Patents
Literature
138 results about "Shot noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Shot noise or Poisson noise is a type of noise which can be modeled by a Poisson process. In electronics shot noise originates from the discrete nature of electric charge. Shot noise also occurs in photon counting in optical devices, where shot noise is associated with the particle nature of light.
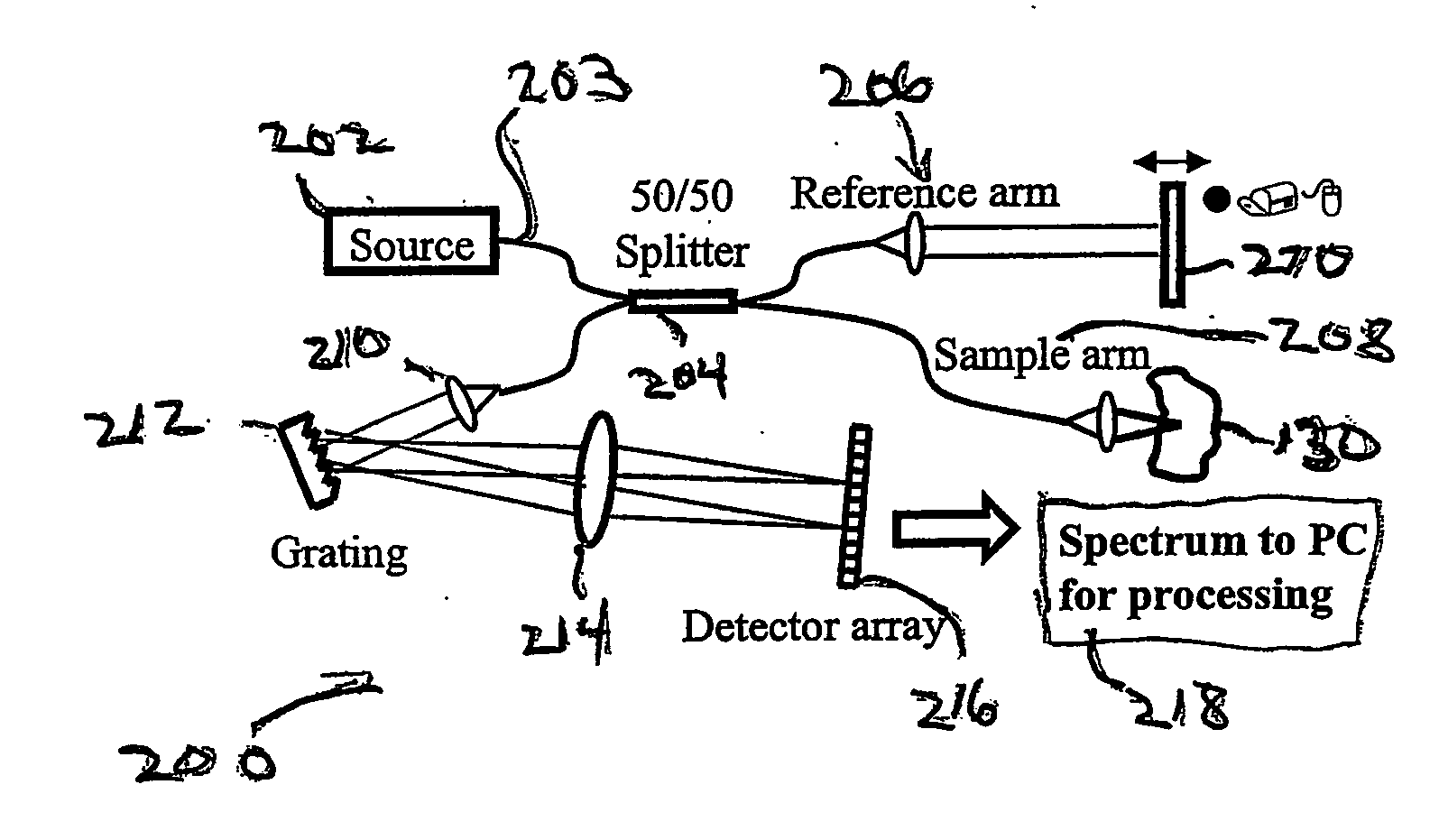
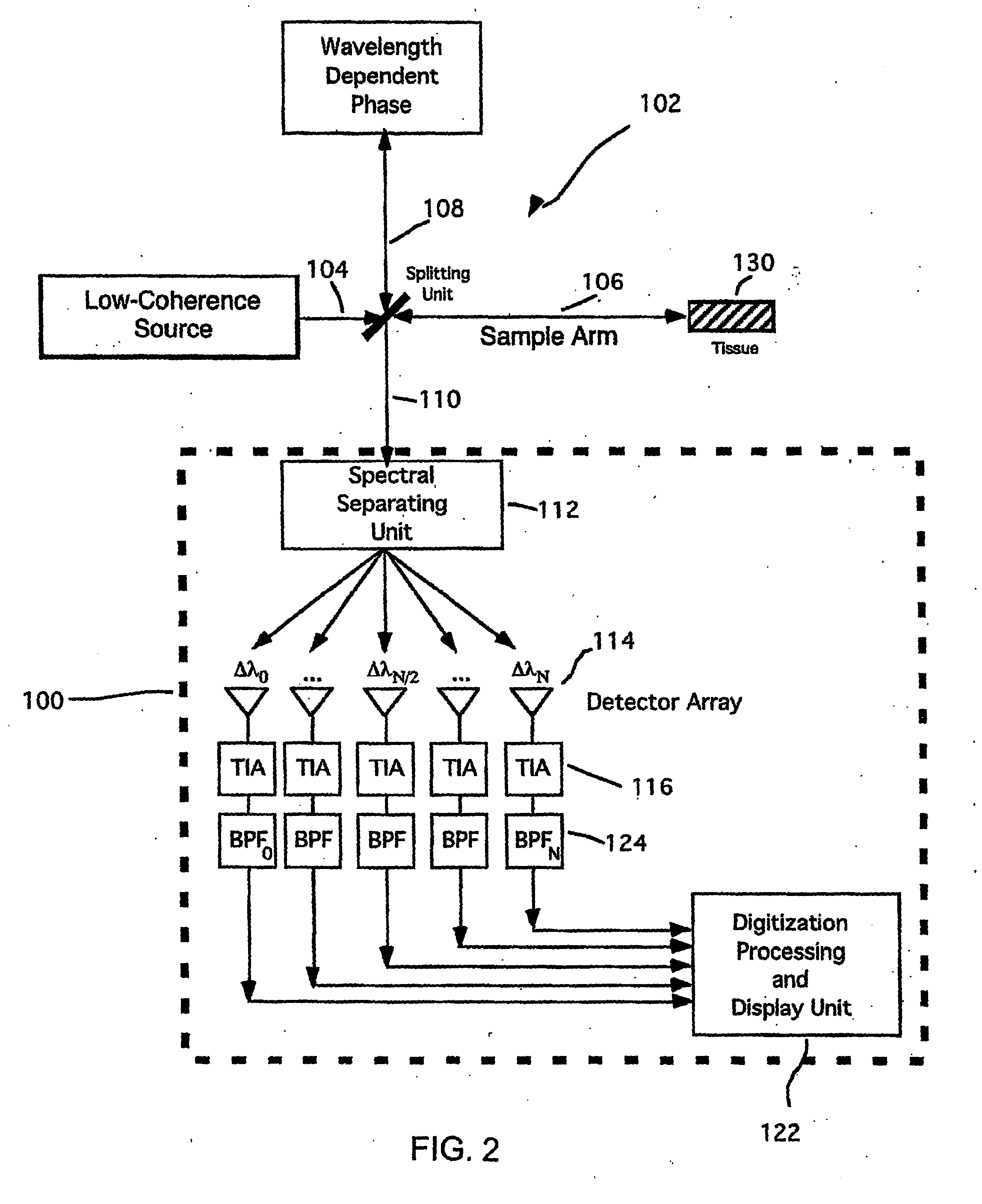
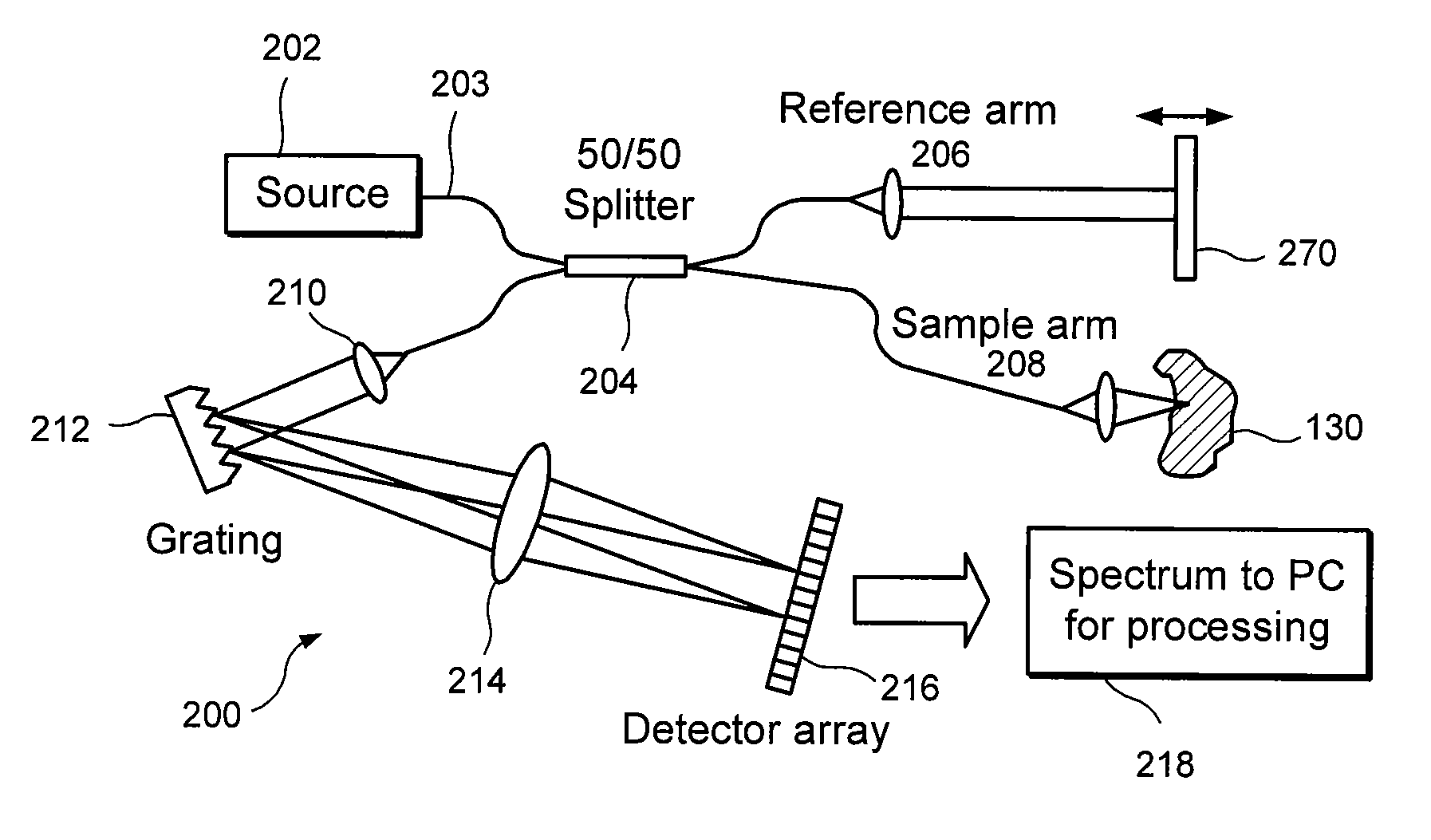
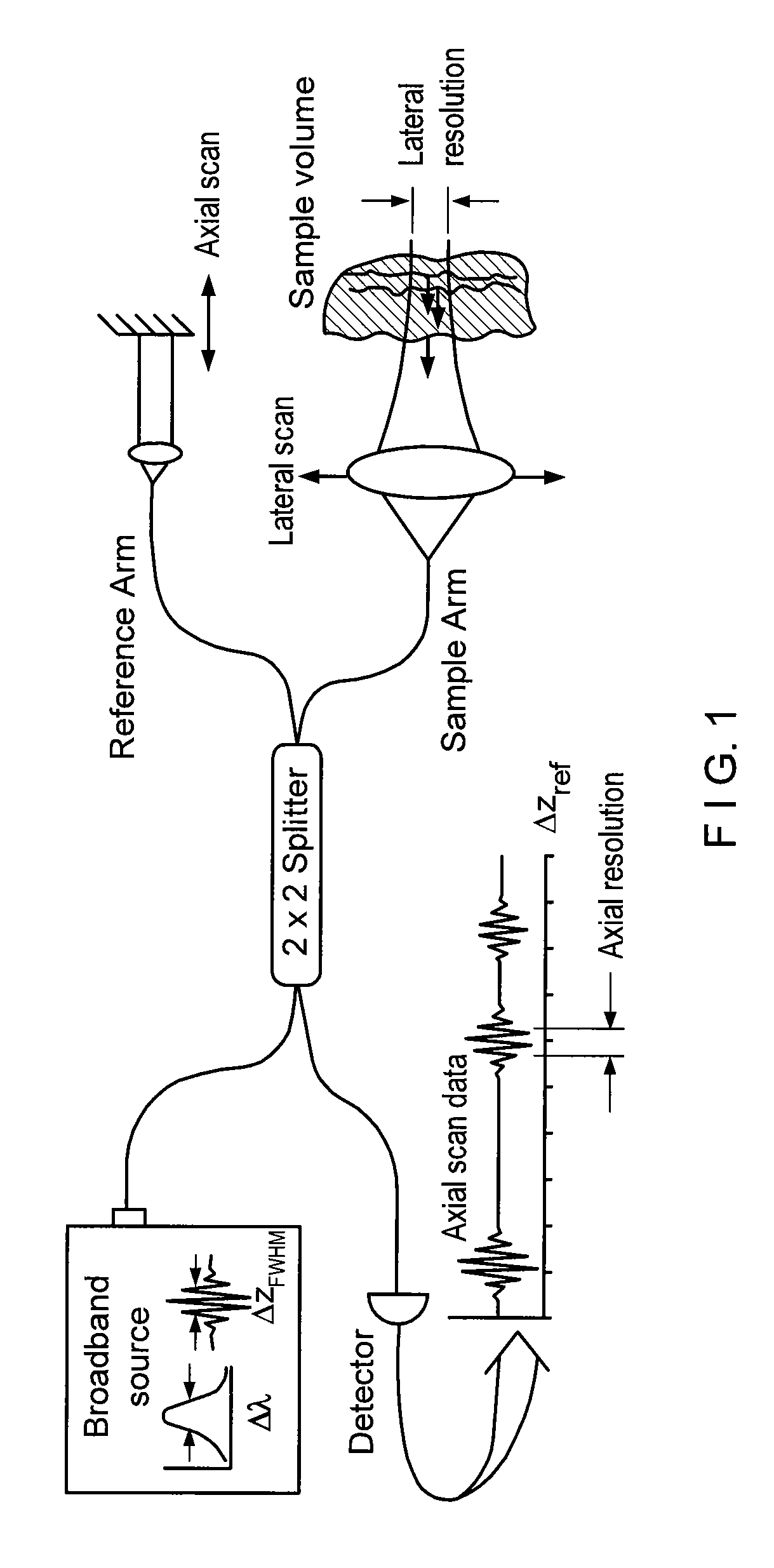
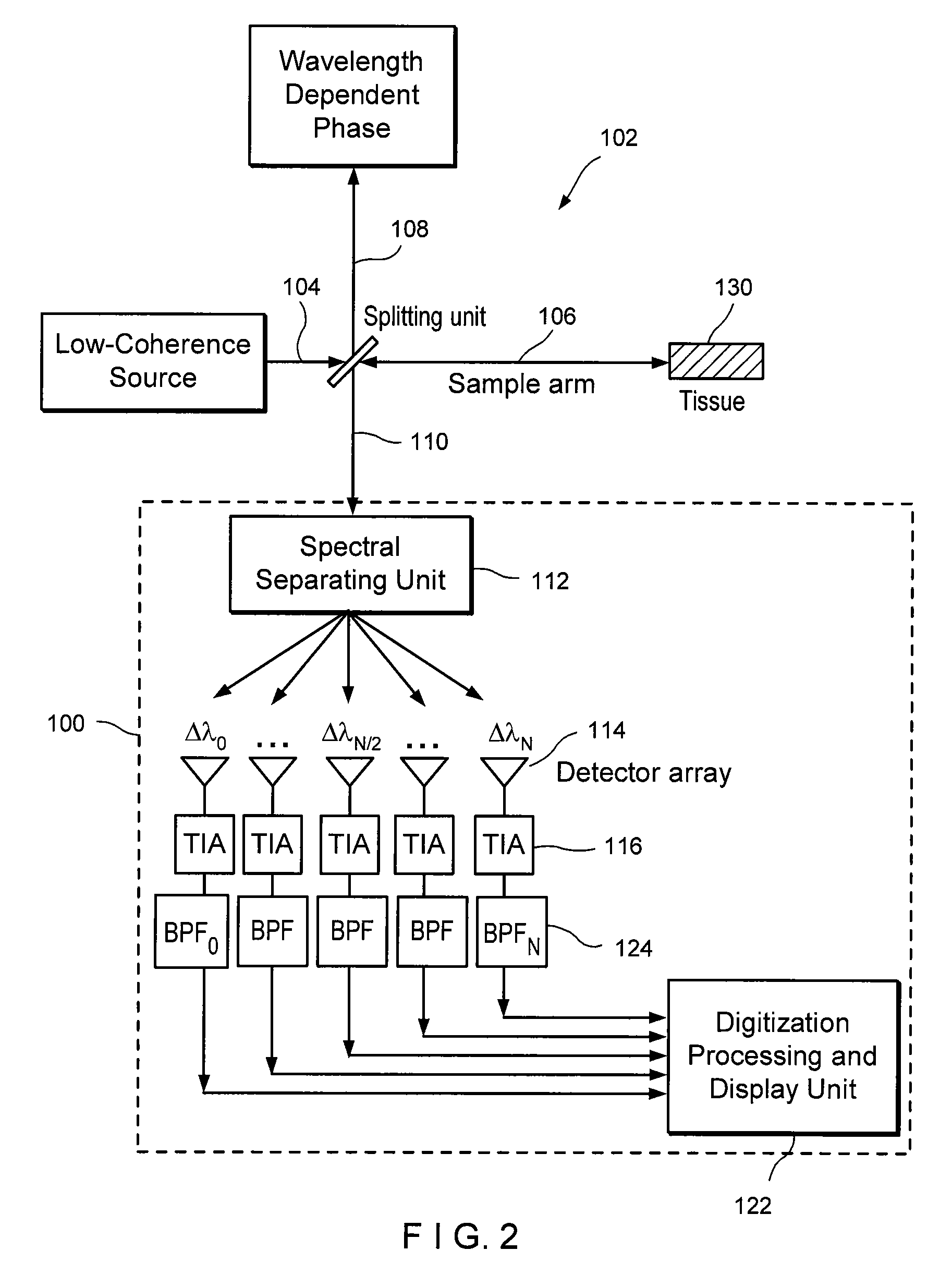
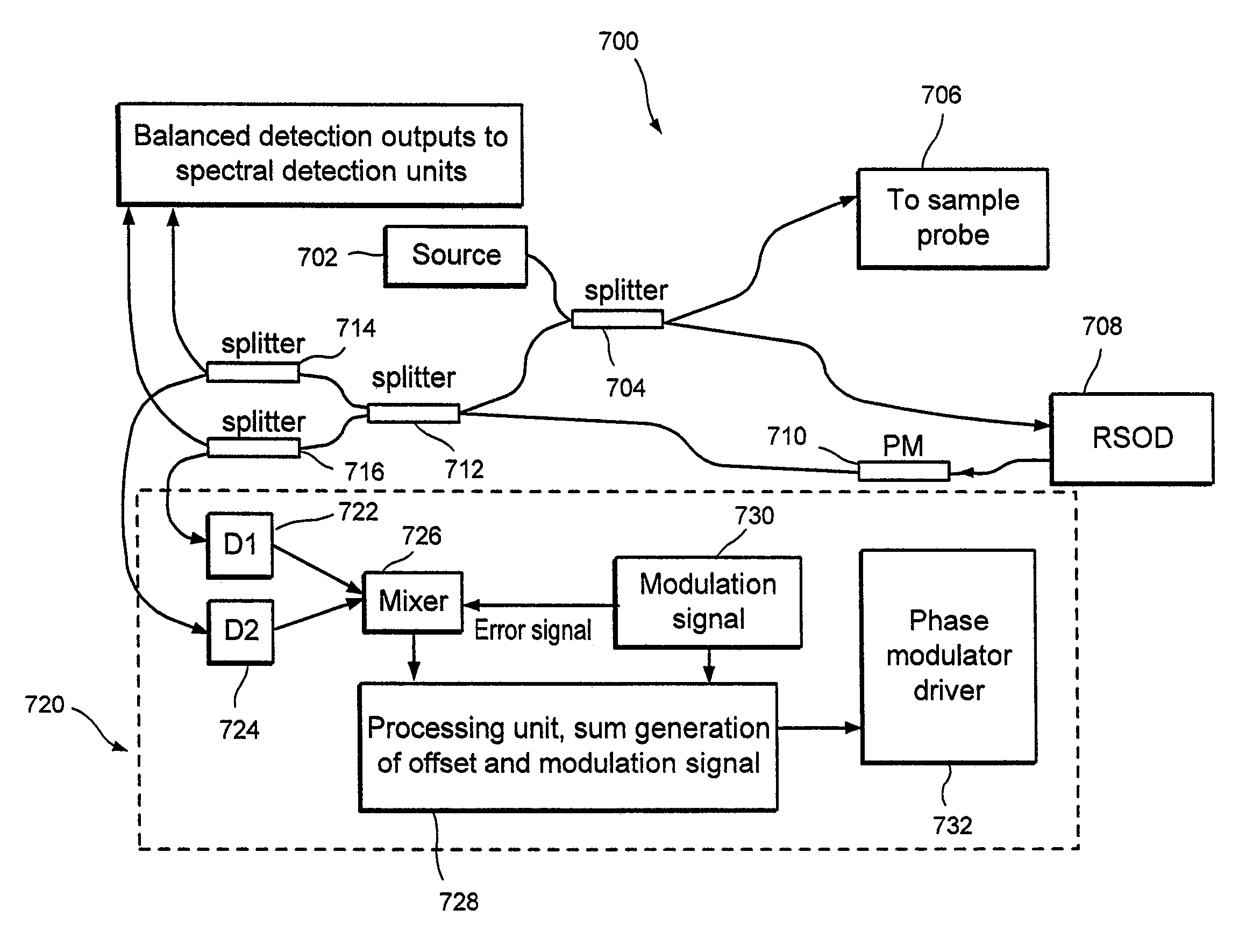
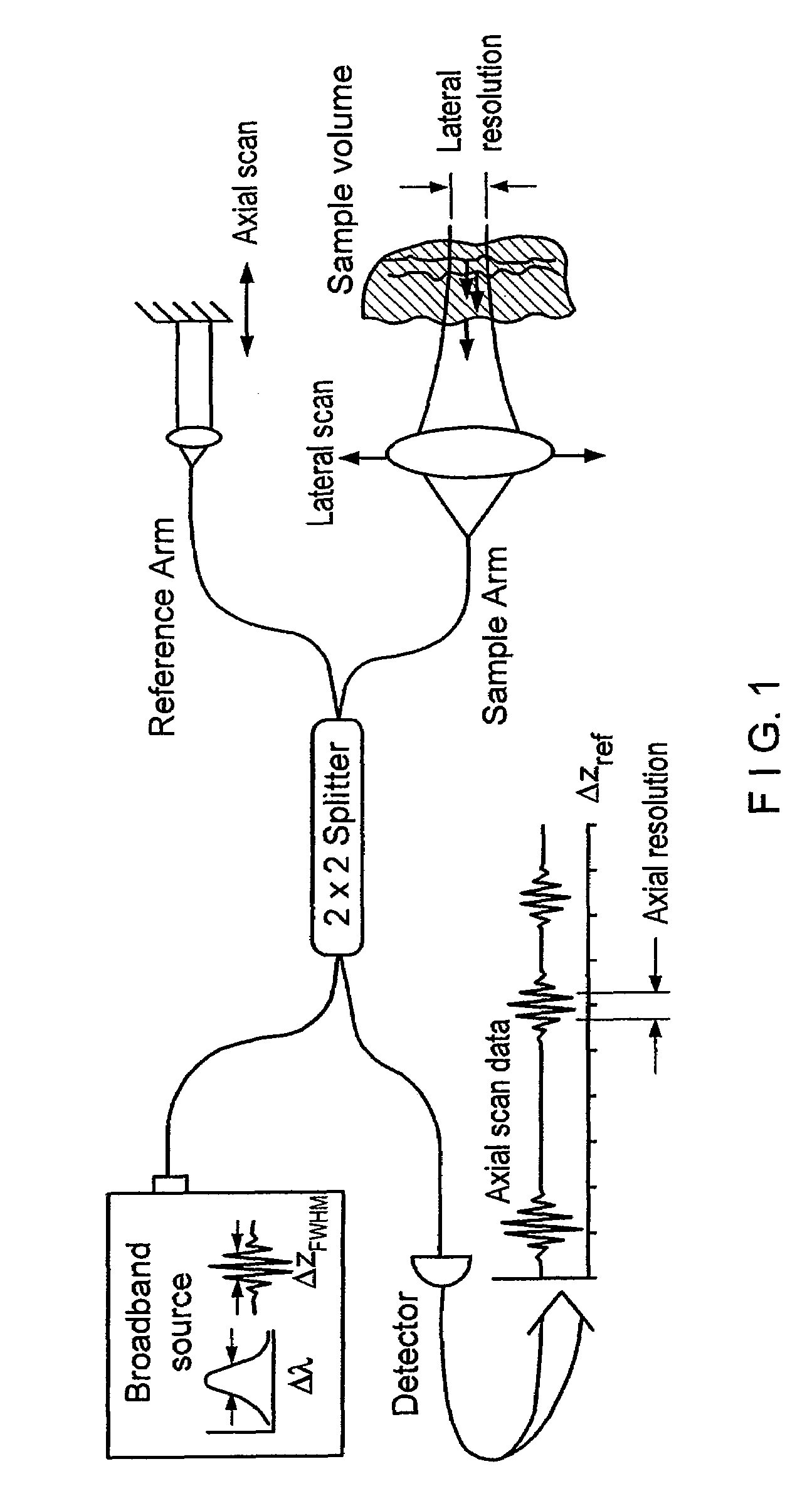
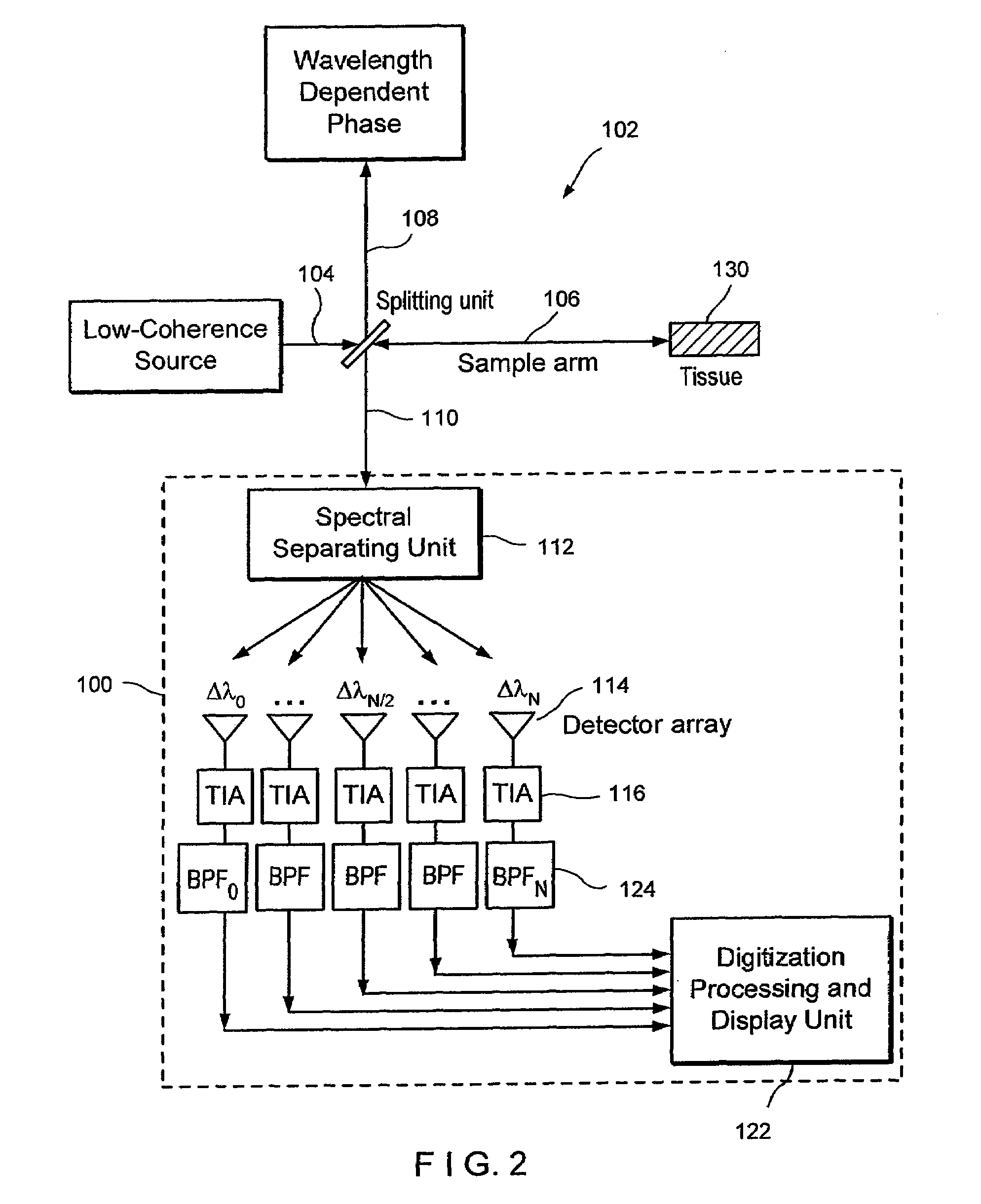
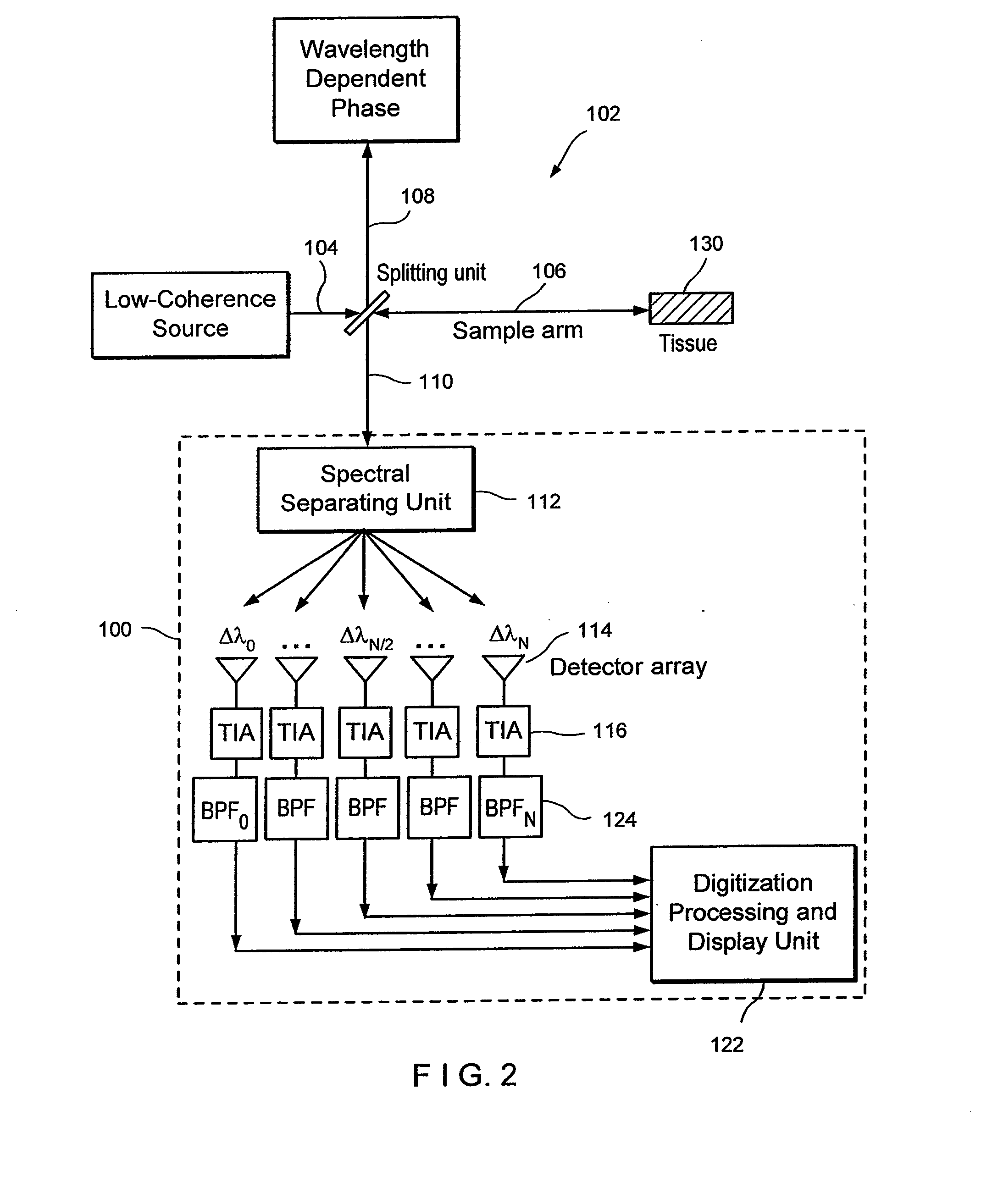
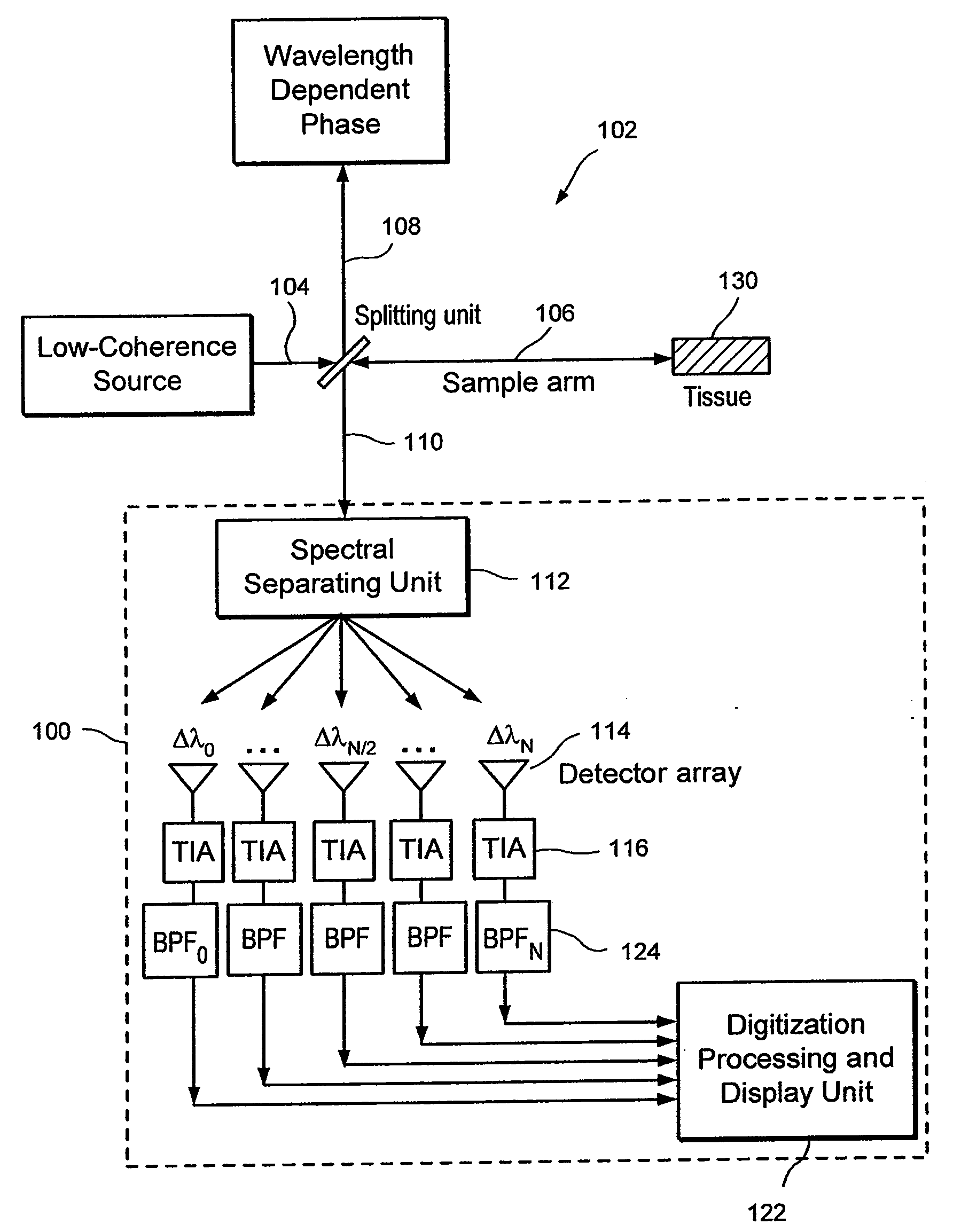
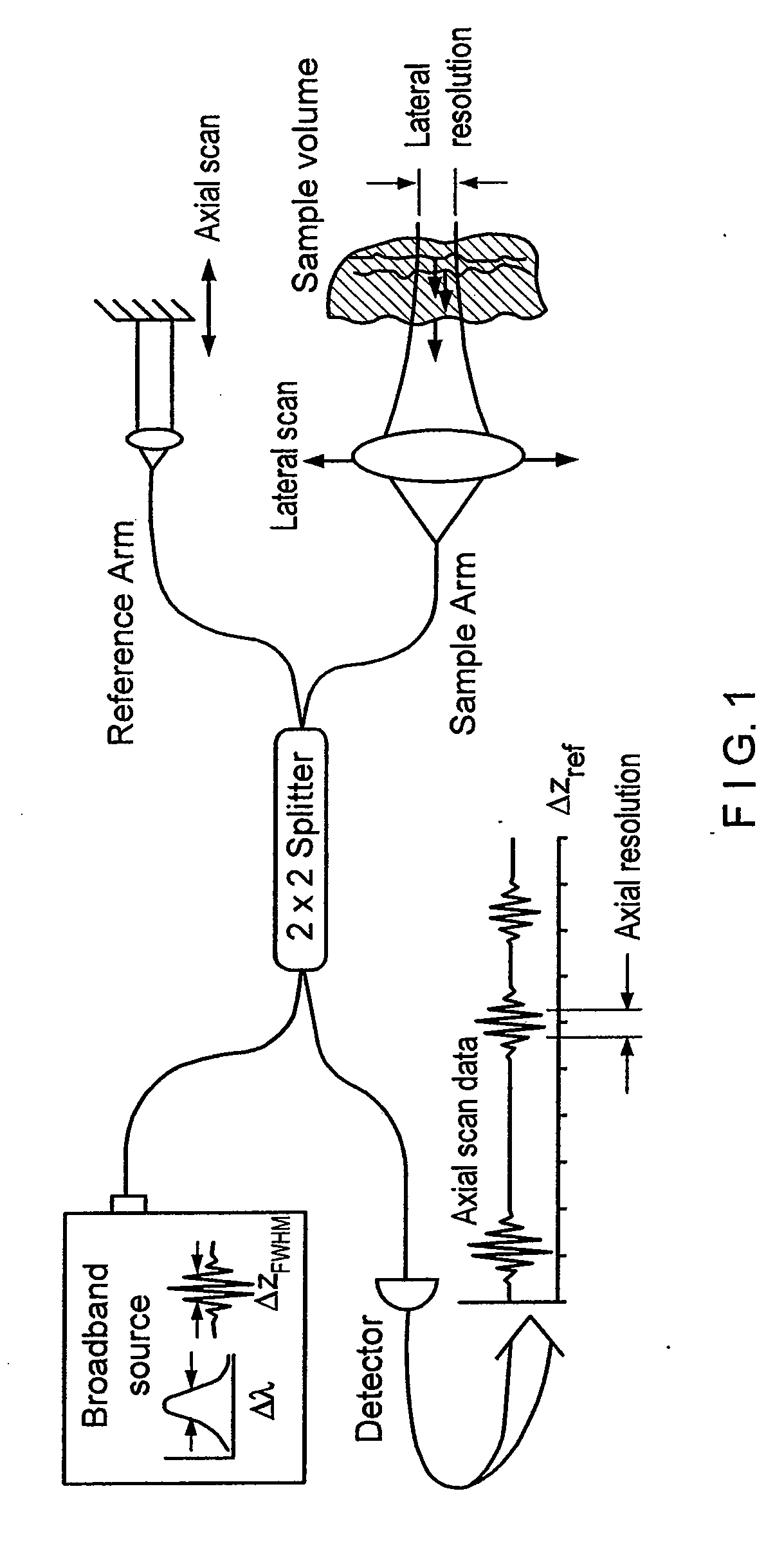
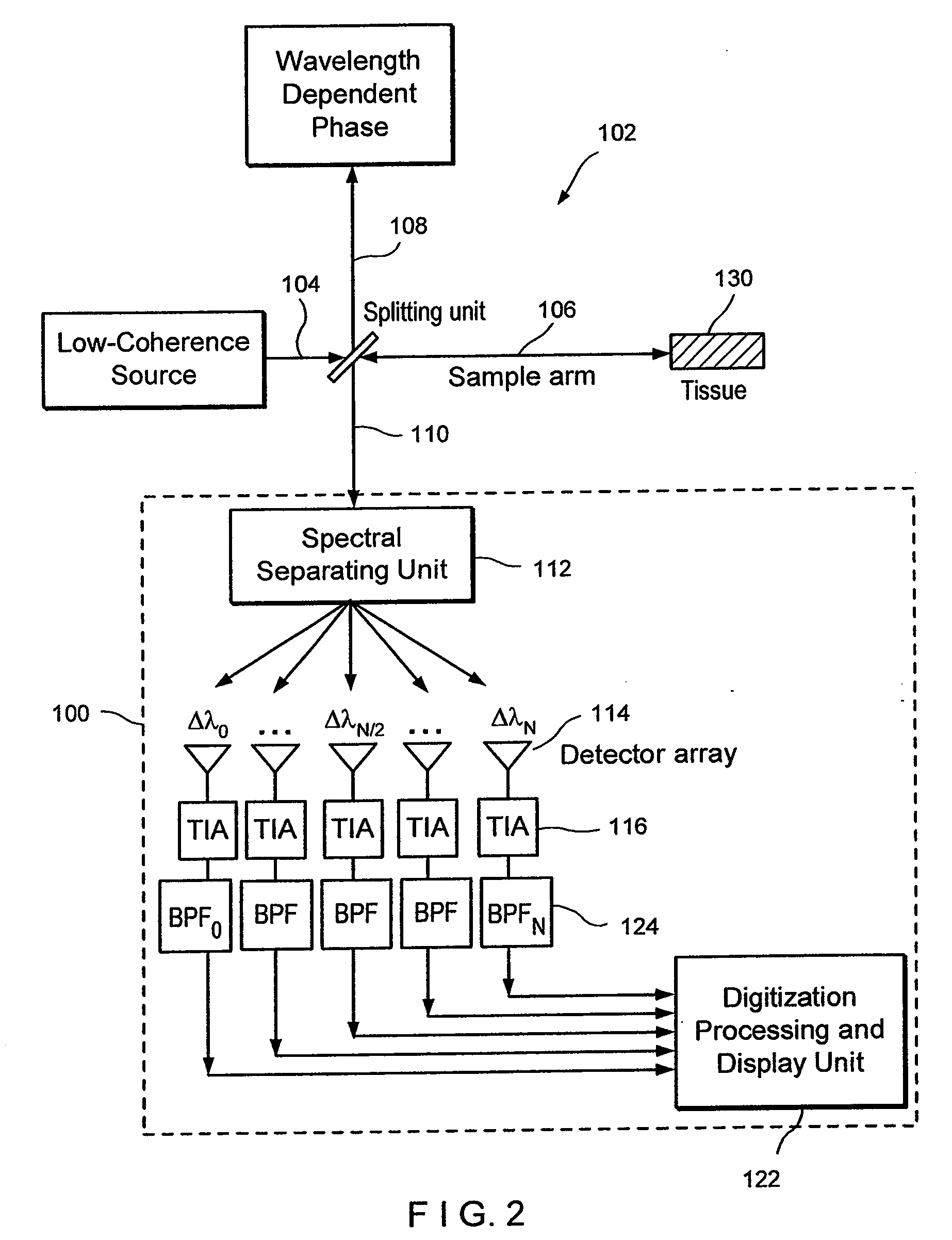
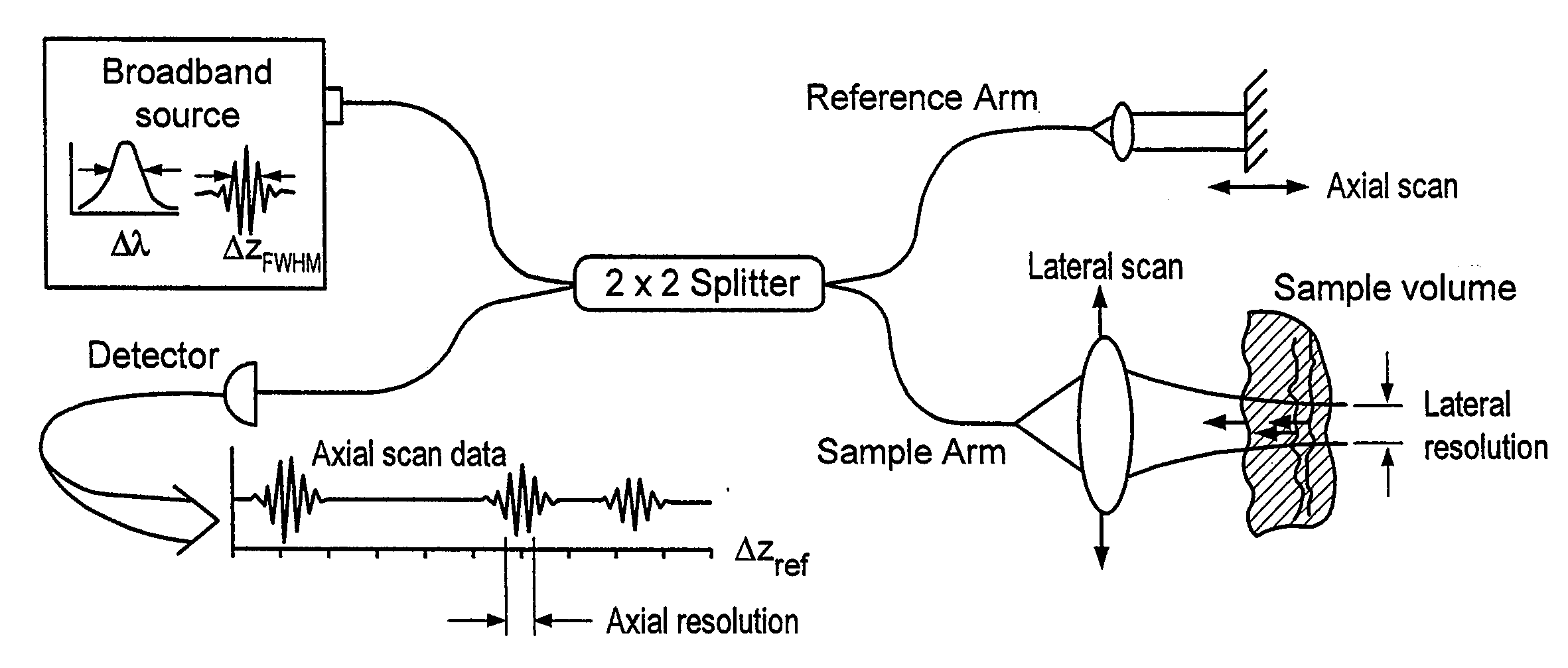
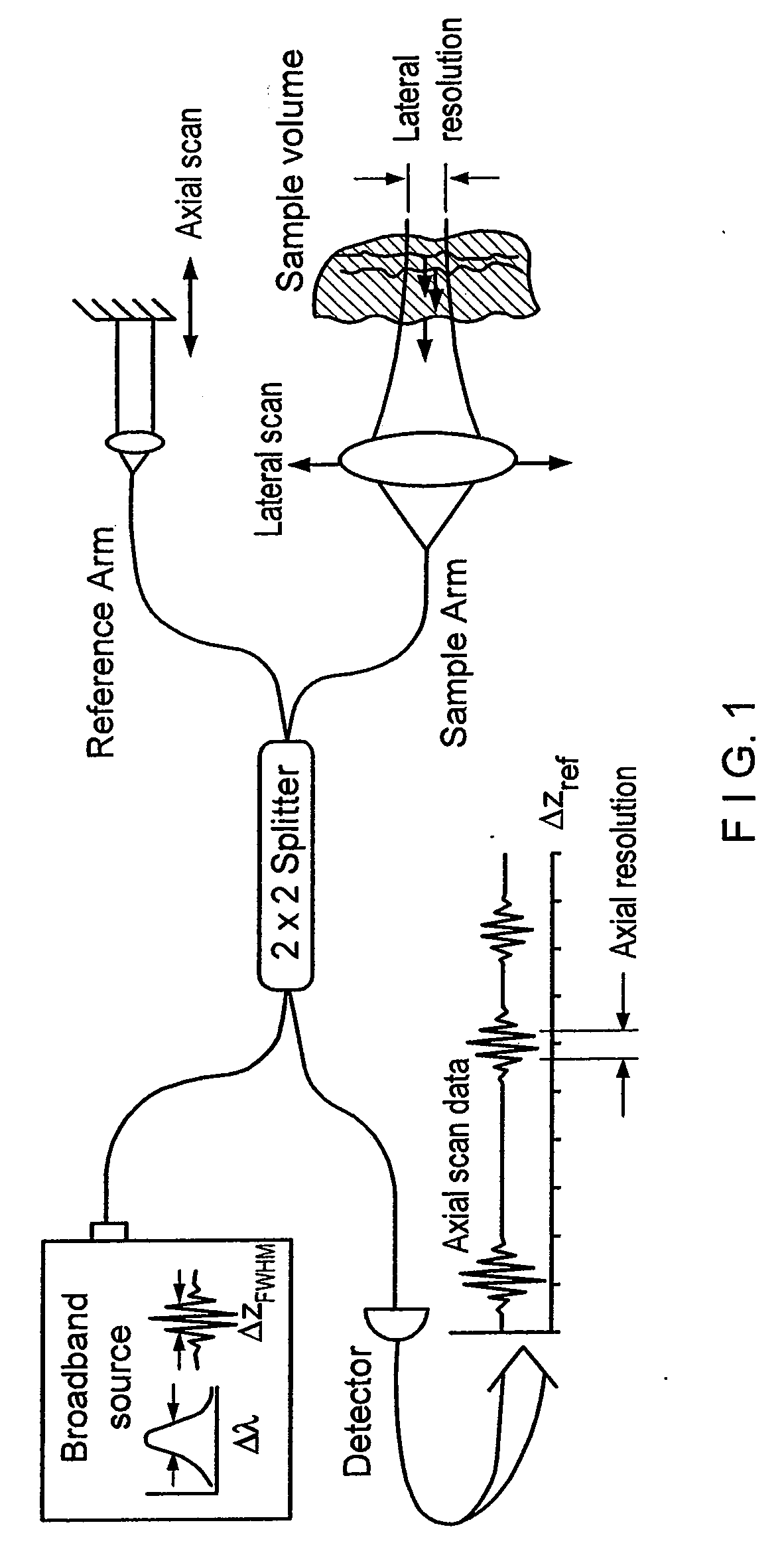
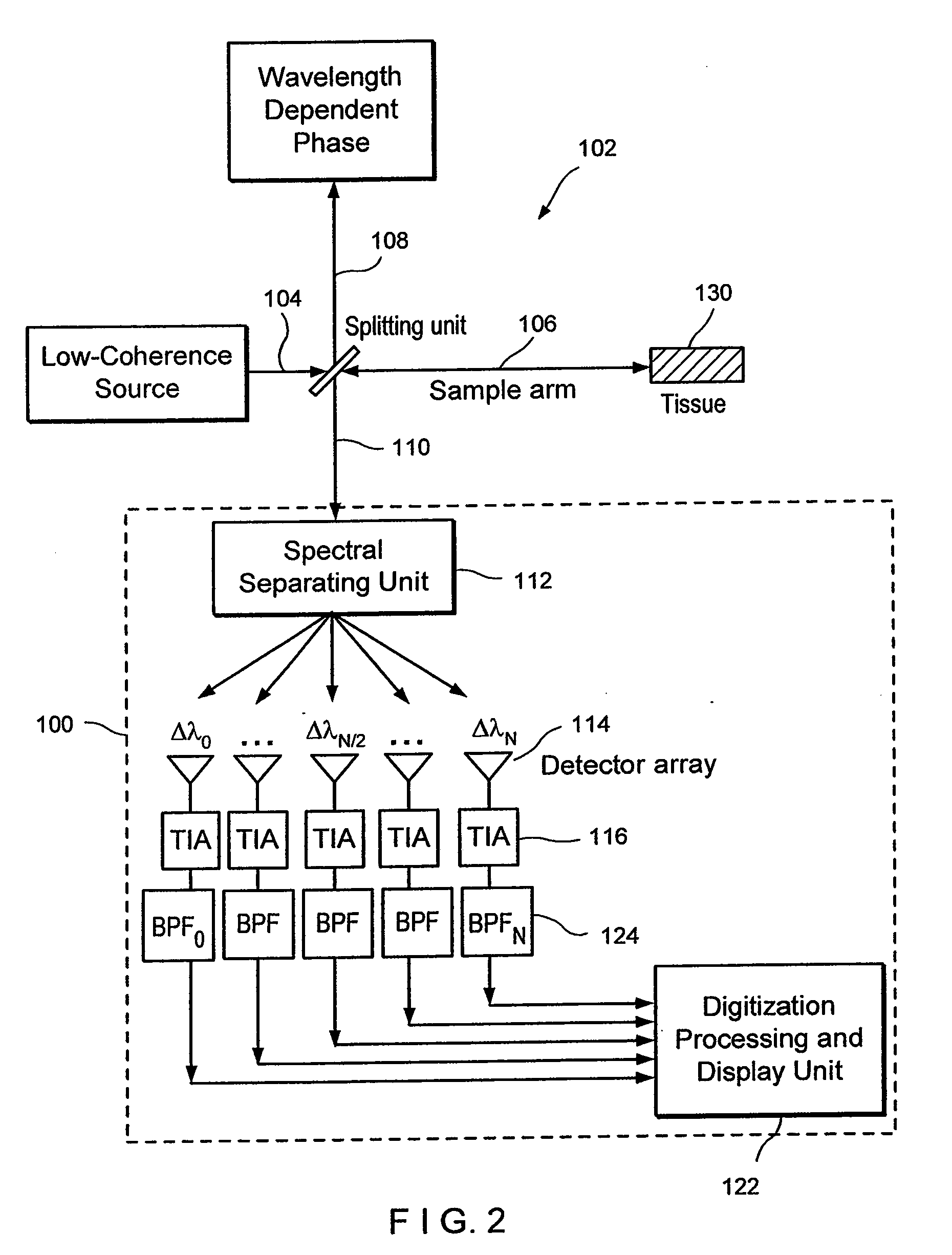
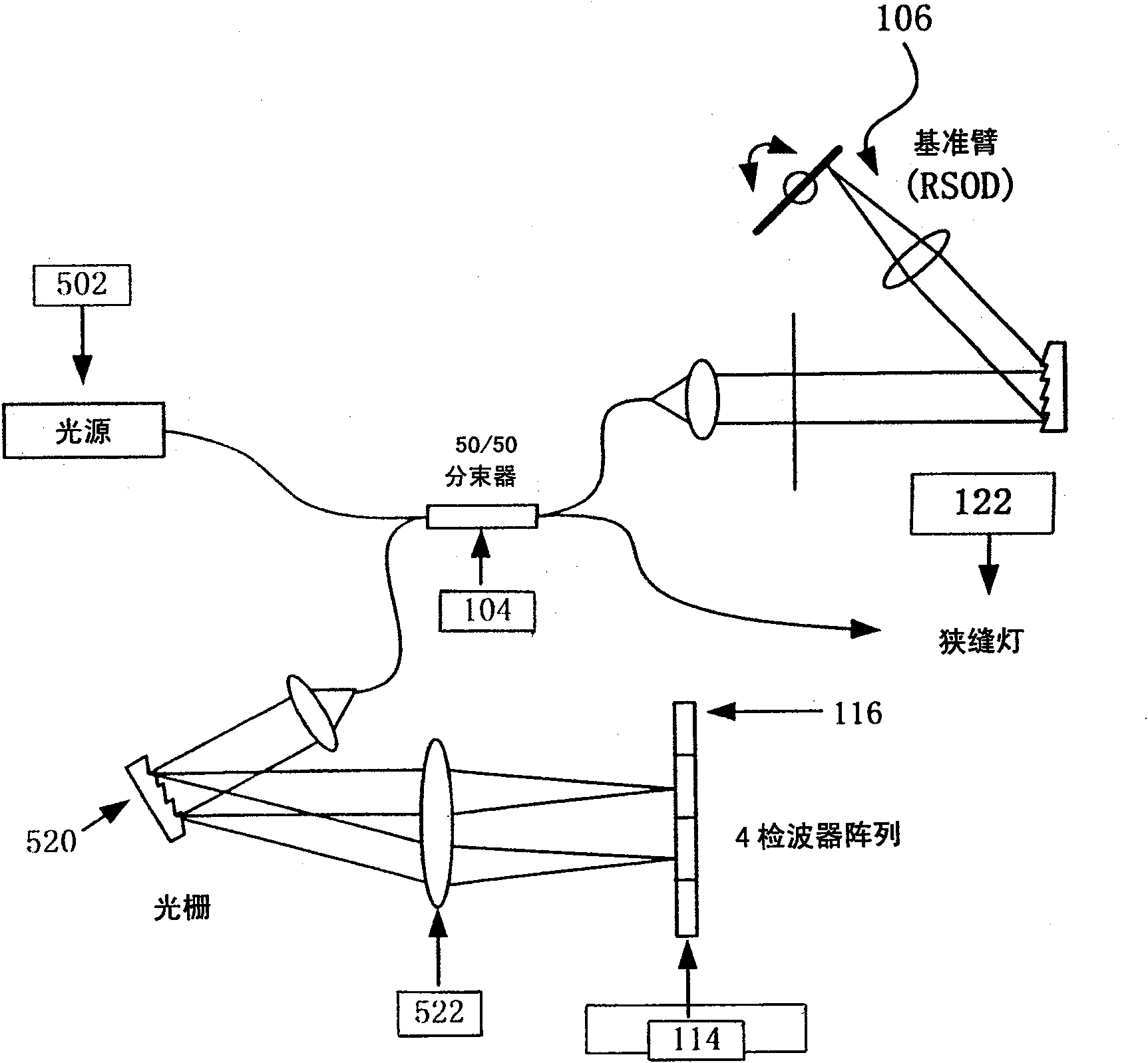
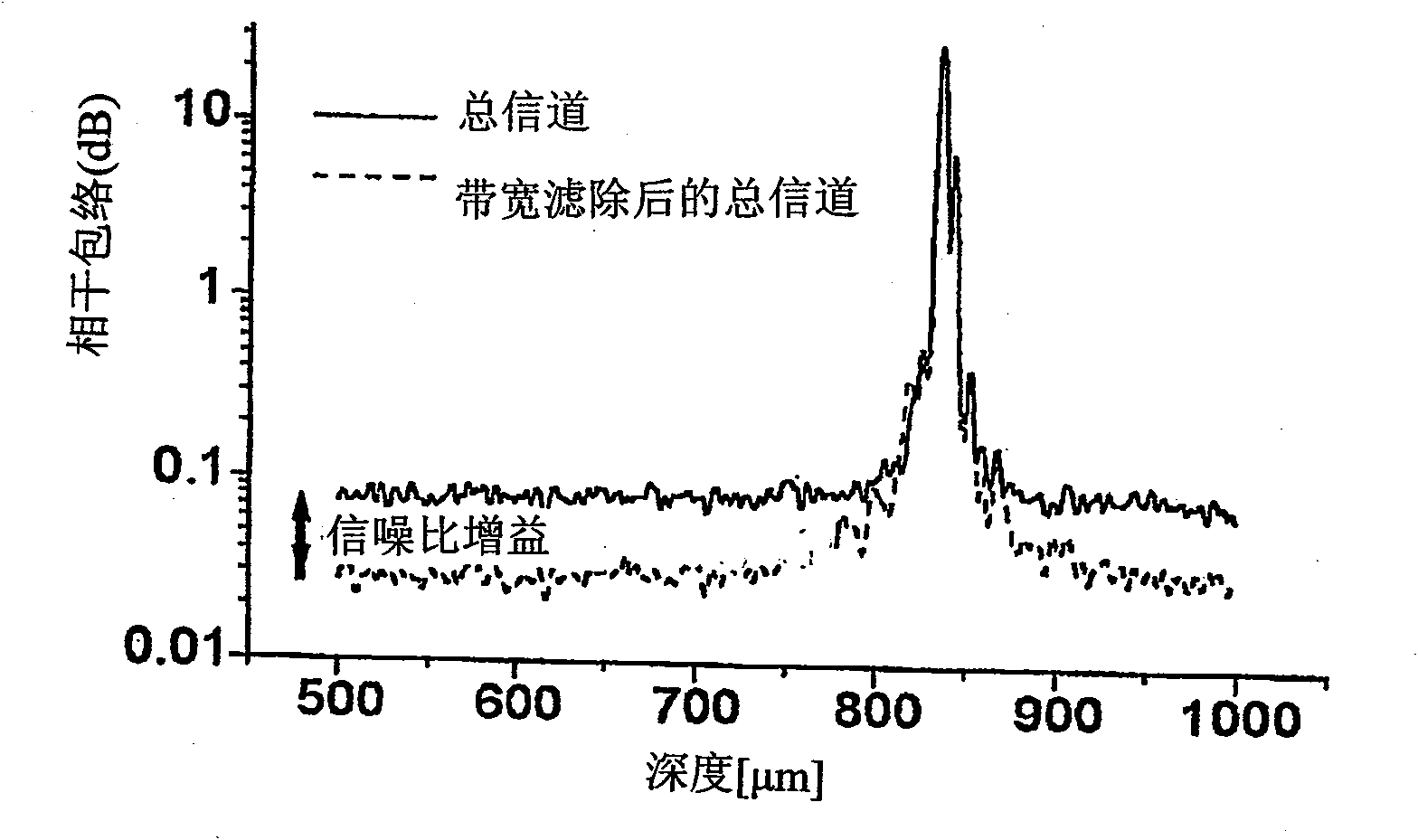
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20050018201A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS7355716B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS7643153B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20080094637A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
ActiveUS20080094613A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for rangings and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20080097709A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
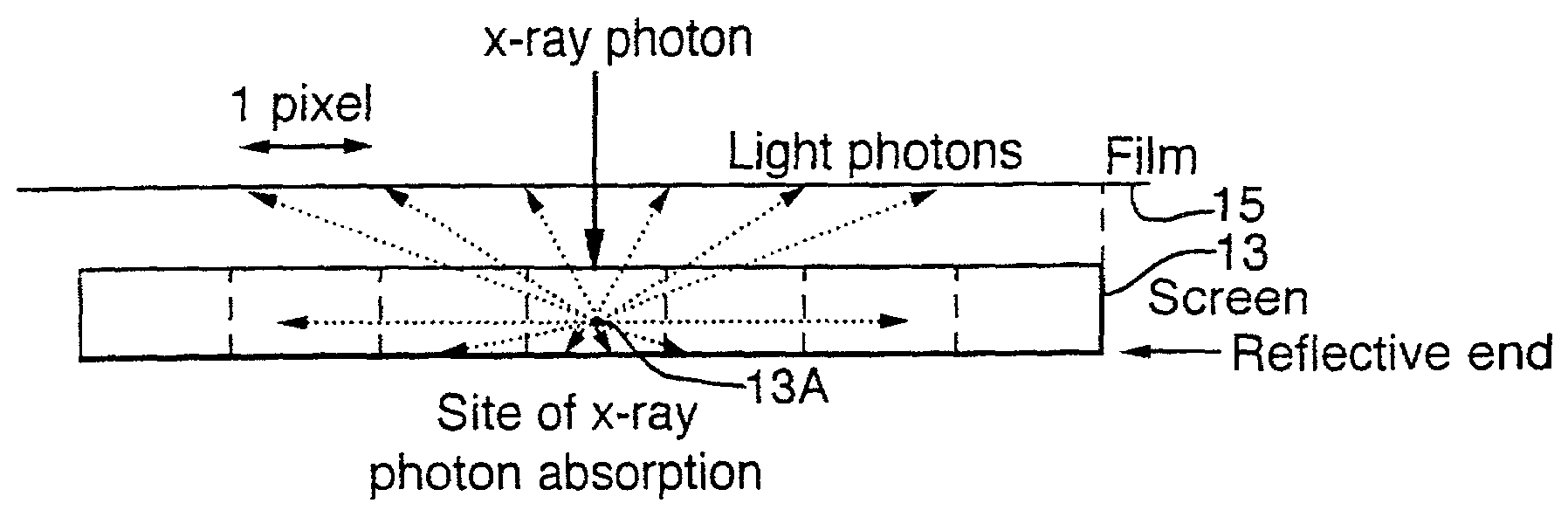
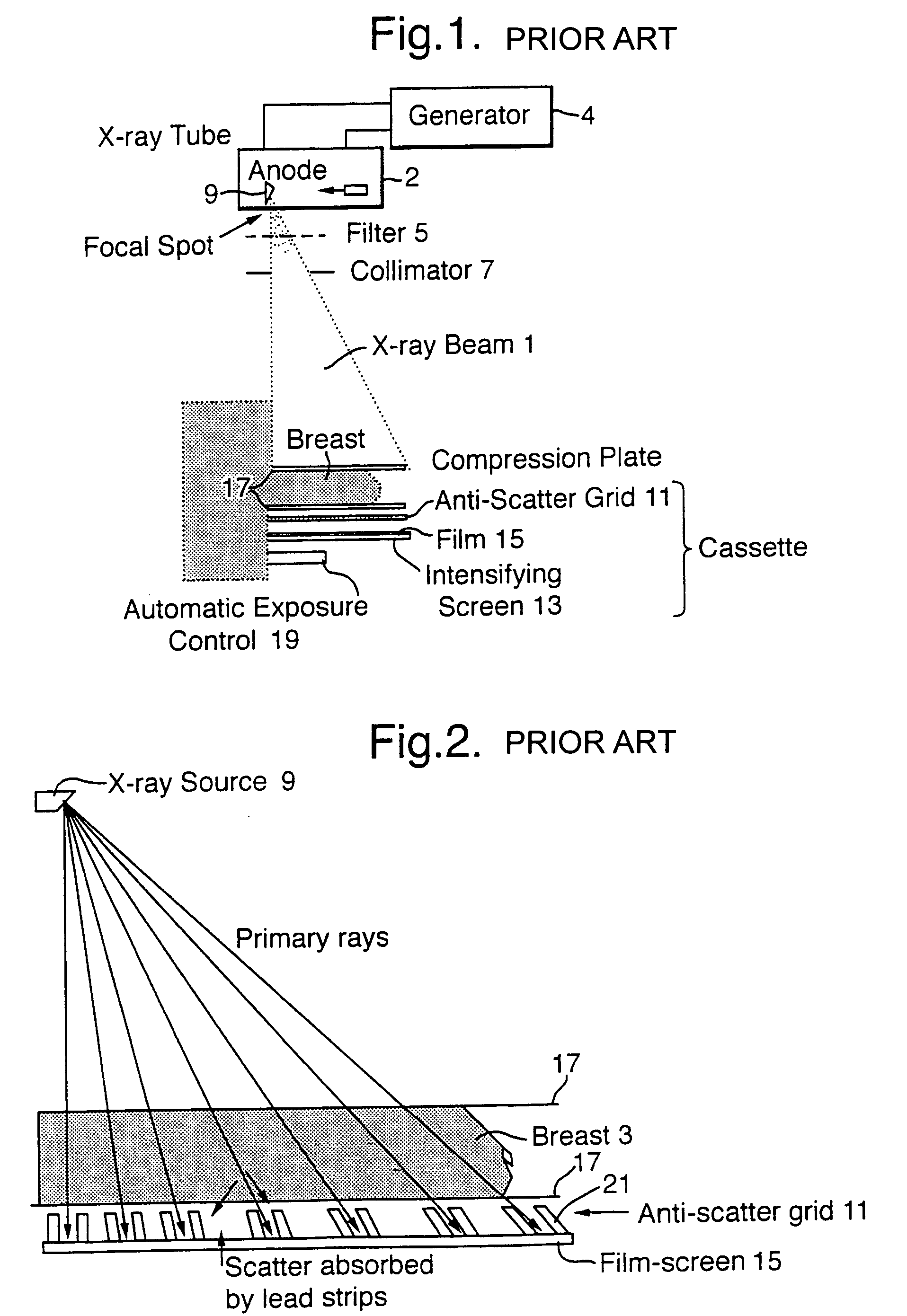
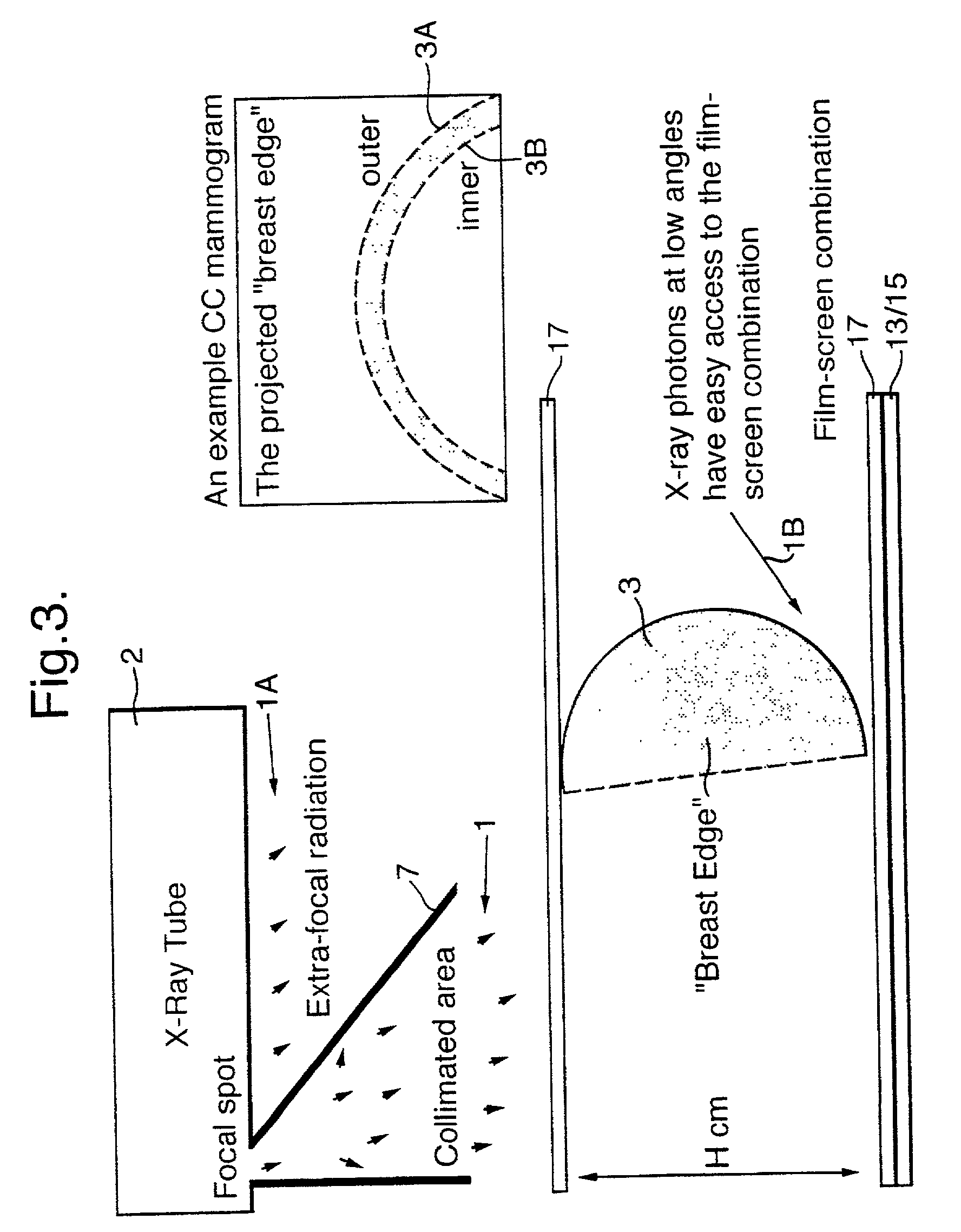
X-ray image processing
A method of enhancing and normalizing x-ray images, particularly mammograms, by correcting the image for digitizer blur, glare from the intensifying screen and the anode-heel effect. The method also allows the calculation of the compressed thickness of the imaged breast and calculation of the contribution to the mammograms of the extra focal radiation. The correction of the image for glare from the intensifying screen allows the detection of noise, such as film shot noise, in the image, and in particular the differentiation between such noise and microcalcifications.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
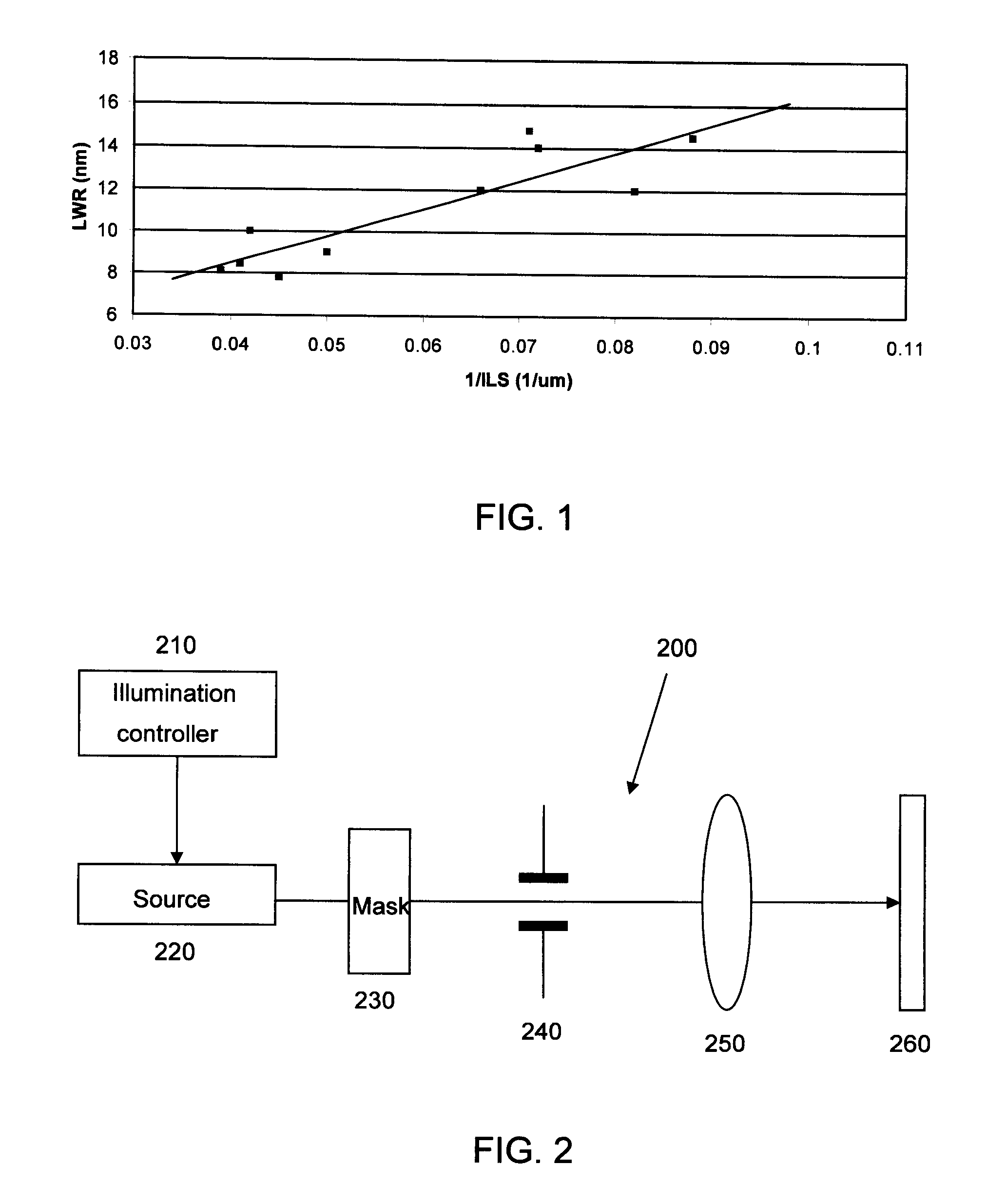
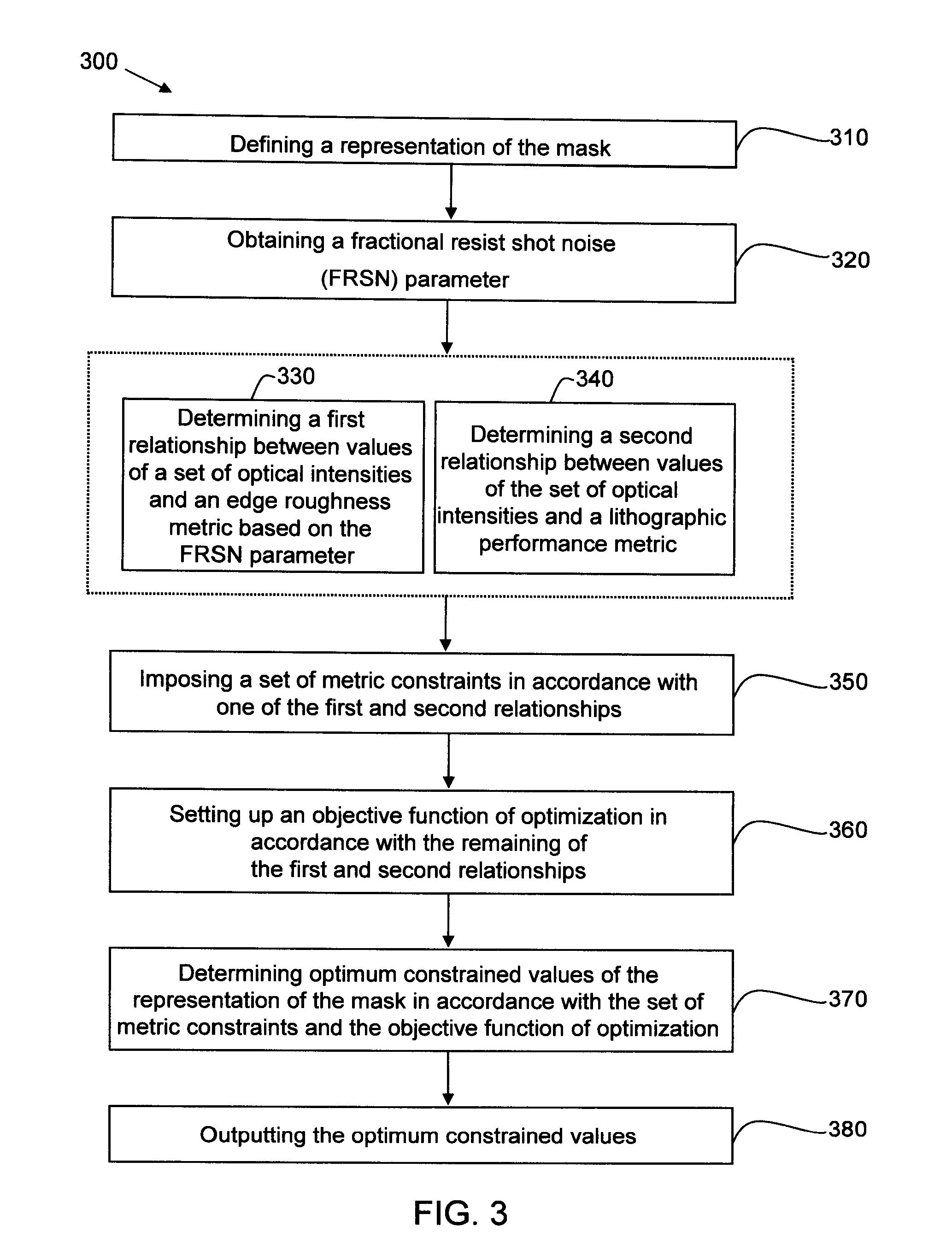
Method for optimizing source and mask to control line width roughness and image log slope
ActiveUS20120052418A1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusControl lineShot noise
A method for illuminating a mask with a source to project a desired image pattern through a lithographic system onto a photoactive material including: defining a representation of the mask; obtaining a fractional resist shot noise (FRSN) parameter; determining a first relationship between a first set of optical intensity values and an edge roughness metric based on the FRSN parameter; determining a second relationship between a second set of optical intensity values and a lithographic performance metric; imposing a set of metric constraints based on one of the first and second relationships; setting up an objective function of optimization based on the remaining of the two relationships; determining optimum constrained values of the representation of the mask based on the set of metric constraints and the objective function; and outputting these values.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system
InactiveCN101825710AMake up for the defect of environmental interferenceSolve the problem of all-fiber miniaturizationElectromagnetic wave reradiationNon-linear opticsRadar systemsOperability
The invention discloses a 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system, which consists of a 2 mu m off-axis Cassegrain optical antenna system, a 2 mu m laser beam splitting system, a 2 mu m seed implantation laser amplifier, a 2 mu m monitoring detector system, and a 2 mu m balanced heterodyne detection system. The system overcomes the defect of ambient interference existing in a free space optical path, overcomes the influence of shot noise on heterodyne reception signal-to-noise ratio, and solves the problems of all fiber and miniaturization of the 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system, so that the 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system has a more compact structure. In addition, the system has the characteristics of safe laser for human eye, optical path connection by adopting flexible optical fiber devices, high operability and stability, low cost, good real time, long effectively measured distance, high measurement accuracy (speed measurement and distance measurement) and the like, and has high practical value in the field of coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
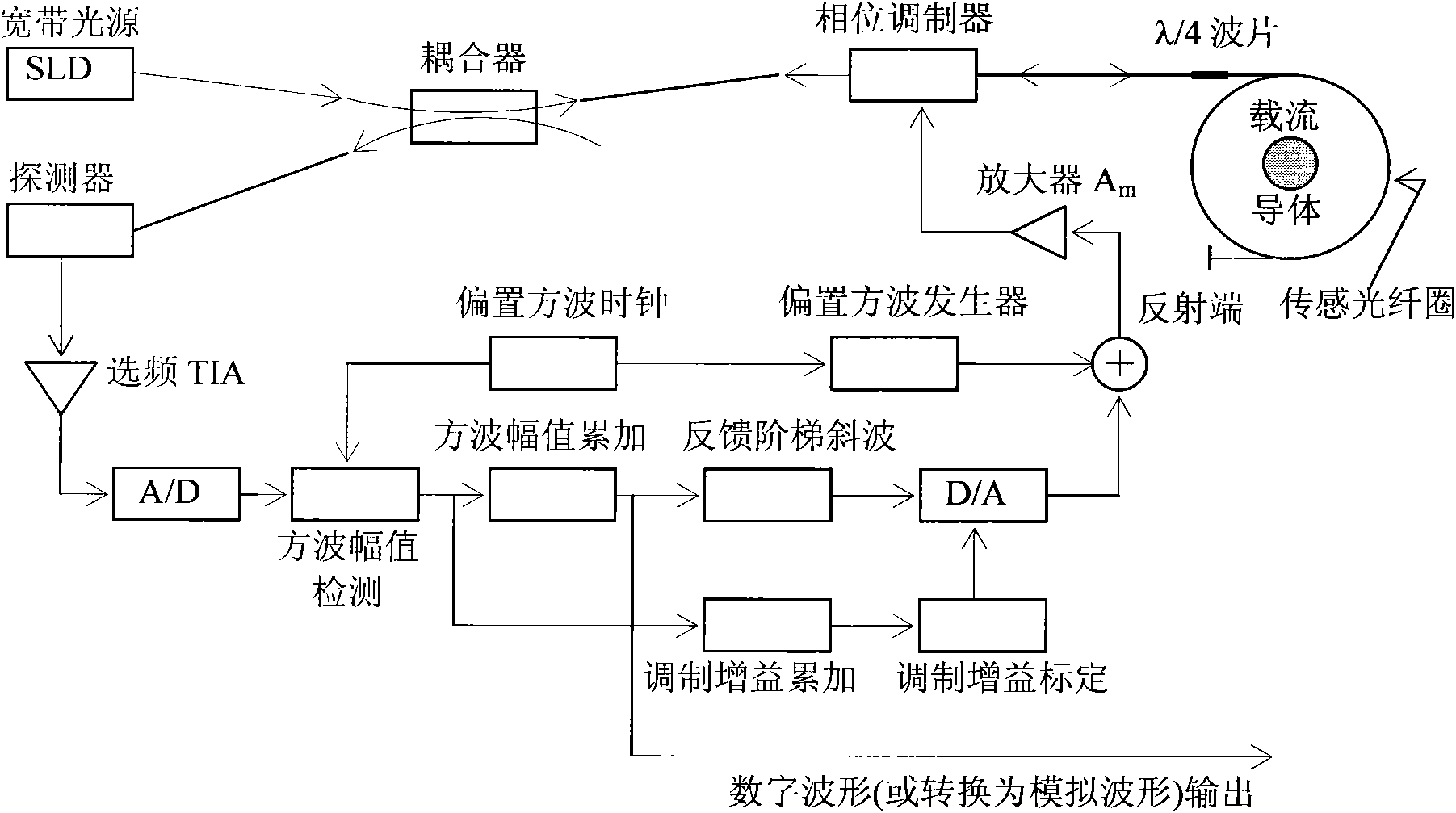
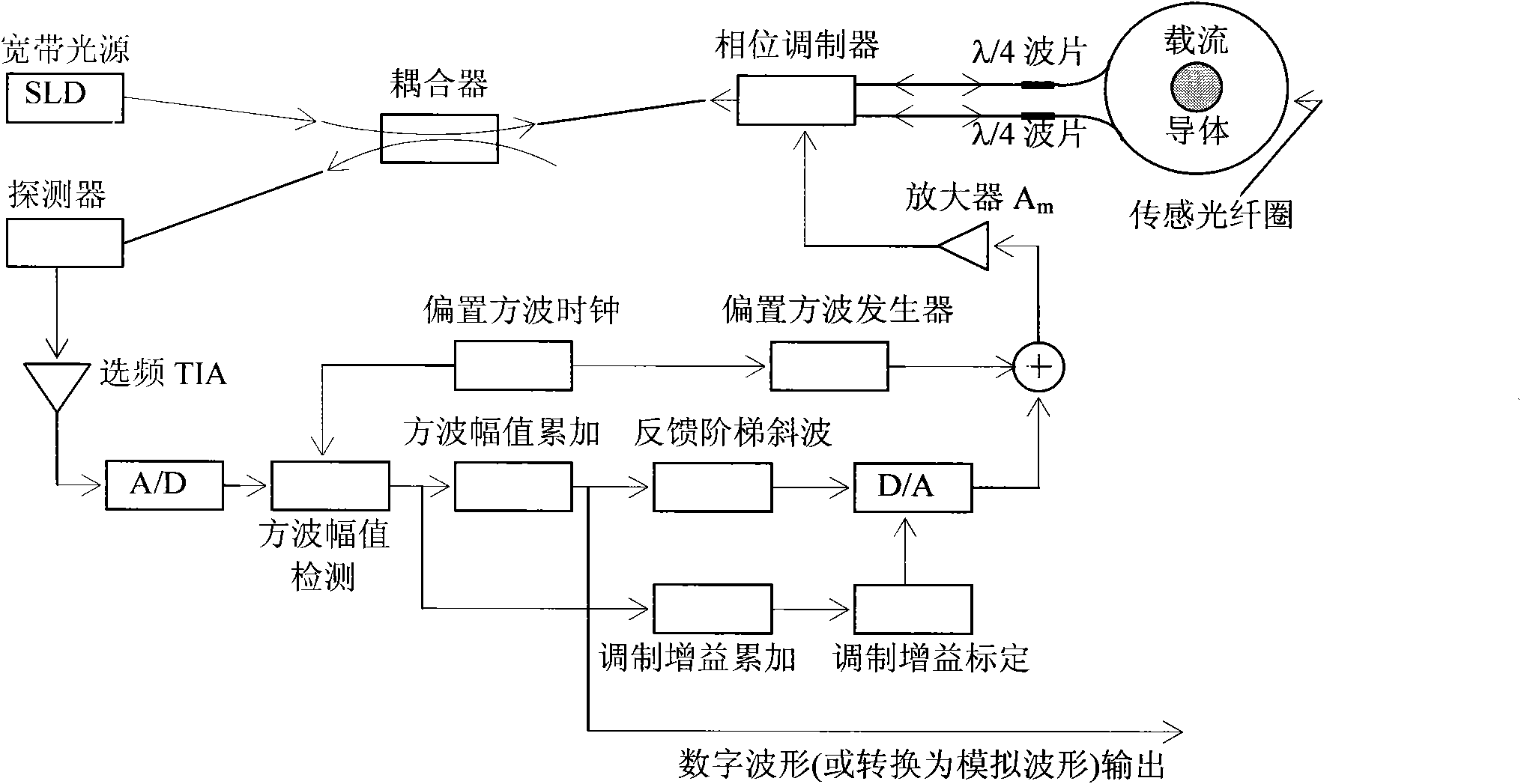
Digital closed loop type optical fiber current sensor
ActiveCN101957399AHigh sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationCurrent transducerNoise level
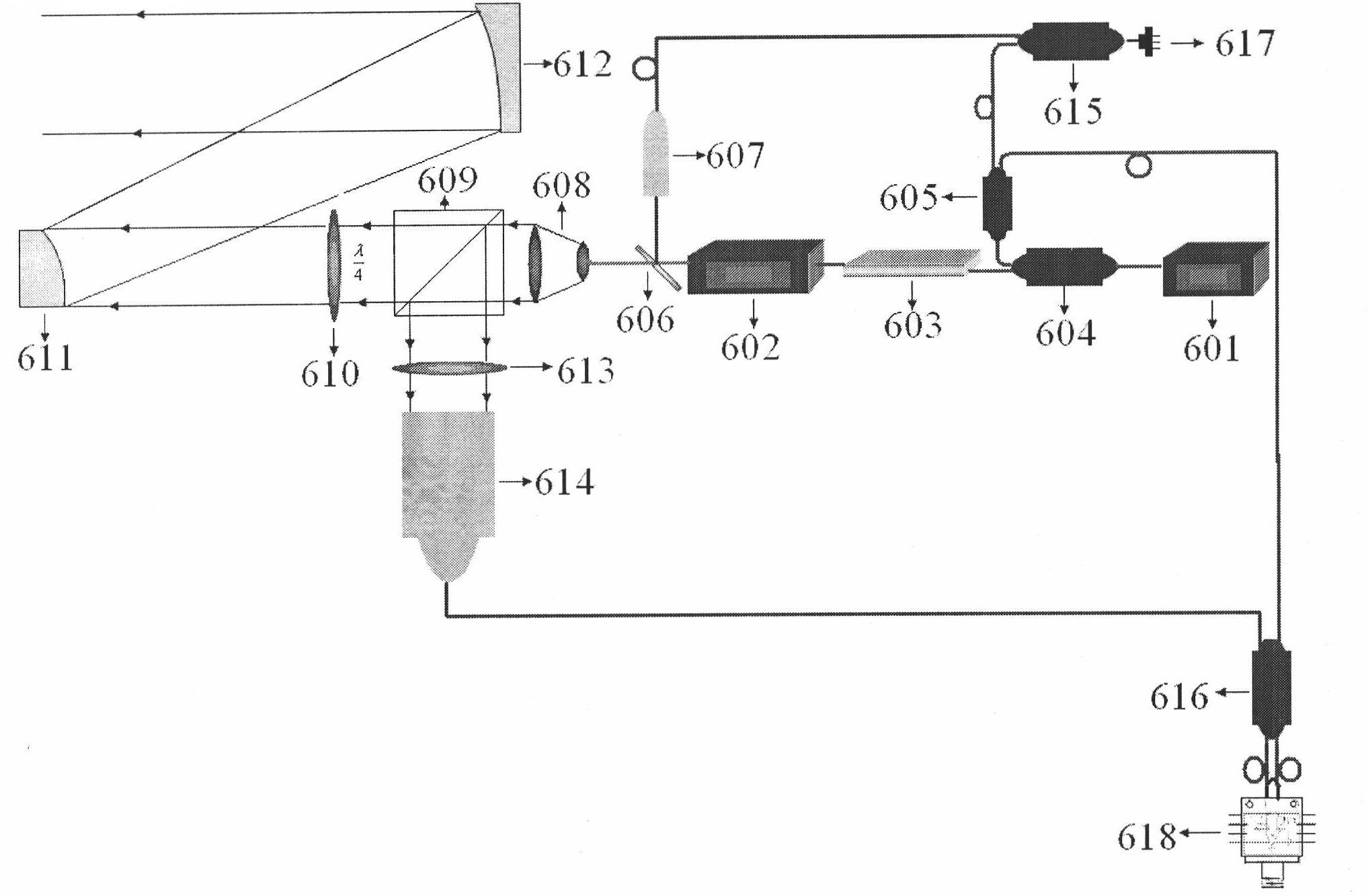
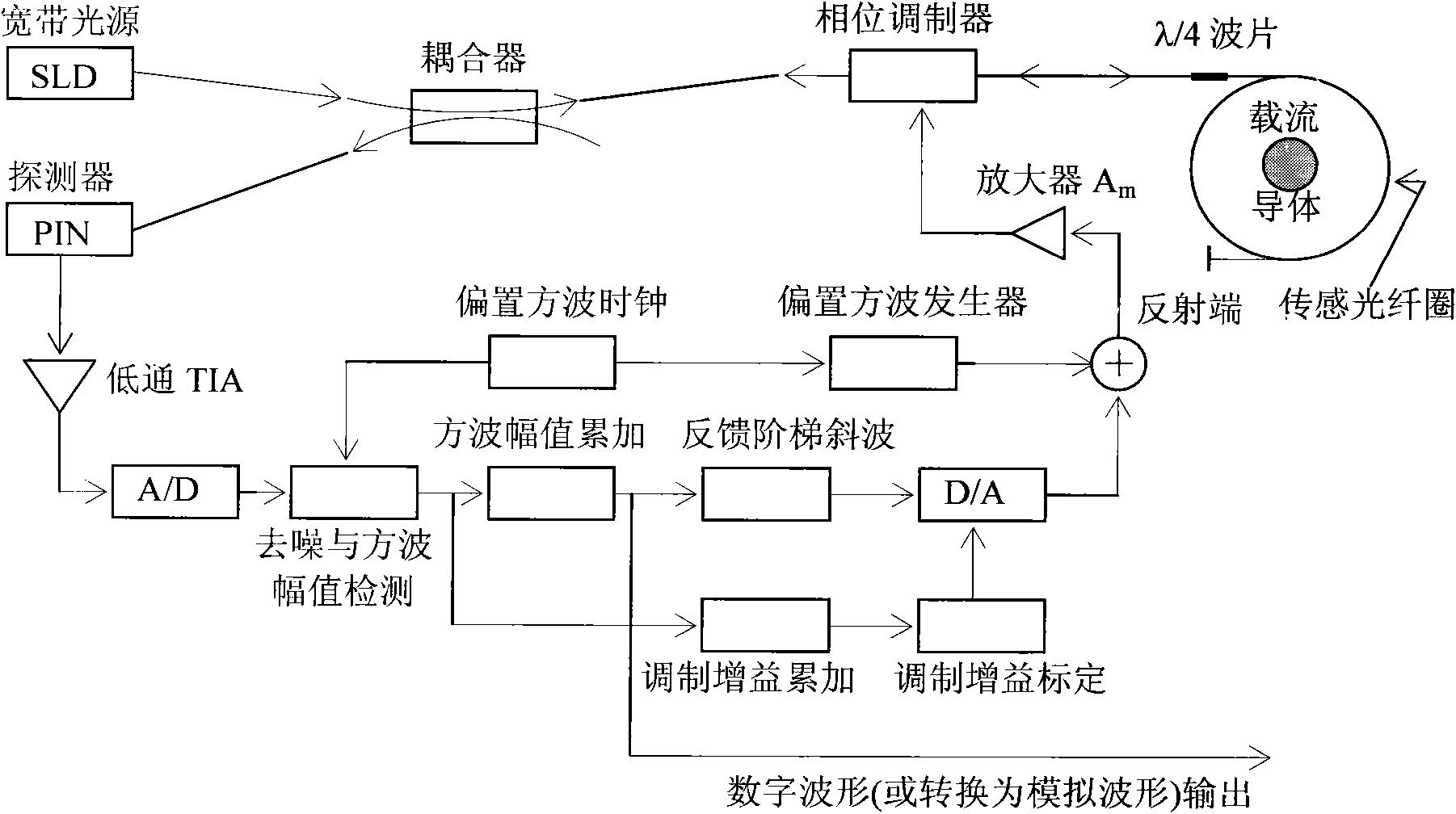
The invention provides a digital closed loop type optical fiber current sensor. A modulation signal of a light wave phase modulator of a sensor optical path system is an amplitude modulation square wave; a signal processing system extracts any harmonic wave of amplitude modulation square wave current output by a photoelectric transducer and extracts tested current information from the current; a pre-amplifier of the signal processing system is a transimpedance amplifier TIA, and the bandwidth is below 1 / 650 when the square wave transient amplitude value (prior art) is directly extracted from the amplitude modulation square wave, so that thermal noise output by the pre-amplifier and the shot noise level are also reduced to be below 1 / 650 of the prior art; and current-voltage conversion gain of the transimpedance amplifier TIA is not determined by the resistance of a feedback network of the TIA, so that a low-resistance resistor is adopted in the feedback network of the TIA while the high current-voltage conversion gain is ensured, and the thermal noise of the resistor which accounts for a significant proportion in the level of the noise output by the TIA is reduced to be negligible.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
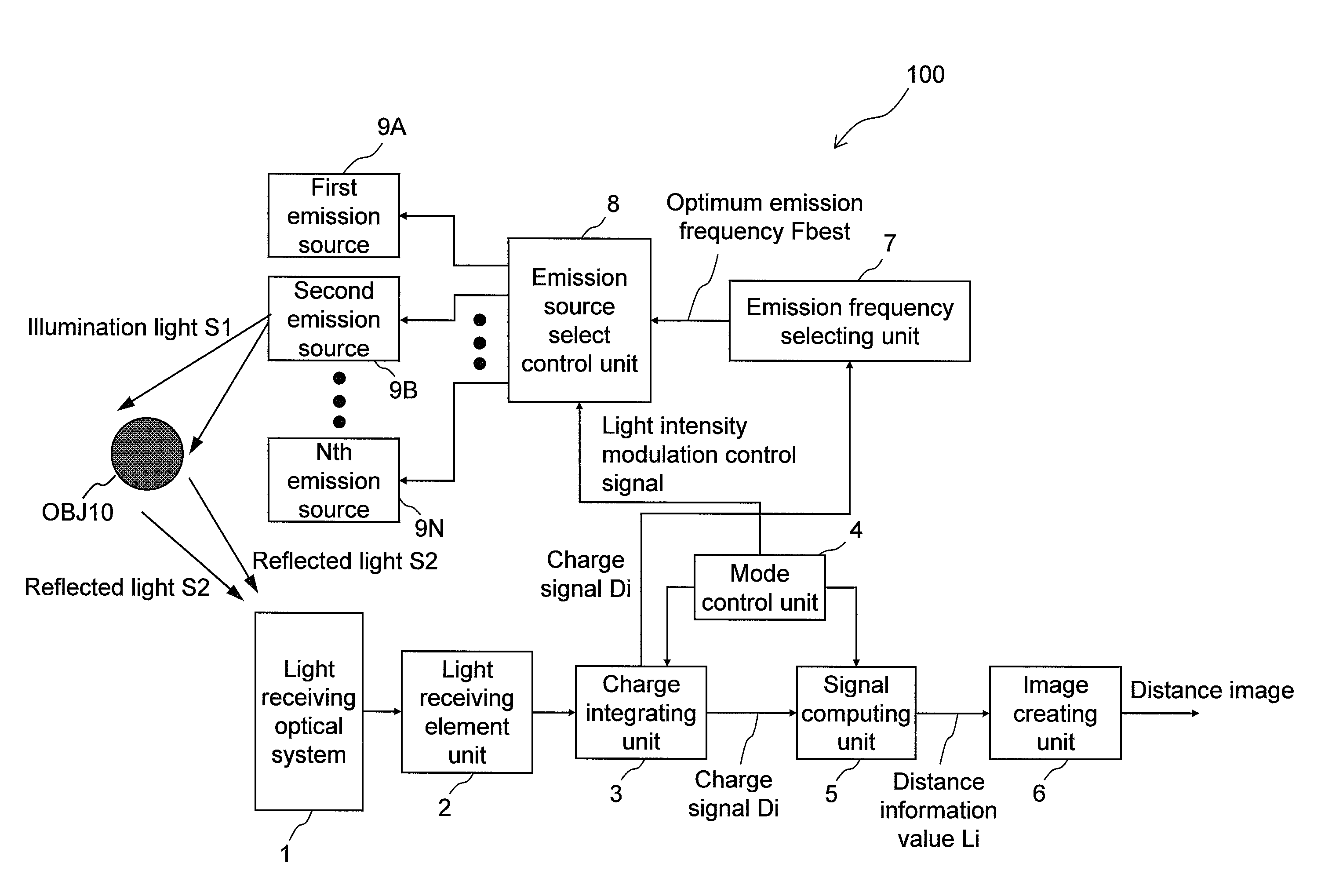
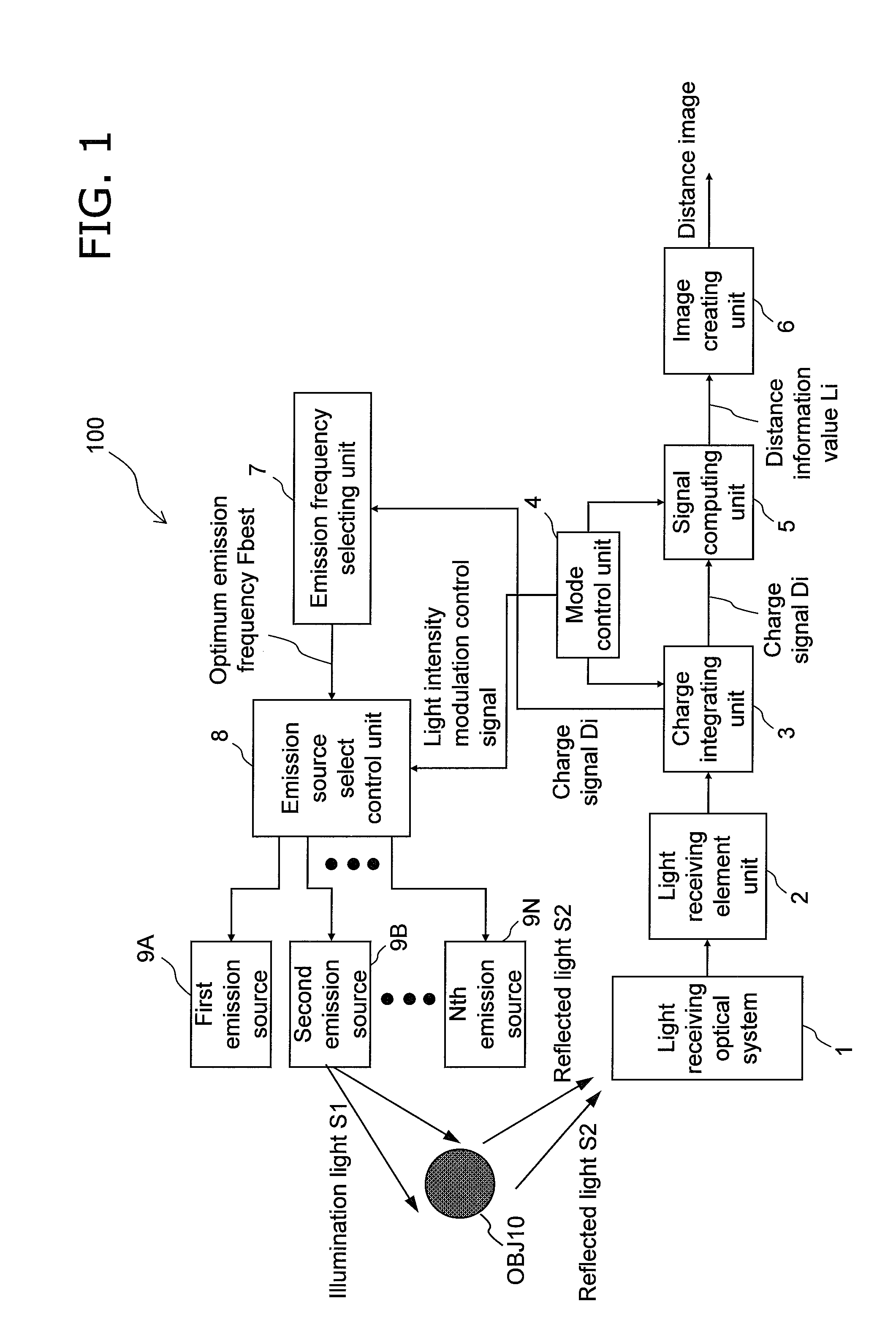
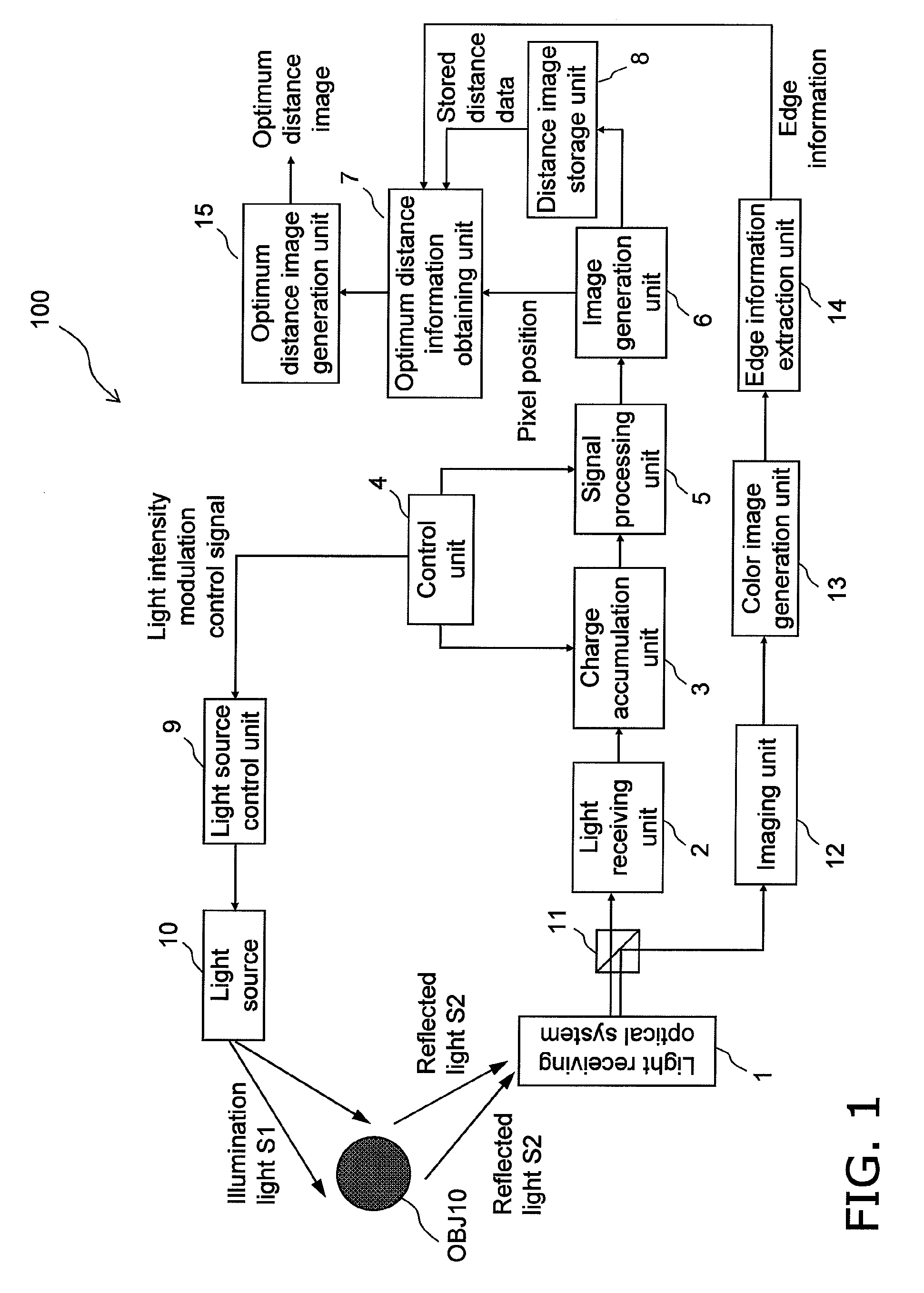
Distance estimating device, distance estimating method, program, integrated circuit, and camera
InactiveUS20110063437A1High resolutionIncrease frame rateColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsHigh frame rateImage resolution
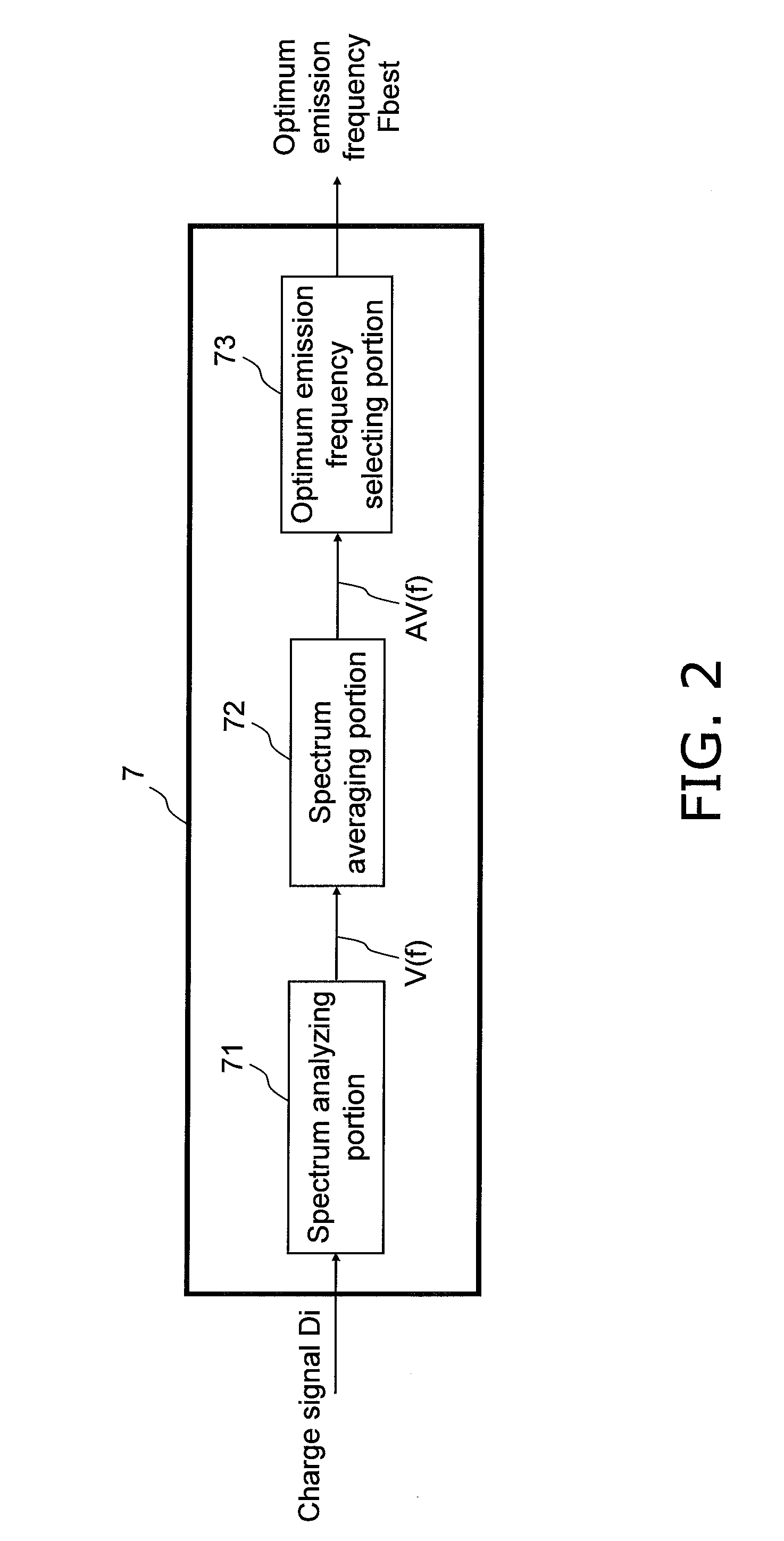
Conventionally, there has been a danger that CCD saturation may occur because of the influence of the shot noise and the environment light if a higher resolution of a distance image showing the distance to an object present in a target space and a higher frame rate are achieved when the distance image is estimated by the TOF method, and the distance accuracy may degrade. An emission frequency selecting unit (7) receives light (S2) reflected from the object when a light source does not emit light and selects illumination light (S1) having an emission frequency insusceptible to the environment light according to the frequency analysis of the reflected light (S2). An image creating unit (6) selects a light source emitting the illumination light having the optimum emission frequency from among prepared light sources (9A to 9N), receives reflected light of the illumination light from the selected light source, and creates the distance image showing the distance to the object. The environment light can be mitigated during light reception, and the noise influence on the distance accuracy can be mitigated when a light-receiving element unit (2) exhibiting higher resolution is used.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetoresistive effect element, magnetic head and magnetic reproducing apparatus
In a CPP element using a metal intermediate layer excellent in shot noise and response to high frequencies unlike a TMR element, its magnetoresistive effect film includes a magnetic layer mainly made of a half-metal exhibiting ferromagnetism, ferrimagnetism or antiferromagnetism, and largely variable in way of conduction in response to spin direction of electrons.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
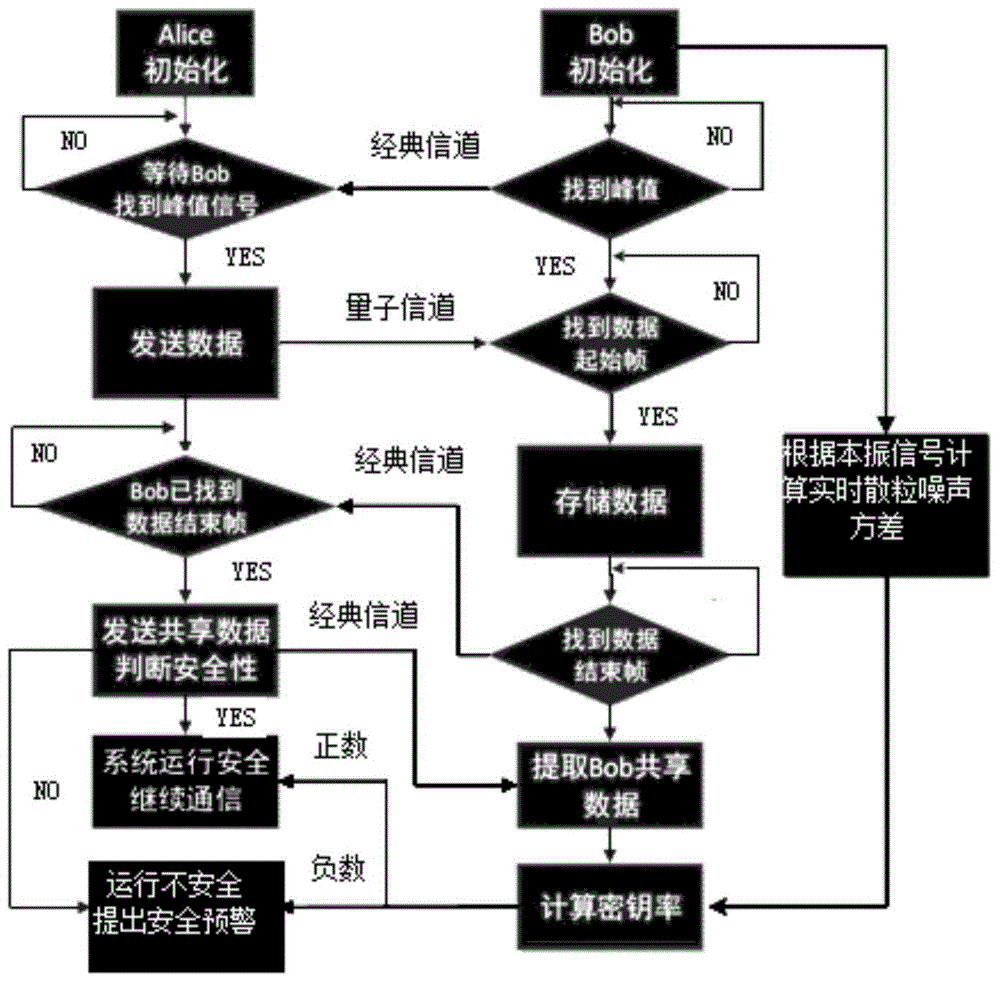
Continuous variable quantum key distribution (CVQKD) security defense method
ActiveCN104539582AAccurately get the key rateDoes not affect key distributionKey distribution for secure communicationEstimation methodsTwo step
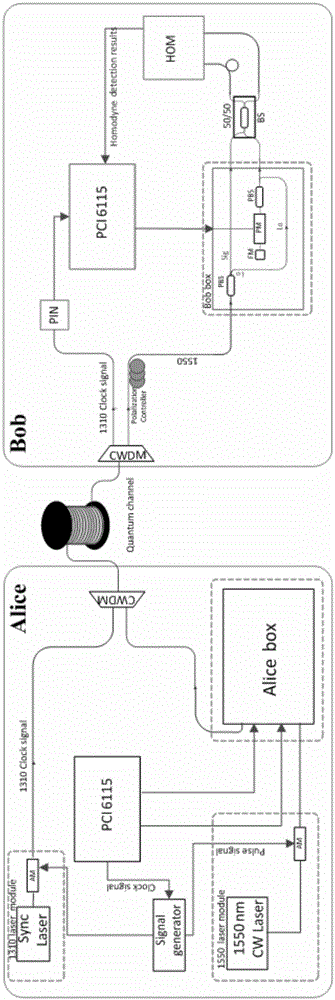
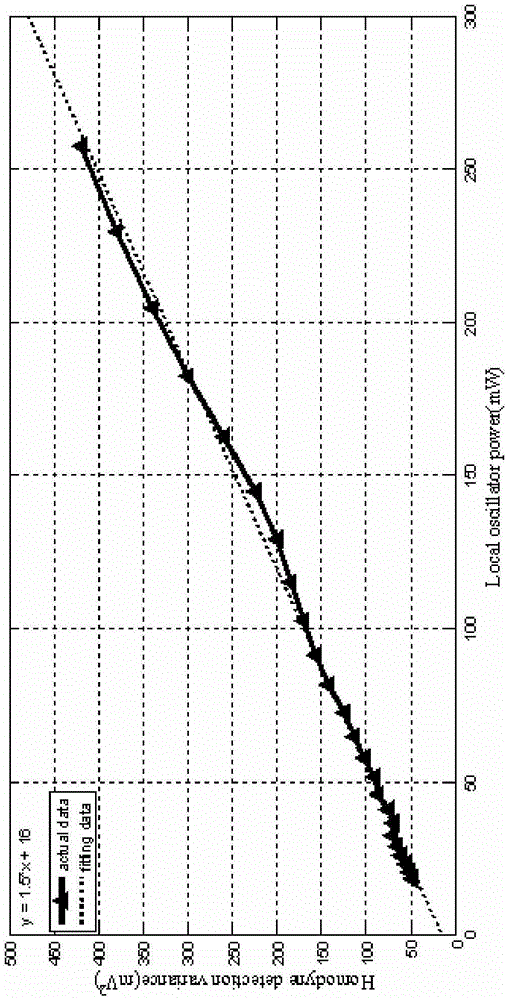
The invention discloses a continuous variable quantum key distribution (CVQKD) security defense method. The method comprises the following steps: A, shot noise monitoring: establishing a shot noise variance by monitoring the local oscillation light intensity of a receiving end in real time; and B, key rate calculation: calculating a running key rate according to the real-time shot noise variance estimated in the step A, wherein the two steps are executed simultaneously and concurrently. The shot noise variance during system running is acquired through a method for monitoring the local oscillation light of the receiving end of a CVQKD system, and the real-time running key rate of the system is acquired in combination with a parameter estimation method, so that security pre-warning is given to system security.
Owner:上海循态量子科技有限公司
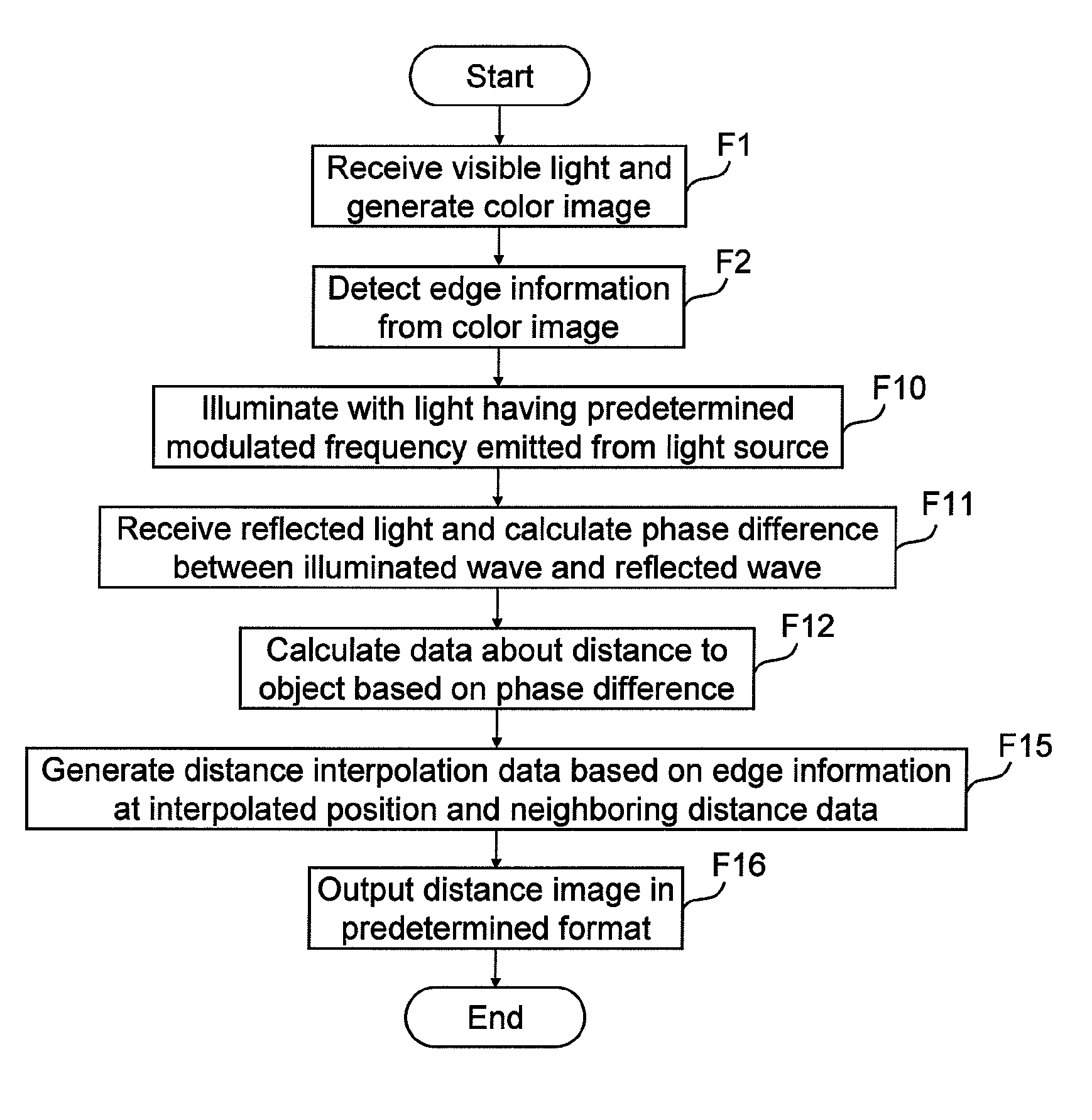
Distance estimation apparatus, distance estimation method, storage medium storing program, integrated circuit, and camera
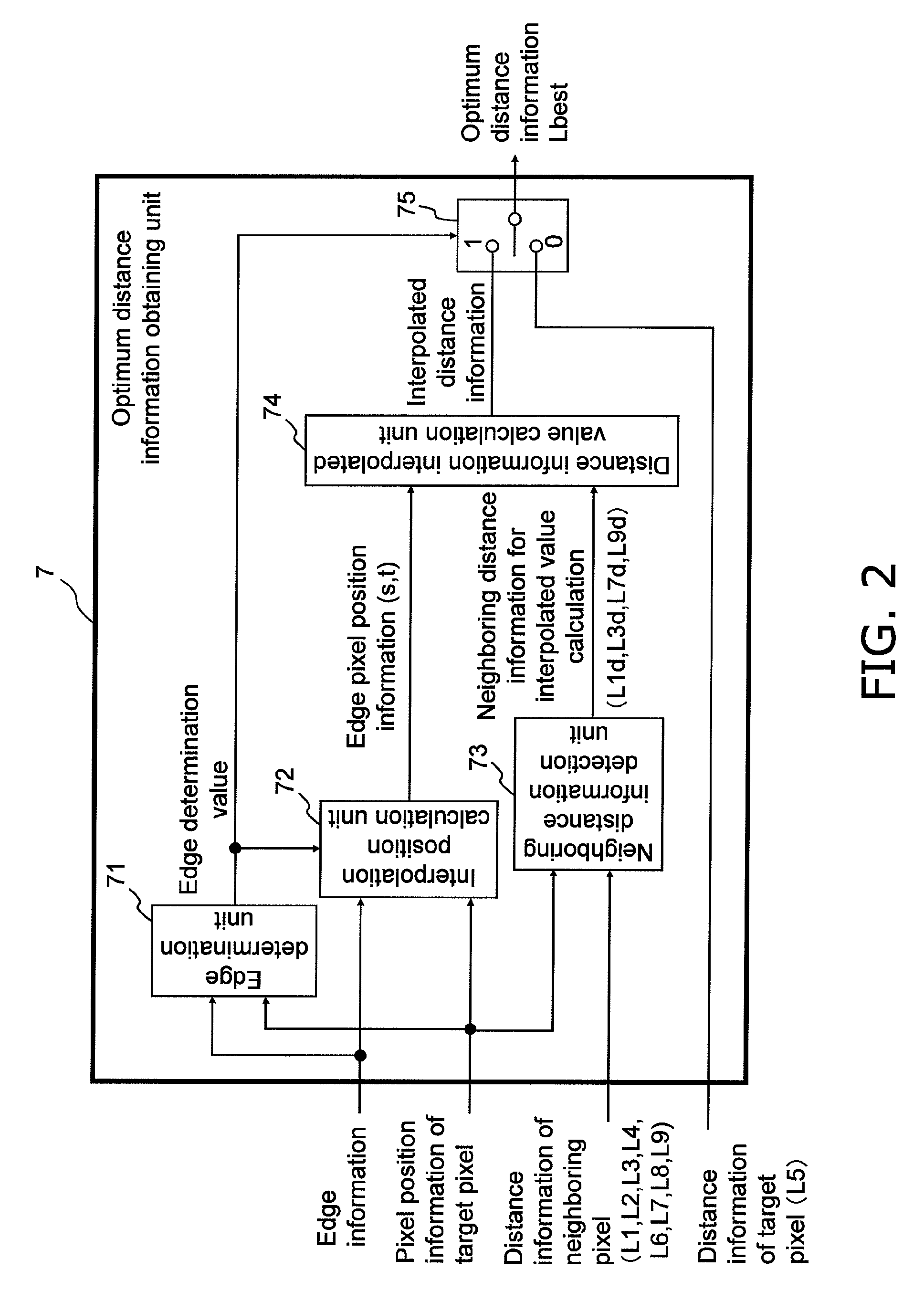
Attempts to achieve a higher resolution and a higher frame rate of a distance image when a distance to an object within a target space is estimated using the TOF method would cause CCD saturation due to shot noise or environment light, and lower distance precision. A distance estimation apparatus illuminates an object with illumination light for distance estimation emitted from a light source that can emit light (electromagnetic wave) having a predetermined illumination frequency, receives reflected light of the illumination light, obtains information about the distance from the apparatus to the object, generates distance image data based on the distance information, extracts edge information of a color image formed using a visible light component obtained in synchronization with the reflected light, and corrects distance information of a target part of the distance image using distance information of a neighboring part of the target part based on the edge information.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Electron beam system and method of manufacturing devices using the system
InactiveUS6853143B2High beam currentSmall shot noisePlug valvesElectric discharge tubesShaped beamThermionic emission
An electron beam system wherein a shot noise of an electron beam can be reduced and a beam current can be made higher, and further a shaped beam is formed by a two-stage lenses so as to allow for an operation with high stability. In this electron beam system, an electron beam emitted from an electron gun is irradiated onto a sample and secondary electrons emanated from the sample are detected. The electron gun is a thermionic emission type and designed to operate in a space charge limited condition. A shaping aperture and a NA aperture are arranged in front locations of the electron gun. An image of the shaping aperture formed by an electron beam emitted from the thermionic emission electron gun is focused onto a surface of the sample through the two-stage lenses.
Owner:EBARA CORP
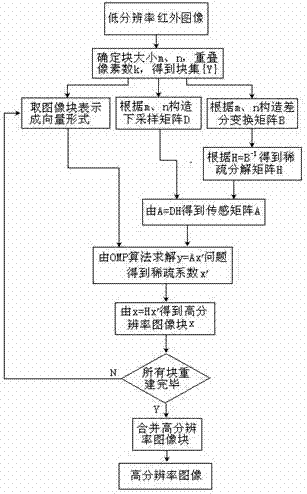
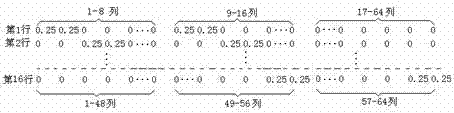
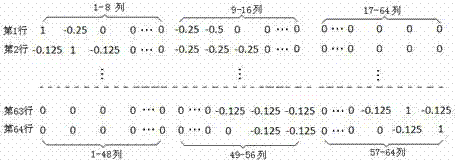
Infrared image super-resolution reestablishing method based on compressed sensing theory
InactiveCN104766273AEliminate shot noiseAvoid complex calculationsGeometric image transformationPattern recognitionImage resolution
The invention relates to an infrared image super-resolution reestablishing method based on the compressed sensing theory. According to the method, low-resolution images are used as a foundation and are subjected to partitioning, low-resolution image blocks are regarded as downsampling observation corresponding to high-resolution image blocks, a downsampling model is established, and a downsampling matrix is written. A sparse transformation matrix of the high-resolution image blocks is established and is multiplied by an observation matrix, and a sensing matrix is obtained. According to the low-resolution blocks and the sensing matrix, an OMP algorithm is used for reestablishing sparse coefficients of the high-resolution image blocks, then the sparse transformation matrix is multiplied by the sparse coefficients, and the high-resolution image blocks are obtained. Finally, all the high-resolution image blocks are spliced, and a high-resolution reestablished image is obtained. The method has the advantages of being easy to achieve, quick in operation, stable in performance and good in anti-noise effect, difference operation is used for generating a difference transformation matrix and achieving sparse transformation, complex computing of redundant dictionary training is avoided, shot noise of images can be well removed, and the noise reduction advantage is achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Electron beam system and method of manufacturing devices using the system
InactiveUS20050133733A1Improve throughputReduce electronic noiseElectric discharge tubesRadiation therapyShaped beamThermionic emission
Owner:EBARA CORP
Image sensor
InactiveUS20070069142A1Reduce Fixed Pattern NoiseReduce pattern noiseTransistorTelevision system detailsElectrical conductorPhotodetector
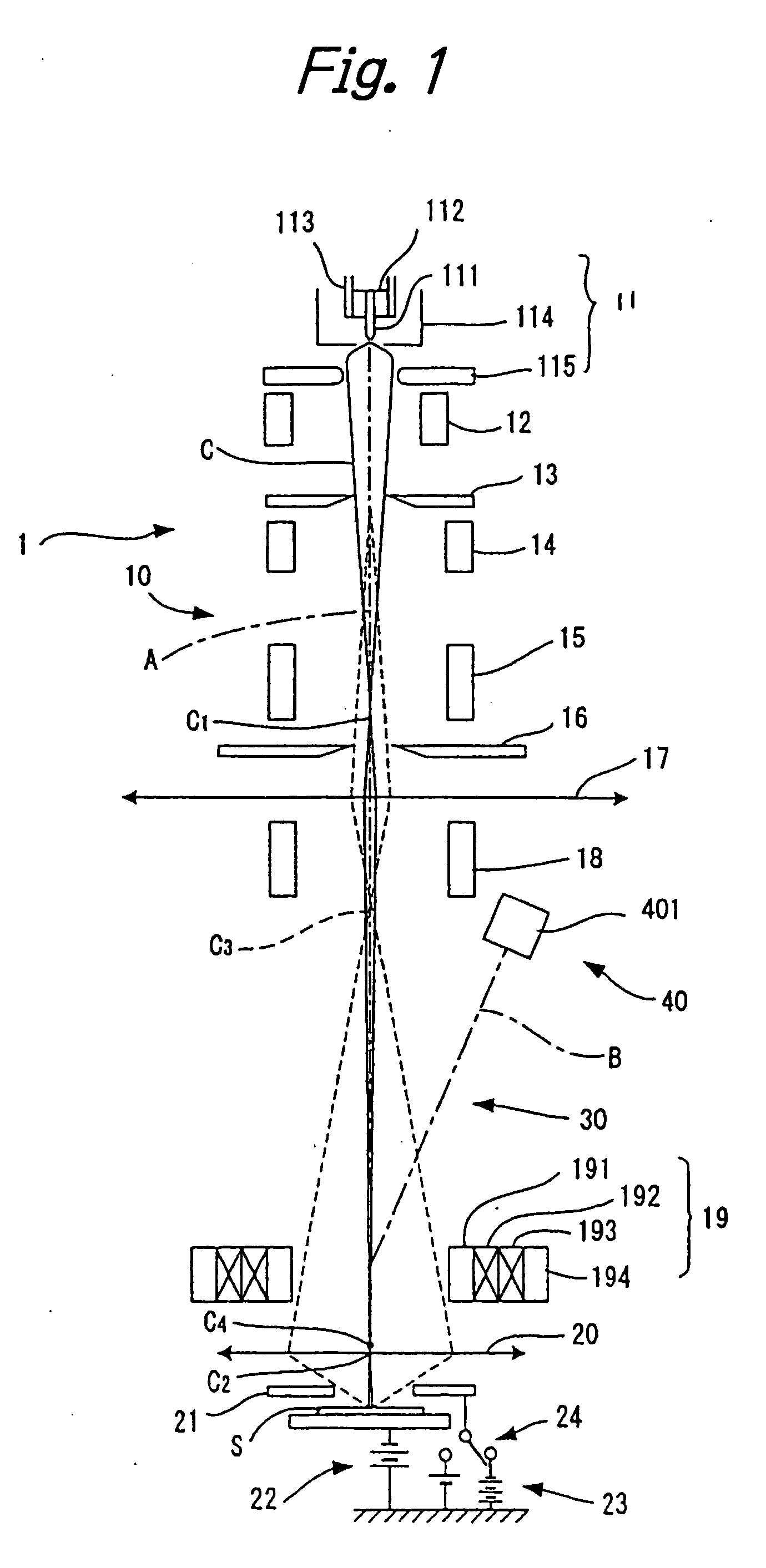
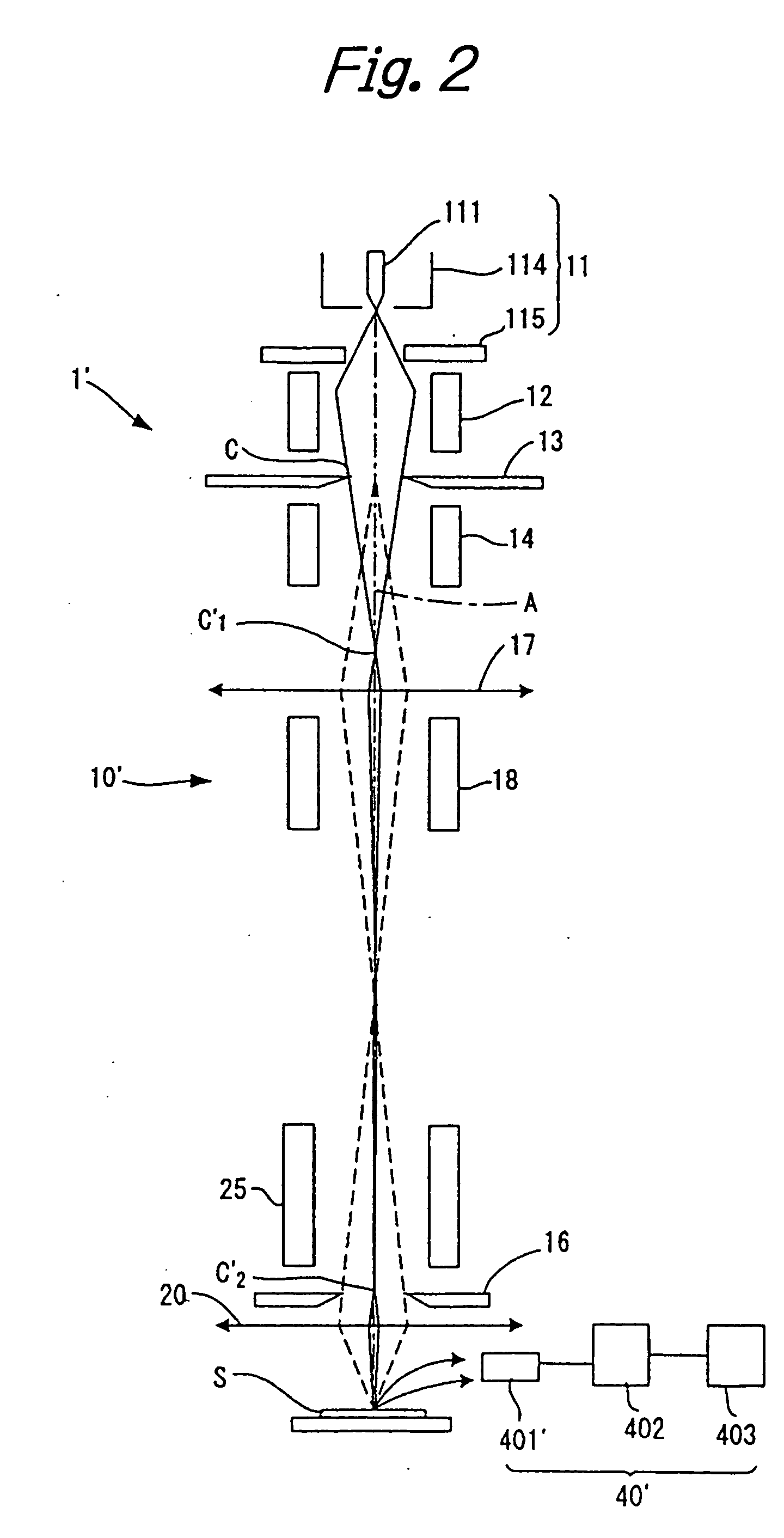
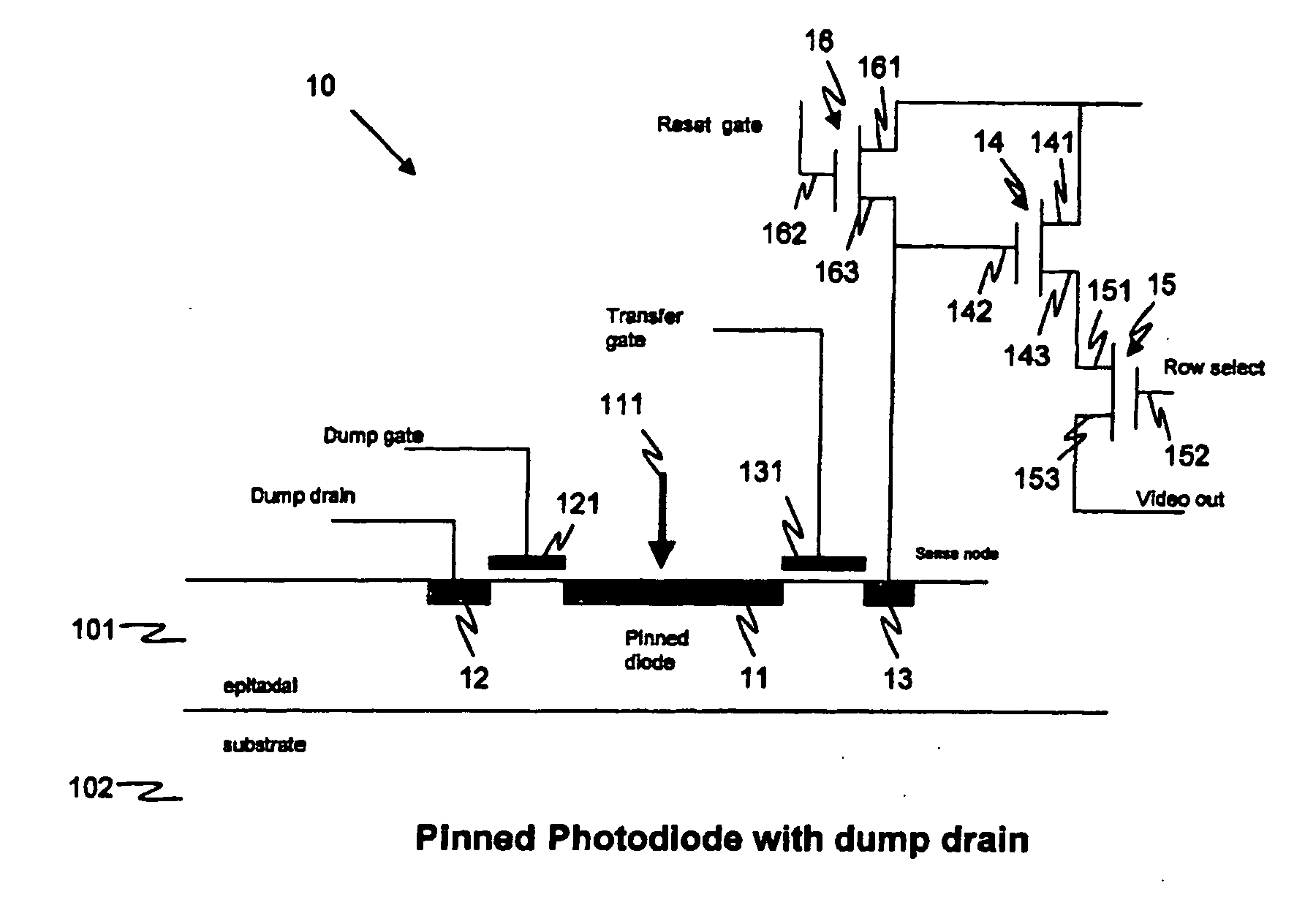
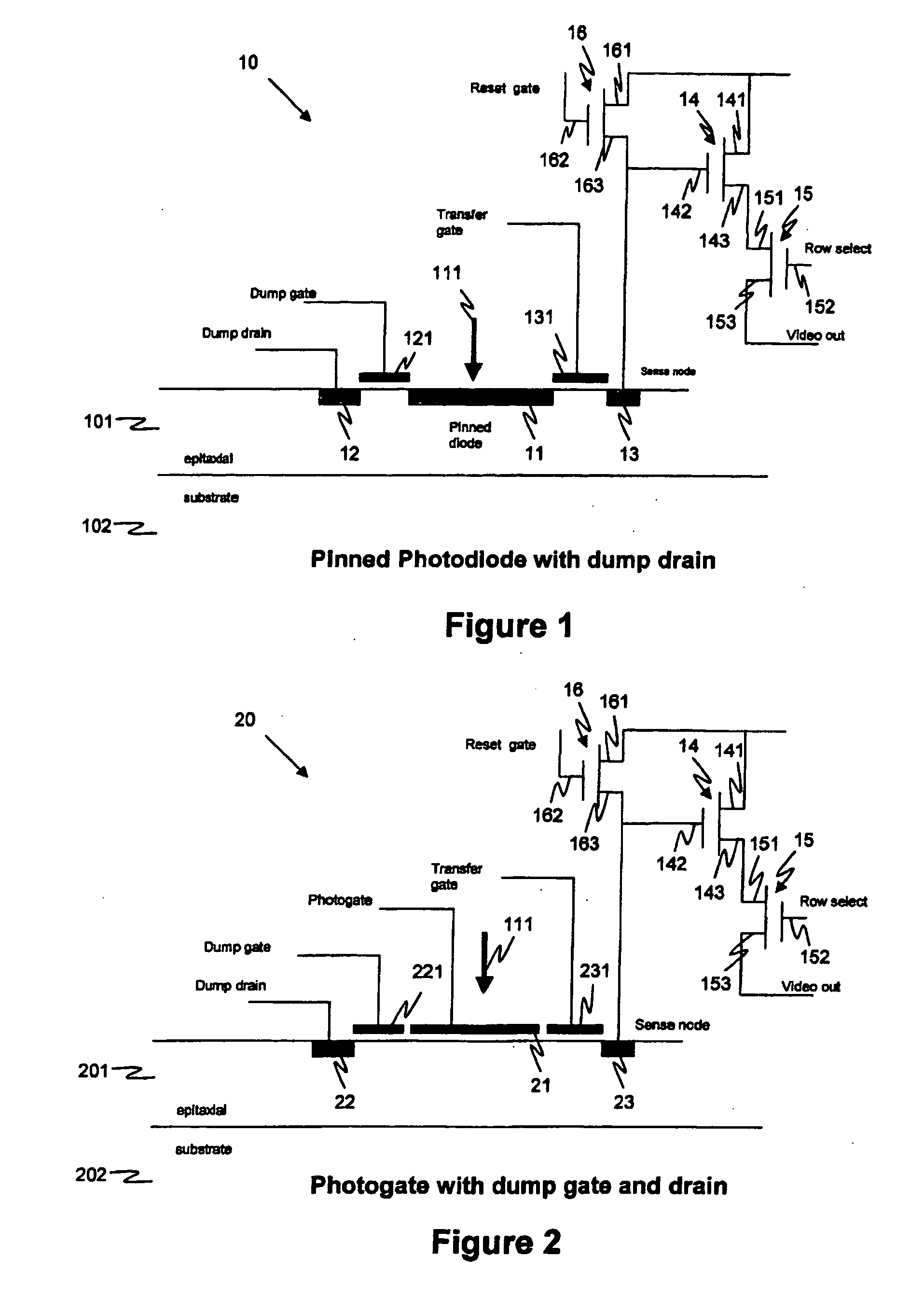
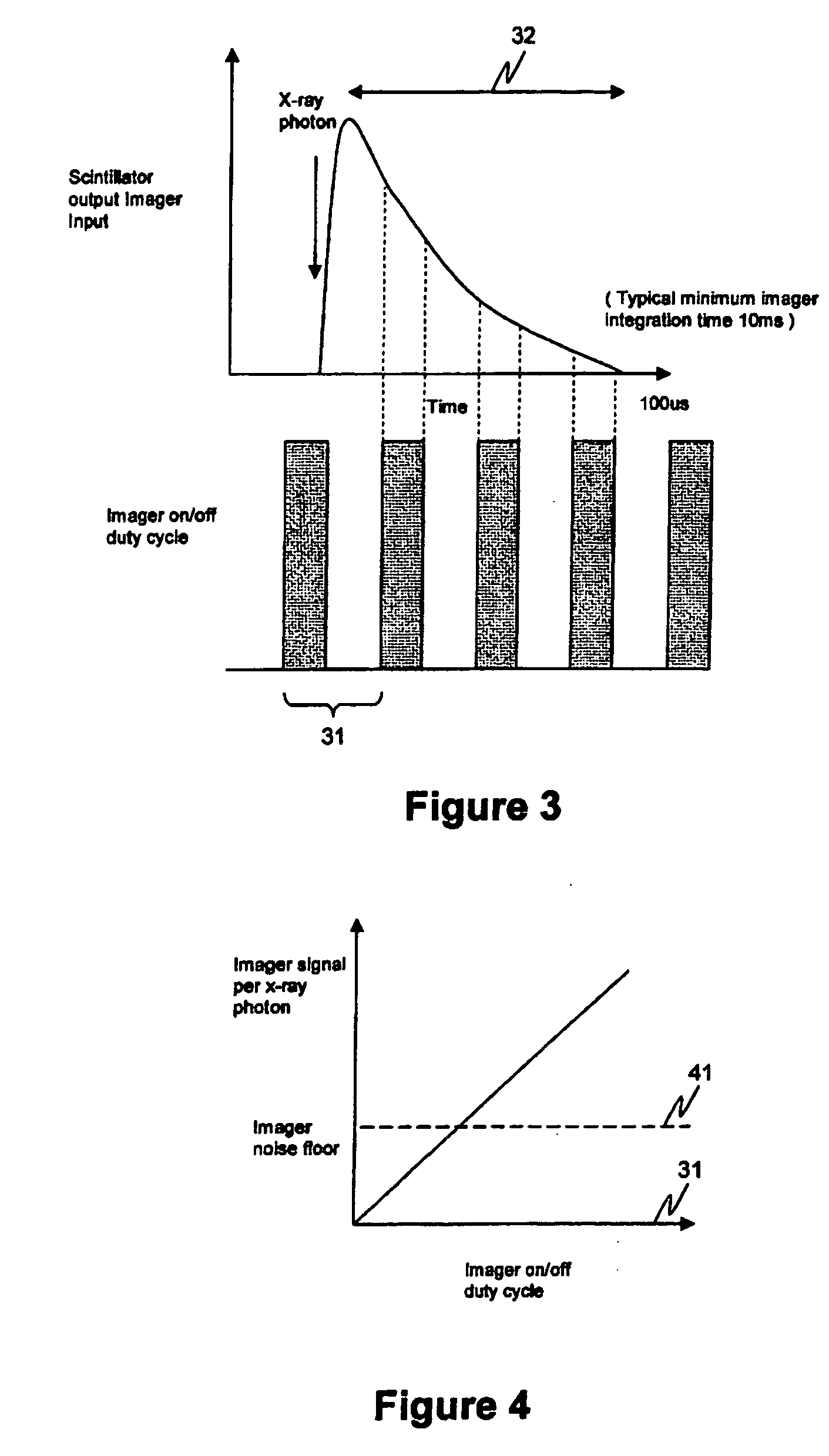
Effective sensitivity of a photodetector of an image sensor is controlled by partitioning signal charge from incident photons, thus producing a manageable yield and a consequently higher, photon shot noise limited, signal to noise ratio than in the prior art, when imaging high flux rates of energetic photons or particles, such as produced by x-ray generators. The invention may be applied, for example, to an image sensor with a photosensitive layer coupled to a charge collection / readout structure, e.g. photoconductor or scintillator on CMOS array, or to an intrinsically sensitive charge collection / readout structure, e.g. deep active layer CMOS. A radiation sensor pixel structure 10 for use in the invention includes a photodetector 11, a transfer gate 131 for controlling charge collection from the photodetector and a dump drain 12 controlled by a dump gate 121, arranged for selectively dumping charge to the dump drain means and collecting charge from the photodetector means, in a duty cycle 31, for varying effective sensitivity of the pixel structure. An image sensor containing such pixel structures may selectively be operated in an integration mode or a photon counting mode. Preferably the image sensor has imaging pixels and control circuitry arranged on a same semiconductor die, such as a CMOS semiconductor die.
Owner:E2V TECH (UK) LTD
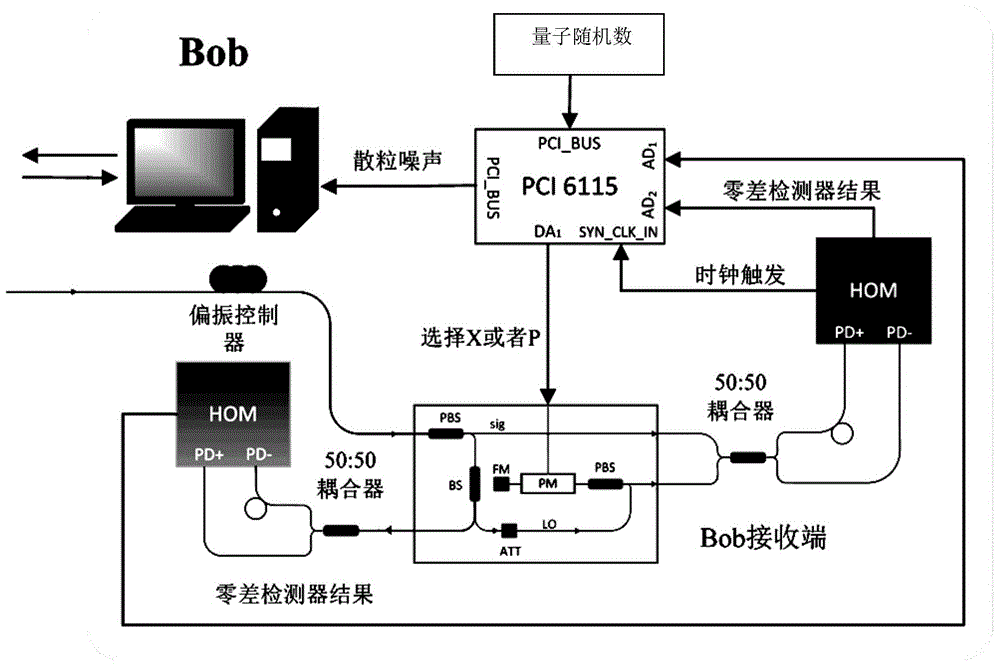
CVQKD system and method for monitoring shot noise variance thereof in real time
ActiveCN105141376ARealize real-time monitoringImprove securityPhotonic quantum communicationElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsBeam splitterSignal light
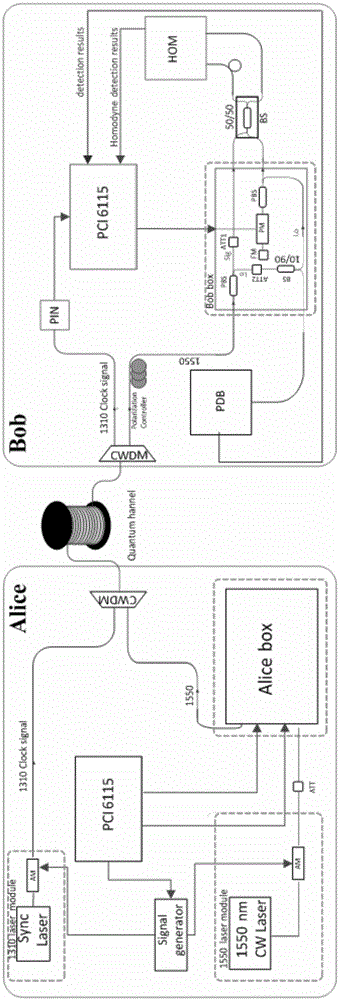
The invention discloses a CVQKD system and a method for monitoring the shot noise variance thereof in real time. According to the CVQKD system, in a receiving end, signal light is split into quantum signal light and local oscillation light after passing through a polarization beam splitter. A first adjustable optical attenuator is arranged on a quantum signal light path, and the quantum signal light enters a 50 / 50 beam splitter. A second adjustable optical attenuator and a 10 / 90 beam splitter are sequentially arranged on a local oscillation light path along the direction of the local oscillation light. 10% of the local oscillation light output by the 10 / 90 beam splitter is sent to a photoelectric detector, and 90% of the local oscillation light sequentially enters the 50 / 50 beam splitter after passing through the polarization beam splitter, a phase modulator and a Faraday mirror, and interferes with the quantum signal light. The output end of the 50 / 50 beam splitter is connected with a Homodyne detector. The output ends of the Homodyne detector and the photoelectric detector are connected to a Bob-end control circuit. The method and the system can effectively resist the attack of Eve to local oscillation light, and therefore, the safety of the CVQKD system is effectively improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
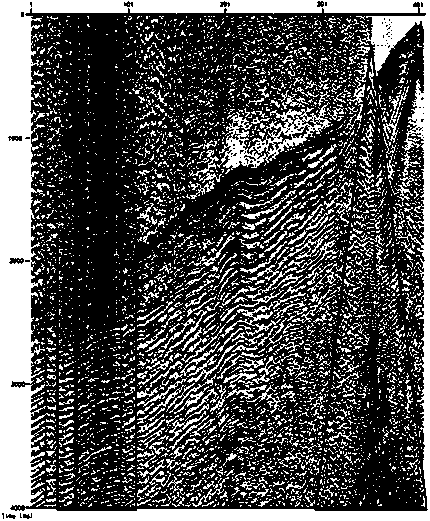
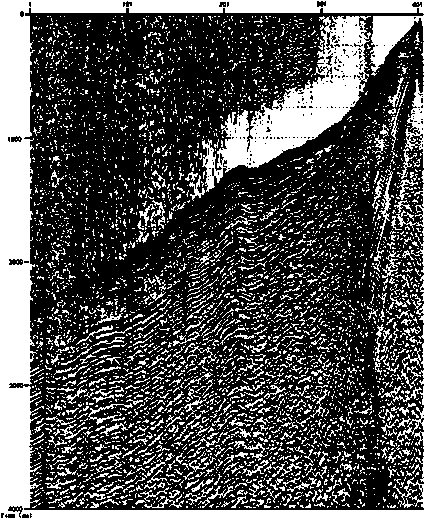
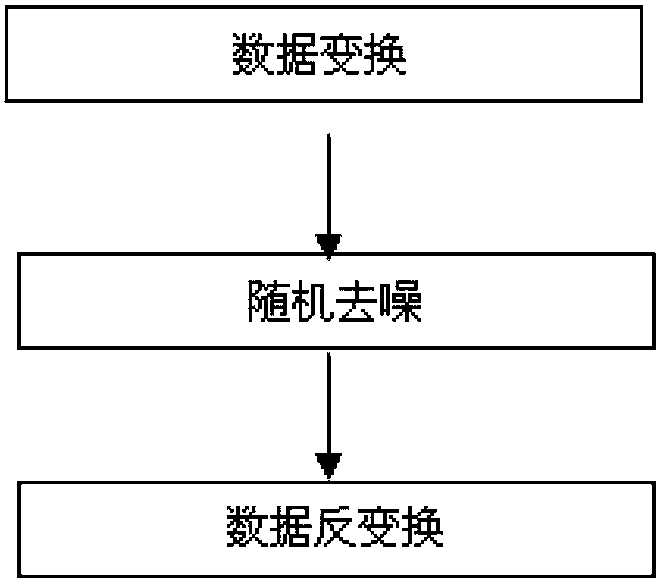
Multi-source seismic wave field separating method by utilizing random denoising technology
The invention provides a multi-source seismic wave field separating method by utilizing a random denoising technology, and belongs to the field of oil exploration. The method comprises the following steps: performing data exchange first, that is, converting common-shot-gather data into non-common-shot-gather data; then utilizing a random denoising method to remove the interference shot noise generated by interference shot signals in the non-common-shot-gather data; finally, performing data inverse transformation, that is, converting the non-common-shot-gather data into the common-shot-gather data again, so as to realize the wave field separation of multi-source seismic data. As for the seismic data of 10 or more synchronous-source seismic events, when the method is adopted for respectively performing conventional processing, pre-stack time shift and post-stack depth migration, a better imaging effect can be always achieved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
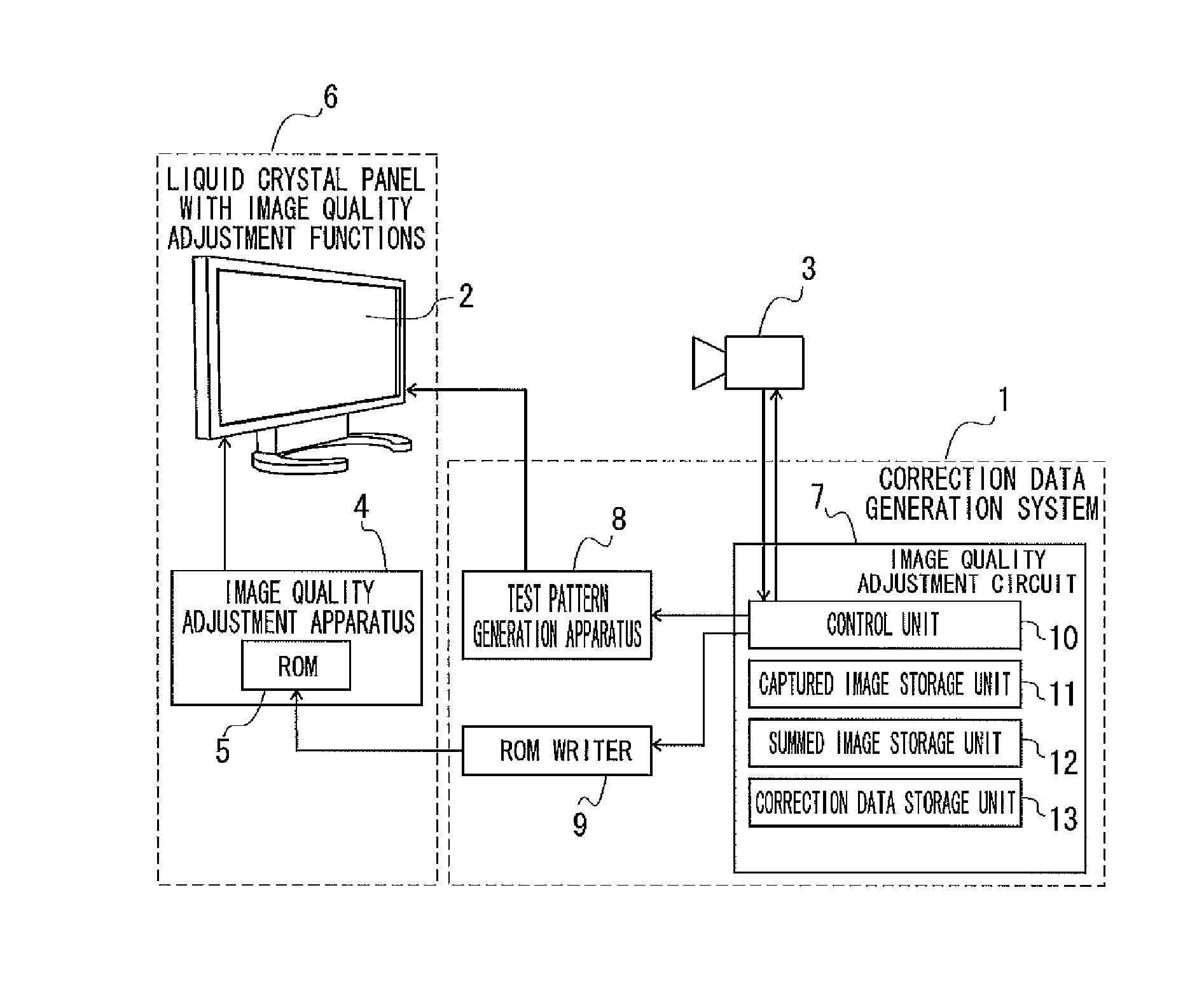
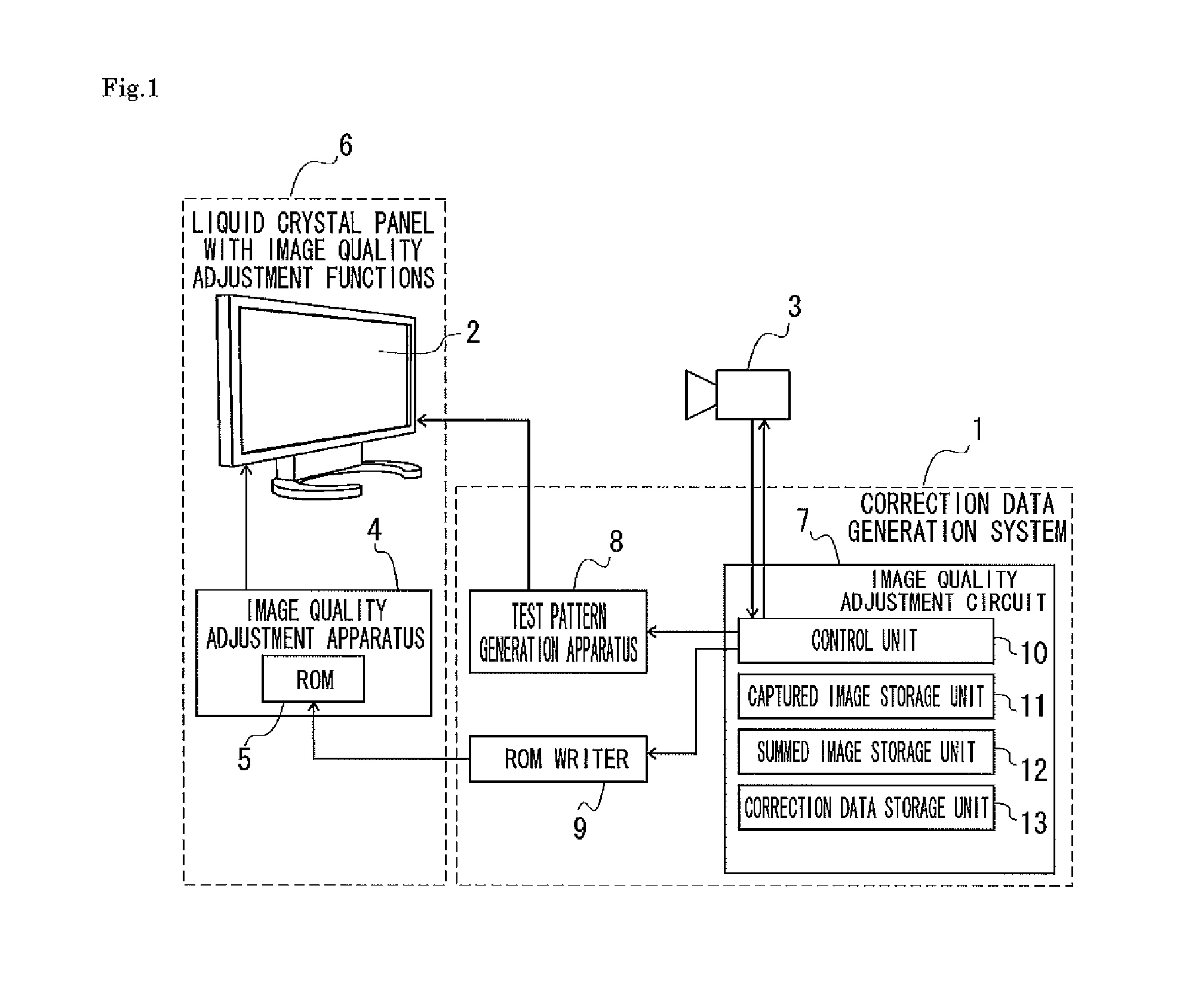
Correction data generation method, correction data generation system, and image quality adjustment technique using the method and system
InactiveUS20140232625A1Highly accurate correction dataInhibition effectStatic indicating devicesImaging qualityShot noise
Provided is a correction data generation method that can generate highly accurate correction data while suppressing the influence of photon shot noise. According to the correction data generation method of the present invention, test patterns are displayed on a liquid crystal panel (2) in units of specific gradation values, the displayed test patterns are captured by a camera (3) a plurality of times for each specific gradation value, and a summed image is generated for each specific gradation value by summing a plurality of captured images of the test patterns. Based on the summed image for each specific gradation value, correction data is generated for reducing unevenness in display of the liquid crystal panel (2) through correction of a signal input to the liquid crystal panel (2).
Owner:IIX
Noise suppression device and noise suppression method for distributed polarization crosstalk measurement of optical polarizer
ActiveCN105043718AAvoid the influence of interferometric beat noiseImprove signal-to-noise ratioTesting optical propertiesFiberCrosstalk measurement
The present invention relates to the technical field of optical fiber measurement and specifically relates to a noise suppression device and a noise suppression method for the distributed polarization crosstalk measurement of an optical polarizer. The noise suppression device for the distributed polarization crosstalk measurement of the optical polarizer comprises a broadband optical source, a polarizer, a first fiber-optic rotary connector, a second fiber-optic rotary connector, a to-be-detected optical fiber device, an optical path correlator, and a polarization crosstalk detecting and signal recording device. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the transmission light and the coupled light are thoroughly separated by means of a polarization beam splitter, so that the noise influence on the interference beat length can be avoided. On the basis of the thermal noise of a control circuit, the transmission light is attenuated by an attenuator, and the coupled light is enabled to be main detecting light. In this way, the shot noise becomes the main noise for limiting the signal noise ratio of the system. Based on the above method, the parameters of the device are adjusted to be appropriate. In this way, on the premise that the dynamic range of the system is kept unchanged, the signal noise ratio of the system is improved by 20 to 40 dB. Therefore, the measurement sensitivity is effectively increased.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
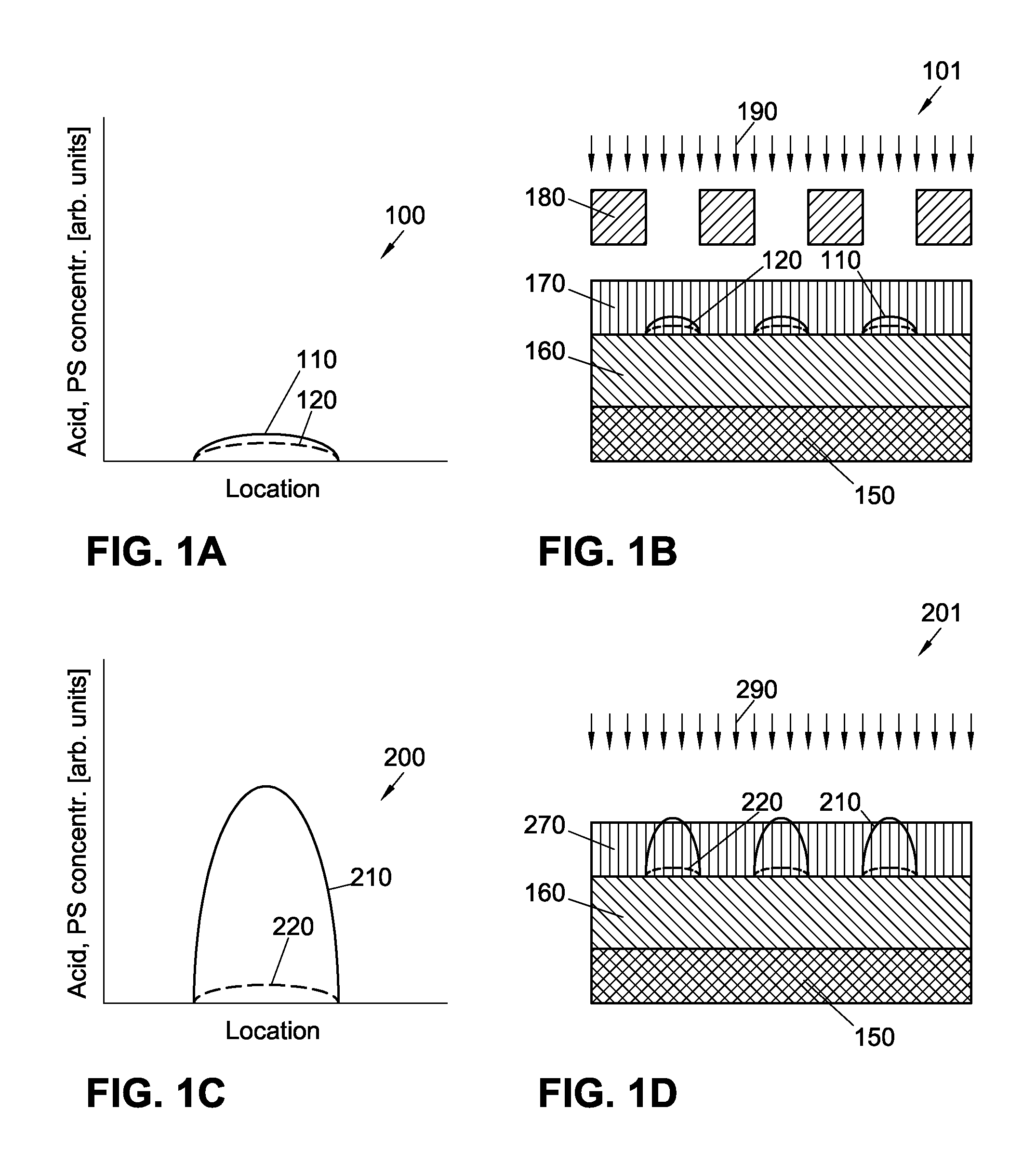
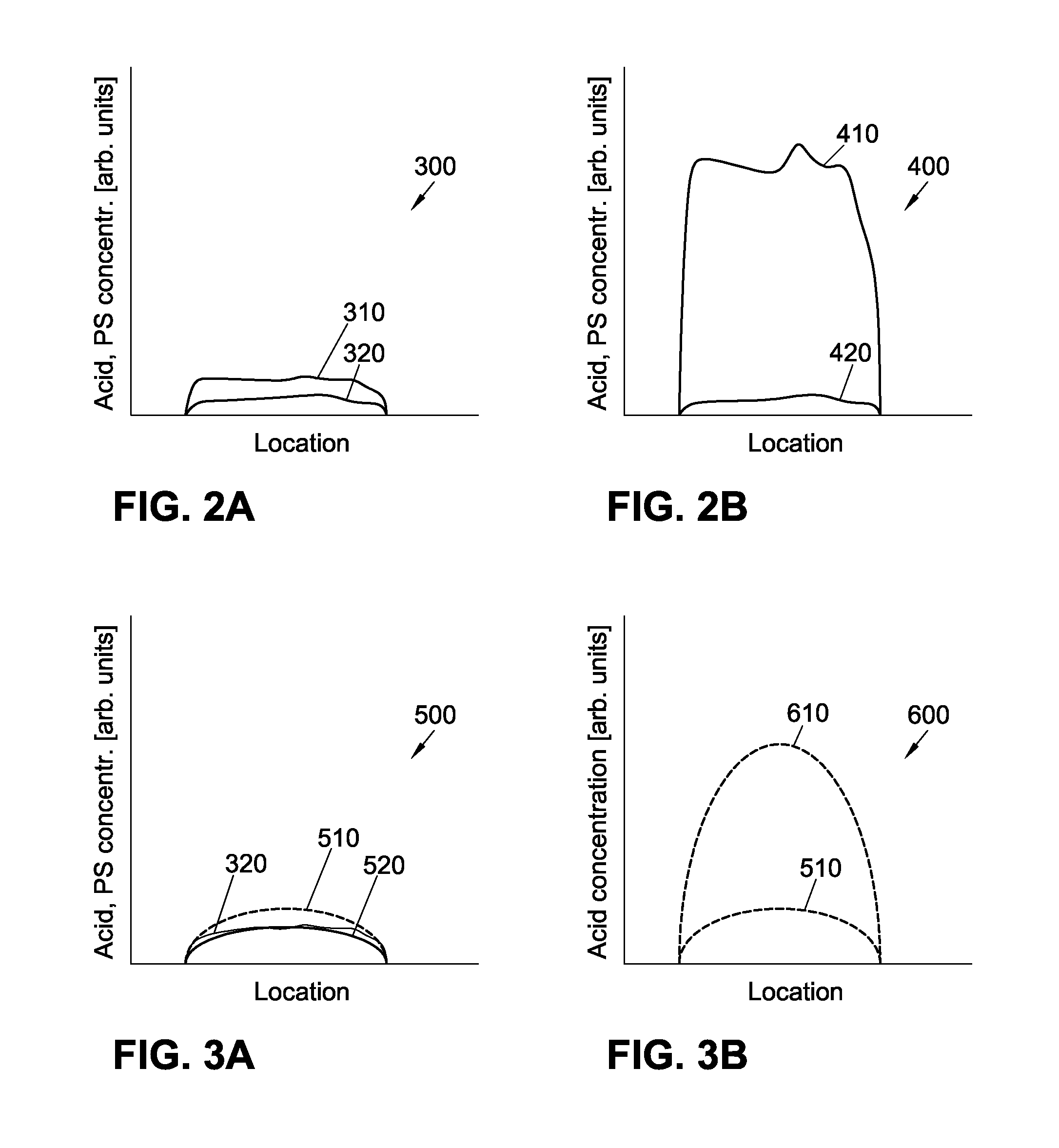
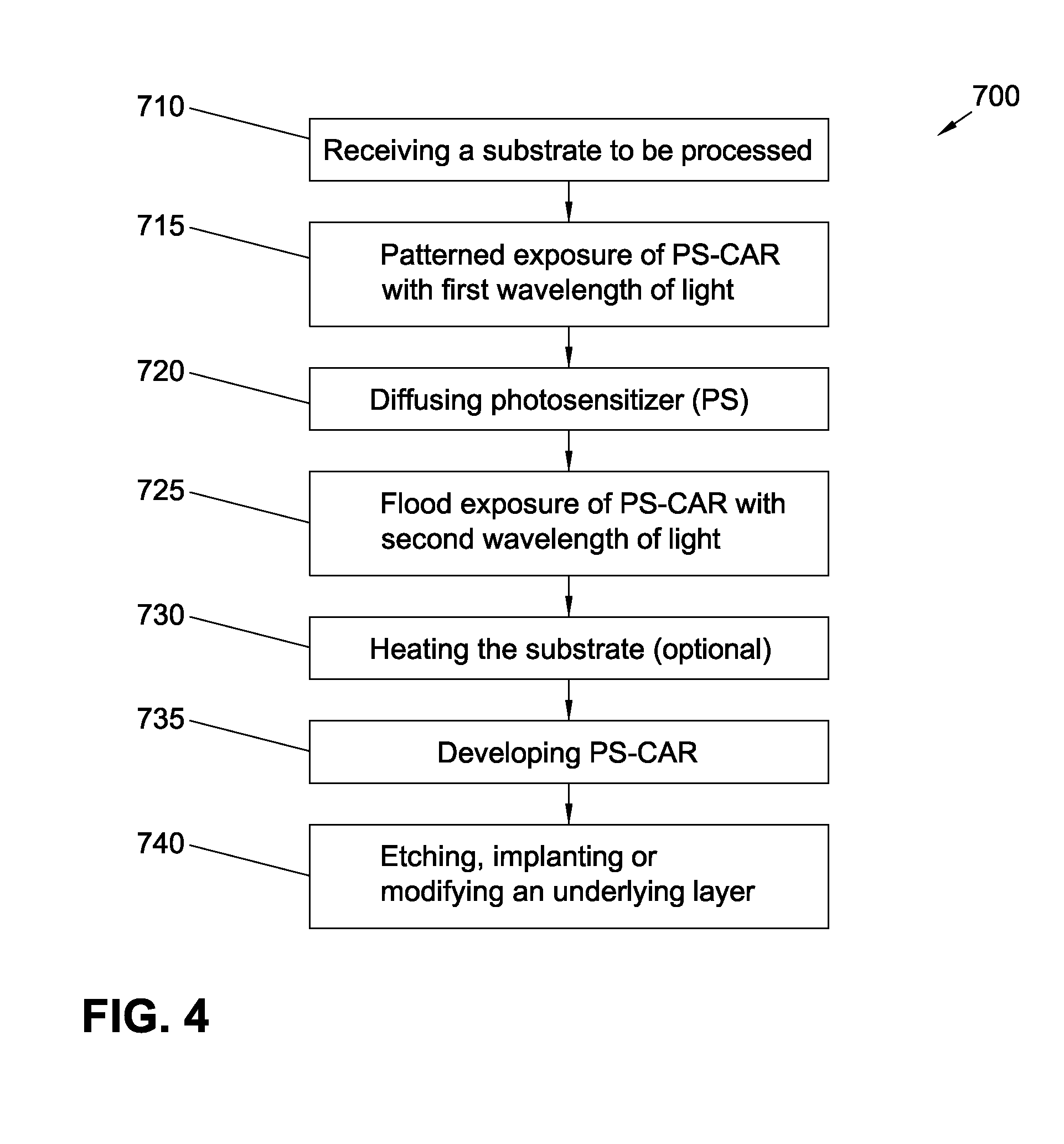
Mitigation of EUV shot noise replicating into acid shot noise in photo-sensitized chemically-amplified resist (ps-car)
ActiveUS20150241781A1Reduce unevennessDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistPhotosensitizer
A method for mitigating shot noise in extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography and patterning of photo-sensitized chemically-amplified resist (PS-CAR) is described. The method includes a first EUV patterned exposure to generate a photosensitizer and a second flood exposure at a wavelength different than the wavelength of the first EUV patterned exposure, to generate acid in regions exposed during the first EUV patterned exposure, wherein the photosensitizer acts to amplify acid generation and improve contrast. The resist may be exposed to heat, liquid solvent, solvent atmosphere, or a vacuum to mitigate the effects of EUV shot noise on photosensitizer concentration which may accrue during the first EUV patterned exposure.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
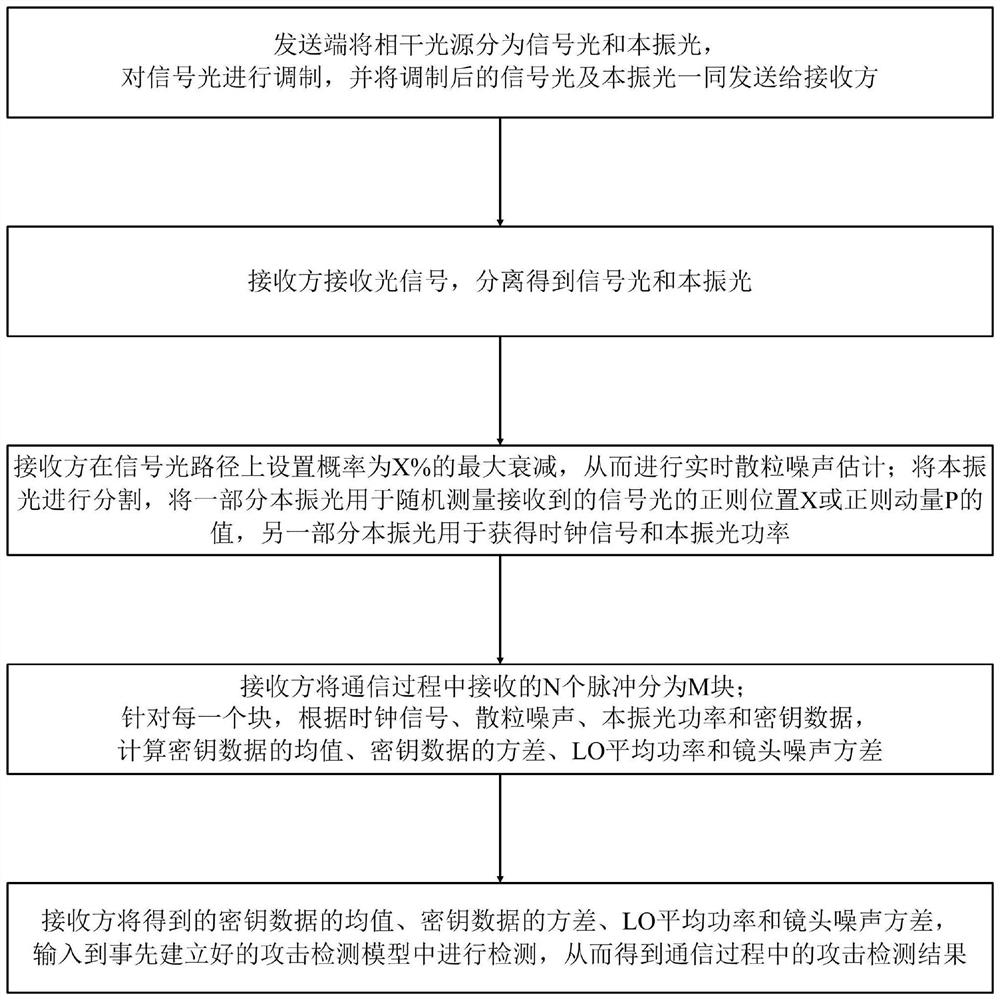
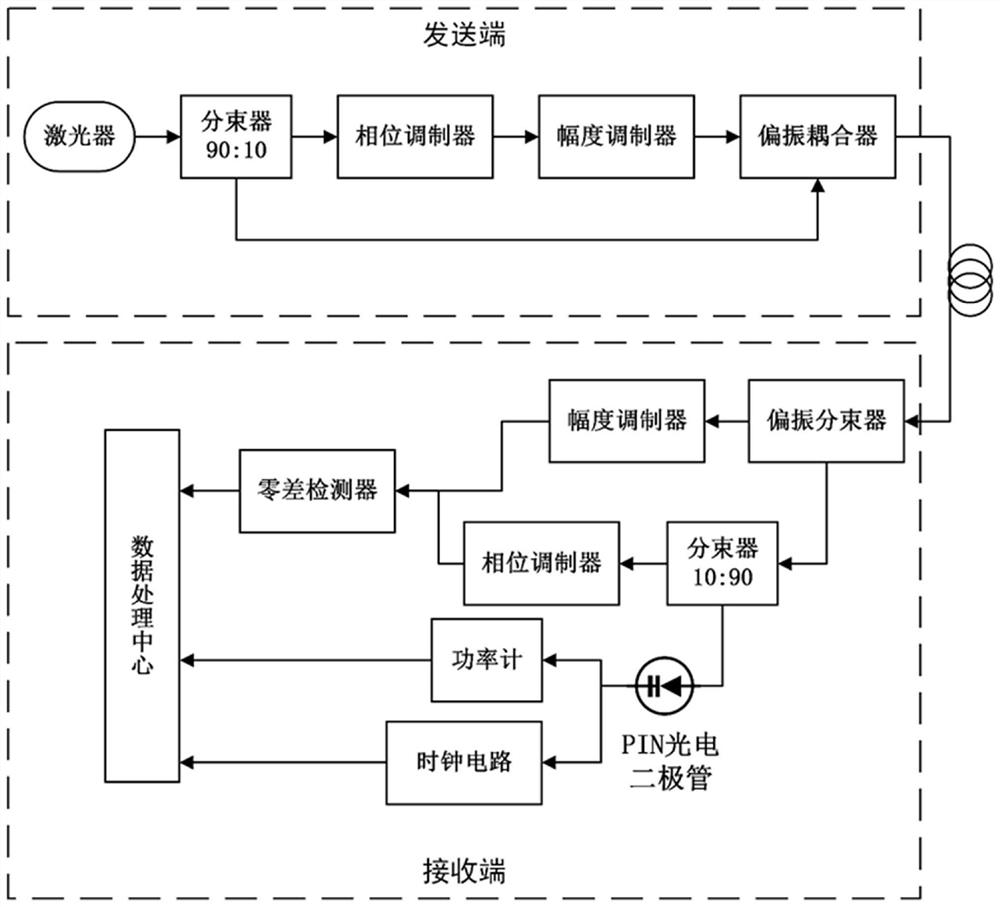
Continuous variable quantum key distribution attack detection method and detection system thereof
ActiveCN111970279AImprove reliabilityImprove accuracyKey distribution for secure communicationElectromagnetic receiversOptical power meterSignal light
The invention discloses a continuous variable quantum key distribution attack detection method. The method comprises the steps that a sending end modulates signal light and sends the signal light andlocal oscillation light to a receiver; the receiver separates the signal to obtain the signal light and the local oscillation light; the receiver performs real-time granular noise estimation on the signal light; the receiver segments the local oscillation light so that one part of the local oscillation light is used for randomly measuring the value of the regular position X or the canonical momentum P of the received signal light, and the other part of the local oscillation light is used for obtaining a clock signal and local oscillation light power; and the receiver calculates the mean valueof the key data, the variance of the key data, the LO average power and the lens noise variance, and inputs the same into a pre-established attack detection model for detection to obtain an attack detection result in the communication process. The invention also discloses a detection system for realizing the continuous variable quantum key distribution attack detection method. According to the invention, the attack mode detection of the continuous variable quantum key distribution process is realized, the reliability is high, the practicability is good, and the accuracy is high.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
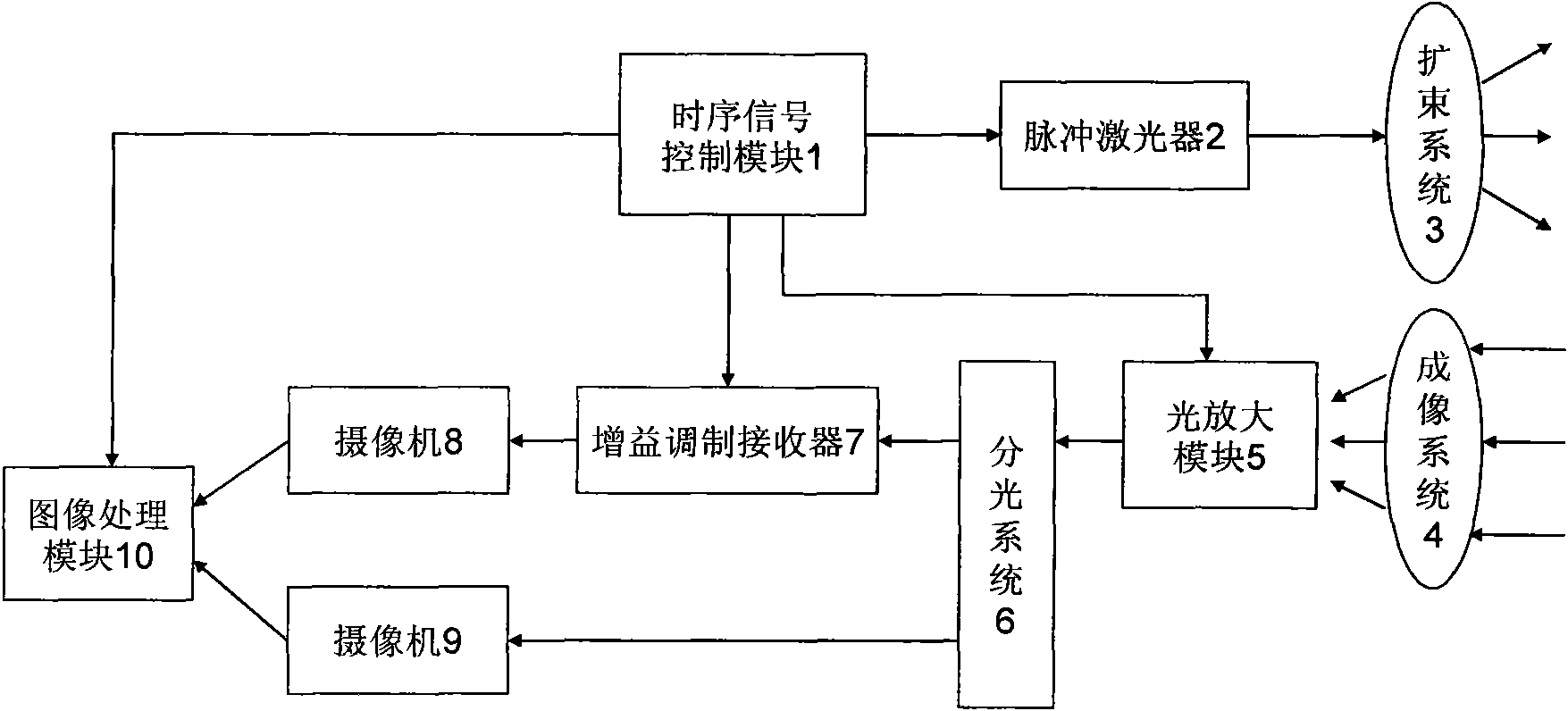
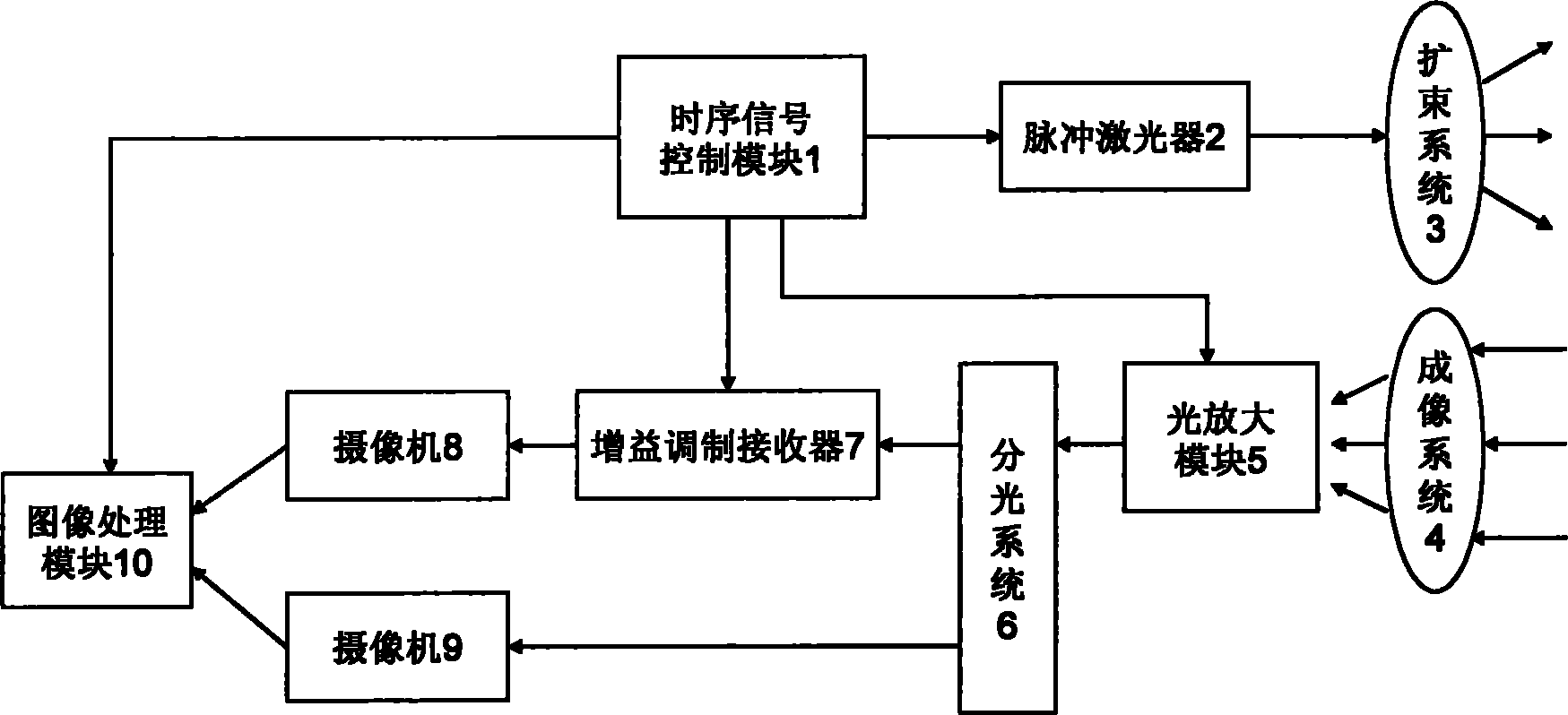
Light amplification type three-dimensional imaging method and system
InactiveCN101788667AReduce the impactImprove ranging accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical elementsImaging processingSignal light
The invention discloses a light amplification type three-dimensional imaging method and a system. A first output of a sequence scheduling control module controls a pulsed laser to emit intense pulsed lights; the intense pulsed lights irradiate at an object to be tested after penetrating through a beam expanding system; returned signal lights enter into a light amplification module for amplifying after penetrating through an imaging system; after the amplified lights are split, part of lights are received by a first vidicon after penetrating through a gainmodulation receiver, and the other parts of lights are received by a second vidicon; and the other three routes of the sequence scheduling control module respectively control the light amplification module, the gainmodulation receiver and an image processing module. Images obtained by the two vidicons are processed by the image processing module, and the distances from each pixel point of the image to the object are worked out to obtain the three-dimensional image of the object. Under the conditions that the light source power and the gate time are not changed, the invention can reduce the influence of random shot noise to signal lights and improve the precision of ranging.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
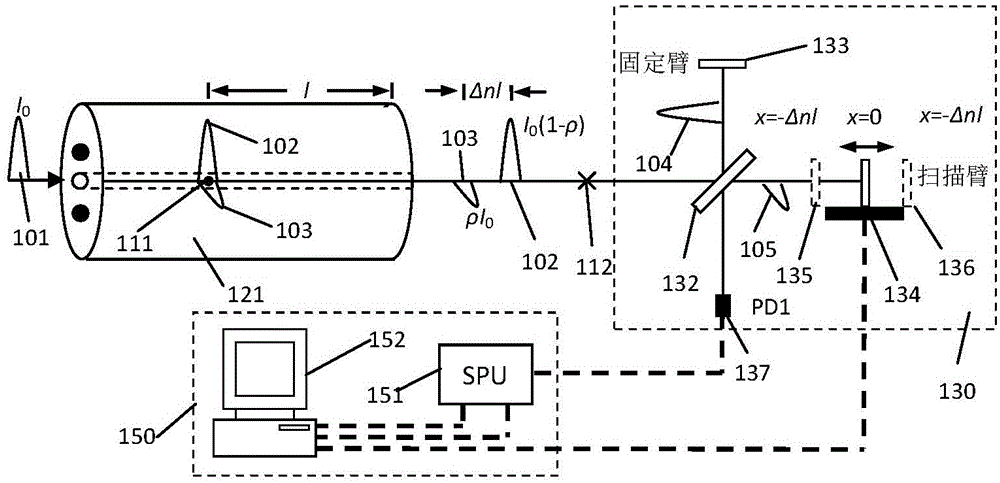
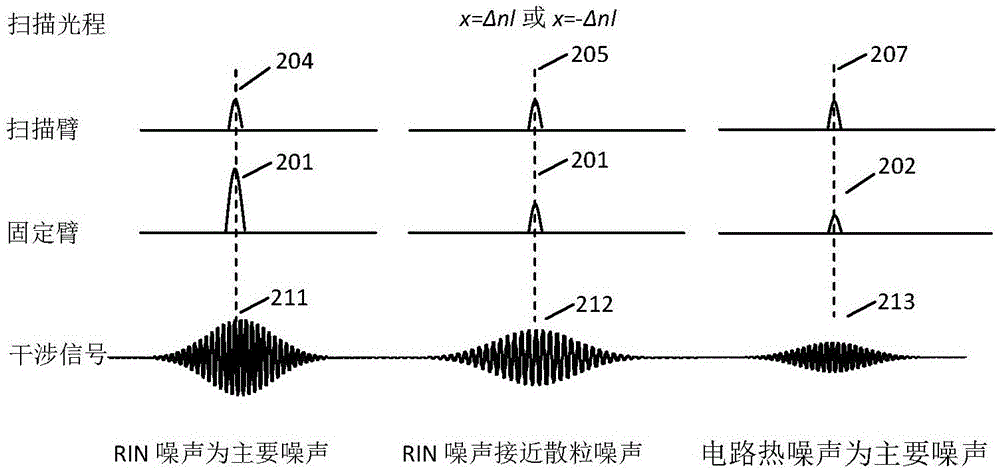
Method for separating thermal noise, shot noise and intensity noise of optical fiber gyroscope
InactiveCN101008570AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionSagnac effect gyrometersTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsFiberDigital collections
This invention discloses one light fiber top noise, discrete noise and intensity noise separation method, which comprises the following steps: processing phase modulation on system according to selection phase; high speed digital collection circuit processes sample of output signal in different modulation depth; through sample sequence analyzing getting relative noise even and variance; according to different function, computing three kinds of noise value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system
InactiveCN101825712AMake up for the defect of environmental interferenceSolve the problem of all-fiber miniaturizationCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsOperability
The invention discloses a 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system, which consists of a 2 mu m off-axis Cassegrain optical antenna system, a 2 mu m laser beam splitting system, a 2 mu m seed implantation laser amplifier, a 2 mu m monitoring detector system, and a 2 mu m balanced heterodyne detection system. The system overcomes the defect of ambient interference existing in a free space optical path, overcomes the influence of shot noise on heterodyne reception signal-to-noise ratio, and solves the problems of all fiber and miniaturization of the 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system, so that the 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system has a more compact structure. In addition, the system has the characteristics of safe laser for human eye, optical path connection by adopting flexible optical fiber devices, high operability and stability, low cost, good real time, long effectively measured distance, high measurement accuracy (speed measurement and distance measurement) and the like, and has high practical value in the field of coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
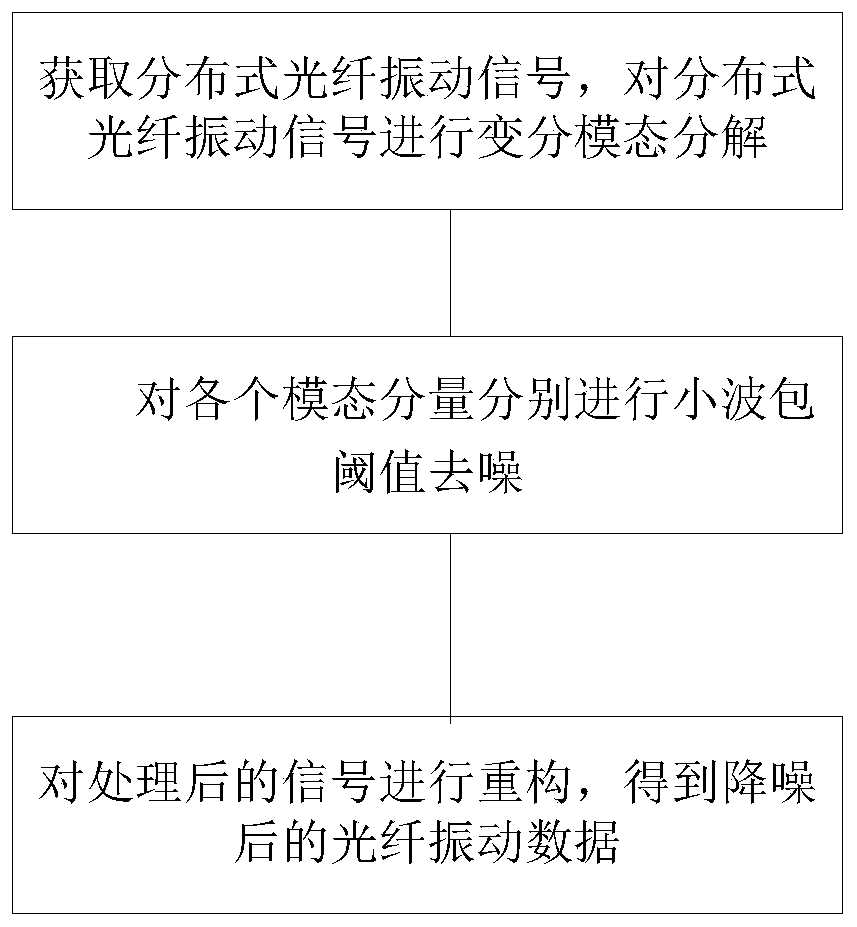
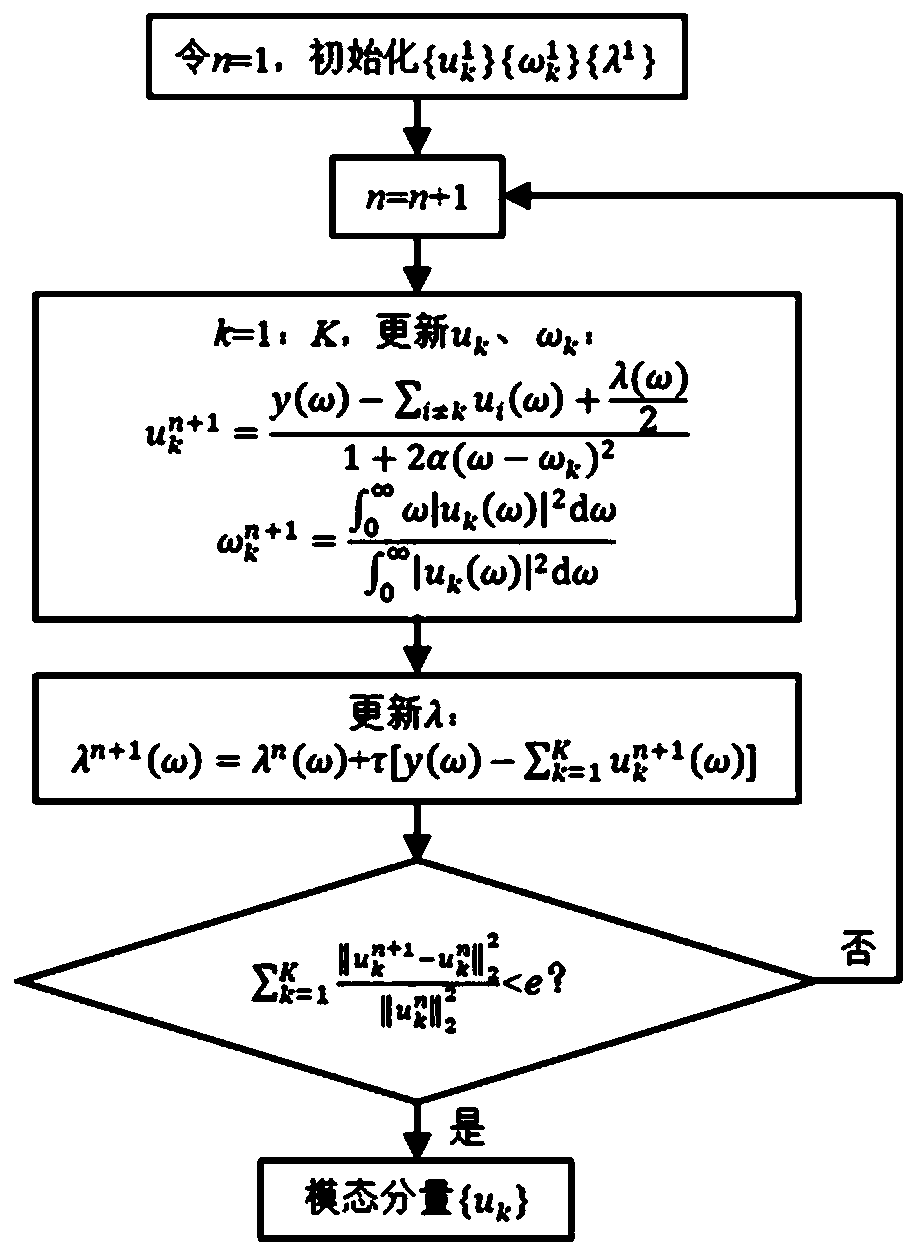
A distributed optical fiber vibration signal noise reduction method based on variational mode decomposition
PendingCN109726642AImprove accuracyImprove signal-to-noise ratioSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Decomposition
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber vibration signal noise reduction method based on variational mode decomposition. The method comprises the steps that distributed optical fiber vibration signals are acquired, variational mode decomposition is conducted on the distributed optical fiber vibration signals, original signals can be divided into components of different modes, high-frequency noise in the vibration signals can be filtered out in the decomposition process, high-frequency noise of the vibration signals is filtered out, and good signal-to-noise separation performance isachieved; Wavelet packet threshold denoising is carried out on each modal component, and types of noise such as granular noise and low-frequency noise in environment noise can be further filtered out. And the processed signal is reconstructed to obtain the denoised optical fiber vibration data, so that the signal-to-noise ratio of the optical fiber vibration data and the optical fiber vibration signal processing accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
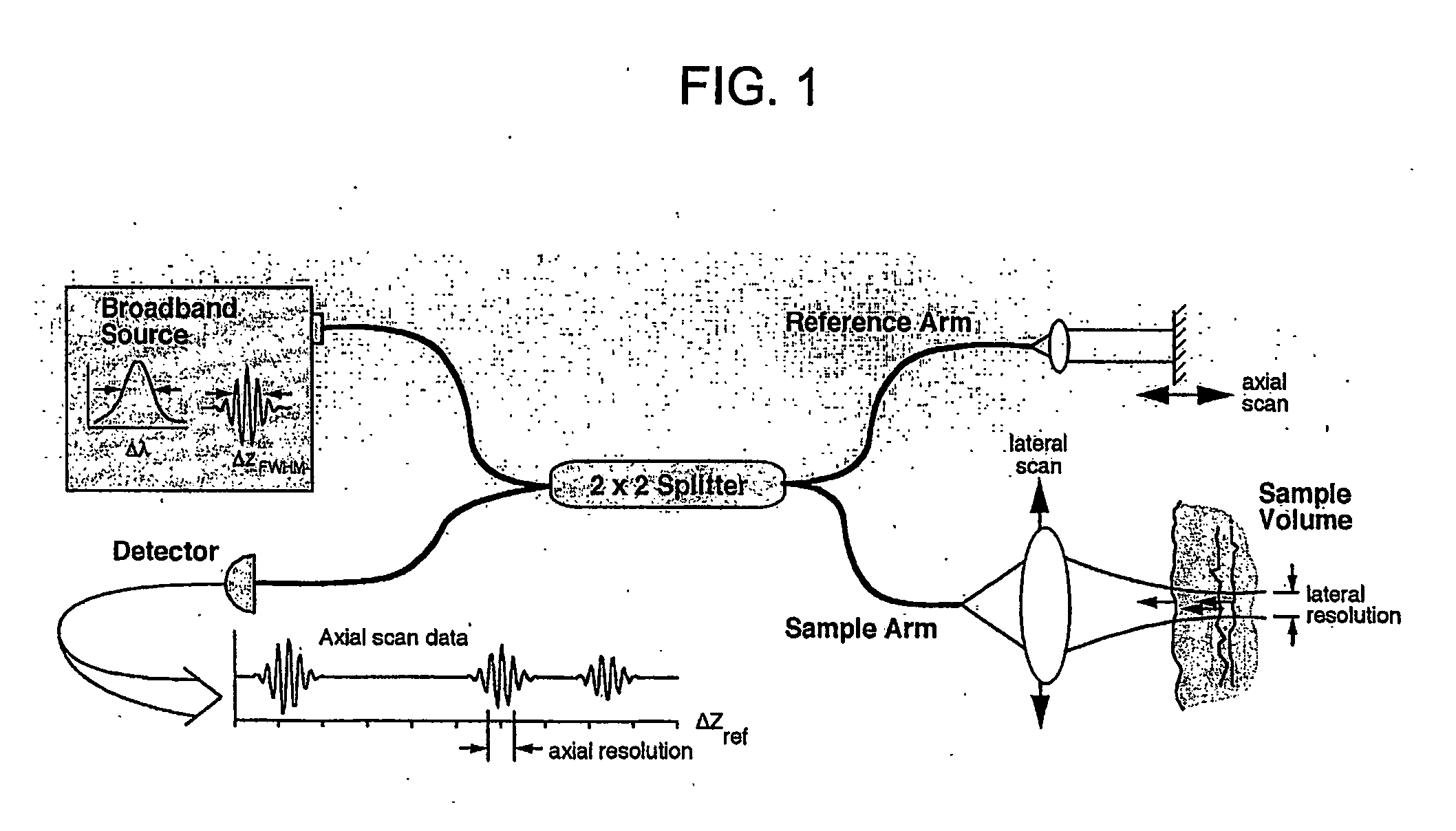
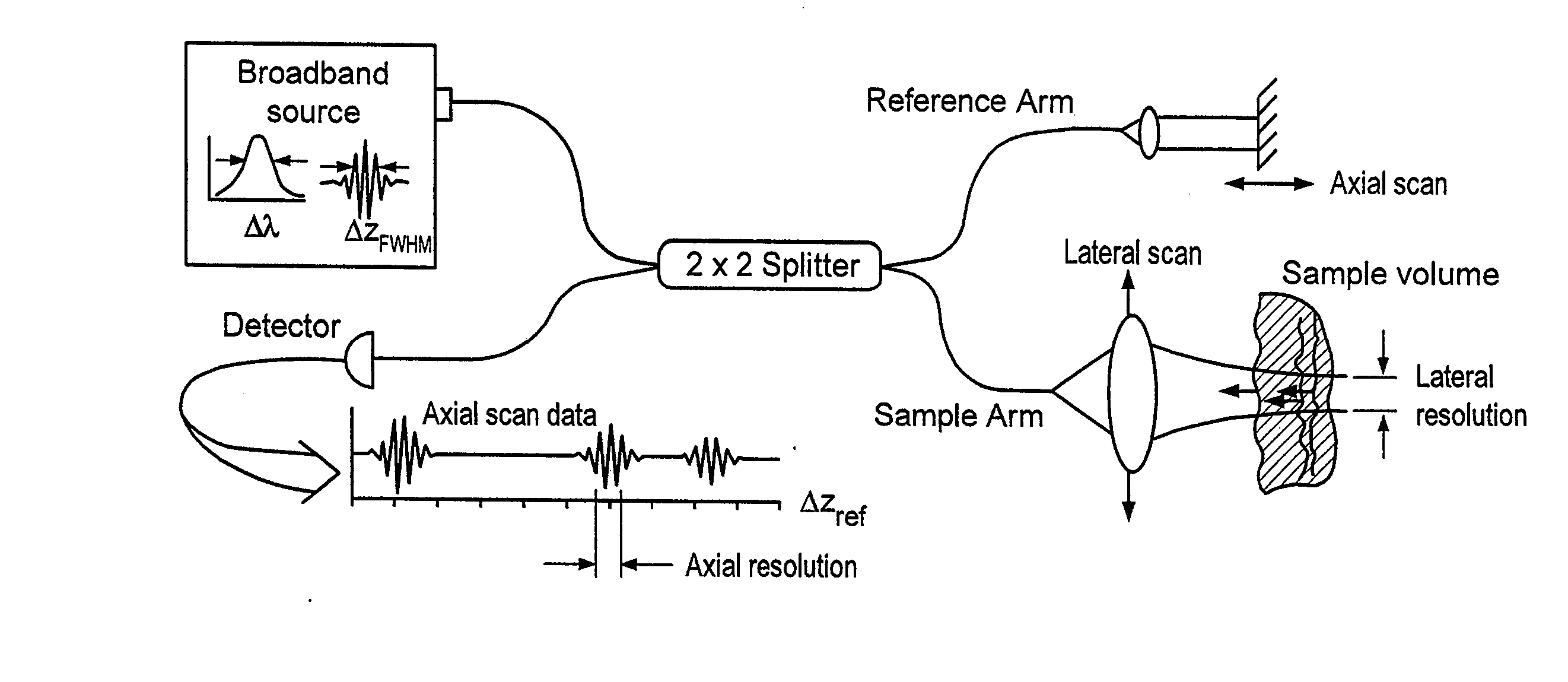
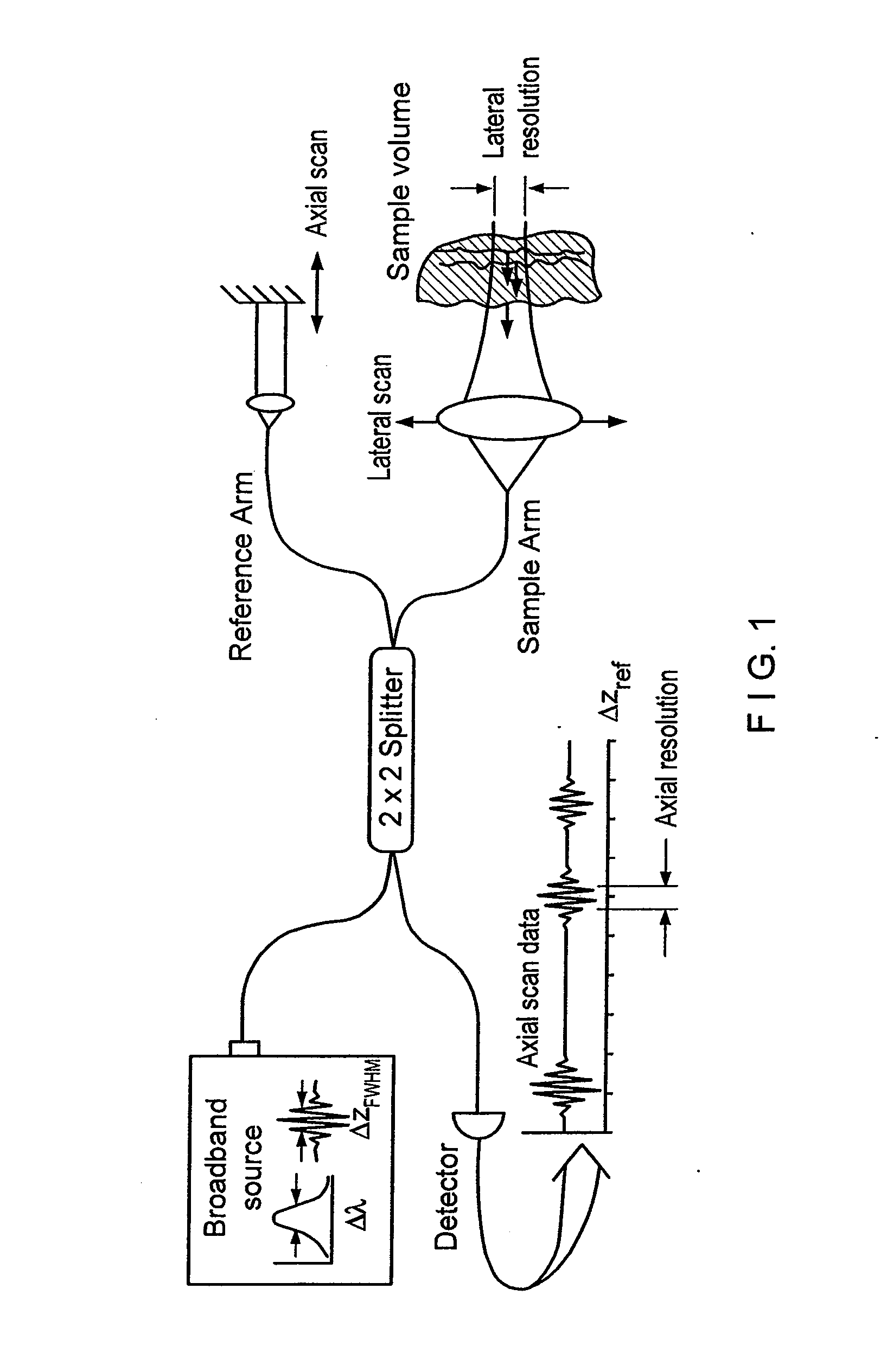
Apparatus and method for rangings and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry (LCI) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) signals
InactiveCN101793823AImprove signal-to-noise ratioFast imagingSurgeryPhase-affecting property measurementsSpectral bandsOptical frequencies
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (''LCI'') signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
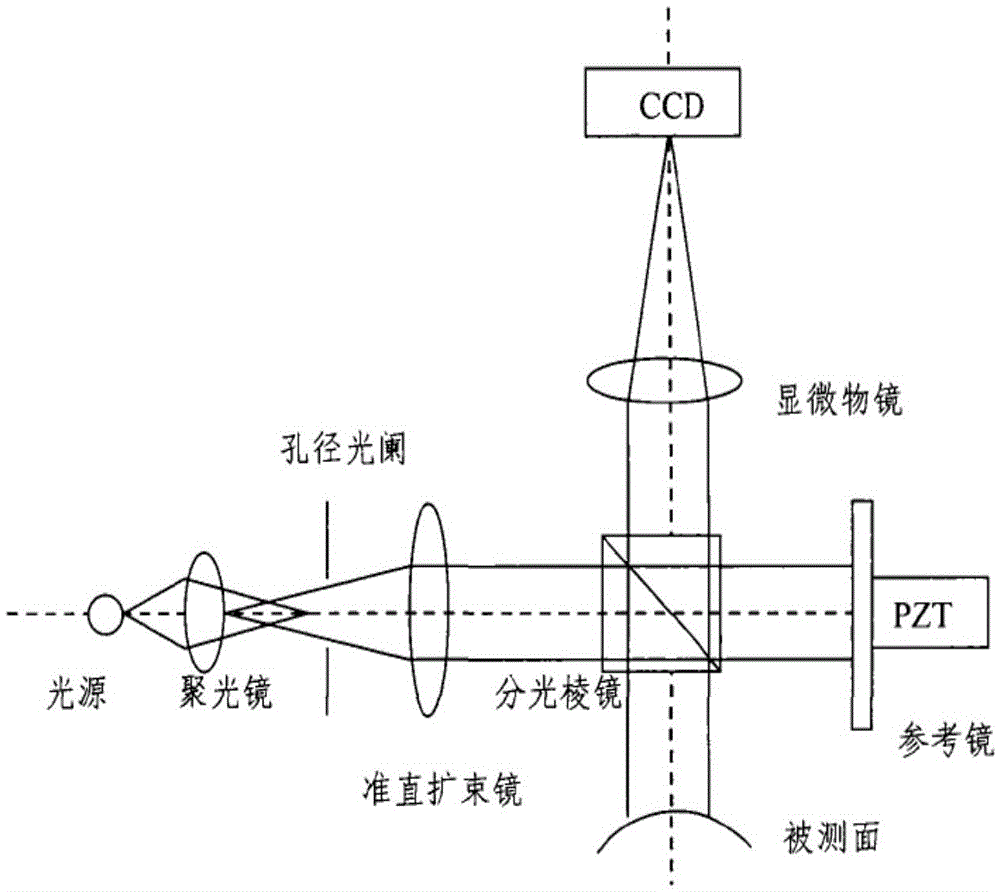
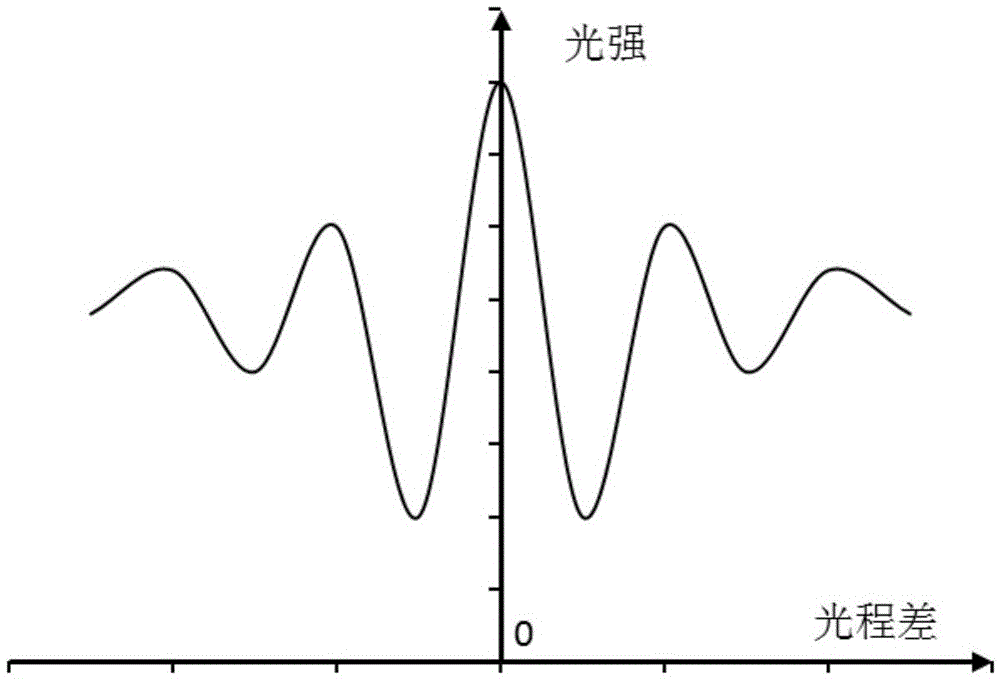
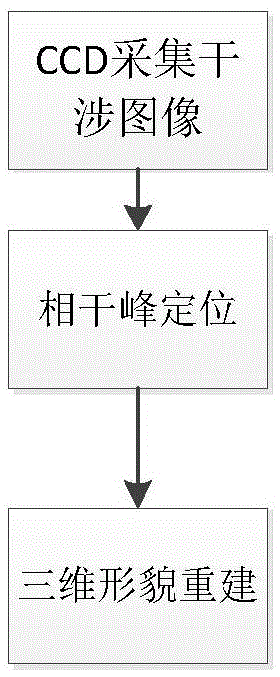
Modified coherence peak demodulation method for fiber end face detection
The invention discloses a modified coherence peak demodulation method for fiber end face detection, and belongs to the technical field of a fiber end face measuring instrument. The demodulation method comprises quickly limiting phase extraction in a zero order stripe through a modified extremum method, and reducing the random error caused by environment disturbance and CCD shot noise; and performing phase correction for the extracted light intensity maximum based on a Carre phase shift algorithm, and eliminating the influence of the linear phase shift error on the fiber end face height value. During the process for calculating the fiber end face height value, the modified coherence peak demodulation method has no demand for performing phase unwrapping operation, thus improving the calculating speed, and has the advantages of being insensitive to the linear error Epsilon of a phase shifter, and being high in precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com