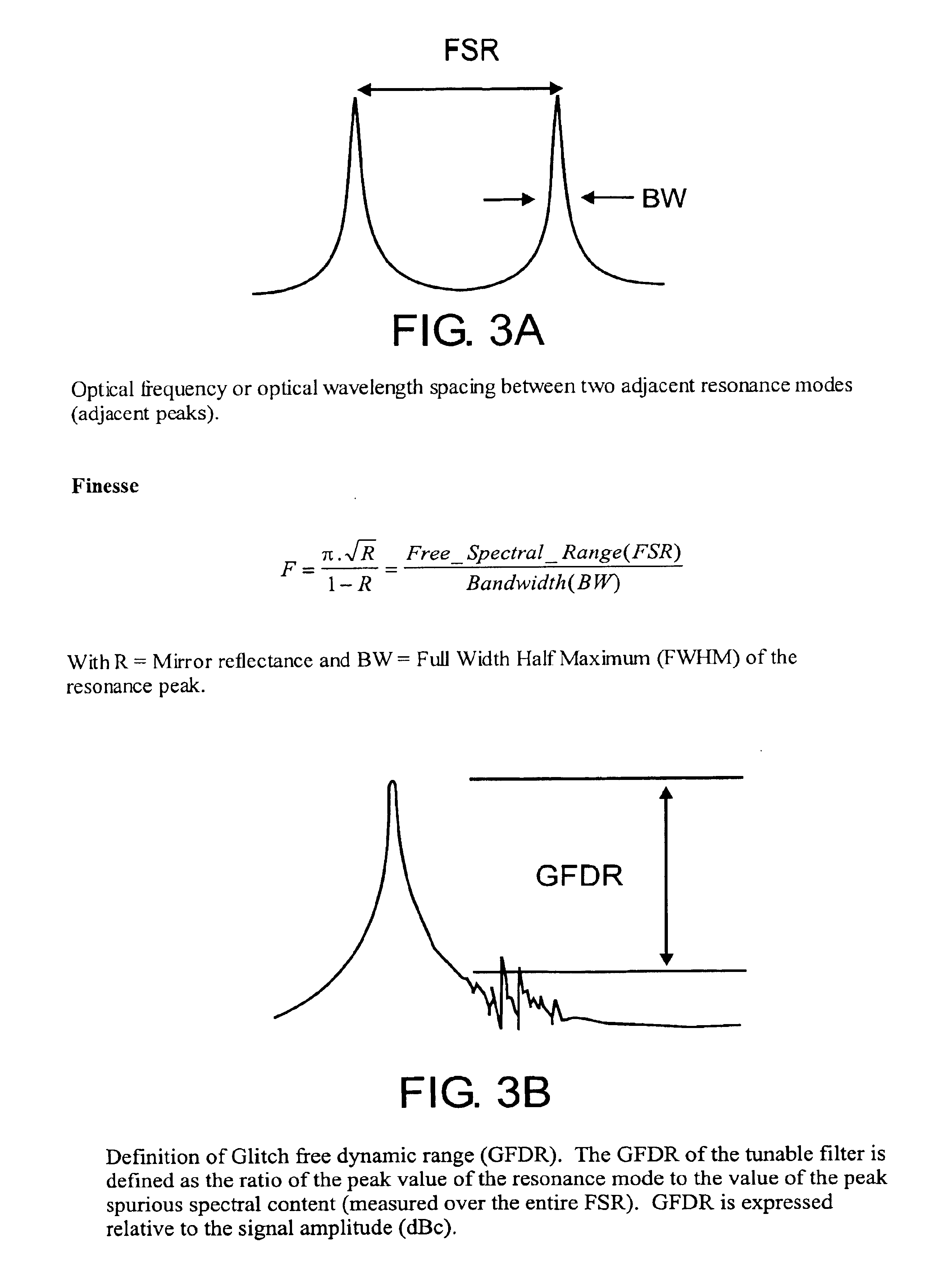
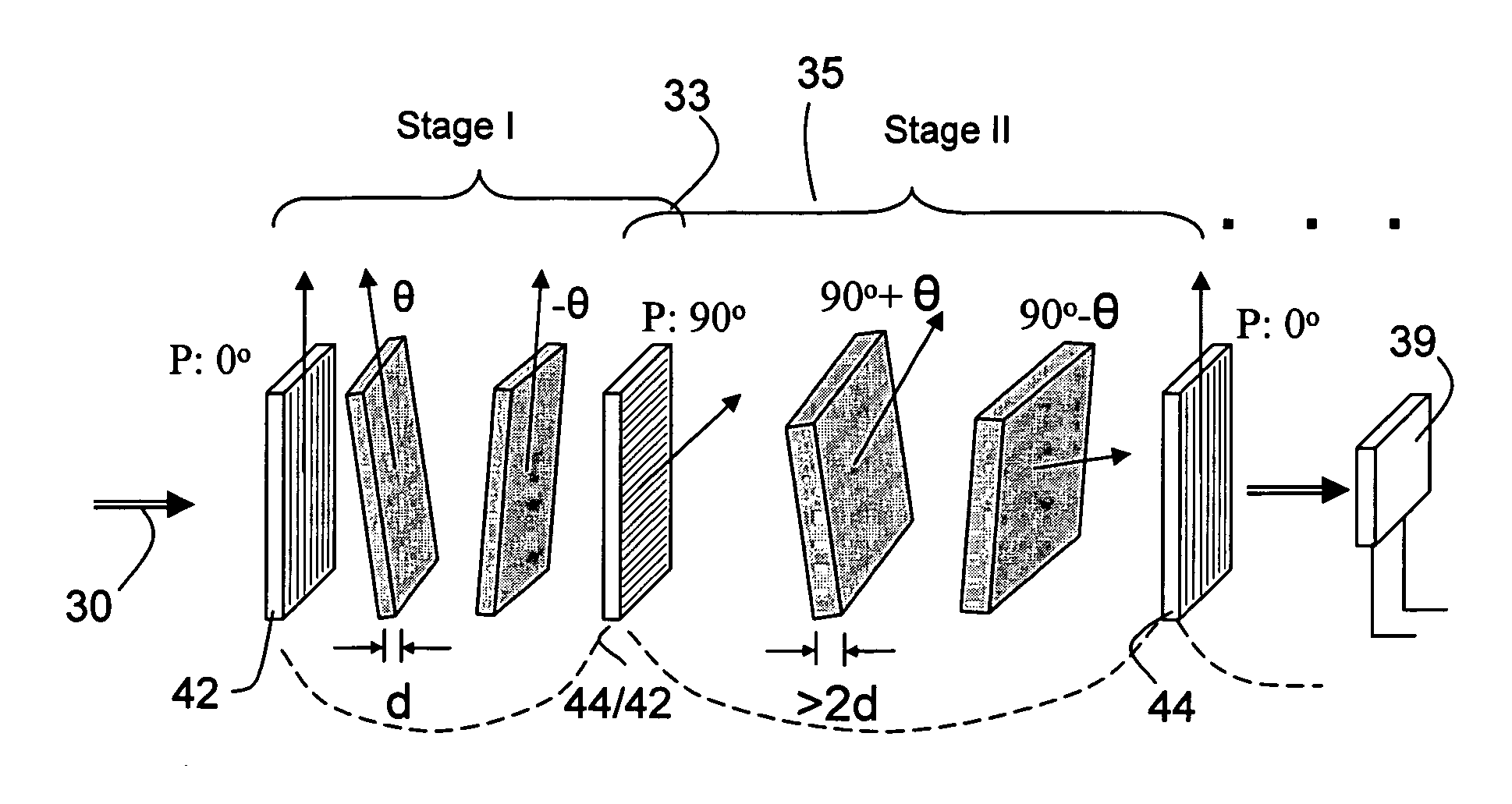
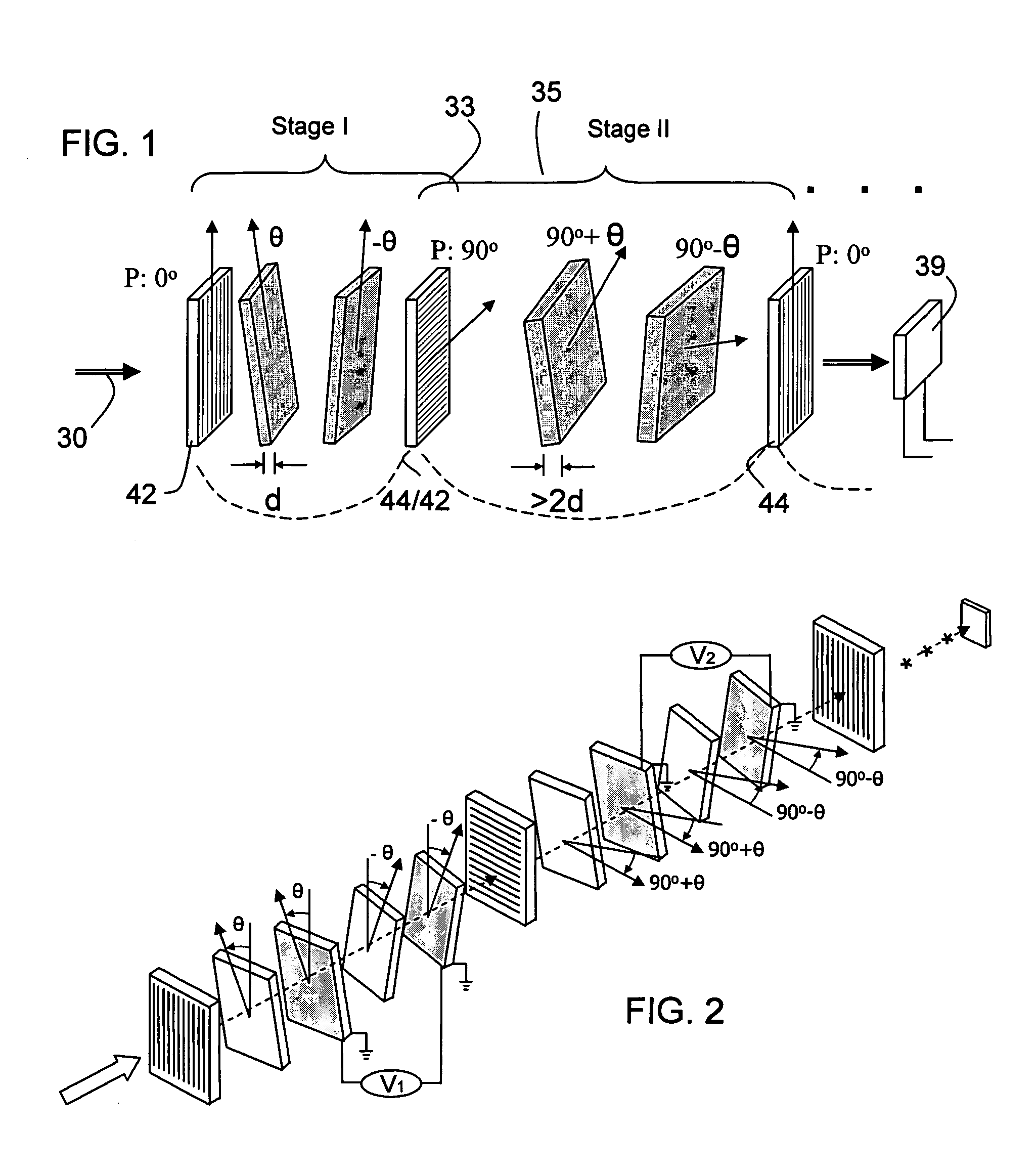
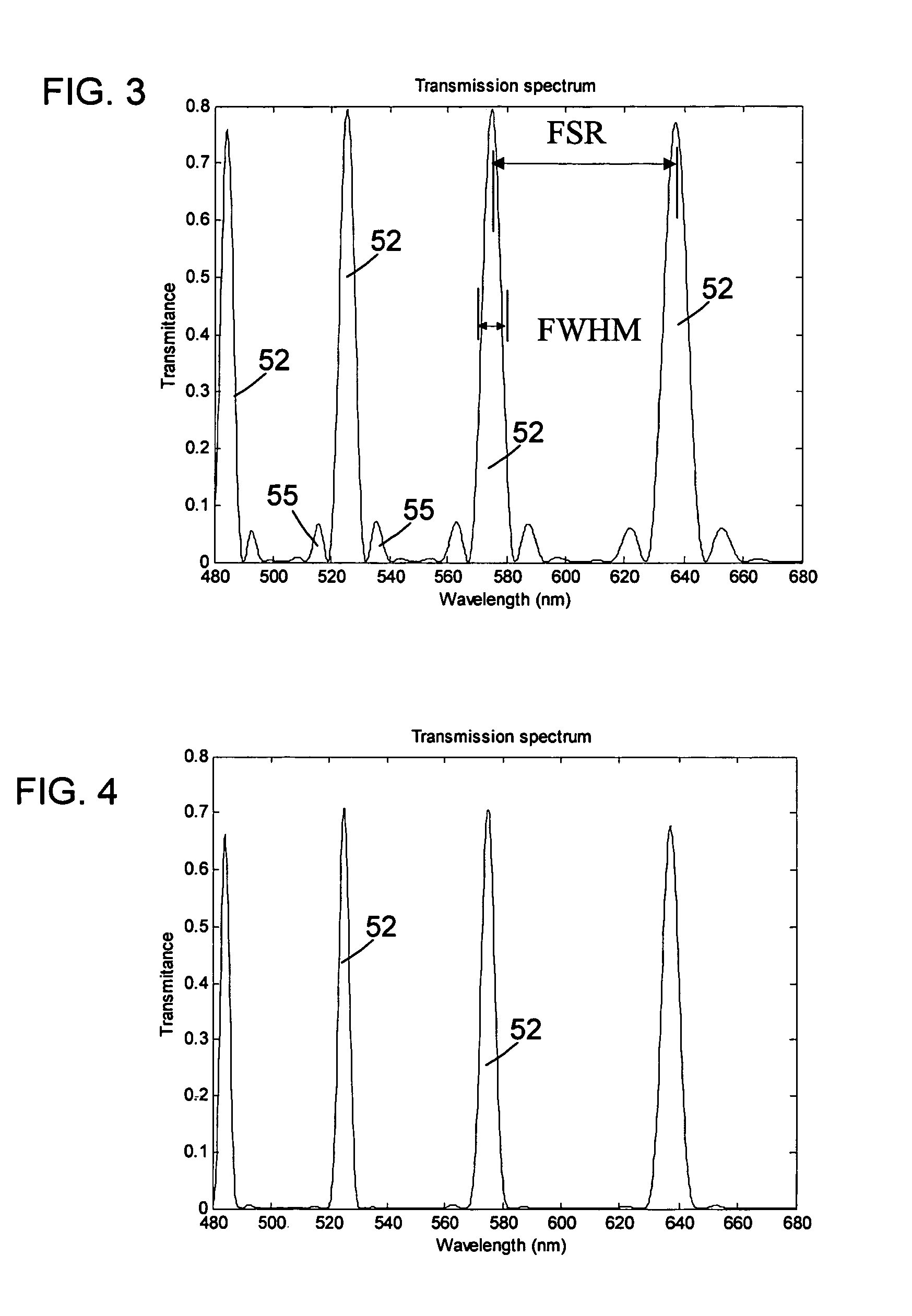
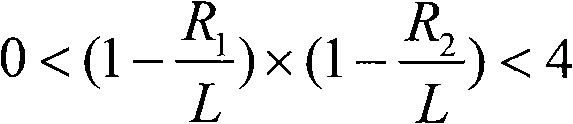Patents
Literature
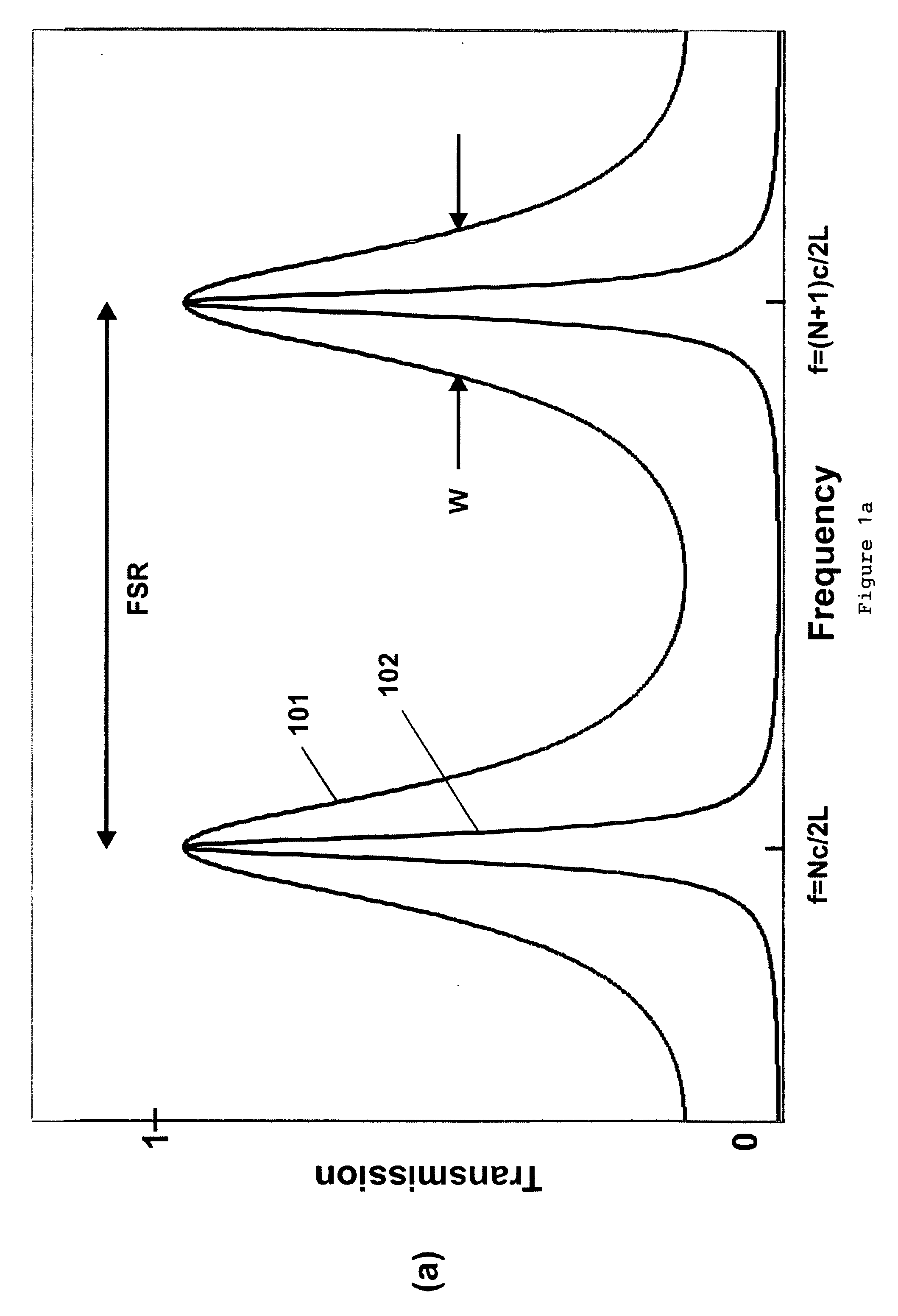
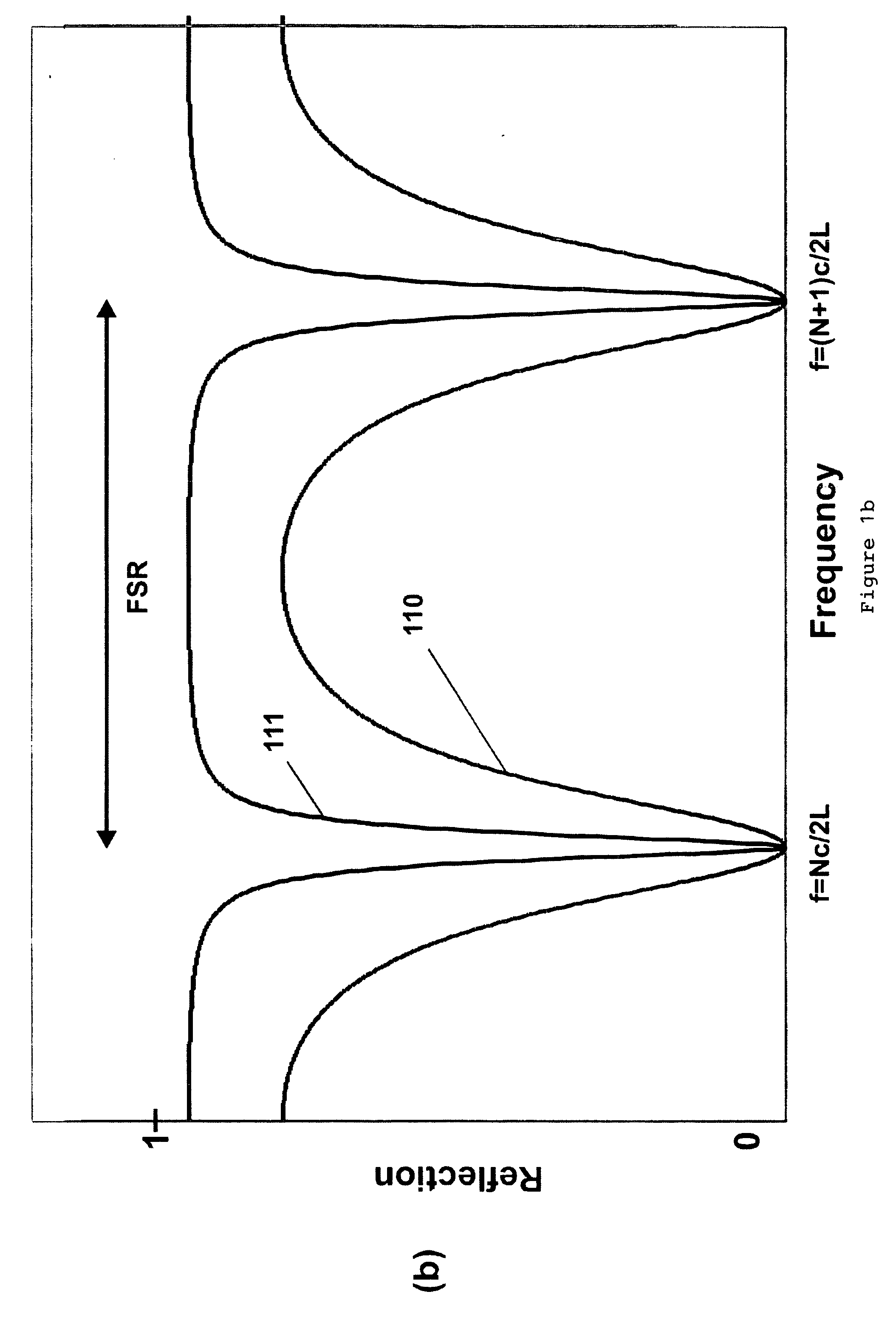
95 results about "Finesse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In contract bridge and similar games, a finesse is a card play technique which will enable a player to win an additional trick or tricks should there be a favorable position of one or more cards in the hands of the opponents.
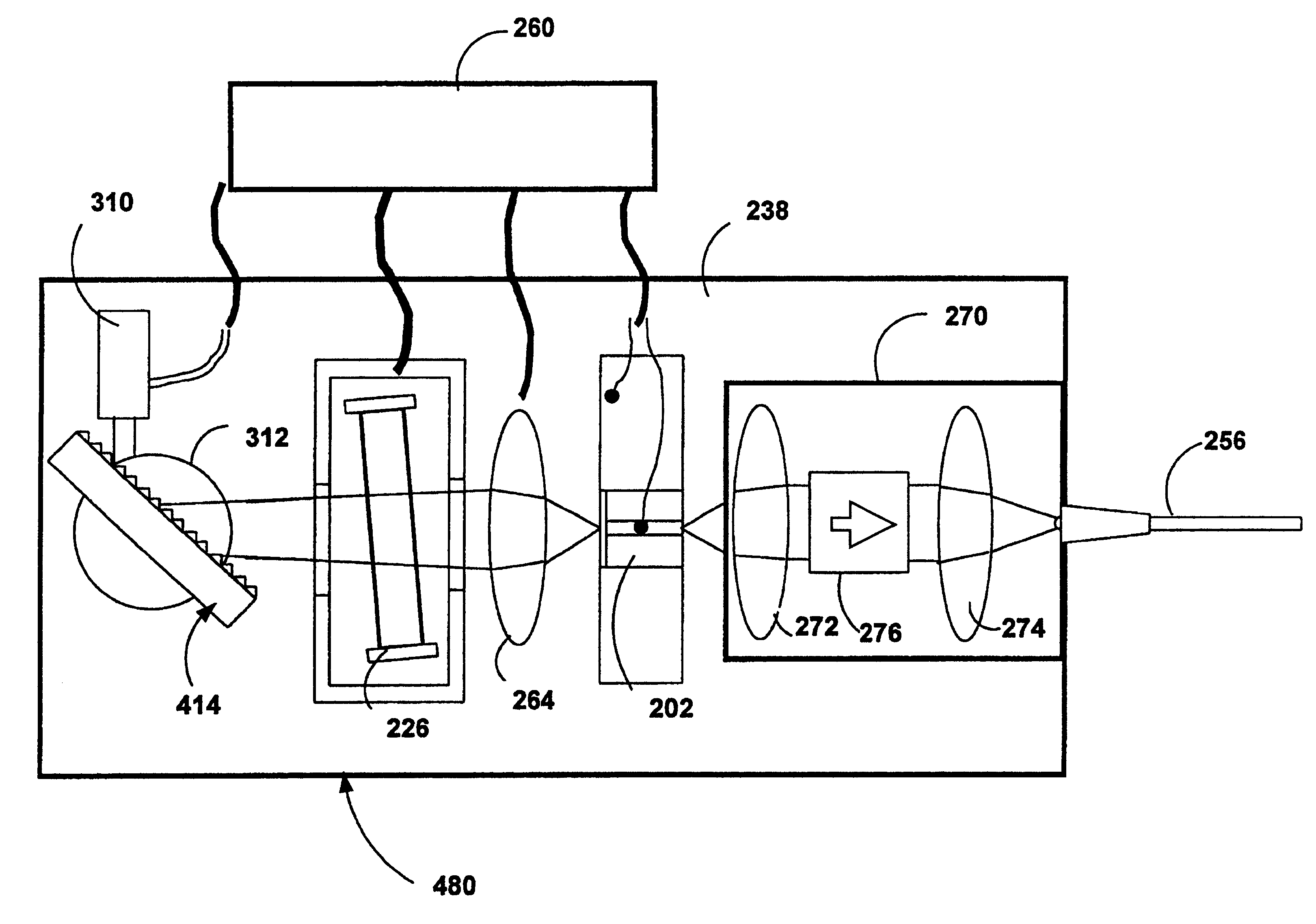
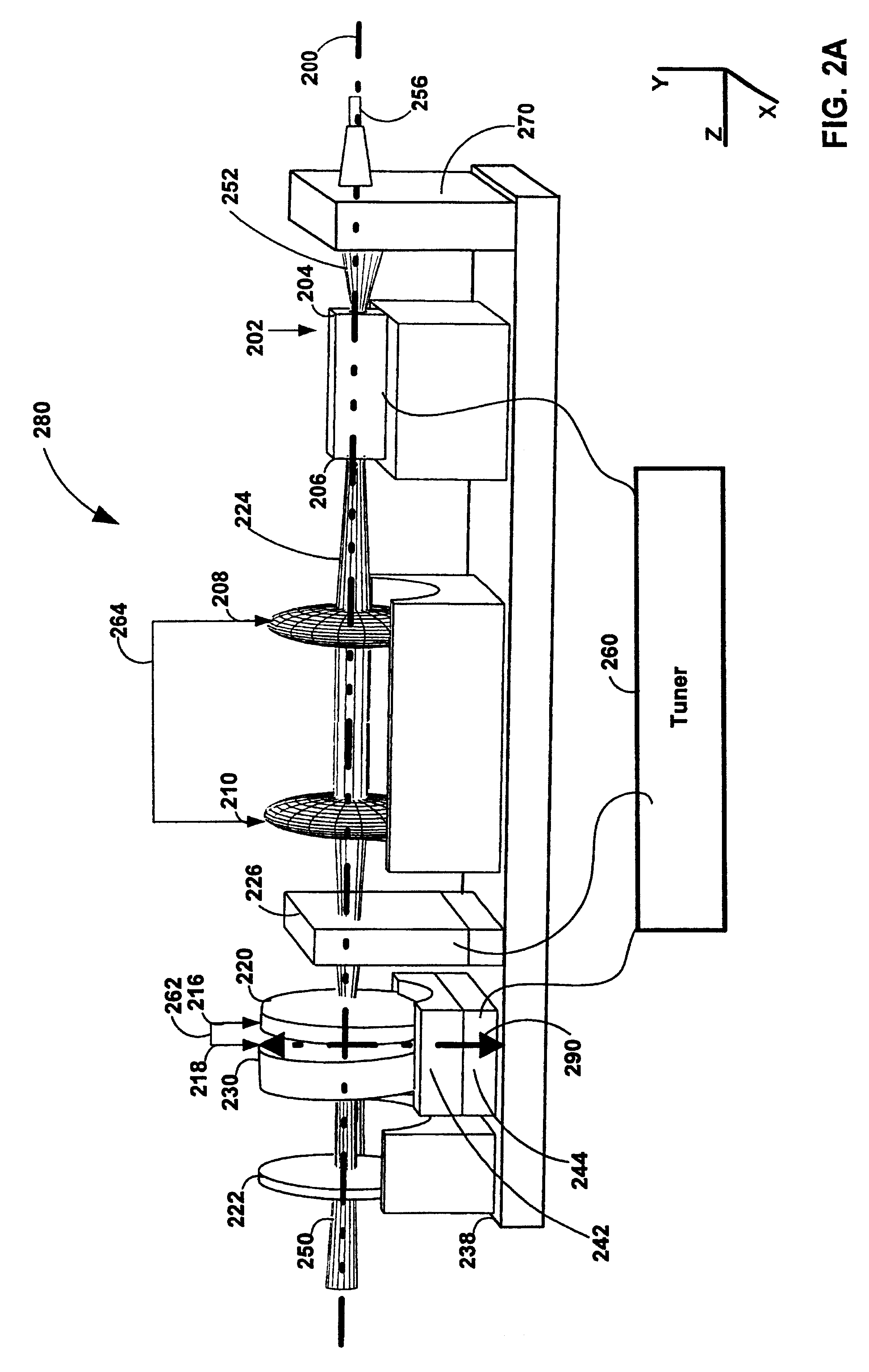
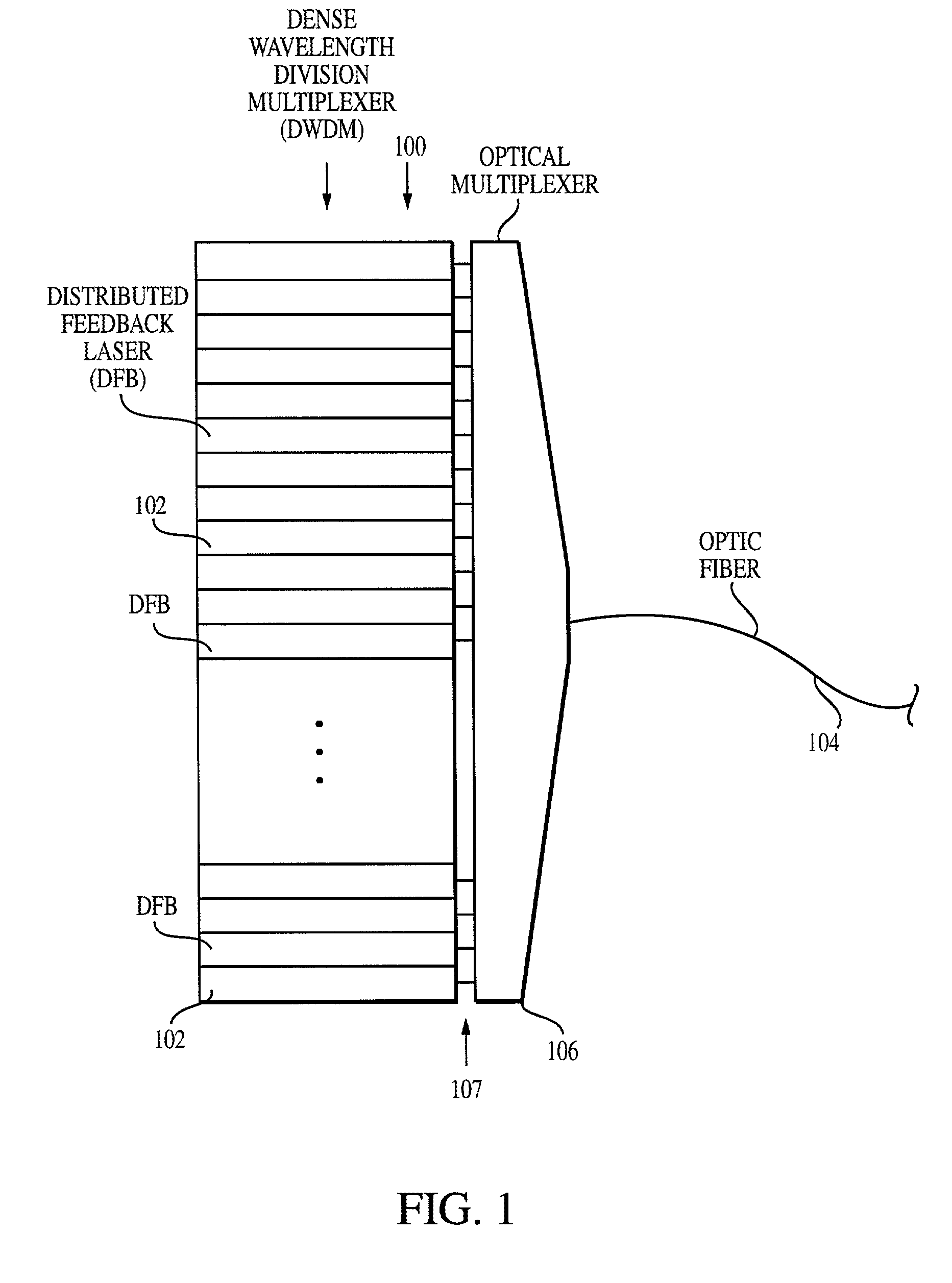
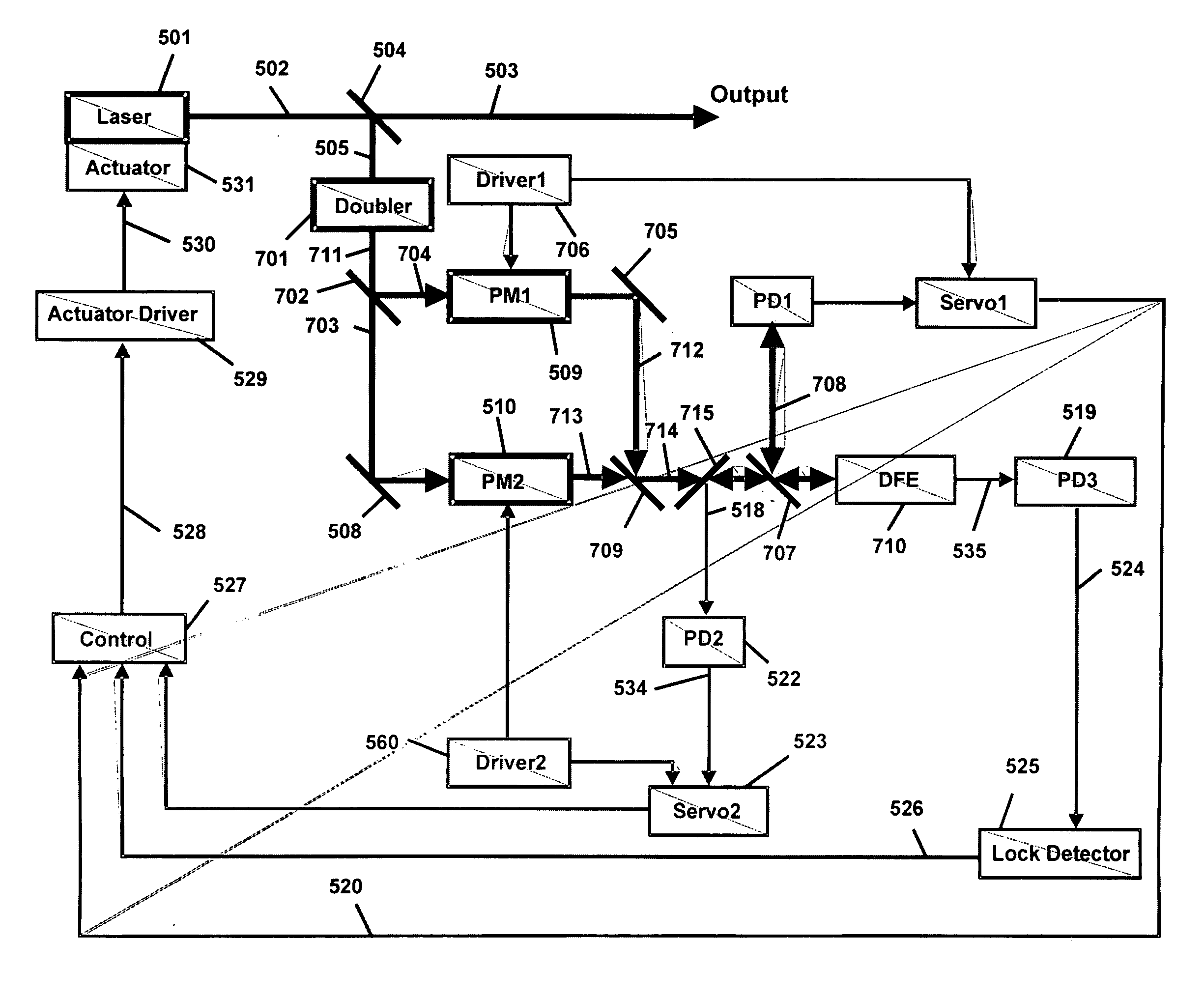
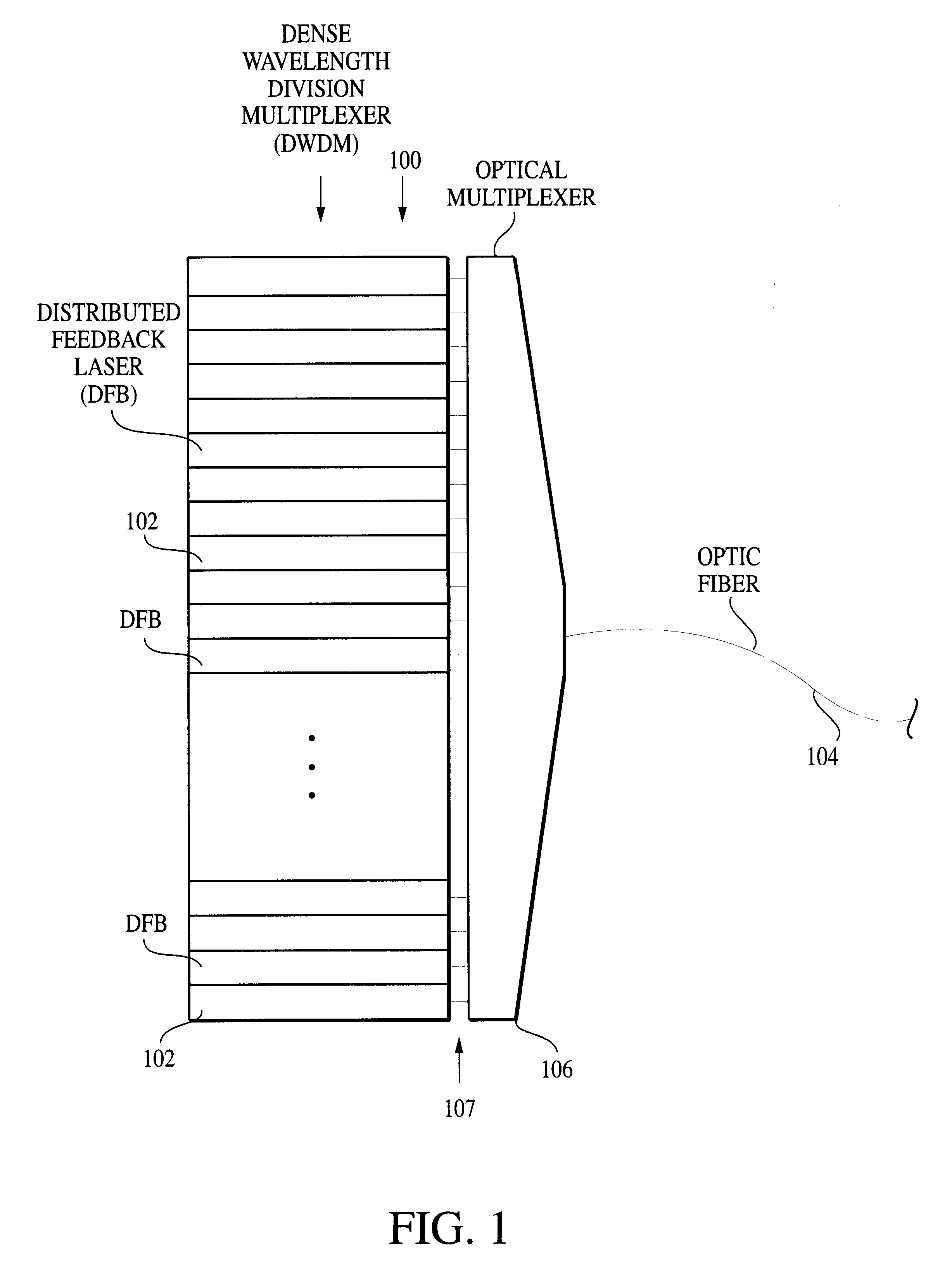
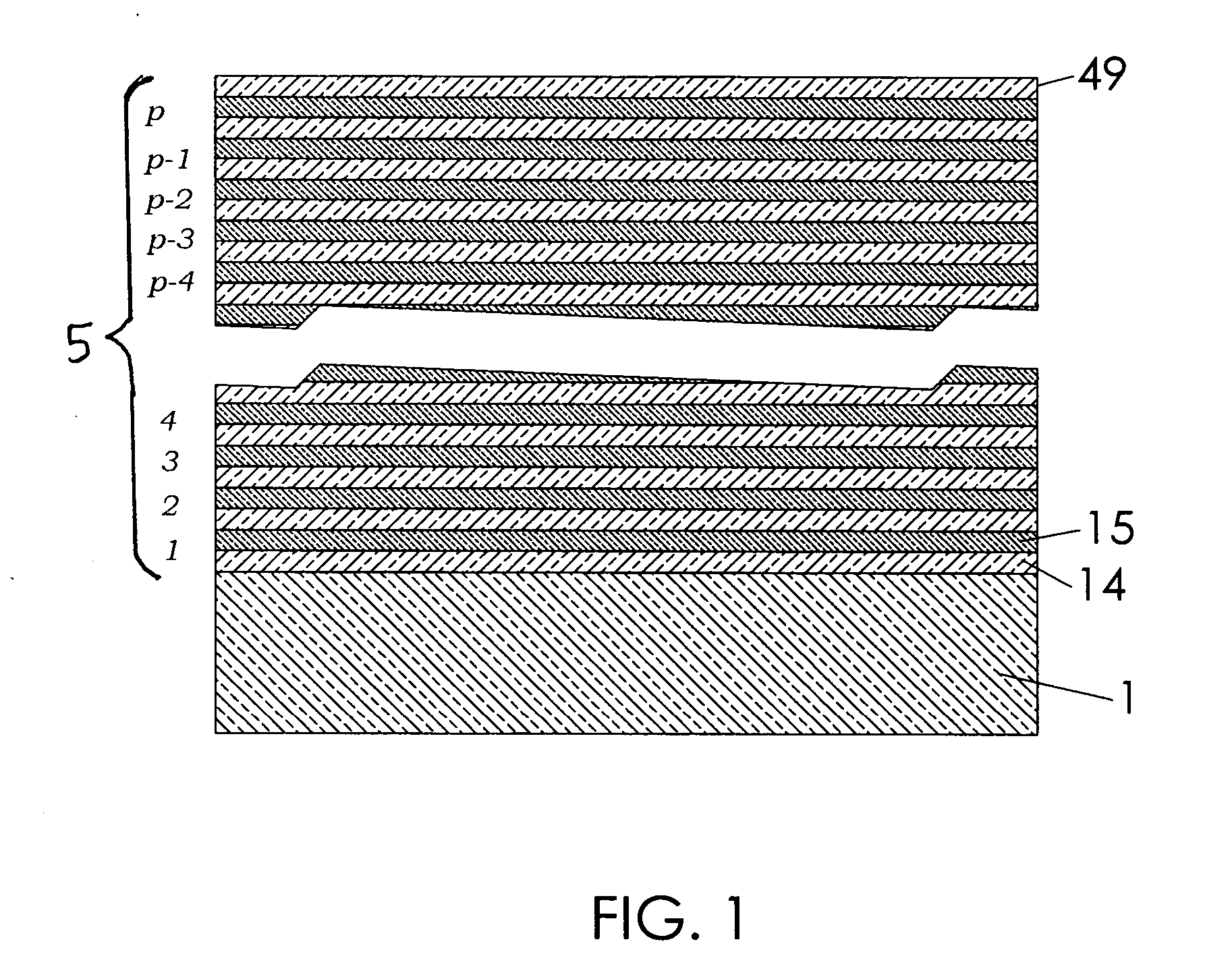
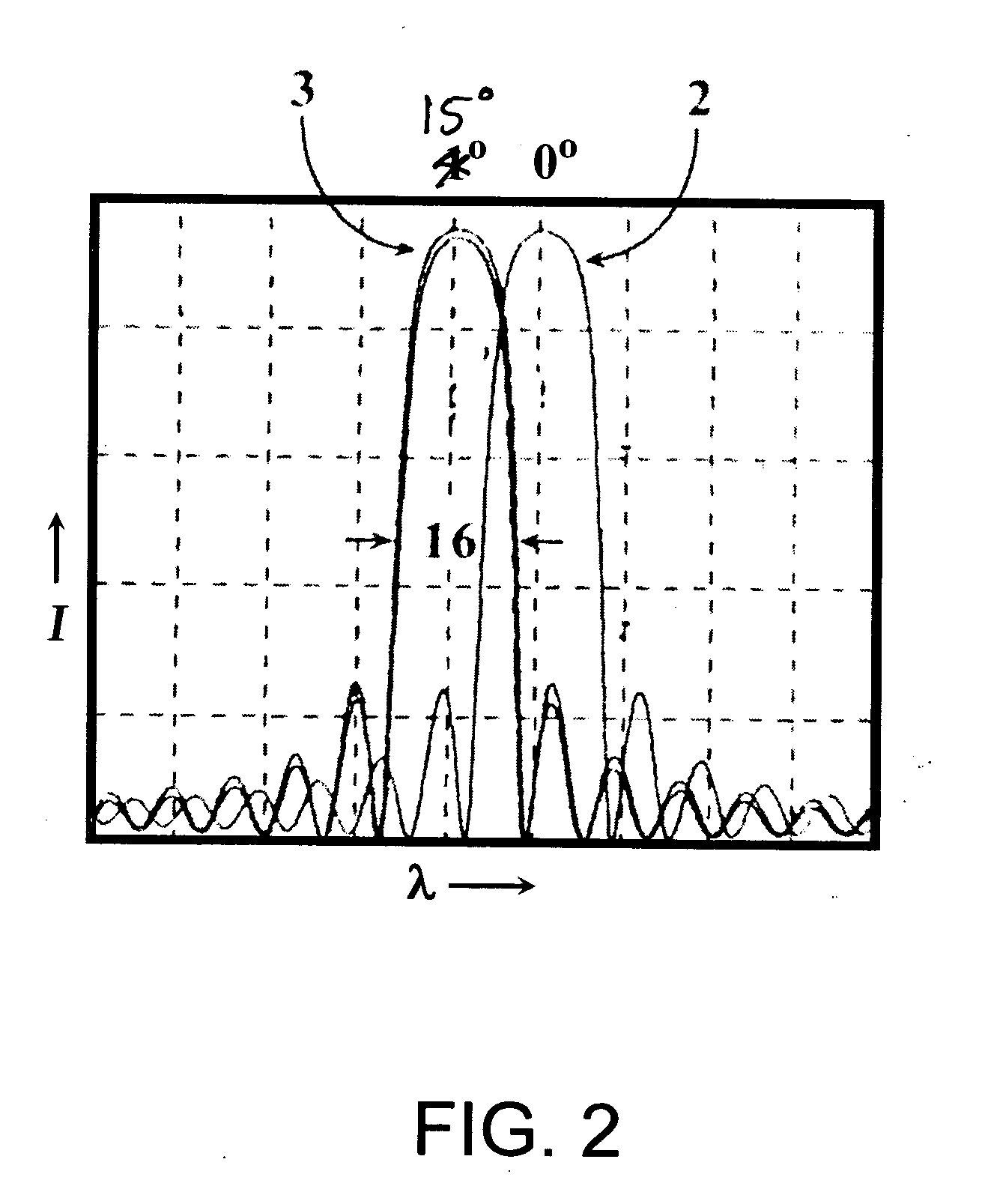
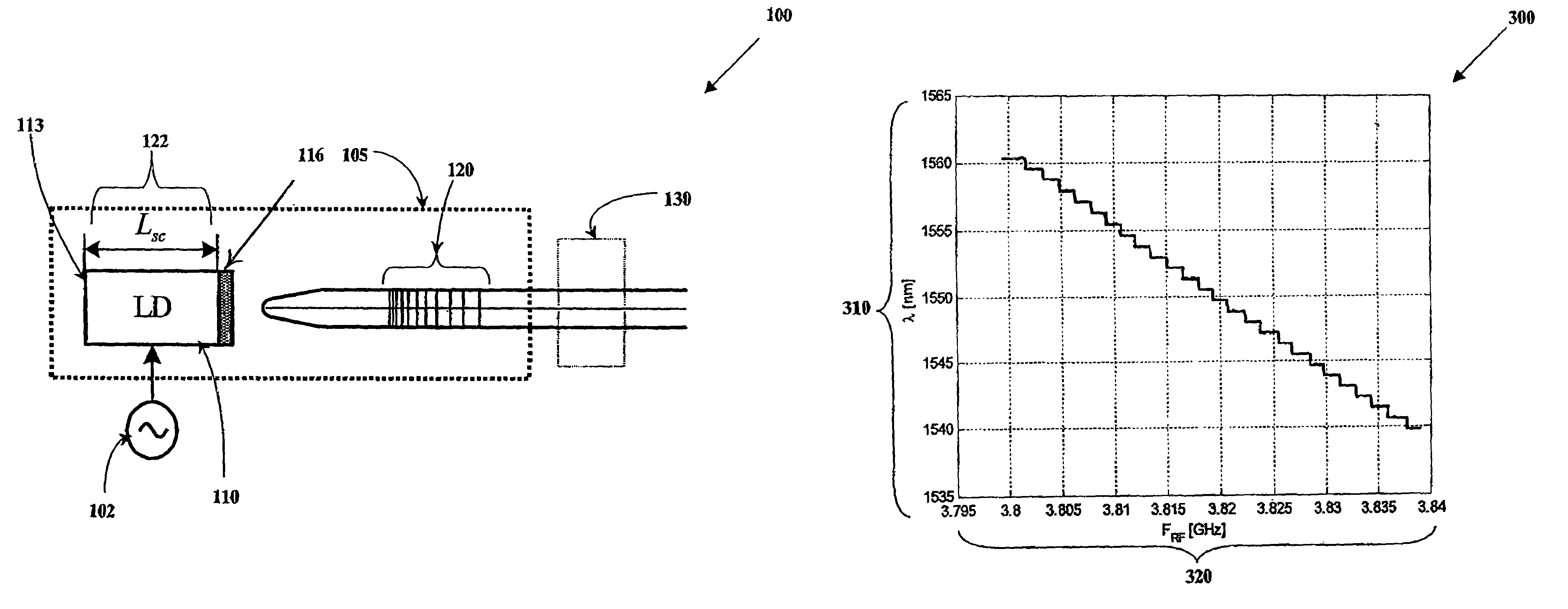
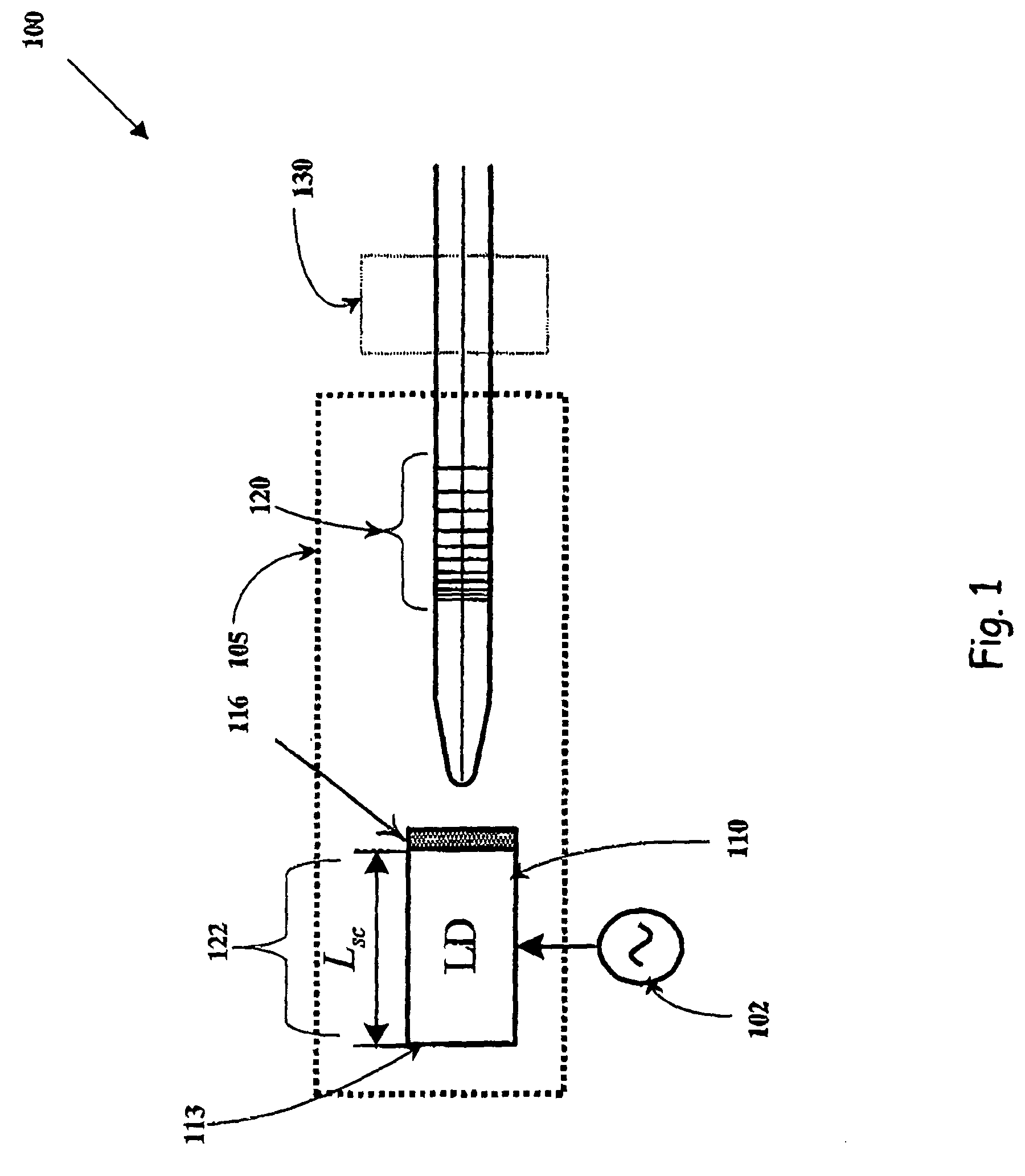
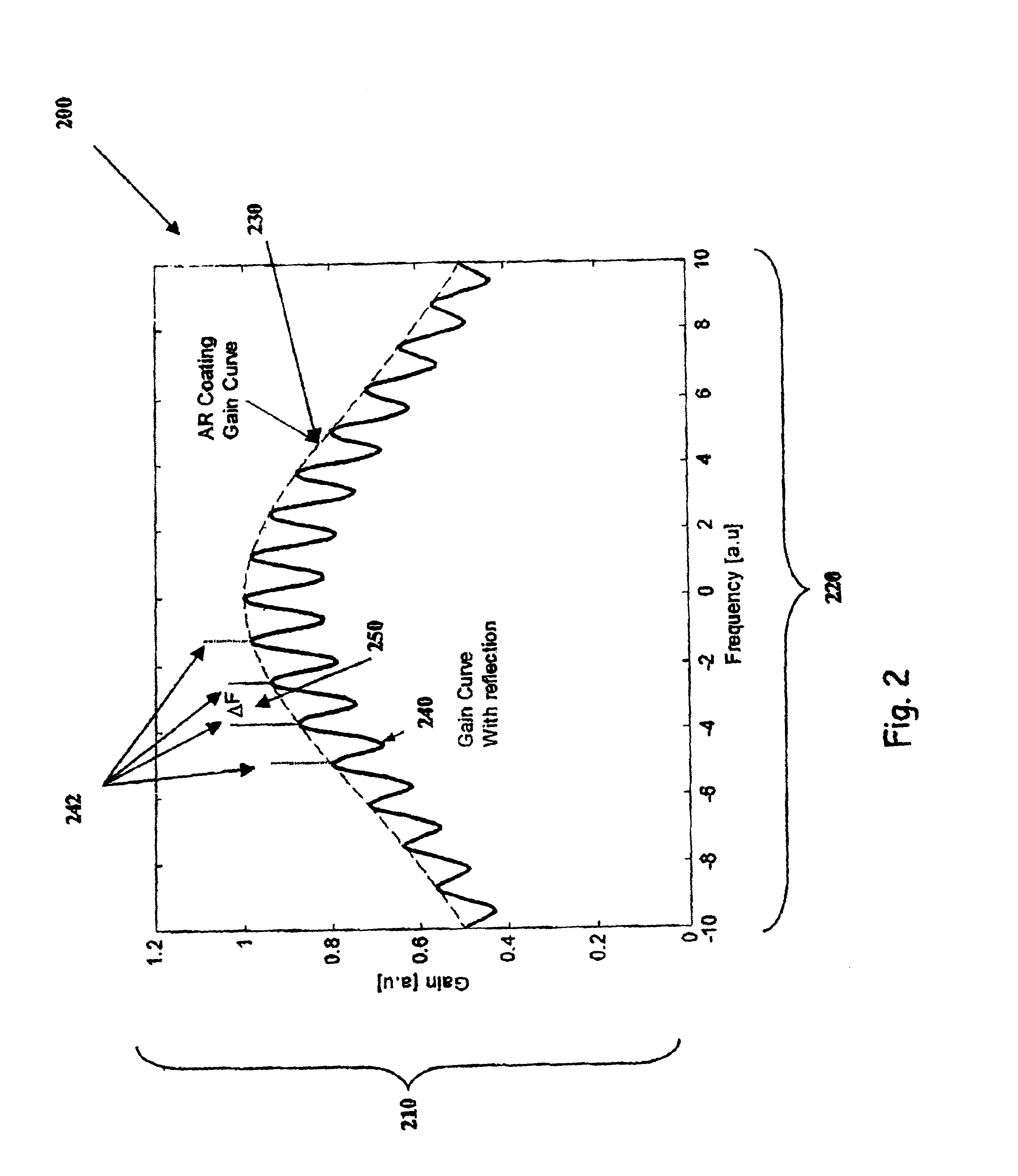
Tunable laser transmitter with internal wavelength grid generators
InactiveUS6526071B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsCapacitanceLaser transmitter
The present invention provides a continuously tunable external cavity laser (ECL) with a compact form factor and precise tuning to a selected center wavelength of a selected wavelength grid. The ECL may thus be utilized in telecom applications to generate the center wavelengths for any channel on the ITU or other optical grid. The ECL does not require a closed loop feedback. A novel tuning mechanism is disclosed which provides for electrical or mechanical tuning to a known position or electrical parameter, e.g., voltage, current or capacitance, with the required precision in the selected center wavelength arising as a result of a novel arrangement of a grid generator and a channel selector. The grid generator exhibits first pass bands which correspond to the spacing between individual channels of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses side band modes of the laser. The channel selector exhibits second pass bands that are wider than the first pass bands. In an embodiment of the invention the second pass bands have a periodicity substantially corresponding with the separation between the shortest wavelength channel and the longest wavelength channel of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses channels adjacent to the selected channel. The broad second pass bands of the channel selector reduce the sensitivity of the ECL to tuning variations about the selected channel, thus avoiding the requirement of a closed loop feedback system to control the channel selector.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
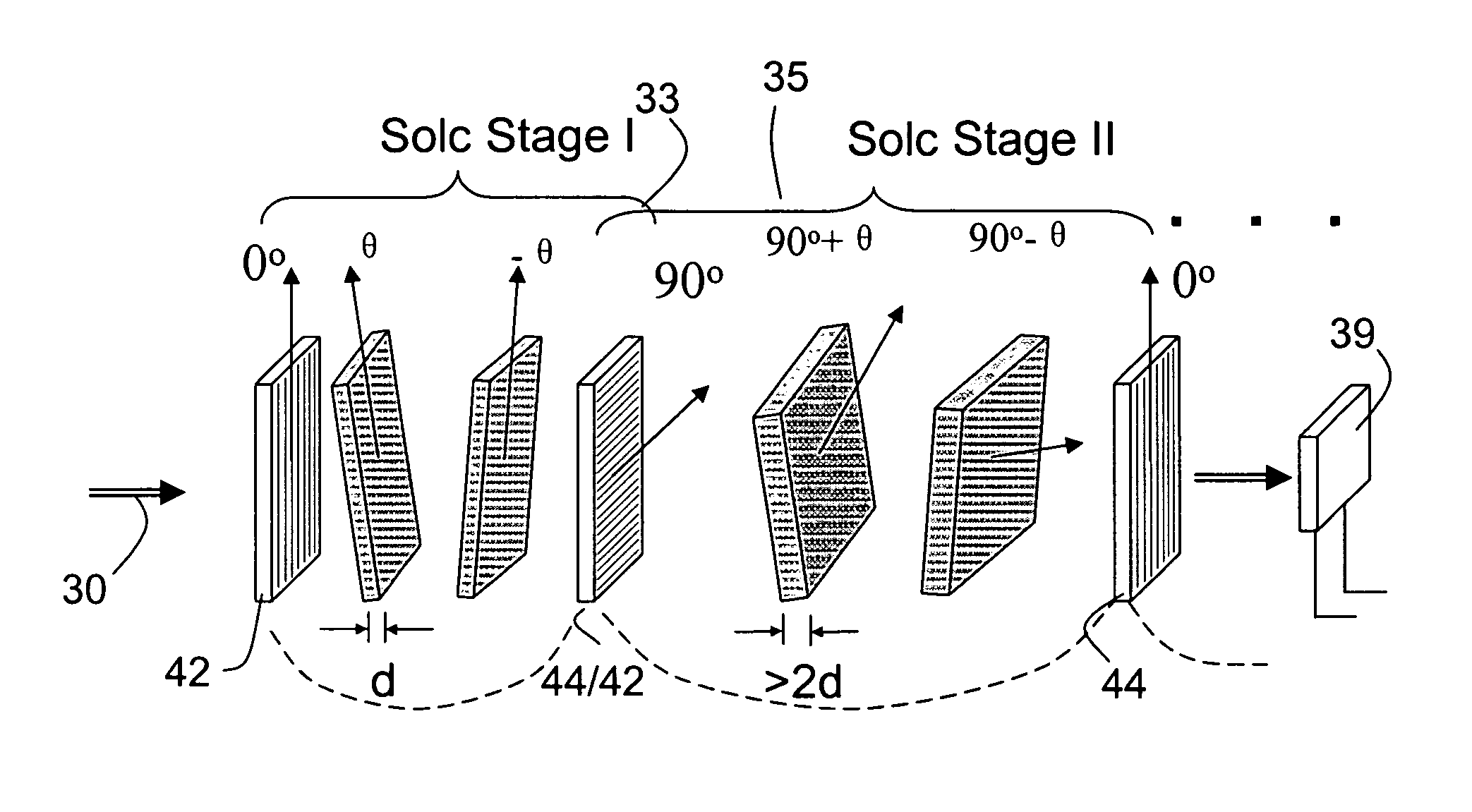
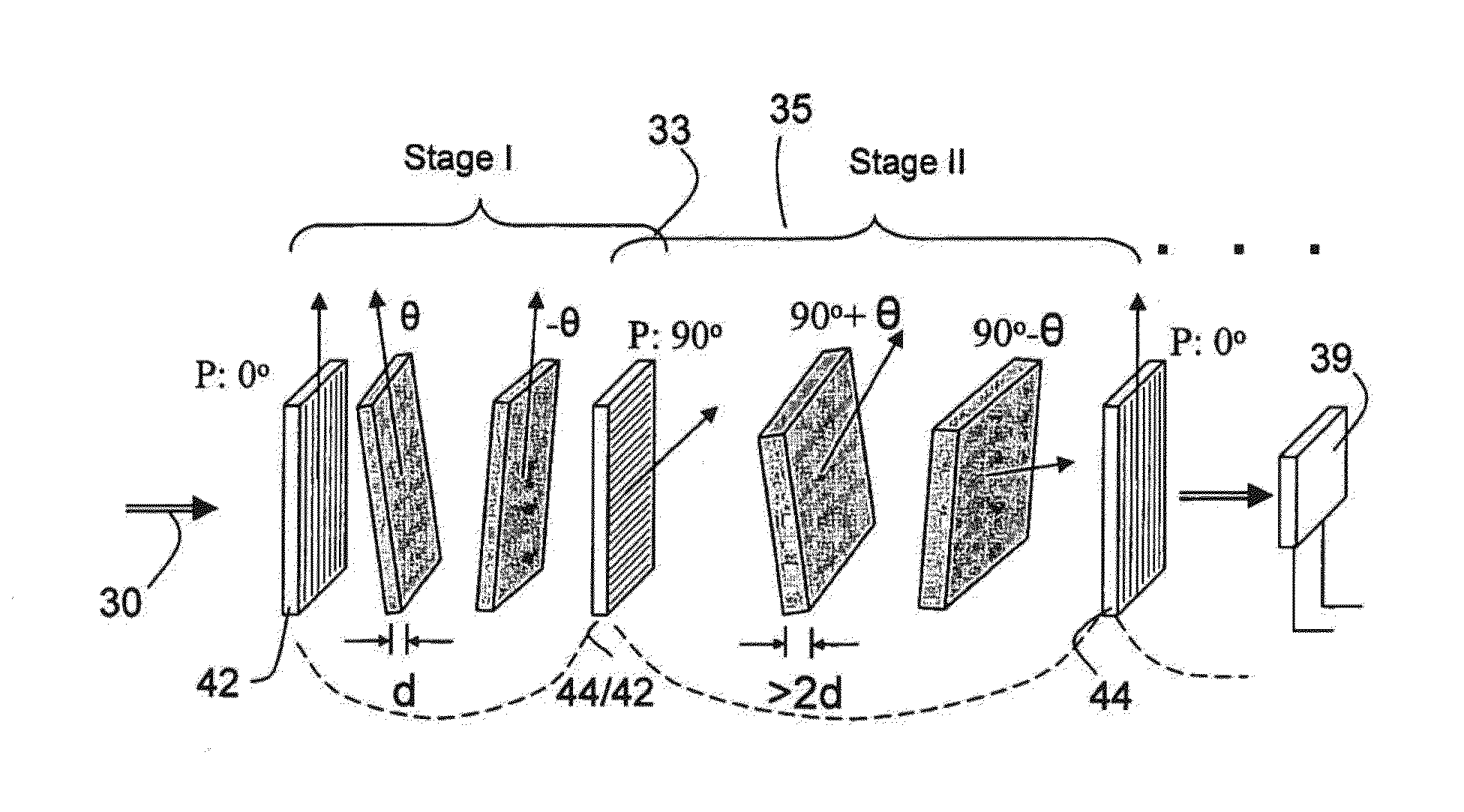
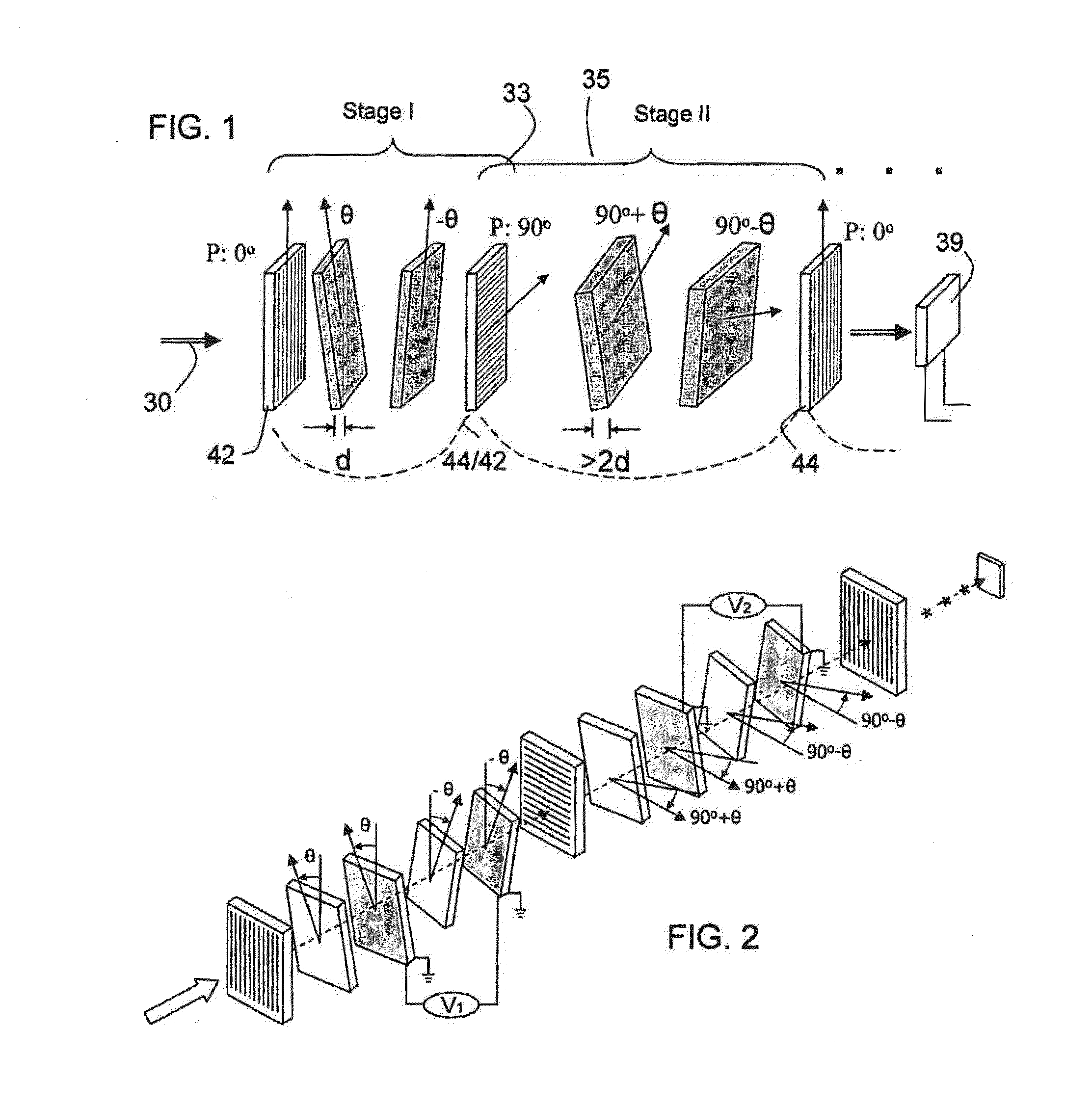
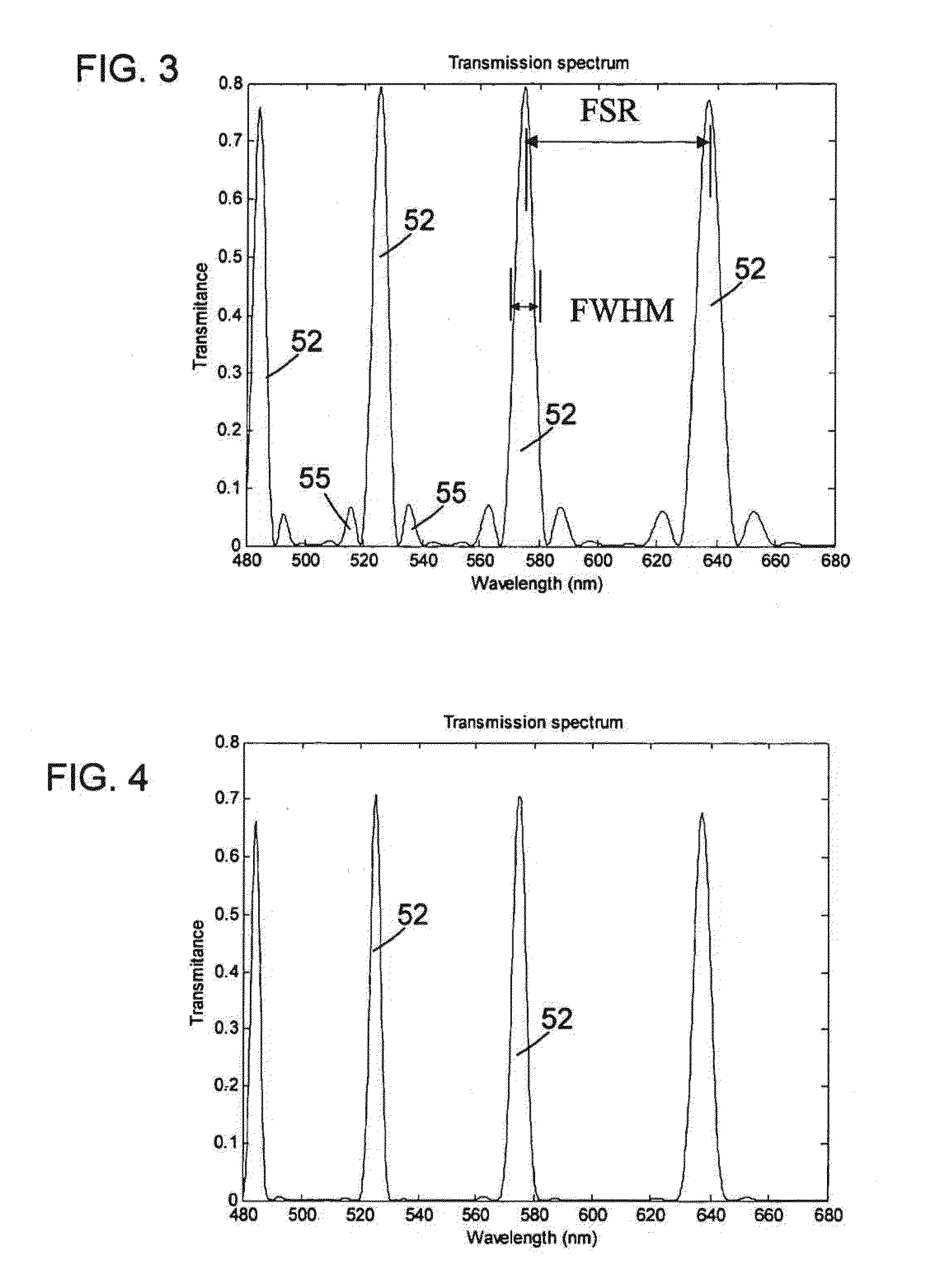
Multi-conjugate liquid crystal tunable filter
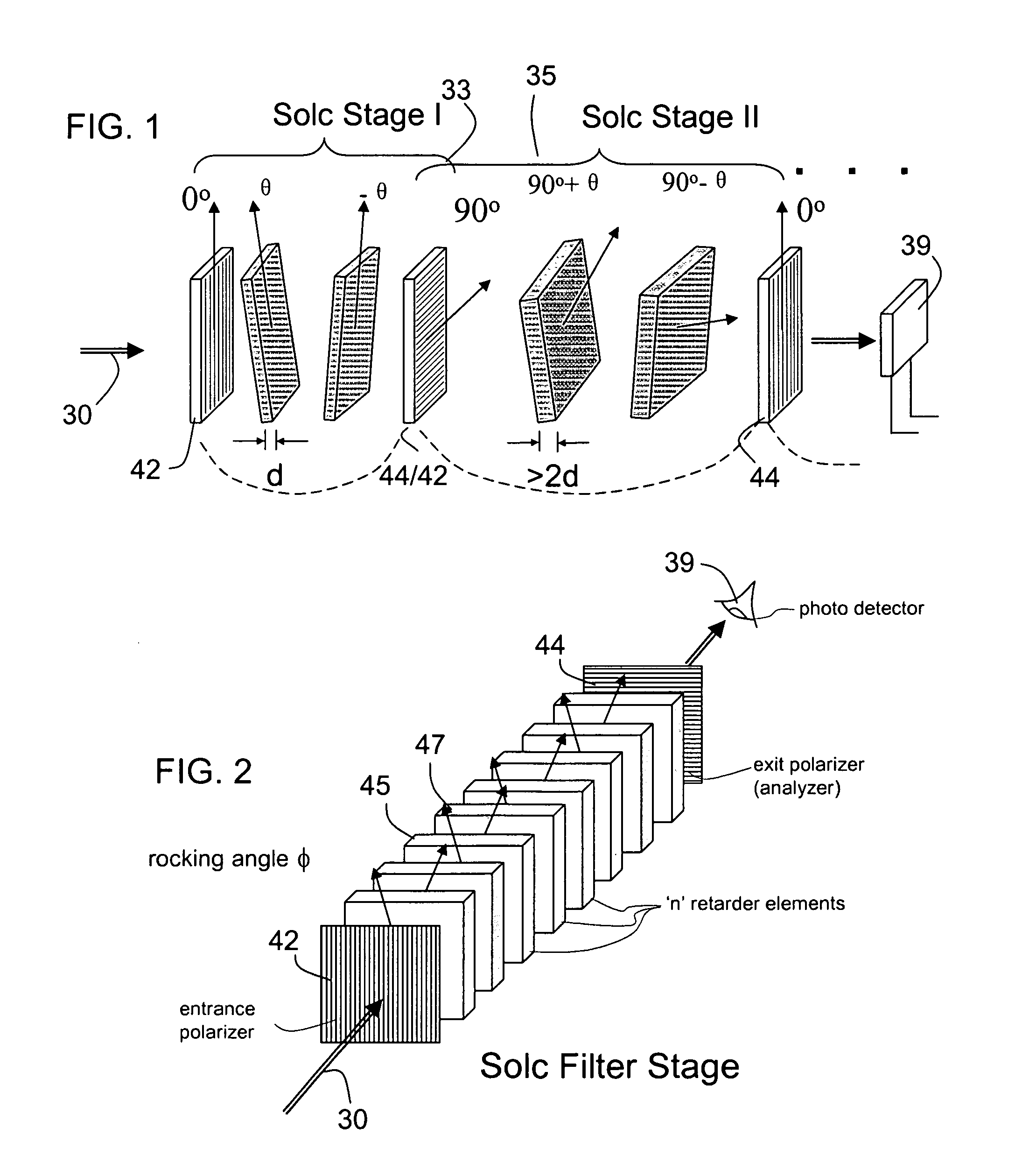
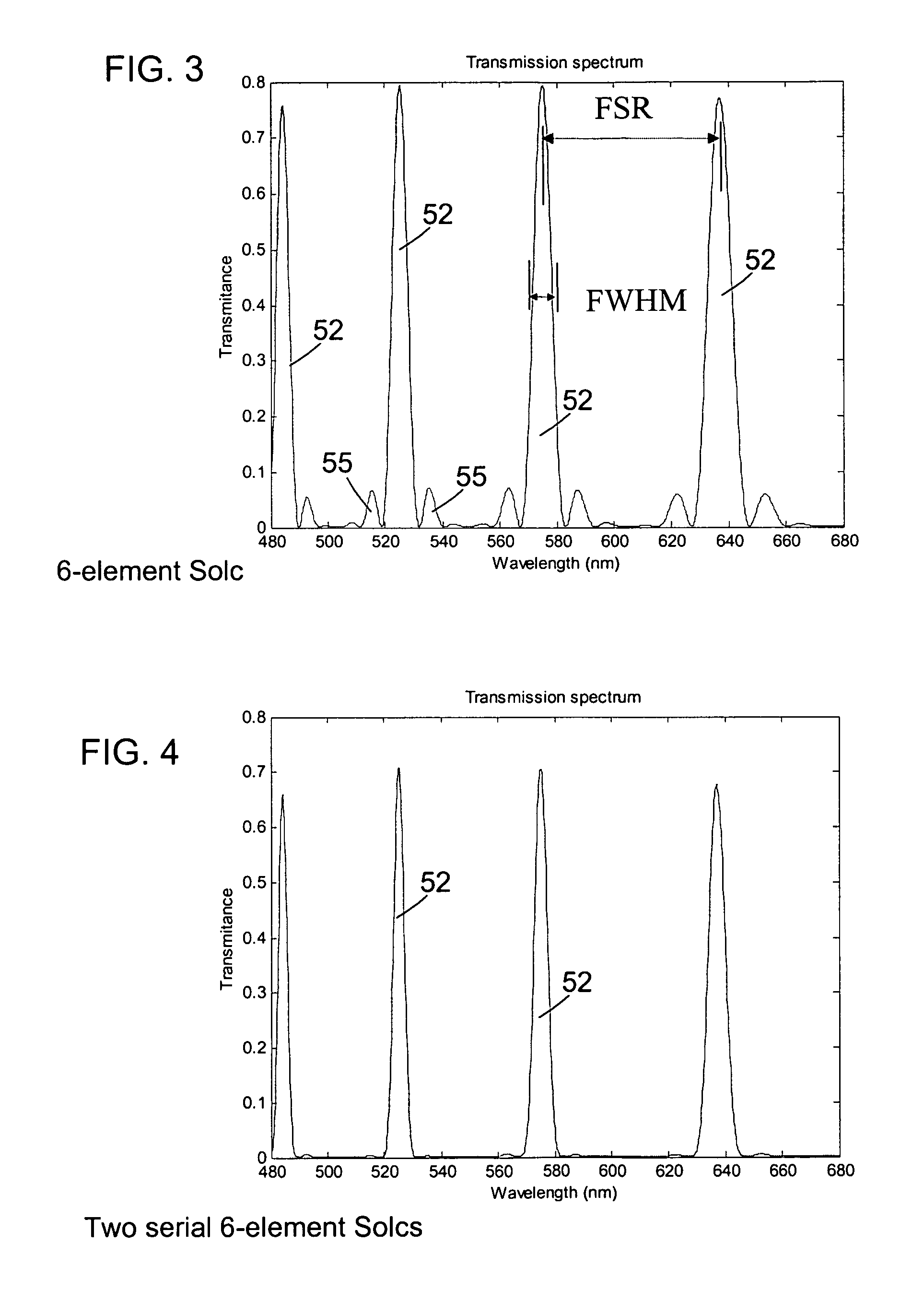
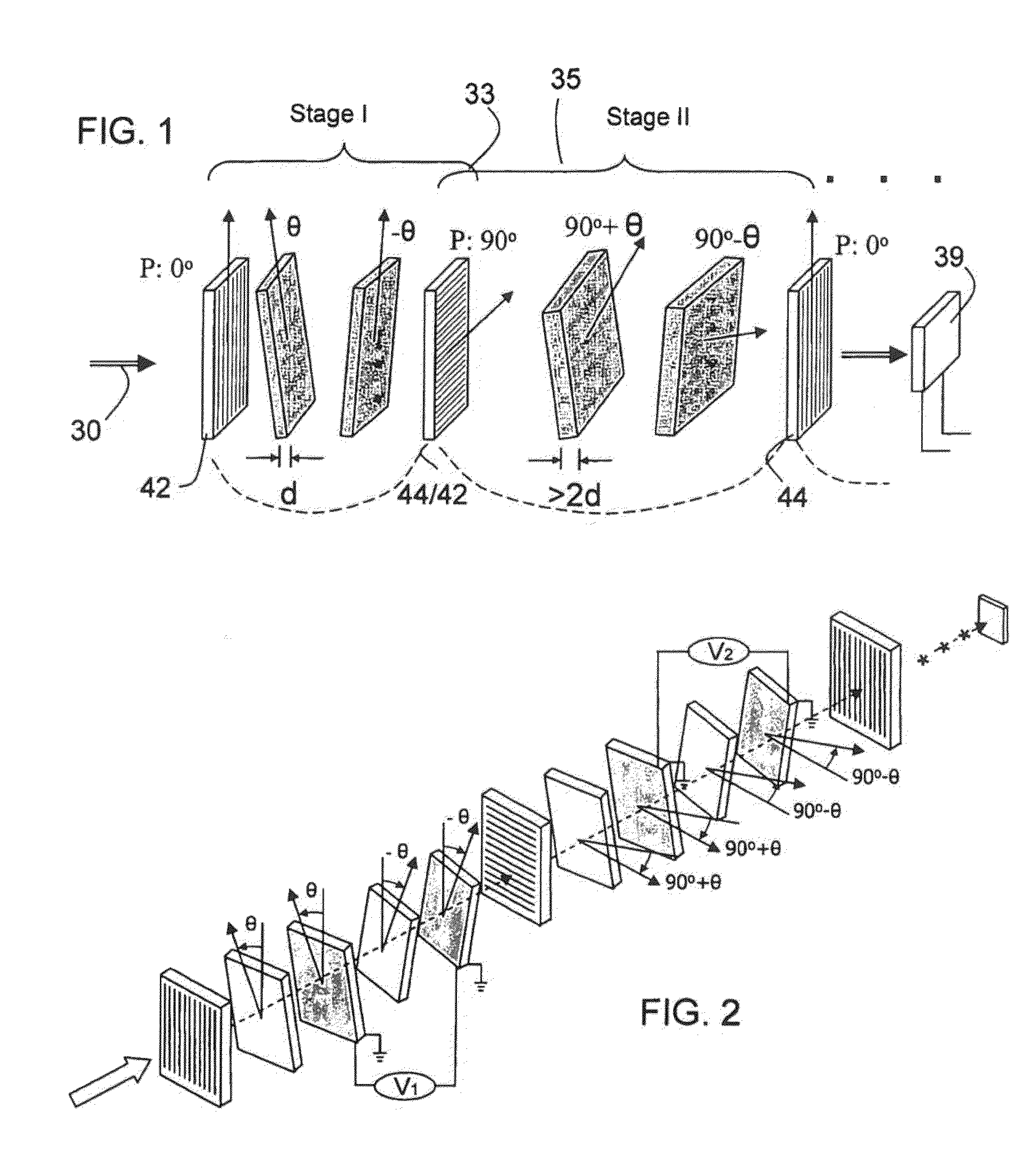
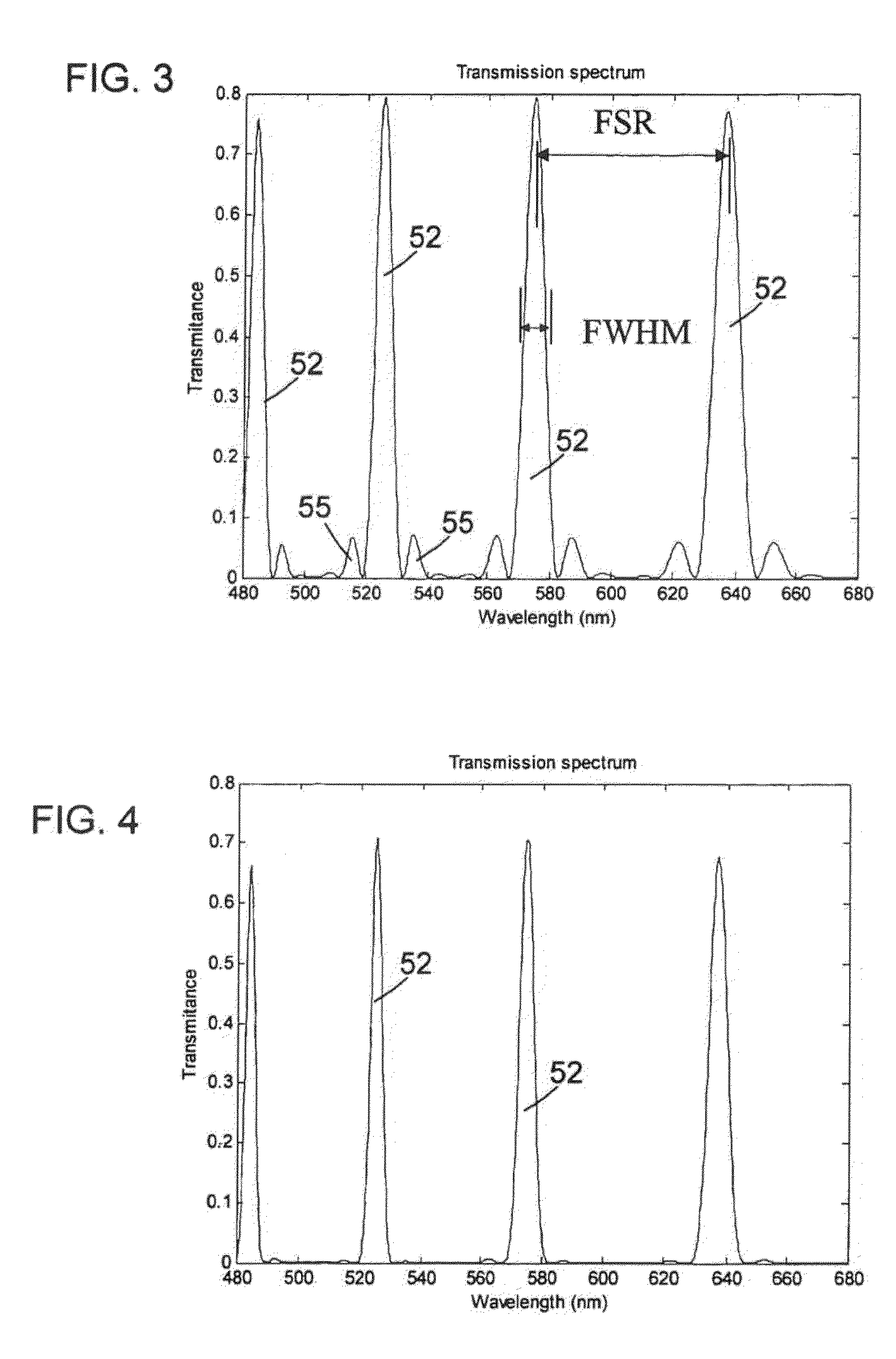
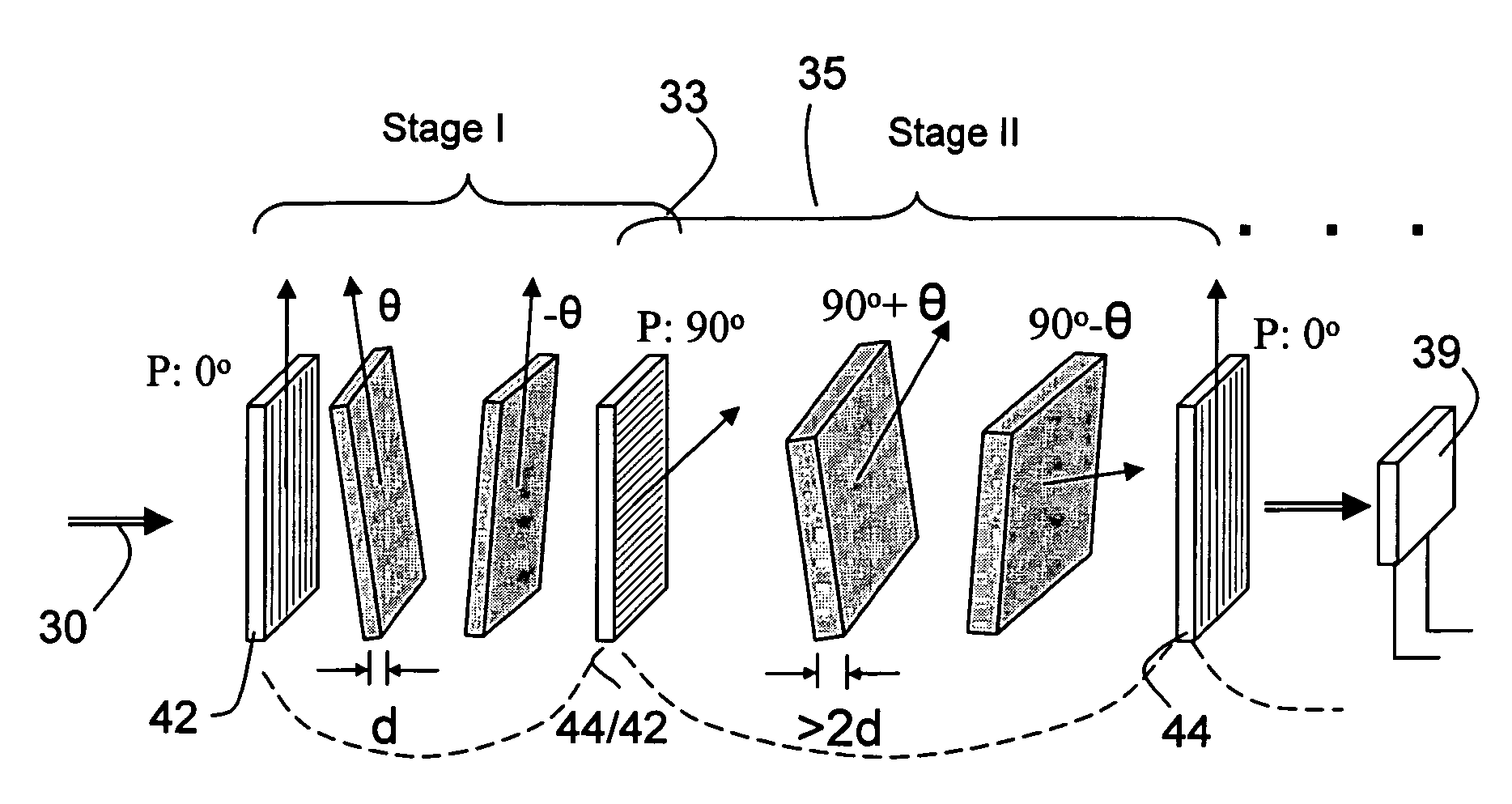
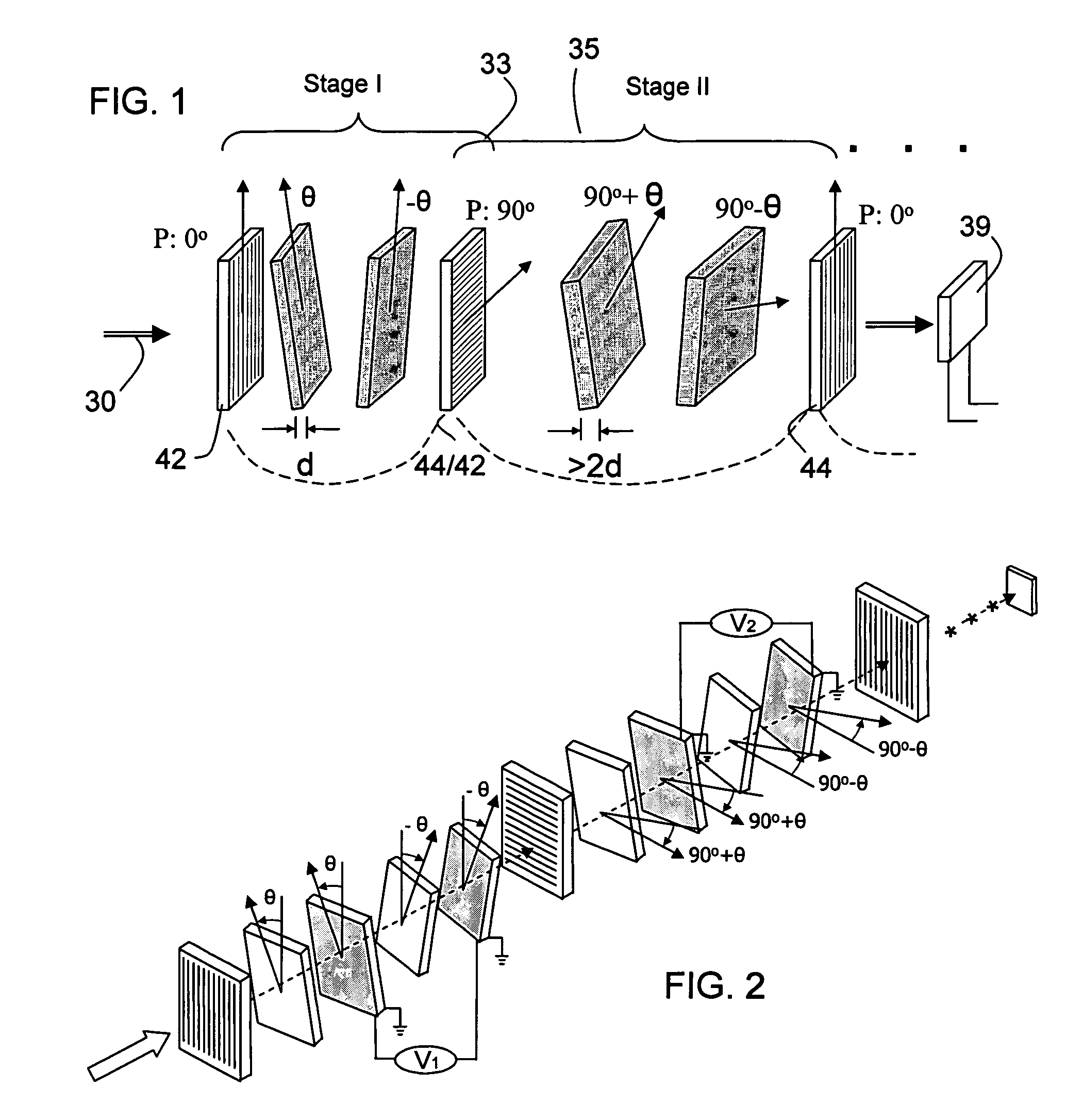
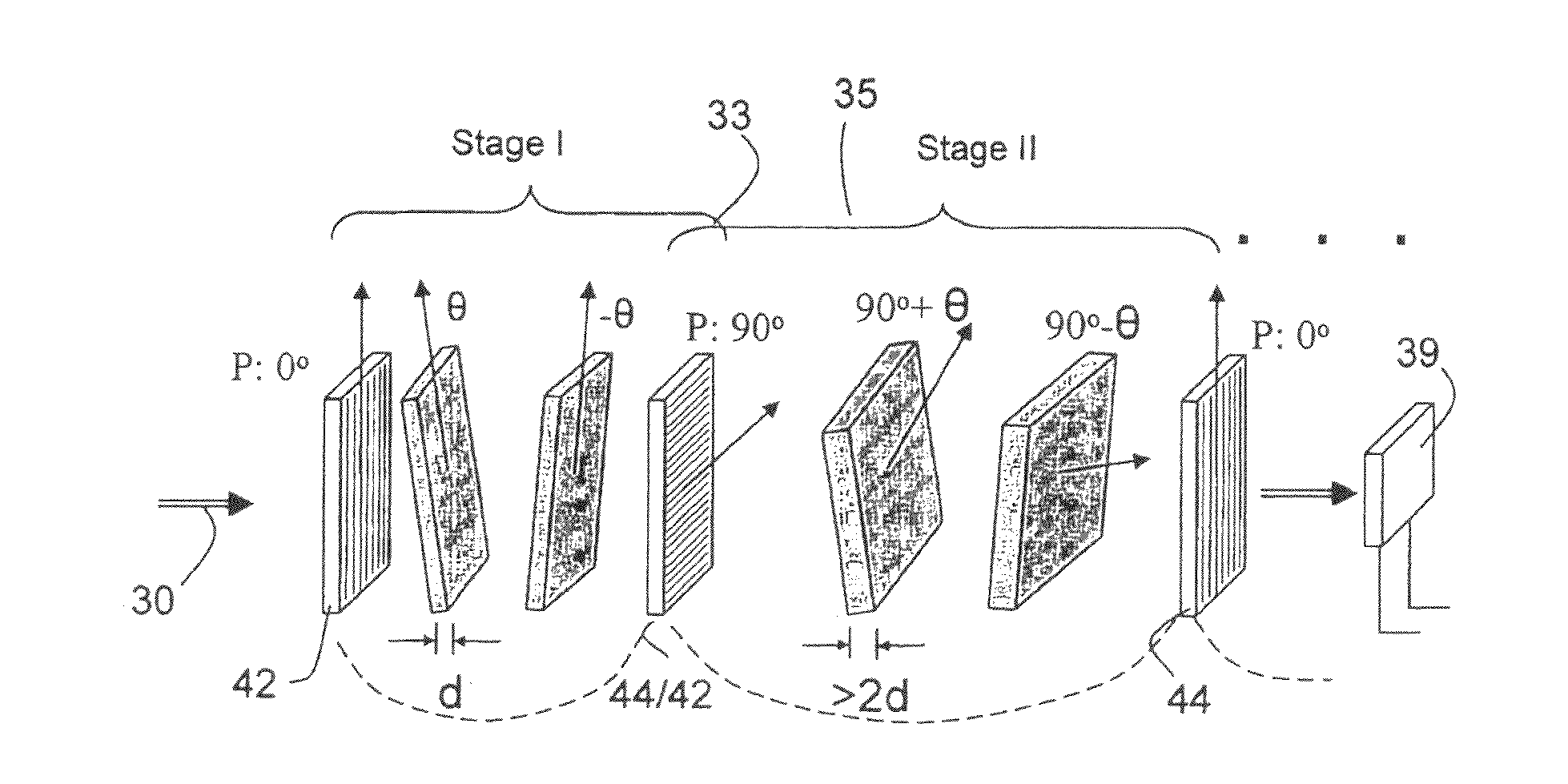
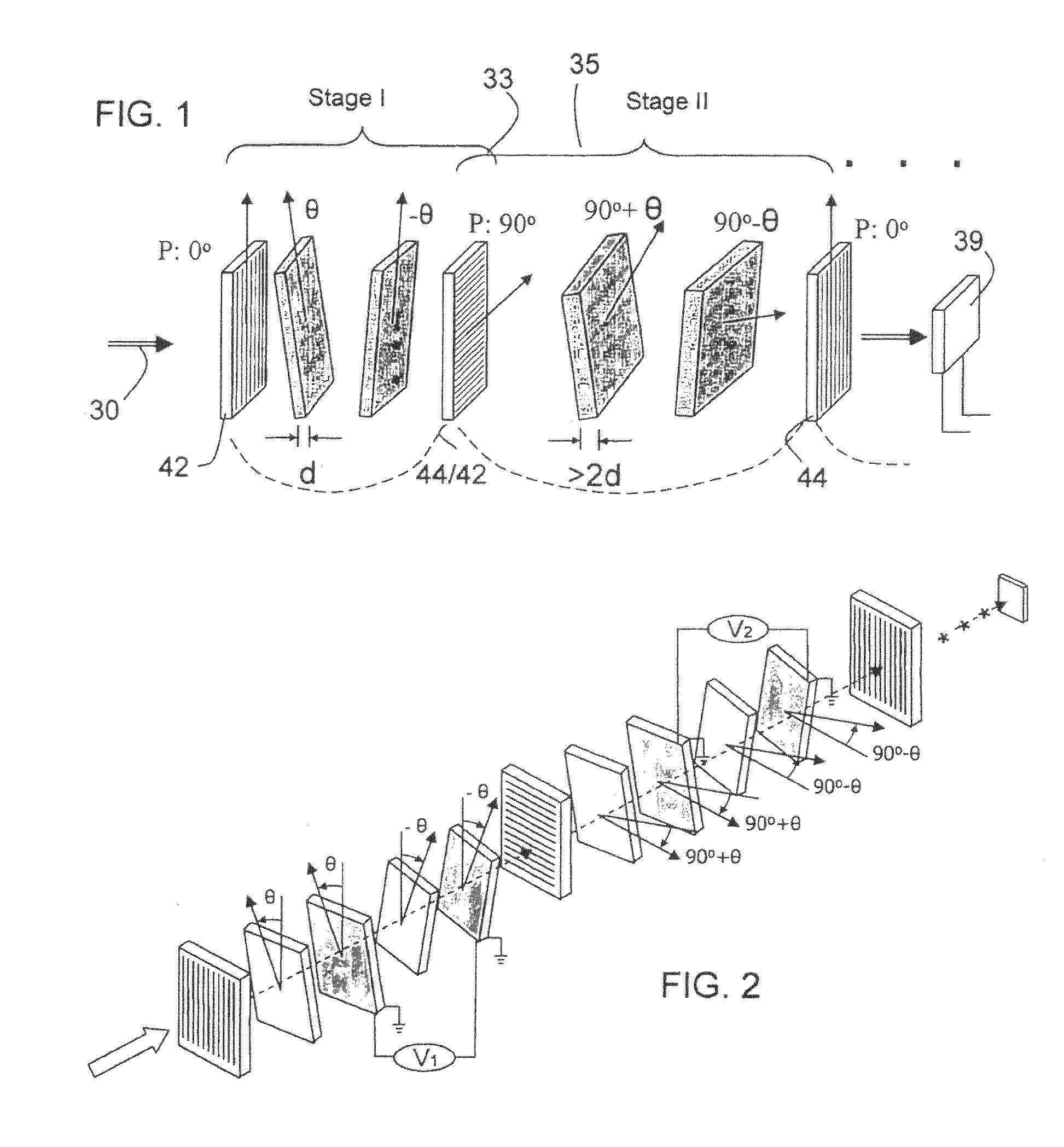
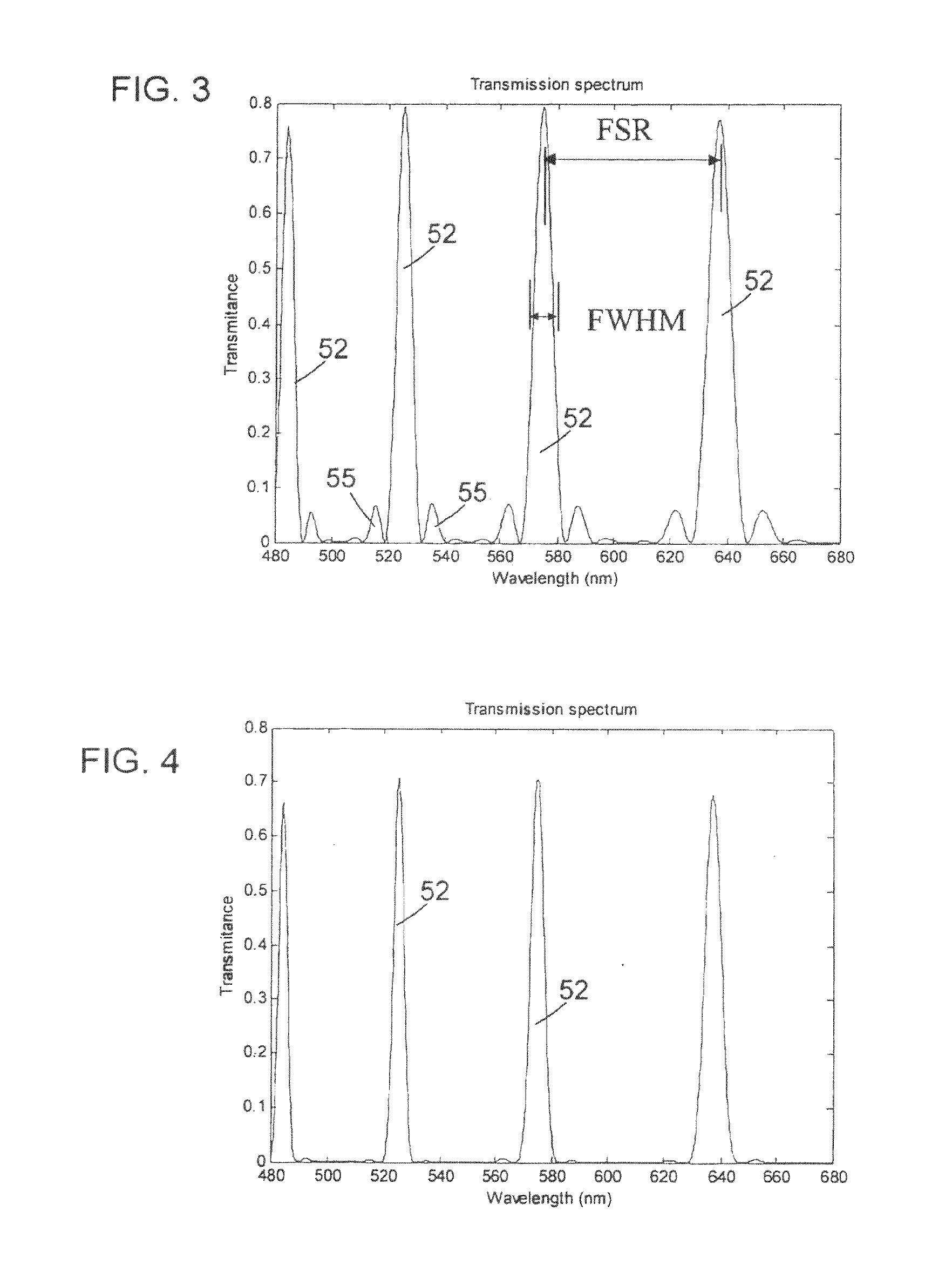
ActiveUS6992809B1Maximize finesseIncrease gear ratioPolarisation spectroscopyNon-linear opticsFinesseOut of band rejection
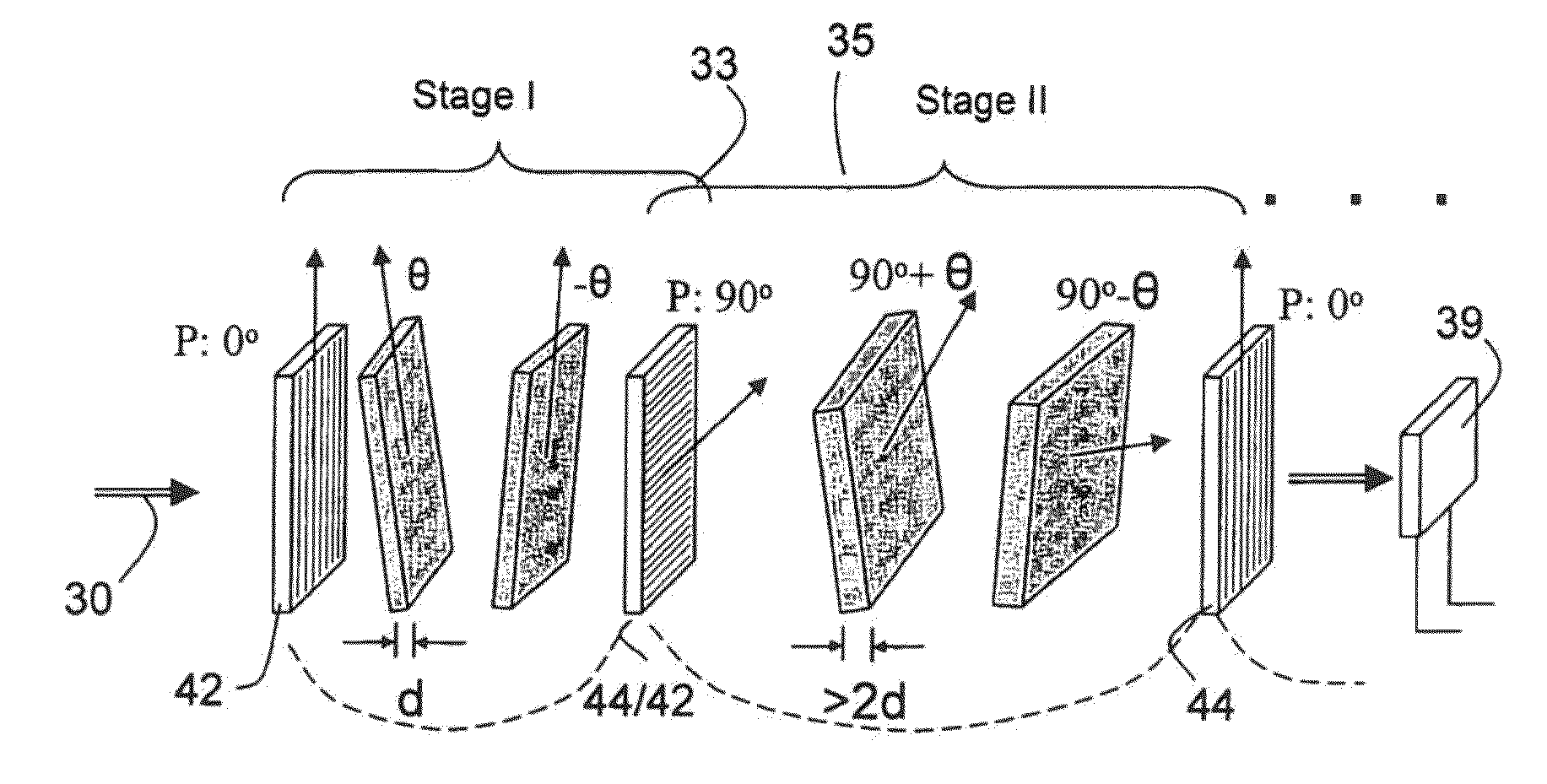
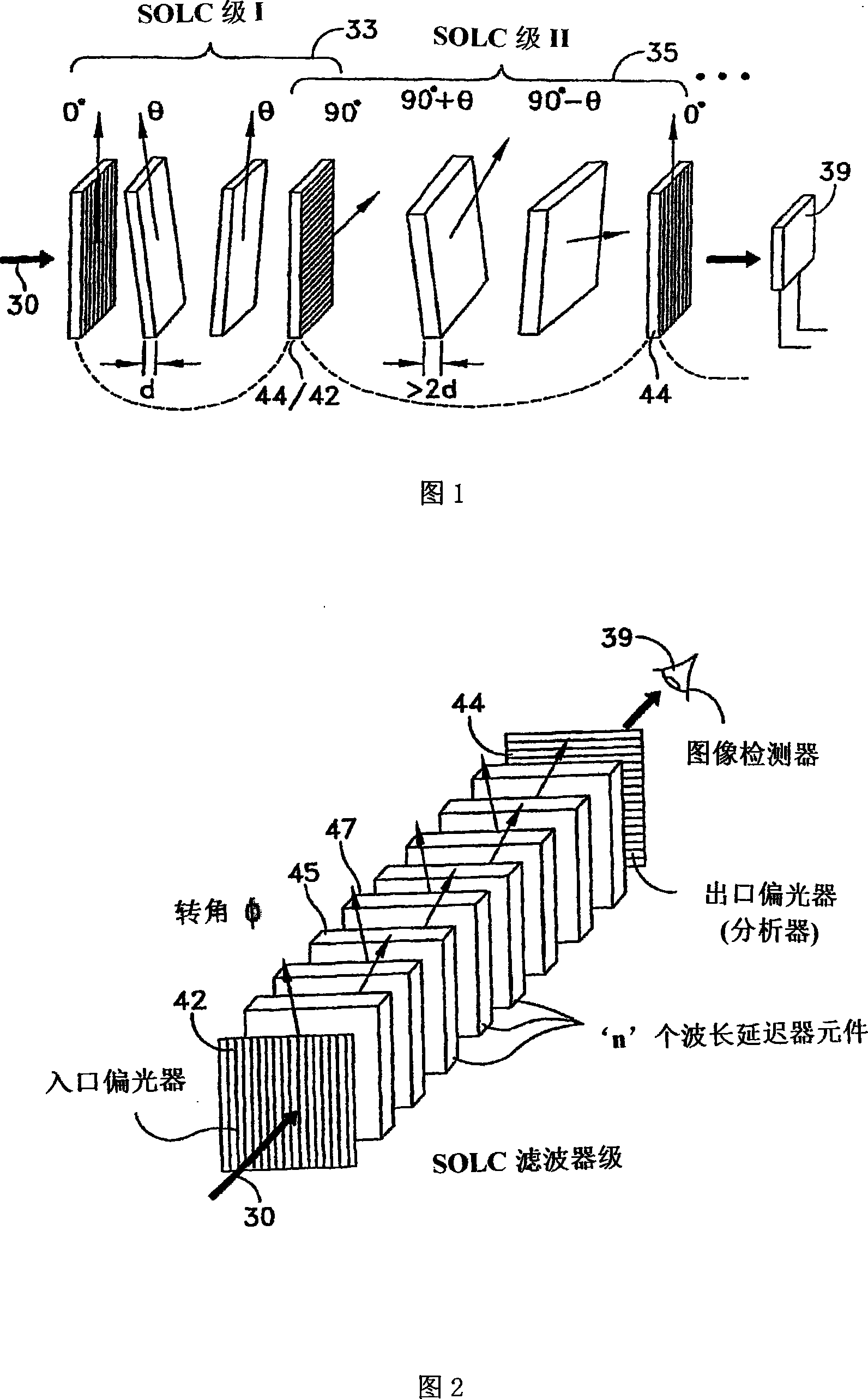
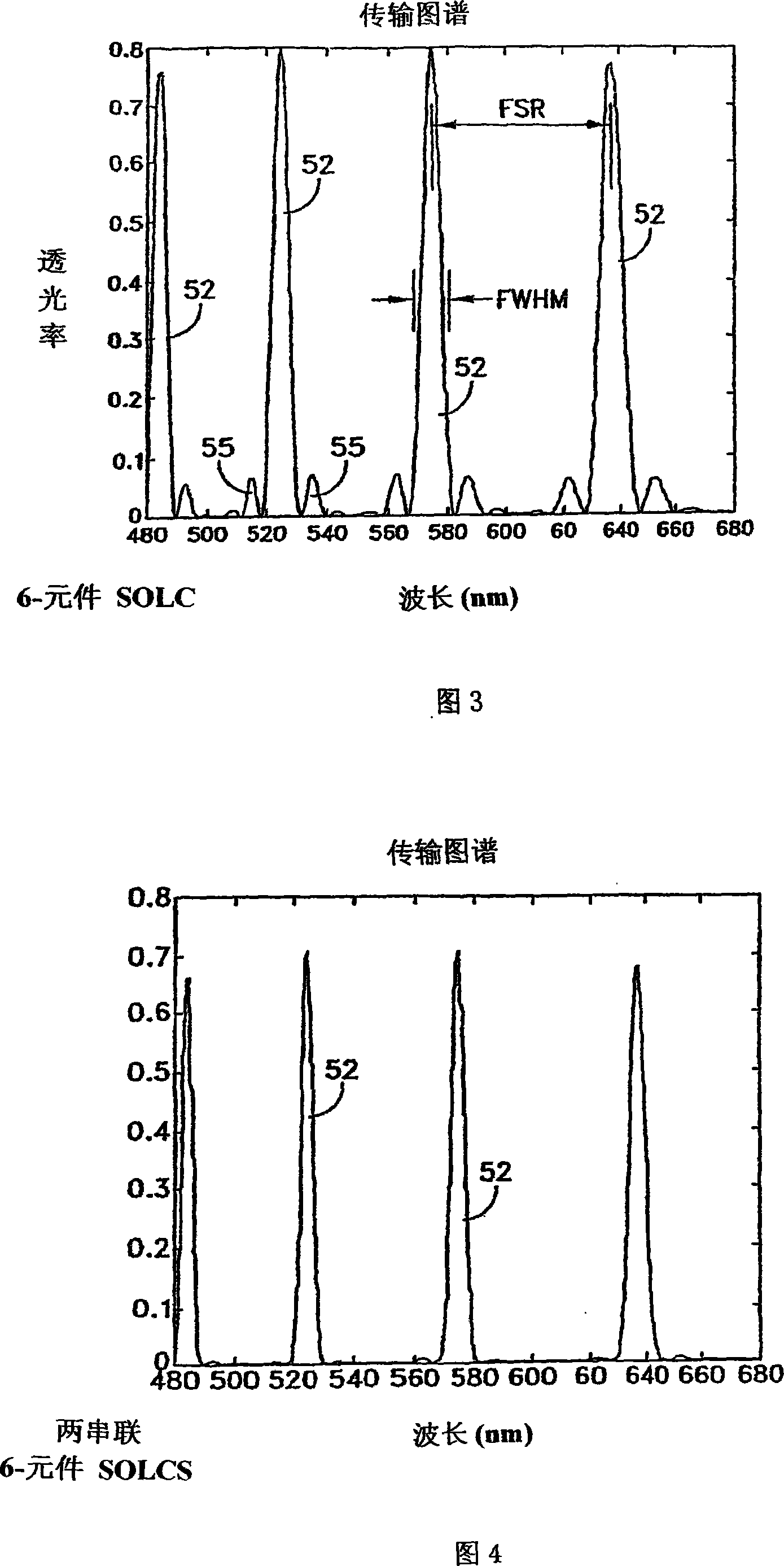
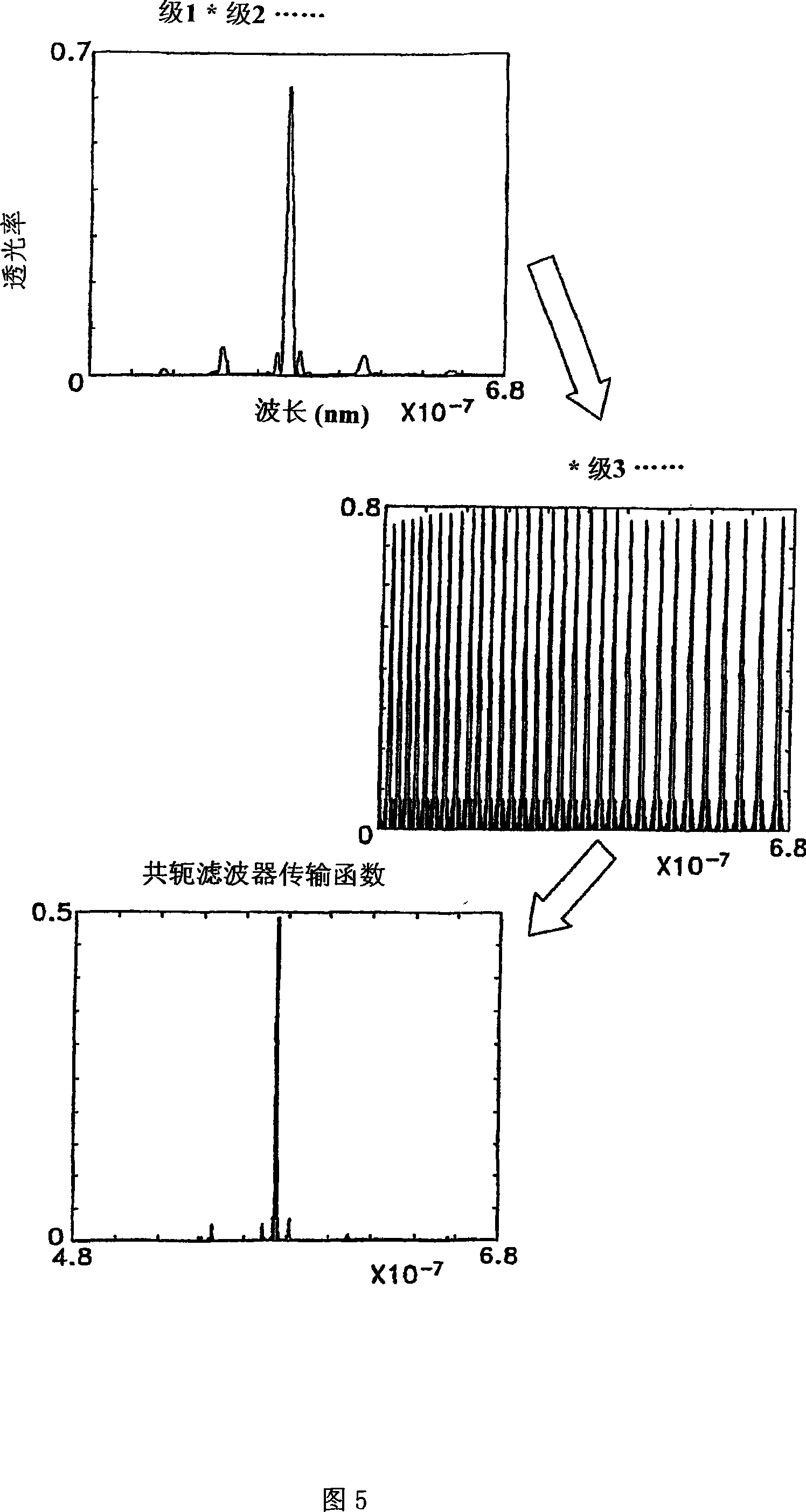
A hyper-spectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path in a Solc filter configuration. Angularly distributed retarder elements of equal birefringence are stacked in each stage, with a polarizer between stages. The retarders can include tunable (such as abutted liquid crystals tuned in unison), fixed and / or combined tunable and fixed birefringences. Although the retardations are equal within each stage, distinctly different retardations are used for two or more different stages. This causes some stages to pass narrow bandpass peaks and other stages to have widely spaced bandpass peaks. The transmission functions of the serial stages are superimposed with selected preferably-tunable peaks coinciding. The resulting conjugate filter has a high finesse ratio, and good out of band rejection.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
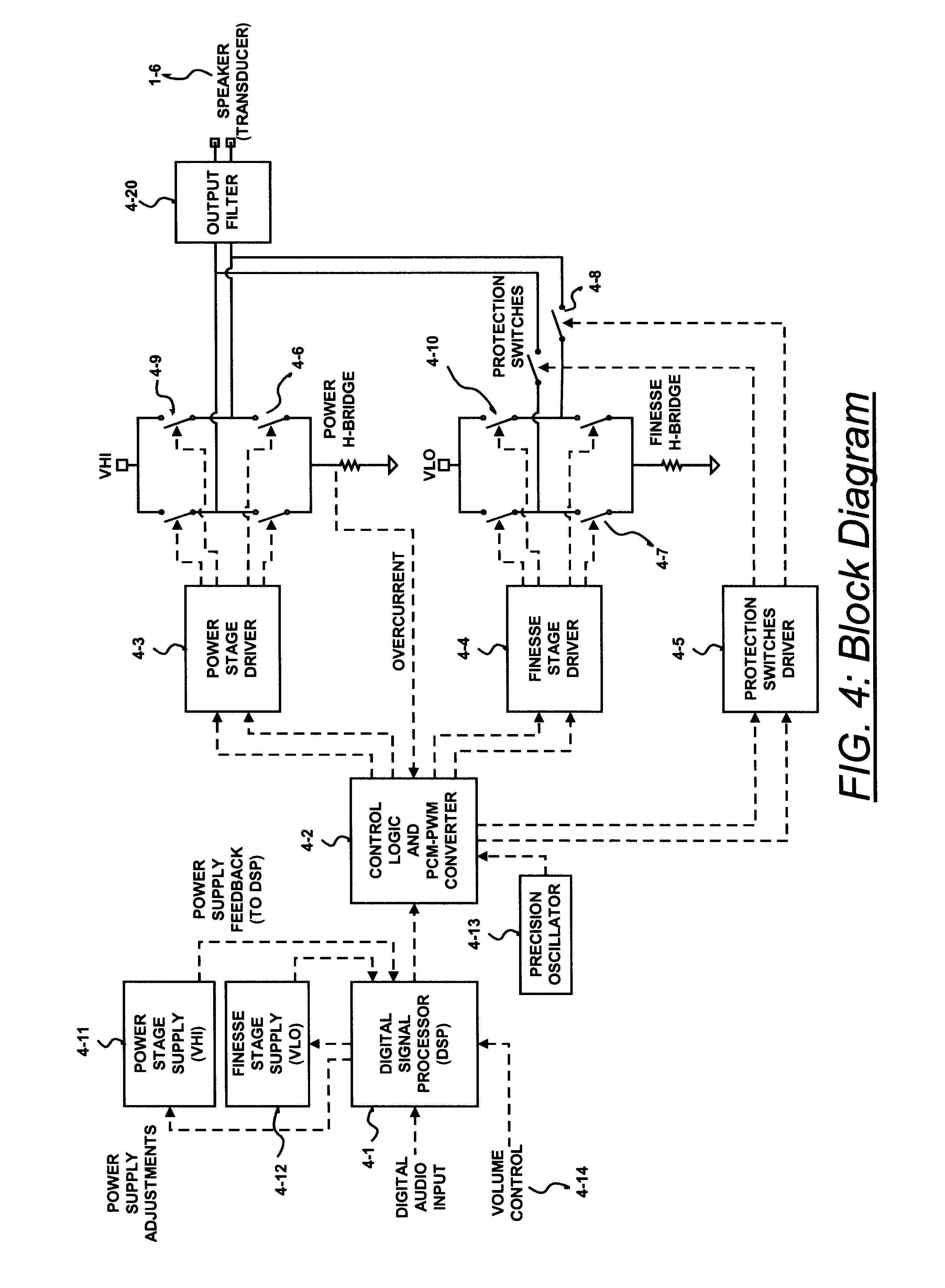
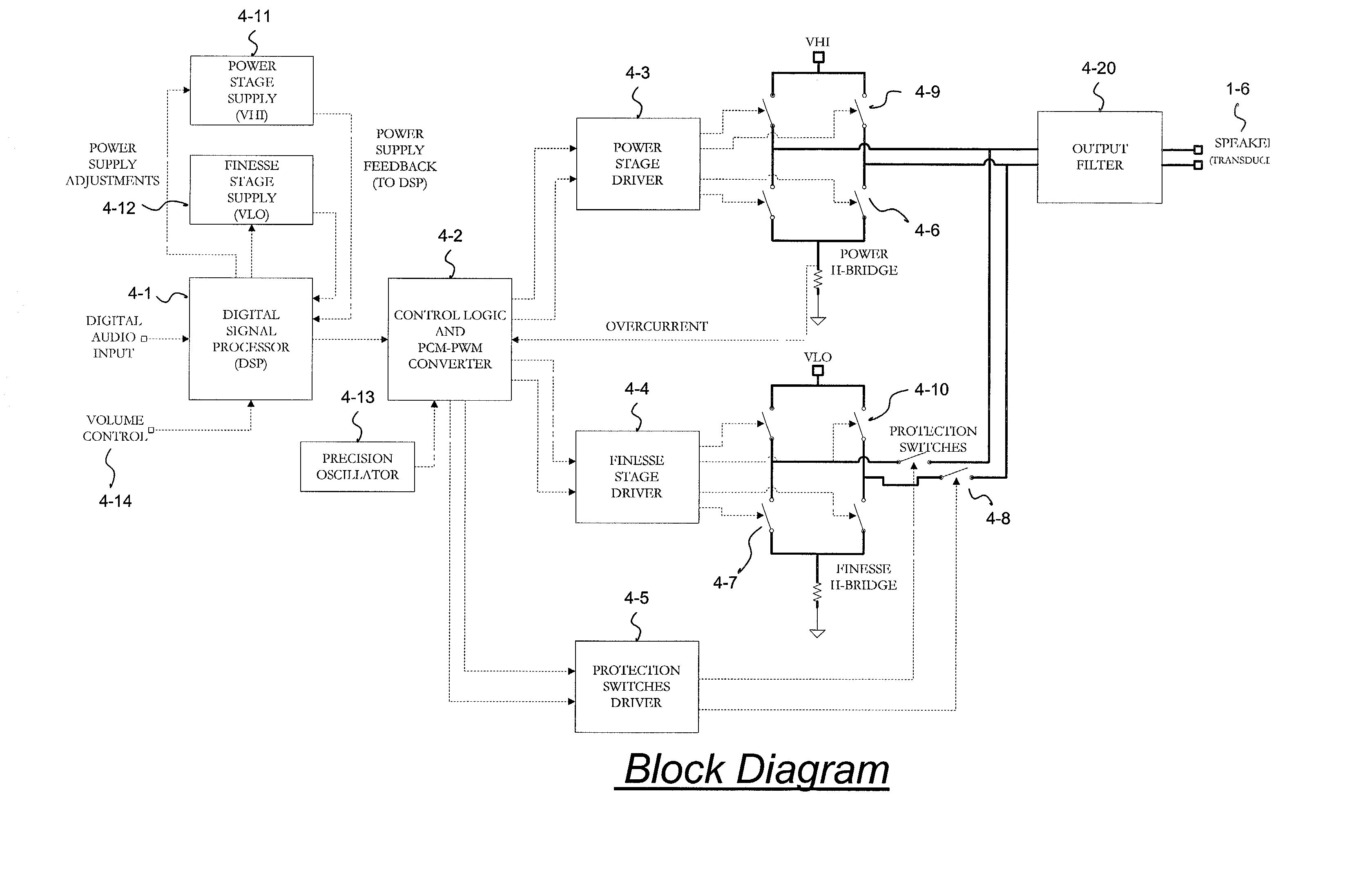
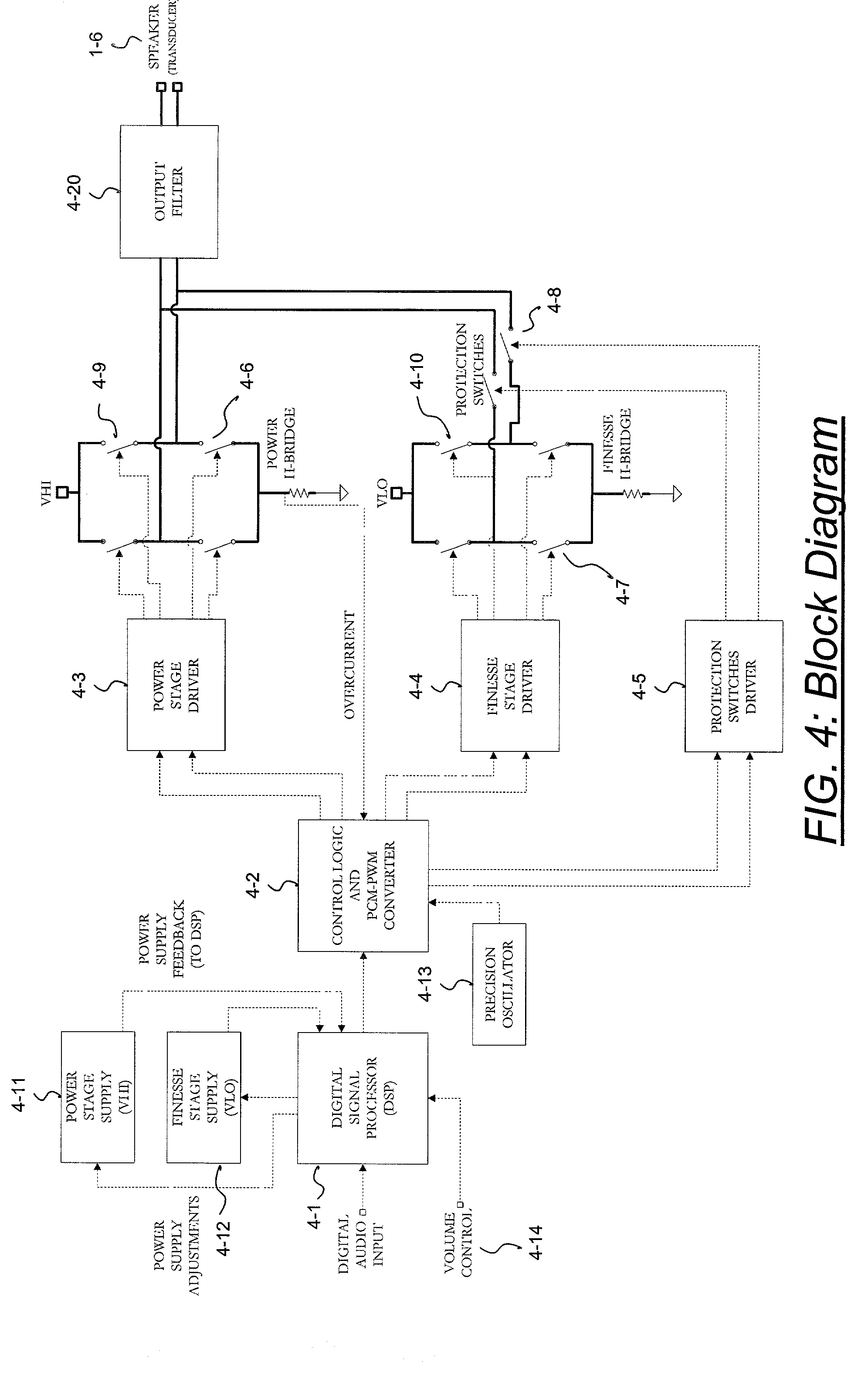
Digital amplifier with improved performance
InactiveUS6593807B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersDigital dataLow-pass filter
A class D amplifier uses a summation of two or more PWM output stages to achieve an increased dynamic range and improved linearity for any given clock operating speed. The amplifier accepts a digital data stream as its input, such as from a compact disk, or other compatible media, at a data rate, Fa, that could be 44.1 kHz, 96 kHz, or any other rate appropriate for audio data. In the preferred embodiment, the input audio data resolution, N bits, would be split into two data samples, of J and K.Internal switching frequency, Fs, switches the PWM with an over sampling factor M, where Fs=M*Fa. The time resolution of the PWM is determined by a precision oscillator that operates at Fc=Fs*(max(J,K)-log2(M)+1).The J most significant bits would be routed to a power PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VHI. The K least significant bits are routed to a finesse PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VLO.The ratio of VLO to VHI will be appropriate for the ratio of K and J so the summation of the power PWM stage and the finesse PWM stage will provide the full range of N bits. This summation is accomplished with a low pass filter and time-division multiplexing of the two PWM stages.A micro controller (MCU) is used to apply a sample packet distribution algorithm to provide more resolution by reducing quantization noise in the audio band of interest. The MCU is also used to calibrate the VLO or VHI, or to calibrate the PWM timing of the two PWM stages to achieve appropriate performance.
Owner:GROVES JR WILLIAM HARRIS +1
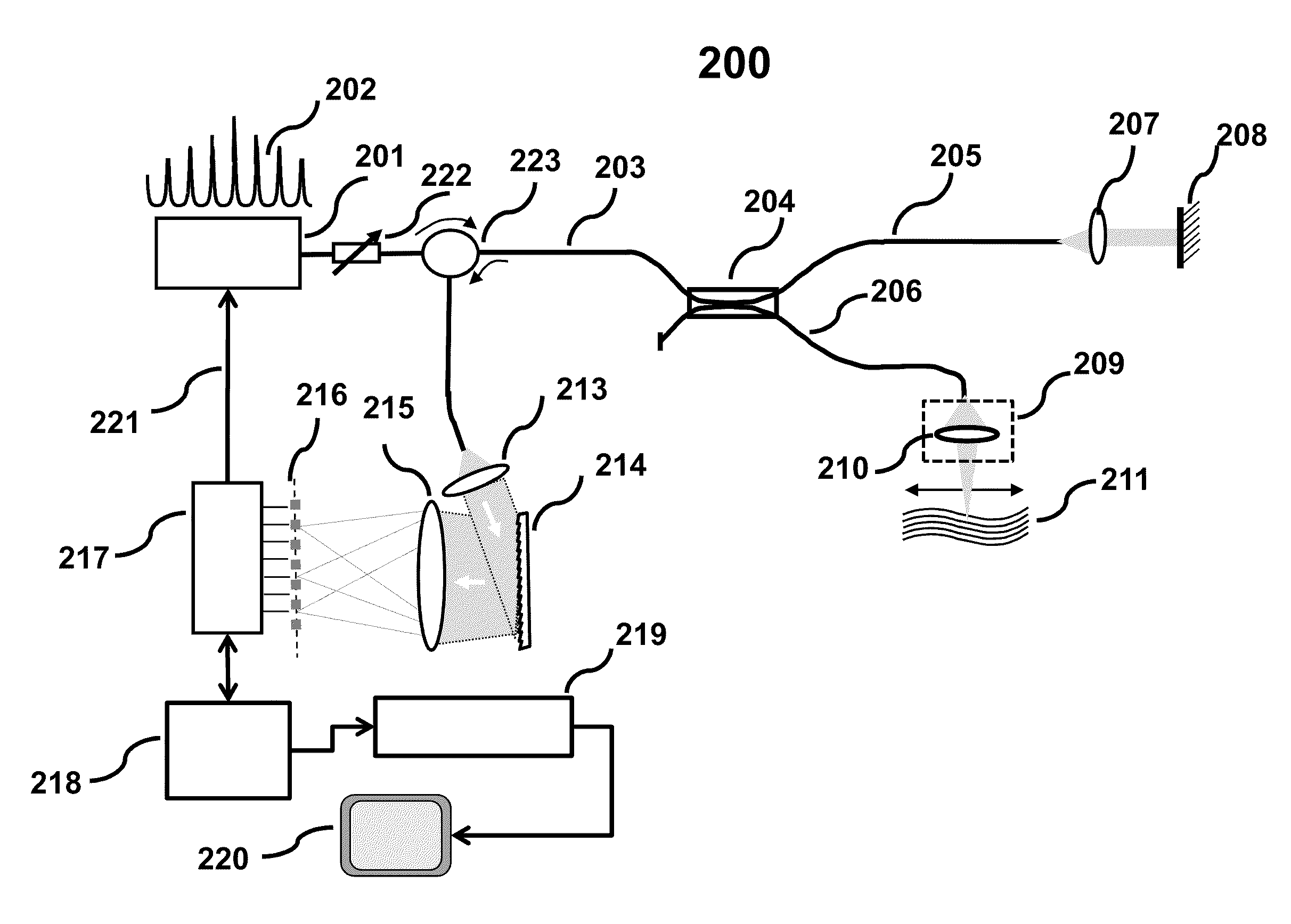
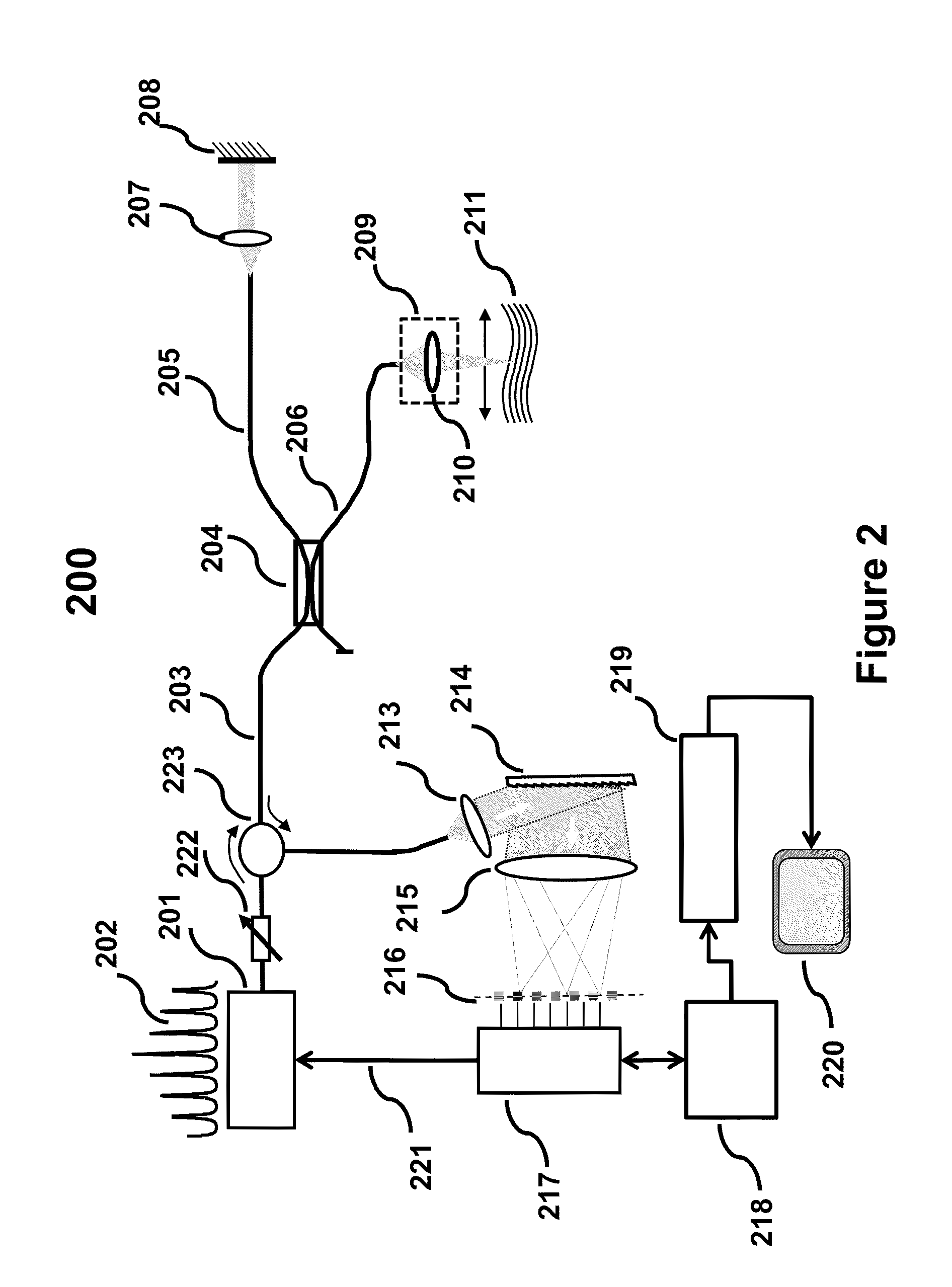
Discrete Spectrum Broadband Optical Source
ActiveUS20110292399A1Increase output peak powerHigh detection sensitivityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionSpectral emissionFrequency spectrum
A new broadband source having a discrete set of spectral emission lines having high peak power in each line is provided by placing a gain medium in a reflective cavity comprising reflective front and back surfaces. A cavity feedback factor less than unity is achieved by providing reflectivity of one surface substantially lower than the reflectivity of the other surface such that spontaneous emission in the gain medium is linearly amplified just below the lasing threshold. In an alternative arrangement, a movable external back surface placed at a prescribed distance from the gain medium provides a means to achieve a free spectral range and finesse of the emission lines to match a pitch of a detector array in a SD-OCT system. By simultaneously providing high power to each detector element of the array, sensitivity and imaging speed of SD-OCT system are significantly improved.
Owner:GDAC PHOTONICS INC
Fast Switching Arbitrary Frequency Light Source for Broadband Spectroscopic Applications
ActiveUS20130228688A1Enlarged cavityQuick switchRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using multiple reflectionSpectroscopySignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
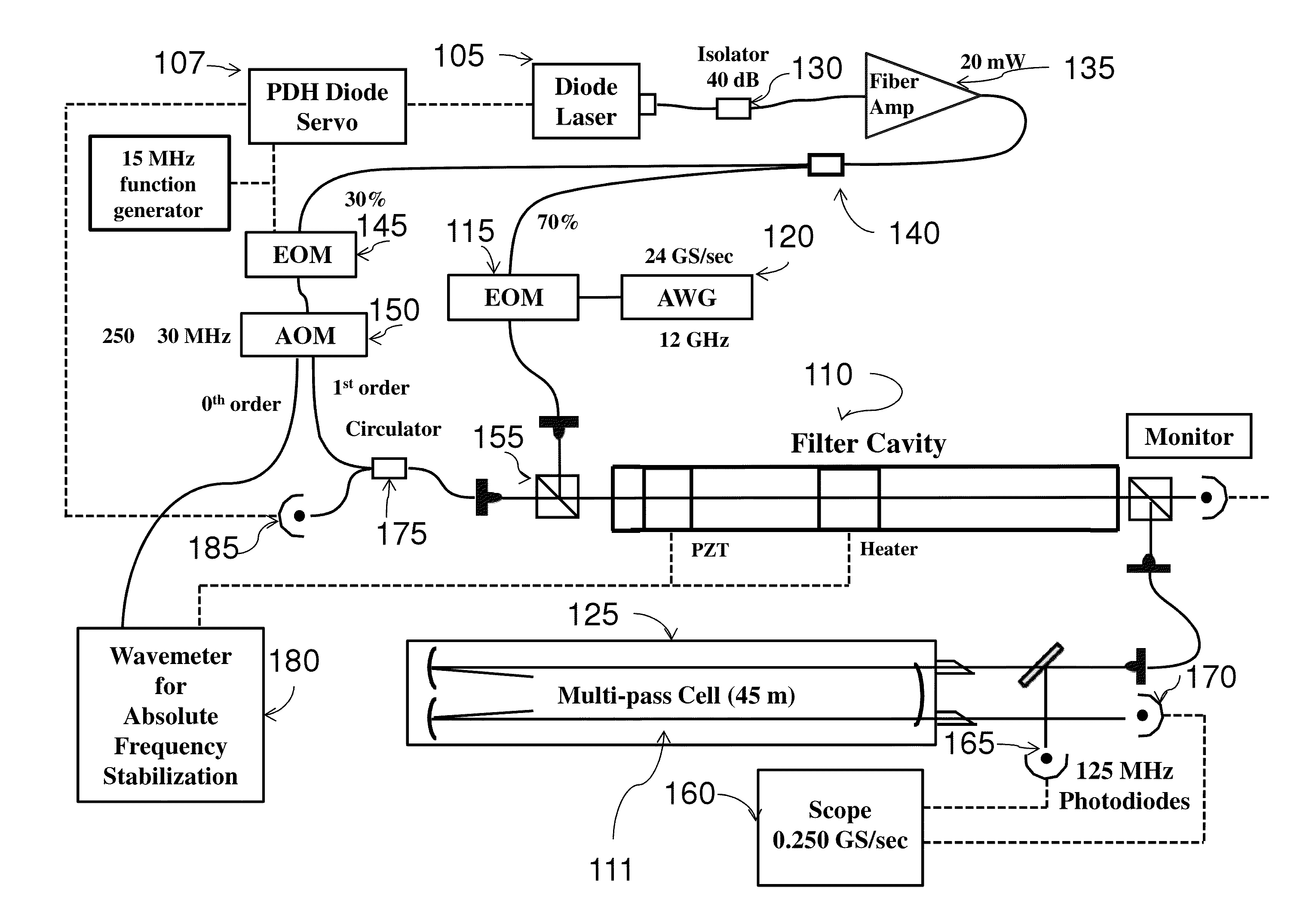
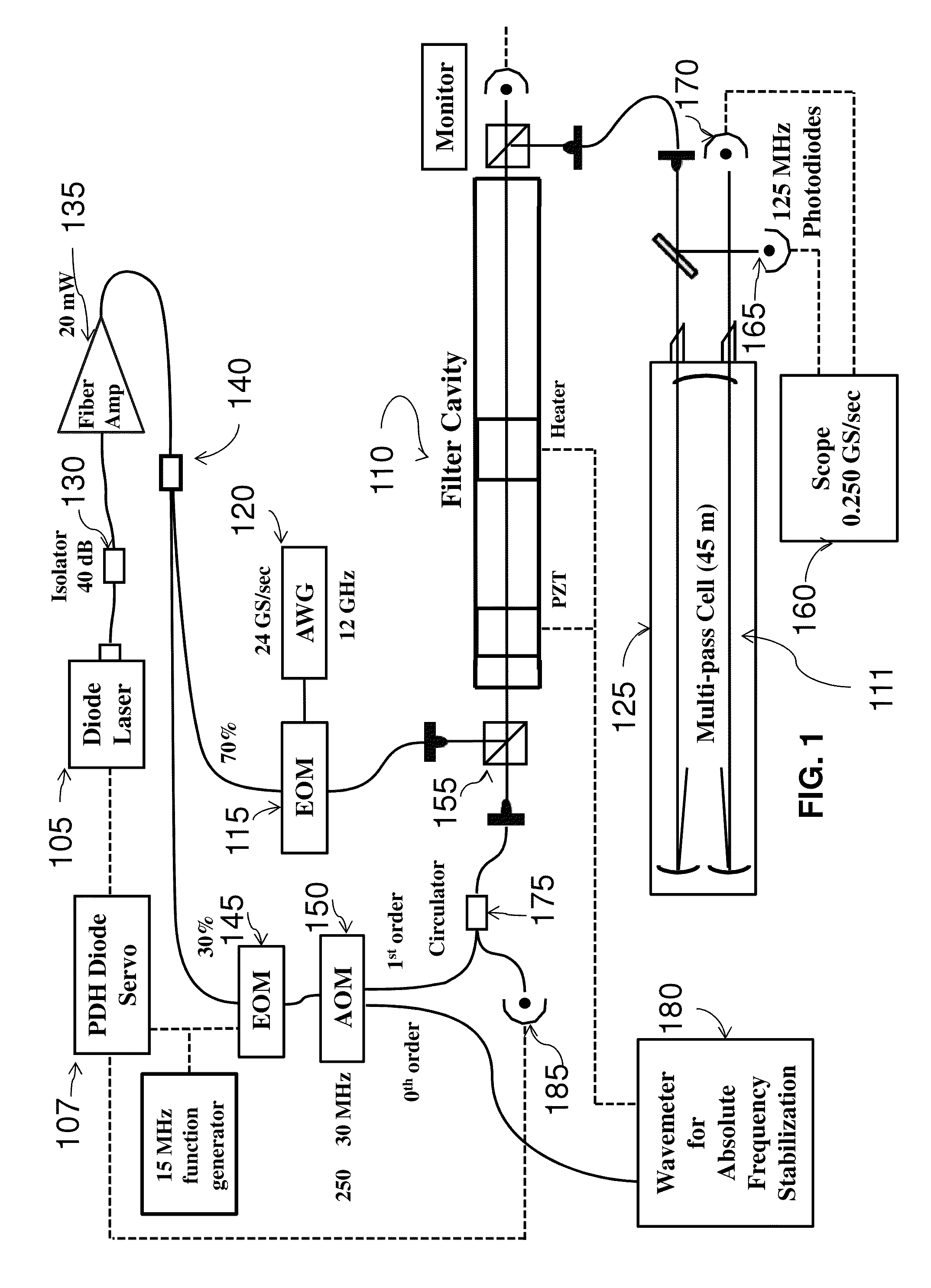
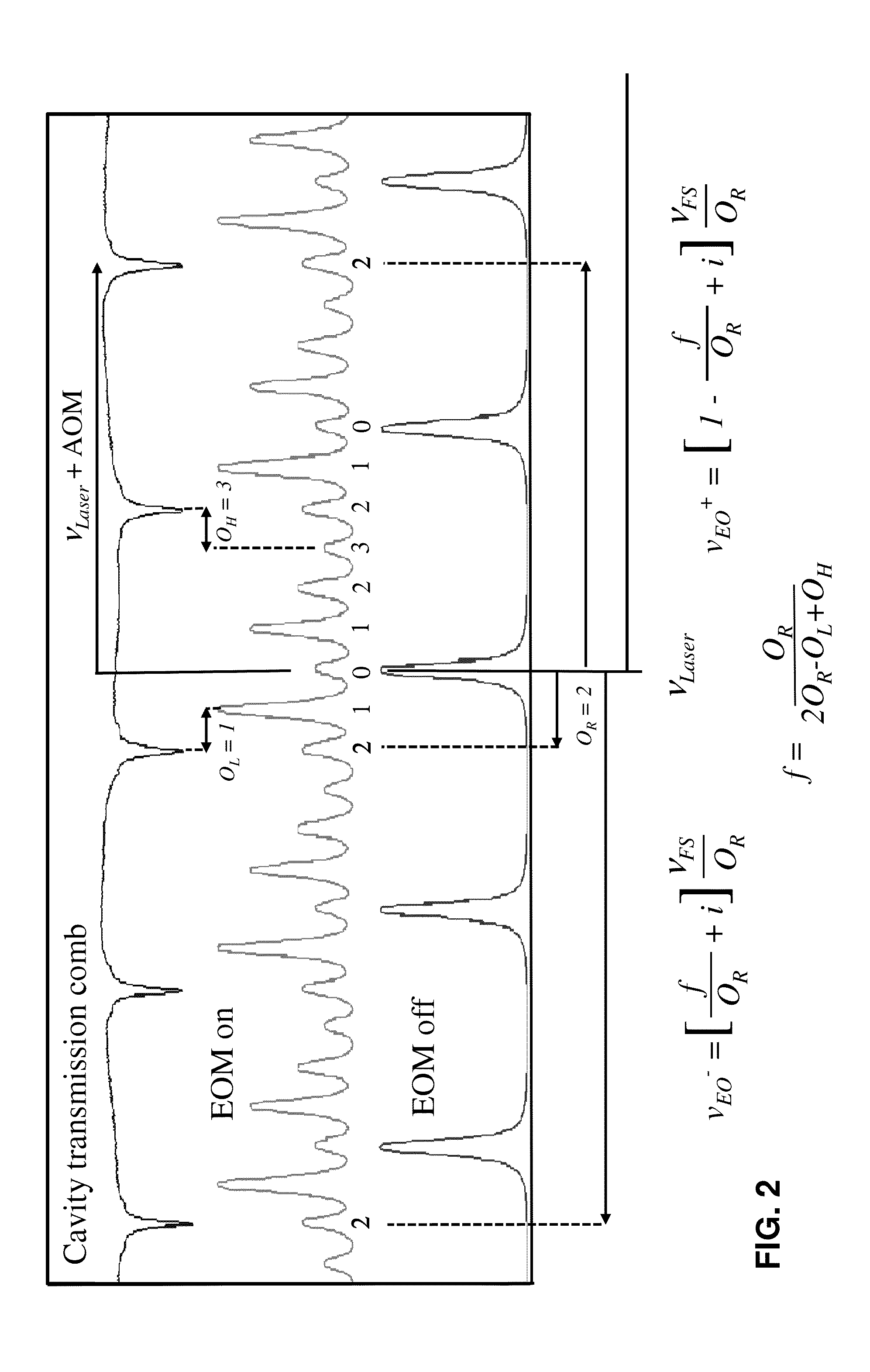
A fast switching arbitrary frequency light source for broadband spectroscopic applications. The light source may operate near 1.6 um based on sideband tuning using an electro-optic modulator driven by an arbitrary waveform generator. A Fabry-Perot filter cavity selects a single sideband of the light source. The finesse (FSR / ΔνFWHM) of the filter cavity may be chosen to enable rapid frequency switching at rates up to 5 MHz over a frequency range of 40 GHz (1.3 cm−1). The bandwidth, speed and spectral purity are high enough for spectroscopic applications where rapid and discrete frequency scans are needed. Significant signal-to-noise advantages may be realized using the rapid and broadband scanning features of this system in many areas of spectroscopy, e.g., process monitoring and control, reaction dynamics, and remote sensing (e.g., greenhouse gas monitoring, biological / chemical agent screening).
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY
VIS-SNIR multi-conjugate liquid crystal tunable filter
ActiveUS20120300143A1Improve transmittanceExcellent out-of-band rejection ratioPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsWavelength filterPolarizer
A VIS-NIR hyperspectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path with angularly distributed birefringent retarders and polarizers. The retarders can include active retarders such as tunable liquid crystal birefringent elements, passive retarders such as fixed retarders, and / or combinations thereof. Distinctly different periodic transmission spectra are provided by different filter stages, each having multiple retarders, in particular with some stages having broad bandpass peaks at wide spectral spacing and other stages have very narrow closely spaced peaks. The respective spectra include at least one tunably selectable band at which the transmission spectra of the filter stages coincide, whereby the salutary narrow bandpass and wide spectral spacing ranges of different stages apply together, resulting in a high finesse wavelength filter suitable for spectral imaging. The filter may be configured to provide faster switching speed and increased angle of acceptance and may operate in the rage of approximately 400-1100 nm.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
Multi-conjugate liquid crystal tunable filter
ActiveUS7362489B2High finesse spectral filtersIncrease gear ratioPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsWavelength filterPolarizer
A hyper-spectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path with angularly distributed birefringent retarders and polarizers forming interference filters. The retarders can include tunable birefringent elements such as liquid crystals controlled in unison, fixed retarders and / or combined tunable and fixed birefringences. Distinctly different periodic transmission spectra are provided by different filter stages, each having multiple retarders, in particular with some stages having broad bandpass peaks at wide spectral spacing and other stages have very narrow closely spaced peaks. The respective spectra include at least one tunably selectable band at which the transmission spectra of the filter stages coincide, whereby the salutary narrow bandpass and wide spectral spacing ranges of different stages apply together, resulting in a high finesse wavelength filter suitable for spectral imaging.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
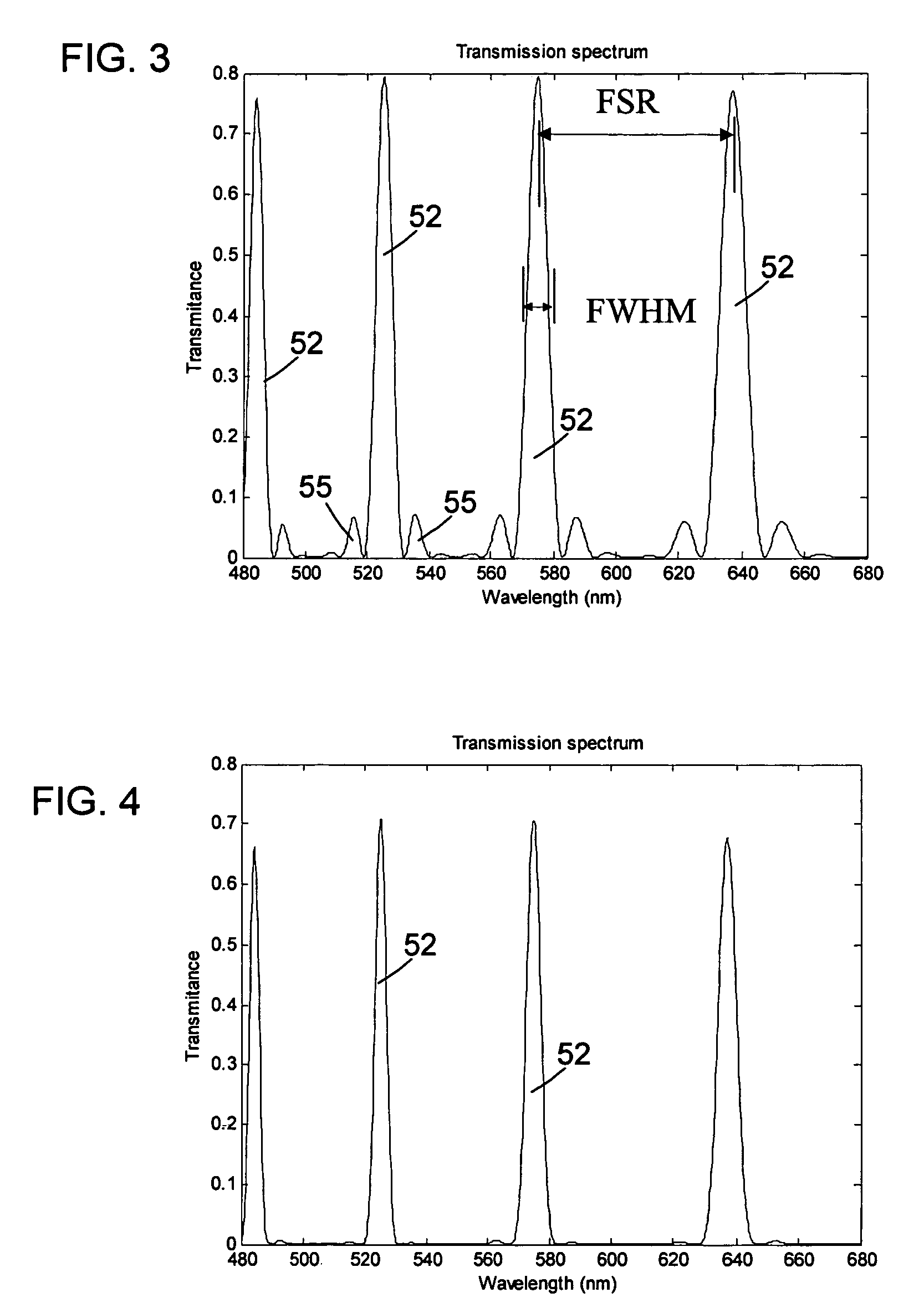
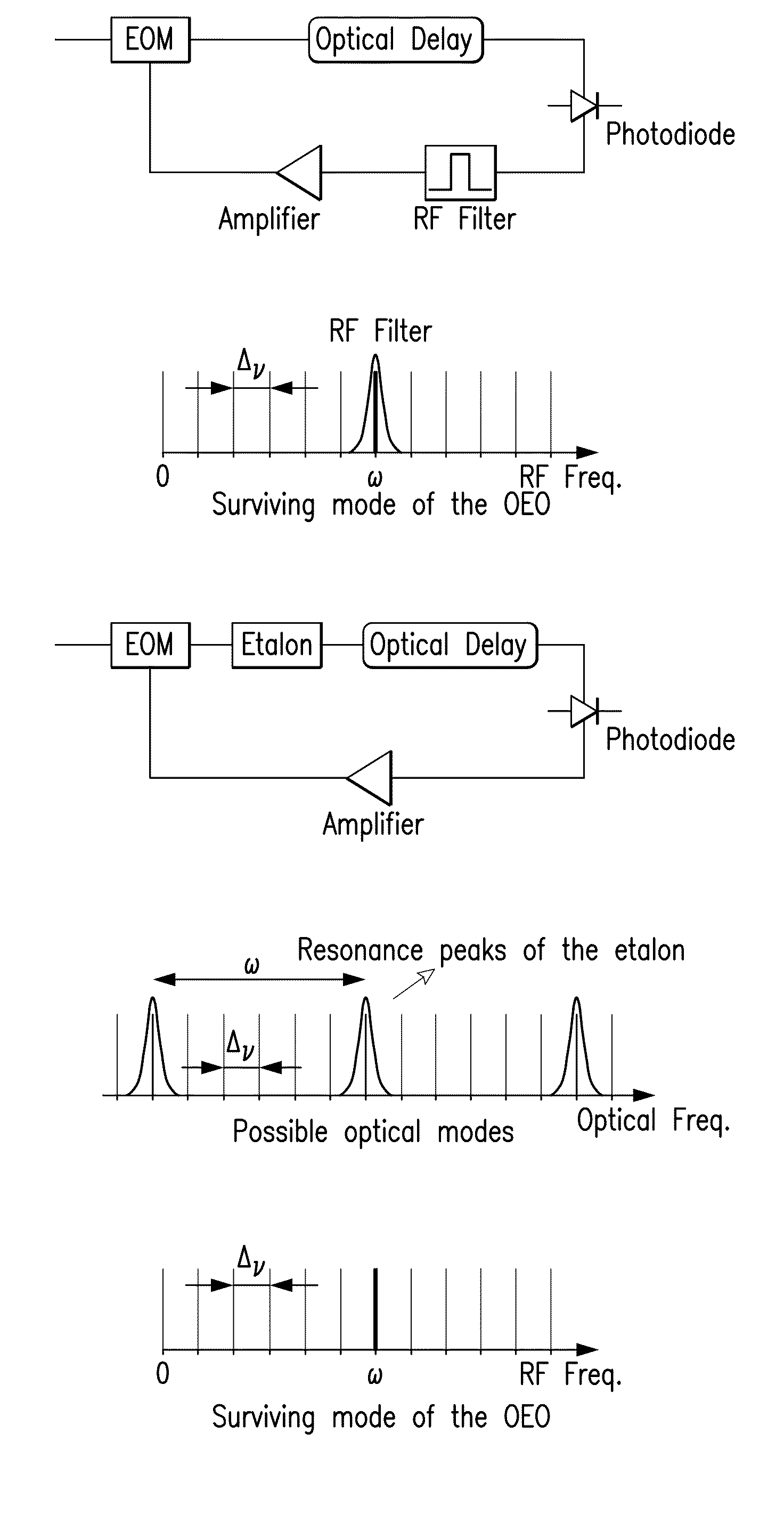
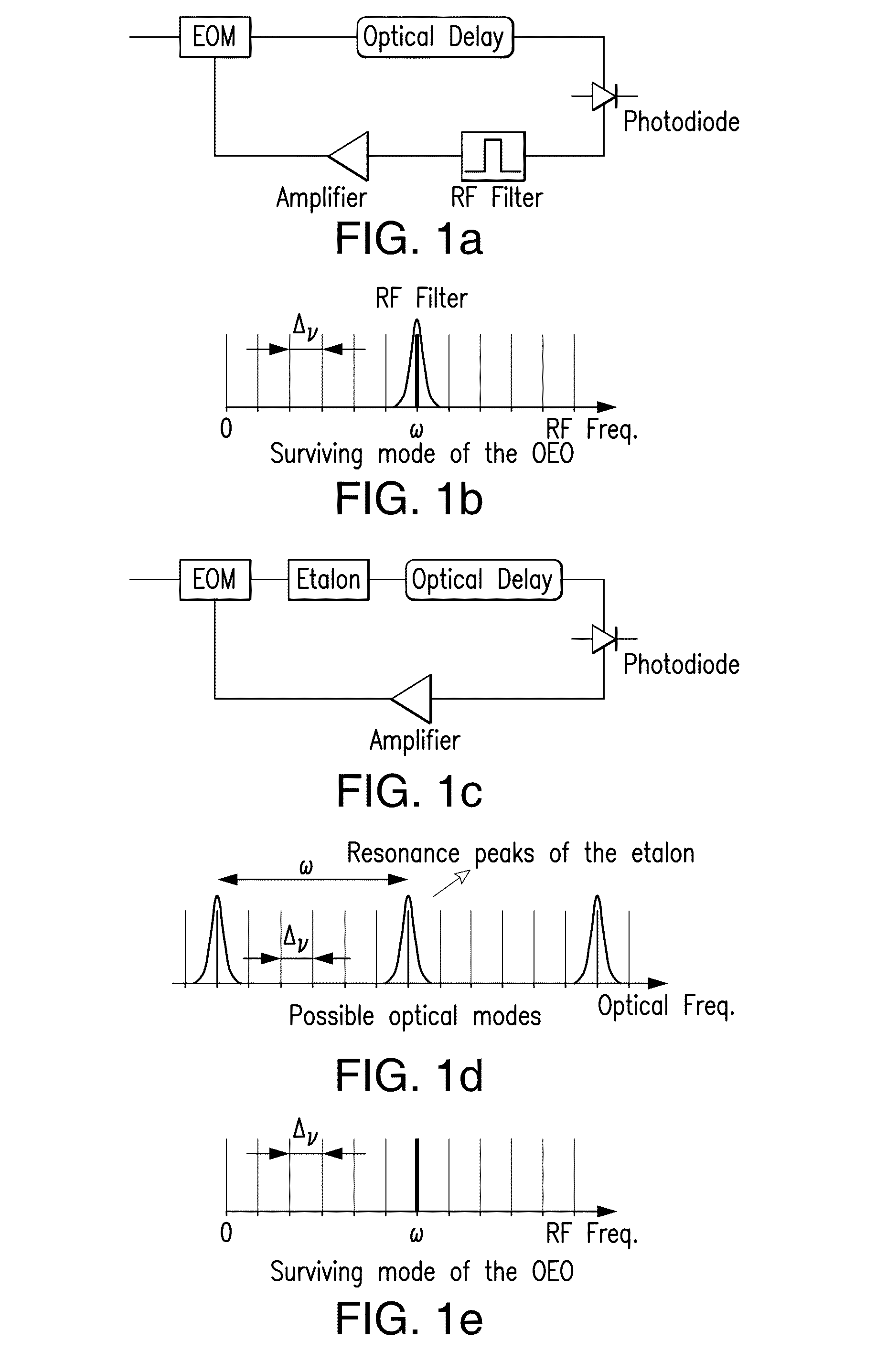
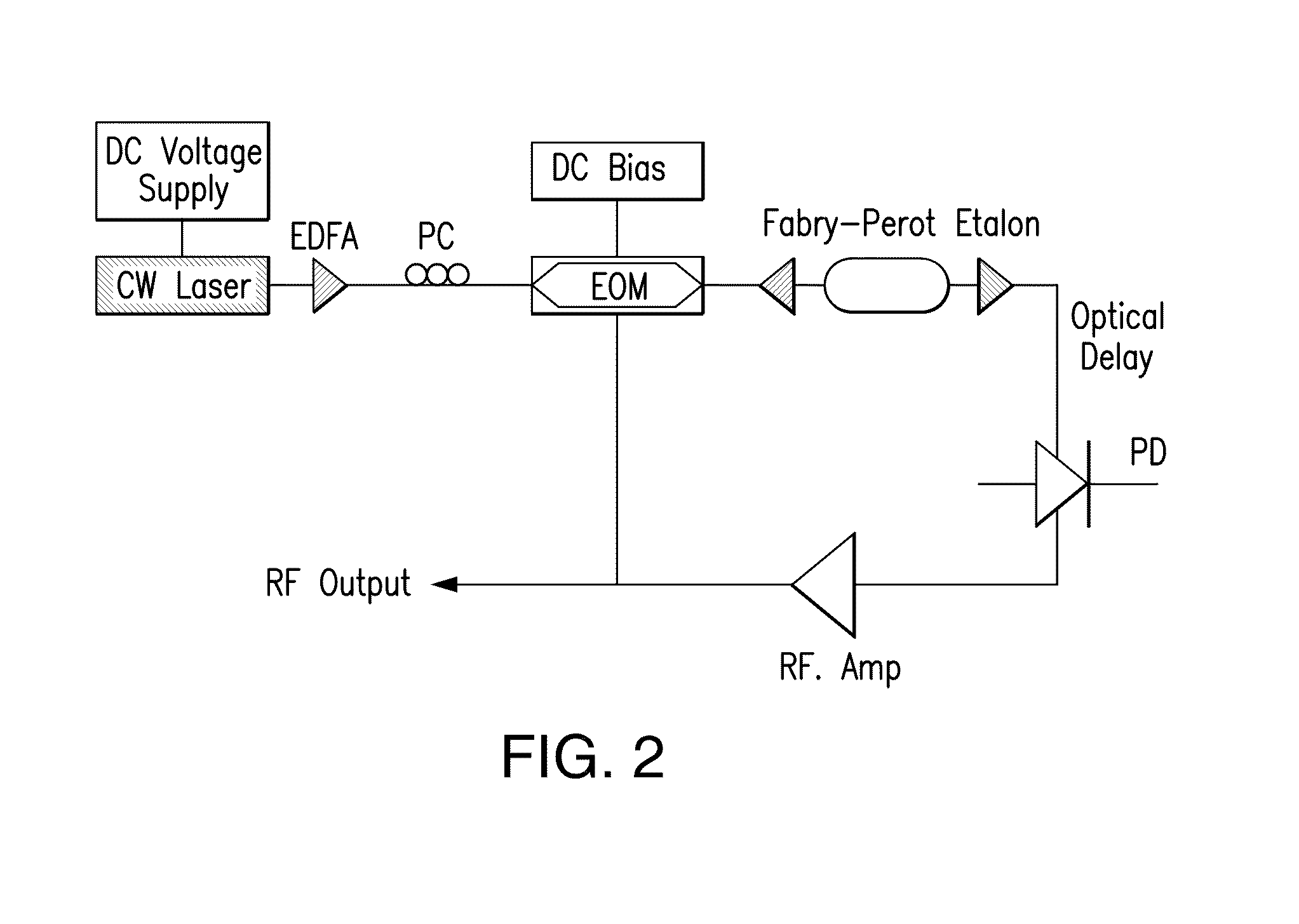
Optoelectronic oscillator using a high finesse etalon
An optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is used to provide a continuous, high Q, modulated signal for a variety of purposes, including a carrier wave for communications, and radar emissions. The OEO of this invention replaces an RF filter in the conventional OEO with an interferometer, preferably a high finesse Fabry-Perot etalon as the mode selector, providing lower phase noise and higher RF frequency stability.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
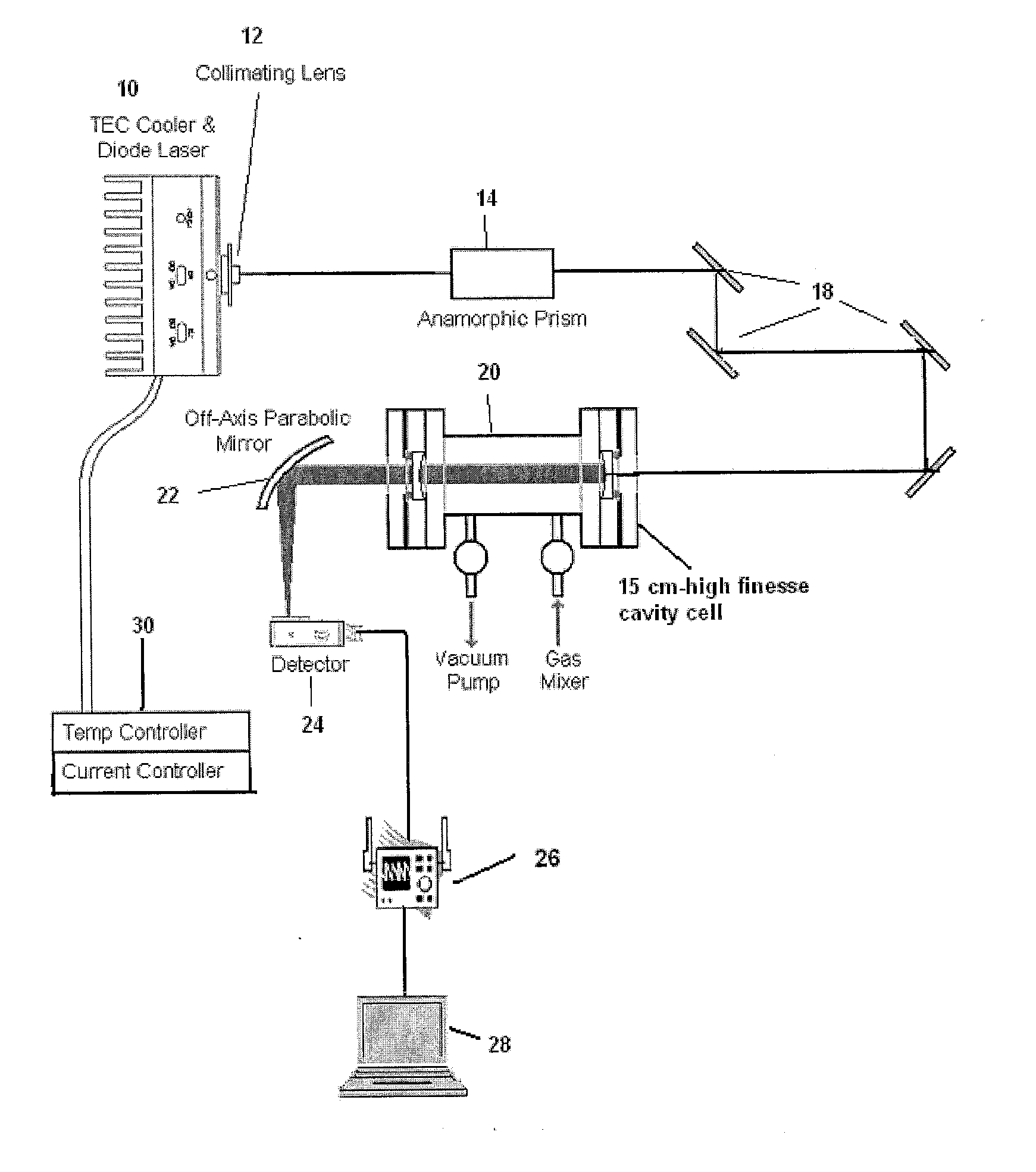
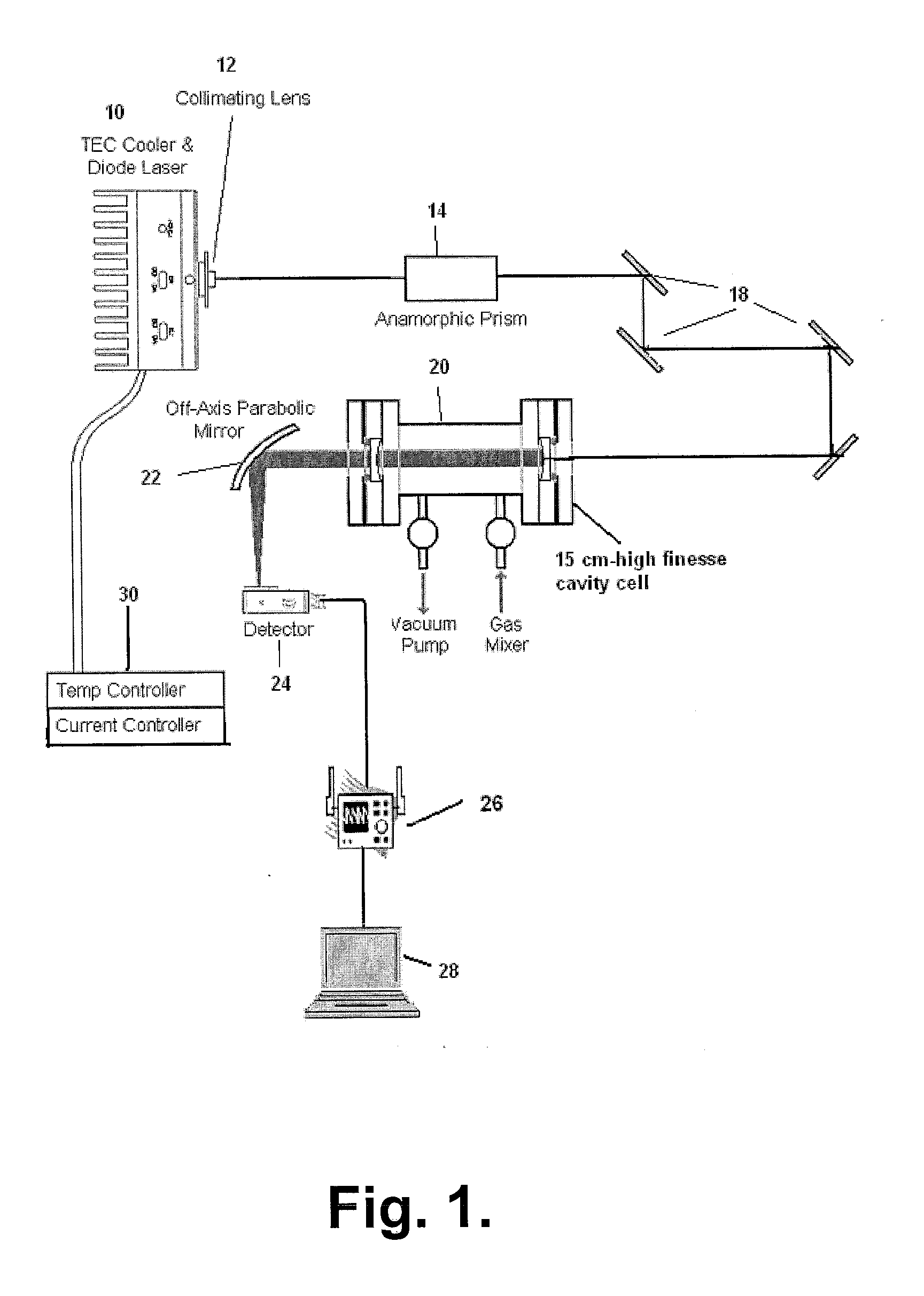
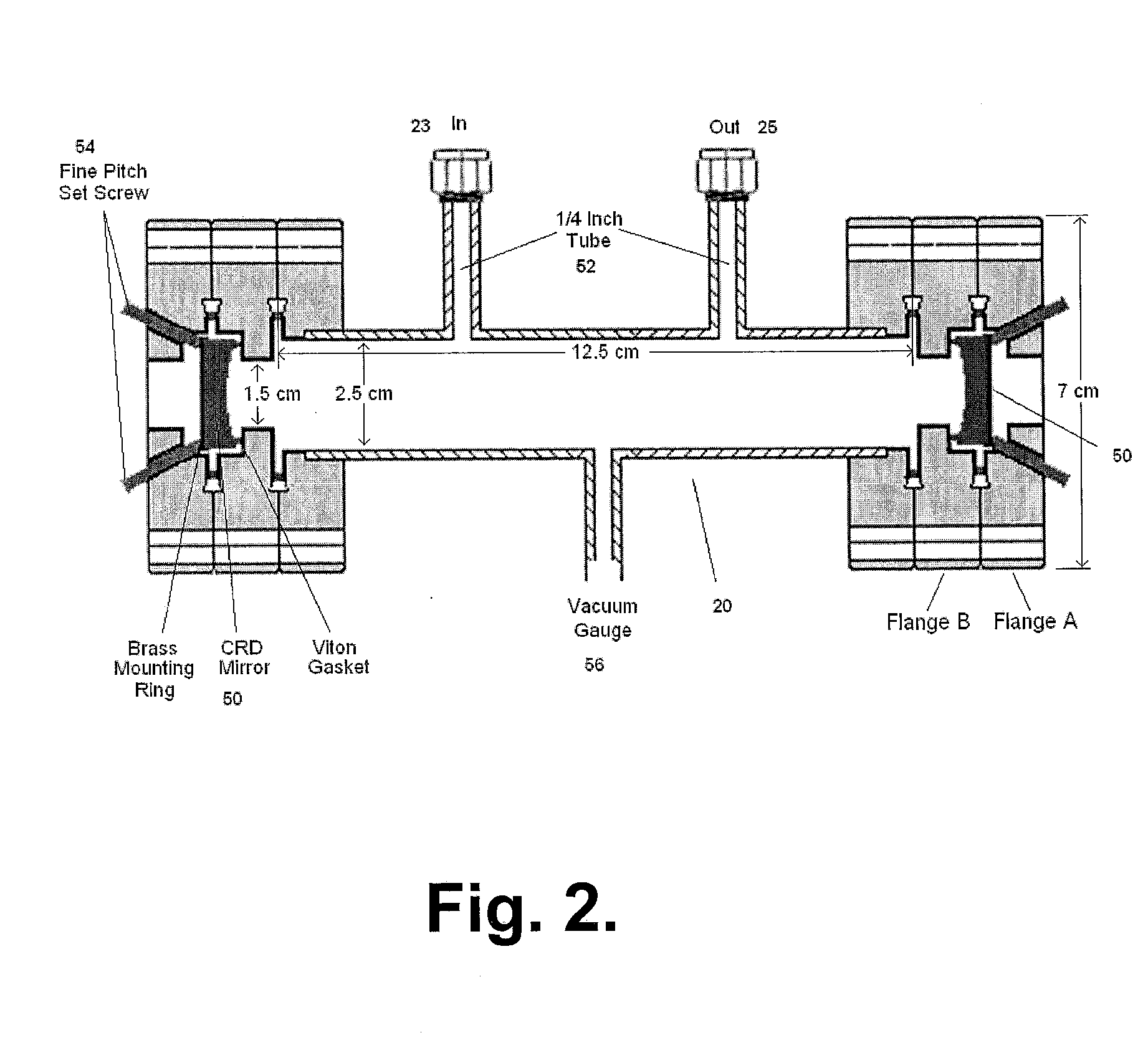
Sensitive and Compact Sensor Employing a Visible Diode Laser and A High Finesse Optical Cavity for Trace Gas Detection (NO2)
InactiveUS20120170043A1Low costHigh detection sensitivityTransmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsLow noisePath length
A sensor with high sensitivity and selectivity for the detection of NO2 uses a simple diode laser operating nominally at 405 nm in the visible region, a high finesse optical cavity and a low noise photon detector. The sensor employs the multimode broad output of the diode laser with the high finesse optical cavity in an essentially off-axis arrangement that can provide large path lengths of the order of a km in a small volume cell. The detected absorption signal corresponds to multiple line integrated absorption spectroscopy (MLIS). Because the sensor uses visible radiation it can employ optics in the visible region that are normally less expensive. Also, the sensor is free from interference from atmospheric water vapor which is often a severe problem for sensors based on mid-infrared quantum cascade lasers operating in the mid-infrared (for example 1650 cm−1) region.
Owner:ADELPHI UNIVERSITY
Method and system for locking transmission wavelengths for lasers in a dense wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS20020163650A1Heat is lostChange in refractive indexSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser output parameters controlFiberFinesse
Owner:SPECTRASENSORS INC
Digital amplifier with improved performance
InactiveUS20020135419A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorDigital dataLow-pass filter
A class D amplifier uses a summation of two or more PWM output stages to achieve an increased dynamic range and improved linearity for any given clock operating speed. The amplifier accepts a digital data stream as its input, such as from a compact disk, or other compatible media, at a data rate, Fa, that could be 44.1 kHz, 96 kHz, or any other rate appropriate for audio data. In the preferred embodiment, the input audio data resolution, N bits, would be split into two data samples, of J and K. Internal switching frequency, Fs, switches the PWM with an over sampling factor M, where Fs=M*Fa. The time resolution of the PWM is determined by a precision oscillator that operates at Fc=Fs*(max(J,K)-log2(+1). The J most significant bits would be routed to a power PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VHI. The K least significant bits are routed to a finesse PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VLO. The ratio of VLO to VHI will be appropriate for the ratio of K and J so the summation of the power PWM stage and the finesse PWM stage will provide the full range of N bits. This summation is accomplished with a low pass filter and time-division multiplexing of the two PWM stages. A micro controller (MCU) is used to apply a sample packet distribution algorithm to provide more resolution by reducing quantization noise in the audio band of interest. The MCU is also used to calibrate the VLO or VHI, or to calibrate the PWM timing of the two PWM stages to achieve appropriate performance.
Owner:GROVES JR WILLIAM HARRIS +1
Short-Wavelength Infrared (SWIR) Multi-Conjugate Liquid Crystal Tunable Filter
InactiveUS20140362331A1Fast tuningImprove transmittanceSpectrum investigationSpectrum generationWavelength filterPolarizer
A SWIR hyperspectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path with angularly distributed birefringent retarders and polarizers. The retarders can include active retarders such as tunable liquid crystal birefringent elements, passive retarders such as fixed retarders, and / or combinations thereof. Distinctly different periodic transmission spectra are provided by different filter stages, each having multiple retarders, in particular with some stages having broad bandpass peaks at wide spectral spacing and other stages have very narrow closely spaced peaks. The respective spectra include at least one tunably selectable band at which the transmission spectra of the filter stages coincide, whereby the salutary narrow bandpass and wide spectral spacing ranges of different stages apply together, resulting in a high finesse wavelength filter suitable for spectral imaging. The filter may be configured to provide faster switching speed and increased angle of acceptance and may operate in the rage of approximately 850-1700 nm.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
Short wave infrared multi-conjugate liquid crystal tunable filter
ActiveUS20110279744A1Fast tuningImprove transmittancePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsWavelength filterPolarizer
A SWIR hyperspectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path with angularly distributed birefringent retarders and polarizers. The retarders can include active retarders such as tunable liquid crystal birefringent elements, passive retarders such as fixed retarders, and / or combinations thereof. Distinctly different periodic transmission spectra are provided by different filter stages, each having multiple retarders, in particular with some stages having broad bandpass peaks at wide spectral spacing and other stages have very narrow closely spaced peaks. The respective spectra include at least one tunably selectable band at which the transmission spectra of the filter stages coincide, whereby the salutary narrow bandpass and wide spectral spacing ranges of different stages apply together, resulting in a high finesse wavelength filter suitable for spectral imaging. The filter may be configured to provide faster switching speed and increased angle of acceptance and may operate in the rage of approximately 850-1700 nm.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
Apparatus and method for stabilizing lasers using dual etalons
ActiveUS20060192970A1Fast rebuildImprove skillsLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryFinesseControl system
Method and apparatus are disclosed that enable lasers to be stabilized in frequency to a high precision while simultaneously enabling rapid re-acquisition of stabilization control loops in the event of frequency locking loss. The principle of operation is to incorporate two etalons, one having a high finesse for frequency high stability, and one having a low finesse for wide error signal locking range, and electronics that pass control between two control systems in such a manner that any loss of frequency locking is rapidly re-acquired.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN COHERENT TECH
Waferless fiber Fabry-Perot filters
ActiveUS6904206B2Reduce light lossReduce alignment sensitivityElectrical apparatusCoupling light guidesFiberFinesse
Improved fiber Fabry-Perot (FFP) filter configurations are provided in which at least one of the mirror-ended fiber ends forming the FFP has a concave fiber core end. The mirror at that fiber core end is thus concave. The invention provides waferless FFP configurations in which the FFP cavity is an air-gap cavity formed by two highly reflective dielectric mirrors deposited directly on optical fiber ends. The air gap cavity can be tuned using various methods to tune the filter. Use of a concave mirror at the fiber core enables filters with improved performance characteristics: including very wide FSR (>12000 GHz), very high finesse (>5,000), and high glitch-free dynamic range (GFDR) (>40 dB). The invention also provides improved wafer-based FFP fixed and tunable filters that incorporate a concave mirror at a fiber core forming the FFP cavity and a fiber (SMF) waveguide within the cavity.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Multi-conjugate liquid crystal tunable filter
ActiveUS20080007813A1Increase gear ratioLimiting rejectionPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsWavelength filterPolarizer
A hyper-spectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path with angularly distributed birefringent retarders and polarizers forming interference filters. The retarders can include tunable birefringent elements such as liquid crystals controlled in unison, fixed retarders and / or combined tunable and fixed birefringences. Distinctly different periodic transmission spectra are provided by different filter stages, each having multiple retarders, in particular with some stages having broad bandpass peaks at wide spectral spacing and other stages have very narrow closely spaced peaks. The respective spectra include at least one tunably selectable band at which the transmission spectra of the filter stages coincide, whereby the salutary narrow bandpass and wide spectral spacing ranges of different stages apply together, resulting in a high finesse wavelength filter suitable for spectral imaging.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
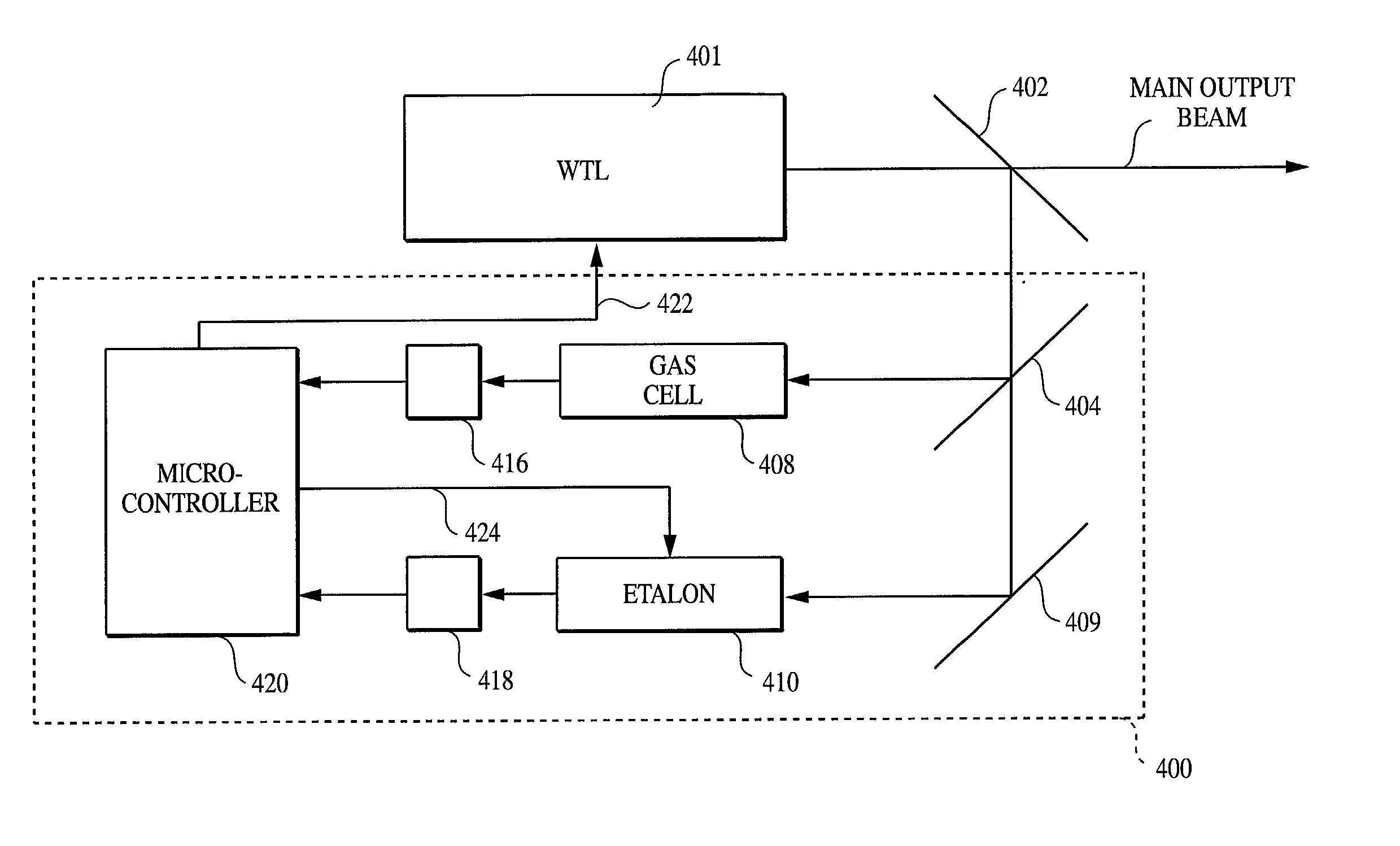
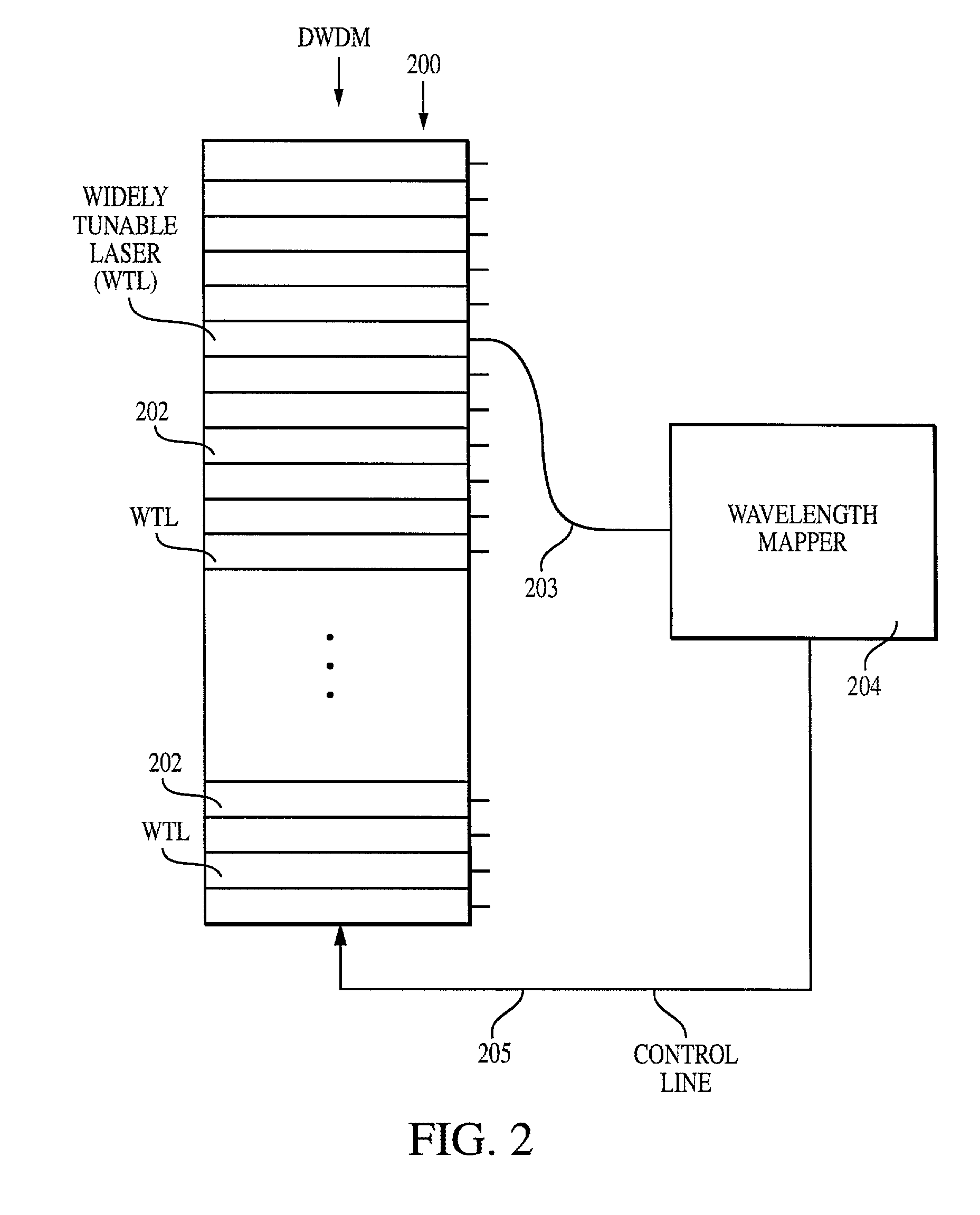
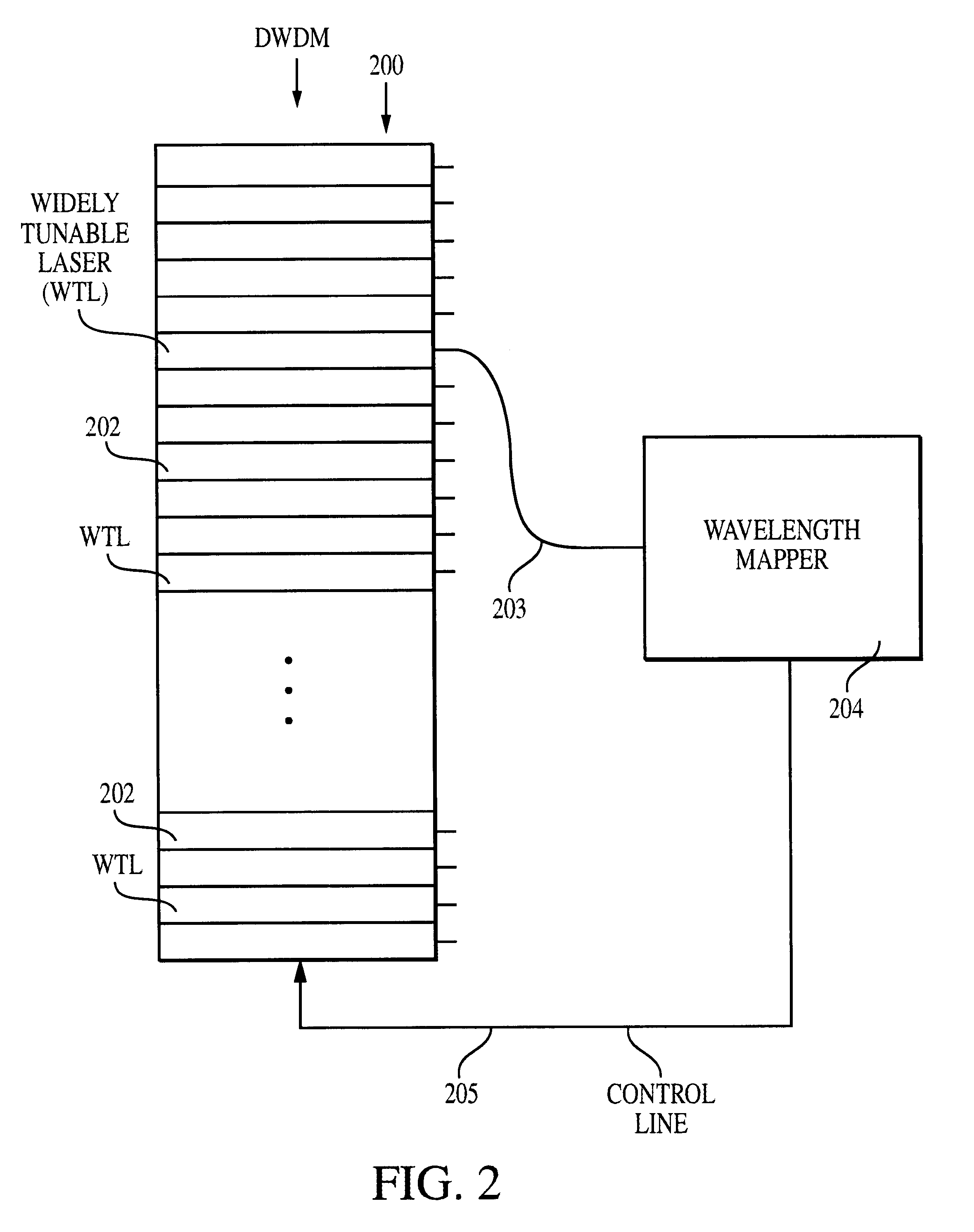
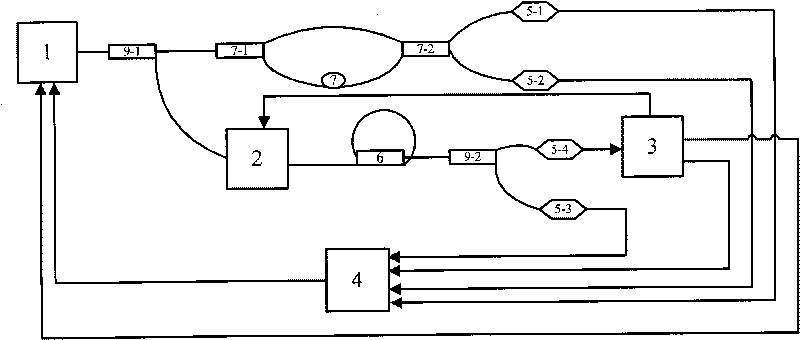
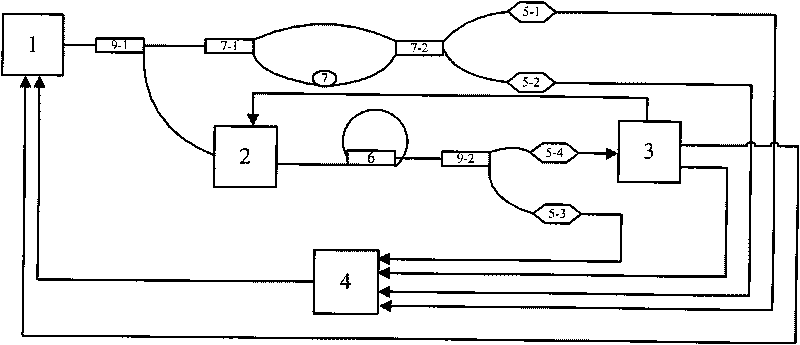
Method and system for locking transmission wavelengths for lasers in a dense wavelength division multiplexer utilizing a tunable etalon
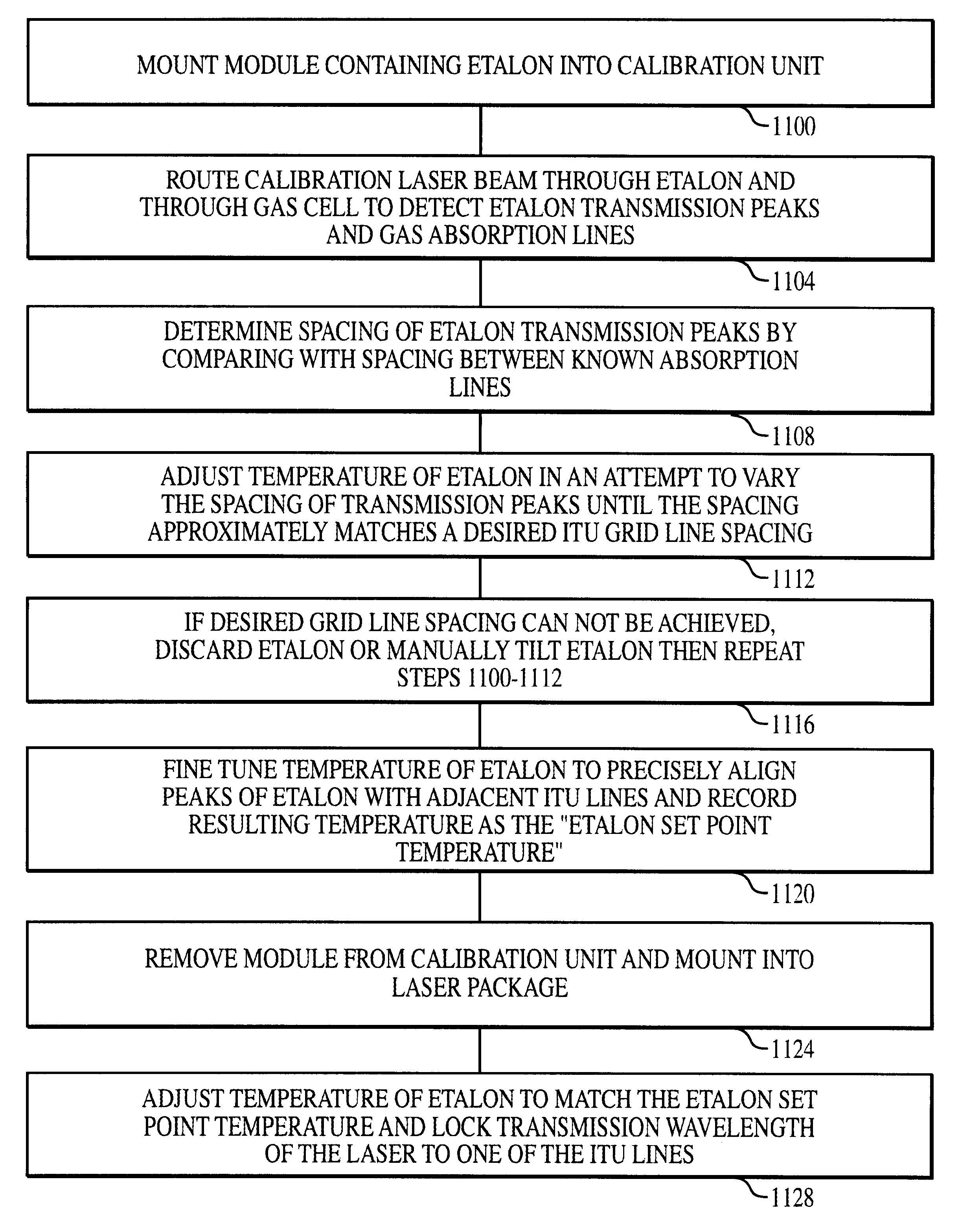
The method and system operate to calibrate a transmission laser of the dense wavelength division multiplexer (DWDM) and to lock the laser to a selected transmission wavelength. In one example, the transmission laser is a widely tunable laser (WTL) to be tuned to one of a set of International Telecommunications Union (ITU) transmission grid lines for transmission through an optic fiber. To lock the WTL to an ITU grid line, a portion of the output beam from the WTL is routed through the etalon to split the beam into a set of transmission lines for detection by a detector. Another portion of the beam is routed directly to another detector. A wavelength-locking controller compares signals from the two detectors and adjusts the temperature of the etalon to align the wavelength of one of the transmission lines of the etalon with the wavelength of the output beam, then controls the WTL in a feedback loop to lock the laser to the etalon line. The wavelength-locking controller thereafter monitors the temperature of the etalon and keeps the temperature constant to prevent any wavelength drift in the etalon. In one example, the etalon is a silicon etalon configured to have finesse of about 20 and to provide a free spectral range of about 8 GHz. With these parameters, the system is able to lock the wavelength of the WTL to within a precision of about 0.2 GHz. In another example, the etalon is first calibrated during manufacture to determine a "set point" operating temperature sufficient to align transmission peaks of the etalon with desired ITU grid lines. The etalon is thereafter mounted within a WTL and the etalon is adjusted to the set point temperature so as to align transmission peaks of the etalon with the desired ITU grid lines to permit wavelength locking. This later technique allows for rapid switching between channels and obviates the need for a gas cell within the WTL.
Owner:SPECTRASENSORS INC
Optical cavity and laser
InactiveUS20050163184A1Less thermal gradientExpand selectionOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialFinesseOptical cavity
A novel laser cavity structure is disclosed which pertains to laser resonator geometries possessing circular symmetry, such as in the case of disk or spherical lasers. The disclosed invention utilizes a very-high finesse Bragg reflector (VHF-BR) thin film reflectors of many layer pairs of very small refractive index difference, the VHF-BR deposited on a surface of revolution, thereby forming an optical cavity. These dielectric reflectors are disposed in such a way as to allow selection of preferred low order modes and suppression of parasitic modes while allowing a high cavity Q factor for preferred modes. The invention disclosed, in its preferred embodiments, is seen as particularly useful in applications requiring high efficiency in the production and coupling of coherent radiation. This is accomplished in a cavity design that is relatively compact and economical. Of particular novelty is the combination of the disclosed cavity design with polymer multilayers. The ability to deposit an unusually large number of polymer thin films without loss of specularity, while maintaining very low extinction, renders the disclosed polymer-based cavity particularly well-suited for higher mode discrimination, more rugged and light-weight cavities, as well as economical fabrication.
Owner:HILLIARD DONALD BENNETT
Semiconductor laser all-fiber frequency stabilizing system
InactiveCN101694921AGuaranteed Polarization CharacteristicsImprove anti-interference abilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFrequency stabilizationFinesse
The invention discloses a semiconductor laser all-fiber frequency stabilizing system, which belongs to the field of laser frequency-sweeping interferometery. The frequency stabilizing system consists of a non-mode-hopping frequency scanning semiconductor laser, an all-fiber reference interferometer, a high-finesse fiber ring resonator and a data acquisition processing and controlling system. In the semiconductor laser all-fiber frequency stabilizing system, the all-fiber reference interferometer is used for monitoring frequency changes of an external-cavity semiconductor laser, and frequency of the laser is stabilized to be equal to resonance frequency of the fiber ring resonator by using a feed back method when the laser frequency approaches resonance frequency of the fiber ring resonator after scanning. The semiconductor laser all-fiber frequency stabilizing system has the advantages of small volume, light weight, high precision and fine stabilizing degree and is adaptable to laser frequency-sweeping interferometering systems.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
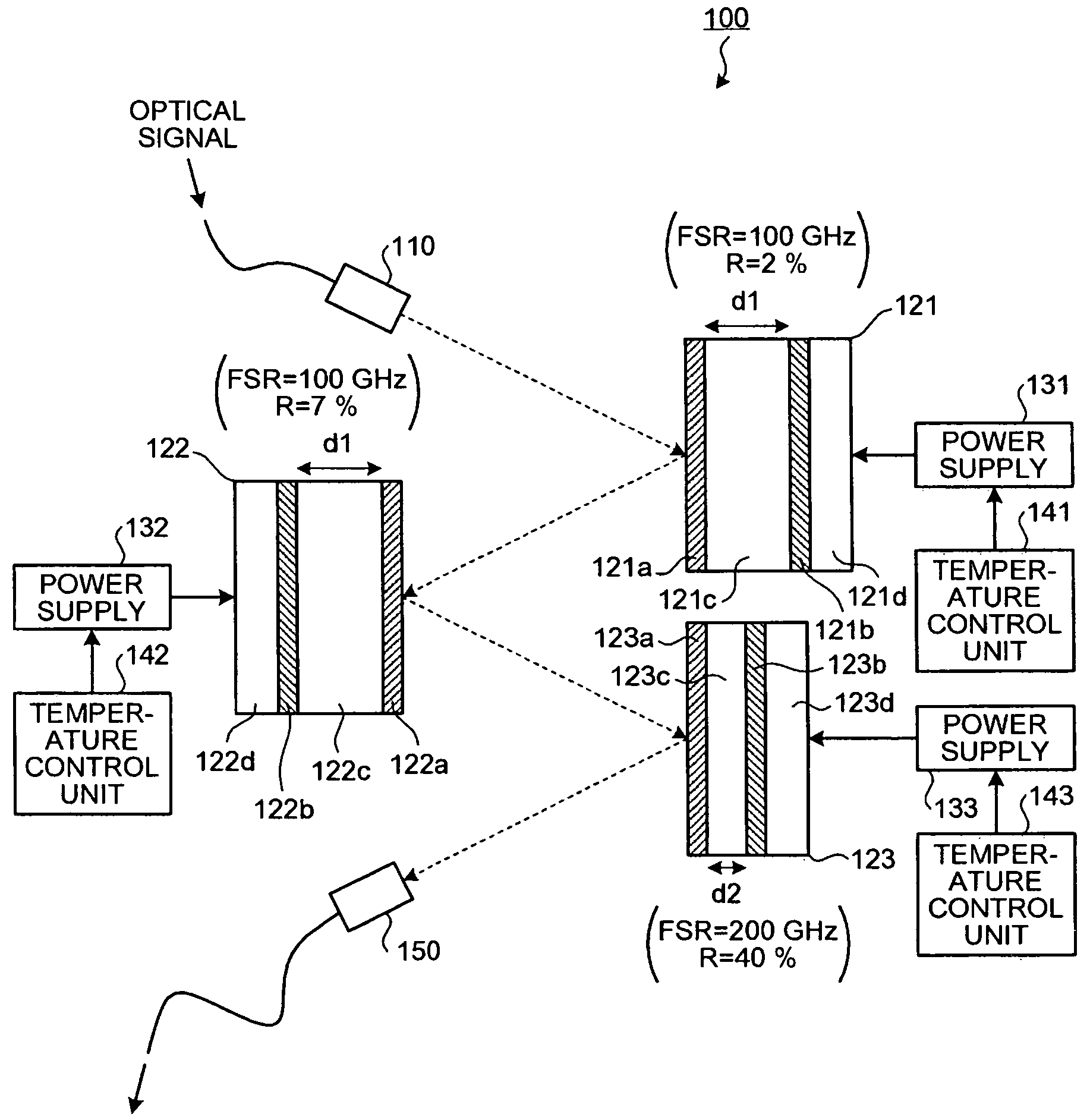
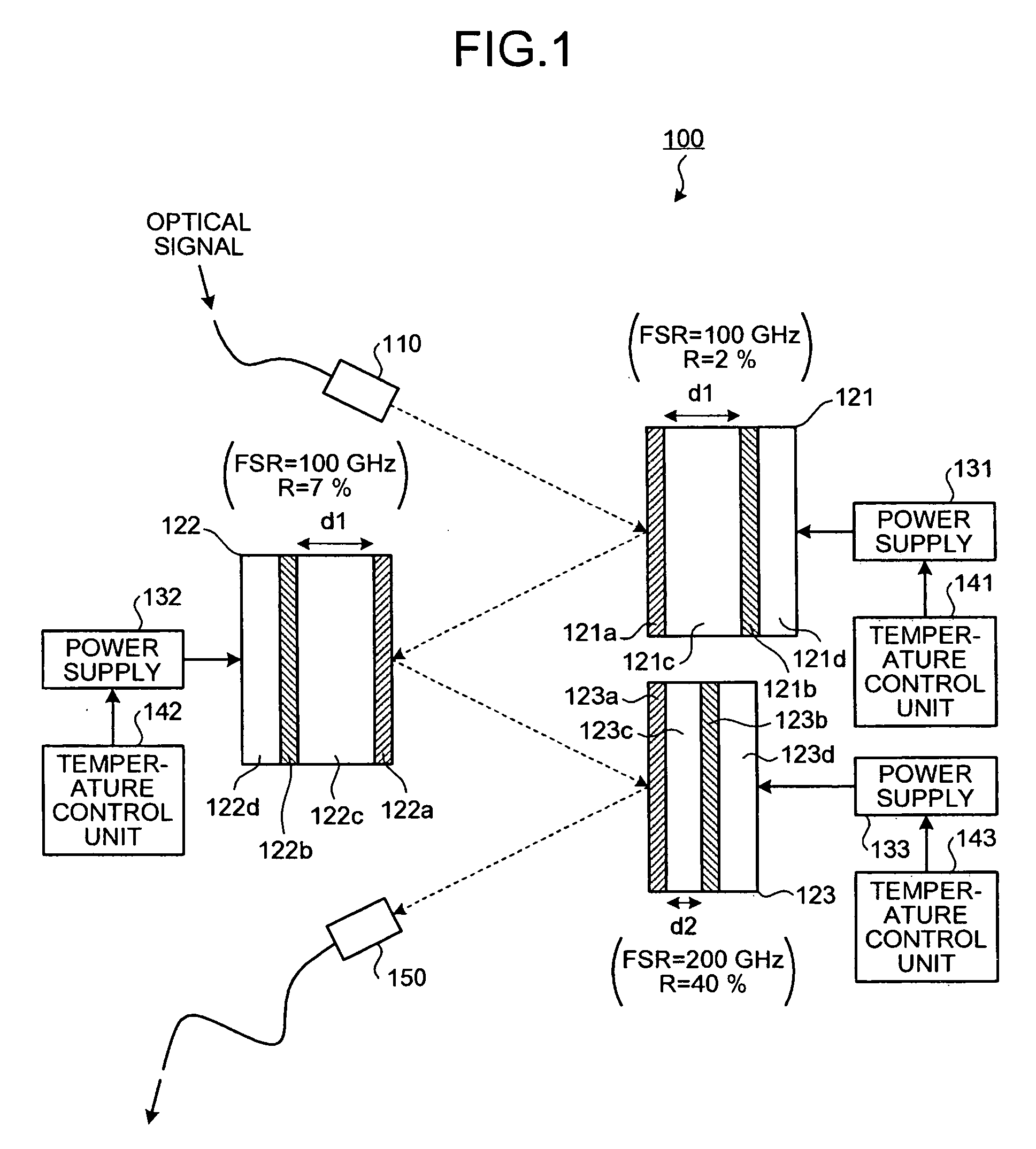
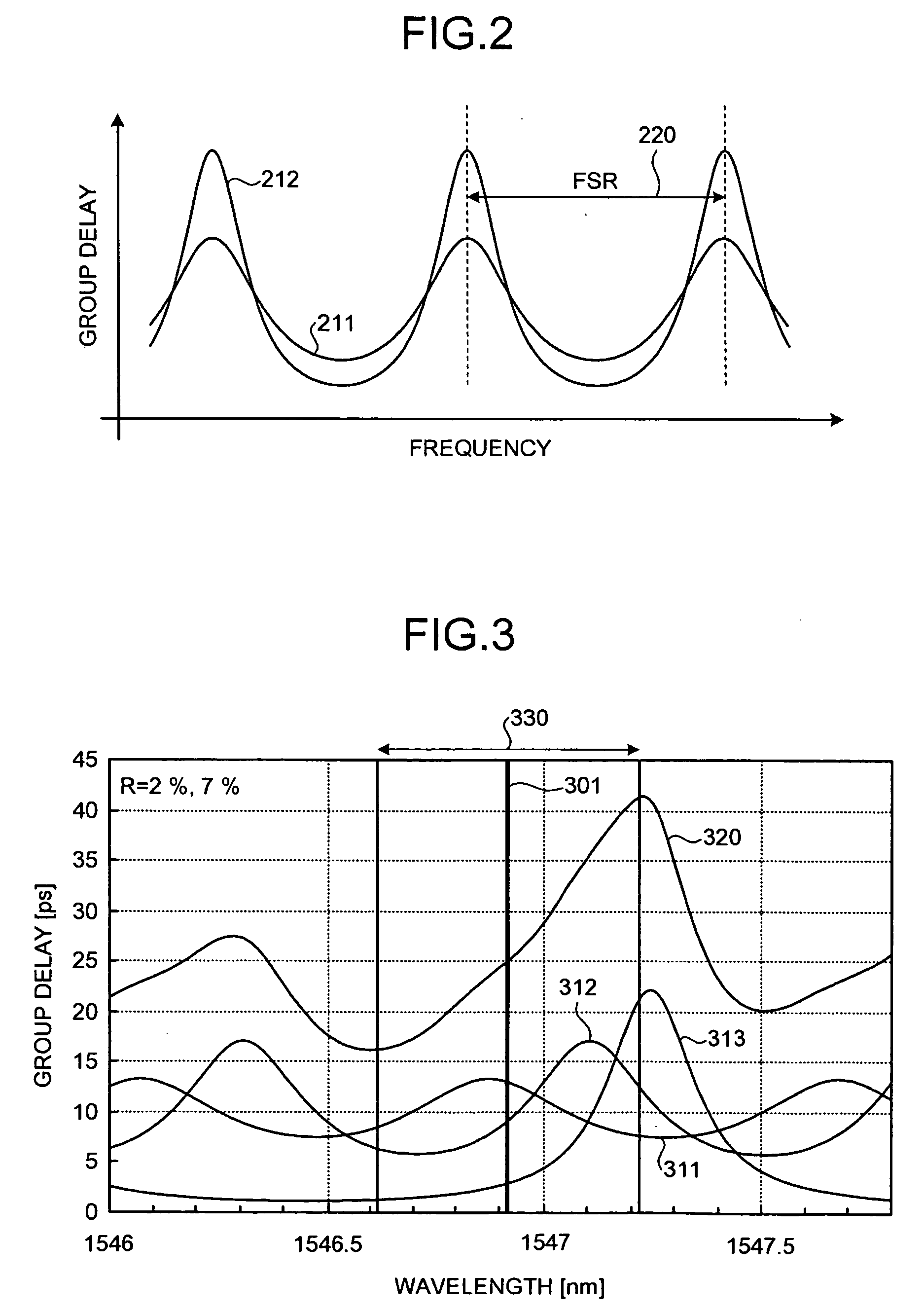
Dispersion compensating apparatus
InactiveUS20090123165A1Distortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersTemperature controlFinesse
A dispersion compensating apparatus compensates dispersion of an optical signal using reflection-type etalons. Each of the etalons reflects the optical signal and at least one etalon has, with respect to a group delay characteristic, a wavelength cycle and a finesse that are larger than those of the other etalons. Power supplies and temperature control units respectively shift, in terms of the wavelength, the group delay characteristics of the etalons.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
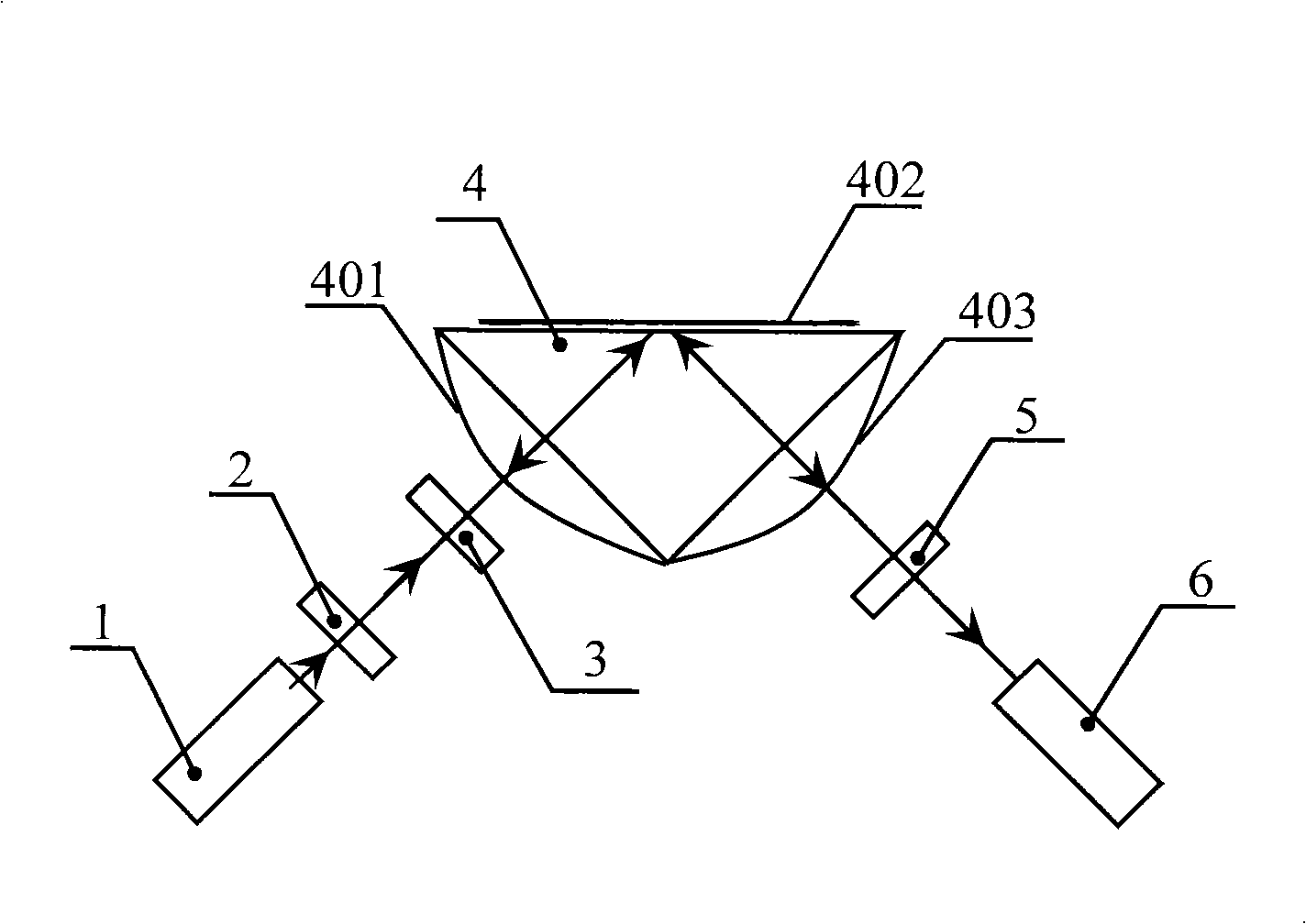
High-fineness cavity surface plasma resonance sensing equipment
InactiveCN101294900ASimple compositionHigh detection sensitivityPhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsPrismOpto electronic
The invention relates to a high-finesse cavity surface plasma resonance sensing device. The prior sensing device has low detection sensitivity. The sensing device comprises a laser source, a surface plasma sensor and a photo electrical detector. The surface plasma sensor is an isosceles triple prism, the bottom of the triple prism is plated with a plane metallic reflecting film, the side faces thereof are respectively plated with an incident high reflecting film and an outgoing high reflecting film, the sloping sides are an incident face and an outgoing face of a beam, the bottom surface is a sensing plane, and the incident face and the outgoing face of the beam are the high reflectivity surface of the beam, thus forming a high-finesse cavity. The light intensity of the detecting beam of the detector, which exits the prism, is the beam produced by the effects of repeated surface plasma resonance. The sensing device is characterized in high detection sensitivity, high modularization degree, simple system, etc.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
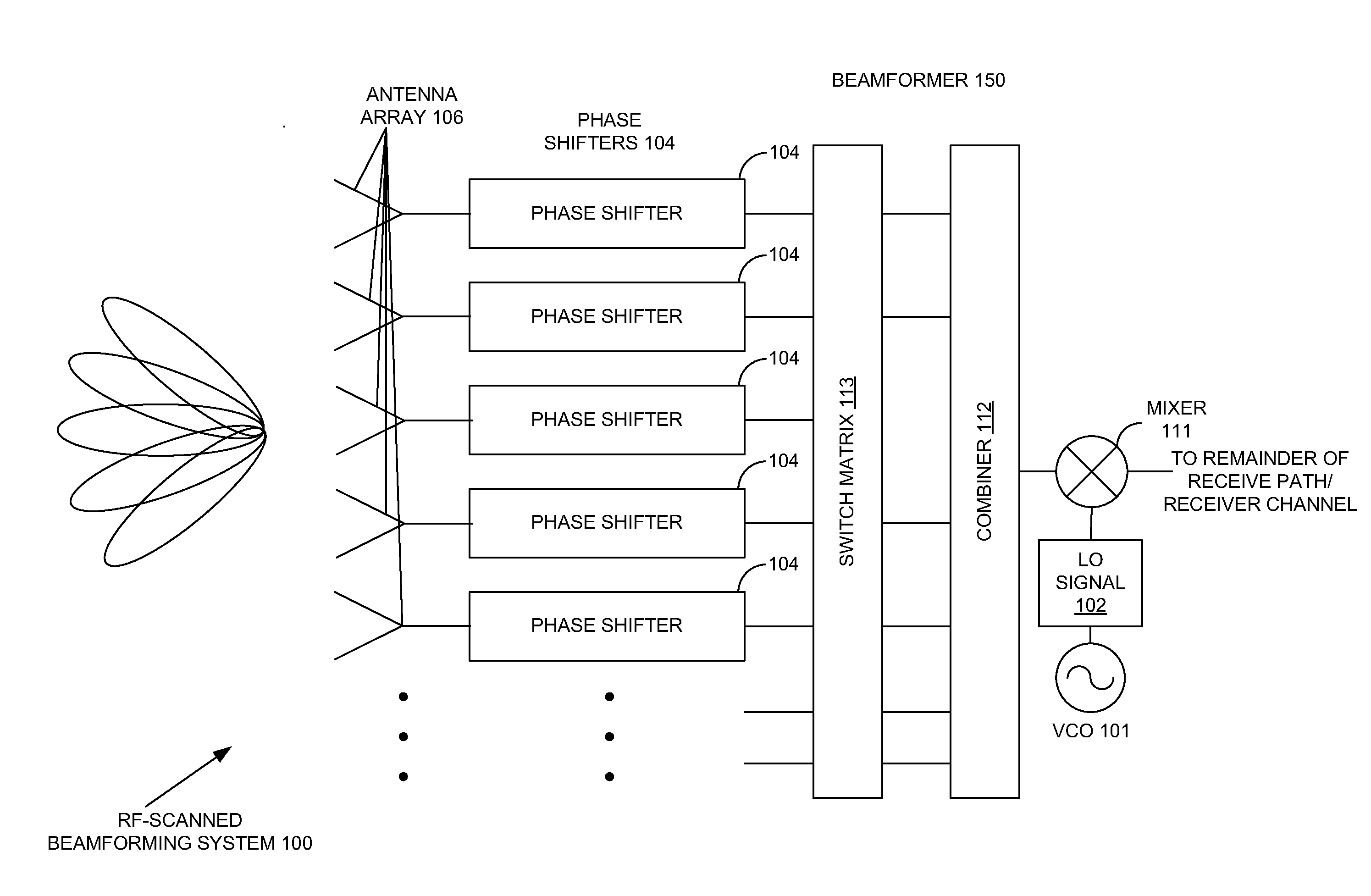
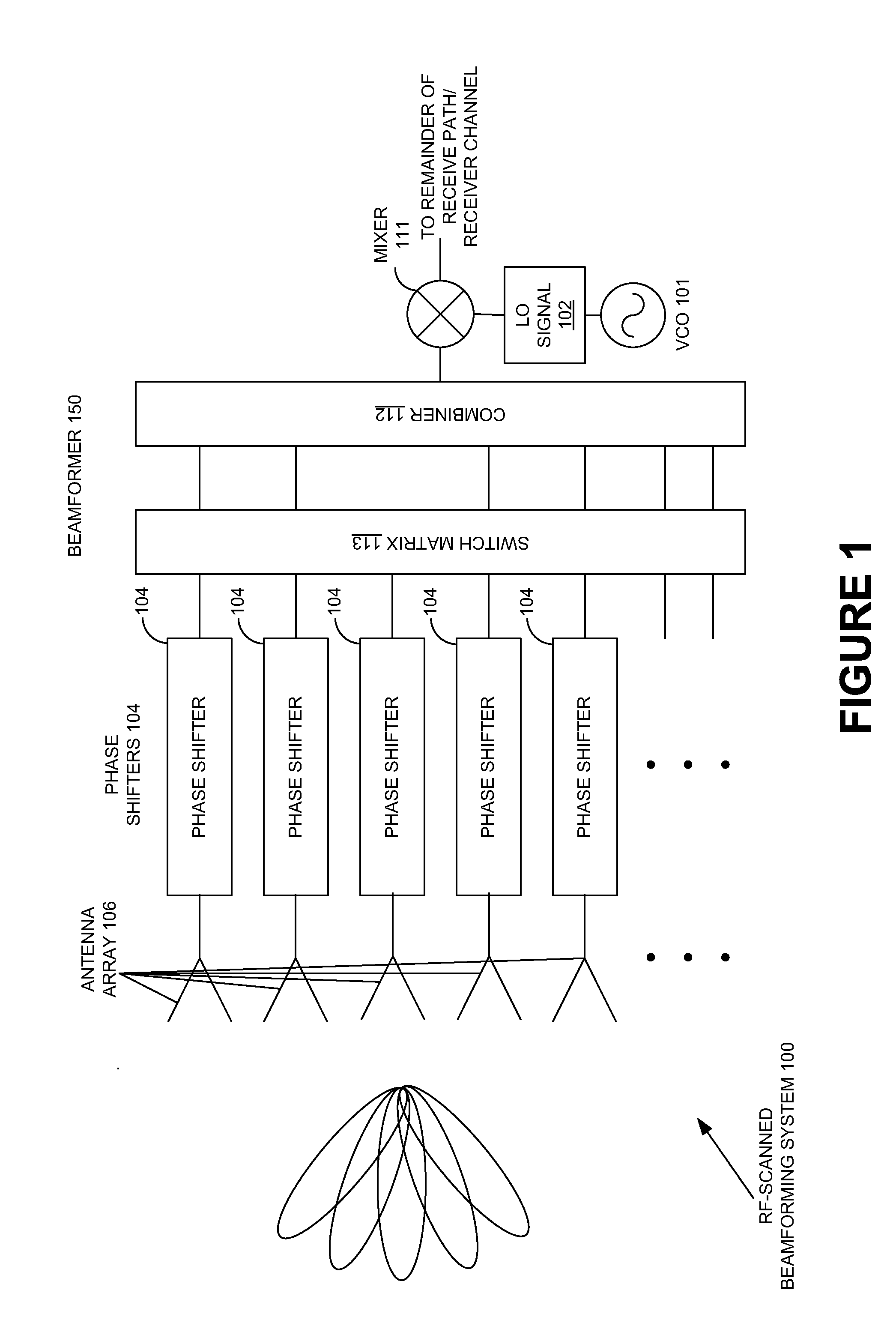
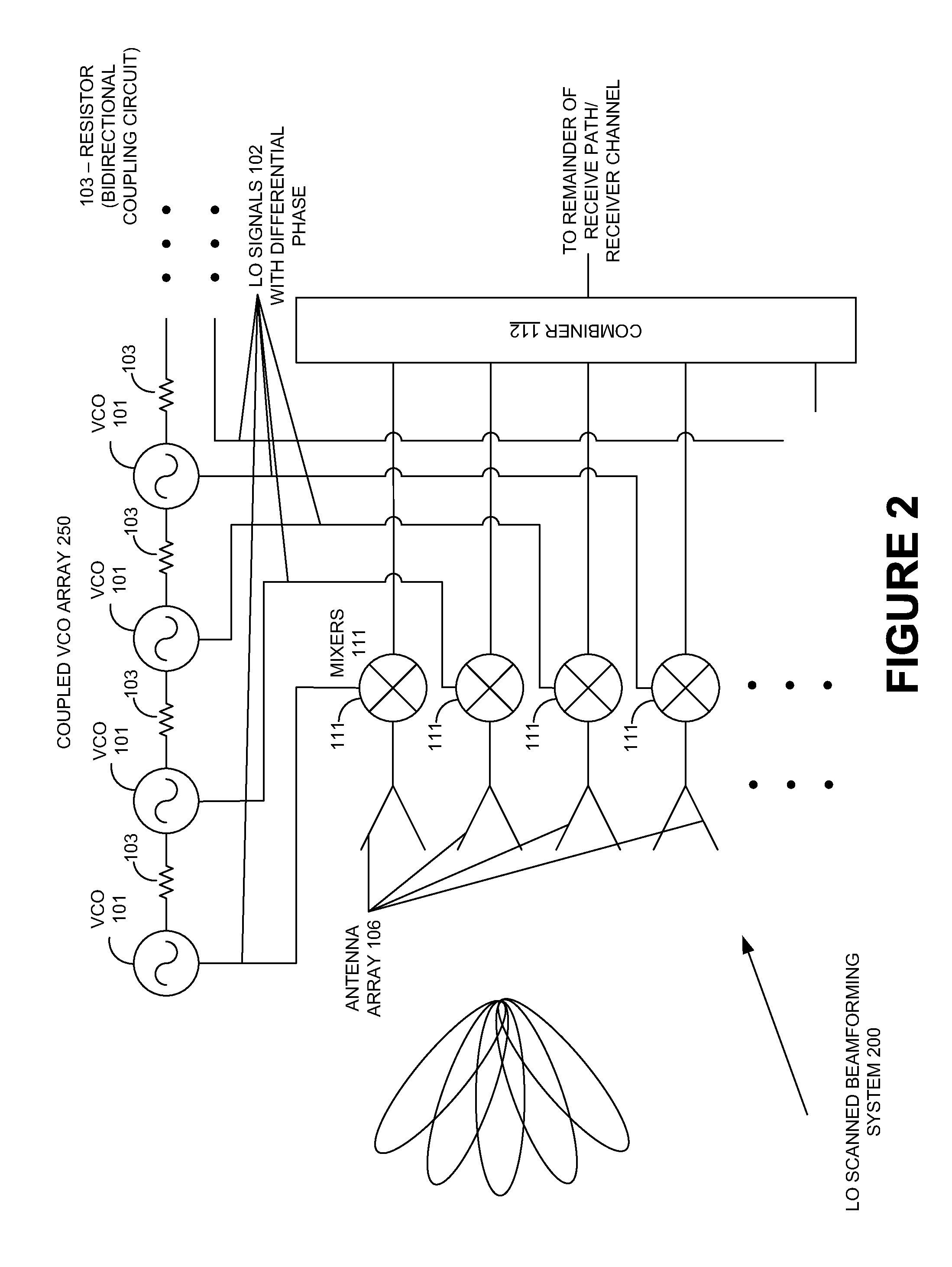
Extending beamforming capability of a coupled voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) array during local oscillator (LO) signal generation through fine control of a tunable frequency of a tank circuit of a vco thereof
ActiveUS20140273817A1Extending beamforming capabilityRadio transmission for post communicationAntennasFinesseDifferential phase
A method includes implementing a coupled Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) array with a number of VCOs, and arranging a number of switched capacitor elements in a geometric proportion in a tank circuit of each VCO to provide for finesse in control of a tunable frequency of the tank circuit. The method also includes utilizing a voltage control input of a varactor element of the tank circuit solely for achieving phase separation between the each VCO and another VCO of the coupled VCO array based on the provision of finesse in the control of the tunable frequency of the tank circuit, and mixing Local Oscillator (LO) signals generated through the number of VCOs of the coupled VCO array with signals from antenna elements of an antenna array to introduce differential phase shifts in signal paths coupled to the antenna elements during performing beamforming with the antenna array.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
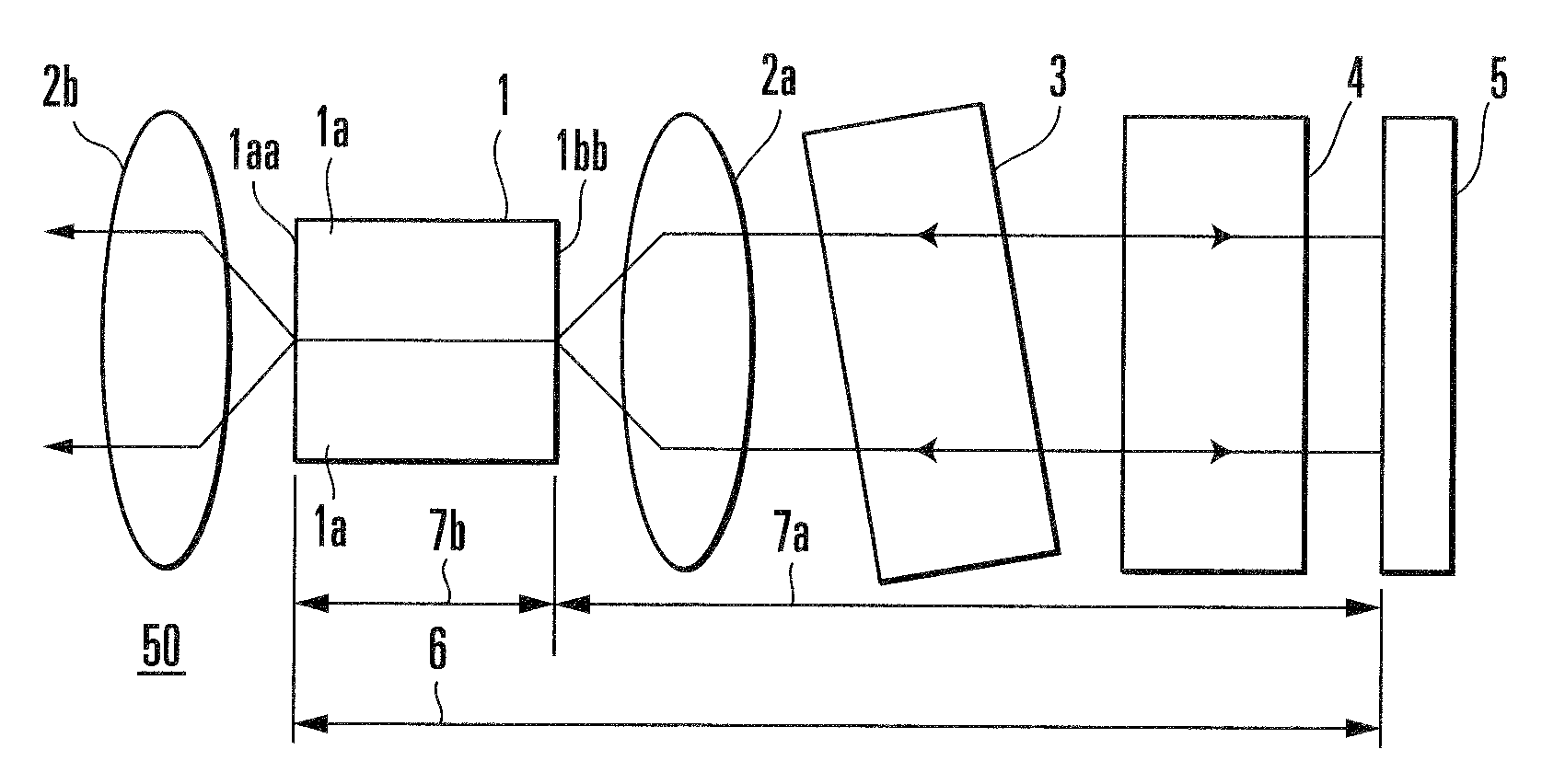
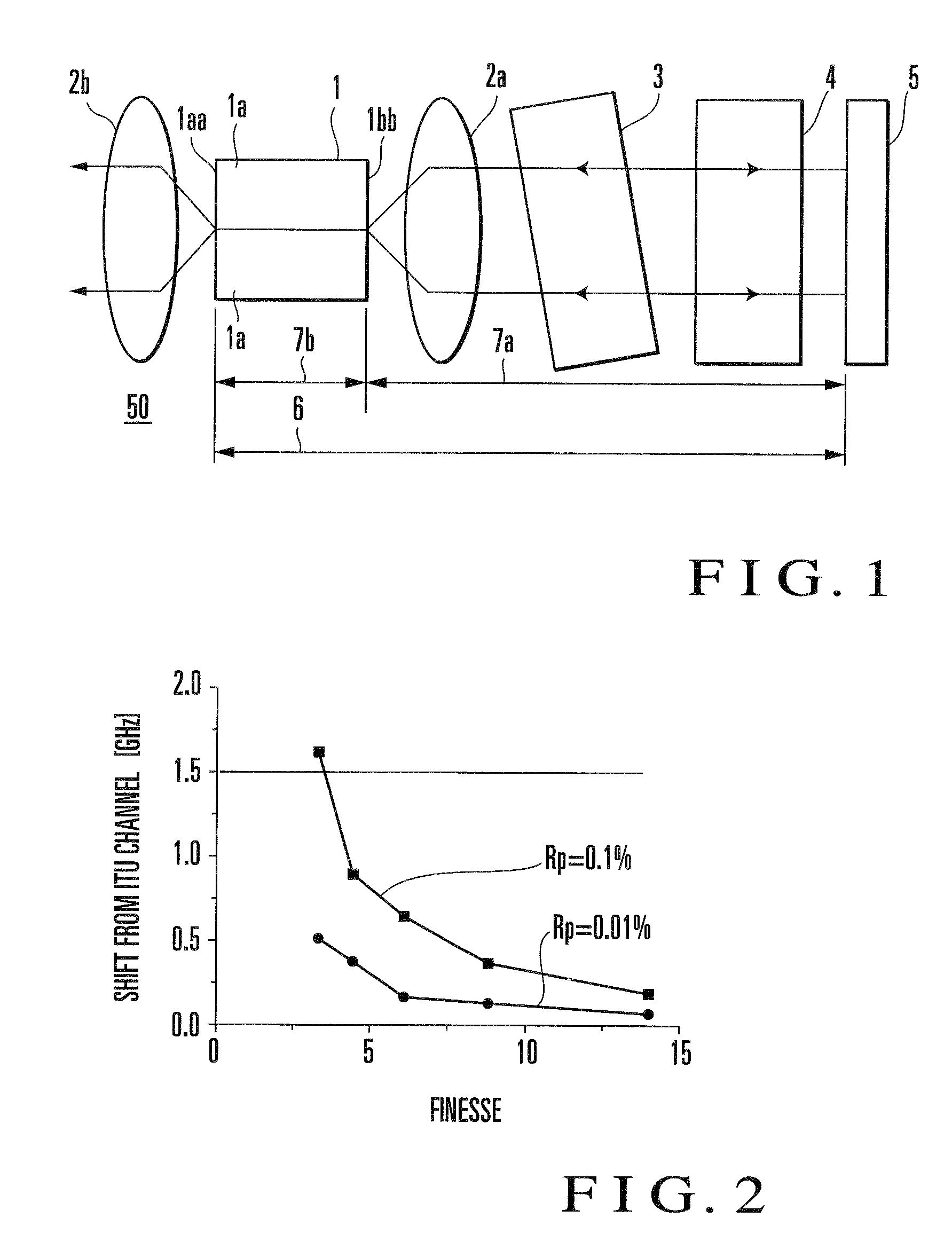
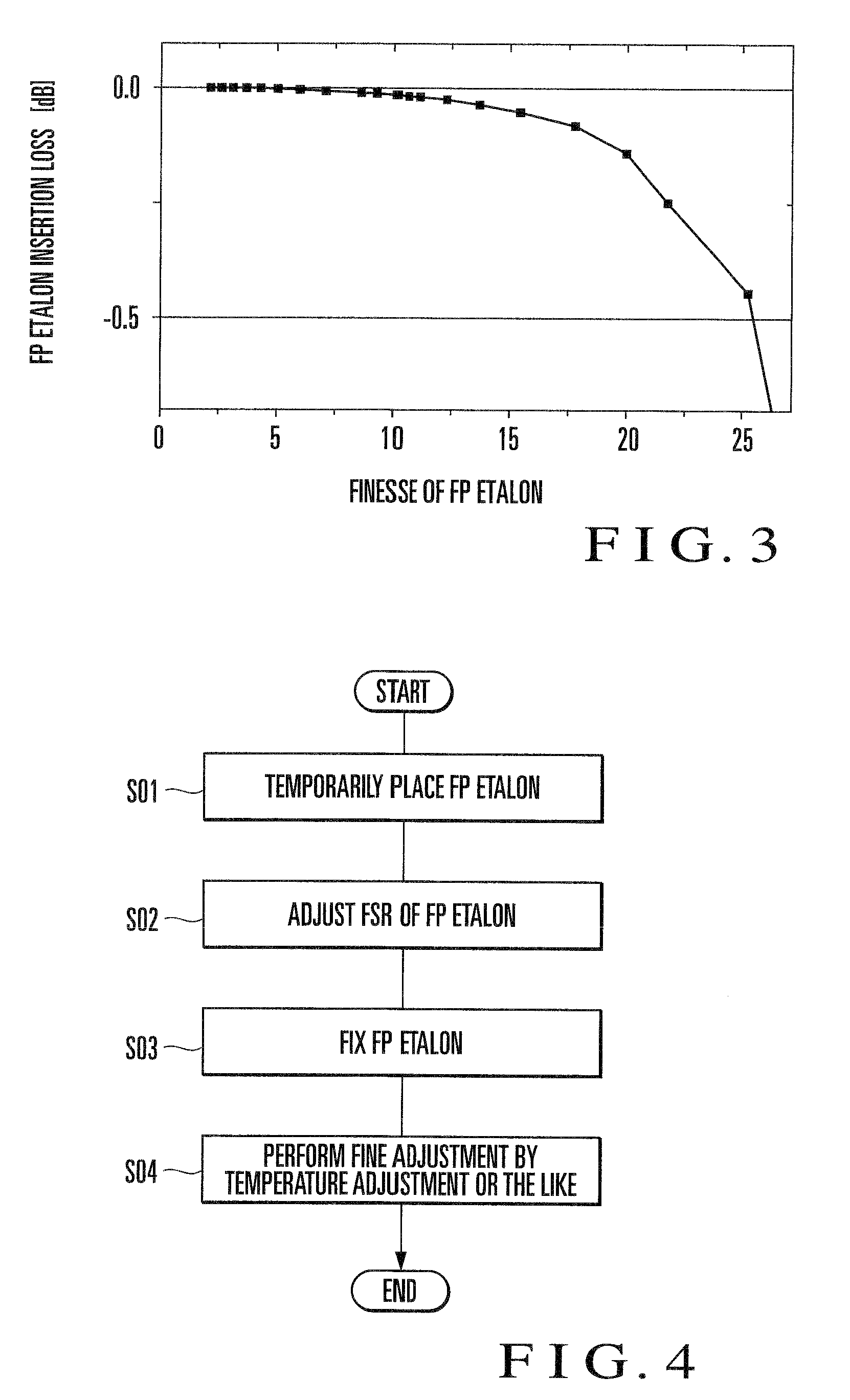
External resonator variable wavelength laser and its packaging method
InactiveUS20090257460A1High wavelength accuracyInhibition transitionLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFinesseLength wave
The reflectance of a semiconductor optical amplifier (1) on the side where an external cavity is formed is 0.1% at most. The finesse value obtained by dividing the period of the transmission characteristic of the wavelength selection filter (3) by the half value width of the transmission characteristic is 4 or more and 25 or less. Even when the reflectance of a cavity side end face (1bb) of the semiconductor optical amplifier (1) is about 0.1%, a wavelength accuracy of ±1.5 GHz can be achieved by setting the finesse to 4 or more. In addition, a wavelength accuracy of about ±0.5 GHz can be achieved by setting the finesse to 8 or more. In order to suppress insertion loss, it is preferable to set the finesse of the FP etalon to 25 or less. This makes it possible to implement an external cavity wavelength tunable laser with high wavelength accuracy.
Owner:NEC CORP
Day and night camera, filter and optical system thereof
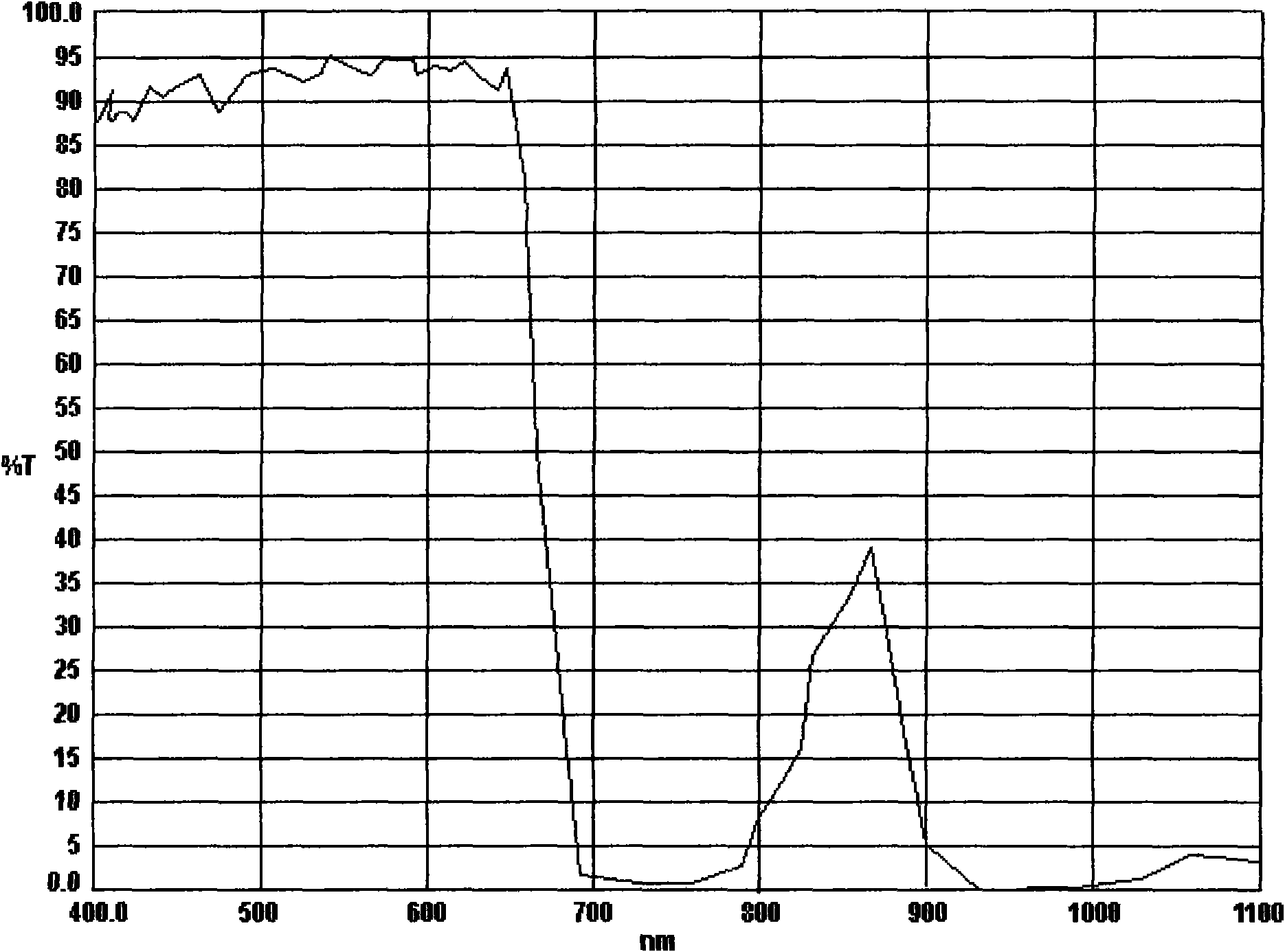
InactiveCN101610355AReduce light transmittanceAvoid damageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFinesseCamera lens
The invention discloses a day and night camera, a filter and an optical system thereof. The day and night camera comprises the optical system which comprises a lens, an image sensor and the filter arranged between the lens and the sensor; the optical system has color finesse D greater than 34.15 and infrared inductivity E greater than 1.45%, wherein, D=(Tkj*Tkl*delta C) / (Thj*Thl*delta CMAX), E=(Thj*Thl*Ths), the Tkj is transmittance of the lens for visible light, the Tkl is the transmittance of the filter for the visible light, the Thj is mean transmittance of the lens for infrared light between 800nm and 900nm, the Thl is the mean transmittance of the filter for the infrared light between 800nm and 900nm, the Ths is inductive capacity of the image sensor for the infrared light between 800nm and 900nm, the delta CMAX is a maximum difference of the mean inductive capacities of various RGB pixels in the image sensor for the infrared light between 800nm and 900nm, and the delta C is a maximum difference of the inductive capacities of two pixels in the delta CMAX for the visible light. The invention can achieve better technical effects of shooting by the day and night camera.
Owner:SHENZHEN ADVANCE RIVER SYST TECH CO LTD
Tunable laser with a fixed and stable wavelength grid especially useful for WDM in fiber optic communication systems
InactiveUS7046704B2Efficient modulationAccurate placementLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionFrequency stabilizationOptical frequencies
A wavelength tunable mode-locked laser system including a complex laser cavity comprising a broadband reflective mirror at one end and a wavelength chirped selective mirror at the other end. The system further includes a gain element and a low finesse Fabry-Perot etalon element inside the laser cavity. The gain element may be a semiconductor laser chip, with a broadband high reflection coating at one end and a partially reflecting coating at its other end. The gain element has a well-defined length, such that its longitudinal modes match a required optical frequency grid. The system also includes an active modulation element applied externally on said complex laser cavity to provide mode-locking of a specific cavity length among said defined predetermined cavity lengths, such that all possible optical frequencies emitted by the laser system are stabilized to the linear grid dictated by the Fabry-Perot longitudinal modes, that could be in accordance with the International Telecommunications Union Standards.
Owner:MRV COMM LTD 50
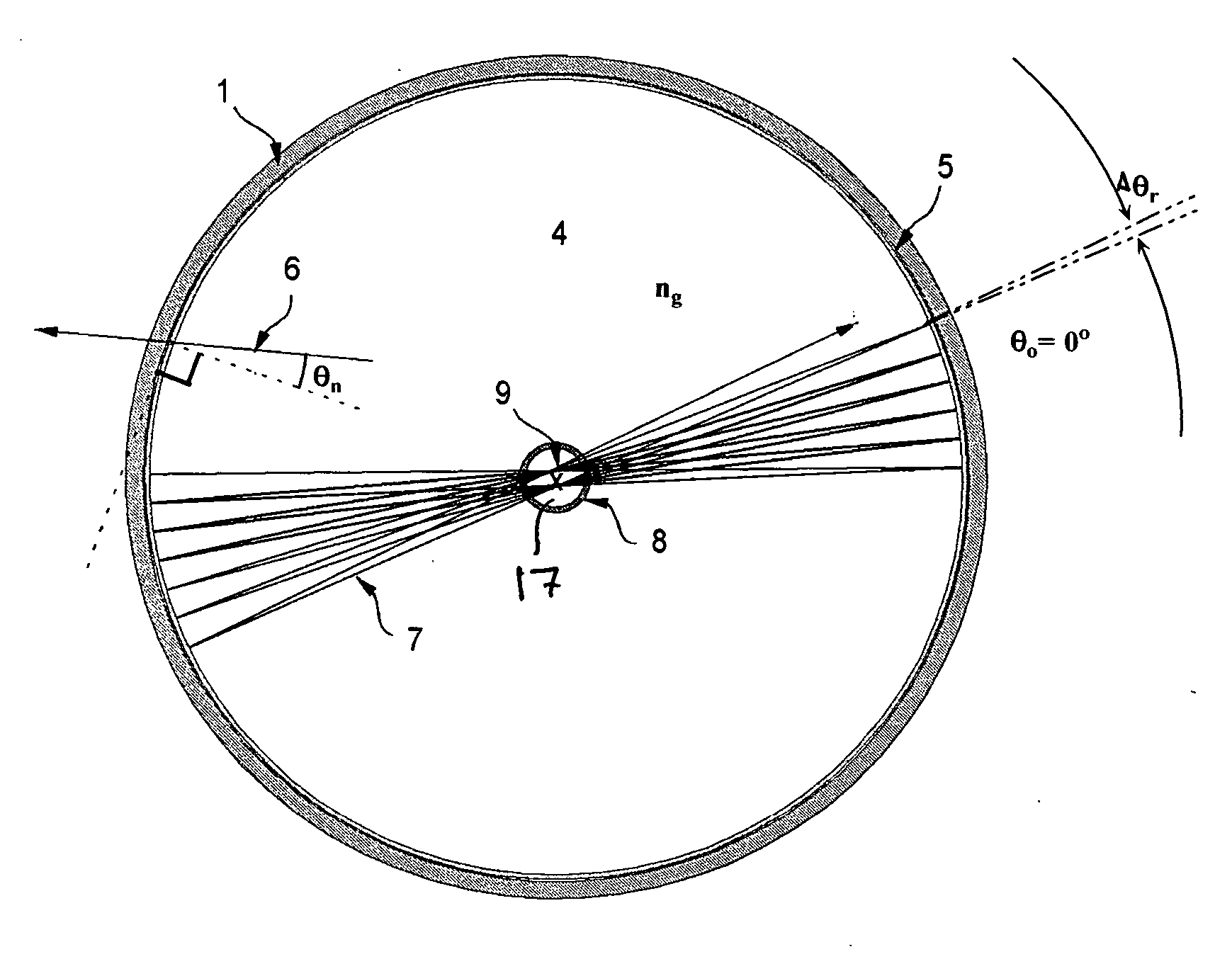
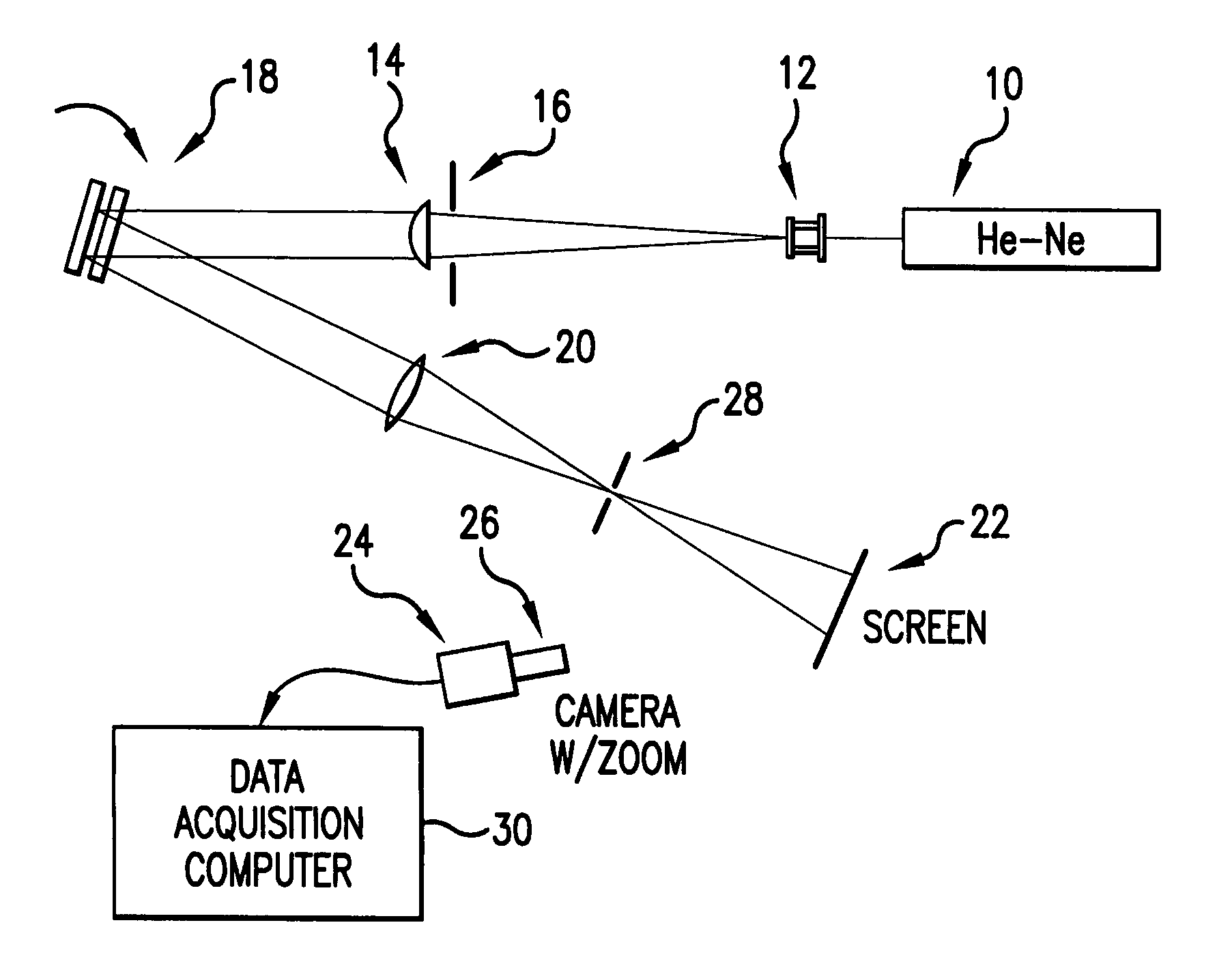
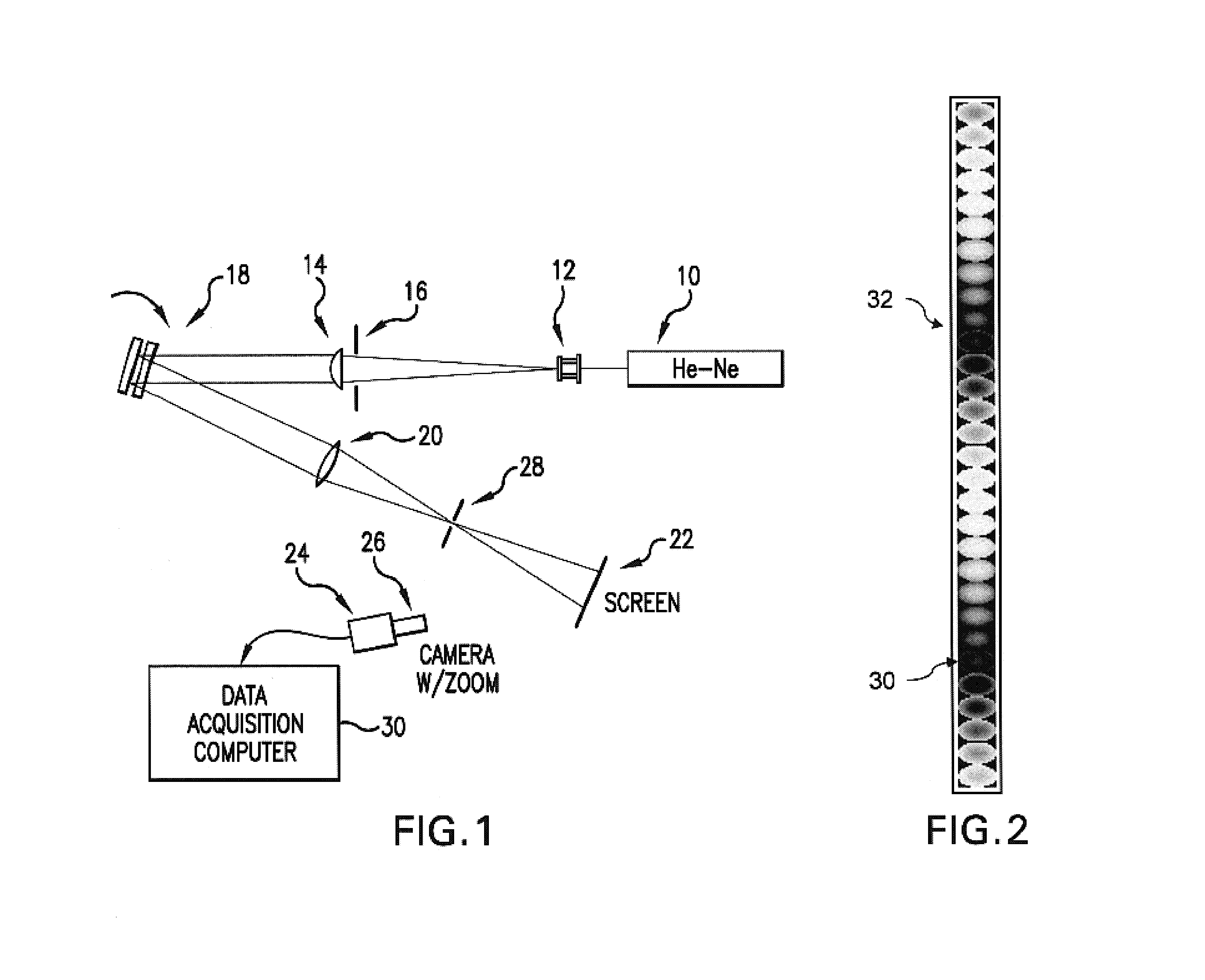
Etalon testing system and process
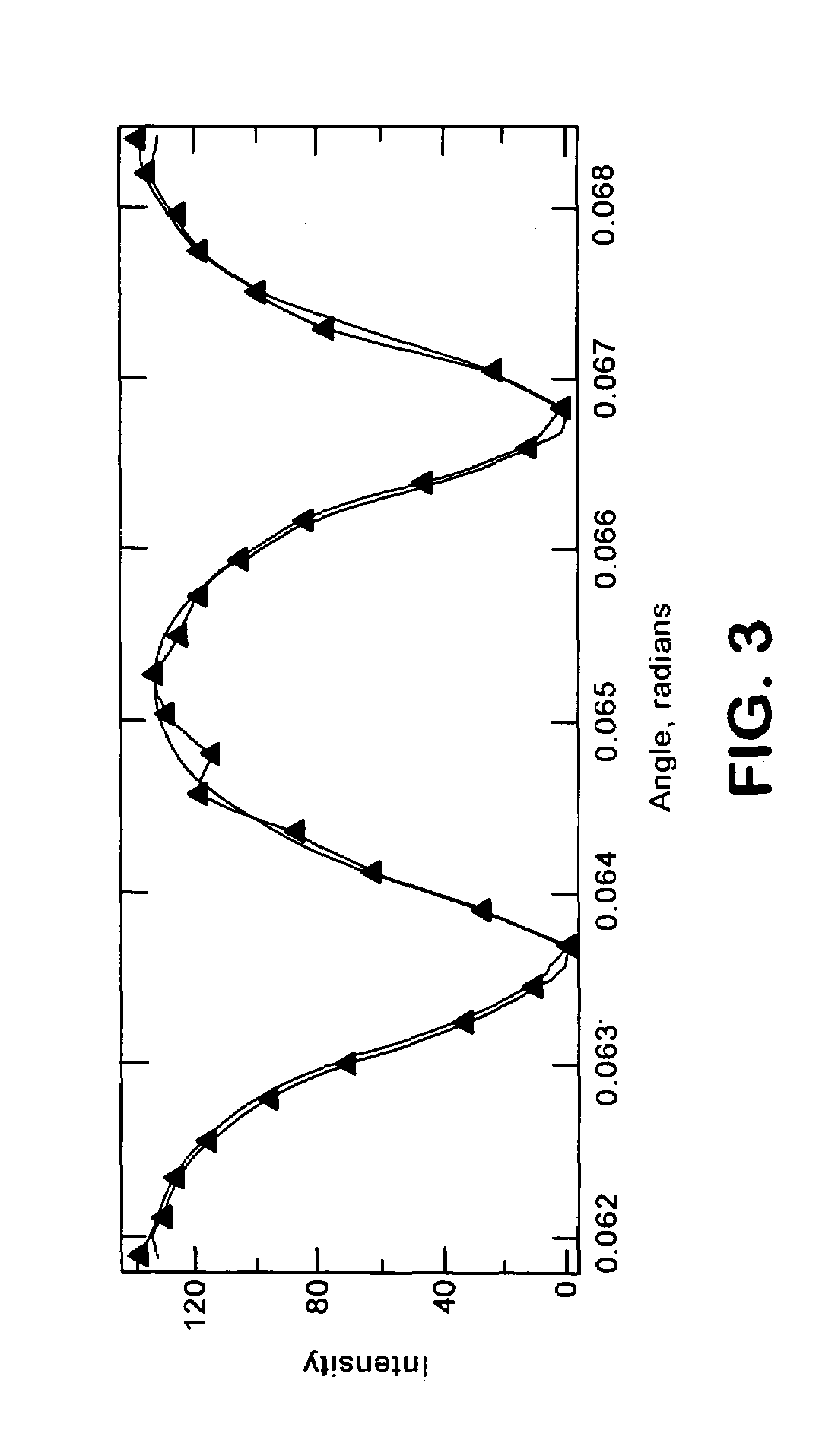
The present invention provides a relatively simple etalon testing system and process for measuring cavity error of etalons to high precision. It works equally well on solid and air-spaced designs. This invention should be a great aid in the manufacture of high performance etalons, separating out the geometric and reflectivity finesses. The present invention permits measurement of etalon spacings to an accuracy of better than λ / 1000 (i.e., about 63 picometers [6.3×10−11 m] when using a HeNe test laser). In a preferred process an etalon under examination is mounted on a rotational stage illuminated with a collimated beam from a HeNe laser. Reflections from the etalon are imaged on a screen to produce interference fringes which are monitored by a CCD camera. The etalon is then pivoted about an axis perpendicular to the laser beam and images of the interference patterns are recorded periodically to produce a plot of intensity vs. pivot angle over a pivot range sufficient to include at least one extinction cycle. (Extinction occurs when the etalon is positioned at such an angle that interference in the etalon causes almost complete extinction of the reflected beam). The interference pattern, as a function of pivot angle, are then analyzed to determine the etalon spacing.
Owner:CYMER INC
Multi-conjugate liquid crystal tunable filter
InactiveCN101137926AExcellent optical propertiesImprove operating characteristicsPolarisation spectroscopyNon-linear opticsFinesseWavelength filter
A hyper-spectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path with angularly distributed birefringent retarders and polarizers forming interference filters. The retarders can include tunable birefringent elements such as liquid crystals controlled in unison, fixed retarders and / or combined tunable and fixed birefringences. Distinctly different periodic transmission spectra are provided by different filter stages, each having multiple retarders, in particular with some stages having broad bandpass peaks at wide spectral spacing and other stages have very narrow closely spaced peaks. The respective spectra include at least one tunably selectable band at which the transmission spectra of the filter stages coincide, whereby the salutary narrow bandpass and wide spectral spacing ranges of different stages apply together, resulting in a high finesse wavelength filter suitable for spectral imaging.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
Rapid composite material image damage detection method based on infrared imaging
ActiveCN105548258AThe detection process is fastSingle detection area is largeMaterial flaws investigationSurface finishFinesse
The invention belongs to the technical field of infrared heat wave nondestructive detection, and concretely relates to a rapid composite material image damage detection method based on infrared imaging. Compared with the prior art, the rapid composite material image damage detection method based on infrared imaging, using hot air as an excitation source, has the advantages of large one-time detection area, fast detection speed, no need of treatment of the surface finesse, and suitableness for onsite detection.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG INST OF TECH PHYSICS
System for Providing Quantitative Process Control of Finesse Polishing
InactiveUS20090186556A1Prevent operator errorAccurate procedurePolishing machinesGrinding feed controlFinesseControl system
A system for providing quantitative process control of a finesse polishing based upon feedback to the operator as to whether he / she is meeting the one or more predetermined key control characteristics (KCCs). One or more sensors provide data to a controller, wherein the controller provides the operator feedback regarding his / her operational compliance with respect to the KCCs, and disables operation in the event of operator noncompliance, with the intention to promote proper operator procedure and prevent operator error when polishing a flawed painted surface.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Light-emitting device containing flattened anisotropic colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals and processes for manufacturing such devices
ActiveCN104302572AMaterial nanotechnologyElectroluminescent light sourcesSpectral emissionDisplay device
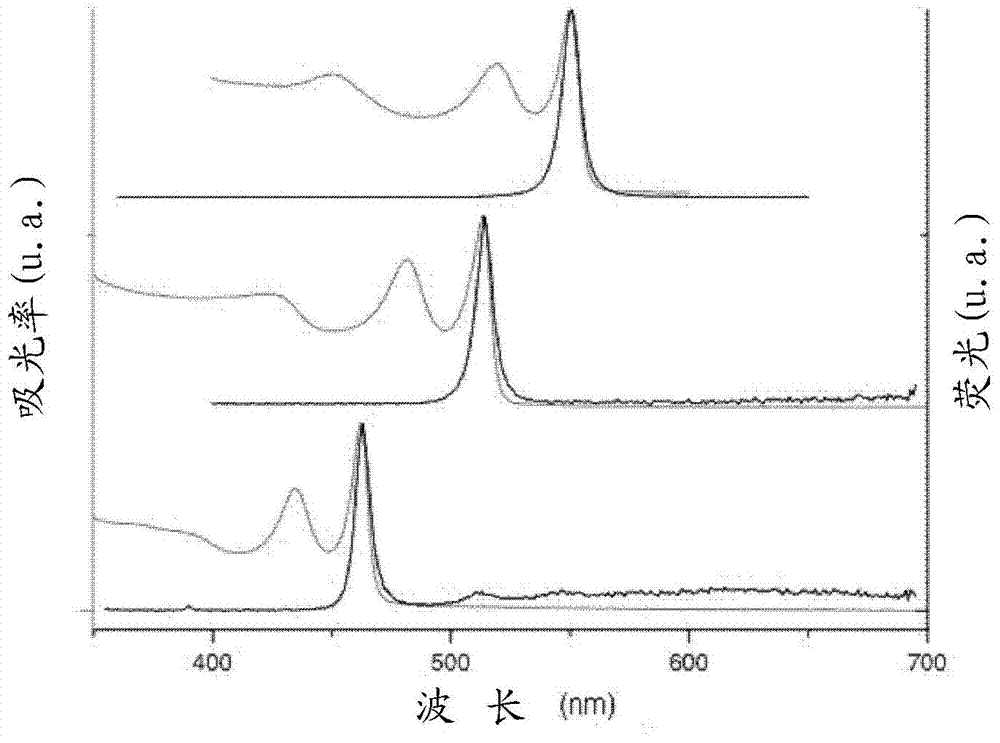
A device that emits light in response to an electrical or optical excitation, such as LEDs, displays, e-readers, device includes at least one anisotropic flat colloidal semiconductor nanocrystal whose smallest dimension, namely the thickness, is smaller than the other two by a factor of at least 1.5, the emitted light having an intensity and a polarization that vary according to the angle formed by the light emitting direction and the normal to the largest surface of the flat nanocrystal. The device allows to realize a light-emitting device exhibiting simultaneously a high emission spectral finesse and allows proper control of the wavelength, the directivity and / or polarization of the emitted light, and thus increases the brightness and color gamut of displays composed of such a device. Such devices are found for example in displays, televisions, mobile phones, tablets, or computers. The various embodiments of these devices are also presented.
Owner:NEXDOT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com