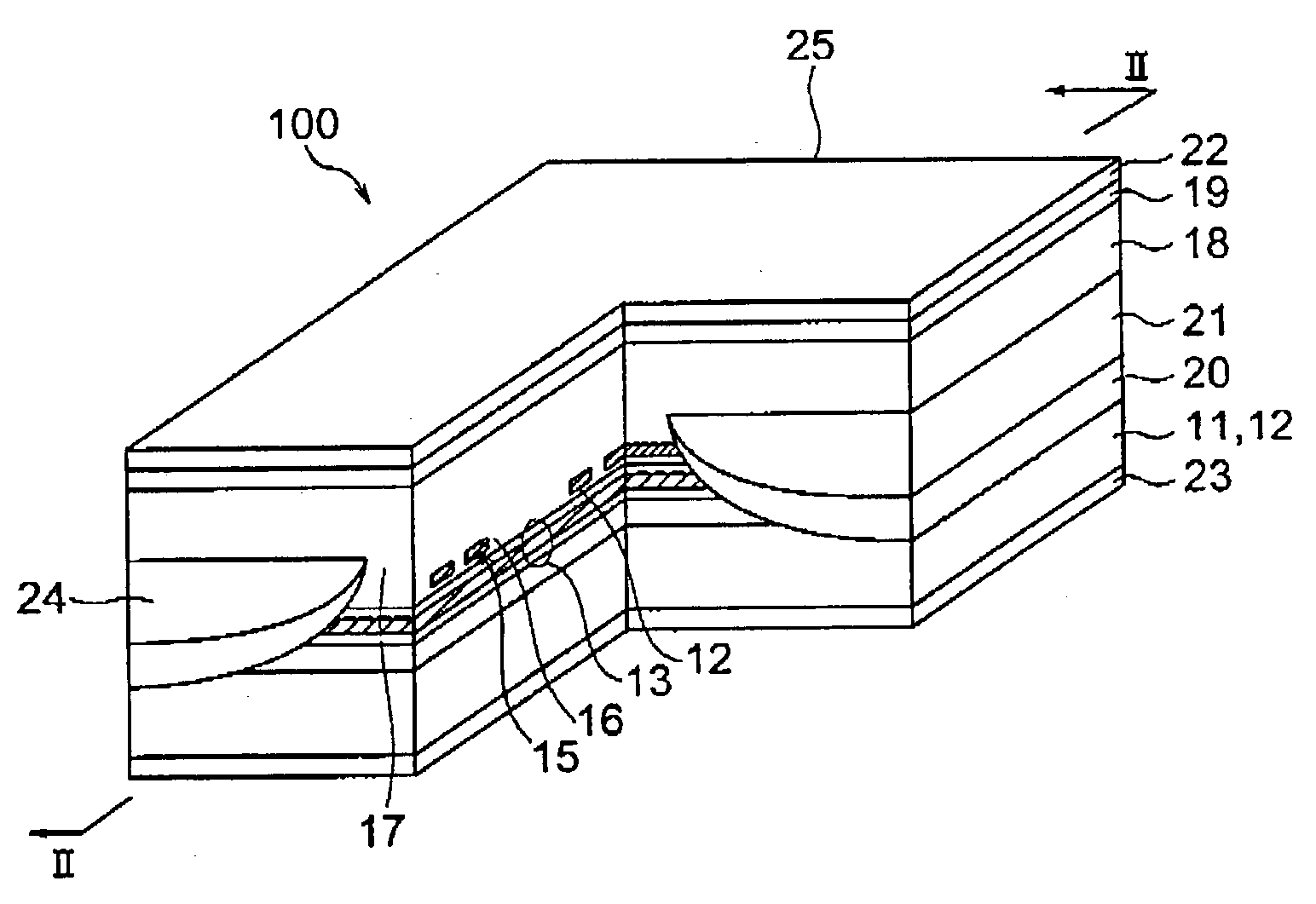
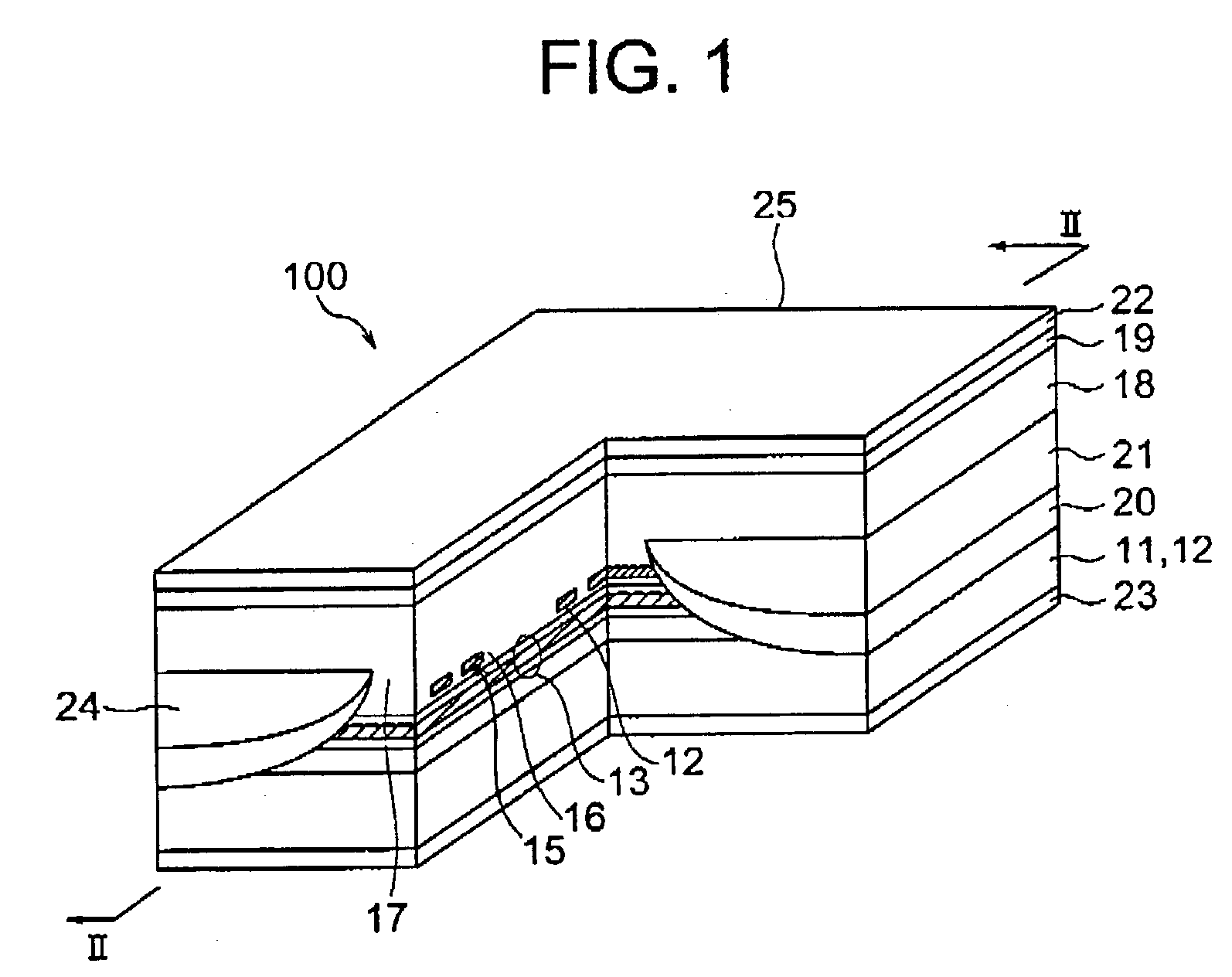
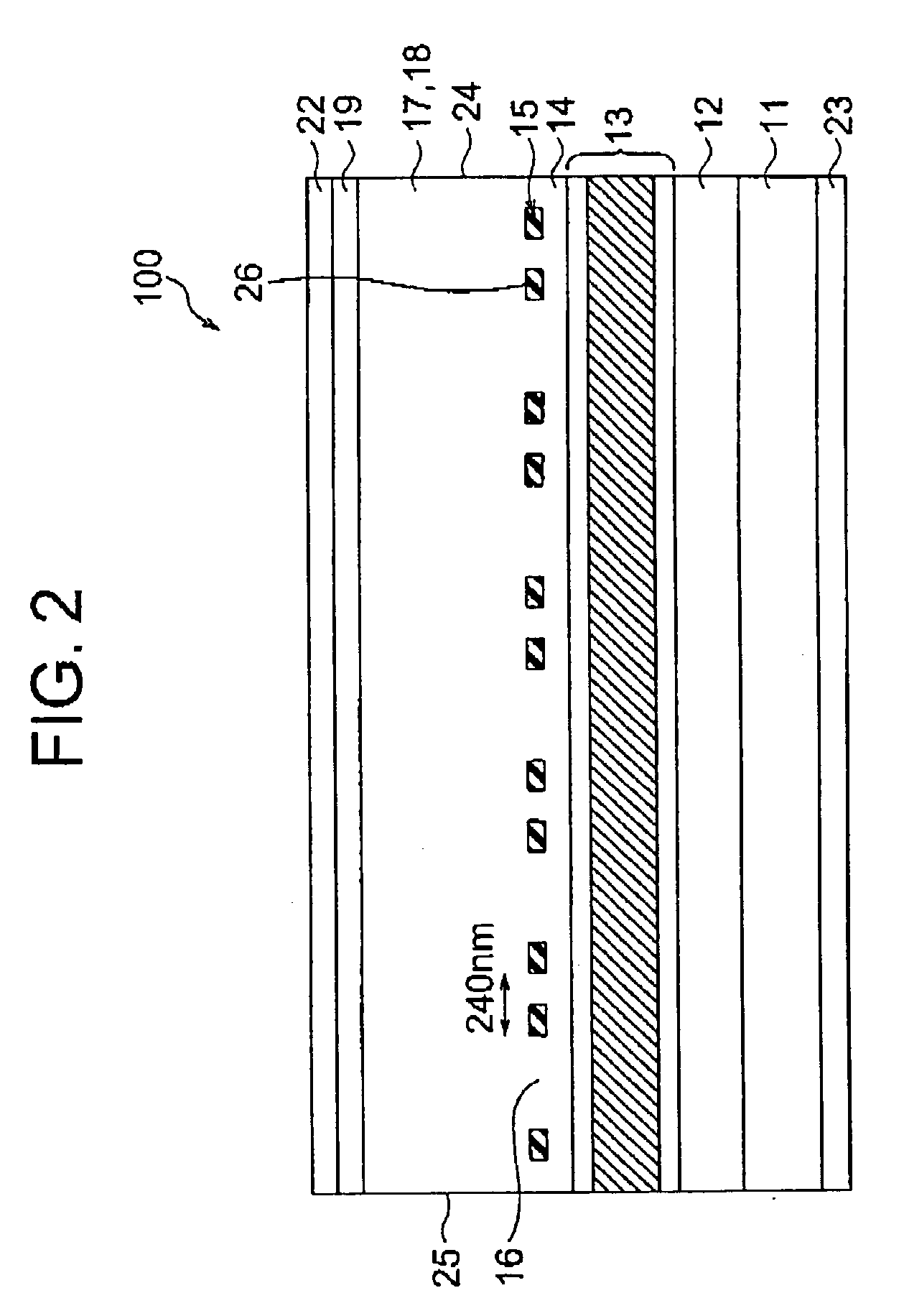
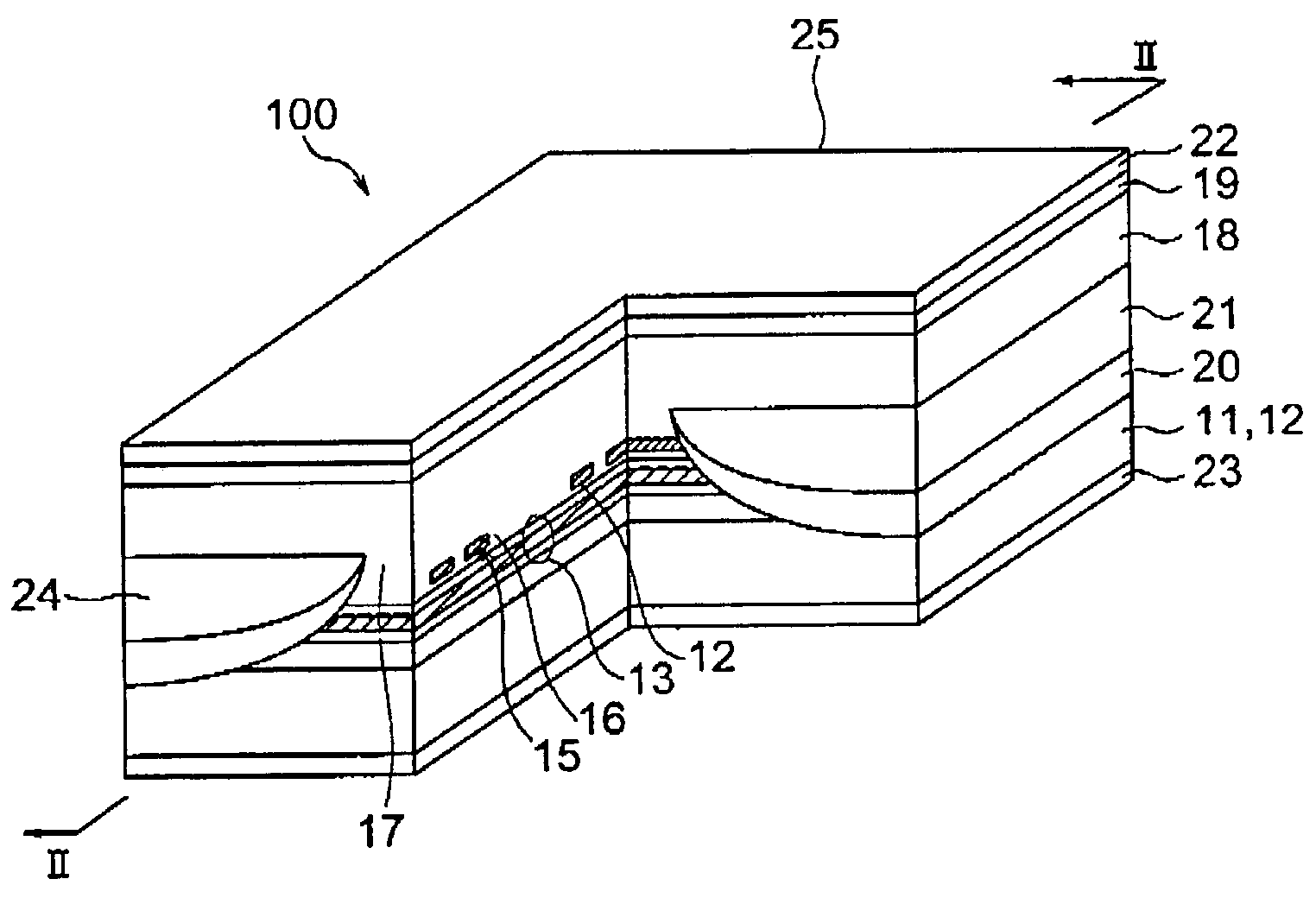
Patents
Literature
155results about How to "Improve optical output power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
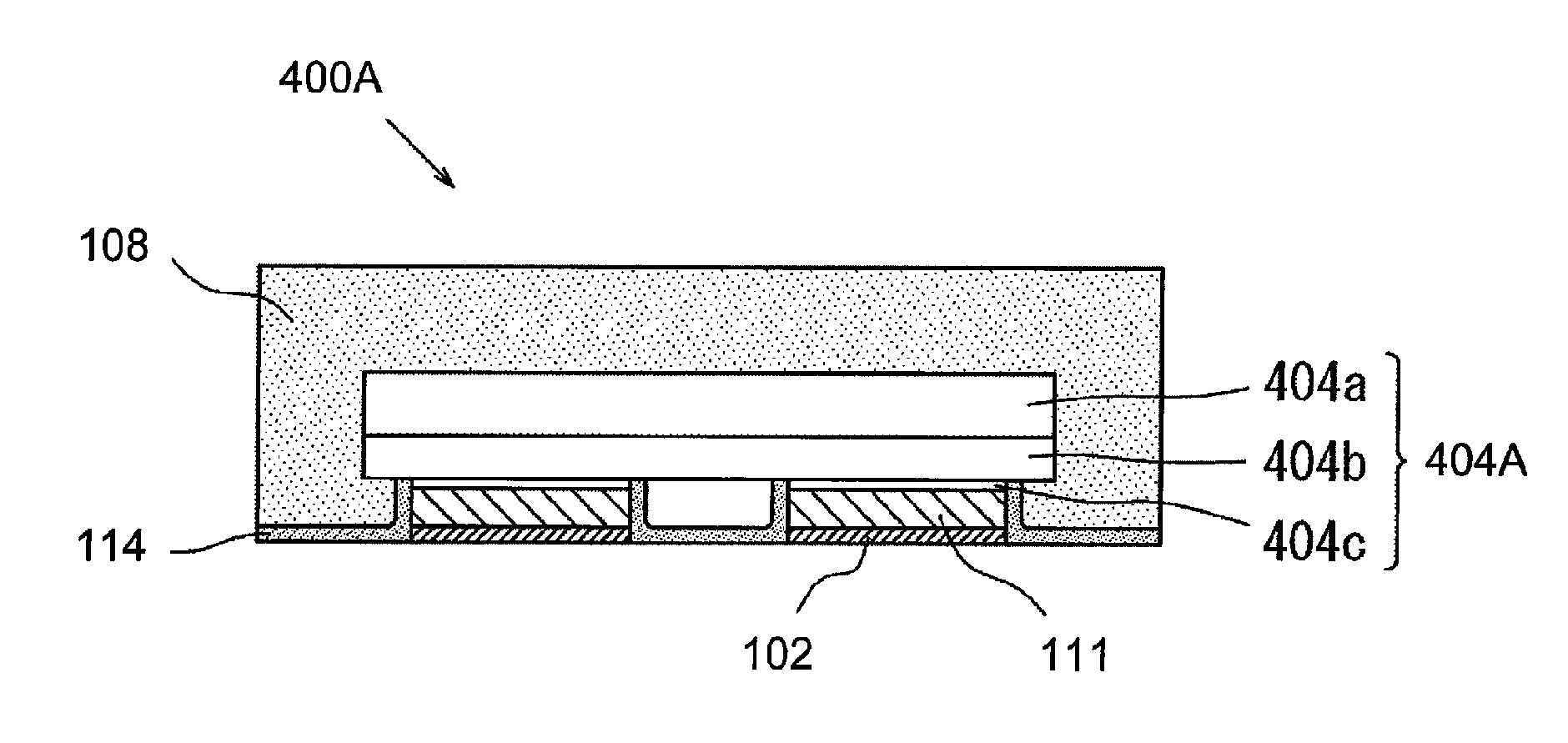
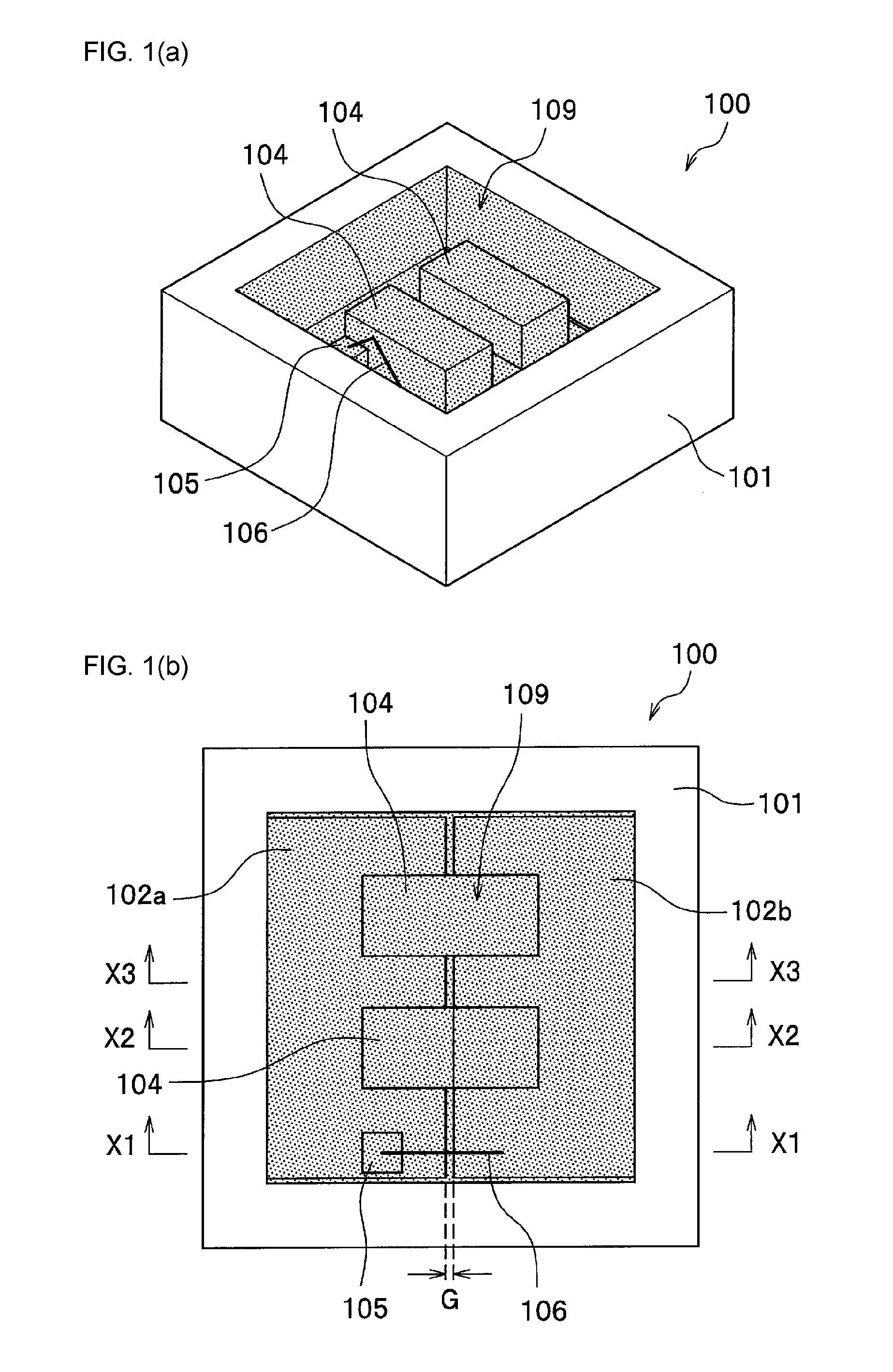
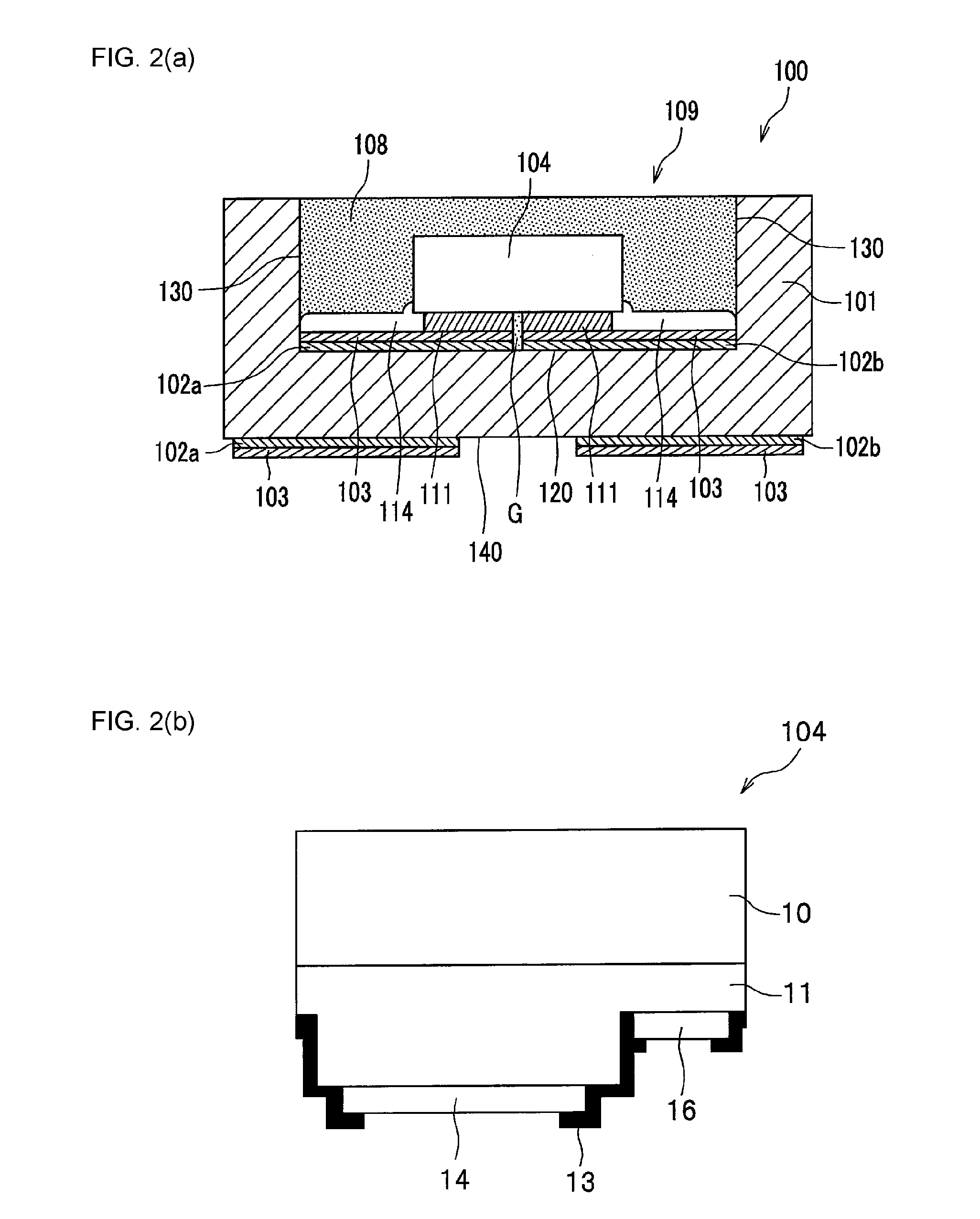
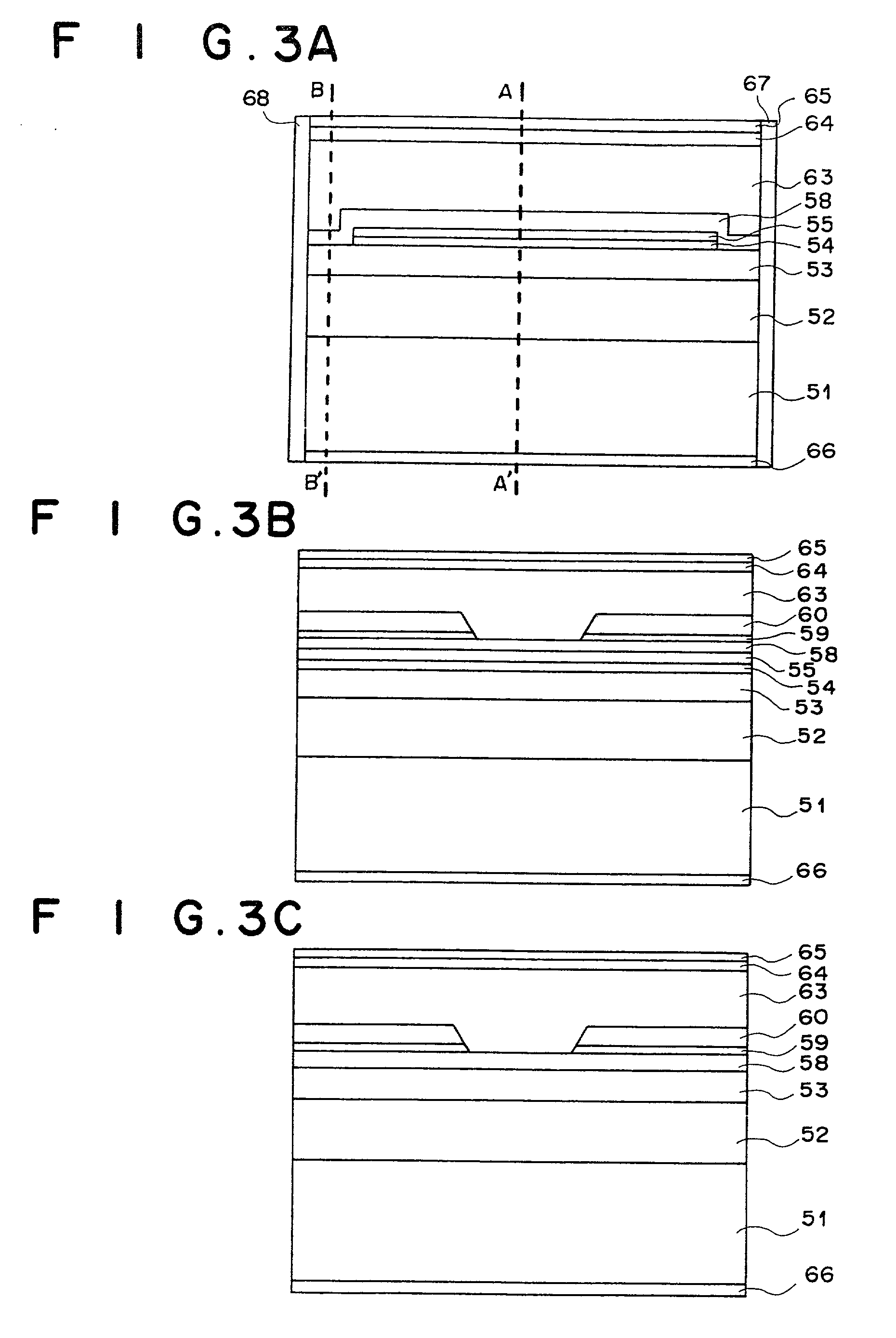
Light emitting device and method for manufacturing light emitting device
ActiveUS20130037842A1Increase productionAvoid light leakageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceLight-emitting diode
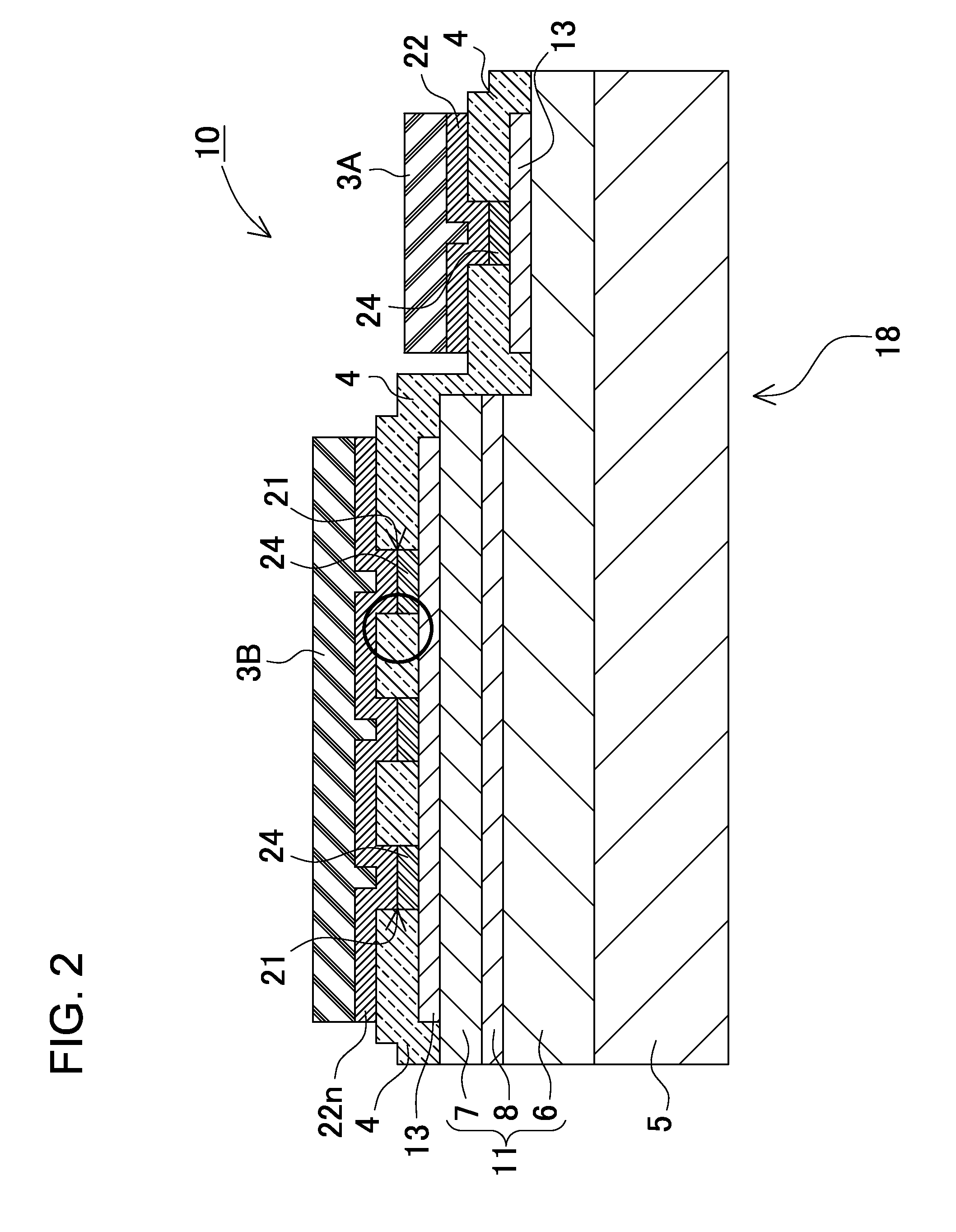
A light emitting device (100) includes a base member (101), electrically conductive members (102a, 102b) disposed on the base member (101), a light emitting element (104) mounted on the electrically conductive members (102a, 102b), an insulating filler (114) covering at least a portion of surfaces of the electrically conductive members (102a, 102b) where the light emitting element (104) is not mounted, and a light transmissive member (108) covering the light emitting element (104).
Owner:NICHIA CORP
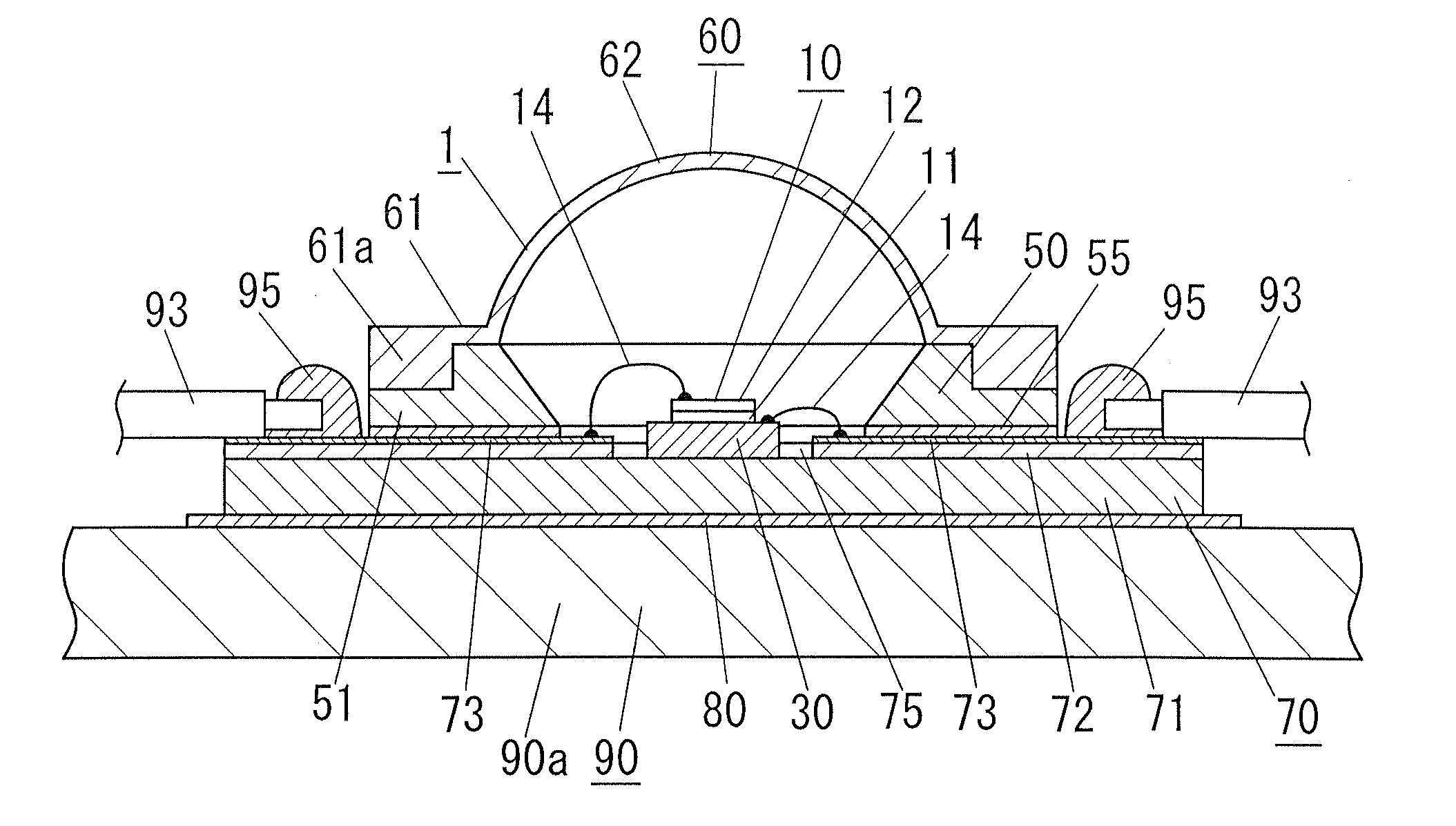
Light-emitting device
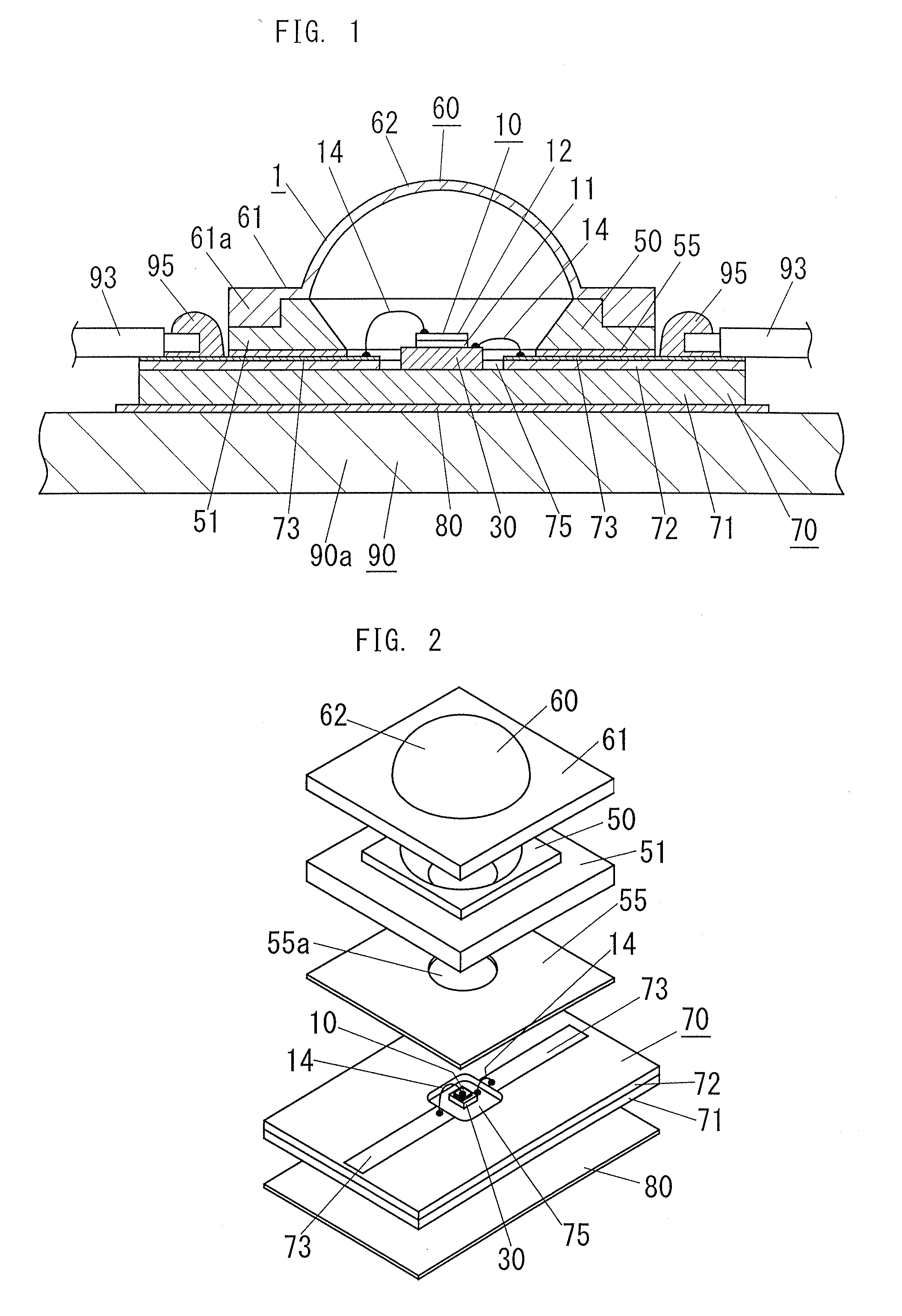
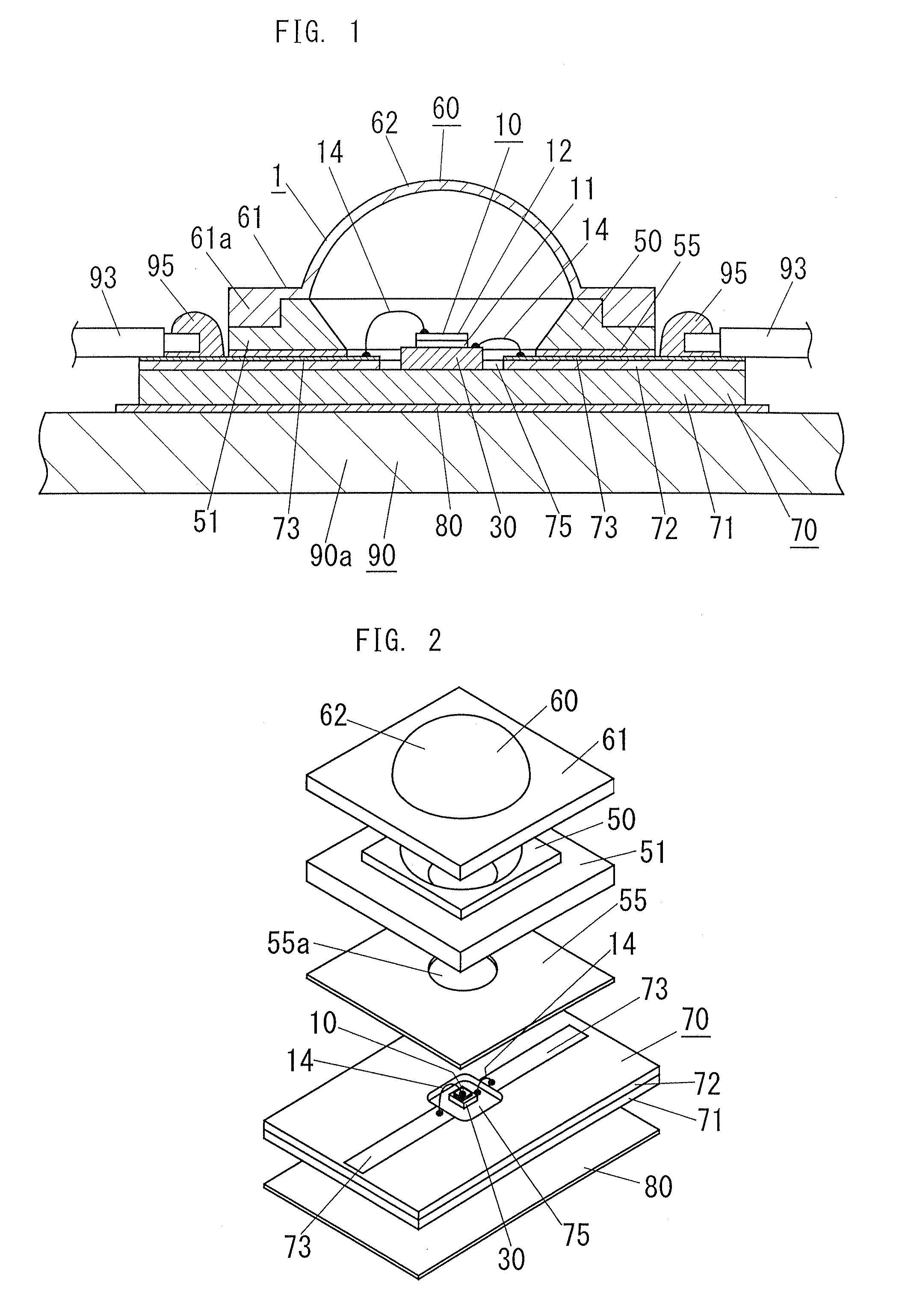
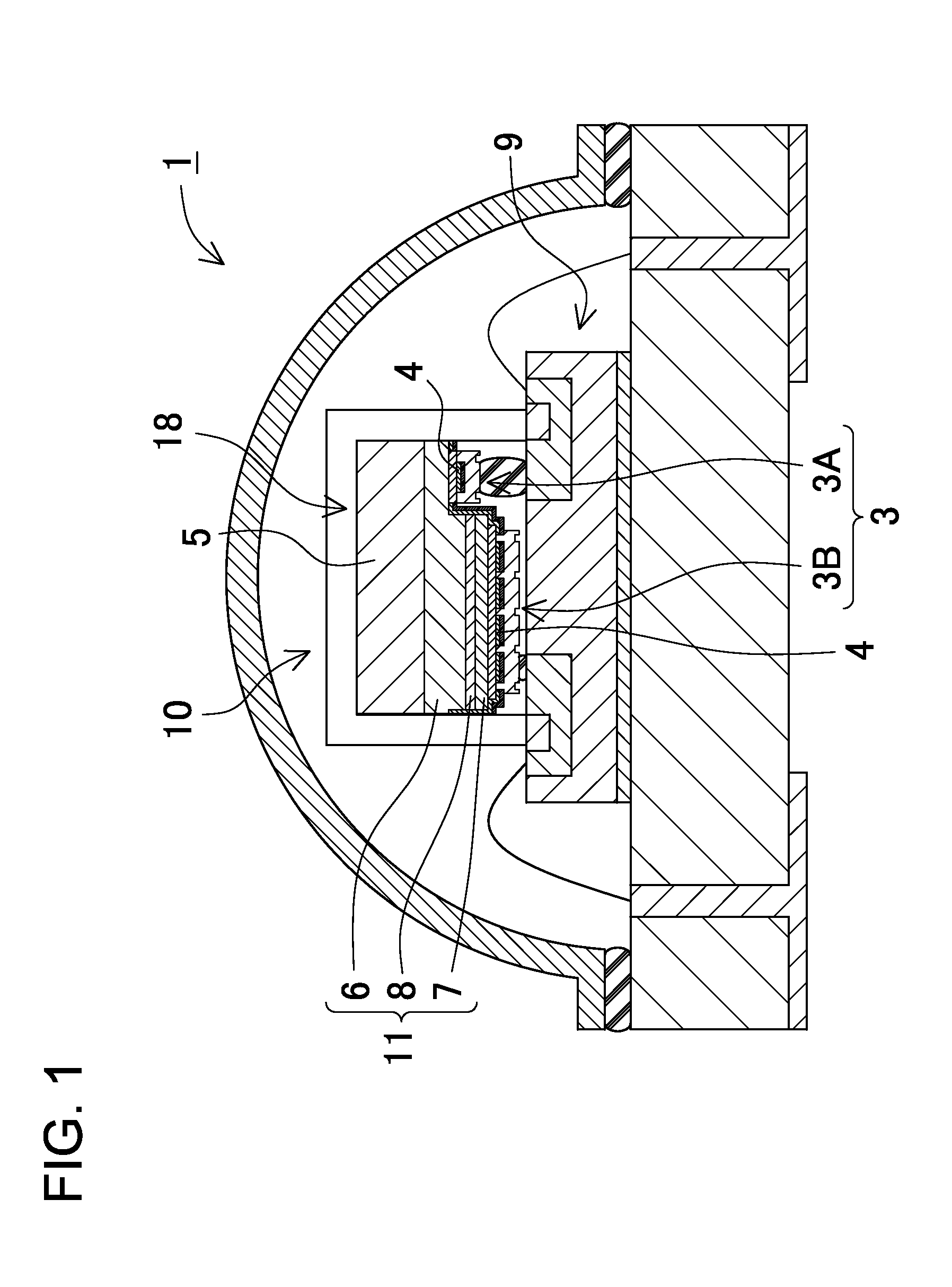
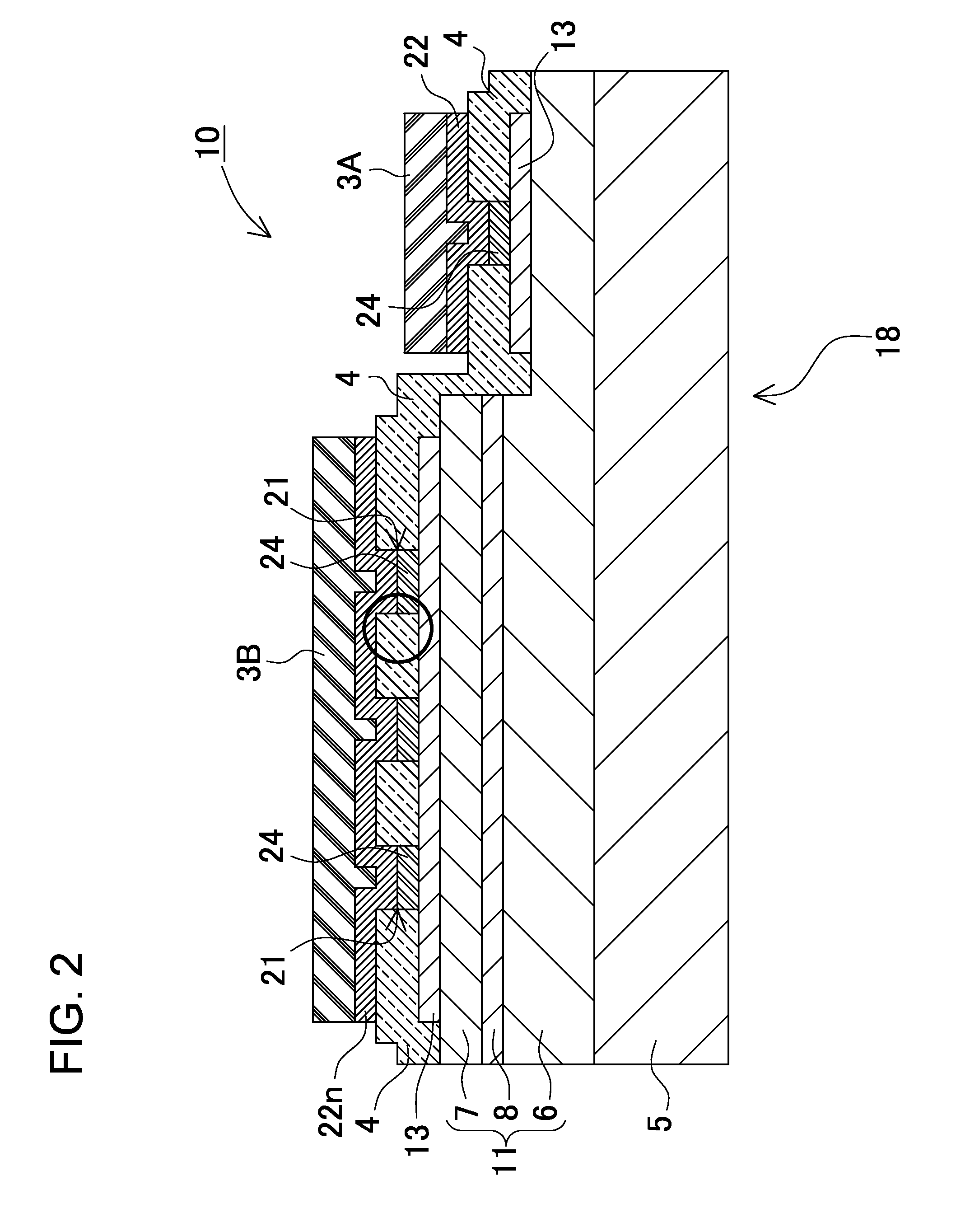
ActiveUS20090026485A1Increase creepage distanceImproved surge protectionPlanar light sourcesLighting support devicesEngineeringElectrical conductor
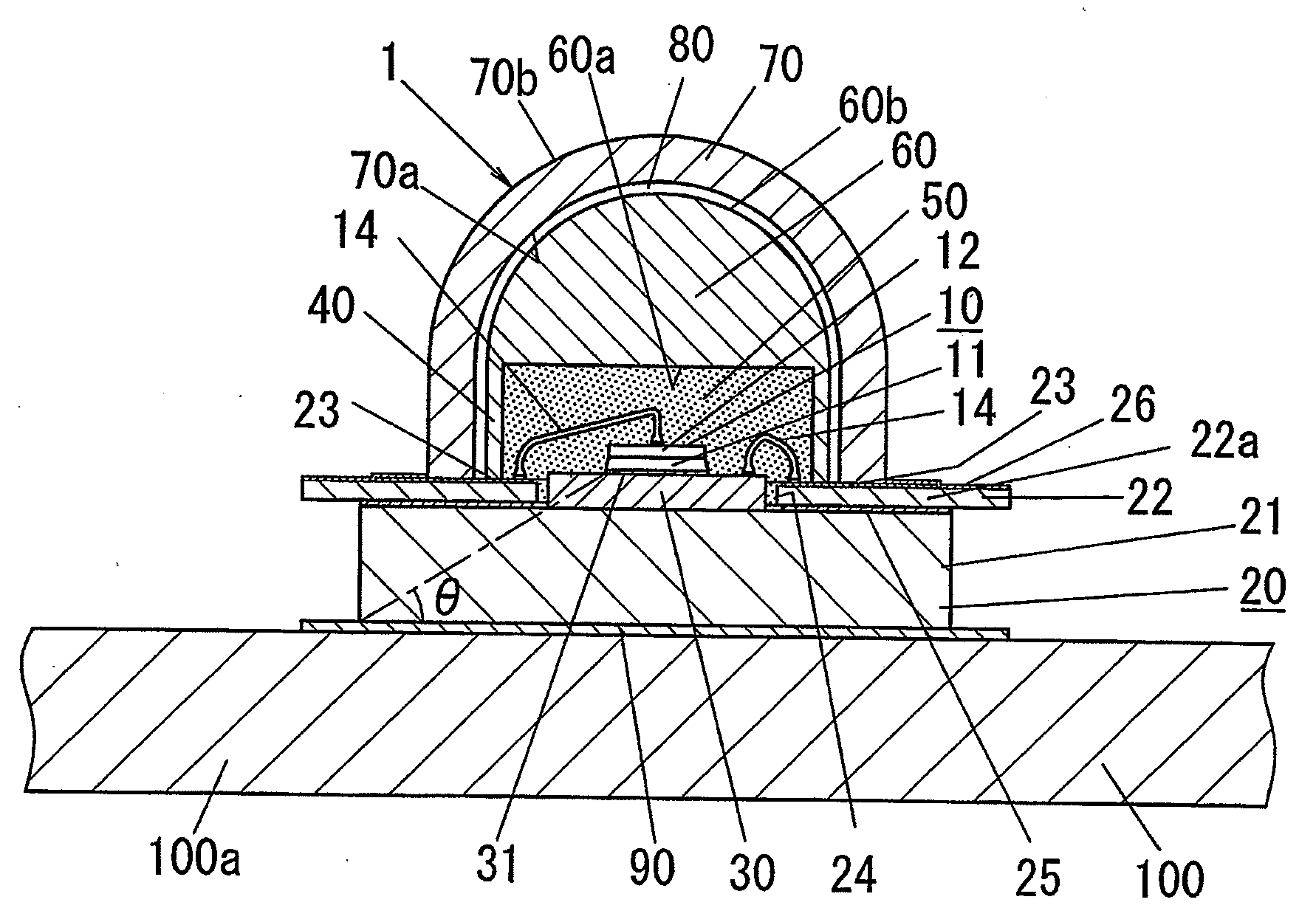
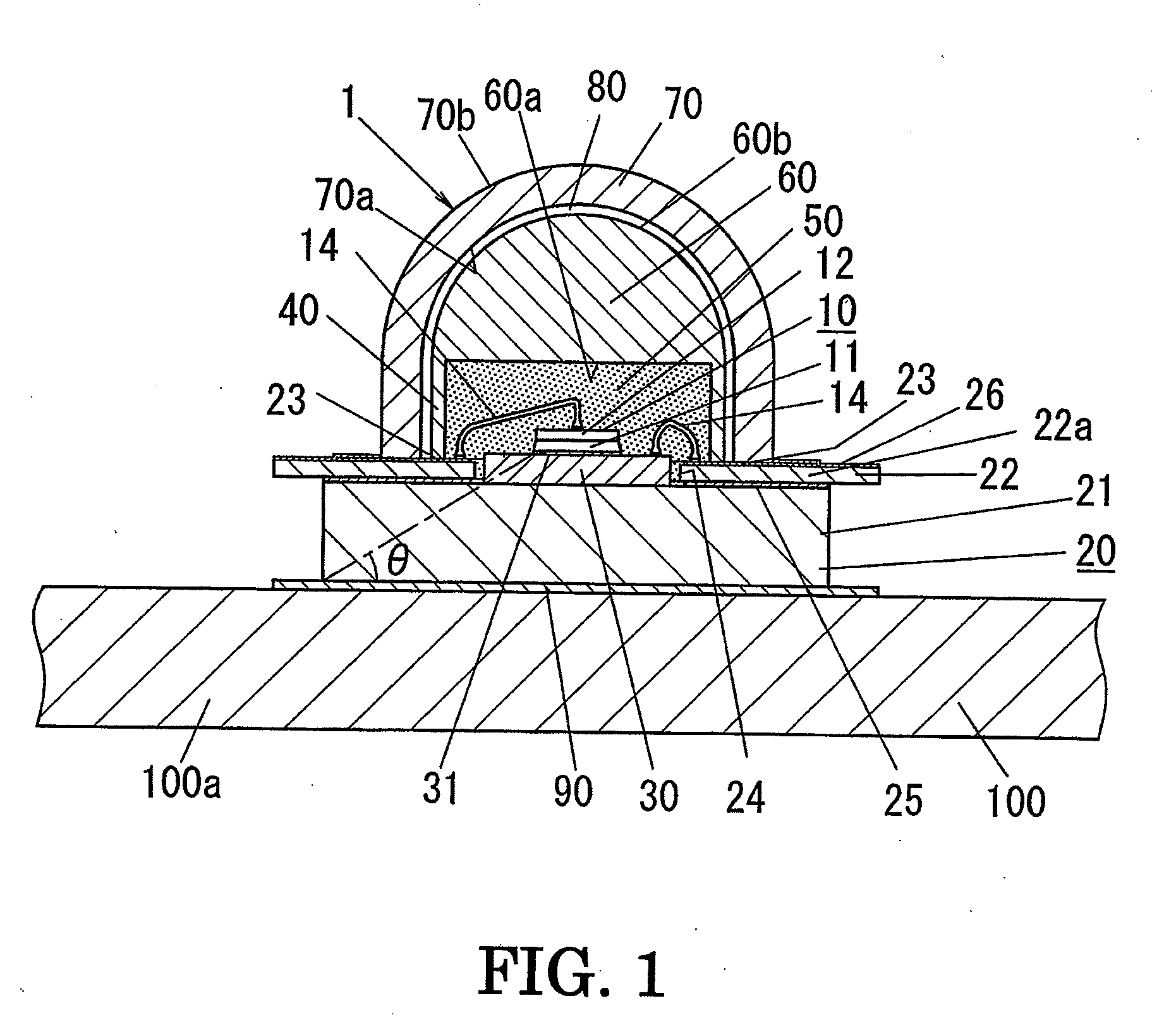
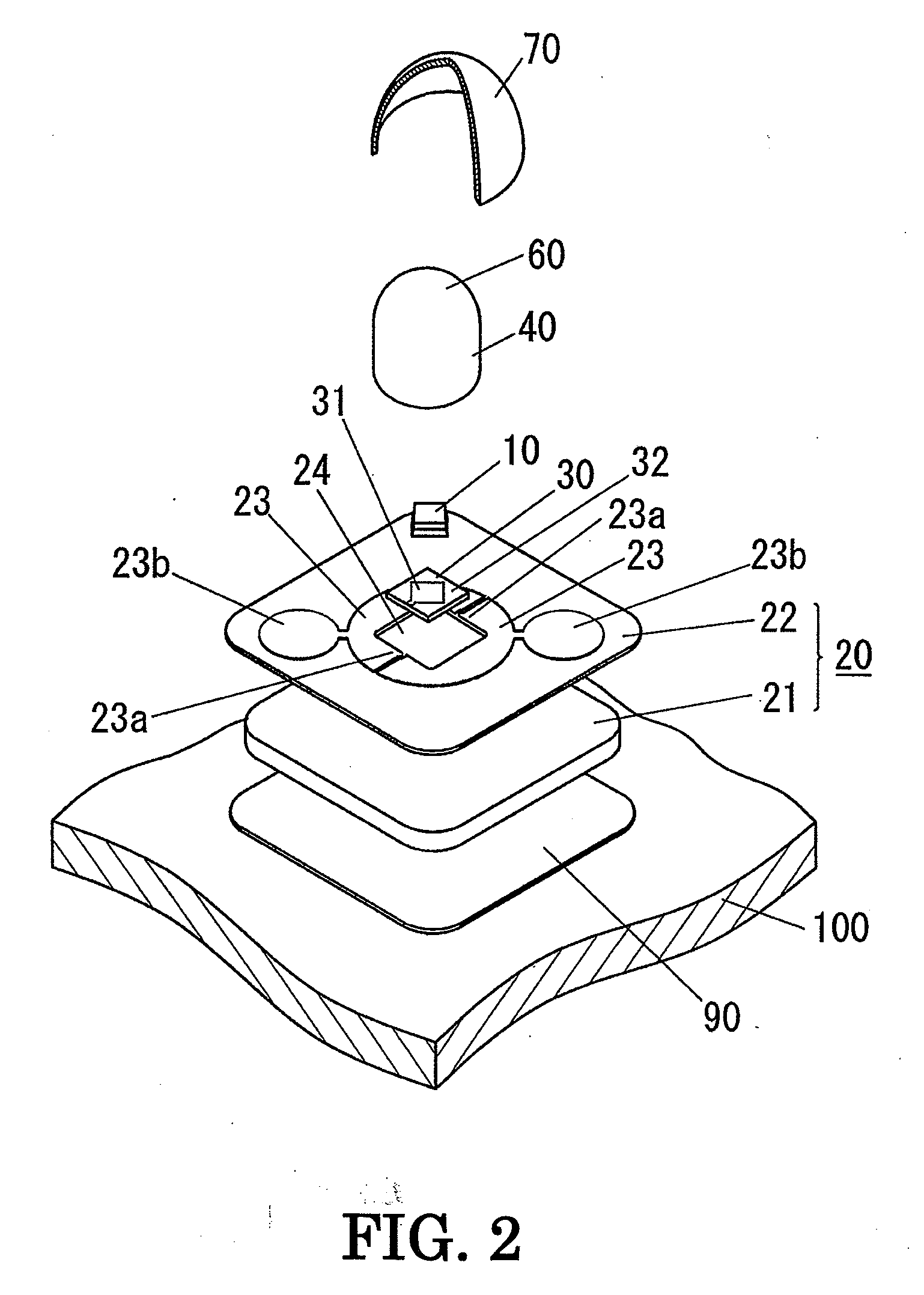
A light-emitting device of the present invention includes: a LED chip 10; a chip mounting member 70 having a conductive plate (heat transfer plate) 71 one surface side of which the LED chip 10 is mounted on and a conductor patterns 73, 73 which is formed on the one surface side of the conductive plate 71 through an insulating part 72 and electrically connected to the LED chip 10; and a sheet-shaped connecting member 80 disposed on the other surface side of the conductive plate 71 to connect the conductive plate 71 to a body of the luminaire 90 which is a metal member for holding the chip mounting member 70. The connecting member 80 is made of a resin sheet which includes a filler and whose viscosity is reduced by heating, and the connecting member 80 has an electrical insulating property and thermally connects the conductive plate 71 and the body 90 of the luminaire to each other.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Light-emitting device
ActiveUS7800124B2Improve optical output powerIncrease powerPlanar light sourcesLighting support devicesLight equipmentElectrical conductor
A light-emitting device of the present invention includes: a LED chip 10; a chip mounting member 70 having a conductive plate (heat transfer plate) 71 one surface side of which the LED chip 10 is mounted on and a conductor patterns 73, 73 which is formed on the one surface side of the conductive plate 71 through an insulating part 72 and electrically connected to the LED chip 10; and a sheet-shaped connecting member 80 disposed on the other surface side of the conductive plate 71 to connect the conductive plate 71 to a body of the luminaire 90 which is a metal member for holding the chip mounting member 70. The connecting member 80 is made of a resin sheet which includes a filler and whose viscosity is reduced by heating, and the connecting member 80 has an electrical insulating property and thermally connects the conductive plate 71 and the body 90 of the luminaire to each other.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Direct cooling of LEDs
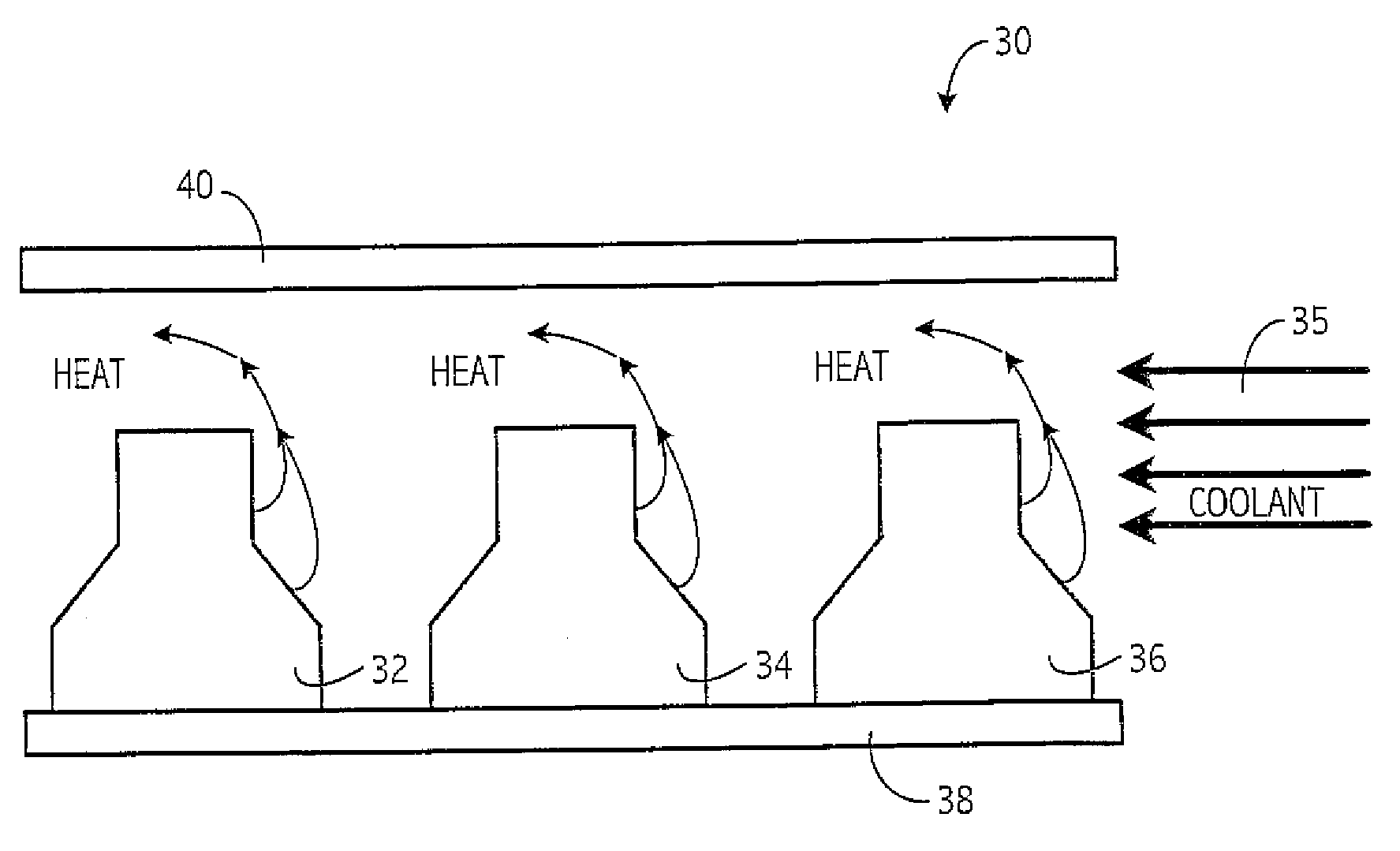
ActiveUS20050253252A1Effective coolingImprove light outputPoint-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLed arrayDevice material
A thermal management system is provided for semiconductor devices such as an LED array, wherein coolant directly cools the LED array. Preferably, the coolant may be selected, among other bases, based on its index of refraction relative to the index associated with the semiconductor device.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
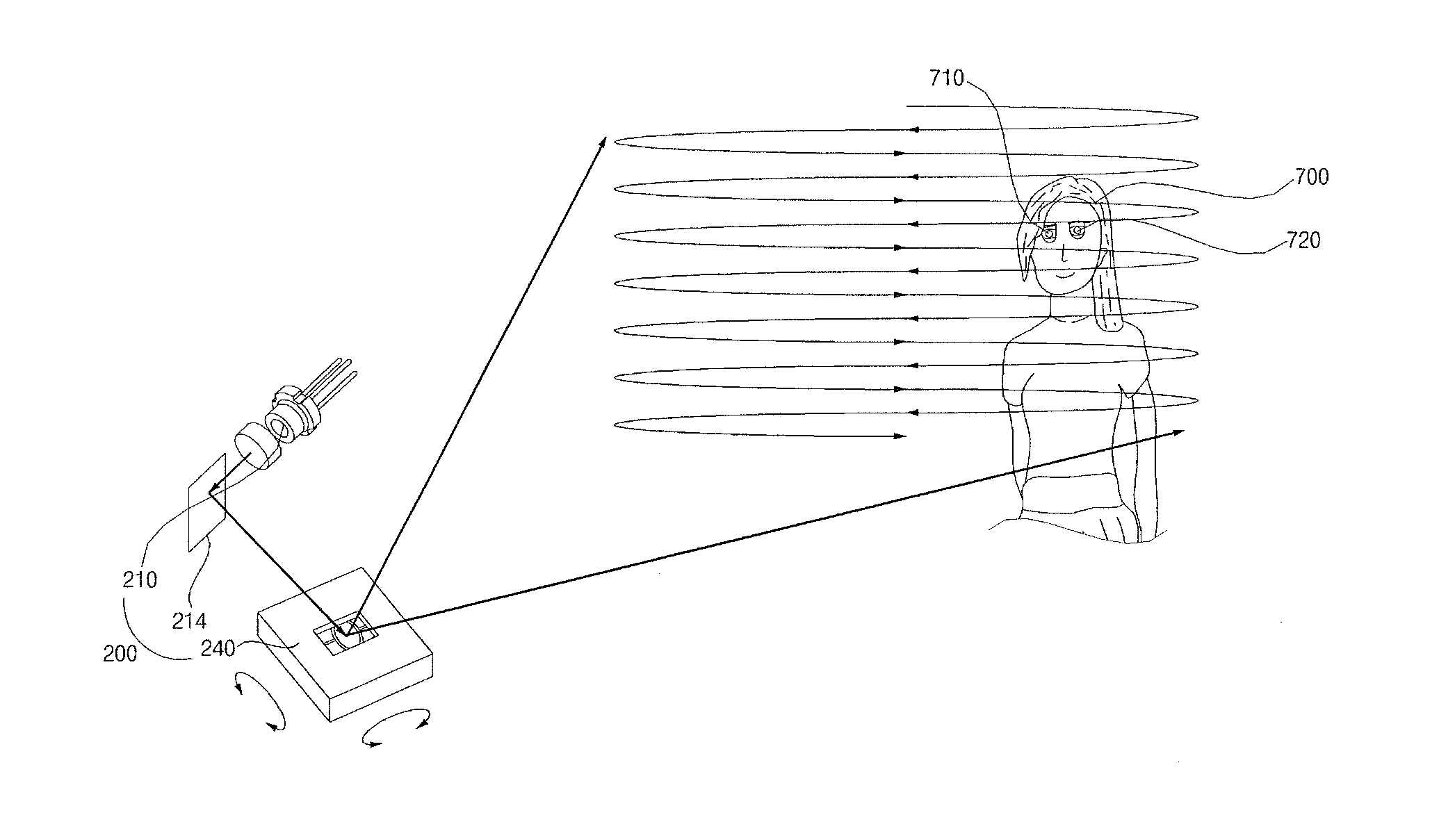
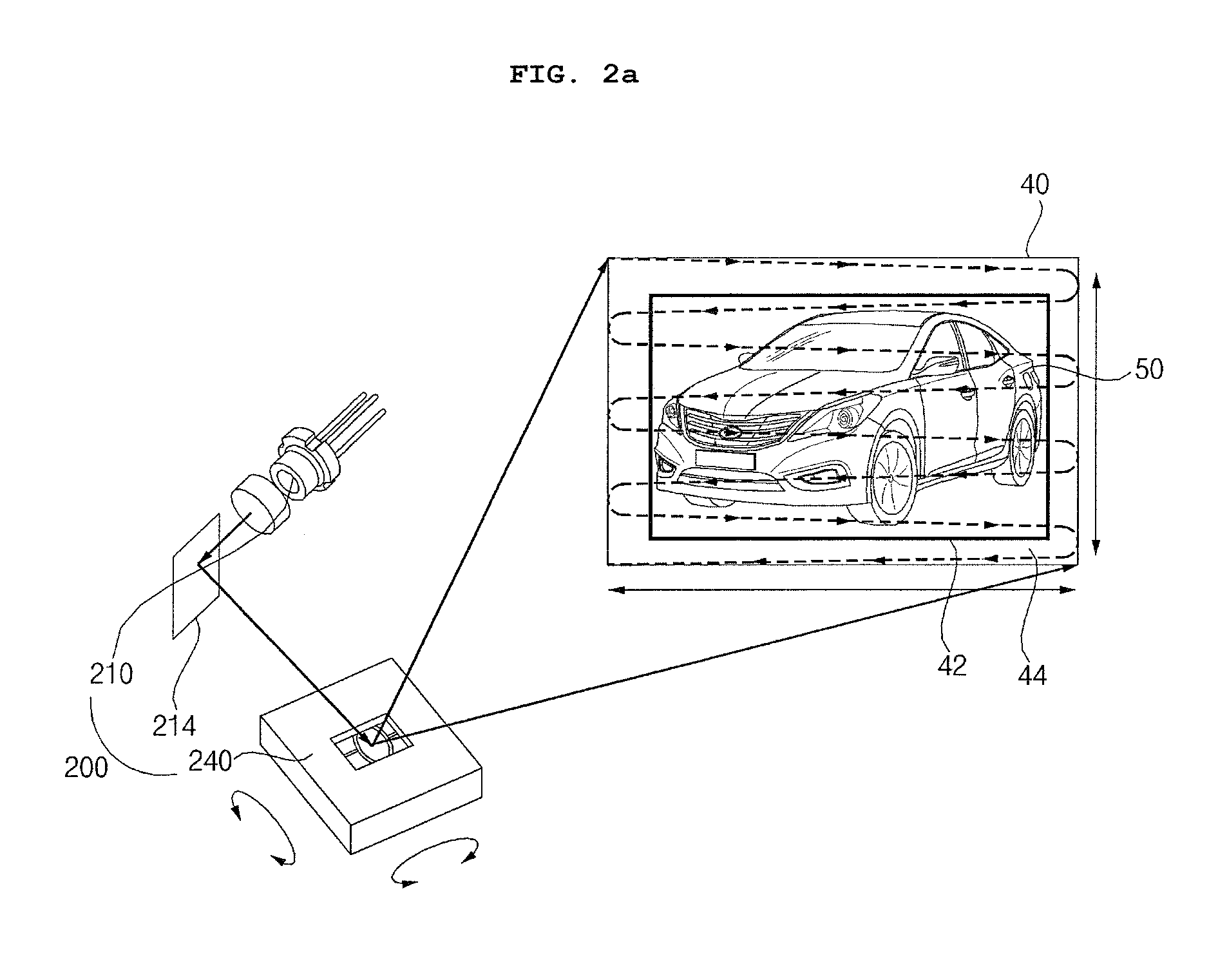
Distance detecting device capable of increasing power of output light and image processing apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20140240317A1Improve optical output powerOptical rangefindersUsing optical meansElectricityImaging processing
A distance detecting device and an image processing apparatus including the same are disclosed. The distance detecting device includes a light source to output light based on a first electric signal, a scanner to sequentially perform first direction a scanner to perform first direction scanning and second direction scanning to output the output light, a detecting unit to detect light received from an external target corresponding to the output light and to convert the received light into a second electric signal, and a processor to calculate a distance from the external target based on the first electric signal and the second electric signal and to control the light source to vary intensity or level of the output light. Consequently, power of light output to the external target is increased.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
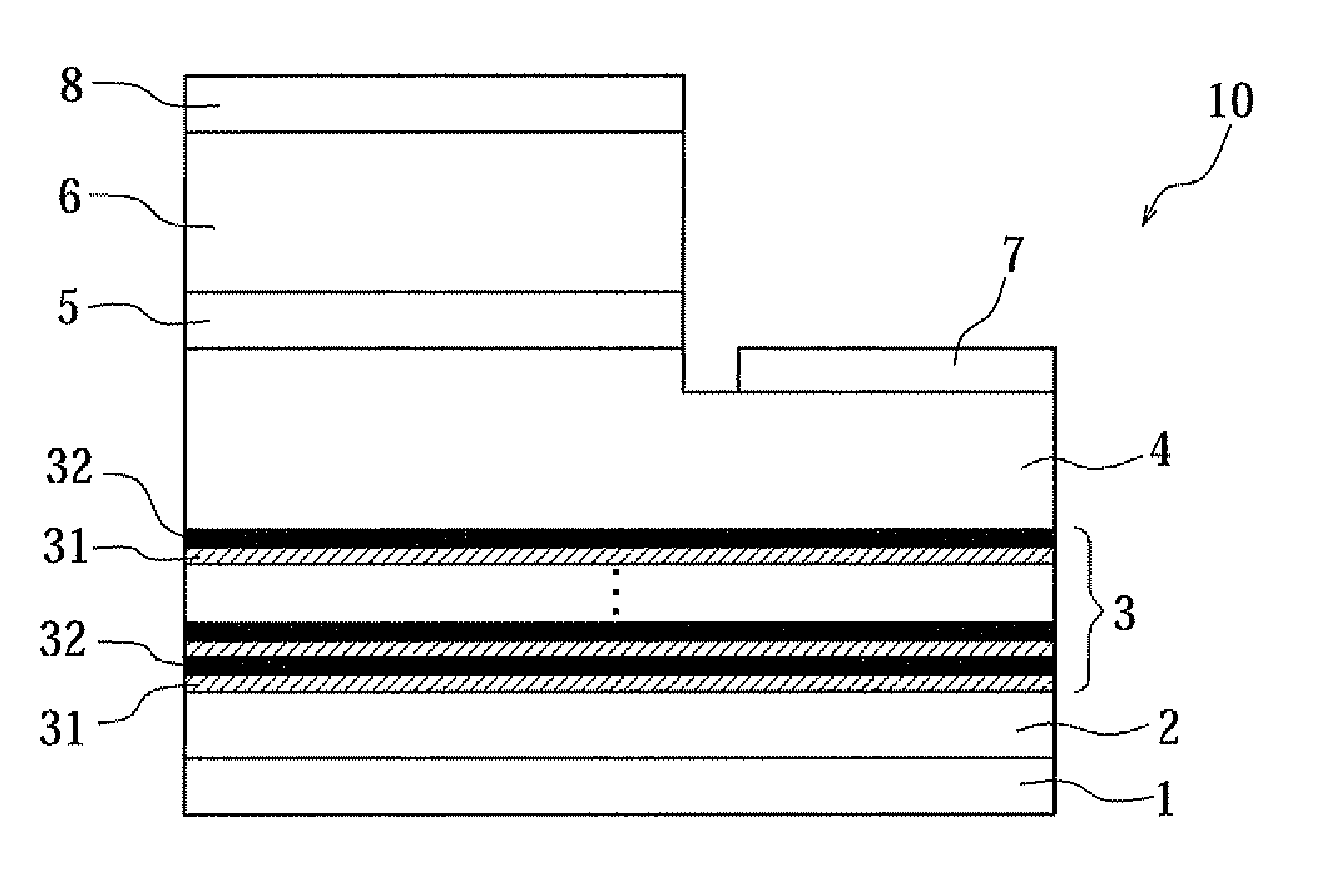
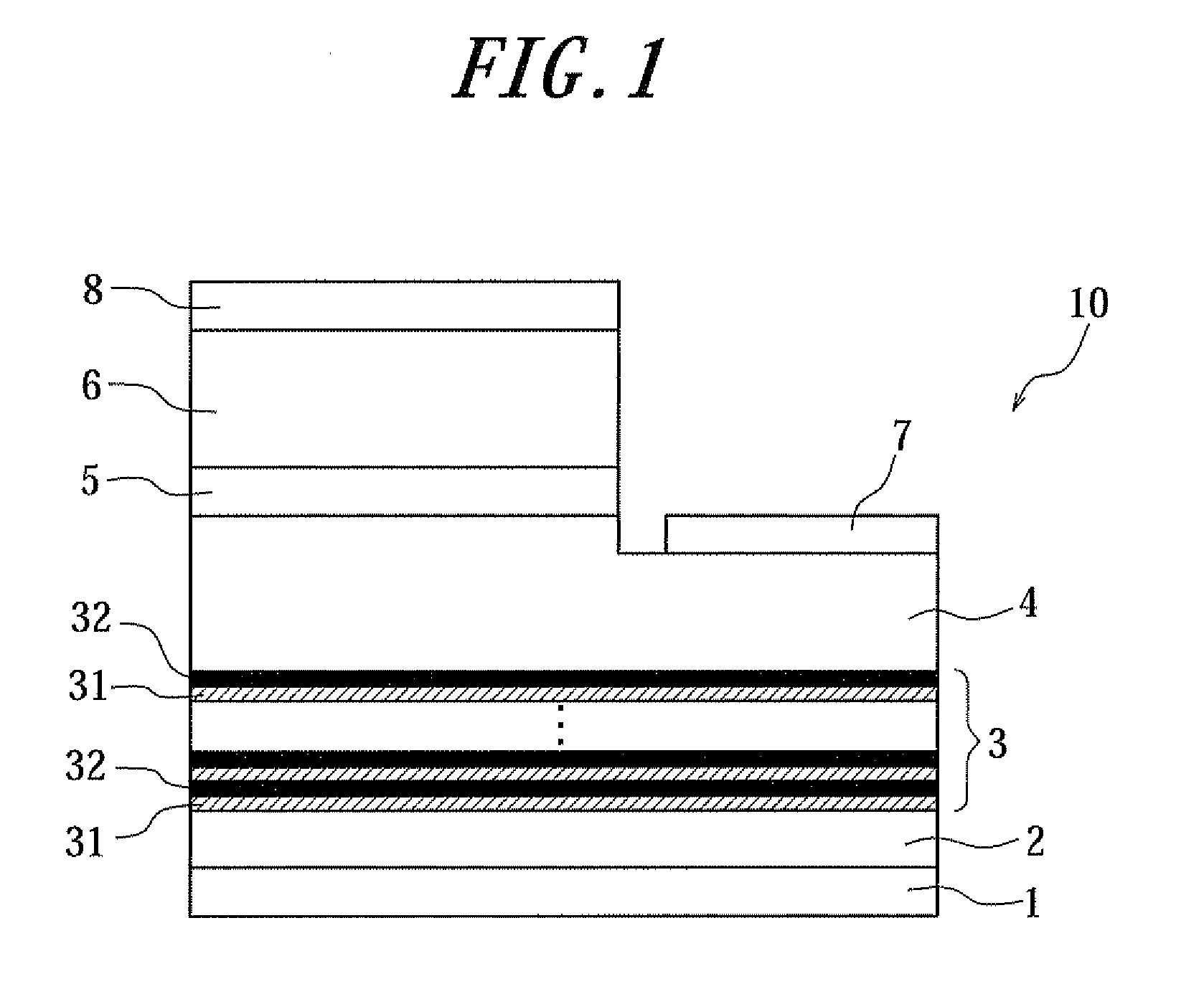
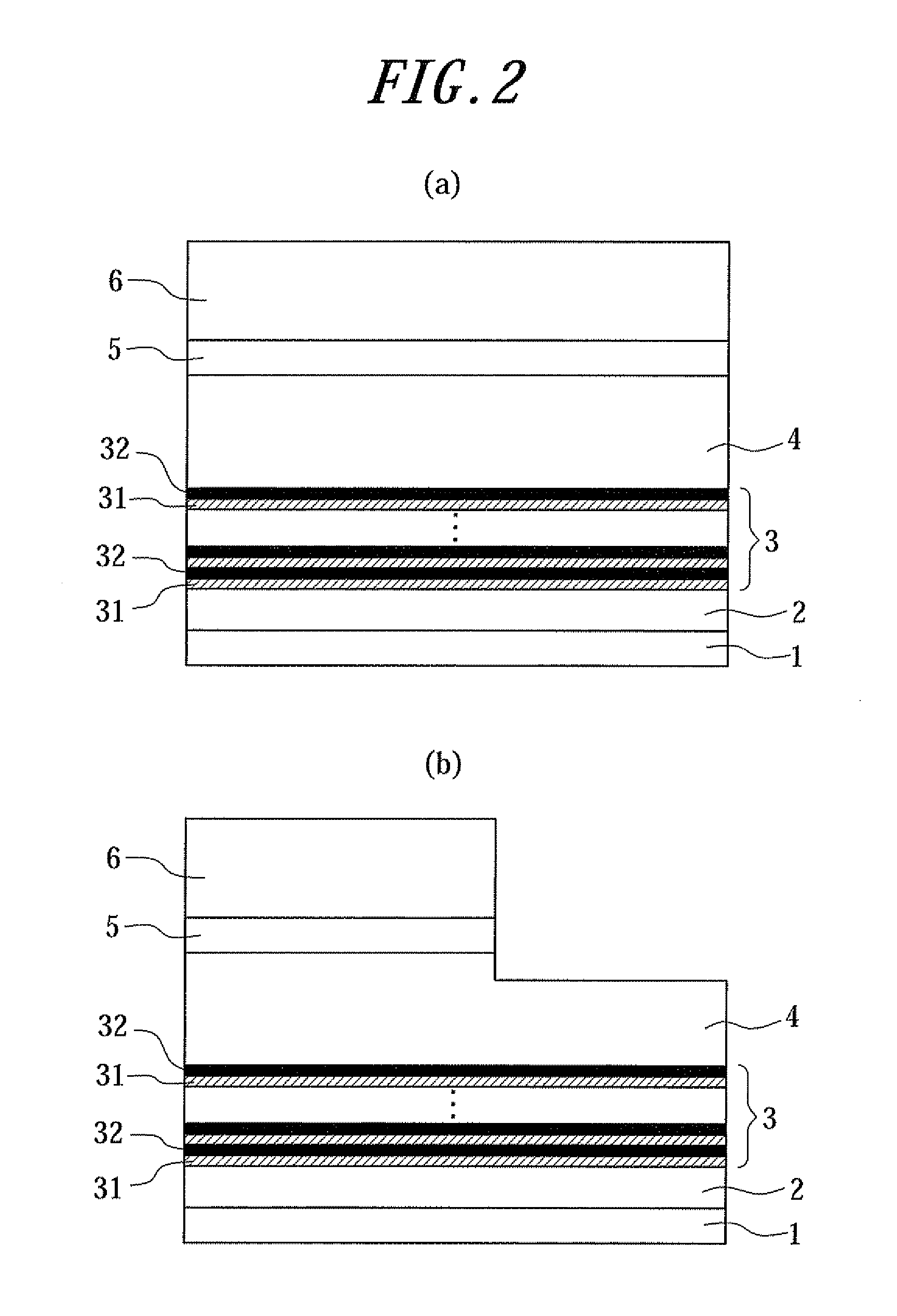
Nitride semiconductor device and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20120175589A1Improve current characteristicsImprove flatnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceCrystallinity
A nitride semiconductor device is provided, in which a superlattice strain buffer layer using AlGaN layers having a low Al content or GaN layers is formed with good flatness, and a nitride semiconductor layer with good flatness and crystallinity is formed on the superlattice strain buffer layer. A nitride semiconductor device includes a substrate; an AlN strain buffer layer made of AlN formed on the substrate; a superlattice strain buffer layer formed on the AlN strain buffer layer; and a nitride semiconductor layer formed on the superlattice strain buffer layer, and is characterized in that the superlattice strain buffer layer has a superlattice structure formed by alternately stacking first layers made of AlxGa1−xN (0≦x≦0.25), which further contain p-type impurity, and second layers made of AlN.
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
Semiconductor light emitting device including metal reflecting layer
ActiveUS20130049053A1Improve reliabilityImprove optical output powerSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureReflective layer
A semiconductor light emitting device includes a semiconductor structure, a transparent electrically-conducting layer, a dielectric film, and a metal reflecting layer. The semiconductor structure includes an active region. The transparent electrically-conducting layer is formed on the upper surface of the semiconductor structure. The dielectric film is formed on the upper surface of the transparent electrically-conducting layer. The metal reflecting layer is formed on the upper surface of the dielectric film. The dielectric film has at least one opening whereby partially exposing the transparent electrically-conducting layer. The transparent electrically-conducting layer is electrically connected to the metal reflecting layer through the opening. A barrier layer is partially formed and covers the opening so that the barrier layer is interposed between the transparent electrically-conducting layer and the metal reflecting layer.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
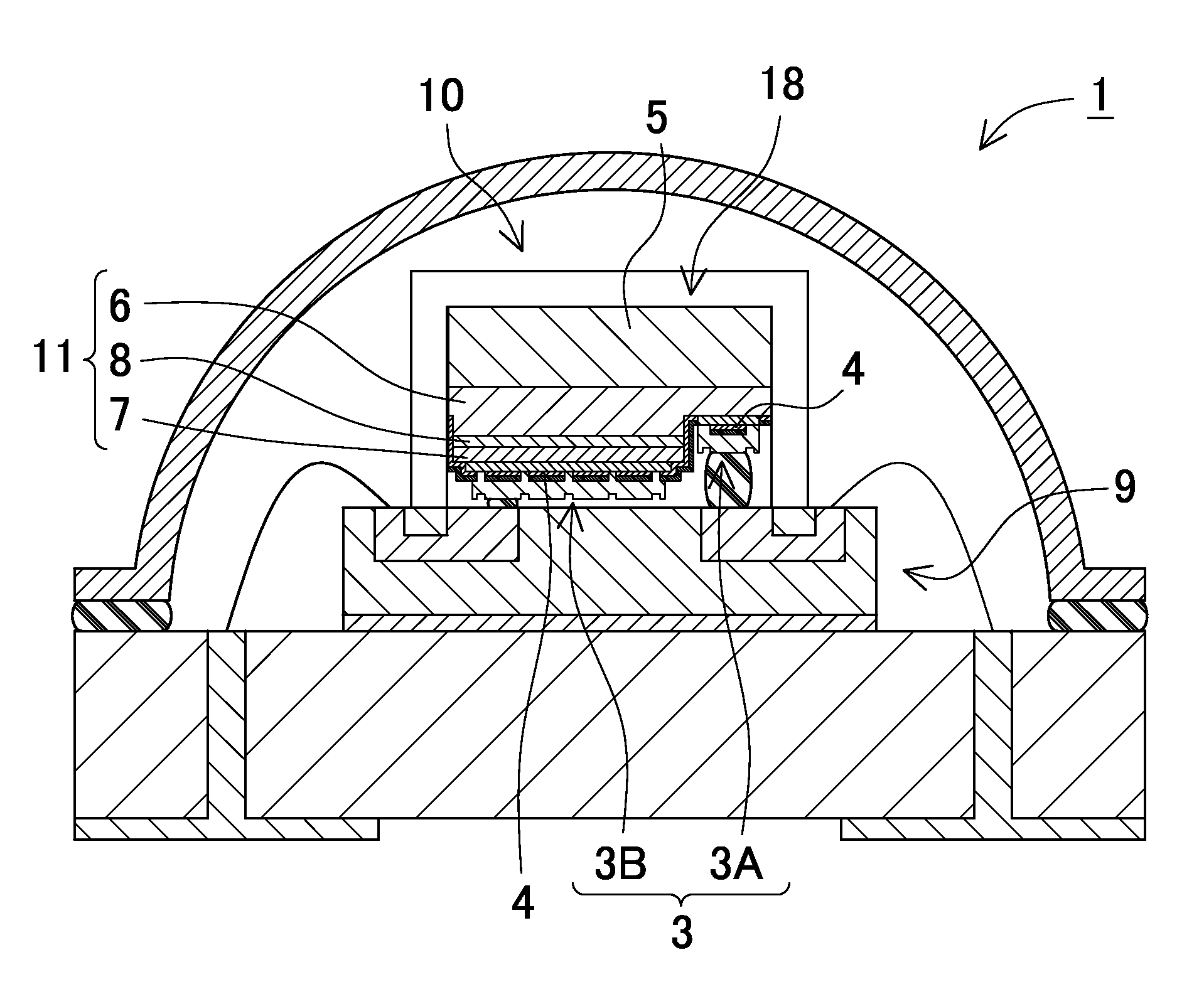
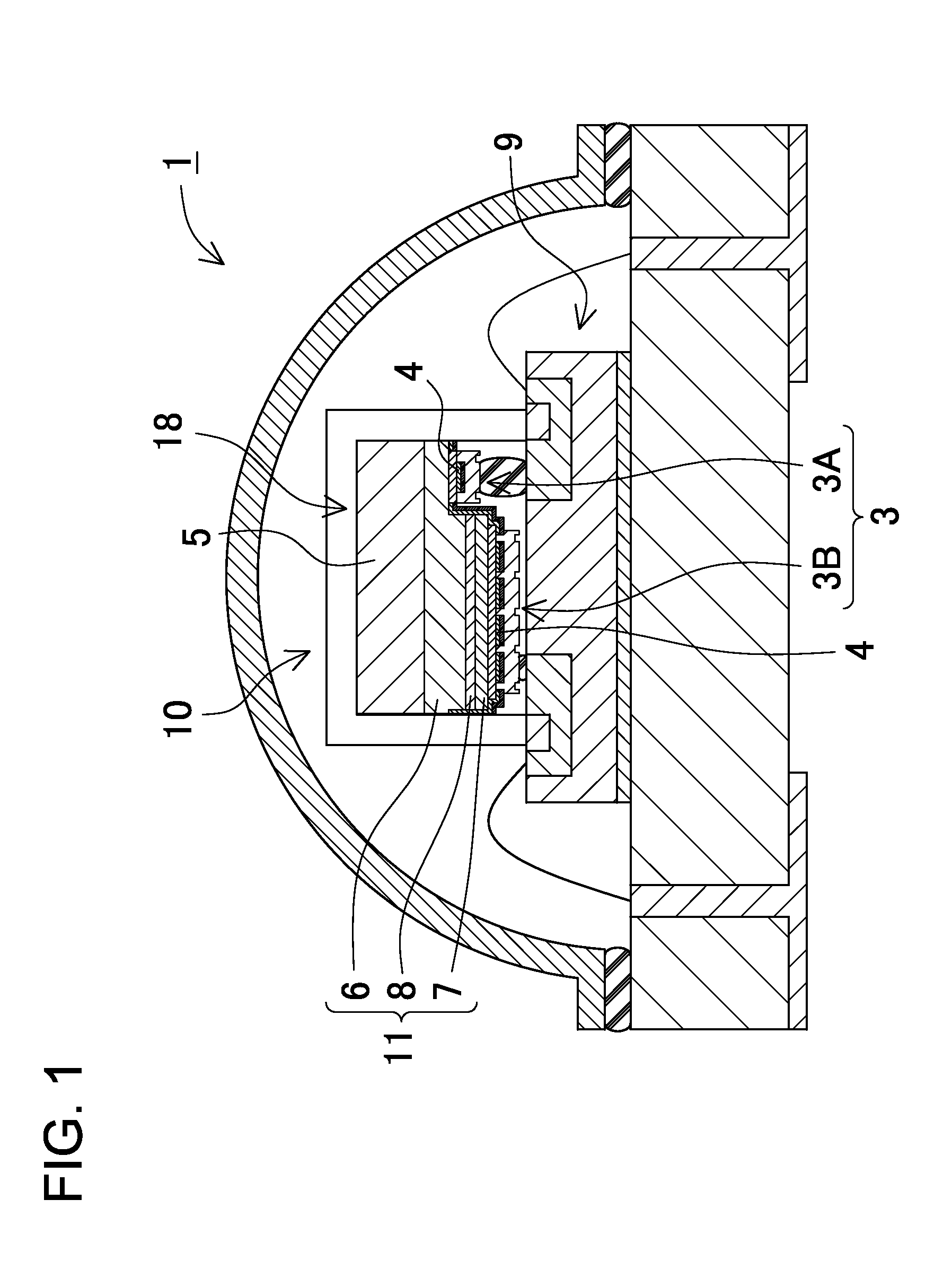
LED lighting fixture
InactiveUS20100148196A1Inhibit transferIncrease temperatureLighting support devicesSolid-state devicesConductive materialsColor changes
A light-emitting device held on a fixture body includes an LED chip, a heat transfer plate made of a thermally conductive material on which the LED chip is mounted, a wiring board having, on one side, patterned conductors, for supplying an electric power to the LED chip and formed with an aperture (exposure part) through which a LED chip mount surface of the heat transfer plate is exposed, an encapsulation part in which the LED chip is encapsulated on the one side of the wiring board, and a dome-shaped color-changing member made of a fluorescent material and an optically transparent material and placed on the one side of the wiring board. The light-emitting device is bonded to the fixture body with an insulating layer interposed therebetween, and the insulating layer has electrical insulating properties and is interposed between the heat transfer plate and the fixture body to thermally couple the same.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
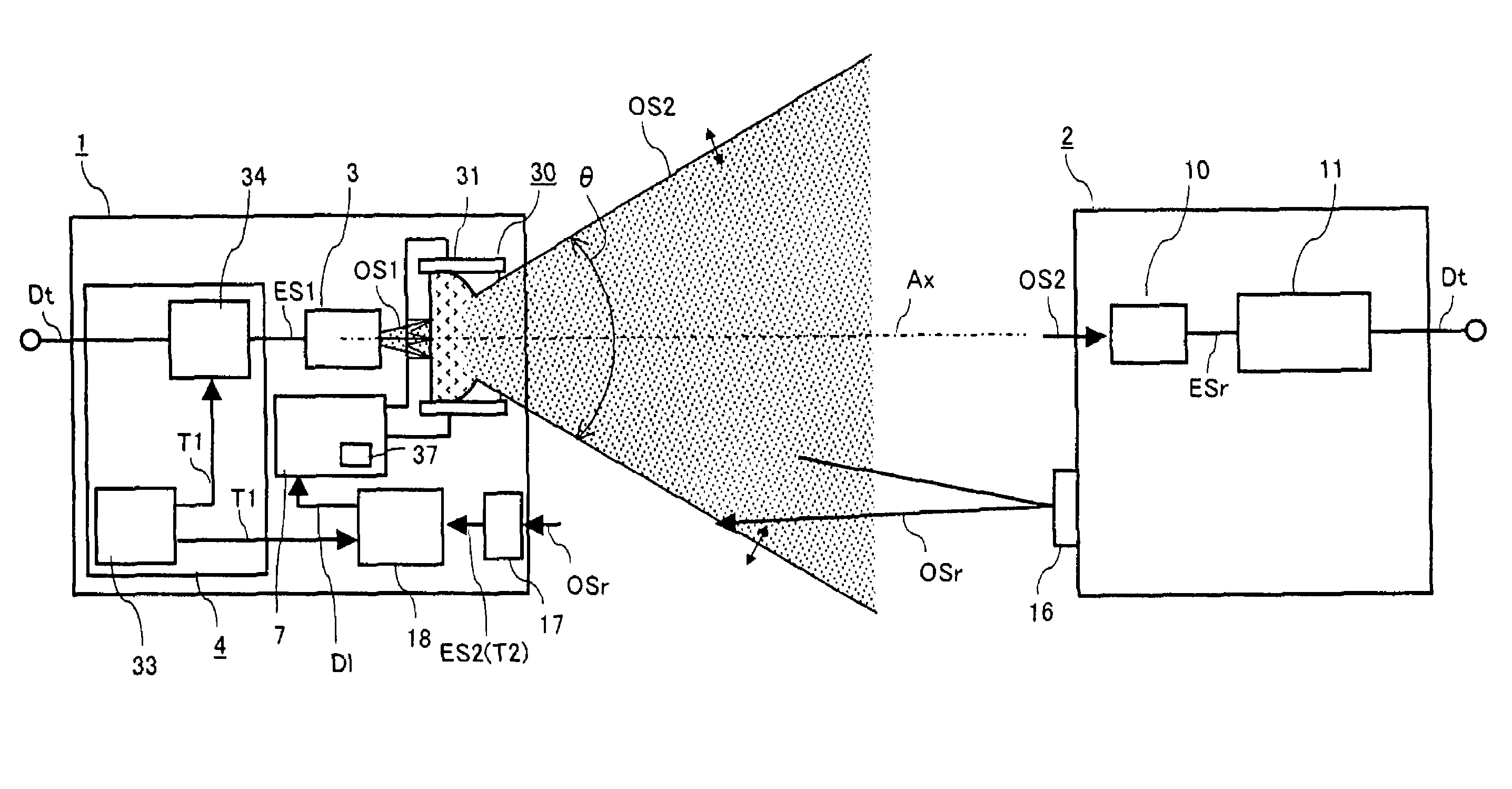
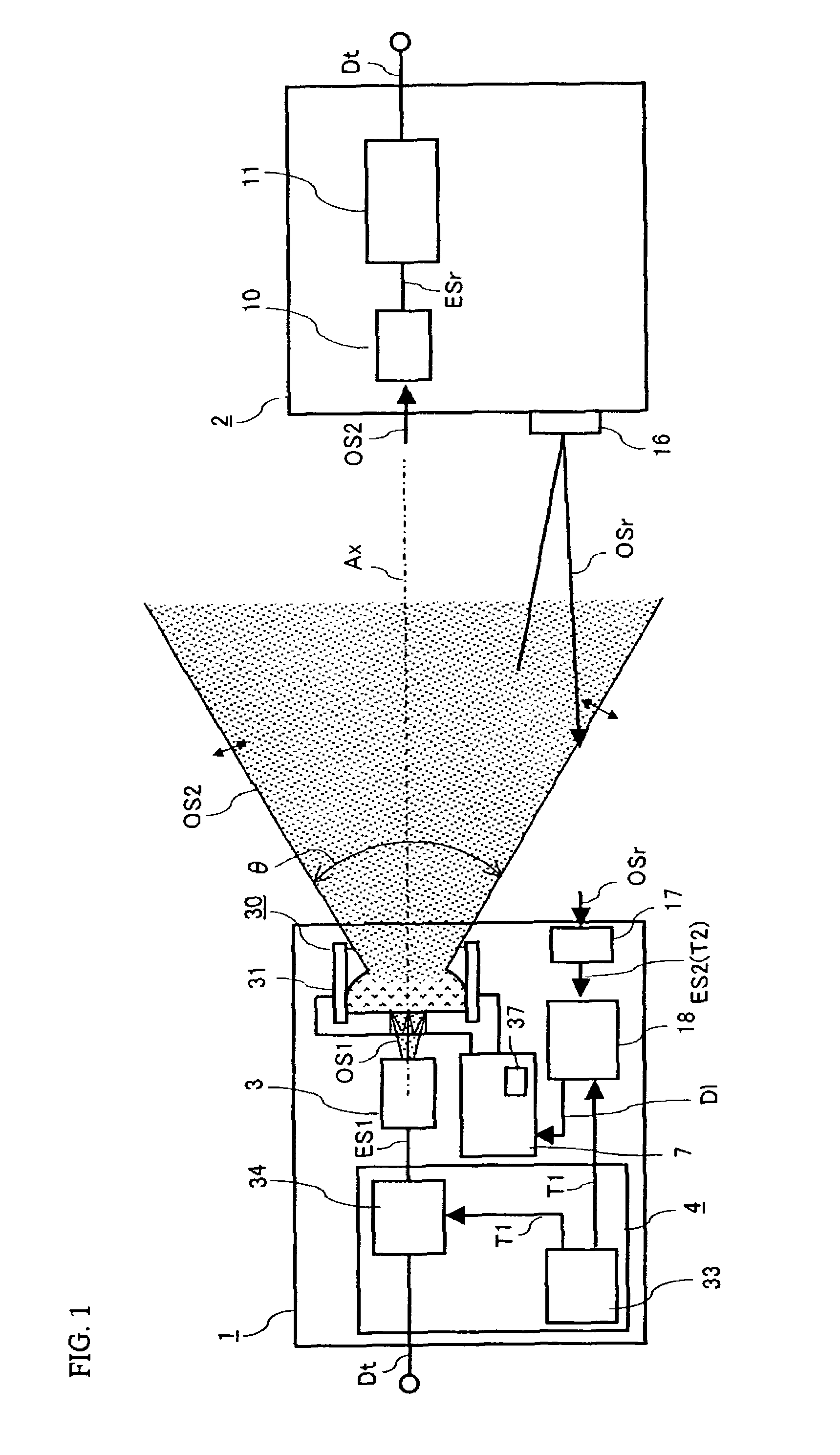
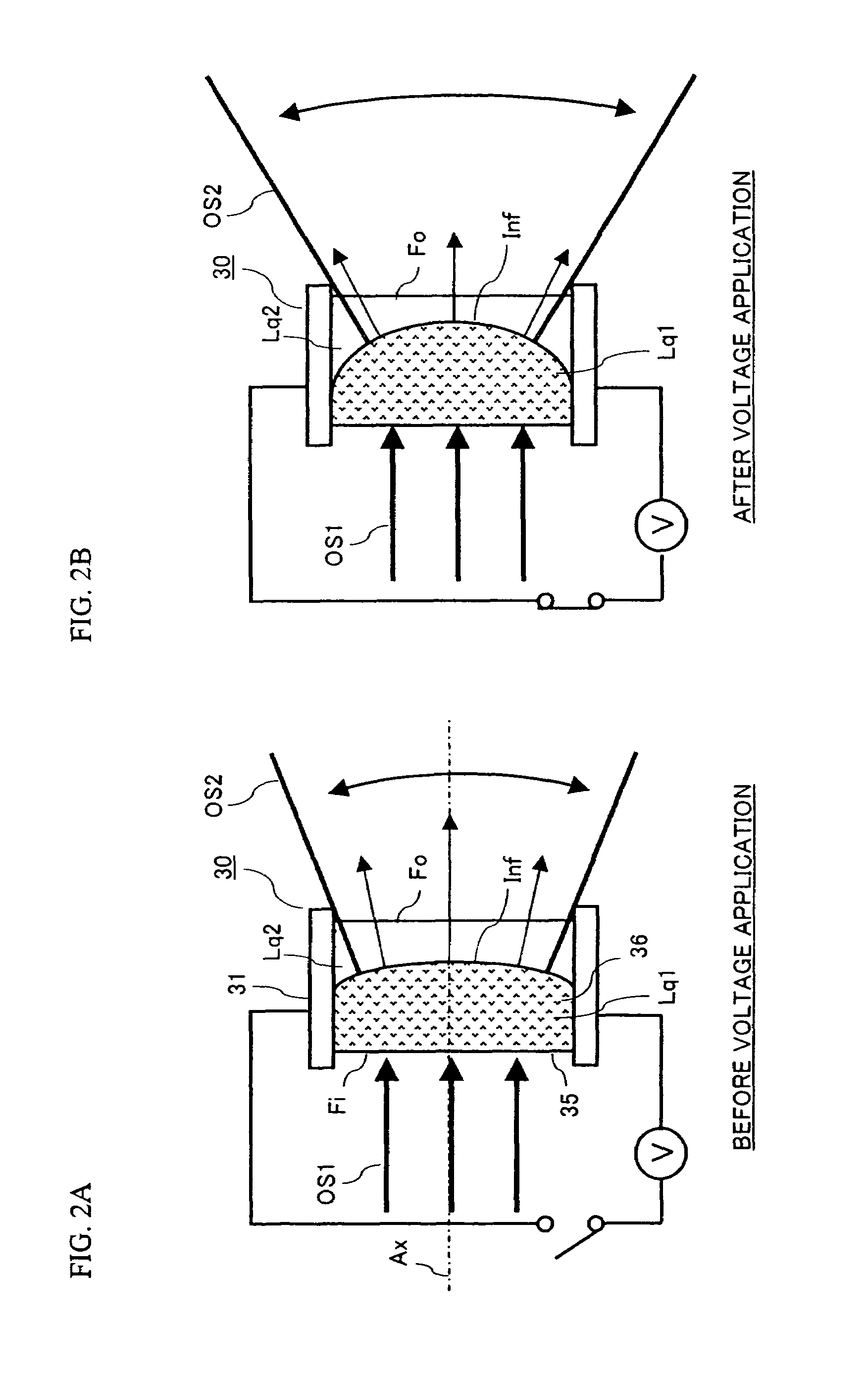
Optical transmitter
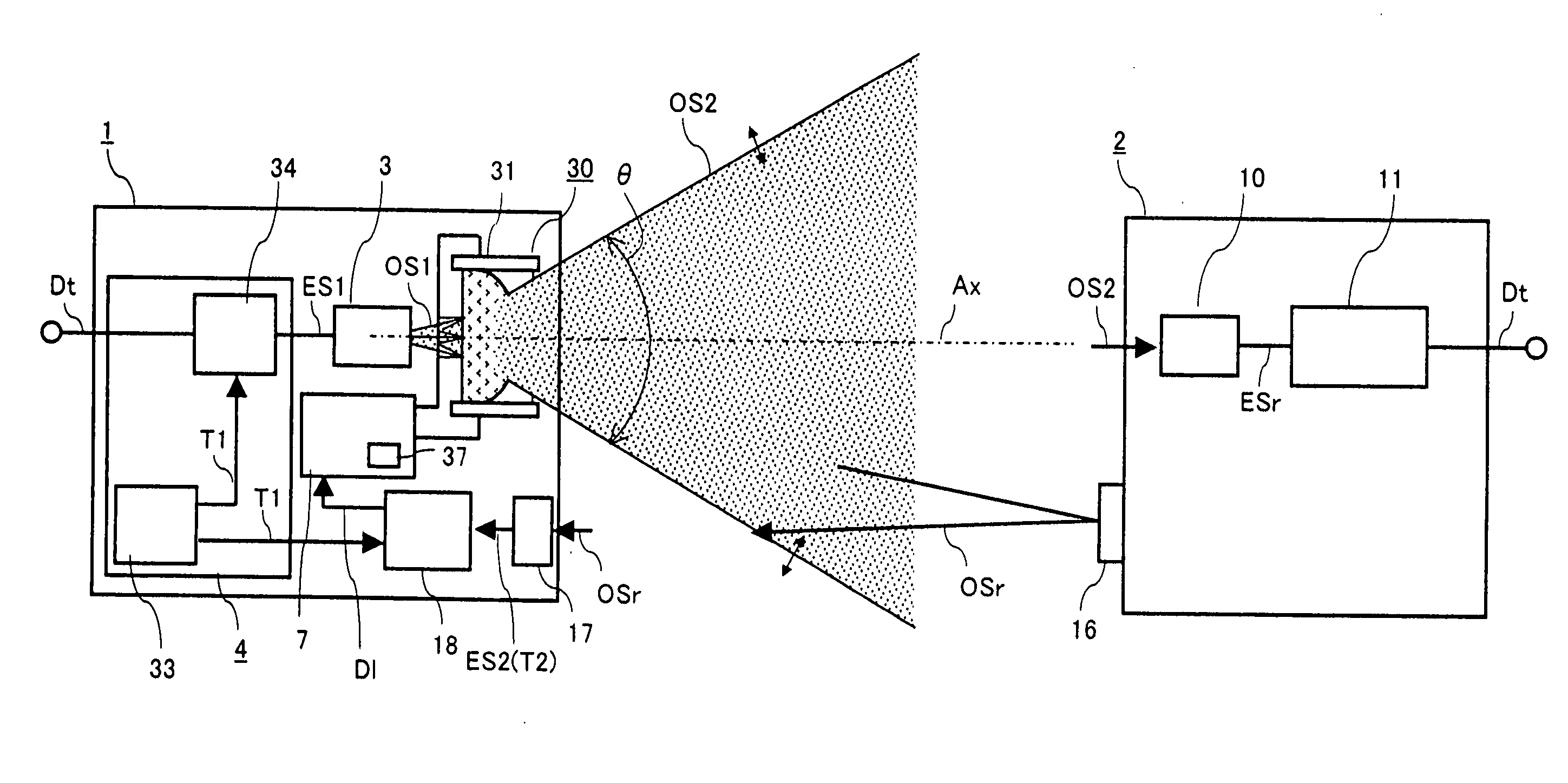
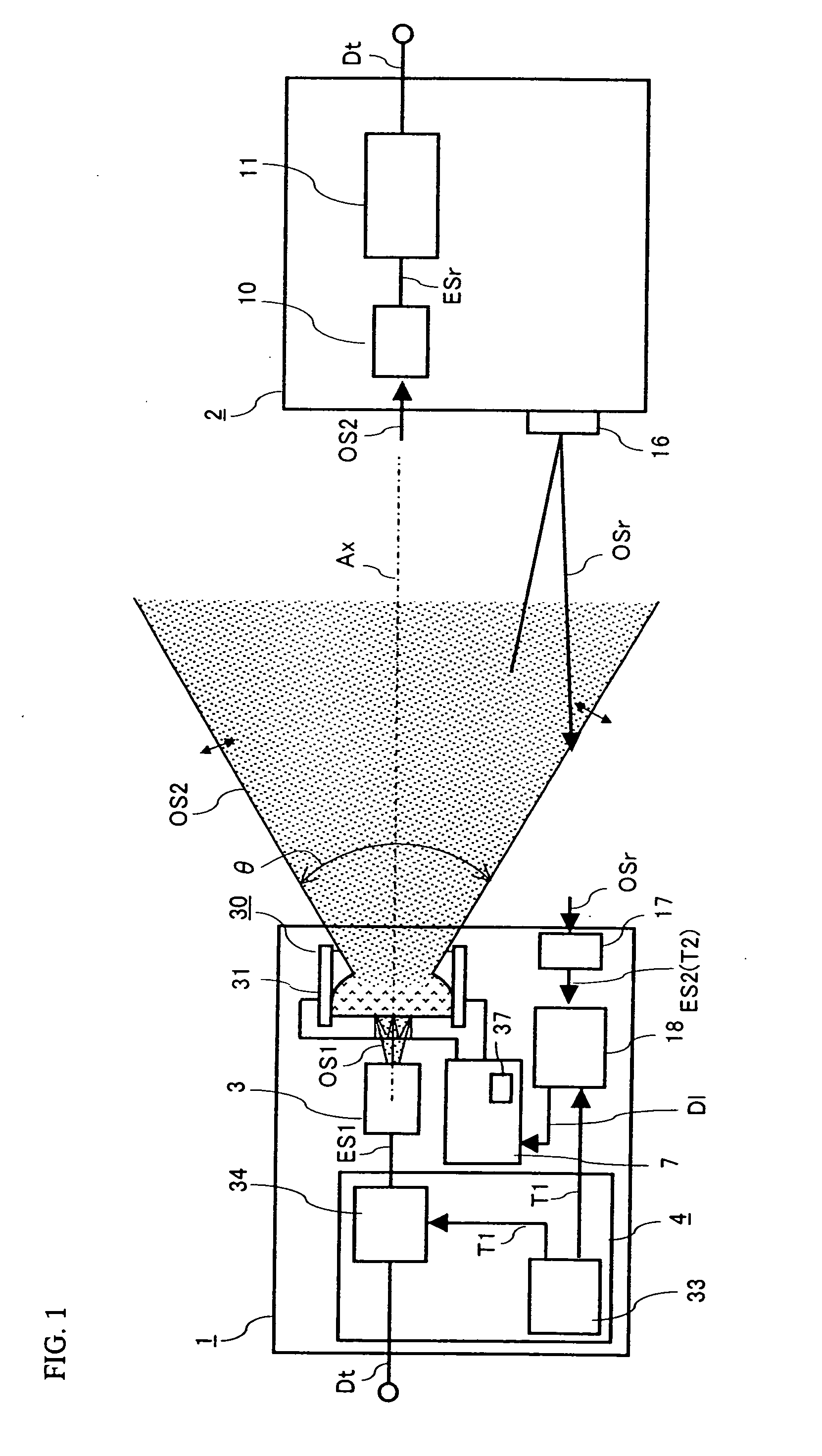
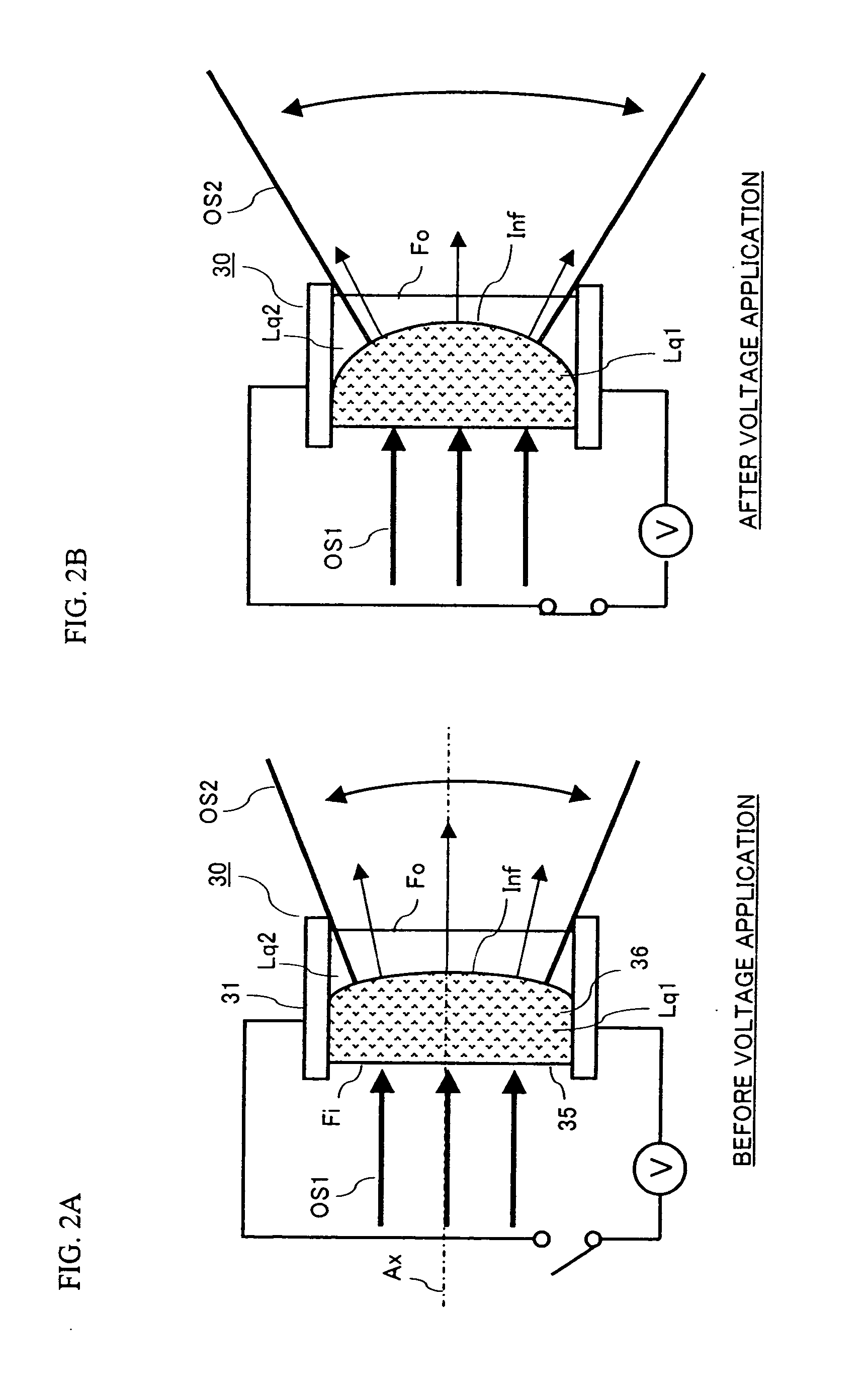
InactiveUS20070206952A1Improve optical output powerIncrease output powerDiffusing elementsElectromagnetic transmissionOptical axisEngineering
An optical transmission apparatus is provided in which high optical output power is secured in an optical transmitter, the fine adjustment of the optical axis is unnecessary, and the propagation range of the optical output signal can be adaptively changed. A diffusing liquid lens includes a first liquid and a second liquid containing a scattering material that scatters light, and the curvature of the boundary surface between the first and the second liquids is changed according to the control voltage applied from a controlling unit. A first optical signal outputted from a light emitting device is diffused in the first liquid, and emitted as a second optical signal having a spread angle corresponding to the curvature of the boundary surface and a substantially uniform radiant intensity distribution.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor optical device and module using the same
InactiveUS20060274802A1Increase output powerImprove featuresOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsSingle mode waveguidesWaveguide
A semiconductor laser device capable of providing high output power operation is provided which has a structure in which high output power and kink suppression can be simultaneously attained as well as these characteristics can be realized by a short chip length. In a waveguide structure of an MMI laser diode, a taper waveguide is intentionally inserted between a single mode waveguide and a multimode waveguide, and further, a single mode waveguide is used as a passive waveguide. These individual units or combination thereof can solve the above-described problems.
Owner:OPNEXT JAPAN INC
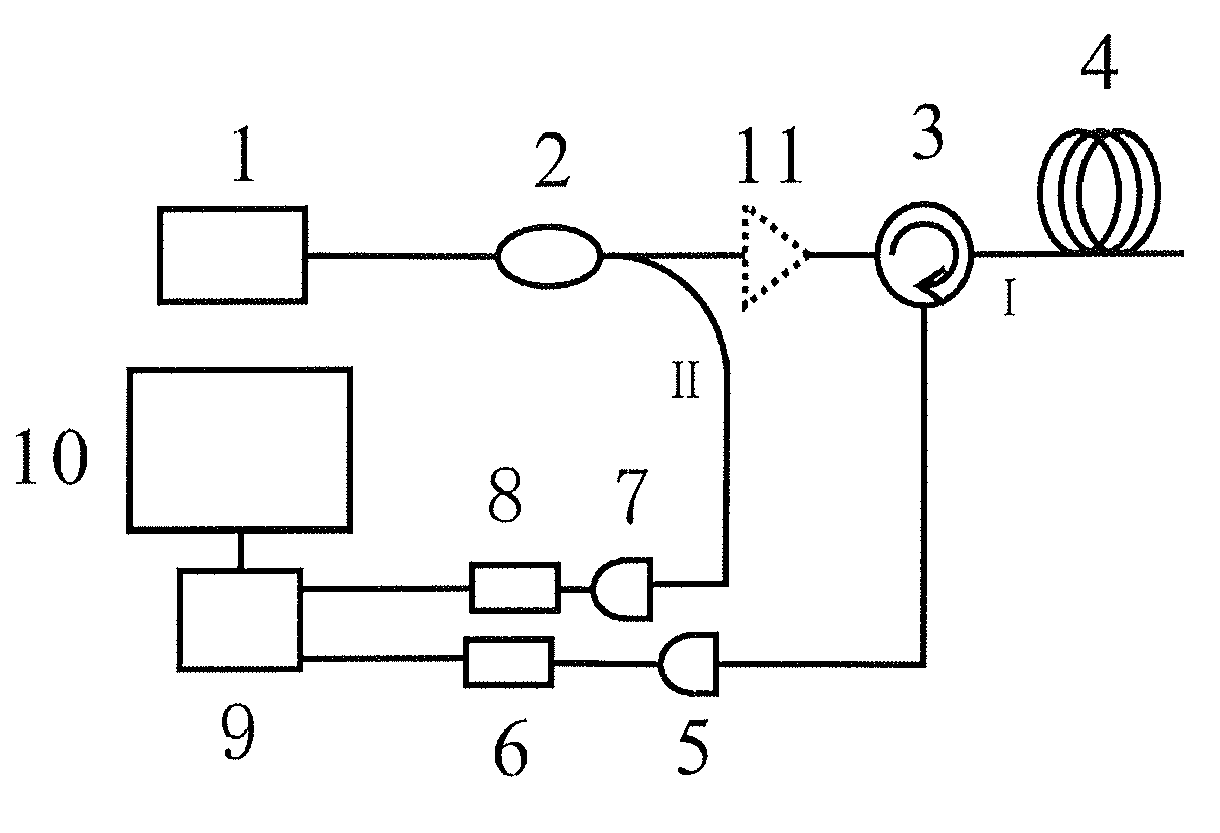
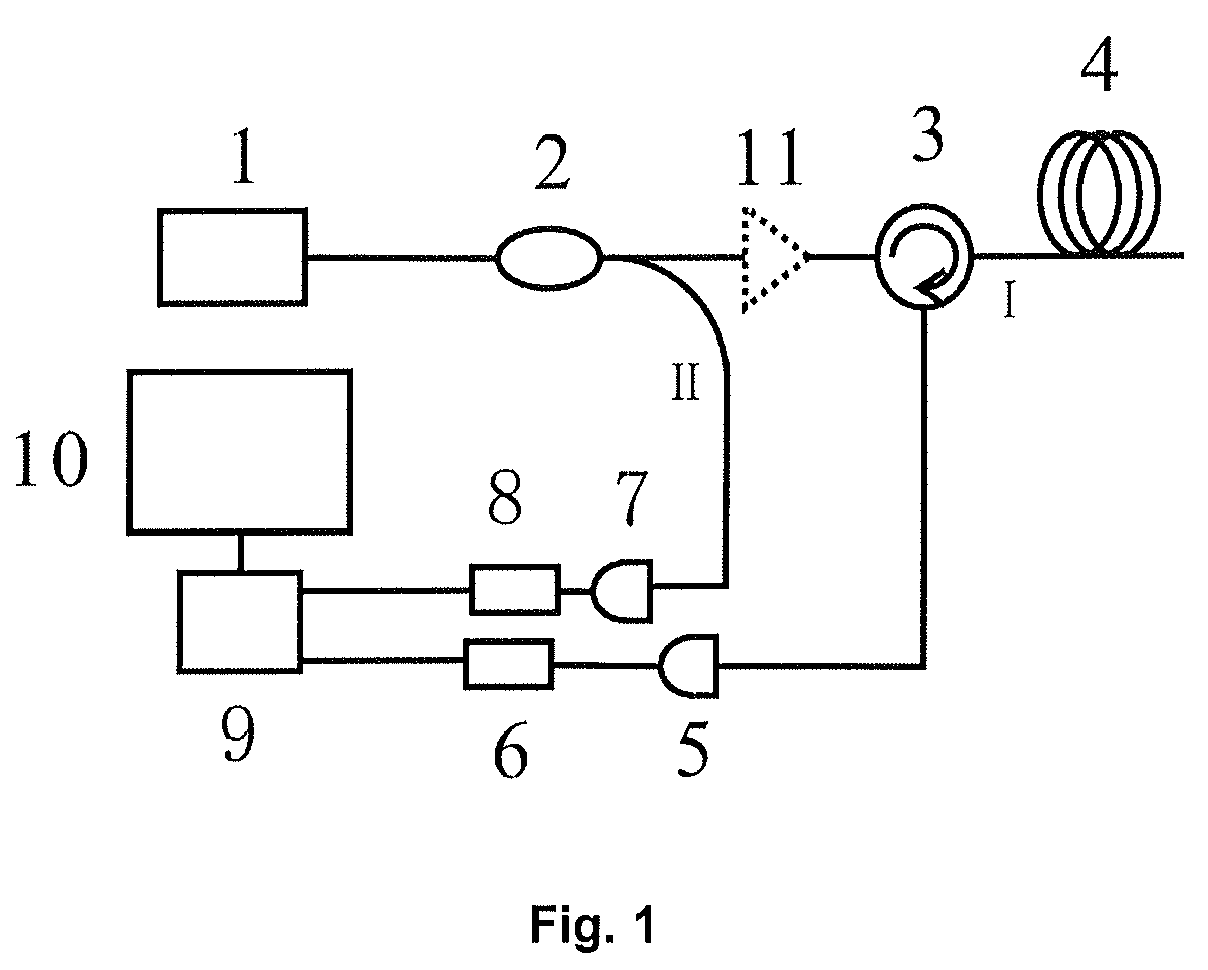
Chaotic optical time domain reflectometer method and apparatus
ActiveUS8502964B2High resolutionSimple structureAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser transmitterPhotodetector
In a method and a corresponding apparatus for performing chaotic optical time domain reflectometer, the chaotic laser signal, generated by the chaotic laser transmitter, is split into probe signal I and reference signal II by a fiber coupler. Through an optical circulator, the probe signal I is launched into the test fiber and the echo light is converted into electrical signal by a photodetector and digitalized by an A / D converter. The reference signal II is converted into electrical signal by a photodetector and digitalized by another A / D converter. Two digital signals received from two A / D converters are correlated in a signal processing device to locate the exact position of faults in fibers. The result output is then displayed on a display device. This invention was developed to overcome the tradeoff problem between resolution and dynamic range of the pulse-based OTDR.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor light emitting device substrate and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS7427772B2Enhanced glowIncrease output powerSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsSingle crystal
A substrate for semiconductor light emitting devices is provided. The substrate is characterized in that the substrate is a single crystal material and has a nanocrystal structure capable of diffracting an electromagnetic wave. The nanocrystal structure is disposed on a surface portion of the substrate and includes an etched region and an unetched region, wherein the etched region has a depth of 10-200 nm. Due to the periodicity of the nanocrystal structure, the semiconductor material grown on the substrate has fewer defects, and the material stress is reduced.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Light emitting device and method of manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS20120049225A1Improve optical output powerPrevent discolorationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtomic layer depositionLight emitting device
Provided is a method of manufacturing a light emitting device capable of maintaining high optical output power while suppressing discoloration of the reflective film. A method of manufacturing a light emitting device according to an embodiment includes steps in an order of, preparing an electrically conductive member provided with a reflective film, disposing a light emitting element on the reflective film, and forming a protective film on the reflective film by using an atomic layer deposition method.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Semiconductor light emitting device including metal reflecting layer
ActiveUS8823031B2Improve reliabilityDeterioration of the metal reflecting layer can be preventedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureReflective layer
A semiconductor light emitting device includes a semiconductor structure, a transparent electrically-conducting layer, a dielectric film, and a metal reflecting layer. The semiconductor structure includes an active region. The transparent electrically-conducting layer is formed on the upper surface of the semiconductor structure. The dielectric film is formed on the upper surface of the transparent electrically-conducting layer. The metal reflecting layer is formed on the upper surface of the dielectric film. The dielectric film has at least one opening whereby partially exposing the transparent electrically-conducting layer. The transparent electrically-conducting layer is electrically connected to the metal reflecting layer through the opening. A barrier layer is partially formed and covers the opening so that the barrier layer is interposed between the transparent electrically-conducting layer and the metal reflecting layer.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Direct cooling of leds
ActiveUS20060216865A1Effective coolingImprove light outputPoint-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLed arrayDevice material
A thermal management system is provided for semiconductor devices such as an LED array, wherein coolant directly cools the LED array. Preferably, the coolant may be selected, among other bases, based on its index of refraction relative to the index associated with the semiconductor device.
Owner:PHOSEON TECHNOLOGY INC
Nitrogen polar surface LED based on metal nitride semiconductor and preparation method
ActiveCN104835893ALower turn-on voltageReduce built-in electric field strengthSemiconductor devicesDevice materialOhmic contact
The invention discloses a nitrogen polar surface LED based on a metal nitride semiconductor, belonging to the technical field of semiconductor devices. The LED successively comprises an n-type semiconductor layer of the nitrogen polar surface, a multi-quantum well active region of the nitrogen polar surface, an electron barrier layer of the nitrogen polar surface and a p-type semiconductor layer of the nitrogen polar surface from bottom to top, and the upper layer of the p-type semiconductor layer of the nitrogen polar surface is provided with a p-type electrode. The LED further comprises an n-type semiconductor layer of a metal polar surface, the n-type semiconductor layer of the metal polar surface is arranged at the lateral side of the n-type semiconductor layer of the nitrogen polar surface and completely bonded to the n-type semiconductor layer of the nitrogen polar surface, and the upper surface of the n-type semiconductor layer of the metal polar surface is provided with an n-type electrode. Compared with the prior art, the n-type semiconductor layer of the metal polar surface serves as an ohmic contact layer of the n-type semiconductor layer of the nitrogen polar surface LED, so as to overcome the problem that an ohmic electrode is not easy to prepare on the n-type semiconductor layer of the nitrogen polar surface, the preparation technology is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
DFB semiconductor laser device having ununiform arrangement of a diffraction grating
ActiveUS20040042516A1Avoid changeImprove optical output powerLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A DFB semiconductor laser device includes a diffraction grating extending parallel to a laser cavity. The diffraction grating has ununiform structure wherein some of the corrugation patterns of diffraction grating are omitted periodically, the diffraction grating has different duty ratio between the area near the front facet of the laser cavity and the area near the rear facet, or the length of the diffraction grating is smaller than the cavity length and the width of the diffraction grating reduces in the vicinity of the rear end of the diffraction grating down to zero at the rear end.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
DFB semiconductor laser device having ununiform arrangement of a diffraction grating
ActiveUS7180930B2Avoid short lengthSuppressing the inter-mode transitionLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A DFB semiconductor laser device includes a diffraction grating extending parallel to a laser cavity. The diffraction grating has ununiform structure wherein some of the corrugation patterns of diffraction grating are omitted periodically, the diffraction grating has different duty ratio between the area near the front facet of the laser cavity and the area near the rear facet, or the length of the diffraction grating is smaller than the cavity length and the width of the diffraction grating reduces in the vicinity of the rear end of the diffraction grating down to zero at the rear end.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Light emitting diode structure utilizing zinc oxide nanorod arrays on one or more surfaces, and a low cost method of producing such zinc oxide nanorod arrays
InactiveUS20110108873A1Increase brightnessImprove optical output powerLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthZinc oxides/hydroxidesAqueous solutionZinc oxide nanorod
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Direct cooling of LEDs
ActiveUS7235878B2Effective coolingImprove light outputPoint-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLed arrayRefractive index
A thermal management system is provided for semiconductor devices such as an LED array, wherein coolant directly cools the LED array. Preferably, the coolant may be selected, among other bases, based on its index of refraction relative to the index associated with the semiconductor device.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Liquid lens optical transmitter system
InactiveUS7657182B2Improve optical output powerIncrease output powerDiffusing elementsElectromagnetic transmissionOptical axisEngineering
An optical transmission apparatus is provided in which high optical output power is secured in an optical transmitter, the fine adjustment of the optical axis is unnecessary, and the propagation range of the optical output signal can be adaptively changed. A diffusing liquid lens includes a first liquid and a second liquid containing a scattering material that scatters light, and the curvature of the boundary surface between the first and the second liquids is changed according to the control voltage applied from a controlling unit. A first optical signal outputted from a light emitting device is diffused in the first liquid, and emitted as a second optical signal having a spread angle corresponding to the curvature of the boundary surface and a substantially uniform radiant intensity distribution.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Super-luminescent diode and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN103022897AReduce polarization sensitivityReduce coating requirementsOptical wave guidanceLaser active region structureContact layerDiode
The invention discloses a super-luminescent diode and a method for manufacturing the same. The super-luminescent diode comprises a substrate. The method includes sequentially forming a buffer layer, a lower limiting layer, an active region, an upper limiting layer and a first p-type covering layer on the substrate so as to form a primary epitaxial slice by an epitaxial growth technology; sequentially growing a second p-type covering layer and an n-type covering layer on the surface of the primary epitaxial slice so as to form a secondary epitaxial slice by the epitaxial growth technology; growing a covering layer and a contact layer on the surface of the secondary epitaxial slice so as to form a tertiary epitaxial slice by the epitaxial growth technology; and manufacturing the tertiary epitaxial slice into a super-luminescent diode chip by photoetching, etching, slice grinding and sputtering processes sequentially, and coating an antireflection film on a light emergent end surface of the chip. The super-luminescent diode and the method have the advantages of low polarization sensitivity and ripple coefficient, high power, wide spectrum and the like.
Owner:WUHAN HUAGONG GENUINE OPTICS TECH
Phase-change radiating device
InactiveCN101471538AEven heat dissipationAccurate temperature controlLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNonlinear optical crystalHigh power lasers
The invention provides a phase-change heat dissipating device and a laser. The phase-change heat dissipating device comprises a vaporizing chamber, a condensation chamber, and a heat conducting end for conducting heat generated by an object to the vaporizing chamber, wherein the heat conducting end comprises a heat absorption assembly covering the object. According to the above technical scheme, the phase-change heat dissipation device has the advantages of simple structure, high heat dissipation efficiency, uniform heat dissipation, high reliability, wide application range, etc., and can be used for dissipating heat of large-power optical components, such as laser crystals, nonlinear optical crystals or semiconductor laser chip of a large-power laser, thereby uniformly dissipating heat, improving the heat dissipation efficiency, effectively improving the light emission efficiency, light output power, beam quality and service life of the large-power laser, and achieving more stable and reliable performance. In addition, the heat dissipating device has relative simple structure, wide application range, environment-friendly energy source and actual value for scale production, and can effectively reduce the size of the large-power laser.
Owner:PHOEBUS VISION OPTO ELECTRONICS TECH +1
Nano coarsening composite graphical sapphire substrate and manufacturing method
InactiveCN104241465AImprove light extraction efficiencyImprove optical output powerAfter-treatment detailsNanotechnologyNanometreSapphire substrate
Provided are a nano coarsening composite graphical sapphire substrate and a manufacturing method thereof. The sapphire substrate is provided with a composite graphic formed by combining micron dimension graphics with nano dimension graphics, and the nano dimension graphics are arranged on the micron dimension graphics. The manufacturing method includes the steps that (1) the micron dimension graphics are manufactured on the sapphire substrate; (2) a silicon dioxide film is deposited on the micron dimension graphics; (3) a silver film is further deposited on the silicon dioxide film; (4) the silver film is agglomerated into silver nanoparticles; (5) silver nanoparticle graphics are transferred onto the silicon dioxide film; (6) the silver nanoparticles are corroded; (7) the nano dimension graphics are manufactured on the sapphire micron graphics; (8) a silicon dioxide mask layer is removed in a corroded mode; (9) the substrate is cleaned. Nano coarsening is carried out on the micron dimension graphics, the light propagation direction can be changed more efficiently, the light escape probability is increased, and the light extraction efficiency and light output power of a GaN-based LED of the sapphire substrate are improved.
Owner:SHANDONG INSPUR HUAGUANG OPTOELECTRONICS
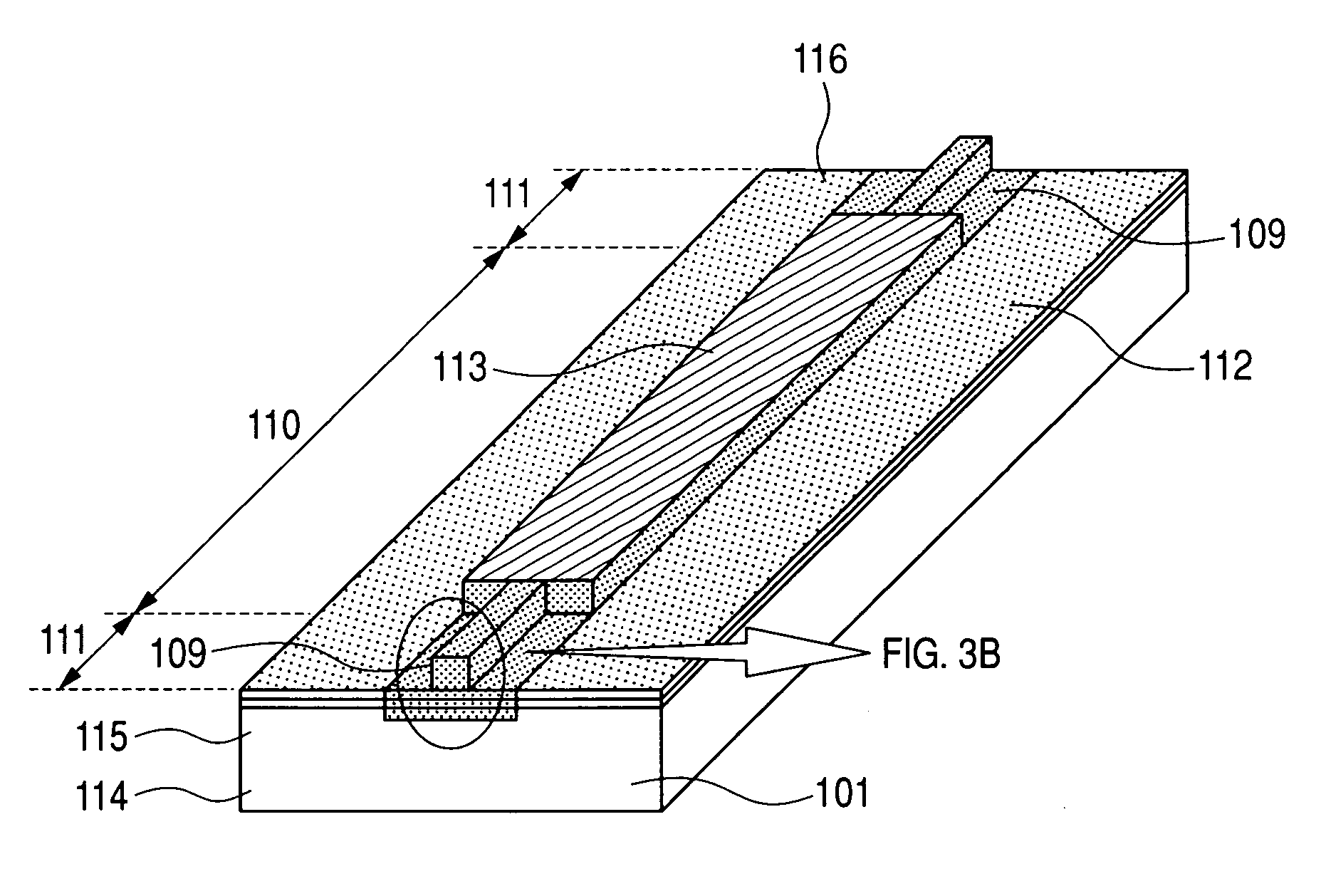
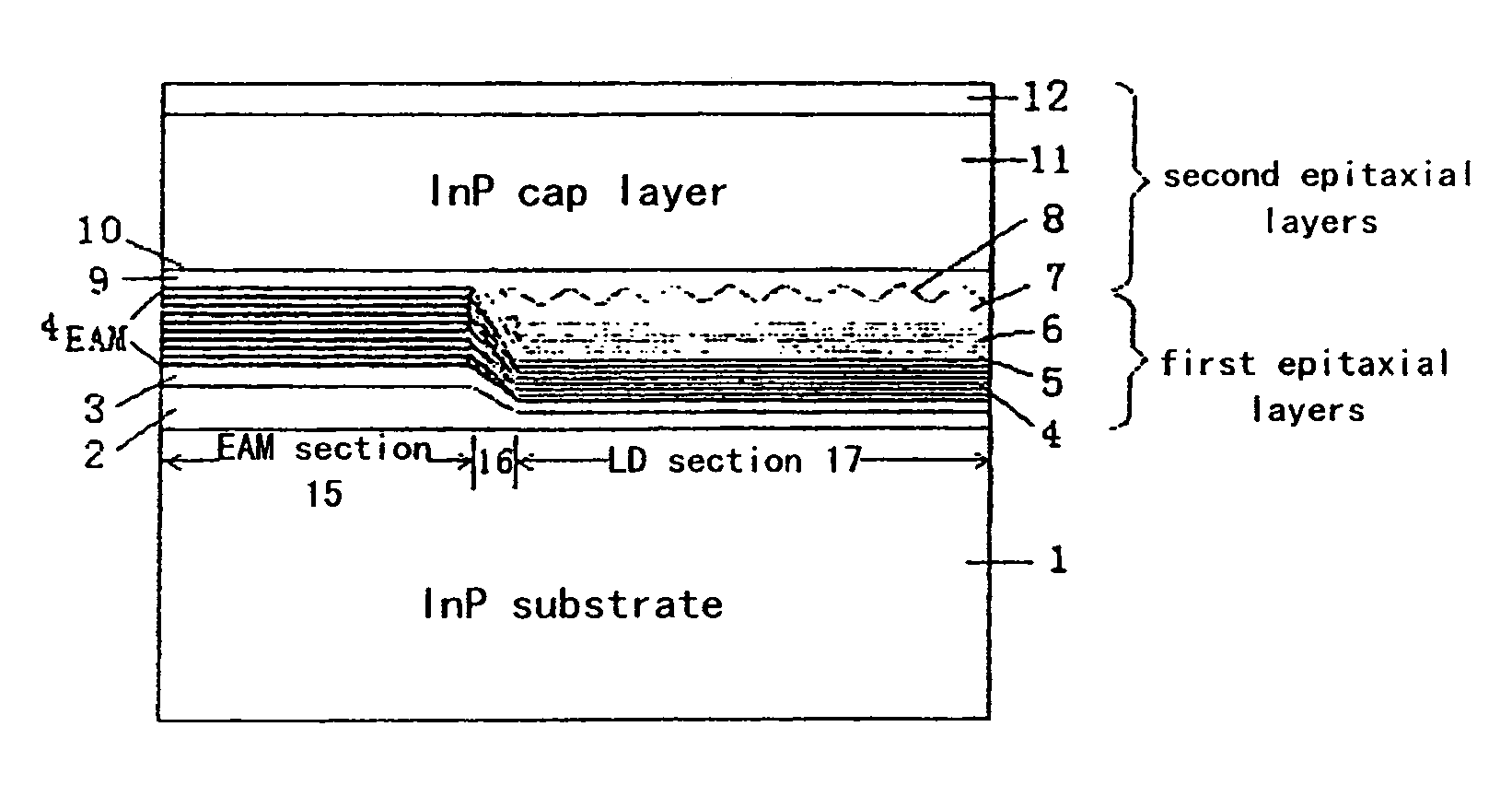
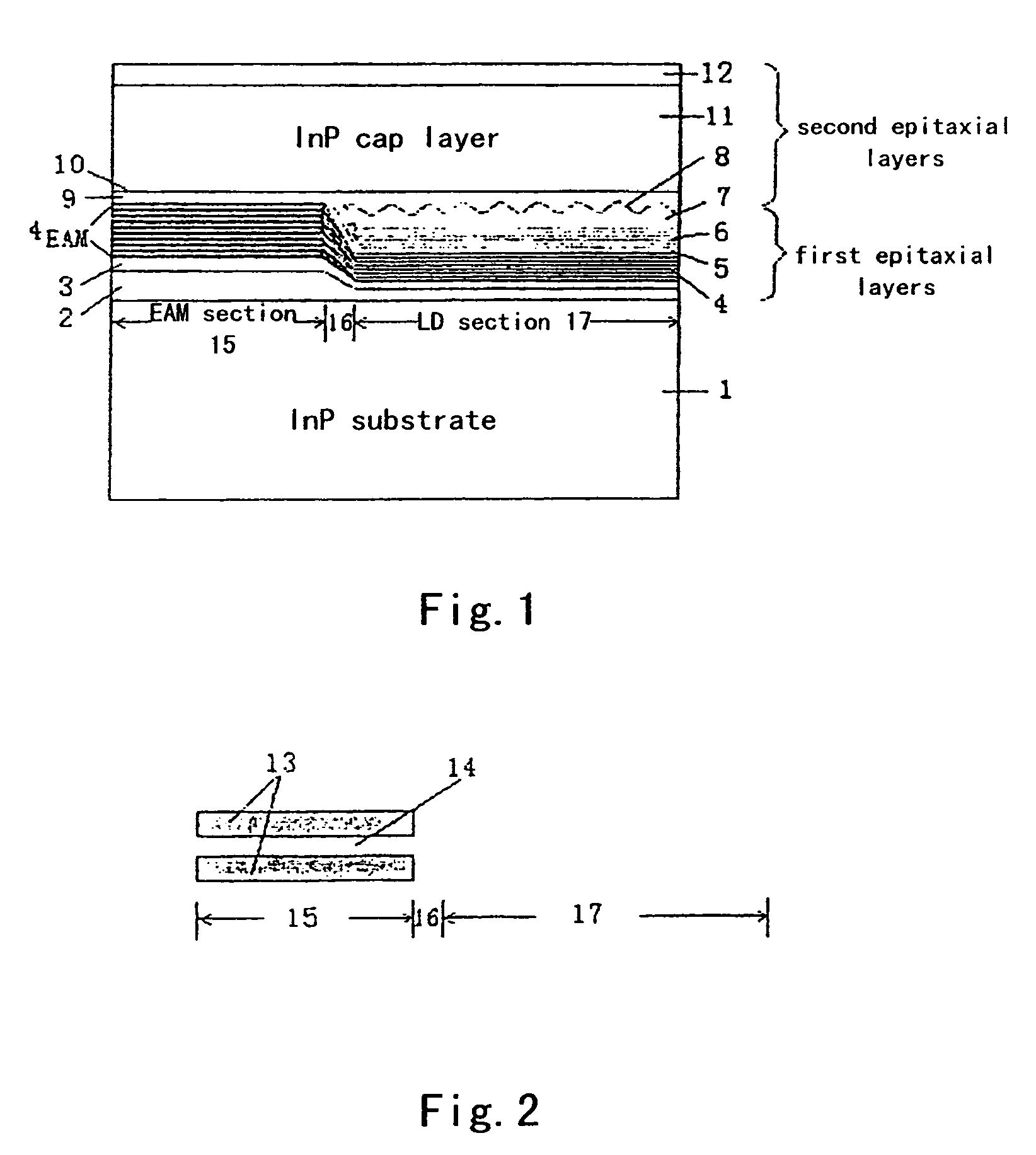
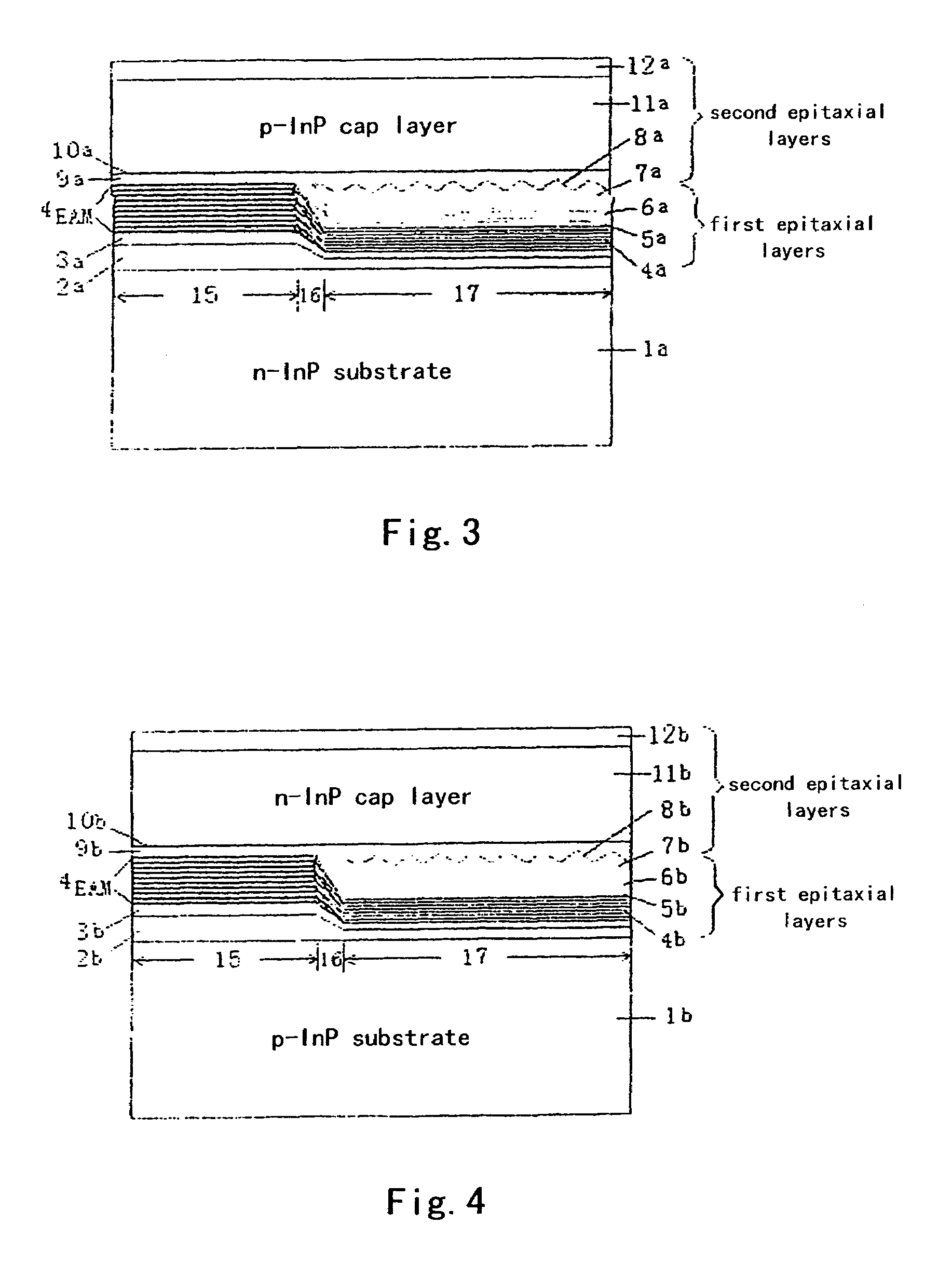
Method for manufacturing selective area grown stacked-layer electro-absorption modulated laser structure
ActiveUS7476558B2Improve featuresLow thresholdLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingGrating
This invention relates to a method for manufacturing selective area grown stacked-layer electro-absorption modulated laser structure, comprising: step 1: forming a selective growth pattern of a modulator section on a substrate; step 2: simultaneously growing a 2-stacked-layer active region structure of a modulator MQW layer and a laser MQW layer by the first epitaxy step; step 3: etching gratings, and removing the laser MQW layer in the modulator section by selective etching; and step 4: completing the growth of the entire electro-absorption modulated laser structure by a second epitaxy step.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-brightness light-emitting bipolar body with transparent base and light-emitting bipolar crystallite
The high-brightness light-emittnig bipolar body includes one seat plate, one compound crystal light-emitting bipolar body crystallite with transparent base plate and one covering plate. The covering plate has one central hole with inclined side wall and the light-emitting bipolar body crystallite is held inside the hole. The seat plate is divided into two parts by one middle insulating area and the two parts are connected separately to two electrodes of the light-emitting bipolar body crystallite. The seat plate is made of matter with high heat conductivity and high electric conductivity for conducting great current and dissipating heat. The central hole is filled and the light-emitting bipolar body crystallite is packed with transparent resin or epoxy resin. The present invention can emit high-strength light.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Laser COD eliminating method suitable for mass production
InactiveCN1877935AImprove affordabilityImprove optical output powerLaser detailsLaser active region structureZinc atomOptoelectronics
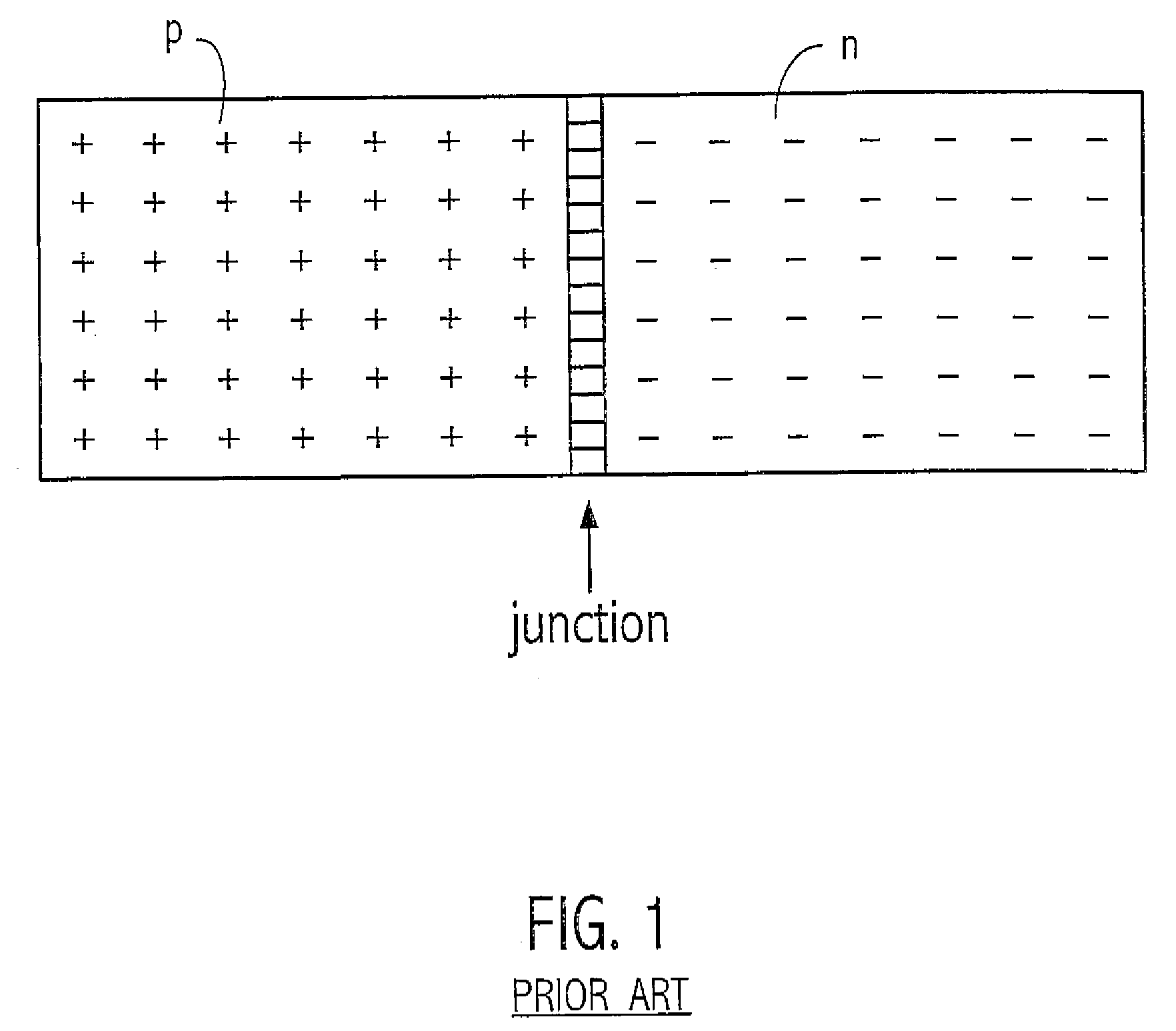
The invention discloses a COD eliminating method of laser and optical non-absorbing window making technology, which is characterized by the following: diffusing zinc atom in the diffusion induced III group element or V group element of III-V group semiconductor compound through quantum confounding elementary; providing new zinc-expanding method; fitting for large-power semiconductor laser; improving optical output power obviously.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-power semiconductor laser device in which near-edge portions of active layer are removed
InactiveUS20010017871A1Low heat generationEnhanced light absorptionOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionLayered structureLaser light
In a semiconductor laser device, a GaAs substrate of a first conductive type, a lower cladding layer of the first conductive type, a lower optical waveguide layer made of InGaP of an undoped type or the first conductive type, an active layer made of InGaAsP or InGaAs, a first upper optical waveguide layer made of InGaP of an undoped type or a second conductive type, a second upper optical waveguide layer made of InGaP of an undoped type or the second conductive type, an upper cladding layer of the second conductive type, and a contact layer of the second conductive type are formed in this order to form a layered structure. Near-edge portions of the active layer and the first upper optical waveguide layer, which are adjacent to opposite end faces of the layered structure, are removed, and the second upper optical waveguide layer is formed over the first upper optical waveguide layer and near-edge areas of the lower optical waveguide layer, where the opposite end faces are perpendicular to the direction of laser light which oscillates in the semiconductor laser device.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
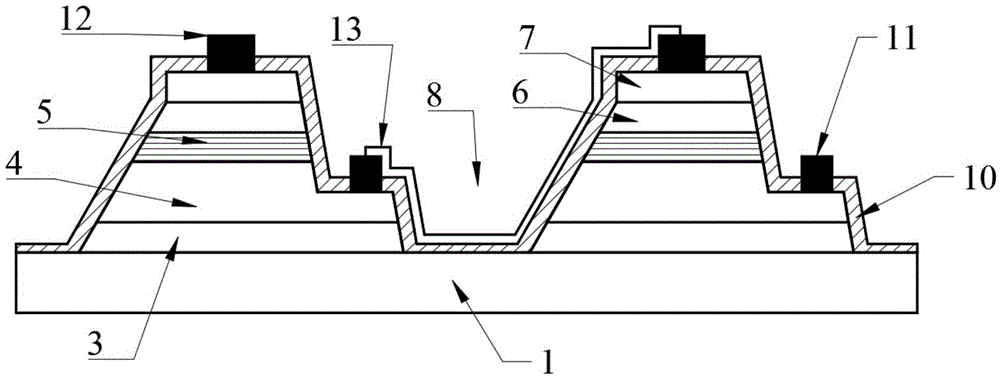
High-voltage direct-current GaN-based light emitting diode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105655462AImprove optical output powerImprove yieldSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh-voltage direct currentIndium tin oxide
The invention provides a high-voltage direct-current GaN-based light emitting diode and a preparation method of the high-voltage direct-current GaN-based light emitting diode. The high-voltage direct-current GaN-based light emitting diode comprises a substrate and a plurality of epitaxial layers arranged on the substrate, wherein the epitaxial layer comprises a GaN buffer layer, an n-type GaN layer, a multiple quantum well active layer and a p-type GaN layer, which are sequentially arranged on the surface of the substrate, an ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) transparent conductive layer is arranged on the epitaxial layer to form an LED unit cell, and the adjacent LED unit cells are interconnected by a metal wire. Compared with the prior art, the high-voltage direct-current GaN-based light emitting diode has the beneficial effects that: the three-dimensional ITO transparent conductive layer can effectively improve the light output power, the ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) etching process parameter is adjusted to make the base angle of a trapezoid-shaped isolating groove to be 120-150 degrees, and the interconnected metal wire can be conformally covered onto the isolating groove, so that the overall yield is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Semiconductor device
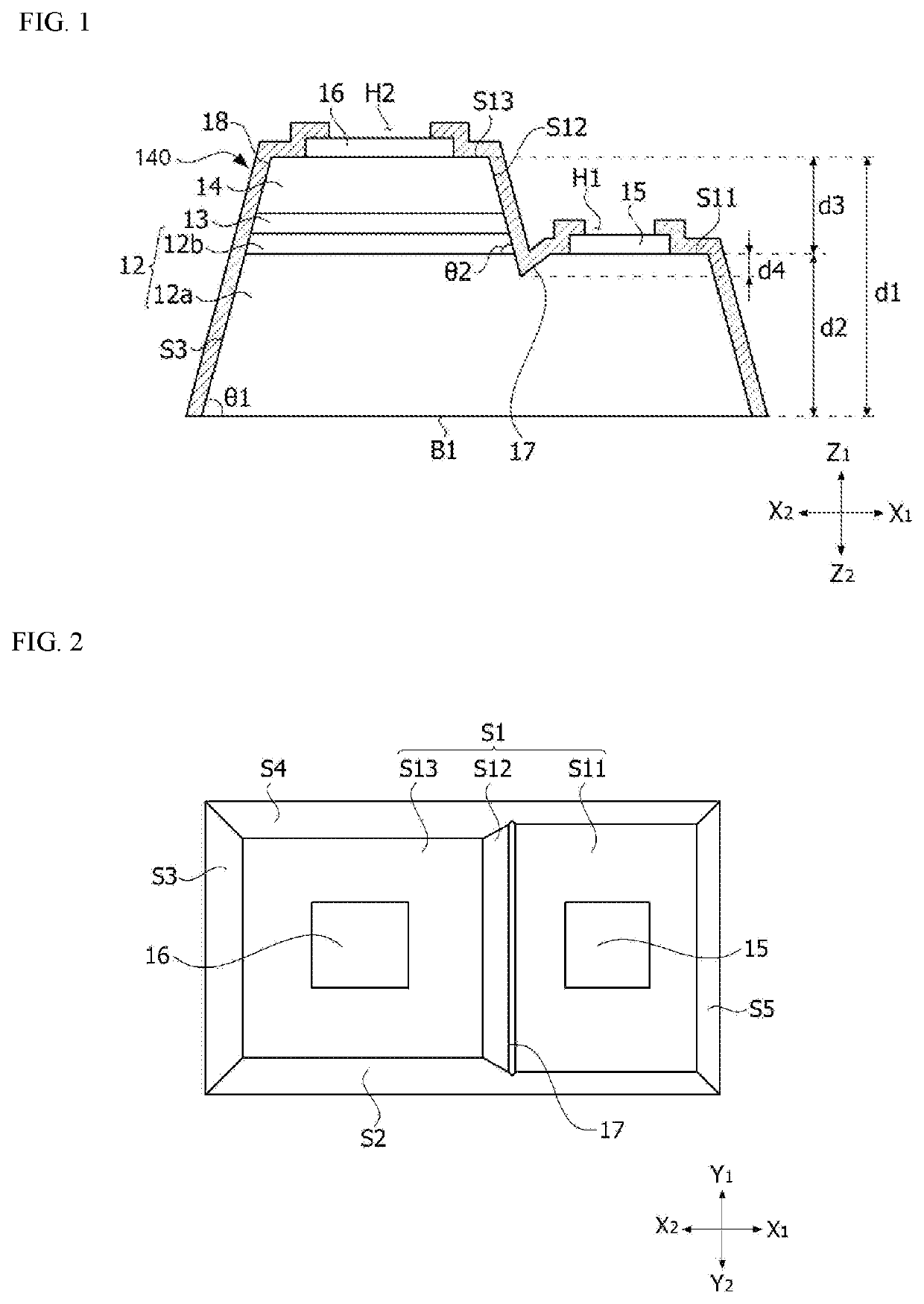
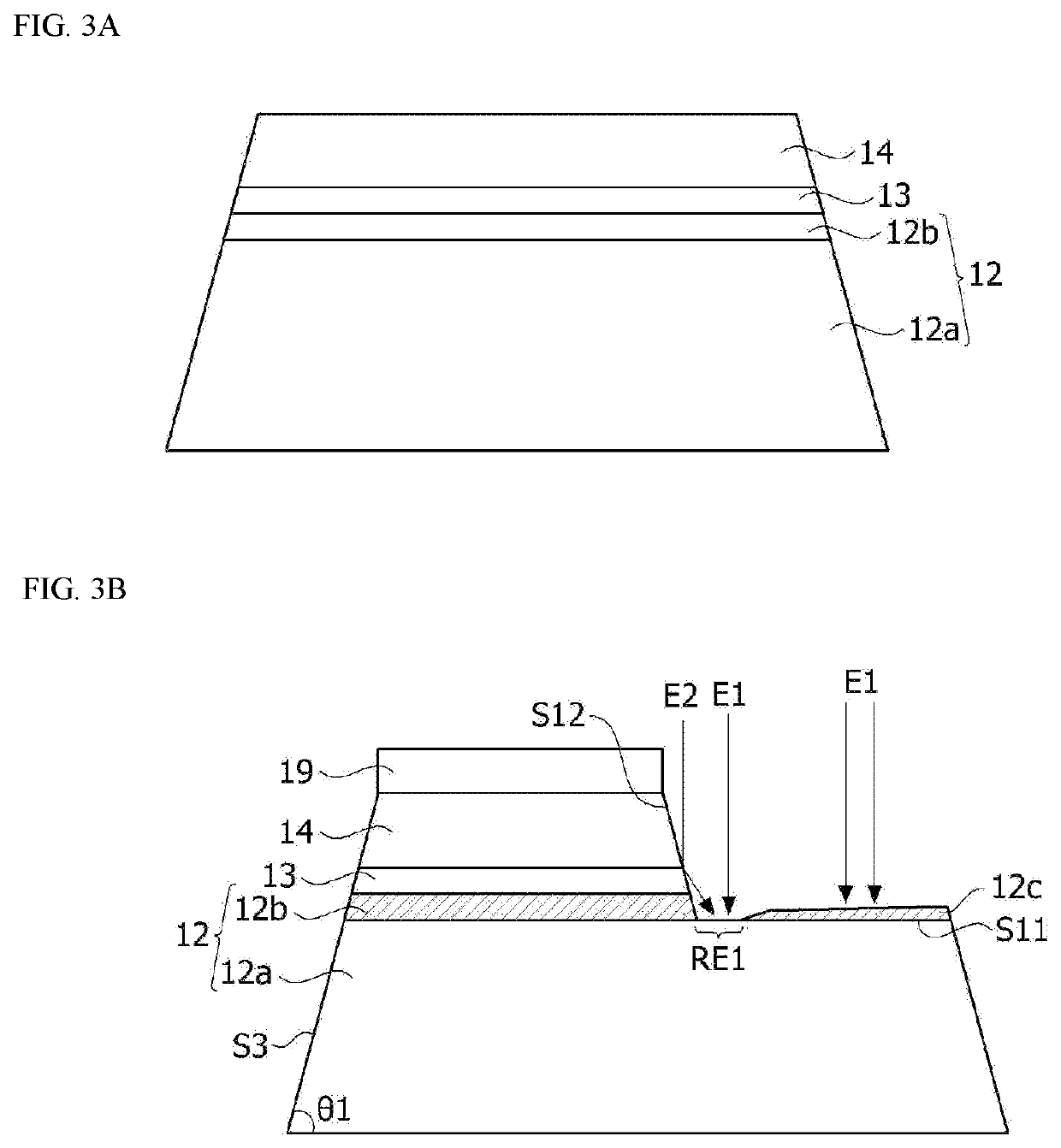
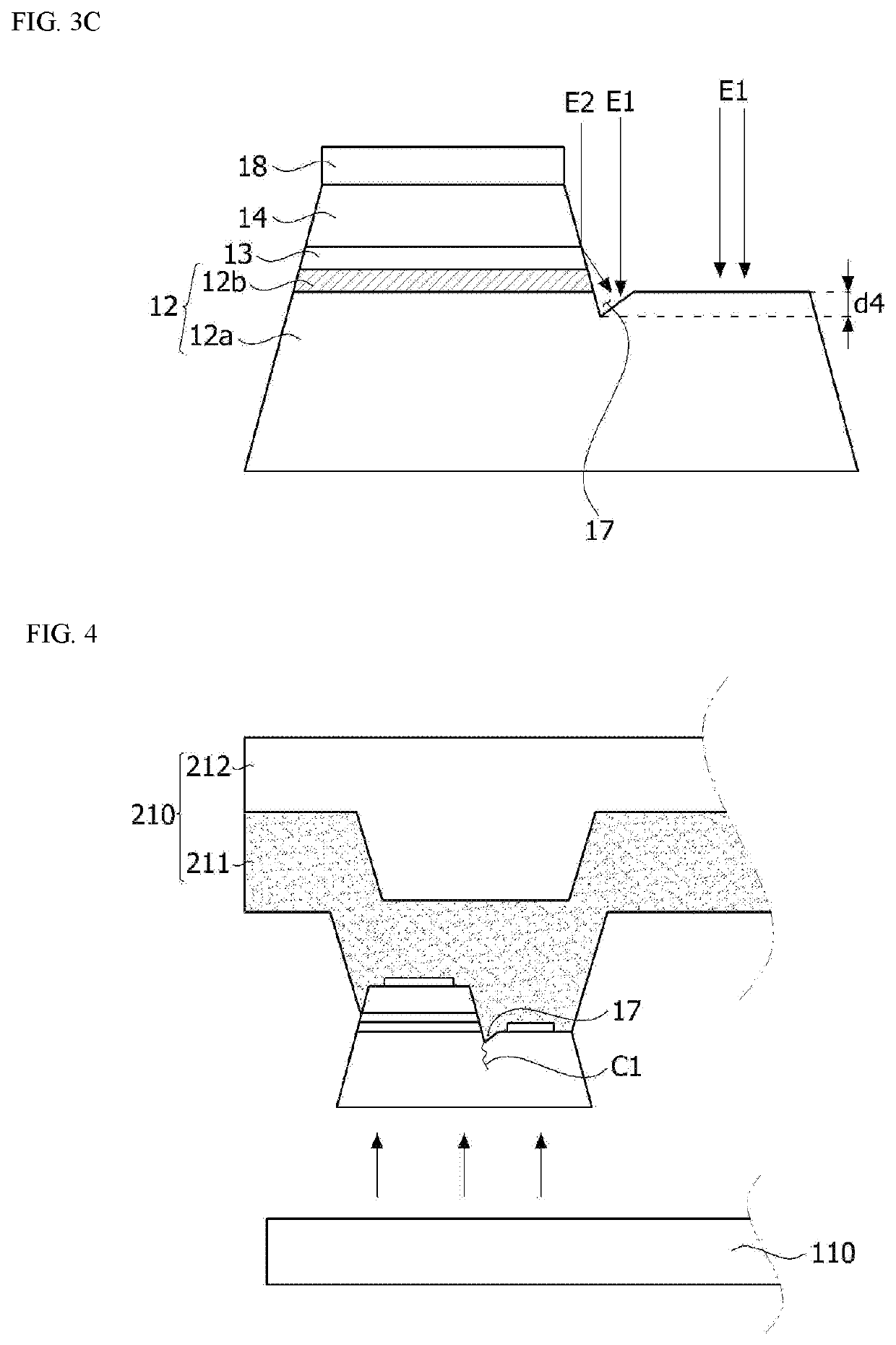
ActiveUS20210036187A1Robust external impactImprove optical output powerSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureDevice material
Disclosed is a semiconductor device including a semiconductor structure including a first semiconductor layer, a second semiconductor layer, and an active layer disposed between the first semiconductor layer and the second semiconductor layer, a first electrode electrically connected to the first semiconductor layer, and a second electrode electrically connected to the second semiconductor layer. The semiconductor structure includes a first upper surface on which the first semiconductor layer is exposed, a second upper surface on which the second semiconductor layer is disposed, an inclined surface connecting the first upper surface and the second upper surface, and a recess formed between the first upper surface and the inclined surface. The recess has a depth less than or equal to 30% of a vertical distance between the first upper surface and the second upper surface.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com