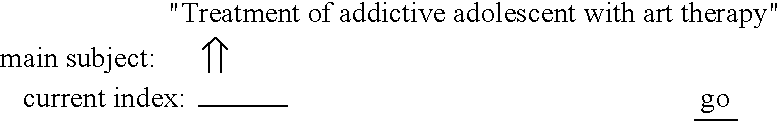Patents
Literature
360 results about "Database index" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A database index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. Indexes are used to quickly locate data without having to search every row in a database table every time a database table is accessed. Indexes can be created using one or more columns of a database table, providing the basis for both rapid random lookups and efficient access of ordered records.
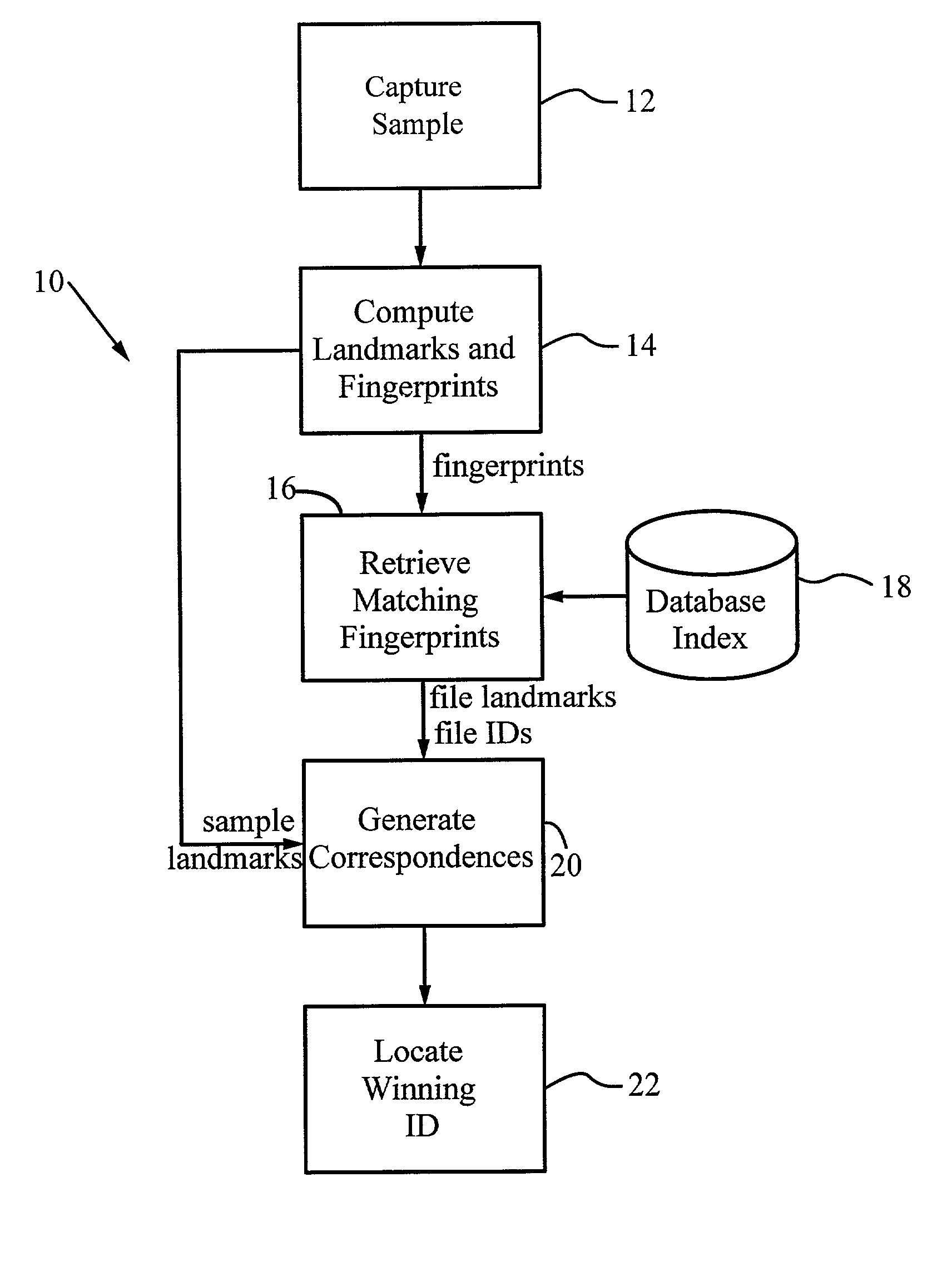
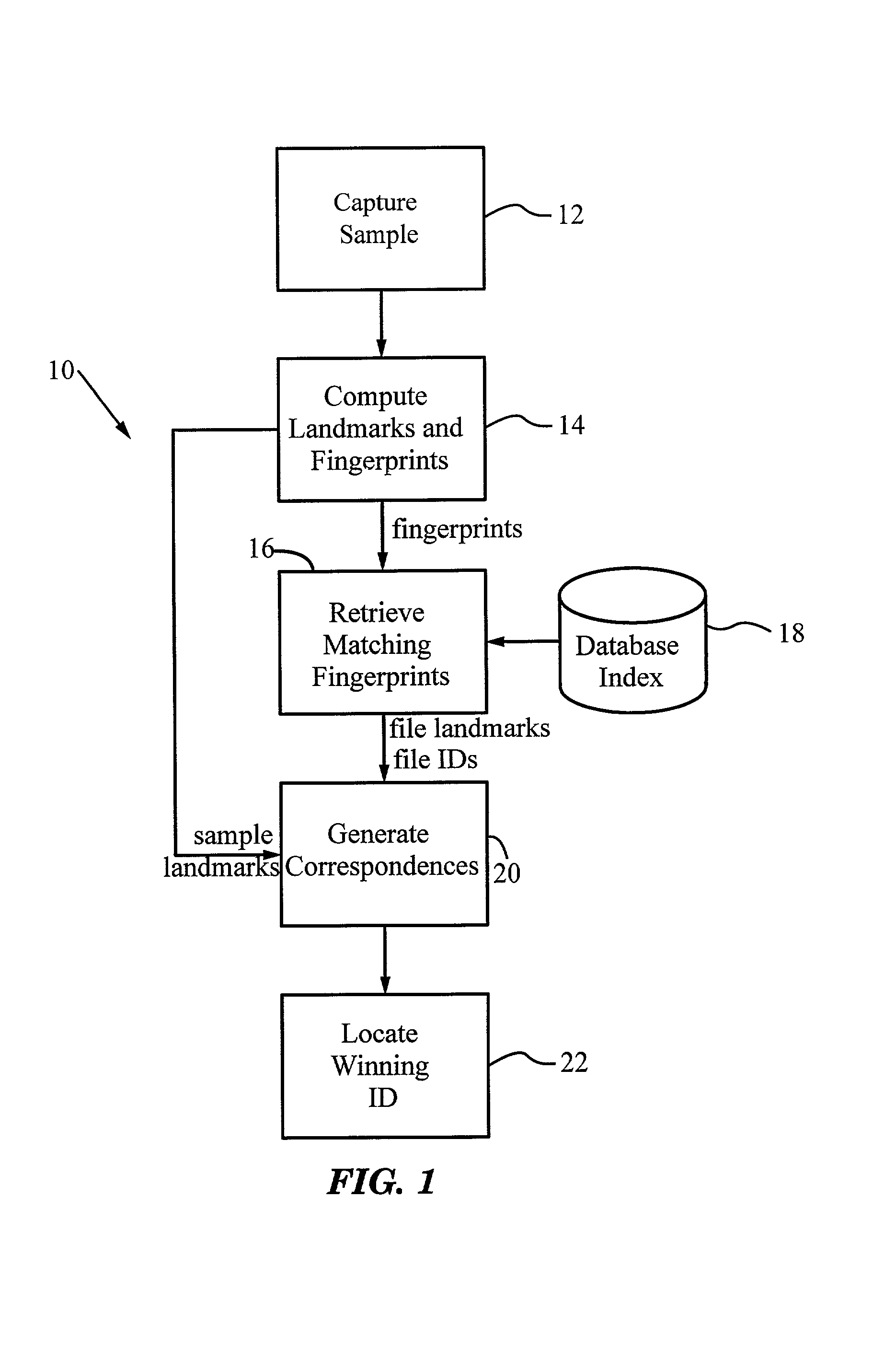
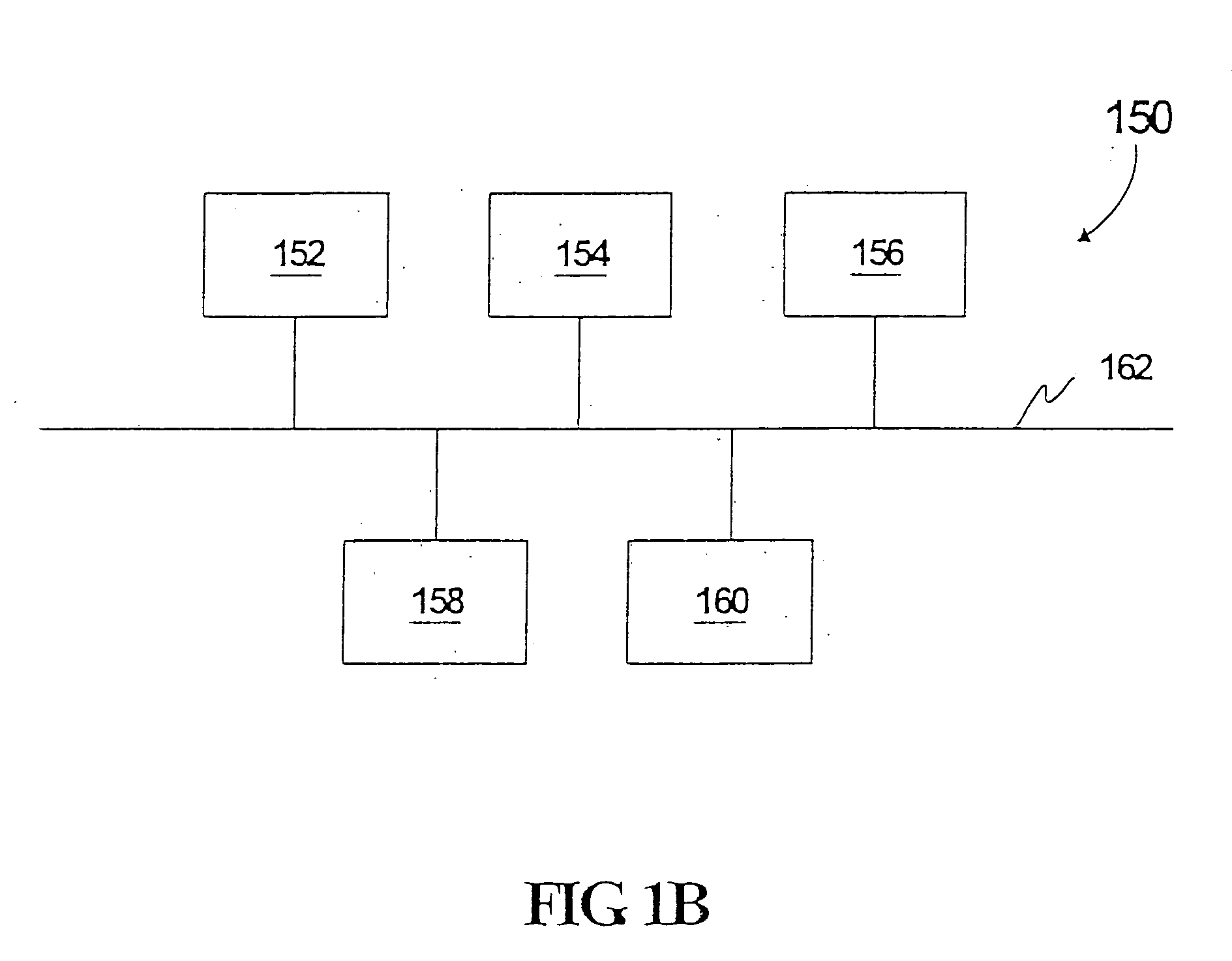
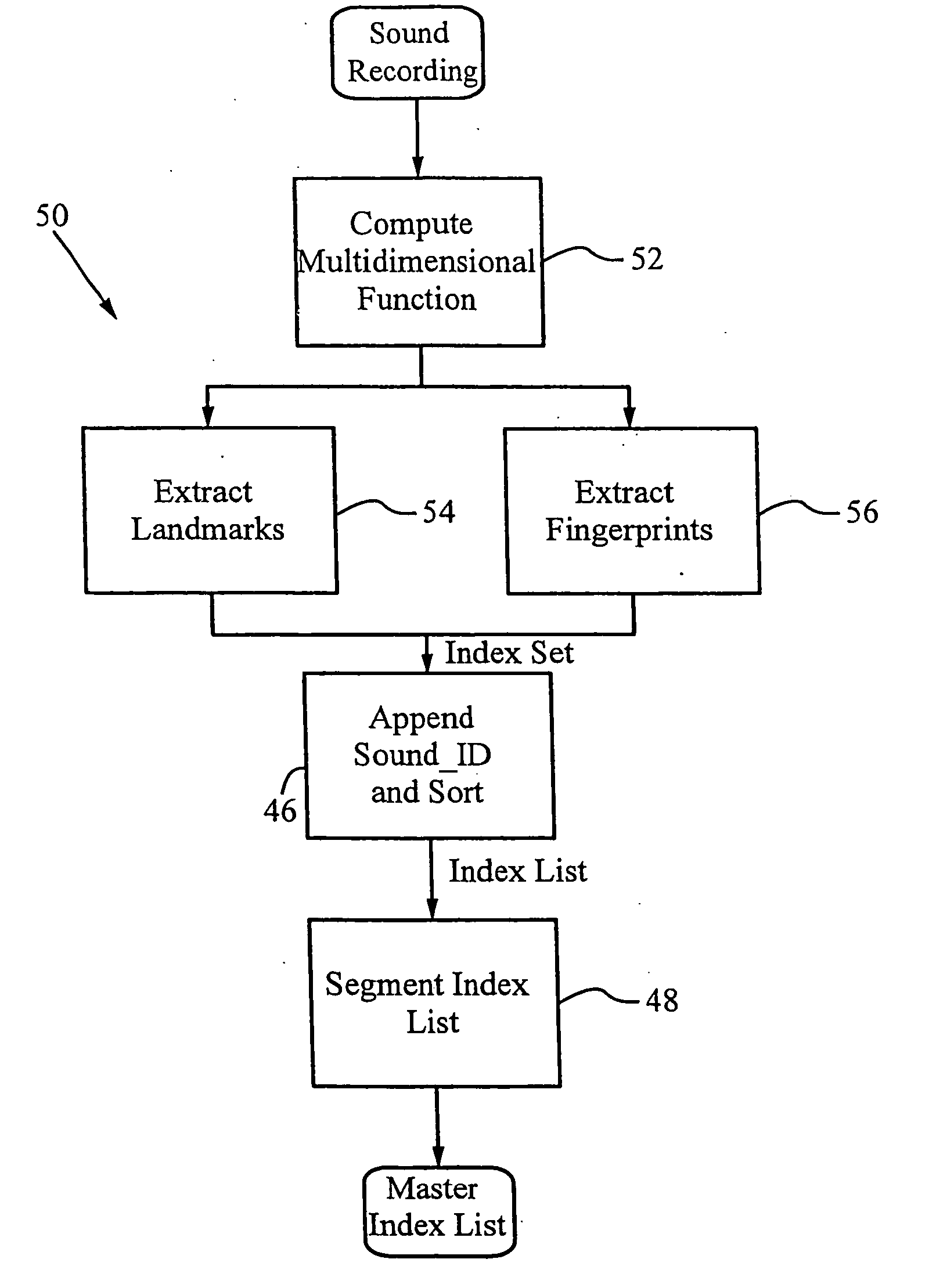
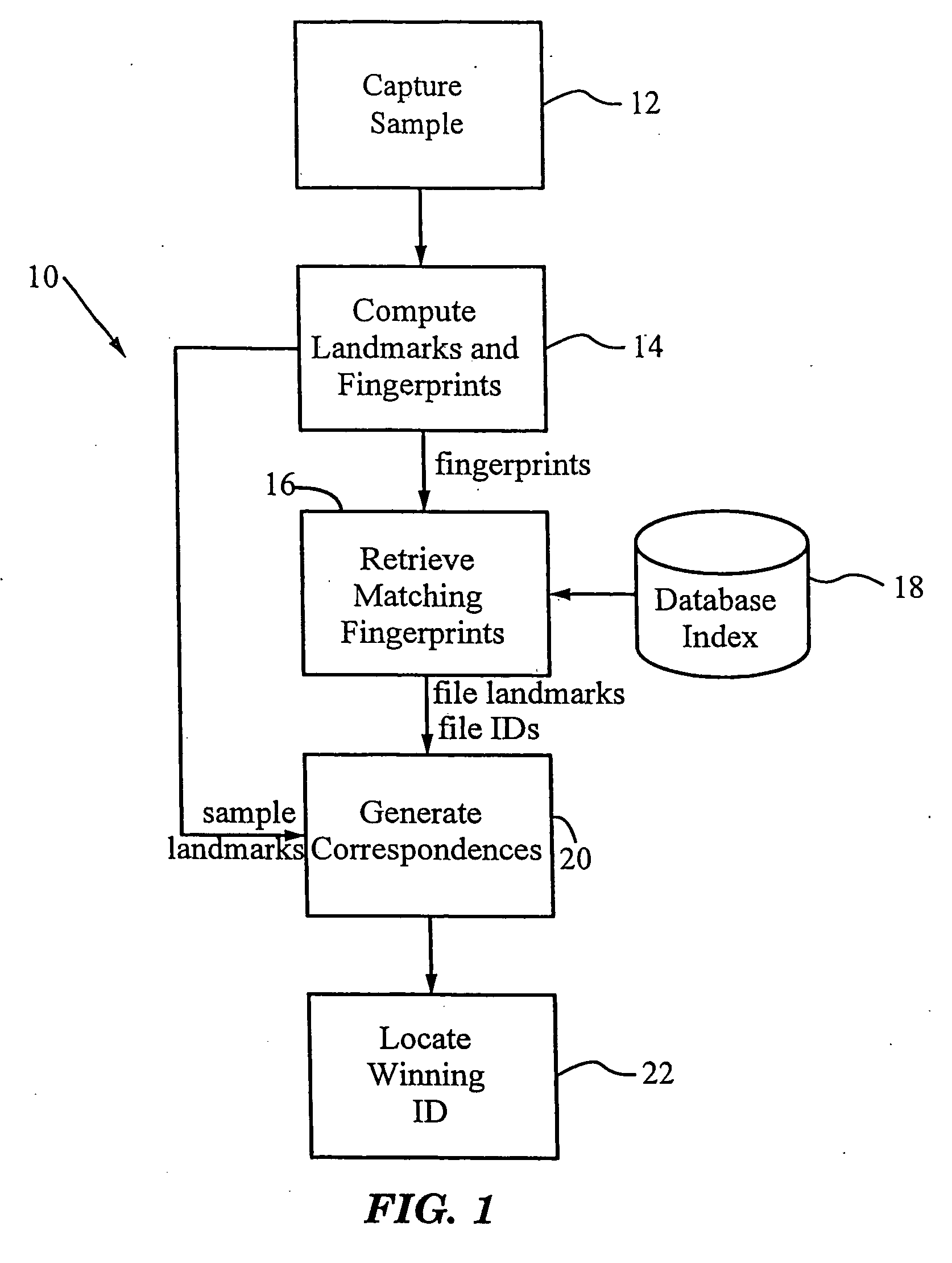
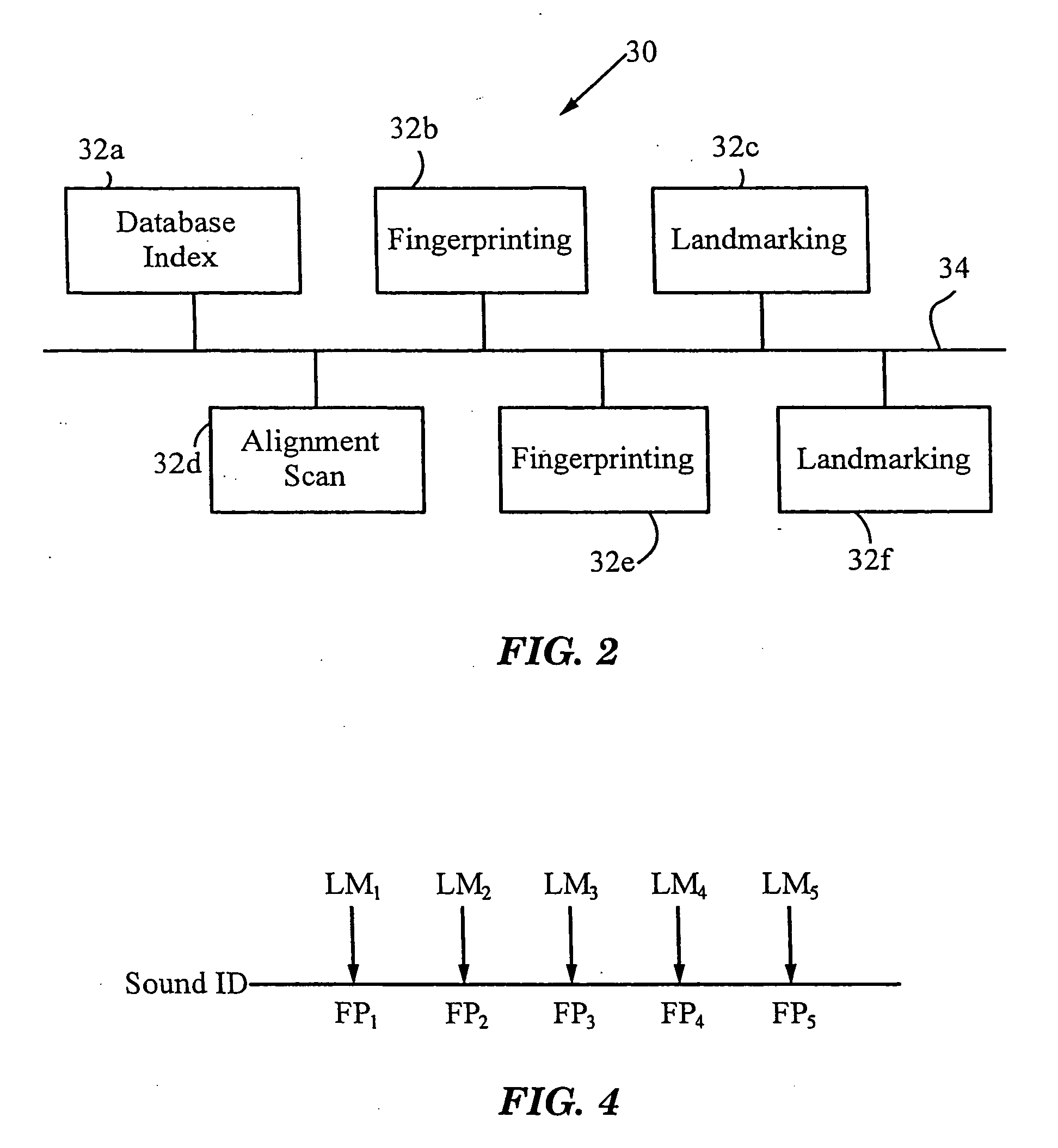
System and methods for recognizing sound and music signals in high noise and distortion
ActiveUS6990453B2High of distortionHigh levelGearworksMusical toysNonlinear distortionLinear correlation
A method for recognizing an audio sample locates an audio file that most closely matches the audio sample from a database indexing a large set of original recordings. Each indexed audio file is represented in the database index by a set of landmark timepoints and associated fingerprints. Landmarks occur at reproducible locations within the file, while fingerprints represent features of the signal at or near the landmark timepoints. To perform recognition, landmarks and fingerprints are computed for the unknown sample and used to retrieve matching fingerprints from the database. For each file containing matching fingerprints, the landmarks are compared with landmarks of the sample at which the same fingerprints were computed. If a large number of corresponding landmarks are linearly related, i.e., if equivalent fingerprints of the sample and retrieved file have the same time evolution, then the file is identified with the sample. The method can be used for any type of sound or music, and is particularly effective for audio signals subject to linear and nonlinear distortion such as background noise, compression artifacts, or transmission dropouts. The sample can be identified in a time proportional to the logarithm of the number of entries in the database; given sufficient computational power, recognition can be performed in nearly real time as the sound is being sampled.
Owner:APPLE INC
Query optimization in a multi-tenant database system
ActiveUS20050065925A1Great semantic knowledgeBroaden their knowledgeDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDatabase indexQuery optimization
More efficient querying of a multi-tenant database using dynamic tuning of database indices. A layer of meta-data associates data items with tenants, e.g., via tags, and the meta-data is used to optimize searches by channeling processing resources during a query to only those pieces of data bearing the relevant tenant's unique tag.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Search engine with suggestion tool and method of using same
InactiveUS20060248078A1Easy to understandDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsHuman search engineDatabase index
A method and a tool for suggesting search terms and other information during information search based on characters entered by users. Search terms may be suggested based on a heuristic that may take into account frequency of use and indexing of a database.
Owner:IDEALAB HLDG
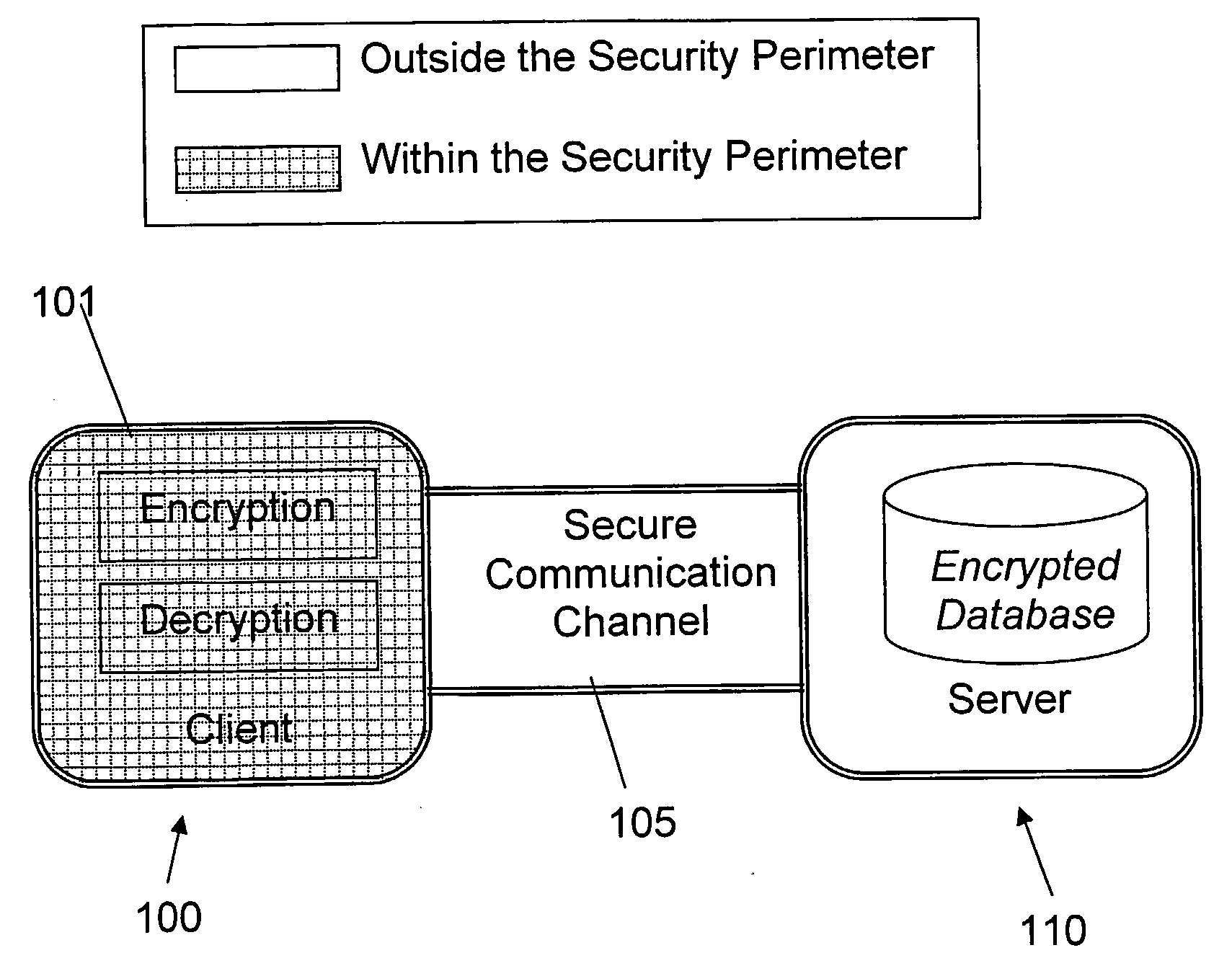
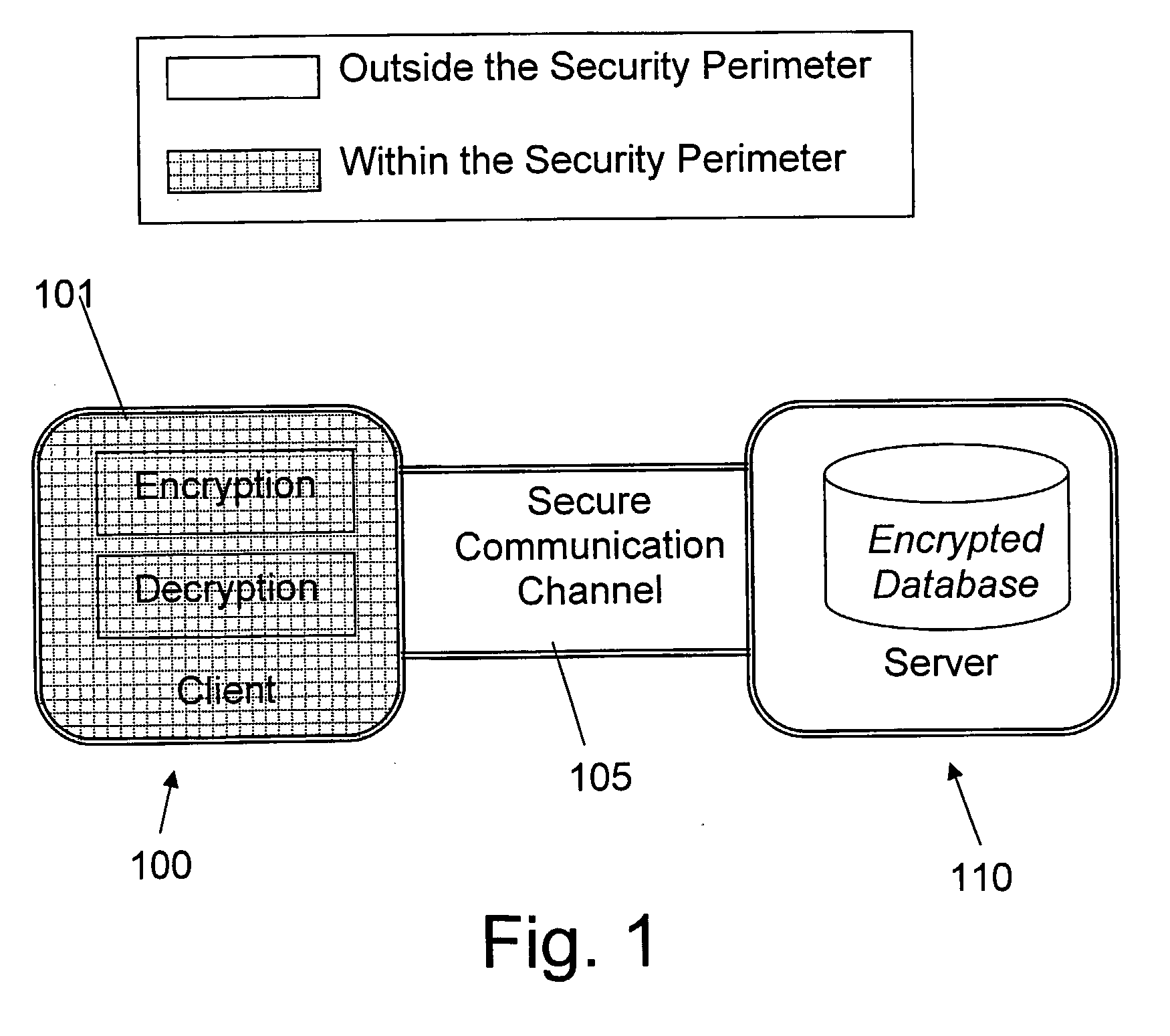
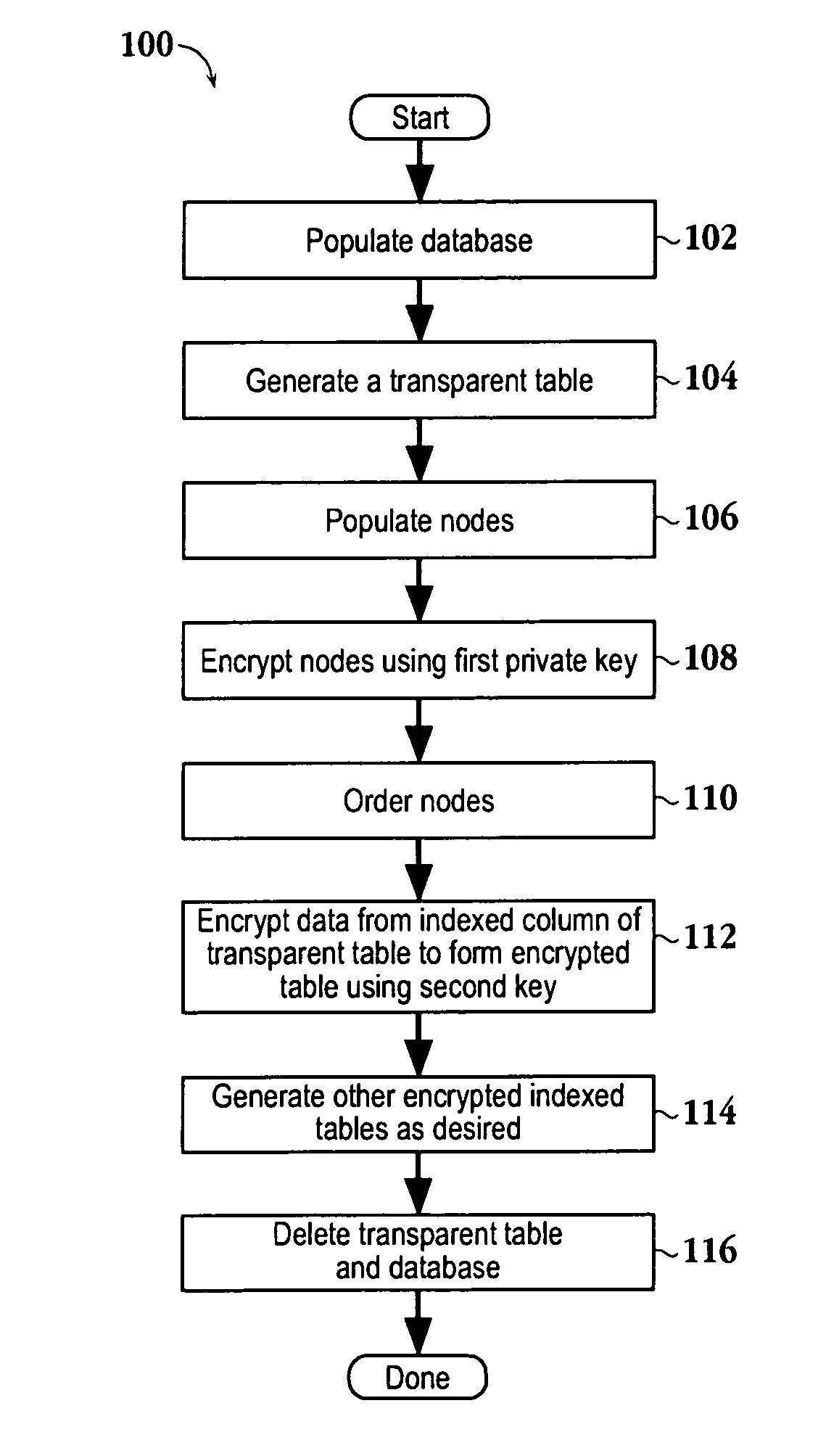
Structure Preserving Database Encryption Method and System
ActiveUS20080133935A1Easy accessAvoid contactKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageDatabase indexMulti user environment
A database encryption system and method, the Structure Preserving Database Encryption (SPDE), is presented. In the SPDE method, each database cell is encrypted with its unique position. The SPDE method permits to convert a conventional database index into a secure one, so that the time complexity of all queries is maintained. No one with access to the encrypted database can learn anything about its content without the encryption key. Also a secure index for an encrypted database is provided. Furthermore, secure database indexing system and method are described, providing protection against information leakage and unauthorized modifications by using encryption, dummy values and pooling, and supporting discretionary access control in a multi-user environment.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Database System with Methodology for Automated Determination and Selection of Optimal Indexes
ActiveUS20050203940A1Superior cost benefitImprove performanceData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase queryCost effectiveness
A database system with methodology for automated determination and selection of optimal indexes is described. In one embodiment, for example, in a database system, a method of the present invention is described for recommending database indexes to be created for optimizing system performance, the method comprises steps of: capturing a workload representative of database queries employed during system use; creating virtual indexes for optimizing system performance during execution of the database queries captured in the workload; computing cost benefits for different combinations of the virtual indexes; and recommending physical indexes to be created based on virtual indexes that have favorable cost benefits for the captured workload.
Owner:IANYWHERE SOLUTIONS
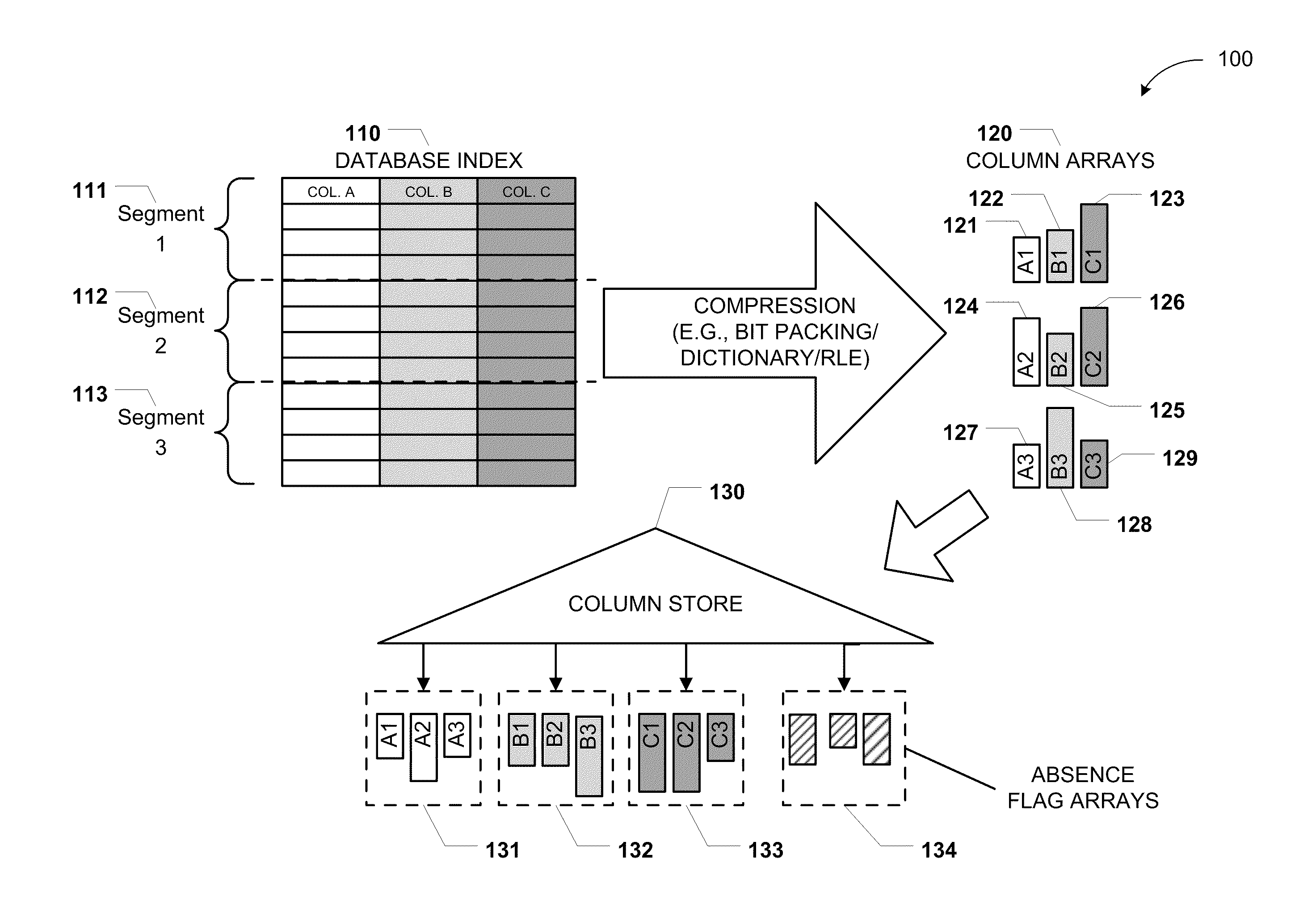
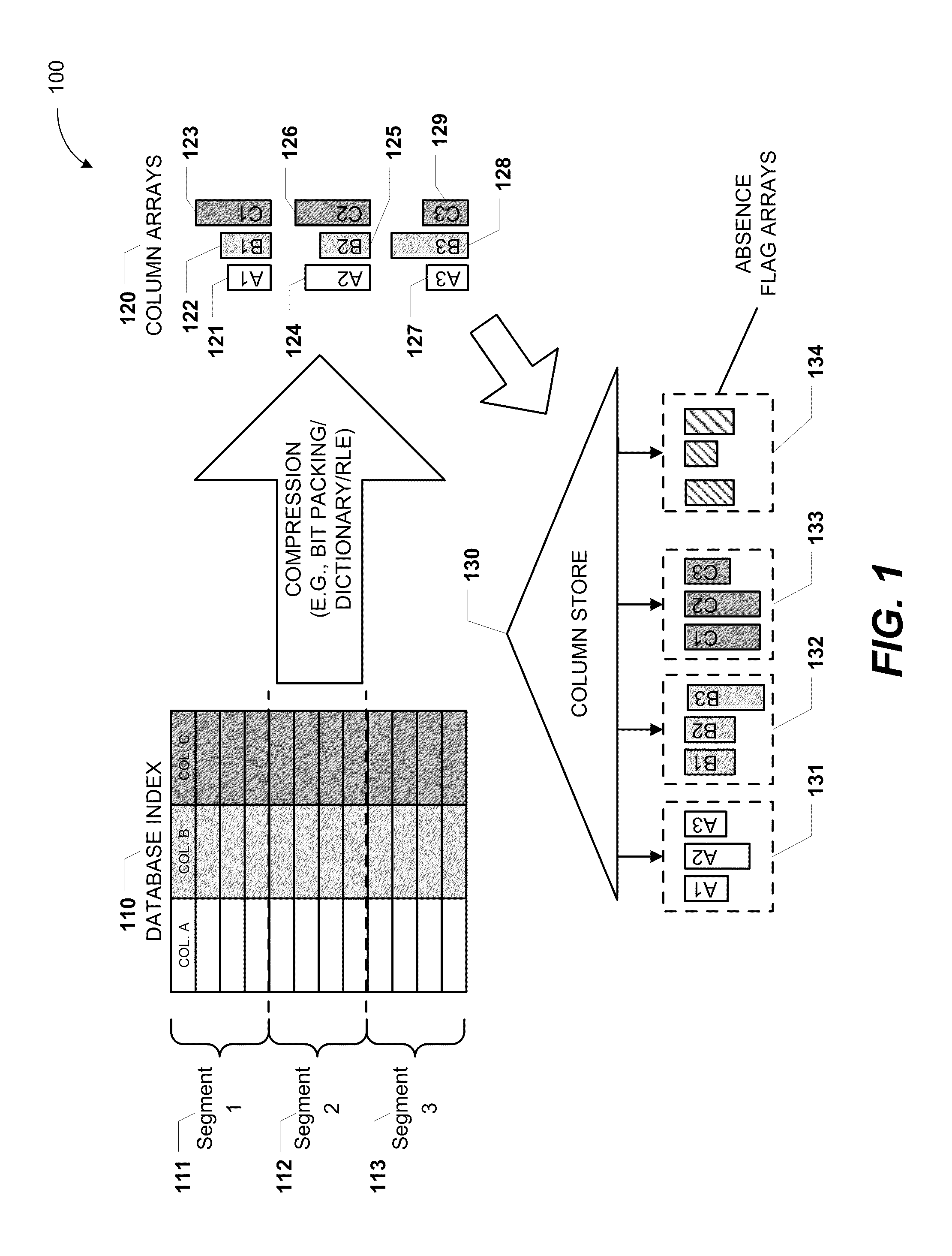
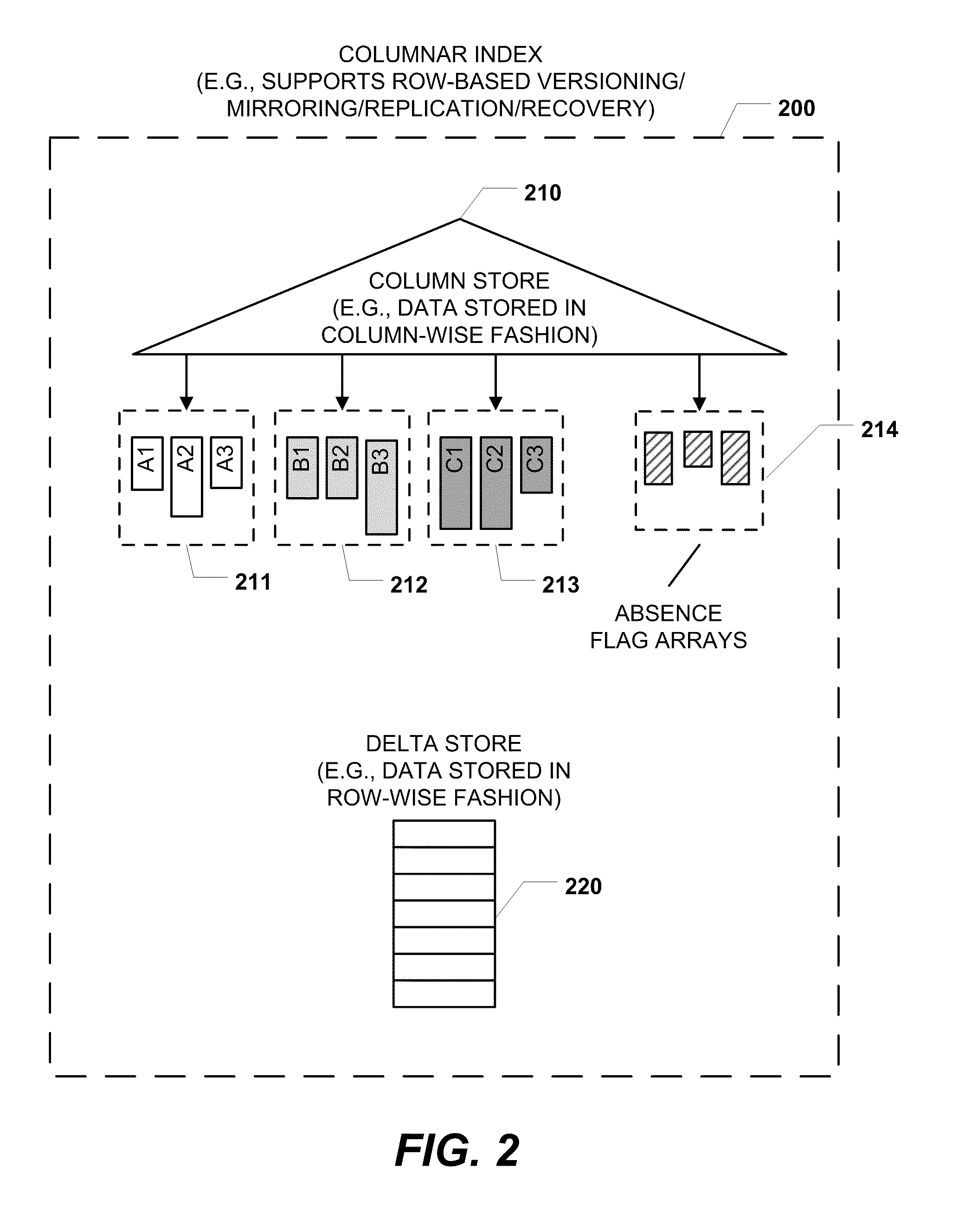
Columnar storage of a database index
ActiveUS20110219020A1Fast column-wise processing of queryMaintain compatibilityDigital data processing detailsHierarchical databasesArray data structureDatabase index
Methods, systems, and computer-readable media of columnar storage of a database index are disclosed. A particular columnar index includes a column store that stores rows of the columnar index in a column-wise fashion and a delta store that stores rows of the columnar index in a row-wise fashion. The column store also includes an absence flag array. The absence flag array includes entries that indicate whether certain rows have been logically deleted from the column store.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Query optimization in a multi-tenant database system
InactiveUS7529728B2Great semantic knowledgeBroaden their knowledgeData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDatabase indexQuery optimization
More efficient querying of a multi-tenant database using dynamic tuning of database indices. A layer of meta-data associates data items with tenants, e.g., via tags, and the meta-data is used to optimize searches by channeling processing resources during a query to only those pieces of data bearing the relevant tenant's unique tag.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
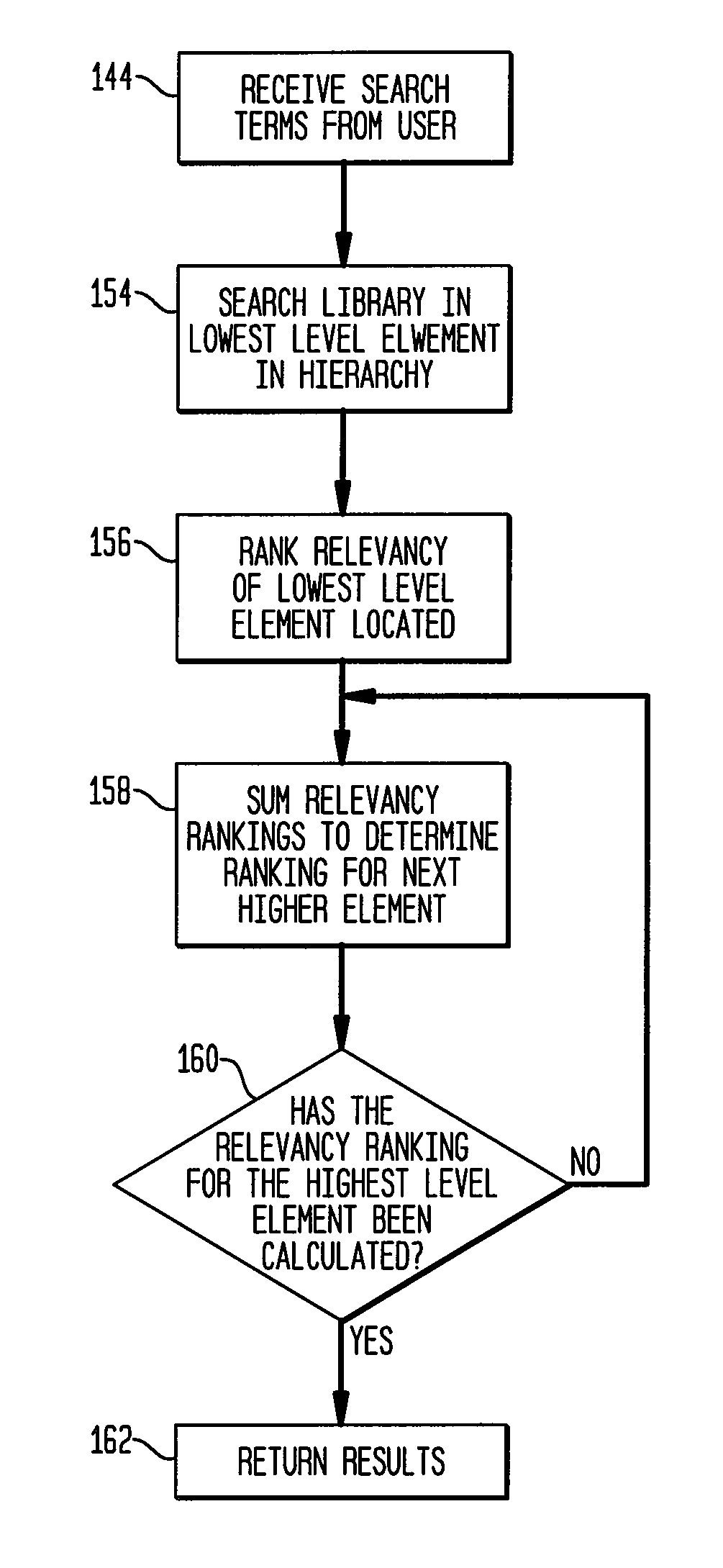
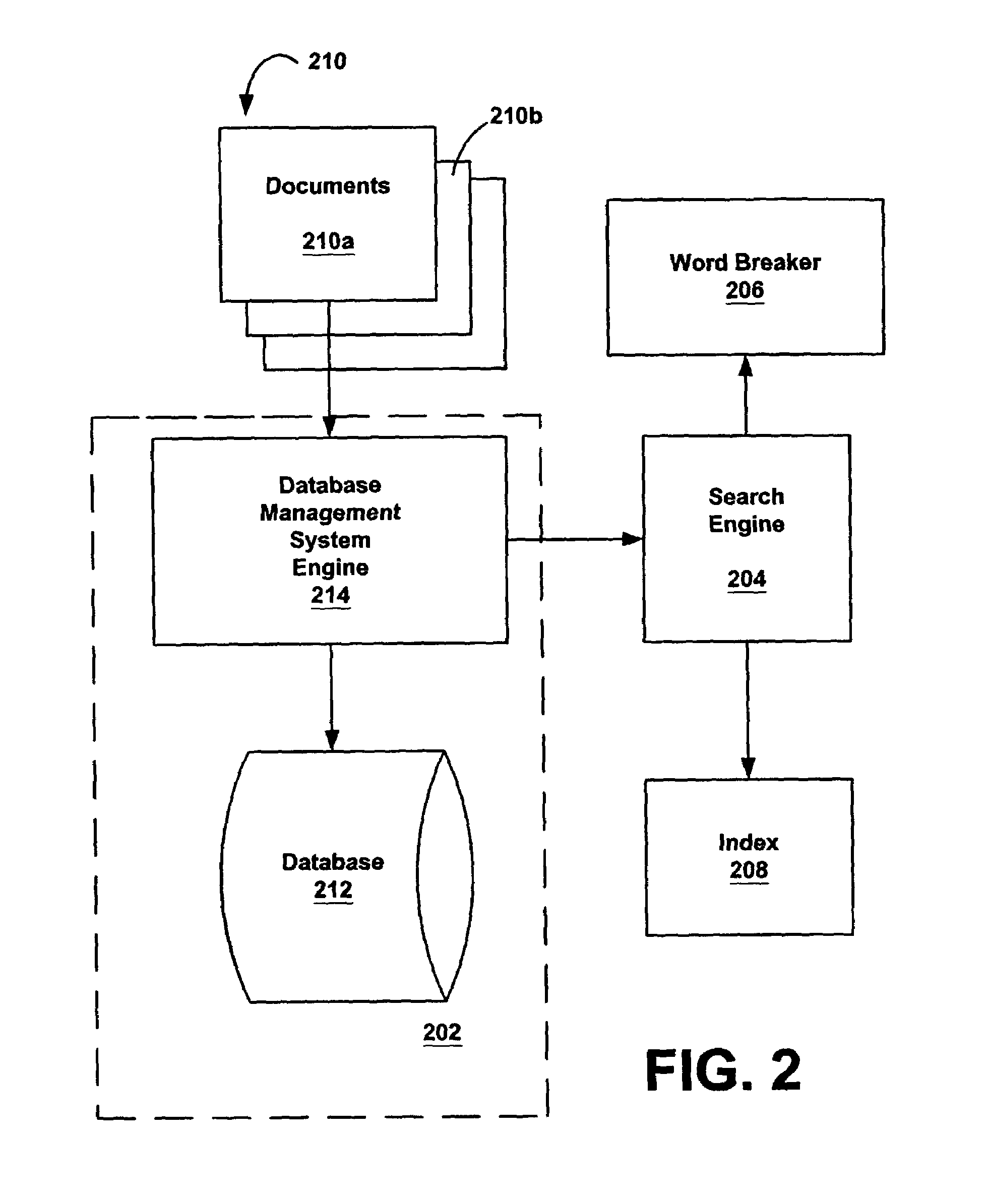
System and method for providing a searchable library of electronic documents to a user
InactiveUS7287214B1Efficient methodData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsDigital dataElectronic document
A method and system for publishing a plurality of books for user access includes selecting a plurality of books, converting each book from a layout or publication digital data form, by providing and applying a tool to detect characteristic features (such as layout, typeface, and hierarchical or organizational features such as chapter headings, captions, drawings and tables), and extracting text or data information of the book tagged with the features. This produces a searchable publishing database indexed by book structure such that a user may remotely, access the database, search desired text data, and view an image of a portion of the book with the desired data. A search engine may score search results based on their position in the hierarchy or other factors, determining degree of relevance of text or data information located by the search engine.
Owner:CREDIT SUISSE CAYMAN ISLANDS BRANCH +1
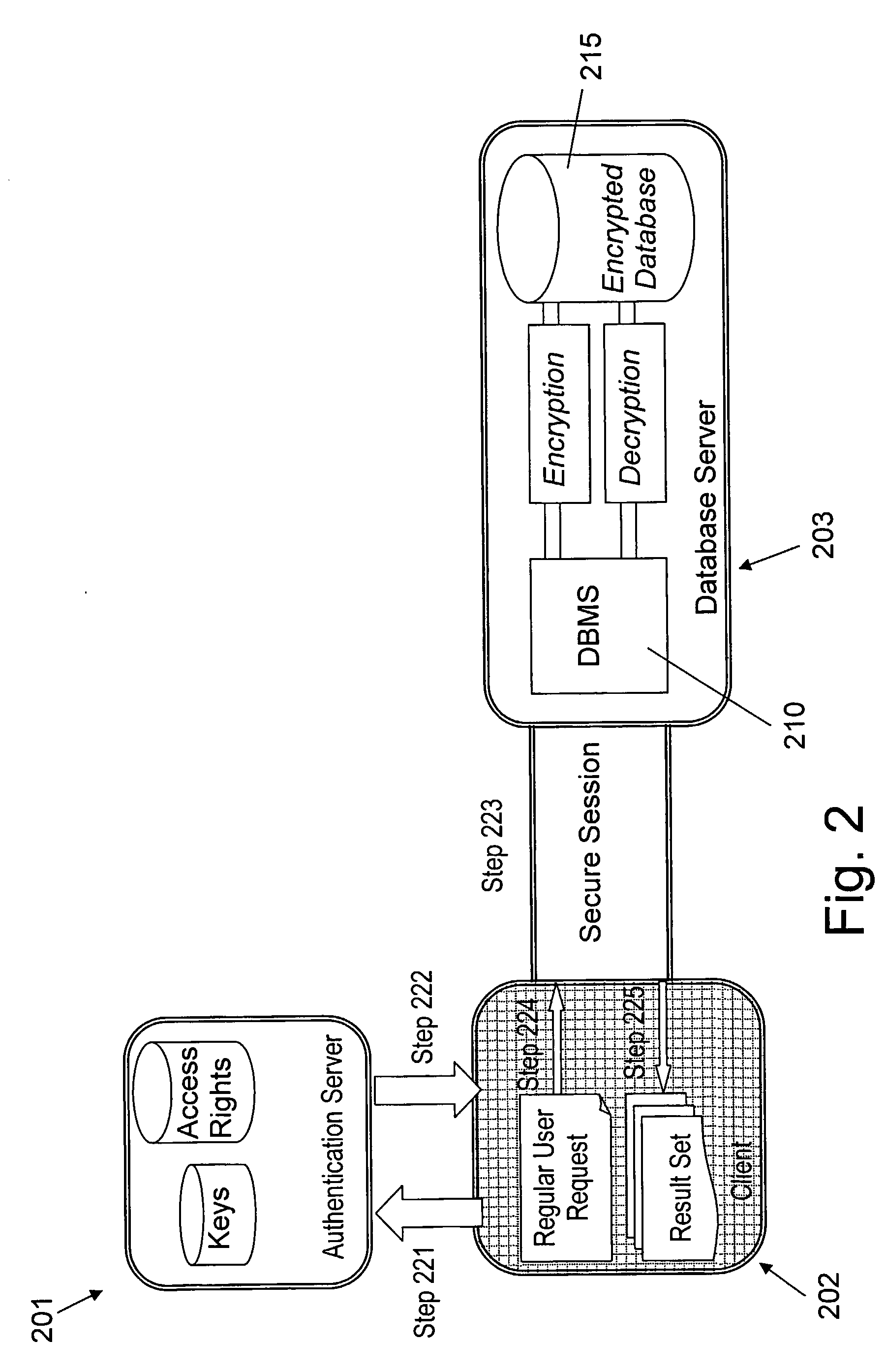
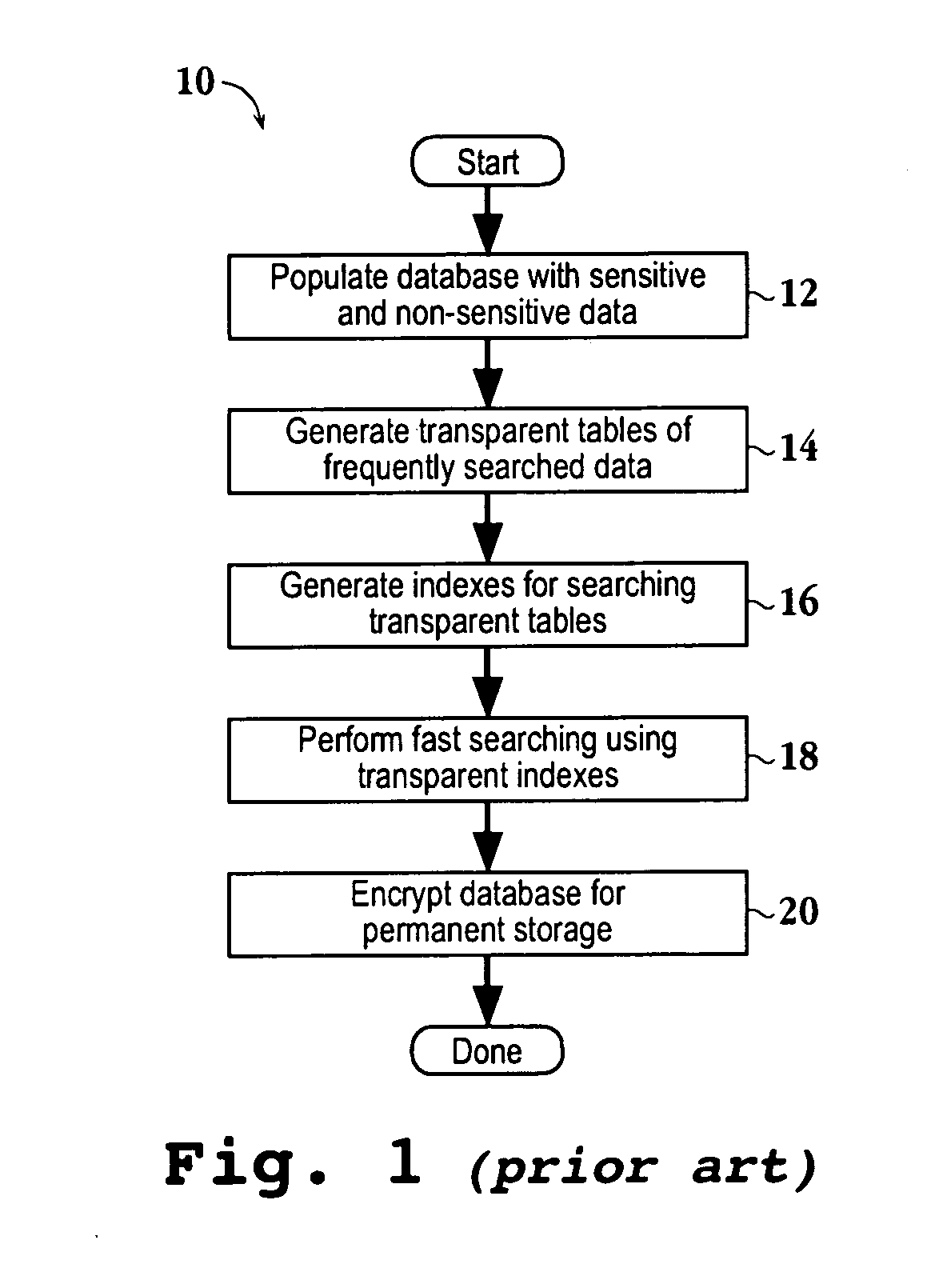
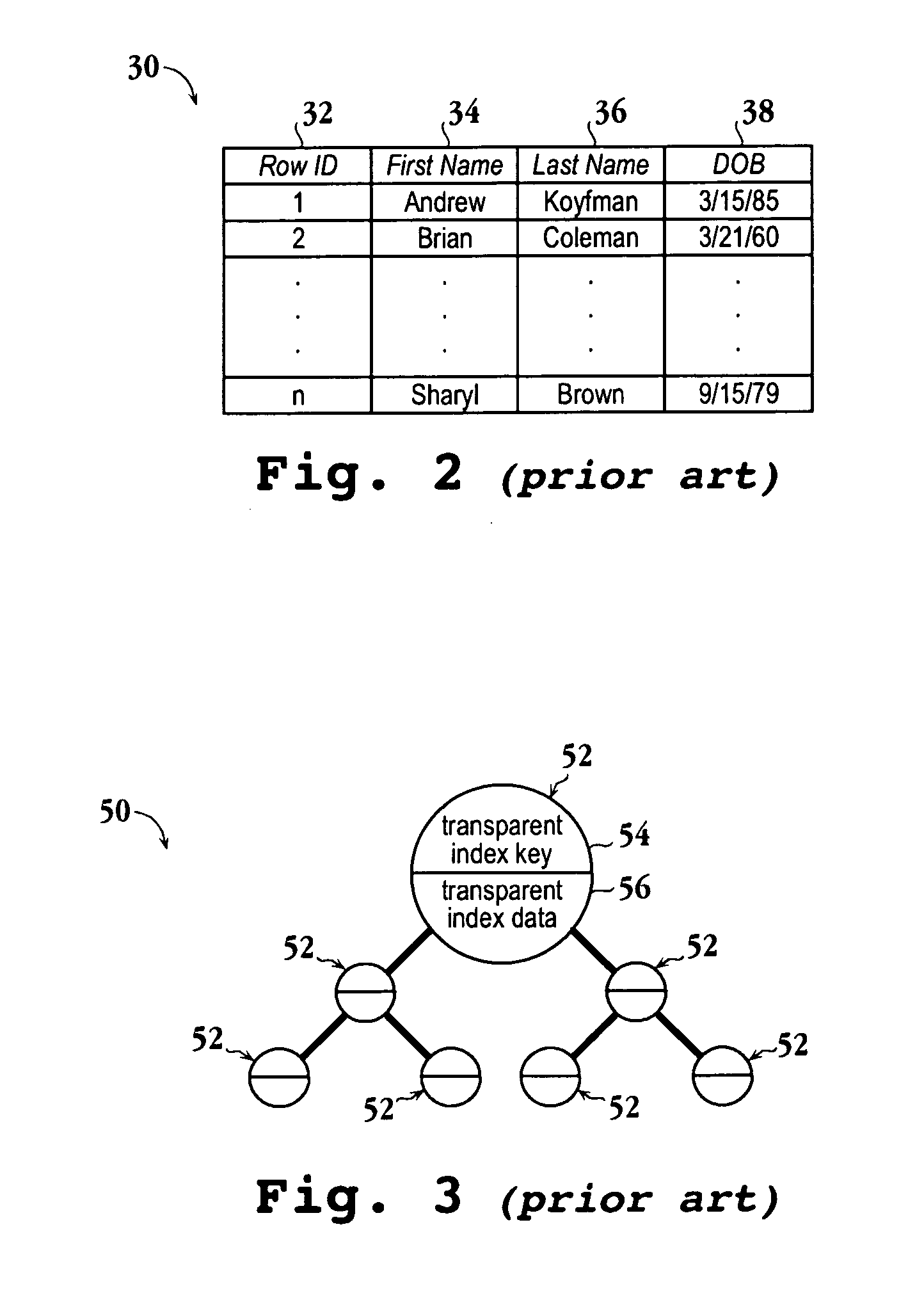
Encrypted table indexes and searching encrypted tables
The present invention teaches a variety of methods for building and searching secure, indexed database tables. Sensitive portions of the database tables and database indexes are encrypted, ordered and searched according to Boolean functions arranged to work with encrypted data. Also disclosed is a database management system that allows authorized users to build and search encrypted tables.
Owner:THALES DIS CPL USA INC
Database system and method for data acquisition and perusal
InactiveUS20050027702A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDatabase indexData source
A data acquisition and perusal system and method including a database selection module, a database index generator module and a search module. The database selection module enables selection of a plurality of files for inclusion into at least one selectable database. The database index generator module enables generation of a searchable index of the data contained in the selectable database. The search module enables a search to be performed of the searchable index according to search criteria. The data acquisition and perusal system and method may also allow users to view, acquire, and generate single- or multiple-data sources locally or remotely, and allow users to compile, index, modify, and append the data sources according to default or user defined criteria. The data acquisition and perusal system and method may also selectively acquire and display data contained within remote databases depending upon the user's access permissions to such databases. Such a system allows for the capture of HTML data which is automatically indexed without human intervention and has the ability to automatically and accurately locate or “pinpoint,” and highlight specific text or groups of text designated by the user within the resulting database. Such a system contains a link module that enables custom links to be defined between selected terms of selected files of the selectable database including the custom links so that the searchable index includes only valid links.
Owner:INTEGRATED DATA CONTROL
System and methods for recognizing sound and music signals in high noise and distortion
InactiveUS20060122839A1High of distortionHigh levelDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionNonlinear distortionLinear correlation
A method for recognizing an audio sample locates an audio file that most closely matches the audio sample from a database indexing a large set of original recordings. Each indexed audio file is represented in the database index by a set of landmark timepoints and associated fingerprints. Landmarks occur at reproducible locations within the file, while fingerprints represent features of the signal at or near the landmark timepoints. To perform recognition, landmarks and fingerprints are computed for the unknown sample and used to retrieve matching fingerprints from the database. For each file containing matching fingerprints, the landmarks are compared with landmarks of the sample at which the same fingerprints were computed. If a large number of corresponding landmarks are linearly related, i.e., if equivalent fingerprints of the sample and retrieved file have the same time evolution, then the file is identified with the sample. The method can be used for any type of sound or music, and is particularly effective for audio signals subject to linear and nonlinear distortion such as background noise, compression artifacts, or transmission dropouts. The sample can be identified in a time proportional to the logarithm of the number of entries in the database; given sufficient computational power, recognition can be performed in nearly real time as the sound is being sampled.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for smart search engine and other applications
InactiveUS20030101182A1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsDatabase indexApplication software
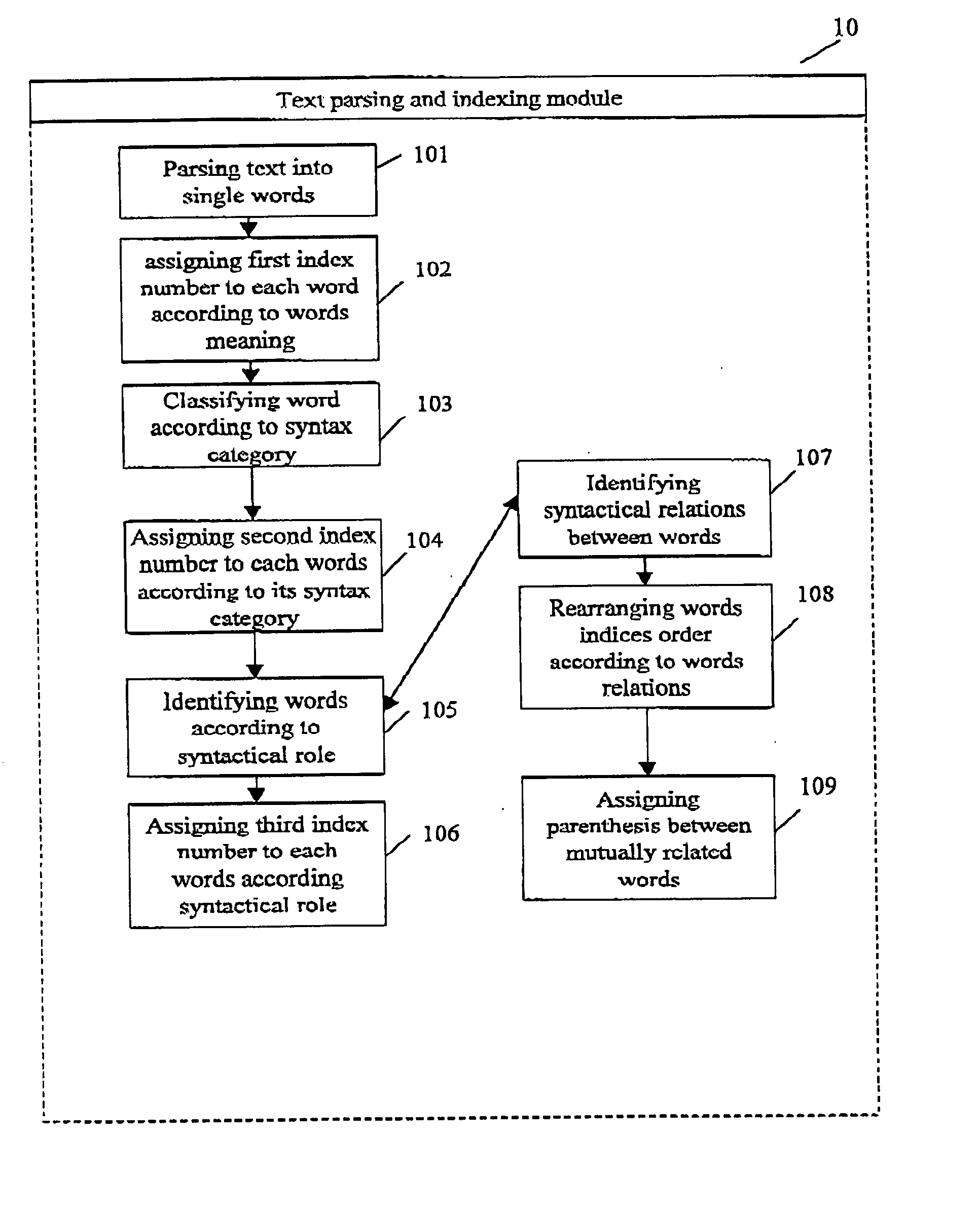
The present invention provides a new method for indexing a given text objects, using text parsing module and words indexing databases. According to this method each word is assigned a first index code according to words meaning, a second index code according to each word syntax category and a third index code according to word syntactical role. The words indices are arranged according to hierarchical order based on syntactical relations between the text words. At the last stage, differentiating symbols, which represent indices hierarchical order, are assigned between adjacent words indices. The indexing process may be implemented as automatic computerized program or as wizard application enabling human intervention in the indexing process. The indexing method can be utilized for enabling text search utilities based on matching between The query indices and source text indices.
Owner:GOVRIN OMRI +1
Method and system for dynamically partitioning very large database indices on write-once tables
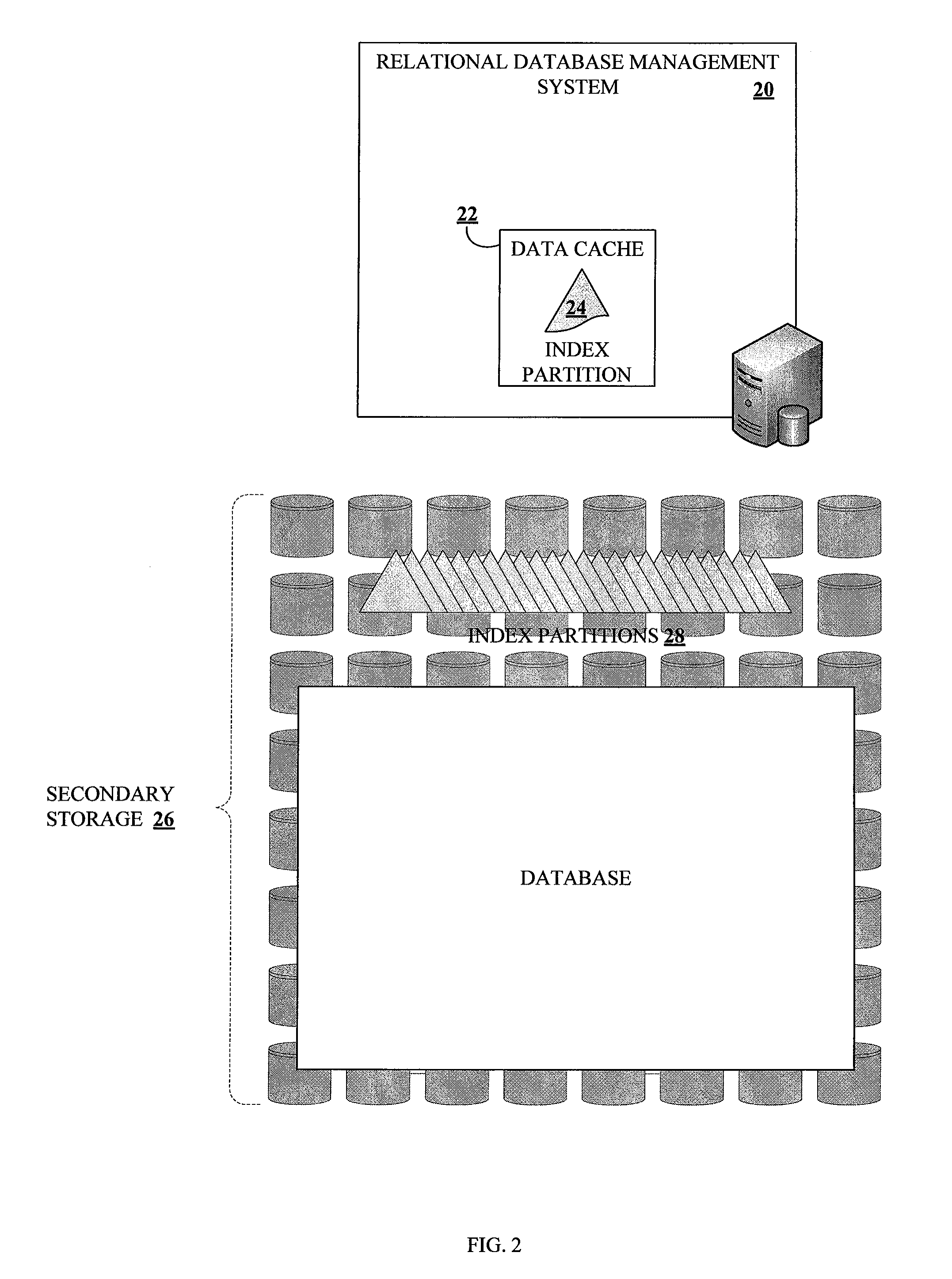
ActiveUS20100161569A1Increase in sizeAvoid performance degradationDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesDatabase indexIncrease size
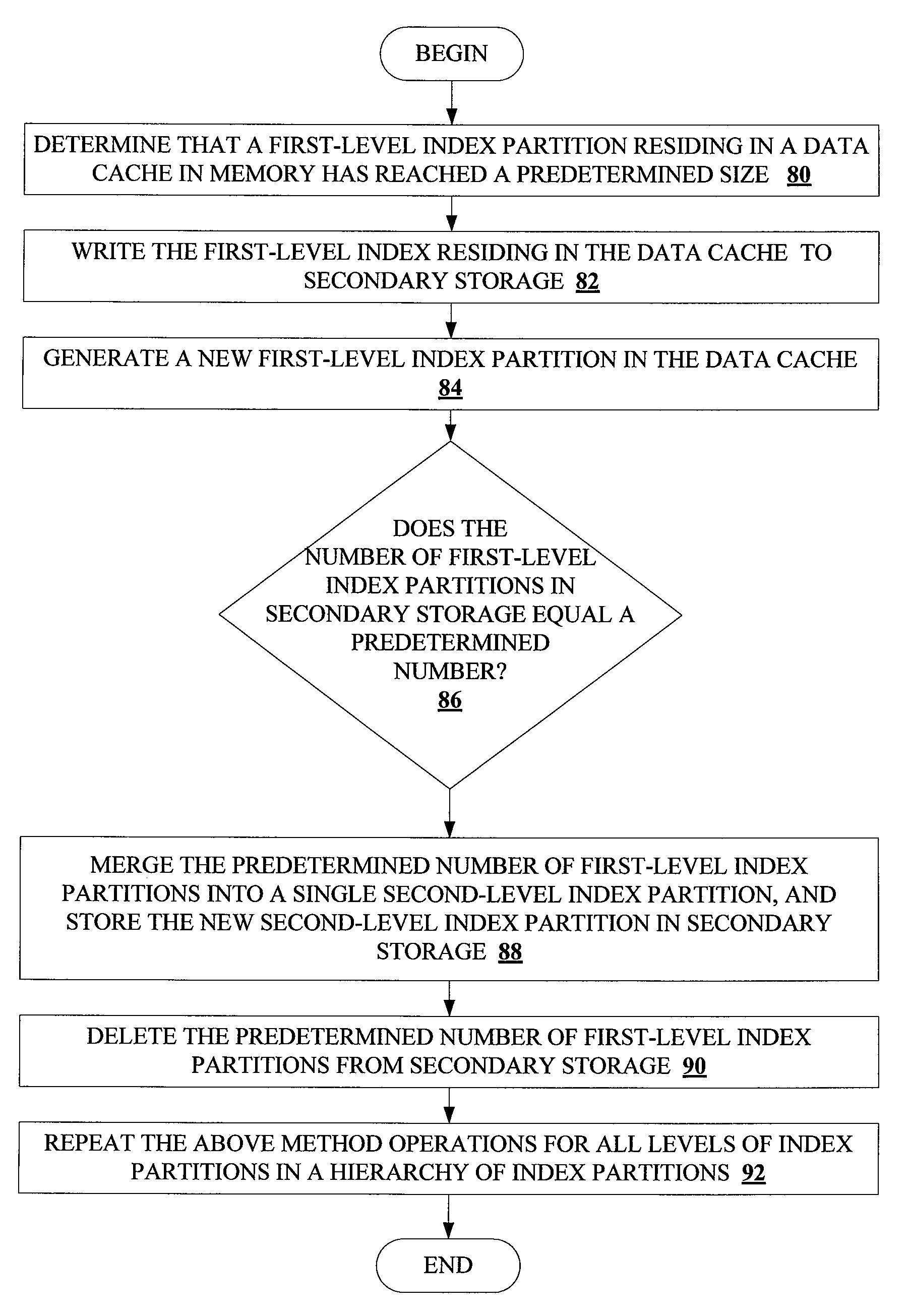
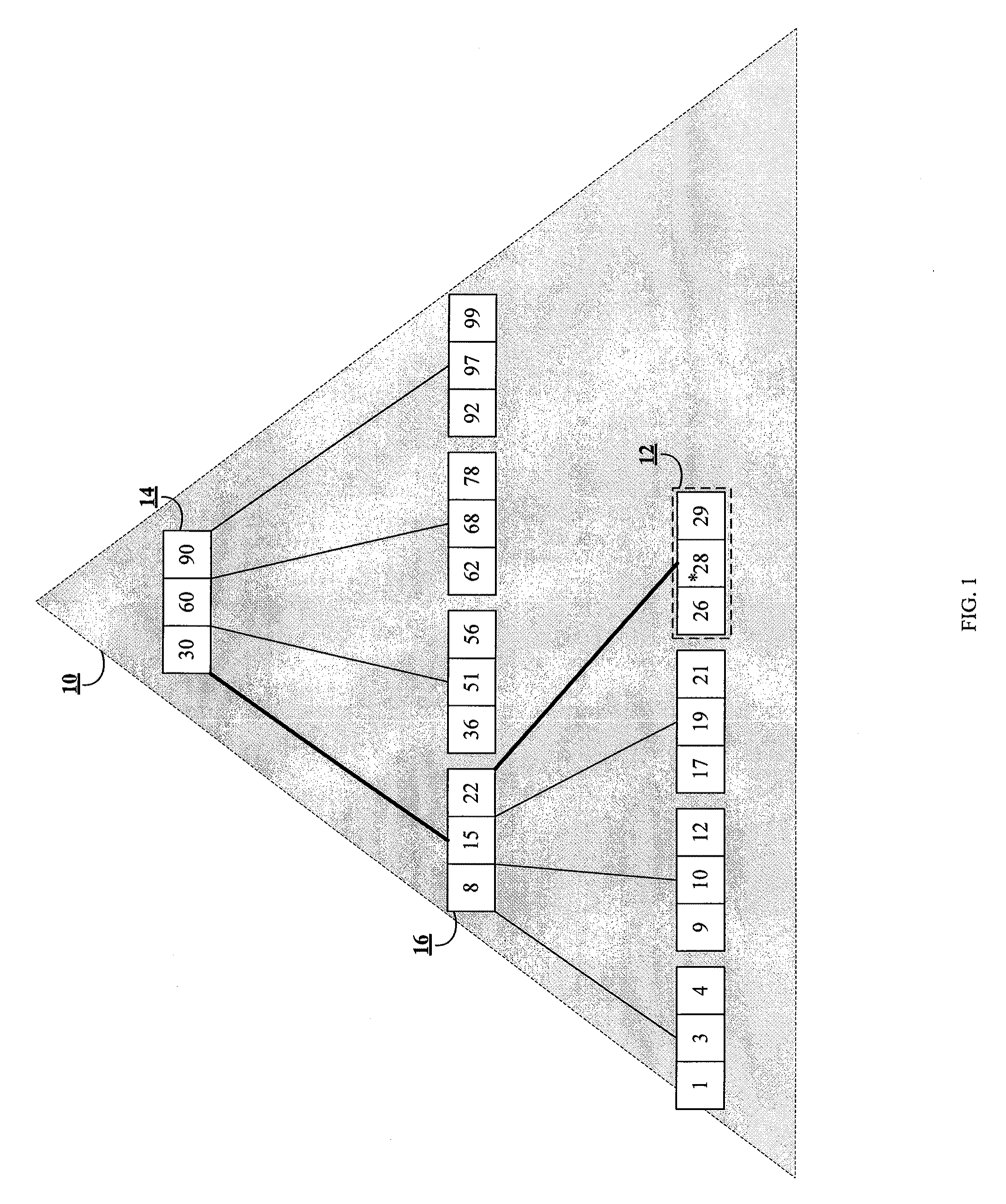
Methods and systems for partitioning and dynamically merging a database index are described. A database index includes a single first-level index partition stored in a data cache. As the first-level index partition in the data cache reaches a predetermined size, it is copied to secondary storage and a new index partition is generated in the data cache. When the number of index partitions in secondary storage reaches some predetermined number, the index partitions are merged to create a single index partition of a higher level in a hierarchy of index partitions having an exponentially increasing size with each increase in level within the hierarchy.
Owner:SAP AG
Systems and methods for automated programming of RFID tags using machine readable indicia
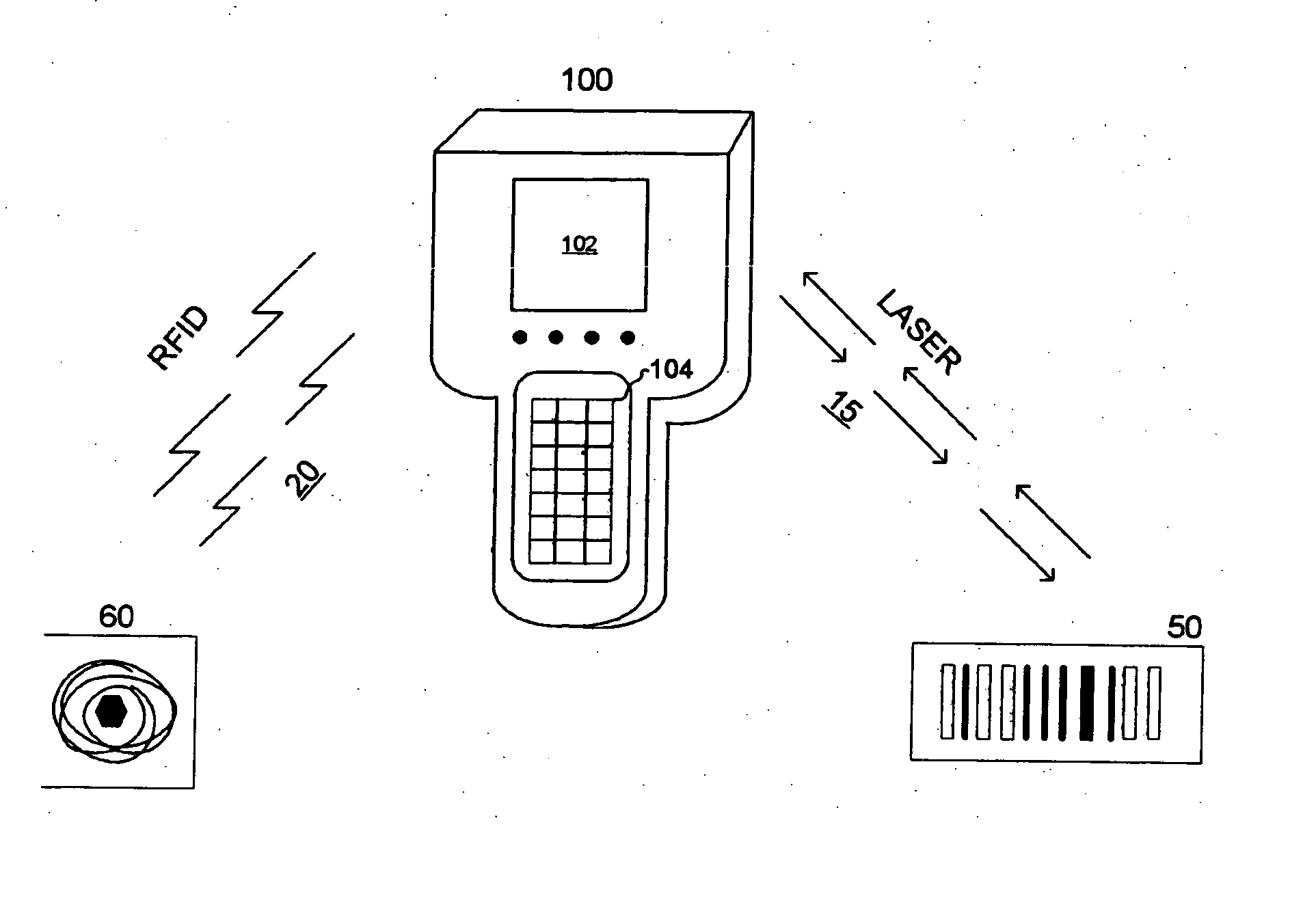
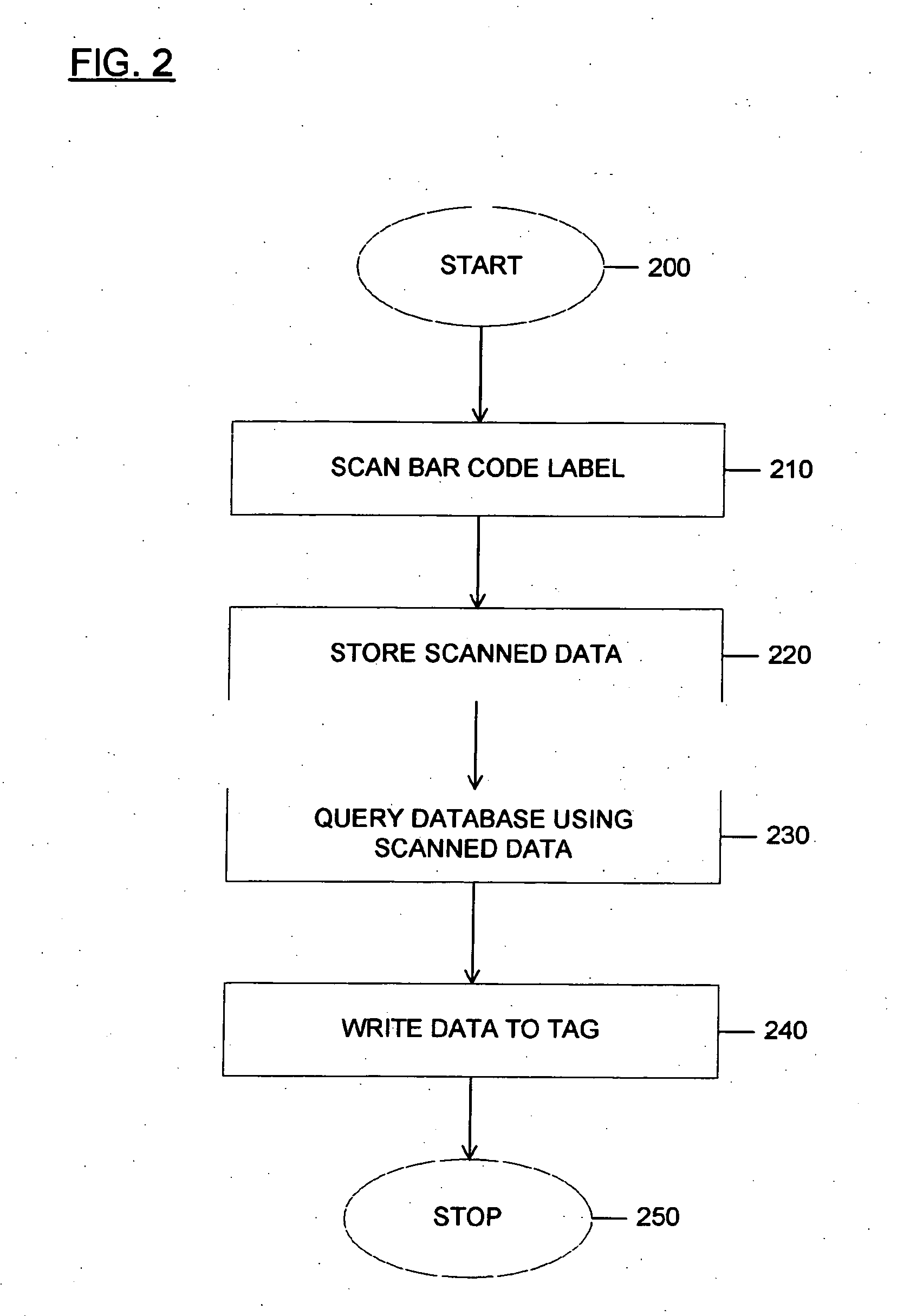
ActiveUS20070188306A1Less reliantCharacter and pattern recognitionSubscribers indirect connectionComputer hardwareDatabase index
Methods and systems for automatically programming an RFID tag using machine readable indicia. A dual mode device performs a bar code scan of a bar coded label. Information obtained from the bar code scan is stored. This information may be used to query a database indexed by the bar code information that contains detailed product information. The bar code information as well as the detailed information may be transmitted in an RF signal by the dual mode device to an RFID tag to be stored in a memory structure in the tag. The dual mode device may perform a read operation on the tag after the write operation to confirm that the data was successfully stored and provide an indication thereof. The indication may be a visual indication, a textual indication, an audible indication or combinations of these.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
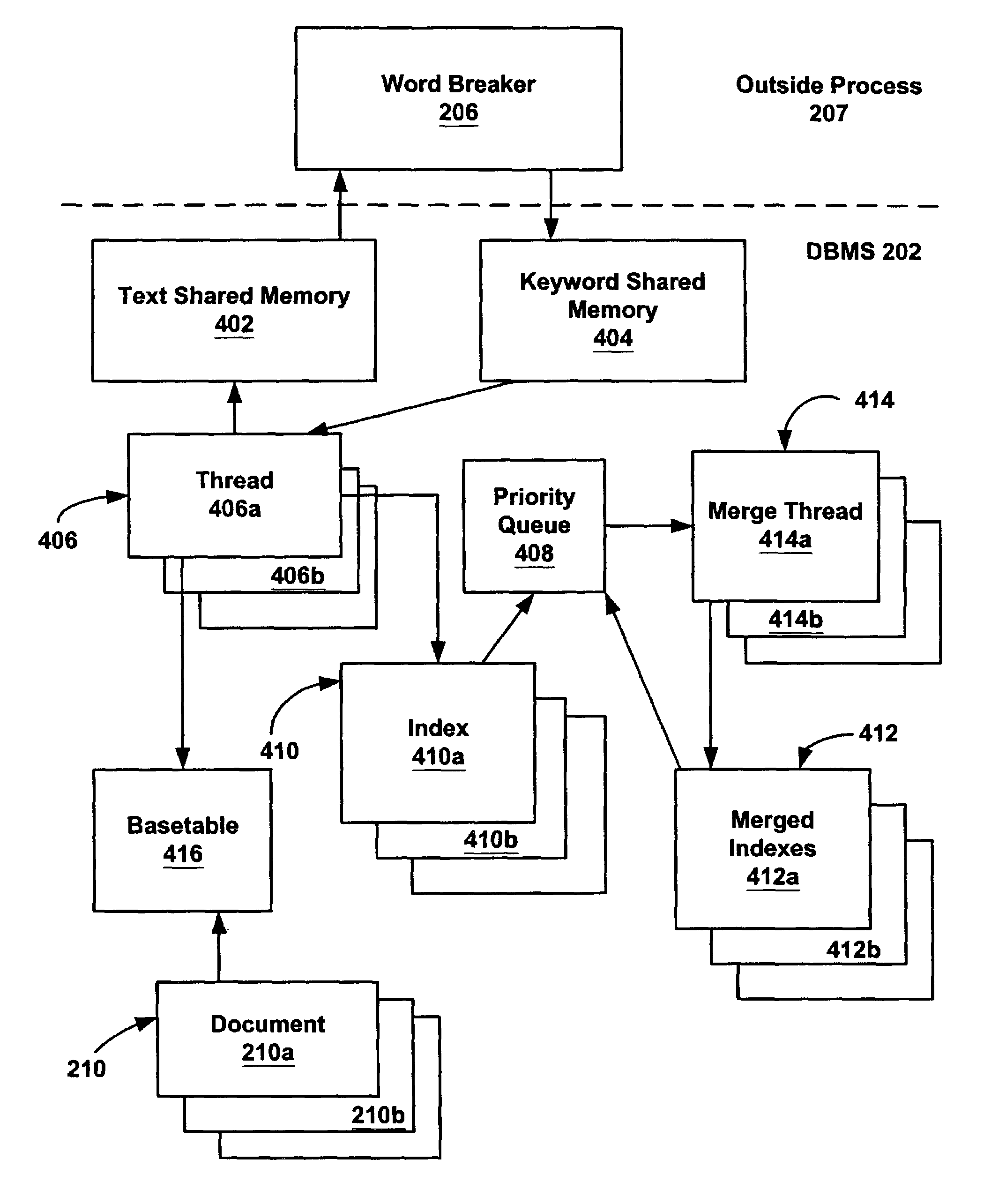
Prioritized merging for full-text index on relational store
A full-text search index system and method is generated by creating instances of a database index from an in-memory inverted list of keywords associated with a text identifier and the occurrences of the keyword in the text. Instances of the index are placed in a priority queue. A merge scheduling process determines when a merge should be initiated, selects instances of the index to be merged and selects a type of merge to perform.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
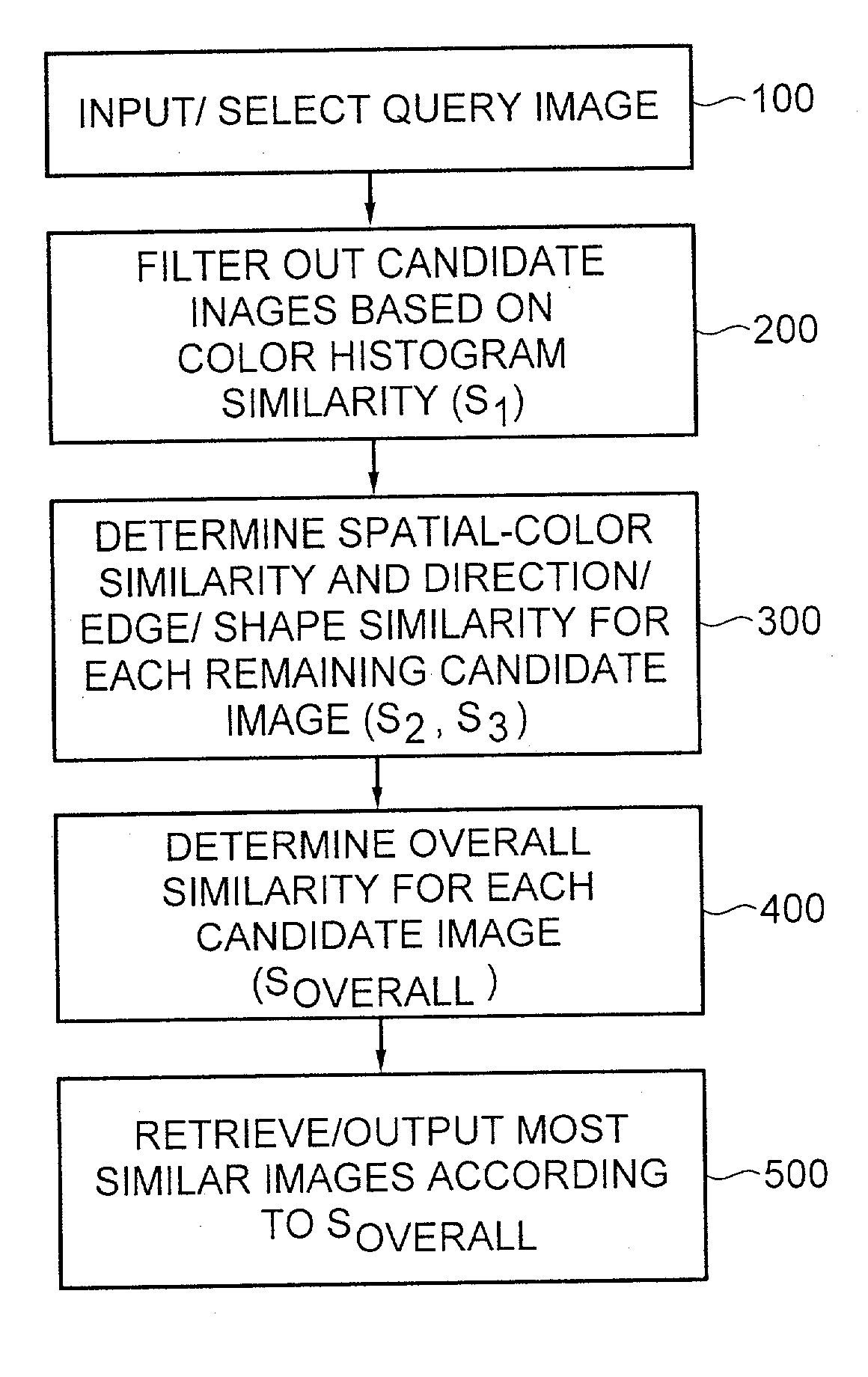
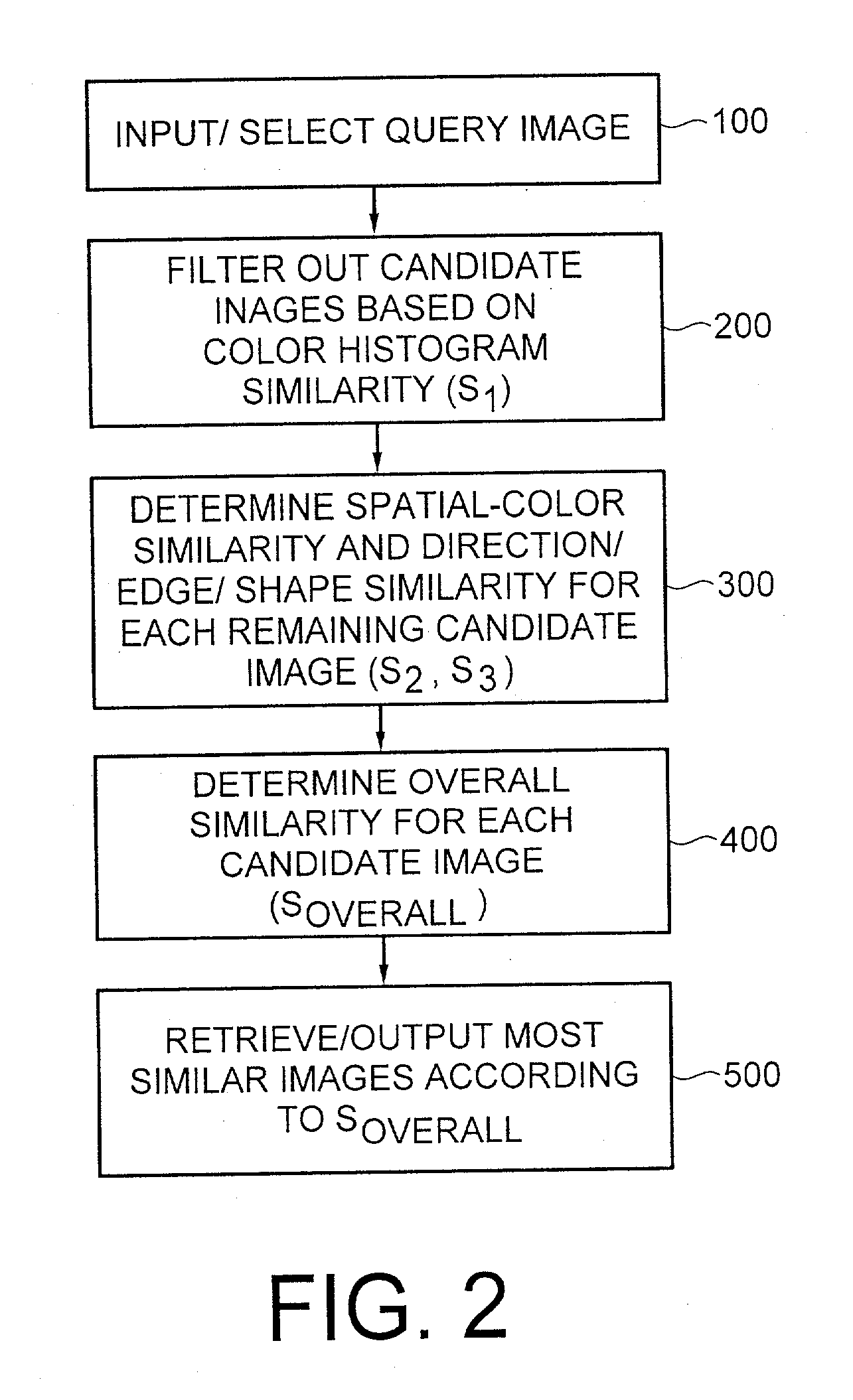
Method for automatic retrieval of similar patterns in image databases
InactiveUS20030179213A1Fast and accurate imageCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDecompositionDatabase index
An image retrieval system and method that combines histogram-based features with Wavelet Frame decomposition features, as well as two-pass progressive retrieval process. The proposed invention is robust against illumination changes as well as geometric distortions. During the first round of retrieval, moment features of image histograms in the Karhunen-Loeve color space are derived and used to filter out most of the dissimilar images. During the second round of retrieval, multi-resolution WF decomposition is recursively applied to the remaining images. A set of coefficients of low-pass filtered subimages at the coarsest level, after being mean-subtracted and normalized, are utilized as features containing spatial-color information. Modulus and direction coefficients are calculated from the high-pass filtered X-Y directional subimages at each level, and central moments are derived from the direction histogram of the most significant direction coefficients to obtain TRSI direction / edge / shape features. Since the proposed invention is fast and robustness against illumination and geometric distortions, the invention is quite appealing for real-time image / video database indexing and retrieval applications.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
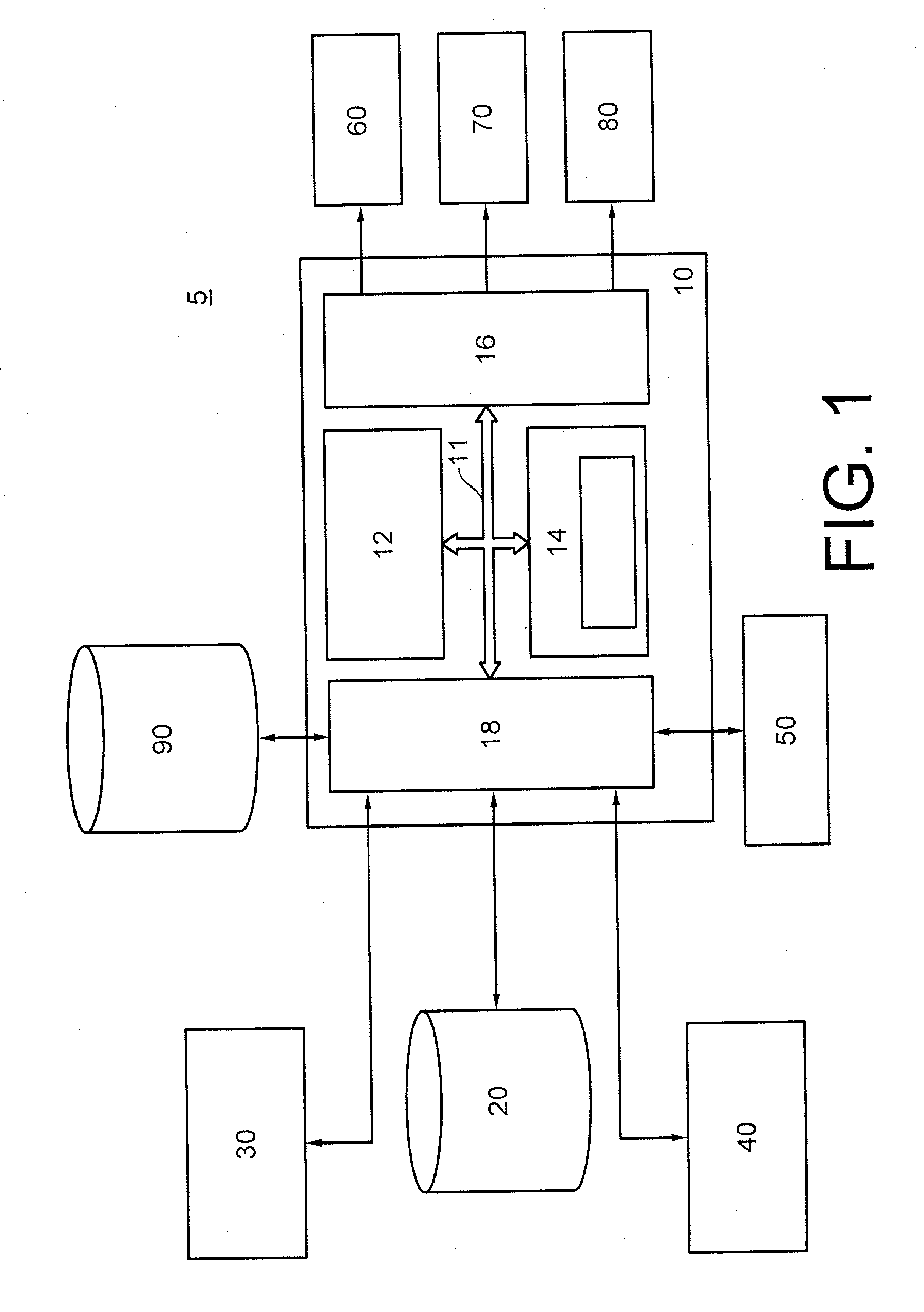
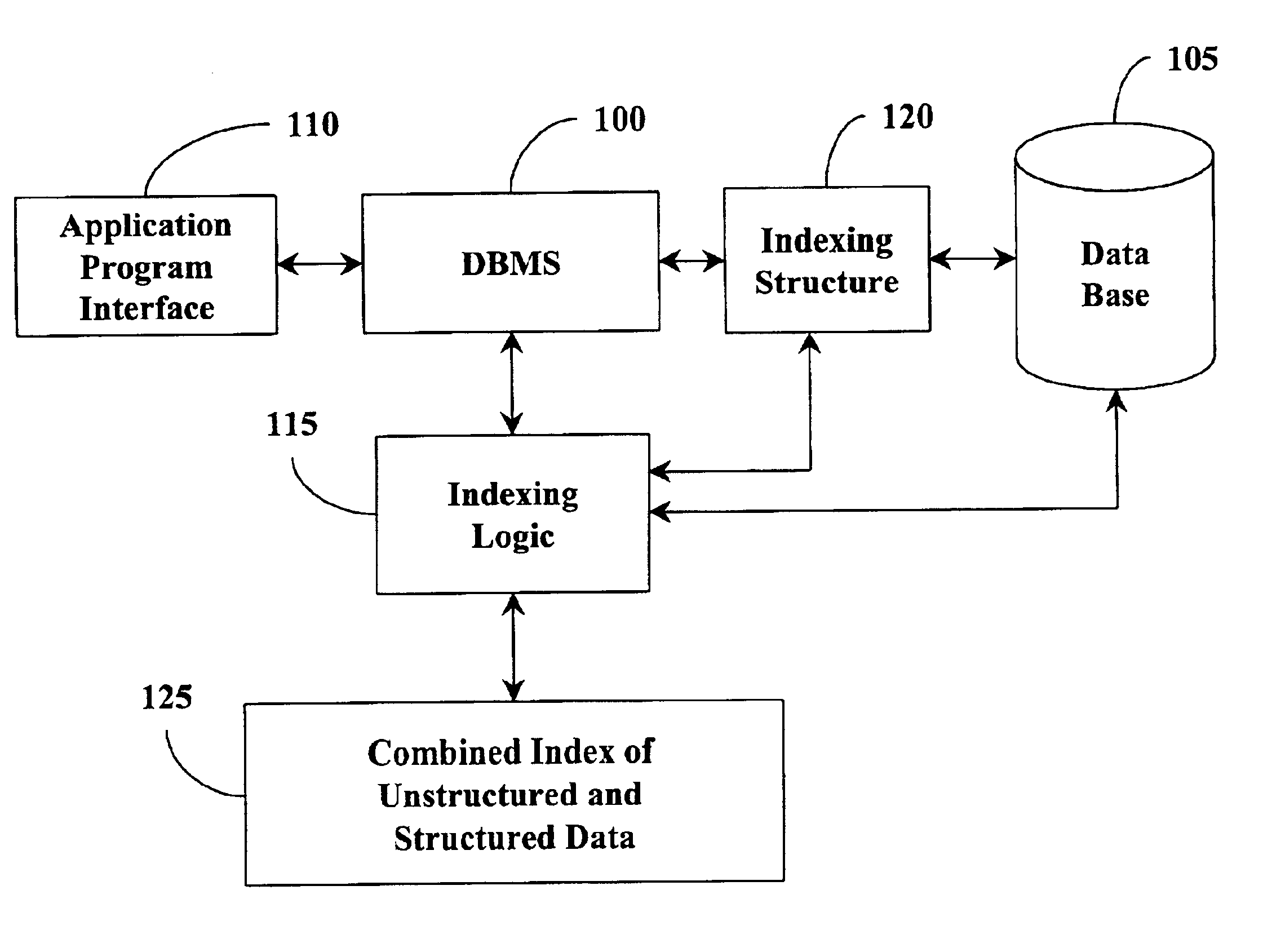
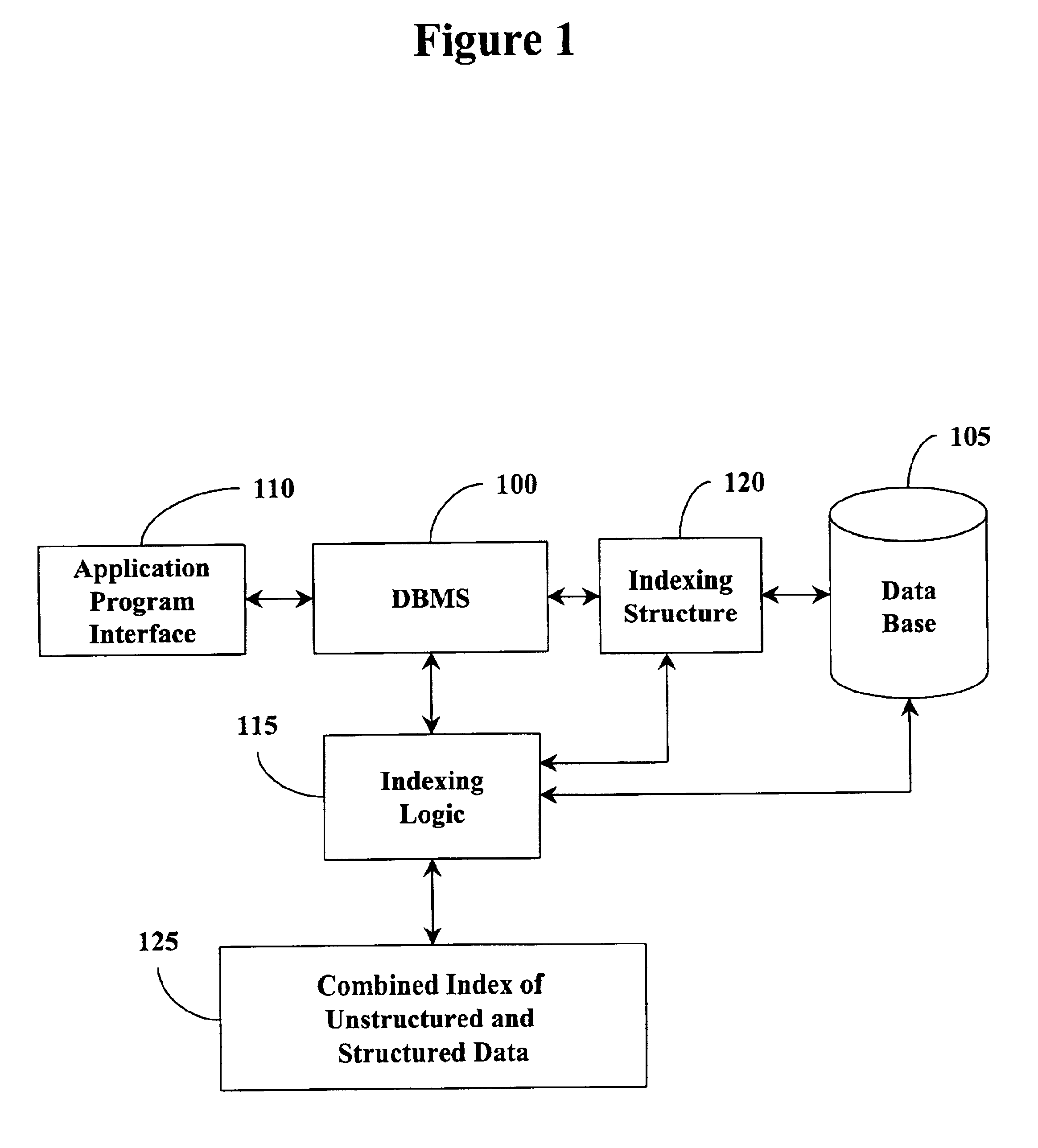
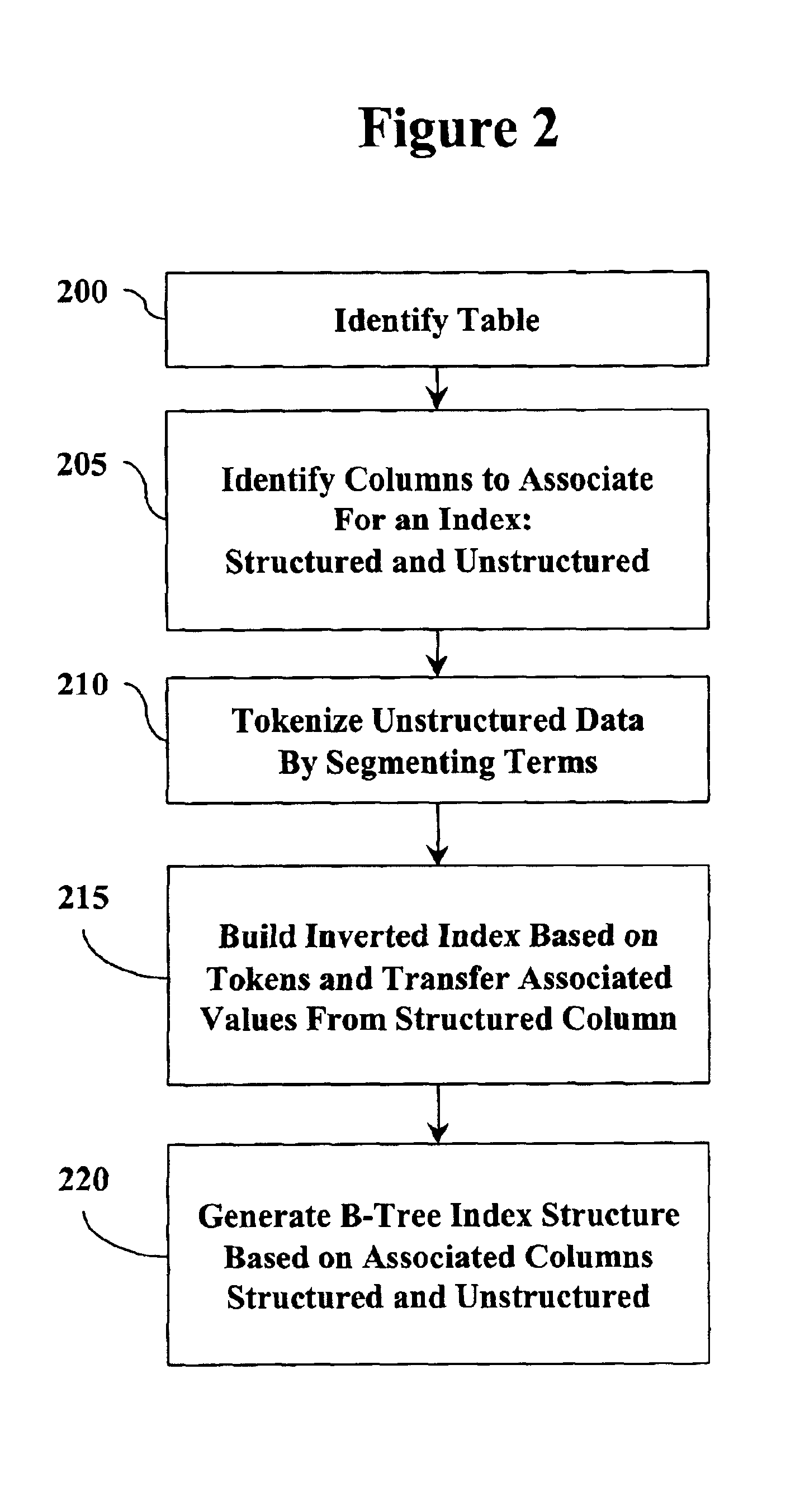
Combined database index of unstructured and structured columns
InactiveUS6980976B2Optimal use of memoryEasy retrievalDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDatabase indexUnstructured data
A database management system and method provides access to a data table having structured data and unstructured data. A user interface allows a user to issue instructions to the database management system such as to build an index based on the structured and unstructured data and to search the data table. An indexing logic generates an index structure by combining the structured and unstructured data. With this index structure, a single query can contain search conditions from both the structured data and the unstructured data. In this manner, efficiency for searching the data table for combined structured and unstructured conditions is improved.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
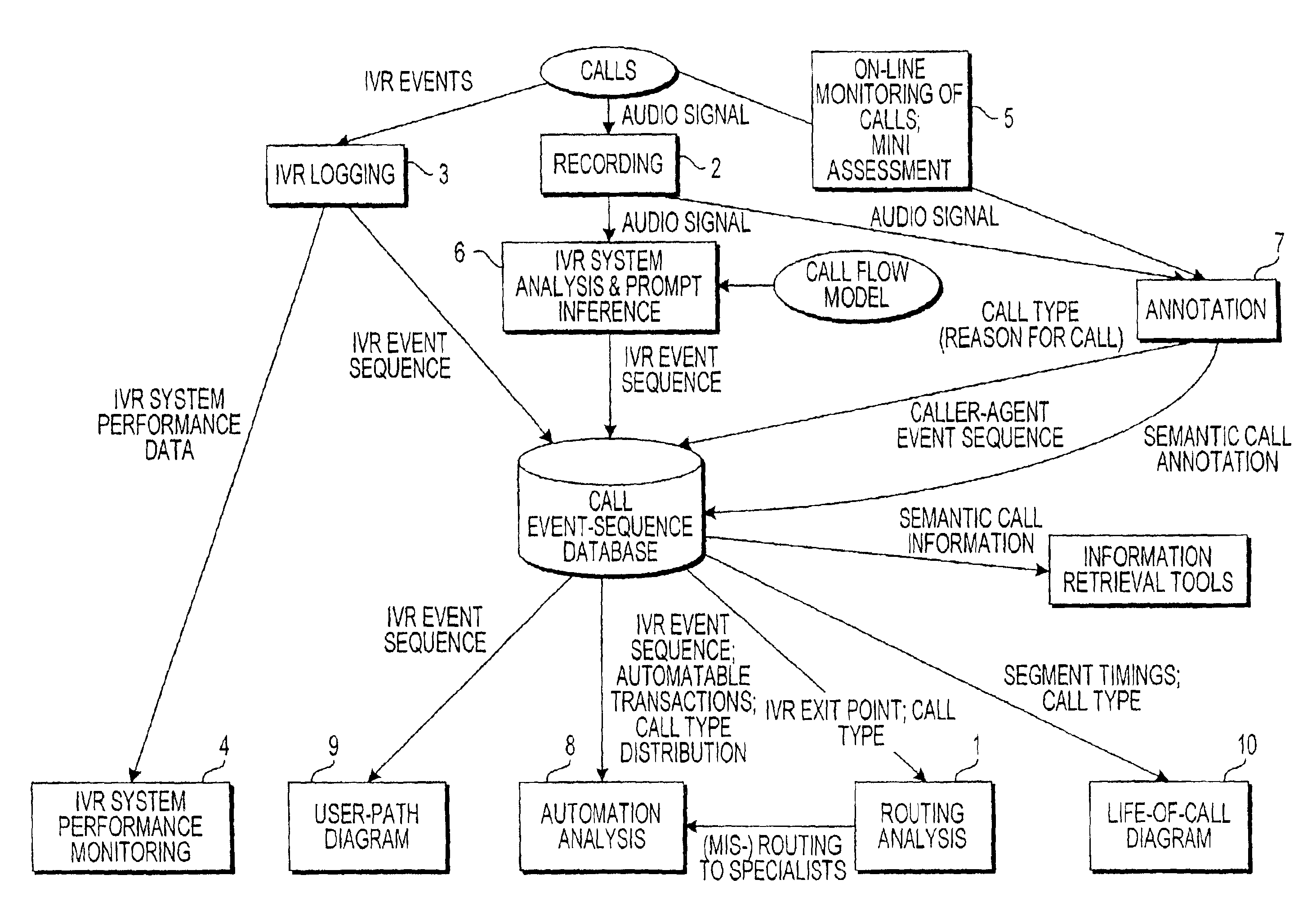
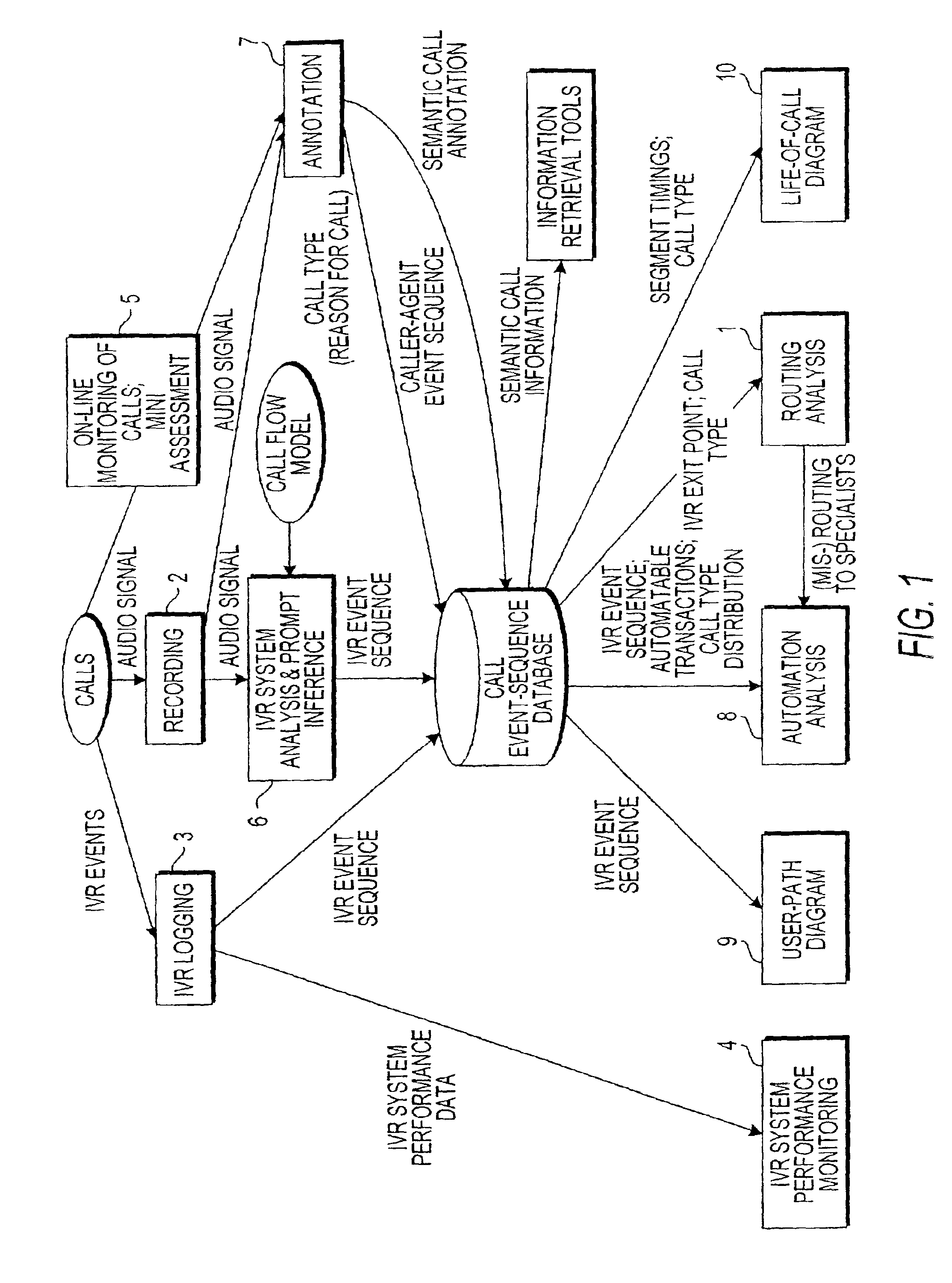
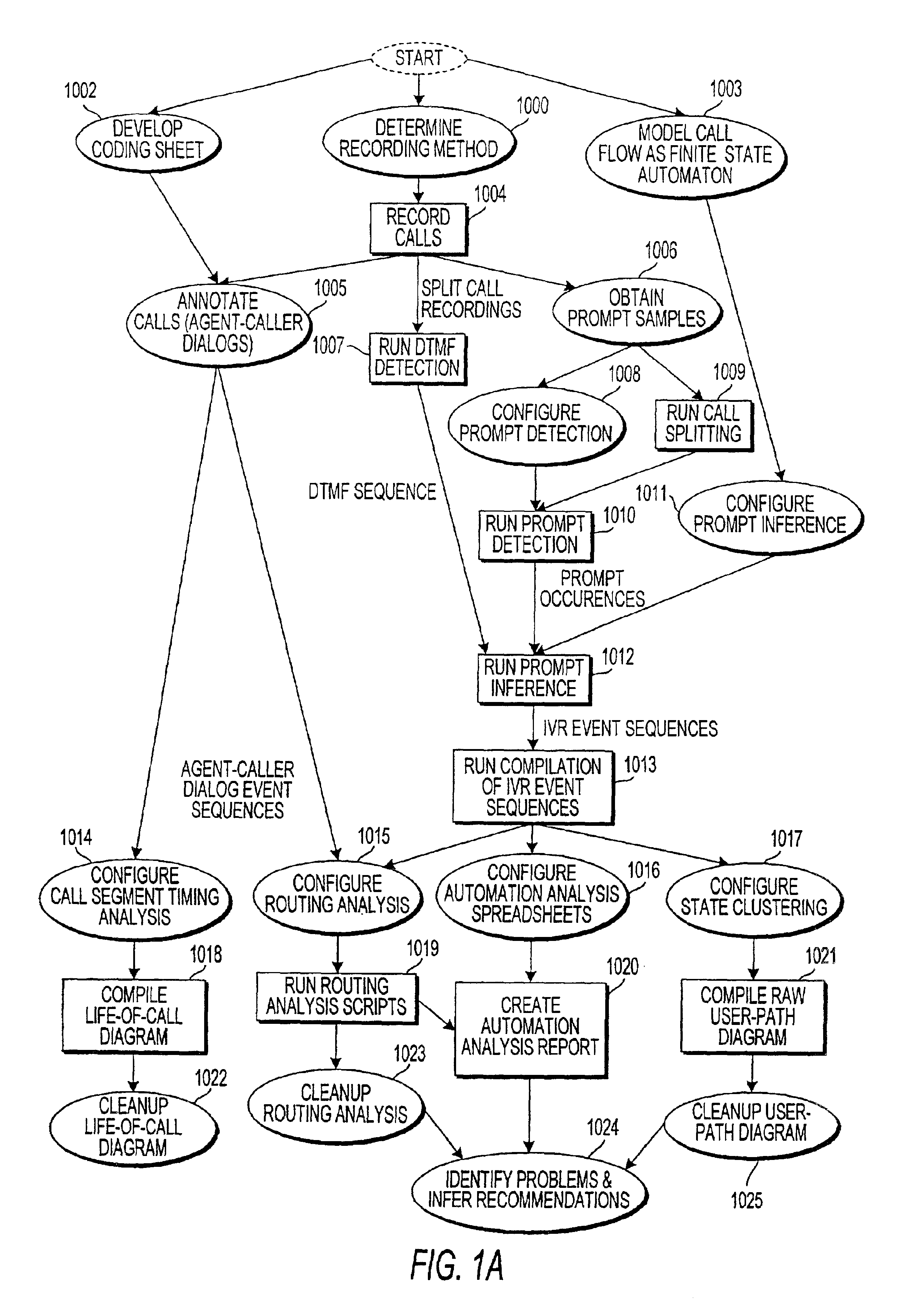
System and method for annotating recorded information from contacts to contact center
ActiveUS6898277B1Overcome deficienciesData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsAudio miningDatabase index
A system for forming a database indexed with content-based parameters, corresponding to recordings of contacts to a contact center, includes an analysis unit, a mining unit, and a correlation unit. The analysis unit performs automated-portion analysis techniques to ascertain predetermined events occurring in recordings of automated portions of the contacts to the contact center. The mining unit performs audio mining of recordings of agent portions of the contacts to the contact center. The correlation unit correlates an event occurring in an agent portion of the recordings with a corresponding one of a plurality of content-based parameters selected to be used as indices of the database, and makes an entry in the database based on the correlated event and the corresponding content-based parameter.
Owner:CX360 INC +1
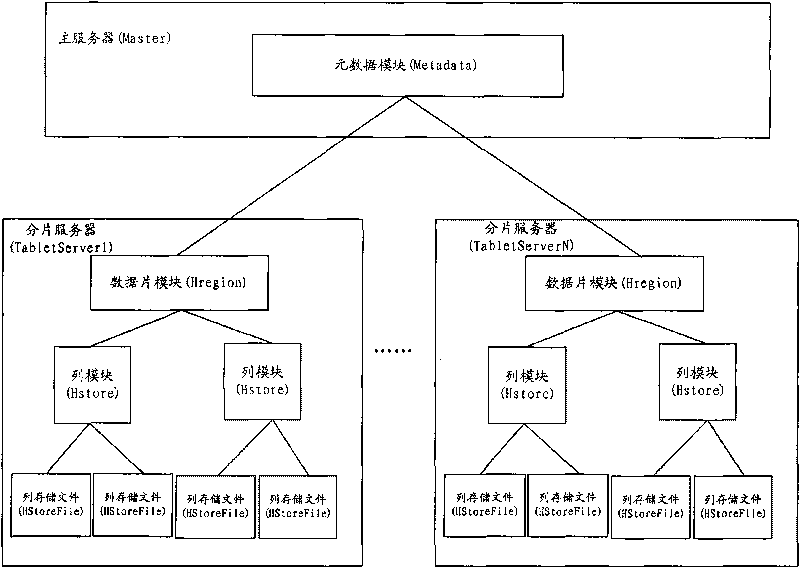
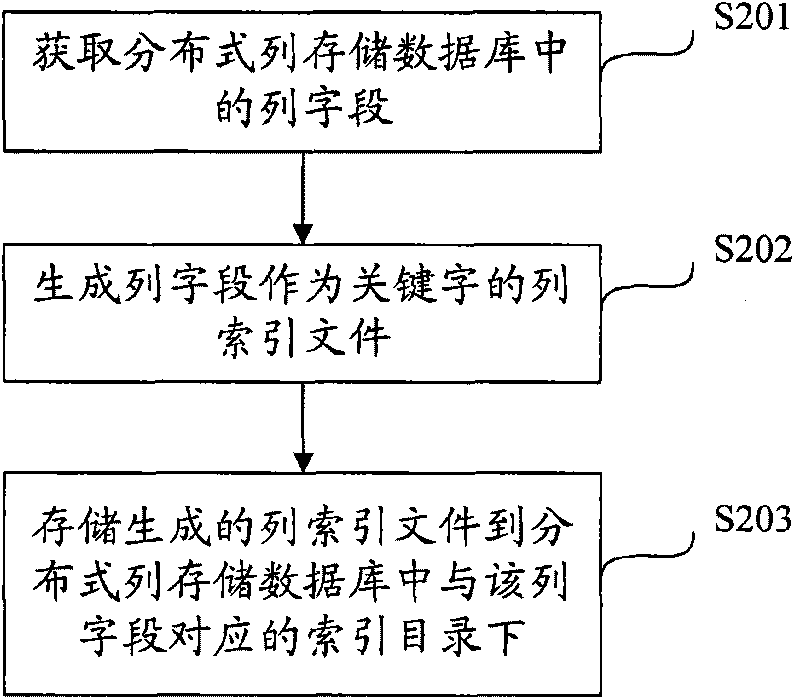
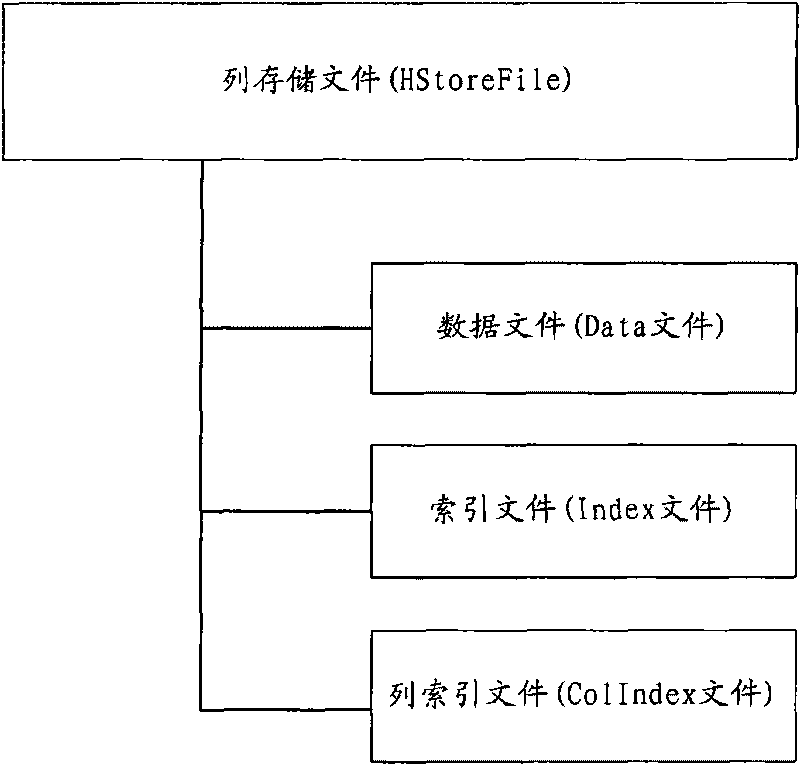
Methods for establishing and inquiring index of distributed column storage database, device and system thereof
ActiveCN101727465AEfficient queryDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase indexClient-side
The invention discloses methods for establishing and inquiring index of a distributed column storage database, a device and a system thereof. The method for establishing index of a distributed column storage database comprises the steps of obtaining the column fields in the distributed column storage database to generate a column index file with the column fields as keywords, wherein the column index file contains the mapping relation between the values of the column fields in the distributed column storage database and the values of the corresponding Row fields; storing the column index file into the index directory corresponding to the column fields in the distributed column storage database. The method for inquiring index is implemented by matching corresponding index files to obtain corresponding values of Row fields when a client launches an inquiry request with the column fields as inquiry condition and result. By adopting the invention, fast inquiry of other column fields except for the Row fields can be realized in the prior distributed column storage database.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE SUZHOU SOFTWARE TECH CO LTD +2
Deferred incorporation of updates for spatial indexes
ActiveUS20060074977A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDatabase indexSystem maintenance
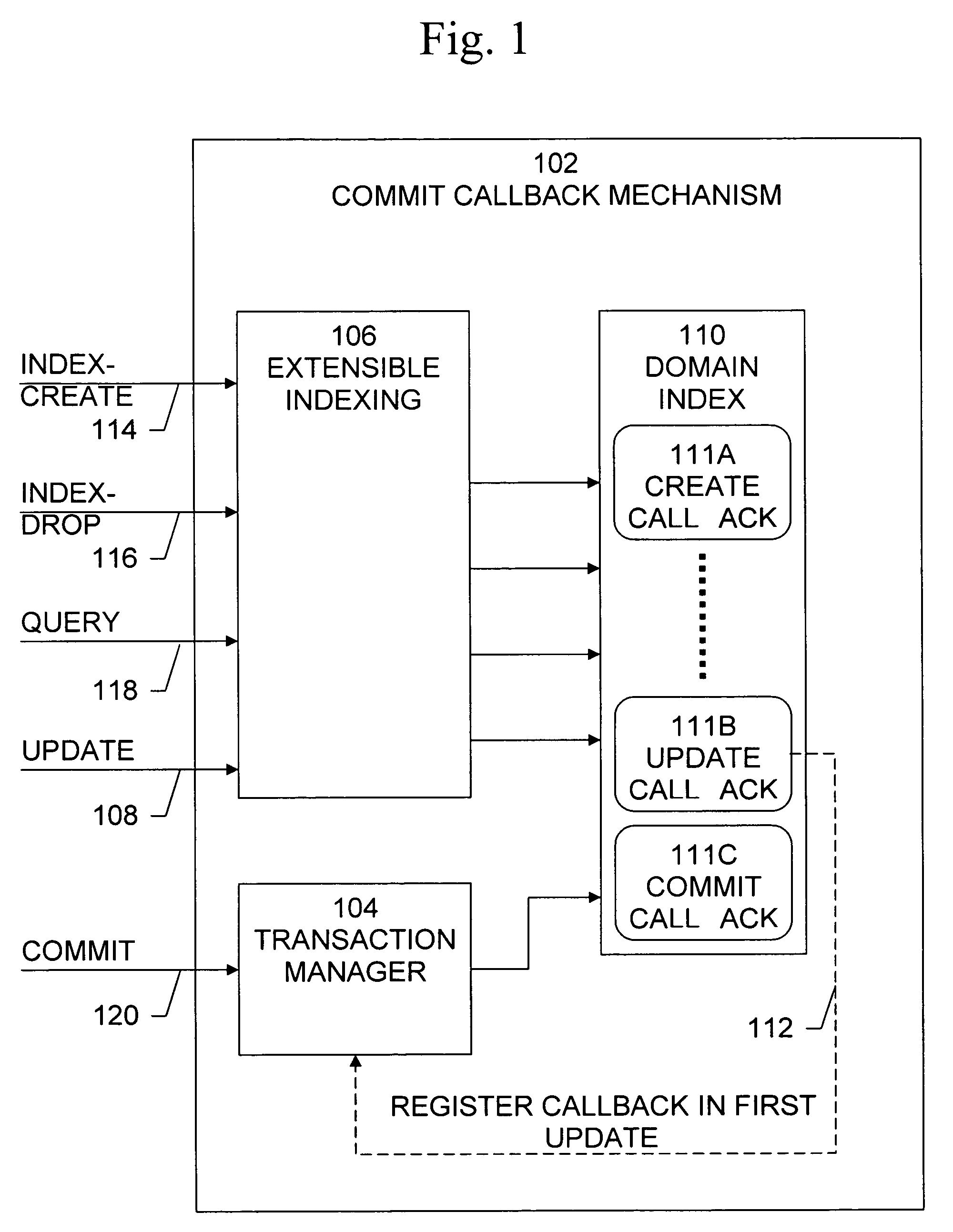
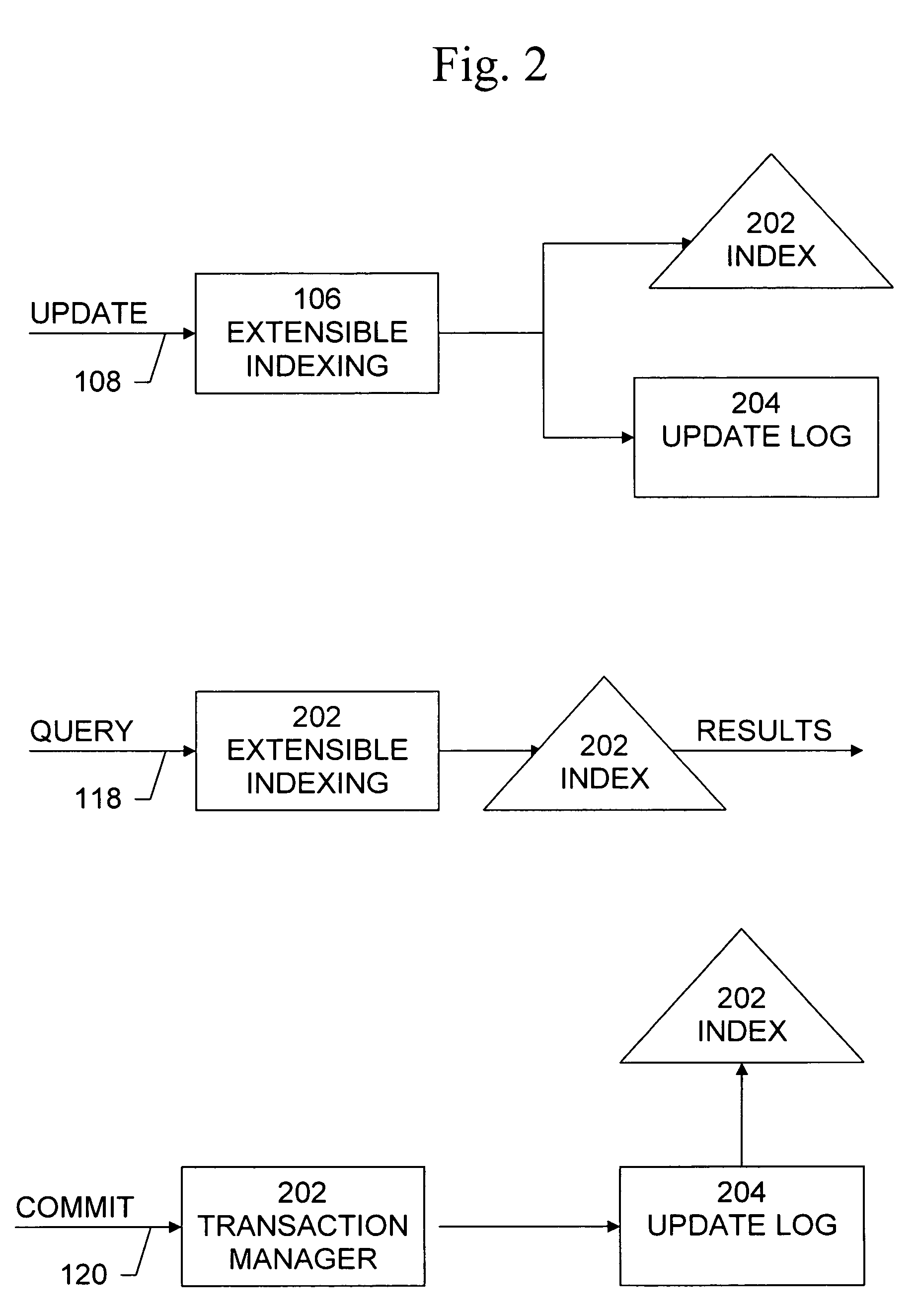
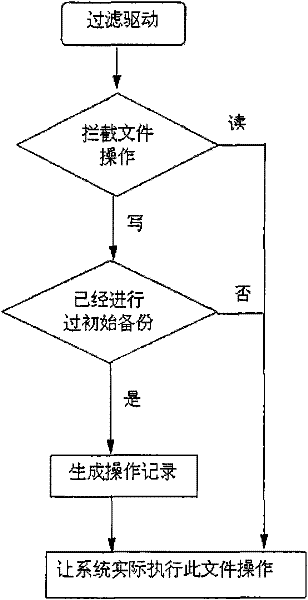
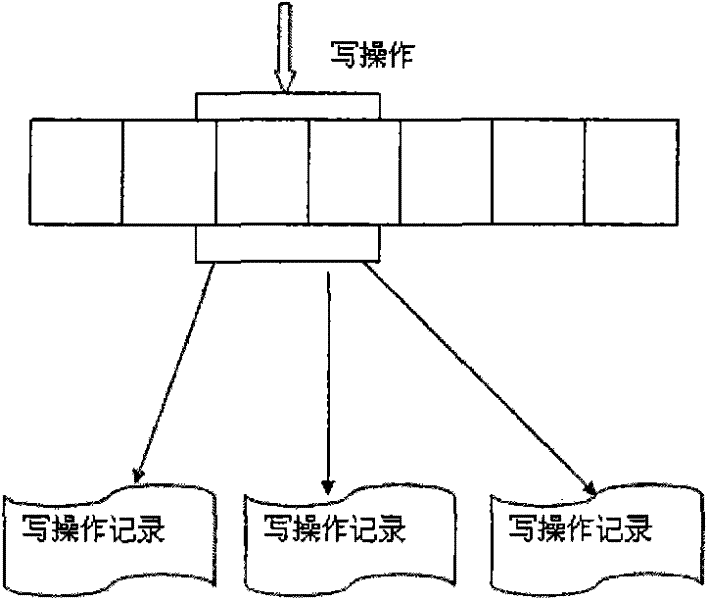
The present invention provides techniques by which updates may be incorporated in database indexes without causing deadlocks of user transactions. In deferred-incorporate update, the updates are propagated to the index only at transaction commit time. A method of handling transactions including updates in a database management system comprises the steps of receiving an update to a database maintained by the database management system, the update operable to cause an index of the database to be modified, recording the update in a log, and receiving an indication that the transaction is to be committed and in response, incorporating the update from the log into an index of the database. The update may comprise an insert operation and / or a delete operation.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and computer system for enabling a user to construct a web-site navigation
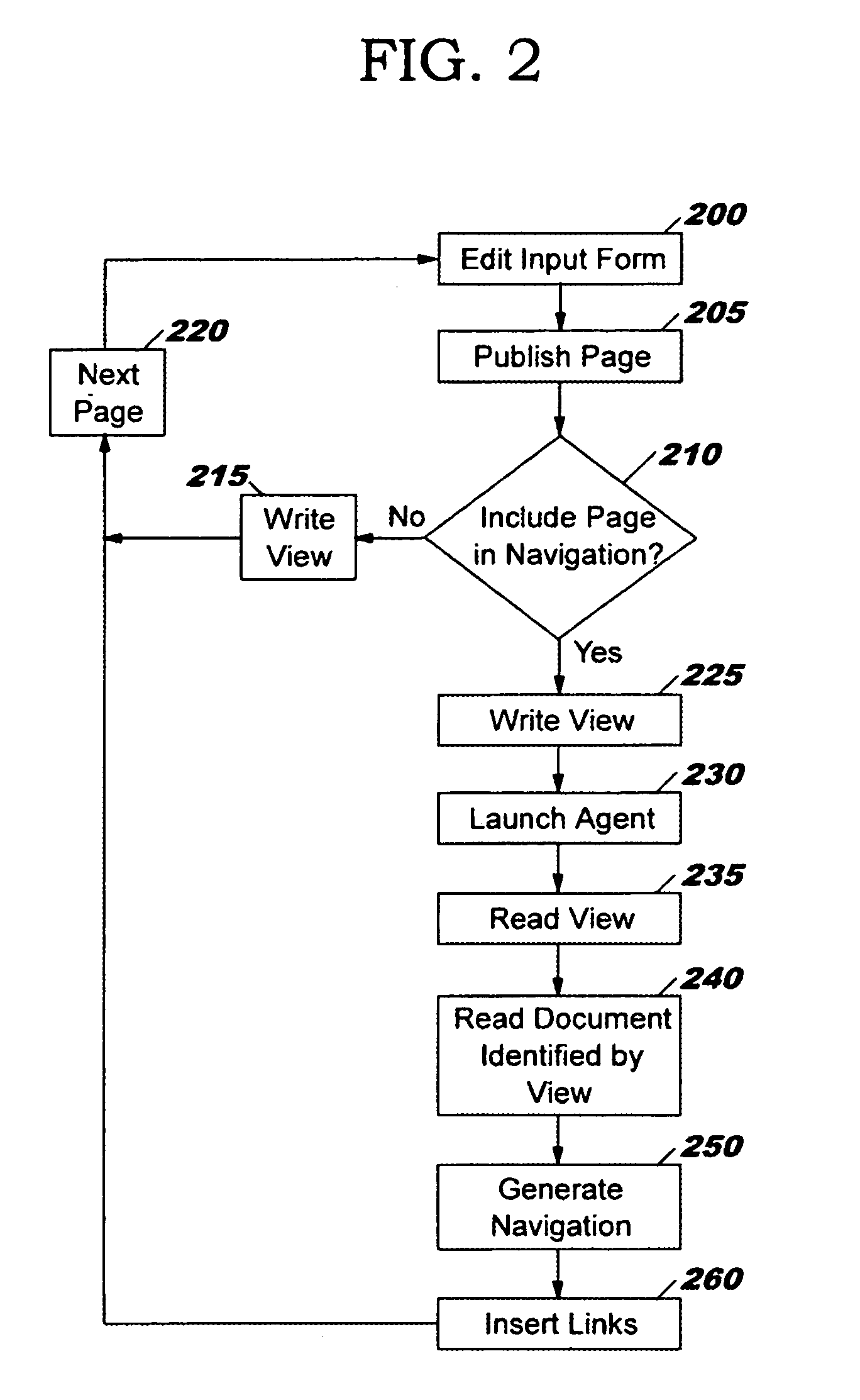
InactiveUS7185275B2Simple and economical and effectiveDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingWeb siteDocumentation procedure
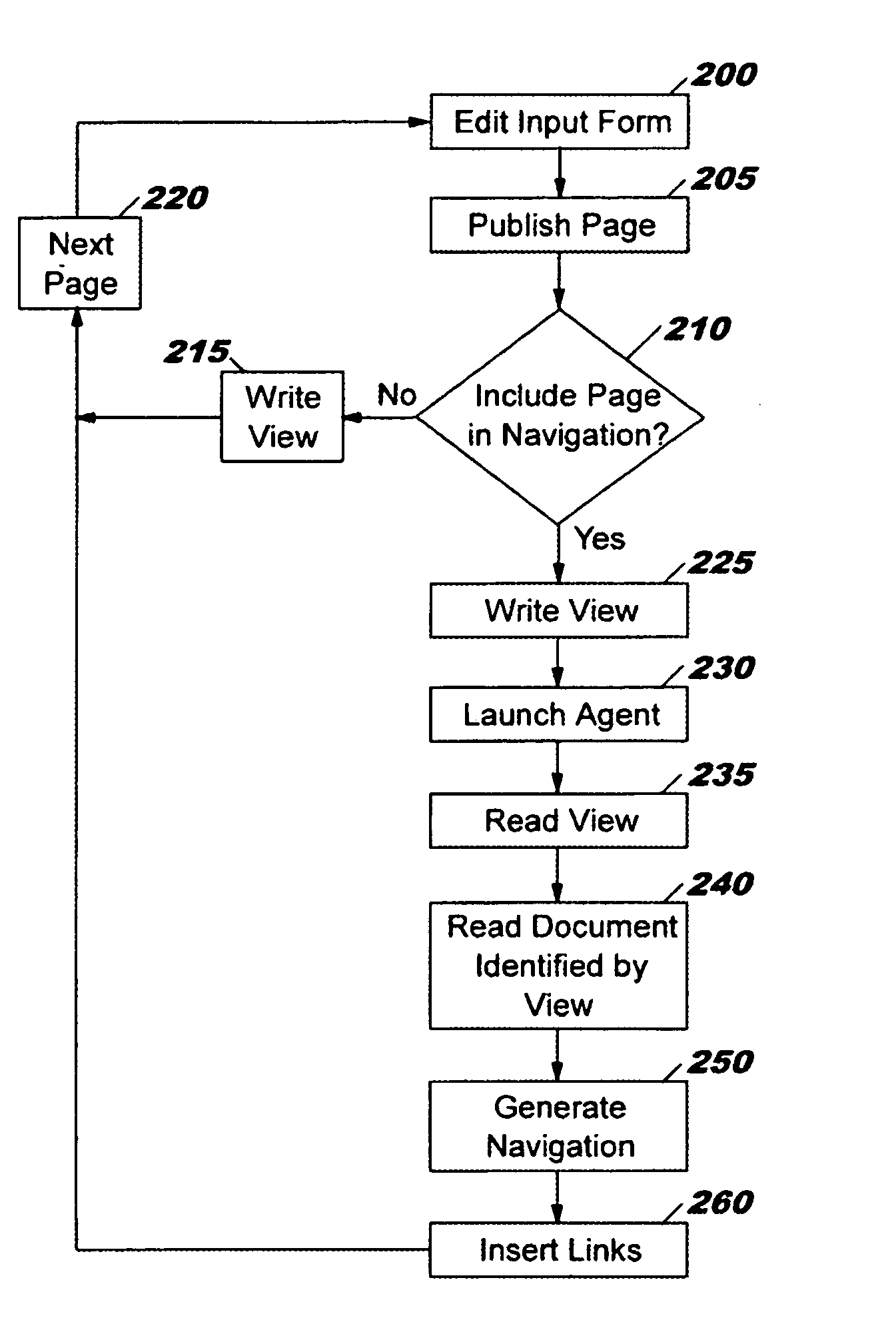
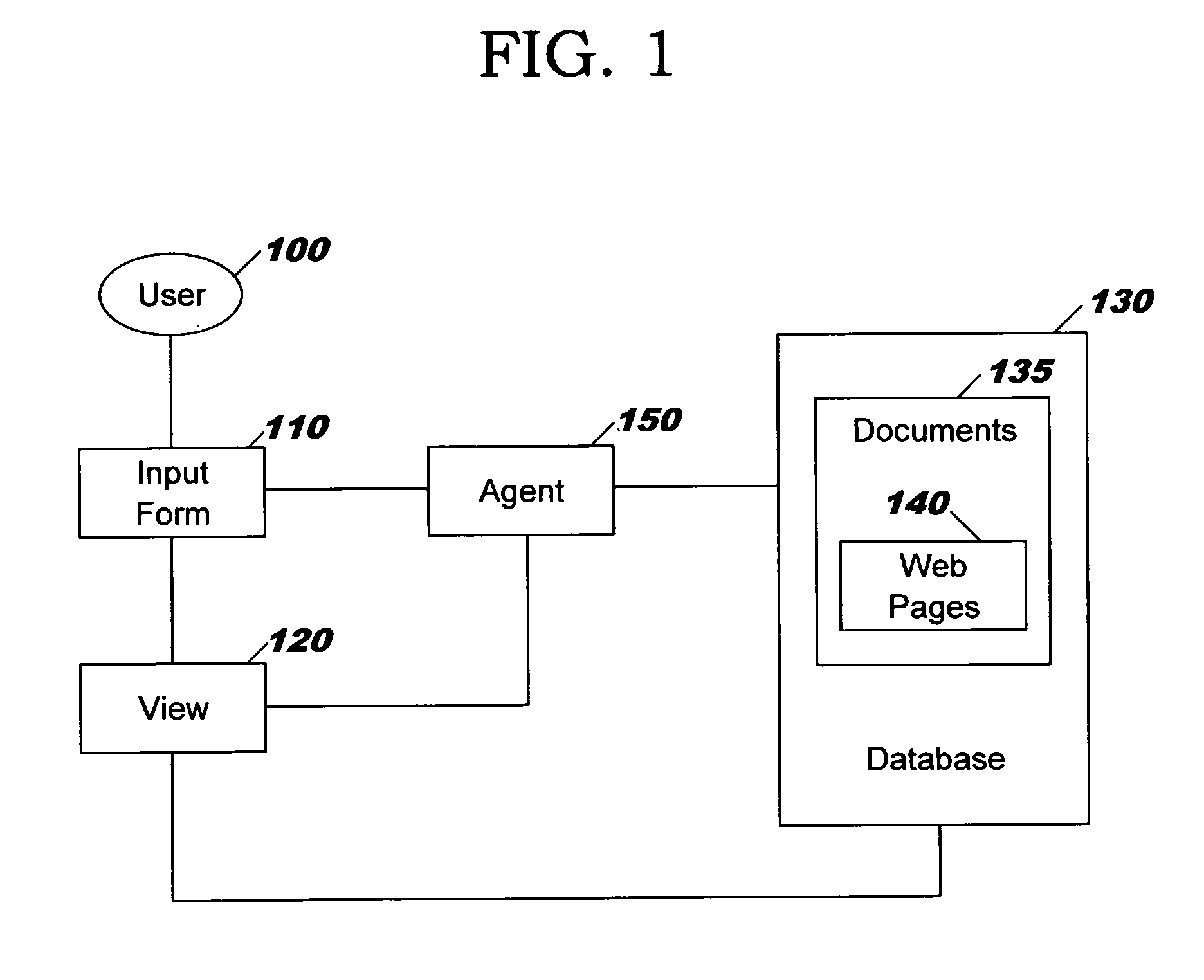
A computer system for generating web page navigations. A user interacts with an input form for creating a web page and accepting input that specifies inclusion of the page in a navigation and the hierarchical level of the inclusion. The specifications of the input form are recorded in a view that provides an index into a database. A Java agent reads the view and a set of documents such as Lotus Notes documents indexed by the view and associated with a plurality of web pages to be included in the navigation. Based upon static HTML information contained in the documents, the agent generates the navigation, and inserts links associated with the navigation into the plurality of web pages.
Owner:IBM CORP
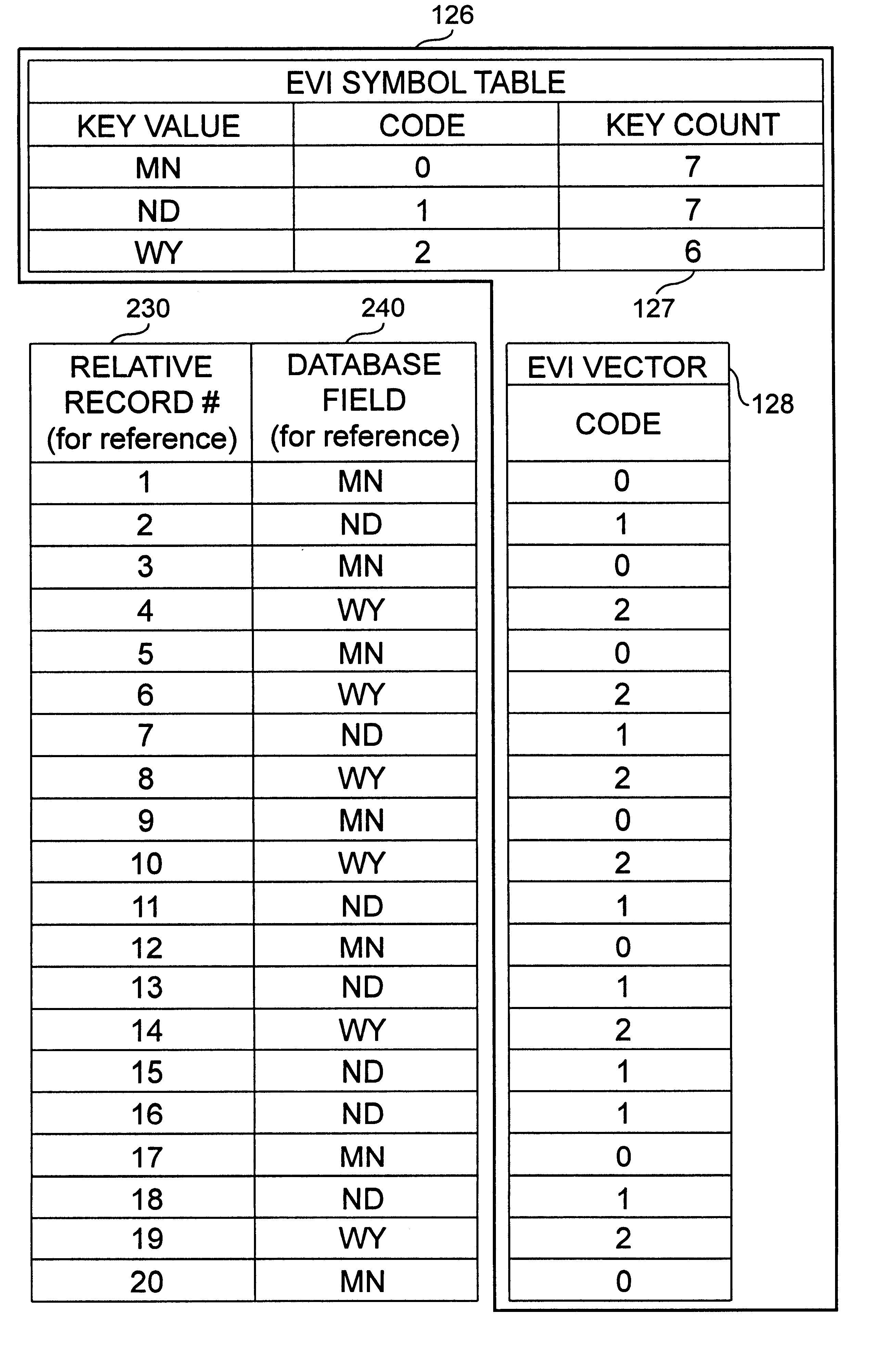
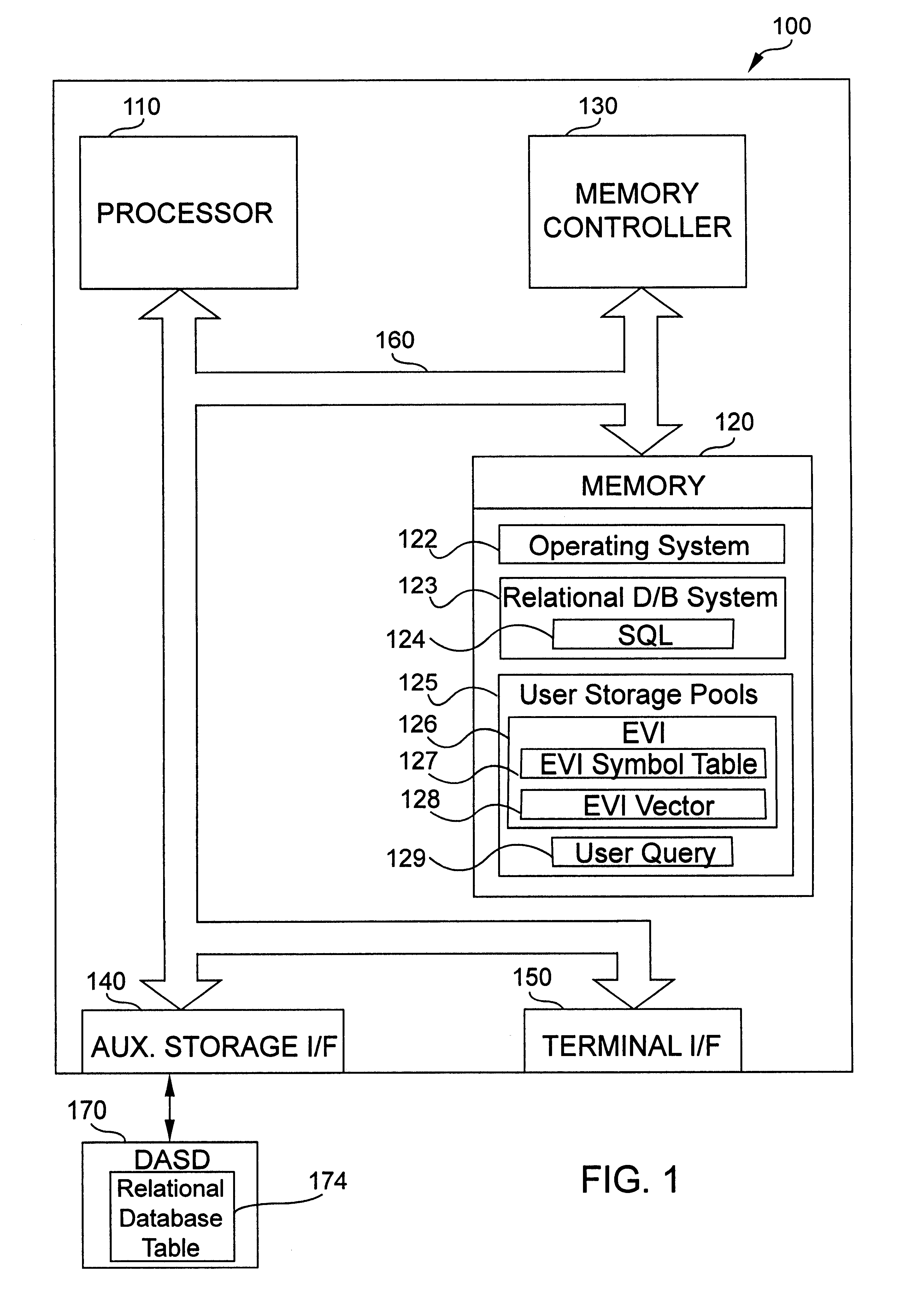
Utilizing encoded vector indexes for statistics in database processing
InactiveUS6405187B1Improve performanceQuick functionData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDatabase indexData mining
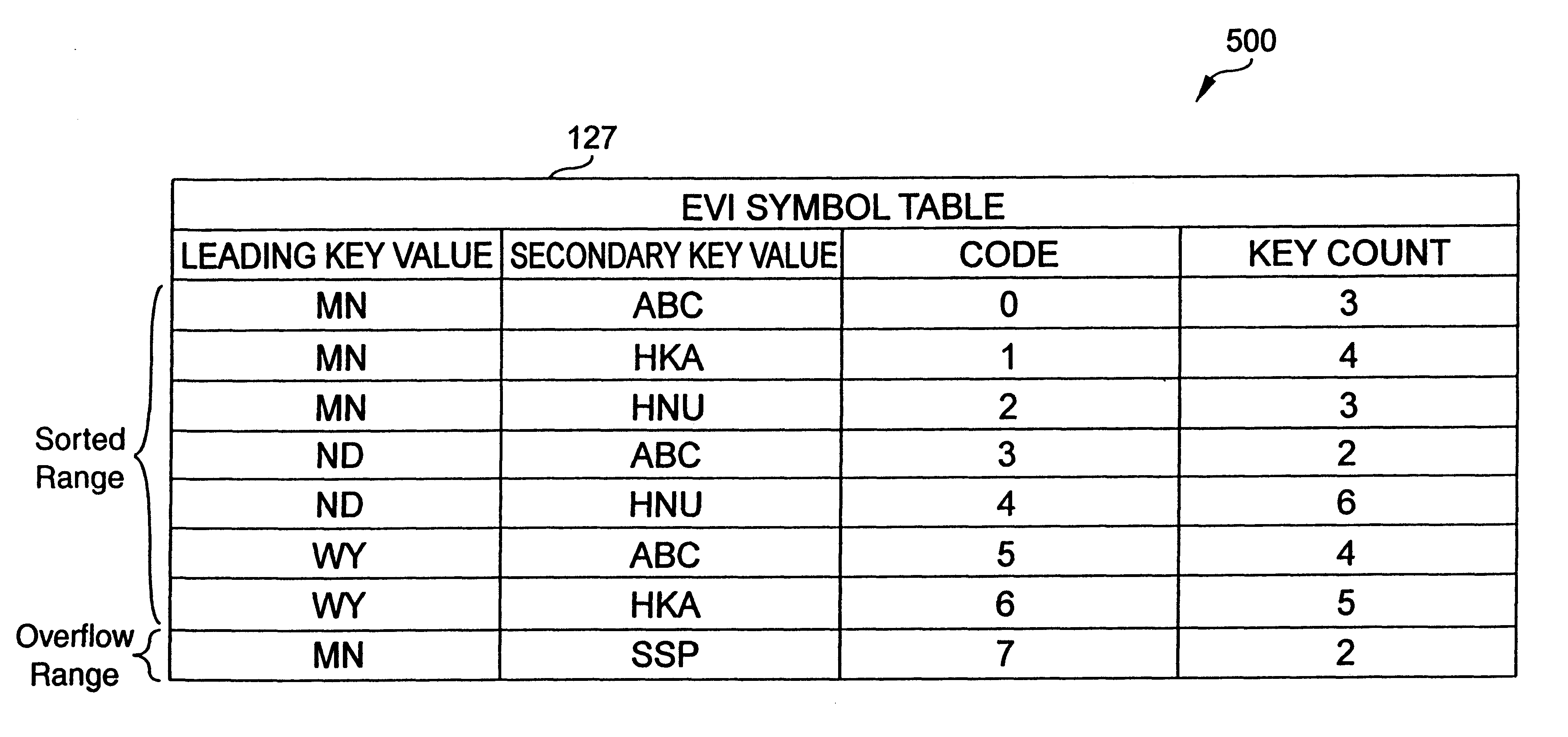
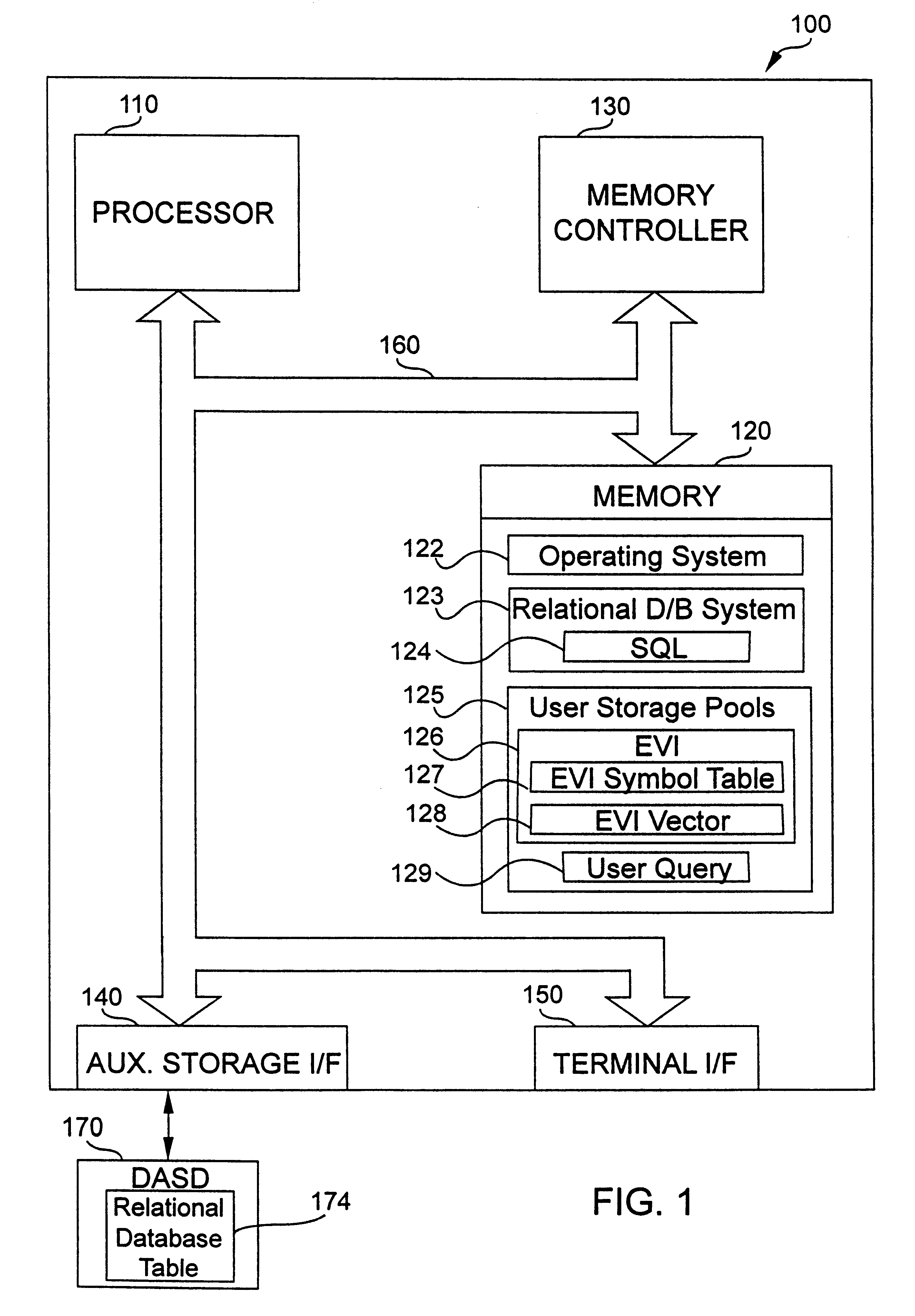
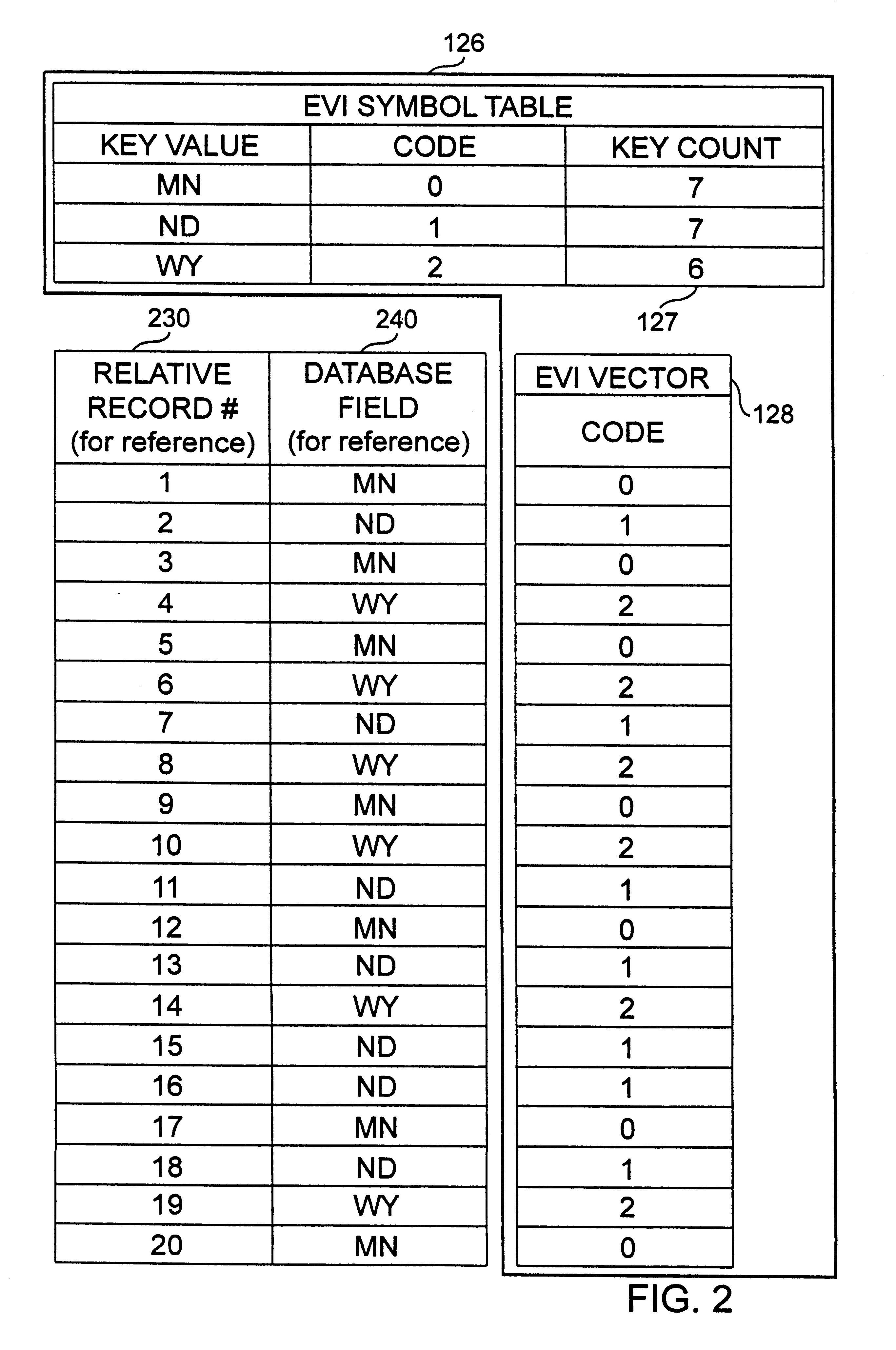
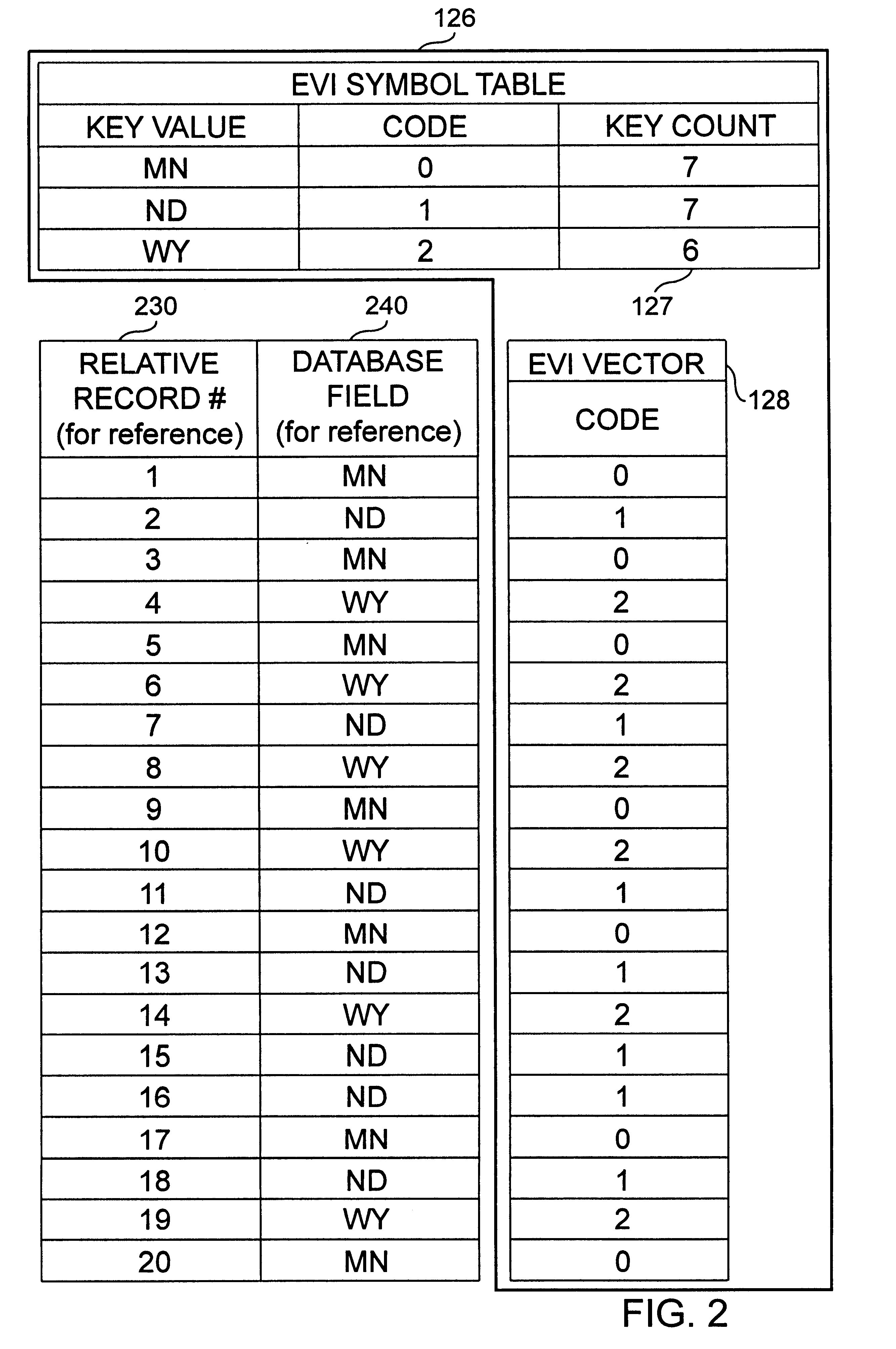
An apparatus and method to significantly improve performance of SQL function processing through the use of an encoded vector index (EVI). An EVI provides the data necessary to count the number of records in a database that match criteria provided by a SQL function. The resulting count can then be used to determine, from among two or more candidate approaches, an approach to use in processing an SQL function. By processing the EVI symbol table in lieu of more traditional database indexes, and / or in lieu of the database table itself, statistics for SQL functions are generated significantly faster.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for online reorganization of databases
InactiveUS7117229B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDatabase indexData mining
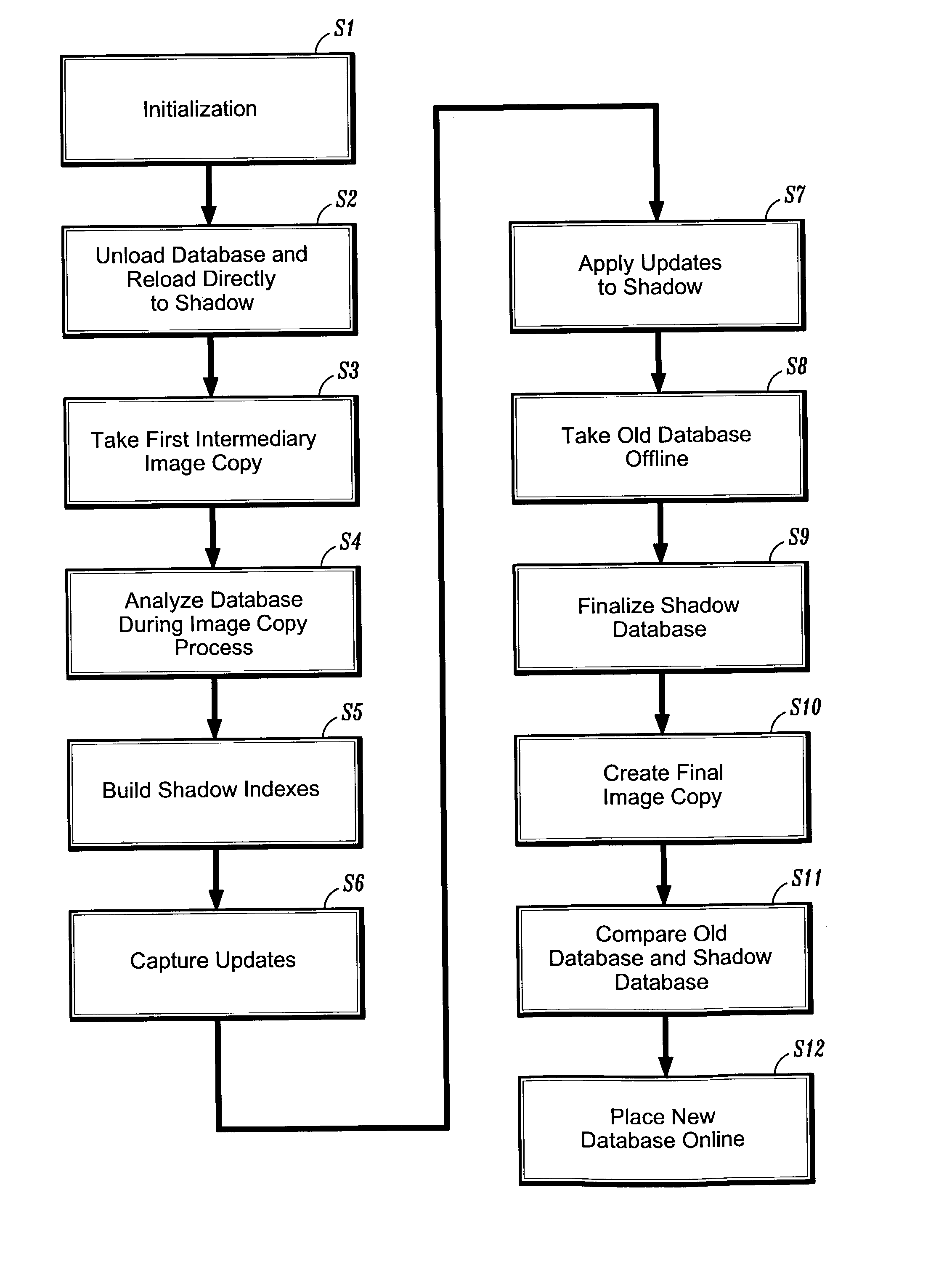
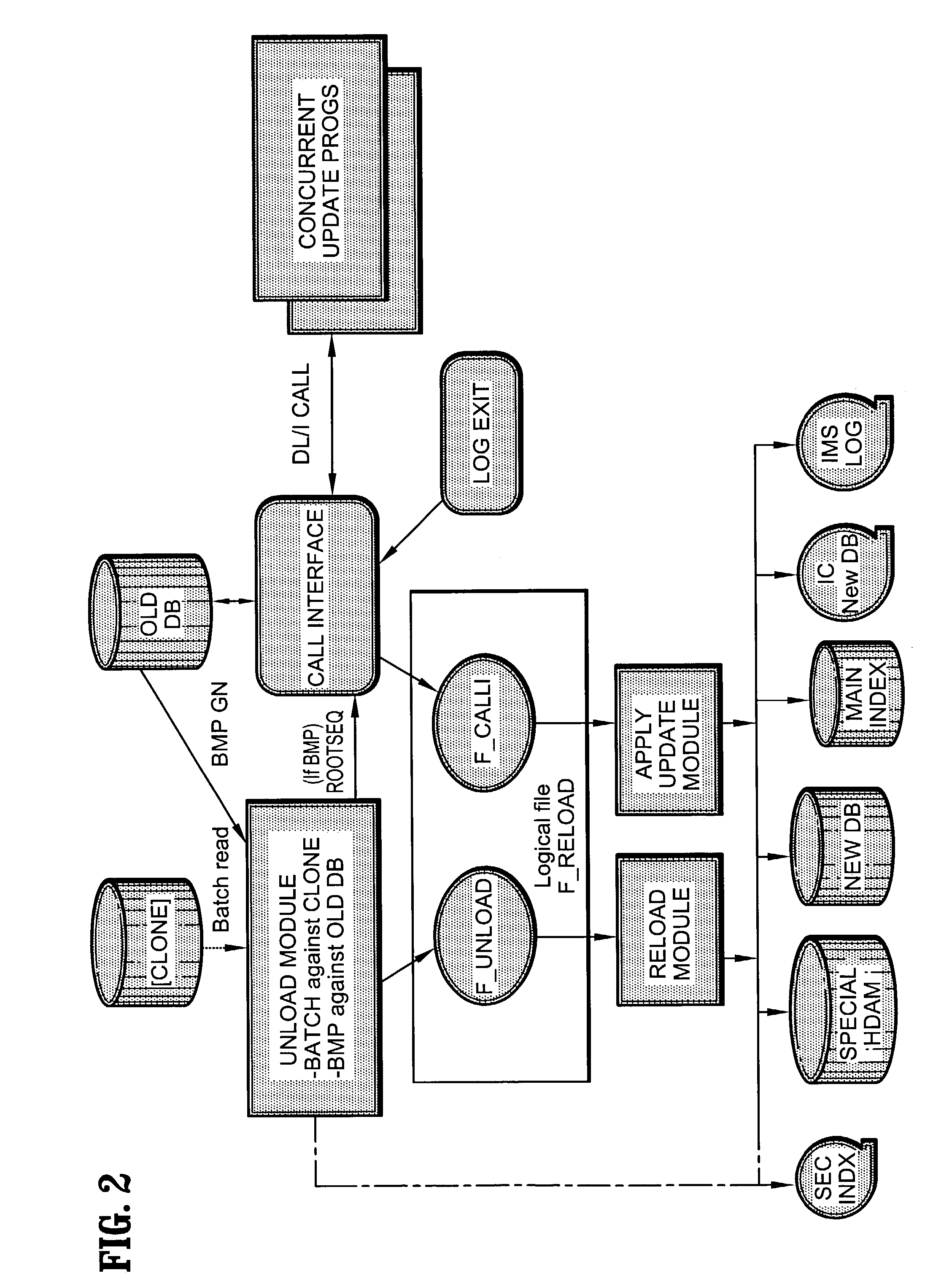
A system and method for online reorganization of an existing database that occurs while read and update activity of the existing database continues. The system and method comprise unloading the existing database, reloading the existing database directly to a shadow database, building shadow database indexes, creating a first intermediary image copy of the existing database, analyzing the existing database, capturing updates for the existing database, applying the captured updates to the shadow database, taking the existing database offline, finalizing the shadow database with any remaining updates, creating a final image copy, comparing the existing database and the finalized shadow database, and placing the finalized shadow database online.
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
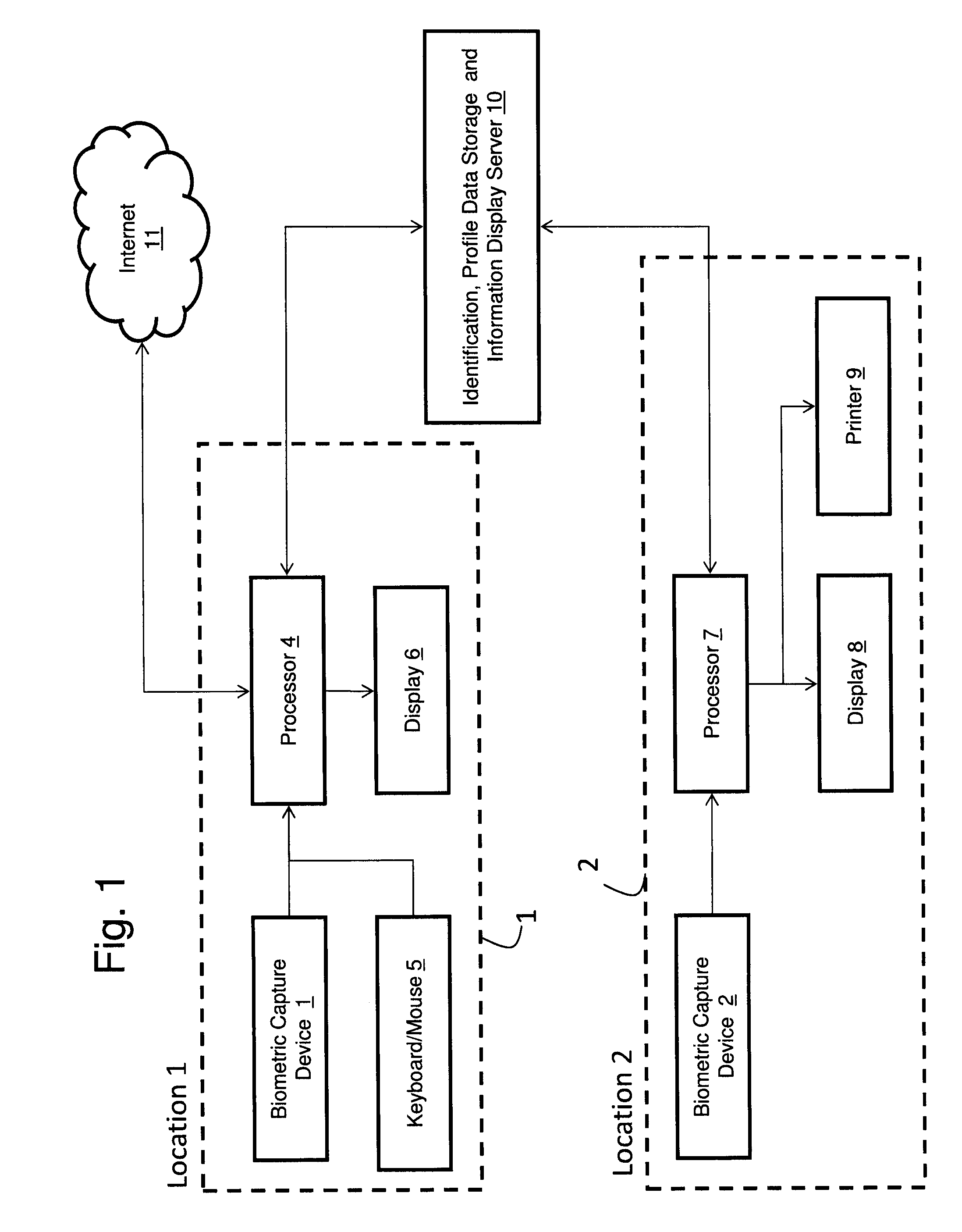
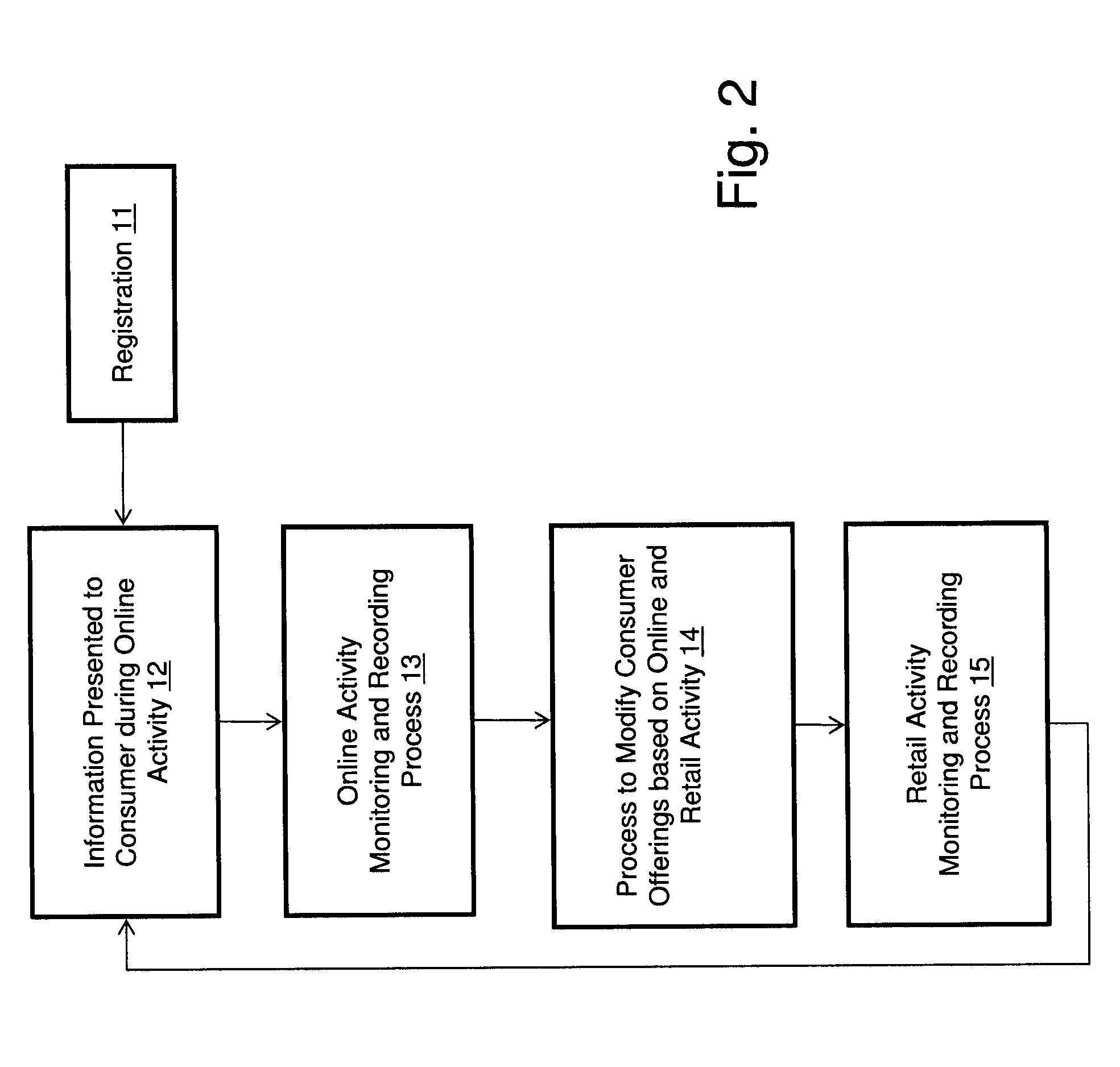
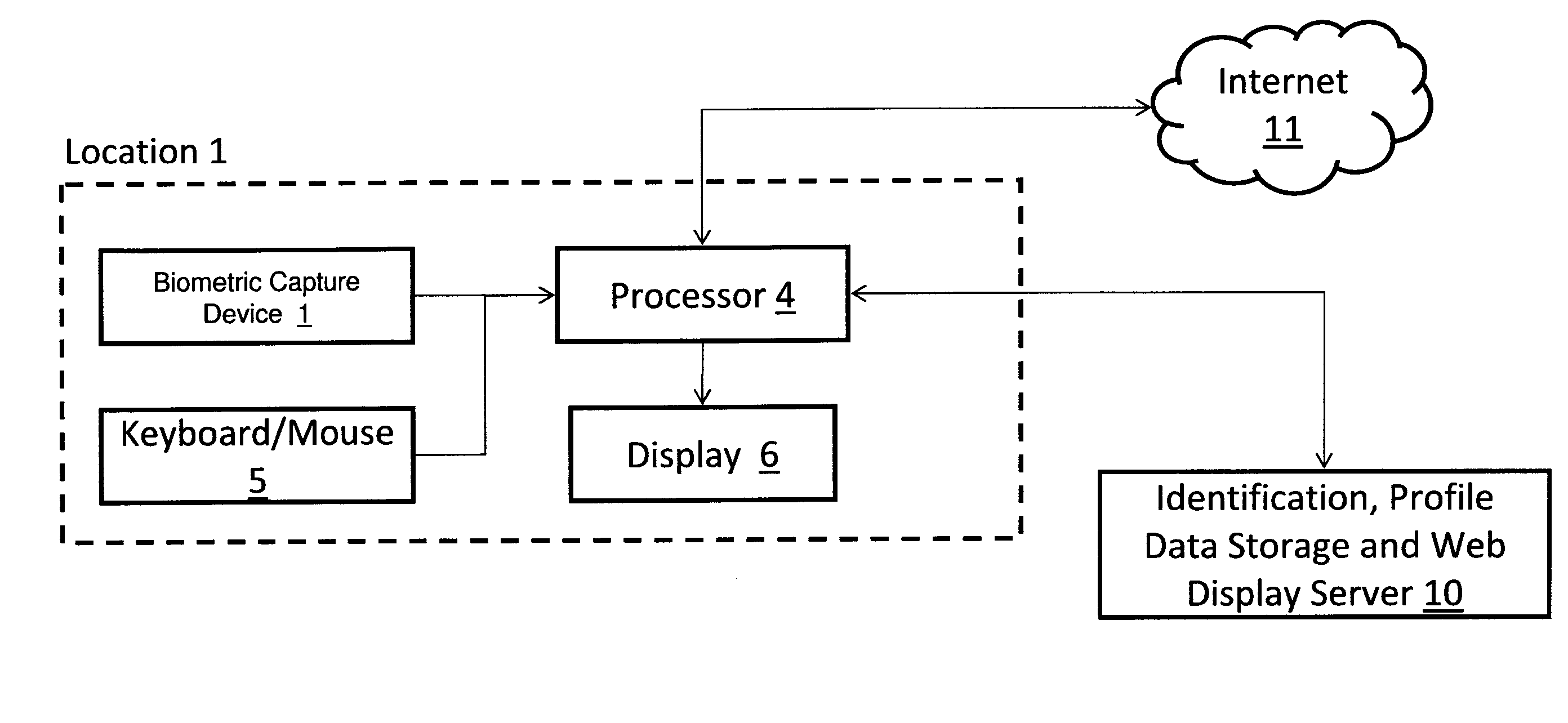
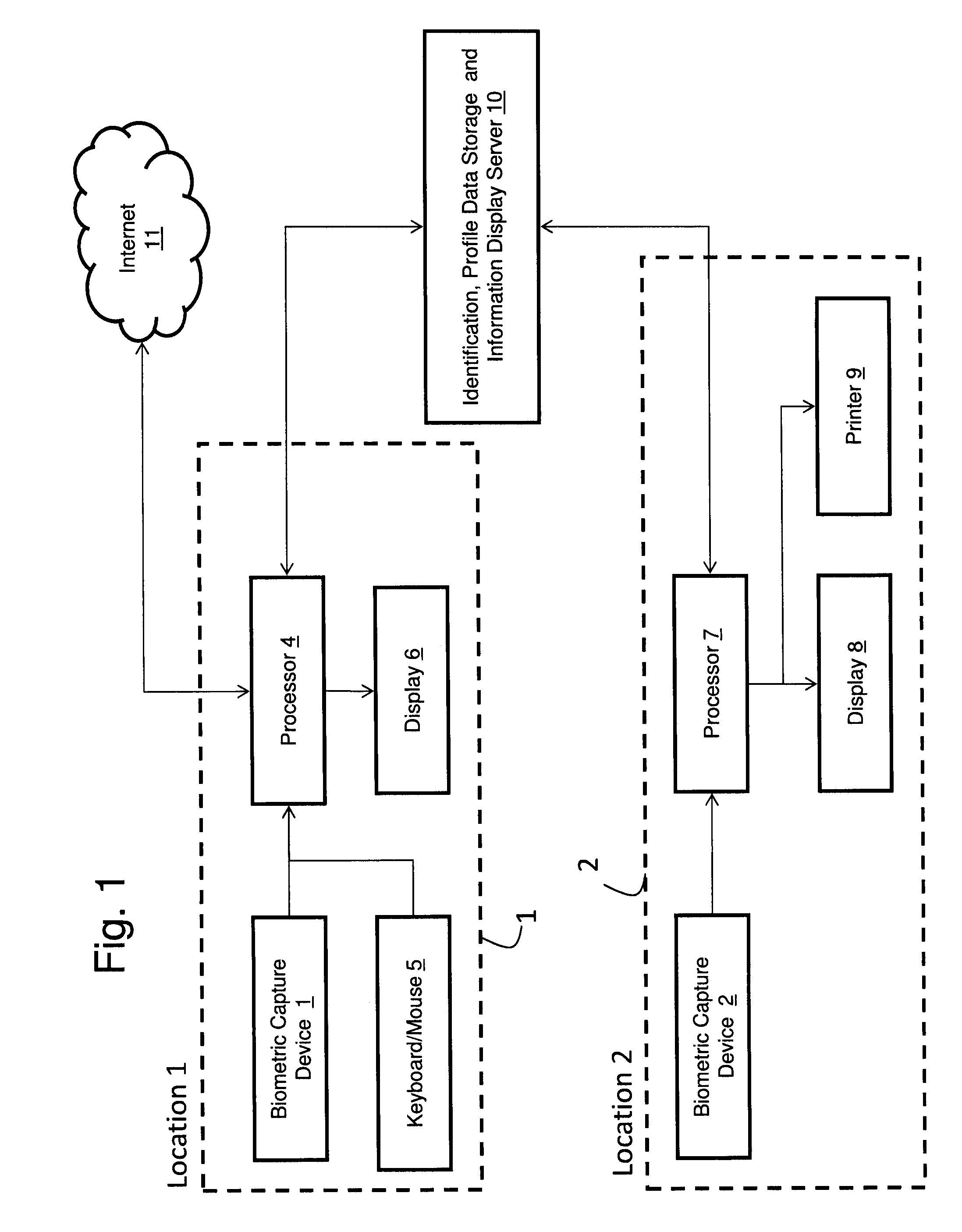
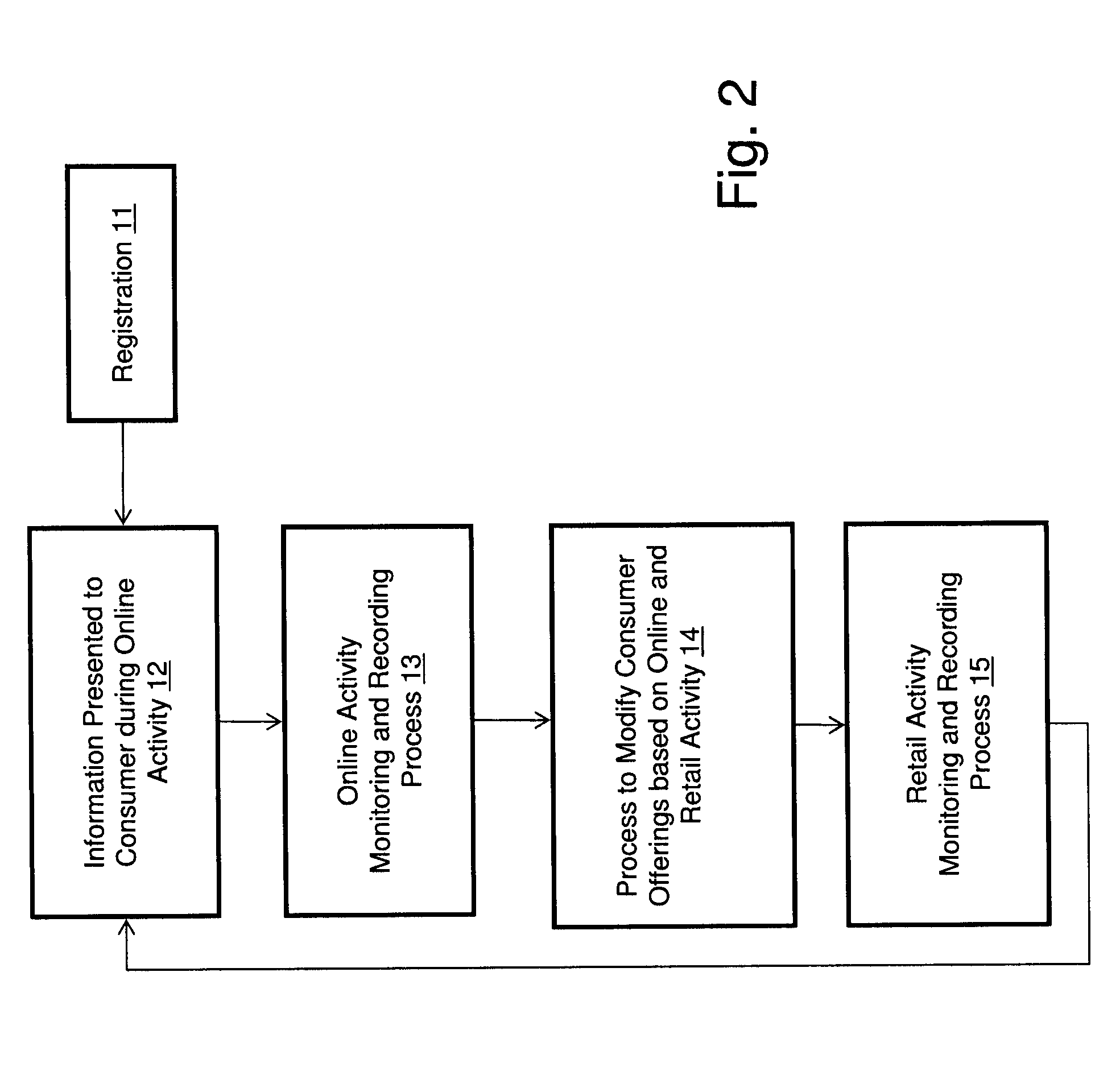
Measuring Effectiveness of Advertisements and Linking Certain Consumer Activities Including Purchases to Other Activities of the Consumer
InactiveUS20110119111A1Improve efficiencyEfficient preparationMarket predictionsDatabase indexUnique identifier
A method for linking online computer activity with non-online consumer activity by creating a unique identifier for each consumer; storing online and non-online consumer activity in a database indexed by the unique identifier; and modifying online or non-online consumer offerings based on processing the stored online and non-online consumer activity.
Owner:EYELOCK
Utilize encoded vector indexes for distinct processing
InactiveUS6356888B1Improve performanceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDatabase indexSQL
According to the present invention, an apparatus and method to significantly improve performance of the SQL DISTINCT function processing through the use of an encoded vector index (EVI) is disclosed. An EVI provides the data necessary to generate query results for SQL DISTINCT functions that specify one or more database fields upon which the EVI is built. Sequentially scanning through the EVI symbol table, each unique value or combination of values in the one or more database fields specified in the DISTINCT function are returned to provide the requested query results. By processing the EVI symbol table in lieu of more traditional database indexes, and / or in lieu of the database table itself, query results for SQL DISTINCT functions are generated significantly faster.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for distributing portable computer virus definition records with binary file conversion
InactiveUS7231440B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDatabase indexObject code
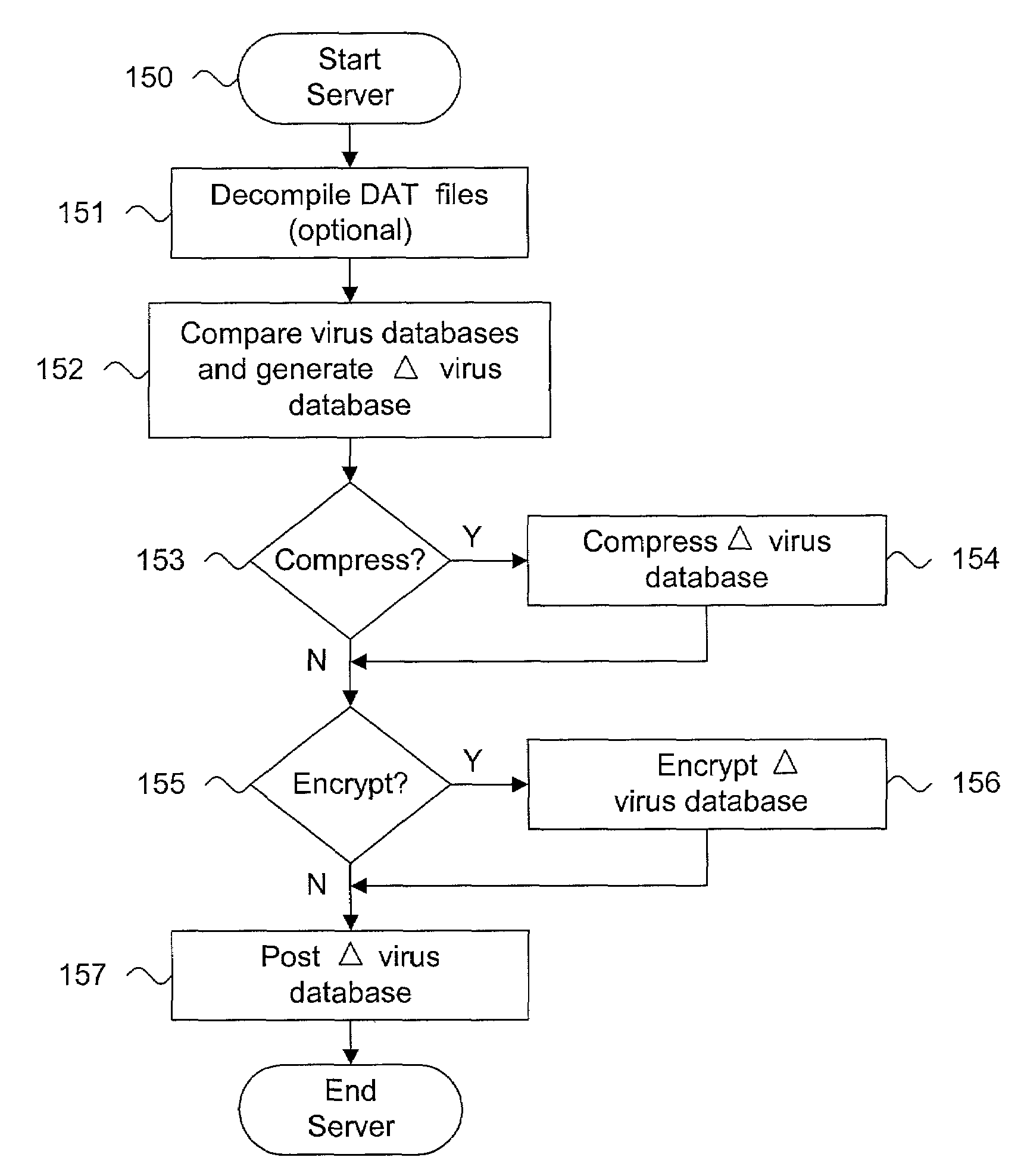
A system and method for distributing portable computer virus definition records with binary file conversion are described. One or more virus definition records are stored into a structured virus database. Each virus definition record includes an identifier uniquely identifying a computer virus, at least one virus name associated with the computer virus, a virus definition sentence comprising object code providing operations to detect the identified computer virus within a computer system, and a virus removal sentence comprising object code providing operations to clean the identified computer virus from the computer system. At least one updated virus definition record is stored into the structured virus database indexed by the identifier and the at least one virus name for each virus definition record. The virus definition records stored in the structured virus database are converted into a virus data file. The virus data file includes virus definition sets. Each virus definition set includes binary data encoding instructions to detect the computer virus within a computer system, instructions to clean the computer virus from the computer system, and names associated with the computer virus.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Data protection method for managing increment file based on digital identifiers
ActiveCN102236589AReduce path lengthPrevent leakageRedundant operation error correctionSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase indexData store
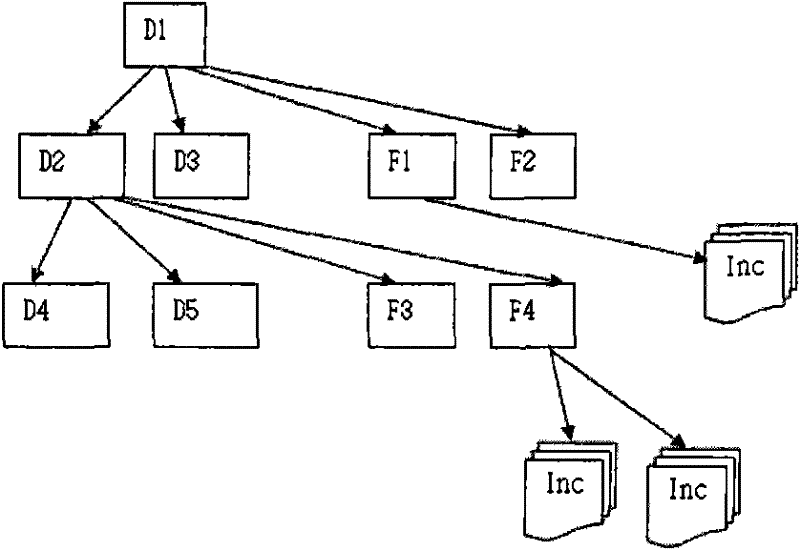
The invention relates to a data protection method for managing an increment file by using digital identifiers, and belongs to the technical field of data storage and backup. The method comprises the following steps of: numbering a catalogue and representing the catalogue by using the digital identifiers; numbering files under the catalogue and representing the files by using the digital identifiers; and synthesizing operating records into the increment file and representing the synthesized increment file by using the digital identifiers. An index is created for fields of the digital identifiers by using a database indexing technology. During recovery, all increment information of the file to be recovered can be quickly found, so that the file version at any modification time can be quickly recovered.
Owner:NANJING UNARY INFORMATION TECH
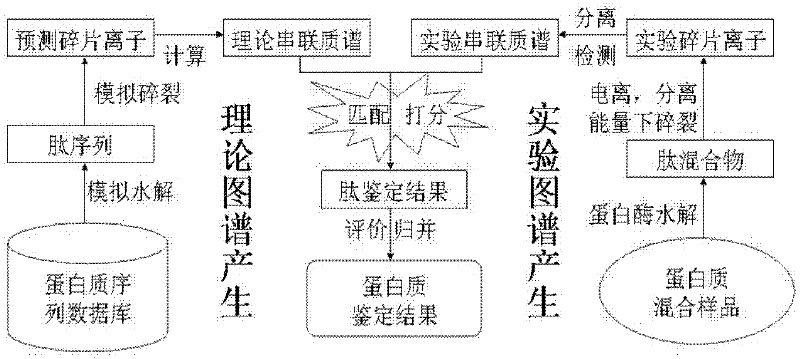
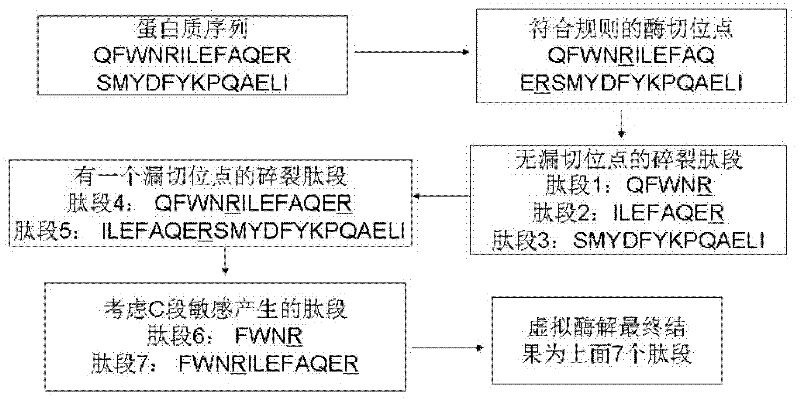
Protein secondary mass spectrometric identification method based on probability statistic model
InactiveCN102495127AMore identificationThe result of the identification method is excellentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein DatabasesMass number
The invention discloses a protein secondary mass spectrometric identification method based on a probability statistic model. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, virtualizing an enzymolysis protein database array, and establishing a peptide section database and a peptide section database index for peptide sections processed by the enzymolysis according to the mass number of the peptide sections; secondly, finding out standby peptide sections meeting the requirements from the peptide section database according to a nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio of parent ions in an experiment map to be analyzed, and generating a theoretical map meeting the requirements by all the standby peptide sections; thirdly, removing isotopes and noises from the experiment map to be analyzed; matching the processed experiment map to be analyzed and the theoretical map of each standby peptide section and grading, and selecting the standby peptide section with the highest score as an identification result of the experiment map; and finally, carrying out whole false positive control according to all the experiment map identification results. According to the invention, the quantity of effective massspectrums and the quantity of the protein peptide sections are higher than those of an existing algorithm; and the method has the advantages of capability of dynamically selecting peaks and fast operation speed.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Measuring Effectiveness of Advertisements and Linking Certain Consumer Activities Including Purchases to Other Activities of the Consumer
InactiveUS20120239458A9Improve efficiencyEfficiently identify an individualMarket predictionsDatabase indexUnique identifier
A method for linking online computer activity with non-online consumer activity by creating a unique identifier for each consumer; storing online and non-online consumer activity in a database indexed by the unique identifier; and modifying online or non-online consumer offerings based on processing the stored online and non-online consumer activity.
Owner:EYELOCK
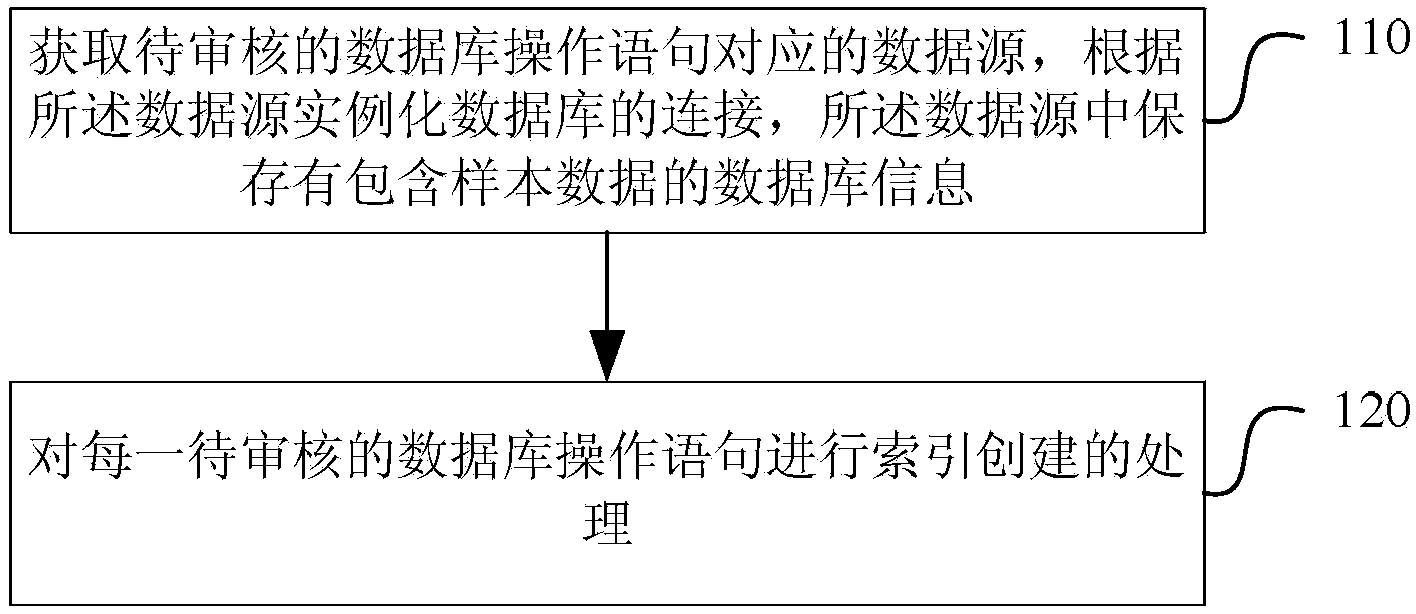
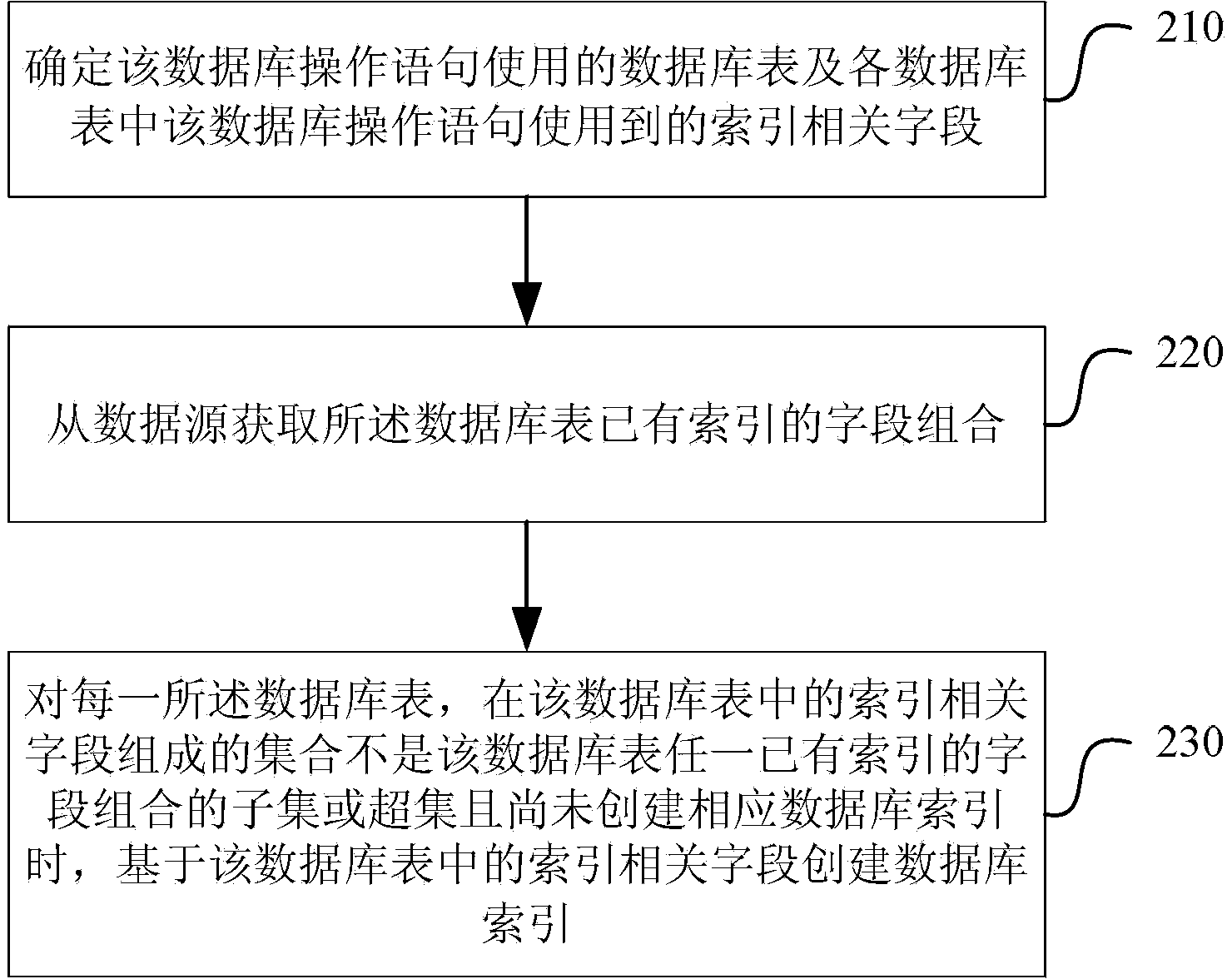
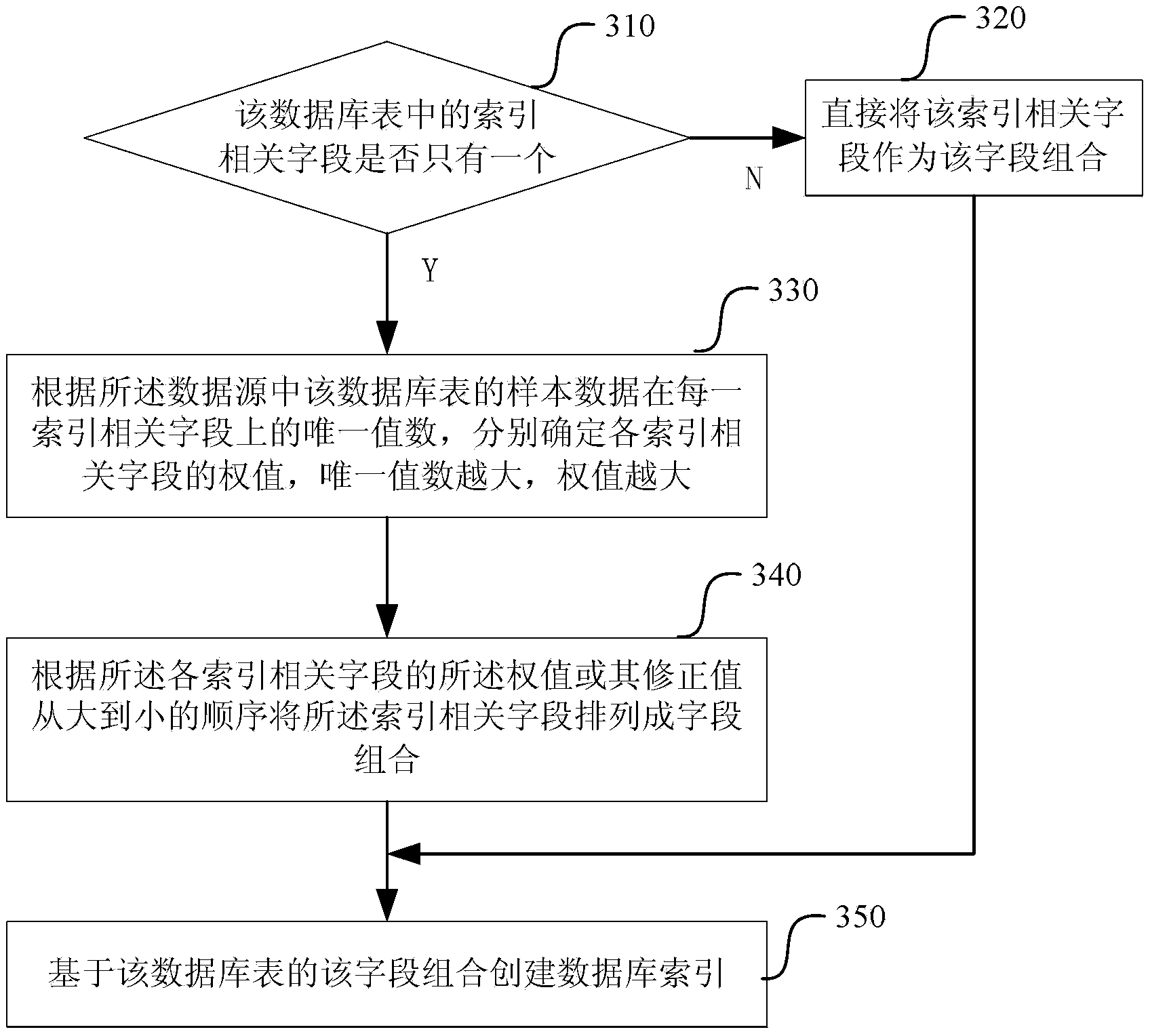
Automated database index creation method and system
ActiveCN103810212ARealize automatic creationImprove creation efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsDatabase indexData source
The invention discloses an automated database index creation method and system. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a data source corresponding to a database operation statement to be approved and instantiating the database connection; processing each database operation statement to be approved in a way of determining a database table used in the database operation statement and an index related field used in each database table; obtaining a field combination of an existing index of the database table from the data source; for each database table, creating a database index when a set formed by the index related fields in the database table is not a sub-set or a superset of the combination of each existing index of the database table and a corresponding database index is not created yet. The invention also provides the corresponding system. According to the automated database index creation method and system, automatic creation of indexes is realized according to the database operation statement to be approved and sample data, and the efficiency of the index creation is improved.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com