Patents
Literature
919 results about "Entropy encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
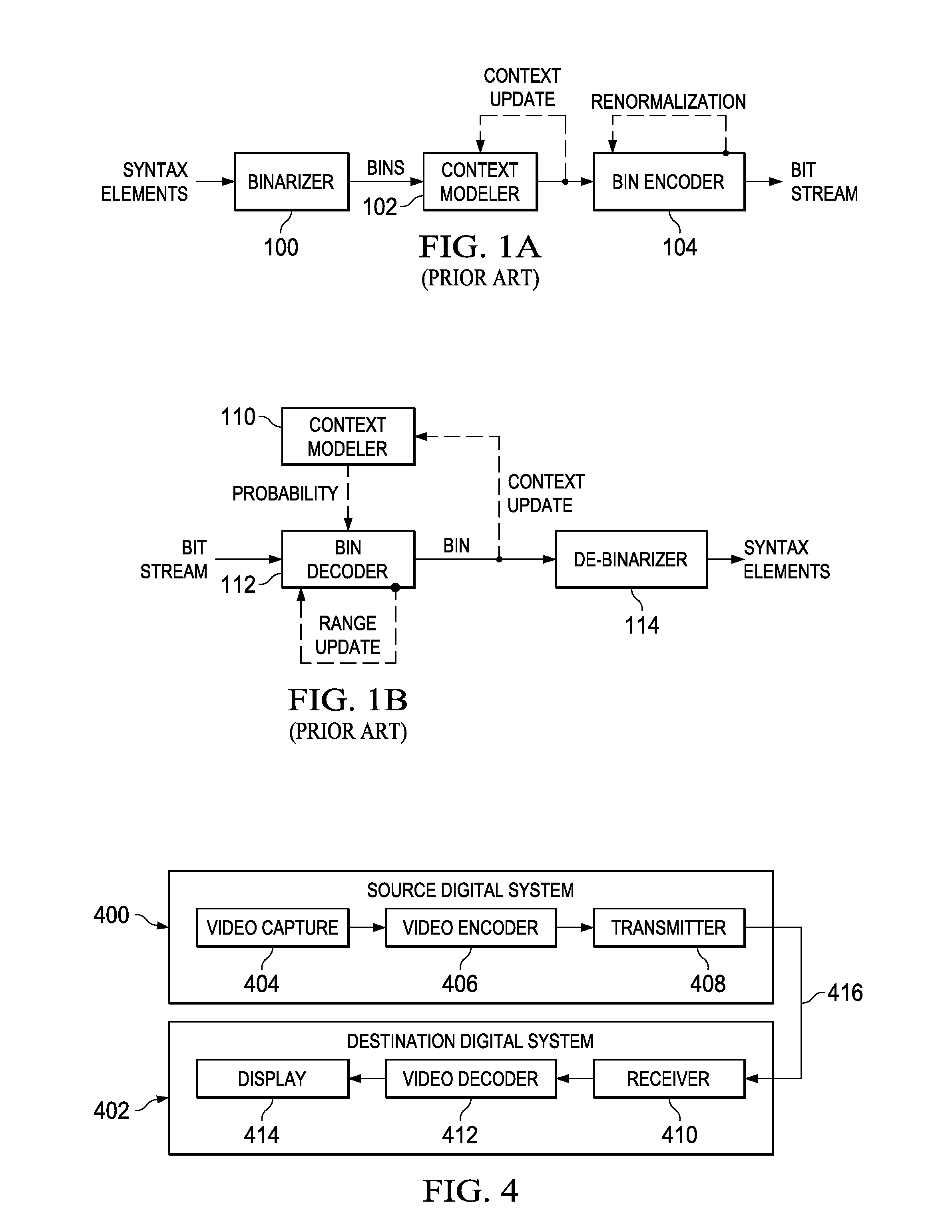
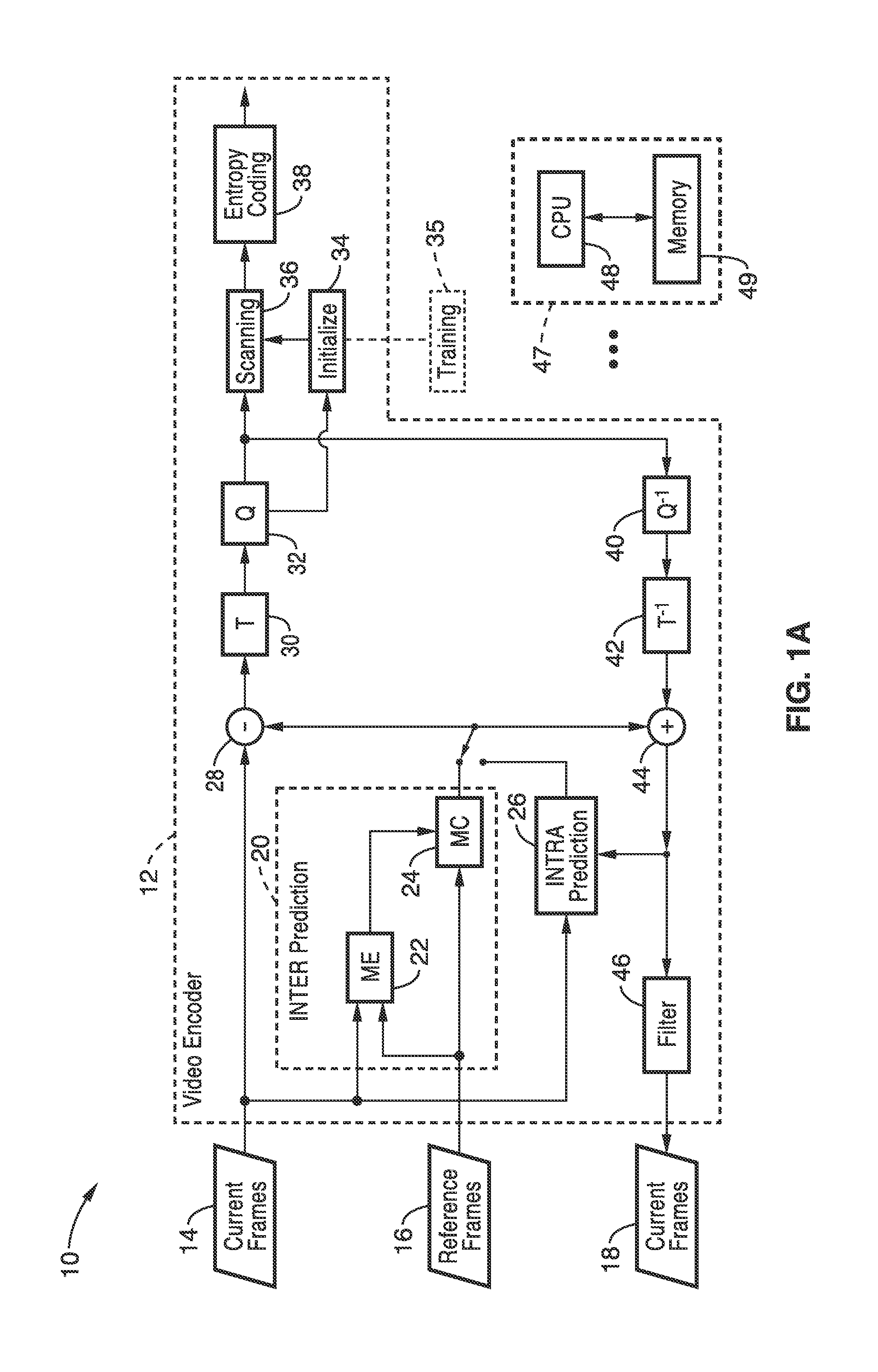
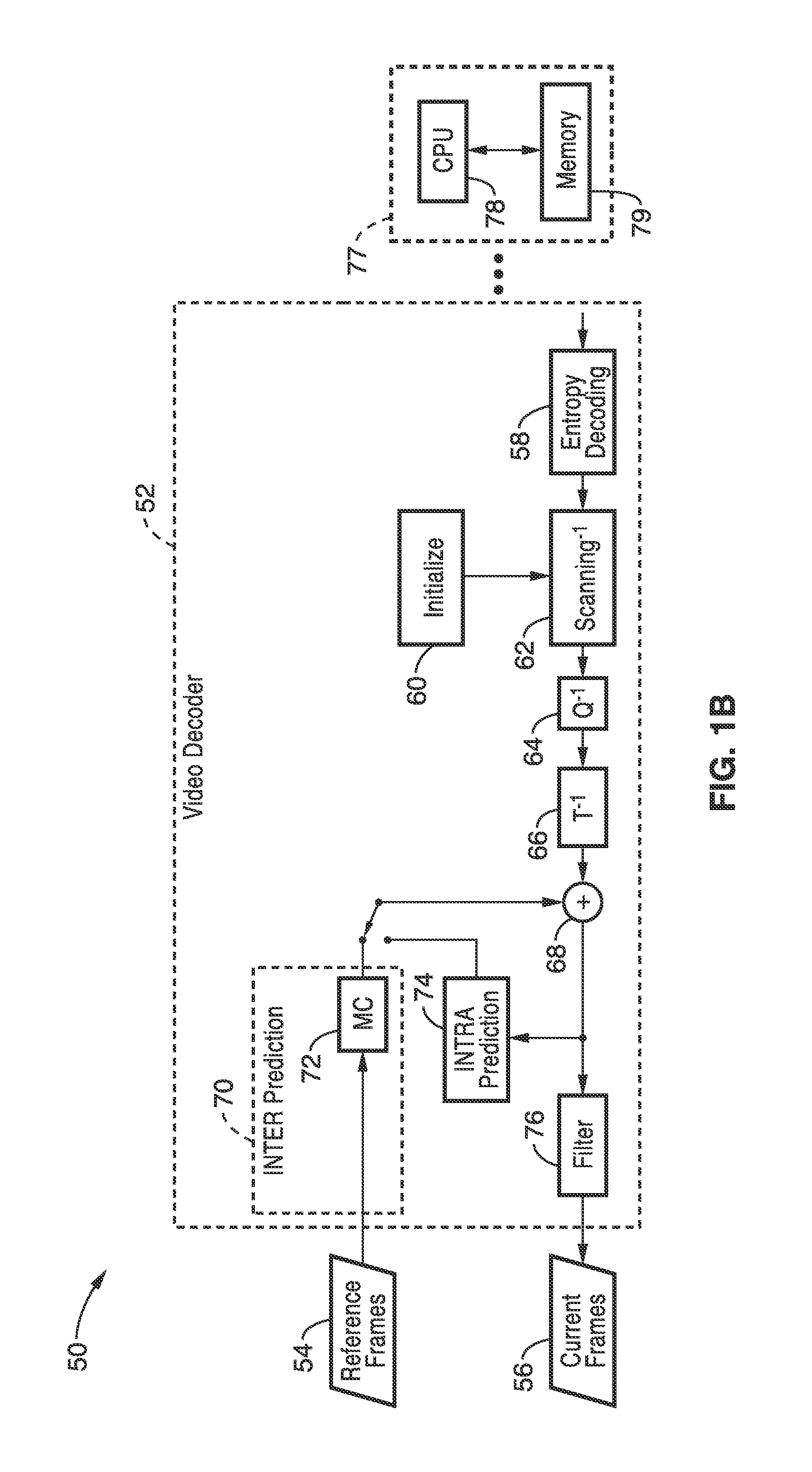
In information theory an entropy encoding is a lossless data compression scheme that is independent of the specific characteristics of the medium. One of the main types of entropy coding creates and assigns a unique prefix-free code to each unique symbol that occurs in the input. These entropy encoders then compress data by replacing each fixed-length input symbol with the corresponding variable-length prefix-free output codeword. The length of each codeword is approximately proportional to the negative logarithm of the probability. Therefore, the most common symbols use the shortest codes.
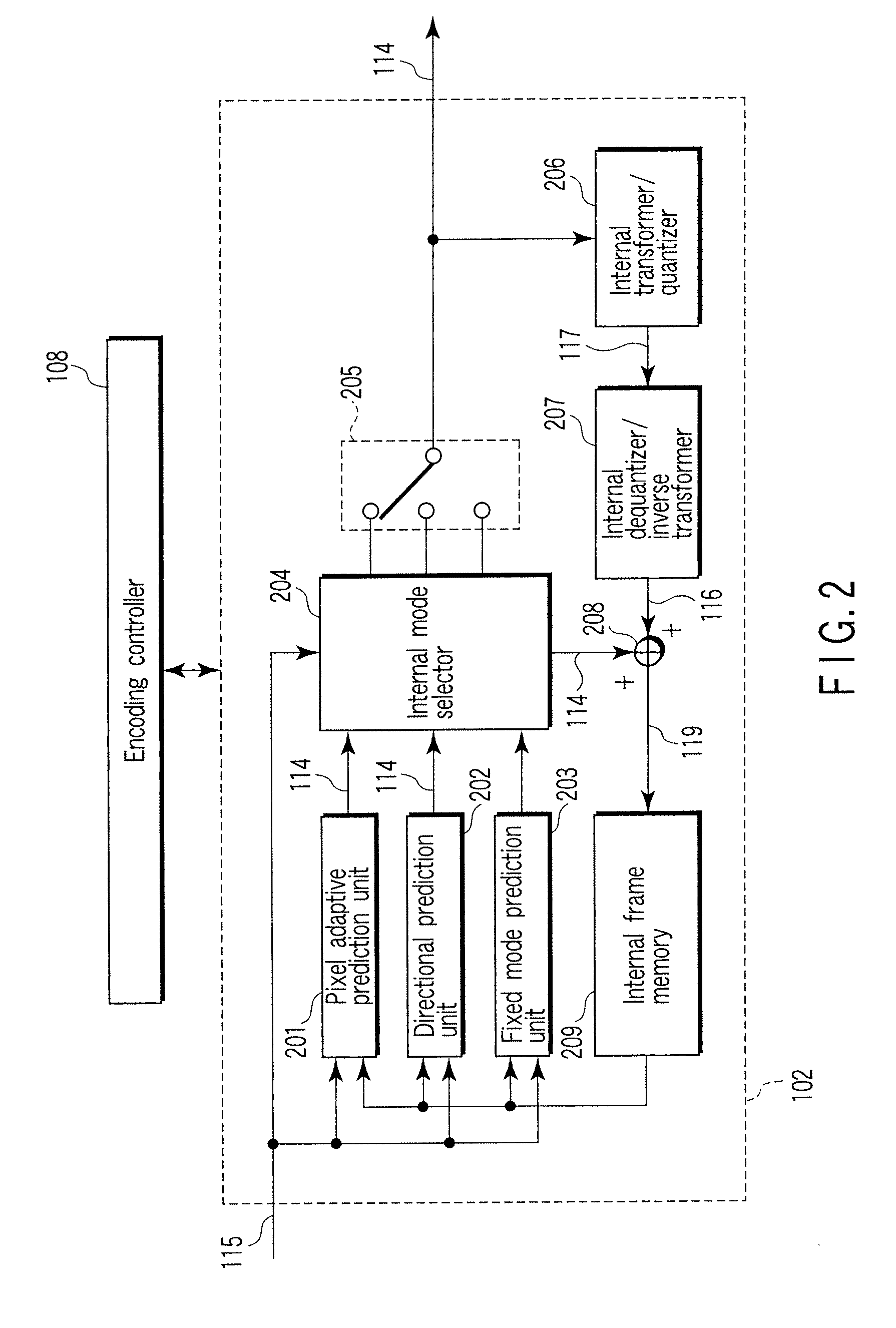
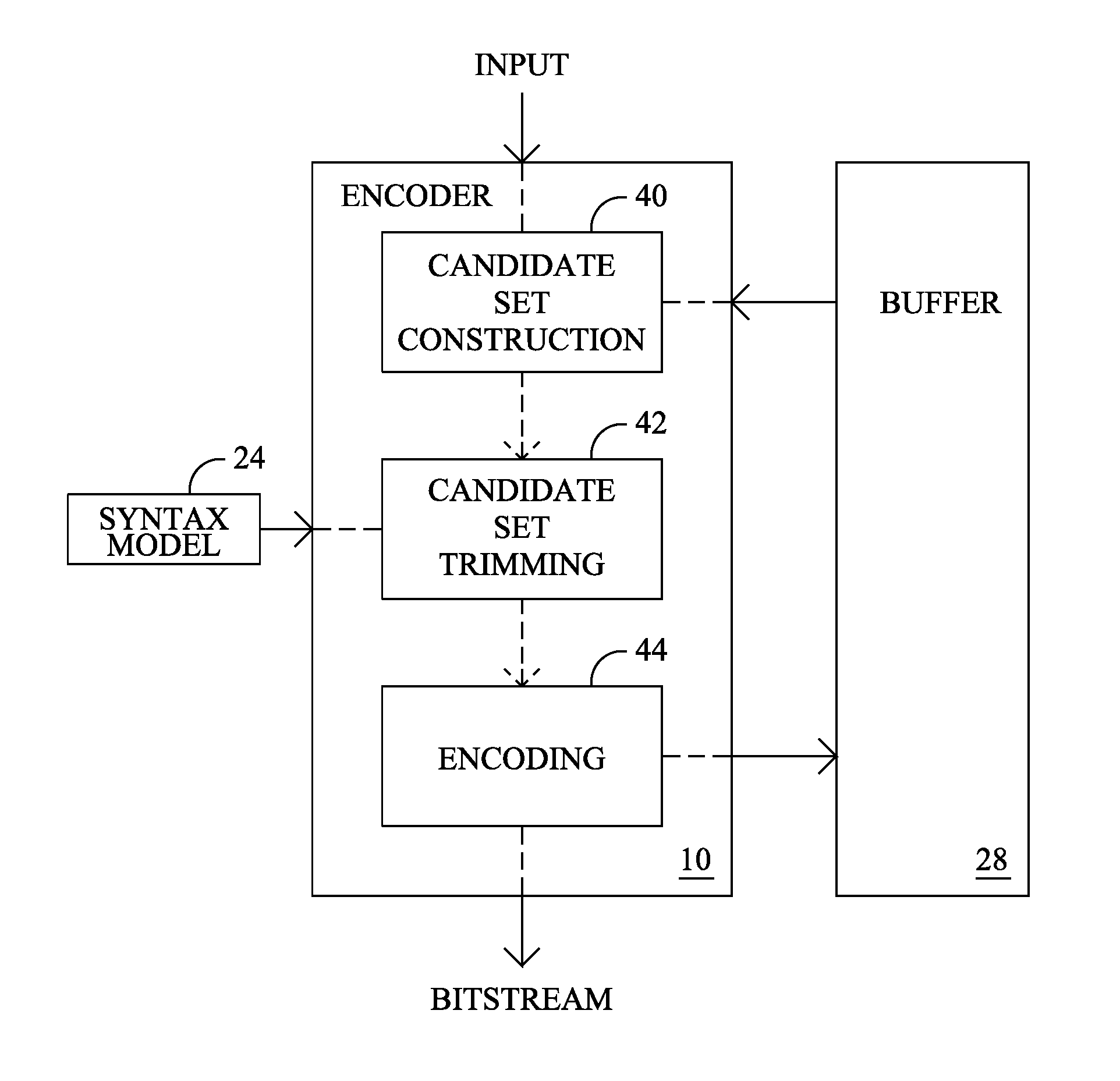
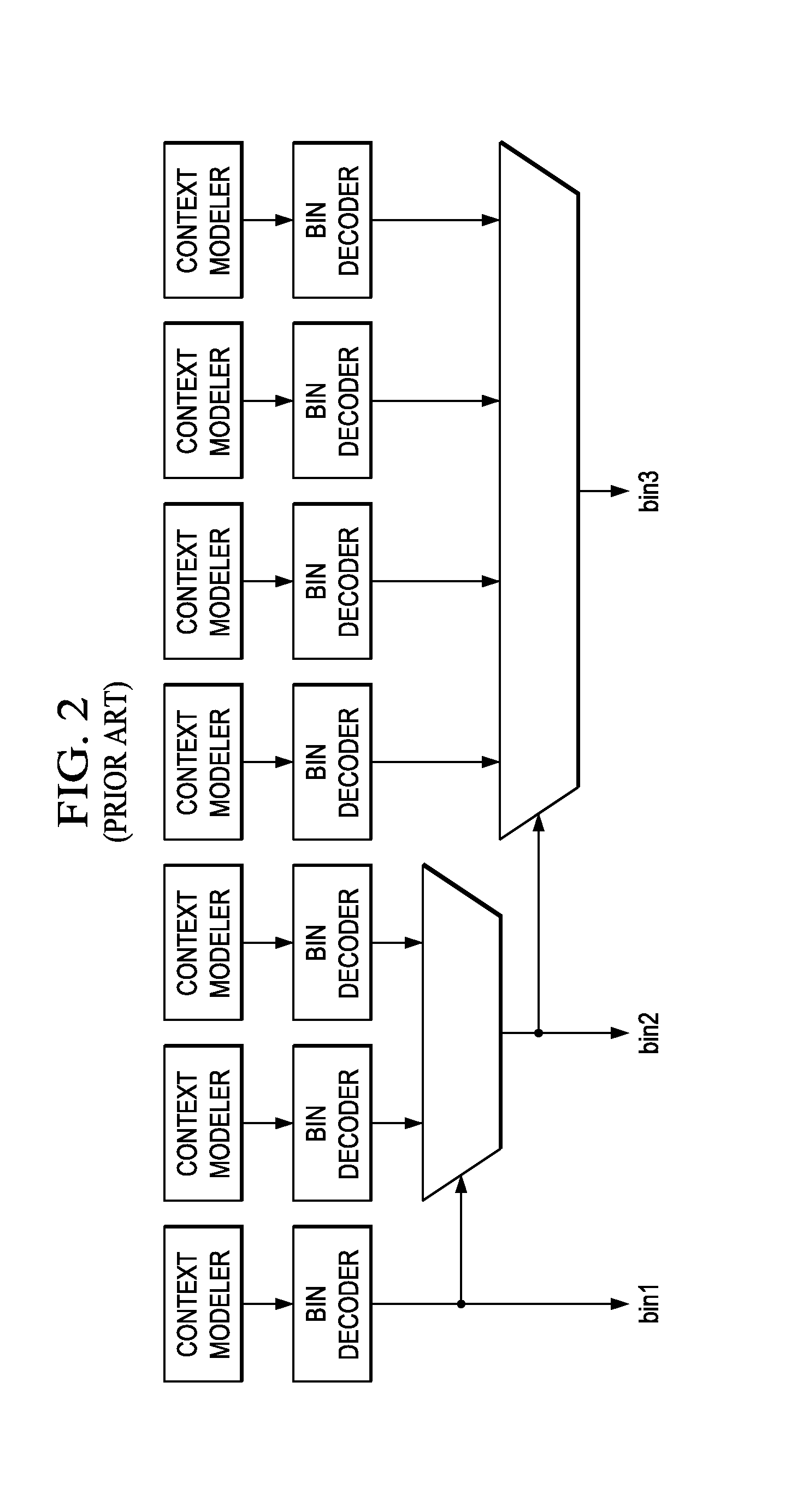
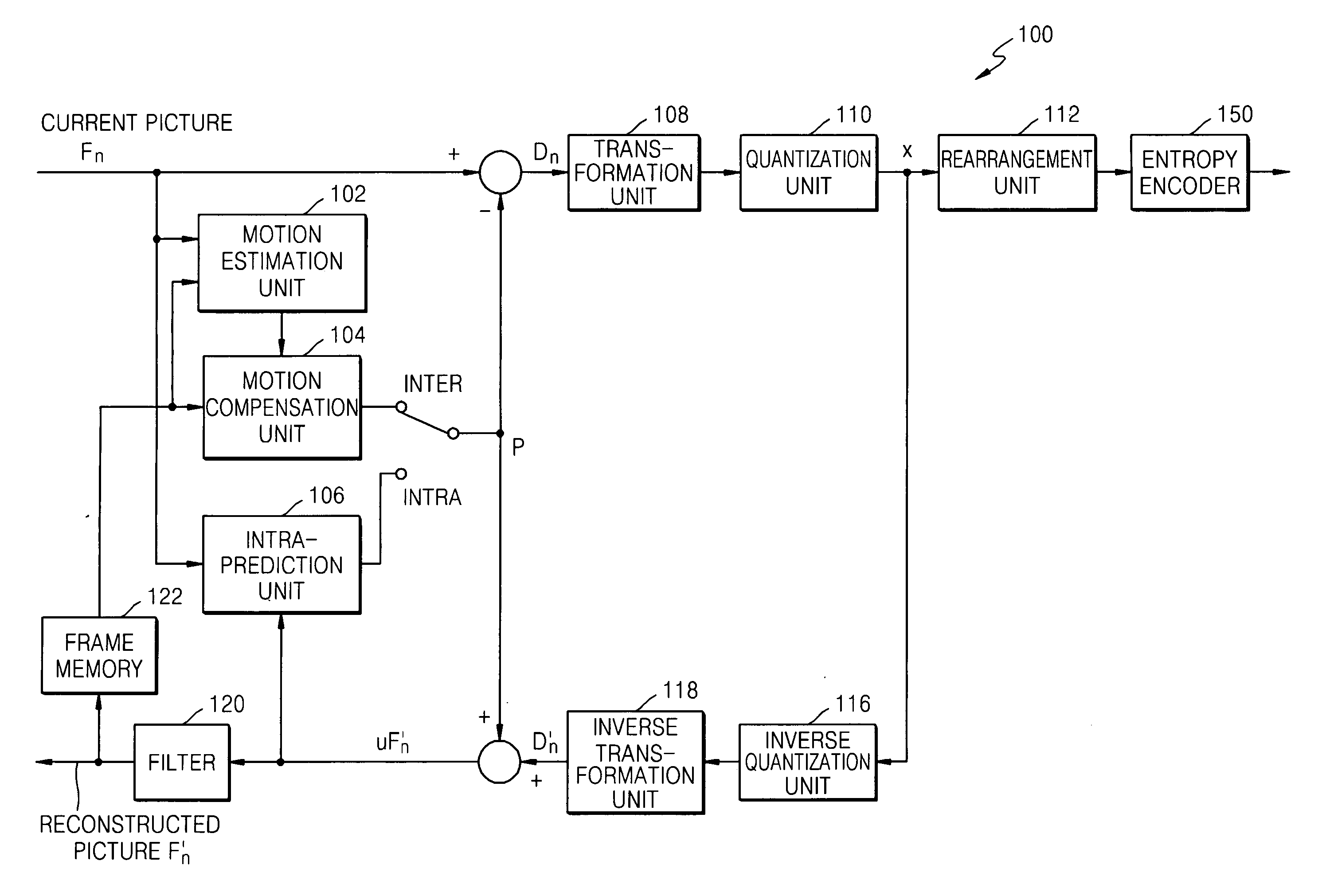
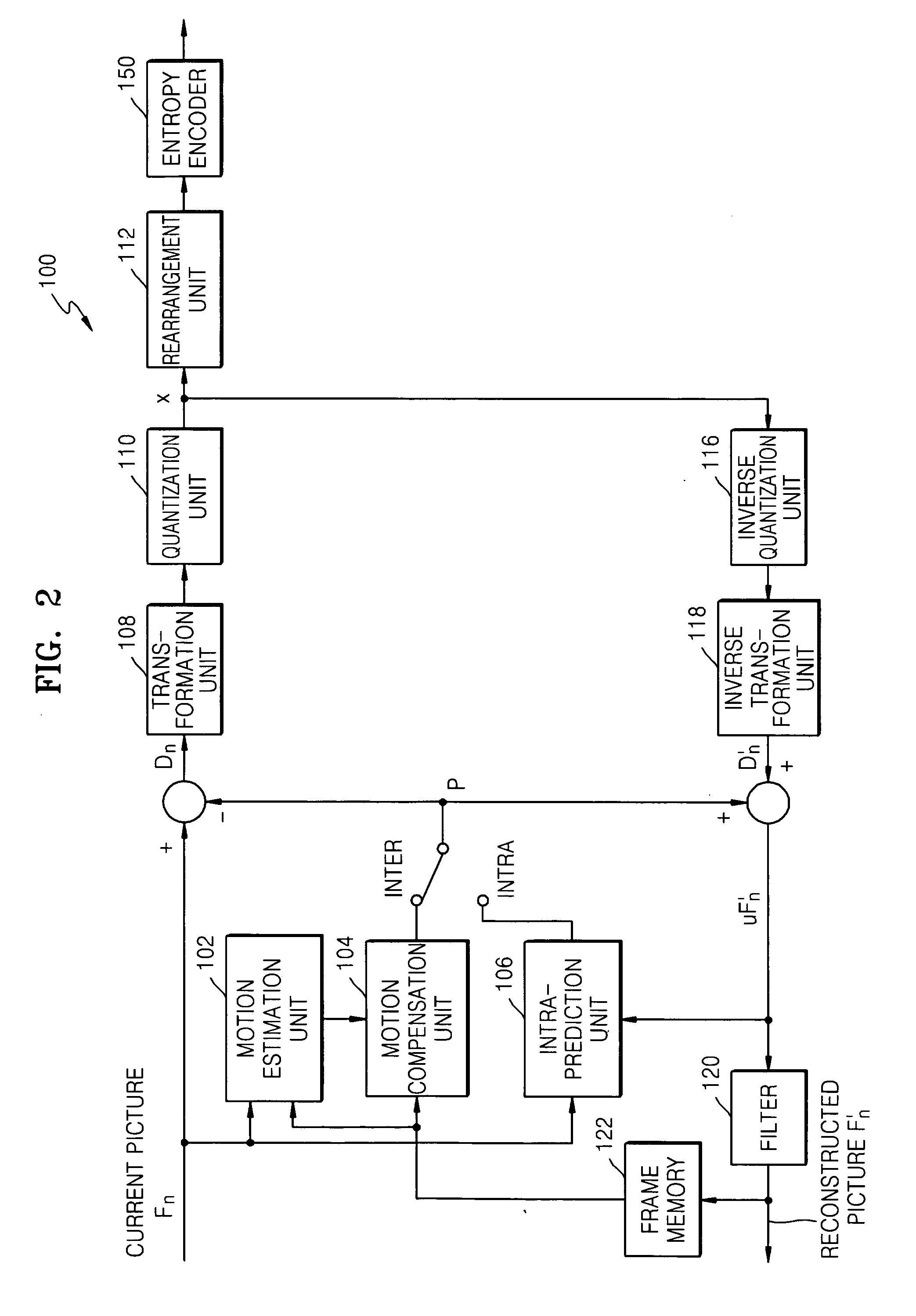
Method and apparatus for adaptively selecting context model for entropy coding
ActiveUS20060233254A1Reduce amountColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureContext model
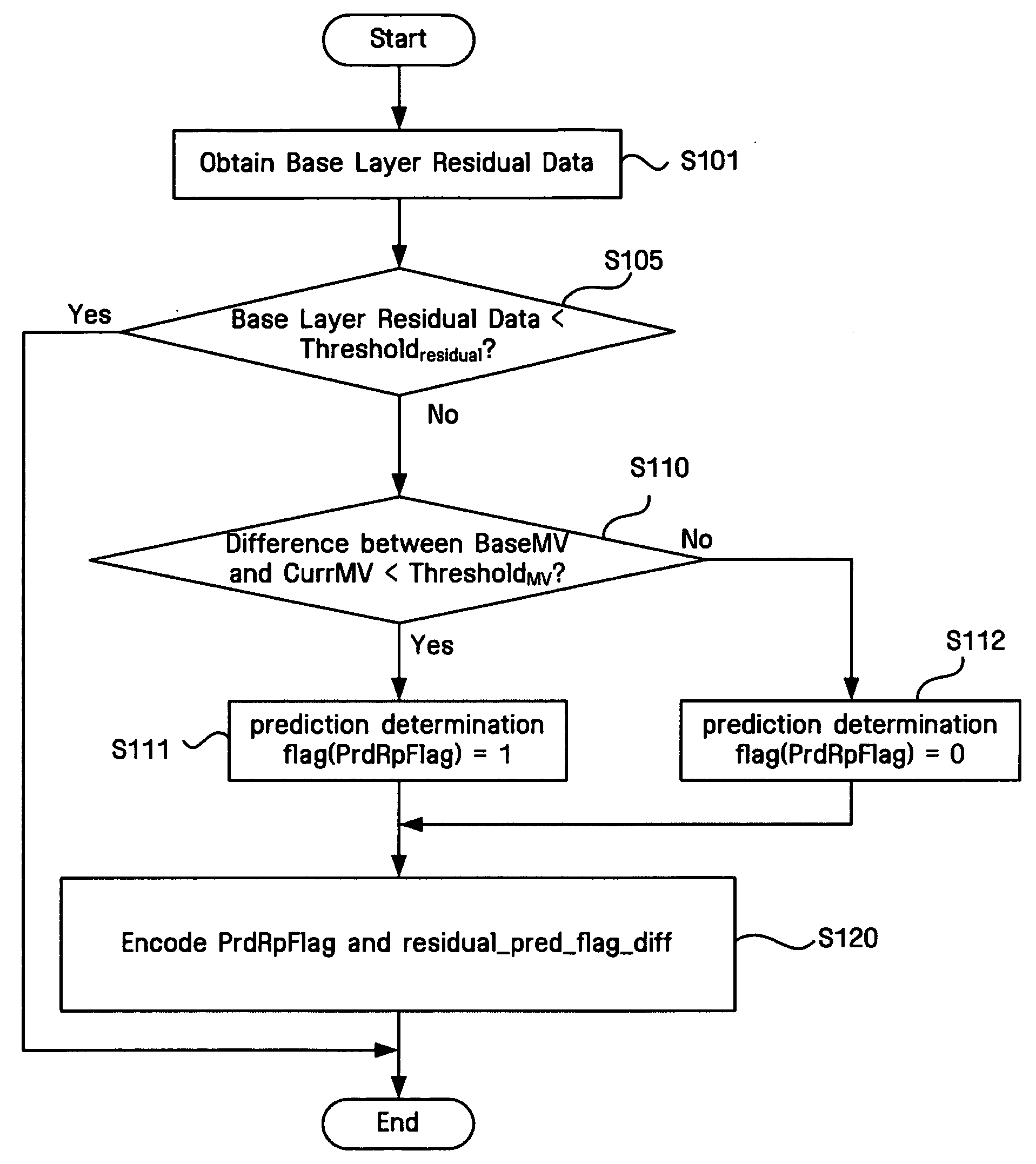
A method and apparatus for adaptively selecting a context model for entropy coding and a video decoder are provided. A method of coding a residual prediction flag indicating whether residual data for an enhancement layer block of a multi-layered video signal is predicted from residual data for a lower layer block corresponding to the residual data for the enhancement layer block includes the steps of calculating the energy of the residual data for the lower layer block, determining a coding method for the residual prediction flag according to the energy, and coding the residual prediction flag using the determined coding method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
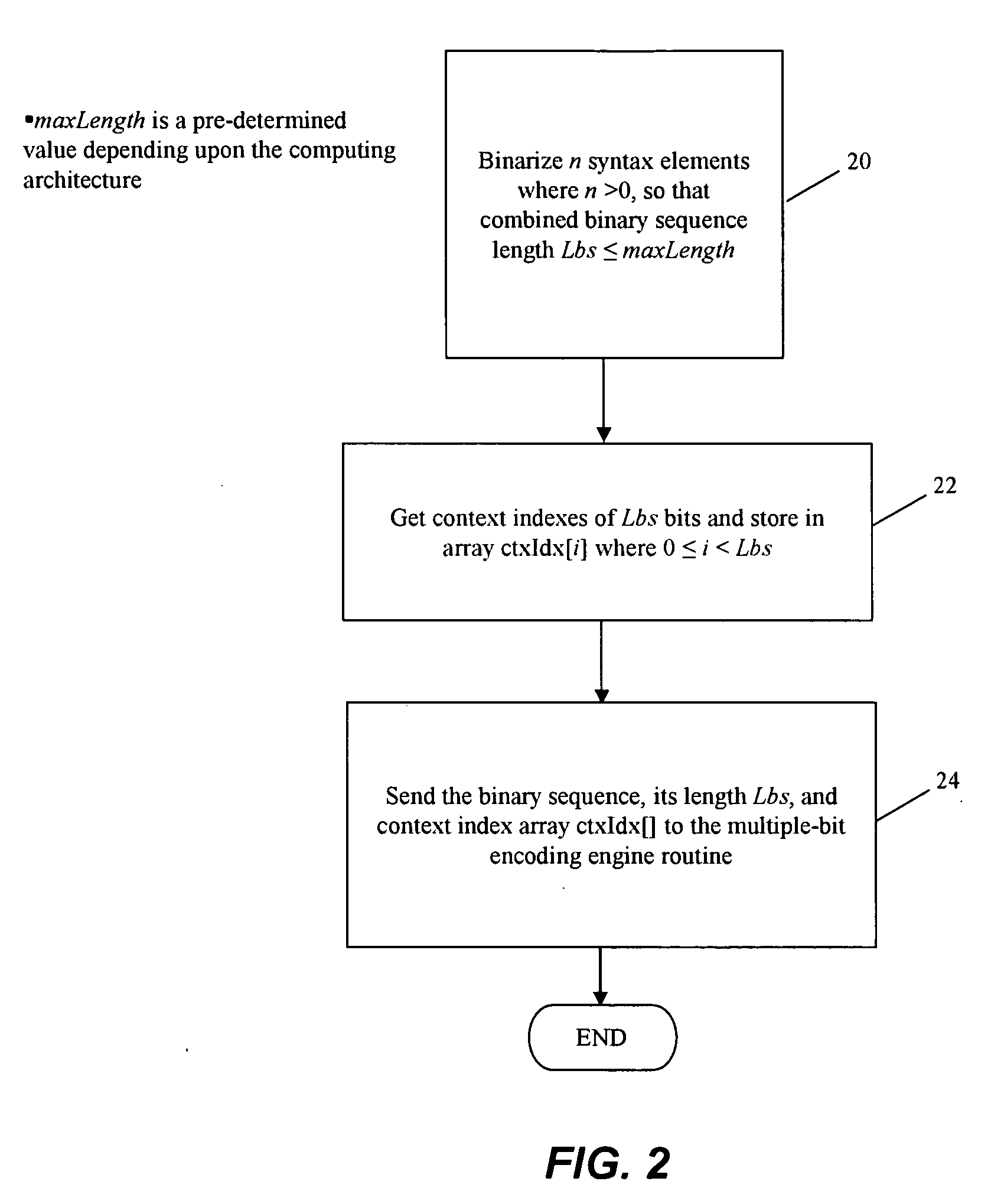
Entropy coding
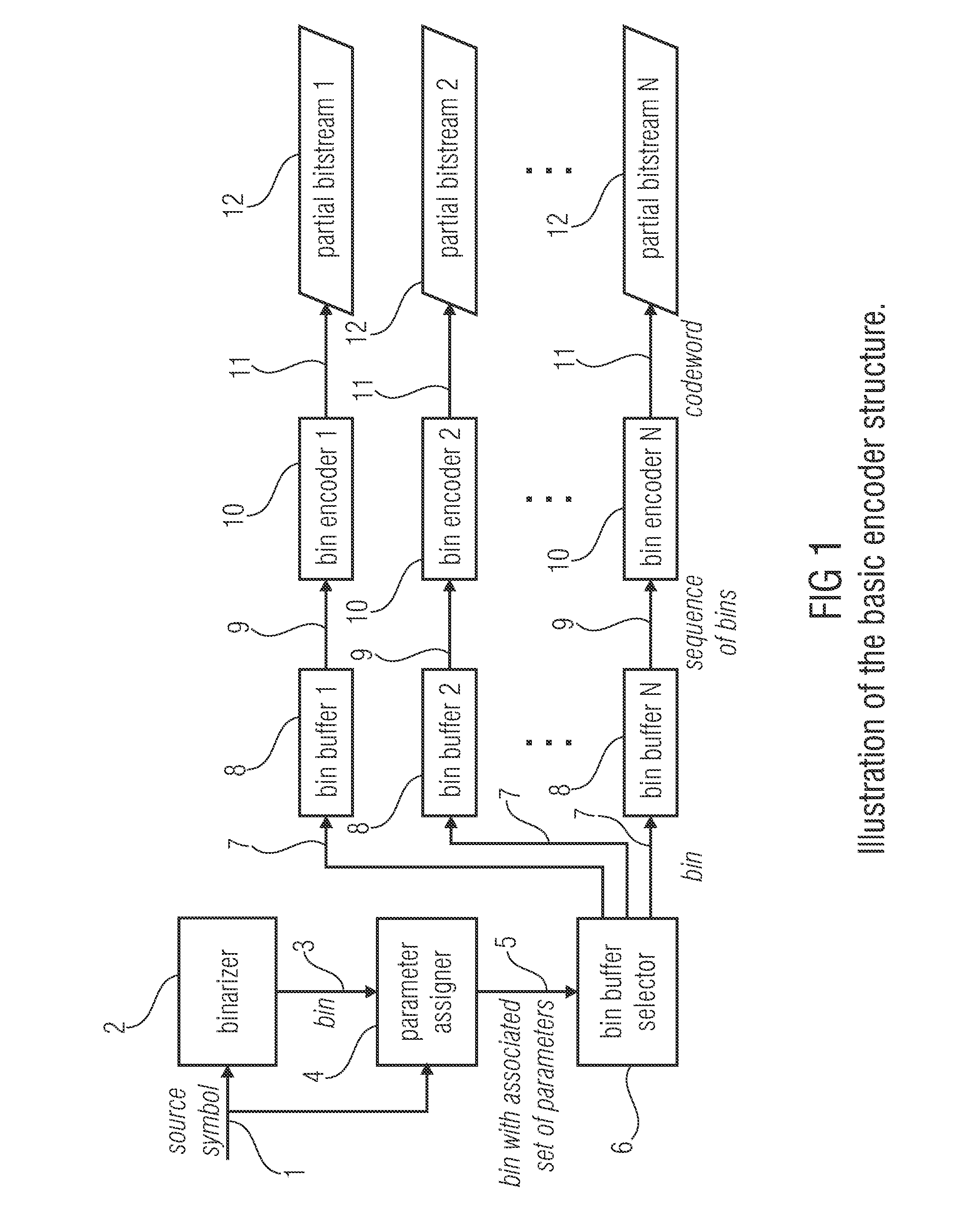
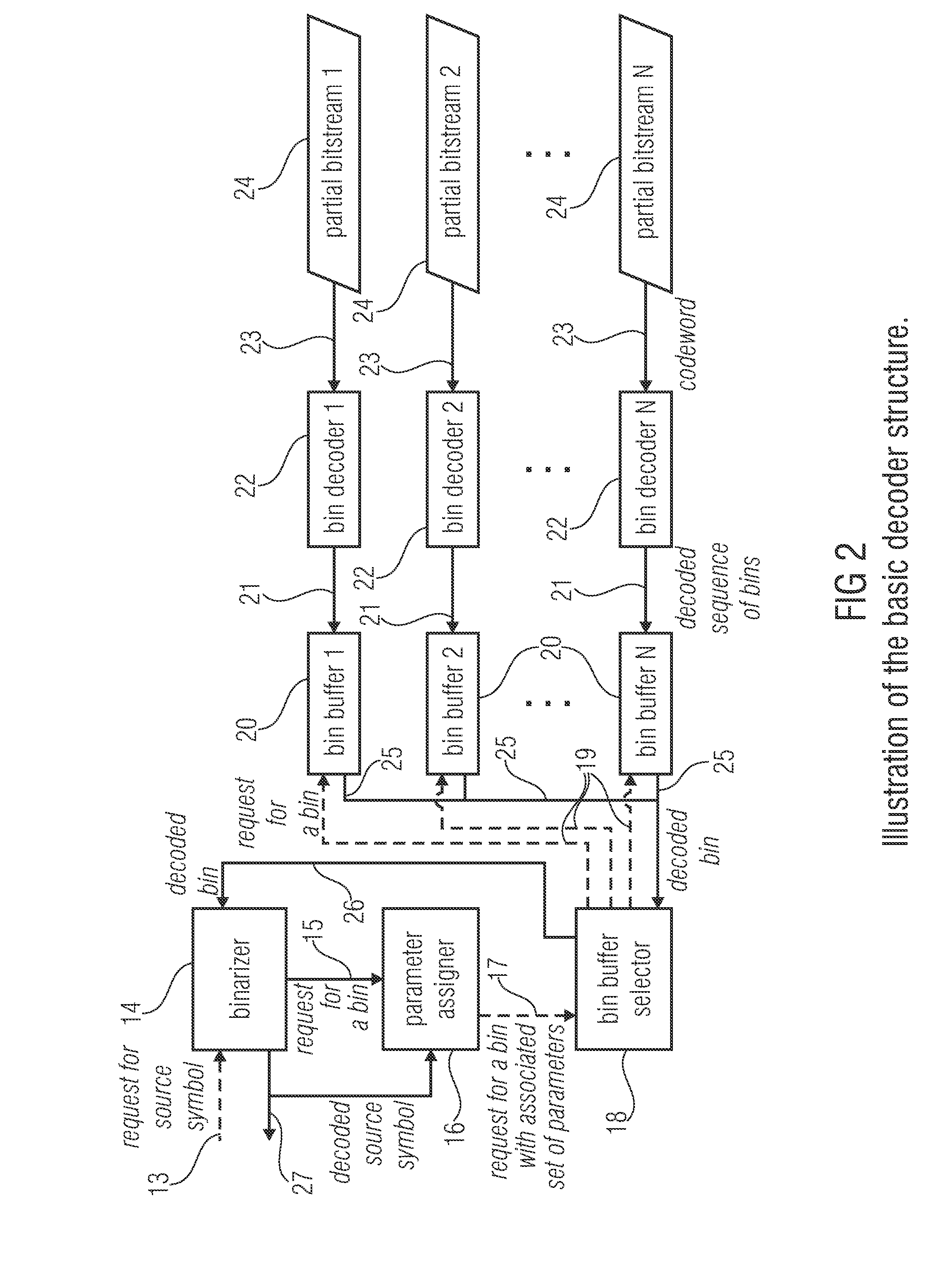
ActiveUS20130027230A1Reduce complexityOverhead for transmitting the partial bitstream can be kept smallCode conversionDigital video signal modificationEntropy encodingComputer science
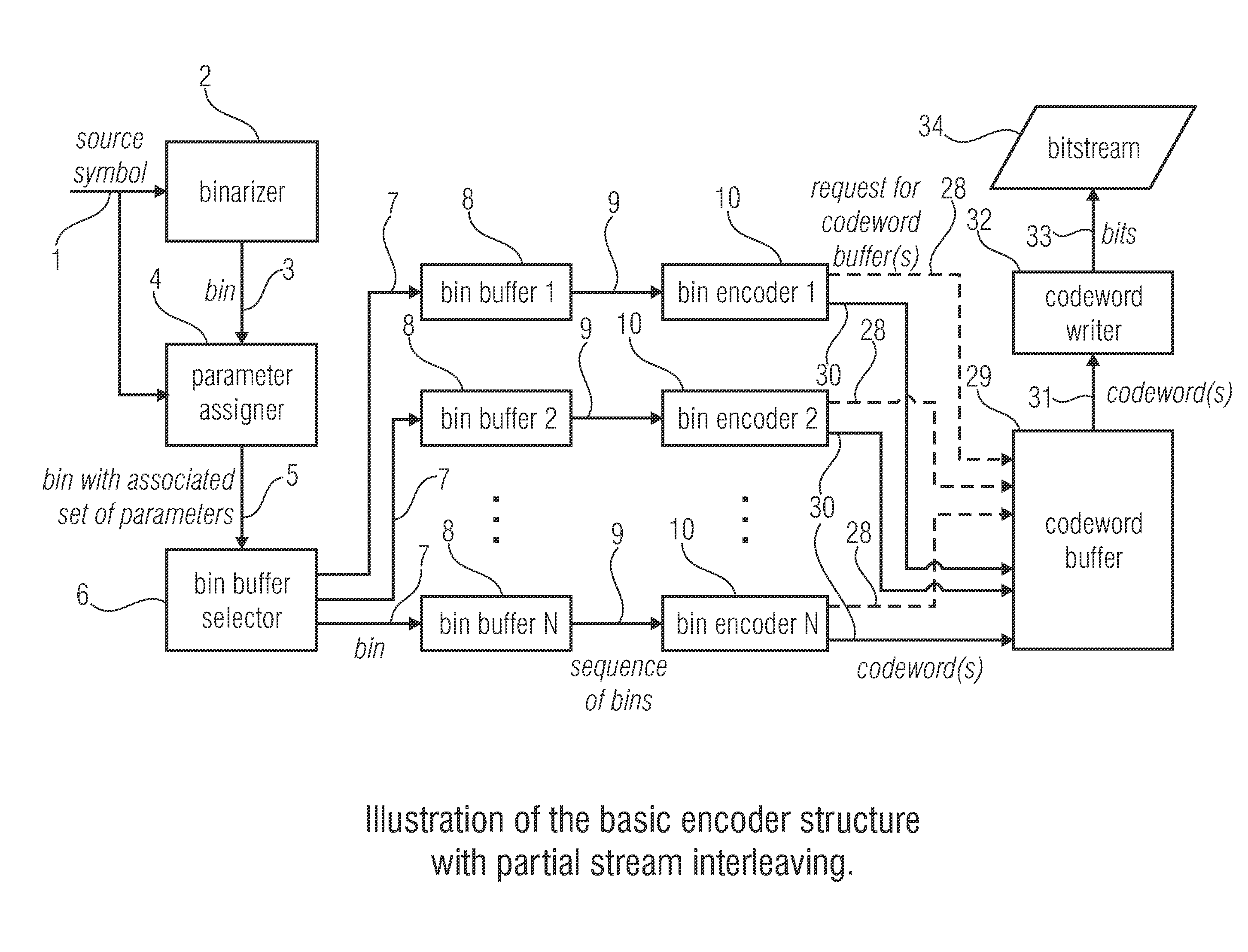
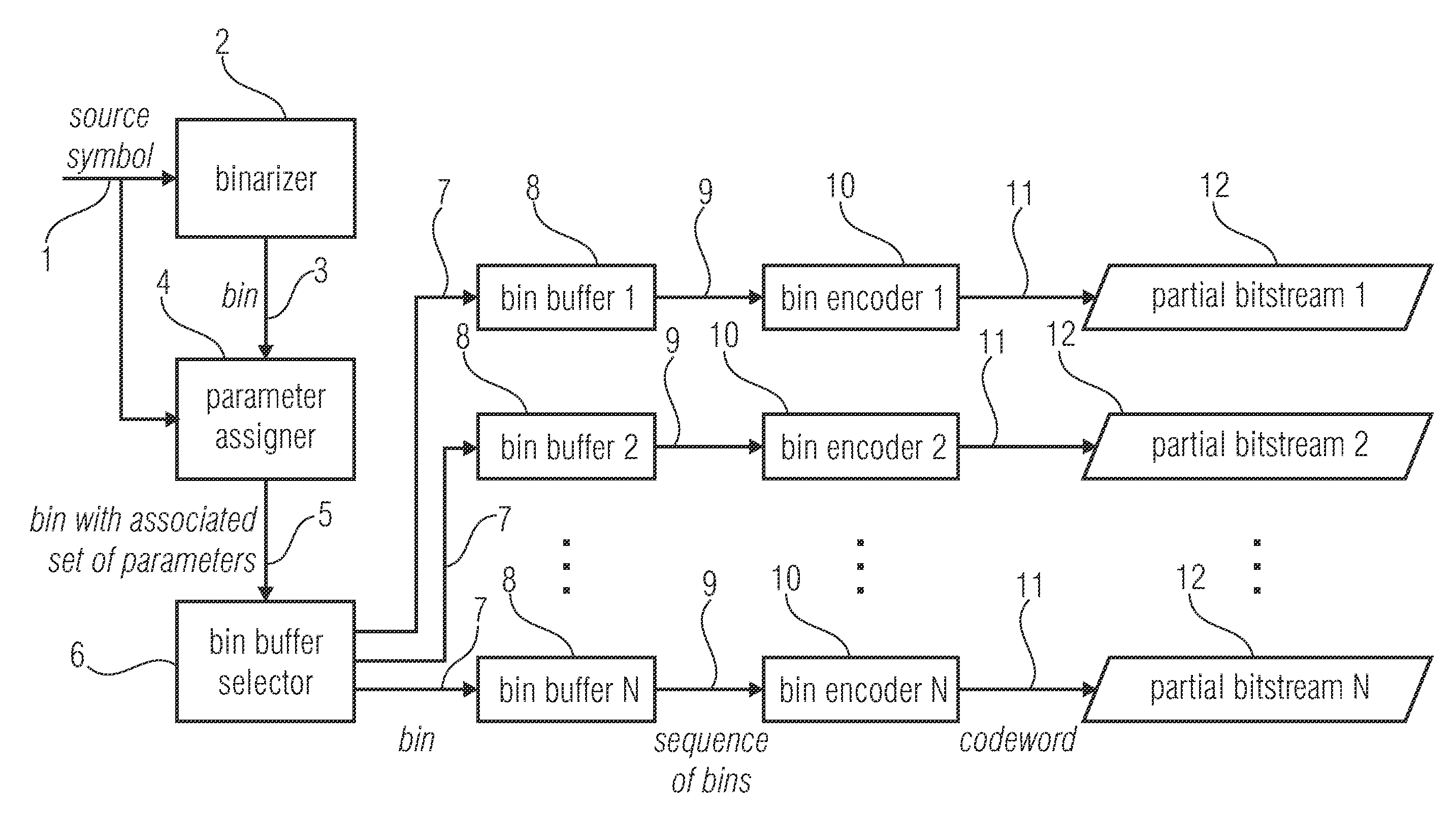
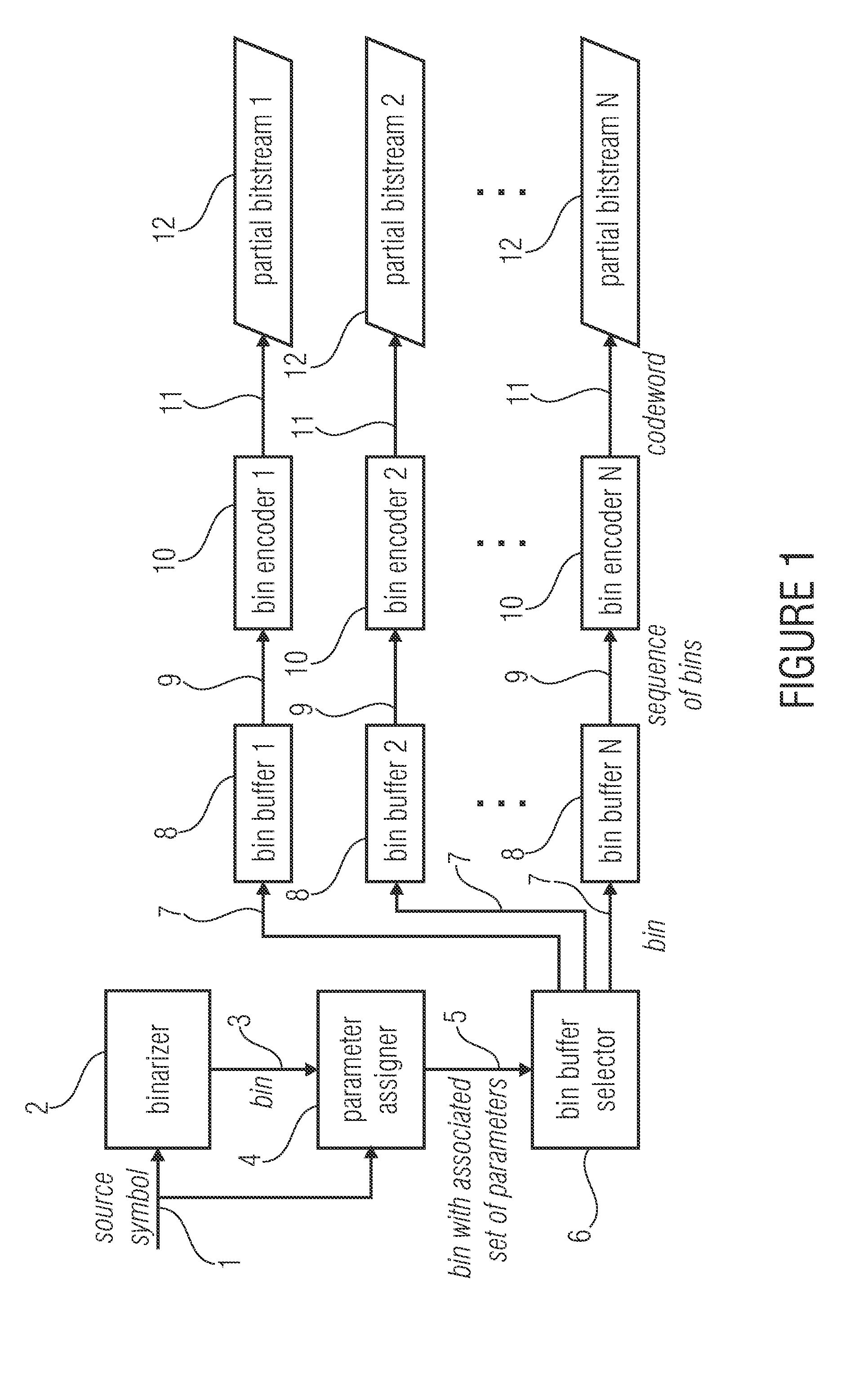
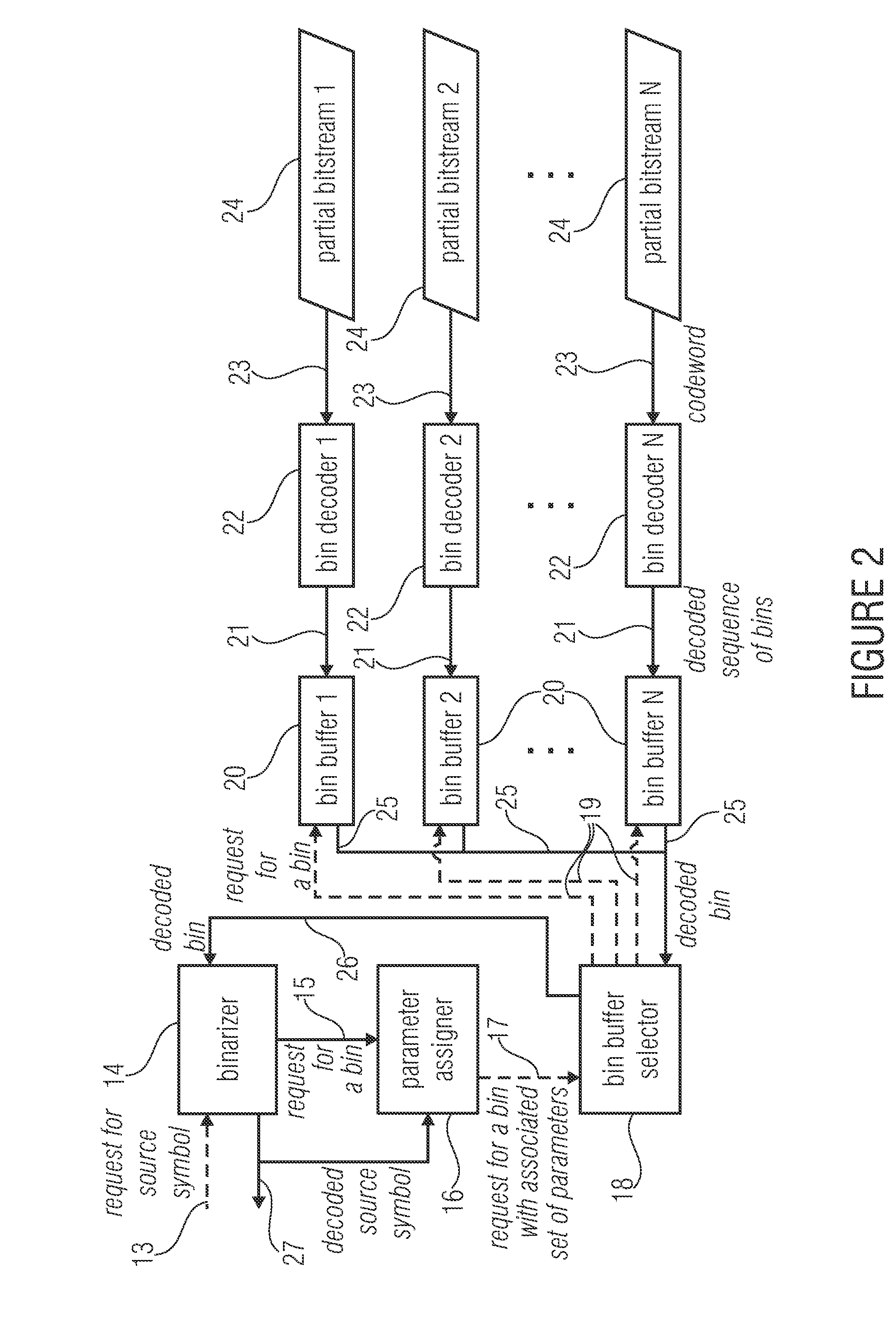
An encoder for encoding a sequence of symbols is described which includes an assigner configured to assign a number of parameters to each symbol of the sequence of symbols based on information contained within previous symbols of the sequence of symbols; a plurality of entropy encoders each of which is configured to convert the symbols forwarded to the respective entropy encoder into a respective bitstream; and a selector configured to forward each symbol to a selected one of the plurality of entropy encoders, the selection depending on the number of parameters assigned to the respective symbol.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Image encoding/image decoding method and image encoding/image decoding apparatus
InactiveUS20070121731A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithmImage signal
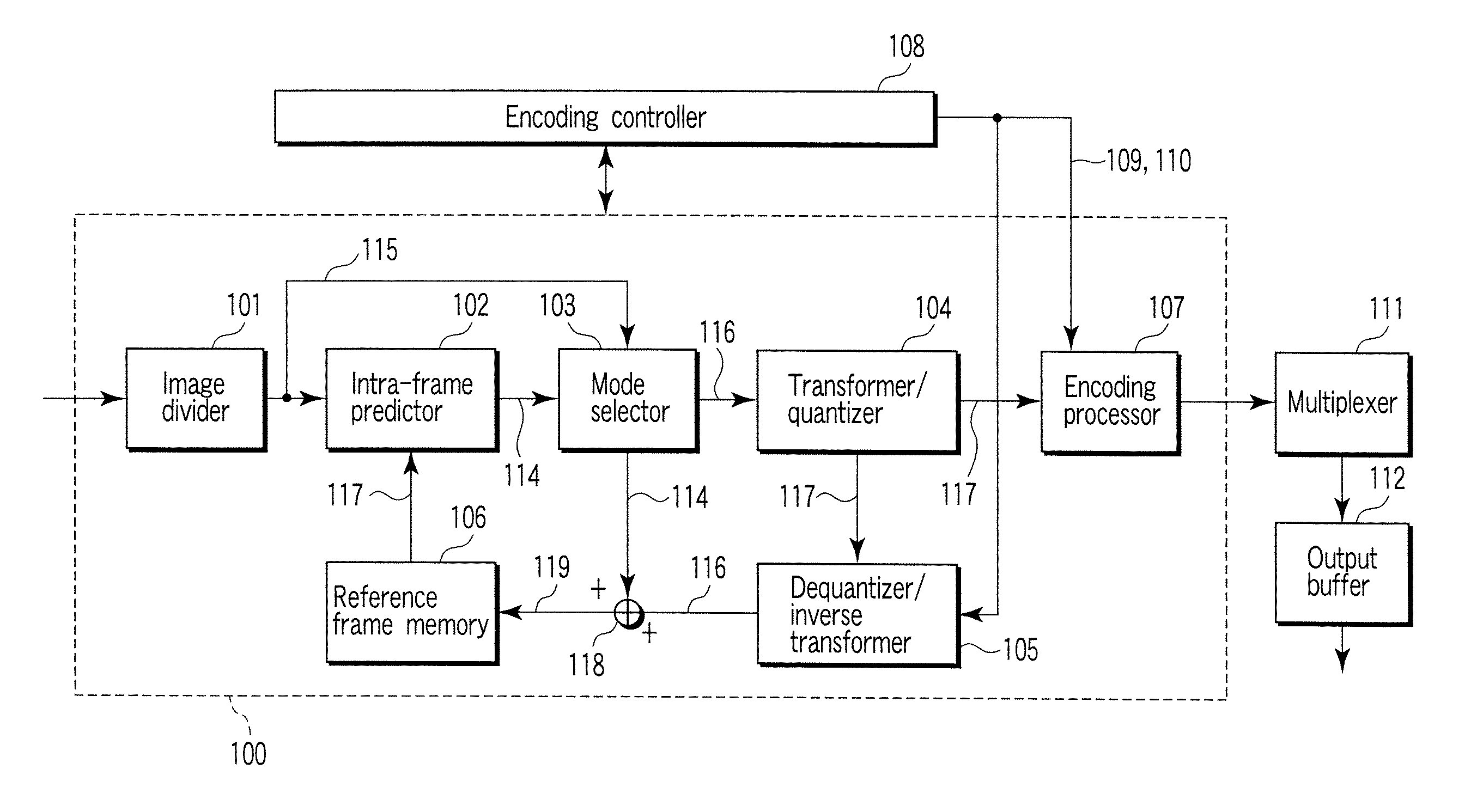
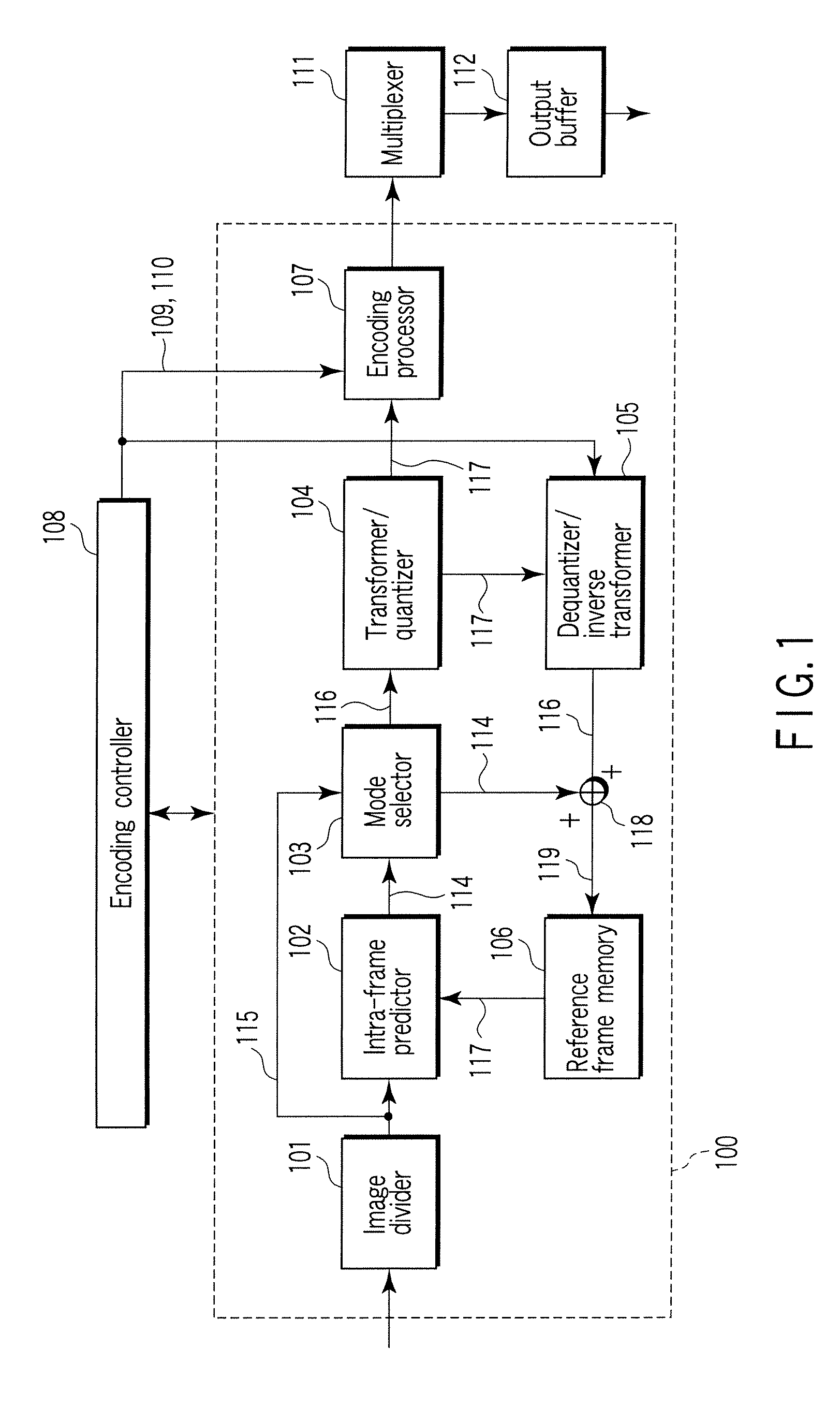
An image coding method includes dividing an input picture into a plurality of pixel block signals, performing intra prediction for extrapolating or interpolating a prediction pixel using reference pixels changed in number according to a distance between the prediction pixel and a reference pixel in plural prediction modes each representing a prediction direction, generating a predictive image signal by extrapolating or interpolating the prediction pixel, calculating a prediction error signal from the pixel block signal and the predictive image signal, selecting one prediction mode of the plural prediction modes using the prediction error signal, and performing entropy-coding using the prediction error signal based on the selected prediction mode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
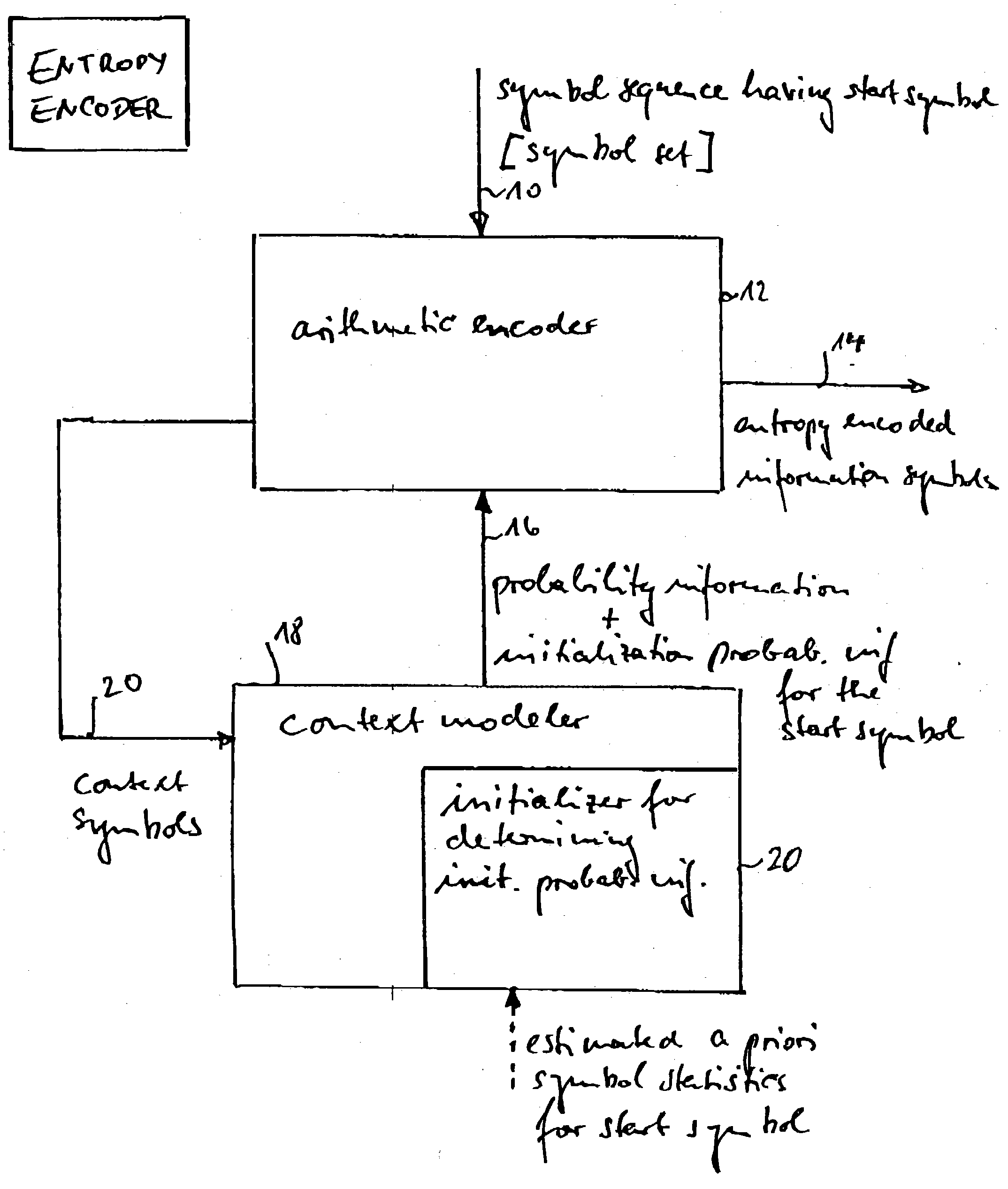
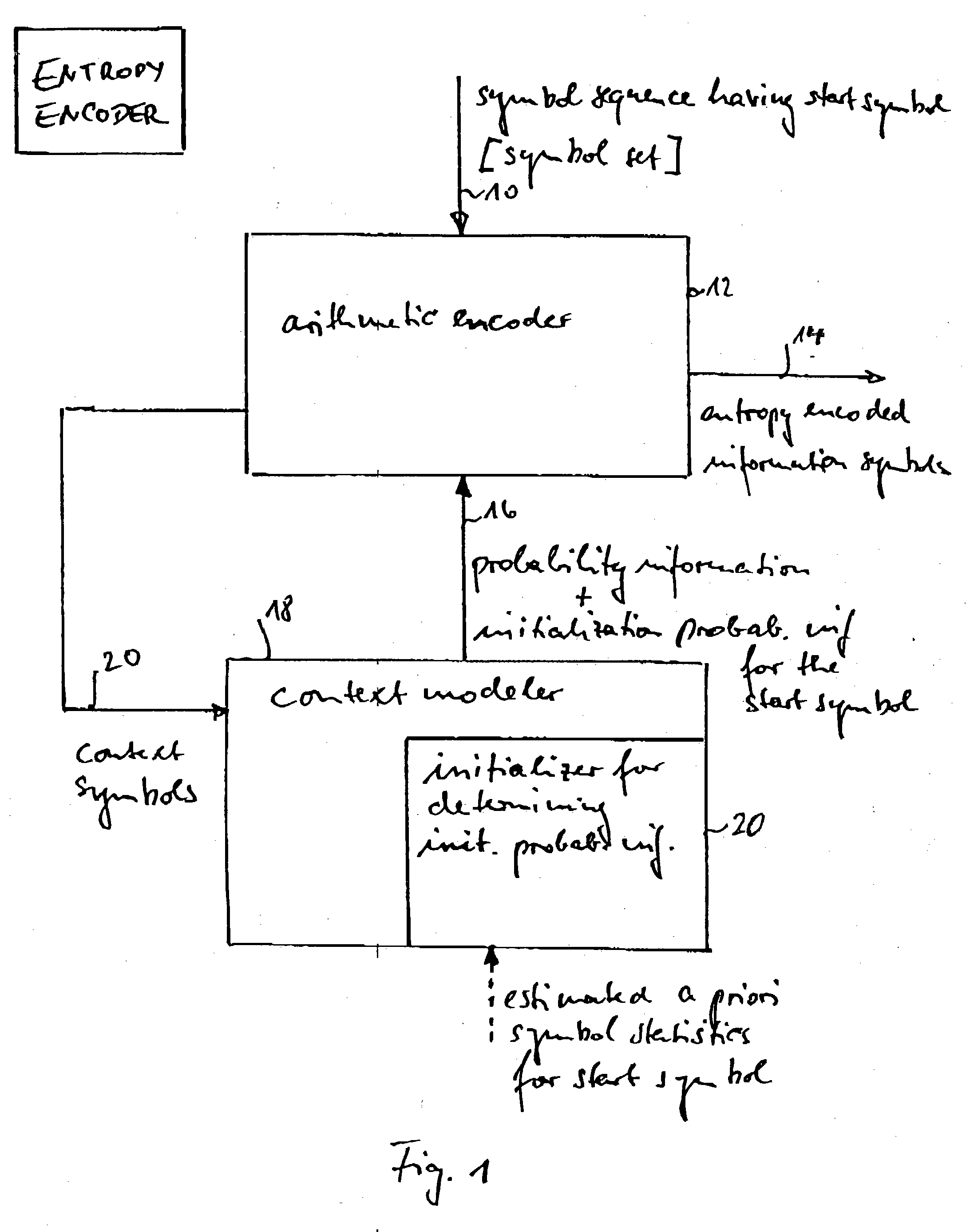
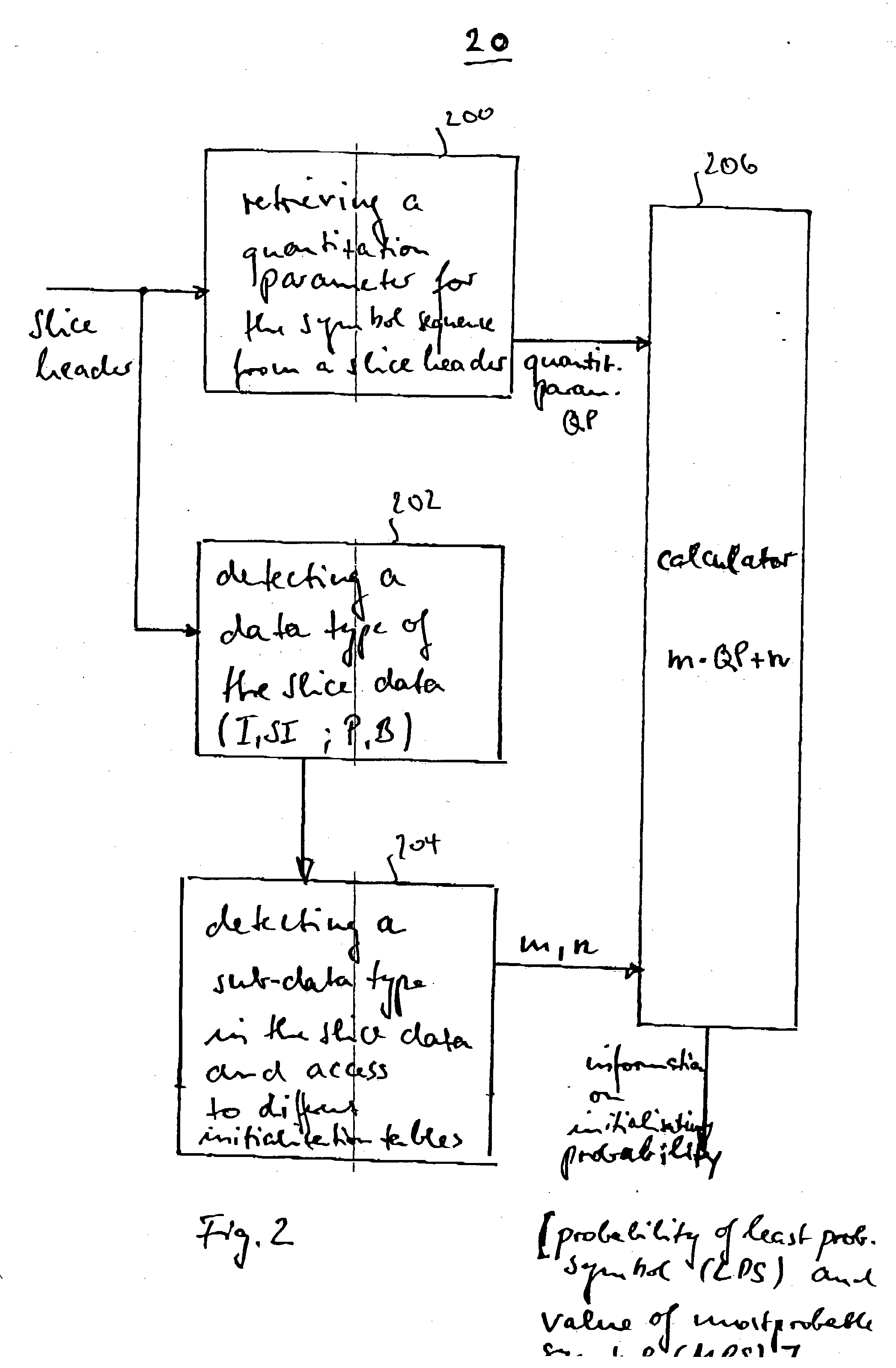
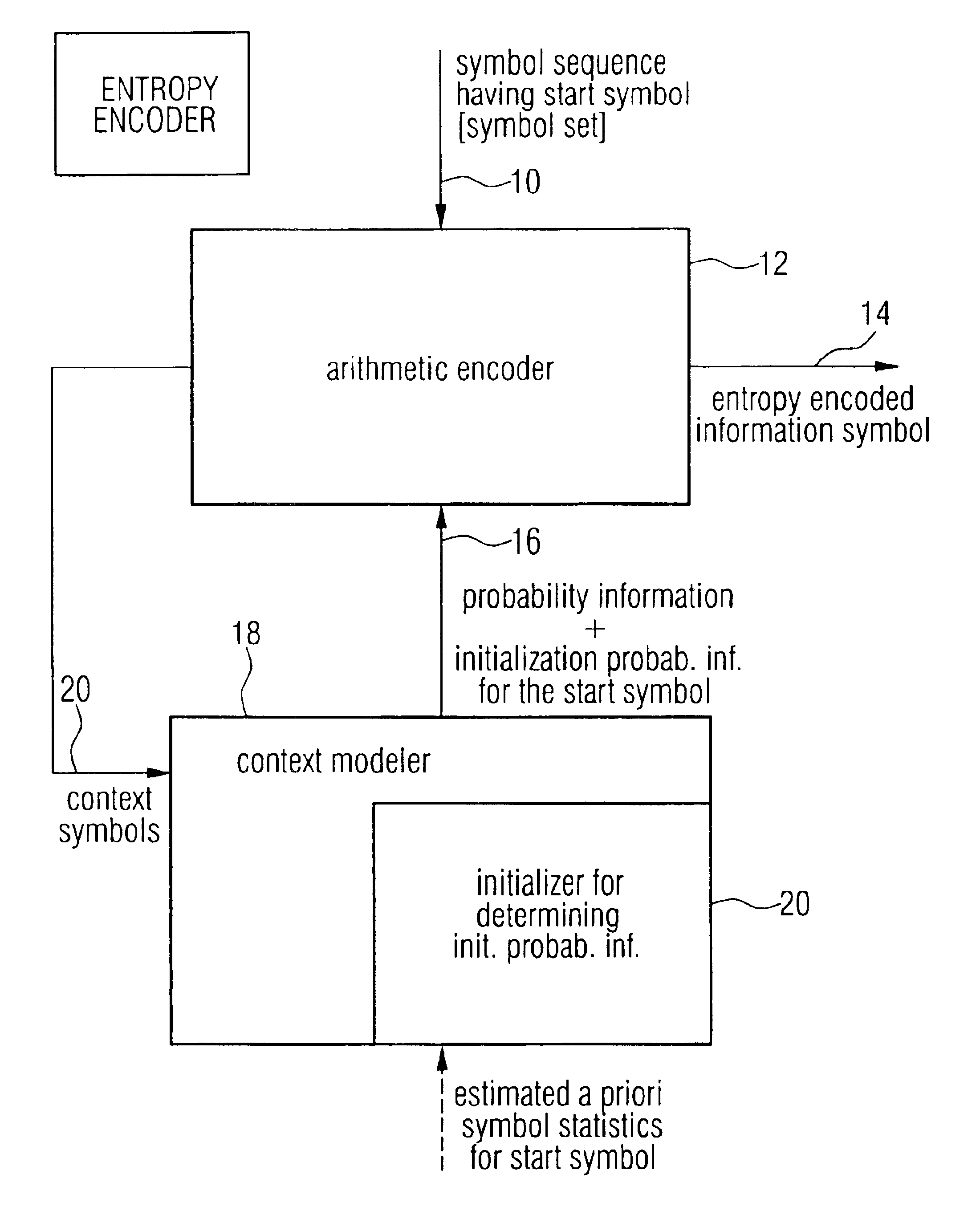
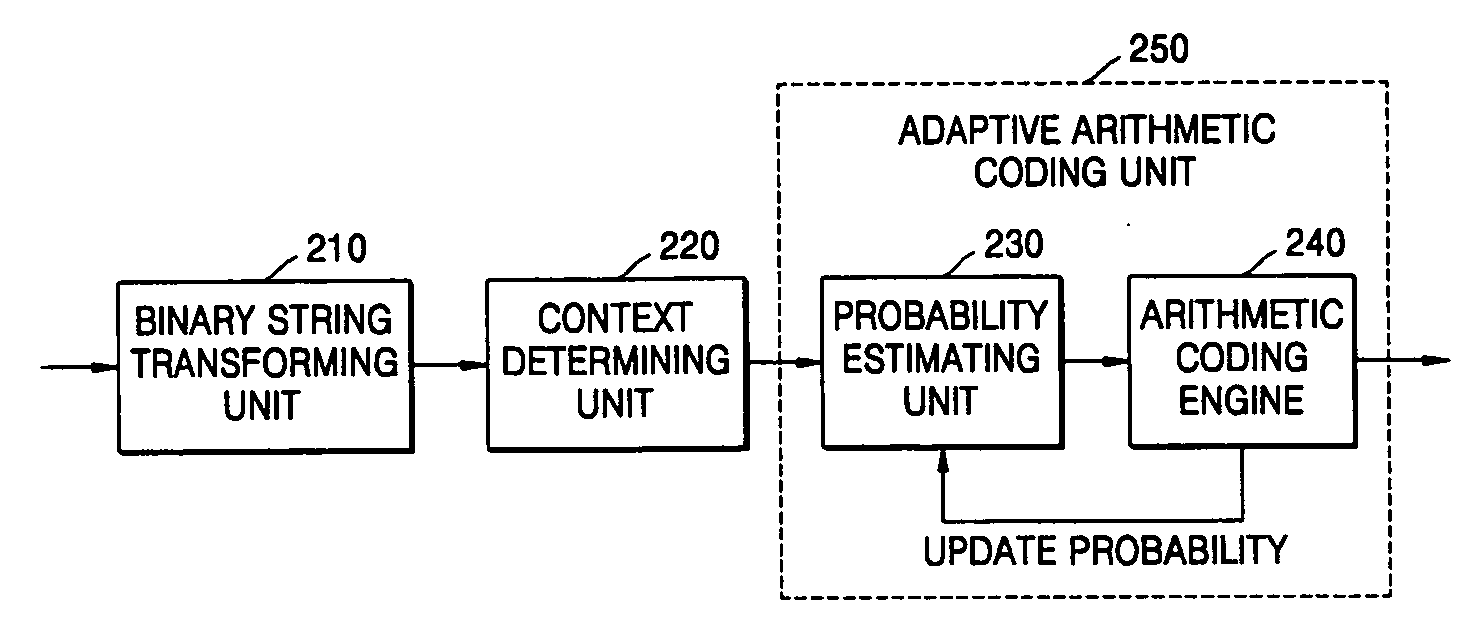
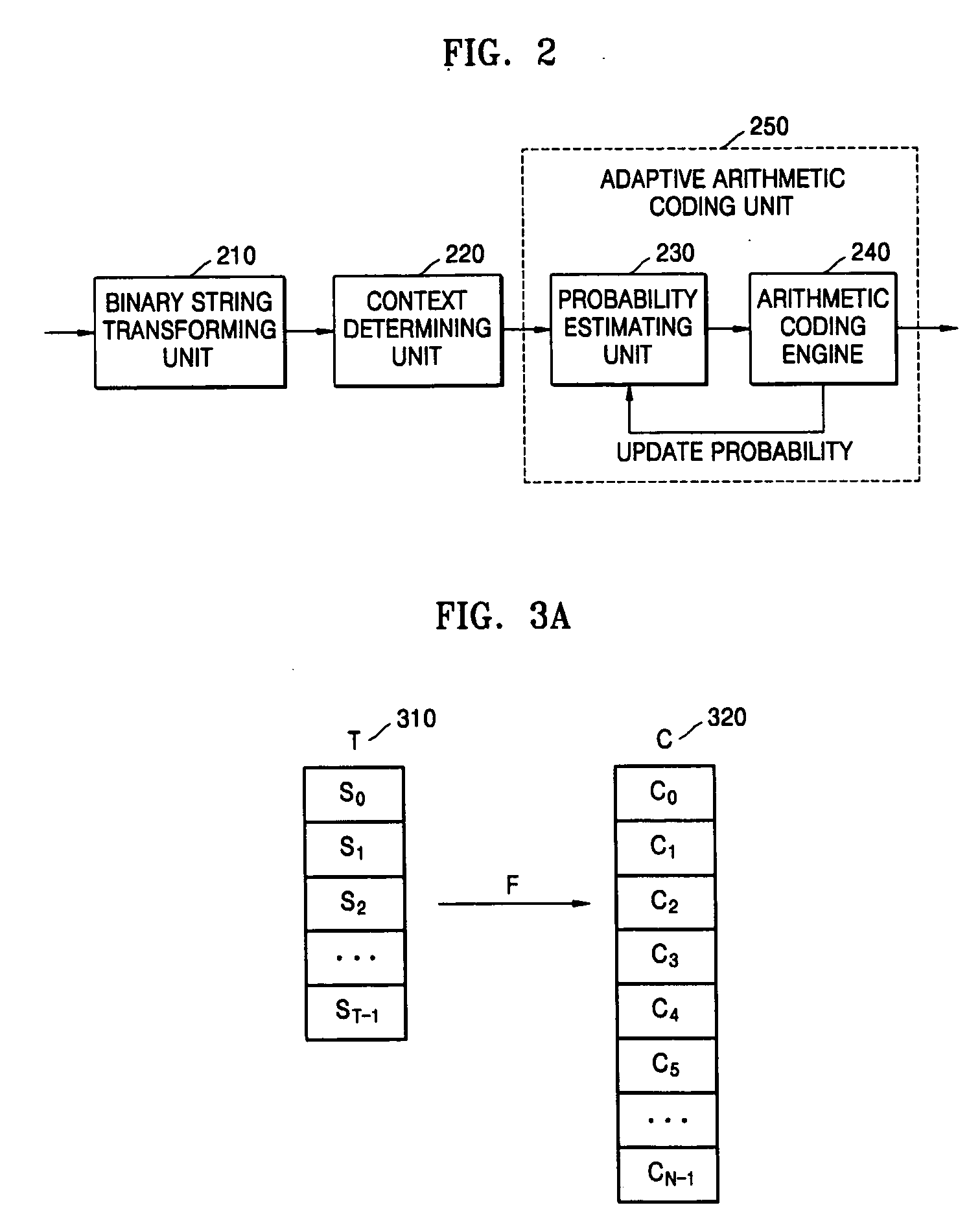
Apparatus and methods for entropy-encoding or entropy-decoding using an initialization of context variables
ActiveUS20050012648A1Improved entropy encoding designImprove compression efficiencyCode conversionTelevision systemsContext variableContext based
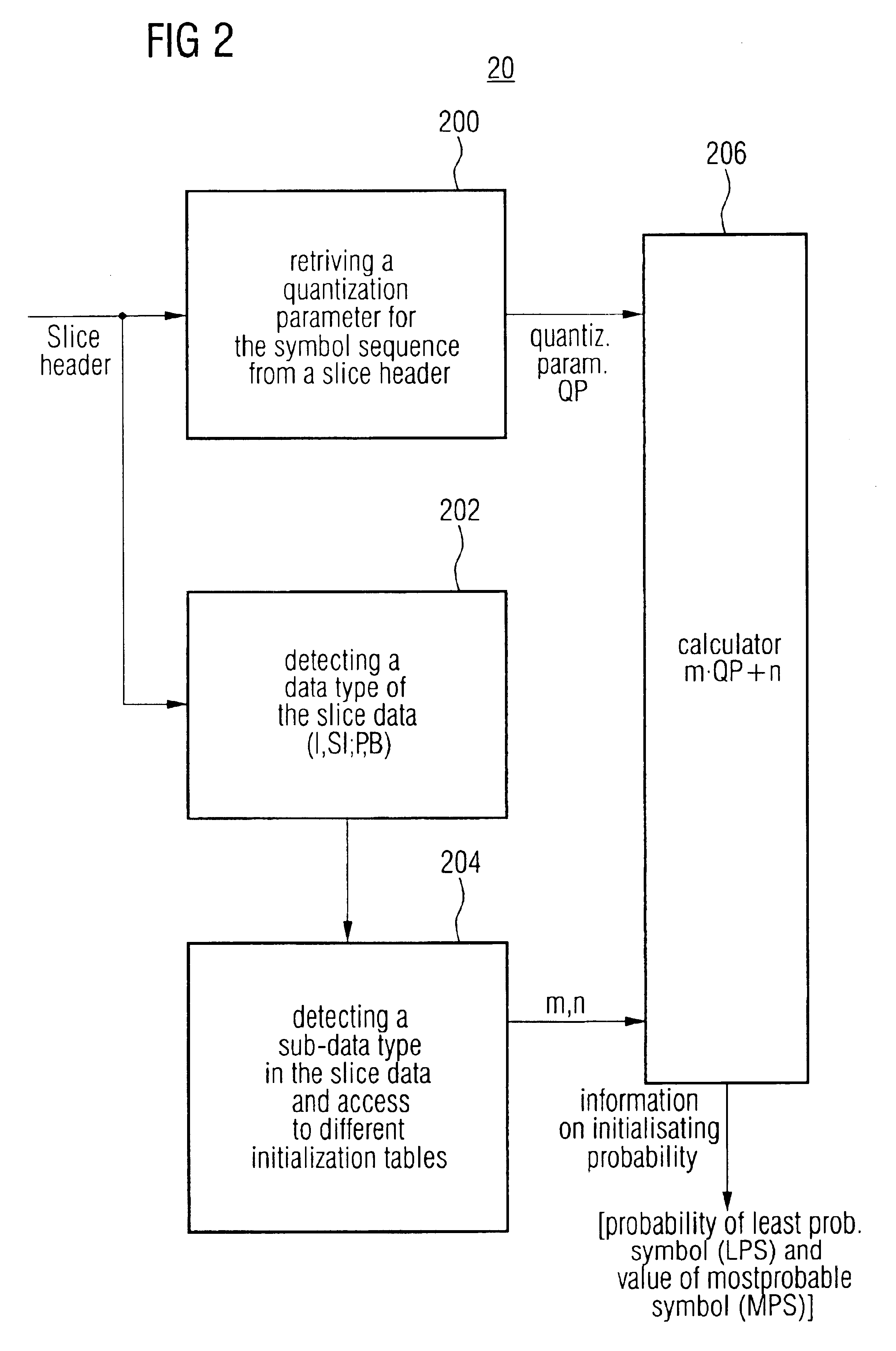
An entropy encoding / decoding scheme uses an arithmetic encoder / decoder together with a context modeler for performing a context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding, which is especially suited for video compression applications. The context modeler includes an initializer for initializing the context modeler by determining and providing initialization probability information to the arithmetic encoder, the initialization probability information to be used by the arithmetic encoder for processing a start symbol of a symbol sequence. The initializer is operative to determine the initialization probability information based on an estimation of the symbol statistics relating to the start symbol such that an initialization probability distribution is different from an equi-probable distribution for all symbols of the symbol set. By means of the initialization, the context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding / decoding scheme is optimally adjusted before processing a start symbol of the symbol sequence so that no bit rate compression losses because of a delayed context-based adaptation are introduced.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
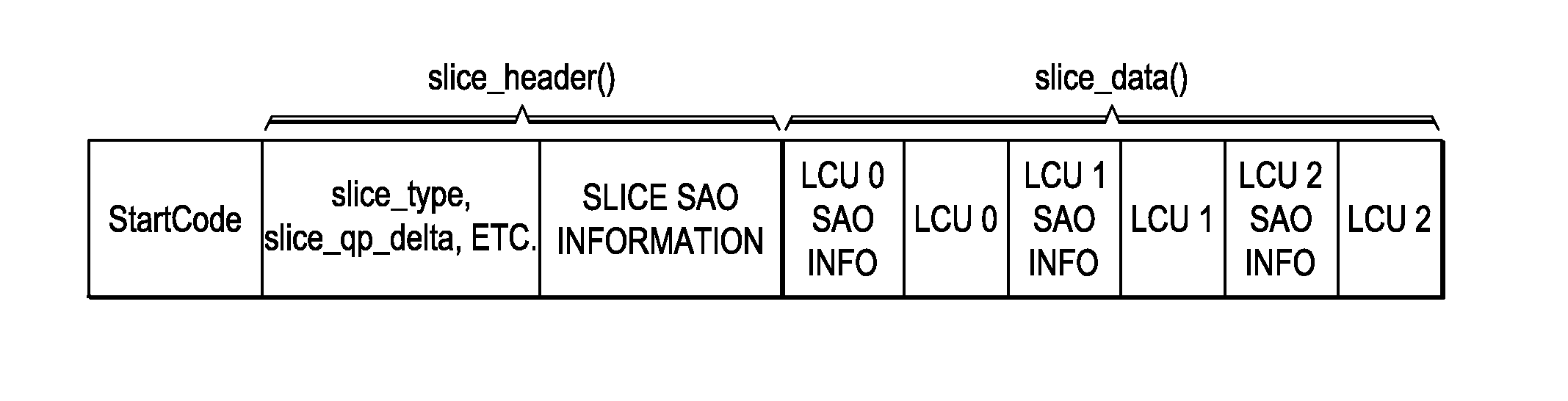
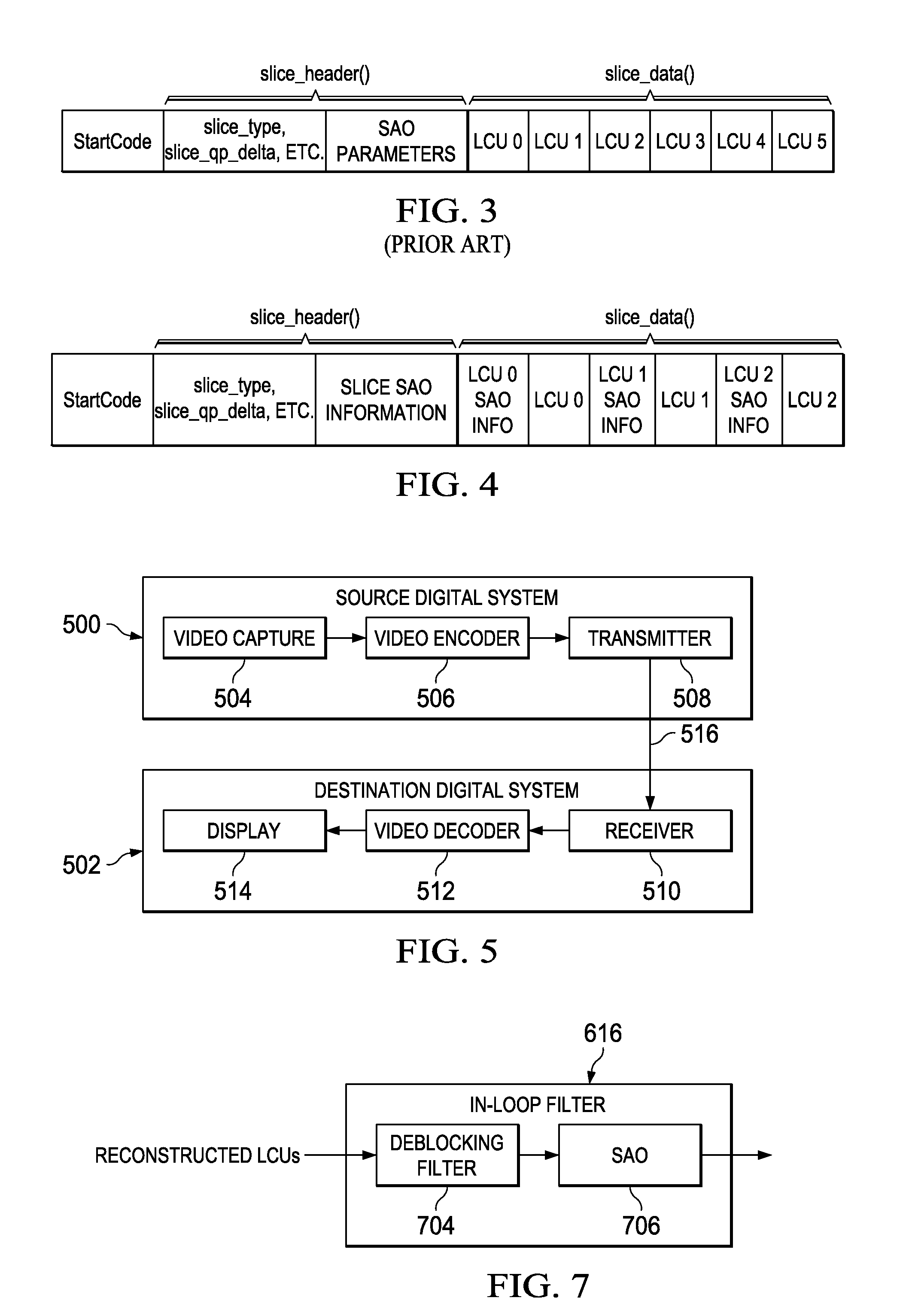
Sample Adaptive Offset (SAO) Parameter Signaling
ActiveUS20130051454A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo bitstream
A method for sample adaptive offset (SAO) filtering and SAO parameter signaling in a video encoder is provided that includes determining SAO parameters for largest coding units (LCUs) of a reconstructed picture, wherein the SAO parameters include an indicator of an SAO filter type and a plurality of SAO offsets, applying SAO filtering to the reconstructed picture according to the SAO parameters, and entropy encoding LCU specific SAO information for each LCU of the reconstructed picture in an encoded video bit stream, wherein the entropy encoded LCU specific SAO information for the LCUs is interleaved with entropy encoded data for the LCUs in the encoded video bit stream. Determining SAO parameters may include determining the LCU specific SAO information to be entropy encoded for each LCU according to an SAO prediction protocol.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
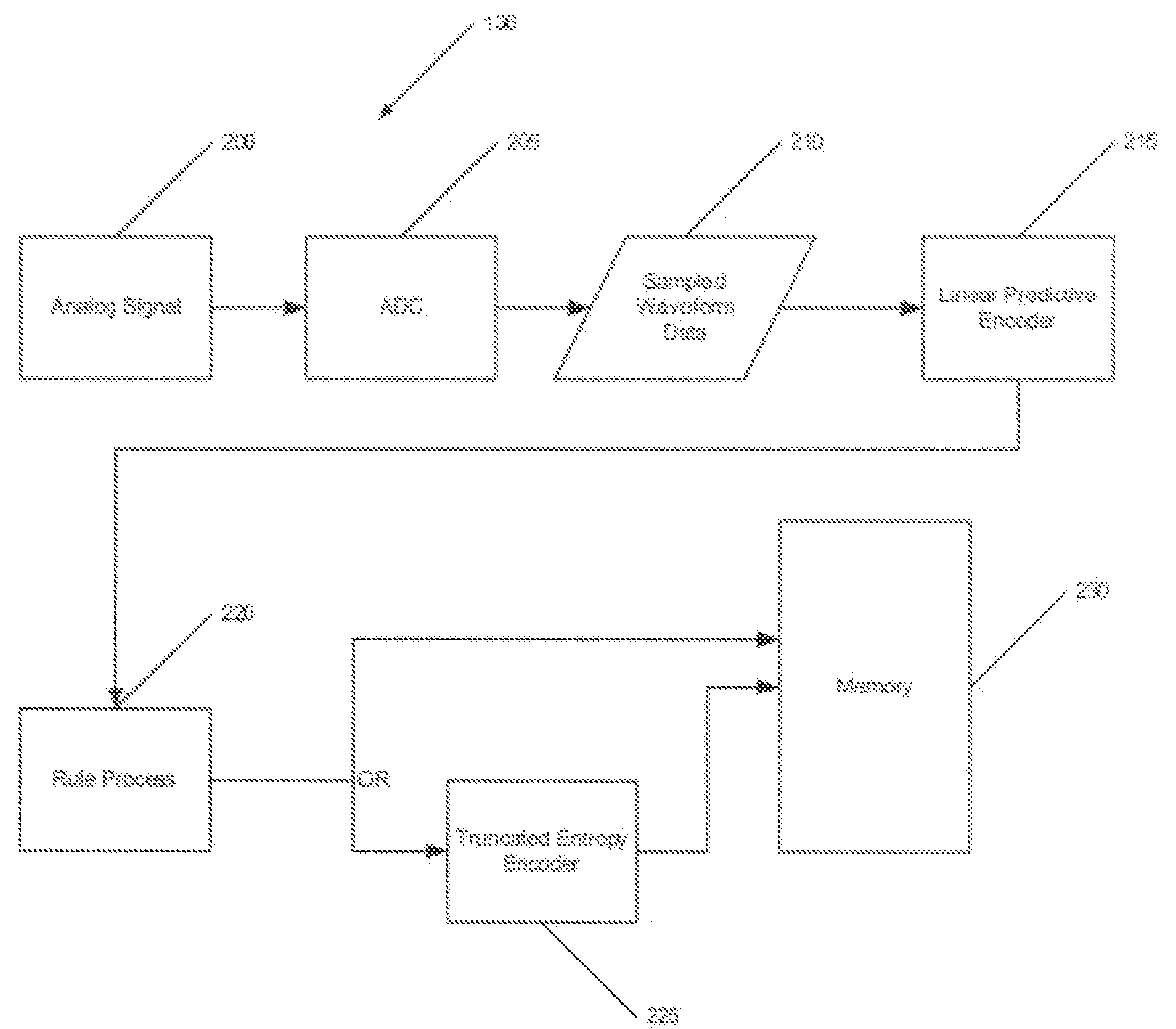
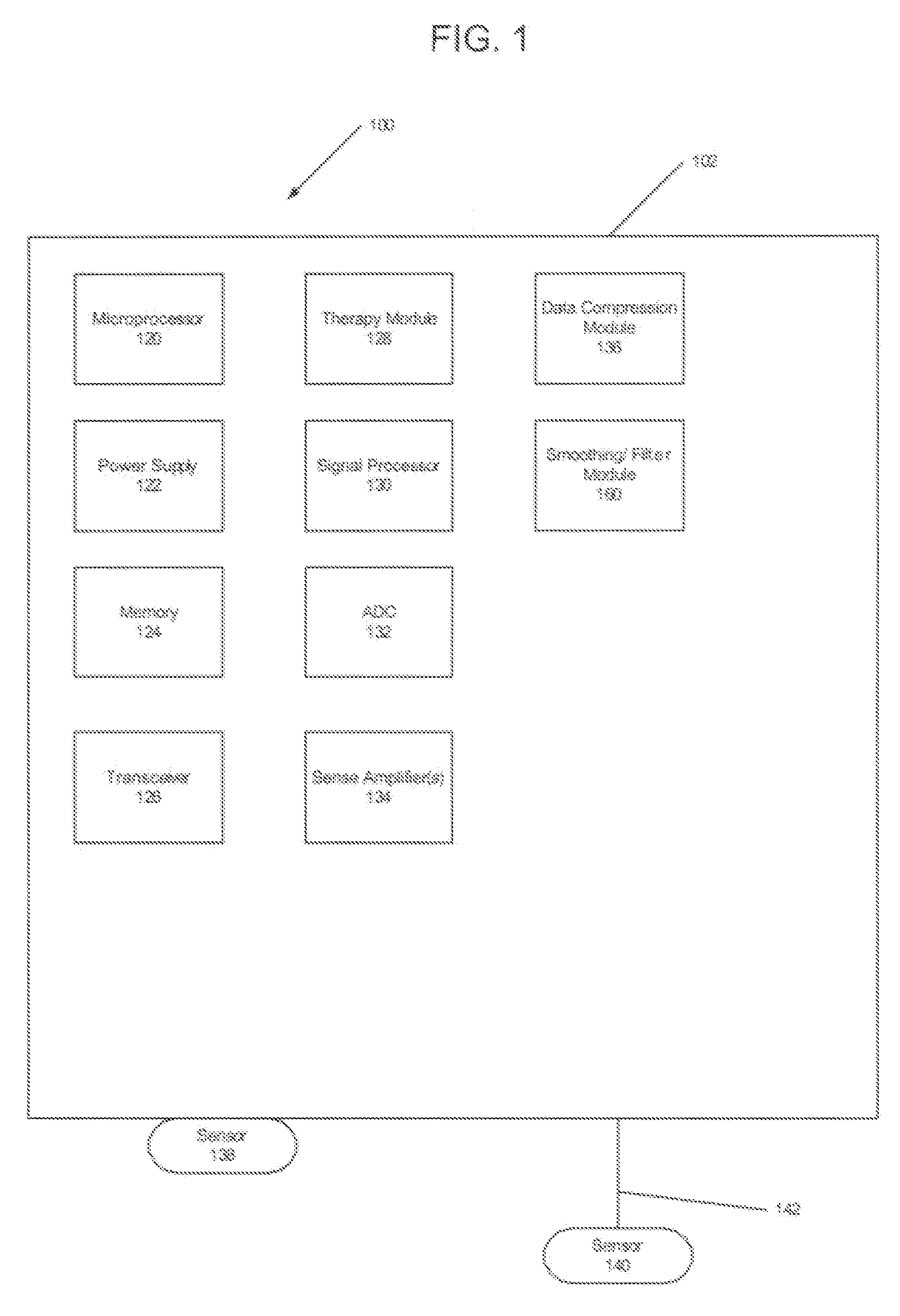
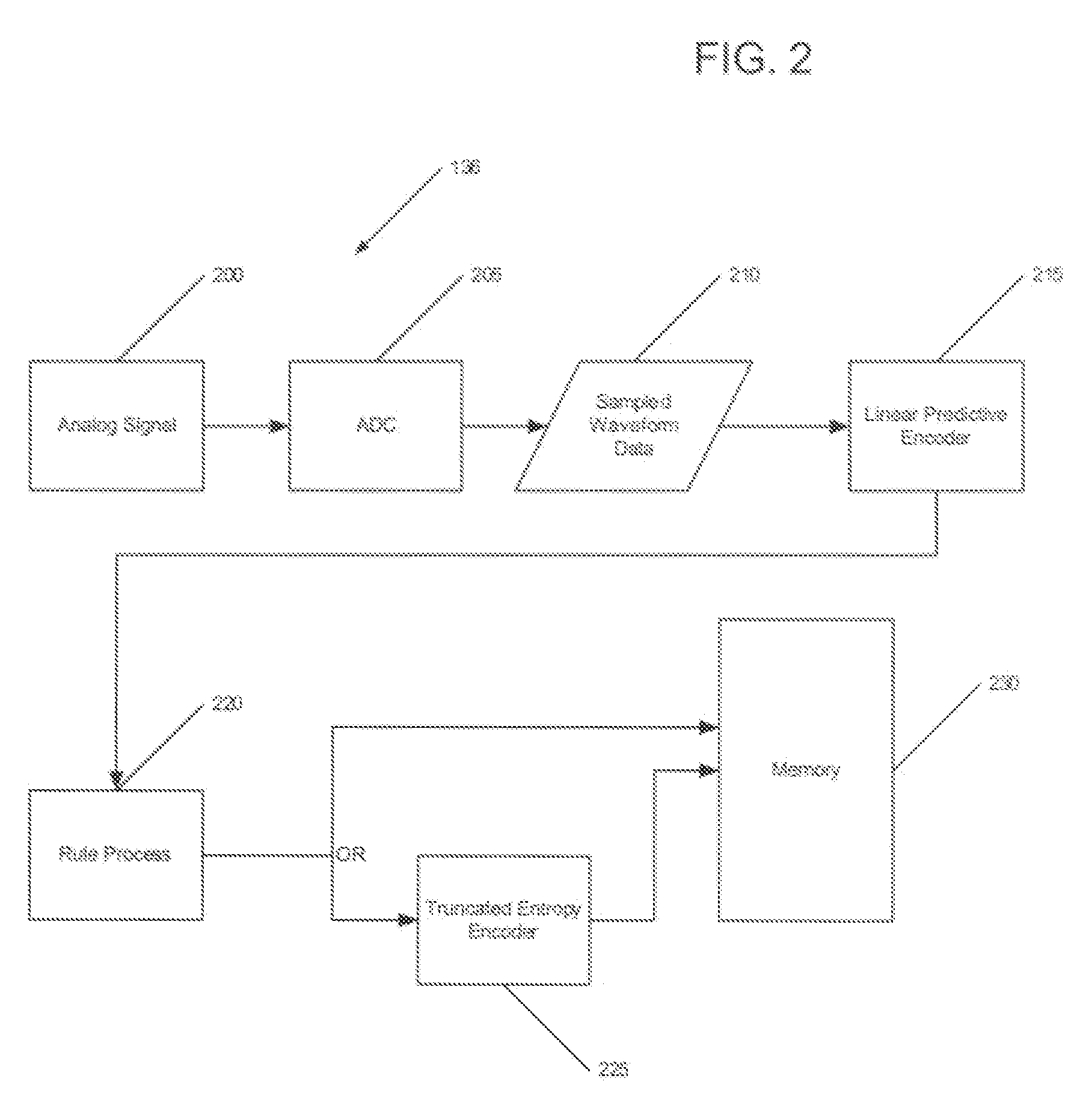
Method of compressing waveform data with differential entropy based compression
Waveforms are digitally sampled and compressed for storage in memory. The compression of the data includes generating a truncated entropy encoding map and using the values within the map to obtain good compression. An encoder further sub-selects values to be encoded and values to remain unencoded to provide an overall compression of the data.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
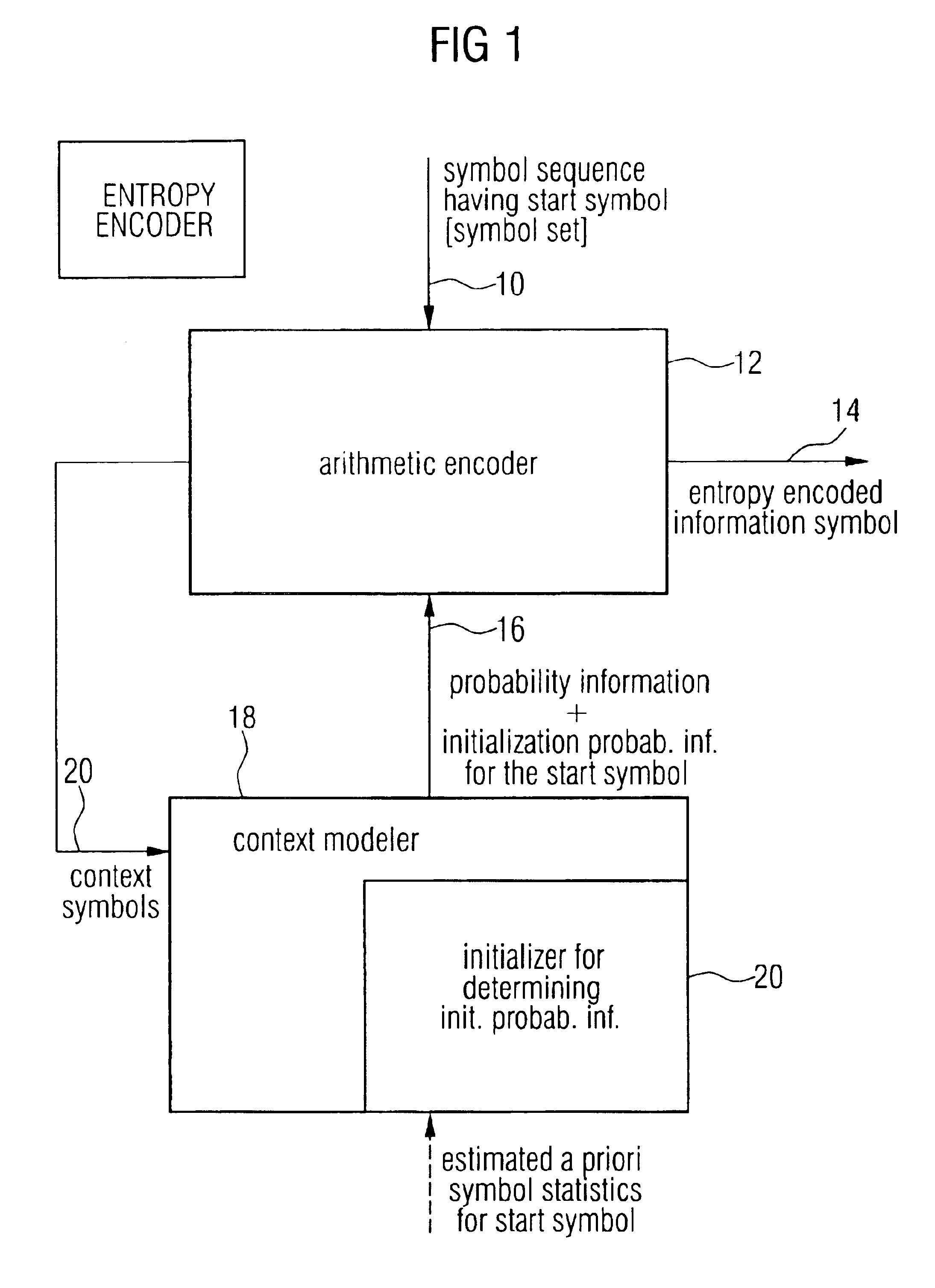
Apparatus and methods for entropy-encoding or entropy-decoding using an initialization of context variables
InactiveUS6894628B2Simple designImprove compression efficiencyCode conversionTelevision systemsContext basedSelf adaptive
An entropy encoding / decoding scheme uses an arithmetic encoder / decoder together with a context modeler for performing a context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding, which is especially suited for video compression applications. The context modeler includes an initializer for initializing the context modeler by determining and providing initialization probability information to the arithmetic encoder, the initialization probability information to be used by the arithmetic encoder for processing a start symbol of a symbol sequence. The initializer is operative to determine the initialization probability information based on an estimation of the symbol statistics relating to the start symbol such that an initialization probability distribution is different from an equi-probable distribution for all symbols of the symbol set. By means of the initialization, the context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding / decoding scheme is optimally adjusted before processing a start symbol of the symbol sequence so that no bit rate compression losses because of a delayed context-based adaptation are introduced.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Image encoding device, image encoding method, image decoding device, image decoding method, program, and storage medium
ActiveUS20100208802A1Improve efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionComputer vision
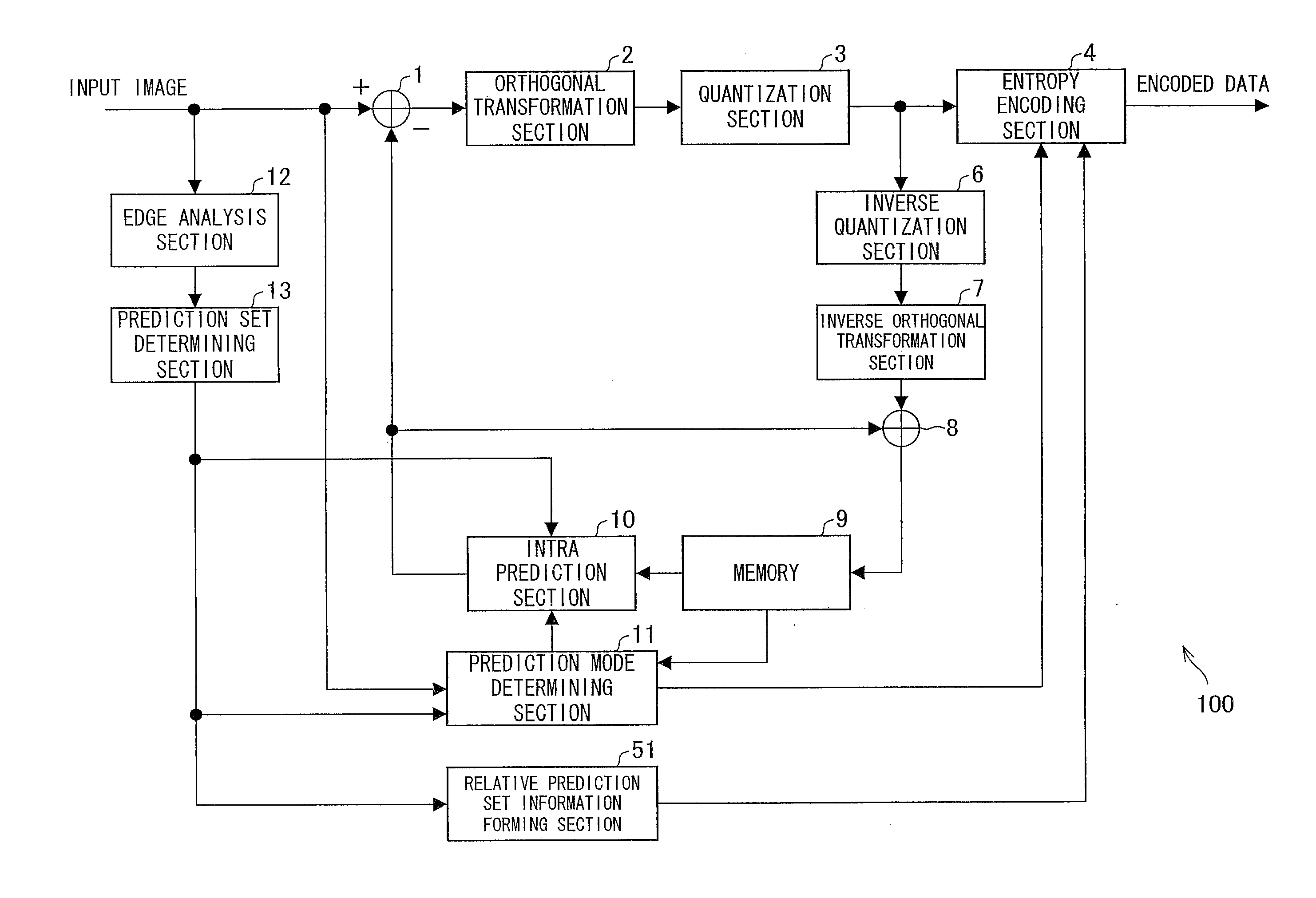
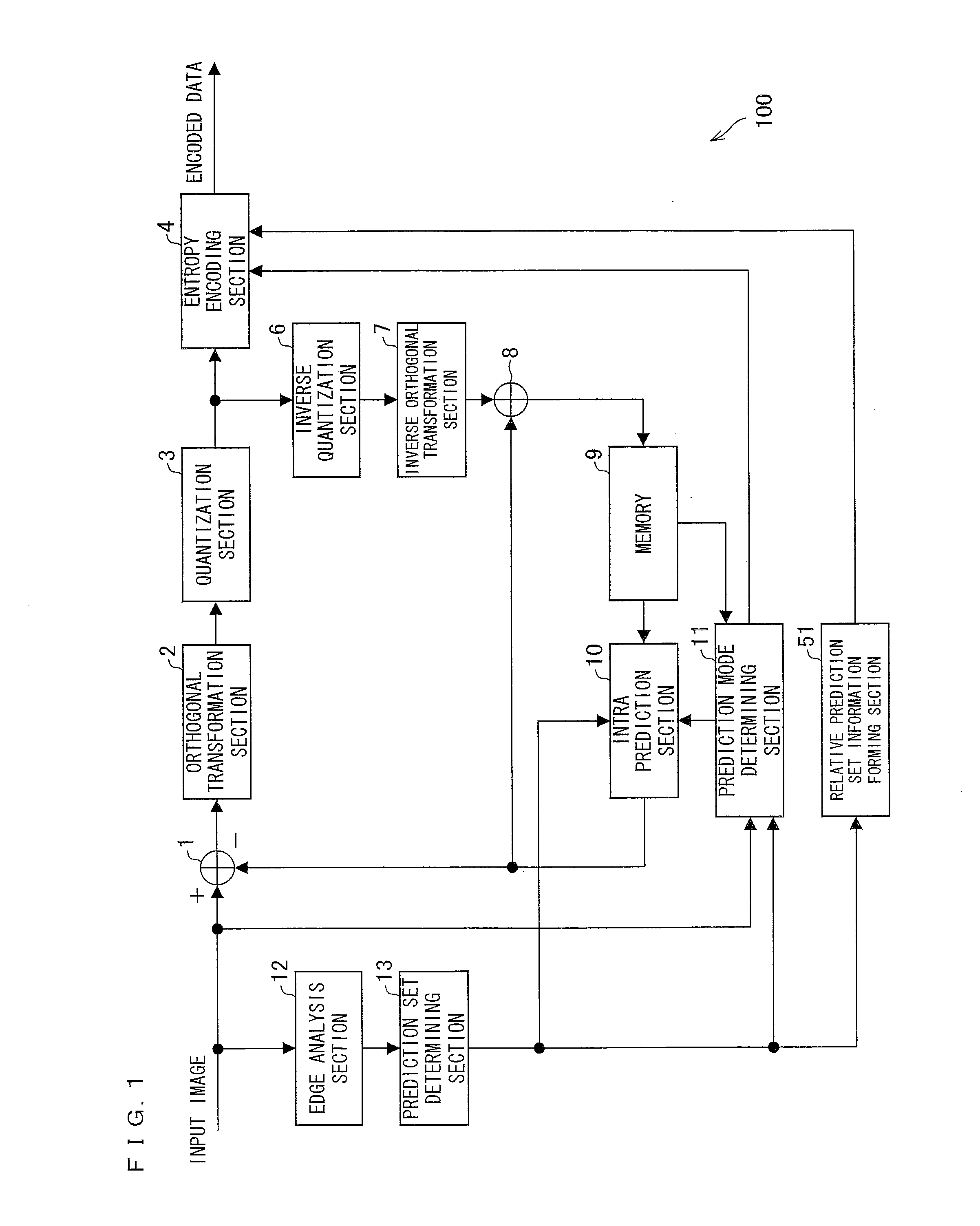
A prediction set determining section (13) selects a prediction set from a prediction set group including a plurality of prediction sets having different combinations of prediction modes corresponding to different prediction directions. Further, a prediction mode determining section (11) selects a prediction mode from the prediction set thus selected. An entropy encoding section (4) encodes the prediction set thus selected, the prediction mode thus selected, and residual data between an input image and a predicted image formed on the basis of the prediction set and the prediction mode. This allows an image encoding device to carry out predictions from more various angles, thereby improving prediction efficiency.
Owner:VELOS MEDIA LLC
Reentry into compressed data
InactiveUS6941019B1Efficiently manipulatedStorage requirement is minimizedCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsData streamJPEG
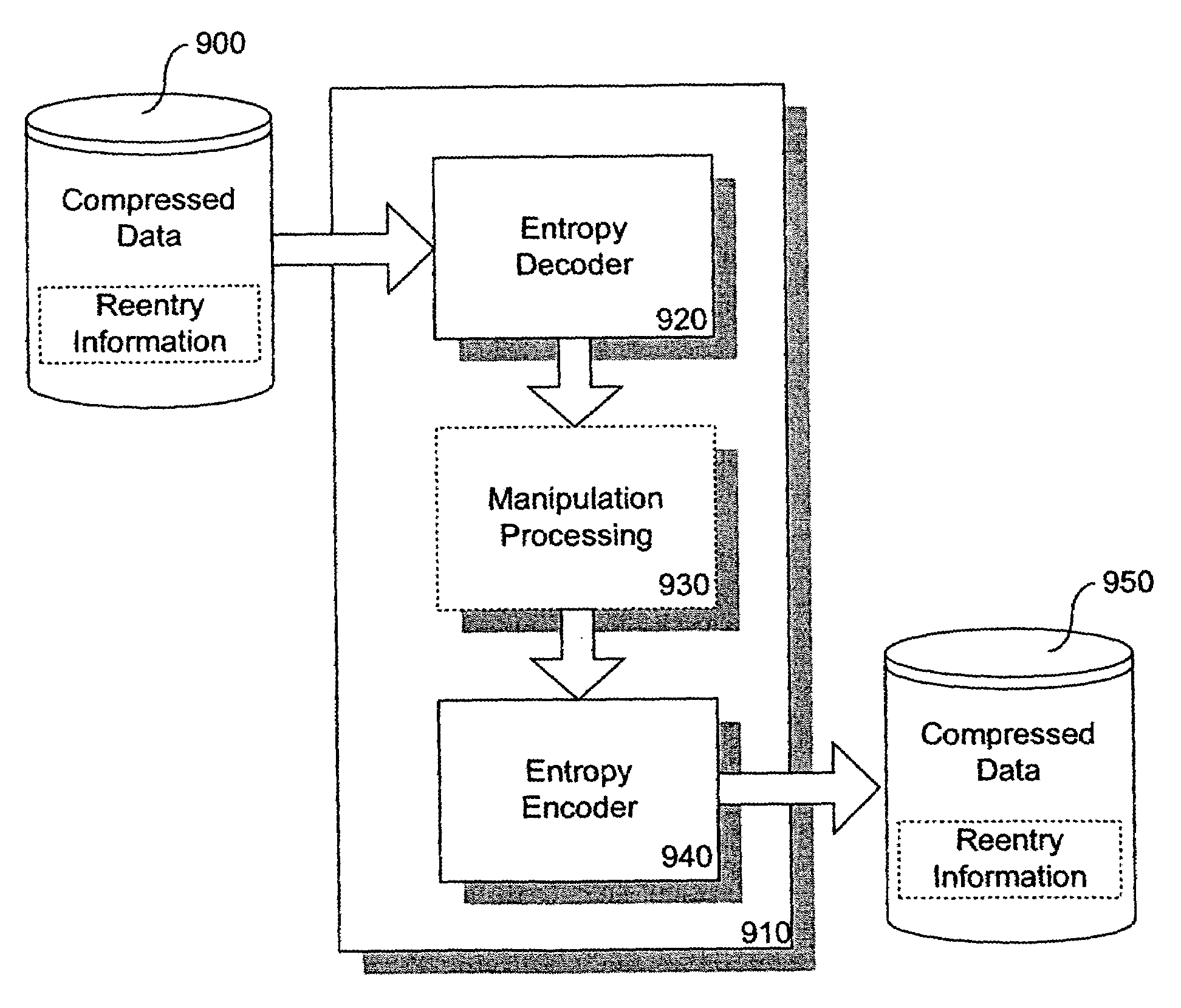
Apparatus and methods are provided for entering compressed data streams at selected reentry points to initiate decoding thereby allowing efficient manipulation of the compressed data and minimizing storage requirements. The reentry information preferably includes bit-level pointers and sufficient state information to initialize the decoder properly. This enables decoding without having to resume at independently decodable points, such as JPEG restart markers. For example, in the context of a JPEG image, in addition to the typical information available to the decoder that has been passed in earlier markers, the reentry information for a given MCU boundary may include: a bit-level pointer to the first block's DC Huffman code, the position of the output, and a DC predictor for each component of the MCU. This allows decompression to be performed in the appropriate order to accomplish various data manipulation operations, such as rotation, thus significantly reducing buffering requirements. Reentry information into a compressed data stream can be generated during encoding, decoding, partial encoding, partial decoding, entropy encoding, and / or entropy decoding. In addition, a reentry decoder may quickly interpret the compressed data sufficiently to preserve desired reentry information and discard unneeded output of the decoding process and terminate immediately after the last desired reentry point. This enables buffering of pieces of compressed data with associated reentry information rather than buffering the entire decompressed data. Additionally, when a subset of the reconstructed data is needed the step of recompressing the individual pieces can be avoided by saving reentry information with the associated pieces of compressed data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Simplified Context Selection For Entropy Coding of Transform Coefficient Syntax Elements
InactiveUS20130003858A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTheoretical computer scienceSyntax
A method for entropy encoding syntax elements of transform coefficient levels in a video encoder to generate a compressed video bit stream is provided that includes selecting a context for a first significant coefficient flag corresponding to a first transform coefficient level in a 32×32 transform block, wherein the first transform coefficient level is at a lowest frequency position in the 32×32 transform block, entropy encoding the first significant coefficient flag using the context, selecting the context for a second significant coefficient flag corresponding to a second transform coefficient level in a 16×16 transform block, wherein the second transform coefficient level is at a lowest frequency position in the 16×16 transform block, and entropy encoding the second significant coefficient flag using the context.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
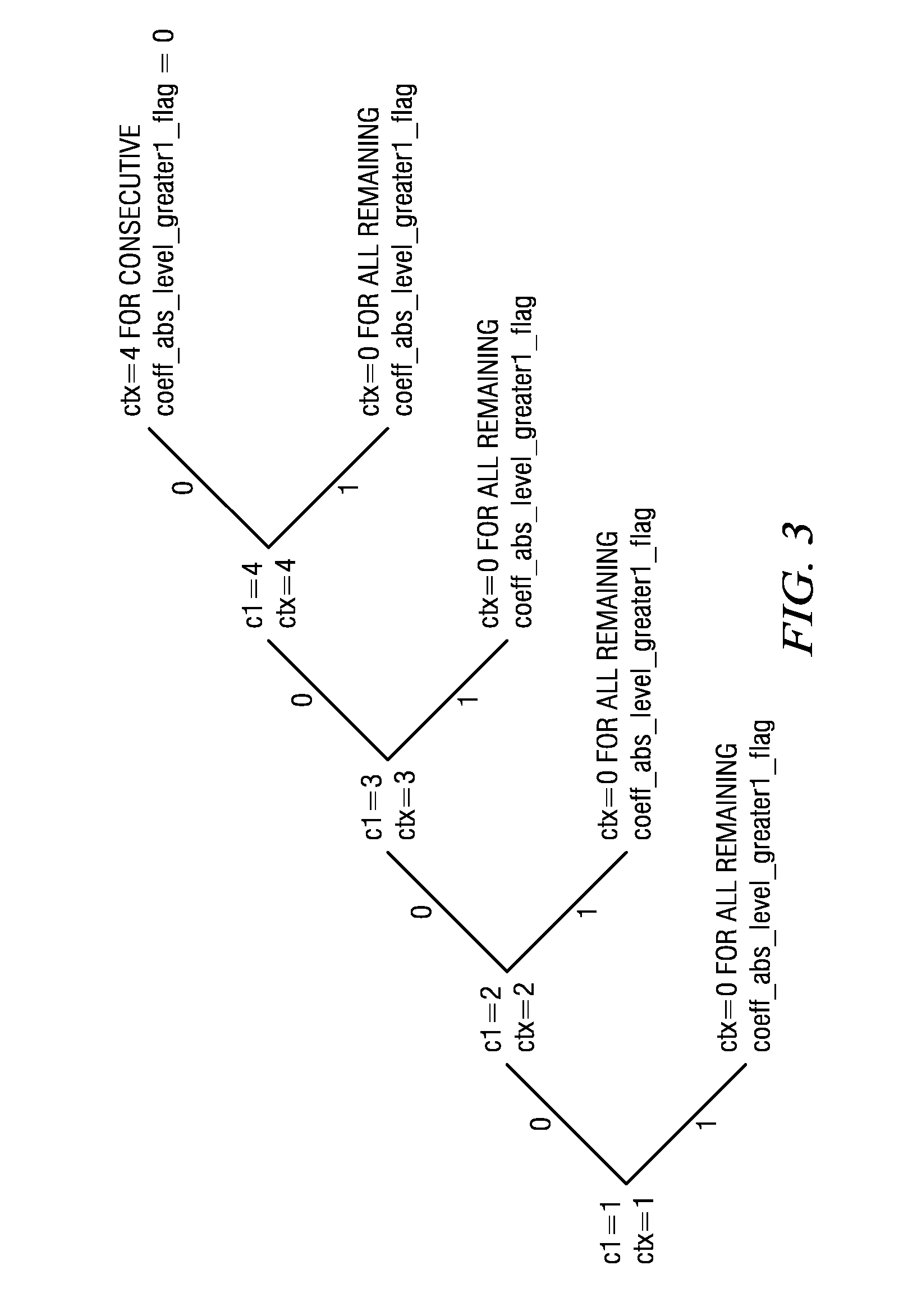
Entropy coding by adapting coding between level and run-length/level modes
An audio encoder performs adaptive entropy encoding of audio data. For example, an audio encoder switches between variable dimension vector Huffman coding of direct levels of quantized audio data and run-level coding of run lengths and levels of quantized audio data. The encoder can use, for example, context-based arithmetic coding for coding run lengths and levels. The encoder can determine when to switch between coding modes by counting consecutive coefficients having a predominant value (e.g., zero). An audio decoder performs corresponding adaptive entropy decoding.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System for nested entropy encoding
ActiveUS20120082229A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTheoretical computer scienceEntropy encoding
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Apparatus for encoding a multi-view moving picture
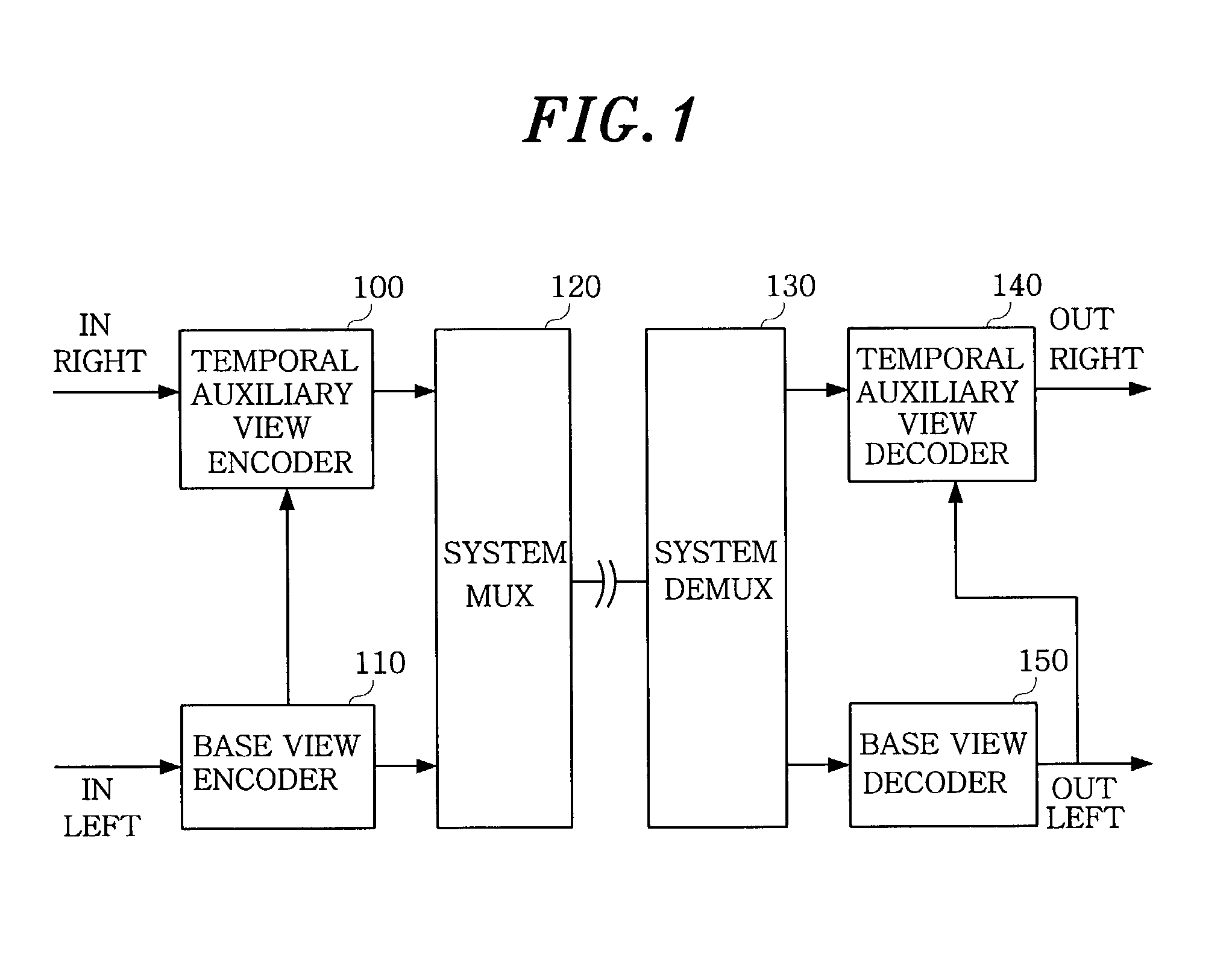
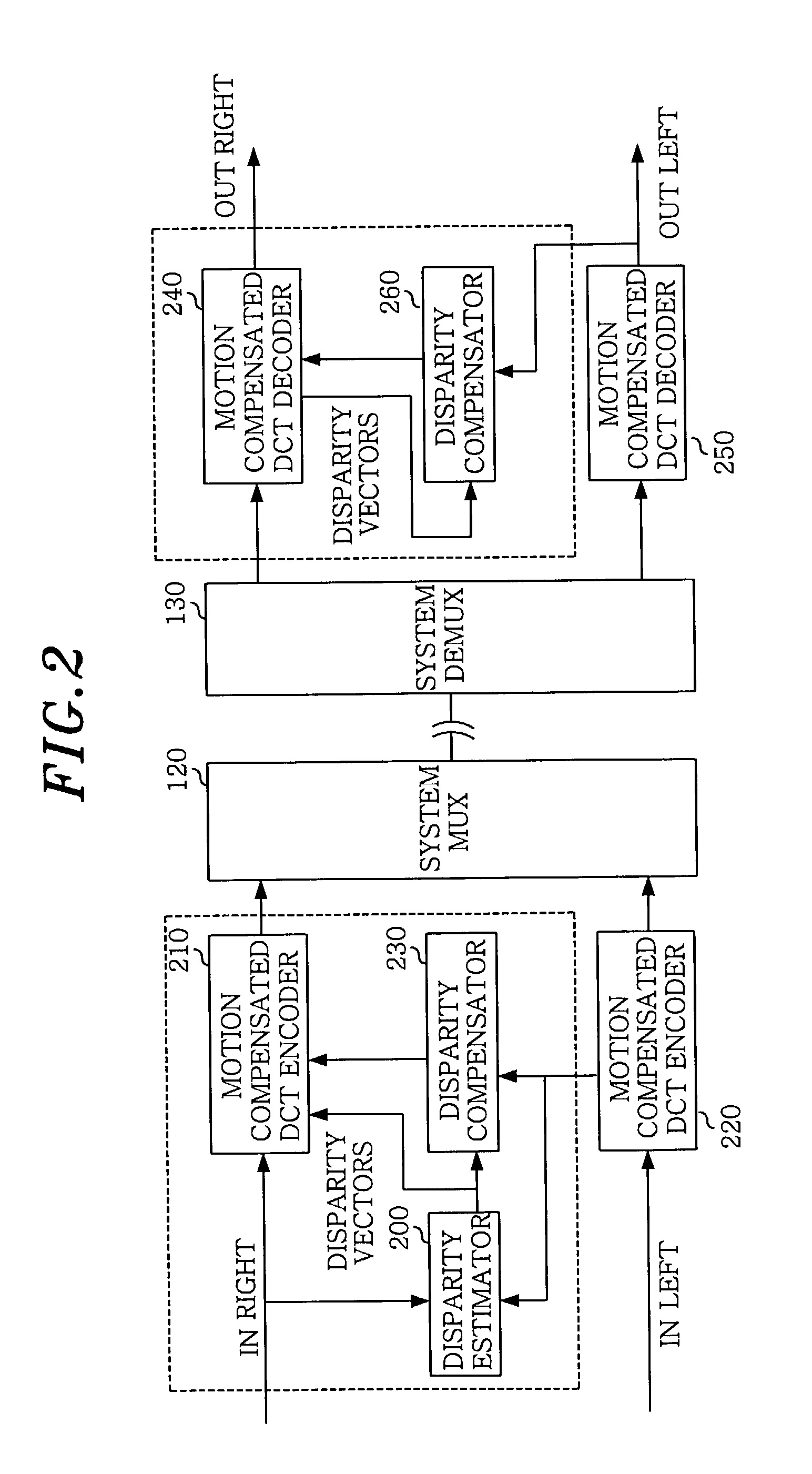
ActiveUS6999513B2Minimize informationImprove picture qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningParallaxMotion vector
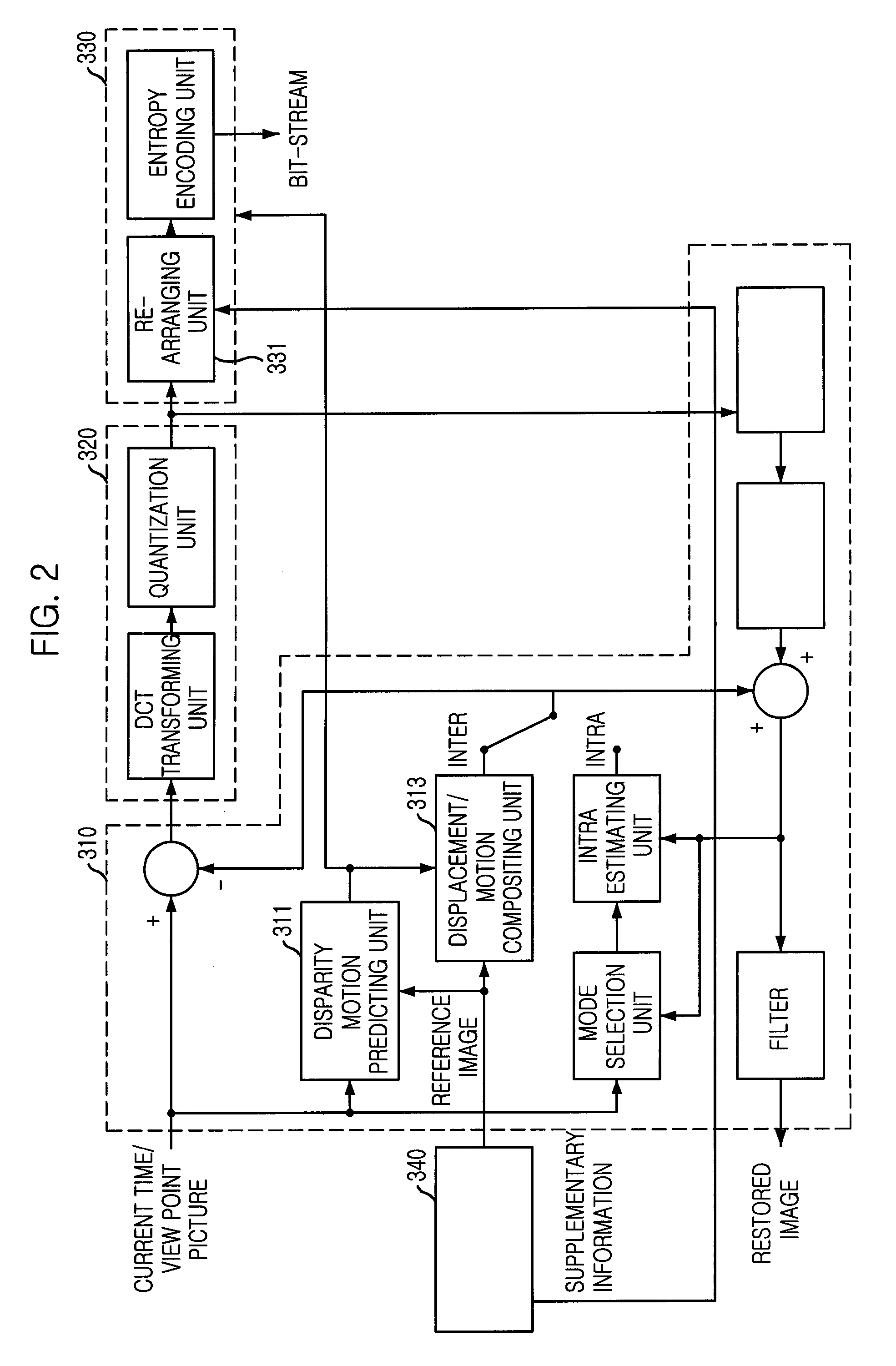
A disparity prediction stage and a motion prediction stage predict a disparity vector and a motion vector by extending a MPEG-2 structure into a view axis and using spatial / temporal correlation. A disparity / motion compensation stage compensates an image reconstructed by the disparity prediction stage and the motion prediction stage by using a sub-pixel compensation method. A residual image encoding stage performs an encoding to provide a better visual quality and a three-dimensional effect of an original image and the reconstructed image. A bit rate control stage controls a bit rate for assigning an effective amount of bit to each frame on the reconstructed image according to a bit rate. An entropy encoding stage generates a bit stream on multi-view video source data according to the bit rate.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRONICS TECH INST
Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) with Scalable Throughput and Coding Efficiency
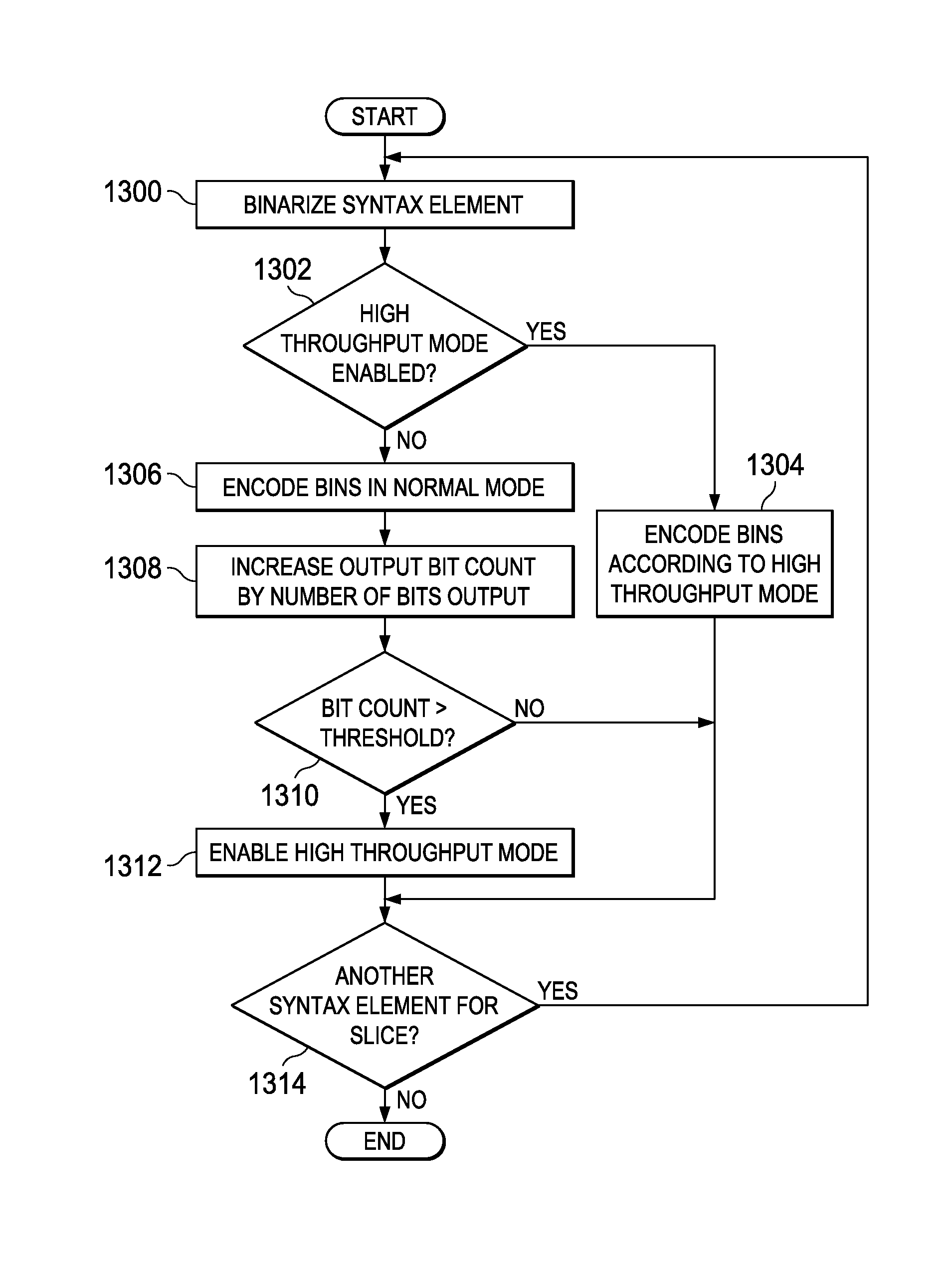
ActiveUS20130177069A1Reduce in quantityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureVideo sequence
A method for encoding a video sequence is provided that includes entropy encoding syntax elements representative of transform coefficients generated as the video sequence is processed, wherein entropy encoding syntax elements representative of a transform coefficient includes binarizing the syntax elements representative of the transform coefficient to generate a plurality of binary symbols (bins), coding a portion of the plurality of bins in context coding mode, and coding a remaining portion of the plurality of bins in bypass coding mode. The method further includes reducing the number of bins that are coded in context coding mode for each transform coefficient in a plurality of subsequent transform coefficients that are entropy encoded after a specified number of transform coefficients have been entropy encoded.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
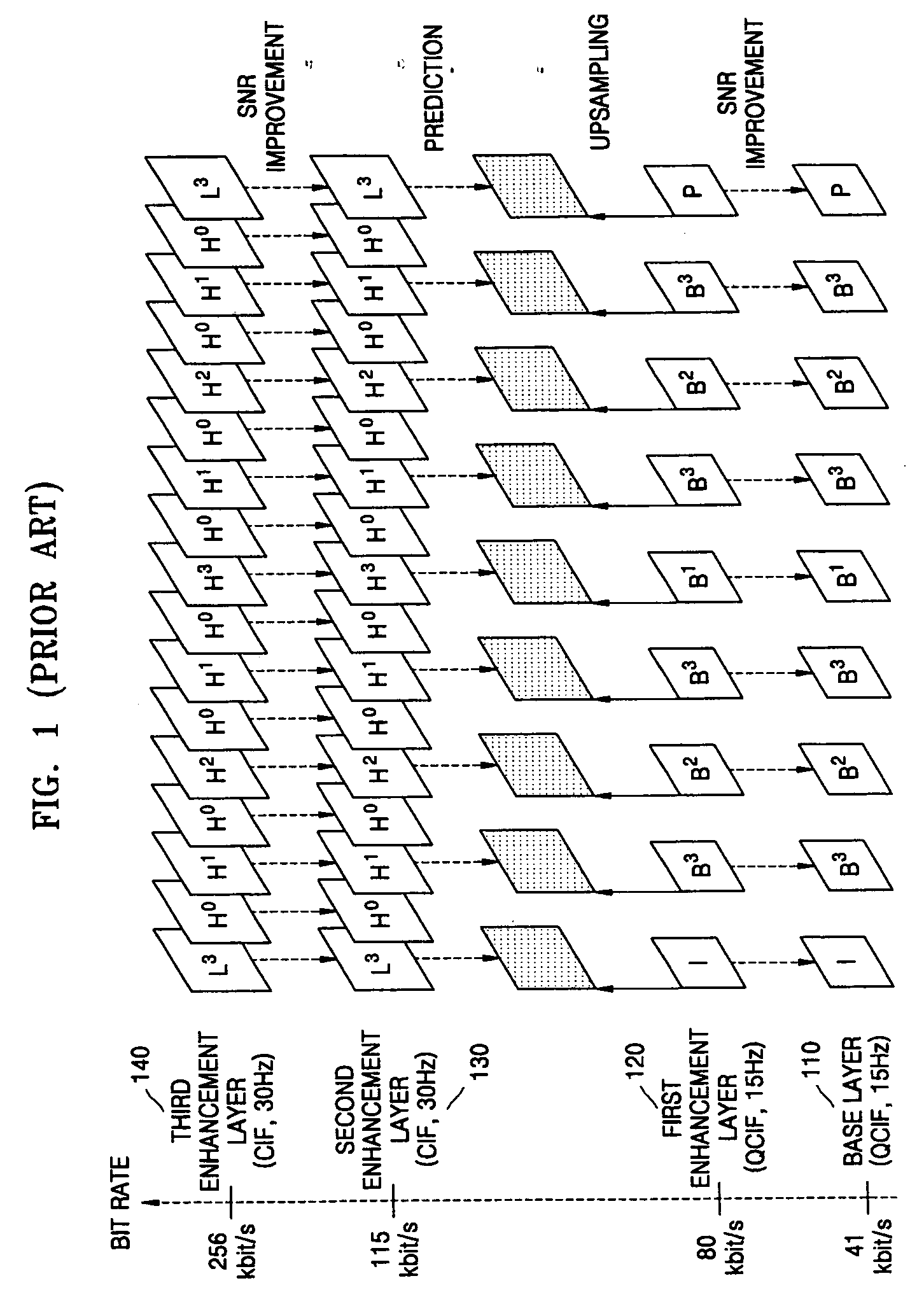
Methods of and apparatuses for adaptive entropy encoding and adaptive entropy decoding for scalable video encoding
ActiveUS20060158355A1Improve efficiencyAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsVideo encodingContext model
Methods and apparatuses are provided for adaptive entropy encoding and adaptive entropy decoding using various context models. A scalable entropy encoding method includes determining a context by referring to both syntax elements in the same layer as a block including a syntax element to be encoded and syntax elements in lower layers or only the syntax elements in the lower layers and performing entropy encoding on the syntax element using the determined context.
Owner:SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIVERSITY +1
Method and apparatus for hybrid entropy encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20070009047A1Reduce complexityIncrease the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionEntropy encoding
An apparatus and method for entropy encoding and decoding of video data. The method for entropy encoding video data includes dividing the video data into at least one partial video data portion and determining an entropy encoding mode to be used for each of the partial video data portion between at least two different entropy encoding modes and performing entropy encoding on each of the partial video data portions using the determined entropy encoding mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for effectively encoding and decoding electronic information
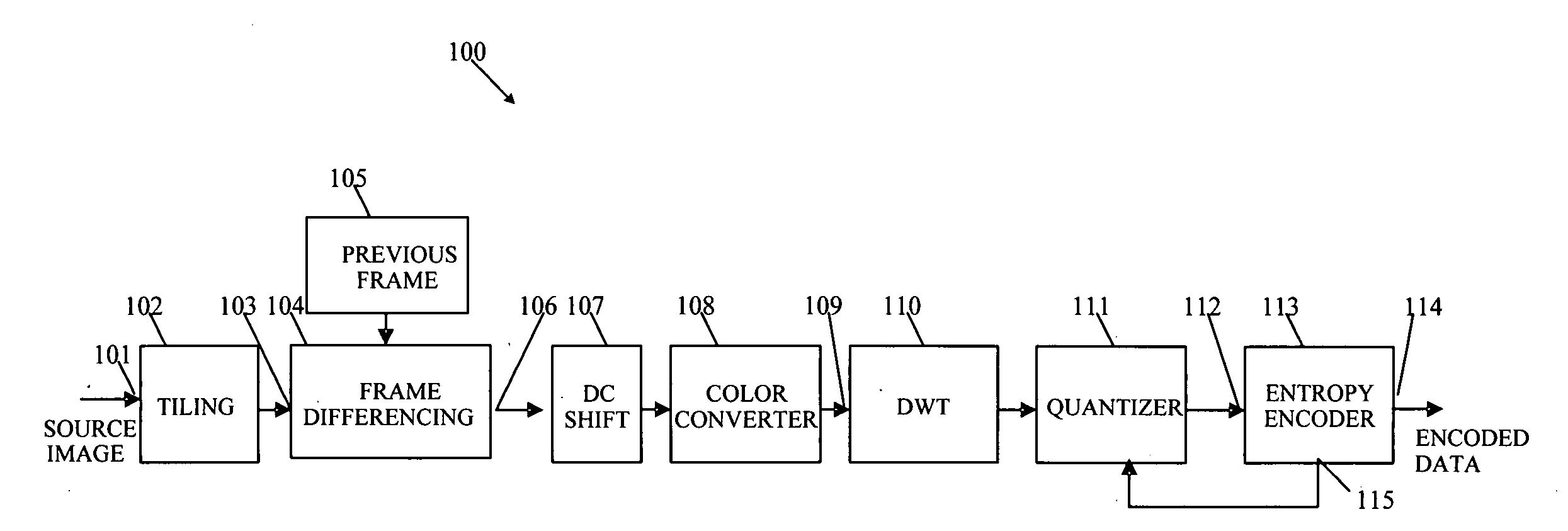
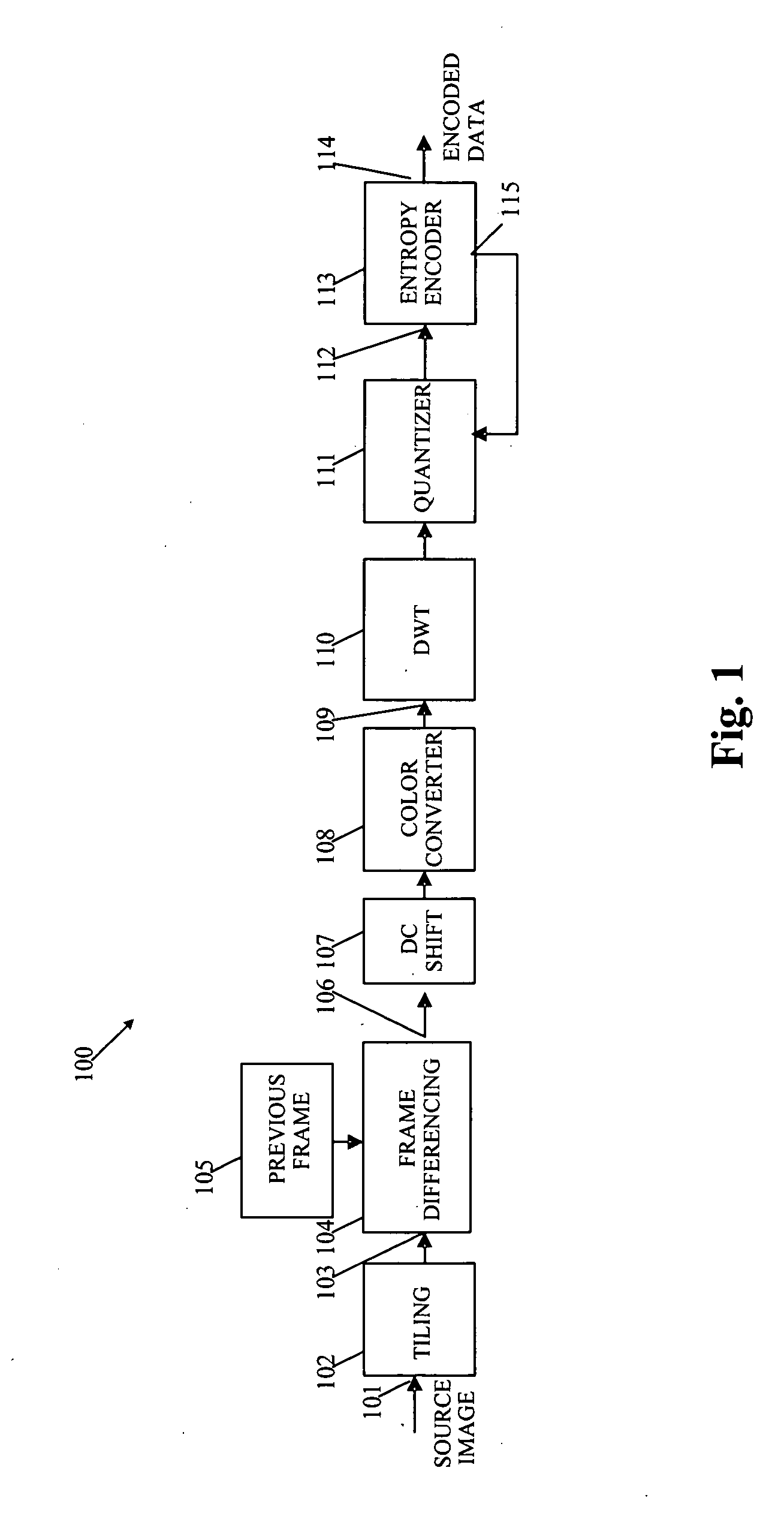
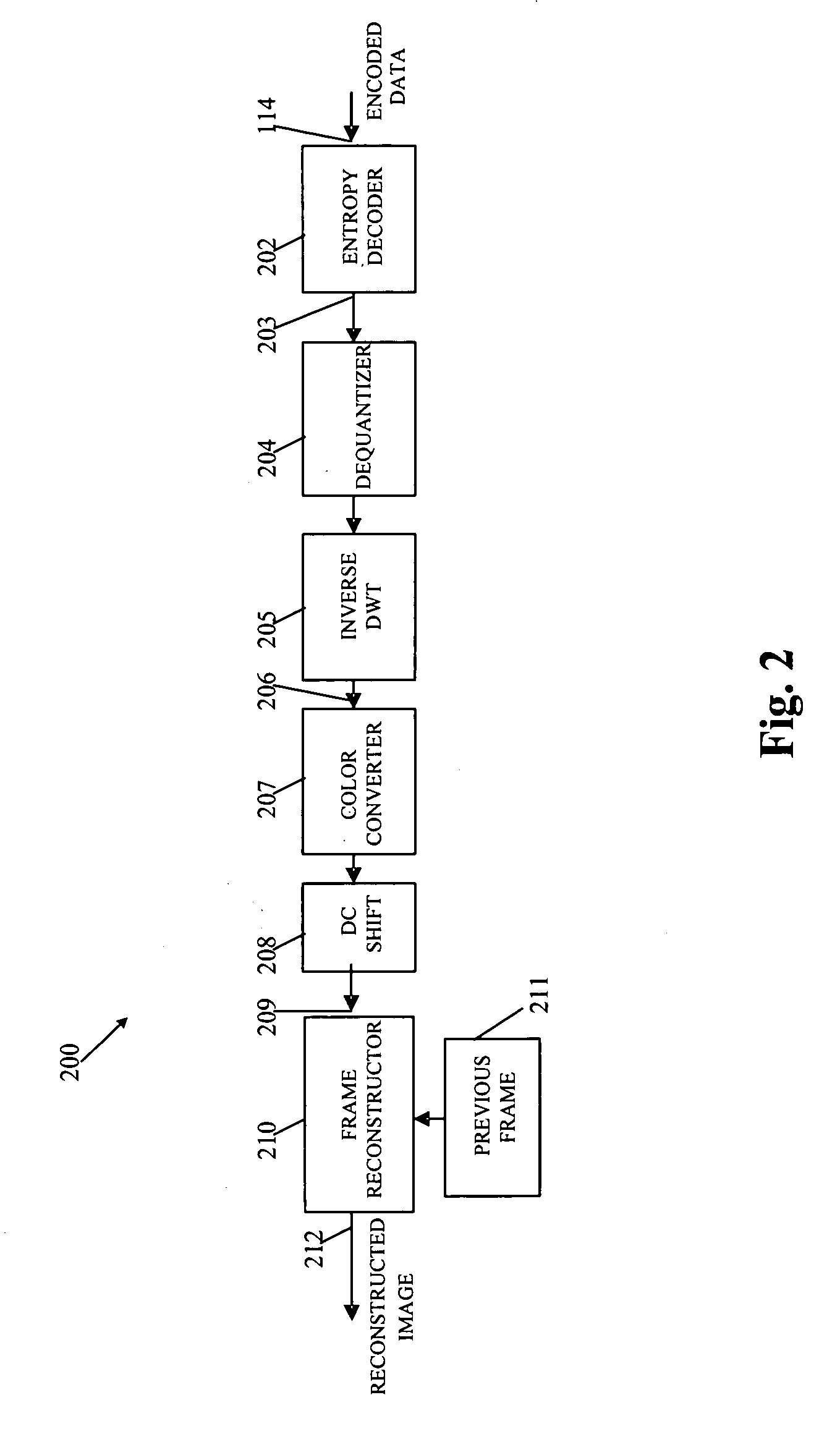
ActiveUS20080112489A1Effective informationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionFrame differenceSource image
A system and method for effectively encoding and decoding electronic information includes an encoding system with a tiling module that initially divides source image data into data tiles. A frame differencing module then outputs only altered data tiles to various processing modules that convert the altered data tiles into corresponding tile components. A quantizer performs a compression procedure upon the tile components to generate compressed data according to an adjustable quantization parameter. An adaptive entropy selector then selects one of a plurality of available entropy encoders to most effectively perform an entropy encoding procedure to thereby produce encoded data. The entropy encoder may also utilize a feedback loop to adjust the quantization parameter in light of current transmission bandwidth characteristics.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
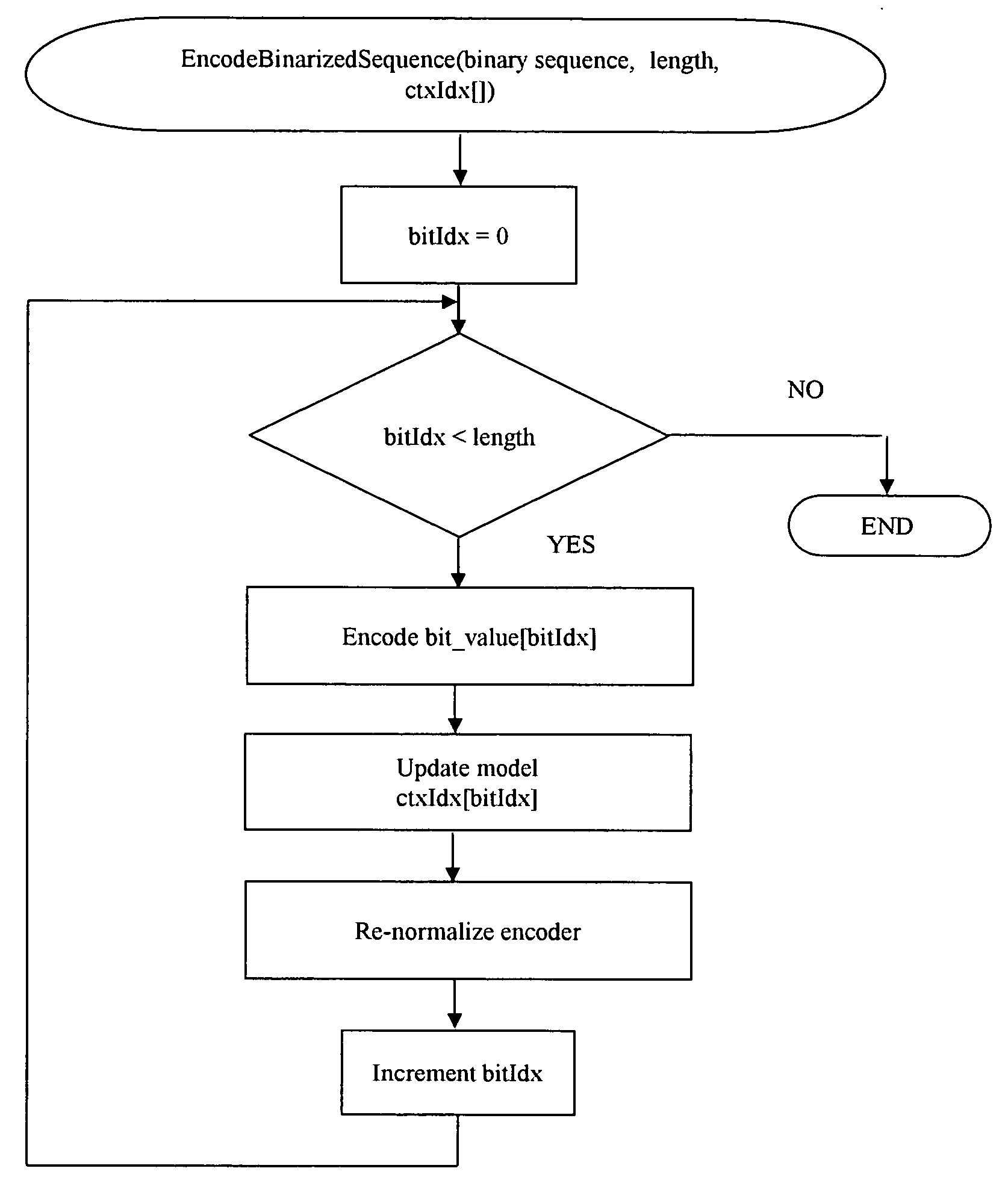
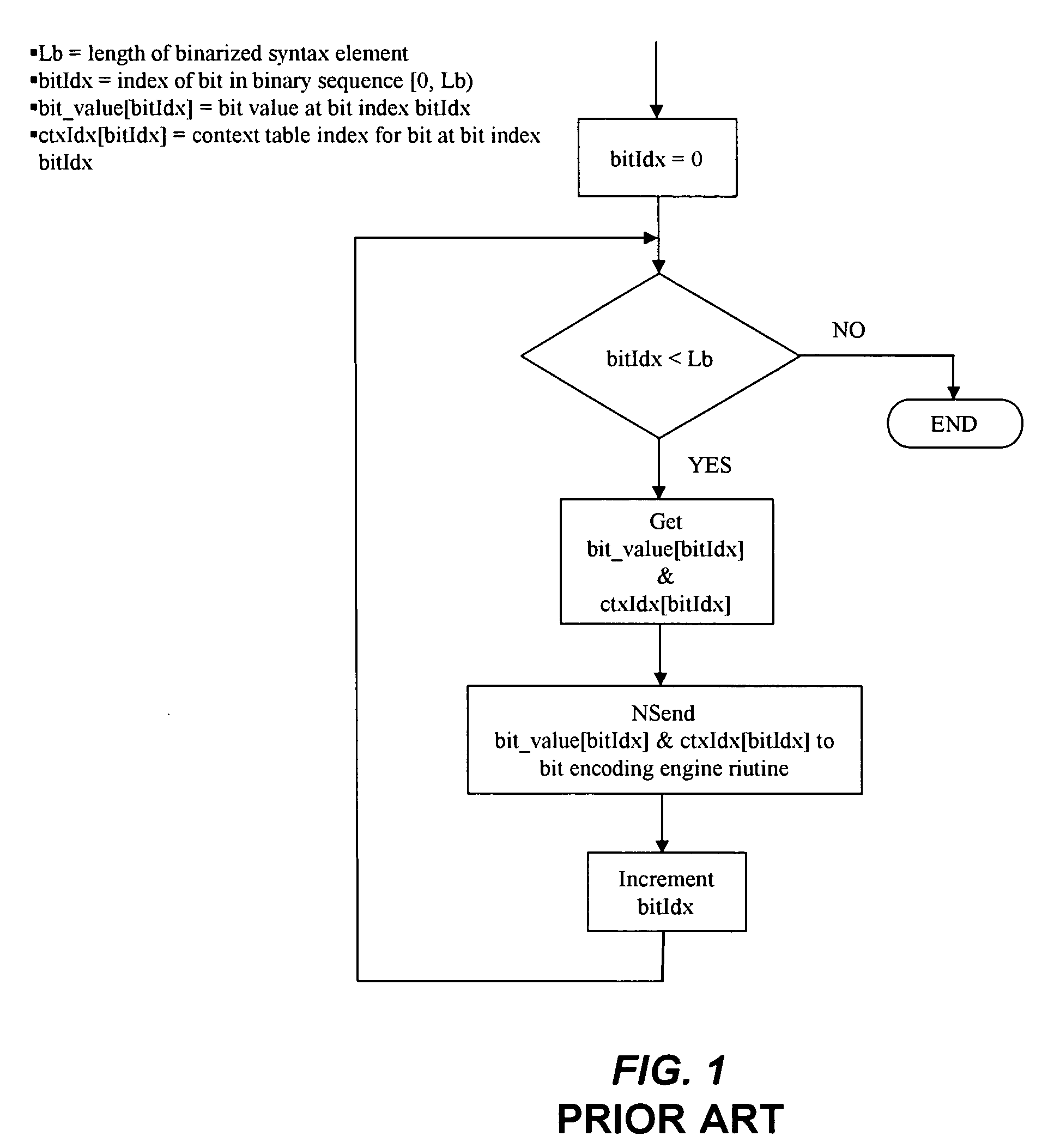
Method and system for fast context based adaptive binary arithmetic coding
InactiveUS20070040711A1Increasing instruction level parallelismReduces function call overheadCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionProcedure callsContext-adaptive variable-length coding
A method for efficient and fast implementation of context-based adaptive binary arithmetic encoding in H.264 / AVC video encoders is disclosed. The H.264 / AVC video standard supports two entropy coding mechanisms. These include Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) and Context Adaptive Variable Length Coding (CAVLC). The entropy coding efficiency of CABAC exceeds that of CAVLC by a clear margin. The method further provides techniques that make the implementation of CABAC on digital signal processors (DSPs) and other processing devices significantly faster. In one aspect, the method increases decoupling between the binarization process and the arithmetic encoding process from bit level to single or multiple syntax element(s) level. The binarized data is provided to the arithmetic encoding engine in bulk, thereby significantly reducing the overhead due to procedure calls. In another aspect, a CABAC arithmetic encoding engine format is provided which decreases data writing overhead and better exploits parallelism in the encoding process. This aspect is particularly advantageous to, for example, very long instruction word (VLIW) DSPs and media processors. In yet another aspect, the method discloses efficient CABAC binarization schemes for syntax elements.
Owner:STREAMING NETWORKS PVT
Encoding device, encoding method, encoding program, decoding device, decoding method, and decoding program
InactiveUS20090074052A1Improve image qualityImprove subjective image qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging qualityBit plane
The present invention relates to an encoding apparatus, an encoding method, an encoding program, a decoding apparatus, a decoding method and a decoding program for adaptively controlling an encoding bit rate. Coefficient data obtained using wavelet transform is quantized, and segmented into bit planes. The coefficient data is entropy encoded from the bit plane of the MSB in a direction from an upper bit position to a lower bit position. Entropy encoding is stopped at a bit position where an amount of code has reached a target amount. On the bit plane, the coefficient data is entropy encoded from a lower frequency region to a higher frequency region. Data greatly affecting subjective image quality of a decoded image is selectively output while the amount of code is easily controlled.
Owner:SONY CORP
Entropy coding
ActiveUS20140210652A1Improve coding efficiencyReduce complexityCode conversionDigital video signal modificationComputer scienceEntropy encoding
An encoder for encoding a sequence of symbols is described which has an assigner configured to assign a number of parameters to each symbol of the sequence of symbols based on information contained within previous symbols of the sequence of symbols; a plurality of entropy encoders each of which is configured to convert the symbols forwarded to the respective entropy encoder into a respective bitstream; and a selector configured to forward each symbol to a selected one of the plurality of entropy encoders, the selection depending on the number of parameters assigned to the respective symbol.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
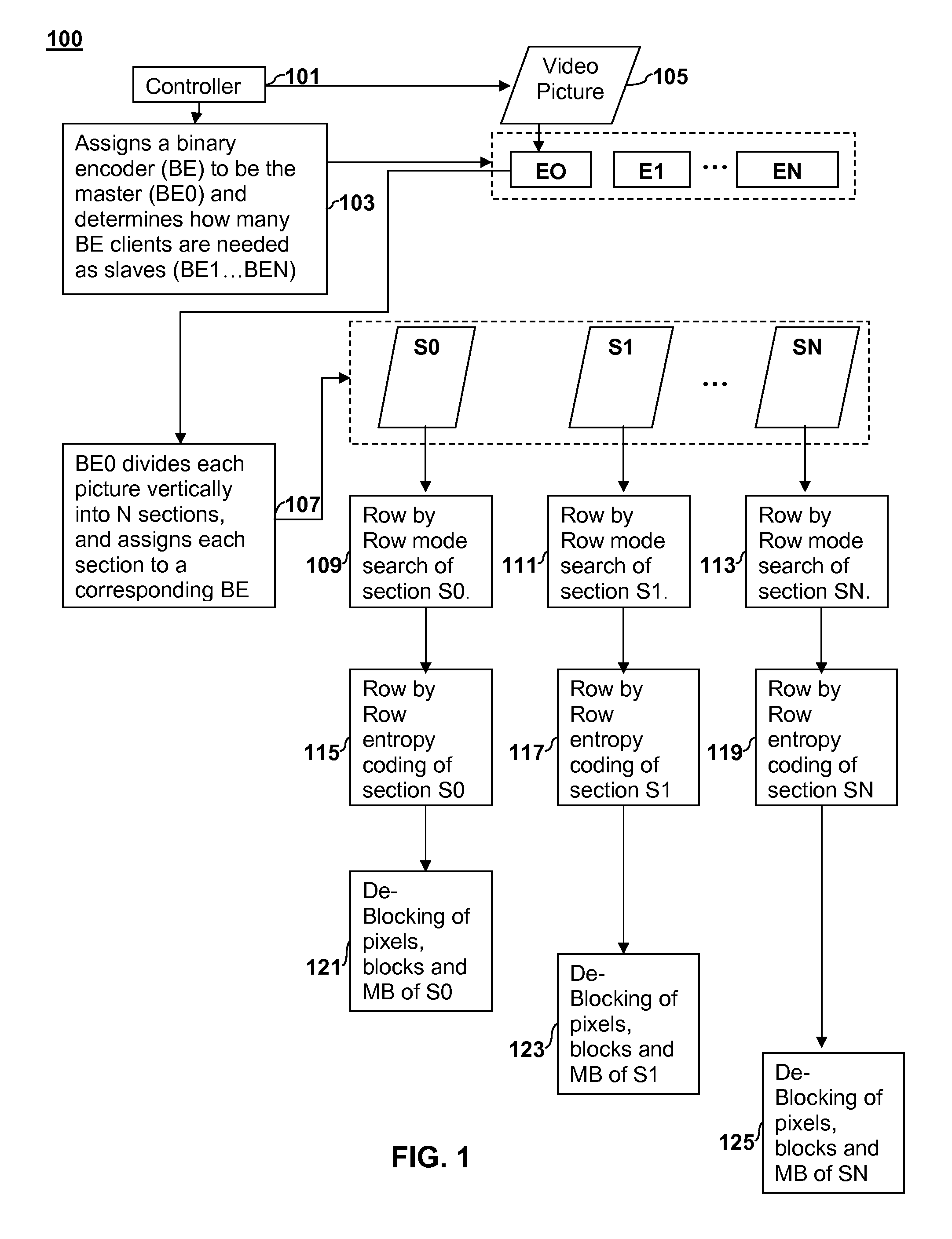
Parallel digital picture encoding
ActiveUS20110051811A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionCritical sectionDigital pictures
Apparatus and Method for parallel digital picture encoding are disclosed. A digital picture is partitioned into two or more vertical sections. An encoder unit is selected to serve as a master and one or more encoder units are selected to serve as slaves. The total number of encoder units used equals the number of vertical sections. A mode search is performed on the two or more vertical sections on a row-by-row basis. Entropy coding is performed on the two or more vertical sections on a row-by-row basis. The entropy coding of each vertical section is performed in parallel such that each encoder unit performs entropy coding on its respective vertical section. De-blocking is performed on the two or more vertical sections in parallel on a row-by-row basis.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Method and system for entropy coding for scalable video codec
InactiveUS20060008009A1Small sizeImprove visual qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionCoding blockNonzero coefficients
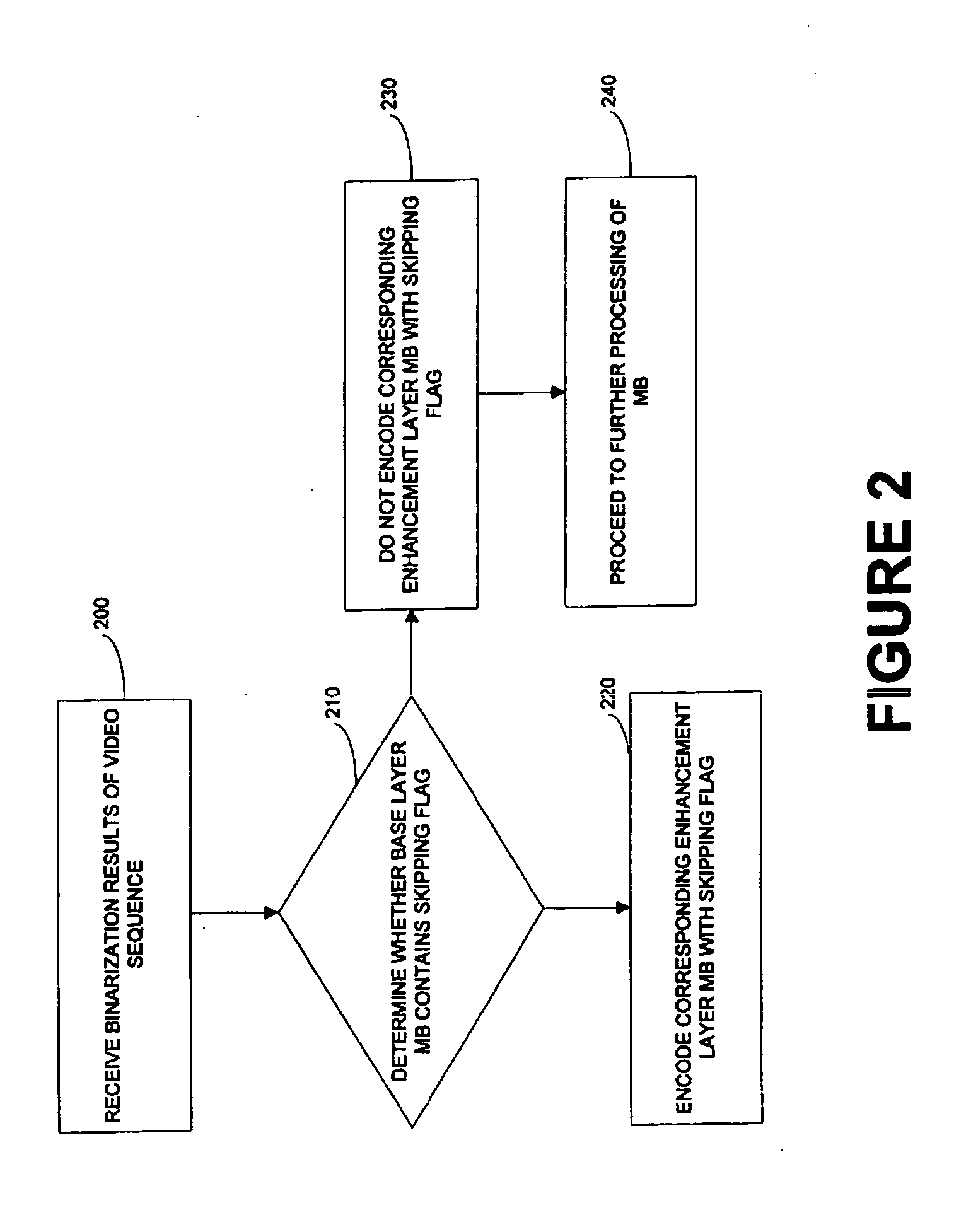
A method, program product and apparatus for encoding a scalable bit stream from the binarization results of a video sequence by selectively encoding syntax elements and avoiding redundancy in coding. The result is a decrease in the size of the compressed bit stream of an enhancement layer. One method includes determining whether a skipping flag in the base layer macro block of the video data is set, and encoding an enhancement layer macro block of the video data, corresponding to the base layer macro block, with a skipping flag only if the base layer macro block skipping flag is set. Another method includes determining which of a plurality of blocks in a base layer macro block contain zero coefficients, generating a coded block pattern (CBP) of an enhancement layer macro block, where the CBP includes a number of digits equal to the number of blocks in said base layer macro block containing only zero coefficients, and then encoding the CBP of the enhancement layer. Yet another method includes encoding a CBP value of a base layer macro block and differentially encoding a CBP value of an enhancement layer macro block relative to the CBP of the base layer macro block. An additional method includes determining the zero-value coefficients in a block of a base layer, determining whether any of the zero-coefficients become non-zero coefficients in a corresponding block in an enhancement layer, and encoding a coding block flag in an enhancement layer based on that determination.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Apparatus of Predictive Coding/Decoding Using View-Temporal Reference Picture Buffers and Method Using the Same
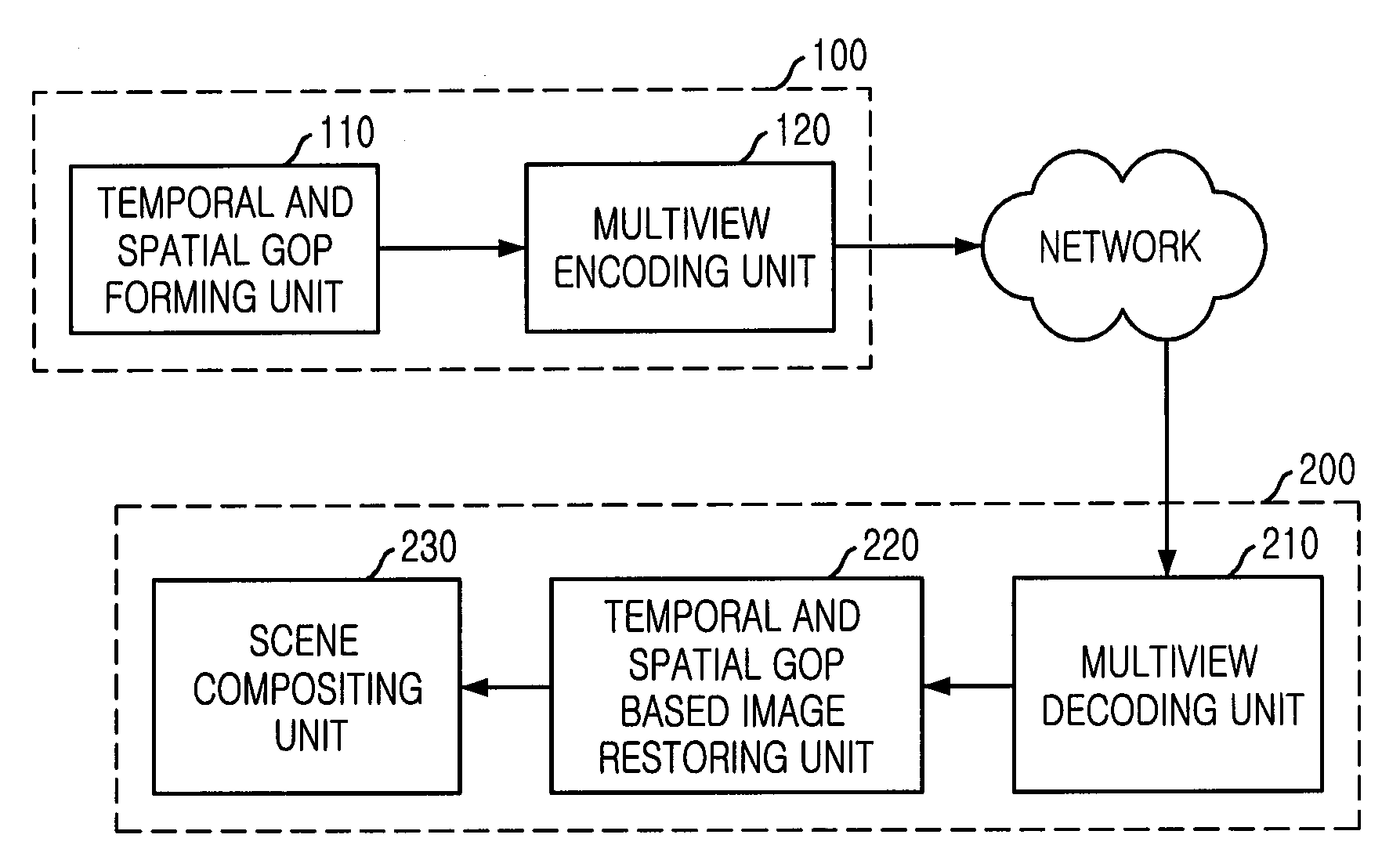
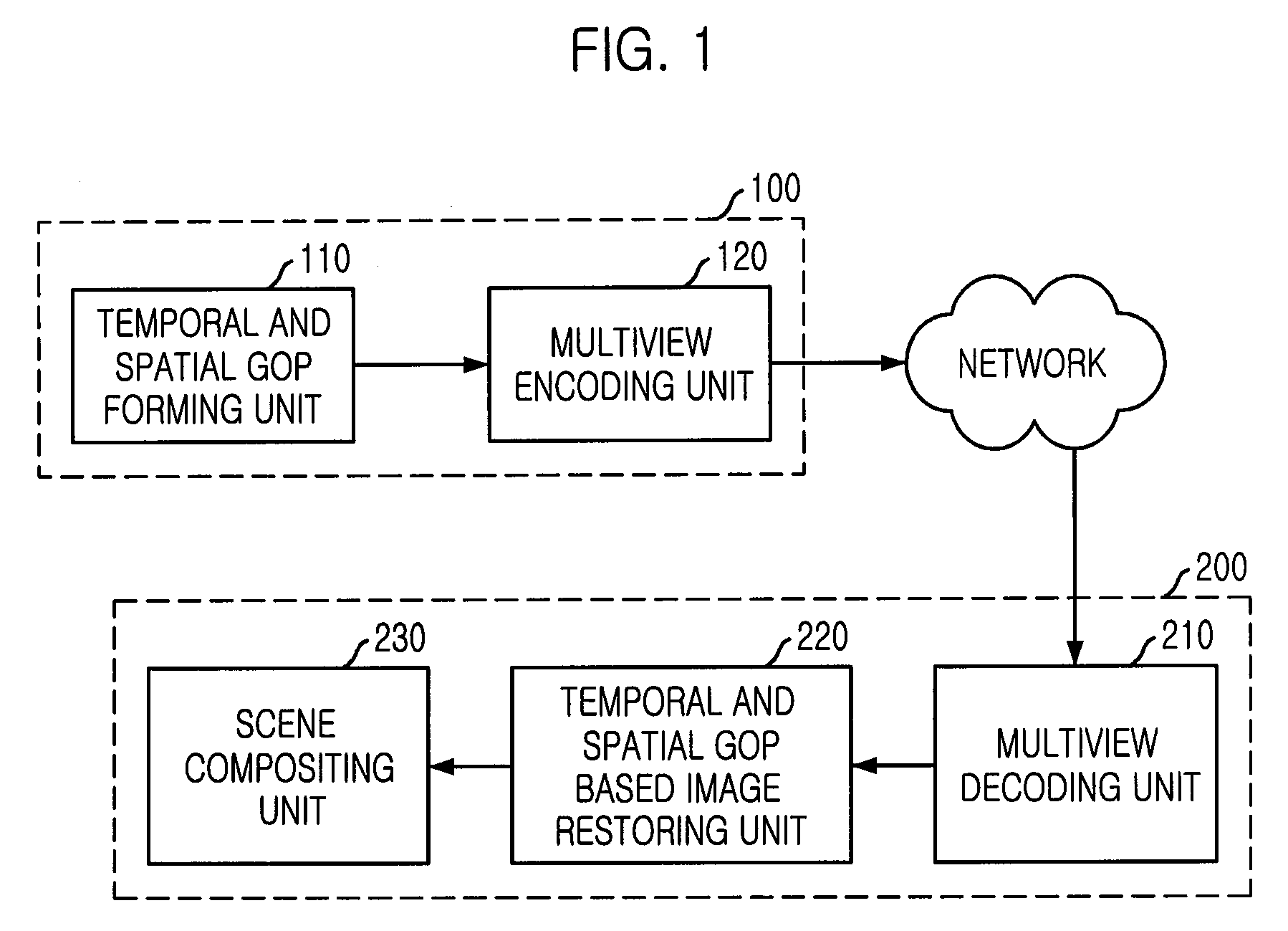
InactiveUS20080219351A1Efficient executionIncrease the compression ratioTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesAlgorithmReference image
Provided are an apparatus and method for predictive coding / decoding for improving a compression rate of multiview video using one or two additional reference frame buffers. The predictive encoding apparatus includes: a multiview reference picture providing unit for providing a reference picture for a predictive encoding according to temporal and spatial GOP structure information; a prediction unit for creating a vector by predicting which part of the reference picture inputted from the multiview reference picture providing unit is referred by a picture to currently encode; a transforming and quantizing unit for obtaining a difference signal between the predicted signal inputted from the prediction unit and a picture signal to currently encode, transforming the obtained difference signal, quantizing the transformed signal, and compressing the quantized signal; and an entropy encoding unit for encoding the quantized signal and the vectors according to a predetermined scheme and outputting the encoded signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Coding of animated 3-D wireframe models for internet streaming applications: methods, systems and program products
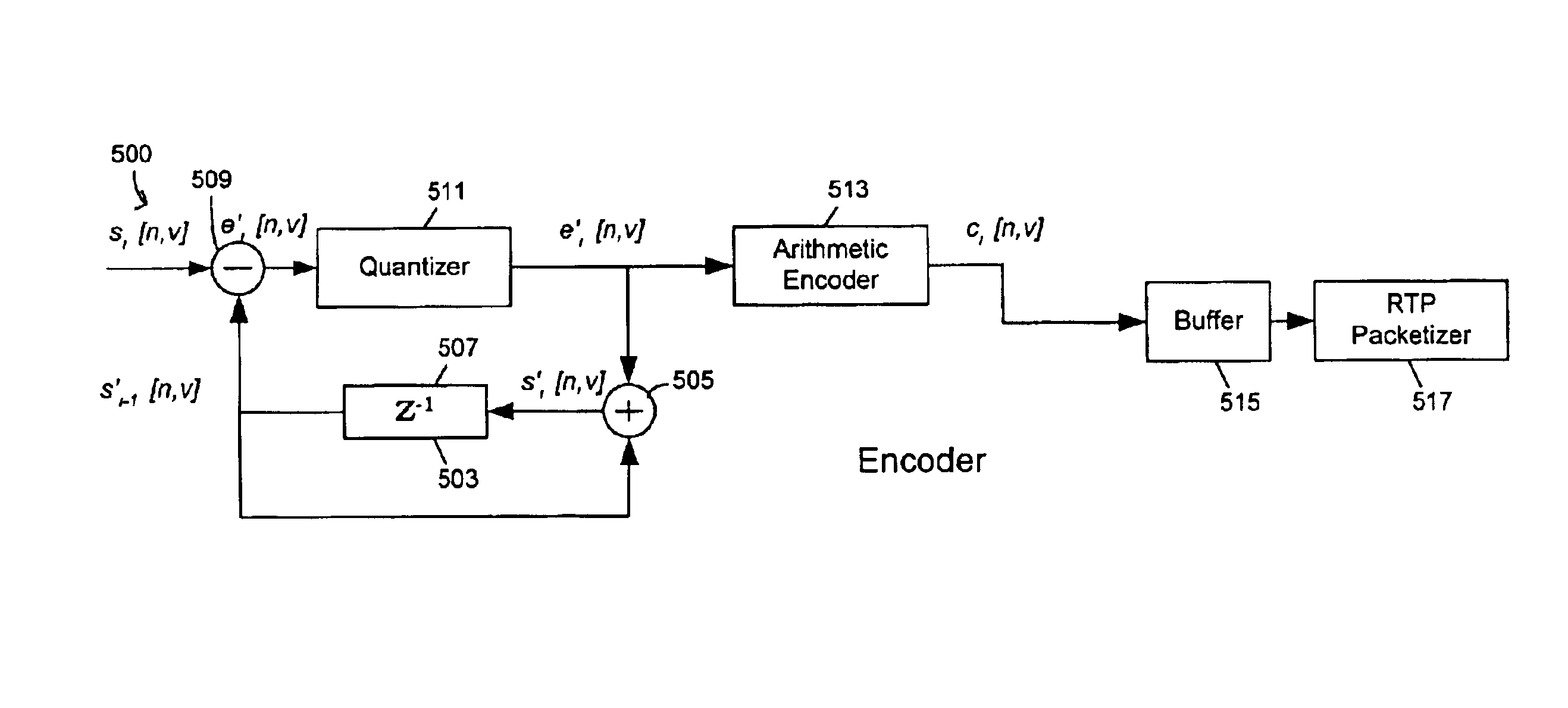
A 3-D wireframe model expressed in terms of nodes and vertices receives a 3-D video or like signal representative of a scene expressed in terms of a reference model, I frames and P frames. A DPCM coder takes advantage of the temporal correlation of the displacement of each vertex along every axis in the 3-D space. The 3-D signal is a set of non-zero displacements of all vertices and all nodes (sl[n, v]) at time tl. The decoded set (animation frame) of the previous instance is used as the predicted value (si-l[n, v]). The prediction error el[n, v], i.e. the difference between the current displacement set and the predicted one, is computed and quantised (el[n, v]). Finally, the quantised samples are entropy coded (ci[n, v]) using an adaptive arithmetic coding algorithm to handle the unknown data statistics. The predictive scheme described above prevents quantization error accumulation. A DPCM decoder first decodes arithmetically the received samples (‘e’ [n, v]) and computers the decoded samples (si′ [n, v]).
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Adaptive quantization using code length in image compression
InactiveUS6882753B2Low memory and bus bandwidth requirementImprove processing efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionLandau quantization
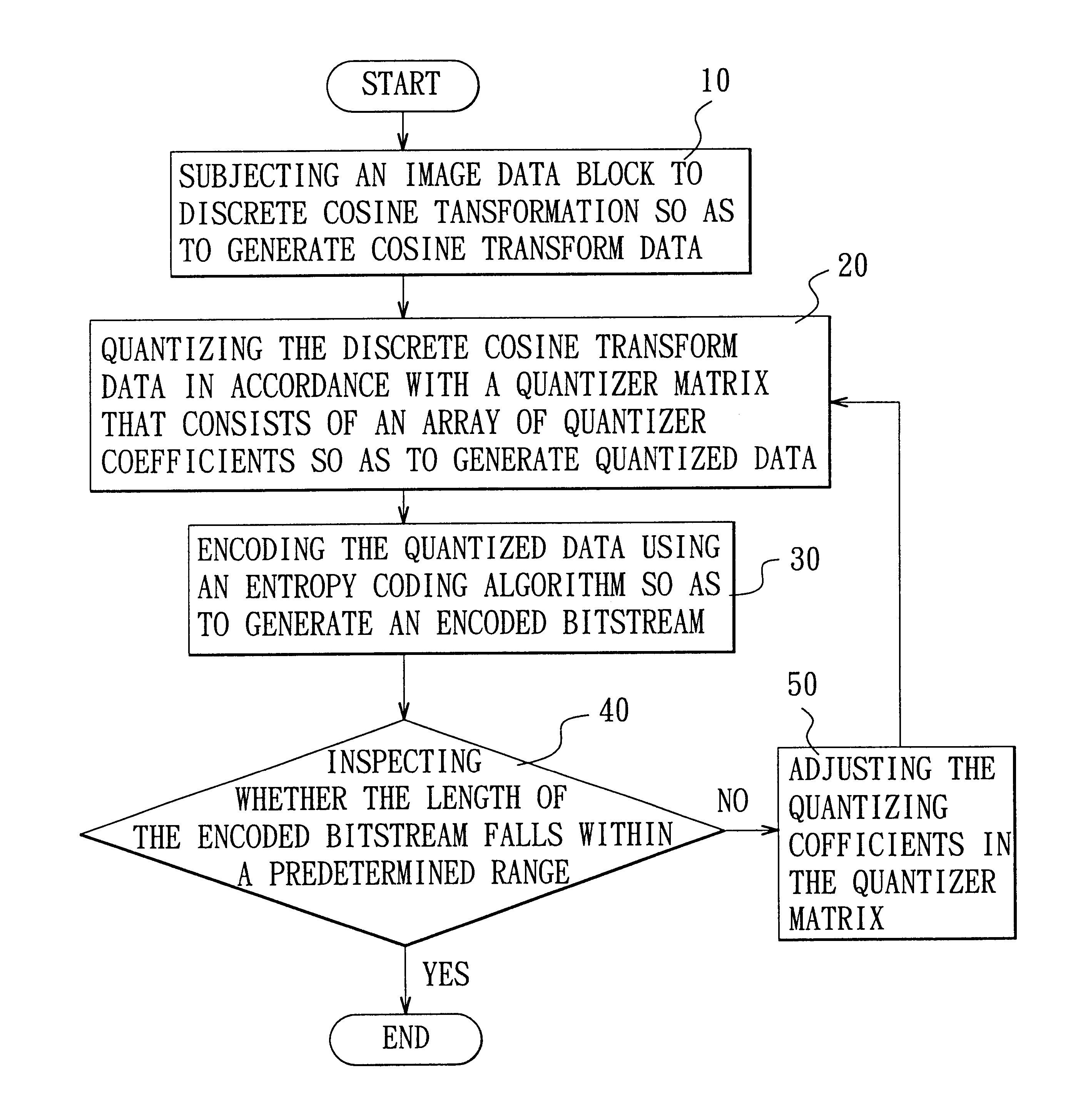
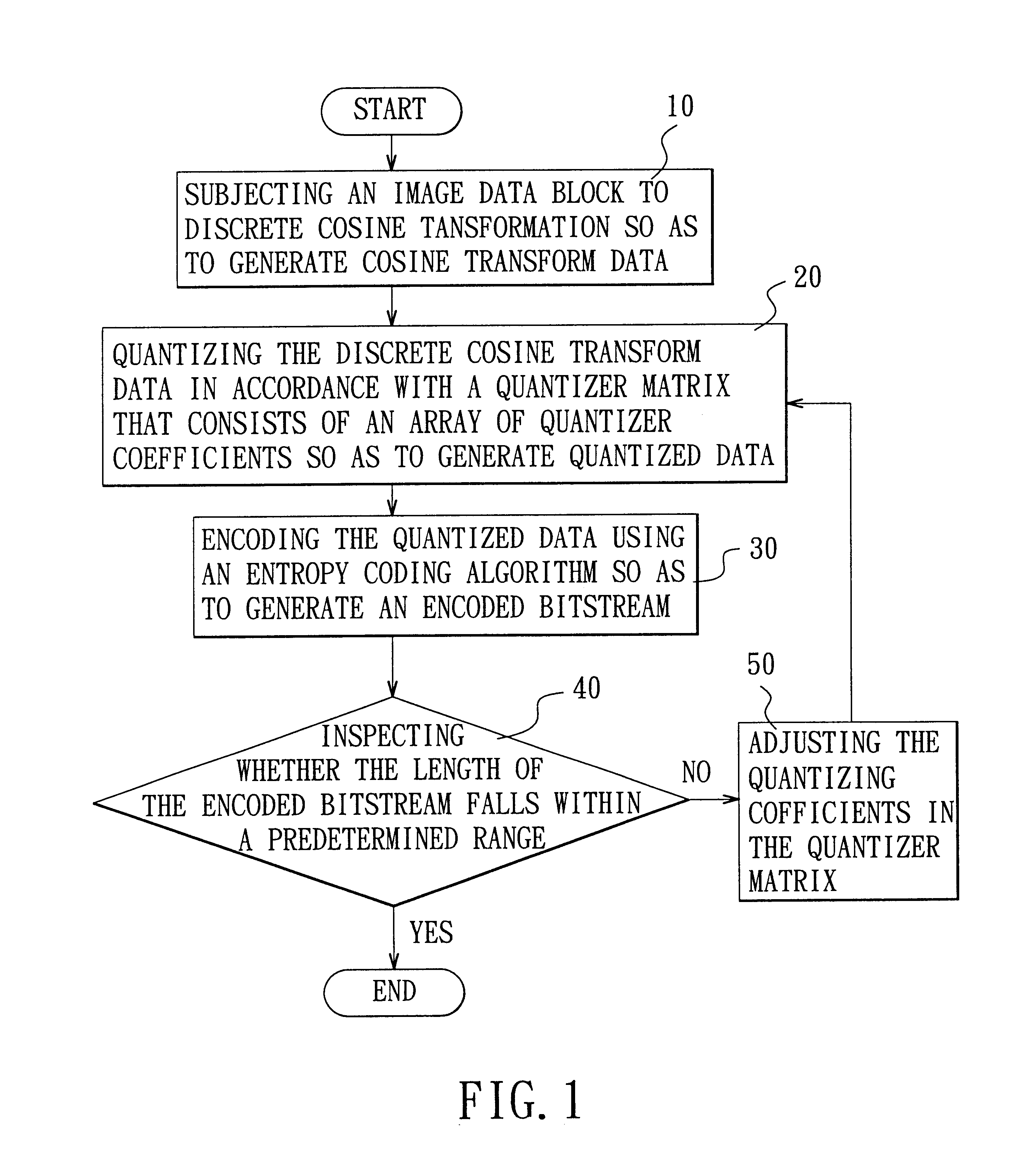
A method is adapted for compressing an image data block, and includes the steps of:(a) subjecting the image data block to discrete cosine transformation so as to generate discrete cosine transform data;(b) quantizing the discrete cosine transform data in accordance with a quantizer matrix that consists of an array of quantizing coefficients so as to generate quantized data;(c) encoding the quantized data using an entropy coding algorithm so as to generate an encoded bitstream; and(d) when the length of the encoded bitstream does not fall within a predetermined range, adjusting the quantizing coefficients in the quantizer matrix and repeating steps (b) and (c) until the length of the encoded bitstream falls within the predetermined range.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
Method of and apparatus for lossless video encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20070065026A1Increase the compression ratioCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionVideo encoding
Provided are a method of and apparatus for lossless video encoding and decoding, in which a differential residual block generated by calculating a difference between pixels of a residual block resulting from interprediction is encoded, thereby improving the compression rate. The method of lossless video encoding includes performing interprediction between a reference frame and a current frame in units of a predetermined-size block to generate a predicted block of a current block to be encoded, generating a residual block composed of residual signals corresponding to differences between pixels of the predicted block and the current block, calculating differences between the residual signals of the residual block in a predetermined direction and generating a differential residual block based on the calculated differences, and performing entropy-encoding on the differential residual block.
Owner:IND ACAD COOP GRP OF SEJONG UNIV +1
2-bin parallel decoder for advanced video processing
ActiveUS20090196355A1Low transfer rateIncrease speedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo processingParallel computing
A critical phase of video processing is the decoding of bit streams coming from standard based heavy compressed sources. Entropy coding can be effectively decoded by adopting parallelism to speed up the process. Reasonable assumptions make possible for example the multiple bits at a time processing for the Context-based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) algorithm. In particular, a clever arithmetic section reduces single propagation for the timing critical path while decoding done for only two sequence elements at a time by calculating and maintaining most probable bit values. This in turn making accelerated path using pre-determined probability outcome through parallelism not cost.
Owner:DIGITAL VIDEO SYSTEMS +1
Methods of and apparatuses for adaptive entropy encoding and adaptive entropy decoding for scalable video encoding
InactiveCN101099391AImprove coding efficiencyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingContext model
Methods and apparatuses are provided for adaptive entropy encoding and adaptive entropy decoding using various context models. A scalable entropy encoding method includes determining a context by referring to both syntax elements in the same layer as a block including a syntax element to be encoded and syntax elements in lower layers or only the syntax elements in the lower layers and performing entropy encoding on the syntax element using the determined context.
Owner:SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIVERSITY +1
Video encoding device
InactiveCN1878309ASmall sizeReduce capacityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionVideo encoding
The present invention provides a video encoding device in which a capacity of a binary data storing unit is small, a size of the video encoding device is small, a video signal can be processed in real time, and reduction in quality of images generated from the eventually obtained data can be prevented. The video encoding device according to the present invention includes: a video encoding unit which encodes a video signal; a binarization unit which binarizes an encoded value obtained from the video encoding unit; and an entropy encoding unit which subjects entropy encoding to binary data obtained from the binarization unit. Here, the video encoding unit encodes the video signal based on a characteristic of the binarization performed by the binarization unit, so that an amount of binary data obtained from the binarization unit by binarizing the encoded value that is encoded based on the characteristic is less than an amount of binary data obtained by binarizing an encoded value that is encoded without being based on the characteristic.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
QP adaptive coefficients scanning and application
InactiveUS20110249726A1Improved scanning pattern initializationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionNonzero coefficients
Entropy encoding is performed in the inventive apparatus and method in response to the scanning of transform coefficients following an initial scanning pattern selected on the basis of probability statistics of non-zero coefficients for each block position. These non-zero probability statistics are ranked for a given combination of coding characteristics within the current block to arrive at an initial scanning pattern. The same initial scanning pattern selection is performed in the decoder to allow the transform coefficients to be extracted in their proper order from encoded video data. The pattern selection is applicable to both intra prediction and inter prediction. Transform coefficients are more accurately ordered in response to the invention because in adapting pattern initialization to quantization step size, high-frequency basis functions are properly taken into account.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com