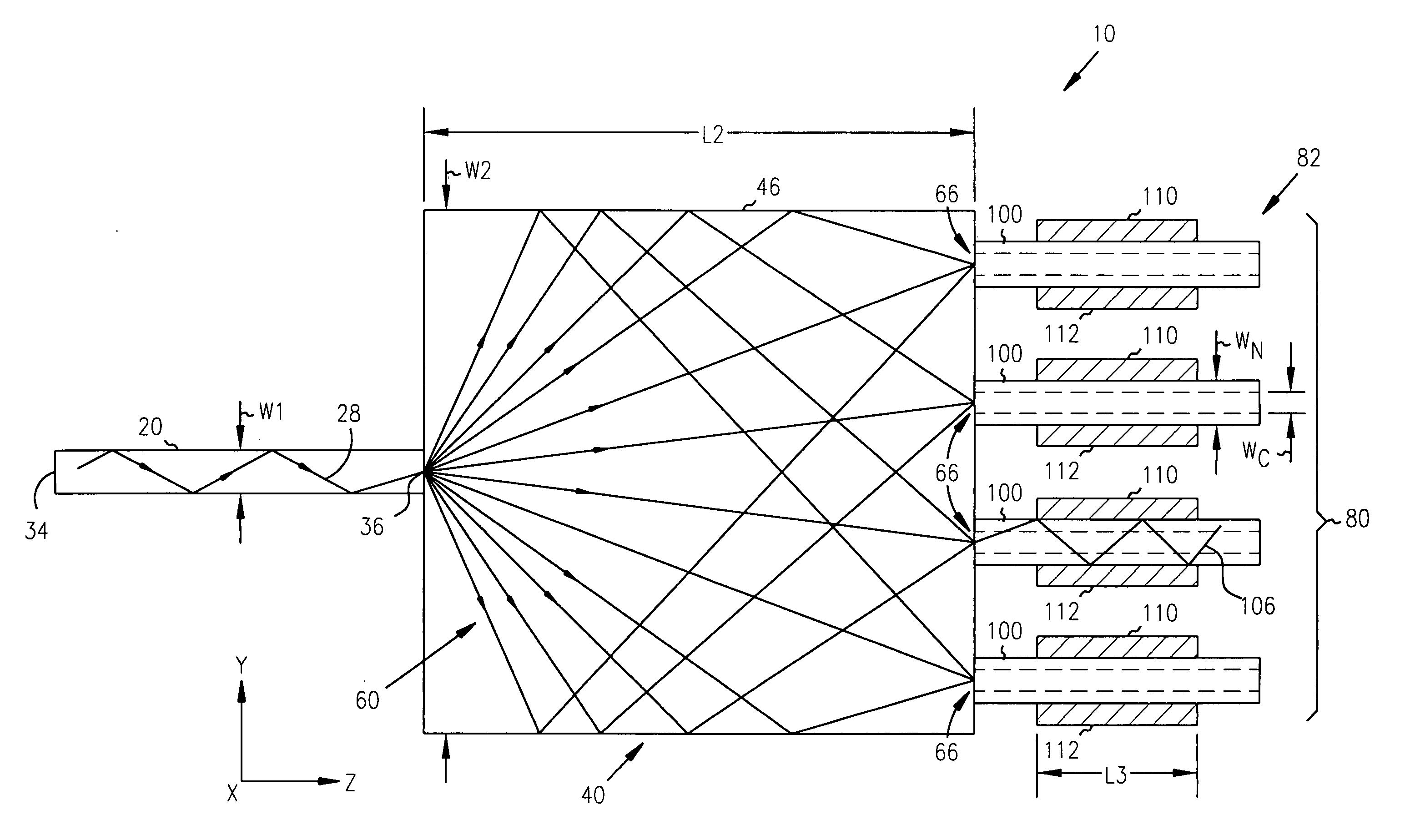
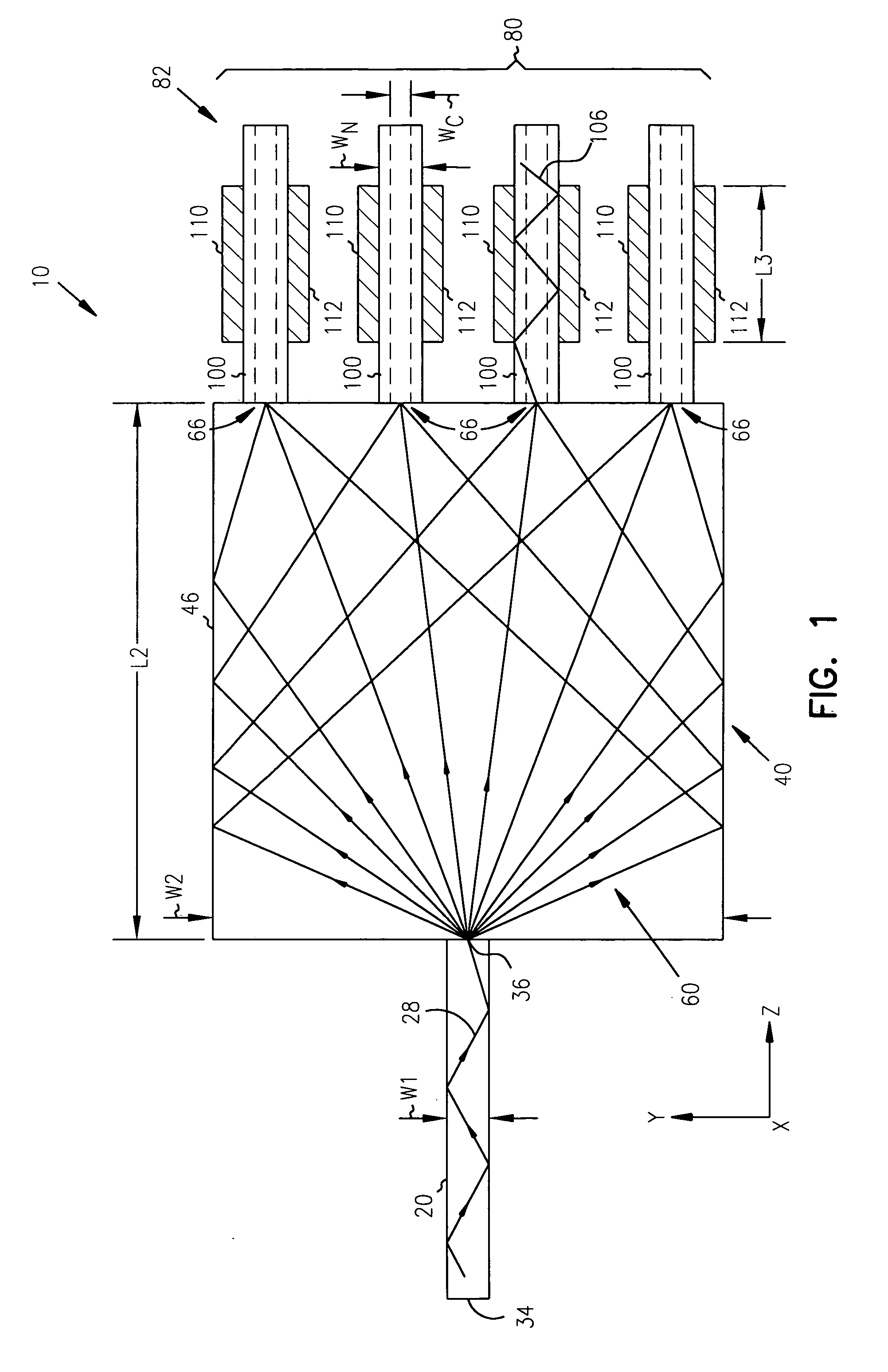
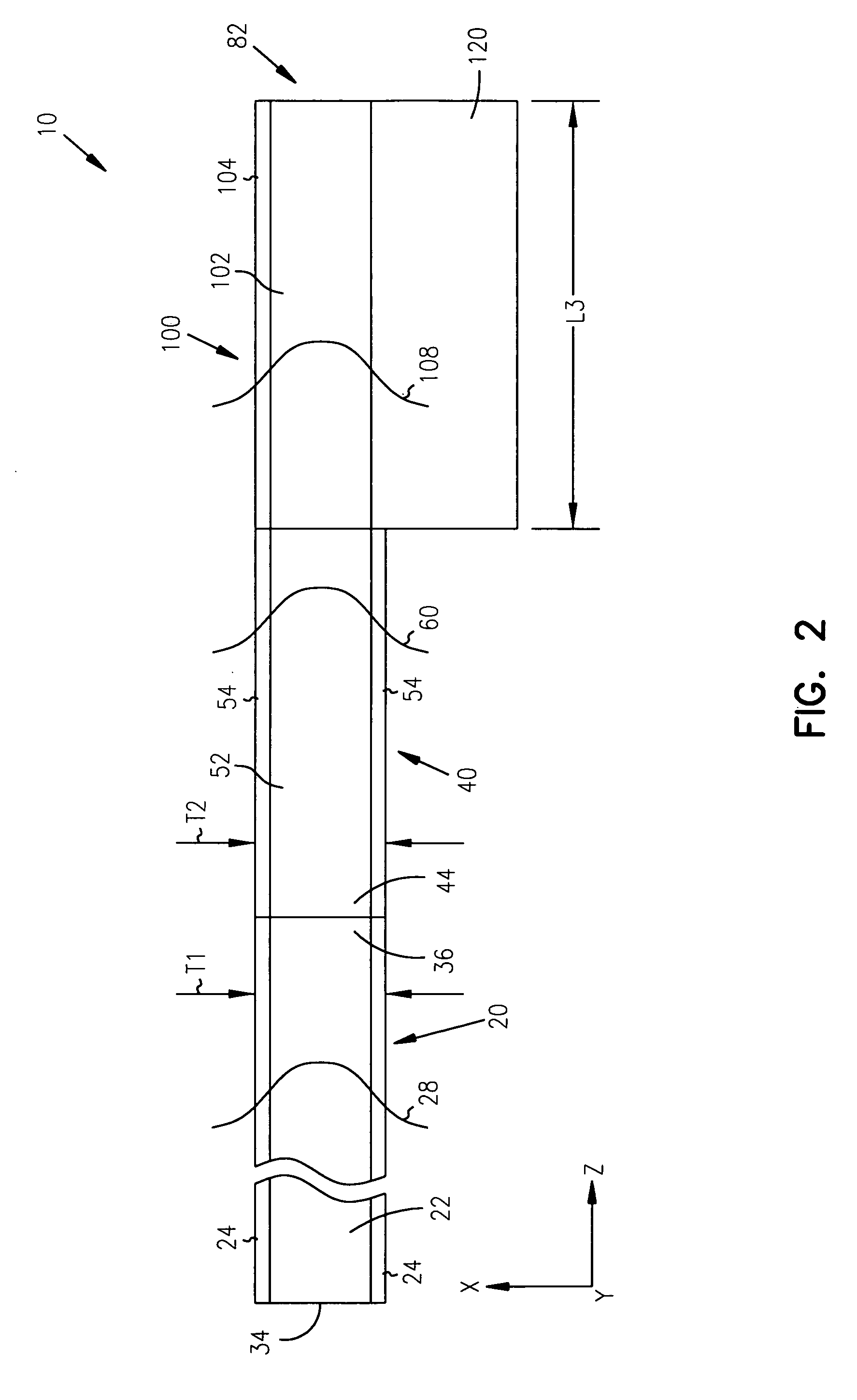
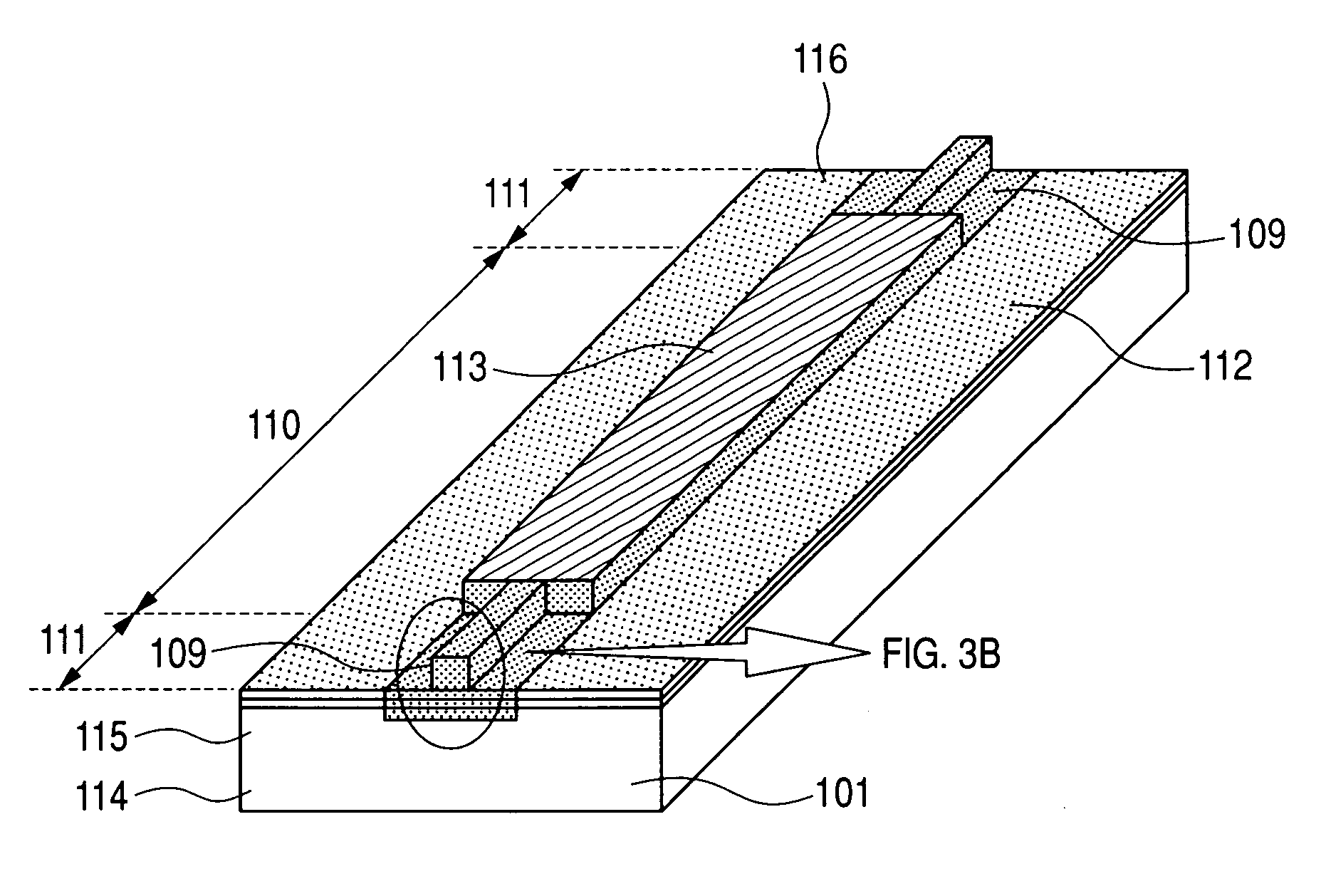
Patents
Literature
209 results about "Single mode waveguides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
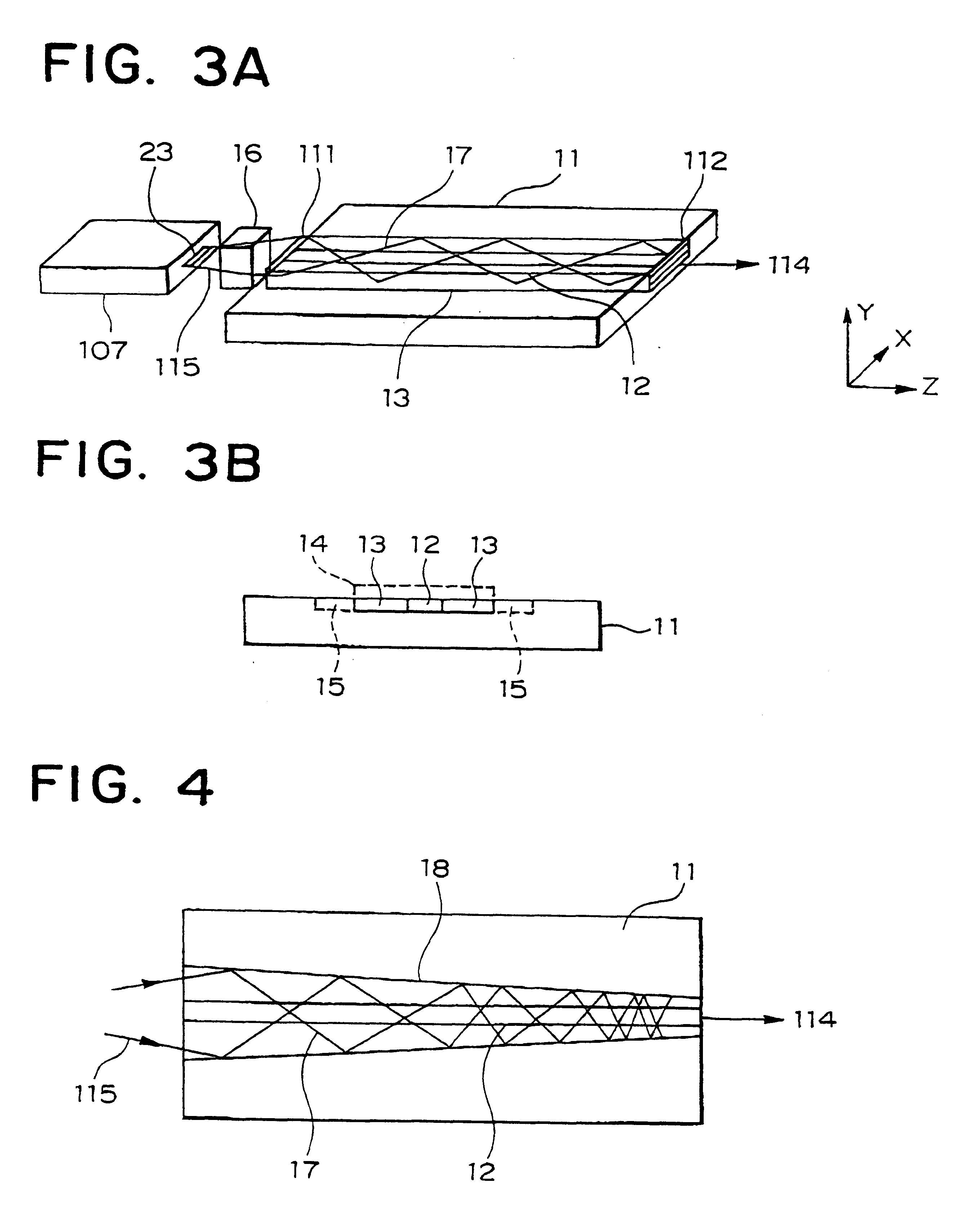
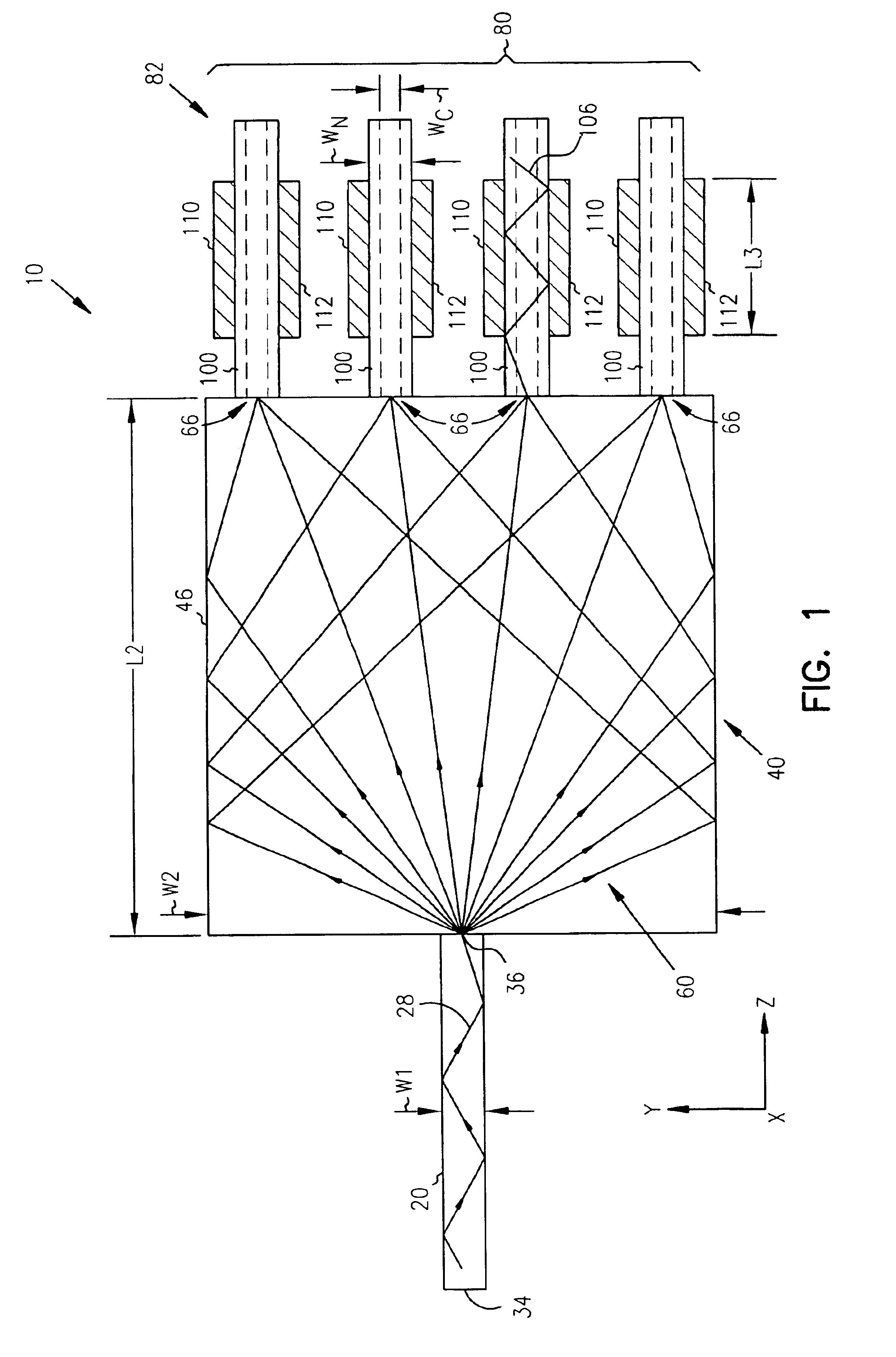
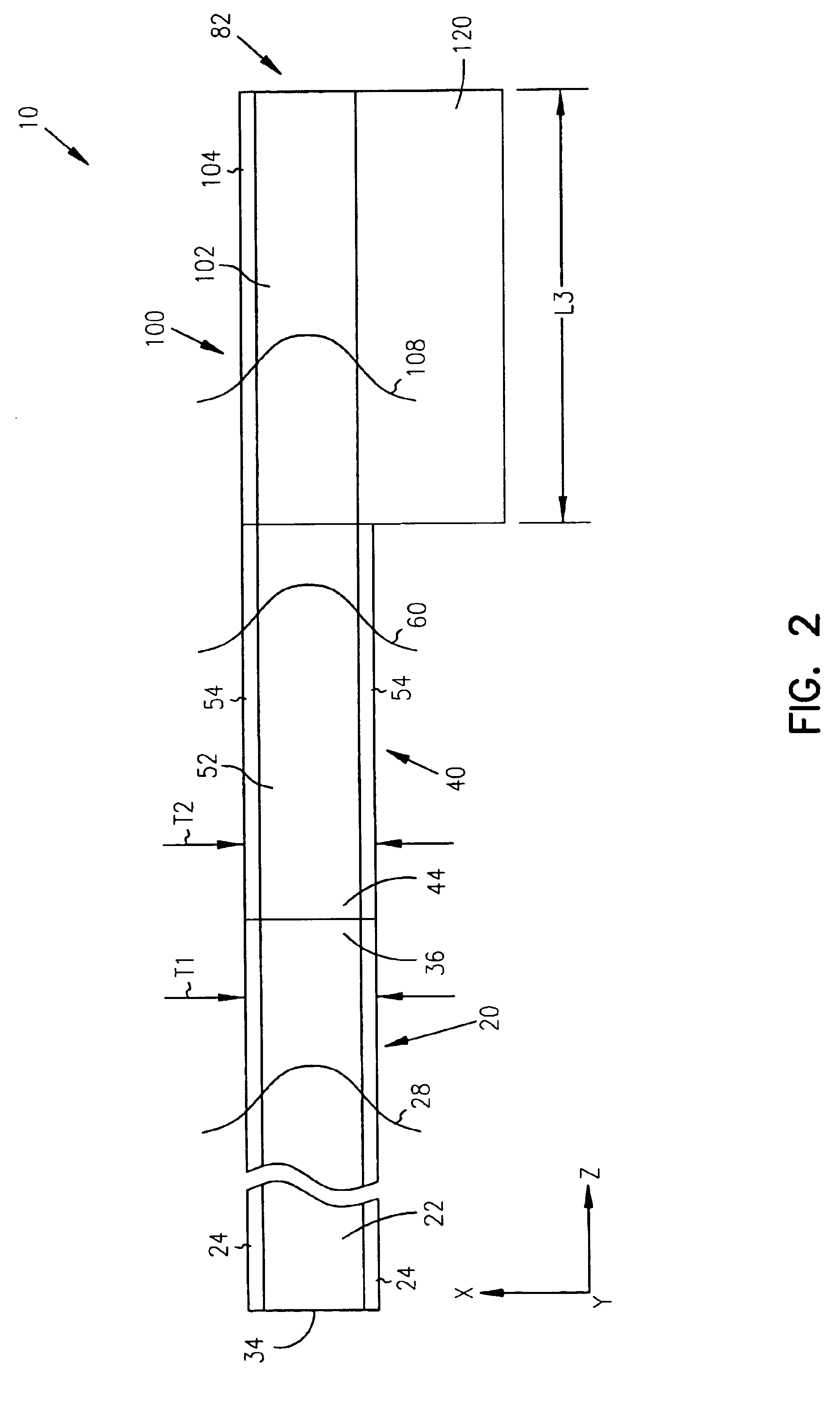
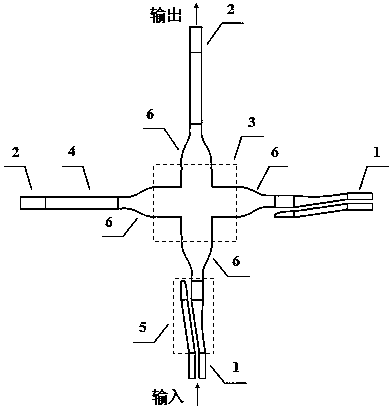
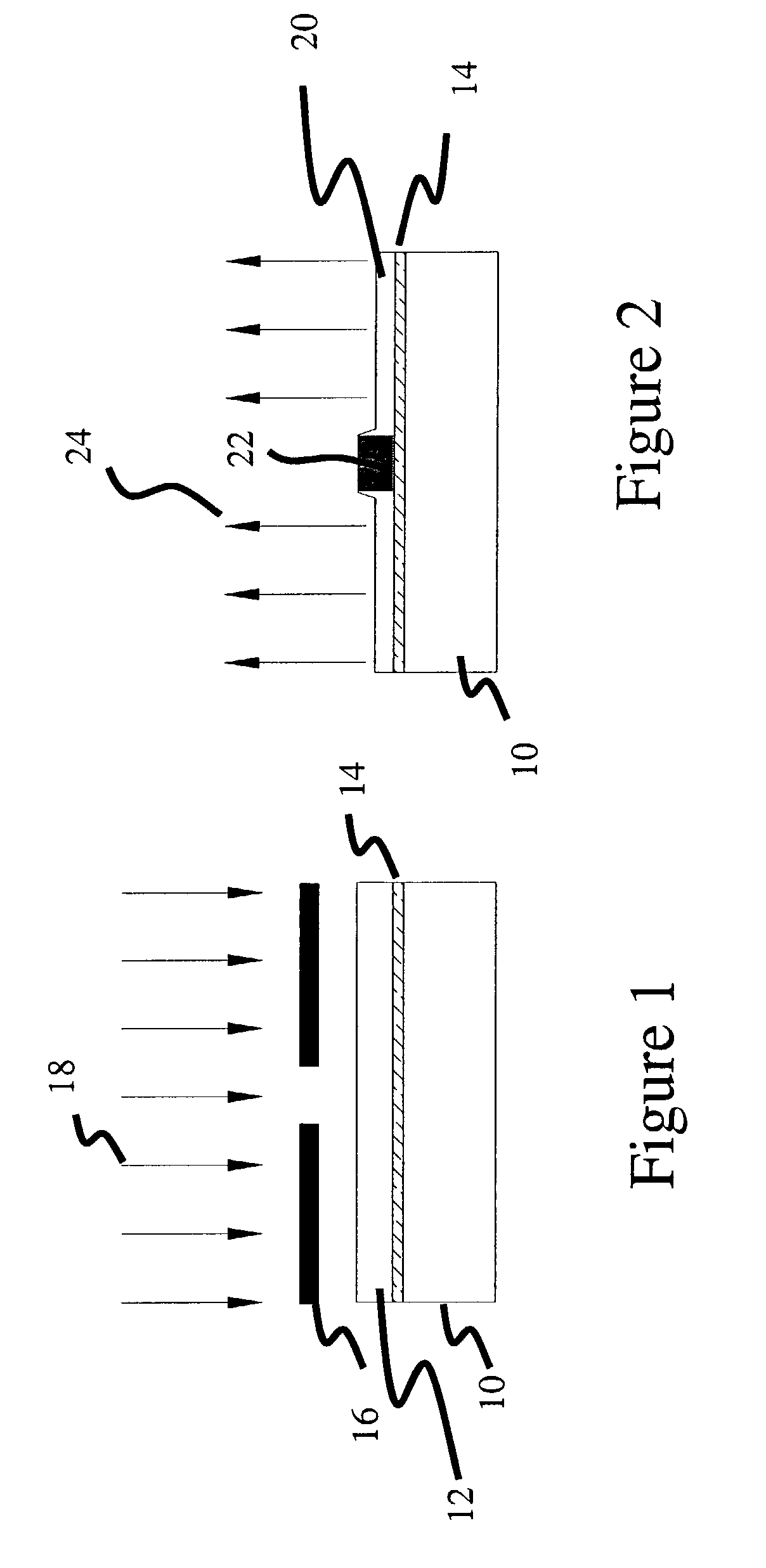
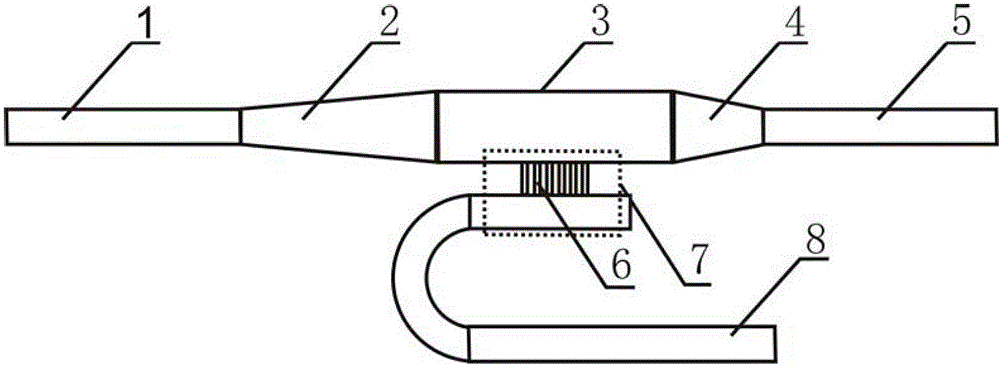
Tapered rib waveguide
InactiveUS6108478AEasy constructionEasy to makeCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesWaveguide
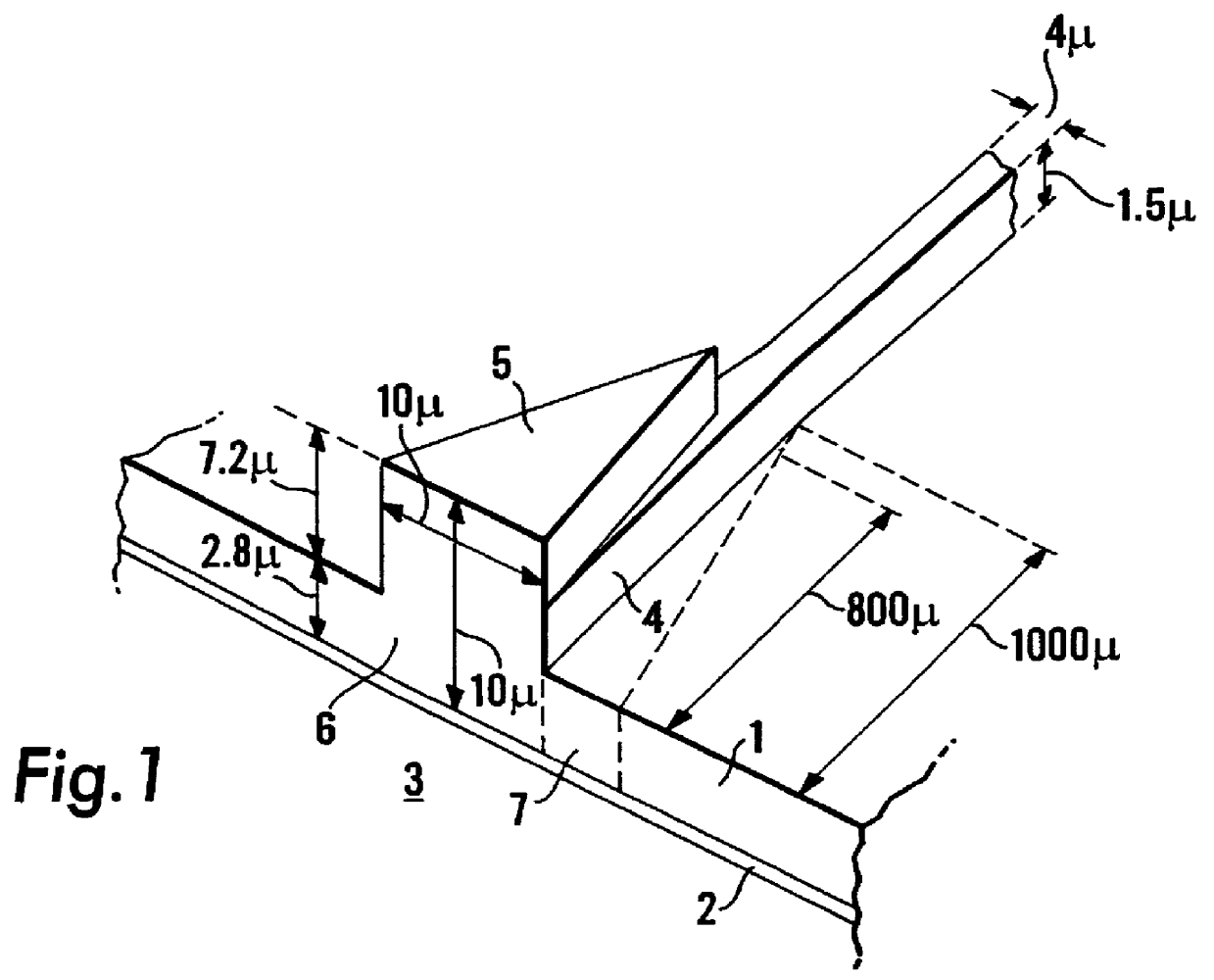
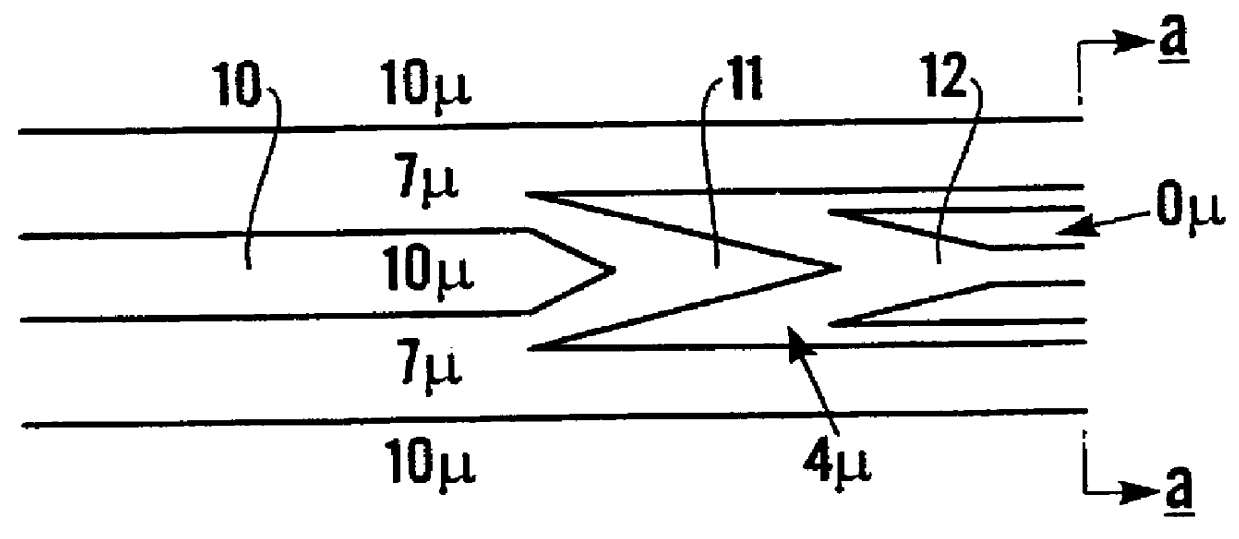
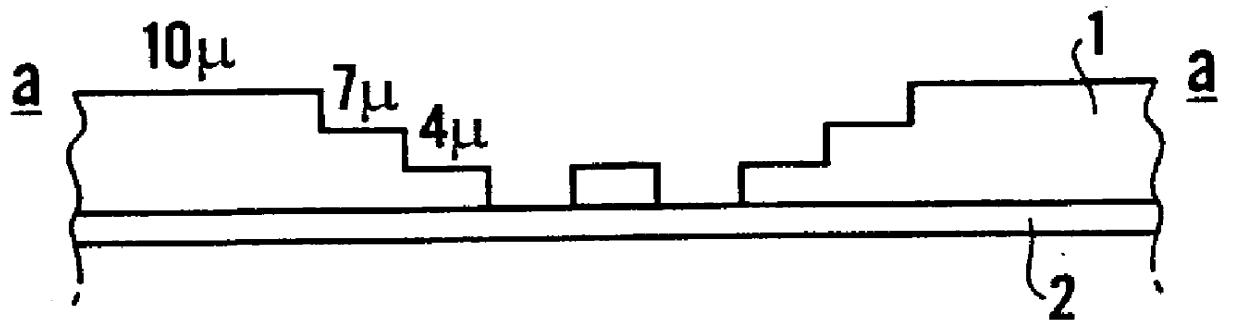
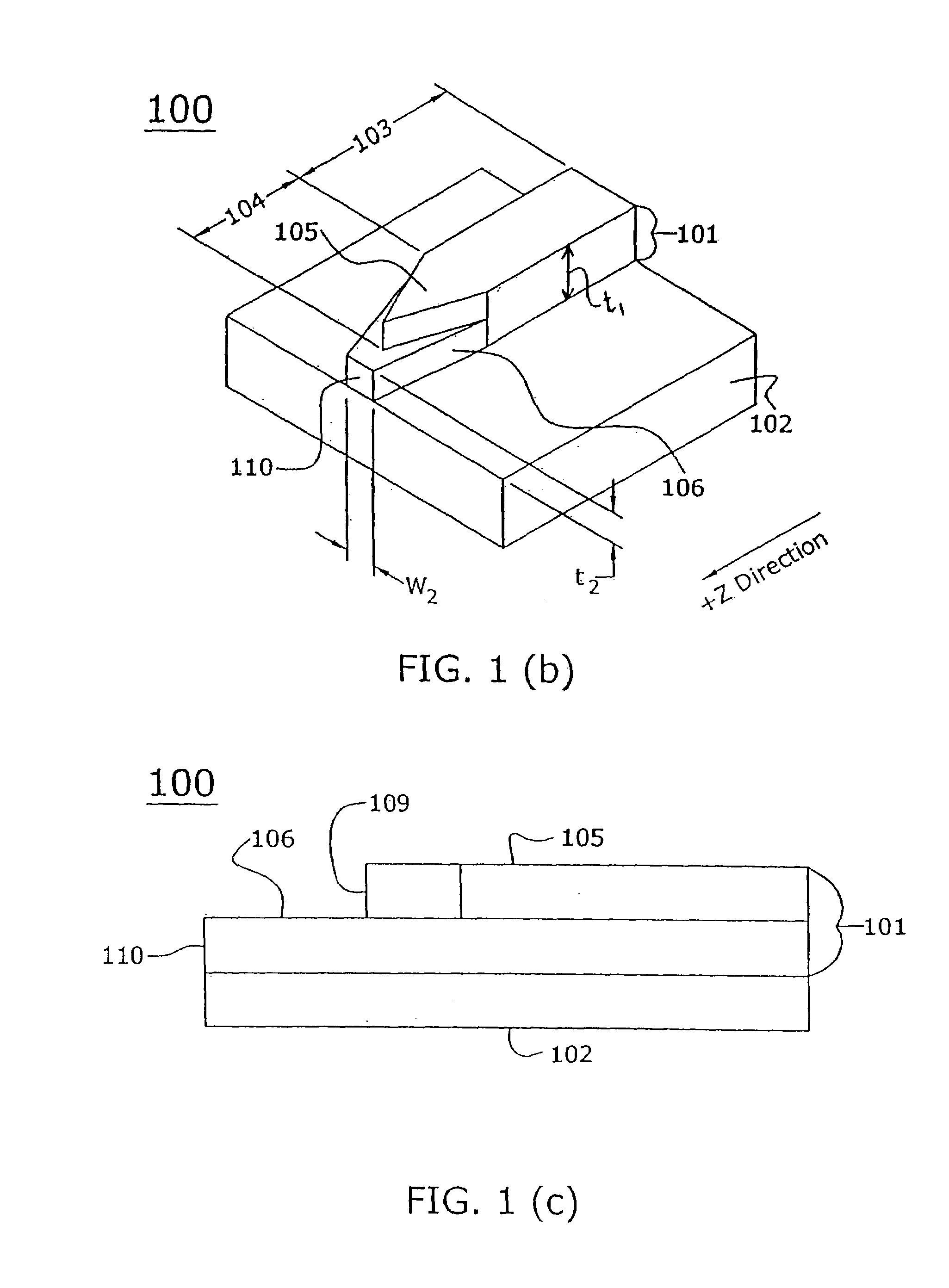
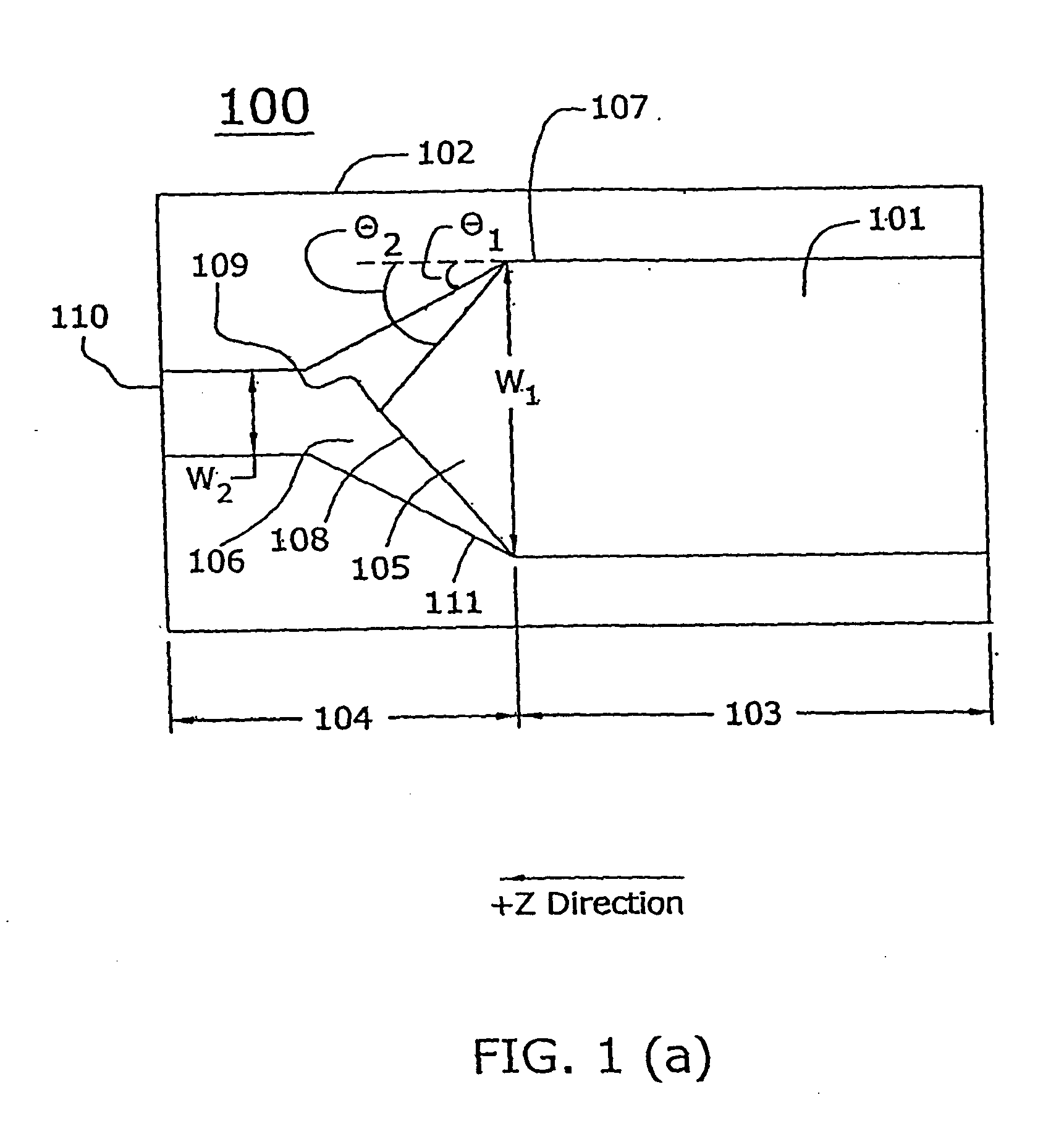
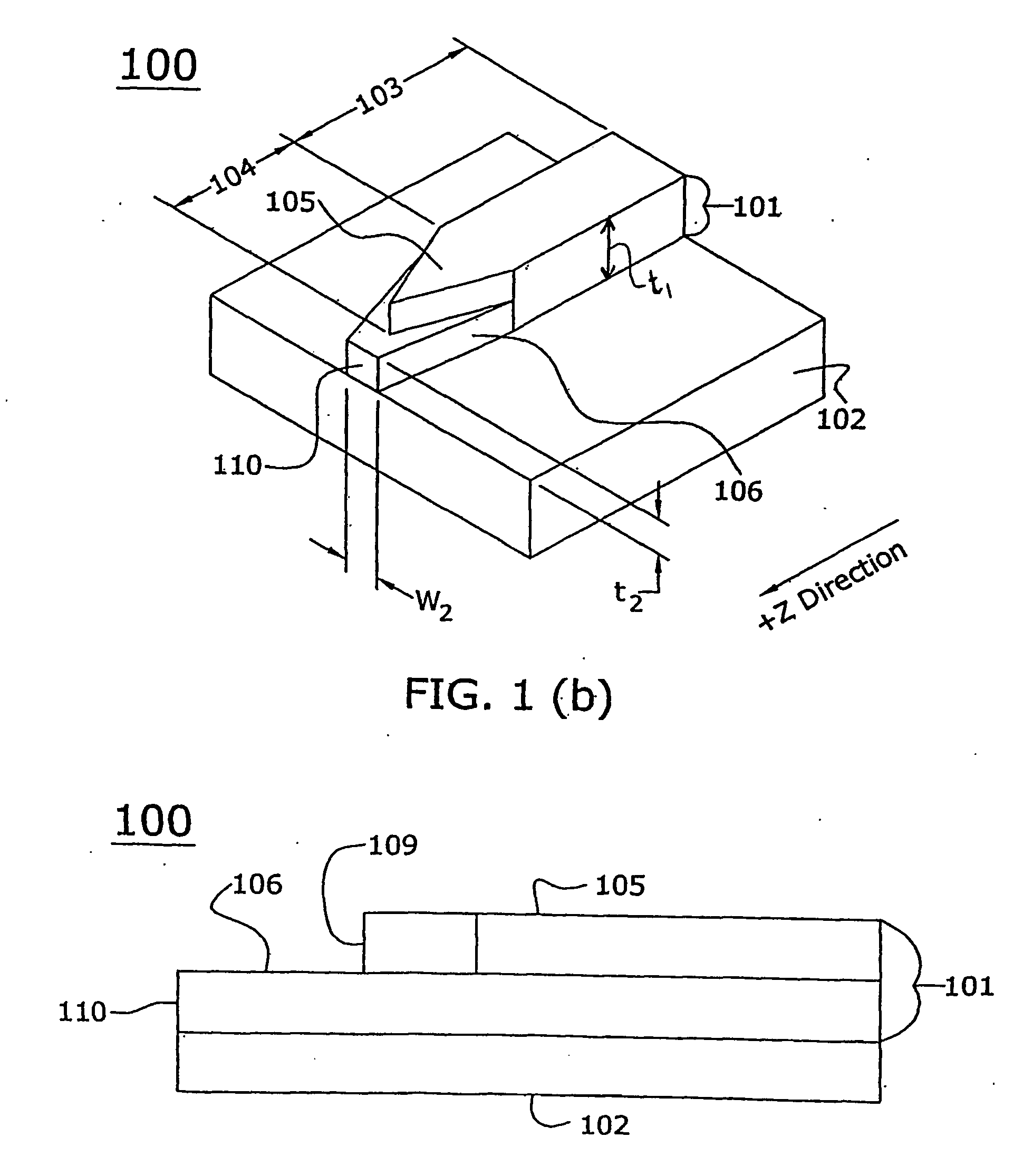
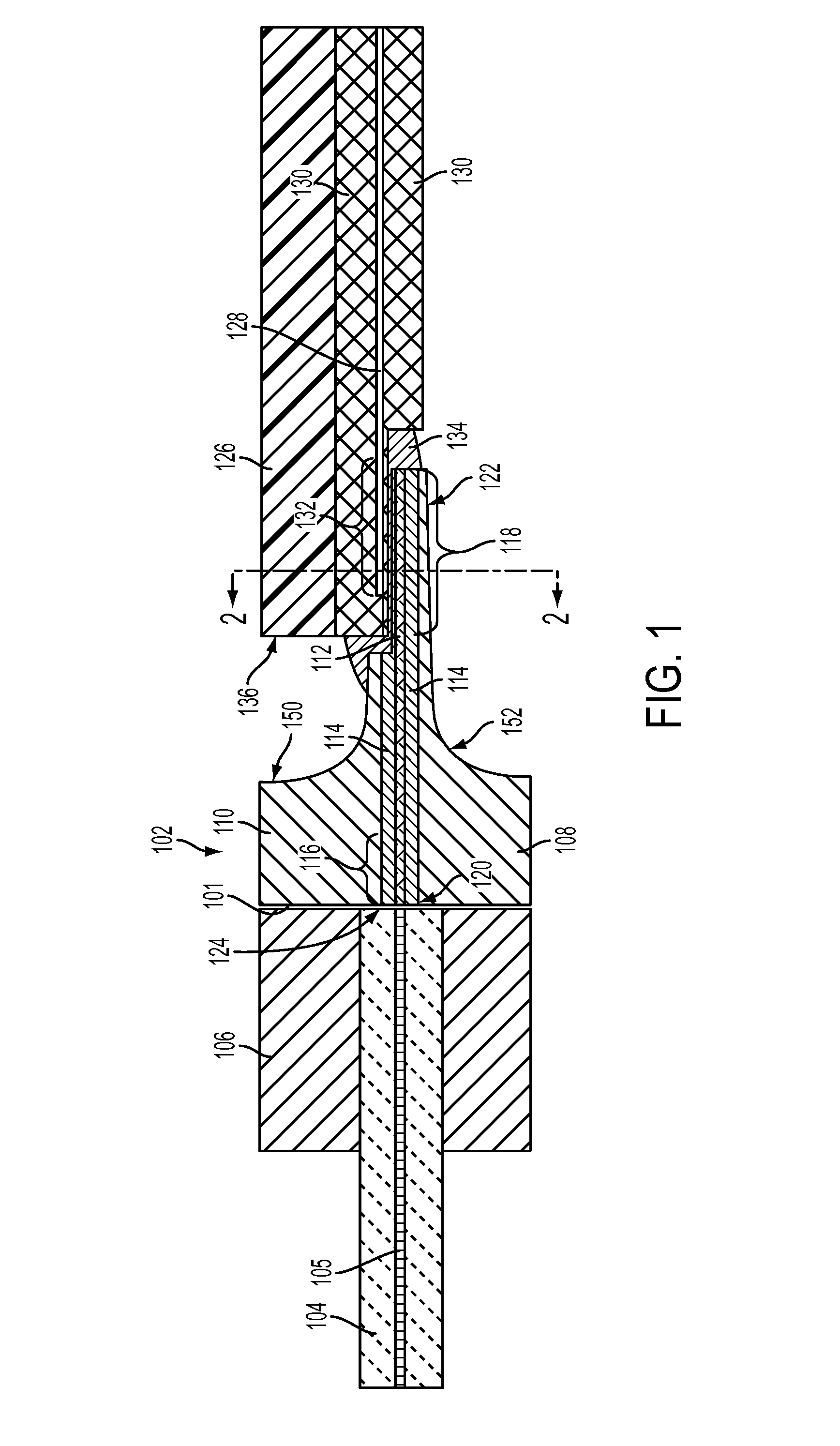
A tapered rib waveguide tapering from a large, multi-mode optical waveguide to a smaller, single-mode optical waveguide, the tapered rib waveguide comprising two portions (4,5) formed of the same material: a lower portion (4) which tapers laterally from the large waveguide to the smaller waveguide and an upper portion (5) formed on the lower portion (4), which tapers to a point (or other form of termination), the dimensions of the two portions (4,5) being such that substantially all of a fundamental mode propagated in the large multi-mode waveguide is coupled to the smaller, single-mode waveguide.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Multi-core optical fiber and method of making and using same
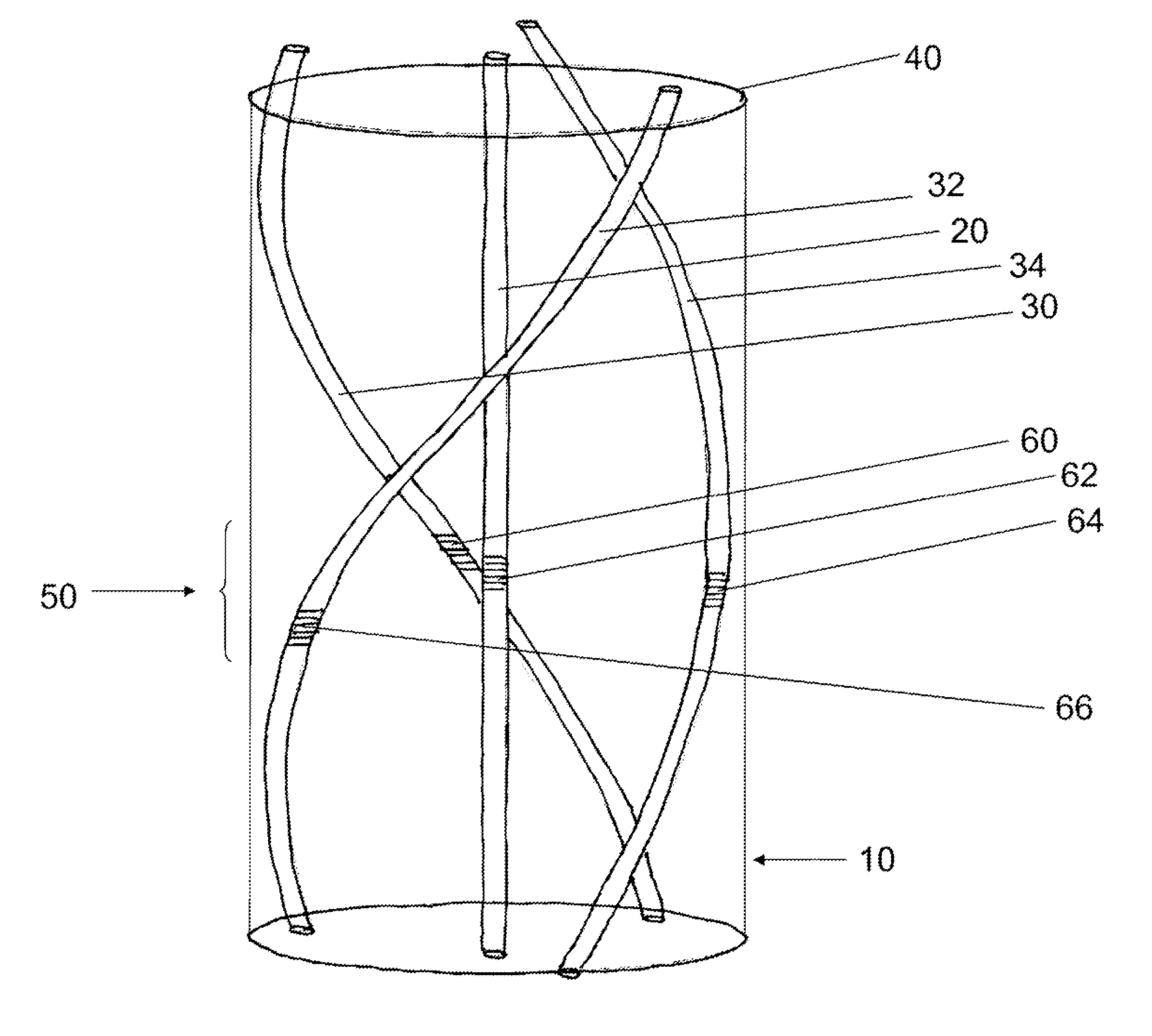
The apparatus includes a fiber comprising an axial center, a central single-mode waveguiding core and a plurality of peripheral single-mode waveguiding cores. The central core is located at a first distance from the axial center. The plurality of peripheral cores is located at respective second distances from the axial center. Each of the respective second distances is greater than the first distance, and each peripheral core of the plurality of peripheral cores follows a respective first helix about the axial center. The central core and the plurality of peripheral cores include an optical strain sensor rosette.
Owner:NAVY USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC THE
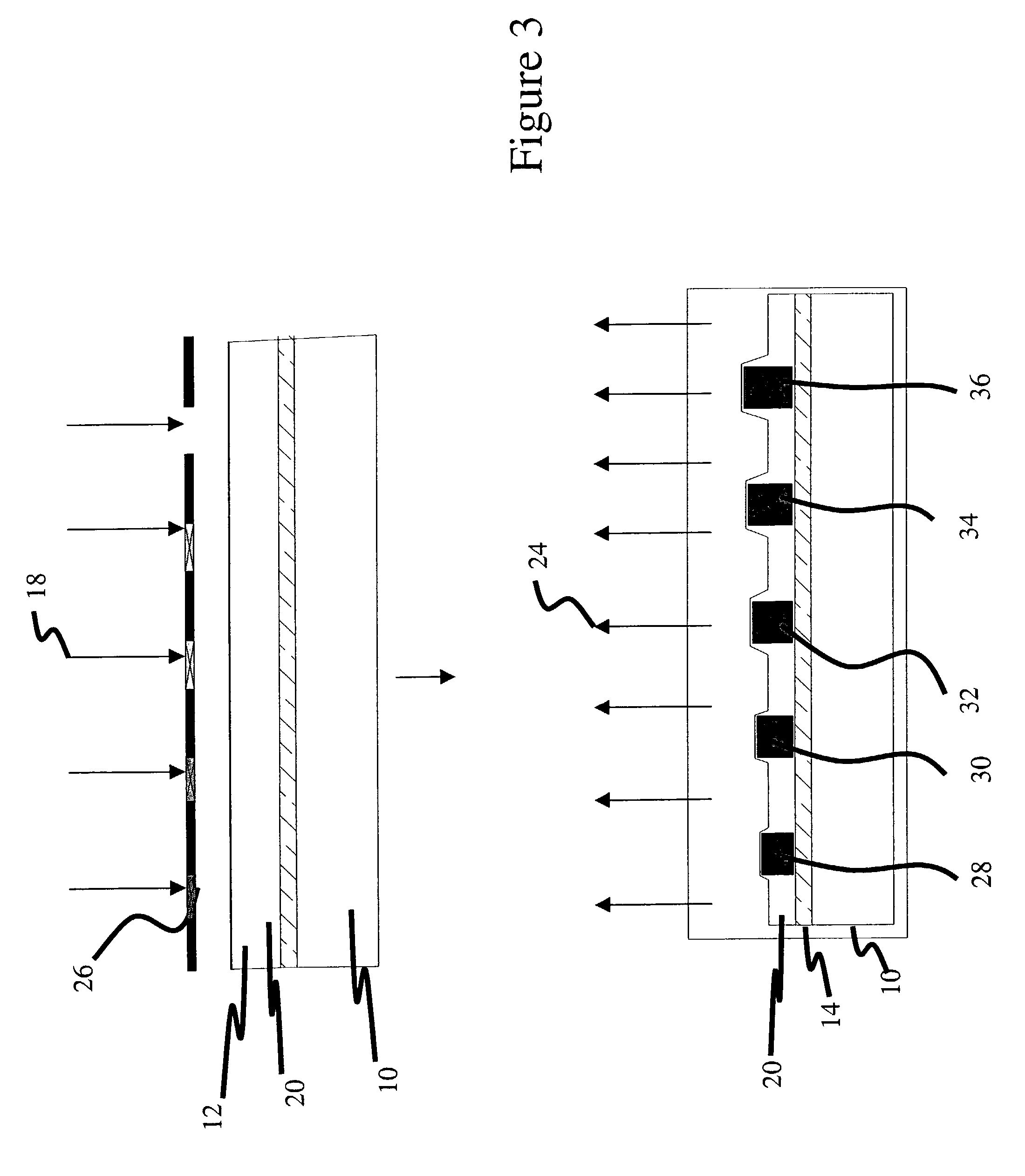
Apparatus, system and method for an adiabatic coupler for multi-mode fiber-optic transmission systems
InactiveUS20050265653A1Low insertion lossIncrease system bandwidthLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberRefractive index
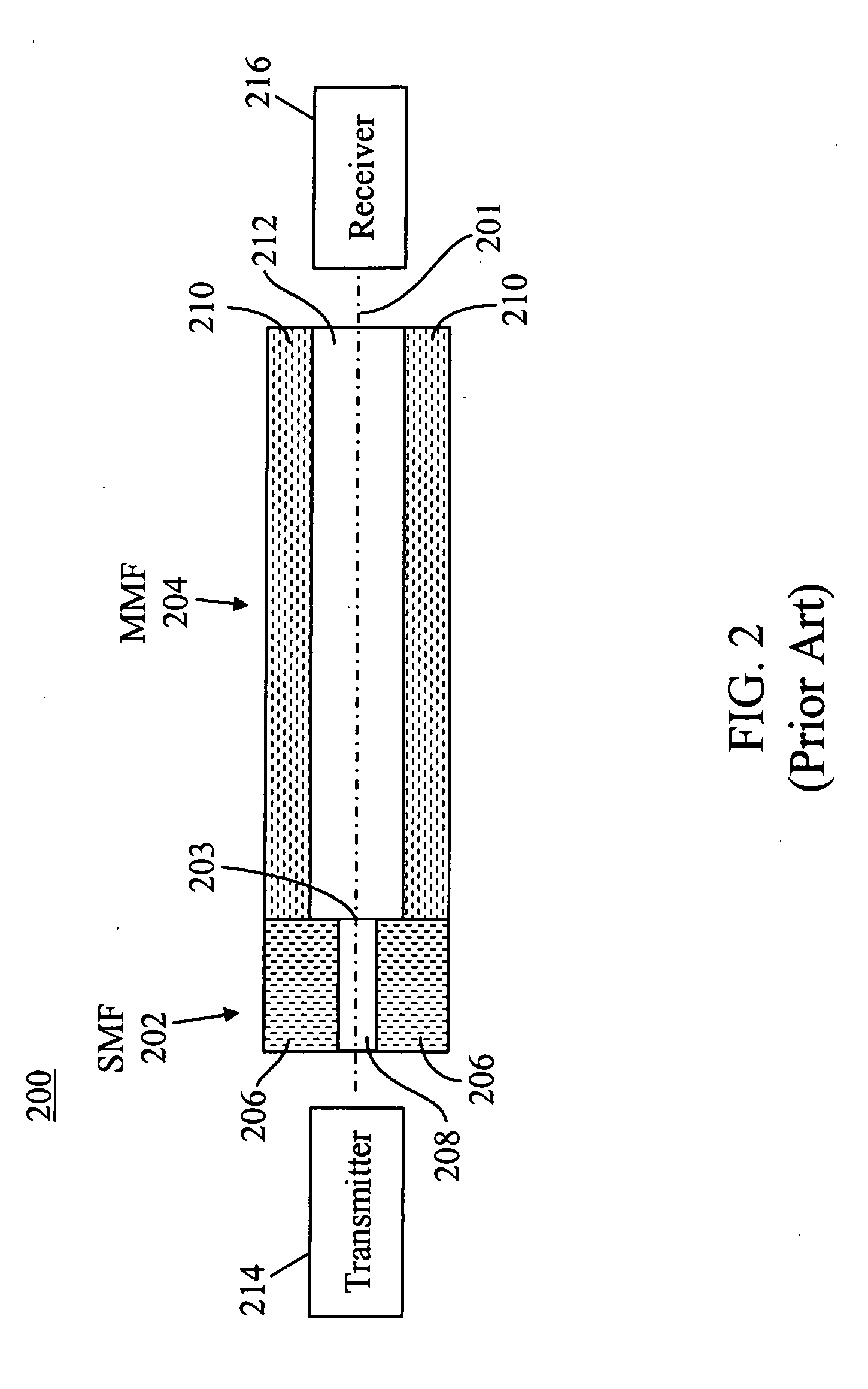
An improved fiber-optic communications system comprises a multi-mode waveguide carrying an optical signal, a single-mode waveguide optically coupled to and receiving the optical signal from the multi-mode waveguide and an adiabatic coupler optically coupled between the multi-mode waveguide and the single-mode waveguide. The multi-mode and single-mode waveguides may be optical fibers. The adiabatic coupler may comprise a tapered core surrounded by a cladding. Alternatively, the adiabatic coupler may comprise a core surrounded by a cladding, wherein the refractive index of at least one of the core and the cladding varies over the length of the adiabatic coupler.
Owner:OCLARO NORTH AMERICA
Fiber to wafer interface
An interface device includes a body portion having a single-mode waveguide portion including a substantially optically transparent material, a cladding portion defined by channels contacting the waveguide portion, the cladding portion including a substantially optically transparent polymer material, an engagement feature operative to engage a portion of a wafer, and a guide portion operative to engage a portion of an optical fiber ferrule.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
Apparatus, system and method for an adiabatic coupler for multi-mode fiber-optic transmission systems
InactiveUS7184623B2Low insertion lossIncrease system bandwidthLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberRefractive index
An improved fiber-optic communications system comprises a multi-mode waveguide carrying an optical signal, a single-mode waveguide optically coupled to and receiving the optical signal from the multi-mode waveguide and an adiabatic coupler optically coupled between the multi-mode waveguide and the single-mode waveguide. The multi-mode and single-mode waveguides may be optical fibers. The adiabatic coupler may comprise a tapered core surrounded by a cladding. Alternatively, the adiabatic coupler may comprise a core surrounded by a cladding, wherein the refractive index of at least one of the core and the cladding varies over the length of the adiabatic coupler.
Owner:OCLARO NORTH AMERICA
Waveguide lens with multimode interference
In one embodiment, a waveguide lens of the invention has a pair of planar waveguides, e.g., a single-mode waveguide connected to a multimode waveguide. The widths of the two waveguides and the length of the multimode waveguide are selected such that particular mode coupling between the waveguides and multimode interference (MMI) effects in the multimode waveguide cause the latter to output a converging beam of light similar to that produced by a conventional waveguide lens. Advantageously, waveguide lenses of the invention may be used to implement low-loss, low-crosstalk waveguide crossings and / or compact waveguide turns. In addition, waveguide lenses of the invention can be readily and cost-effectively incorporated into waveguide devices designated for large-scale production.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
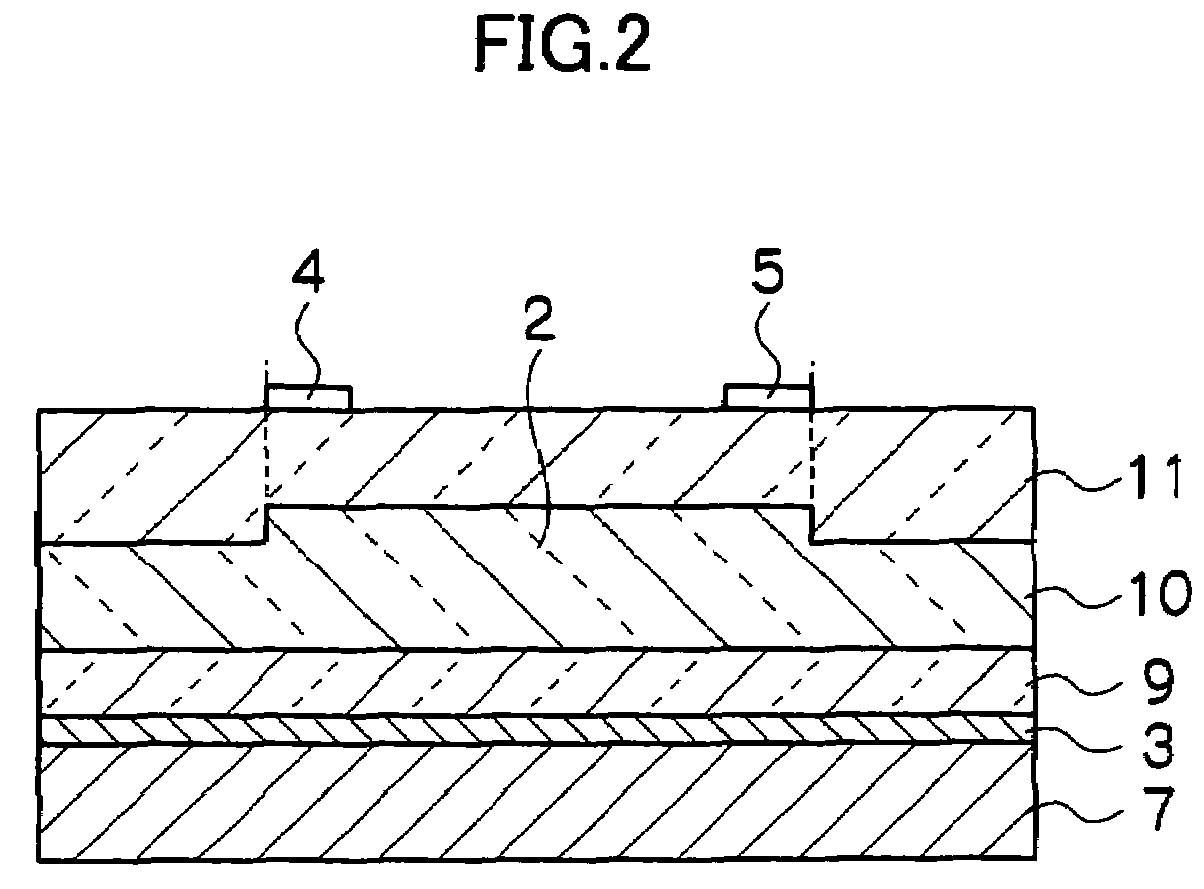
Optical waveguide termination with vertical and horizontal mode shaping
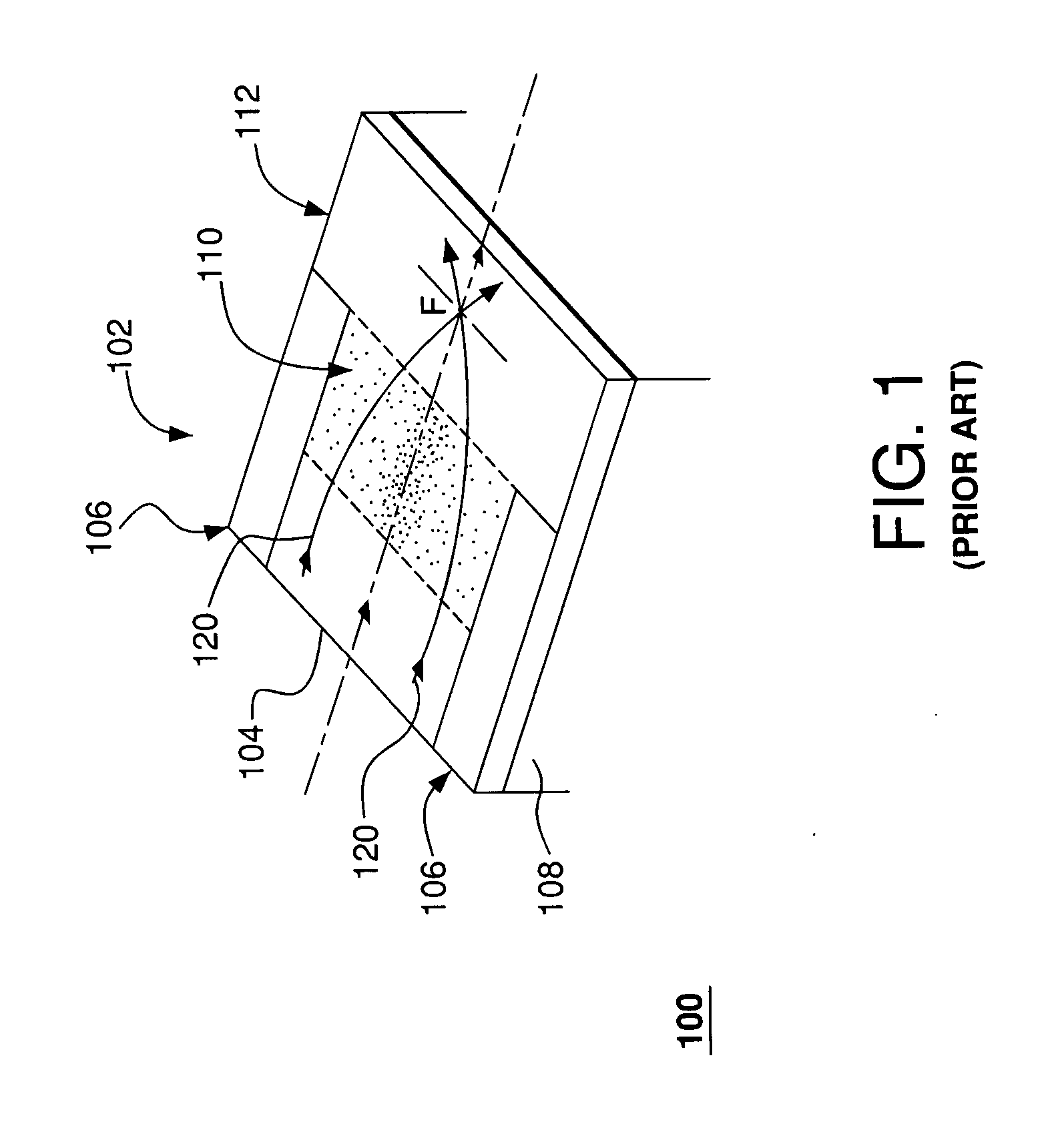
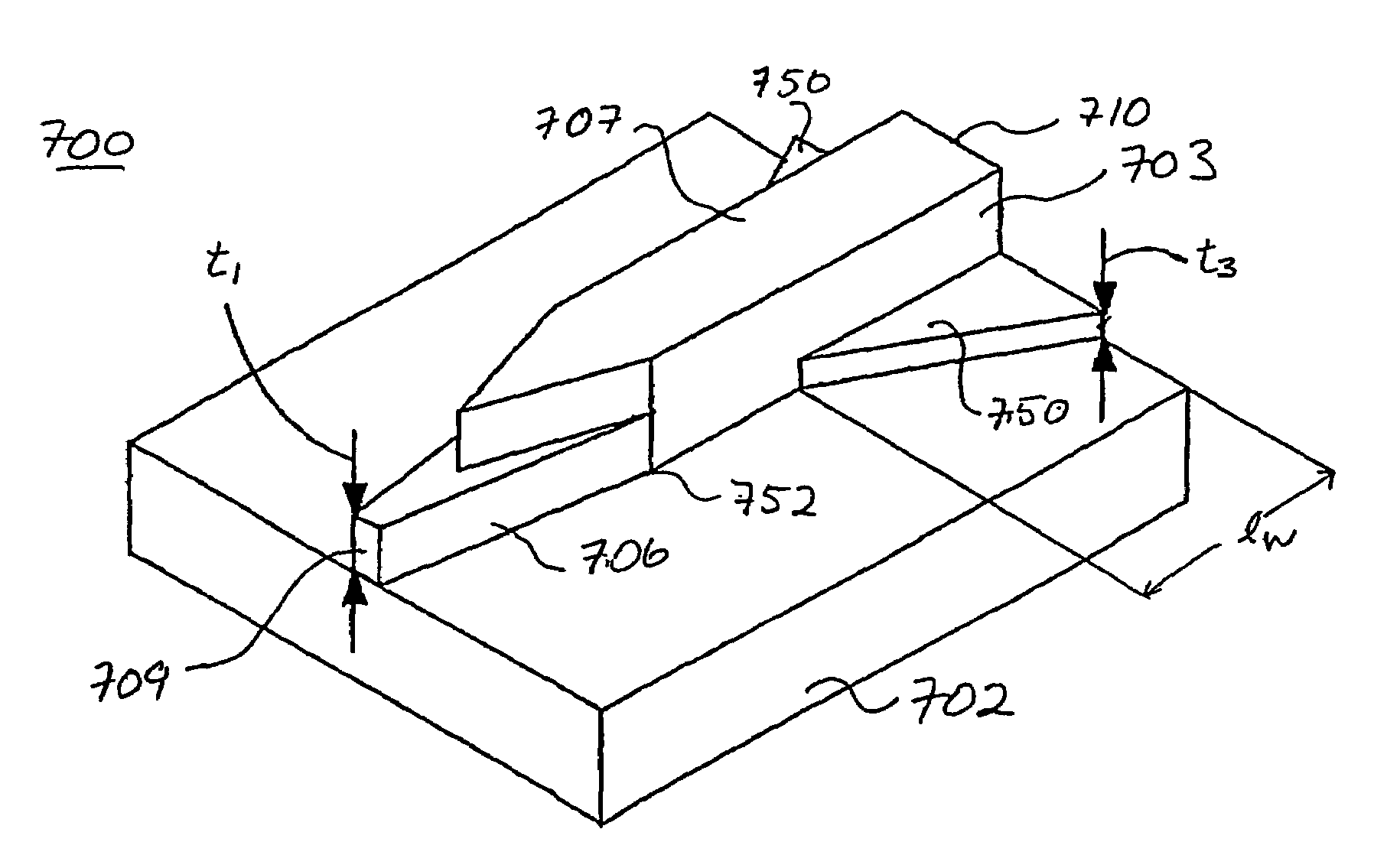
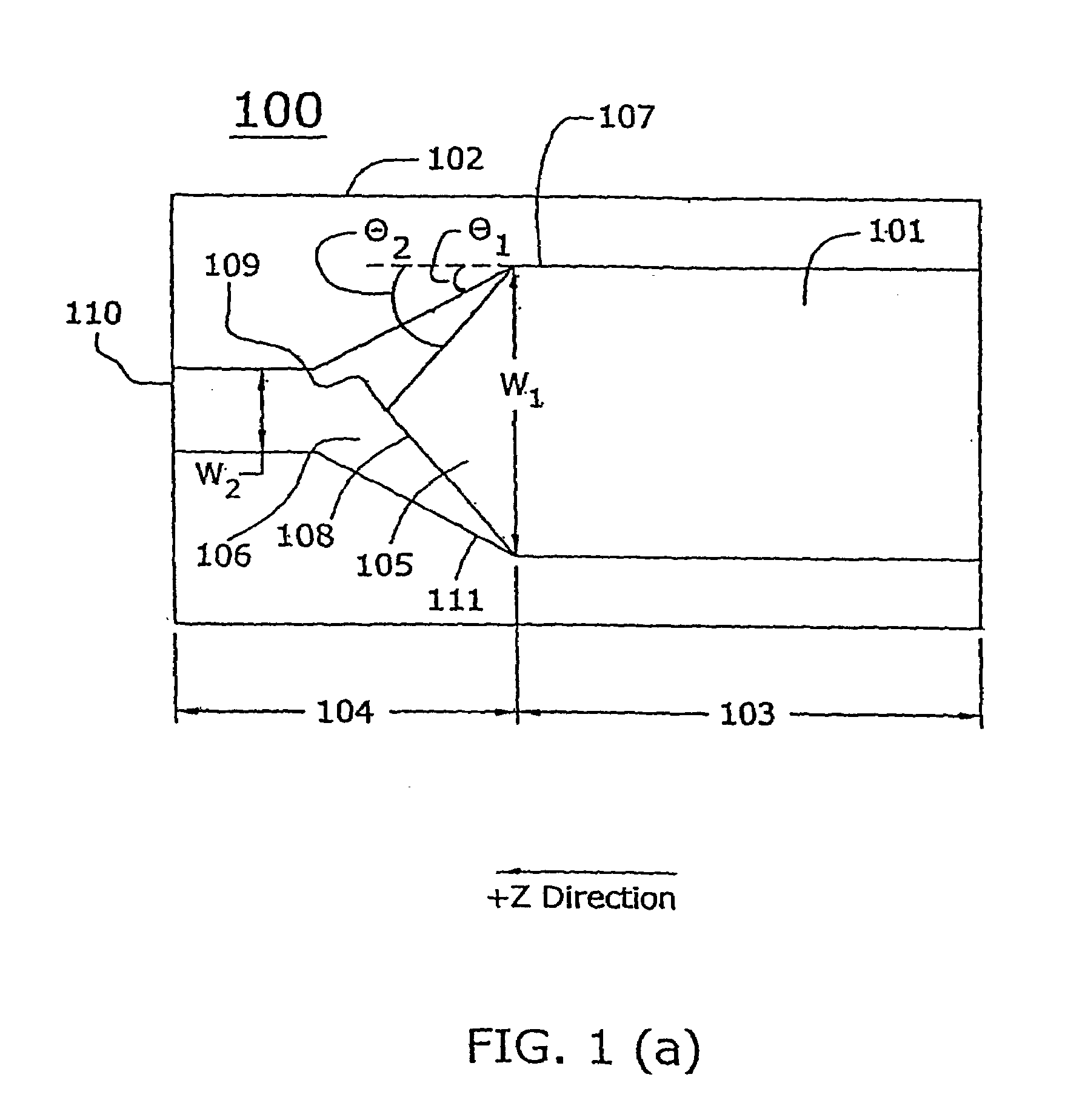
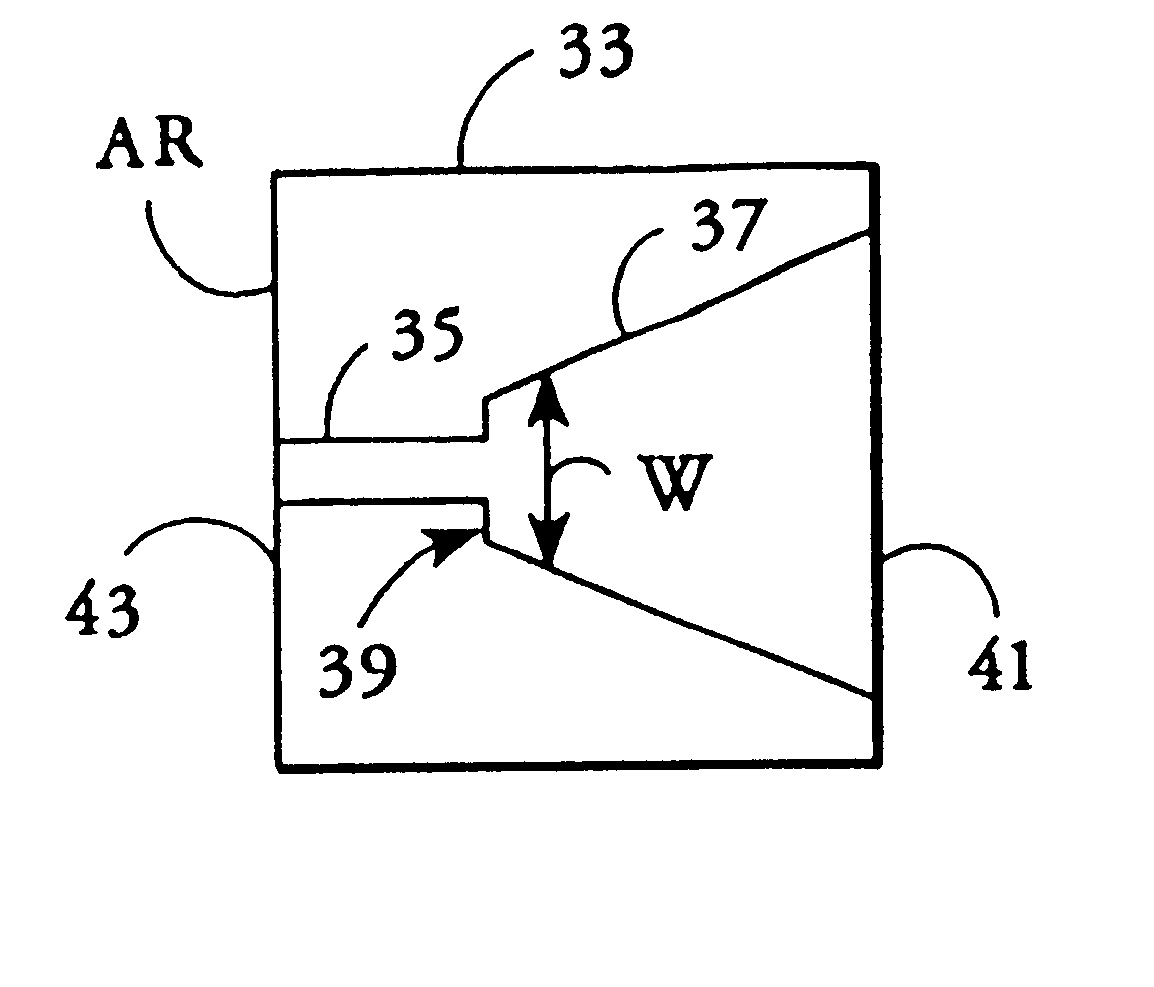
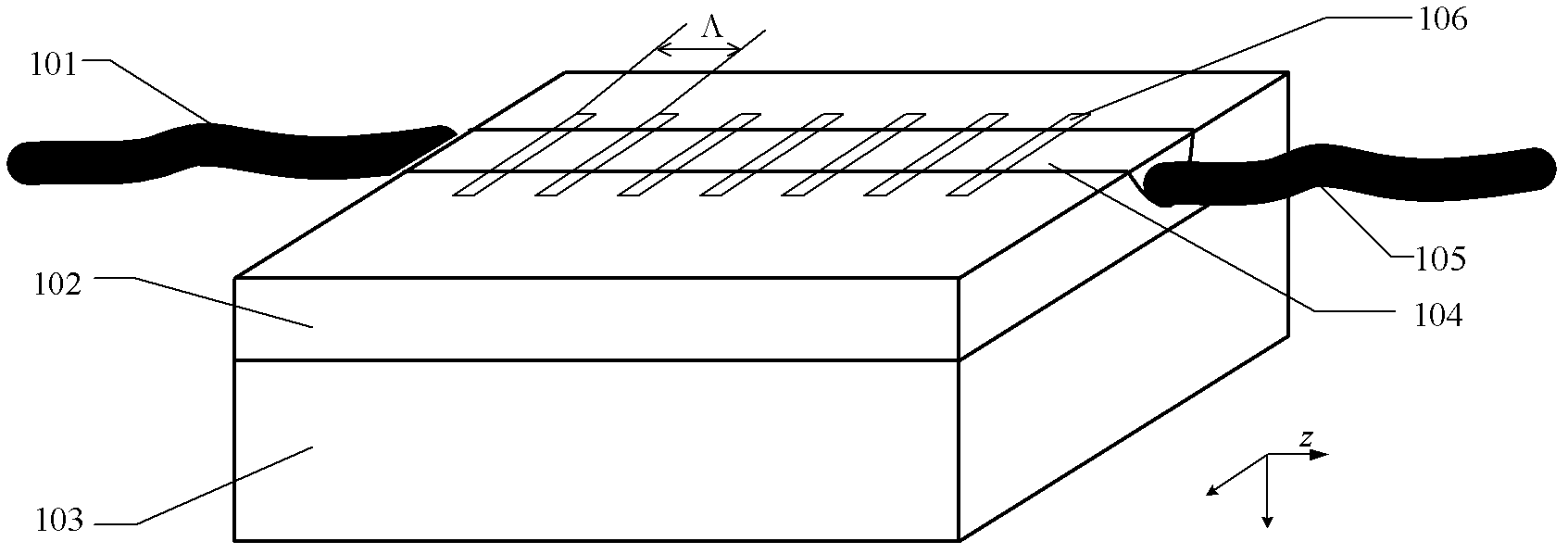
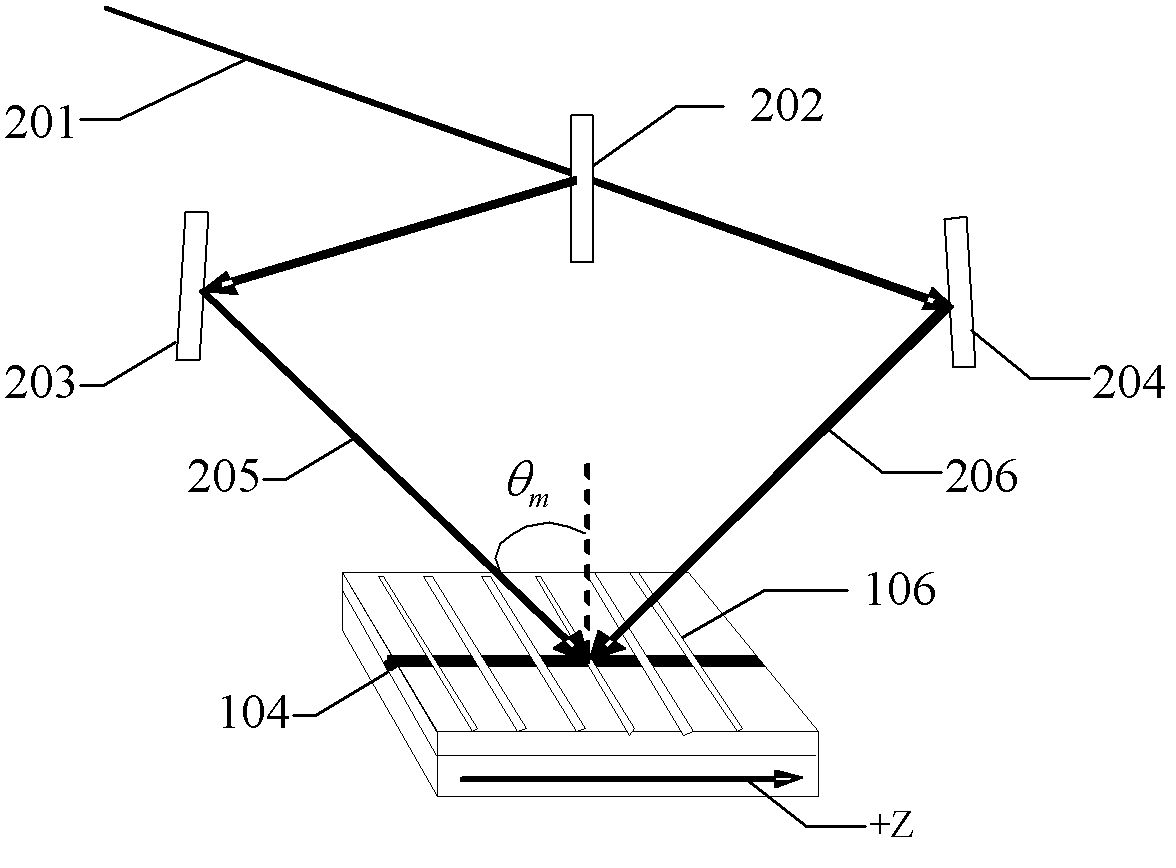
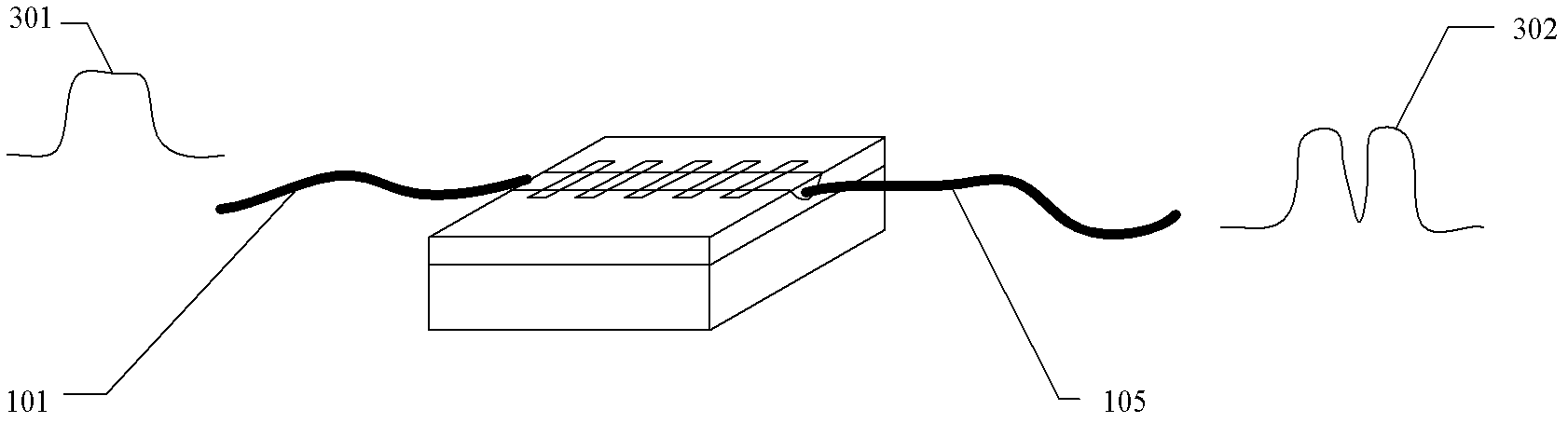
InactiveUS7251406B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryWaveguide modeSingle mode waveguides
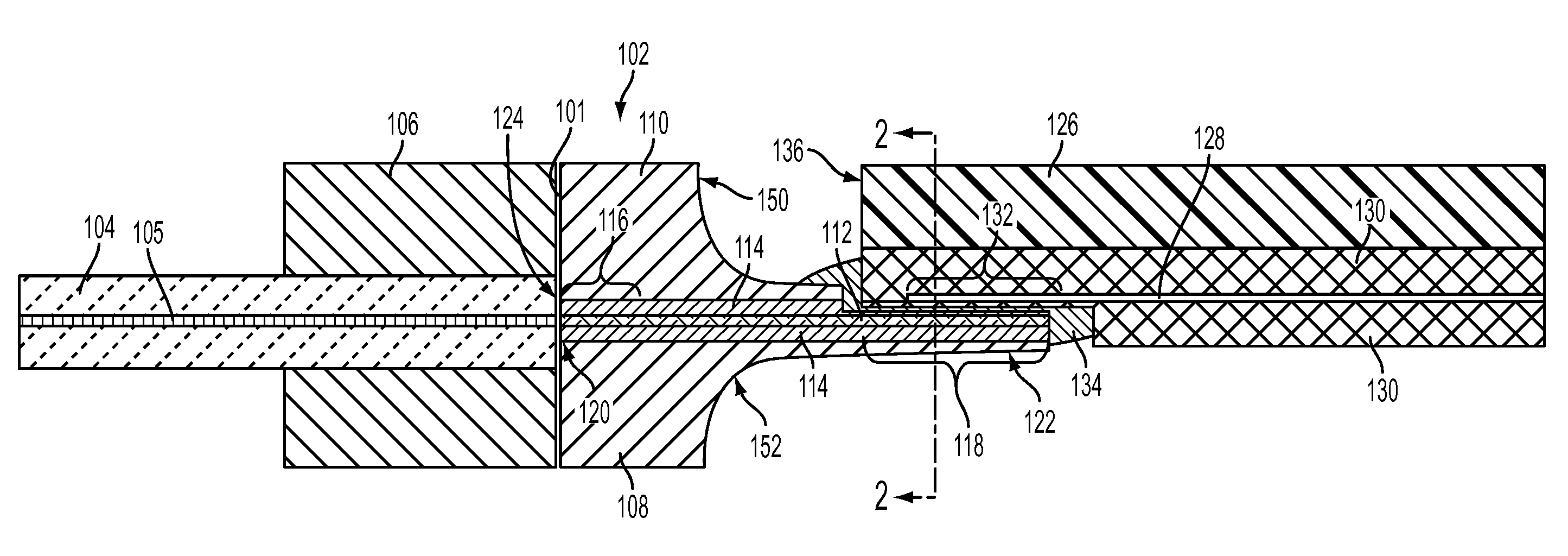
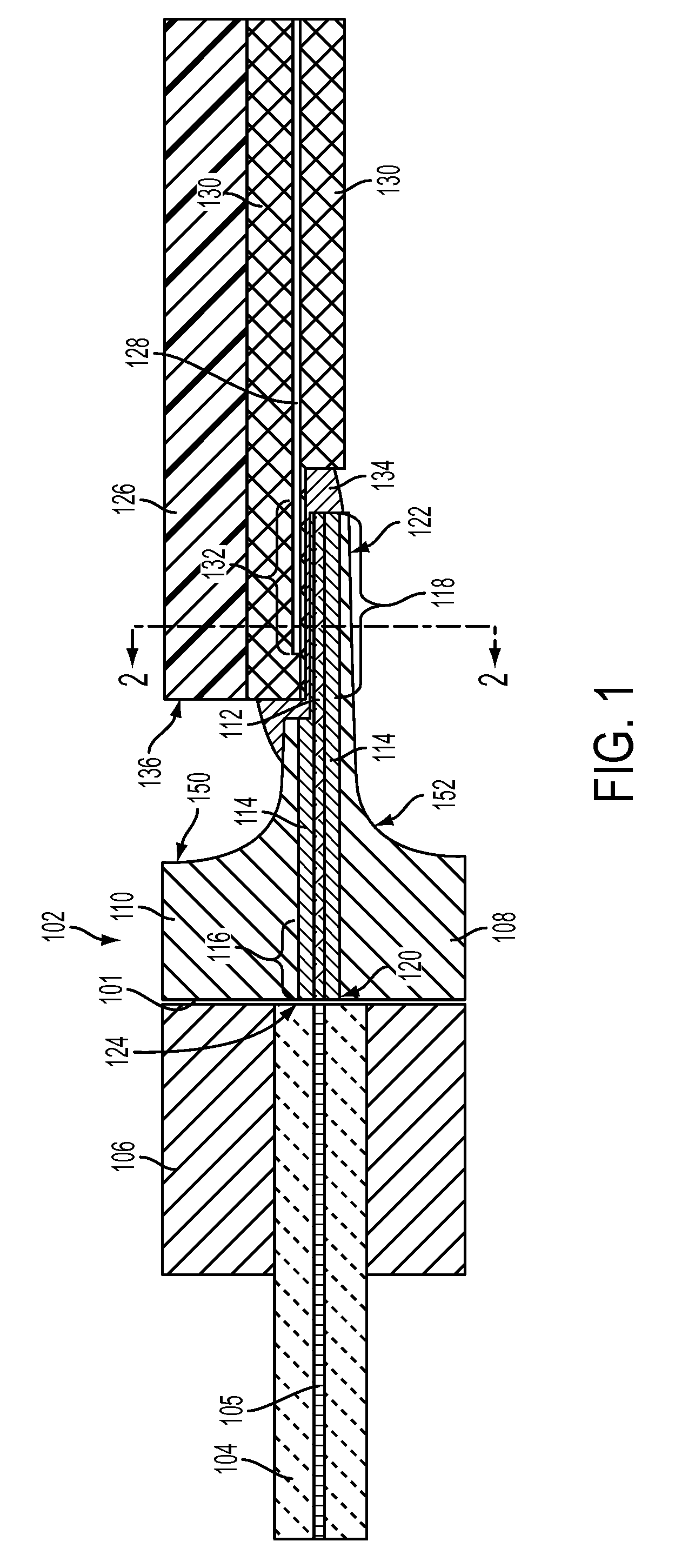
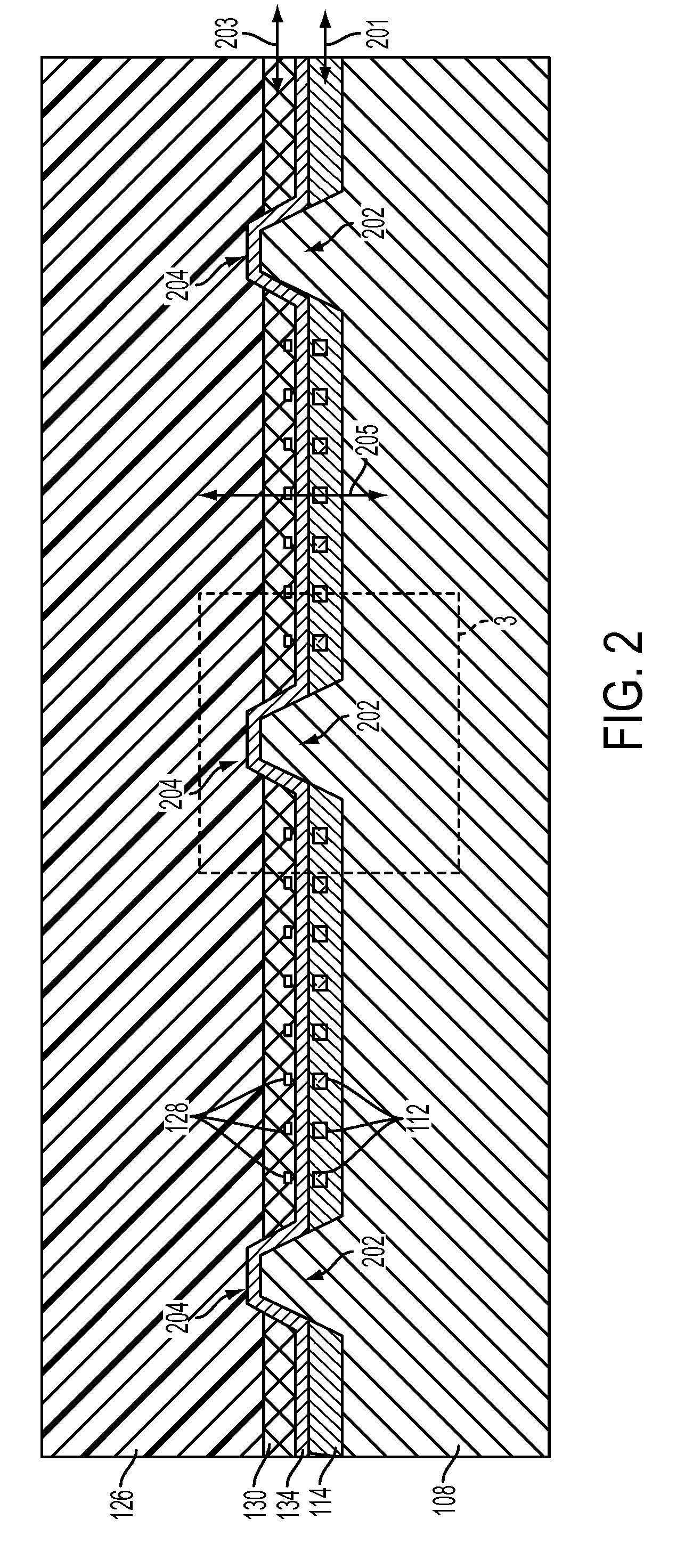
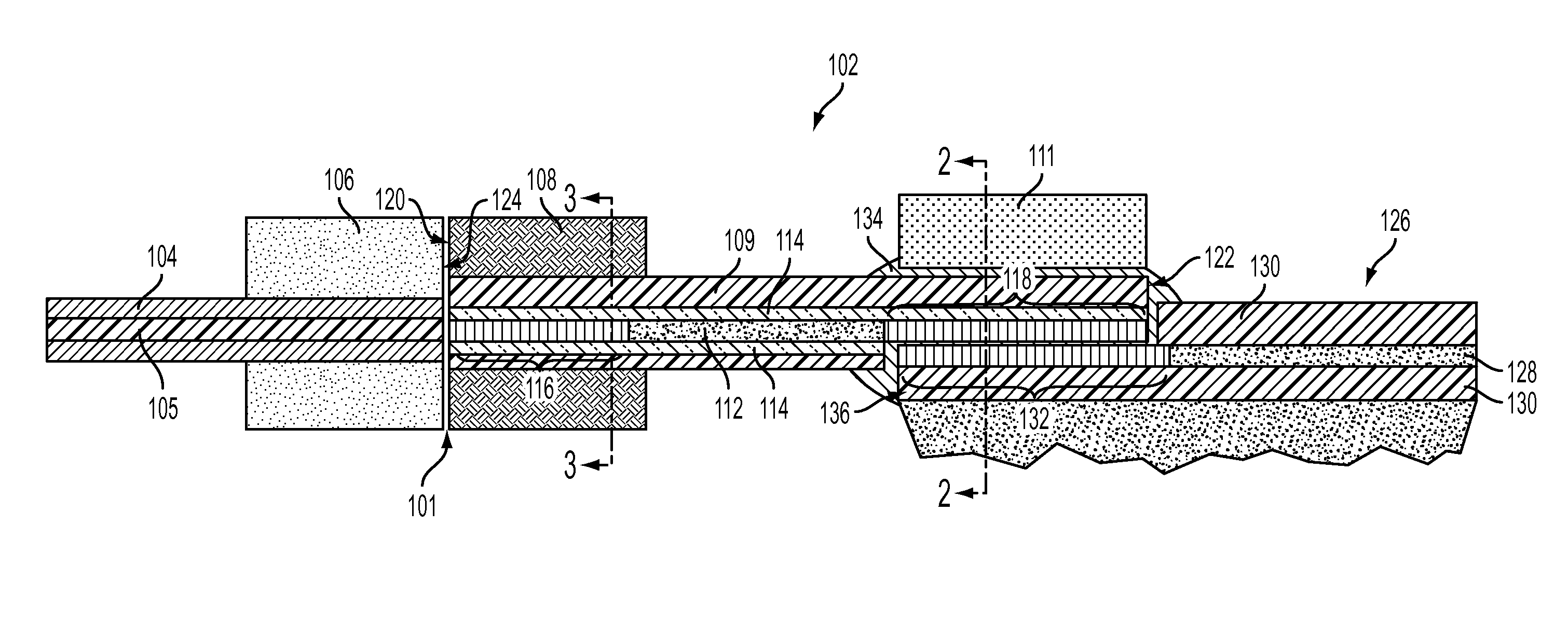
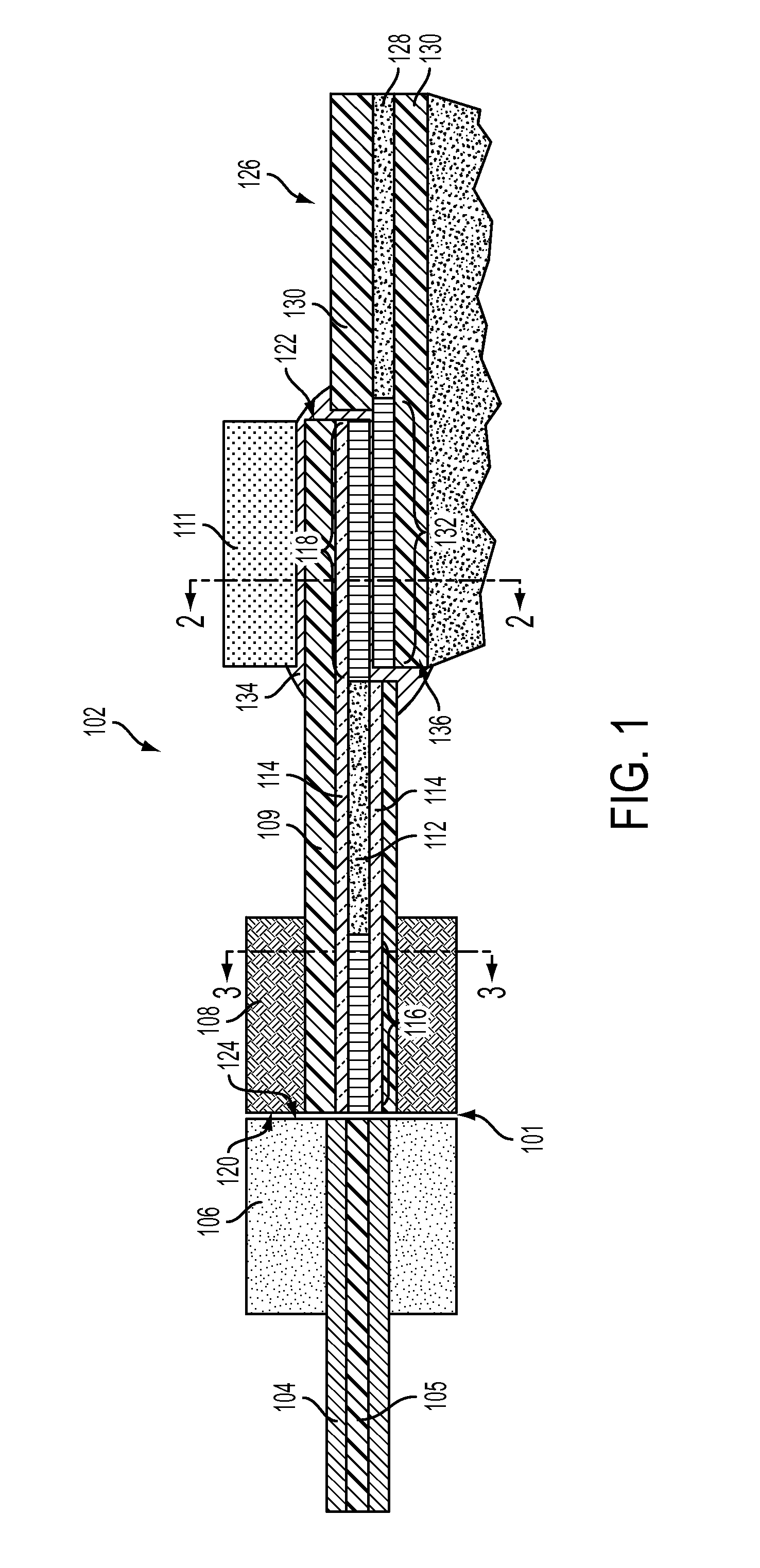
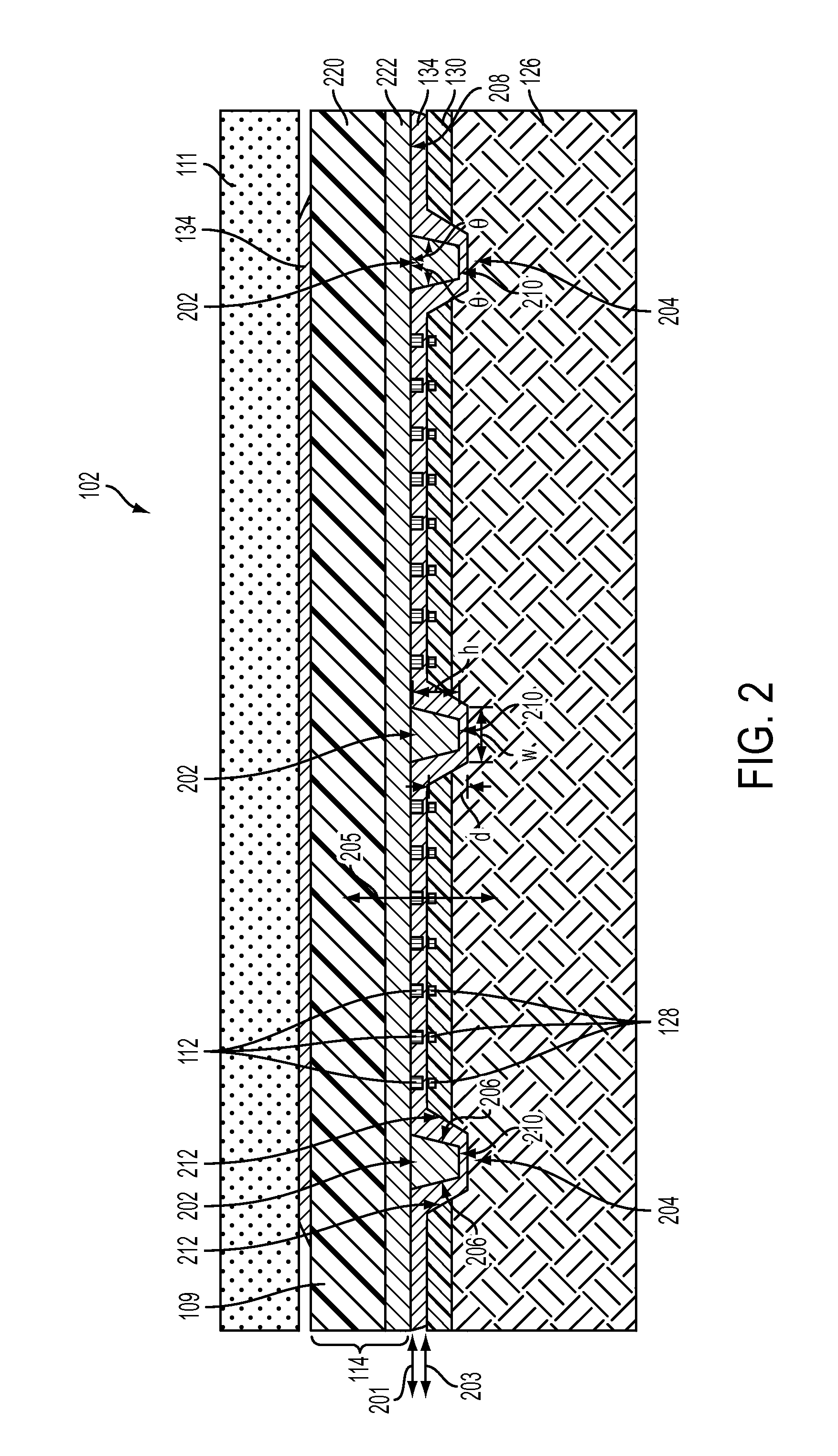
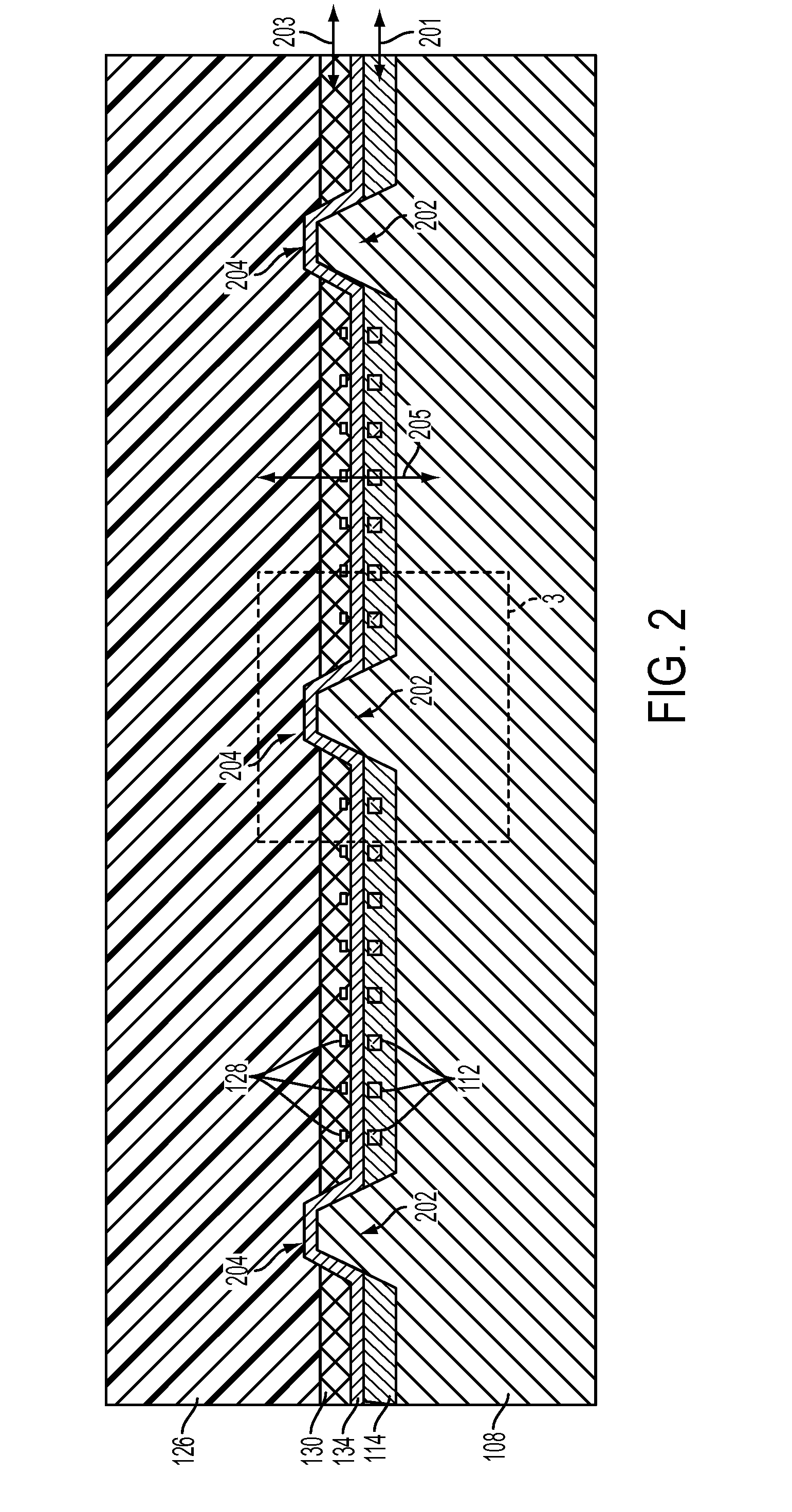
An optical device is disclosed which includes a single-mode waveguide (700) which supports a first optical mode in a first region and a second optical mode in a second region. The waveguide includes a guiding layer (703) having at least one wing (750) extended outwardly from the guiding layer (703). The guiding layer (703) may desirably have a rib waveguide (706, 707) cross sectional shape at the wings. The wings (750) decrease in width along the length of the guiding layer to convert a rib waveguide mode at the wings to a channel waveguide mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
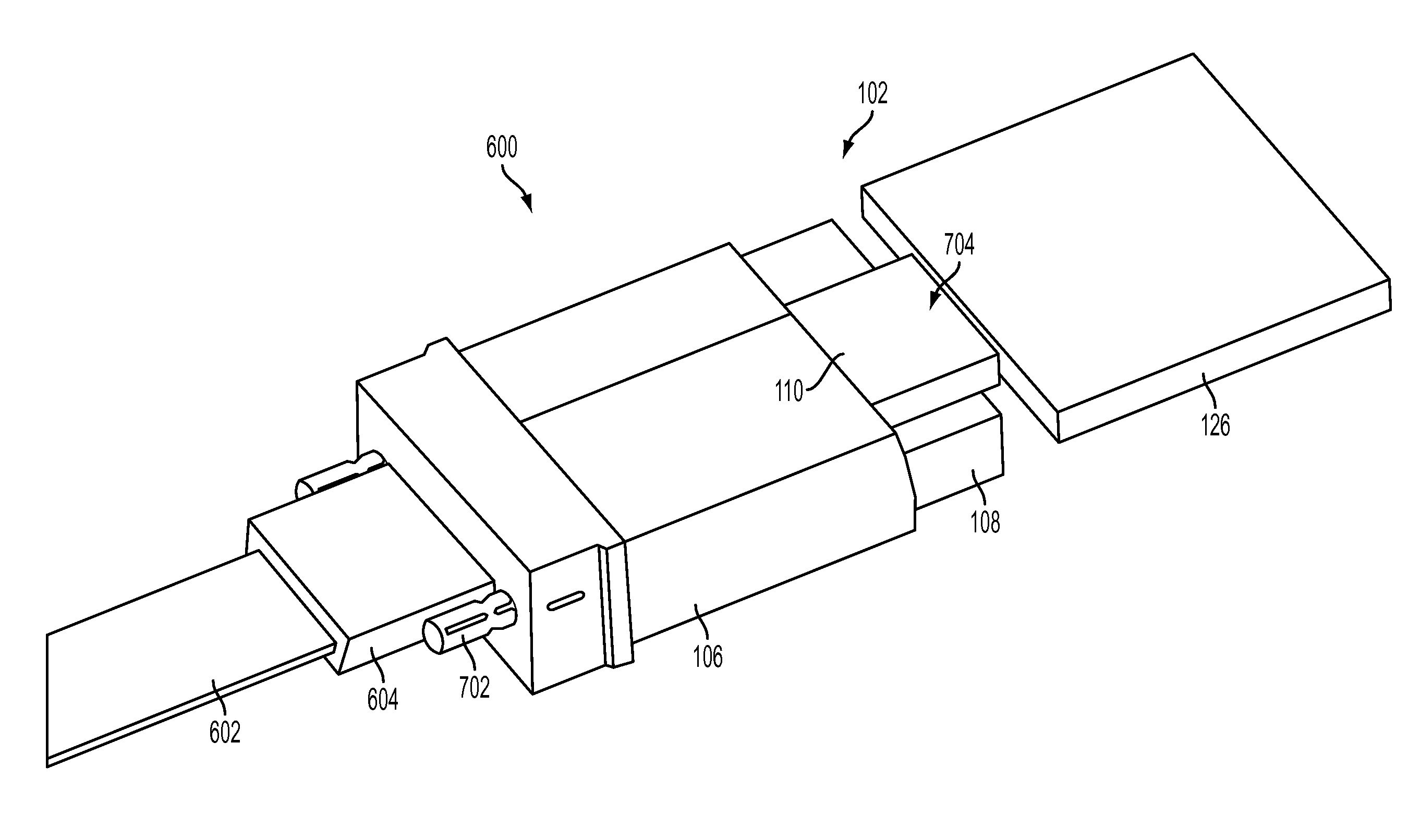
Flexible fiber to wafer interface
ActiveUS8534927B1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesMechanical engineering
An interface device includes a flexible substrate portion, a flexible cladding portion arranged on the substrate portion, a flexible single-mode waveguide portion arranged on the cladding portion including a substantially optically transparent material, a first engagement feature operative to engage a portion of a wafer, and a connector portion engaging a first distal end of the flexible substrate portion, the connector portion operative to engage a portion of an optical fiber ferrule.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
1 x N fanout waveguide photodetector
Owner:INTEL CORP
Semiconductor optical device and module using the same
InactiveUS20060274802A1Increase output powerImprove featuresOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsSingle mode waveguidesWaveguide
A semiconductor laser device capable of providing high output power operation is provided which has a structure in which high output power and kink suppression can be simultaneously attained as well as these characteristics can be realized by a short chip length. In a waveguide structure of an MMI laser diode, a taper waveguide is intentionally inserted between a single mode waveguide and a multimode waveguide, and further, a single mode waveguide is used as a passive waveguide. These individual units or combination thereof can solve the above-described problems.
Owner:OPNEXT JAPAN INC
Optical device
InactiveUS6288833B1Laser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionAudio power amplifierSingle mode waveguides
An optical waveguide including a single-mode waveguide in which an induced radiation ray generated by exciting the ion propagates in a single-mode in both of a thickness direction and a width direction in the single-mode waveguide; and multi-mode waveguides disposed along both of side surfaces of the single-mode waveguide in which the ray propagates in a single-mode in a thickness direction of the multi-mode waveguide and propagates in a multi-mode in a width direction. In accordance with the present invention, the exciting ray is easily absorbed because the ray propagates to cross the single-mode waveguide without a skew-mode propagation, and the laser and the photo-amplifier which can obtain a higher output in the single-mode is provided.
Owner:NEC CORP
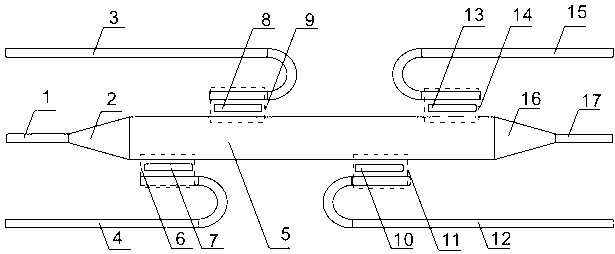
Mode add-drop multiplexing and demultiplexing device based on grating-assisting type coupler
InactiveCN103217738AAdjustable coupling coefficientHigh bandwidthOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexWaveguide grating
The invention discloses a mode add-drop multiplexing and demultiplexing device based on a grating-assisting type coupler. The device comprises three add single-mode waveguides, an add mode converter, a bus multi-mode waveguide, two add Bragg waveguide gratings, a drop mode converter, three drop single-mode waveguides, two drop Bragg waveguide gratings, two add coupling areas and two drop coupling areas. The Bragg waveguide gratings are arranged between the bus multi-mode waveguide and the add and drop single-mode waveguides, and the energy exchange between the multi-mode waveguide and the single-mode waveguides is realized due to the micro-interference function of the refraction rate. The device has the advantages that the coupling is realized between the single-mode waveguides and the multi-mode waveguide in different modes; the coupling coefficient is adjustable, the bandwidth is large, the number of information carrying channels is multiple, and the like; the design structure is simple, and the size is compact; the device manufacturing process is compatible with a CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) process, so the integration and the extension are easy, the low-cost manufacturing is convenient, and the device can be widely applied to the on-chip and high-density integrated type optical interconnection system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optical waveguide termination with vertical and horizontal mode shaping
InactiveUS20050202554A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryWaveguide modeSingle mode waveguides
An optical device is disclosed which includes a single-mode waveguide (700) which supports a first optical mode in a first region and a second optical mode in a second region. The waveguide includes a guiding layer (703) having at least one wing (750) extended outwardly from the guiding layer (703). The guiding layer (703) may desirably have a rib waveguide (706, 707) cross sectional shape at the wings. The wings (750) decrease in width along the length of the guiding layer to convert a rib waveguide mode at the wings to a channel waveguide mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flexible fiber to wafer interface
ActiveUS20130251304A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesMechanical engineering
An interface device includes a flexible substrate portion, a flexible cladding portion arranged on the substrate portion, a flexible single-mode waveguide portion arranged on the cladding portion including a substantially optically transparent material, a first engagement feature operative to engage a portion of a wafer, and a connector portion engaging a first distal end of the flexible substrate portion, the connector portion operative to engage a portion of an optical fiber ferrule.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Optical modulator and optical modulator array
InactiveUS20050175281A1Easy to produceImprove robustnessCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesWaveguide
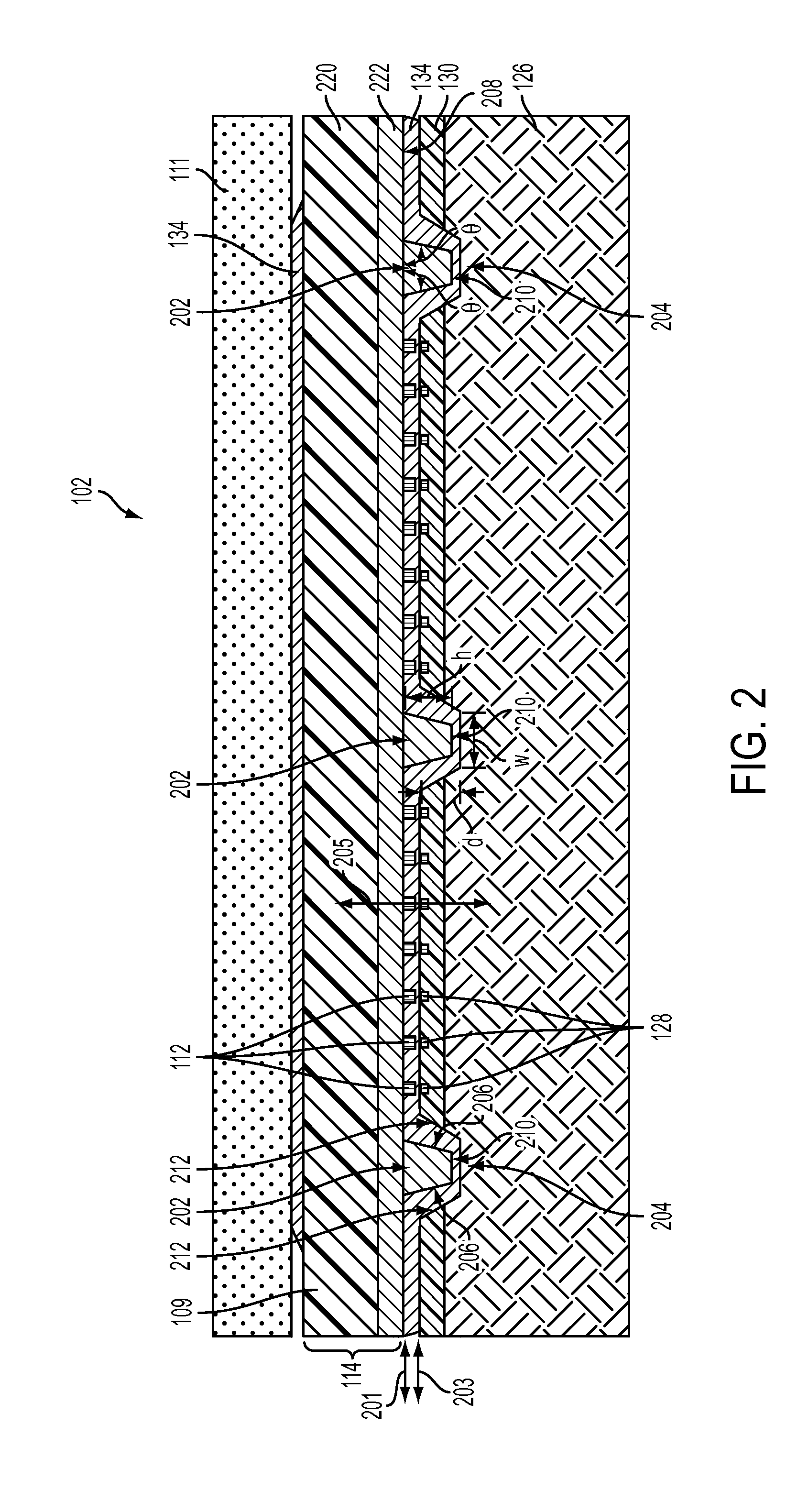
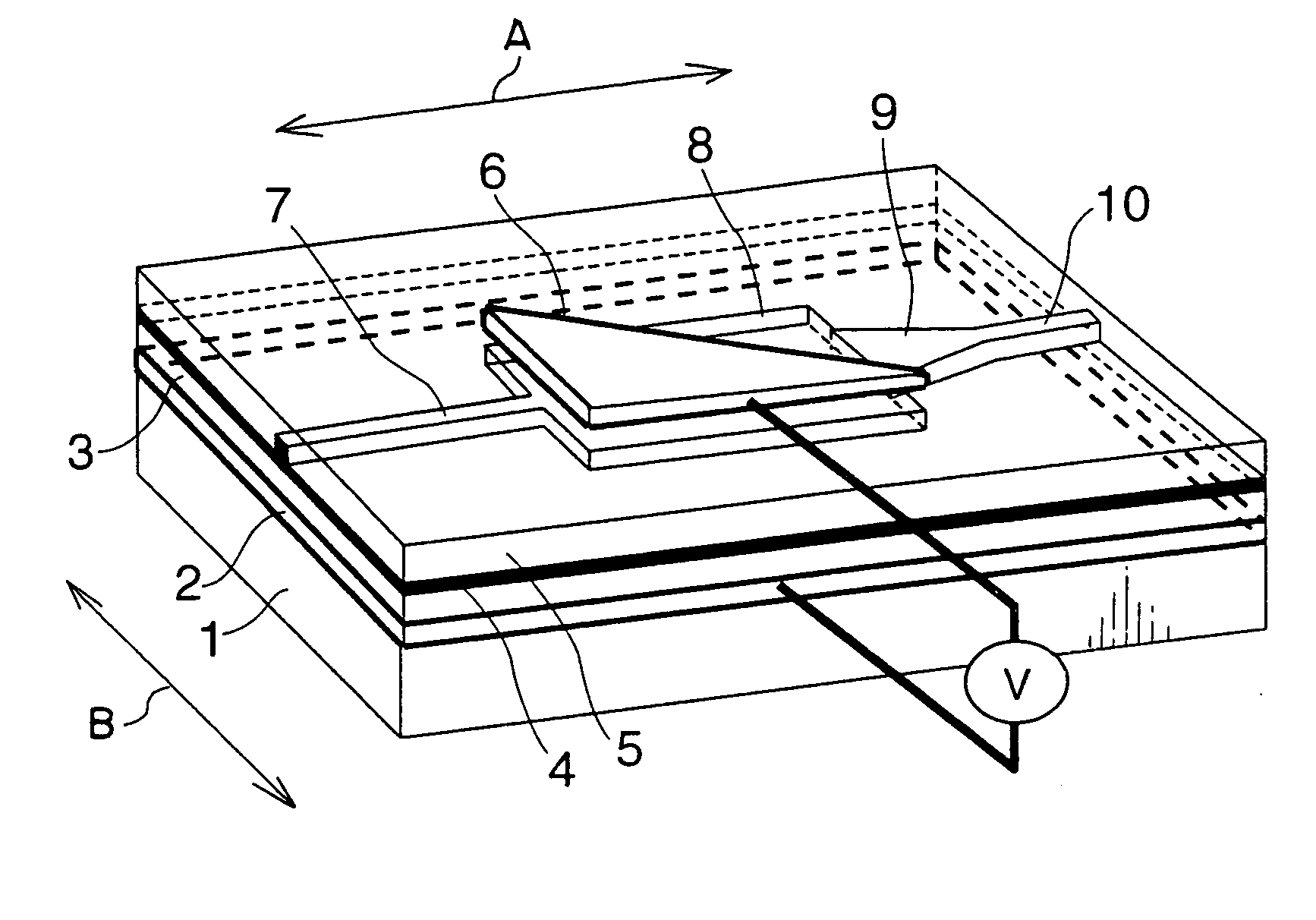
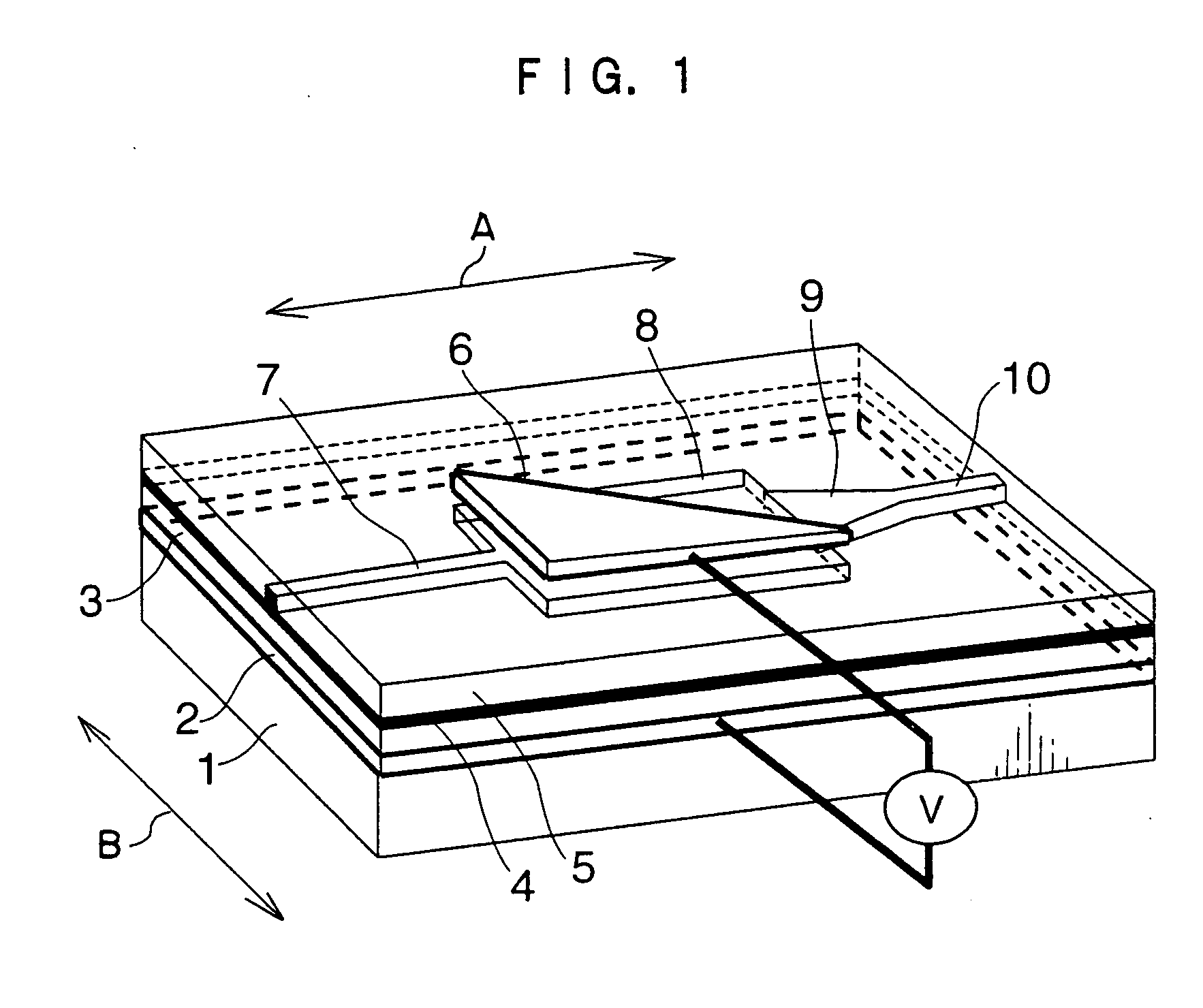
An optical modulator is provided with an optical waveguide including an input-side single-mode waveguide for propagating inputted light at single mode, a multi-mode waveguide for propagating the light propagated from the input-side single-mode waveguide at plural guided modes, and an output-side single-mode waveguide for propagating the light propagated from the multi-mode waveguide at single mode to output the light. A lower electrode layer is disposed below the multi-mode waveguide, and an upper electrode is disposed above the multi-mode waveguide. The upper electrode cooperates with the lower electrode layer to apply an electric field to the multi-mode waveguide. A phase of each of the guided modes propagating through the multi-mode waveguide is modulated by applying an electric field to the multi-mode waveguide, and intensity of the light outputted from the output-side single-mode waveguide is modulated by an interference of the phase-modulated guided modes.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
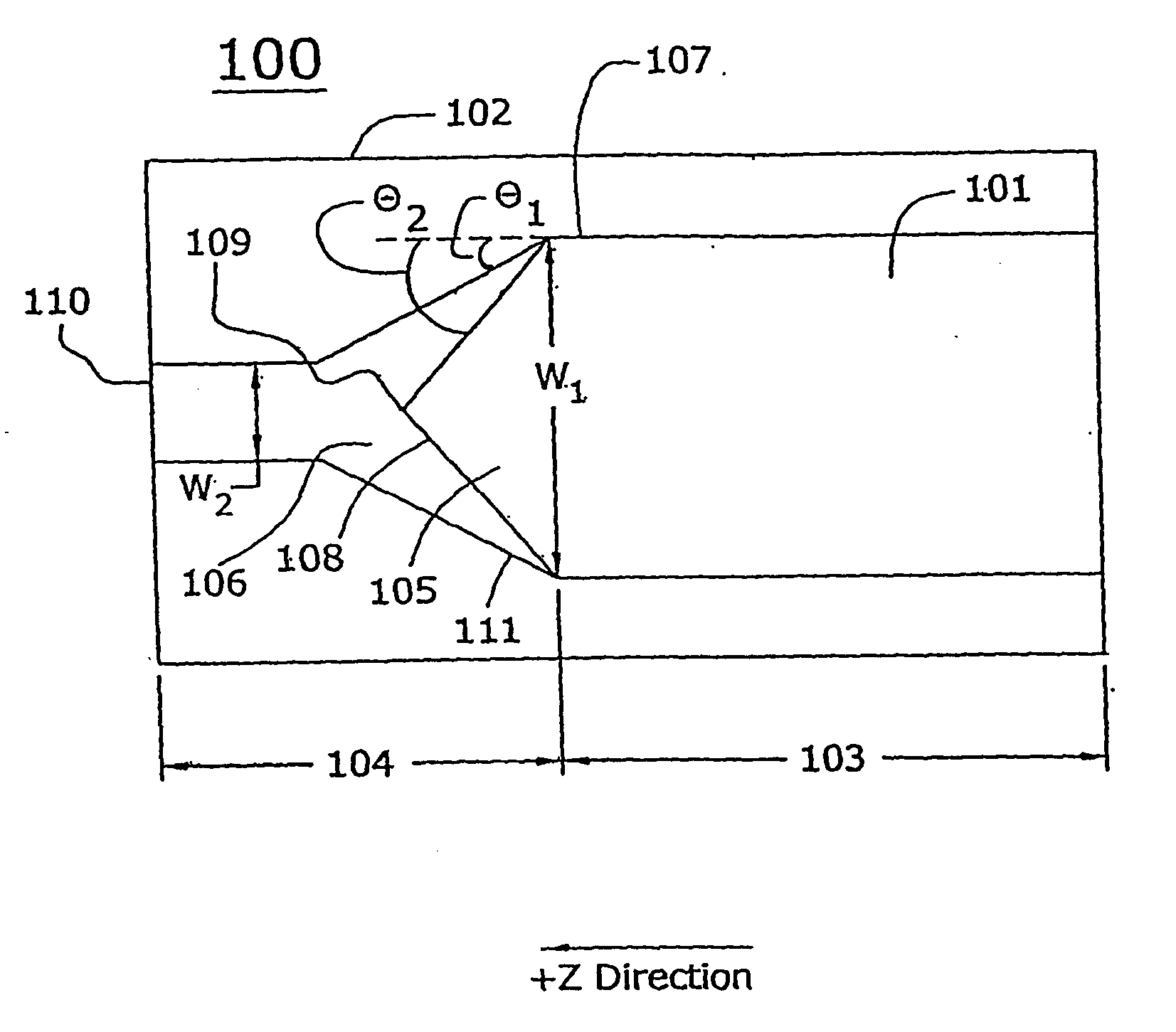
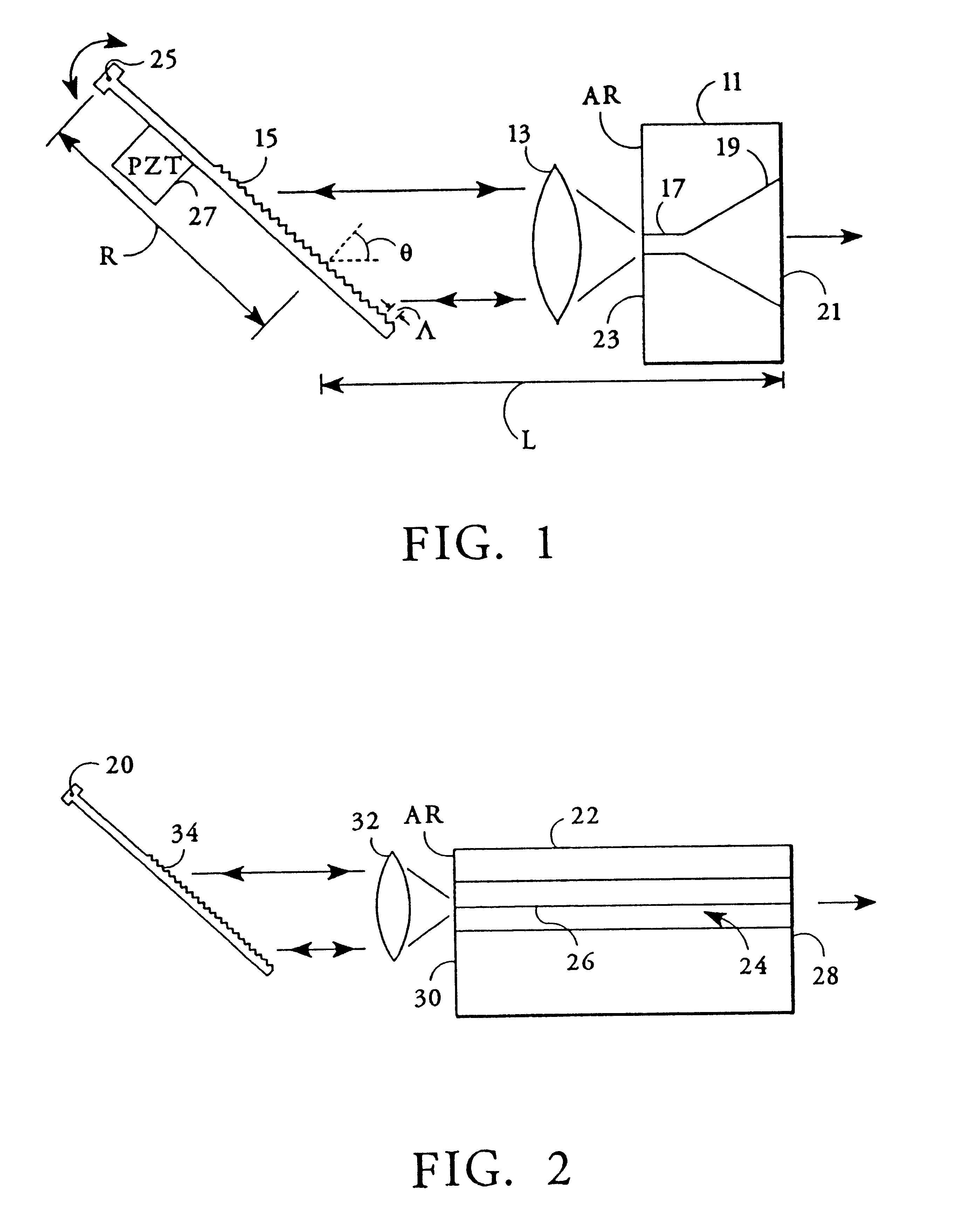
Semiconductor laser with integral spatial mode filter
InactiveUSRE37354E1Increase powerOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionResonant cavityGrating
A semiconductor laser having a light amplifying diode heterostructure with a flared gain region in an external resonant cavity. The flared gain region has a narrow aperture end which may be coupled to a single mode waveguide and a wide output end. A light emitting surface of the heterostructure proximate to the wide end of the flared gain region is partially reflective and combines with an external reflector to form a resonant cavity that is effectively unstable. The intracavity light-emitting surface proximate to the narrow aperture end is antireflection coated. The external reflector may be a planar mirror or a grating reflector. A lens or an optical fiber may couple the aperture end of the flared gain region to the external reflector. Frequency-selective feedback is provided by orienting the grating reflector or providing a prism in the cavity in front of the external planar mirror. Other filtering elements may also be placed in the external cavity. The flared gain region and waveguide may be differentially pumped or modulated with current provided by separate contacts.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
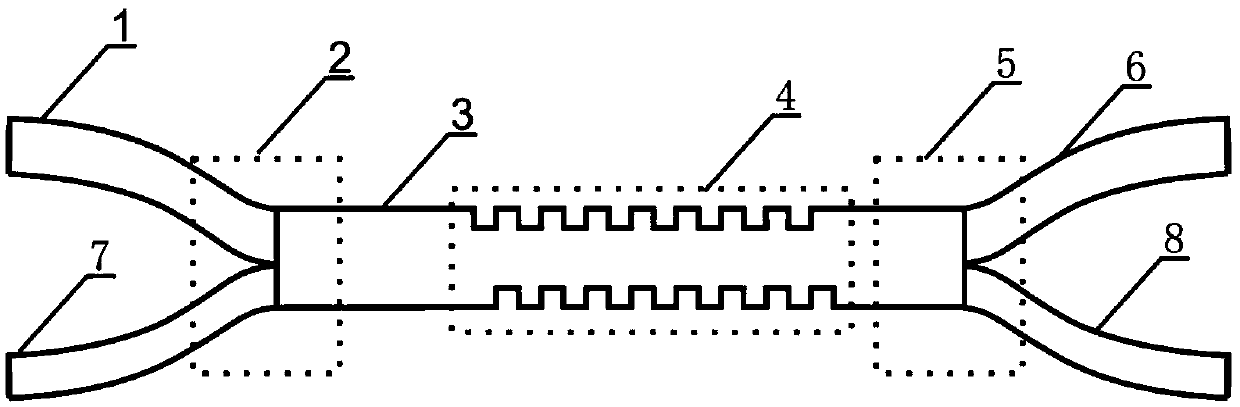
Adjustable-bandwidth filter based on silicon-based waveguide optical grating
The invention discloses an adjustable-bandwidth filter based on a silicon-based waveguide optical grating. The filter comprises a two-stage optical grating filter. A left downloading end of the first-stage optical grating filter is connected with an input single-mode waveguide of the second-stage optical grating filter. A right direct-connection end of the second-stage optical grating filter is connected with the lower port of a right asymmetric gradual-change directional coupler of the first-stage optical grating filter, thereby achieving the signal recycling. The cascading of the filter is employed for adjusting the range of an overlapping range of two-stage optical grating spectral lines through a thermode, thereby forming the filter. The filter employs the asymmetric gradual-change directional coupler, so the filter is large in tolerance and is small in insertion loss. Based on the optical grating filters, the bandwidth adjustment range is not limited by FSR. The asymmetric gradual-change directional coupler is used for enabling a signal of the direct-through end of the second optical grating filter to be uploaded and synthesized in a no-loss manner, thereby achieving no bandwidth loss. The filter is manufactured through the technology of planar integrated optical waveguides, is formed through one-time etching, is low in cost, is high in performance, and is small in loss.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optical add drop multiplexer based on antisymmetric multimode waveguide Bragg grating
InactiveCN105866893ARealize optical signal add-drop multiplexing functionRealize add-drop multiplexing functionWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical light guidesMultiplexingHigh density
The invention discloses an optical add drop multiplexer based on an antisymmetric multimode waveguide Bragg grating. When being input from a single-mode input waveguide, TE light is converted into a base mode of a multi-mode waveguide when passing through an input gradual change waveguide; the antisymmetric multimode waveguide Bragg grating reversely couples incident light meeting the phase matching condition into one step mode of the multi-mode wave guide; reflecting light is converted into a TE mode of a lower-path single-mode waveguide when passing through a lower-path coupling region; transmission light is output from a single-mode output waveguide through the output gradual change waveguide. Identically, the ET light is input from an upper path single-mode waveguide, an upper-path coupling region converts the TE light into the TE one step mode of the multi-mode waveguide; the antisymmetric multimode waveguide Bragg grating reversely couples the incident light meeting the phase matching conditions into a base mode of the multi-mode waveguide; reflecting light is output from the single-mode output waveguide through the output gradual change waveguide. The optical add drop multiplexer has the advantage that the optical signal add drop multiplexing function is realized, and the optical add drop multiplexer can be applied to an on-chip high-density integrated optical interconnection system.
Owner:LONGYAN UNIV
Photorefractive long-period waveguide grating filter and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102590951AHigh reuse rateEasy to installCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesFiberSingle mode waveguides
The invention relates to a photorefractive long-period waveguide grating filter, which comprises input tail fiber and output tail fiber. The photorefractive long period waveguide grating filter further comprises a photorefractive long period waveguide grating that comprises a substrate. The substrate is a LiNbO3 crystal that is tangential in X or Y direction and conductive in Z direction and a cladding is arranged on the substrate. A Z-directional single mode waveguide is arranged on the cladding. A photorefractive holographic grating is manufactured on the single mode waveguide. Two end surfaces of the single mode waveguide are respectively connected with the input tail fiber and the output tail fiber. The invention further provides a manufacturing method of the photorefractive long-period waveguide grating filter. The photorefractive long-period waveguide grating filter has a simplified structure, is convenient to manufacture and has higher recycle rate of materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Fiber to Wafer Interface
InactiveUS20130156365A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideFiberSingle mode waveguides
An interface device includes a body portion having a single-mode waveguide portion including a substantially optically transparent material, a cladding portion defined by channels contacting the waveguide portion, the cladding portion including a substantially optically transparent polymer material, an engagement feature operative to engage a portion of a wafer, and a guide portion operative to engage a portion of an optical fiber ferrule.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Filter based on axial direction apodized grating
ActiveCN106896446ARealize downloadLarge toleranceOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesSideband
The present invention discloses a filter based on axial direction apodized grating. Input single mode waveguide is connected with the upper end port of the left end of an asymmetrical gradual changing directional coupler through input gradual changing waveguide, and the lower end port of the left end of the asymmetrical gradual changing directional coupler is connected with bending waveguide to realize reflection signal download; and the upper end port of the right end of the asymmetrical gradual changing directional coupler is connected with the left end of an antisymmetrical multimode waveguide grating, and the right end of the antisymmetrical multimode waveguide grating is connected with the output single mode waveguide through output gradual changing waveguide. The separation of grating reflection signals employs the asymmetrical gradual changing directional coupler with large tolerance and small insertion loss to realize download of the grating signals; based on a grating filter, the filter based on axial direction apodized grating is large in tolerance and wide in bandwidth regulation range and cannot be limited by the FSR so as to realize filters with various different bandwidth demands; and moreover, the axial direction position regulation of grating teeth realizes apodization so as to realize a grating filter with large sideband suppression ratio and greatly improve the performance of the grating filter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Semiconductor optical amplifier
InactiveUS6148132ALaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionAudio power amplifierSingle mode waveguides
A semiconductor optical amplifier wherein poalization independent gain, high saturation input light intensity, and high saturation gain are obtained. The semiconductor optical amplifier of the present invention comprises a 1x1 multi mode interference (MMI) light waveguide region and a couple of single mode waveguide regions, each of which is connected with each end of the multi mode region. The length of the multi mode waveguide region is about 340 mu m and the length of the single mode waveguide regions is about 20 mu m. The width of the multi mode waveguide region is about 12 mu m while the widths of the single mode waveguide regions 2,3 are about 1 mu m.
Owner:NEC CORP
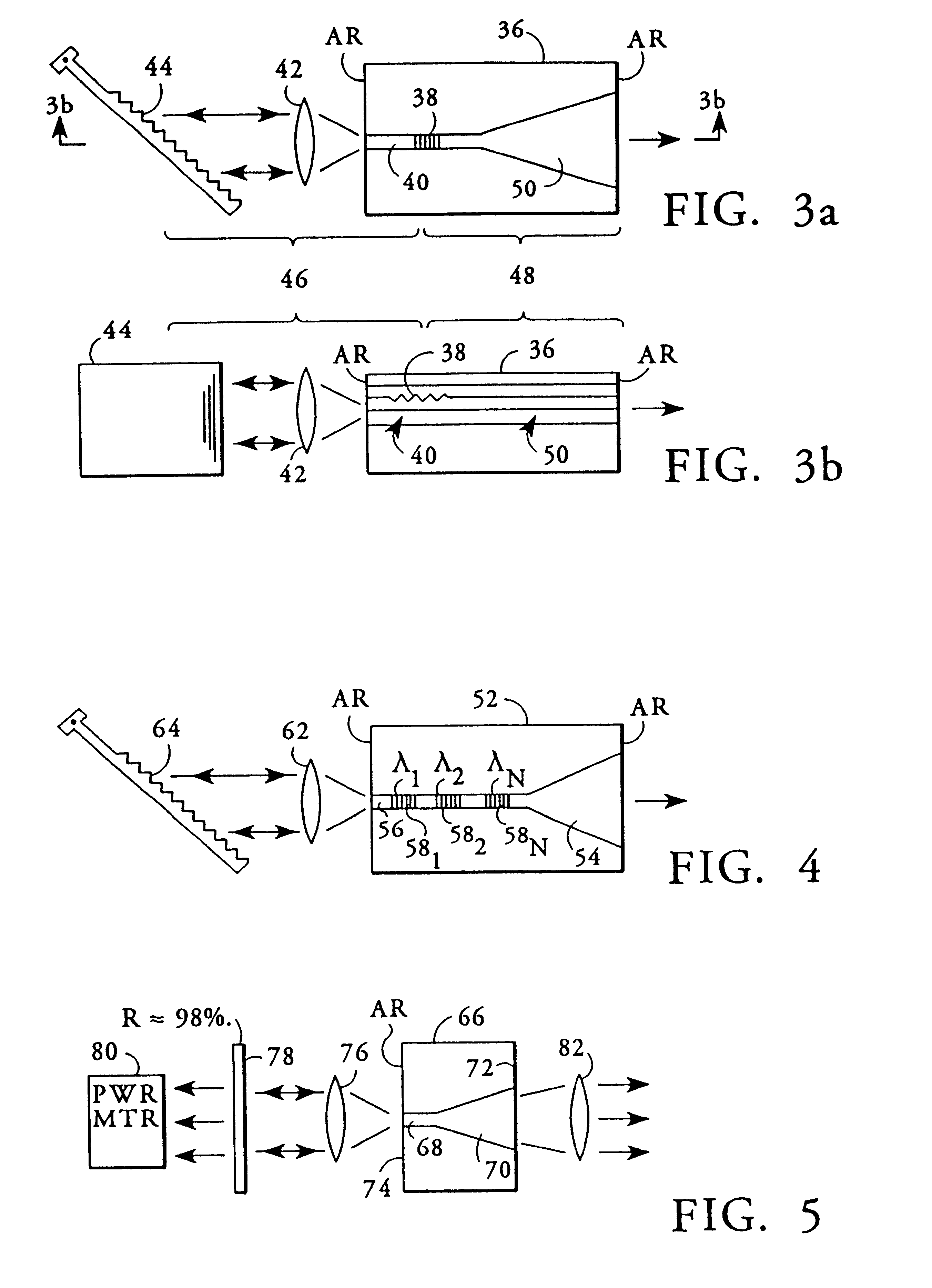
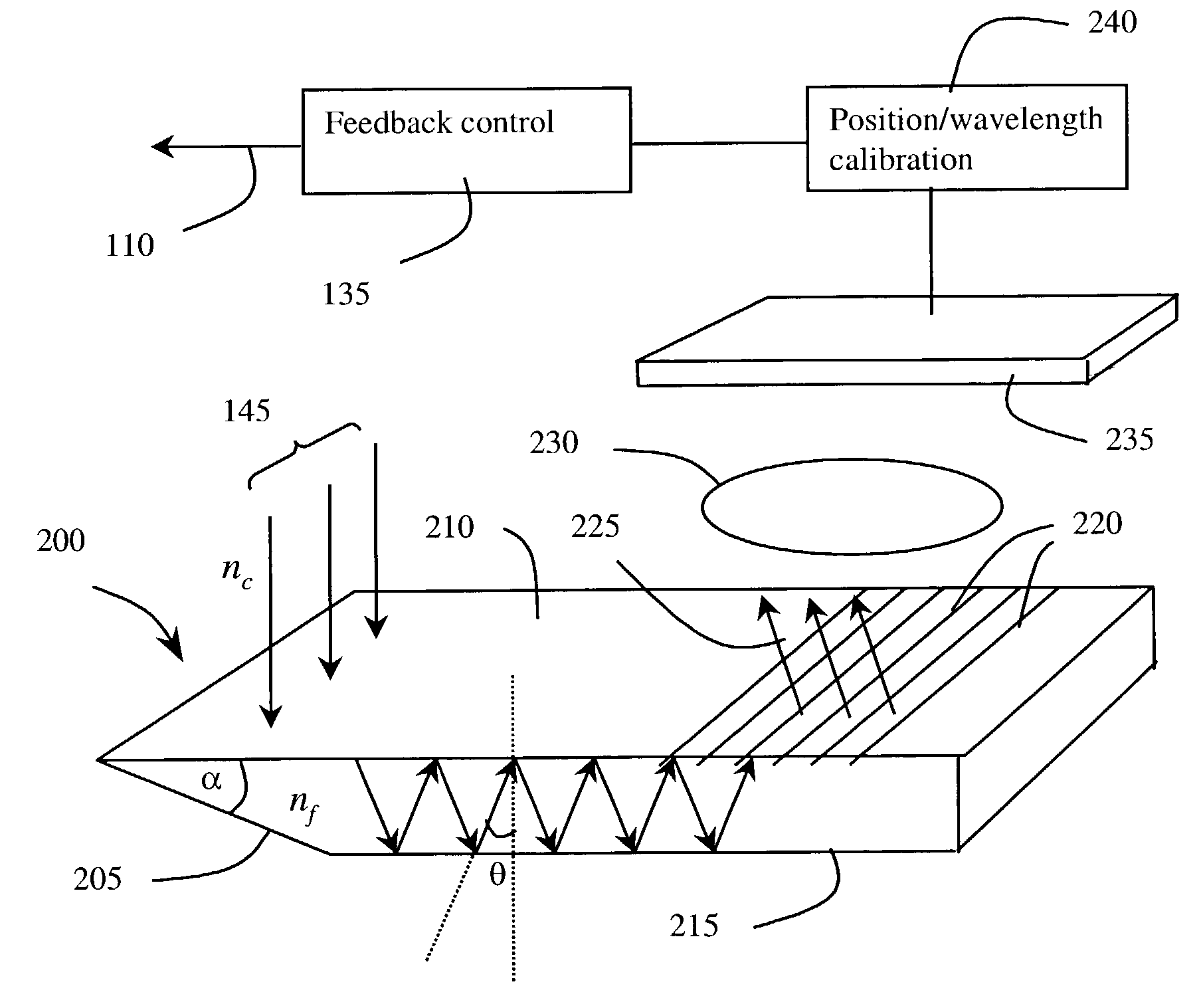
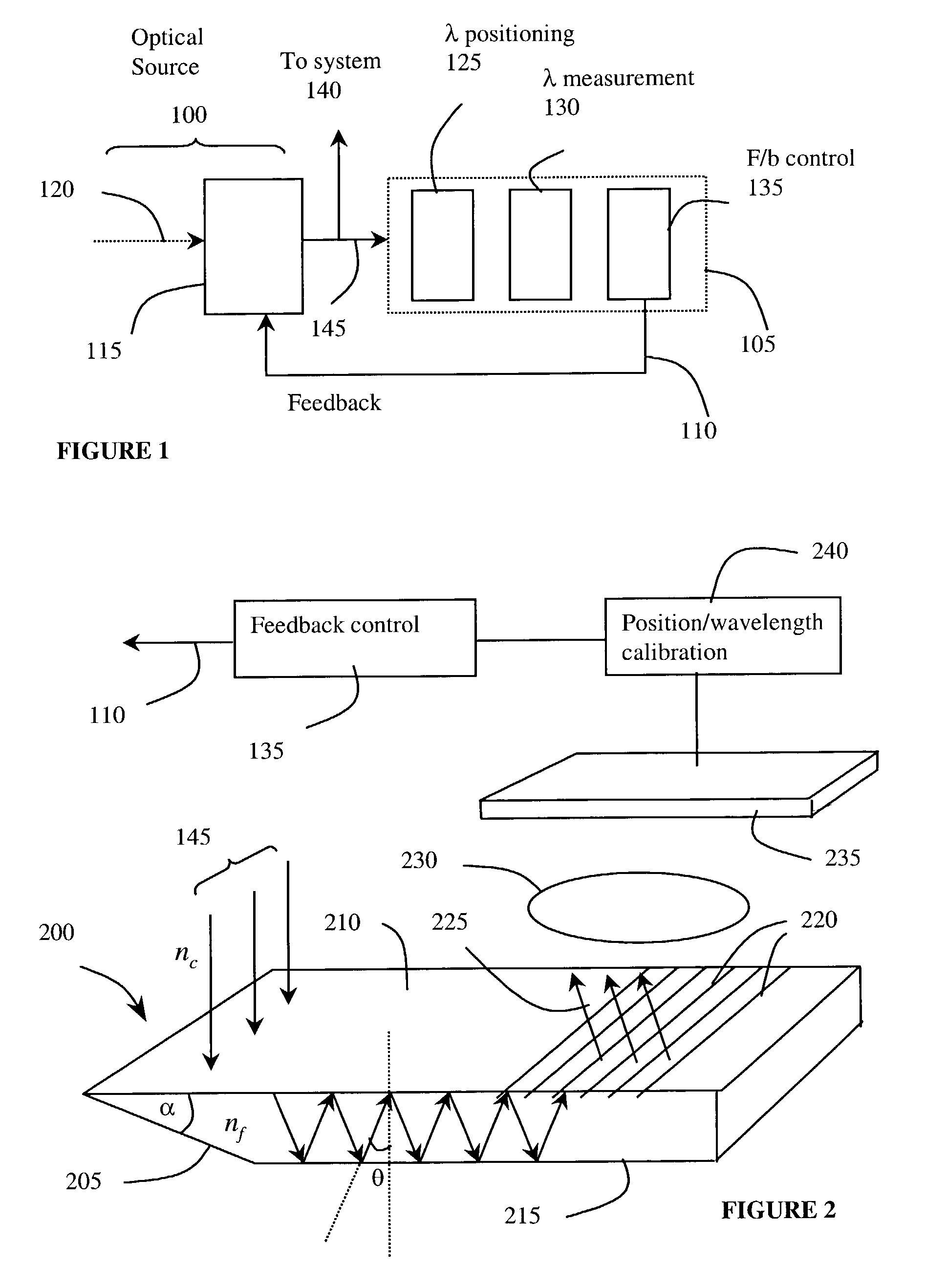
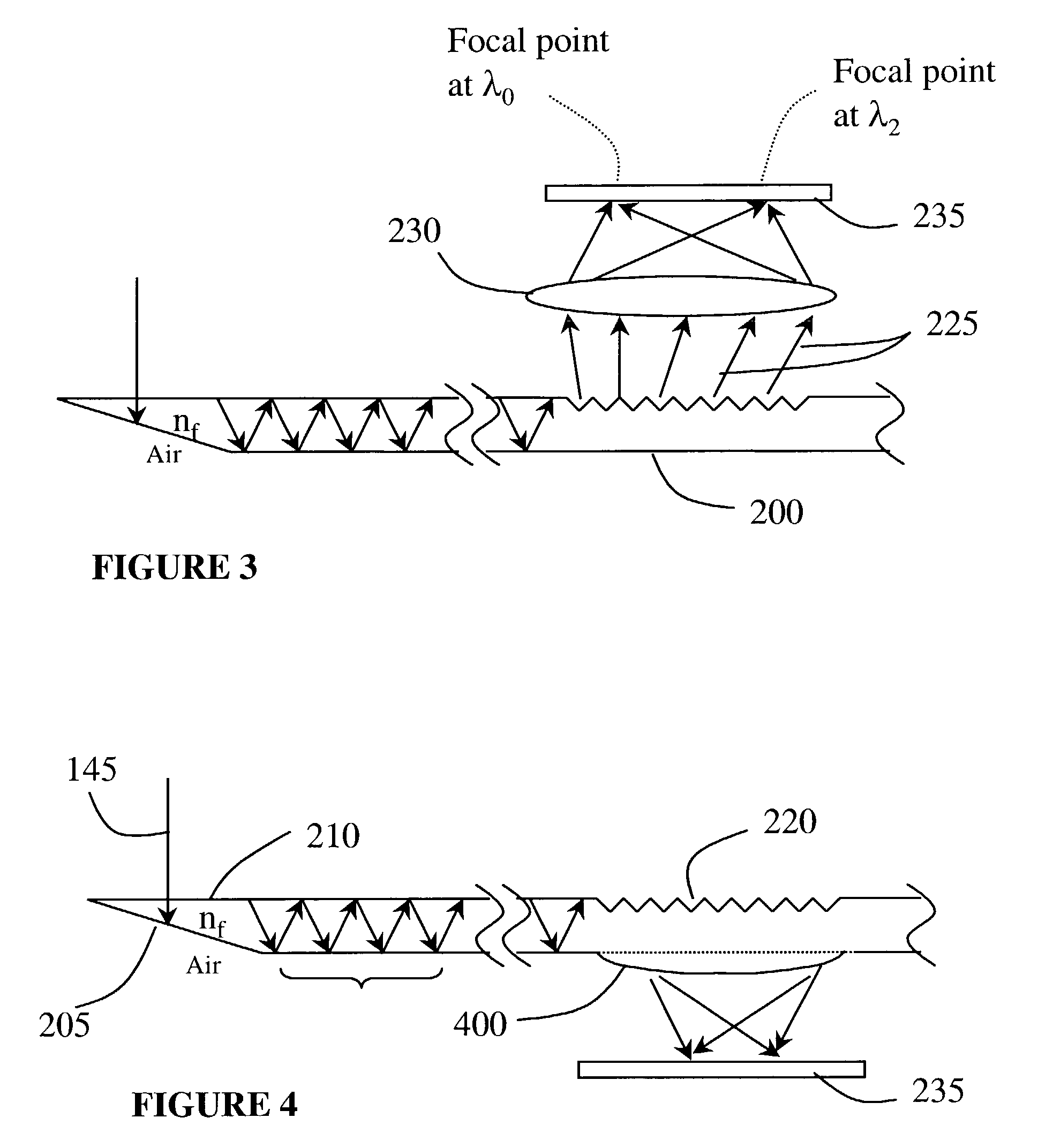
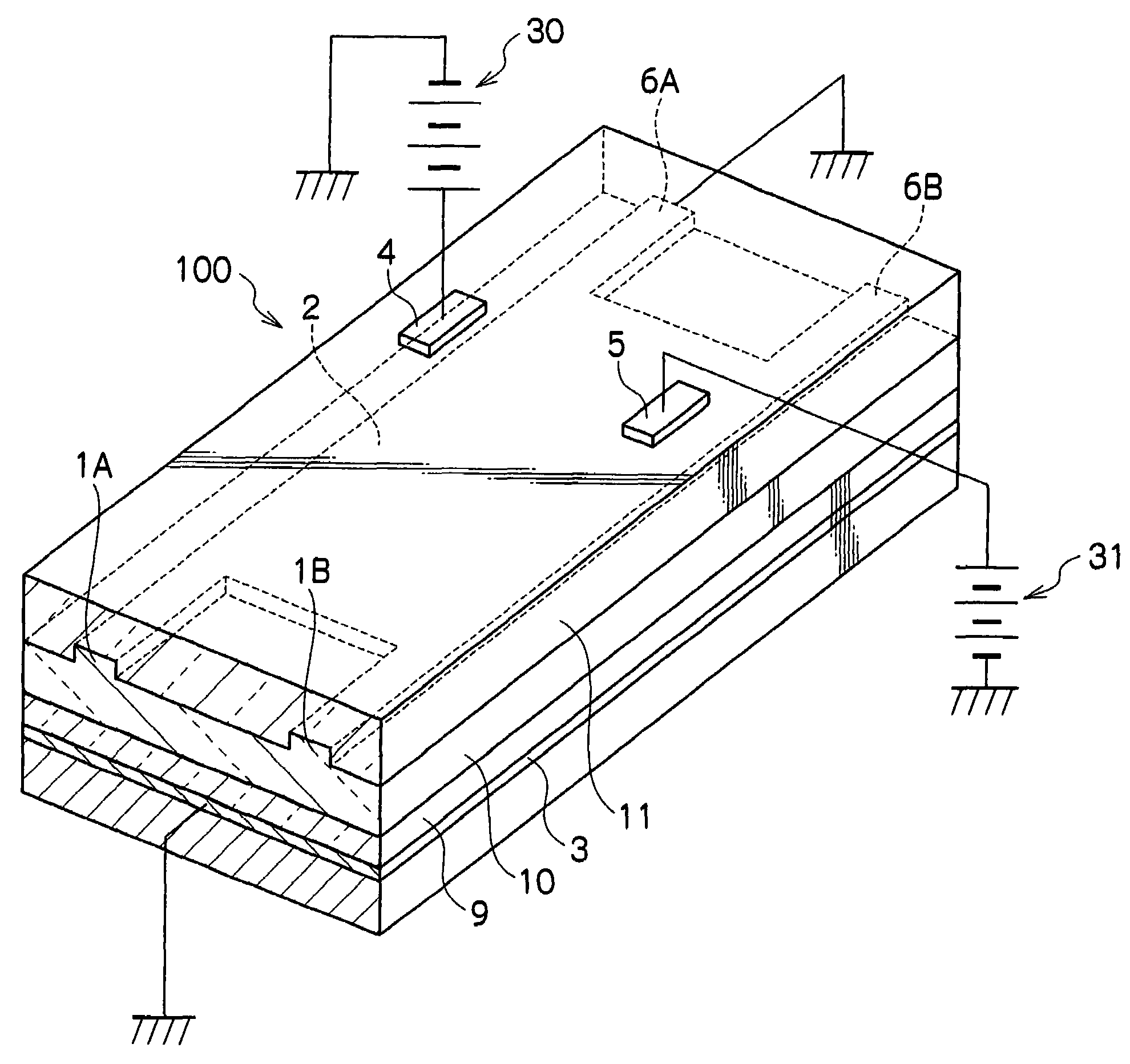
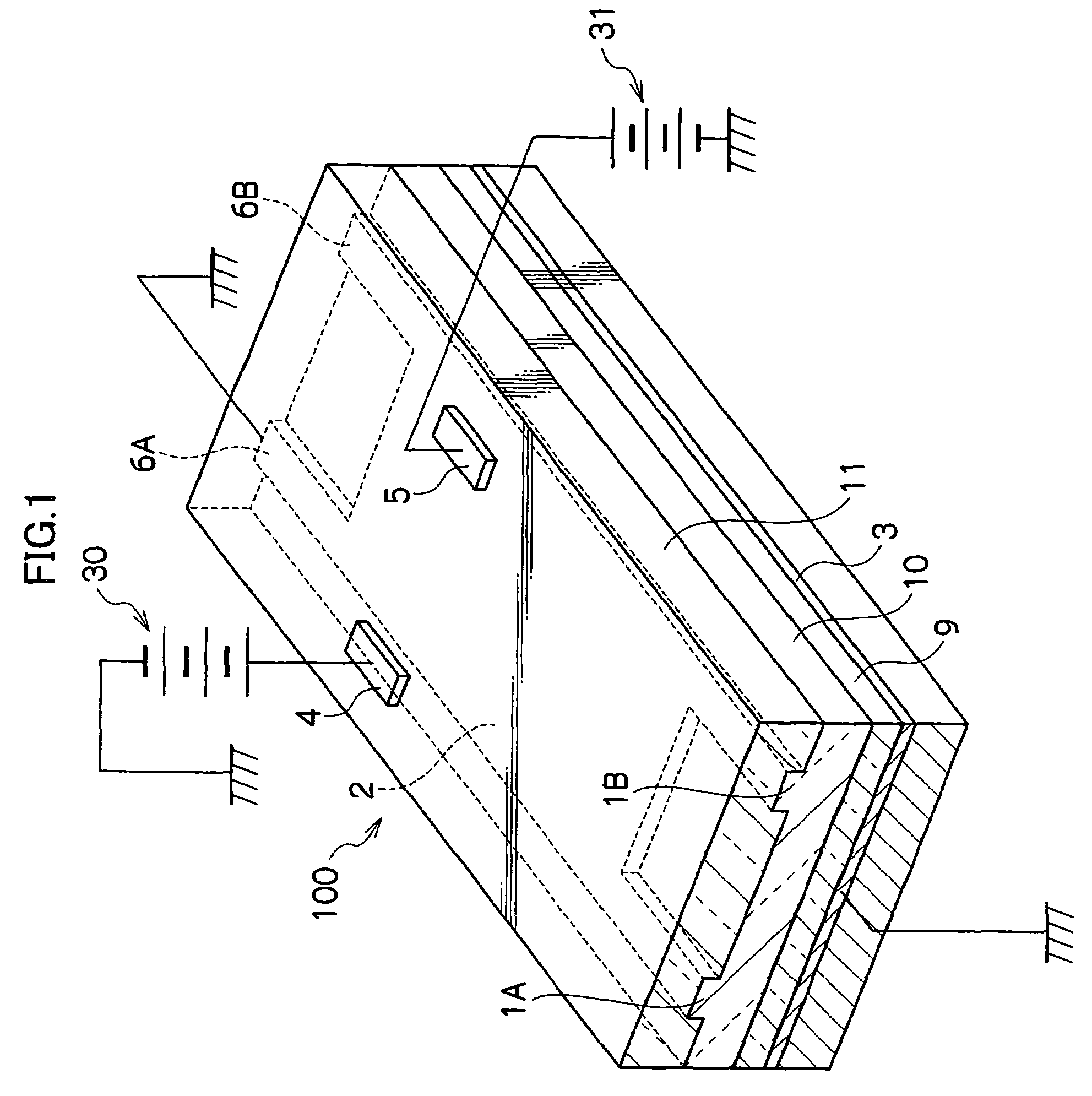
Optical wavelength measuring device using guiding body and diffractive structure
InactiveUS7355162B2Easy to manufactureNarrow line widthRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpatially resolvedImage resolution
An optical characterization device has a guiding body and a diffractive structure integrated with it. The guiding body delivers radiation to the diffractive structure at a preselected angle and the diffractive structure diffracts at least a portion of radiation guided to it to give spatial resolution according to wavelength. A position sensitive detector detects the position of the spatially resolved radiation and thus the radiation can be characterized according to wavelength. Embodiments can be used to monitor and adjust the wavelength of a radiation source, using a feedback connection. By using the integrated approach, a very small structure can be realized and the structure can be relatively simply fabricated and assembled. The guiding body might be either capable of supporting multimode propagation of the radiation or might be a single mode waveguide. Where it is capable of supporting multimode propagation, an input to the guiding body acts to select a mode for propagation of the radiation.
Owner:OPTITUNE
1xN fanout waveguide photodetector
InactiveUS6856733B2Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideQuantum efficiencyCharge carrier
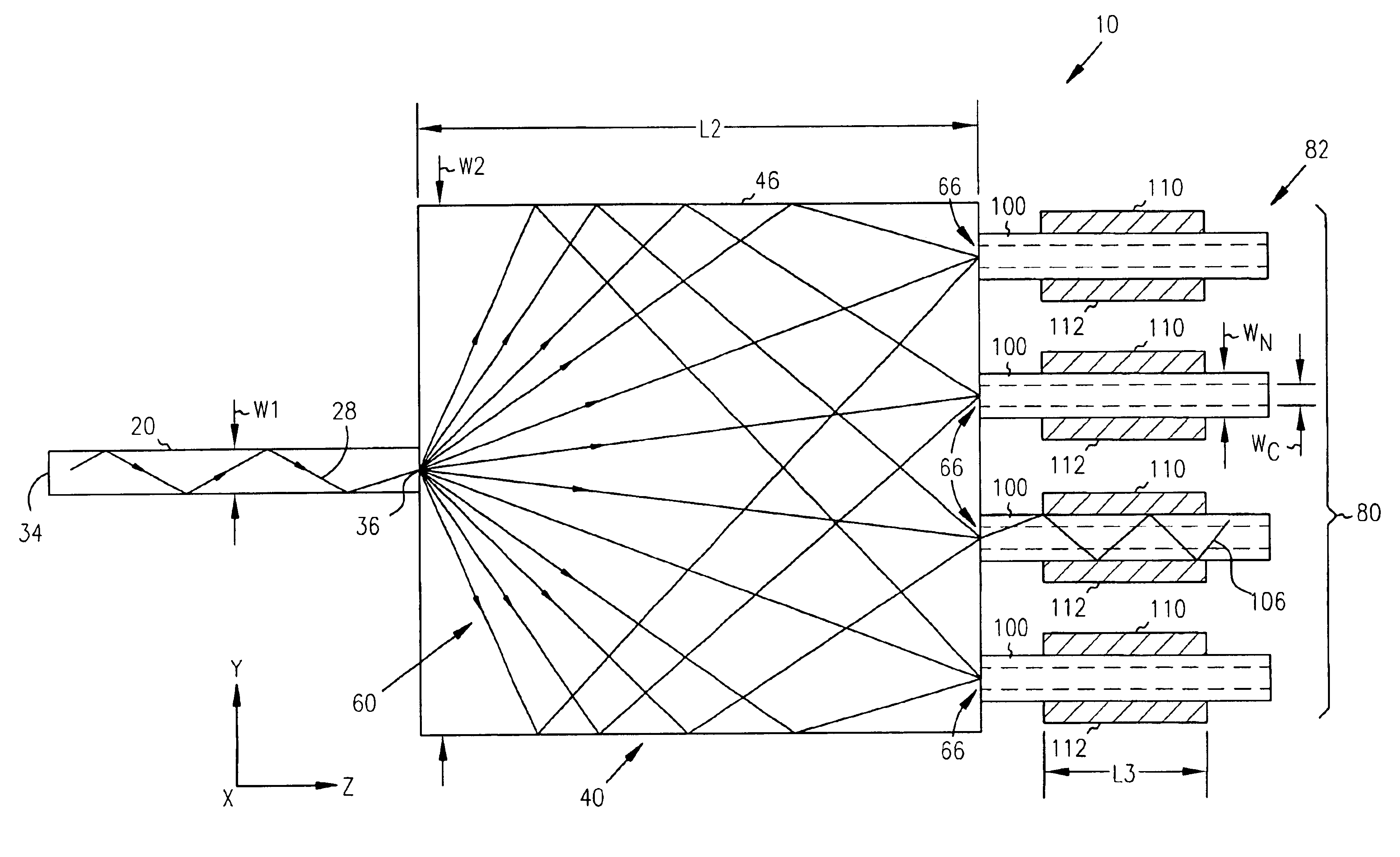
A 1×N fanout waveguide detector is disclosed. The detector includes a multiple-mode interference (MMI) cavity with input and output ends. A single-mode waveguide is optically coupled to the input end of the MMI cavity so that the optical power in the guided mode is distributed over N modes. The MMI cavity forms N interference nodes at or near its output end. N waveguide detectors are optically coupled to the output end at or near the N interference nodes. The waveguide detectors each have a waveguide that is evanescently coupled to an intrinsic region of a PIN detector. The width of the detector waveguide core, which can be sub-micron, defines the carrier collection distance between the electrodes of the PIN detector. Further, the length of the detector waveguide can be selected to maximize optical absorption to provide optimum quantum efficiency. The waveguide detectors are connected in parallel to provide a high-output photocurrent.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Optical switching element
InactiveUS7403678B2Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideMultimode interferenceEngineering
An optical switching element comprising: a multimode waveguide having an electro-optical effect; one or a plurality of first single mode waveguides; a plurality of second single mode waveguides; a first electrode arranged in the vicinity of one edge on one side of the multimode waveguide; a second electrode arranged in the vicinity of the other edge on the same side of the multimode waveguide; and a third electrode arranged on the other side of the multimode waveguide, over the first electrode and the second electrode being arranged so as to be positioned on bright spots formed by multimode interference in an optical mode field generated by the light propagating through the multimode waveguide, and an optical path being switched between the first single mode waveguide and the second single mode waveguide by applying voltage between the first electrode and the third electrode and between the second electrode and the third electrode, is provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Optical device having a waveguide lens with multimode interference
In one embodiment, a waveguide lens of the invention has a pair of planar waveguides, e.g., a single-mode waveguide connected to a multimode waveguide. The widths of the two waveguides and the length of the multimode waveguide are selected such that particular mode coupling between the waveguides and multimode interference (MMI) effects in the multimode waveguide cause the latter to output a converging beam of light similar to that produced by a conventional waveguide lens. Advantageously, waveguide lenses of the invention may be used to implement low-loss, low-crosstalk waveguide crossings and / or compact waveguide turns. In addition, waveguide lenses of the invention can be readily and cost-effectively incorporated into waveguide devices designated for large-scale production.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Blended crossing device for silicon-based nanowire
InactiveCN103513333AReduce widthImprove transmission efficiencyOptical light guidesNanowireWaveguide mode
The invention discloses a blended crossing device for a silicon-based nanowire. The crossing device comprises two groove waveguide mode switching units, two slab waveguide mode switching units, a sine switching waveguide and a crossing multimode waveguide, wherein the two groove waveguide mode switching units and the two slab waveguide mode switching units are respectively connected through the sine switching waveguide and the crossing multimode waveguide, each groove waveguide mode switching unit is opposite to one slab waveguide mode switching unit, each groove waveguide mode switching unit comprises a groove waveguide for inputting an optical signal and a mode switcher, each mode switcher is connected between each groove waveguide and the sine switching waveguide, each slab waveguide mode switching unit comprises a slab waveguide and a single-mode waveguide for outputting the optical signal, and each single-mode waveguide is connected between each slab waveguide and the sine switching waveguide. The crossing device has the advantages of high transmission efficiency, compact structure, low loss, low manufacturing difficulty, relatively low cost and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Optical device structures based on photo-definable polymerizable composites
InactiveUS20040101268A1Significant differenceSmall bending radiusOptical waveguide light guideLensRefractive indexSingle mode waveguides
An optical device structure comprising a substrate and at least one topological feature. The topological feature comprises a polymeric composite material formed from a polymerizable binder and an uncured monomer. The topological feature has a controlled topological profile and a controlled refractive index across the topological feature. The optical device structure may be a multimode waveguide device, a single mode waveguide device, an optical data storage device, thermo-optic switches, or microelectronic mechanical system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Add/drop filter based on antisymmetric multimode Bragg waveguide grating
InactiveCN105572796ARealize the function of adding and dropping signalsCompatible with CMOS processOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesLength wave
The invention discloses an add / drop filter based on an antisymmetric multimode Bragg waveguide grating. When TE light is input from a single-mode input waveguide, a drop asymmetric Y-branch waveguide converts the TE light into a TE fundamental mode of a multimode waveguide; the antisymmetric Bragg waveguide grating carries out back-coupling on the incident light meeting phase matching condition wavelength to form reflected light; the reflected light is converted into a TE mode of a drop single-mode waveguide when passing through the drop asymmetric Y-branch waveguide, and the TE mode is output from the drop end; transmission light passes through an add asymmetric Y-branch waveguide and is output from a single-mode output waveguide; similarly, add light is input from an add single-mode input waveguide; the add asymmetric Y-branch waveguide converts the add light into a TE first-order mode of the multimode waveguide; and the antisymmetric Bragg waveguide grating enables the reflected light meeting the phase matching condition wavelength to be converted into a TE mode of the single-mode output waveguide when the reflected light passes through the add asymmetric Y-branch waveguide, and the TE mode is output from the output end. The add / drop filter realizes signal adding / dropping function, and can be applied to an on-chip super-integrated optical interconnection system.
Owner:LONGYAN UNIV
Mode beam-splitting converter based on grating-assisted coupler
InactiveCN104950391AImprove conversion efficiencyLarge toleranceOptical waveguide light guideCMOSHigh density
The invention discloses a mode beam-splitting converter based on a grating-assisted coupler. The converter comprises a single-mode input waveguide, an input mode converter, a bus multi-mode waveguide, a downlink Bragg waveguide grating, an output mode converter, a single-mode output waveguide, a downlink single-mode waveguide and a downlink coupling zone, wherein the input mode converter converts a TM (transverse magnetic) mode in the single-mode input waveguide into a TE (transverse electric) first-order mode in the bus multi-mode waveguide, and by the aid of the Bragg waveguide grating assisted coupler, the TE first-order mode of the multi-mode waveguide and the TE mode of the single-mode waveguide exchange energy. The converter realizes separation of the TE mode and the TM mode which are transmitted in the waveguide, converts the TM mode into the TE mode and has the advantages of simple structure, compactness, large work bandwidth, low crosstalk and the like, the production technology has CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) technology compatibility, the device is easy to integrate and extend, low-cost production is facilitated, and the device can be widely applied to on-chip high-density-integrated optical interconnection systems.
Owner:LONGYAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com