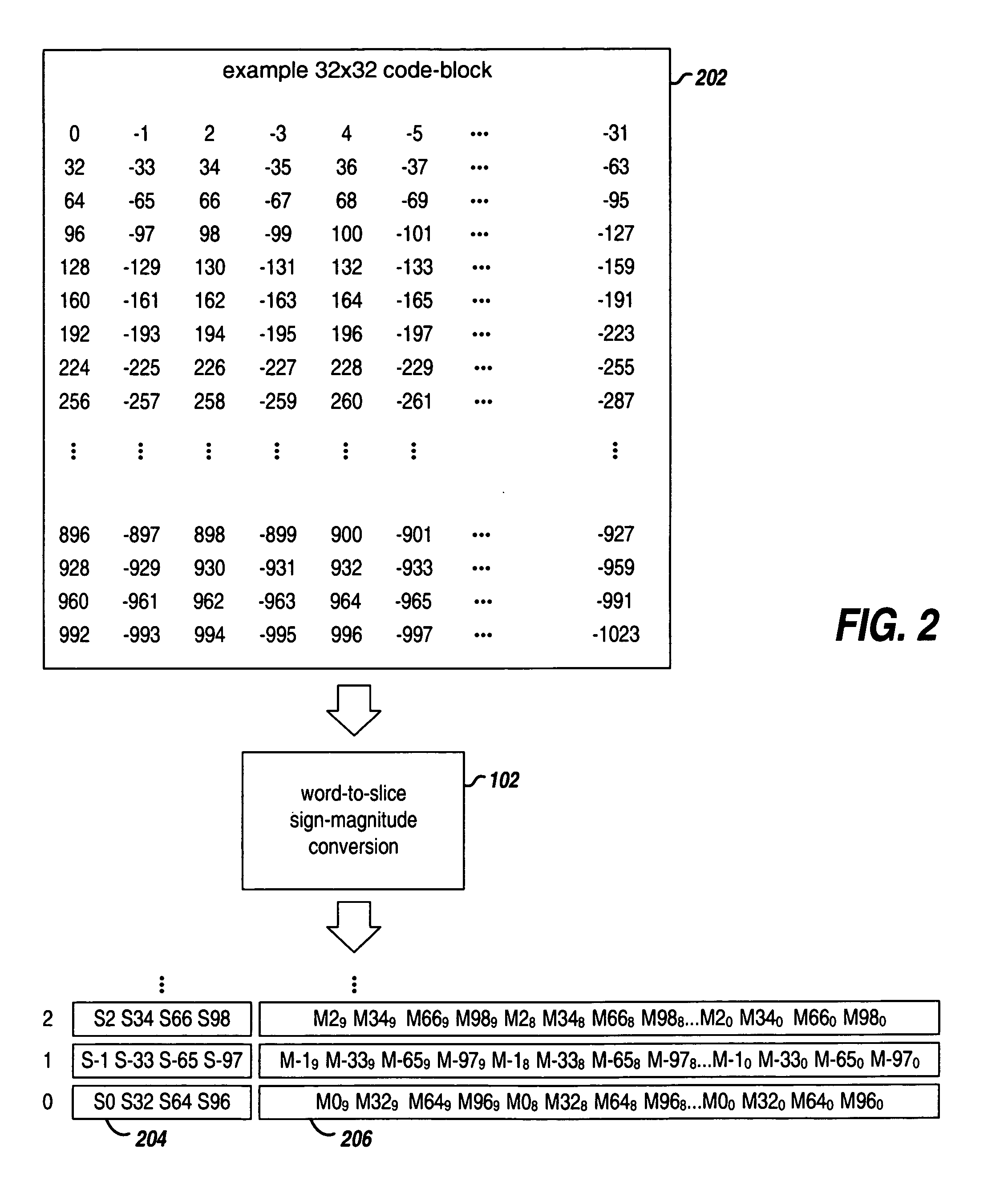
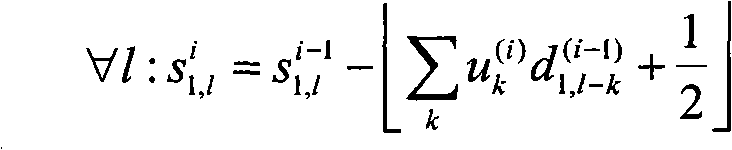Patents
Literature
104 results about "Bit plane coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
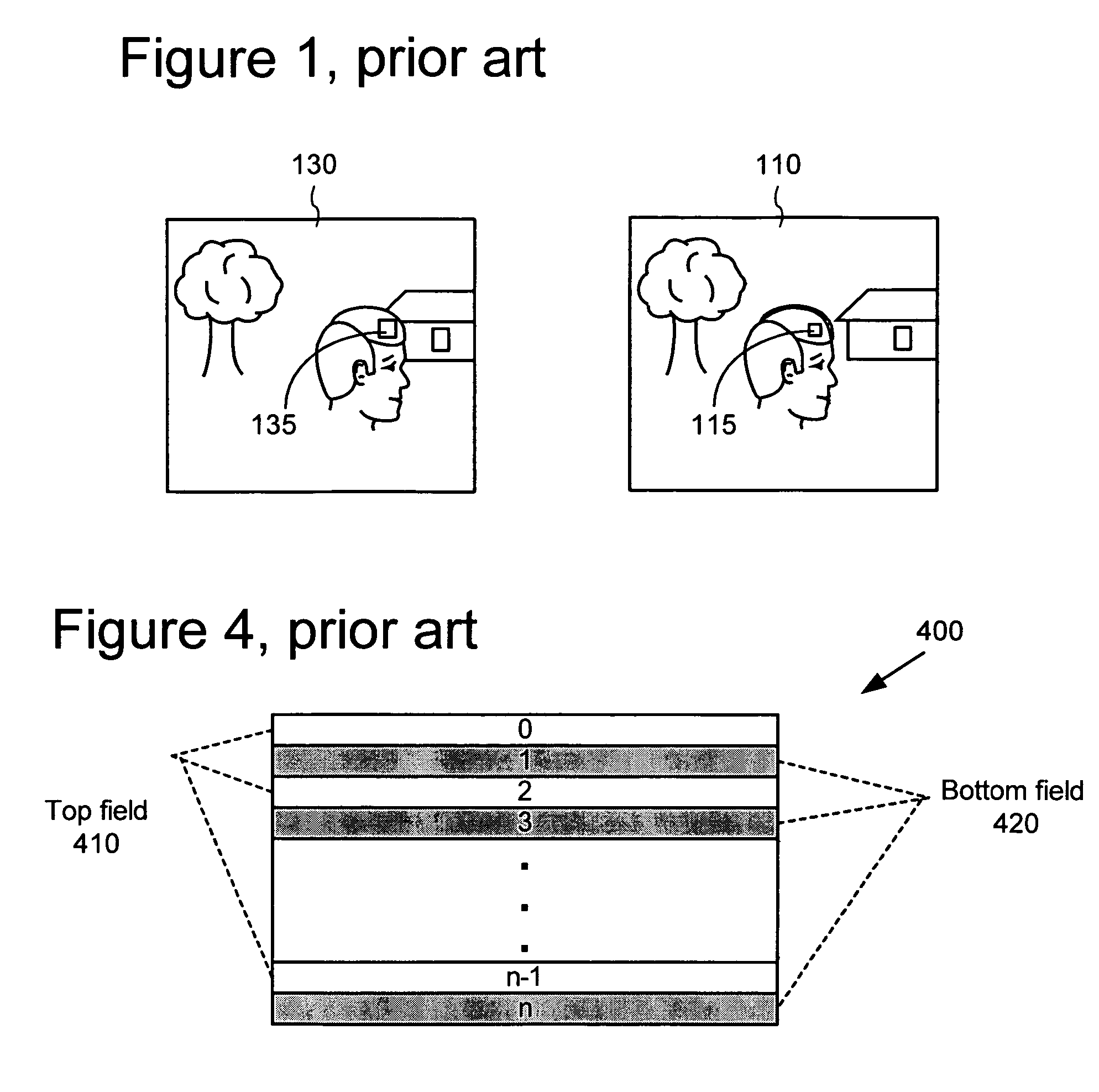
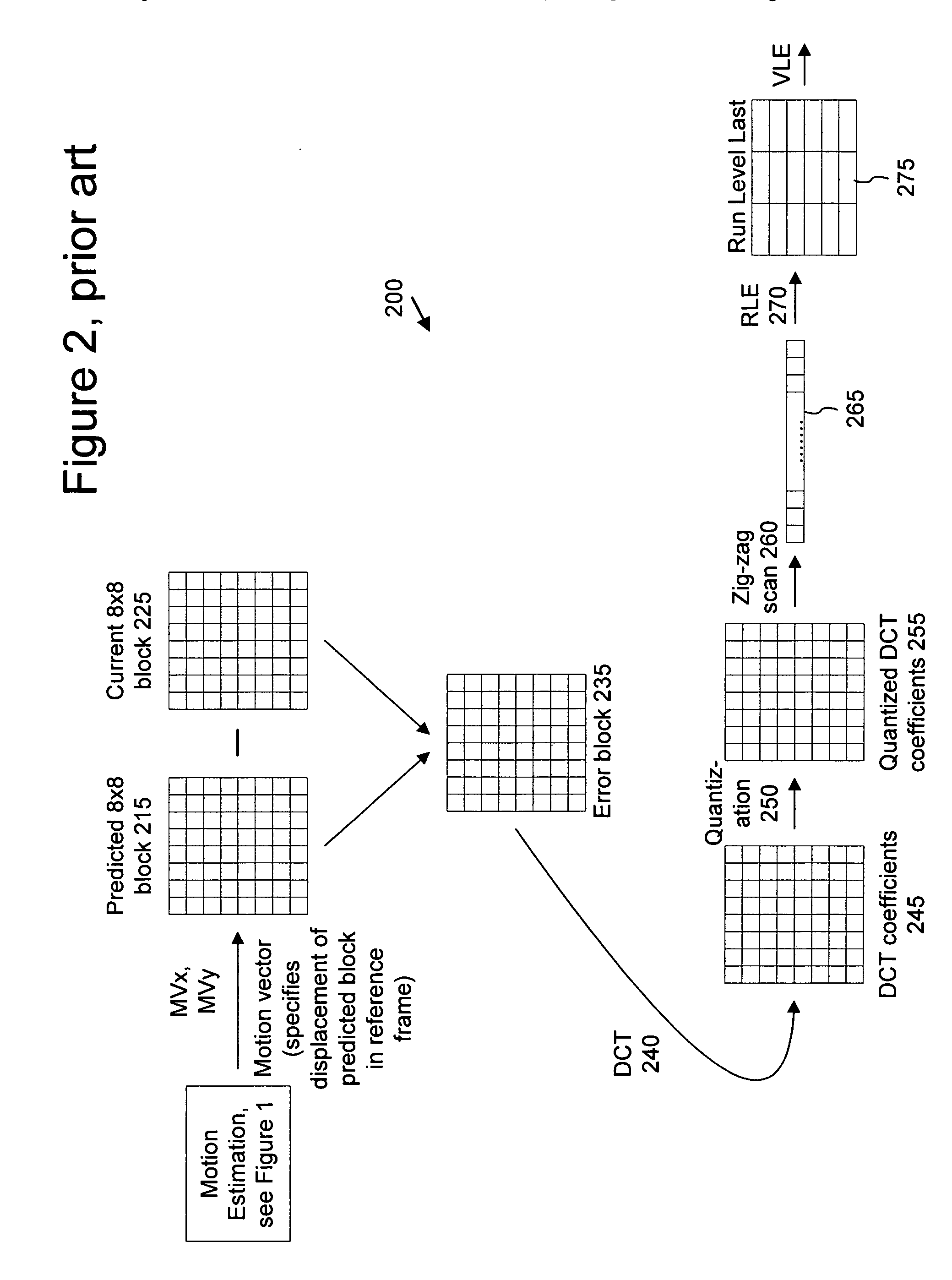
Advanced bi-directional predictive coding of video frames
ActiveUS20050013365A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionEncoder decoderMotion vector
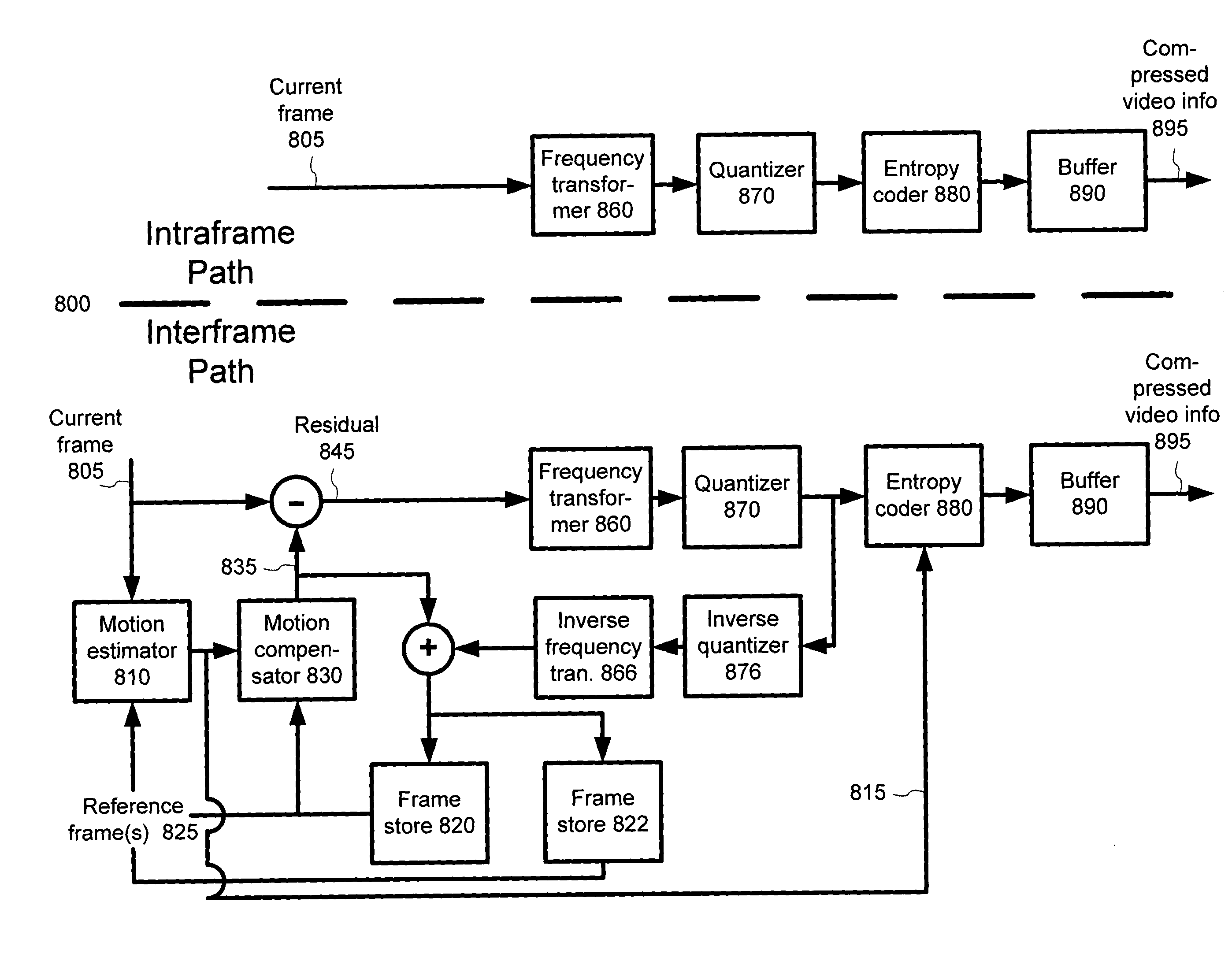
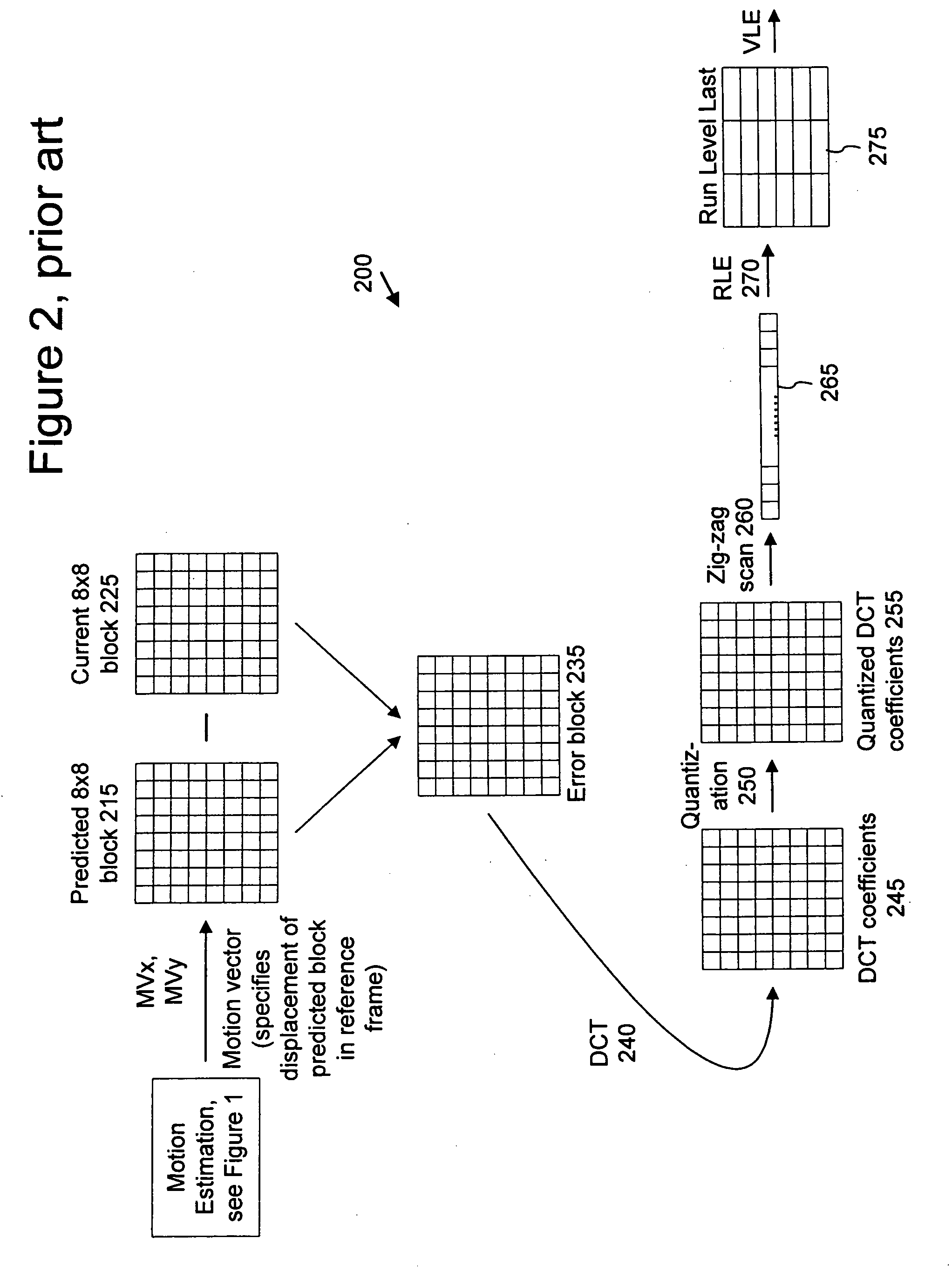
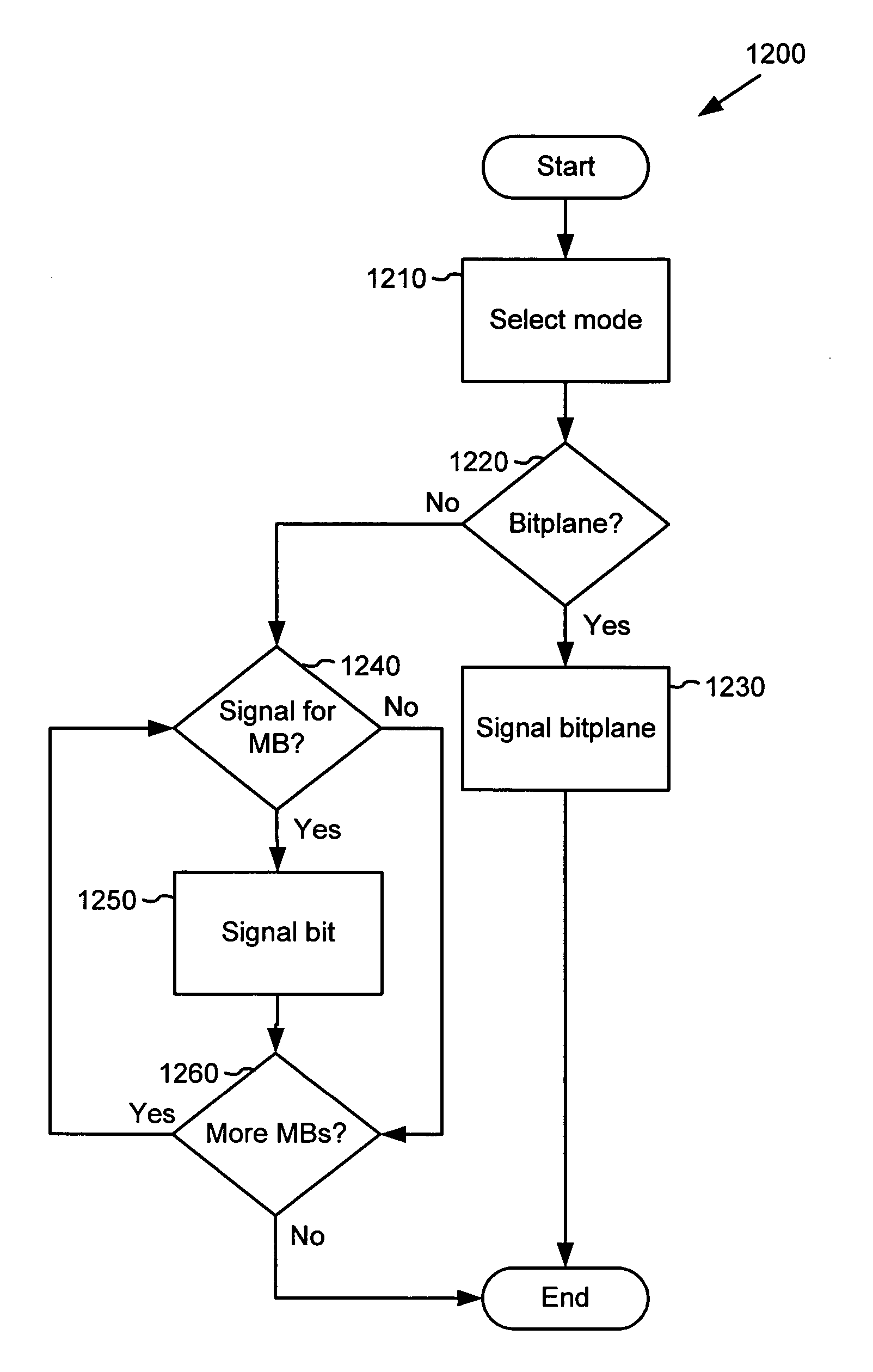
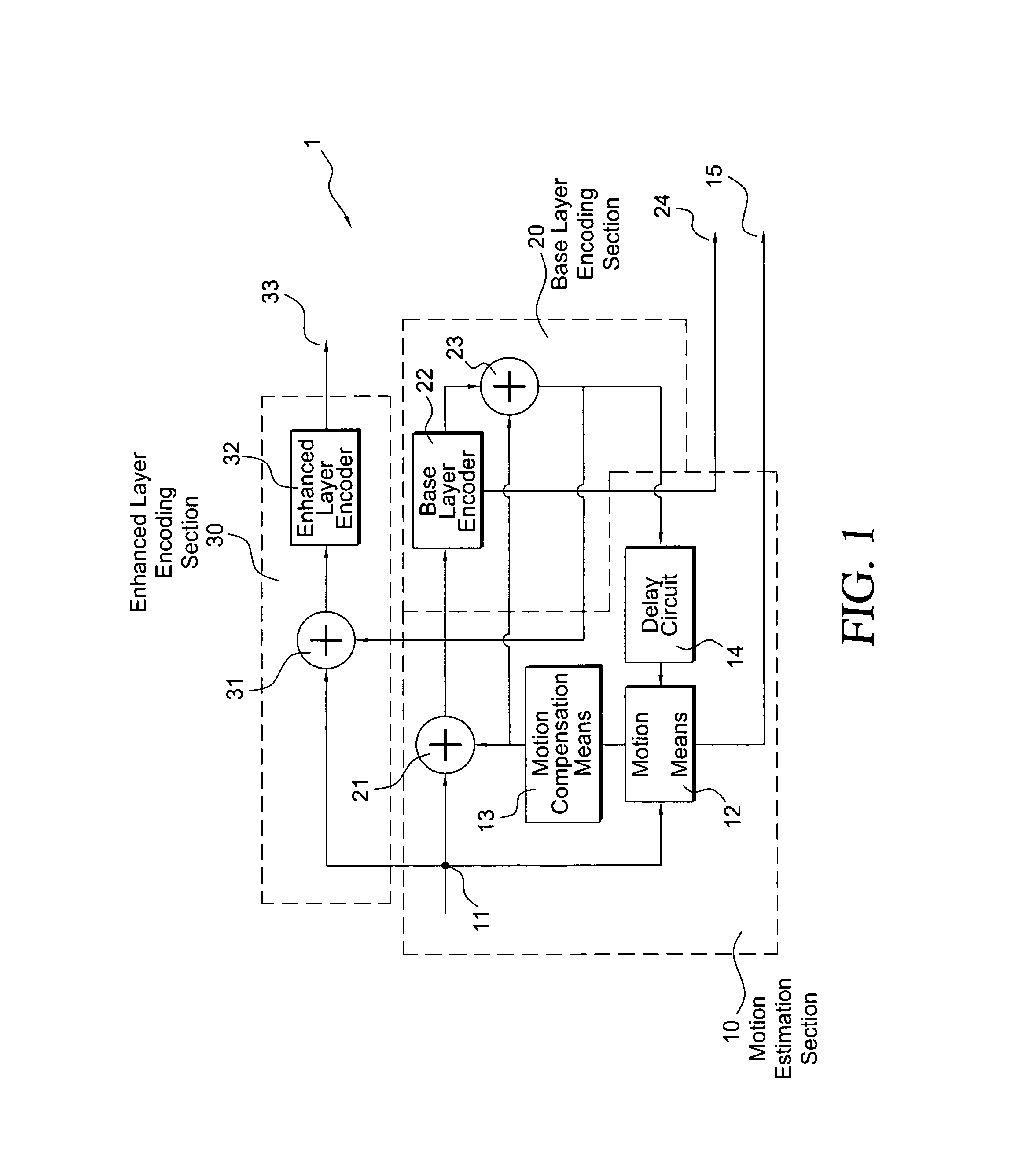
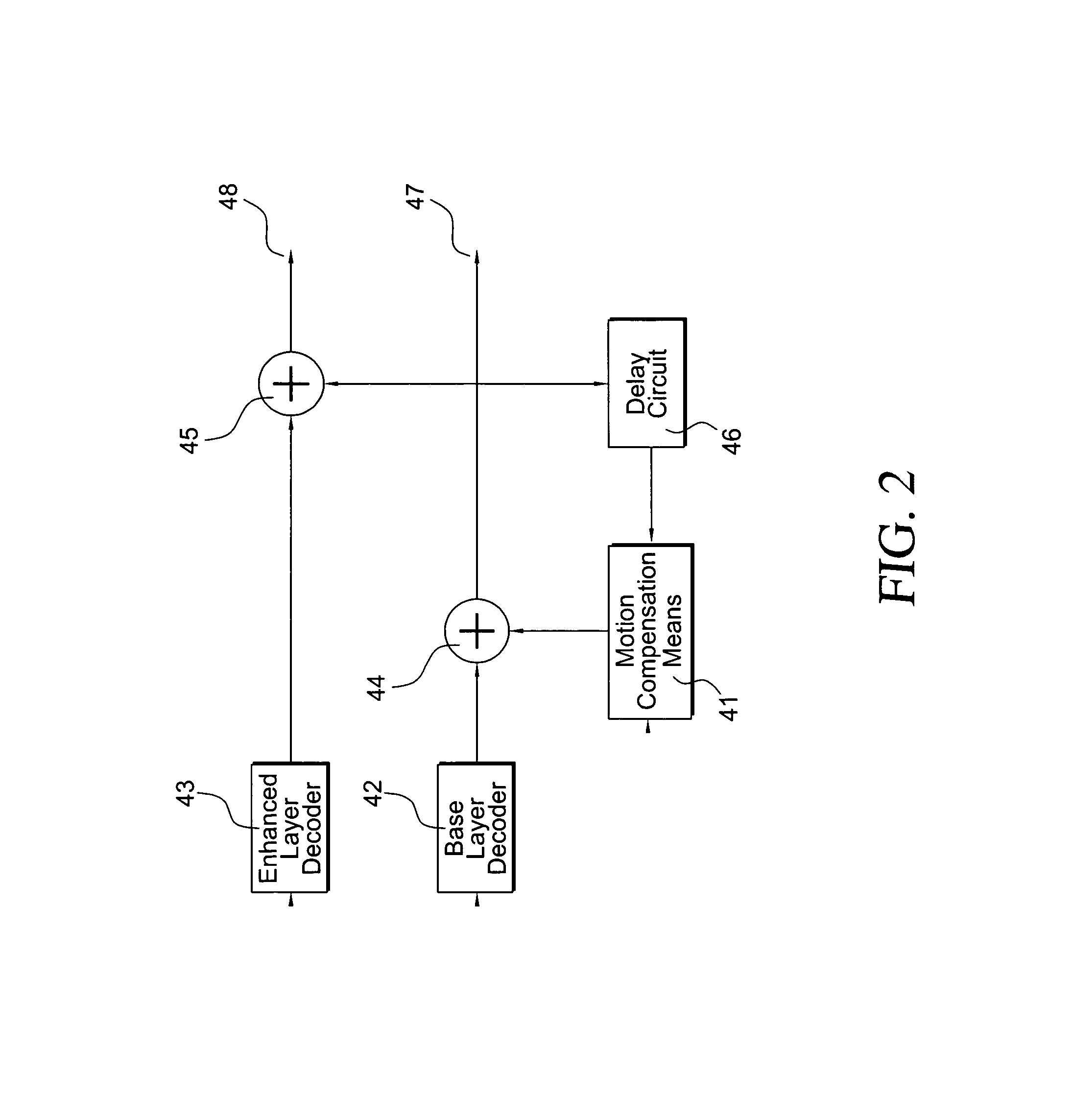
Techniques and tools for coding / decoding of video images, and in particular, B-frames, are described. In one aspect, a video encoder / decoder determines a fraction for a current image in a sequence. The fraction represents an estimated temporal distance position for the current image relative to an interval between a reference images for the current image. The video encoder / decoder processes the fraction along with a motion vector for a first reference image, resulting in a representation of motion (e.g., constant or variable velocity motion) in the current image. Other aspects are also described, including intra B-frames, forward and backward buffers for motion vector prediction, bitplane encoding of direct mode prediction information, multiple motion vector resolutions / interpolation filters for B-frames, proactive dropping of B-frames, and signaling of dropped predicted frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Video coding
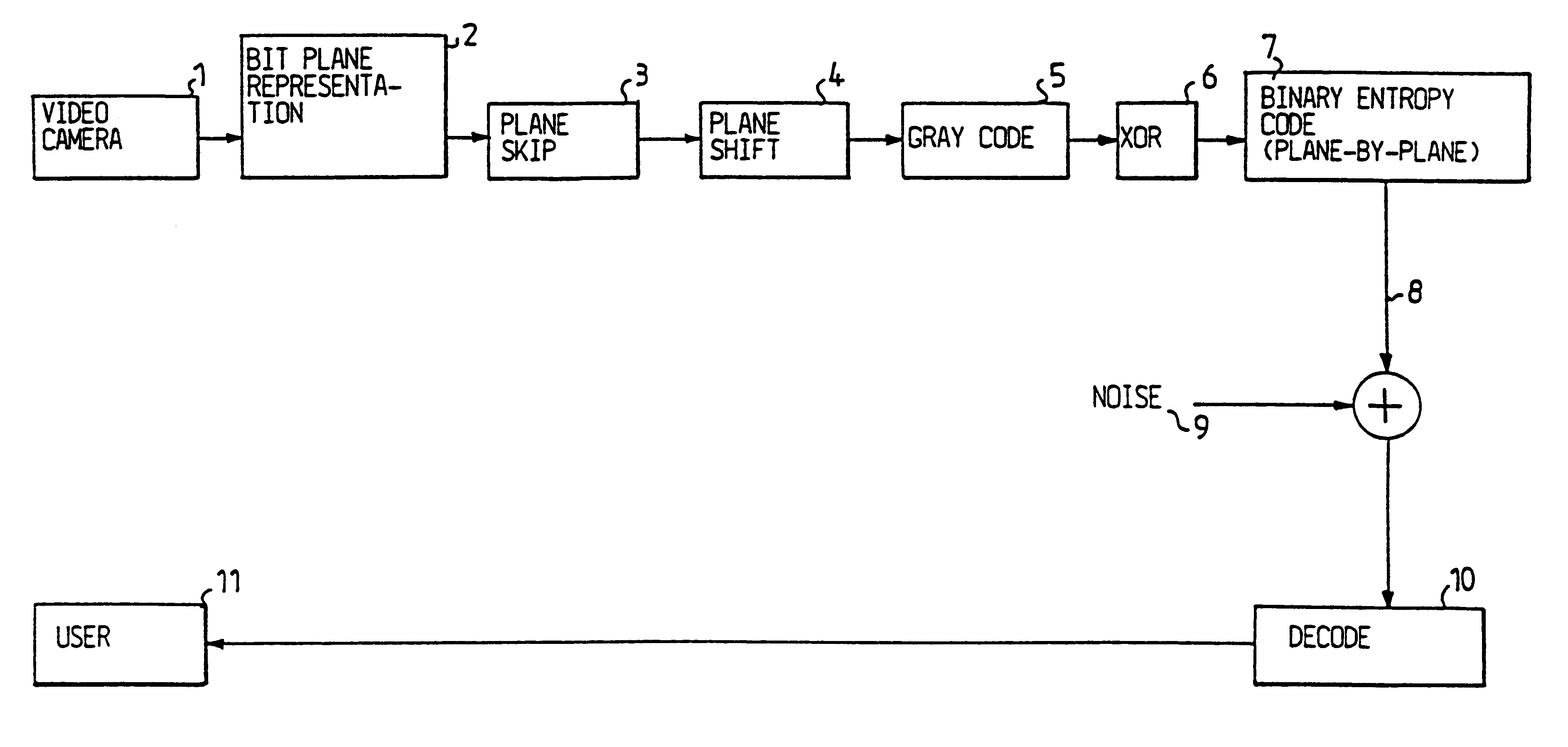
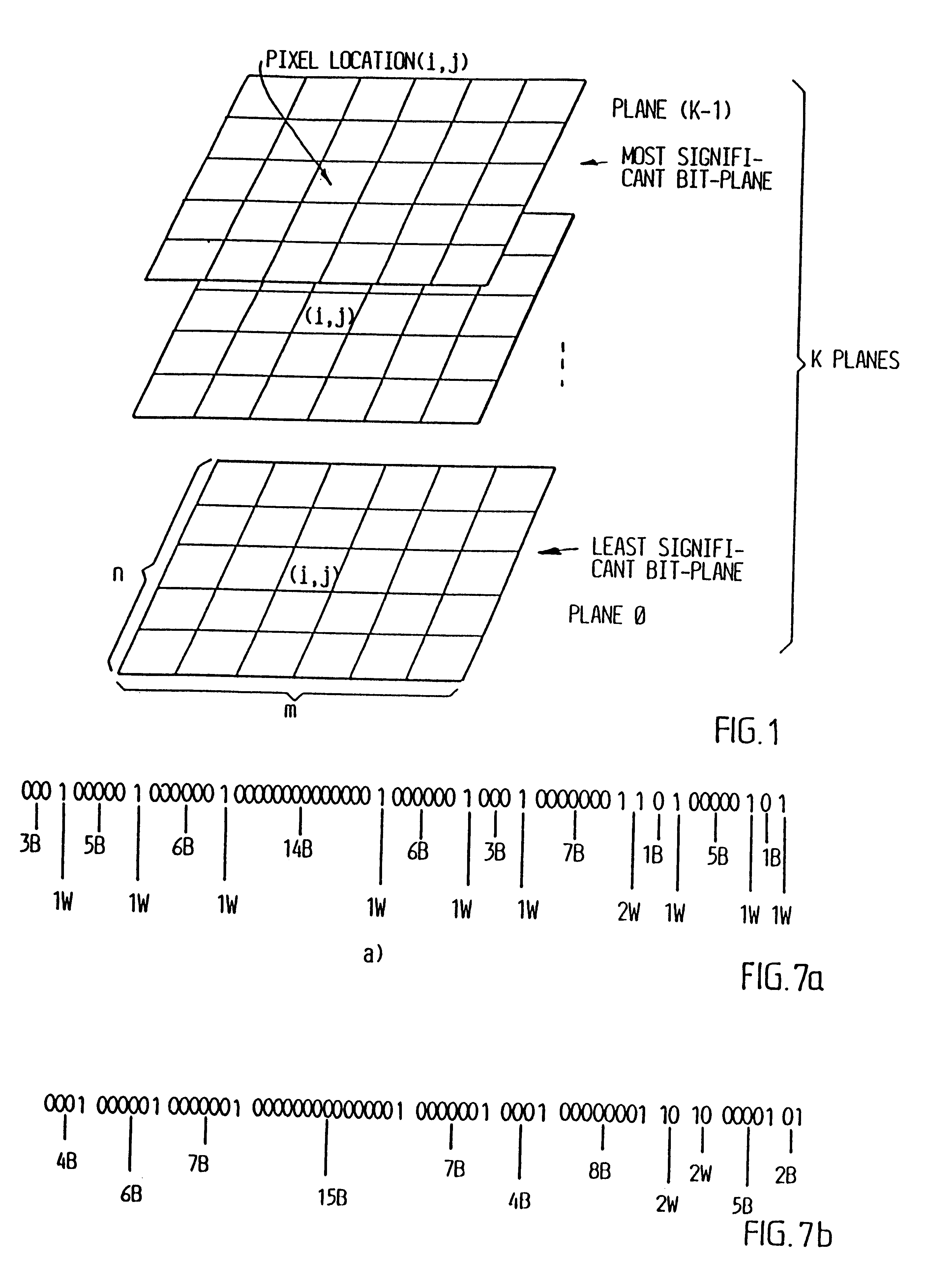
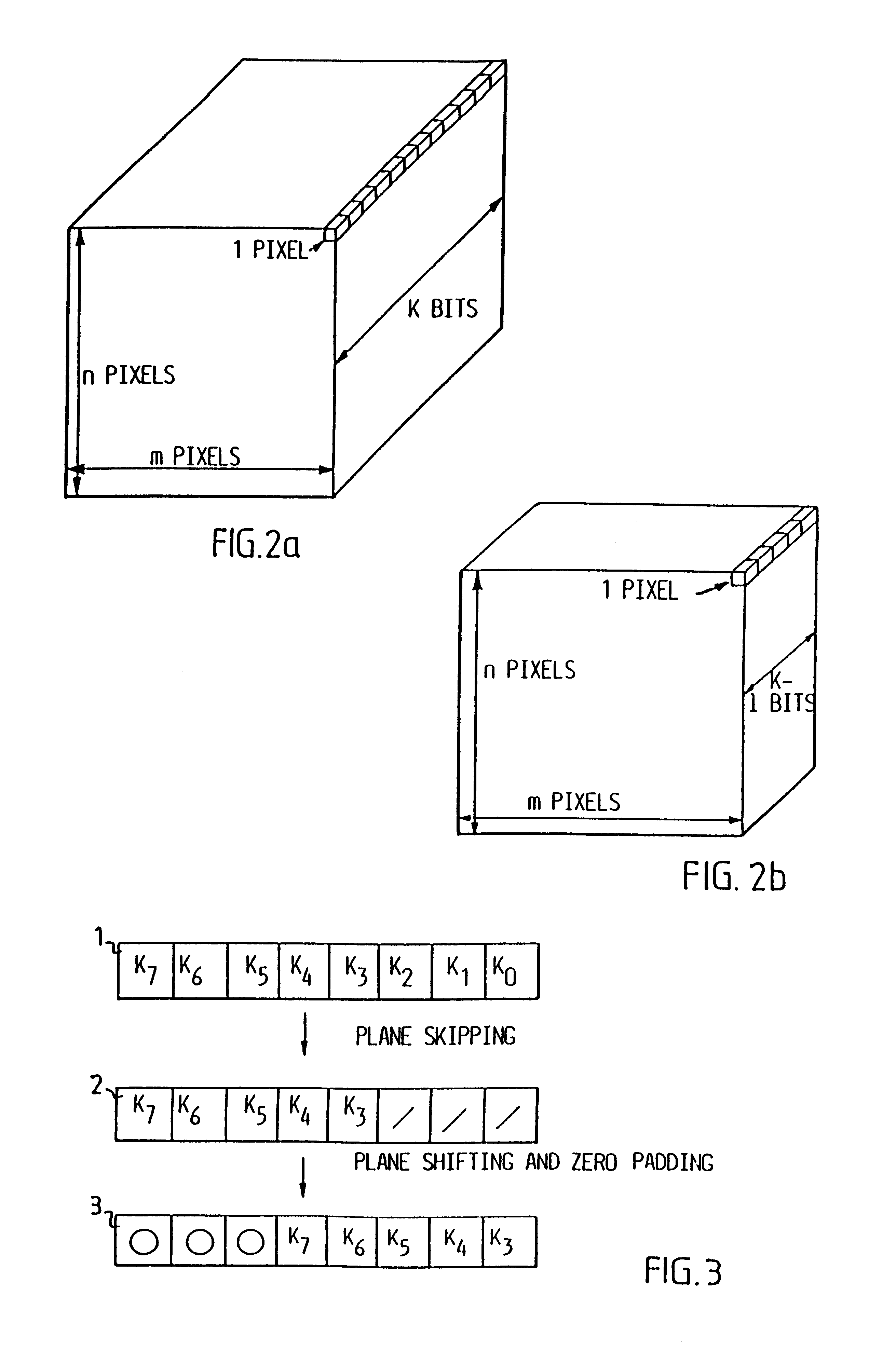
InactiveUS6208761B1Reduce in quantityEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsVideo sequenceBit plane coding
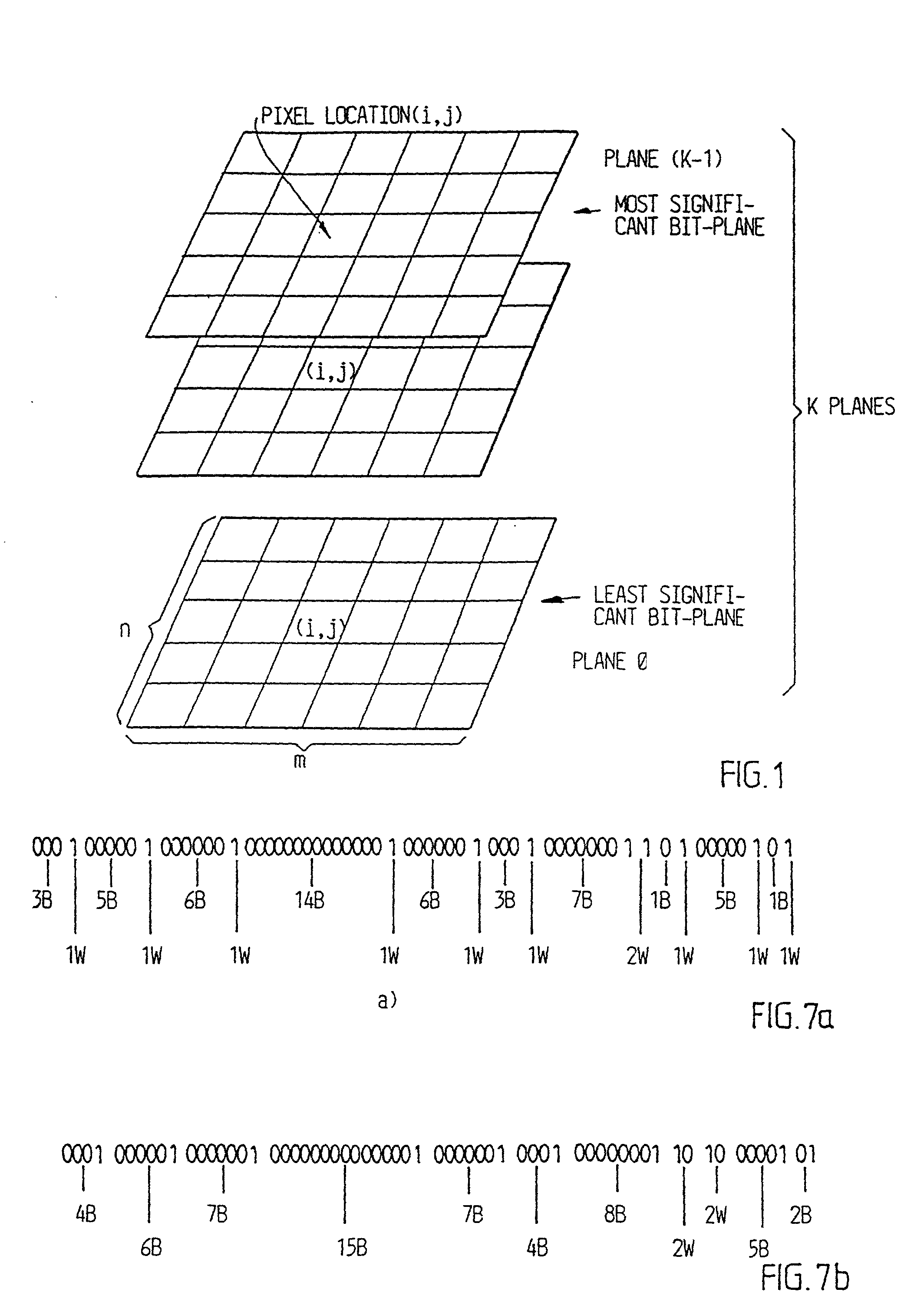
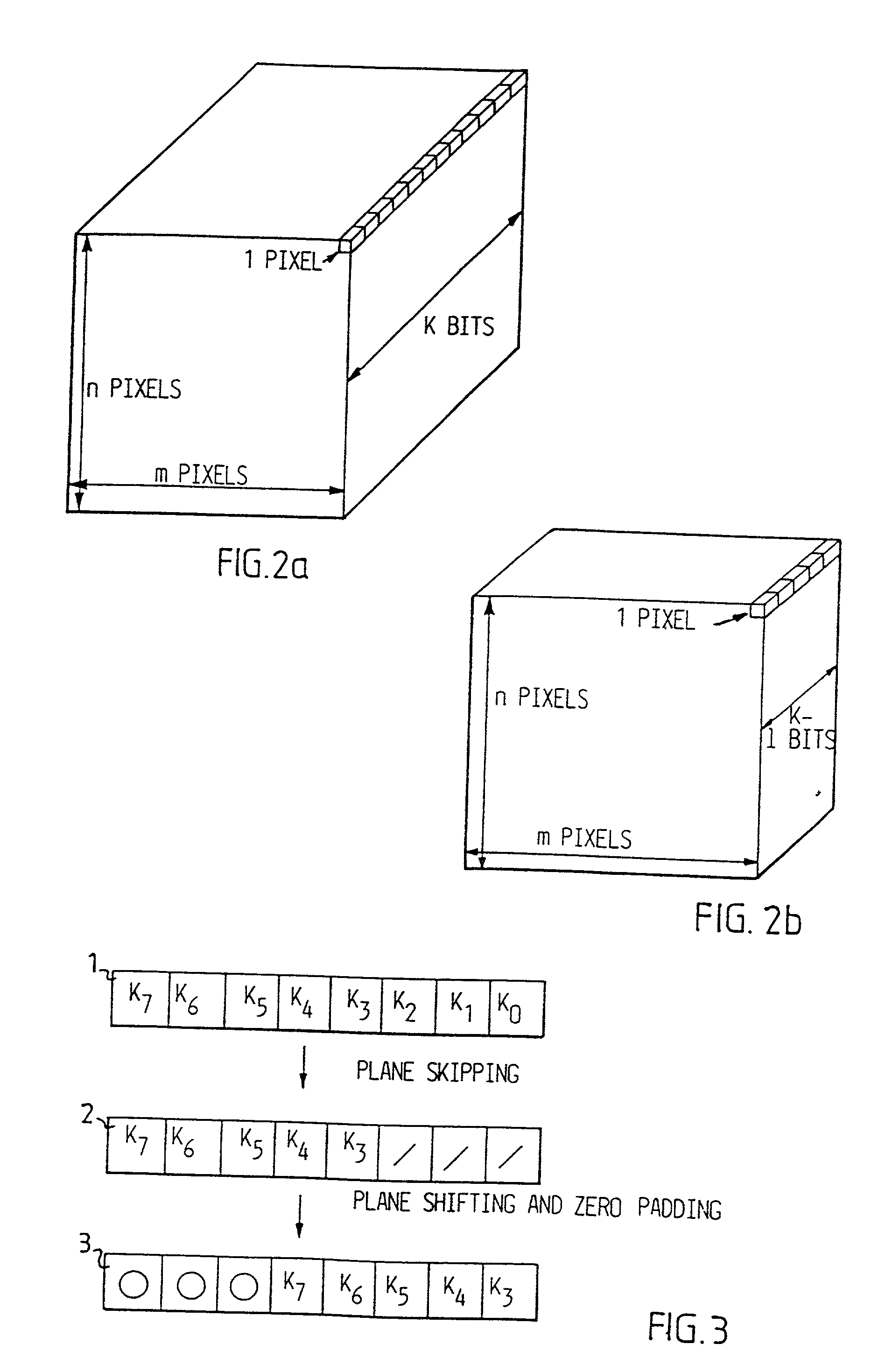
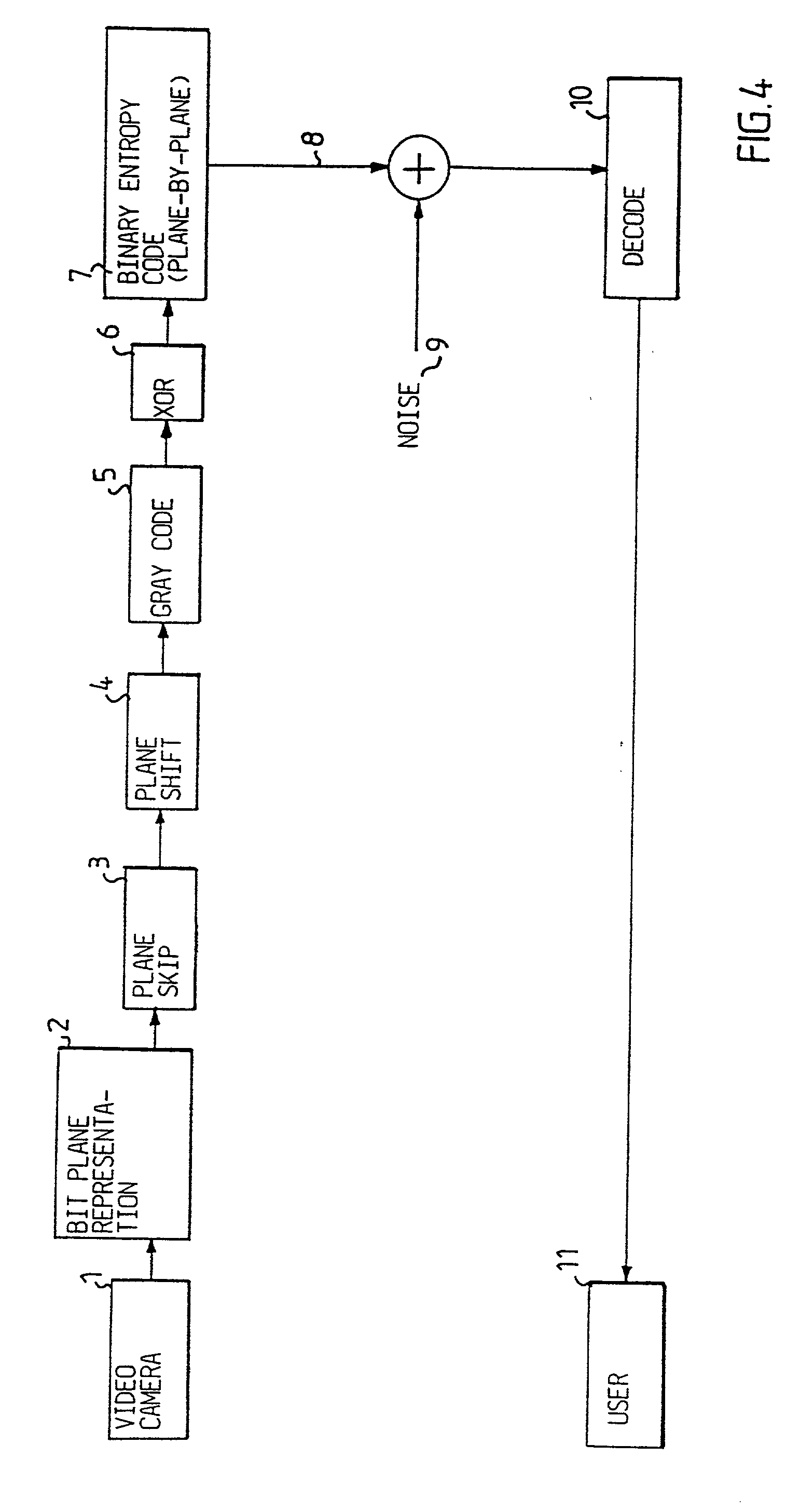
Digitalized video images are compressed in several steps in order to provide a system for transmitting moving video pictures via narrow band channels, such as the telephone network. The system is based on any extension of the bit-plane coding technique to video sequences and lossy conditions. The compression technique can also be advantageously used in a lossless compression system. The system involves the steps of bit plane representation and skipping the least significant bit plane(s), shifting the pixels, coding with a Gray code, the use of segmentation, and motion-estimation / motion compensation and application of a transmit / not transmit / motion compensate (TX / NT / MC) procedure, exploiting of the temporal redundancy of two corresponding bit planes via an XOR operation on two successive images, and a plane-by-plane application of an extended RLEID technique. The RLEID technique includes coding a run of like binary symbols with one word, the run including a transition between the penultimate and ultimate binary symbol.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Bitplane coding for macroblock field/frame coding type information
ActiveUS20050053296A1Reduced flexibilityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInterlaced videoComputer graphics (images)
In one aspect, for a first interlaced video frame in a video sequence, a decoder decodes a bitplane signaled at frame layer for the first interlaced video frame. The bitplane represents field / frame transform types for plural macroblocks of the first interlaced video frame. For a second interlaced video frame in the video sequence, for each of at least one but not all of plural macroblocks of the second interlaced video frame, the decoder processes a per macroblock field / frame transform type bit signaled at macroblock layer. An encoder performs corresponding encoding.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
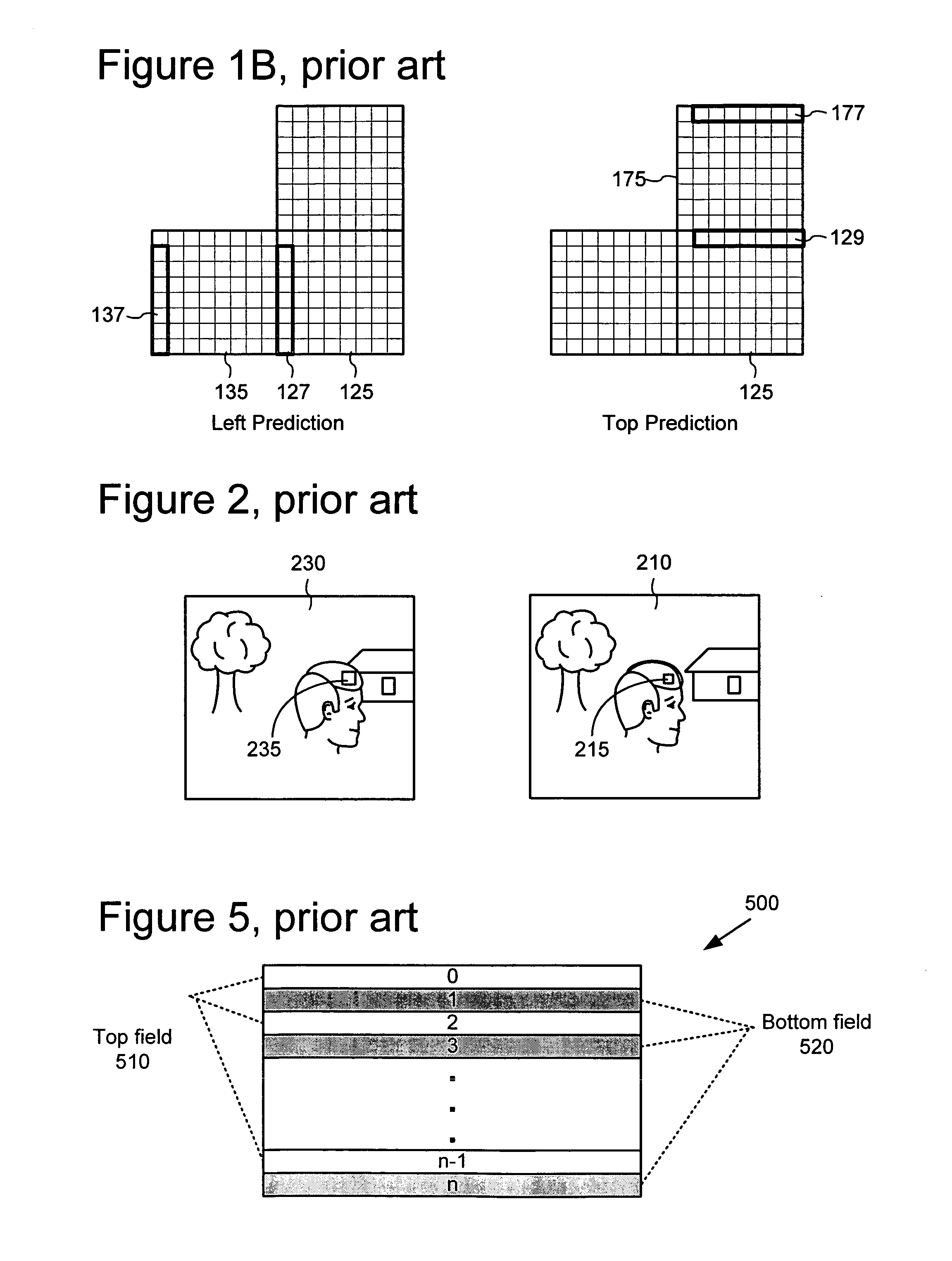
Bitplane coding of prediction mode information in bi-directionally predicted interlaced pictures
ActiveUS20050053300A1Reduce encoding overheadStable supportPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionInterlaced videoBinary information
An encoder sends binary information indicating whether a prediction mode is forward or not-forward for one or more macroblocks in an interlaced B-field. For example, the encoder sends forward / not-forward decision information at B-field level in a compressed bitplane. Sending forward / not-forward prediction mode decision information in a compressed bitplane at B-field level can reduce coding overhead for prediction mode coding. A decoder performs corresponding decoding.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for Encoding a Digital Signal Into a Scalable Bitstream; Method for Decoding a Scalable Bitstream
ActiveUS20070274383A1Reduce amountPromote regenerationElectrophonic musical instrumentsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMultiplexingBit plane coding
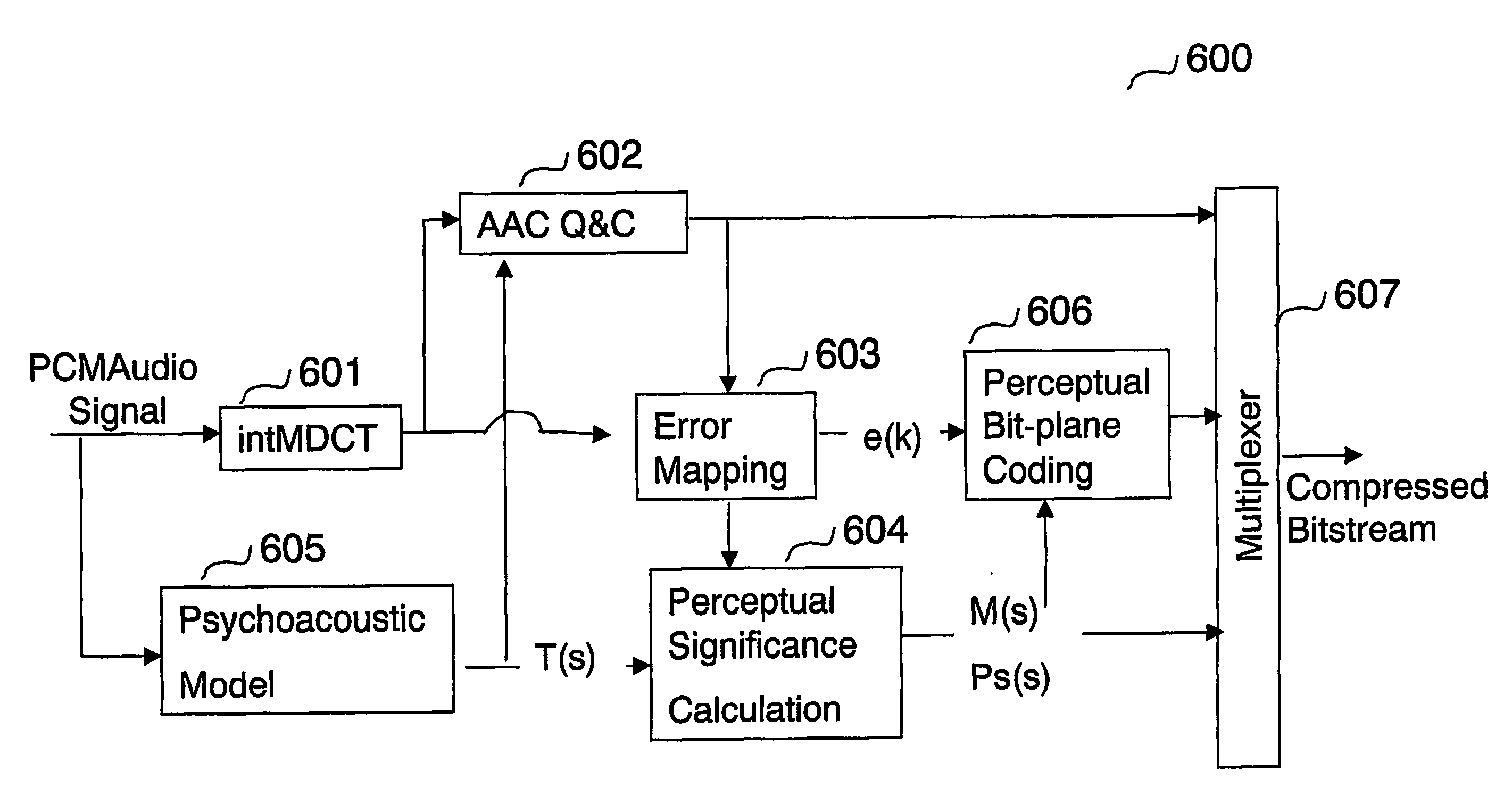
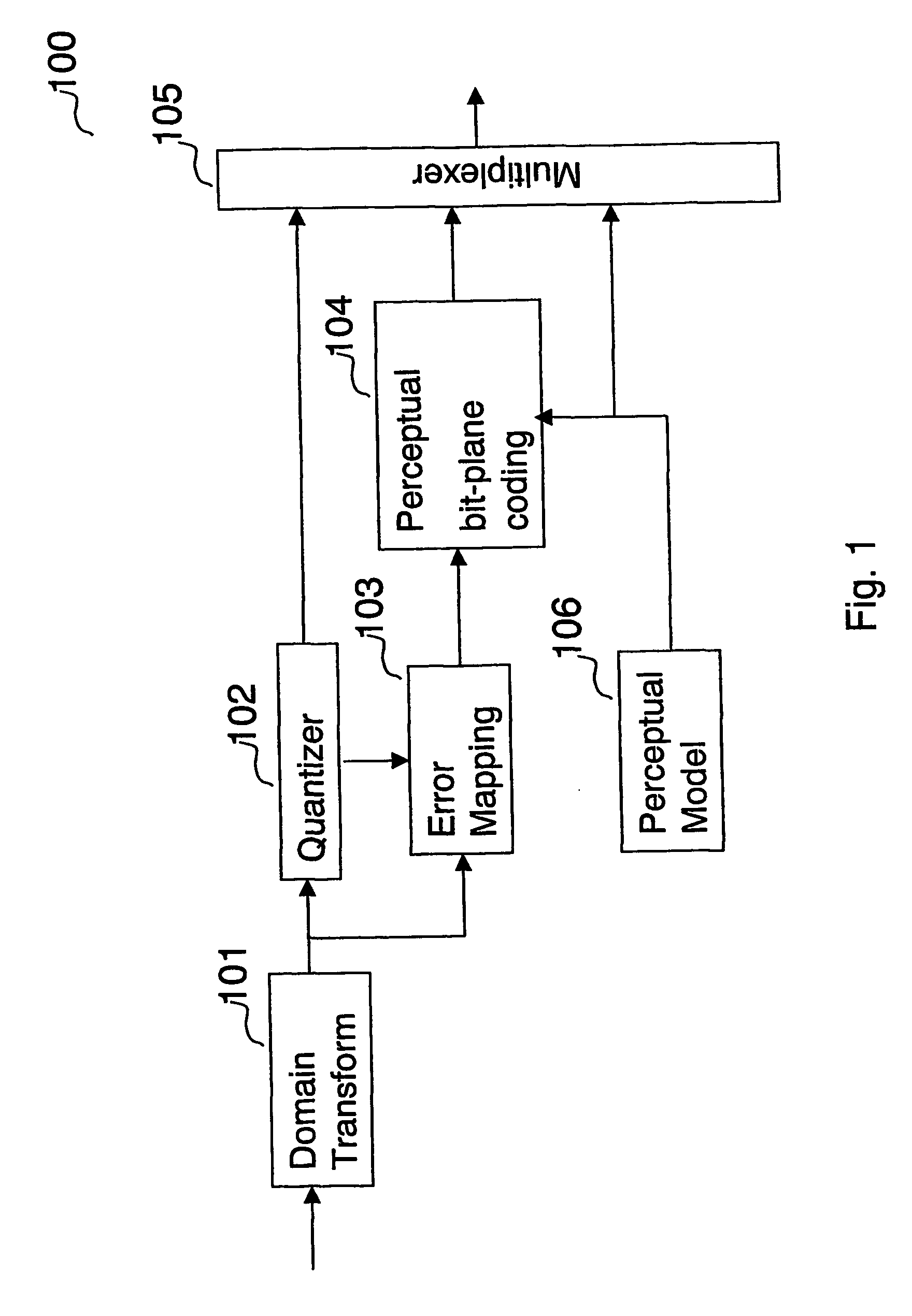
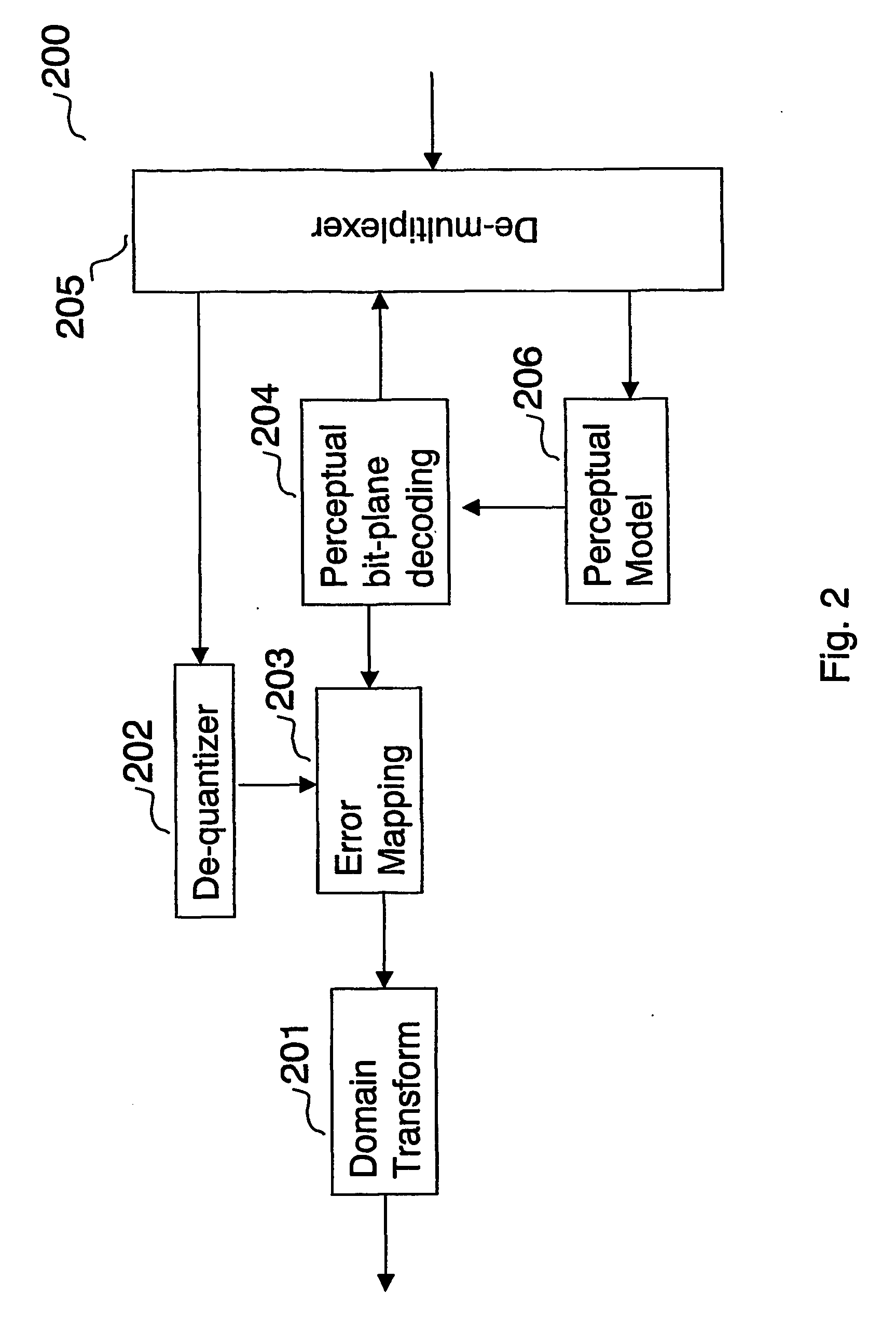
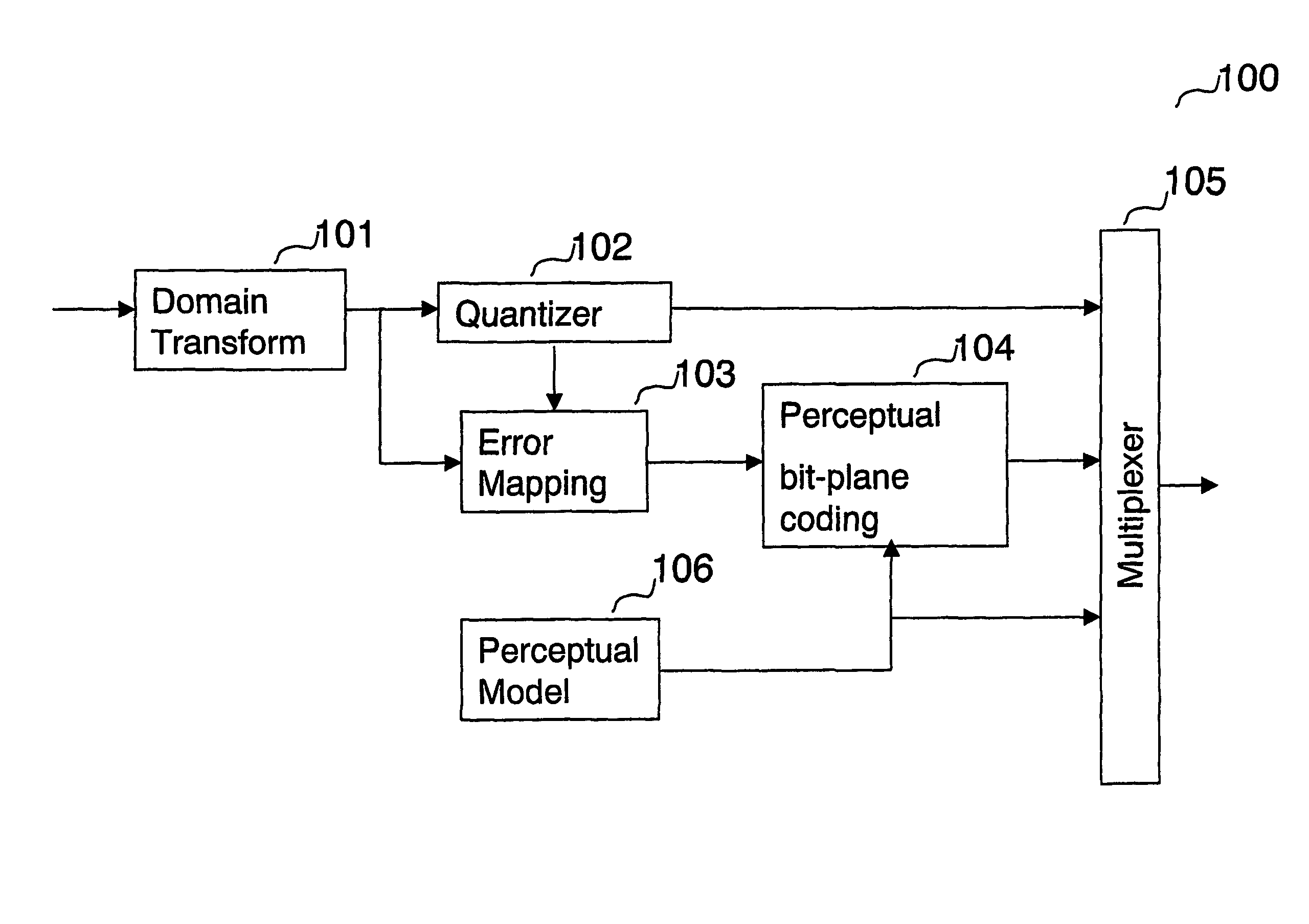
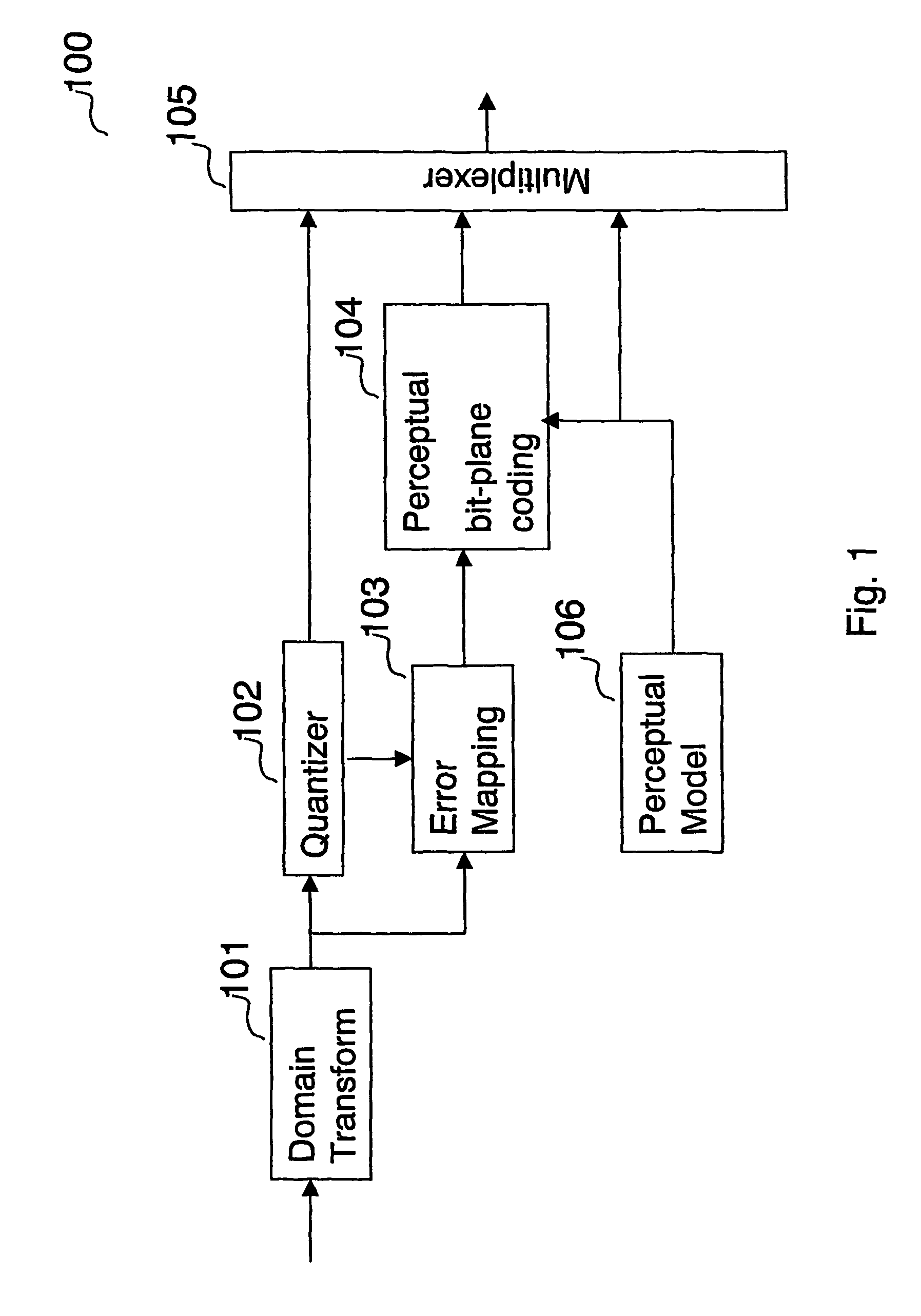
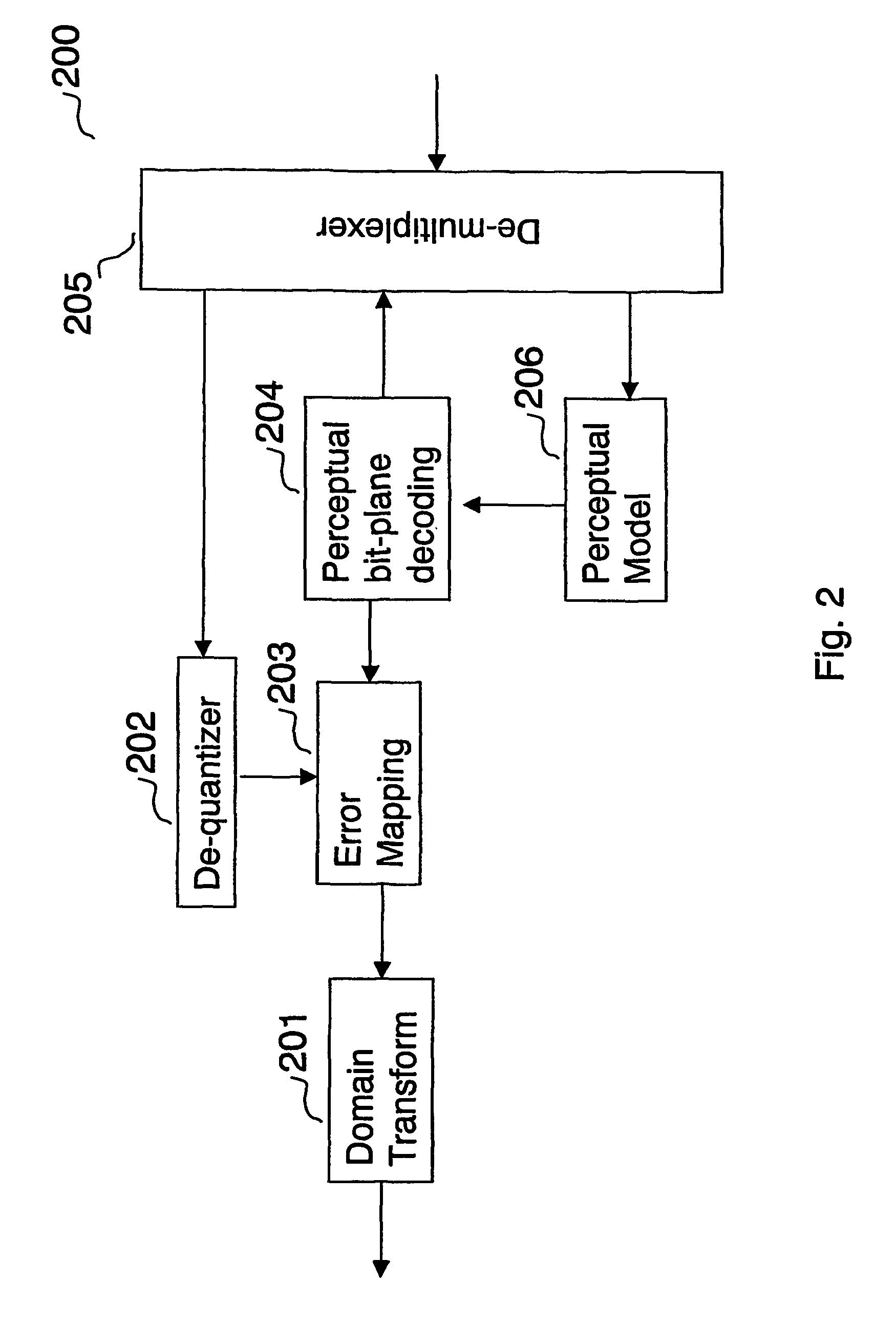
A method for encoding a digital signal into a scalable bitstream comprising quantizing the digital signal, and encoding the quantized signal to form a core-layer bitstream, performing an error mapping based on the digital signal and the core-layer bitstream to remove information that has been encoded into the core-layer bitstream, resulting in an error signal, bit-plane coding the error signal based on perceptual information of the digital signal, resulting in an enhancement-layer bitstream, wherein the perceptual information of the digital signal is determined using a perceptual model, and multiplexing the core-layer bitstream and the enhancement-layer bitstream, thereby generating the scalable bitstream. A method for decoding a scalable bitstream into a digital signal comprising de-multiplexing the scalable bitstream into a core-layer bitstream and an enhancement-layer bitstream, decoding and de-quantizing the core-layer bitstream to generate a core-layer signal, bit-plane decoding the enhancement-layer bitstream based on perceptual information of the digital signal, and performing an error mapping based on the bit-plane decoded enhancement-layer bitstream and the de-quantized core-layer signal, resulting in an reconstructed transformed signal, wherein the reconstructed transformed signal is the digital signal.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
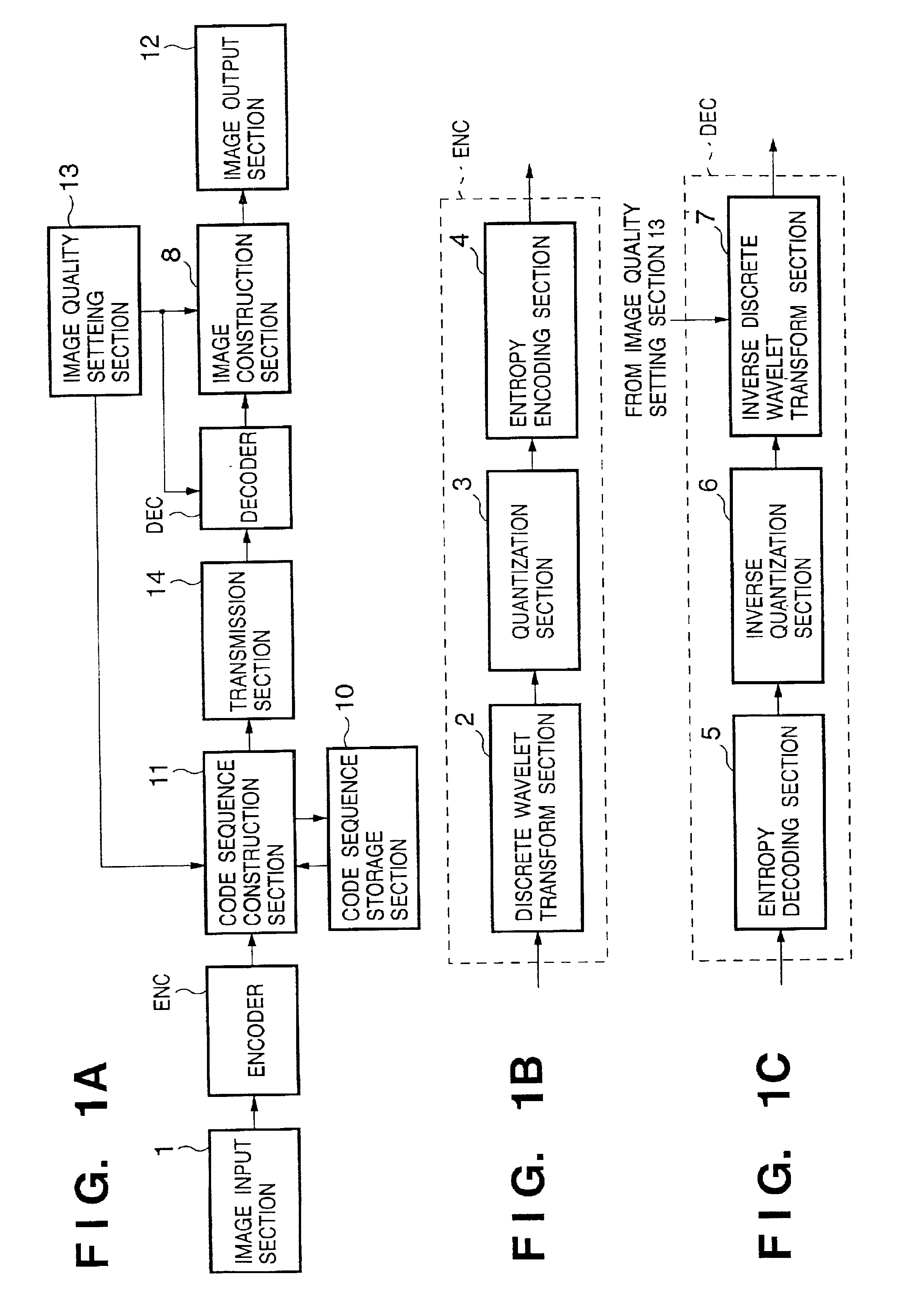
Decoding bit-plane-encoded data using different image quality for display
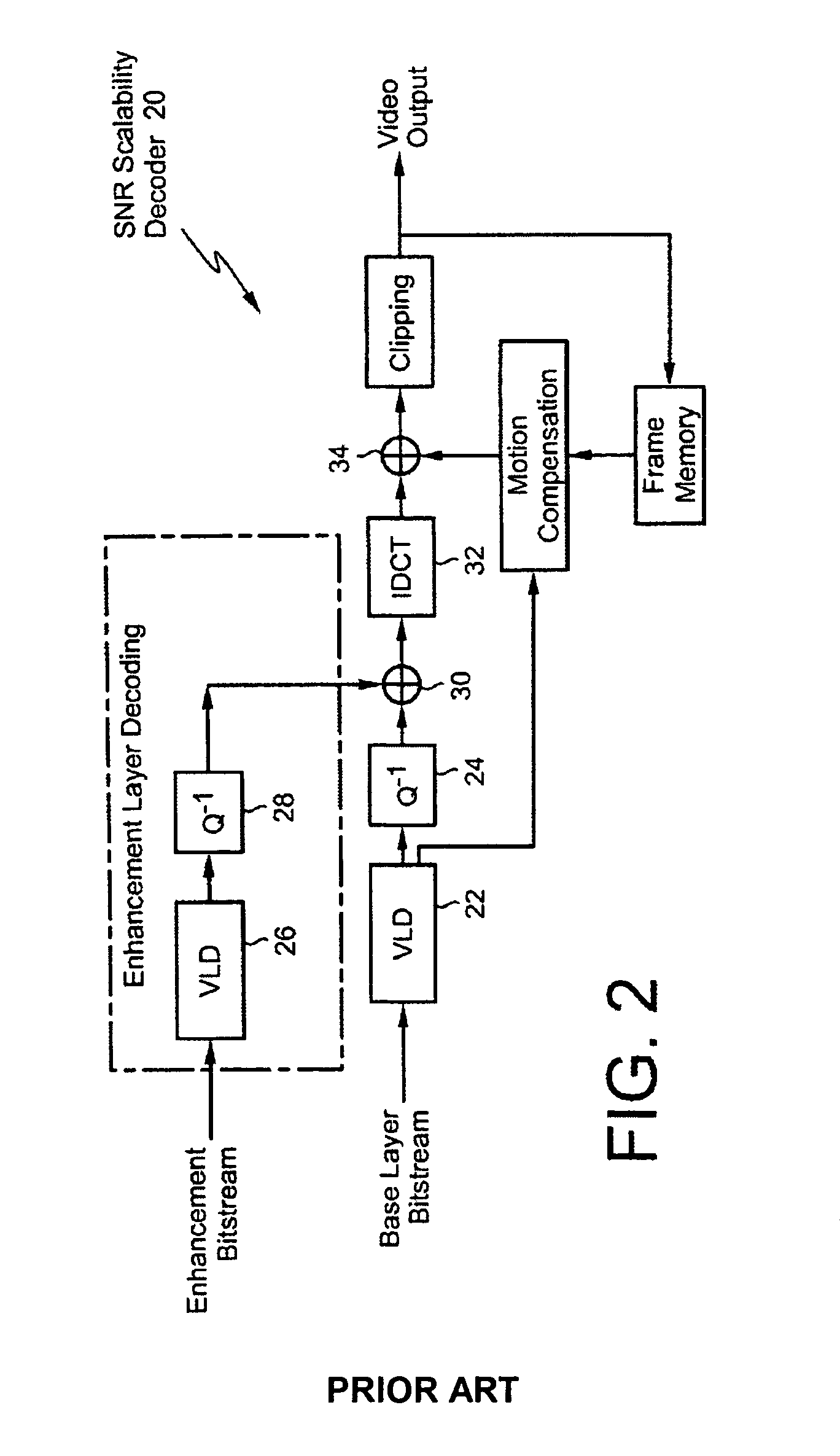
InactiveUS6879727B2Image degradationMaintain qualityCode conversionImage codingPattern recognitionImaging processing
An image processing apparatus includes an encoding section and a decoding section. The encoding section includes means for encoding an input image to generate encoded data, means for receiving a designation of an image quality for display of the input image, and means for outputting, of the encoded data, encoded data necessary to display the input image at an image quality equal to or higher than the designated image quality. The decoding section includes means for decoding the encoded data output from the encoding section to generate image data, and means for, when an image based on the image data has an image quality higher than the designated image quality, converting the image data into image data having the designated image quality.
Owner:CANON KK
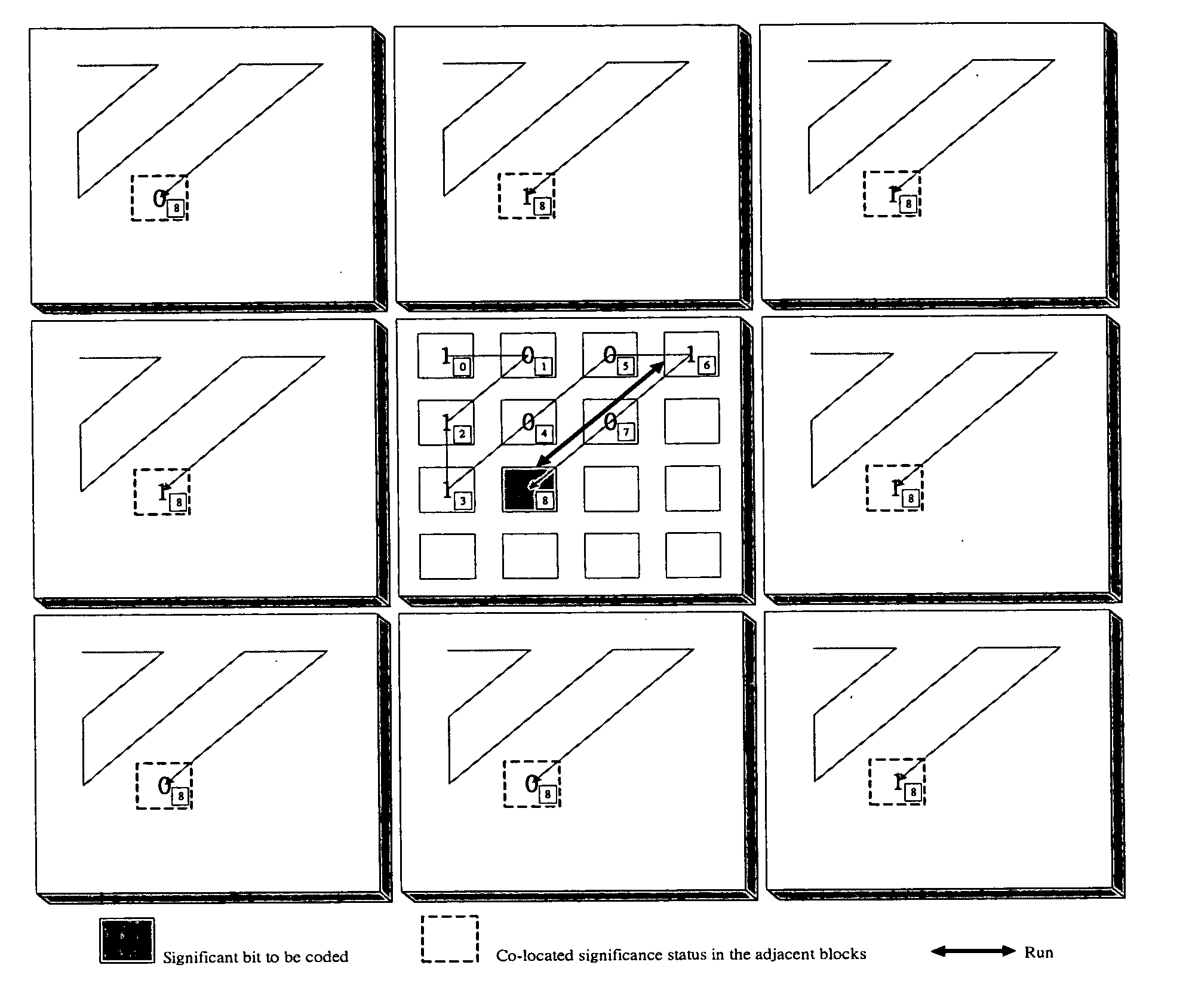
Method for performing context adaptive binary arithmetic coding with stochastic bit reshuffling for fine granularity scalability
InactiveUS20070071090A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove subjective qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSpatial correlationSide information
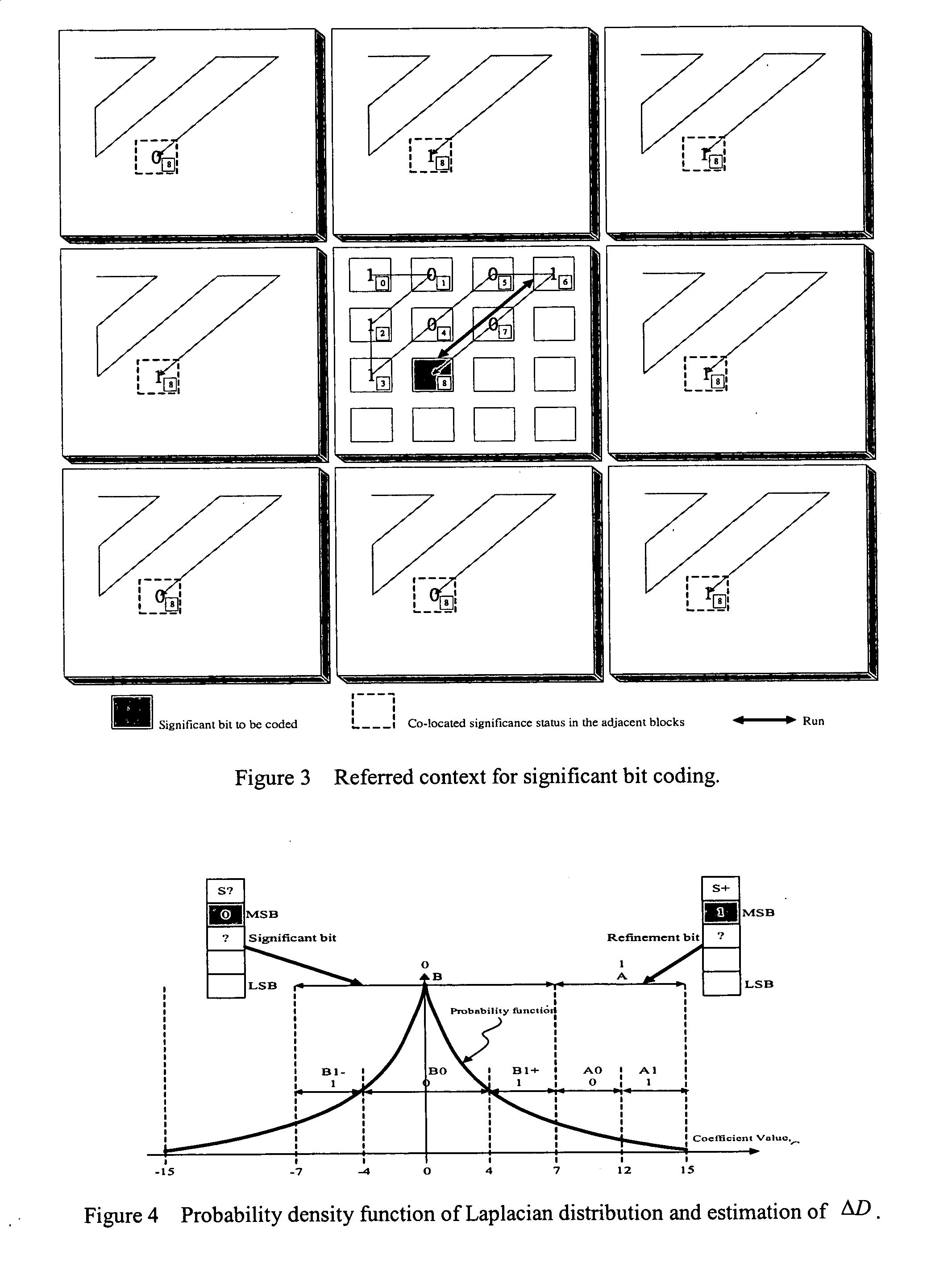
The disclosure relates to a method for performing context based binary arithmetic coding with a stochastic bit-reshuffling scheme in order to improve MPEG-4 fine granularity scalability (FGS) based bit-plane coding. The method comprises steps of: replacing 8×8 DCT with 4×4 integer transform coefficient in MPEG-4 AVC (Advance Video-Coding); partitioning each transform coefficient into significant bit and refinement bit; setting up significant bit context based on energy distribution within a transform block and spatial correlation in adjacent blocks; using an estimated Laplacian distribution to derive coding probability for the refinement bit; and using the context across bit-planes to partition each significant bit-plane for saving side information bit.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Apparatus and method for performing bitplane coding with reordering in a fine granularity scalability coding system
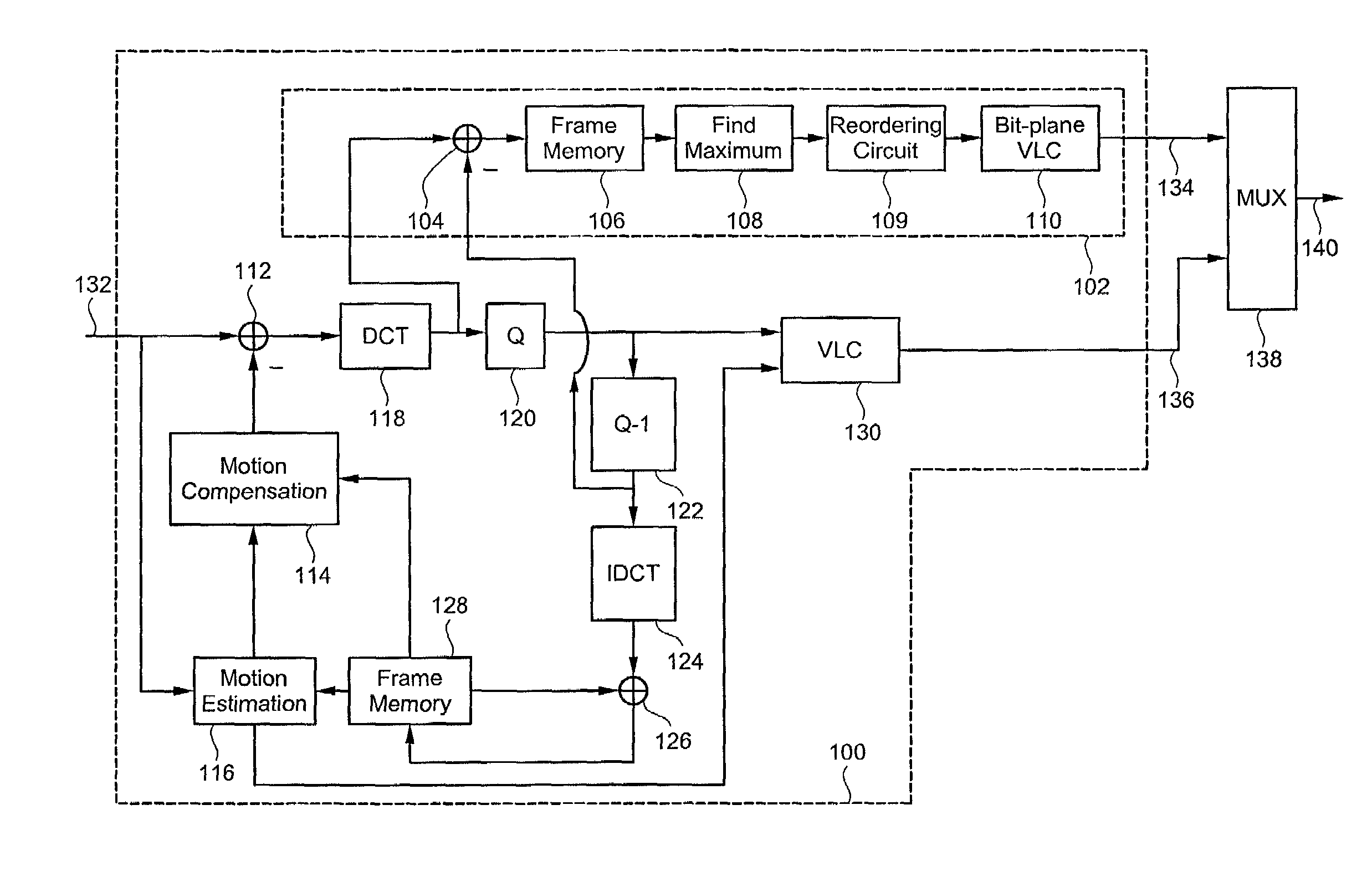
ActiveUS7062096B2Fine degree of spatial quality controlImproved flexibility in qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureGranularity
An apparatus and method for performing bitplane coding with reordering, that may be used in a Fine Granularity Scalability (FGS) system. The apparatus and method reorder coefficients each time after a bitplane is coded. By reordering, the apparatus and method separate the coefficients into two groups. When coding a bitplane, bits in the first group are copied into the bitstream, while the bits in the second group are subject to common run-length, VLC, or arithmetic coding. The apparatus and method may also be used with or in a conventional SNR, temporal and / or spatially scalable architectures, for example, as utilized within an MPEG-4 framework.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Bitplane coding and decoding for AC prediction status information
ActiveUS20050053156A1Reduced flexibilityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionTelecommunicationsBit plane coding
In one aspect, an encoder / decoder selects a bitplane mode from a group of plural available bitplane modes, and processes a bitplane according to the selected bitplane mode, wherein the bitplane indicates AC prediction status information for plural macroblocks of a video picture. In another aspect, an encoder encodes a bitplane that indicates AC prediction status information for plural macroblocks of a video picture and signals the encoded bitplane. In another aspect, a decoder receives an encoded bitplane and decodes the bitplane, wherein the bitplane indicates AC prediction status information for plural macroblocks of a video picture.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
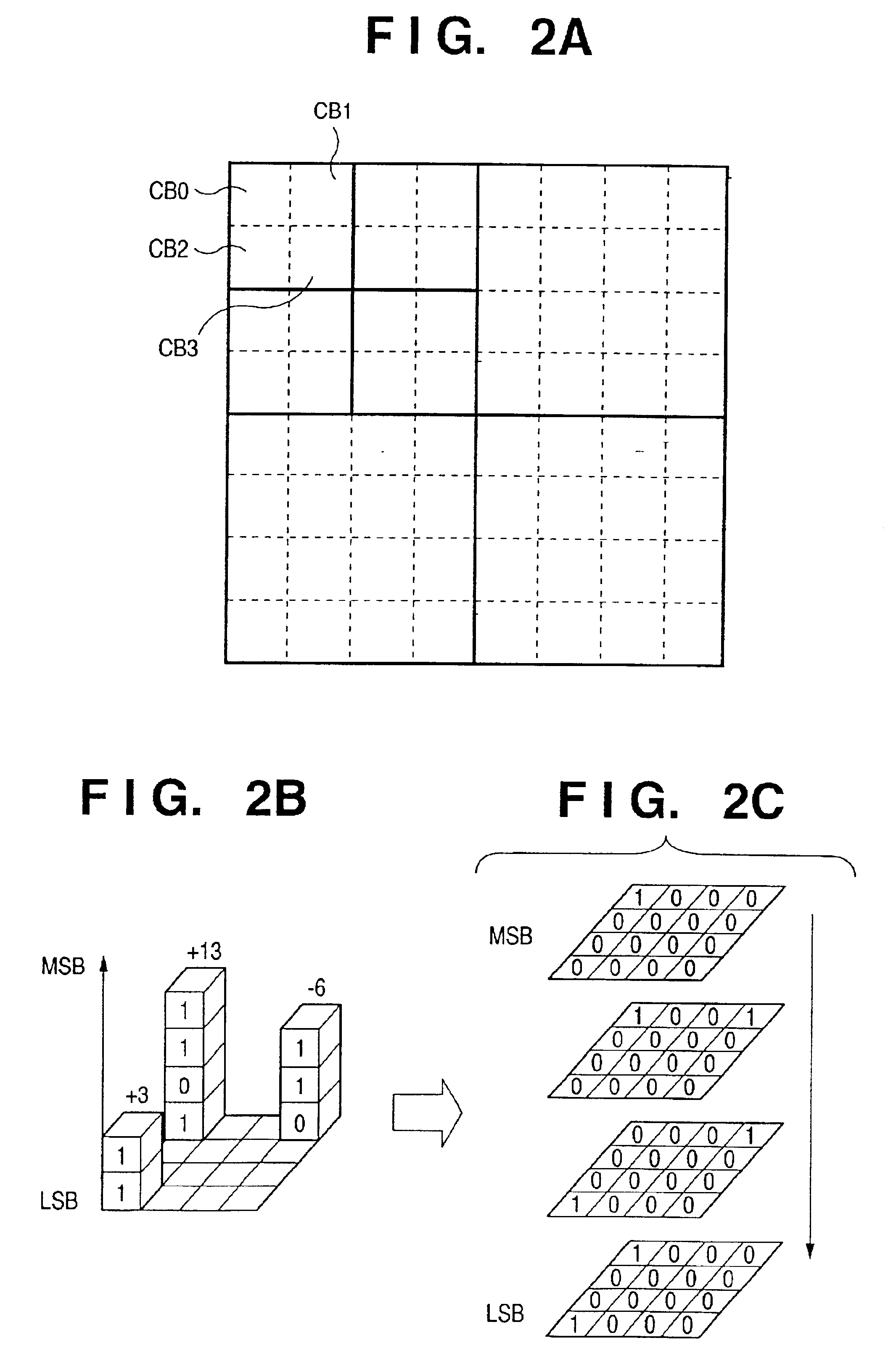
Image compression by economical quaternary reaching method
InactiveUS20070071331A1Reduce in quantityReduce stepsCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationCoding blockNonzero coefficients
In wavelet-based image compression schemes, a very sparse representation of the image signal may be obtained after quantization to transform coefficients. In addition, the nonzero coefficients 2-dimensionally cluster around the edge or texture areas. In existing systems, for example JPEG2000, in the bit-plane coding process, coefficients are repeatedly scanned and encoded in a 1-dimensional pattern within code-blocks. A large number of zeros have to be encoded to record the distribution of significant coefficients. It inevitably causes a big loss of compression performance. Quaternary reaching method emphasizes reaching and encoding the significant coefficients in 2-dimensional pattern. It fully adapts to the 2-dimensional character of the significance distribution of quantized coefficients. Besides, it admits very economical implementation. The recording of redundant information is drastically reduced. As result, it magnificently enhances both compression performance and computation performance against existing systems.
Owner:LIU XITENG
Macroblock information signaling for interlaced frames
ActiveUS20050053145A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionVariable-length codeInterlaced video
A decoder decodes skipped macroblocks of an interlaced frame. Skipped macroblocks use exactly one motion vector and have no motion vector differential information, and lack residual information. The skipped macroblock signal indicates one-motion-vector coding. The skipped macroblock signal can be a compressed bitplane (in a selected bitplane coding mode) sent at frame layer in a bitstream, or an individual bit sent at macroblock layer. In another aspect, an encoder jointly encodes motion compensation type and field / frame coding type for a macroblock in an interlaced P-frame. The encoder also can jointly encode other information for the macroblock (e.g., the presence of a differential motion vector). A decoder decodes a joint code (e.g., a variable length code in a variable length code table) to obtain both motion compensation type and field / frame coding type (and potentially other information) for the macroblock.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
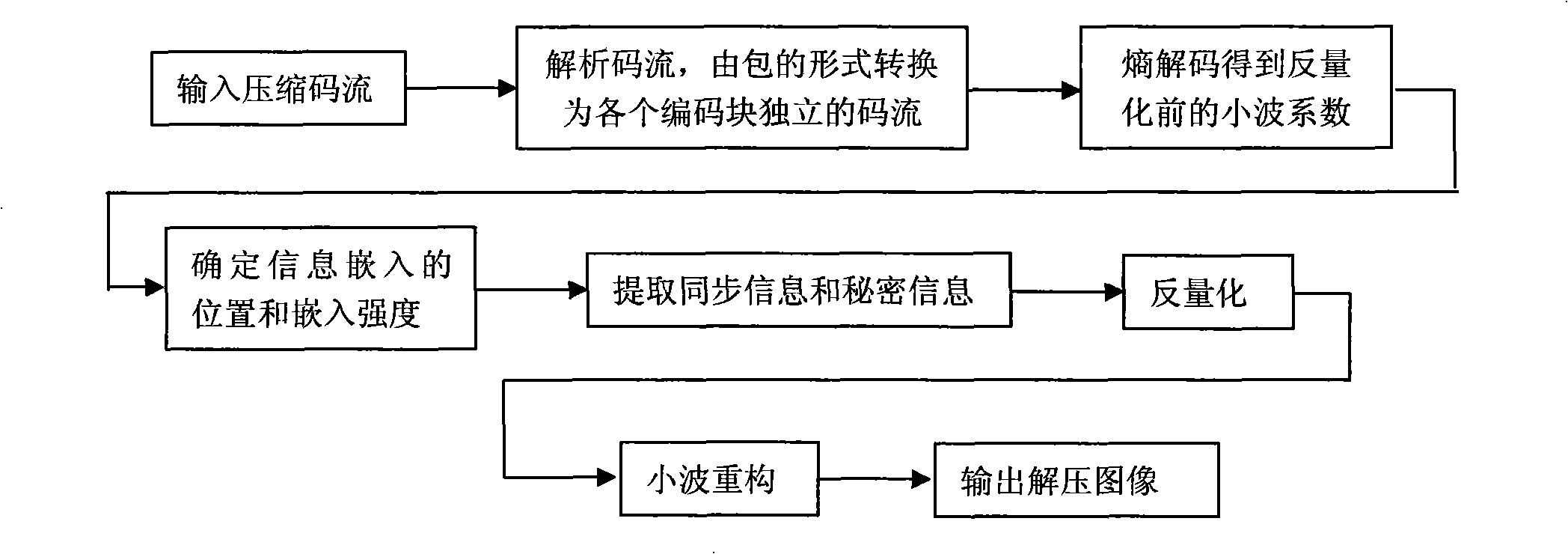
Considerable information hide method using JPEG2000 compression image as carrier
InactiveCN101304522AIncrease hidden capacityNormal decodingPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage codingCoding blockRate distortion
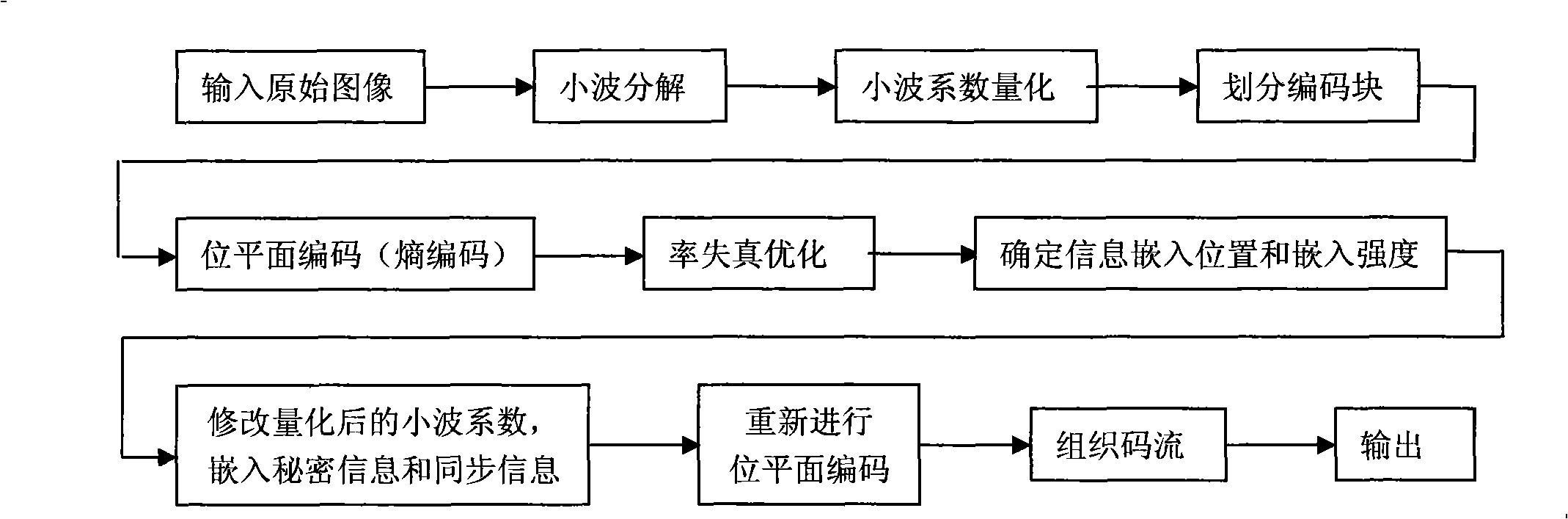
The invention relates to a high capacity information hiding method using JPEG2000 compressing images as the carrier. The operation steps are: applying wavelet decomposition, wavelet coefficients quantification and bit-plane coding to images, and determining the truncation position of the code flow of all coding blocks and the lowest bit-plane of the embeddable information by rate-distortion optimization; primarily choosing a wavelet coefficient which is more than the threshold value as the embedding point, and making a redundancy estimation and adjusting the embedding point and the embedding strength; embedding the synchronous information and the hidden information into the quantified wavelet coefficient in an order of the bit plane from the lowest to the highest starting from the lowest embeddable bit-plane; making a second bit-plane coding and organizing the code flow after embedding the information. The high capacity information hiding method is based on a second coding strategy to determine the embedding position and improves the information hiding volume by self-adaptively choosing the embedding point and adjusting the embedding strength, The high capacity information hiding method has the advantages of being transparent completely for the standard JPEG2000 decoders and being able to be conveniently integrated in the JPEG2000 coders. Meanwhile, the code flow still can decode normally after being embedded with hiding information.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
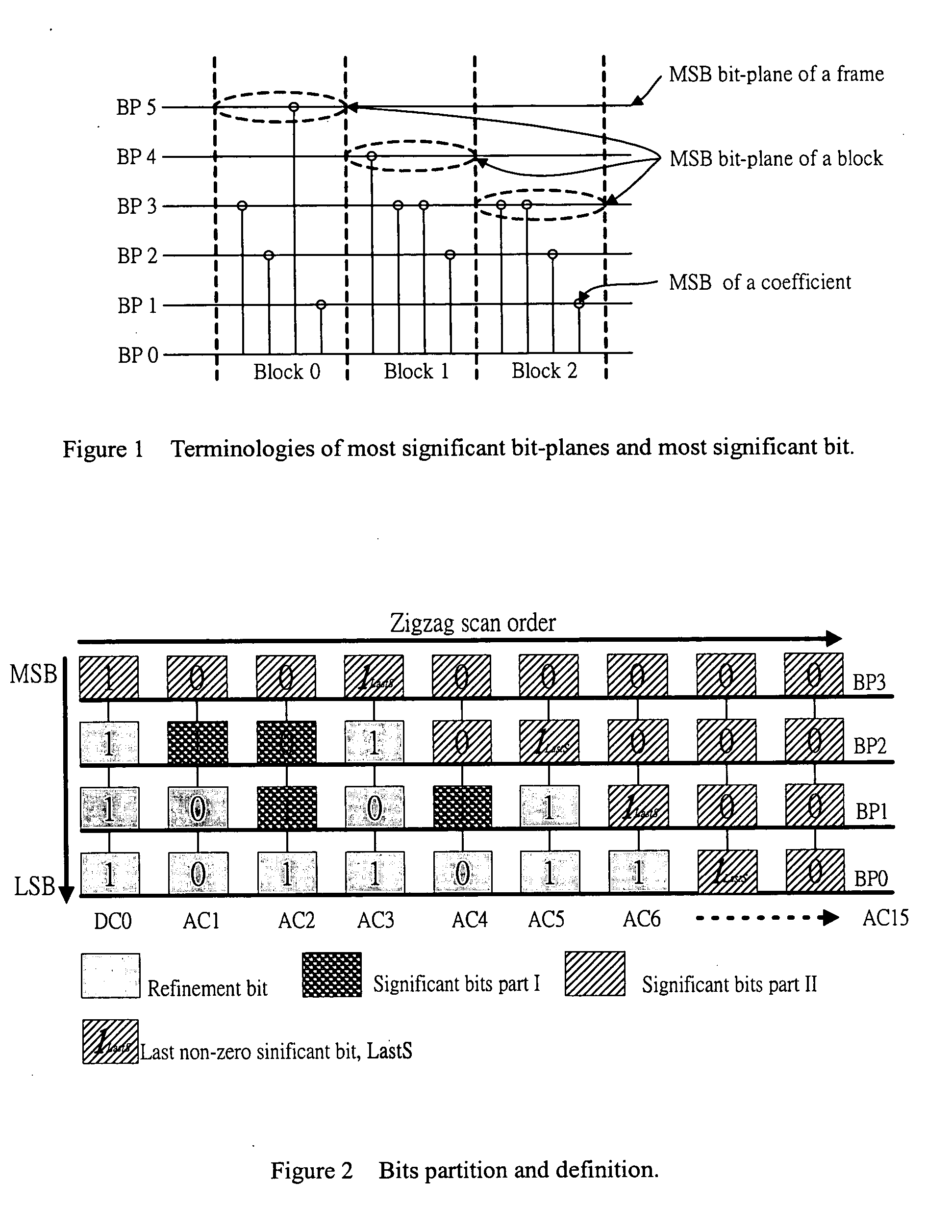
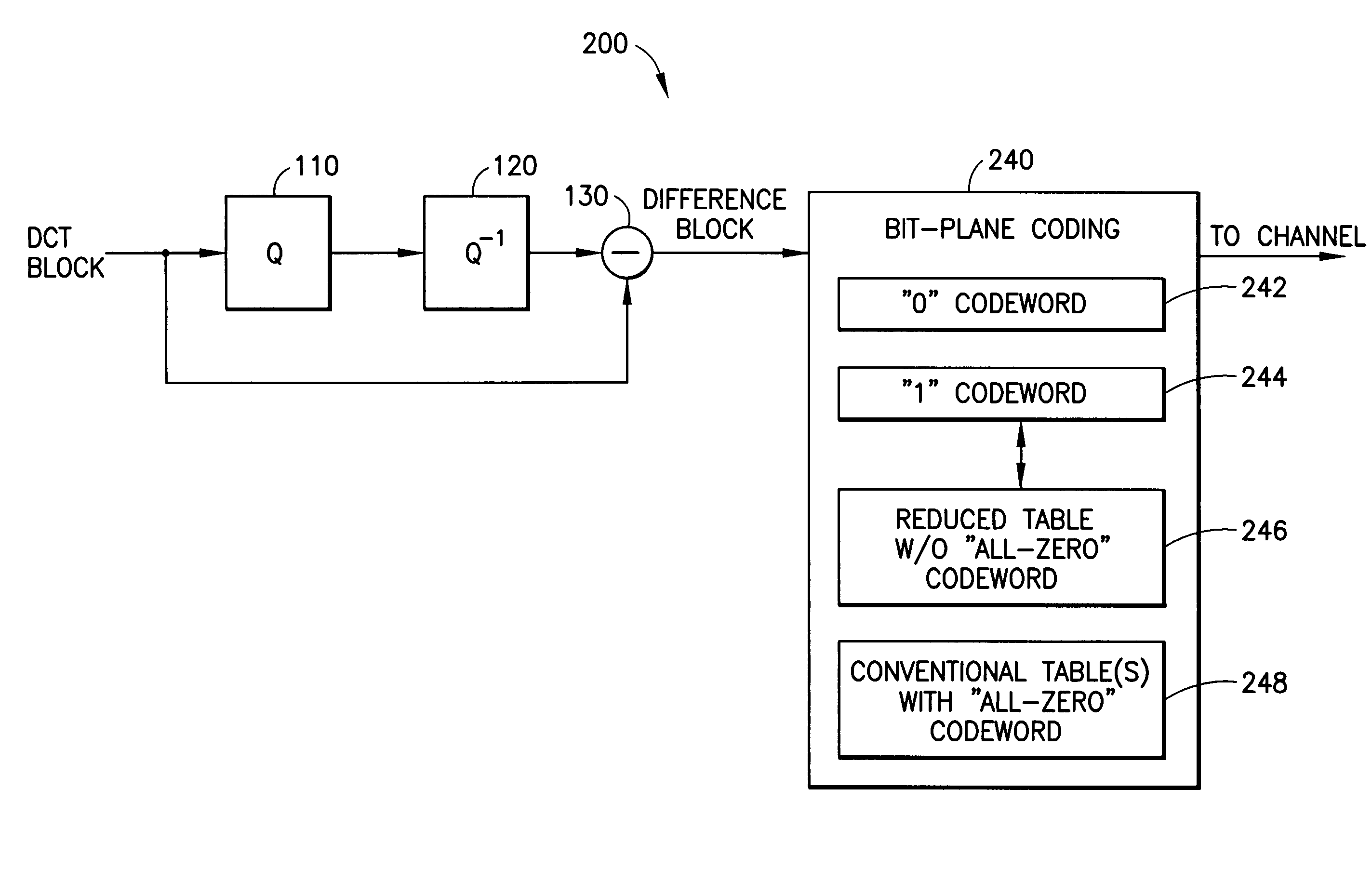
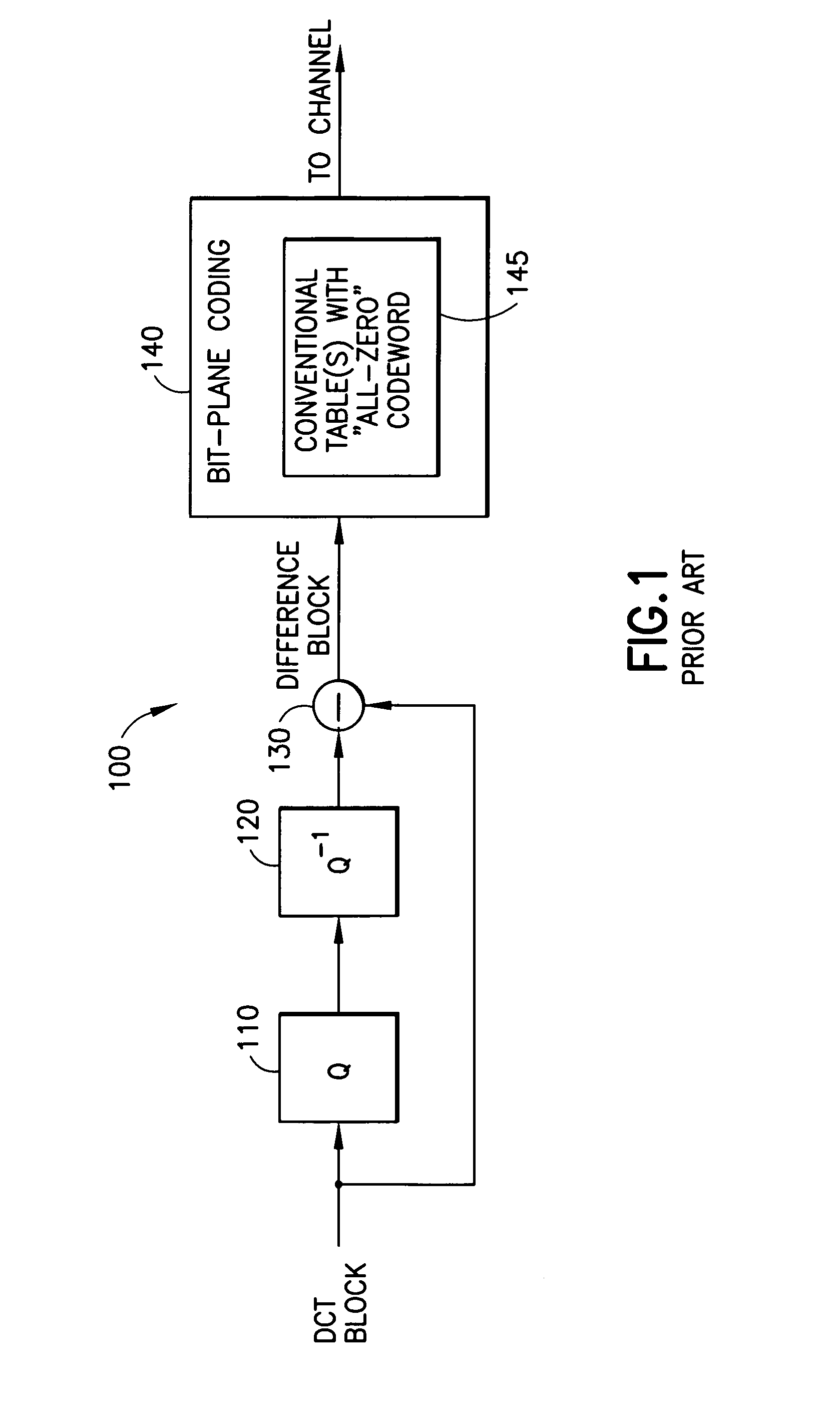
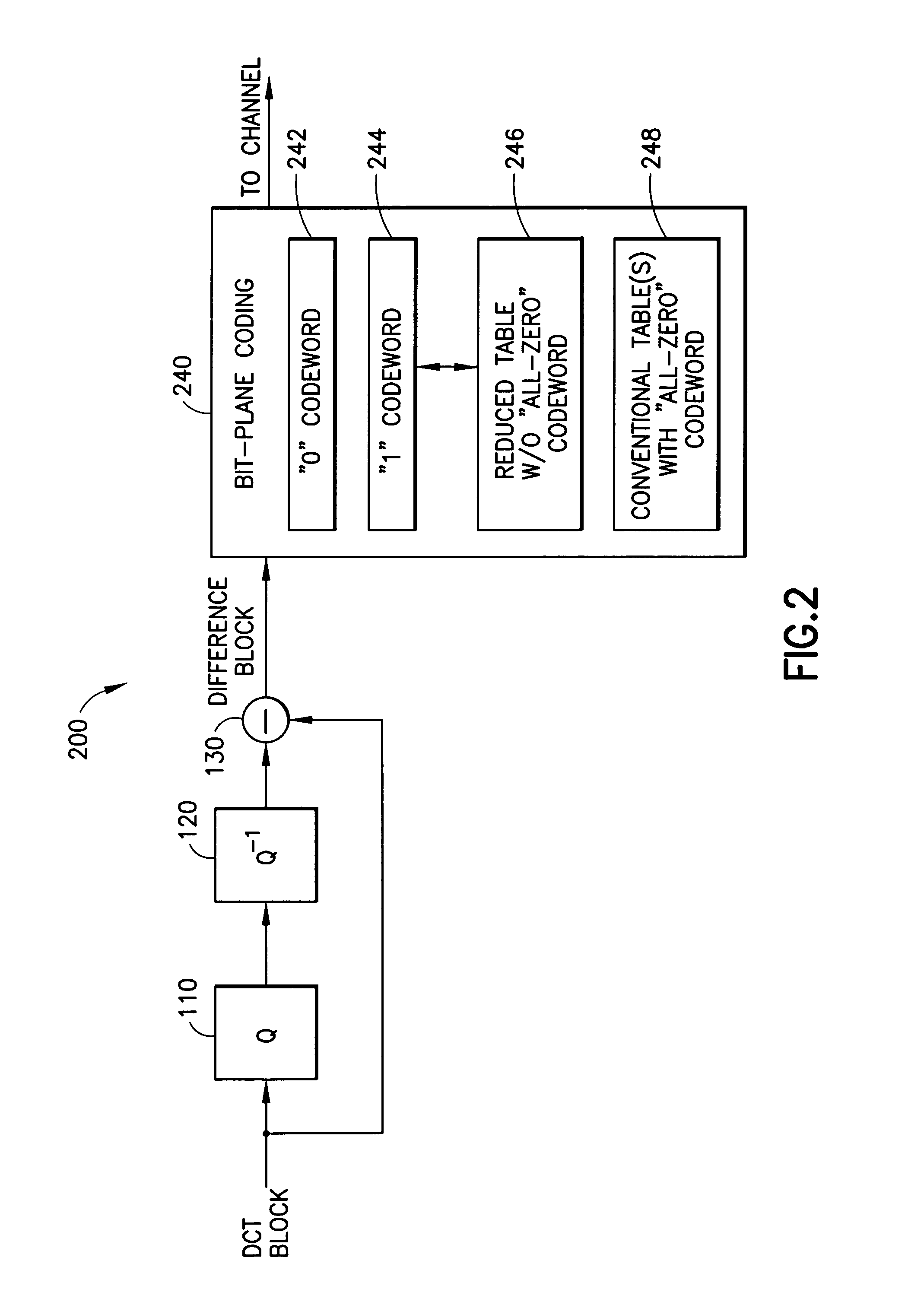
Fine granularity scalability using bit plane coding of transform coefficients
InactiveUS6980597B1Reduce in quantitySmall sizeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureGranularity
A system for efficient bit plane coding of transform coefficient data, such as DCT data used in a video coding system. Decimal values for the transform coefficients are converted to binary values, where each bit occupies a corresponding bit plane, from the most significant bit to the least significant bit. One bit from each coefficient is provided in a common bit plane. A one-bit flag or codeword is used for coding one or more initial all-zero bit planes, while another one-bit flag is used for designating the first subsequent non-all-zero plane. For the first non-all-zero plane, a reduced coding table is used to provide codewords that follow the one-bit flag.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Video coding
InactiveUS20010041011A1Reduce in quantityEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsVideo sequenceBit plane coding
Digitalized video images are compressed in several steps in order to provide a system for transmitting moving video pictures via narrow band channels, such as the telephone network. The system is based on any extension of the bit-plane coding technique to video sequences and lossy conditions. The compression technique can also be advantageously used in a lossless compression system. The system involves the steps of bit plane representation and skipping the least significant bit plane(s), shifting the pixels, coding with a Gray code, the use of segmentation, and motion-estimation / motion compensation and application of a transmit / not transmit / motion compensate (TX / NT / MC) procedure, exploiting of the temporal redundancy of two corresponding bit planes via an XOR operation on two successive images, and a plane-by-plane application of an extended RLEID technique. The RLEID technique includes coding a run of like binary symbols with one word, the run including a transition between the penultimate and ultimate binary symbol.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
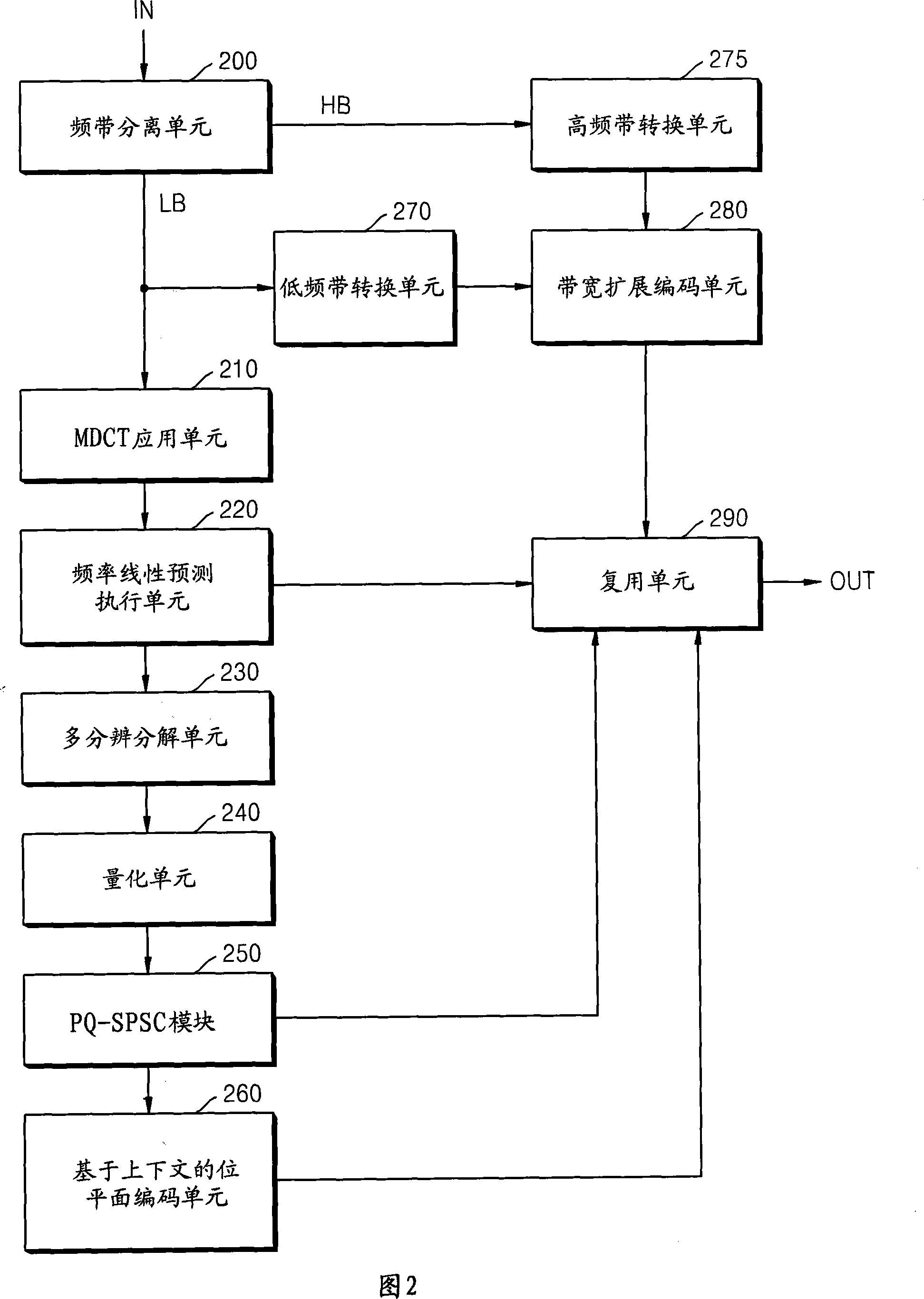
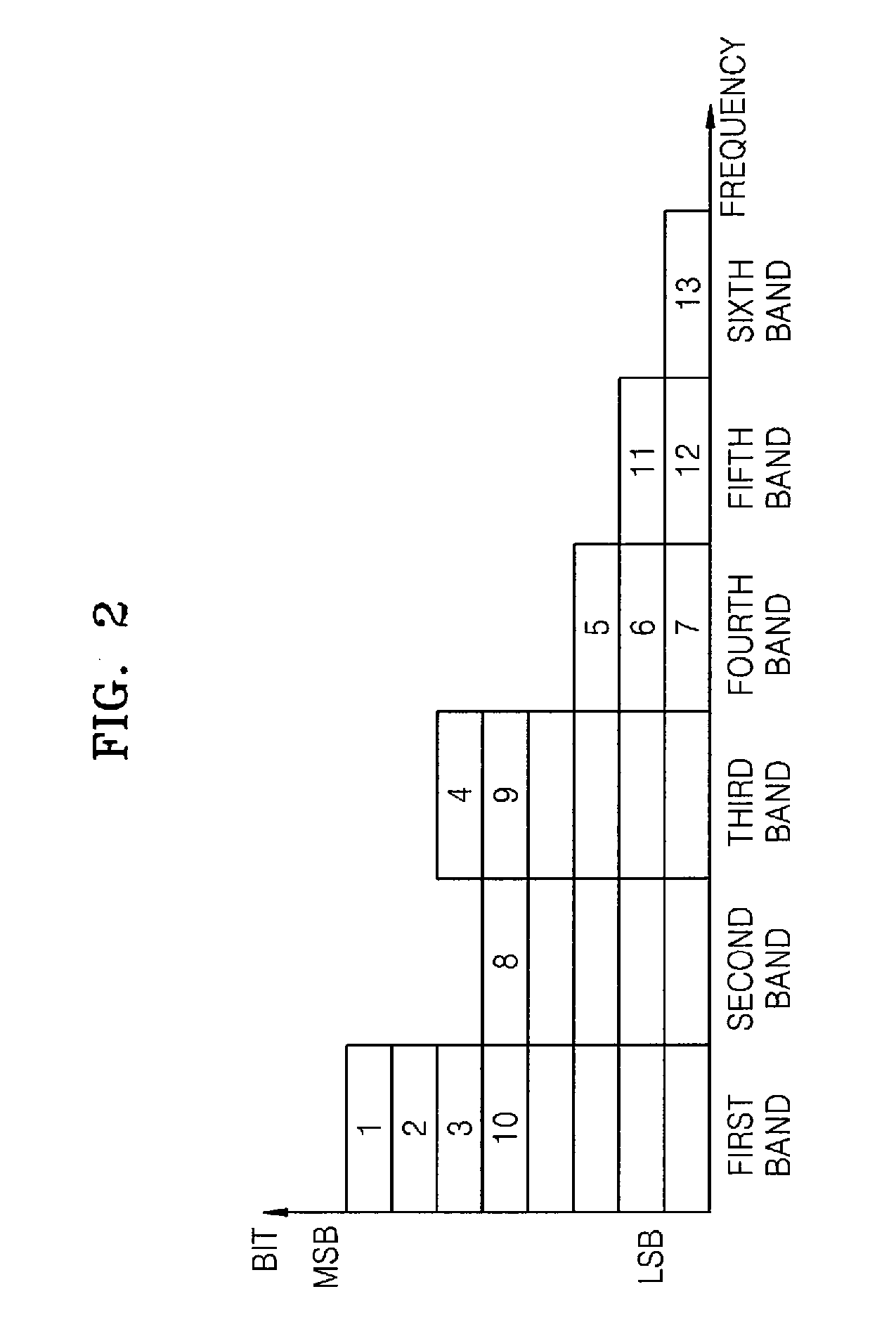
Method and apparatus to encode and decode audio signal by using bandwidth extension technique
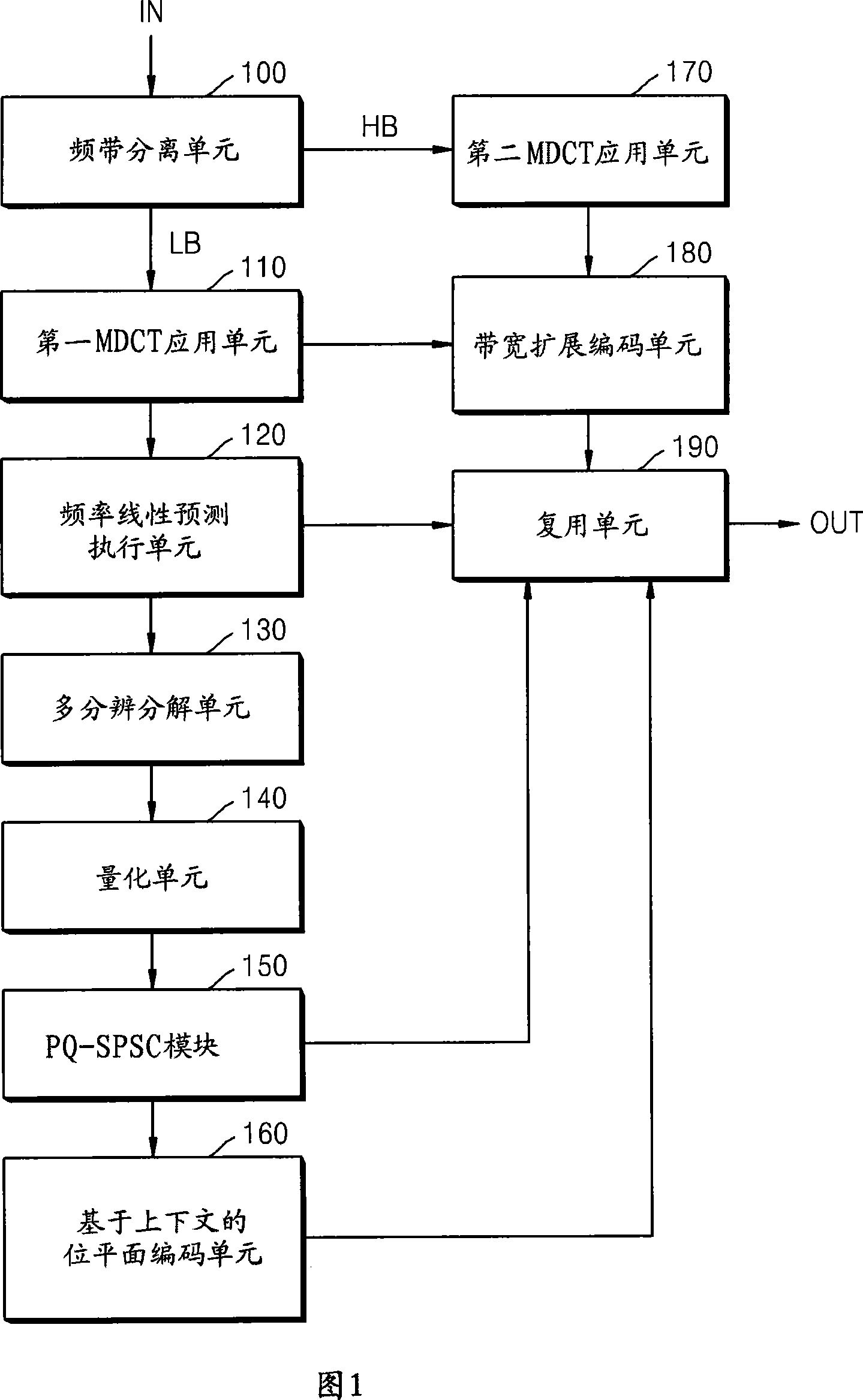
A method and an apparatus for encoding / decoding an audio signal by using bandwidth expansion technique are provided to output an encoded bitplane and encoded bandwidth expansion information as an encoded result of an input signal, thereby efficiently encoding high frequency components at a limited bit rate and accordingly improving sound quality. An audio signal encoding method comprises the following steps of: splitting an input signal into a high band signal and a low band signal(1300); converting each of the high and low band signals from a time domain to a frequency domain(1310); performing quantization and context-dependent bitplane encoding of the converted low band signal(1320); generating and encoding bandwidth expansion information showing a characteristic of the converted high band signal by using the converted low band signal(1330); and outputting the encoded bitplane and the encoded bandwidth expansion information as an encoded result of the input signal(1340).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
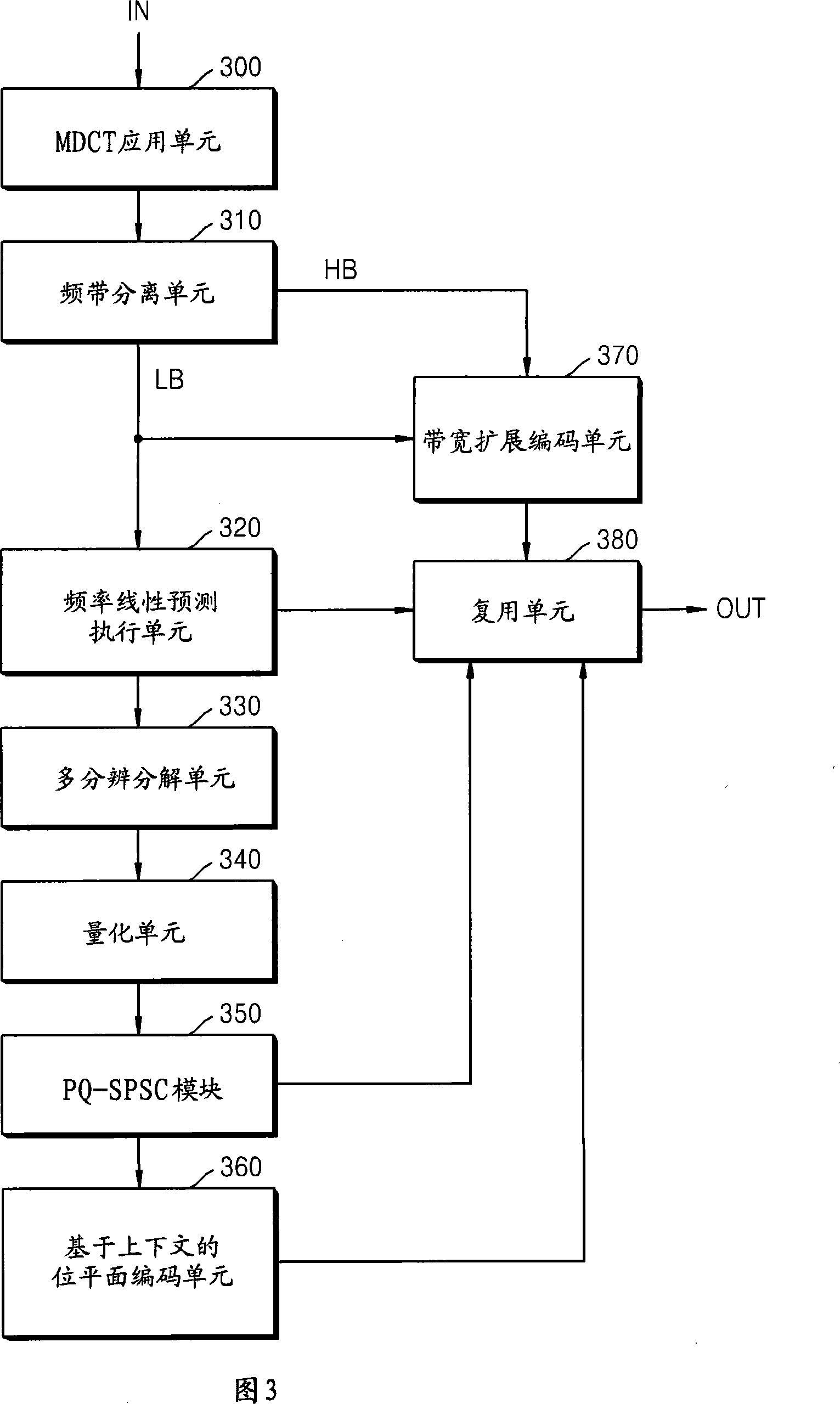
Method and apparatus to encode/decode audio signal
A method and apparatus to encode / decode an audio signal, in which a bit rate for each bit plane can be controlled. A method of encoding an audio signal for each of a plurality of bit plane can include dividing the audio signal into a plurality of frequency bands and encoding the bit planes of the frequency bands from a low frequency band to a high frequency band, wherein, in the encoding the bit planes of the frequency bands, the bit planes are encoded from the most significant bit (MSB) to the least significant bit (LSB) within bits allocated for the frequency bands, and when there are allocated bits remaining after the encoding of the currently encoded frequency band, un-encoded bit planes corresponding to the MSB in a frequency band that has the fewest encoded bit planes among frequency bands with a lower frequency than the currently encoded frequency band are encoded using the remaining allocated bits. Accordingly, when encoding / decoding an audio signal, an encoding sequence of bit planes is determined so that an audio signal that significantly affects audio quality during decoding is first encoded, thereby reducing audio quality deterioration at a low bit rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Scalable audio communications utilizing rate-distortion based end-to-end bit allocation
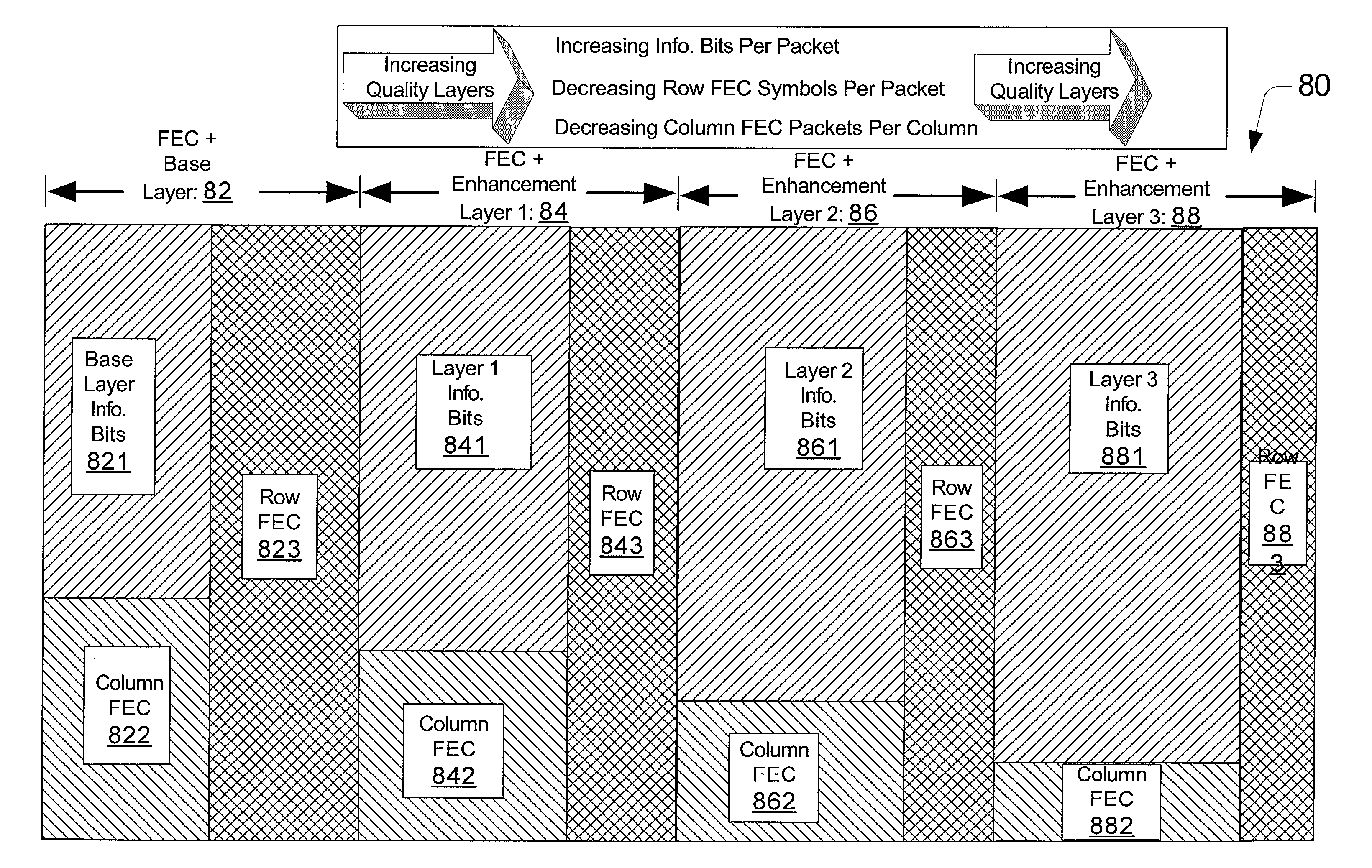
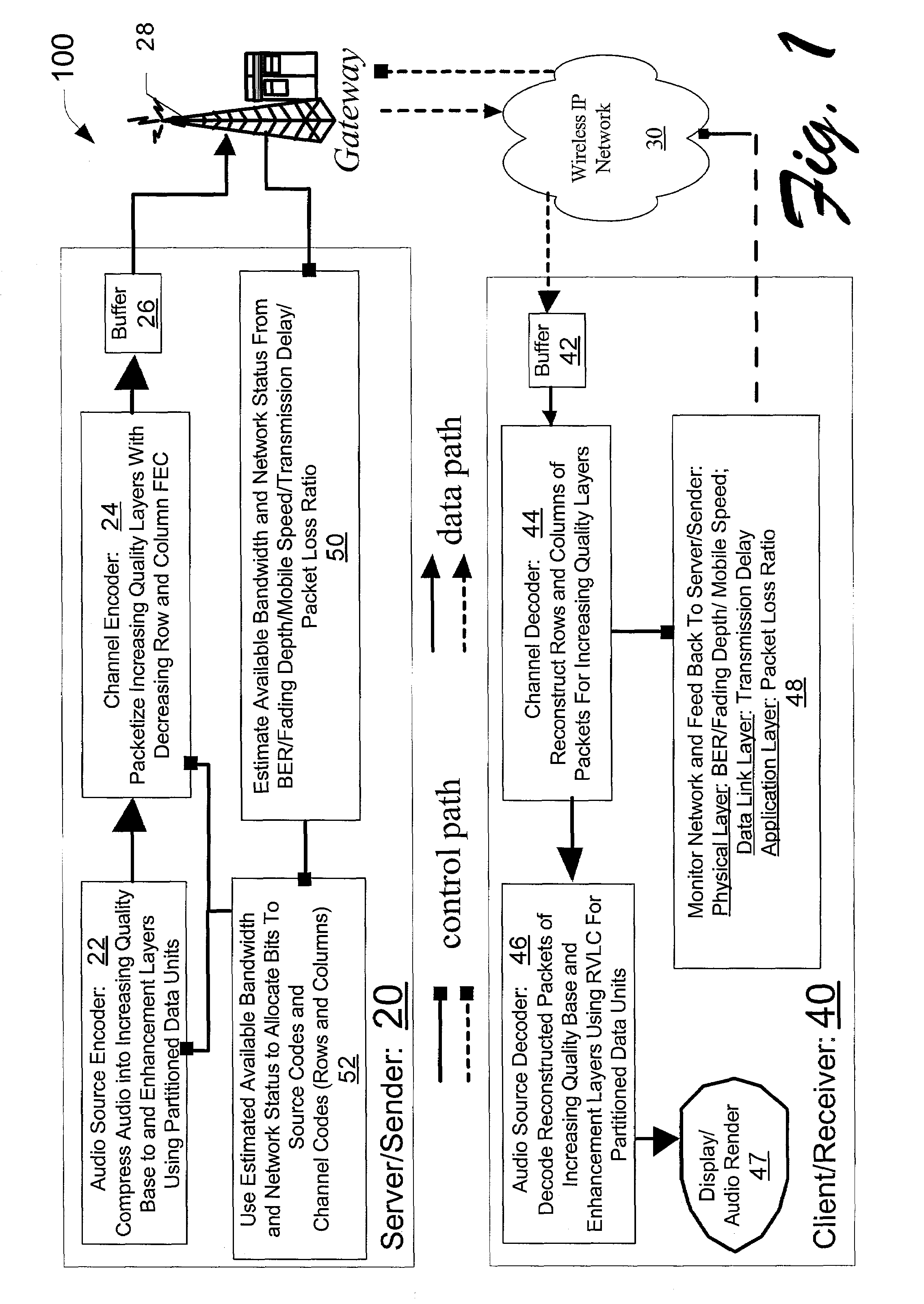
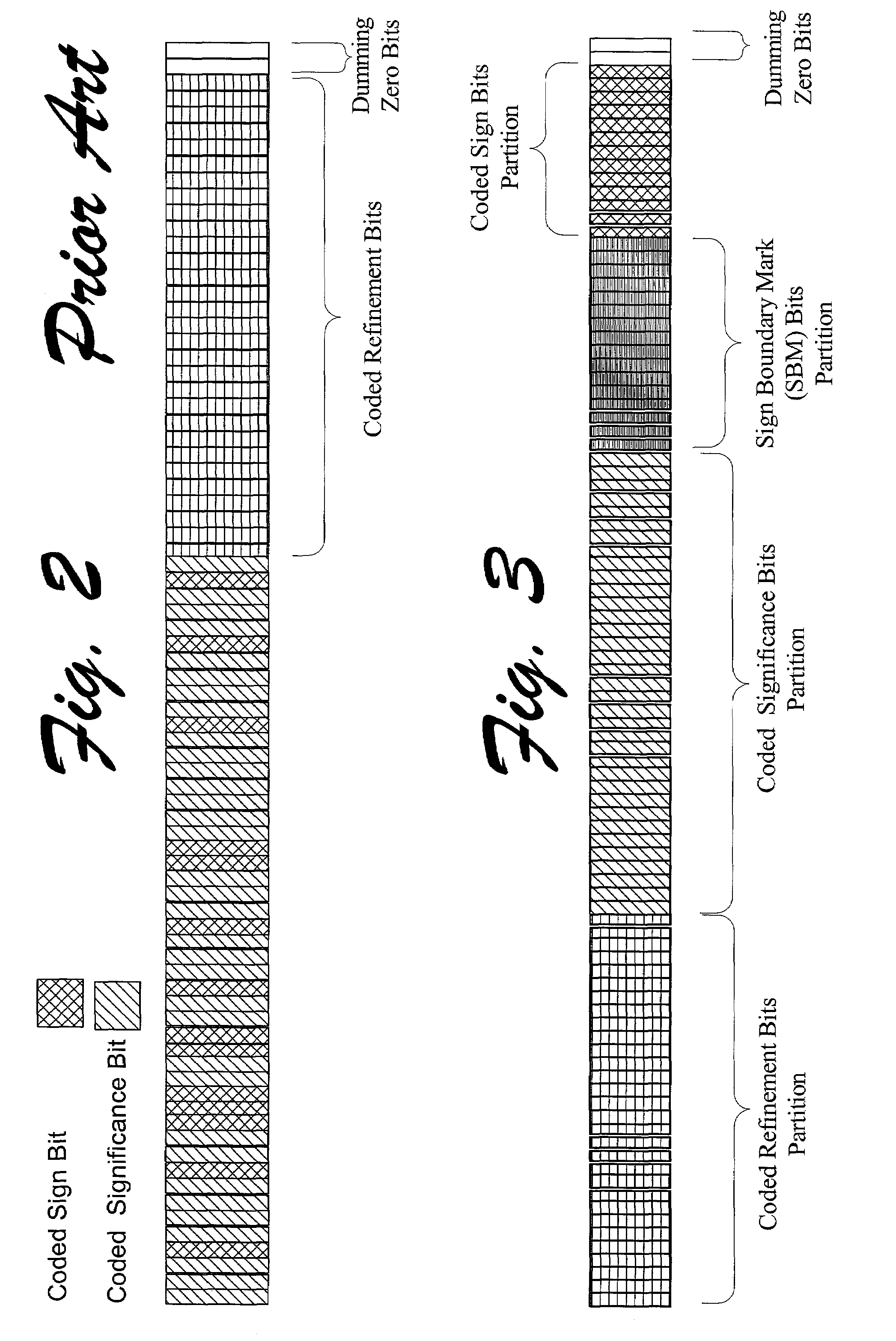
InactiveUS7283966B2Minimize expected end-to-end distortionImprove scalabilitySpeech analysisSign bitBit allocation
A source encoder encodes audio signals into increasing quality layers defined in bit planes. Each bit plane has a data unit that includes a beginning partition having one or more contiguous refinement bits, a second partition having one or more contiguous coded significance bits, a third partition having one or more contiguous sign boundary mark bits, and a fourth partition having one or more contiguous coded sign bits. A channel encoder encodes the bit planes into respective columns containing multiple rows. Unequal error protection coding is provided according to the quality of each layer such that each row has row and column channel protection codes for the respective row and column that correspond to the respective quality layer. For the corresponding row and column, each row contains the row channel protection codes and either the compressed audio data from the respective layer or the column channel protection codes. A server machine can use a network feedback transmission to allocate bits to the source encoder and the channel encoder.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
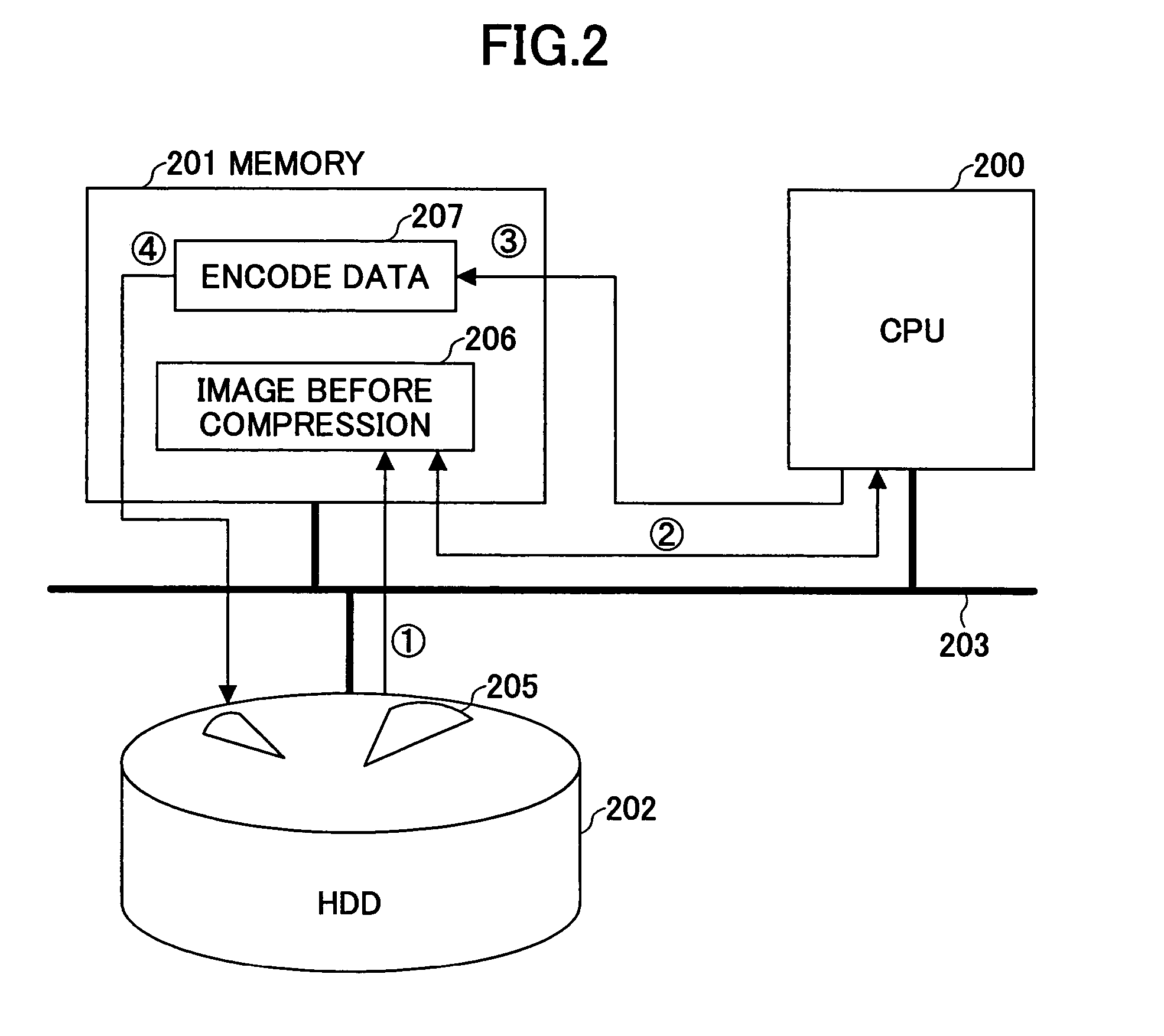
Method and system for improving coding efficiency in image codecs
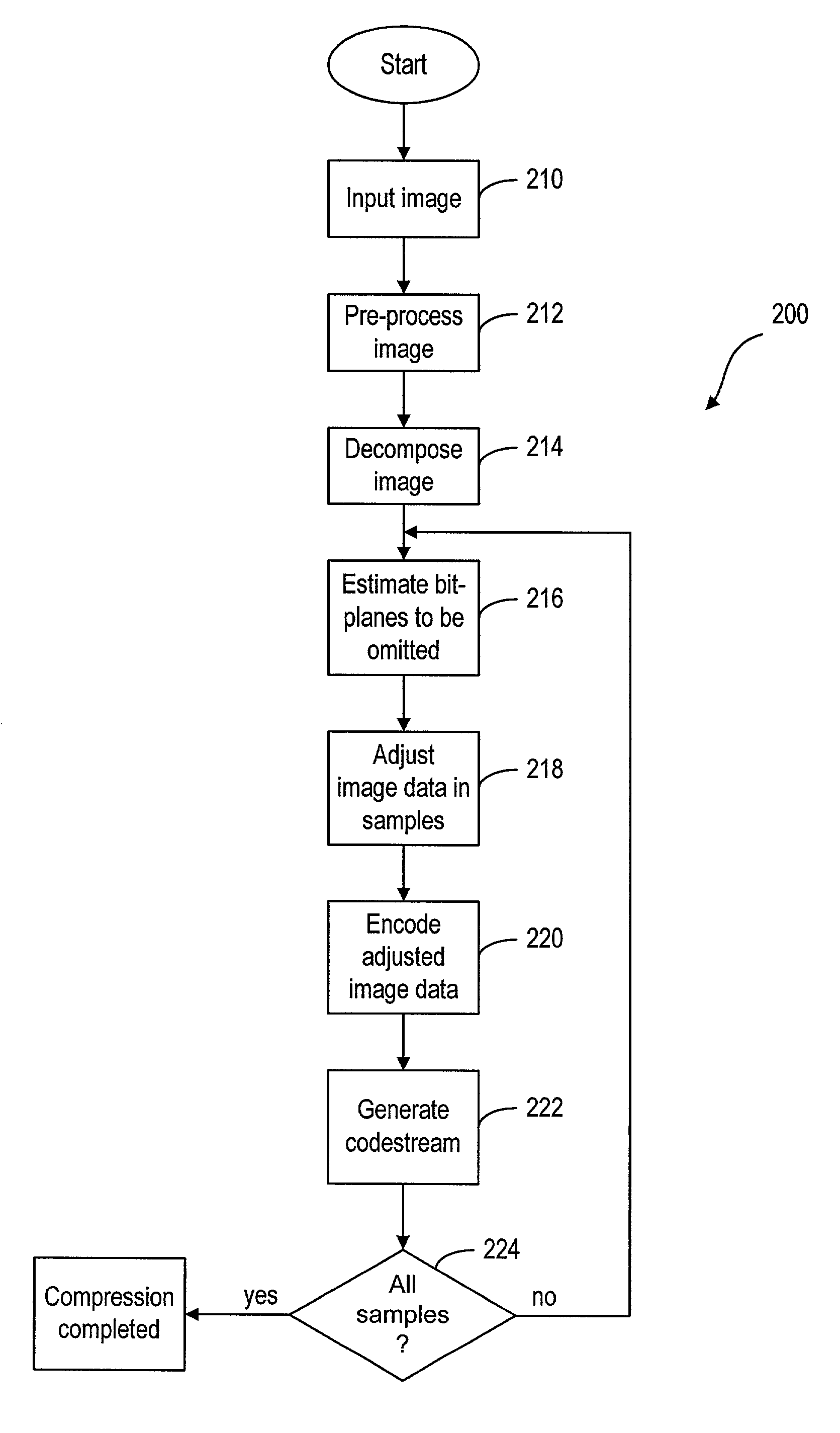
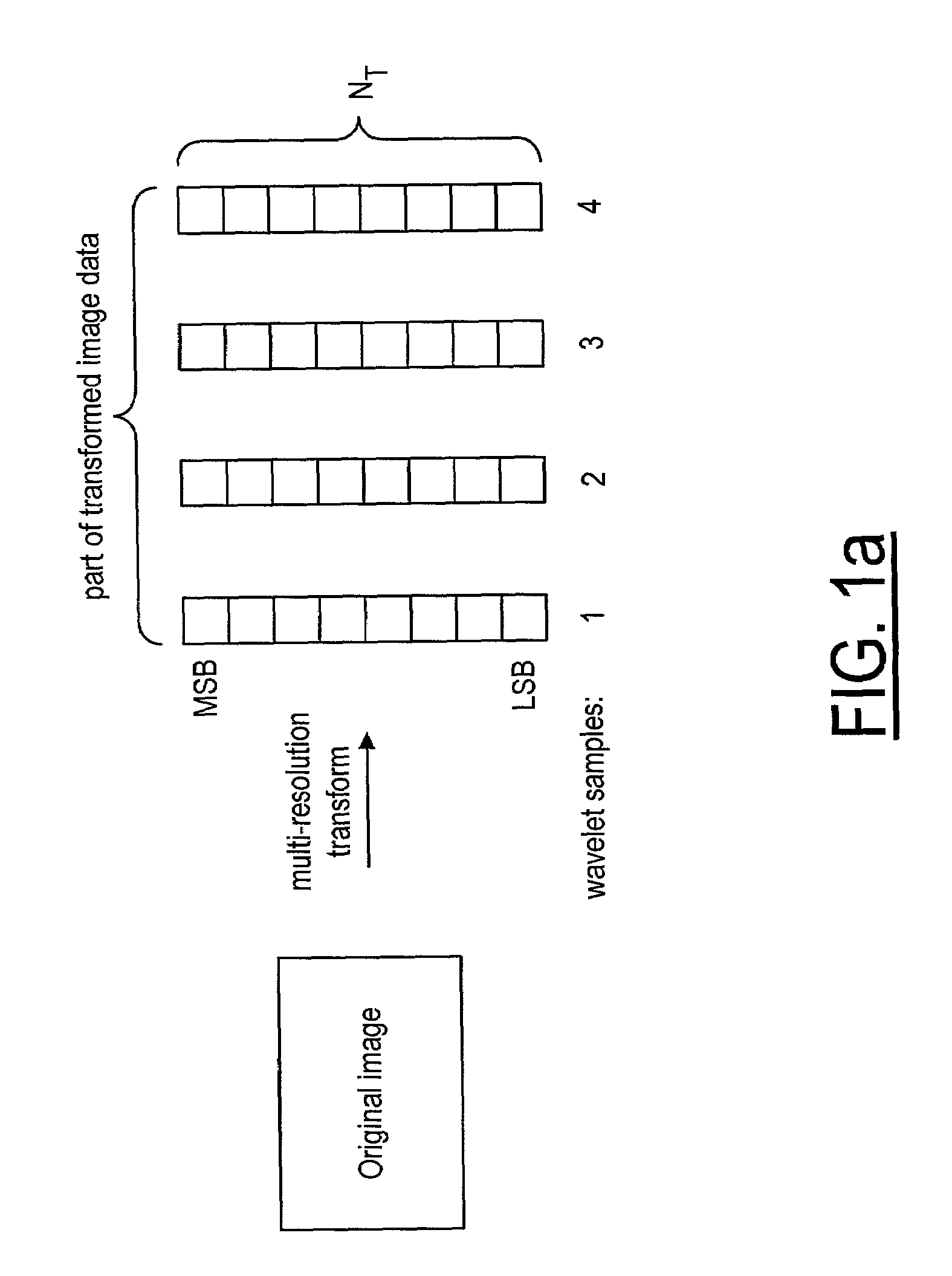
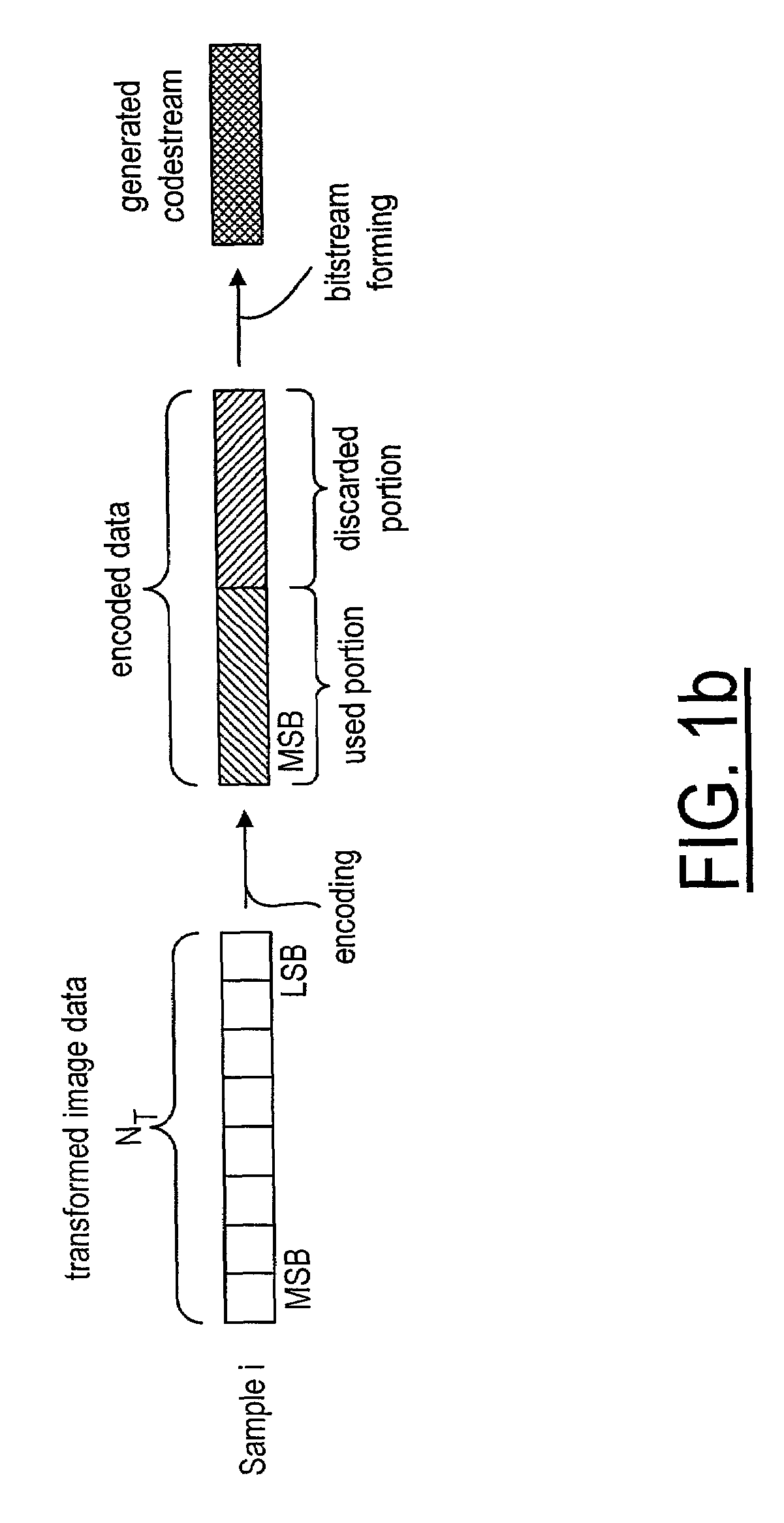
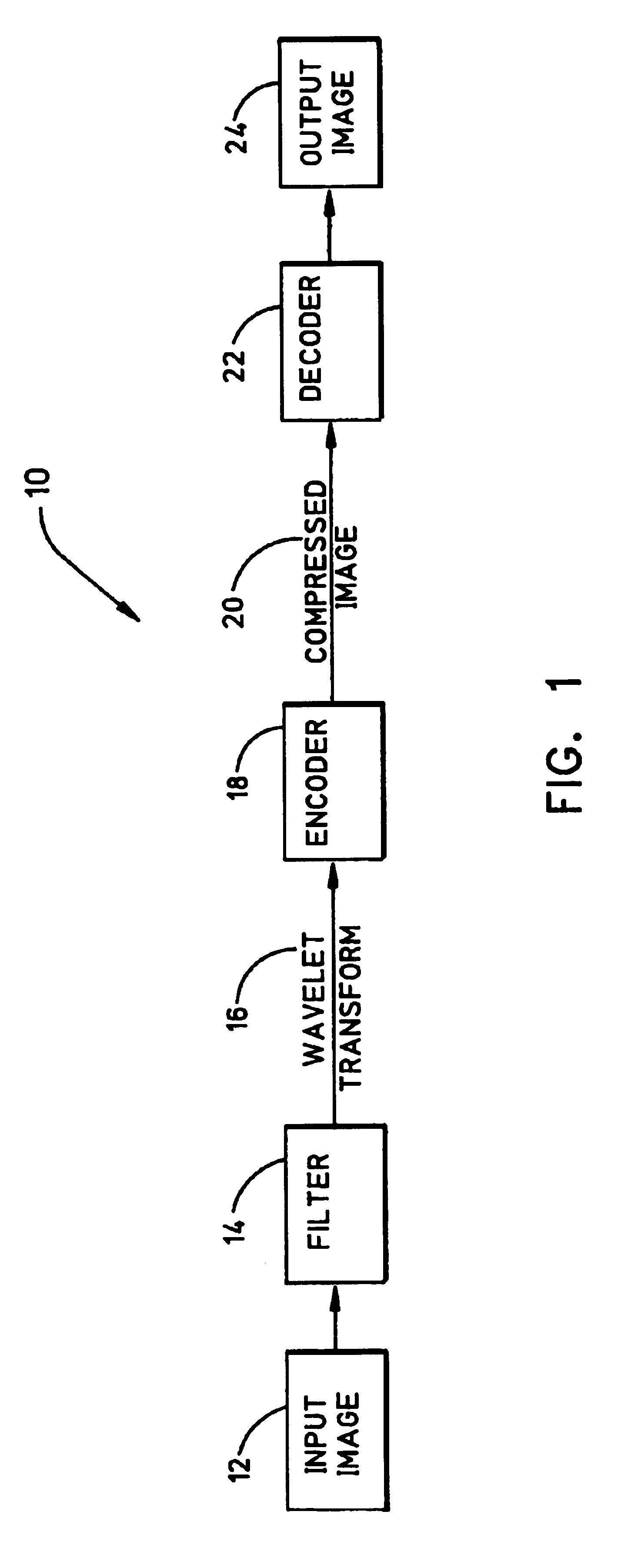
A method and system for encoding an image for providing encoded data for transmission or storage. After the image is decomposed by a transform into sub-bands containing blocks or samples of transformed image data organized in a number of bit-planes, it is adjusted to reduce the number of bit-planes prior to being encoded by a bit-plane coder into encoded data. The reduction of the bit-planes is based on the compression factor of the encoding process, the transmission target bit-rate, the type of sub-band and the resolution level of the transformed image data.
Owner:SISVEL INT
Apparatus for and method for SNR scalable quad-tree bit-plane coding
InactiveUS6915015B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Array data structure
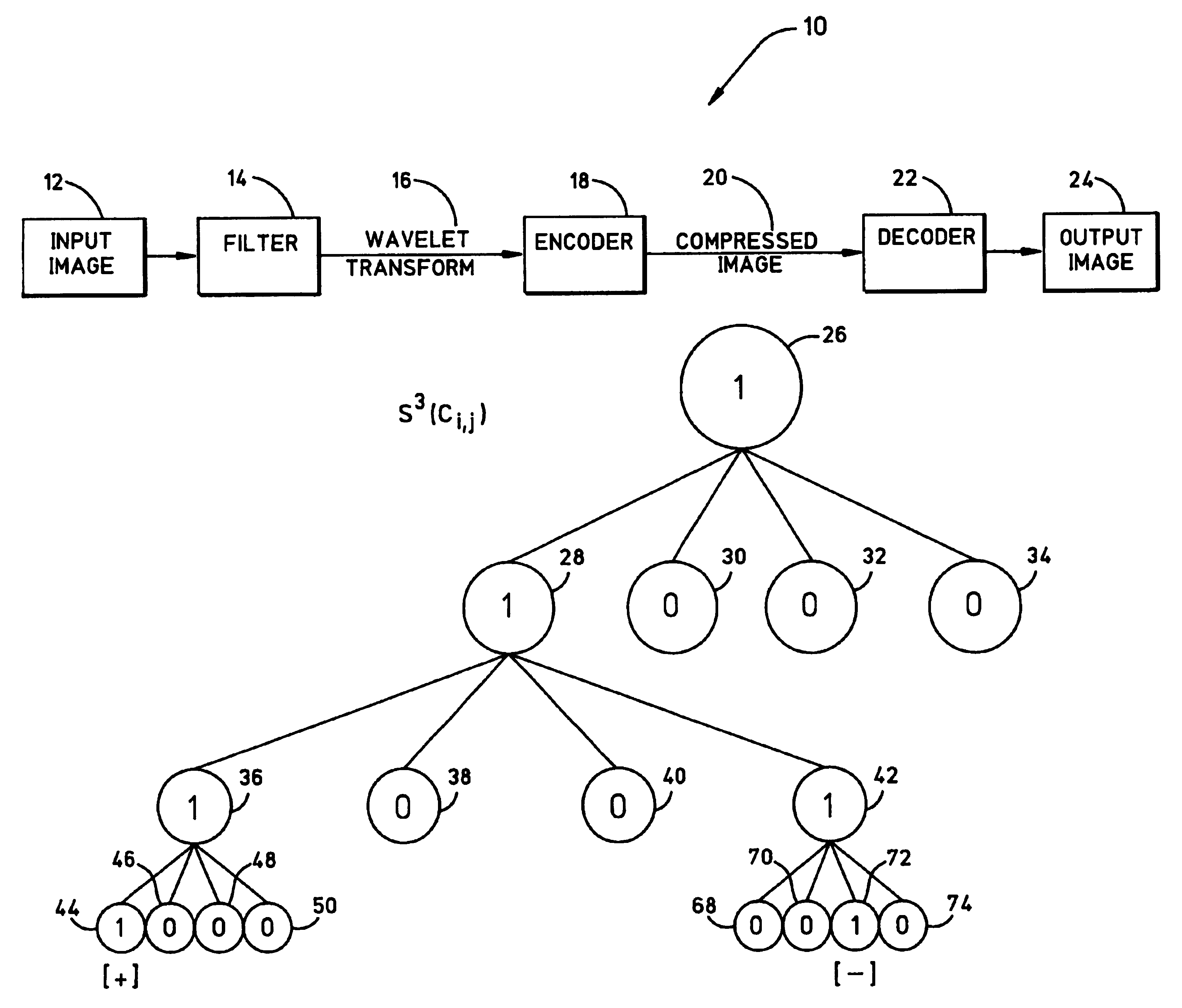
An apparatus for and a method of coding the bit-planes of an array of numbers. The values in the array of numbers are converted to binary. The binary values are truncated to a predetermined level of accuracy. The number of bit-planes is determined based on the largest absolute value. A tree structured description of the array is generated based on a modified quad-tree coding technique. An SNR (signal to noise ratio) scalable encoding of the significance information for each bit-plane is generated by describing new branches and leaves of the tree corresponding to each bit-plane in a bottom-up-depth-first manner. An encoding of refinement information for each bit-plane is generated. A SNR scalable description of the array is generated by concatenating the encoding of the significance information and the refinement information generated for each bit-plane.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
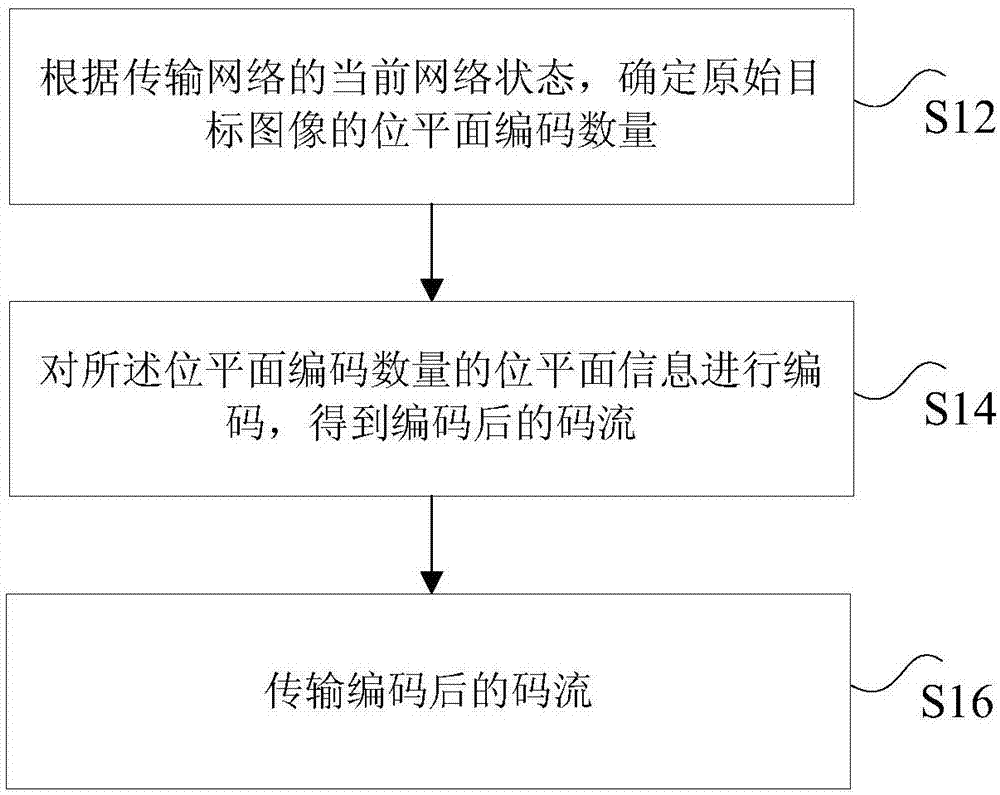
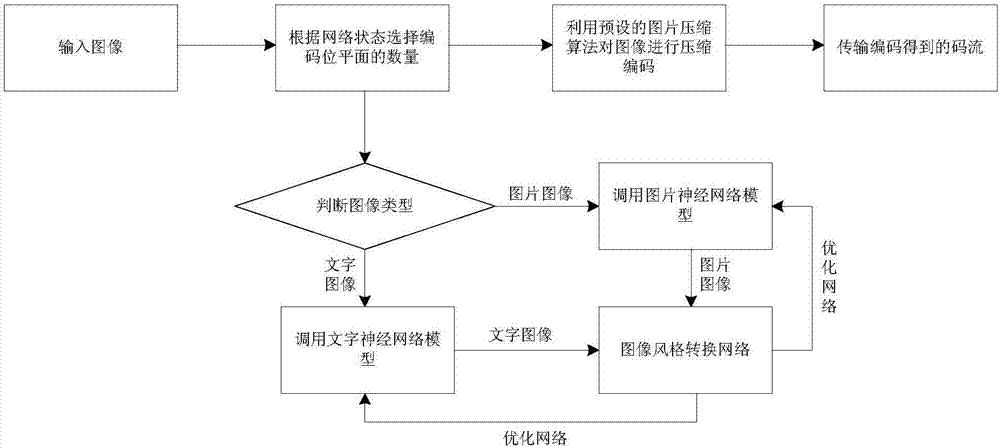
Image transmission method, device and system
ActiveCN107172428ATroubleshoot technical issues with high bandwidth requirementsRealize the effect of real-time transmissionDigital video signal modificationNeural learning methodsComputer hardwareBit plane coding
The invention discloses an image transmission method, an image transmission device and an image transmission system. The method comprises the steps of determining a bit plane code quantity of an original target image according to the current network state of a transmission network, wherein the original target image is an image to be transmitted; coding bit plane information of the bit plane code quantity, thus acquiring a coded code stream; and transmitting the coded code stream. According to the method, the device and the system provided by the invention, the technical problem that in the prior art, video data occupies relatively large bandwidth when in transmission, and thus the requirement on network bandwidth is relatively high is solved.
Owner:XIAN WANXIANG ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
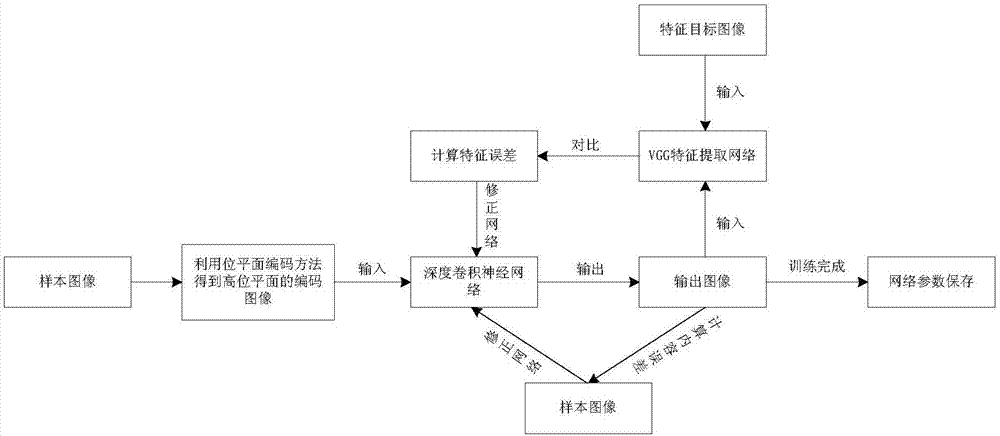
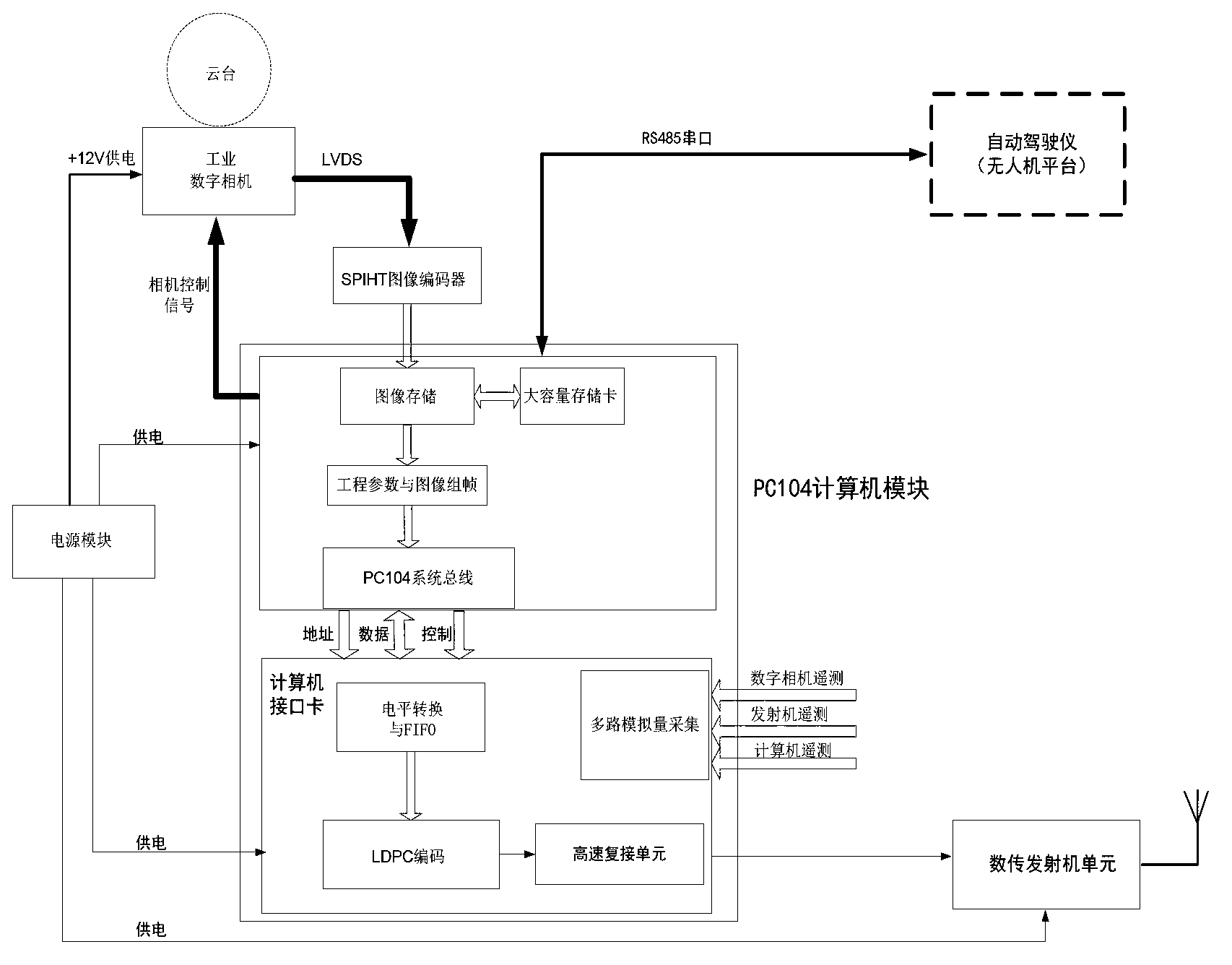
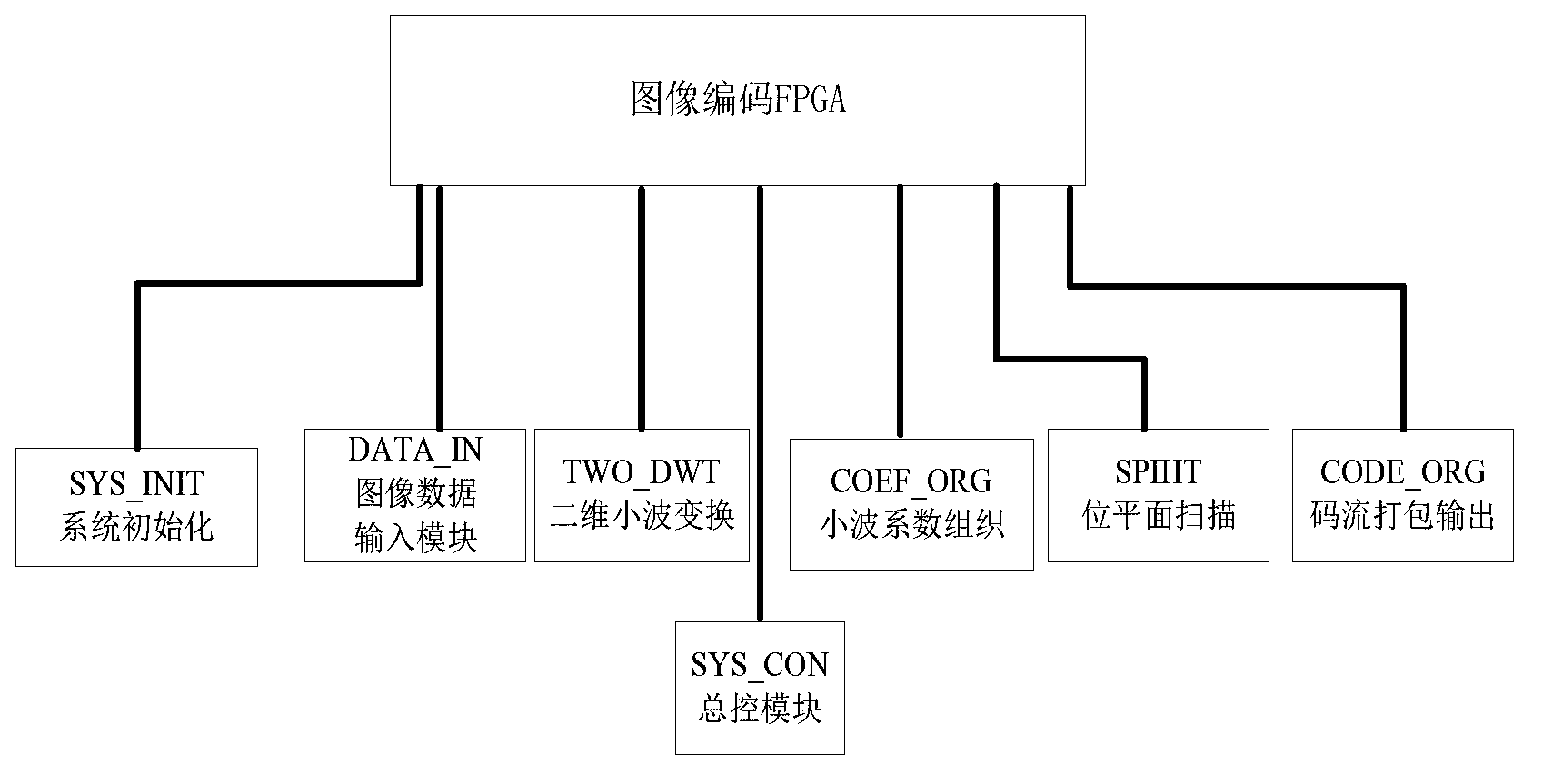
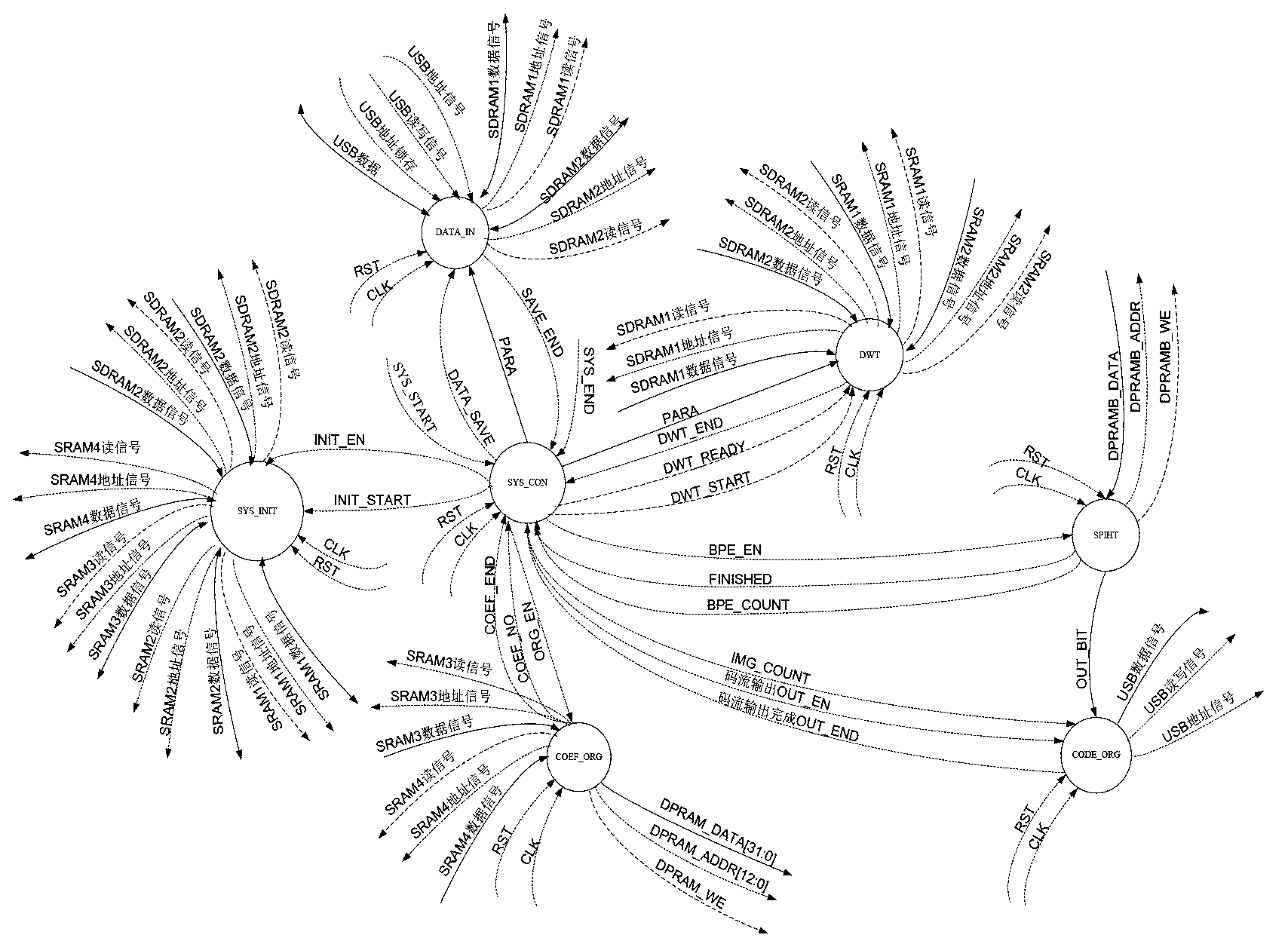
FPGA encoding method and system and control method for unmanned aerial vehicle image transmission device
The invention relates to an FPGA encoding method and system and a control method for an unmanned aerial vehicle image transmission device. The system comprises an image input module, a wavelet transformation processing module and an SPIHT algorithm encoding module. The image input module is used for receiving collected image data in real time and conducting conversion in the aspect of a data interface protocol on the collected image data. The wavelet transformation processing module is used for conducting wavelet transformation on image original data after the interface protocol is converted so that wavelet coefficients can be obtained. The SPIHT algorithm encoding module is used for encoding in a bit-plane mode, conducting bit-plane division on the wavelet coefficients to form n bit planes which are scanned in parallel and processing each bit plane to obtain encoded binary code streams. The system further comprises an image encoder general control function module and a system initialization function module, wherein the image encoder general control function module is used for controlling the enable of various function modules in the FPGA encoding system and the enable of a state transition process including an input data processing process, an output data processing process and a middle data processing process, and the system initialization function module is used for initializing the various function modules, memories and registers in the FPGA encoding system and for setting a default state.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
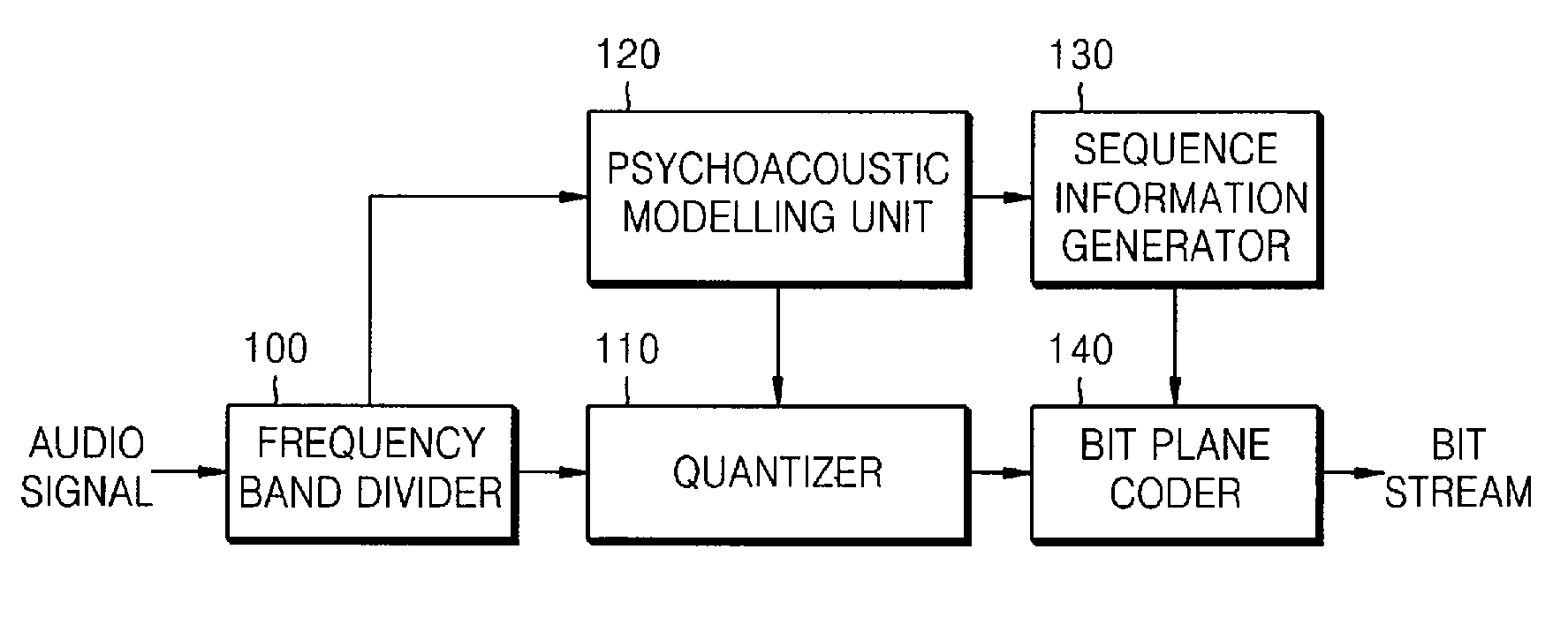
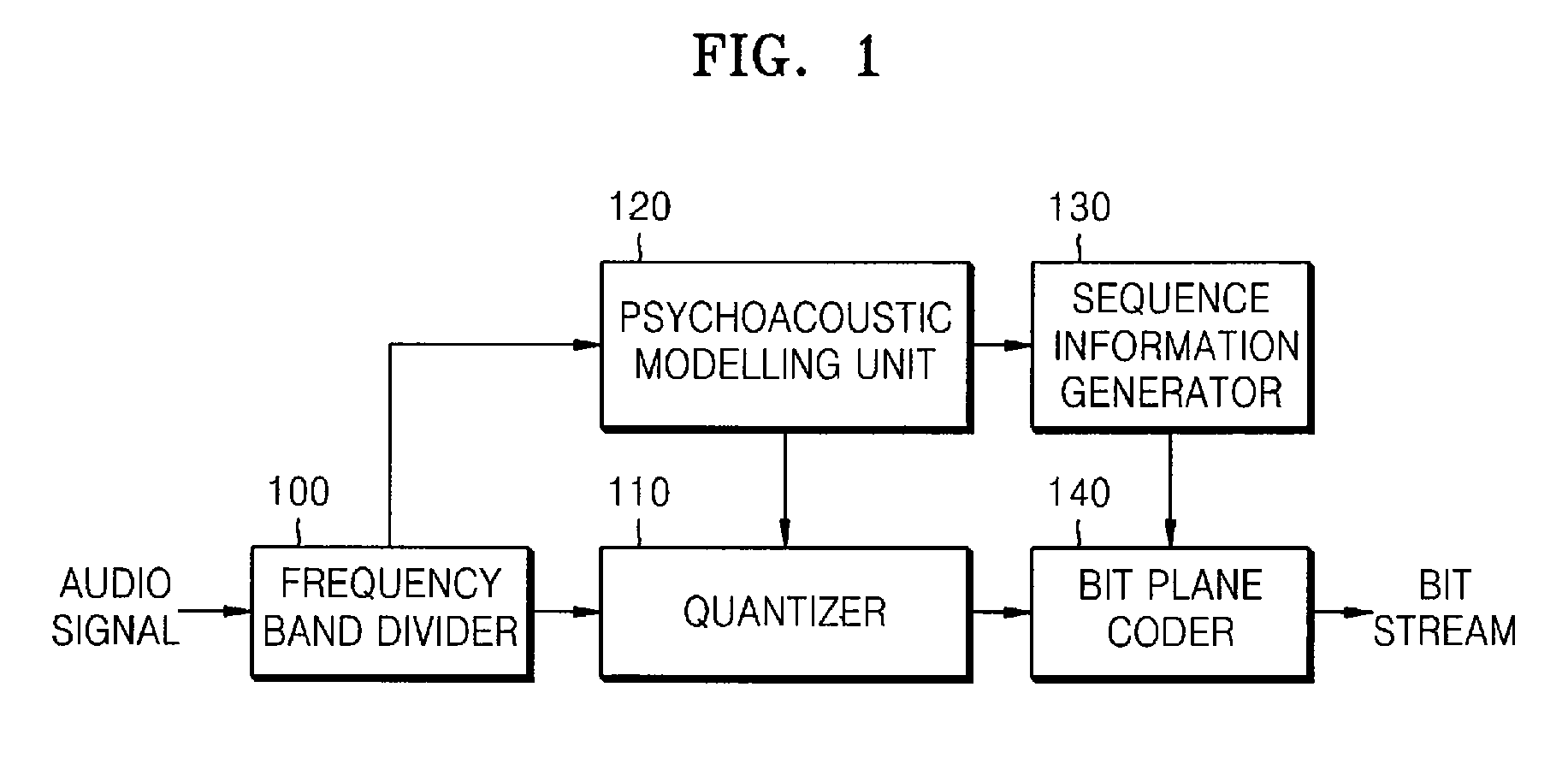
Method, medium, and apparatus encoding and/or decoding an audio signal
ActiveUS8224658B2Minimized in sizeImprove efficiencySpeech analysisDigital computer detailsBit plane codingAudio frequency
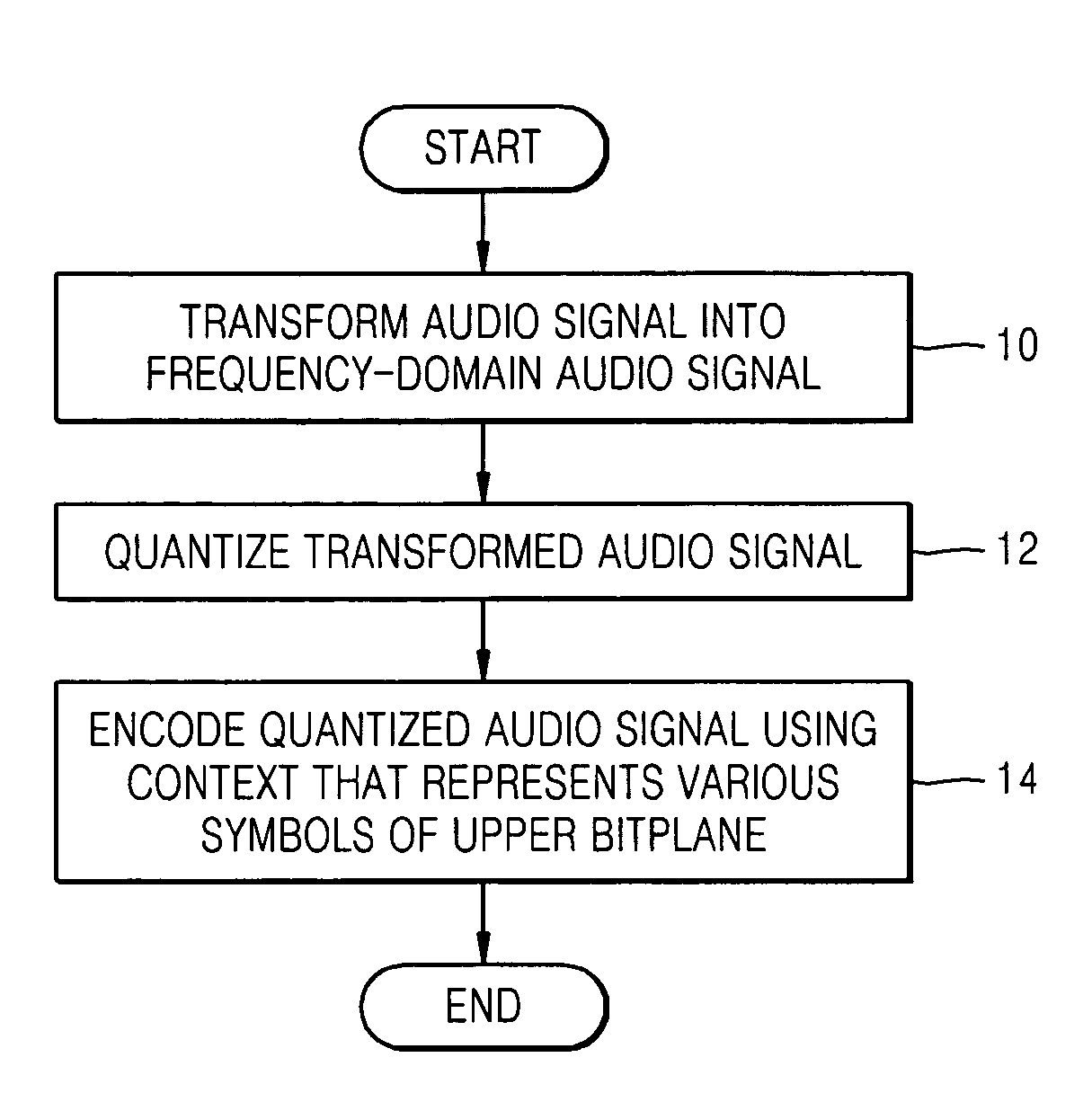
A method, medium, and apparatus encoding and / or decoding an audio signal. The method of encoding an audio signal includes transforming an input audio signal into an audio signal in a frequency domain, quantizing the frequency-domain transformed audio signal, and performing bitplane coding on the quantized audio signal using a context that represents various available symbols of an upper bitplane.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
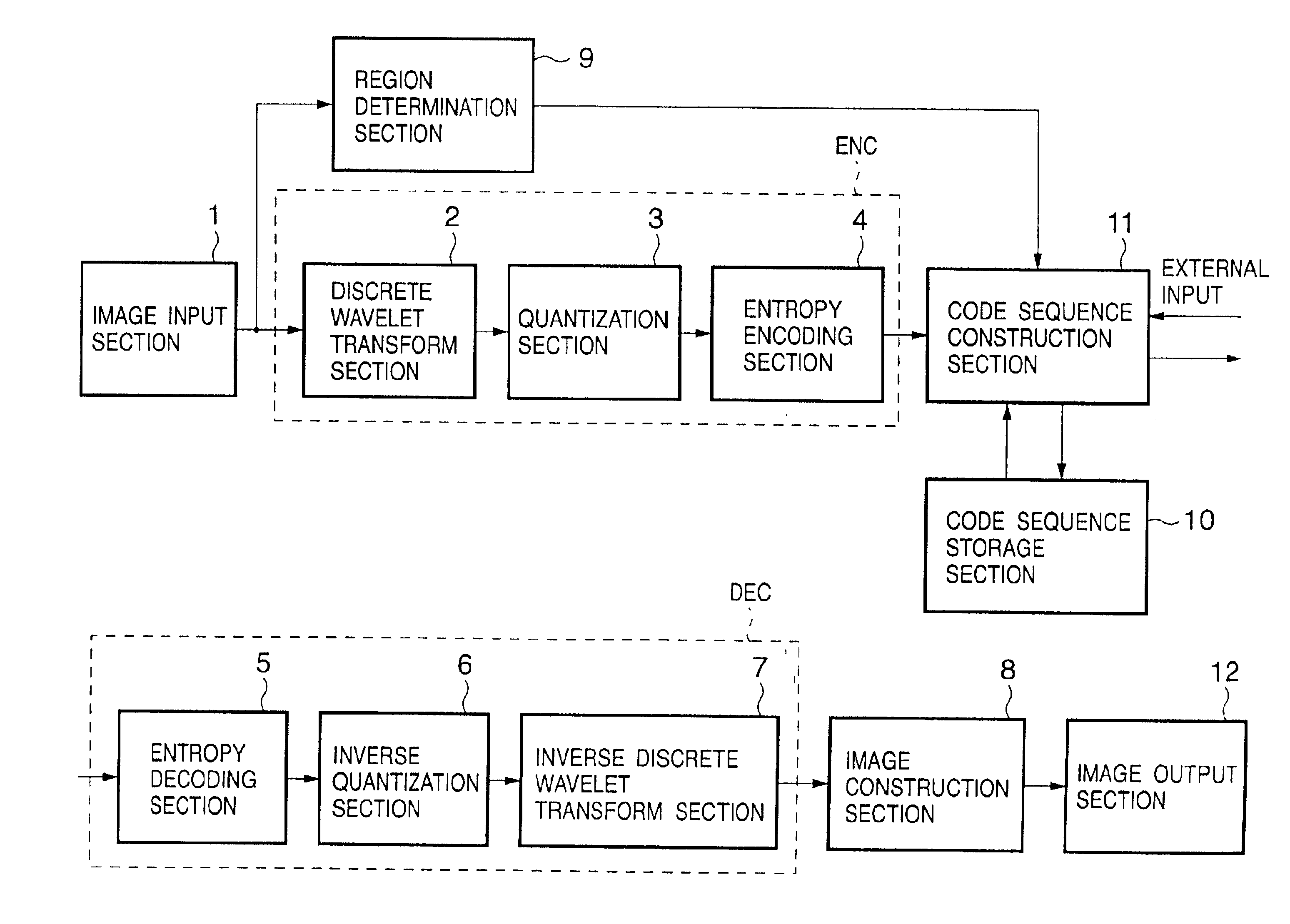
Image coding apparatus and method, and program and recording medium
InactiveUS7224846B2Increase speedShorten the timePrinted circuit assemblingPrinted circuit aspectsCoding blockTheoretical computer science
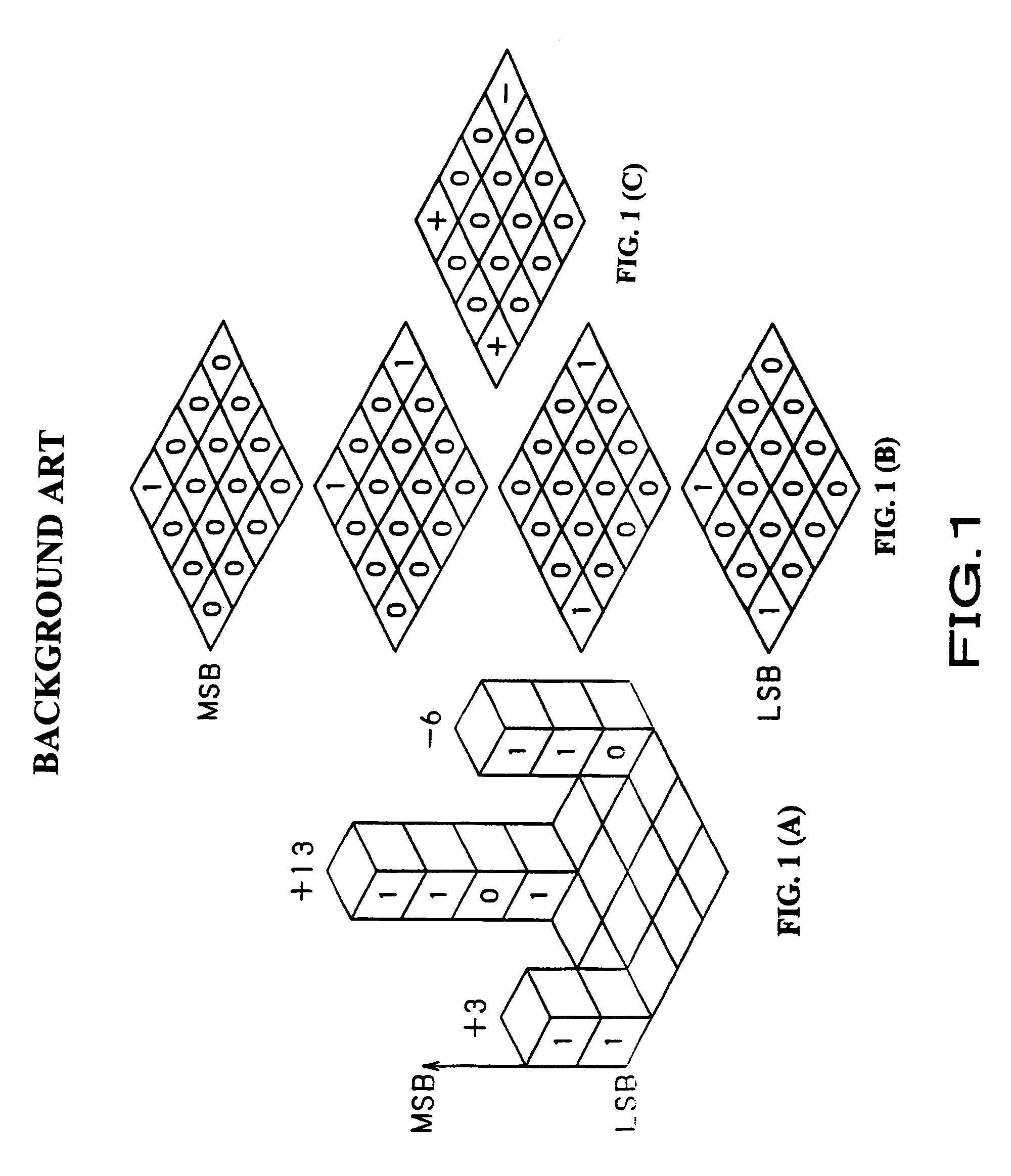
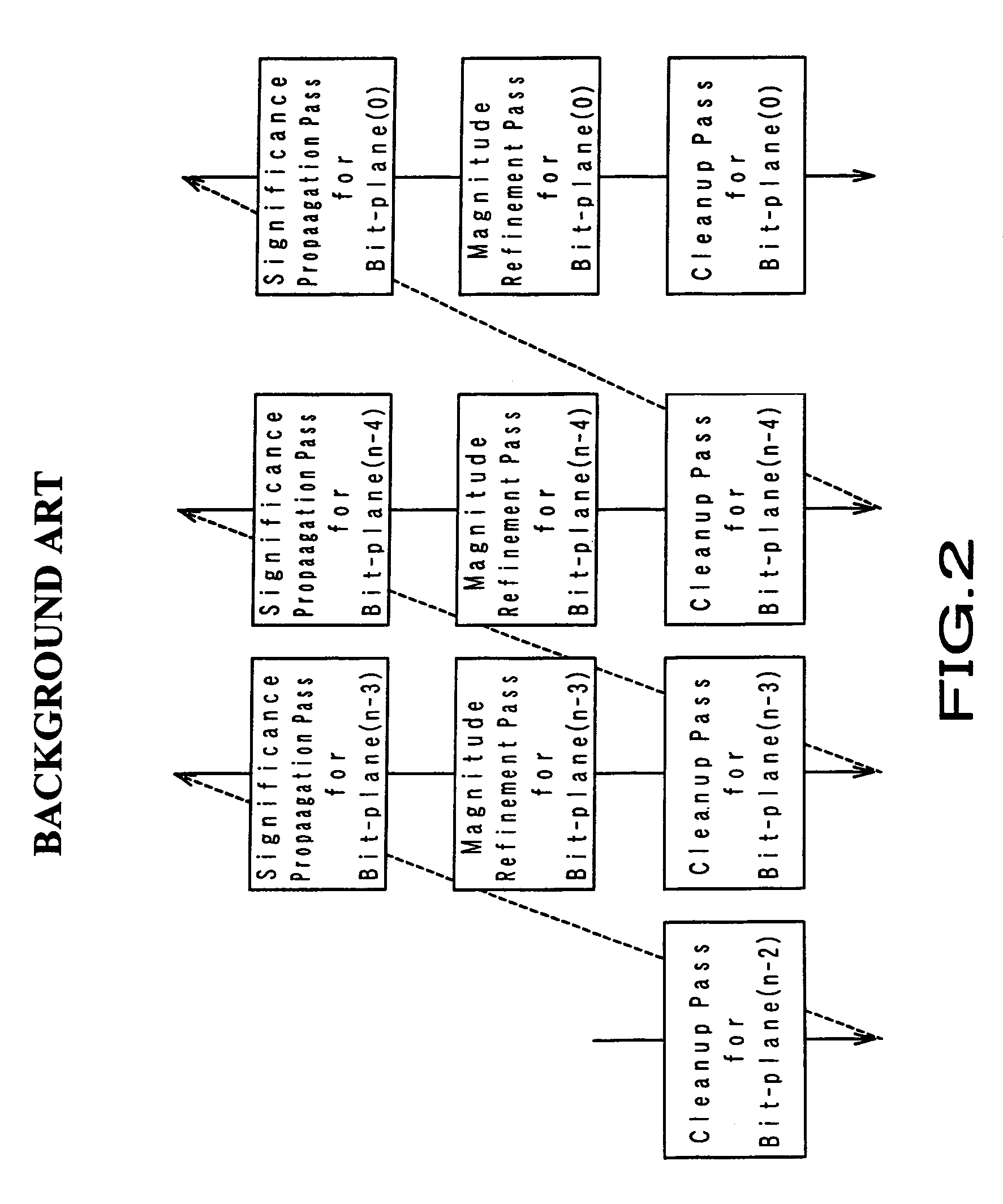
An bit-plane coding pass generator is provided in which for SP-pass processing quantization coefficient of each code block divided into bit planes, “significant (S)” or “non-significant (N)” data in a predetermined area and those around the area and compared with an S / N matching pattern. The S / N matching pattern has been set when a jump can be made from an arbitrary sample point to a next sample point to be processed by SP pass. The jump is made to the next sample point to be processed by SP pass according to a jump address value obtained from a pattern coincident with a current S / N matching pattern. Thus, by reducing the time for the significant propagation (SP) pass defined in JPEG-2000, a code block can be coded at a higher speed by three coding passes.
Owner:SONY CORP
Parallel coefficient bit modeling
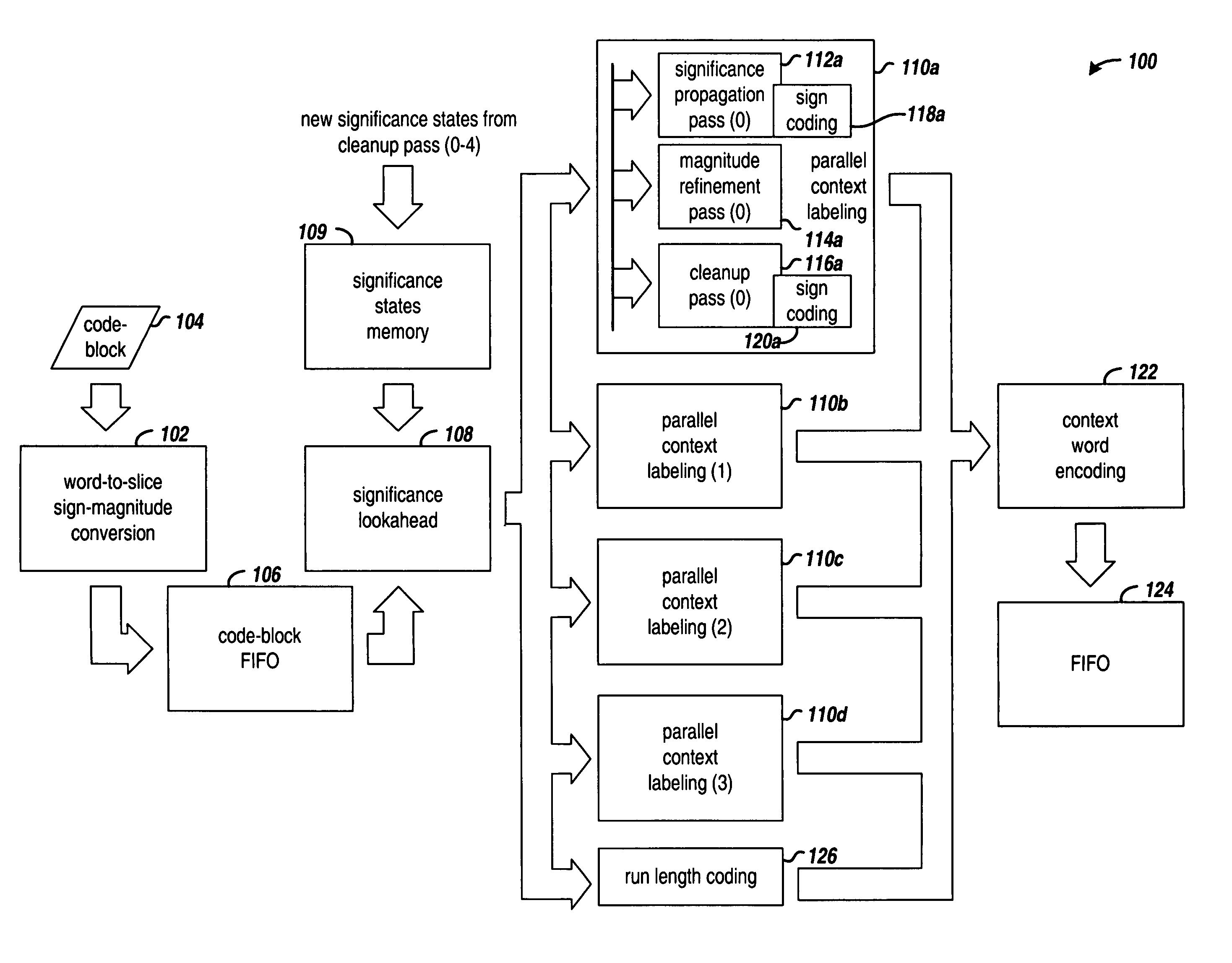
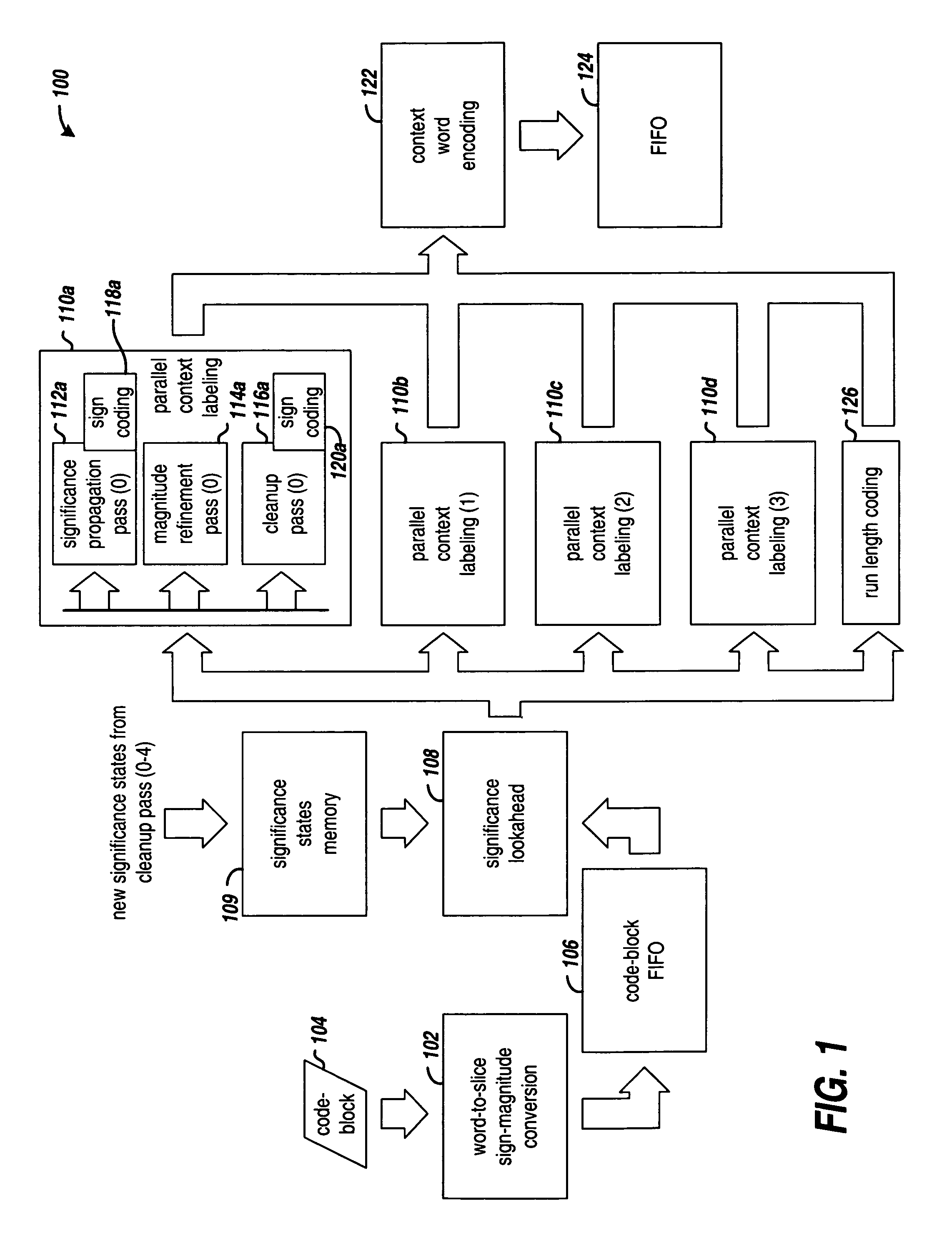
ActiveUS7760948B1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationCoding blockMultiple context
Owner:XILINX INC
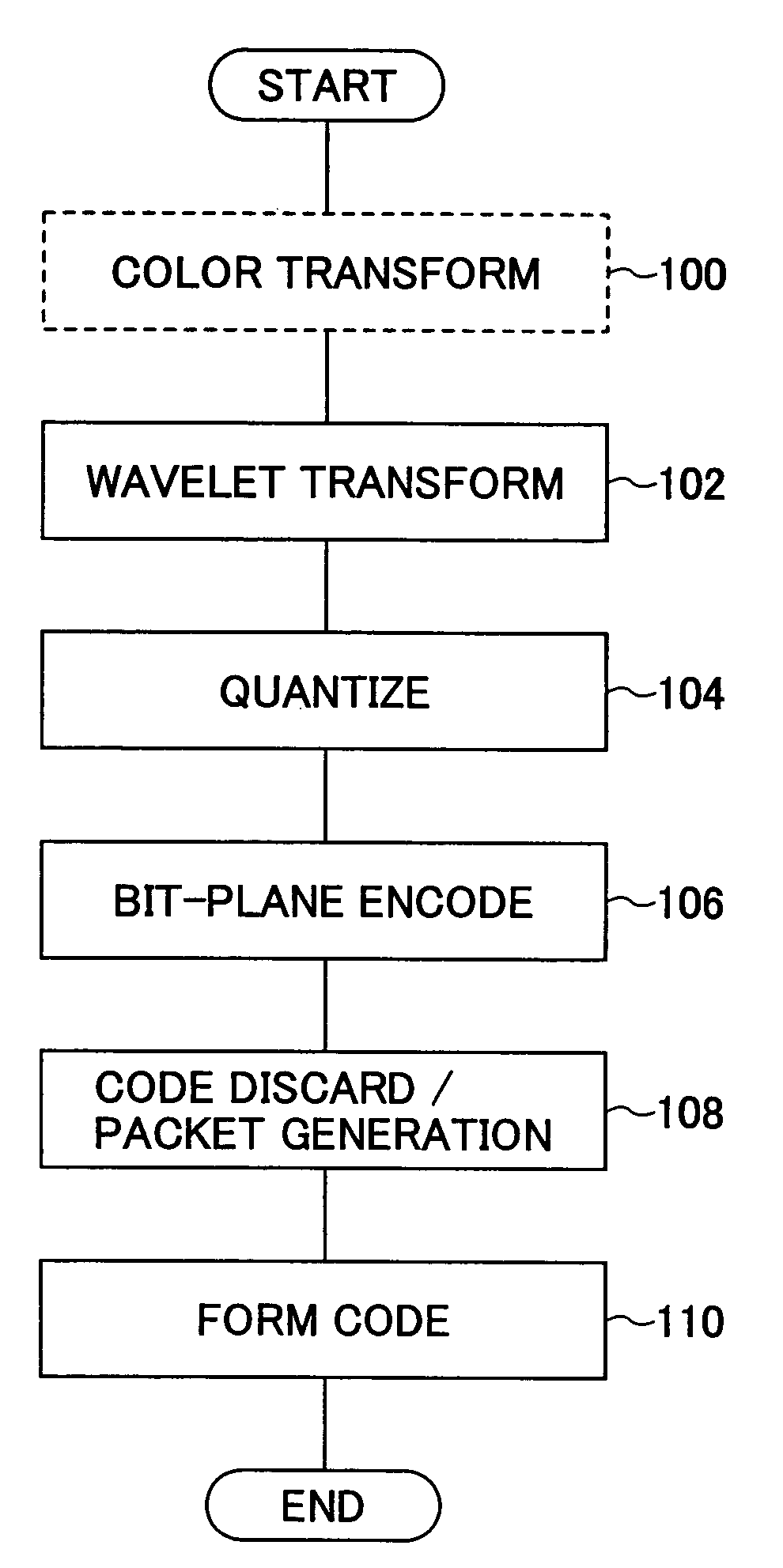
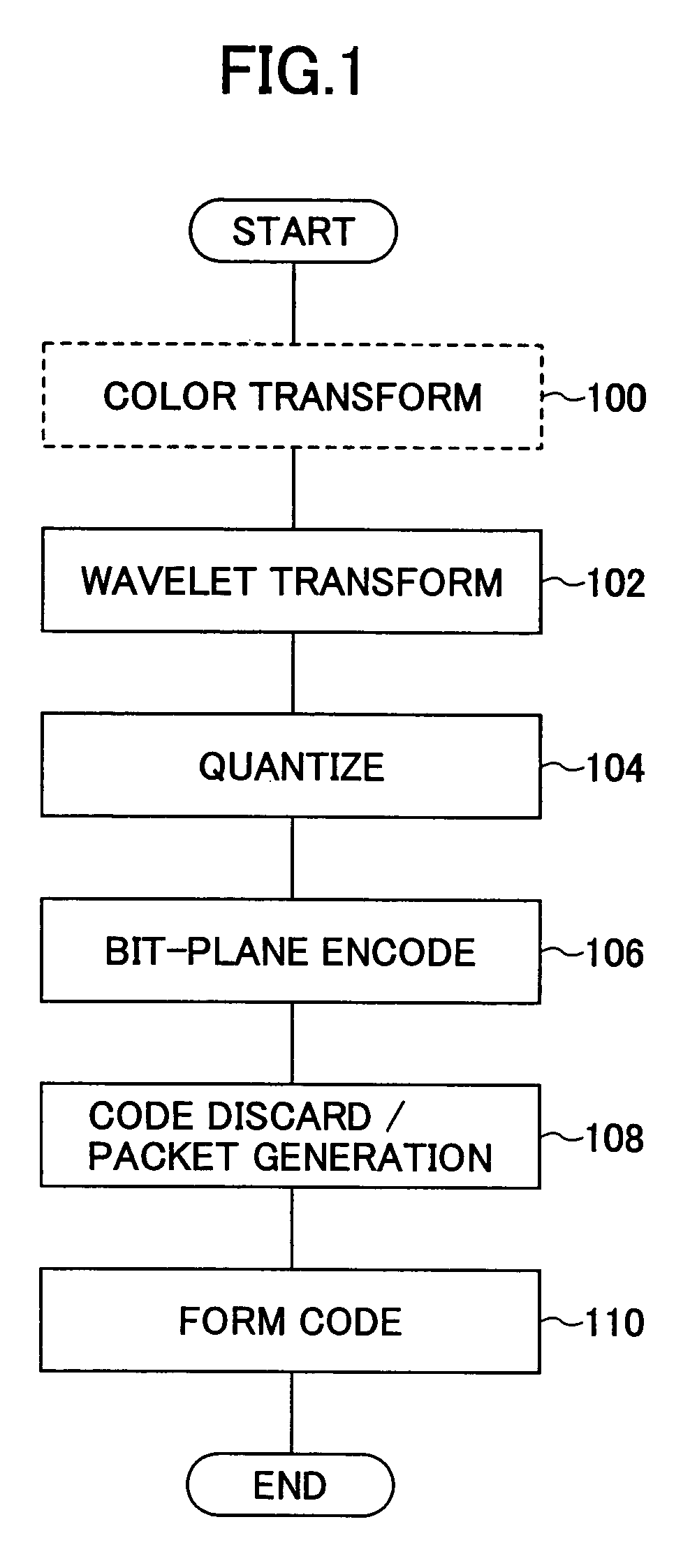
Picture-encoding apparatus and picture-encoding method
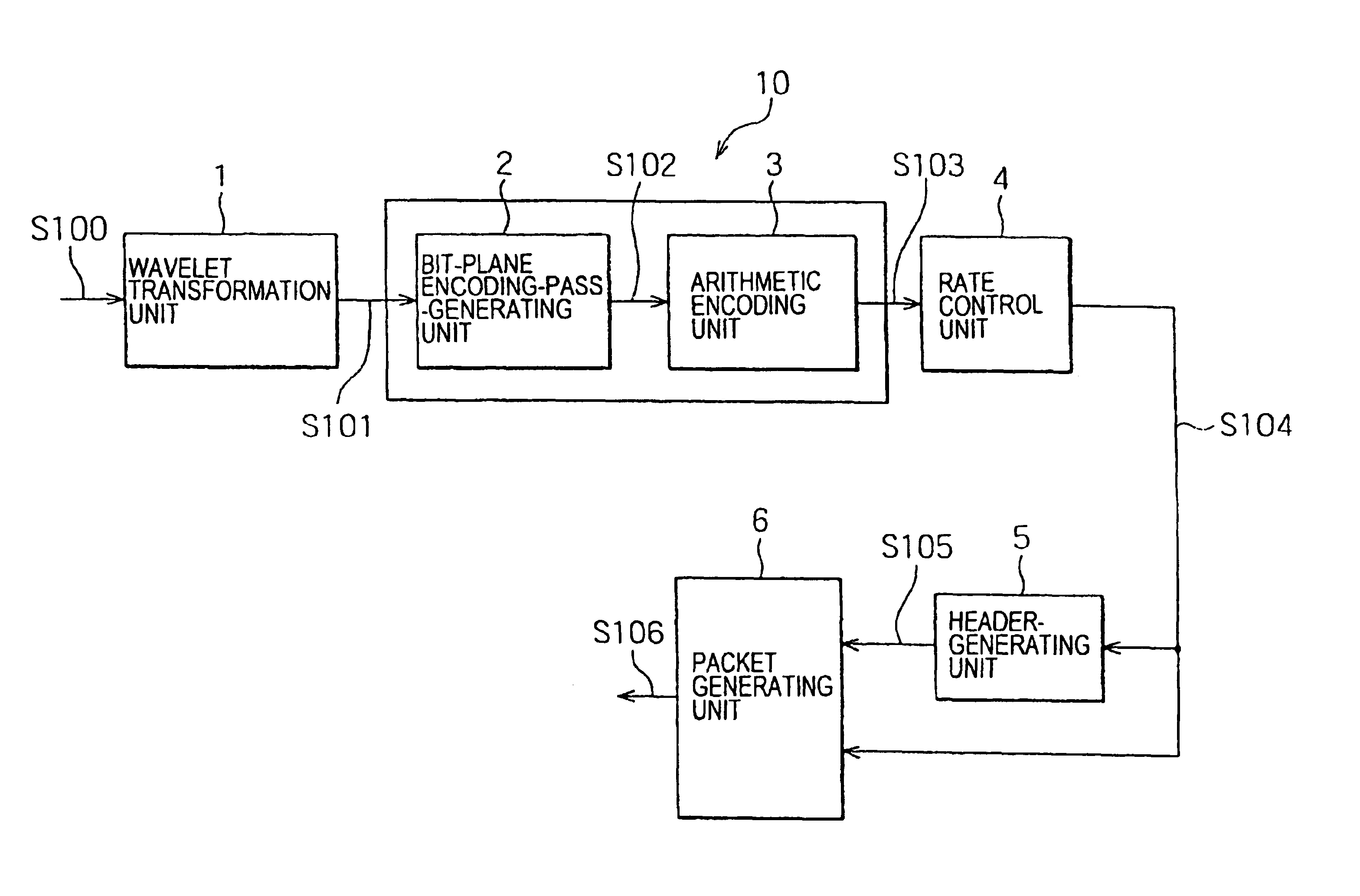
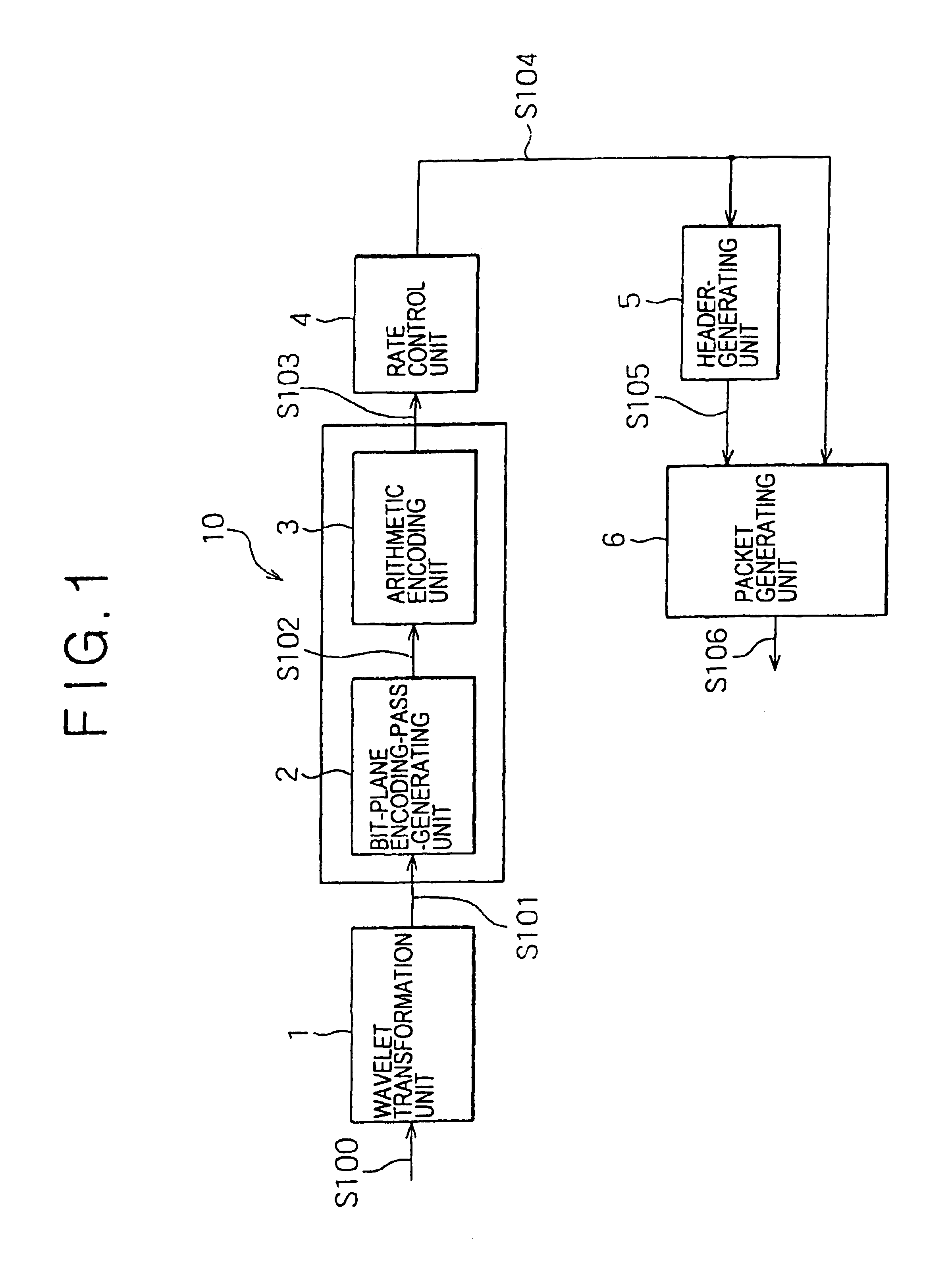
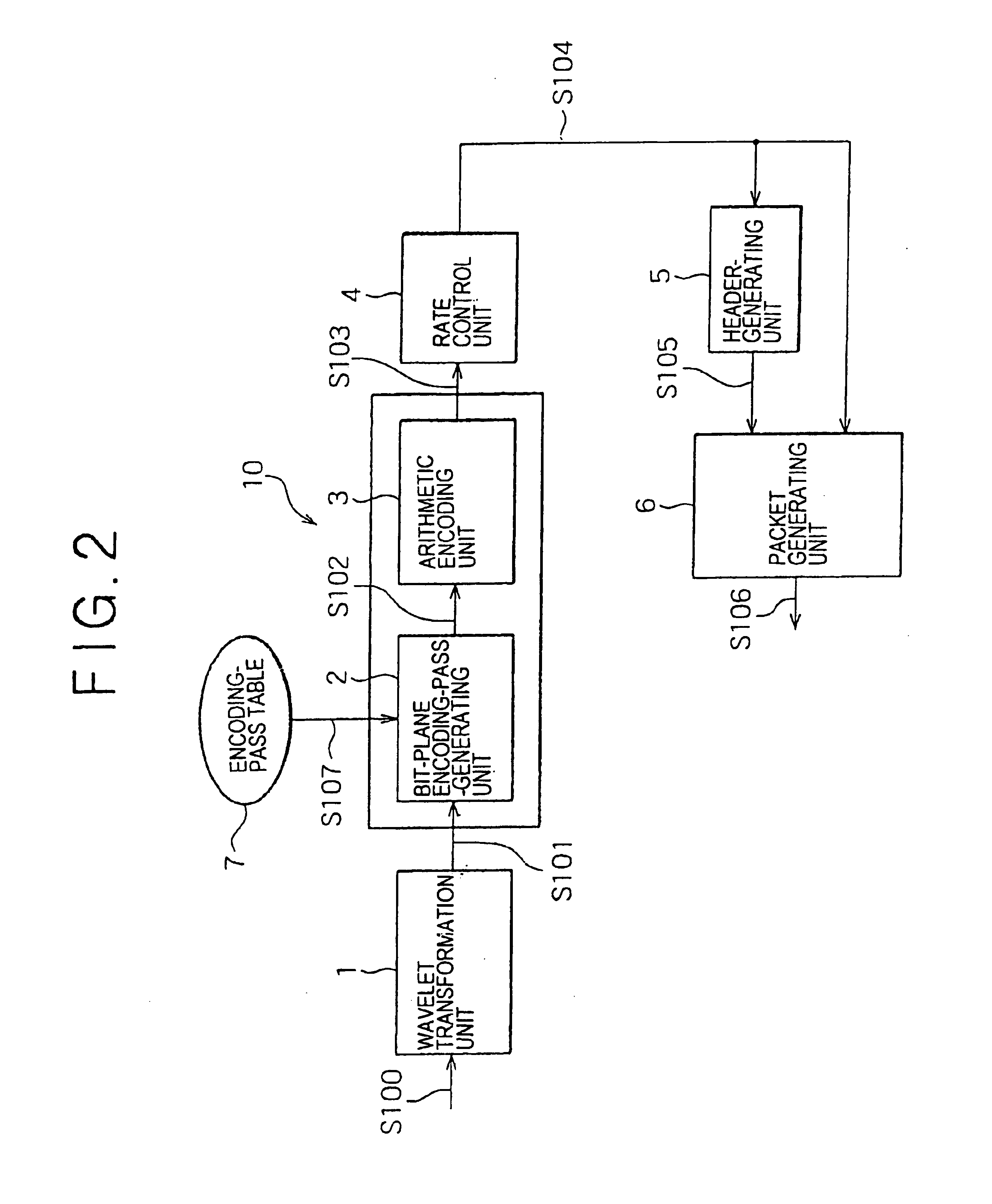
InactiveUS6876772B2Efficient implementationReduce computing loadPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionParallel computingTransformation unit
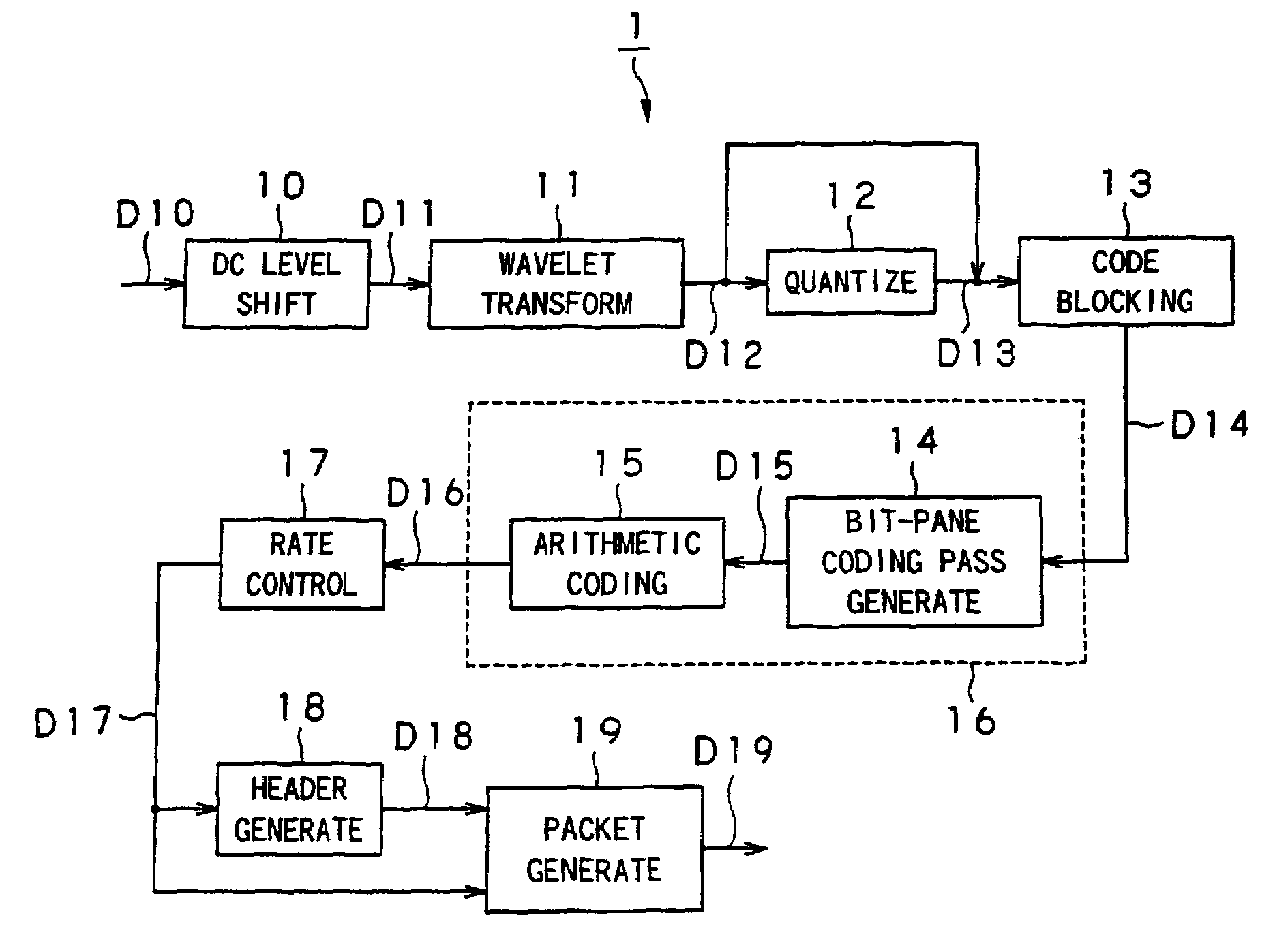
A picture-encoding apparatus provided by the present invention includes a wavelet transformation unit for carrying out wavelet transformation on an input picture to generate wavelet-transformation coefficients, a bit-plane encoding-pass-generating unit for spreading the wavelet-transformation coefficients over bit-planes, an arithmetic encoding unit for carrying out an arithmetic encoding process in an encoding pass, a rate control unit for controlling an encoded-data quantity of the generated arithmetic code so as to achieve a target encoded-data quantity, a header-generating unit for generating a header, a packet-generating unit for generating a packet by addition of the header to the arithmetic code experiencing control of the encoded-data quantity executed by the rate control unit, and an encoded-code-stream-truncating means for truncating an encoded-code stream completing processing through all the encoding passes by discarding a rear portion of the stream so as to make an encoded-data quantity of the stream equal to a target encoded-data quantity.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image compression method capable of reducing tile boundary distortion
InactiveUS7333664B2Reducing tile boundary distortionReduce distortion problemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionComputer architectureFrequency conversion
An image compressing apparatus divides an image into plural tiles, decomposes each tile into plural sub band by frequency conversion, and conducts bit plane encoding of each sub band for each encoding unit, wherein the image compressing apparatus includes a code discarding unit selectively discarding a code obtained by the bit plane encoding for each encoding unit, and wherein the code discarding unit includes a discard amount setting unit that makes generally even the amount of code discarding in the encoding units that are in mutually adjacent relationship across a tile boundary.
Owner:RICOH KK
Compression-type coding scheme of curve vector data based on integer wavelet transformation
The invention discloses a lossless compression method of curve vector data based on integer wavelet transformation and bit plane coding. In the invention, the integer wavelet transformation is introduced in a vector data compression algorithm. The integer wavelet transformation can compress the majority of energy of the data in a low-frequency coefficient and only the minority of energy in a high-frequency coefficient. In the invention, the low-frequency coefficient is coded by using the Huffman coding scheme and the high-frequency coefficient is coded by using a plane coding scheme. The embedded coding of the vector data can be achieved by the bit plane coding. The designed bit plane coder can sequence the bit streams to be coded according to the different importance, and the coding is finished at any time according to the requirements of a target code rate or a degree of distortion. Similarly, a given code stream decoder can finish decoding at any time, and the reconstruction vector curve of the target code rate at a corresponding place where the code stream is cut off can be obtained. Experiments show that the compression scheme achieves the embedded coding of the vector data, can progressively transmit and display the compressed code streams of the vector data, and simultaneously obtains a relatively high lossless compression ratio.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for encoding and decoding JPEG2000 image based on vision potential attention target area
InactiveCN102036073ATelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationVision basedImage decompression
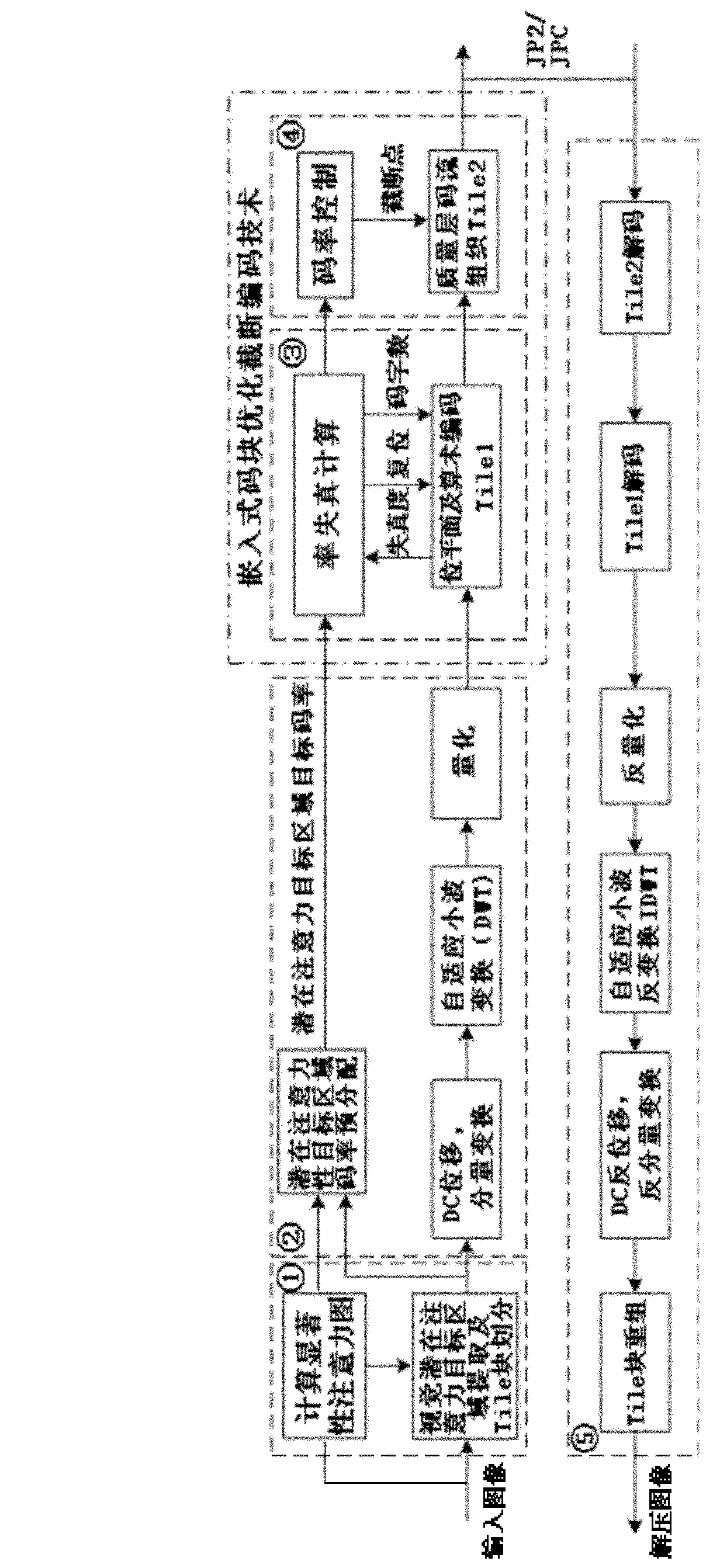
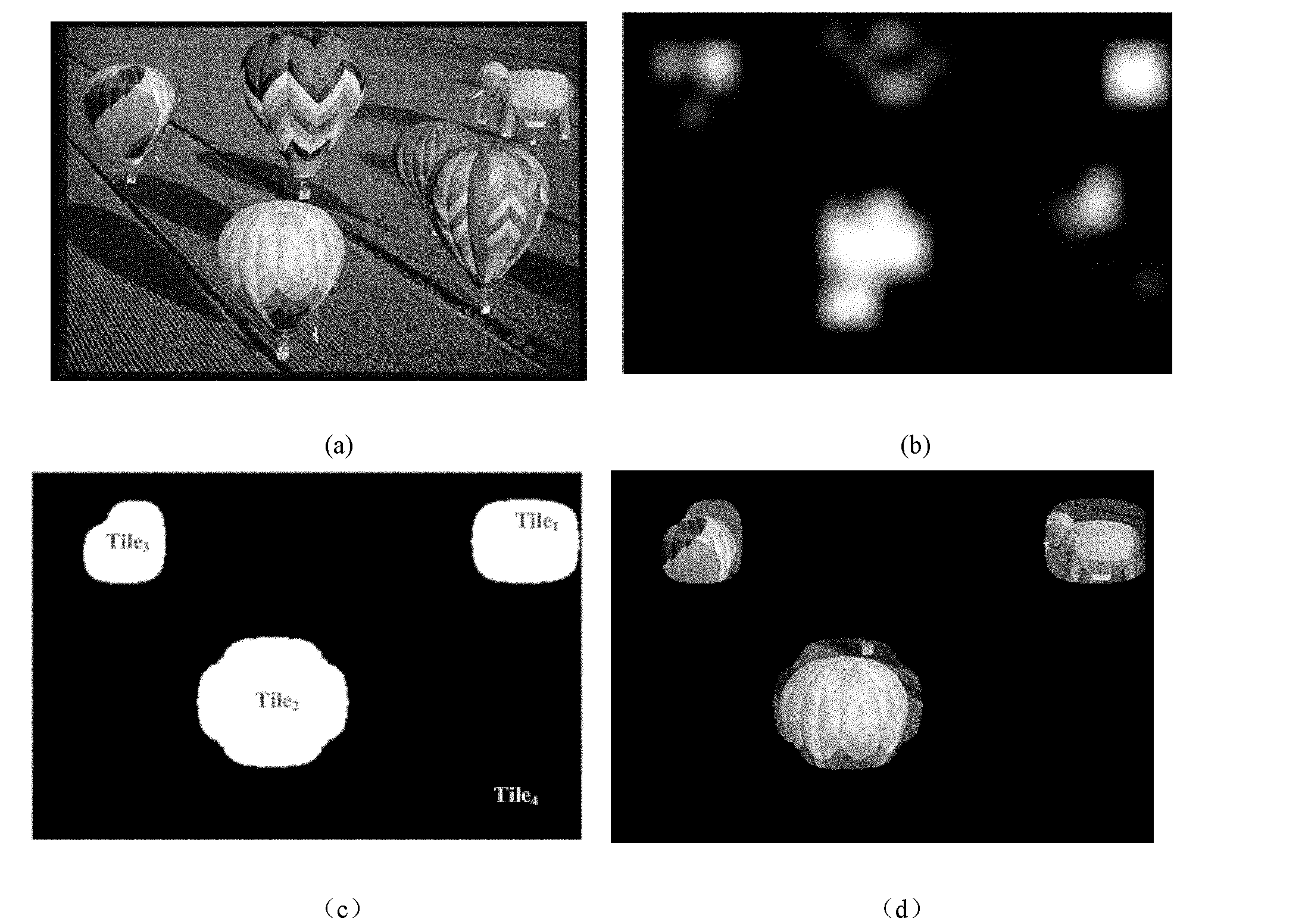
The invention discloses a method for effectively encoding and decoding a JPEG2000 image based on a vision potential attention target area. The method comprises the following steps of: before the image is encoded, dividing the image into a plurality of Tile blocks based on the potential target area of different attentions and pre-assigning corresponding target code rates according to vision potential attention target area extraction technology; and then carrying out code stream organization and packaging to realize image compression through quantization, adaptive wavelet transformation, and a bit plane encoding and arithmetic encoder code word reset mechanism on the basis of potential attention target area quality layer code rate control. When network band width is insufficient, the image reconstruction quality of a more-concerned target area can be exchanged at the expense of part of code rates of the target area with smaller potential attention; simultaneously, retractable high-efficiency image encoding and decoding technology is combined with a qualified content based on the potential attention target area.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Coding and decoding of video data
InactiveUS7242812B2Eliminate spaceRemove temporal redundancyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureBit plane coding
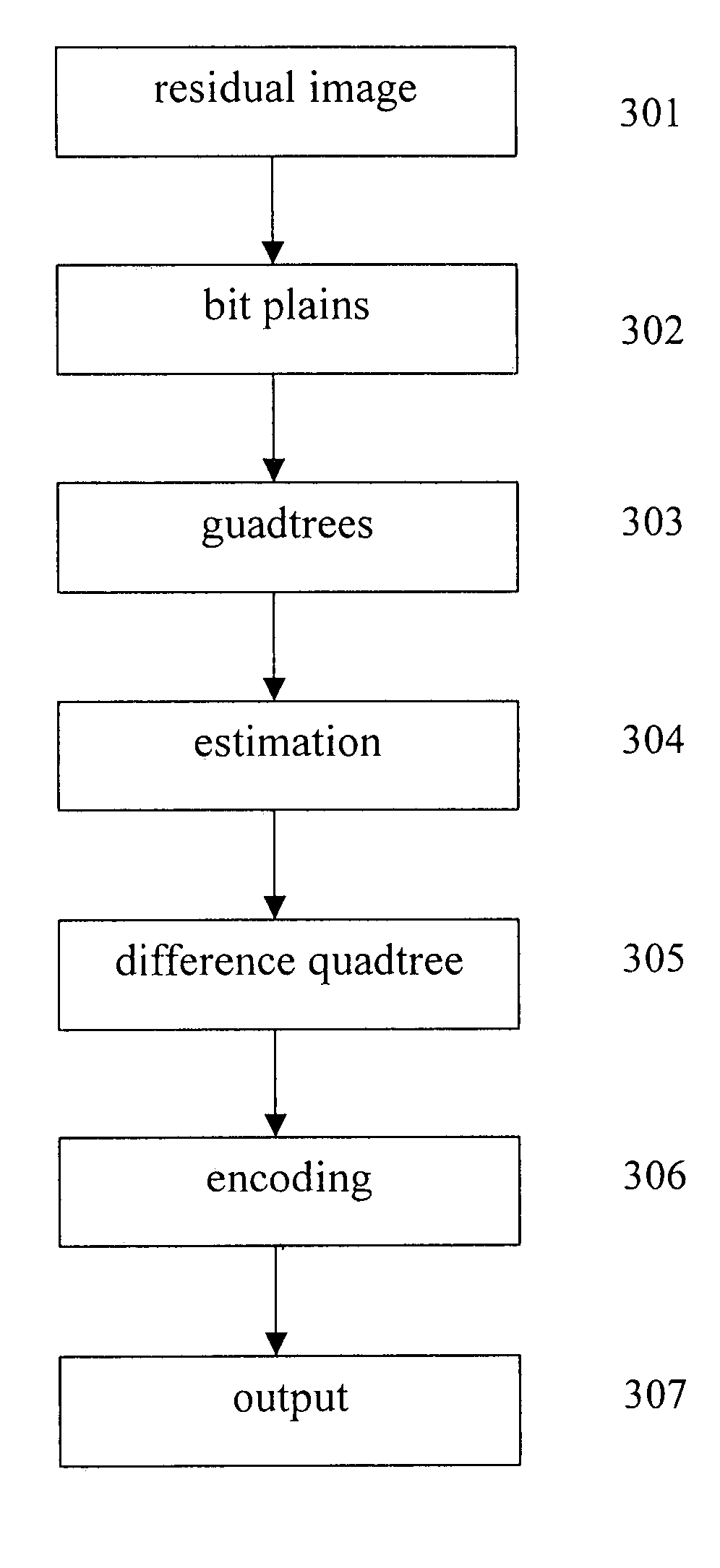
A novel method for coding and decoding video data and codec thereof are disclosed. The invented method provides an FGS (fine grained scalability) algorithm using bit plane coding technique. While conducting the bit plane encoding, the spatial and temporal dependence between bit planes is used to exploit the redundancy in the bit planes. In the embodiment of this invention, the bit plains are represented by quadtrees and bit plane prediction is made to remove the spatial and temporal redundancy in a video. The scalability of the video data is fine grained since atoms of the motion residuals do not have to be grouped as coding units.
Owner:HWANG WEN LIANG
Method for encoding a digital signal into a scalable bitstream; method for decoding a scalable bitstream
ActiveUS8446947B2Perceptual scalability of the scalable bitstreamReduce the amount requiredElectrophonic musical instrumentsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesBit plane codingComputer science
A method for encoding a digital signal into a scalable bitstream comprising quantizing the digital signal, and encoding the quantized signal to form a core-layer bitstream, performing an error mapping based on the digital signal and the core-layer bitstream to remove information that has been encoded into the core-layer bitstream, resulting in an error signal, bit-plane coding the error signal based on perceptual information of the digital signal, resulting in an enhancement-layer bitstream, wherein the perceptual information of the digital signal is determined using a perceptual model, and multiplexing the core-layer bitstream and the enhancement-layer bitstream, thereby generating the scalable bitstream. A method for decoding a scalable bitstream into a digital signal comprising de-multiplexing the scalable bitstream into a core-layer bitstream and an enhancement-layer bitstream, decoding and de-quantizing the core-layer bitstream to generate a core-layer signal, bit-plane decoding the enhancement-layer bitstream based on perceptual information of the digital signal, and performing an error mapping based on the bit-plane decoded enhancement-layer bitstream and the de-quantized core-layer signal, resulting in an reconstructed transformed signal, wherein the reconstructed transformed signal is the digital signal.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com