Patents
Literature
76 results about "Lasing threshold" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The lasing threshold is the lowest excitation level at which a laser's output is dominated by stimulated emission rather than by spontaneous emission. Below the threshold, the laser's output power rises slowly with increasing excitation. Above threshold, the slope of power vs. excitation is orders of magnitude greater. The linewidth of the laser's emission also becomes orders of magnitude smaller above the threshold than it is below. Above the threshold, the laser is said to be lasing. The term "lasing" is a back formation from "laser," which is an acronym, not an agent noun.
Wavelength tunable laser
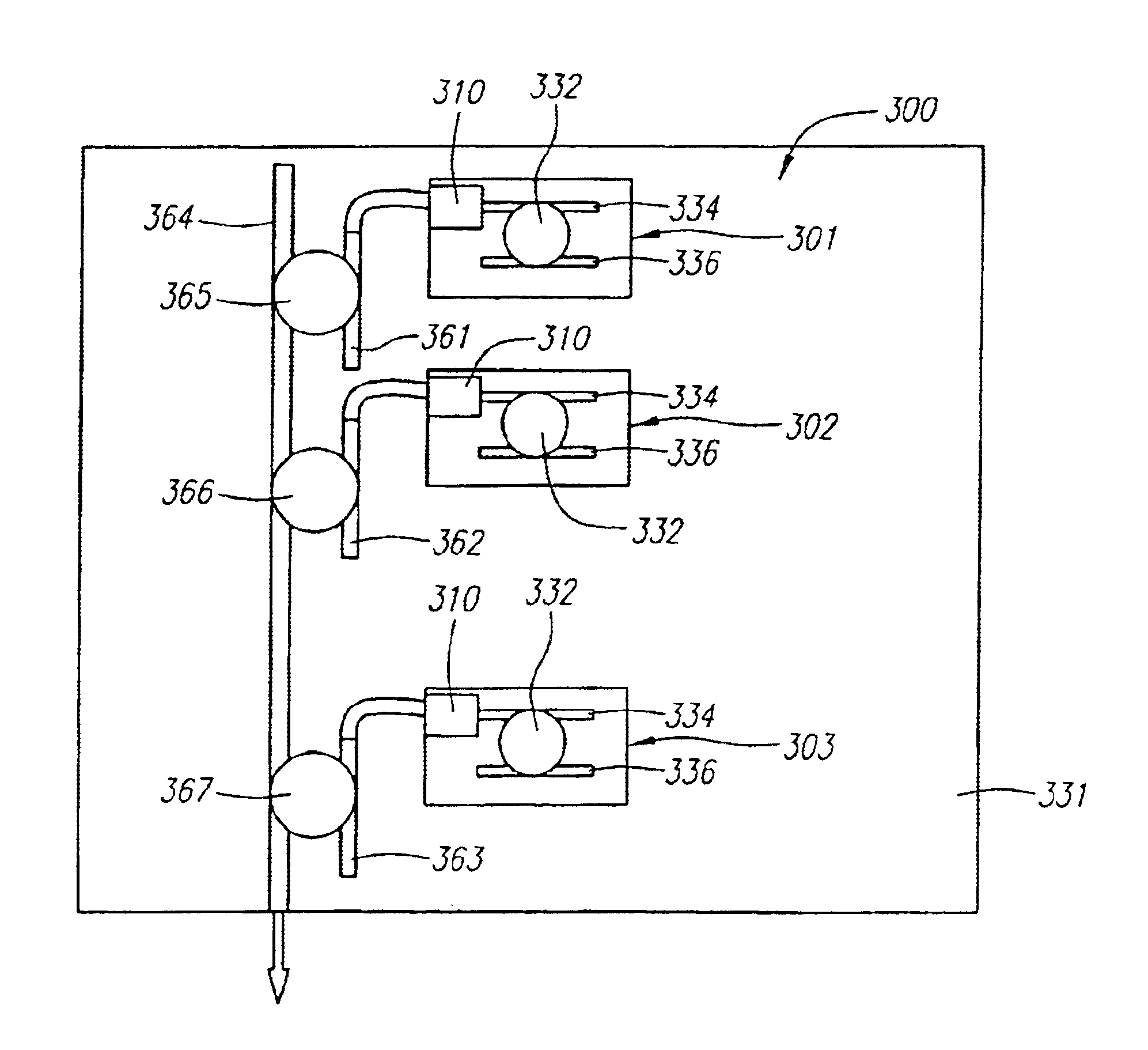
InactiveUS6891865B1Increase speedBroad band wavelength tuningLaser optical resonator constructionLaser using scattering effectsResonance wavelengthWaveguide
A wavelength tunable laser comprising a laser diode and a closed external cavity formed by one or more optical resonators either horizontally or vertically coupled to adjacent waveguides. The optical resonator primarily functions as a wavelength selector and may be in the form of disk, ring or other closed cavity geometries. The emission from one end of the laser diode is coupled into the first waveguide using optical lens or butt-joint method and transferred to the second waveguide through evanescent coupling between the waveguides and optical resonator. A mirror system or high reflection coating at the end of the second waveguide reflects the light backwards into the system resulting in a closed optical cavity. Lasing can be achieved when the optical gain overcomes the optical loss in this closed cavity for a certain resonance wavelength which is tunable by changing the resonance condition of the optical resonator through reversed biased voltage or current injection. Multiple optical resonators may be used to reduce the lasing threshold and provide higher power output. With monolithic integration, more optical devices can be integrated with the tunable laser into the same substrate to produce optical devices that are capable of more complex functions, such as tunable transmitters or waveguide buses.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC +1
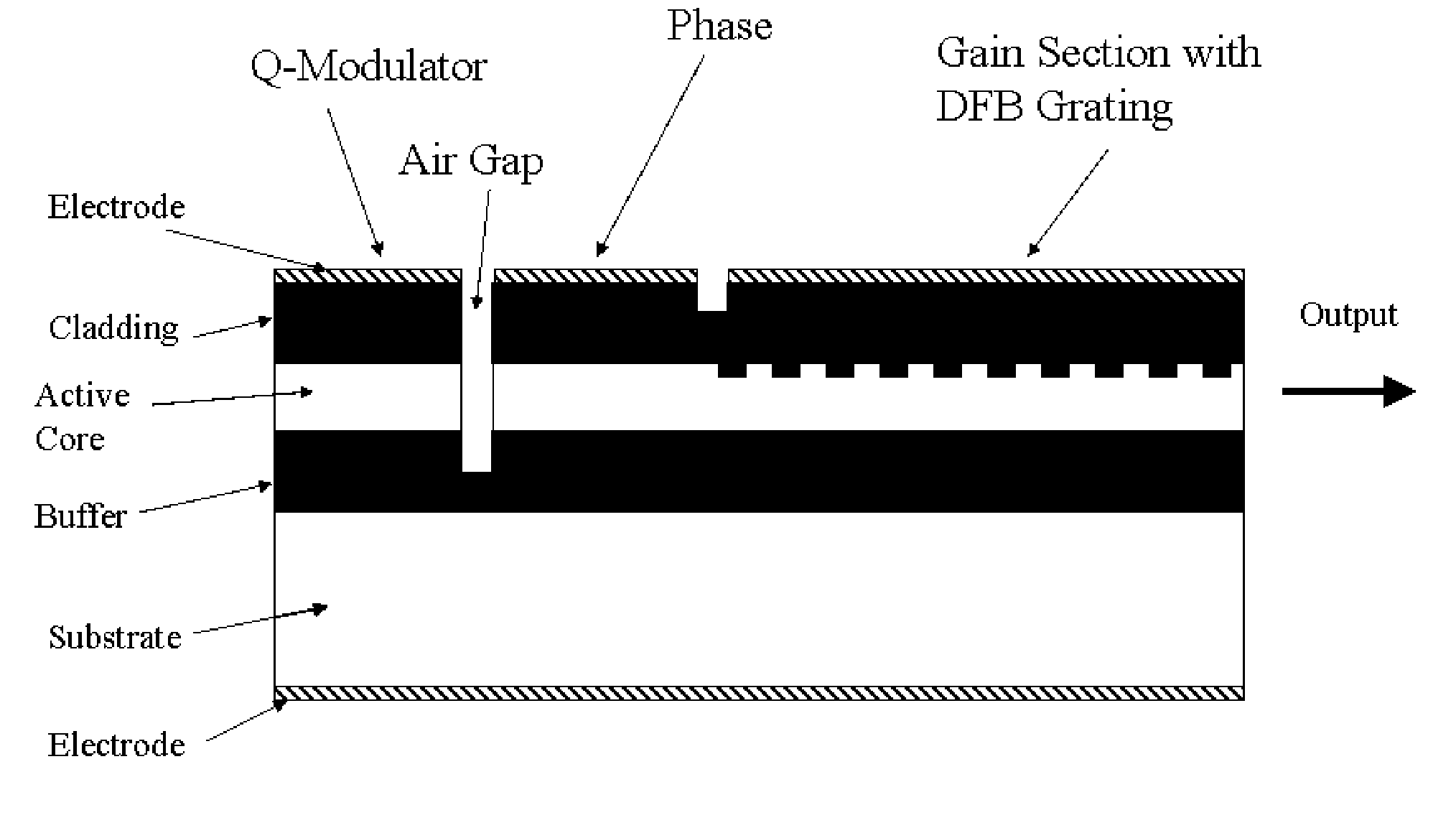
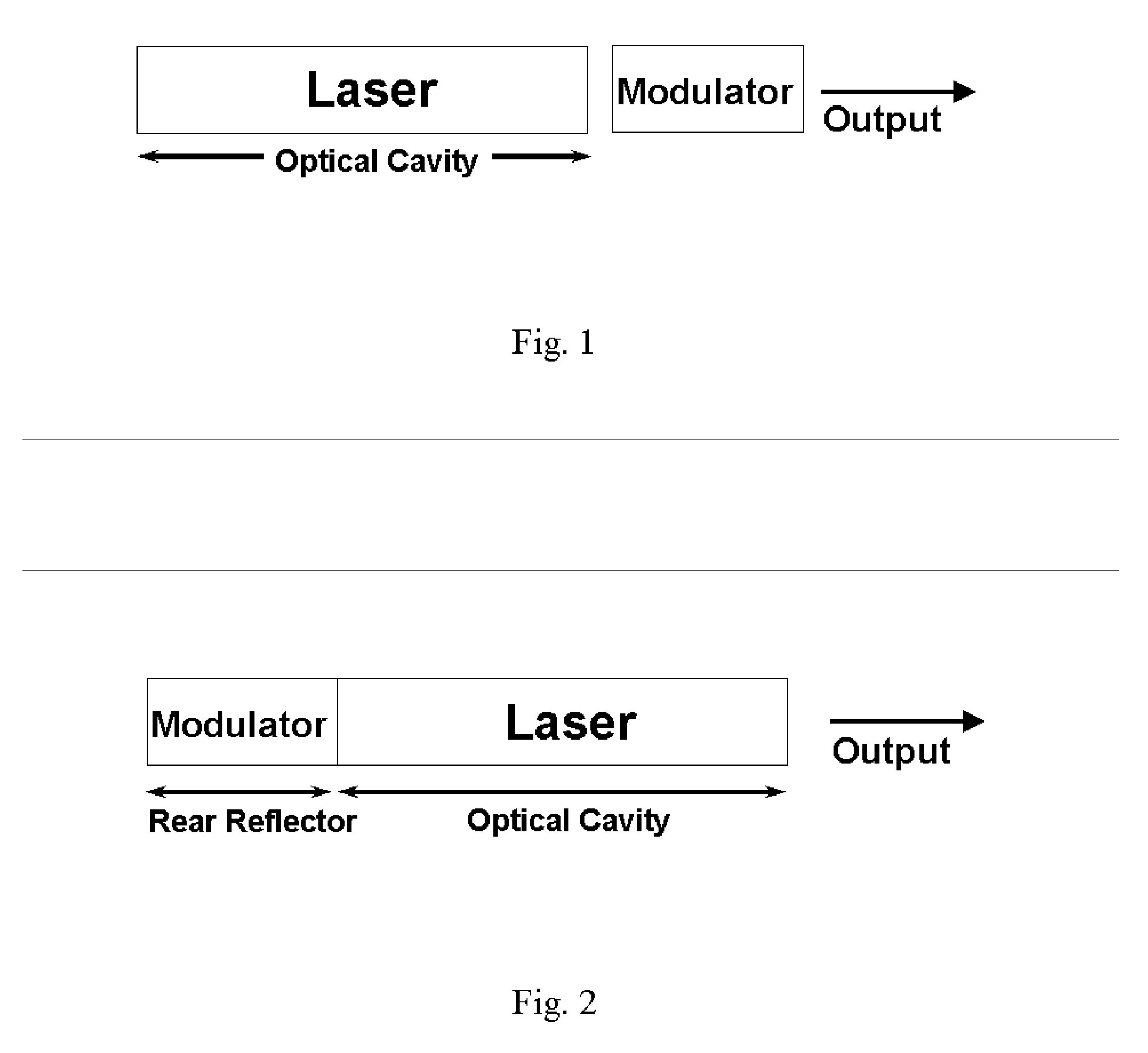
Q-modulated semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20060088066A1Effective refractive indexLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionElectro-absorption modulatorDistributed Bragg reflector
A Q-modulated semiconductor laser comprises an optical gain section and an electro-absorptive modulator section, separated by a vertically etched air gap acting as a partially reflecting mirror. The modulator section is placed inside an anti-resonant Fabry-Perot cavity and acts as the rear reflector of the laser. The change of the absorption coefficient in the modulator section results in a change in the Q-factor of the laser, and consequently the lasing threshold and output power. Different embodiments are disclosed, which involve a distributed feedback (DFB) laser, a Fabry-Perot laser, a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) laser, or a wavelength switchable multi-cavity laser. The integrated Q-modulated laser has advantages of high speed, high extinction ratio, low wavelength chirp and low cost.
Owner:LIGHTIP TECH
Wavelength tunable laser
InactiveUS20050025199A1Increase speedMechanically simple, scaleable and reliableLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionResonance wavelengthWaveguide
A wavelength tunable laser comprising a laser diode and a closed external cavity formed by one or more optical resonators either horizontally or vertically coupled to adjacent waveguides. The optical resonator primarily functions as a wavelength selector and may be in the form of disk, ring or other closed cavity geometries. The emission from one end of the laser diode is coupled into the first waveguide using optical lens or butt-joint method and transferred to the second waveguide through evanescent coupling between the waveguides and optical resonator. A mirror system or high reflection coating at the end of the second waveguide reflects the light backwards into the system resulting in a closed optical cavity. Lasing can be achieved when the optical gain overcomes the optical loss in this closed cavity for a certain resonance wavelength which is tunable by changing the resonance condition of the optical resonator through reversed biased voltage or current injection. Multiple optical resonators may be used to reduce the lasing threshold and provide higher power output. With monolithic integration, more optical devices can be integrated with the tunable laser into the same substrate to produce optical devices that are capable of more complex functions, such as tunable transmitters or waveguide buses.
Owner:PETRIE DATA CO +2
Discrete Spectrum Broadband Optical Source
ActiveUS20110292399A1Increase output peak powerHigh detection sensitivityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionSpectral emissionFrequency spectrum
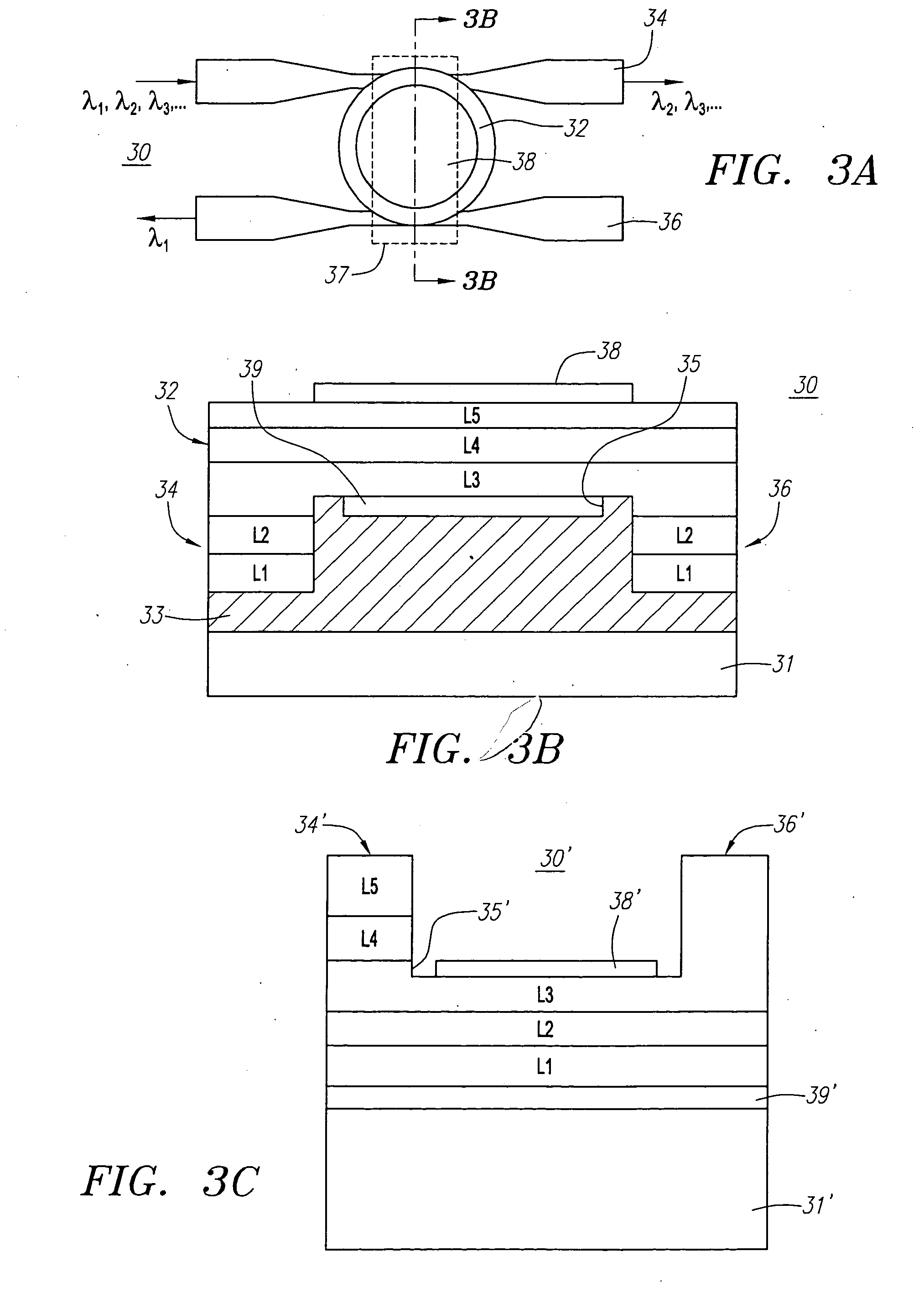
A new broadband source having a discrete set of spectral emission lines having high peak power in each line is provided by placing a gain medium in a reflective cavity comprising reflective front and back surfaces. A cavity feedback factor less than unity is achieved by providing reflectivity of one surface substantially lower than the reflectivity of the other surface such that spontaneous emission in the gain medium is linearly amplified just below the lasing threshold. In an alternative arrangement, a movable external back surface placed at a prescribed distance from the gain medium provides a means to achieve a free spectral range and finesse of the emission lines to match a pitch of a detector array in a SD-OCT system. By simultaneously providing high power to each detector element of the array, sensitivity and imaging speed of SD-OCT system are significantly improved.
Owner:GDAC PHOTONICS INC
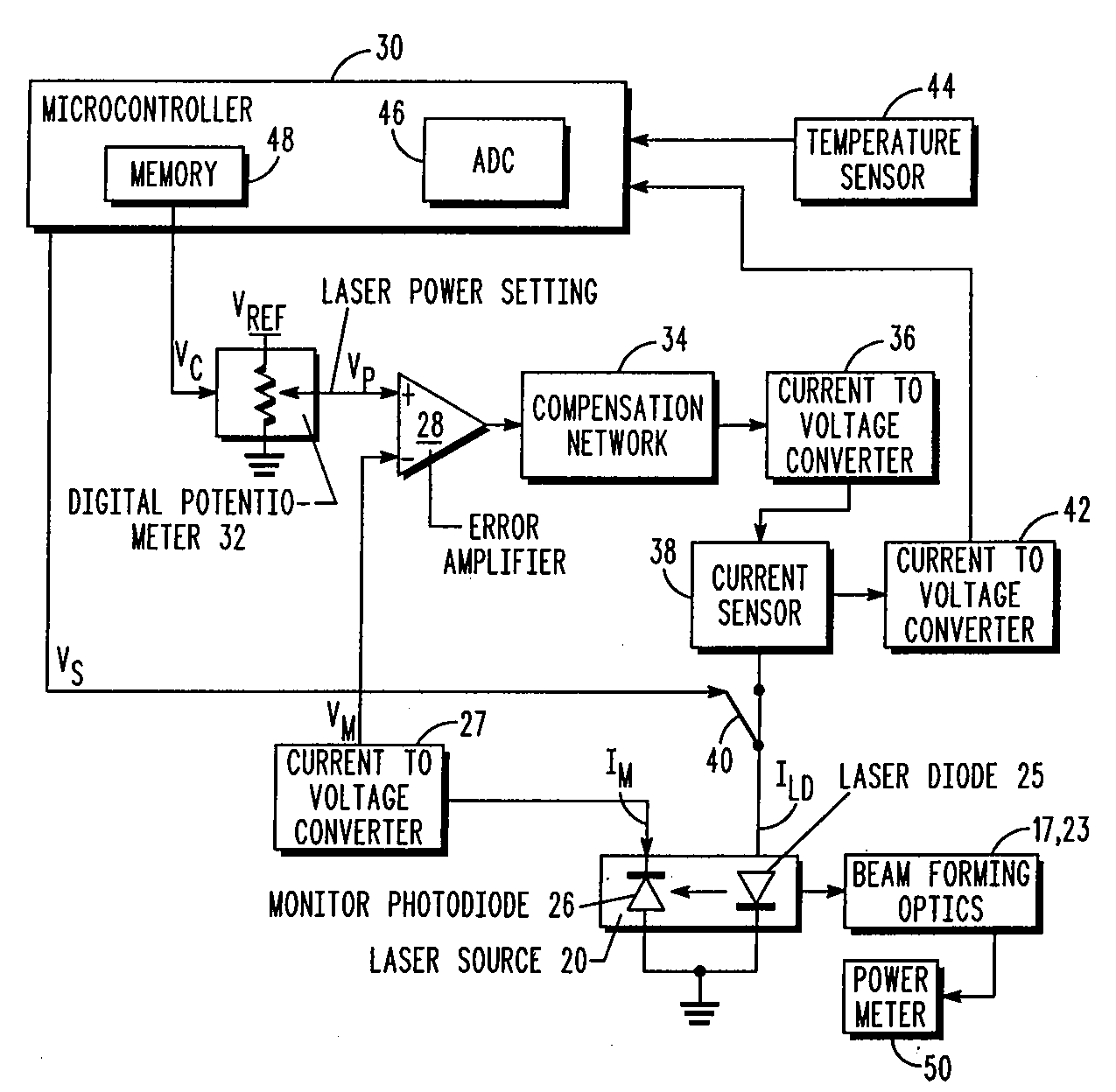
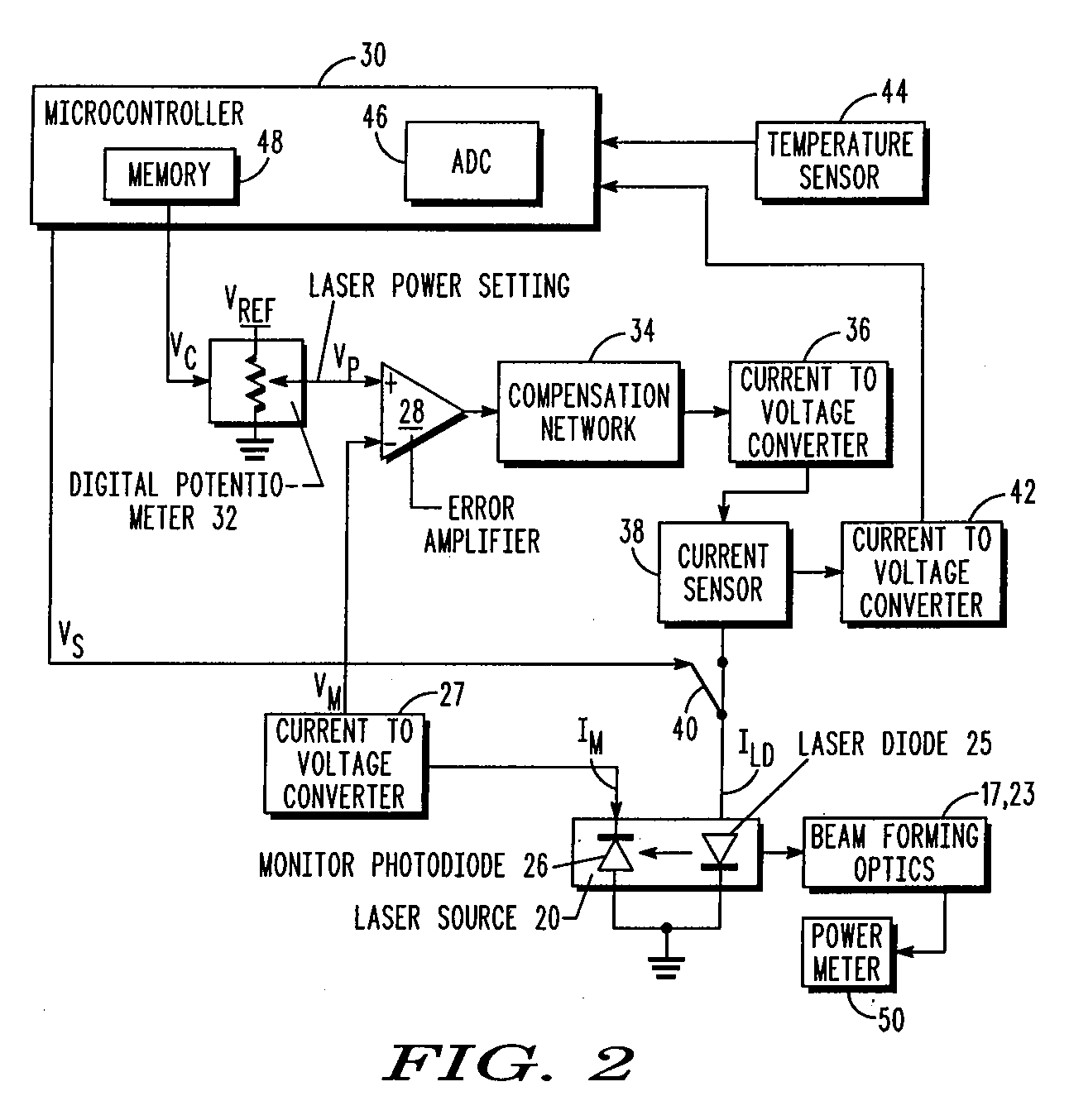
Method and apparatus for controlling and monitoring laser power in barcode readers
A method of monitoring the output power of a laser diode in a barcode reader. The method includes sampling a threshold monitoring-current that is related the driving-current passing through the laser diode during a first time period when this current is at the lasing threshold of the laser diode. The method includes generating a threshold-compensated monitoring-current by subtracting the threshold monitoring-current from the above-threshold monitoring-current. The method includes monitoring the output power of the laser diode in the barcode reader at least partially based on the threshold-compensated monitoring-current.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
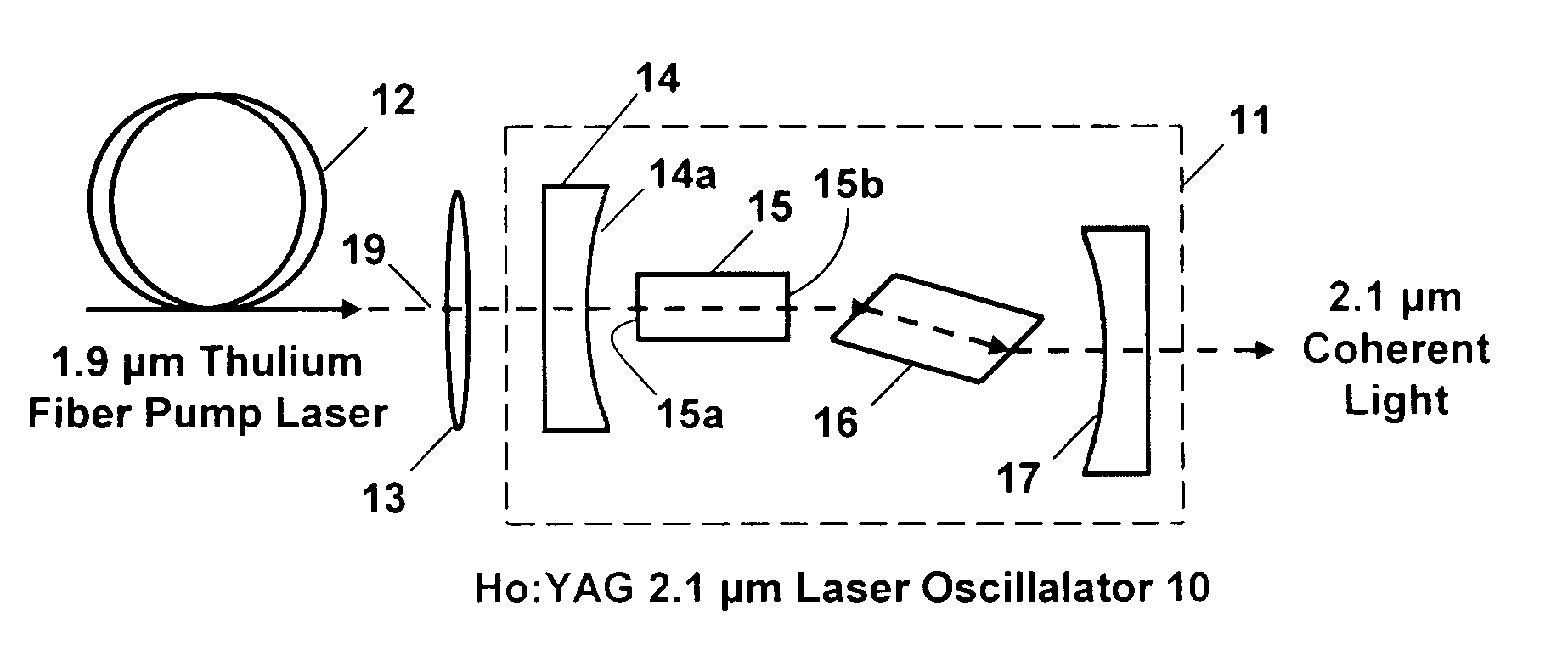
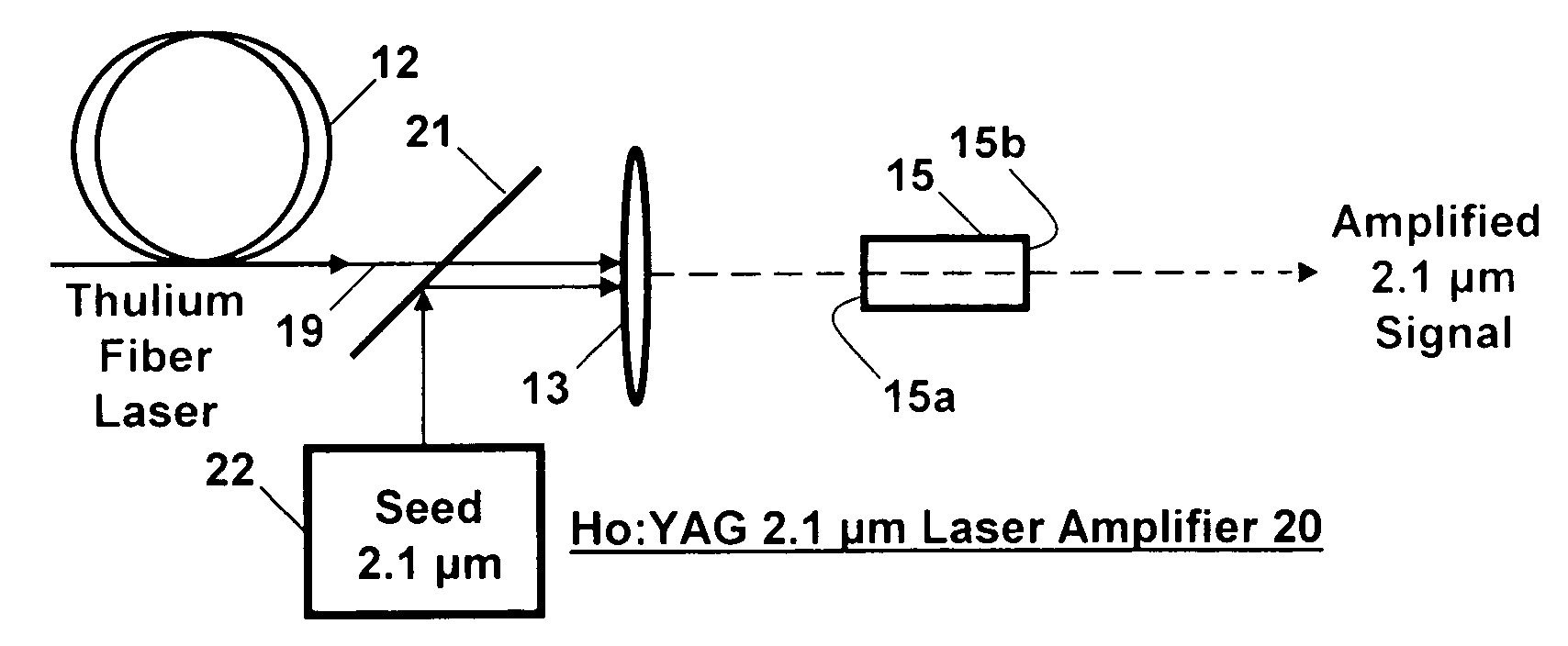
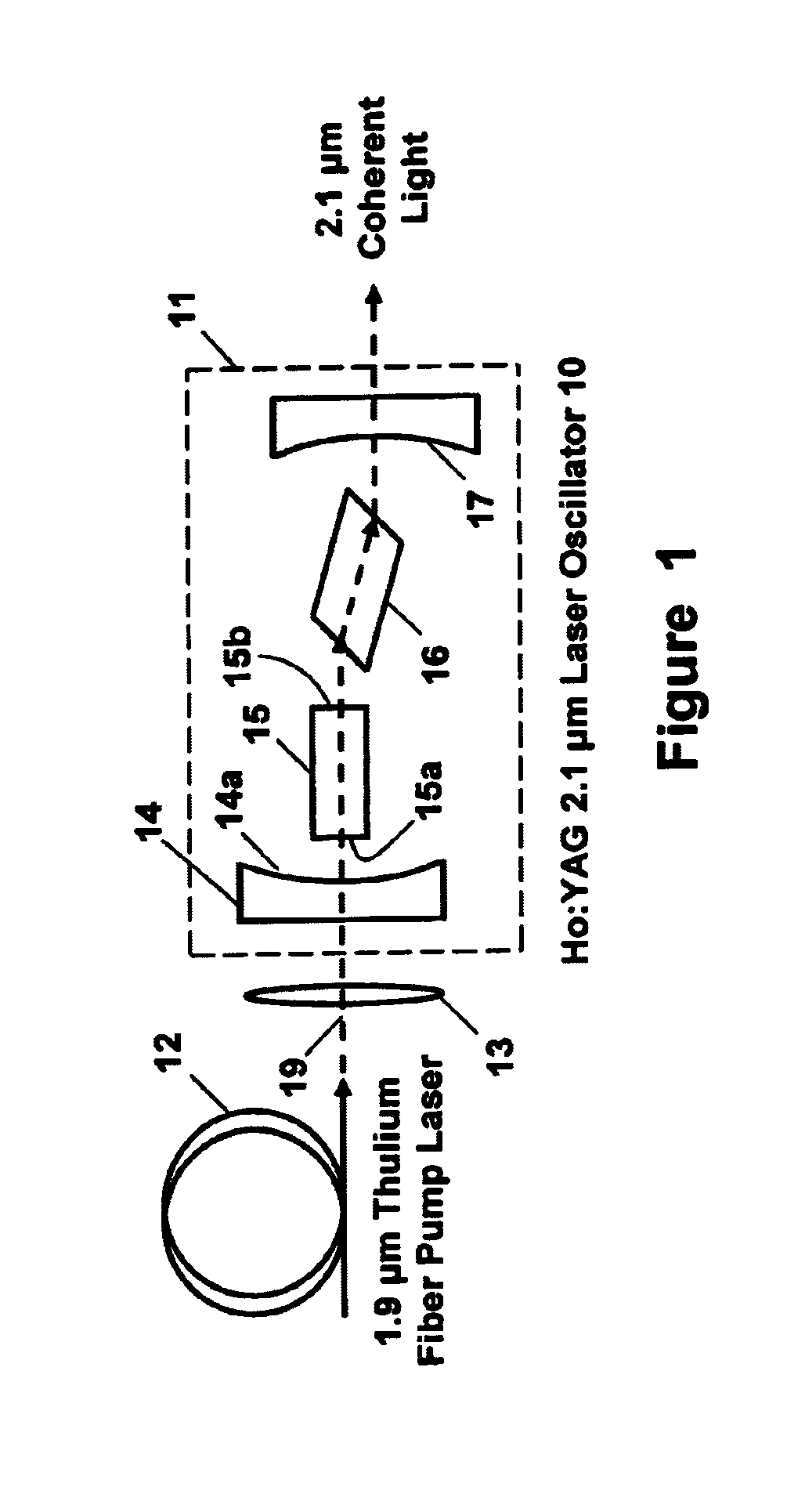
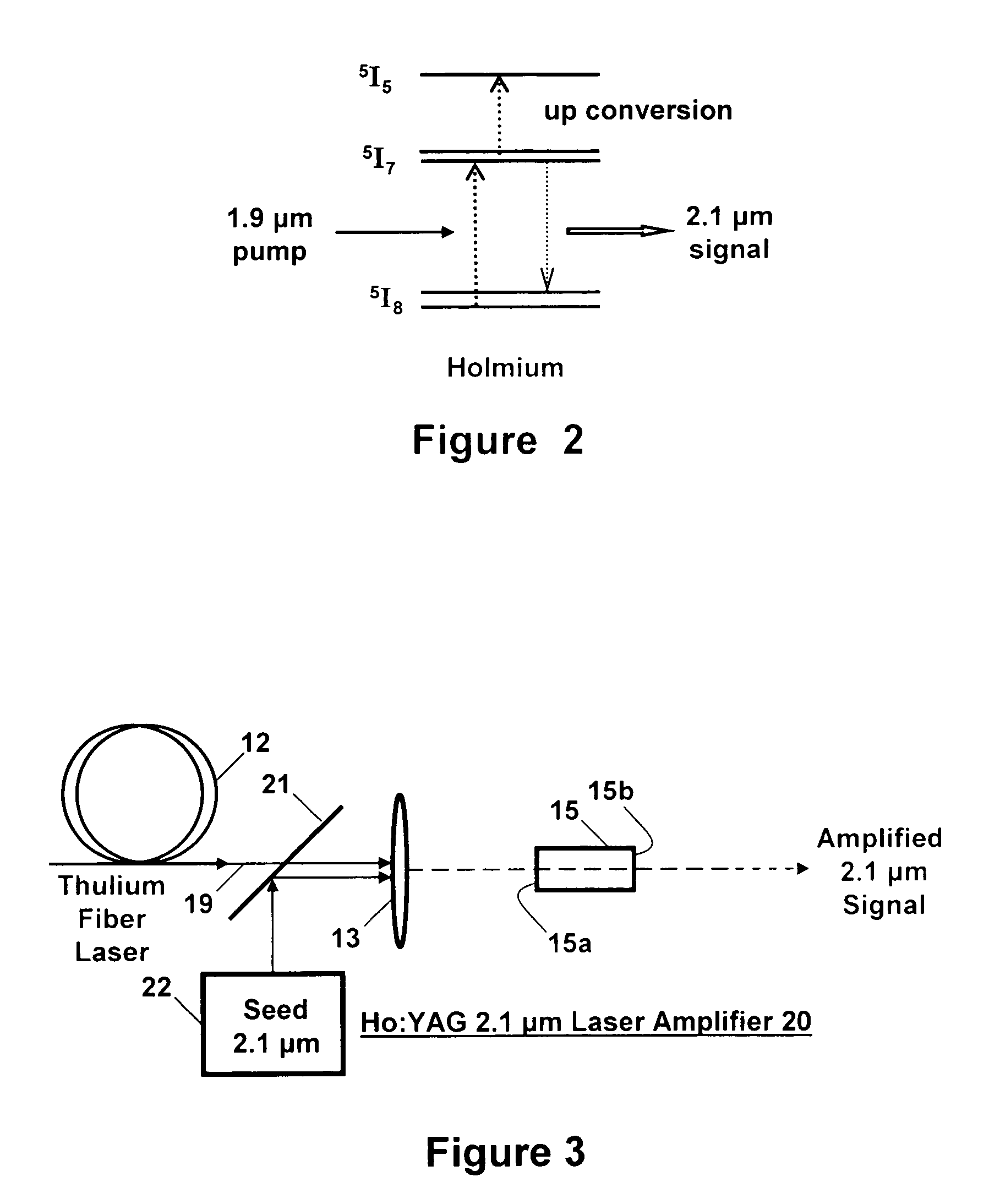
Holmium doped 2.1 micron crystal laser
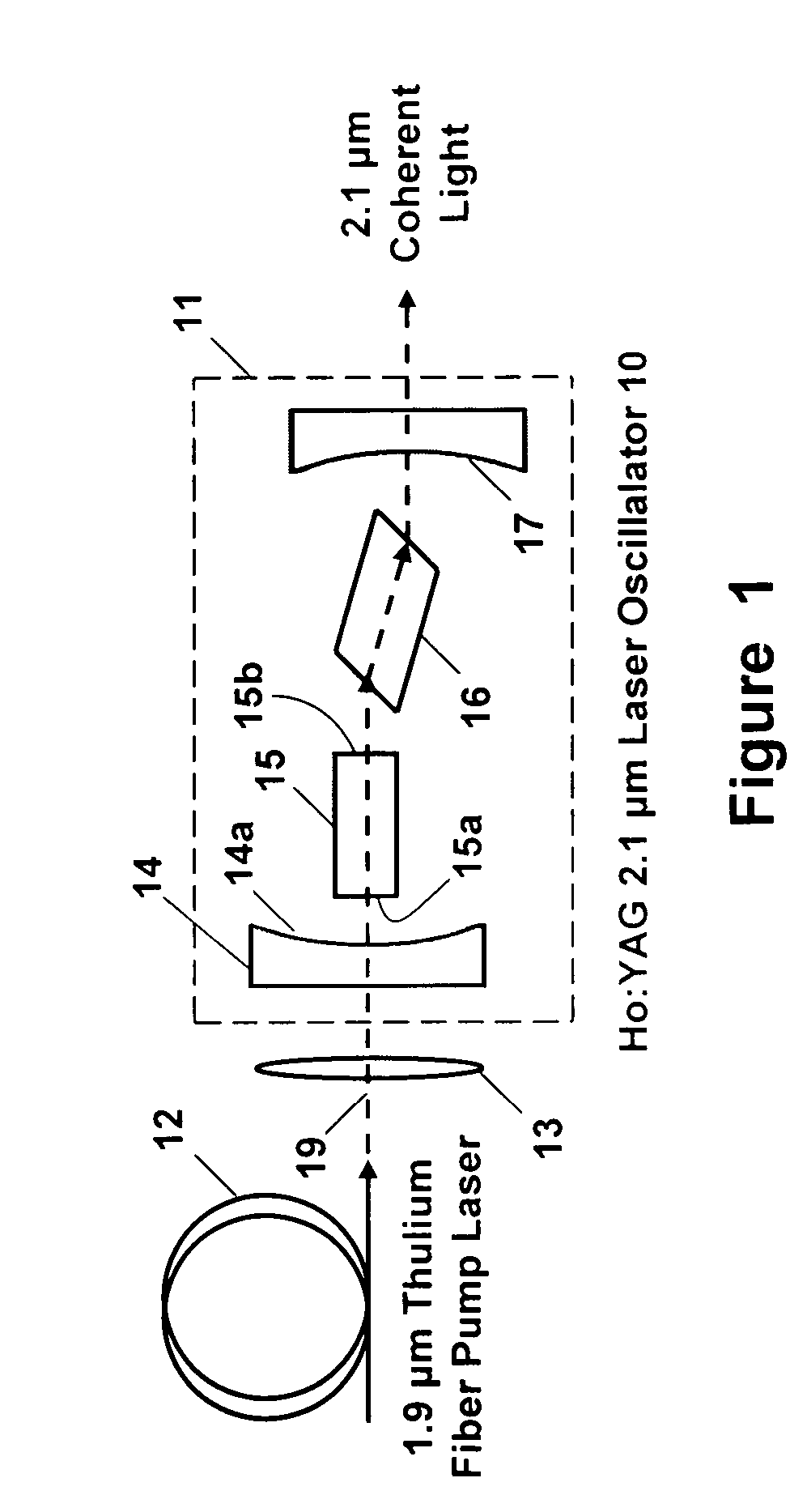
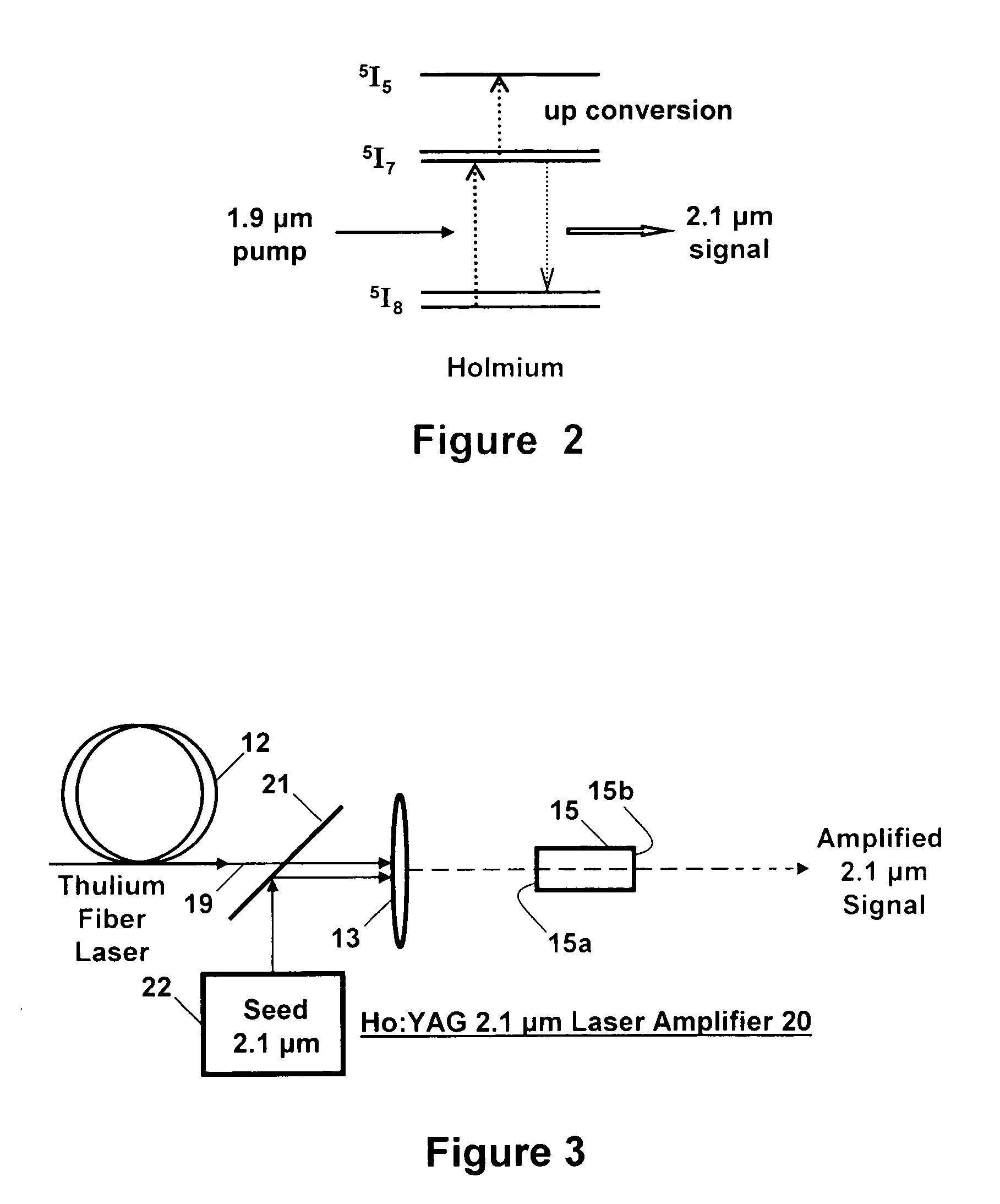
ActiveUS20060146901A1Less-detrimental heatLess conversionActive medium materialOptoelectronicsUp conversion
A Ho:YAG crystal laser is disclosed which is doped with less than 2% holmium to reduce the lasing threshold and up-conversion, thereby increasing the operating efficiency of the laser. The laser does not need sensitizer ions so energy mismatches introduced by the sensitizer ions ale eliminated to the thereby increase the efficiency of the laser while minimizing detrimental thermal loading in the laser caused by up-conversion loss processes. The Ho:YAG crystal laser is directly pumped by a Thulium fiber laser at 1.9 μm at the holmium 5I7 to 5I8 transition to produce an output at 2.1 μm yielding a very low quantum defect. The laser is embodied as a thulium fiber laser pumped oscillator or an amplifier.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Thin-film large-area coherent light source, filter and amplifier apparatus and method
InactiveUS7242702B2Increase productionSpace utilizationOptical beam sourcesExcitation process/apparatusAudio power amplifierLight beam
Lasing at the edge of the reflection band or at a defect state within the reflection band of a thin one-dimensional feedback structure is used to create a large-area, thin-film laser source with transverse dimensions that can be much greater than the film thickness. Angular confinement of radiation propagating perpendicular to the layers leads to a spreading of the beam inside the medium which is much greater than the diffraction divergence. This enhances the spatial extent of correlation at the output surface of the thin film. When a pump source induces gain at the lasing threshold in a wide region, a spatially coherent monochromatic light beam is emitted perpendicular to the film surface from the entire gain region. Alternate embodiments of the present invention include a passive spatial filter and an active amplifier.
Owner:CHIRAL PHOTONICS
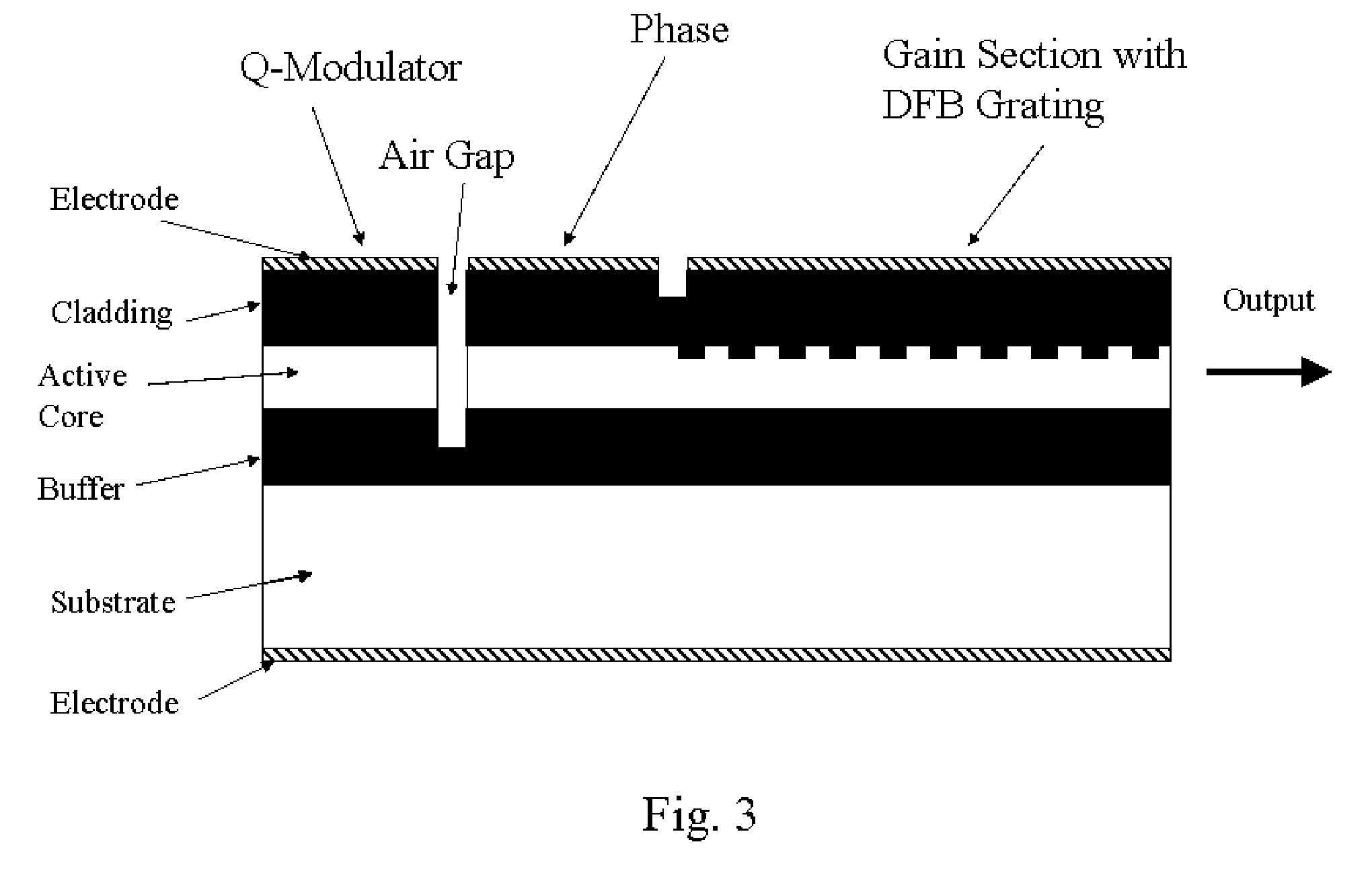
Q-modulated semiconductor laser with electro-absorptive grating structures
A Q-modulated semiconductor laser comprises a λ / 4-phase-shifted distributed-feedback grating. Two isolated electrodes are deposited on top of the grating, and one electrode is deposited on the back side of the laser substrate as a common ground. The first top-side electrode covers a portion of the grating including the phase-shift region, and provides an optical gain for the laser when a constant current is injected. The second top-side electrode covers the remaining portion of the grating away from the phase-shift region, which acts as a Q-modulator of the laser. An electrical signal is applied on the second electrode to change the absorption coefficient of the waveguide in the modulator section, resulting in a change in the Q-factor of the laser, and consequently the lasing threshold and output power. The integrated Q-modulated laser has advantages of high speed, high extinction ratio, low wavelength chirp and low cost.
Owner:LIGHTIP TECH
Semiconductor laser device and circuit for and method of driving same
ActiveUS20100260220A1Sufficient powerEasy to controlLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionData signalEngineering
A directly driven laser includes multiple contacts, with at least one of the contacts for injecting current into the laser such that the laser reaches at least a lasing threshold and at least one of the contacts for providing a data signal to the laser. In some embodiments a differential data signal is effectively provided to a front and a rear section of the laser, while lasing threshold current is provided to a central portion of the laser.
Owner:T&S COMM
Method and device for generating a laser beam, a laser treatment device and a laser detection device
InactiveUS20100069897A1Increase flexibilityTimeDiagnosticsControlling energy of instrumentOptoelectronicsLaser detection
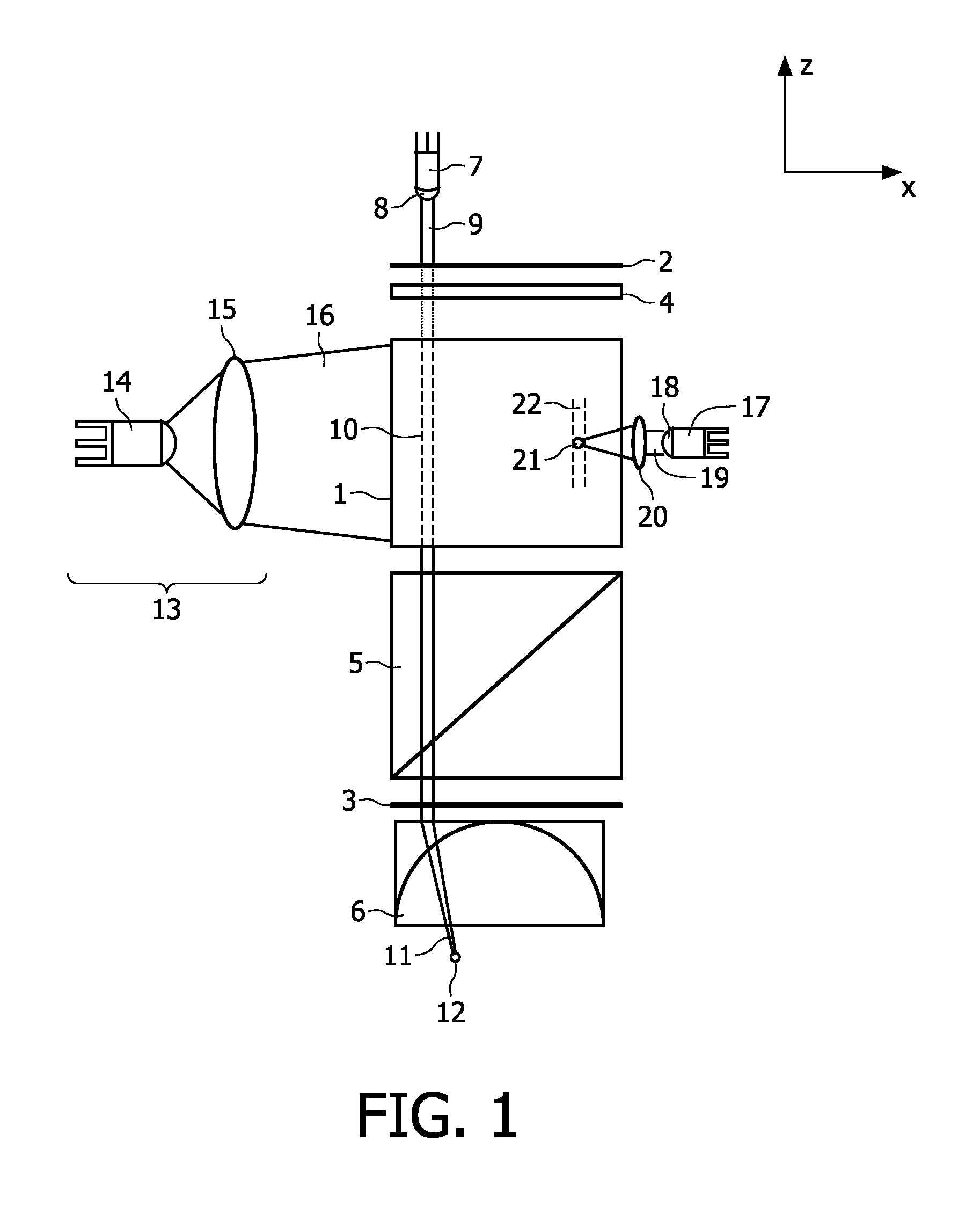
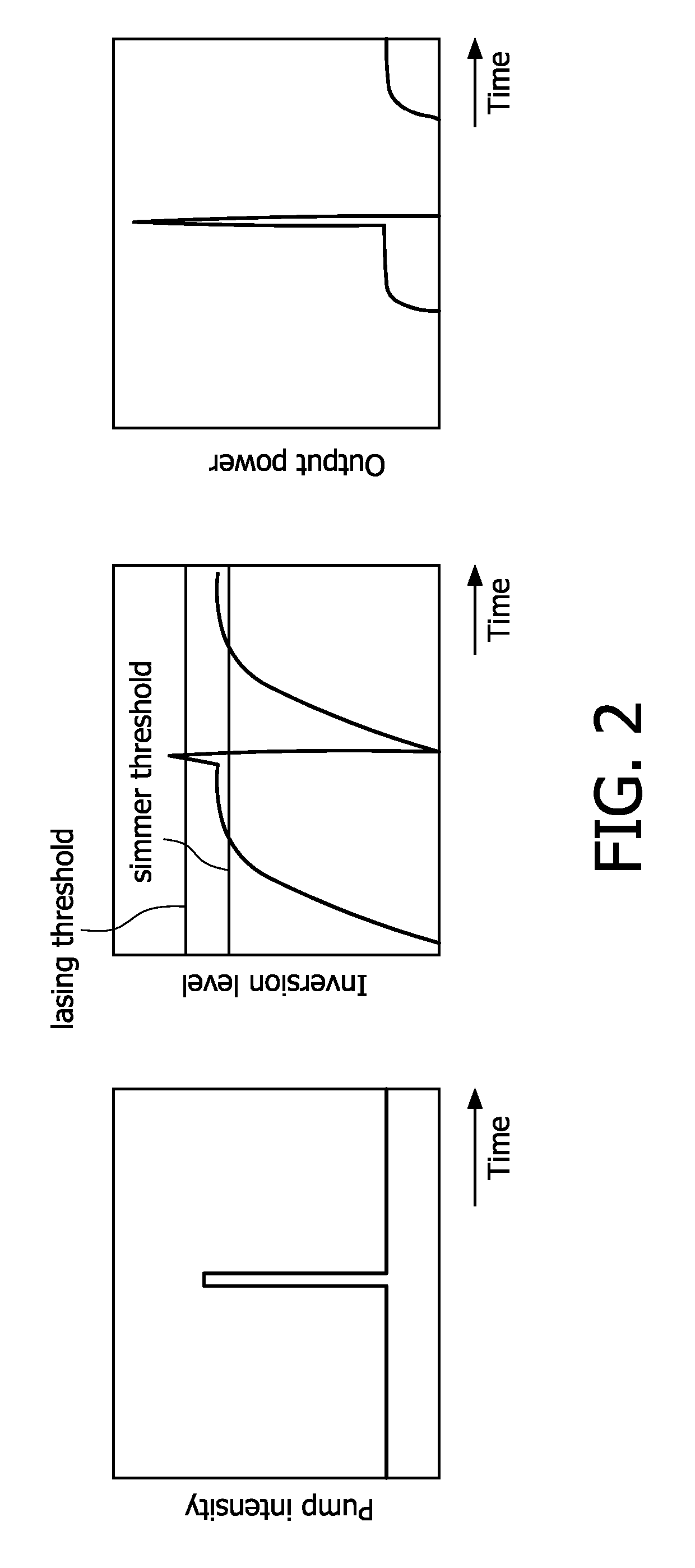
The invention relates to a laser device, comprising a laser material (1) brought into a simmer mode. A controllable source (7, 17) of additional energy (16, 20) supplies energy to the laser material (1), such that in only a desired part of the laser material (1) a lasing threshold is exceeded, and a laser beam (10) is emitted from only a desired part of the laser surface. This device makes possible to provide a laser beam in just the desired part of the laser, which allows a flexible and localized output. The invention further relates to a hair-removing device comprising a laser device according to the invention and further comprising an optical system (6) for focusing the laser beam pulses on a focal spot (12) and for positioning the focal spot in a target position, wherein the optical system (6) comprises a movable lens or a plurality of individually addressable lenses.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
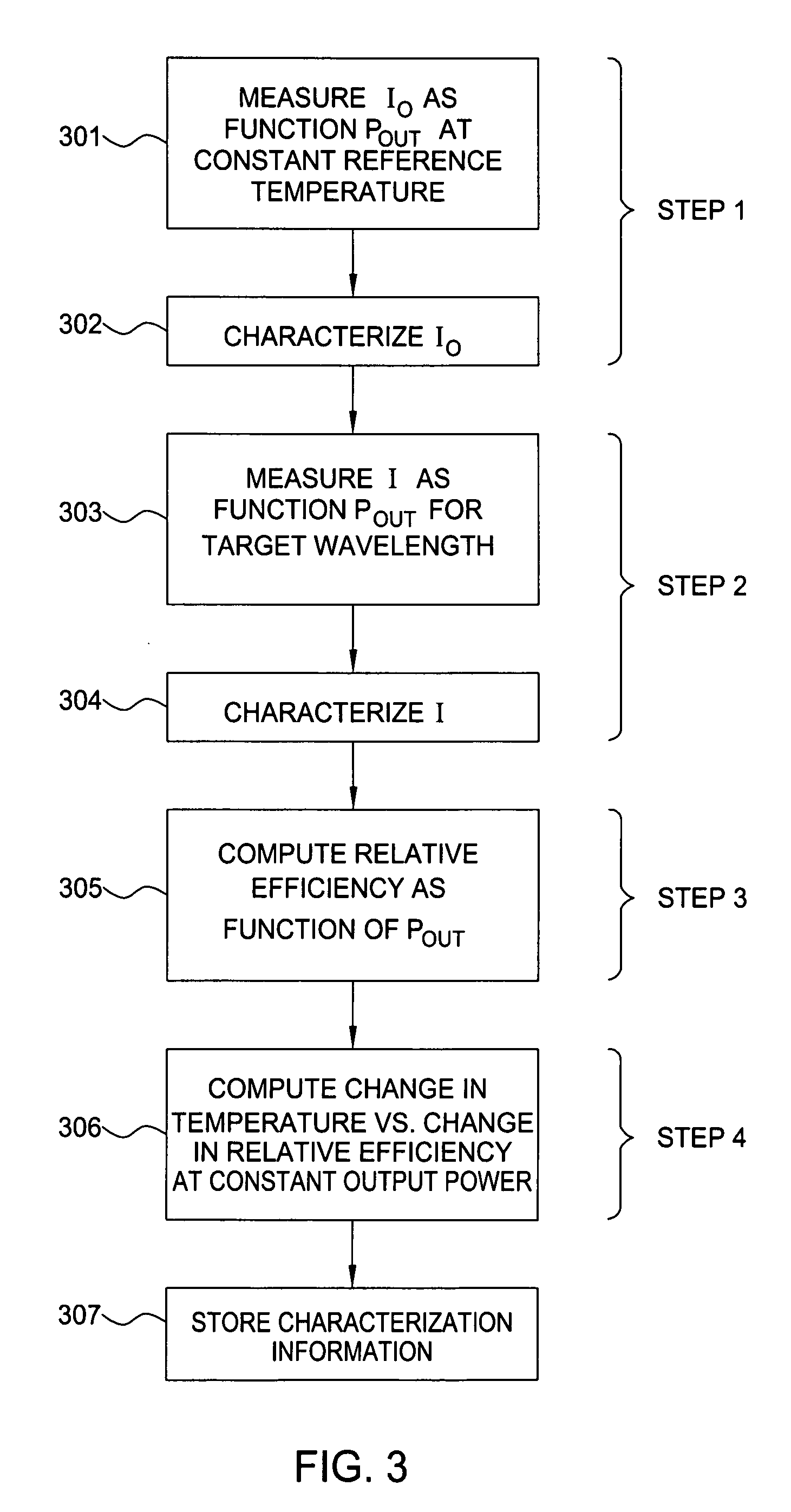
Laser wavelength control arrangement and method
InactiveUS20060182157A1Practical and inexpensive and accurateLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSingle mode laserLength wave
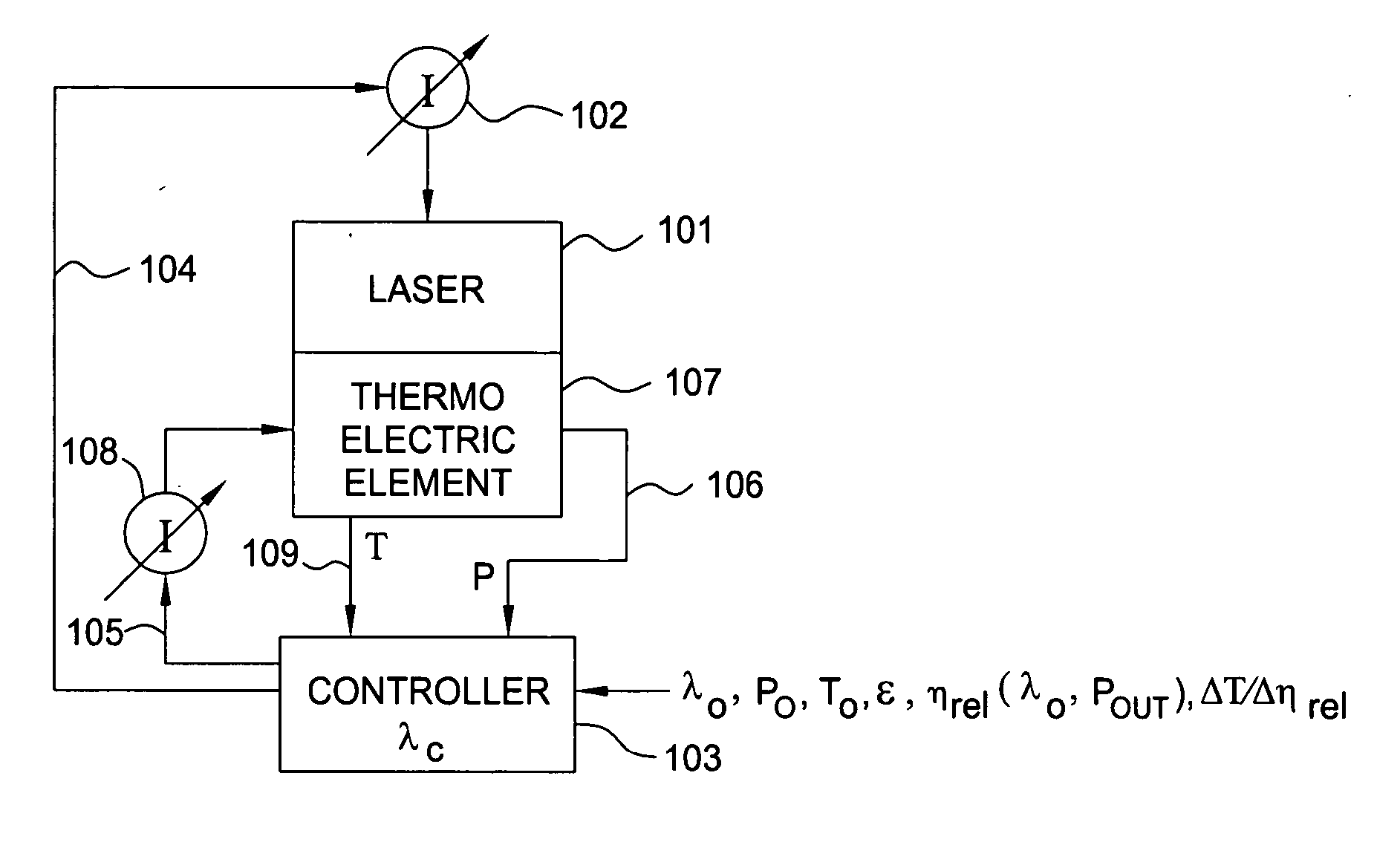
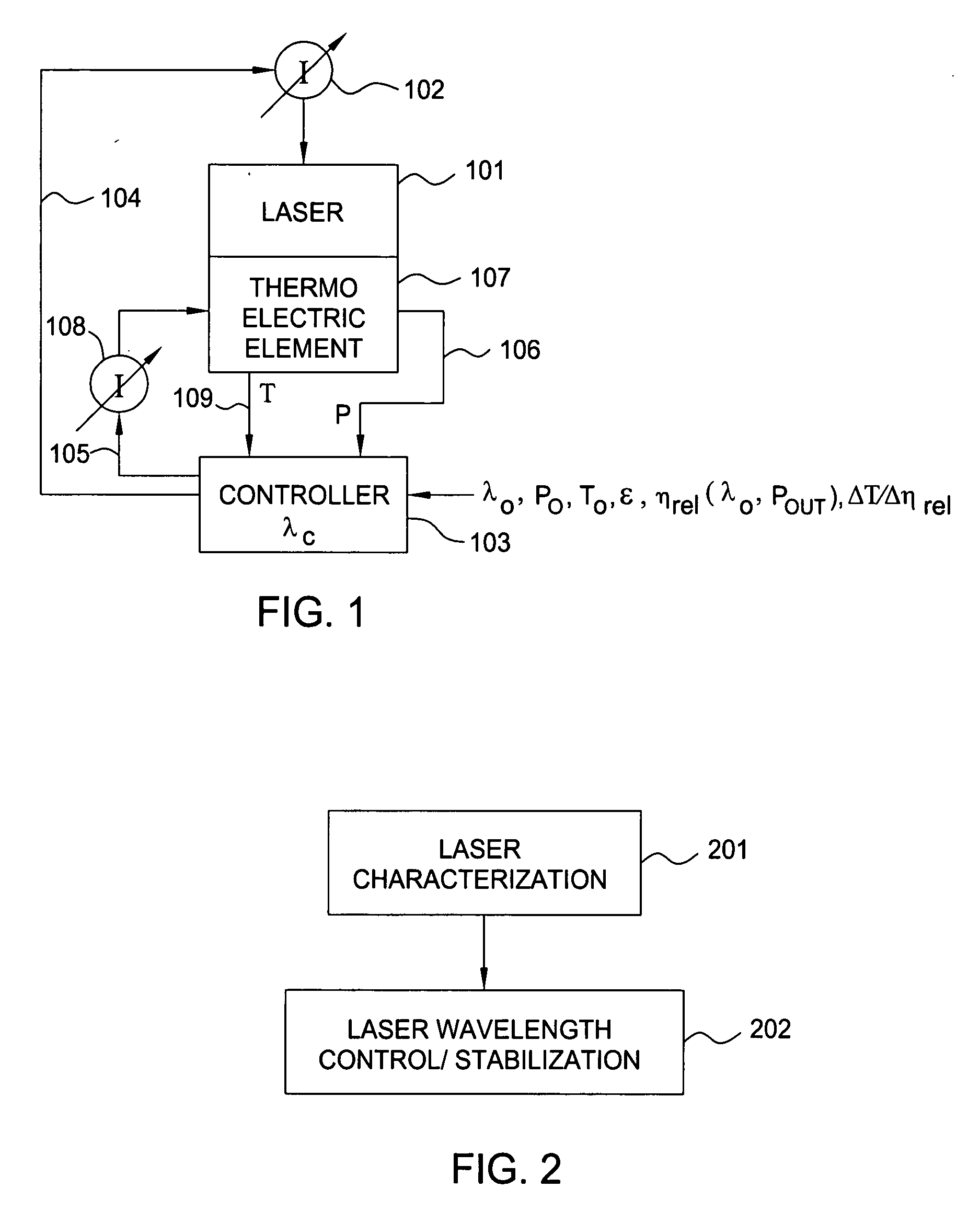
Wavelength control and stabilization of a laser is achieved by a practical, inexpensive, and accurate technique adapted for most optical transmission system applications by a method involving a laser characterization phase and a laser wavelength control and stabilization phase. This technique is applicable to both single mode lasers and multimode lasers. It is especially useful in those applications where the desired laser output power can vary over a wide range, including relatively low power above the lasing threshold.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Simplified laser oscillator-amplifier system
InactiveUS7003005B1Good energy extraction efficiencyHigh gainOptical resonator shape and constructionUv laserAudio power amplifier
The present invention contemplates a simplified laser oscillator-amplifier system for deep UV generation. The simplified system employs same type of gain media in both the oscillator and the amplifier and utilizes a single pump pulse split to pump both the oscillator and the amplifier. A short cavity oscillator is operated near lasing threshold to produce a seed pulse with a narrow spectral bandwidth and long pulse duration. A short cavity amplifier is Q-switched to amplify the seed pulse to produce a single short pulse with good energy extraction efficiency. The amplifier is simply a short cavity, Q-switched laser. Short pulse is obtained with short cavity length and high gain of the amplifier. Consequently, the simplified laser oscillator-amplifier system can accommodate a long pump pulse to produce a nanosecond pulse suitable for deep UV laser generation.
Owner:LAI MING +2
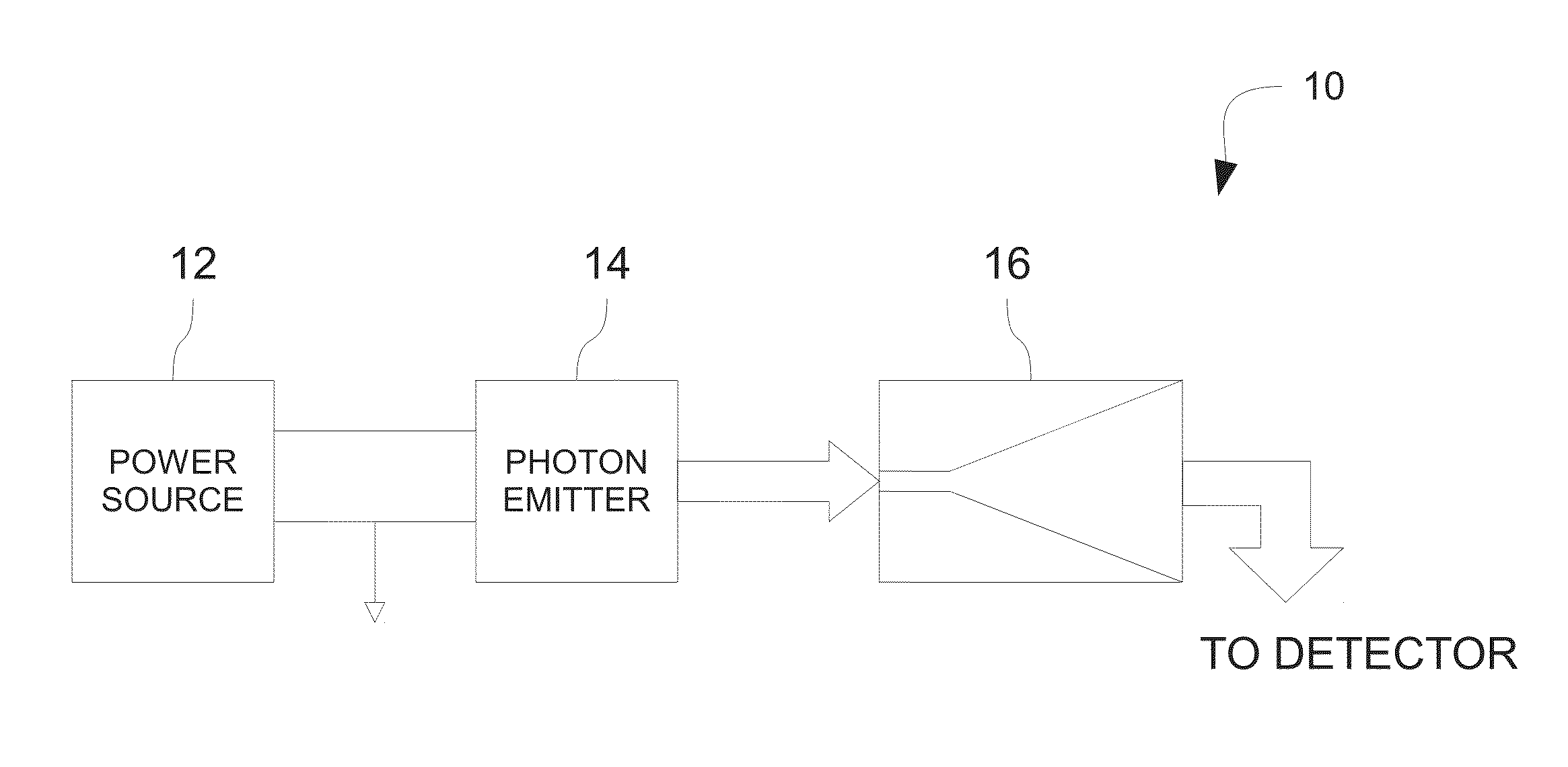
Quantum random number generator
ActiveUS20150193207A1Desensitize the photon generatorHigh bandwidthRandom number generatorsComputing modelsMultiplexingAudio power amplifier
A quantum random number generator (QRNG) and a photon generator for a QRNG are provided. The photon generator may be operated in a spontaneous mode below a lasing threshold to emit photons. Photons emitted from the photon generator may have at least one random characteristic, which may be monitored by the QRNG to generate a random number. In one embodiment, the photon generator may include a photon emitter and an amplifier coupled to the photon emitter. The amplifier may enable the photon generator to be used in the QRNG without introducing significant bias in the random number and may enable multiplexing of multiple random numbers. The amplifier may also desensitize the photon generator to fluctuations in power supplied thereto while operating in the spontaneous mode. In one embodiment, the photon emitter and amplifier may be a tapered diode amplifier.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method and device for generating a laser beam, a laser treatment device and a laser detection device
InactiveCN101652907AHigh sensitivityDiagnosticsControlling energy of instrumentOptoelectronicsLaser detection
The invention relates to a laser device, comprising a laser material (1) brought into a simmer mode. A controllable source (7, 17) of additional energy (16, 20) supplies energy to the laser material (1), such that in only a desired part of the laser material (1) a lasing threshold is exceeded, and a laser beam (10) is emitted from only a desired part of the laser surface. This device makes possible to provide a laser beam in just the desired part of the laser, which allows a flexible and localized output. The invention further relates to a hair- removing device comprising a laser device according to the invention and further comprising an optical system(6) for focusing the laser beam pulses on a focal spot (12) and for positioning the focal spot in a target position, wherein the optical system (6) comprises a movable lens or a plurality of individually addressable lenses.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and Method for Seed Laser Mode Stabilization
InactiveUS20140072006A1Output maximizationLaser detailsX-ray apparatusUltrasound attenuationOperating point
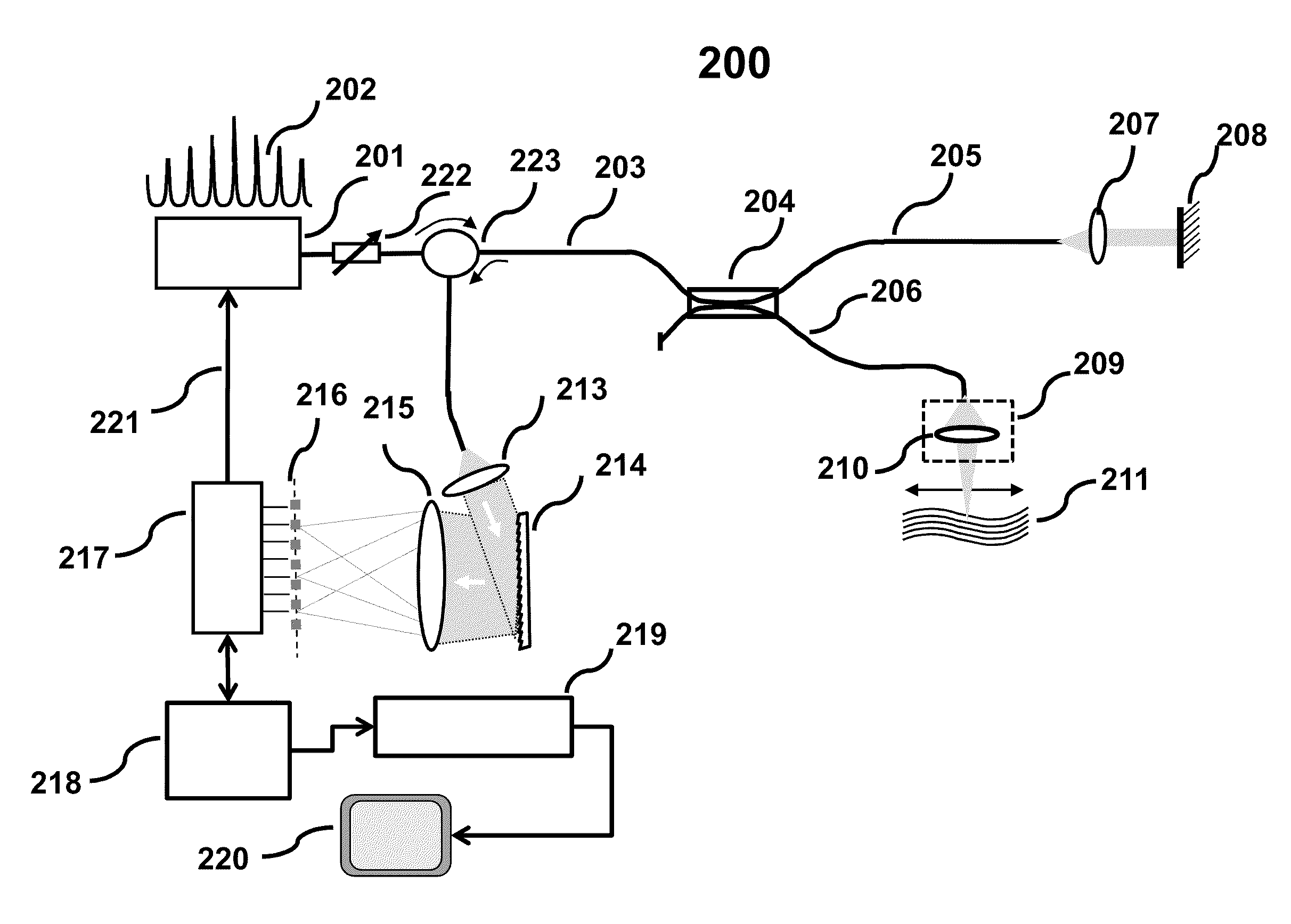
A method and apparatus for stabilizing the seed laser in a laser produced plasma (LPP) extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light system are disclosed. In one embodiment, the cavity length of the laser may be adjusted by means of a movable mirror forming one end of the cavity. The time delay from the release of an output pulse to the lasing threshold next being reached is measured at different mirror positions, and a mirror position selected which results in a cavity mode being aligned with the gain peak of the laser, thus producing a minimum time delay from an output pulse of the laser to the next lasing threshold. A Q-switch in the laser allows for pre-lasing and thus jitter-free timing of output pulses. Feedback loops keep the laser output at maximum gain and efficiency, and the attenuation and timing at a desired operating point.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Laser emitting material, method for making the same and use thereof
InactiveUS20070091967A1Low thresholdActive medium materialOptical light guidesLaser dyeHost material
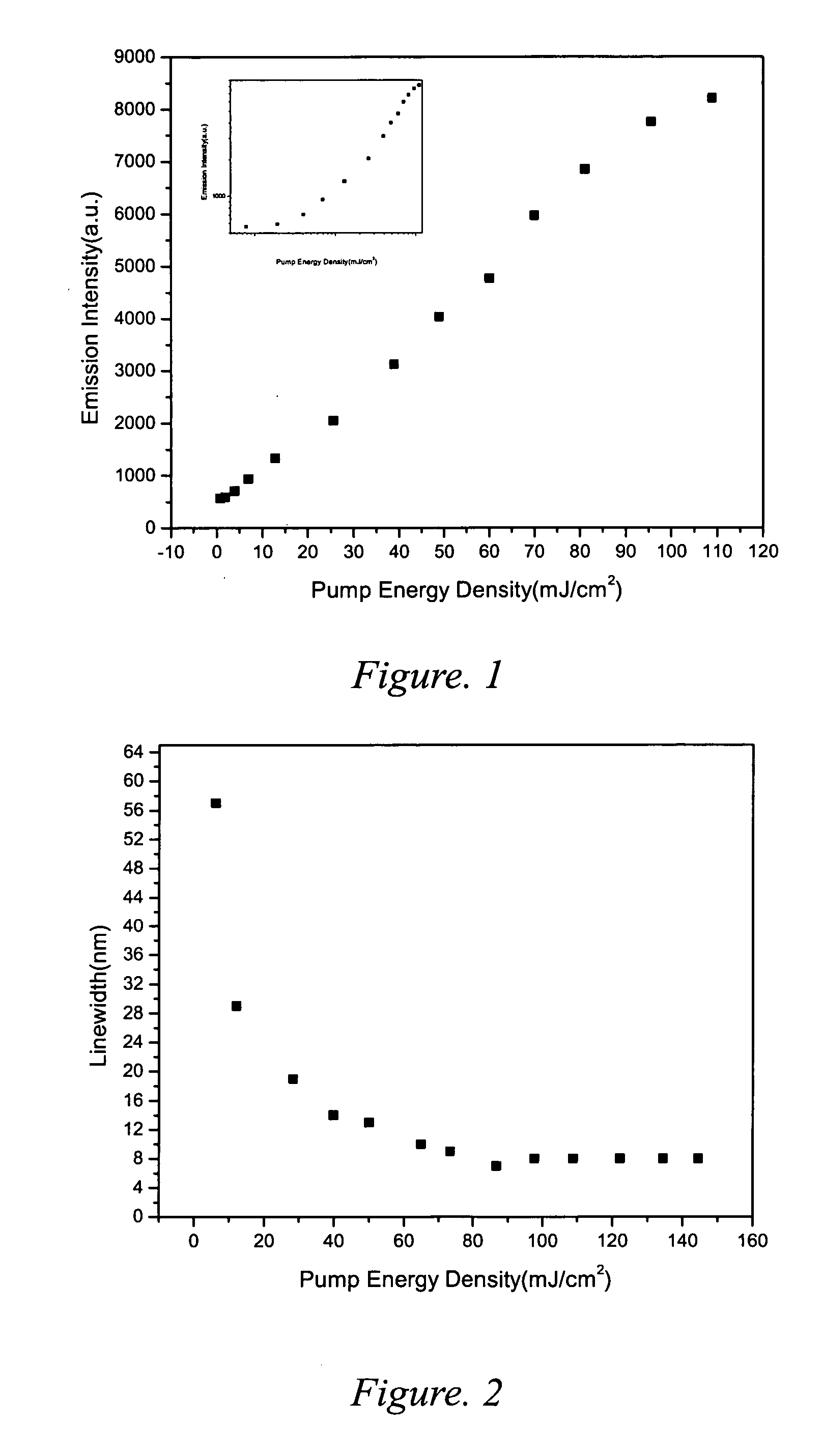
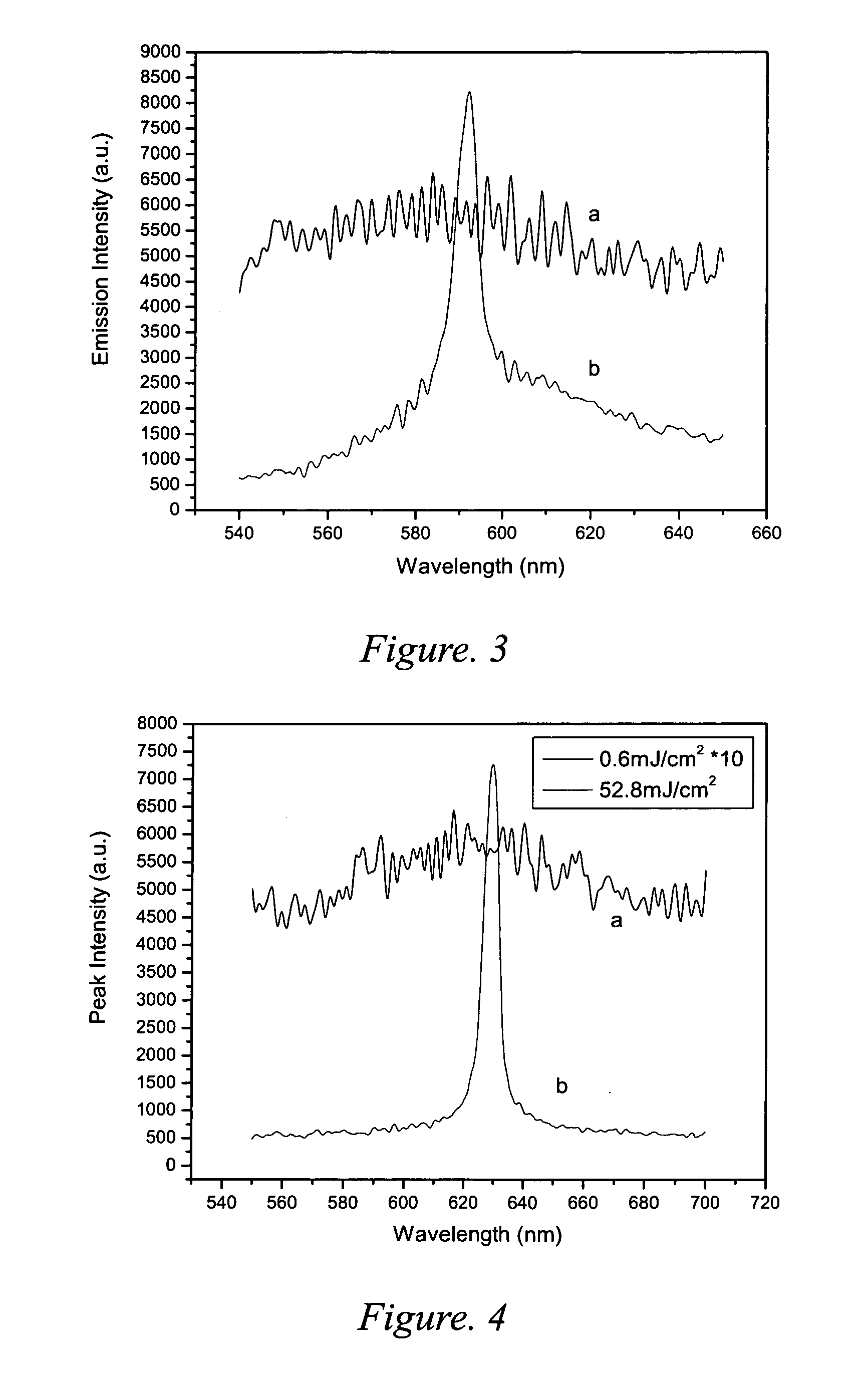
A solid-state laser emitting material for use in conjunction with a light source includes a polymer matrix functioning as host materials, containing laser dye of rhodamine 590 or rhodamine 610 as gain materials and nano-submicron particles as scatters therein. The lowest lasing threshold of the laser emitting material is approximately 5 mJ / cm2 for 585 nm emission and 2 mJ / cm2 for 630 nm emission.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Wavelength control of a dual-ring laser
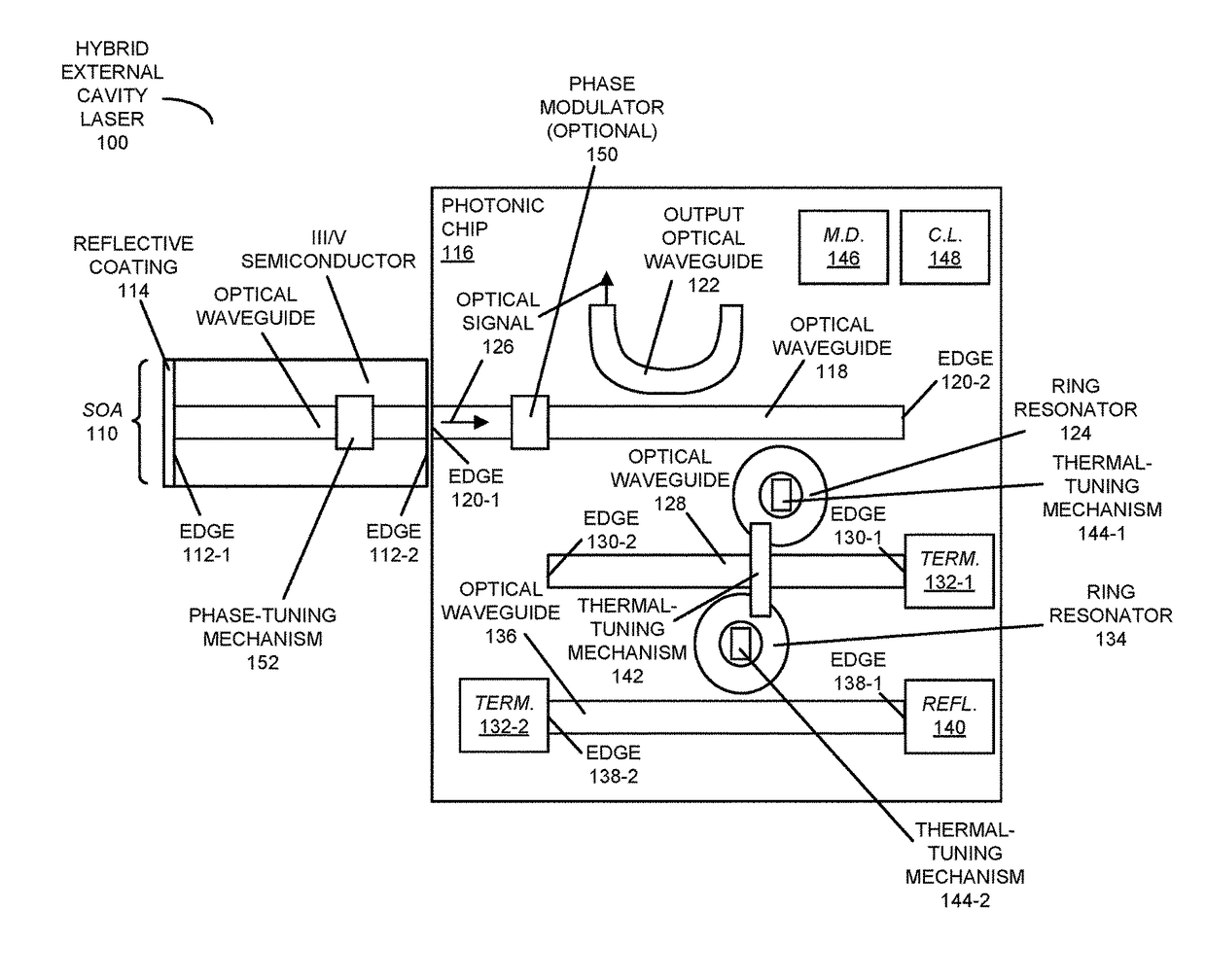
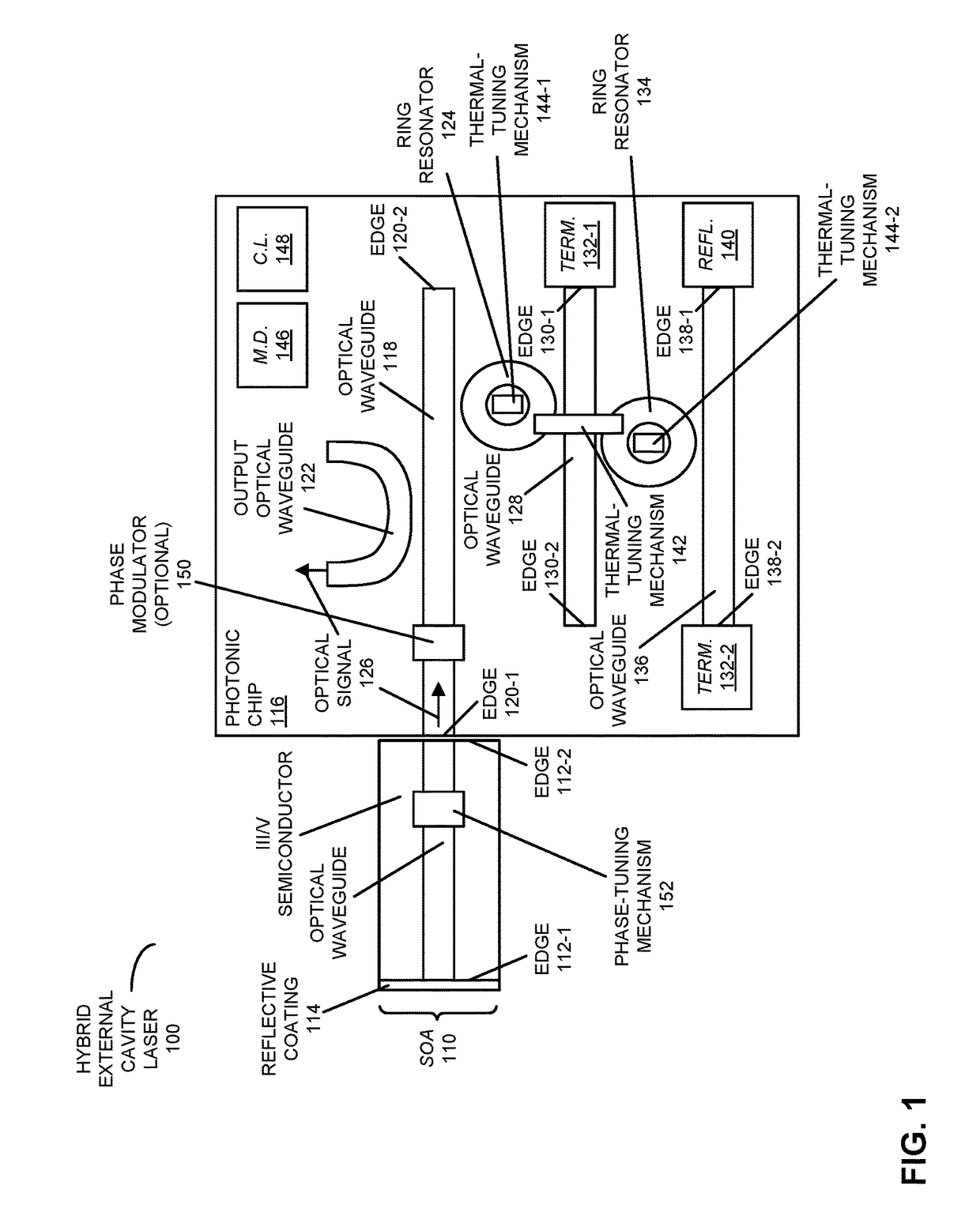
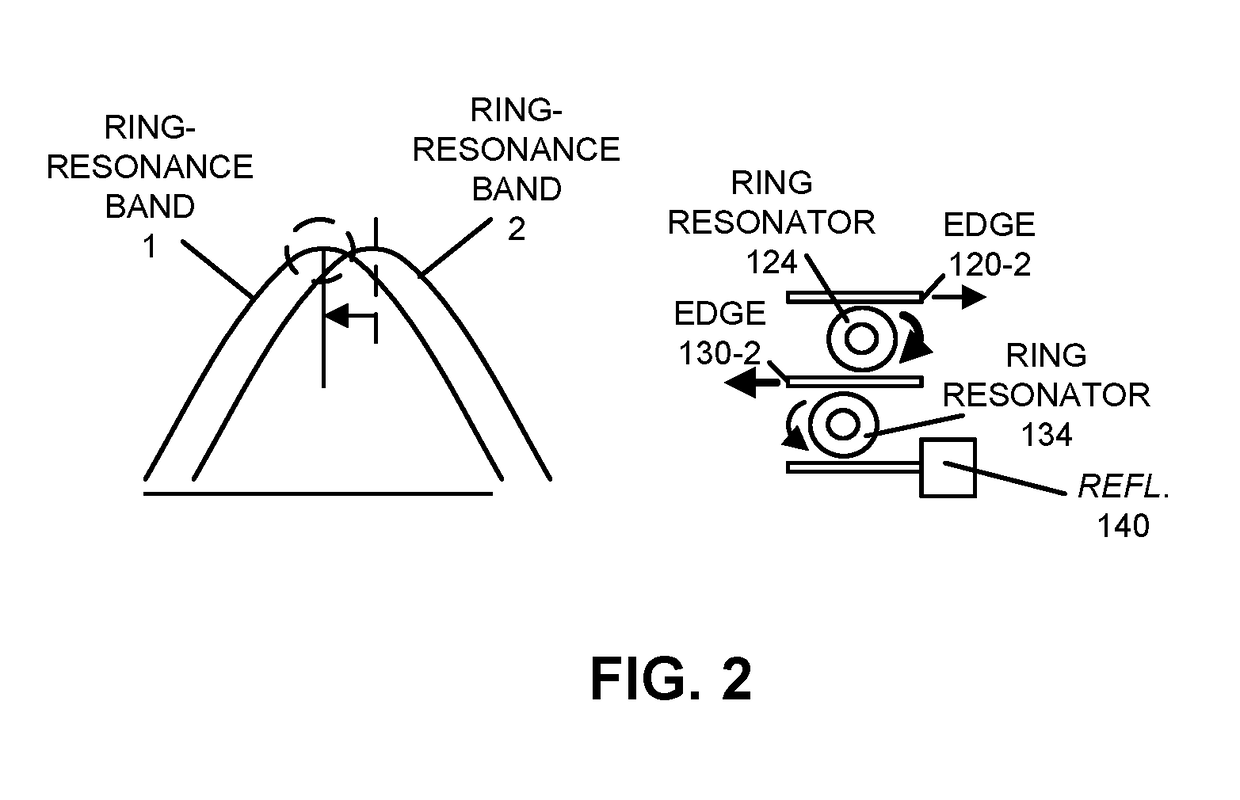
ActiveUS9608406B1Minimize powerMaintain alignmentLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionRing laserPhoton
An optical source includes a semiconductor optical amplifier that provides an optical signal, and a photonic chip with first and second ring resonators that operate as Vernier rings. When the optical source is operated below a lasing threshold, one or more thermal-tuning mechanisms, which may be thermally coupled to the first ring resonator and / or the second ring resonator, may be adjusted to align resonances of the first ring resonator and the second ring resonator based on measured optical power on a shared optical waveguide that is optically coupled to the first and second ring resonators. Then, when the optical source is operated above the lasing threshold, a common thermal-tuning mechanism may be adjusted to lock the aligned resonances with an optical cavity mode of the optical source based on a measured optical power on an optical waveguide that is optically coupled to the first ring resonator.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Pulsed laser system with a thulium-doped saturable absorber Q-switch
A pulsed laser system having a Tm3+-doped saturable absorber Q-switch unit, capable of outputting laser pulses sequentially by inputting a stable continuous-wave pump light source, is disclosed. When the gain excited in the Er3+ laser resonator exceeds the lasing threshold, the photons start resonating and being amplified in the Er3+ laser resonator. At the same moment, the Tm3+-doped saturable absorber Q-switch unit absorbs the resonant photons and quickly reaches the situation of absorption saturation. Then, sequentially Q-switched Er3+ laser pulses at 1570 nm are passively produced. In addition, the Tm3+-doped saturable absorber Q-switch unit can be designated as the gain material of a second laser resonator for producing a gain-switched Tm3+ laser pulse at 1950 nm after each of the Q-switched Er3+ laser pulses. Moreover, the Tm3+ and Ho3+ co-doped crystal can be designated as the saturable absorber Q-switch unit, for producing a gain-switched Ho3+ laser pulses at 2090 nm.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
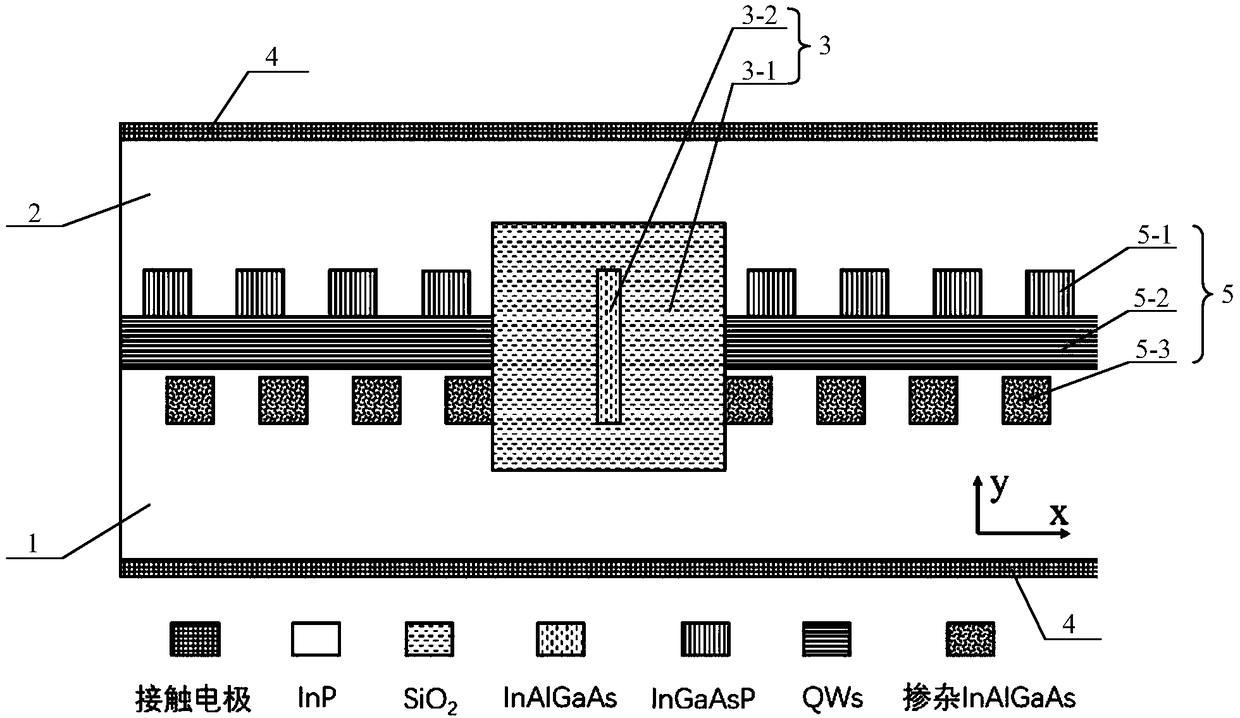
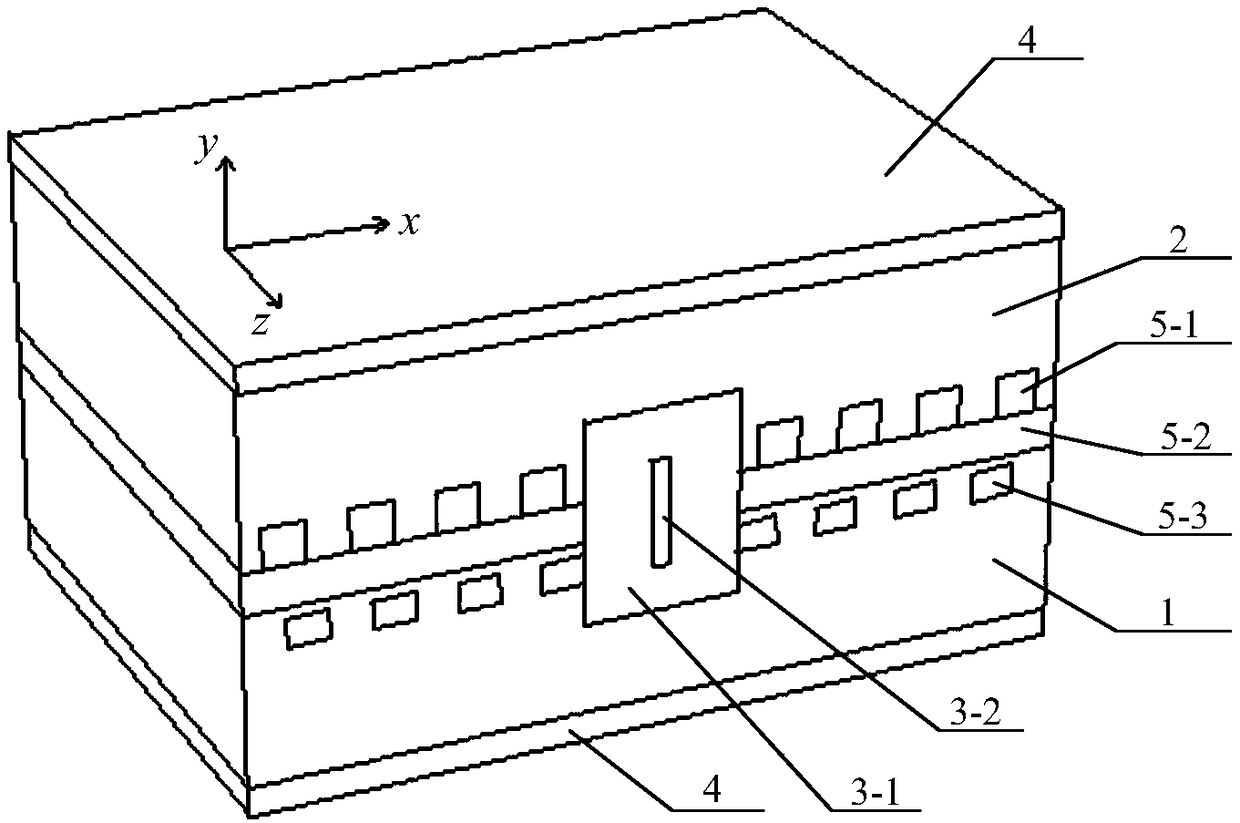
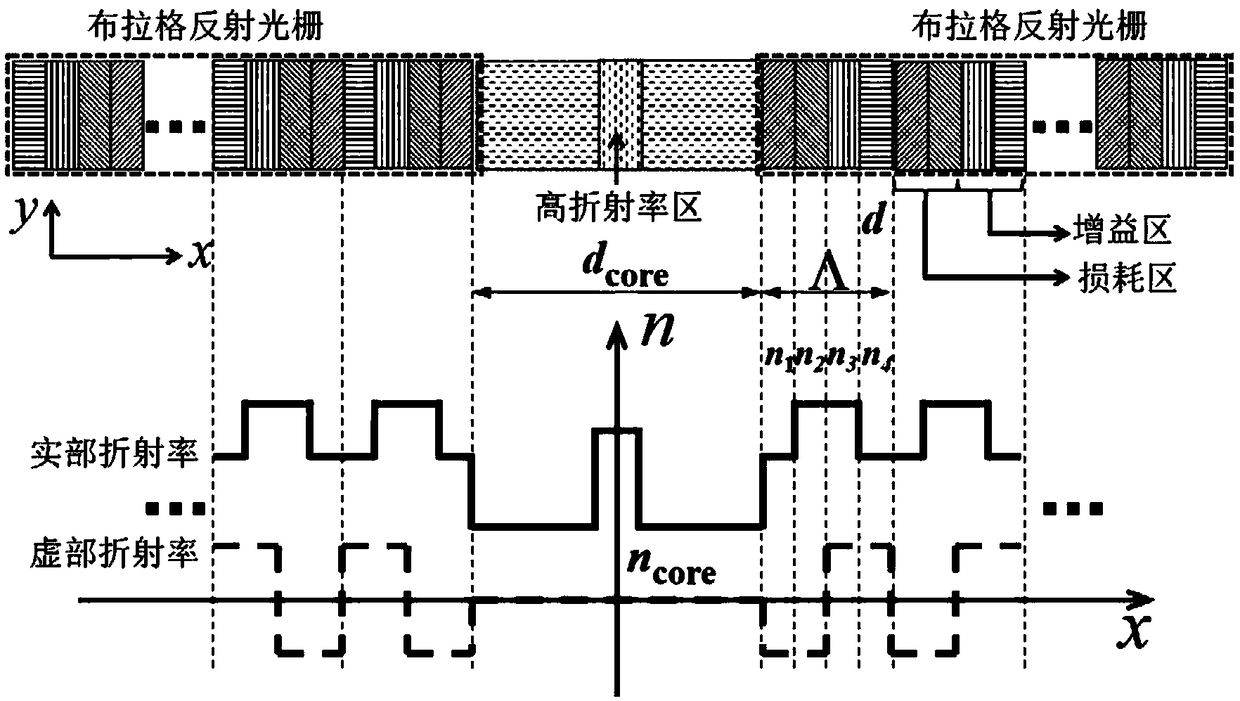
A high-power semiconductor laser based on PT Bragg reflection waveguide and a preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109244828AGuaranteed normal outputLasing mode stableLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPower semiconductor deviceLaser technology
The invention relates to a high-power semiconductor laser based on PT Bragg reflection waveguide and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the semiconductor laser technology. The device comprises an InP substrate and an InP cladding layer, wherein a low-refractive-index central cavity and a PT Bragg reflection grating region on both sides of the low-refractive-index central cavity are arranged in the InP substrate and the InP cladding layer; The low refractive index central cavity is composed of a low refractive index material wrapped in a high refractive index strip waveguide, and thePT Bragg reflective grating region includes a quantum well structure. At that same time, the lase has the advantages of high energy conversion efficiency (PCE), high COD threshold value, low lase emission threshold value, easy heat dissipation and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Holmium doped 2.1 micron crystal laser
ActiveUS7286587B2Reduce heat loadReducing up-conversion lossesActive medium materialOptoelectronicsUp conversion
A Ho:YAG crystal laser is disclosed which is doped with less than 2% holmium to reduce the lasing threshold and up-conversion, thereby increasing the operating efficiency of the laser. The laser does not need sensitizer ions so energy mismatches introduced by the sensitizer ions ale eliminated to the thereby increase the efficiency of the laser while minimizing detrimental thermal loading in the laser caused by up-conversion loss processes. The Ho:YAG crystal laser is directly pumped by a Thulium fiber laser at 1.9 μm at the holmium 5I7 to 5I8 transition to produce an output at 2.1 μm yielding a very low quantum defect. The laser is embodied as a thulium fiber laser pumped oscillator or an amplifier.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
Non-annular cavity type semiconductor laser
InactiveCN101714744AImprove electro-optical conversion efficiencyImprove optical output powerLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor materialsResonance
The invention provides a non-annular cavity type semiconductor laser, adopting a non-annular cavity and comprising an upper electrode (8), an upper waveguide layer (9), an active gain region (10), a lower waveguide layer (11), a substrate (12) and a lower electrode (13) which are all non-annular and sequentially connected. The lower electrode (13) of the non-annular cavity type semiconductor laser is formed by welding solder on a copper heat sink, Compared with a non-circular dick cavity type semiconductor laser, the non-annular resonance cavity not only keeps optical orientation output, but also improves the current injection rate by more than 20%, decreases the lasing threshold of a laser device by more than 20%, improves the electro-optic conversion efficiency of the device by 15-20%, improves the optical output rate by 10-15% and overcomes the defects of the conventional structure. The laser can be applied to a semiconductor material system of an III-V group or a semiconductor material system of an II-VI group and can be also applied to organic fluorescent or laser material systems.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Silica-based germanium electrical injection laser and production method thereof
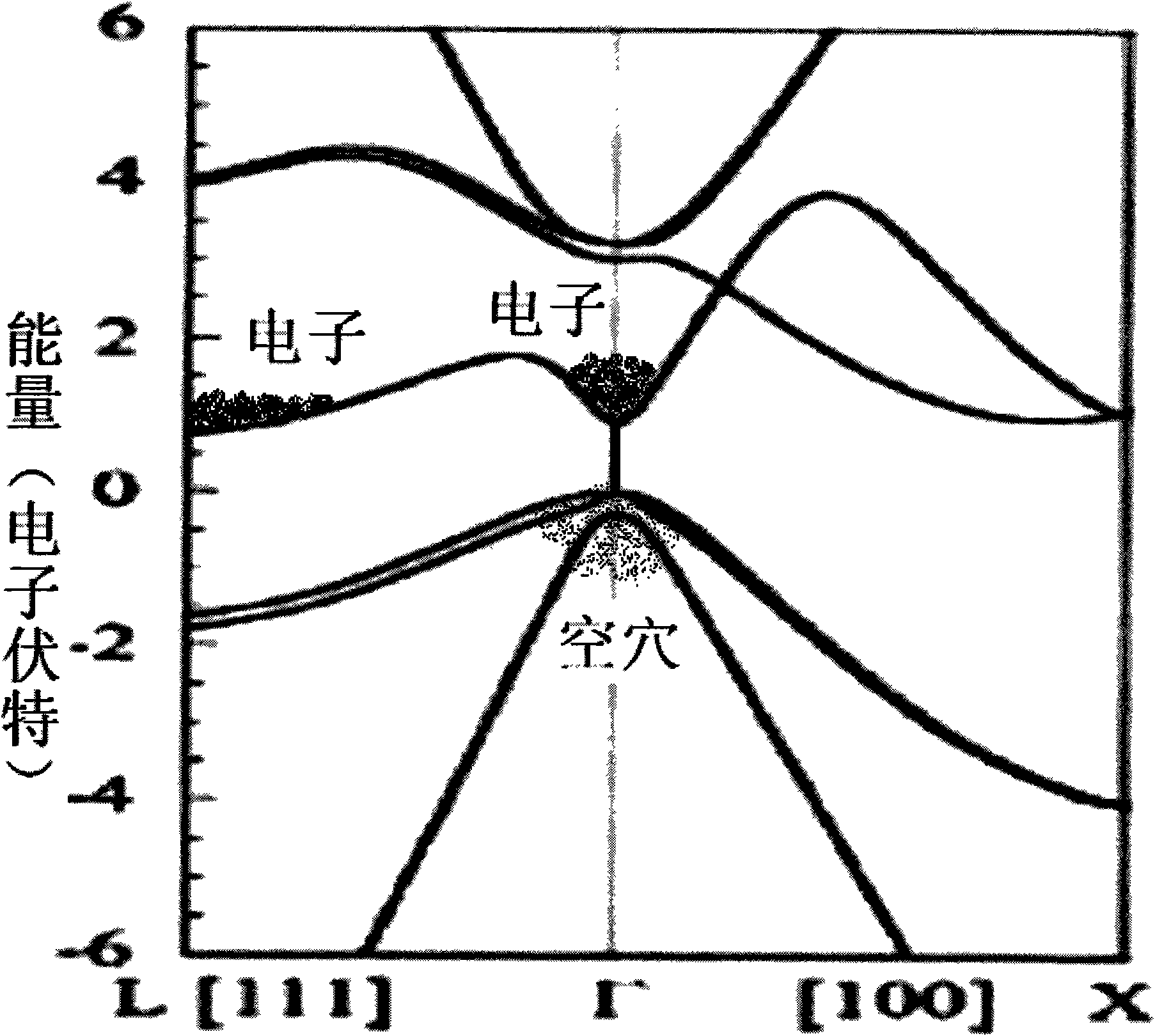
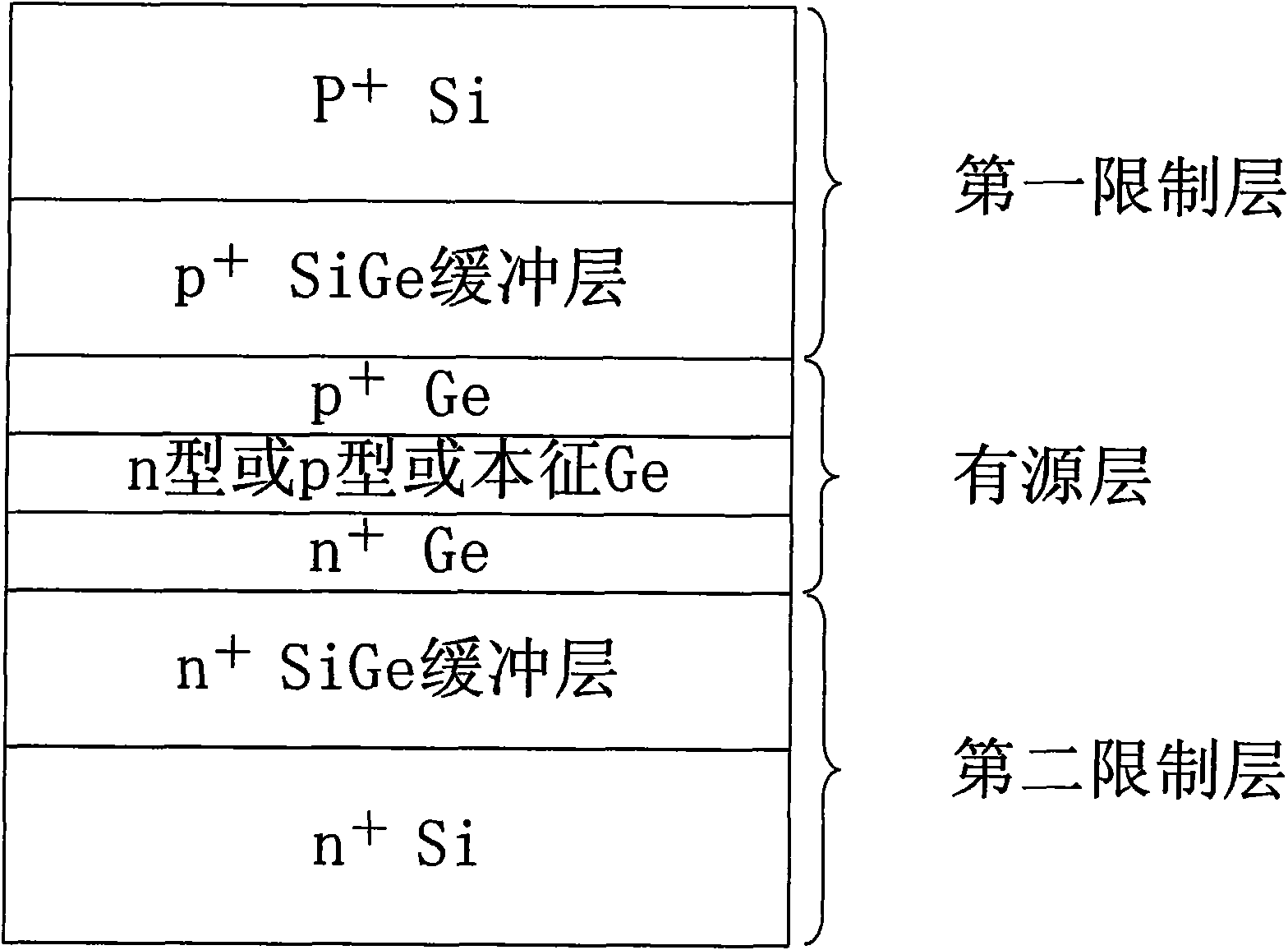
The invention relates to a silica-based germanium electrical injection laser and a production method thereof. An active layer of the laser forms a p-i-n structure on the basis of an extension germanium-based single crystalline layer on a monocrystal line silicon. A first limiting layer is positioned at the upper part of the active layer, and a second limiting layer is positioned at the lower part of the active layer. Under the injection of large electric current, when the injected electric current is larger than or equal to a laser ejection threshold, the laser utilizes Auger effect and a laser resonant cavity to form positive feedback to adjust the electronic condensation proportion of a germanium L conduction band valley and a germanium inverse-L conduction band valley so as to realize the higher electronic condensation of the germanium inverse-L conduction band valley, therefore, the silica-based germanium electrical injection laser which realizes high efficiency and low working current density and is based on germanium direct bandgap near infrared (-1.55 microns) light emission is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Micro-nano semiconductor edge emission FP laser and manufacturing method thereof
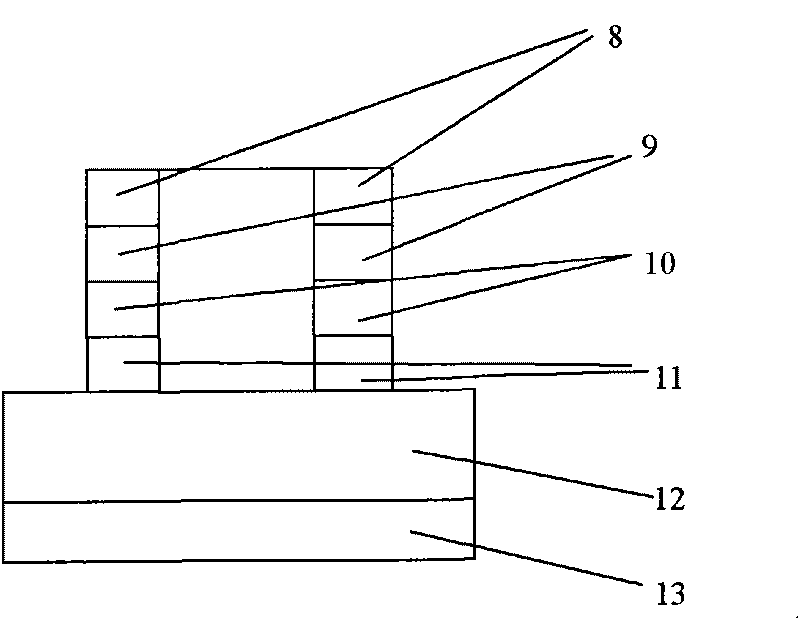
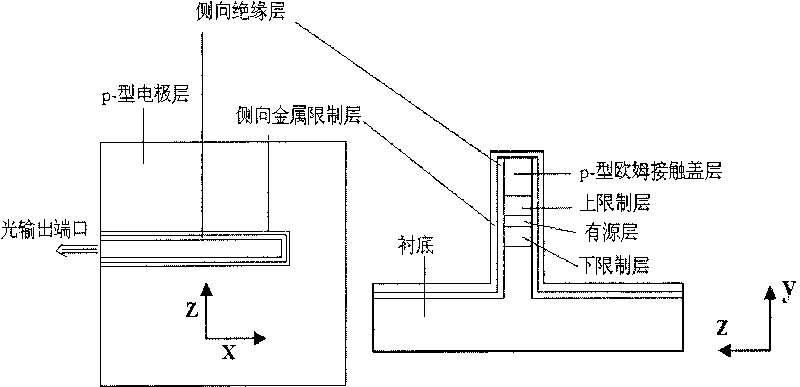
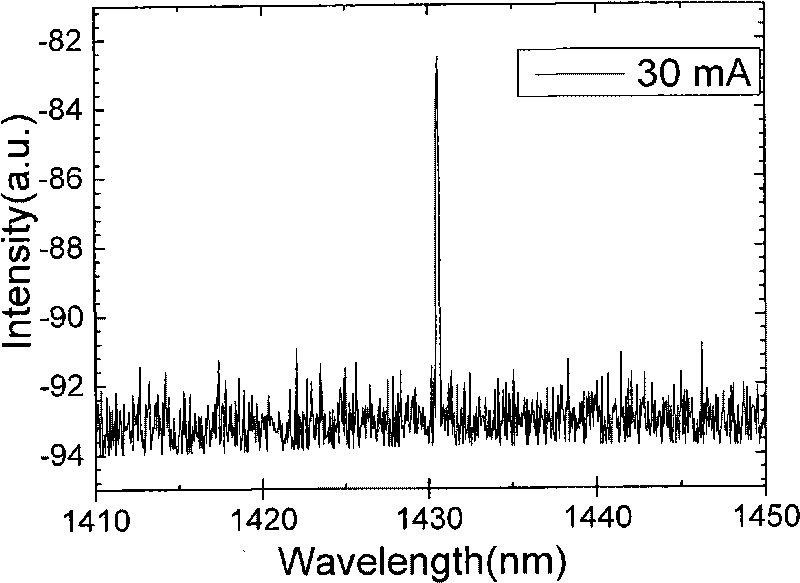
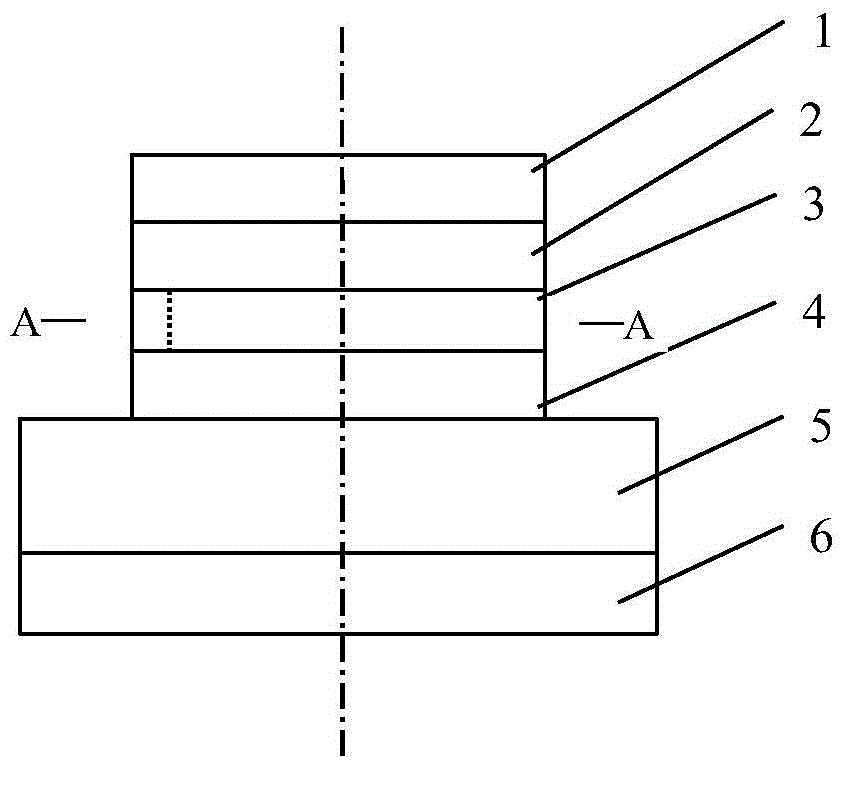
InactiveCN101764353AOvercoming the problem of directional outputEasy to analyzeLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionMicro nanoLower limit
The invention discloses a micro-nano semiconductor edge emission FP laser and manufacturing method thereof. The edge emission FP laser comprises an n-shape underlay (1), a lower limiting layer (2), an active layer (3), an upper limiting layer (4), a P-type ohm contact cap layer (5), a side surface insulating layer (6) and an anode-cathode layer (7) in sequence from up to down; wherein the side surface insulating layer (6) and a P-type electrode layer in the anode-cathode layer (7) are used for laterally limiting a light field, enhancing the lateral light field or the mode limitation of a cavity, reducing the laser emission threshold of the cavity, and improving the exiting efficiency of the end surface of the cavity and the output power of the laser. The invention can be used to overcome the problem of directional output of the micro-nano semiconductor laser, and is easy to analyze the FP mode exited by the laser. A laser source in opto-electronic integration can reach a nano size on a 2D direction and the integration level of opto-electronic apparatuses is improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor polarization mode converter having a diffraction grating
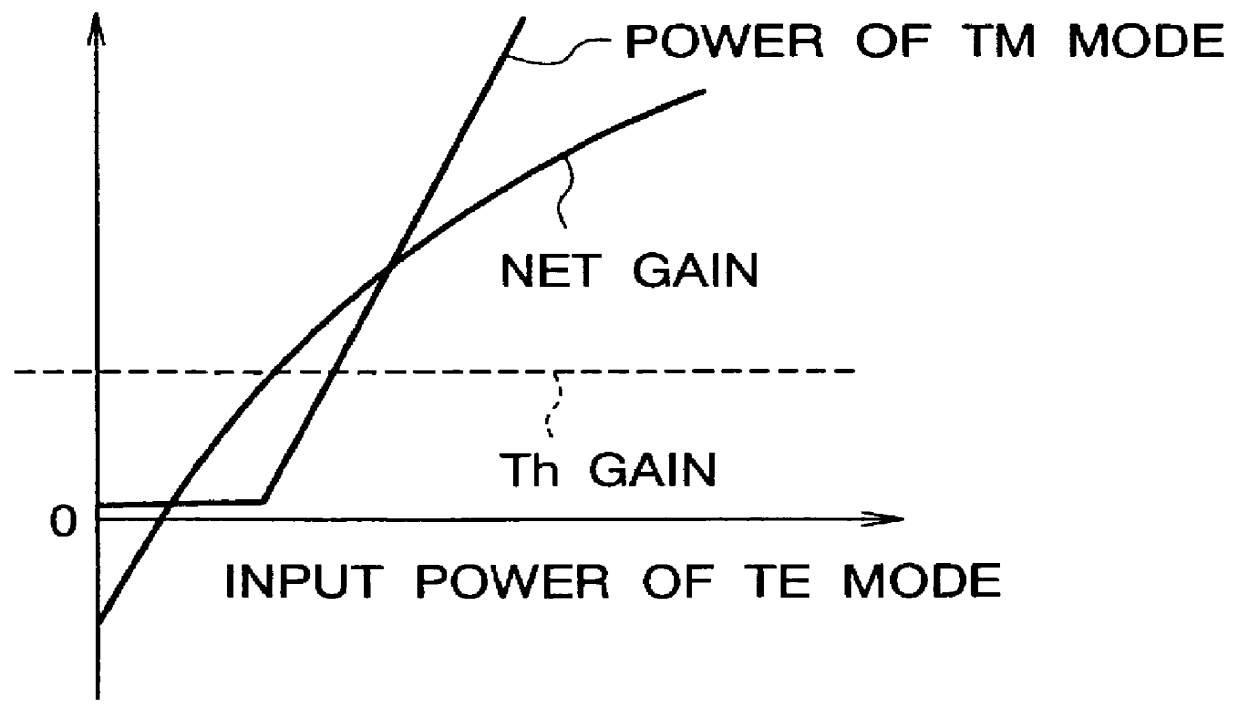
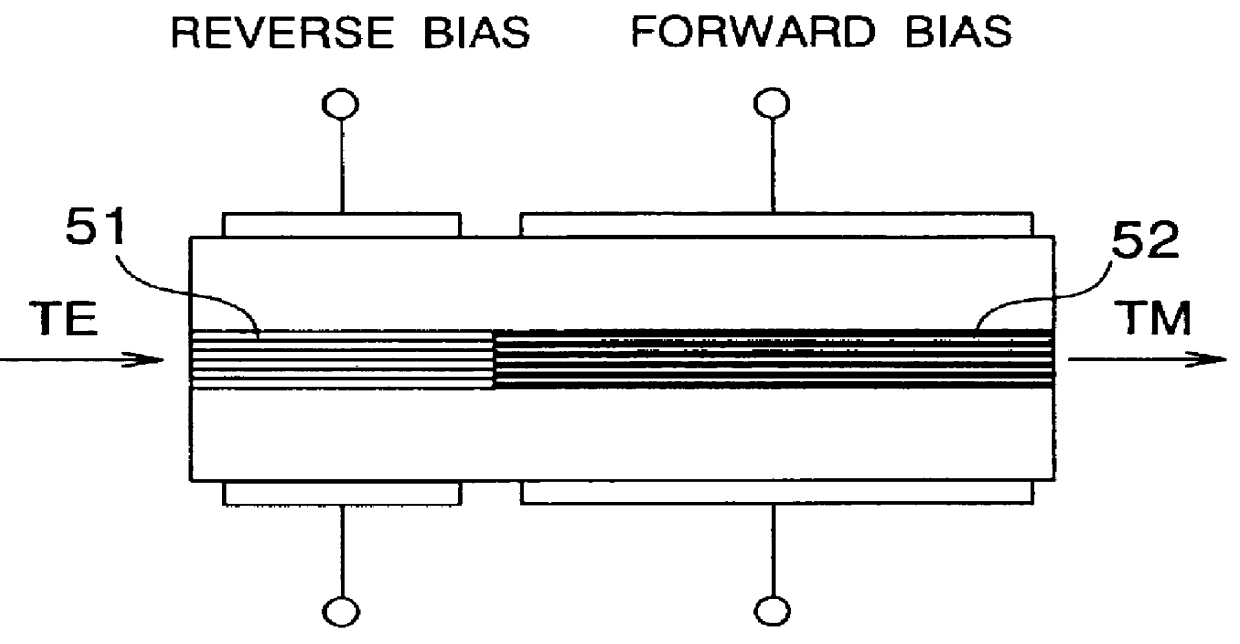
InactiveUS6104850ALaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionSelective reflectionSemiconductor waveguides
A semiconductor TE / TM mode converter comprises a semiconductor waveguide layer including a compressive-strained first region and a tensile-strained second region, and a diffraction grating formed on the first region. The first region and second region are reversed-biased and forward-biased, respectively. TE mode light incident on the facet of the first region generates TM mode light outgoing from the facet of the second region. The diffraction grating in the first region has selective reflectance against TM mode light and reflects the TM mode light toward the second region, to lower the lasing threshold of TM mode light and raise the conversion efficiency.
Owner:NEC CORP
Elliptic ring microcavity laser with high-resistance area
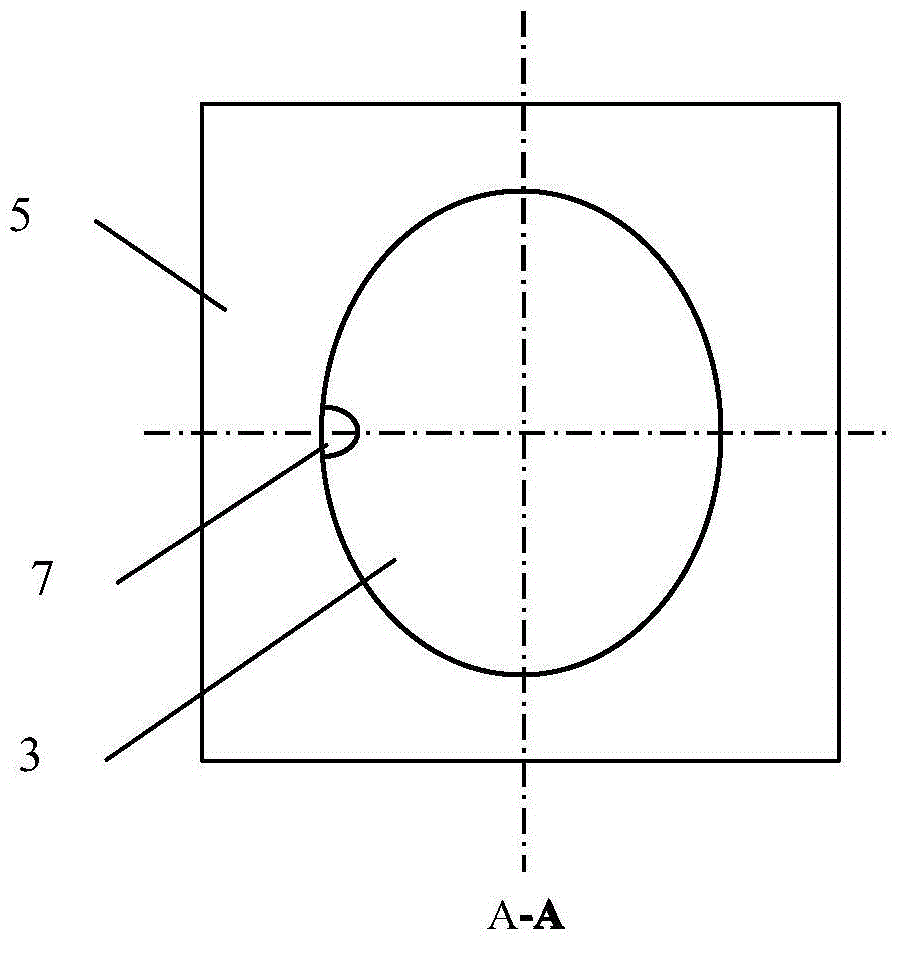
ActiveCN104377546ANarrow widthImprove electro-optical conversion efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser output parameters controlHigh resistanceProtonation
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor lasers, discloses an elliptic ring microcavity laser with a high-resistance area, and aims to solve the problems that existing elliptic plate microcavity lasers are high in laser emission threshold, low in electro-optical conversion efficiency, high in temperature rise and low in light output power and existing elliptic ring microcavity semiconductor lasers are low in yield and difficult in realization of high light output power. The elliptic ring microcavity laser with the high-resistance area comprises an upper electrode, an upper waveguide layer, an active gain layer, a lower waveguide layer, a substrate and a lower electrode sequentially from top to bottom. The lower electrode is welded onto a copper heat sink, the upper electrode, the upper waveguide layer, the active gain layer and the lower waveguide layer are shaped in elliptic plates, and one end of an ellipse minor axis at the outer boundary of the active gain layer is provided with a semi-elliptic cut. The elliptic ring microcavity laser is characterized in that a central area of the upper waveguide layer is the high-resistance area, and the high-resistance area is formed by means of photomask and protonation before the upper electrode is made on the upper waveguide layer.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Two section blue laser diode with reduced output power droop
InactiveUSRE40230E1Reduce power consumptionReduces transient heatingLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAudio power amplifierReverse bias
A III-V nitride blue laser diode has an amplifier region and a modulator region. The amplifier region has a constant current to keep the region near the lasing threshold. The modulator region has a small varying forward current or reverse bias voltage which controls the light output of the laser. This two section blue laser diode requires much lower power consumption than directly modulated lasers which reduces transient heating and “drooping” of the light output.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Implementation and enhancement method for ZnO single-mode ultraviolet lasers
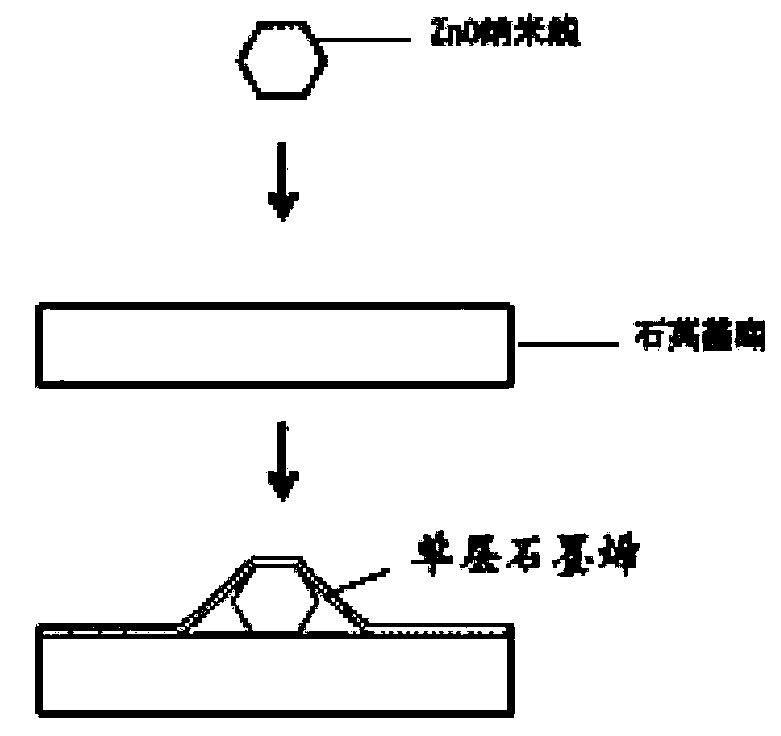
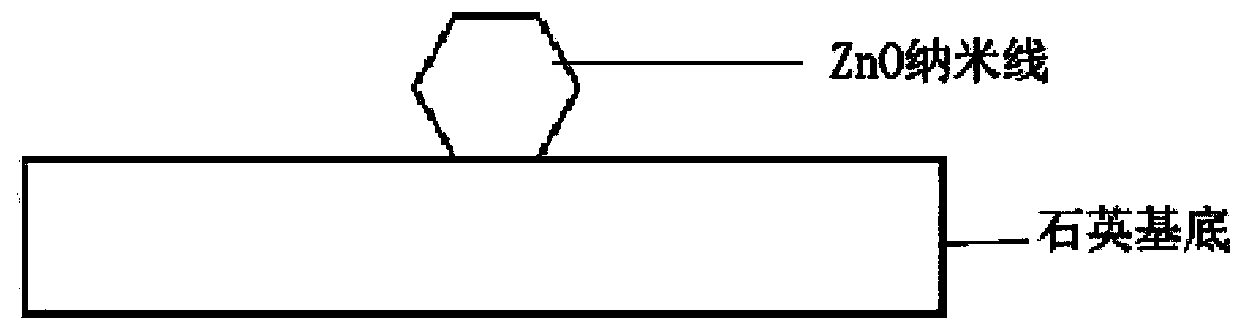
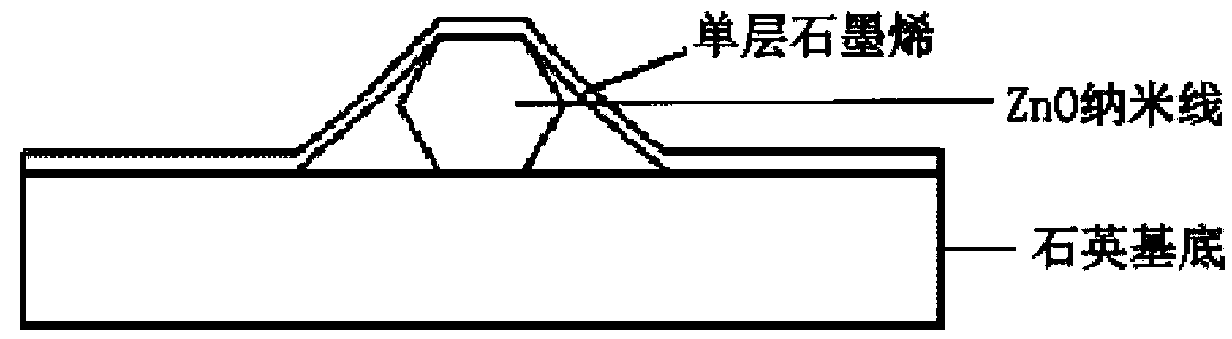
InactiveCN104242053APromote formationSmall cavity sizeLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionNanolithographyInformation processing
The invention discloses an implementation and enhancement method for ZnO single-mode ultraviolet lasers. Single-layer graphene prepared according to the chemical vapor deposition method or the mechanical exfoliation method is transferred onto the surfaces of ZnO nanowires respectively with the submicron diameter in a covering mode, so that graphene / ZnO nanowire composite structure microcavities are formed. Due to the fact that the range of a light field is effectively limited by plasmas on the surface of the graphene, the optical loss of the ZnO nanowires can be greatly reduced, the lasing threshold value is effectively reduced, the quality factor of a micro laser device is improved, and the intensity of the ultraviolet lasers of the micro laser device is enhanced. The very beneficial method is provided for a composite high-performance photoelectric device, and meanwhile the potential applications of the device to the aspects of ultrafast information processing, nanometer microimaging, nanometer photolithography, biomedicine, super sensing and the like are developed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Dual-wavelength passive self-modulated mode-locked semiconductor laser diode
InactiveUS6868098B1Increase currentRealize the operationLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser optical deviceLength waveDual wavelength
Method of generating laser pulses using a semiconductor laser diode as a lasing amplification medium of an extended laser cavity are presented. Passive self-modulated mode-locked operation of the semiconductor laser diode is achieved by providing an above lasing threshold direct current input current to the semiconductor laser diode while the semiconductor laser diode is operational in a slightly misaligned extended laser cavity favoring the amplification of wavelengths shorter than a center wavelength of a continuous wave operational mode of the semiconductor laser diode at threshold.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
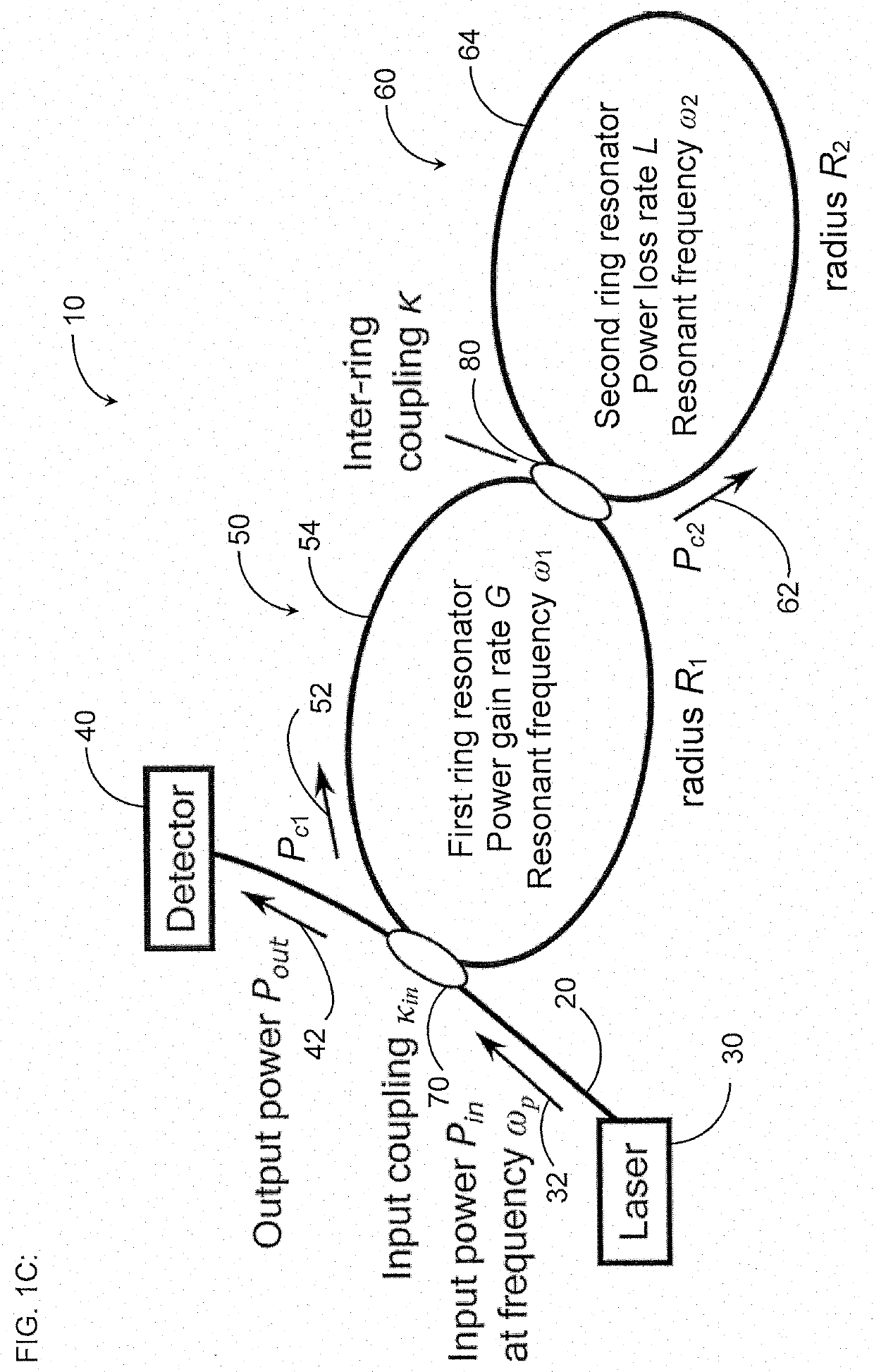
Gain-coupled resonator gyroscope
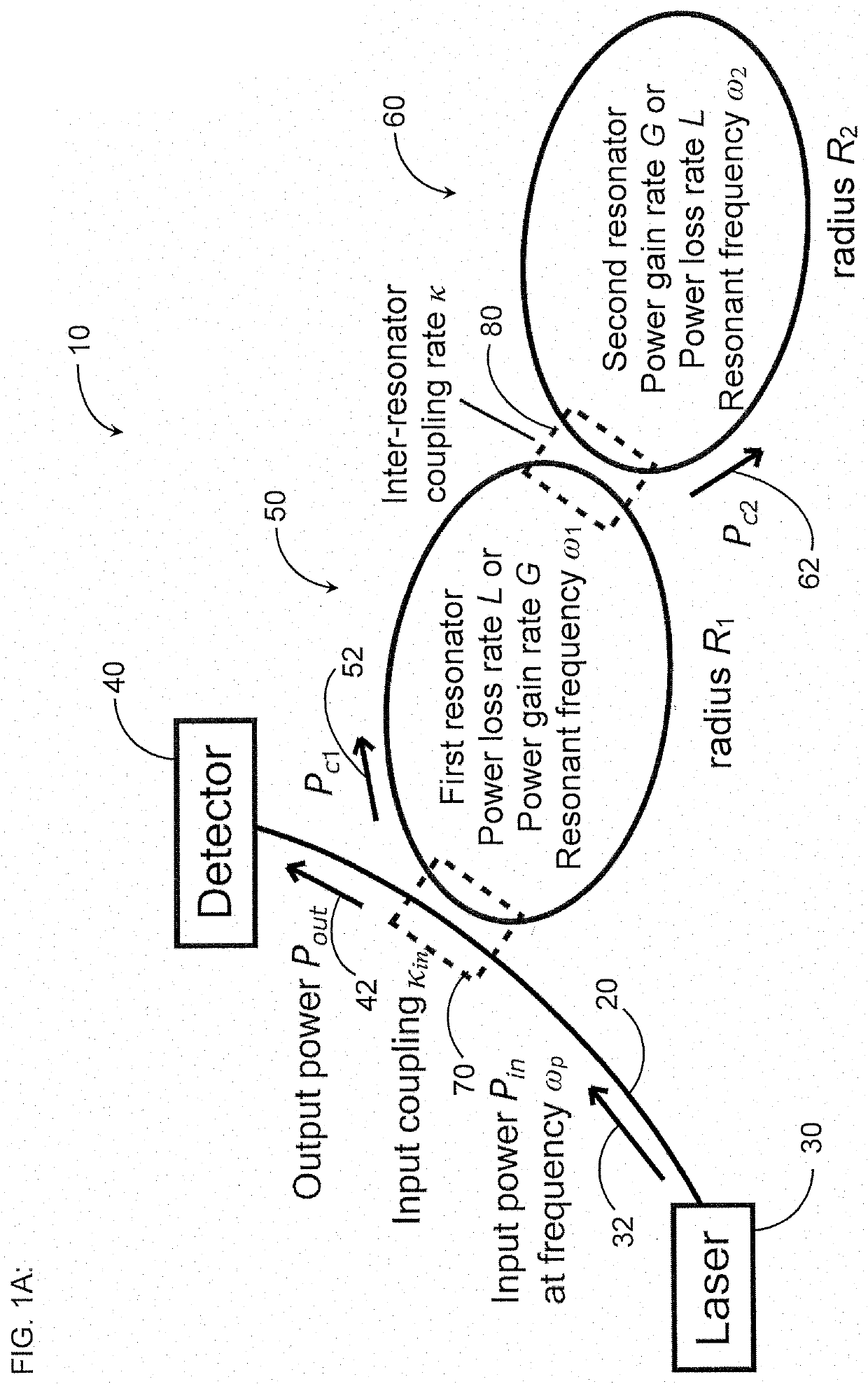
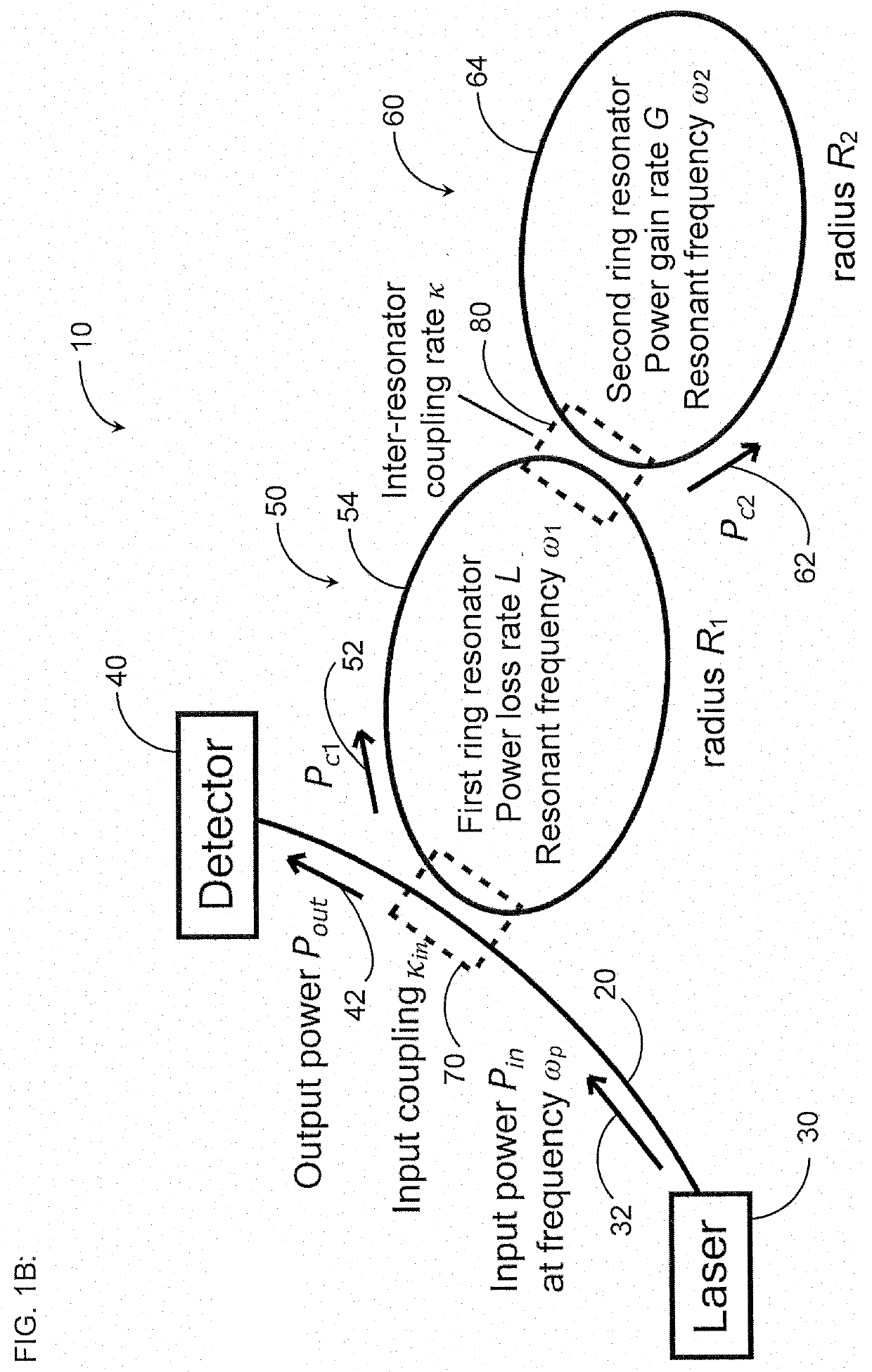
A gyroscope includes a first optical resonator in optical communication with at least one optical waveguide and a second optical resonator in optical communication with the first optical resonator. One of the first optical resonator and the second optical resonator has a power loss rate L greater than zero and the other of the first optical resonator and the second optical resonator has a power gain rate G greater than zero. The at least one optical waveguide, the first optical resonator, and the second optical resonator are configured to be below lasing threshold. The gyroscope further includes at least one optical detector in optical communication with the at least one optical waveguide, and the at least one optical waveguide is configured to receive, from at least one light source, light having an input power Pin at a frequency ωp and to transmit at least a portion of the light having an output power Pout to the at least one optical detector.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Quantum random number generator
ActiveUS9335973B2Desensitize the photon generatorHigh bandwidthRandom number generatorsMultiplexingPhoton emission
A quantum random number generator (QRNG) and a photon generator for a QRNG are provided. The photon generator may be operated in a spontaneous mode below a lasing threshold to emit photons. Photons emitted from the photon generator may have at least one random characteristic, which may be monitored by the QRNG to generate a random number. In one embodiment, the photon generator may include a photon emitter and an amplifier coupled to the photon emitter. The amplifier may enable the photon generator to be used in the QRNG without introducing significant bias in the random number and may enable multiplexing of multiple random numbers. The amplifier may also desensitize the photon generator to fluctuations in power supplied thereto while operating in the spontaneous mode. In one embodiment, the photon emitter and amplifier may be a tapered diode amplifier.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com