Patents
Literature
2987 results about "Data cache" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
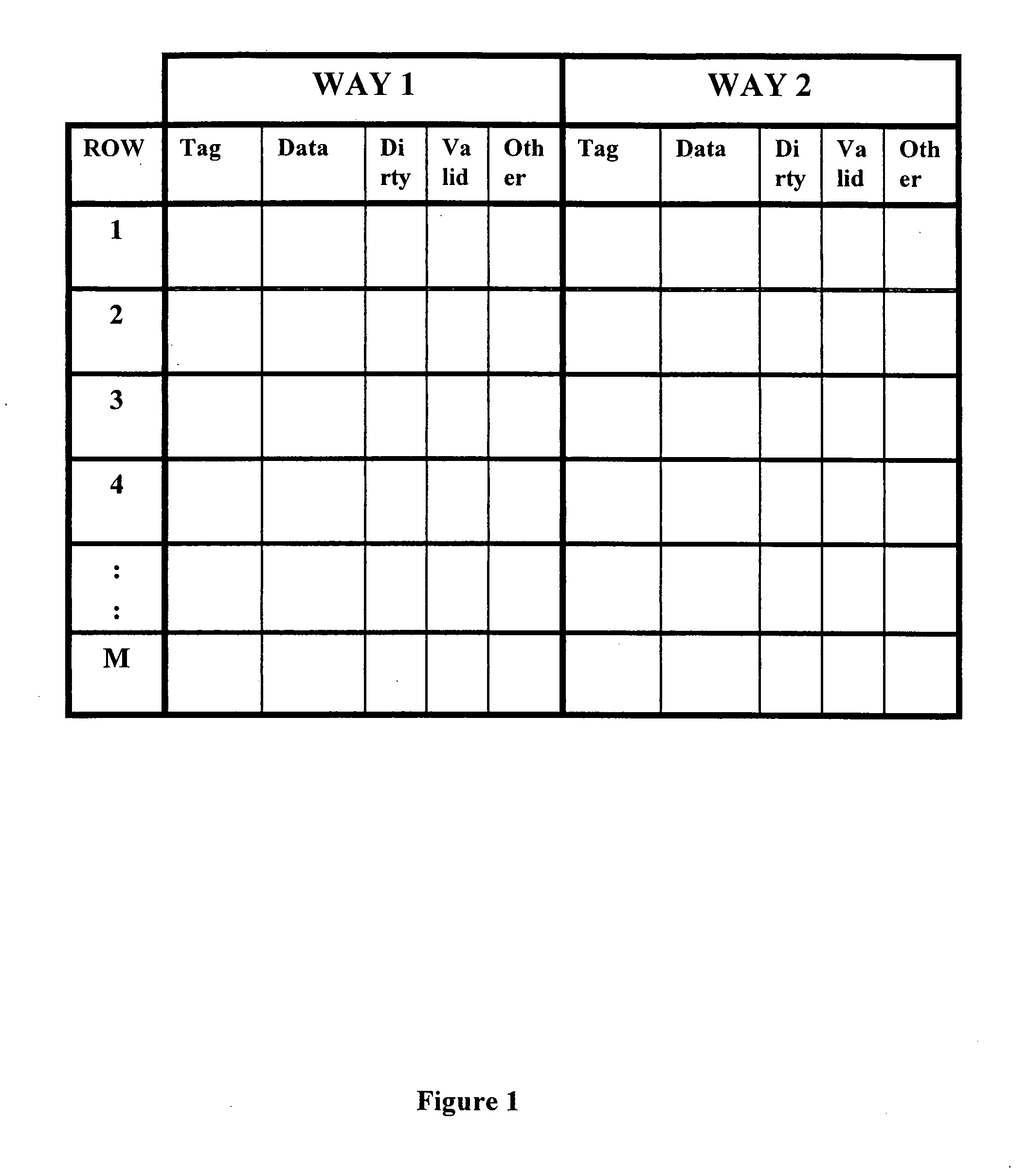
Data Caching : Data caching means caching data from a data source. As long as the cache is not expired, a request for the data will be fulfilled from the cache. When the cache is expired, fresh data is obtained by the data source and the cache is refilled.
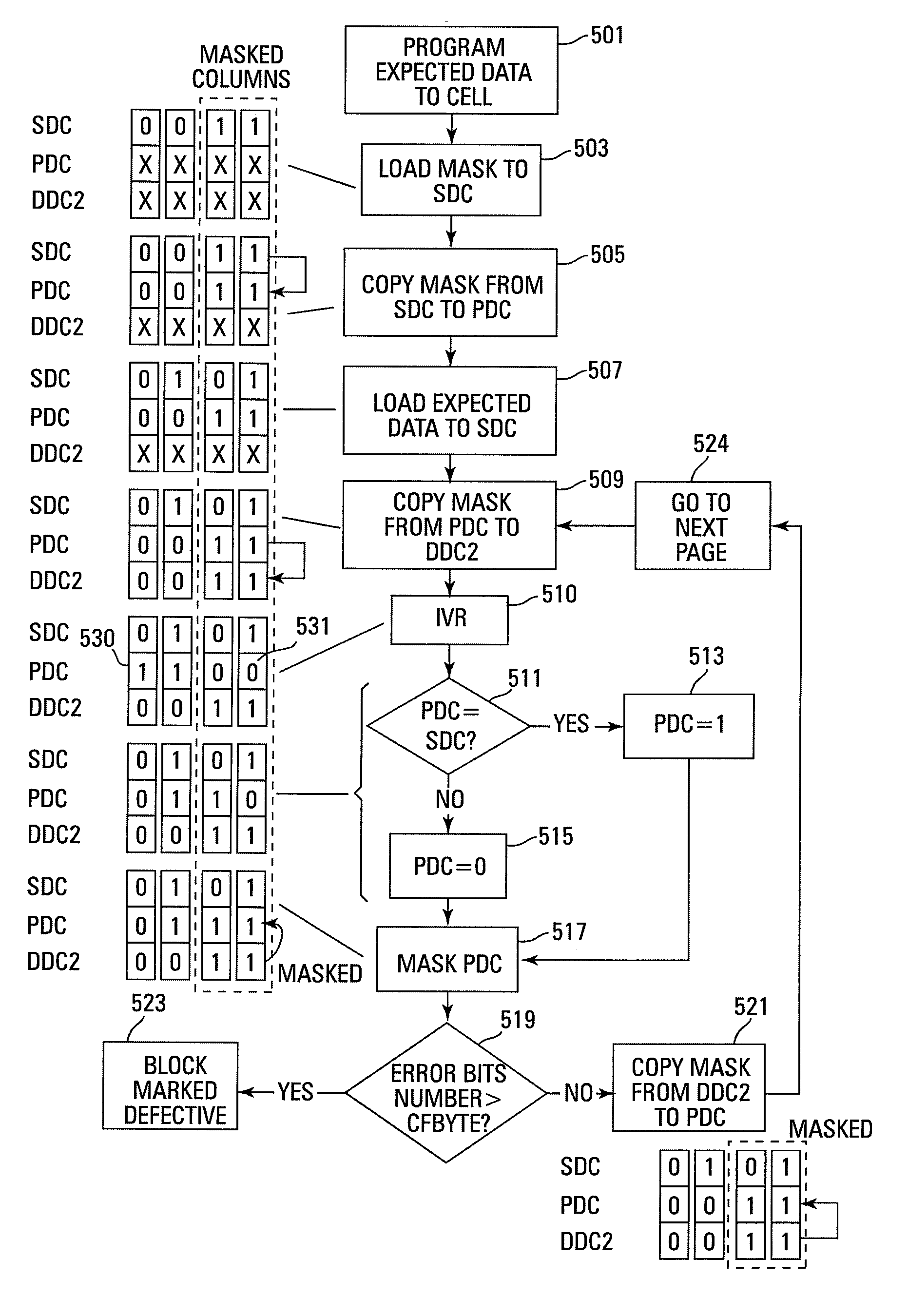
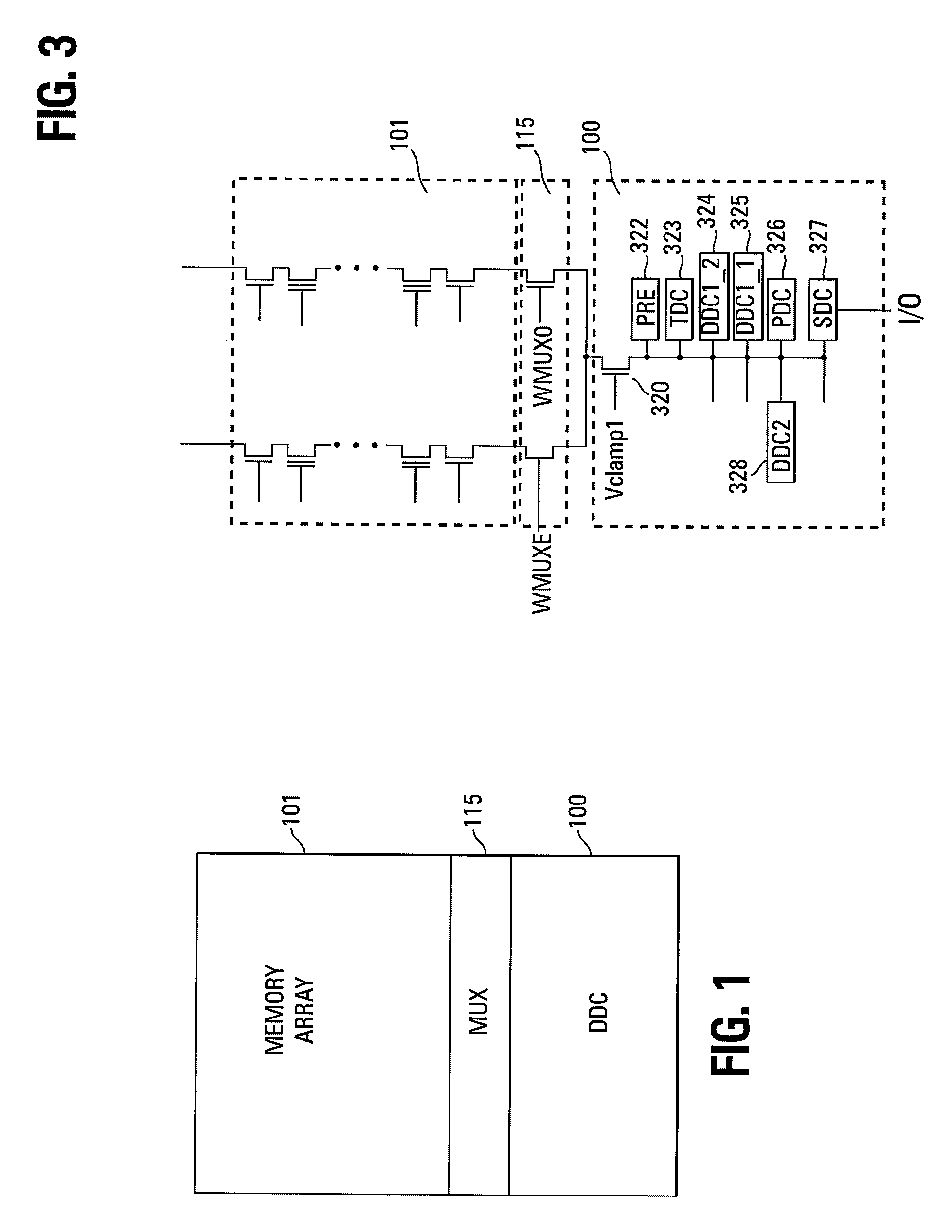
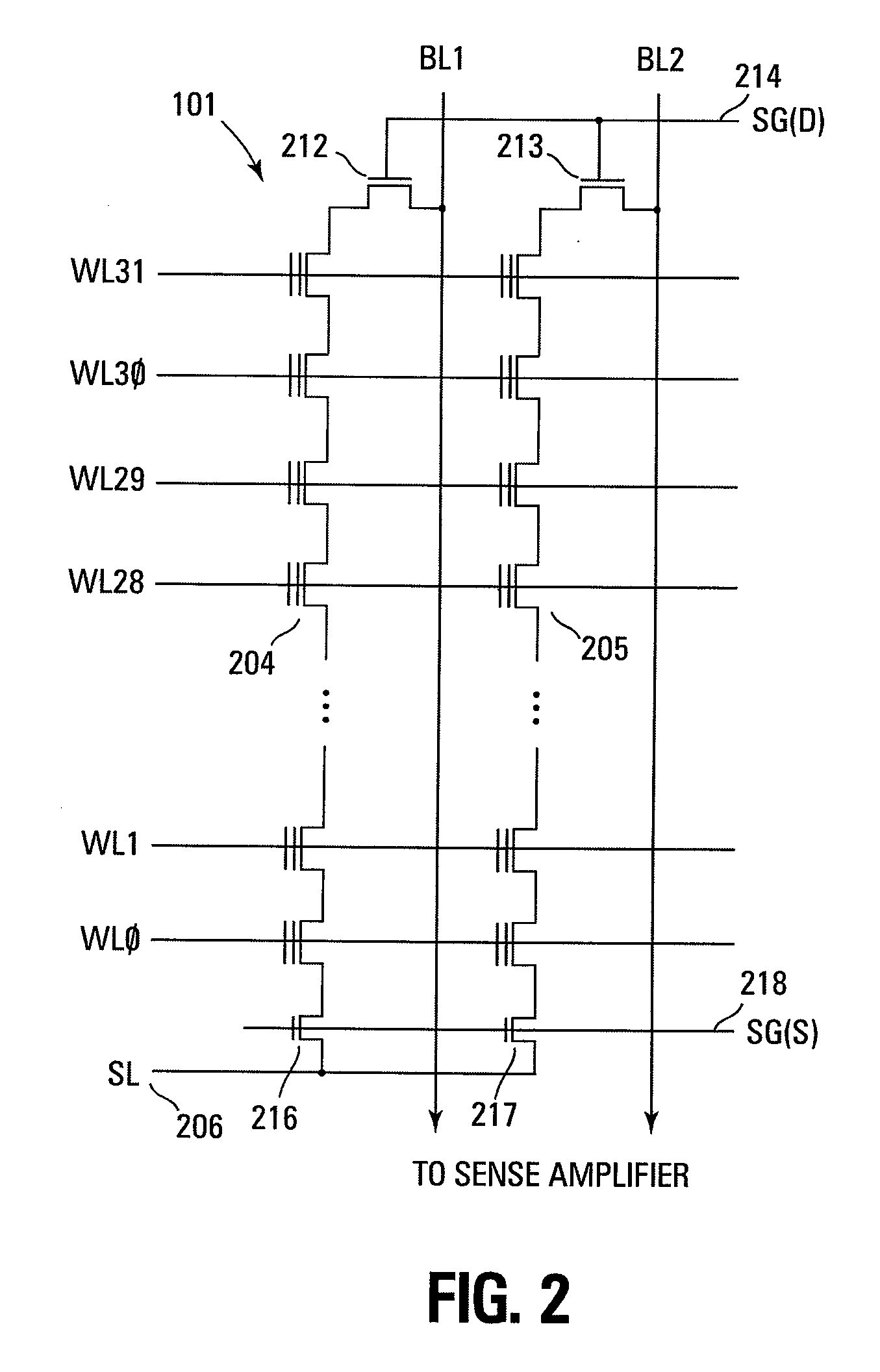
Small unit internal verify read in a memory device
Methods for small unit internal verify read operation and a memory device are disclosed. In one such method, expected data is programmed into a grouping of columns of memory cells (e.g., memory block). Mask data is loaded into a third dynamic data cache of three dynamic data caches. The expected data is loaded into a second data cache. After a read operation of programmed columns of memory cells, the read data is compared to the expected data and error bit indicators are stored in the second data cache in the error bit locations. The second data cache is masked with the mask data so that only those error bits that are unmasked are counted. If the number of unmasked error bit indicators is greater than a threshold, the memory block is marked as unusable.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
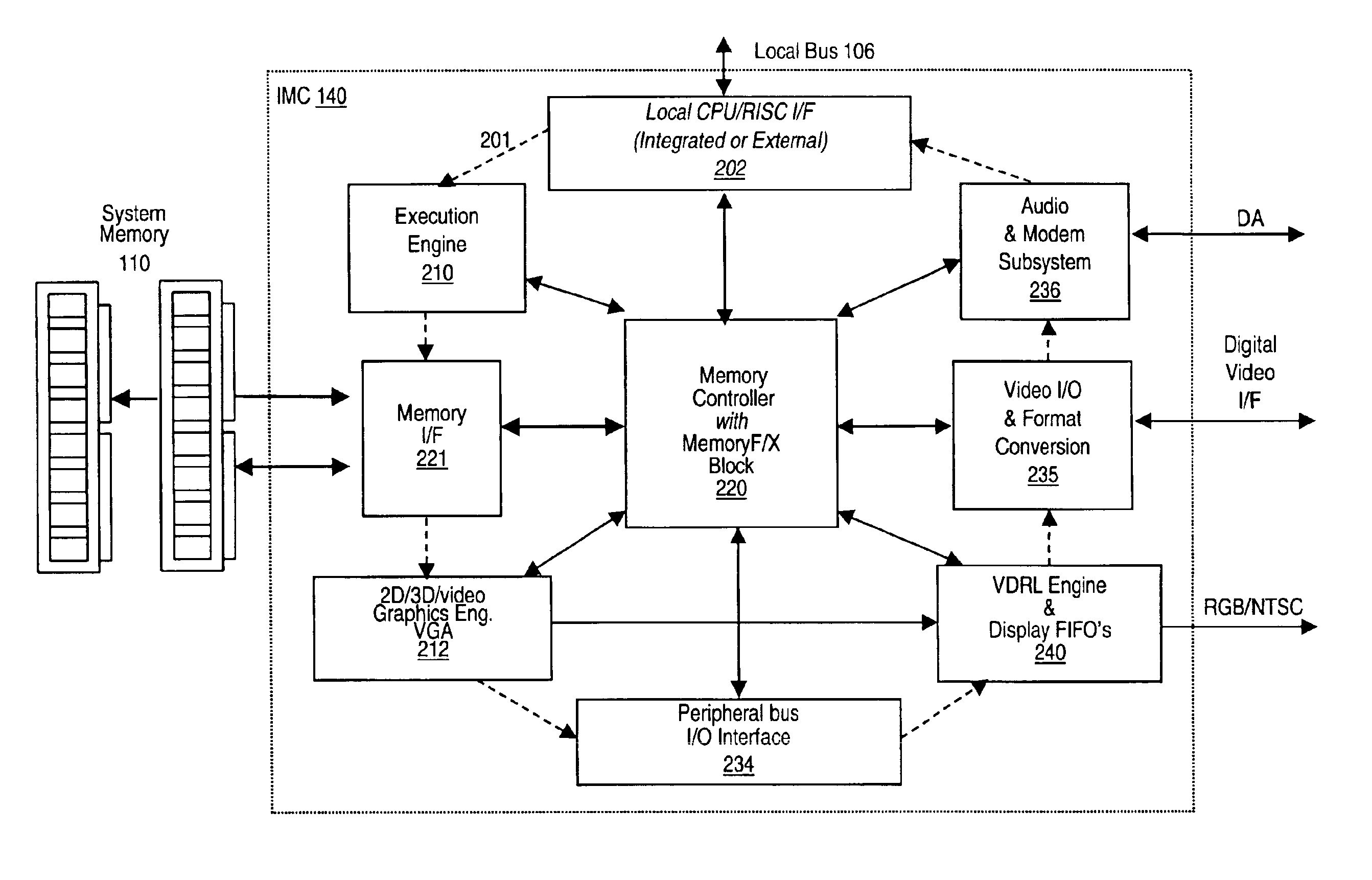
Memory module including scalable embedded parallel data compression and decompression engines
InactiveUS6879266B1Low costSmall data storage requirementMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTParallel compressionParallel computing
An memory module including parallel data compression and decompression engines for improved performance. The memory module includes MemoryF / X Technology. To improve latency and reduce performance degradations normally associated with compression and decompression techniques, the MemoryF / X Technology encompasses multiple novel techniques such as: 1) parallel lossless compression / decompression; 2) selectable compression modes such as lossless, lossy or no compression; 3) priority compression mode; 4) data cache techniques; 5) variable compression block sizes; 6) compression reordering; and 7) unique address translation, attribute, and address caches. The parallel compression and decompression algorithm allows high-speed parallel compression and high-speed parallel decompression operation. The memory module-integrated data compression and decompression capabilities remove system bottlenecks and increase performance. This allows lower cost systems due to smaller data storage, reduced bandwidth requirements, reduced power and noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Method and apparatus for efficient scalable storage management
ActiveUS7181578B1Improve performanceSolve the lack of spaceMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingHandling systemDatapath
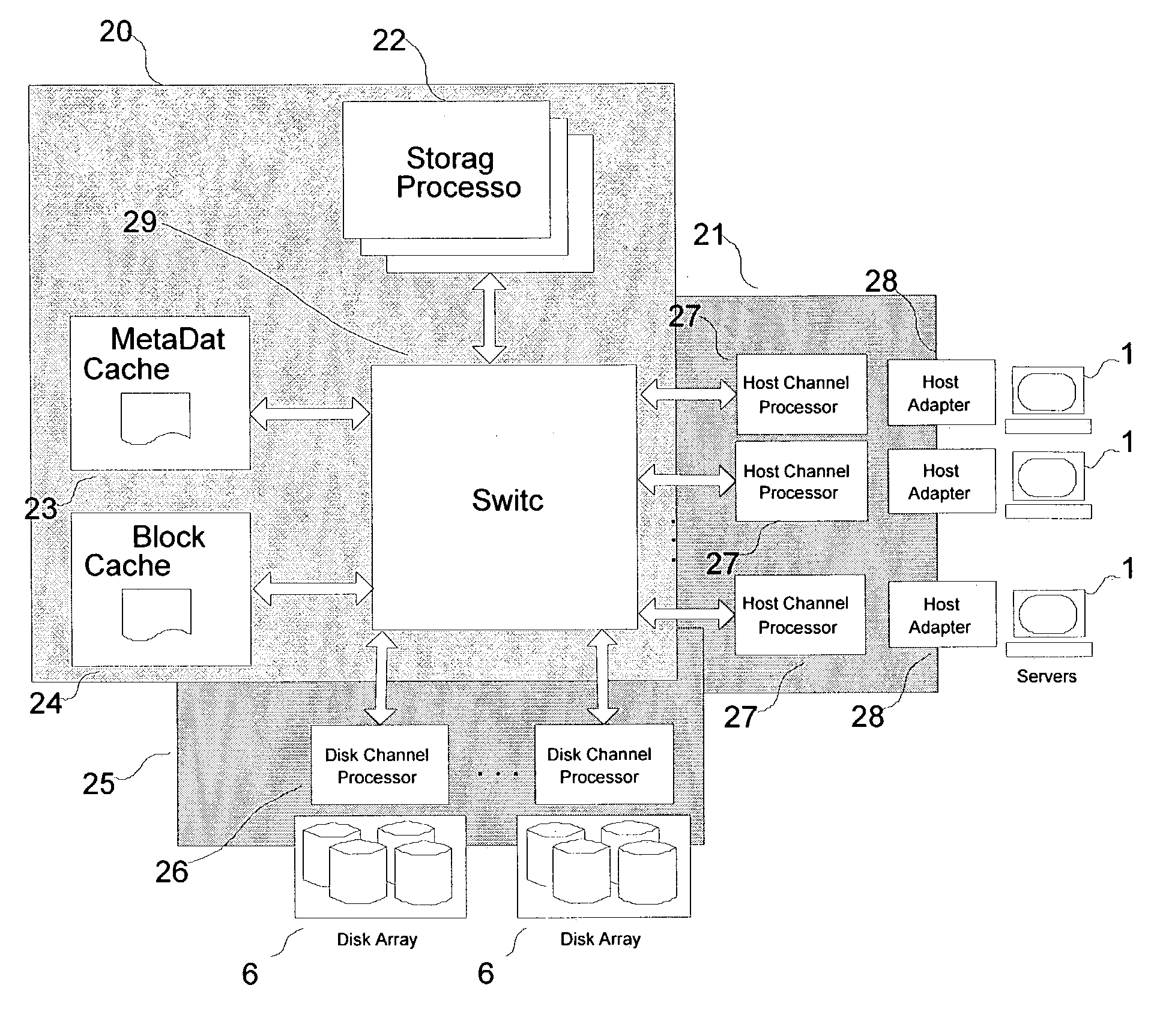
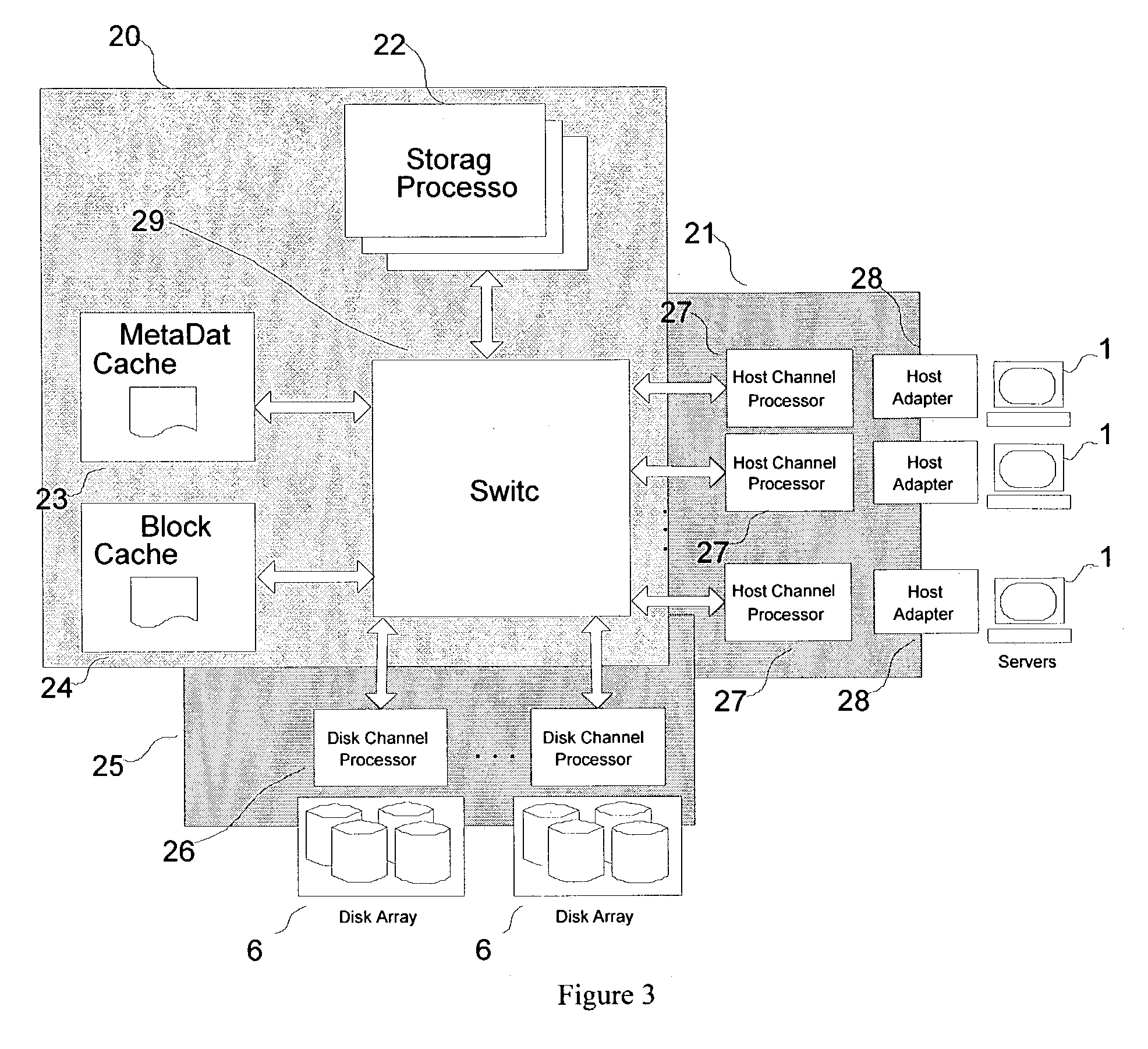
A hybrid centralized and distributed processing system includes a switching device that connects a storage processor to one or more servers through a host channel processor. The switching device also connects the storage processor to one or more storage devices such as disk drive arrays, and to a metadata cache and a block data cache memory. The storage processor processes access request from one or more servers in the form of a logical volume or logical block address and accesses the metadata cache to determine the physical data address. The storage processor monitors the performance of the storage system and performs automatic tuning by reallocating the logical volume, load balancing, hot spot removal, and dynamic expansion of storage volume. The storage processor also provides fault-tolerant access and provides parallel high performance data paths for fail over. The storage processor also provides faster access by providing parallel data paths for, making local copies and providing remote data copies, and by selecting data from a storage device that retrieves the data the earliest.
Owner:COPAN SYST INC +1
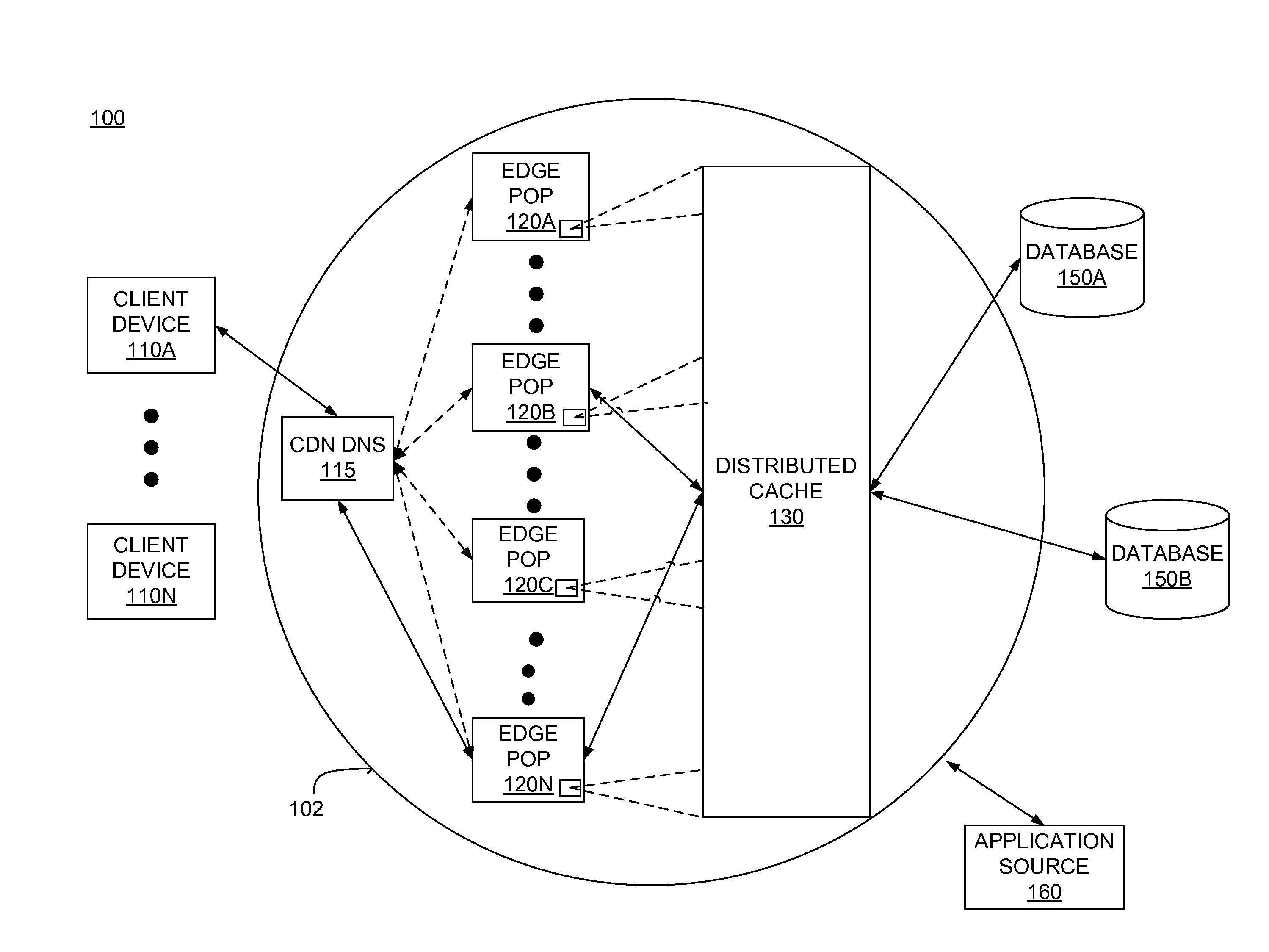
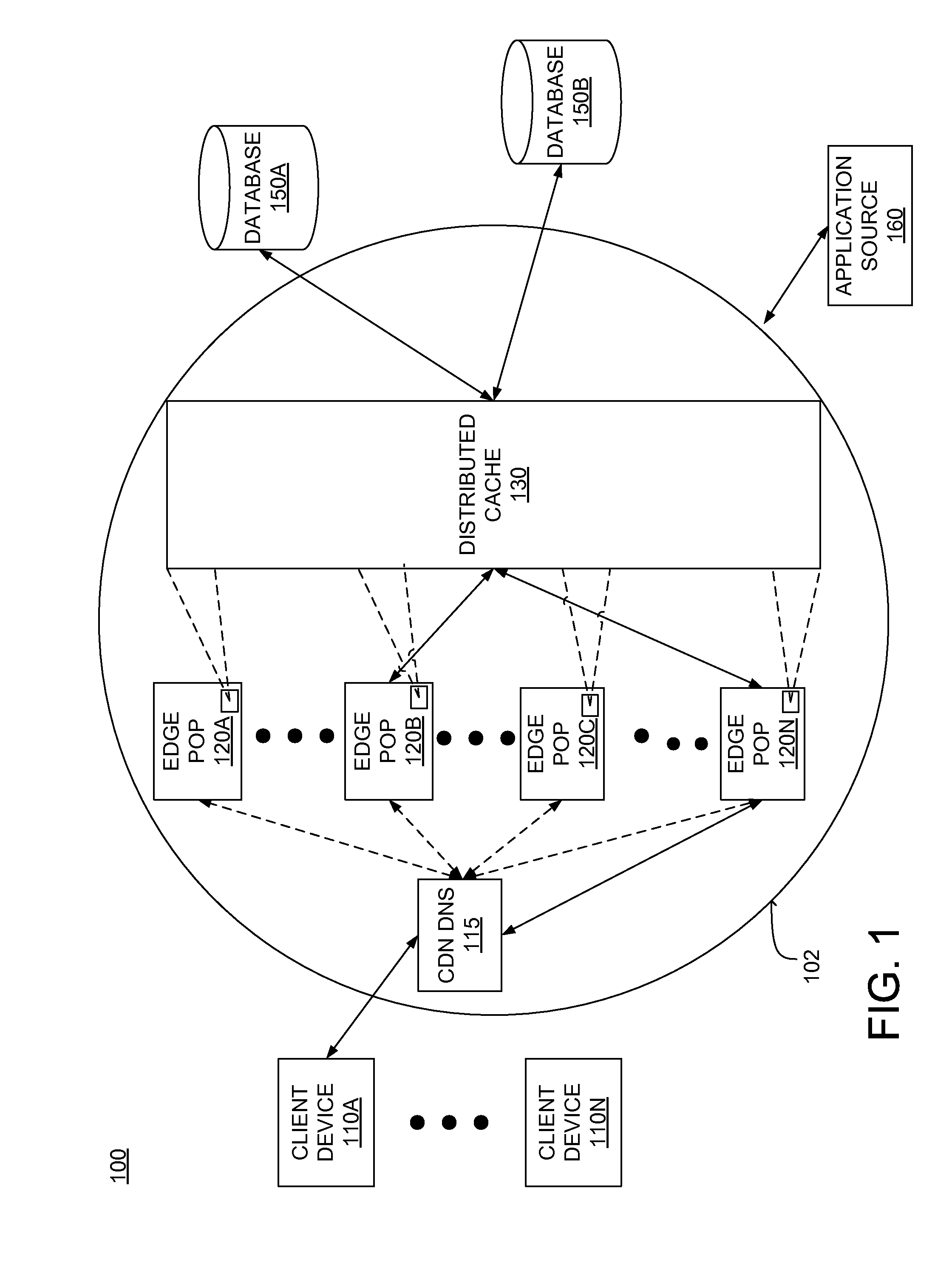
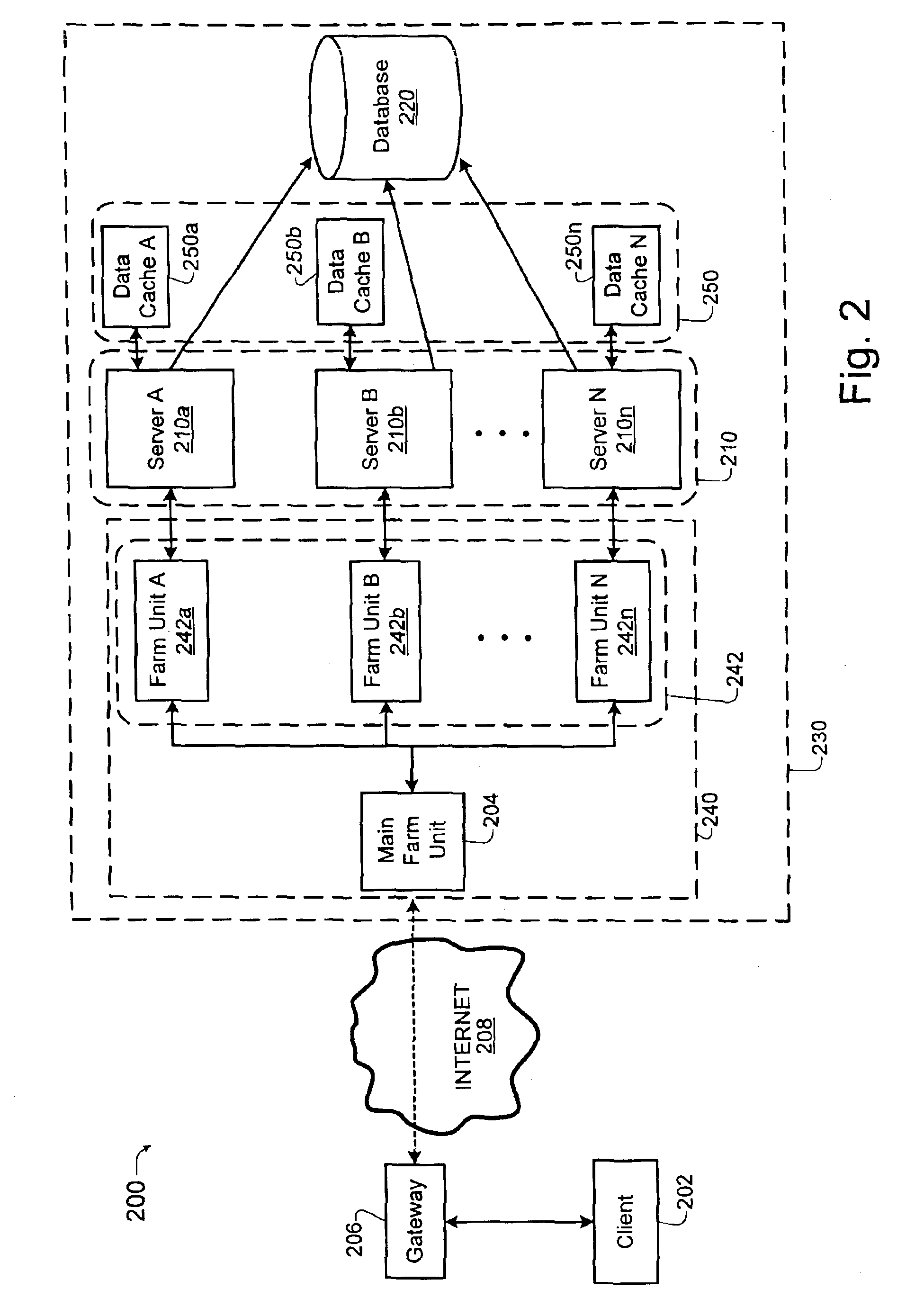
Distributed data cache for on-demand application acceleration
ActiveUS20120041970A1Decreasing application executionShorten the timeDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsApplication softwareDistributed computing
A distributed data cache included in a content delivery network expedites retrieval of data for application execution by a server in a content delivery network. The distributed data cache is distributed across computer-readable storage media included in a plurality of servers in the content delivery network. When an application generates a query for data, a server in the content delivery network determines whether the distributed data cache includes data associated with the query. If data associated with the query is stored in the distributed data cache, the data is retrieved from the distributed data cache. If the distributed data cache does not include data associated with the query, the data is retrieved from a database and the query and associated data are stored in the distributed data cache to expedite subsequent retrieval of the data when the application issues the same query.
Owner:CDNETWORKS HLDG SINGAPORE PTE LTD
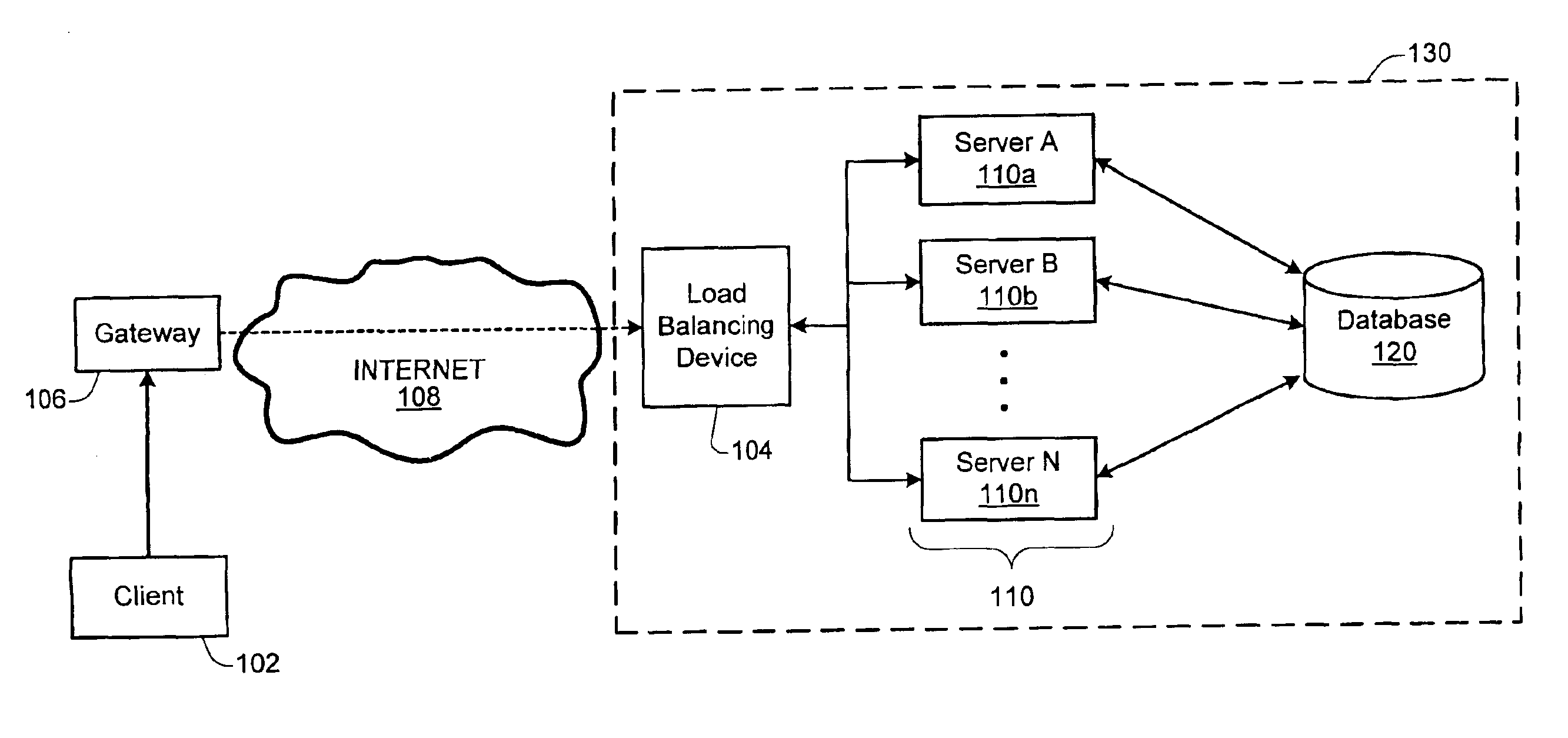
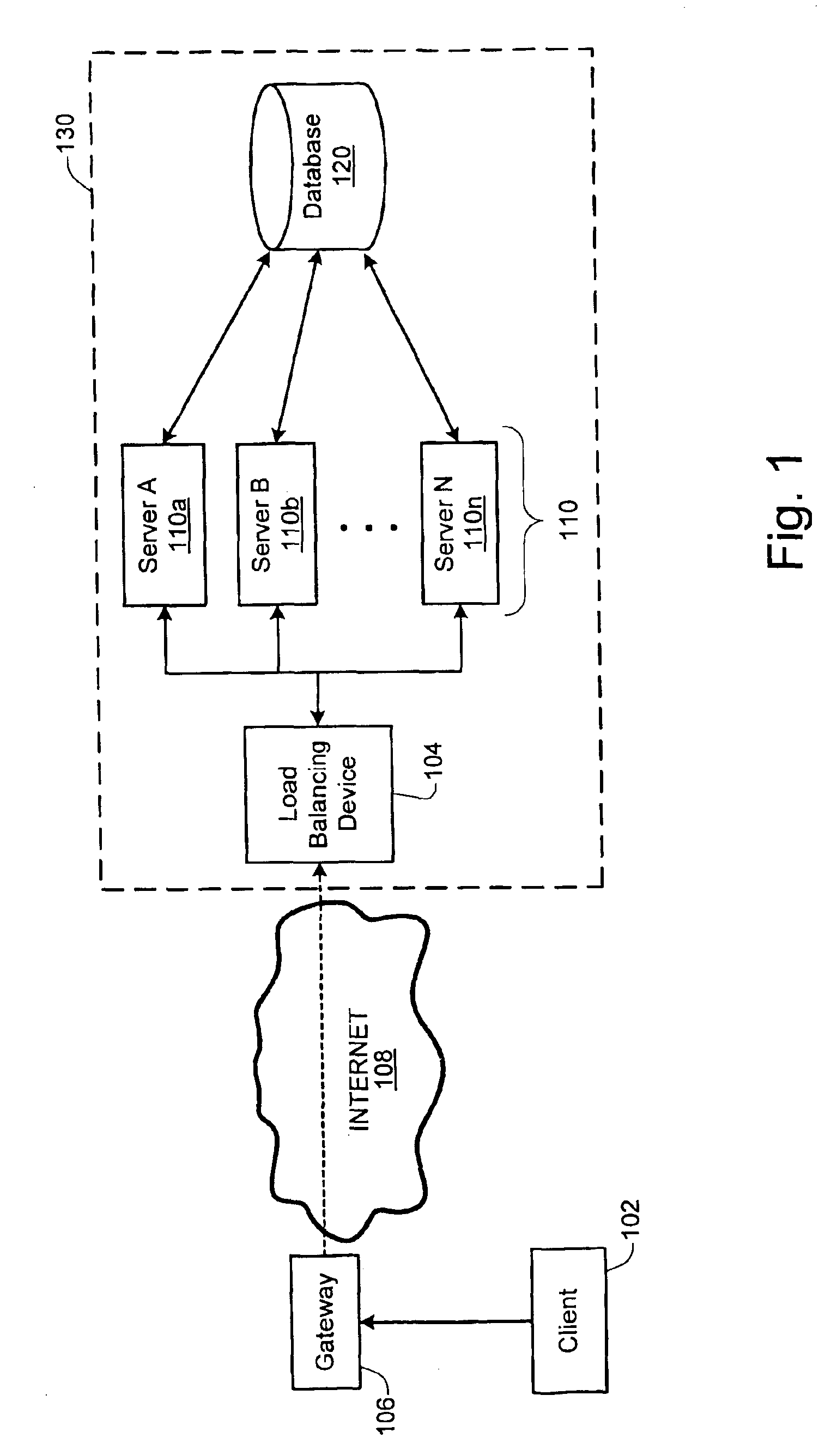
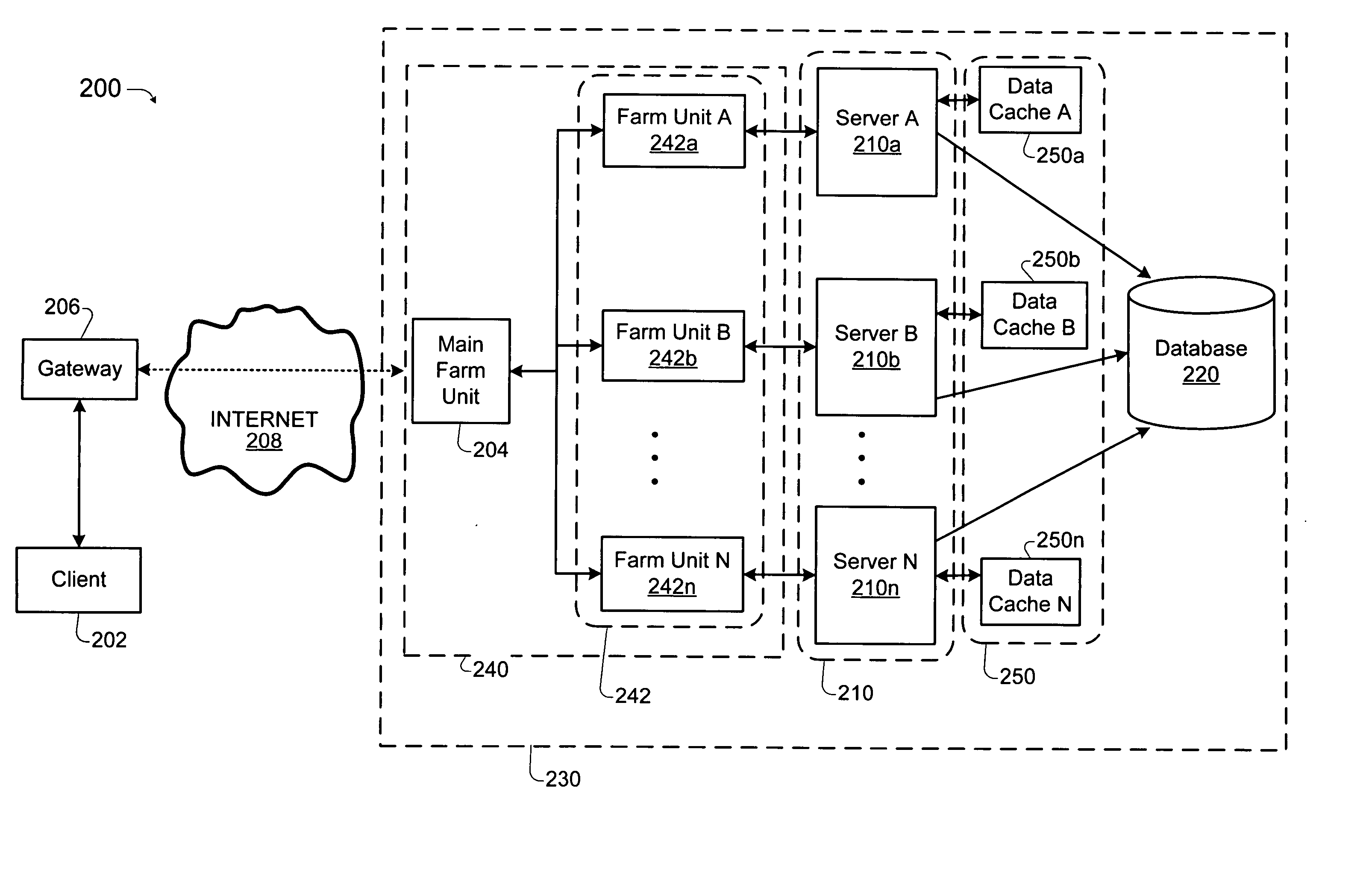
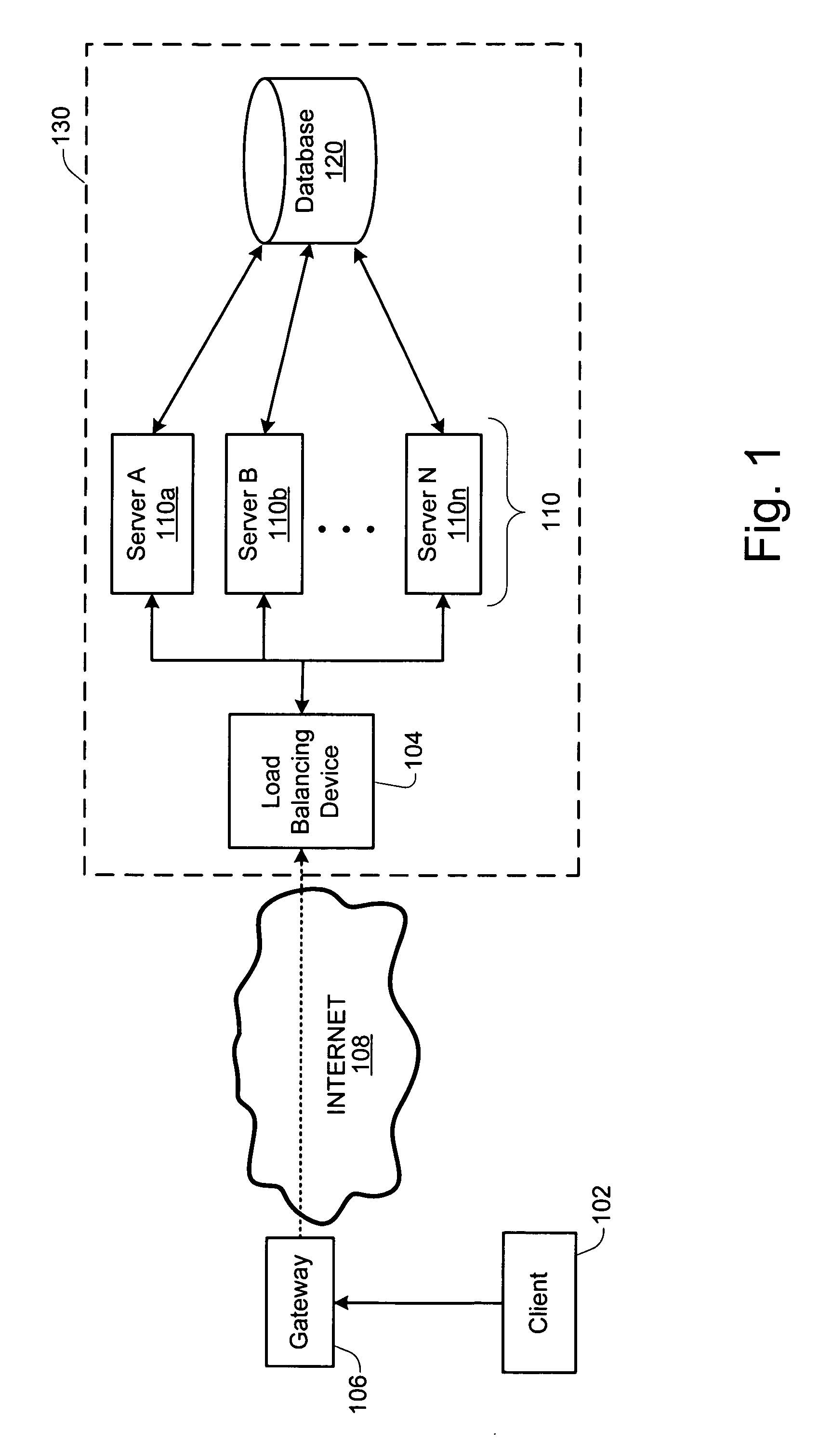
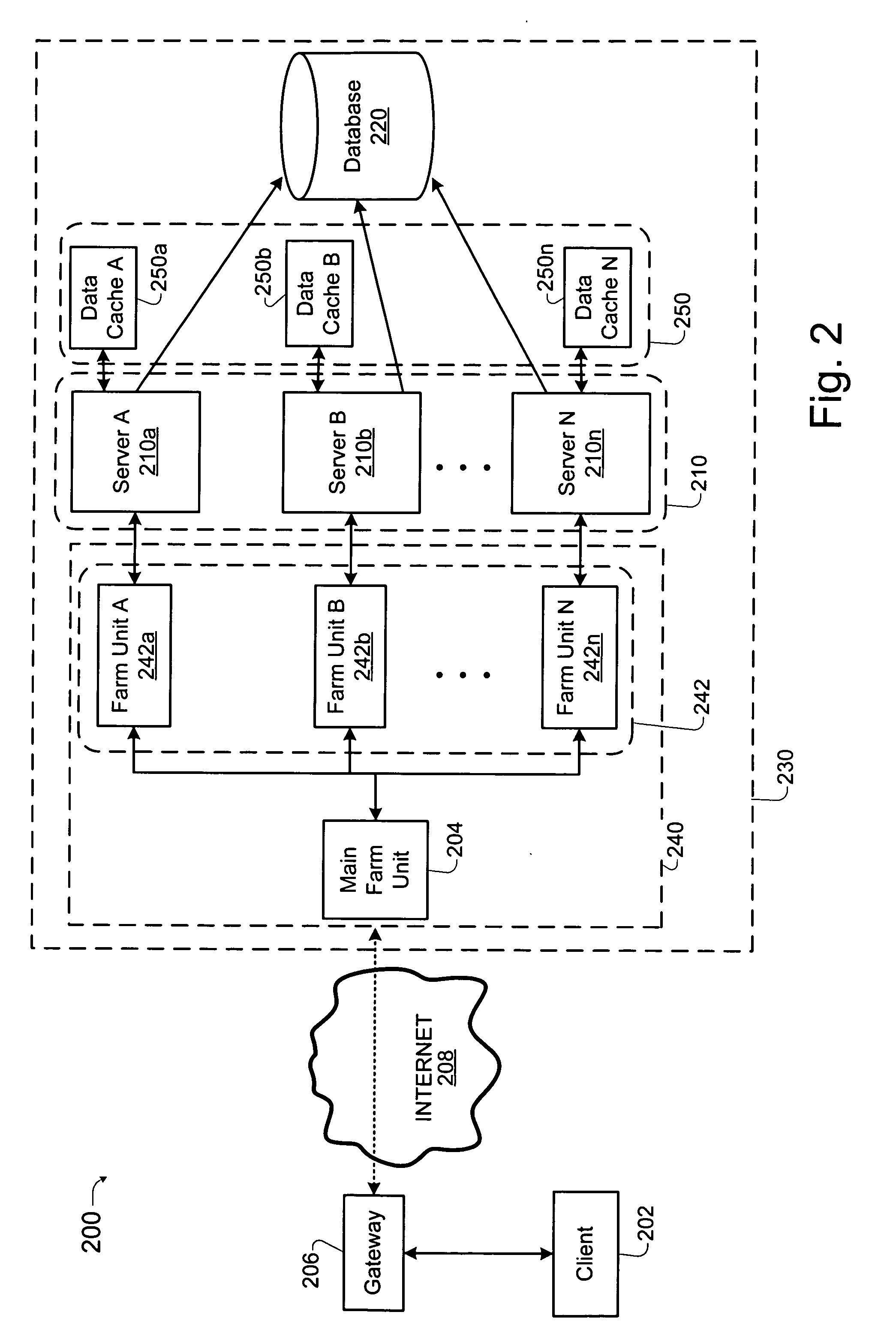
Load balancing technique implemented in a data network device utilizing a data cache
InactiveUS7197547B1Easy to useDigital data information retrievalMultiprogramming arrangementsE-commerceClient-side
A technique for implementing a load balanced server farm system is described which may be used for effecting electronic commerce over a data network. The system comprises a load balancing system and a plurality of servers in communication with the load balancing system. Each of the plurality of servers may include a respective data cache for storing state information relating to client session transactions conducted between the server and a particular client. The load balancing system is configured to select, using a load balancing protocol, an available first server from the plurality of servers to process an initial packet received from a source device such as, for example, a client machine of a customer. The load balancing system is also configured to route subsequent packets received from the source device to the first server. In this way, a “stickiness” scheme may be implemented in the server farm system whereby, once an electronic commerce session has been initiated between the first server and the source device, the first server may handle all subsequent requests from the source device in order to make optimal use of the state data stored in the first server's data cache. Before generating its response, the first server may verify that the state information relating to a specific client session stored in the data cache is up-to-date. If the first server determines that the state information stored in the data cache is not up-to-date, then the first server may be configured to retrieve the desired up-to-date state information from a database which is configured to store all state information relating to client sessions which have been initiated with the server farm system.
Owner:JUNE RAY
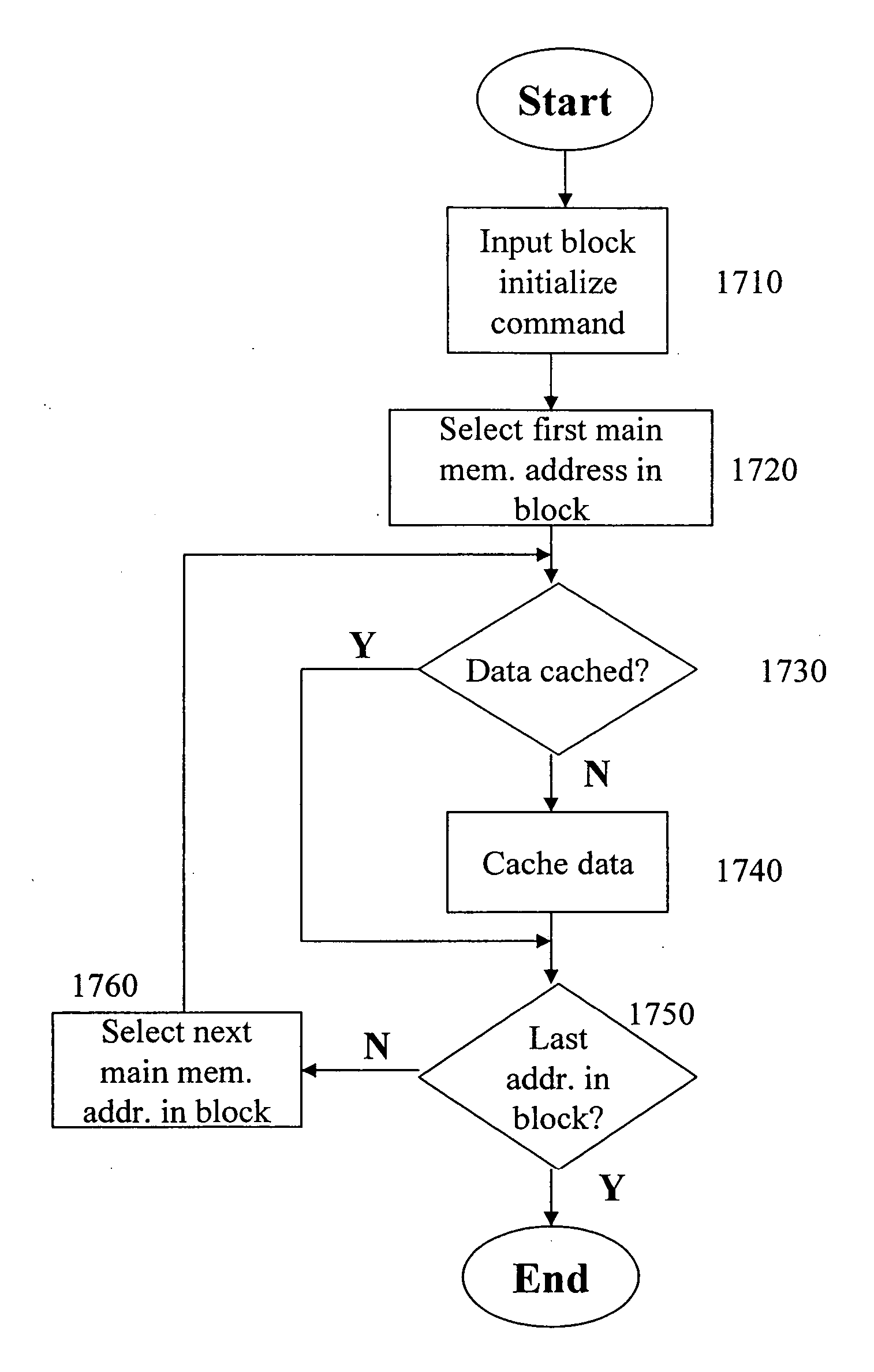
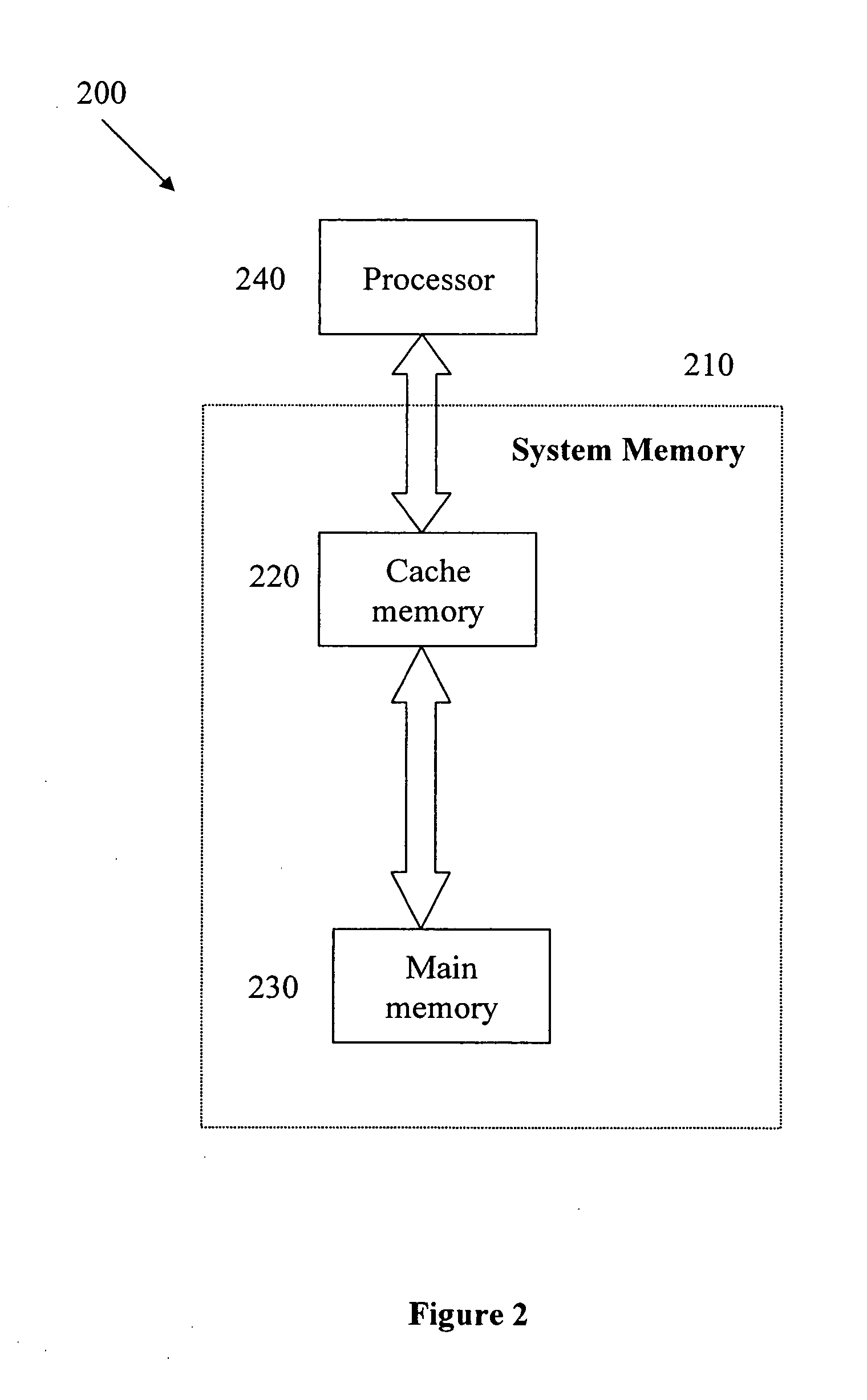
Cache memory background preprocessing
A cache memory preprocessor prepares a cache memory for use by a processor. The processor accesses a main memory via a cache memory, which serves a data cache for the main memory. The cache memory preprocessor consists of a command inputter, which receives a multiple-way cache memory processing command from the processor, and a command implementer. The command implementer performs background processing upon multiple ways of the cache memory in order to implement the cache memory processing command received by the command inputter.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
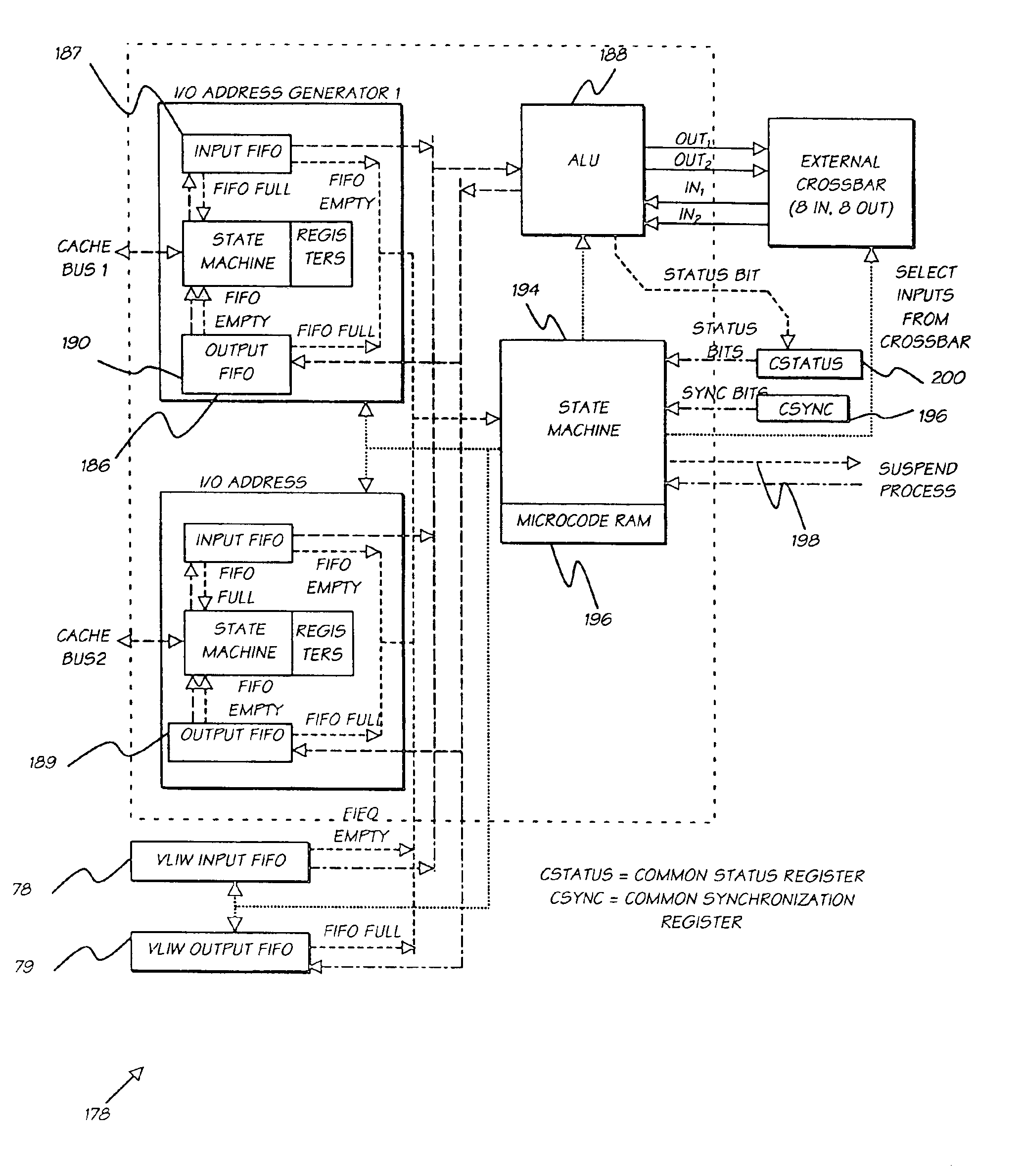
Digital camera system containing a VLIW vector processor
InactiveUS6879341B1Material nanotechnologyTelevision system detailsCrossbar switchArithmetic logic unit
A digital camera has a sensor for sensing an image, a processor for modifying the sensed image in accordance with instructions input into the camera and an output for outputting the modified image where the processor includes a series of processing elements arranged around a central crossbar switch. The processing elements include an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) acting under the control of a writeable microcode store, an internal input and output FIFO for storing pixel data to be processed by the processing elements and the processor is interconnected to a read and write FIFO for reading and writing pixel data of images to the processor. Each of the processing elements can be arranged in a ring and each element is also separately connected to its nearest neighbors. The ALU receives a series of inputs interconnected via an internal crossbar switch to a series of core processing units within the ALU and includes a number of internal registers for the storage of temporary data. The core processing units can include at least one of a multiplier, an adder and a barrel shifter. The processing elements are further connected to a common data bus for the transfer of a pixel data to the processing elements and the data bus is interconnected to a data cache which acts as an intermediate cache between the processing elements and a memory store for storing the images.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Business intelligence system with interface that provides for immediate user action
InactiveUS20060089939A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A business intelligence system includes a business activity monitor with a data cache to receive and store enterprise data integrated from a plurality of enterprise applications, the data cache being updated in real-time as the enterprise data changes. A computer coupled with the data cache runs a program that produces a graphical user interface on a display. The graphical user interface provides a user with a real-time report of the enterprise data and a page that allows the user to specify at least one action affecting operation of the enterprise. The page also including a button selection of which causes the computer to send a first message designating one or more selected actions to the BAM. In response, the BAM sends a second message to one or more of the enterprise applications to execute the one or more selected actions in real-time. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
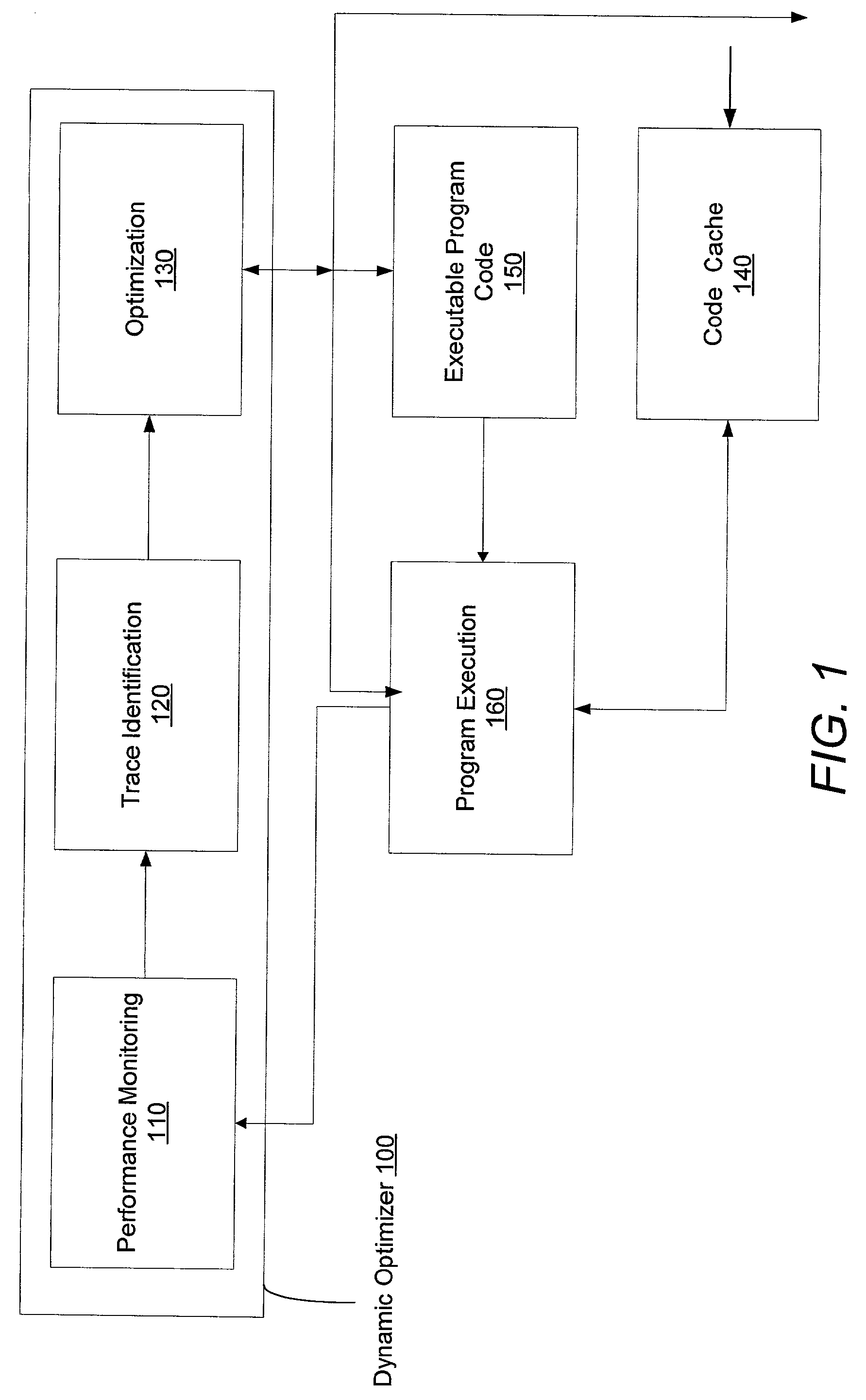
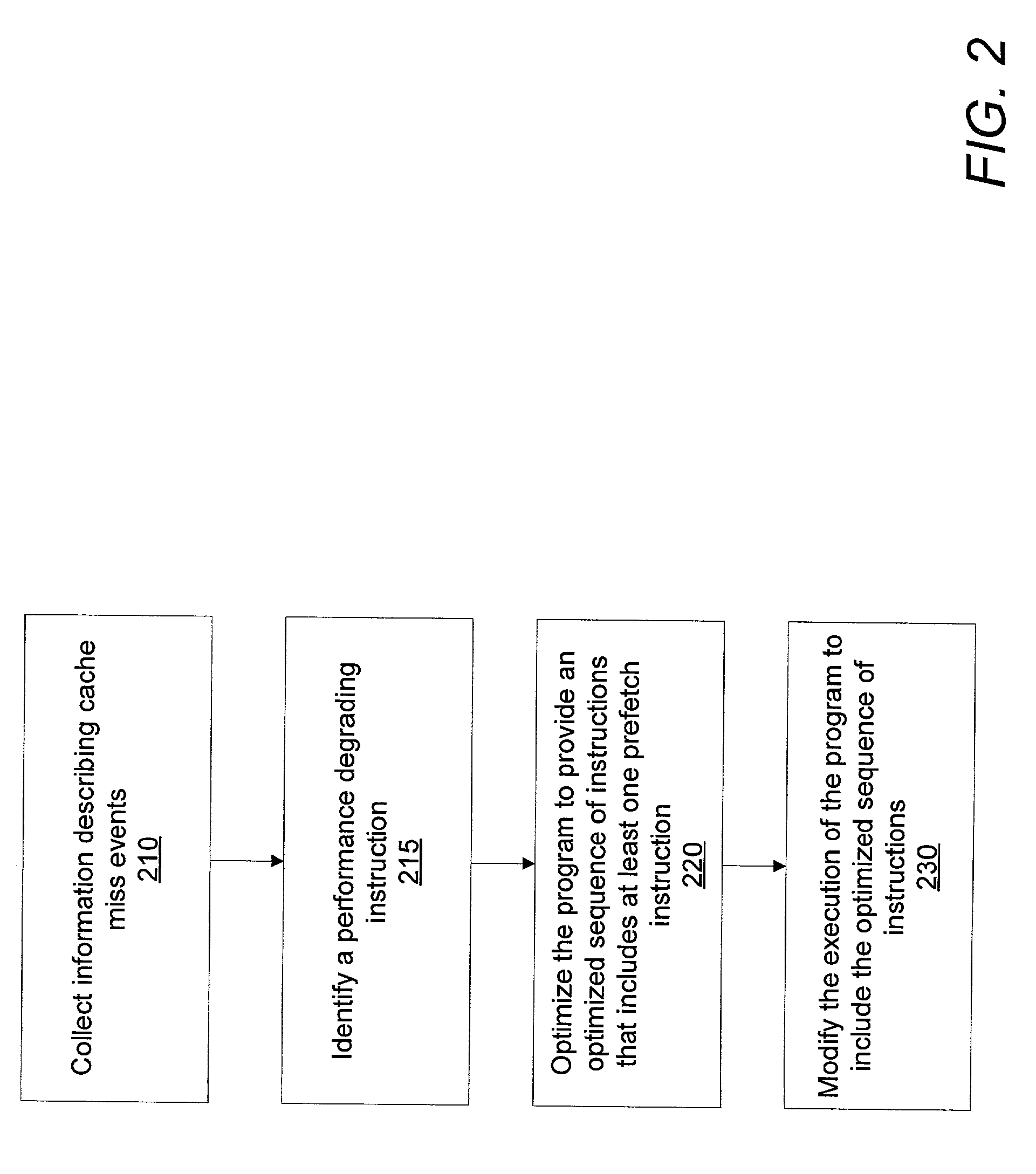
Method of efficient dynamic data cache prefetch insertion
InactiveUS20030145314A1Reducing subsequent cache missesMemory architecture accessing/allocationSoftware engineeringCache missData cache
A system and method for dynamically inserting a data cache prefetch instruction into a program executable to optimize the program being executed. The method, and system thereof, monitors the execution of the program, samples on the cache miss events, identifies the time-consuming execution paths, and optimizes the program during runtime by inserting a prefetch instruction into a new optimized code to hide cache miss latency.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Load balancing technique implemented in a data network device utilizing a data cache
InactiveUS20050261985A1Easy to useDigital data information retrievalMultiprogramming arrangementsLoad SheddingData pack
Techniques for implementing a load balanced server system are described which may be used for effecting electronic commerce over a data network. The system comprises a load balancing system and a plurality of servers in communication with the load balancing system. Each of the plurality of servers may include a respective data cache for storing state information relating to client session transactions conducted between the server and a particular client. The load balancing system can be configured to select, using a load balancing protocol, an available first server from the plurality of servers to process an initial packet received from a source device such as, for example, a client machine of a customer. The load balancing system can also configured to route subsequent packets received from the source device to the first server. Before generating its response, the first server may verify that the state information relating to a specific client session stored in the data cache is up-to-date. If the first server determines that the state information stored in the data cache is not up-to-date, then the first server may be configured to retrieve the desired up-to-date state information from a database which is configured to store all state information relating to client sessions which have been initiated with the server system.
Owner:JUNE RAY
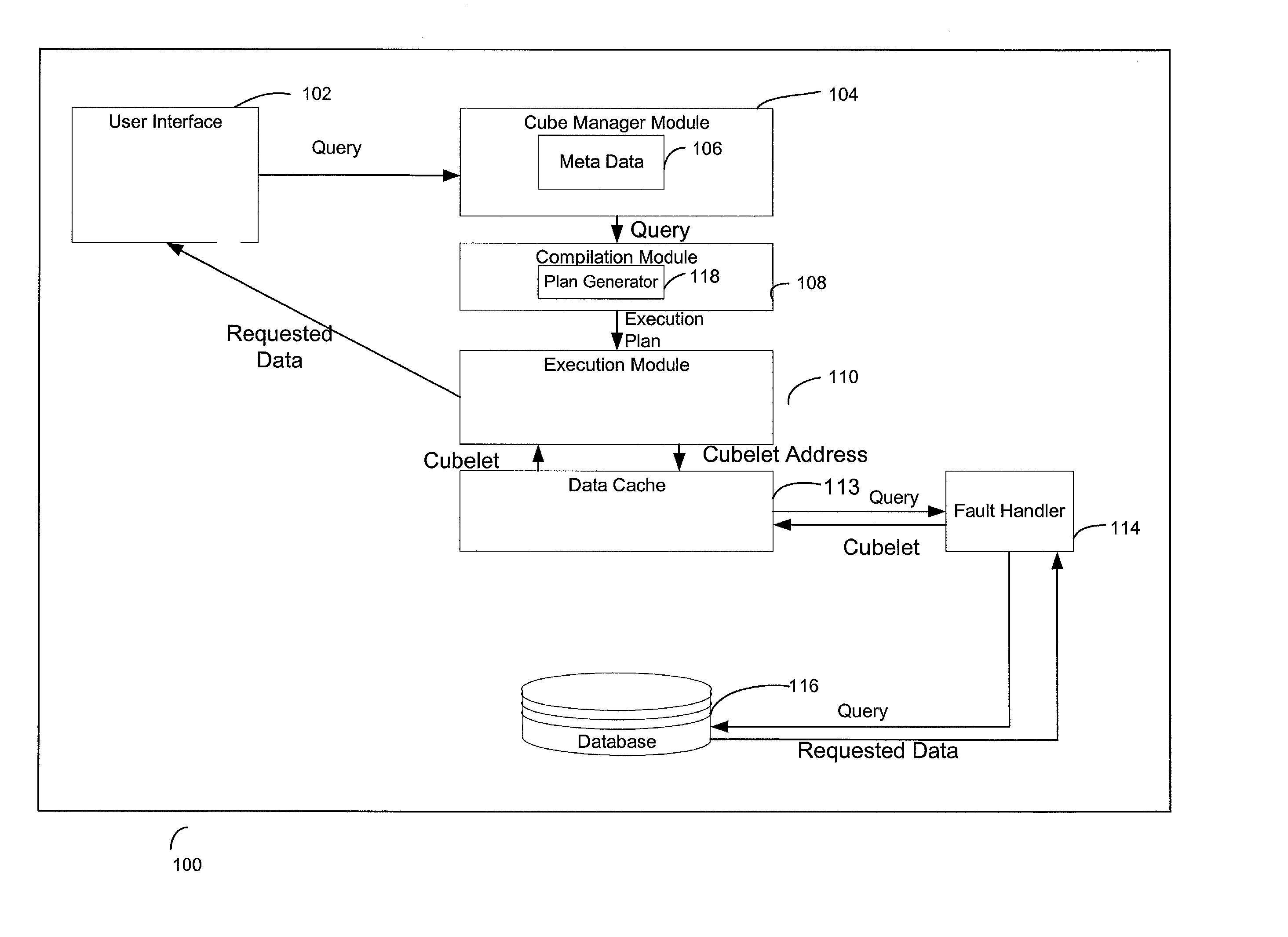
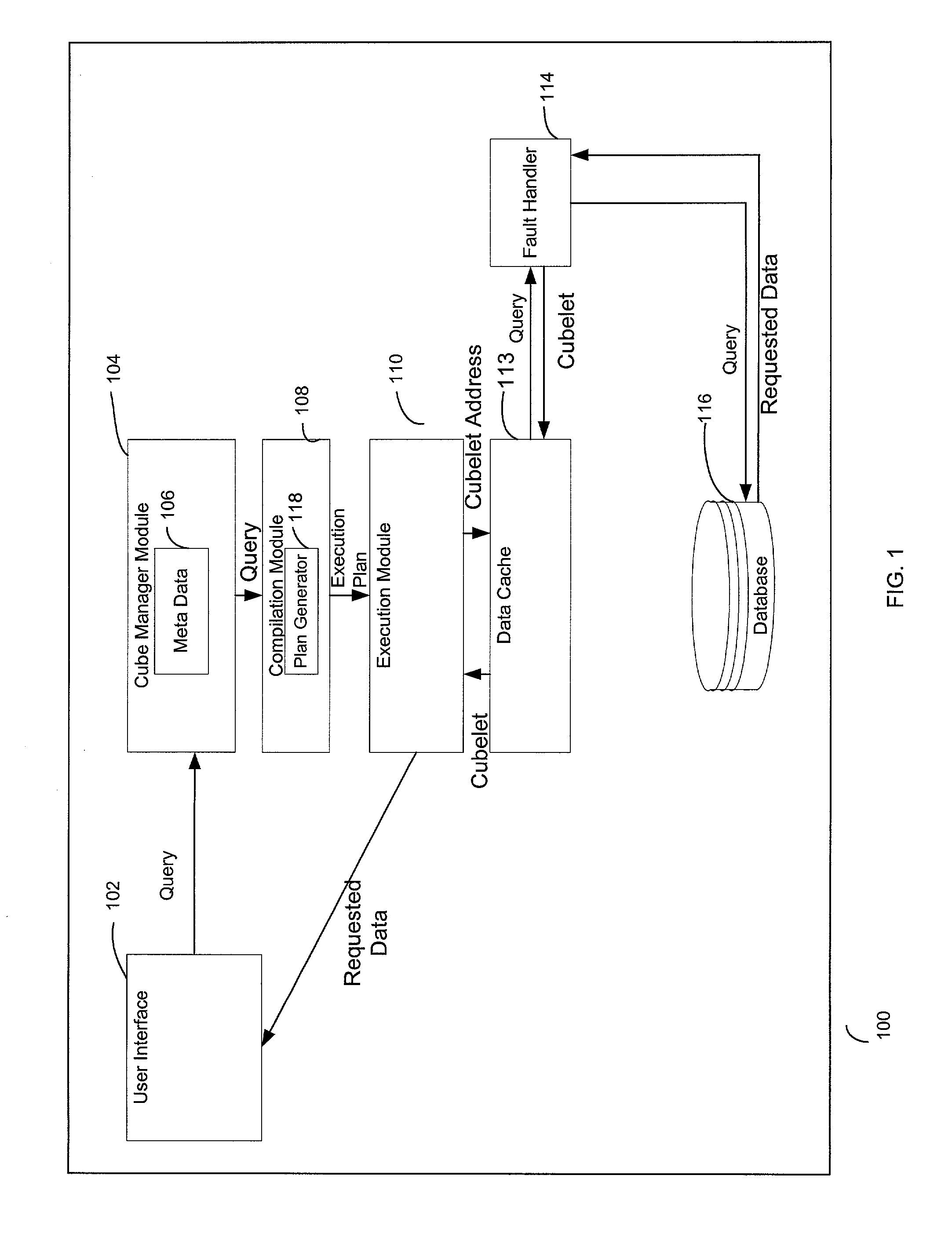
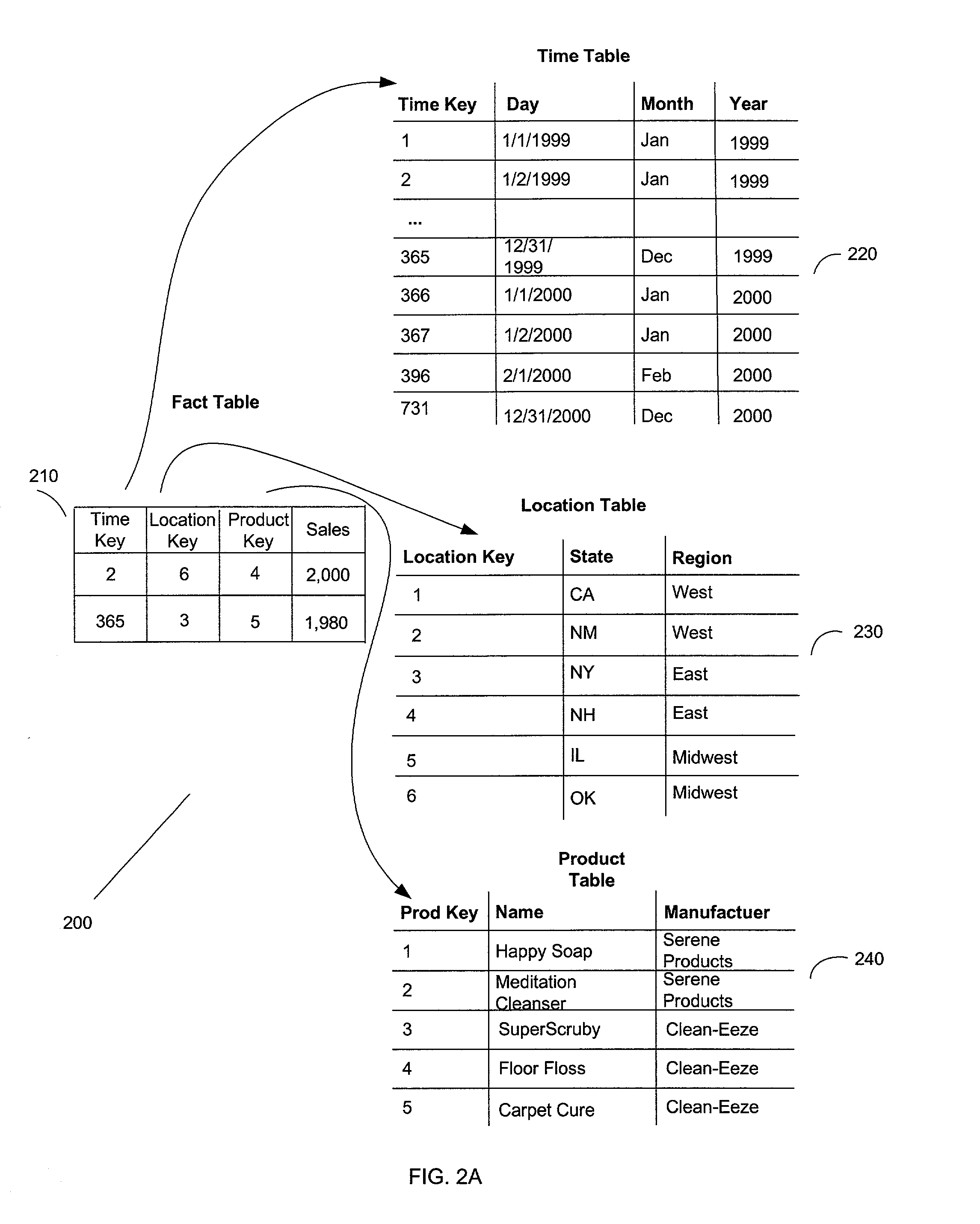
Caching scheme for multi-dimensional data
InactiveUS20020126545A1Data processing applicationsDigital storageLocality of referenceError processing
A system, method, and a computer program product for caching multi-dimensional data based on an assumption of locality of reference. A user sends a query for data. A described compilation module converts the query into a set of cubelet addresses and canonical addresses. In the described embodiment, if the data corresponding to the cubelet address is found in a data cache, the data cache returns the cubelet, which may contain the requested data and data for "nearby" cells. The data corresponding to the canonical addresses is extracted from the returned cubelet. If the data is not found in a data cache, a fault handler queries a back-end database for the cubelet identified by the cubelet address. This cubelet includes the requested data and data for "nearby" cells. The requested data and the data for "nearby cells" are in the form of values of measure attributes and associated canonical addresses. The returned cubelet is then cached and the data corresponding to the canonical addresses is extracted.
Owner:IBM CORP
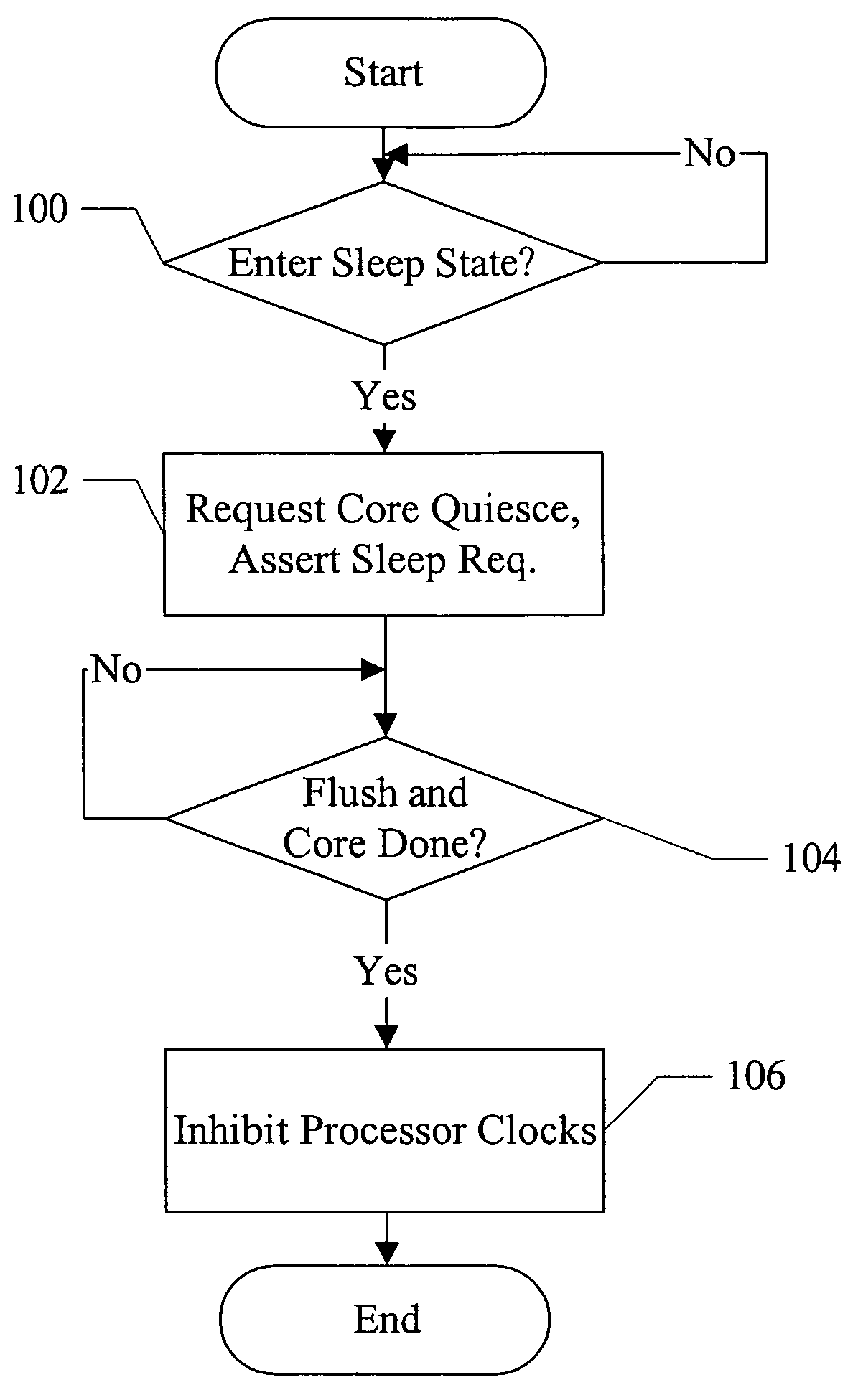
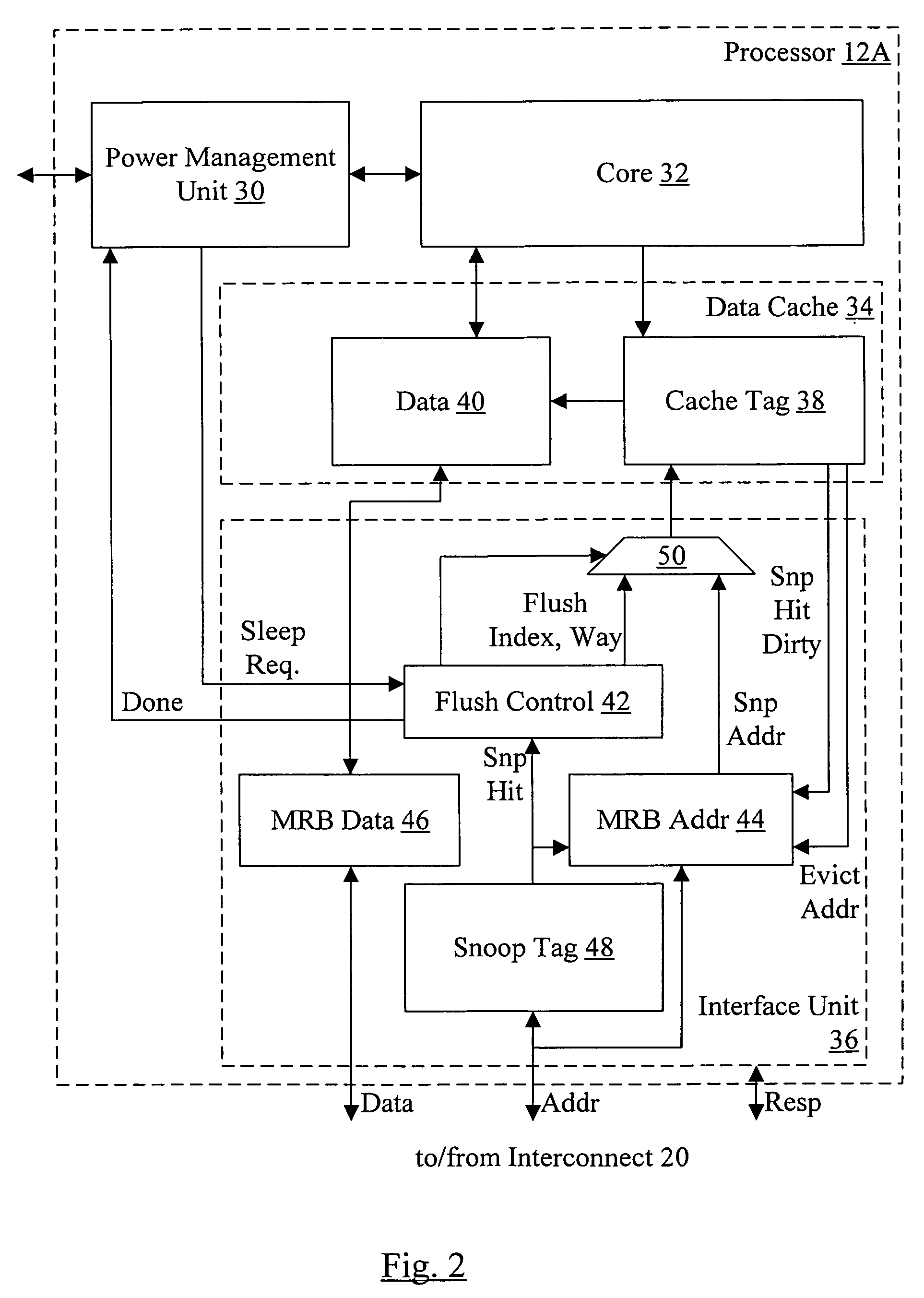
Fast L1 flush mechanism
In one embodiment, a processor comprises a data cache configured to store a plurality of cache blocks and a control unit coupled to the data cache. The control unit is configured to flush the plurality of cache blocks from the data cache responsive to an indication that the processor is to transition to a low power state in which one or more clocks for the processor are inhibited.
Owner:APPLE INC
Data caching based on data contents
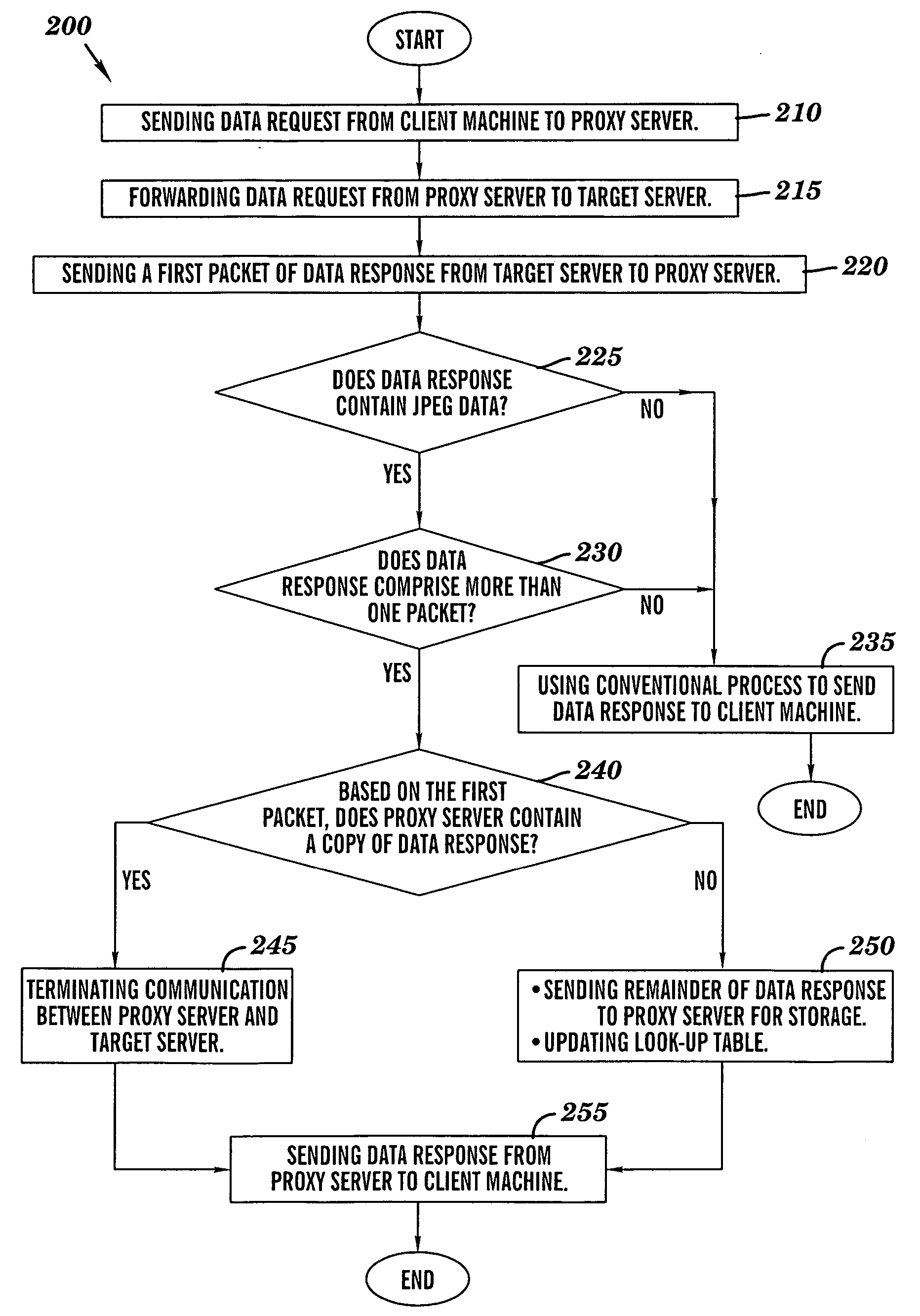
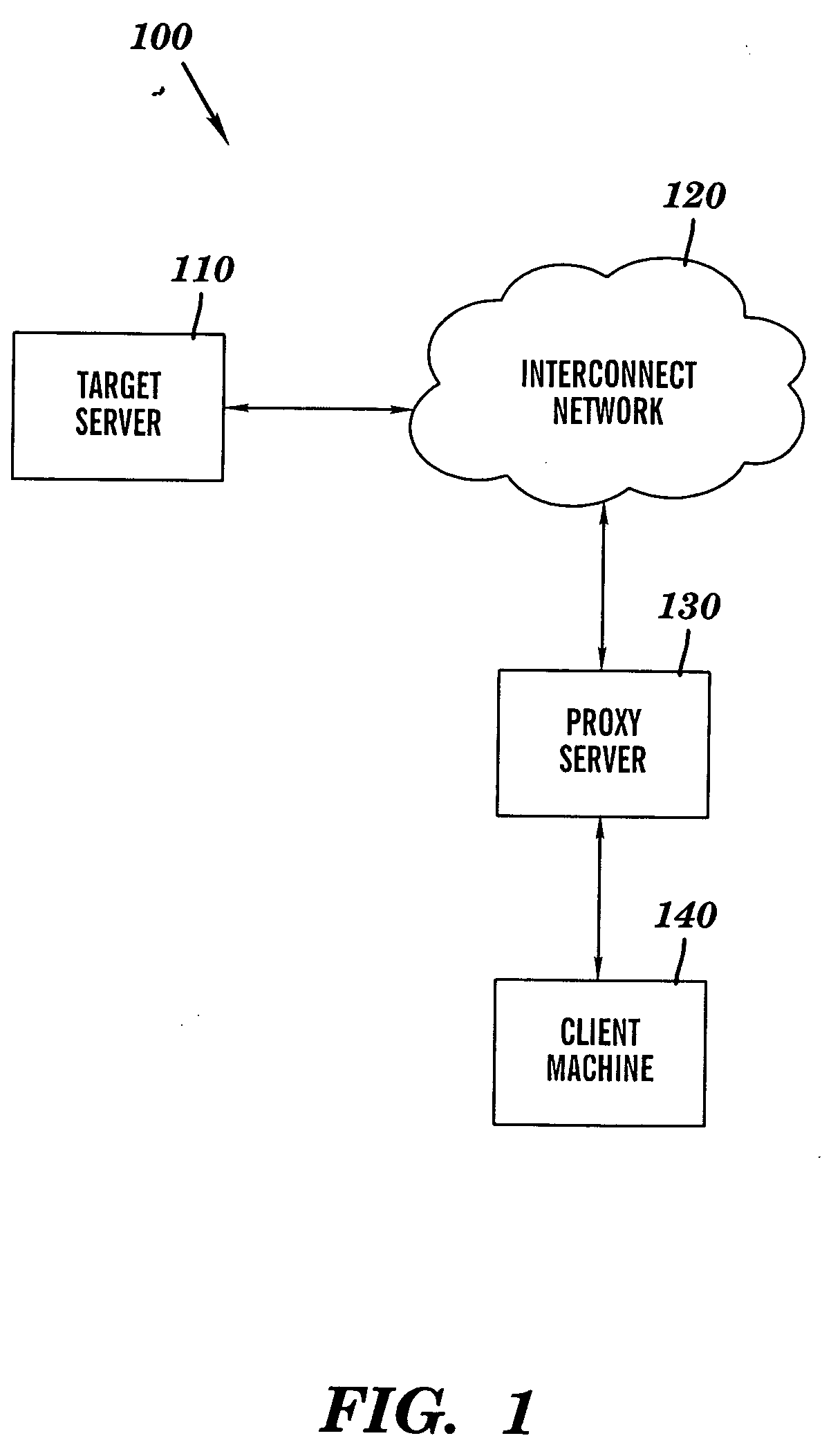
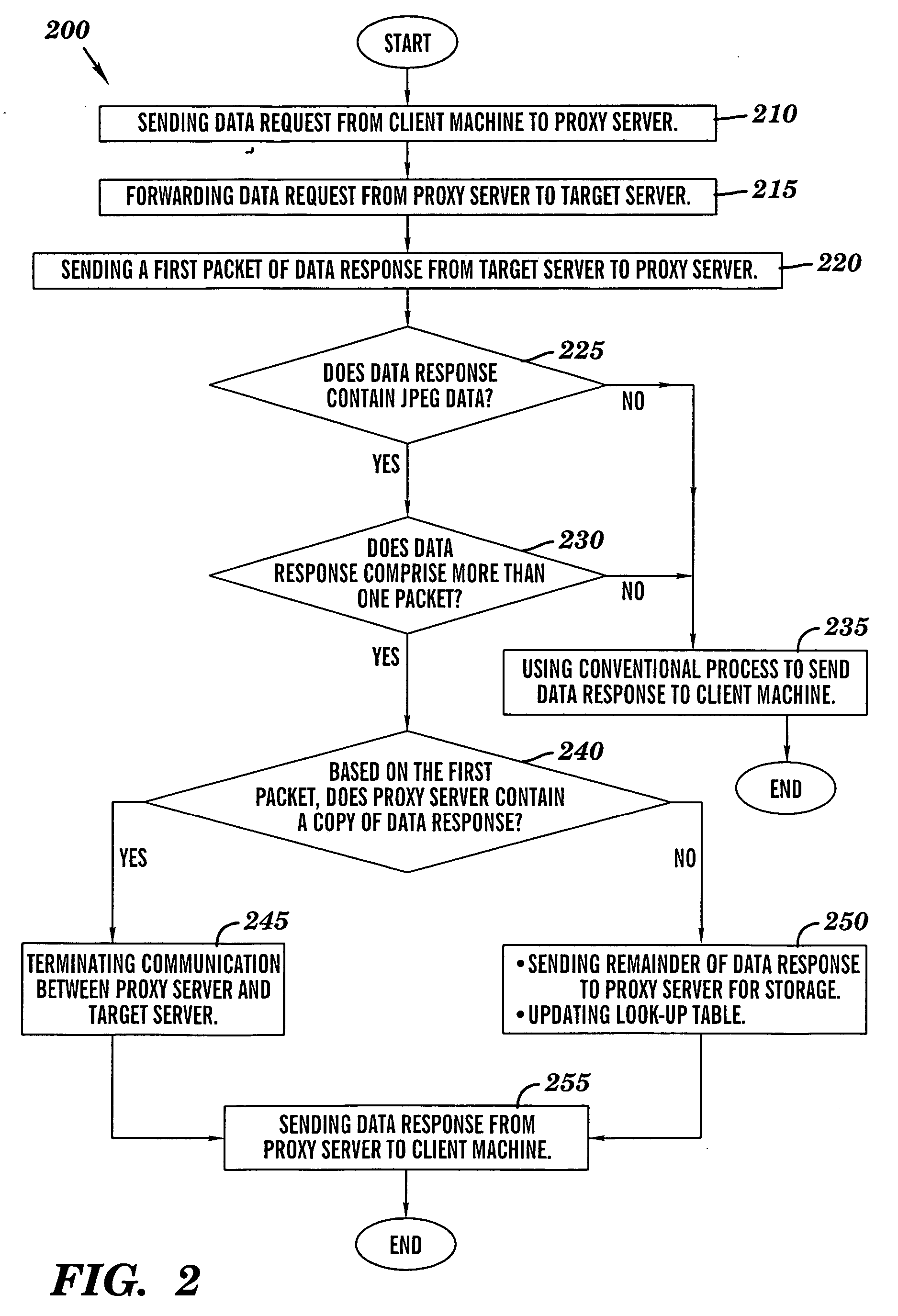
ActiveUS20060167969A1LessMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData contentClient machine
A novel method and structure in which data caching is based on data contents. The method comprises the steps of (a) sending a data request from a processing circuit to a target server; (b) in response to the target server receiving the data request, sending a first response portion of a data response from the target server to the processing circuit; and {circle around (c)} in response to the processing circuit receiving the first response portion, using the processing circuit to examine the first response portion so as to determine whether the processing circuit contains a copy of the data response; and (d) in response to the processing circuit determining that the processing circuit contains a copy of the data response, sending the copy of the data response from the processing circuit to a client machine.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Method and article of manufacture for component based task handling during claim processing
A computer program is provided for developing component based software capable of handling insurance-related tasks. The program includes a data component that stores, retrieves and manipulates data utilizing a plurality of functions. Also provided is a client component which includes an adapter component that transmits and receives data to / from the data component. The client component also includes a business component that serves as a data cache and includes logic for manipulating the data. A controller component is also included which is adapted to handle events generated by a user utilizing the business component to cache data and the adapter component to ultimately persist data to a data repository. In use, the client component allows a user to define tasks that achieve an insurance-related goal upon completion. In addition, the user is able to input rules which dictate which tasks should be selected based on a set of predetermined events. Events are then received from any source, such as a common event queue. Finally, tasks are selected and outputted based on the received events.
Owner:DUCK CREEK TECH LTD
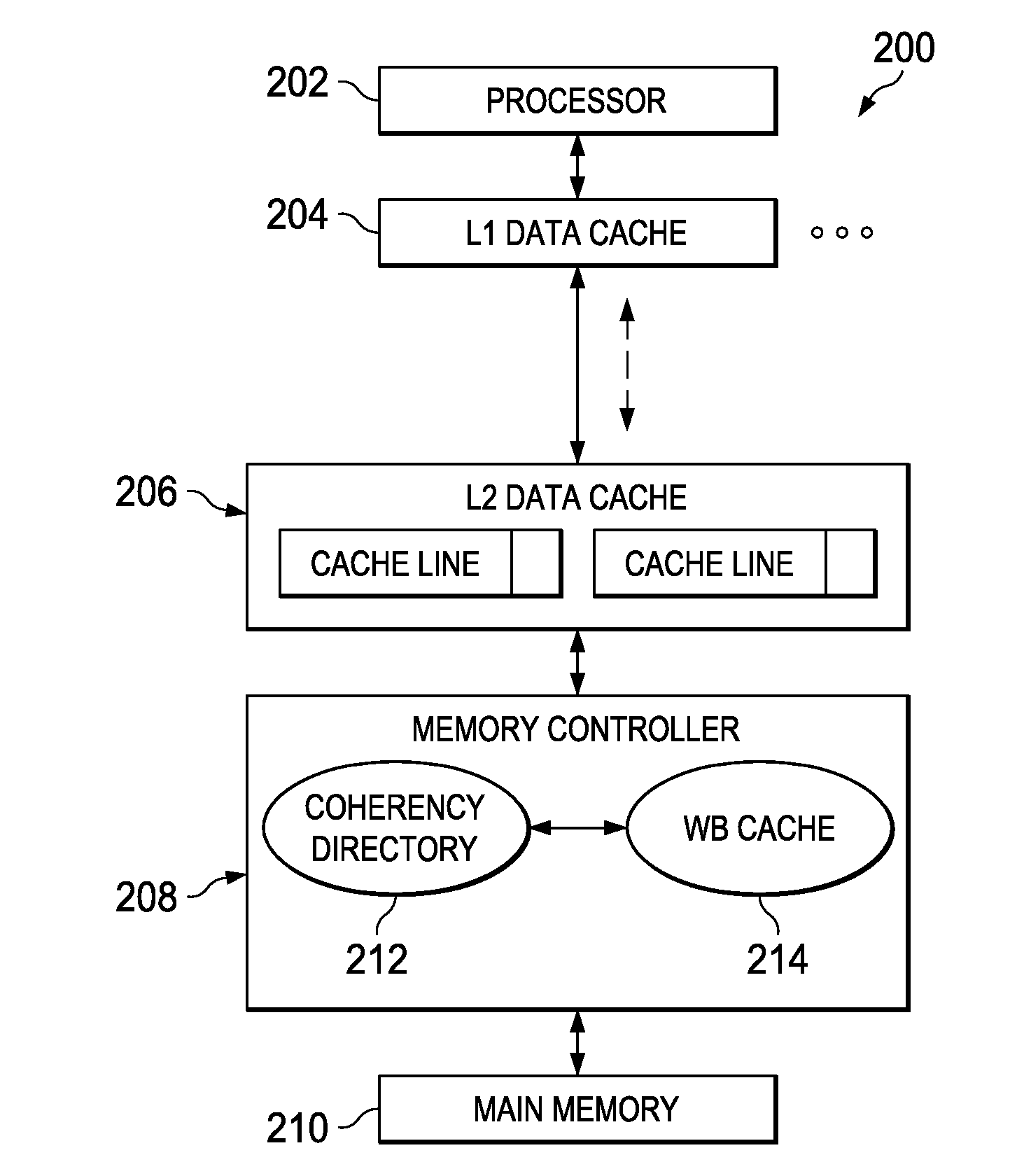
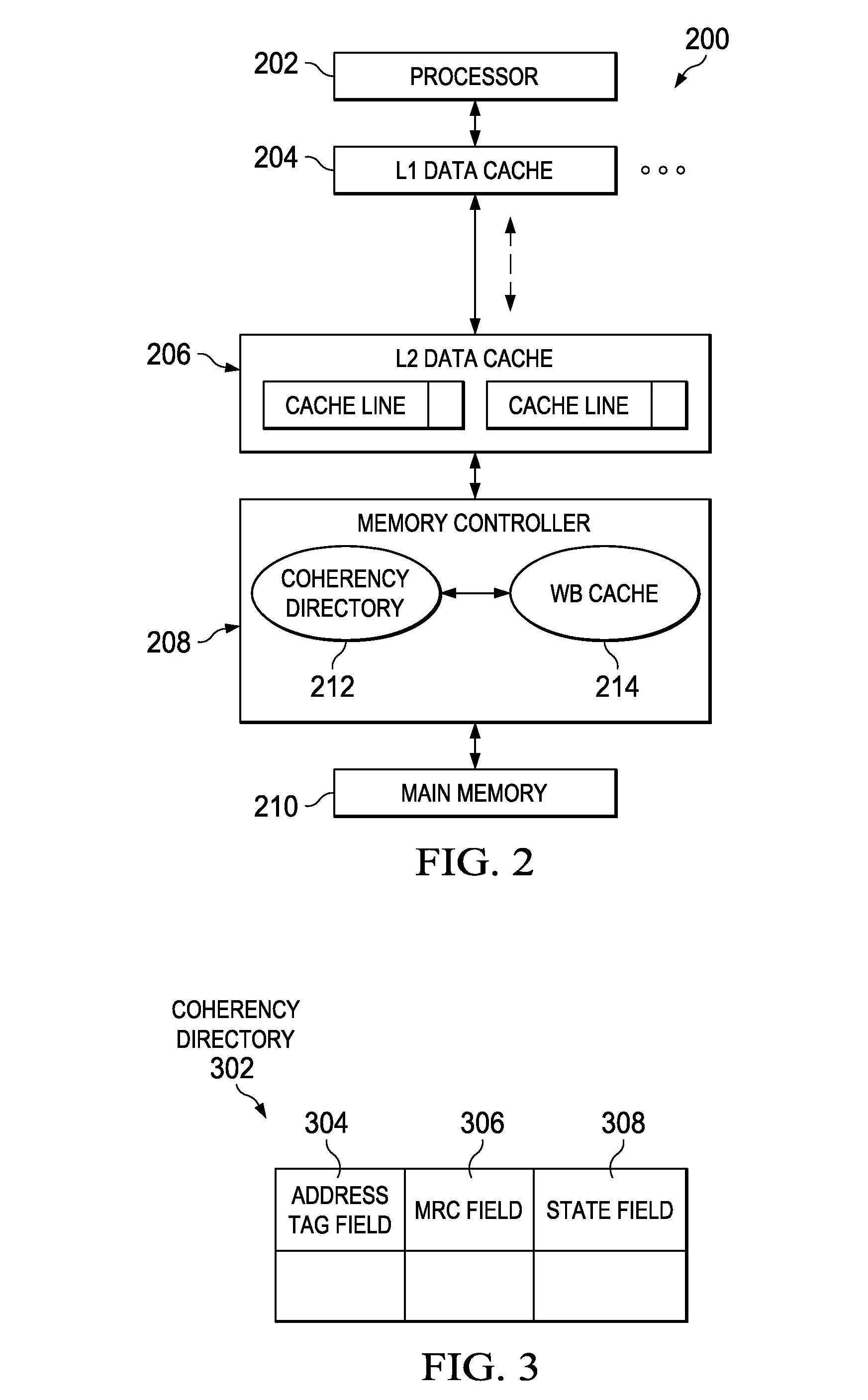
Write-Back Coherency Data Cache for Resolving Read/Write Conflicts
ActiveUS20100325367A1Improve system performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingMemory controller
A write-back coherency data cache for temporarily holding cache lines. Upon receiving a processor request for data, a determination is made from a coherency directory whether a copy of the data is cached in a write-back cache located in a memory controller hardware. The write-back cache holds data being written back to main memory for a period of time prior to writing the data to main memory. If the data is cached in the write-back cache, the data is removed from the write-back cache and forwarded to the requesting processor. The cache coherency state in the coherency directory entry for the data is updated to reflect the current cache coherency state of the data based on the requesting processor's intended use of the data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for dynamically partitioning very large database indices on write-once tables
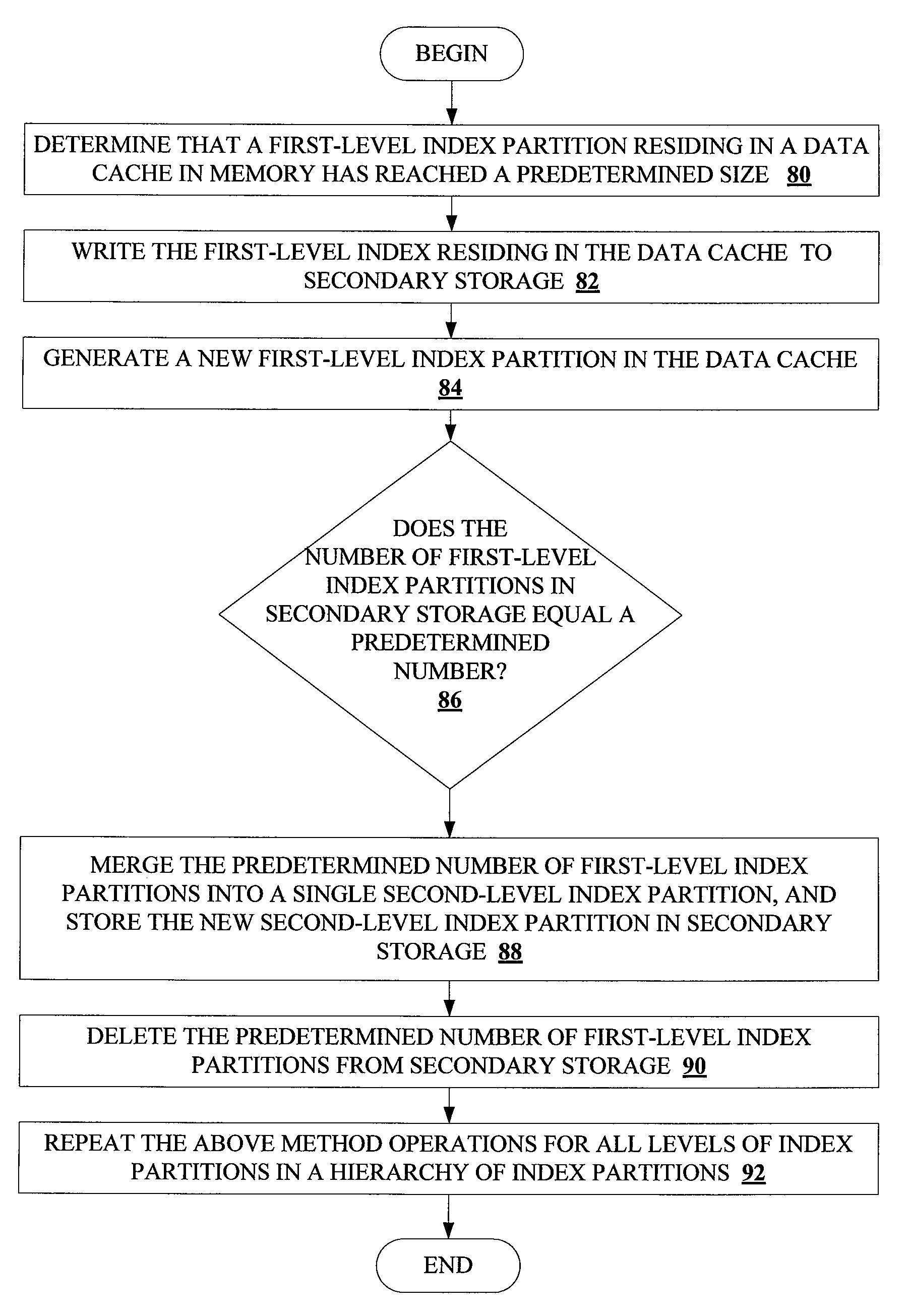
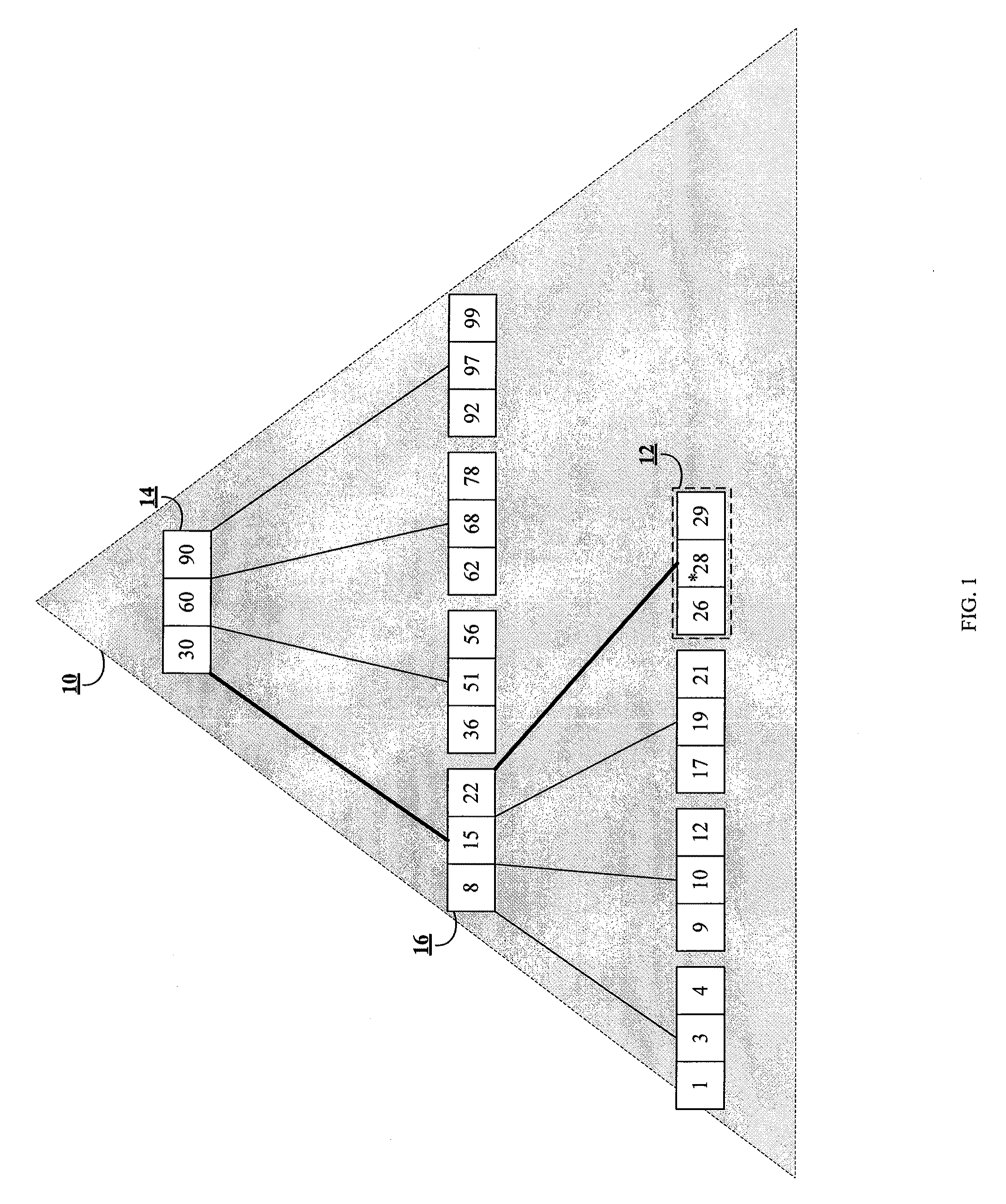
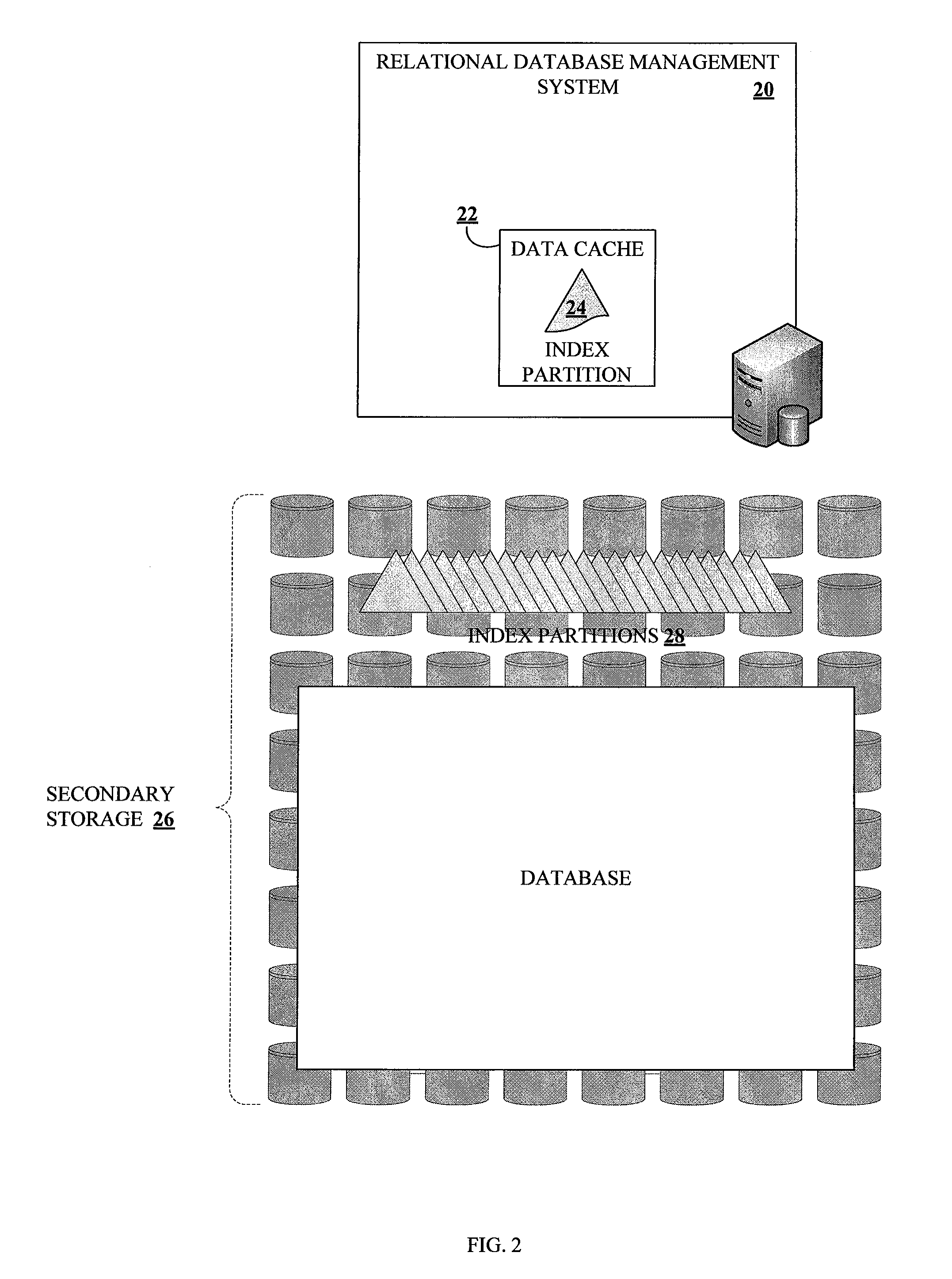
ActiveUS20100161569A1Increase in sizeAvoid performance degradationDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesDatabase indexIncrease size
Methods and systems for partitioning and dynamically merging a database index are described. A database index includes a single first-level index partition stored in a data cache. As the first-level index partition in the data cache reaches a predetermined size, it is copied to secondary storage and a new index partition is generated in the data cache. When the number of index partitions in secondary storage reaches some predetermined number, the index partitions are merged to create a single index partition of a higher level in a hierarchy of index partitions having an exponentially increasing size with each increase in level within the hierarchy.
Owner:SAP AG
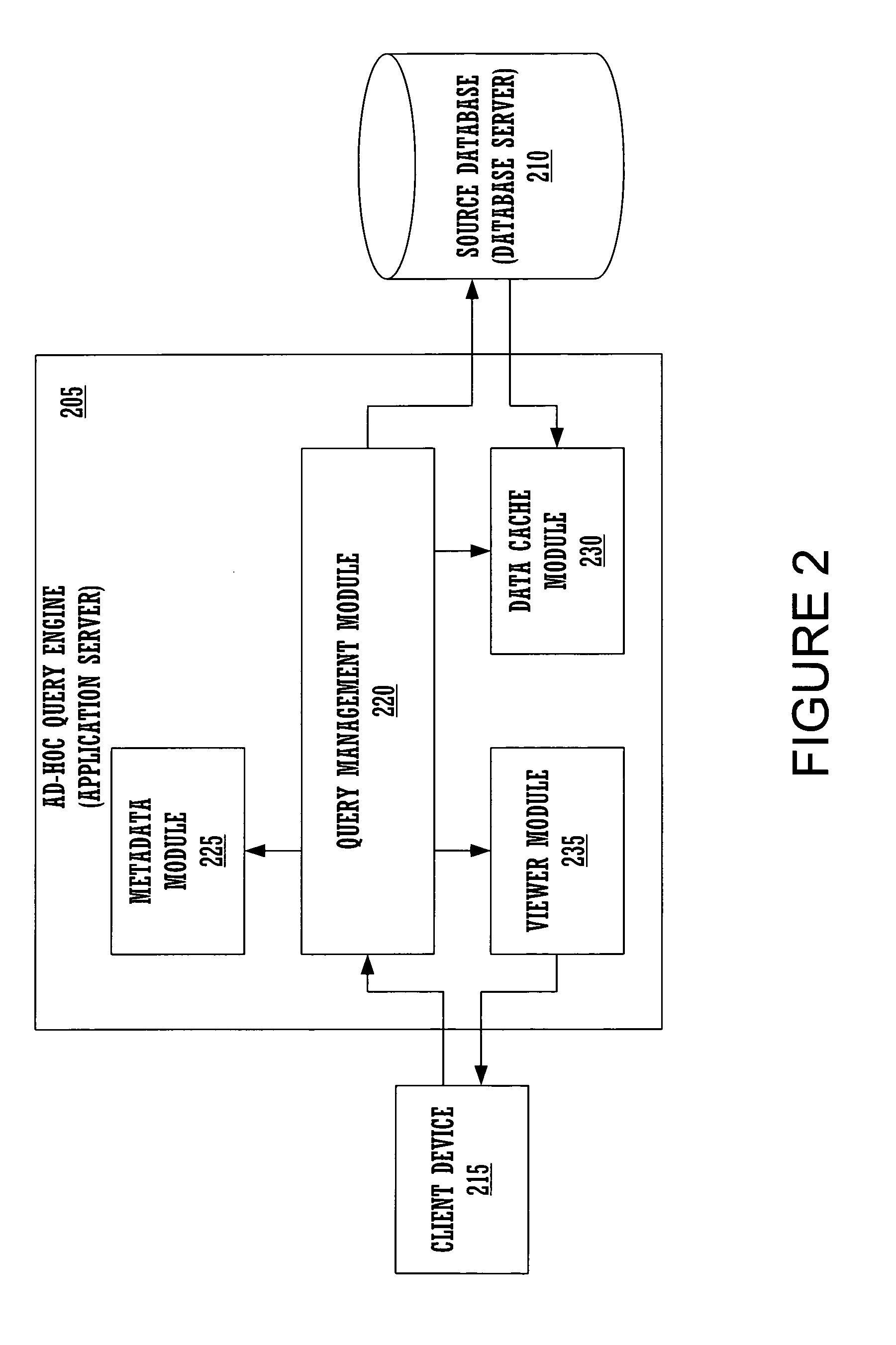
Enhanced ad-hoc query aggregation
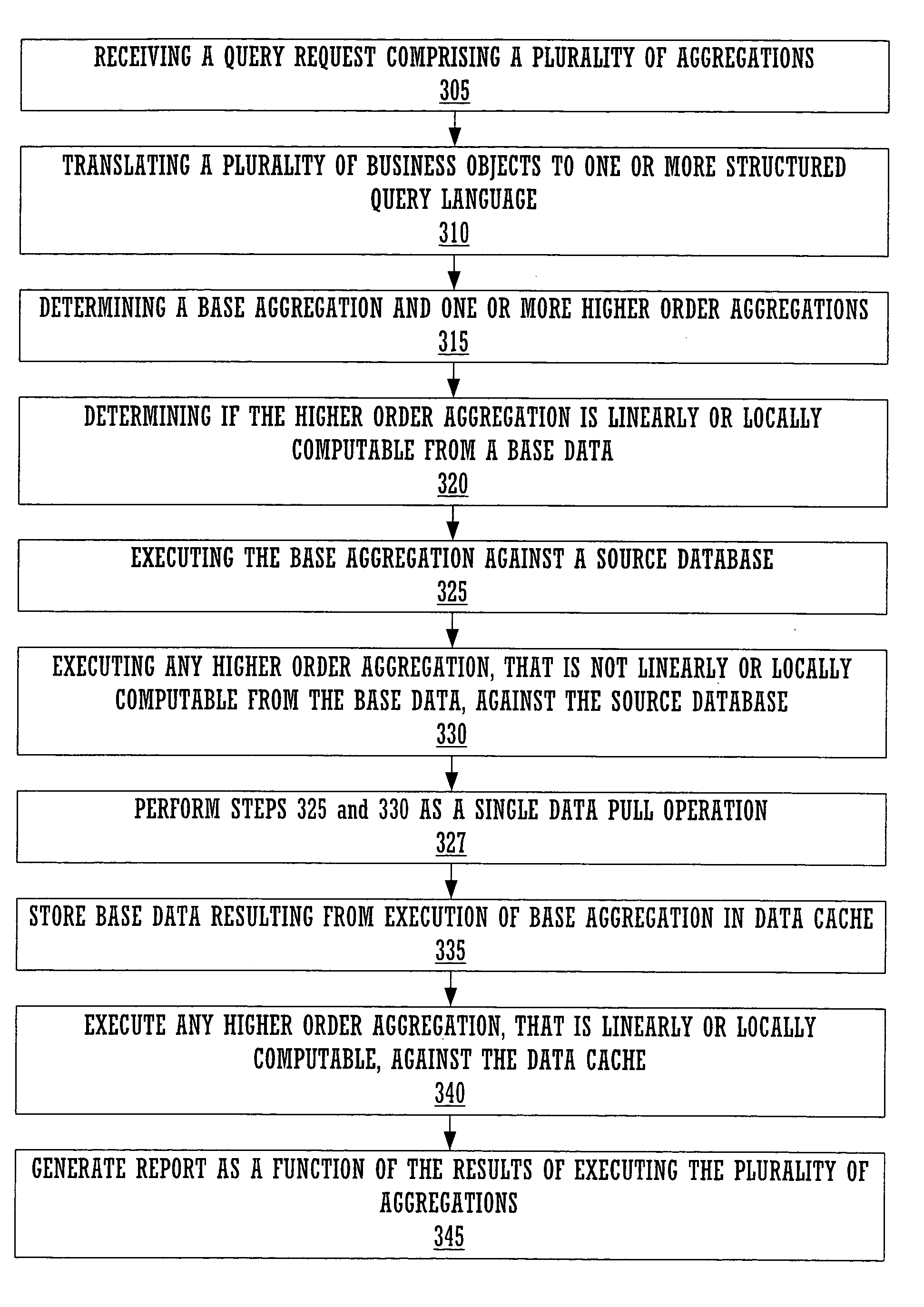
ActiveUS7110997B1Reduce utilizationImprove performanceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalClient-sideQuery language
Embodiments of the present invention provide an ad-hoc query engine. The ad-hoc query engine comprises a query management module, a metadata module, a data cache module and a viewer module. The query management module receives a query request from a client device. The query request is specified in terms of a plurality of business objects. The query management module utilizes the metadata module to translate the business objects into a structured query language statement as a function of the content of the data cache module. The SQL statement comprises a plurality of aggregation. The query management module dynamically causes each aggregation to be re-directed to execute against the content of the data cache module, when the aggregation is locally or linearly computable from said content of said data cache module. The query management utilizes the viewer module to generate a report as a function of the results of the executed SQL statement.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
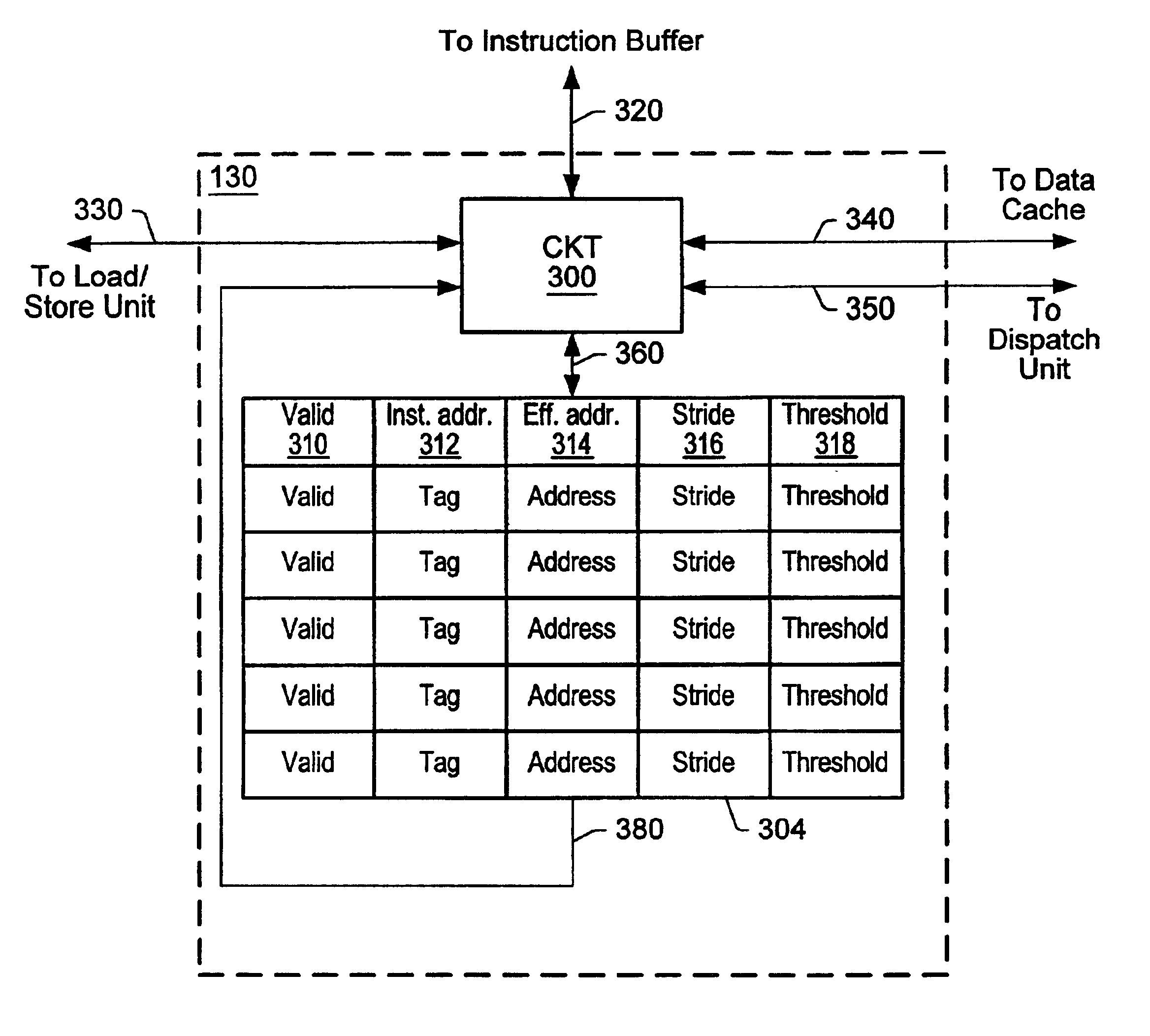
Threshold-based load address prediction and new thread identification in a multithreaded microprocessor
ActiveUS6907520B2Memory access latencyTake advantage ofMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital computer detailsLoad instructionInstruction window
A method and apparatus for predicting load addresses and identifying new threads of instructions for execution in a multithreaded processor. A load prediction unit scans an instruction window for load instructions. A load prediction table is searched for an entry corresponding to a detected load instruction. If an entry is found in the table, a load address prediction is made for the load instruction and conveyed to the data cache. If the load address misses in the cache, the data is prefetched. Subsequently, if it is determined that the load prediction was incorrect, a miss counter in the corresponding entry in the load prediction table is incremented. If on a subsequent detection of the load instruction, the miss counter has reached a threshold, the load instruction is predicted to miss. In response to the predicted miss, a new thread of instructions is identified for execution.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
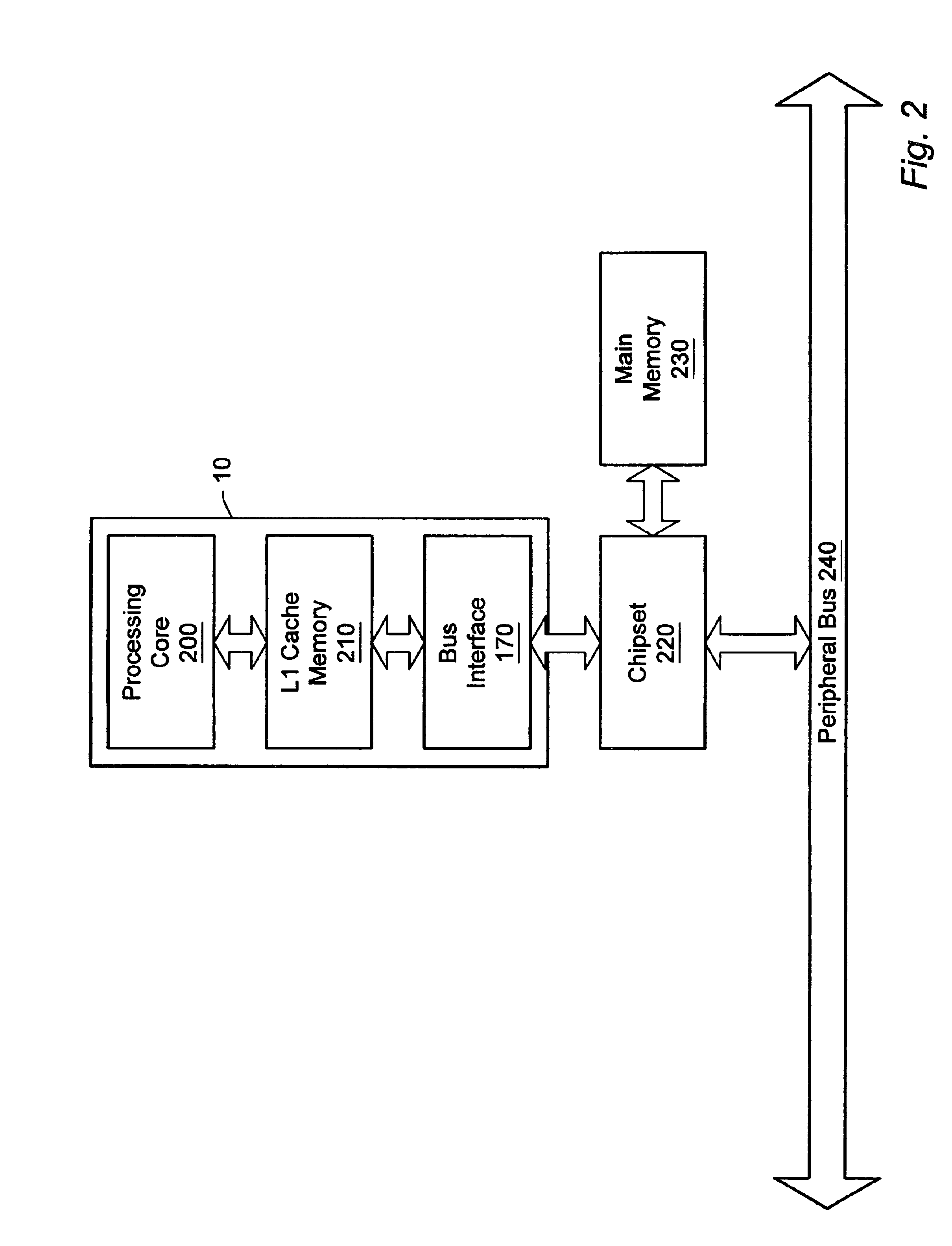
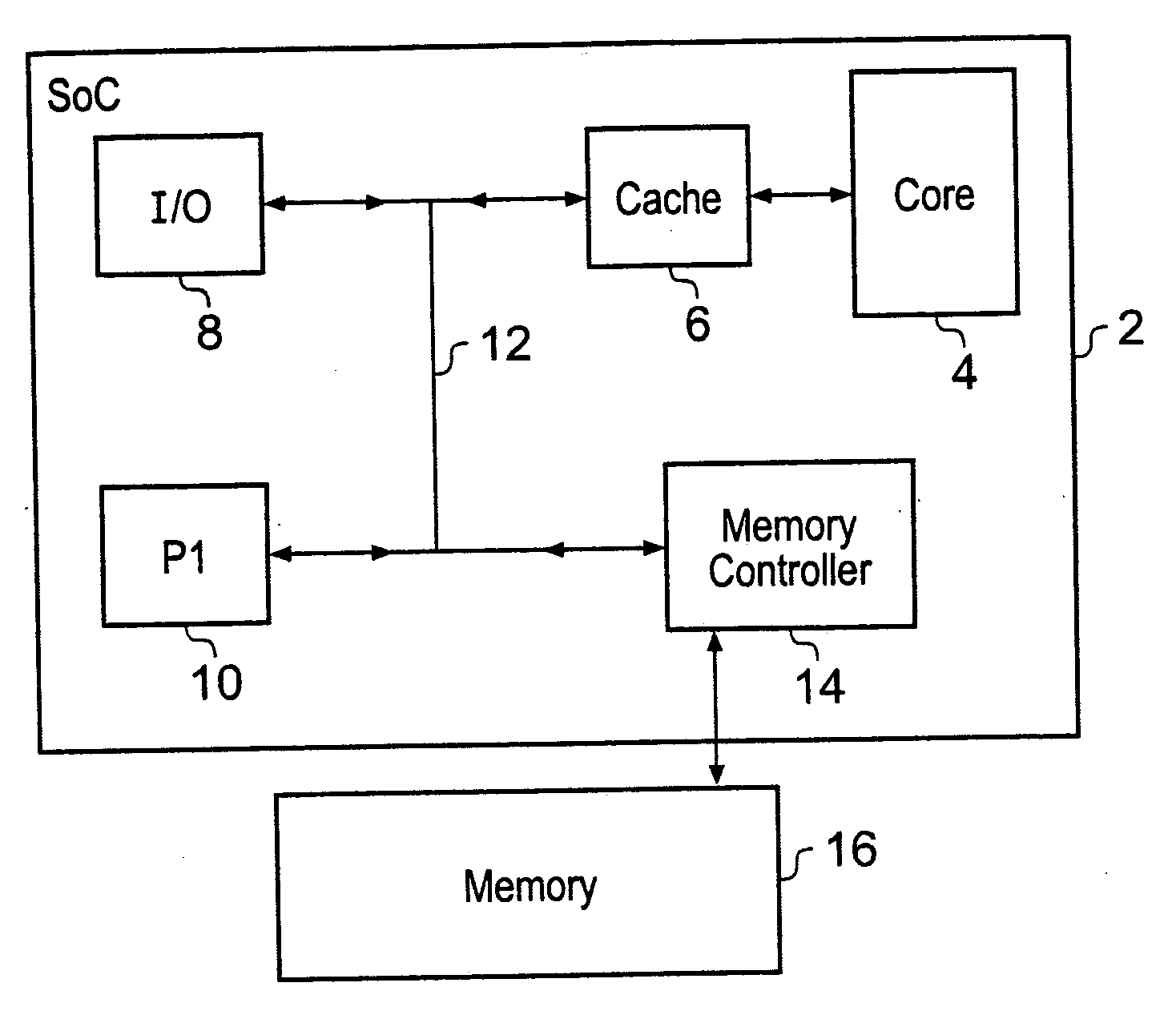
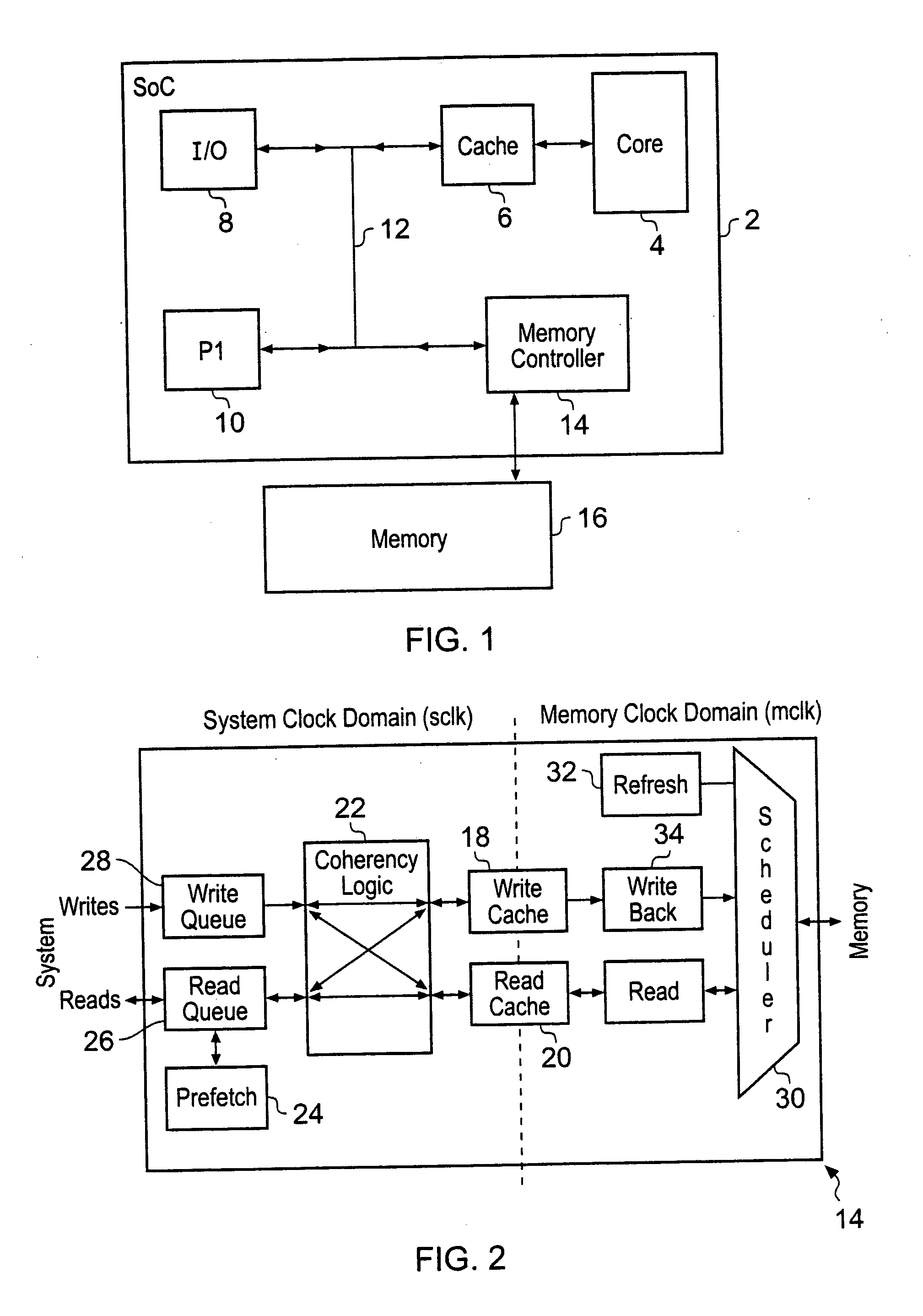
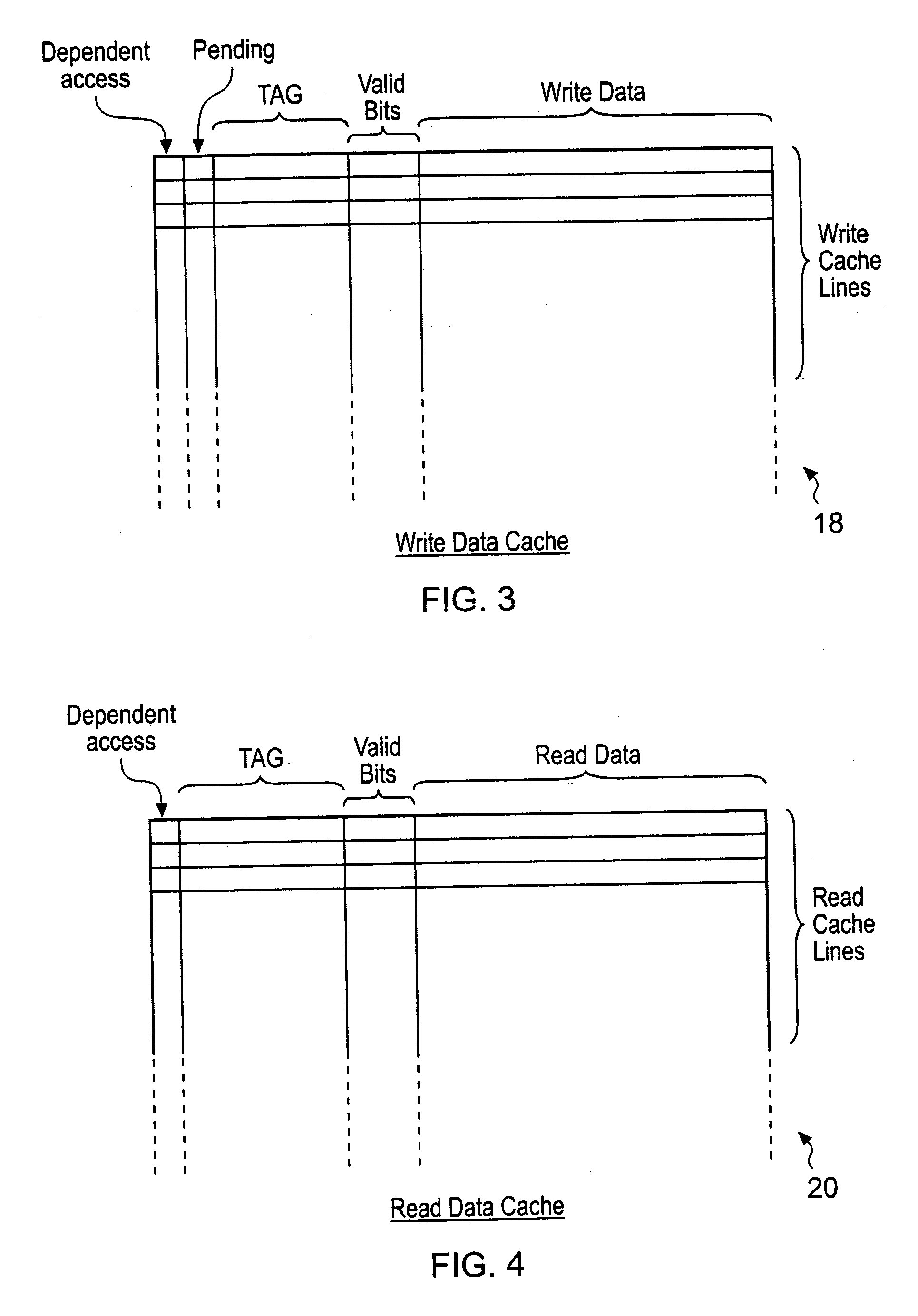
Memory controller with write data cache and read data cache
A memory controller 14 includes a write data cache 18, a read data cache 20 and coherency circuitry 22. The coherency circuitry 22 manages coherency of data between the write data cache 18, the read data cache 20 and data stored within a main memory 16 when servicing read requests and write requests received by the memory controller 14. Write complete signals are issued back to a write requesting circuit as soon as a write request has had its write data stored within the write data cache 18.
Owner:ARM LTD
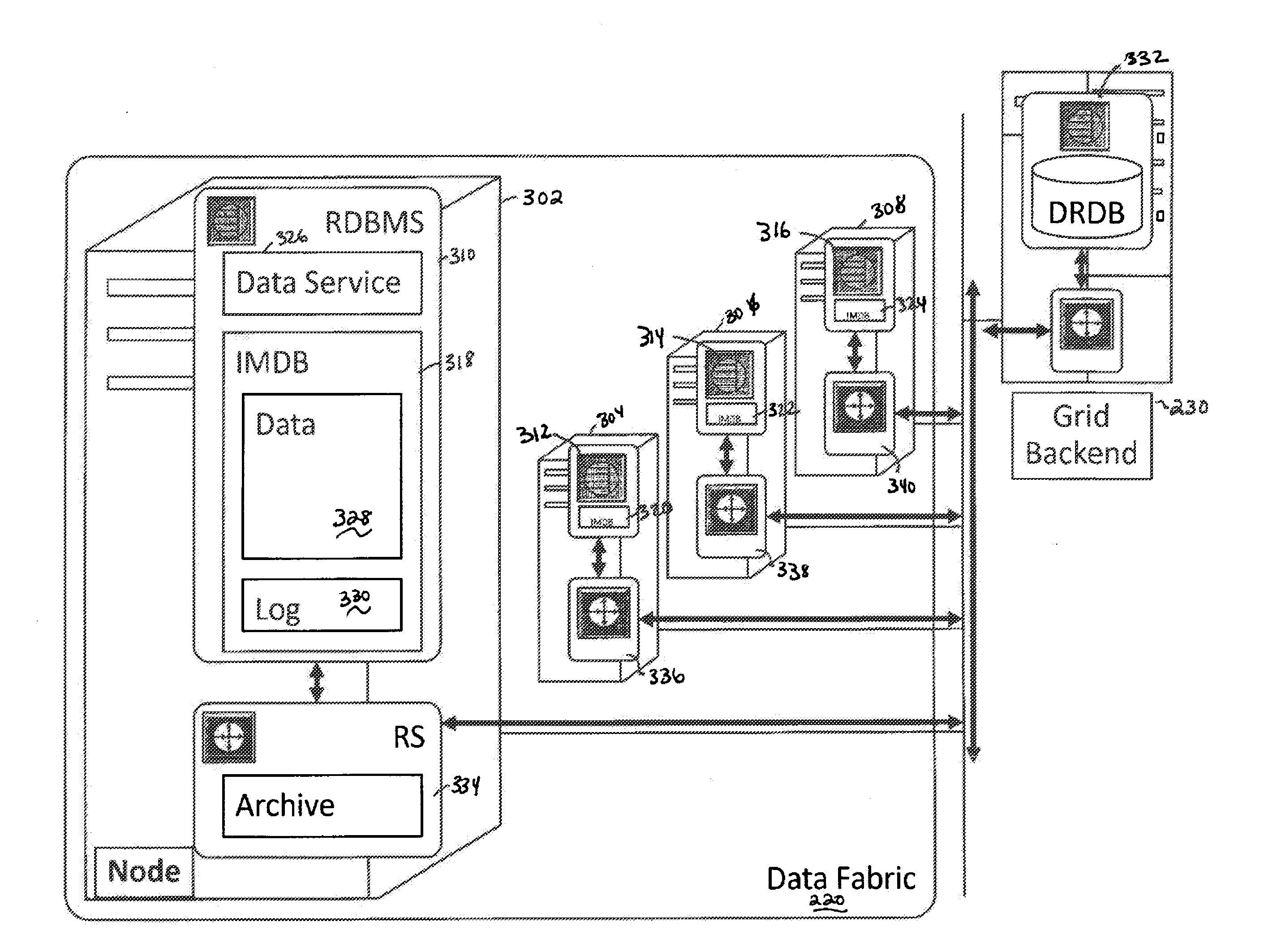
Distributed data cache database architecture
InactiveUS20120158650A1Digital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationIn-memory databaseGranularity
System, method, computer program product embodiments and combinations and sub-combinations thereof for a distributed data cache database architecture are provided. An embodiment includes providing a scalable distribution of in-memory database (IMDB) system nodes organized as one or more data fabrics. Further included is providing a plurality of data granularity types for storing data within the one or more data fabrics. Database executions are managed via the one or more data fabrics for a plurality of applications compatible with at least one data granularity type.
Owner:SYBASE INC
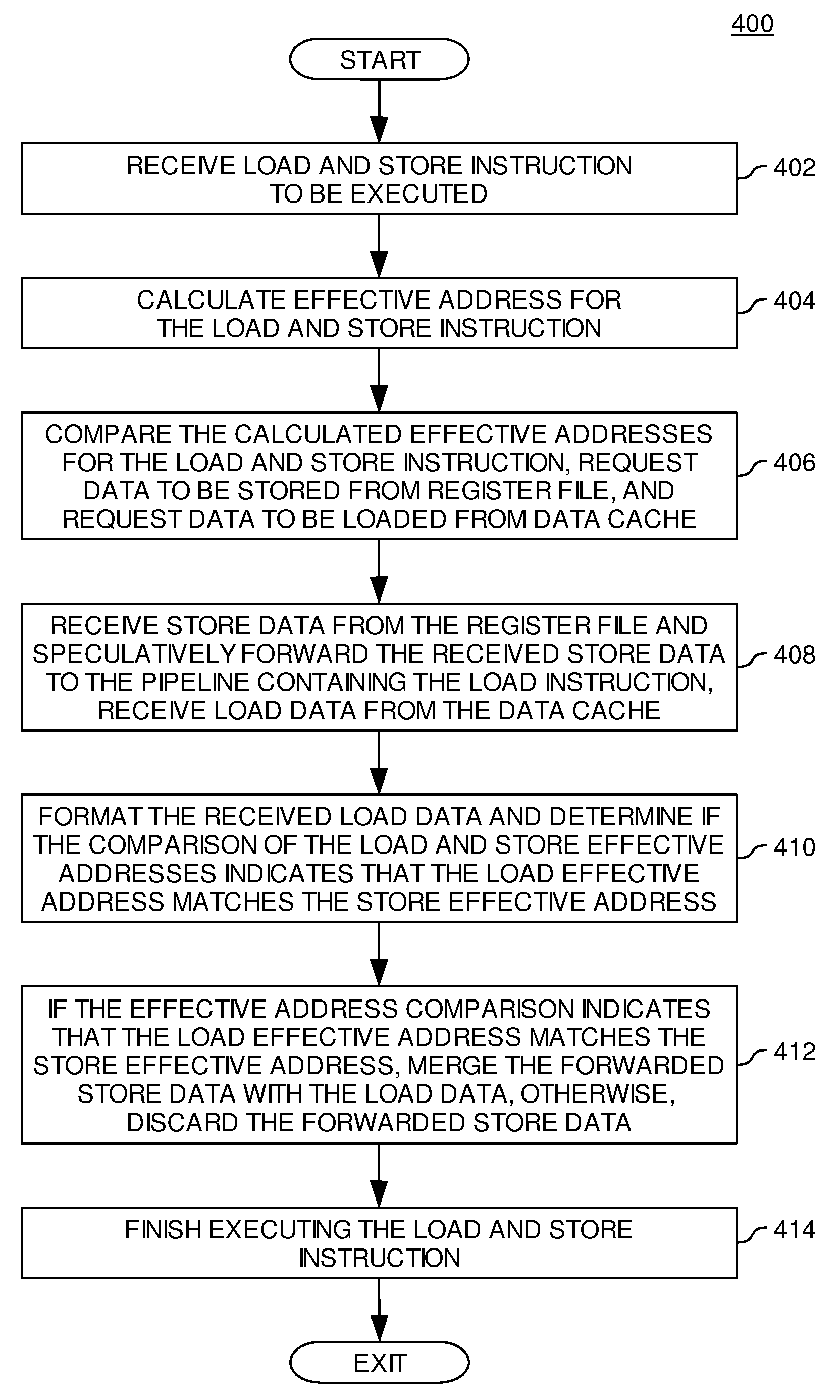
A Fast and Inexpensive Store-Load Conflict Scheduling and Forwarding Mechanism
InactiveUS20070288725A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsLoad instructionParallel computing
Embodiments provide a method and apparatus for executing instructions. In one embodiment, the method includes receiving a load instruction and a store instruction and calculating a load effective address of load data for the load instruction and a store effective address of store data for the store instruction. The method further includes comparing the load effective address with the store effective address and speculatively forwarding the store data for the store instruction from a first pipeline in which the store instruction is being executed to a second pipeline in which the load instruction is being executed. The load instruction receives the store data from the first pipeline and requested data from a data cache. If the load effective address matches the store effective address, the speculatively forwarded store data is merged with the load data. If the load effective address does not match the store effective address the requested data from the data cache is merged with the load data.
Owner:IBM CORP
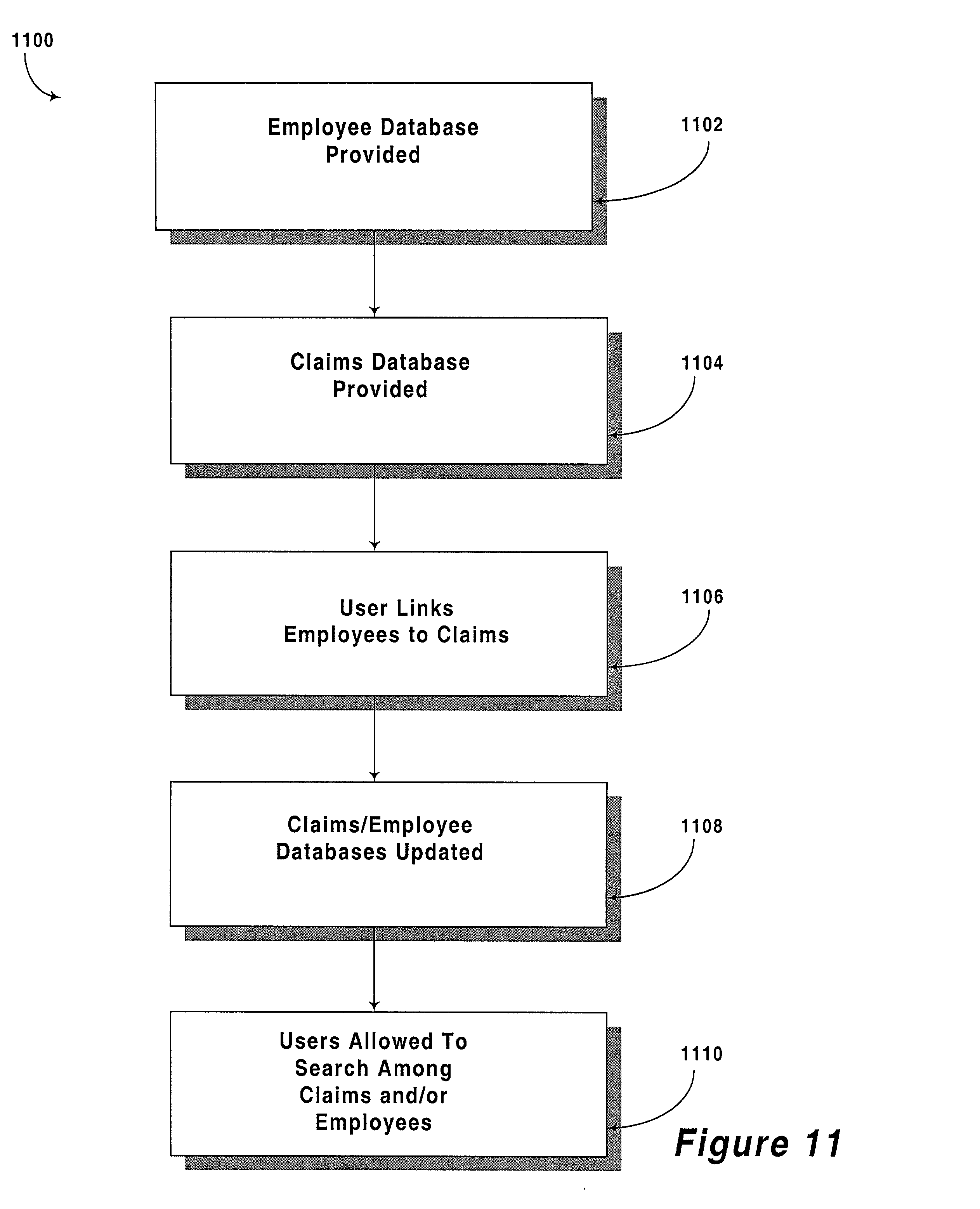
Component based organizing of projects and members of an organization during claim processing
A computer program is provided for developing component based software capable of organizing projects and members of an organization during insurance claim processing. The program includes a data component that stores, retrieves and manipulates data utilizing a plurality of functions. Also provided is a client component that includes an adapter component that transmits and receives data to / from the data component. The client component also includes a business component that serves as a data cache and includes logic for manipulating the data. A controller component is also included which is adapted to handle events generated by a user utilizing the business component to cache data and the adapter component to ultimately persist data to a data repository. In use, the client component is provided with a plurality of first data sets relating to unique projects. In addition, a plurality of second data sets relating to unique members of an organization are also provided. The first data sets are then linked with the second data sets according to the instructions of a user. The user is then allowed to obtain a list of projects linked to a member upon selection of a member, or a list of members linked to a project up selection of a project.
Owner:ACCENTURE LLP
Data Cache Invalidate with Data Dependent Expiration Using a Step Value
InactiveUS20090019228A1Energy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingData storing
According to embodiments of the invention, a step value and a step-interval cache coherency protocol may be used to update and invalidate data stored within cache memory. A step value may be an integer value and may be stored within a cache directory entry associated with data in the memory cache. Upon reception of a cache read request, along with the normal address comparison to determine if the data is located within the cache a current step value may be compared with the stored step value to determine if the data is current. If the step values match, the data may be current and a cache hit may occur. However, if the step values do not match, the requested data may be provided from another source. Furthermore, an application may update the current step value to invalidate old data stored within the cache and associated with a different step value.
Owner:IBM CORP
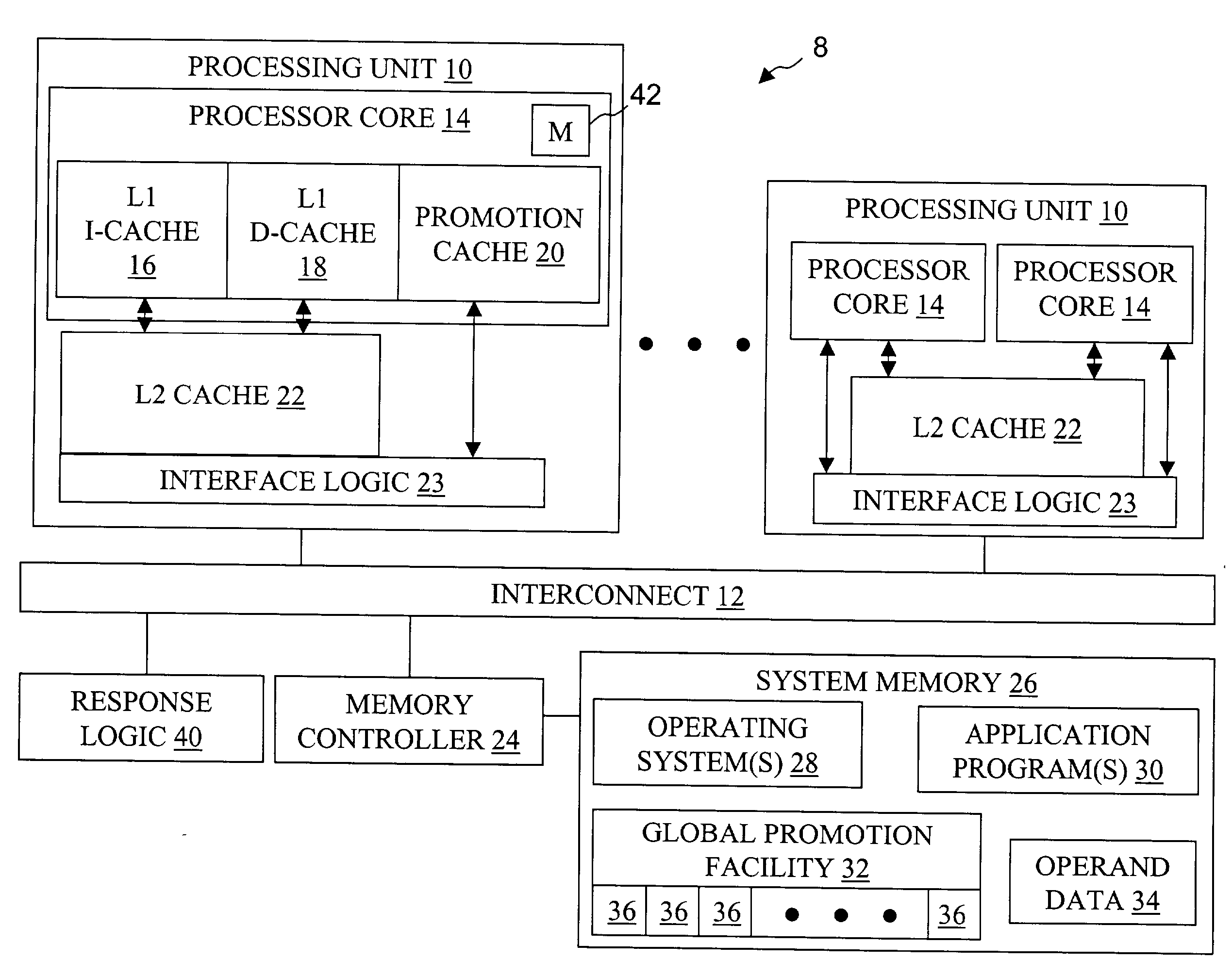
High speed promotion mechanism suitable for lock acquisition in a multiprocessor data processing system
InactiveUS20040073909A1Program synchronisationUnauthorized memory use protectionData processing systemBit field
A multiprocessor data processing system includes a plurality of processors coupled to an interconnect and to a global promotion facility containing at least one promotion bit field. A first processor executes a high speed instruction sequence including a load-type instruction to acquire a promotion bit field within the global promotion facility exclusive of at least a second processor. The request may be made visible to all processors coupled to the interconnect. In response to execution of the load-type instruction, a register of the first processor receives a register bit field indicating whether or not the promotion bit field was acquired by execution of the load-type instruction. While the first processor holds the promotion bit field exclusive of the second processor, the second processor is permitted to initiate a request on the interconnect. Advantageously, promotion bit fields are handled separately from data, and the communication of promotion bit fields does not entail the movement of data cache lines.
Owner:IBM CORP
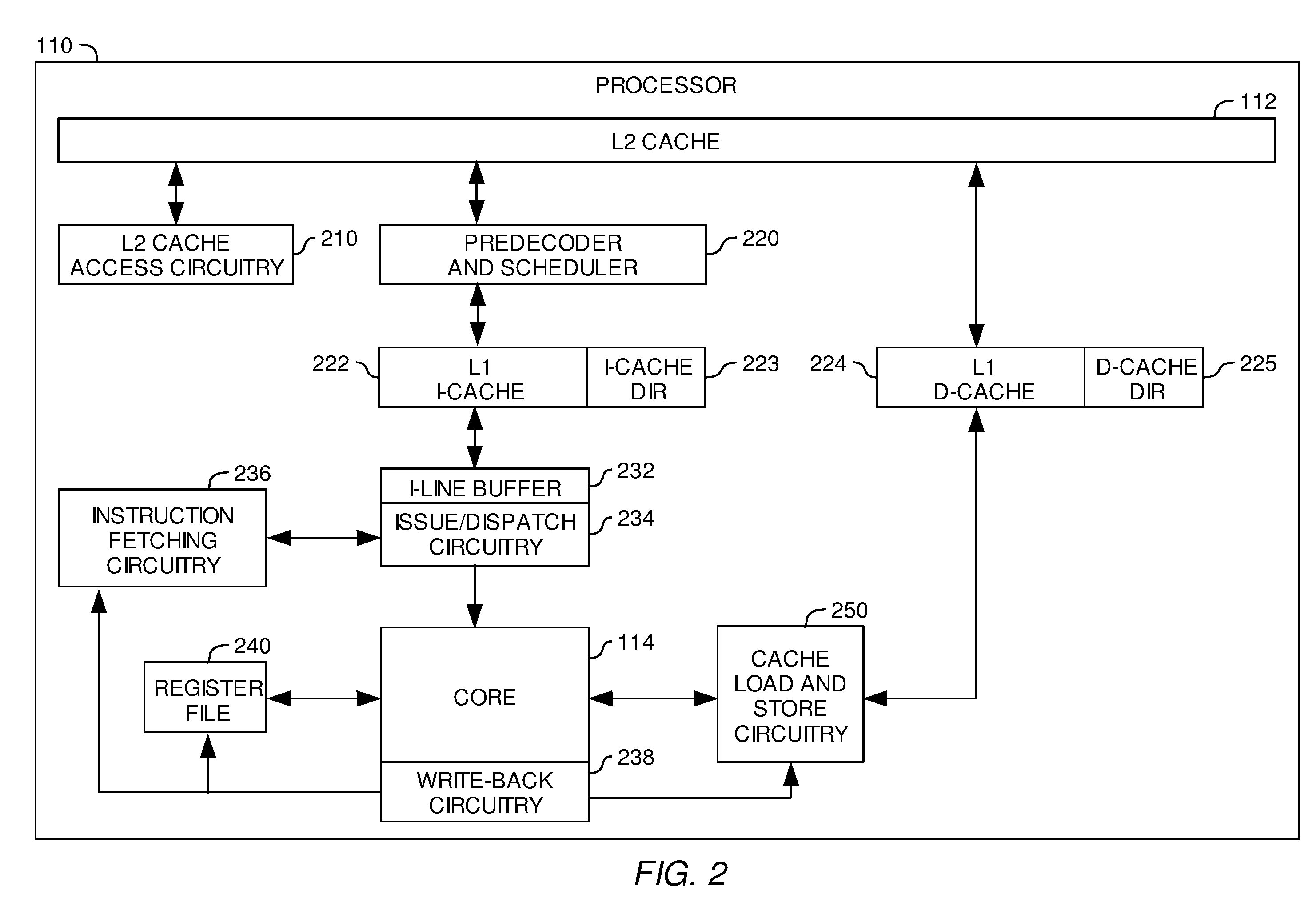
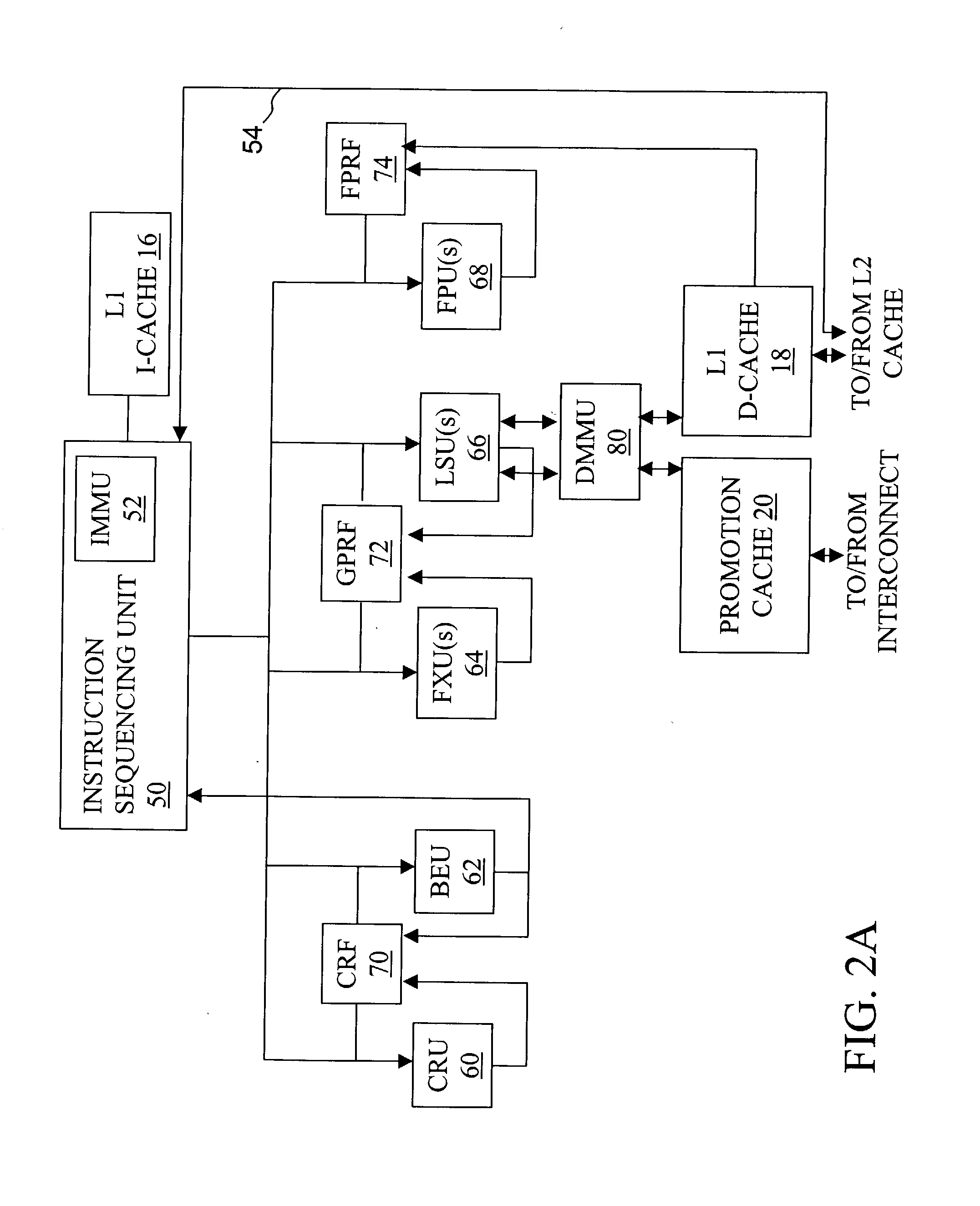
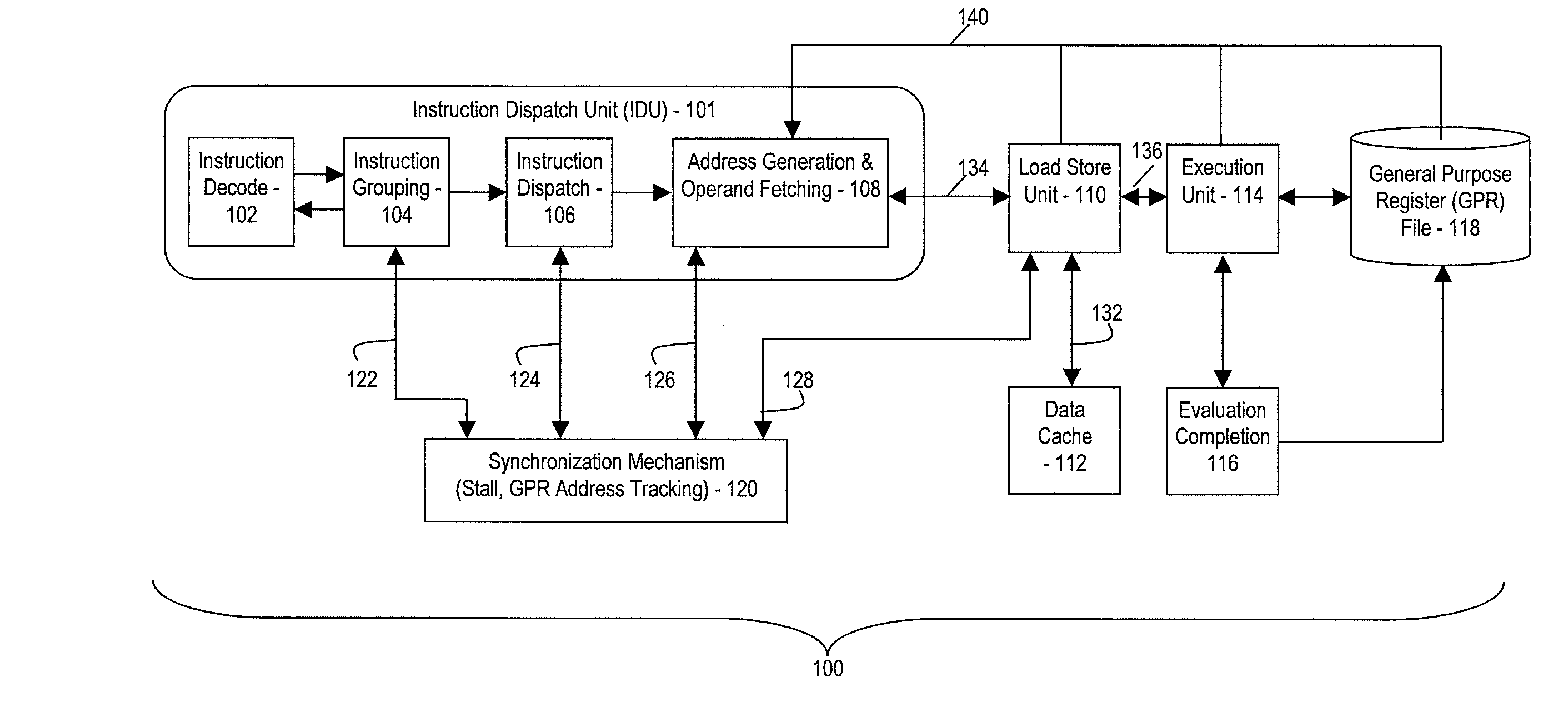
Processor and method for synchronous load multiple fetching sequence and pipeline stage result tracking to facilitate early address generation interlock bypass
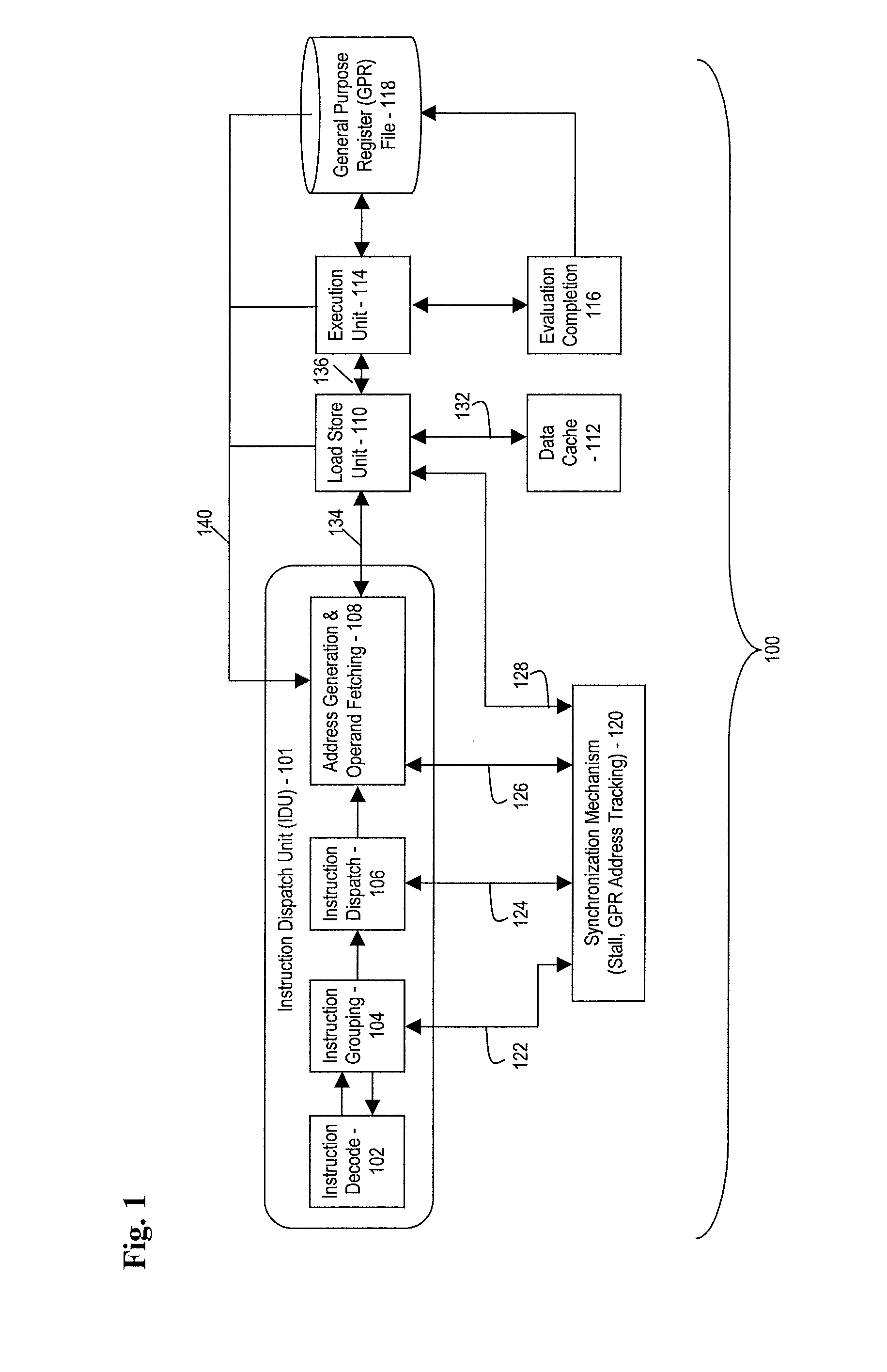
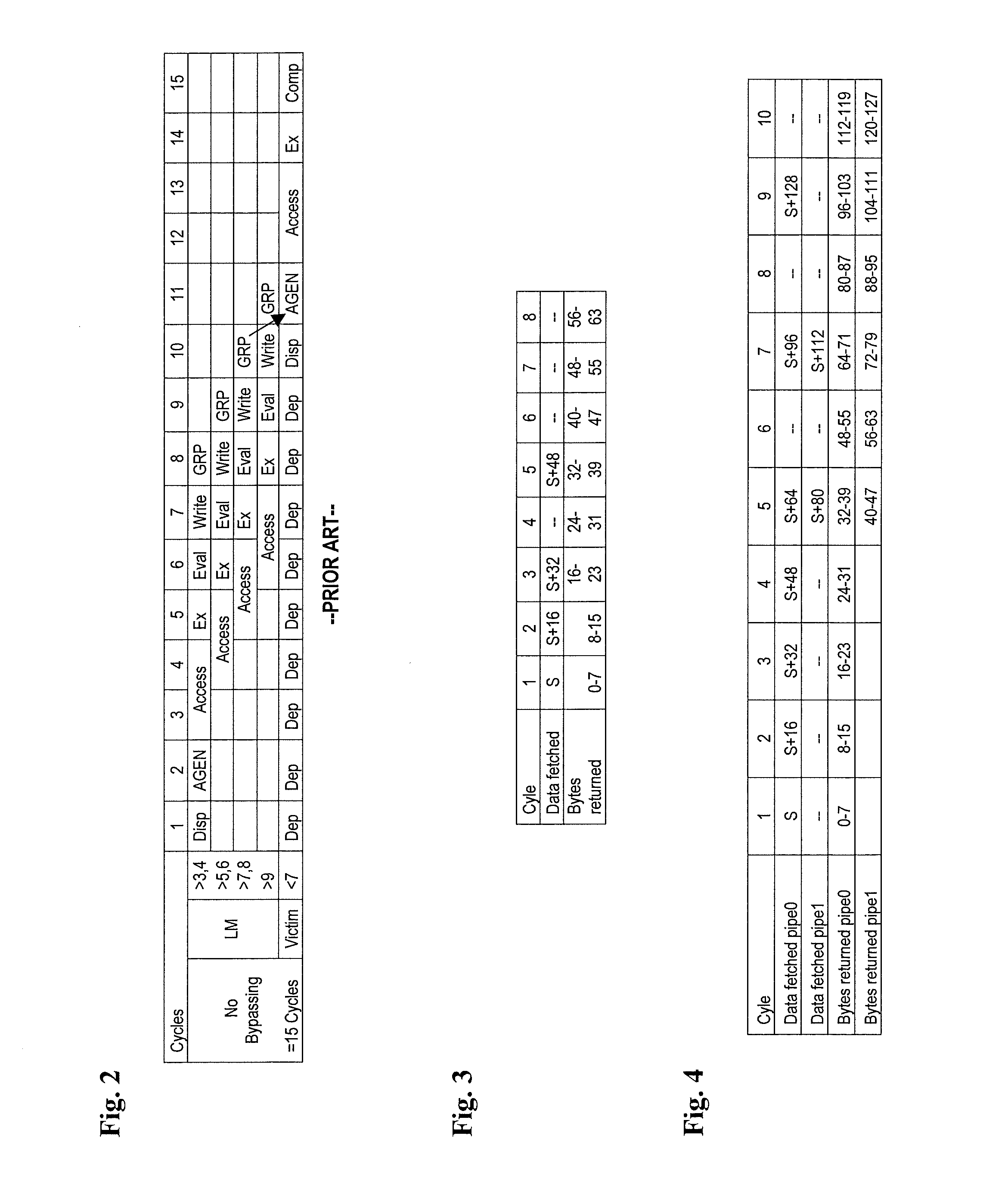
A pipelined processor including an architecture for address generation interlocking, the processor including: an instruction grouping unit to detect a read-after-write dependency and to resolve instruction interdependency; an instruction dispatch unit (IDU) including address generation interlock (AGI) and operand fetching logic for dispatching an instruction to at least one of a load store unit and an execution unit; wherein the load store unit is configured with access to a data cache and to return fetched data to the execution unit; wherein the execution unit is configured to write data into a general purpose register bank; and wherein the architecture provides support for bypassing of results of a load multiple instruction for address generation while such instruction is executing in the execution unit before the general purpose register bank is written. A method and a computer system are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
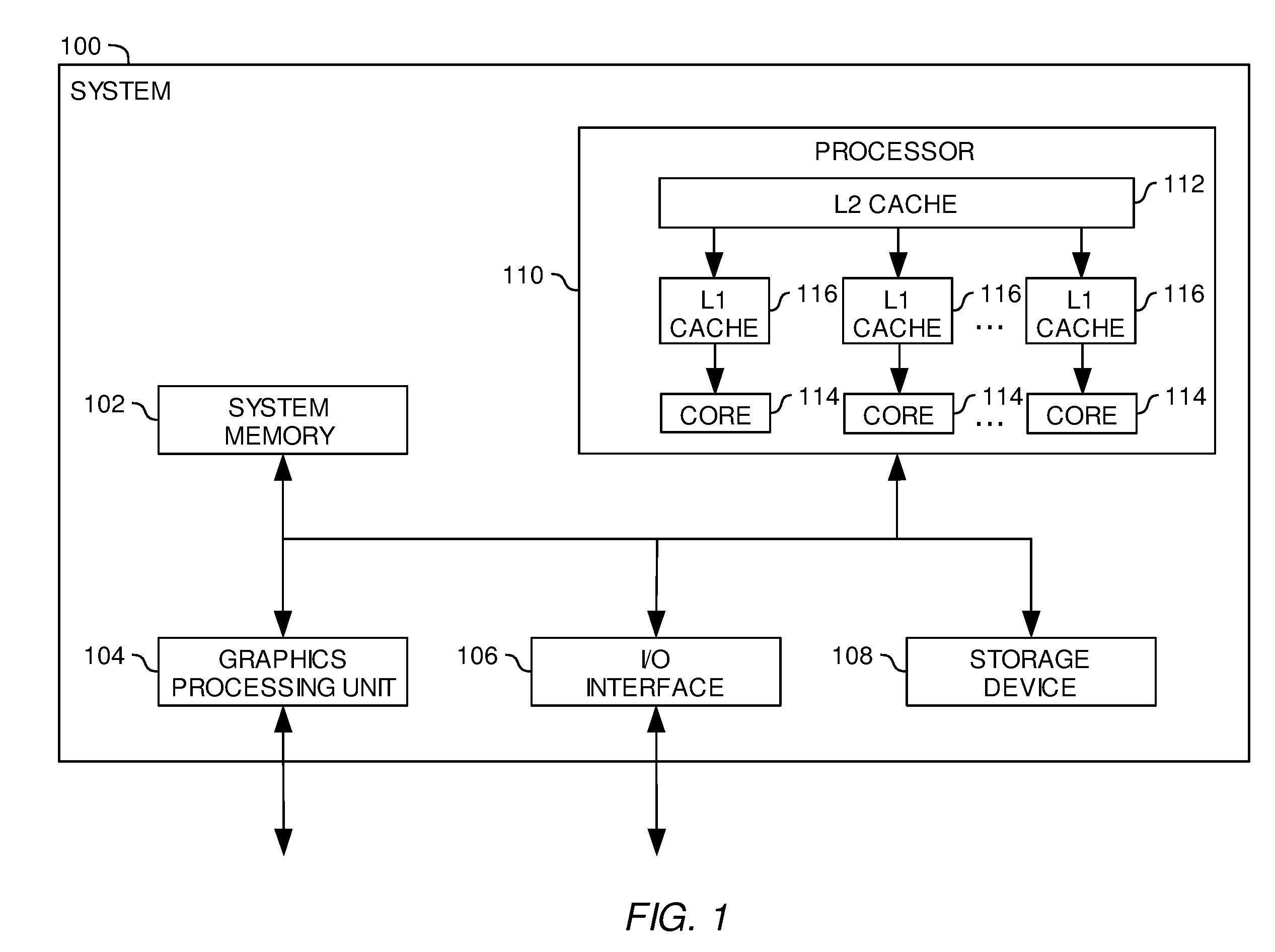
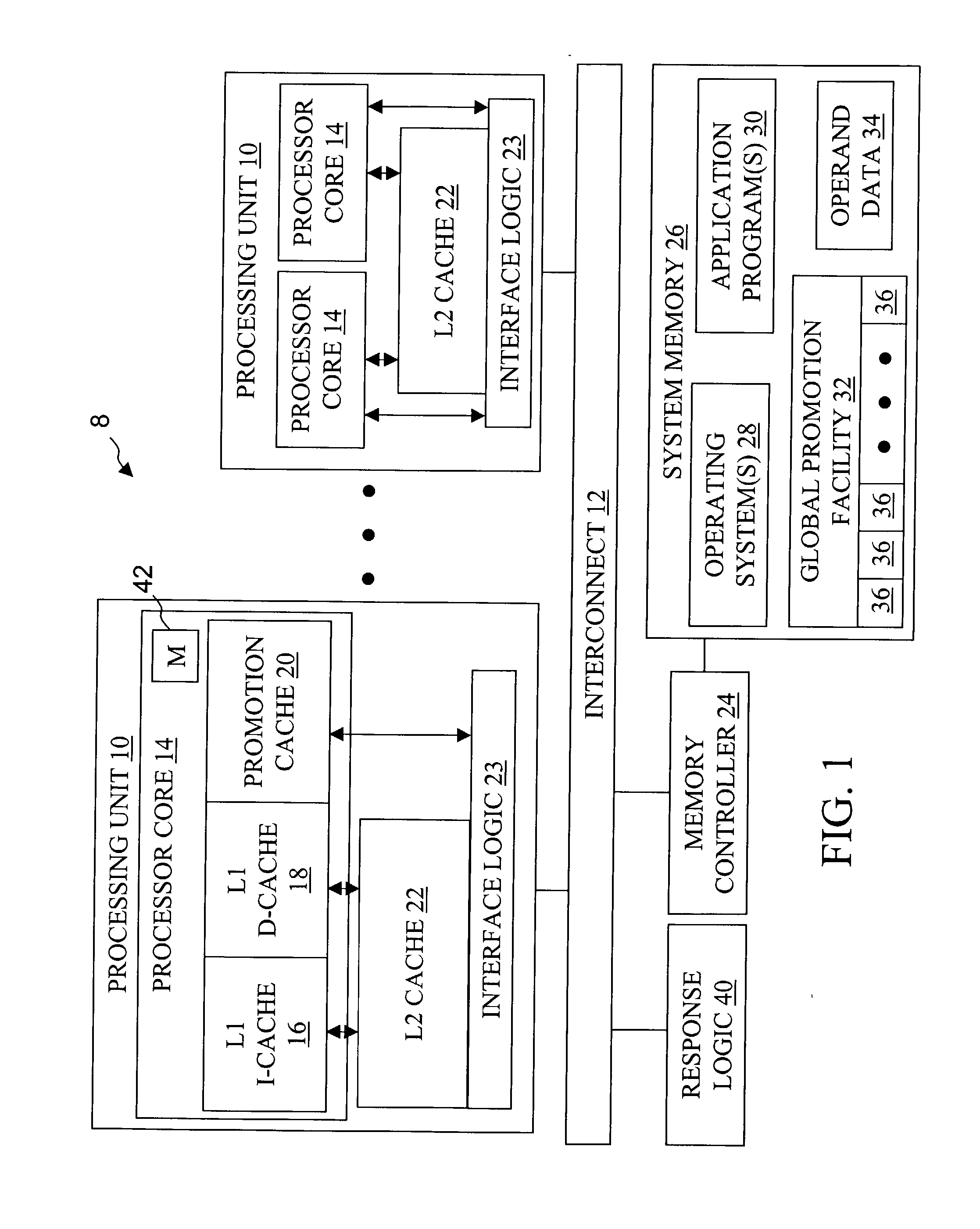
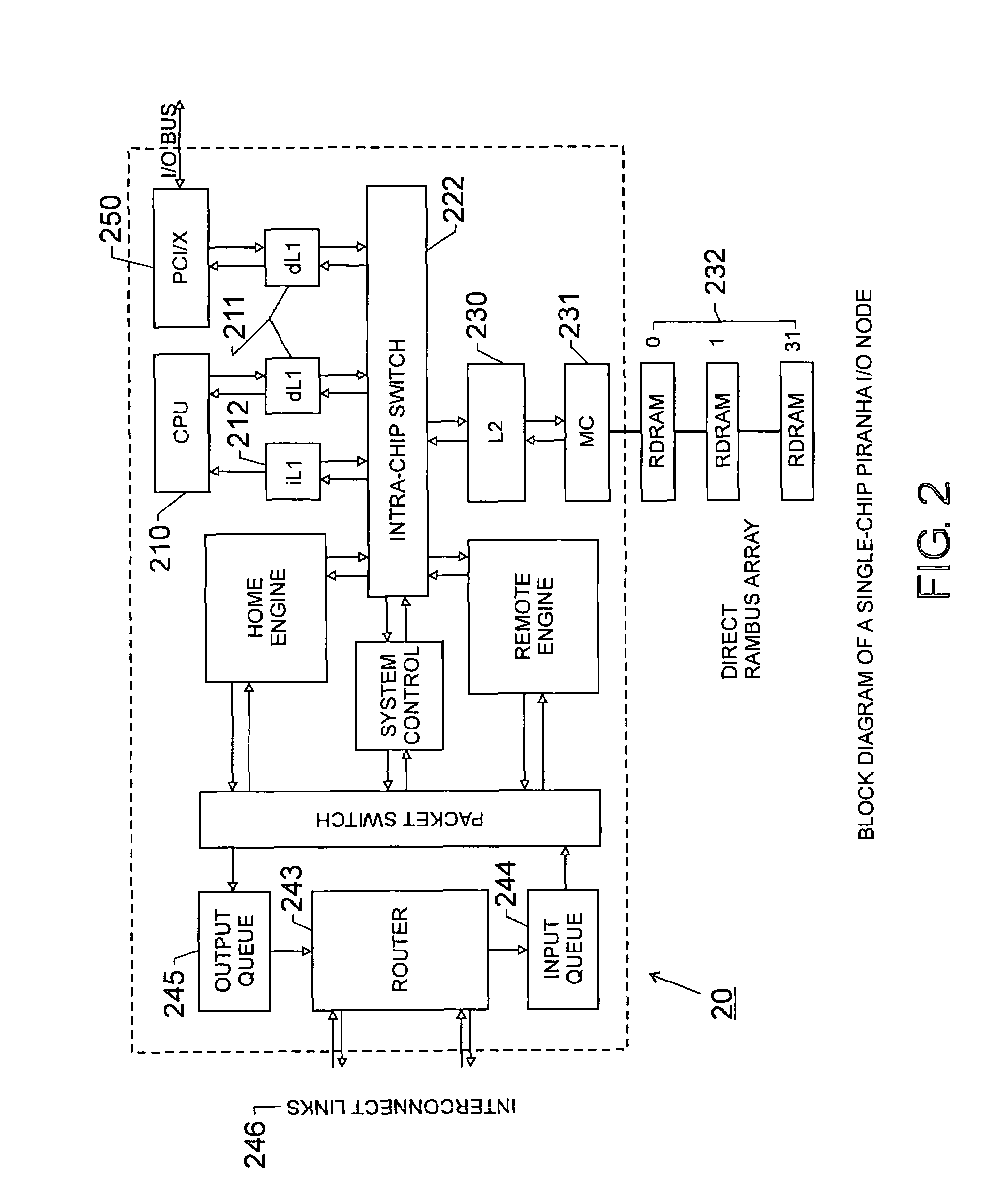
Scalable architecture based on single-chip multiprocessing
InactiveUS6988170B2Short timeSmall investmentMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCache hierarchyProcessing core
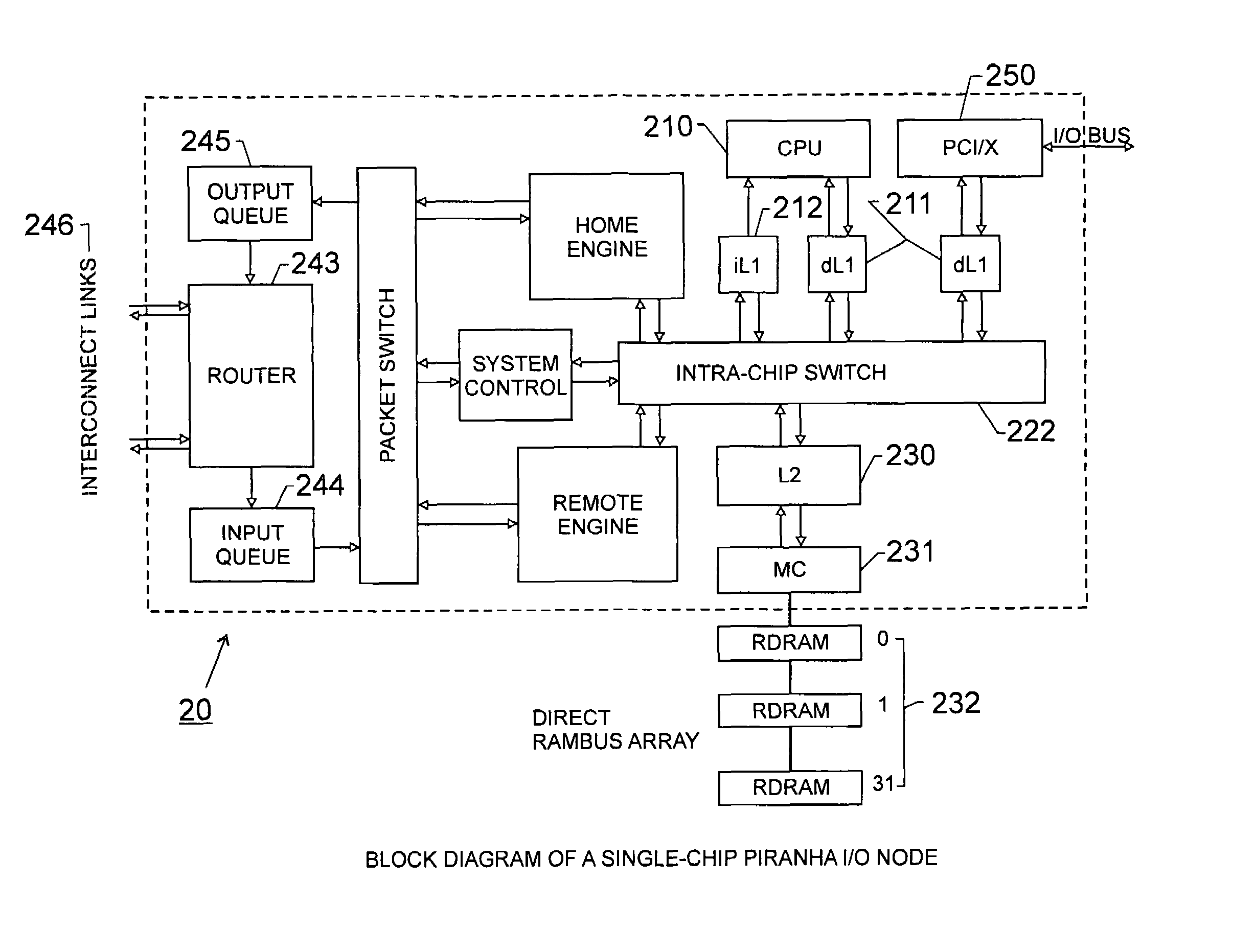
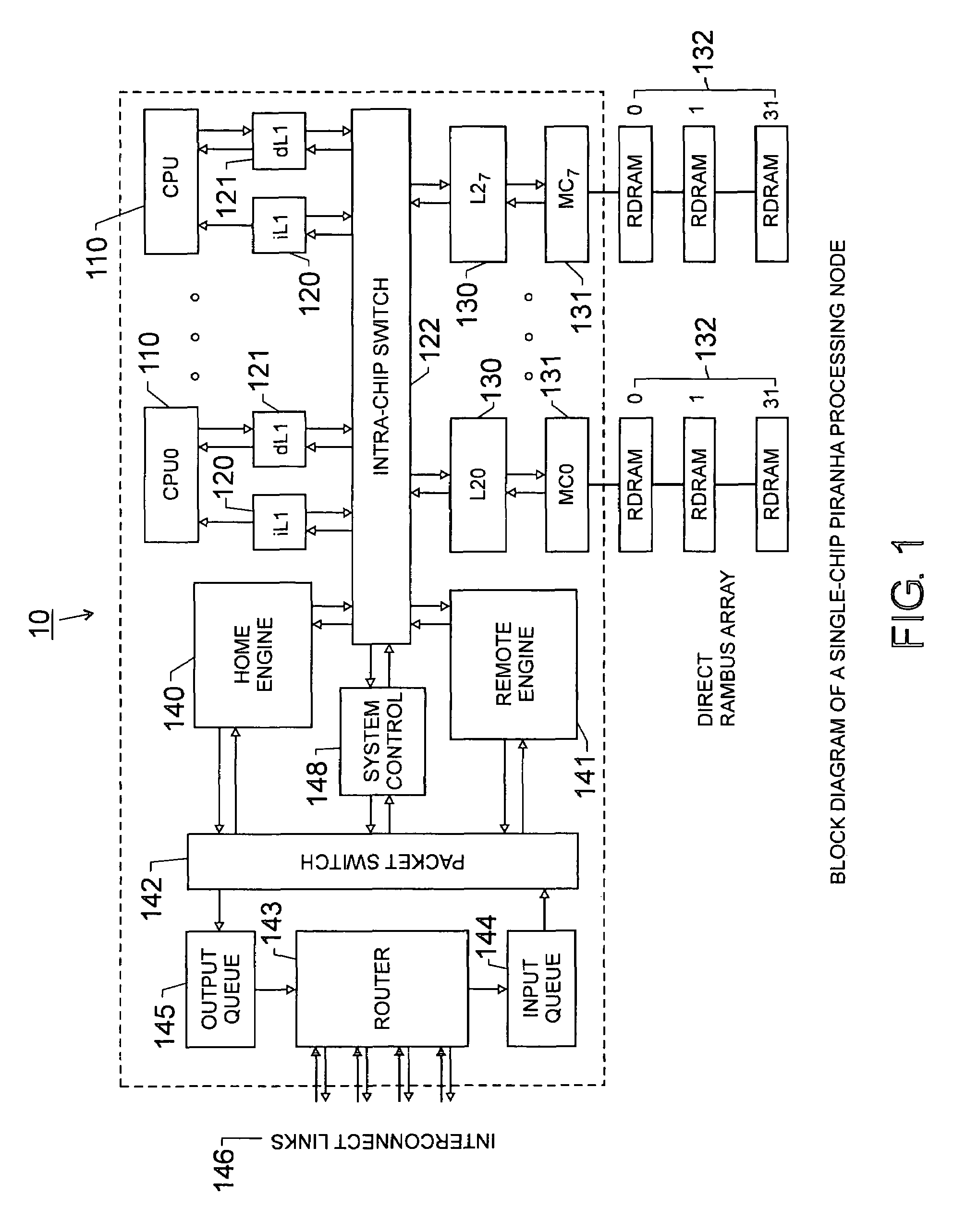
A chip-multiprocessing system with scalable architecture, including on a single chip: a plurality of processor cores; a two-level cache hierarchy; an intra-chip switch; one or more memory controllers; a cache coherence protocol; one or more coherence protocol engines; and an interconnect subsystem. The two-level cache hierarchy includes first level and second level caches. In particular, the first level caches include a pair of instruction and data caches for, and private to, each processor core. The second level cache has a relaxed inclusion property, the second-level cache being logically shared by the plurality of processor cores. Each of the plurality of processor cores is capable of executing an instruction set of the ALPHA™ processing core. The scalable architecture of the chip-multiprocessing system is targeted at parallel commercial workloads. A showcase example of the chip-multiprocessing system, called the PIRAHNA™ system, is a highly integrated processing node with eight simpler ALPHA™ processor cores. A method for scalable chip-multiprocessing is also provided.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
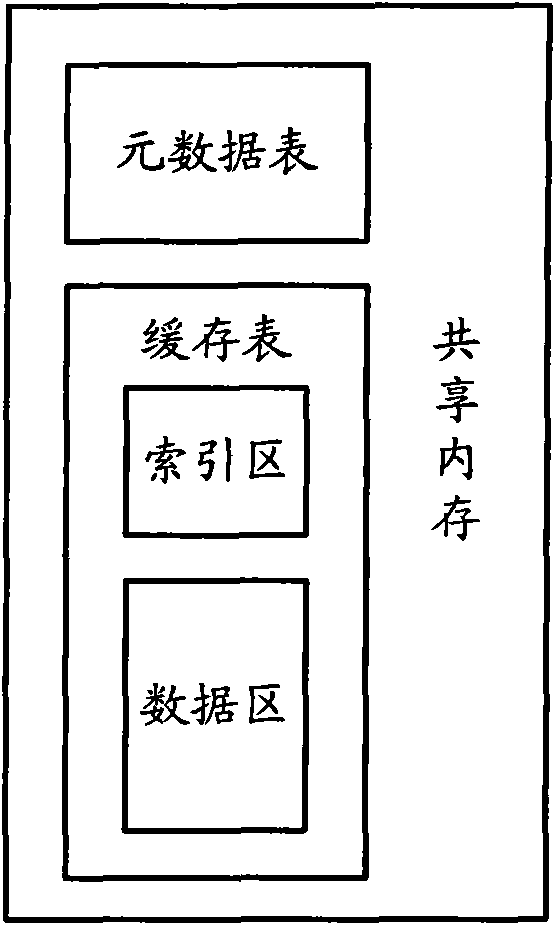
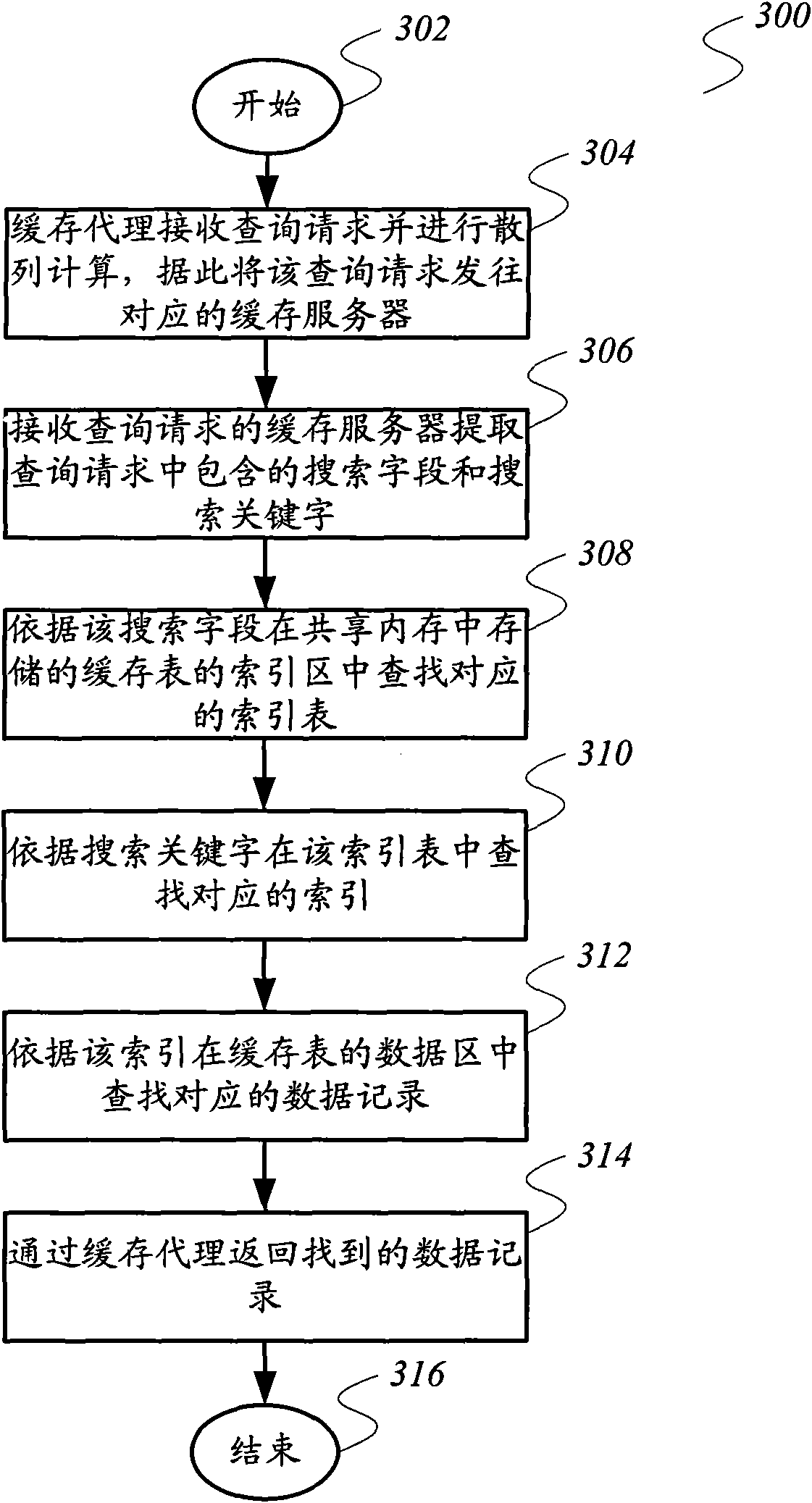
Data caching system and data query method
InactiveCN102117309AEasy to manageEasy to useTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsCache serverDependability
The invention relates to the cache technique, and provides a data caching system and a data query method, in order to overcome the disadvantages that the existing Memcached system does not support multi-index and the like. The data caching system comprises a cache proxy, and at least one cache server in communication connection with the cache proxy, wherein the cache proxy is used for receiving aquery quest and carrying out hash calculation, and sending the query quest to the corresponding cache server; and the cache server is used for extracting the search field and the search keyword contained in the query quest, searching the corresponding index table in an index region of a cache table of the search field stored in a shared memory, searching the corresponding index in the index tableaccording to the search keyword, searching the corresponding data record in a data region in the cache table according to the index, and returning to the searched data record through the cache proxy.The invention also provides a data query method. The technical scheme provided by the invention is helpful in improving the overall reliability and the security of the data caching system.
Owner:卓望数码技术(深圳)有限公司
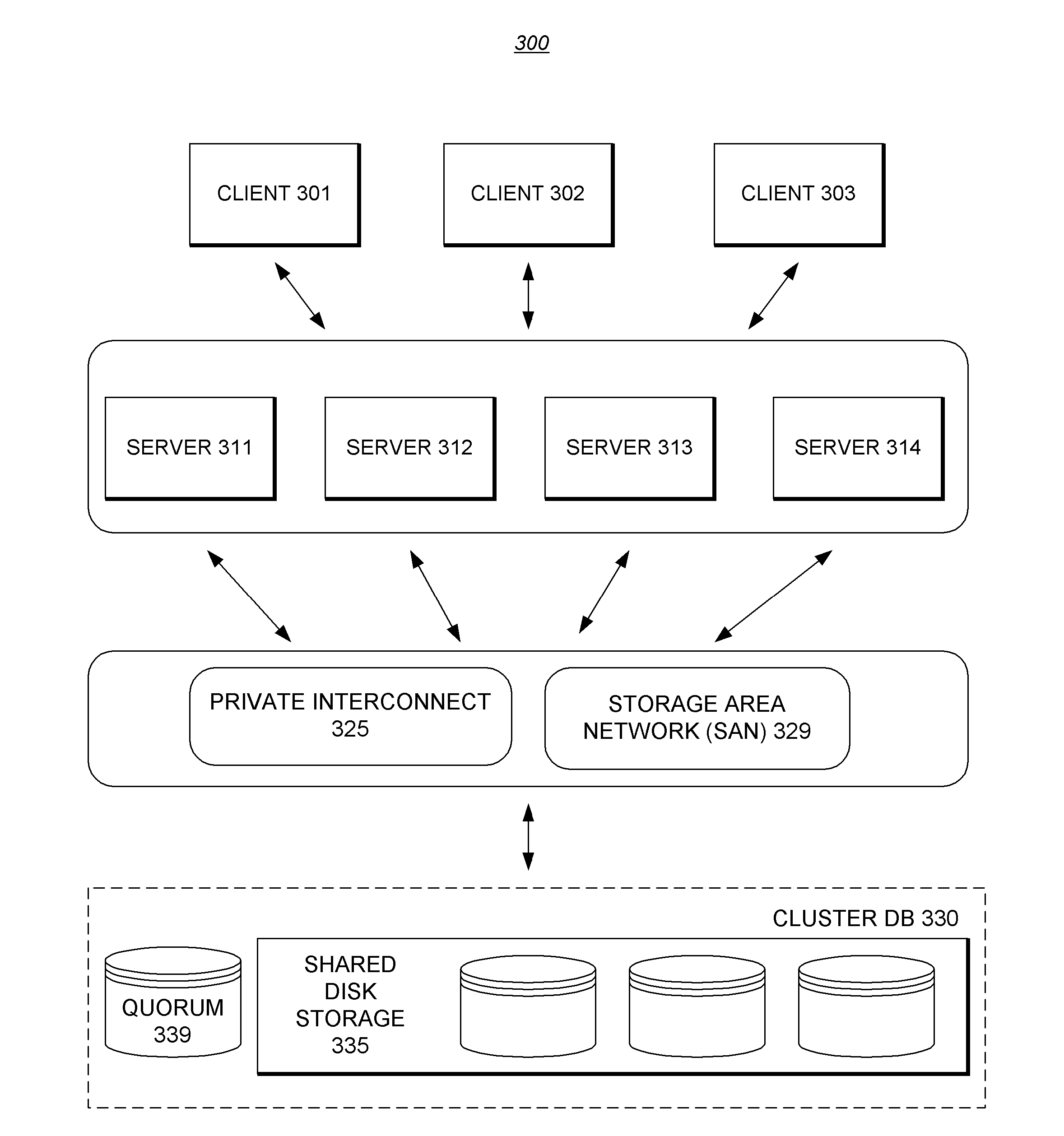
Storage area network file system
ActiveUS7165096B2Read data quicklyInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsStorage area networkNetwork connection
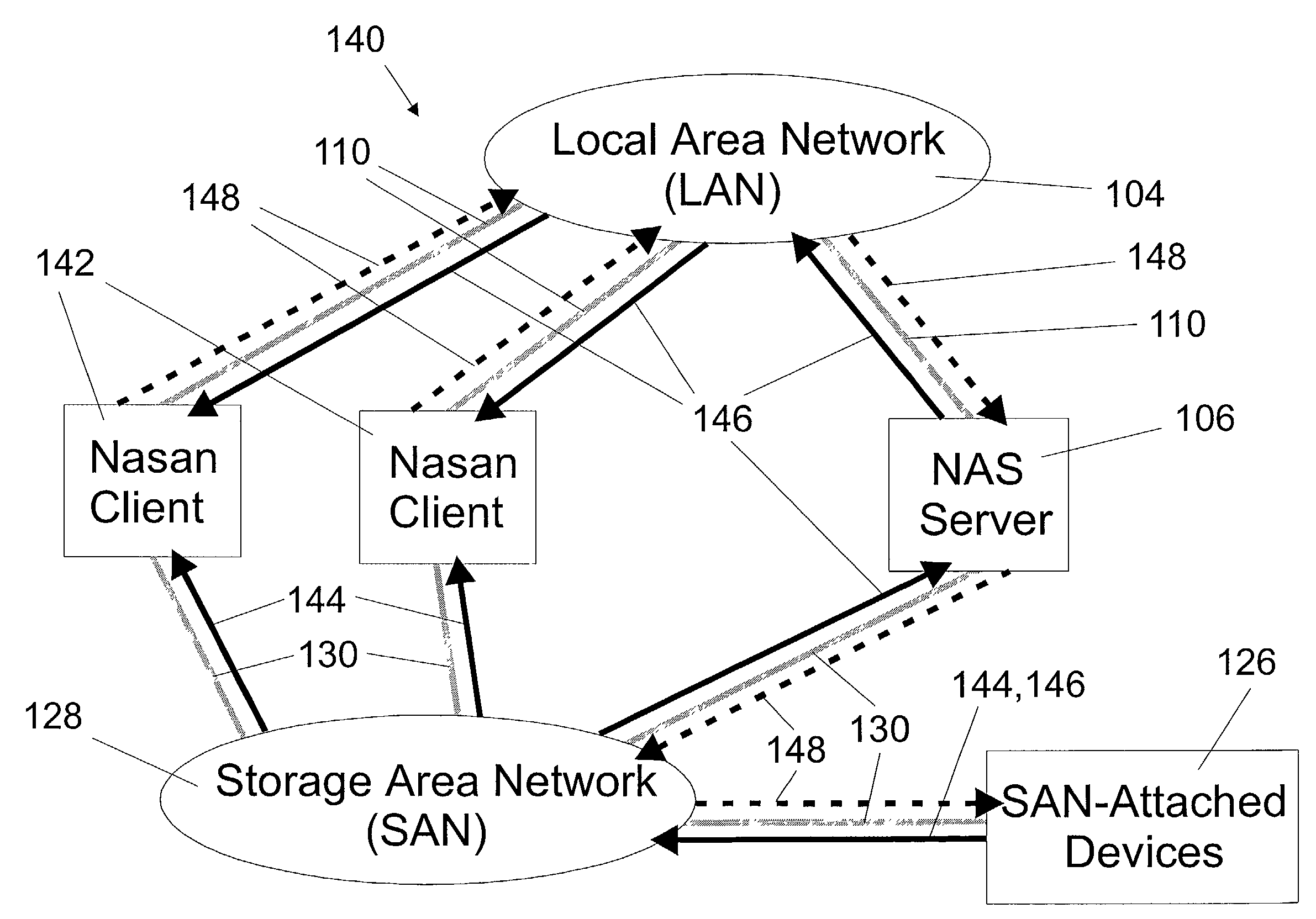
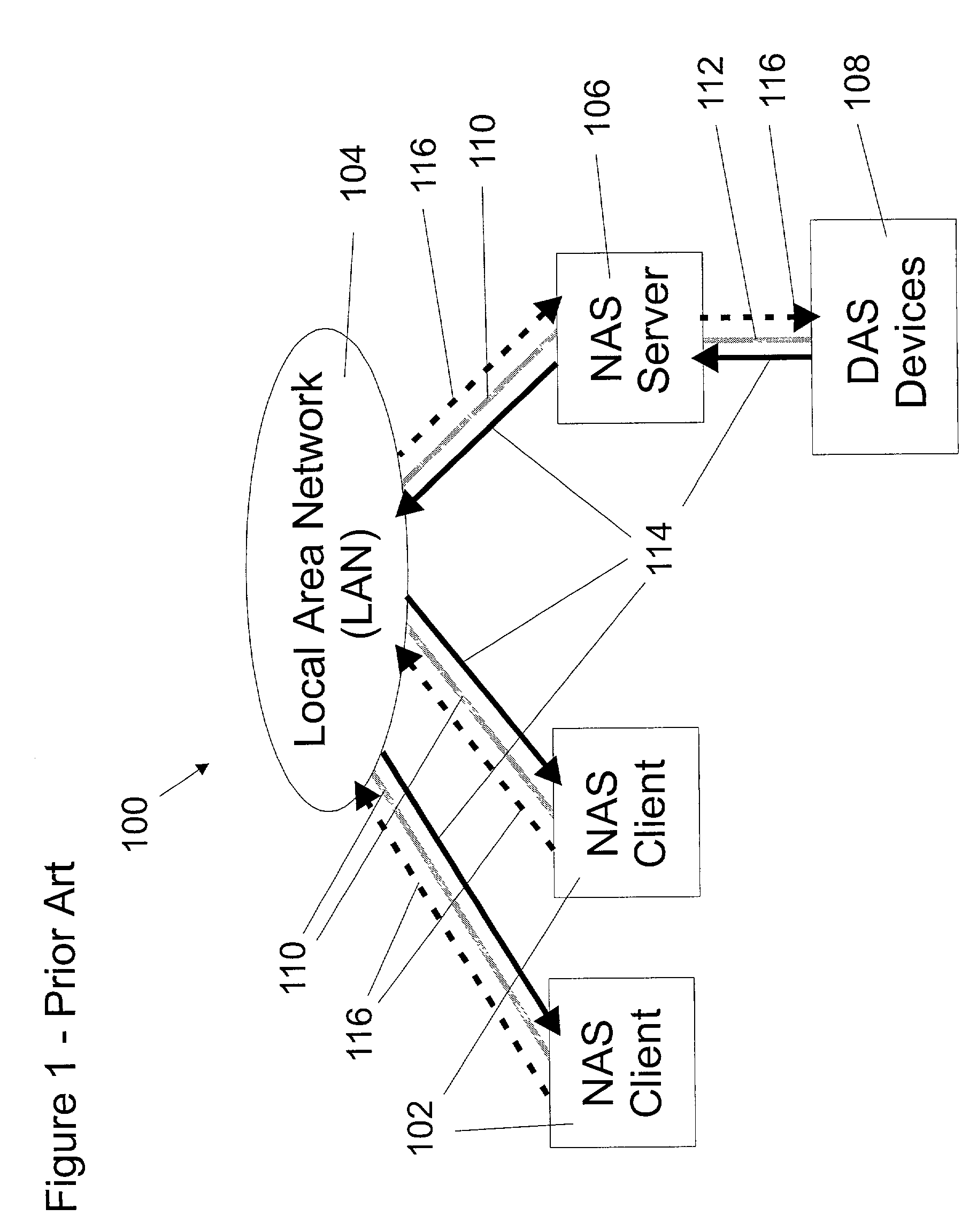
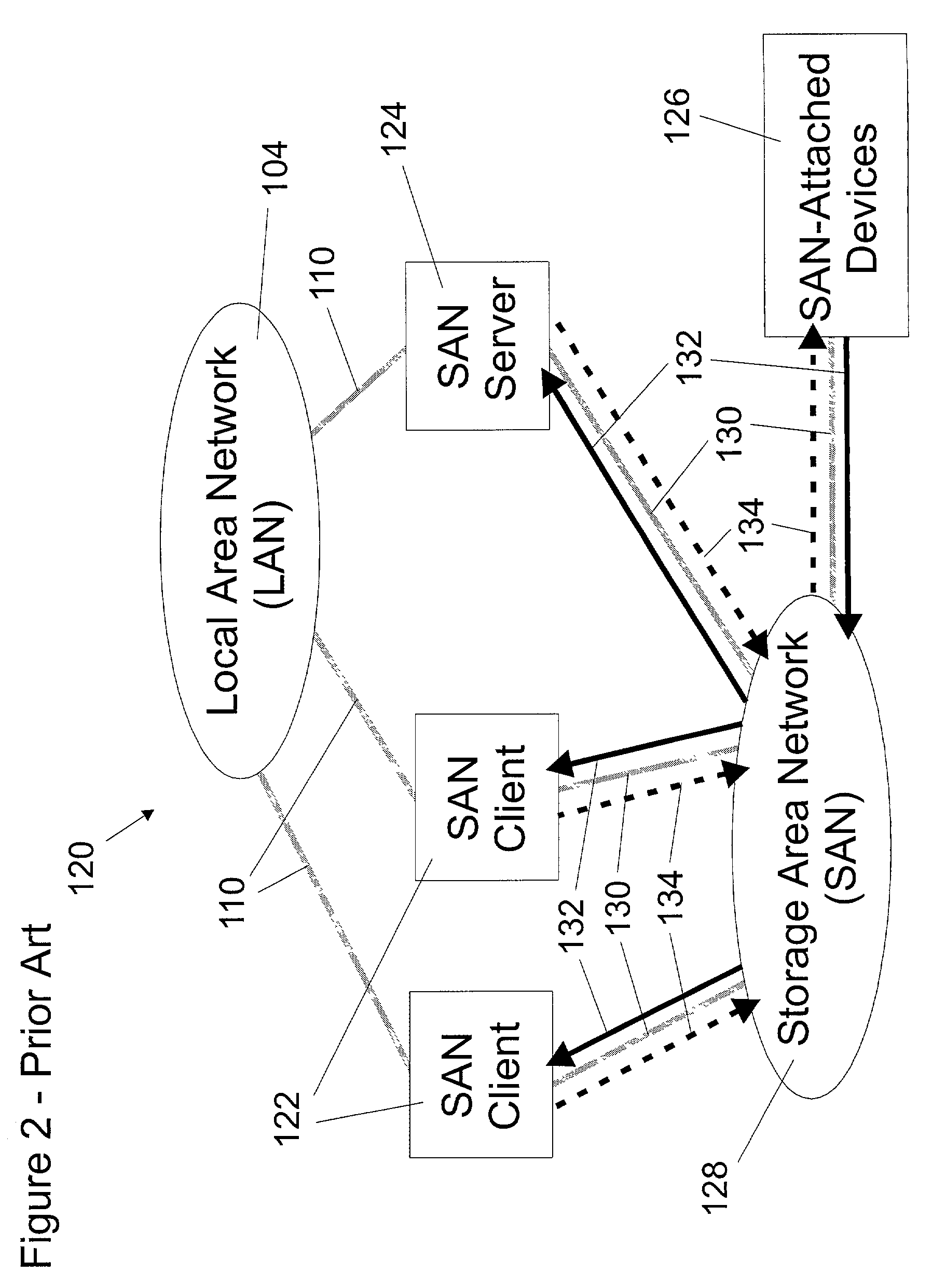
A shared storage distributed file system is presented that provides applications with transparent access to a storage area network (SAN) attached storage device. This is accomplished by providing clients read access to the devices over the SAN and by requiring most write activity to be serialized through a network attached storage (NAS) server. Both the clients and the NAS server are connected to the SAN-attached device over the SAN. Direct read access to the SAN attached device is provided through a local file system on the client. Write access is provided through a remote file system on the client that utilizes the NAS server. A supplemental read path is provided through the NAS server for those circumstances where the local file system is unable to provide valid data reads.Consistency is maintained by comparing modification times in the local and remote file systems. Since writes occur over the remote file systems, the consistency mechanism is capable of flushing data caches in the remote file system, and invalidating metadata and real-data caches in the local file system. It is possible to utilize unmodified local and remote file systems in the present invention, by layering over the local and remote file systems a new file system. This new file system need only be installed at each client, allowing the NAS server file systems to operate unmodified. Alternatively, the new file system can be combined with the local file system.
Owner:DATAPLOW
System and method for hierarchical data storage
InactiveUS6865650B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingData storing
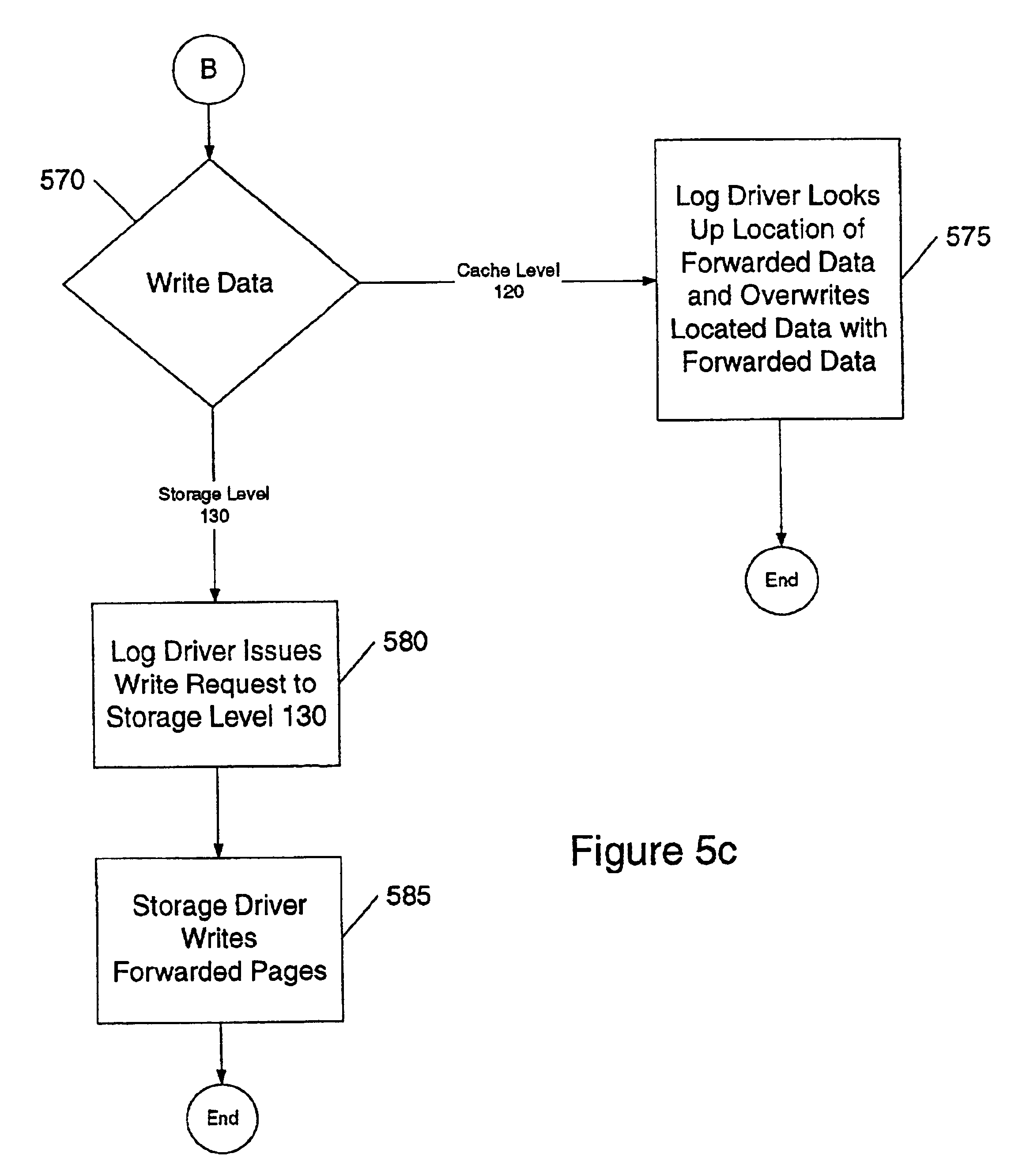
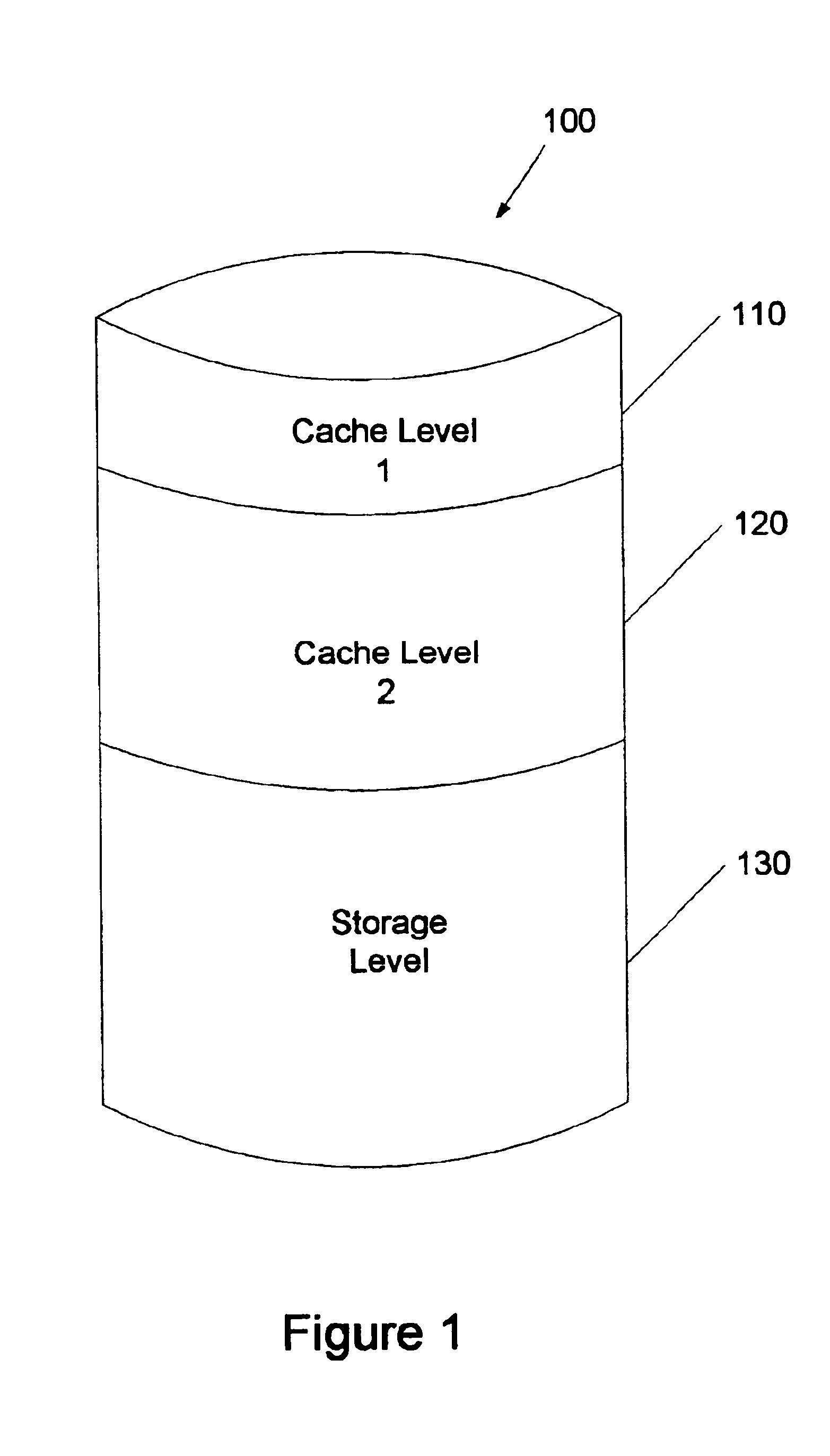
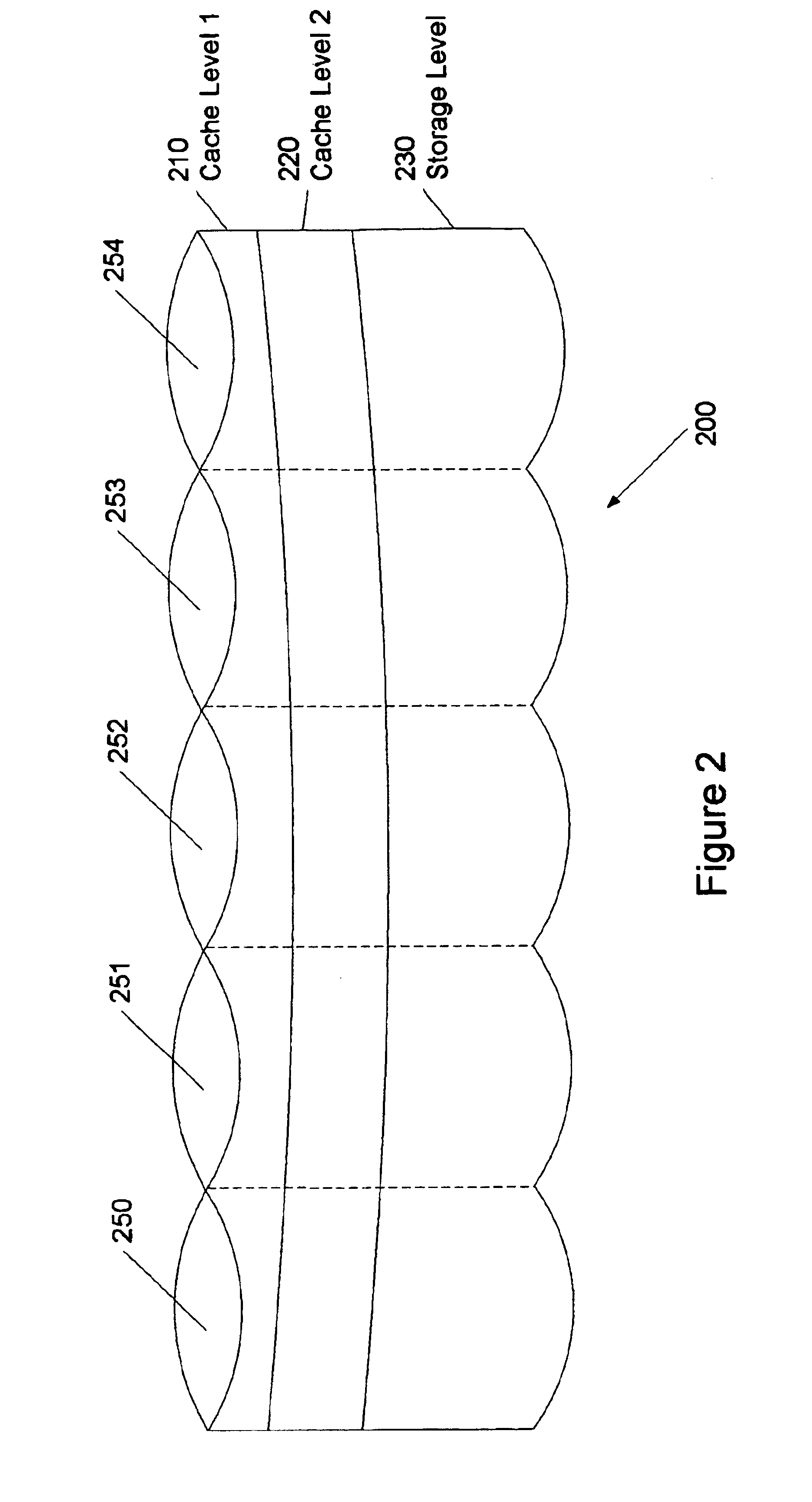
A system and method for storing data, the system having one or more storage devices, caches data from a sender into a first random-access structure located in a first cache level, caches data from the first cache level into a log structure located in a second cache level, and stores data from CL into a second random-access structure located in a storage level, wherein CL is the first cache level or the second cache level. In further embodiments of the invention, the second cache level caches in the log structure parity data for the data cached in the log structure. In a still further embodiment of the invention, the storage level stores in the second random-access structure parity data for the data stored in the second random-access structure.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
System and Methodology Providing Multiple Heterogeneous Buffer Caches
ActiveUS20080140937A1Efficient accessMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsUser inputParallel computing
A method for temporarily storing data objects in memory of a distributed system comprising a plurality of servers sharing access to data comprises steps of: reserving memory at each of the plurality of servers as a default data cache for storing data objects; in response to user input, allocating memory of at least one of the plurality of servers as a named cache reserved for storing a specified type of data object; in response to an operation at a particular server requesting a data object, determining whether the requested data object is of the specified type corresponding to the named cache at the particular server; if the data object is determined to be of the specified type corresponding to the named cache, storing the requested data object in the named cache at the particular server; and otherwise, using the default data cache for storing the requested data object.
Owner:SAP AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com