In-pixel high dynamic range imaging system and imaging sensor pixels
An imaging sensor and pixel technology, applied in radiation control devices, diodes, transistors, etc., can solve the problems of reducing dynamic range and signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
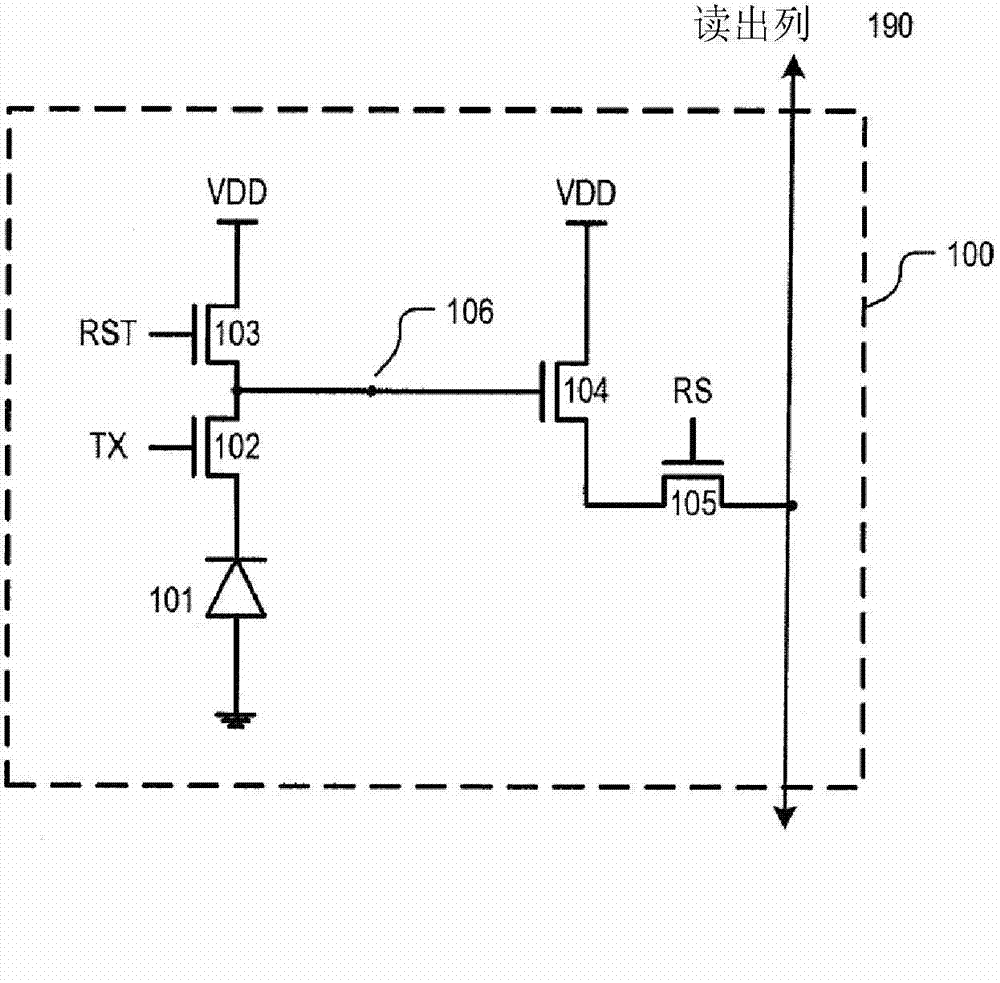
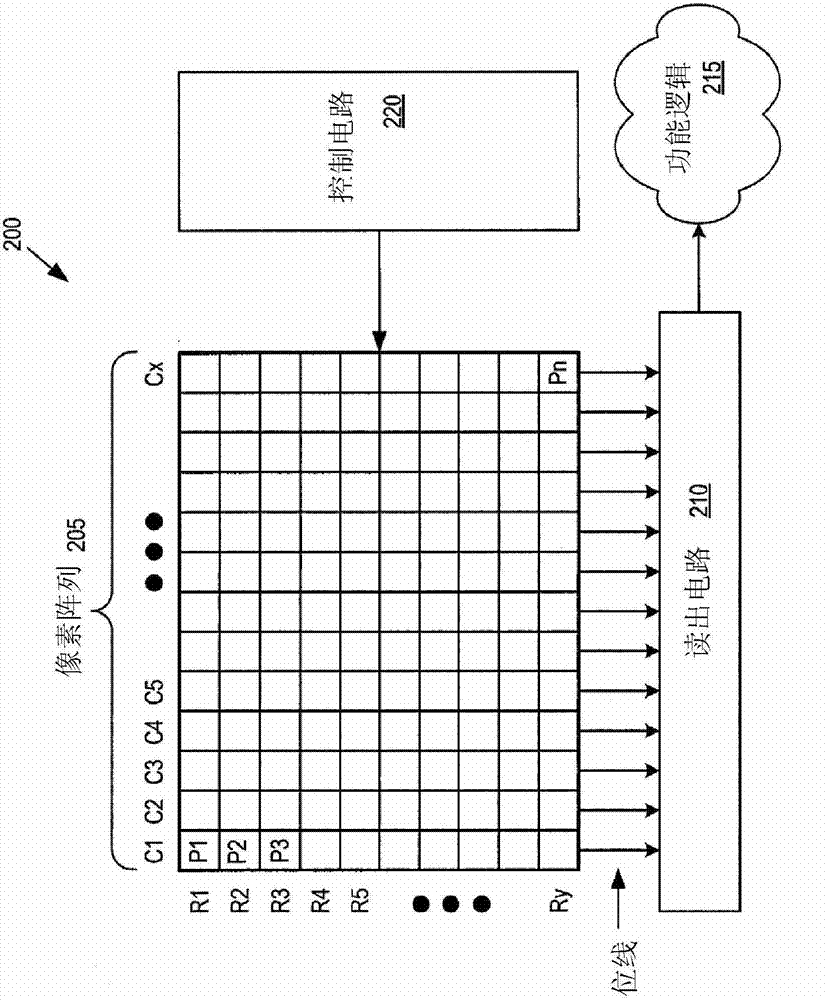
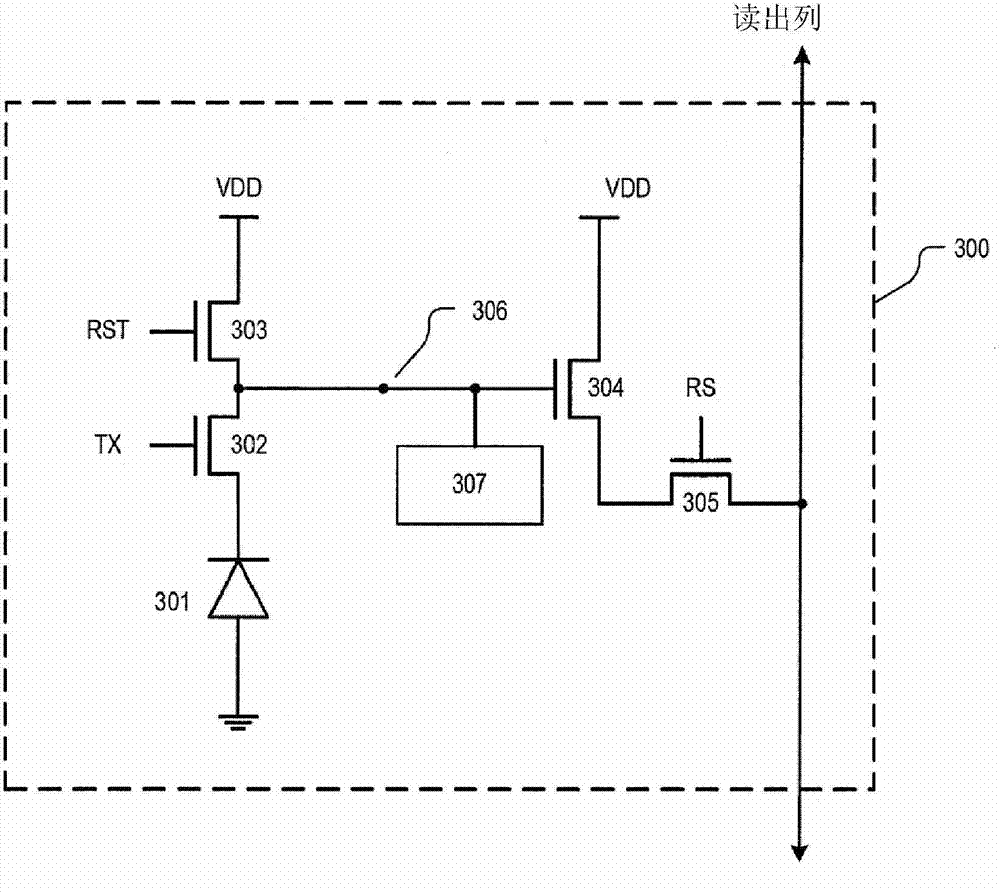
[0020] Embodiments of the present invention describe providing high dynamic range imaging (HDRI or just HDR) to imaging pixels by coupling their floating diffusion nodes to multiple metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) capacitive regions. It should be understood that the MOS capacitive region "turns on" (i.e., changes the voltage of the floating diffusion node) only when the voltage at the floating diffusion node (or the voltage difference between the gate node and the floating diffusion node) is greater than the threshold voltage of the MOS capacitive region. total capacitance); until the MOS capacitance region is "on", it has no effect on the total capacitance or conversion gain of the imaging pixel.
[0021] Each of the multiple MOS capacitive regions utilized by embodiments of the present invention may have a different threshold voltage, thereby "turning on" under different lighting conditions. This increases the dynamic range of the imaging pixels, thereby providing HDR for th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com