Patents
Literature
945 results about "Lossless compression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lossless compression is a class of data compression algorithms that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data. By contrast, lossy compression permits reconstruction only of an approximation of the original data, though usually with improved compression rates (and therefore reduced media sizes).
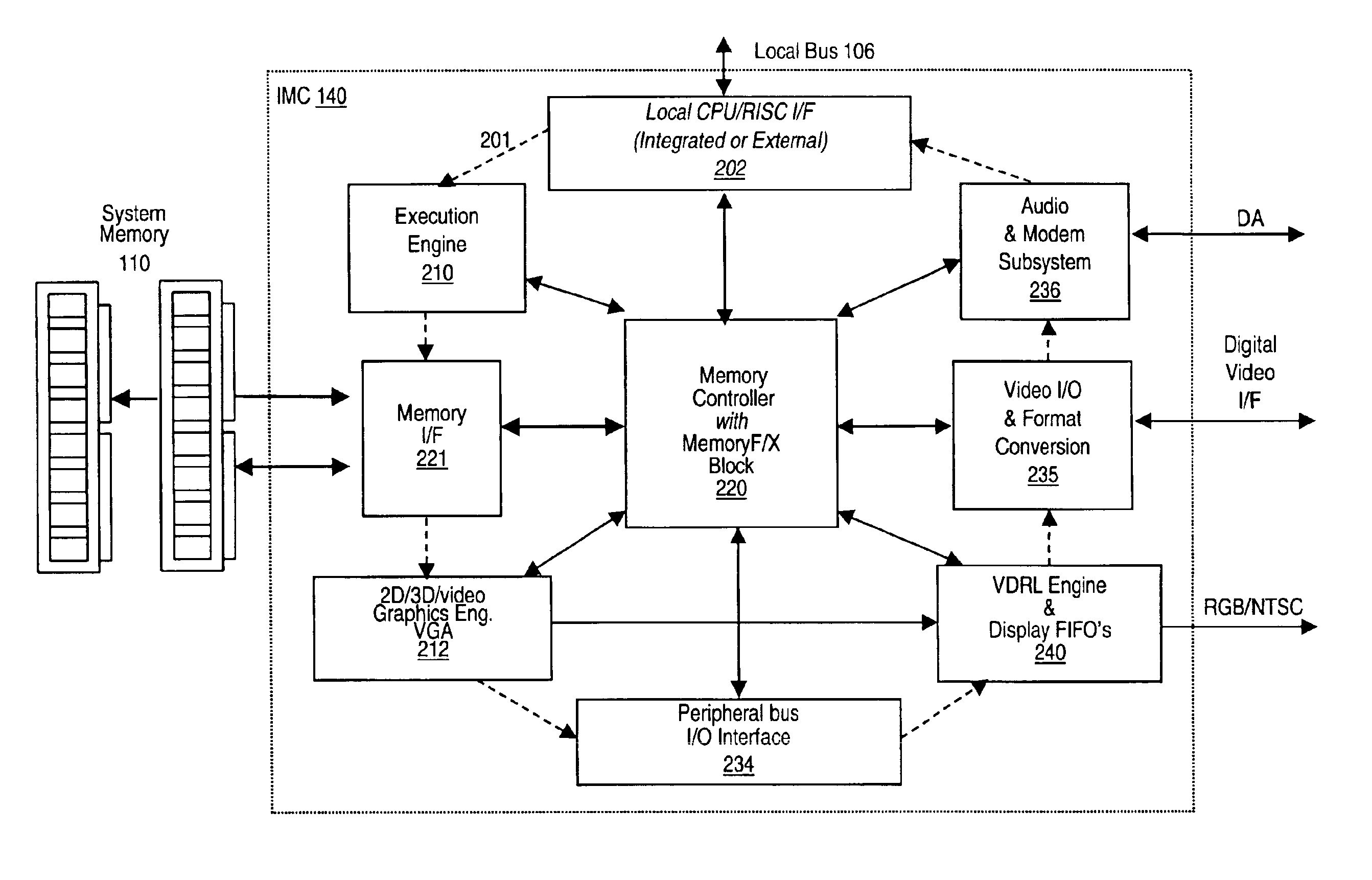
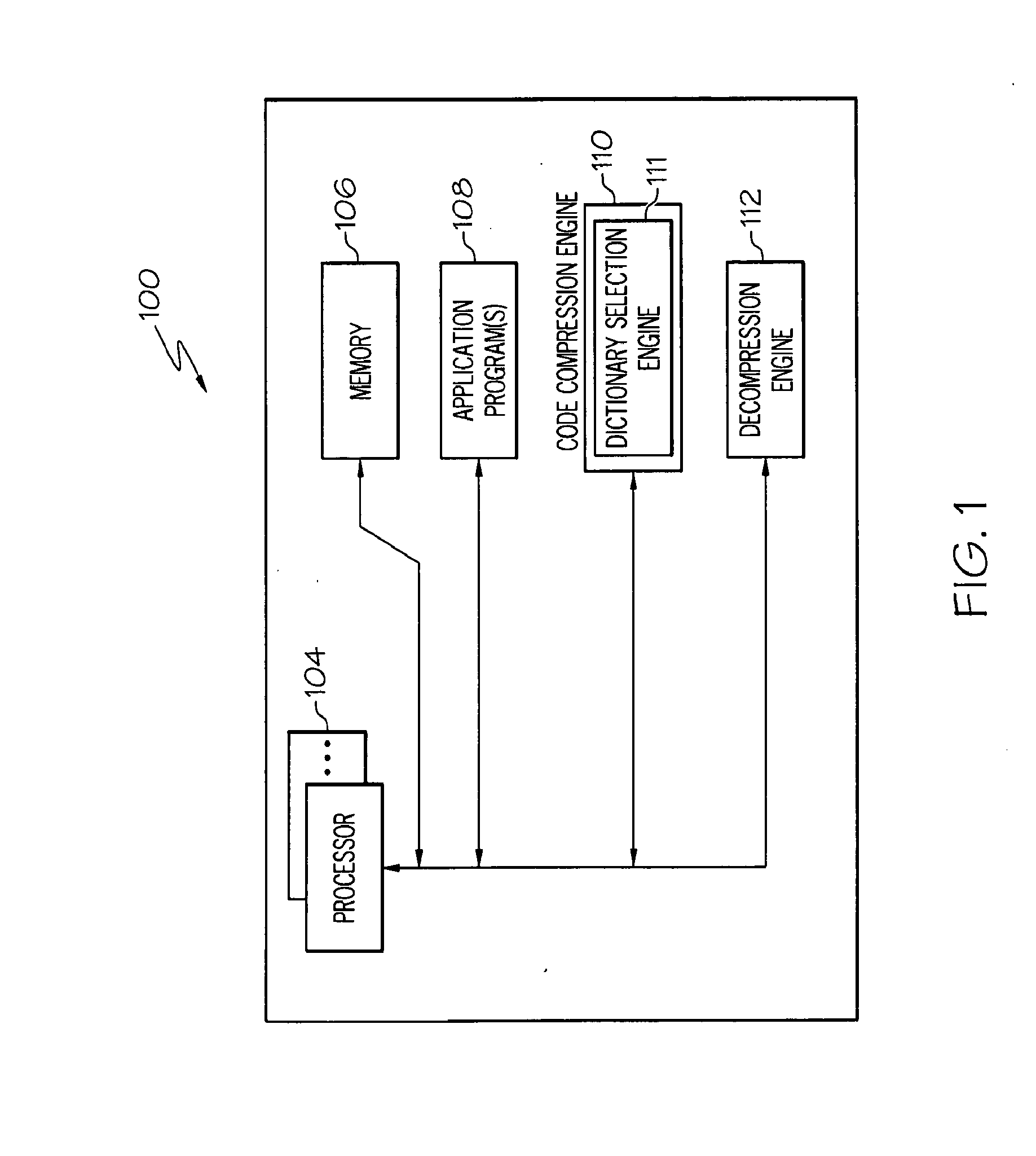
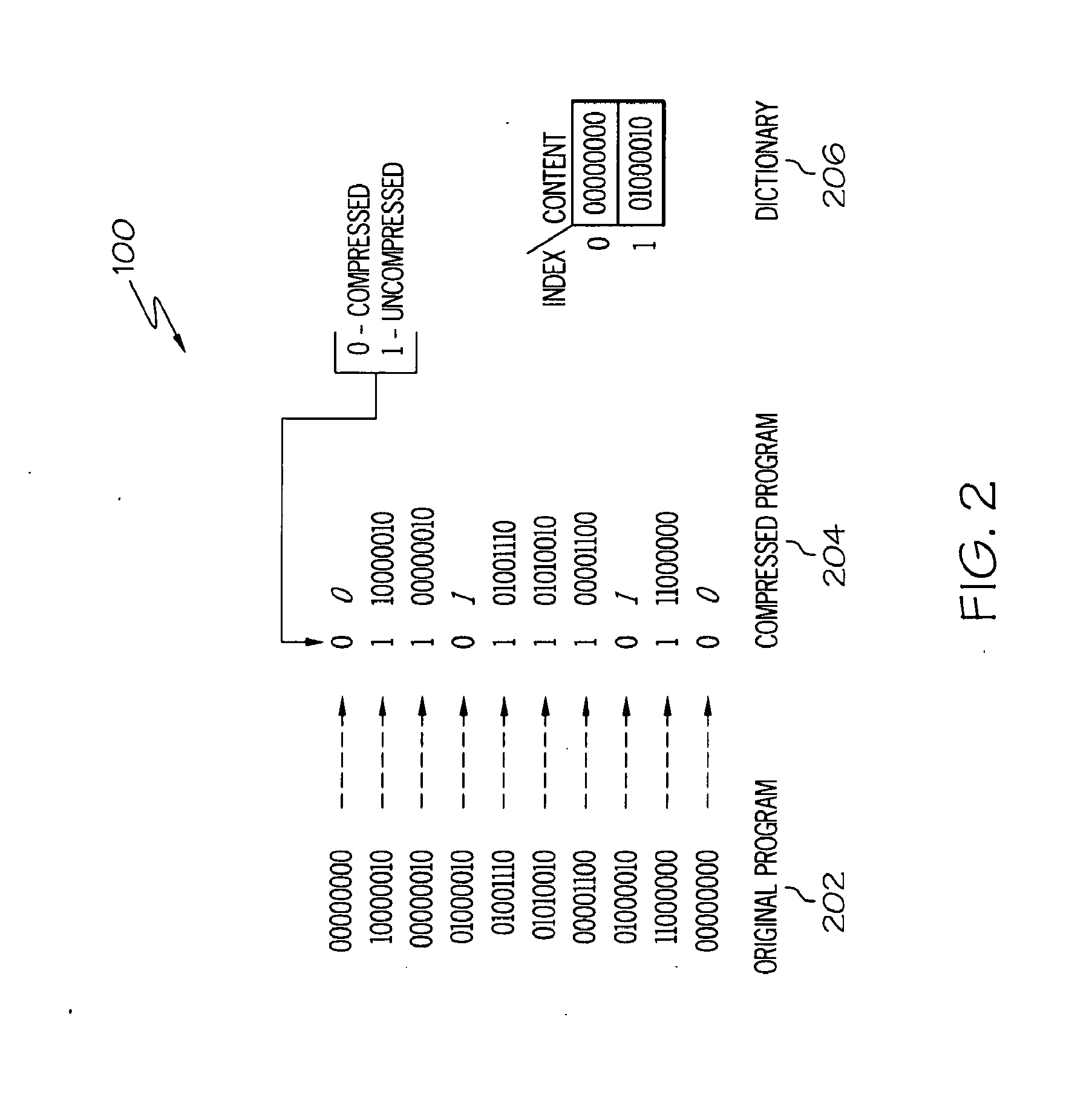
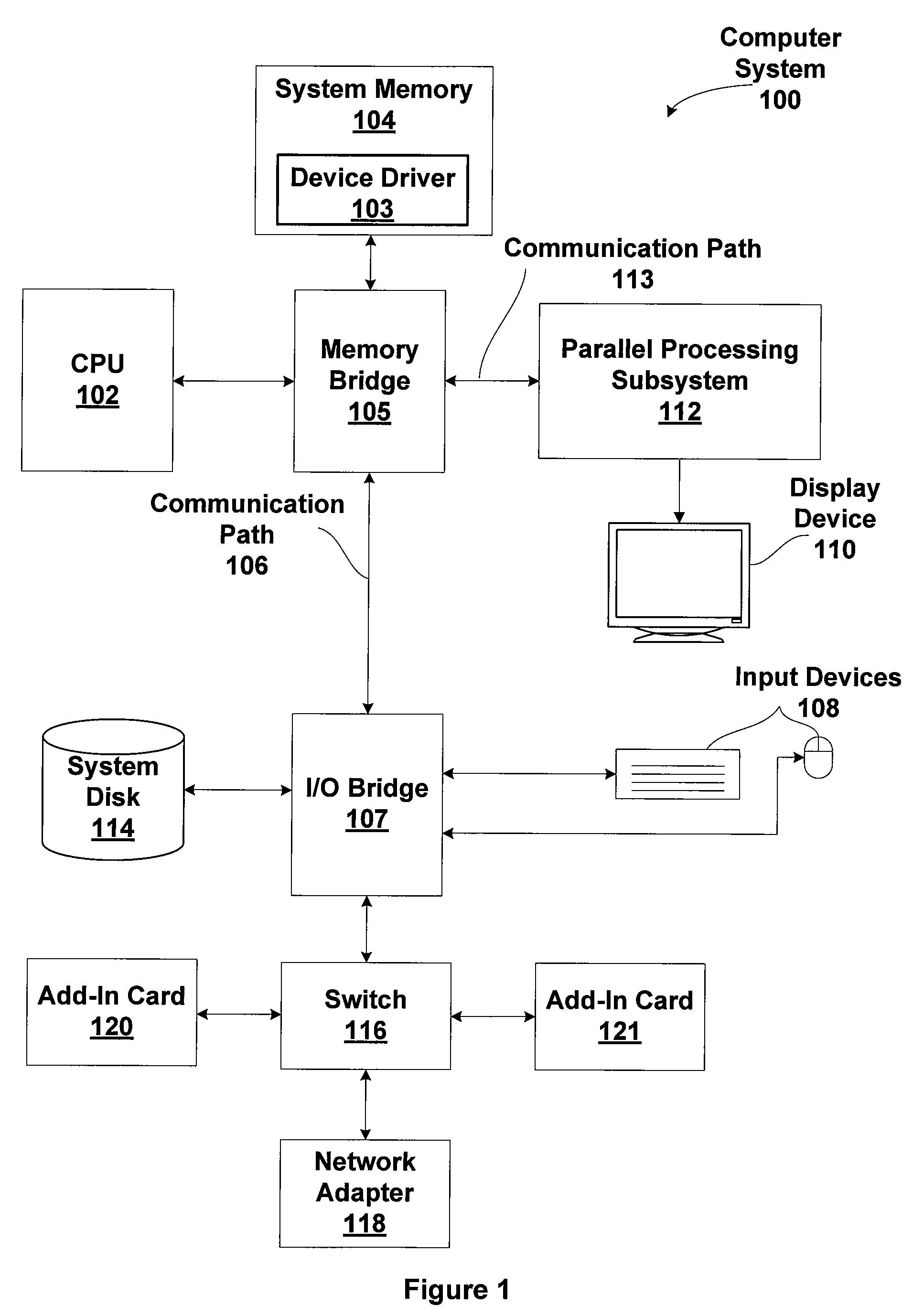
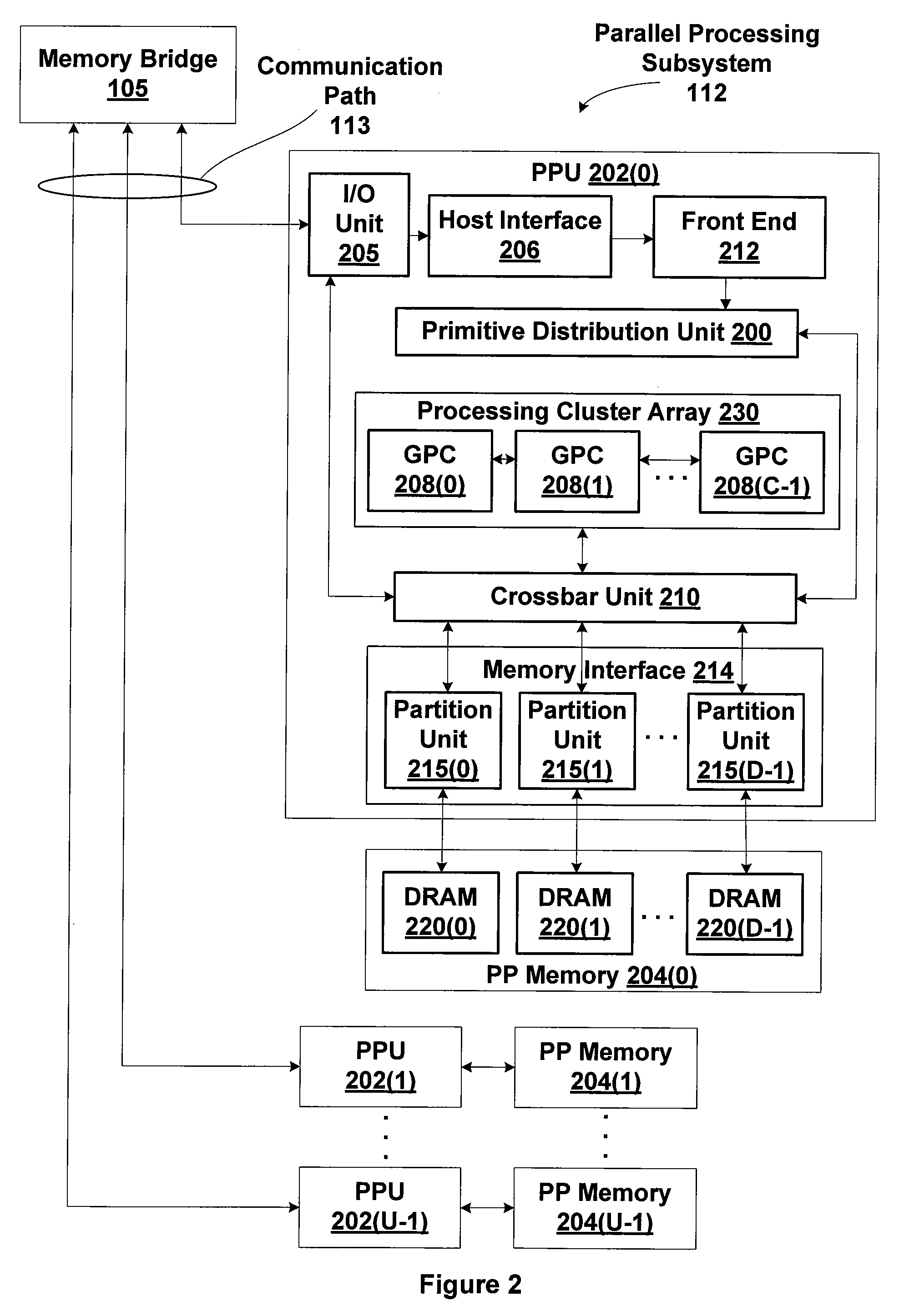
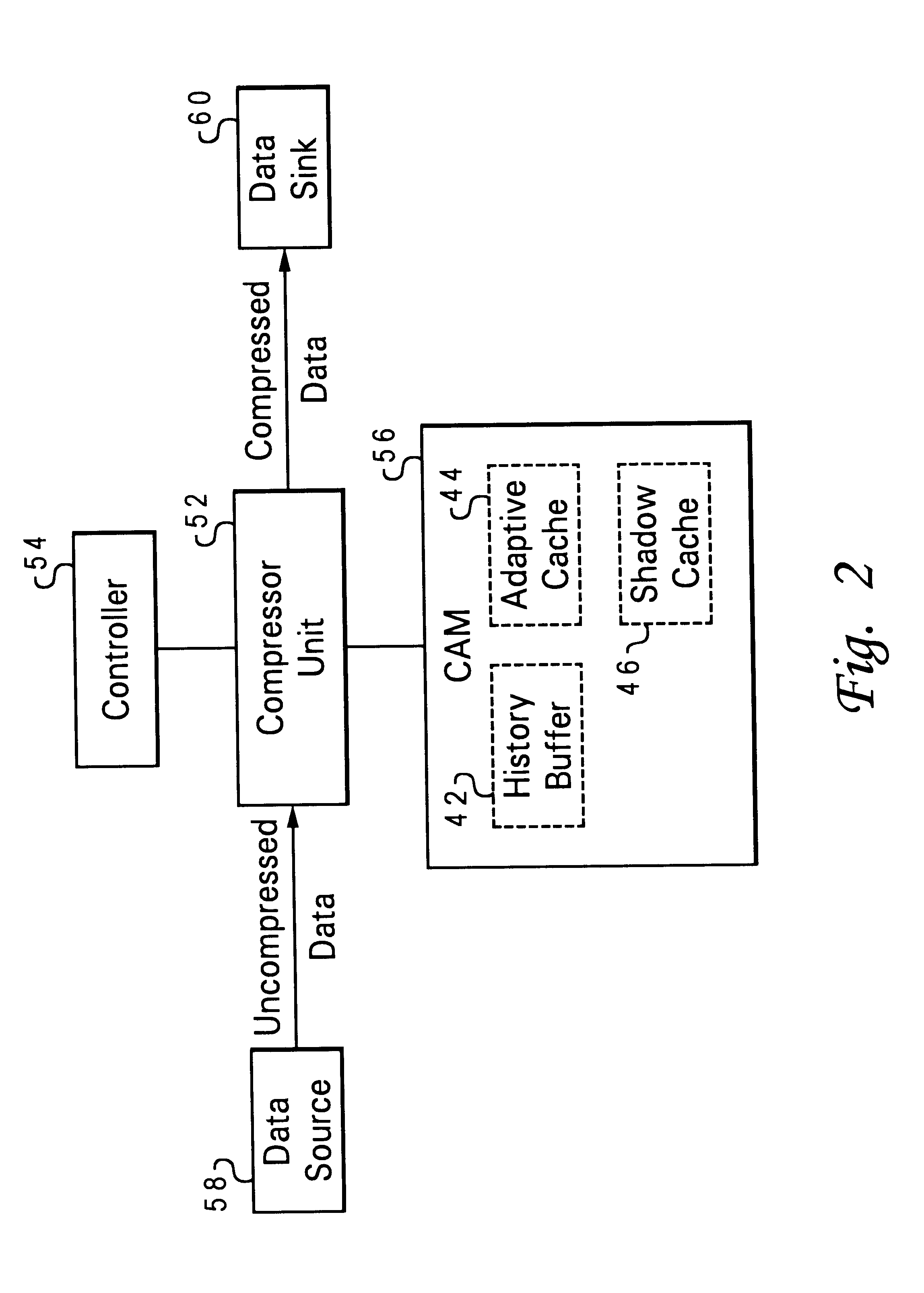
Memory module including scalable embedded parallel data compression and decompression engines
InactiveUS6879266B1Low costSmall data storage requirementMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTParallel compressionParallel computing
An memory module including parallel data compression and decompression engines for improved performance. The memory module includes MemoryF / X Technology. To improve latency and reduce performance degradations normally associated with compression and decompression techniques, the MemoryF / X Technology encompasses multiple novel techniques such as: 1) parallel lossless compression / decompression; 2) selectable compression modes such as lossless, lossy or no compression; 3) priority compression mode; 4) data cache techniques; 5) variable compression block sizes; 6) compression reordering; and 7) unique address translation, attribute, and address caches. The parallel compression and decompression algorithm allows high-speed parallel compression and high-speed parallel decompression operation. The memory module-integrated data compression and decompression capabilities remove system bottlenecks and increase performance. This allows lower cost systems due to smaller data storage, reduced bandwidth requirements, reduced power and noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
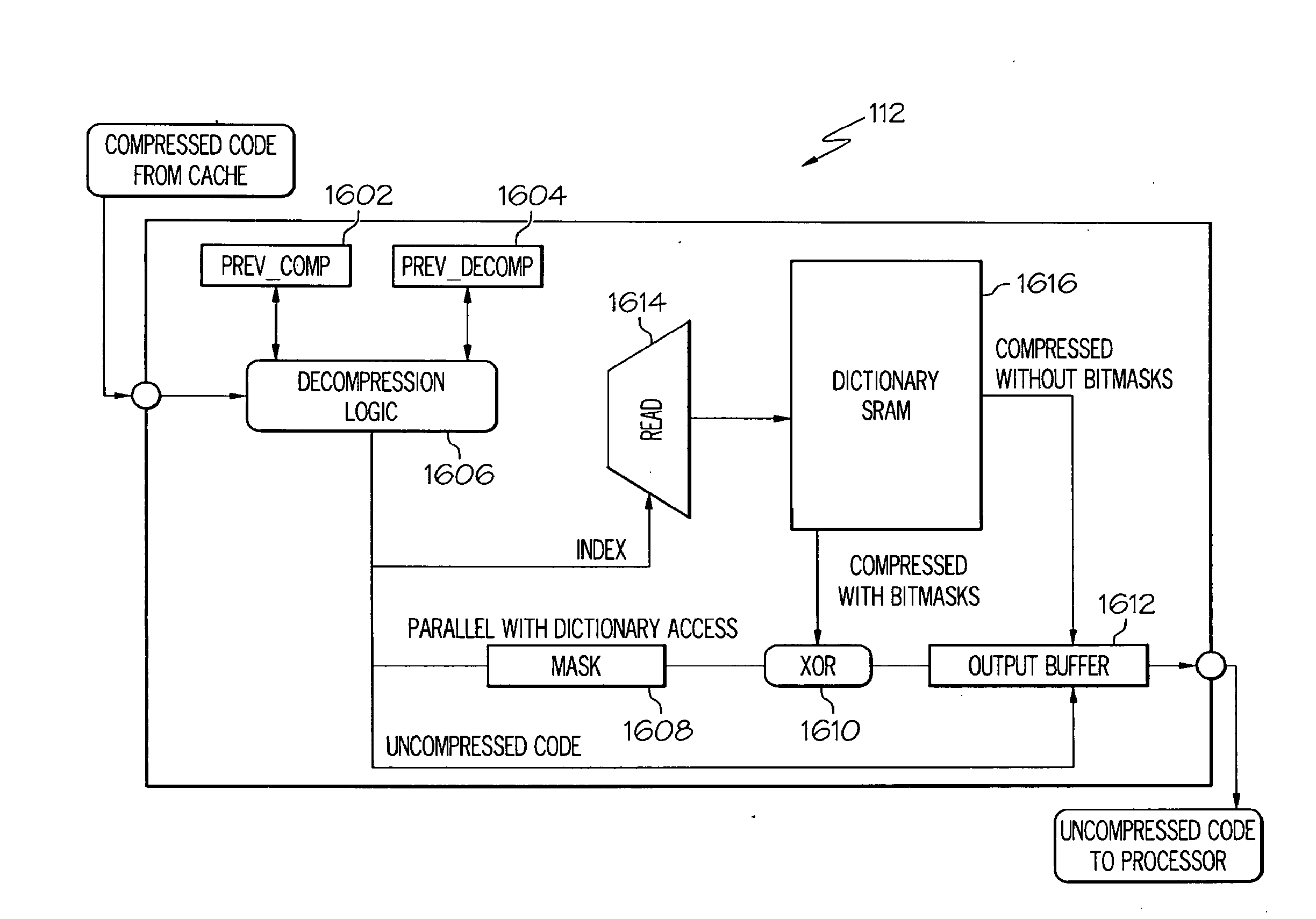
Lossless data compression and real-time decompression
InactiveUS20100223237A1Maximizing compressing efficiencyMinimizes decompression penaltyDigital data processing detailsCode conversionInformation processingMaximal set
A method, information processing system, and computer program storage product store data in an information processing system. Uncompressed data is received and the uncompressed data is divided into a series of vectors. A sequence of profitable bitmask patterns is identified for the vectors that maximizes compression efficiency while minimizes decompression penalty. Matching patterns are created using multiple bit masks based on a set of maximum values of the frequency distribution of the vectors. A dictionary is built based upon the set of maximum values in the frequency distribution and a bit mask savings which is a number of bits reduced using each of the multiple bit masks. Each of the vectors is compressed using the dictionary and the matching patterns with having high bit mask savings. The compressed vectors are stored into memory. Also, an efficient placement is developed to enable parallel decompression of the compressed codes.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
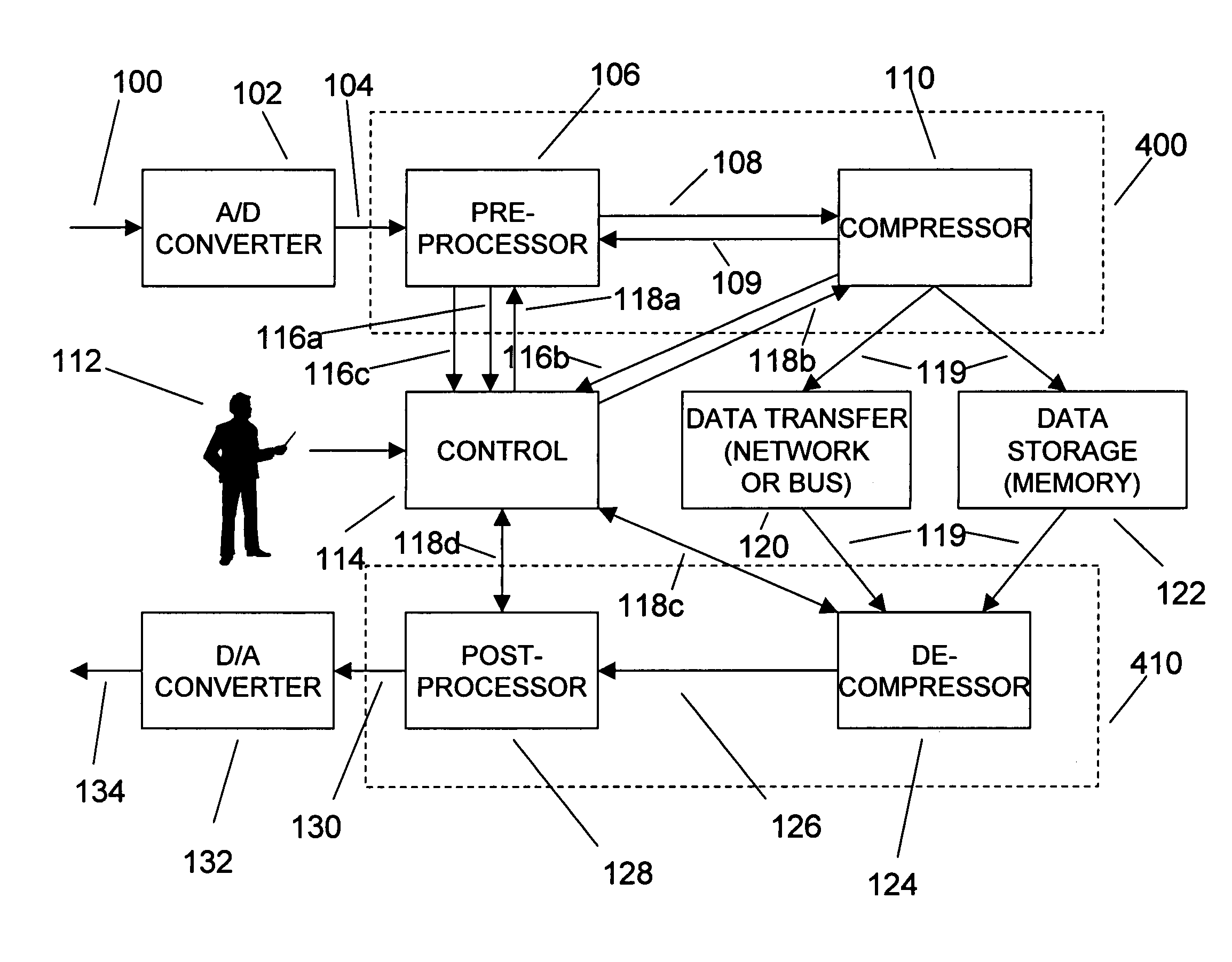
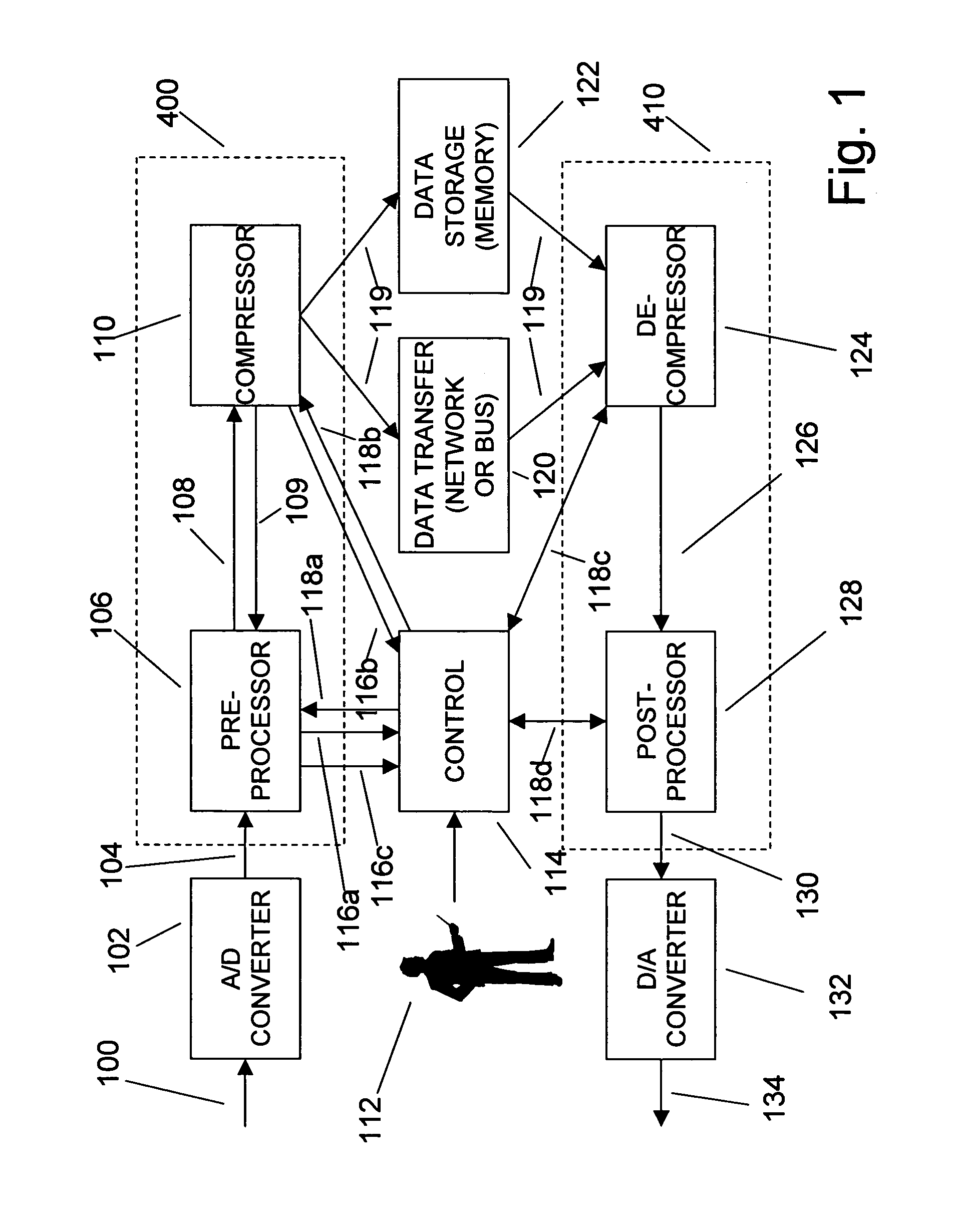
Adaptive compression and decompression of bandlimited signals
InactiveUS7009533B1Less bandwidthLess storageCode conversionPictoral communicationAdaptive compressionSpectrum analyzer
An efficient method for compressing sampled analog signals in real time, without loss, or at a user-specified rate or distortion level, is described. The present invention is particularly effective for compressing and decompressing high-speed, bandlimited analog signals that are not appropriately or effectively compressed by prior art speech, audio, image, and video compression algorithms due to various limitations of such prior art compression solutions. The present invention's preprocessor apparatus measures one or more signal parameters and, under program control, appropriately modifies the preprocessor input signal to create one or more preprocessor output signals that are more effectively compressed by a follow-on compressor. In many instances, the follow-on compressor operates most effectively when its input signal is at baseband. The compressor creates a stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters that represent the original sampled input signal using fewer bits. The decompression subsystem uses a decompressor to decompress the stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters. After decompression, the decompressor output signal is processed by a post-processor, which reverses the operations of the preprocessor during compression, generating a postprocessed signal that exactly matches (during lossless compression) or approximates (during lossy compression) the original sampled input signal. Parallel processing implementations of both the compression and decompression subsystems are described that can operate at higher sampling rates when compared to the sampling rates of a single compression or decompression subsystem. In addition to providing the benefits of real-time compression and decompression to a new, general class of sampled data users who previously could not obtain benefits from compression, the present invention also enhances the performance of test and measurement equipment (oscilloscopes, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, logic analyzers, etc.), busses and networks carrying sampled data, and data converters (A / D and D / A converters).
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
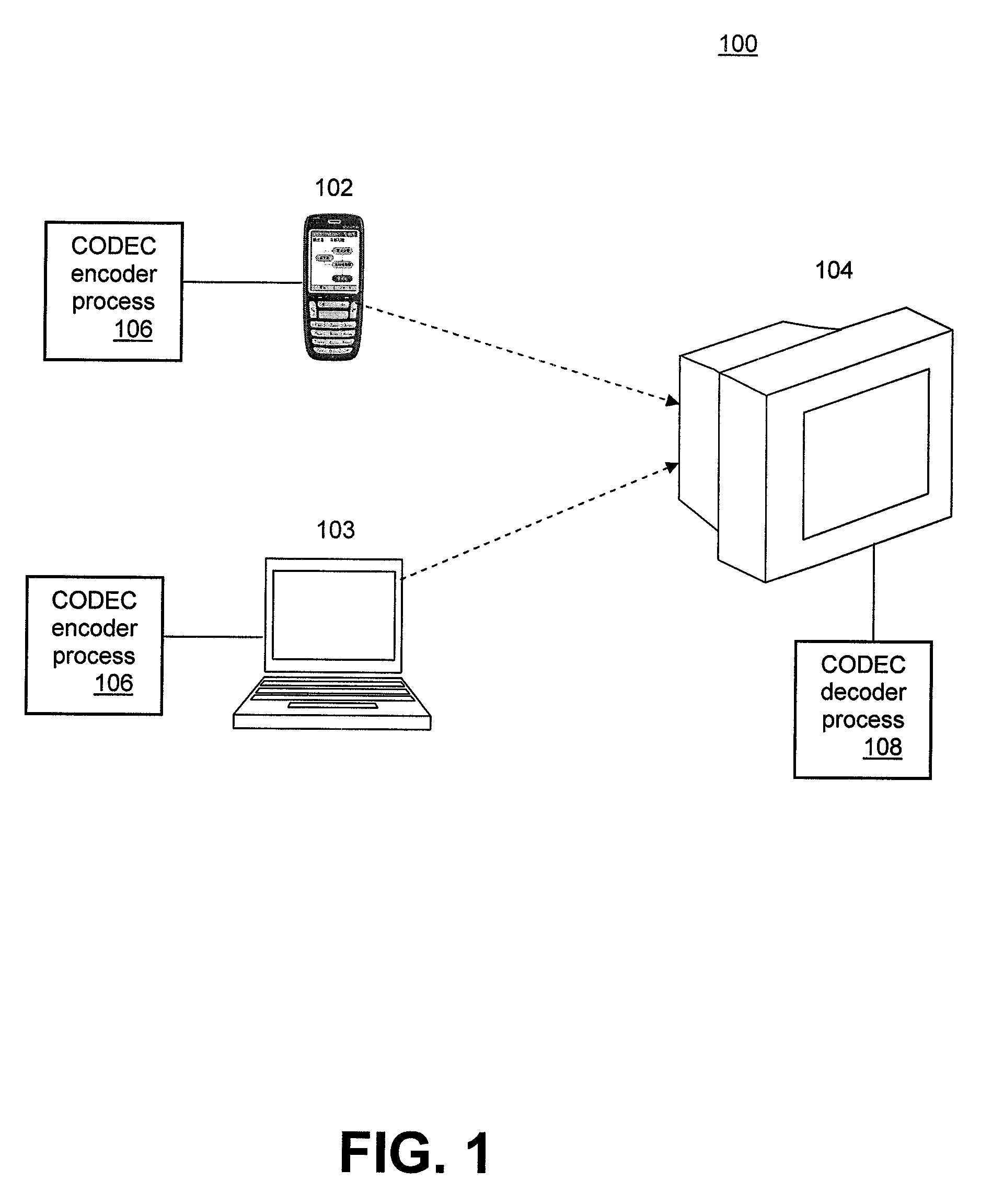
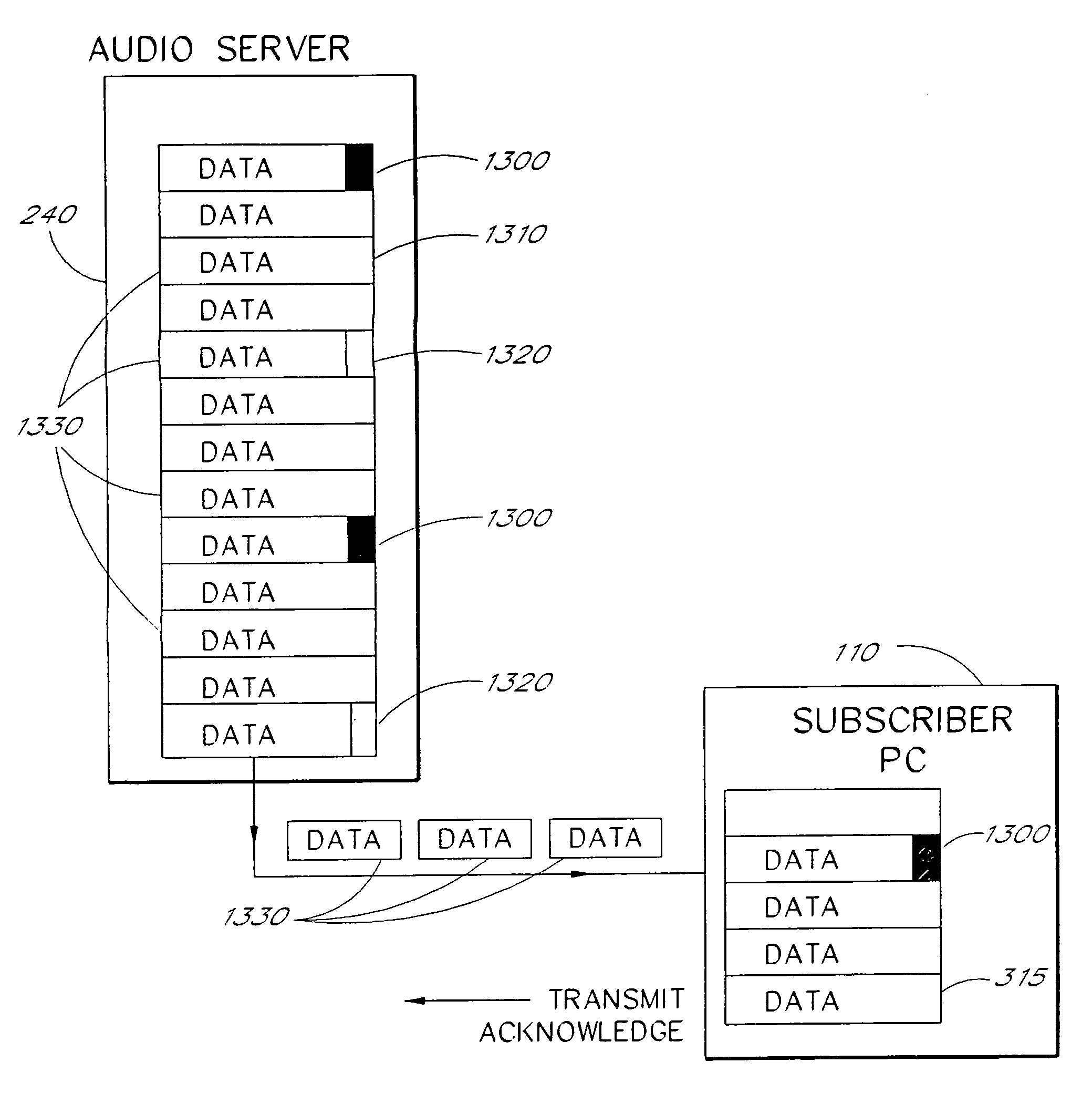
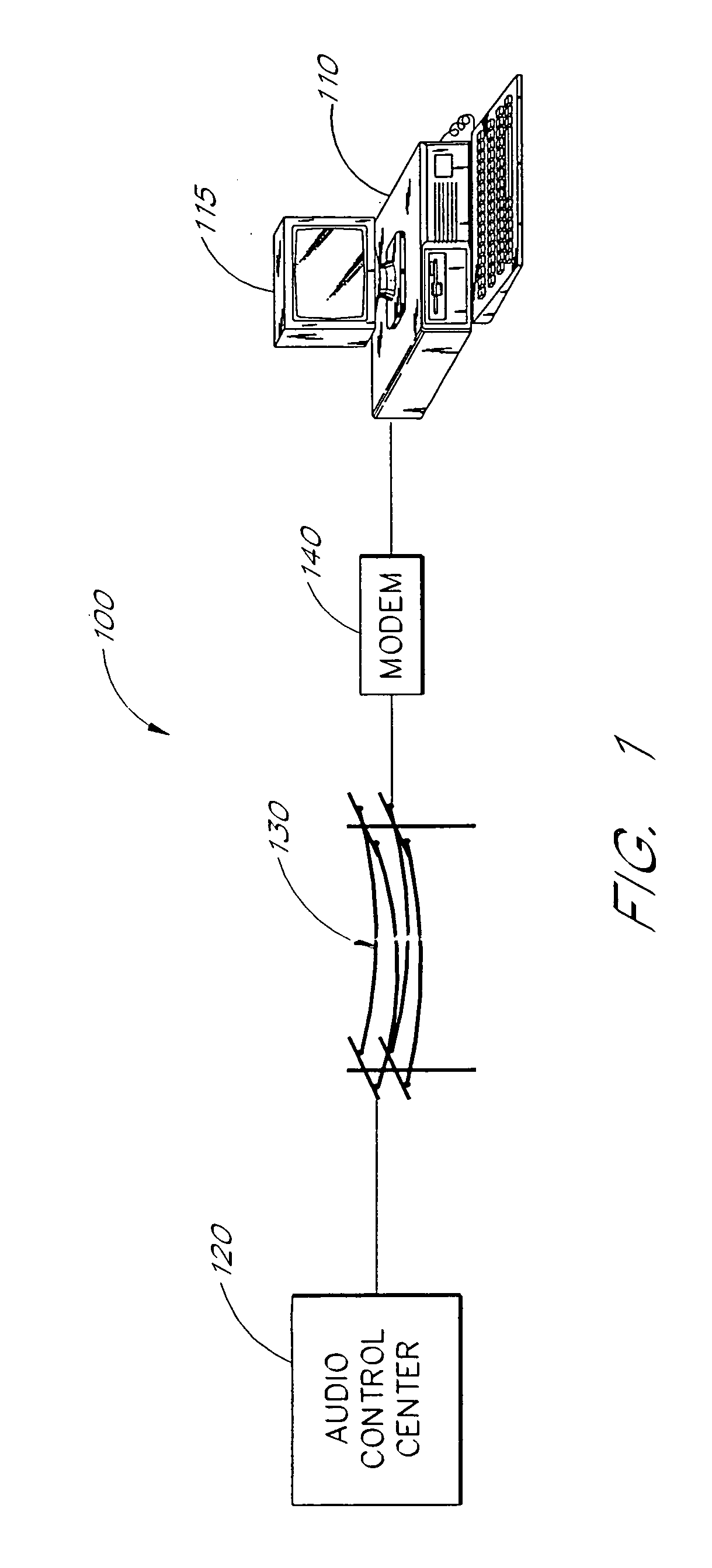
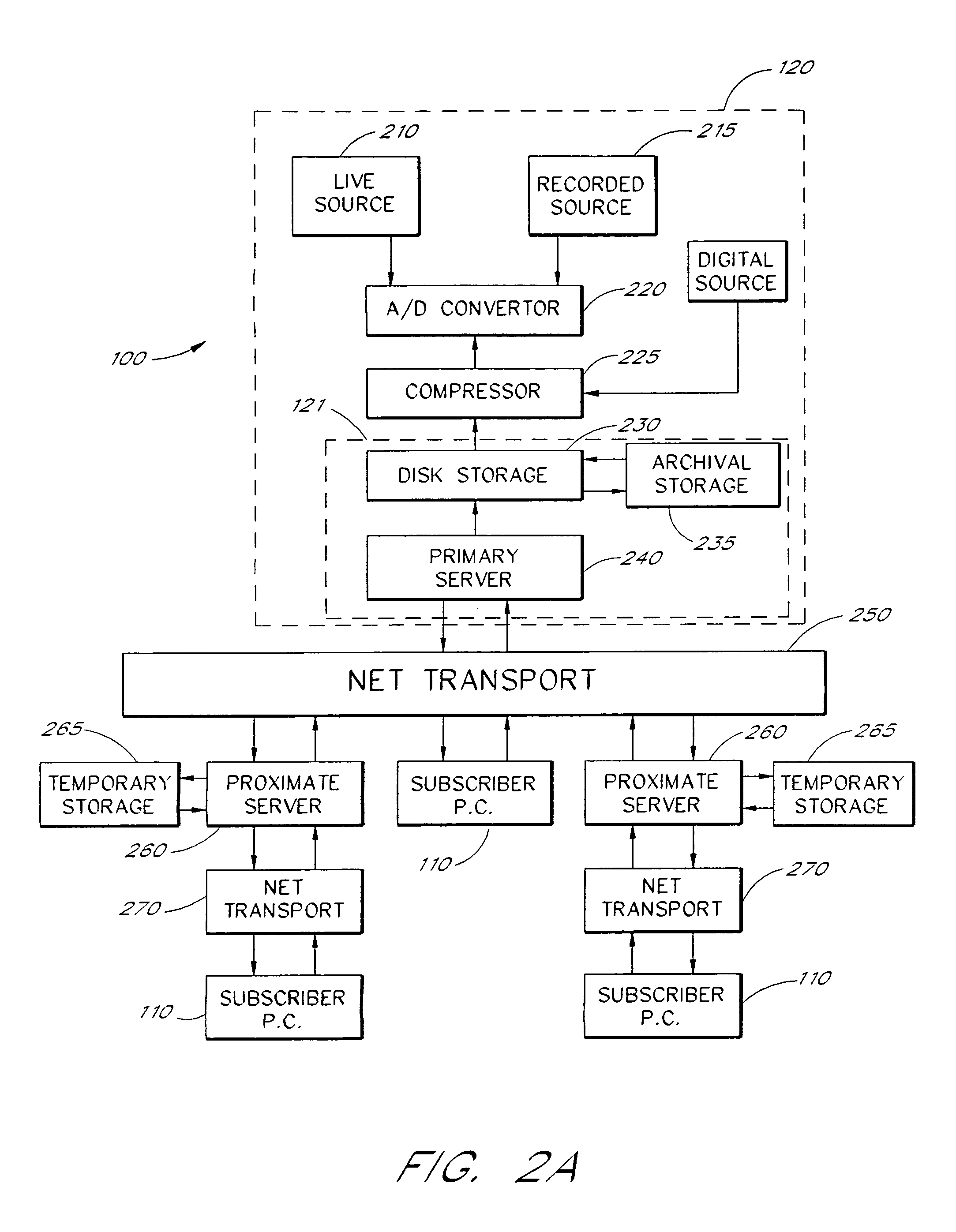
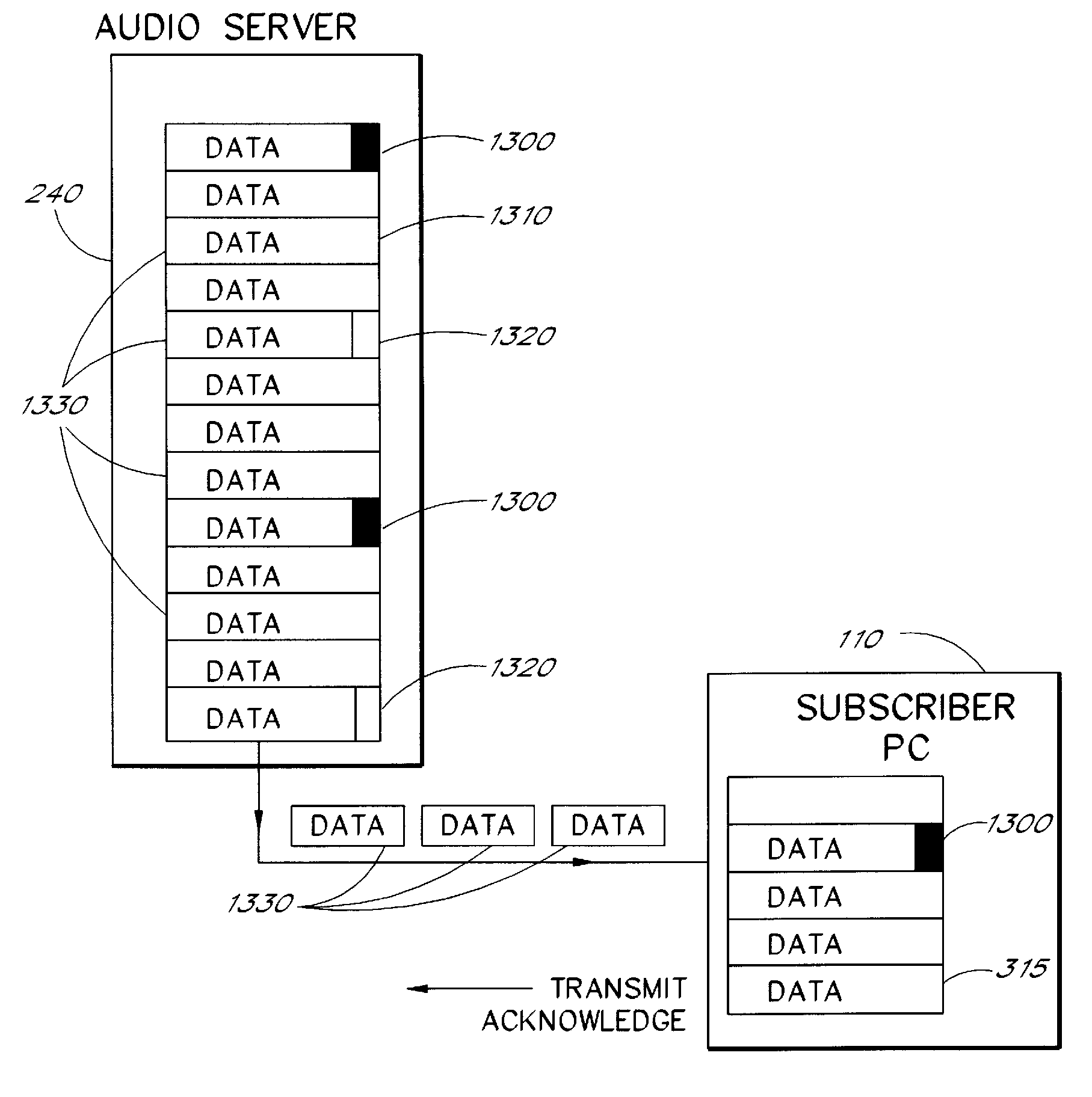
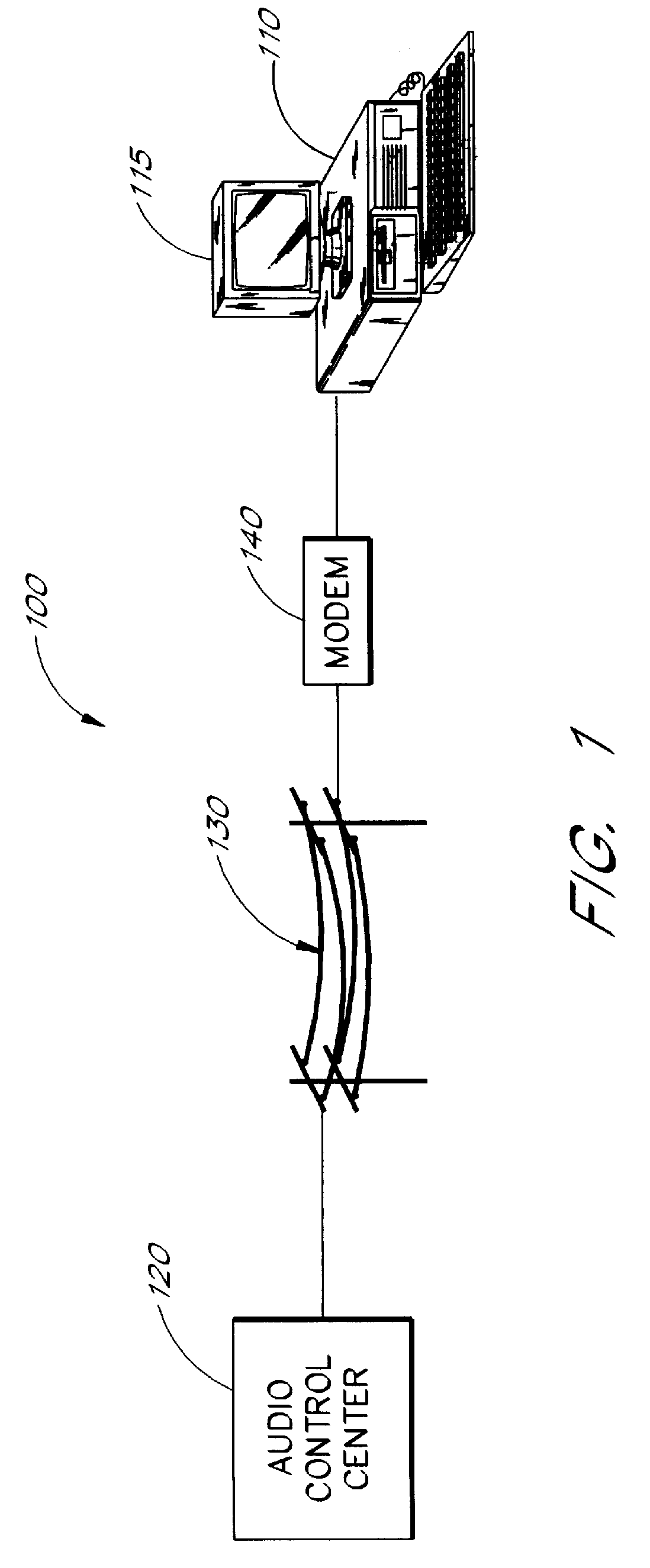
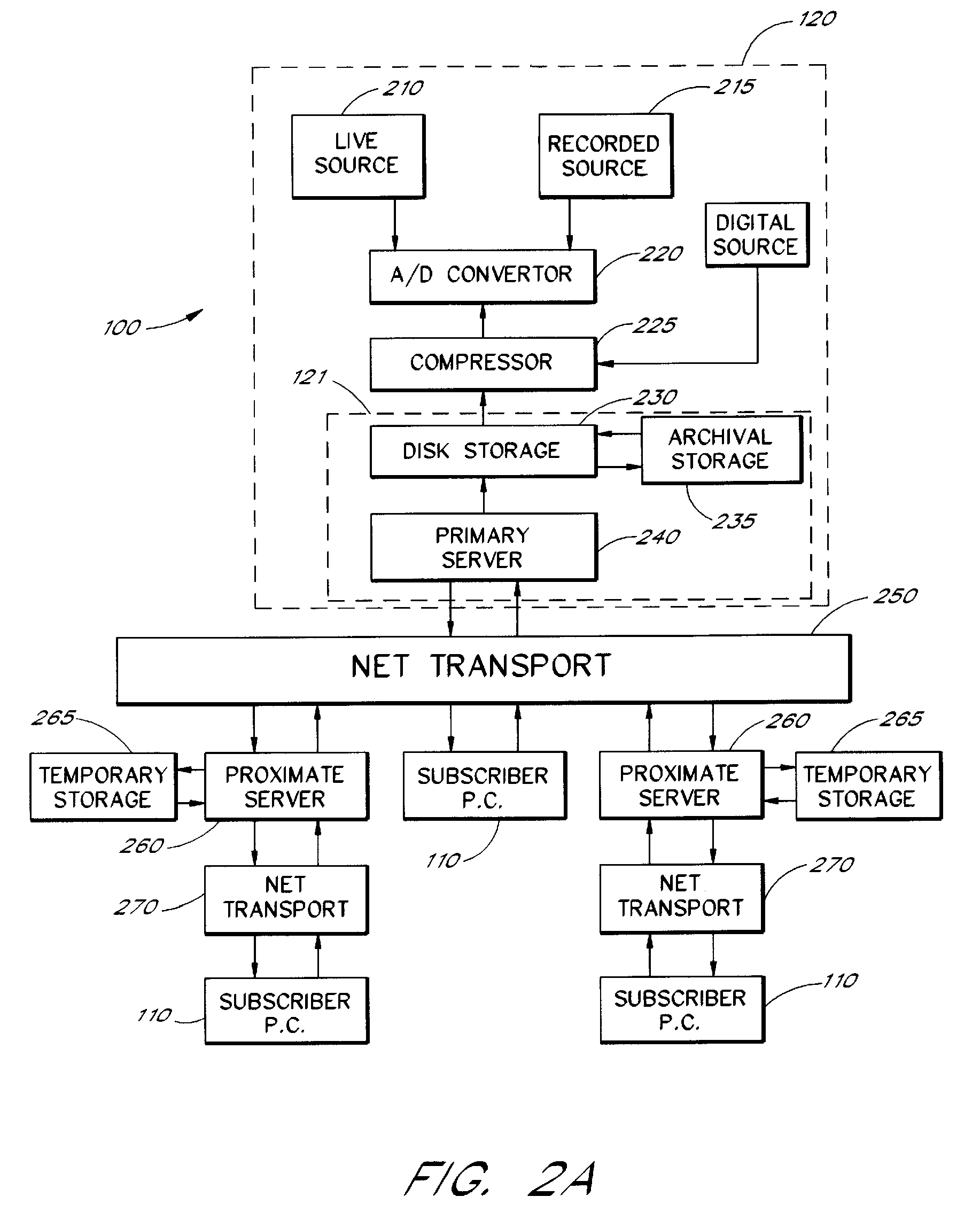
Multimedia communications system and method for providing audio on demand to subscribers
InactiveUS6985932B1Quality improvementHigh audio signalSpecific information broadcast systemsBroadcast transmission systemsCommunications systemTelecommunications link
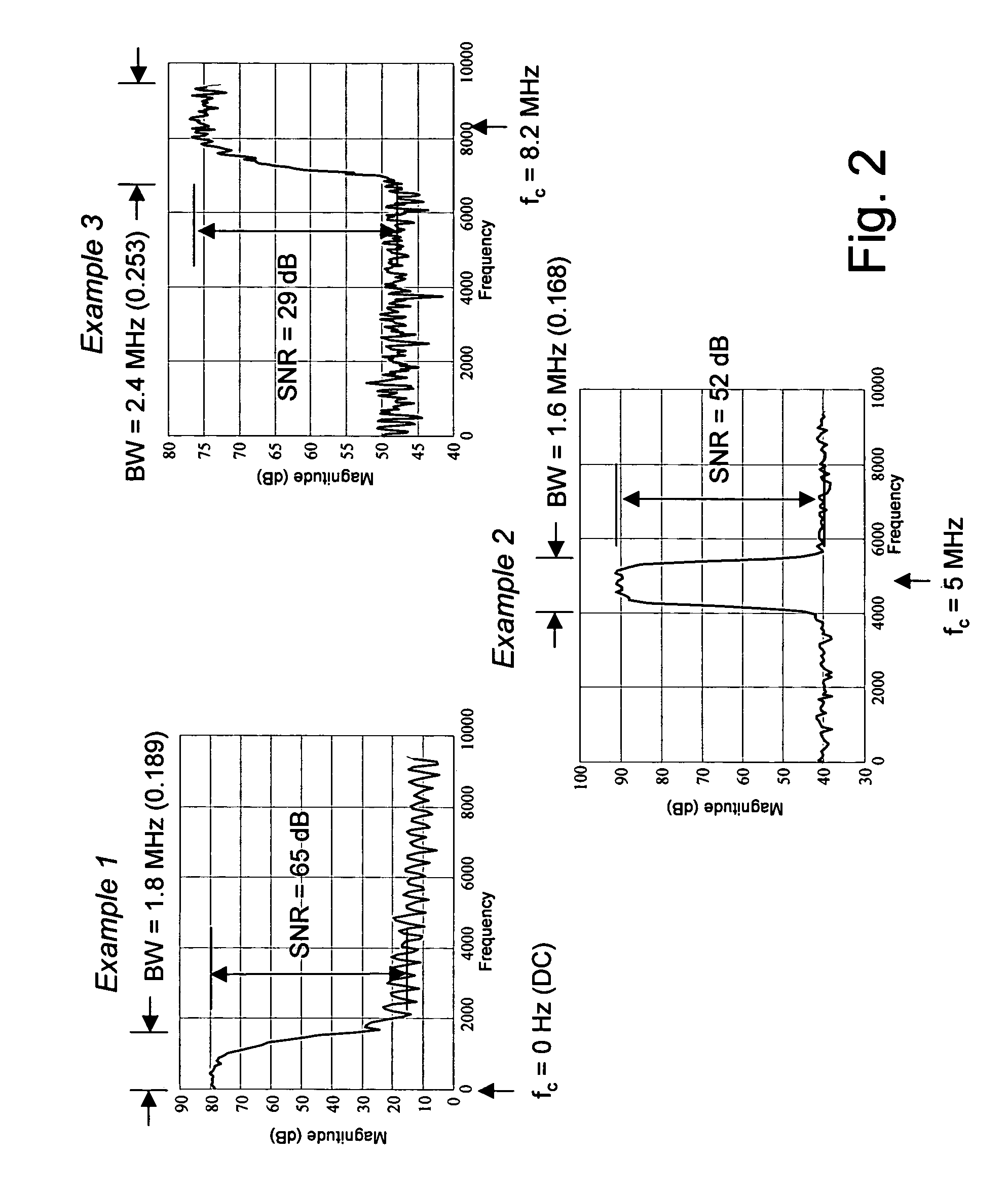
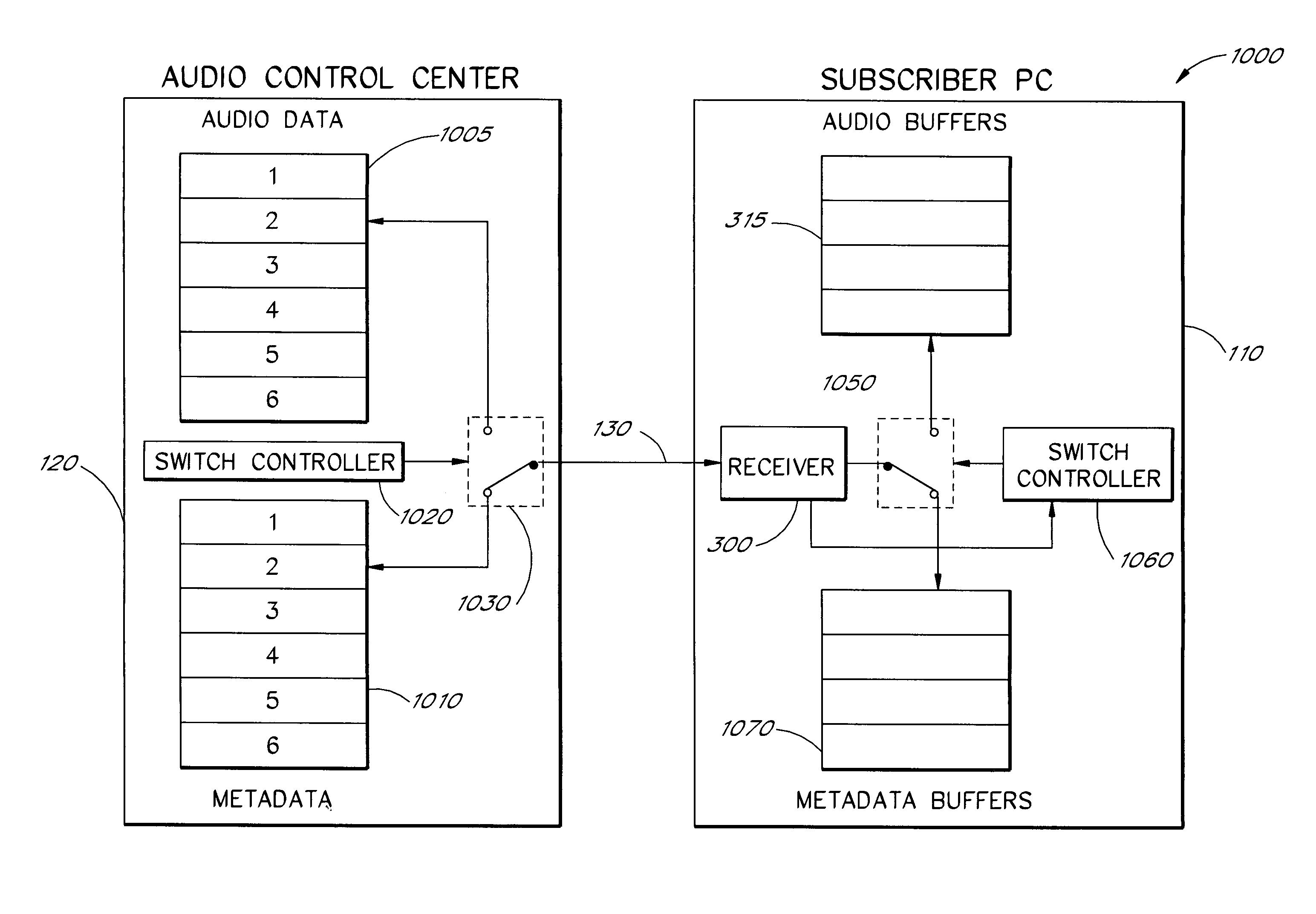
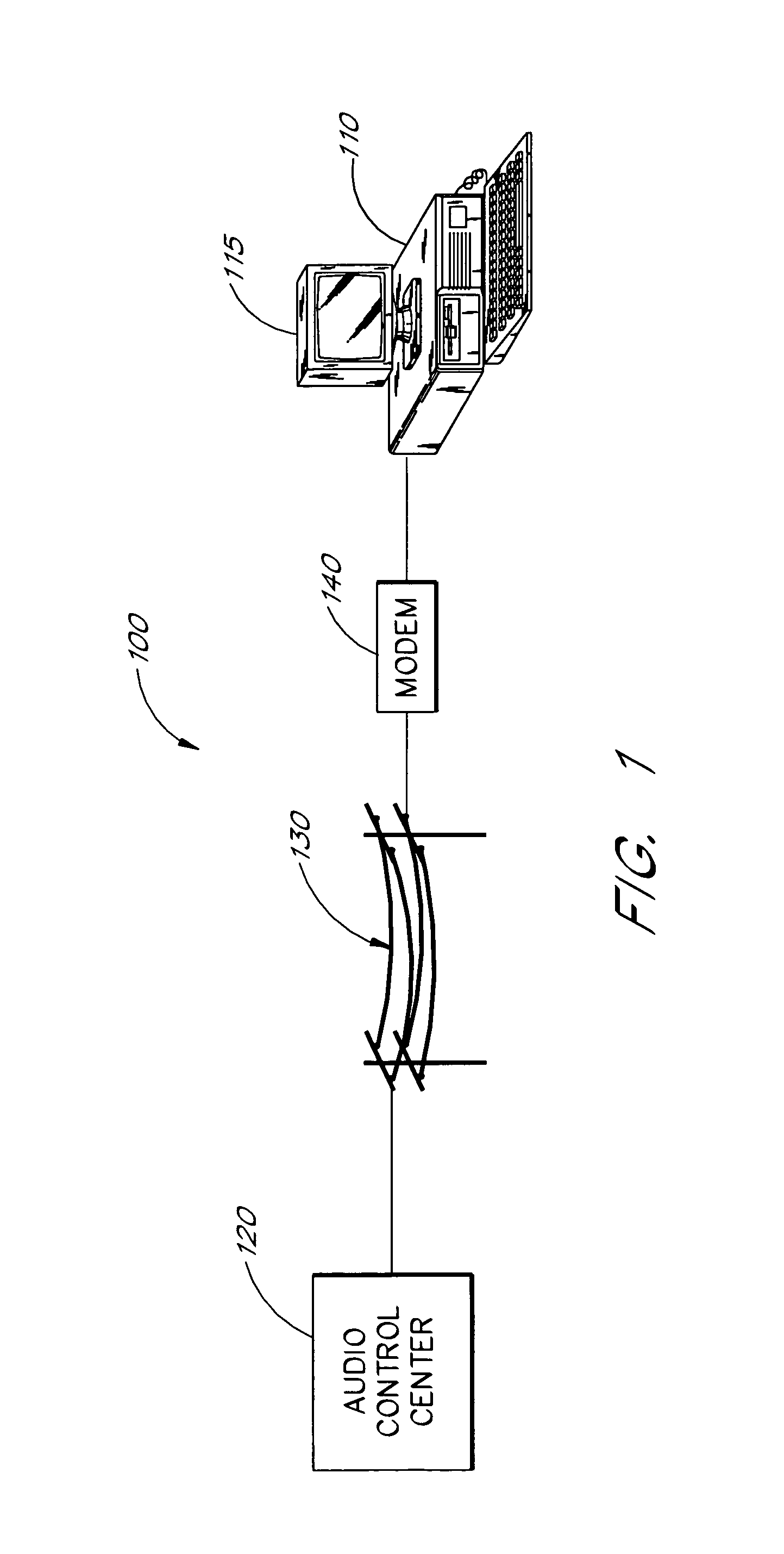
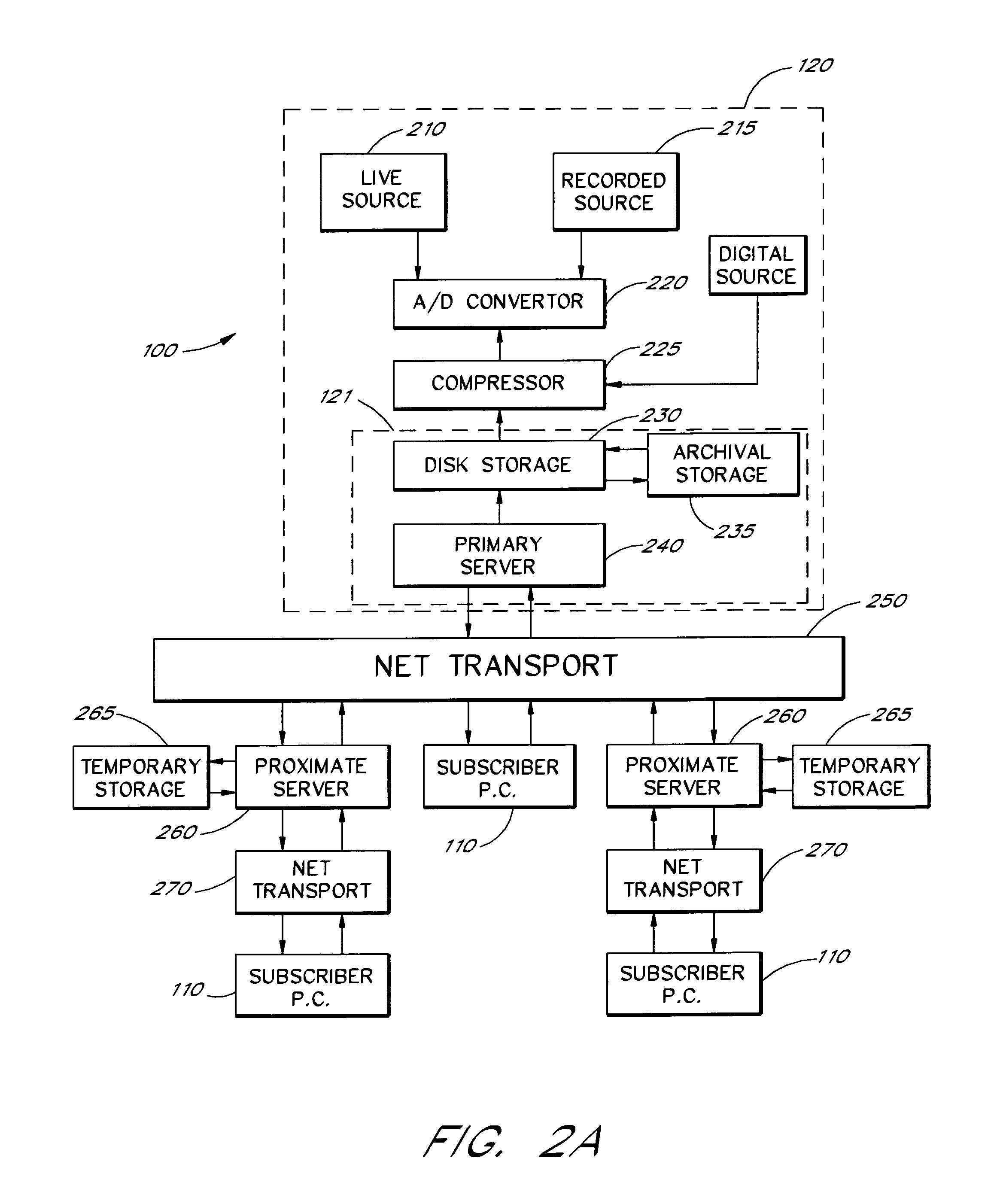
An audio-on-demand communication system provides real-time playback of audio data transferred via telephone lines or other communication links. One or more audio servers include memory banks which store compressed audio data. At the request of a user at a subscriber PC, an audio server transmits the compressed audio data over the communication link to the subscriber PC. The subscriber PC receives and decompresses the transmitted audio data in less than real-time using only the processing power of the CPU within the subscriber PC. According to one aspect of the present invention, high quality audio data compressed according to lossless compression techniques is transmitted together with normal quality audio data. According to another aspect of the present invention, metadata, or extra data, such as text, captions, still images, etc., is transmitted with audio data and is simultaneously displayed with corresponding audio data. The audio-on-demand system also provides a table of contents indicating significant divisions in the audio clip to be played and allows the user immediate access to audio data at the listed divisions. According to a further aspect of the present invention, servers and subscriber PCs are dynamically allocated based upon geographic location to provide the highest possible quality in the communication link.
Owner:INTEL CORP
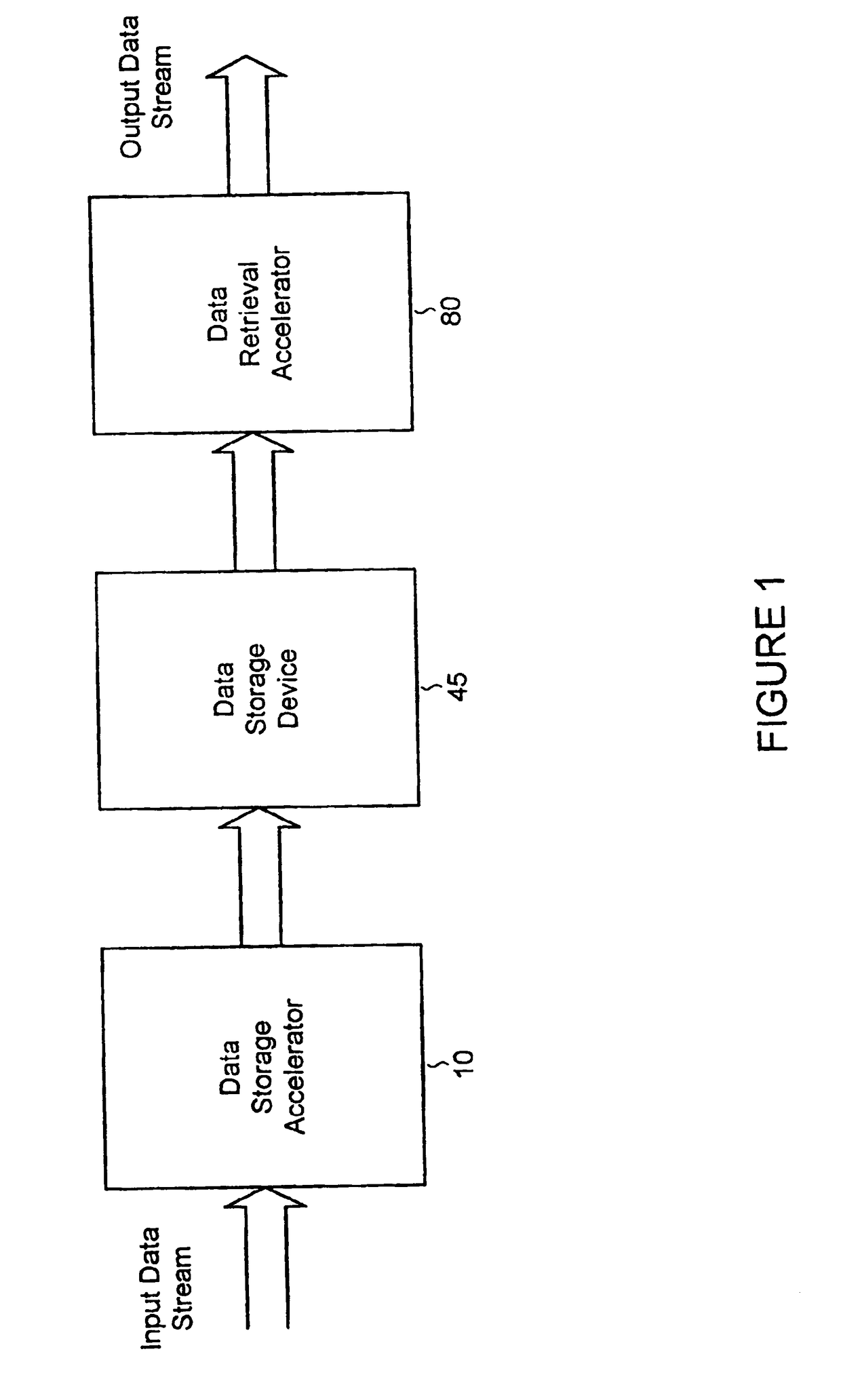
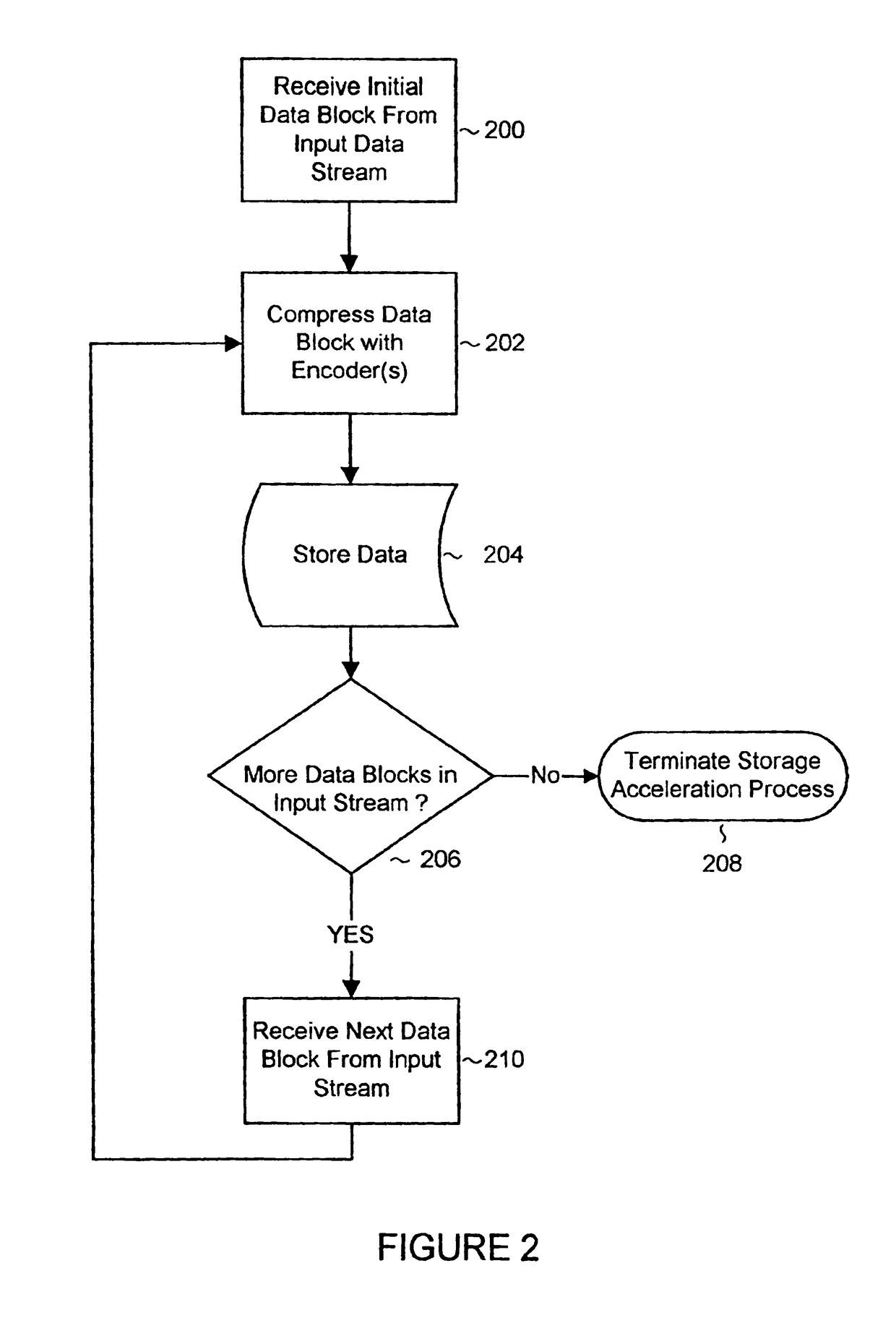
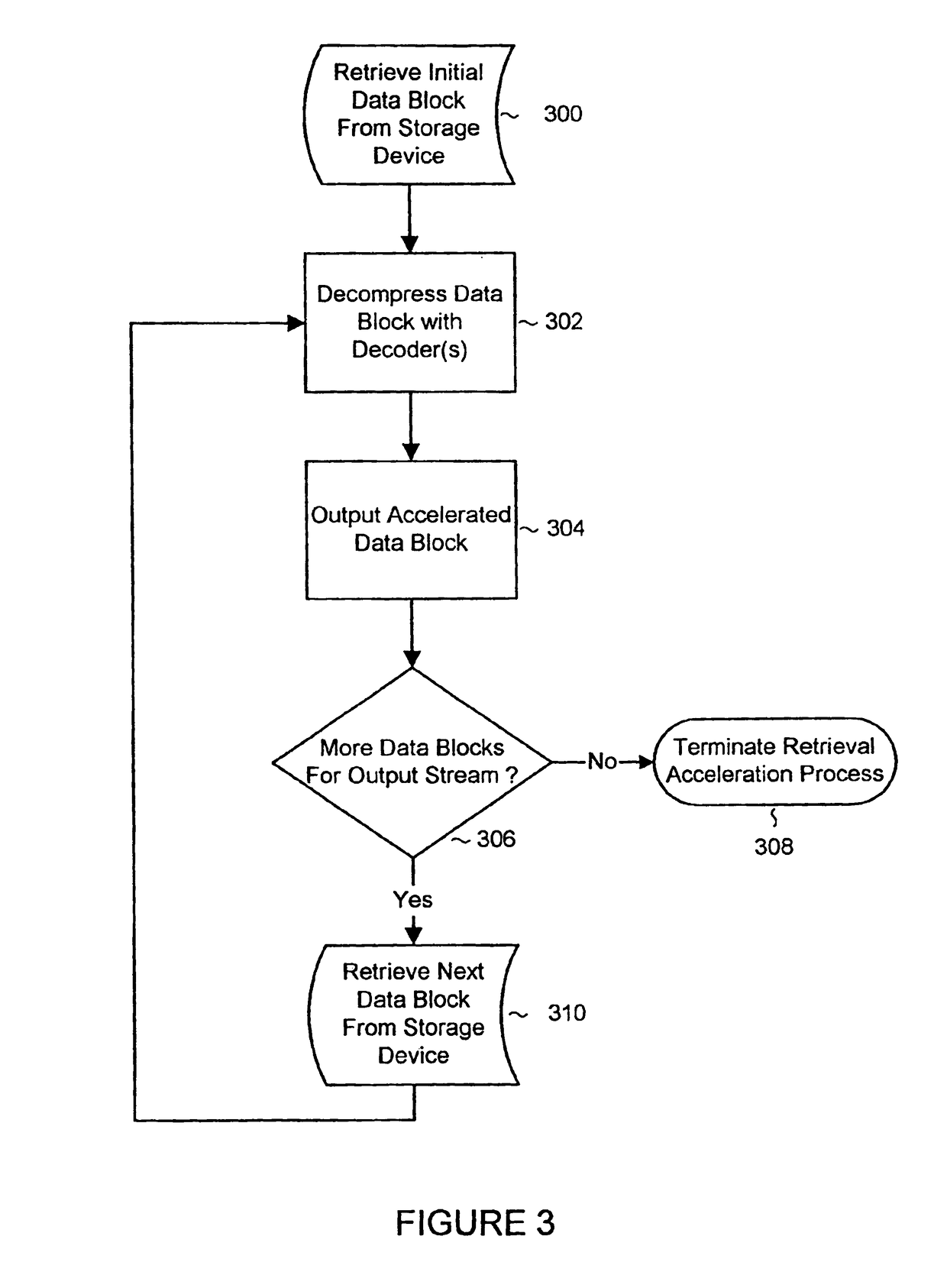
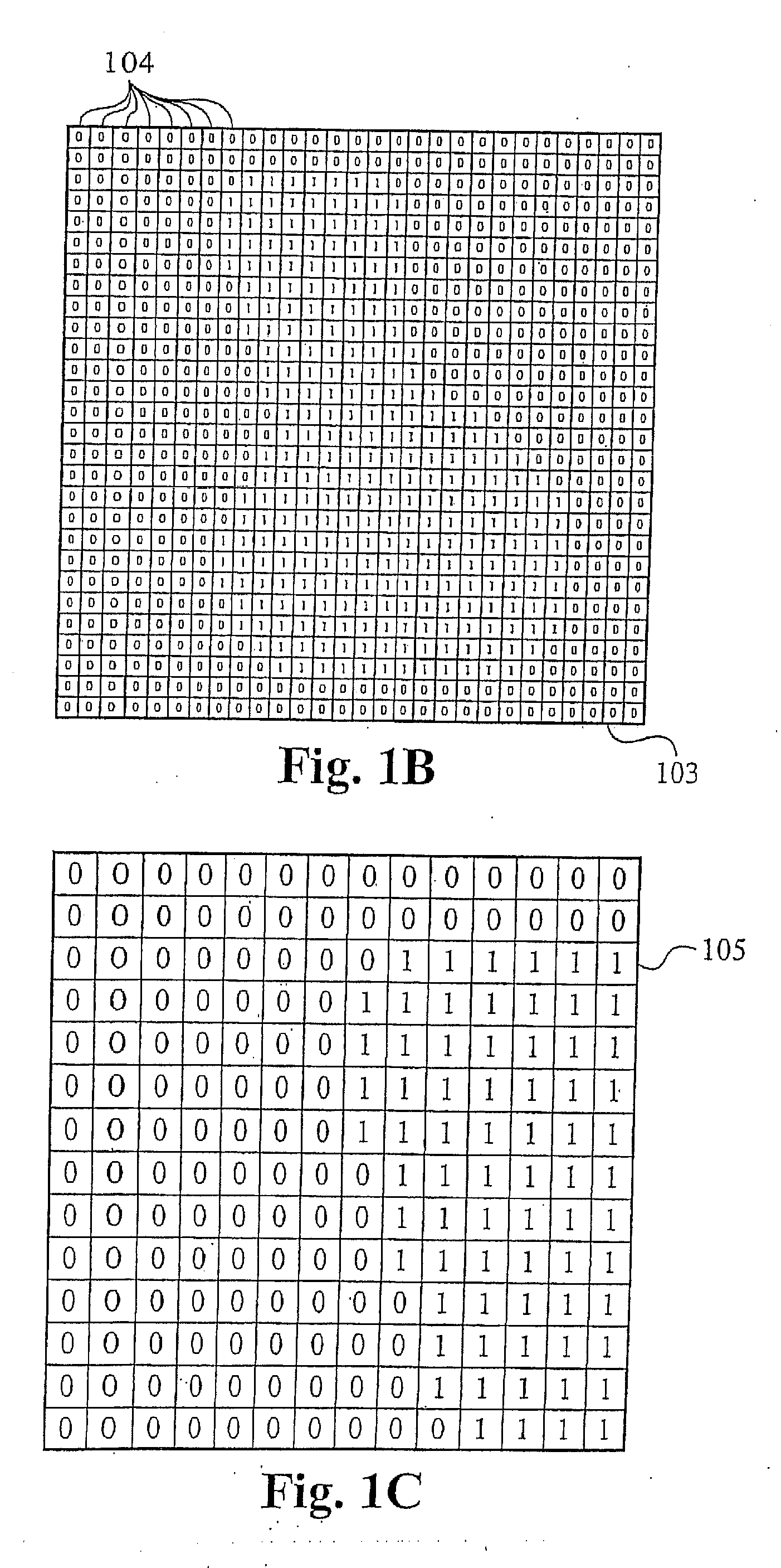
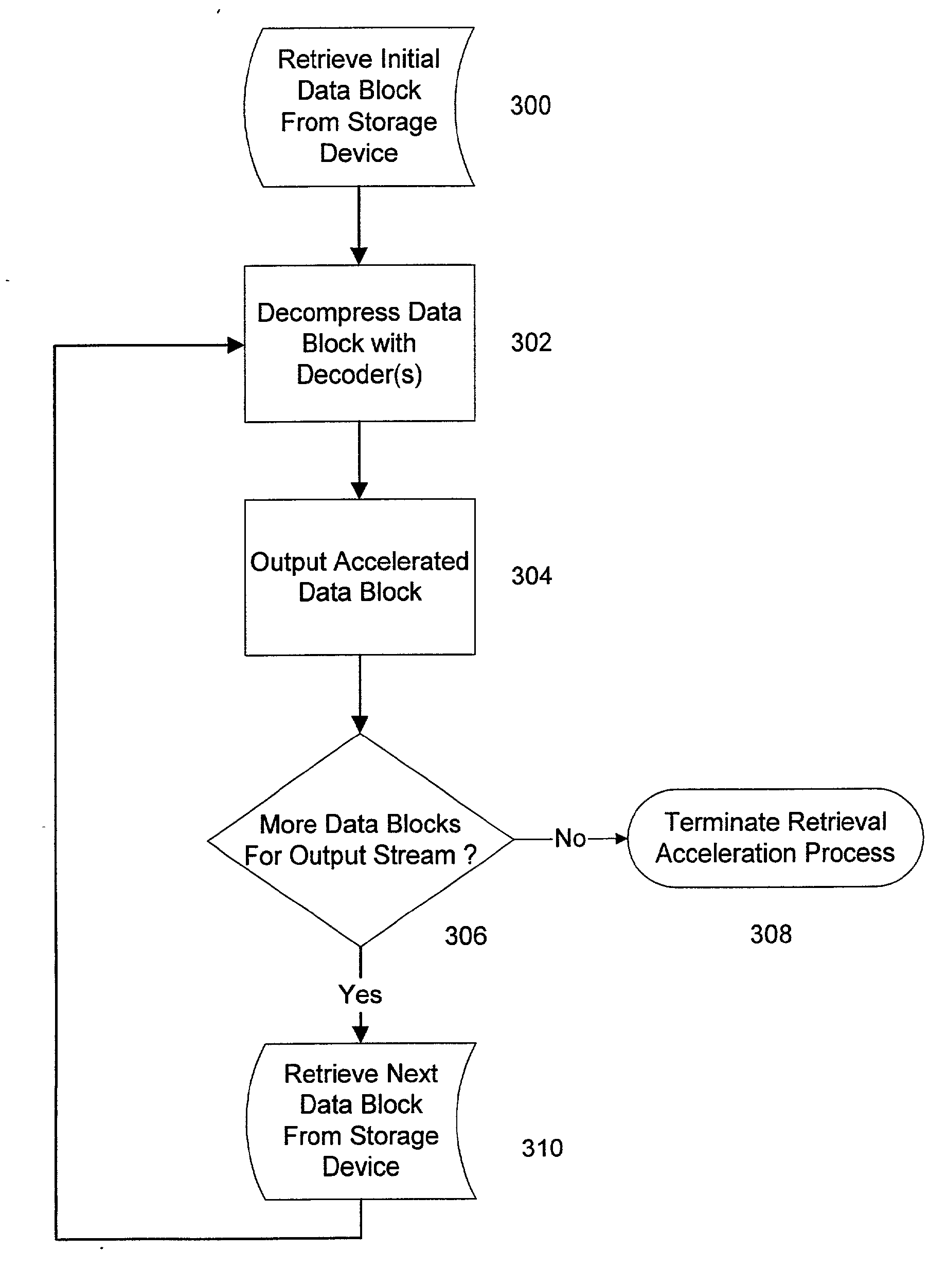
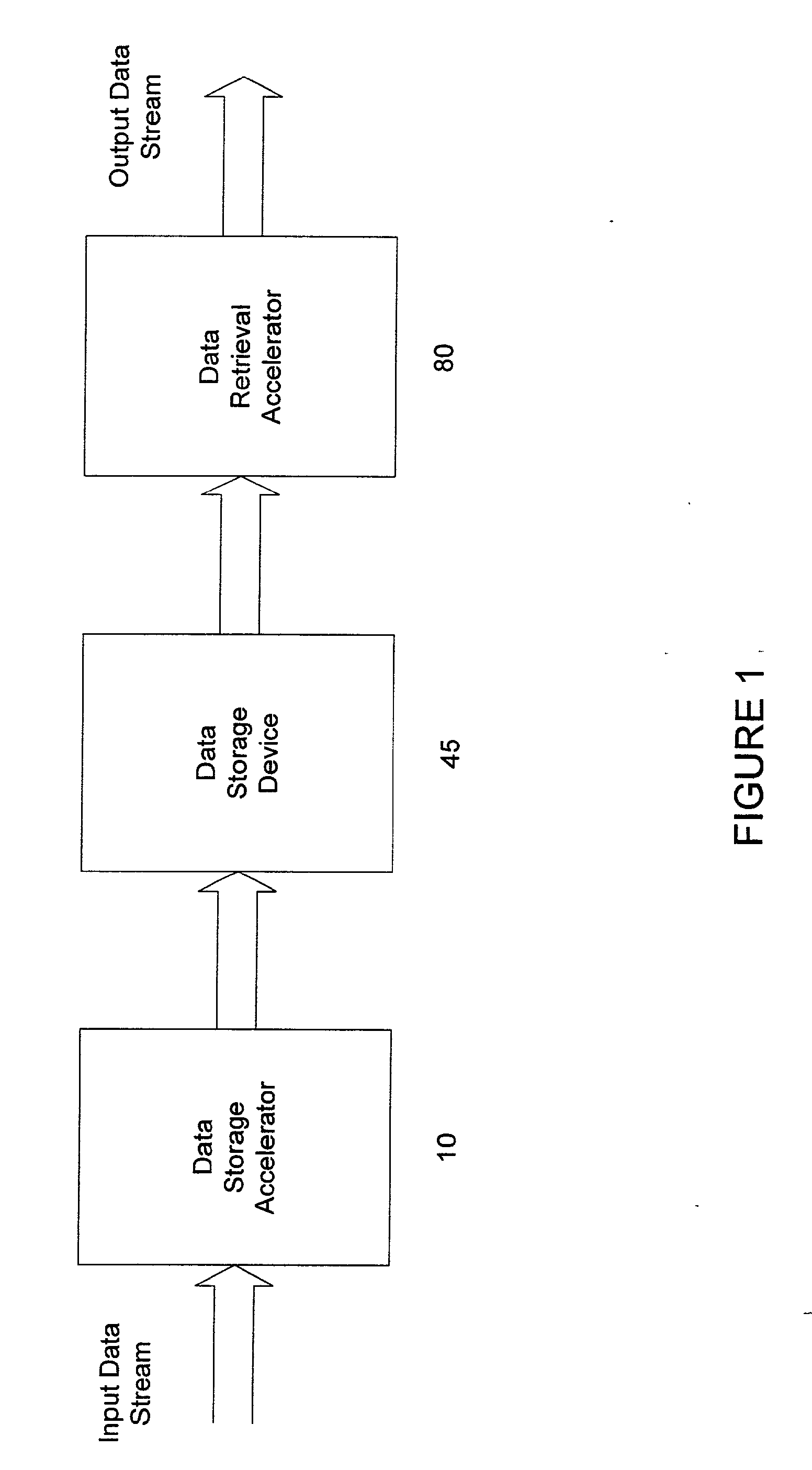
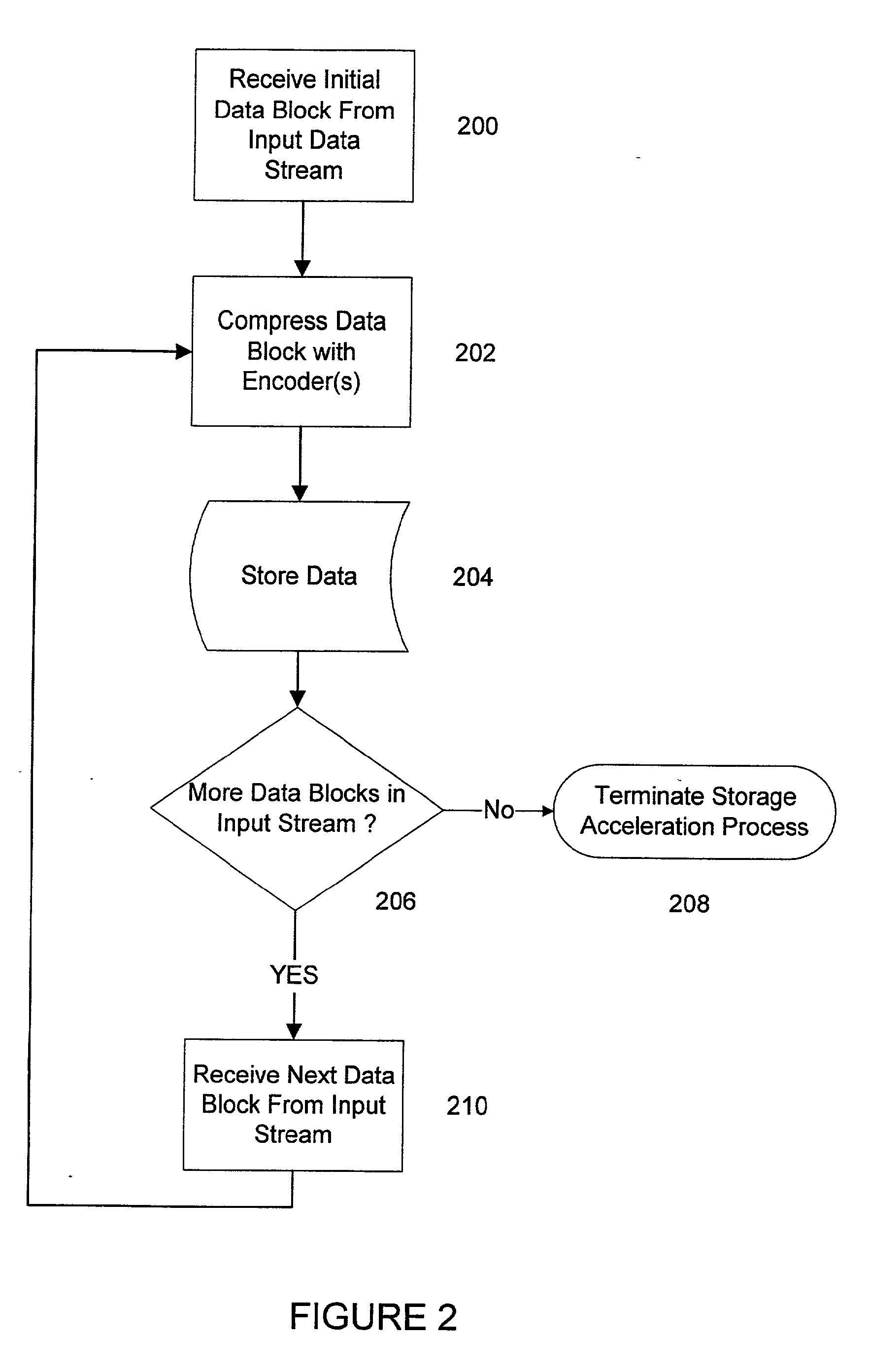
System and methods for accelerated data storage and retrieval
InactiveUS7130913B2High bandwidthData augmentationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsData streamData retrieval
Systems and methods for providing accelerated data storage and retrieval utilizing lossless data compression and decompression. A data storage accelerator includes one or a plurality of high speed data compression encoders that are configured to simultaneously or sequentially losslessly compress data at a rate equivalent to or faster than the transmission rate of an input data stream. The compressed data is subsequently stored in a target memory or other storage device whose input data storage bandwidth is lower than the original input data stream bandwidth. Similarly, a data retrieval accelerator includes one or a plurality of high speed data decompression decoders that are configured to simultaneously or sequentially losslessly decompress data at a rate equivalent to or faster than the input data stream from the target memory or storage device. The decompressed data is then output at rate data that is greater than the output rate from the target memory or data storage device. The data storage and retrieval accelerator method and system may employed: in a disk storage adapter to reduce the time required to store and retrieve data from computer to disk; in conjunction with random access memory to reduce the time required to store and retrieve data from random access memory; in a display controller to reduce the time required to send display data to the display controller or processor; and / or in an input / output controller to reduce the time required to store, retrieve, or transmit data.
Owner:REALTIME DATA
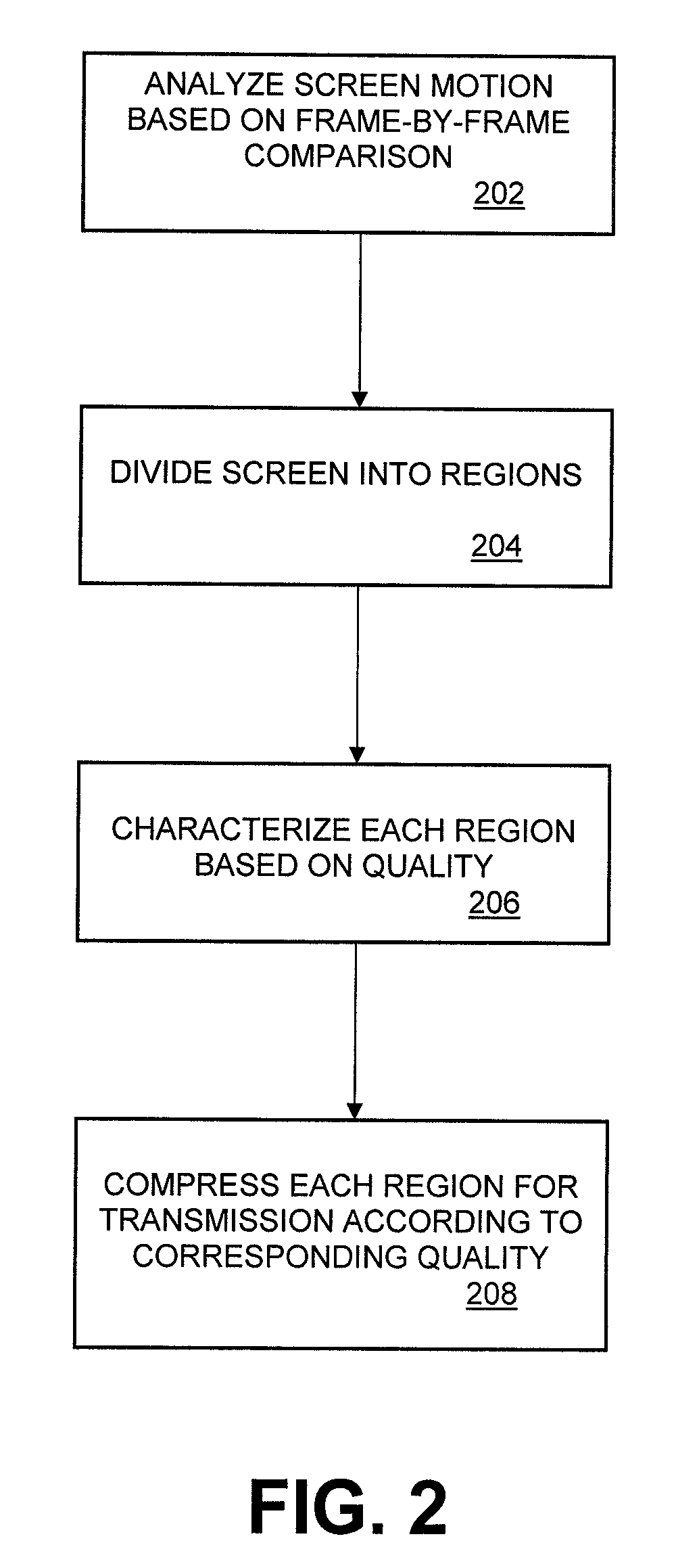
Remote Transmission and Display of Video Data Using Standard H.264-Based Video Codecs
ActiveUS20100104021A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionQuality levelComputer graphics (images)
Embodiments include implementing a remote display system (either wired or wireless) using a standard, non-custom codec. In this system, the decoder side can be fully implemented using an existing standard from a decode / display point of view and using a single stream type. The encoder side includes a pre-processing component that analyzes screen images comprising the video data to determine an amount of difference between consecutive frames of the screen images, divides each screen image into a plurality of regions, including no change regions, high quality regions, and low quality regions. The pre-processor characterizes each region as requiring a minimum quality level, encodes the low quality regions for compression in accordance with the H.264 encoding standard; and encodes the high quality regions using the lossless compression scheme of the H.264 standard. A no change region is encoded using a version of the H.264 encoding standard that adaptively and dynamically selects between lossless and lossy compression in a manner that optimizes efficiency of the compression operation.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Audio-on-demand communication system
InactiveUS7349976B1Quality improvementHigh audio signalAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsTelecommunications linkCommunications system
An audio-on-demand communication system provides real-time playback of audio data transferred via telephone lines or other communication links. One or more audio servers include memory banks which store compressed audio data. At the request of a user at a subscriber PC, an audio server transmits the compressed audio data over the communication link to the subscriber PC. The subscriber PC receives and decompresses the transmitted audio data in less than real-time using only the processing power of the CPU within the subscriber PC. According to one aspect of the present invention, high quality audio data compressed according to lossless compression techniques is transmitted together with normal quality audio data. According to another aspect of the present invention, metadata, or extra data, such as text, captions, still images, etc., is transmitted with audio data and is simultaneously displayed with corresponding audio data. The audio-on-demand system also provides a table of contents indicating significant divisions in the audio clip to be played and allows the user immediate access to audio data at the listed divisions. According to a further aspect of the present invention, servers and subscriber PCs are dynamically allocated based upon geographic location to provide the highest possible quality in the communication link.
Owner:INTEL CORP
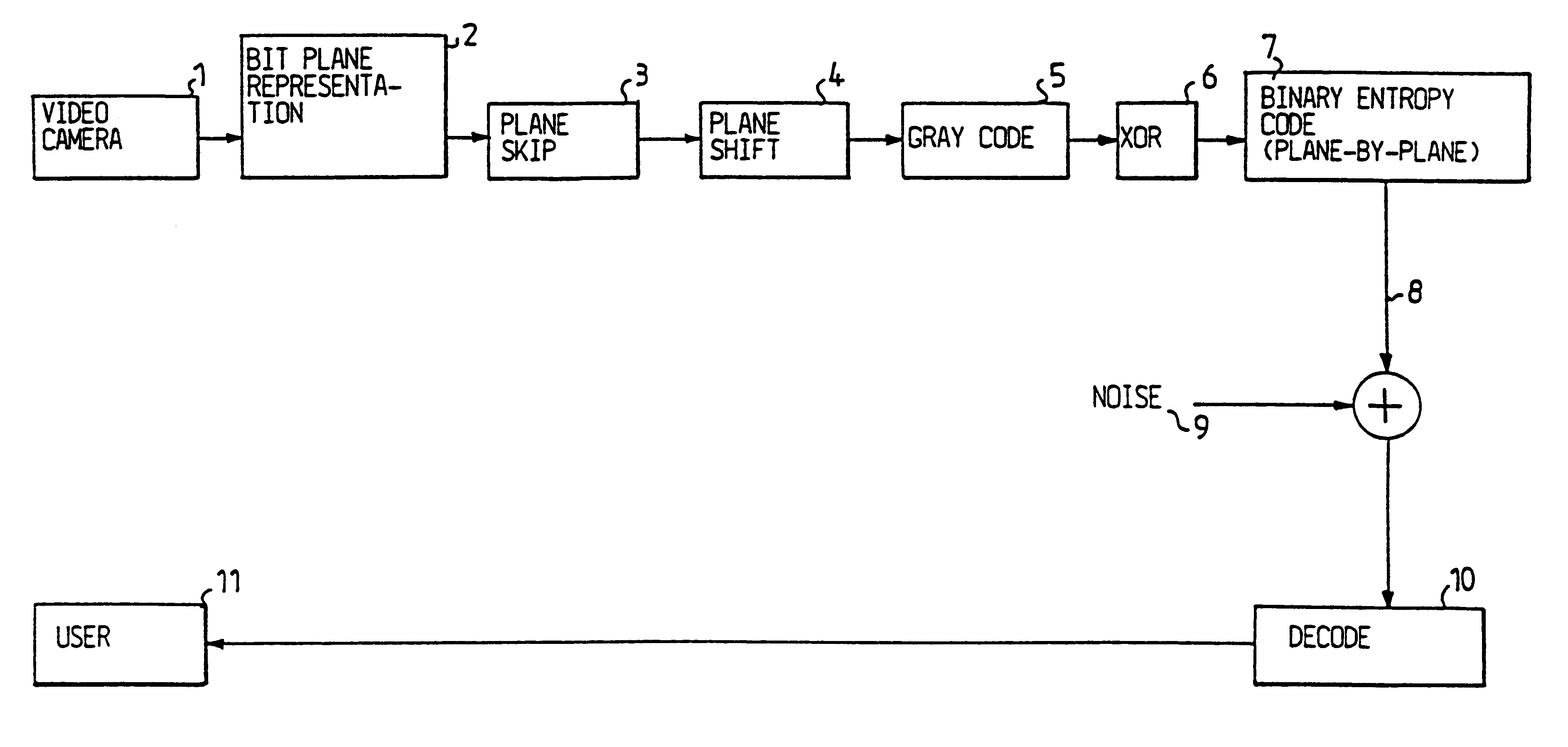
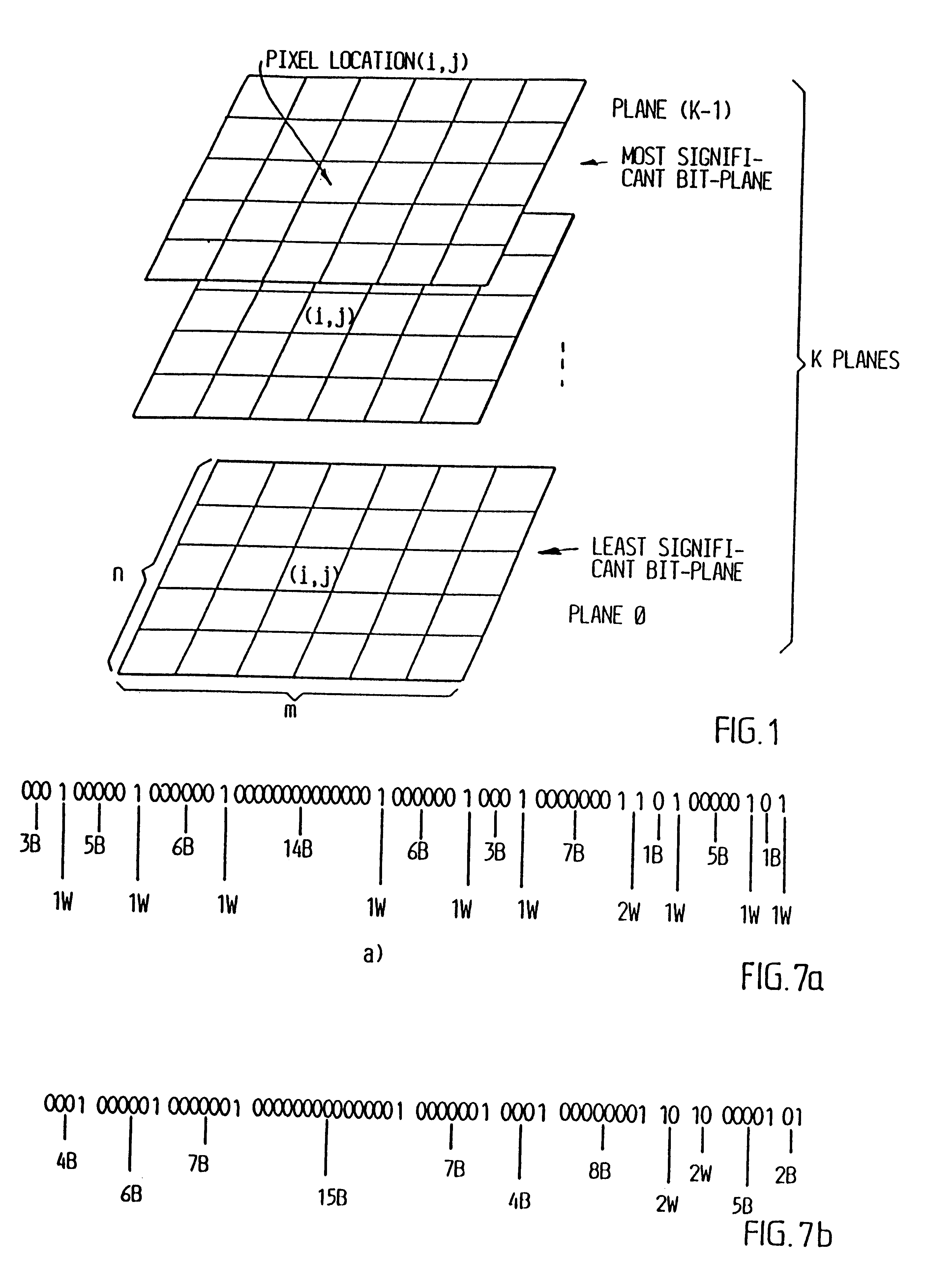
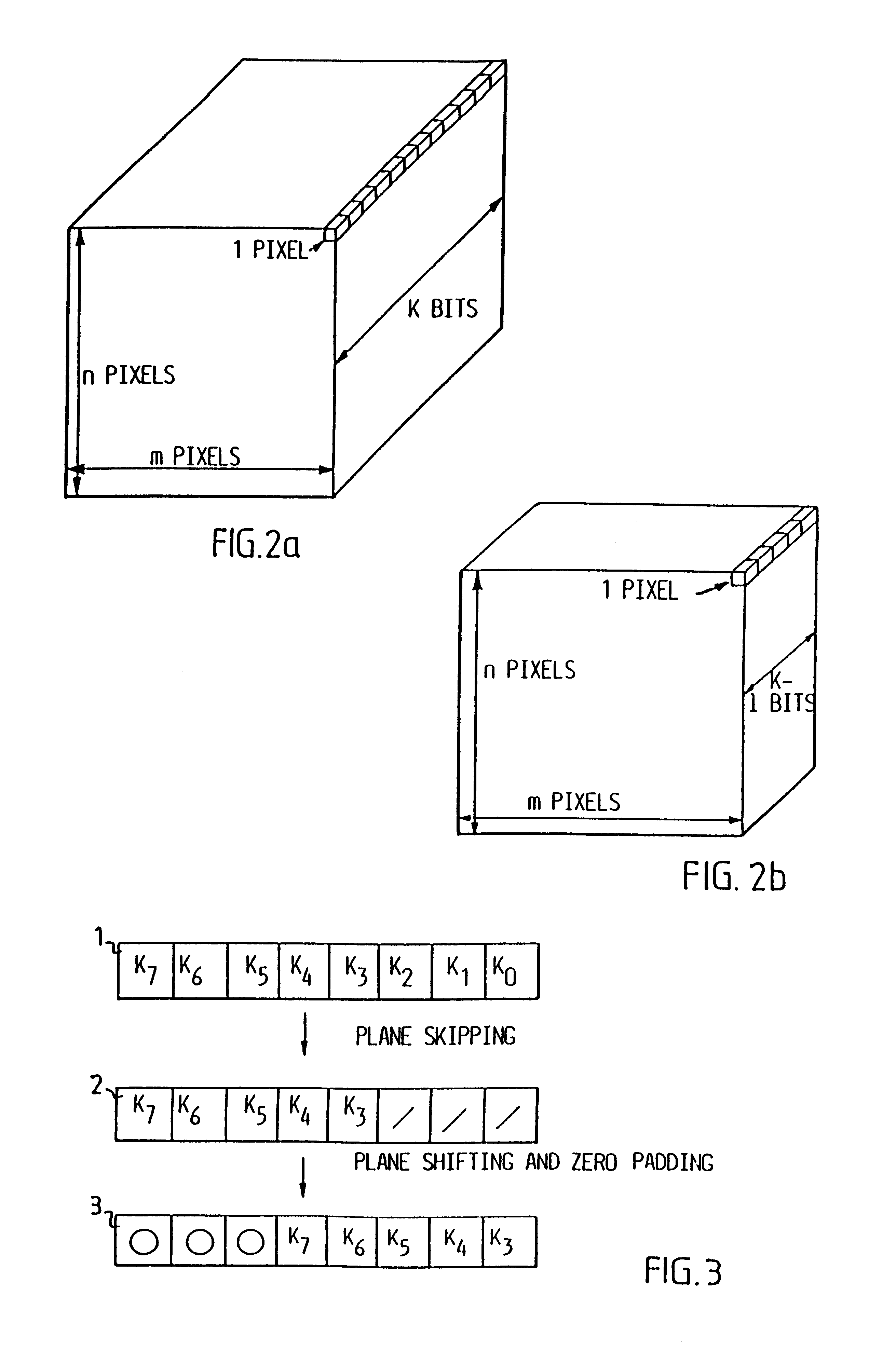
Video coding
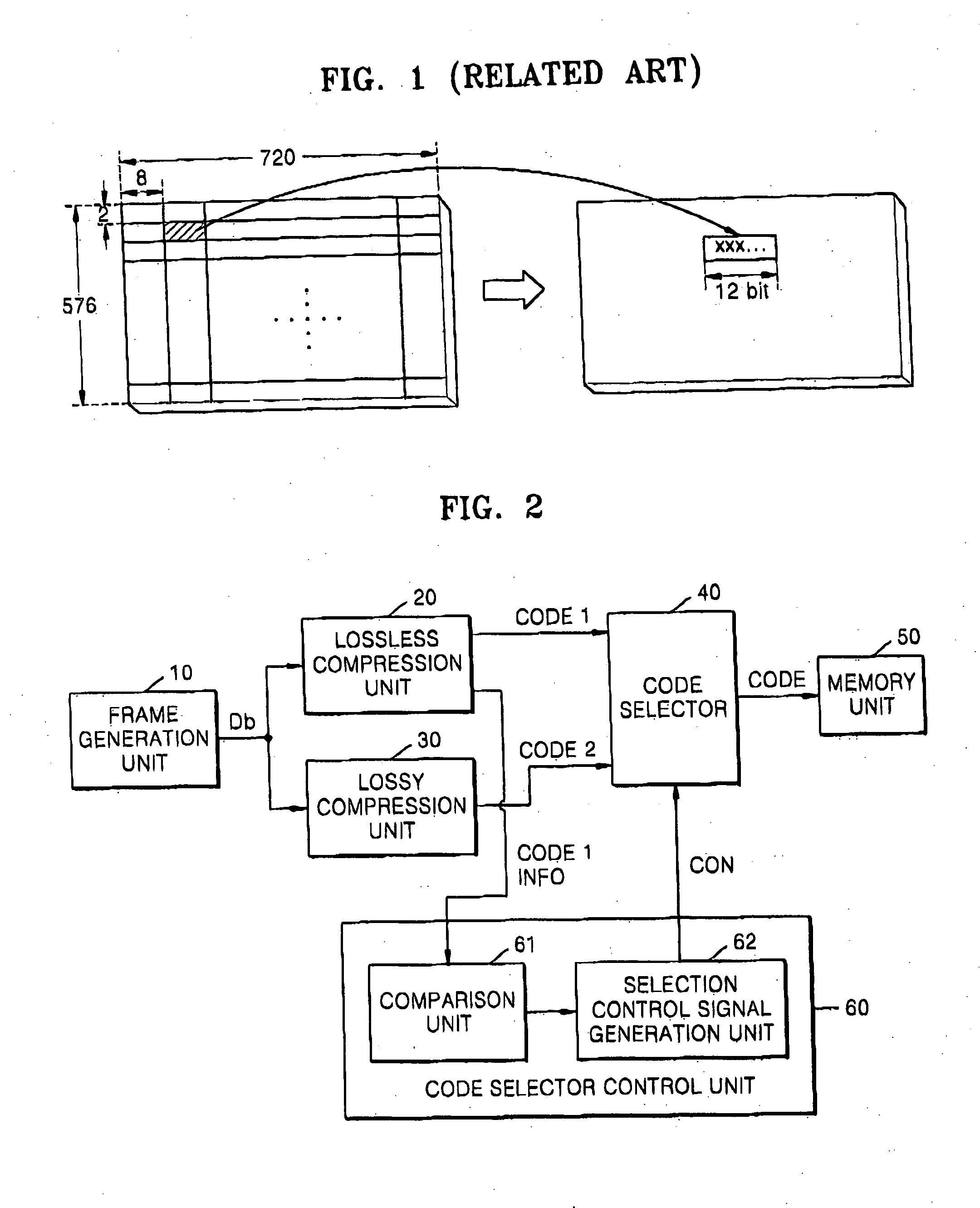
InactiveUS6208761B1Reduce in quantityEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsVideo sequenceBit plane coding
Digitalized video images are compressed in several steps in order to provide a system for transmitting moving video pictures via narrow band channels, such as the telephone network. The system is based on any extension of the bit-plane coding technique to video sequences and lossy conditions. The compression technique can also be advantageously used in a lossless compression system. The system involves the steps of bit plane representation and skipping the least significant bit plane(s), shifting the pixels, coding with a Gray code, the use of segmentation, and motion-estimation / motion compensation and application of a transmit / not transmit / motion compensate (TX / NT / MC) procedure, exploiting of the temporal redundancy of two corresponding bit planes via an XOR operation on two successive images, and a plane-by-plane application of an extended RLEID technique. The RLEID technique includes coding a run of like binary symbols with one word, the run including a transition between the penultimate and ultimate binary symbol.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
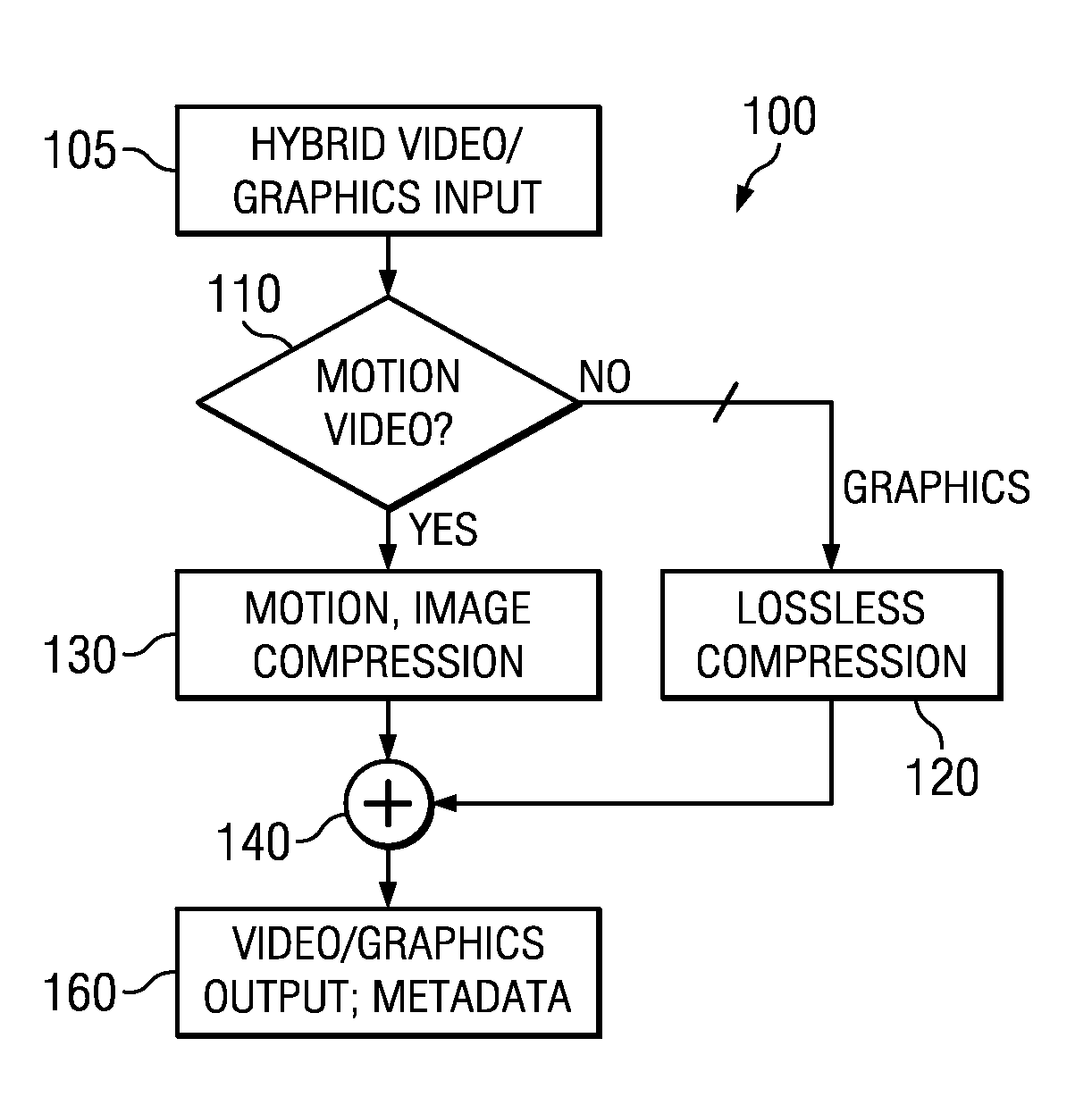
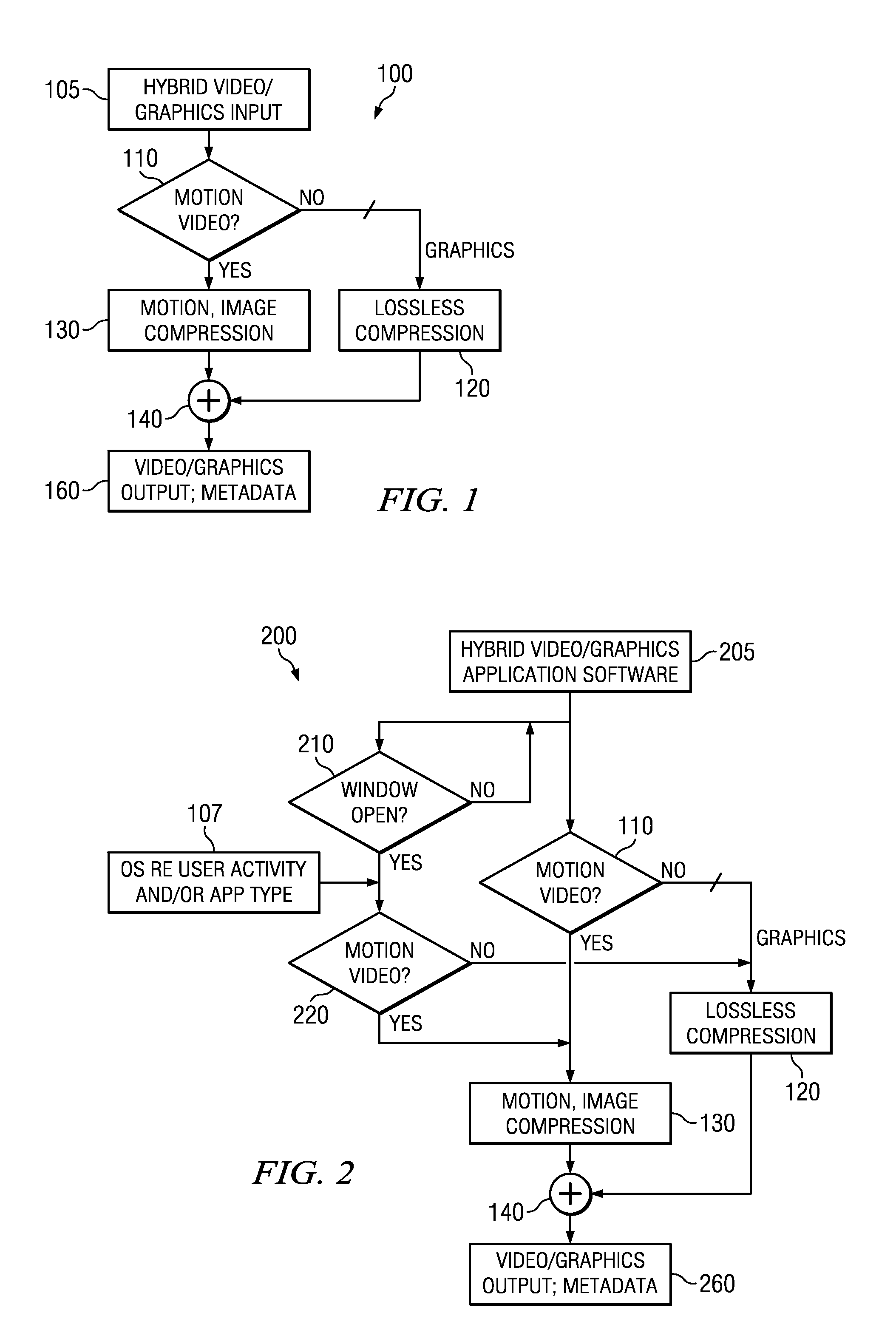
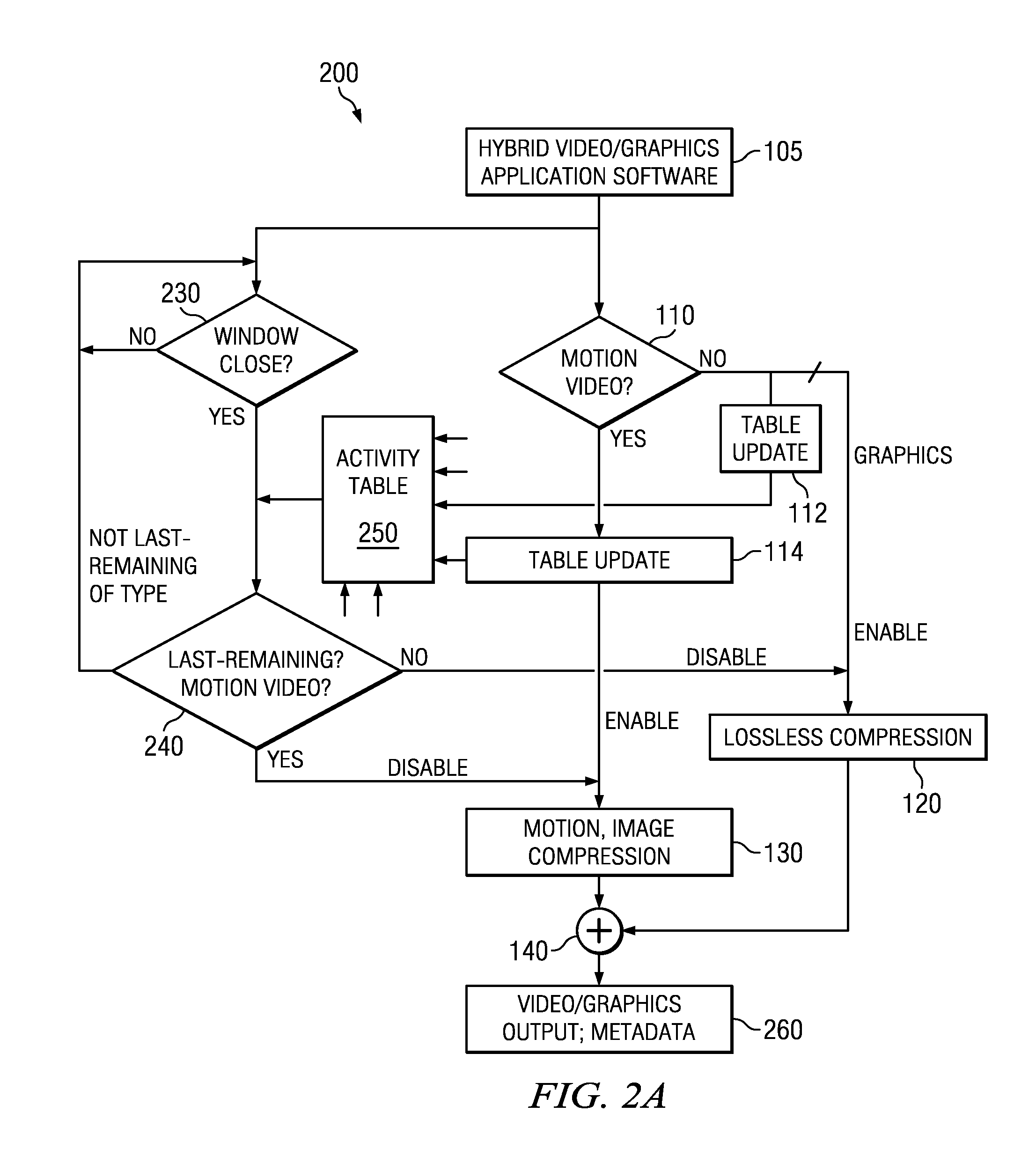
Hybrid video and graphics system with automatic content detection process, and other circuits, processes, and systems
A computing device (300) includes a storage (325) that over time is operable to include video and graphics content and the storage has a first set of instructions representing lossy video compression (130) and a second set of instructions representing lossless compression (120); and a processor (320) coupled with said storage (325), and said processor (320) operable to electronically analyze (110) at least a portion of the content for motion based on magnitudes of motion vectors and, on detection of a significant amount of motion, further operable to activate the first set of instructions (130) to compress at least the motion video, and otherwise to activate the second set of instructions representing lossless compression (120) to compress at least the graphics. Other devices, systems, and processes are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Hybrid image data processing system and method
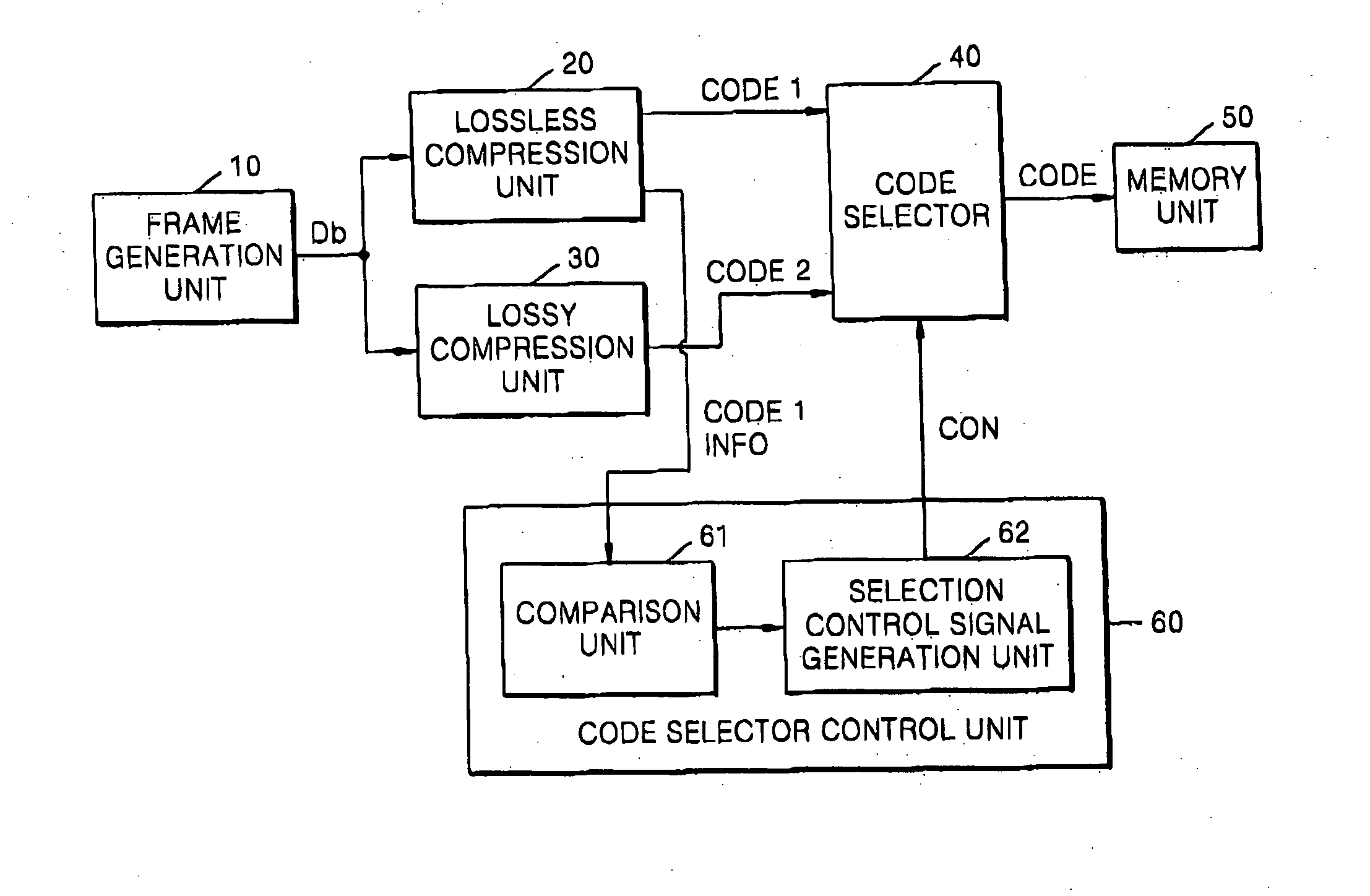
ActiveUS20070098283A1Efficient compressionCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationData processing systemLossless compression
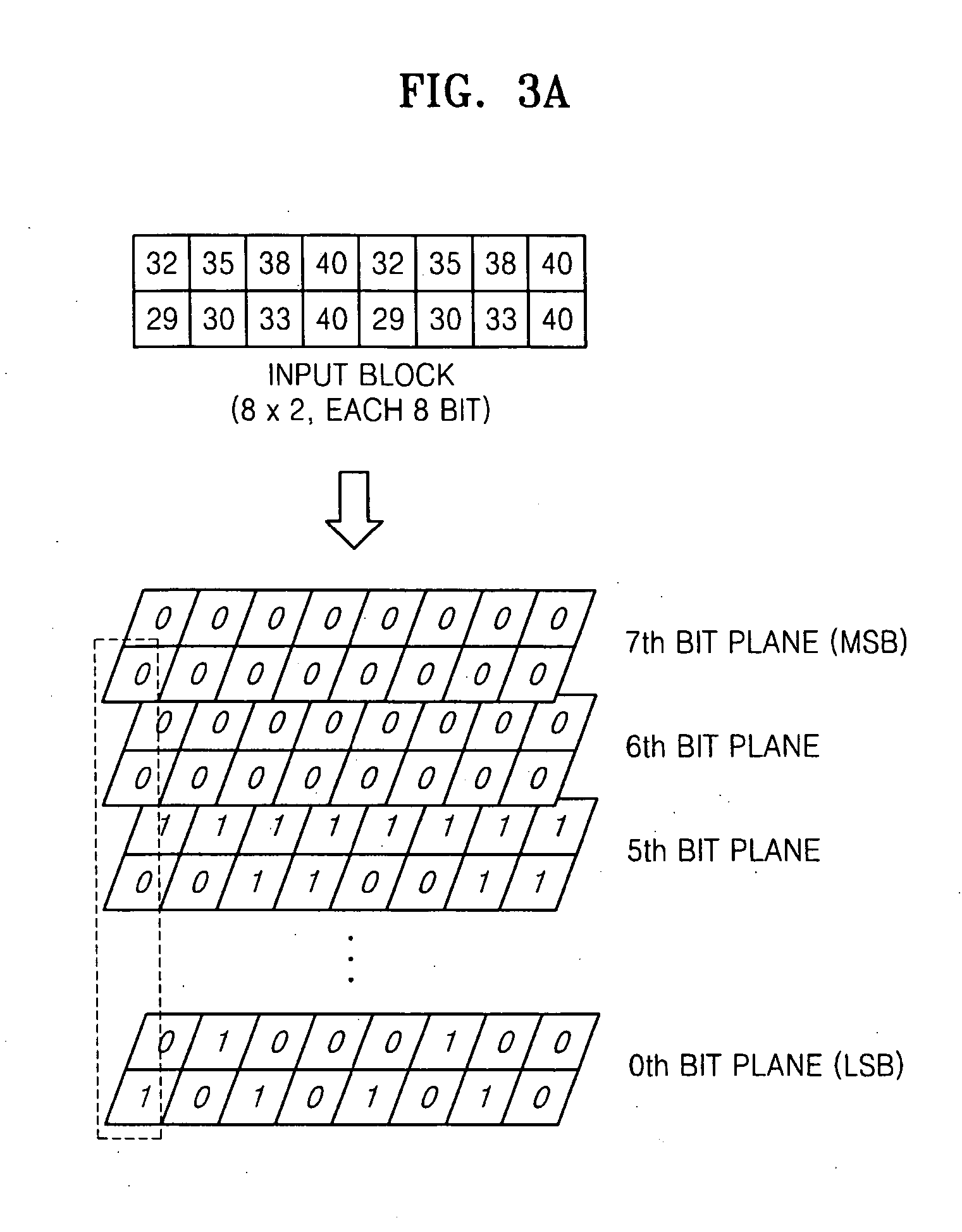
An image data compression system, for compressing a frame represented as a plurality of blocks, can include: a lossless compression unit to receive the plurality of blocks and to perform lossless compression thereon resulting in a first code; a lossy compression unit to receive the plurality of blocks and to perform lossy compression thereon resulting in a second code; and a code selection circuit to selectively output one of the first and second codes based upon a figure of merit evaluated for at least one of the first and second codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hierarchical lossless compression
ActiveUS20100299454A1Code conversionMultiple digital computer combinationsRepresentative elementLossless compression
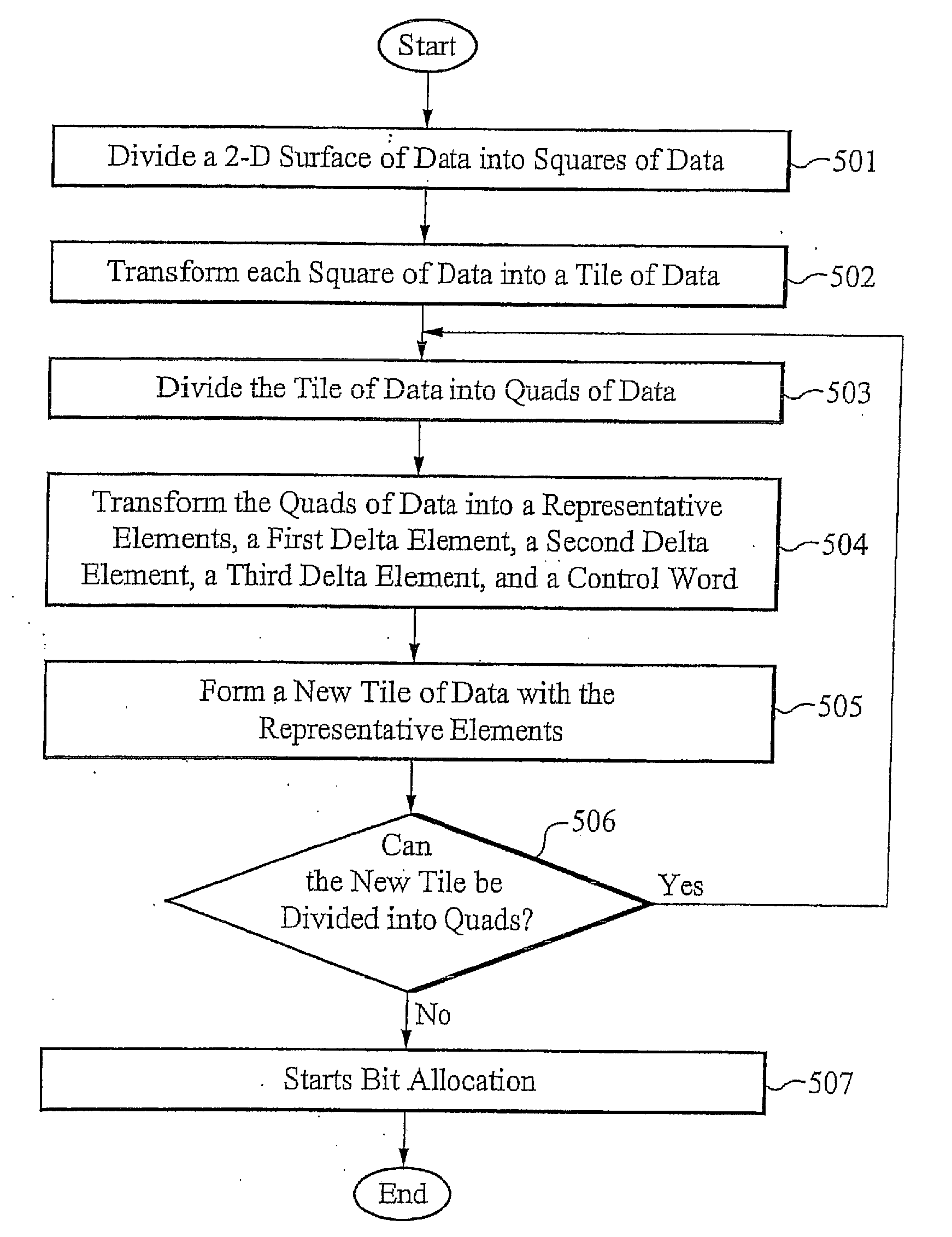
A method is provided for data compression. The data compression method transforms a square of data into a tile of data. The tile of data is then divided into quads of data that are converted into a representative element, a first delta element, a second delta element, a third delta element, and a control word. A new tile of data is then formed with the representative elements, and the process is repeated until a single representative element remains. The single representative element is then embedded into an output stream with the control words and corresponding delta elements. Decompression of the data is symmetrical to the encoding once the bit stream has been parsed.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
System and methods for accelerated data storage and retrieval
InactiveUS20070050515A1High bandwidthData augmentationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsData streamData retrieval
Systems and methods for providing accelerated data storage and retrieval utilizing lossless data compression and decompression. A data storage accelerator includes one or a plurality of high speed data compression encoders that are configured to simultaneously or sequentially losslessly compress data at a rate equivalent to or faster than the transmission rate of an input data stream. The compressed data is subsequently stored in a target memory or other storage device whose input data storage bandwidth is lower than the original input data stream bandwidth. Similarly, a data retrieval accelerator includes one or a plurality of high speed data decompression decoders that are configured to simultaneously or sequentially losslessly decompress data at a rate equivalent to or faster than the input data stream from the target memory or storage device. The decompressed data is then output at rate data that is greater than the output rate from the target memory or data storage device. The data storage and retrieval accelerator method and system may employed: in a disk storage adapter to reduce the time required to store and retrieve data from computer to disk; in conjunction with random access memory to reduce the time required to store and retrieve data from random access memory; in a display controller to reduce the time required to send display data to the display controller or processor; and / or in an input / output controller to reduce the time required to store, retrieve, or transmit data.
Owner:REALTIME DATA
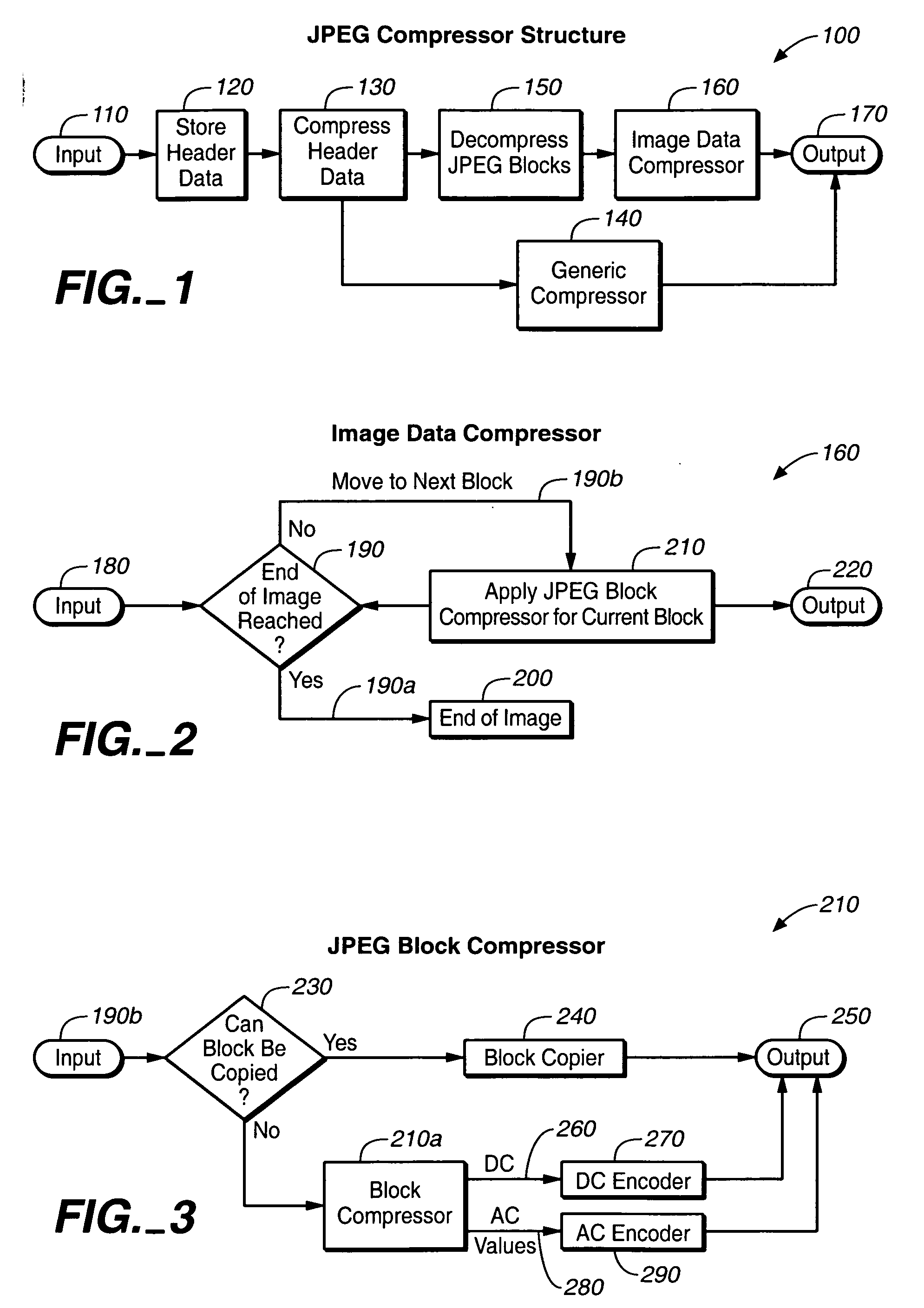
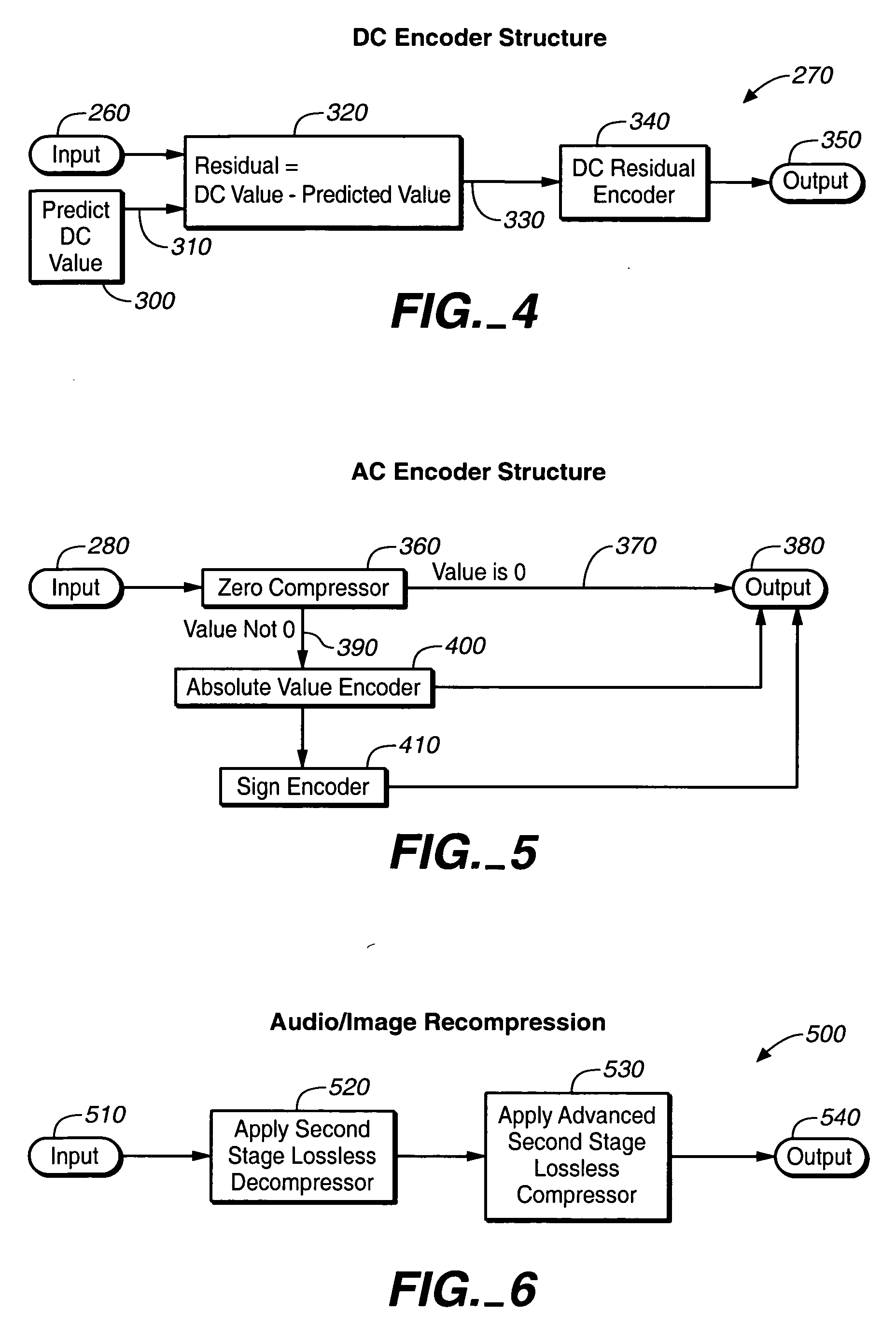
System and method for lossless compression of already compressed files
ActiveUS20060104526A1Promote resultsCompressing video files losslesslyCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputational scienceComputer hardware
A system and method for losslessly compressing already compressed files, such as JPEG files. The inventive method involves full or partial decompression of the original file, and re-compression using various advanced data compression techniques. Decompression involves decompression using the advanced techniques and re-compression using the original techniques. This method and system saves on data storage space and allows for the reconstruction of an original compressed file for use in applications that require or support the original compressed format.
Owner:SMITH MICRO SOFTWARE INC
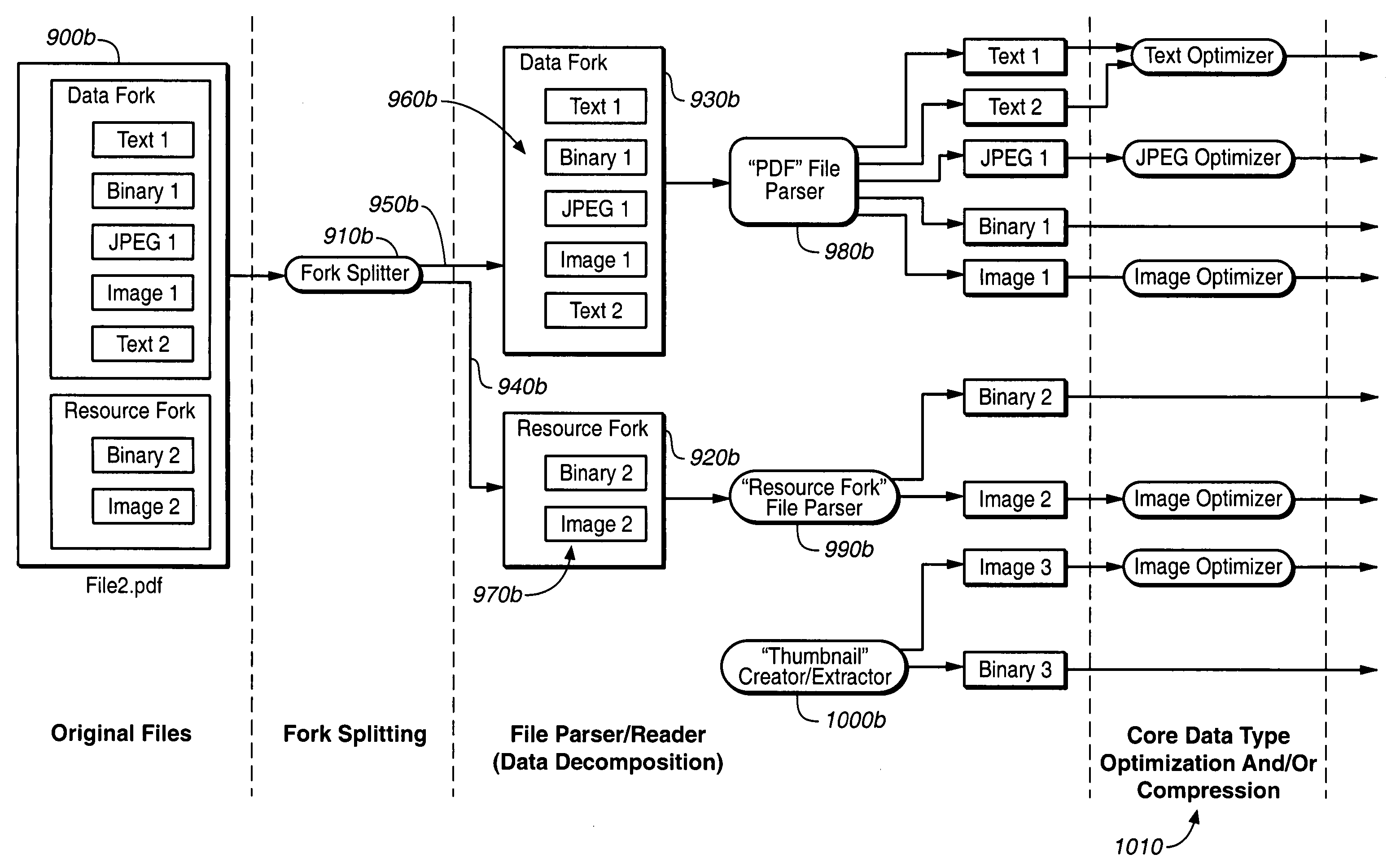
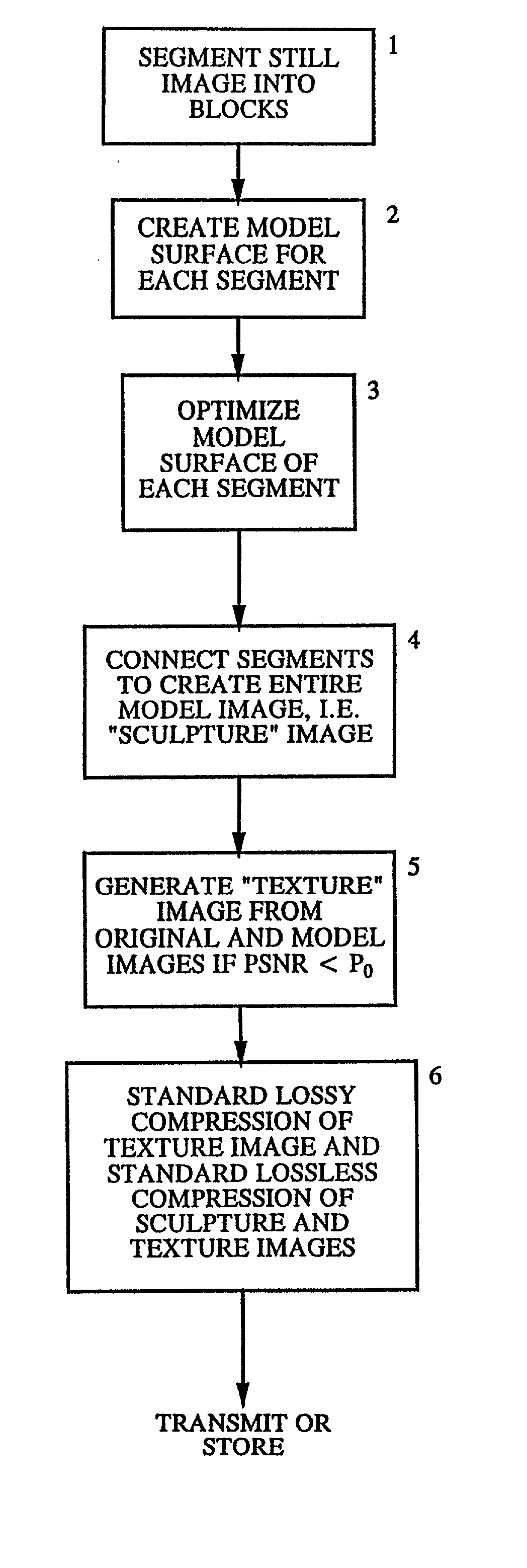
Method of isomorphic singular manifold projection still/video imagery compression
InactiveUS20020176624A1Reduction procedureReduce redundancyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingPattern recognitionImage compression
Methods and apparatuses for still image compression, video compression and automatic target recognition are disclosed. The method of still image compression uses isomorphic singular manifold projection whereby surfaces of objects having singular manifold representations are represented by best match canonical polynomials to arrive at a model representation. The model representation is compared with the original representation to arrive at a difference. If the difference exceeds a predetermined threshold, the difference data are saved and compressed using standard lossy compression. The coefficients from the best match polynomial together with the difference data, if any, are then compressed using lossless compression. The method of motion estimation for enhanced video compression sends I frames on an "as-needed" basis, based on comparing the error between segments of a current frame and a predicted frame. If the error exceeds a predetermined threshold, which can be based on program content, the next frame sent will be an I frame. The method of automatic target recognition (ATR) including tracking, zooming, and image enhancement, uses isomorphic singular manifold projection to separate texture and sculpture portions of an image. Soft ATR is then used on the sculptured portion and hard ATR is used on the texture portion.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Radiologist workstation
InactiveUS6909436B1Reduce flickerReconstruction from projectionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDICOMNetwork link
A radiologist workstation program capable of performing the methods of: (a) losslessly compressing an image by using a sample of pixel neighborhoods to determine a series of predictive coefficients values related to the pixel neighborhoods; (b) lossy compressing an image to a predetermined ratio by adjusting the quality parameter in a quality controlled compression routine; (c) adjusting the compression ratio of image data based upon the available bandwidth of a network link across which the image is transmitted; (d) encapsulating audio data in a DICOM object and selectively retrieving the data; (e) performing an improved integer based ray tracing method by establishing a ray angle from an observer position and adjusting the ray angle such that the directional components of the ray angle are rational numbers; and (f) reducing flicker caused by a magnifying window moving across an image on the display screen by determining what portion of a first window position is not covered by a new window position and restoring from memory that portion of the image which corresponds to the portion of the first window not covered by the second window.
Owner:THE BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA
Lossless frame buffer color compression
ActiveUS20120050303A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital video signal modificationGraphicsPattern recognition
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for lossless compression of color data. Color data for a packet including multiple sub-pixel samples is compressed using a predictor map that is selected based on the sampling format specified for the graphics surface storing the color data. The predictor map defines one of the samples as an anchor that is represented exactly and a transform indicating which neighboring samples are used to compute difference samples for the other samples in the packet. The difference samples are truncated and tested to determine if the difference samples can fit into one or more compressed data formats, i.e., if the color data can be compressed without loss. When compression can be performed without loss, the transformed packet is output. Otherwise, the original packet is output.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Audio-on-demand communication system
InactiveUS20060271989A1Quality improvementHigh audio signalSpecific information broadcast systemsBroadcast transmission systemsTelecommunications linkAudio on demand
An audio-on-demand communication system provides real-time playback of audio data transferred via telephone lines or other communication links. One or more audio servers include memory banks which store compressed audio data. At the request of a user at a subscriber PC, an audio server transmits the compressed audio data over the communication link to the subscriber PC. The subscriber PC receives and decompresses the transmitted audio data in less than real-time using only the processing power of the CPU within the subscriber PC. According to one aspect of the present invention, high quality audio data compressed according to lossless compression techniques is transmitted together with normal quality audio data. According to another aspect of the present invention, metadata, or extra data, such as text, captions, still images, etc., is transmitted with audio data and is simultaneously displayed with corresponding audio data. The audio-on-demand system also provides a table of contents indicating significant divisions in the audio clip to be played and allows the user immediate access to audio data at the listed divisions. According to a further aspect of the present invention, servers and subscriber PCs are dynamically allocated based upon geographic location to provide the highest possible quality in the communication link.
Owner:INTEL CORP
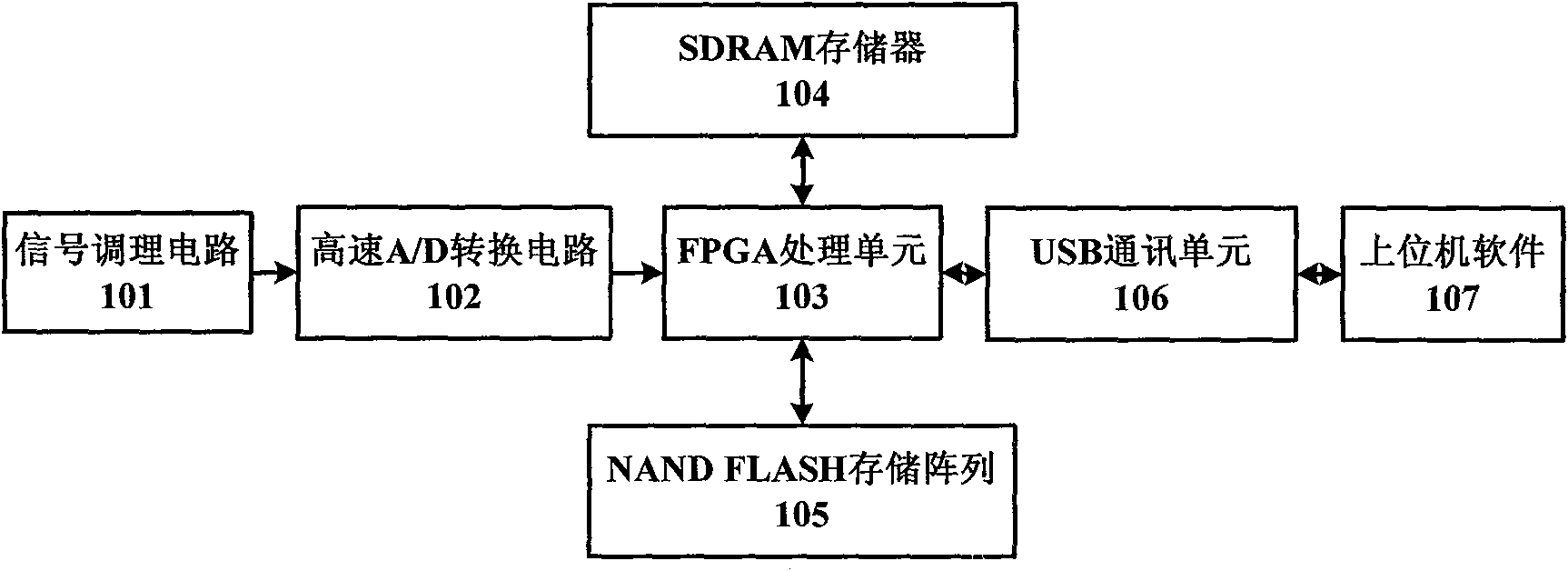
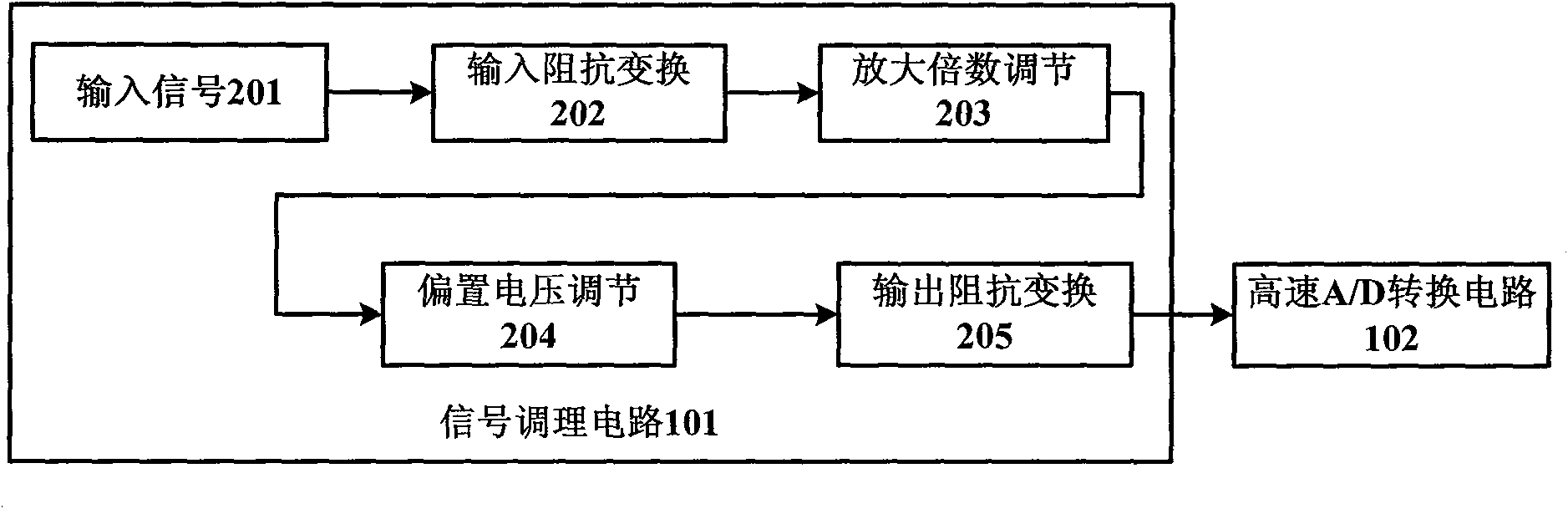
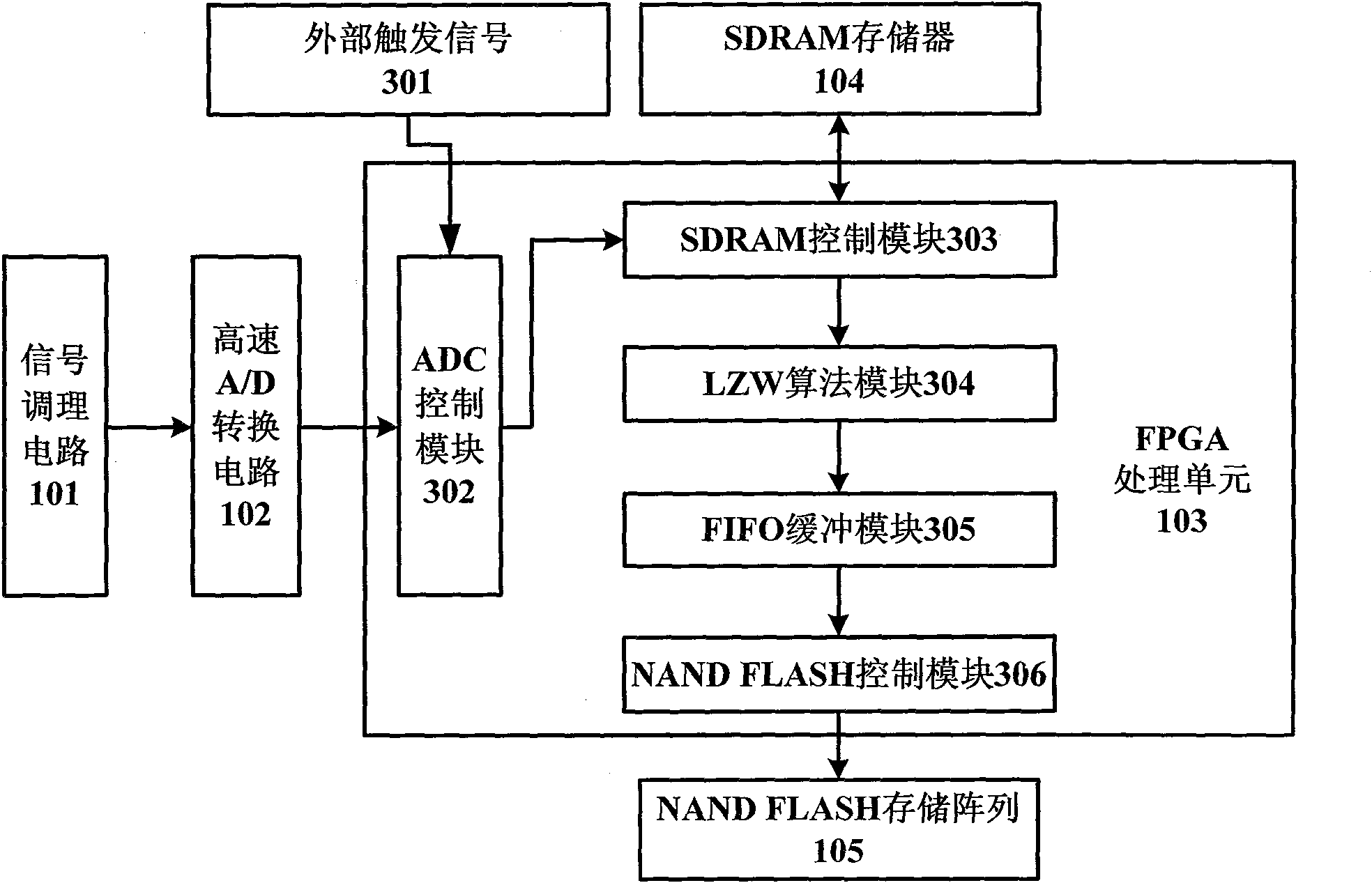
High-speed signal acquisition, storage and playback device based on FPGA
InactiveCN101807214AReduce storageHigh sampling frequencyData acquisition and loggingSignal conditioning circuitsCommunication unit
The invention discloses a high-speed signal acquisition, storage and playback device based on FPGA. The device is composed of a signal conditioning circuit, a high-speed A / D conversion circuit, an FPGA processing unit, an SDRAM, a NAND FLASH storage array, a USB 2.0 communication unit and upper computer software. In an acquisition mode, after being processed by the signal conditioning circuit, an analog signal is converted into a digital signal by the high-speed A / D conversion circuit, and the FPGA processing unit caches the digital signal, carries out lossless compression by using an LZW algorithm and then writes into the NAND FLASH storage array. In the signal playback mode, the FPGA reads data from the NAND FLASH, the USB 2.0 communication unit sends the data to the upper computer, and the upper computer software receives and analyzes the data.
Owner:湖南亿能电子科技有限公司
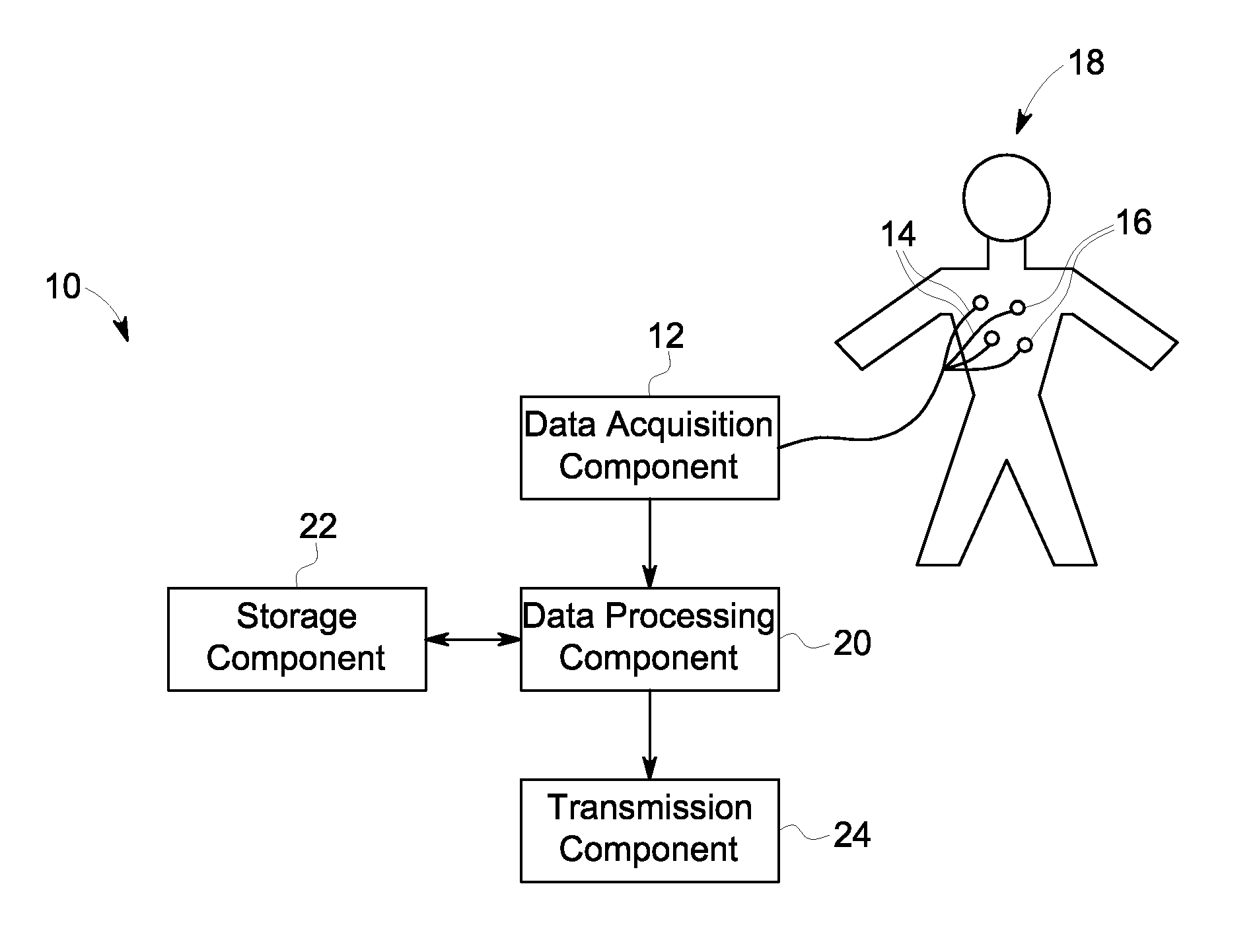
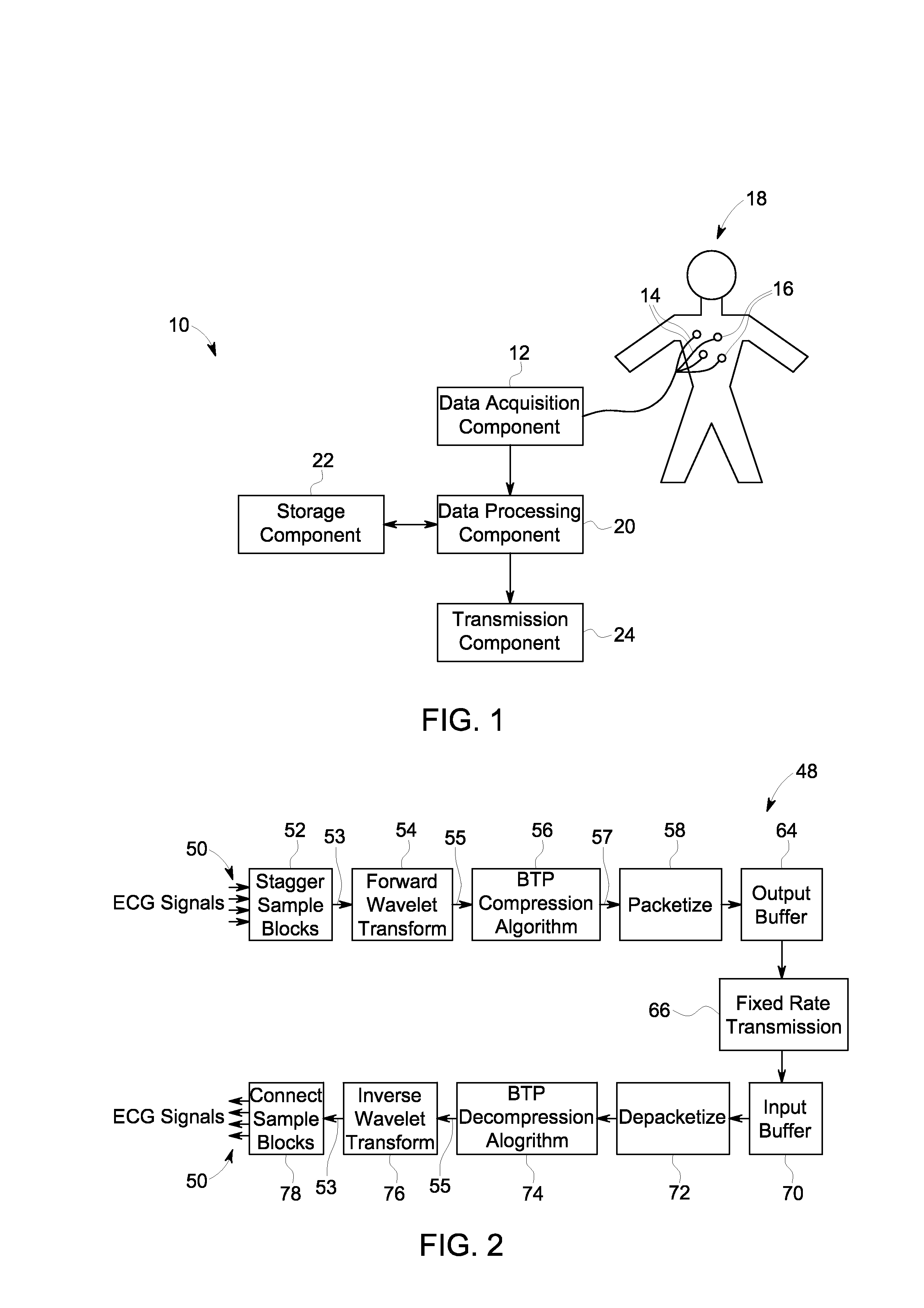
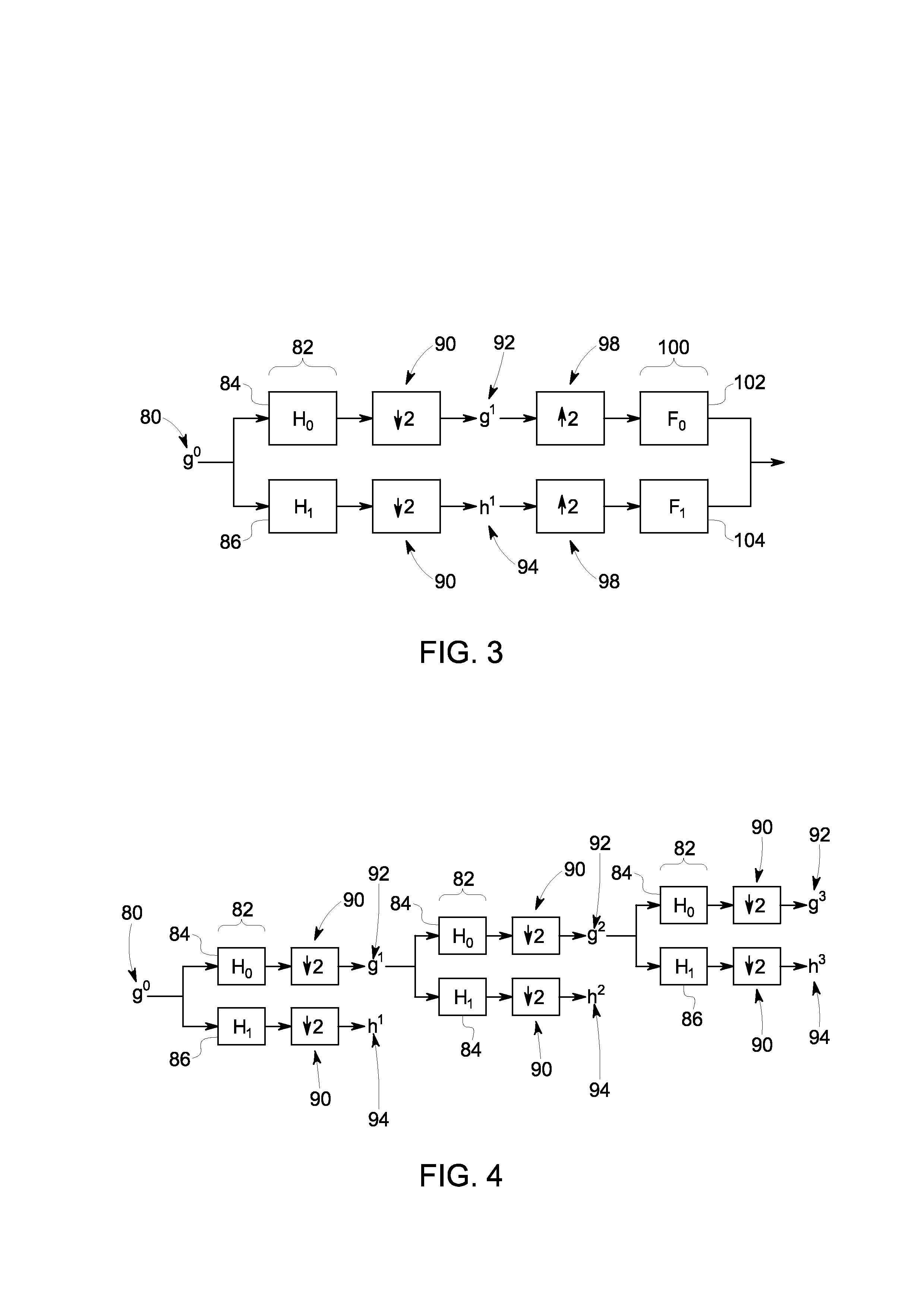
Compression of electrocardiograph signals
A generally lossless compression system suitable for compression of data in a real-time, remote monitoring application is disclosed. In one embodiment, the real-time monitoring application is subject to a fixed-delay transmission constraint. In one implementation, a specific set partitioning method (e.g., binary tree partitioning) is employed on blocks of data that are wavelet transformed in a reversible manner so that encoded blocks may be transmitted losslessly or truncated and transmitted with some loss.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
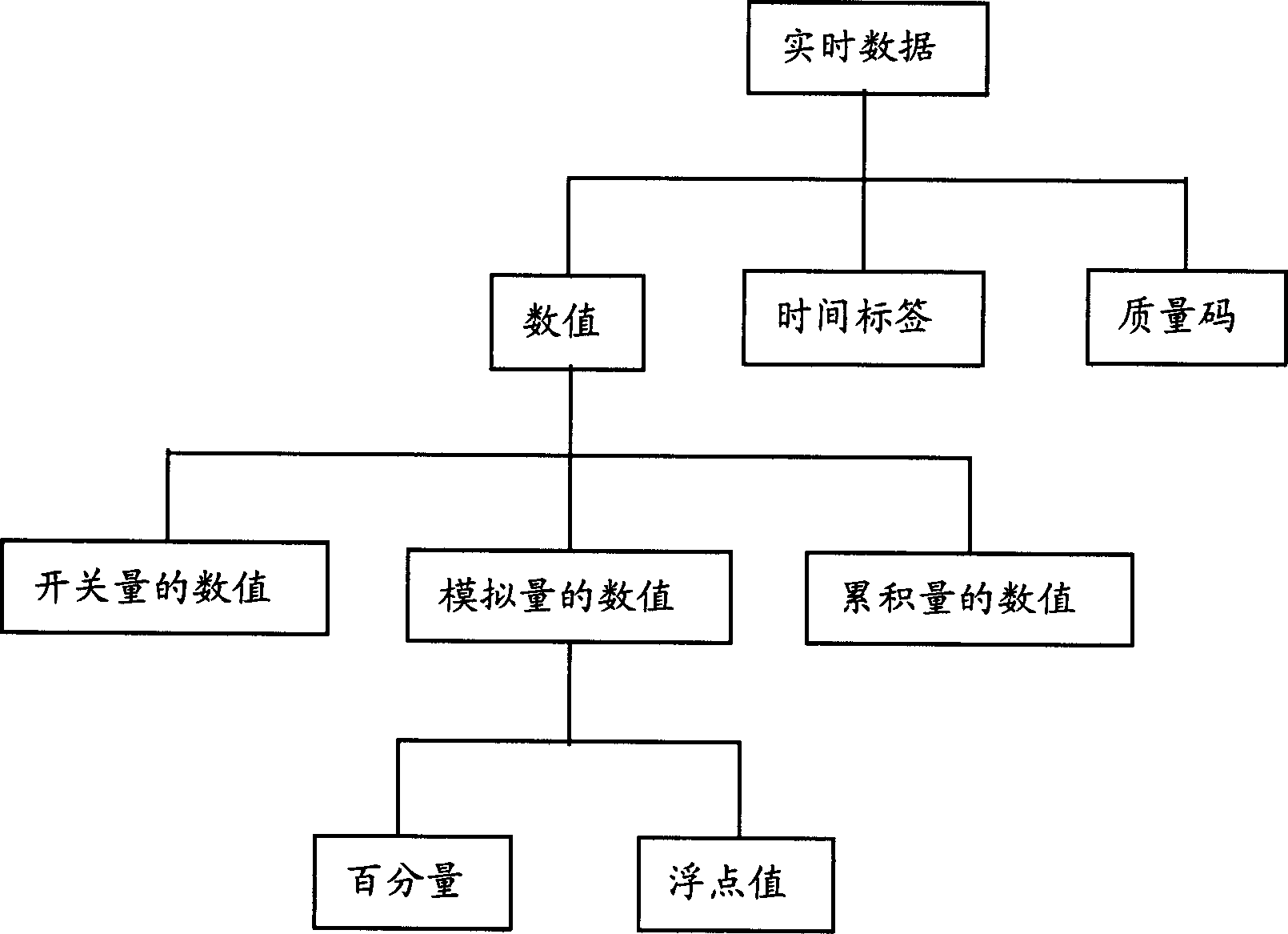
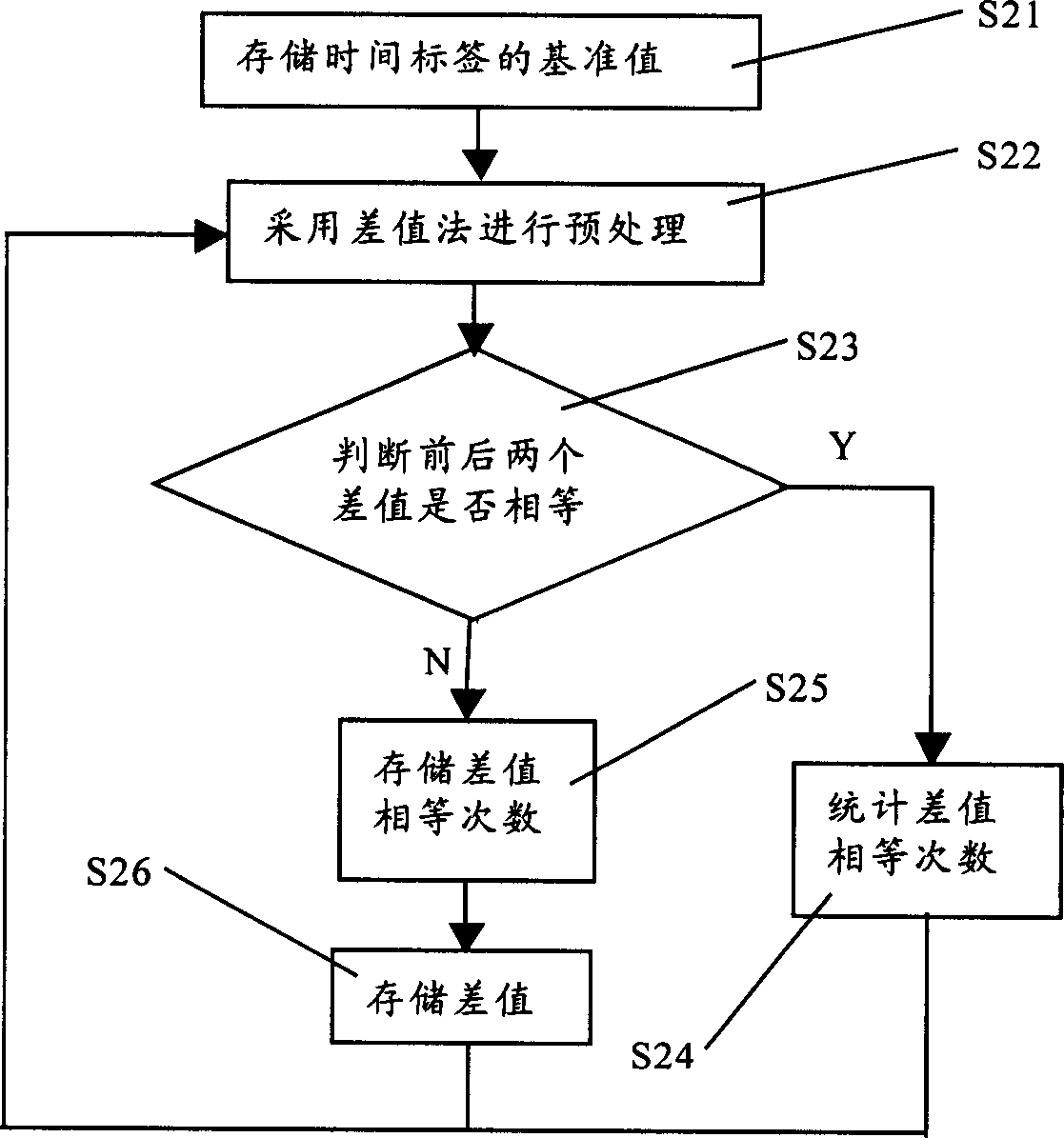
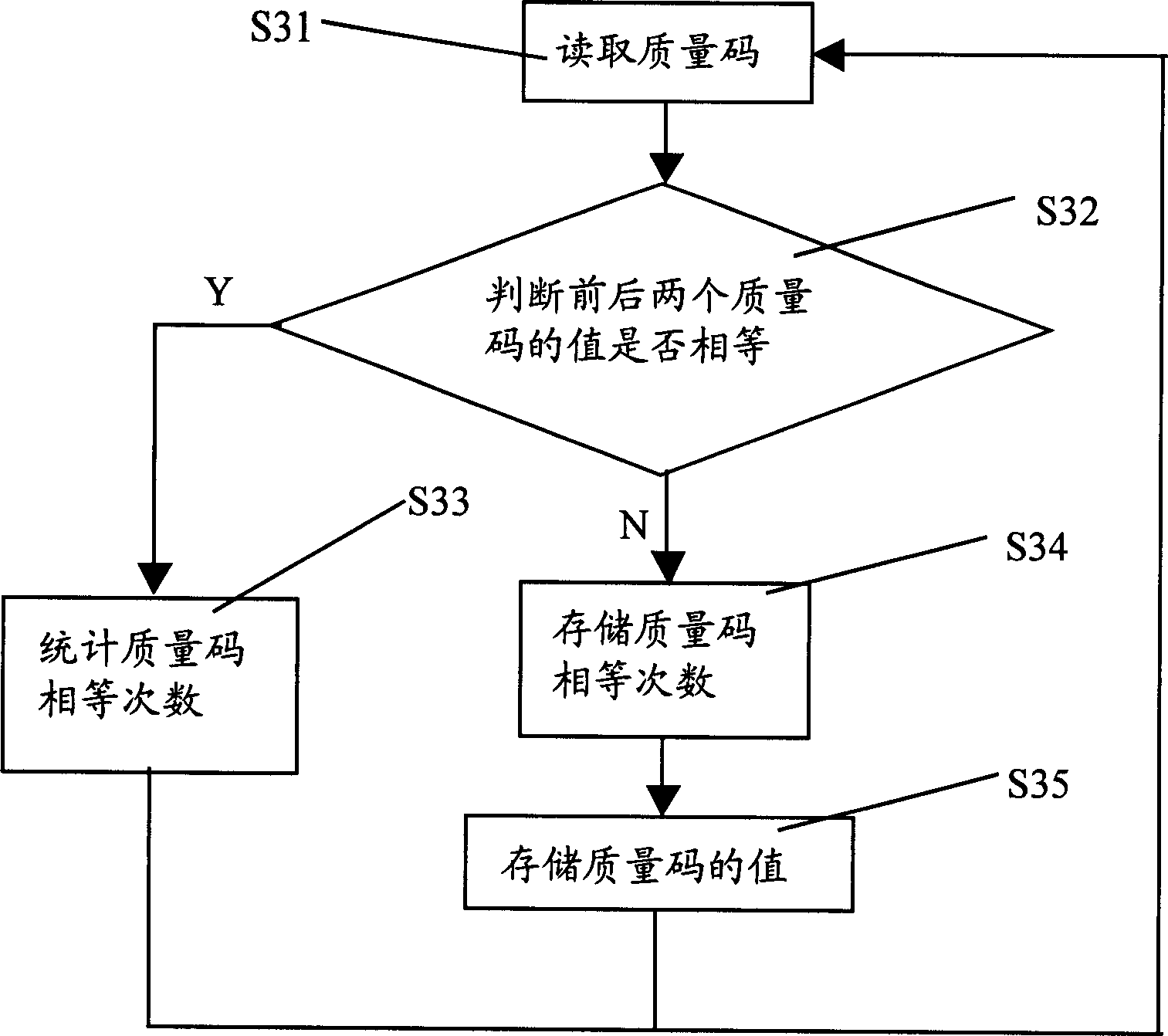
Real-time data compression method
ActiveCN1786939AAchieve lossless compressionFulfil requirementsCode conversionComplex mathematical operationsReal-time dataNetwork packet
The invention relates to a real time data compressing method, for compressing in-data packet data in a process control system, where the real time data comprises numerical values of analogue quantities and the method comprises: 1) initializing a dictionary, i.e. initializing characters that possibly occur during compressing into a dictionary; 2) reading in numerical valves; 3) making subtraction of adjacent data to obtain difference values and storing the first read-in numerical value in compressed files; 4) adopting LZW algorithm to compress the difference values. The invention realizes the lossless compression of real time data and the compressing course is safe and reliable. The invention has very good rapidness and can meet the requirements of real time databases and raises the history data inquiring efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUPCON TECH
Undamaged encoding and decoding method and system based on interweave forecast
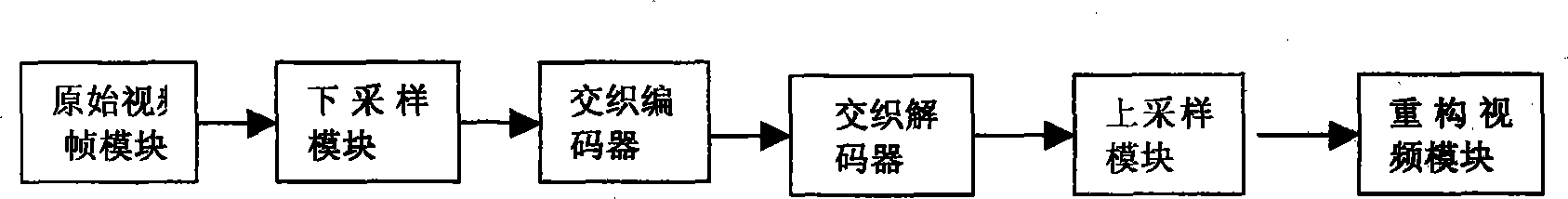
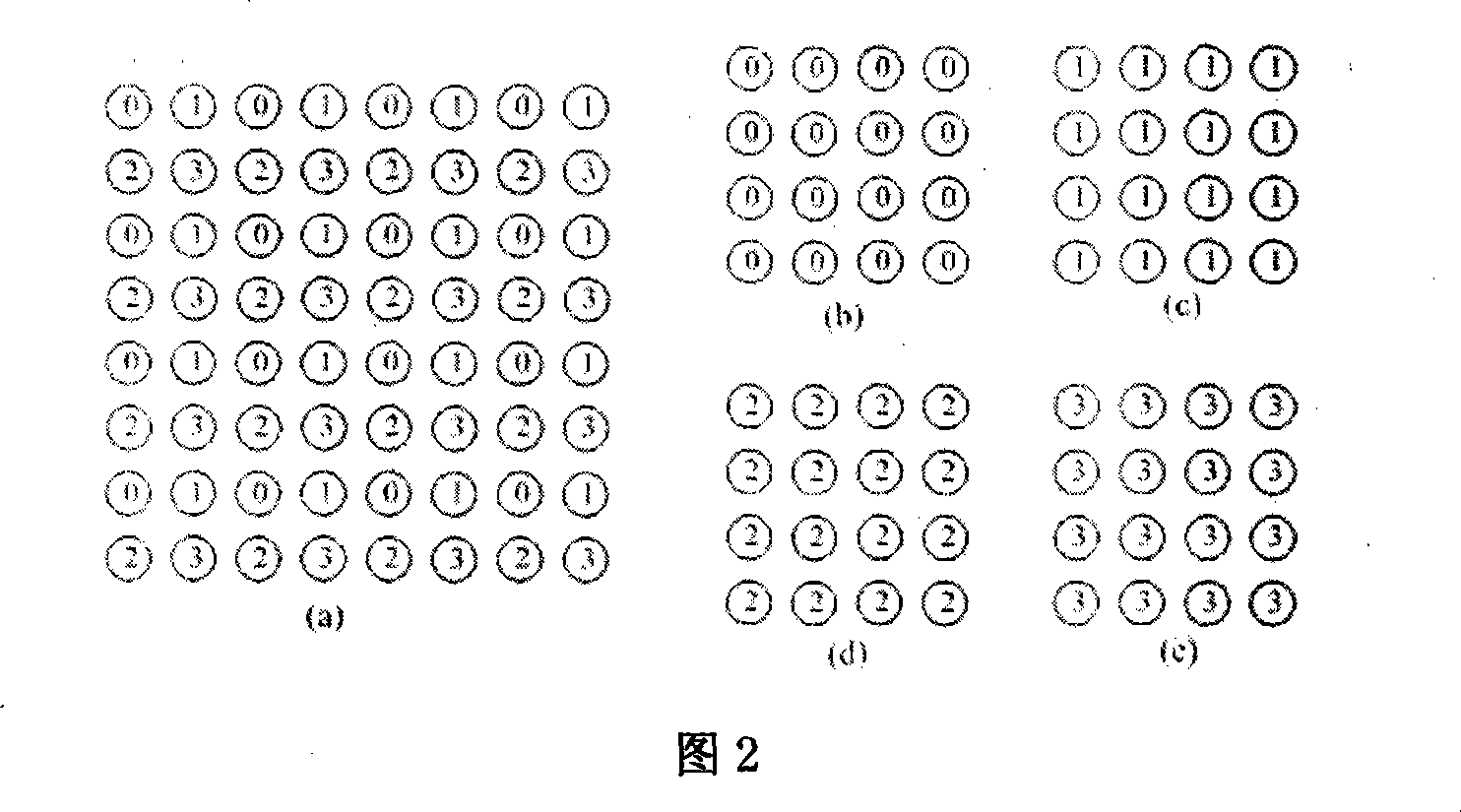
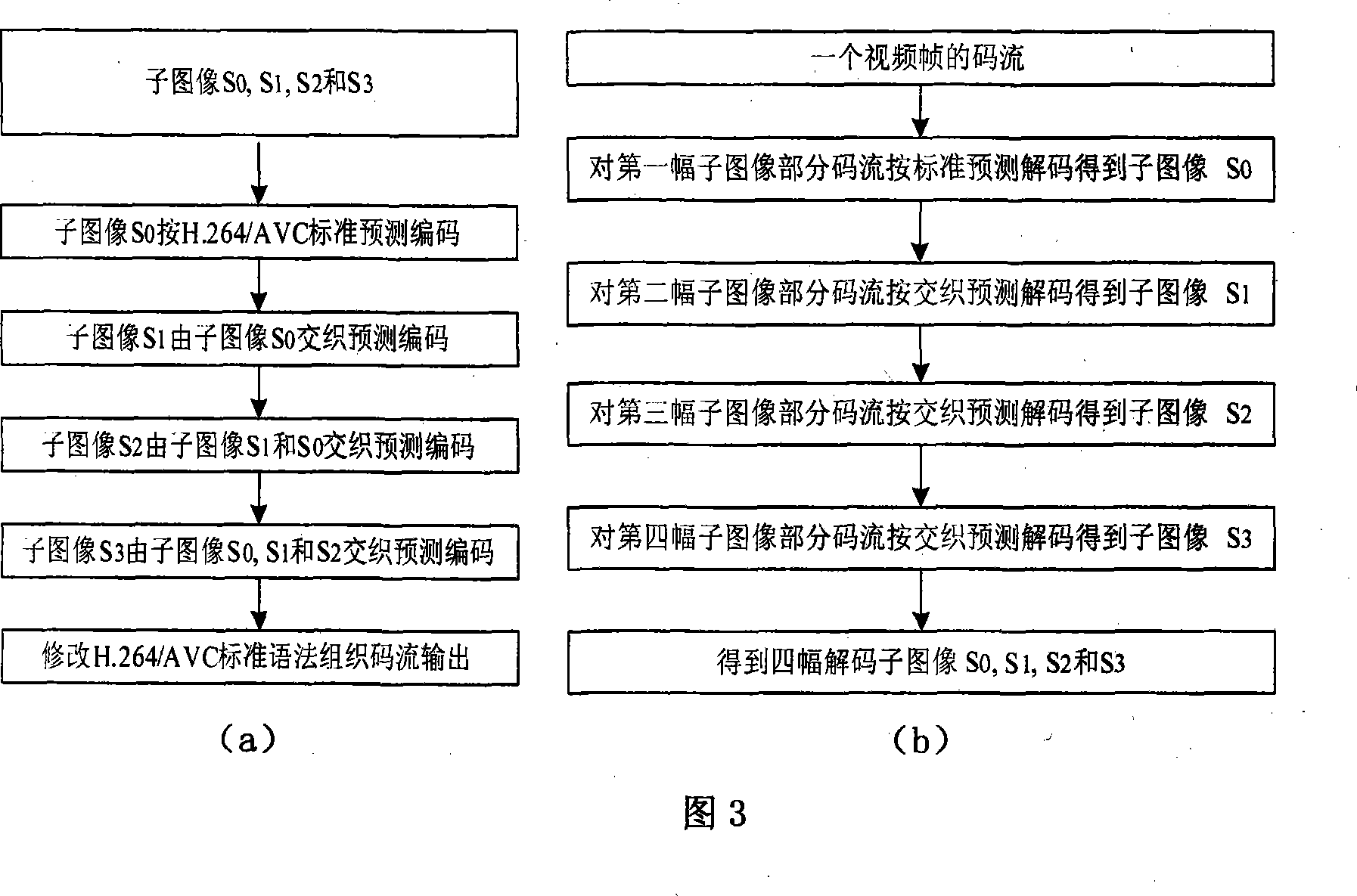
ActiveCN101252686ASignificant improvementFine forecastColor television with pulse code modulationTelevision systemsVideo encodingLossless compression
The invention relates to a video intraframe lossless encoding and decoding method based on interleaving prediction and the system thereof, and belongs to the technical field of the video encoding and decoding for signal processing. In the encoder end, each intra-frame coding frame (I frame) is down-sampled to form four subimages in certain sequence, encoding based on standard prediction is adopted for the first subimage, and decoding based on the interleaving prediction is adopted for the three subsequent subimages in sequence; in the decoder, each received I frame code stream is used for decoding the code stream of the first subimage section according to the standard prediction, and decoding the code stream of the three subsequent subimages on the basis of the pixel level interleaving prediction, and finally up-sampling combination is performed to the four decoded subimages to obtain I frame decoding image. Compared with the standard prediction method, the interleaving prediction method of the invention is provided with better prediction performance, thereby improving the video intraframe lossless compression performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT OF DIGITAL TELEVISION
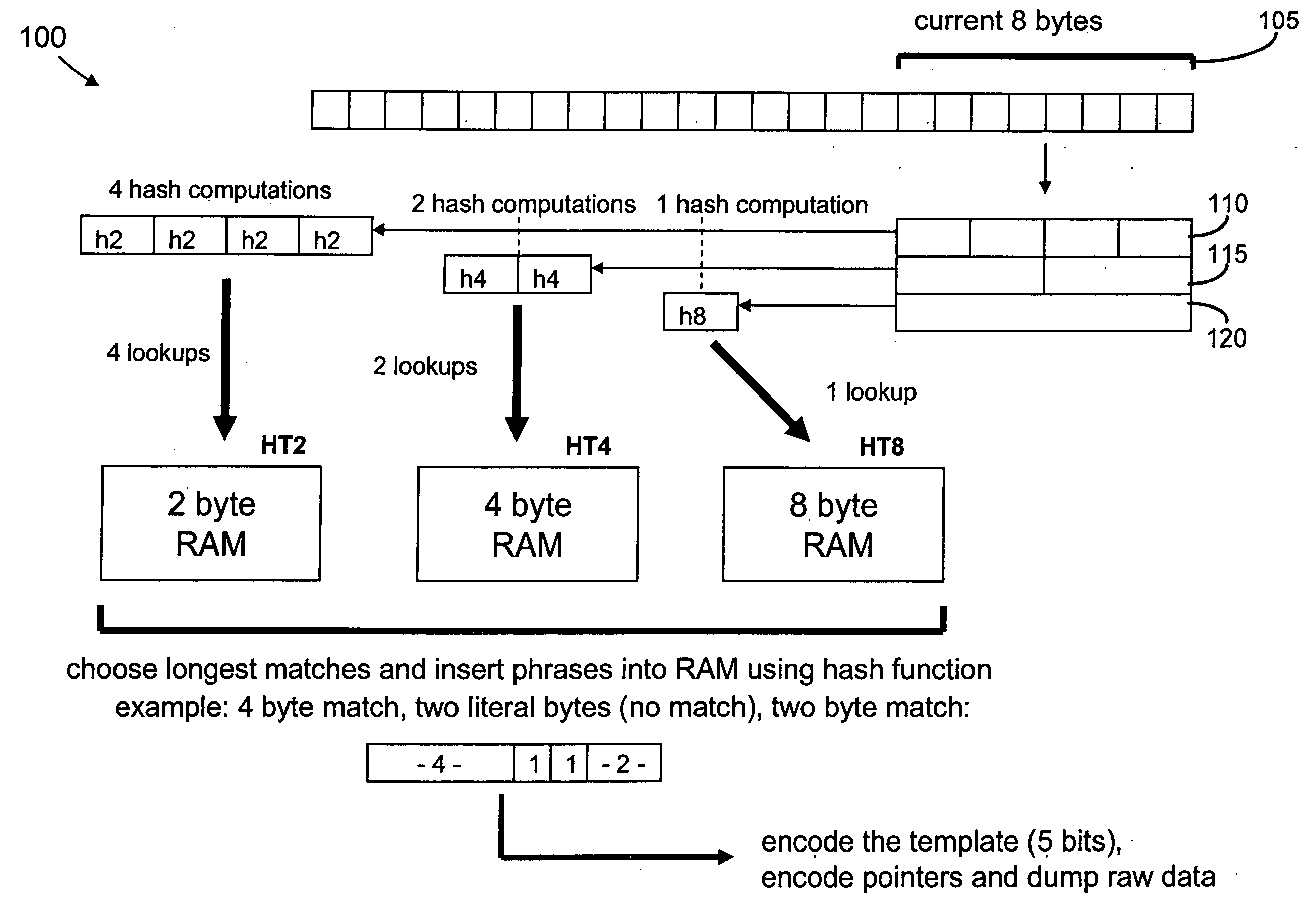
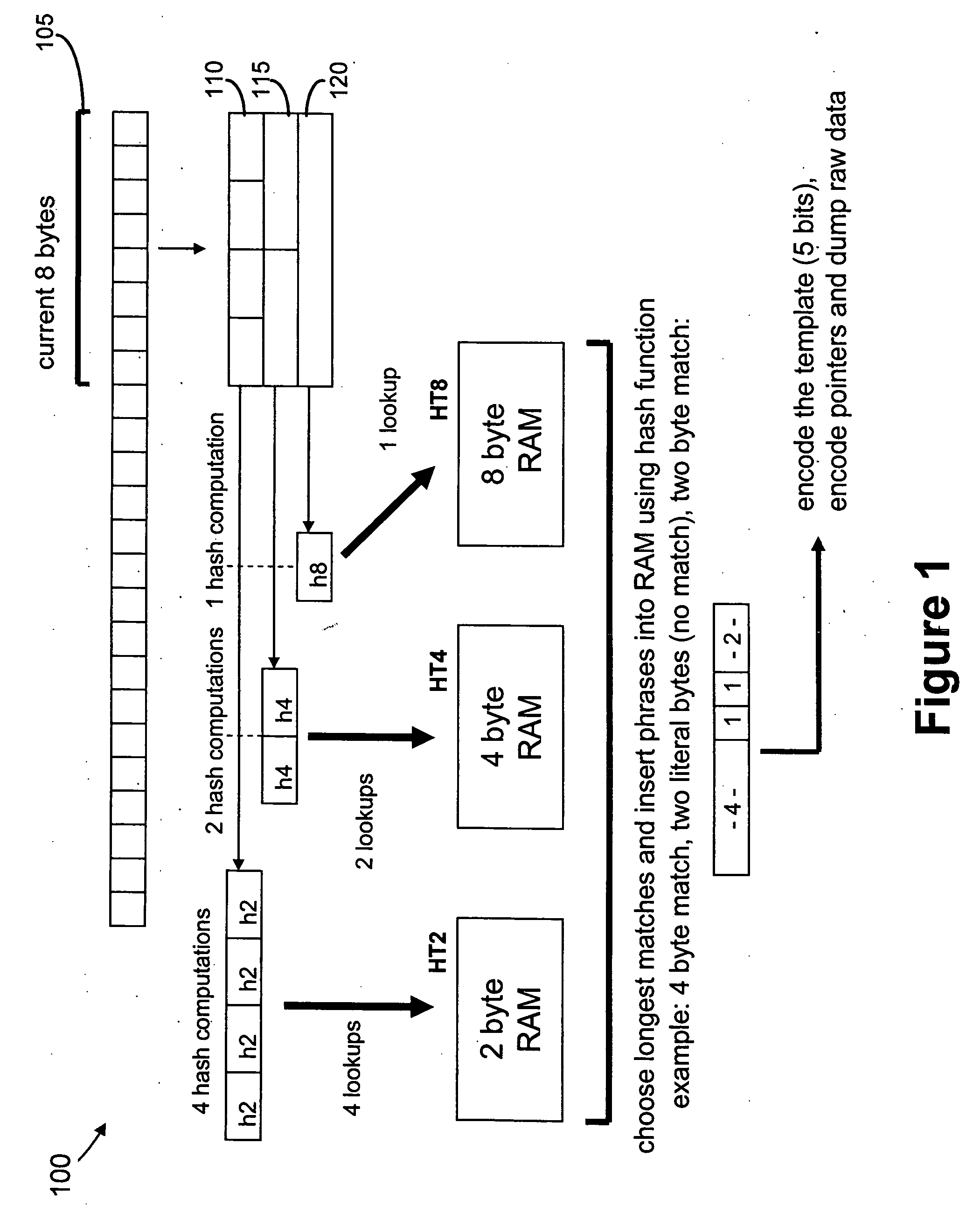
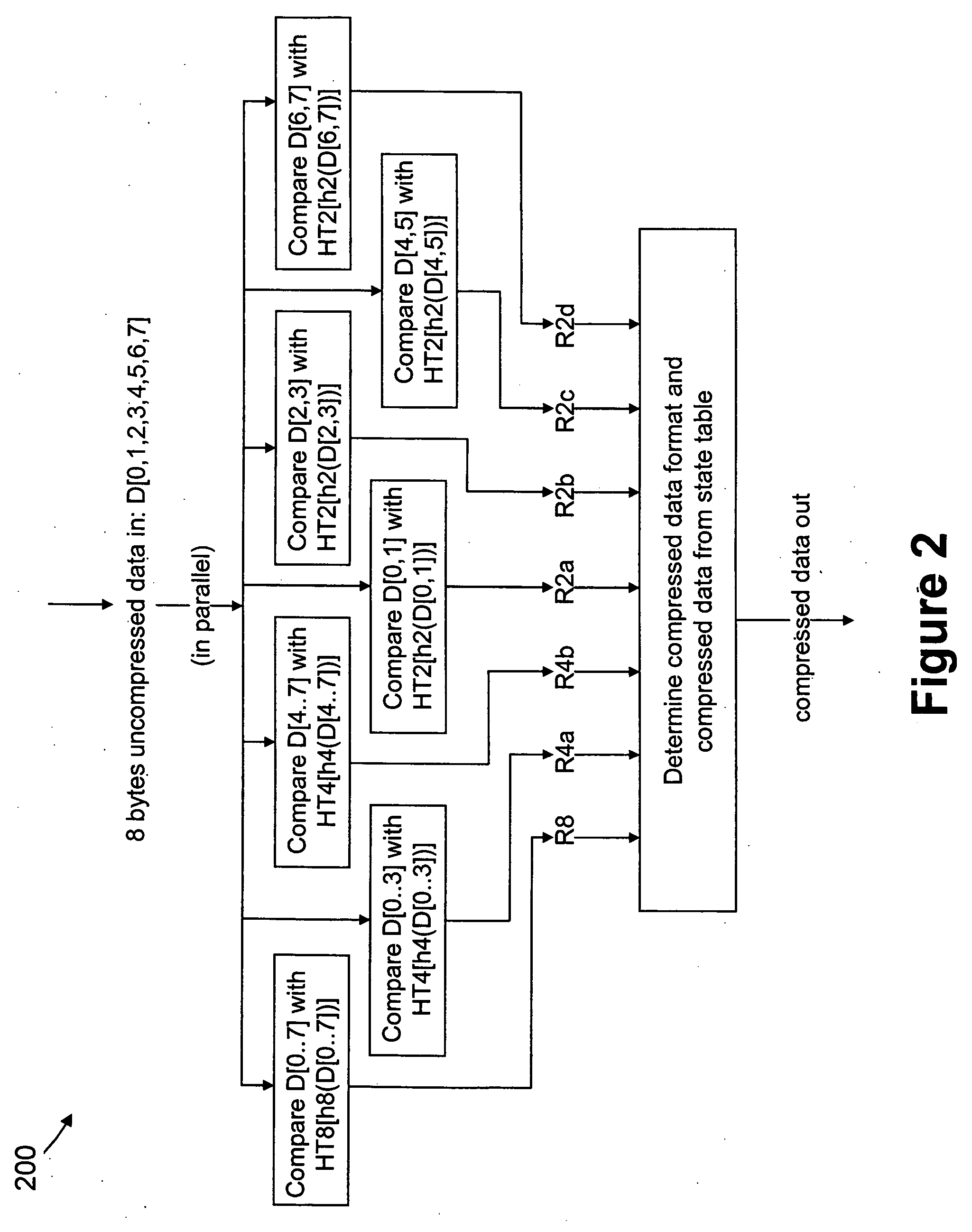
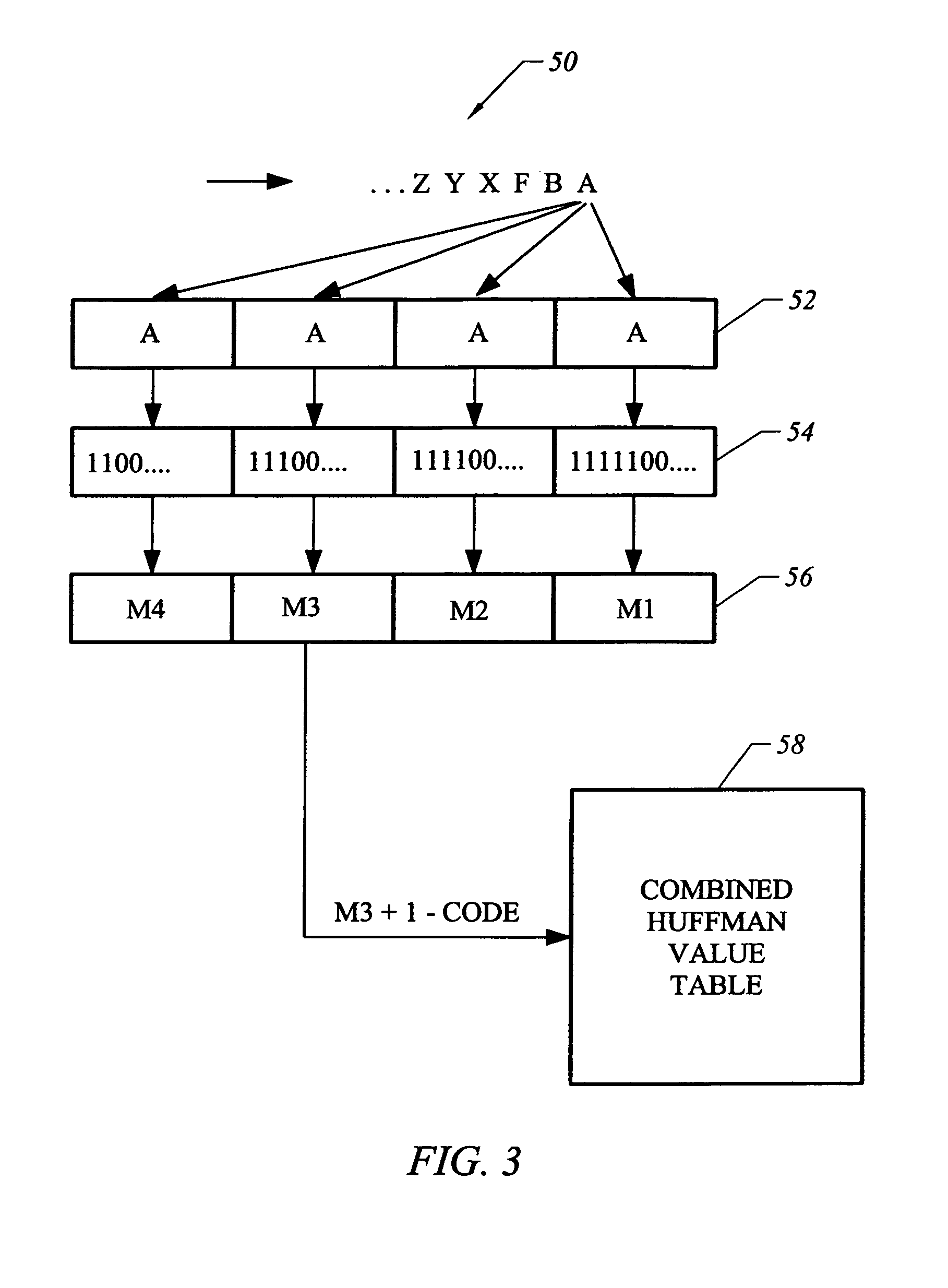
Data compression using a nested hierarchy of fixed phrase length dictionaries
InactiveUS20060106870A1Digital data processing detailsCode conversionLossless compressionComputer science
Exemplary embodiments are described herein whereby blocks of data are losslessly compressed and decompressed using a nested hierarchy of fixed phrase length dictionaries. The dictionaries may be built using information related to the manner in which data is commonly organized in computer systems for convenient retrieval, processing, and storage. This results in low cost designs that give significant compression. Further, the methods can be implemented very efficiently in hardware.
Owner:IBM CORP
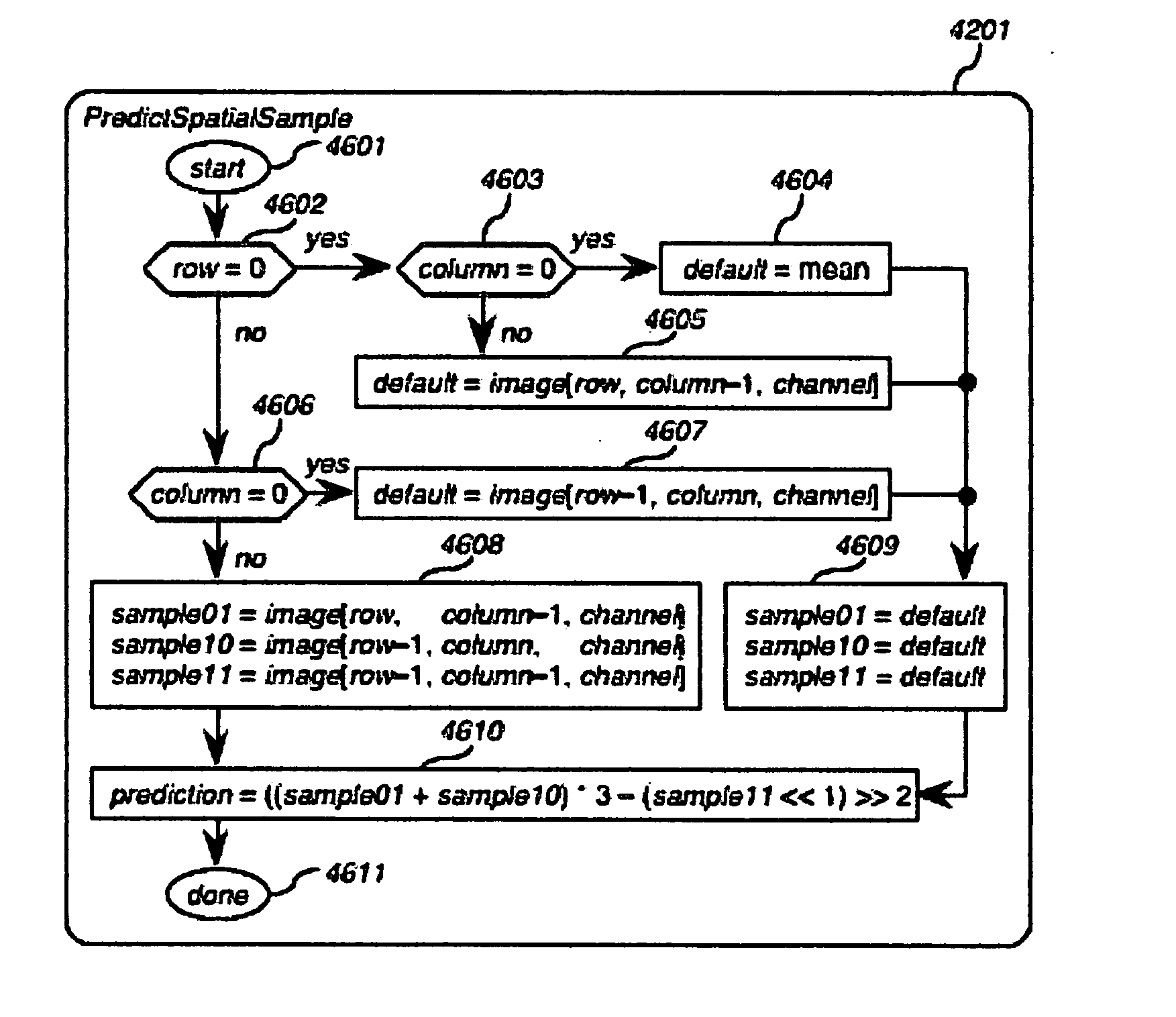
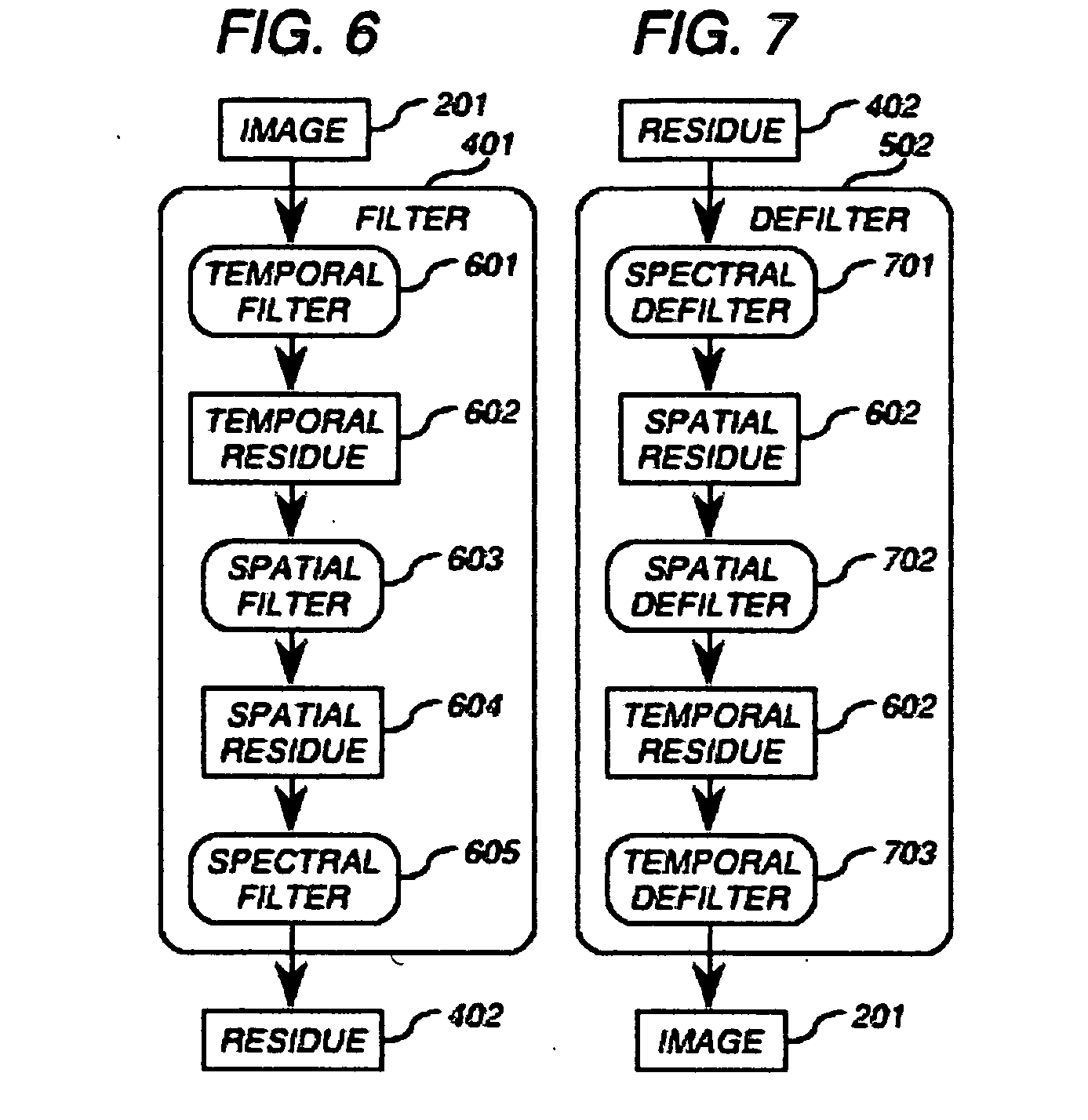
Method and apparatus for faster-than-real-time lossless compression and decompression of images
InactiveUS20080219575A1Maximize compression ratioMinimized on demandCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationFrequency spectrumContext independent
The present invention is a method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing data. In particular, the present invention provides for (de-)compressing naturalistic color-image and moving-image data, including high-precision and high-definition formats, with zero information loss, one-sample latency and in faster than real time on common computing platforms, resulting in doubled transmission, storage, and playback speed and doubled transmission bandwidth and storage capacity, and hence in doubled throughput for non-CPU-bound image-editing tasks in comparison with uncompressed formats. The present invention uses a nearly symmetrical compression-decompression scheme that provides temporal, spatial, and spectral compression, using a reversible condensing / decondensing filter, context reducer, and encoder / decoder. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the compression filter is implemented as a cascade of quasilinear feedforward filters, with temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral stages, where appropriate, in that order, whose support consists of adjacent causal samples of the respective image. The decompressor cascades quasilinear feedback inverse filters in the reverse order. The filters can be implemented with mere integer addition, subtraction, and either one-dimensional table lookup or constant multiplication and binary shifting, depending on the computing environment Tables permit the data precision to be constrained throughout to that of the image samples. The encoder uses a table of prefix codes roughly inversely proportional in length to their probability, while the decoder uses chunked decode tables for accelerated lookup. In the fastest and simplest mode, the code tables are context-independent. For greater power, at the cost of a reduction in speed, the code tables are based on the temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral adjacent causal residue samples, where contexts with similar probability distributions are incoherently collapsed by a context reducer using one-dimensional lookup tables followed by implicitly multidimensional lookup tables, to minimize the overall table size. The invention's minimal resource requirements makes it ideal for implementation in either hardware or software.
Owner:WITTENSTEIN ANDREAS
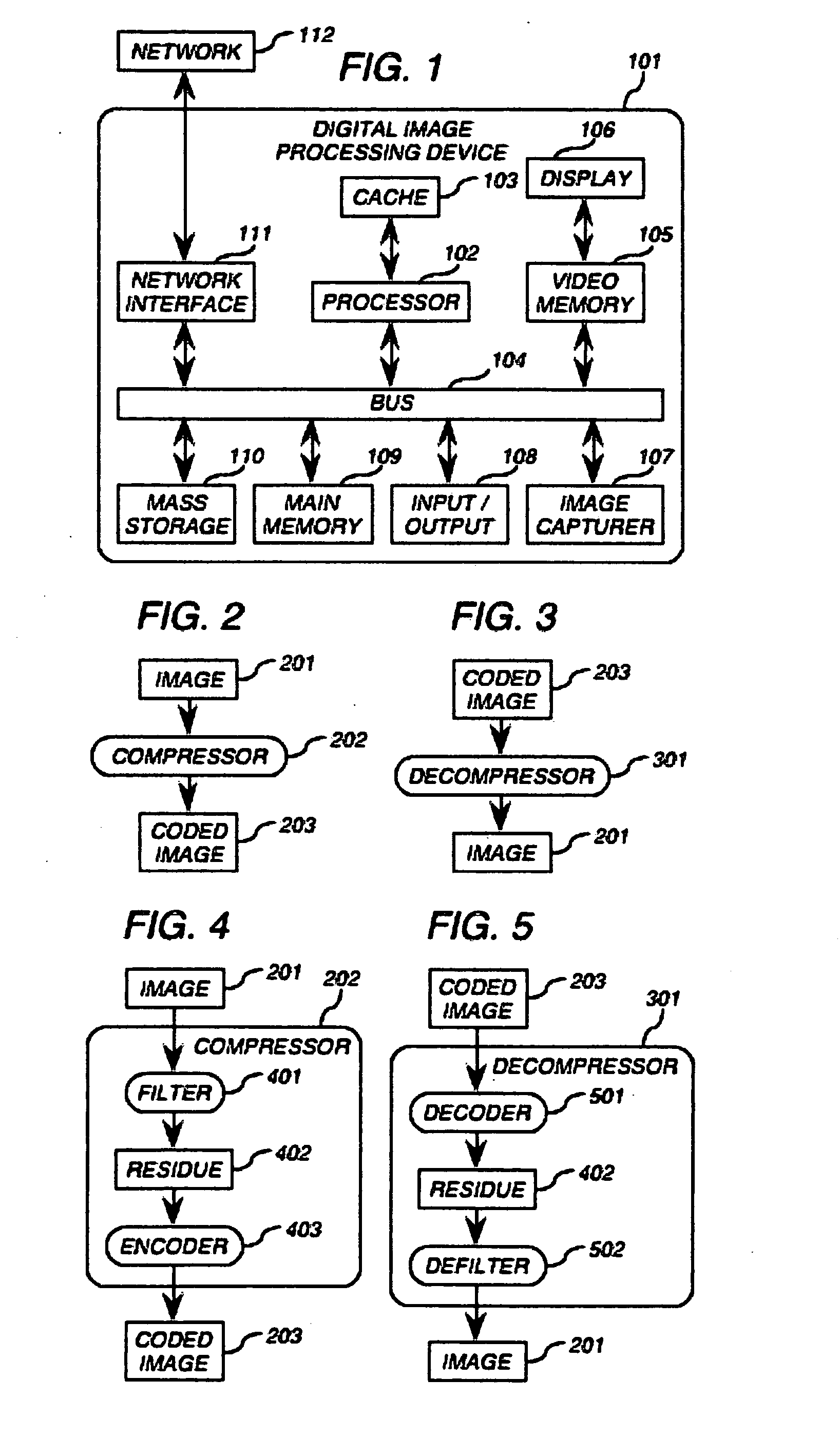
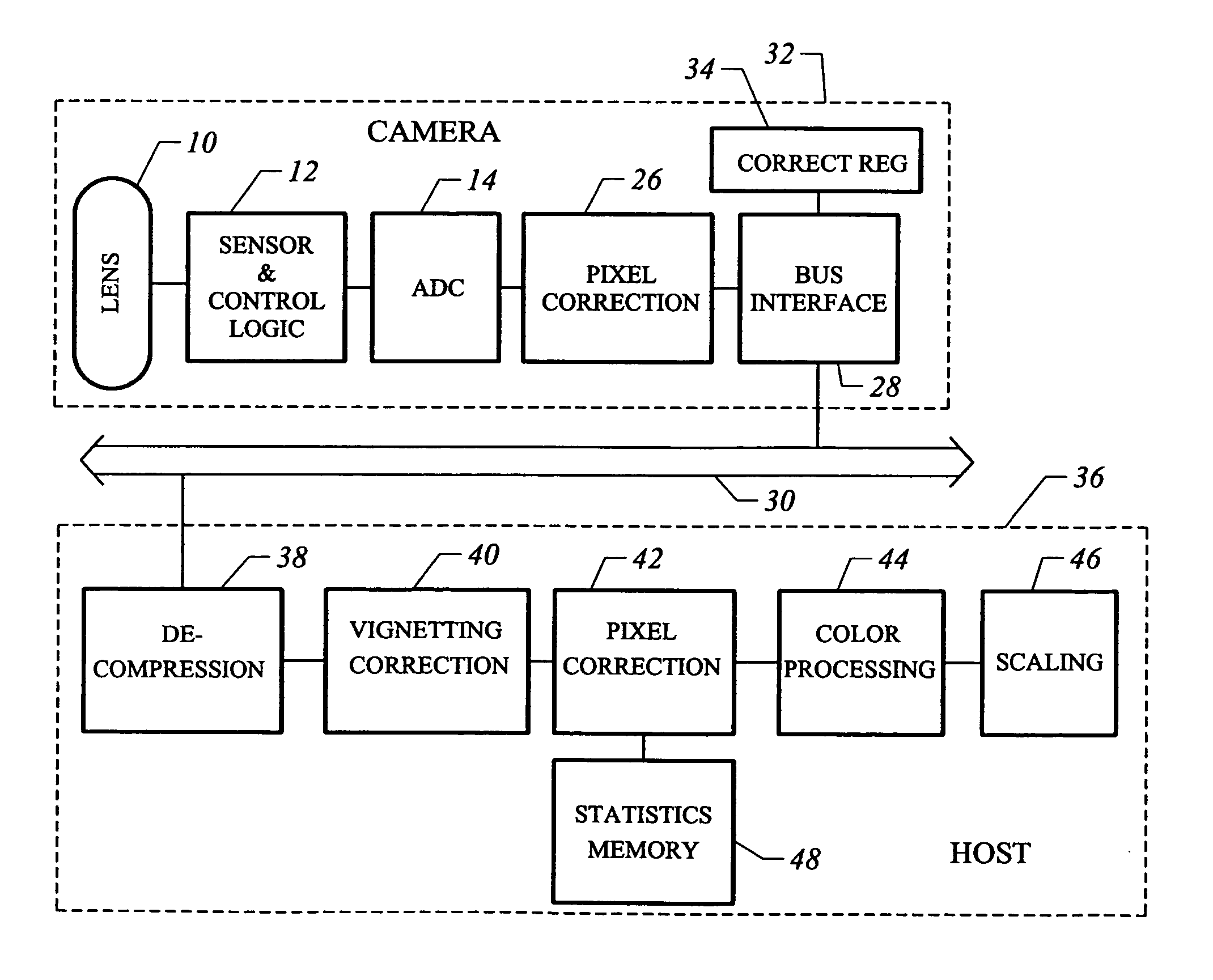
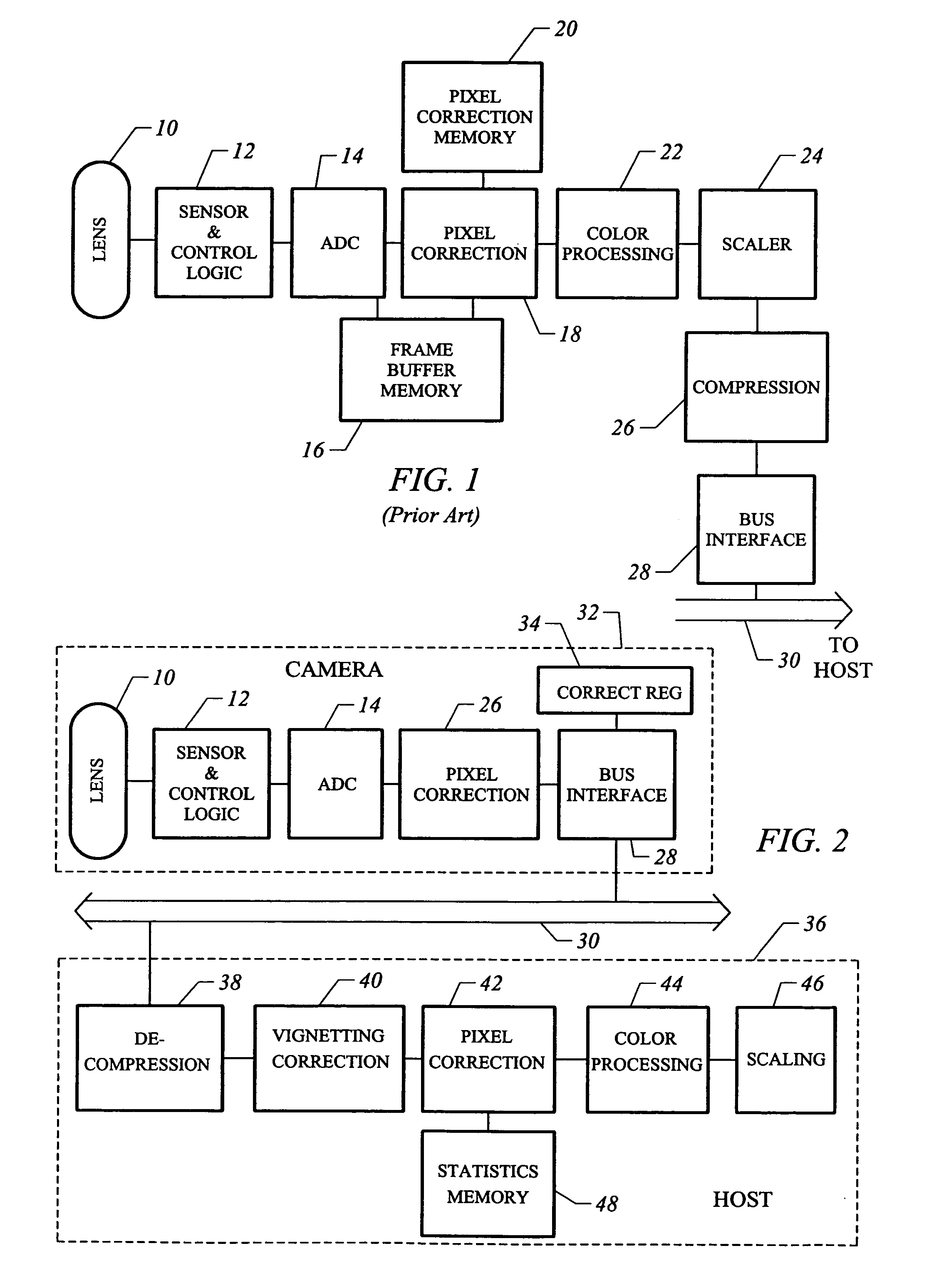
Video camera with major functions implemented in host software
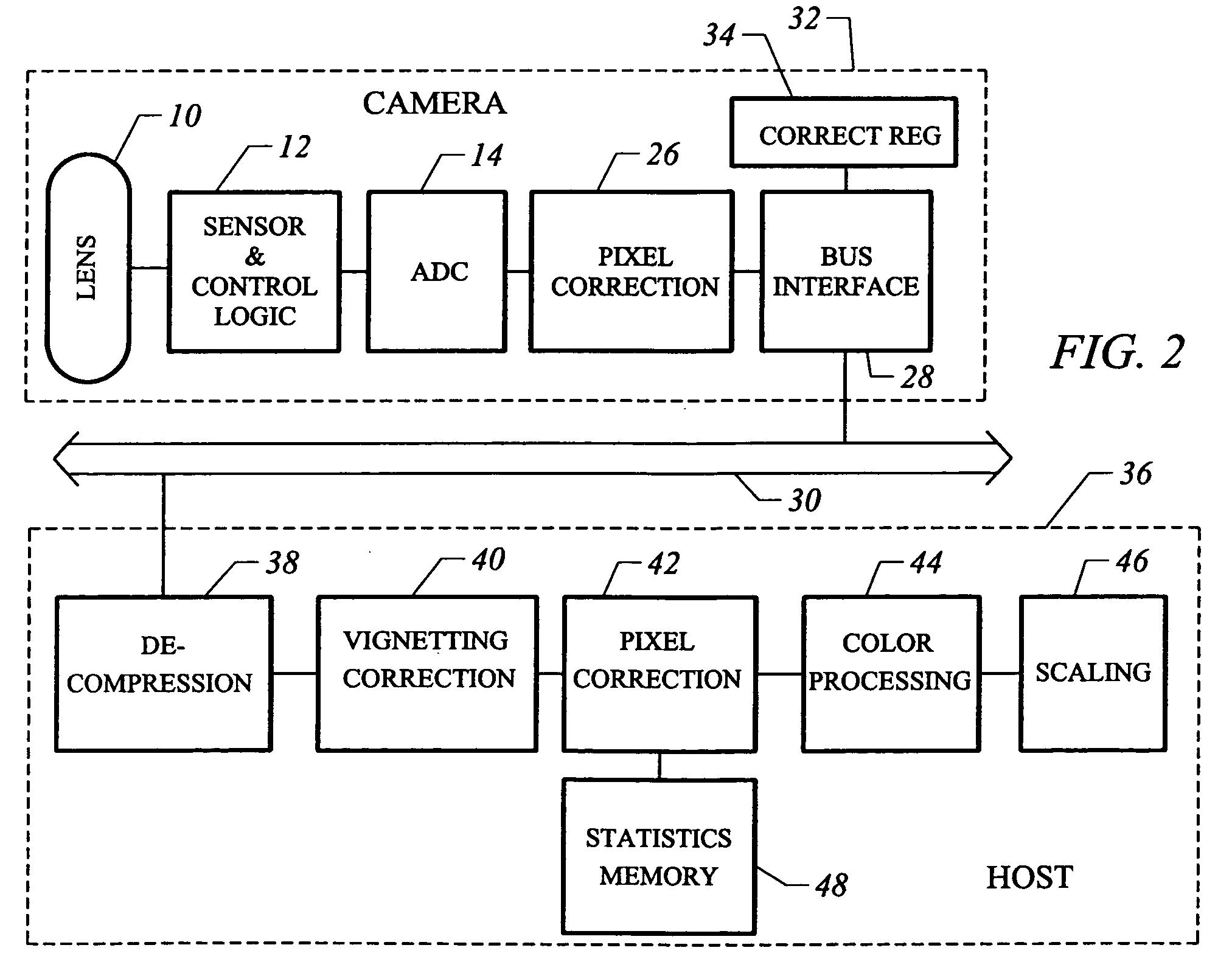
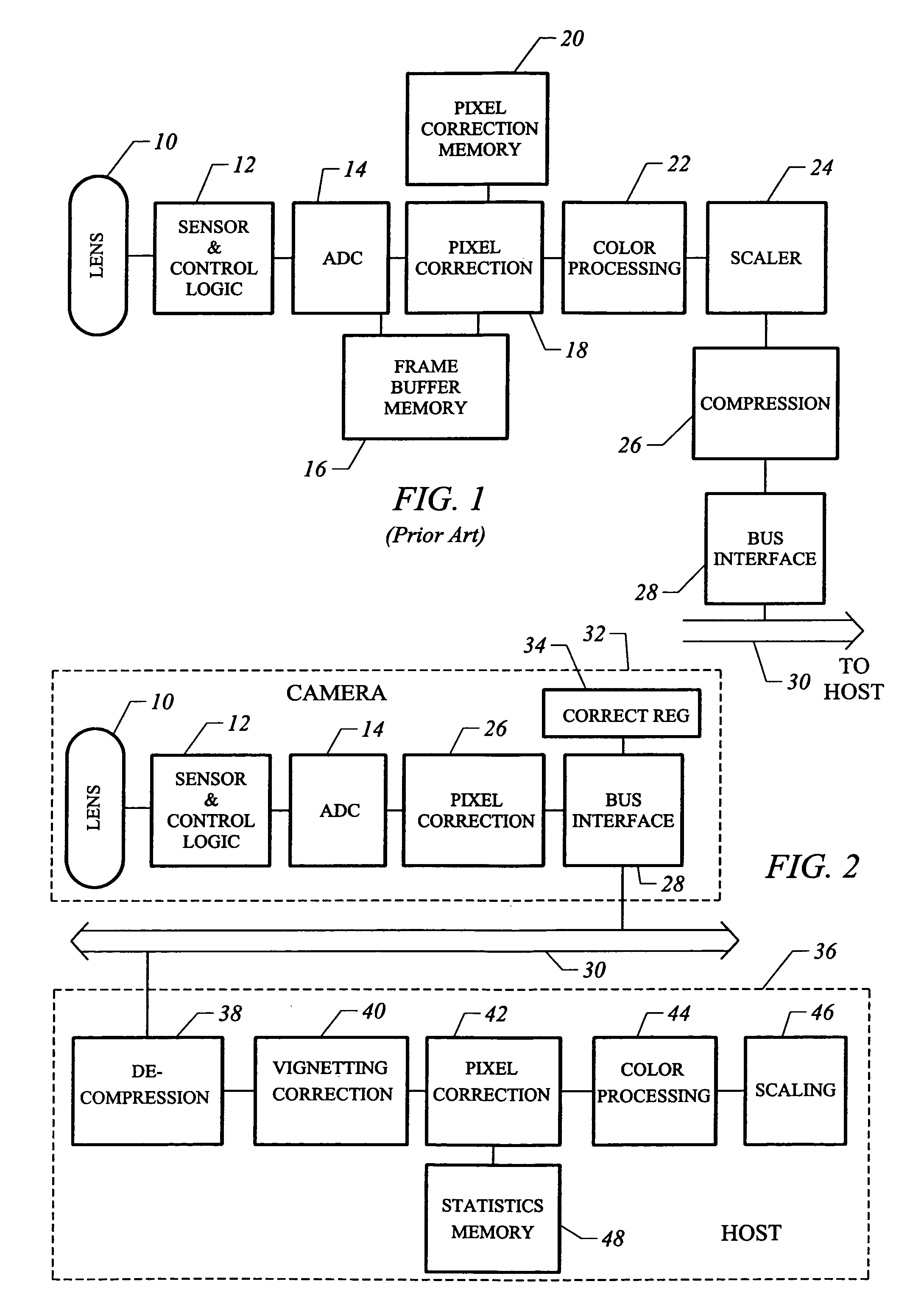
InactiveUS20050162531A1Low costIncrease volumeTelevision system detailsCode conversionComputer hardwareHigh bandwidth
A low cost camera by implementing the major functions in host software is provided. This is accomplished by sending raw, digitized data from the camera directly to the host. The increased volume of raw data is handled by either an improved compression / decompression scheme using lossless compression, using lossy compression or using a shared bus with higher bandwidth. By moving such functions as color processing and scaling to the host, the pixel correction can also be moved to the host. This in turn allows the elimination of the frame buffer memory from the camera. Finally, the camera can use a low cost lens by implementing vignetting, distortion, gamma or aliasing correction with a correction value stored in a register of the camera for later access by the host to perform corrections.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
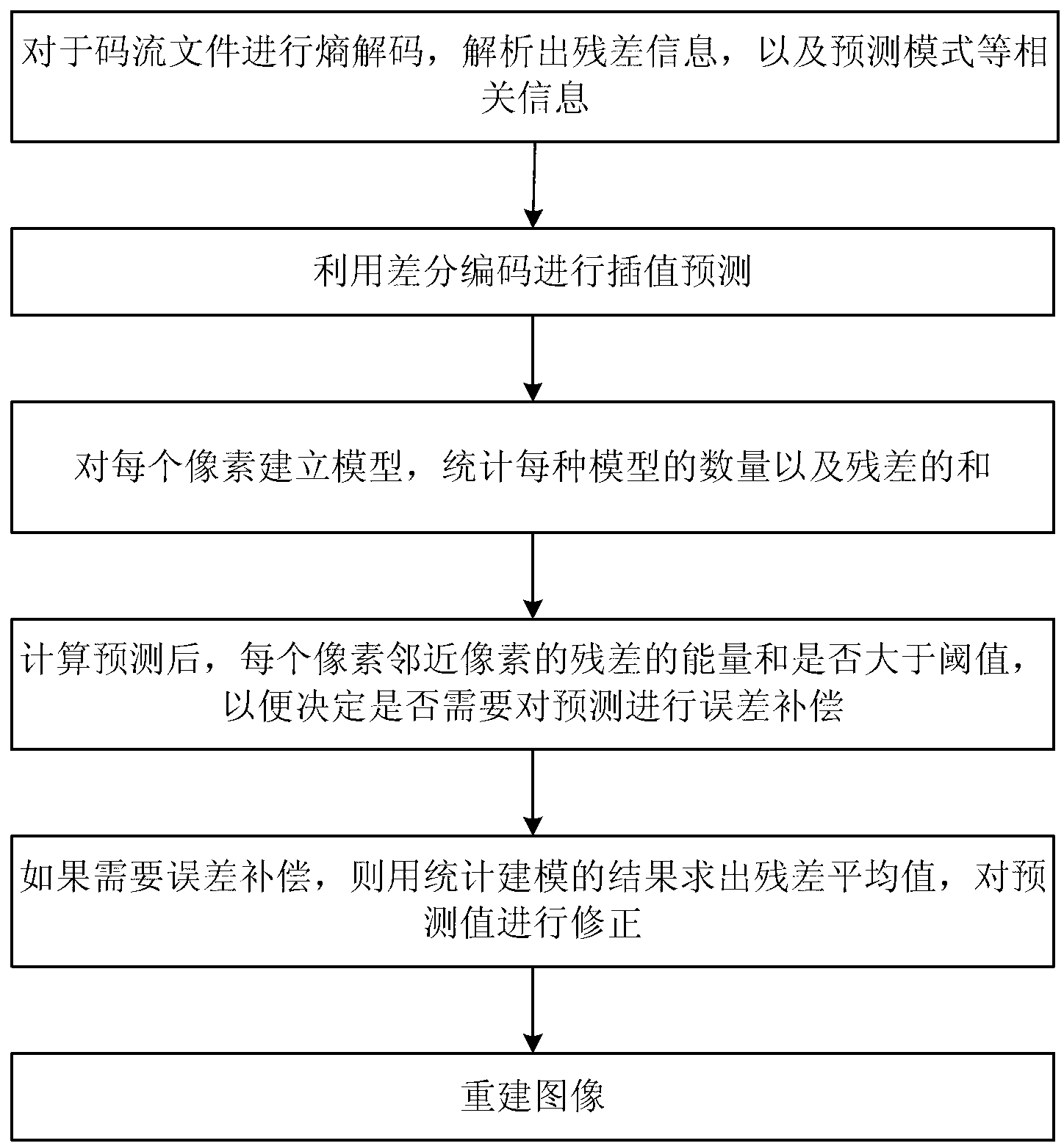
Intra-frame lossless compression coding method based on HEVC (high efficiency video coding) frame
ActiveCN103024383AReduce bit rateImprove forecast accuracyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDistribution characteristicPulse-code modulation
The invention discloses an intra-frame lossless compression coding method based on an HEVC (high efficiency video coding) frame, wherein the method is low in time complexity and high in prediction accuracy and increases compression ratio. By the aid of the HEVC frame, a coding unit can be adaptively divided according to image flatness, the best division scheme is determined, and the optimal prediction mode is selected. DPCM (differential pulse code modulation) differential codes are used for preliminary prediction, prediction errors are possibly large when only the differential codes are used for an area with complex texture, and accordingly, prediction values are corrected for the area by means of error compensation. By combining the two methods, reduction of time complexity and improvement of prediction accuracy can be effectively compromised. Distribution characteristics of residual errors depend on the prediction mode, so that the scanning sequence of the residual errors is determined according to the prediction mode, and entropy coding can be more effective.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
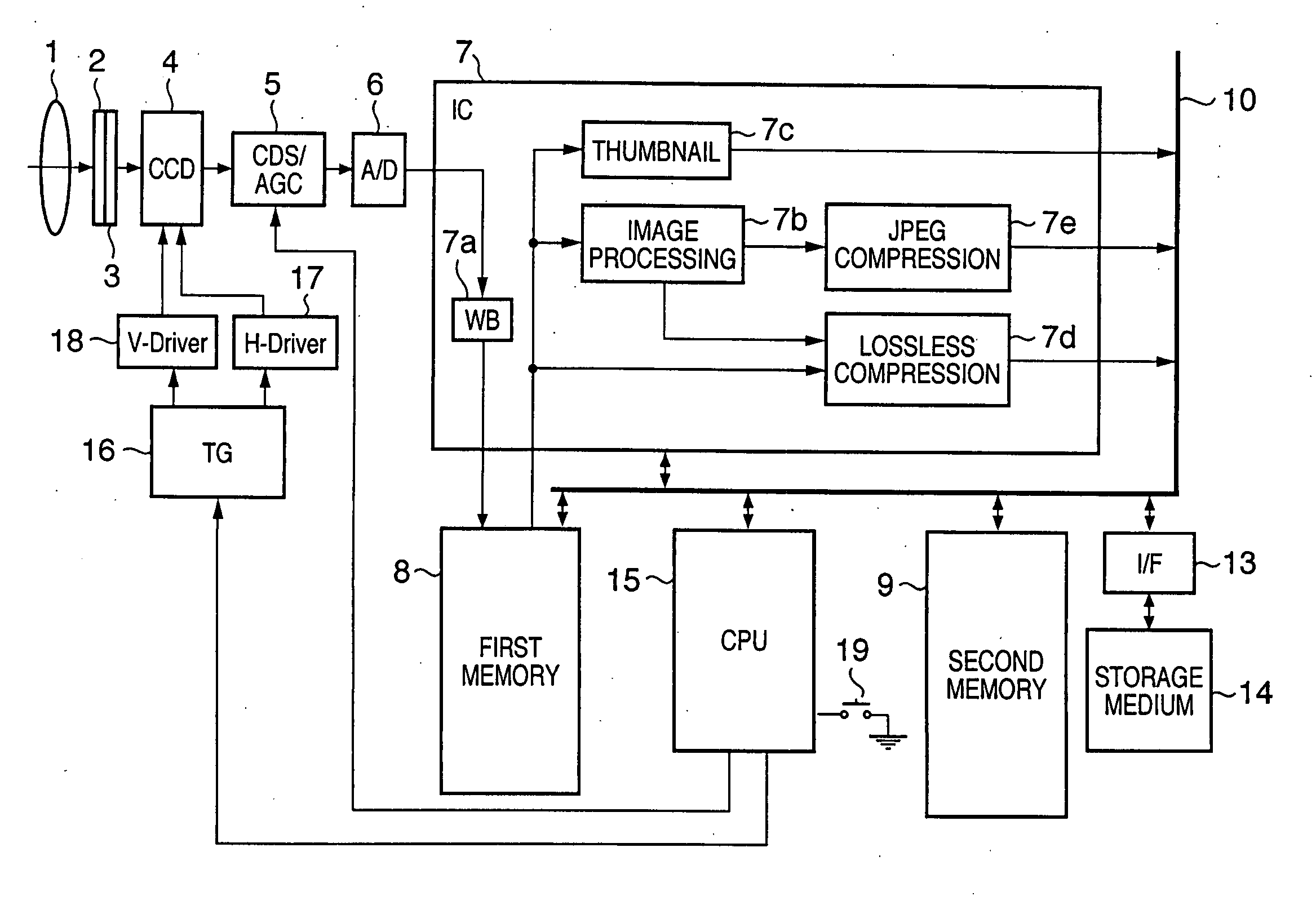
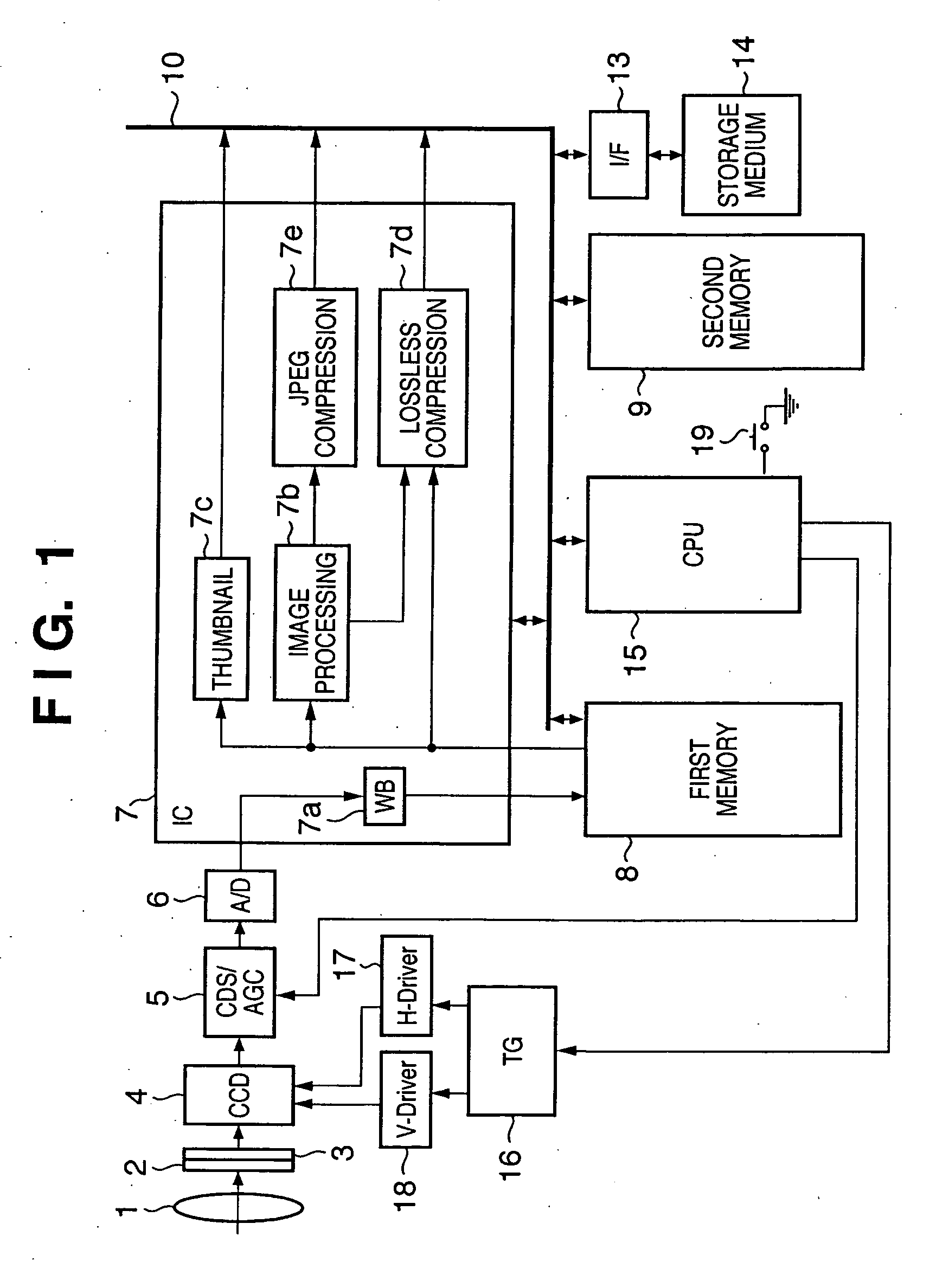
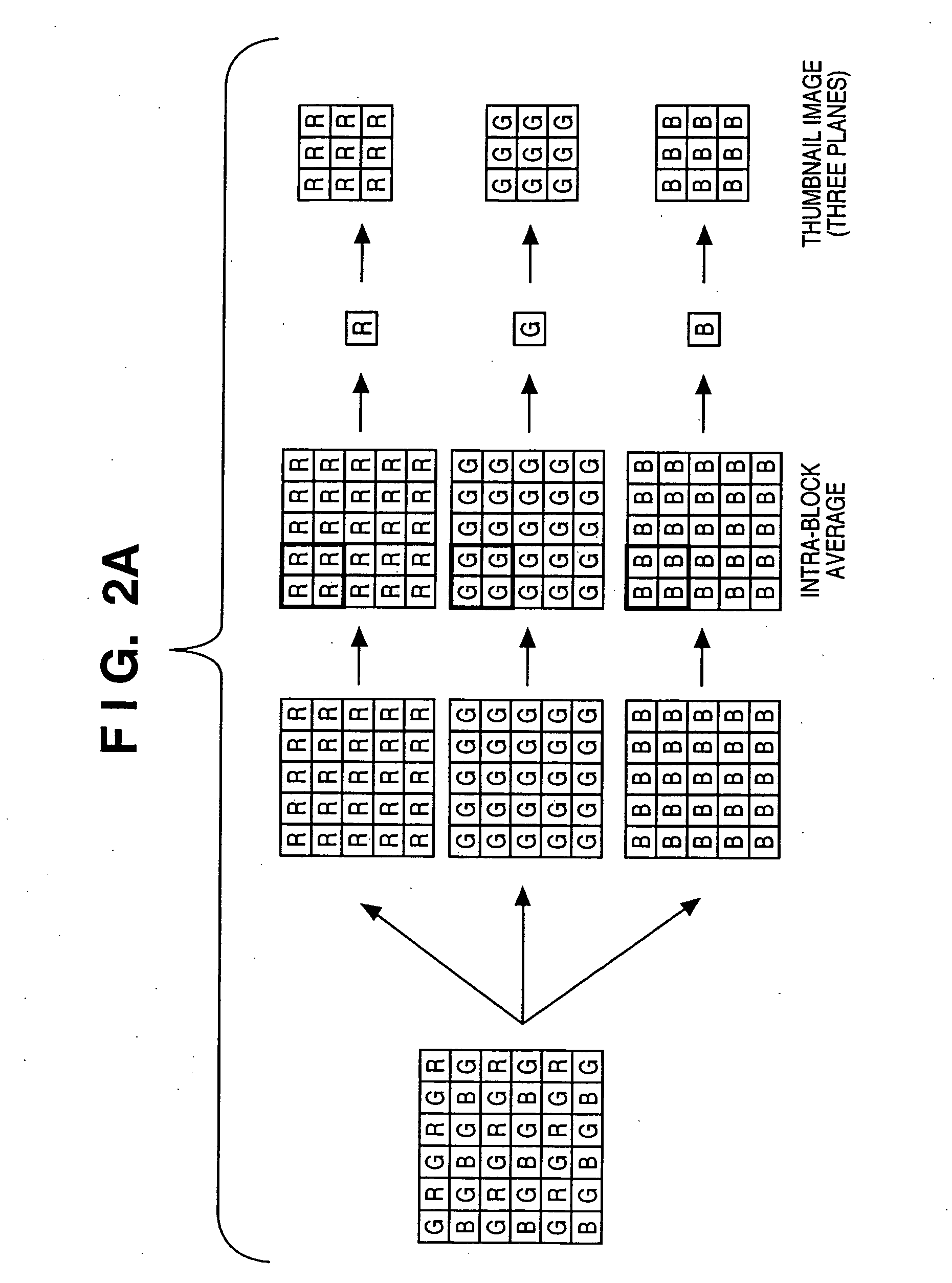
Image capturing apparatus, image processing method, program, and storage medium
InactiveUS20070127095A1Reduce image quality degradationDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingColor interpolation
This invention reduces degradation in quality of a resized image in obtaining the resized image. An image capturing apparatus includes an image sensor which converts an optical image into an electrical signal, an A / D conversion unit which converts an image signal output from the image sensor into digital image data, a color interpolation unit which executes color interpolation of the digital image data, a separation unit which separates the digital image data that has undergone color interpolation by the color interpolation unit into a luminance component and color difference components, an image size conversion unit which converts the image size of the luminance component and color difference components, and a lossless compression unit which losslessly compresses the luminance component and color difference components generated by the image size conversion unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Video camera with major functions implemented in host software
InactiveUS6995794B2Low costIncrease volumeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer hardwareHigh bandwidth
A low cost camera by implementing the major functions in host software is provided. This is accomplished by sending raw, digitized data from the camera directly to the host. The increased volume of raw data is handled by either an improved compression / decompression scheme using lossless compression, using lossy compression or using a shared bus with higher bandwidth. By moving such functions as color processing and scaling to the host, the pixel correction can also be moved to the host. This in turn allows the elimination of the frame buffer memory from the camera. Finally, the camera can use a low cost lens by implementing vignetting, distortion, gamma or aliasing correction with a correction value stored in a register of the camera for later access by the host to perform corrections.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
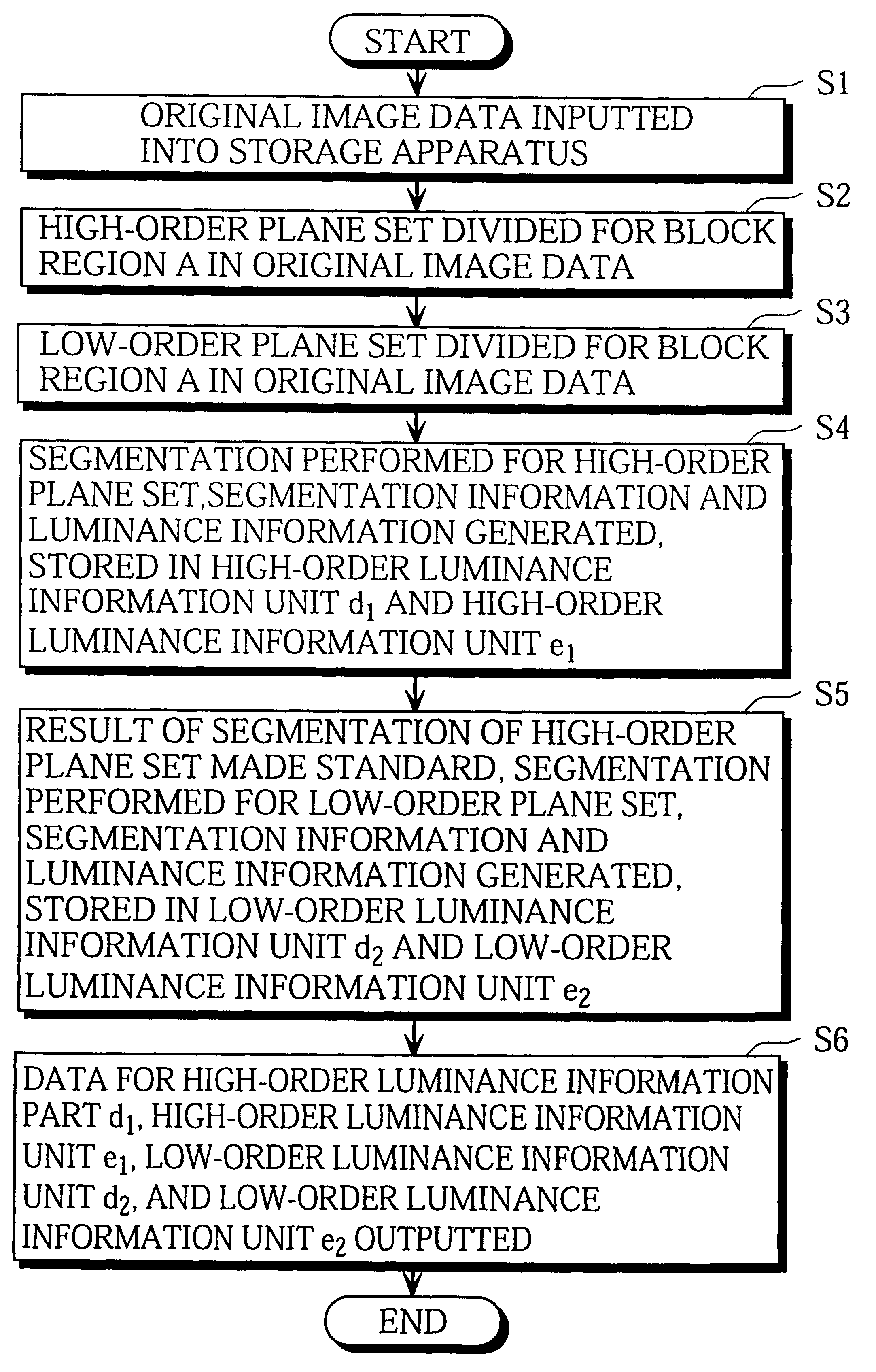
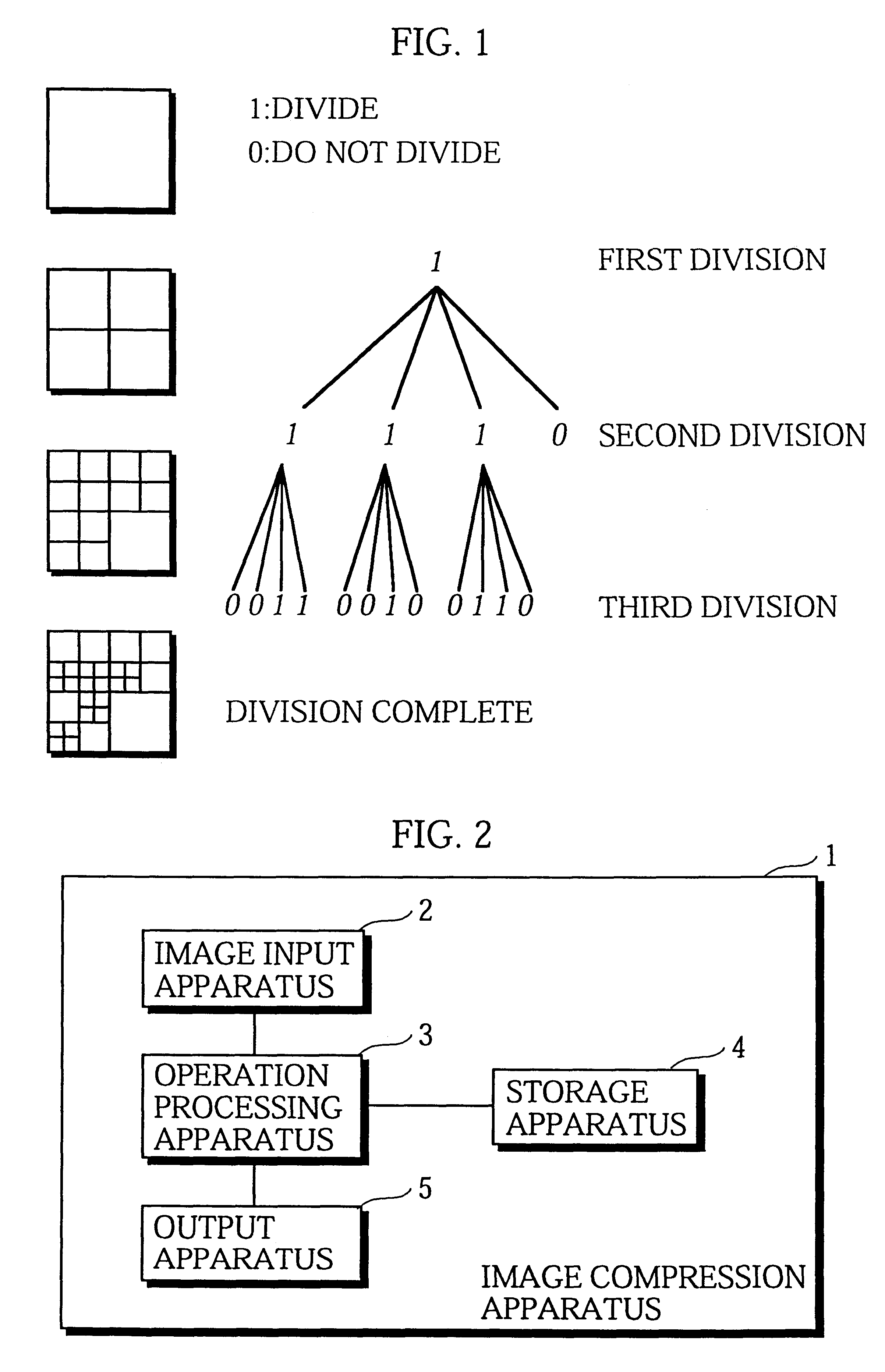
Image compression apparatus and decoding apparatus suited to lossless image compression
InactiveUS6614939B1Character and pattern recognitionImage codingImage compressionLossless compression
An image compression apparatus for outputting compressed image information that is suited to progressive image reproduction where completely lossless reproduction is possible without having to use large amounts of compressed image information. A decoding apparatus decodes the compressed image information and performs reproduction. The image compression apparatus performs image compression with a first segmentation for a first plane set that includes at one bit plane in block image information in the original image information. As a result, first region information composed of segmentation information showing a first segmentation result and luminance information is produced. The image compression apparatus also performs image compression with a second segmentation for a second plane set that includes at least one bit plane adjacent to the first plane set. Here, the first segmentation result is used as a standard. As a result, second region information composed of segmentation information and luminance information is produced. Compressed image information is then generated and outputted based on the first and second region information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and system for improving lossless compression efficiency
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
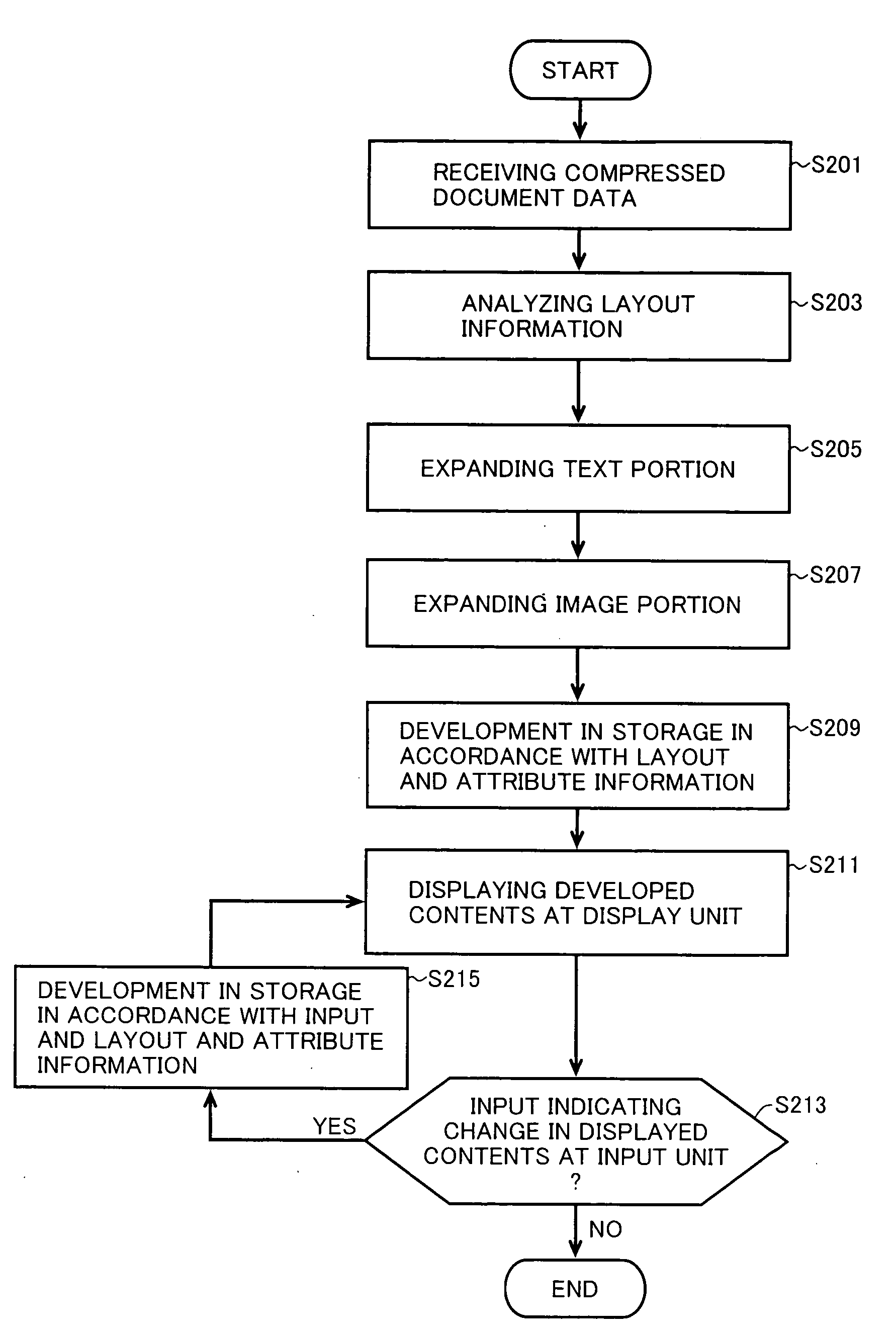
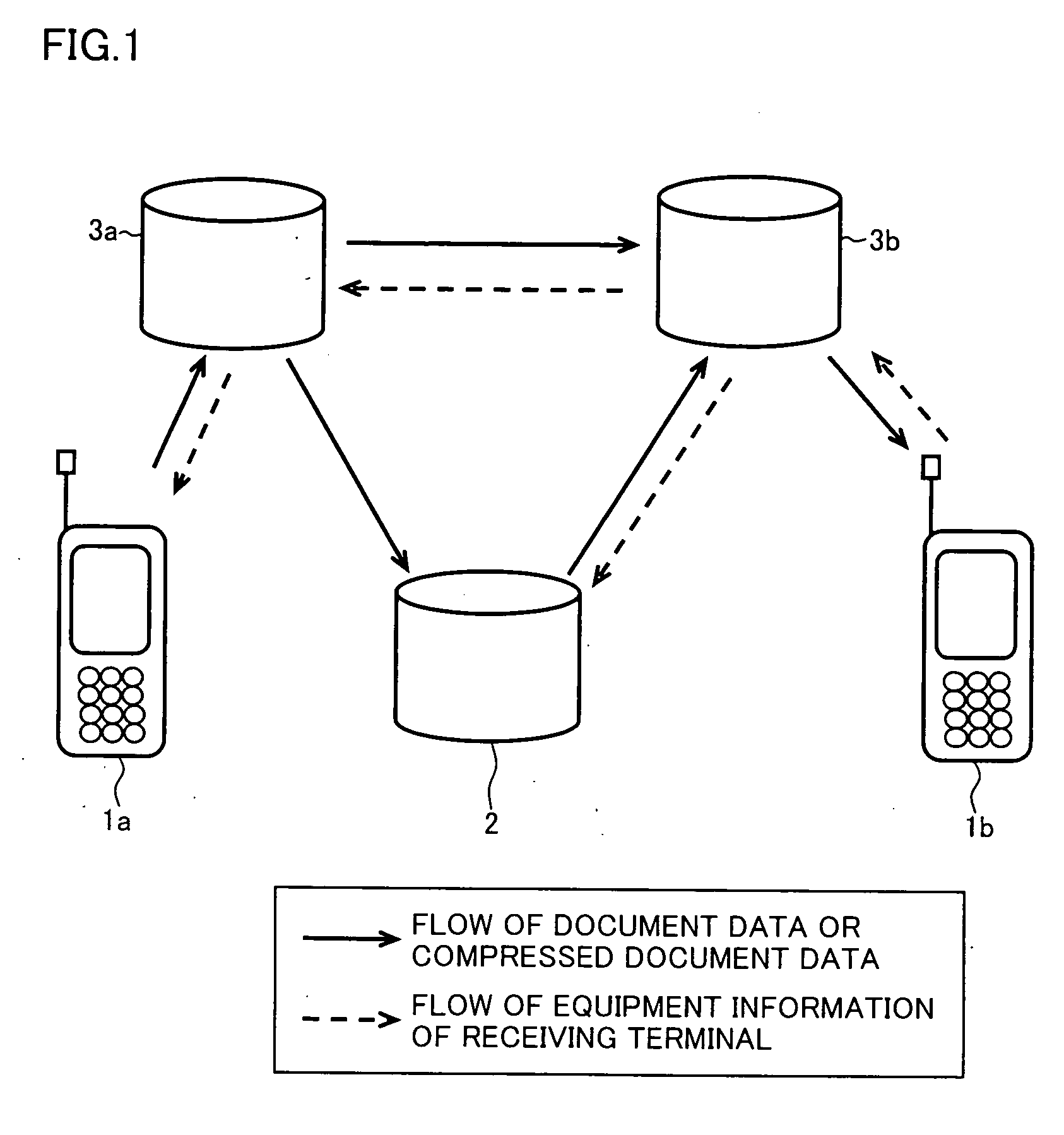
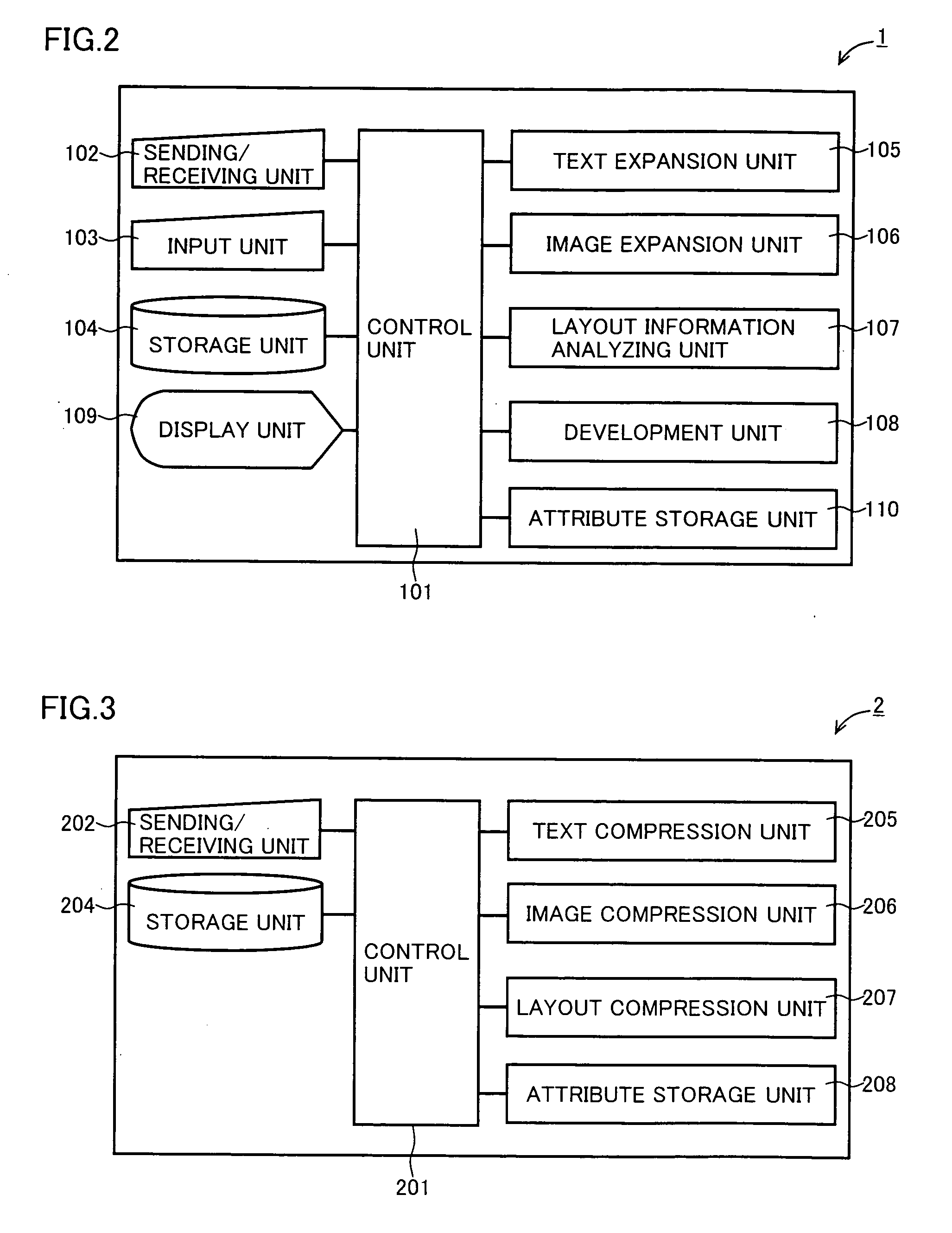
Document data output device capable of appropriately outputting document data containing a text and layout information
InactiveUS20070055931A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsData displayOutput device
A document data display system uses document data composed of text and image portions and layout information and creates from it compressed document data by lossless compressing the text portion and lossless or lossy compressing the image portion in order to reduce traffic in communication. A document data display device 1 expands text or image portions from received compressed document data at a text expansion unit or an image expansion unit, and uses the analysis of the layout information by a layout information analyzing unit to arrange the text or image portions at a development unit before being displayed by a display unit.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com