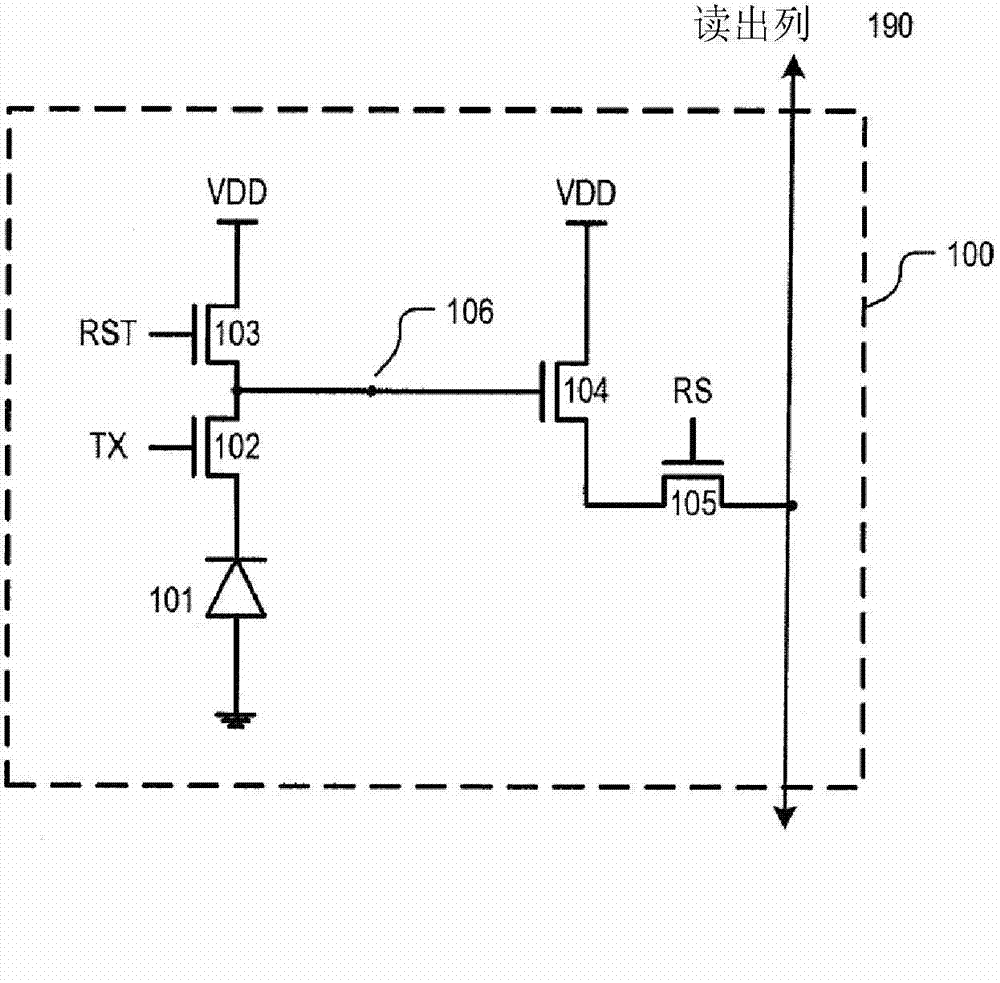
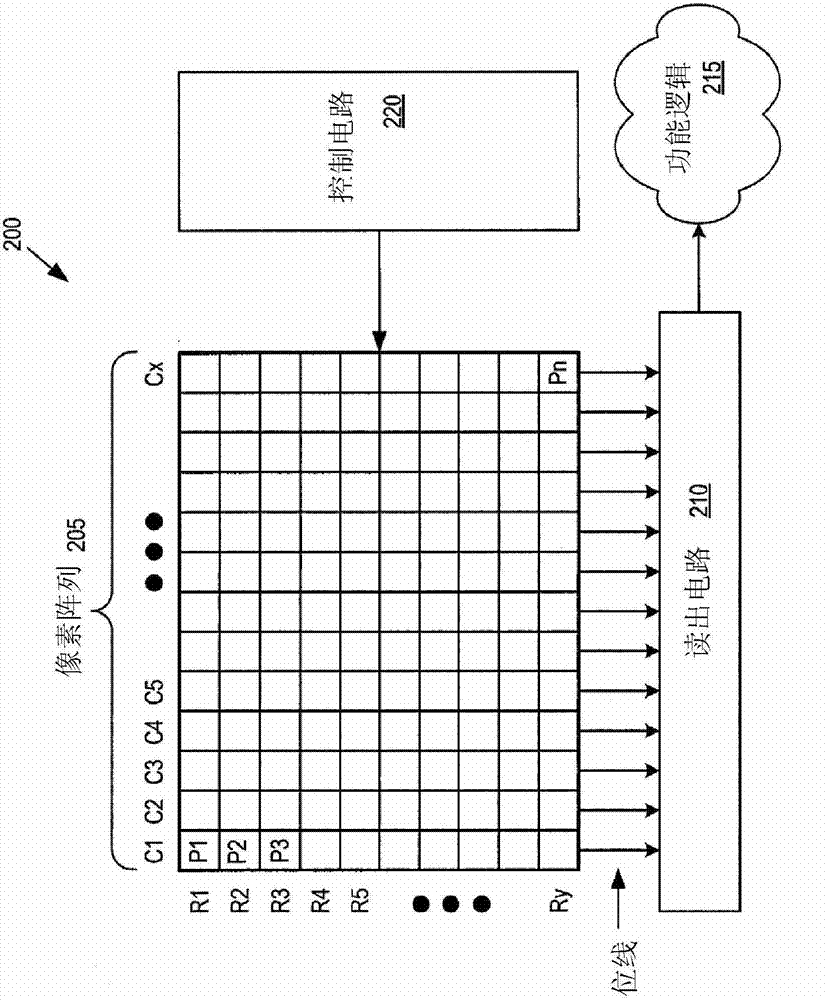
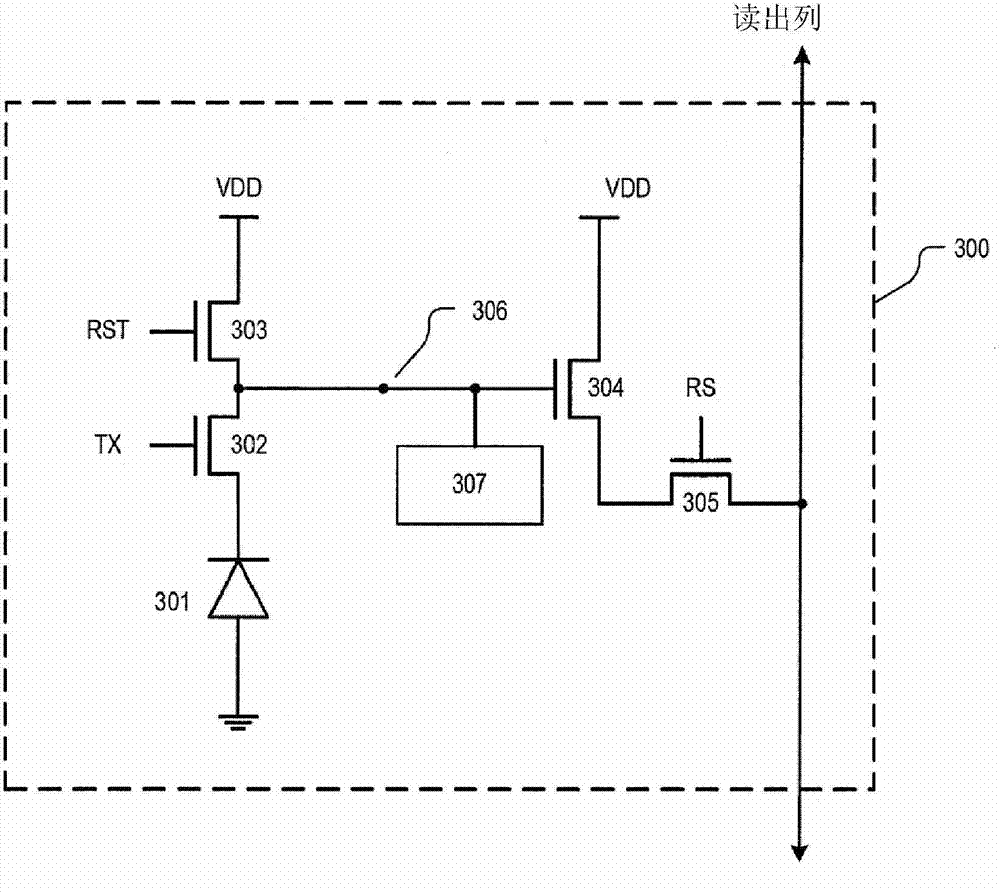
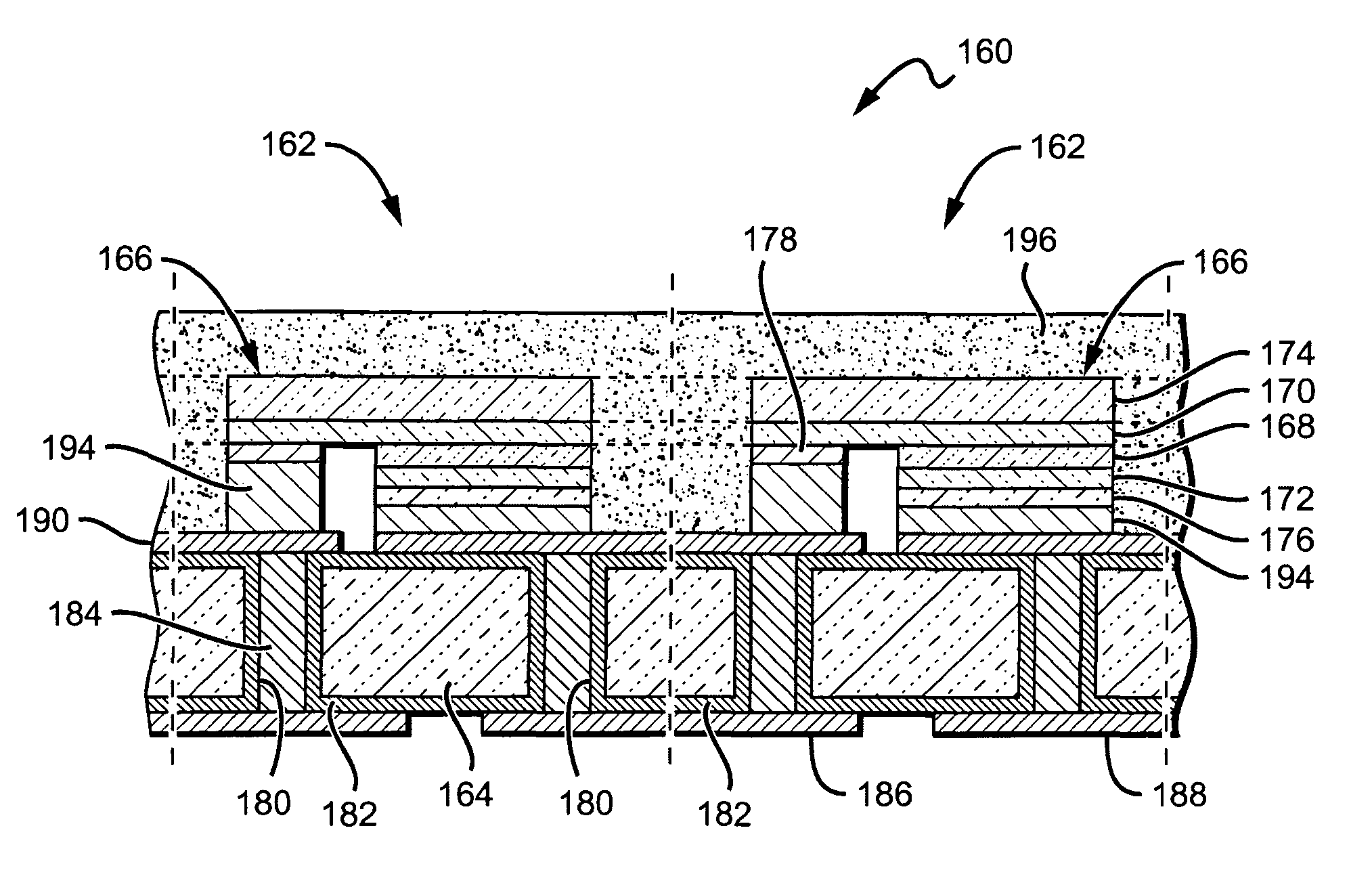
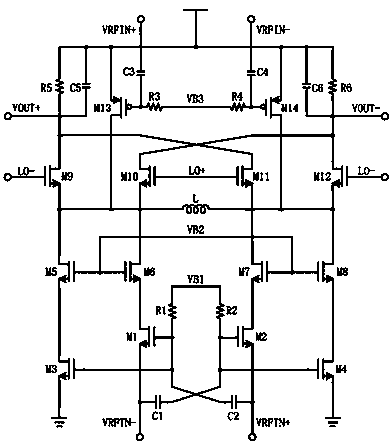
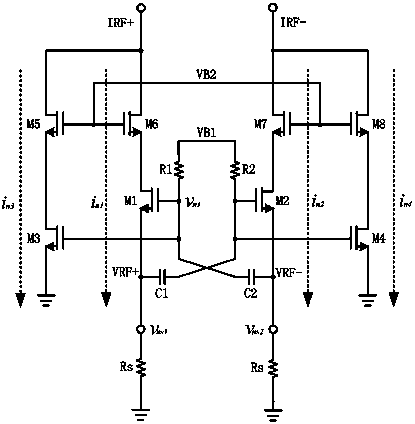
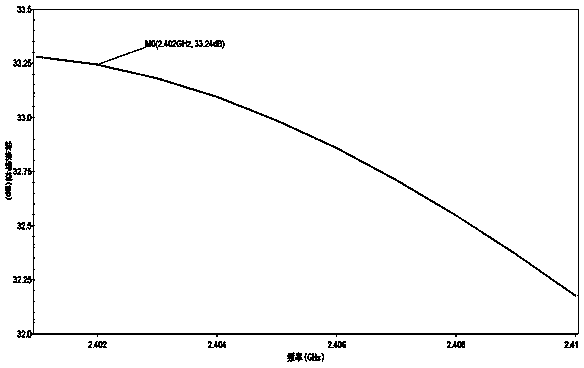
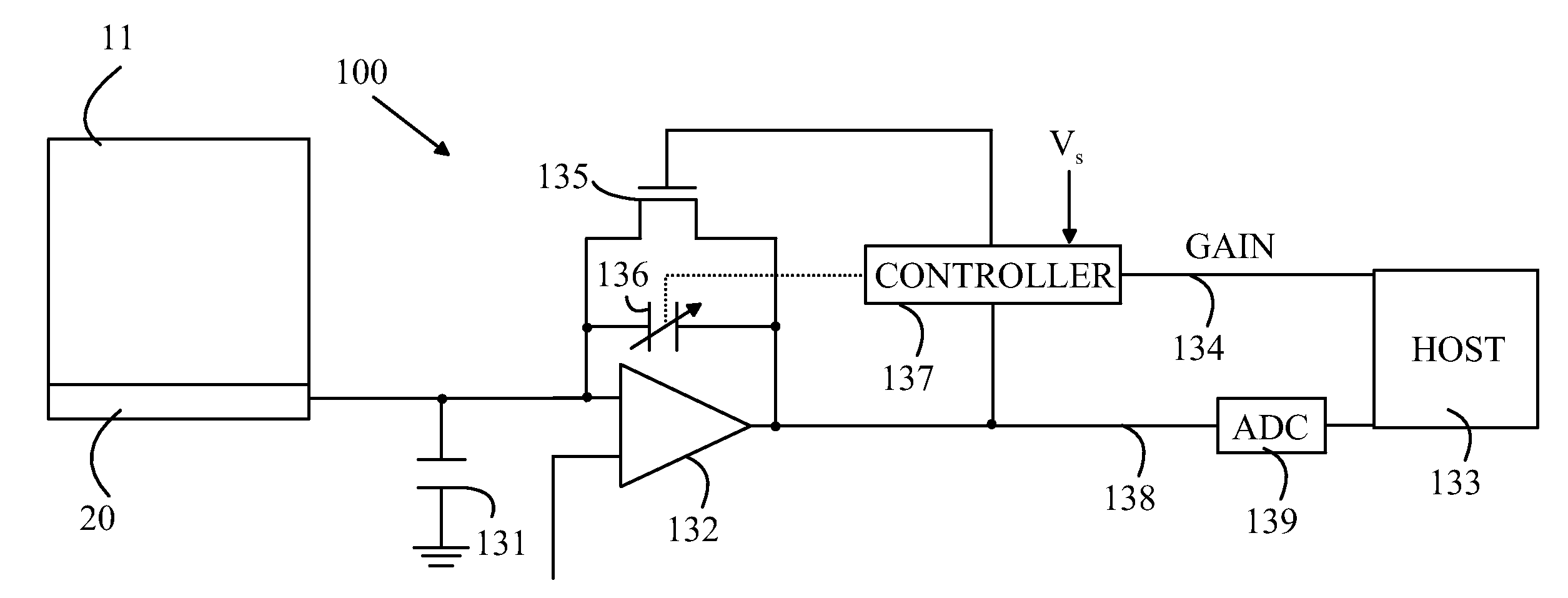
Patents
Literature
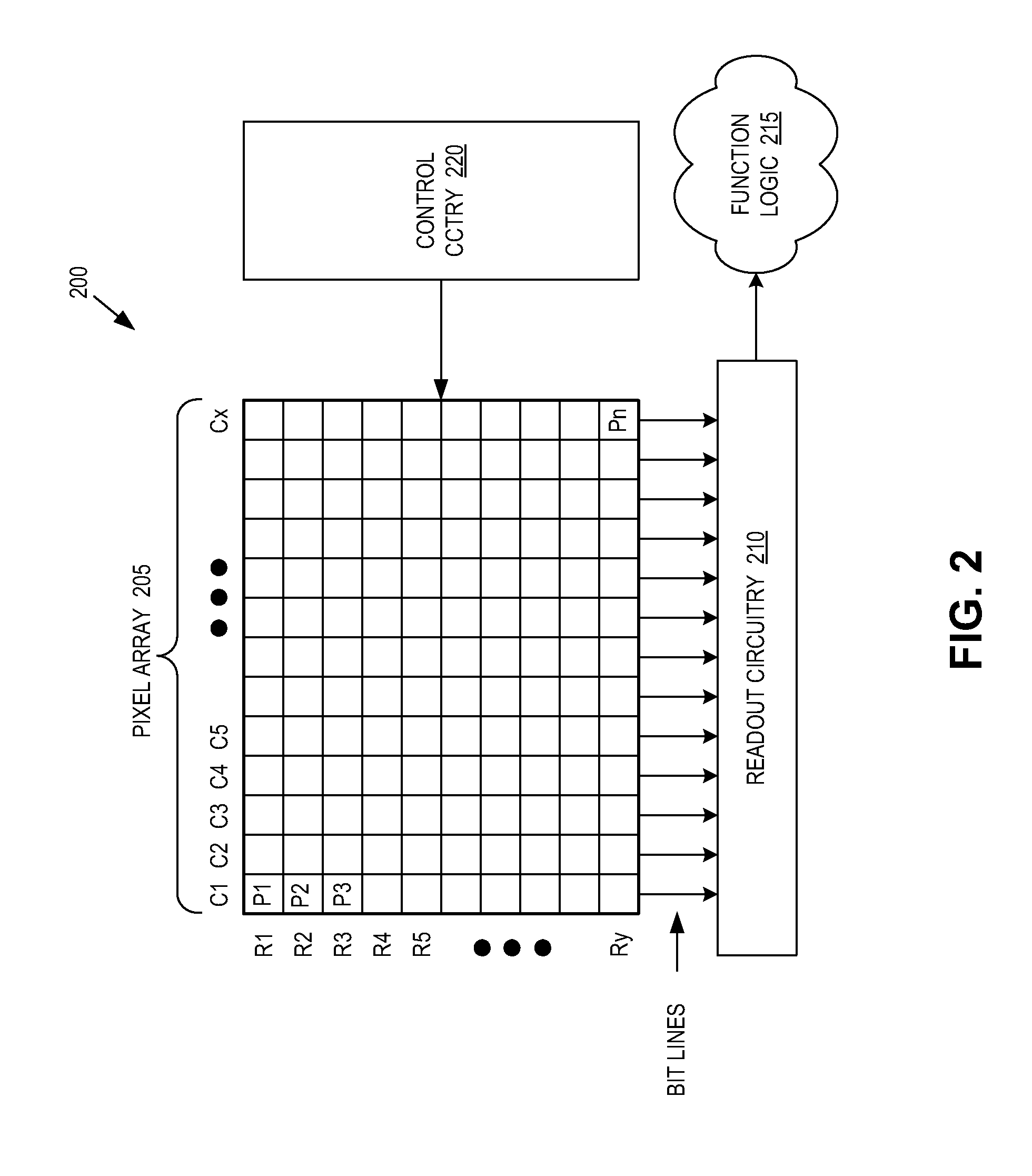
307 results about "Conversion gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
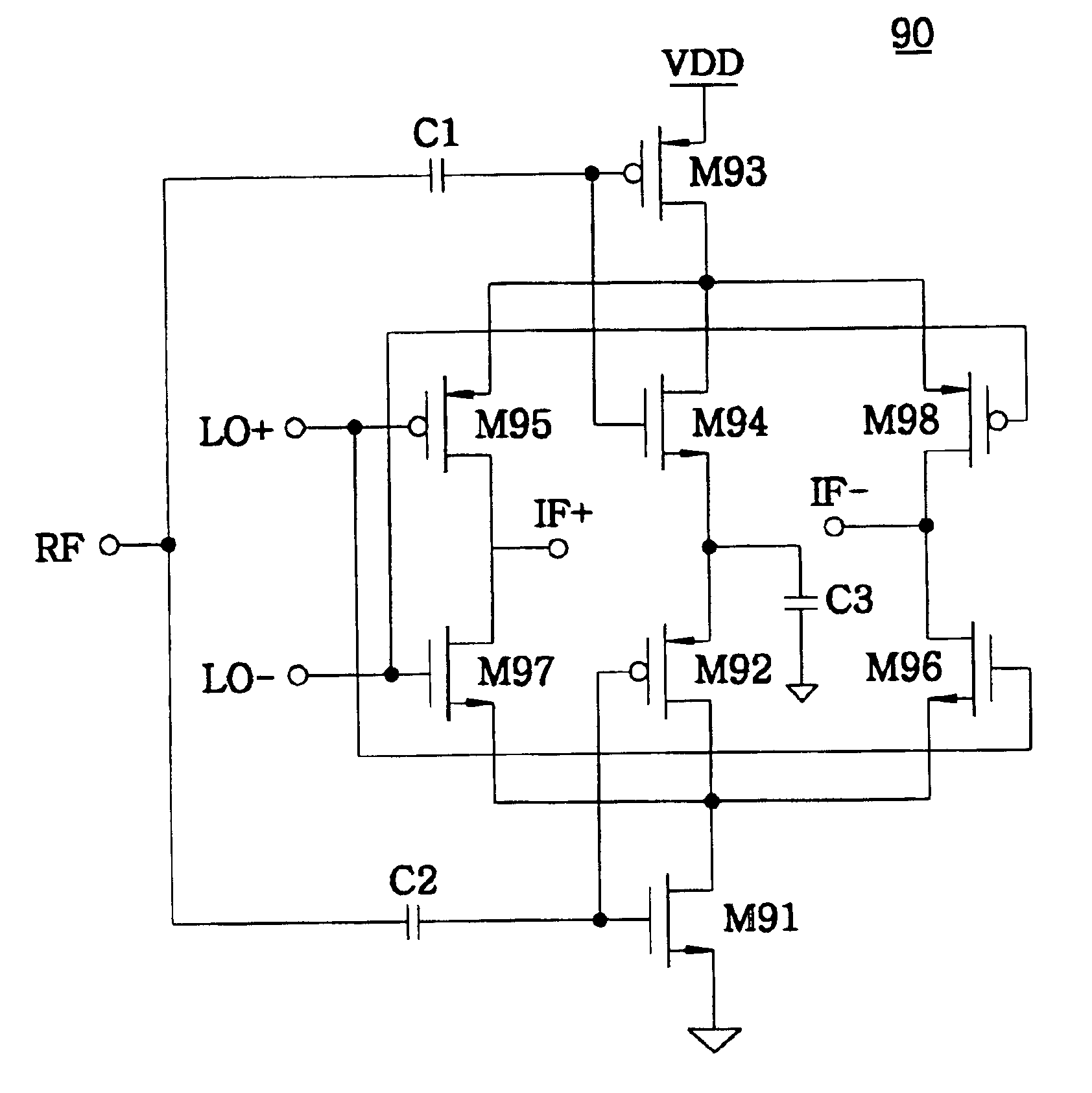
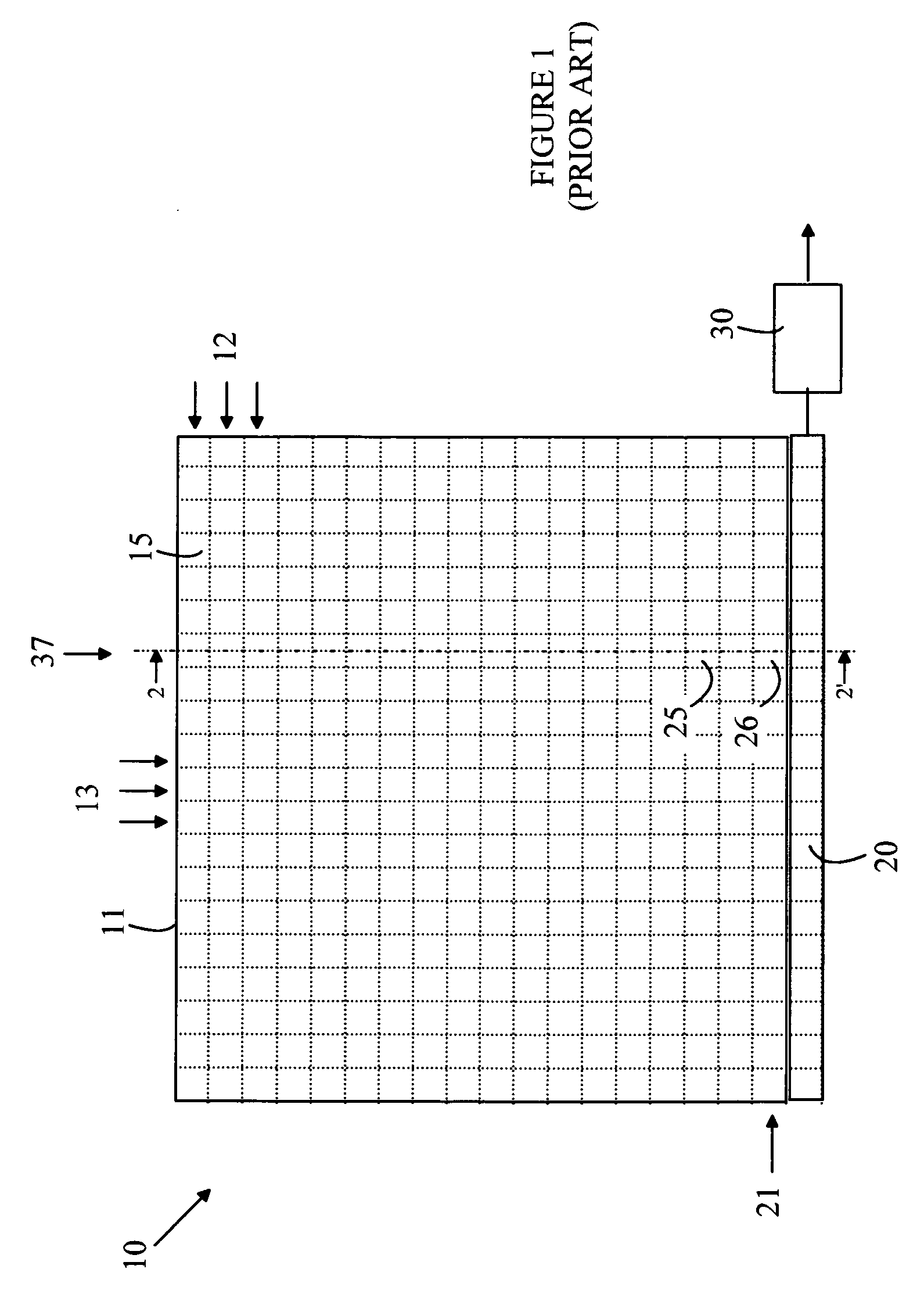
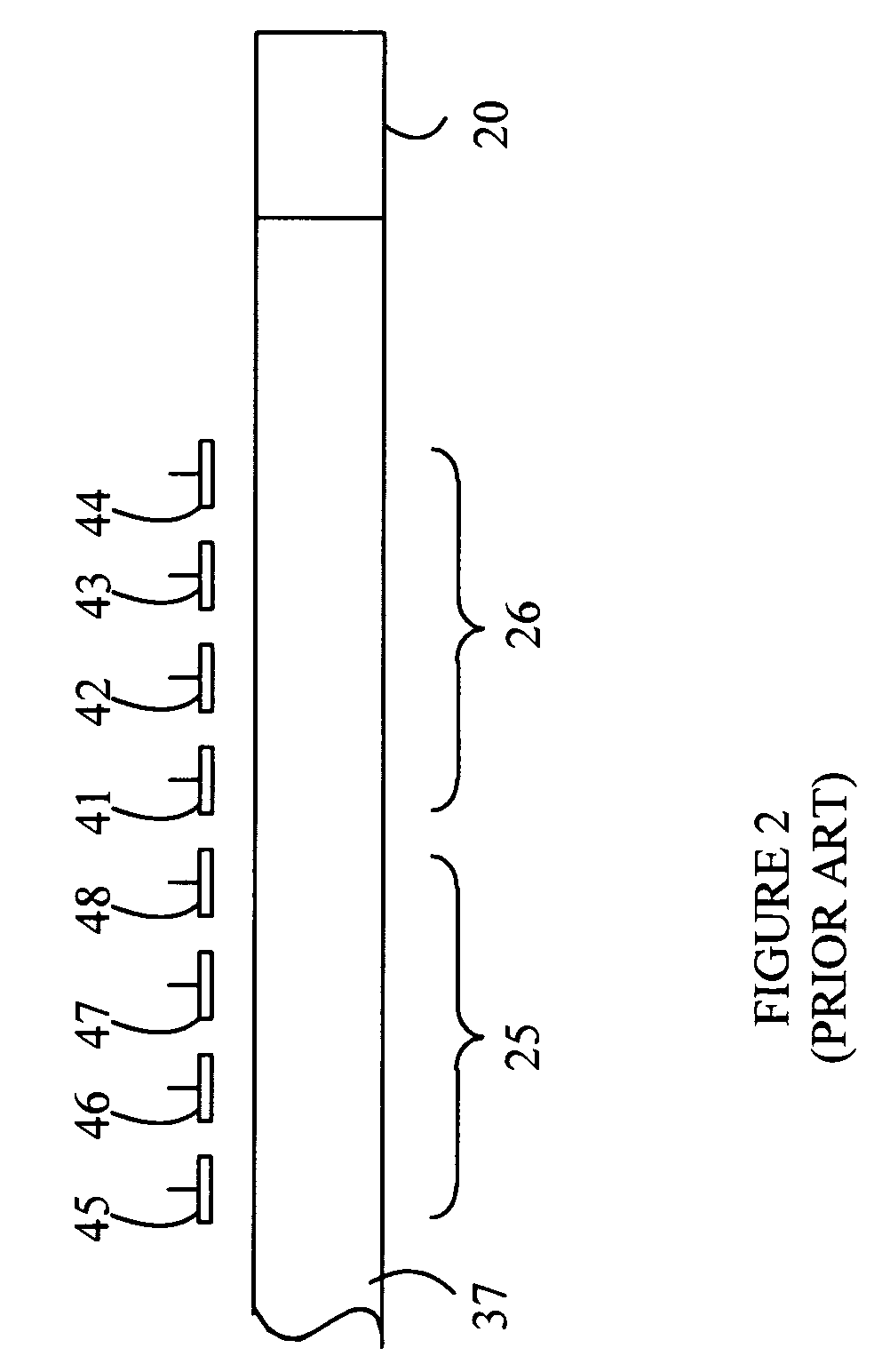
Current-reuse bleeding mixer
InactiveUS6892062B2Good performance in conversion gain and linearity and noise figureModulation transference balanced arrangementsAmplitude demodulationLow noiseLocal oscillator
Owner:INFORMATION & COMM UNIV EDUCATIONAL FOUND
High dynamic range imager circuit and method for reading high dynamic range image
ActiveUS20120256077A1Improve dynamic rangeTransistorTelevision system detailsCapacitanceHigh-dynamic-range imaging
The present invention discloses a high dynamic range imager circuit and a method for reading high dynamic range image with an adaptive conversion gain. The high dynamic range image circuit includes a variable capacitor. The capacitance of the variable capacitor is adjusted according to sensed light intensity or by internal feedback control, to adaptively adjust the conversion gain of the high dynamic range image circuit as it reads a signal which relates to a pixel image sensed by an image sensor device. In each cycle, the signal can be read twice or more with different dynamic ranges, to enhance the accuracy of the signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
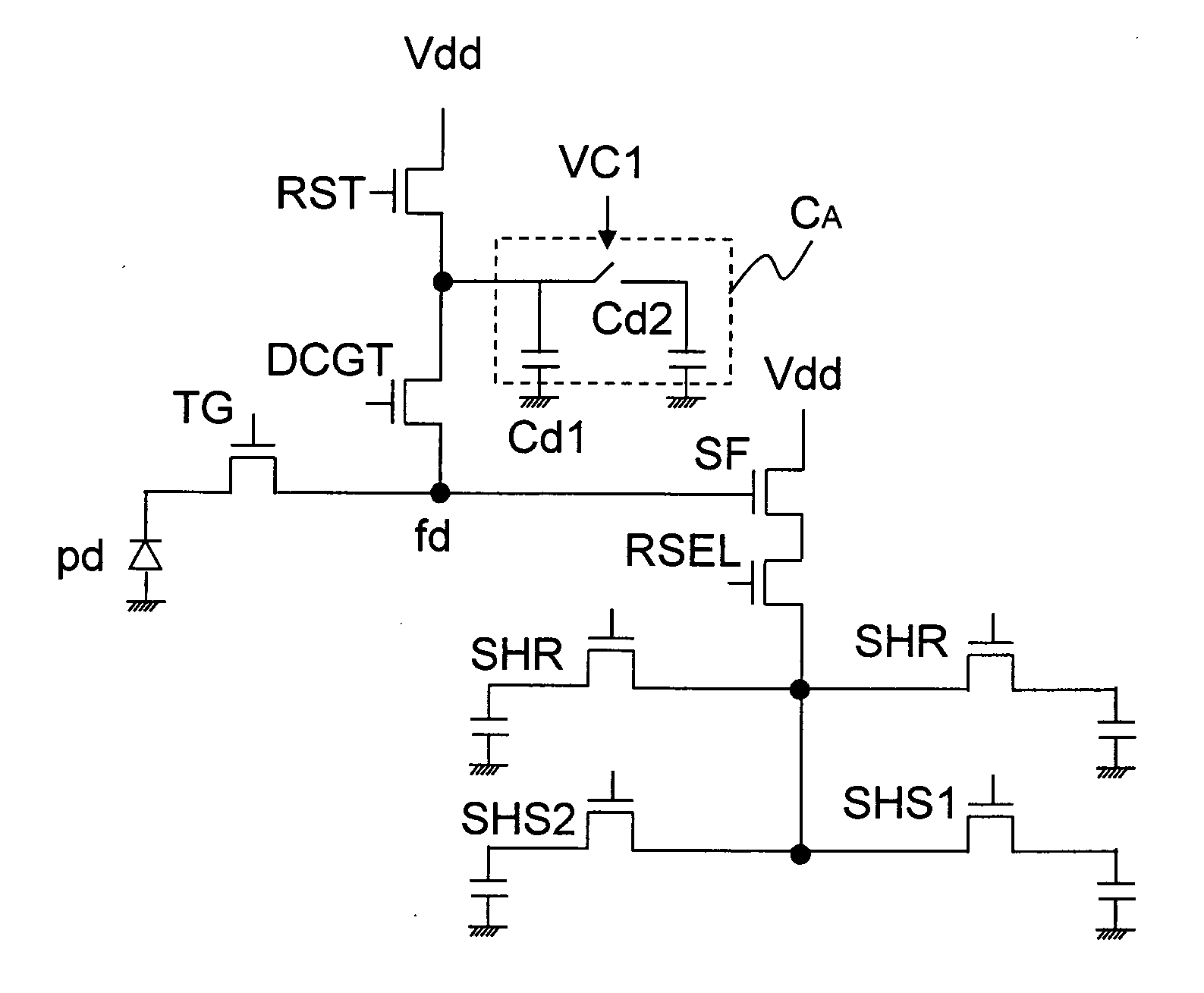
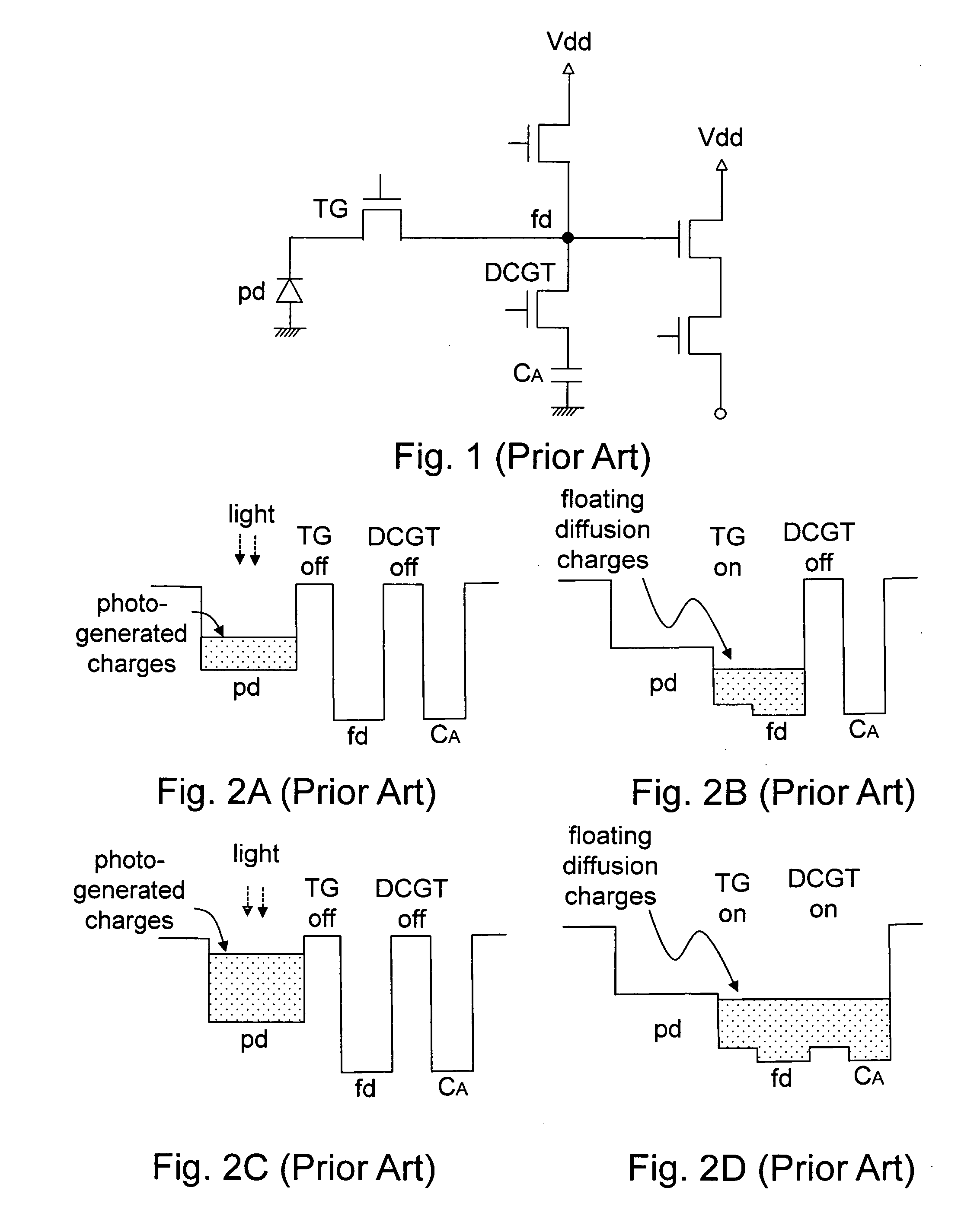
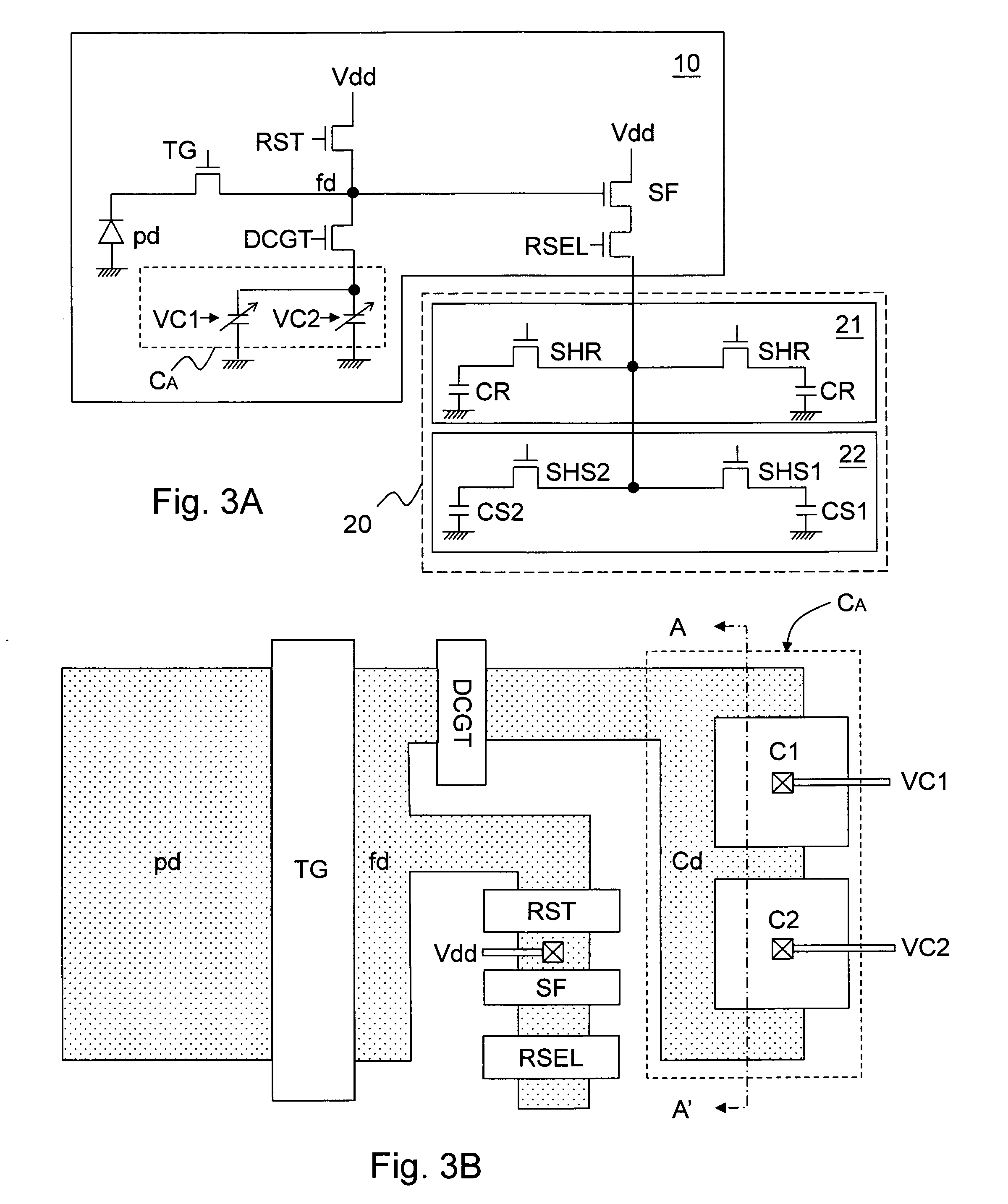
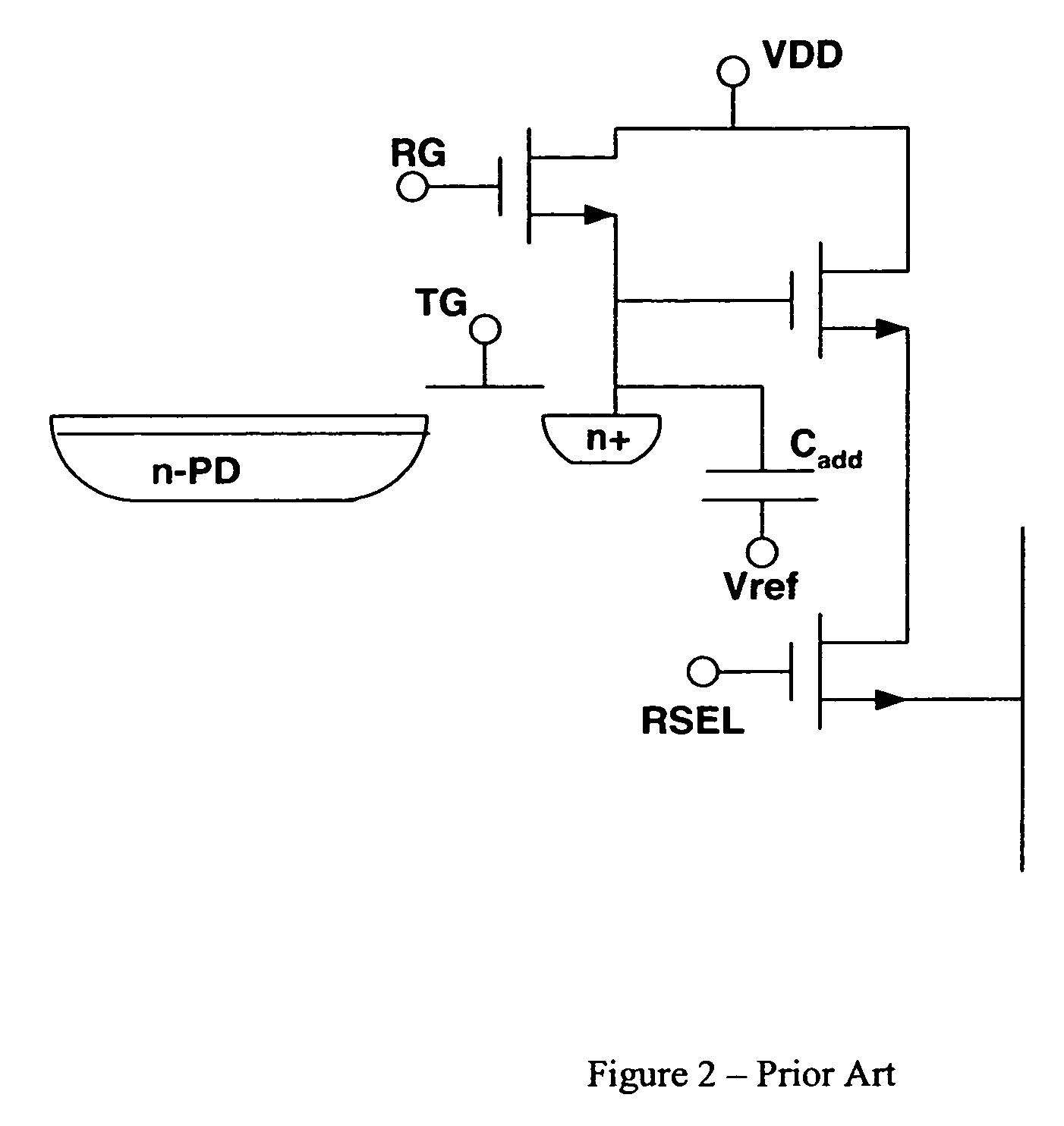
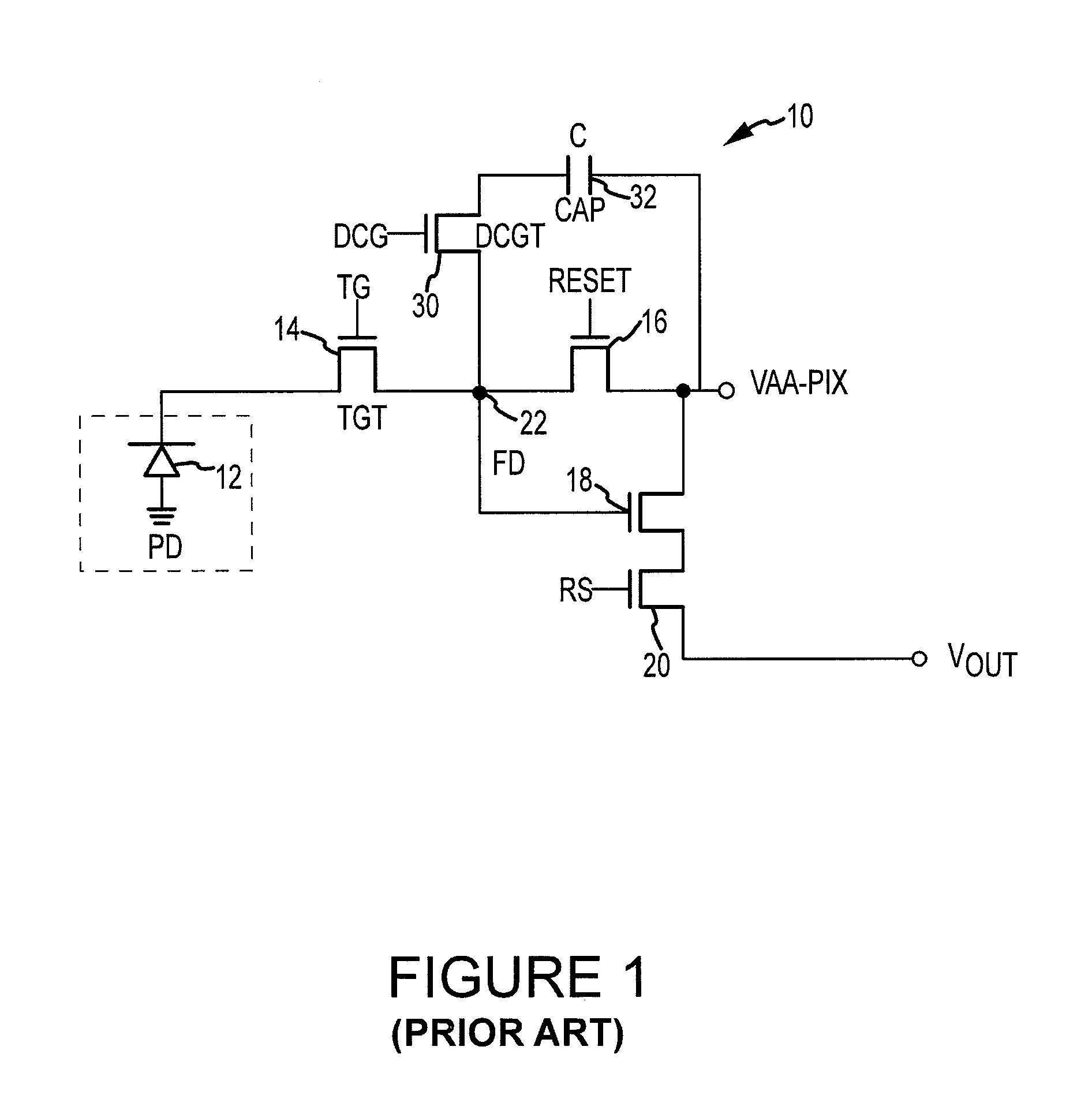
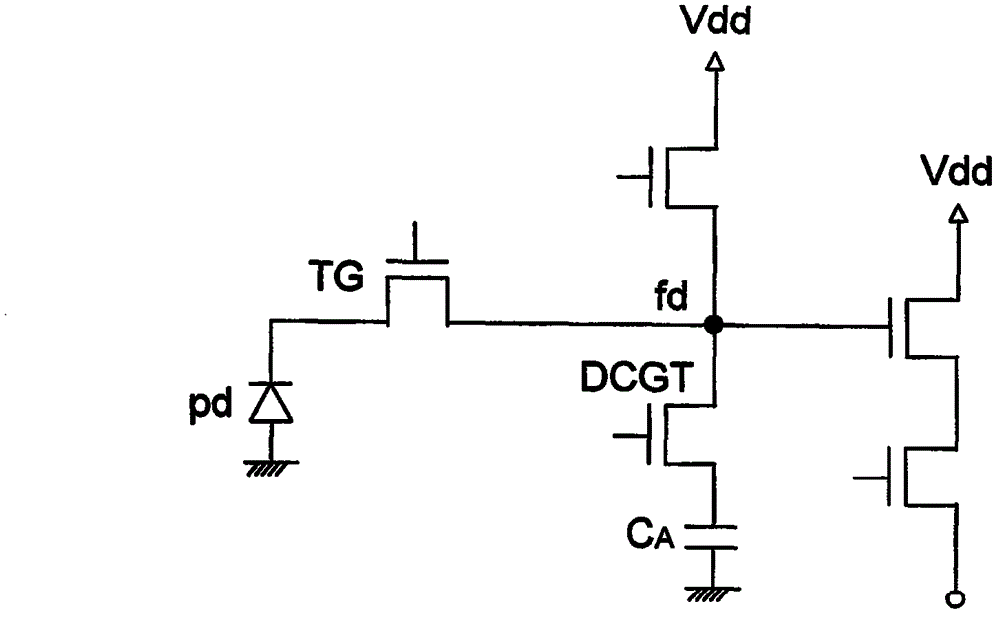
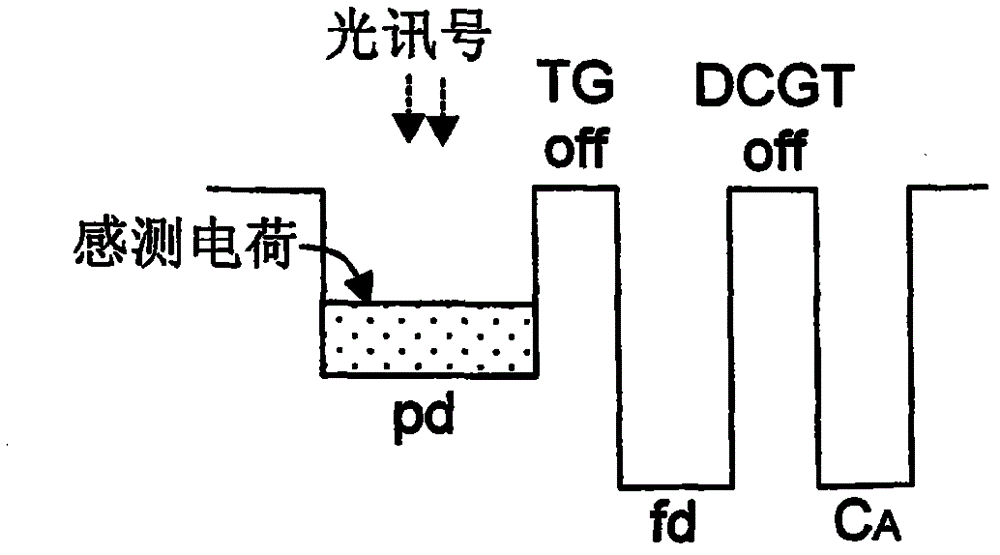
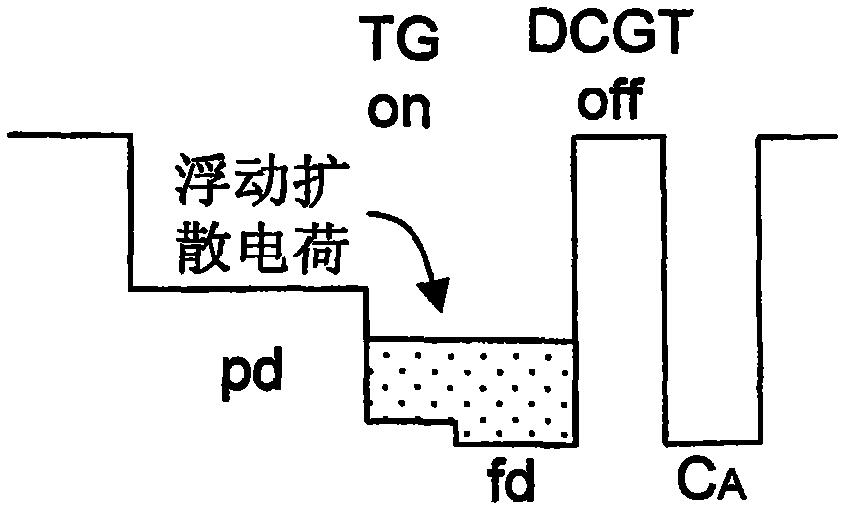
Dual conversion gain gate and capacitor combination
A pixel cell array architecture having a dual conversion gain. A dual conversion gain element is coupled between a floating diffusion region and a respective storage capacitor. The dual conversion gain element having a control gate switches in the capacitance of the capacitor to change the conversion gain of the floating diffusion region from a first conversion gain to a second conversion gain. In order to increase the efficient use of space, the dual conversion gain element gate also functions as the bottom plate of the capacitor. In one particular embodiment of the invention, a high dynamic range transistor is used in conjunction with a pixel cell having a capacitor-DCG gate combination; in another embodiment, adjacent pixels share pixel components, including the capacitor-DCG combination.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Shunting-type isothermal sulfur-tolerant conversion process and equipment thereof
ActiveCN101704513ASatisfy conversion rate requirementsMeet the requirements of adiabatic conversion control temperature riseHydrogenChemical industryShunt typesSulfur
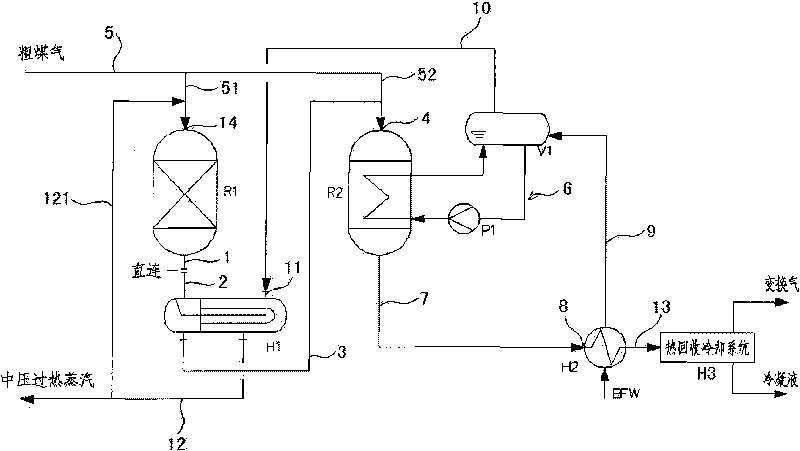
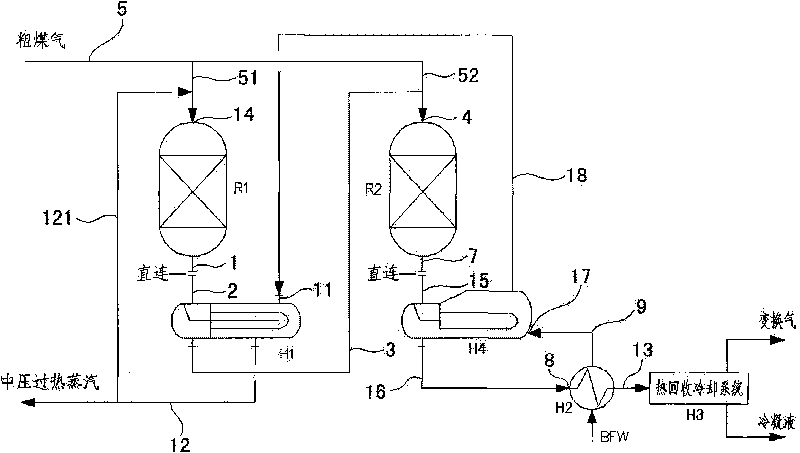
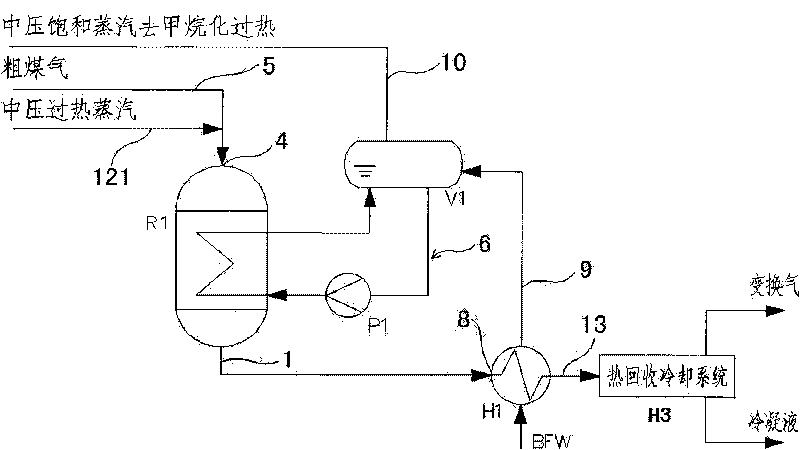
The invention discloses a shunting-type isothermal sulfur-tolerant conversion process. The process comprises the following steps: shunting raw coal gas from exterior into at least two parts; leading overheat stream in the first part of the raw coal gas to increase the temperature to 200-300 DEG C; and then entering a first-stage conversion reaction step to carry out a conversion reaction and generate first conversion gas; and conveying the other part of the raw coal gas to next-stage conversion reaction step to carry out a conversion reaction. The catalyst bed of a shift converter has the advantages of stable temperature, simple control, convenient operation and low output CO content. The invention has the advantages of short conversion flows, few equipment, reduced resistance, great byproduct stream amount, high overheat temperature, stream pressure and heat recovery rate, and the like, thereby achieving the aims of reducing conversion stages, equipment number and resistance fall, decreasing investment, having great byproduct stream amount and high overheat temperature, stream pressure and heat recovery rate, reducing conversion stream consumption and outward wastewater discharge, protecting the environment and easily maximizing the device equipment. The invention also discloses shunting-type isothermal sulfur-tolerant conversion equipment used by the process.
Owner:SHANGHAI INT ENG CONSULTING
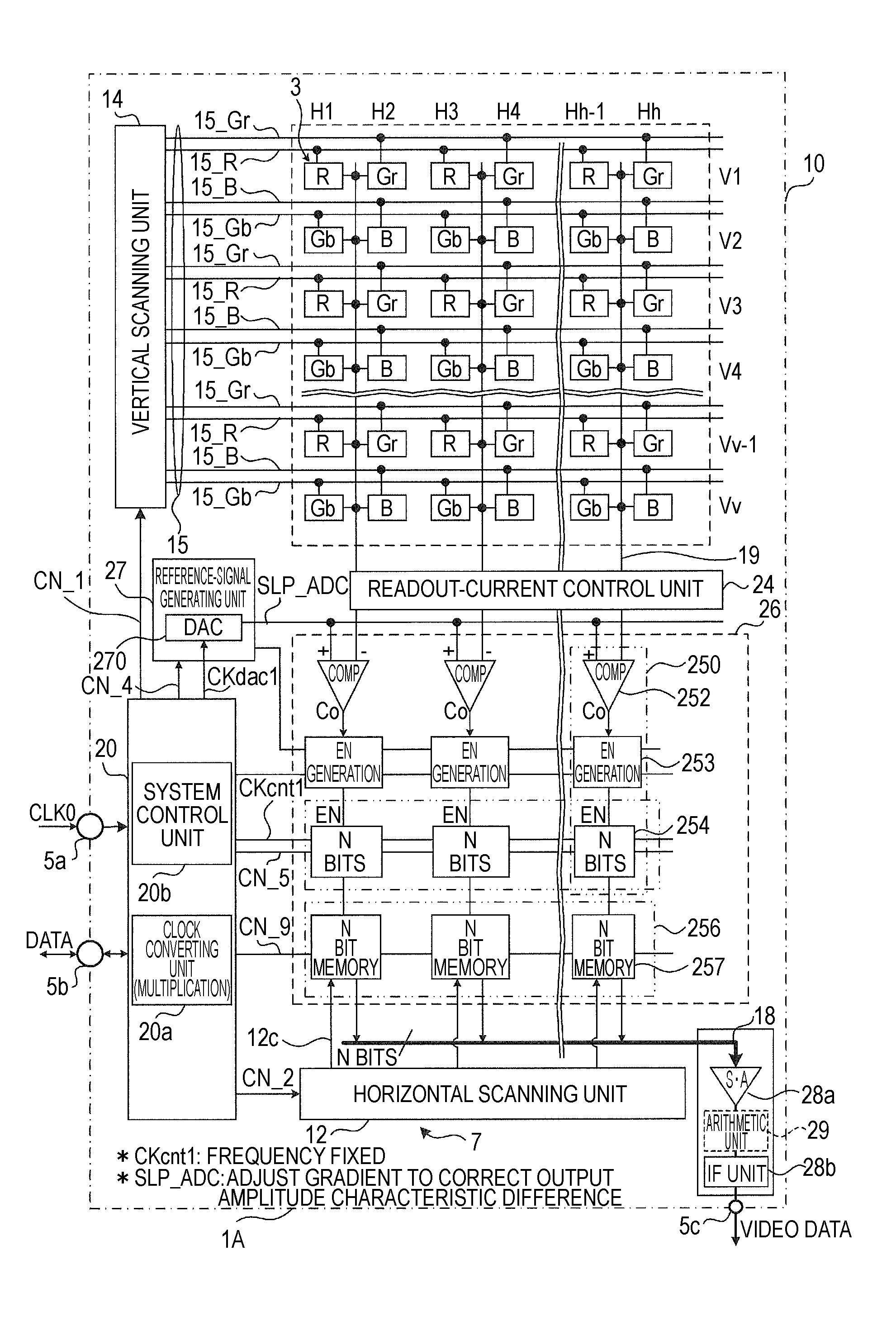
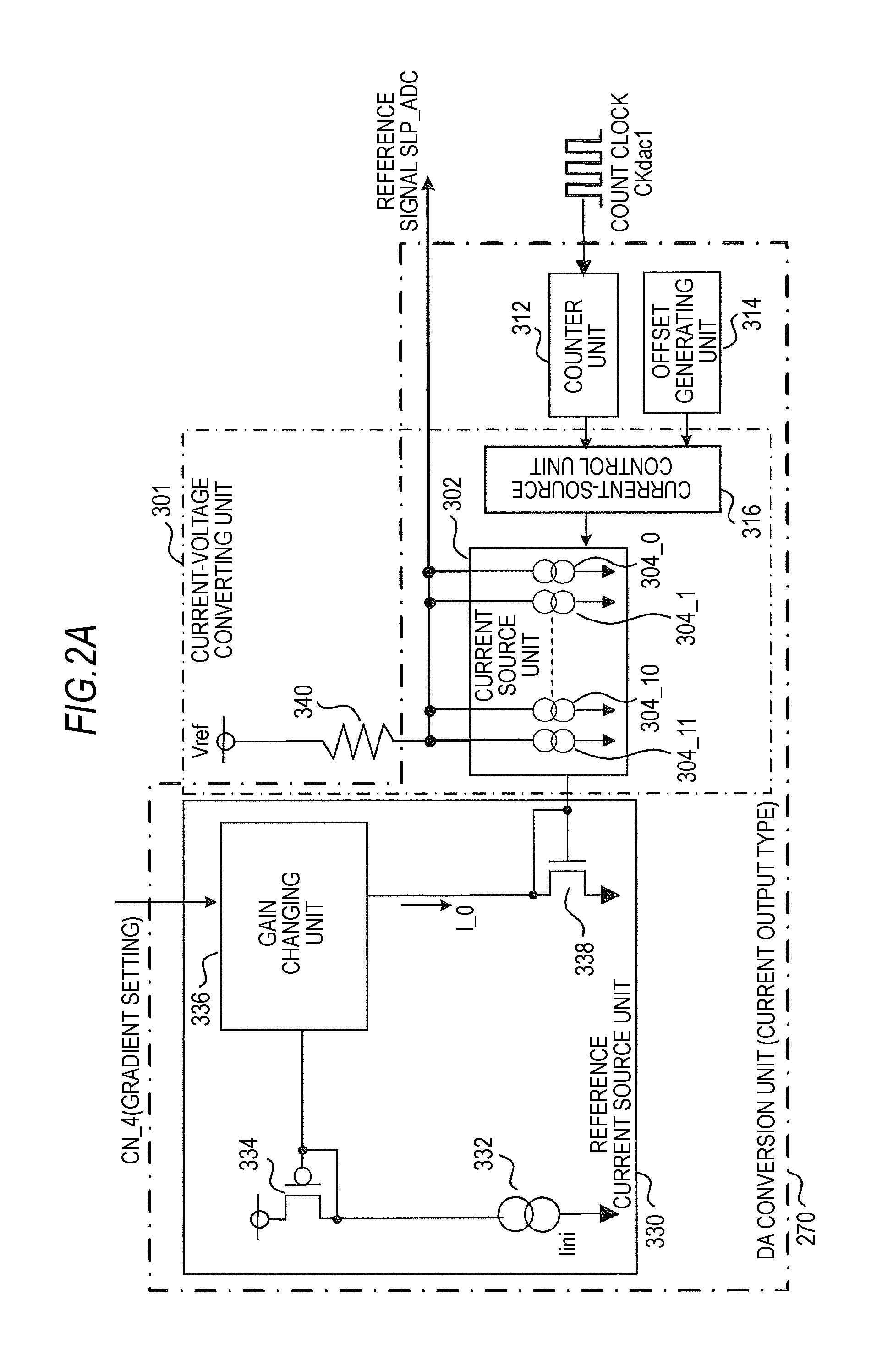
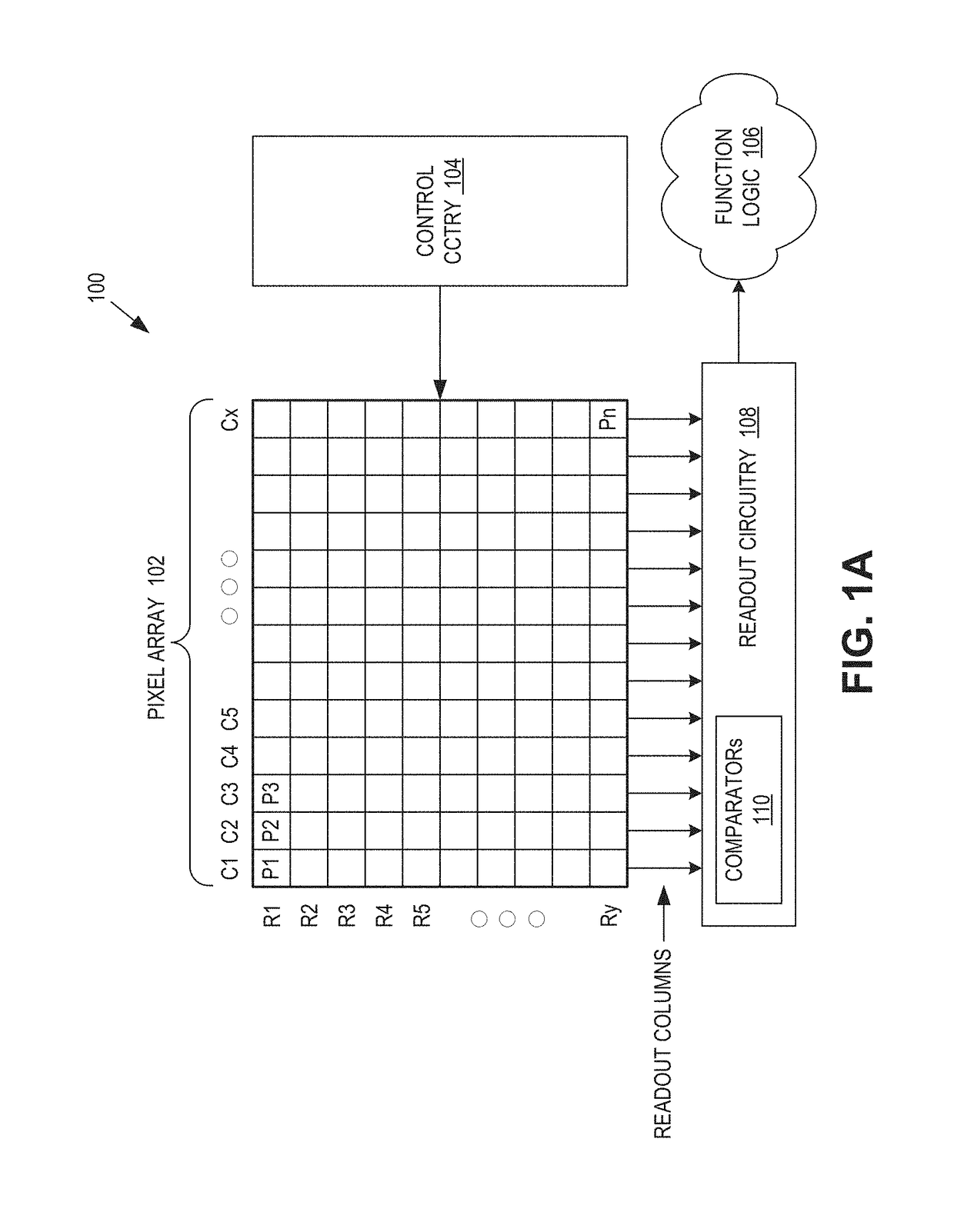
Solid-state imaging device, imaging apparatus, and ad conversion gain adjusting method
ActiveUS20100079611A1Reduce decreaseIncrease in circuit sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsTarget signalExecution control
A solid-state imaging device includes: a pixel unit in which unit pixels outputting processing target signals are arranged in a horizontal direction and scanning lines are wired such that the processing target signals can be read out in order in a vertical direction within a repetition unit of an array of the unit pixels in the horizontal direction; an AD conversion unit including comparing units that compare a reference signal supplied from a reference-signal generating unit and the processing target signals, and counter units that perform count operation, the AD conversion unit performing AD conversion processing based on output data of the counter units; and a driving control unit that performs control to read out the processing target signals in order in the vertical direction and controls the reference-signal generating unit and the AD conversion unit such that AD conversion gains are individually adjusted in order to correct an output amplitude characteristic difference within the repetition unit during AD conversion processing.
Owner:SONY CORP
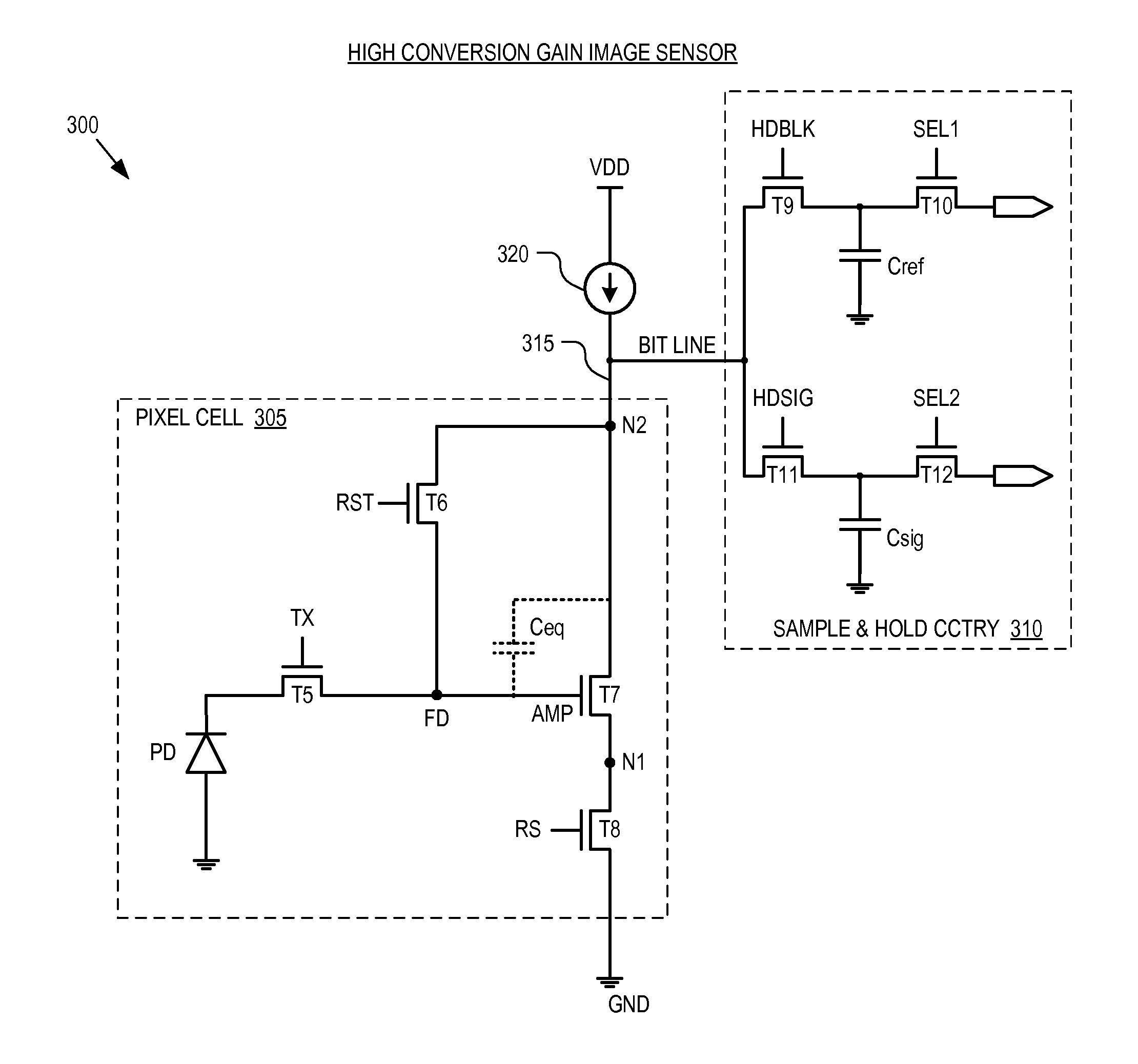
High conversion gain image sensor
ActiveUS20090272879A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierEngineering
An image sensor includes a photosensitive element, a reset circuit, an amplifier transistor, and a current source. The photosensitive element is coupled to generate an image charge in response to incident light and transfer the image charge to a circuit node. The reset circuit is coupled to selectively reset a voltage at the circuit node. The amplifier transistor includes a gate terminal responsive to the voltage at the circuit node. A current source is coupled between a high level power rail and a second terminal of the amplifier transistor.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
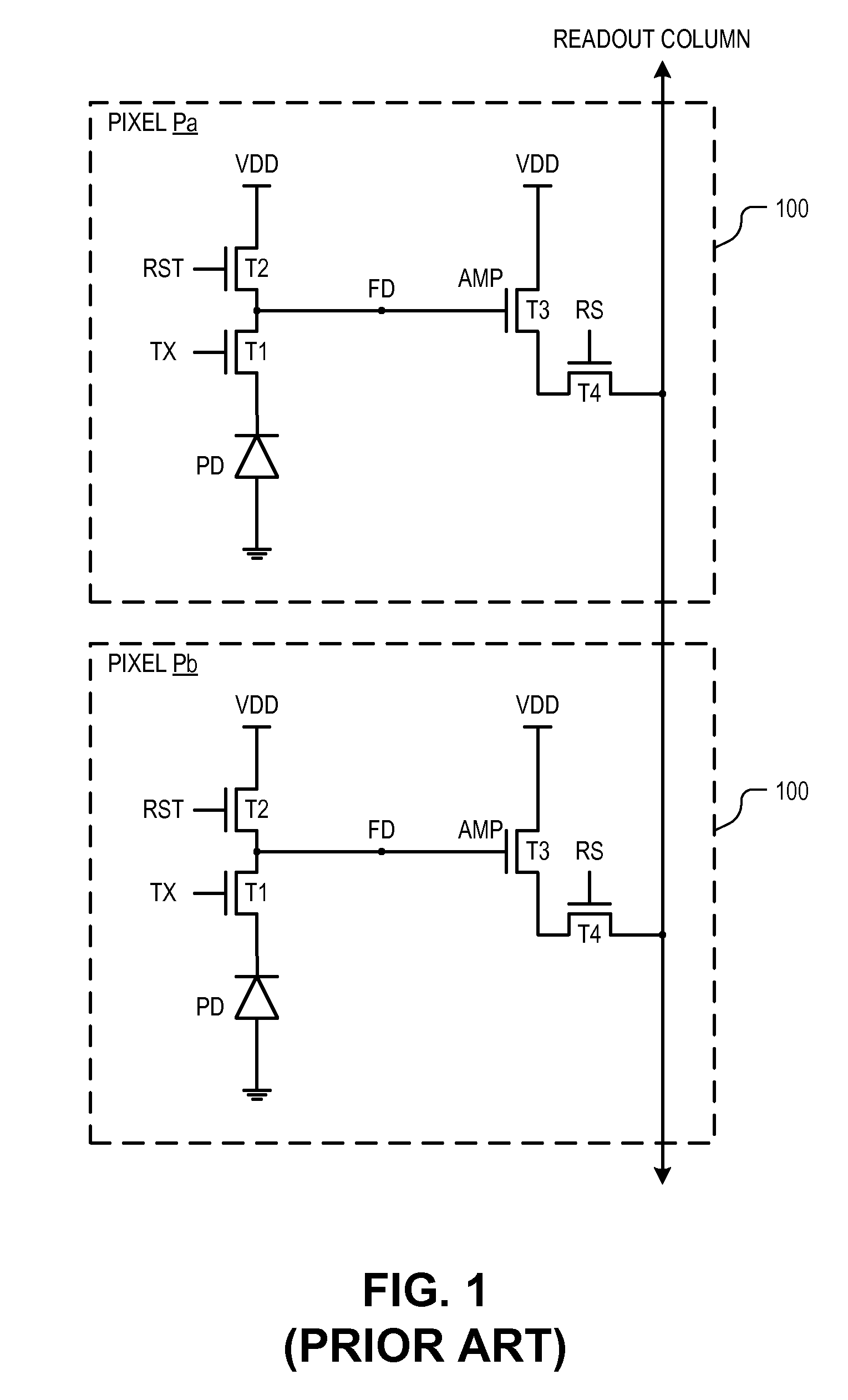
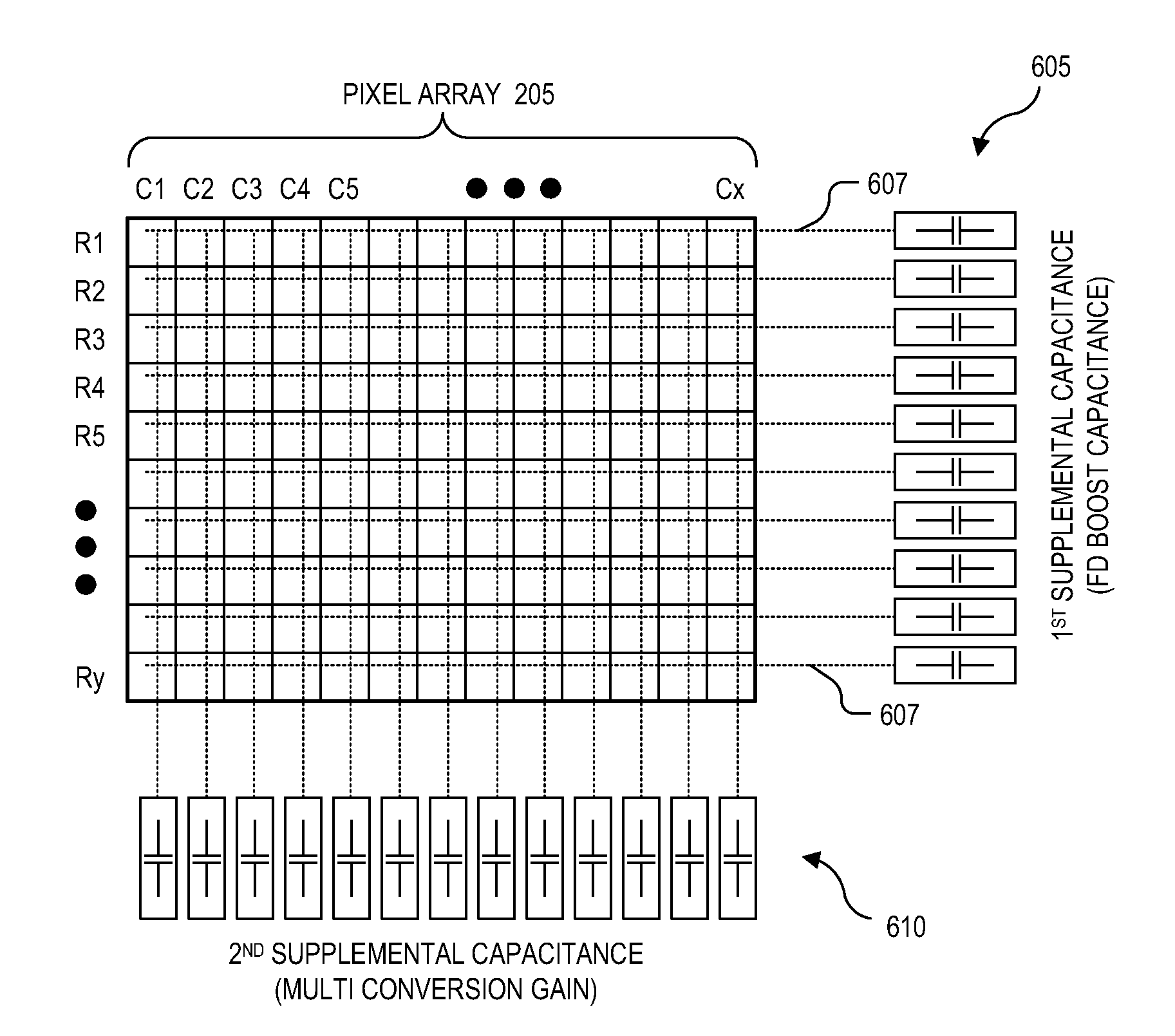
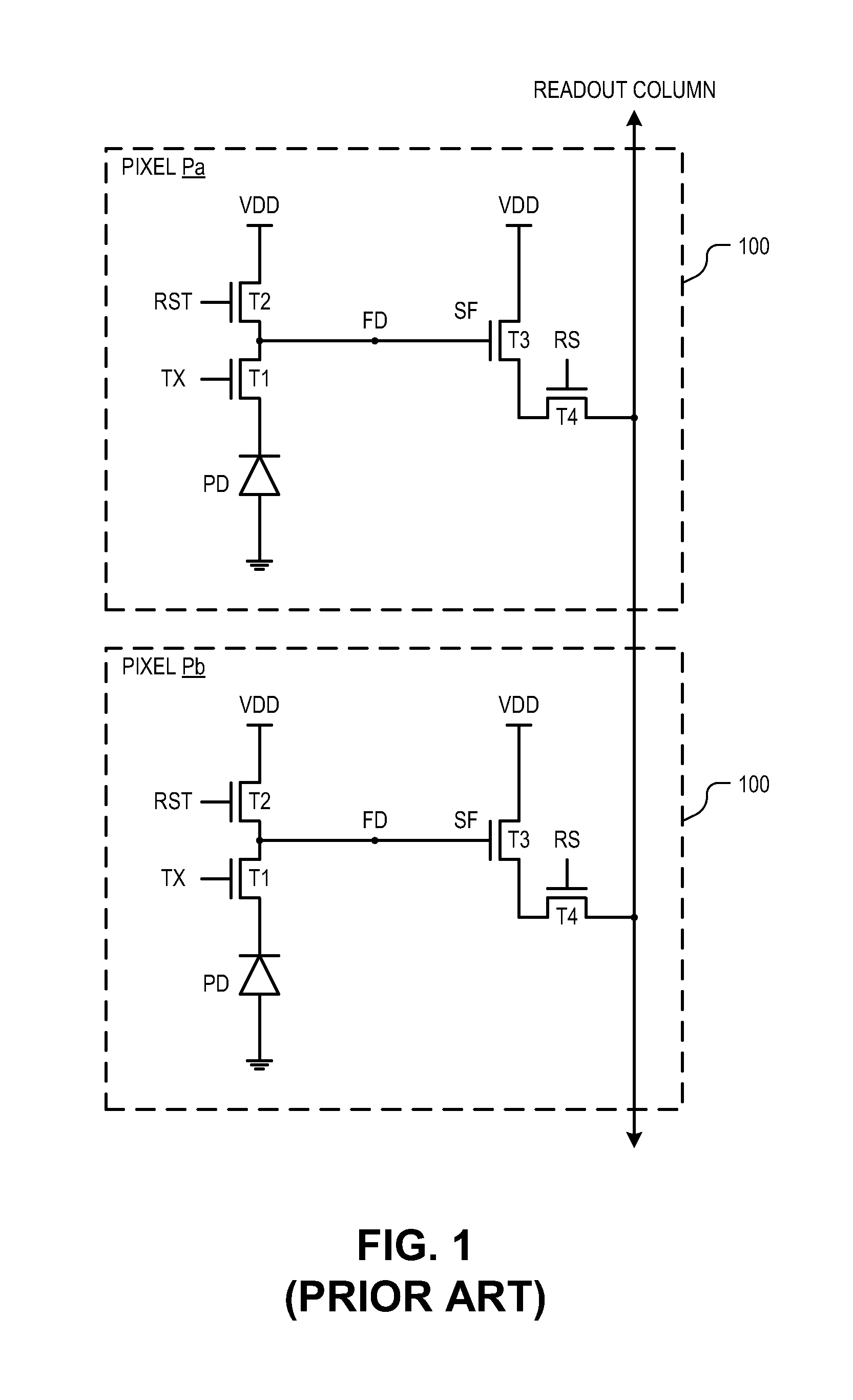
Image sensor having supplemental capacitive coupling node
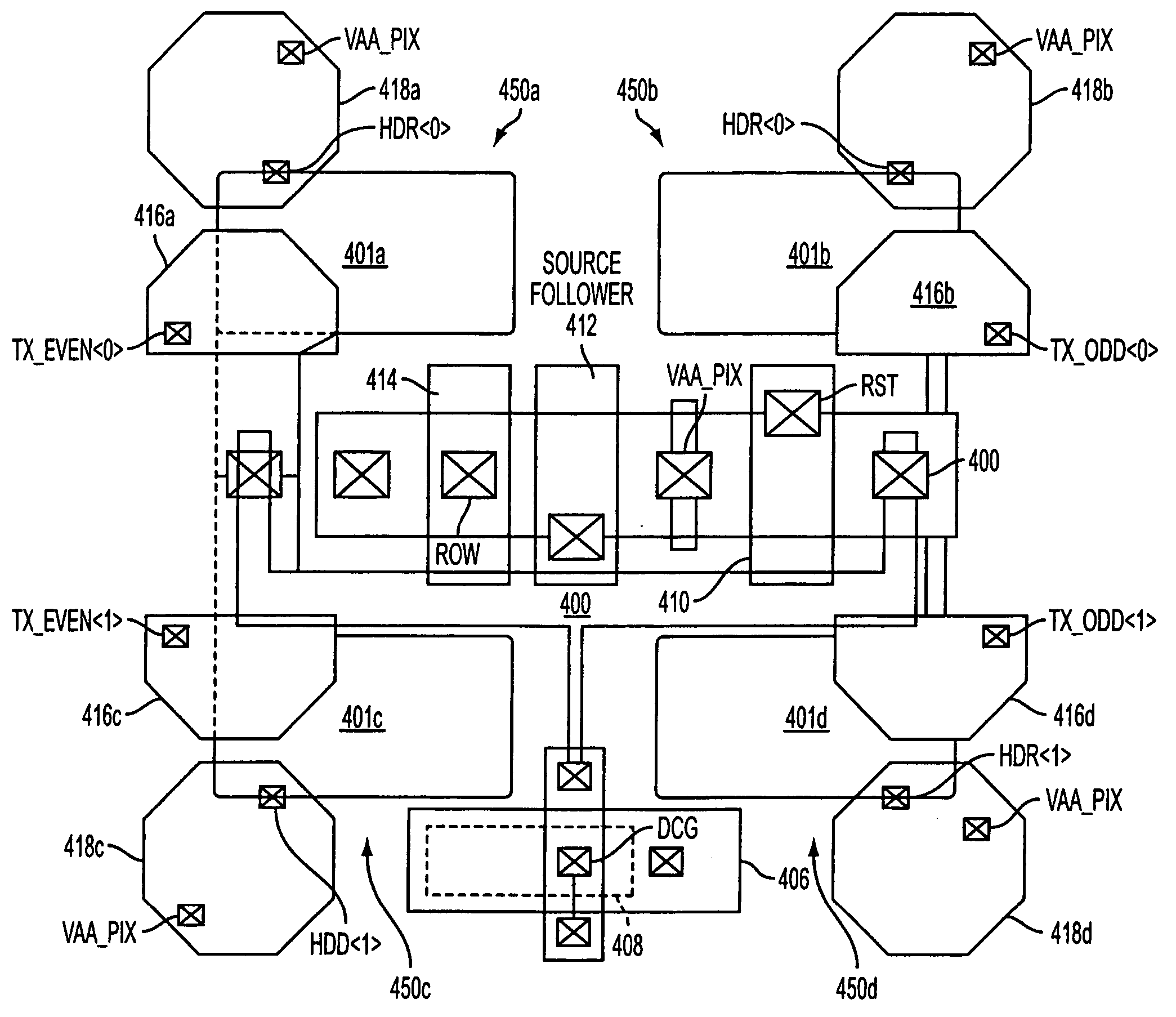
An image sensor includes a pixel array, a bit line, supplemental capacitance node line, and a supplemental capacitance circuit. The pixel array includes a plurality of pixel cells each including a floating diffusion (“FD”) node and a photosensitive element coupled to selectively transfer image charge to the FD node. The bit line is coupled to selectively conduct image data output from a first group of the pixel cells. The supplemental capacitance node line is coupled to the FD node of a second group of the pixel cells to selectively couple a supplemental capacitance to the FD nodes of the second group in response to a control signal. In various embodiments, the first and second group of pixel cells may be the same group or a different group of the pixel cells and may add a capacitive boost feature or a multi conversion gain feature.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Conversion Gain Modulation Using Charge Sharing Pixel
An image sensor including an array of pixel elements is operated according to two operation modes to modulate the conversion gain of the pixel to operate the image sensor based on the impinging light conditions. More specifically, an image sensor pixel element is operated in a high conversion gain mode for low light conditions and in a low conversion gain mode for bright light conditions. The low conversion gain mode implements charge sharing between the floating diffusion and the photodiode. The low conversion gain mode further implements partial reset where the photodiode and the floating diffusion are reset to the same potential and to a potential slightly less than the pinning voltage of the photodiode.
Owner:PIXIM
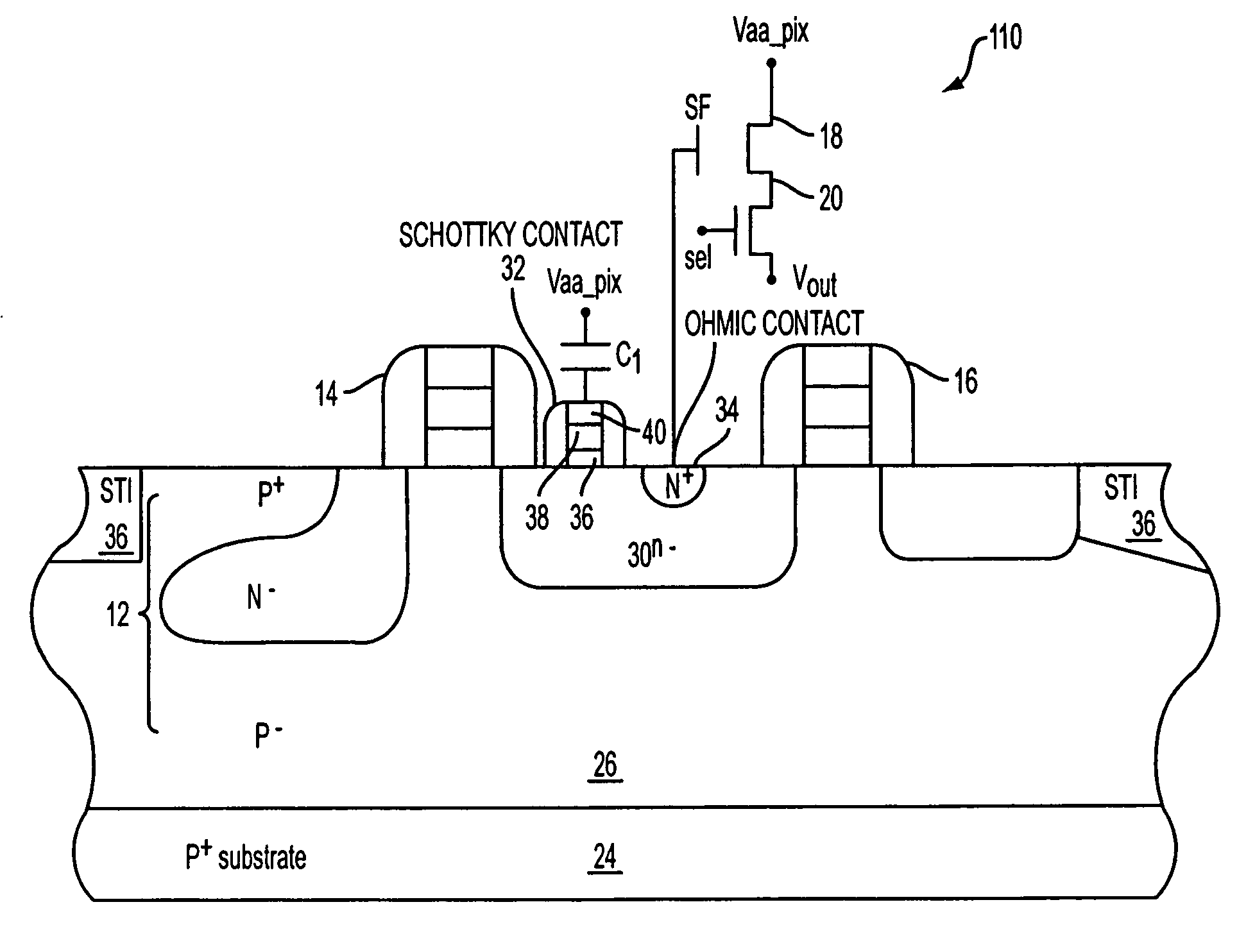
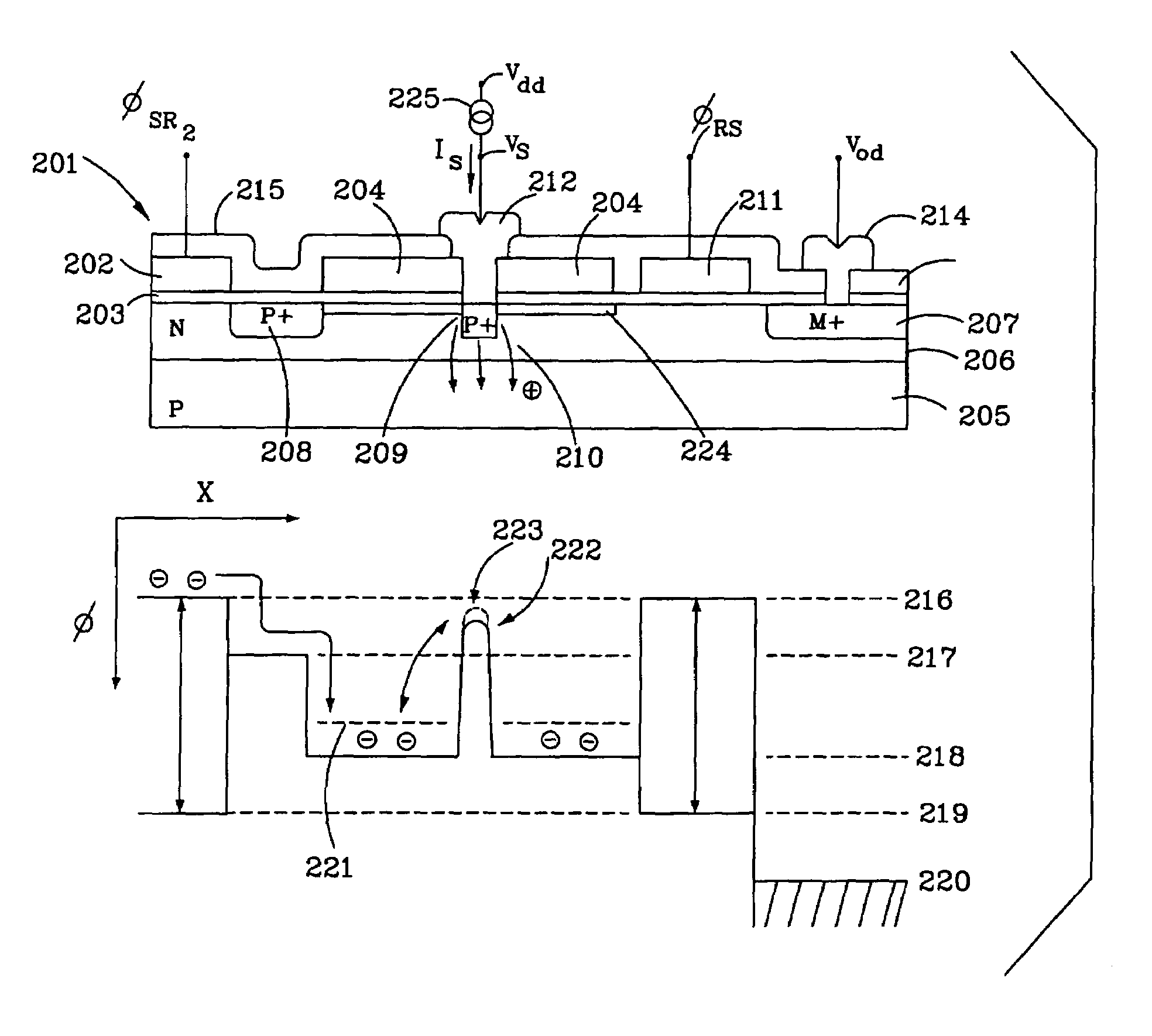
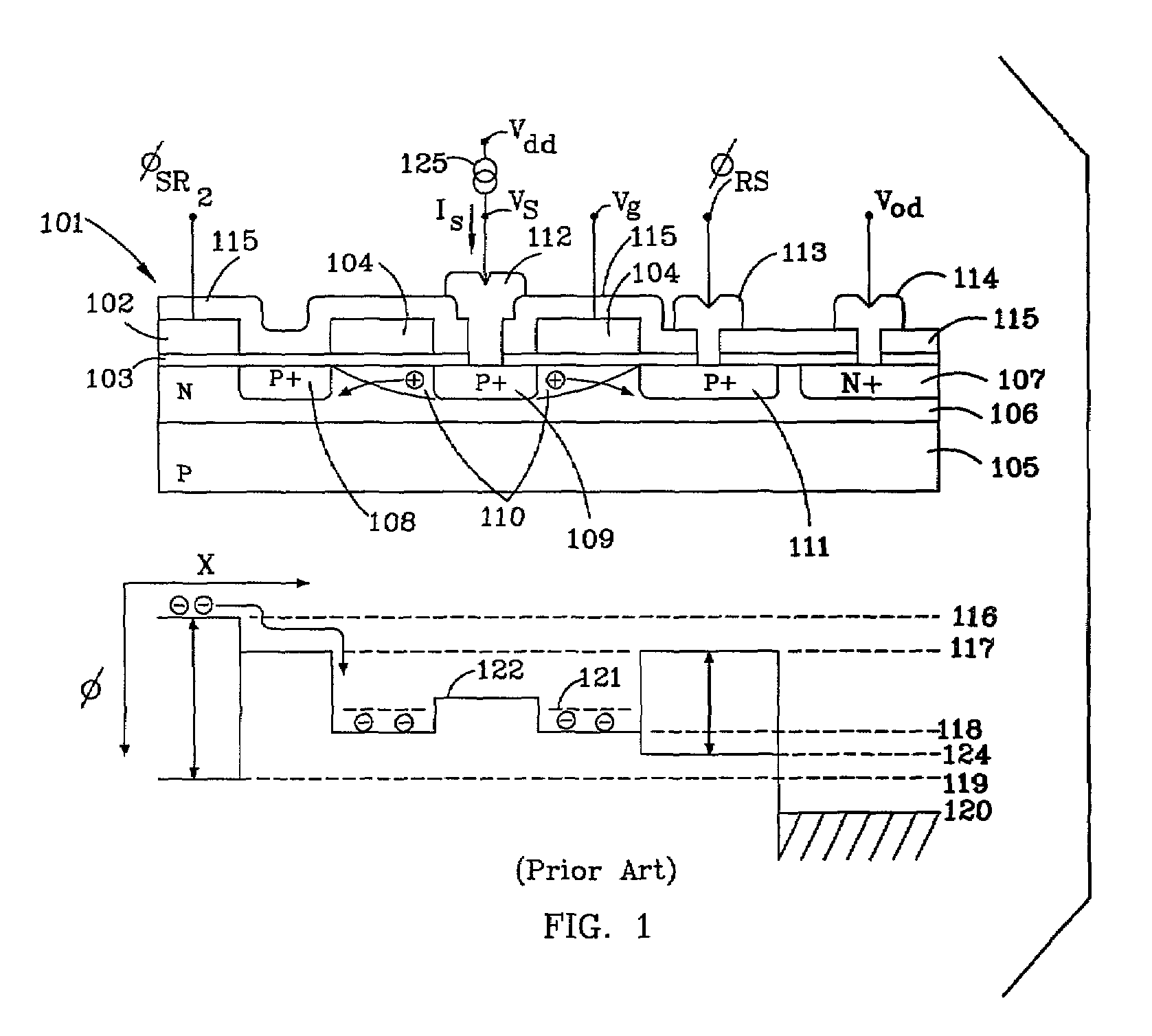
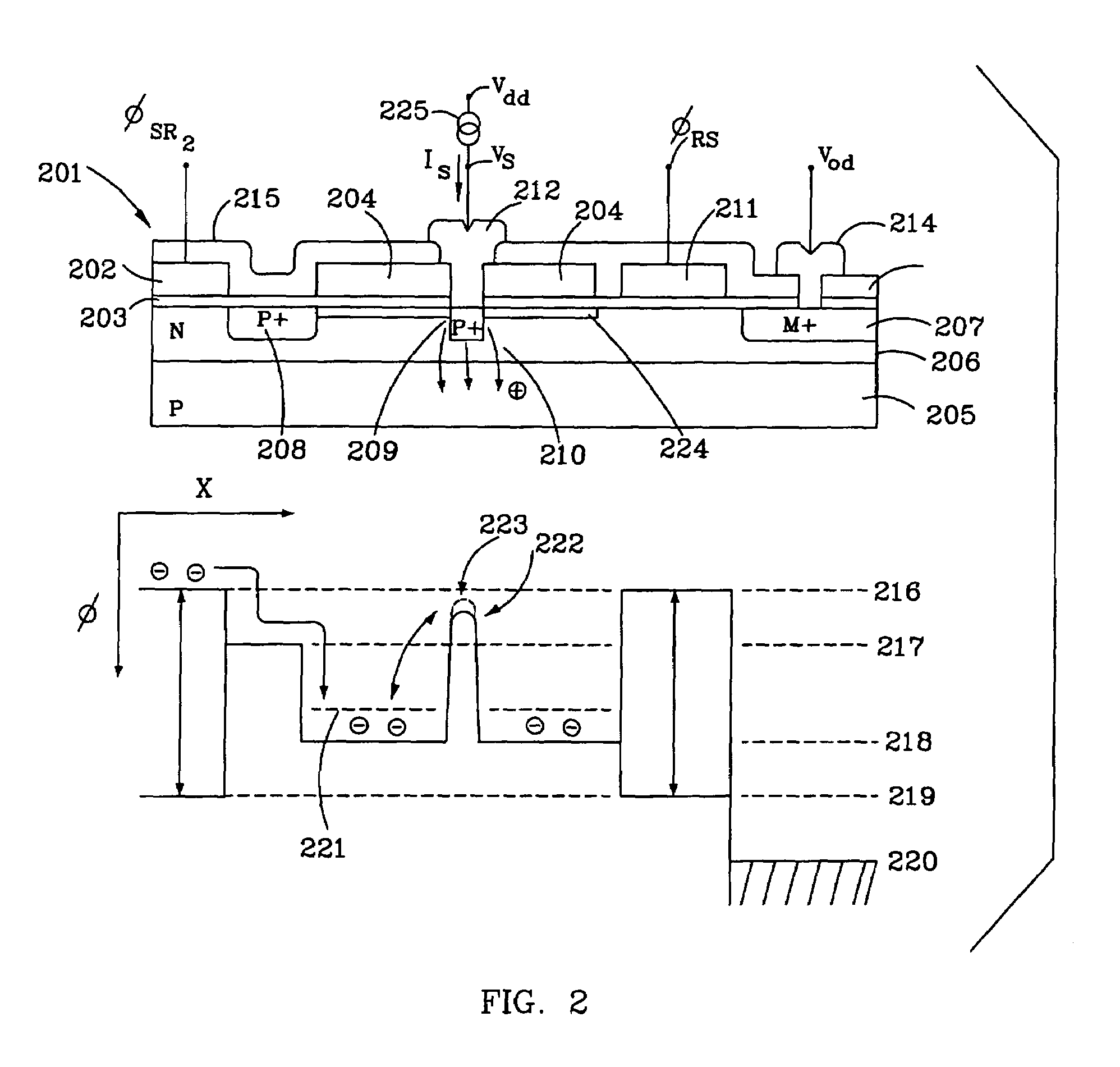
Dual conversion gain pixel using Schottky and ohmic contacts to the floating diffusion region and methods of fabrication and operation
ActiveUS20060231875A1Improve dynamic rangeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceOhmic contact
The exemplary embodiments provide an imager with dual conversion gain charge storage and thus, improved dynamic range. A dual conversion gain element (e.g., Schottky diode) is coupled between a floating diffusion region and a respective capacitor. The dual conversion gain element switches in the capacitance of the capacitor, in response to charge stored at the floating diffusion region, to change the conversion gain of the floating diffusion region from a first conversion gain to a second conversion gain. In an additional aspect, the exemplary embodiments provide an ohmic contact between the gate of a source follower transistor and the floating diffusion region which assists in the readout of the dual conversion gain output signal of a pixel.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
High dynamic range pixel amplifier
ActiveUS7091531B2Increase capacitanceReduce capacitanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A pixel cell with increased dynamic range is formed by providing a floating diffusion region having a variable capacitance, controlled by at least one gate having source and drain regions commonly connected to the floating diffusion region. The gate has an intrinsic capacitance which, when the gate is activated, is added to the capacitance of the floating diffusion region, providing a low conversion gain readout. When the gate is off, the floating diffusion region capacitance is minimized, providing a high conversion gain readout. The gate may also be selectively switched to mid-level. At mid-level, a mid-level conversion gain, which is between the high and low conversion gains, readout is provided, but the gate still provides some capacitance to prevent the floating diffusion region from saturating.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
CMOS image sensor pixel with selectable binning and conversion gain
ActiveUS7705900B2Increase data rateReduce resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSAudio power amplifier
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Gated vertical punch through device used as a high performance charge detection amplifier
ActiveUS7075575B2Large output voltage swingHigh conversion factorTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow noiseCMOS
A charge detection system used in an image sensor consists of the vertical punch through transistor with the gate surrounding its source and connected to it. The charge detector has a large conversion gain, high dynamic range, low reset feed through, and low noise. It senses charge nondestructively, which avoids generation of kTC noise. Additional embodiments of the invention include a standard reset gate option, a resistive reset gate option, and a lateral punch through transistor reset option to minimize the reset feed through. The charge detection system can be used in all know CCD image sensor architectures as well as in most CMOS image sensor architectures.
Owner:ISETEX
Imaging array having variable conversion gain
ActiveUS20070007438A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A CCD imaging array and a charge measurement amplifier for use in such imaging arrays is disclosed. The array includes a plurality of pixels that accumulate charge when exposed to light, a readout amplifier having input and output ports. The readout amplifier has a variable gain that is set by a gain control signal. The readout amplifier also includes a reset path between the input and output ports, the path having an impedance controlled by a reset signal. A controller generates the gain control signal and the reset signal during a charge measurement cycle. Initially the gain is set to a first value after generating the reset signal. The gain is changed to a second value during the charge measurement cycle if the output signal exceeds a first threshold value. The readout amplifier can be constructed from an operational amplifier having a capacitive feedback loop.
Owner:BAE SYST IMAGING SOLUTIONS
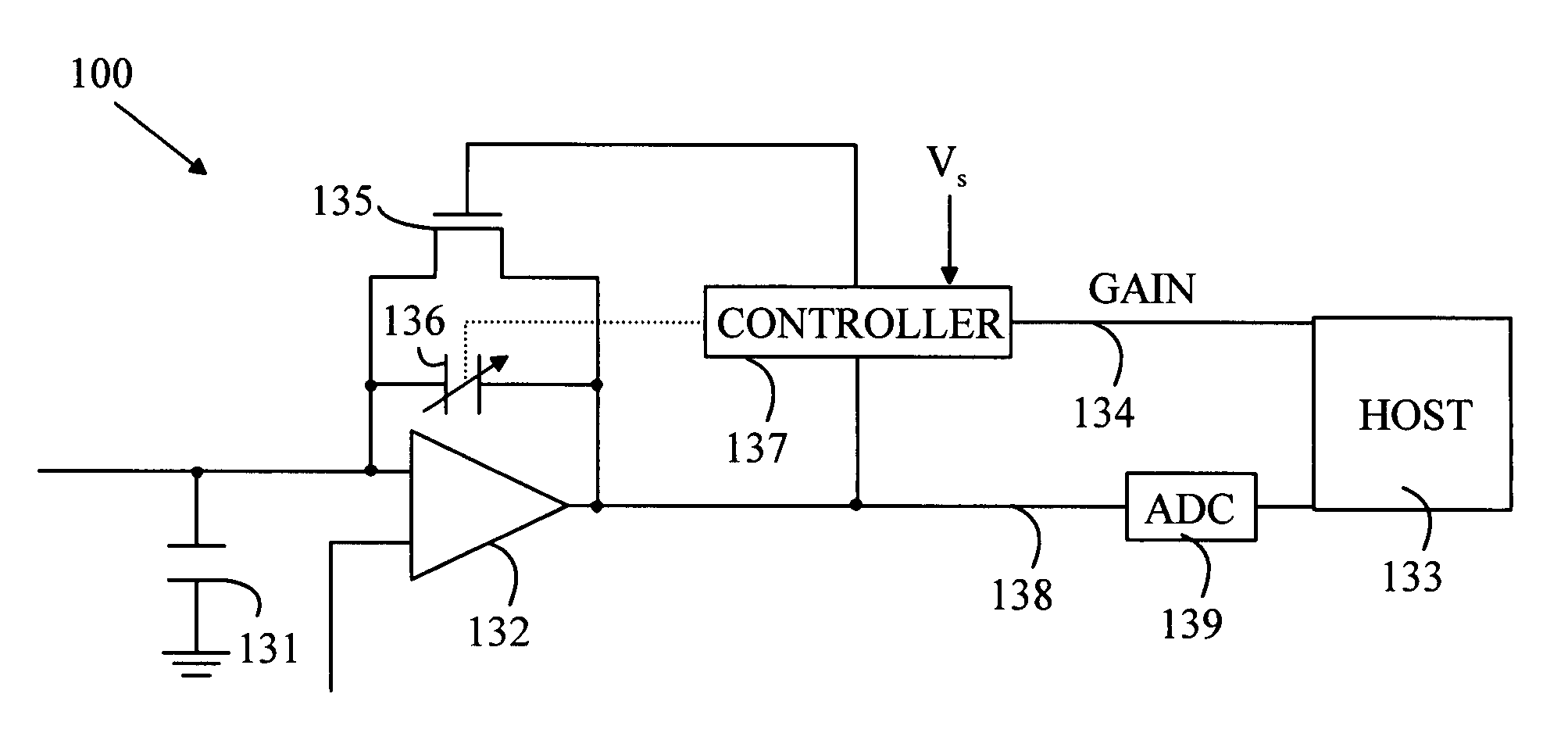
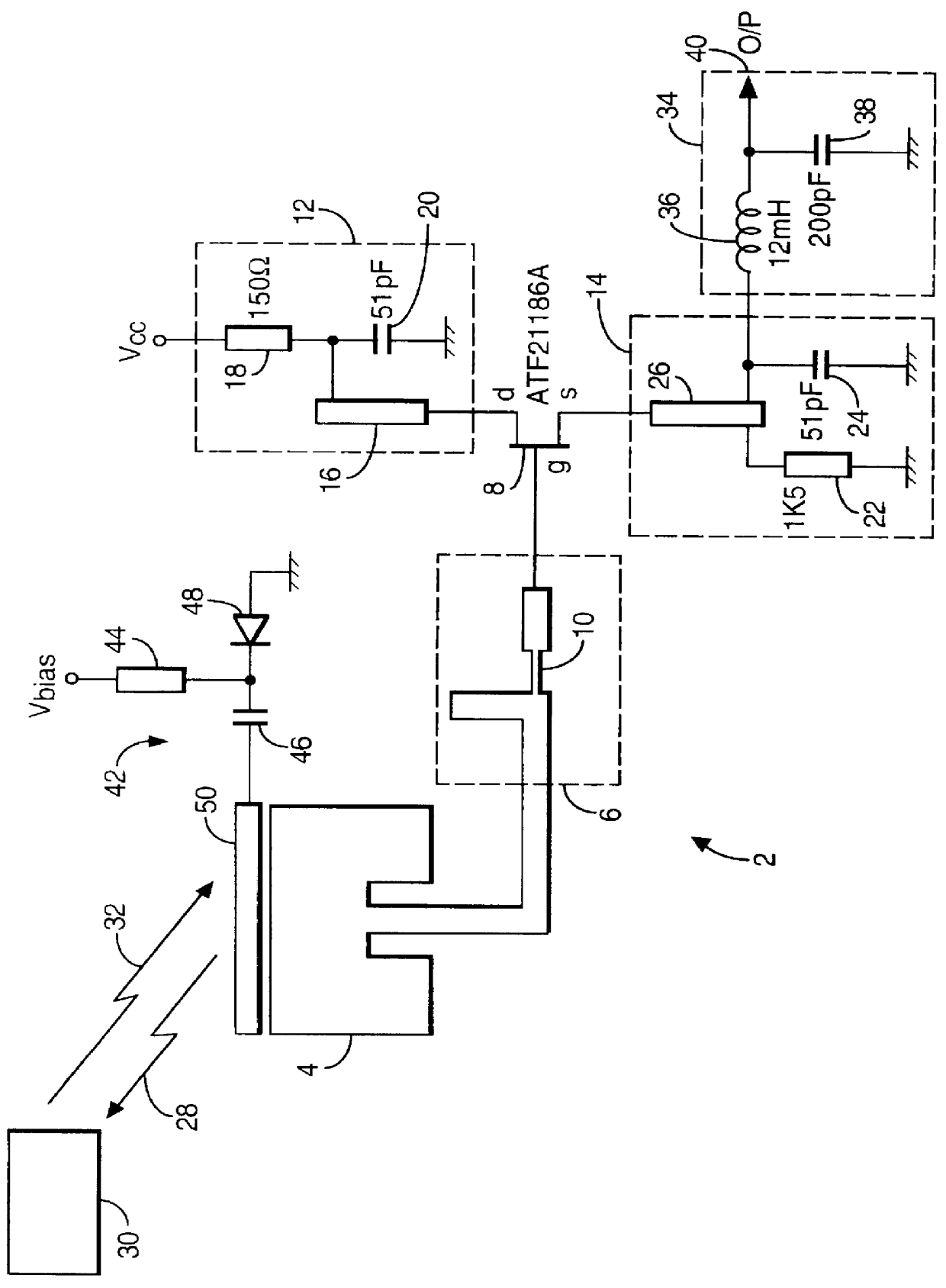
Interrogator circuit arrangement
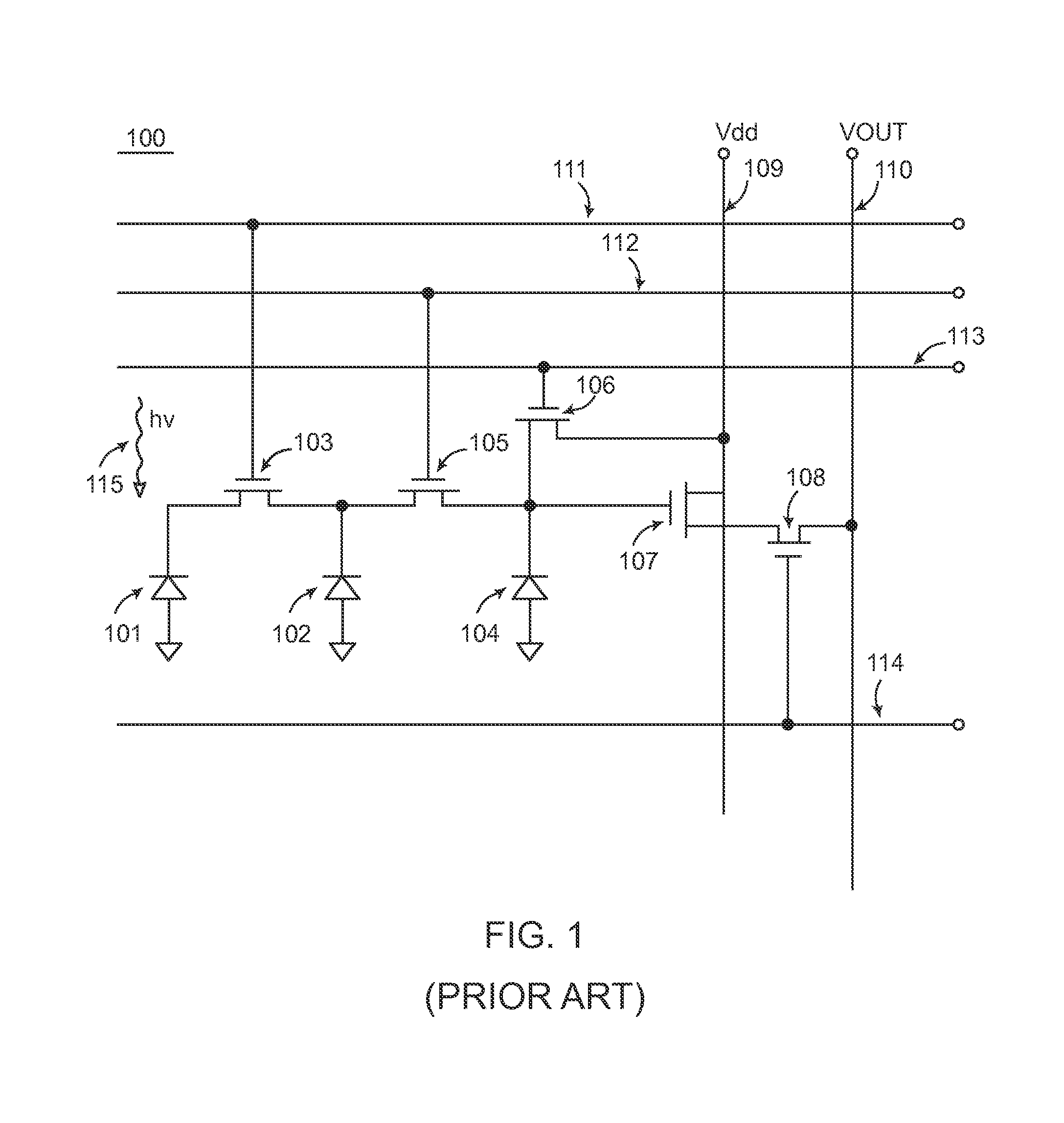
InactiveUS6046668AMemory record carrier reading problemsOscillations generatorsEngineeringTransistor
An interrogator circuit (2) for use with a semi-passive transponder (30) of a type which reflectively modulates an incoming signal (28) is described. The circuit (2) comprises an antenna (4), a transistor (8), a matching network (6) connecting to the antenna (4) to an input of the transistor and means (12, 14) for operating the transistor such that it self-oscillates and radiates power (28) from the antenna (4) and simultaneously acts as a self-oscillating mixer to produce an output (40) which is representative of the modulation of a signal 32 received at the antenna. For an efficient conversion gain the reflection coefficient of the antenna (4) is configured to be low when the circuit is in a stable self-oscillating condition.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
In-pixel high dynamic range imaging system and imaging sensor pixels
The application relates to an in-pixel high dynamic range imaging system and imaging sensor pixels. Embodiments of the invention describe providing high dynamic range imaging (HDRI or simply HDR) to an imaging pixel by coupling a floating diffusion node of the imaging pixel to a plurality of metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) capacitance regions. It is understood that a MOS capacitance region only turns on (i.e., changes the overall capacitance of the floating diffusion node) when the voltage at the floating diffusion node (or a voltage difference between a gate node and the floating diffusion node) is greater than its threshold voltage; before the MOS capacitance region is on it does not contribute to the overall capacitance or conversion gain of the floating diffusion node. Each of the MOS capacitance regions will have different threshold voltages, thereby turning on at different illumination conditions. This increases the dynamic range of the imaging pixel, thereby providing HDR for the host imaging system.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
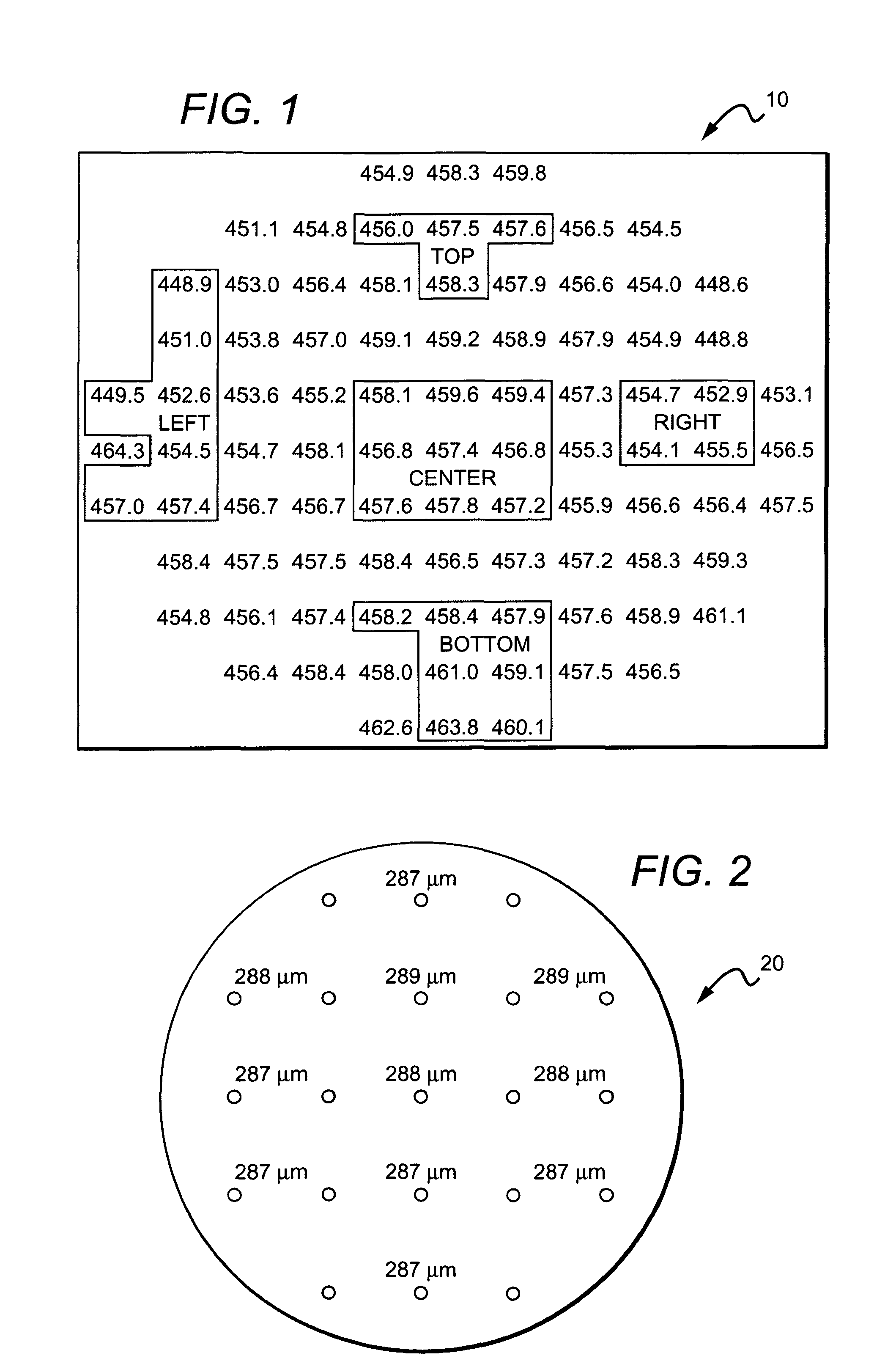
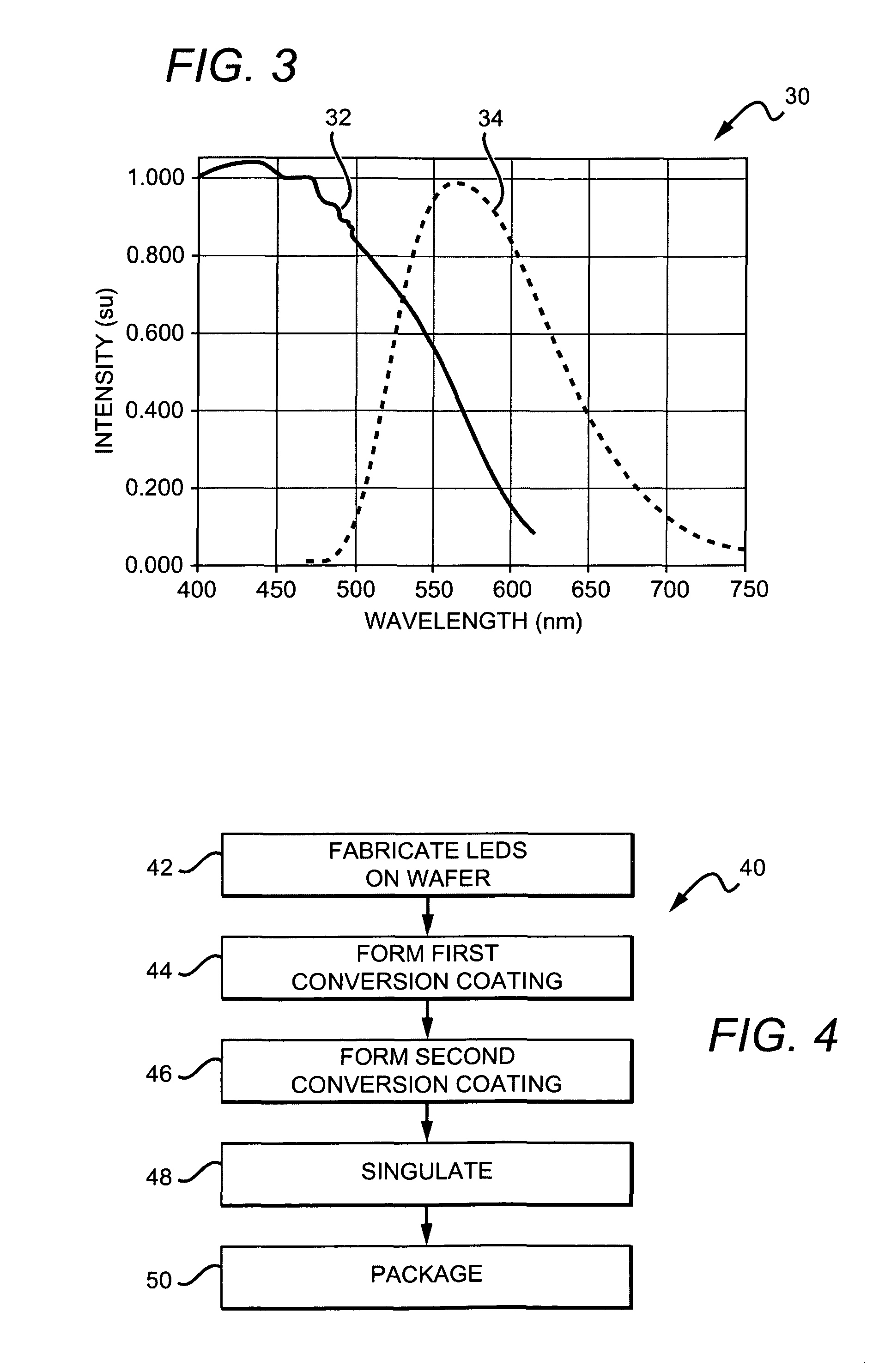
Wafer level phosphor coating technique for warm light emitting diodes
Methods for wafer level fabricating of light emitting diode (LED) chips are disclosed with one embodiment of a method according to the present invention comprising providing a plurality of LEDs and then coating of the LEDs with a layer of first conversion material so that at least some light from the LEDs passes through the first conversion material. The light is converted to different wavelengths of light having a first conversion material emission spectrum. The LEDs are then coated with a layer of second conversion material arranged on the first layer of conversion. The second conversion material has a wavelength excitation spectrum, and at least some light from the LEDs passes through the second conversion material and is converted. The first conversion material emission spectrum does not substantially overlap with the second conversion material excitation spectrum. Methods according to the present invention can also be used in wafer level fabrication of LED chips and LED packages with pedestals for electrically contacting the LEDs through the conversion coatings.
Owner:CREELED INC
Dual conversion gain gate and capacitor combination
A pixel cell array architecture having a dual conversion gain. A dual conversion gain element is coupled between a floating diffusion region and a respective storage capacitor. The dual conversion gain element having a control gate switches in the capacitance of the capacitor to change the conversion gain of the floating diffusion region from a first conversion gain to a second conversion gain. In order to increase the efficient use of space, the dual conversion gain element gate also functions as the bottom plate of the capacitor. In one particular embodiment of the invention, a high dynamic range transistor is used in conjunction with a pixel cell having a capacitor-DCG gate combination; in another embodiment, adjacent pixels share pixel components, including the capacitor-DCG combination.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
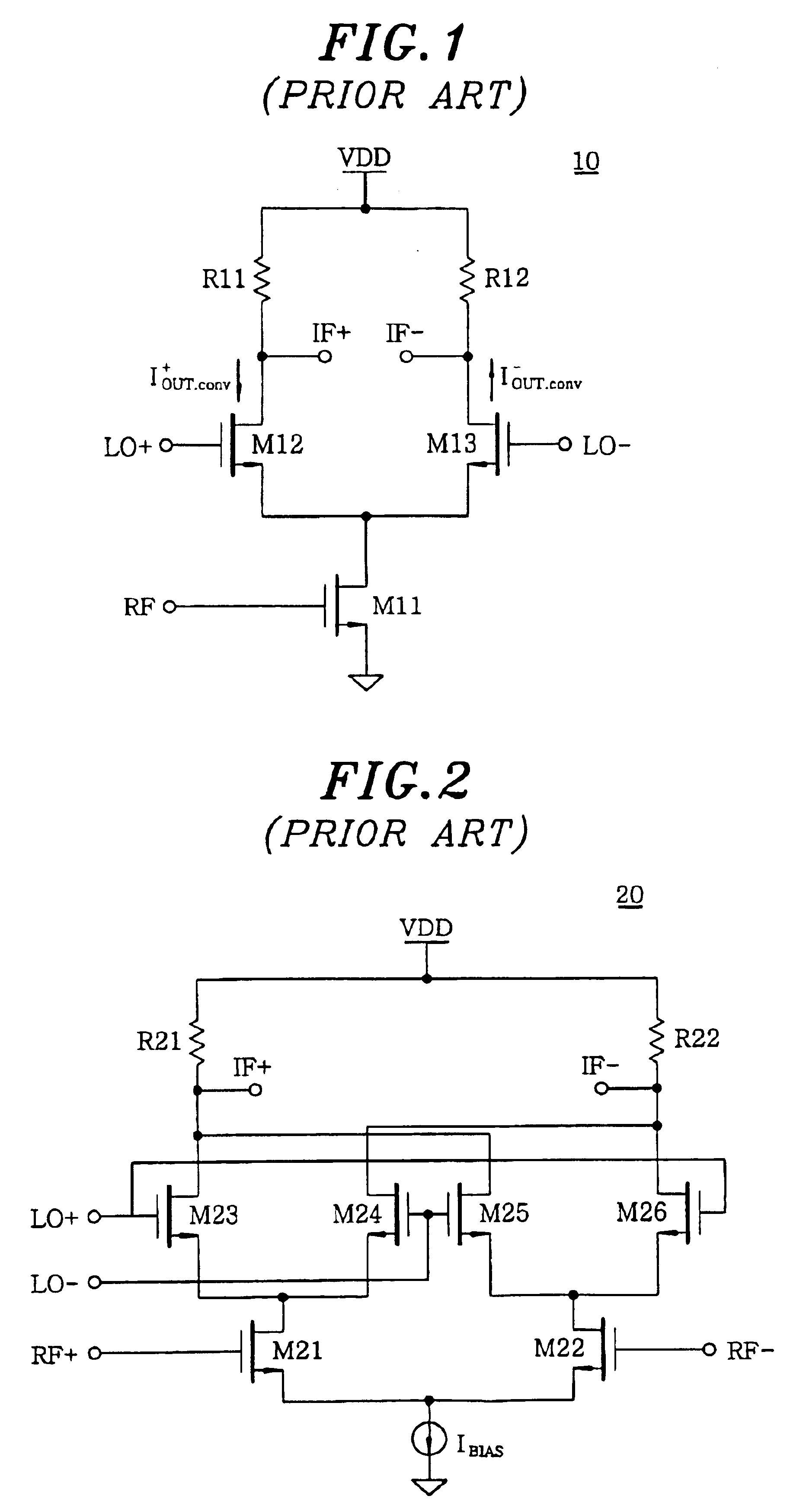
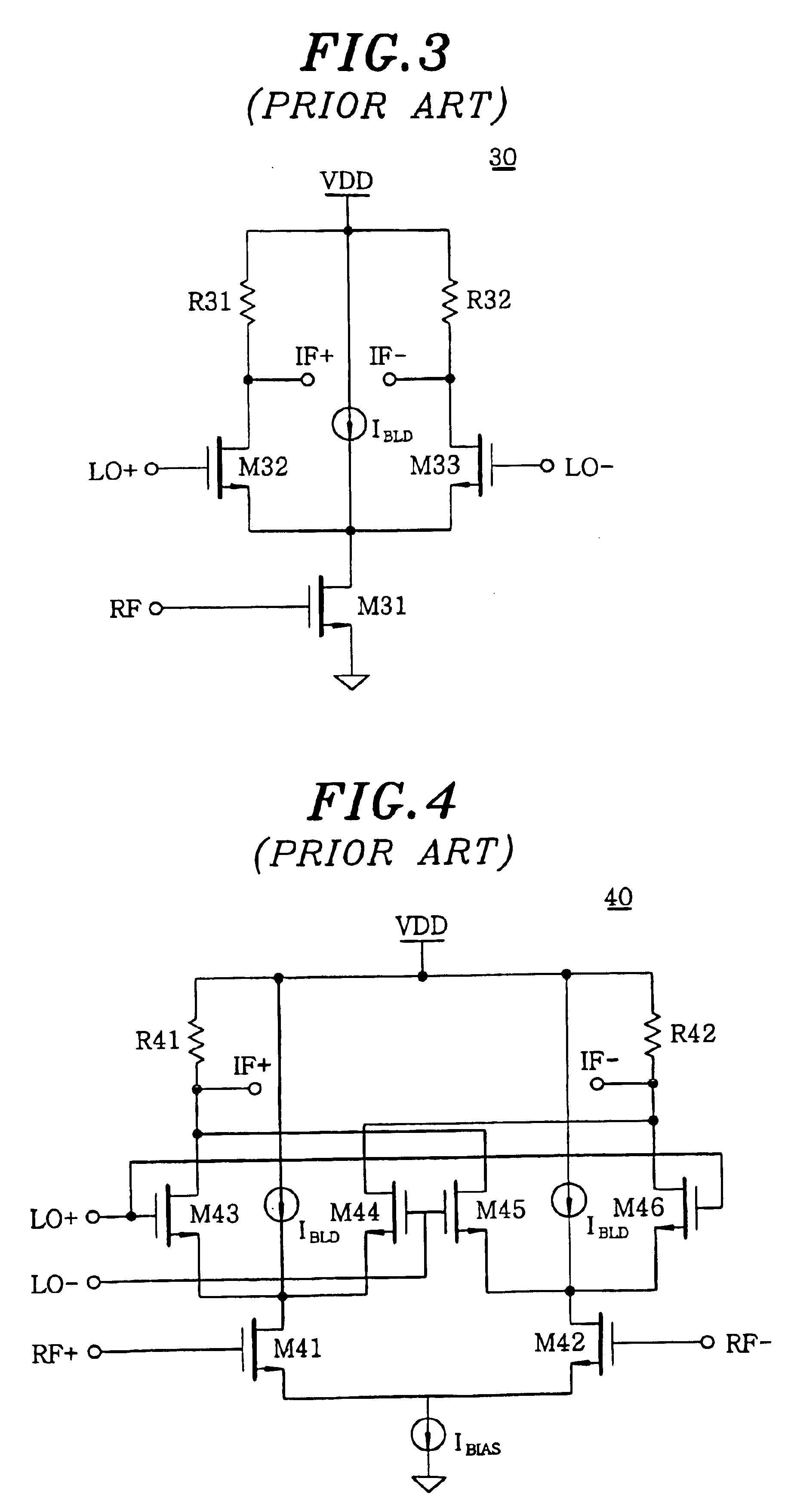
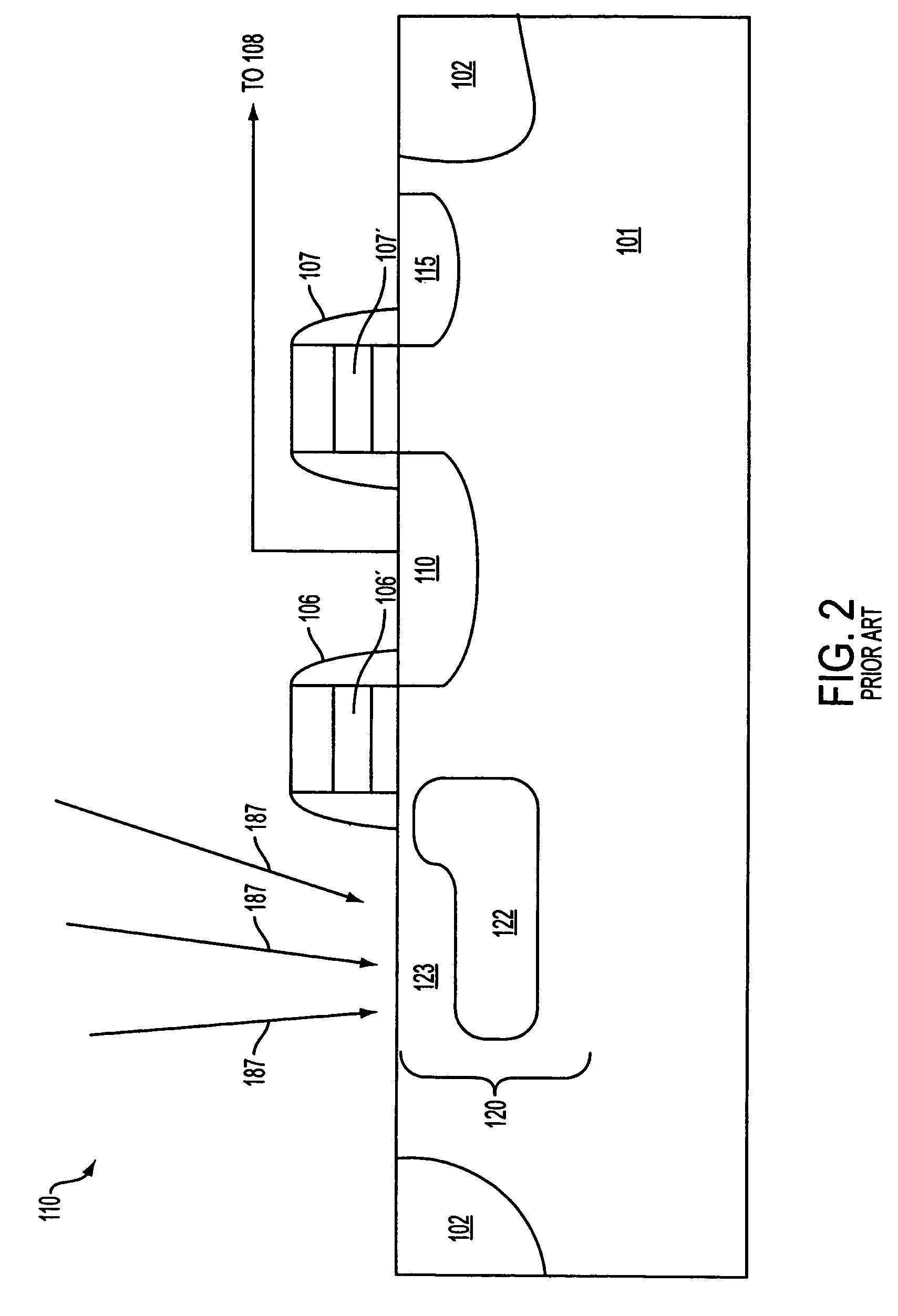
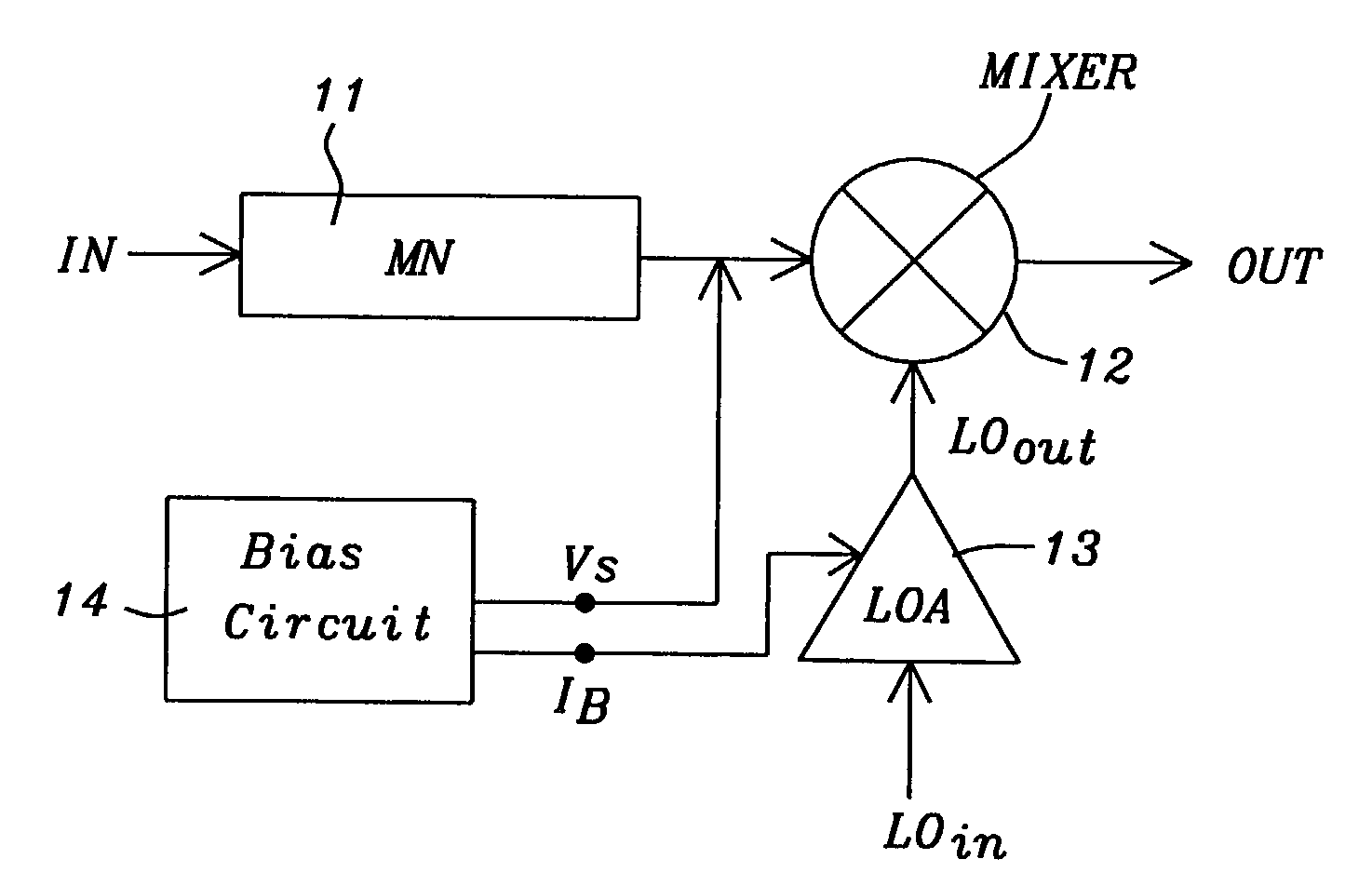
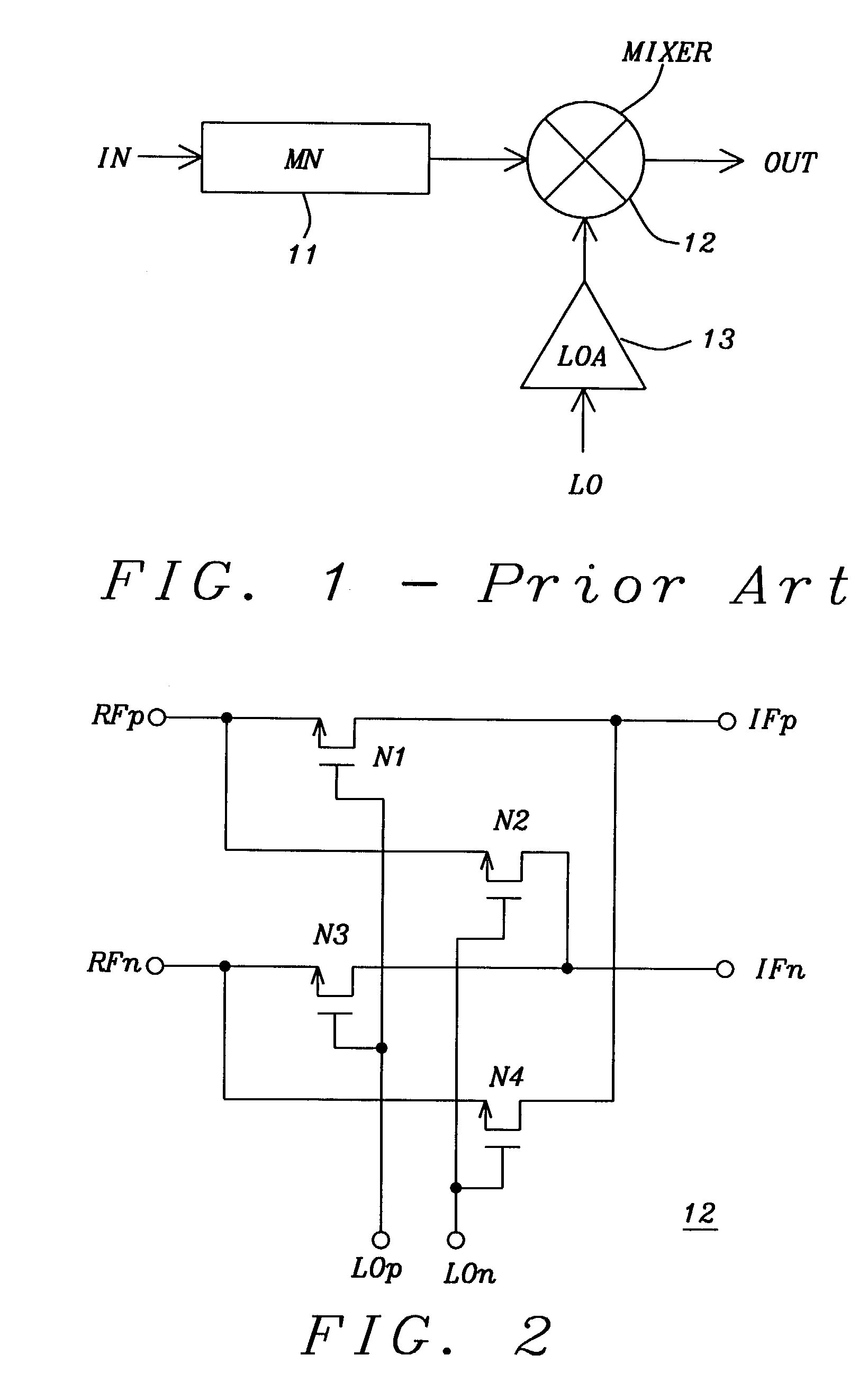
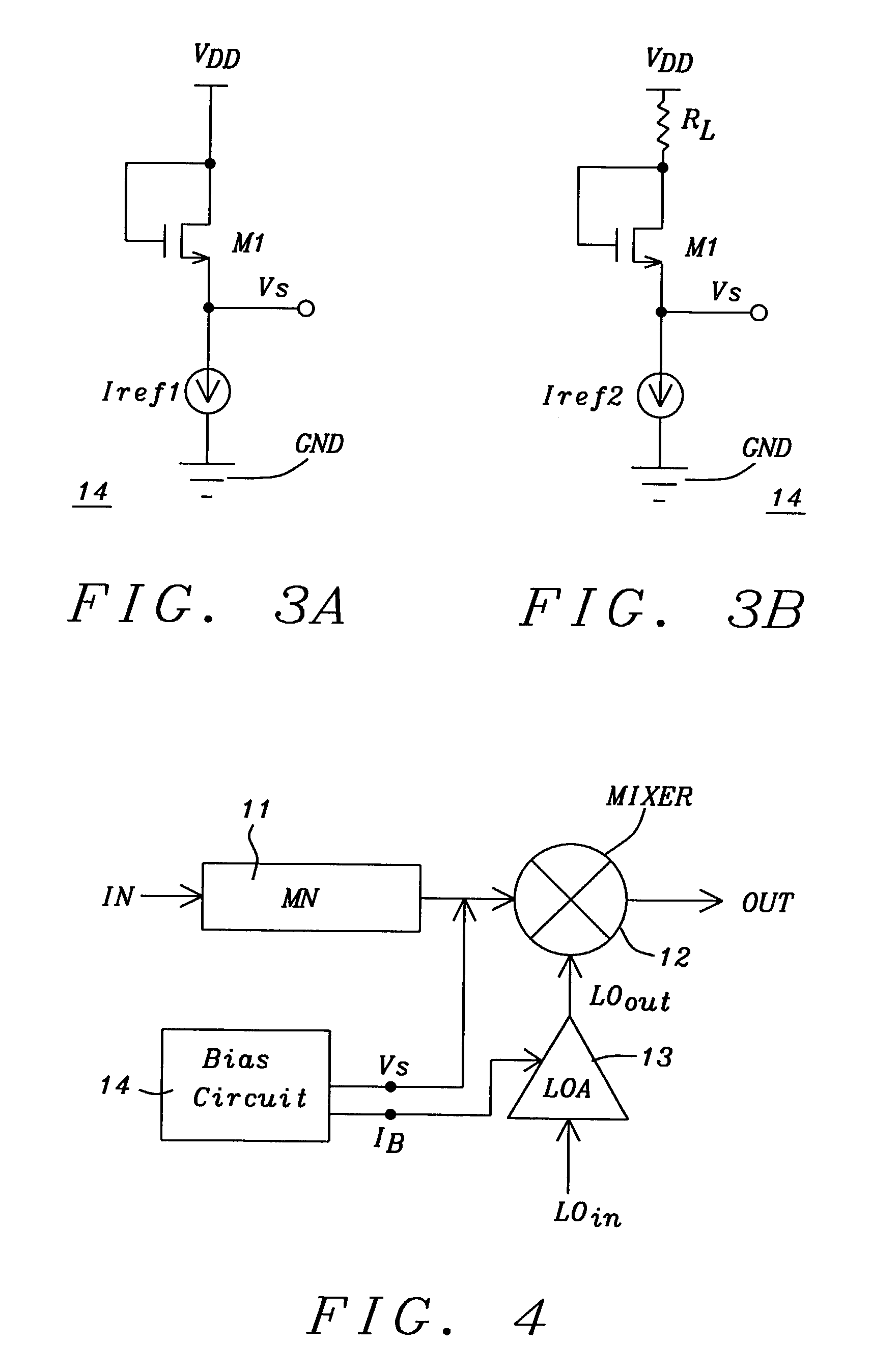
Threshold voltage (Vth), power supply (VDD), and temperature compensation bias circuit for CMOS passive mixer
ActiveUS7092692B2Conversion stabilityLinear stabilityModulation transference balanced arrangementsSolid-state devicesMOSFETReference current
A biasing circuit for a CMOS passive mixer core to stabilize its conversion gain, linearity and noise figure. The RF inputs are fed differentially from the two RF ports, the LO inputs are fed differentially from the two LO ports, and the IF outputs are obtained at the two IF ports. The biasing circuit comprises a reference current derived from the bandgap voltage and a n-channel MOSFET transistor. The conversion gain is stabilized by keeping the Vgs−Vth value of the passive mixer core almost constant at all process corners, temperature and power supply changes. This is achieved by implementing Vs in such a way that it will increase the same amount as VDD decreases, and that Vs will decrease the same amount as Vth increases.
Owner:WIPRO LTD +1
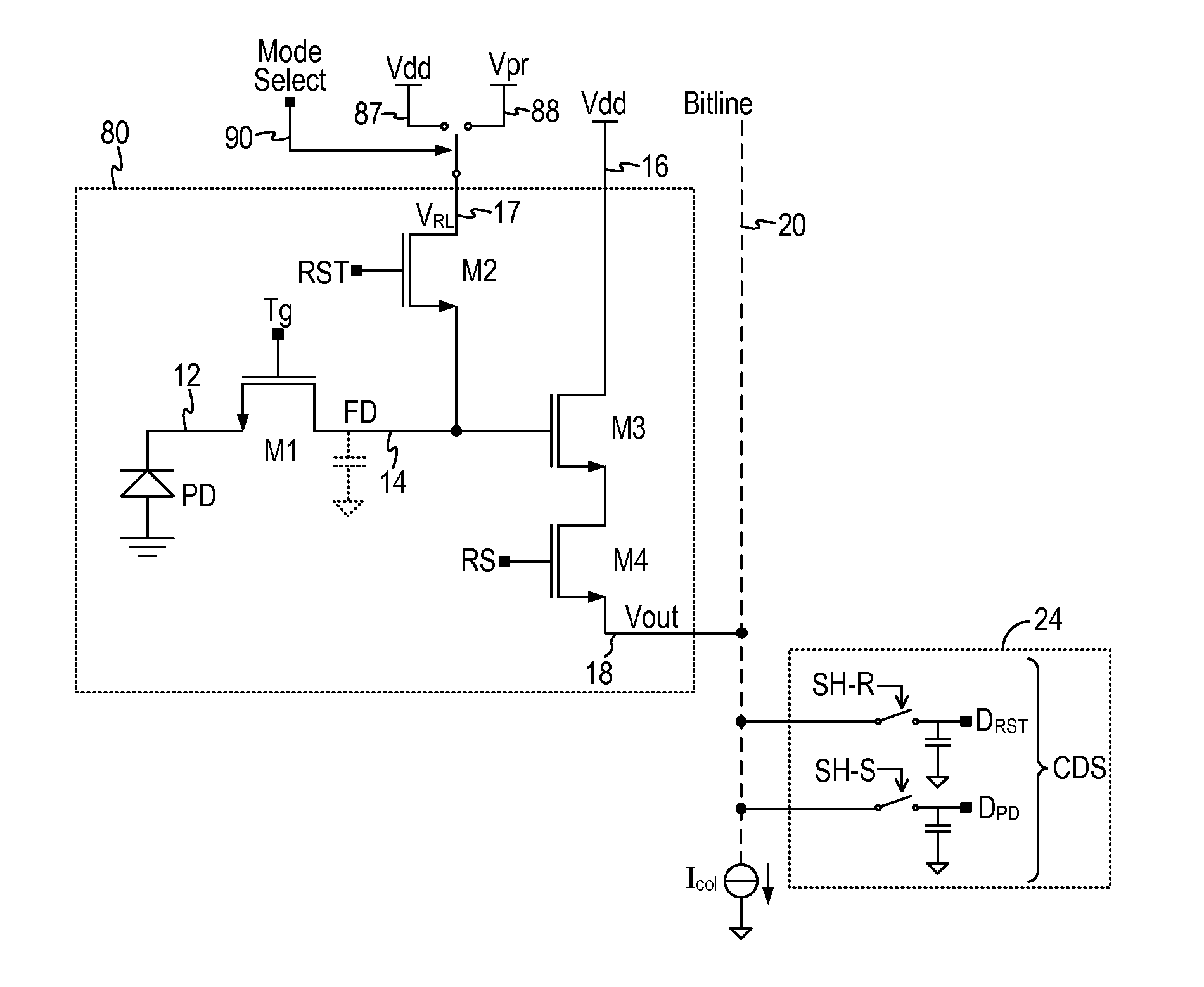
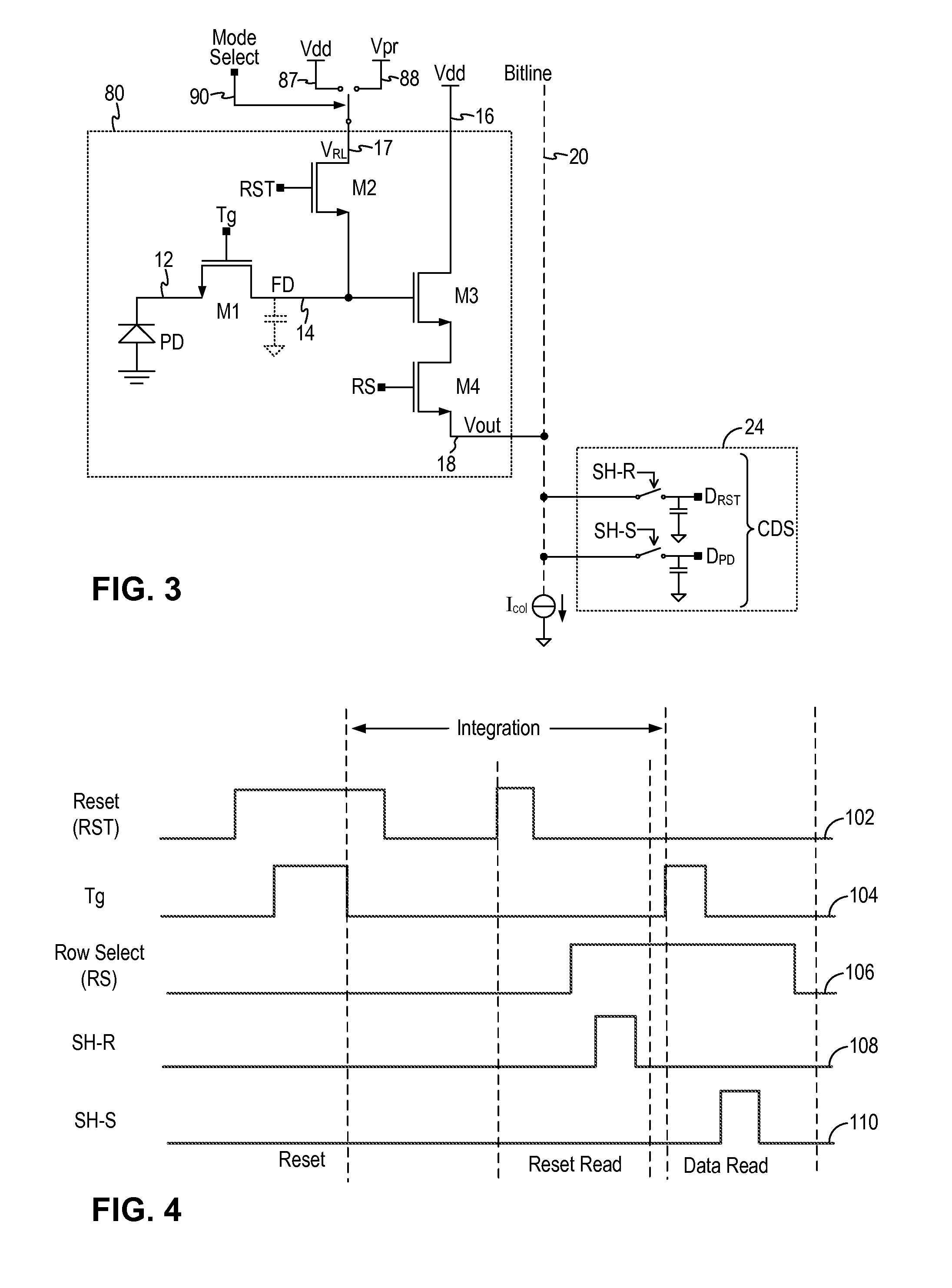
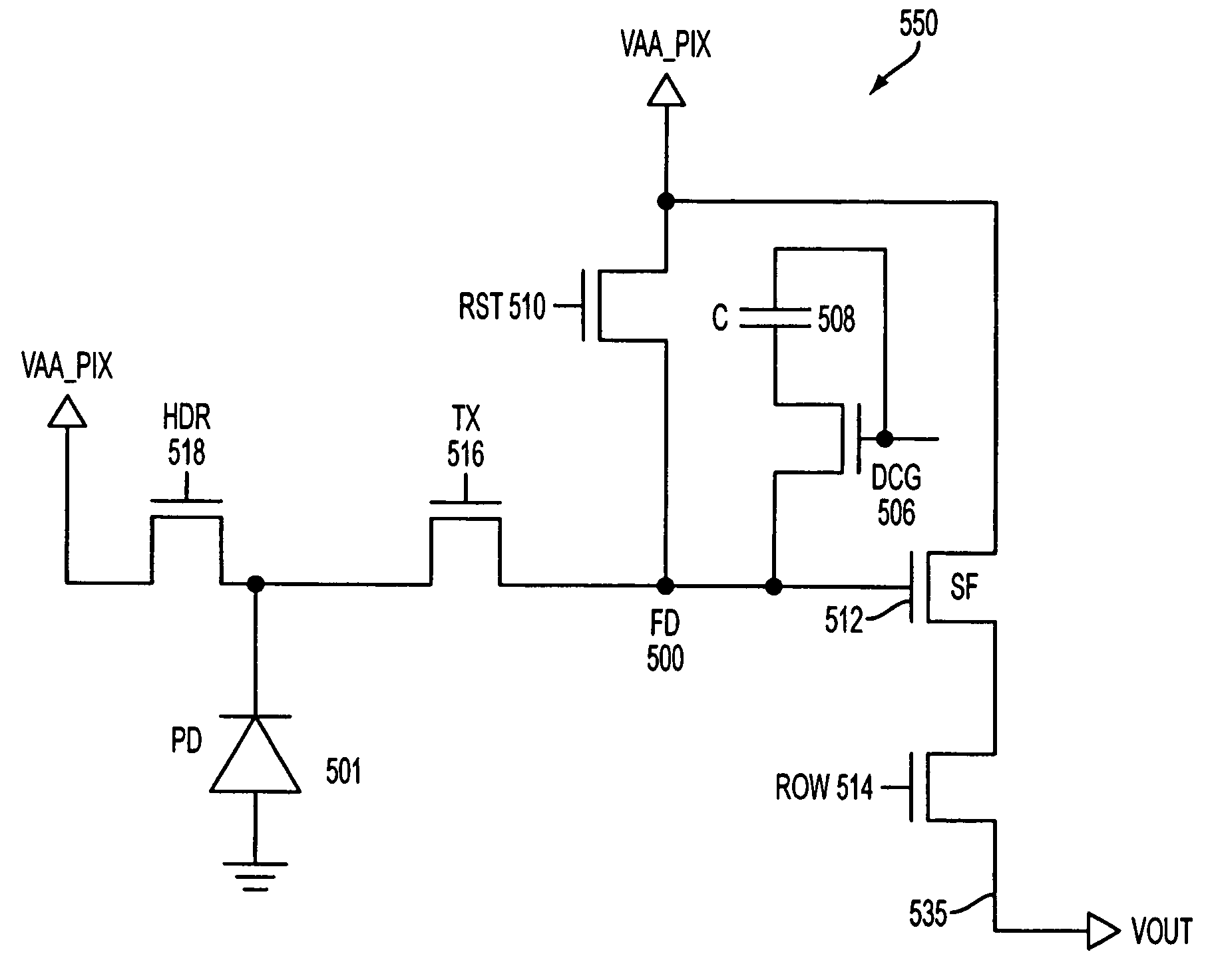
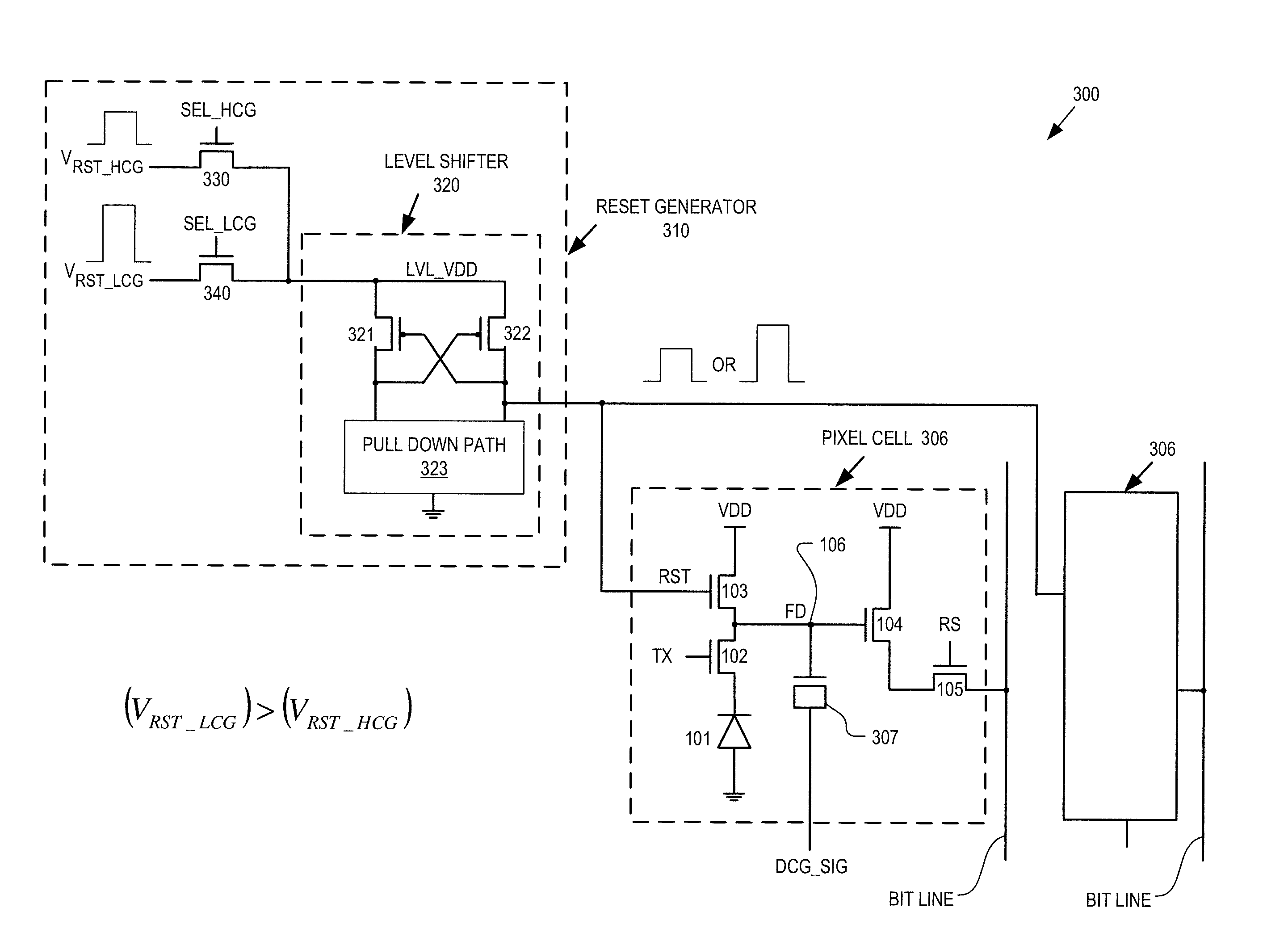
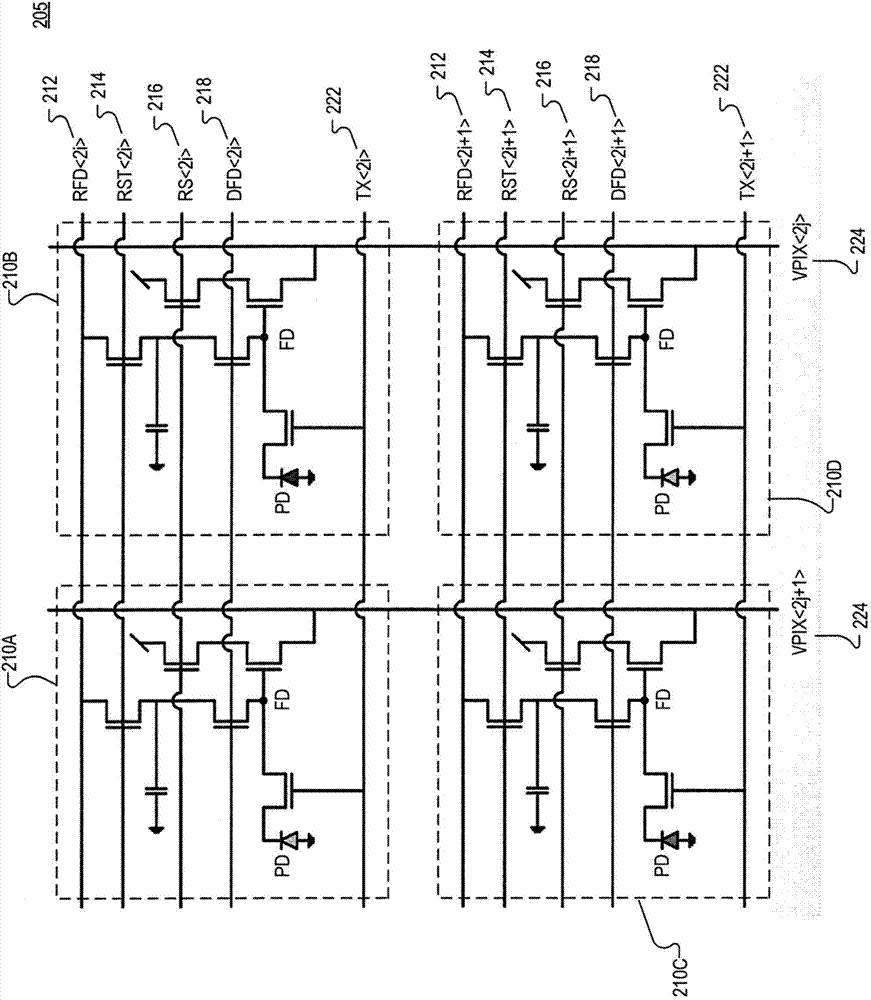
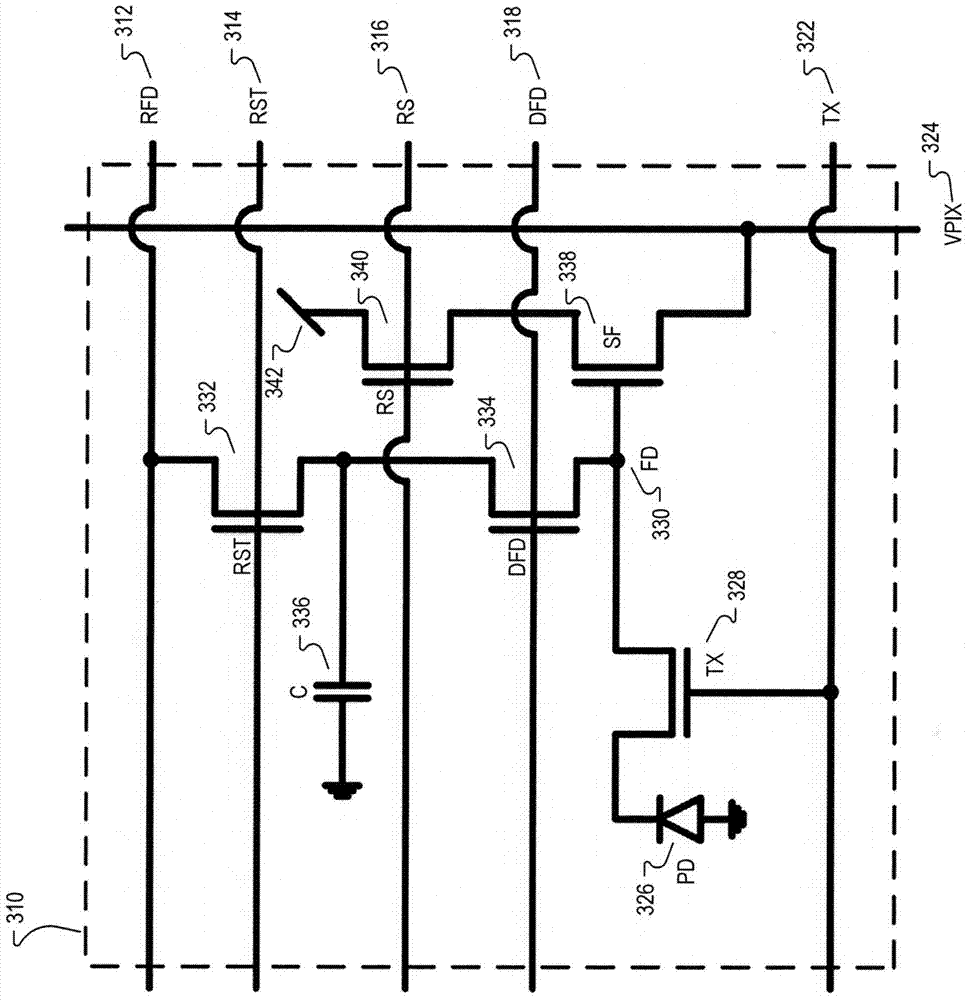
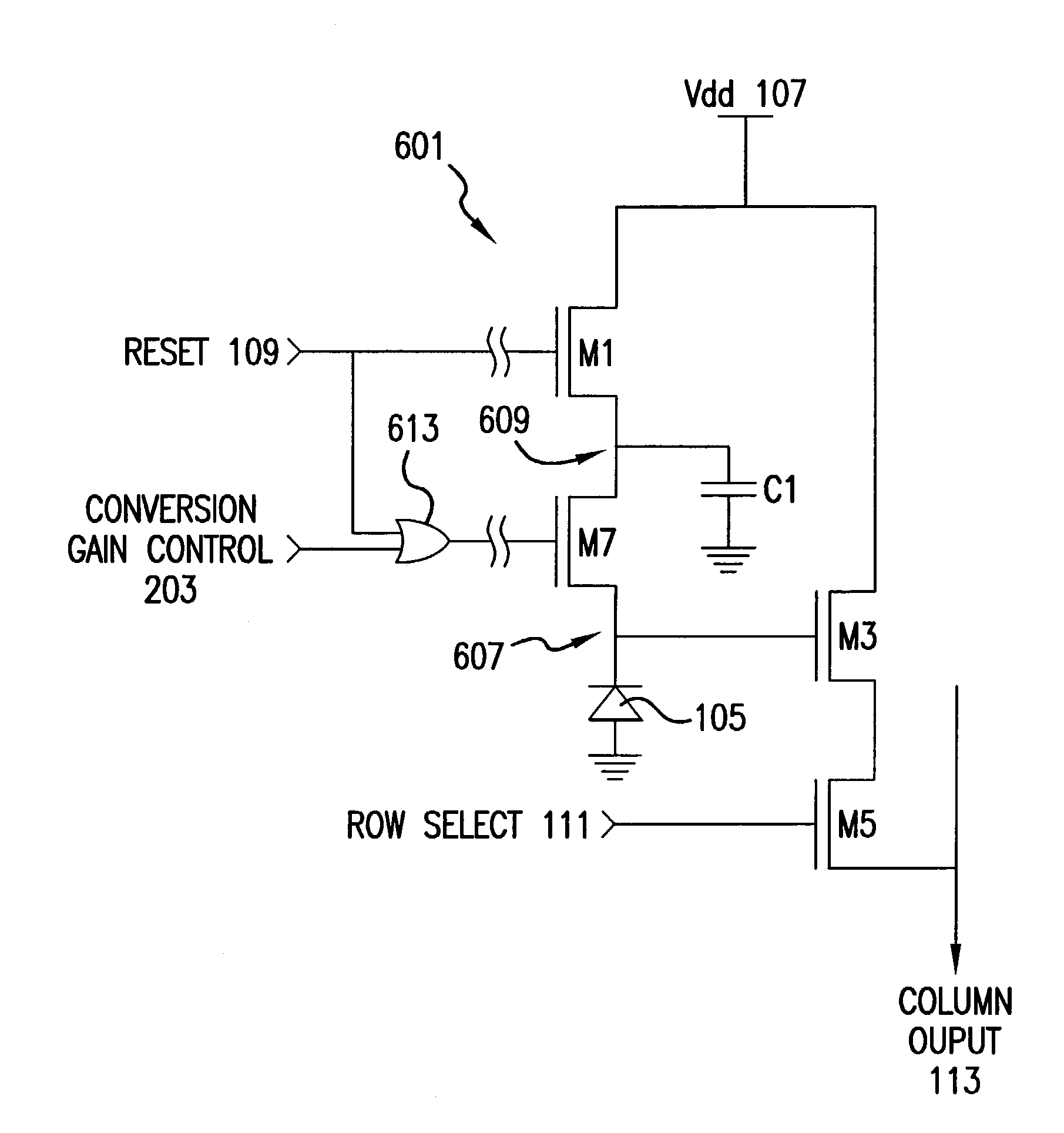
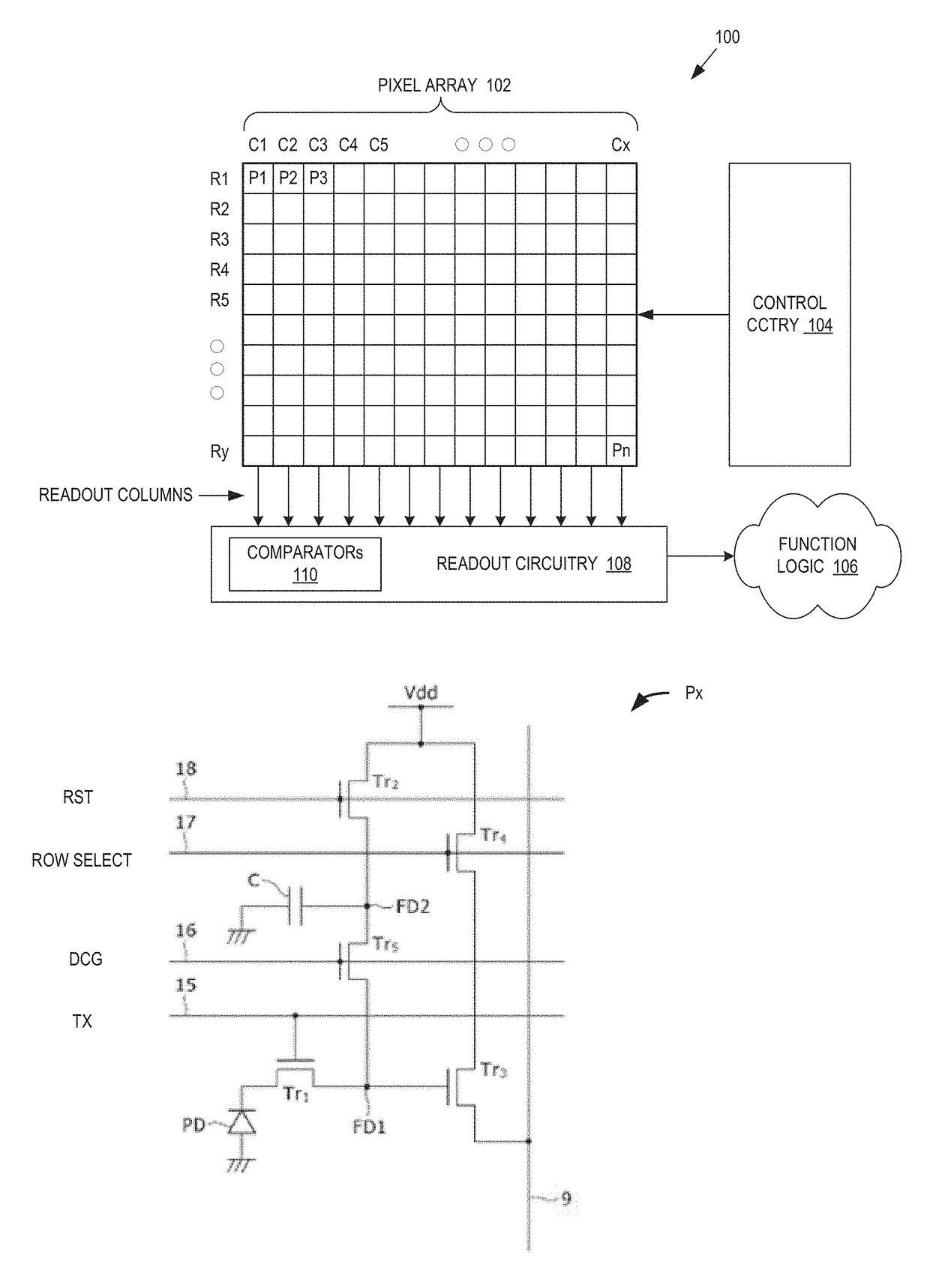
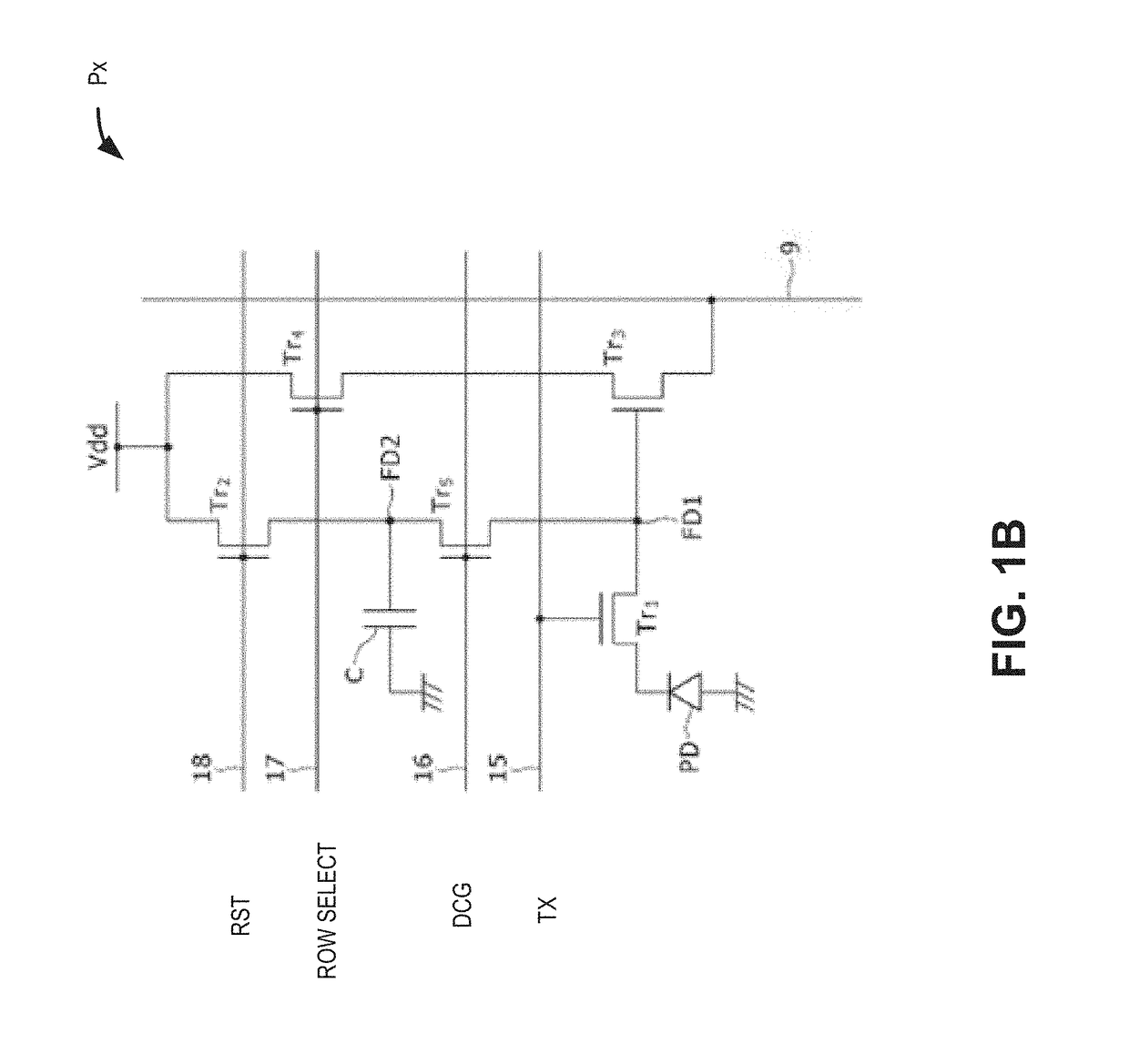
Multilevel reset voltage for multi-conversion gain image sensor
A method of operating an image sensor includes adjusting a capacitance coupled to a circuit node within a pixel cell. The circuit node is coupled to selectively receive an image charge acquired by a photo-sensor of the pixel cell. A conversion gain is selected from multiple conversion gains for the pixel cell by adjusting the capacitance. A voltage level from multiple voltage levels is selected for use as a reset signal when the reset signal is asserted. The reset signal controls resetting of the circuit node during operation of the pixel cell. The voltage level is selected dependent upon which of the multiple conversion gains is selected by adjusting the capacitance. The reset signal is asserted to reset a voltage at the circuit node.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
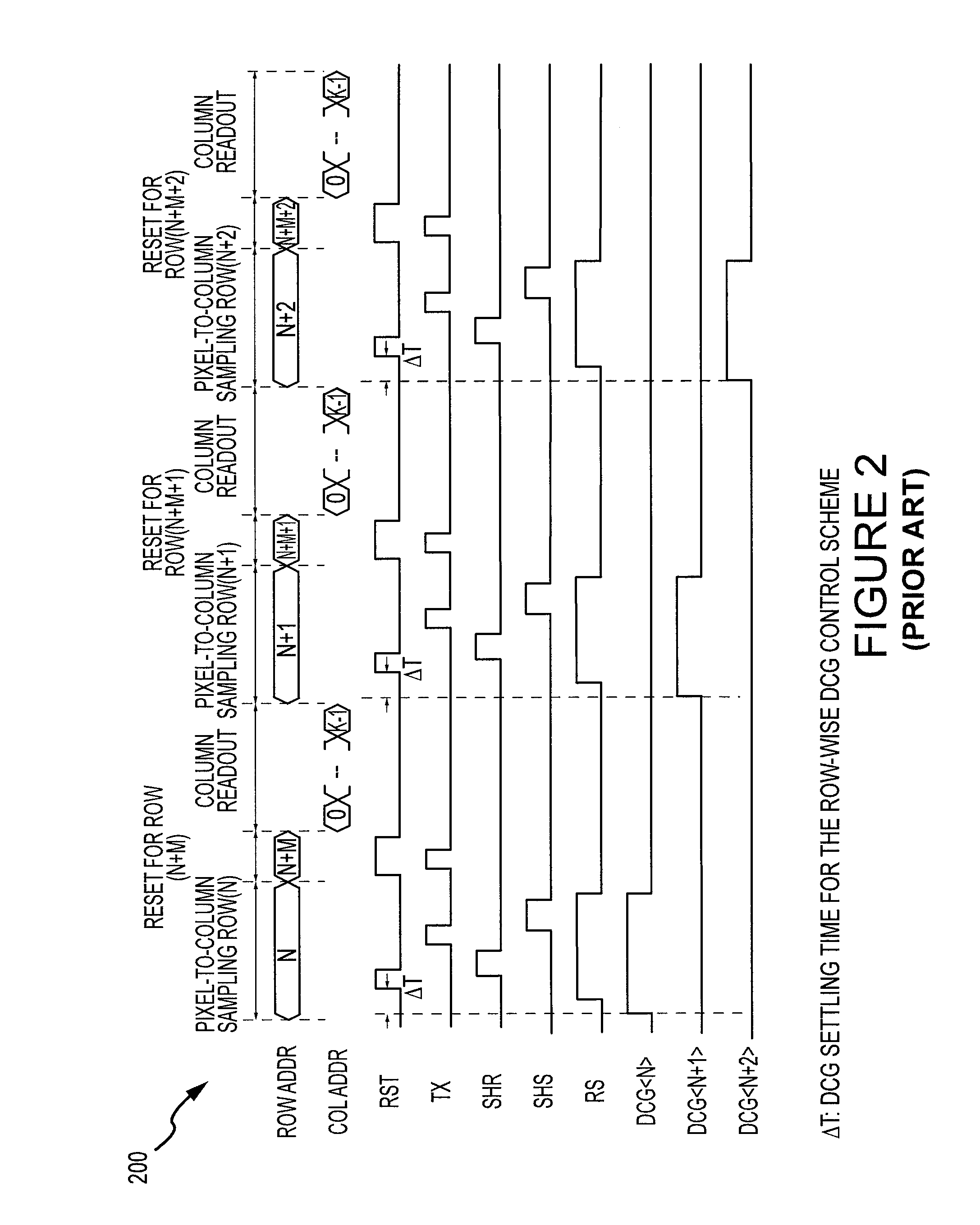
Method and apparatus for controlling dual conversion gain signal in imaging devices
ActiveUS20090096890A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLight sensingControl signal
A image-sensing device includes an array of light-sensing pixels arranged in rows, a readout circuit, and a control logic coupled to the rows of pixels. Each of the pixels has a respective conversion gain that changes to a respective second value from a respective first value within a settling time when a control signal is applied to the pixel. The readout circuit is coupled to the array of pixels and samples the rows of pixels once in an array sampling process. The control logic applies the control signal to the pixels of at least one row after sampling of the pixels in at least one other row of the array has begun but at least the settling time before the at least one row is sampled.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
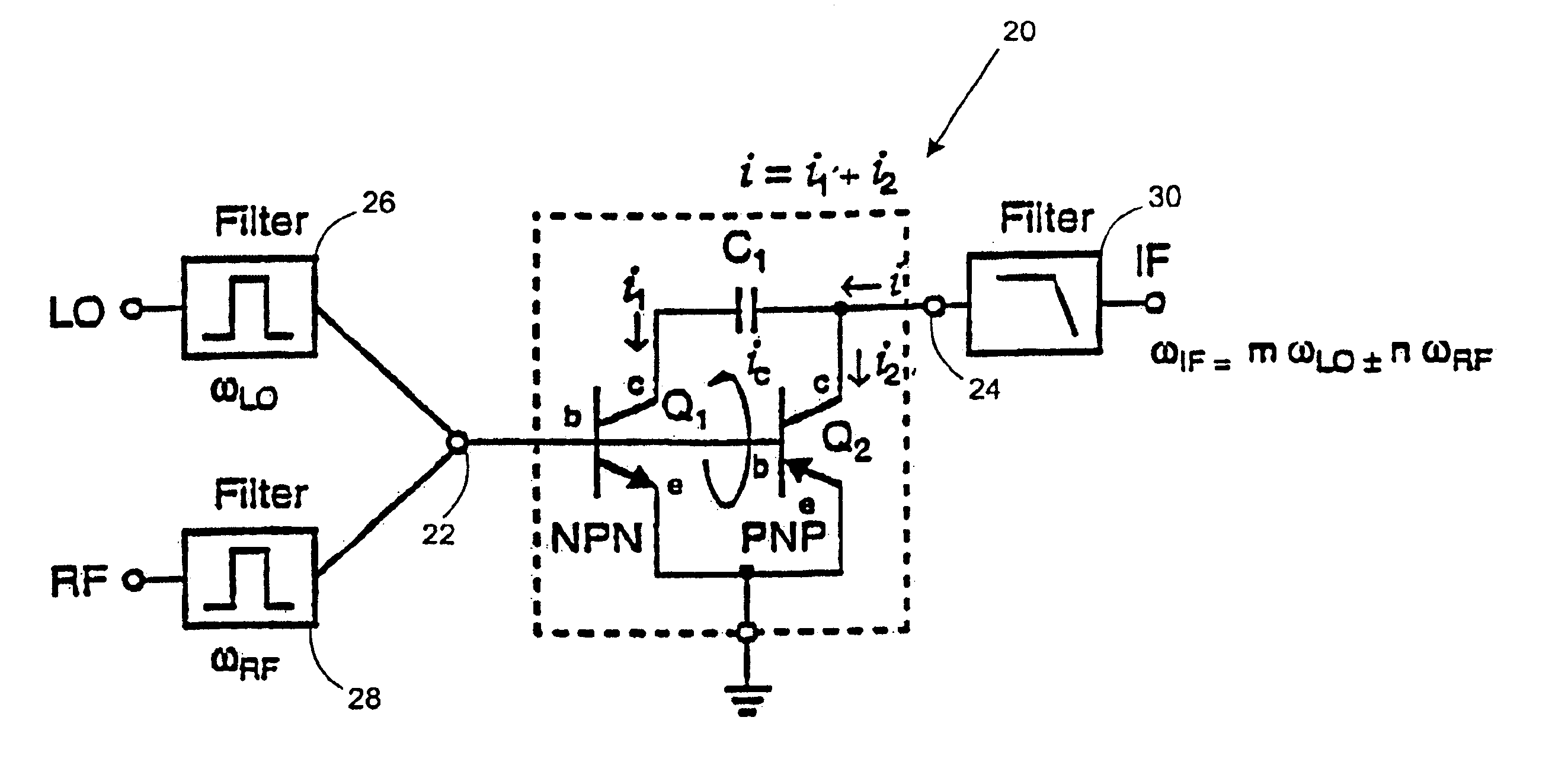
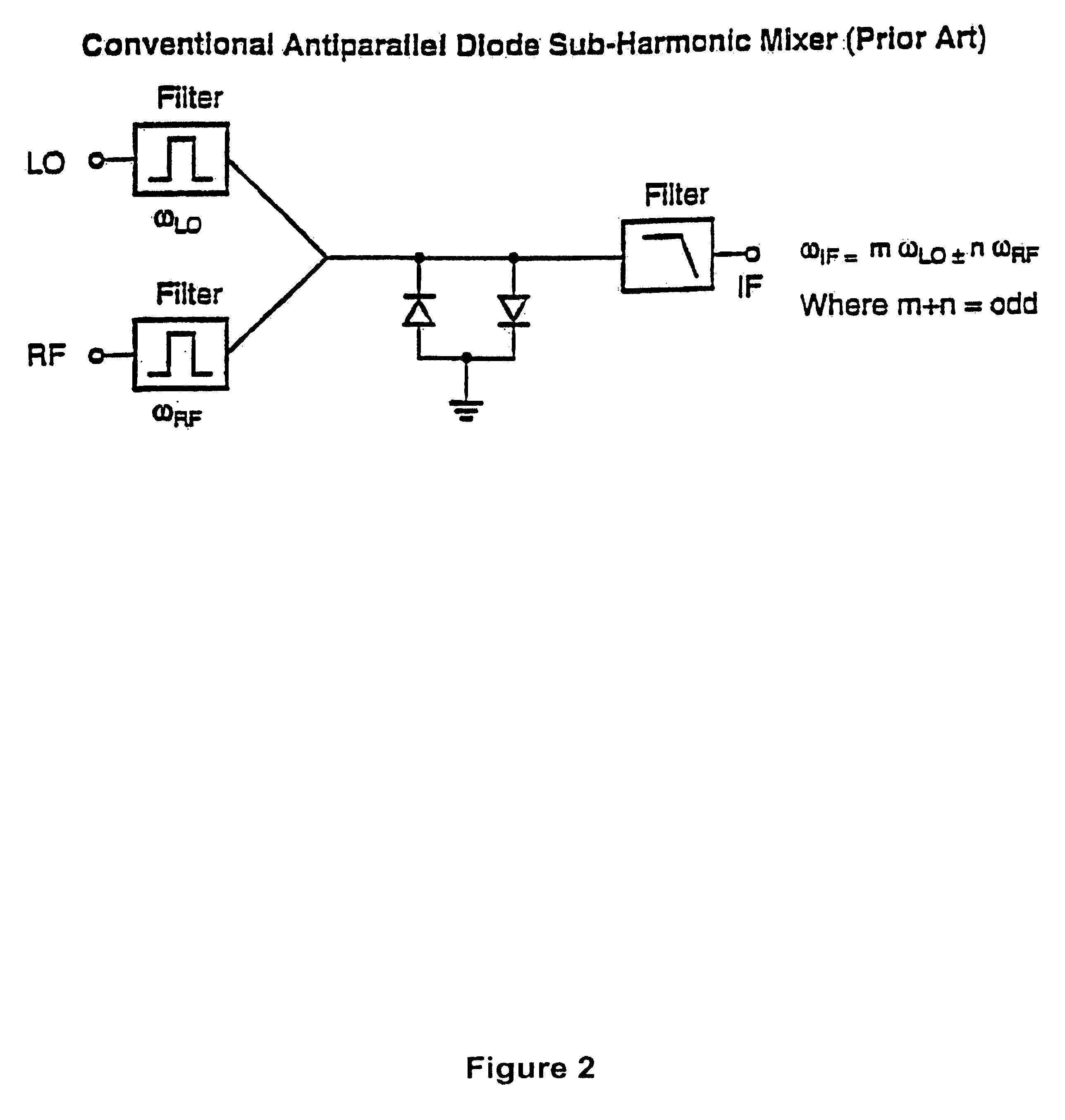
Complementary bipolar harmonic mixer
InactiveUS6901249B1Modulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesTransmissionFrequency mixerHarmonic
A 3-terminal harmonic mixer which solves the conversion gain, port impedance and isolation problems associated with known harmonic mixers. In particular, the 3-terminal harmonic mixer in accordance with the present invention provides harmonically pumped anti-parallel diode mixing operation by utilizing the inherent characteristics of complementary transistors.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method for capturing image data, high dynamic range imaging system and pixel unit
ActiveCN104780326ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh-dynamic-range imagingPhotodetector
A method of reading out a pixel includes resetting a photodetector of the pixel. Light incident on the photodetector is then integrated for a single exposure of a single image capture. A floating diffusion node of the pixel is then reset. The floating pixel is set to low conversion gain and a low conversion gain reset signal is sampled from the floating diffusion node. The floating diffusion is set to high conversion gain and a high conversion gain reset signal is sampled from the floating diffusion node. Charge carriers are transferred from the photodetector to the floating diffusion node and a high conversion image signal is then sampled from the floating diffusion node. The floating diffusion is set to low conversion gain. Charge carriers are transferred again from the photodetector to the floating diffusion node and a low conversion image signal is sampled from the floating diffusion node.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
High-dynamic range image sensing circuit and high-dynamic range image reading method
ActiveCN102752559AAdjust Capacitor ValueEasy to understand technical contentTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCapacitanceComputer science
The invention provides a high-dynamic range image sensing circuit with adaptive conversion gain and a high-dynamic range image reading method. The high-dynamic range image sensing circuit comprises a variable capacitor. The capacitance value of the variable capacitor is adjusted according to sensed lightness or internal feedback control so as to adaptively adjust the conversion gain when a signal representing a pixel image sensed by an image sensing element is read. When signals are read per period, the signals within different dynamic ranges can be respectively read for more than two times so as to enhance the accuracy of the signals.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
CMOS image sensor with variable conversion gain
ActiveUS7327393B2Improve conversion gainHighly sensitive to lightTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceCMOS
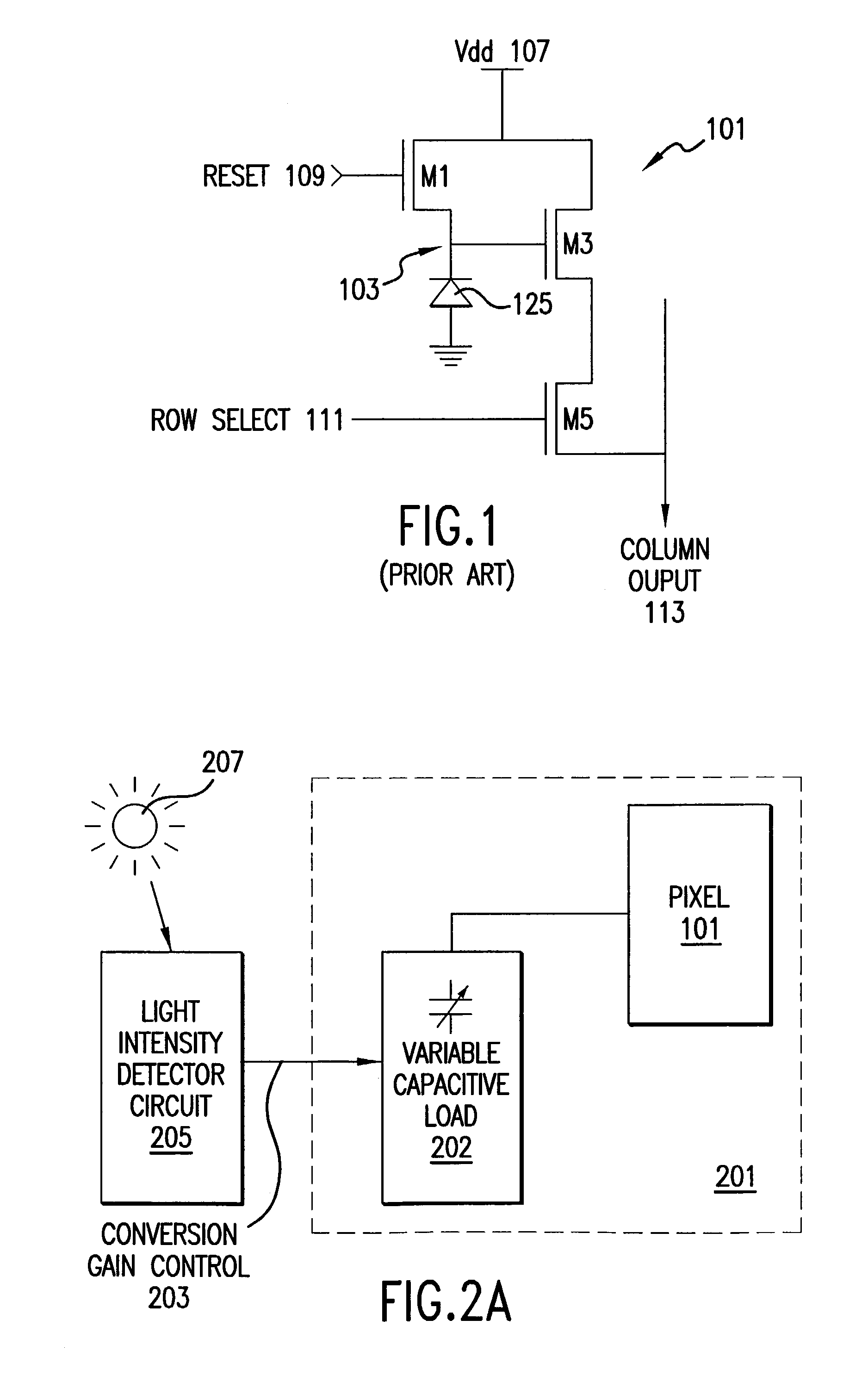
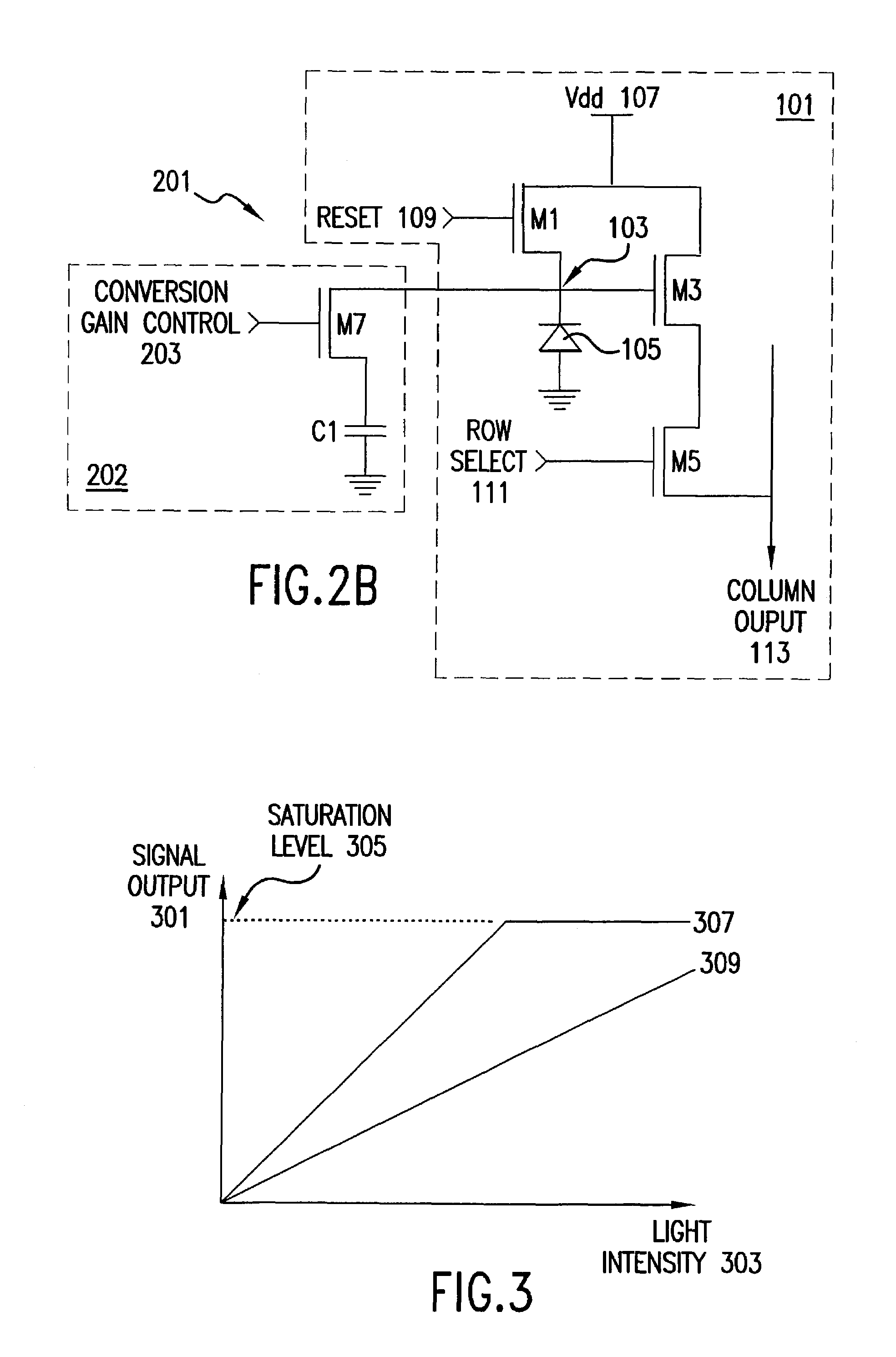
An image sensor pixel has variable conversion gain to prevent overexposure of the pixel without reducing the exposure period. Under dim lighting conditions, the pixel operates with high conversion gain and is highly sensitive to light. When the incident light is bright, the pixel switches into a low conversion gain, low-sensitivity mode. The variable conversion gain is implemented by connecting a variable capacitive load in parallel with the photodiode of the image sensor pixel. When the incident light intensity exceeds a certain threshold, the variable capacitive load is increased to allow the photodiode to absorb more light. Likewise, the variable capacitive load is decreased when the incident light intensity is below a certain threshold.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
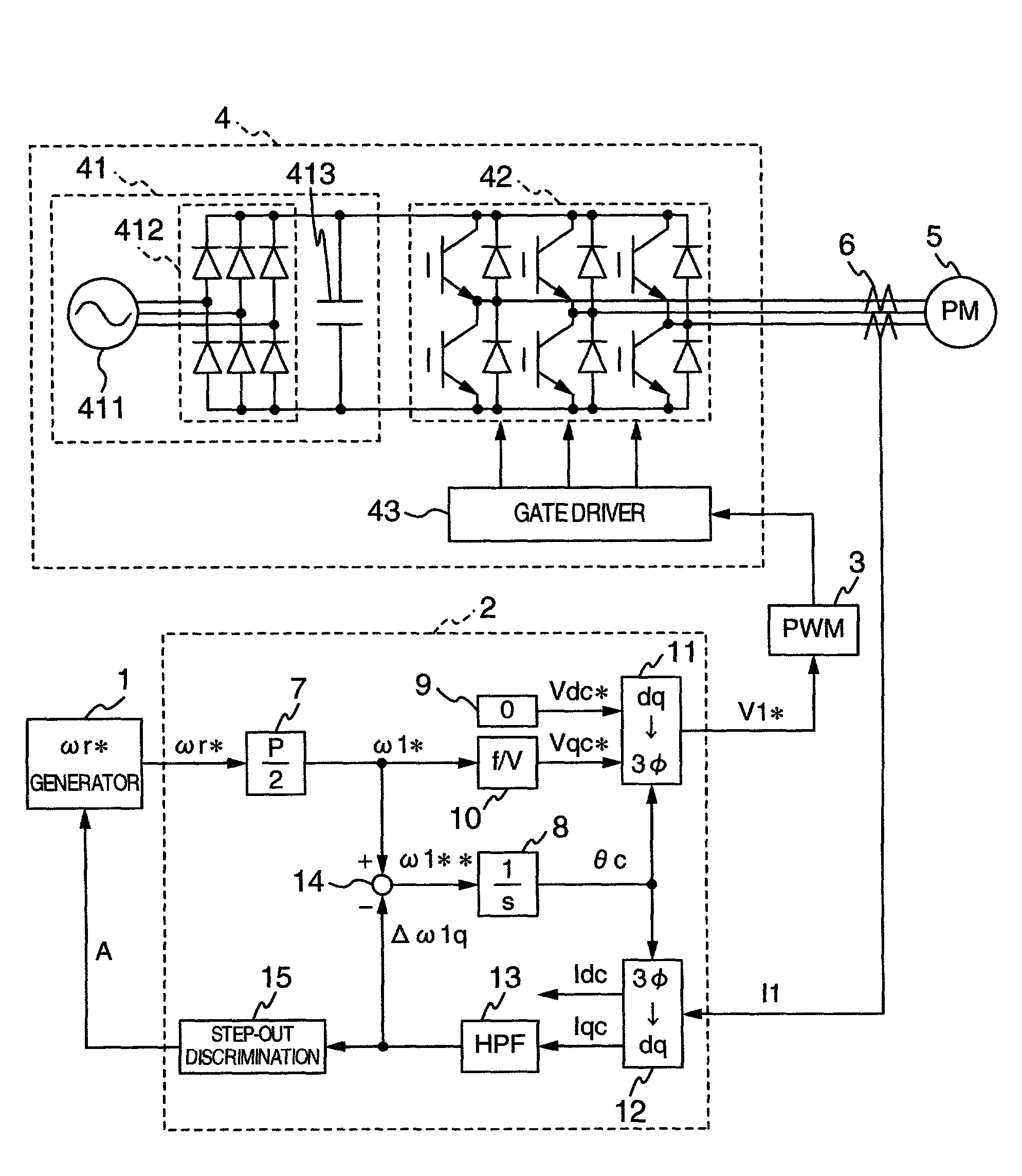
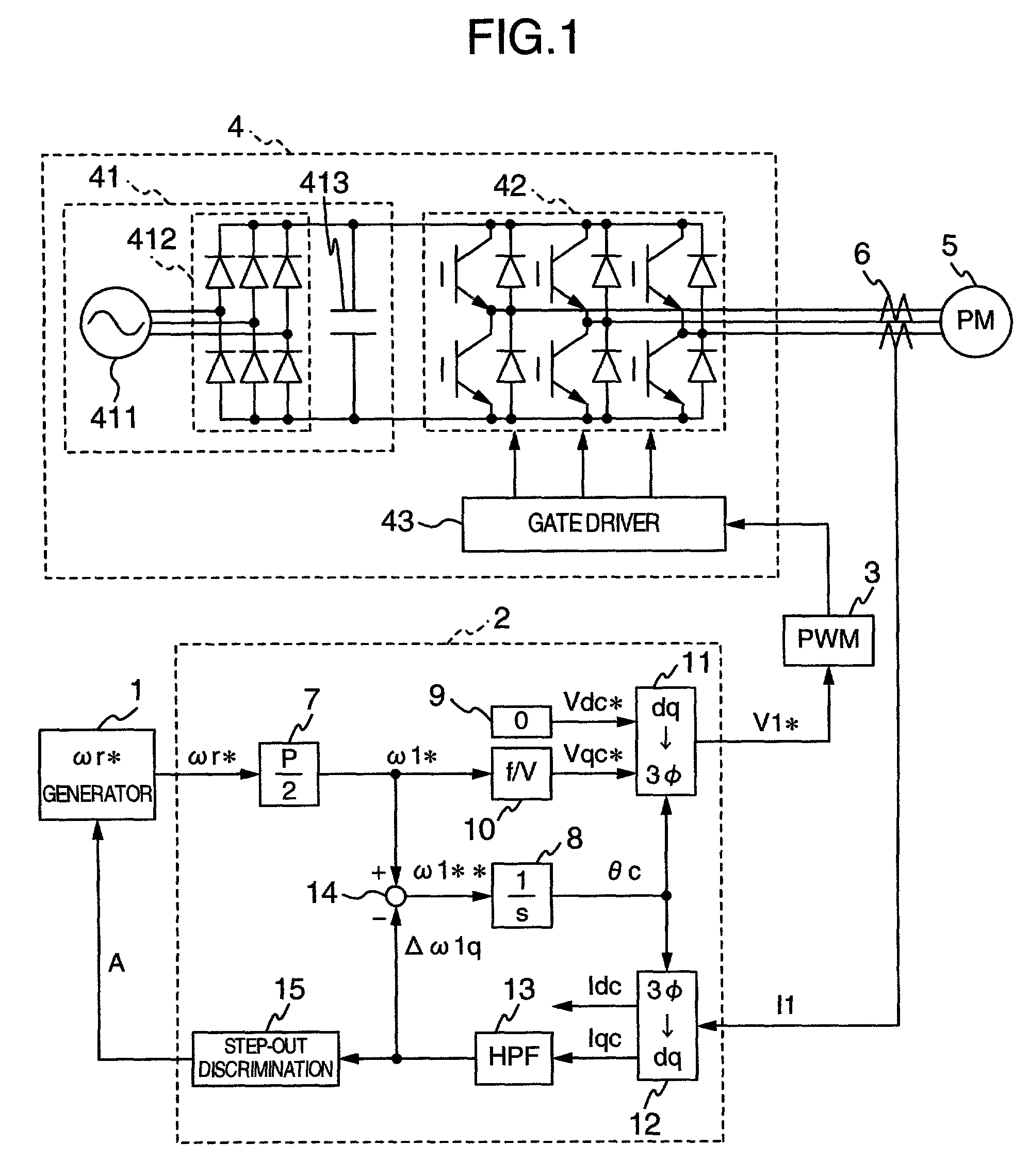
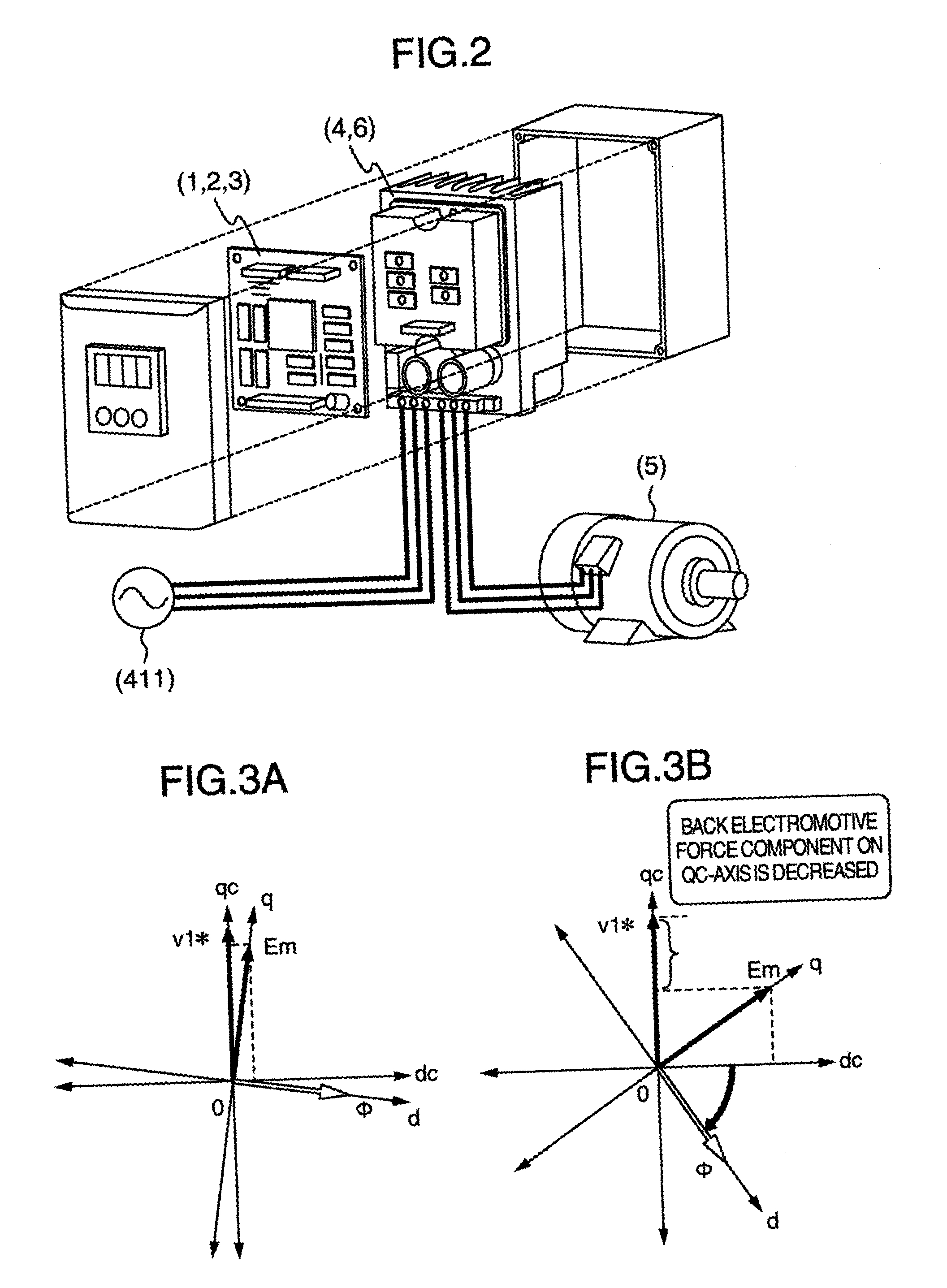
System for driving electric motor
An electric motor driving system has a permanent magnet type synchronous motor, an inverter for driving the motor, a generator for issuing a rotational frequency command to the motor and a controller including a conversion gain for generating a control signal to the inverter on the basis of the rotational frequency command, an integrator, a zero generator, a qc-axis voltage command arithmetic unit, a dq inverter, a dq coordinate converter, a high-pass filter, and an adder, wherein the system includes the high-pass filter for correcting the rotational frequency command to the motor on the basis of current detection values flowing through the motor, and a step-out detector for comparing the correction amount with a threshold value previously set for the coordinate amount to judge when the correction amount exceeds the threshold value at least one or more times that the motor is in the step-out state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dual conversion gain high dynamic range readout for comparator of double ramp analog to digital converter
Example comparators as discussed herein may include a second stage coupled to provide an output in response to an intermediate voltage, a first stage coupled to provide the intermediate voltage in response to an input. The first stage including a pair of cascode devices coupled to a current mirror, a low gain input coupled to inputs of the first stage via first switches, and further selectively coupled to the pair of cascode devices via second switches, and a high gain input coupled to the first and second inputs of the first stage via the first switches, and further selectively coupled to the pair of cascode devices via fourth switches. Based on a low conversion gain mode, the low gain input may be coupled to the inputs by the first switches, and further coupled to the pair of cascode devices by the second switches in response to a control signal being in a first state, and based on a high conversion gain mode, the high gain input may be coupled to the first and second inputs by the first switches, and further coupled to the pair of cascode device by the fourth switch in response to the control signal being in a second state.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Fusion structure of LNA (low noise amplifier) and frequency mixer
InactiveCN103401508AReduce power consumptionReduce noiseDifferential amplifiersMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceLow noiseLevel structure
The invention relates to a fusion structure of an LNA and a frequency mixer. The fusion structure comprises a low noise transconductance amplifier stage, a switching frequency mixing stage and a resistance loading stage, wherein the low noise transconductance amplifier stage is divided into two parts, a first part adopts a cross coupling main-auxiliary noise offset technology, a main transconductance pipe adopts a cross coupling structure so as to double an equivalent transconductance value, an auxiliary transconductance pipe provides an appropriate transconductance value, and the noise of the main transconductance pipe is offset through the main-auxiliary structure; and a second part adopts a common-source-level structure, then gain is provided, direct current flowing through switching tubes is reduced, and flicker noise is reduced. The switching frequency mixing stage modulates radio-frequency current output from the low noise transconductance amplifier stage and outputs intermediate-frequency current, and source electrodes of two groups of switching tubes are connected through an inductor, so that the flicker noise is reduced, and the conversion gain is improved. The resistance loading stage adopts an RC (current limiting resistor) lowpass filtering network to convert the intermediate-frequency current into an intermediate-frequency voltage signal for outputting. The fusion structure of the LNA and the frequency mixer has the characteristics of low noise, high gain and low power consumption.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Imaging array having variable conversion gain
ActiveUS7268338B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A CCD imaging array and a charge measurement amplifier for use in such imaging arrays is disclosed. The array includes a plurality of pixels that accumulate charge when exposed to light, a readout amplifier having input and output ports. The readout amplifier has a variable gain that is set by a gain control signal. The readout amplifier also includes a reset path between the input and output ports, the path having an impedance controlled by a reset signal. A controller generates the gain control signal and the reset signal during a charge measurement cycle. Initially the gain is set to a first value after generating the reset signal. The gain is changed to a second value during the charge measurement cycle if the output signal exceeds a first threshold value. The readout amplifier can be constructed from an operational amplifier having a capacitive feedback loop.
Owner:BAE SYST IMAGING SOLUTIONS
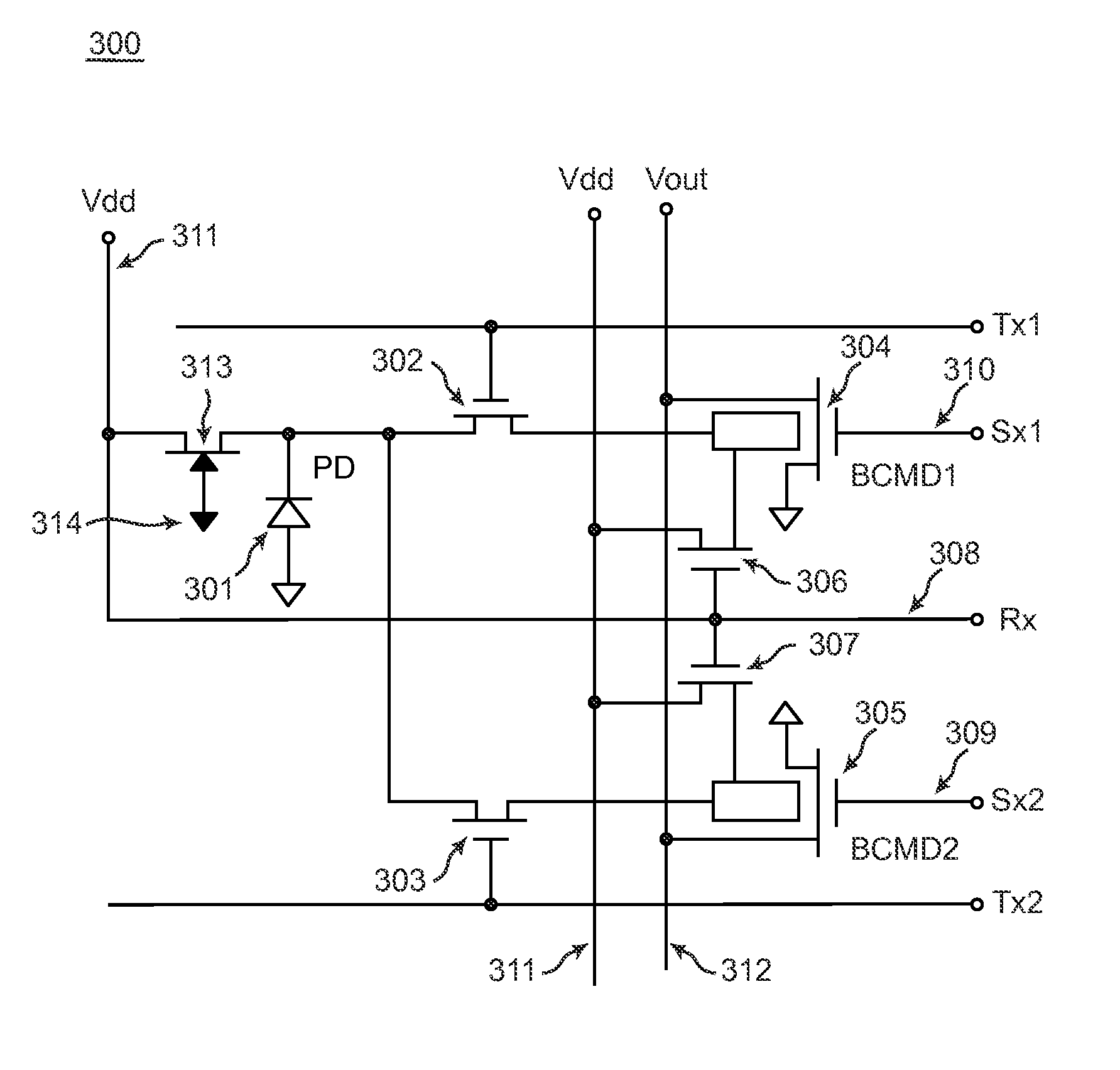
CMOS image sensor with global shutter, rolling shutter, and a variable conversion gain, having pixels employing several BCMD transistors coupled to a single photodiode and dual gate BCMD transistors for charge storage and sensing
The invention describes a solid-state CMOS image sensor array and discloses image sensor array pixels with global and rolling shutter capabilities that utilize multiple BCMD transistors for a single photodiode, for charge storage and sensing. Thus, the valuable pixel area saved by employing the BCMD transistor for charge storage and sensing is used by placing several BCMD transistors coupled to one photodiode. This increases the Dynamic Range (DR) of the sensor, since the same photodiode can integrate charge for different integration times, both long and short. This allows sensing of two different image signals from a single pixel without saturation, a low level signal with long integration time followed by a high level signal with short integration time. The signal processing circuits located at the periphery of the array can then process these signals into a single Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) output. Further disclosed is an image sensor array with pixels that use BCMD transistors for charge storage and sensing having multiple concentric gates, which allows changing the conversion gain of the BCMD transistors by applying various biases to the gates. Variable conversion gain is a useful feature when building WDR sensors since low conversion gain and high well capacity allows detection of high level signals and the same structure can be used to detect, at the same time, low level signals with high conversion gain and thus low noise.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Contactless power supply system and contactless extension plug
ActiveUS20150214747A1Promote generationTransformersCircuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionCoupling
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com