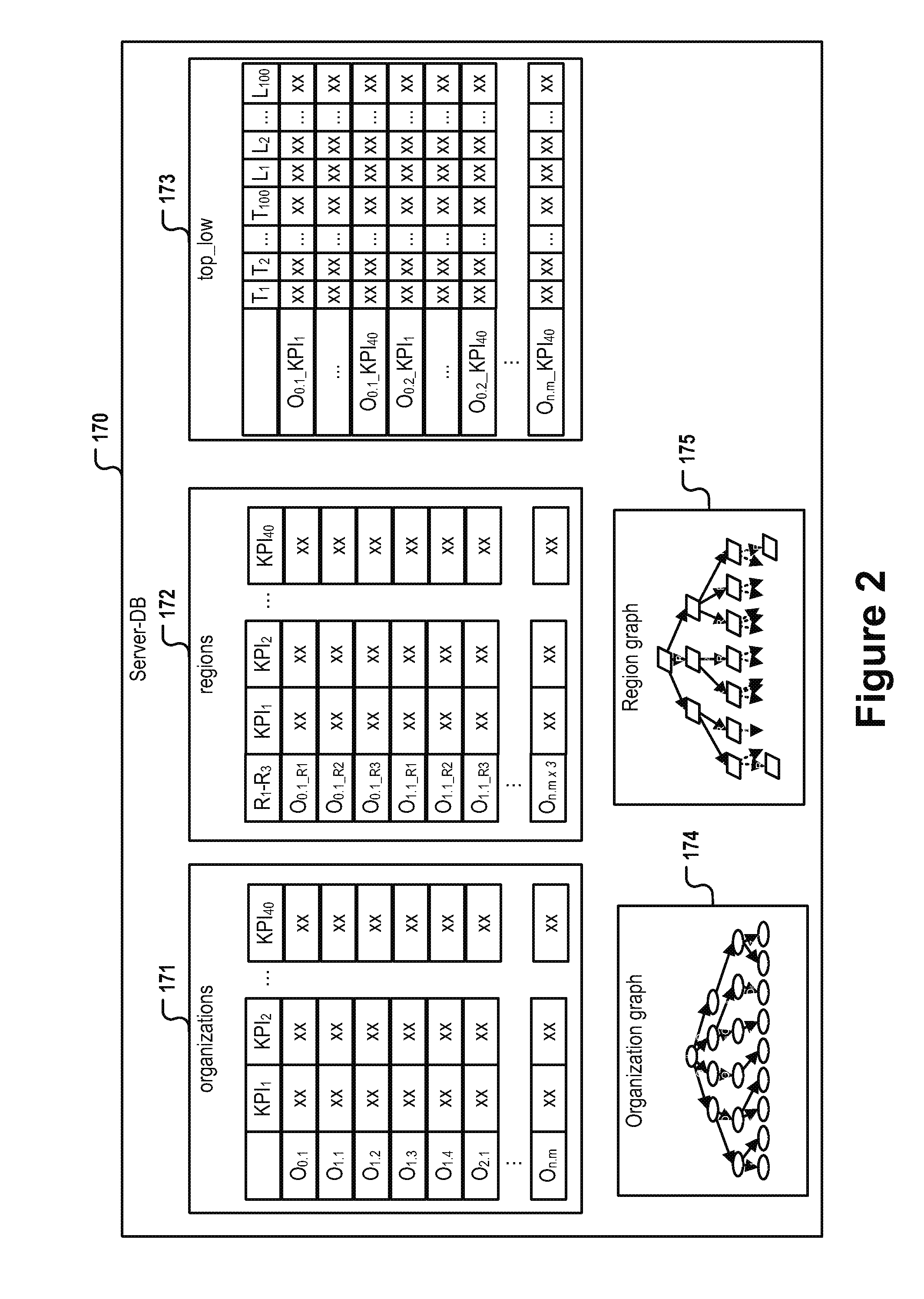
The disclosed subject matter provides for specifying a processing operation by means of a gesture by way of a first and second database, tables, organizational graphs, organizational nodes, KPI-values (including aggregated KPI values, O-aggregated KPI-values), and an application where the application displays the O-aggregated KPI values retrieved from the first database or received from the second database in an organization view of the GUI, the organization view displaying the current organization node and its direct child organization nodes, the organization view enabling the user to navigate within the organization graph, whereby a selection of one of the displayed organization nodes triggers a re-execution wherein the selected organization node is used as the current organization node.
Owner:SOVANTA
Command line interface for creating business objects for accessing a hierarchical database
InactiveUS6141660AData processing applicationsObject oriented databasesCommand-line interfaceEncapsulated data
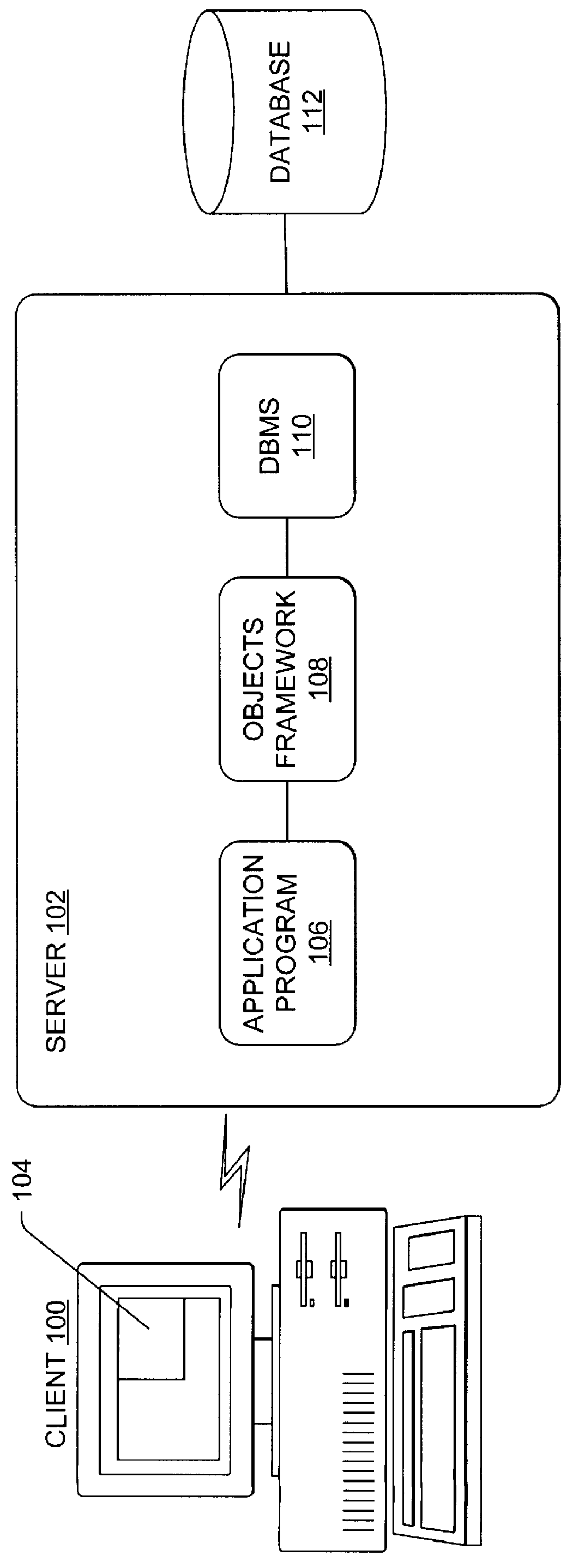
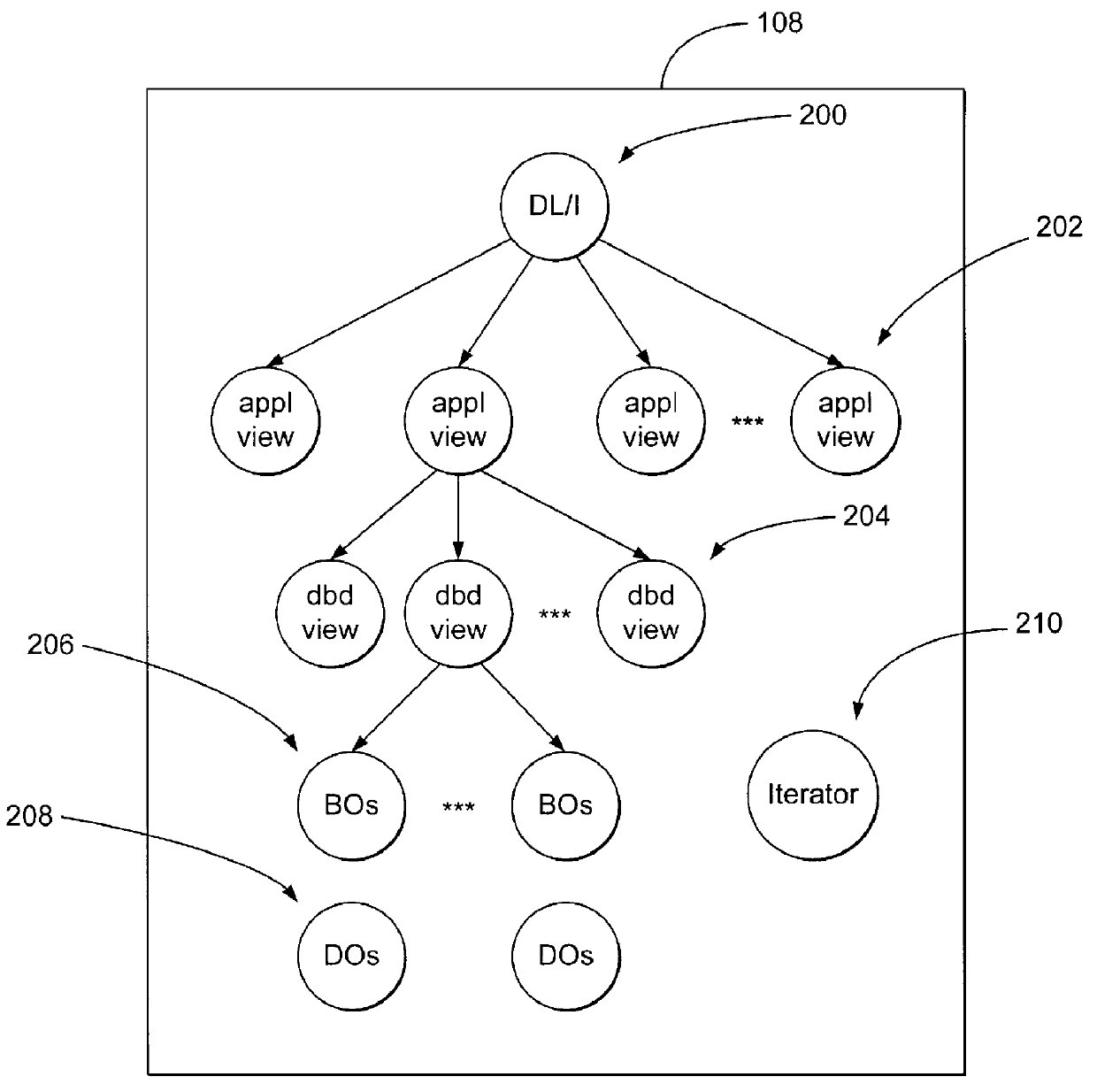
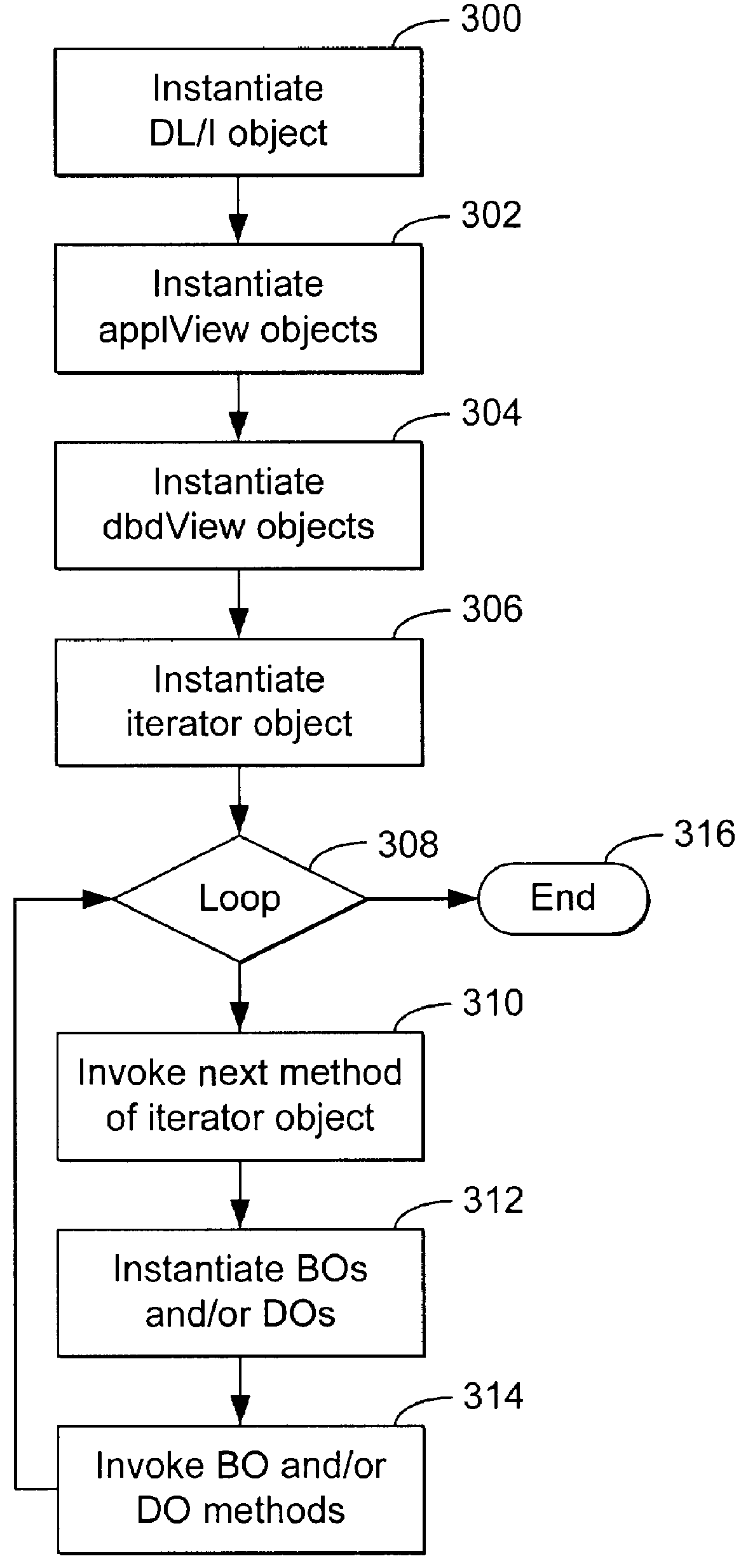
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for generating class specifications for an object-oriented application that accesses a hierarchical database. The class specifications are generated using a command line interface of a class definition tool. A database description and a record layout associated with the hierarchical database are captured and associated to define a specification for the database. Class definitions are then generated from the database specification, wherein the class definitions are instantiated as objects in the objects framework that encapsulate data retrieved from the database.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for information mining and filtering
InactiveUS6915308B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInformation analysisData stream
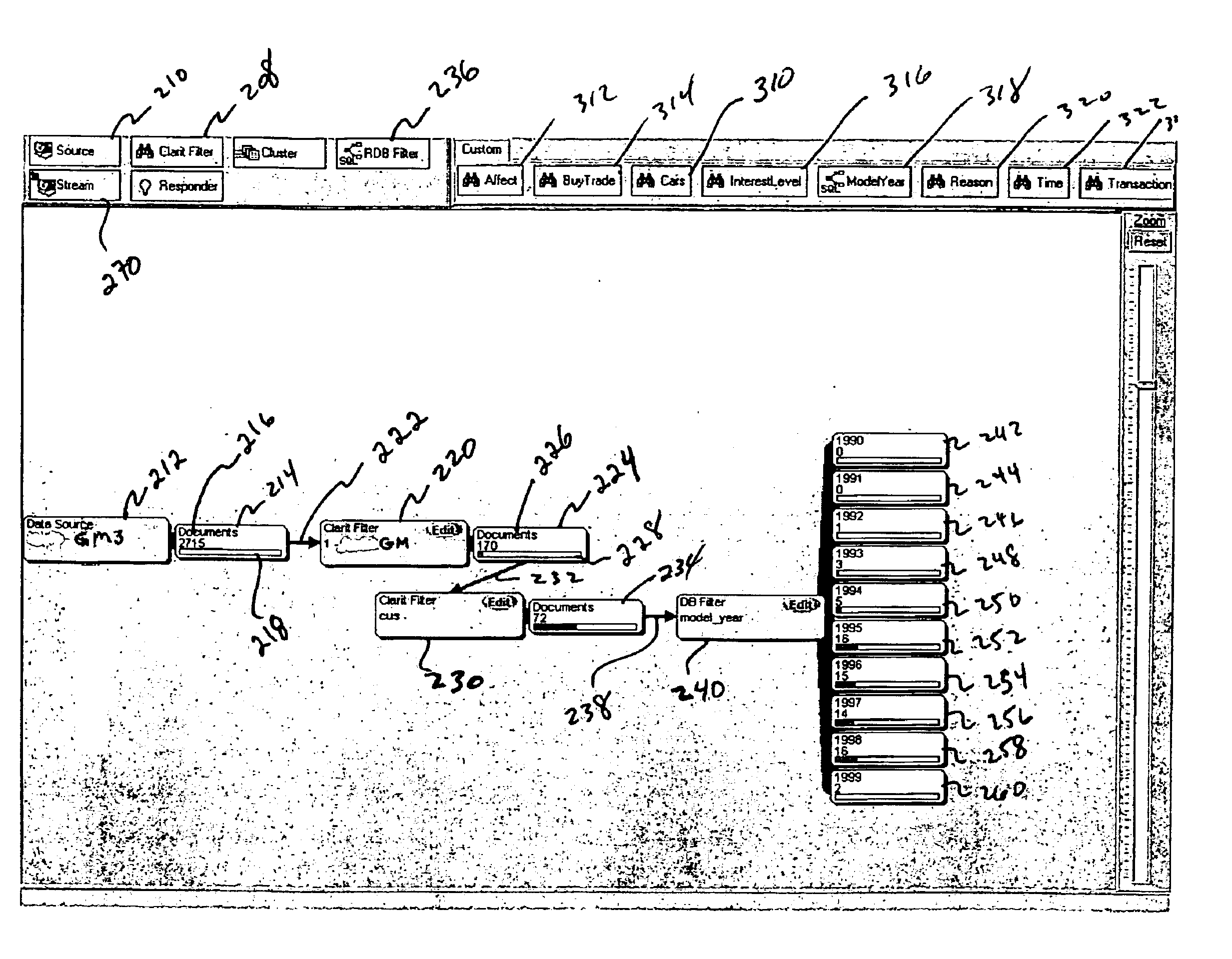
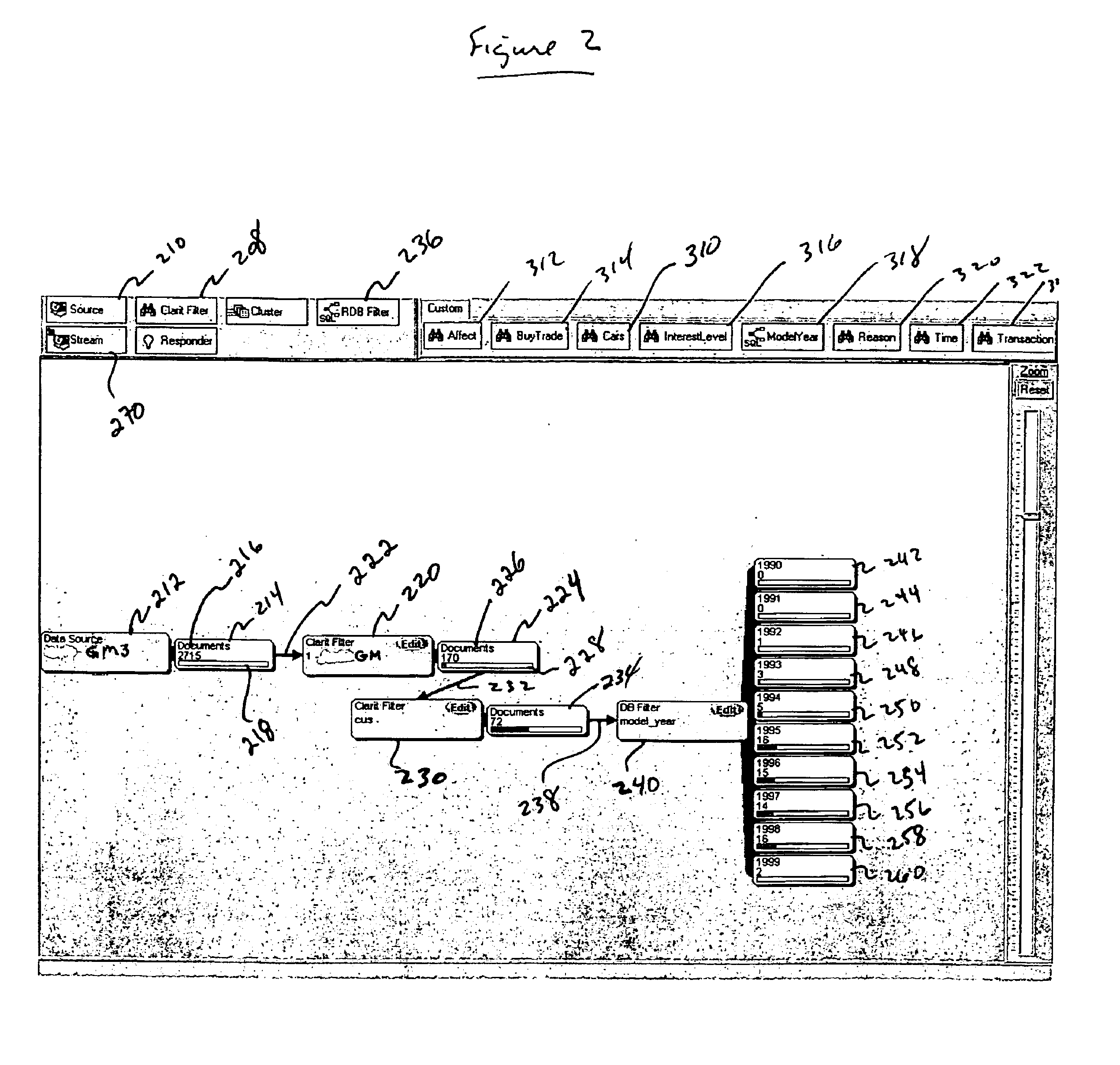
The present invention combines a data processing structure with a graphical user interface (GUI) to create an information analysis tool wherein multiple functions are combined in a network to extract information from multiple data sources. The functional network is created, and graphically represented to the user, by linking individual operations together. The combination of individual operations is not limited by the input or output characteristic of any single operation. The form of the input to or output from a by individual operation, whether from a database or from another operation, is the same. That is, both the input to and the output from an analysis function is a list of document identifiers and corresponding document characteristics. Because the form of the input and output from each operation is the same, arbitrary combinations into of operations may be created. Moreover, functional networks of individual operations can then be used for database retrieval as well as to filter data streams. Furthermore, the user is able to create a visual representation of the structure forming a functional network which may be dynamically updated as new data is added or functions switched in or out. Because, inter alia, the network structure dynamically responds to information as it is presented to the network, the visual representation of the network conveniently provides the user with information concerning the characteristics of the database or stream of data that are substantially unavailable through conventional search, filtering, or clustering techniques alone.
Owner:JUSTSYST EVANS RES
GPS explorer
InactiveUS20040036649A1Instruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsHands freeGlobal Positioning System
This is a portable information system which uses Global Positioning System (GPS) data as a key to automatically retrieve audiovisual data from a database. On a journey the system can automatically identify and describe places of specific interest to the user, landmarks and the history of nearby buildings, or locate hotels, hospitals, shops and products within a radius of the present position. Audible menus and voice command give hands-free and eyes-free control while driving, flying, sailing or walking.
Owner:TAYLOR WILLIAM MICHAEL FREDERICK
Systems and methods for gathering information
ActiveUS7873149B2Interconnection arrangementsSubstation speech amplifiersData libraryDatabase retrieval
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
APU troubleshooting system
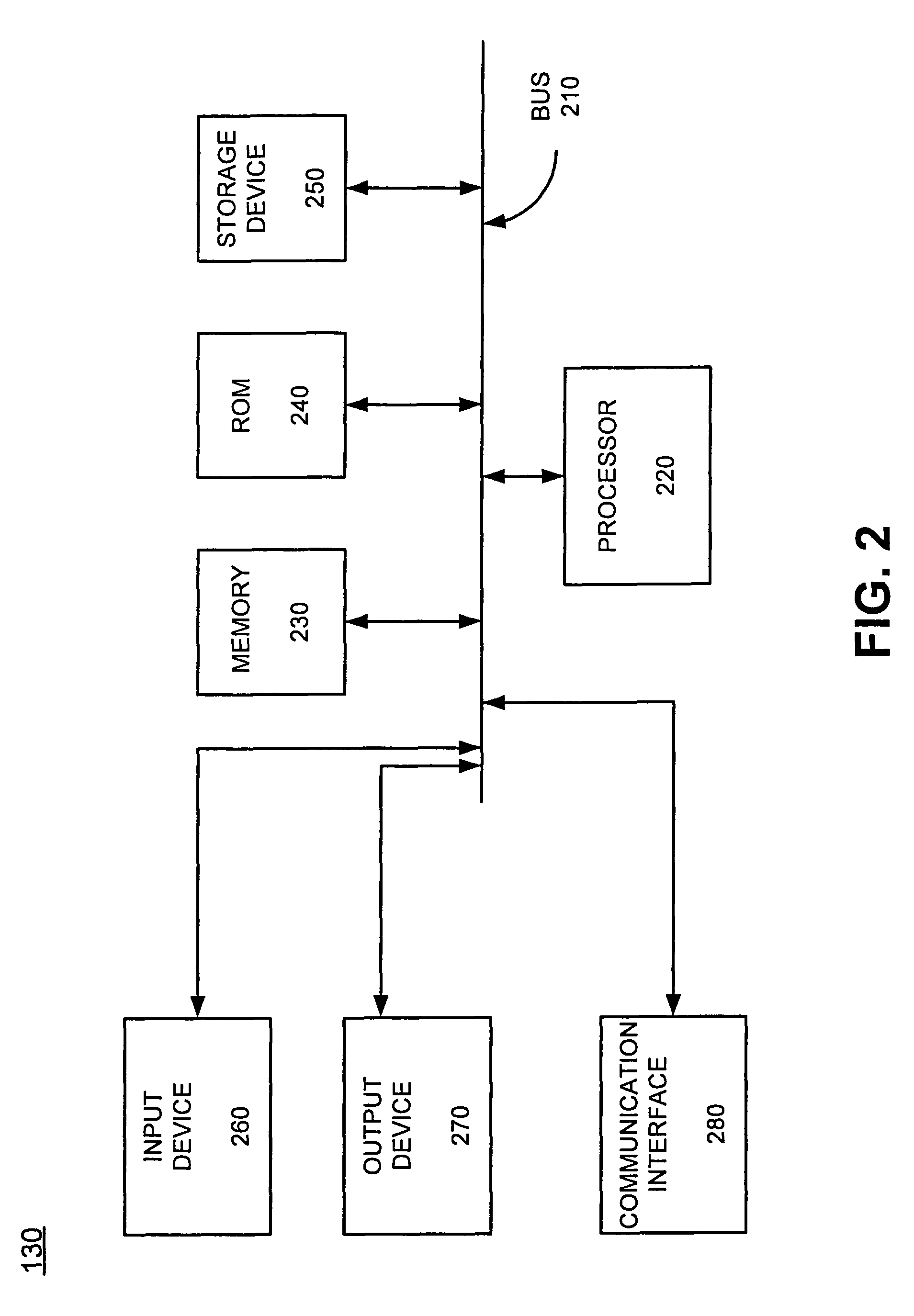
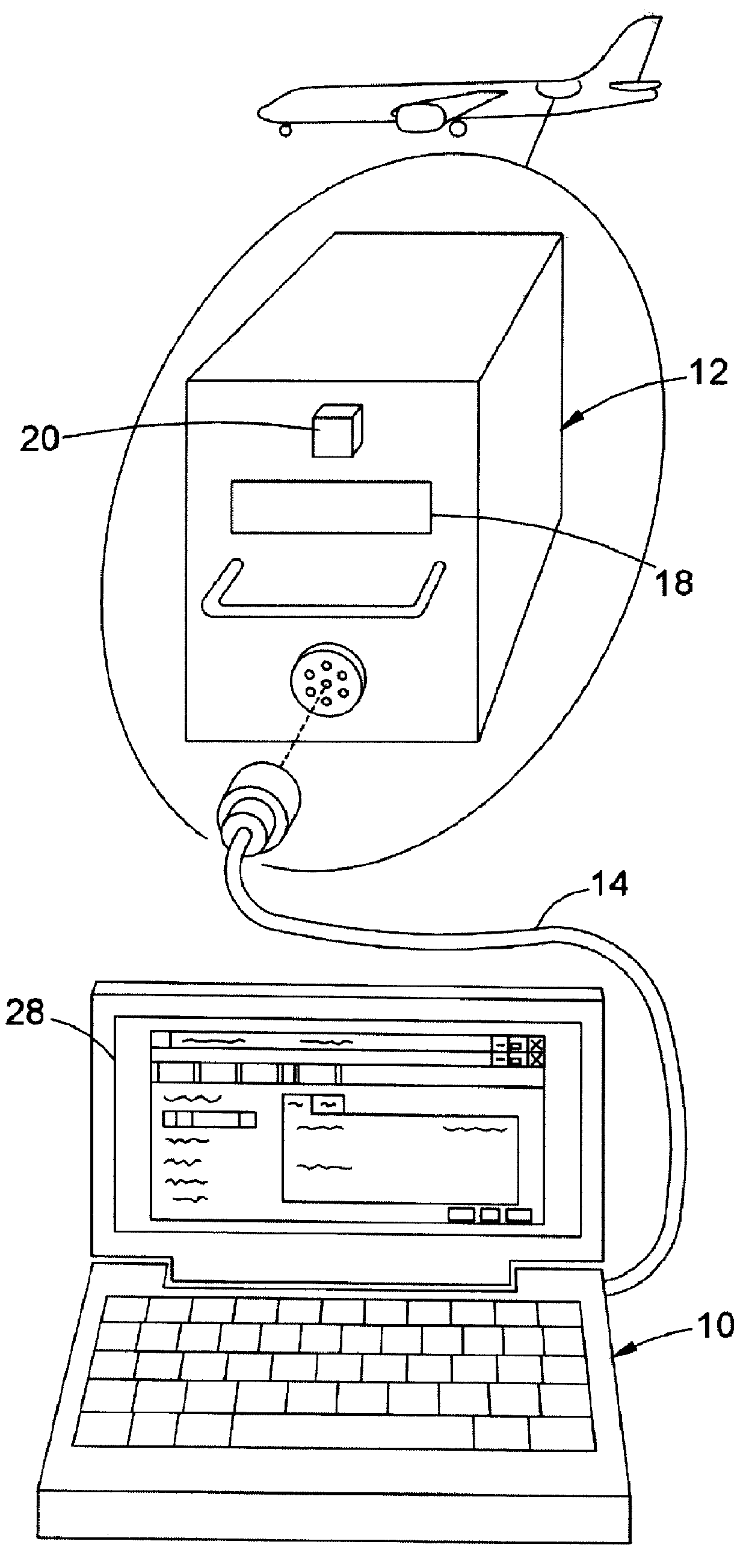
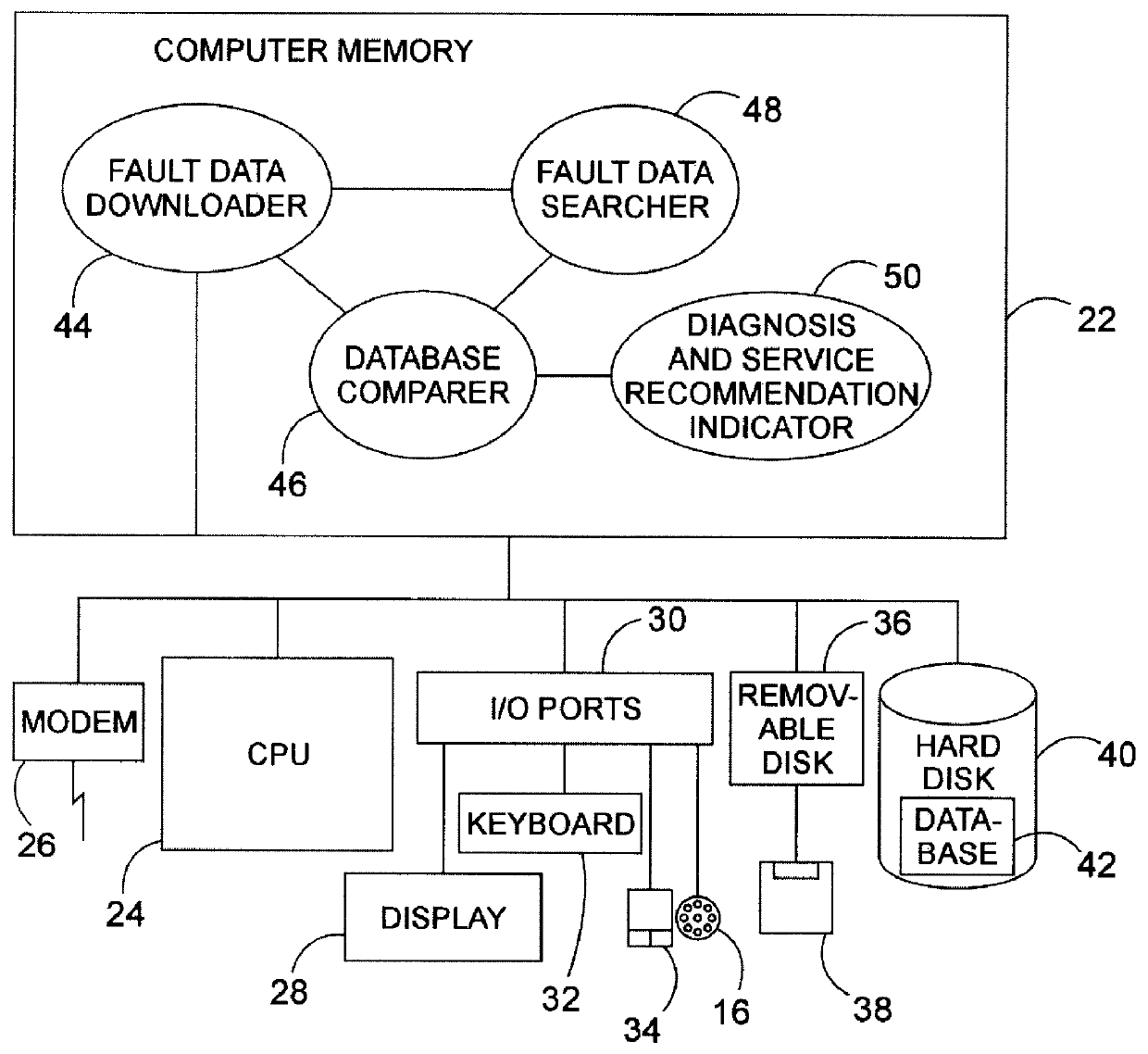
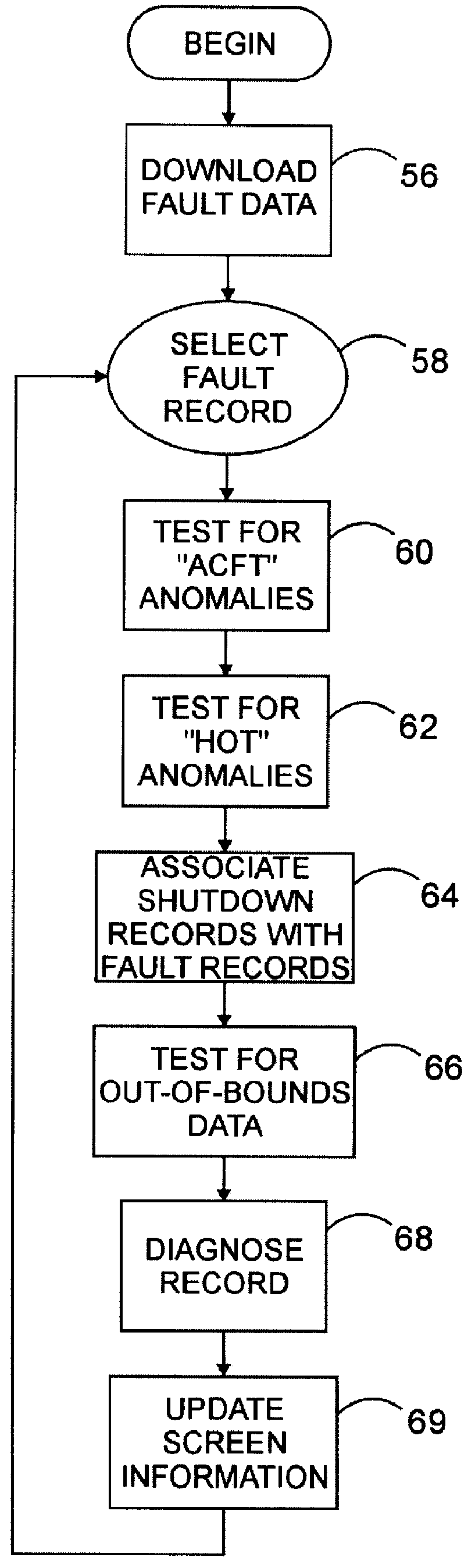
InactiveUS6122575AVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDisplay deviceAuxiliary power unit
A system, method, and computer program product assist a technician in troubleshooting an aircraft auxiliary power unit (APU). A portable computer is couplable of download the fault data captured in a memory of the ECU. The fault data corresponds to one or more instances of APU failure. The computer is further programmed to compare the fault data to predetermined fault patterns stored in a database. Each record of the database has one of the fault patterns, a corresponding fault indication, and a corresponding service recommendation indication. The computer is further programmed so that when a record in which the fault pattern matches the fault data is found, the corresponding fault indication and service recommendation are retrieved from the database and provided to the technician via the computer's display or other suitable output mechanism.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Search engine interface
InactiveUS7089236B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalUser inputUser interface
The invention provides, inter alia, front ends to a database search engine or engines, that process a user query to generate a new search request that will more effectively retrieve information from the database that is relevant to the query of the user. To this end, in one embodiment the systems can be realized as computer programs present to a user interface to a user and which prompt the user to enter one or more key phrases that are representative of a user search request or user query. The user interface can collect the key phrases provided by the user and can analyze these key phrases to identify at least one meaning that can be associated with this user query. The systems can then process the user query and the identified meaning to generate an expanded search request that can be represented as a boolean search strategy. This boolean search strategy can then be processed to create one or more expanded user queries that can be presented to a search engine to collect from a search engine information that is relevant to the interest of the user.
Owner:CONVERSANT
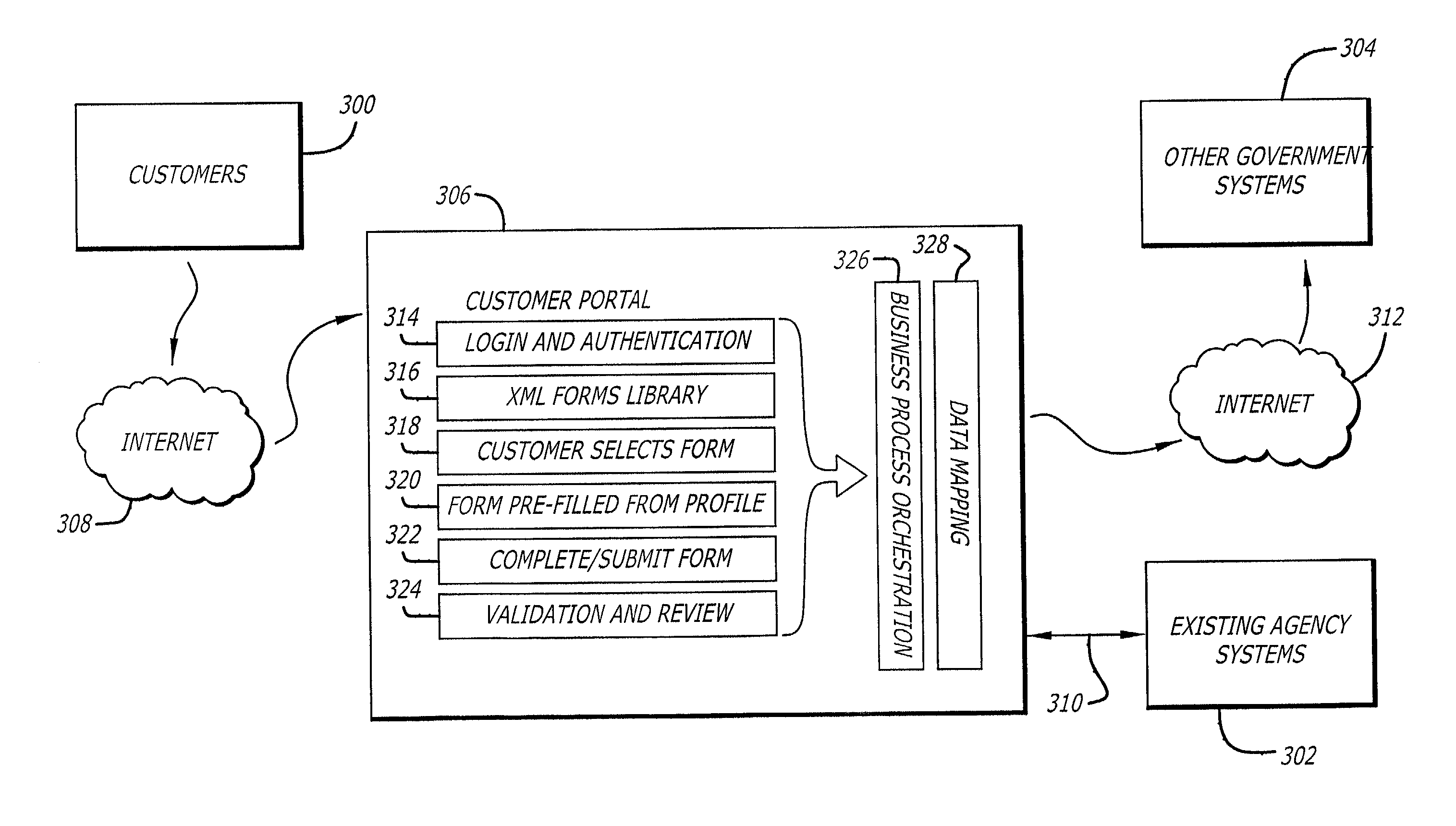
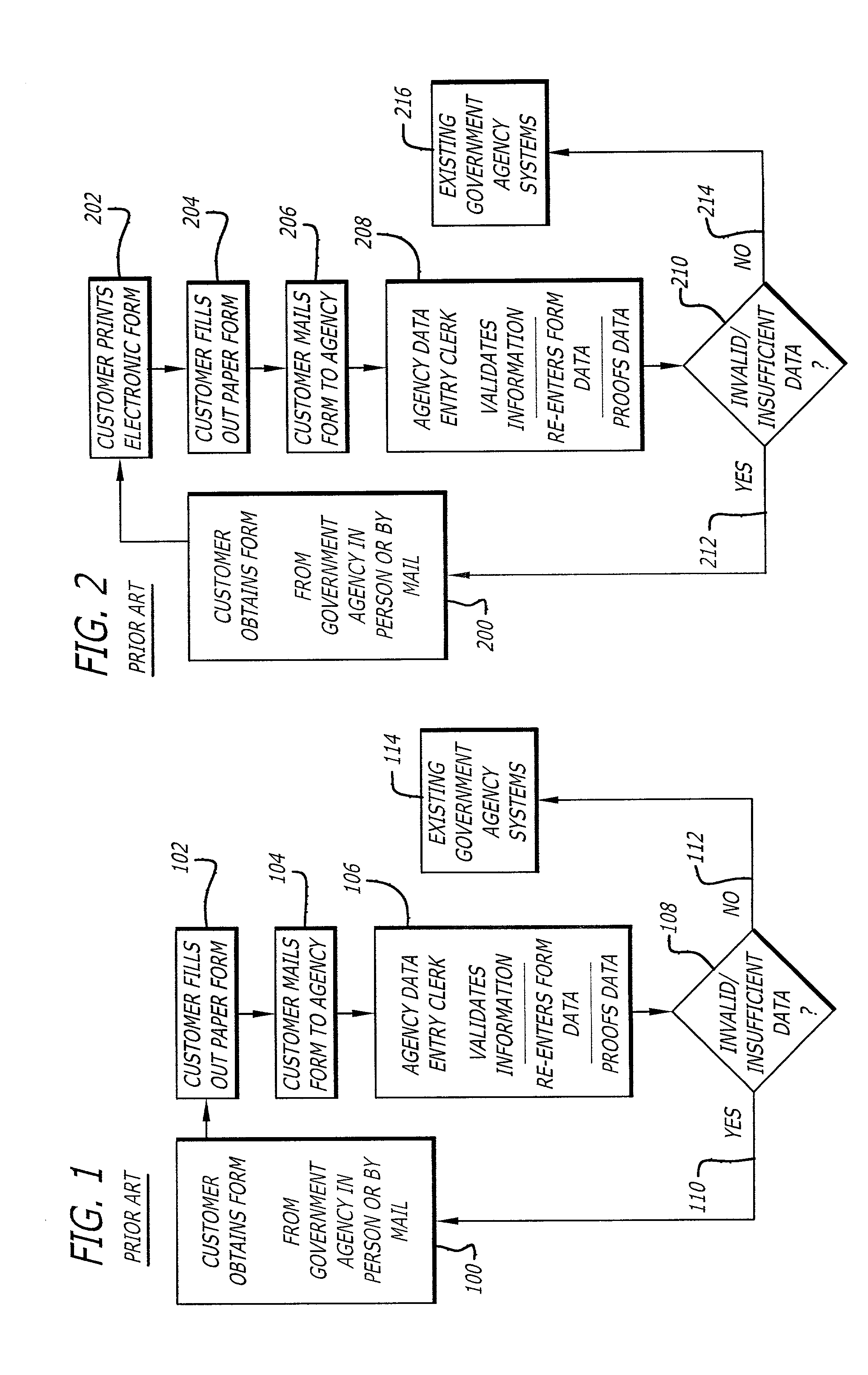
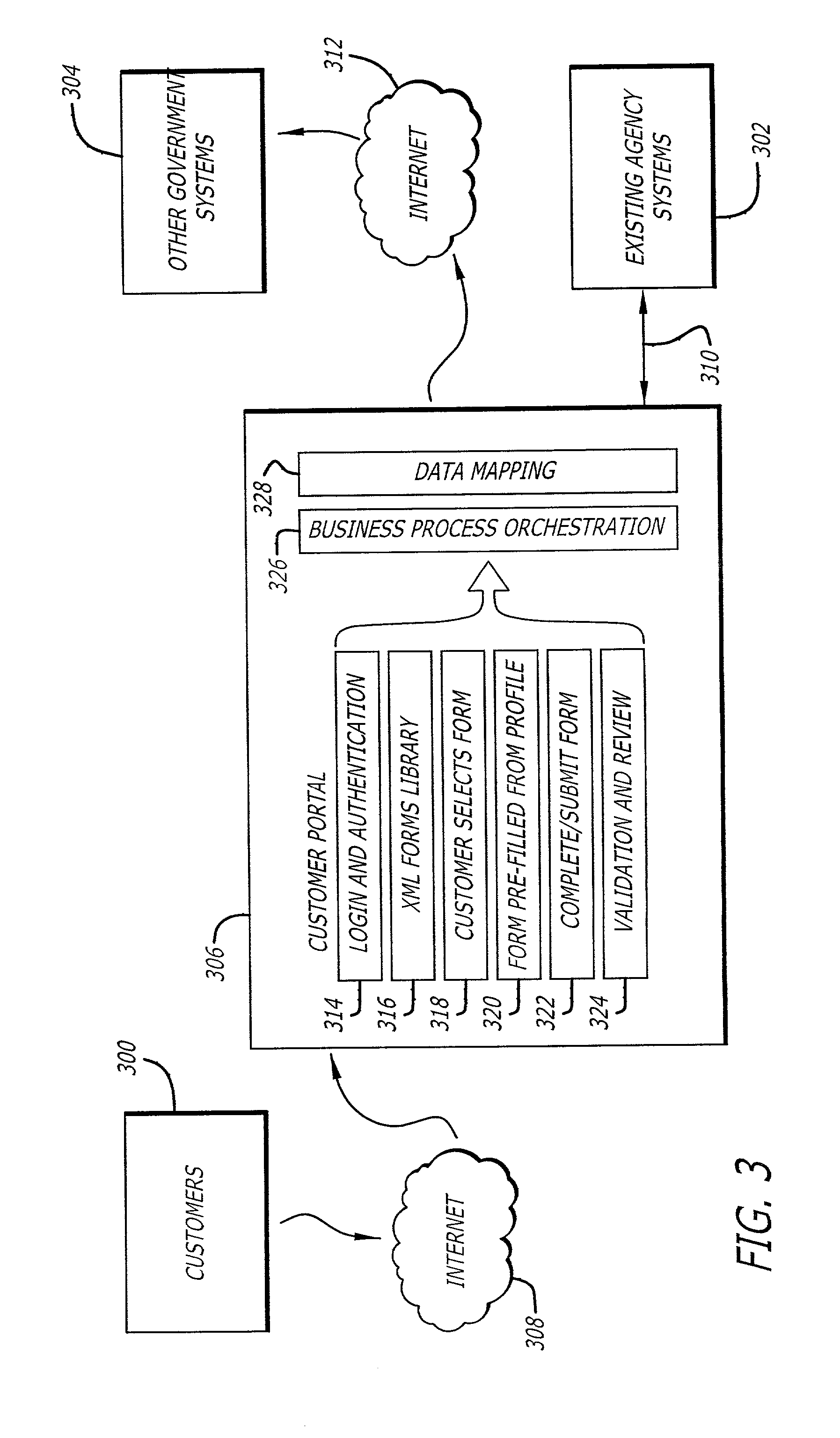
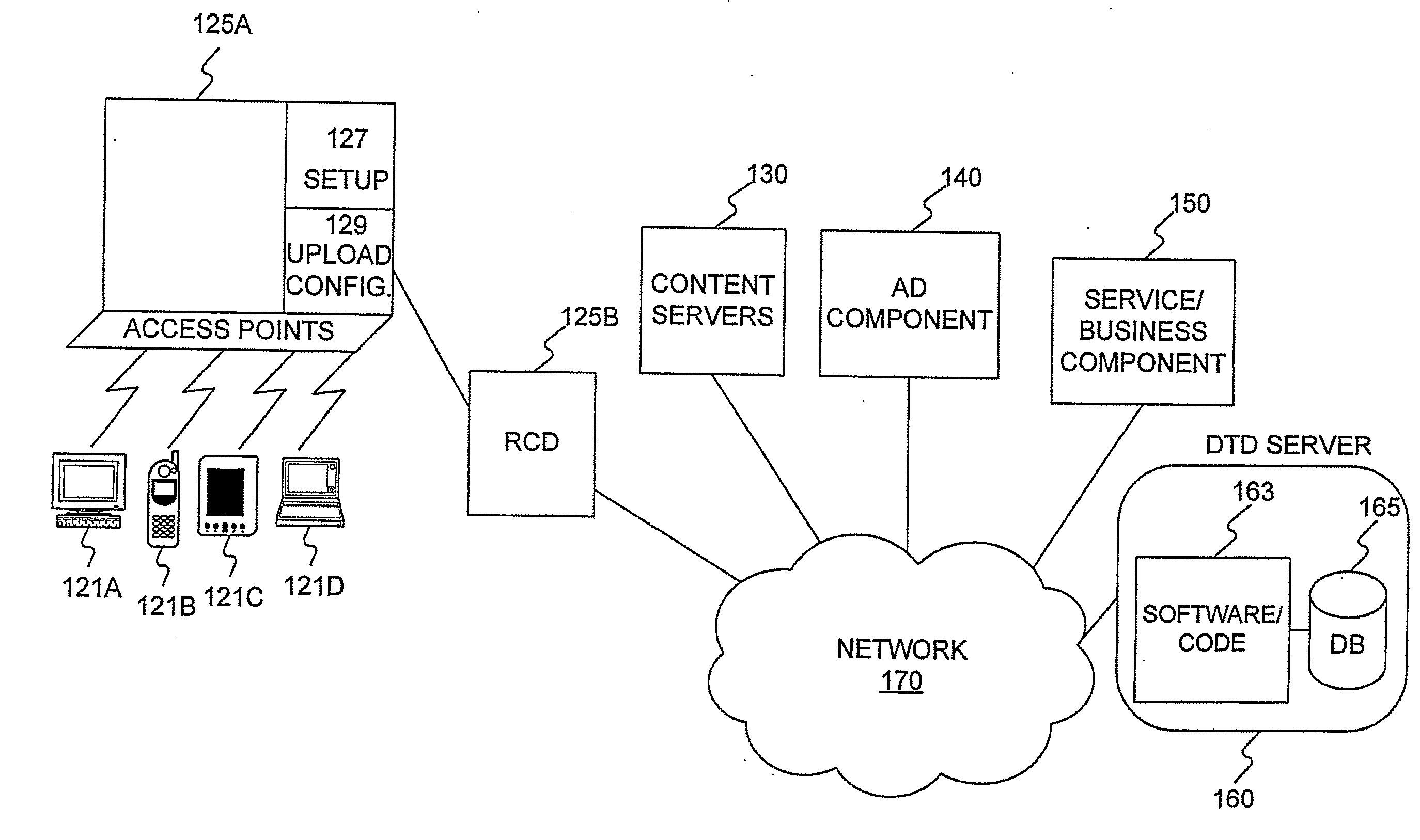
Single access point for filing of converted electronic forms to multiple processing entities
InactiveUS20040205533A1Digital data processing detailsNatural language data processingWeb siteElectronic form
Methods for efficiently publishing electronic versions of traditionally paper-based government forms and utilizing the electronic forms for web-based transactional services are disclosed. Standard paper-based government forms are automatically converted to XML format, including data fields for entry of information by customers. Multiple electronic forms are accessible to the customer at a single access point, such as a web site. At the web site, the customer selects a form for filing with any of a plurality of government agencies. When presented to the customer, the selected form is presented with some of its data fields being pre-populated according to information retrieved from a database and specific to that customer. The customer completes the form, and a back-end system integrated with the web site handles the completed form, determines the appropriate government agency for filing the form, and transmits it as a transaction to the determined government agency.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
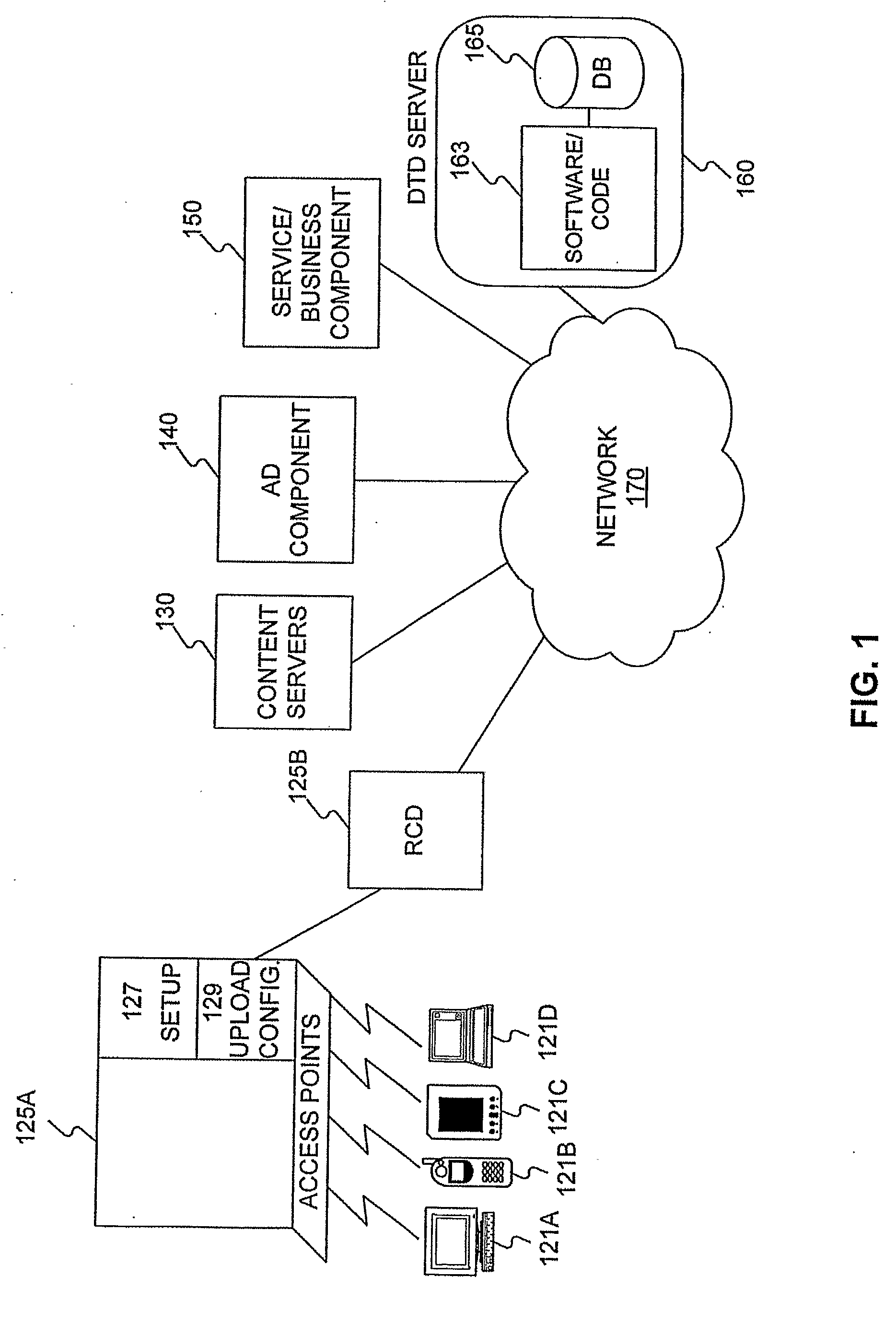
Apparatus, Systems and Methods for Targeted Content Delivery
InactiveUS20080235351A1High bandwidth requirementsIncrease inventoryWeb data retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsRelevant informationThe Internet
According to some embodiments of the present invention, a system, apparatus and method for targeted content delivery is presented. In some embodiments, the method comprises registering users logging-on to a computer network and gathering user-related information from users. Location-centric information for each user logged-on to the network is relayed to a server, and user-profile information for each user is retrieved from a database. User-profile and location-centric information for each user is processed to get targeting information for each user and the targeting information is sent to a content-provider wherein the content-provider uses the targeting information to select content to be displayed to each user. In some embodiments, user-profile and location-centric information may be gathered from wireless access points to which users log-on in order to access the Internet.
Owner:FEEVA
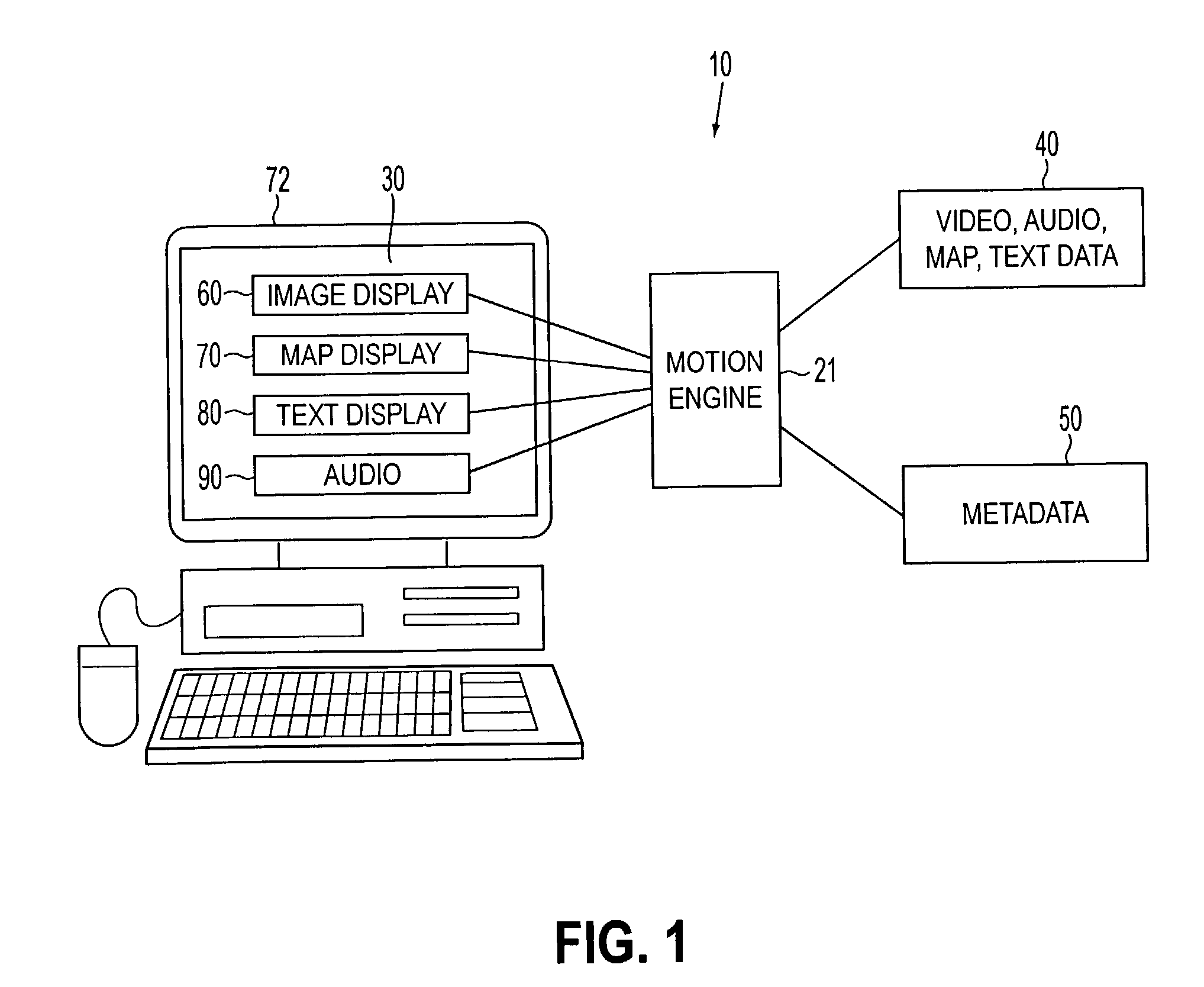
Systems and methods for providing a spatially indexed panoramic video
InactiveUS7096428B2Metadata video data retrievalClosed circuit television systemsComputer graphics (images)User interface
Systems and methods generate a video for virtual reality wherein the video is both panoramic and spatially indexed. In embodiments, a video system includes a controller, a database including spatial data, and a user interface in which a video is rendered in response to a specified action. The video includes a plurality of images retrieved from the database. Each of the images is panoramic and spatially indexed in accordance with a predetermined position along a virtual path in a virtual environment.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Interactive framework for understanding user's perception of multimedia data
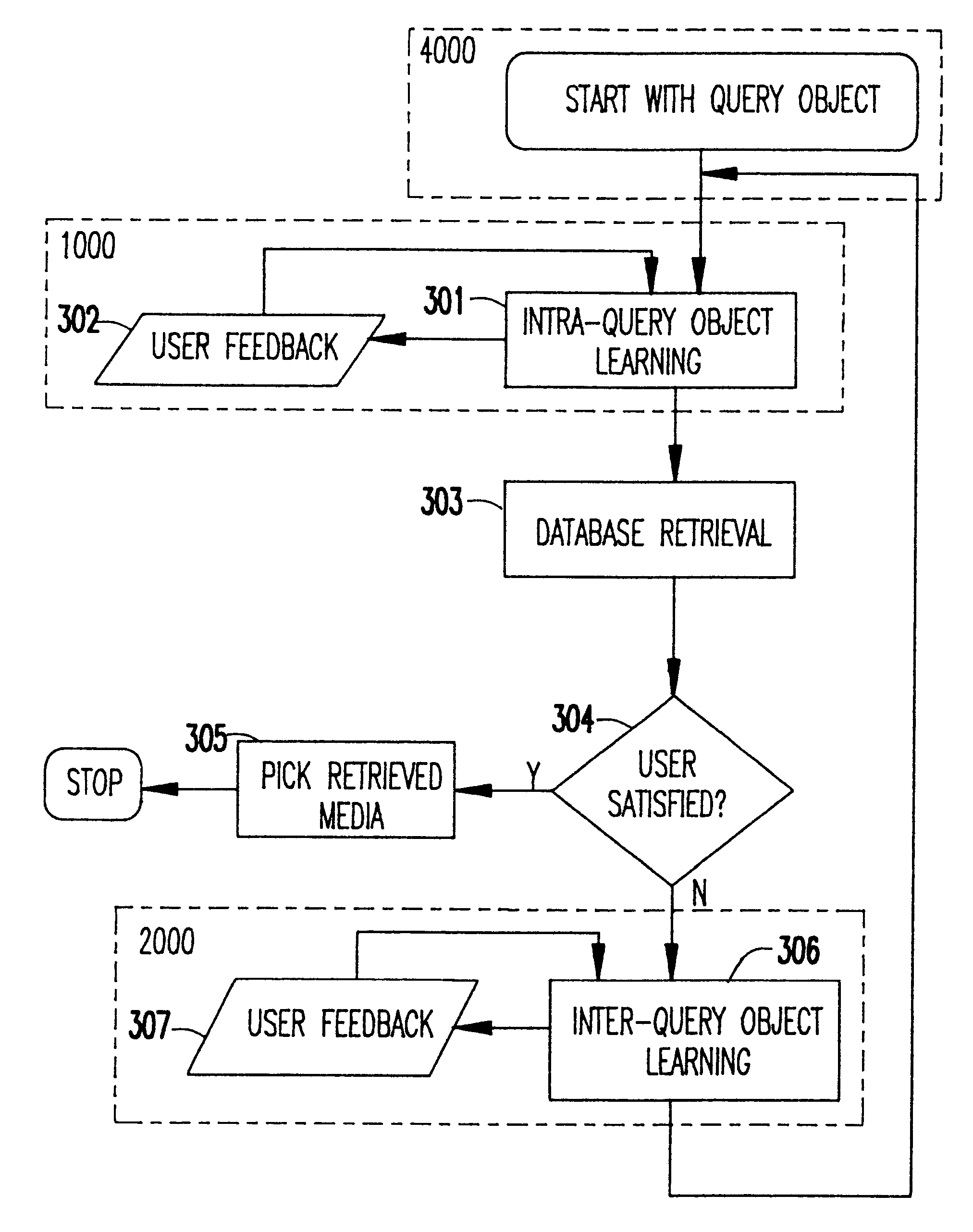
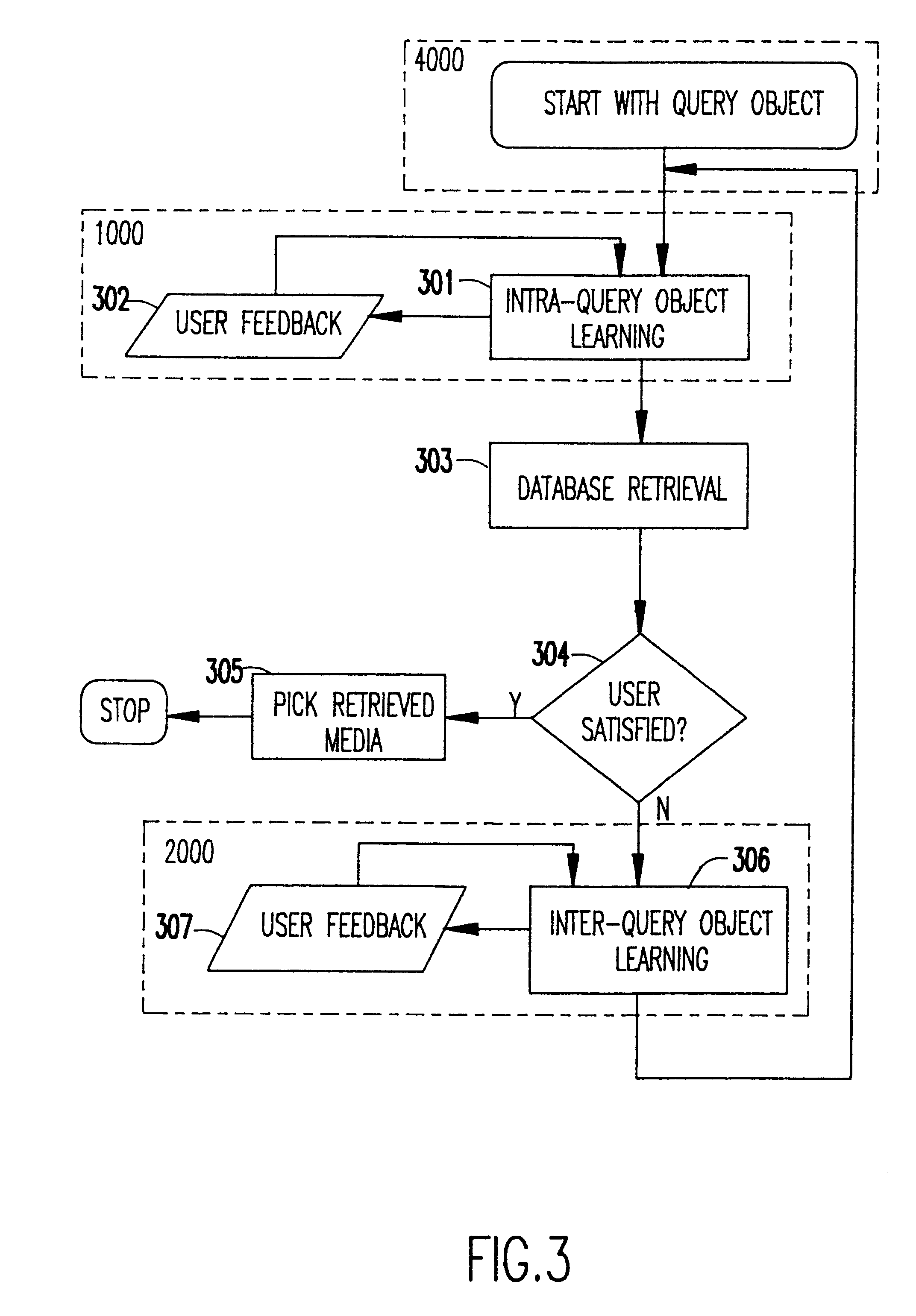
InactiveUS6408293B1Improve approximationReducing being retrievedData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPattern perceptionVideo sequence
A methodology of highly interactive intra-object relevance feedback is used to retrieve multimedia data from a database. The query object could consist of one or more images, images derived from video, a video sequence, or an audio clip. The query is adjusted using the information fed-back by the user about the relevance of previously extracted part(s) from the object itself, such that the adjusted query is a better approximation to the user's perception. The information fed-back by the user during intra-query modification is used for intra-object learning of the user's perception. The refined query is subsequently used for inter-object relevance feedback where data is retrieved from the database based on parameters learnt by intra-query object feedback mechanism, and the user provides feedback by ranking the retrieved objects in order of their relevance to him or her. In the system according to the invention, inter-object learning of user's perception is expedited by utilizing the learnt parameters in the intra-object relevance feedback. Furthermore, the methodology of the invention allows for building refined queries based on part(s) or sub-sequence(s) of the query object rather than the entire object itself, thereby reducing the number of irrelevant objects, retrieved from the database. The methodology allows synthesis and modification of the input query object itself in the event a query object is not directly available, and, also to learn the user's perception.
Owner:PHONENICIA INNOVATIONS LLC SUBSIDIARY OF PENDRELL TECH +1
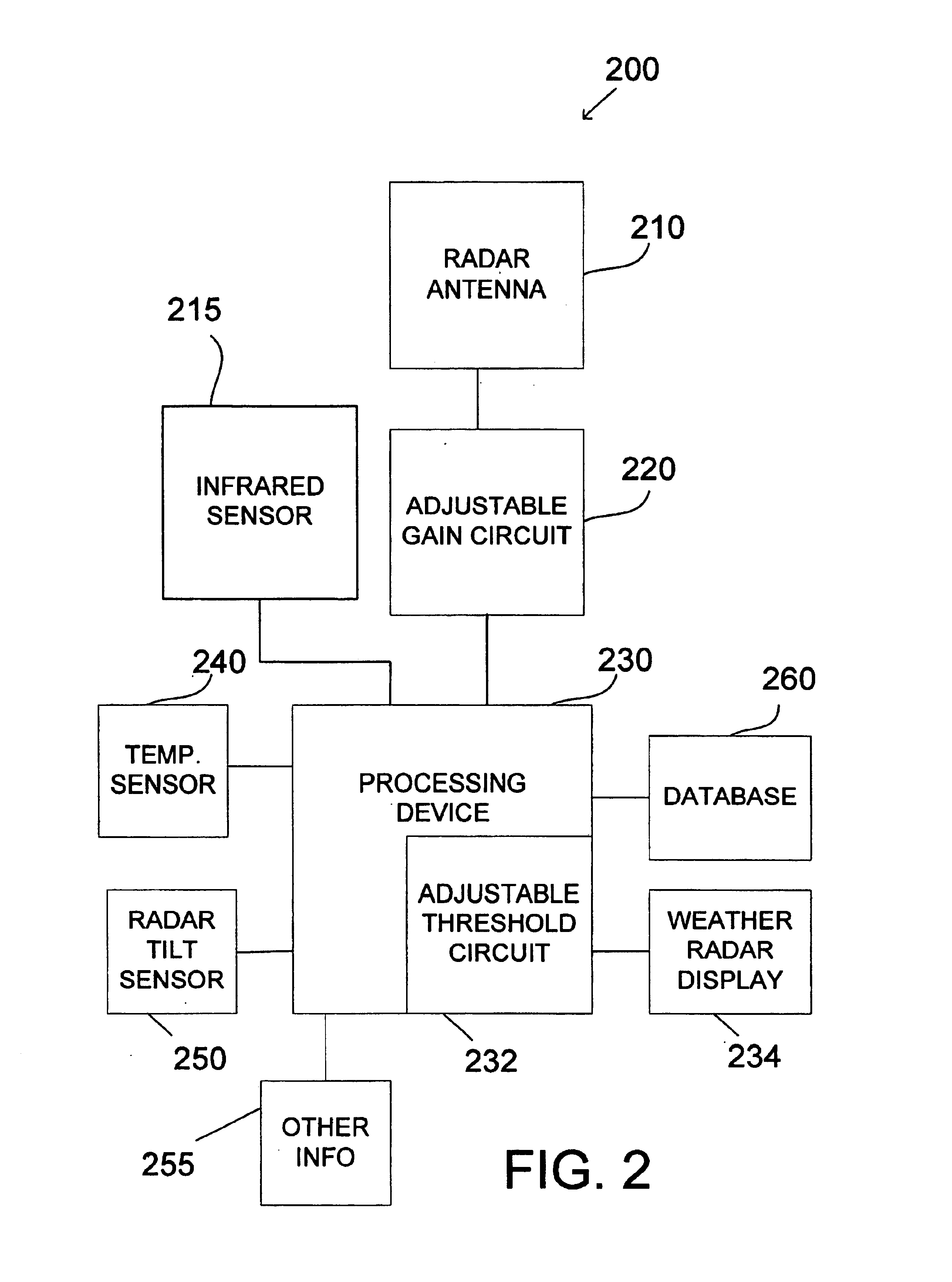
Vertical weather profile display system and method
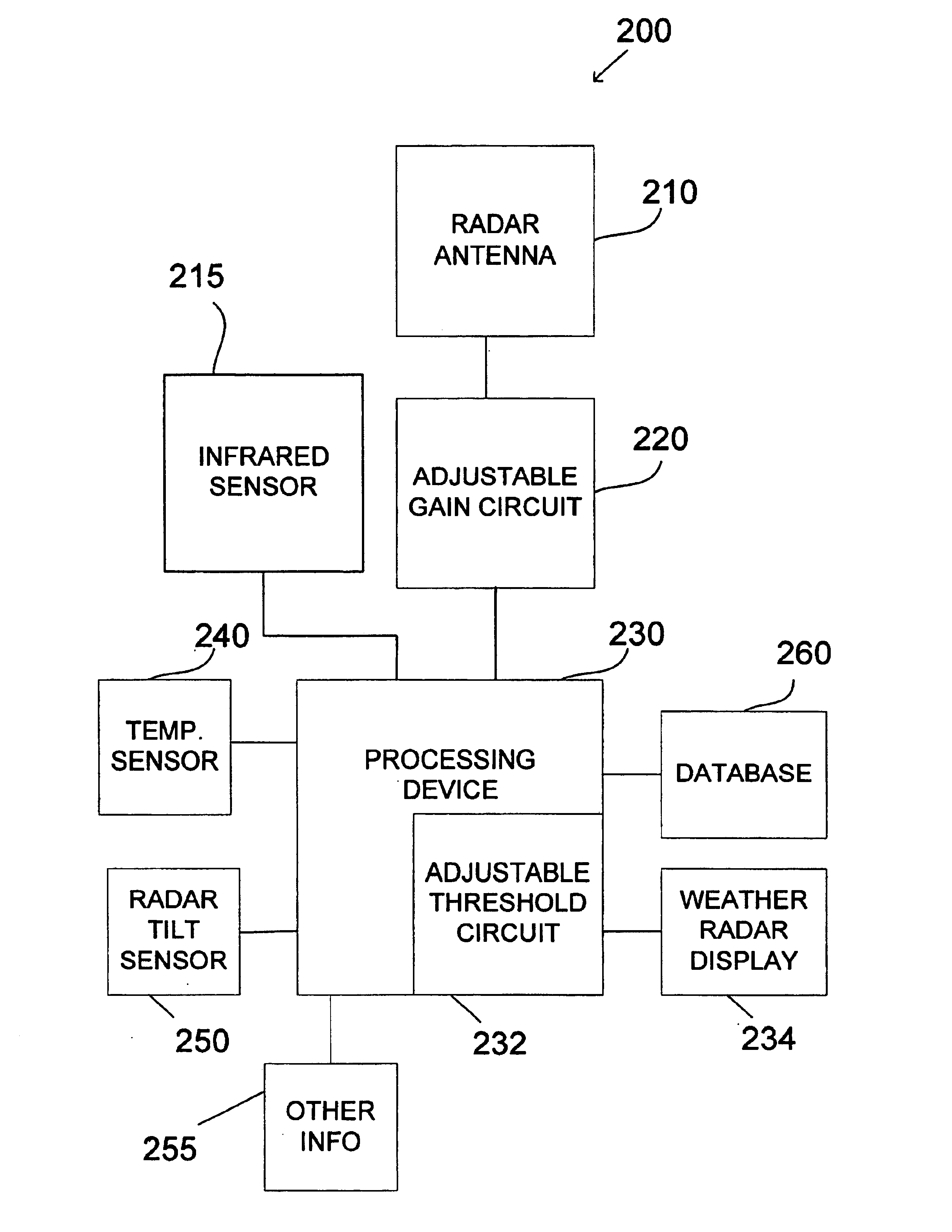
ActiveUS6879280B1Electric/magnetic detectionSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsRadar systems
An aircraft weather radar system is disclosed. The system comprises a radar antenna, aircraft sensors, and a database. The system also comprises a processing device receiving information from the radar antenna and from the aircraft sensors and able to retrieve information from the database. Further, the system comprises a cockpit display coupled to the processing device. The processing device is programmed to estimate storm system characteristics based on the received information from the aircraft sensors and the database and to display the storm system characteristics on a vertical weather profile display using a graphical representation.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
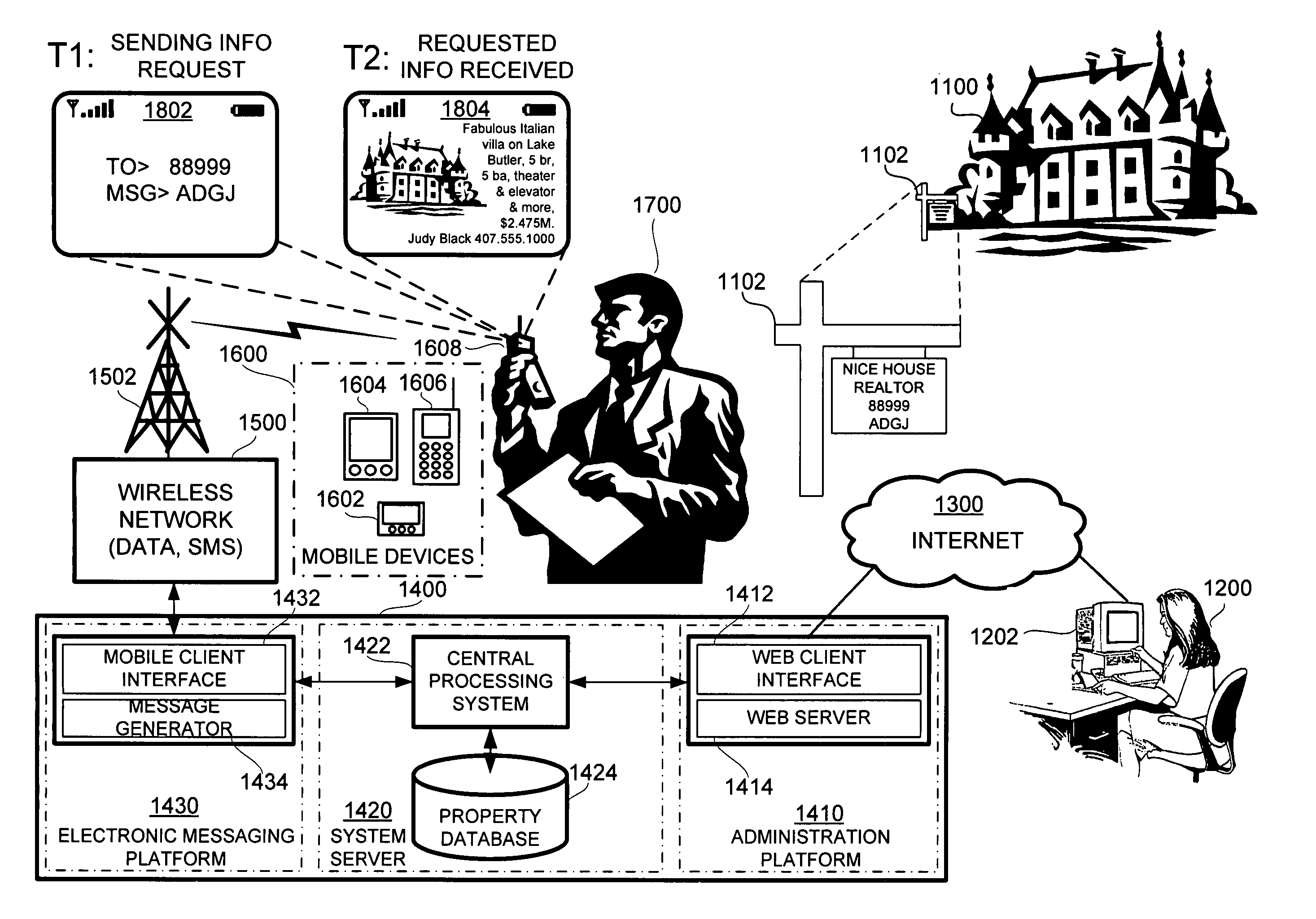
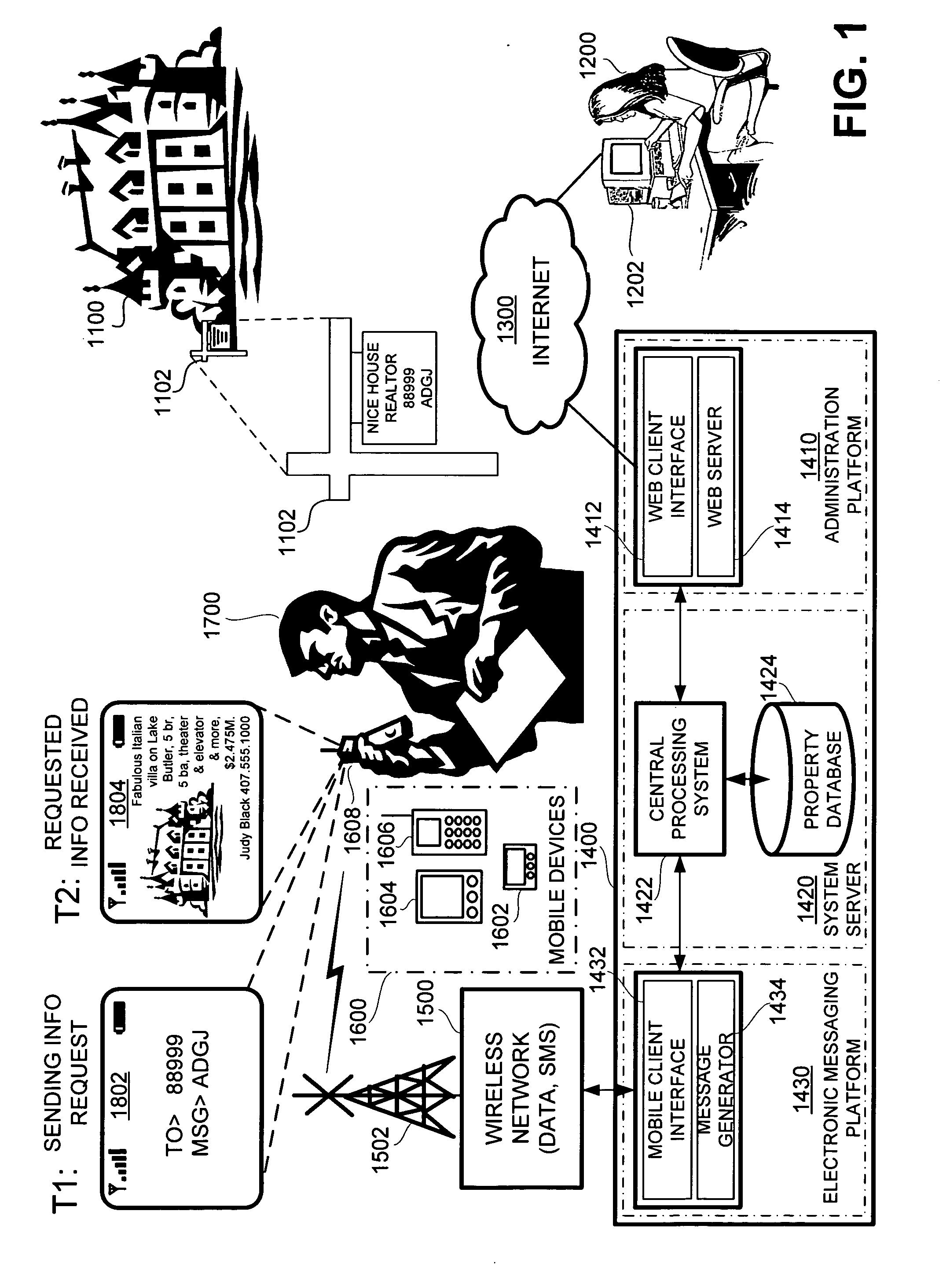
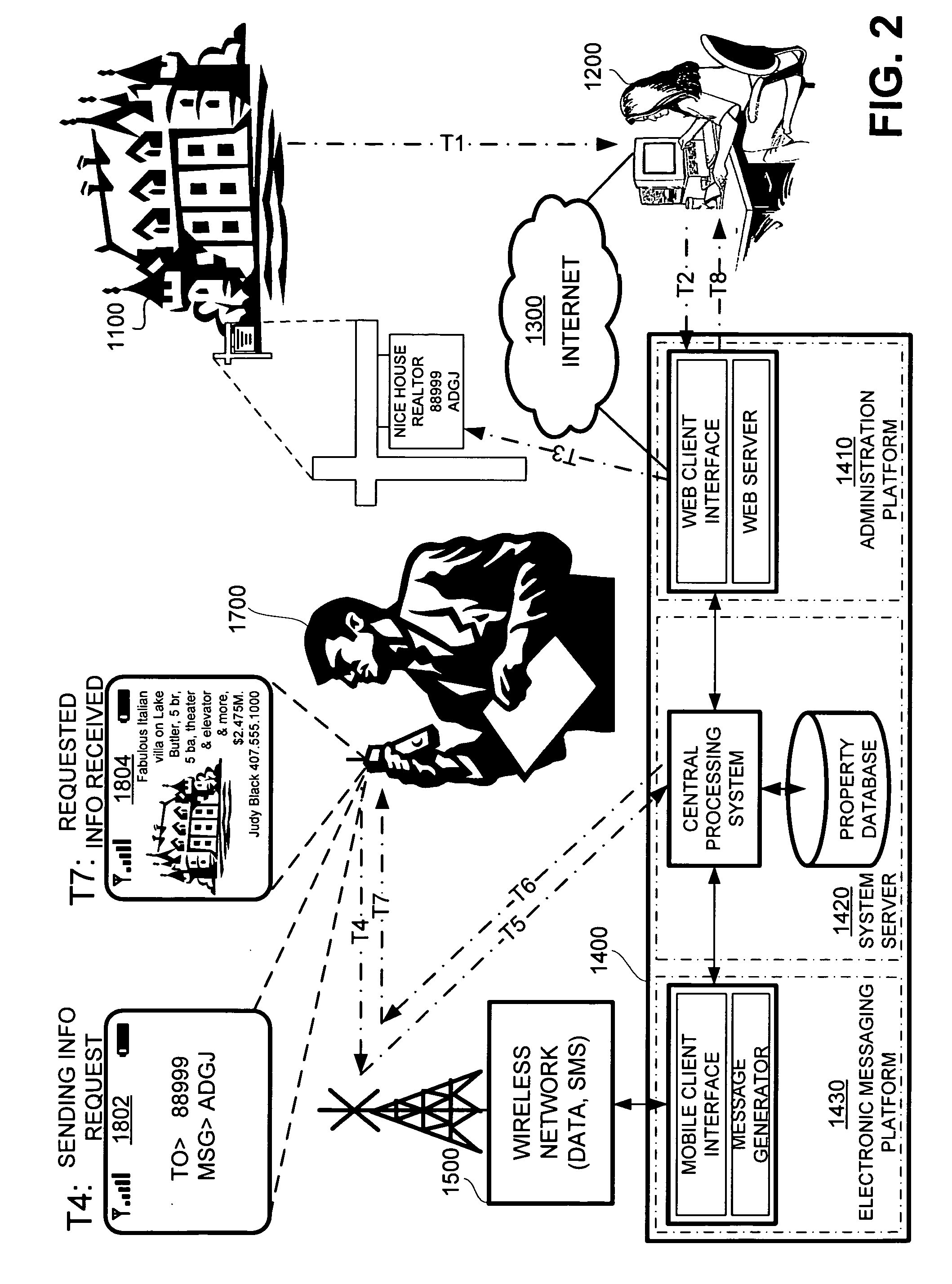
Wireless interactive property advertising system and methods
InactiveUS20060194572A1Special service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile deviceData bank
A system for providing property information about a property over a wireless network to an interested party having a mobile device, comprising: (a) an advertisement associated with the property, the advertisement having a shortcode and a keyword, and (b) a networked computer system having a property database containing property information for the property; the property information being retrievable from the property database based on the shortcode and the keyword. In operation, the interested party requests the property information about the property by sending a message with the shortcode and the keyword over the wireless network using the mobile device and, in response, the networked computer system retrieves the property information about the property associated with the shortcode and the keyword from the property database and transmits the property information to the mobile device of the interested party.
Owner:CLEARSKY MOBILE MEDIA
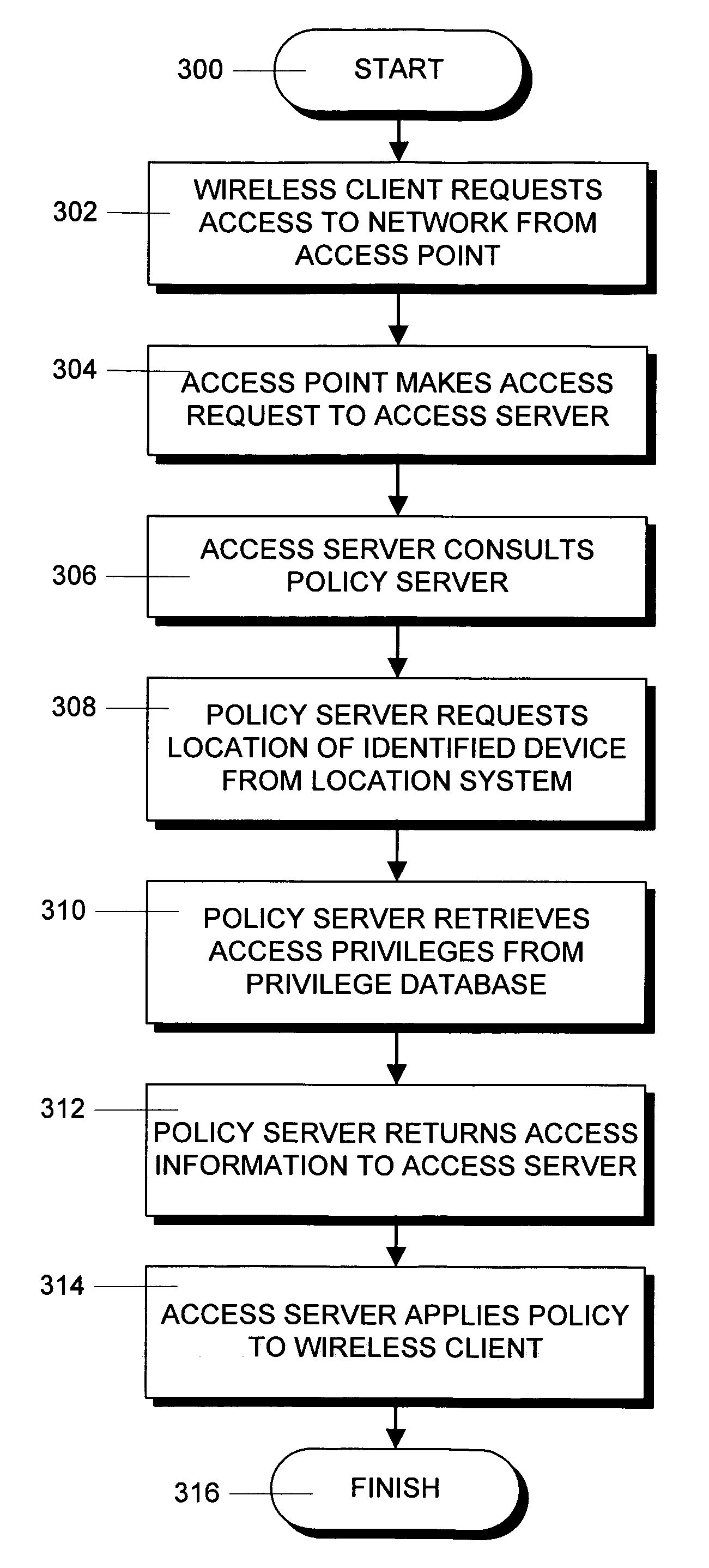
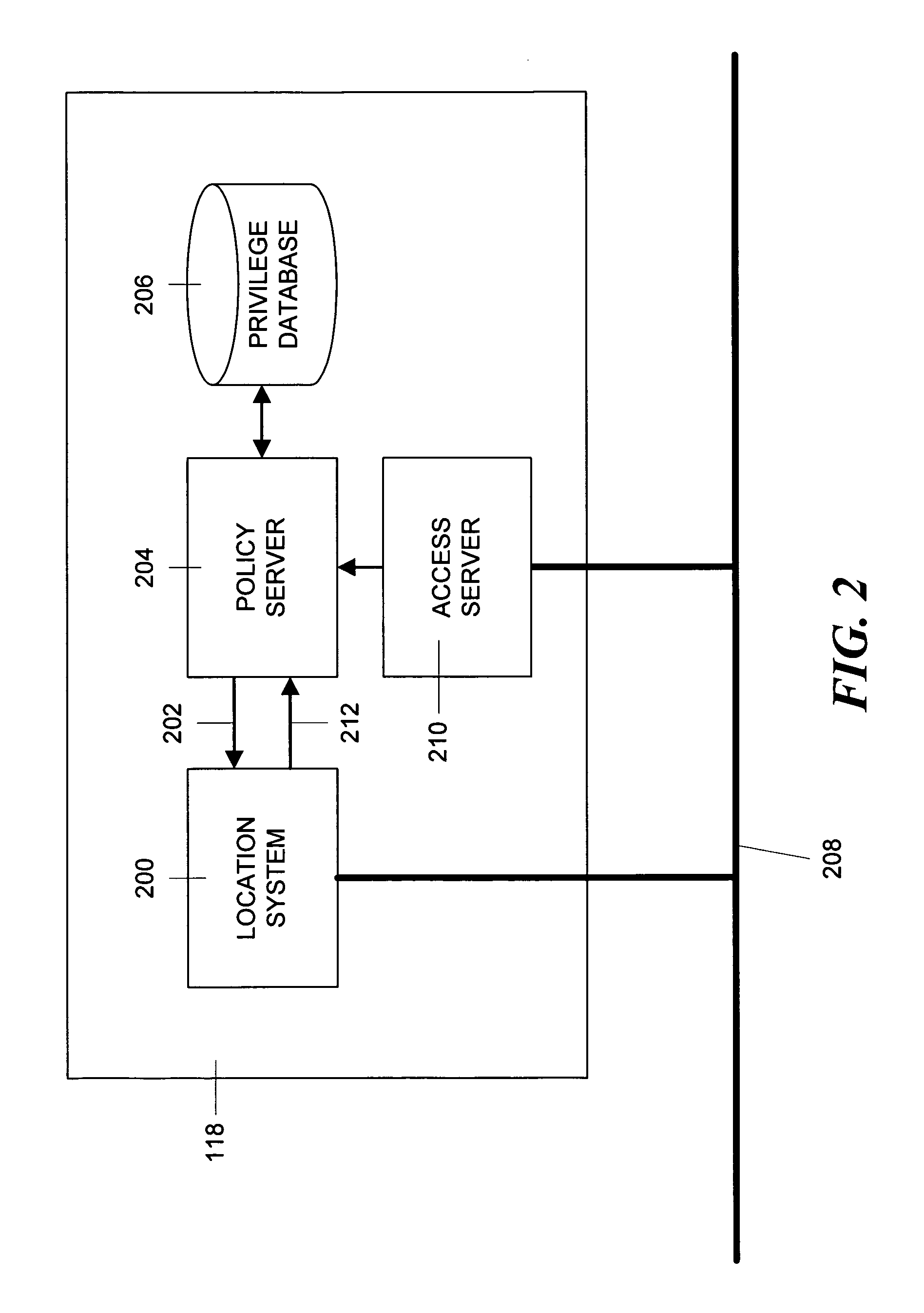
Method and apparatus for controlling wireless network access privileges based on wireless client location
ActiveUS7551574B1Telephonic communicationData switching by path configurationClient-sideLocation determination
An access point through which a wireless device attaches to a wireless network determines the access privileges that will be accorded to the device based on a criteria set, such as the ID and physical location of the device requesting network access, the access point through which the device is connected to the network and user credentials. The location of the device is determined by a location determination system using the signal strength of the device signal. The location information and ID information is provided to an access server that uses the criteria set to retrieve access privileges from a privilege database. The retrieved access privileges are then applied to the wireless device by means of the access point and other devices in the wireless network.
Owner:TRAPEZE NETWORKS
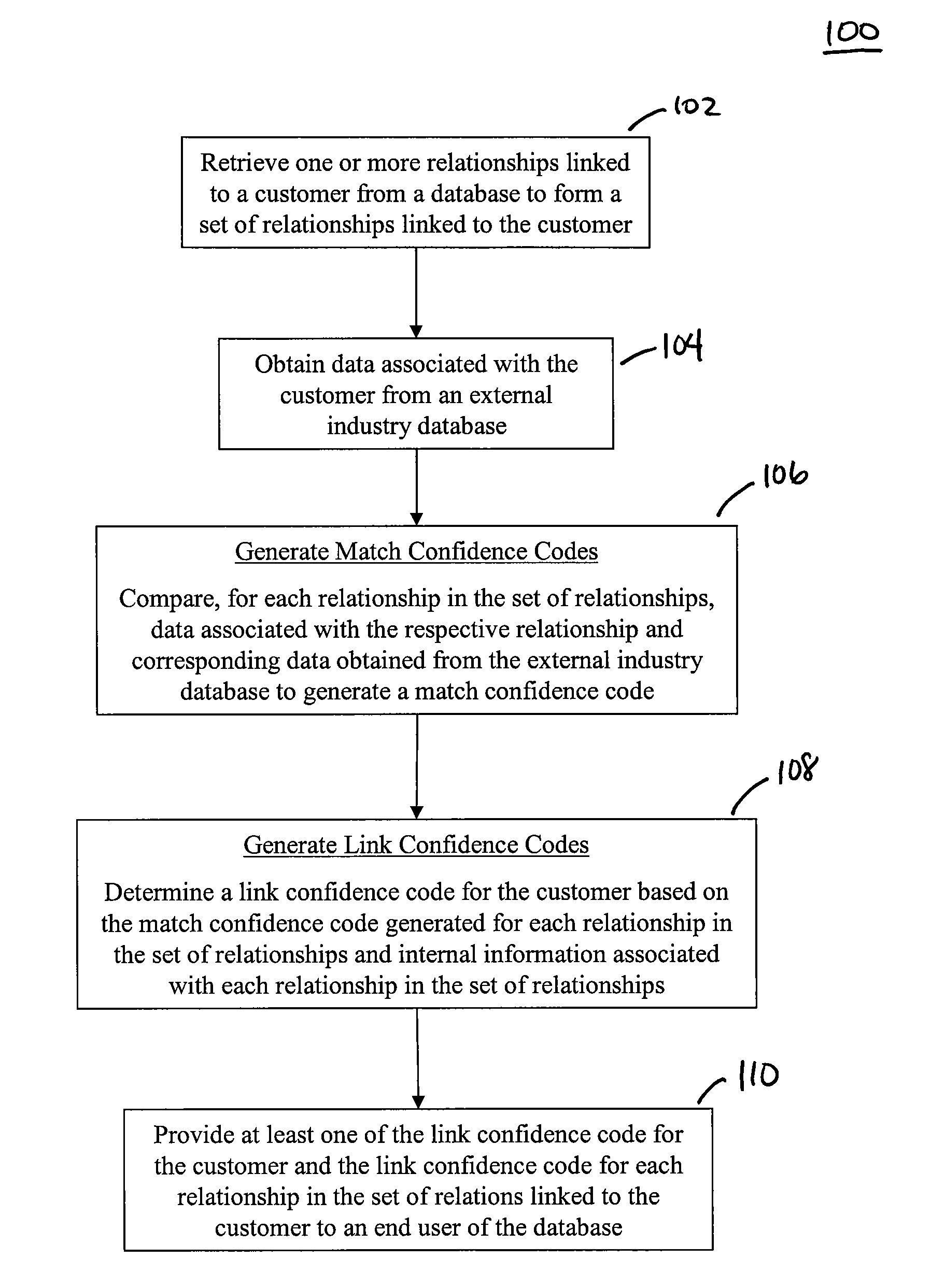
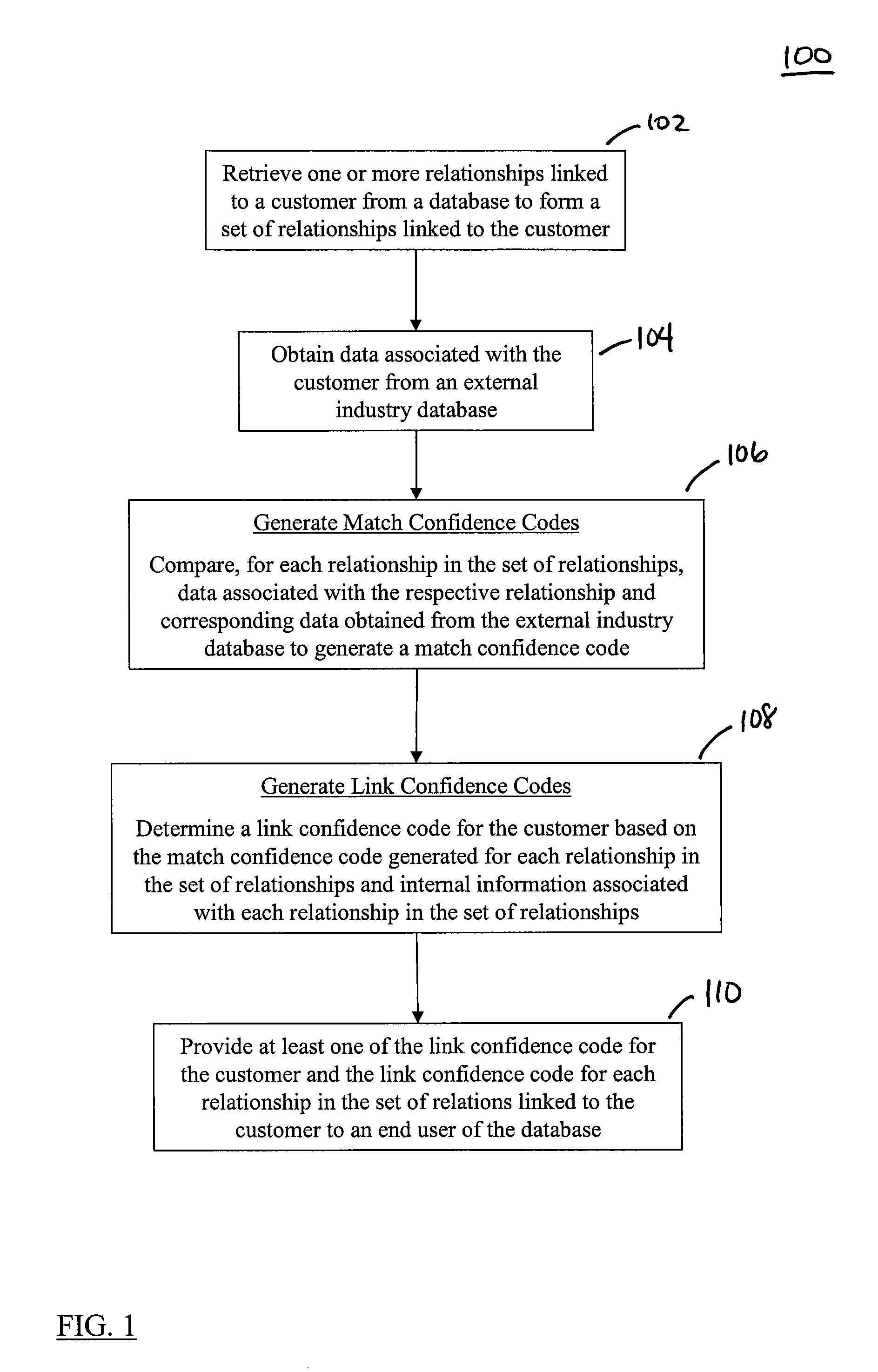
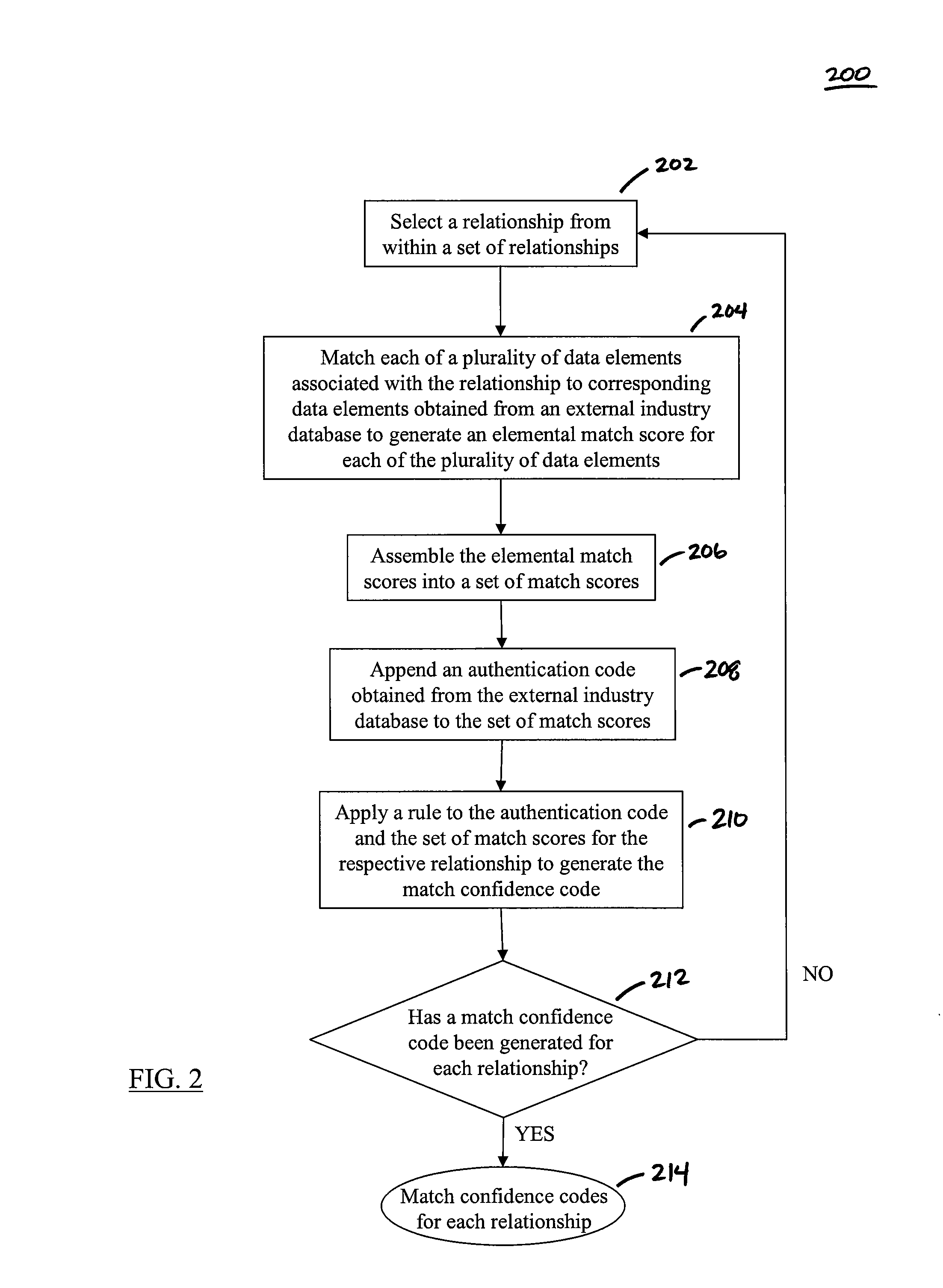
Methods, Systems, and Computer Program Products for Generating Data Quality Indicators for Relationships in a Database
The disclosed methods, systems, and computer-program products allow a business to generate data quality indicators for relationships in a database. In an embodiment, one or more relationships linked to a customer are retrieved from a database to form a set of relationships. A match confidence code is generated for each relationship based on a score generated by the comparison of customer data associated with the respective relationship and corresponding customer data obtained from an external industry database. A link confidence code is subsequently determined for the customer based on a score generated by the scores used to define the match confidence code for each relationship in the set of relationships and on internal data associated with each relationship in the set of relationships. The link confidence code for the customer and the match confidence codes and the respective scores for the set of relationships may be provided to an end user of the database in order to improve decisions made by the end user at the customer level.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Scrolling method and apparatus for zoom display
According to one aspect of the disclosed system, a user supplies character-based queries to retrieve and display a record from a structured database. For every character the user enters, a progressively reduced list of indexes that start with the entered characters is displayed. When a desired index identifying the record is among those indexes being displayed, the user may cease the character entry and scroll a zoom window upon the desired index to explore the record. According to another aspect of the disclosed system, the zoom window maintains a display of an index and at least one field of a record. Consequently, the user can access and display pertinent information of a certain record from a database quickly and efficiently with less keystrokes.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Credit manager method and system
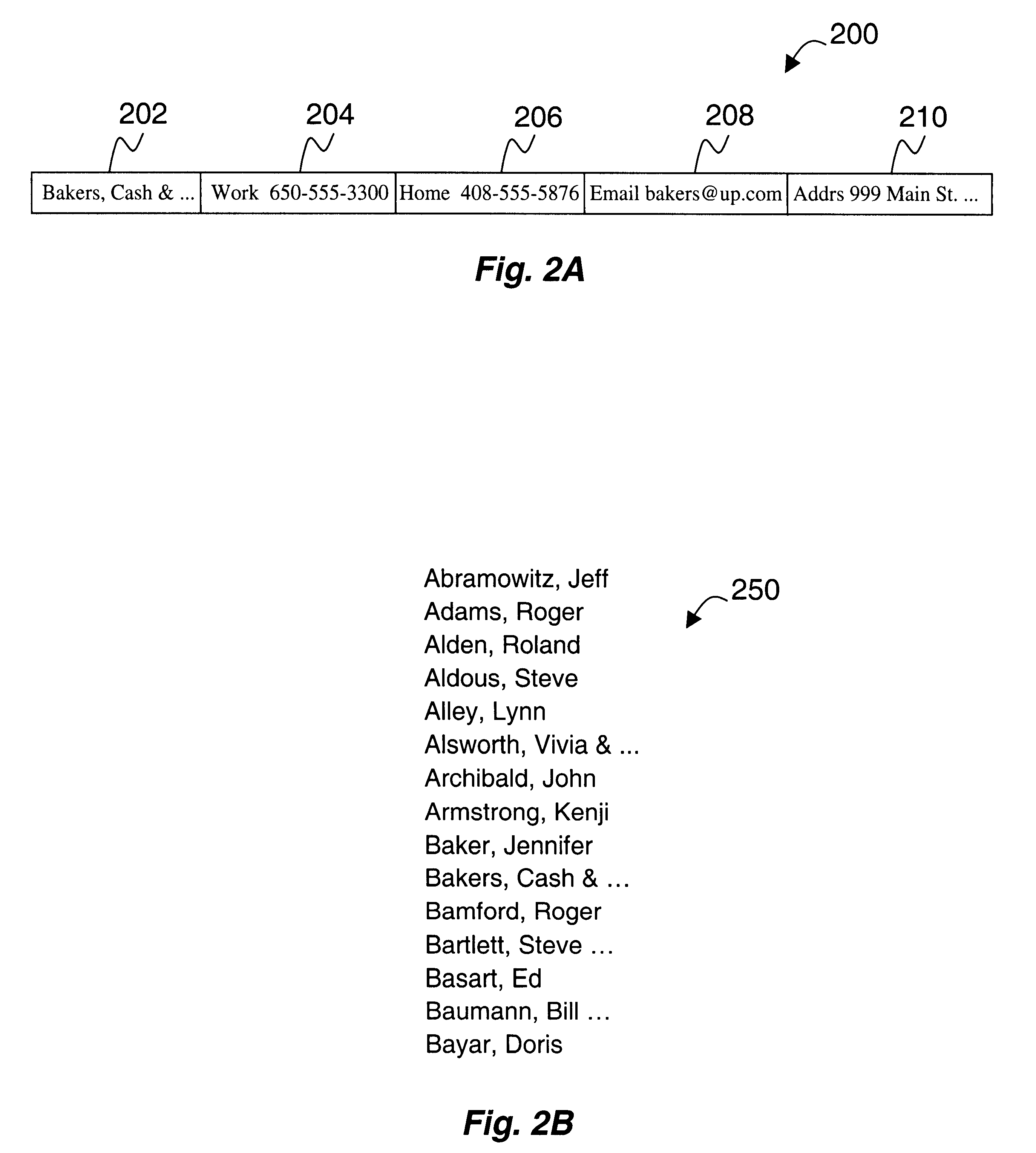
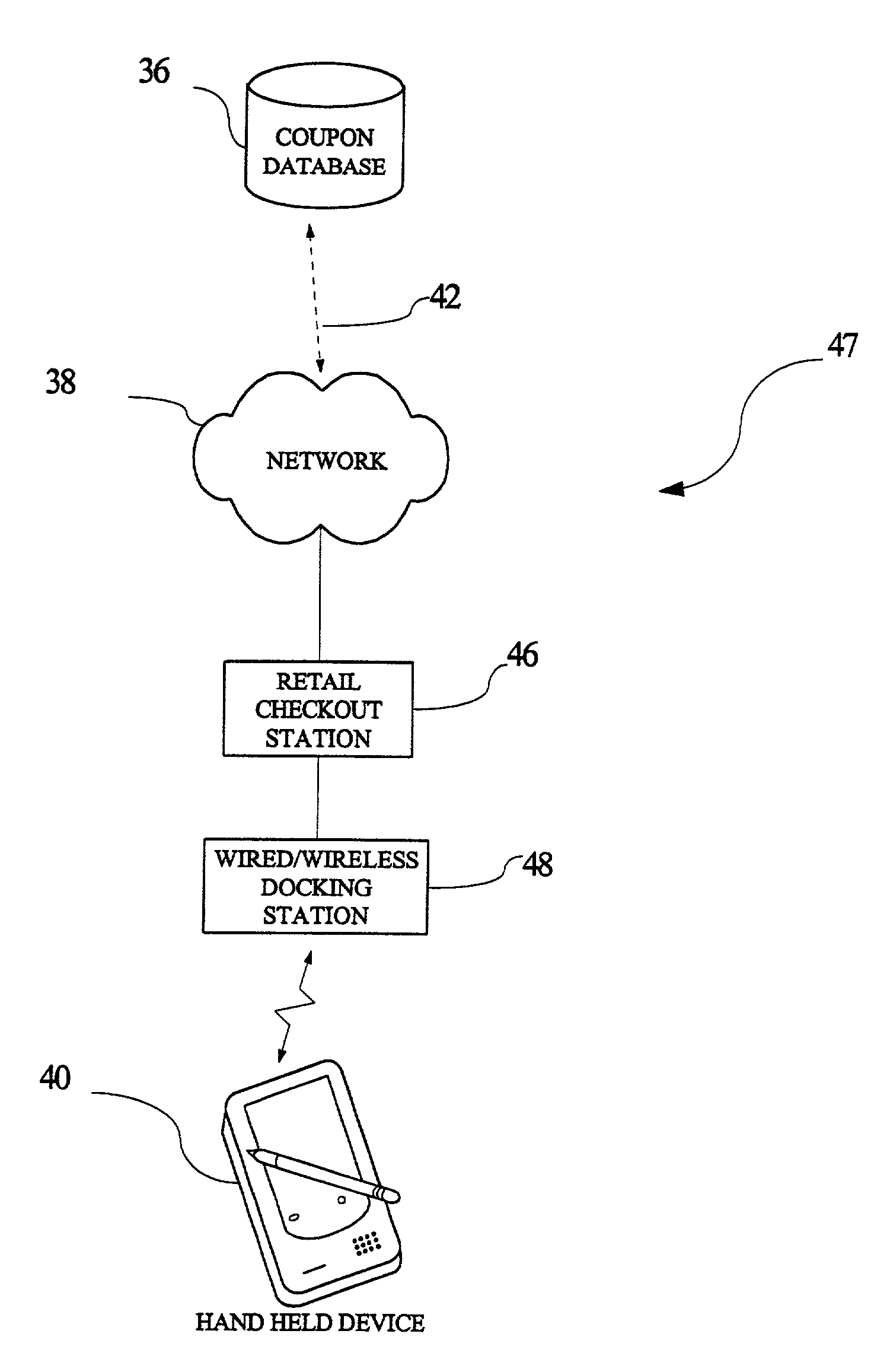
A method and system for processing negotiable economic credits (e.g., cash, credit card, enterprise incentives / award such as frequent flier miles, etc.) through a hand held device. Credits are storable in the form of credit data in a credit database associated with a point of sale and / or hand held device. Credit is retrievable from the credit database, in response to synchronizing a hand held device, such as a PDA, wireless PDA, paging device, cellular telephone, or other hand held computing device, with the point of sale. Credit data may be transferred to / from the hand held device, thereby permitting a user to maintain and manage enterprise credits based on the credit data, utilizing the hand held device. In one embodiment, when a particular number of enterprise credits have been earned, the user may utilize such credits to receive price discounts on enterprise products or services, or awards of such products or services. A user may also use credits earned for enterprise sponsored credit programs unrelated to transactions at unrelated enterprise having compatible points of sale for providing / receiving / processing credits, so long as credits are recognized at a point of sale.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com