Patents
Literature
1179 results about "Least significant bit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
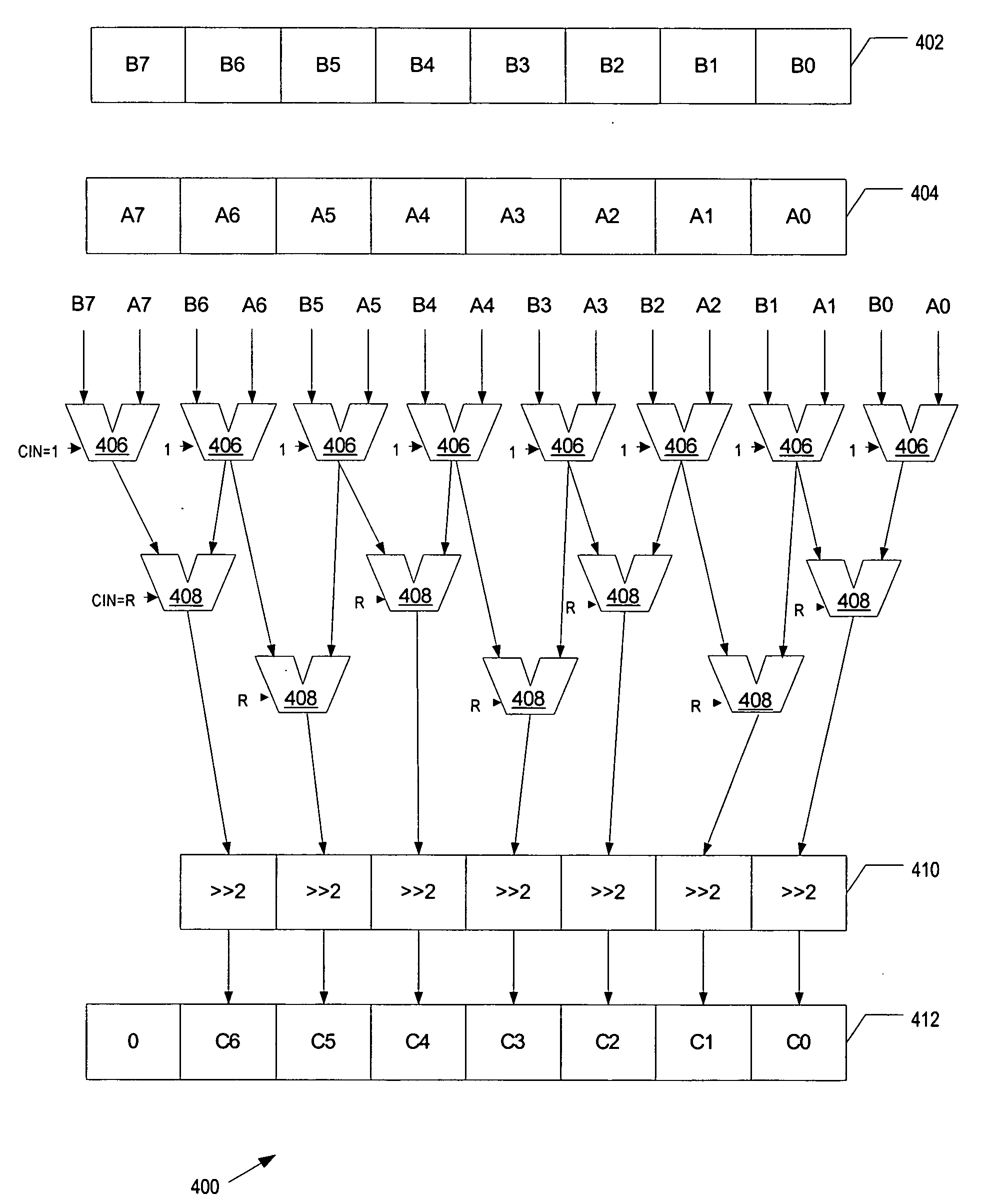
In computing, the least significant bit is the bit position in a binary integer giving the units value, that is, determining whether the number is even or odd. The lsb is sometimes referred to as the right-most bit, due to the convention in positional notation of writing less significant digits further to the right. It is analogous to the least significant digit of a decimal integer, which is the digit in the ones position. It is common to assign each bit a position number, ranging from zero to N-1, where N is the number of bits in the binary representation used. Normally, this is simply the exponent for the corresponding bit weight in base-2. Although a few CPU manufacturers assign bit numbers the opposite way, the term lsb remains unambiguous as an alias for the unit bit. By extension, the least significant bits are the bits of the number closest to, and including, the lsb. The least significant bits have the useful property of changing rapidly if the number changes even slightly. For example, if 1 is added to 3, the result will be 4 and three of the least significant bits will change. By contrast, the three most significant bits stay unchanged.
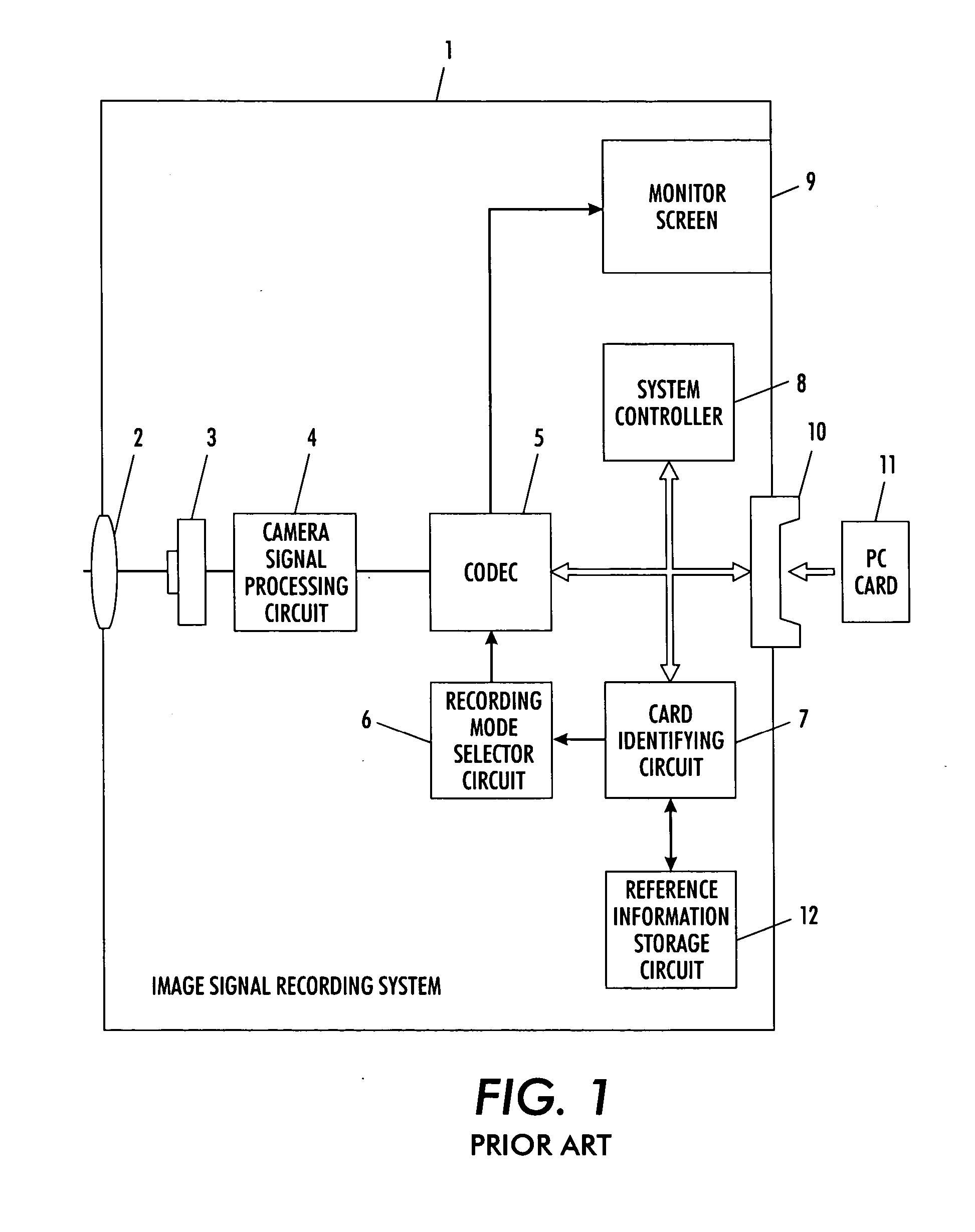
Methods of increasing the reliability of a flash memory
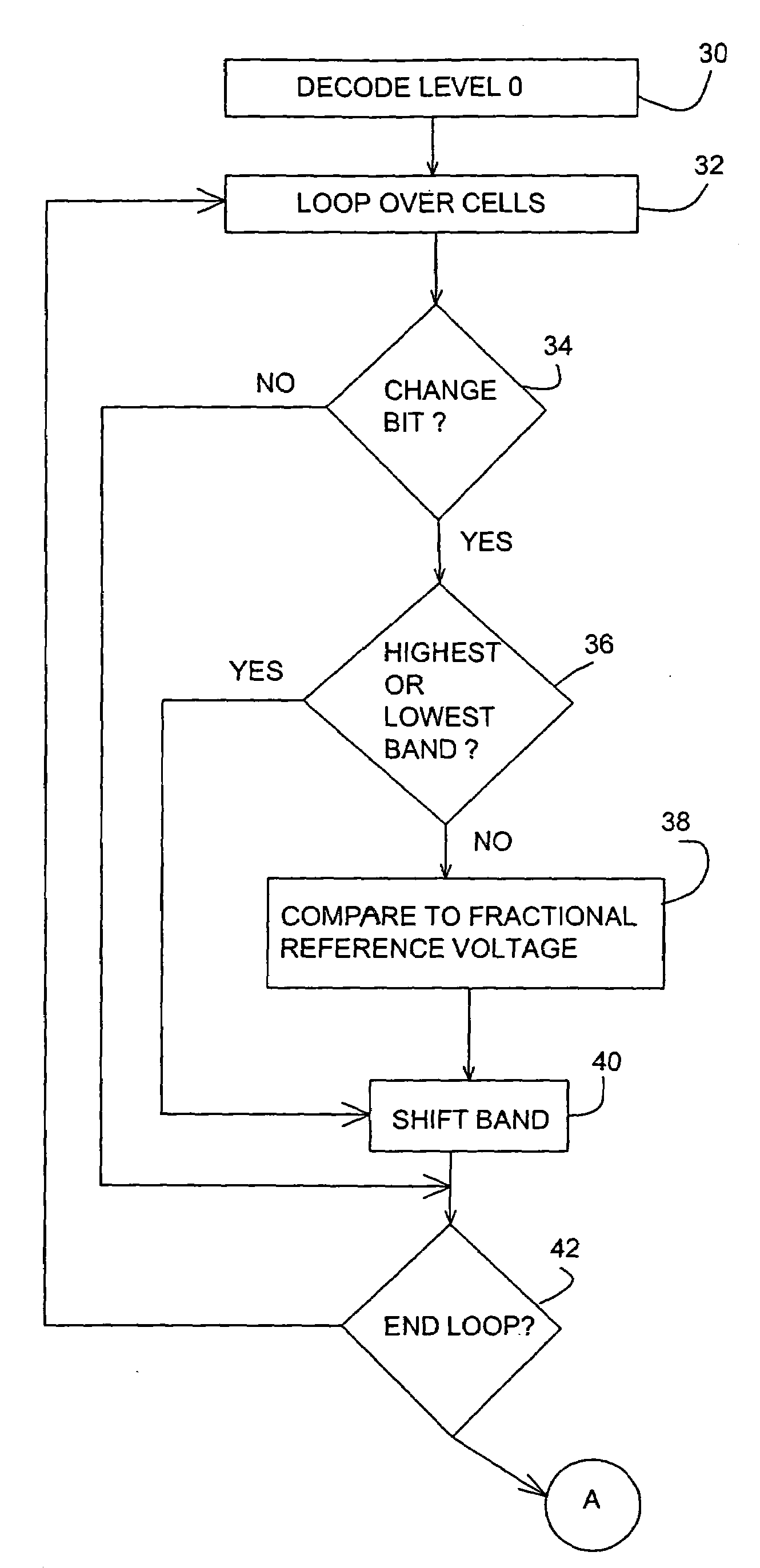
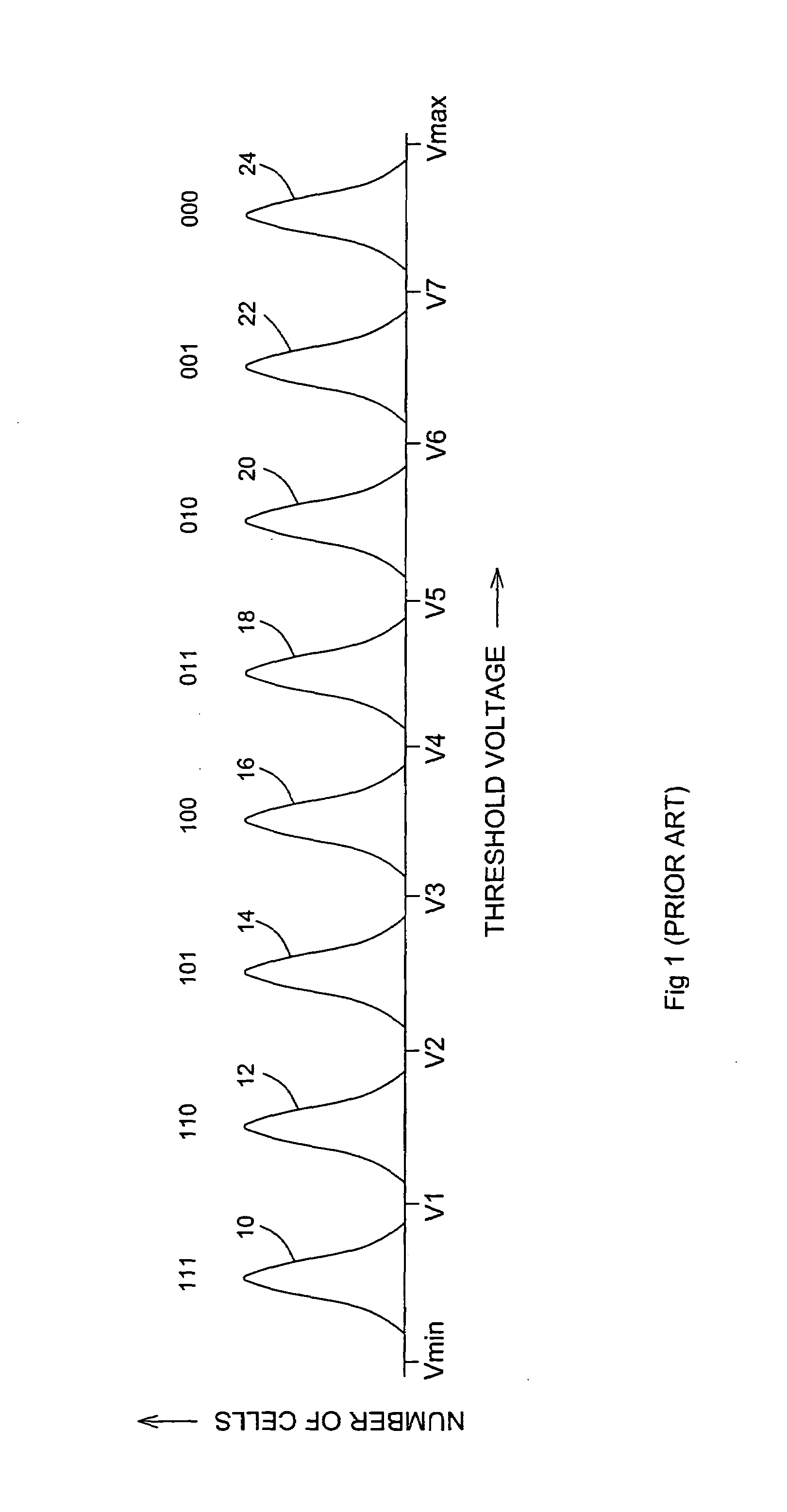
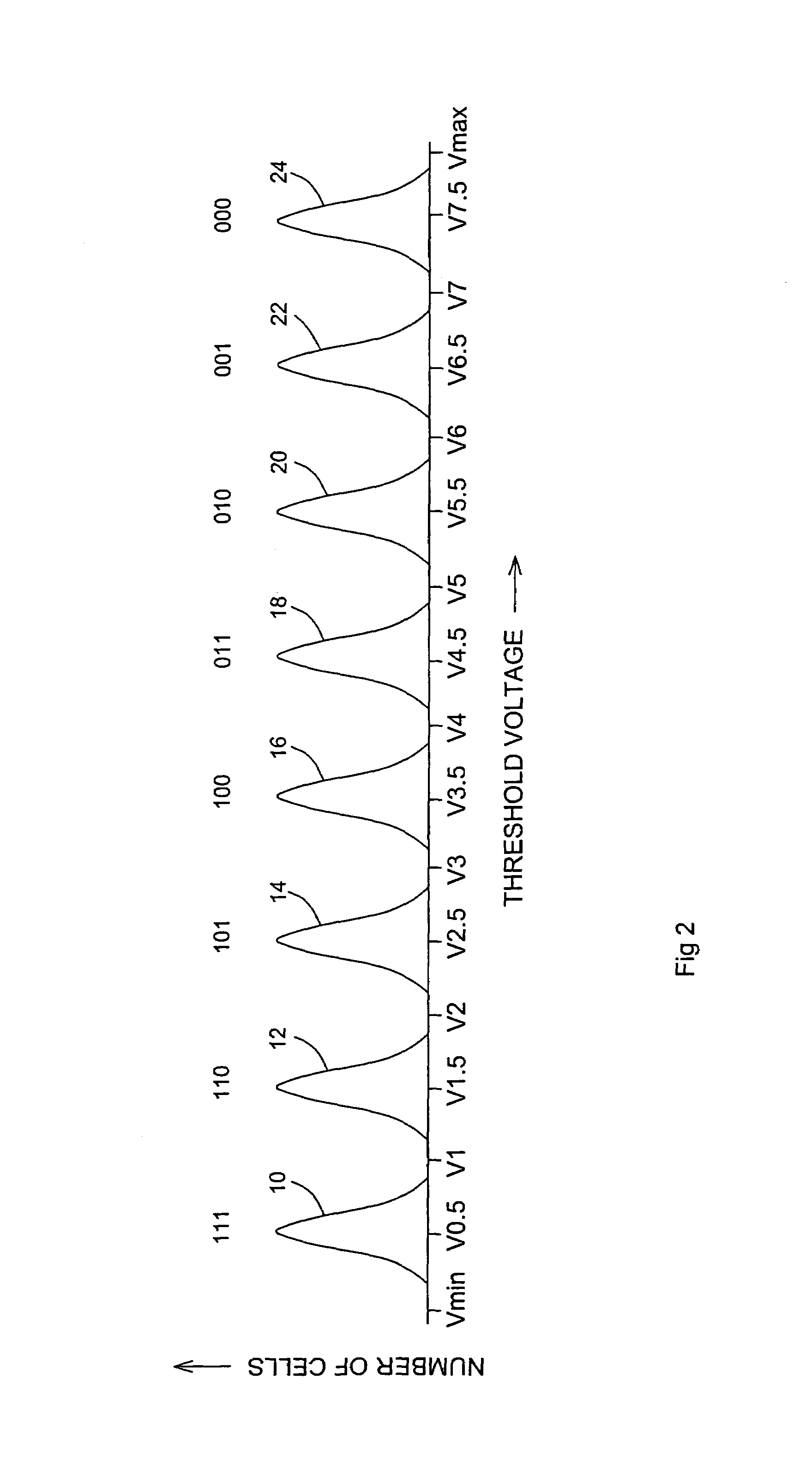
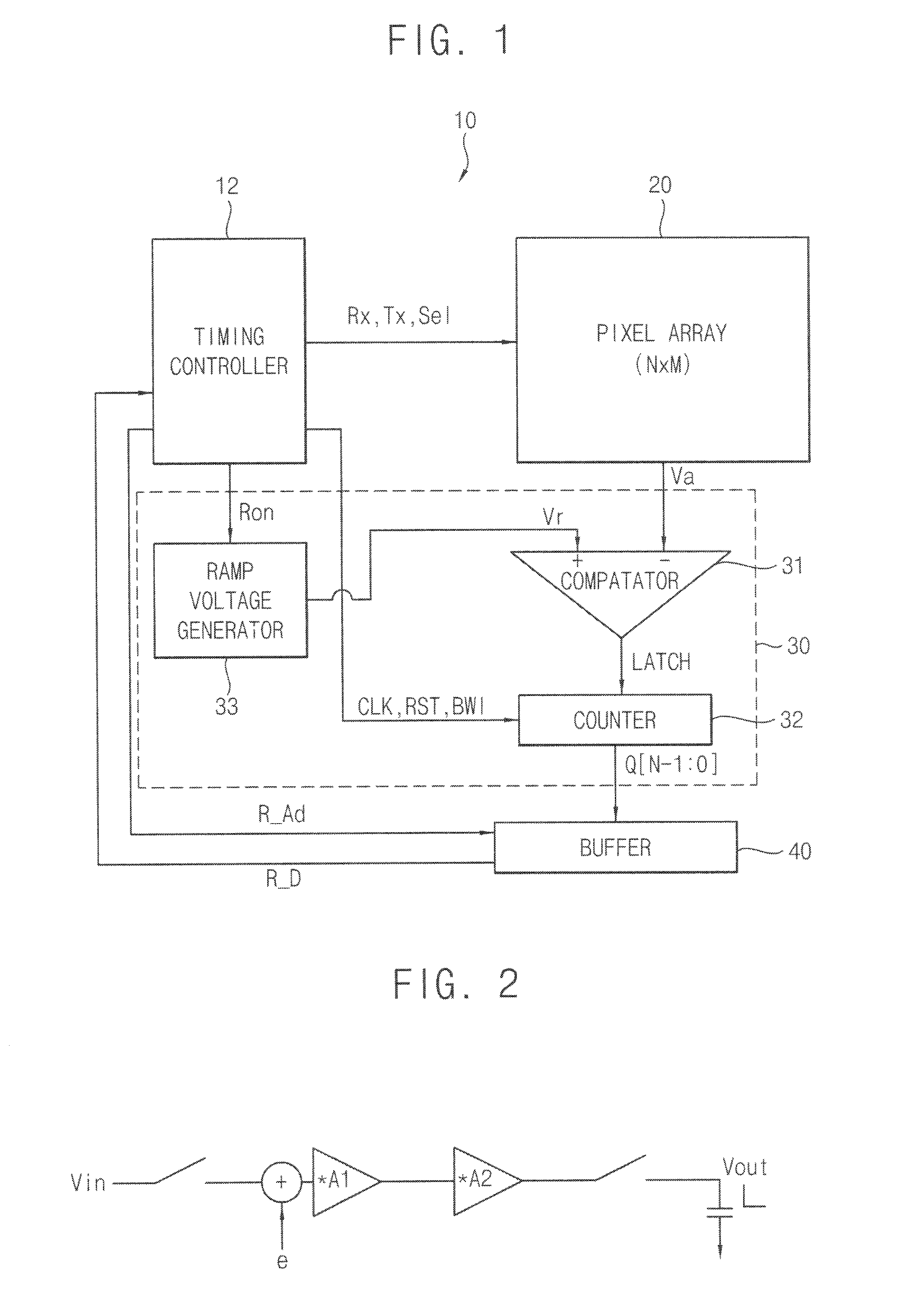
A multi-level flash memory cell is read by comparing the cell's threshold voltage to a plurality of integral reference voltages and to a fractional reference voltage. Multi-level cells of a flash memory are programmed collectively with data and redundancy bits at each significance level, preferably with different numbers of data and redundancy bits at each significance level. The cells are read collectively, from lowest to highest significance level, by correcting the bits at each significance level according to the redundancy bits and adjusting the bits of the higher significance levels accordingly. The adjustment following the correction of the least significant bits is in accordance with comparisons of a cell's threshold voltages to fractional reference voltages.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
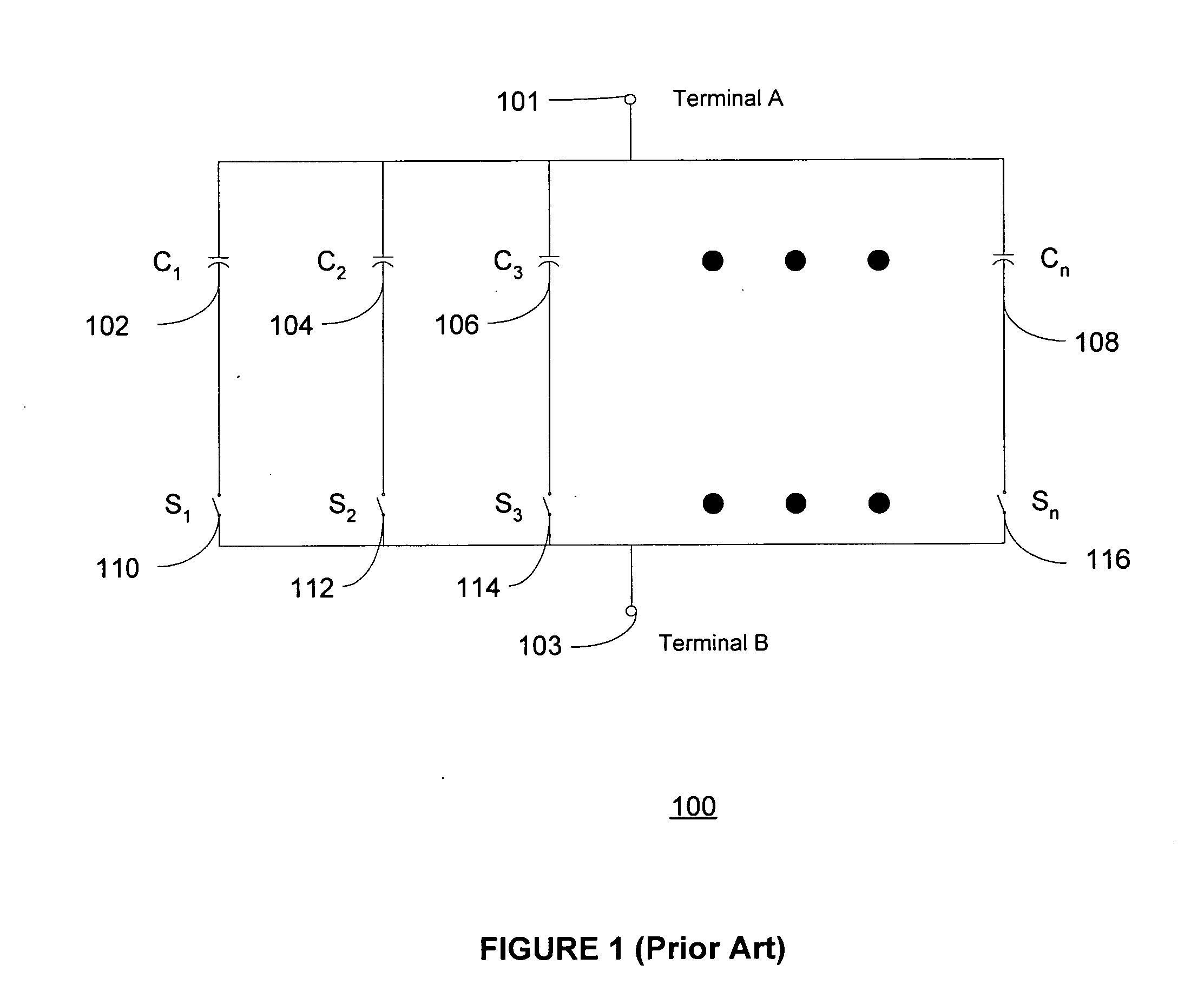
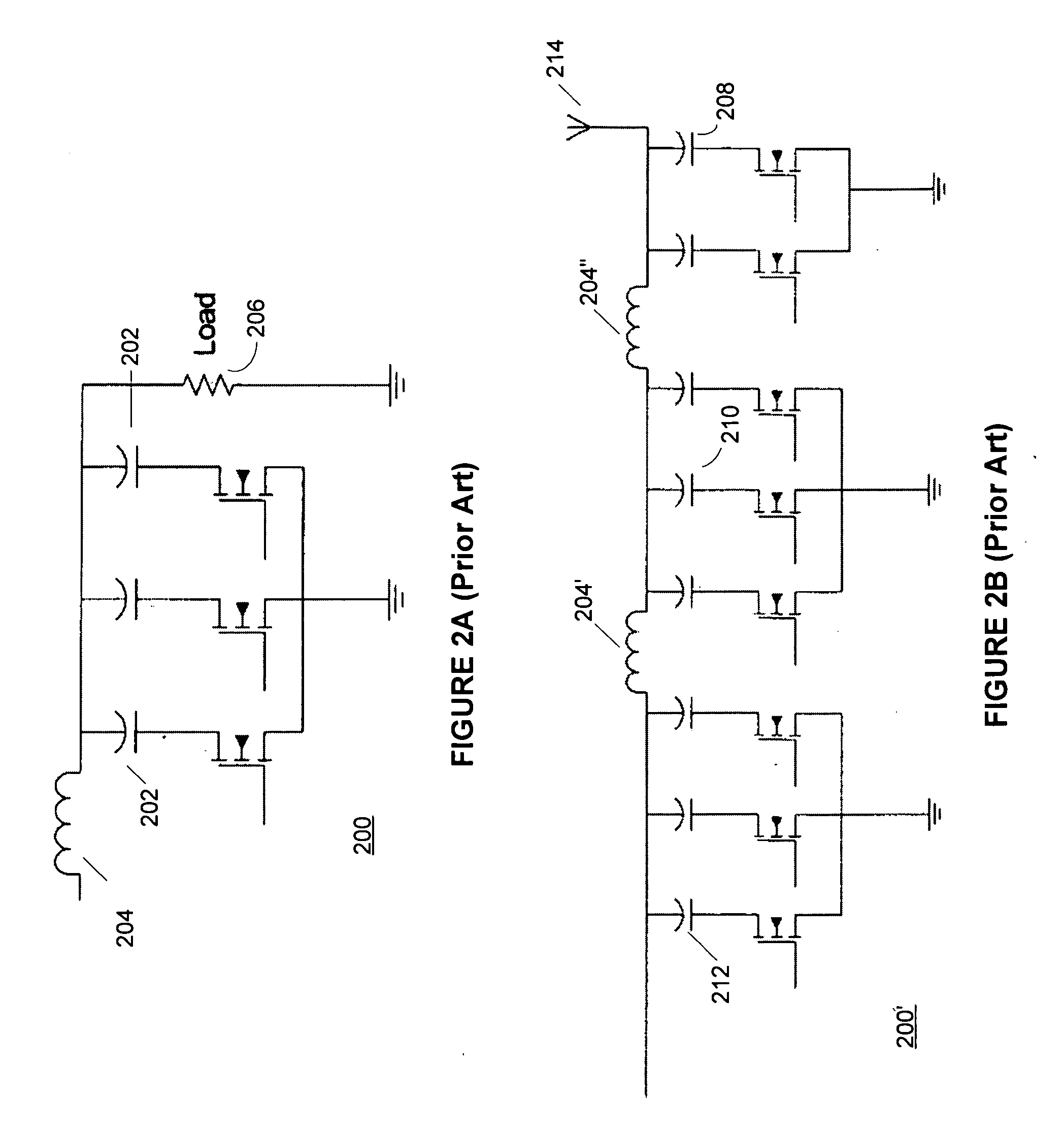
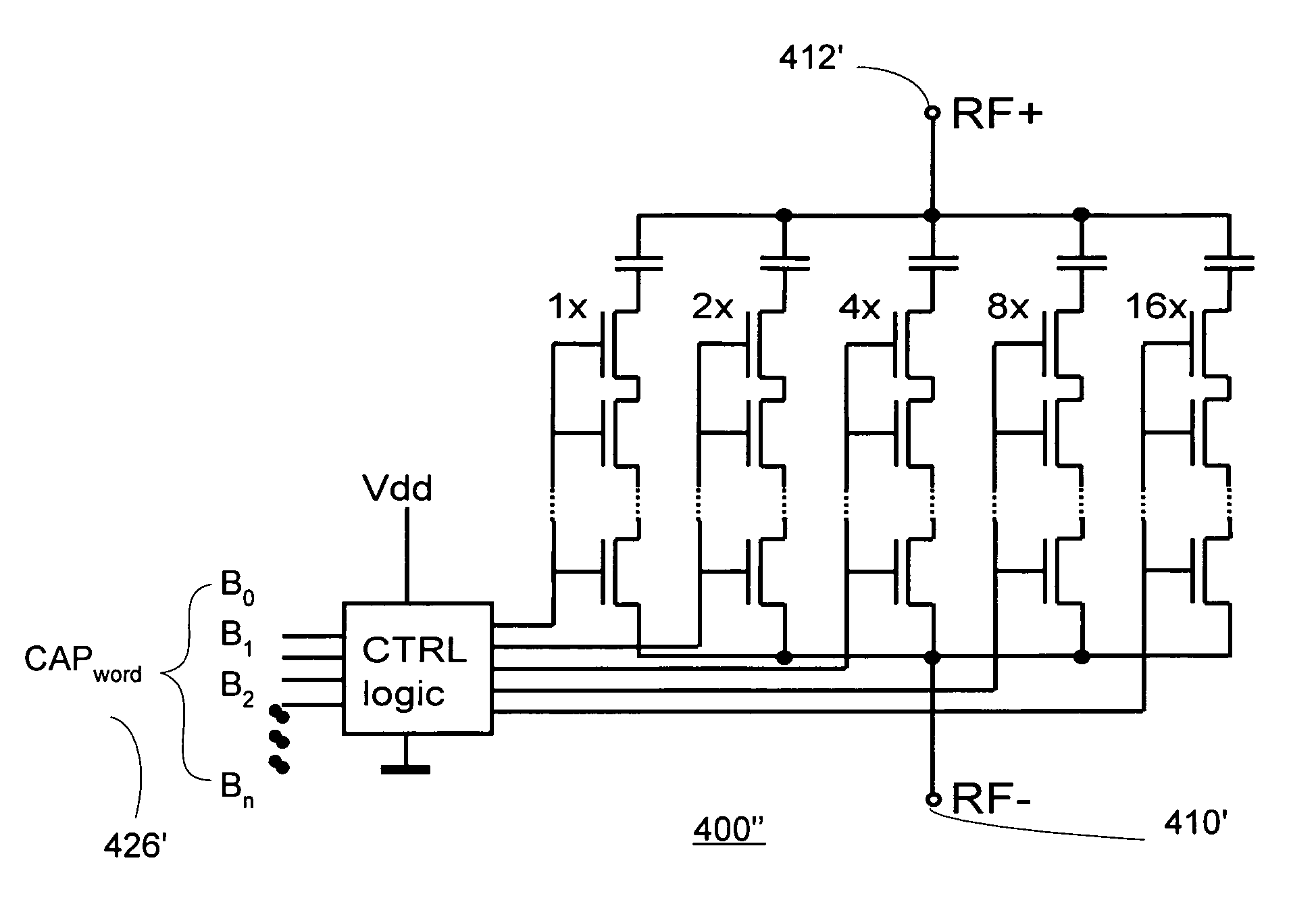
Method and apparatus for use in digitally tuning a capacitor in an integrated circuit device
ActiveUS20110002080A1Easy to controlHigh Power Handling CapabilityAnalogue/digital conversionImpedence matching networksCapacitanceLeast significant bit
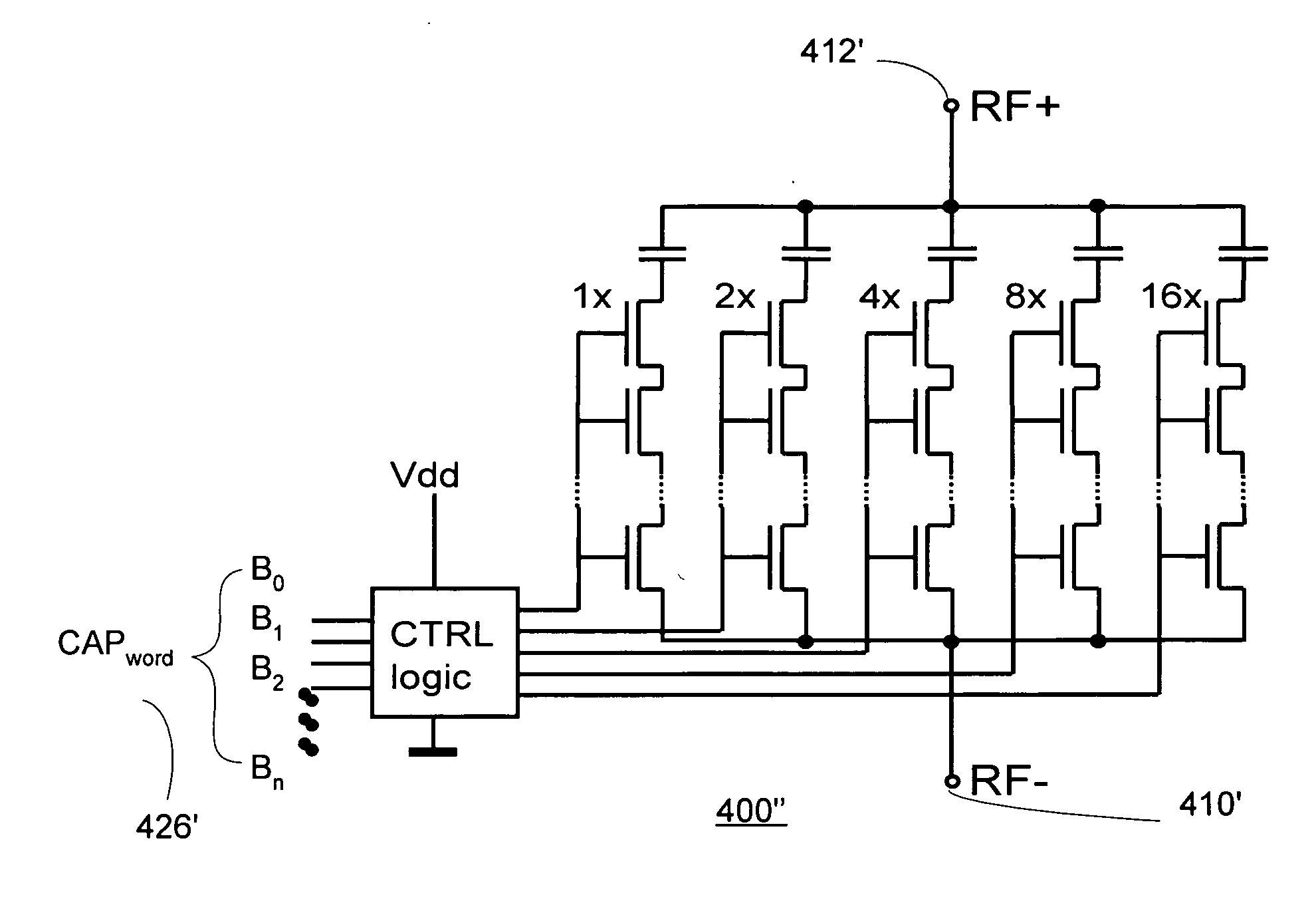
A method and apparatus for use in a digitally tuning a capacitor in an integrated circuit device is described. A Digitally Tuned Capacitor DTC is described which facilitates digitally controlling capacitance applied between a first and second terminal. In some embodiments, the first terminal comprises an FW+ terminal and the second terminal comprises an RF terminal. In accordance with some embodiments, the DTCs comprises a plurality of sub-circuits ordered in significance from least significant bit (LSB) to most significant bit (MSB) sub-circuits, wherein the plurality of significant bit sub-circuits are coupled together in parallel, and wherein each sub-circuit has a first node coupled to the first RF terminal, and a second node coupled to the second FW terminal. The DTCs further include an input means for receiving a digital control word, wherein the digital control word comprises bits that are similarly ordered in significance from an LSB to an MSB.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
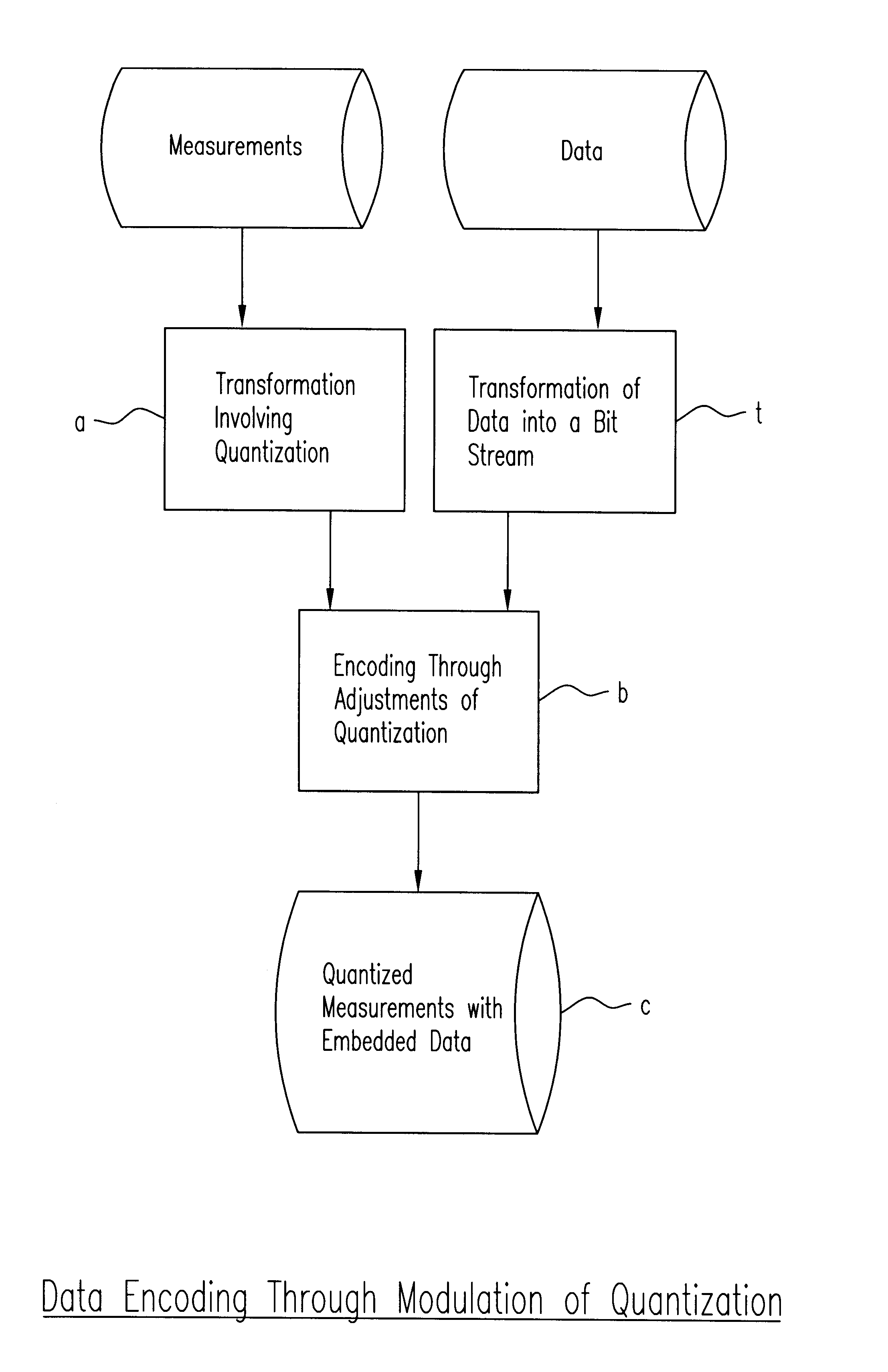
Method of and apparatus for high-bandwidth steganographic embedding of data in a series of digital signals or measurements such as taken from analog data streams or subsampled and/or transformed digital data
InactiveUS6768980B1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisDigital dataData stream
A novel technique for high-bandwidth steganographic embedding of supplemental data in a series of digital signals or measurements, such as taken from analog data streams or subsampled and / or transformed digital data, wherein the series of measurements are derived through functional transformations and involving quantization and / or aliasing, with the supplemental data bits modulating or modifying the quantized and / or aliased components with only slight adjustments thereof to embed the supplemental data without substantially affecting the quality of the measurements; and all, preferably, through not exclusively, with the use of least-significant-bit parity encoding designed to choose the appropriate components to be so modulated or modified
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
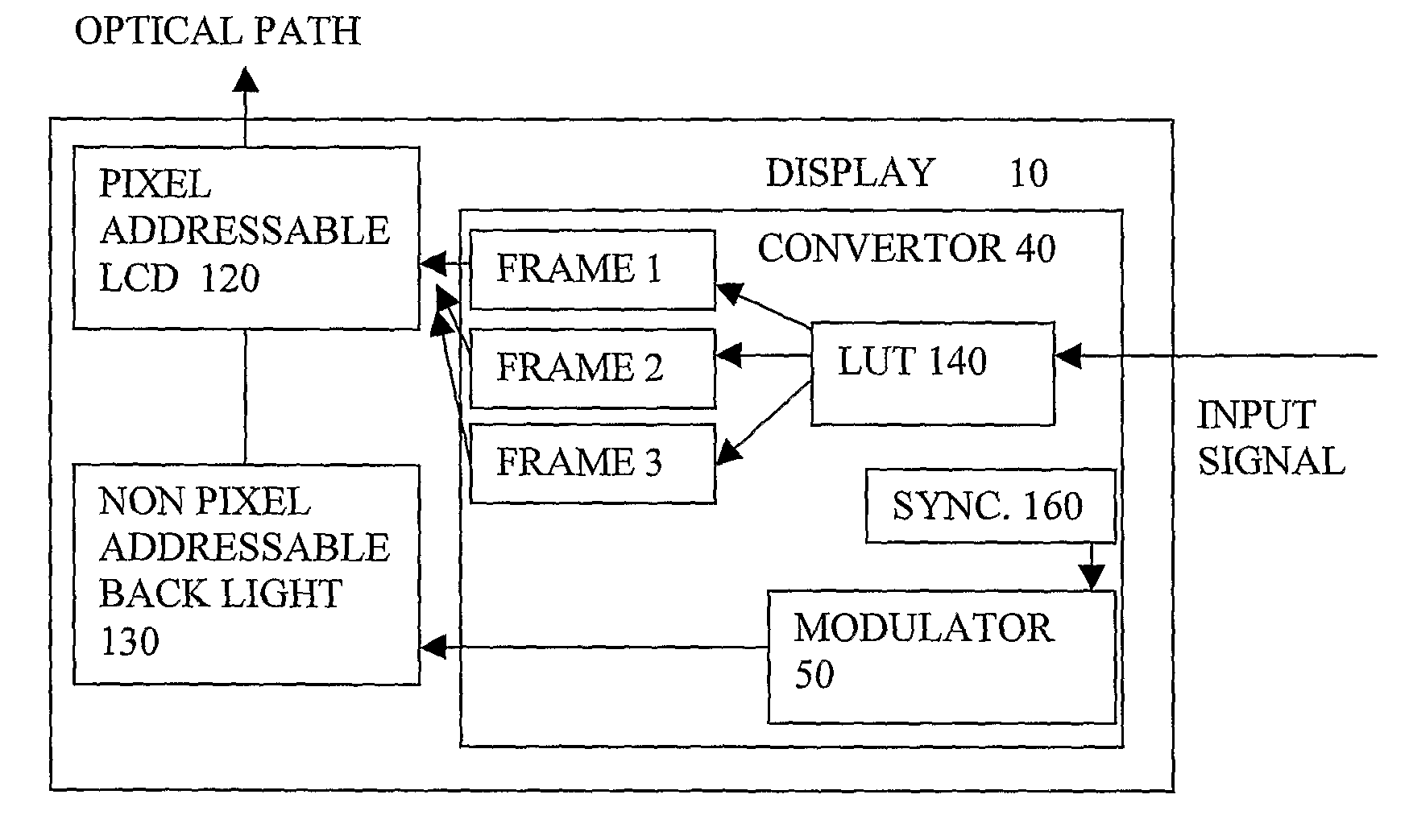
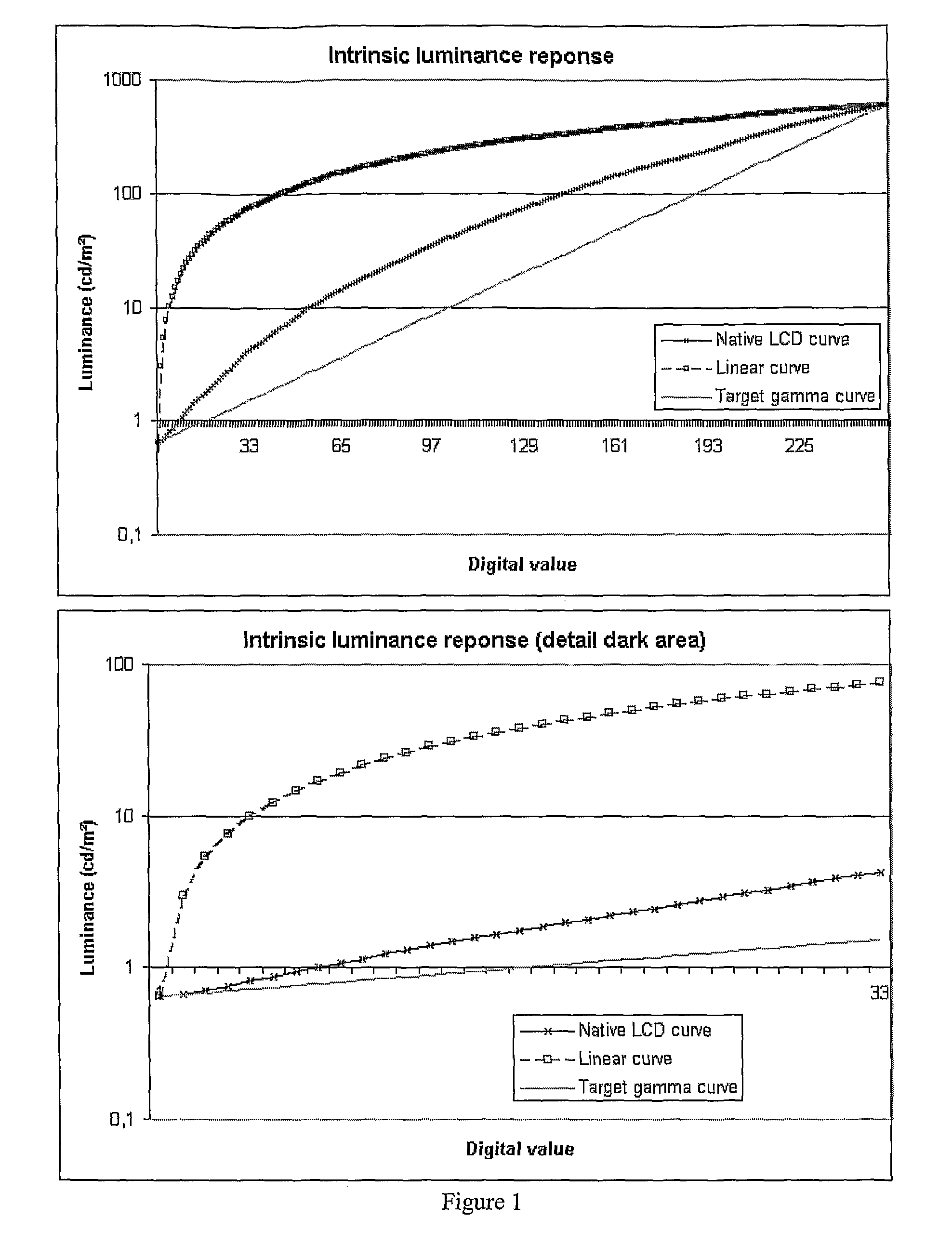
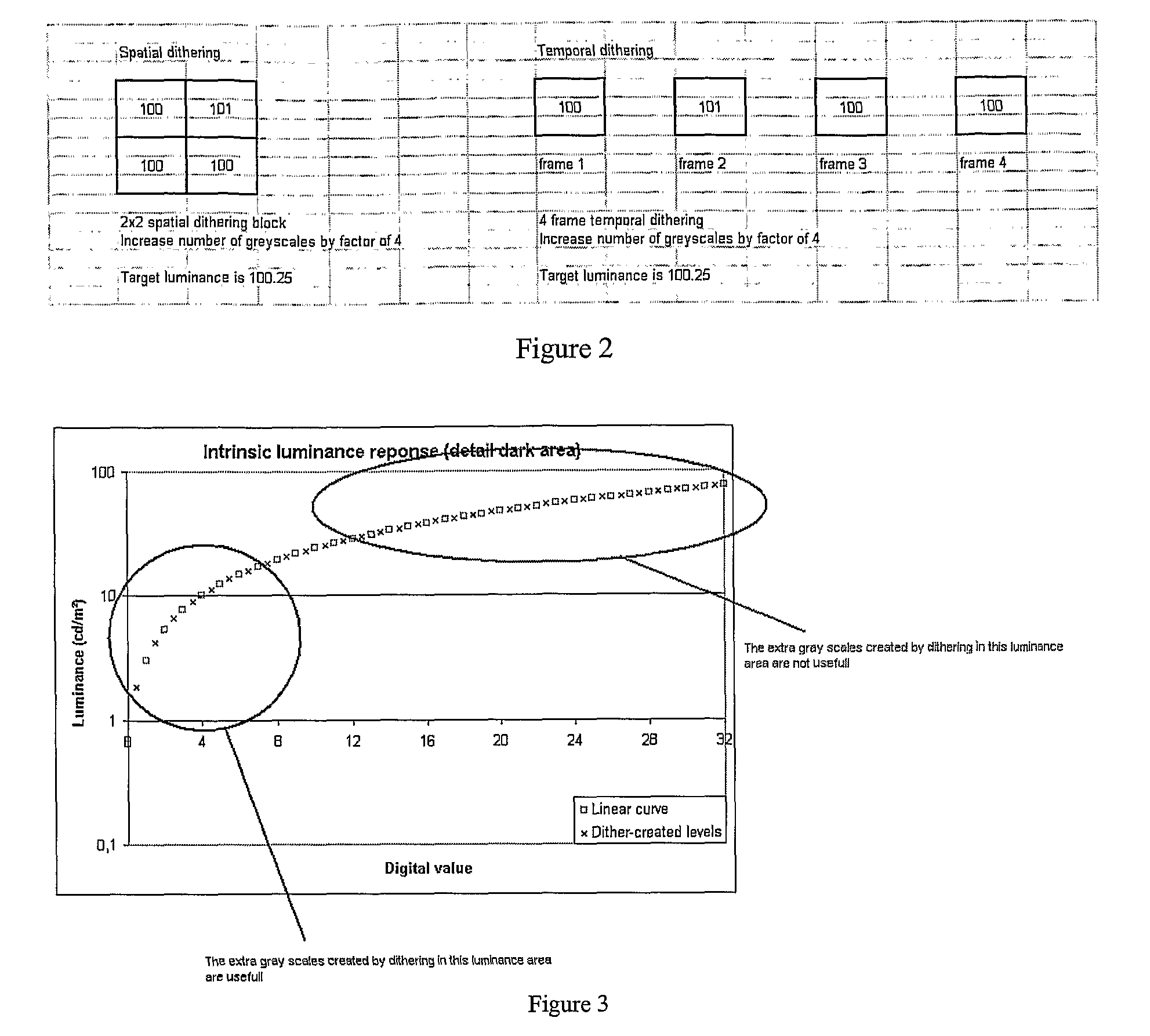
Backlight Modulation For Display
InactiveUS20080094426A1Ease riseEase fall time specificationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceLeast significant bit
A display ( 10 ) has a non pixel addressable backlight ( 130 ), having a temporal modulation applied, a pixel addressable LCD ( 120 ) in an optical path and the pixel addressable part being arranged to output each pixel of a frame as a temporal sequence of output values unrelated to colour components of the pixel, different values of the sequence coinciding with different output levels of the modulated non pixel addressable part. The apparent luminance or colour of the pixels can be made to take intermediate values between the gradations dictated by the stepsize corresponding to a least significant bit of the pixel addressable part, to enable more accurate reproduction of both colour and greyscale images. Additional intermediate output levels are concentrated at low illumination levels. A convertor generates a temporal modulation of the pixels for the LCD according to a value of the pixels in an input signal, and synchronized to the temporal modulation of the backlight.
Owner:BARCO NV
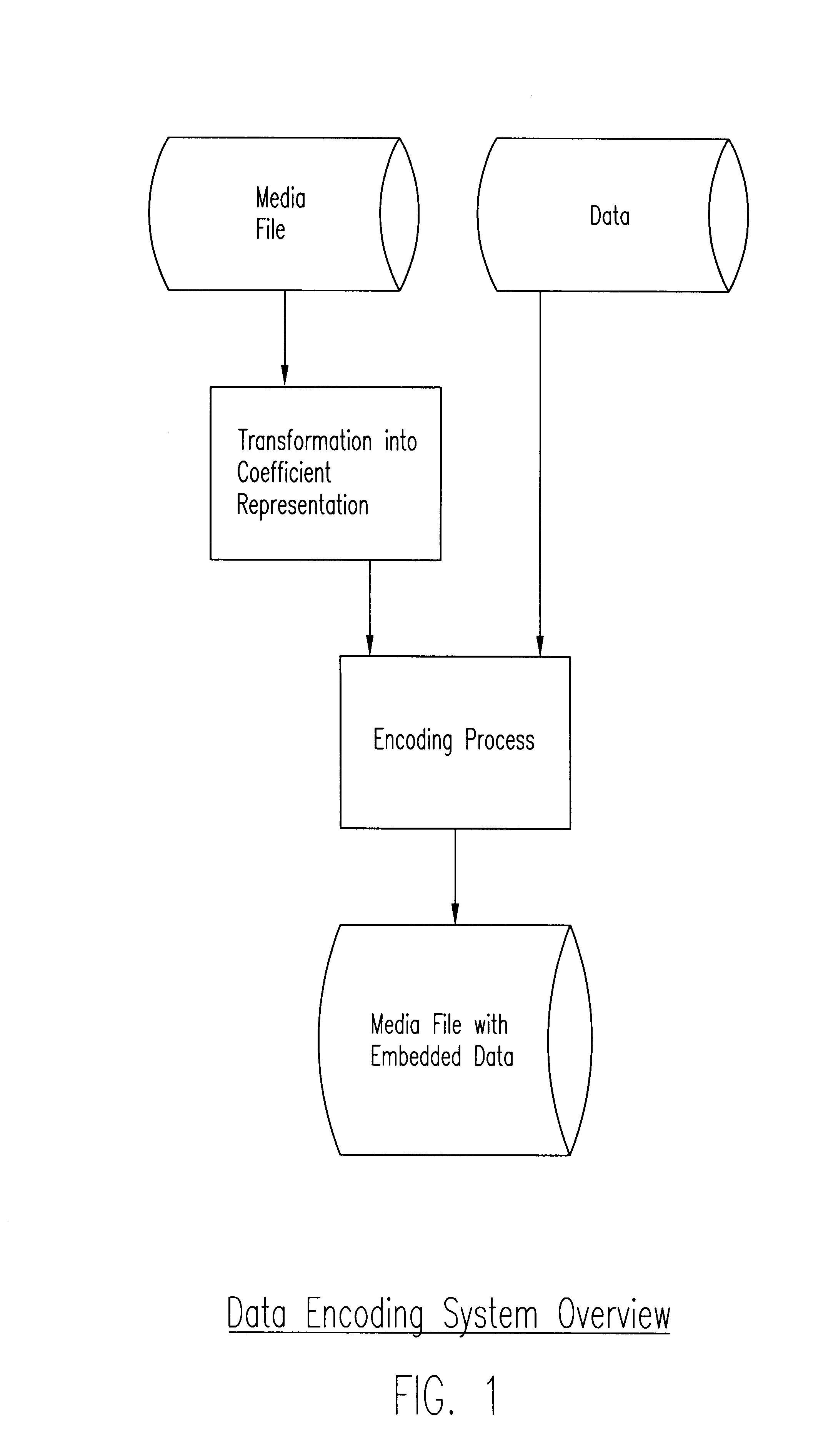
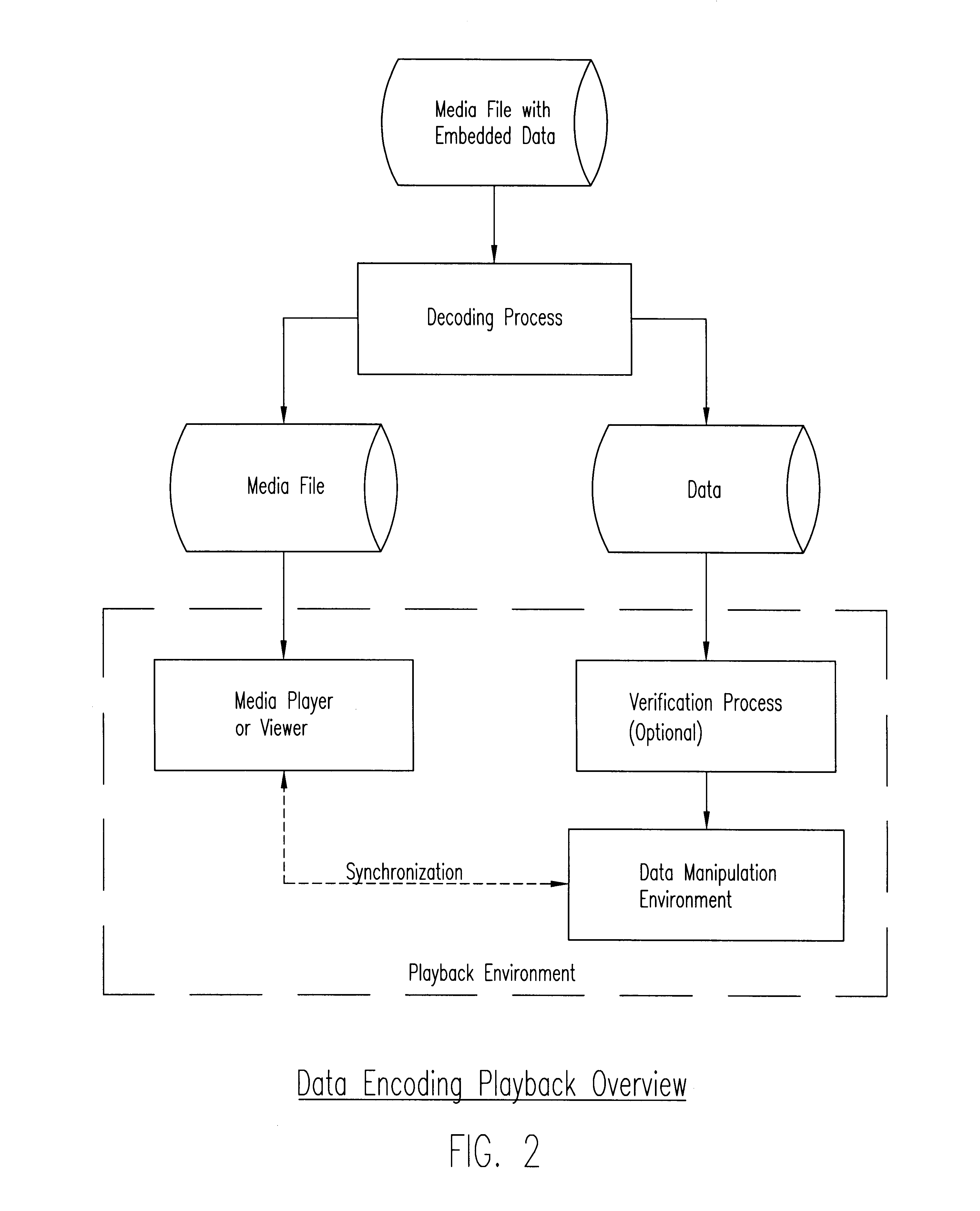
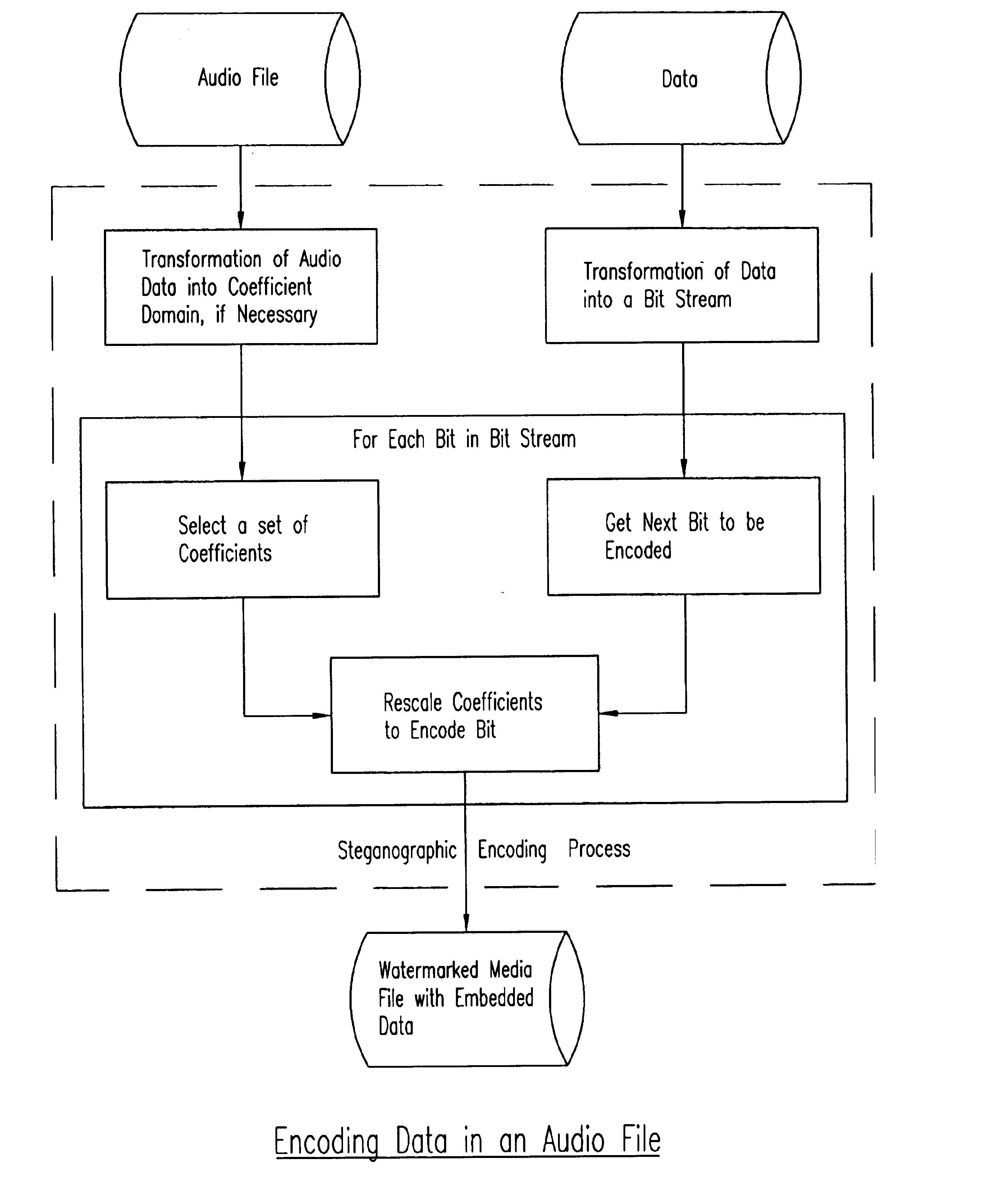
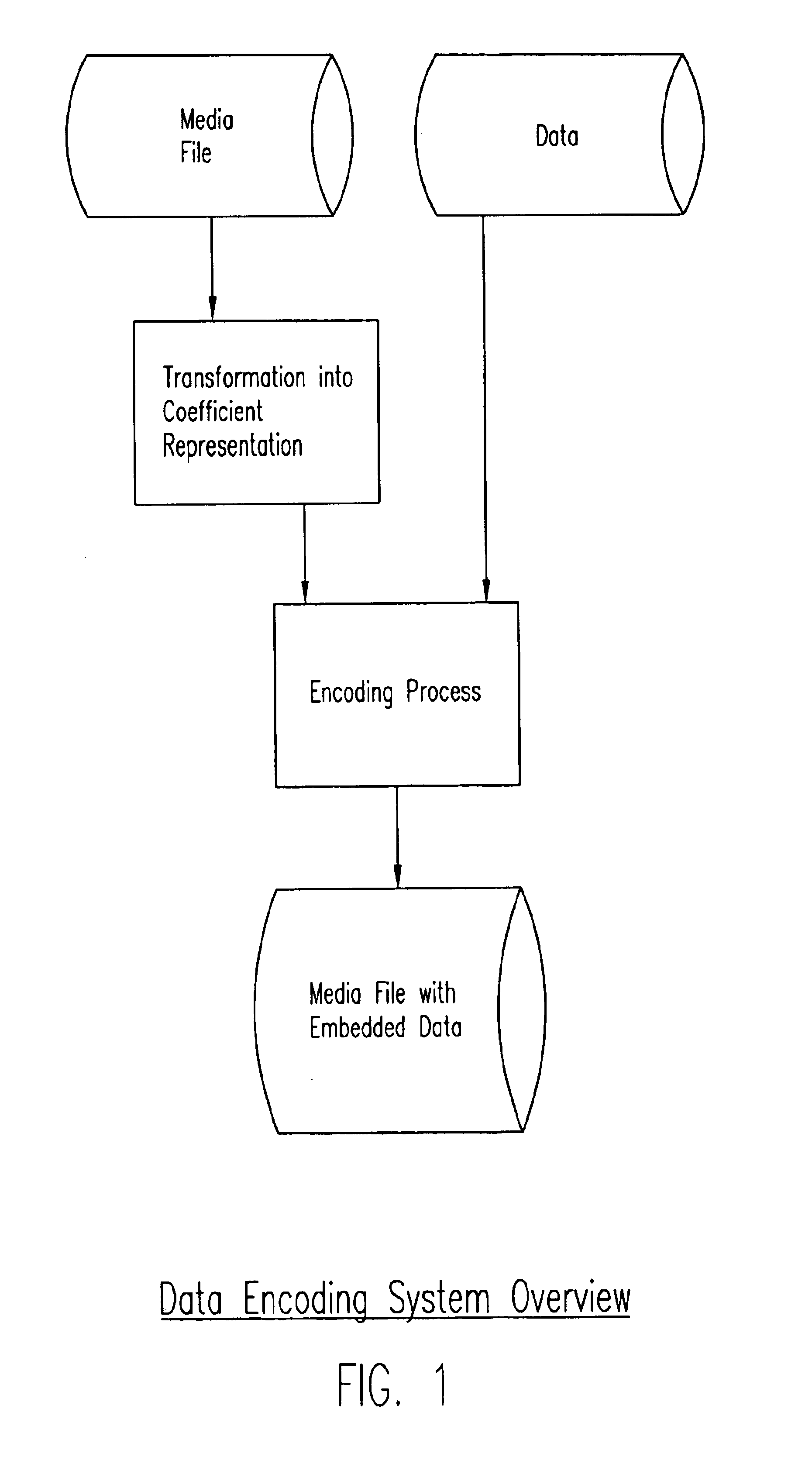
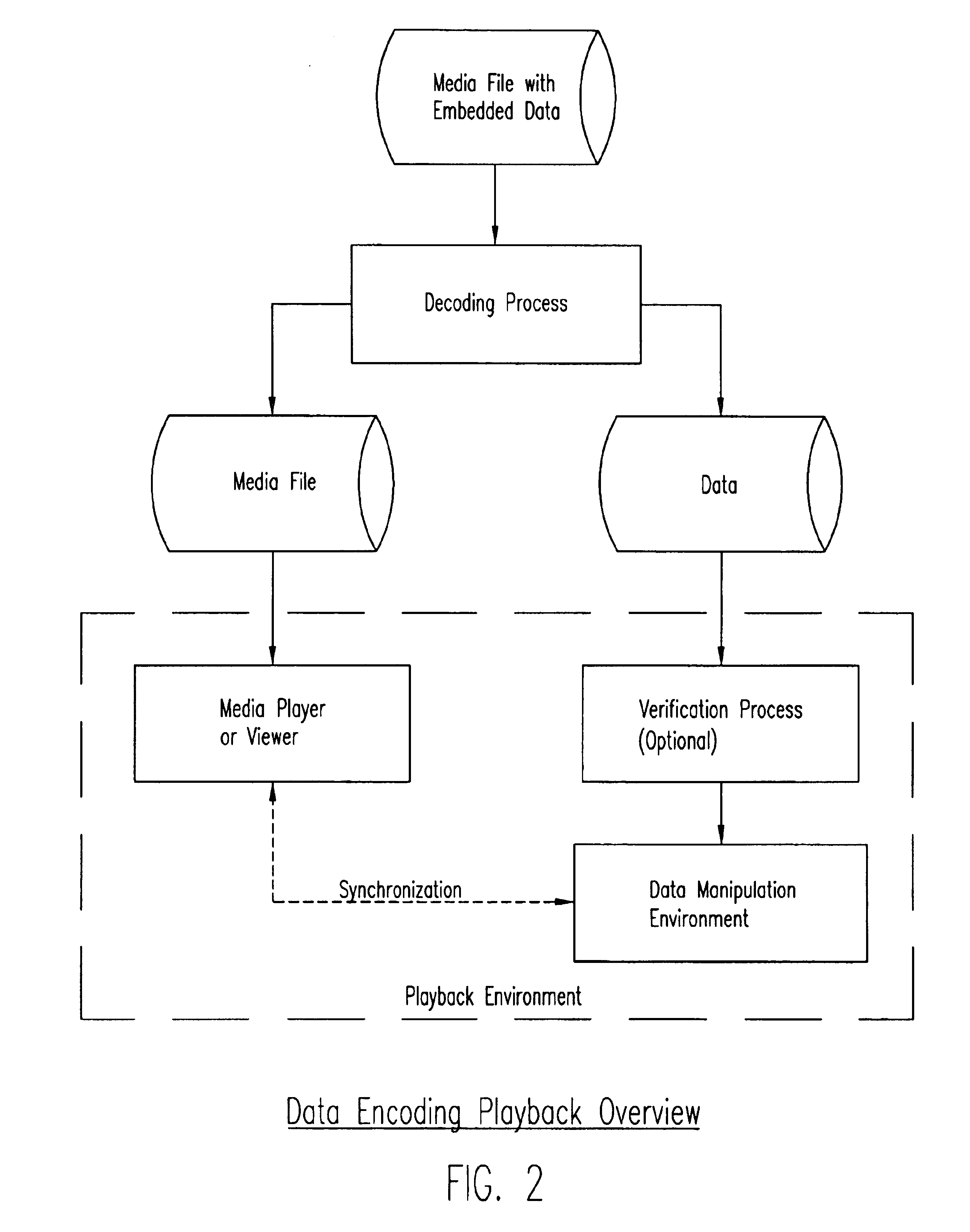
Process, system, and apparatus for embedding data in compressed audio, image video and other media files and the like
InactiveUS6748362B1User identity/authority verificationError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsDigital dataComputer graphics (images)
A novel process and system for enabling the seamless and facile embedding of relatively large quantities of supplemental digital data into pre-prepared digital media files (audio, image, video, 3D, volumetric and multimedia and the like) by compressing such files and encoding them into sets of coefficient representations (preferably frequency-domain coefficient representations) of the pre-prepared media file information, and embedding bits of the supplemental digital data at selected coefficients, preferably, though not exclusively, using the least significant bit of the selected coefficients, and with stenographic encoding processes.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
Video coding
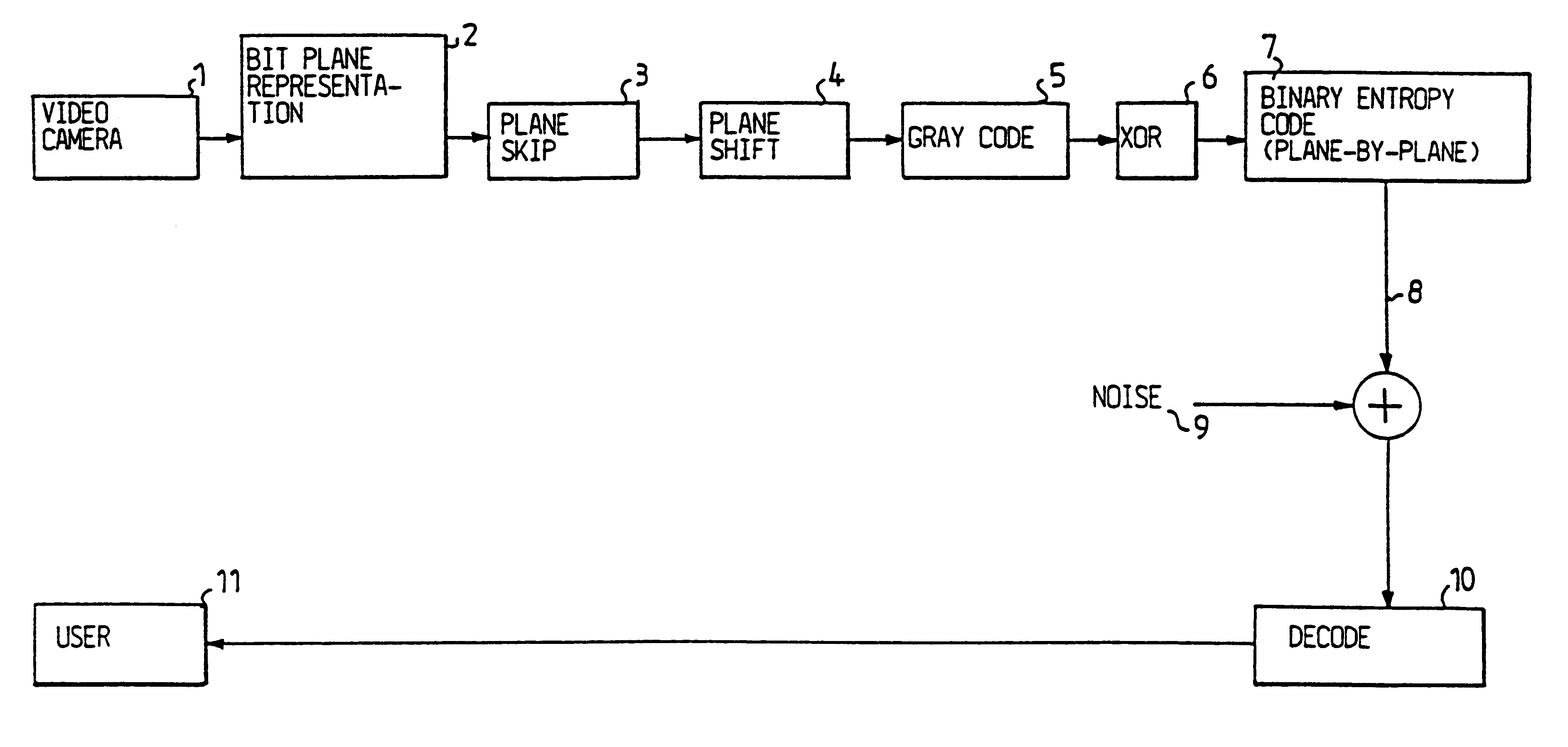
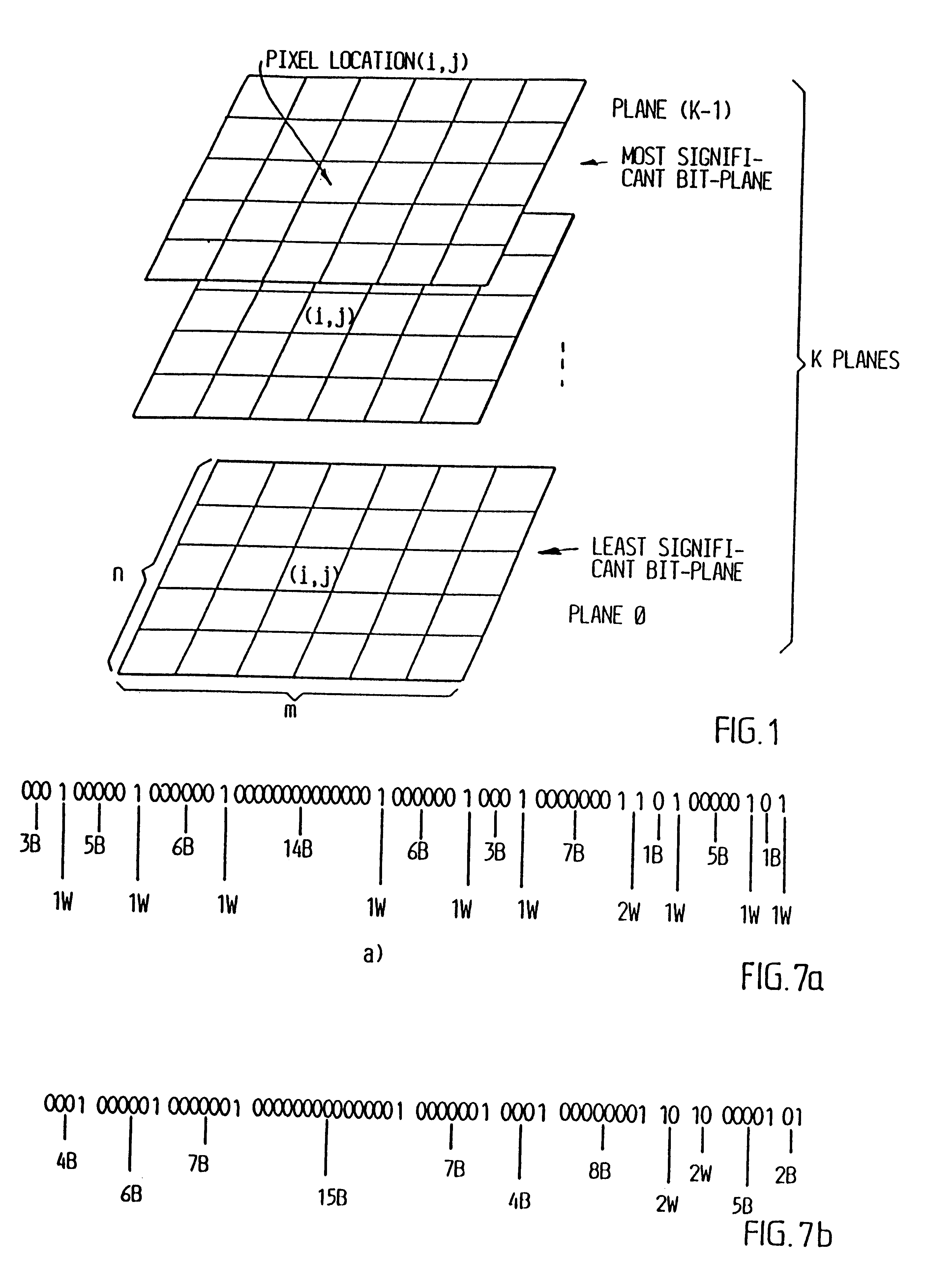
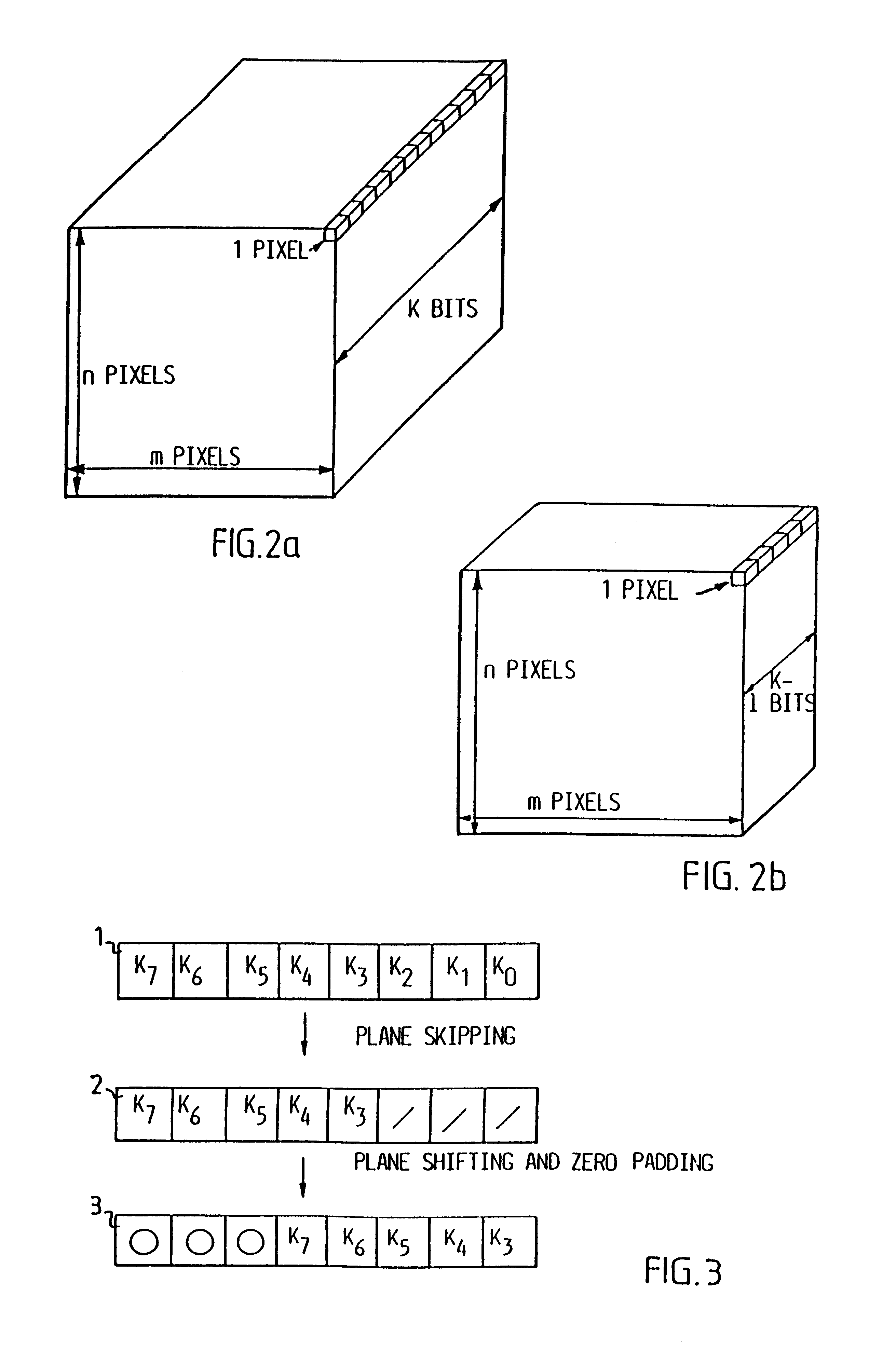
InactiveUS6208761B1Reduce in quantityEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsVideo sequenceBit plane coding
Digitalized video images are compressed in several steps in order to provide a system for transmitting moving video pictures via narrow band channels, such as the telephone network. The system is based on any extension of the bit-plane coding technique to video sequences and lossy conditions. The compression technique can also be advantageously used in a lossless compression system. The system involves the steps of bit plane representation and skipping the least significant bit plane(s), shifting the pixels, coding with a Gray code, the use of segmentation, and motion-estimation / motion compensation and application of a transmit / not transmit / motion compensate (TX / NT / MC) procedure, exploiting of the temporal redundancy of two corresponding bit planes via an XOR operation on two successive images, and a plane-by-plane application of an extended RLEID technique. The RLEID technique includes coding a run of like binary symbols with one word, the run including a transition between the penultimate and ultimate binary symbol.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
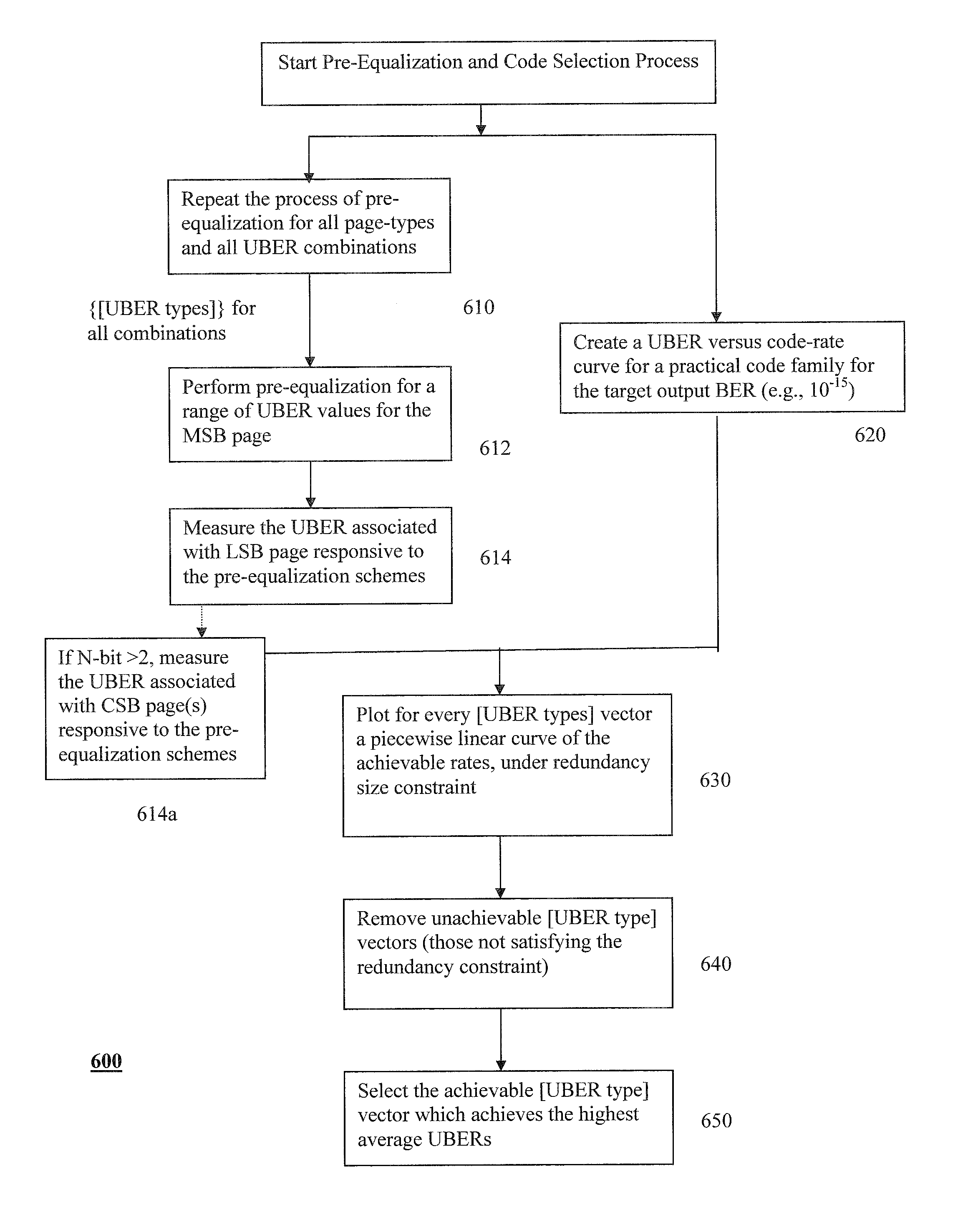
Systems and methods for pre-equalization and code design for a flash memory
ActiveUS20110055461A1High average UBERError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLeast significant bitEqualization
A system, computer readable program, and method for programming flash memory, the method includes: providing multiple pairs of most significant bit (MSB) page uncoded bit error rates (UBERs) and least significant bit (LSB) page UBERs; selecting a selected MSB page code rate and a selected LSB page code rate so that a selected MSB page UBER associated with the selected MSB page code rate and a selected LSB page UBER associated with the selected LSB page code rate support a highest average UBER out of the multiple pairs of MSB page UBERs and LSB page UBERs, wherein the selected MSB page code rate and the selected LSB page code rate are obtainable under a desired code rate constraint; and determining an encoding and programming scheme that may be based on the selected MSB page UBER, the selected MSB code rate, the selected LSB page UBER and the selected LSB code rate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
CAM modified to be used for statistic calculation in network switches and routers
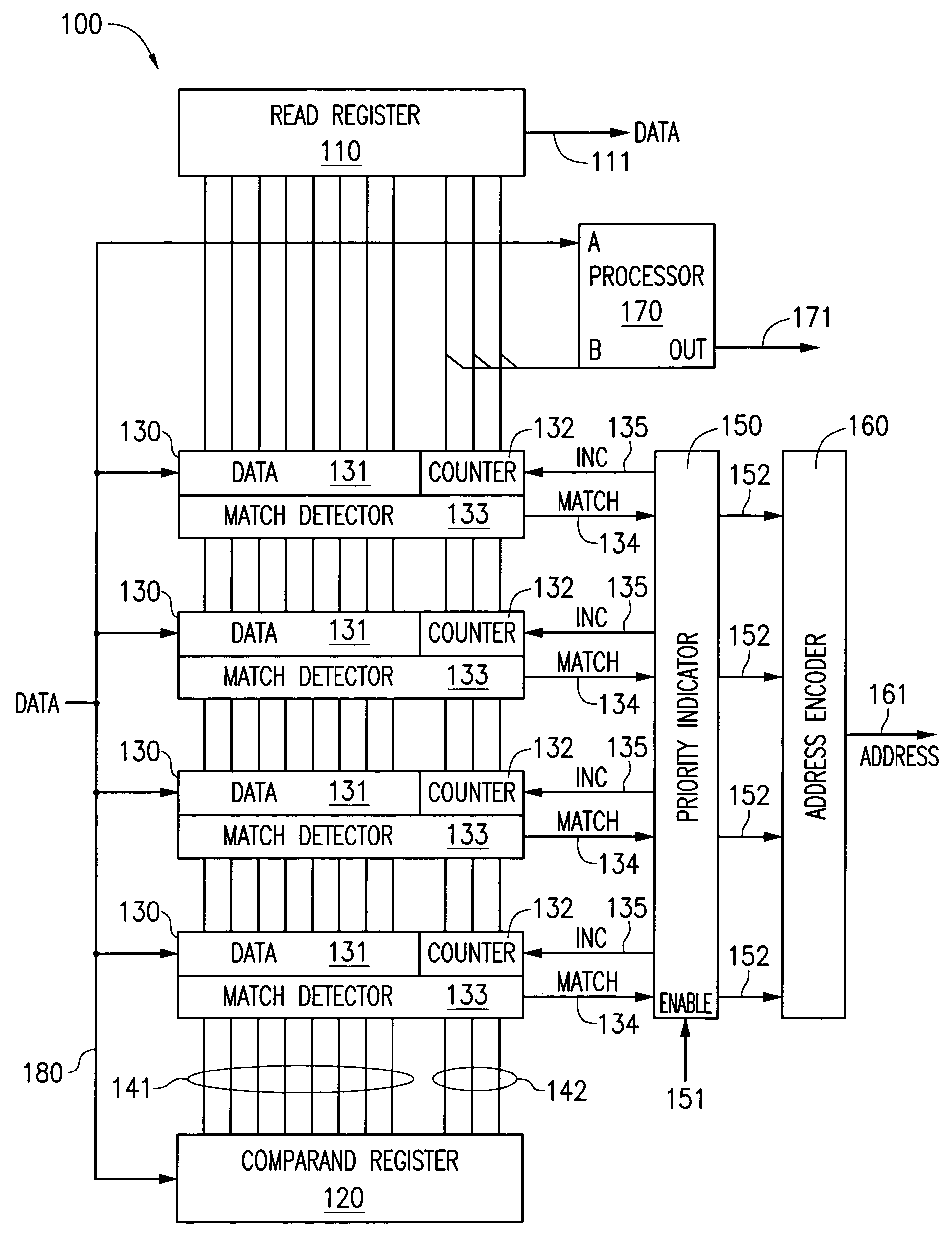
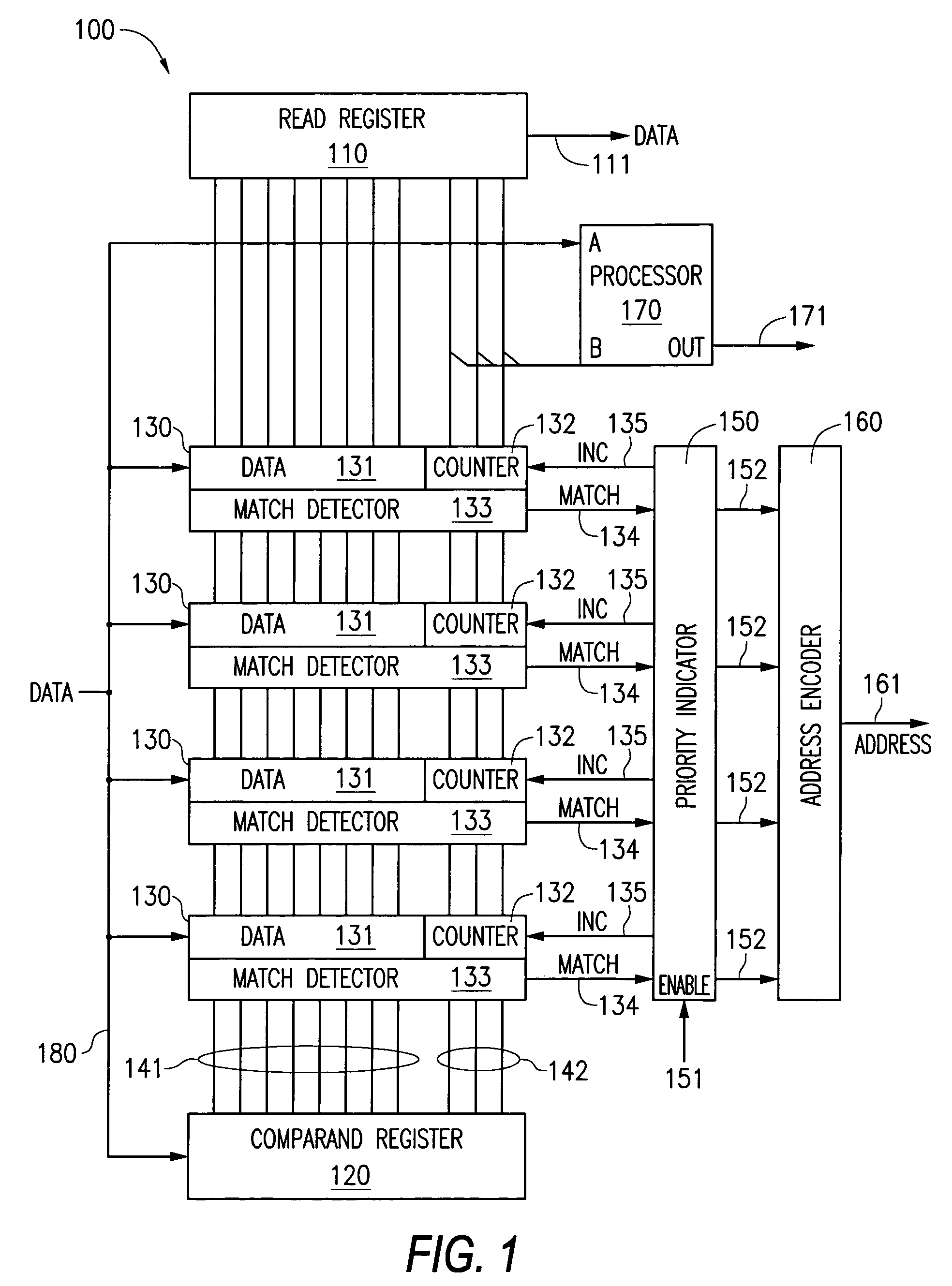
A content addressable memory (CAM) device includes a plurality of entries each having an associated counter. When a CAM entry matches a search word stored in the comparand register of the CAM device, the matching entry's counter may be incremented. Alternatively, if there are multiple matching entries, in some instances only one matching entry has its counter incremented. The counter value can be written or read as part of either the least significant or most significant bits of the CAM entry.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
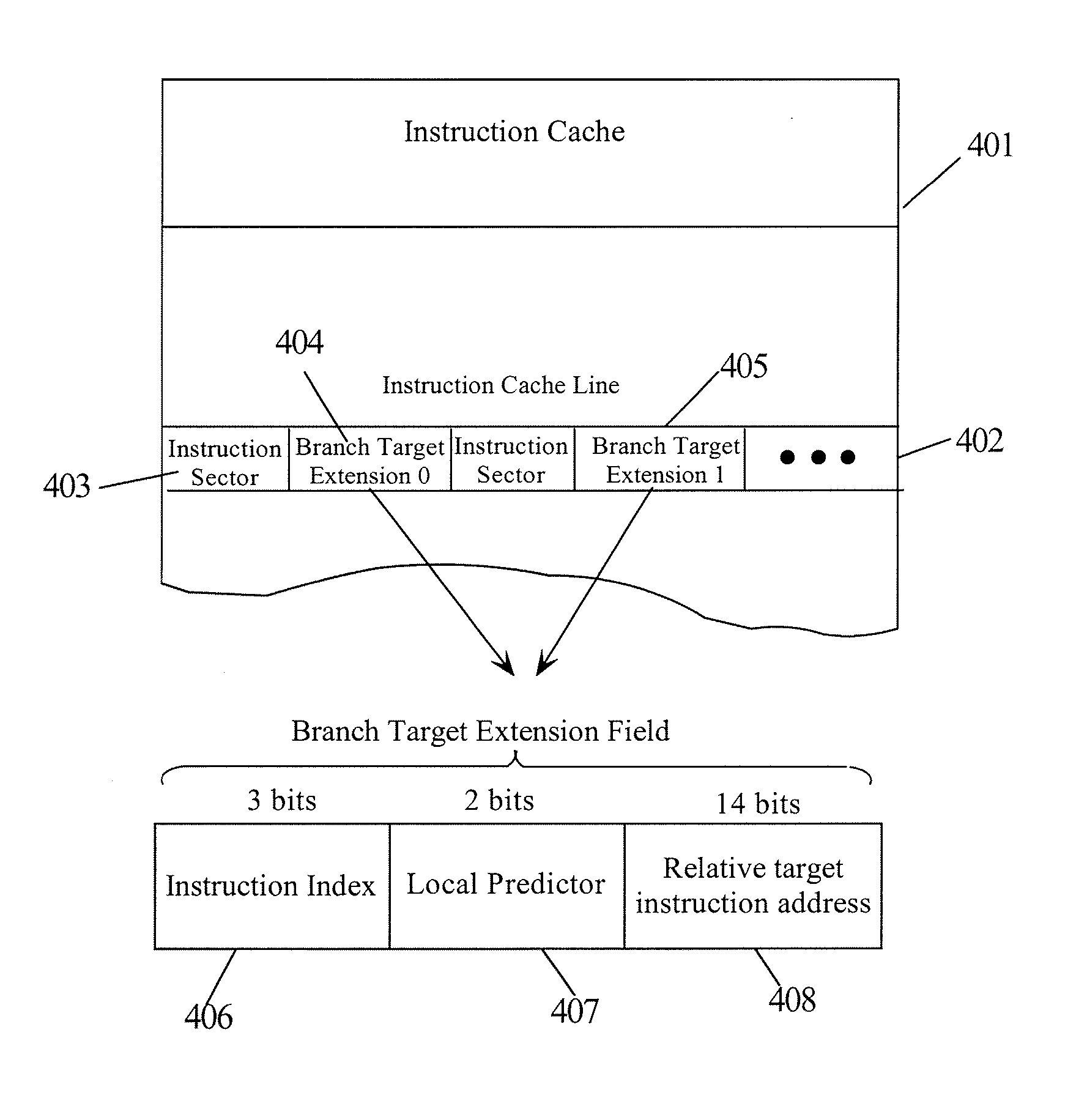
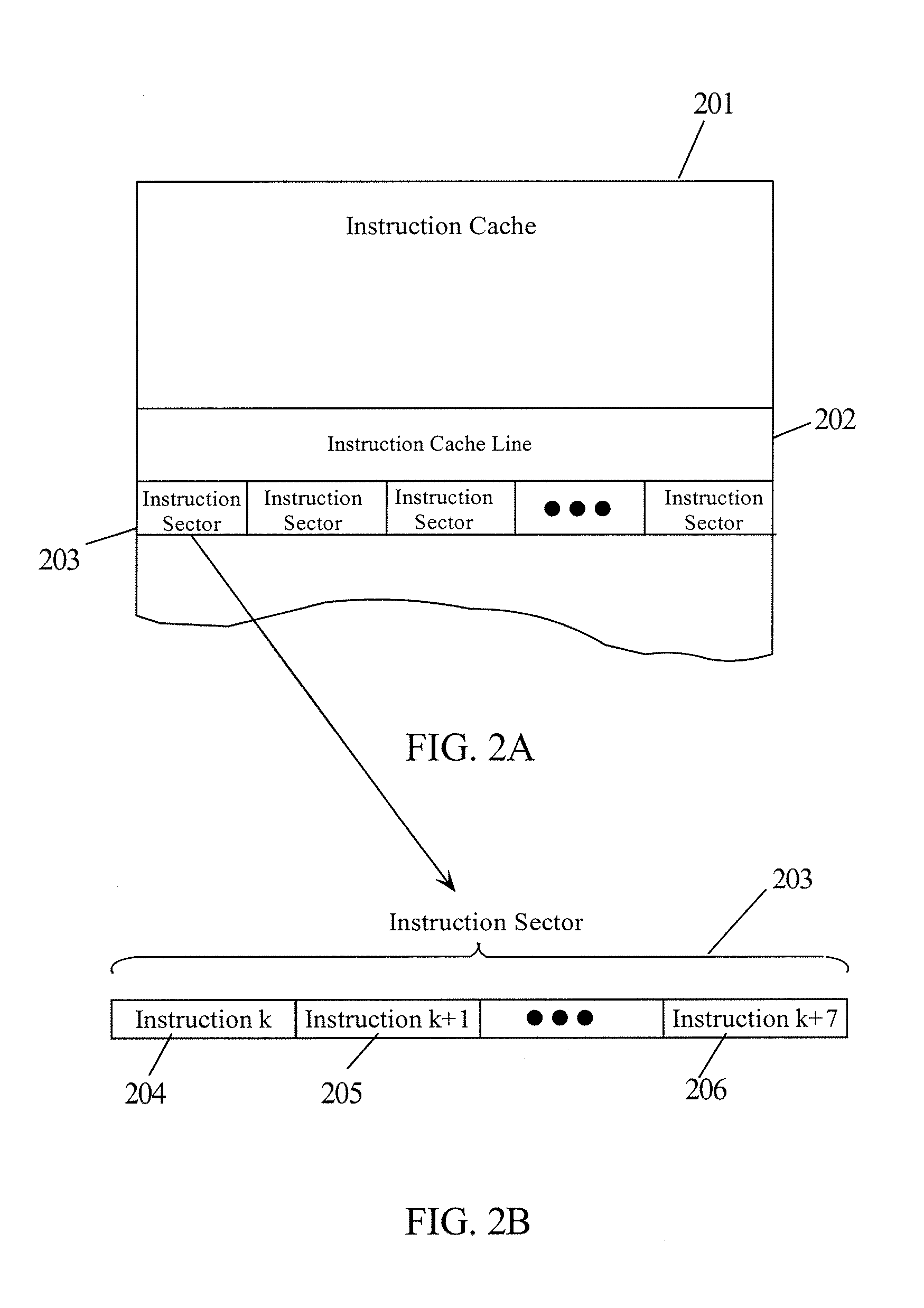
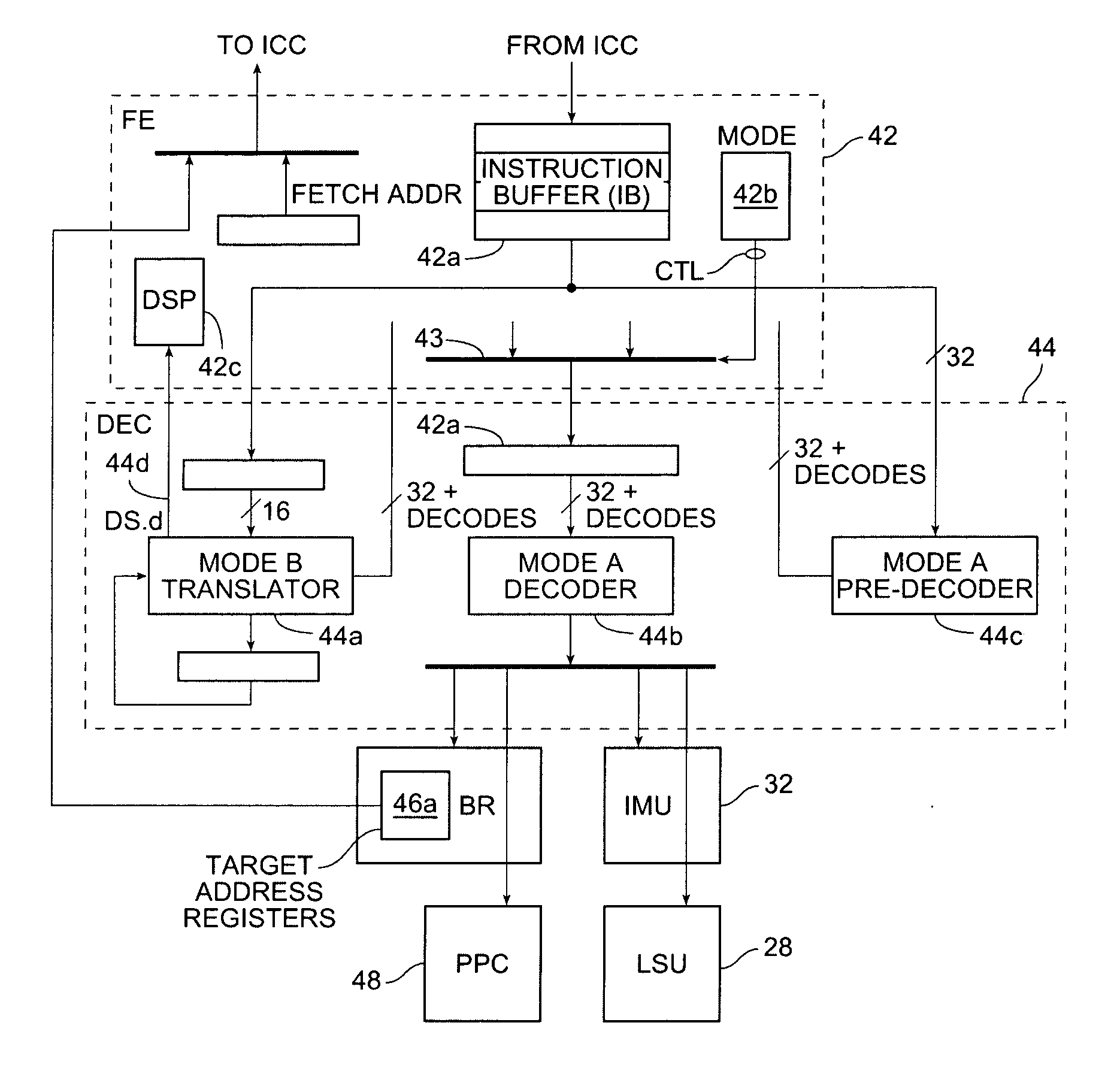
Branch Target Extension for an Instruction Cache
InactiveUS20080126771A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionBranch target addressLeast significant bit
An instruction cache (I-Cache) for a processor is configured to include a Branch Target Extension associated with each Instruction Sector. When an Instruction Sector is fetched, the Branch Target Extension is simultaneously fetched. If the Instruction Sector has a branch instruction that is predicted taken, then the branch target address in the branch extension is used to access the next Instruction Sector. In other embodiments, each Instruction Sector has a plurality of Branch Target Extensions each corresponding to a potential branch instruction in an Instruction Sector. In this case, the Branch Target Extensions are partitioned into an instruction index field for locating branch instruction in the Instruction Sector, a local predictor field for predicted taken status and a target address field for the branch target address. The least significant bits of the instruction fetch address are compared to the instruction indexes to determine a particular Branch Target Extension to use.
Owner:IBM CORP
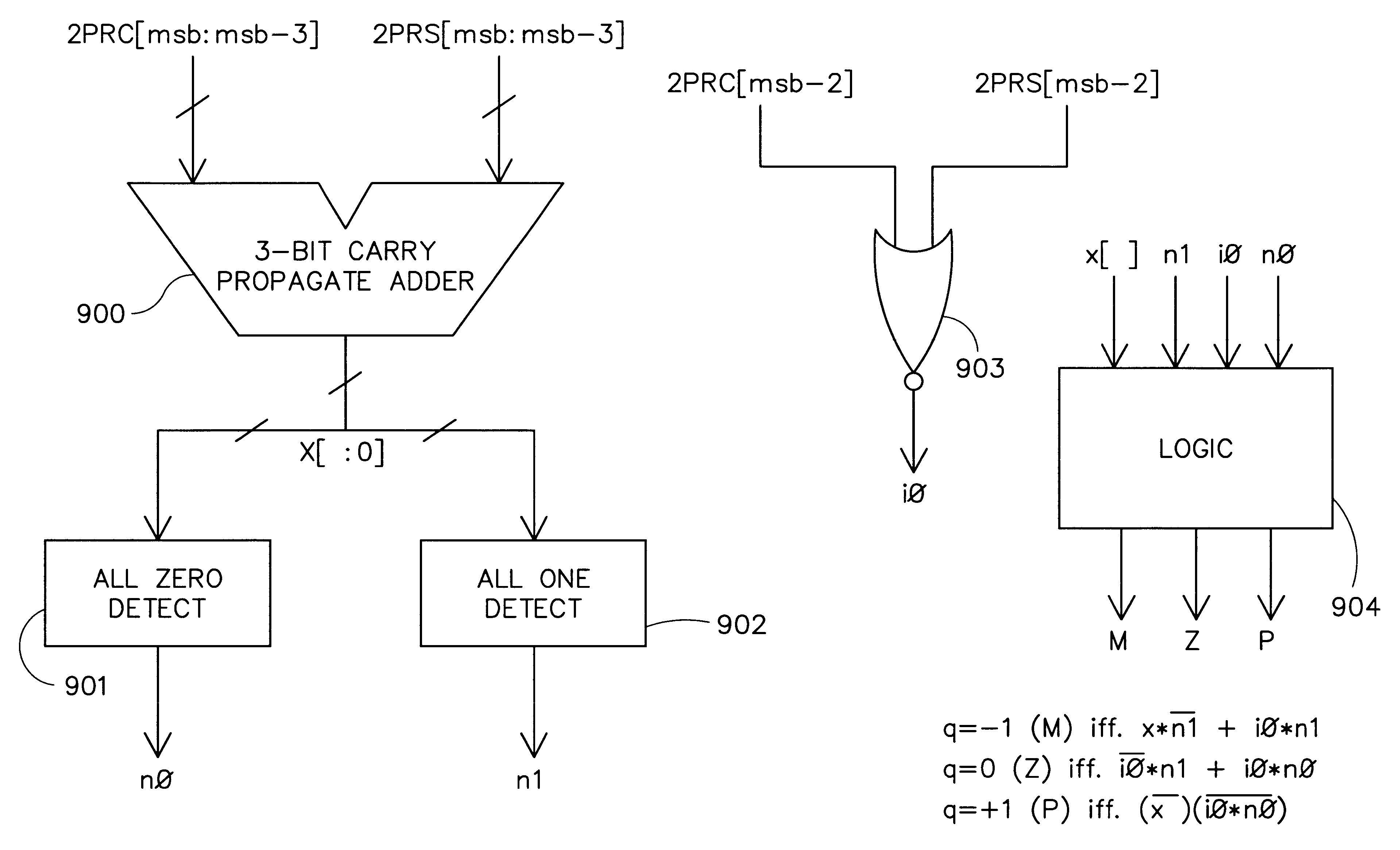
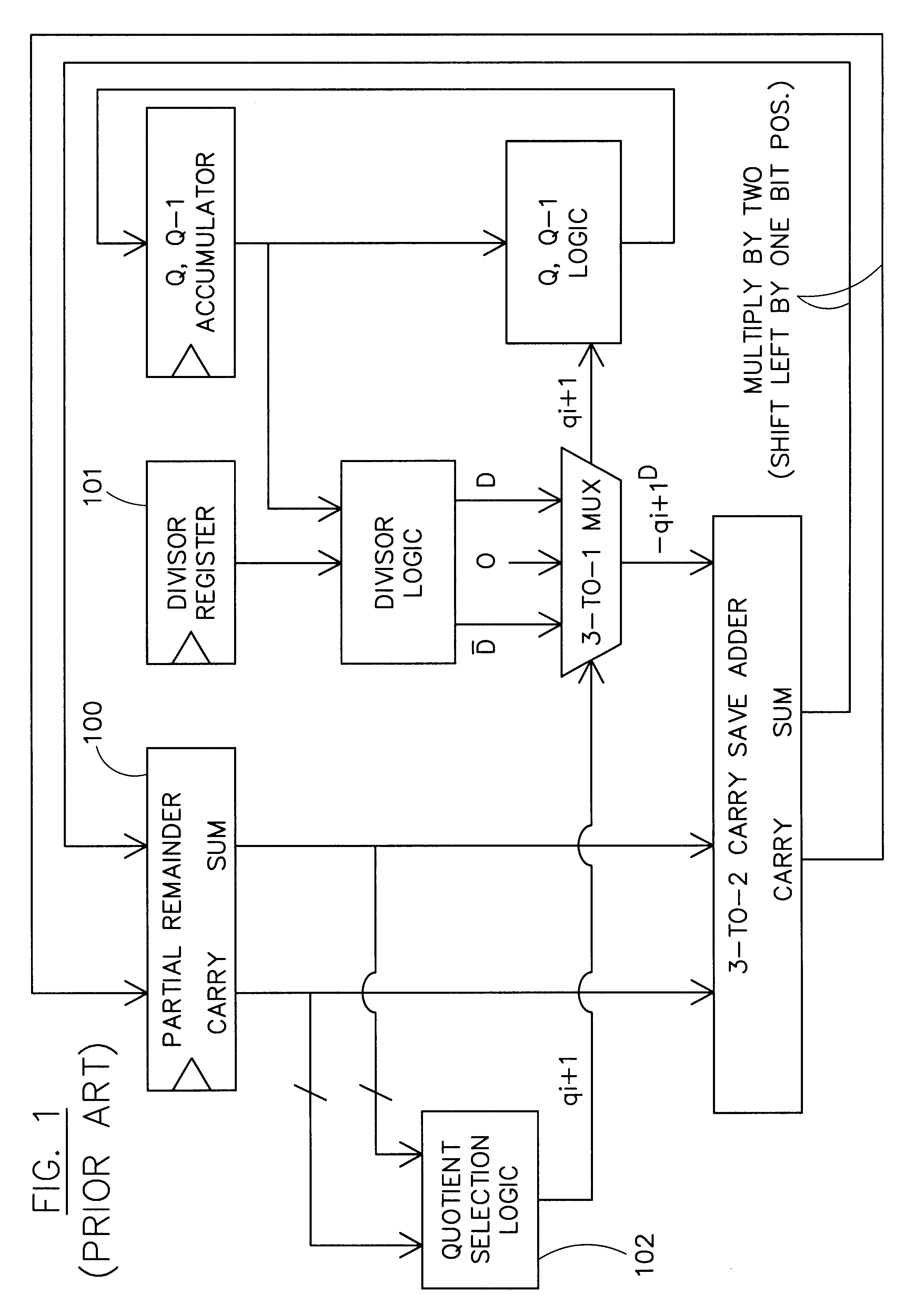
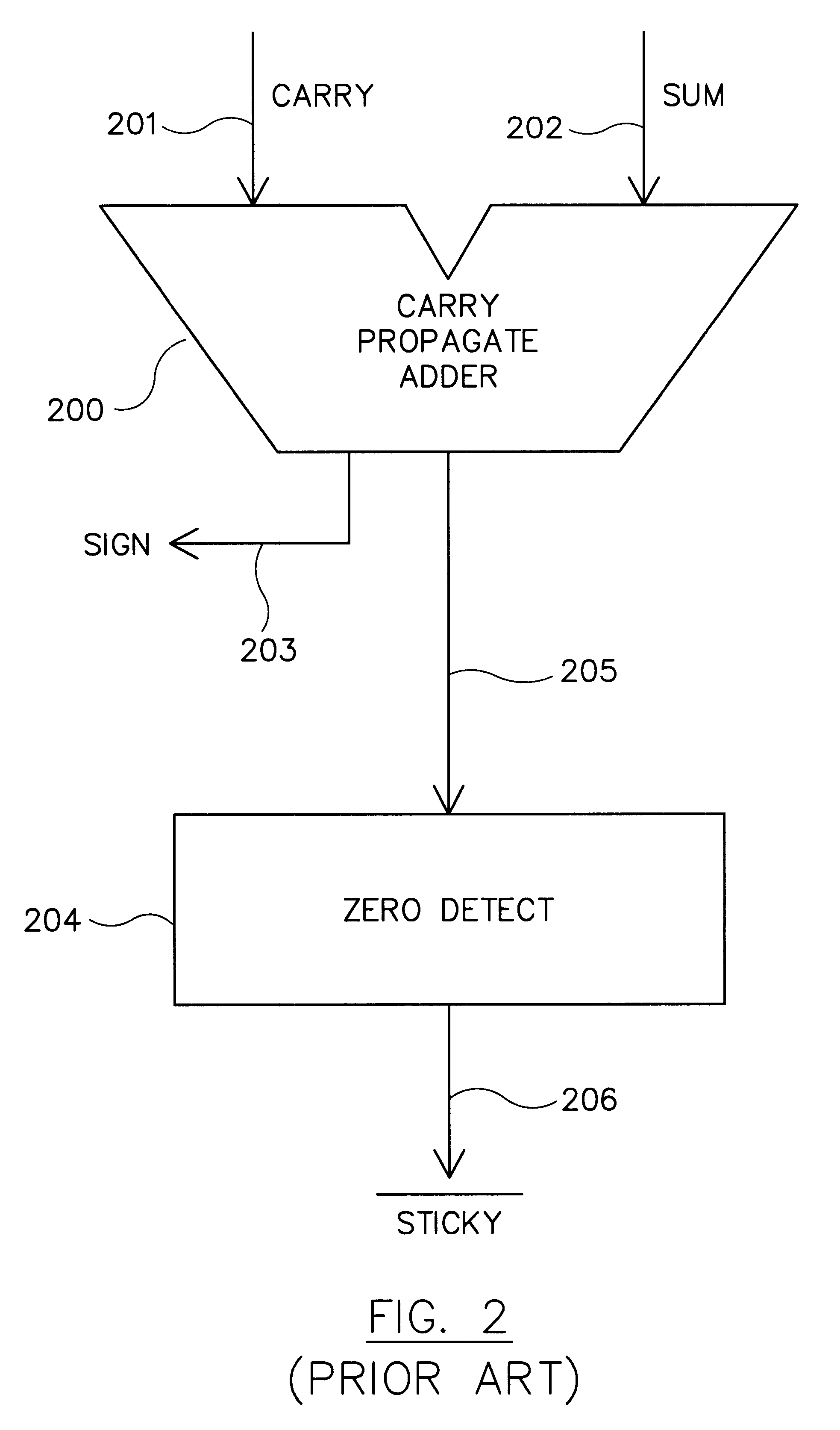
Quotient digit selection logic for floating point division/square root
InactiveUS6594681B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesCarry propagationAlgorithm
Quotient digit selection logic using a three-bit carry propagate adder is presented. An enhanced quotient digit selection function prevents the working partial remainder from becoming negative if the result is exact. The enhanced quotient digit selection logic chooses a quotient digit of zero instead of a quotient digit of one when the actual partial remainder is zero. Using a four bit estimated partial remainder where the upper four bits are zero, a possible carry propagation into fourth most significant bit is detected. This can be accomplished by looking at the fourth most significant sum and carry bits of the redundant partial remainder. If they are both zero, then a carry propagation out of that bit position into the least significant position of the estimated partial remainder is not possible, and a quotient digit of zero is chosen. This provides a one cycle savings since negative partial remainders no longer need to be restored before calculating the sticky bit. Extra hardware is eliminated because it is no longer necessary to provide any extra mechanism for restoring the preliminary final partial remainder. Latency is improved because no additional cycle time is required to restore negative preliminary partial remainders. In an alternative embodiment, where the upper three bits of the estimated partial remainder are ones while the fourth most significant bit is zero, a quotient digit of negative one is chosen. This alternative embodiment allows correct exact results in all rounding modes including rounding toward plus or minus infinity.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Memory system and method of accessing a semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS8027194B2Improve reliabilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTLeast significant bitMulti-level cell
One embodiment of a nonvolatile memory device includes a memory cell array including a plurality of multi-level cells, and a control unit configured to determine a characteristic of data to be stored in the memory cell array. The control unit is configured to select one of plural multi-bit programming methods based on the determination. Data is stored in the memory cell array according to the selected multi-bit programming method, and at least one of the plural multi-bit programming methods maintains least significant bit data when there is a program fail of most significant bit data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
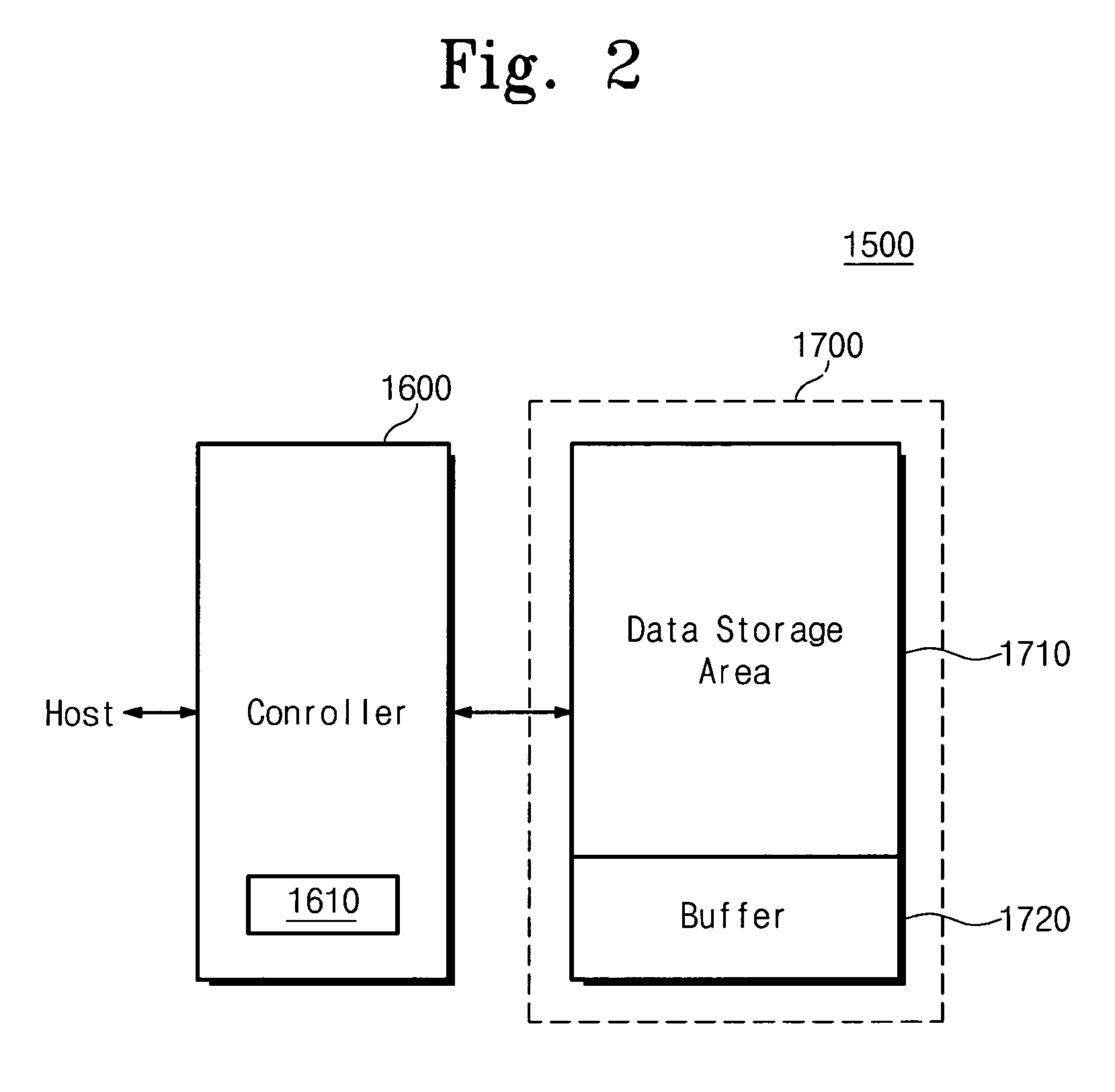
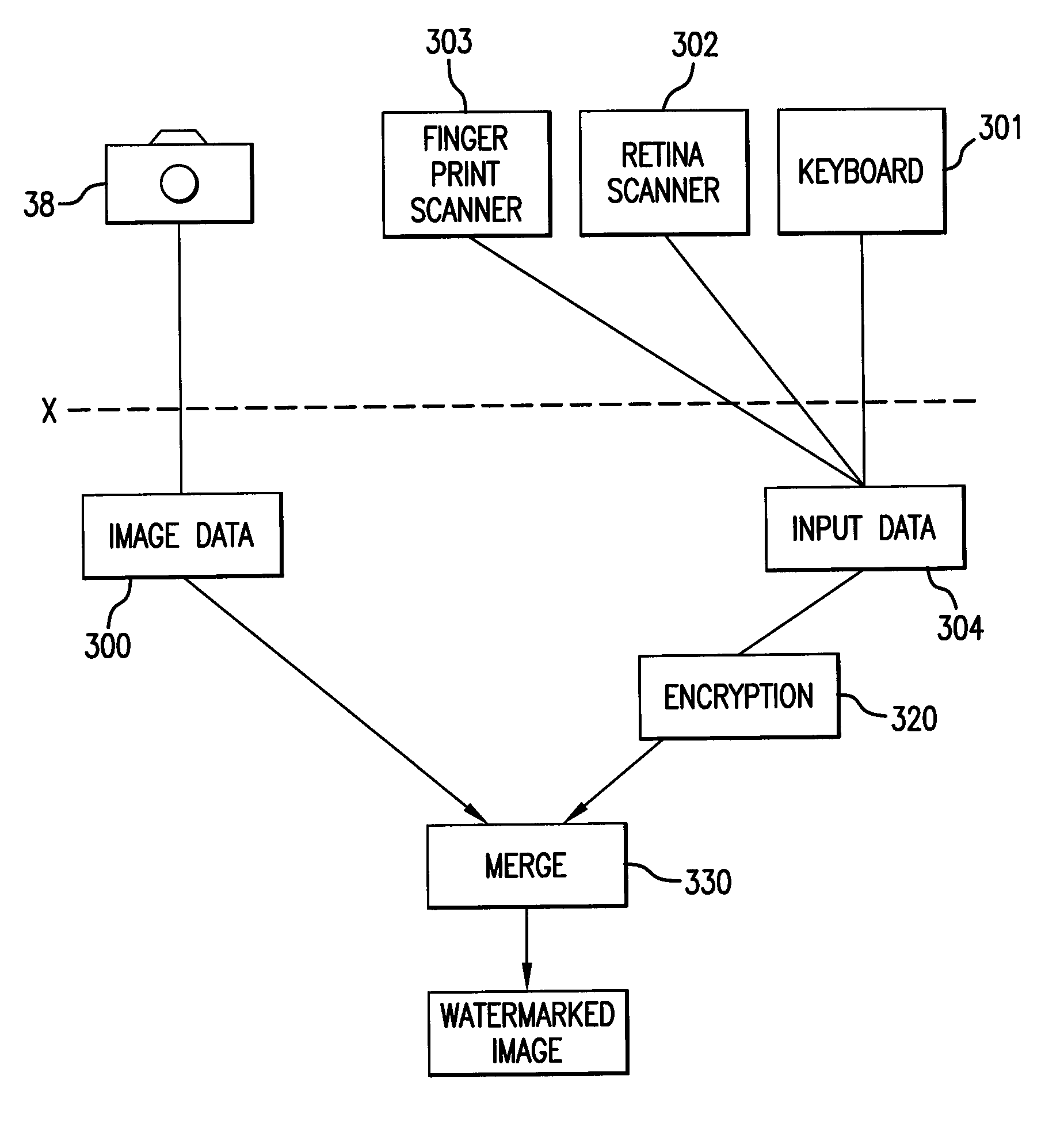
Device and method for digitally watermarking an image with data
InactiveUS20080089554A1Television system detailsImage data processing detailsComputer hardwareData stream
A method for digitally watermarking an image or video by replacing the least significant bit of each pixel of the image with data so that an image or video can be authenticated by removing the least significant bits, reassembling the bits into a data stream and decoding the data stream.
Owner:CATCHER
Method and apparatus for use in digitally tuning a capacitor in an integrated circuit device
ActiveUS9024700B2Easy to controlHigh Power Handling CapabilityMultiple-port networksImpedence matching networksCapacitanceLeast significant bit
Owner:PSEMI CORP
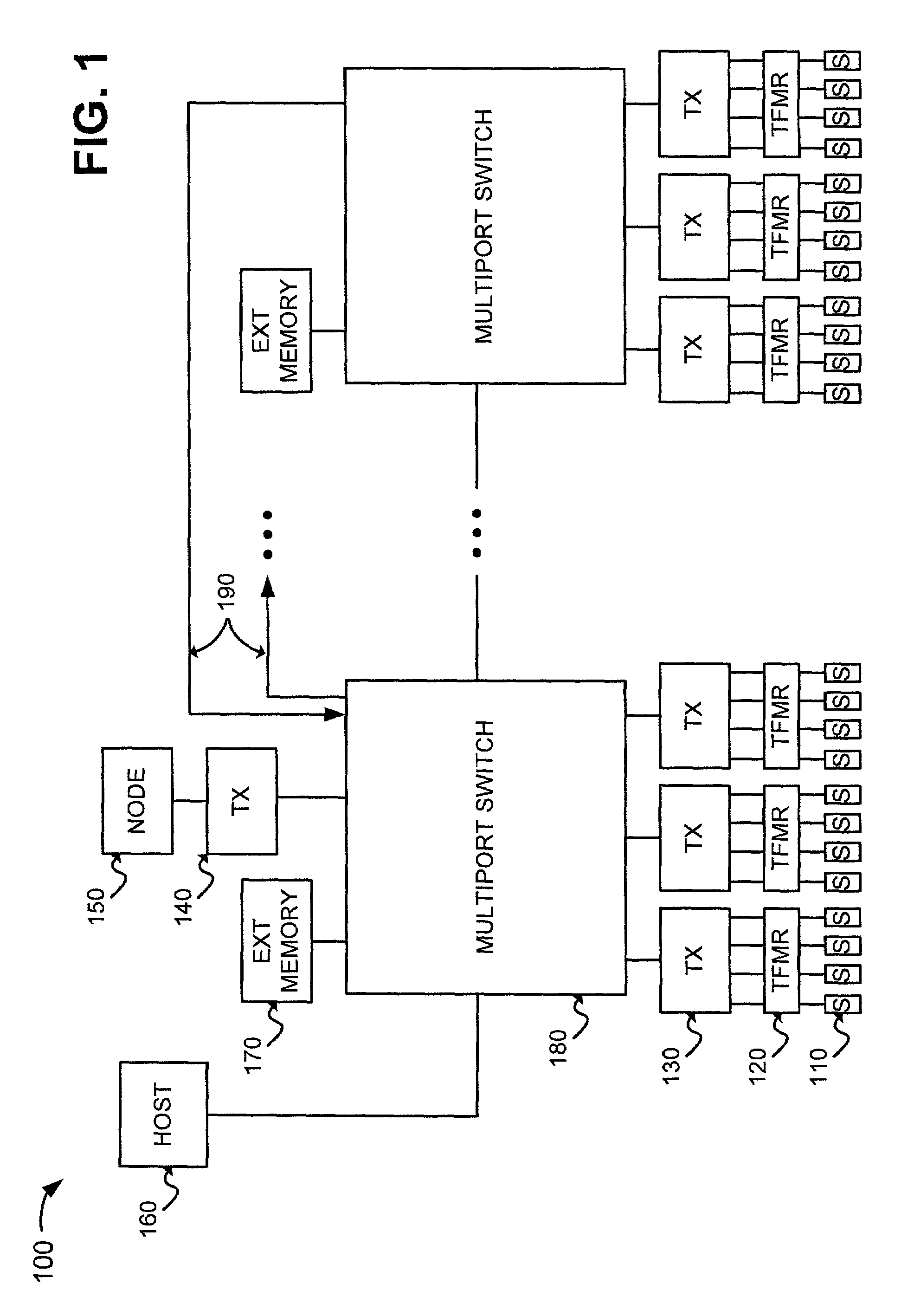
Parallel lookup tables for locating information in a packet switched network
ActiveUS6990102B1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationLeast significant bitParallel computing
An address lookup table in a multiport switch is implemented as a plurality of address sub-tables. Entries in the address sub-tables are stored at row addresses based on a hash of the information in the entry. Entries in the address sub-tables are stored in one of the address sub-tables, as determined by pre-selected information relating to the entry. For example, the least significant bit of a source or destination MAC address may be used to select between two address sub-tables. In this manner, the total memory size of the address table can be increased relative to a single address sub-table while decreasing the length of the longest chain and the length of the average chain.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
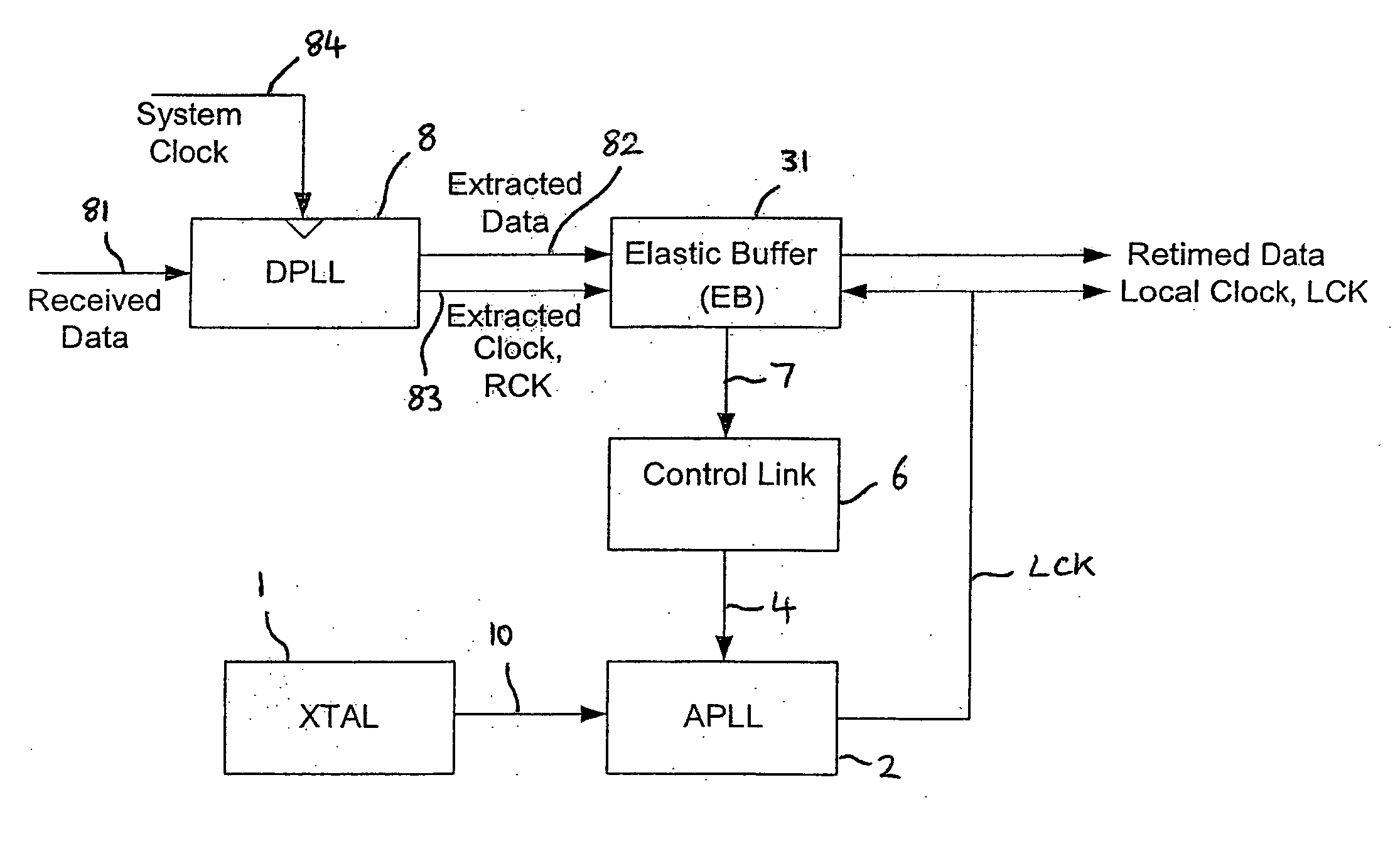
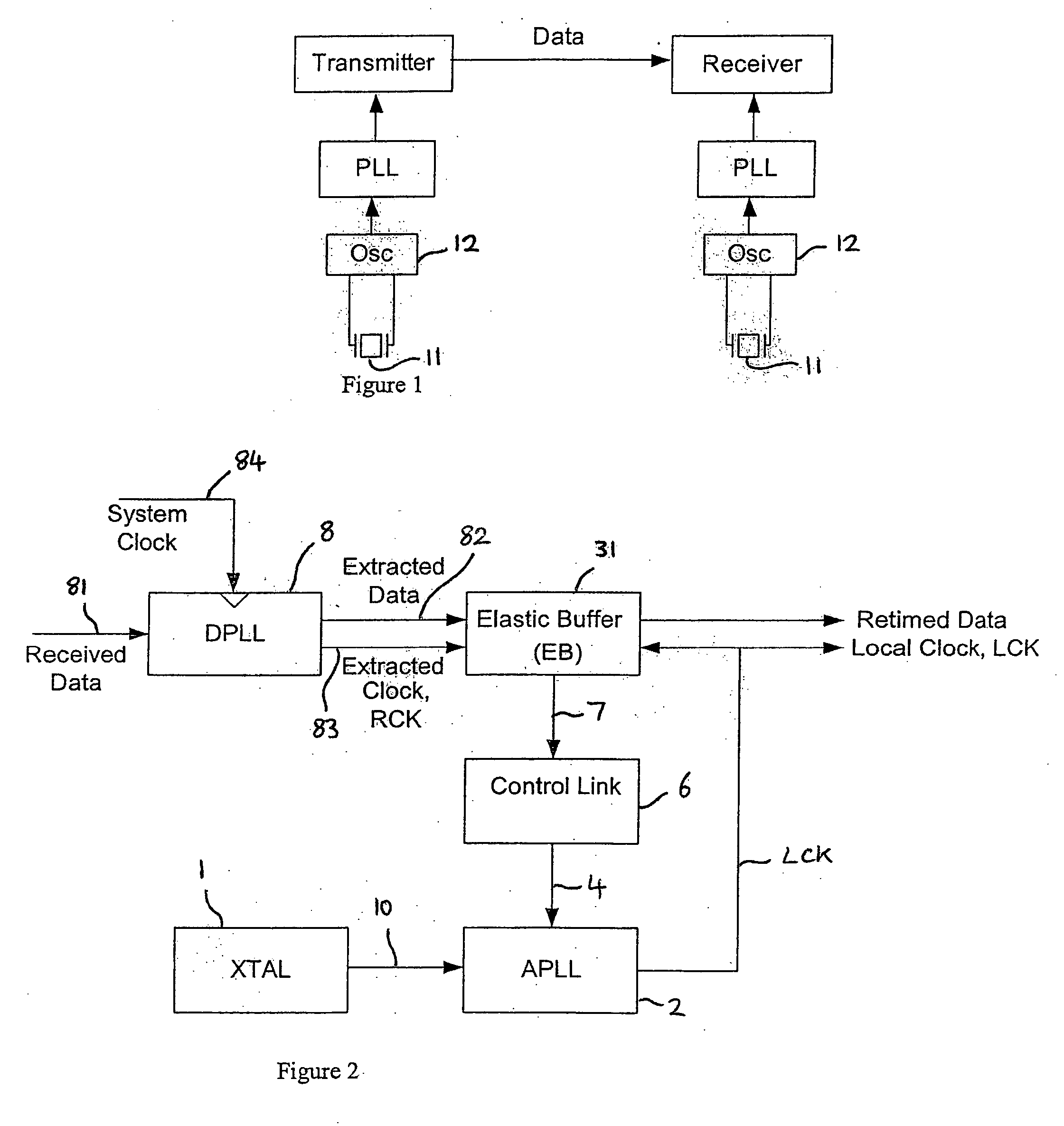
Clock synchroniser and clock and data recovery apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050220240A1Reduce jitterAvoid data lossPulse automatic controlElectric/magnetic signal storageLeast significant bitComputer science
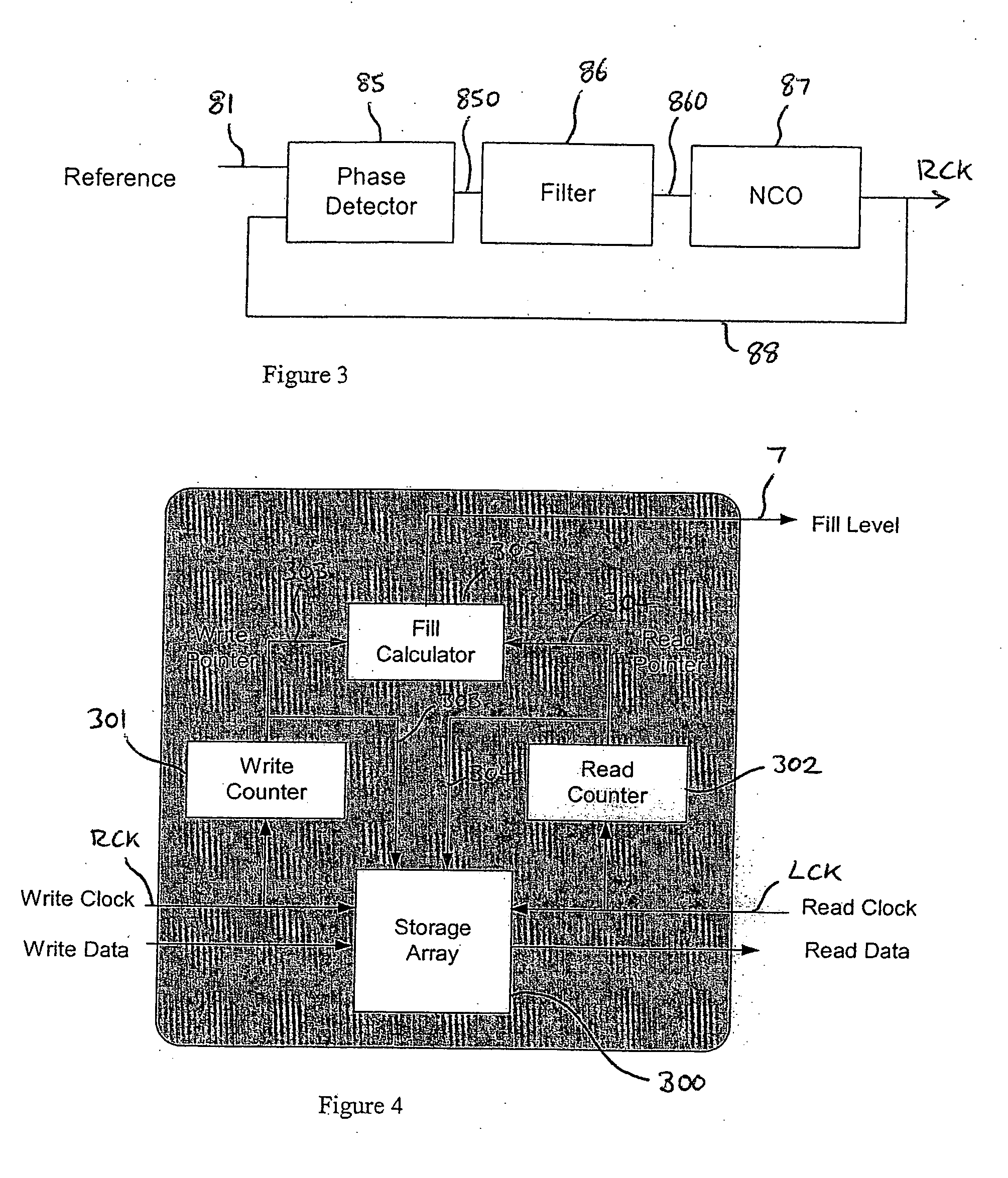
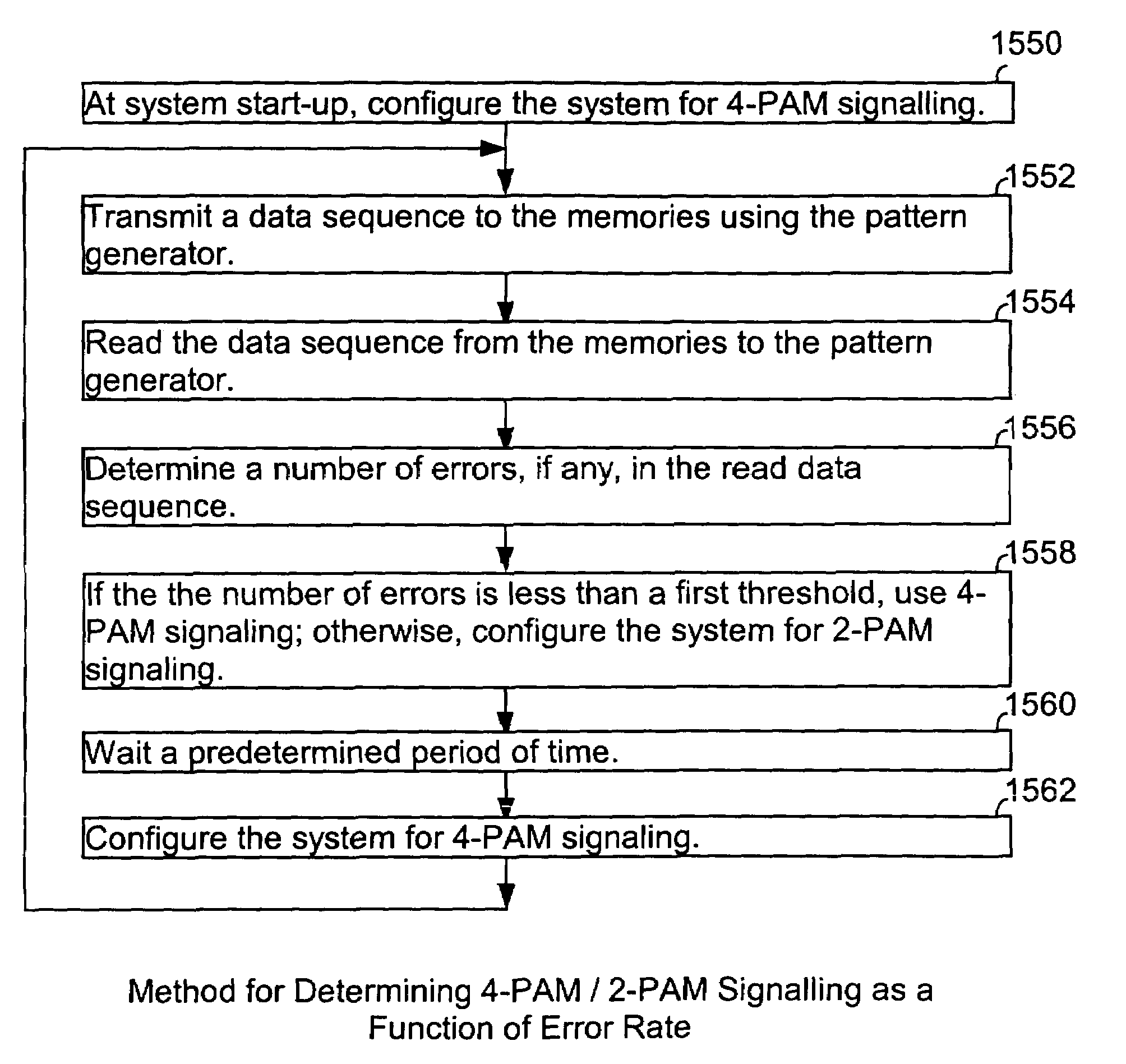
A clock synchroniser, and clock and data recovery apparatus incorporating the clock synchroniser, are described, together with corresponding clock synchronisation methods. The clock synchroniser incorporates an elastic buffer. A received clock signal is used to clock data into the buffer, and a locally generated clock is used to clock data out of the buffer. The local clock is synthesised using a PLL, and a fill-level signal from the elastic buffer is used to control to local clock frequency to maintain a desired average quantity of data in the buffer, thereby achieving synchronisation of the received and local clocks. In preferred embodiments the fill-level signal is used to control a variable divider in the feedback path of the PLL, which is supplied with a highly stable reference signal. A synchronised, and low-jitter local clock is thus produced. Preferably, the elastic buffer employs counters of relatively wide word width, and a storage array of much reduced depth, read and write pointers being provided by just a few of the least significant bits of the words.
Owner:WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
Low latency multi-level communication interface
InactiveUS7124221B1Reduce static power consumptionWide input common mode rangePulse modulation television signal transmissionElectric analogue storesCommunication interfaceLeast significant bit
A memory system uses multiple pulse amplitude modulation (multi-PAM) output drivers and receivers to send and receive multi-PAM sigsnals. A multi-PAM signal has more than two voltage levels, with each data interval now transmitting a “symbol” at one of the valid voltage levels. In one embodiment, a symbol represents two or more bits. The multi-PAM output driver drives an output symbol onto a signal line. The output symbol represents at least two bits that include a most significant bit (MSB) and a least significant bit (LSB). The multi-PAM receiver receives the output symbol from the signal line and determines the MSB and the LSB.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
SIMD four-data element average instruction
InactiveUS20050216545A1Instruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesData averagingLeast significant bit
According to some embodiments, a Single-Instruction / Multiple-Data averaging operation is presented. The averaging operation averages multiple sets of data elements, for example, two data elements each from a first source and a second source, producing a set of averages. In at least one embodiment, in a first adder stage, a first plurality of data elements are added to a second plurality of data elements, generating a plurality of intermediate results. In a second adder stage, multiple different combinations of the plurality of intermediate results are added together, generating a plurality of sum results. The two least significant bits of each sum result are discarded.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Double data rate (DDR) counter, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) using the same, CMOS image sensor using the same and methods in DDR counter, ADC and CMOS image sensor
InactiveUS20100225796A1Television system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsCMOSDouble data rate
In a double data rate (DDR) counter and counting method used in, for example, an analog-to-digital conversion in, for example, a CMOS image sensor and method, a first stage of the counter generates a least significant bit (LSB) of the value in the counter. The counter includes at least one second stage for generating another bit of the value in the counter. An input clock signal is applied to a data input of the first stage and a clock input of the second stage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
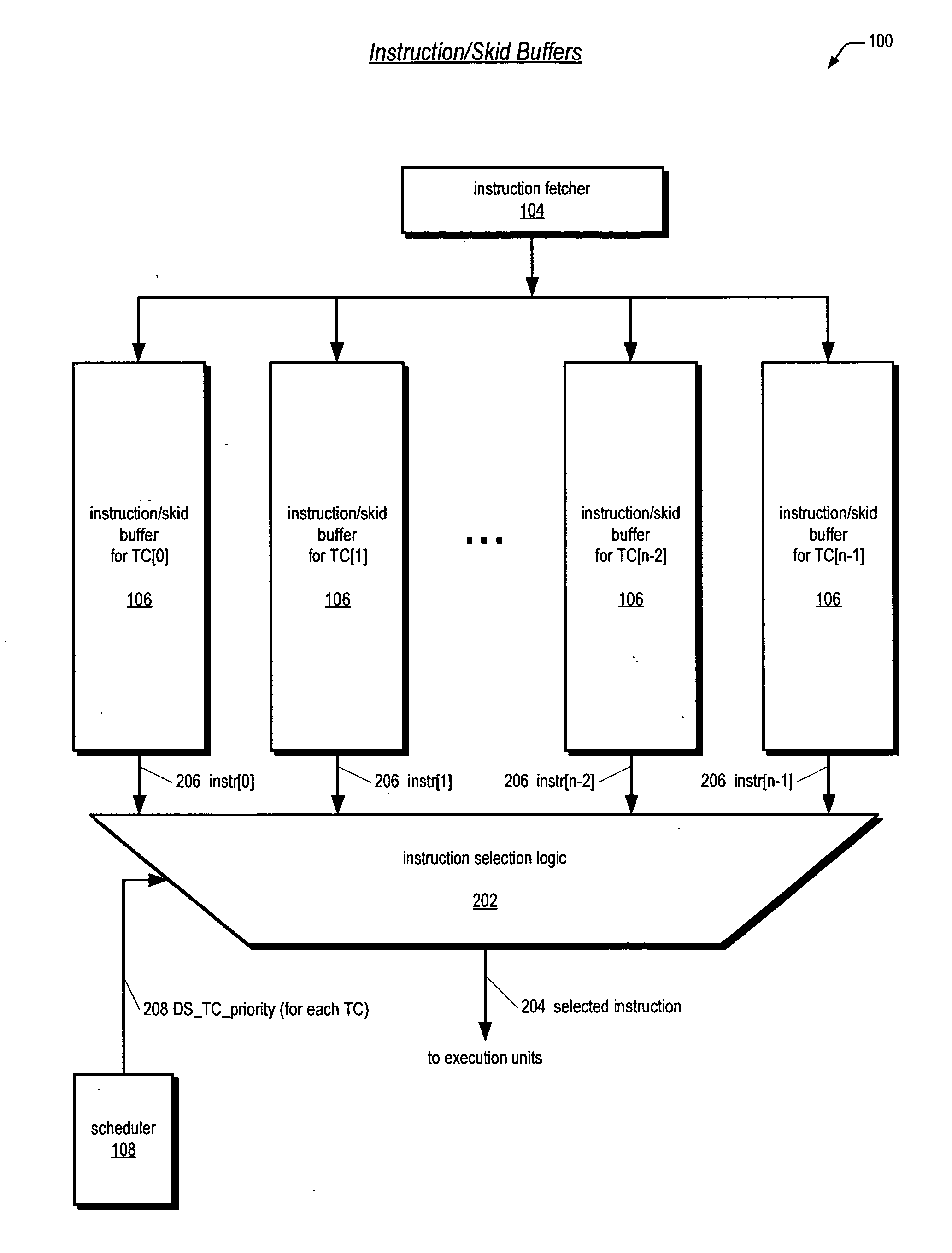
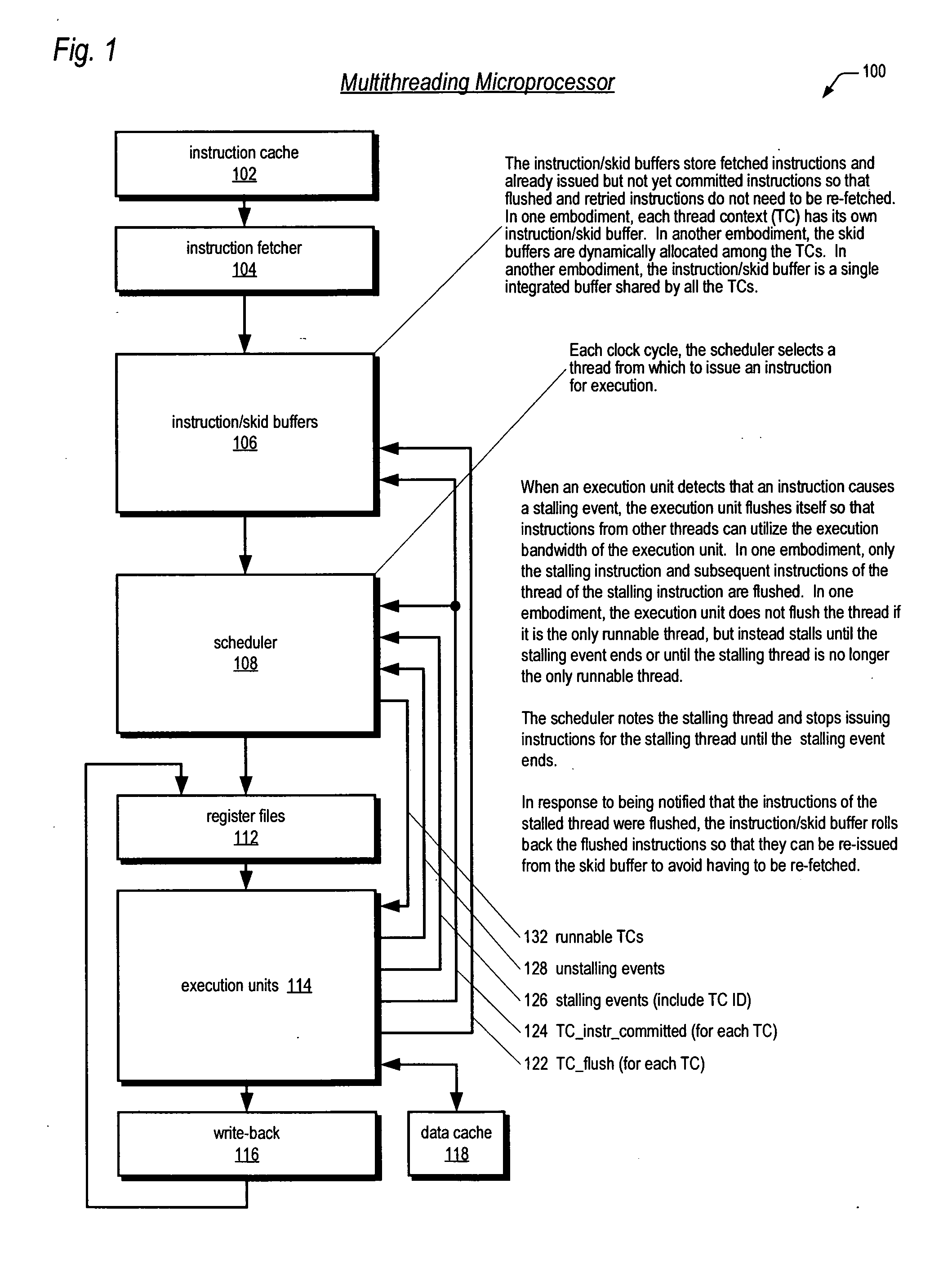
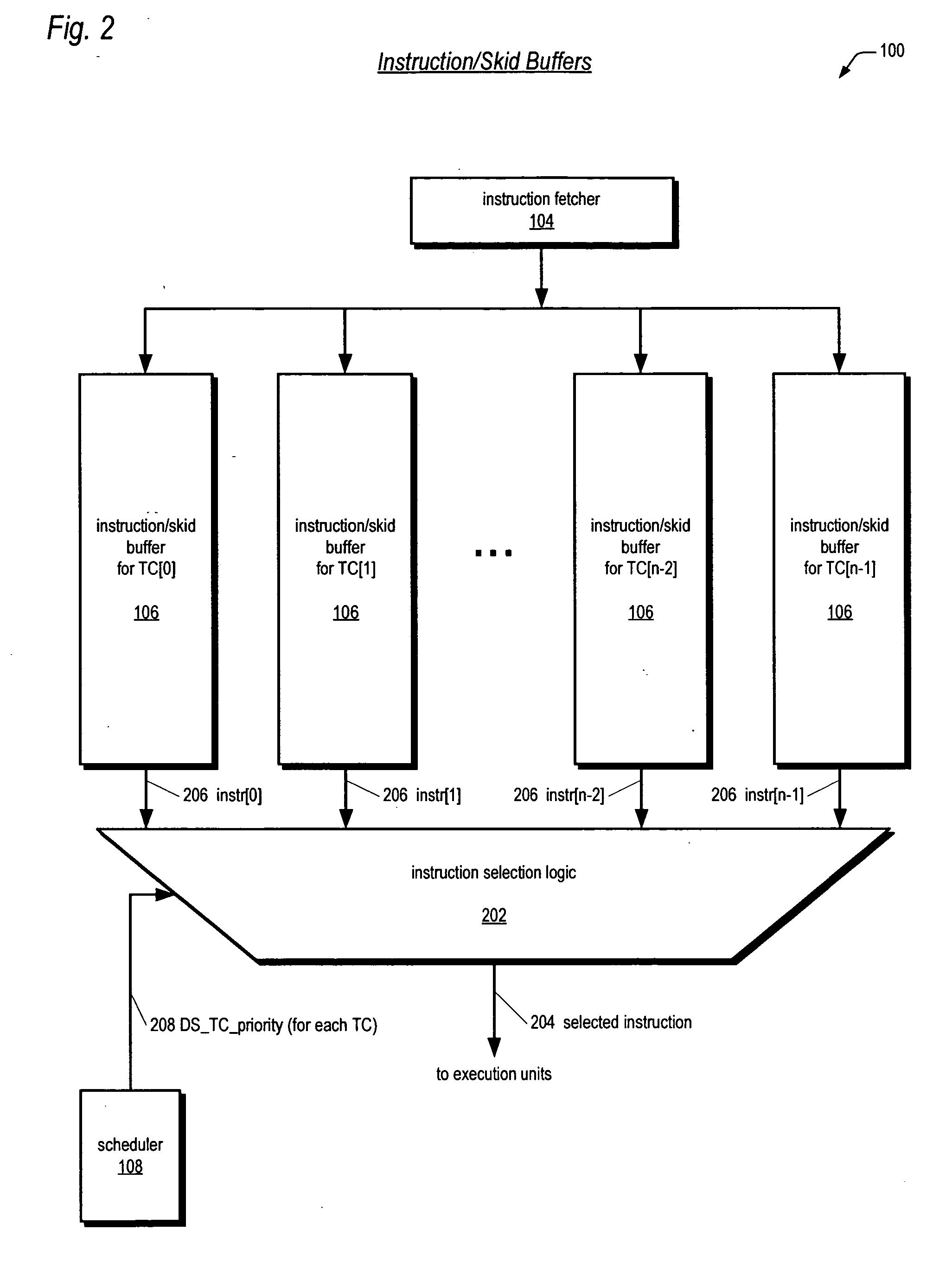
Instruction dispatch scheduler employing round-robin apparatus supporting multiple thread priorities for use in multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS20060206692A1Short clock cycleThe process is simple and fastDigital computer detailsMemory systemsParallel computingLeast significant bit
A dispatch scheduler in a multithreading microprocessor is disclosed. Each of N concurrently executing threads has one of P priorities. P N-bit round-robin vectors are generated, each being a 1-bit left-rotated and subsequently sign-extended version of an N-bit 1-hot input vector indicating the last thread selected for dispatching at the priority. N P-input muxes each receive a corresponding one of the N bits of each of the P round-robin vectors and selects the input specified by the thread priority. Selection logic selects an instruction for dispatching from the thread having a dispatch value greater than or equal to any of the threads left thereof in the N-bit input vectors. The dispatch value of each of the threads comprises a least-significant bit equal to the corresponding P-input mux output, a most-significant bit that is true if the instruction is dispatchable, and middle bits comprising the priority of the thread.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
EL display device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS6351077B1Uniform processGood white balanceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDigital dataComputer graphics (images)
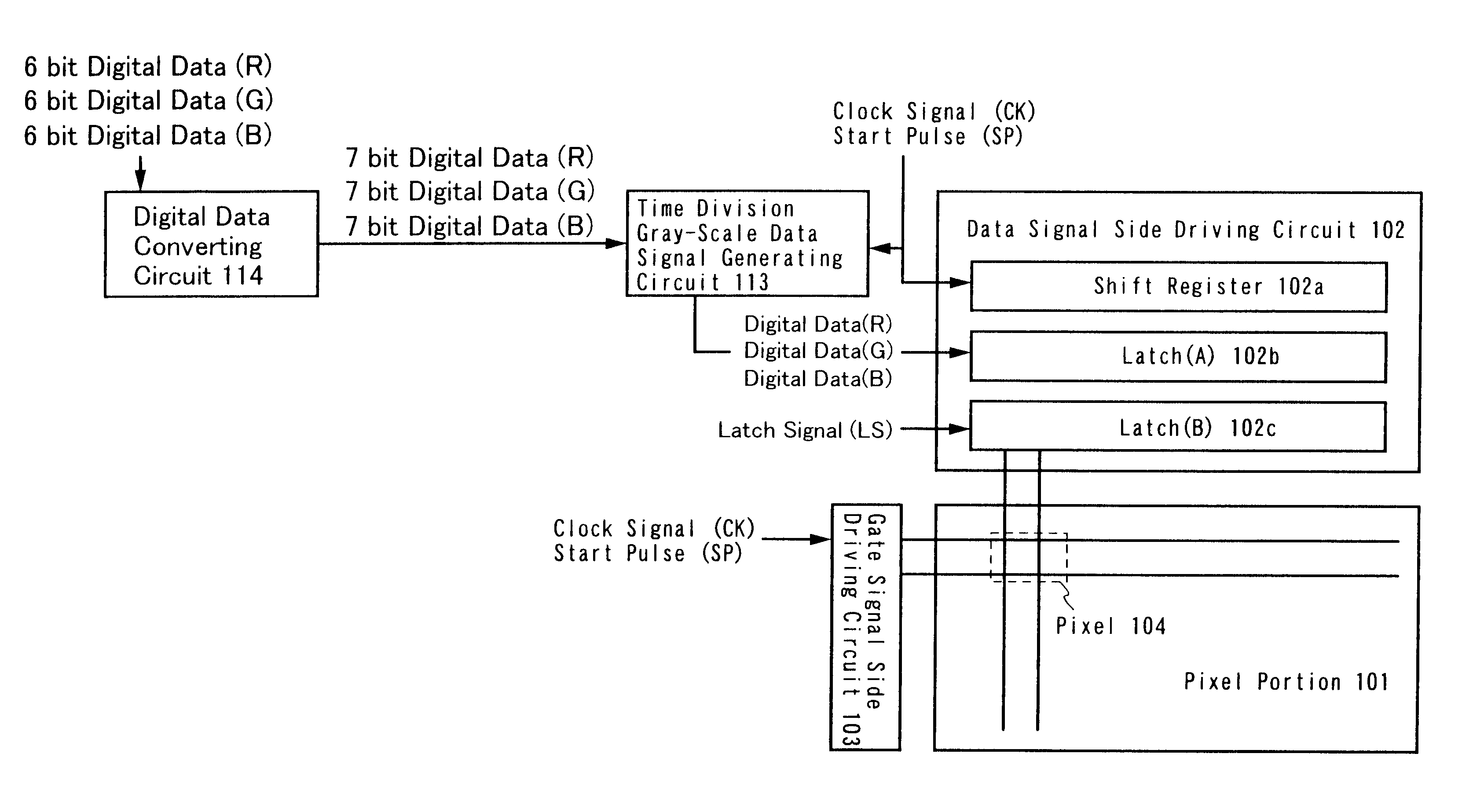
The present invention is characterized by adding a bit having the value of one below the least significant bit of n bit digital data having red image information inputted from the external, adding a bit having the value of zero above the most significant bit of n bit digital data having green image information inputted from the external, and adding a bit having the value of zero above the most significant bit of n bit digital data having blue image information inputted from the external, whereby producing (n+1) bit digital data having red image information, (n+1) bit digital data having green image information, and (n+1) bit digital data having blue image information, respectively, for displaying an image.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
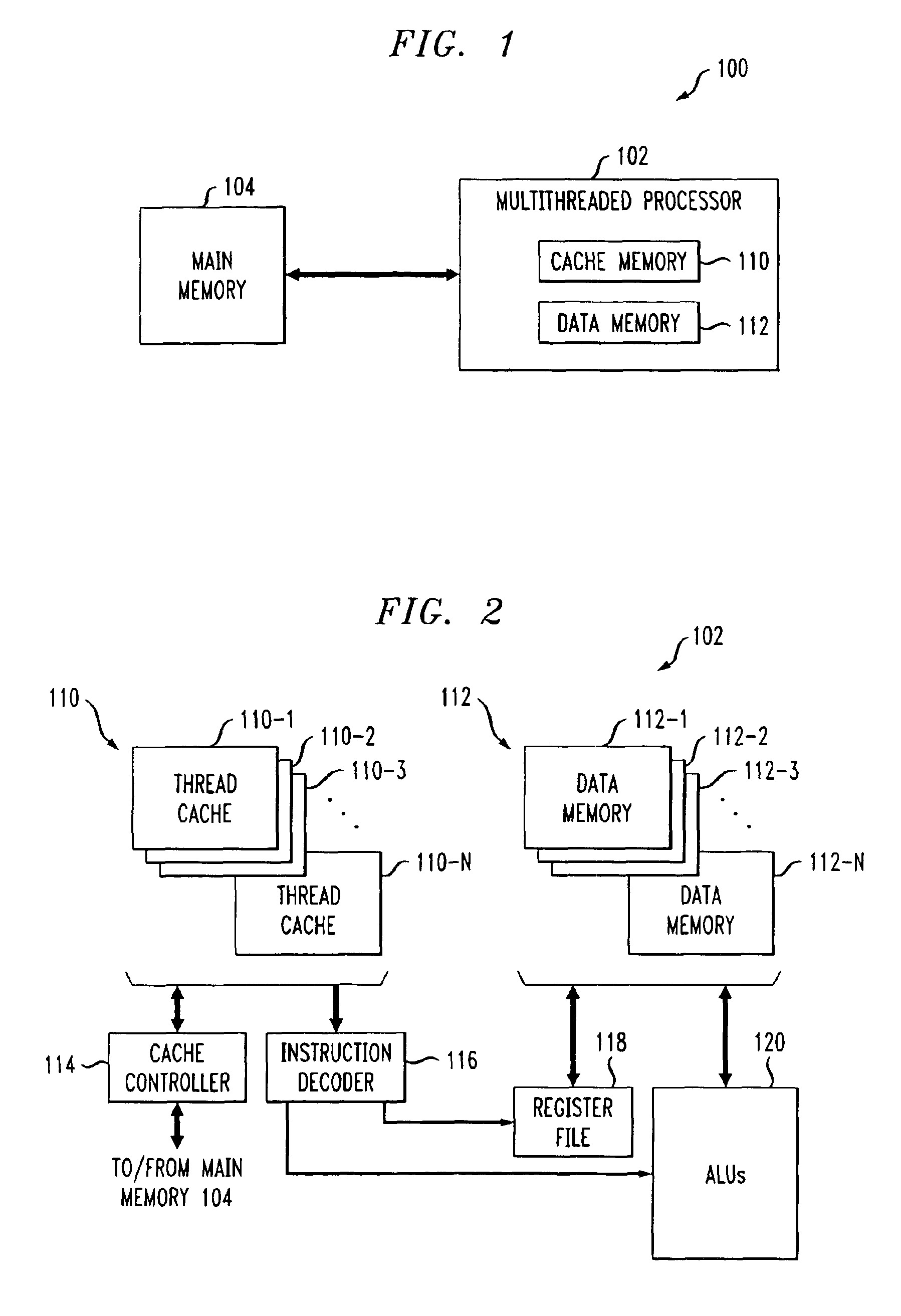
Method and apparatus for register file port reduction in a multithreaded processor
InactiveUS6904511B2Reduce in quantityDecreasing processor power consumptionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInterprogram communicationProcessor registerLeast significant bit
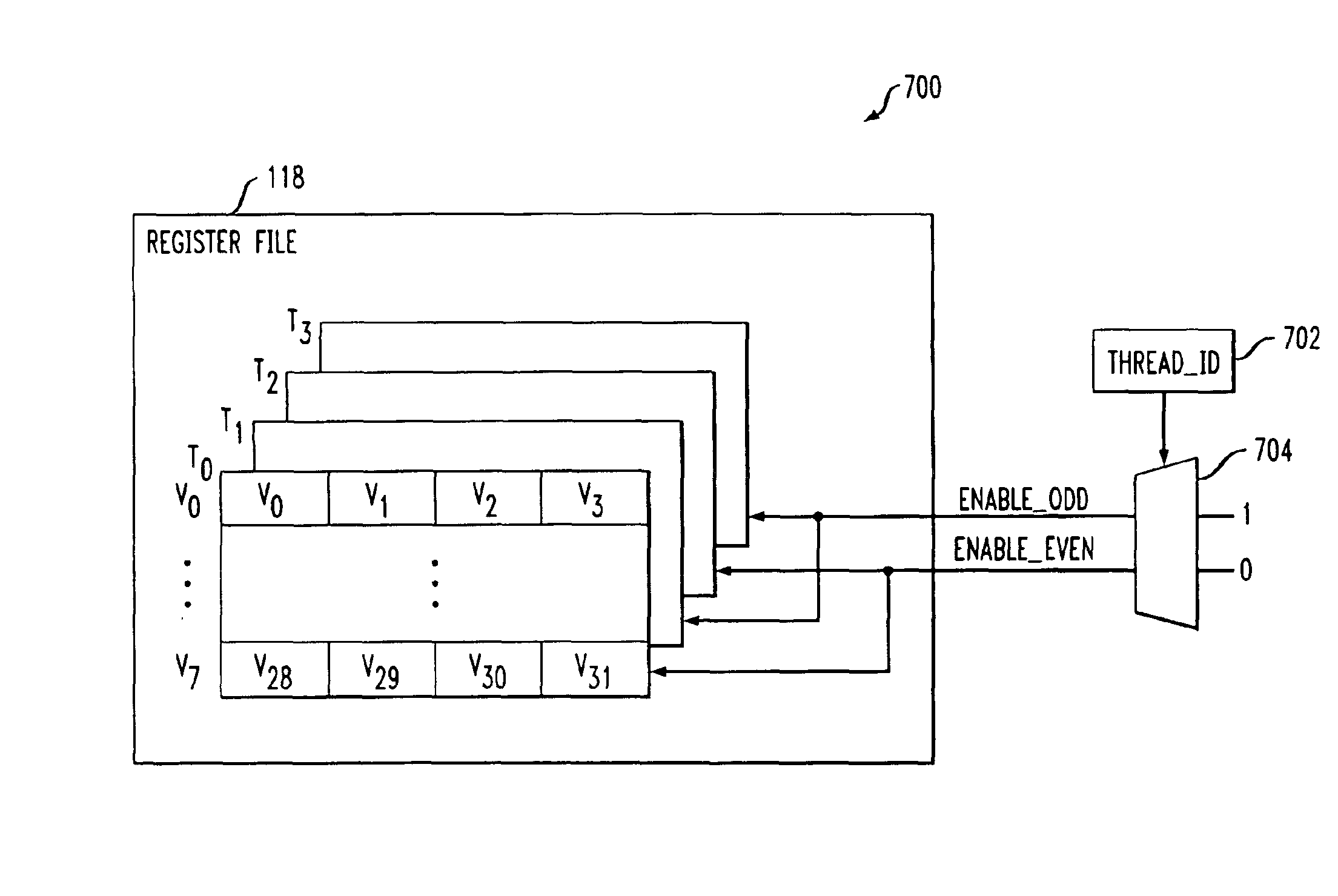
Techniques for thread-based register file access by a multithreaded processor are disclosed. The multithreaded processor determines a thread identifier associated with a particular processor thread, and utilizes at least a portion of the thread identifier to select a particular portion of an associated register file to be accessed by the corresponding processor thread. In an illustrative embodiment, the register file is divided into even and odd portions, with a least significant bit or other portion of the thread identifier being used to select either the even or the odd portion for use by a given processor thread. The thread-based register file selection may be utilized in conjunction with token triggered threading and instruction pipelining. Advantageously, the invention reduces register file port requirements and thus processor power consumption, while maintaining desired levels of concurrency.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
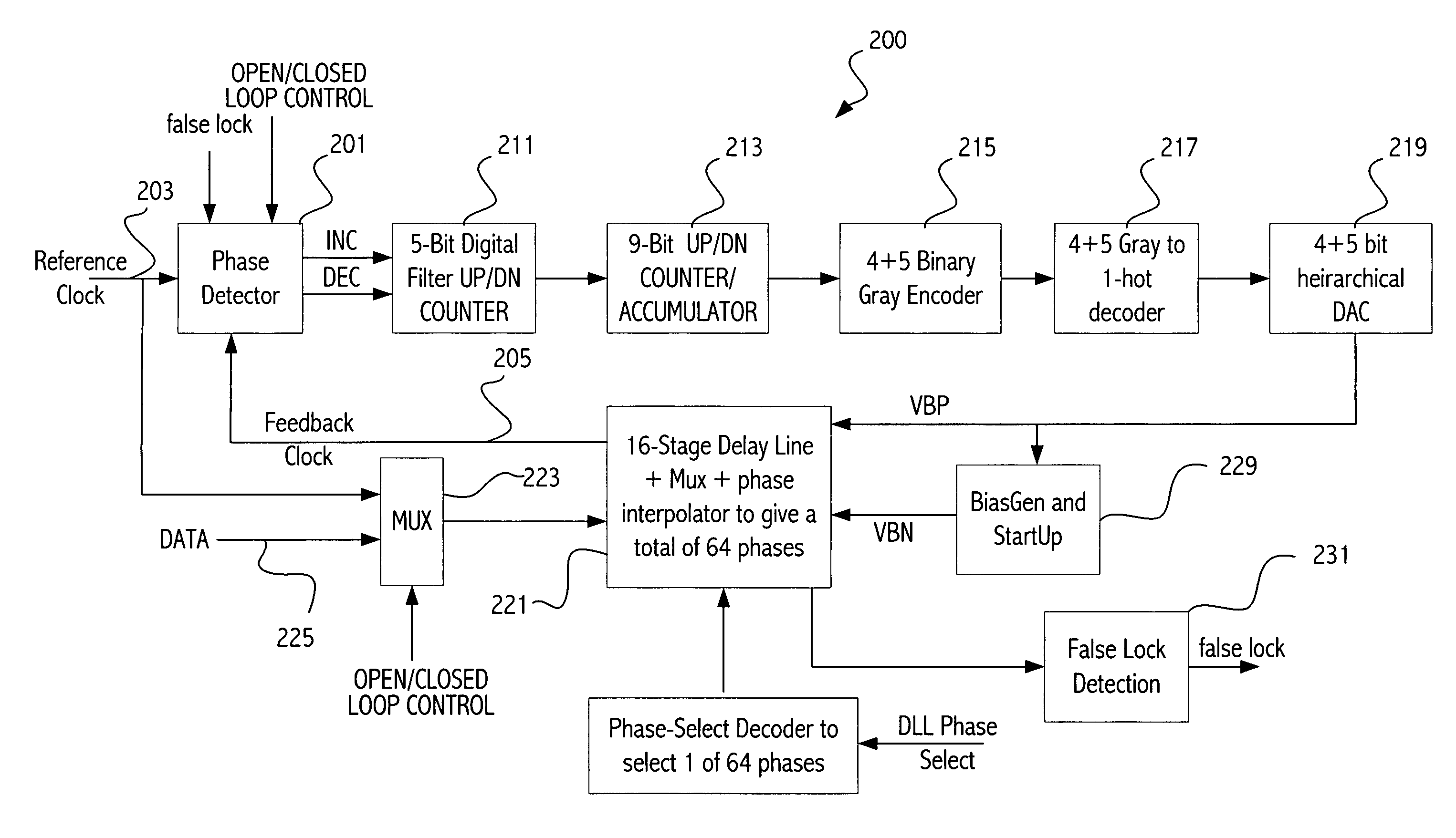
Delay-locked loop having a plurality of lock modes
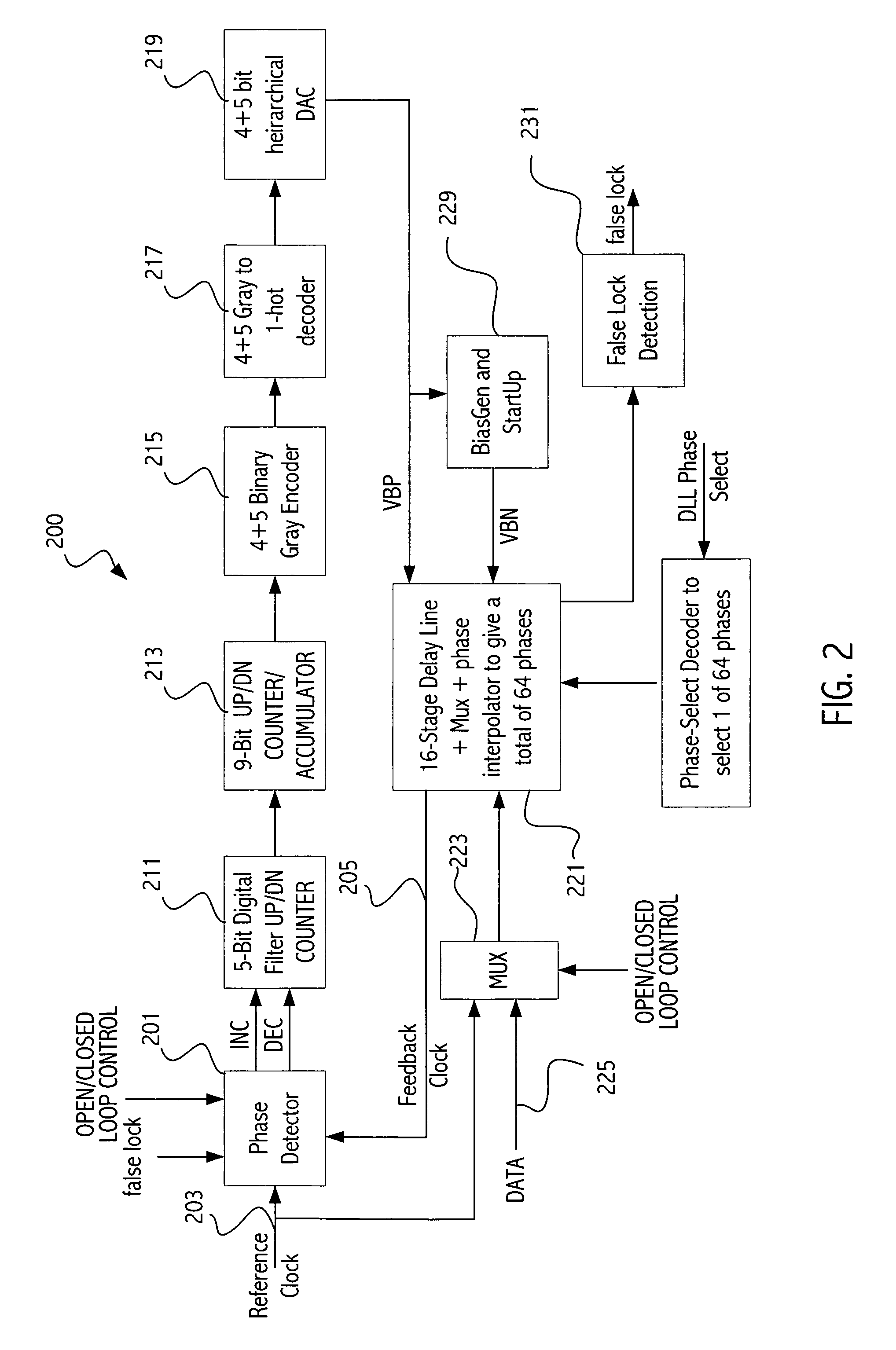
A delay-locked loop (DLL) has a counter that is incremented or decremented by the loop in the process of achieving lock. The counter value is converted using an digital to analog converter (DAC) to an analog voltage that controls the delay through the delay line. During faster lock modes, the loop increments / decrements intermediate bits of the counter (with the bits less significant being held at a constant value, e.g., 0) to provide a coarse lock, rather than incrementing / decrementing the least significant bit of the counter. After coarse lock is achieved, a better lock is then achieved by incrementing / decrementing the counter using a smaller increment, i.e., a less significant bit is updated, until finally, the LSB is utilized to achieve fine lock. Utilizing the coarse lock first, and then one or more finer locks, allows the lock to be achieved more quickly.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
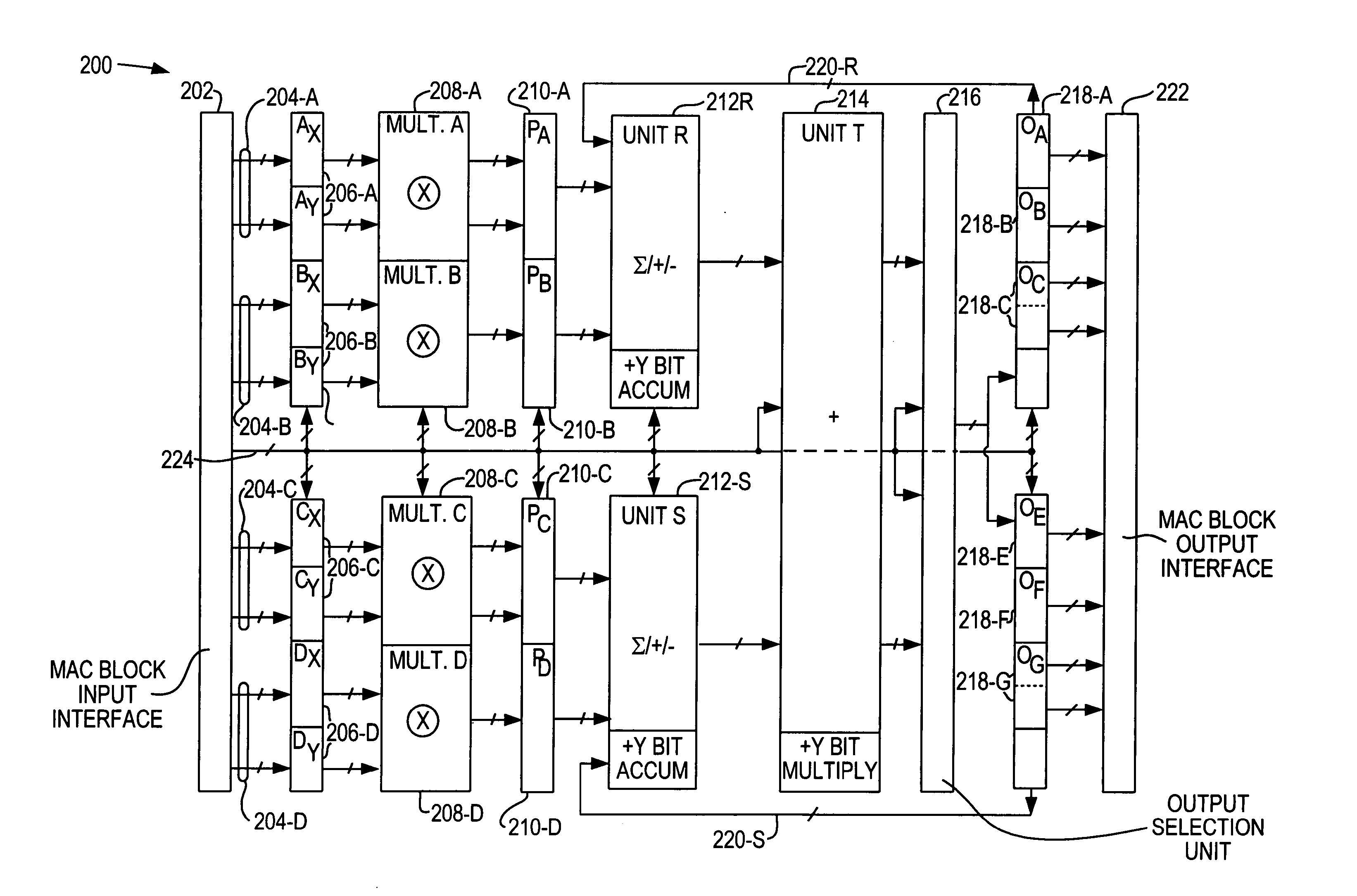
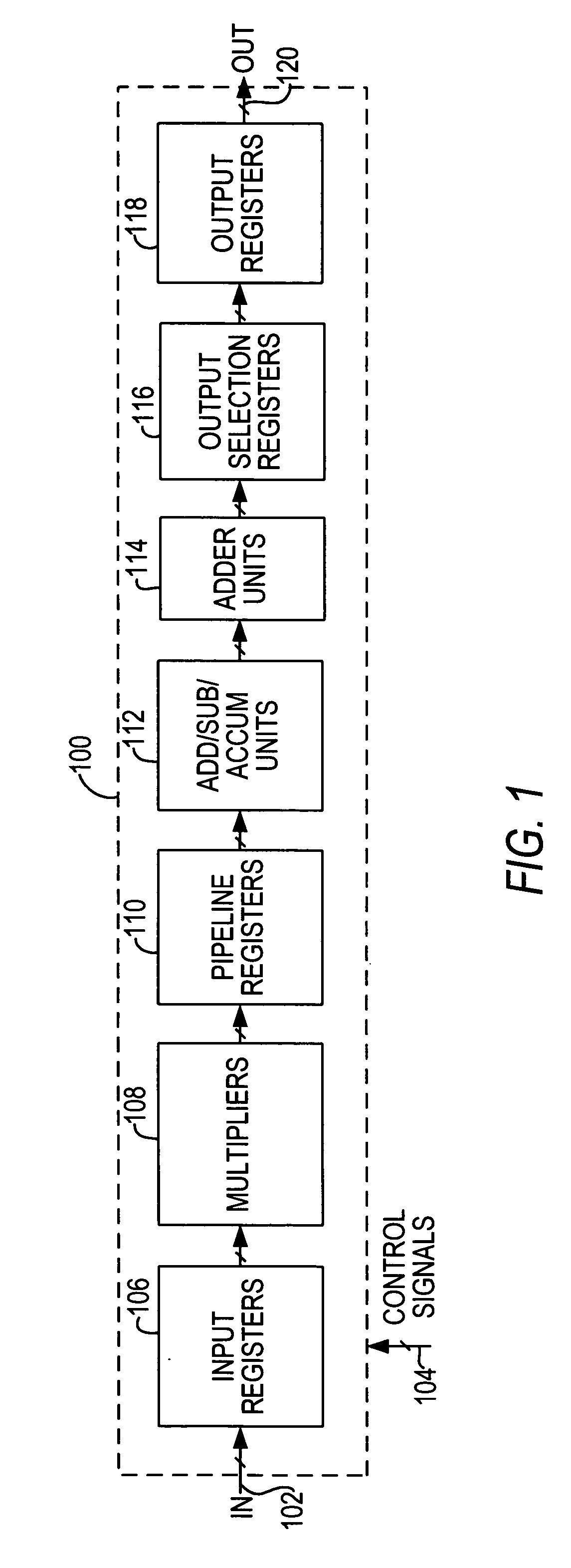
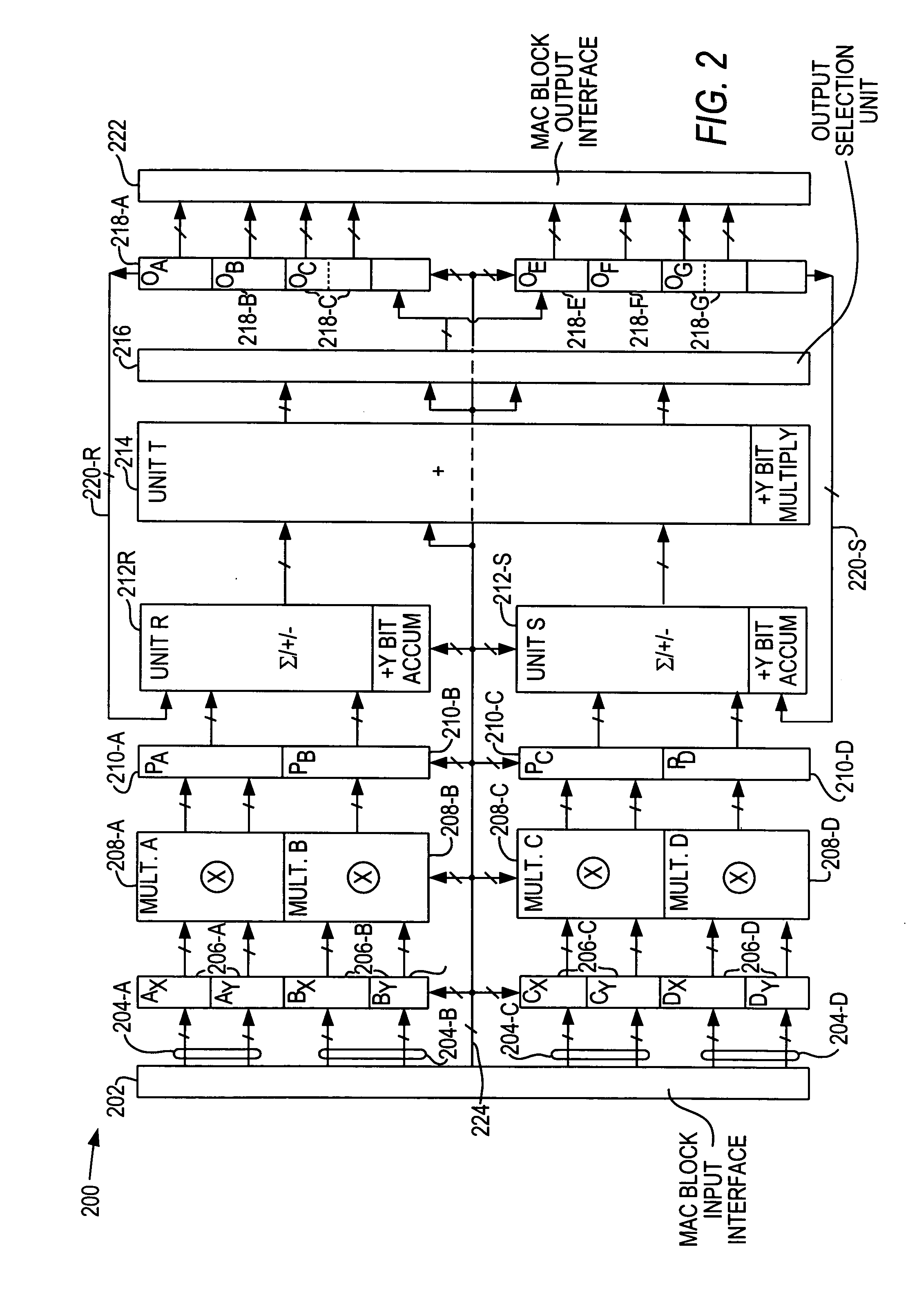
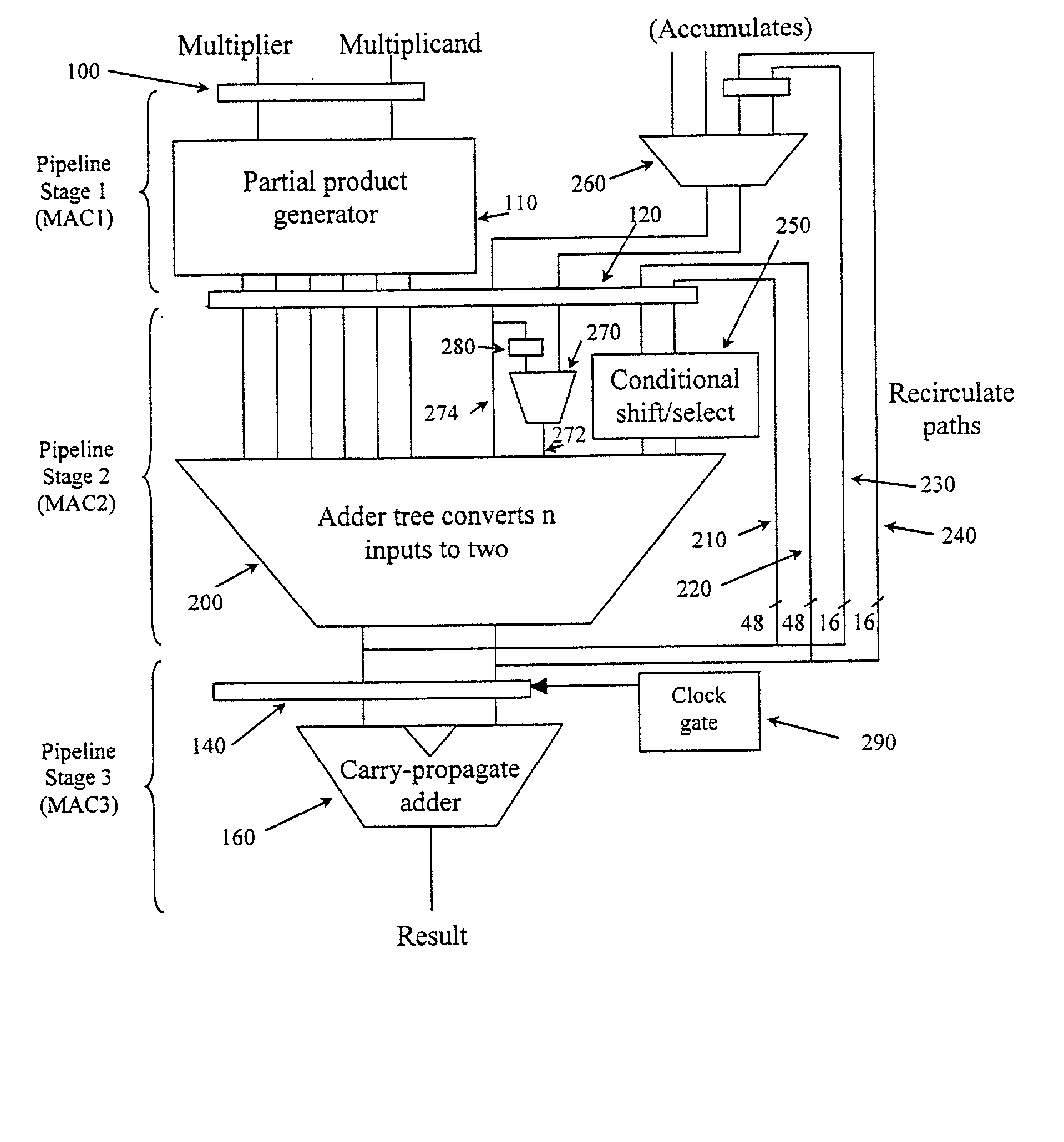
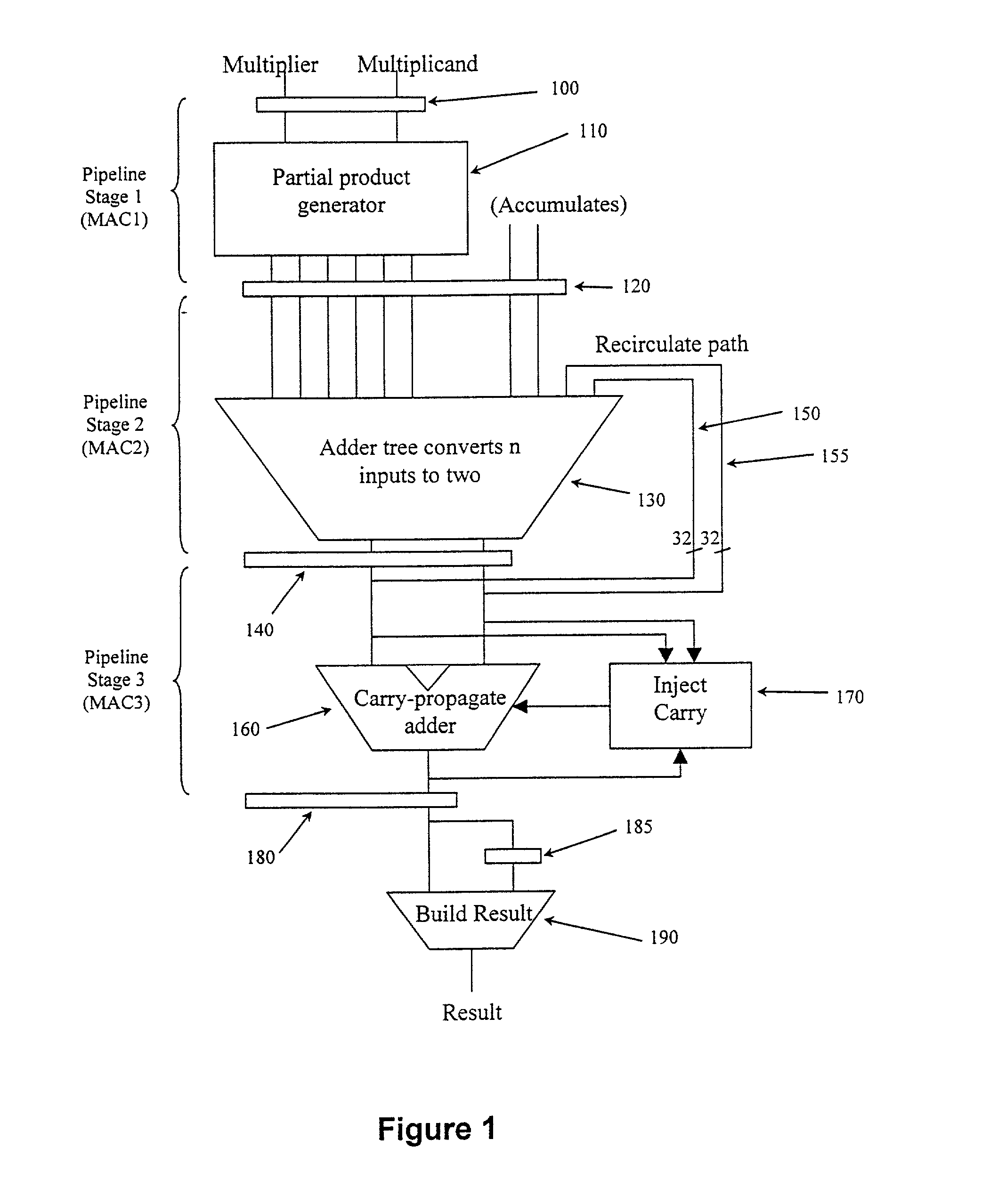
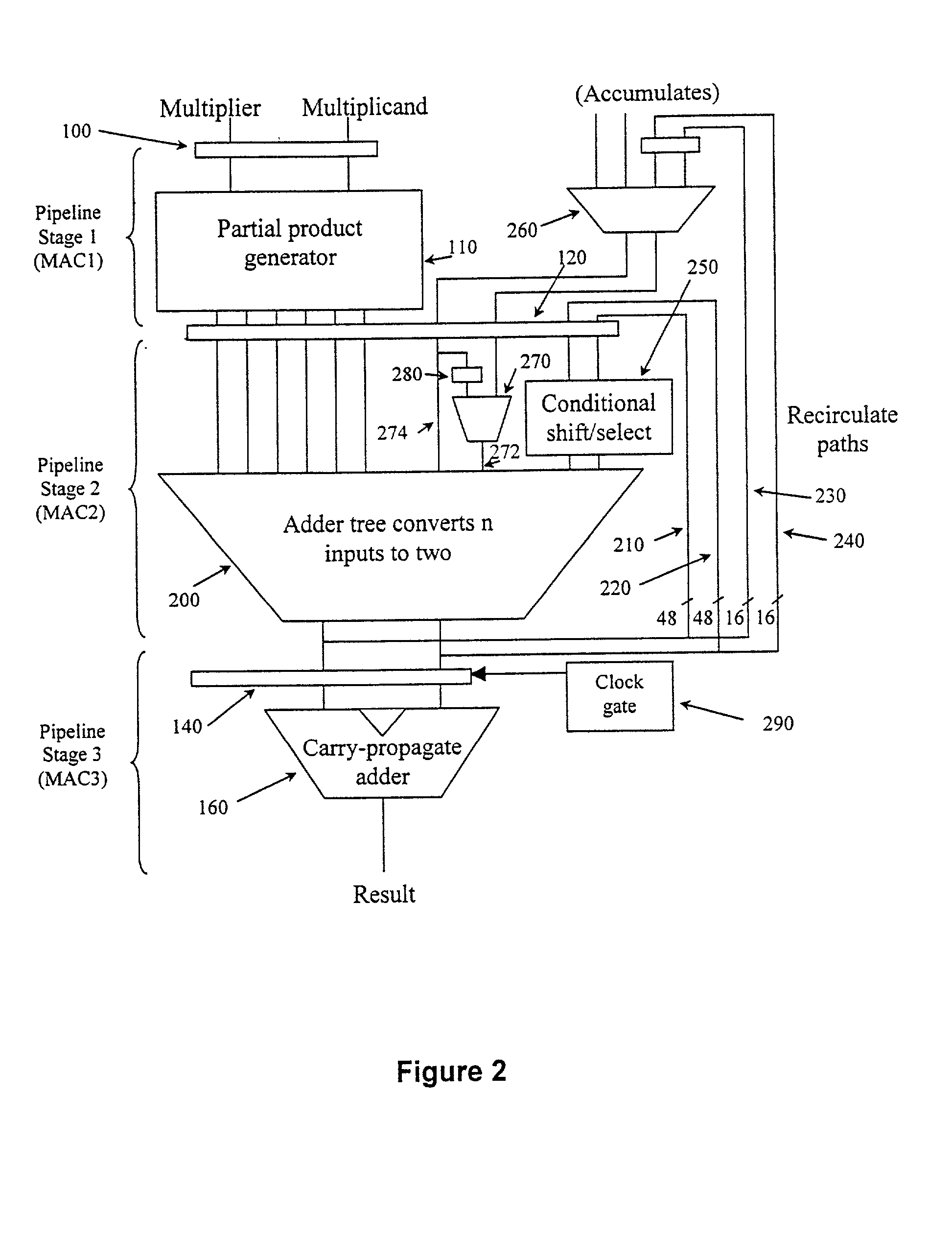
Flexible accumulator in digital signal processing circuitry
InactiveUS20050187997A1Computation using denominational number representationDigital signal processingBinary multiplier
A multiplier-accumulator (MAC) block can be programmed to operate in one or more modes. When the MAC block implements at least one multiply-and-accumulate operation, the accumulator value can be zeroed without introducing clock latency or initialized in one clock cycle. To zero the accumulator value, the most significant bits (MSBs) of data representing zero can be input to the MAC block and sent directly to the add-subtract-accumulate unit. Alternatively, dedicated configuration bits can be set to clear the contents of a pipeline register for input to the add-subtract-accumulate unit. The least significant bits (LSBs) can be tied to ground and sent along the feedback path. To initialize the accumulator value, the MSBs of the initialization value can be input to the MAC block and sent directly to the add-subtract-accumulate unit. The LSBs can be sent to another multiplier that performs a multiply-by-one operation before being sent to the add-subtract-accumulate unit.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Apparatus and method for performing multiplication operations
InactiveUS20020116434A1Reduce power consumptionComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsReverse orderParallel computing
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for processing data using a multiplying circuit for performing a multiplication of a W / 2 bit data value by a W bit data value. An instruction decoder is provided which is responsive to a multiply instruction to control the multiplying circuit to generate a multiplication result for the computation MxN, where M and N are W bit data words. The multiplying circuit is arranged to execute a first operation in the which the data word N is multiplied by the most significant W / 2 bits of the data word M to generate a first intermediate result having 3W / 2 bits, and to then execute a second operation in which the data word N is multiplied by the least significant W / 2 bits of the data word M to generate a second intermediate result having 3W / 2 bits. The first intermediate result is shifted by W / 2 with respect to the second intermediate result and added to the second intermediate result to generate the multiplication result. By performing the two parts of the multiplication in reverse order to the conventional approach, it has been found that the complexity of the circuitry can be reduced, and a reduction in power consumption can be achieved.
Owner:ARM LTD
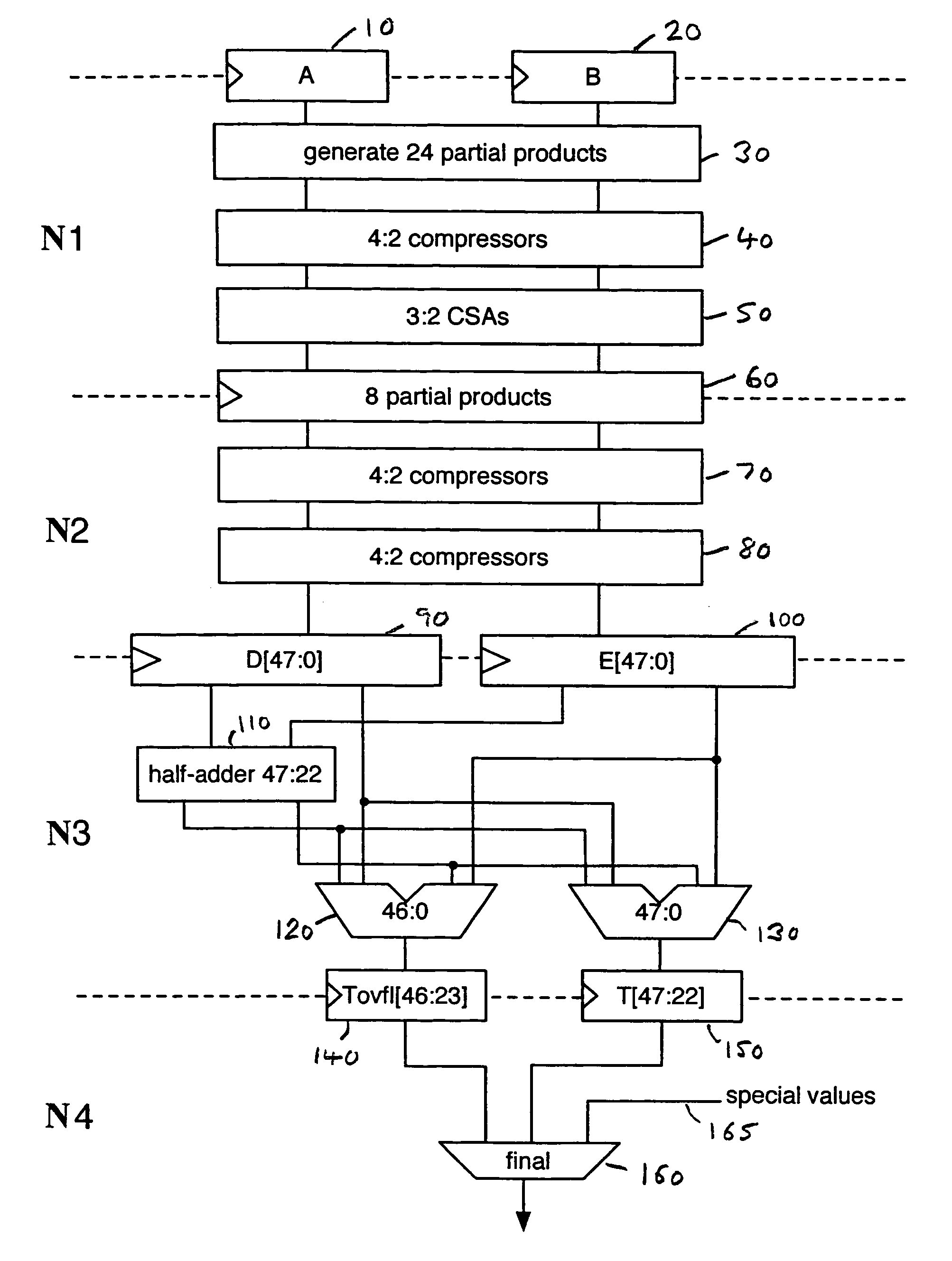
Data processing apparatus and method for performing floating point multiplication
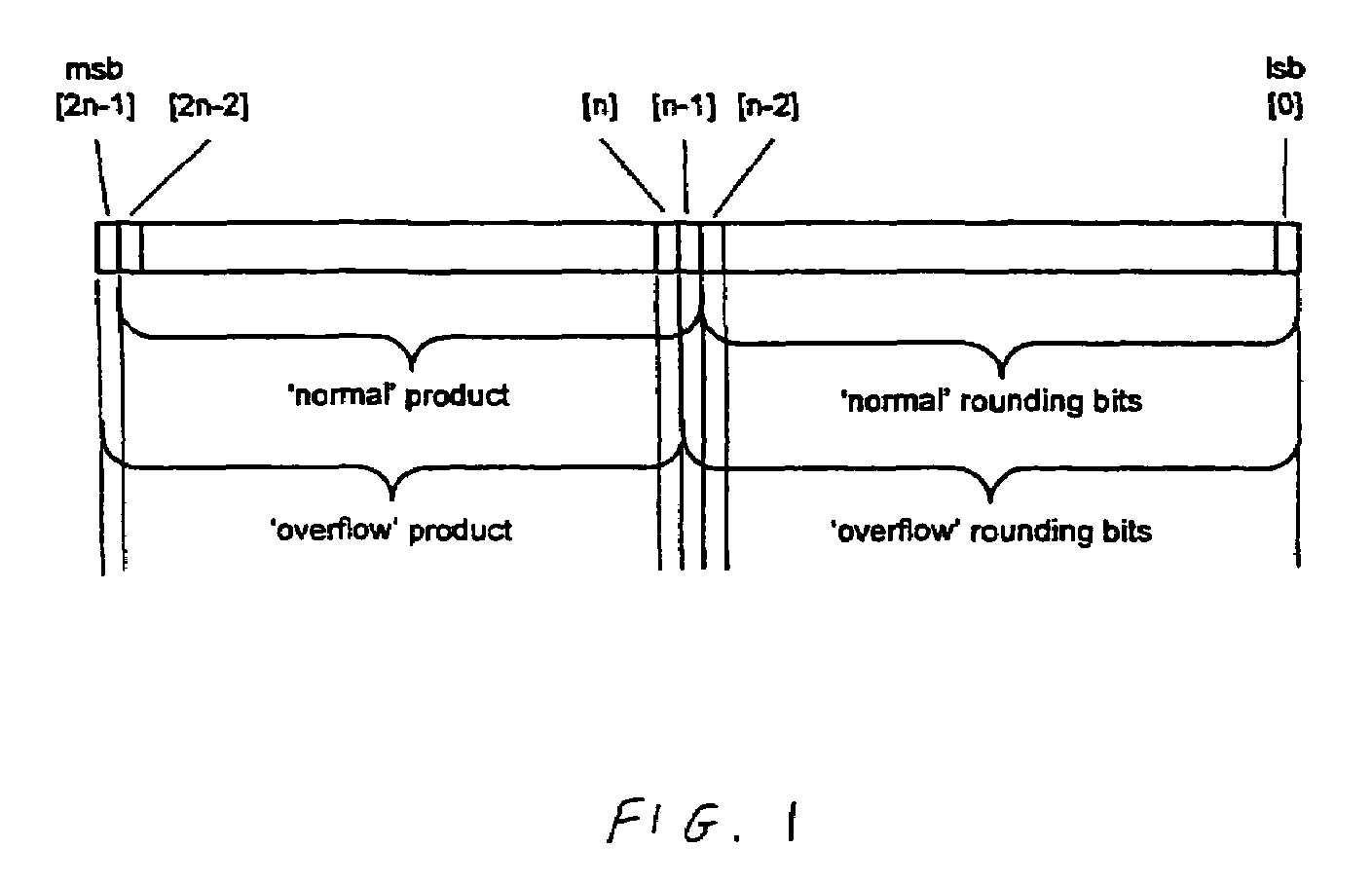
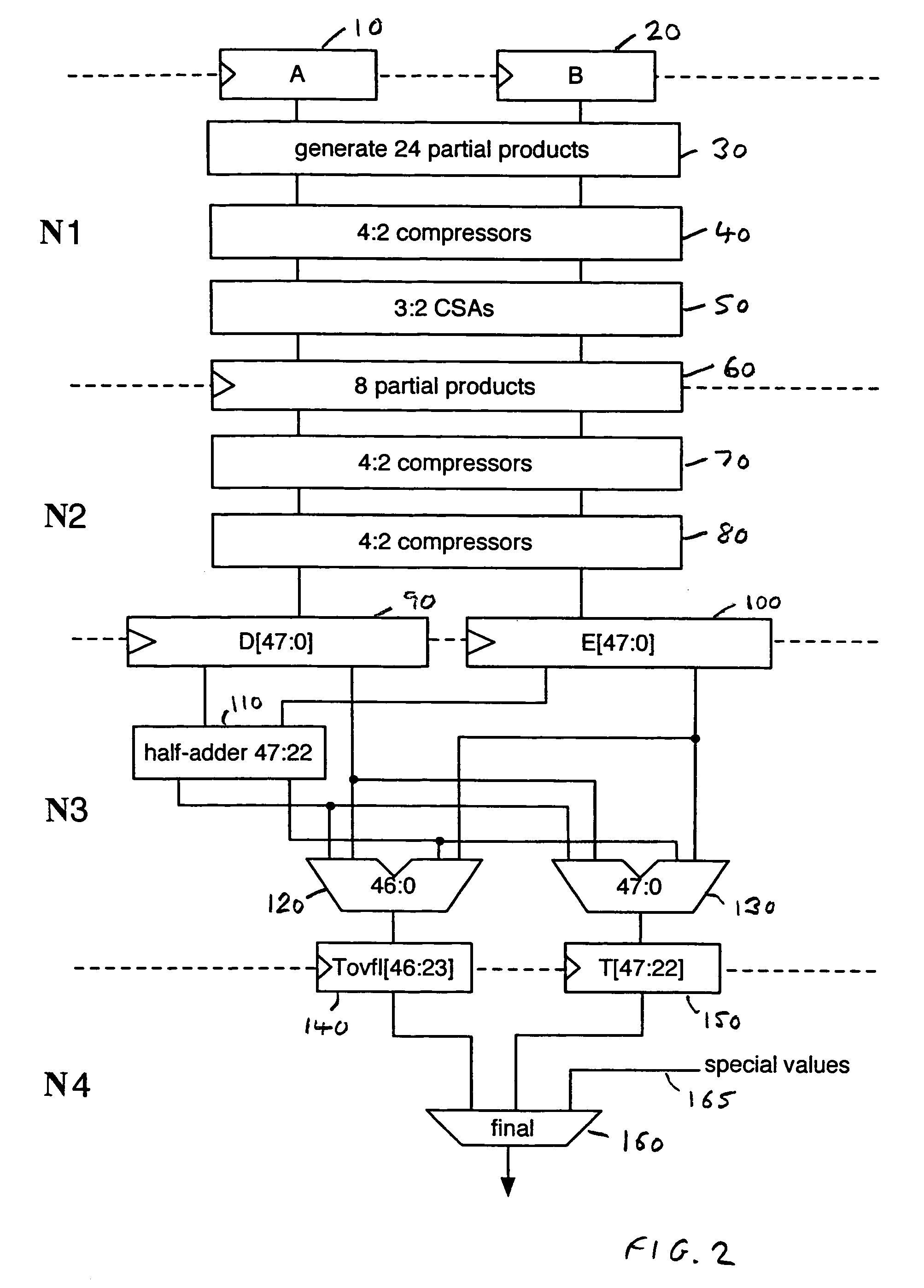
ActiveUS7668896B2Efficient detectionAvoid the needComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesLeast significant bitFloating point multiplication
The first and second n-bit significands are multiplied producing a pair of 2n-bit vectors, and half adder logic produces a corresponding plurality of carry and sum bits. A product exponent is checked for correspondence with a predetermined exponent value. A sum operation generates a first result equivalent to the addition of the pair of 2n-bit vectors. First adder logic uses corresponding m carry and sum bits, the least significant of them carry bits being replaced with the increment value prior to the first adder logic performing the first sum operation. Second adder logic performs a second sum operation and uses the corresponding m−1 carry and sum bits replacing the least significant m−1 carry bits with the rounding increment value prior to the second adder logic second sum operation. The n-bit result is derived from either the first rounded result, the second rounded result or a predetermined result value.
Owner:ARM LTD
Digital amplifier with improved performance
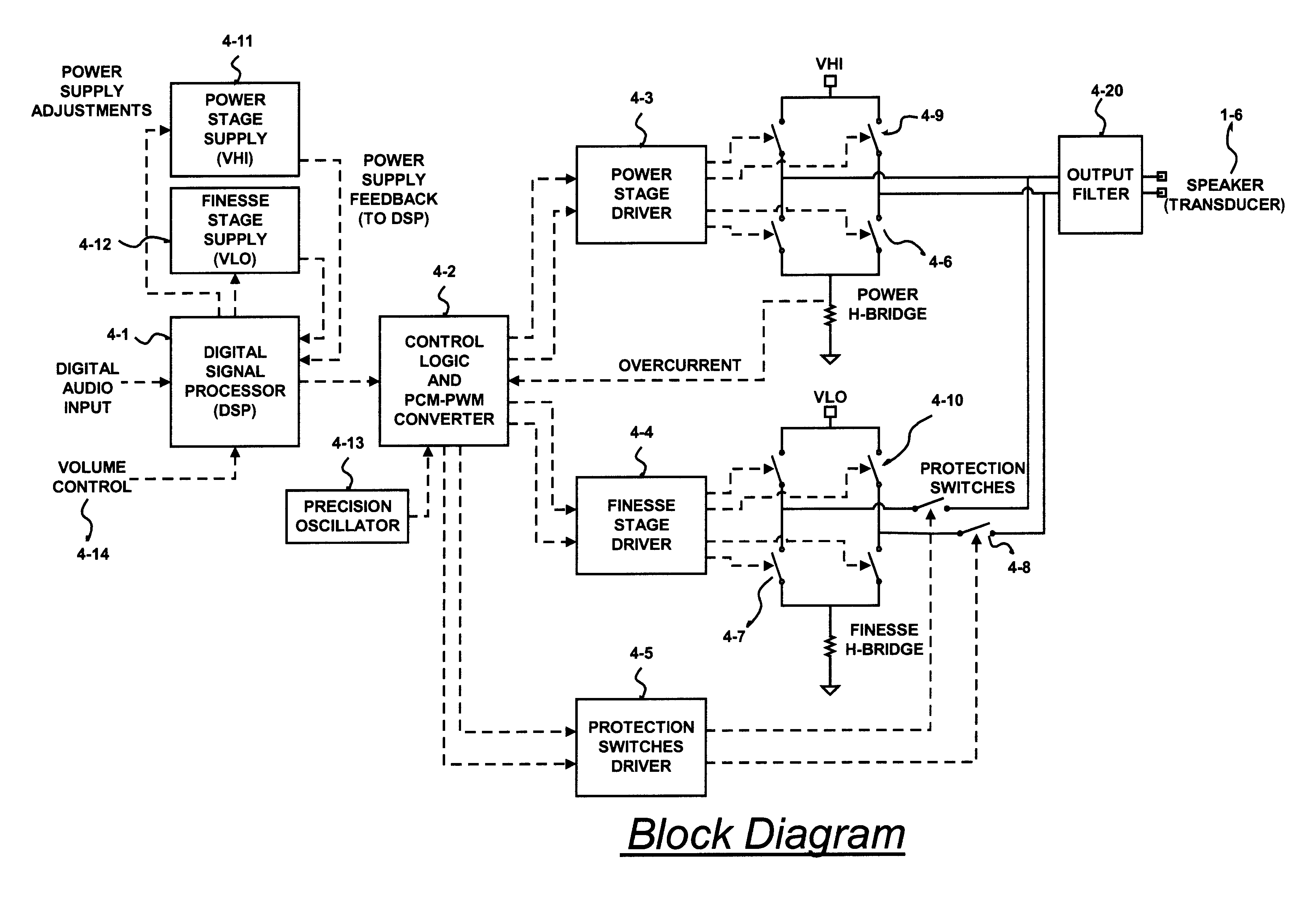
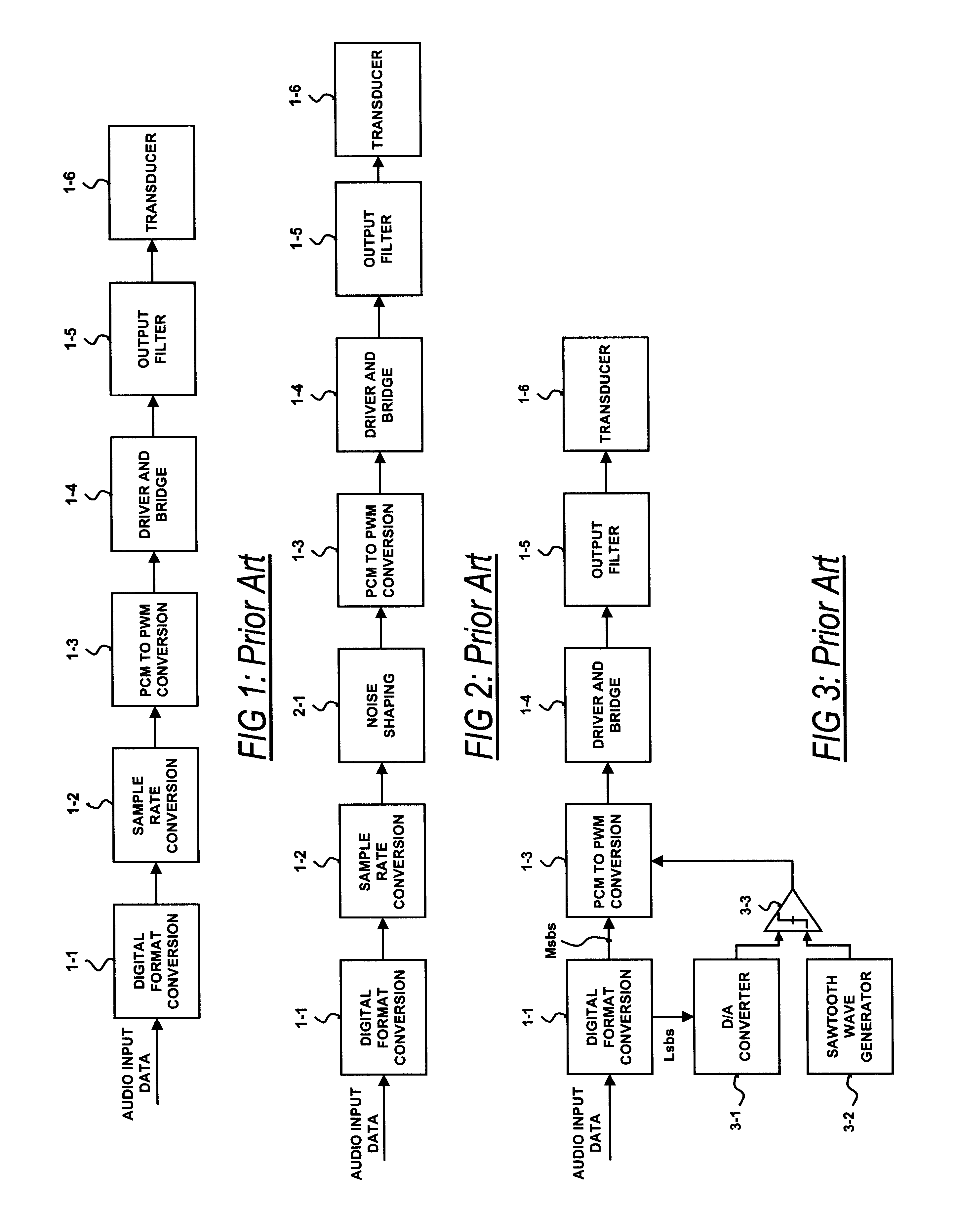
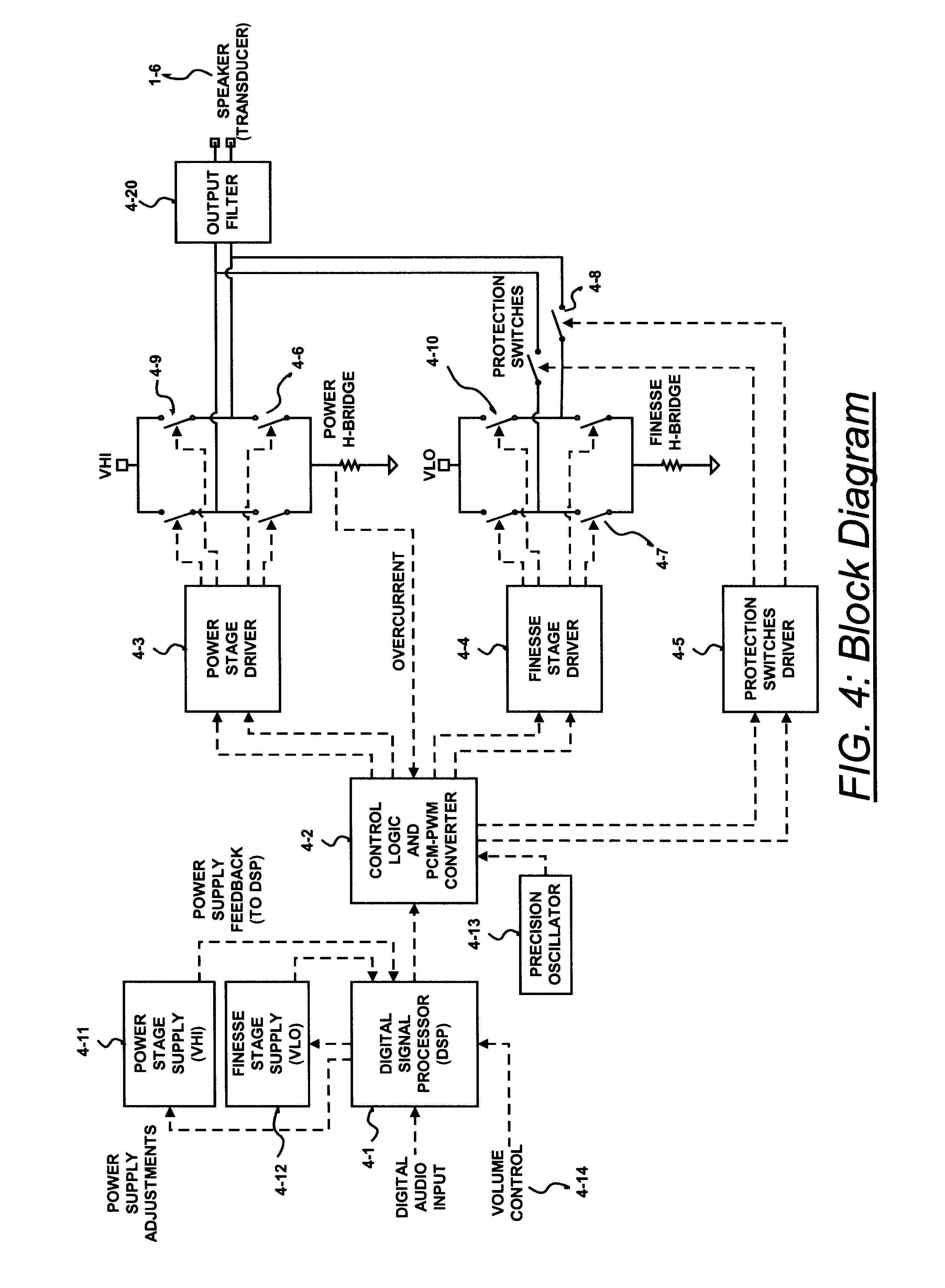
InactiveUS6593807B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersDigital dataLow-pass filter
A class D amplifier uses a summation of two or more PWM output stages to achieve an increased dynamic range and improved linearity for any given clock operating speed. The amplifier accepts a digital data stream as its input, such as from a compact disk, or other compatible media, at a data rate, Fa, that could be 44.1 kHz, 96 kHz, or any other rate appropriate for audio data. In the preferred embodiment, the input audio data resolution, N bits, would be split into two data samples, of J and K.Internal switching frequency, Fs, switches the PWM with an over sampling factor M, where Fs=M*Fa. The time resolution of the PWM is determined by a precision oscillator that operates at Fc=Fs*(max(J,K)-log2(M)+1).The J most significant bits would be routed to a power PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VHI. The K least significant bits are routed to a finesse PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VLO.The ratio of VLO to VHI will be appropriate for the ratio of K and J so the summation of the power PWM stage and the finesse PWM stage will provide the full range of N bits. This summation is accomplished with a low pass filter and time-division multiplexing of the two PWM stages.A micro controller (MCU) is used to apply a sample packet distribution algorithm to provide more resolution by reducing quantization noise in the audio band of interest. The MCU is also used to calibrate the VLO or VHI, or to calibrate the PWM timing of the two PWM stages to achieve appropriate performance.
Owner:GROVES JR WILLIAM HARRIS +1
Processor architecture for executing two different fixed-length instruction sets
InactiveUS20050262329A1High simulationSave memory spaceDigital computer detailsNext instruction address formationProcessor elementLeast significant bit
A processor element, structured to execute a 32-bit fixed length instruction set architecture, is backward compatible with a 16-bit fixed length instruction set architecture by translating each of the 16-bit instructions into a sequence of one or more 32-bit instructions. Switching between 16-bit instruction execution and 32-bit instruction execution is accomplished by branch instructions that employ a least significant bit position of the address of the target of the branch to identify whether the target instruction is a 16-bit instruction or a 32-bit instruction.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
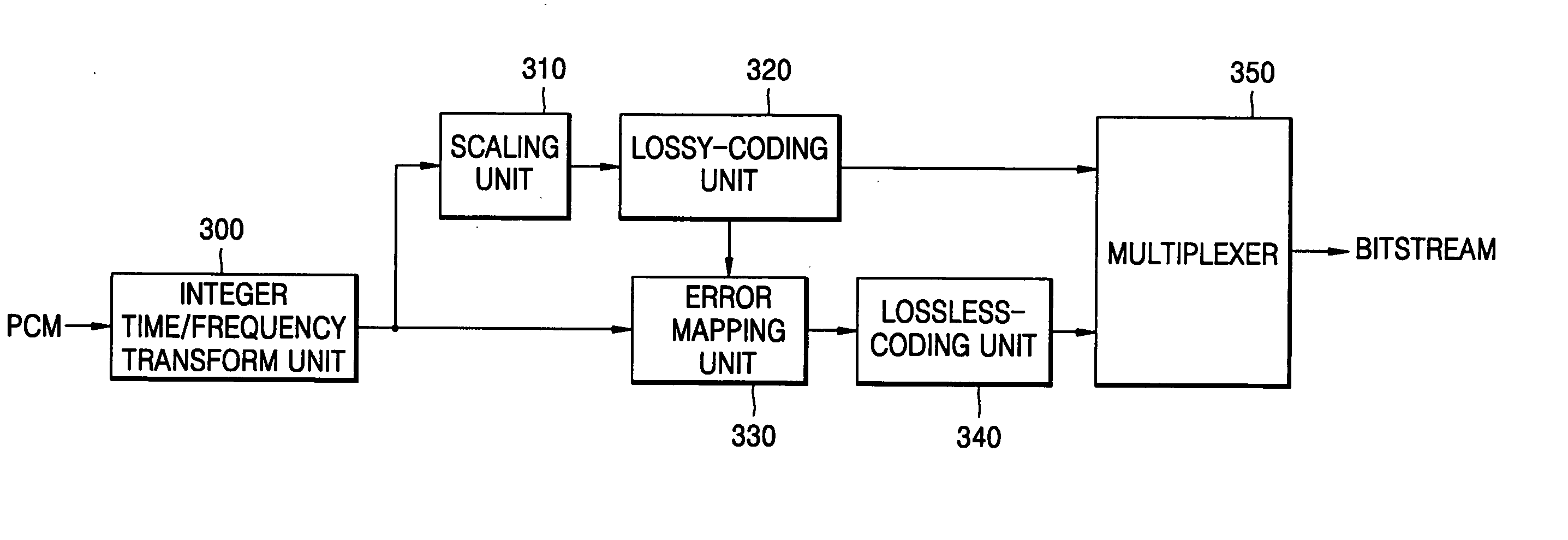
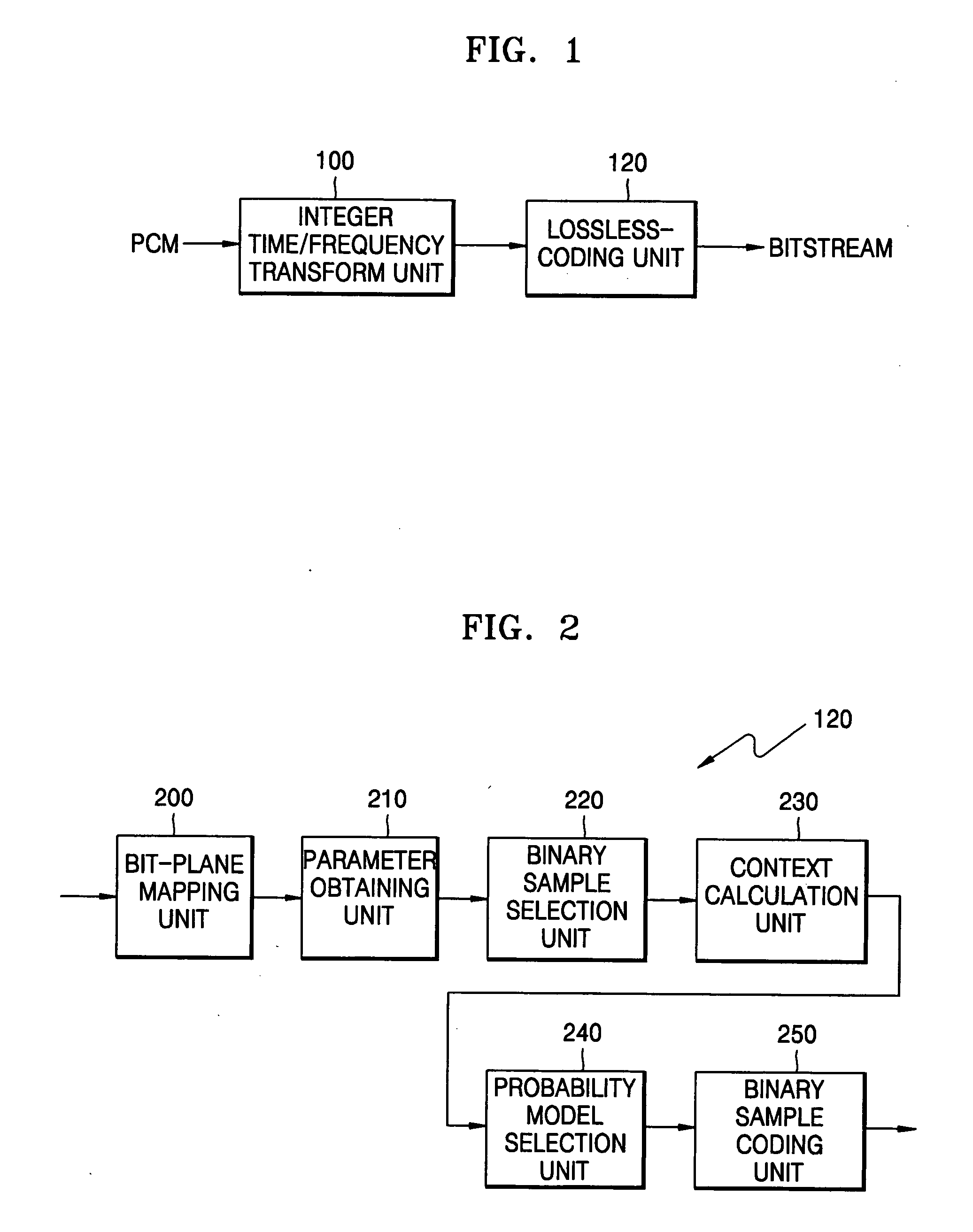
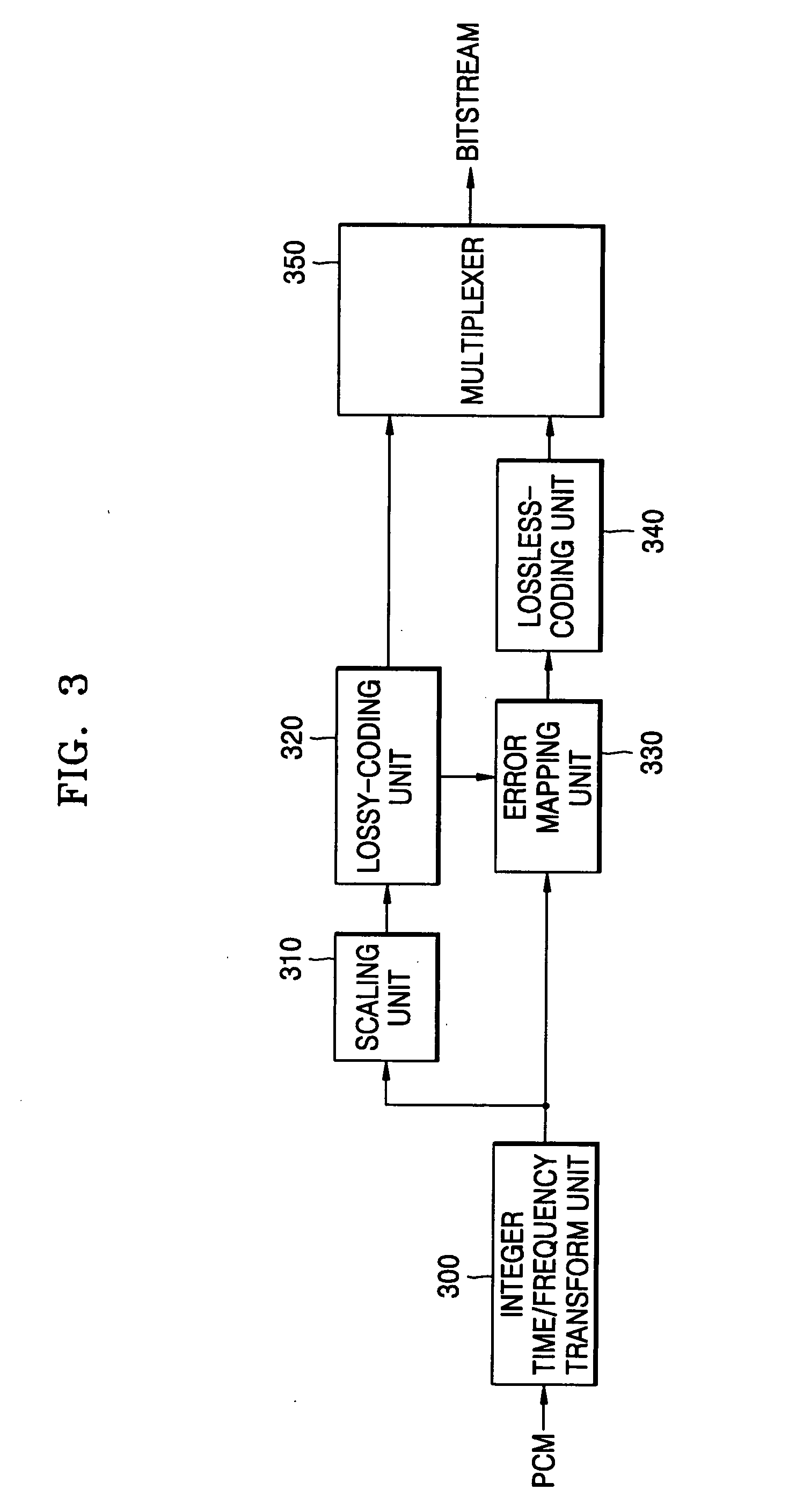
Lossless audio coding/decoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050203731A1Increase the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionProbit modelBit plane
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
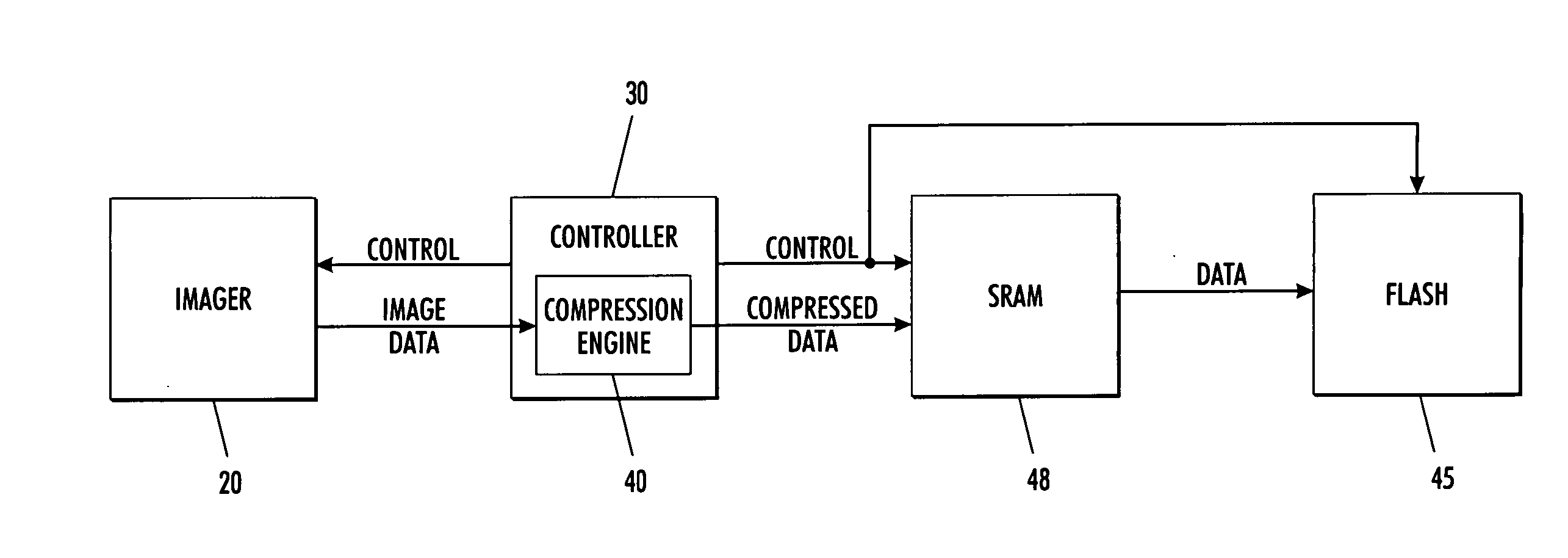
In-stream lossless compression of digital image sensor data
InactiveUS20040135903A1Television system detailsColor television detailsMultiplexingLeast significant bit
A method and system provide in-stream compression of bytes of digital image sensor data. A specified number of least significant bits of the byte of digital image sensor data is masked or dropped to reduce the amount of image data if a frame of image data. After masking, alternate bytes of digital image sensor data are subtracted to produce an entropy-reduced data model. The difference bytes of digital image sensor data are split into a predetermined number of channels, each channel having a bit width such that the sum of the bit widths of each channel equals a bit width of the byte of digital image sensor data. Each channel is operated upon by a distinct cumulative distribution function before being multiplexed. The multiplexed digital image sensor data is encoded by arithmetic compression encoding. The method and system also utilize a division-free method of arithmetic encoding to simplify the hardware requirements of encoding. Lastly, the method and system utilize a round-robin removal approach for adaptively fixing a number of elements in a histogram.
Owner:SMAL CAMERA TECH
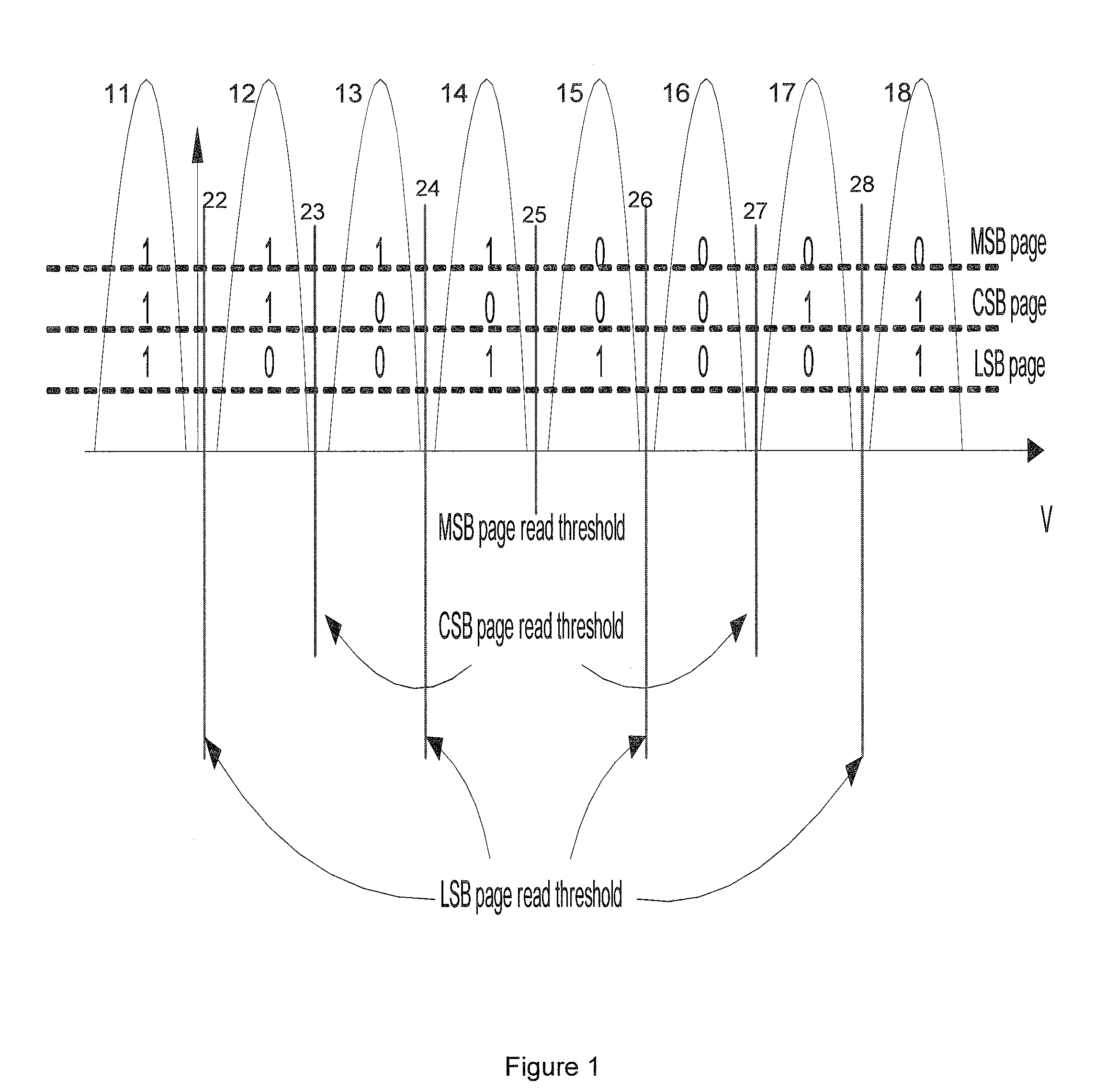
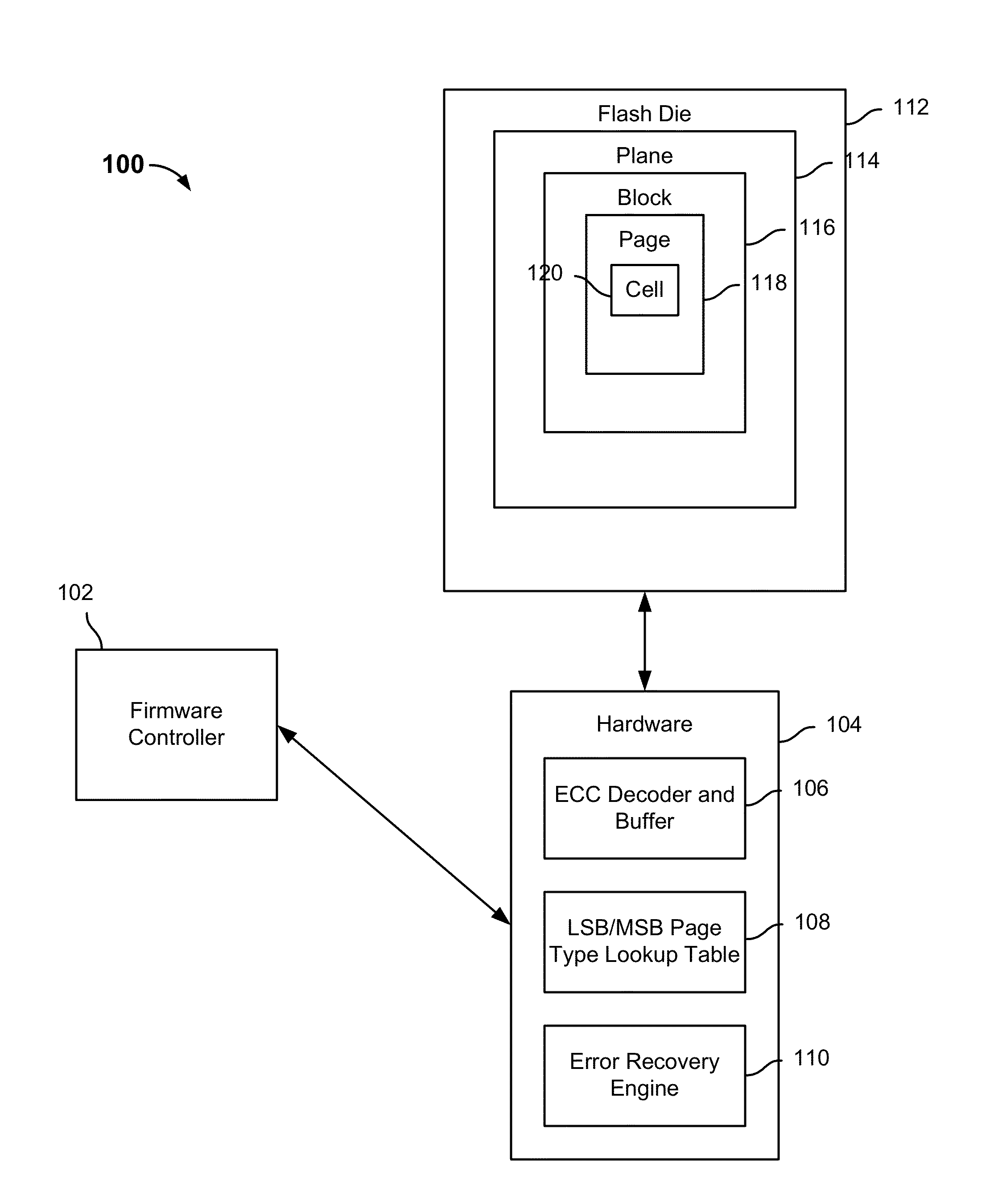
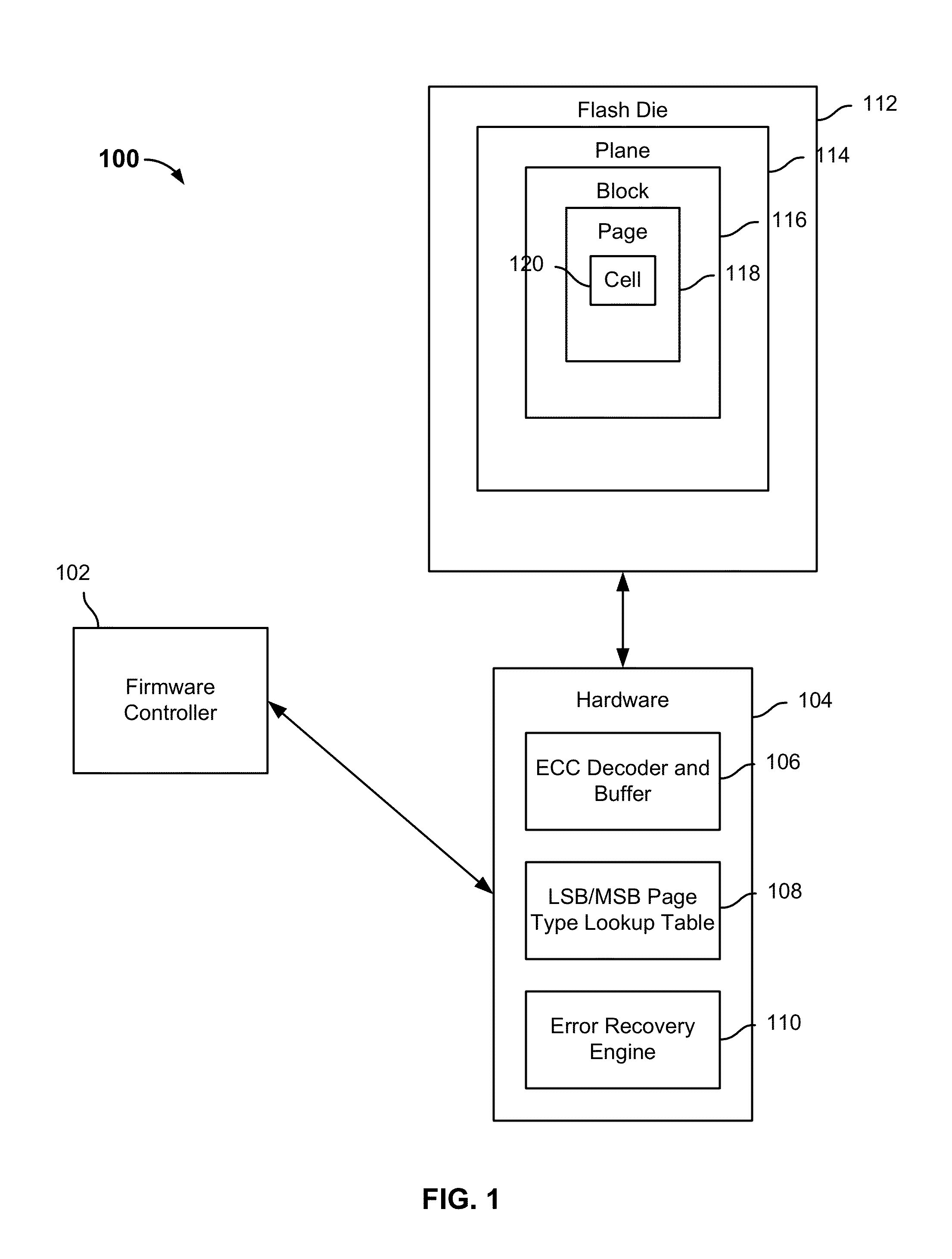
Error recovery for flash memory
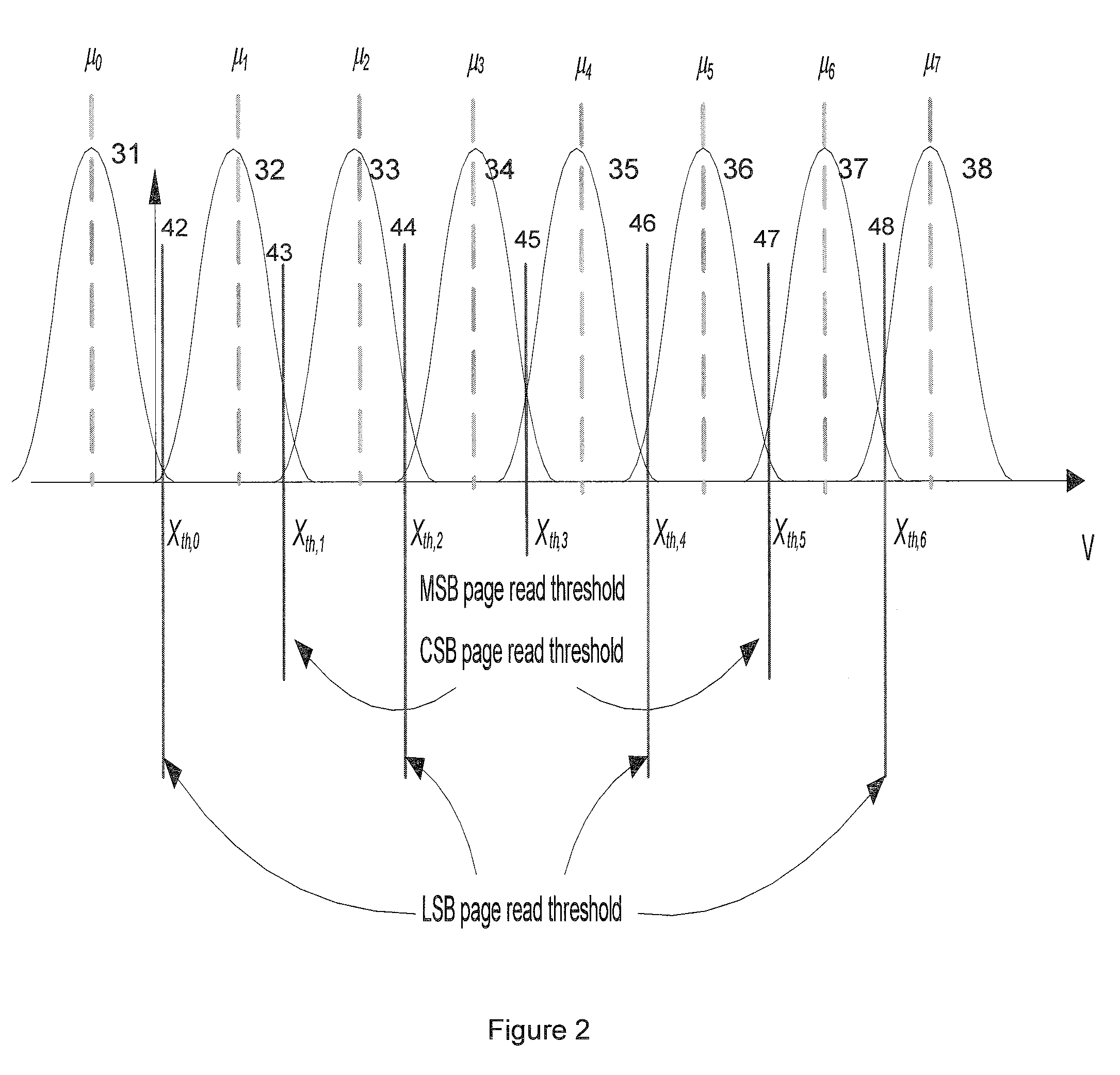
A set of data associated with a page in flash storage is received. Error correction decoding is performed on the set of data; if event error correction decoding fails, it is determined whether the page is a most significant bit (MSB) page or a least significant bit (LSB) page. If it is determined the page is a MSB page, one or more MSB read thresholds are adjusted and the is re-read page using the adjusted MSB read threshold(s). If it is determined the page is a LSB page, one or more LSB read thresholds are adjusted and the page is re-read using the adjusted LSB read threshold(s).
Owner:SK HYNIX MEMORY SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com