Patents
Literature
612results about How to "Reduction procedure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
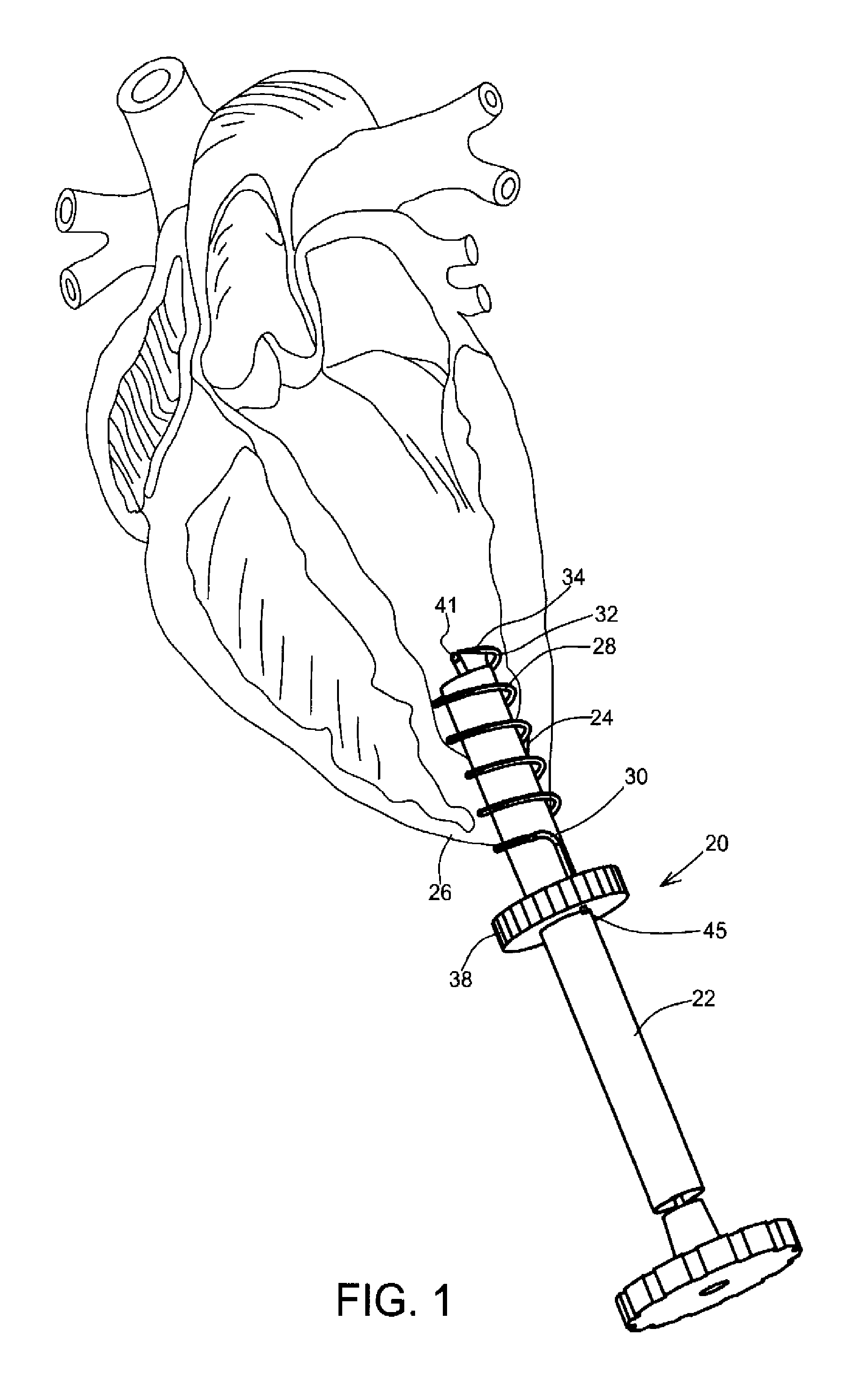
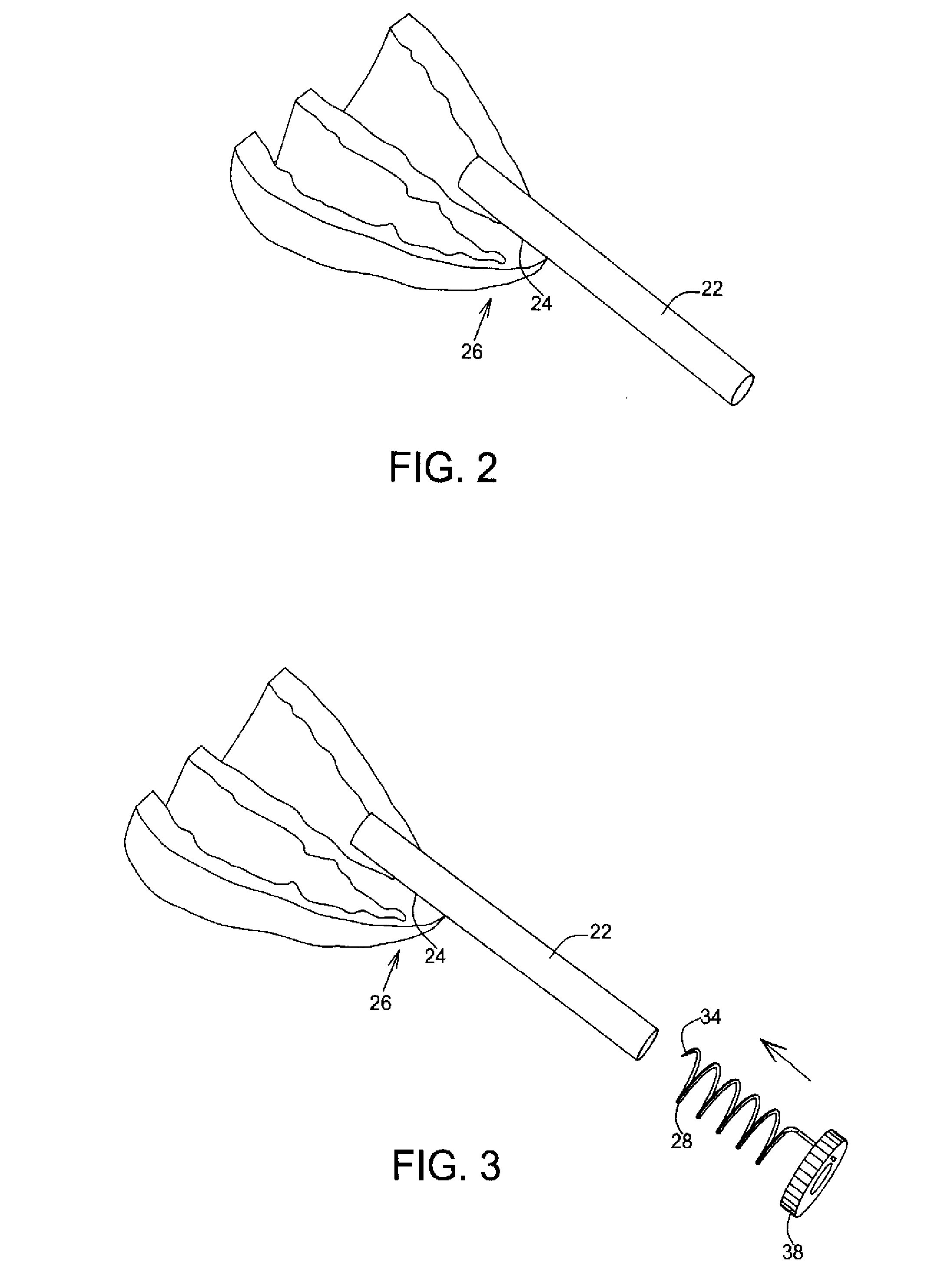
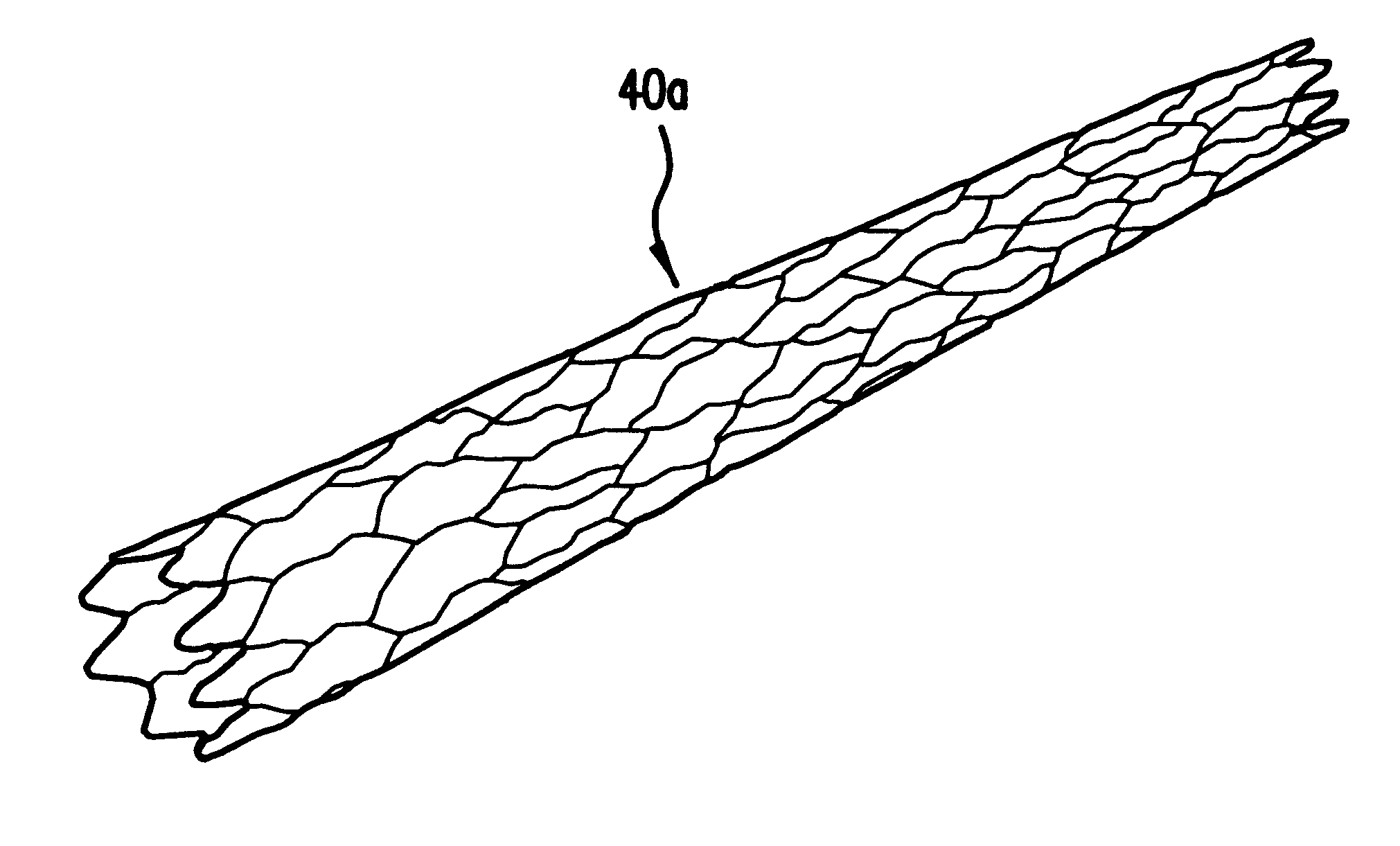
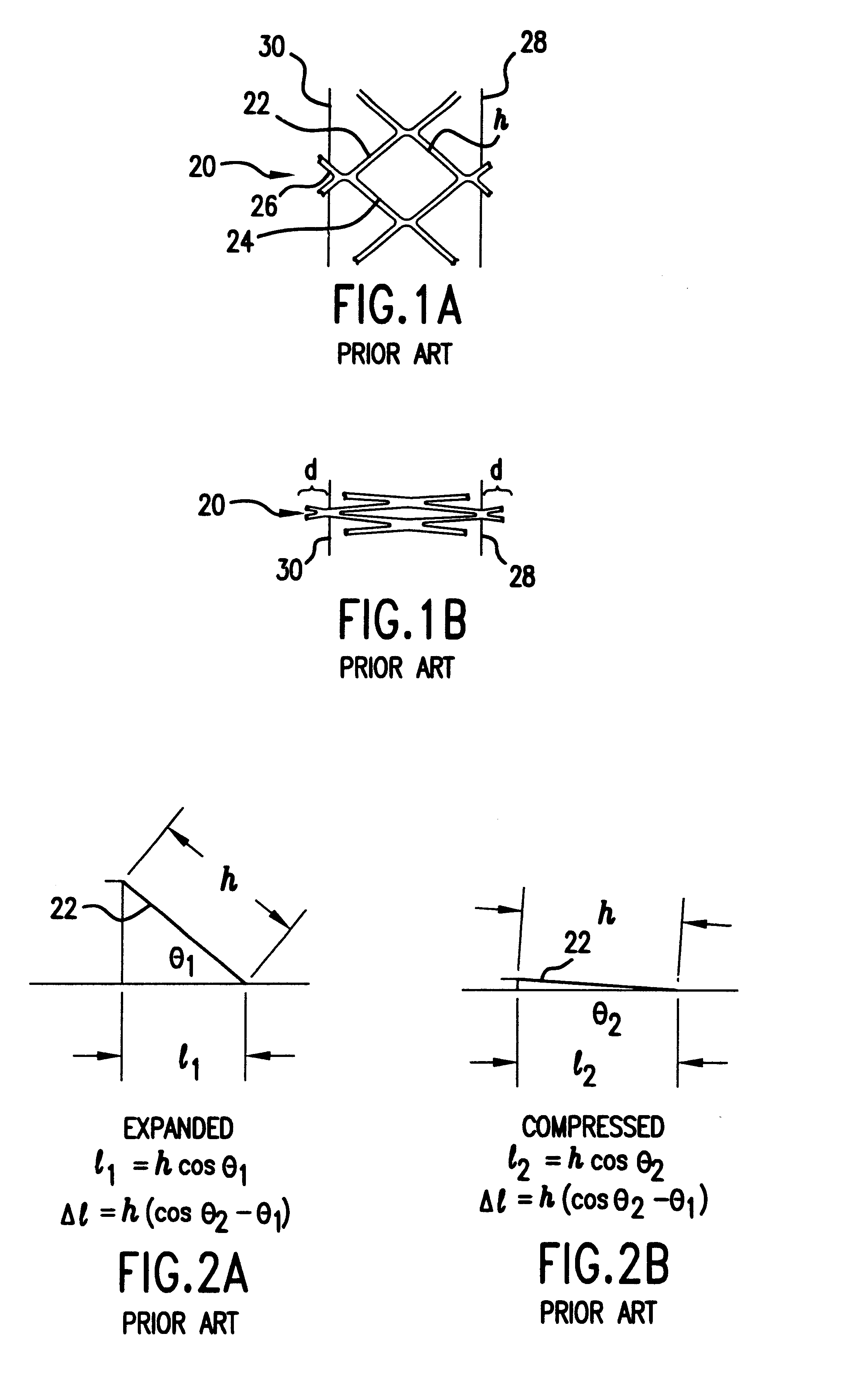
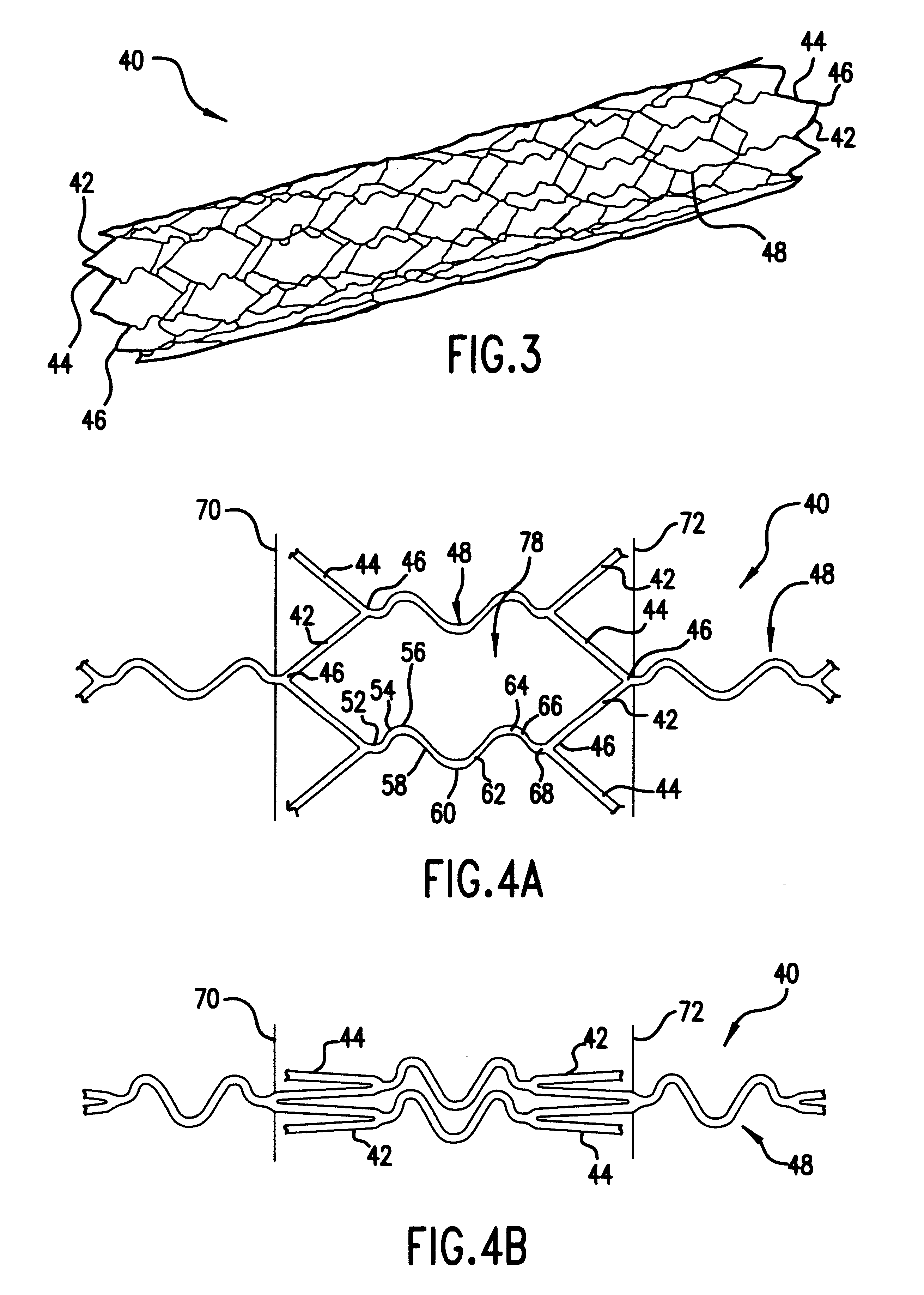
Non-foreshortening intraluminal prosthesis
InactiveUS6106548ADifferent degree of flexibilityVaried flexibilityStentsBlood vesselsProsthesisEngineering
An intraluminal prosthesis is provided with a plurality of annular elements. Each annular element includes a plurality of struts and apices connected to form an annular configuration. Each annular element has a compressed state and an expanded state, and has a longitudinal dimension which is smaller in the expanded state than in the compressed state. A plurality of connecting members connect the apices of adjacent annular elements. The connecting members have a plurality of alternating segments that function to compensate for the smaller longitudinal dimension of each annular element in the expanded state. The stent may be provided with varying flexibility along its length and / or circumference, and may include segments that have different diameters.
Owner:ENDOSYST
Medical suturing device and method for use thereof
ActiveUS20090240264A1Avoid the needEasy to operateSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesGuide wiresSharp point
A suturing device for use with a delivery catheter in a transcatheter procedure, for closing an opening formed in the body. The suturing device comprises: a spiral needle having a central core, a proximal end, and a distal end. The distal end terminates in a sharp point for cutting a spiral passageway through body tissue surrounding the opening that is to be closed. The device also includes a guide wire having a suture eye at one end thereof for receiving suture thread after the guide wire has been advanced through the hollow central core of the spiral needle. The device further includes driving means, for allowing advancing and retracting of the spiral needle and guide wire with respect to the catheter, and for allowing connecting between the suture thread and the suture eye of the guide wire. The present invention also relates to a method for closing an opening formed in the body using a transcatheter procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VENTOR TECH
Non-foreshortening intraluminal prosthesis
InactiveUS6475236B1Different degree of flexibilitySame lengthStentsBlood vesselsProsthesisEngineering
An intraluminal prosthesis is provided with a plurality of annular elements. Each annular element includes a plurality of struts and apices connected to form an annular configuration. Each annular element has a compressed state and an expanded state, and has a longitudinal dimension which is smaller in the expanded state than in the compressed state. A plurality of connecting members connect the apices of adjacent annular elements. The connecting members have a plurality of alternating segments that function to compensate for the smaller longitudinal dimension of each annular element in the expanded state. The stent may be provided with varying flexibility along its length and / or circumference, and may include segments that have different diameters.
Owner:ENDOSYST
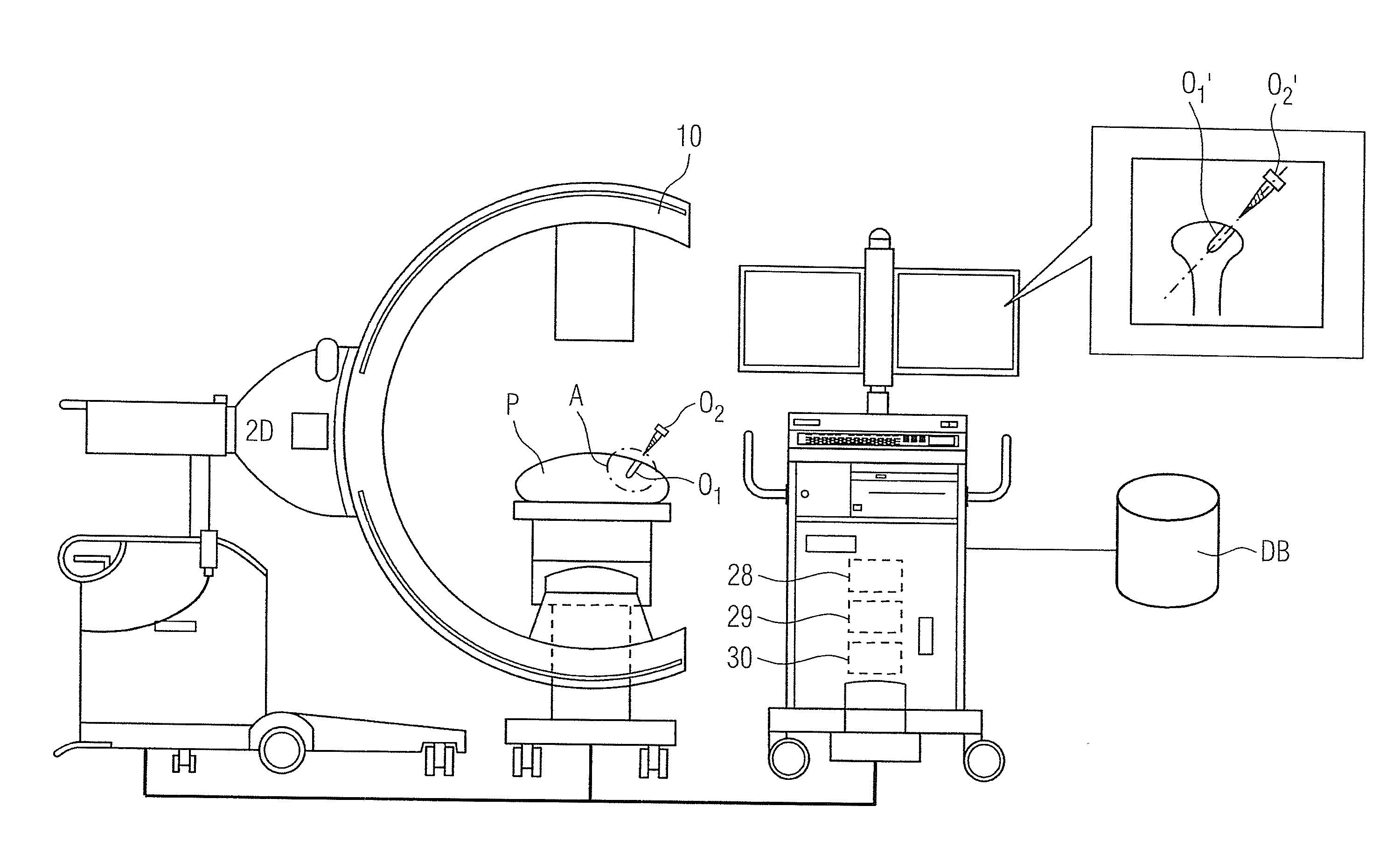
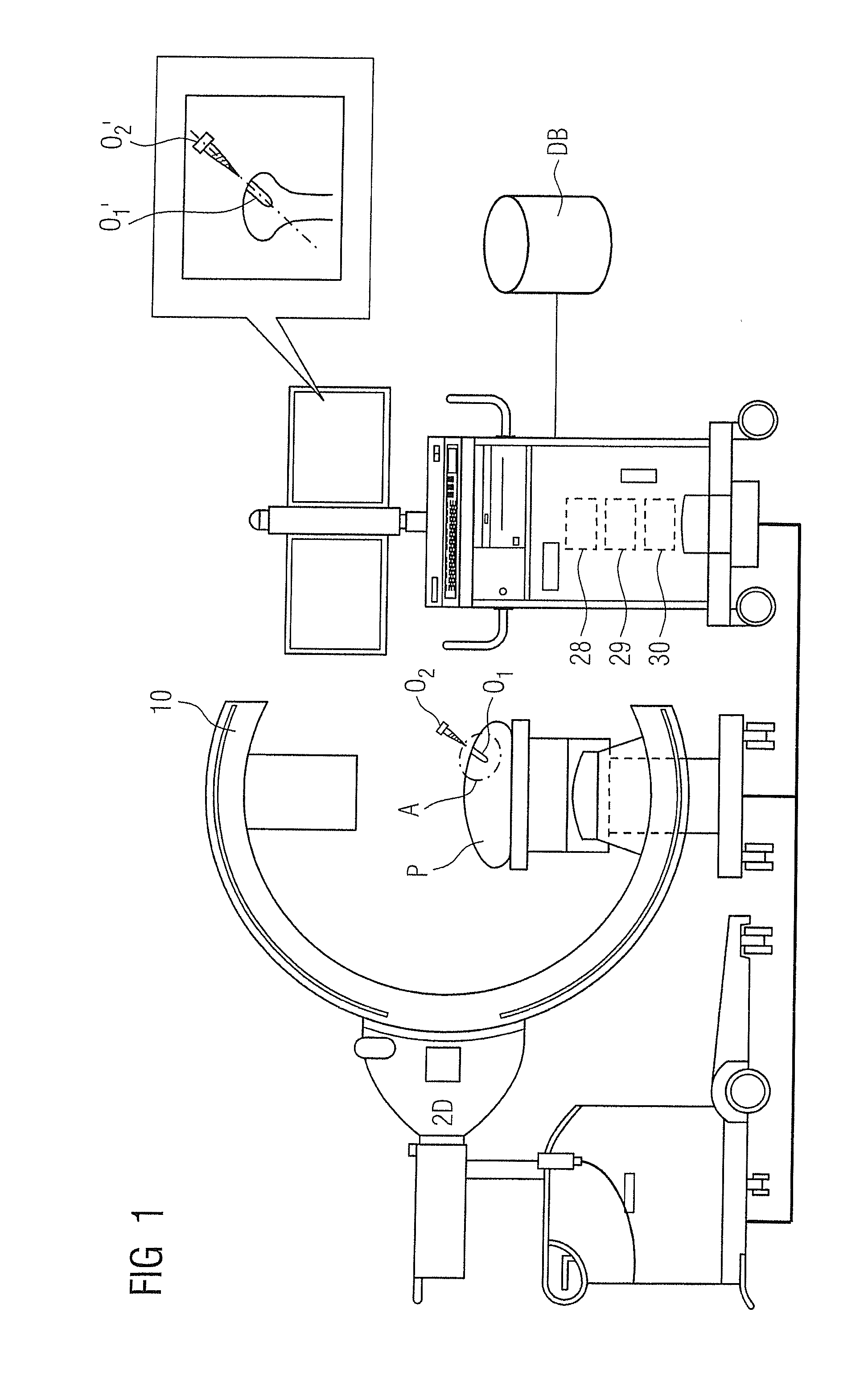
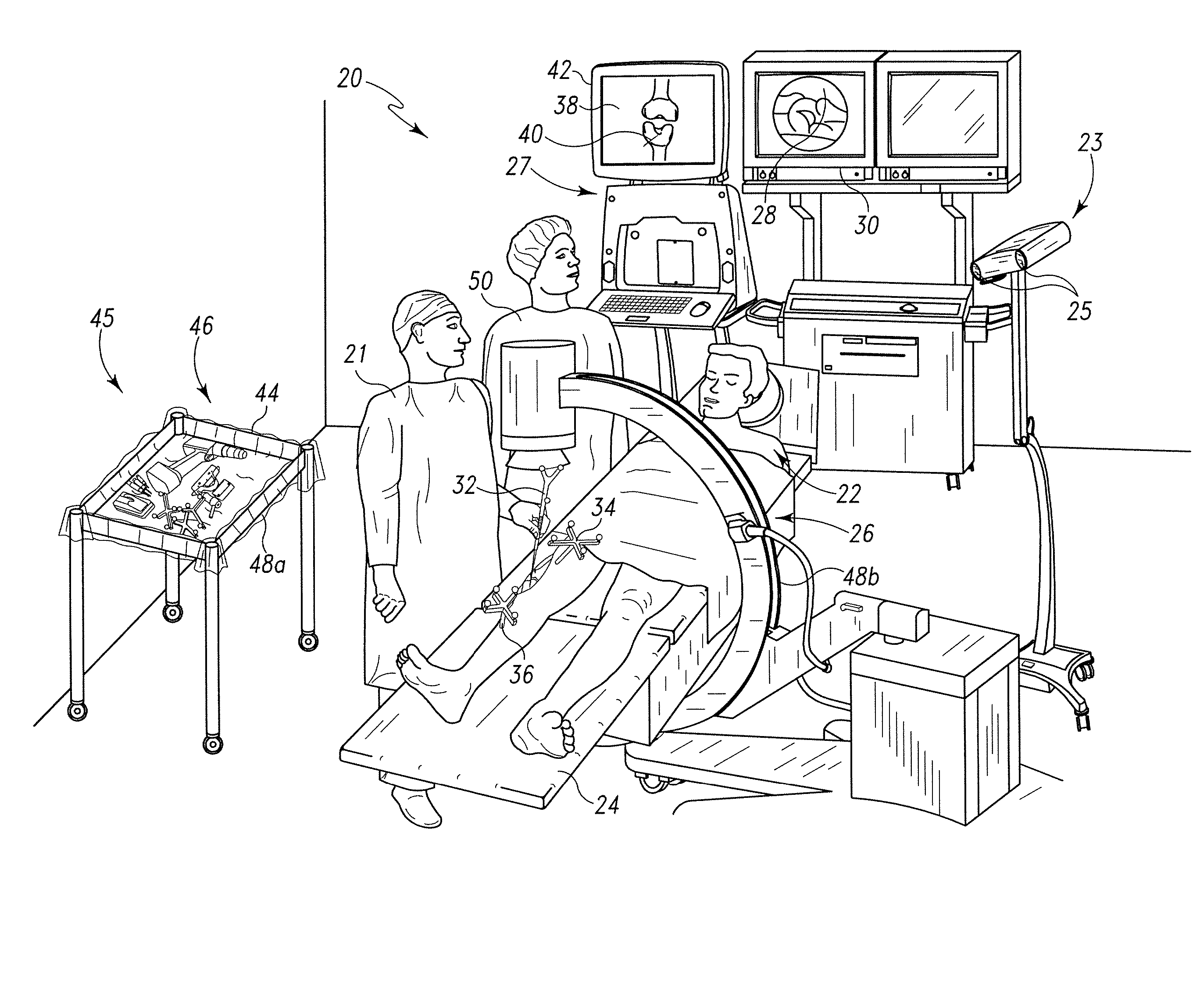
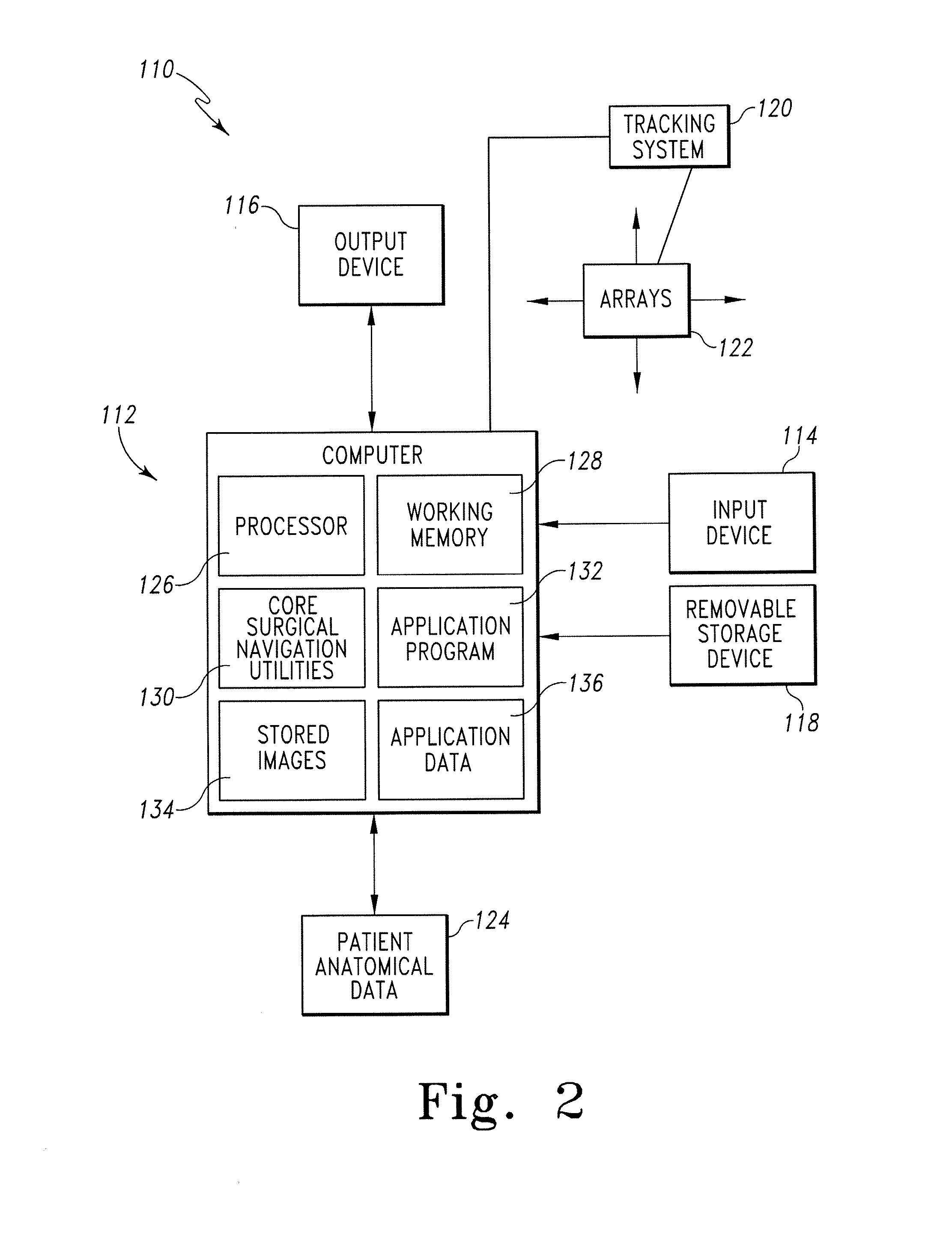
Method and system for determination of 3D positions and orientations of surgical objects from 2d x-ray images
InactiveUS20110282189A1Lower amount of x-ray radiation for the patientShort operating timeImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayX ray image
In a method, a system and a computer readable storage medium encoded with programming instructions, as well as a calculation module for three-dimensional presentation of at least two separate surgical objects within a medical procedure, access to three-dimensional models for the surgical objects takes place based on an acquired two-dimensional x-ray image with the surgical objects. The accessed three-dimensional models are integrated into the acquired two-dimensional x-ray image in order to be shown as a modified x-ray image. The modified x-ray image includes position information, relative positions and orientations of the surgical objects.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
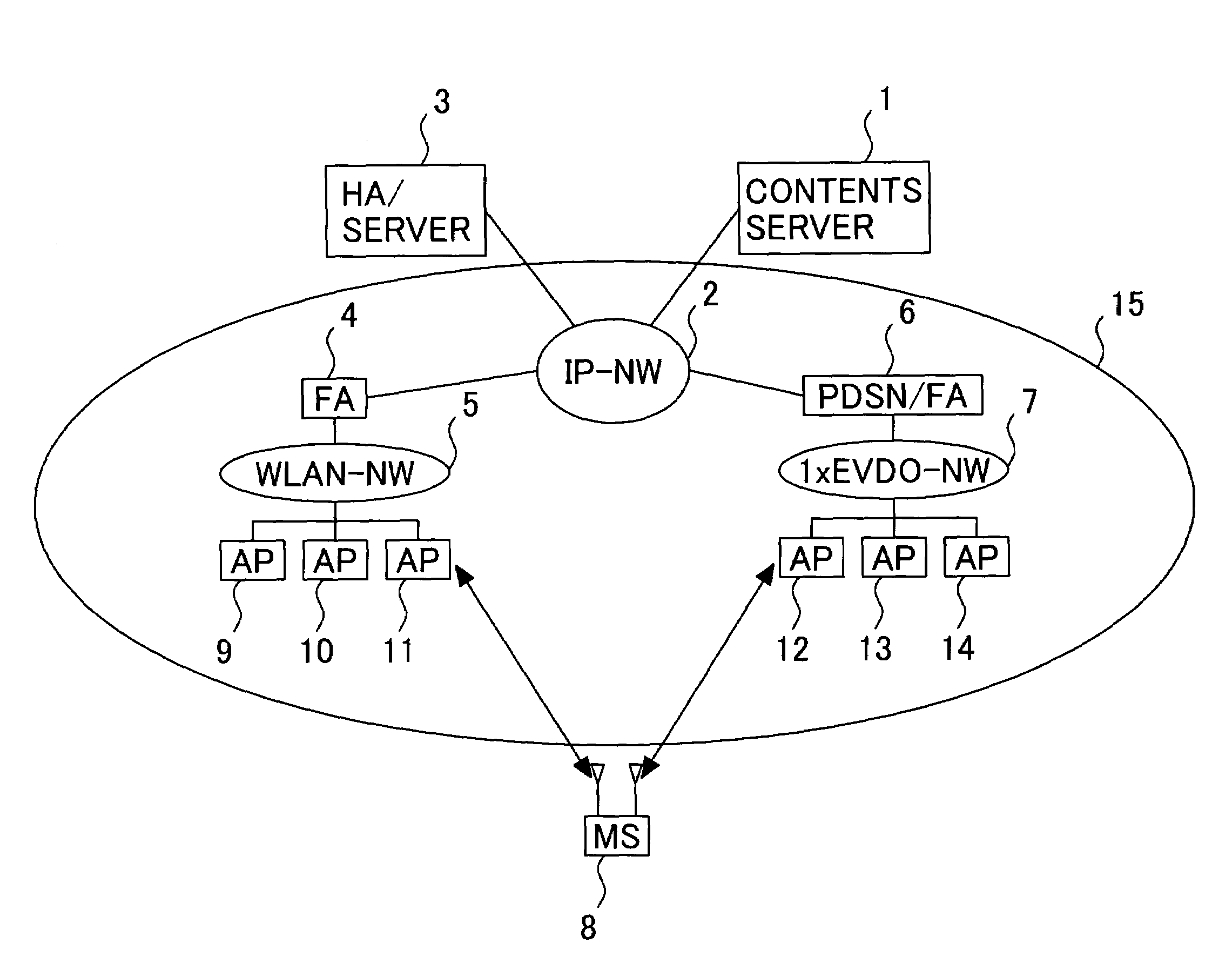
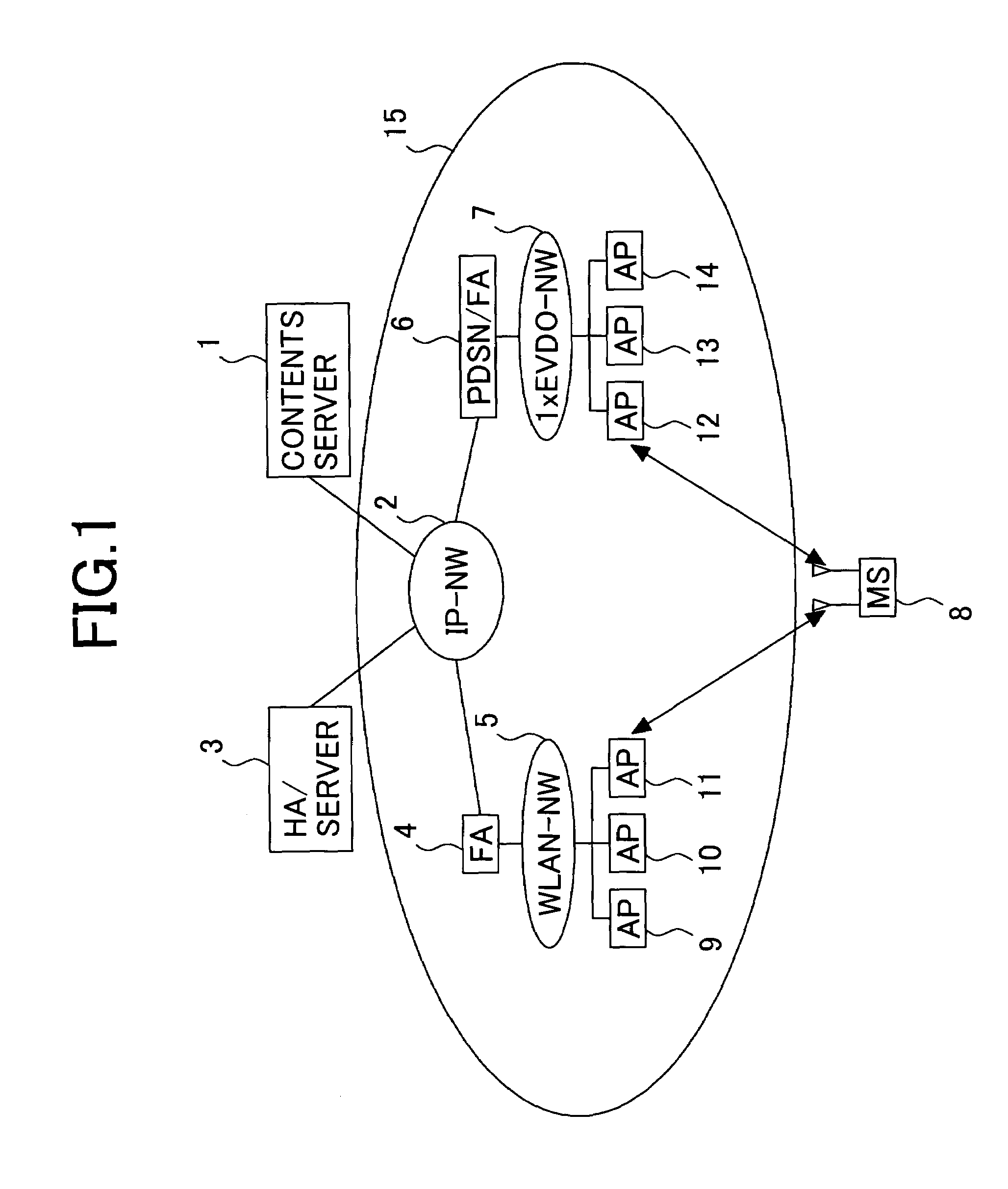
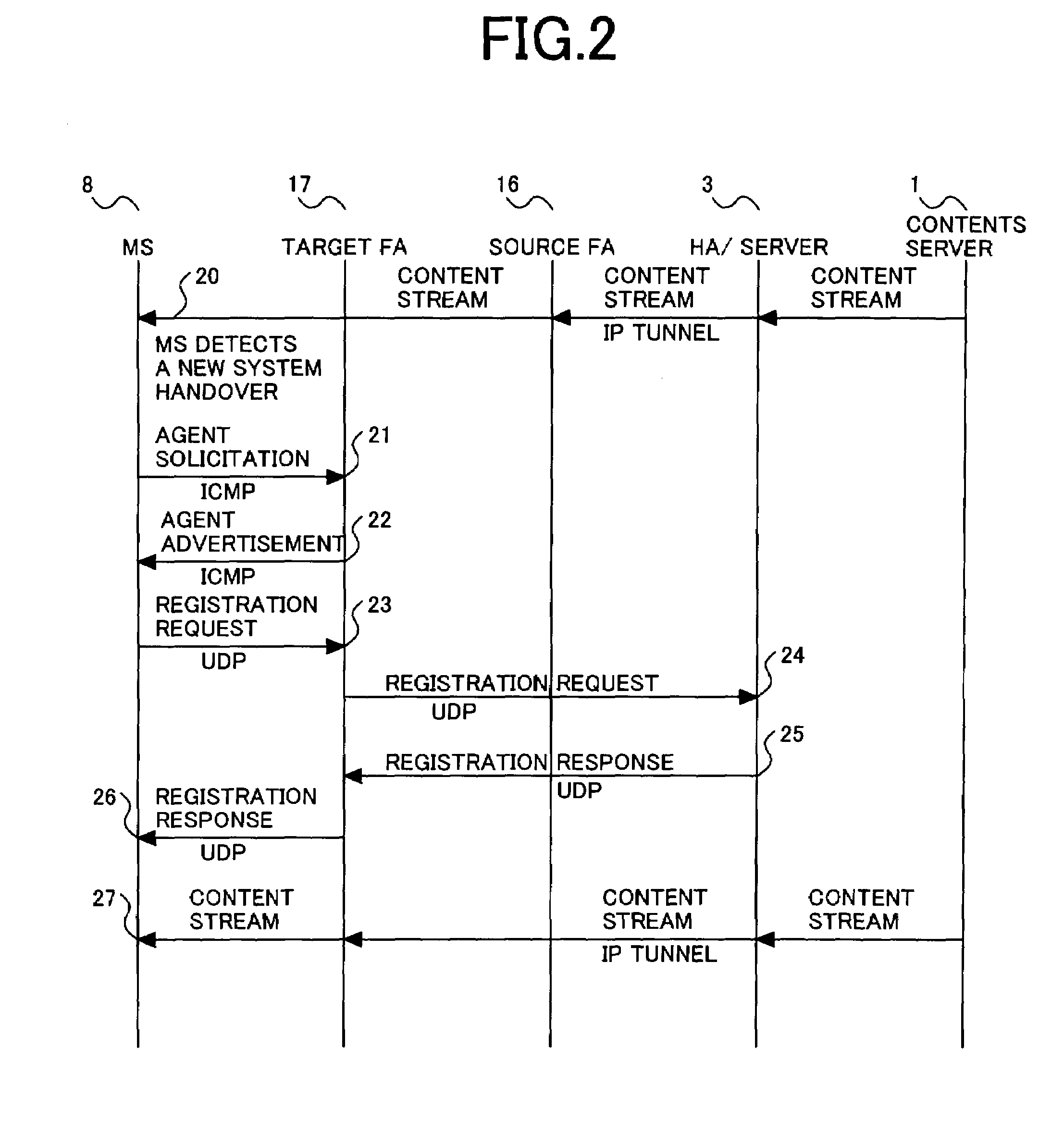
Wireless communication system, server and mobile station therefor
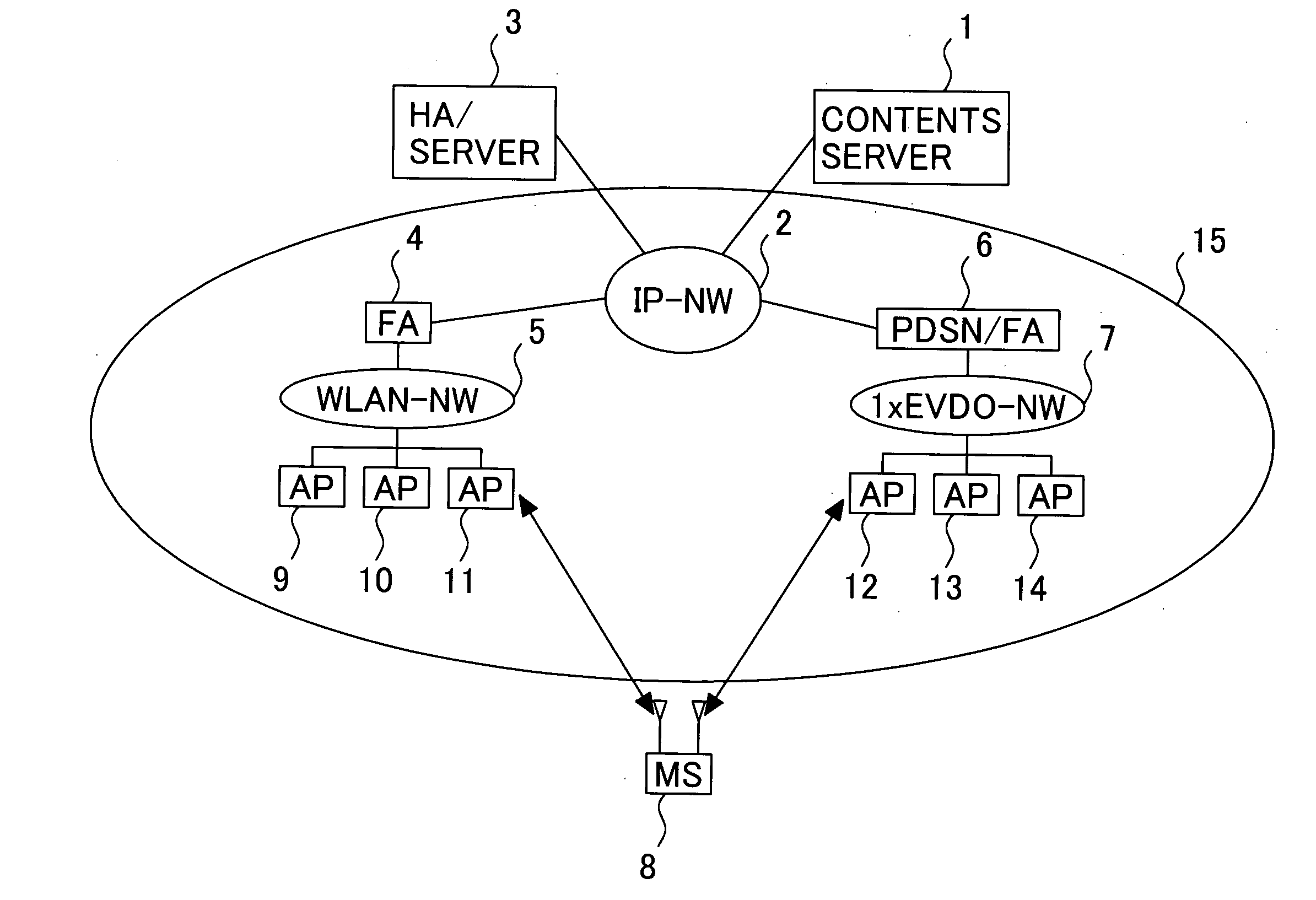
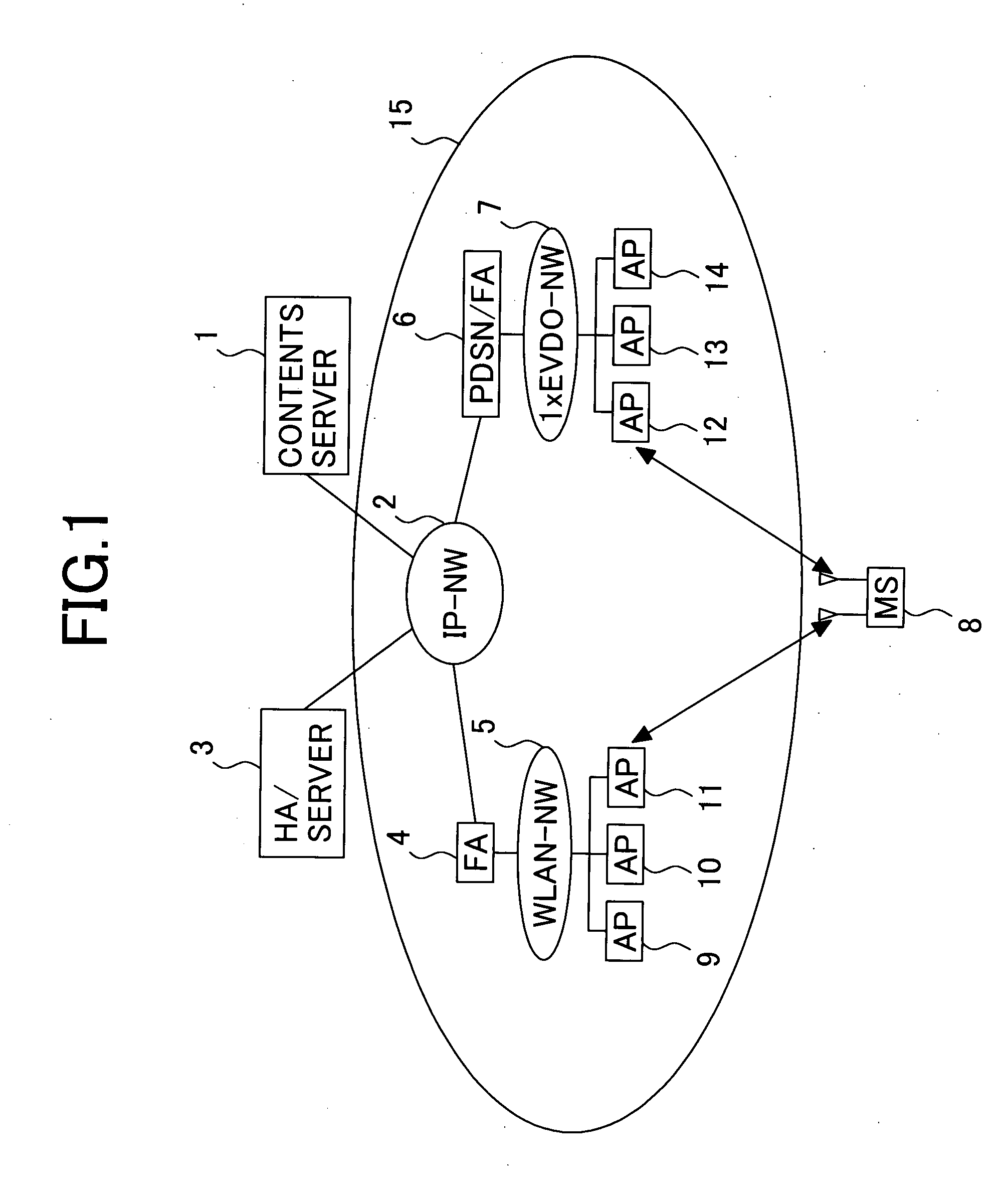
InactiveUS20050119001A1Shorter to authenticateShorten handover timeAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemNetworked system
This invention provides a wireless communication system wherein a network to which a mobile station should be handed over can be selected, using parametric data collected from network components other than the mobile station. Time taken for a handover between different types of network systems is reduced. The wireless communication system of the present invention comprises a mobile station equipped with multiple wireless interfaces, a server connected to a fixed network, and multiple access points. The mobile station determines available wireless interfaces and sends notification of the available interfaces' identifiers to the server. The server collects managerial data from network components and selects a wireless interface, based on the notification from the mobile station and the managerial data. The mobile station registers its locations in visiting networks corresponding to multiple available wireless interfaces with the server. The server retains the registrations of mobile station locations for the above wireless interfaces.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
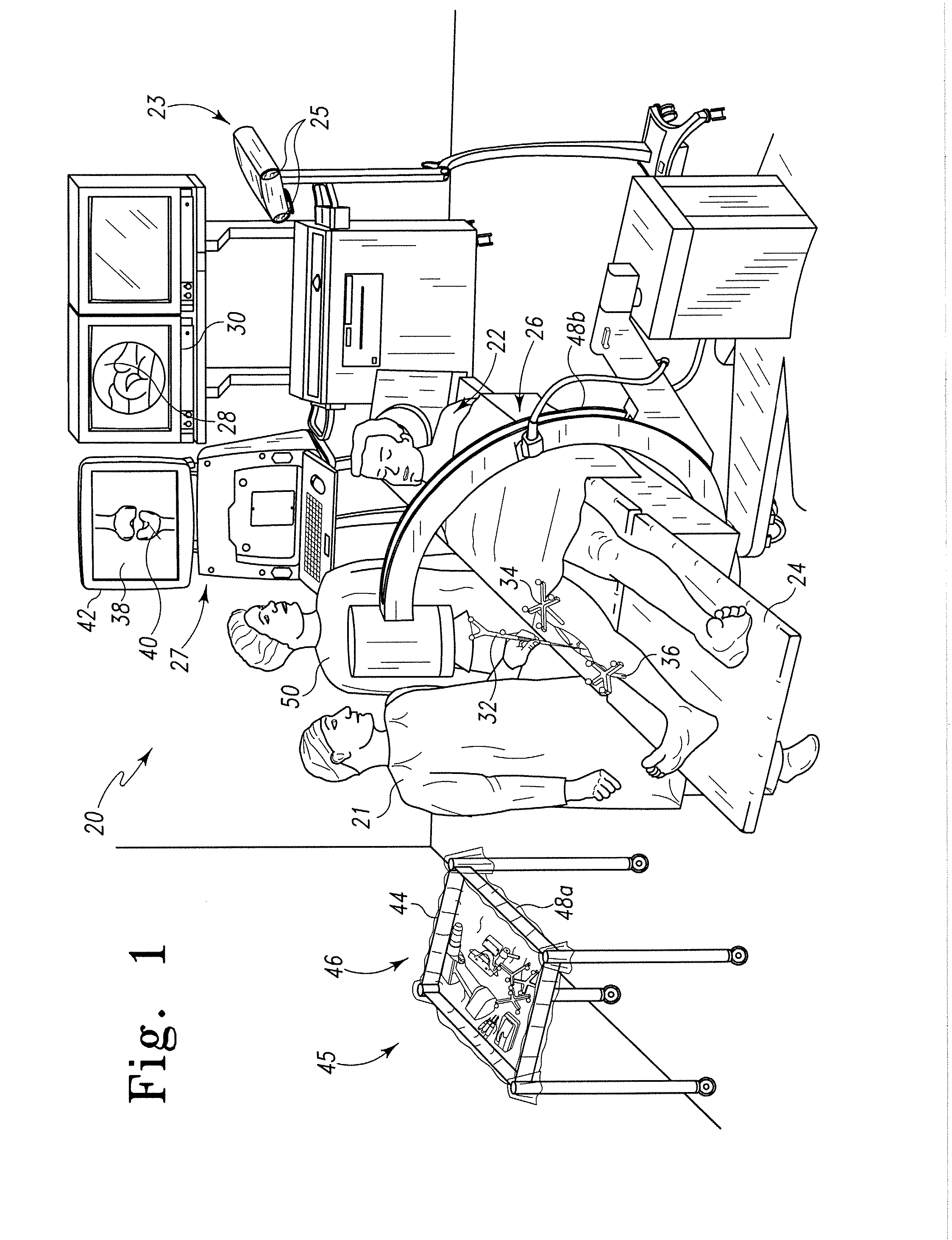
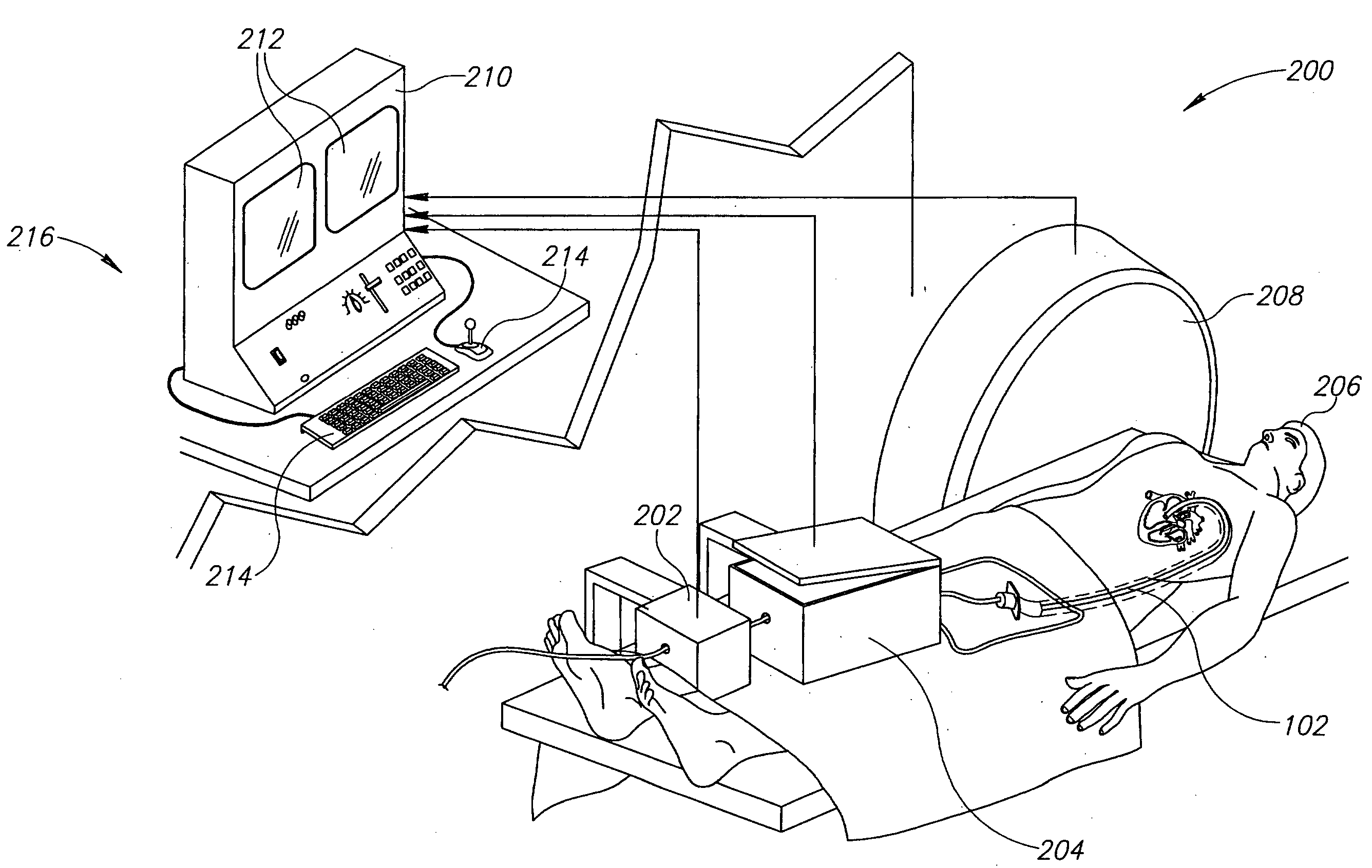
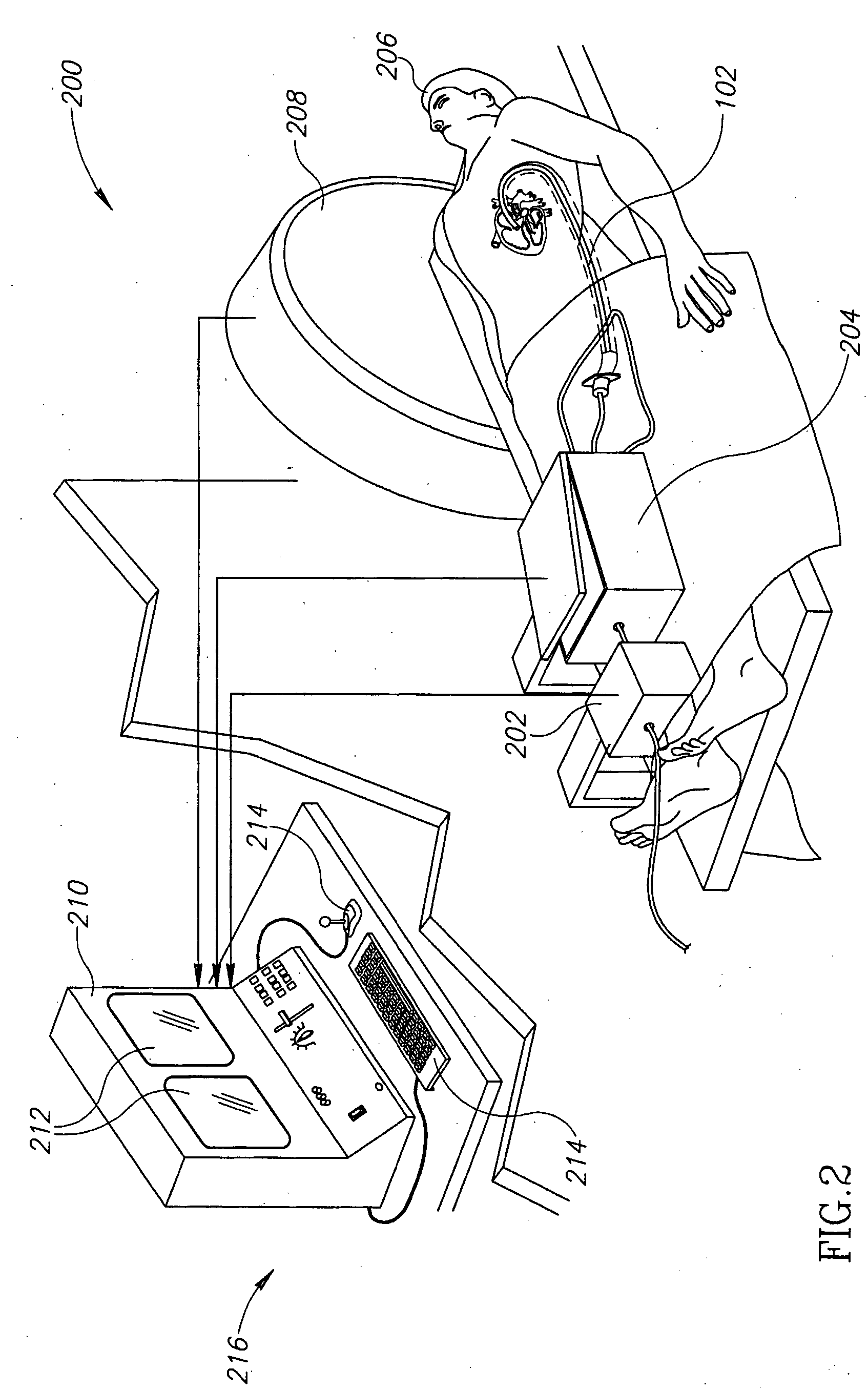
Modeling method and apparatus for use in surgical navigation
ActiveUS20070270680A1Accurate locationShorten the timeSurgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceModel methodRadiology
A modeling method for use in surgical navigation is provided. The method acquires a finite number of pre-defined points from a patient's bone and registers the points with a surgical navigation system. The navigation system generates and displays a three-dimensional image of a warped bone model that is manipulatable and accurate in at least the locations of the points taken and can be used to calculate the locations of bone cuts, implant positions and sizes, as well as display all of this information on the three-dimensional warped model.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
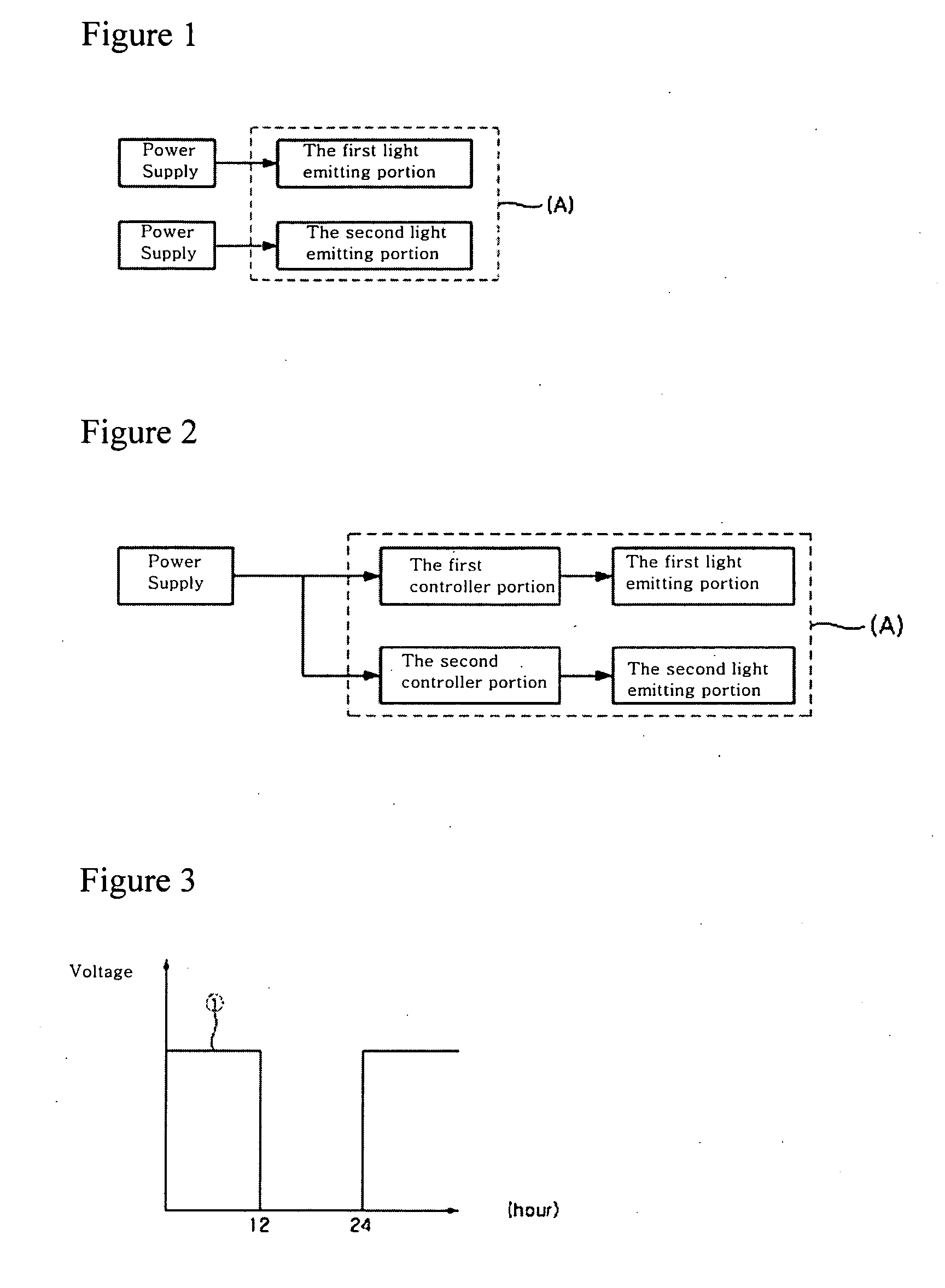
Light emitting device and lighting system having the same
ActiveUS20090303694A1Reduce cumbersome proceduresLow costElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesPhosphorLighting spectrum
The present invention provides a light emitting device comprising a first light emitting portion that emits white light at a color temperature of 6000K or more and a second light emitting portion that emits white light at a color temperature of 3000K or less, which include light emitting diode chips and phosphors and are independently driven. The present invention has an advantage in that a light emitting device can be diversely applied in a desired atmosphere and use by realizing white light with different light spectrums and color temperatures. Particularly, the present invention has the effect on health by adjusting the wavelength of light or the color temperature according to the circadian rhythm of humans.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Methods and devices for combined gastric restriction and electrical stimulation
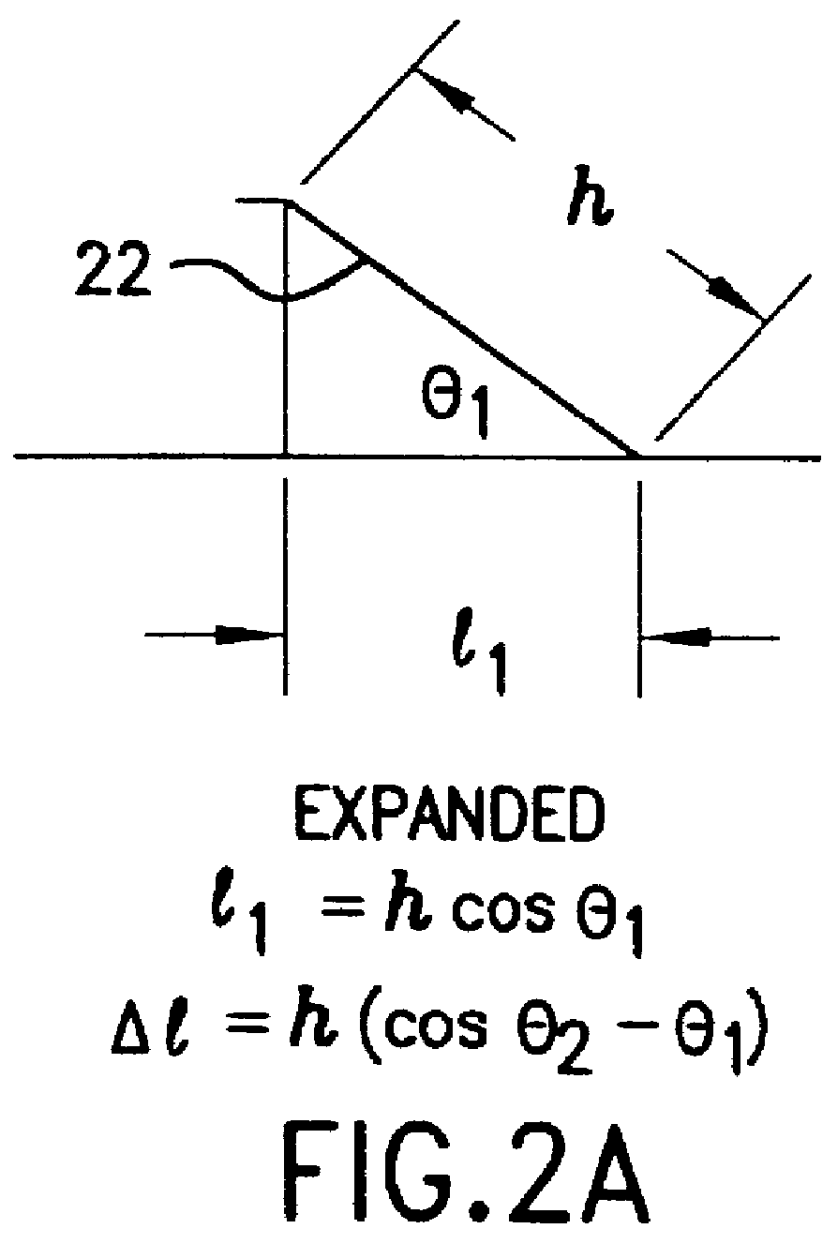
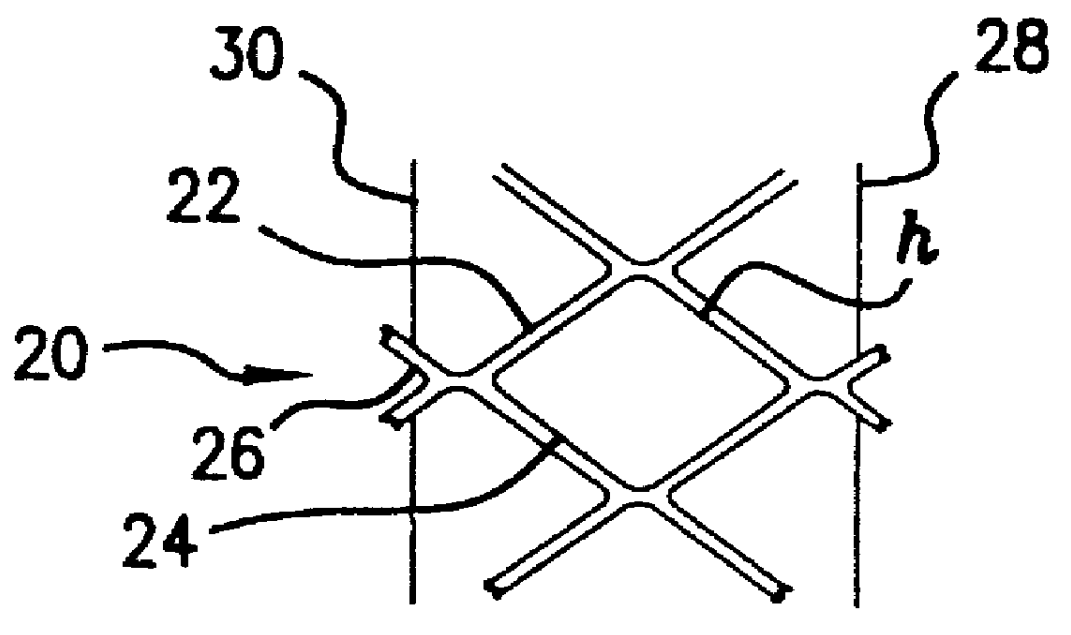
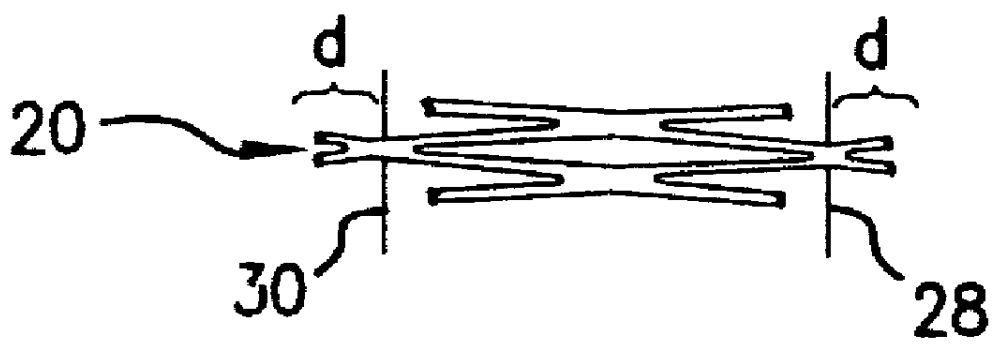
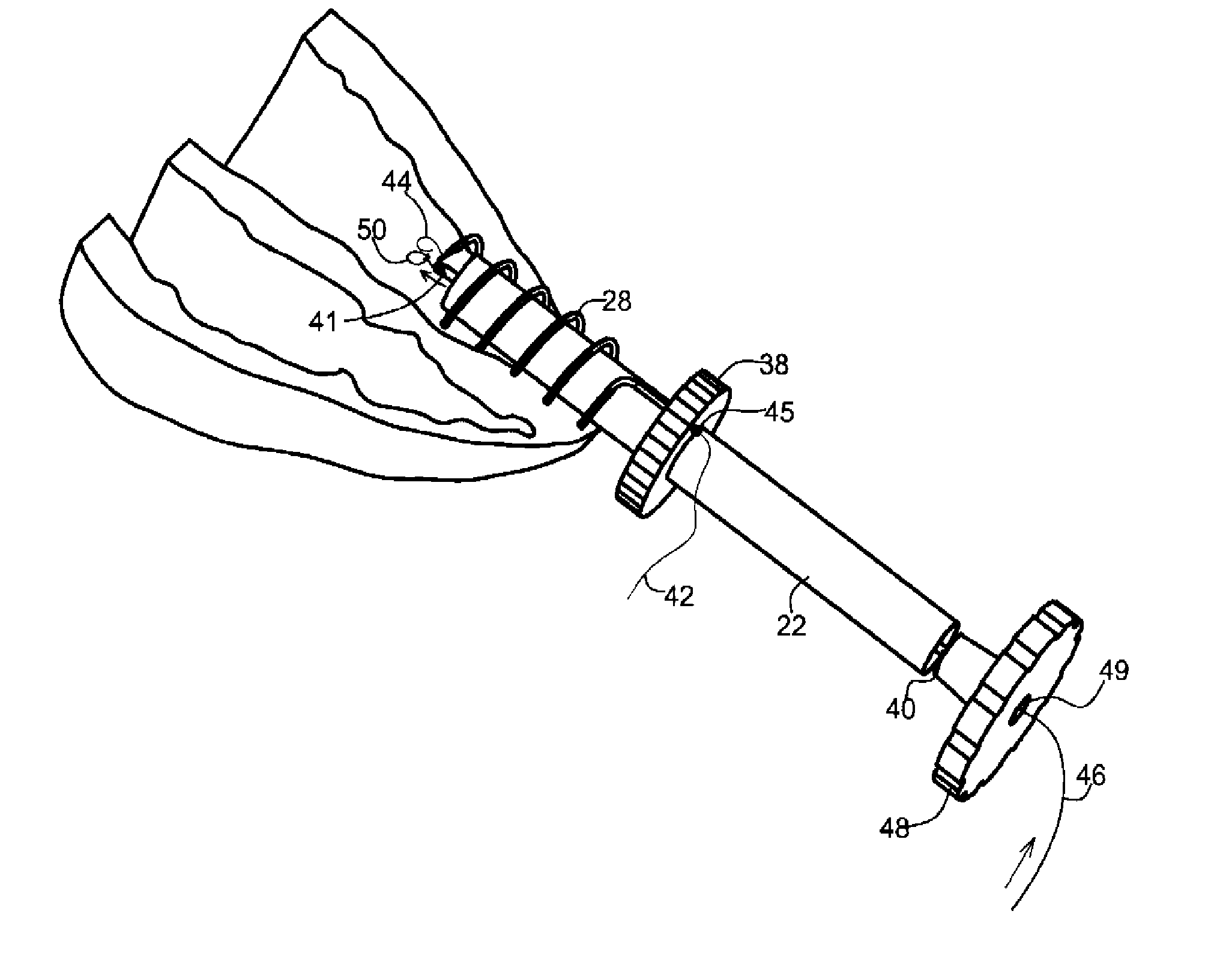
InactiveUS20060074473A1Reduce internal volumeReduction procedureSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesDevice implantGastric restriction
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for implantation into the walls of an organ such as the stomach. Deformable or inflatable anchors with a connector between are used to pull the walls of the organ together, or to implant devices in the wall of the organ. Also disclosed are surgical instruments useful in practicing the disclosed methods.
Owner:GERTNER MICHAEL
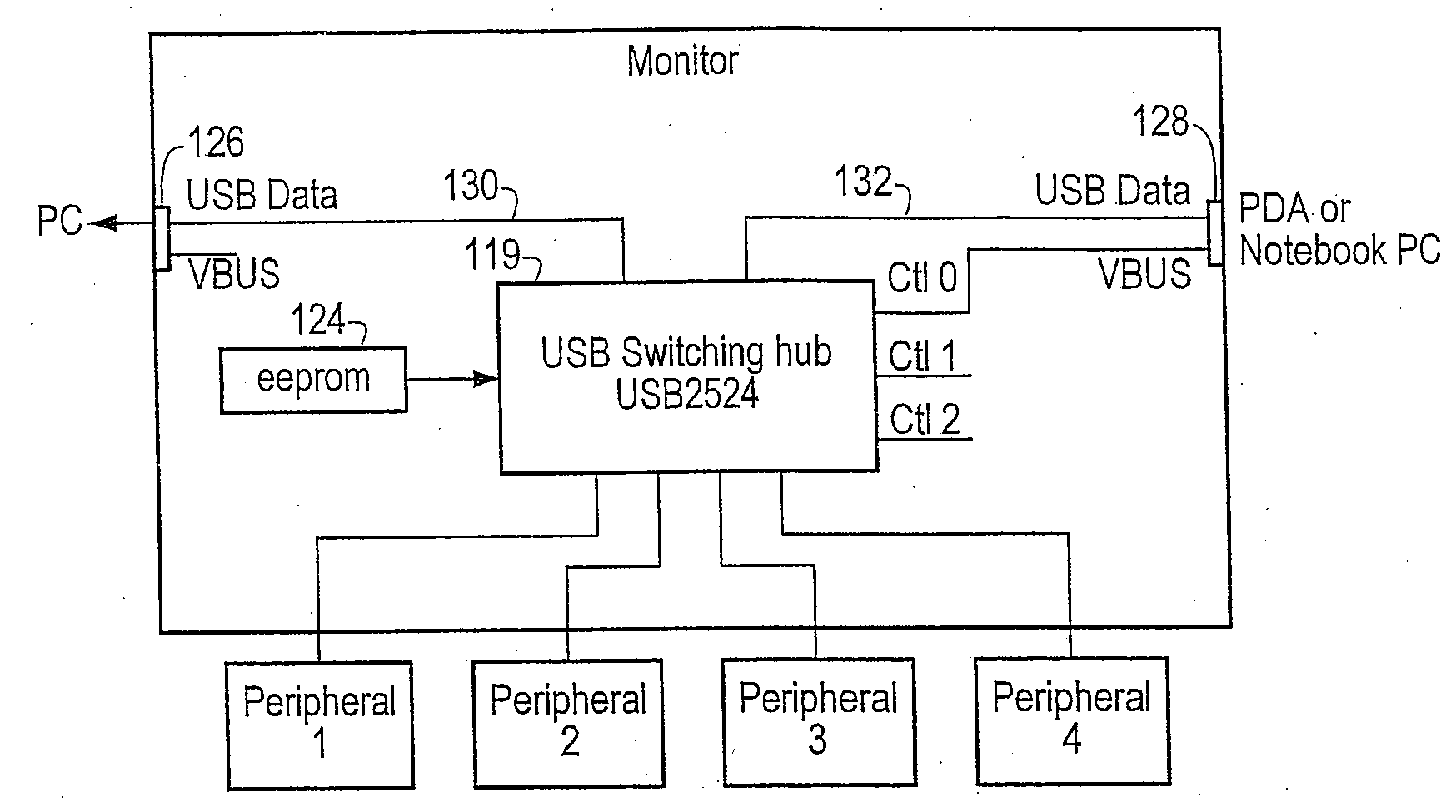
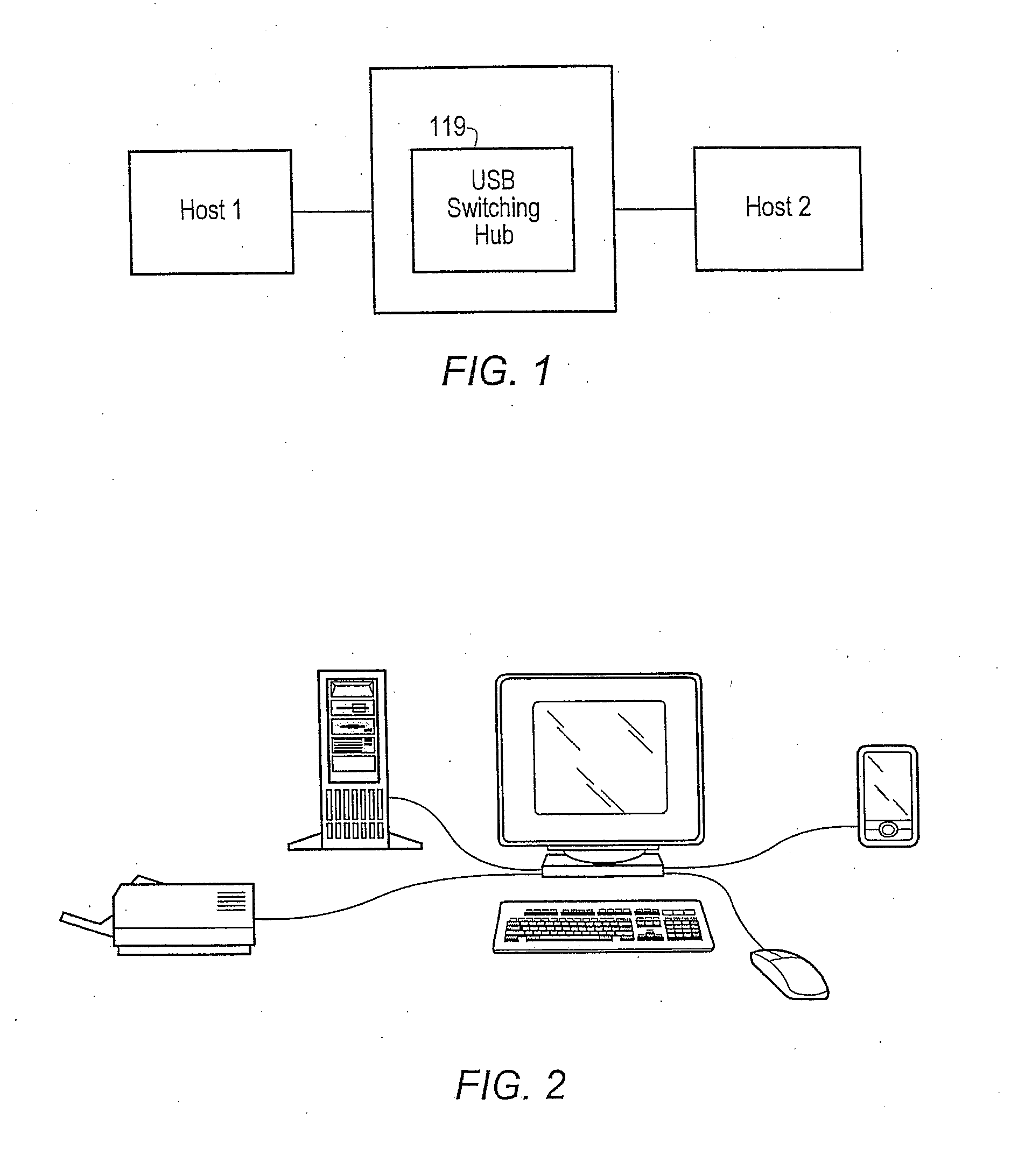
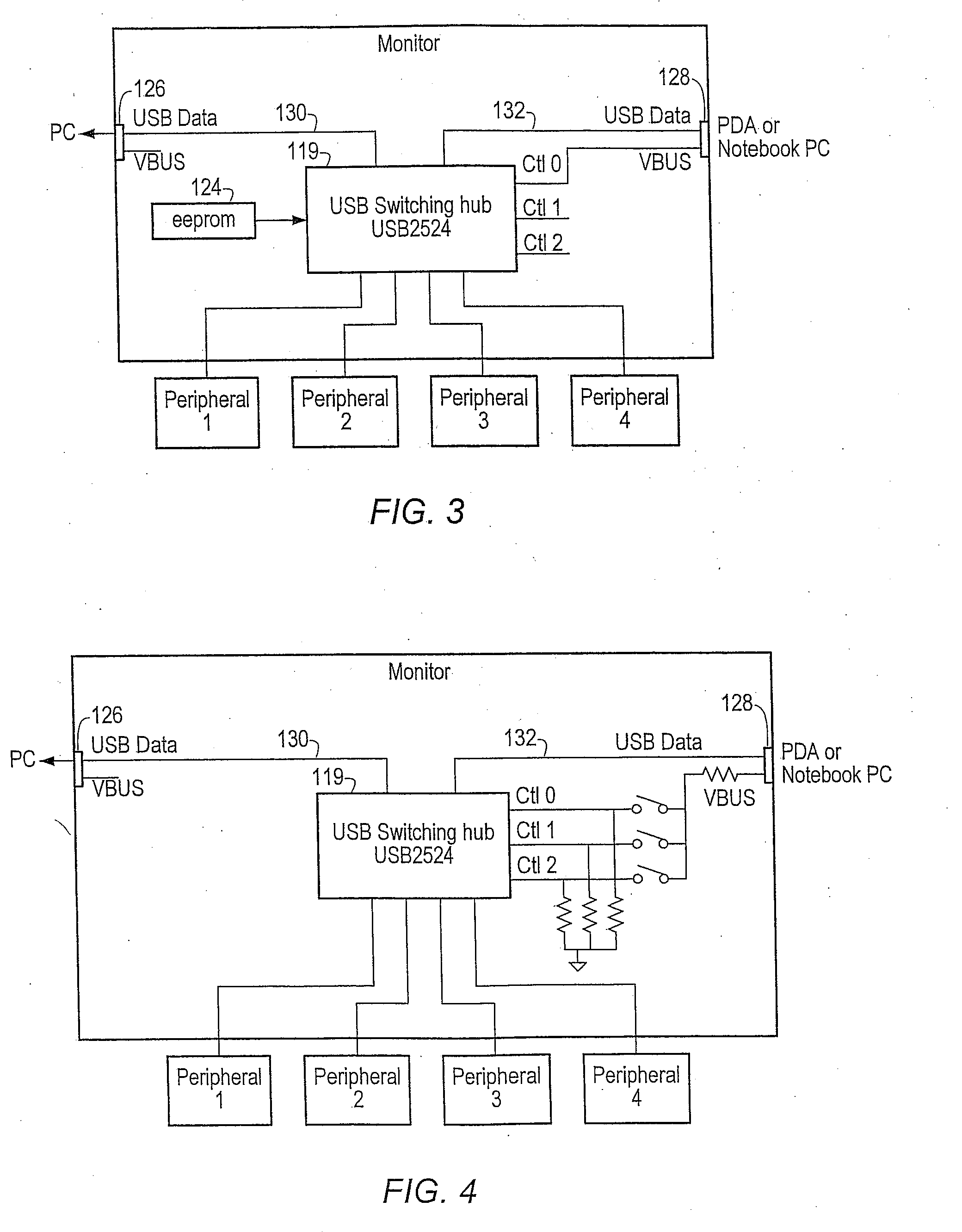
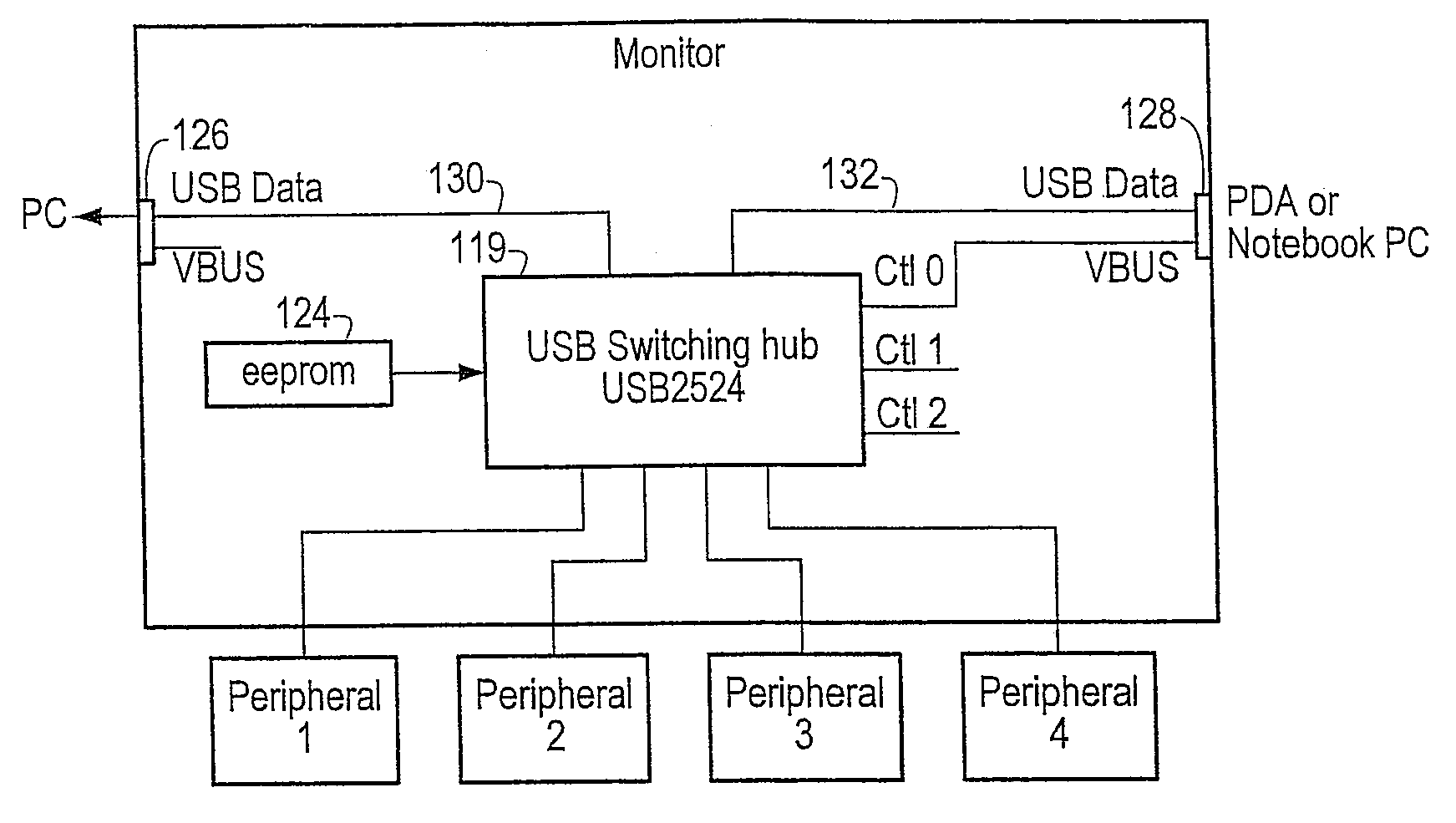
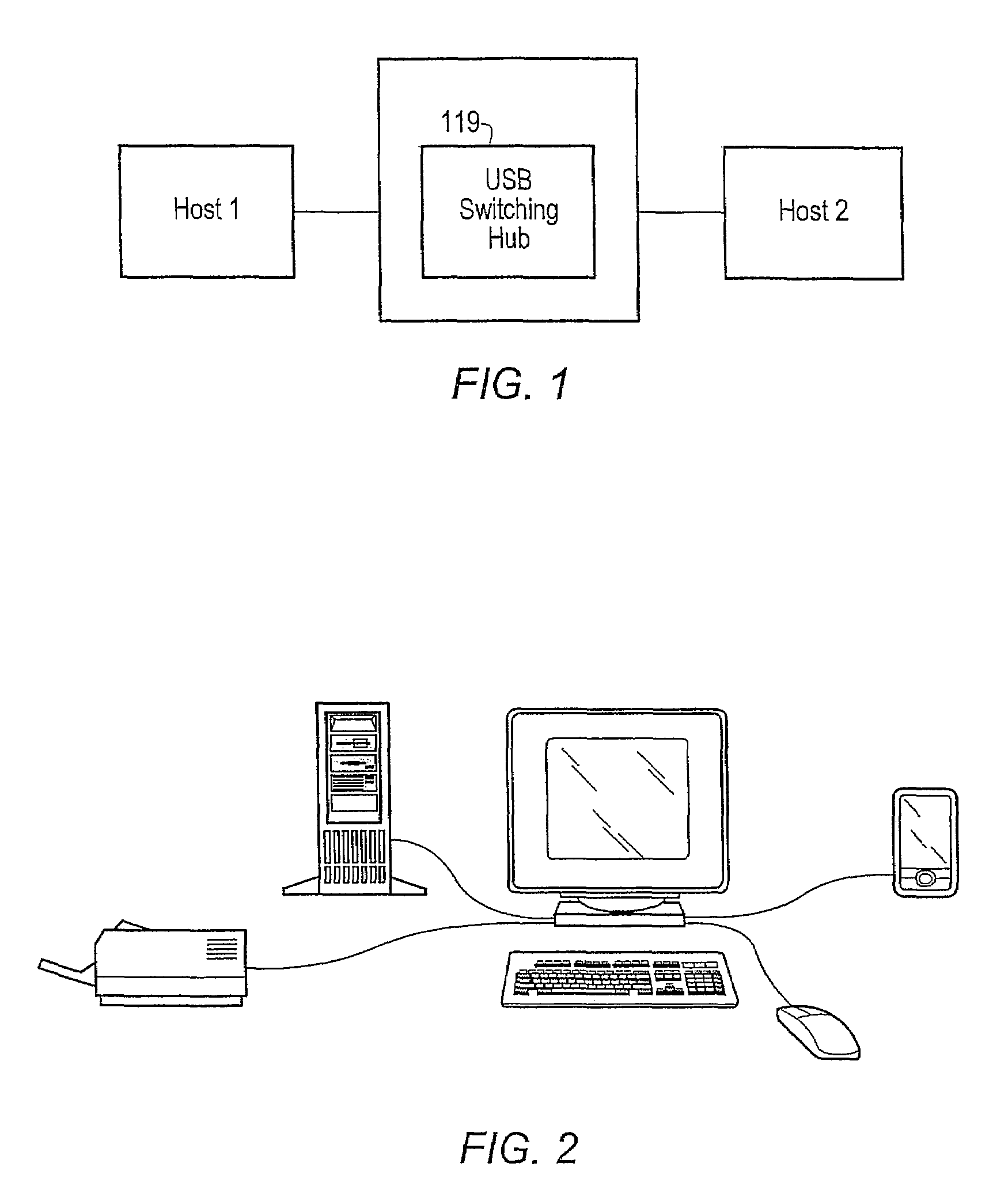
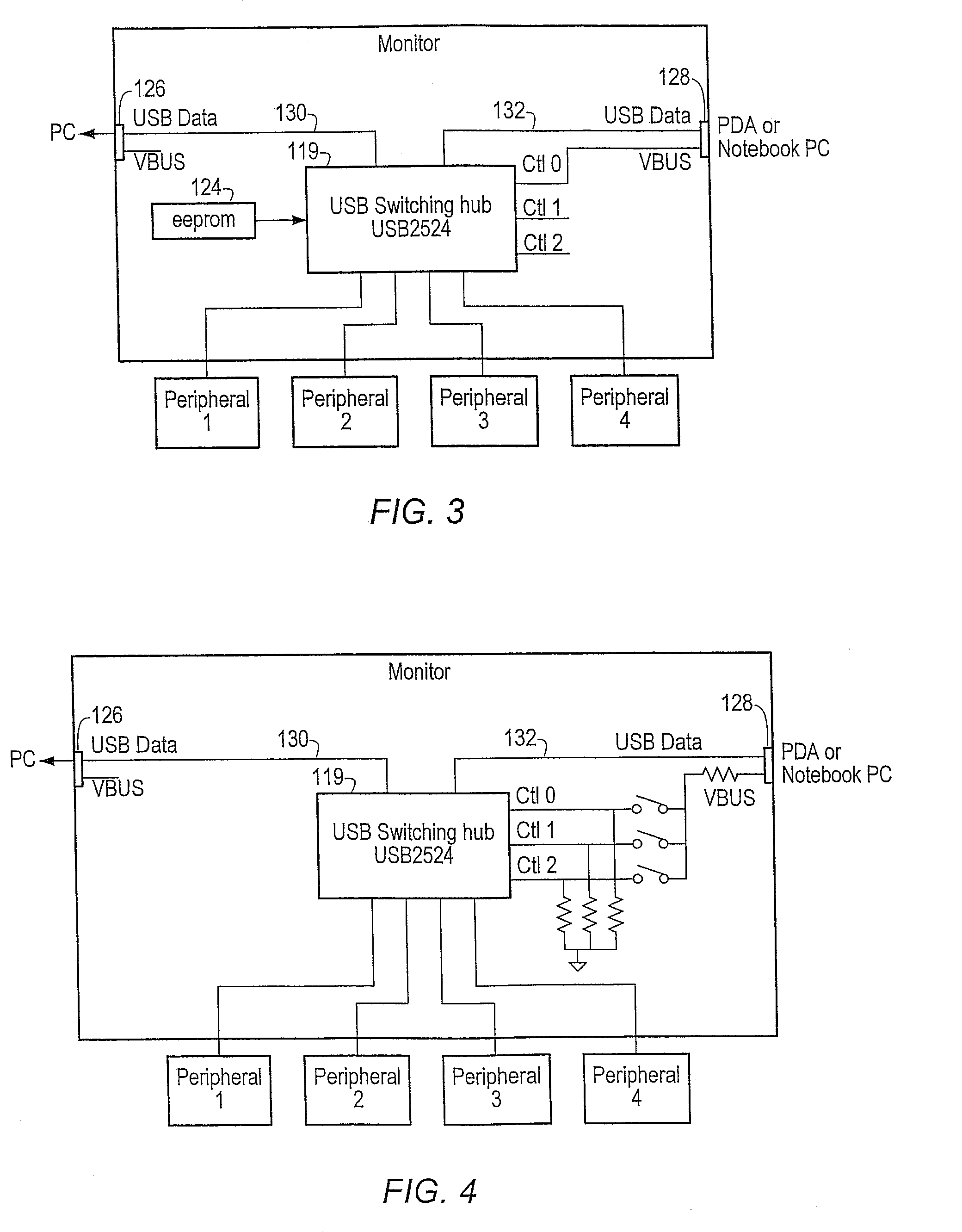
Method for automatically switching USB peripherals between USB hosts
ActiveUS20070245058A1Reduces procedureReduction procedureInput/output processes for data processingEmbedded systemPeripheral
A system for automatically switching peripheral connectivity between two host devices based on respective connectivity of the hosts. The method may be used where peripherals are usually attached to one host and are automatically switched to a second host when the second host is attached to the system. A USB switching hub may be operable to automatically switch connectivity of the peripheral device(s) from the first host device to the second host device when the second host device is connected to the USB device. This automates the process for the end user when normally all peripherals are attached to one host, and some or all peripherals are shared with a second host when the second host is attached.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Method and apparatus for downloading content using NFC
ActiveUS20150133049A1Reduction procedureReduced resourceNear-field transmissionMobile application execution environmentsNetwork-attached storageSmart device
Disclosed are a method and apparatus for downloading content using NFC. The content-downloading method of the present invention is performed by a first device, and comprises the steps of: transmitting a content-downloading request for requesting a download of content using a second device; receiving a confirmation to the content-downloading request from the device which has received the content-downloading request; receiving a wake-up request from the second device; and receiving, from the second device, the content downloaded to the second device in response to the content-downloading request. Accordingly, a user may support a download reservation and transmission by simply placing NFC-supporting devices in contact, support a queue download request and list management using NFC between network attached storage (NAS) and a smart device, and support a queue request and caching using a home network after establishing an NFC link.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
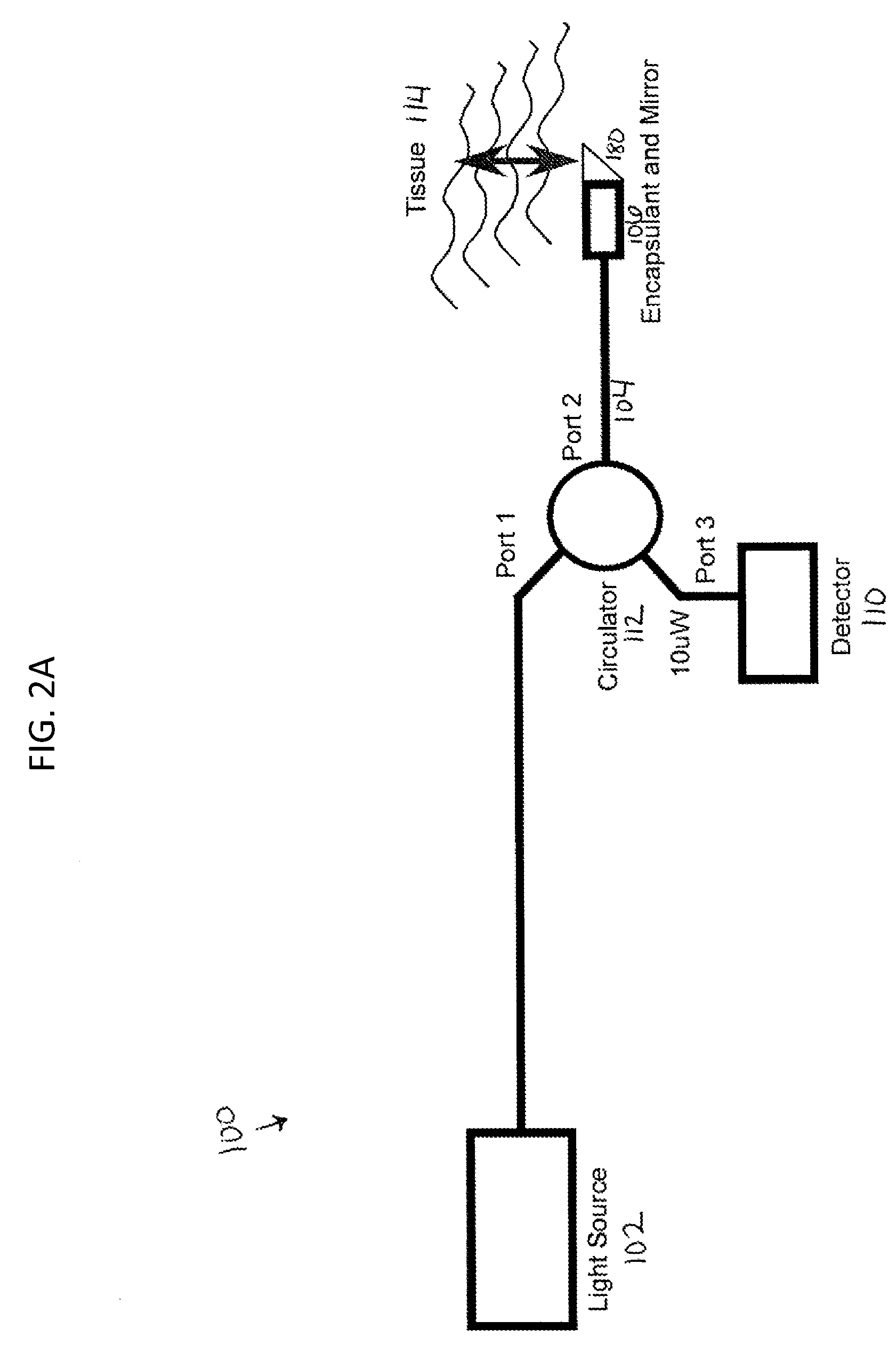
Optical coherence tomography for biological imaging
ActiveUS20100305452A1Shorten operation timeImprovement longCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical radiationRefractive index
Described herein are catheters for use with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) that include an optical fiber core having a first refractive index and an interface medium having a second refractive index, where the first and second refractive indexes are mismatched such that receiving electronics configured to receive optical radiation reflected from the reference interface and the target operate in a total noise range that is within 5 dB of the shot noise limit. These OCT catheters may include a silicon die mirror having a reflective coating that is embedded in the interface medium. The optical fiber can be fixed at just the distal end of the catheter, and may be managed within a handle that is attached to the proximal end of the catheter body, and is configured to allow rotation of the both catheter body and the optical fiber relative to the handle.
Owner:AVINGER
Methods and apparatuses for treatment of hollow organs
InactiveUS20090131955A1Shorten the timeLower performance requirementsElectrocardiographySurgical navigation systemsSensing dataDisplay device
Owner:CORINDUS
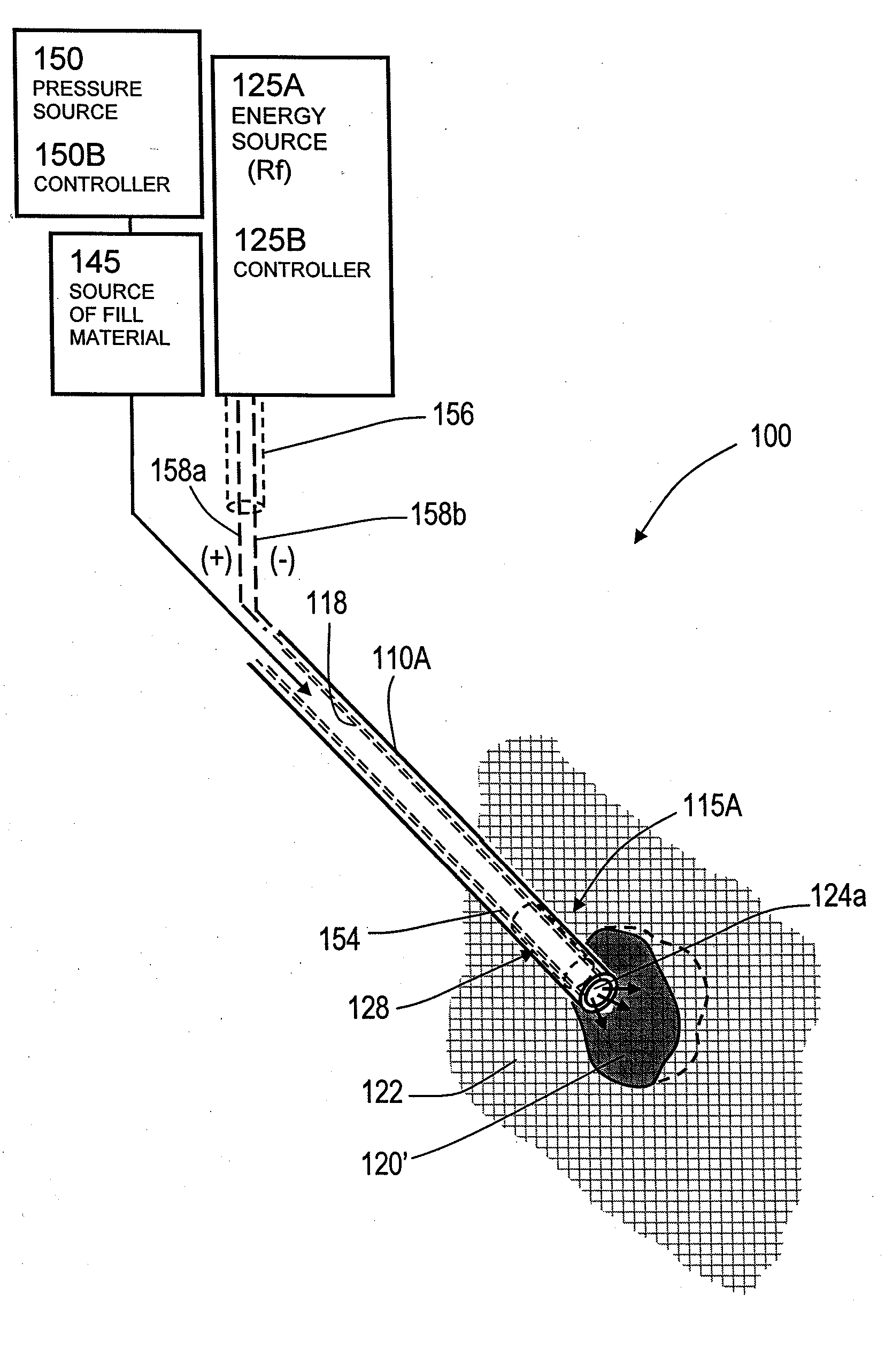
Systems for sensing retrograde flows of bone fill material
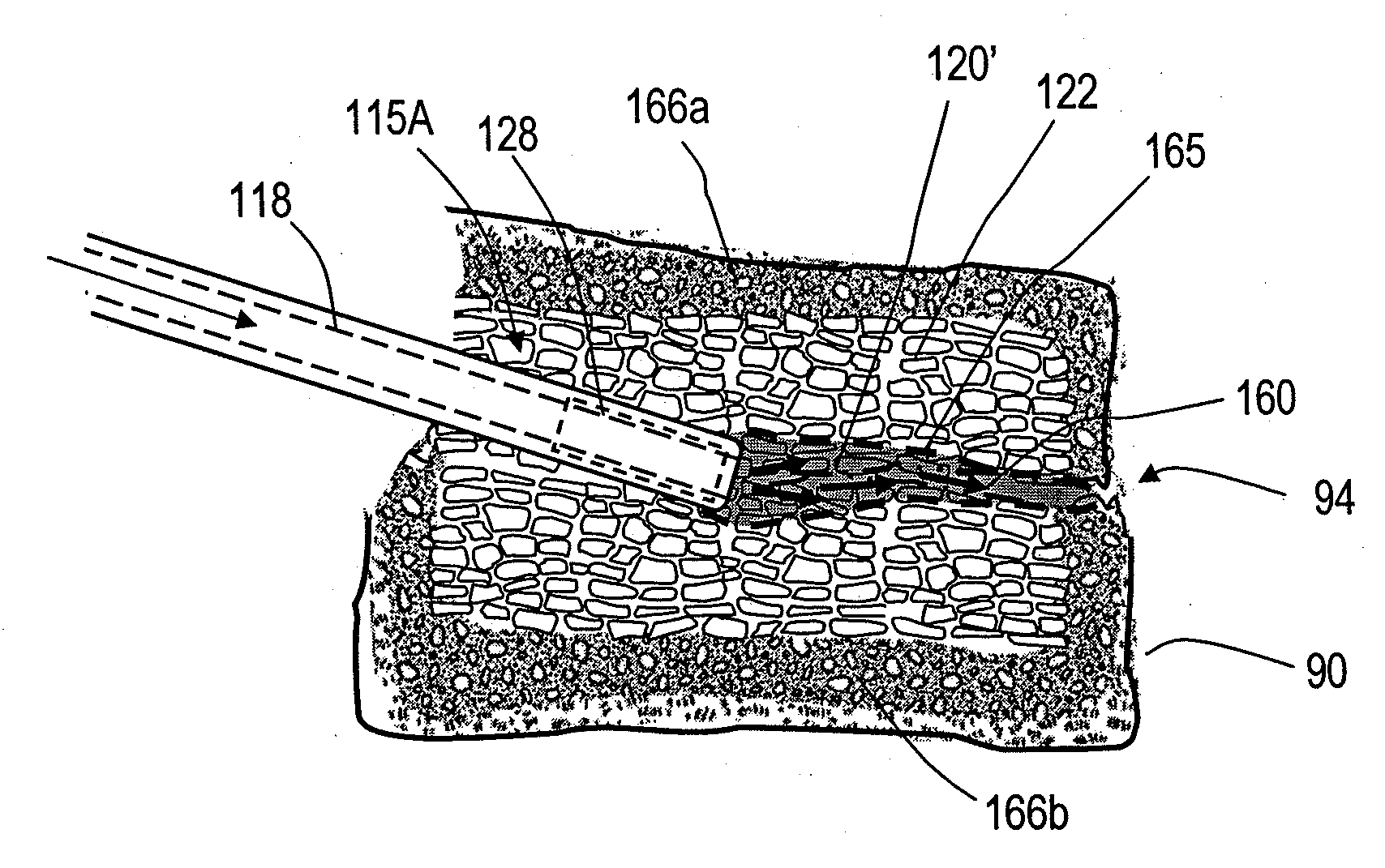
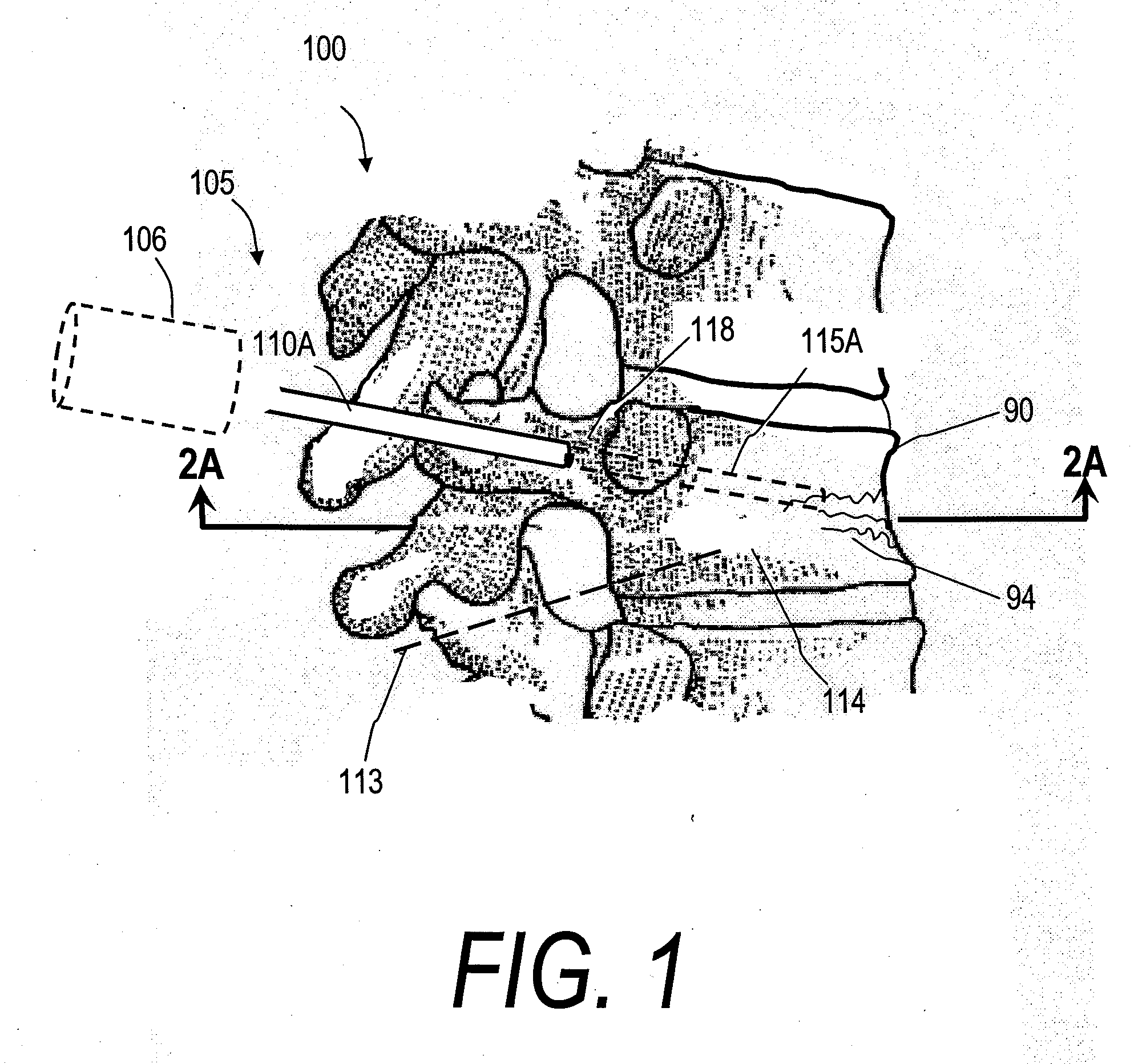
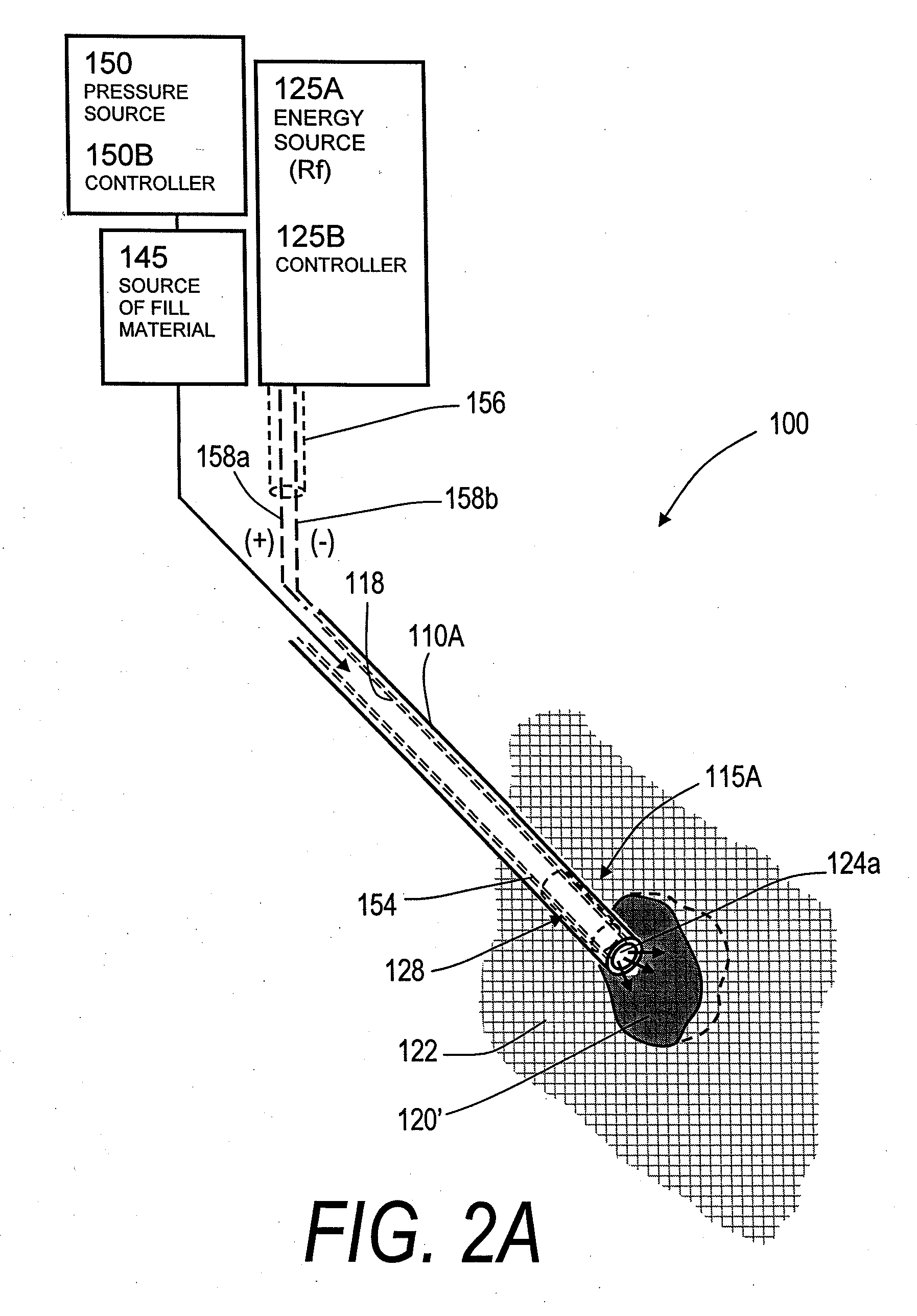
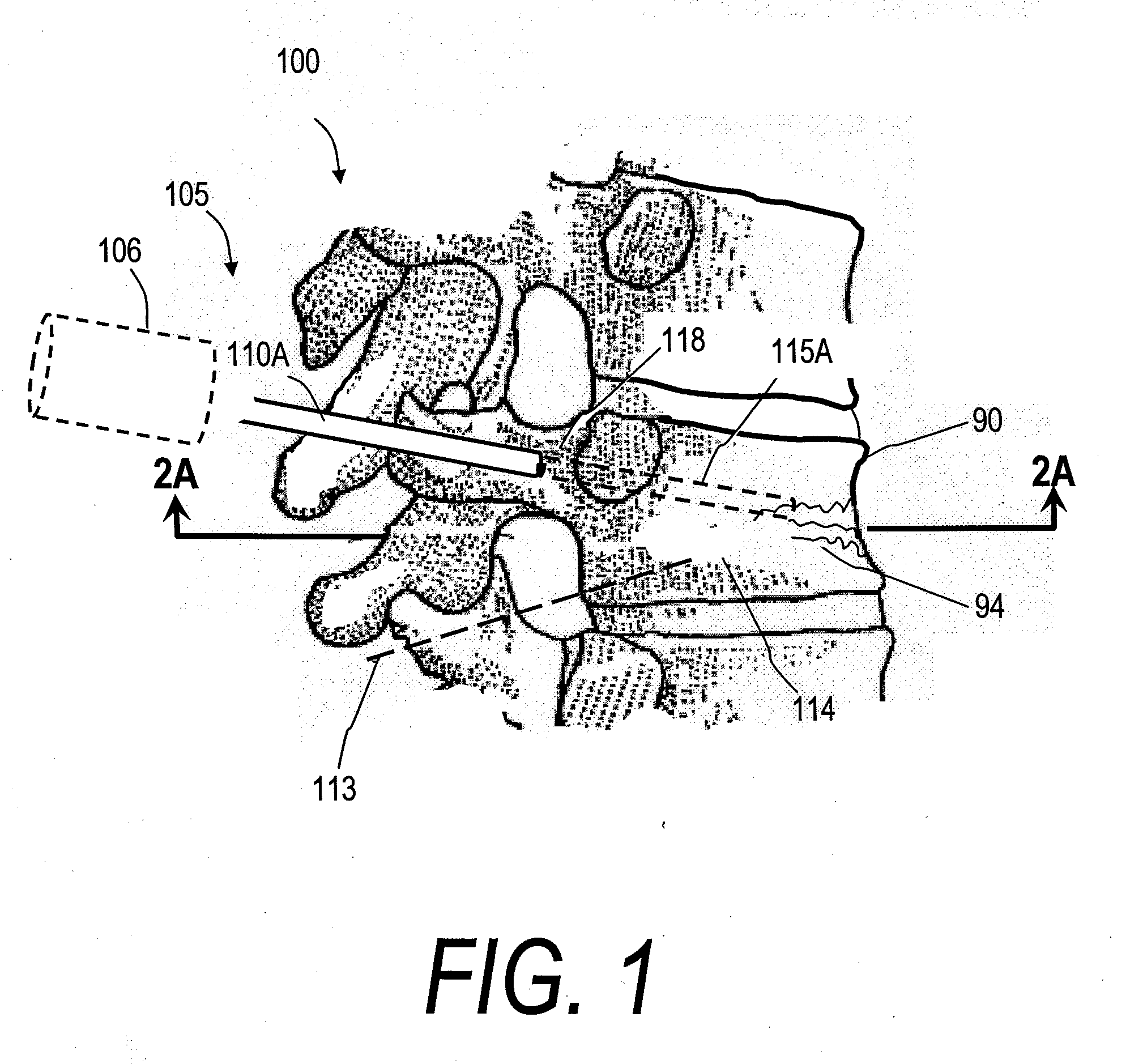
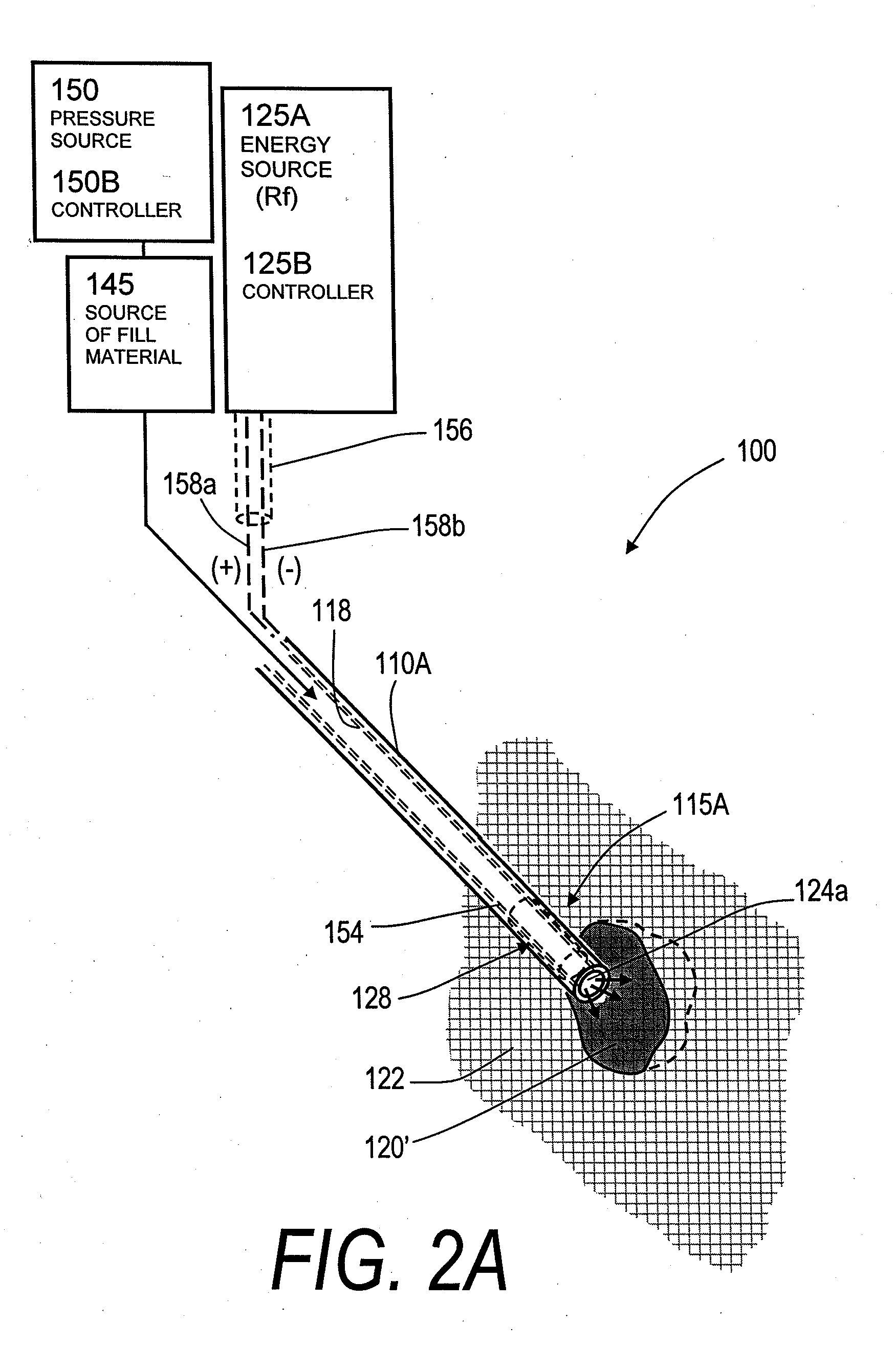
InactiveUS20070118144A1Inhibit migrationReduction procedureDiagnosticsSpinal implantsCounter flowFilling materials
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to medical devices, systems and methods for use in osteoplasty procedures, such as vertebral compression fractures. One device for delivering a bone fill material to a bone, such as a vertebra, includes an elongated sleeve configured for introduction into a bone, the elongated sleeve having an opening to allow a flow of bone fill material therethrough into the bone. The device also includes at least one sensor disposed on an exterior surface of the sleeve, the sensor being configured to sense a retrograde flow of bone fill material about the sleeve and proximate the at least one sensor. One system for treating a bone includes such a device and a controller configured to receive signals from the sensor and controls at least one parameter of bone fill material flow into the bone based at least in part on said signals.
Owner:DFINE INC
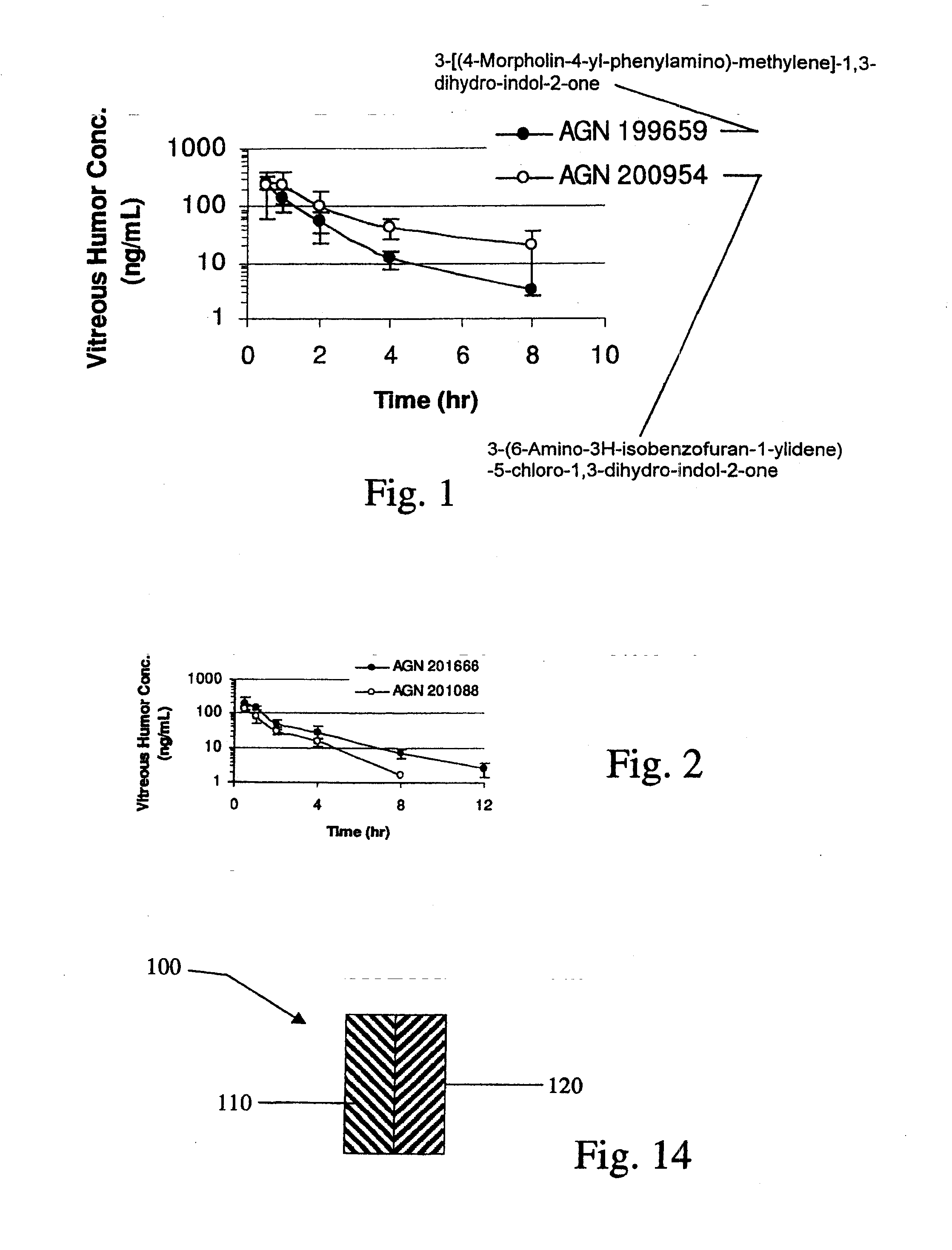
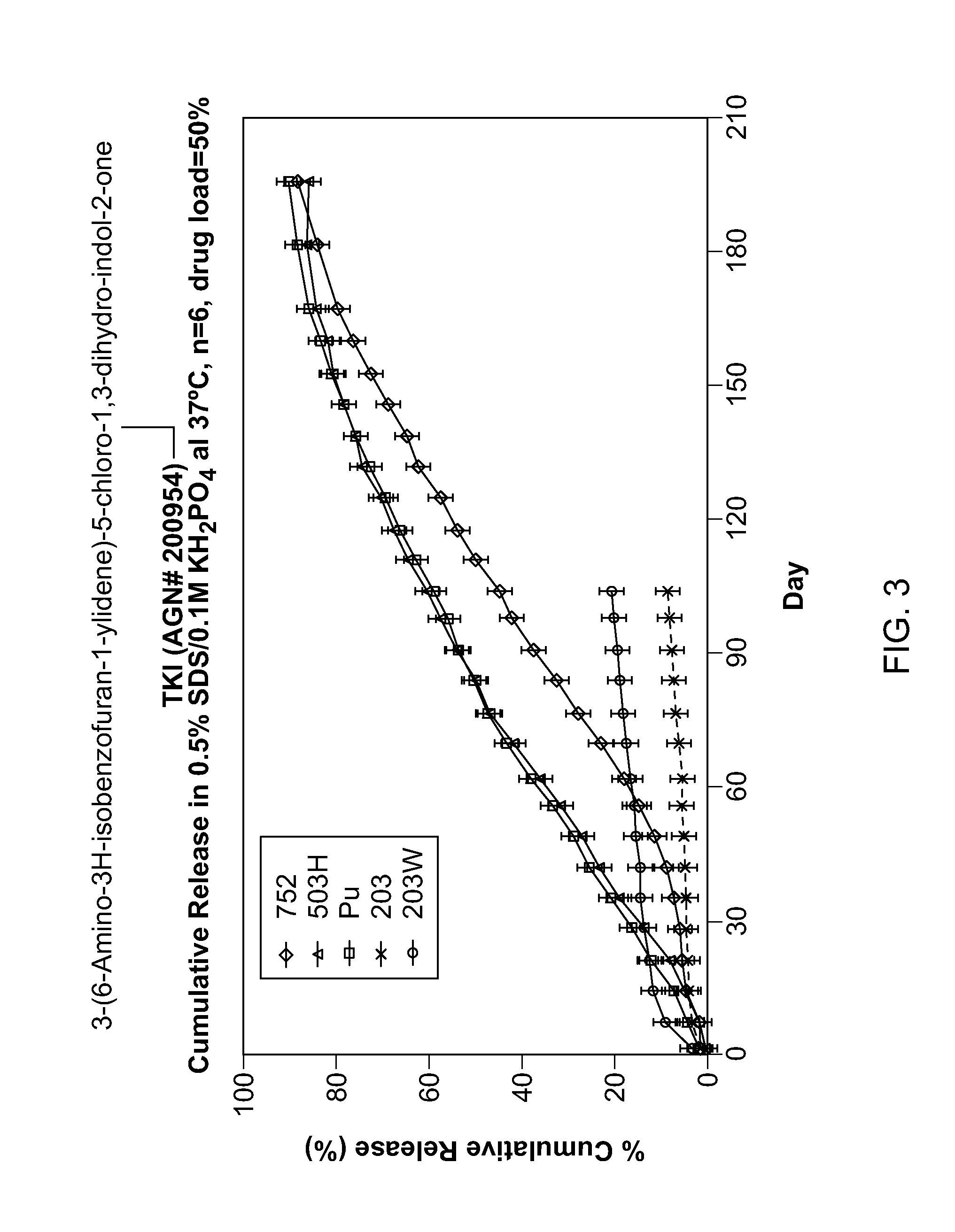
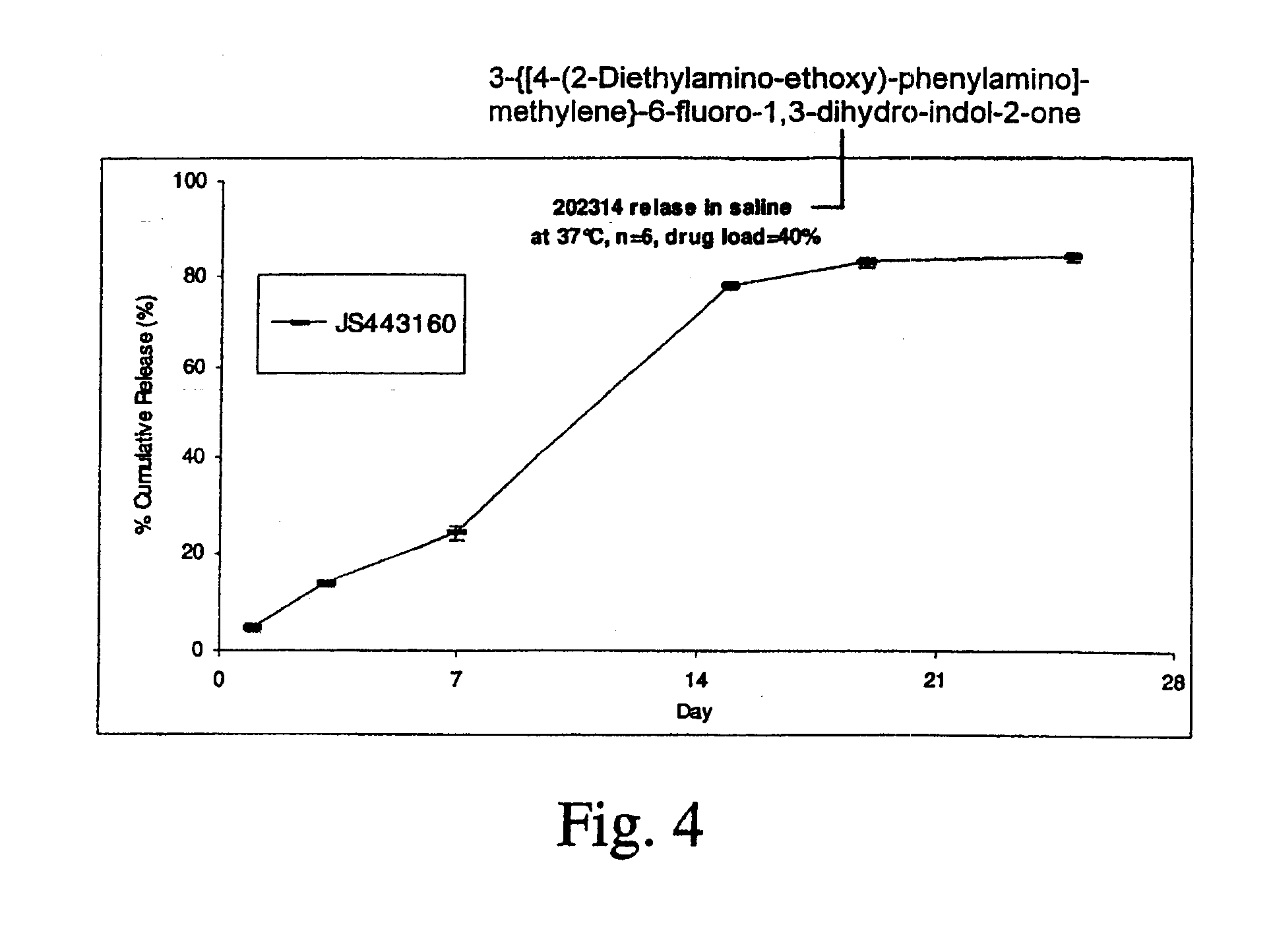
Biodegradable Intravitreal Tyrosine Kinase Implants
ActiveUS20140031408A1Reduce deliveryFacilitate obtaining successful treatment resultsBiocideSenses disorderOphthalmologyPolyvinyl alcohol
Biocompatible intraocular implants include a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and a biodegradable polymer that is effective to facilitate release of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor into the vitreous of an eye for an extended period of time. The therapeutic agents of the implants may be associated with a biodegradable polymer matrix, such as a matrix that is substantially free of a polyvinyl alcohol. The implants can be placed in an eye to treat or reduce the occurrence of one or more ocular conditions.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Method and system for smart contact arrays
ActiveUS20140065847A1Improve convenienceLight weightEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsCoupling device engaging/disengagingCouplingBiomedical engineering
A device includes a device body having an attachment face defined by an attachment area and a contact array disposed in the device body and exposed at a coupling face. The contact array comprises one or more magnets disposed on the coupling face and a plurality of terminals disposed on the coupling face. A periphery of the one or more magnets and the plurality of terminals defines a coupling area. The attachment area is greater than and independent of the coupling area.
Owner:I BLADES
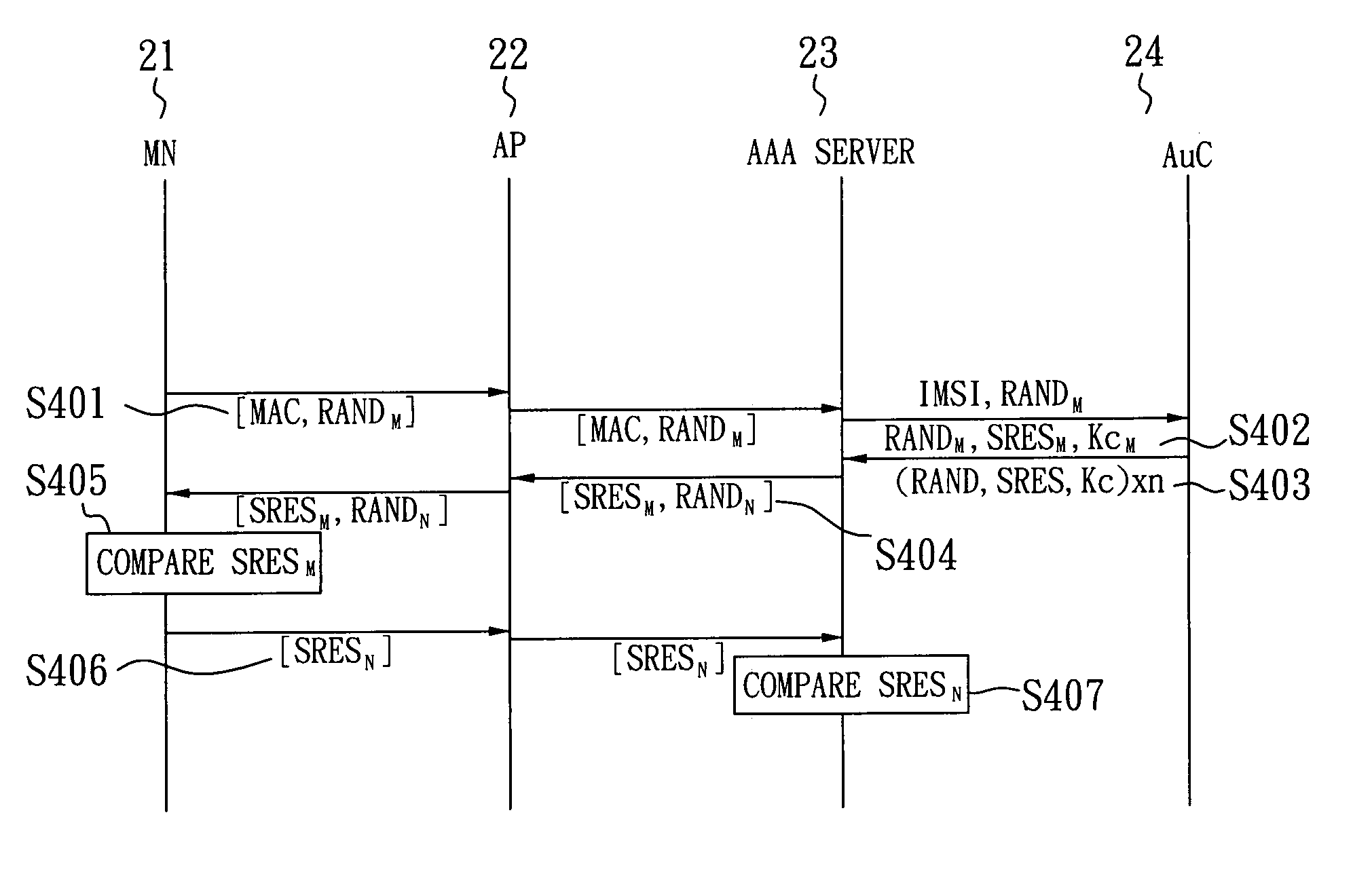
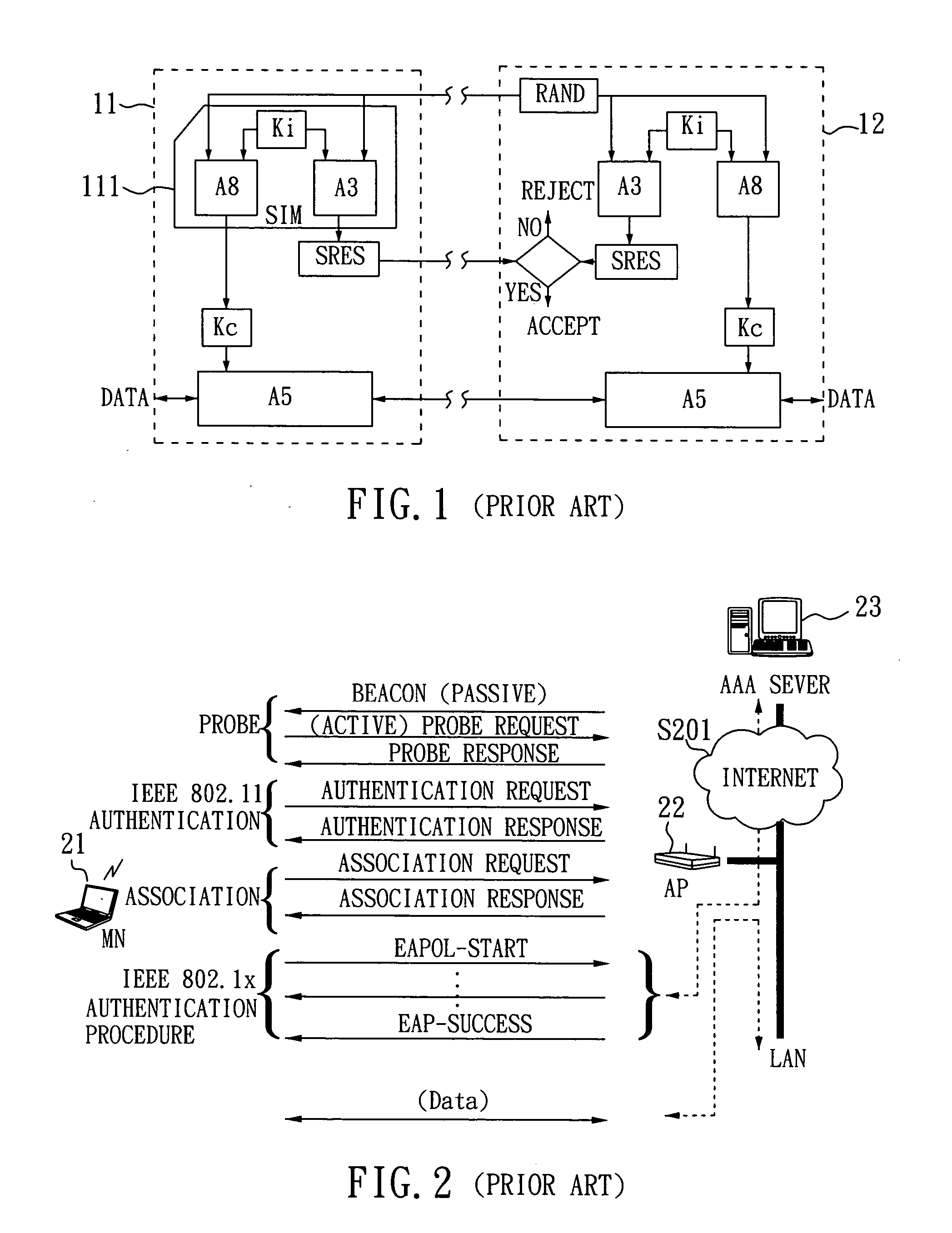
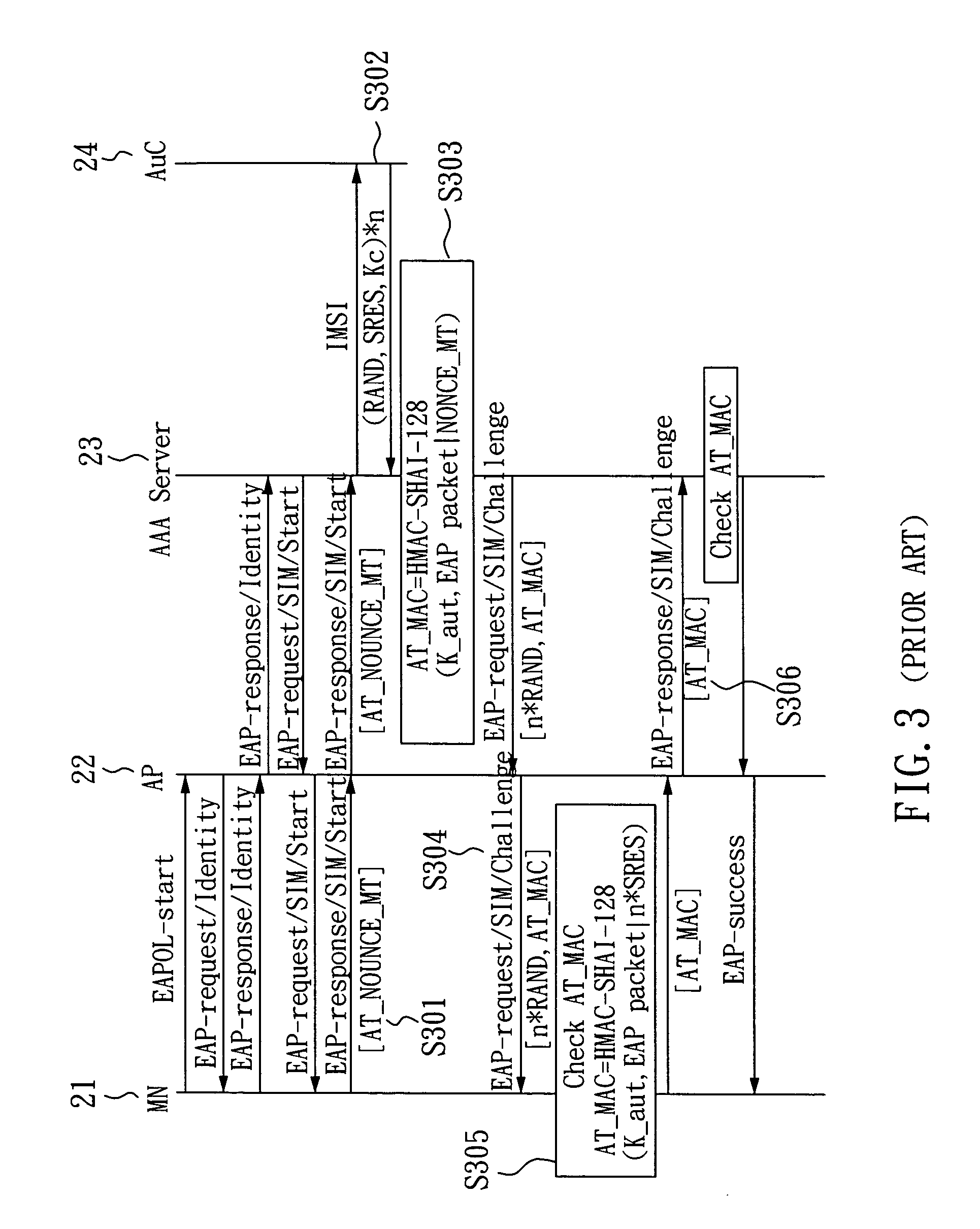
SIM-based authentication method capable of supporting inter-AP fast handover
ActiveUS20050177723A1Blocking in networkSafe WLAN environmentUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsFast handoverWireless lan
The invention relates to a SIM-based authentication method capable of supporting inter-AP fast handover, which can decrease the number of authentication procedures without negatively influencing the security of the wireless LAN by establishing an encrypted channel for each mobile node and using method 1: an aggressive key pre-distribution and method 2: probe request triggering passive key pre-query technique, thereby reducing the time of inter-AP handover for the mobile node. Furthermore, a re-authentication procedure is started to update the key after the key is used for a long time so as to ensure that the key is safe, thereby effectively achieving a fast and safe wireless LAN environment.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Entropy coding
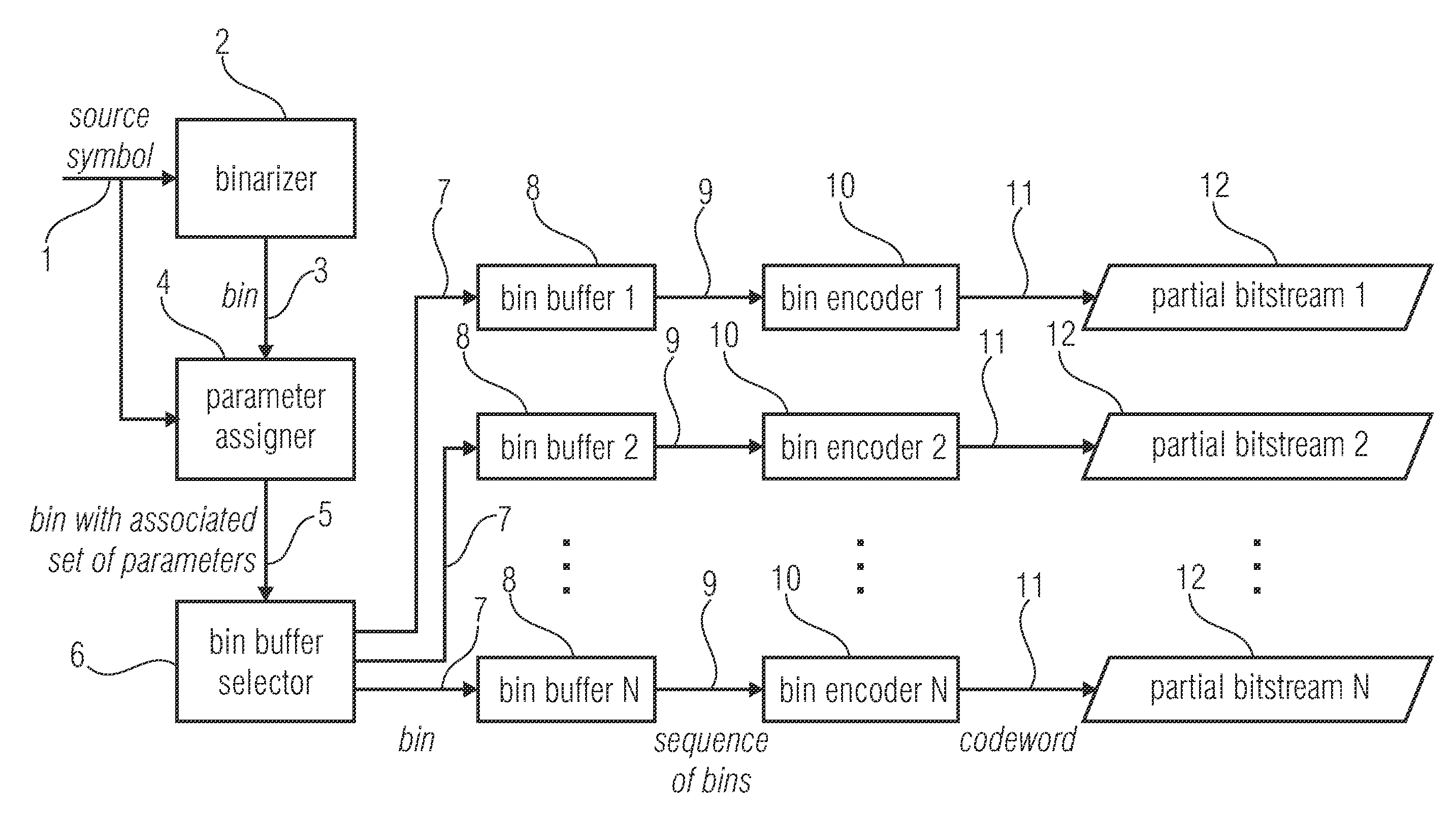
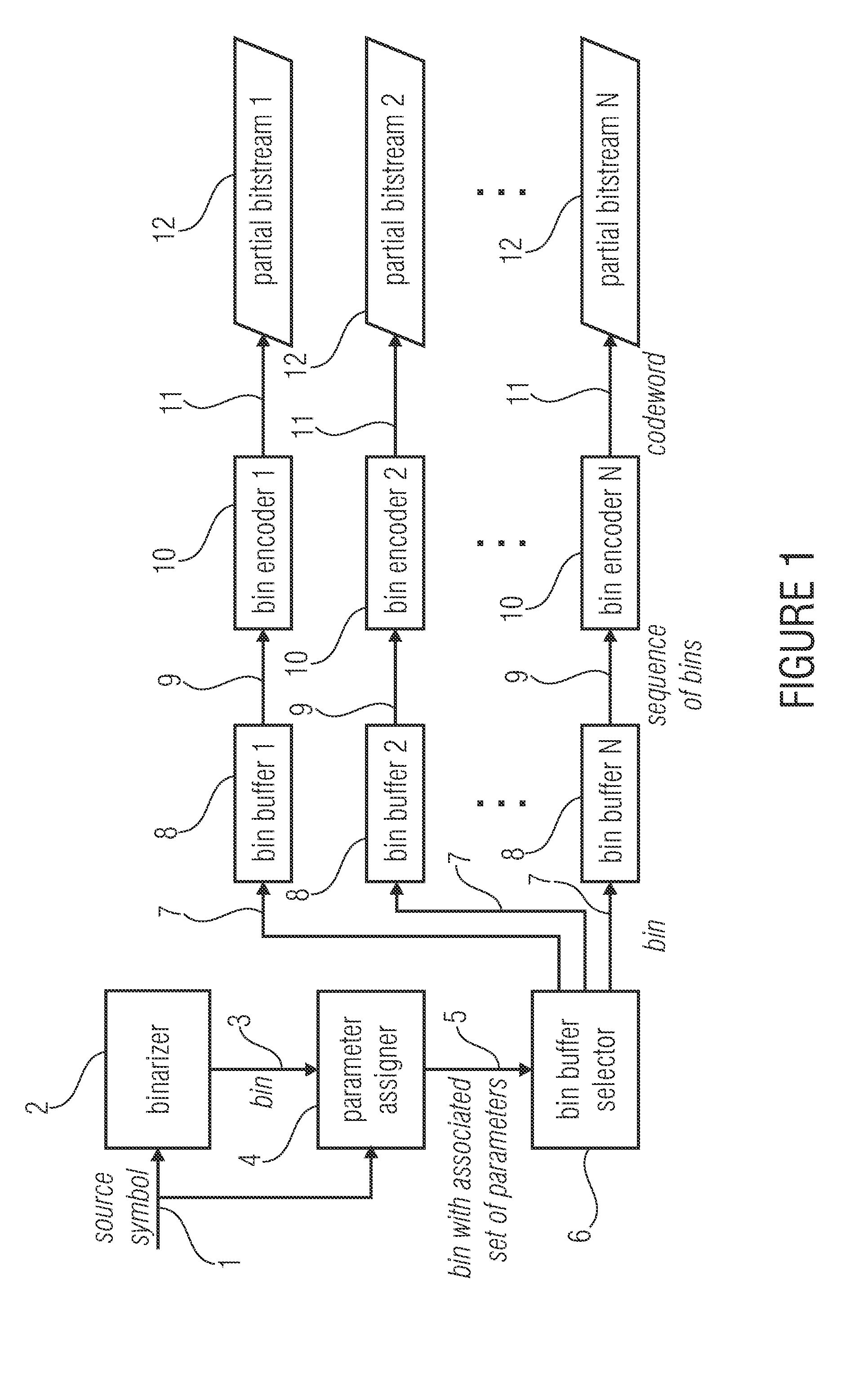
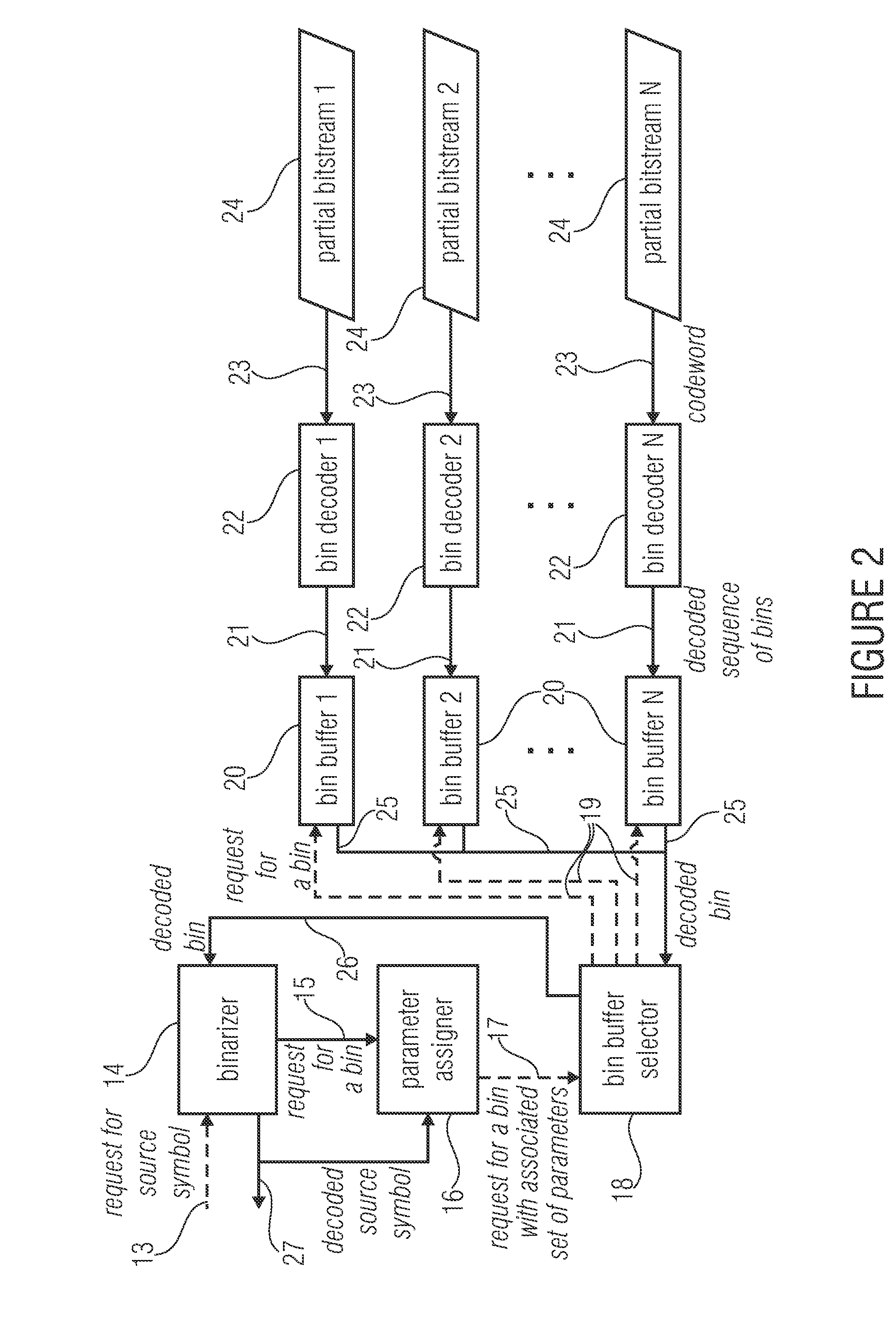
ActiveUS20140210652A1Improve coding efficiencyReduce complexityCode conversionDigital video signal modificationComputer scienceEntropy encoding
An encoder for encoding a sequence of symbols is described which has an assigner configured to assign a number of parameters to each symbol of the sequence of symbols based on information contained within previous symbols of the sequence of symbols; a plurality of entropy encoders each of which is configured to convert the symbols forwarded to the respective entropy encoder into a respective bitstream; and a selector configured to forward each symbol to a selected one of the plurality of entropy encoders, the selection depending on the number of parameters assigned to the respective symbol.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
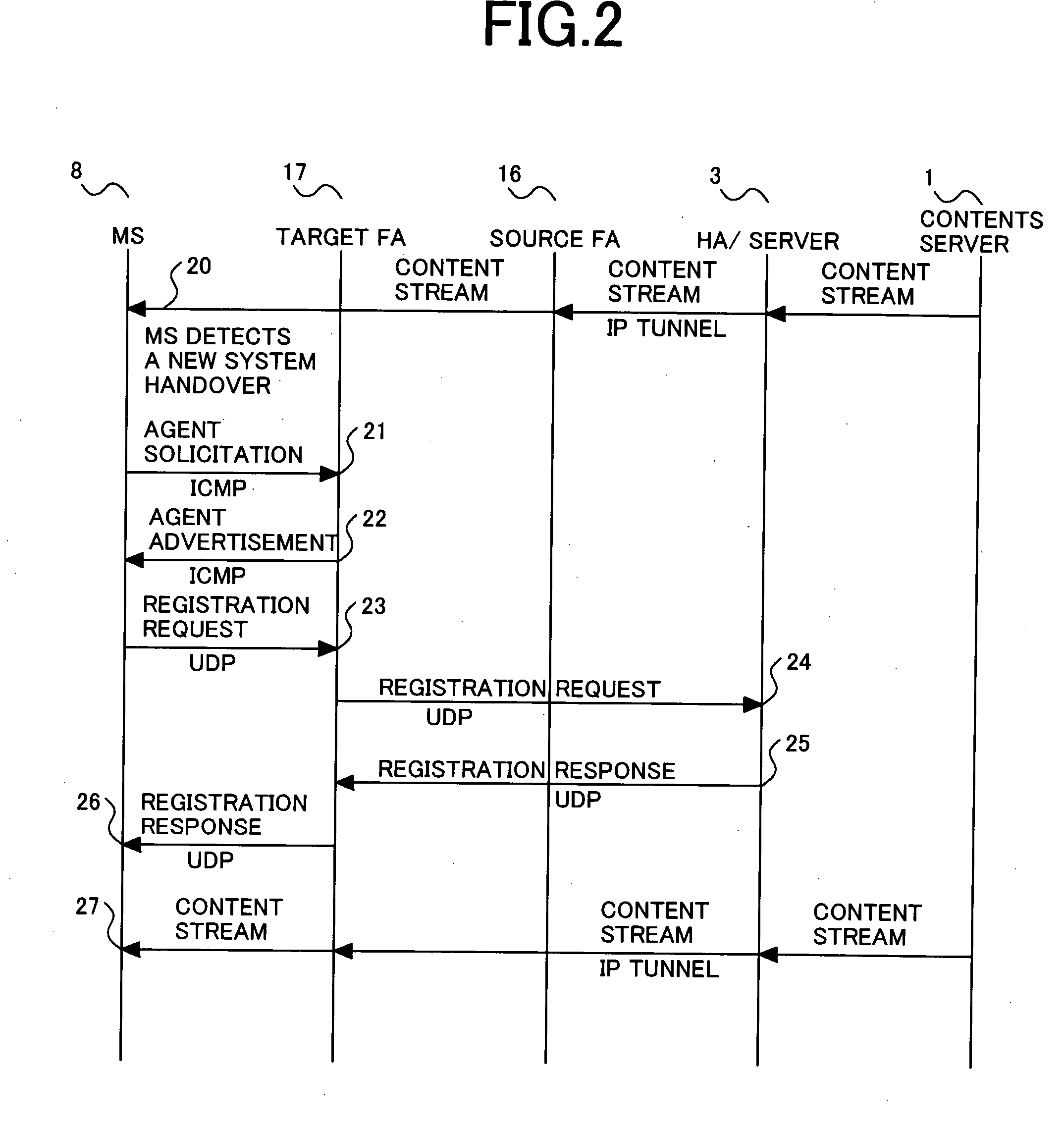
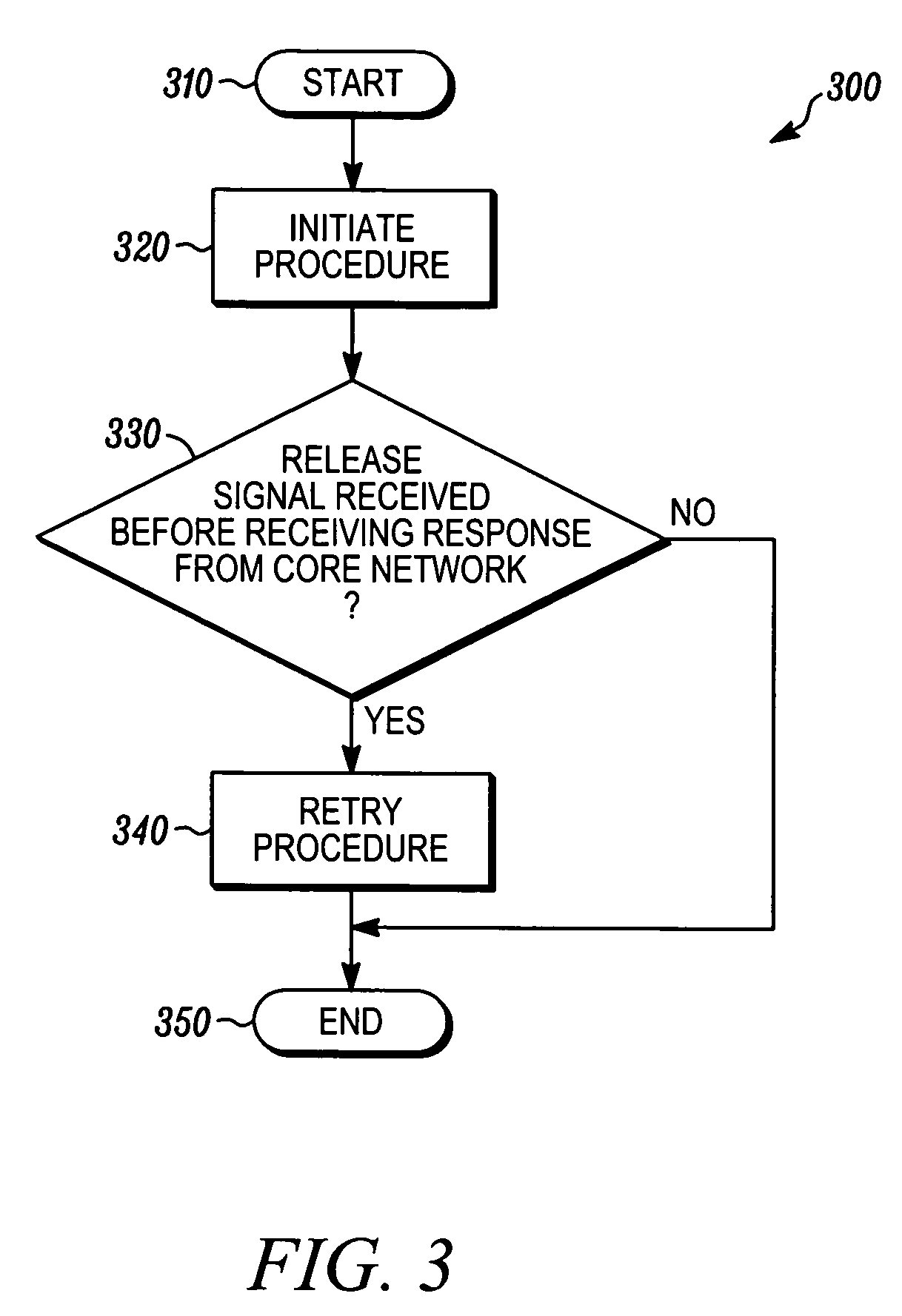
Method for reducing wireless communication procedure failure
InactiveUS20060089137A1Reducing wireless communication procedure failureReduction procedureConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio Resource ControlCore network
A method for reducing wireless communication procedure failure. The method can include initiating a procedure over an existing radio resource control connection on a universal mobile telecommunication system. The method can also include receiving a connection release signal prior to receiving a response from a core network regarding the initiated procedure. The method can further include immediately retrying the procedure.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
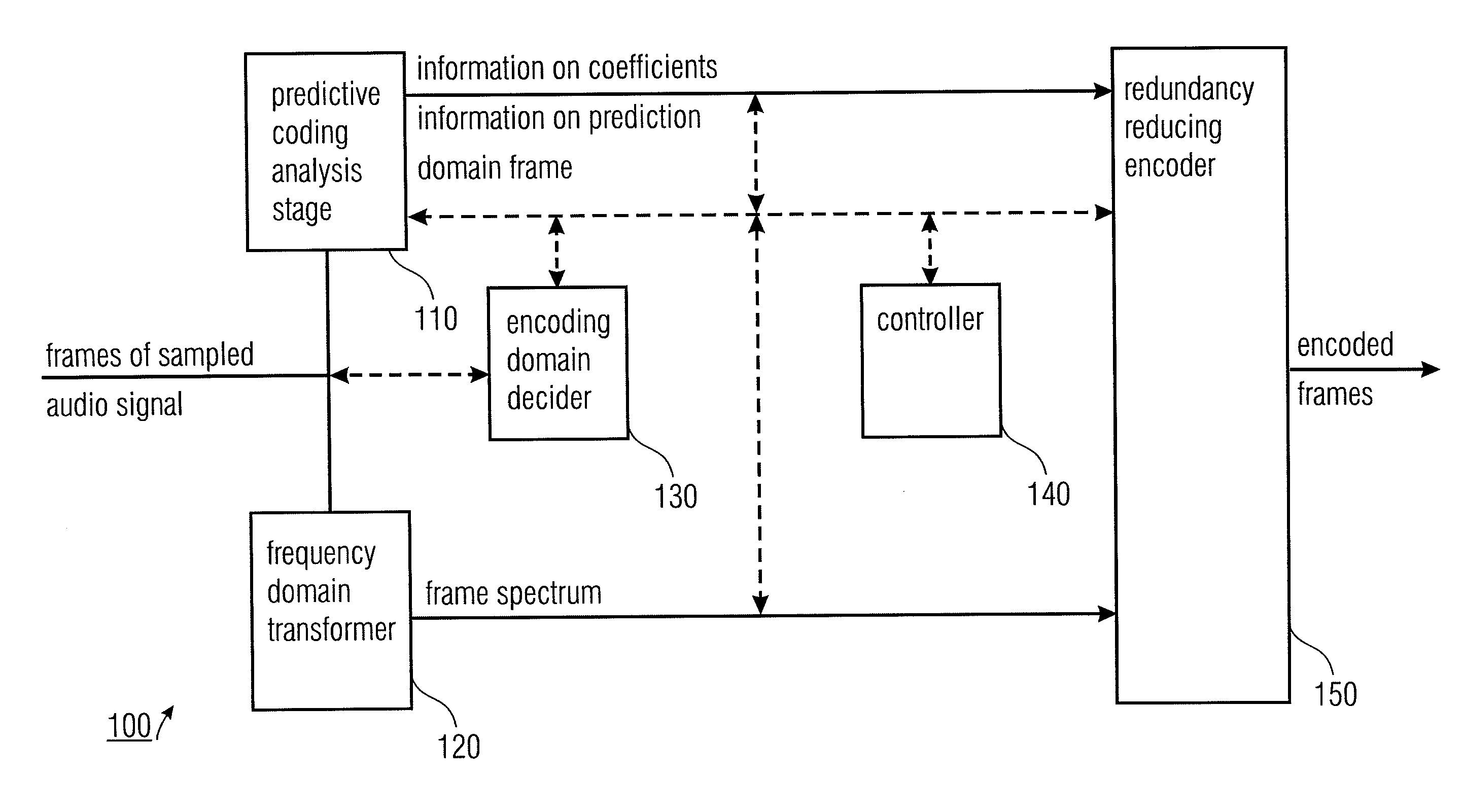
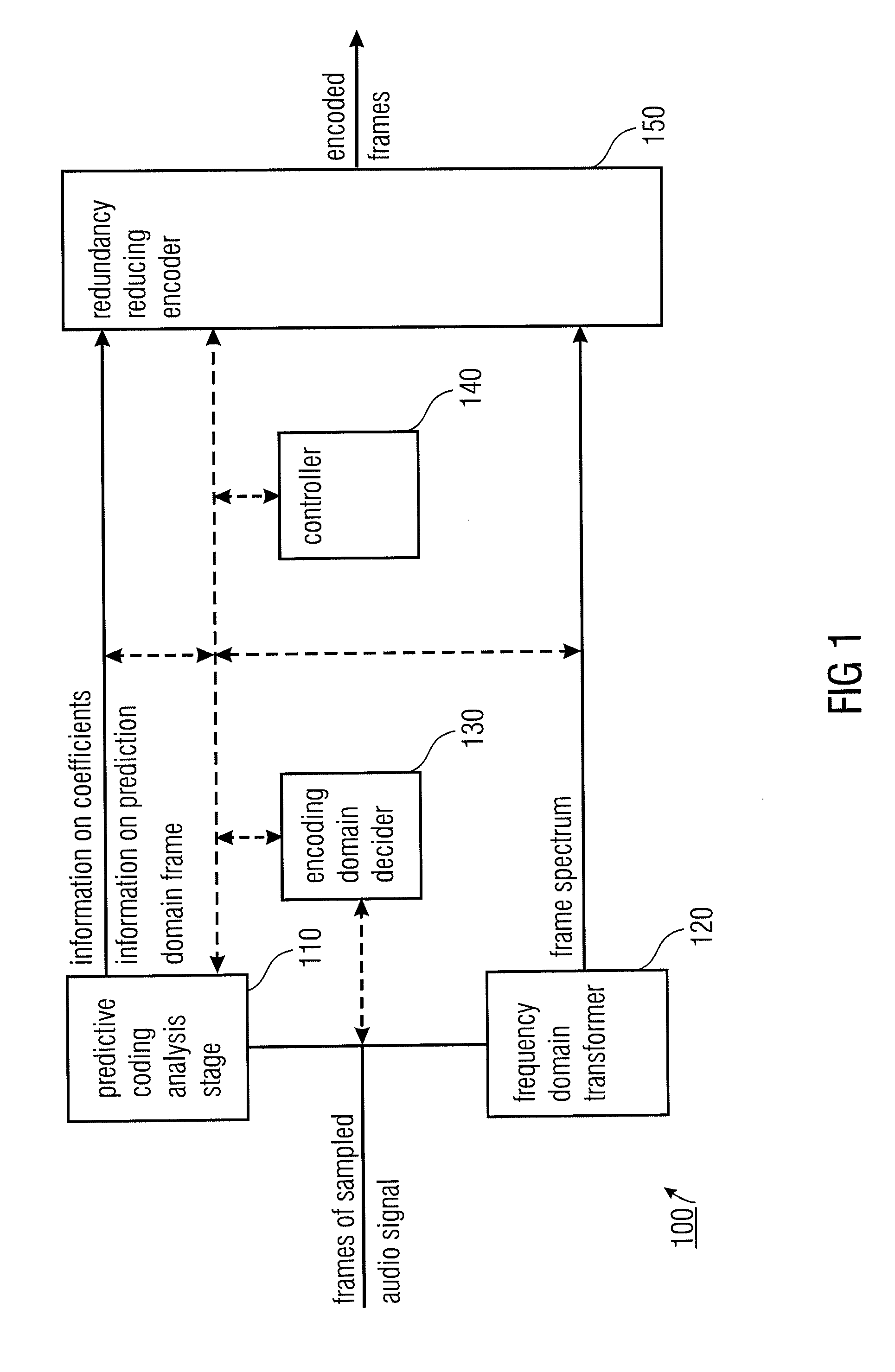
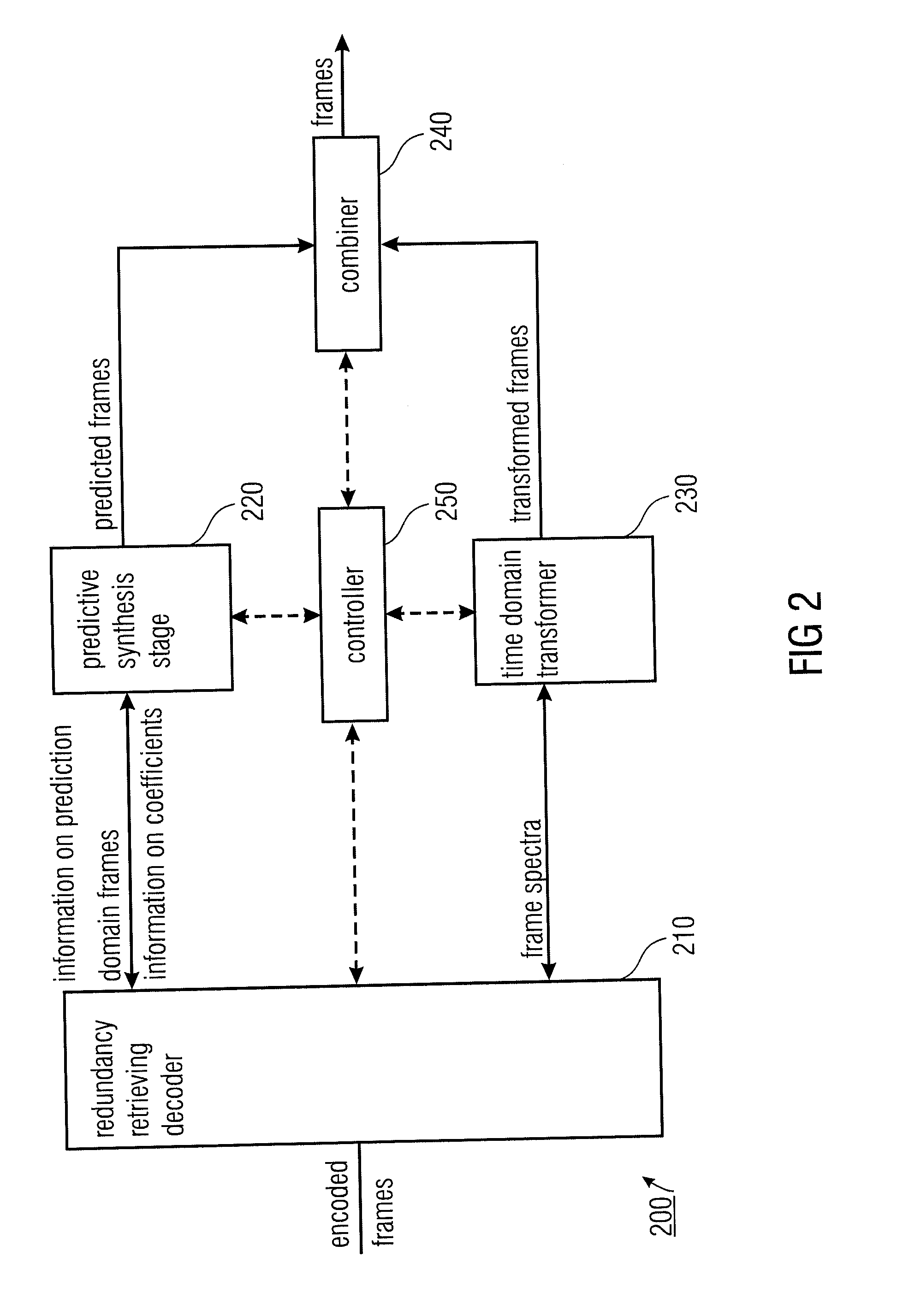
Audio Encoder and Decoder for Encoding Frames of Sampled Audio Signals
An audio encoder adapted for encoding frames of a sampled audio signal to obtain encoded frames, wherein a frame has a number of time domain audio samples, having a predictive coding analysis stage for determining information on coefficients of a synthesis filter and information on a prediction domain frame based on a frame of audio samples. The audio encoder further has a frequency domain transformer for transforming a frame of audio samples to the frequency domain to obtain a frame spectrum and an encoding domain decider for deciding whether encoded data for a frame is based on the information on the coefficients and on the information on the prediction domain frame, or based on the frame spectrum. Moreover, the audio encoder has a controller for determining an information on a switching coefficient when the encoding domain decider decides that encoded data of a current frame is based on the information on the coefficients and the information on the prediction domain frame when encoded data of a previous frame was encoded based on a previous frame spectrum and a redundancy reducing encoder for encoding the information on the prediction domain frame, the information on the coefficients, the information on the switching coefficient and / or the frame spectrum.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Wireless communication system, server and mobile station therefor
InactiveUS7610049B2Fast transmissionProcess in becomes heavyAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemNetworked system
Owner:HITACHI LTD
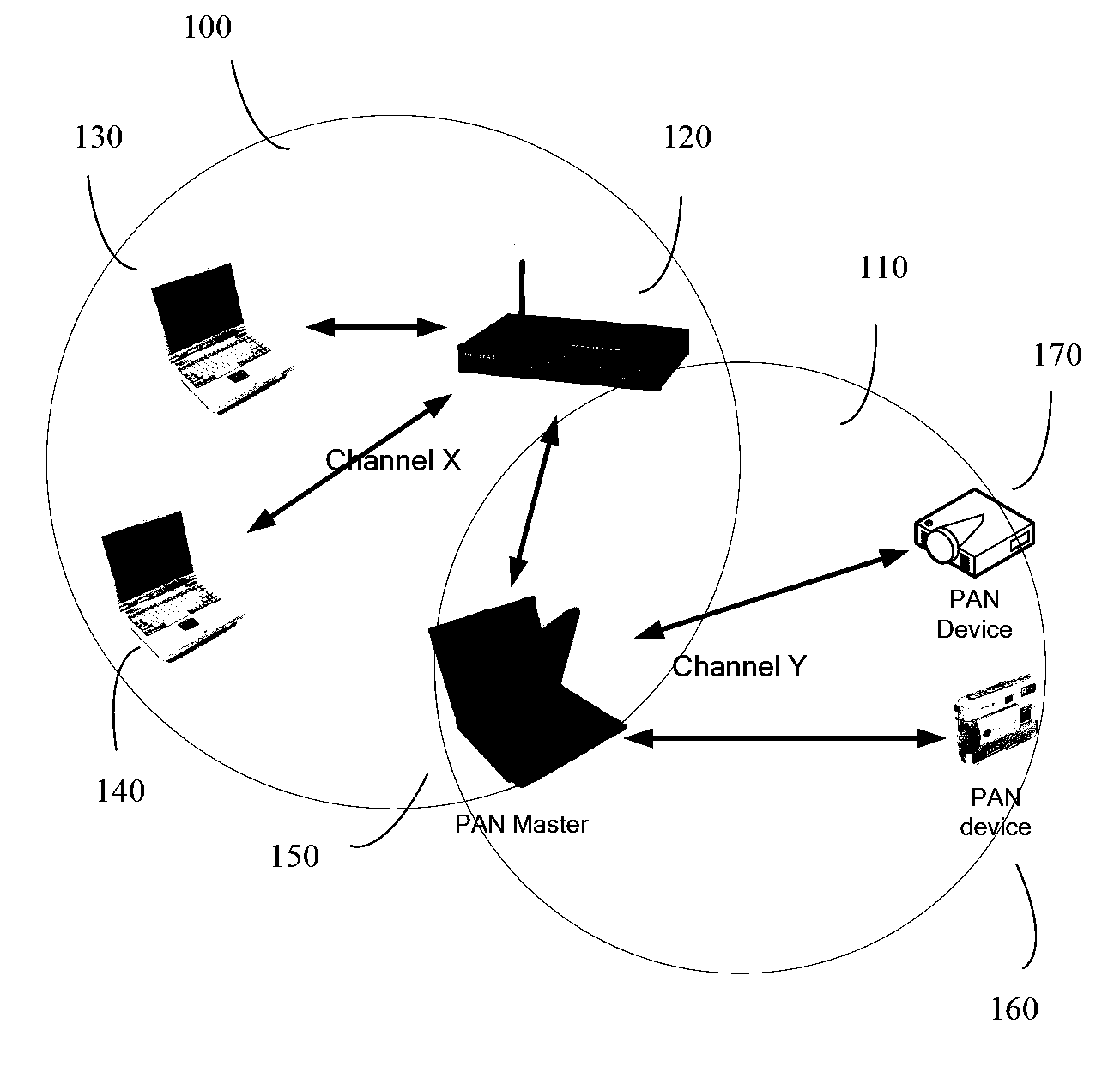
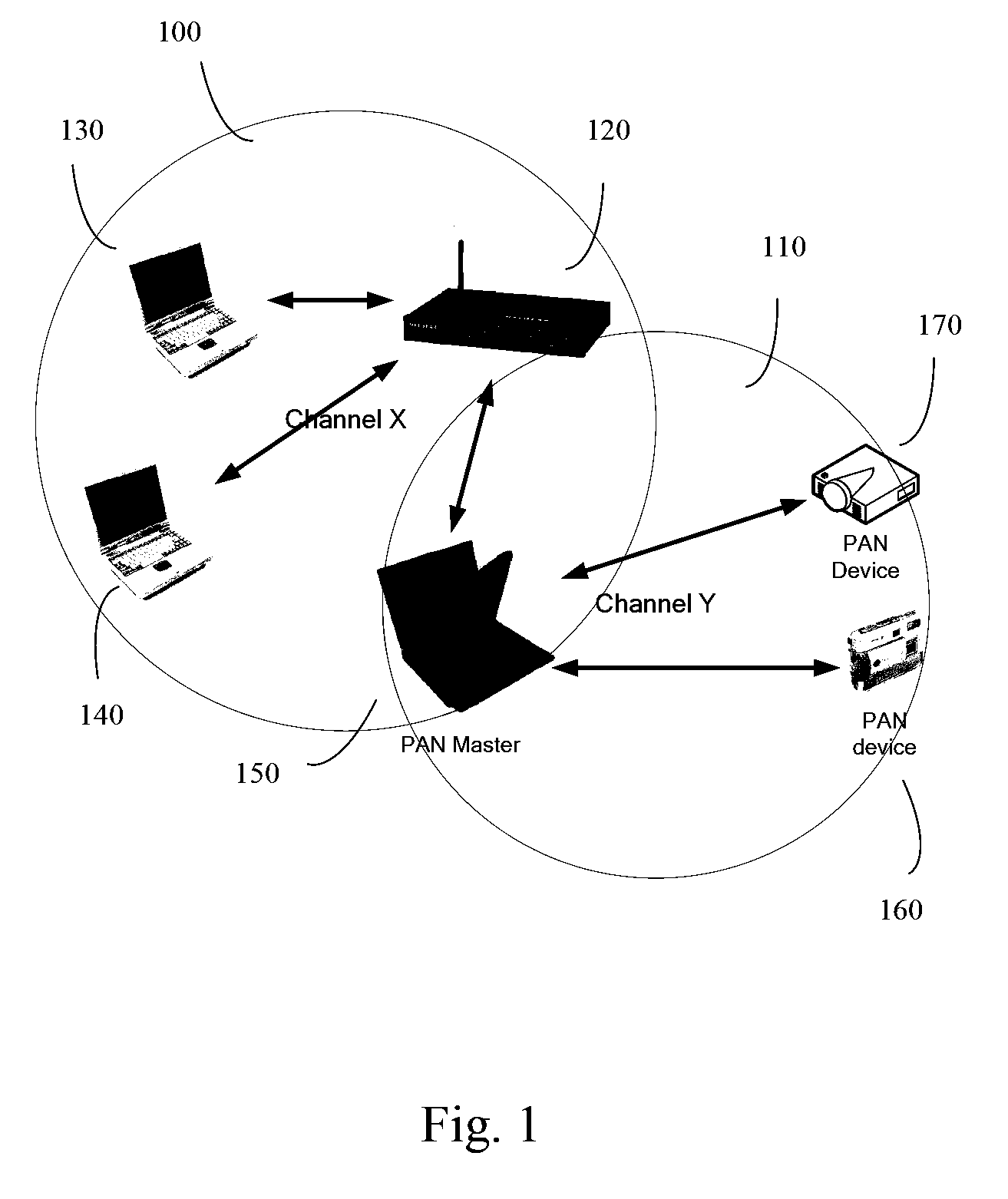
Method and apparatus for improved dual channel operation and access point discovery in wireless communication networks
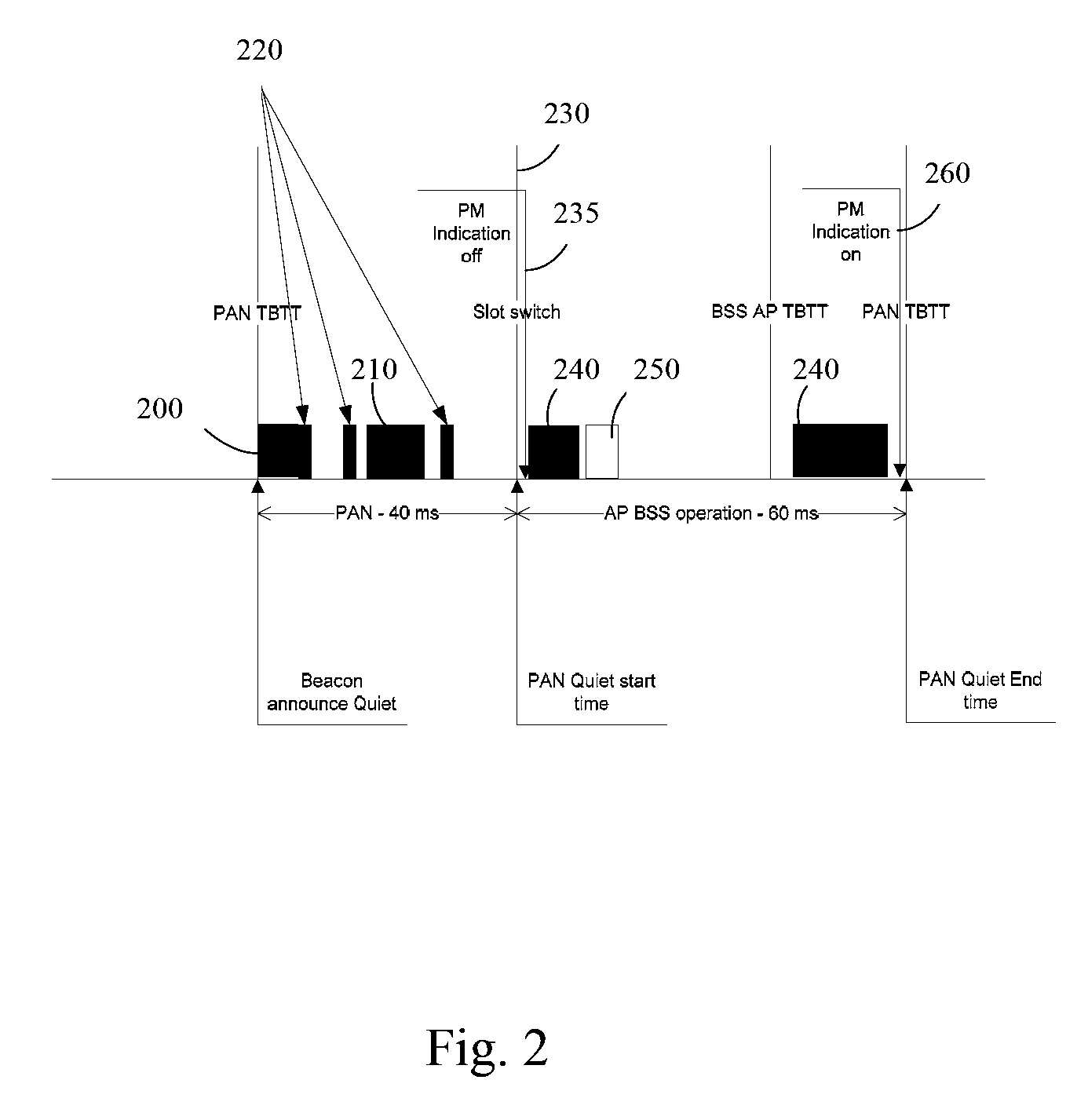
InactiveUS20090046673A1Reduction procedureEasy accessAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessCoordinate time
A method and apparatus of coordinating Time Division Multiple Access operation of wireless communication devices is disclosed. The method comprises an access point announcing a Quiet Period to one or more clients of the access point and transmitting as part of Target Beacons and probe responses an indication to the one or more clients that the access point will be absent from the communication channel for a period of time. The method also comprises the one or more clients establishing a connection with the access point after the Quiet Period when the access point is present on the communication channel on the basis of the indication.
Owner:INTEL CORP
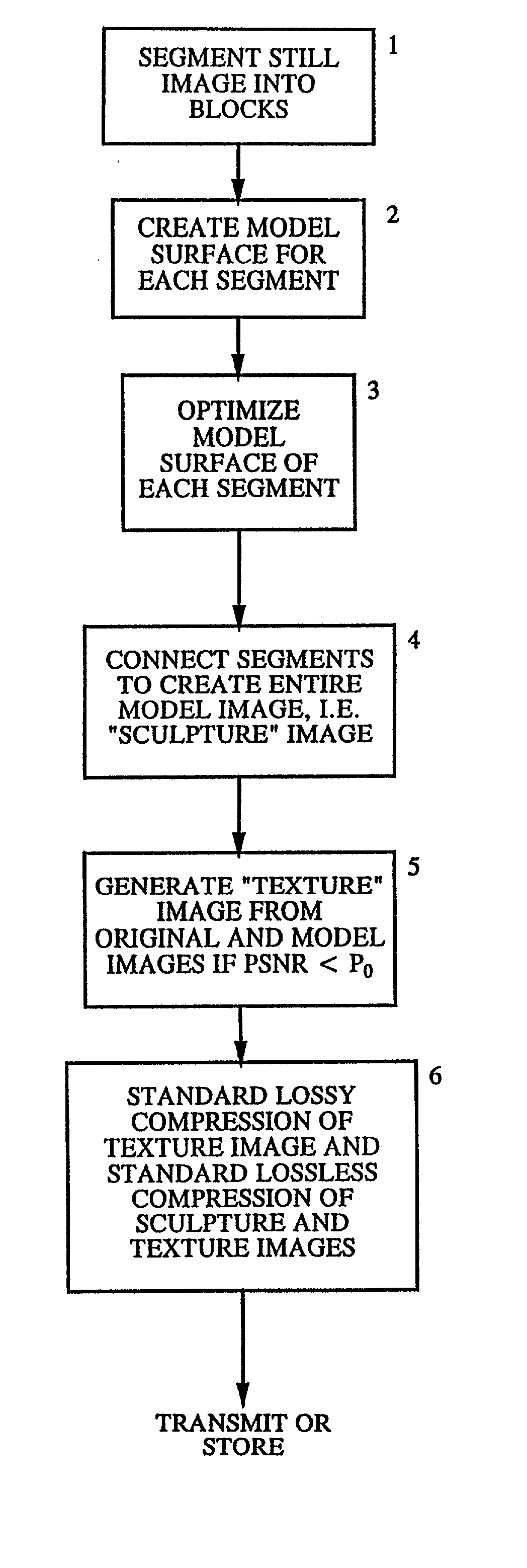
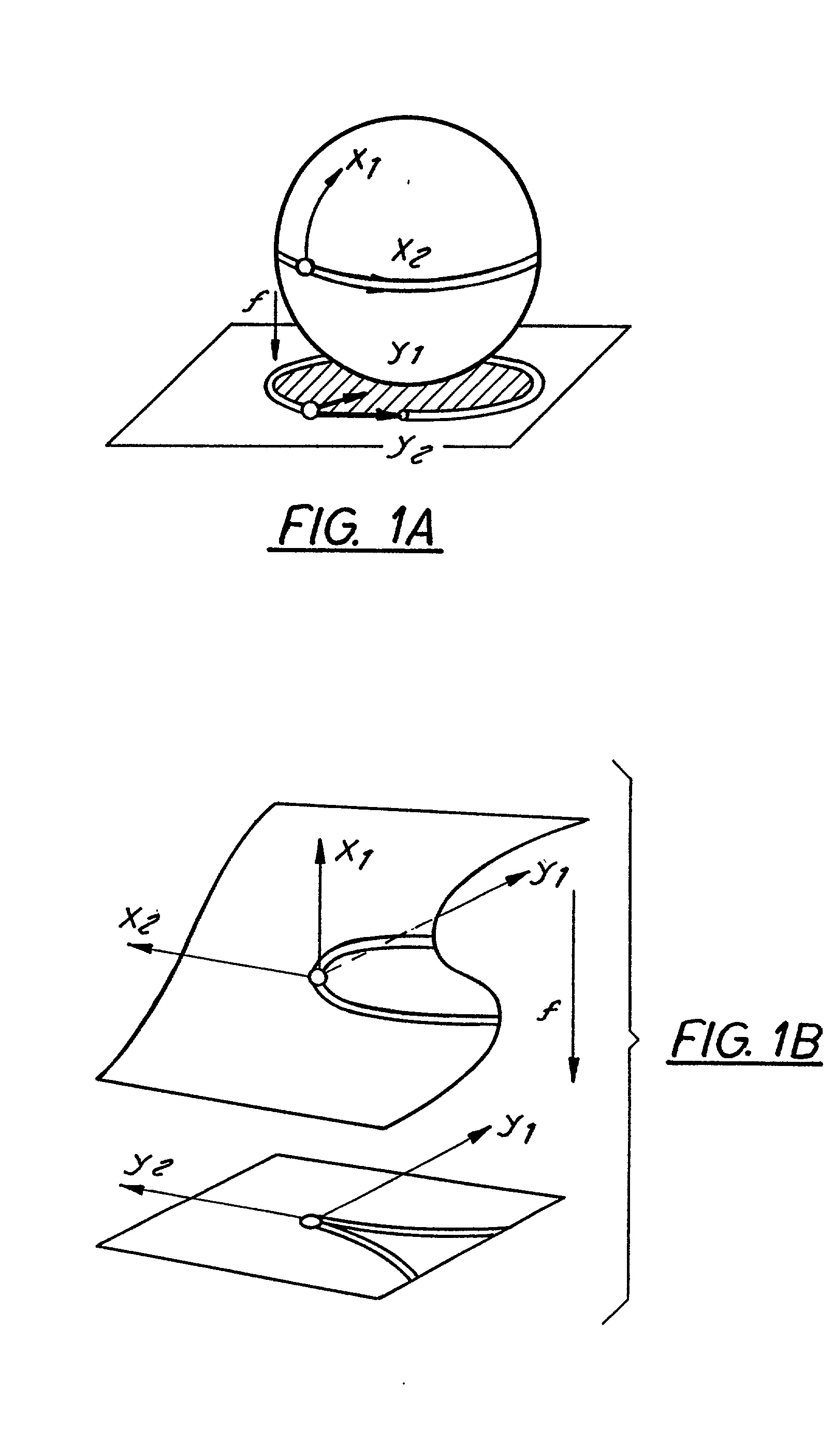
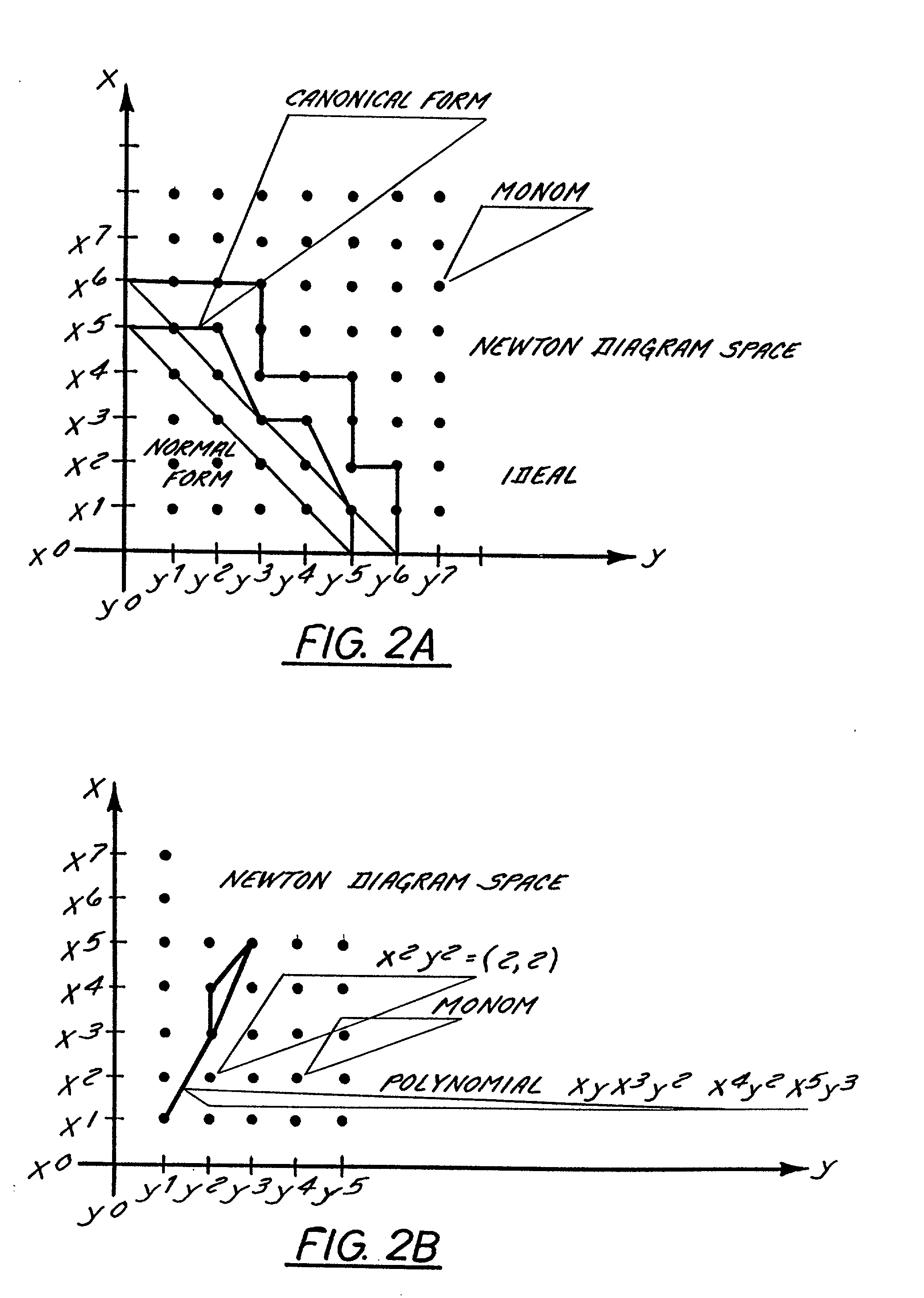
Method of isomorphic singular manifold projection still/video imagery compression
InactiveUS20020176624A1Reduction procedureReduce redundancyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingPattern recognitionImage compression
Methods and apparatuses for still image compression, video compression and automatic target recognition are disclosed. The method of still image compression uses isomorphic singular manifold projection whereby surfaces of objects having singular manifold representations are represented by best match canonical polynomials to arrive at a model representation. The model representation is compared with the original representation to arrive at a difference. If the difference exceeds a predetermined threshold, the difference data are saved and compressed using standard lossy compression. The coefficients from the best match polynomial together with the difference data, if any, are then compressed using lossless compression. The method of motion estimation for enhanced video compression sends I frames on an "as-needed" basis, based on comparing the error between segments of a current frame and a predicted frame. If the error exceeds a predetermined threshold, which can be based on program content, the next frame sent will be an I frame. The method of automatic target recognition (ATR) including tracking, zooming, and image enhancement, uses isomorphic singular manifold projection to separate texture and sculpture portions of an image. Soft ATR is then used on the sculptured portion and hard ATR is used on the texture portion.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
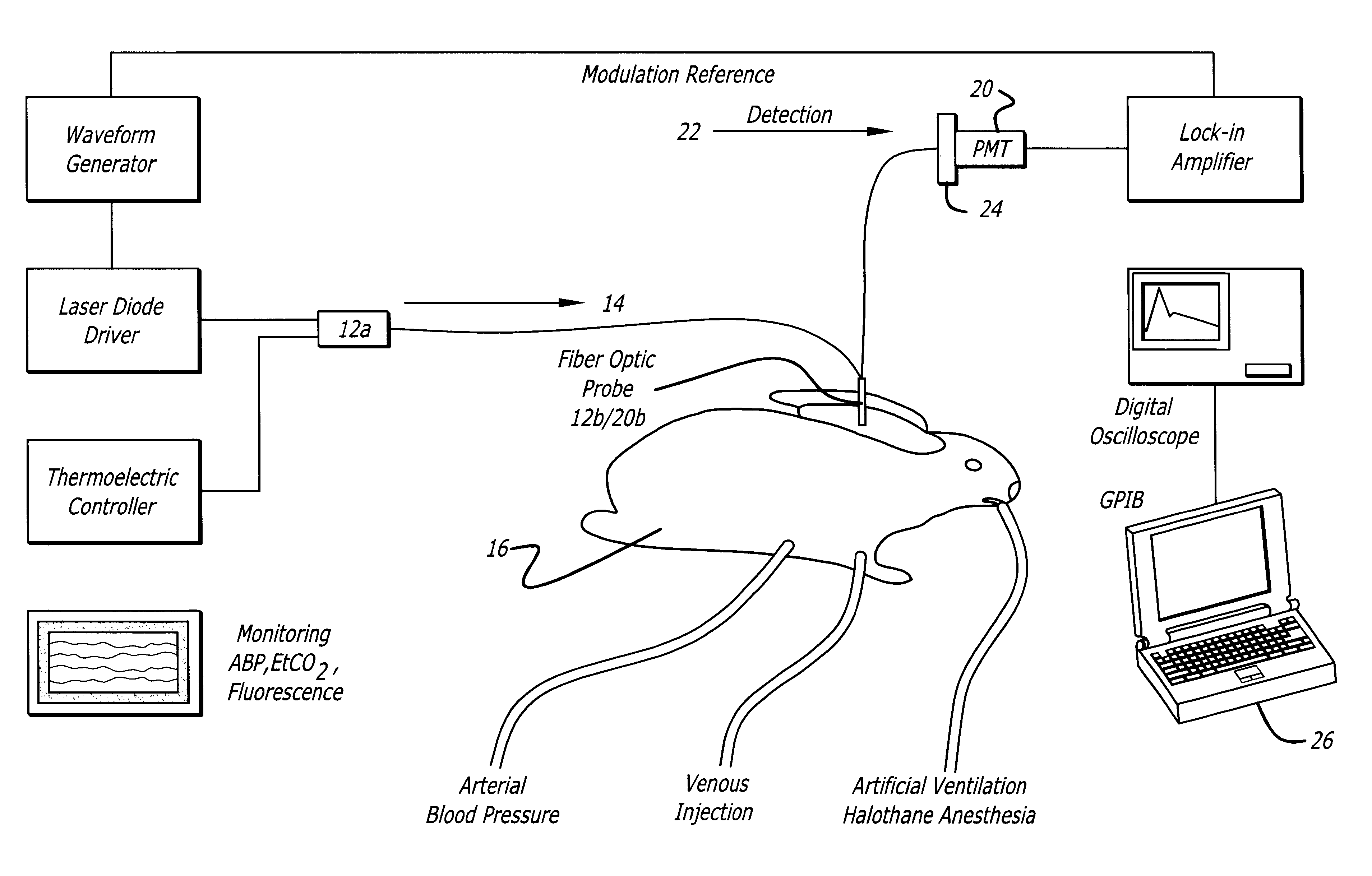
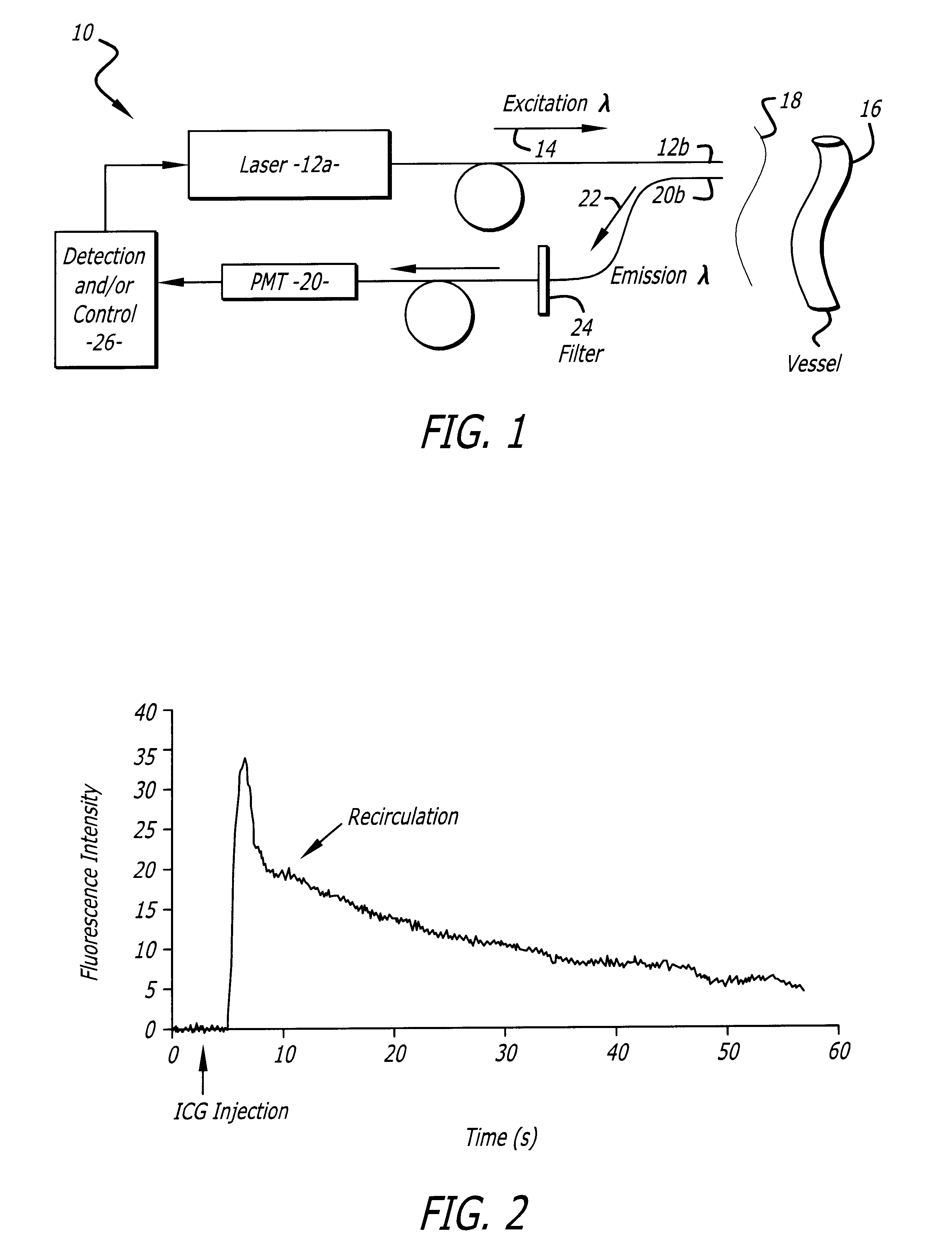
Measurement of cardiac output and blood volume by non-invasive detection of indicator dilution
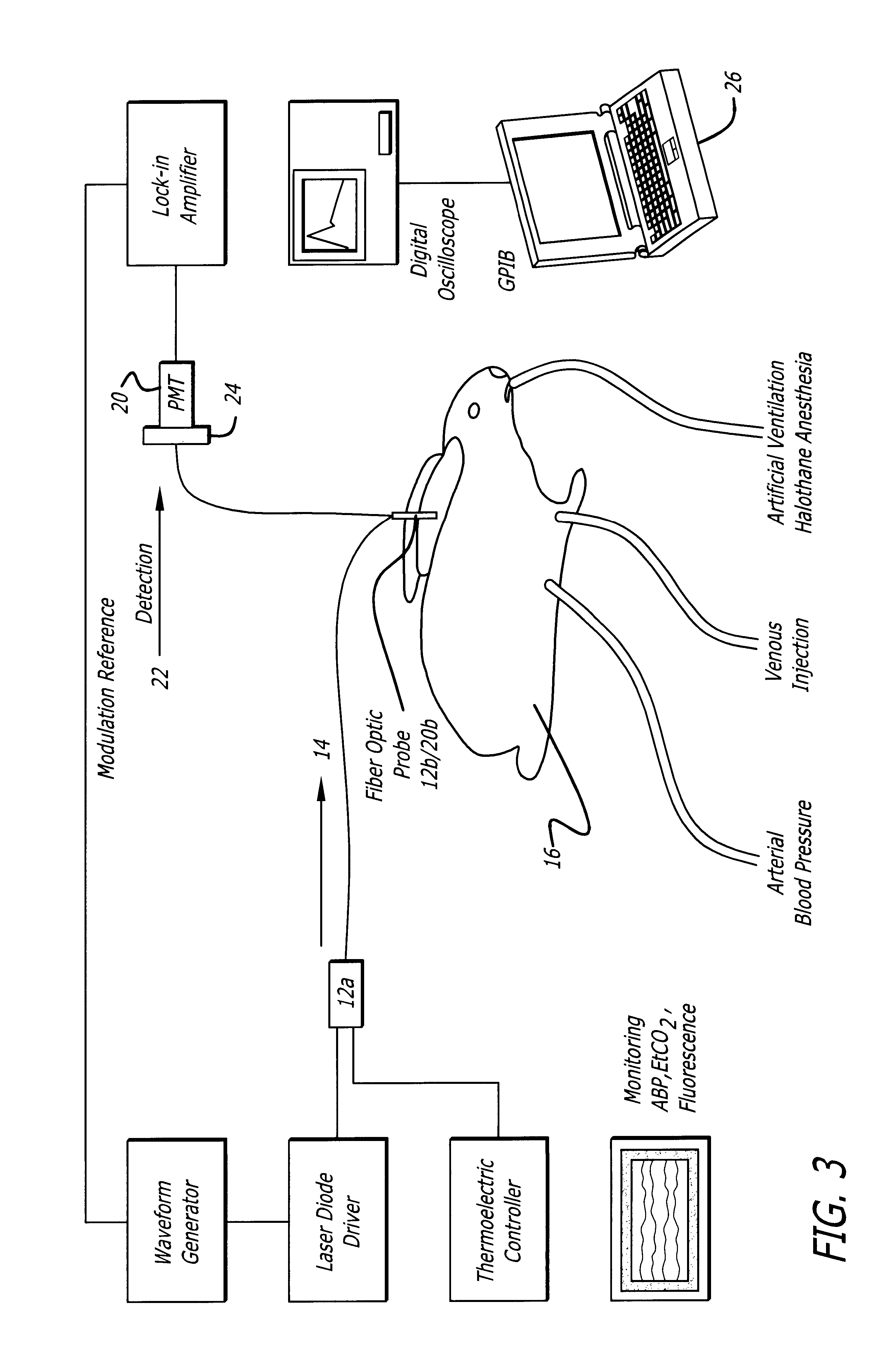
InactiveUS6757554B2Reduce complicationsReduction procedureSensorsBlood flow measurementIndicator dilutionNormal blood volume
A system for evaluating the cardiovascular system parameters using indicator dilution and non-invasive or minimally invasive detection methods is disclosed. Intravascular indicators are stimulated, and emission patterns detected for computation of cardiac output, cardiac index, blood volume and other indicators of cardiovascular health.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
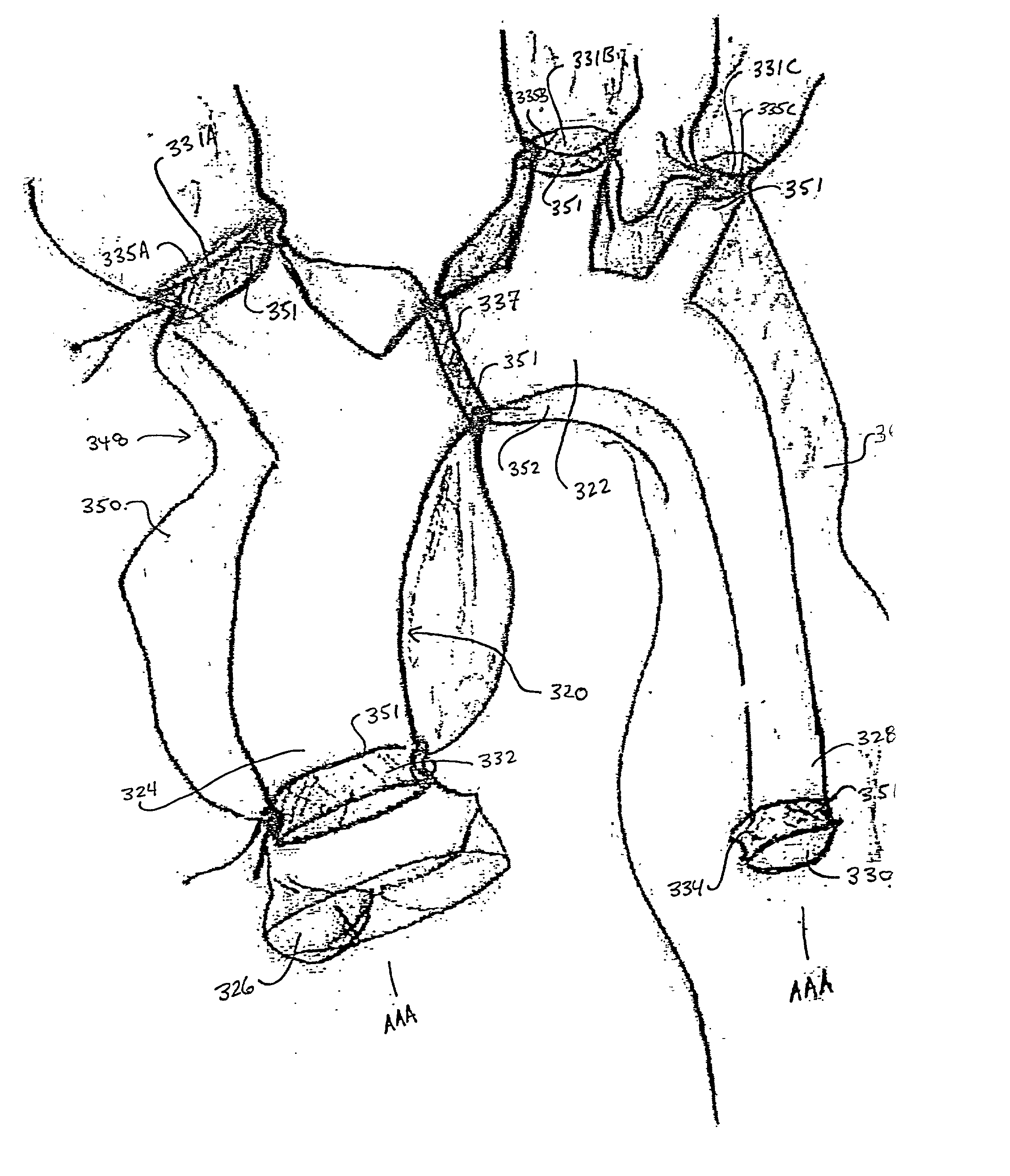
Intravascular prosthetic and method
InactiveUS20020082684A1Easy to operateReduce complexitySuture equipmentsStentsIntravascular stentEndovascular prosthesis
An intravascular prosthetic graft is provided which includes a flexible tubular body having a first end defining at least one opening and a second end defining at least one opening. The flexible tubular body may be elongated and define a longitudinal axis. A first ring member is connected to the first end adjacent to the at least one opening of the first end. A second ring member is connected to the second end adjacent to the at least one opening of the second end. The flexible tubular body can be fabricated from a flexible material, such as, for example, DACRON(R), TEFLON(R), or other suitable material. The first and second ring members may be fabricated from a rigid material, such as metals or polymerics. A method of repairing at least a portion of an arterial system, such as, for example, treatment of an aortic aneurysm is disclosed. The method includes the steps of providing an intravascular prosthetic graft; determining a placement position for the intravascular prosthetic graft at an aneurysm site of the arterial system; introducing the intravascular prosthetic graft to the arterial system; delivering the intravascular prosthetic graft to the aneurysm site; positioning the intravascular prosthetic graft for repairing a diseased portion of an aorta at the placement position; expanding the intravascular prosthetic graft to substantially conform to an inner surface of the aorta; and fixing the intravascular prosthetic graft at the placement position. The step of fixing may include tying a suture about the exterior of the aorta. The method may further include the step of suturing the aorta to the intravascular prosthetic graft from exterior to the aorta.
Owner:MISHALY DAVID
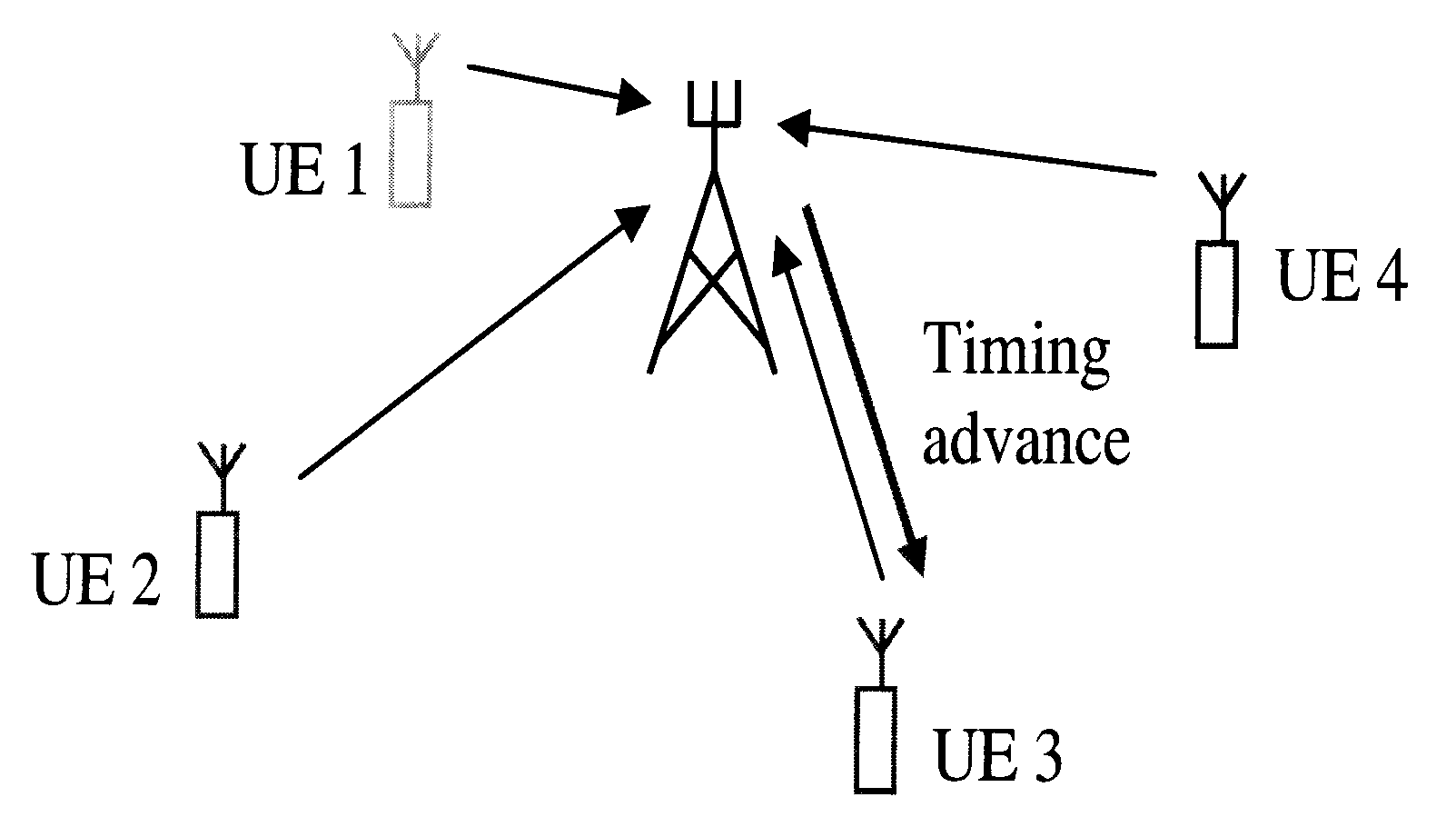
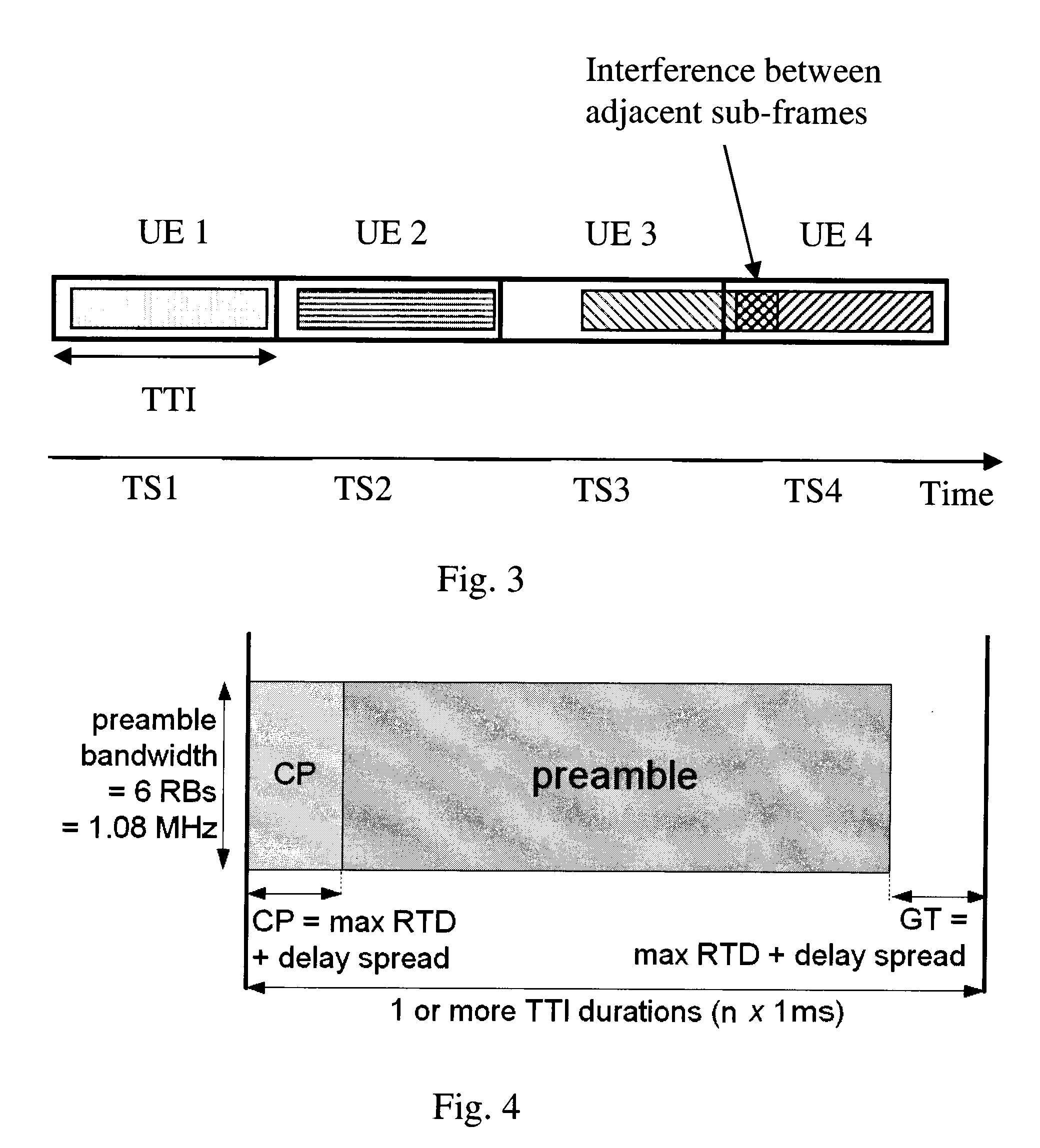
System and method for determining a transmit timing for communication in a radio communication system
ActiveUS20090318175A1Reduction procedureSynchronisation arrangementTransmission control/equalisingTransceiverCommunications system
A method for determining a transmission timing is provided. The method includes steps of, at a first point in time, determining a first transmission timing for transmissions from a user entity to a first radio transceiver, and determining a representation of a first position of the user entity in relation to the first radio transceiver and at least a second and a third radio transceiver. The method further includes, at a second point in time, subsequent to the first point in time, determining a representation of a second position of the user entity in relation to the first, second and third radio transceivers, and adjusting the transmission timing based on a difference of the first position and the second position.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Methods for sensing retrograde flows of bone fill material
InactiveUS20070162043A1Inhibit migrationReduction procedureDiagnosticsSpinal implantsFilling materialsRetrograde Flow
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to medical devices and methods for use in osteoplasty procedures, such as vertebral compression fractures. One method for treating an abnormal vertebra includes flowing a bone fill material through an introducer into a vertebral body along a first direction and sensing a flow of said bone fill material about an outer surface of the introducer in a second direction different from said first direction. In other embodiments, a signal is generated to alert a physician of said bone fill material flow in said second direction.
Owner:DFINE INC
Method for reporting channel state information in wireless communication system and apparatus for same
ActiveUS20200112355A1Improve performanceHigh densitySpatial transmit diversitySignal allocationChannel state informationCommunications system
A method for a terminal reporting channel state information (CSI) in a wireless communication system, according to one embodiment of the present invention, comprises the steps of: receiving, from a base station, channel state information-reference signal (CSI-RS) setting information for receiving a CSI-RS resource; receiving the CSI-RS resource on the basis of the CSI-RS resource setting information; and reporting CSI generated on the basis of the CSI-RS resource to the base station, wherein when the same CSI-RS resource is set for repeated transmission for the terminal, the CSI-RS resource setting information may include indicating information relating to the location of a subcarrier on which the same CSI-RS resource is mapped.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Blood processing information system with blood loss equivalency tracking
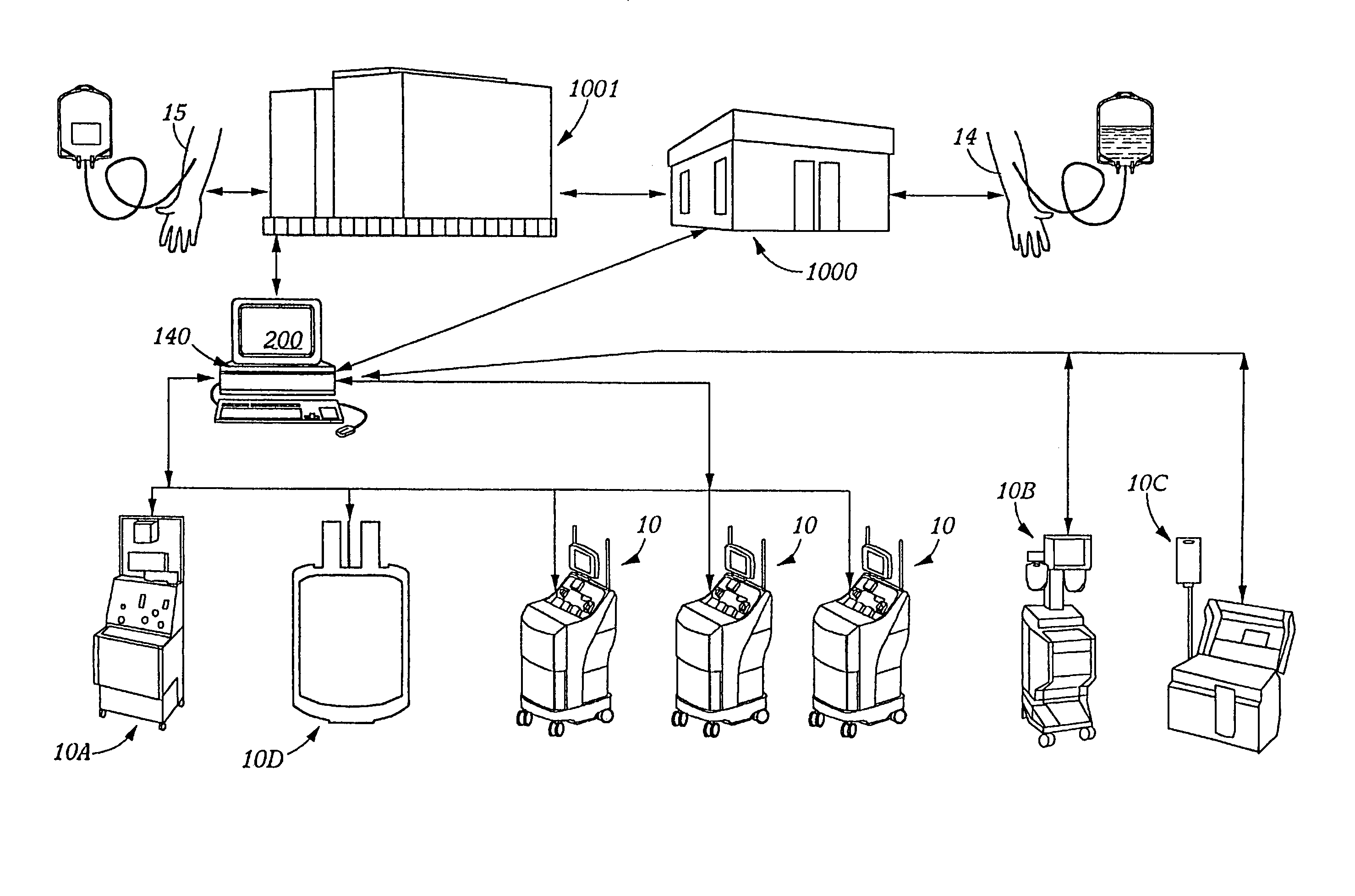
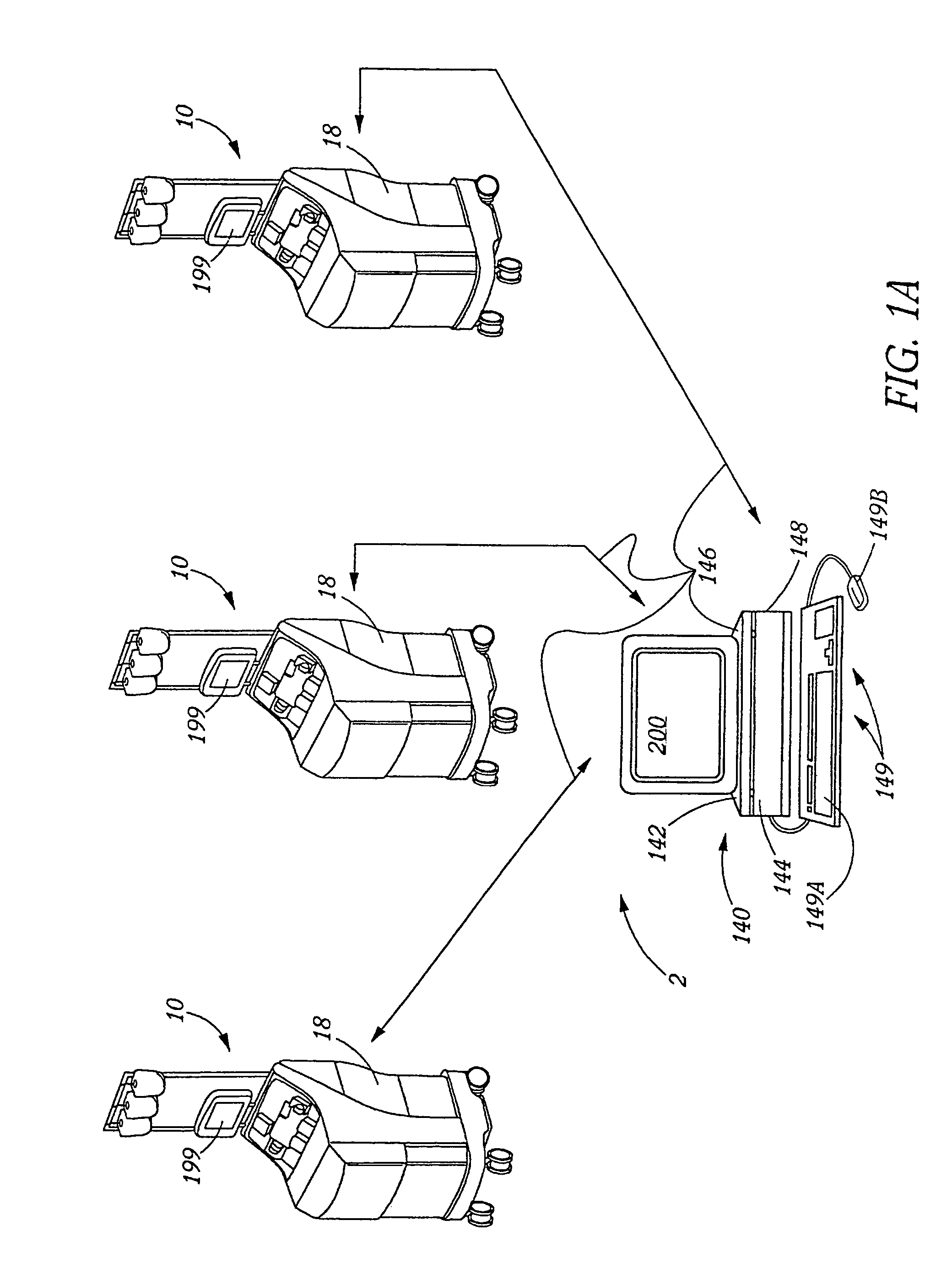
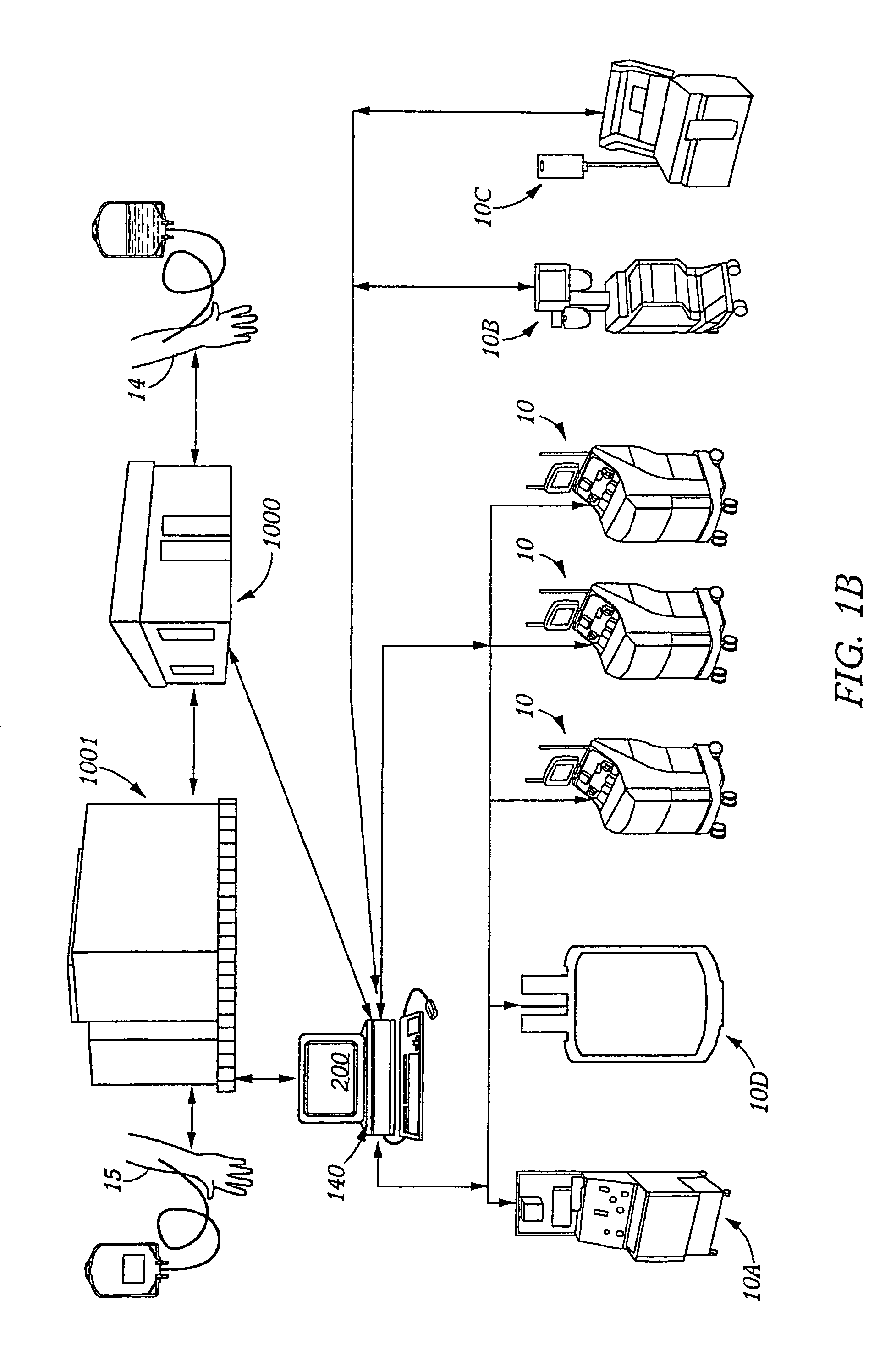
InactiveUS7430478B2Avoid wastingEasy to useOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesBlood componentCollection system
Owner:TERUMO BCT
Method for automatically switching USB peripherals between USB hosts
A system for automatically switching peripheral connectivity between two host devices based on respective connectivity of the hosts. The method may be used where peripherals are usually attached to one host and are automatically switched to a second host when the second host is attached to the system. A USB switching hub may be operable to automatically switch connectivity of the peripheral device(s) from the first host device to the second host device when the second host device is connected to the USB device. This automates the process for the end user when normally all peripherals are attached to one host, and some or all peripherals are shared with a second host when the second host is attached.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Thermopile IR detector package structure
InactiveUS20050081905A1Ease of mass productionReducing fabrication procedureThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsManufacturing technologyThermopile
A thermopile IR detector package structure makes use of the silicon micro-electro-mechanical processing technique fabricate an encapsulation having a cavity. The encapsulation is then installed onto a substrate of a detector to seal thermoelectric components on the substrate. In addition to having the sealing function, the encapsulation also has the function of detecting the spectrum and field of view. Next, a carrier substrate is combined with sensing components to form a surface mount device applicable to assembly and fabrication of various related circuits. The thermopile IR detector package structure not only facilitates mass production and reduces fabrication process, material, volume ad weight, but the formed surface mount device is also in agreement with automatically produced electronic components.
Owner:FORMOSA NANOMEMS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com