Patents
Literature
896 results about "Image pattern" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
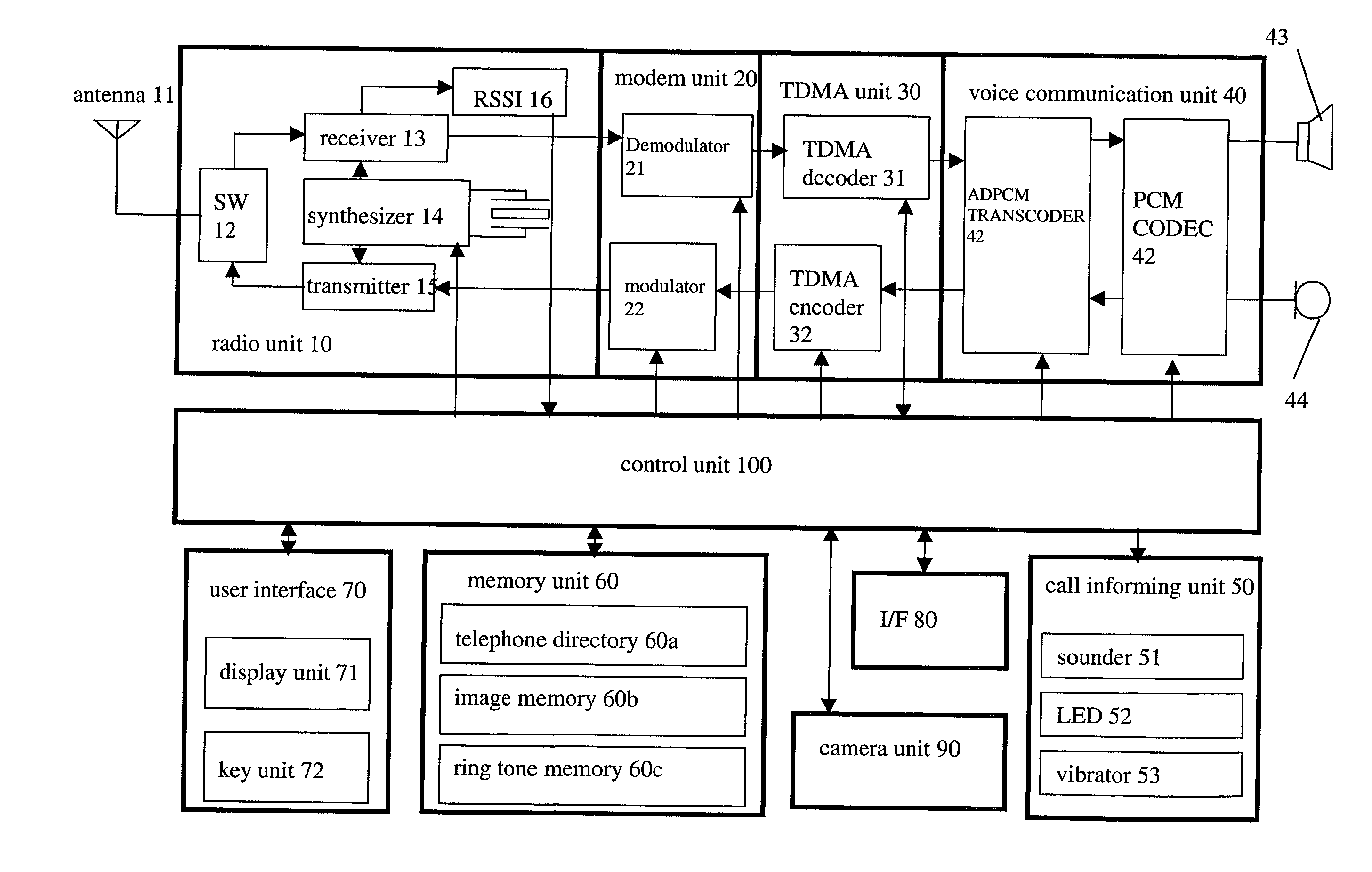
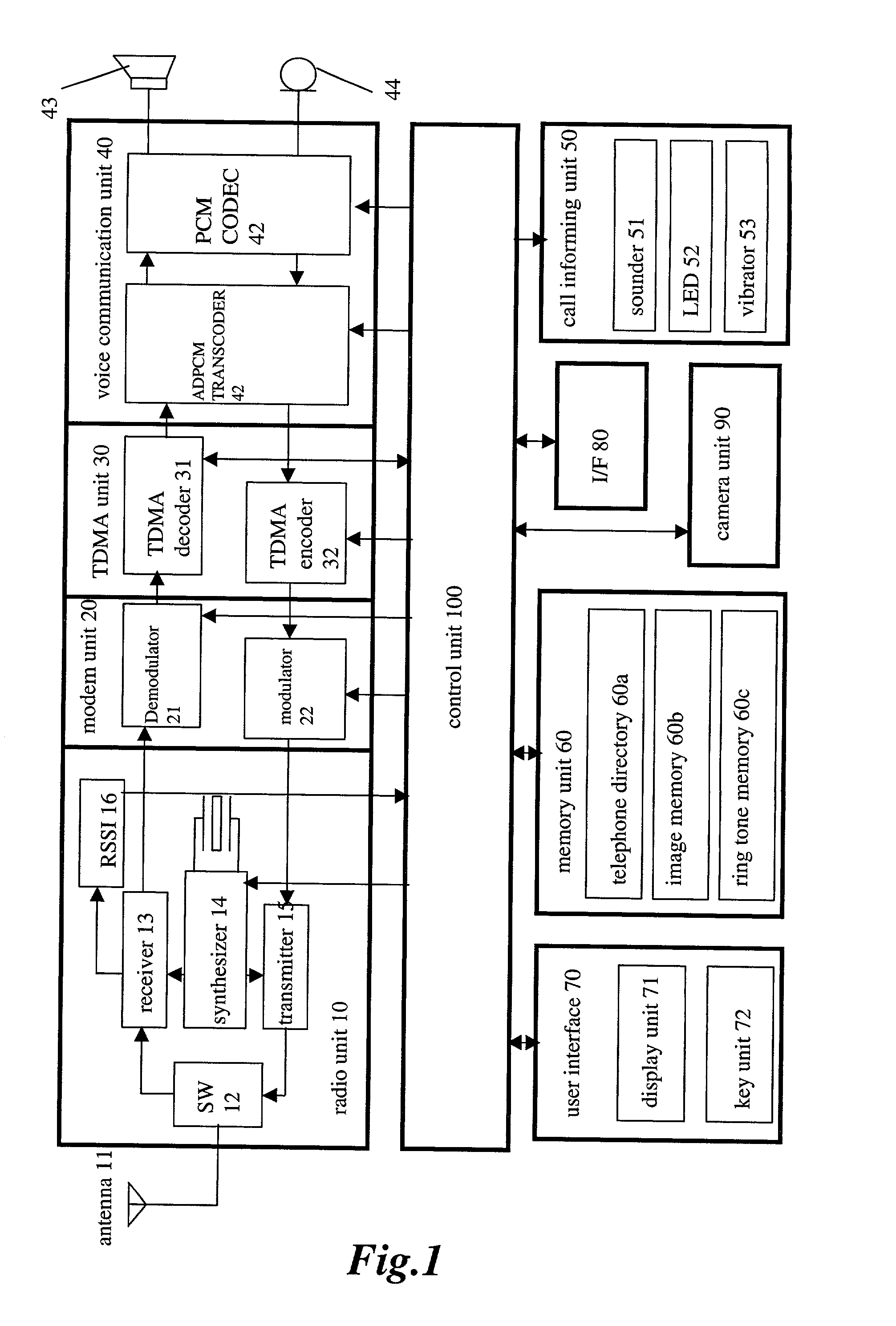
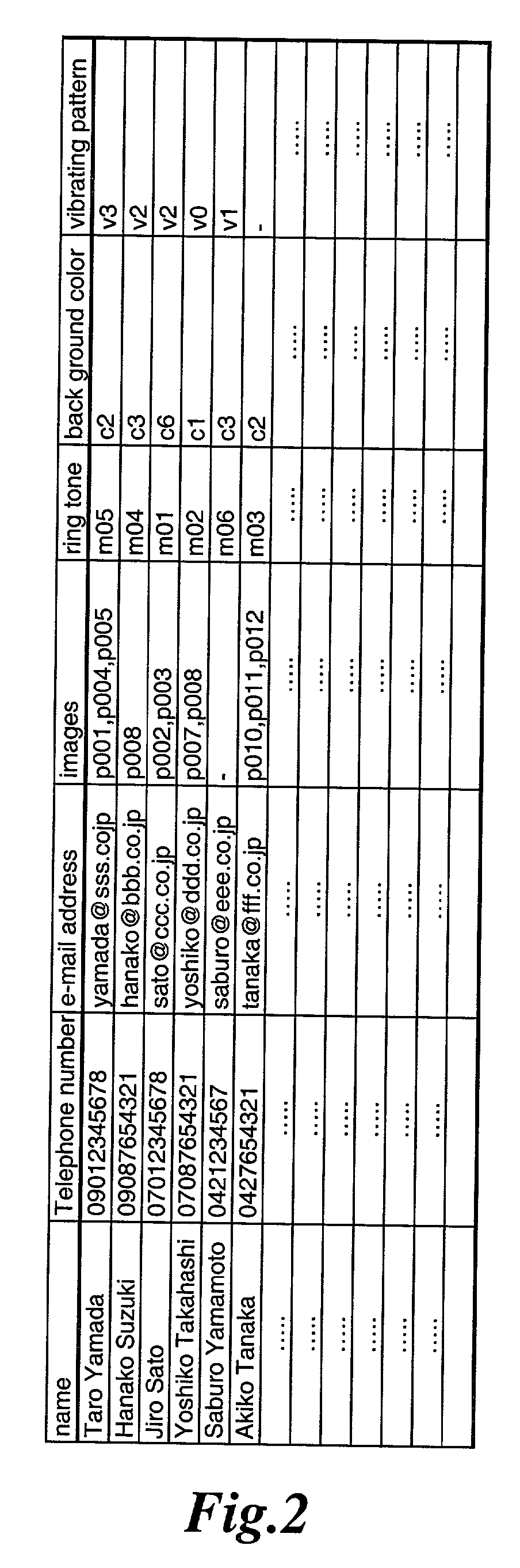
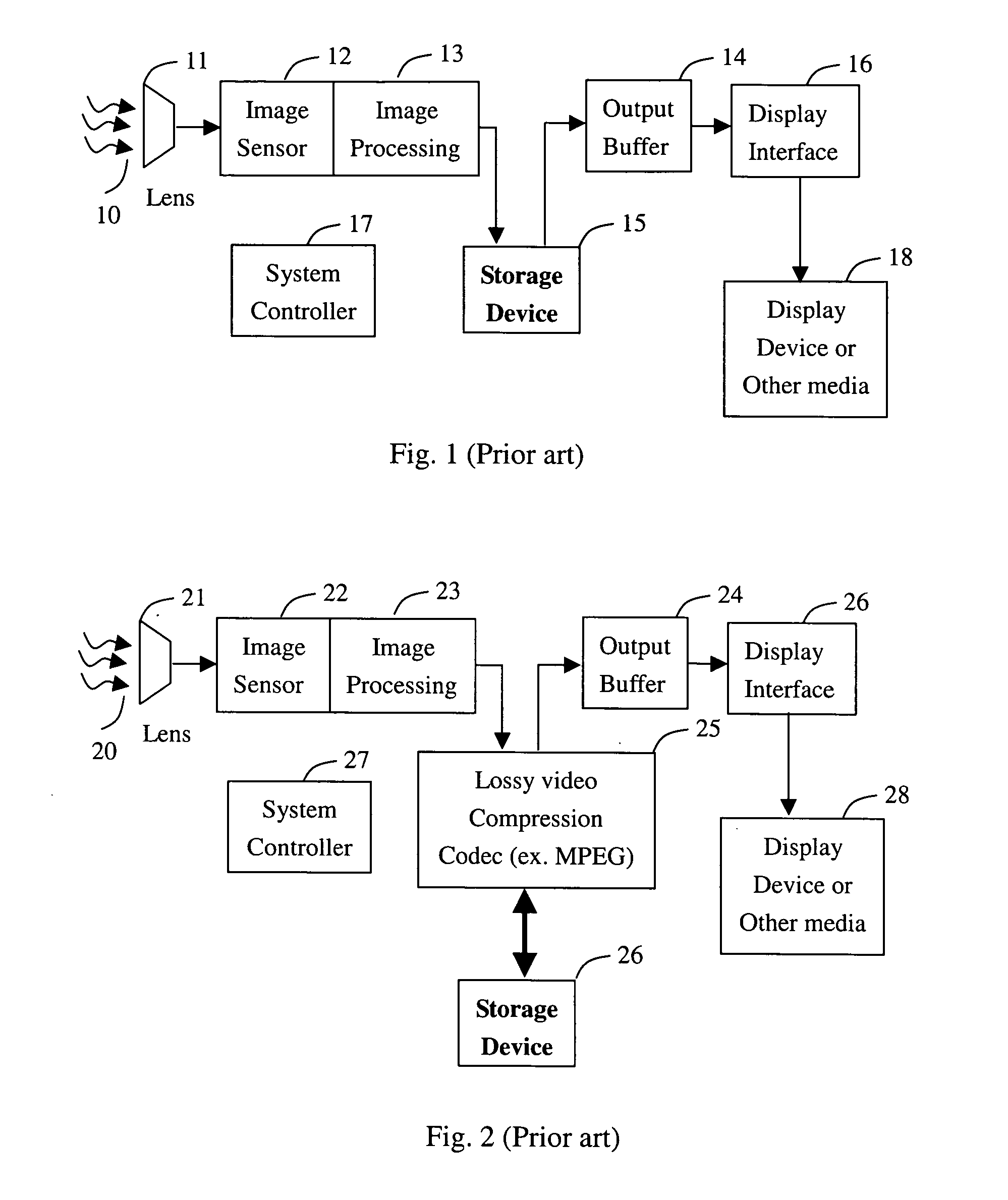
Communication apparatus for use in a communication system providing caller ID functionality
InactiveUS20020094806A1Special service for subscribersCalling susbscriber number recording/indicationData setEmail address
A telephone directory stores a plurality of data sets including a name, a telephone number, e-mail address, image pattern numbers, a ring tone number, a background color number, and a vibrating pattern. An image memory stores images corresponding to each image pattern number. A ring tone memory stores ring tone data corresponding to each ring tone pattern. When a radio communication apparatus receives an incoming call signal, the control unit informs of an incoming voice or message call by repeatedly displaying the images on a display unit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
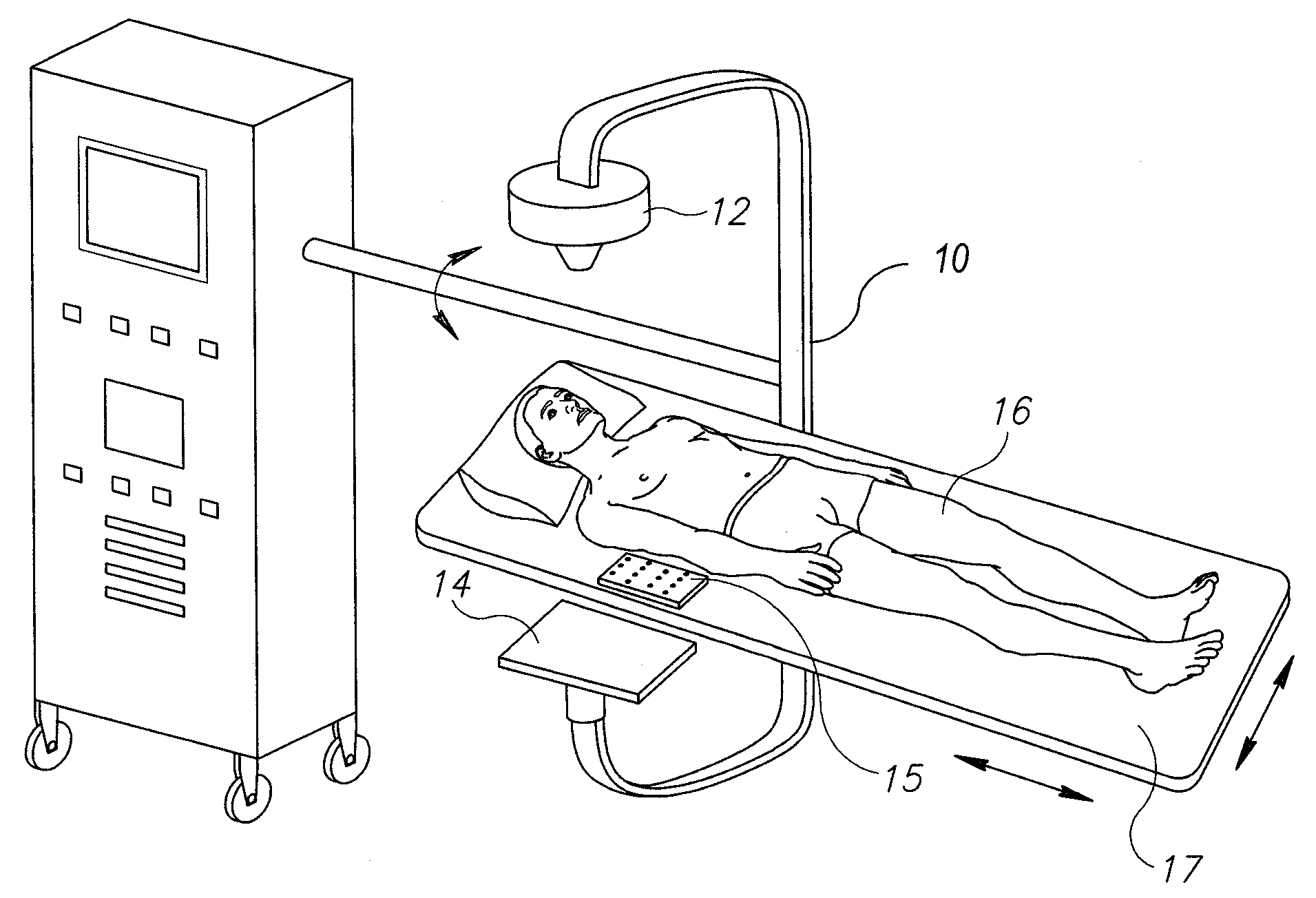
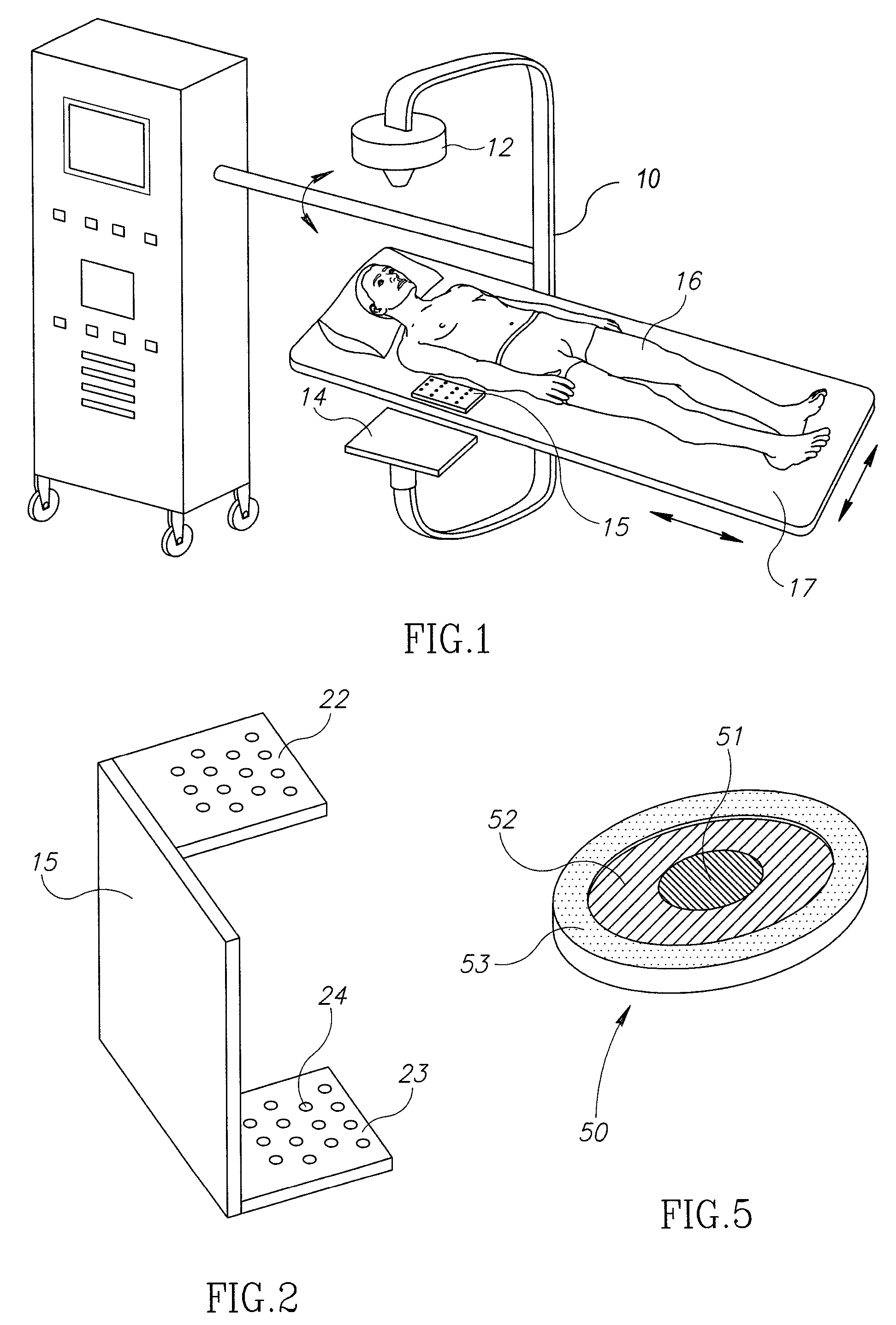
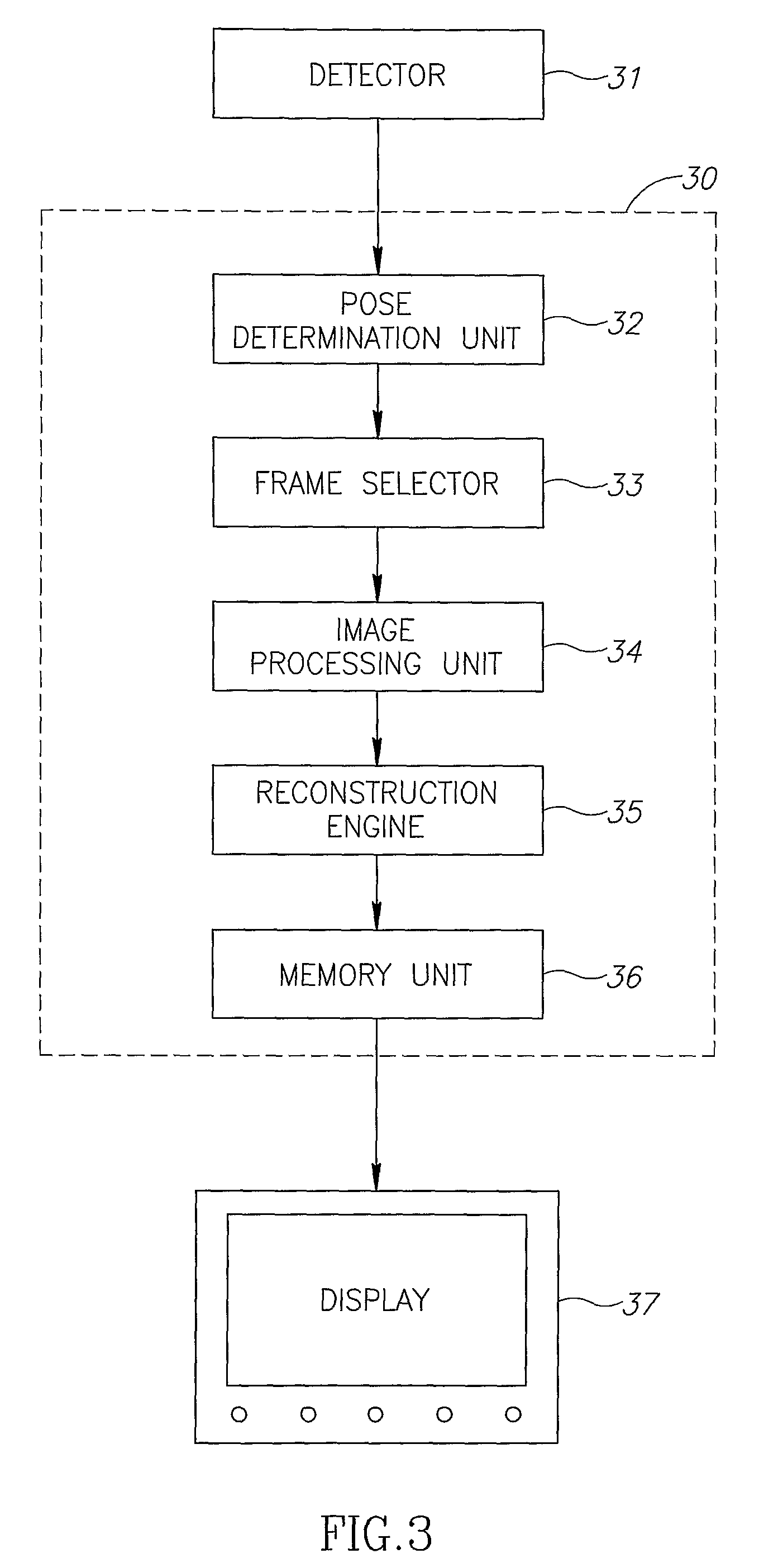
C-arm computerized tomography system
ActiveUS9044190B2Reducing effect of motion of C-armCharacter and pattern recognitionX-ray apparatusData setVideo sequence
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
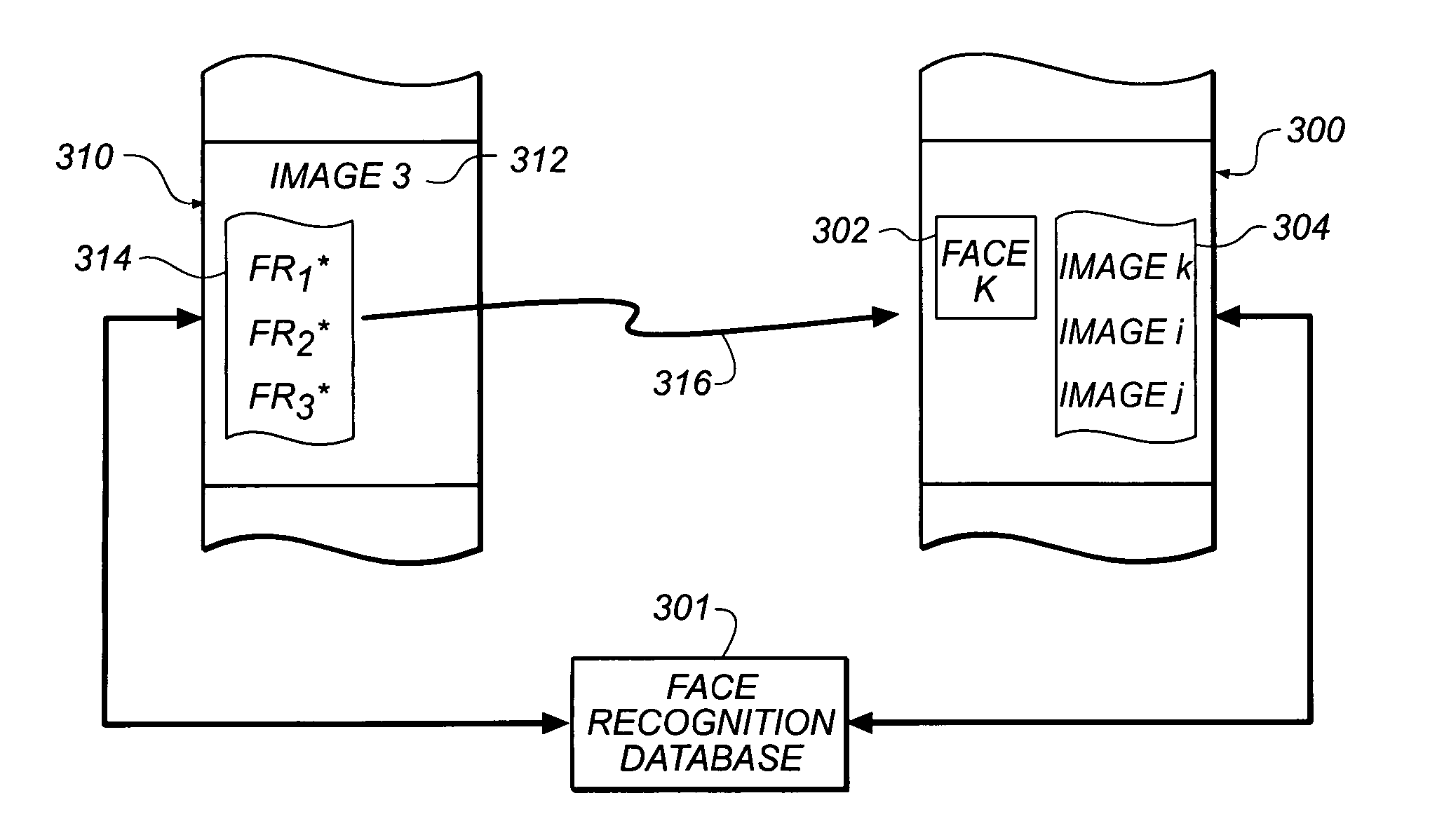
Method for selecting an emphasis image from an image collection based upon content recognition
ActiveUS7382903B2Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFrequency of occurrence
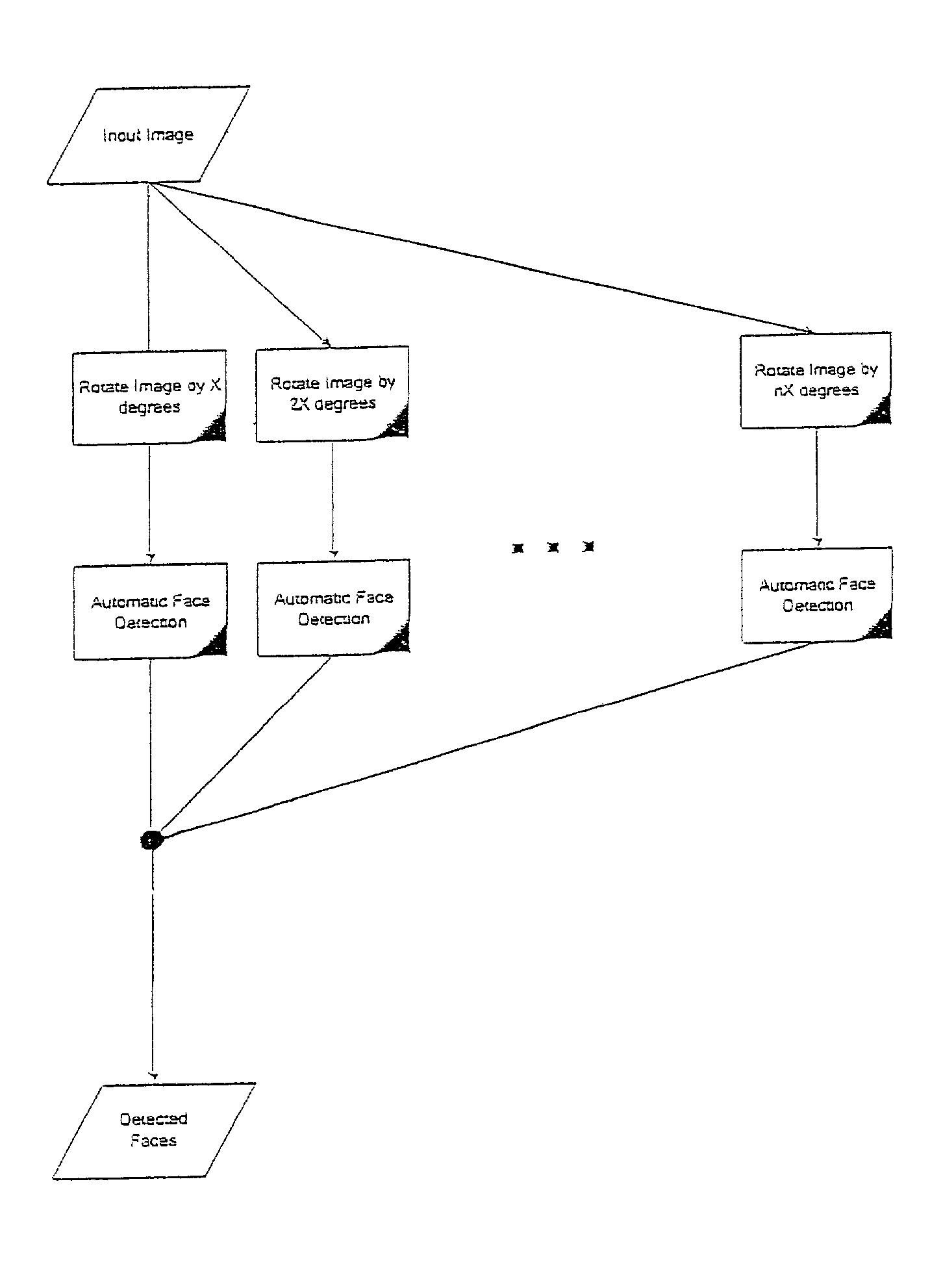
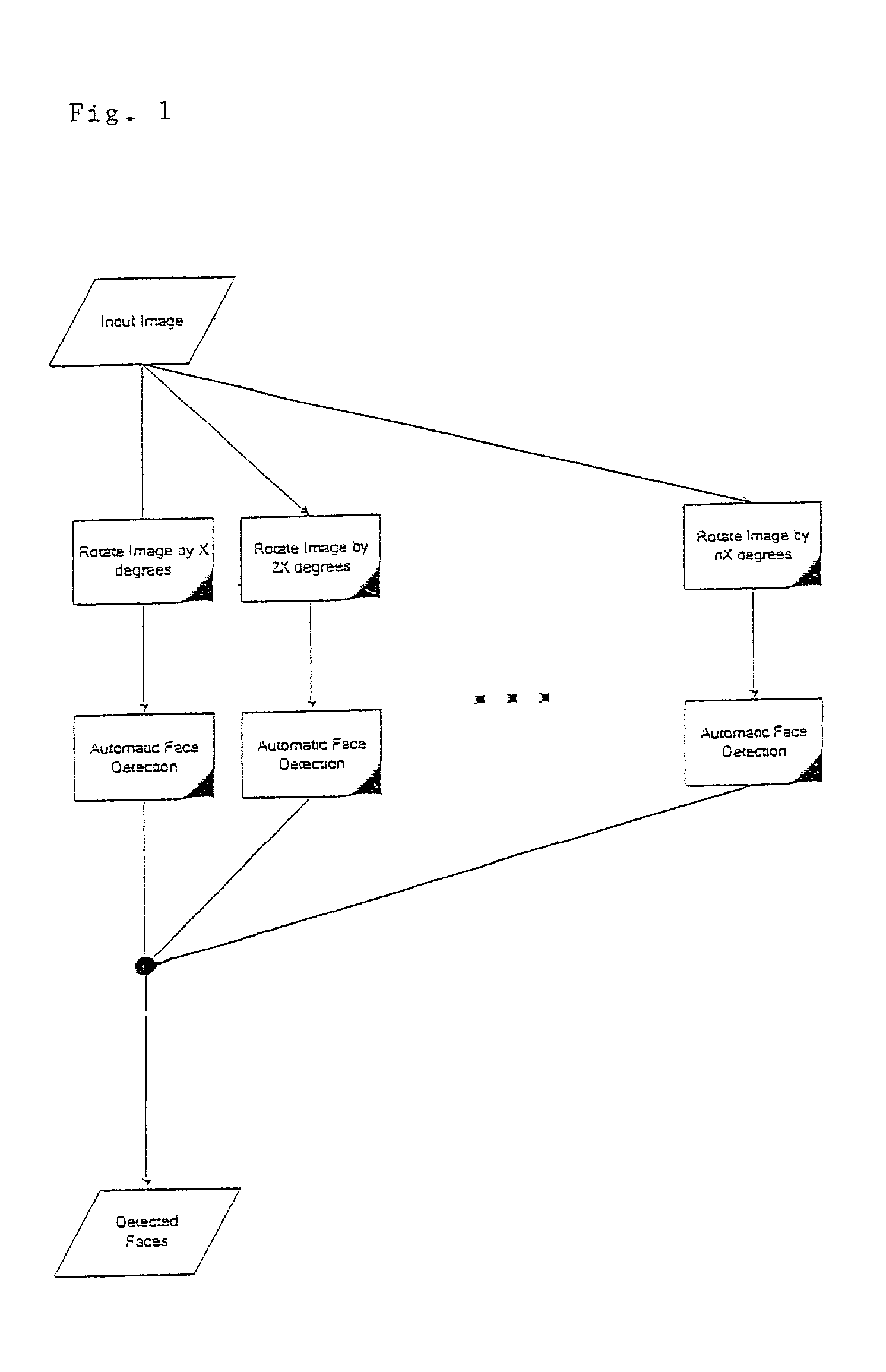
A method for selecting an emphasis image from a collection of images based on facial identification comprises the steps of: (a) obtaining a collection of digital images; (b) detecting image patterns indicative of the presence of one or more faces in the digital images, thereby identifying one or more detected faces for each image in which a face is detected; (c) recognizing one or more faces from the detected faces for each of the images in which a face is detected; and (d) scoring an image based on the relative frequency of occurrence of a recognized face within the collection of images, thereby producing an emphasis image characteristic of the most frequently occurring face in the collection of images.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Flexible organic laser printer
A printing device and method for printing. The printing device includes photoconductor for receiving a charge, a plurality of organic vertical cavity surface emitting lasers for producing a charged image pattern on said photoconductor; a toner application mechanism for applying a toner onto said photoconductor for creating a toner image pattern in accordance with said charged image pattern; and a transfer mechanism for transferring said toner image pattern onto a media.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
3D projection with image recording
ActiveUS6935748B2Increase refresh rateSolve the lack of densityProjectorsCharacter and pattern recognitionLight energyLaser light
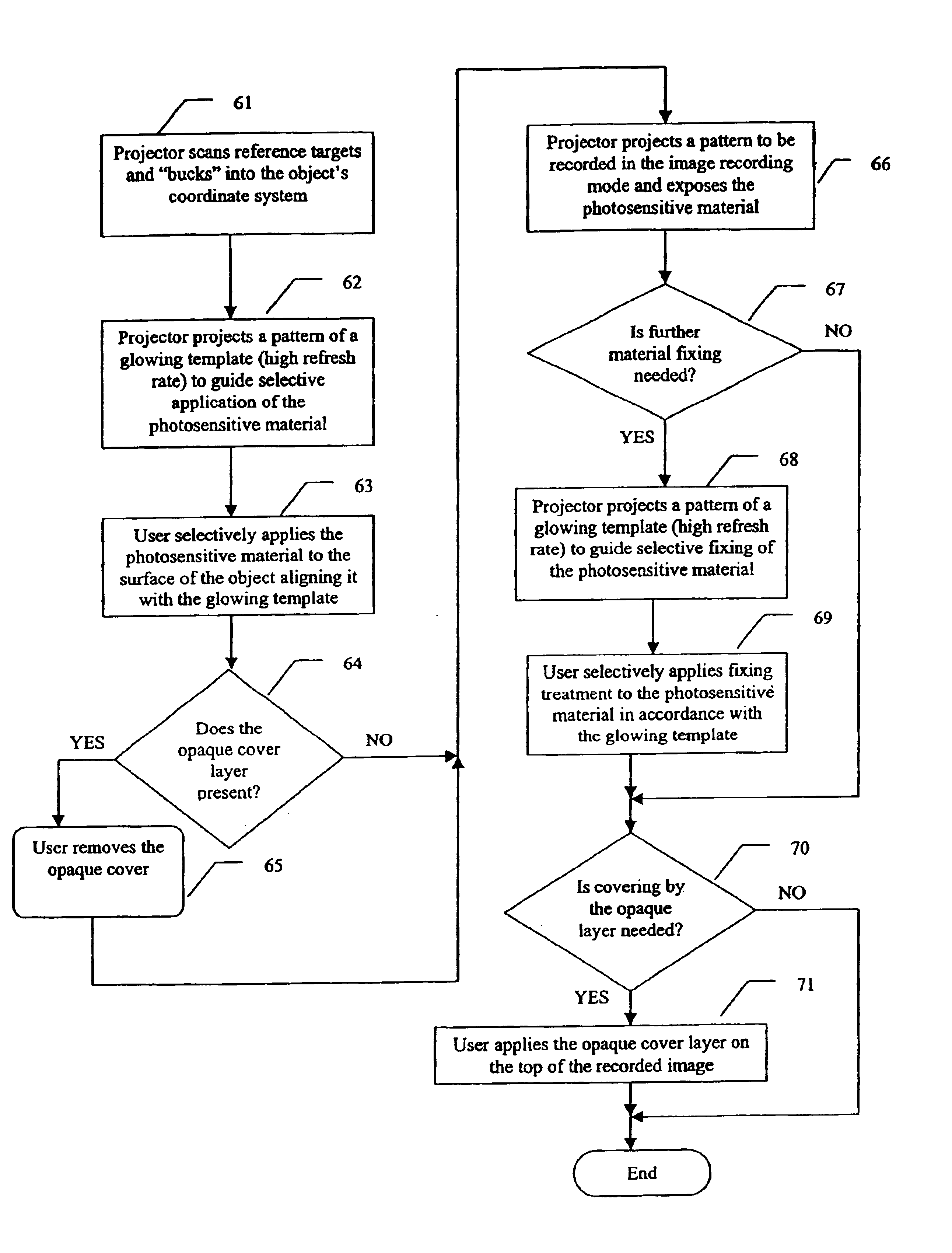
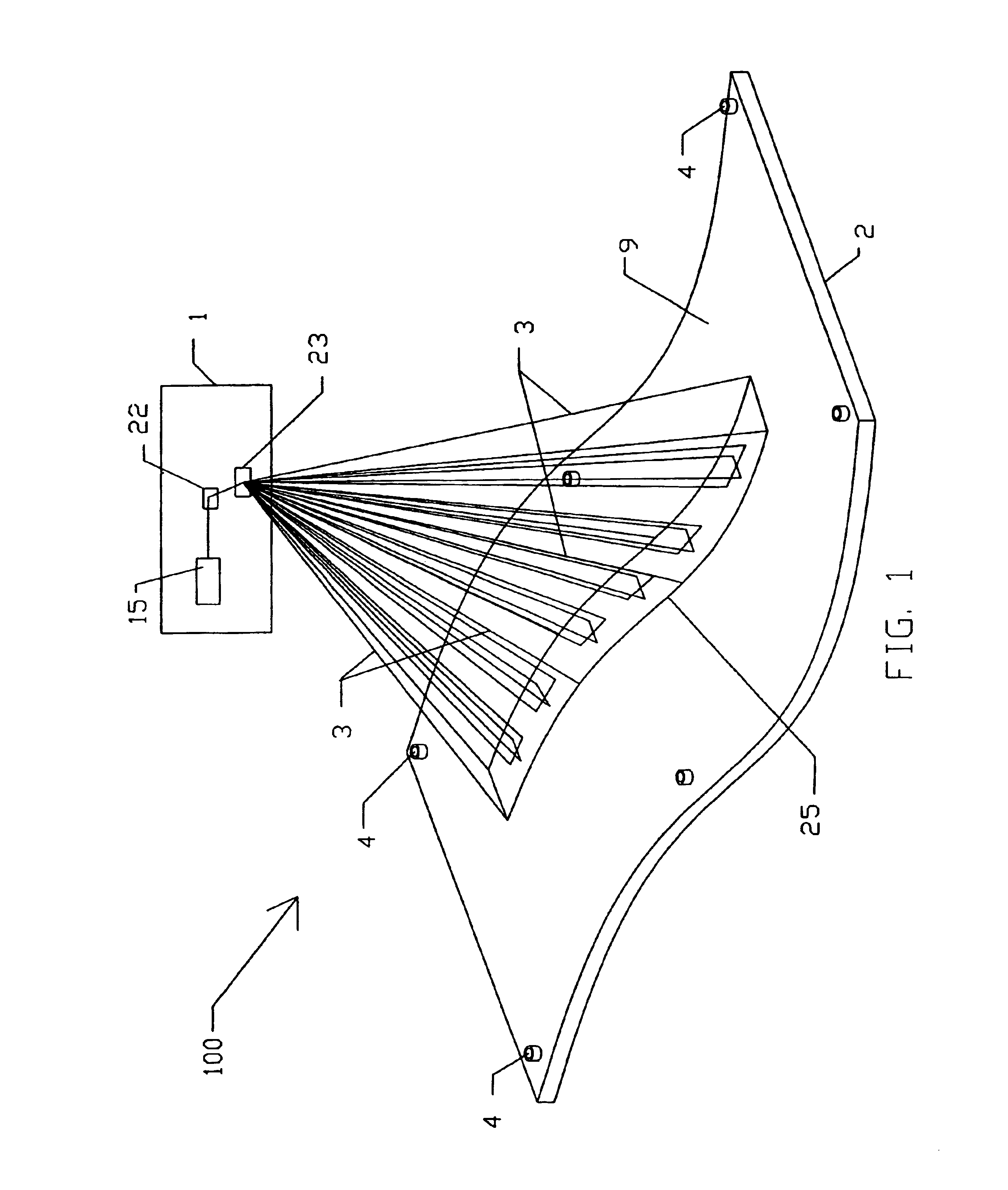
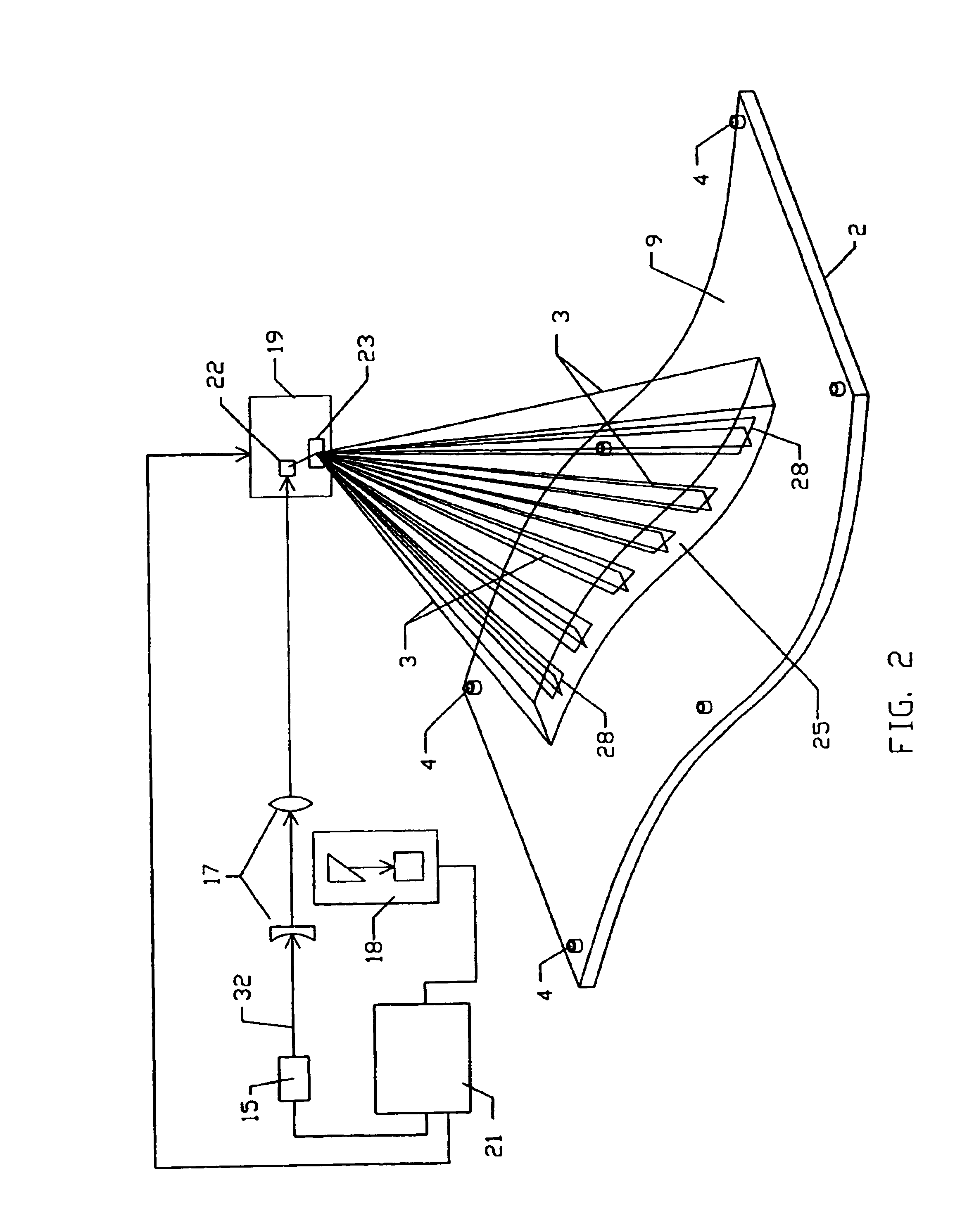
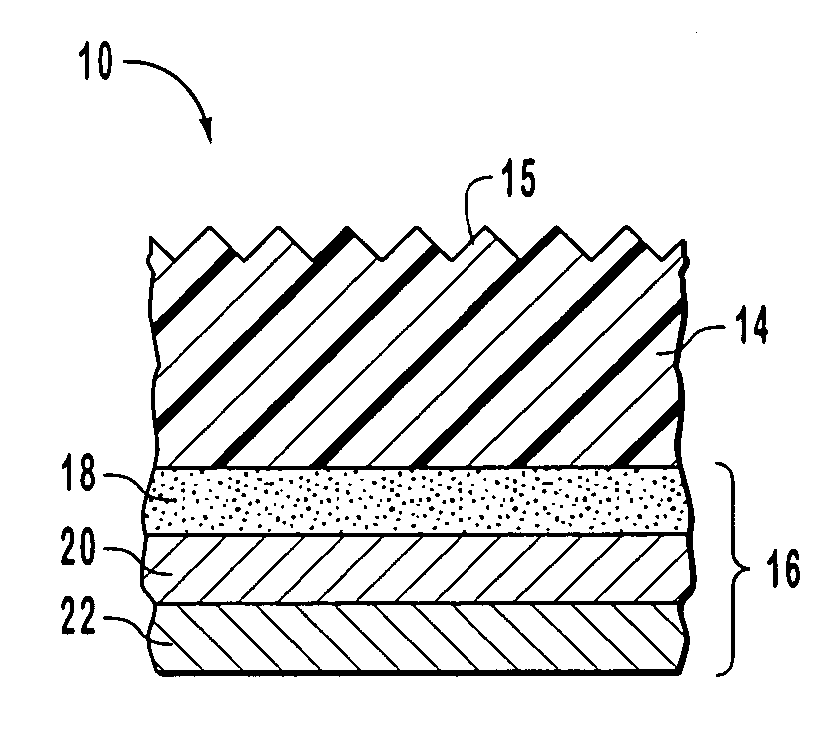
An apparatus and method for recording an image on the surface of a 3D object uses a laser projector that scans a light beam over the surface in an image pattern. The projector operates in a template imaging mode and an image recording mode where the beam scans at a speed that in a single pass / scan mode is typically four to five orders of magnitude slower than in the template imaging mode. A layer of a photosensitive material is applied to the surface of the object either partially or fully. Projection in the template imaging mode can guide the applying. The layer is substantially insensitive to ambient light for at least a period of time necessary to perform a desired processing step on the object. The layer has a maximum spectral sensitivity in the vicinity of the wavelength of the laser light beam. In one or multiple passes of the beam over the image pattern operating in the image record mode, the accumulated light energy dose density is sufficient to react the material and record the image.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Security articles having diffractive surfaces and color shifting backgrounds
InactiveUS20040105963A1Increase the difficulty of counterfeitingOther printing matterDecorative surface effectsOptical diffractionColor shift
A security article includes a light transmissive substrate having a first surface and an opposing second surface, with the first surface having an embossed region with an optical diffraction pattern or a holographic image pattern. A color shifting optical coating is formed on the substrate such as on the opposing second surface, with the optical coating providing an observable color shift as the angle of incident light or viewing angle changes. The security article can be used in a variety of applications and products to provide for enhanced security measures such as anticounterfeiting.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
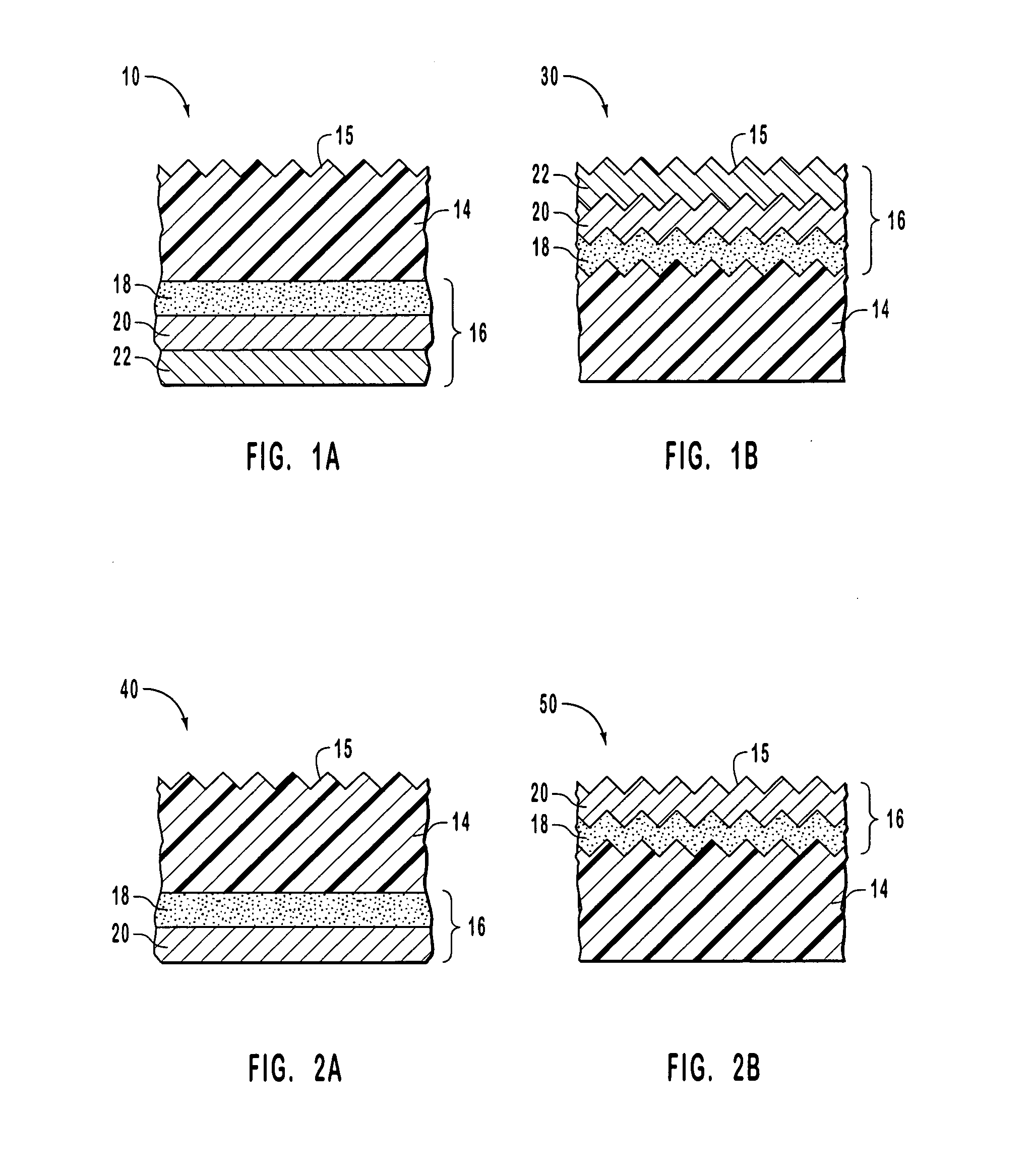
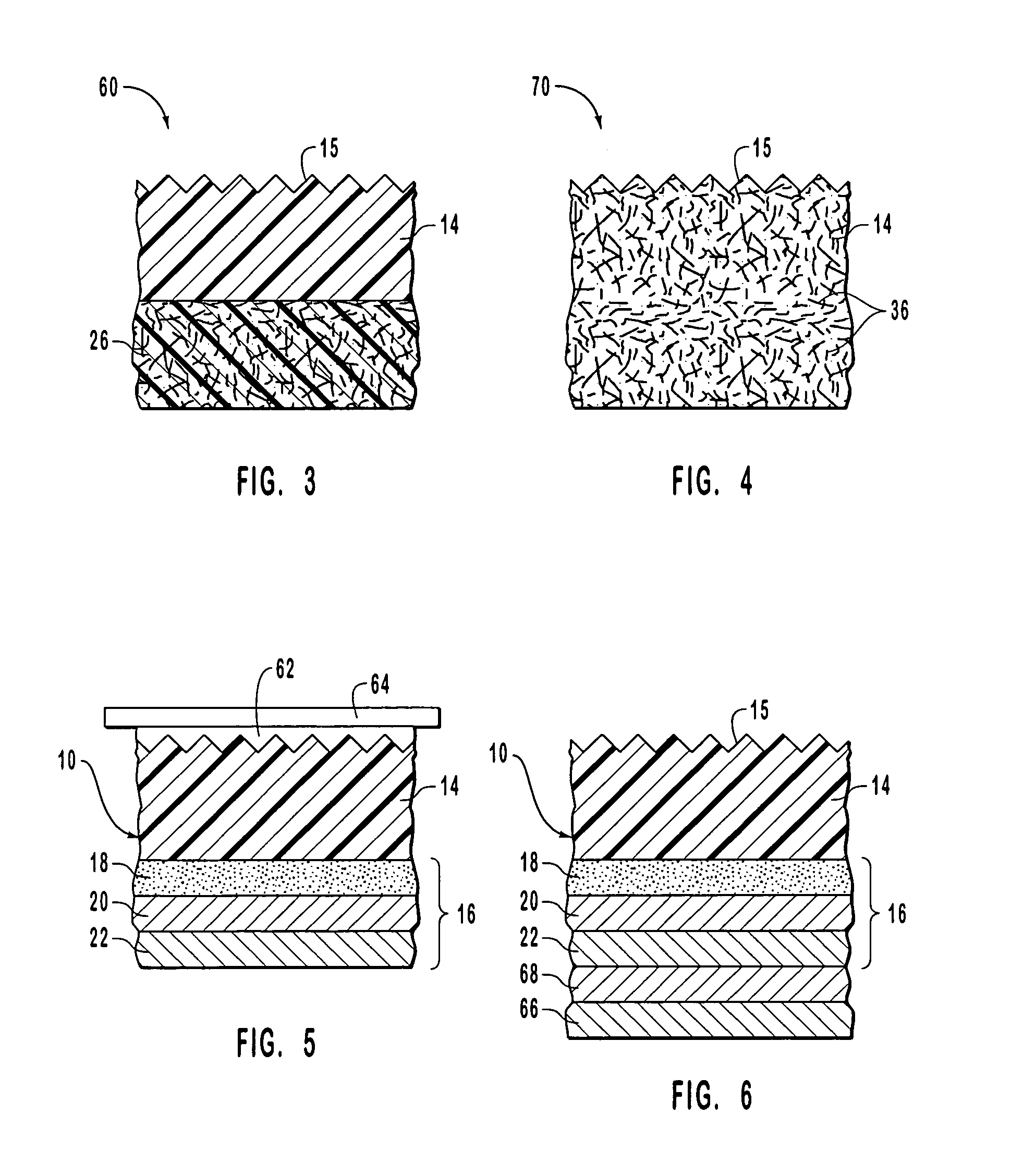
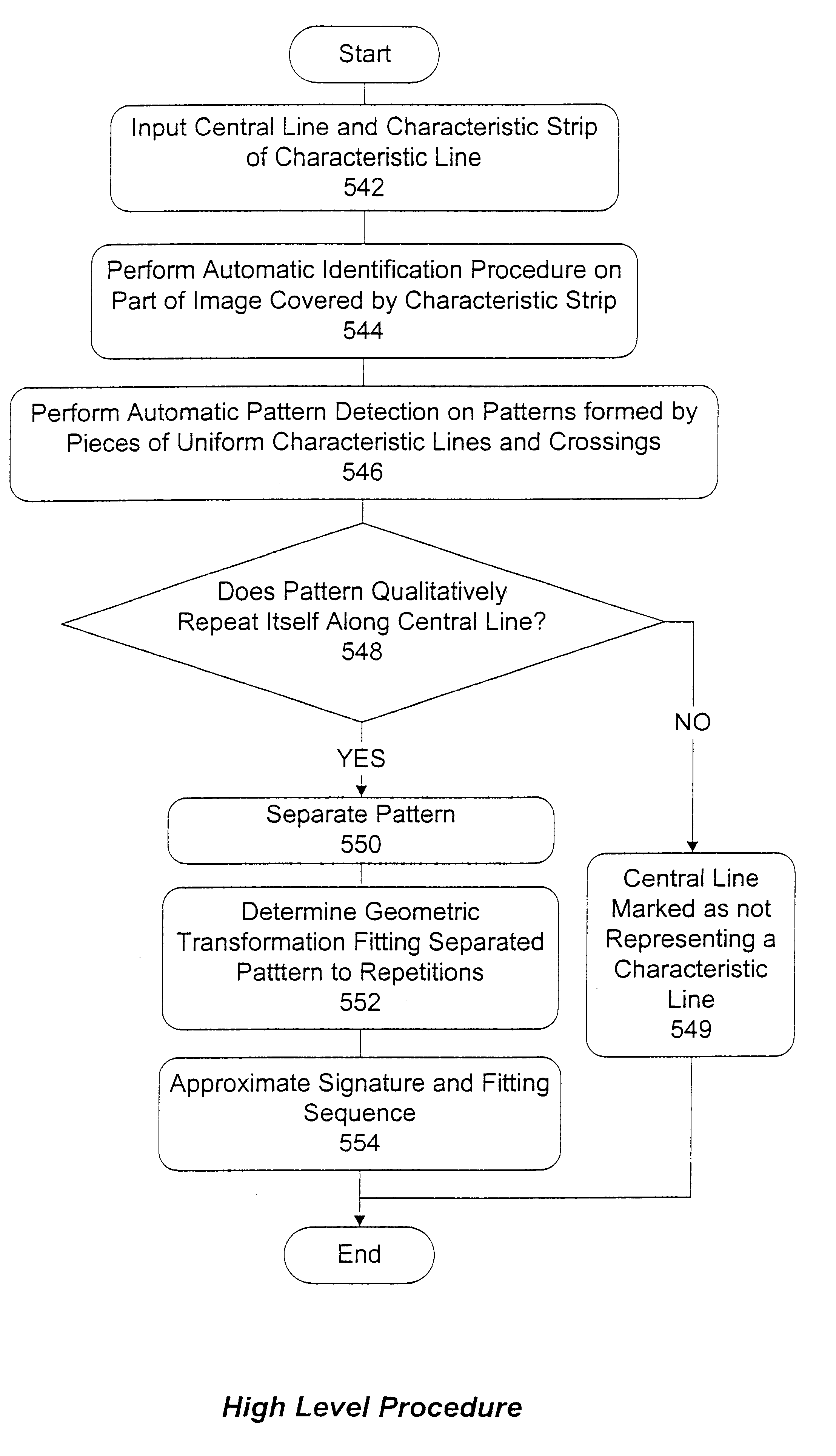
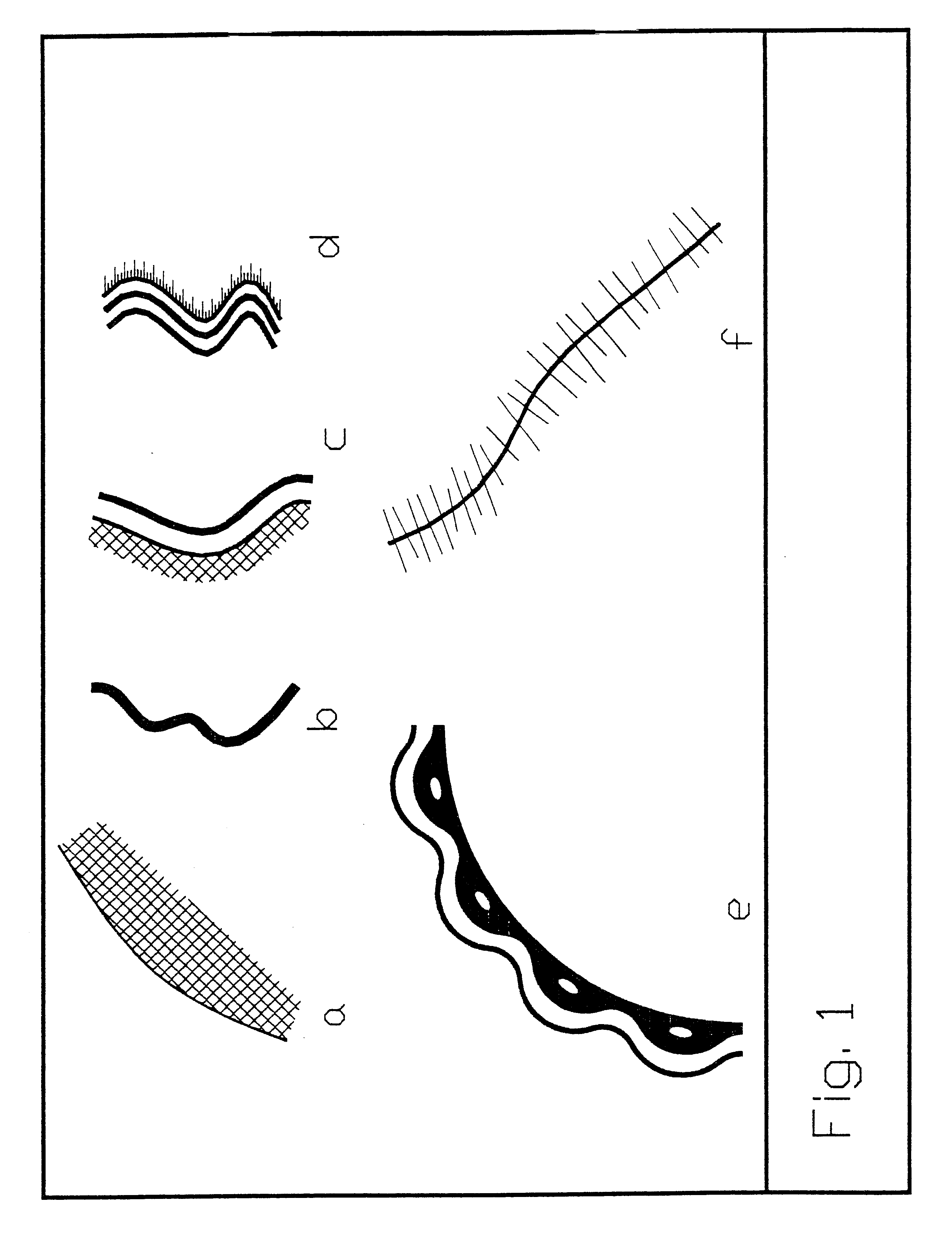
Method and apparatus for image analysis and processing by identification of characteristic lines and corresponding parameters
A method and apparatus is provided for analyzing and processing images by identification of characteristic lines and corresponding parameters. More particularly, the method and apparatus transforms an image into mathematical models derived from the characteristic lines and parameters, based on repetitive image patterns. The parameters include central lines, signatures, cross-sections, characteristic strips, margins, end areas, fitting transformations and fitting sequences. Each of the parameters associated with the identified characteristic lines are representable by mathematical models, which accurately approximate the geometric and brightness (or color) attributes of the respective characteristic lines.
Owner:VIMATIX TECH
3D projection with image recording
ActiveUS20050058332A1Easy to disassembleLow costProjectorsCharacter and pattern recognitionLight energyLaser light
An apparatus and method for recording an image on the surface of a 3D object uses a laser projector that scans a light beam over the surface in an image pattern. The projector operates in a template imaging mode and an image recording mode where the beam scans at a speed that in a single pass / scan mode is typically four to five orders of magnitude slower than in the template imaging mode. A layer of a photosensitive material is applied to the surface of the object either partially or fully. Projection in the template imaging mode can guide the applying. The layer is substantially insensitive to ambient light for at least a period of time necessary to perform a desired processing step on the object. The layer has a maximum spectral sensitivity in the vicinity of the wavelength of the laser light beam. In one or multiple passes of the beam over the image pattern operating in the image record mode, the accumulated light energy dose density is sufficient to react the material and record the image.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Image colour correction based on image pattern recognition, the image pattern including a reference colour
InactiveUS20020150291A1Short timeEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisColor correctionImage pattern
The present invention relates to a method for correcting at least one color of a photographic image including at least one pattern area or image pattern with a predictably known color or memory color, said image being transferred to a digital representation, wherein the method comprises the following steps: said at least one pattern area or image pattern is being detected with respect to its presence and its location, and preferably also with respect to its dimensions; an existing color in the at least one detected pattern area or image pattern is being determined; at least one replacement color value (memory color) is being provided, said value being related to the respective at least one pattern area or image pattern and the determined existing color is replaced by said at least one replacement color value, to correct the color in the image pattern or image area.
Owner:GRETAG IMAGING TRADING
Methods for forming security articles having diffractive surfaces and color shifting backgrounds
InactiveUS20040094850A1Increase the difficulty of counterfeitingOther printing matterOptical articlesOptical diffractionColor shift
A security article includes a light transmissive substrate having a first surface and an opposing second surface, with the first surface having an embossed region with an optical diffraction pattern or a holographic image pattern. A color shifting optical coating is formed on the substrate such as on the opposing second surface, with the optical coating providing an observable color shift as the angle of incident light or viewing angle changes. The security article can be used in a variety of applications and products to provide for enhanced security measures such as anticounterfeiting.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Projector
A projector includes: an image creation unit that projects image information upon a screen, comprising a plurality of picture elements that create an image pattern corresponding to the image information; and an illumination unit in which light emitting members are disposed upon a vertical plane with respect to an optical axis which passes through a center of the image creation unit, at equal distances from the optical axis and moreover in different locations.
Owner:NIKON CORP
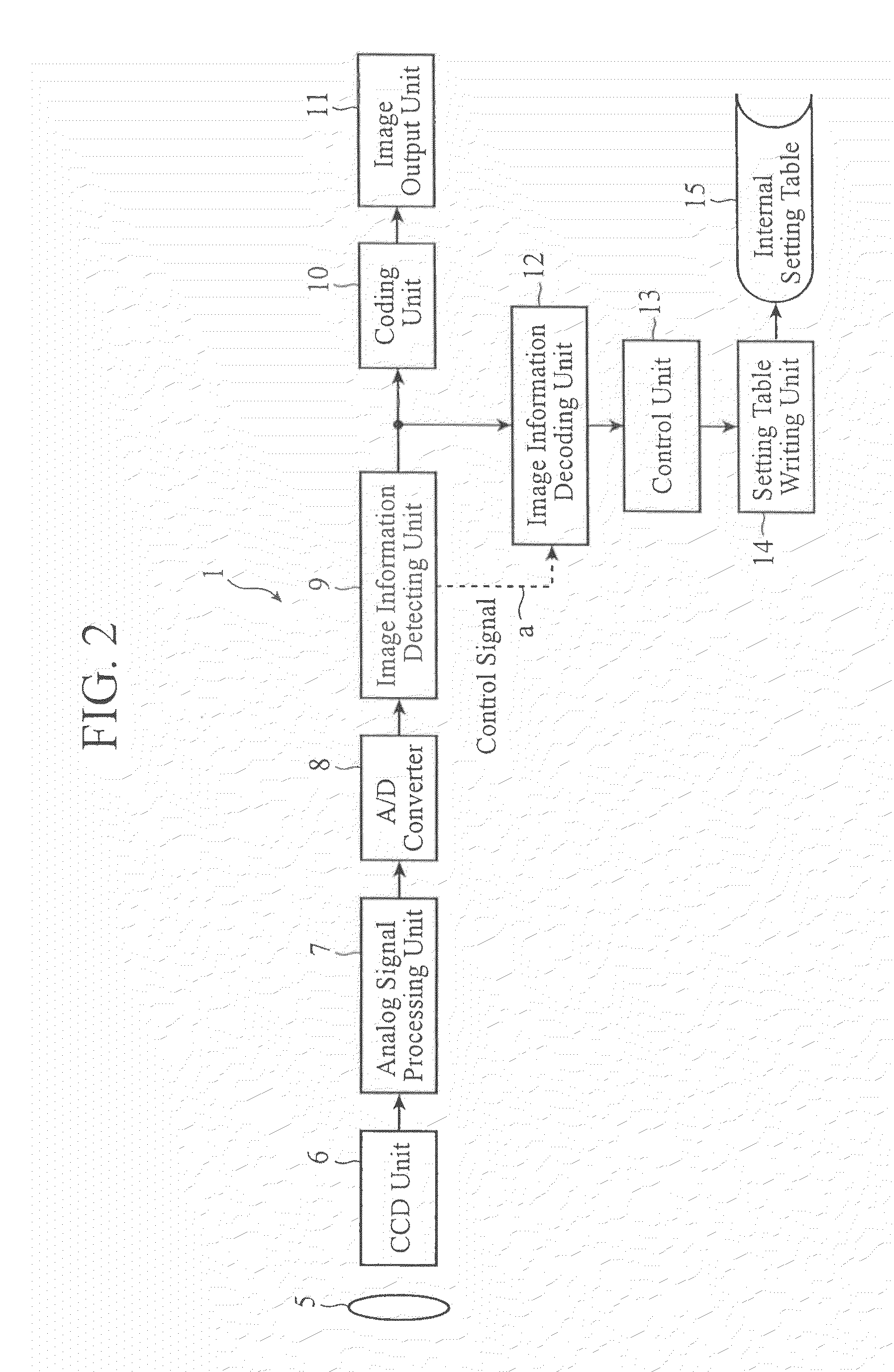
Image reading apparatus and drive control method therefor
InactiveUS20050141048A1Improve ease of useCharacteristicSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSensor arrayElectrical connection
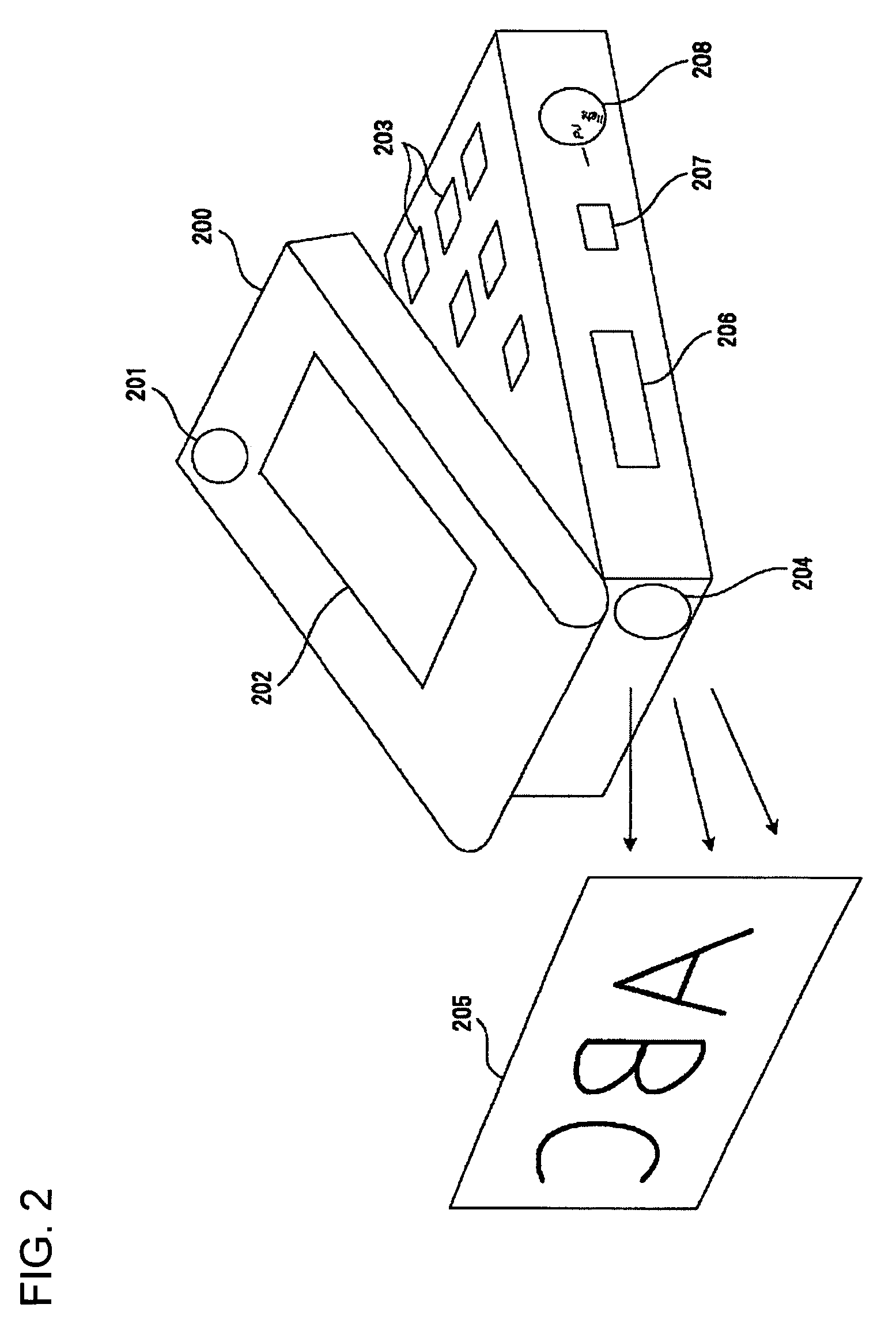
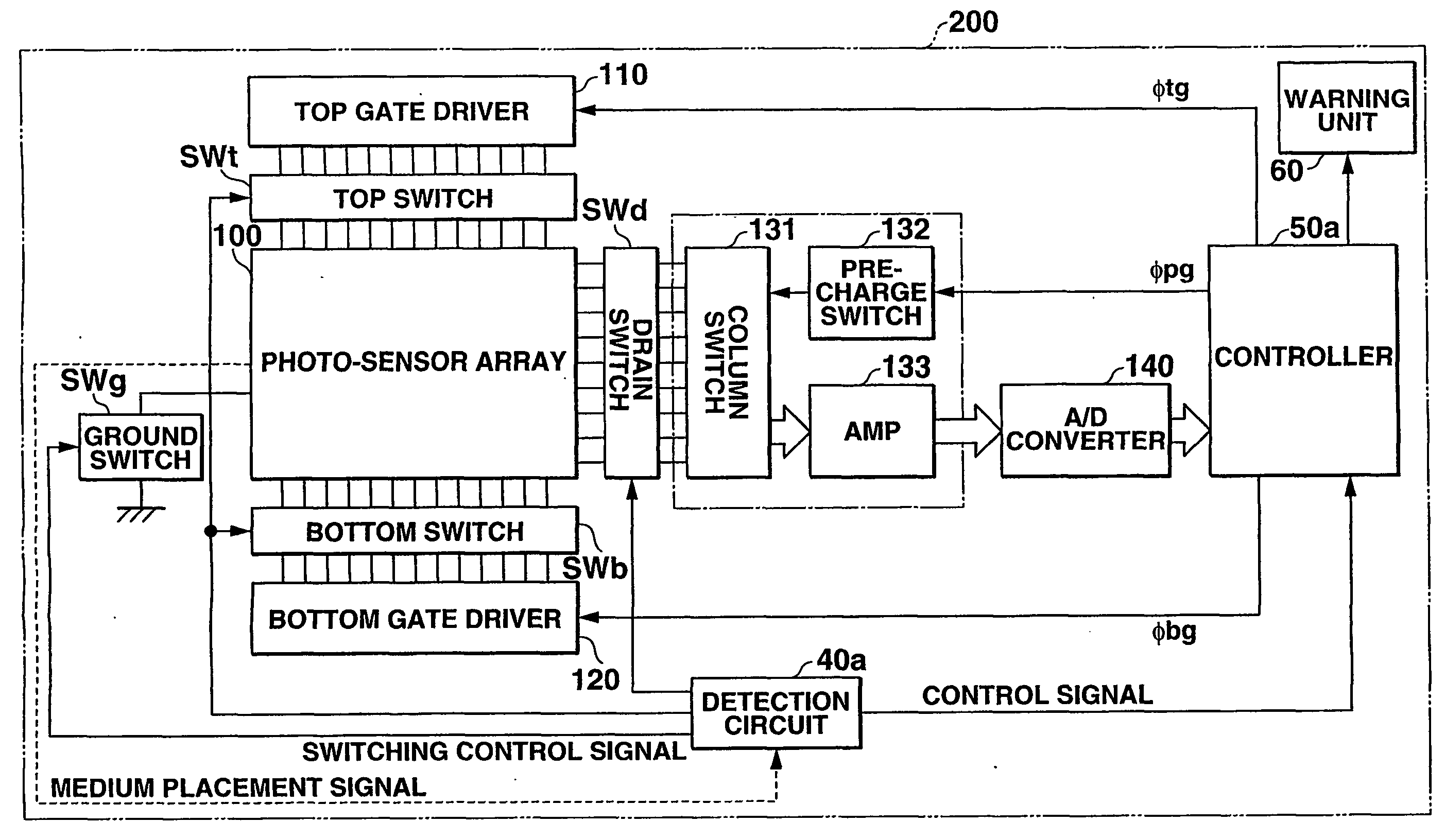
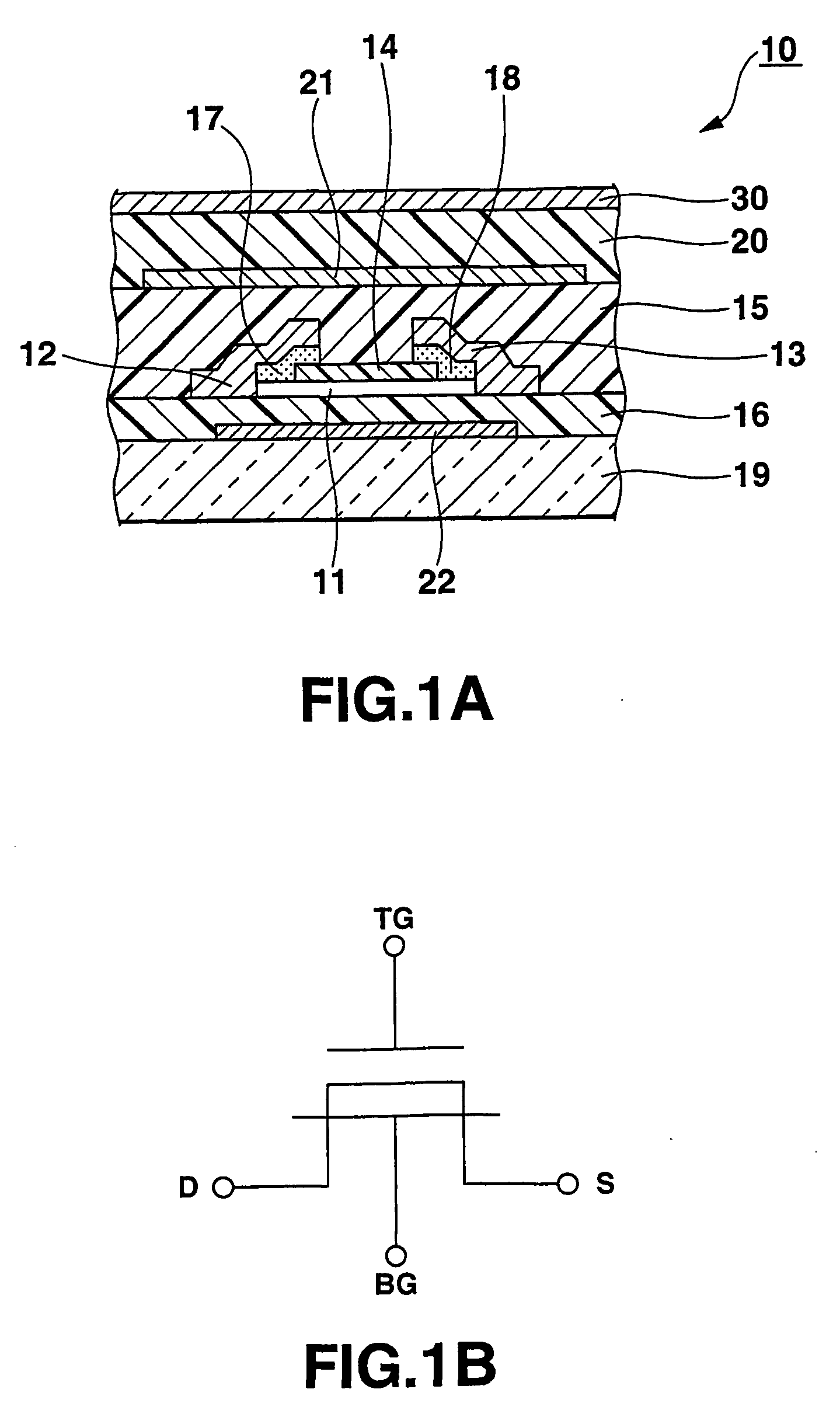
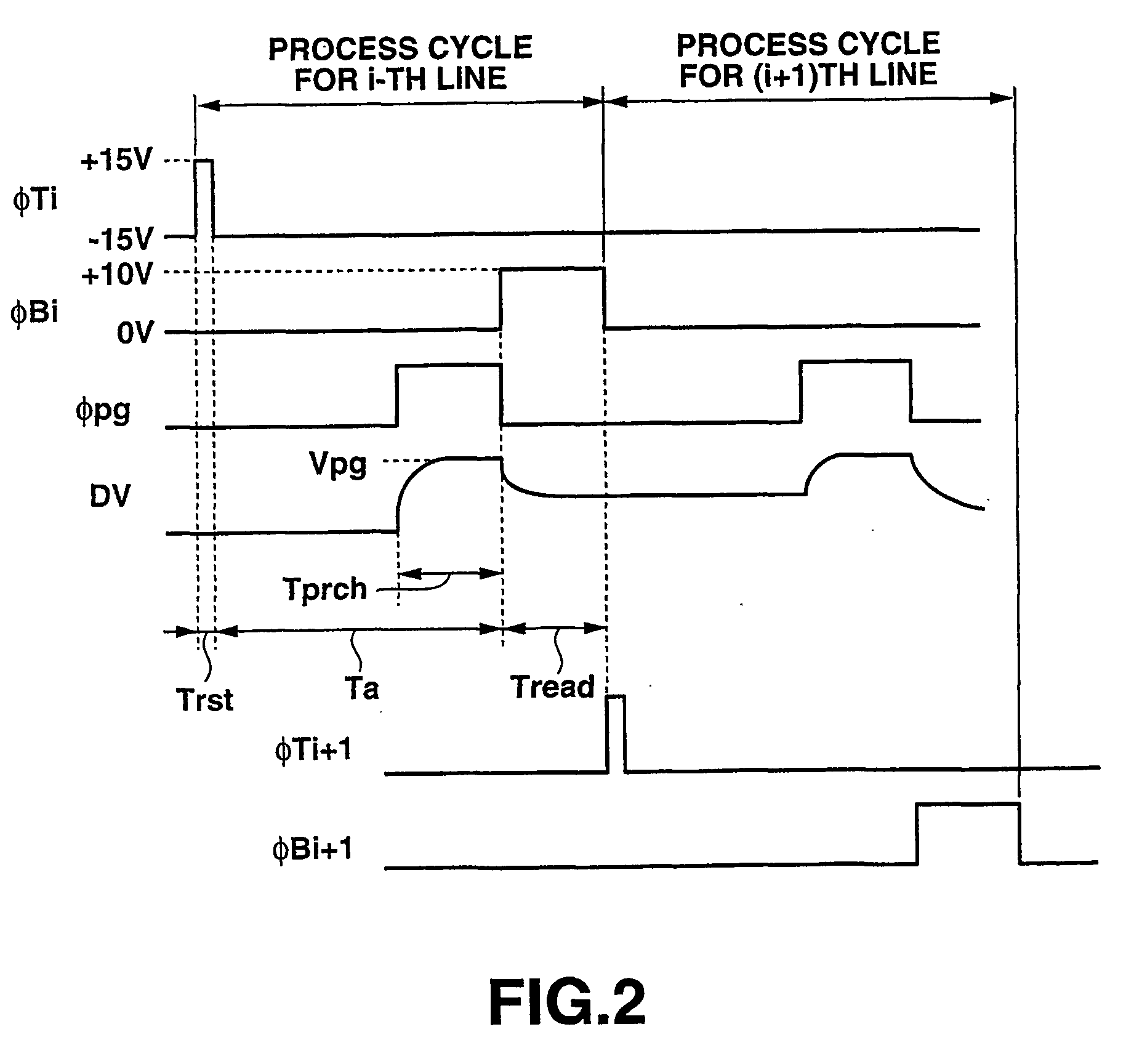
There is provided an image reading apparatus which reads an image pattern of a medium placed on a detection surface of a sensor array (100). In a waiting state, electrical connection between the sensor array (100) and a drive controller (110, 120) is cut off, and whether a medium is placed on the detection surface or not is detected. When a medium is placed on the detection surface, the sensor array (100) and the drive controller (110, 120) are electrically connected and an image reading operation is started. In a case where the medium is separated from the detection surface during the image reading operation, the image reading operation is suspended and the image reading apparatus is set to the waiting state.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Donor sheet, color filter, organic EL element and method for producing them
InactiveUS20050157157A1Excellent ink repellencyReduce manufacturing stepsRecording apparatusInk ribbonsEngineeringSolvent
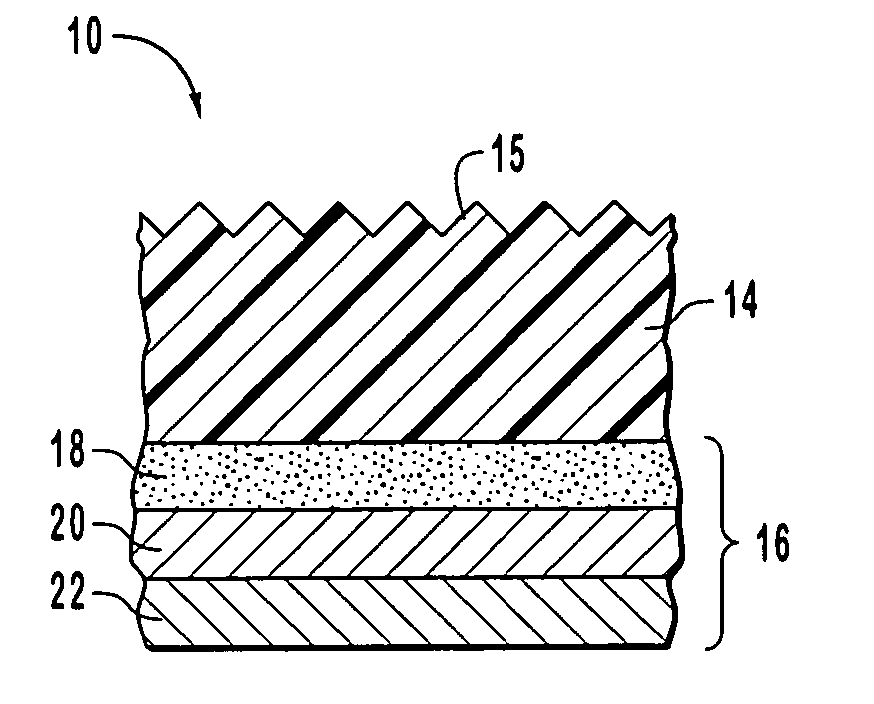
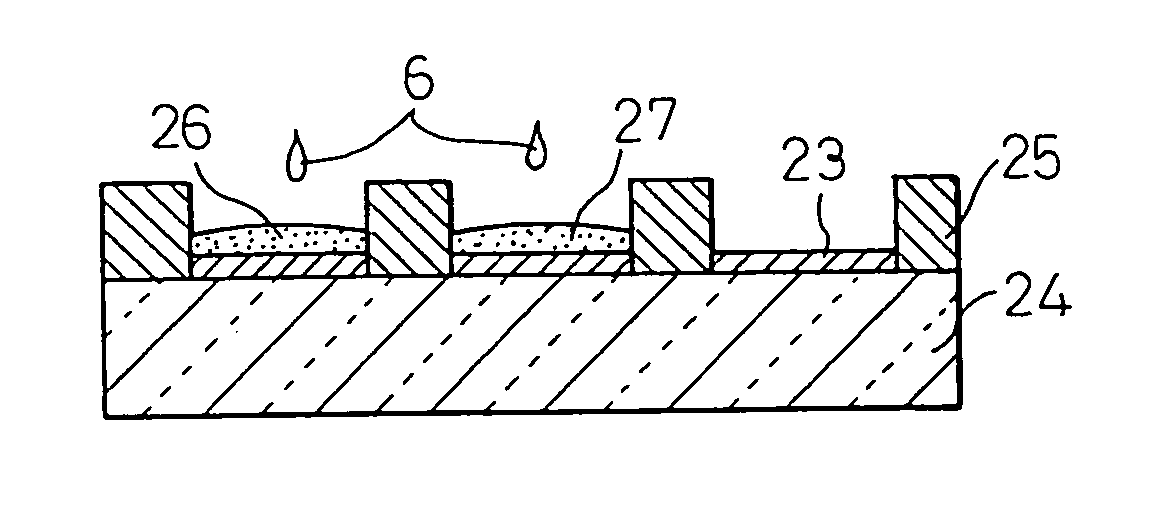
A donor sheet for transferring an image pattern to an image receiving element by a thermal imaging process using laser beam, comprising a base having formed in order on the base a light-to-heat conversion layer, and a transfer layer containing an image component which is melted by heating due to an action of the light-to-heat conversion layer and transferred to the image receiving element in a patterned form, in which the image component of the transfer layer contains an ink-repellent or solvent-repellent compound in an optimized amount. Using the donor sheet, it becomes possible to produce an separation member such as partition pattern and black matrix of a color filter by a shortened manufacturing step with ease and accuracy at high contrast, and can impart excellent ink repellency to the separation member.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO +1
Front end for 3D imaging camera
A three-dimensional imaging system for forming a three dimensional image of an object tooth includes a projection unit capable of generating a projected light pattern and a detector unit capable of detecting an image pattern received from the object tooth. An optical transceiver unit transmits the projected pattern generated by the projection unit to the object tooth and receives the image pattern from the object tooth. The optical transceiver is formed of an integrated body having at least first and second transmitting faces and a reflecting surface that reflects light propagating within the body. In some embodiments, the projected pattern light is polarized in one polarization state and the detected image light is polarized in a second polarization state orthogonal to the first polarization state.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Personal authentication device
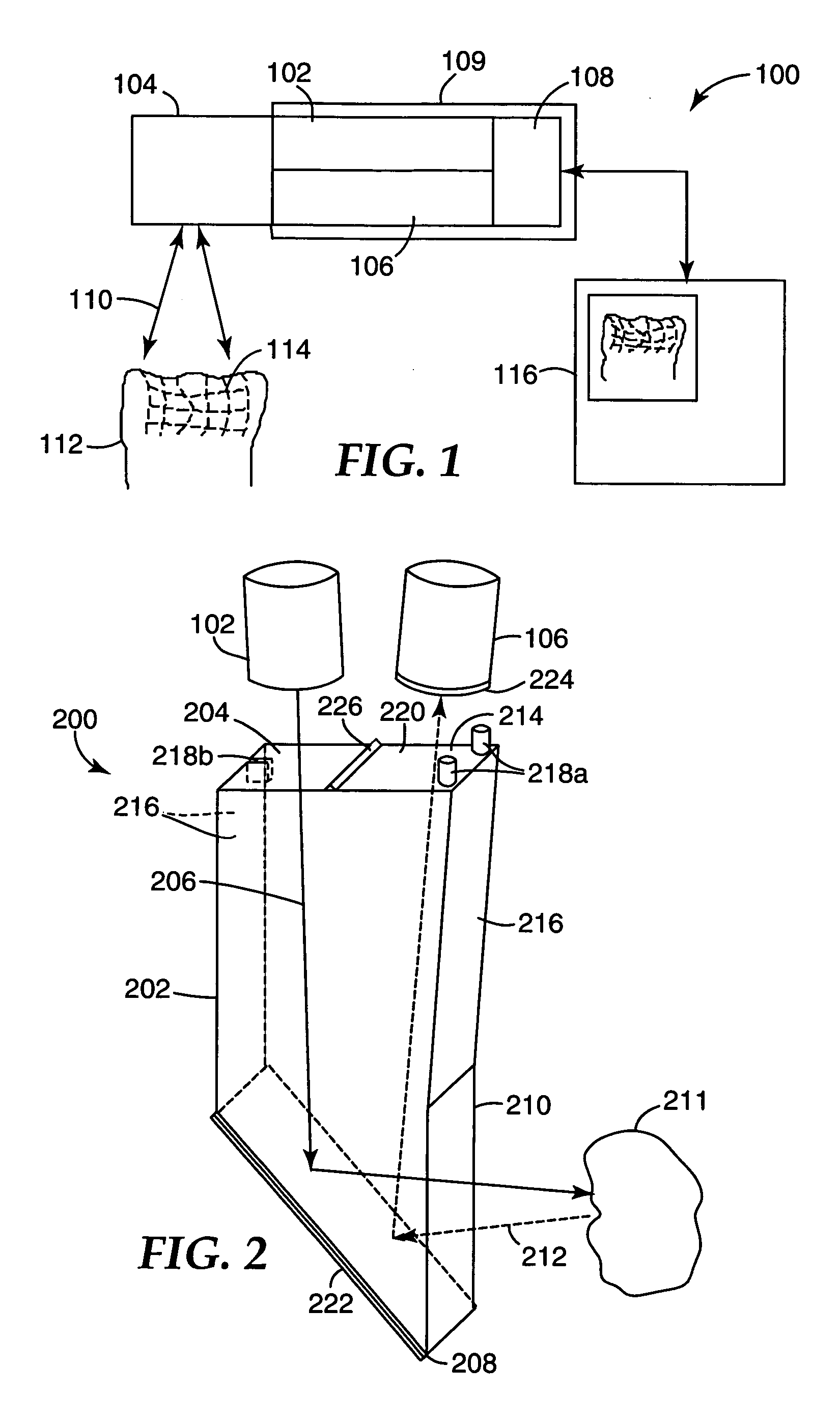
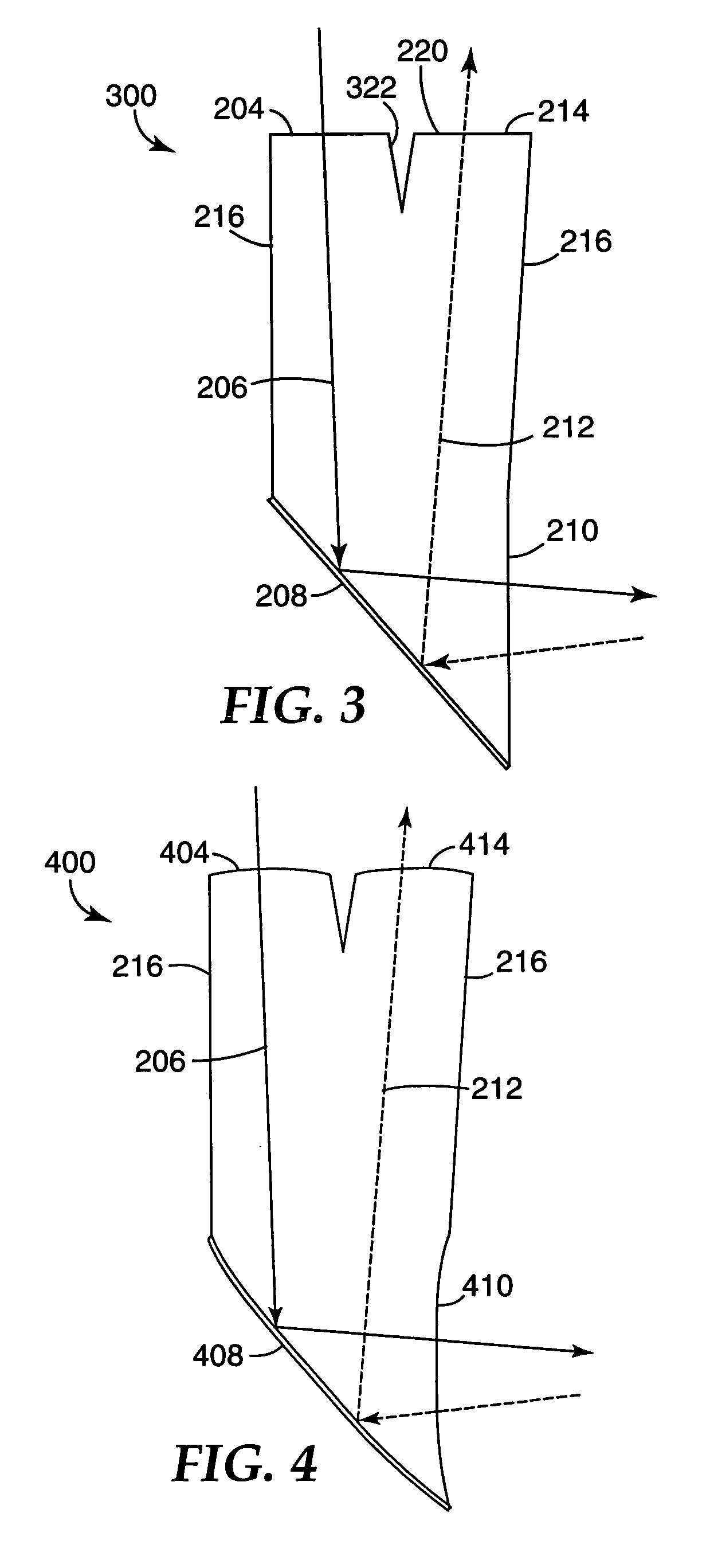
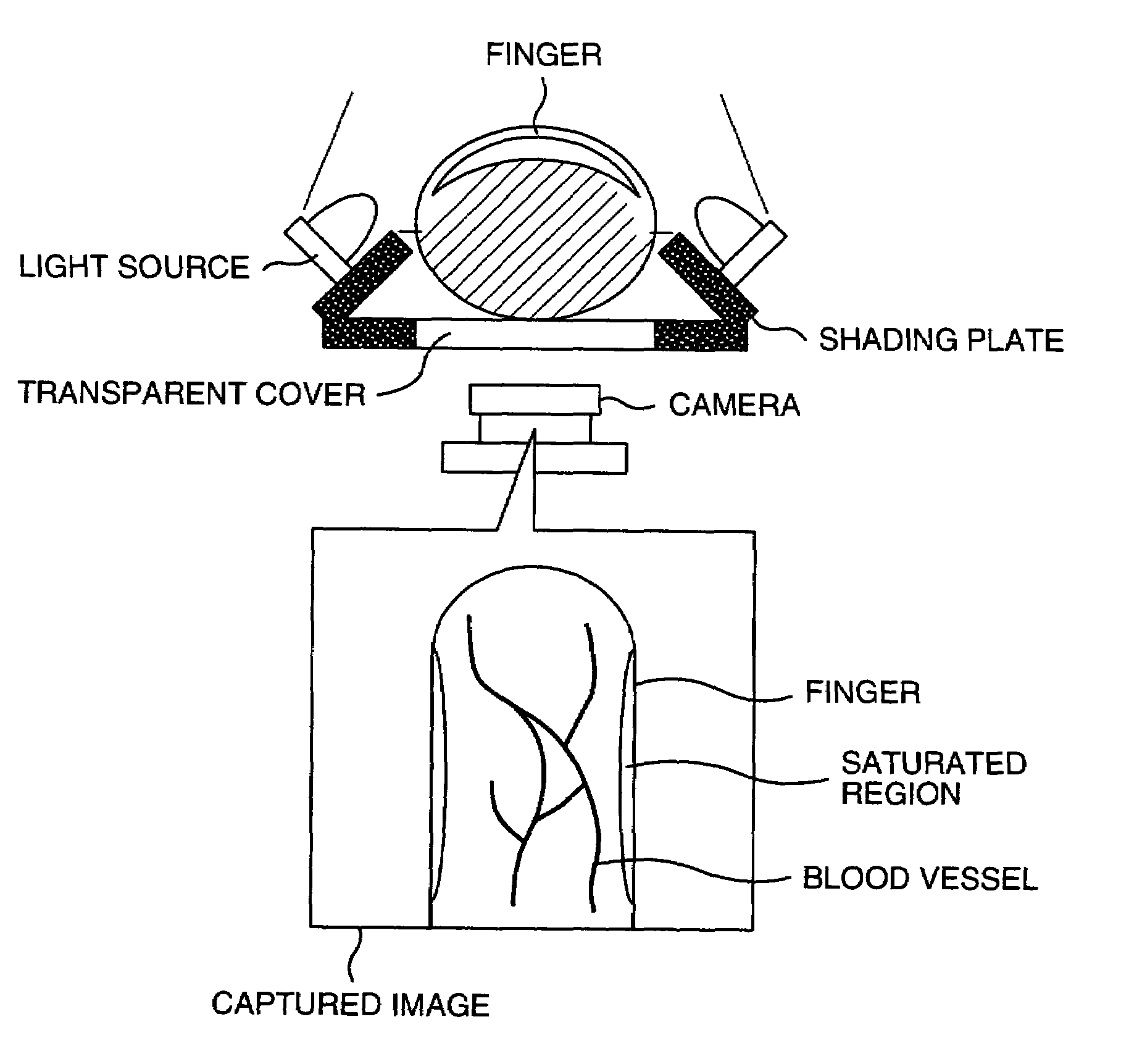
ActiveUS7245745B2Prevent pressureReduce saturated regionPerson identificationImage data processing detailsIrradiationCollation
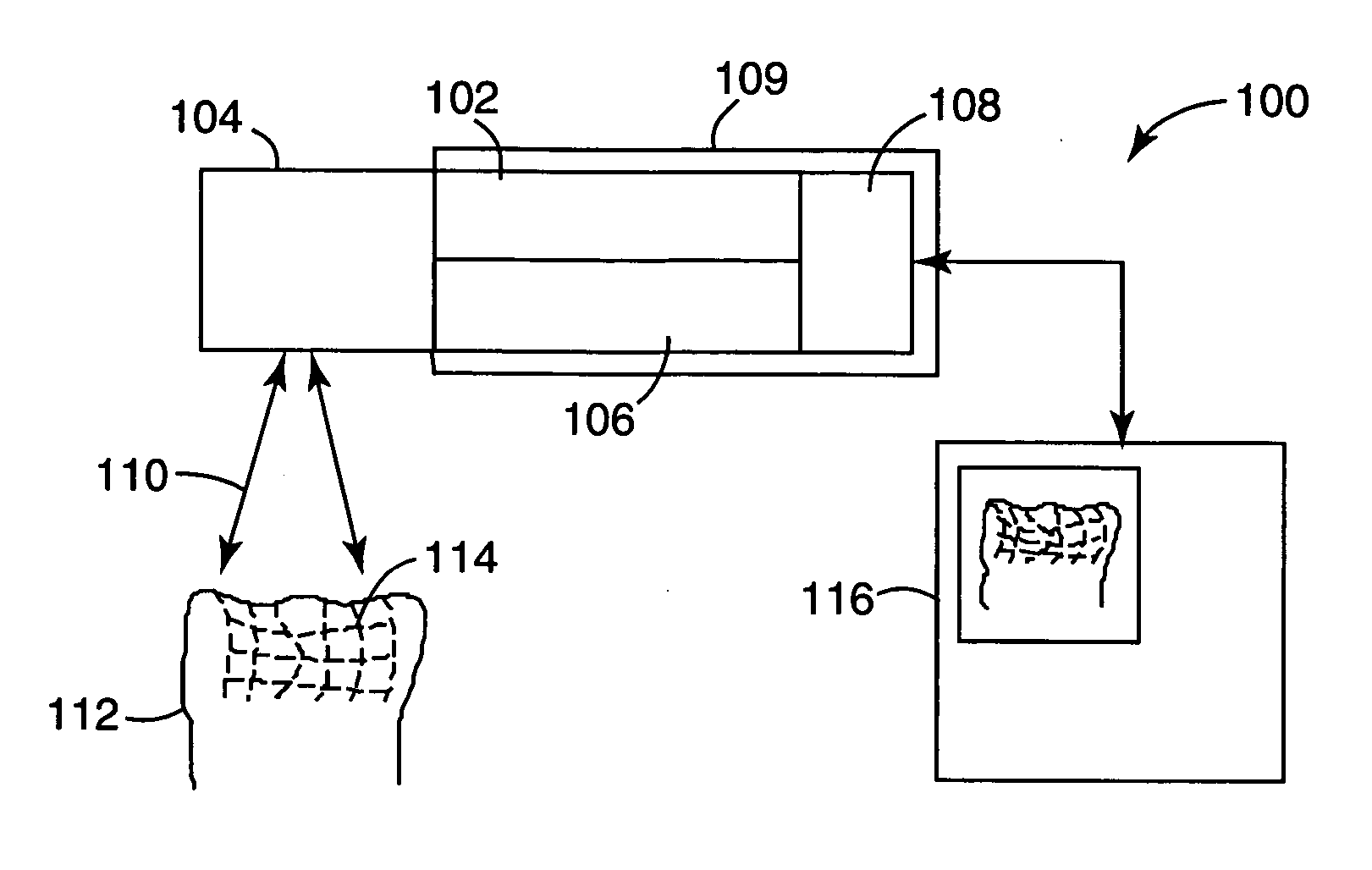
A compact authentication device that prevents user from feeling pressure and is strong against external light, when capturing an image of a finger blood vessel pattern with transmitted light. The device includes a guidance part for determining the finger position, a light source disposed on at least one side of the guidance part to emit light to be transmitted though the finger, an image capture part for capturing the transmitted light, a shading unit for limiting an irradiation region of the light, a finger thickness measuring unit, a unit for controlling a light amount of the light source based on a result of the measurement, a unit for recording registered image patterns of the finger, a unit for collating a captured image pattern from the image capture part with the registered patterns, and a unit for controlling different processing according to the collation result.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
2d/3d switch liquid crystal display panel and 2d/3d selection liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20050285997A1Widen perspectiveReduce distanceSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsCrystallographyLiquid-crystal display
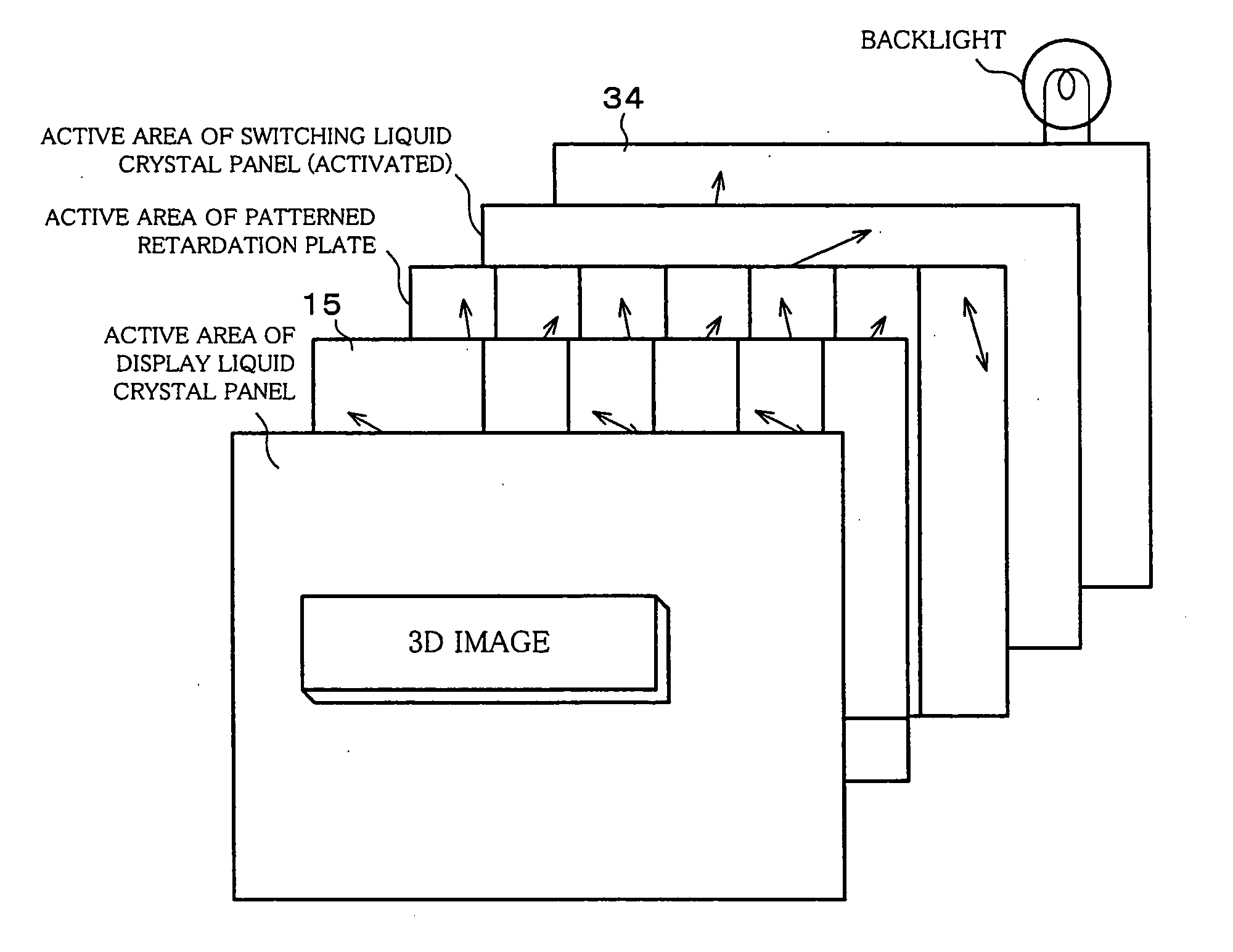
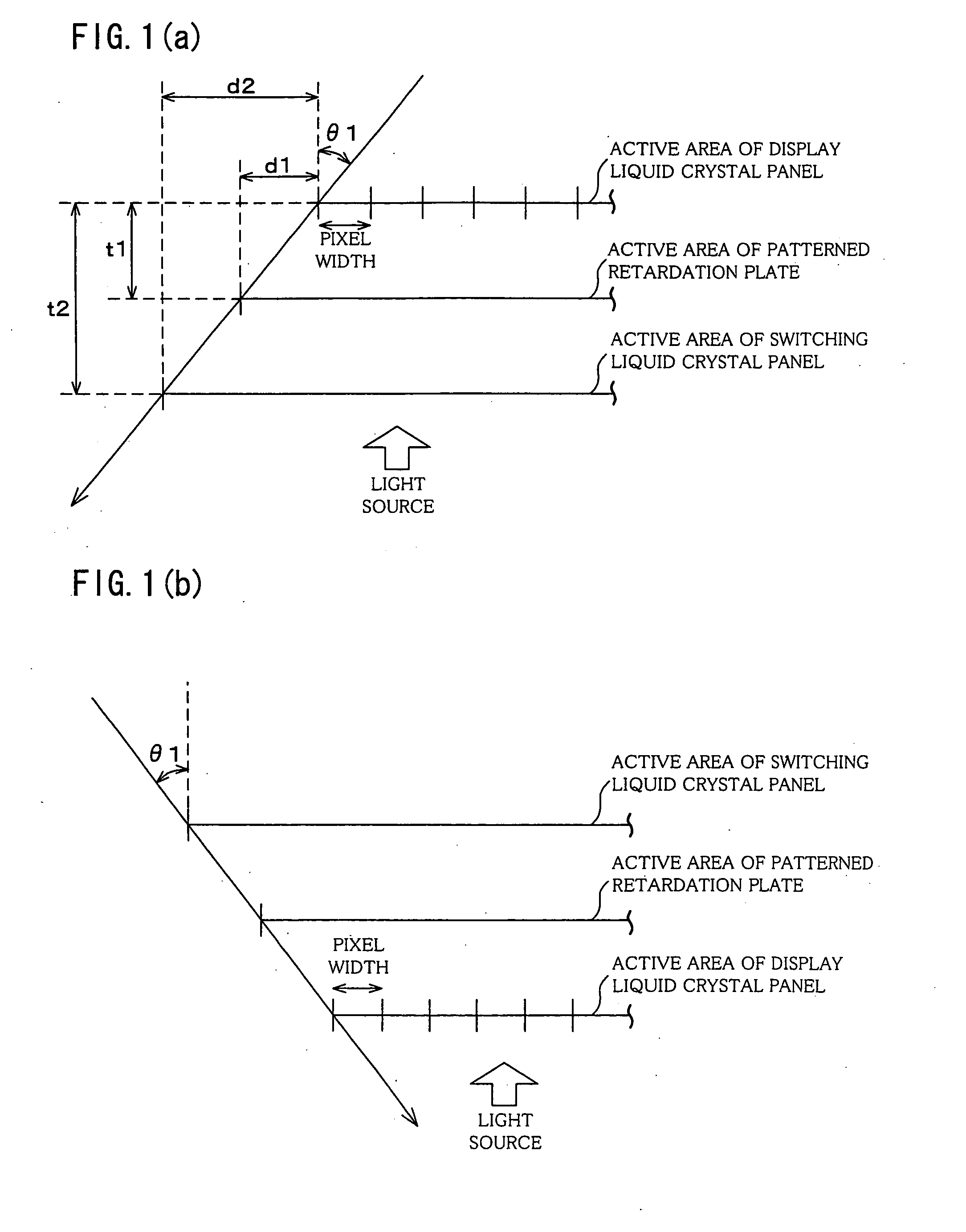
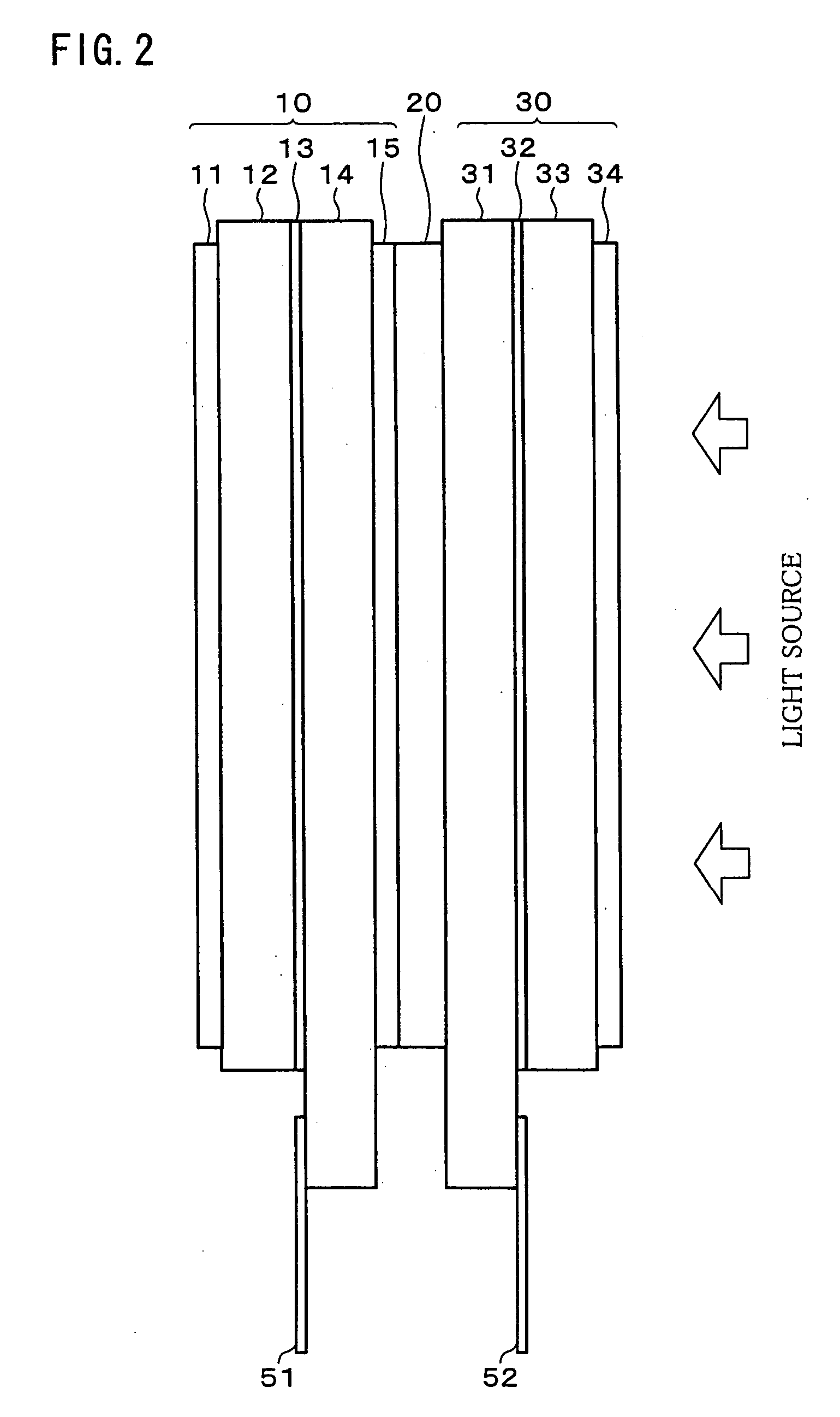
A 2D / 3D switching type liquid crystal display device includes: (i) display liquid crystal panel (10) for generating an image in accordance with input image data; (ii) patterned retardation plate (20) for rendering a certain viewing angle to a display image during 3D display, so as to provide a 3D effect; and (iii) a switching liquid crystal panel (30) for switching 2D display and 3D display by activating and deactivating the effect of the parallax barrier means. The patterned retardation plate (20) and the switching liquid crystal panel (30) respectively have wider active areas than an active area of the display image generating means. With this, the 2D / 3D switching liquid crystal display device allows for a viewing angle in 2D as wide as a viewing angle of 2D-only display.
Owner:SHARP KK
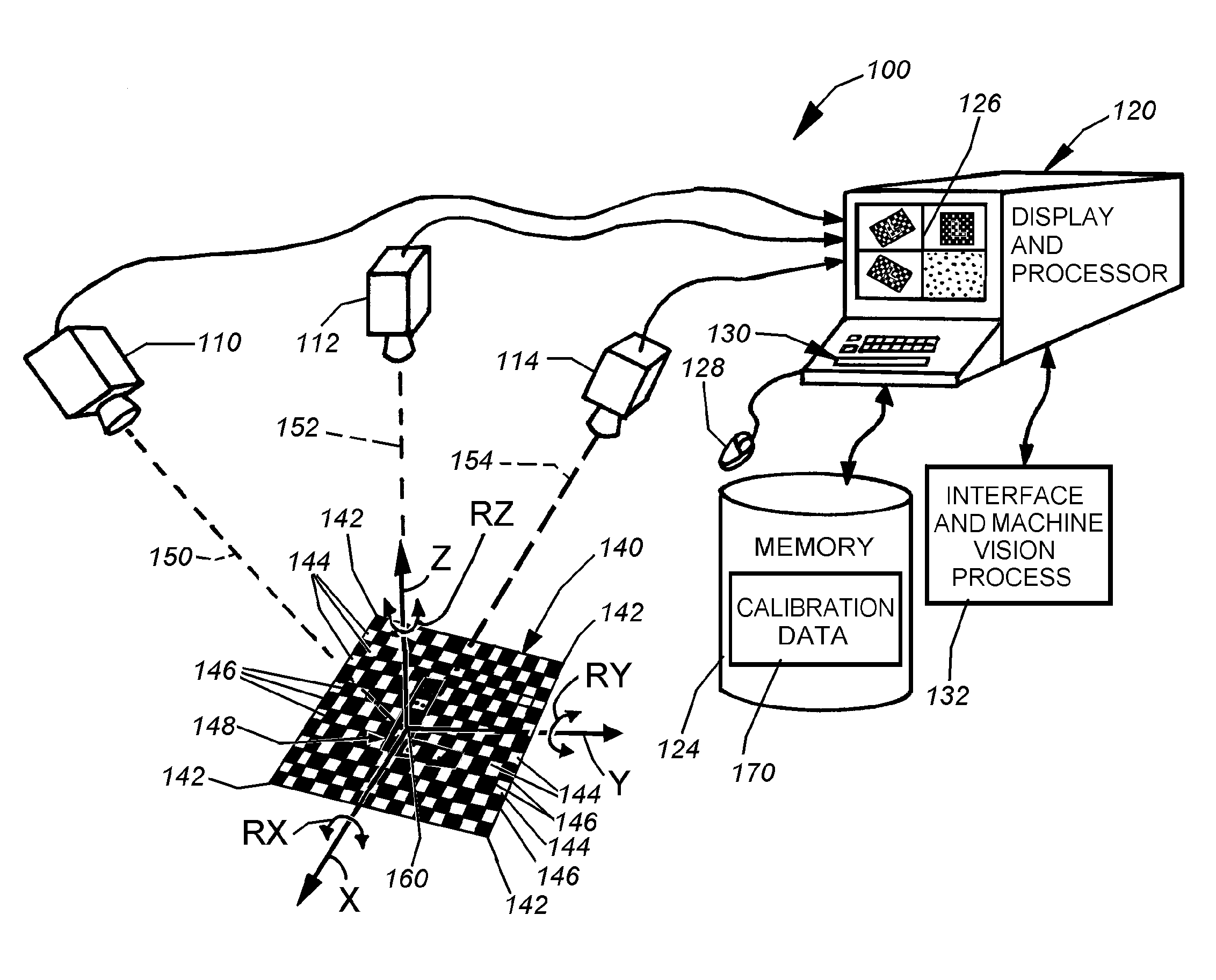
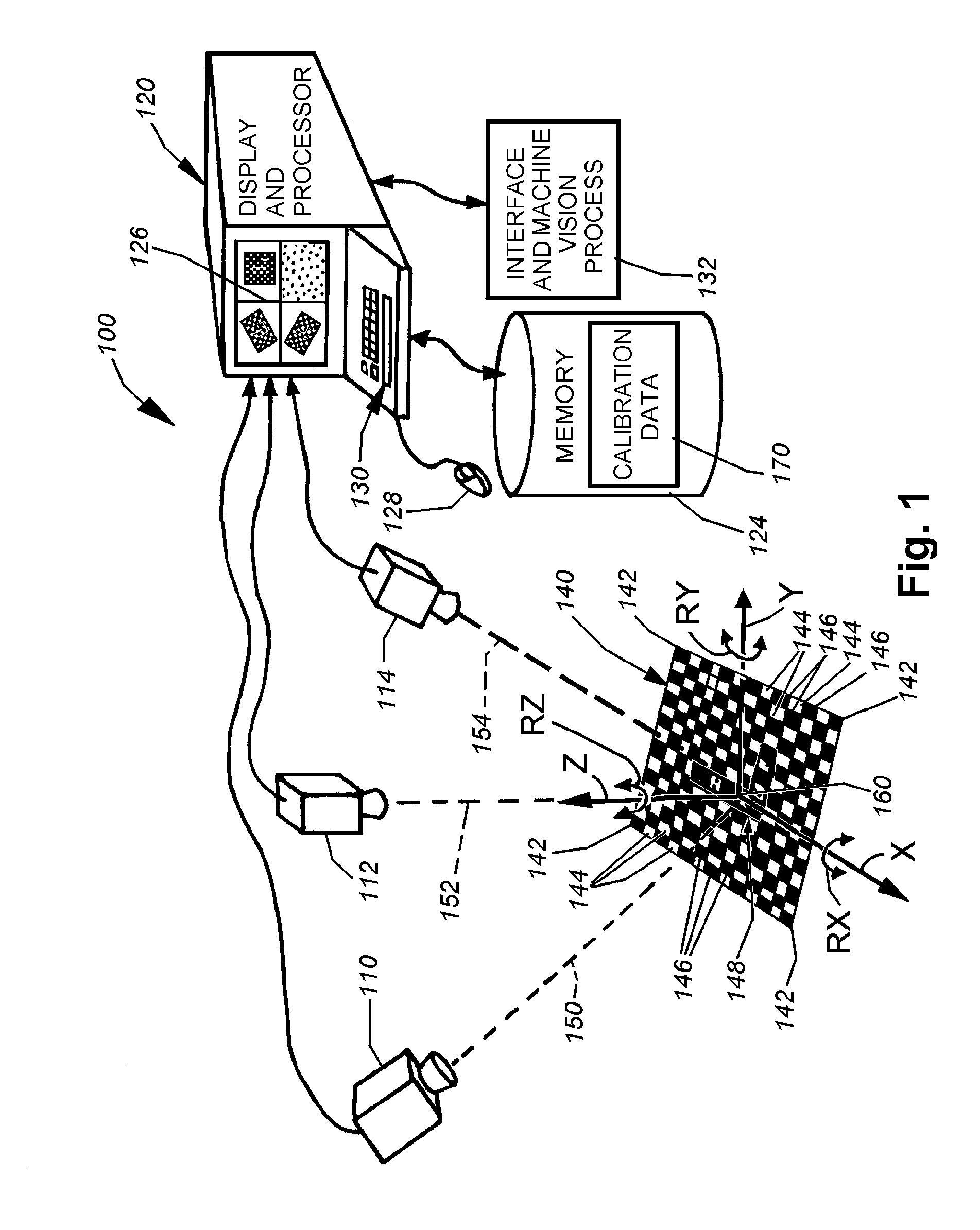
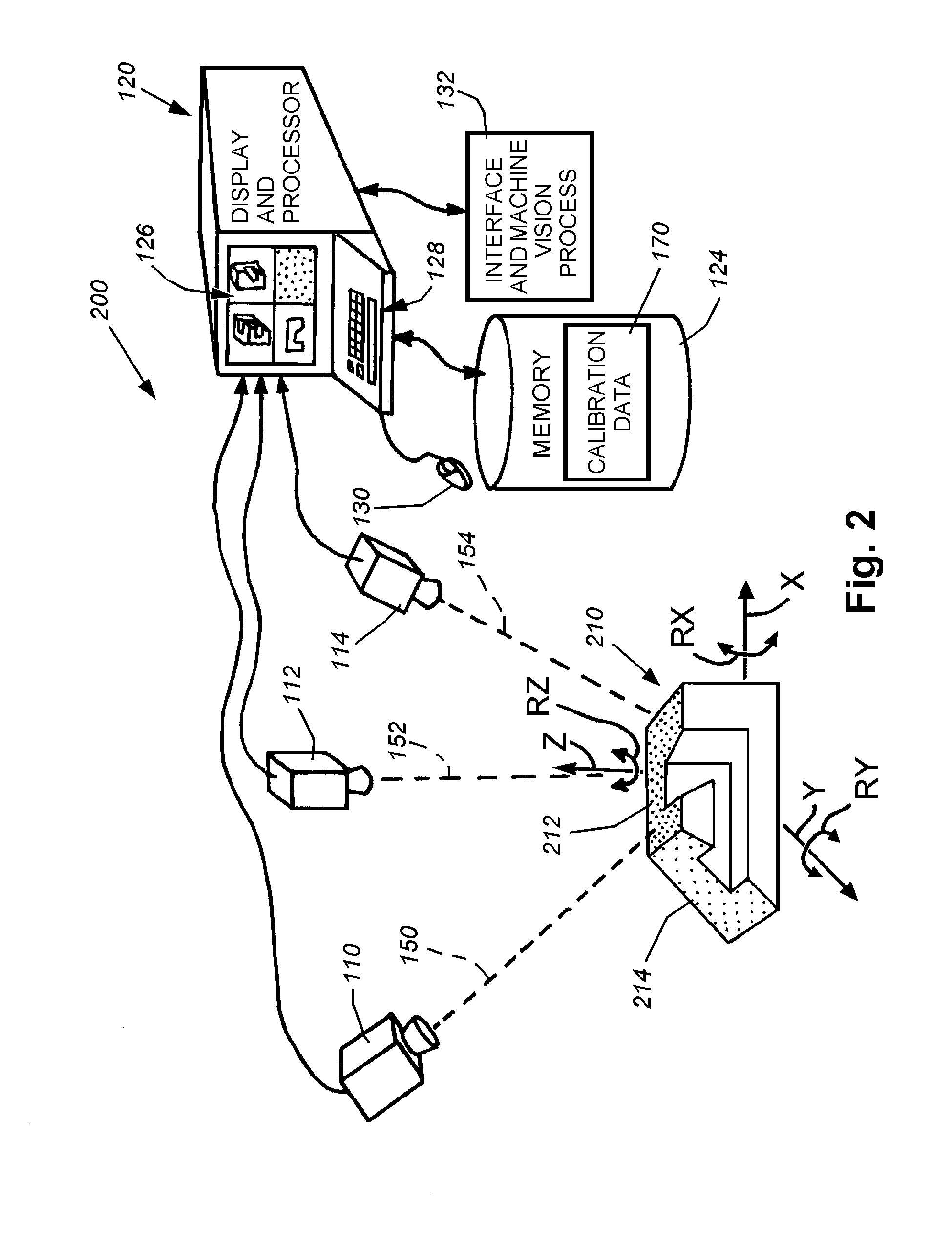
System and method for locating a three-dimensional object using machine vision
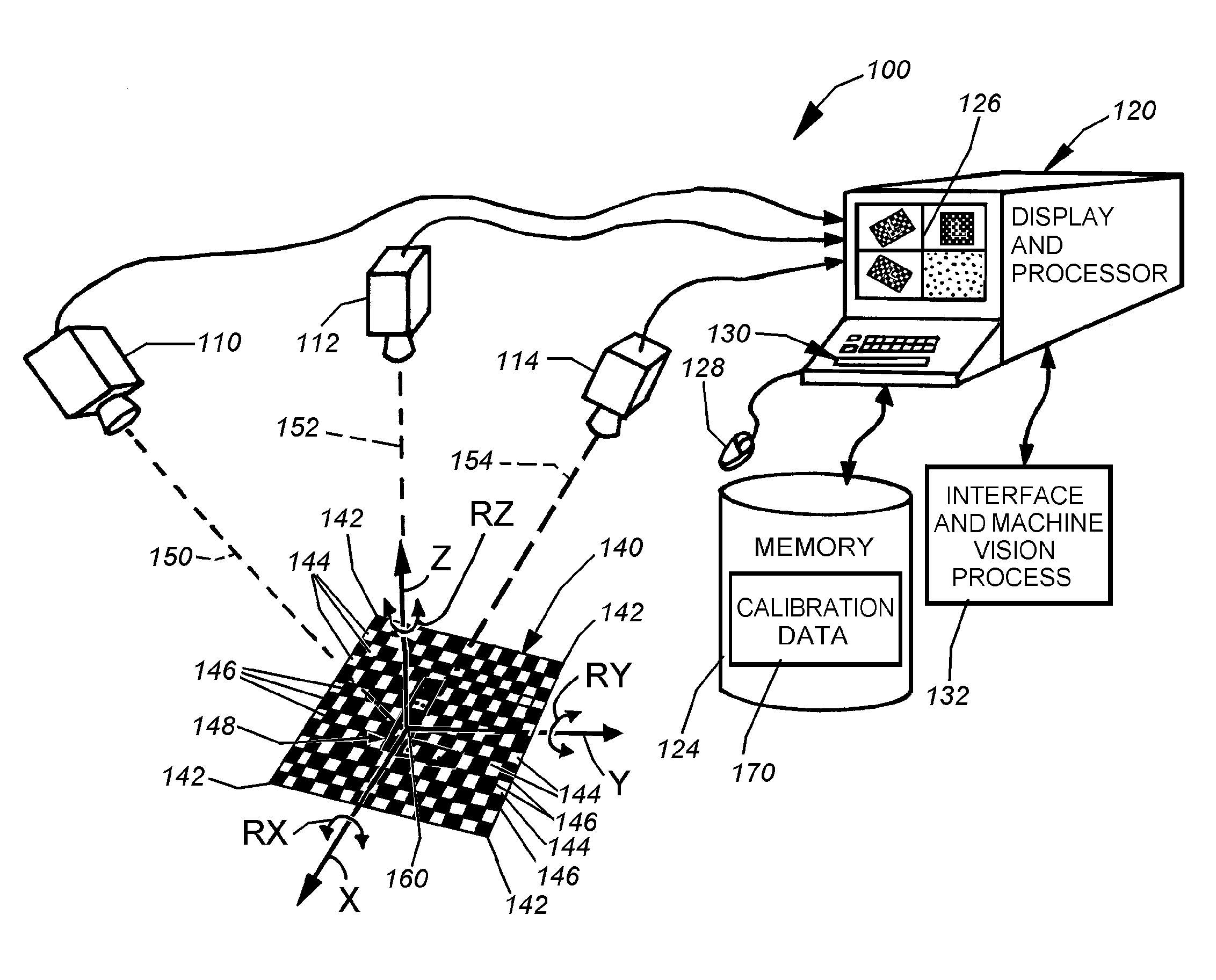
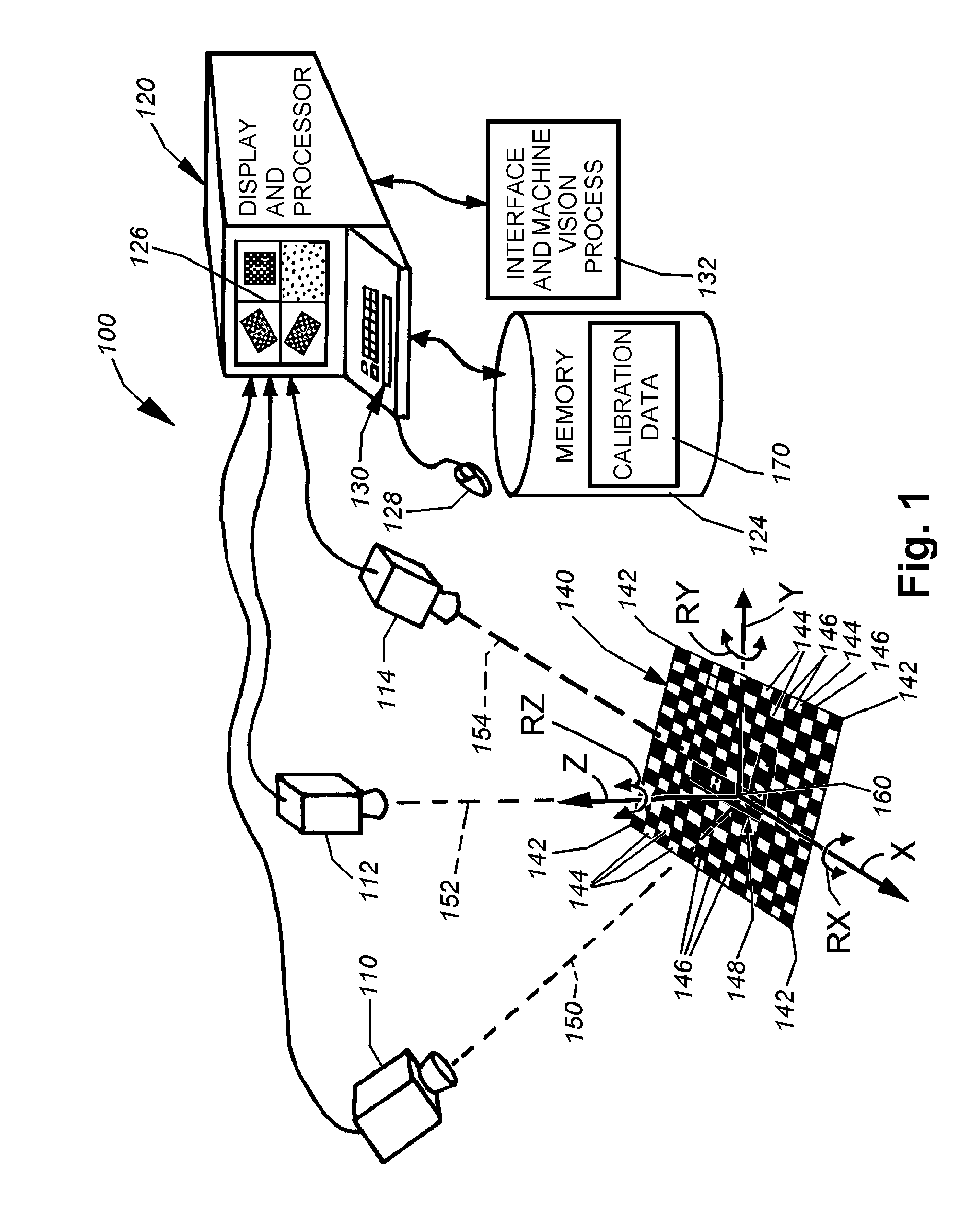
ActiveUS20080298672A1Error minimizationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVision processing
This invention provides a system and method for determining position of a viewed object in three dimensions by employing 2D machine vision processes on each of a plurality of planar faces of the object, and thereby refining the location of the object. First a rough pose estimate of the object is derived. This rough pose estimate can be based upon predetermined pose data, or can be derived by acquiring a plurality of planar face poses of the object (using, for example multiple cameras) and correlating the corners of the trained image pattern, which have known coordinates relative to the origin, to the acquired patterns. Once the rough pose is achieved, this is refined by defining the pose as a quaternion (a, b, c and d) for rotation and a three variables (x, y, z) for translation and employing an iterative weighted, least squares error calculation to minimize the error between the edgelets of trained model image and the acquired runtime edgelets. The overall, refined / optimized pose estimate incorporates data from each of the cameras' acquired images. Thereby, the estimate minimizes the total error between the edgelets of each camera's / view's trained model image and the associated camera's / view's acquired runtime edgelets. A final transformation of trained features relative to the runtime features is derived from the iterative error computation.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer readable storage medium
An image processing apparatus includes a generating unit and a superimposing unit. The generating unit generates an image carrier representing a machine-readable image pattern by using information to be embedded into a first image. The superimposing unit makes a second image translucent, the second image being an image of the image carrier, and superimposes the second image onto the first image in such a manner that the second image can be mechanically read and the first image can be read by a user.
Owner:RICOH KK
Camera device
InactiveUS20100110212A1Easily set setting informationSimple processTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Image pattern
Setting information is converted into a plurality of image patterns (22), and the plurality of image patterns (22) are displayed in time sequence according to a predetermined sequence. A camera device reproduces the setting information from image information (3) which the camera device acquires by capturing the displayed description to set the setting information thereto.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
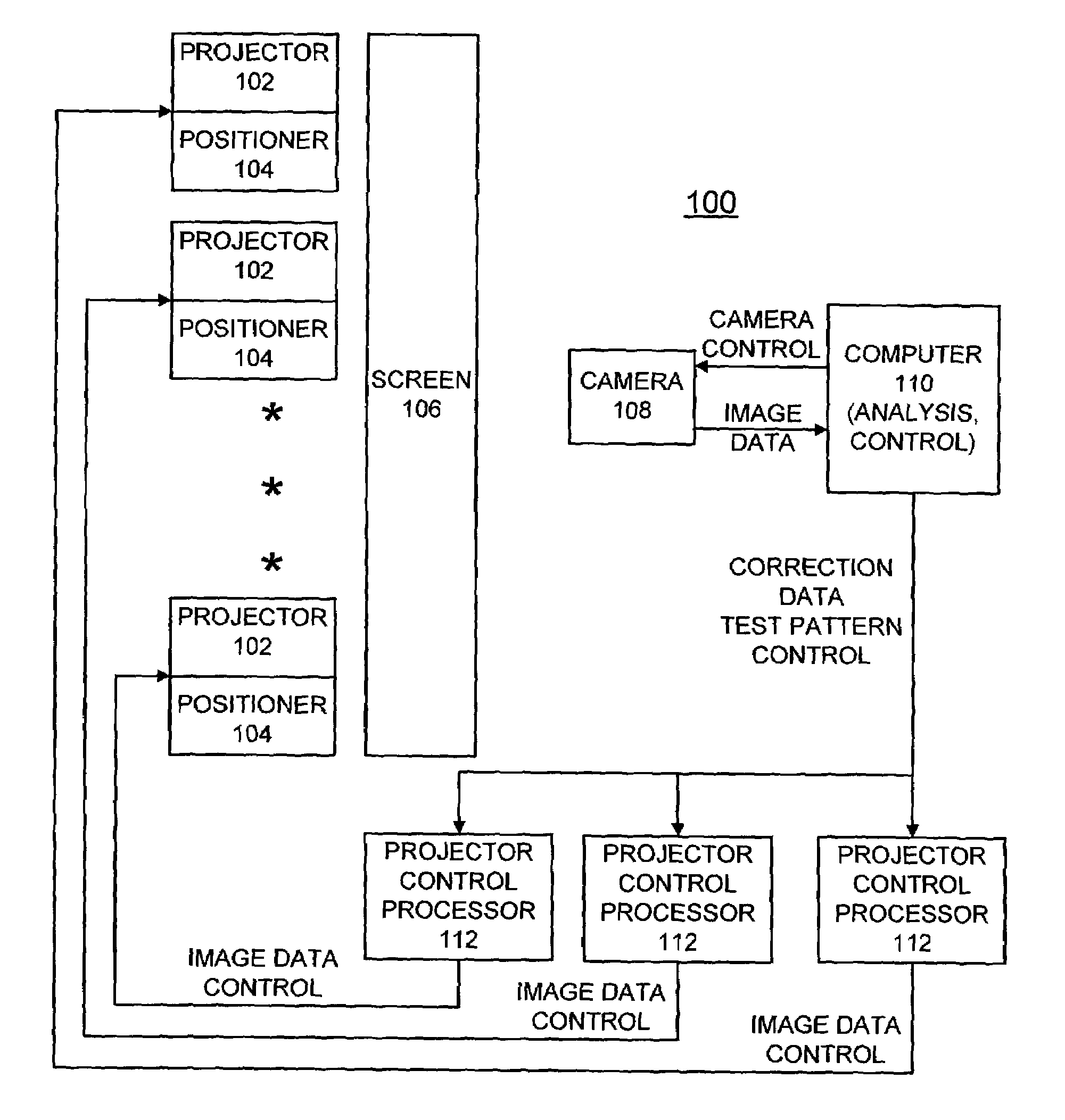
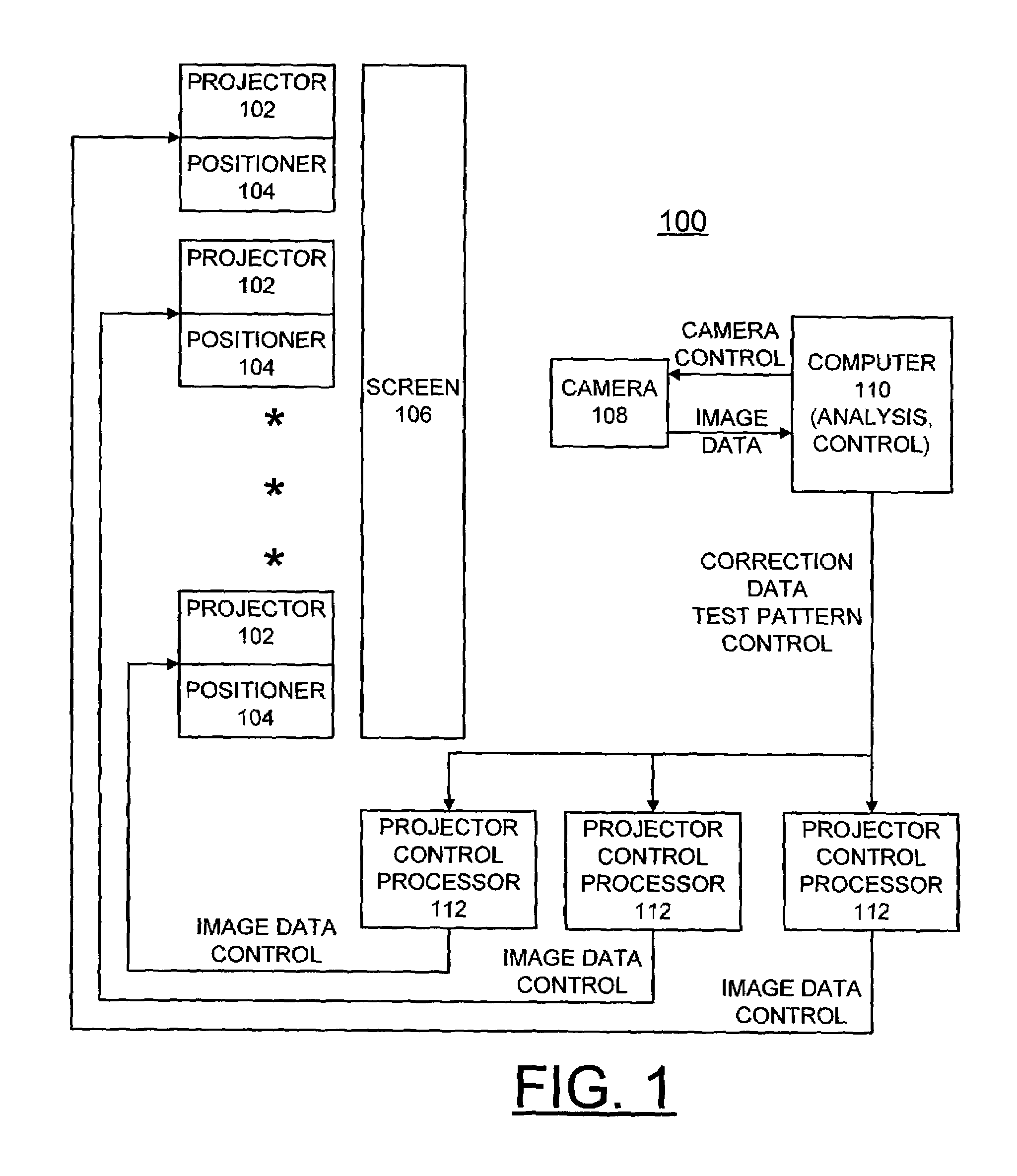
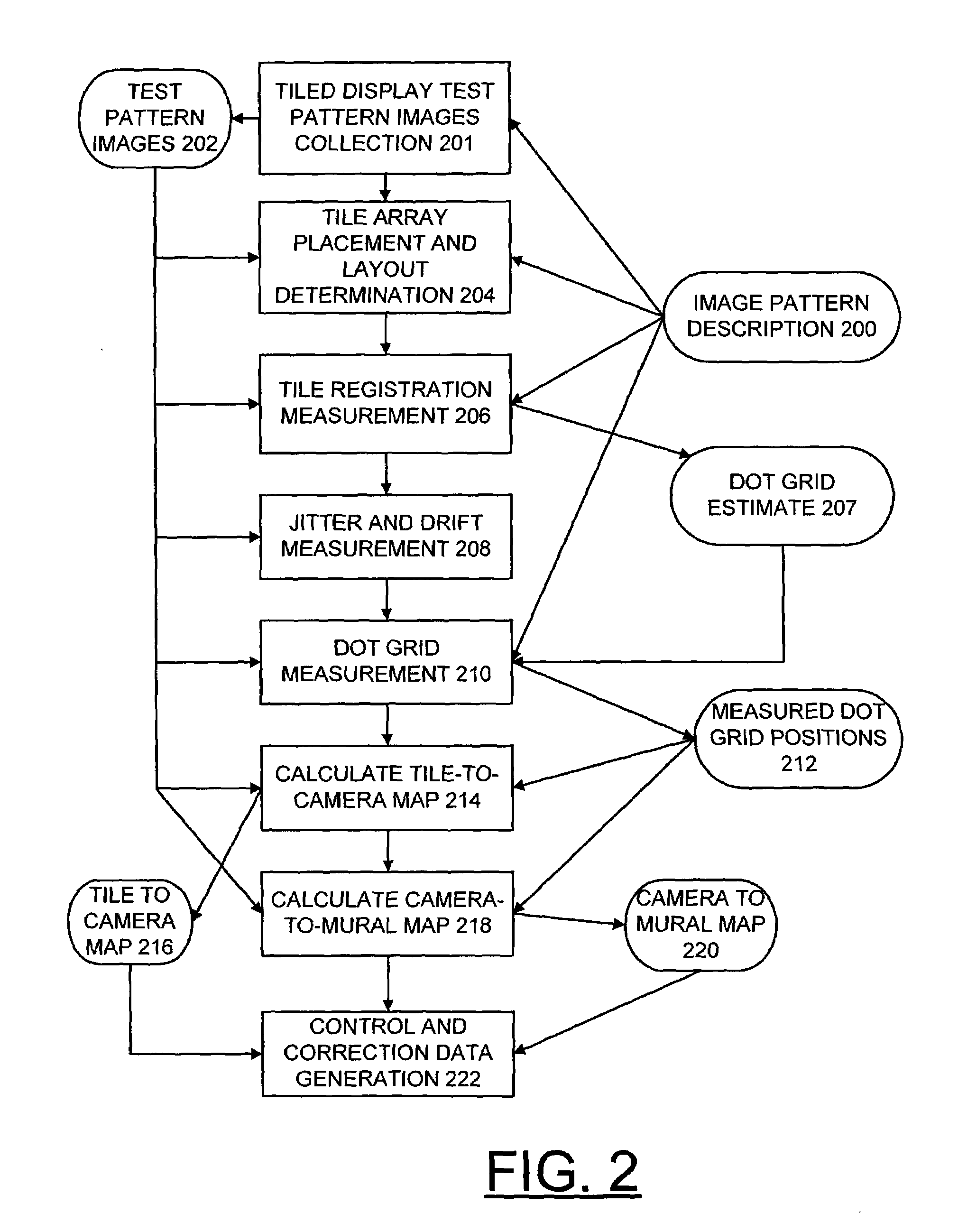
Methods and measurement engine for aligning multi-projector display systems
InactiveUS7019713B2Television system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsMeasurement pointImage pattern
An image pattern description is stored and tiled display test pattern images are captured. The stored image pattern description and at least one captured tiled display test pattern image are used to identify a tile array placement and layout; a tile registration measurement; and a dot grid measurement providing measured dot grid positions. At least one captured tiled display test pattern images and the measured dot grid positions are used for calculating tile-to-camera maps and a camera-to-mural map. The tile-to-camera maps and the camera-to-mural map are used to generate control and correction data.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
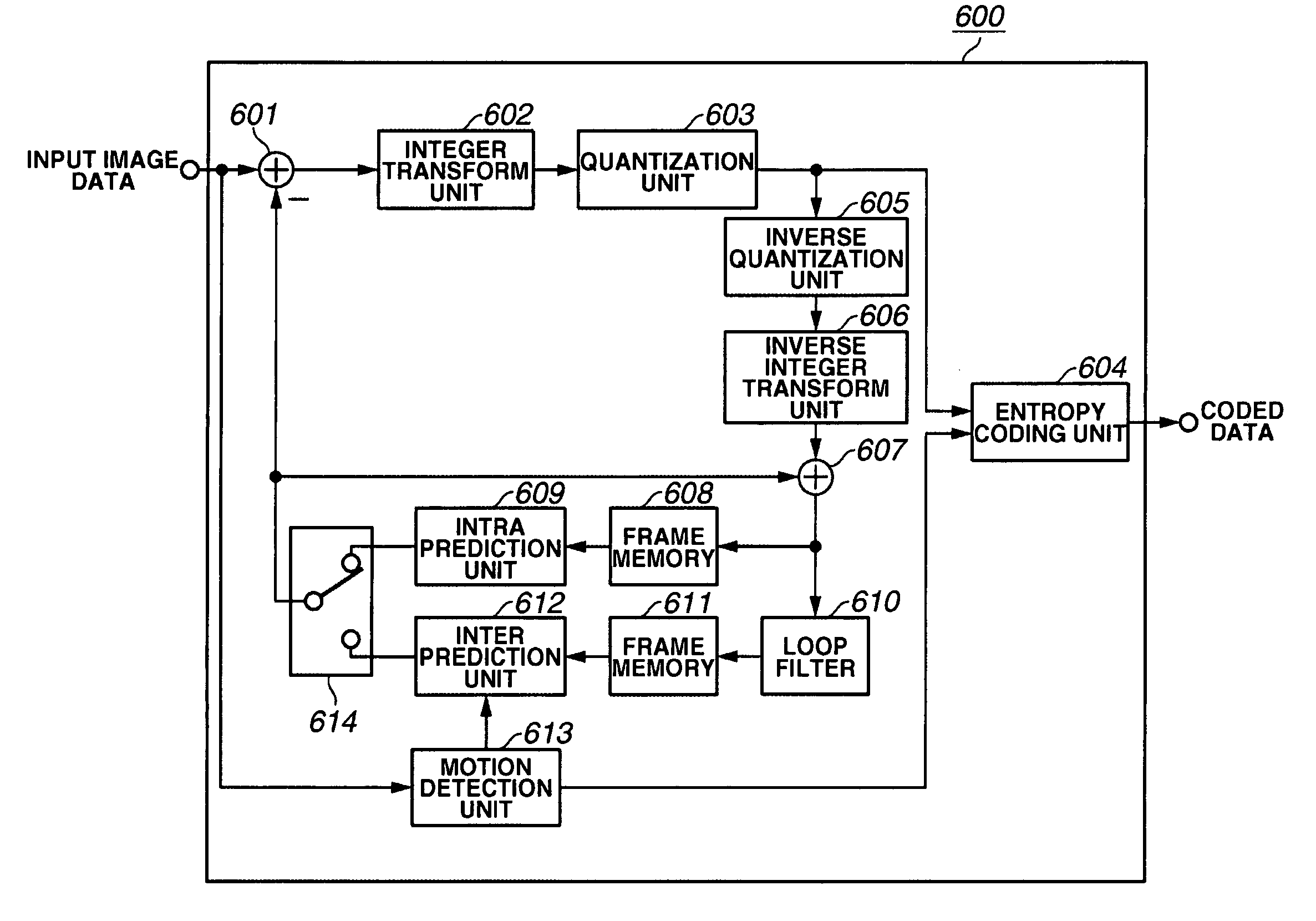
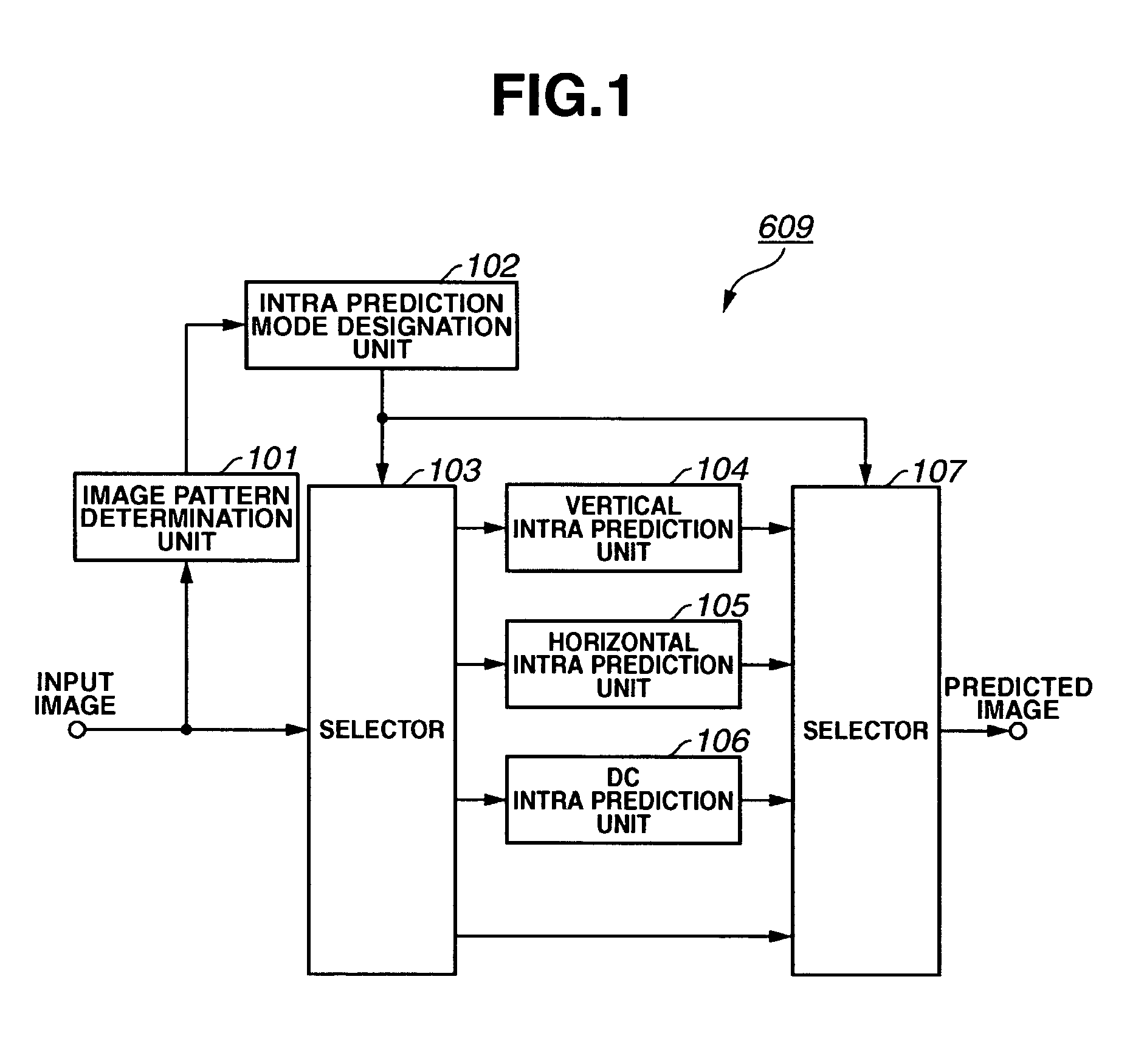
Moving image coding apparatus
ActiveUS20050281337A1Good choiceTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesImage codeImaging data
An image coding apparatus determines an image pattern of image data and, based on the determined image pattern, selects a prediction mode for generating predicted pixel values by predicting pixel values in a frame using pixel values in the same frame. Alternatively, based on photographing information concerning input image data, an image coding apparatus selects a prediction mode for generating predicted pixel values by predicting pixel values in a frame using pixel values in the same frame.
Owner:CANON KK
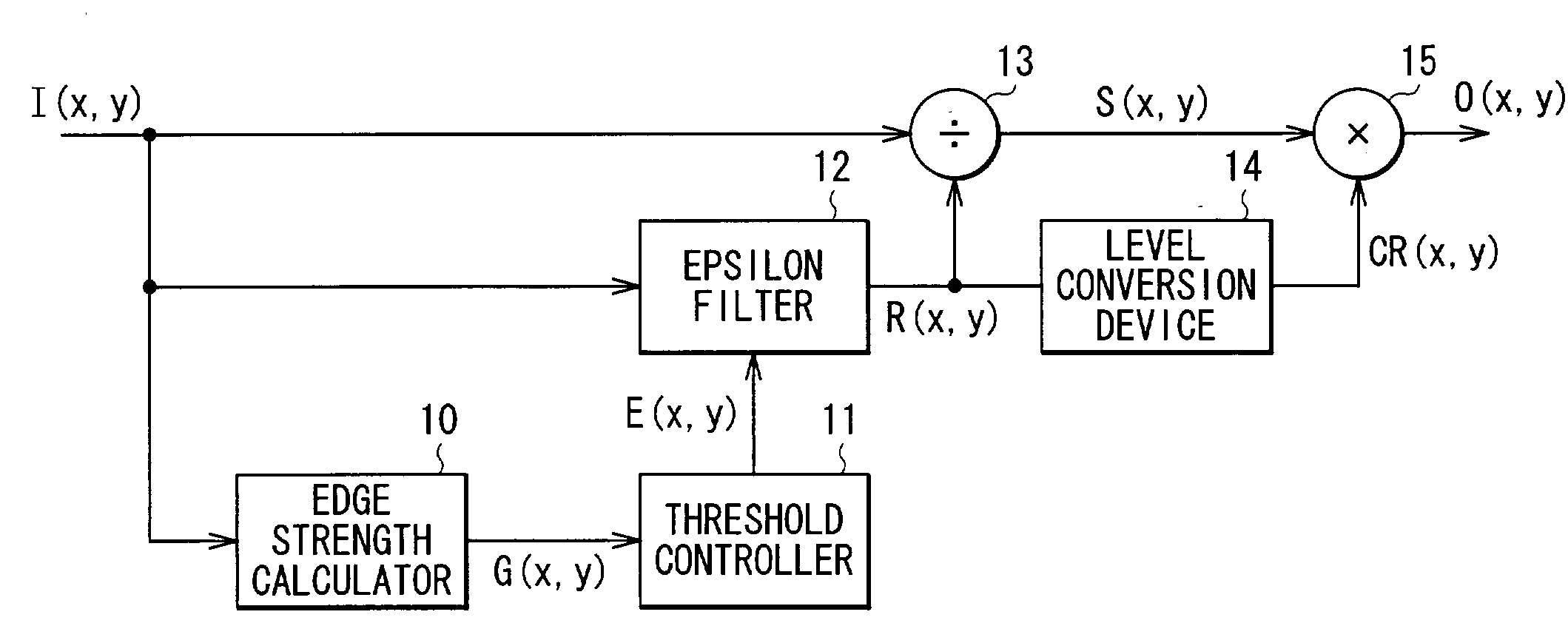
Image processing method and image processing apparatus
ActiveUS7127122B2Reduce the impactAppropriately extractedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingLow-pass filter
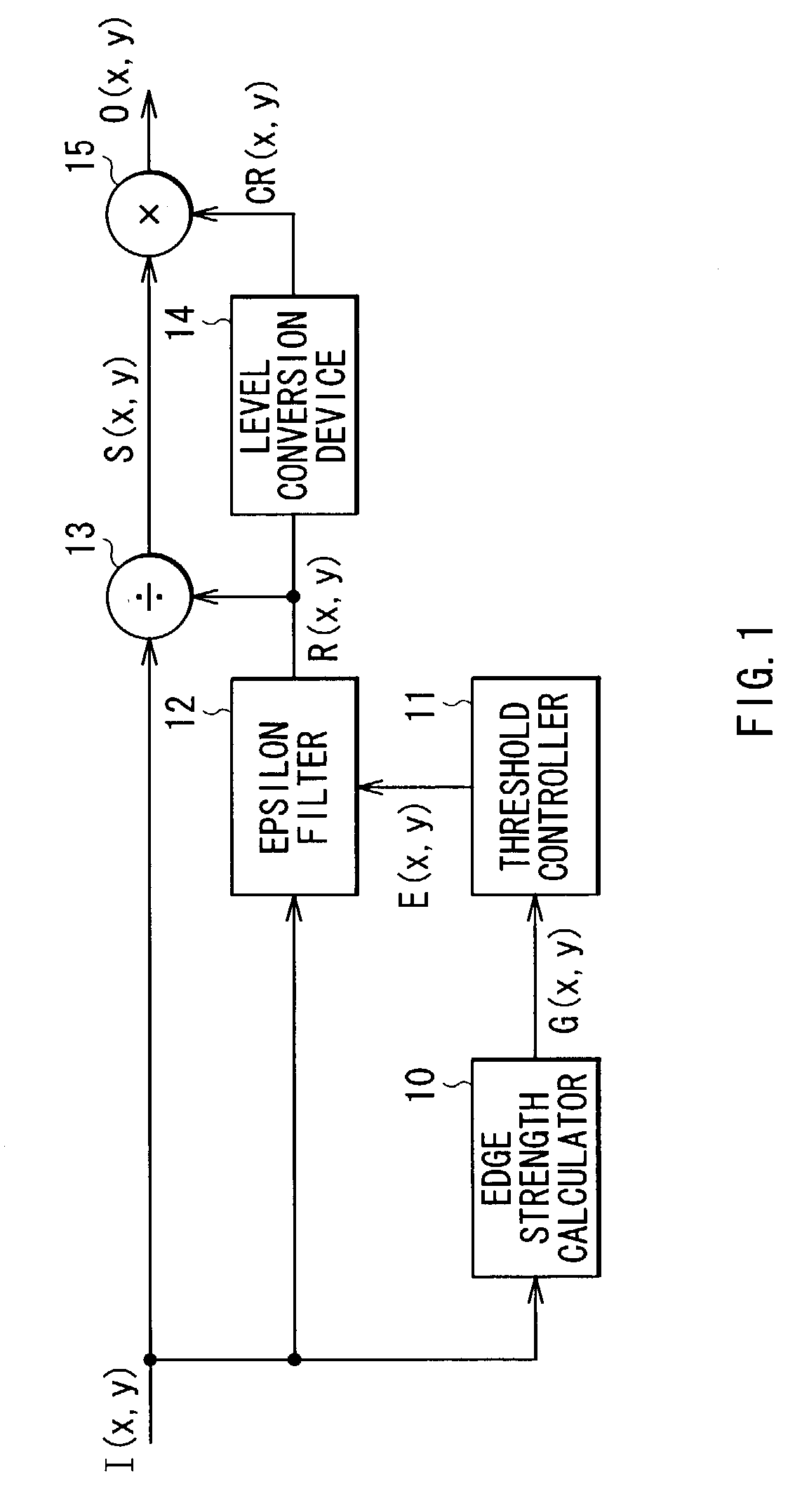
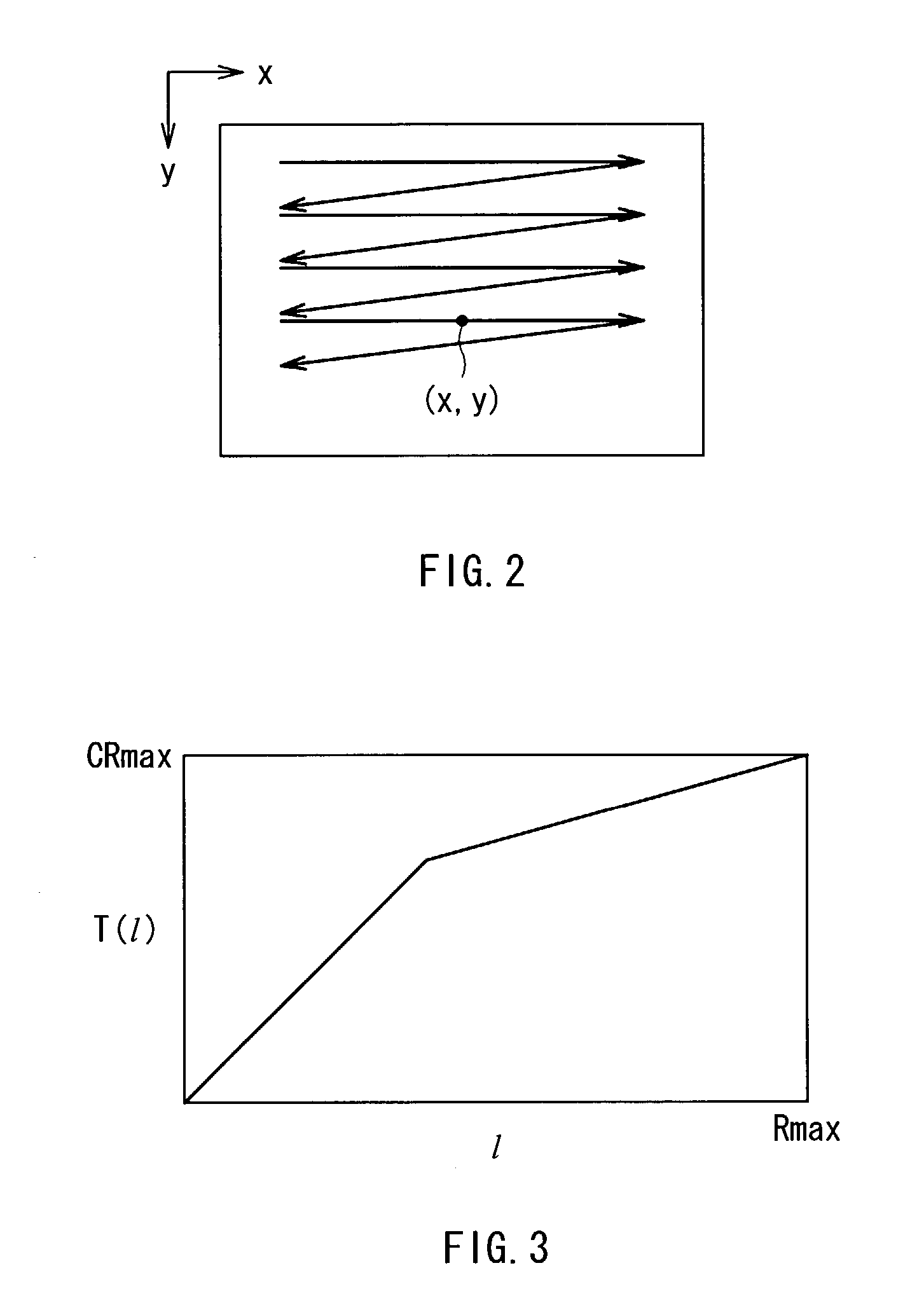
By the use of an epsilon filter, in the case where a plurality of different illuminations exist, a boundary between the illuminations can be appropriately extracted, and an unnatural image pattern can be prevented from being generated, therefore subjectively preferable compression of a dynamic range can be achieved. An edge strength G(x, y) is calculated per position on an input image, and a threshold E(x, y) of an epsilon filter (12) is controlled on the basis of the edge strength G(x, y). The epsilon filter (12) filters the input image on the basis of the controlled threshold E(x, y). On the basis of the edge strength G(x, y), the threshold E of the epsilon filter (12) is adaptively changed according to a local gradient of a pixel value I(x, y), so in the case of using a linear lowpass filter or a fixed threshold epsilon filter, an illumination boundary can be more accurately extracted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Velocity detecting device and multi-color image forming apparatus
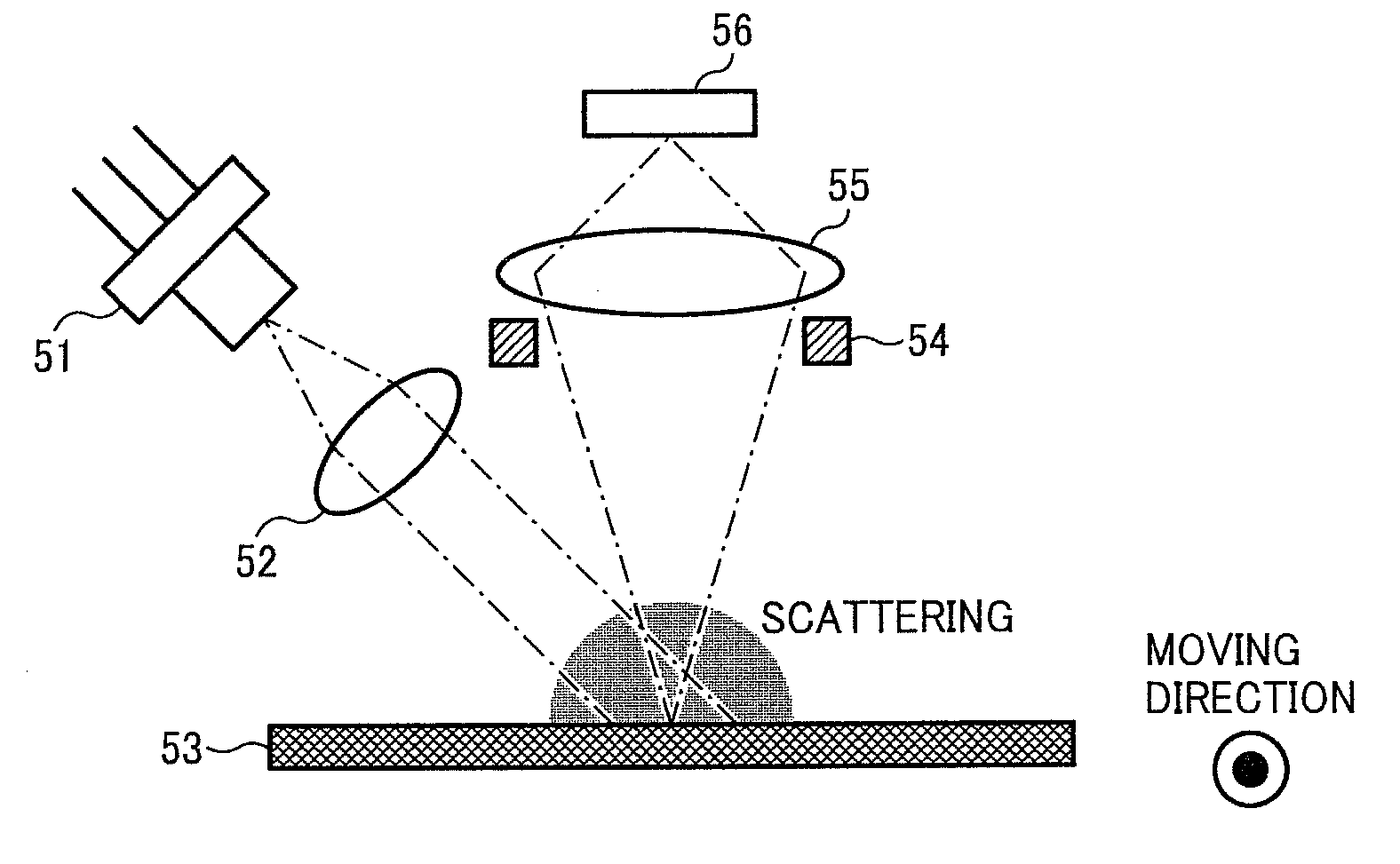
ActiveUS20100310284A1Solve problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionDevices using time traversedColor imageLight beam
A velocity detecting device includes an image-pattern acquiring unit that includes a laser light source and an area sensor that acquires a one-dimensional or a two-dimensional image. The image-pattern acquiring unit includes a lens between a moving member and the area sensor, irradiates a beam emitted from the laser light source to the moving member to make a scattering light of the moving member scattered from the moving member on the area sensor by using the lens, and acquires an image pattern at a predetermined time interval in association with movement of the moving member. A velocity calculating unit calculates the velocity of the moving member by computing the image pattern acquired by the image-pattern acquiring unit. The lens is a reduced optical system that projects a reduced object onto the area sensor.
Owner:RICOH KK
System and method for locating a three-dimensional object using machine vision
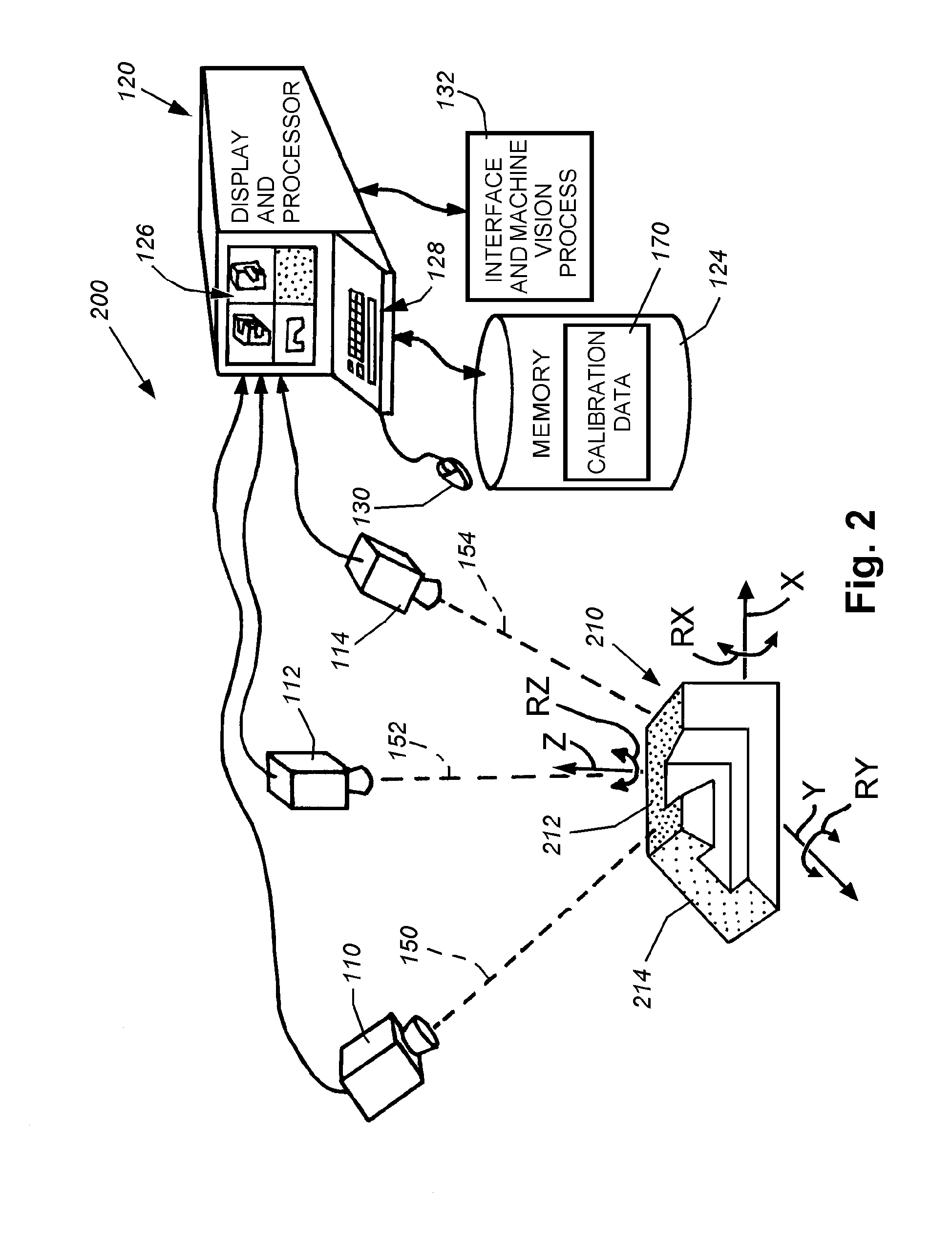
ActiveUS8126260B2Error minimizationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMachine vision
This invention provides a system and method for determining position of a viewed object in three dimensions by employing 2D machine vision processes on each of a plurality of planar faces of the object, and thereby refining the location of the object. First a rough pose estimate of the object is derived. This rough pose estimate can be based upon predetermined pose data, or can be derived by acquiring a plurality of planar face poses of the object (using, for example multiple cameras) and correlating the corners of the trained image pattern, which have known coordinates relative to the origin, to the acquired patterns. Once the rough pose is achieved, this is refined by defining the pose as a quaternion (a, b, c and d) for rotation and a three variables (x, y, z) for translation and employing an iterative weighted, least squares error calculation to minimize the error between the edgelets of trained model image and the acquired runtime edgelets. The overall, refined / optimized pose estimate incorporates data from each of the cameras' acquired images. Thereby, the estimate minimizes the total error between the edgelets of each camera's / view's trained model image and the associated camera's / view's acquired runtime edgelets. A final transformation of trained features relative to the runtime features is derived from the iterative error computation.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Structured light projection module group, depth camera and method for manufacturing structured light projection module group
The invention discloses a structured light projection module group, a depth camera and a method for manufacturing the structured light projection module group. The structured light projection module group comprises a light source which comprises multiple child light sources which are arranged into a two-dimensional array and used for transmitting two-dimensional patterned beams corresponding to the two-dimensional array; a lens which receives and converges the two-dimensional patterned beams; and a diffractive optical element which receives the two-dimensional patterned beams which are emergent through convergence of the lens and projects speckle patterned beams, wherein the speckle patterns include multiple image patterns corresponding to the two-dimensional patterns, and the relationshipbetween the adjacent image patterns of multiple image patterns at least includes two relationship of overlapping, adjoining and spacing. The structured light projection module group can project the speckle patterns having high degree of non-correlation.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
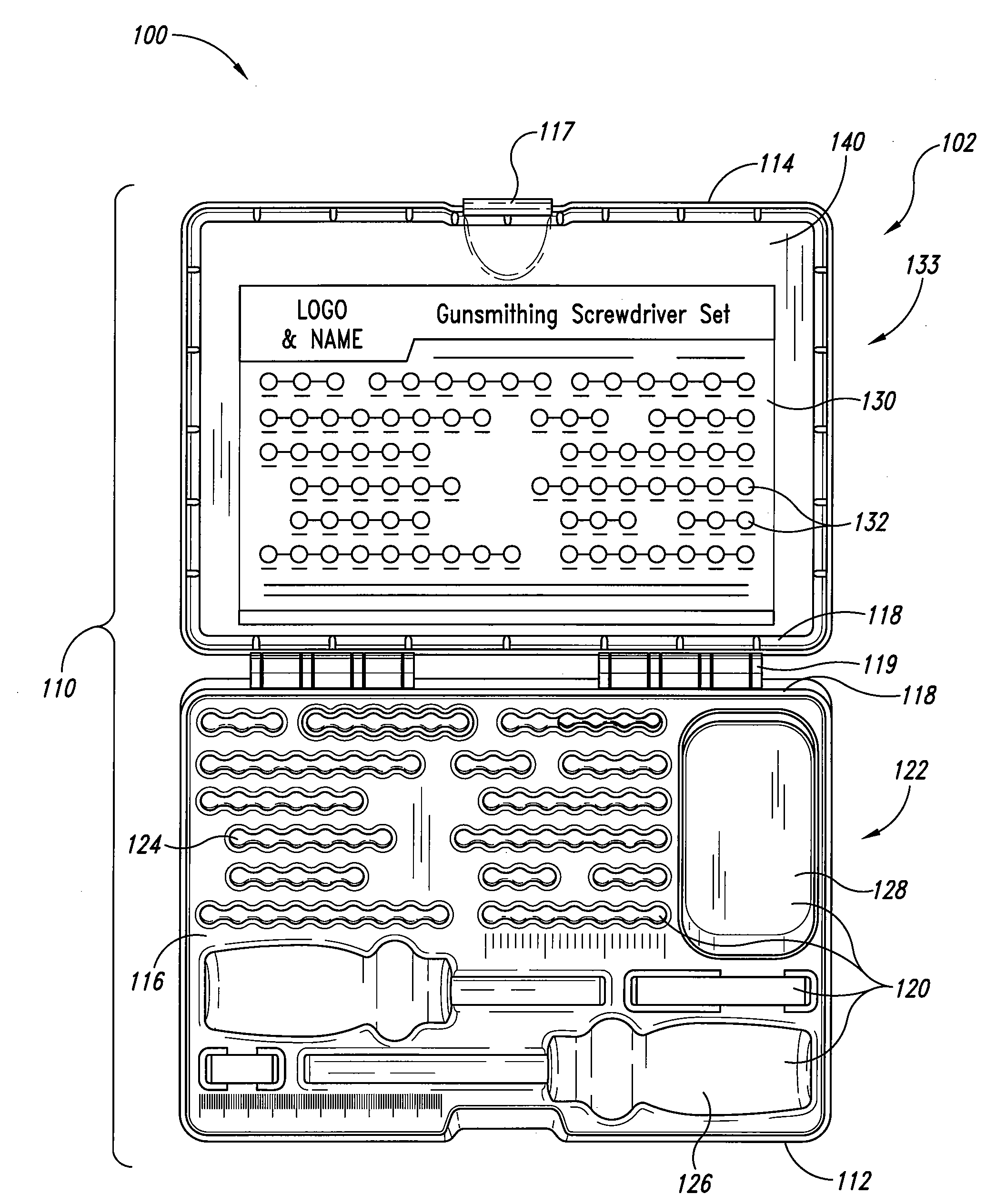
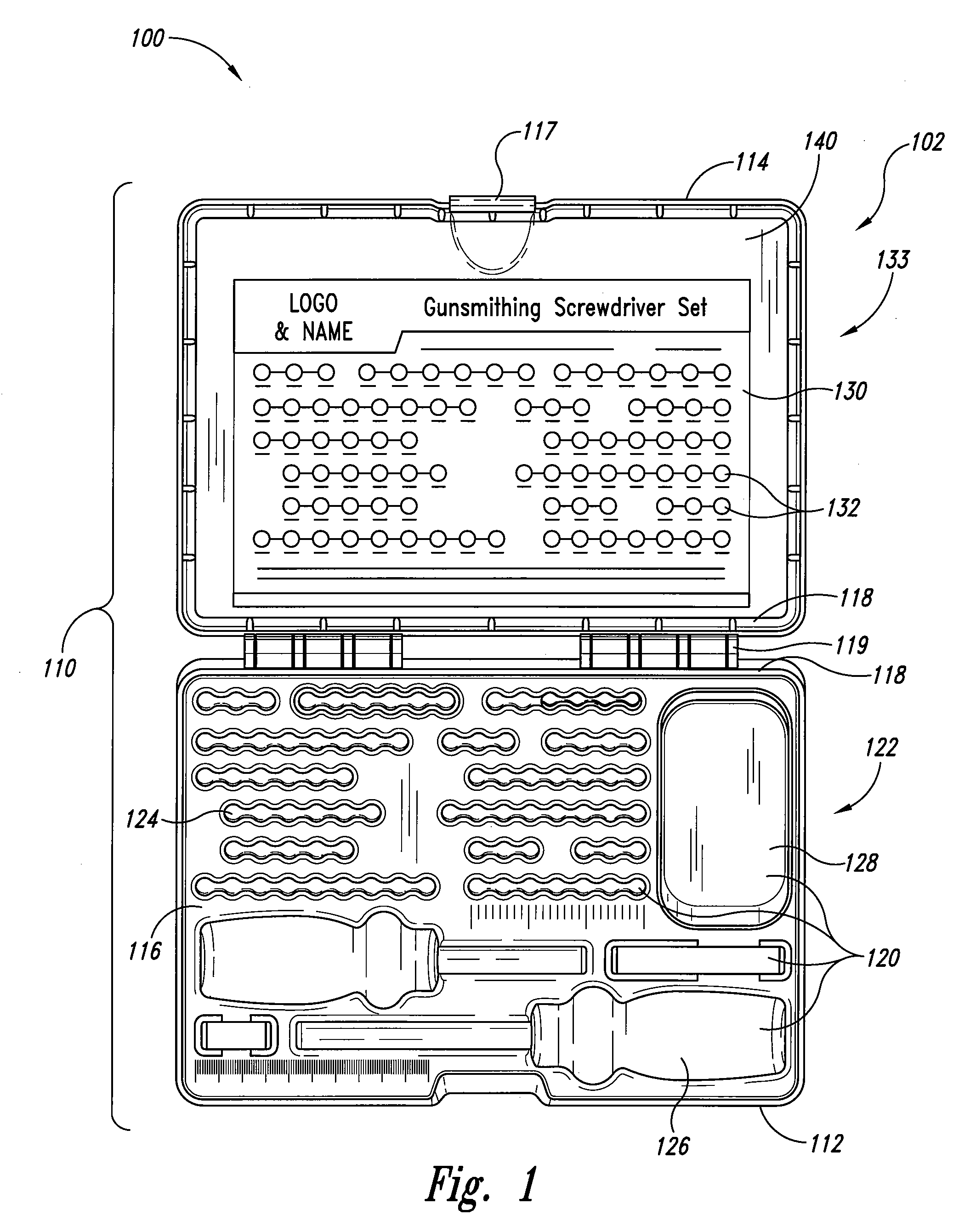
System and container for organizing and carrying tools and tool sets
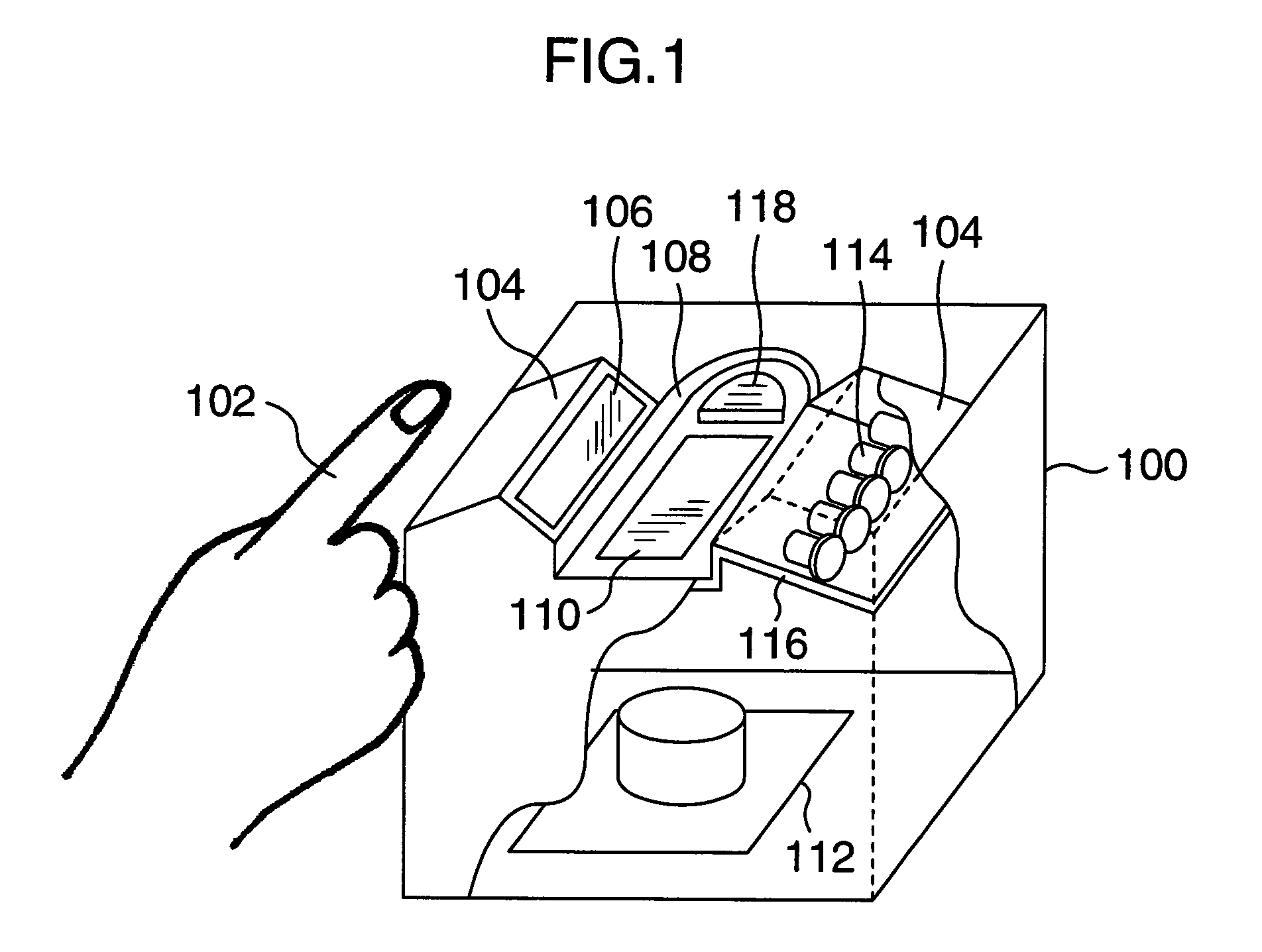
Systems and containers for organizing and carrying tools and tool sets are disclosed herein. One aspect of the invention is directed to systems and containers for efficiently organizing tools for specific work tasks, such as gunsmith tools, etc. In one embodiment, a container for carrying and organizing tools includes a housing having a base portion and a lid portion. The lid portion can be pivotally attached to the base portion. The container can also include a plurality of recesses disposed in an internal portion of the container in a recess pattern. The recesses can be configured to releasably retain the tools in the housing. The container also includes an insertable tool position guide having a plurality of images in an image pattern, wherein the image pattern can correspond to the recess pattern. In addition to tool positional information, the tool position guide can also communicate tool identification information.
Owner:BATTENFELD TECH
Method for selecting an emphasis image from an image collection based upon content recognition
ActiveUS20050105803A1Television system detailsDigital data information retrievalPattern recognitionFrequency of occurrence
A method for selecting an emphasis image from a collection of images based on facial identification comprises the steps of: (a) obtaining a collection of digital images; (b) detecting image patterns indicative of the presence of one or more faces in the digital images, thereby identifying one or more detected faces for each image in which a face is detected; (c) recognizing one or more faces from the detected faces for each of the images in which a face is detected; and (d) scoring an image based on the relative frequency of occurrence of a recognized face within the collection of images, thereby producing an emphasis image characteristic of the most frequently occurring face in the collection of images.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
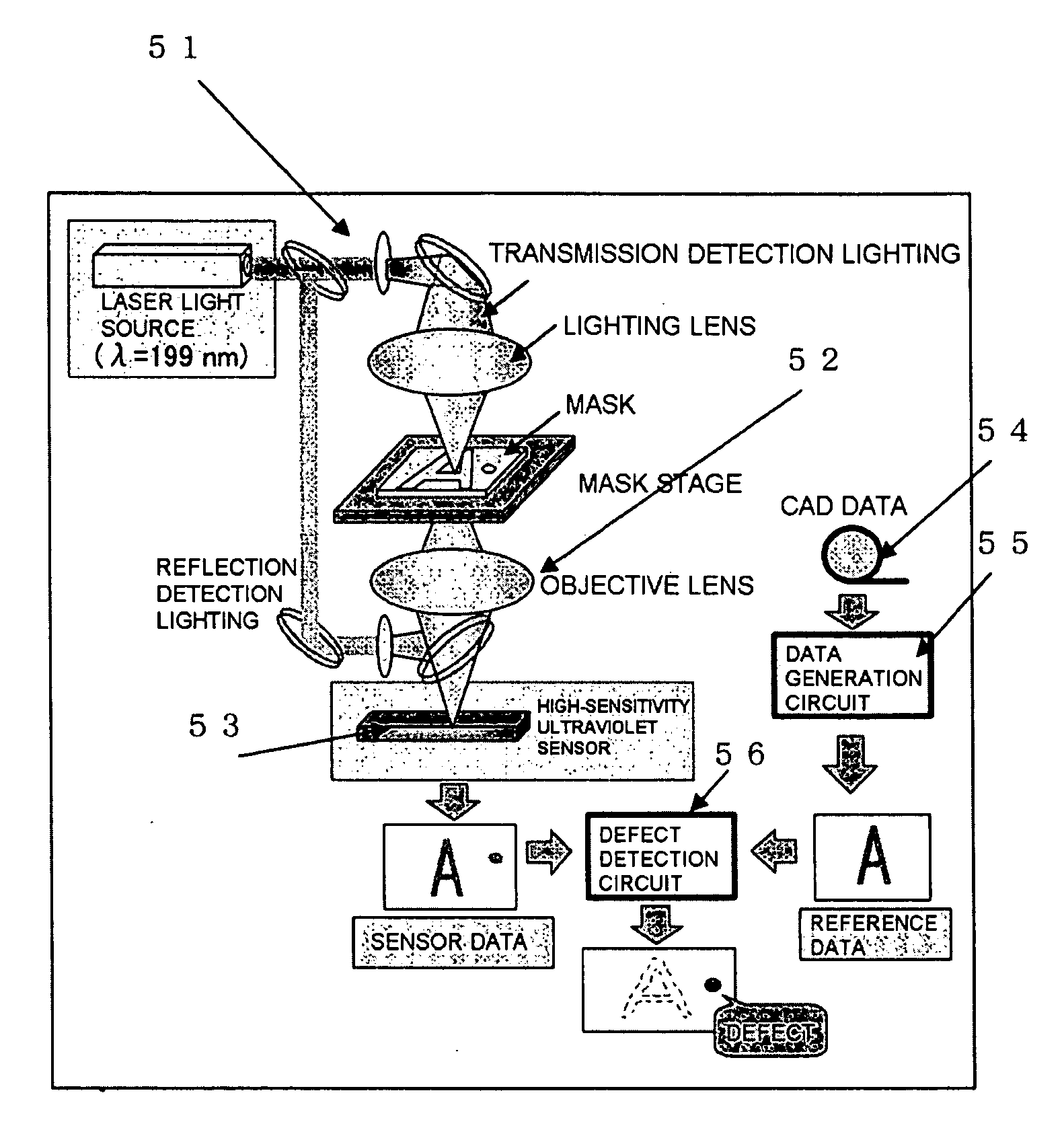
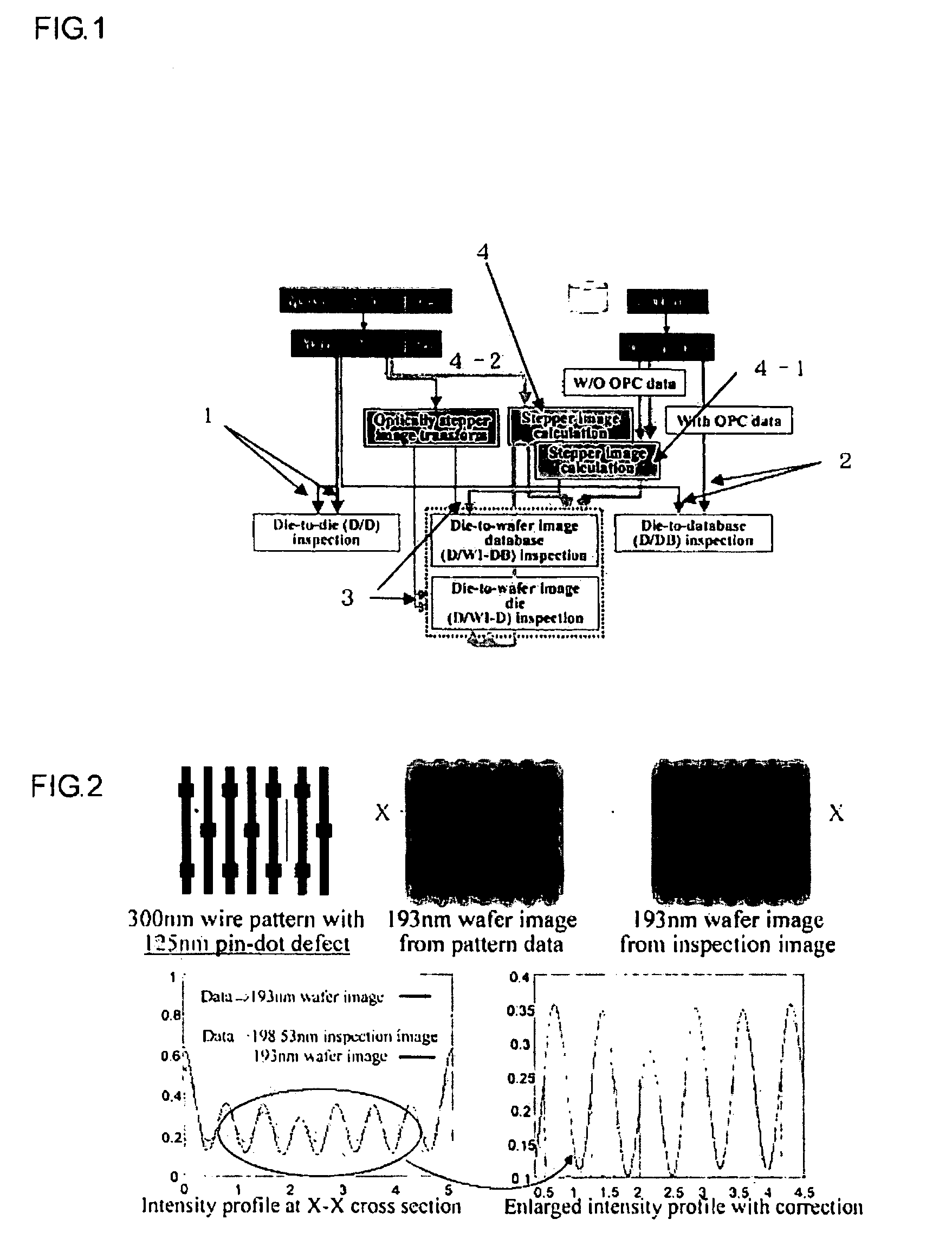
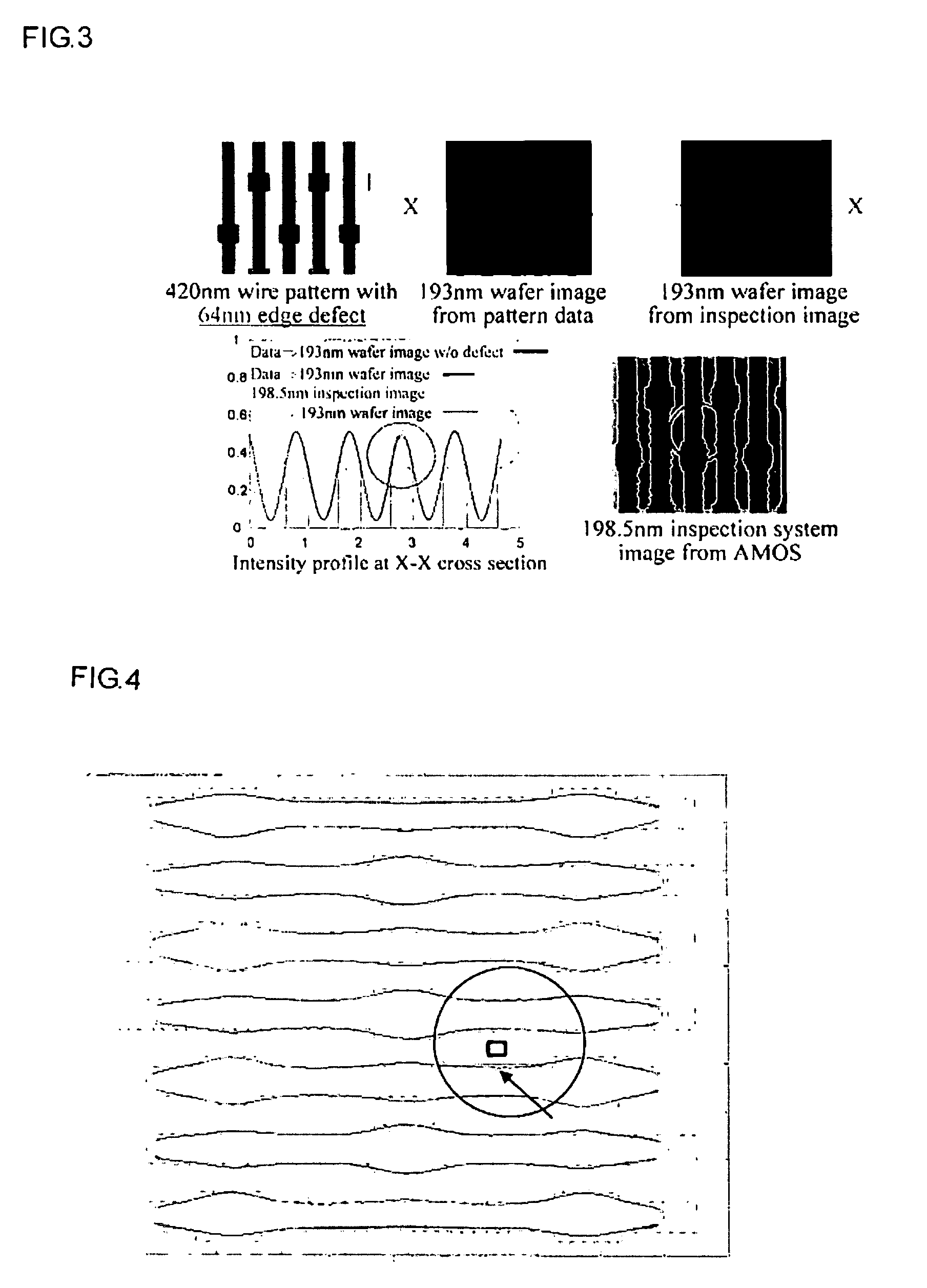
Pattern defect inspection method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060239535A1High detection sensitivitySuppress generationImage enhancementImage analysisDesign patternPhotomask
A method and an apparatus for irradiating a measurement sample with an energy beam, a pattern being formed in the measurement sample, providing an optical system for detecting transmitted energy beam or reflected energy beam from the measurement sample, obtaining a pattern image, and comparing design data of the pattern and an image of the obtained image pattern to inspect a defect of the pattern formed in the measurement sample, wherein the measurement sample is a so-called photomask, a design pattern produced in producing the photomask is used as the design data of the pattern, and, in a procedure of performing inspection by comparing the obtained image and the design data, the design data is converted into an image (hereinafter referred to as wafer image) by a proper method, the wafer image being formed through a stepper used for actually forming the pattern of the photomask on a wafer, the obtained image actually measured is simultaneously converted into a wafer image by a proper method, and the defect is detected by comparing both wafer images to each other.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Medical image processing apparatus and medical image processing method
InactiveUS20050238216A1Way accurateShort timeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
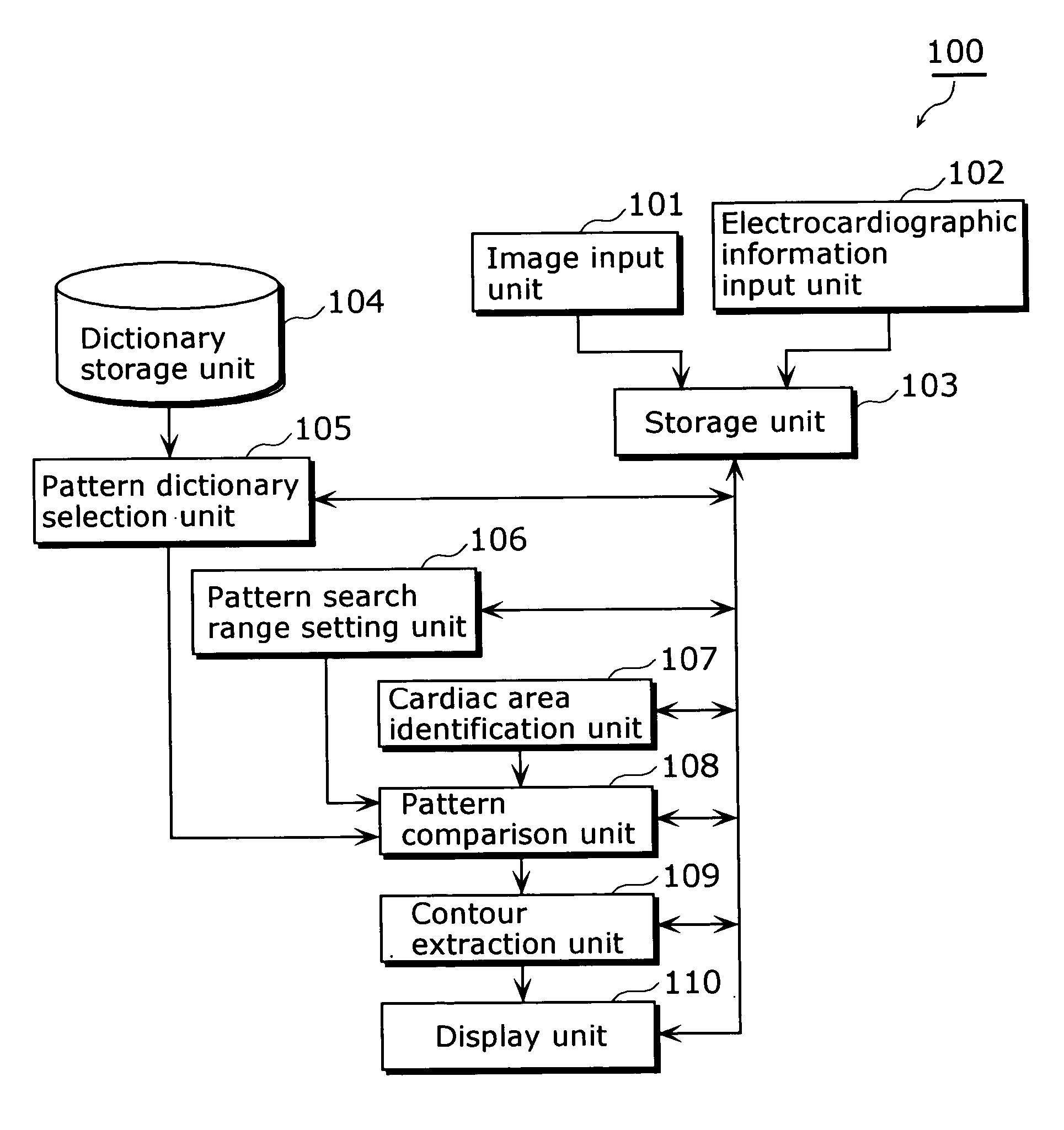
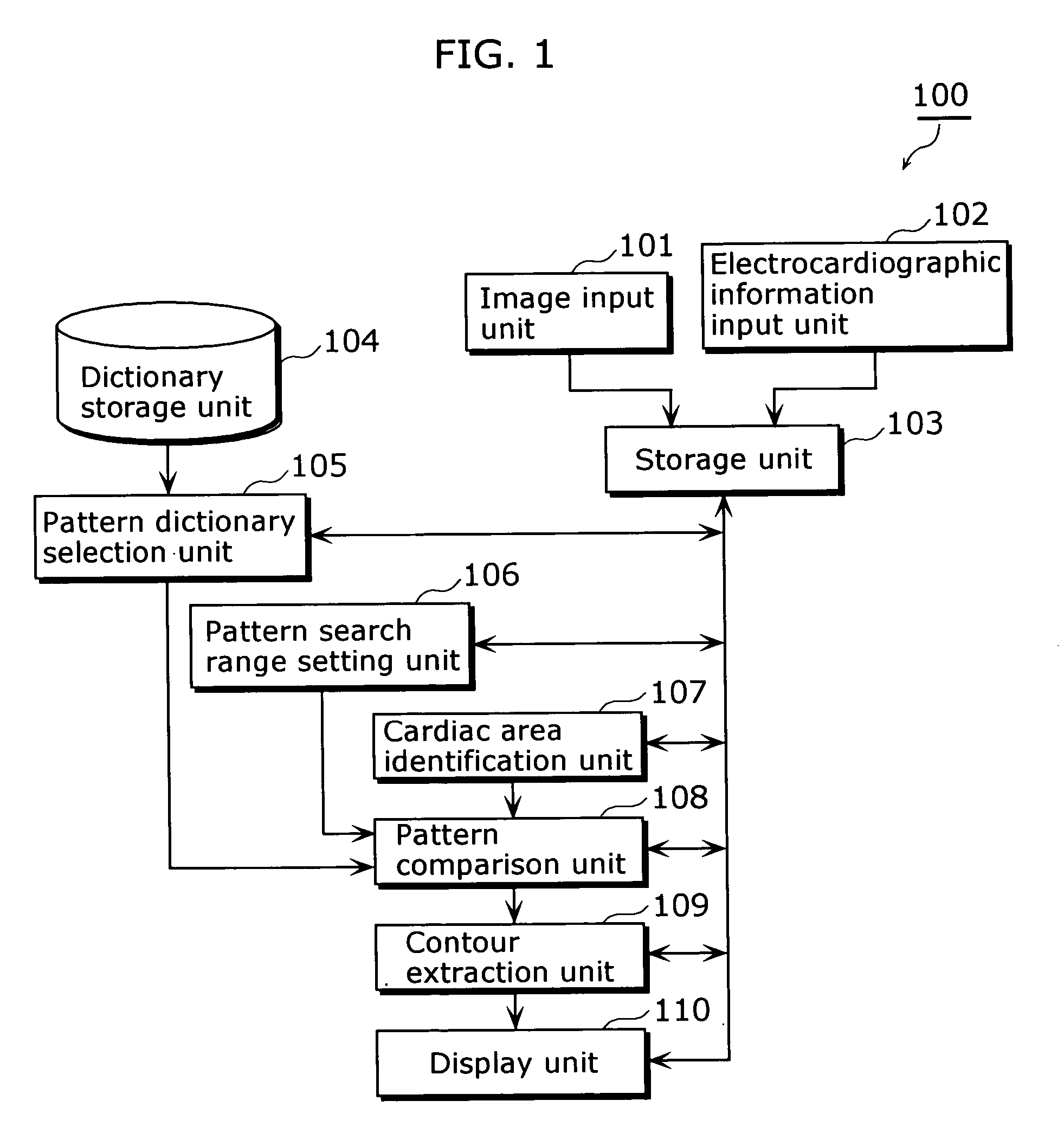
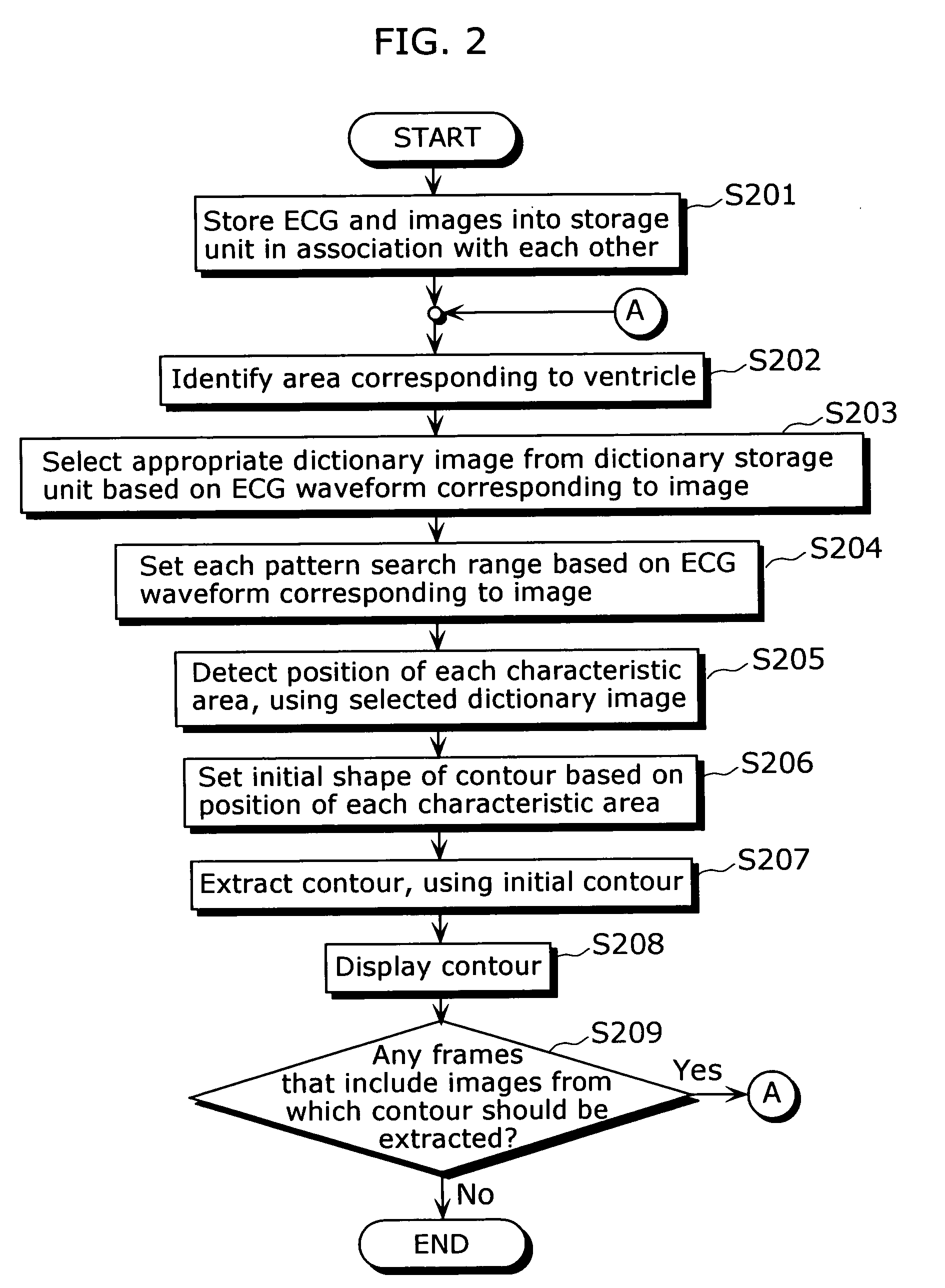
In a medical image processing apparatus 100 that is capable of extracting a contour of an organ or the like in a highly accurate manner within a short time, an image input unit 101 accepts ultrasound images or the like. An electrocardiographic information input unit 102 accepts electrocardiographic information (e.g. ECG waveform). A storage unit 103 stores image data representing the ultrasound images and the electrocardiographic information in association with each other. A dictionary storage unit 104 stores image patterns (dictionary images) used for pattern matching. A pattern dictionary selection unit 105 selects a dictionary image used for pattern matching with reference to the electrocardiographic information. A pattern search range setting unit 106 specifies a range in which pattern matching is to be performed, based on the electrocardiographic information. A cardiac area identification unit 107 detects a cardiac area in the image. A pattern comparison unit 108 identifies the position of each characteristic area in the image by pattern matching. A contour extraction unit 109 extracts a contour based on the position of each characteristic area and the ultrasound image. A display unit 110 displays the extracted contour.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
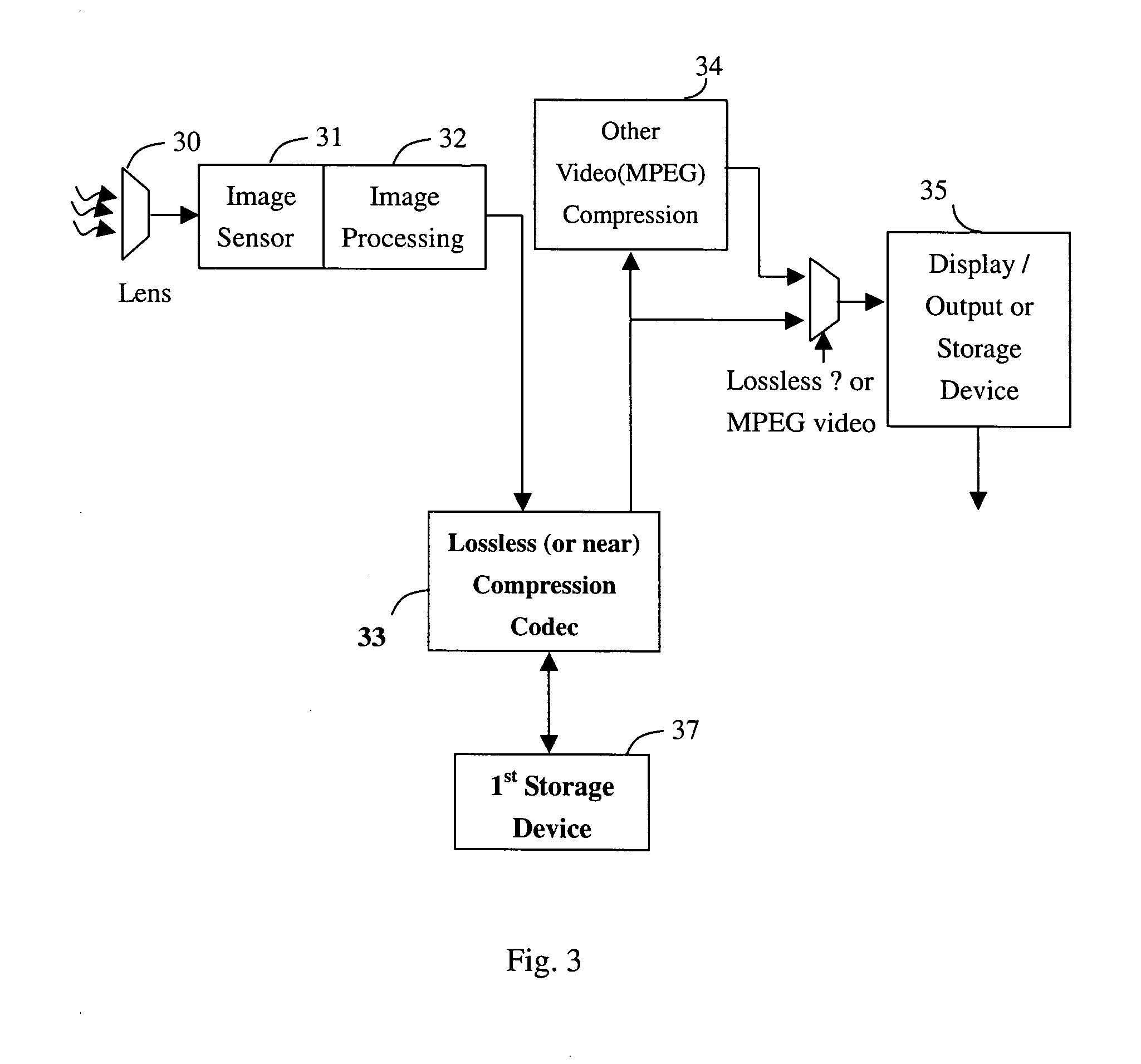
Method and apparatus of high quality video compression
InactiveUS20070092149A1Reduces required storage device densityQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Compression method
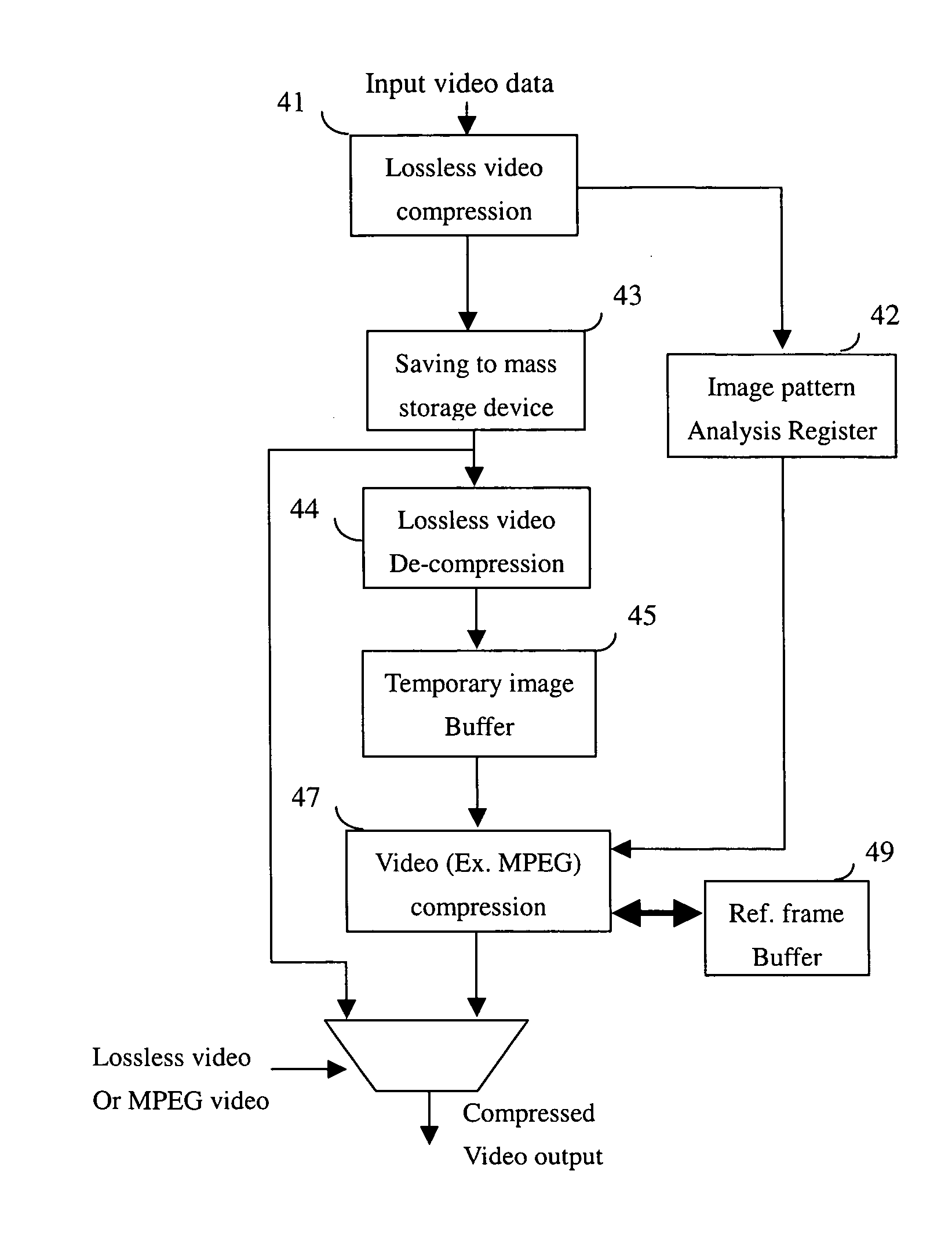
A video compression method compresses the capture video raw data into the 1st compression format and records the image patter complexity of each frame of a predetermined amount of video frames. The information of the image pattern complexity is used to determine the bit rate of each frame for the 2nd time of the video compression. For saving the image buffer size and speeding up the accessing time, a lossless and near lossless video compression algorithm is applied to the 1st video compression algorithm.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com