Patents
Literature
36 results about "Rib waveguides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
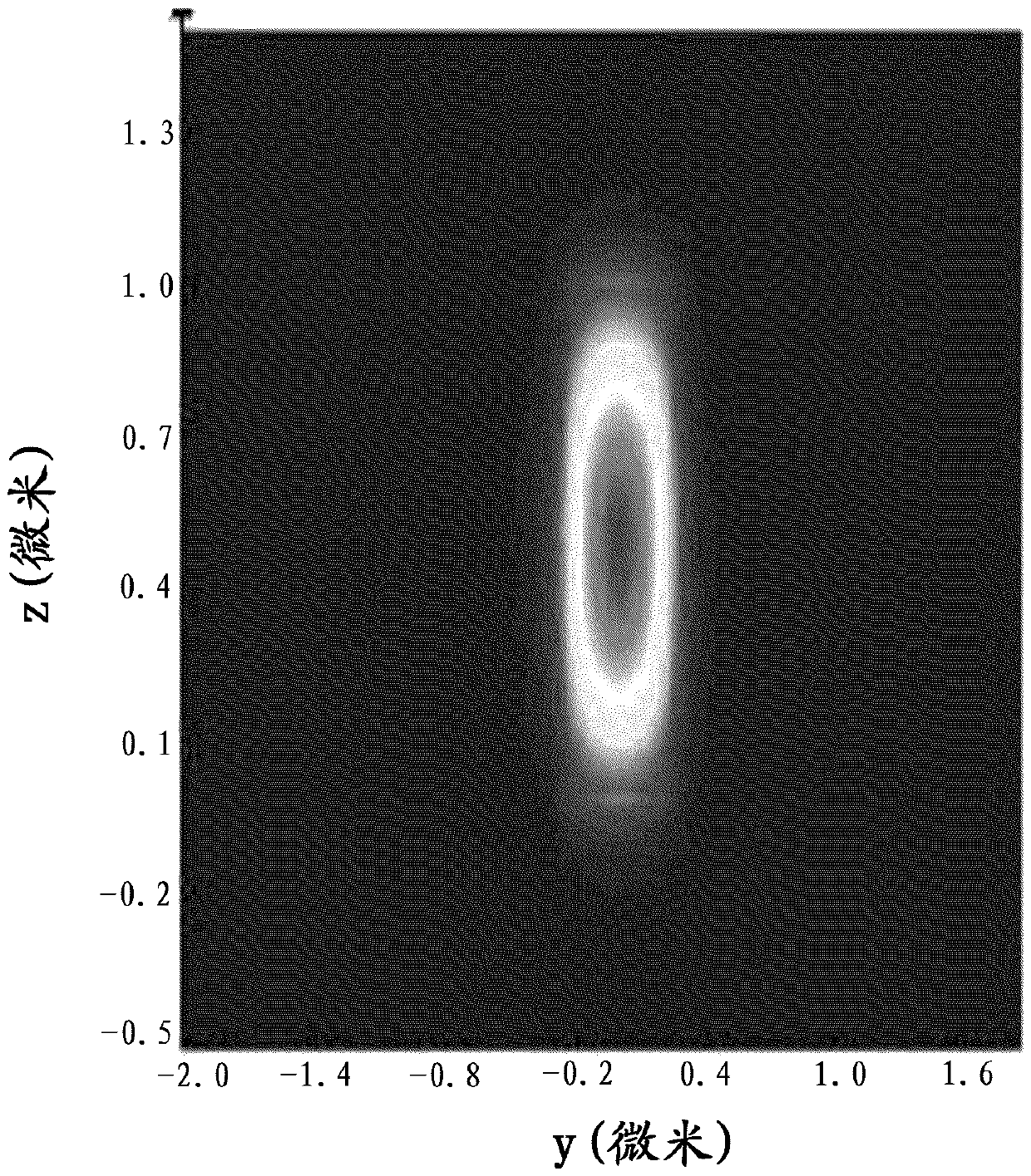
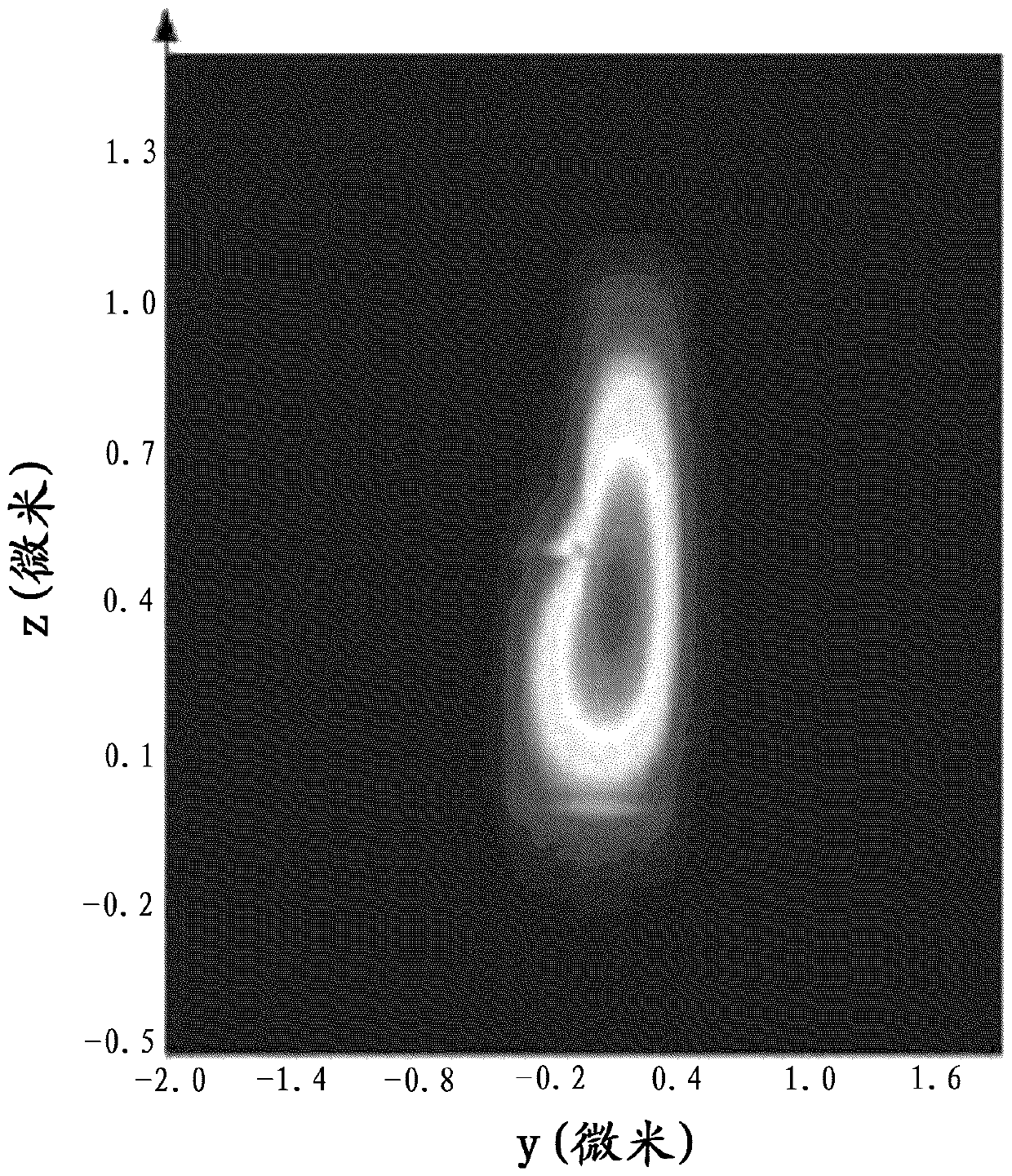
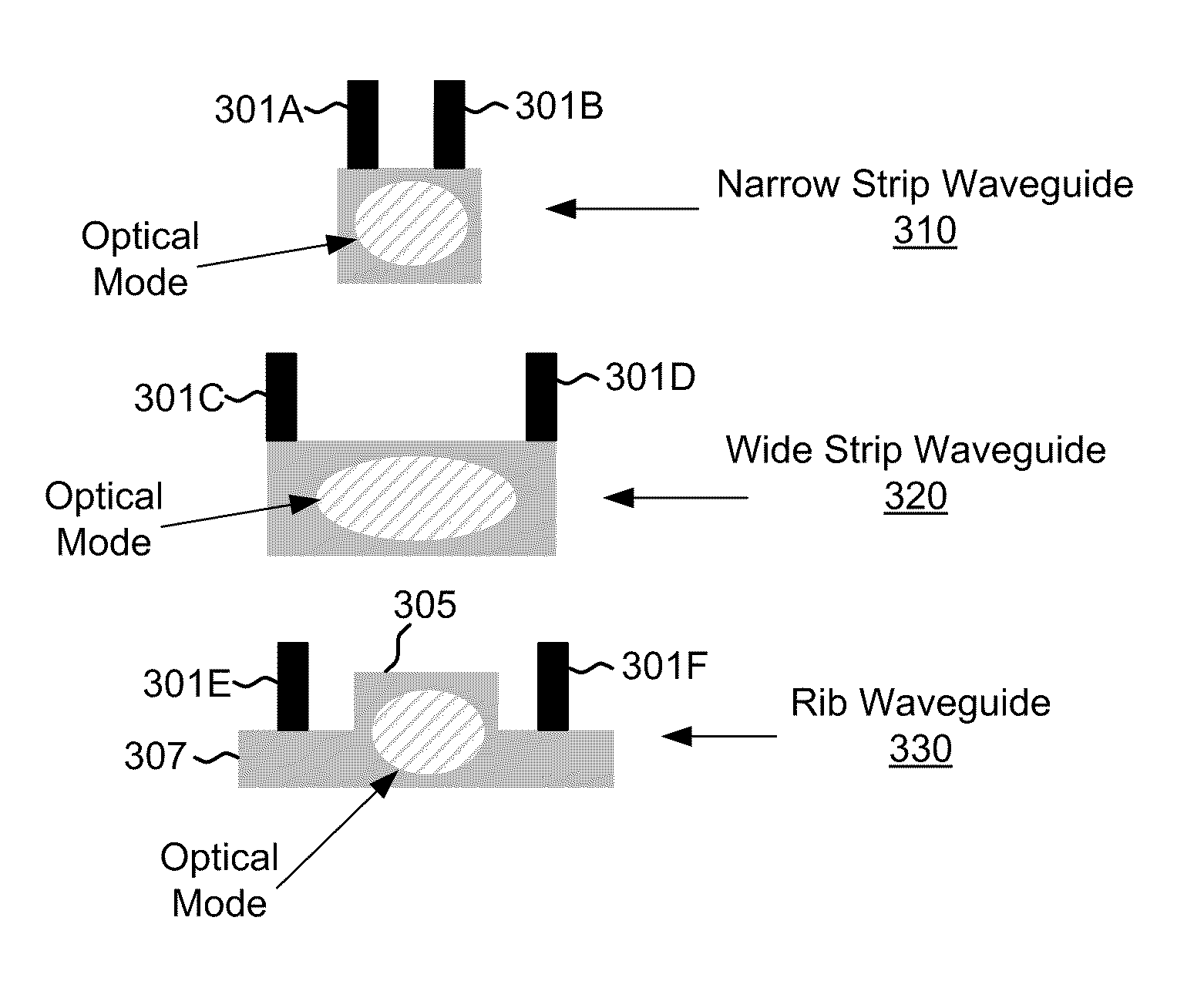
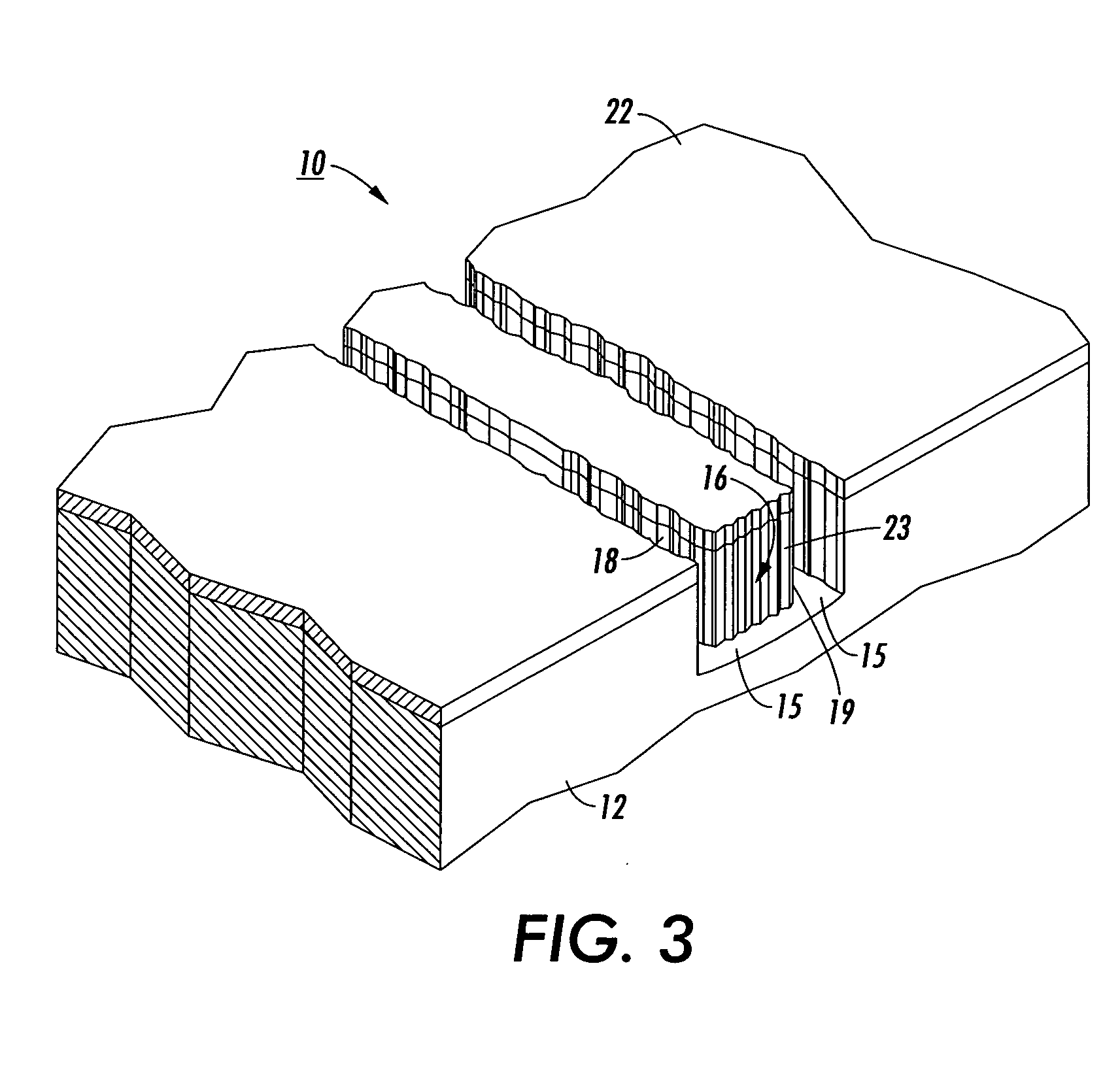
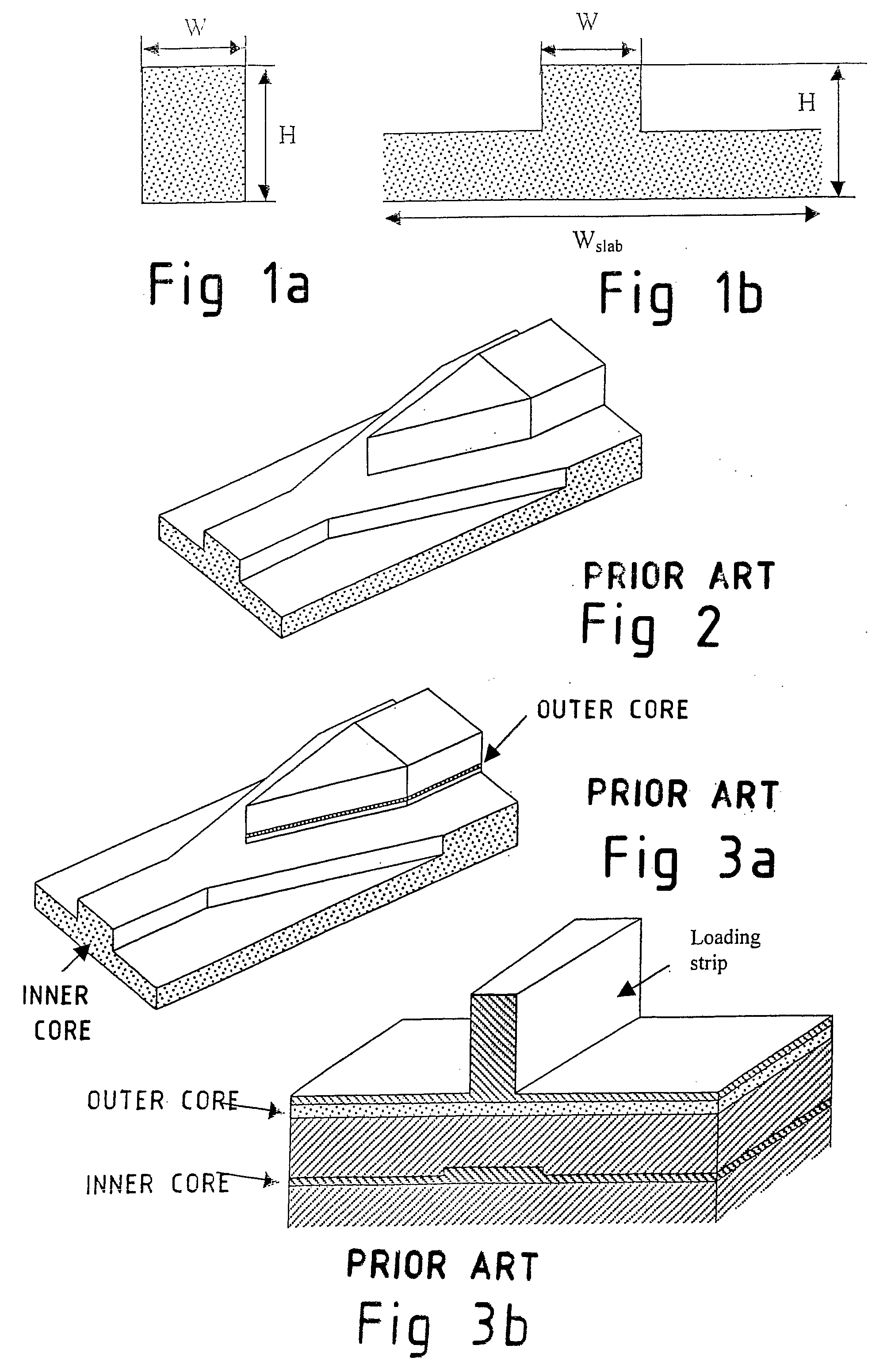
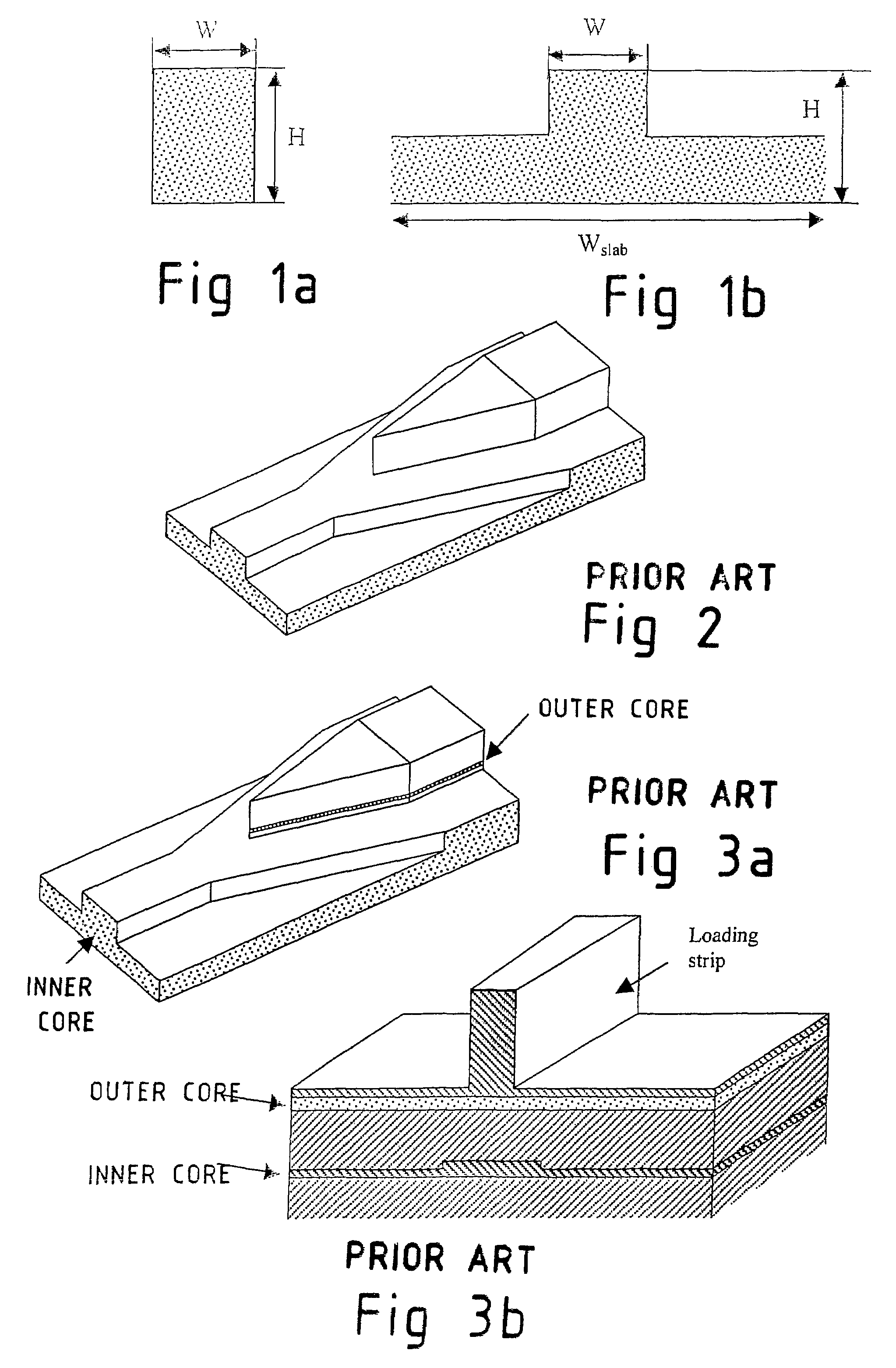
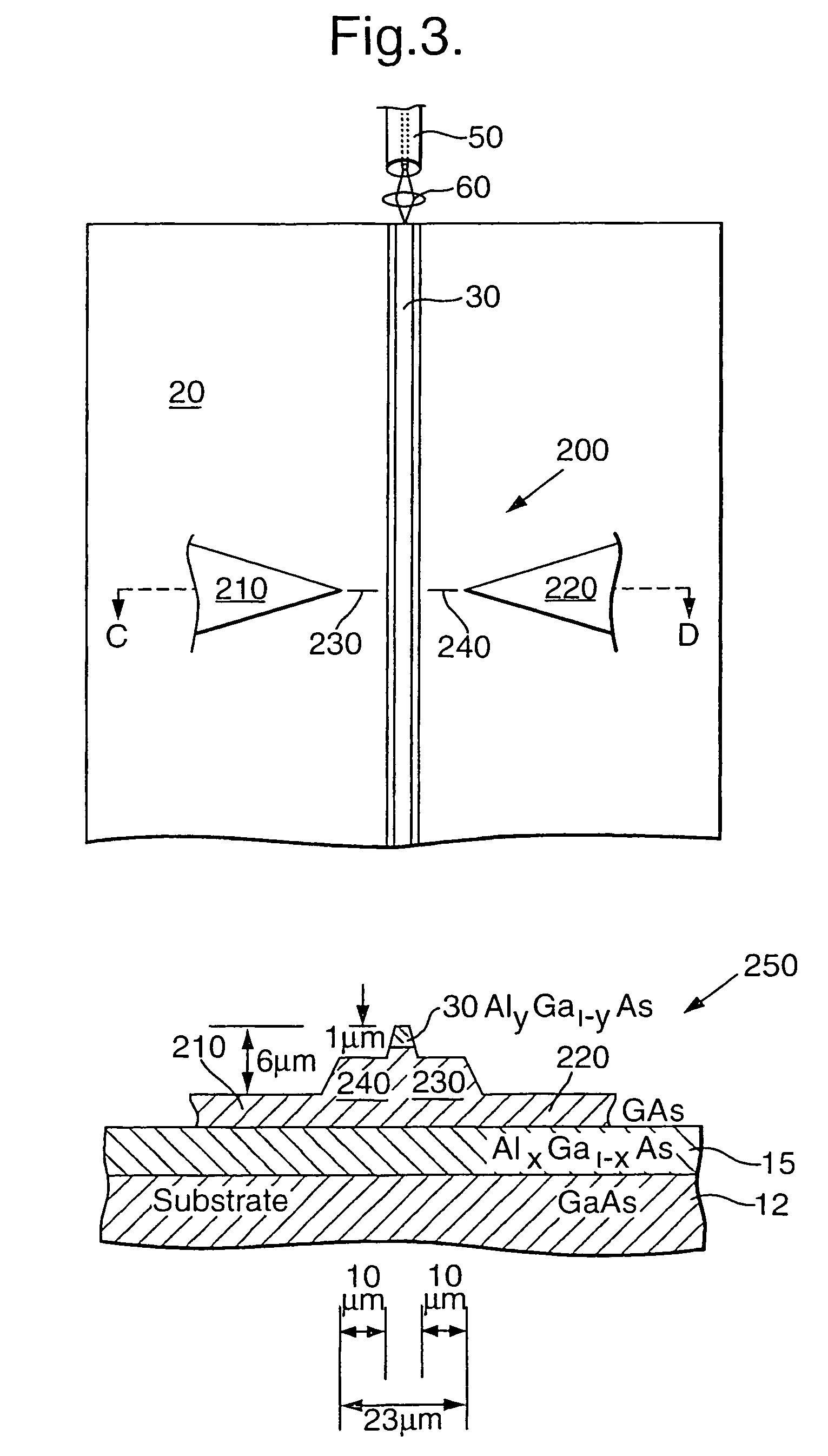
A rib waveguide is a waveguide in which the guiding layer basically consists of the slab with a strip (or several strips) superimposed onto it. Rib waveguides also provide confinement of the wave in two dimensions.
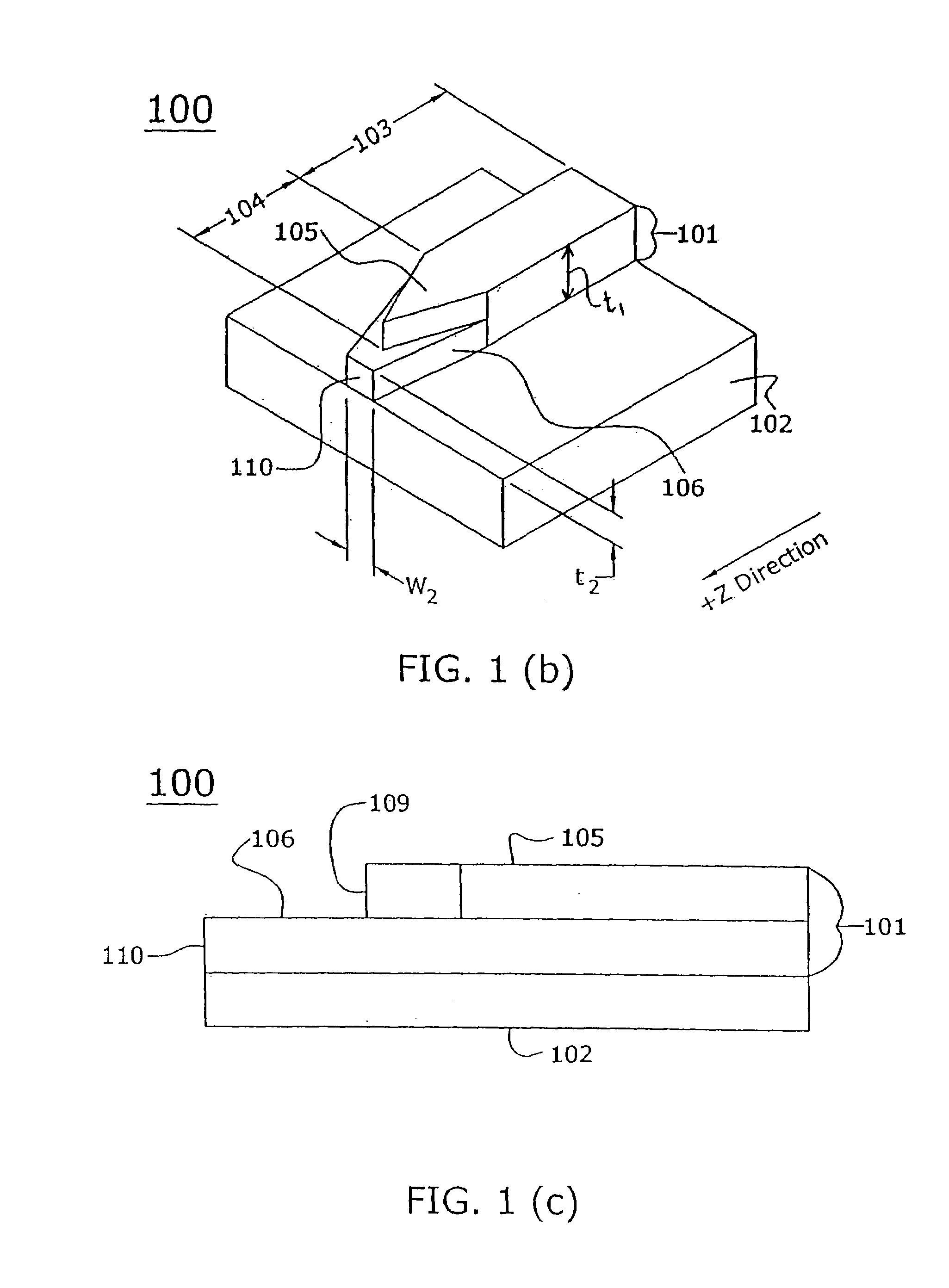
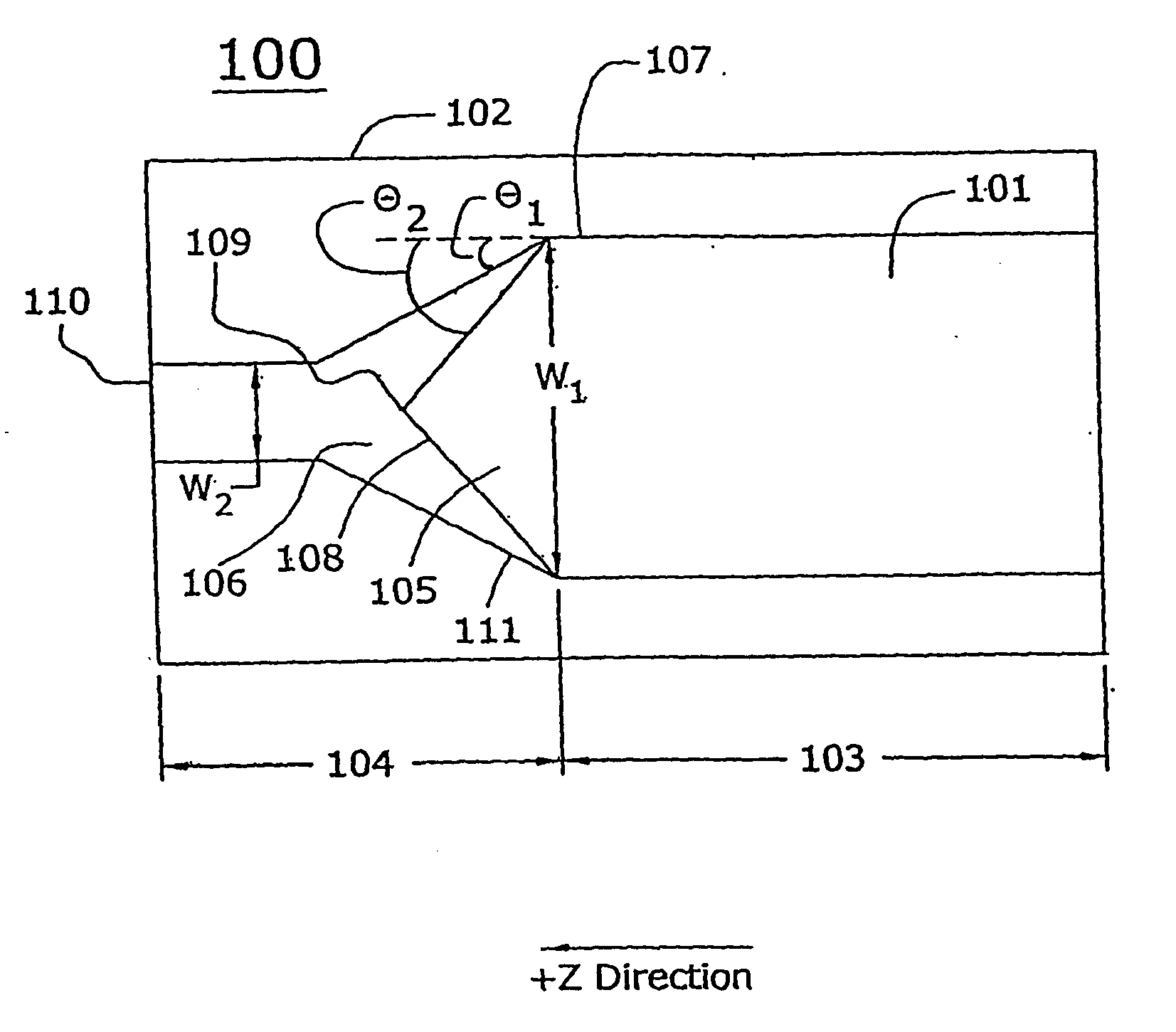
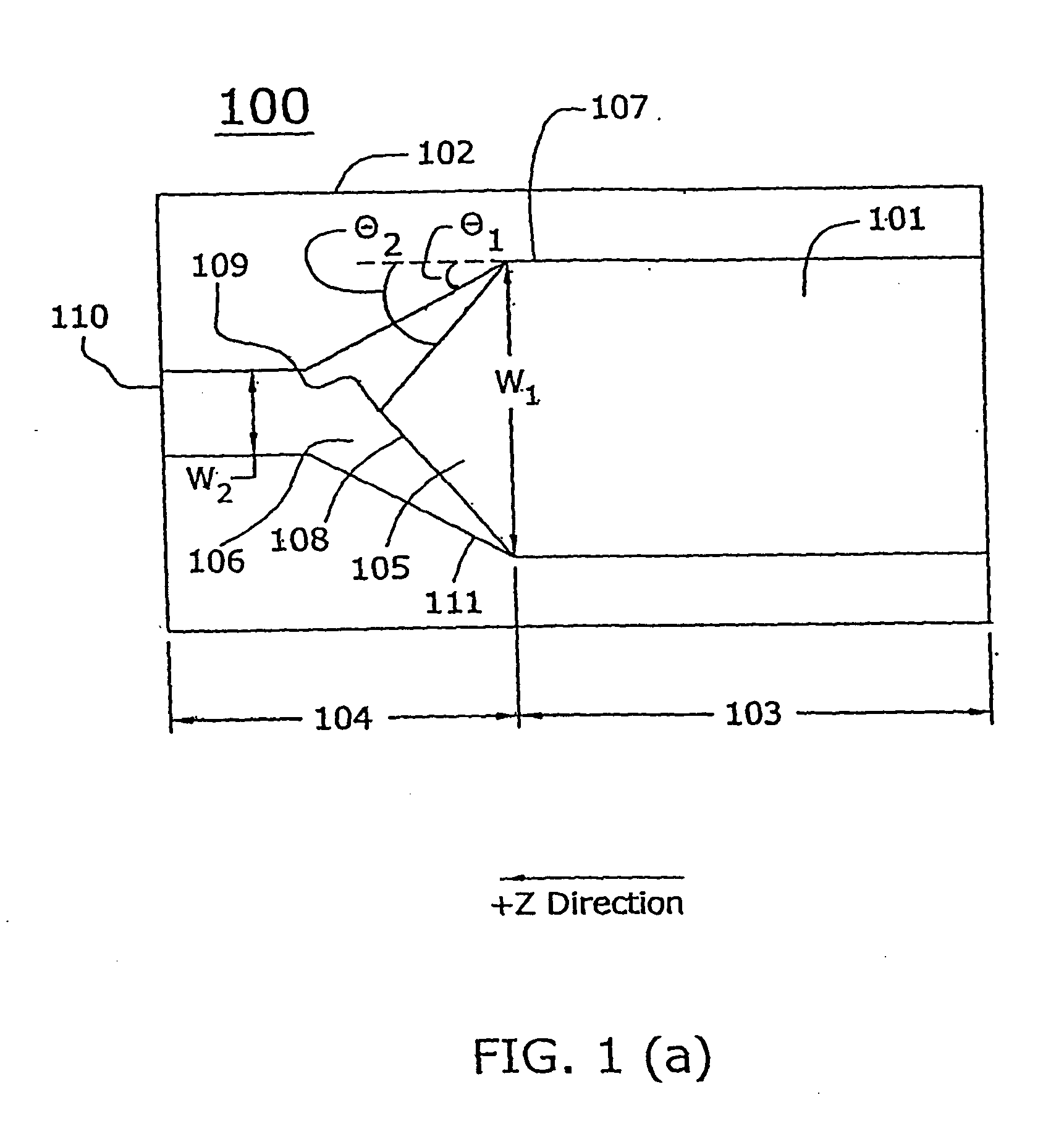
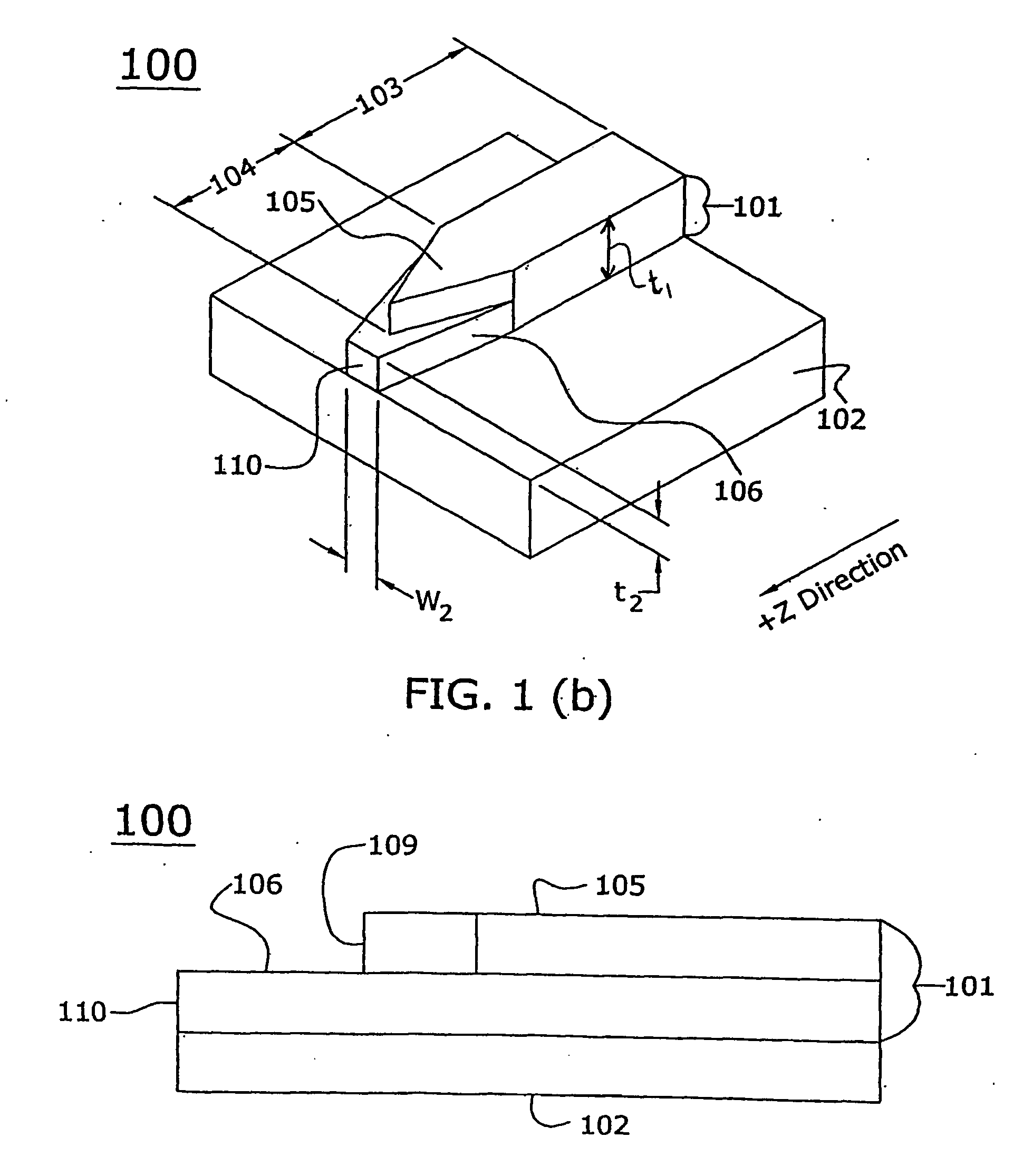
Tapered rib waveguide
InactiveUS6108478AEasy constructionEasy to makeCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesWaveguide
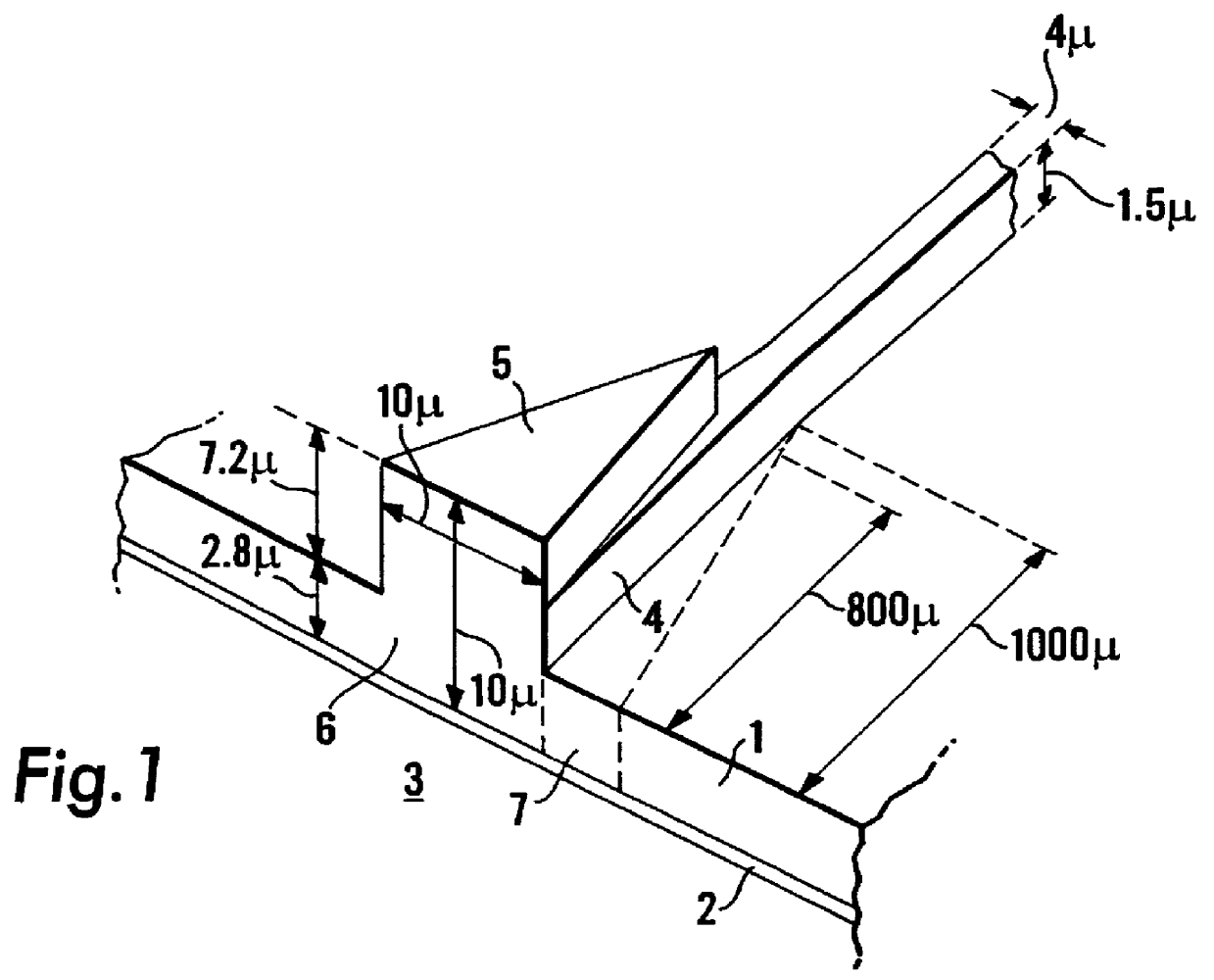
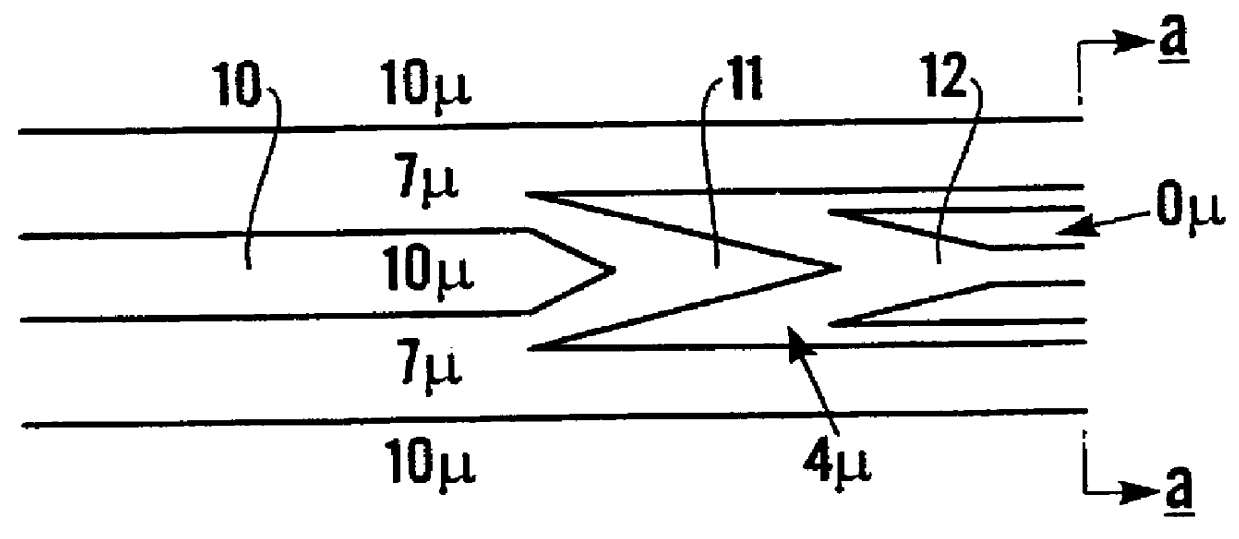
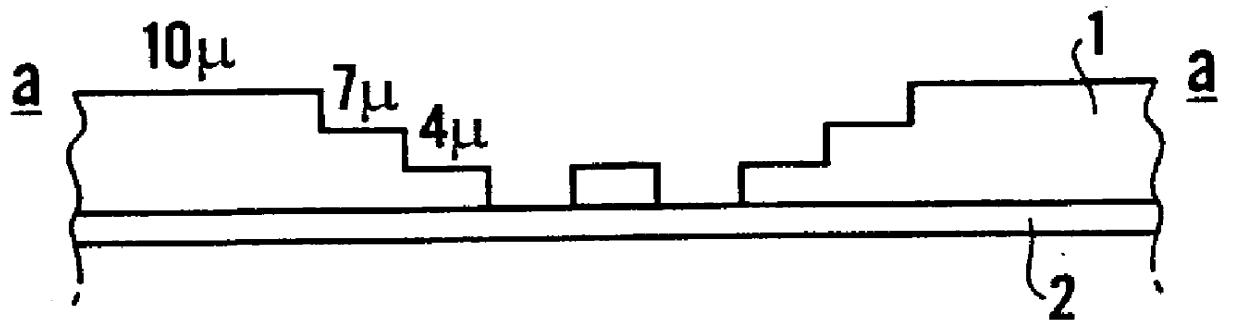
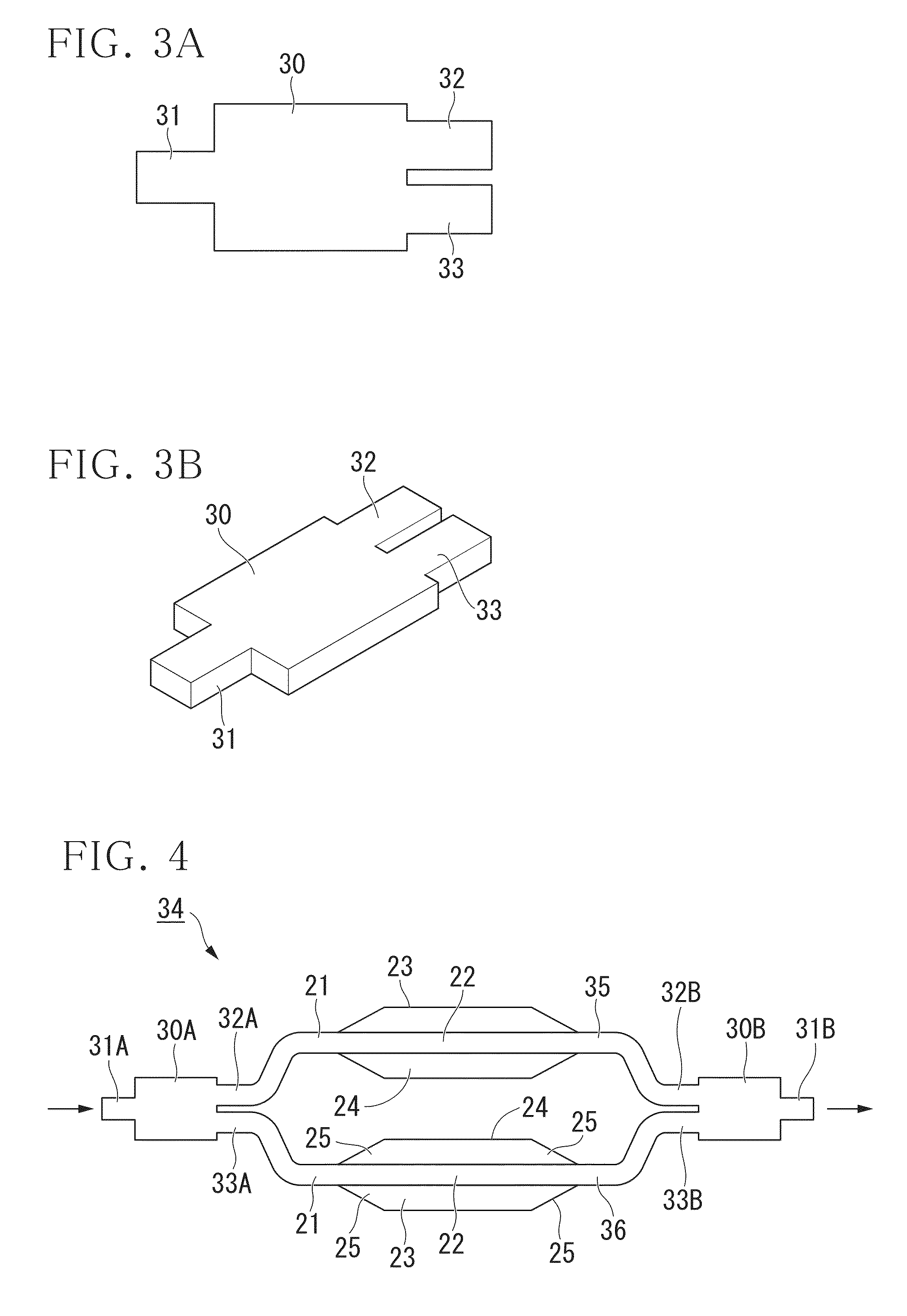
A tapered rib waveguide tapering from a large, multi-mode optical waveguide to a smaller, single-mode optical waveguide, the tapered rib waveguide comprising two portions (4,5) formed of the same material: a lower portion (4) which tapers laterally from the large waveguide to the smaller waveguide and an upper portion (5) formed on the lower portion (4), which tapers to a point (or other form of termination), the dimensions of the two portions (4,5) being such that substantially all of a fundamental mode propagated in the large multi-mode waveguide is coupled to the smaller, single-mode waveguide.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
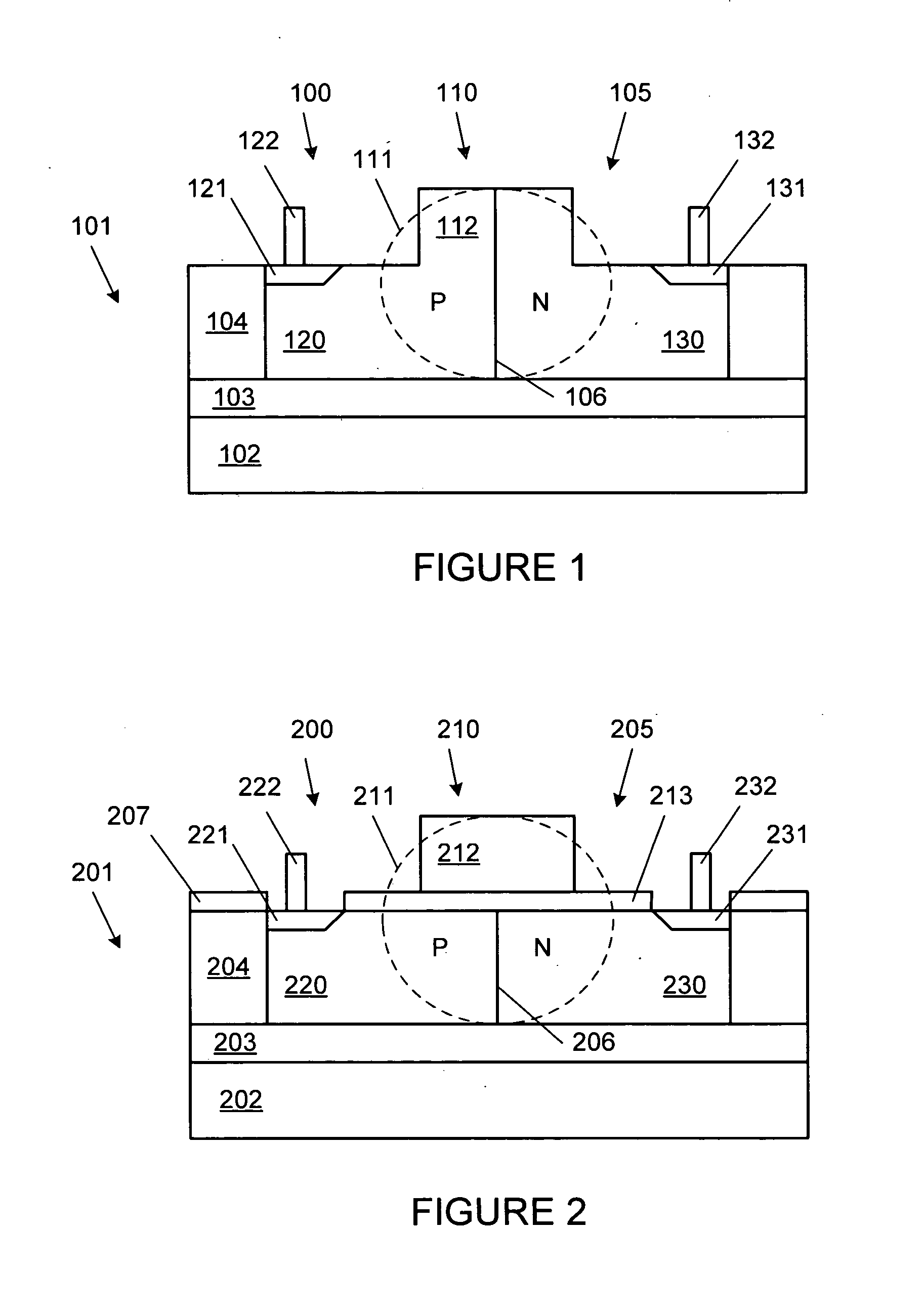
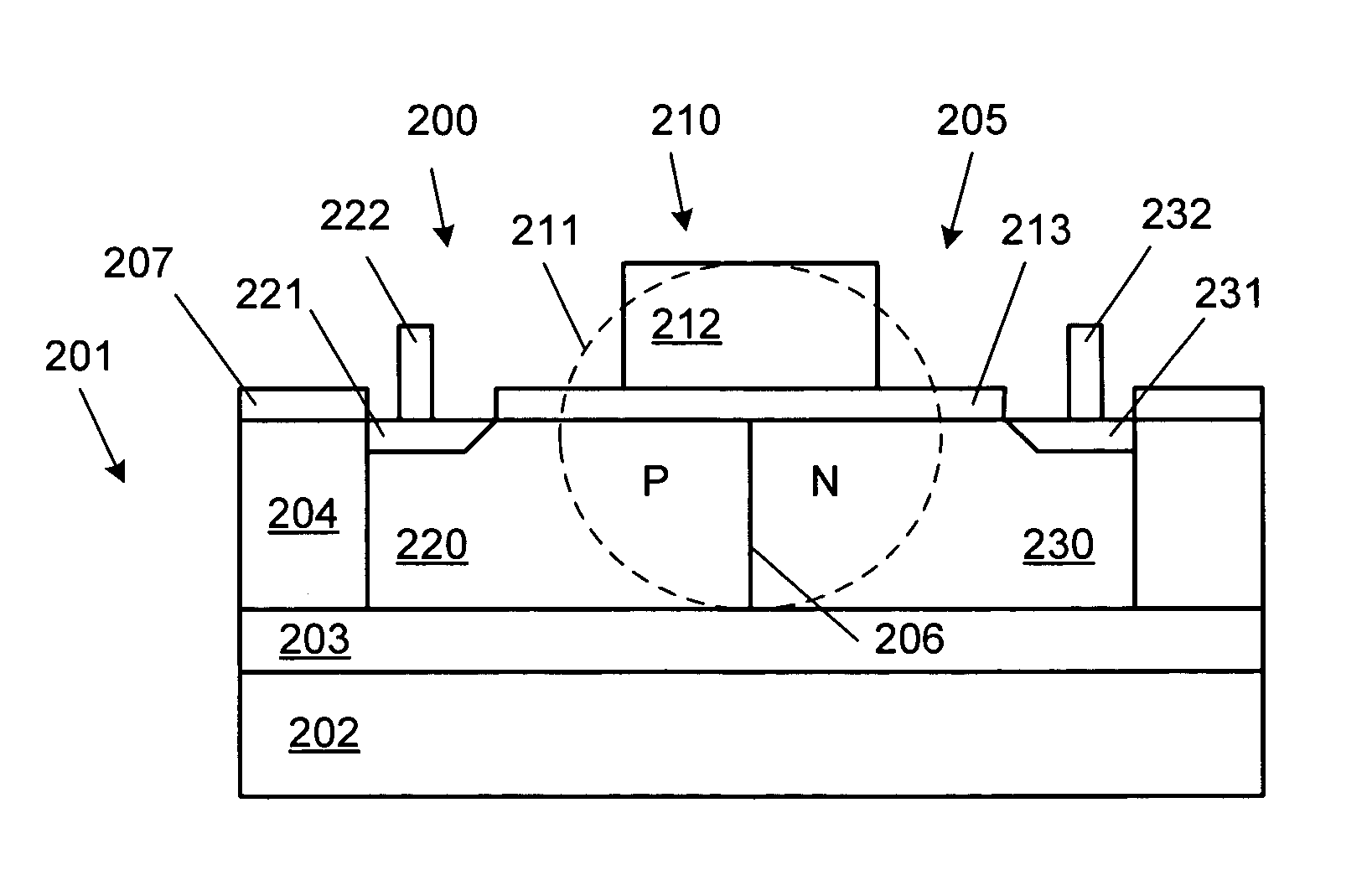
PN diode optical modulators fabricated in rib waveguides
ActiveUS20060008223A1Reduce speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideLow speedPhase shifted
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Light coupler between an optical fibre and a waveguide made on an soi substrate
ActiveUS20100086256A1Reduce widthInvariant widthNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsThin layer
A light coupler between an optical fiber (6) and a waveguide is made on a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate (1), this substrate (1) comprising a thin layer of semiconducting material in which the waveguide is made. The coupler comprises a light injector (5) and an adiabatic collector (4) made up with an inverted nanotip formed from the thin layer of semiconducting material. The injector (5) is formed on the insulator (3) and has a face (7) for receiving an end of the optical fiber (6). The adiabatic collector (4) has a cross-section which increases from a first end located on the side of said end of the optical fiber (6) right up to a second end which is connected to the waveguide, the injector (5) covering the adiabatic collector (4) and having a rib waveguide shape.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Integrated optical circuit
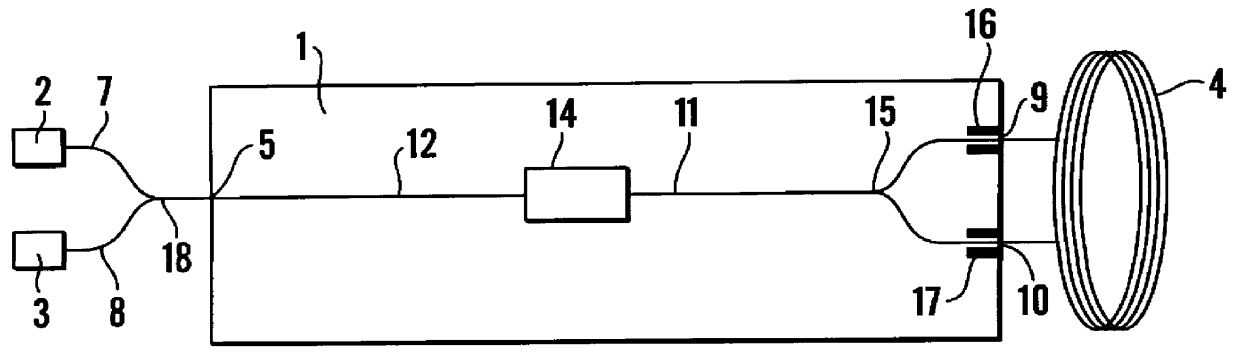
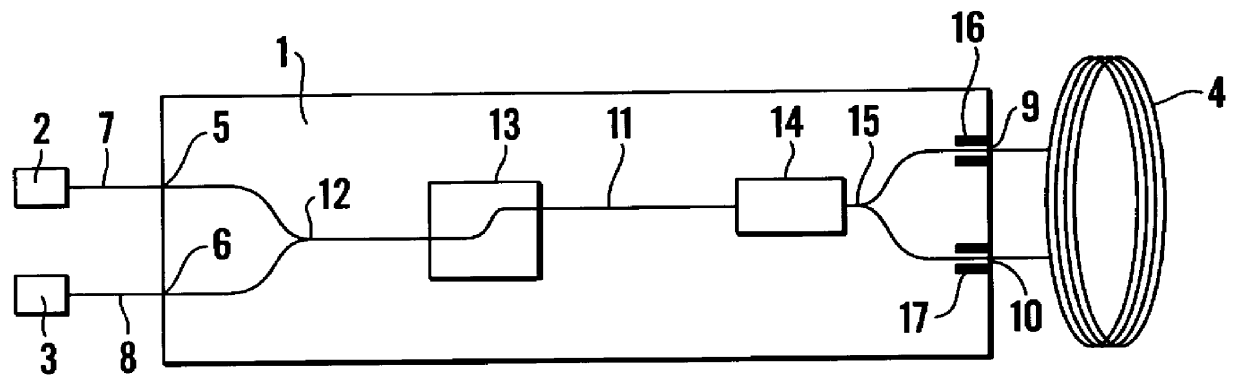
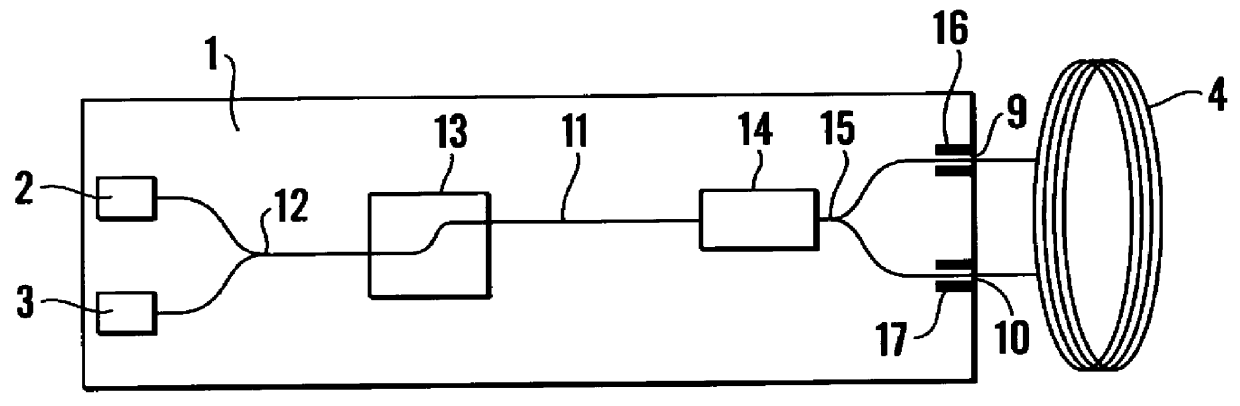
InactiveUS6163632ASagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberPhase shifted
An integrated optical circuit for use in a fibre optic gyroscope which senses rotation rates by determining a phase shift due to the Sagnac Effect between light beams travelling around an optical fibre sensing loop (4) in opposite directions, the circuit being provided on a silicon-on-insulator chip comprising a layer of silicon separated from a substrate by an insulating layer, the circuit comprising: rib waveguides (11) formed in the silicon layer for receiving light from a light source (2) and transmitting light to a light detector (3), fibre optic connectors (9) in the form of grooves etched in the silicon layer for receiving the respective ends of the optical fibre sensing loop (4); rib waveguides (11) formed in the silicon layer for transmitting light to and from said fibre optic connectors (9) so as to direct light beams in opposite directions around the sensing loop (4) and receive light beams returning therefrom, phase determining means and (13,17,31) integrated in silicon layer for determining a phase shift between the light beams returning from the sensing loop (4).
Owner:BOOKHAM TECH
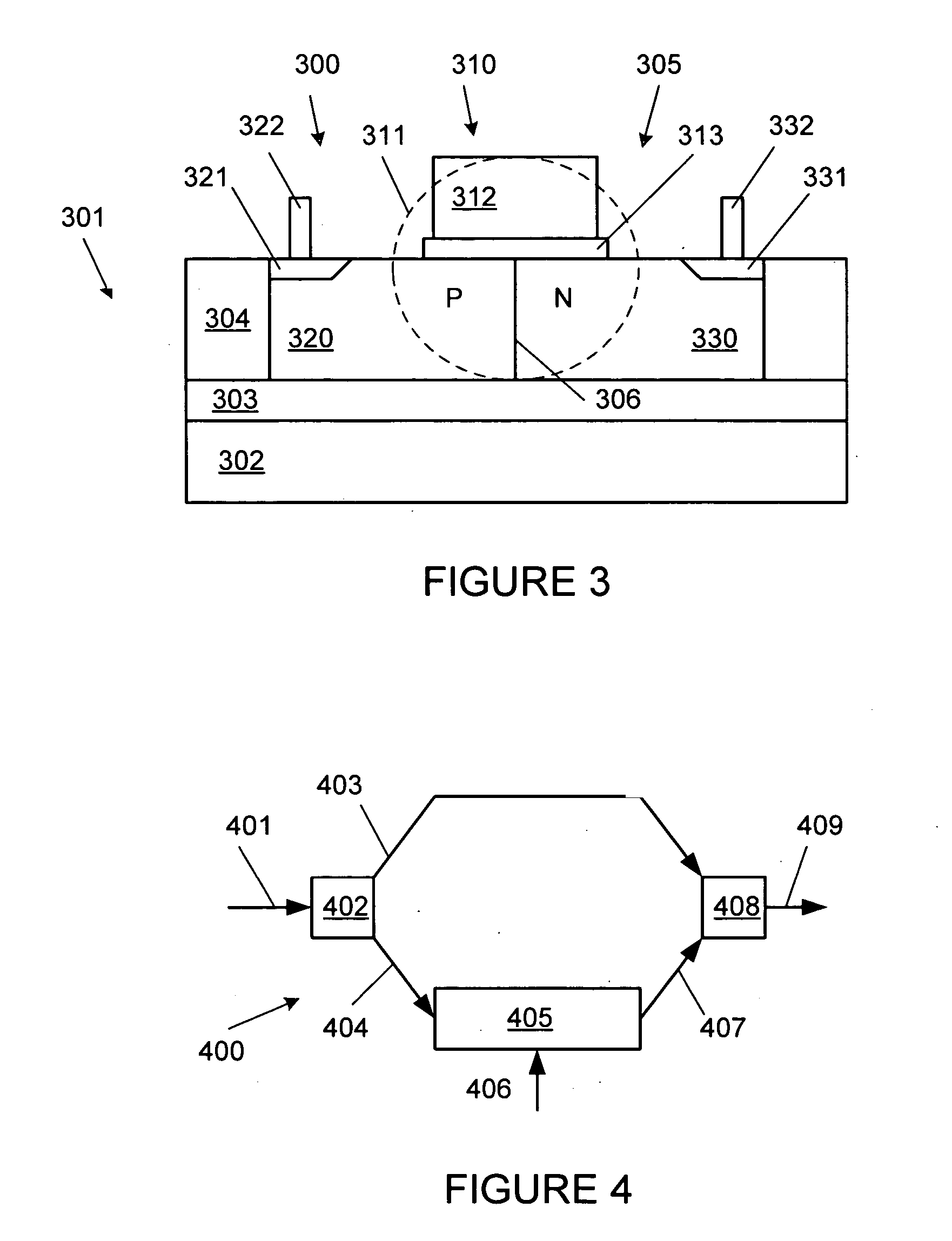
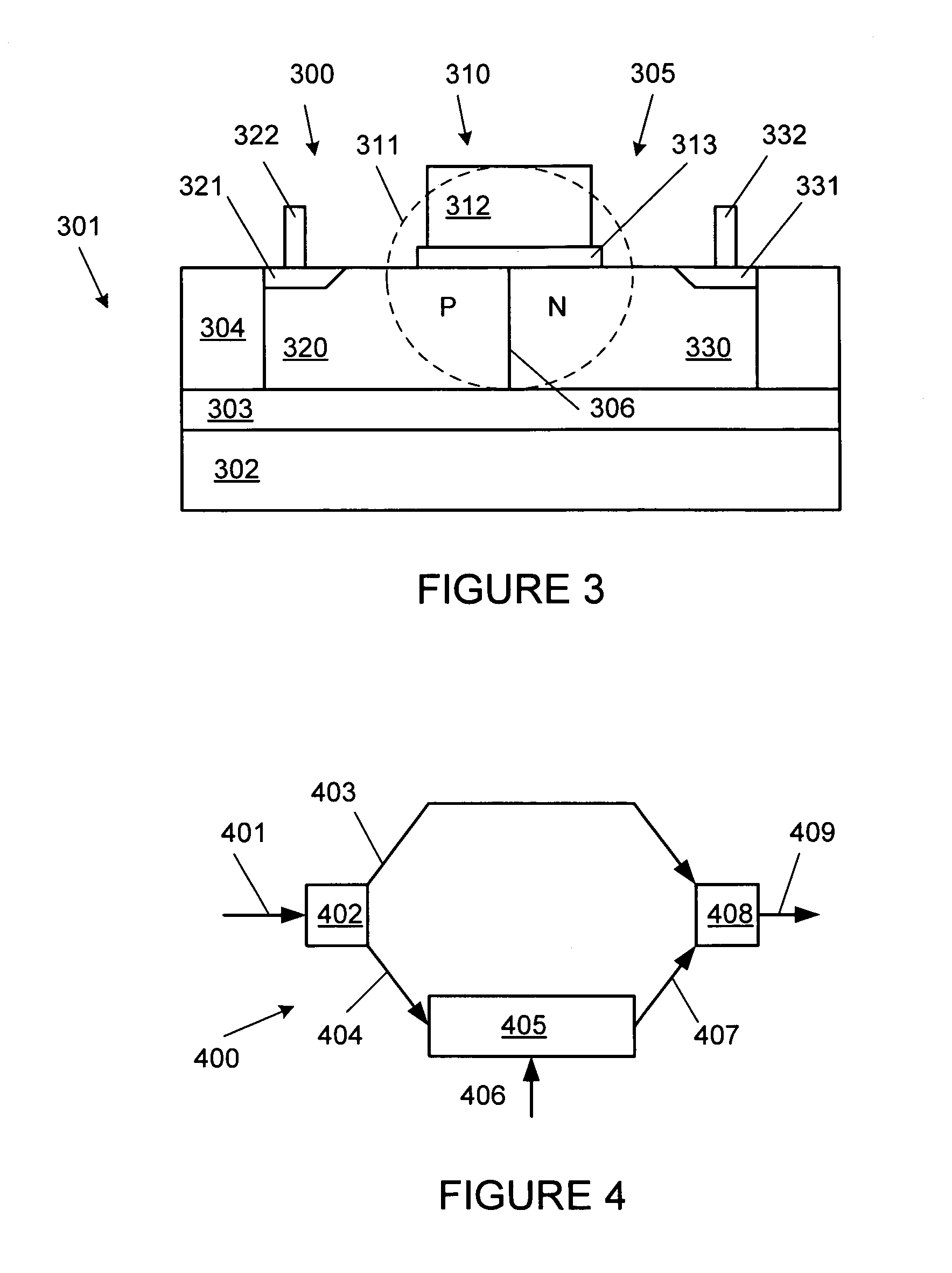
PN diode optical modulators fabricated in strip loaded waveguides
ActiveUS7136544B1Minimal impactDifficult to controlOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsPhase shiftedWaveguide
High speed optical modulators can be made of a lateral PN diode formed in a strip loaded optical waveguide on a SOI or other silicon based substrate. A PN junction is formed at the boundary of the P and N doped regions. The depletion region at the PN junction overlaps with the center of a guided optical mode propagating through the waveguide. Electrically modulating a lateral PN diode causes a phase shift in an optical wave propagating through the waveguide. Due to differences in fabrication methods, forming strip loaded waveguides with consistent properties for use in PN diode optical modulators is much easier than fabricating similar rib waveguides.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Silicon-based electro-optic device
ActiveUS20110211786A1Efficient connectionReduced propagation lossOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsMetal electrodesMaterials science
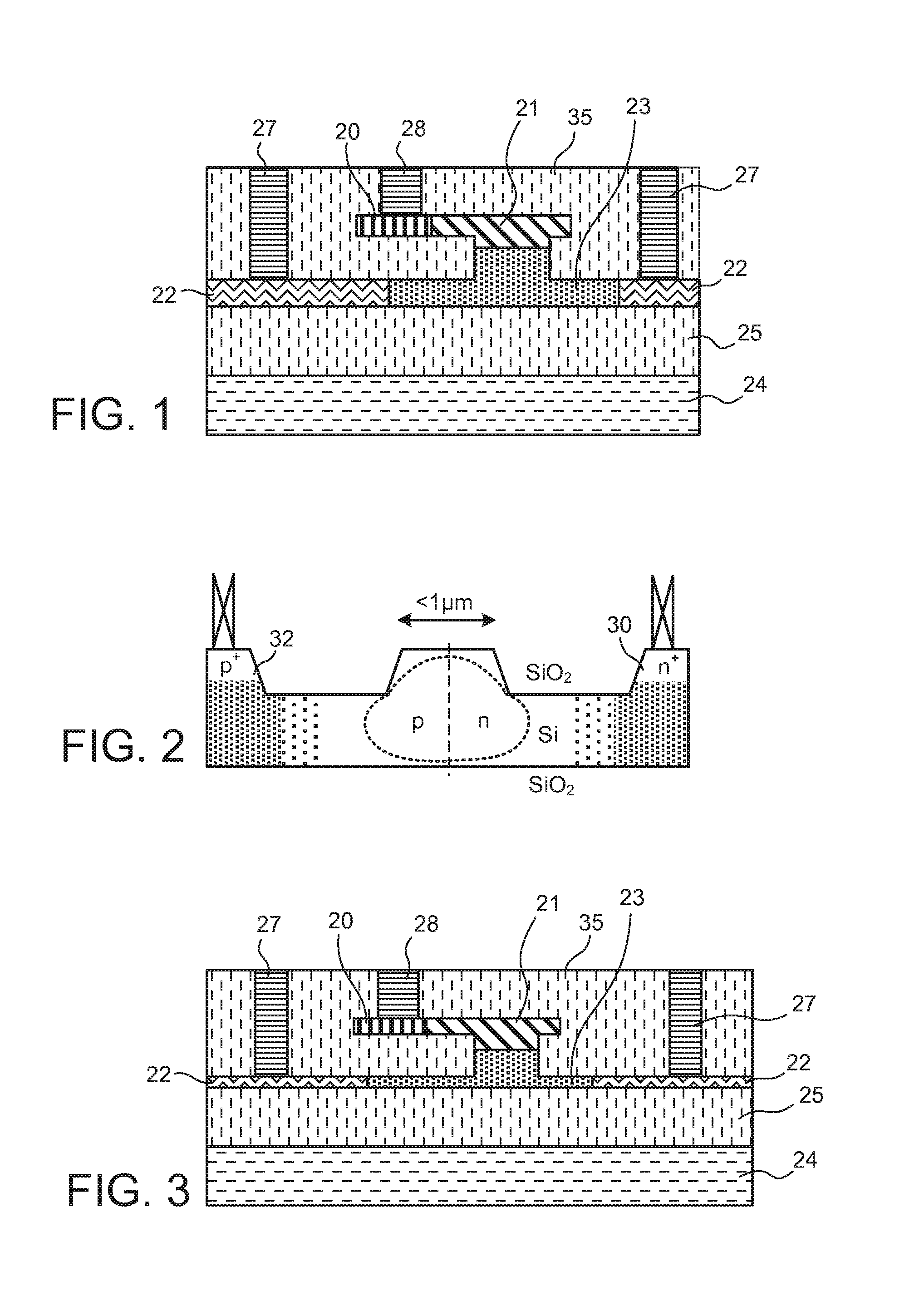
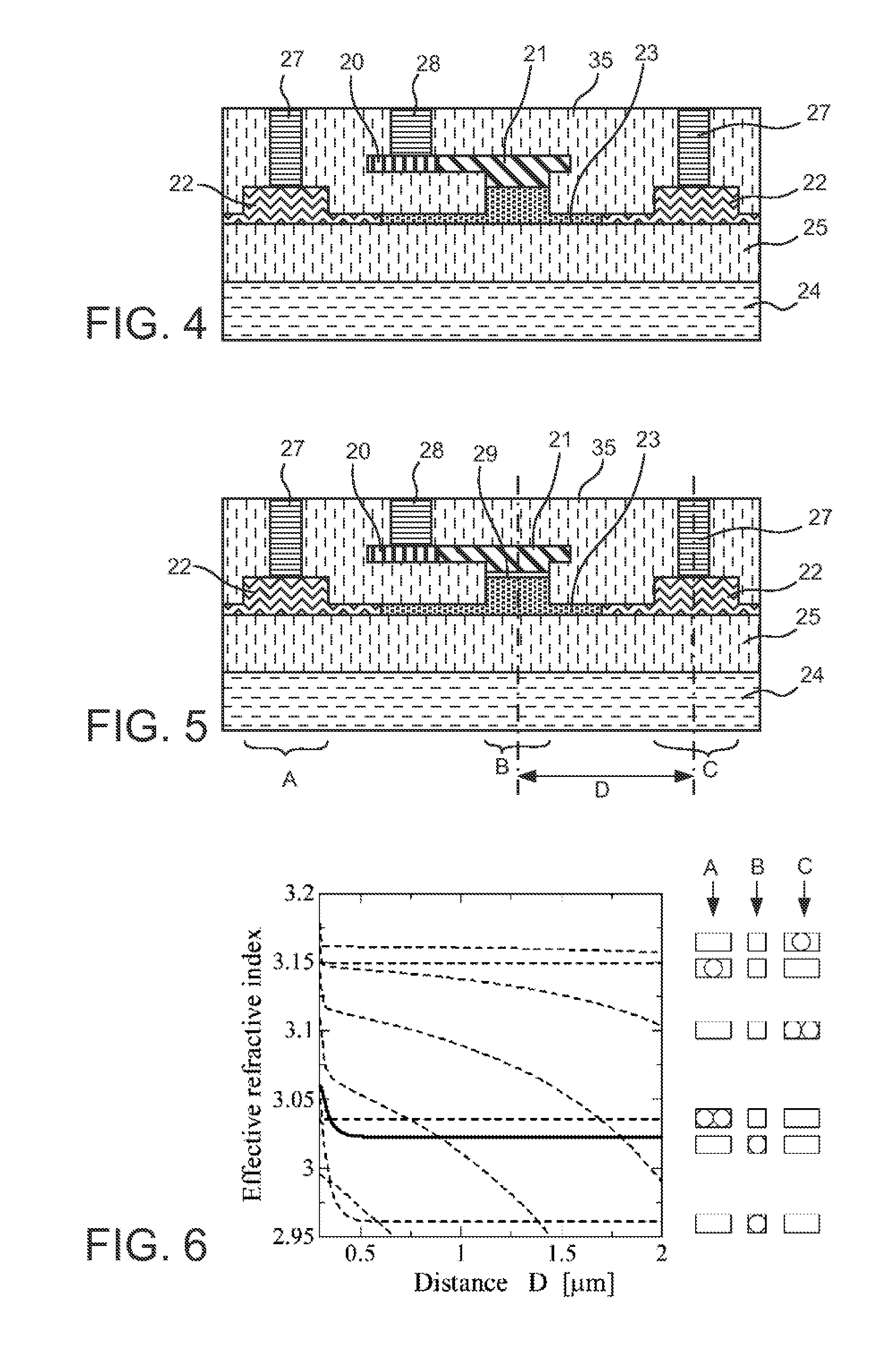
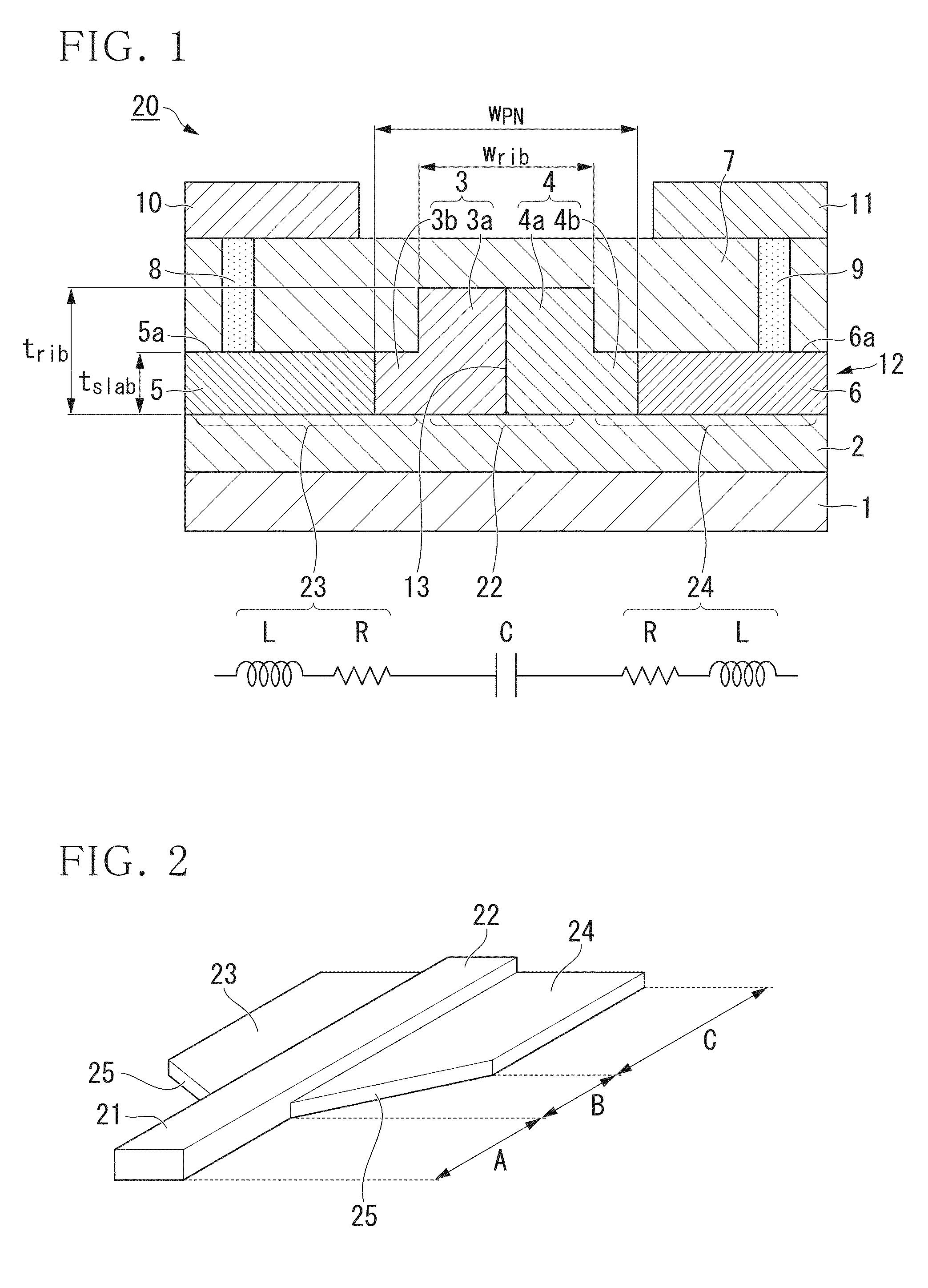
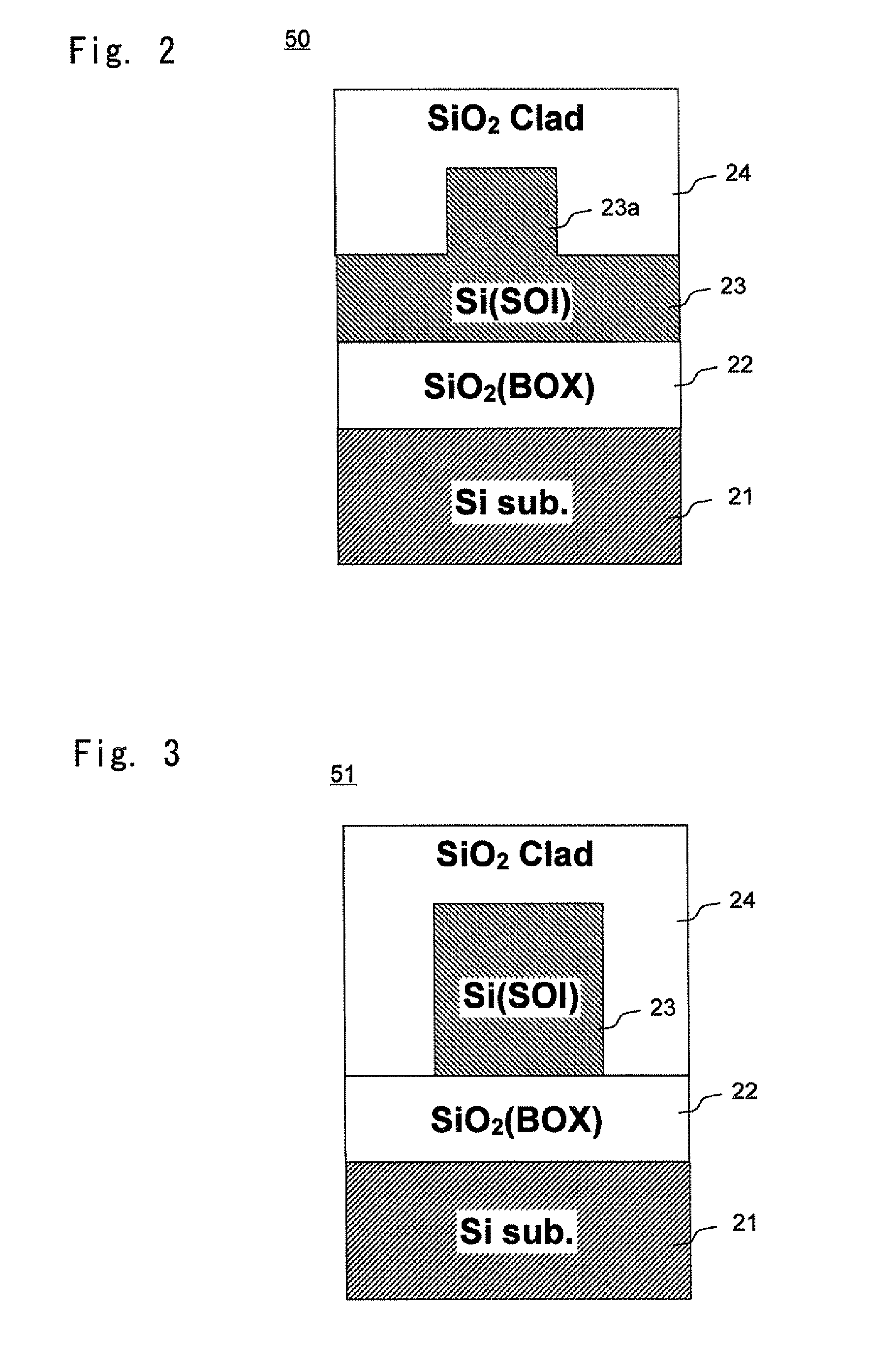
In an electro-optic device, a stack structure including a first silicon layer of a first conductivity type and a second silicon layer of a second conductivity type has a rib waveguide shape so as to form an optical confinement area, and a slab portion of a rib waveguide includes an area to which a metal electrode is connected. The slab portion in the area to which the metal electrode is connected is thicker than a surrounding slab portion. The area to which the metal electrode is connected is set so that a range of a distance from the rib waveguide to the area to which the metal electrode is connected is such that when the distance is changed, an effective refractive index of the rib waveguide in a zeroth-order mode does not change.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FOUNDRY PTE LTD +1
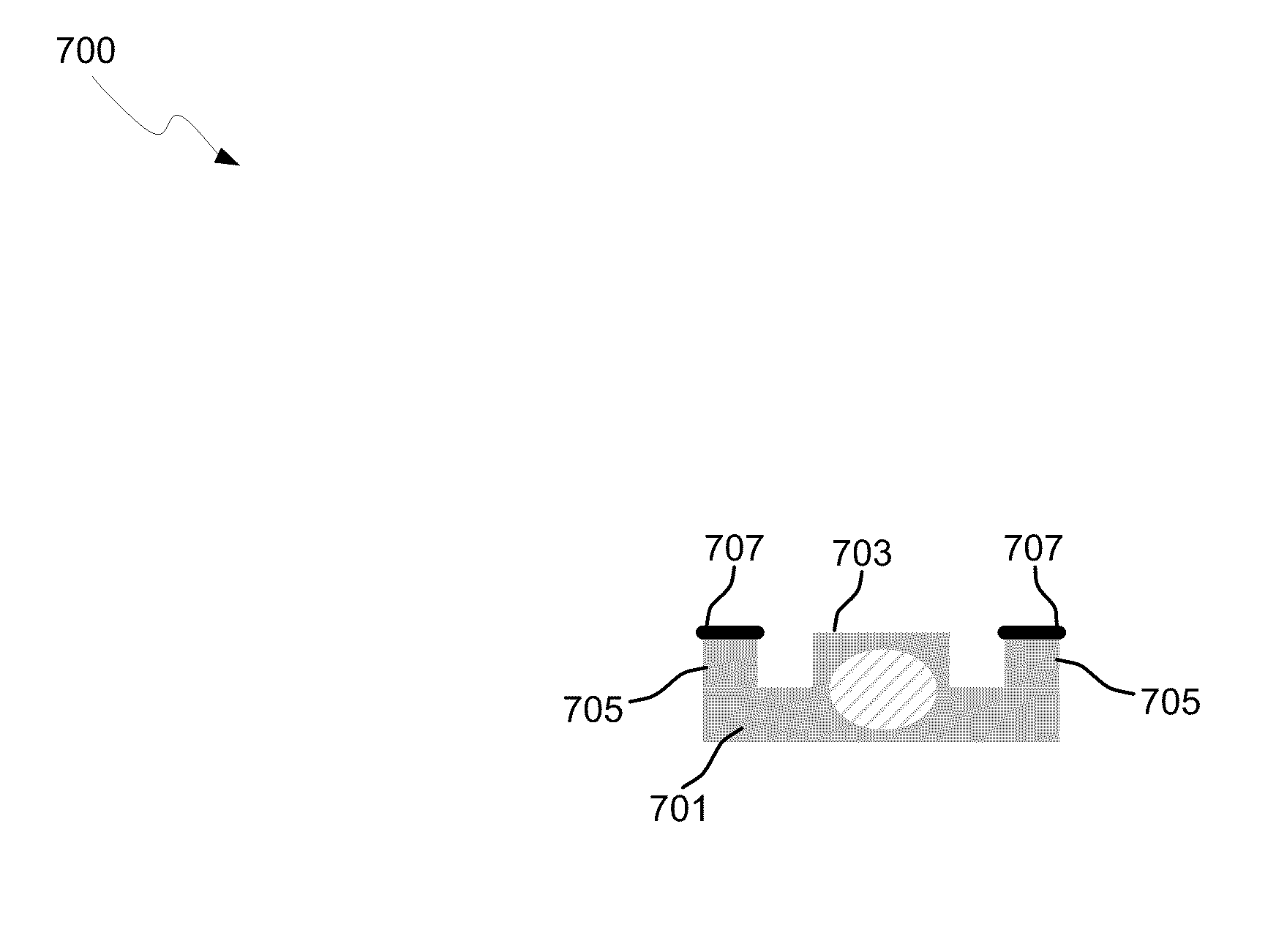
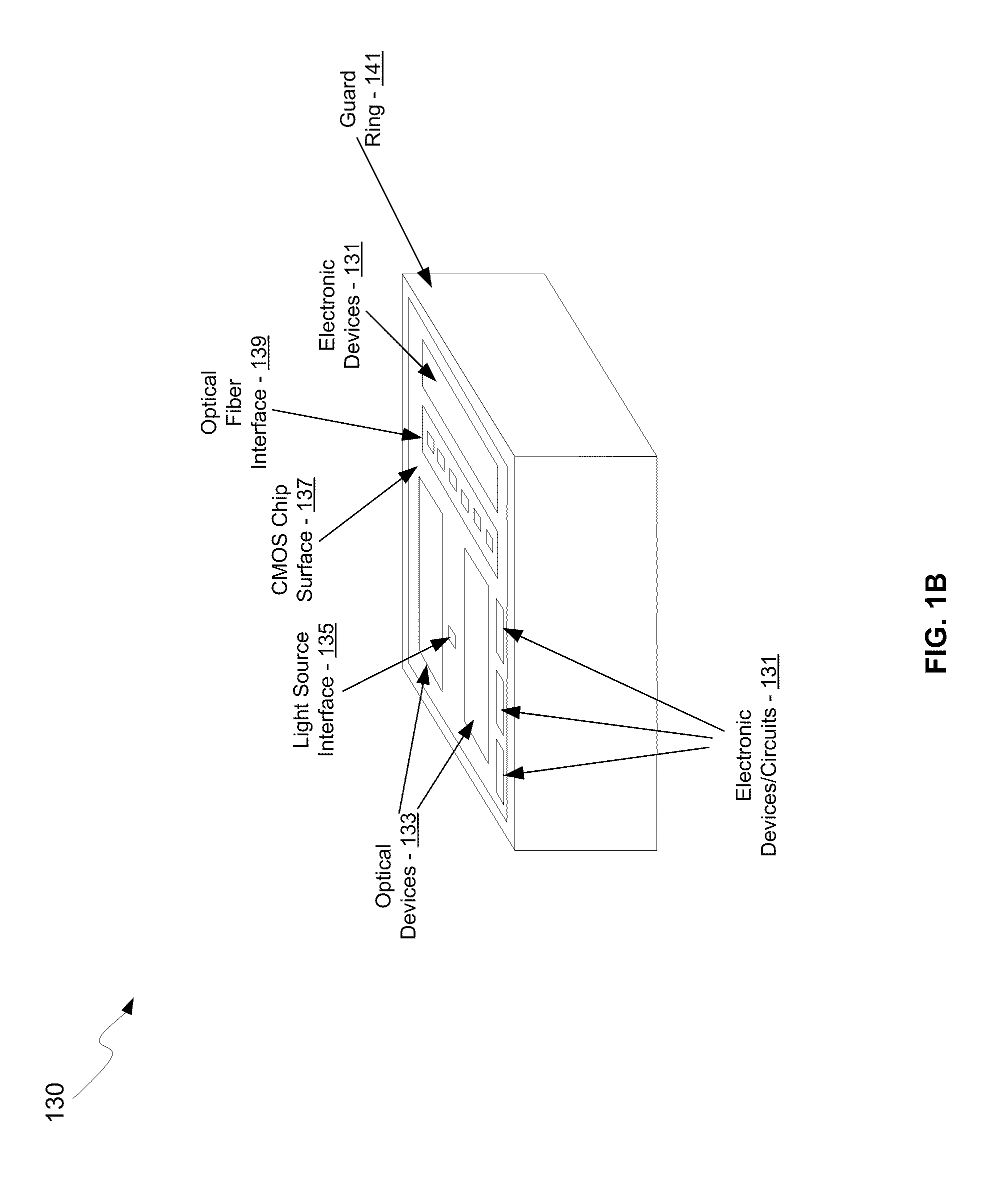
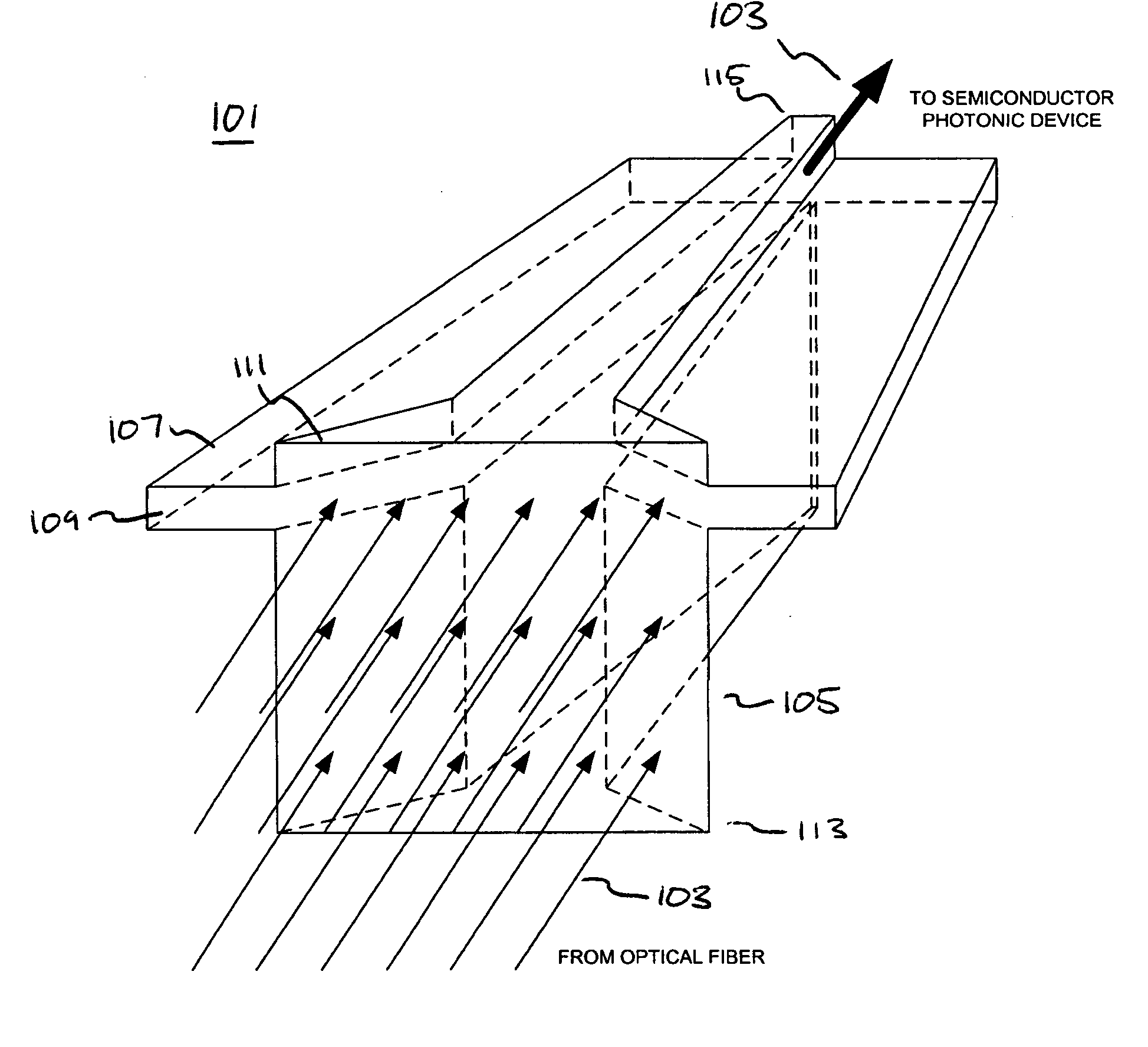
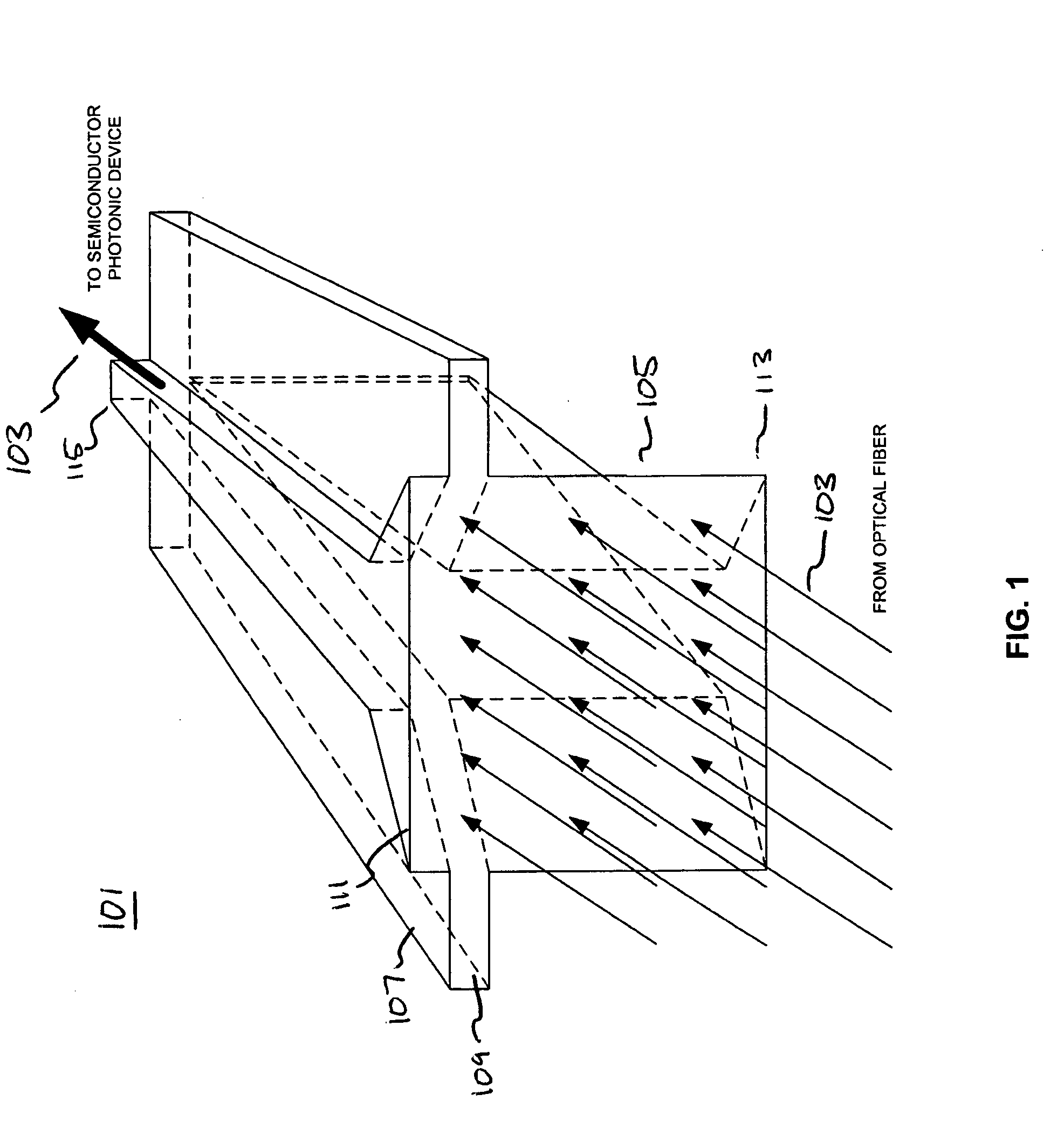
Optical waveguide termination with vertical and horizontal mode shaping
InactiveUS7251406B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryWaveguide modeSingle mode waveguides
An optical device is disclosed which includes a single-mode waveguide (700) which supports a first optical mode in a first region and a second optical mode in a second region. The waveguide includes a guiding layer (703) having at least one wing (750) extended outwardly from the guiding layer (703). The guiding layer (703) may desirably have a rib waveguide (706, 707) cross sectional shape at the wings. The wings (750) decrease in width along the length of the guiding layer to convert a rib waveguide mode at the wings to a channel waveguide mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
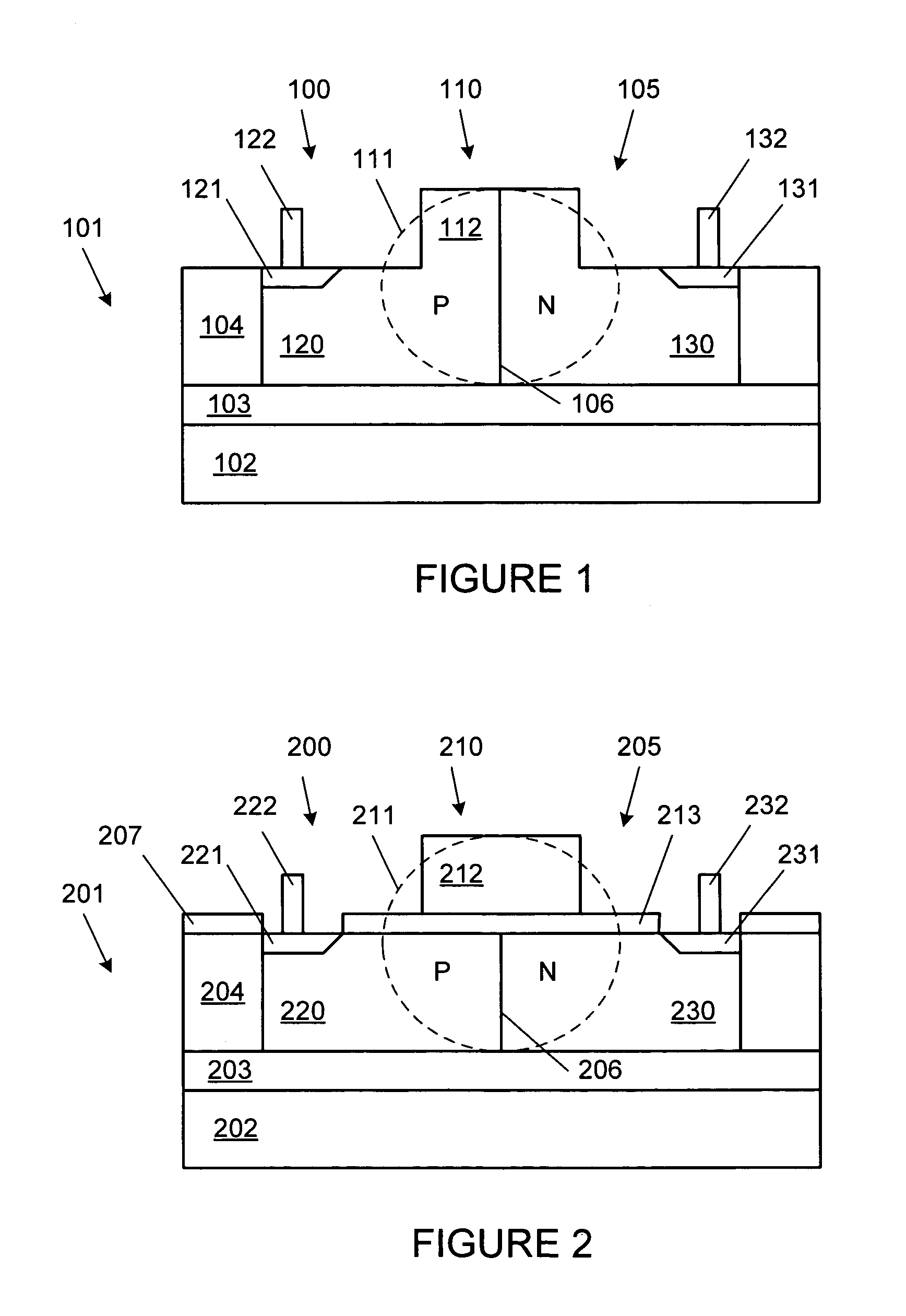
PN diode optical modulators fabricated in rib waveguides
ActiveUS7116853B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideElectricityLow speed
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and System for Waveguide Mode Filters
A method and system for waveguide mode filters are disclosed and may include processing optical signals of a fundamental mode and higher-order modes by filtering the higher-order modes in rib waveguides in a photonic chip. The higher-order modes may be filtered utilizing doped regions and / or patterns in one or more slab sections in the rib waveguides. The patterns may be periodic or aperiodic along the rib waveguides. The higher-order modes may be filtered utilizing varying widths of slab sections, or doped, patterned, and / or salicided ridges on the slab sections in the rib waveguides. The higher-order modes may be attenuated by scattering and / or absorbing the modes. The chip may comprise a CMOS photonic chip.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Mode transformation and loss reduction in silicon waveguide structures utilizing tapered transition regions
ActiveUS6980720B2Mode mismatchCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideOptical reflectionCoupling
A low loss coupling arrangement between a slab / strip waveguide and a rib waveguide in an optical waveguiding structure formed on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) platform utilizes tapered sections at the input and / or output of the rib waveguide to reduce loss. Optical reflections are reduced by using silicon tapers (either vertical tapers, horizontal tapers, or two-dimensional tapers) that gradually transition the effective index seen by an optical signal propagating along the slab / strip waveguide and subsequently into and out of the rib waveguide. Loss can be further reduced by using adiabatically contoured silicon regions at the input and output of the rib waveguide to reduce mode mismatch between the slab / strip waveguide and rib waveguide. In a preferred embodiment, concatenated tapered and adiabatic sections can be used to provide for reduced optical reflection loss and reduced optical mode mismatch.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Low loss silicon waveguide and method of fabrication thereof
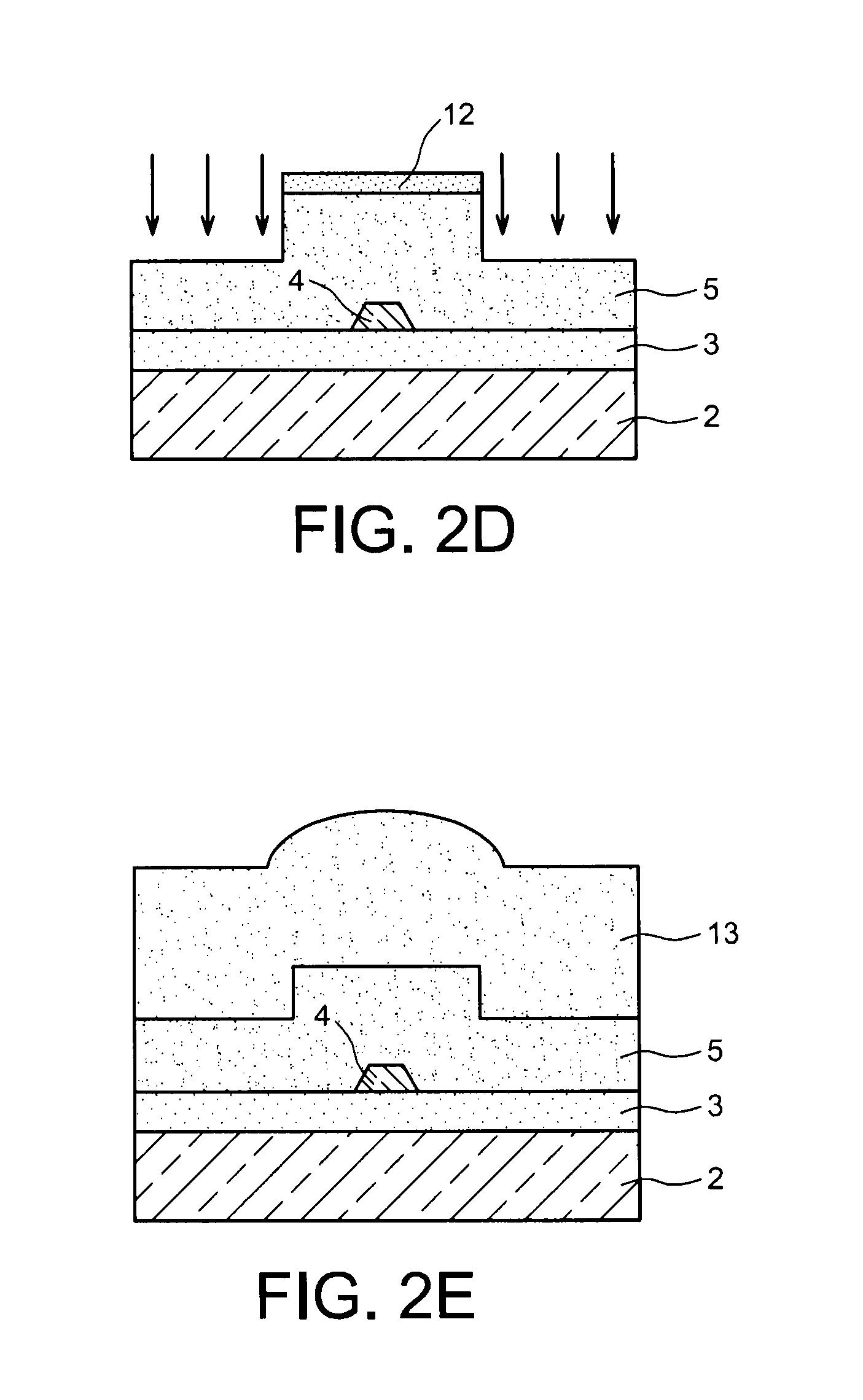
InactiveUS20050158002A1Reduce lossReduce light lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideSilicon on insulator
A silicon rib waveguide that has a silicon nitride cladding layer of predetermined thickness to reduce optical loss of light propagating therethrough. An exemplary embodiment of the waveguide is fabricated by using a silicon-on-insulator structure having a single crystal silicon layer bonded to a silicon wafer with a layer of insulative material. An etch resistant masking layer is deposited on the outer surface of the single crystal silicon layer and patterned to produce vias therein. A RIE etching process is used through the vias in the masking layer to form at least one rib bounded by a pair of parallel trenches. The masking layer is removed and a silicon nitride cladding layer is deposited on the rib side and end walls and on the trenches.
Owner:XEROX CORP
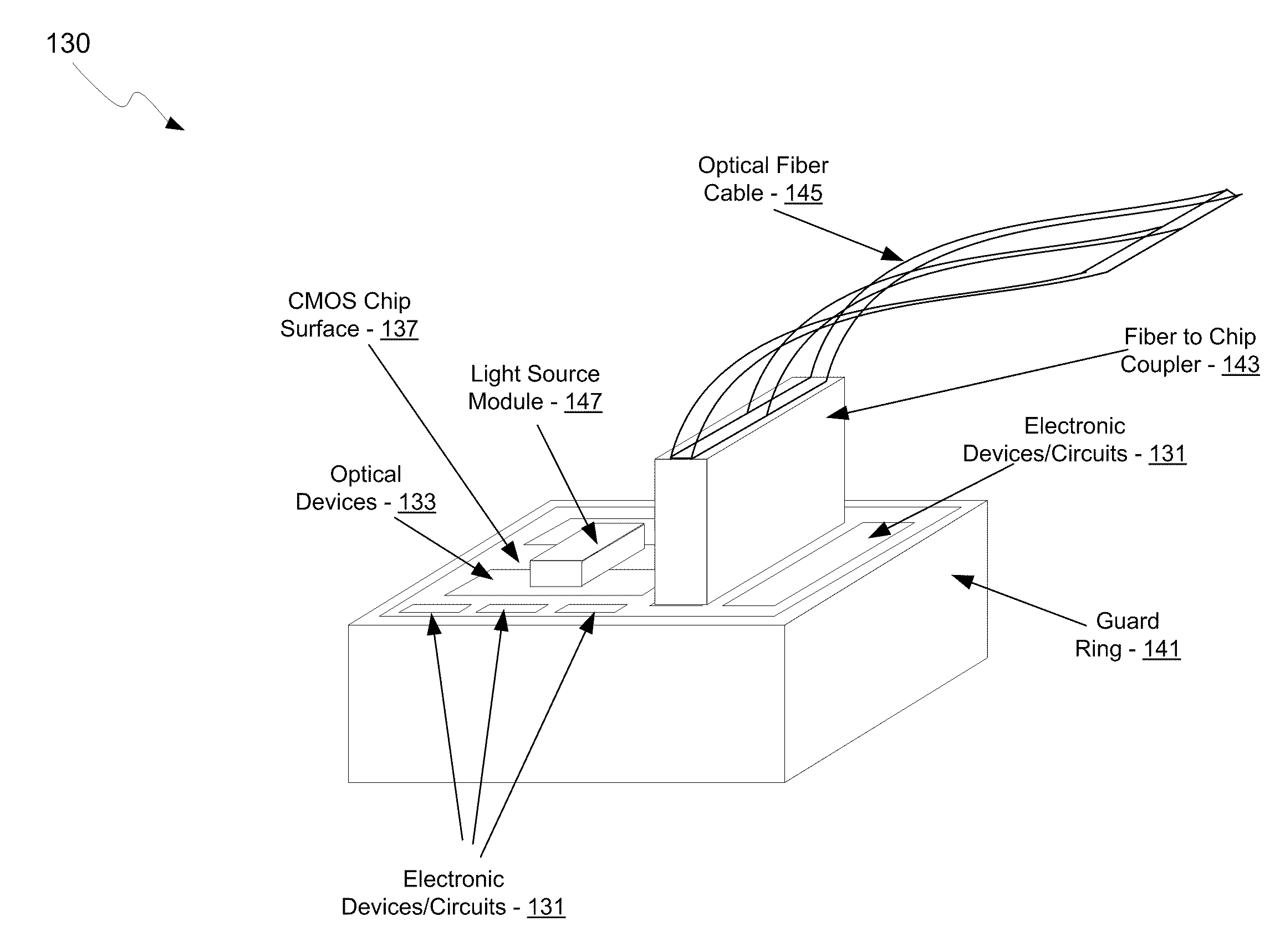
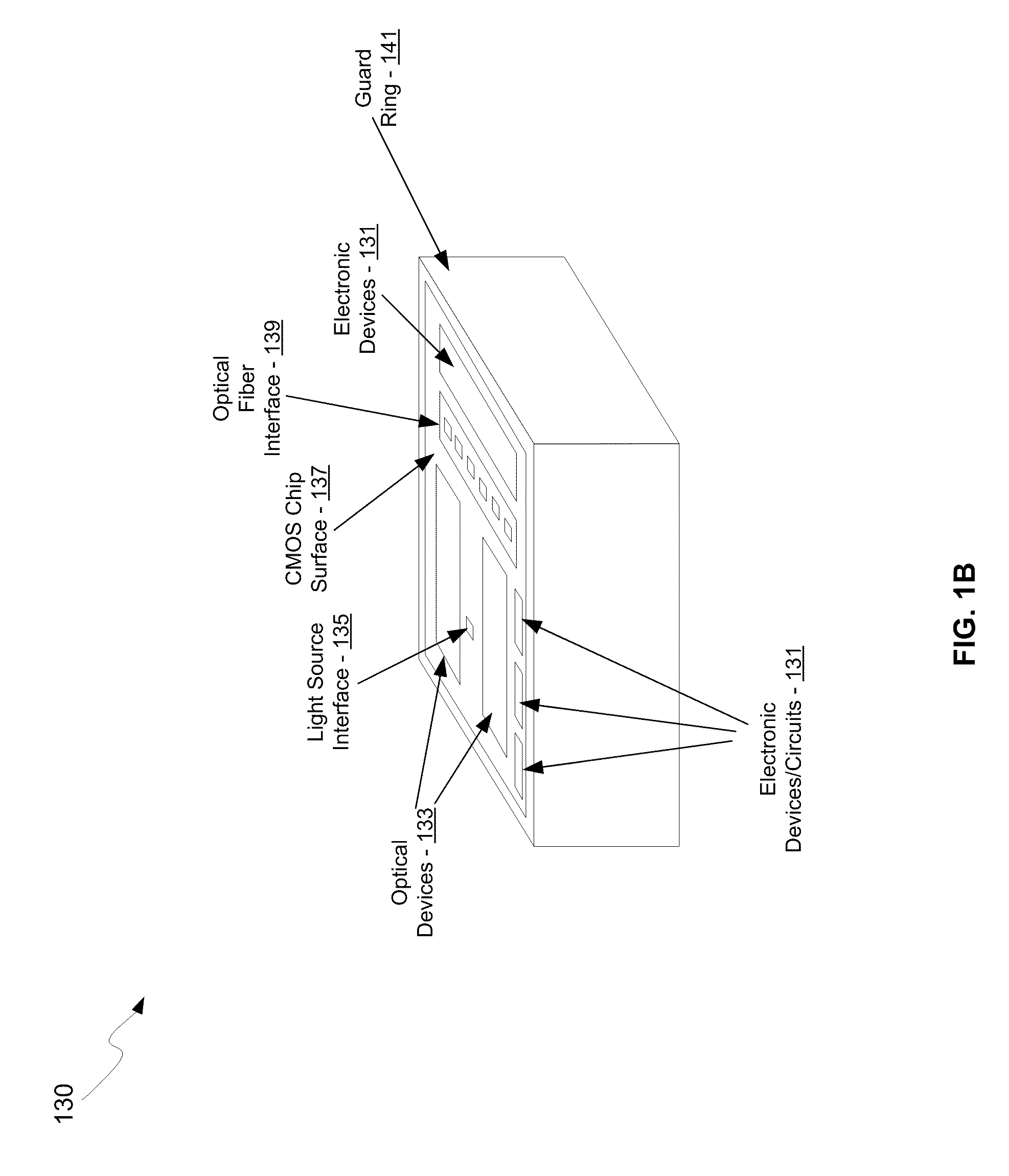
Method and system for multi-mode integrated receivers
A method and system for multi-mode integrated receivers are disclosed and may include receiving an optical signal from an optical fiber coupled to a chip comprising a photonic circuit. The photonic circuit may comprise an optical coupler, one or more multi-mode optical waveguides, and a detector. The received optical signal may be coupled to a plurality of optical modes in the one or more multi-mode optical waveguides, which are communicated to a detector to generate an electrical signal from the communicated modes. The optical coupler may comprise a grating coupler. The chip may comprise a CMOS chip, and the optical fiber may comprise a single-mode or a multi-mode fiber. The detector may comprise a germanium or silicon-germanium photodiode, and / or a waveguide detector. The optical fiber may be coupled to a top surface of the chip and the multi-mode optical waveguides may comprise rib waveguides.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Optical waveguide termination with vertical and horizontal mode shaping
InactiveUS20050202554A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryWaveguide modeSingle mode waveguides
An optical device is disclosed which includes a single-mode waveguide (700) which supports a first optical mode in a first region and a second optical mode in a second region. The waveguide includes a guiding layer (703) having at least one wing (750) extended outwardly from the guiding layer (703). The guiding layer (703) may desirably have a rib waveguide (706, 707) cross sectional shape at the wings. The wings (750) decrease in width along the length of the guiding layer to convert a rib waveguide mode at the wings to a channel waveguide mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
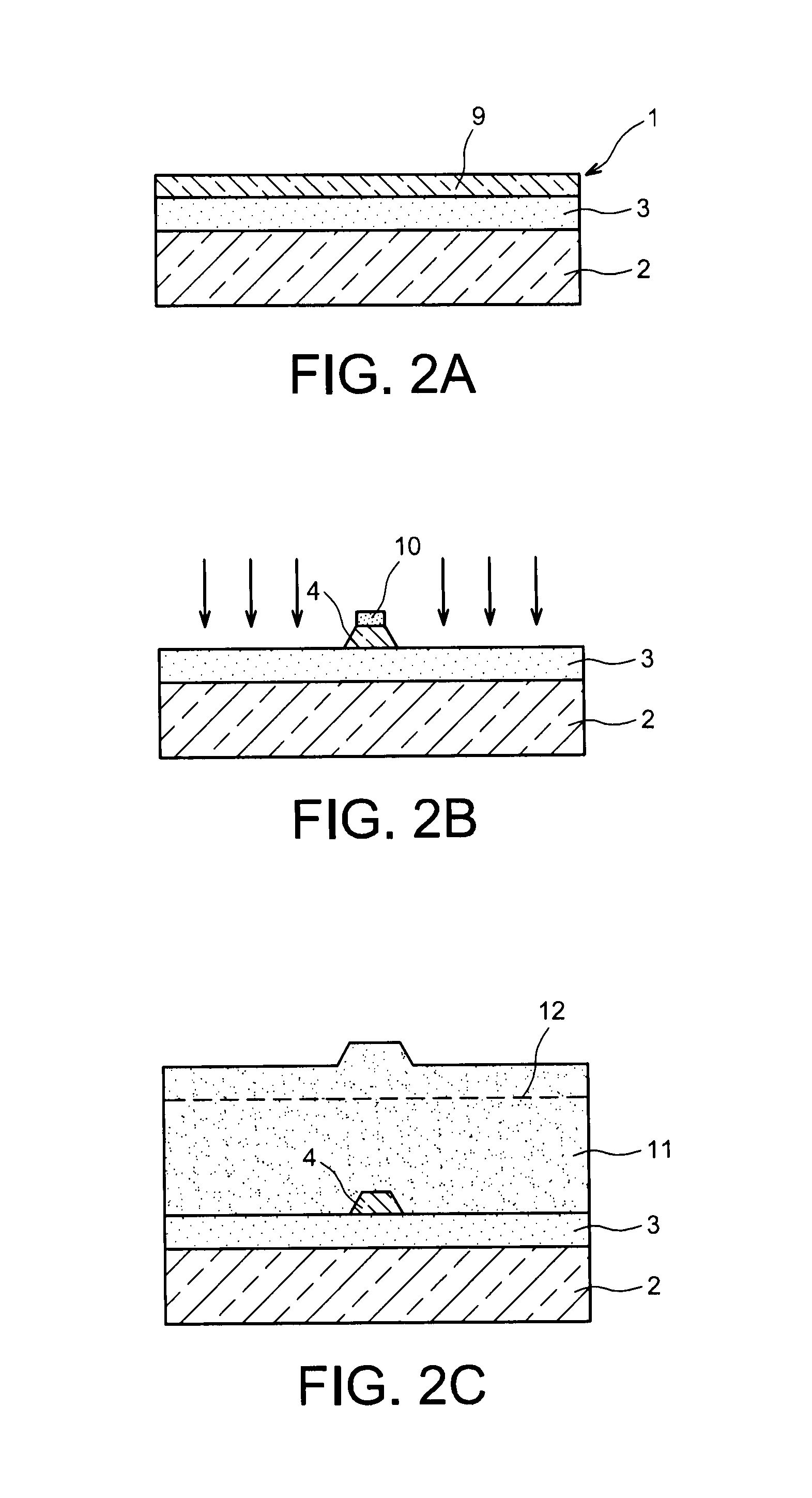
Structure Comprising An Adiabatic Coupler For Adiabatic Coupling Of Light Between Two Optical Waveguides And Method For Manufacturing Such A Structure
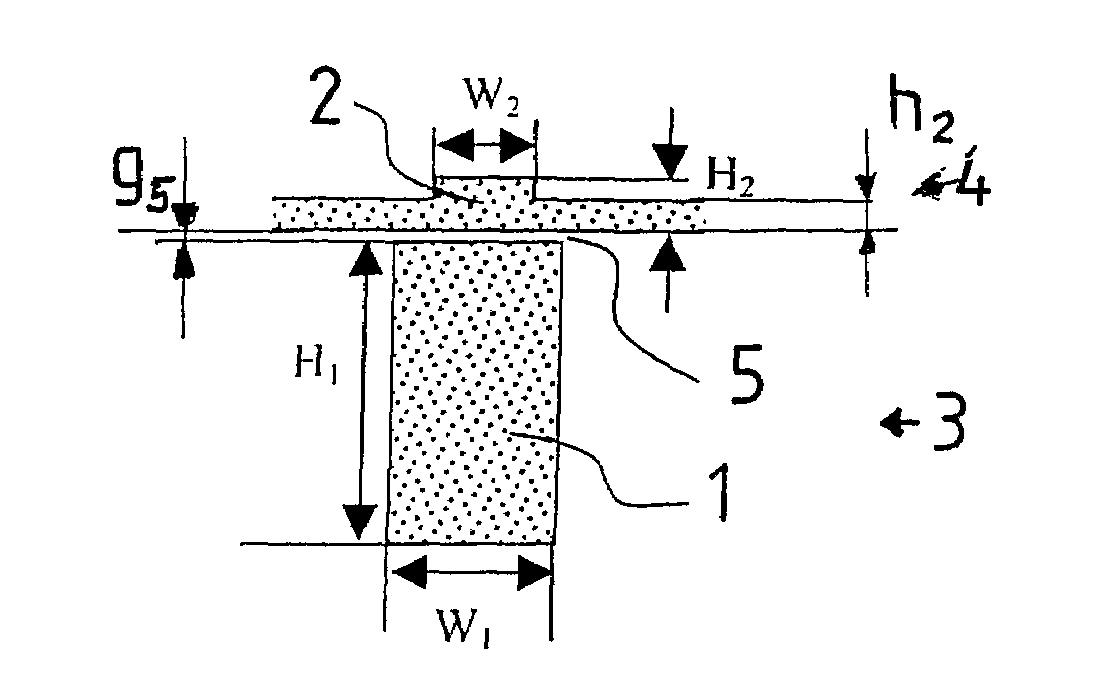
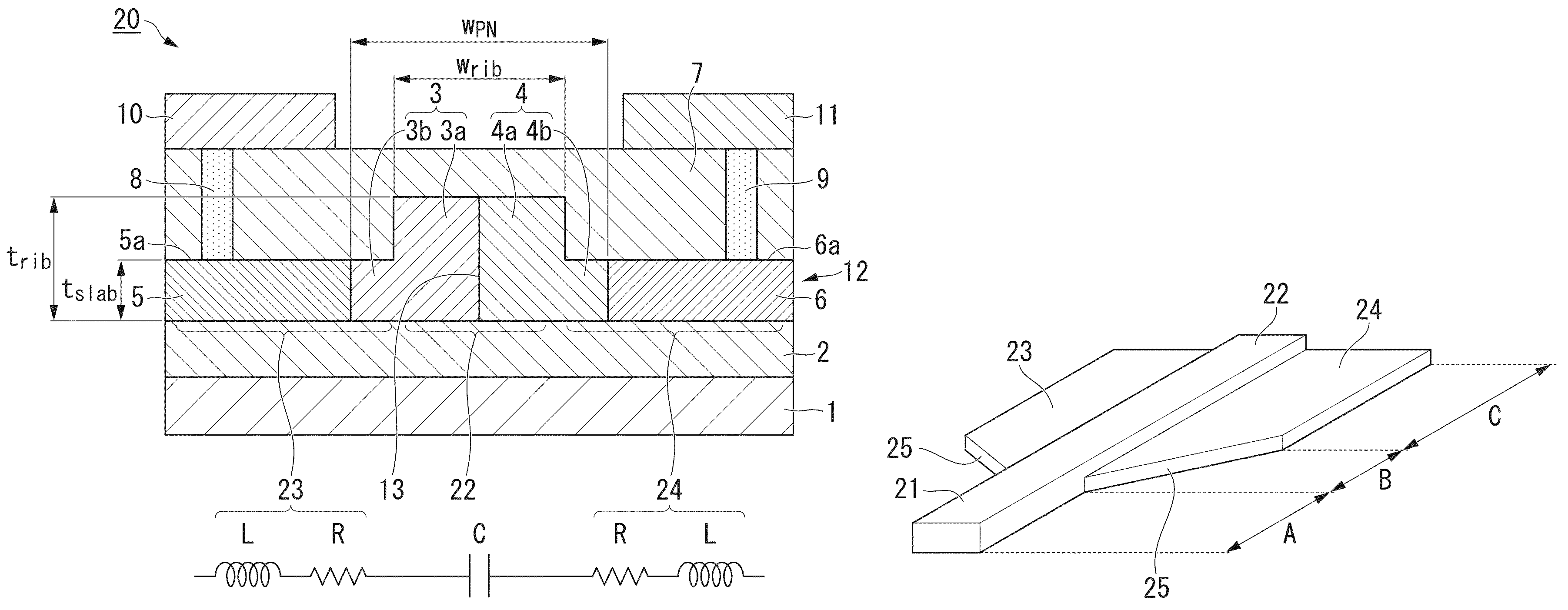
InactiveUS20070286552A1Improve surface qualityIncreasing the thicknessCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCouplingOuter core
A structure comprises an inner strip waveguide (1) and an outer rib waveguide (2) on a common substrate. The thicker inner waveguide (1) is patterned into an inner core layer (3). The thinner outer waveguide (2) is patterned into an outer core layer (4). The inner and outer waveguides are separated by a gap (5) being less than 500 nm. The structure forms an adiabatic coupler. In the method, the first (inner) waveguide (1) is patterned into the thicker inner core layer (3) by etching trenches (8). A thinner outer silicon layer (4) is attached on top of the inner-core layer (3) and the first waveguide (1) to form an outer core layer (4). The second (outer) waveguide (2) is patterned into the outer core layer (4).
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Method and system for waveguide mode filters
A method and system for waveguide mode filters are disclosed and may include processing optical signals of a fundamental mode and higher-order modes by filtering the higher-order modes in rib waveguides in a photonic chip. The higher-order modes may be filtered utilizing doped regions and / or patterns in one or more slab sections in the rib waveguides. The patterns may be periodic or aperiodic along the rib waveguides. The higher-order modes may be filtered utilizing varying widths of slab sections, or doped, patterned, and / or salicided ridges on the slab sections in the rib waveguides. The higher-order modes may be attenuated by scattering and / or absorbing the modes. The chip may comprise a CMOS photonic chip.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for dual tapering an optical waveguide
An apparatus and method for reducing a mode size of an optical beam with a dual taper waveguide device. In one embodiment, an apparatus according to embodiments of the present invention includes a buried tapered waveguide disposed in a semiconductor layer. The apparatus further includes a tapered rib waveguide disposed in the semiconductor layer proximate to the buried tapered waveguide. The tapered rib waveguide includes a rib portion adjoining a slab portion. The slab portion of the rib waveguide adjoins the buried tapered waveguide. An optical beam is directed into a larger end of the buried tapered waveguide and the tapered rib waveguide. The buried tapered waveguide is tapered to guide the optical beam therethrough into the slab portion of the rib waveguide.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Structure comprising an adiabatic coupler for adiabatic coupling of light between two optical waveguides and method for manufacturing such a structure
InactiveUS7469084B2Efficient couplingEasy to optimizeCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringWaveguide
A structure comprises an inner strip waveguide (1) and an outer rib waveguide (2) on a common substrate. The thicker inner waveguide (1) is patterned into an inner core layer (3). The thinner outer waveguide (2) is patterned into an outer core layer (4). The inner and outer waveguides are separated by a gap (5) being less than 500 nm. The structure forms an adiabatic coupler. In the method, the first (inner) waveguide (1) is patterned into the thicker inner core layer (3) by etching trenches (8). A thinner outer silicon layer (4) is attached on top of the inner-core layer (3) and the first waveguide (1) to form an outer core layer (4). The second (outer) waveguide (2) is patterned into the outer core layer (4).
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Optical waveguide element and optical modulator
ActiveUS9448425B2Reduce light lossHigh extinction ratioOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsElectrical conductorWaveguide
An optical waveguide element includes: a rib waveguide and a pair of slab portions including a first slab portion and a second slab portion connected to both sides of the rib portion so as to sandwich the rib portion. The rib portion has a cross-sectional dimension which allows the propagation of a fundamental mode and a higher order mode in a predetermined single polarization state, and has a first P-type semiconductor and a first N-type semiconductor forming a PN junction, the first slab portion has a second P-type semiconductor and a P-type conductor connected to each other, the second P-type semiconductor is connected to the first P-type semiconductor of the rib portion, the second slab portion has a second N-type semiconductor and an N-type conductor connected to each other, and the second N-type semiconductor is connected to the first N-type semiconductor of the rib portion.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Guided wave spatial filter
InactiveUS7174080B2Avoid couplingAvoid radiationCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideFiltrationRadiation mode
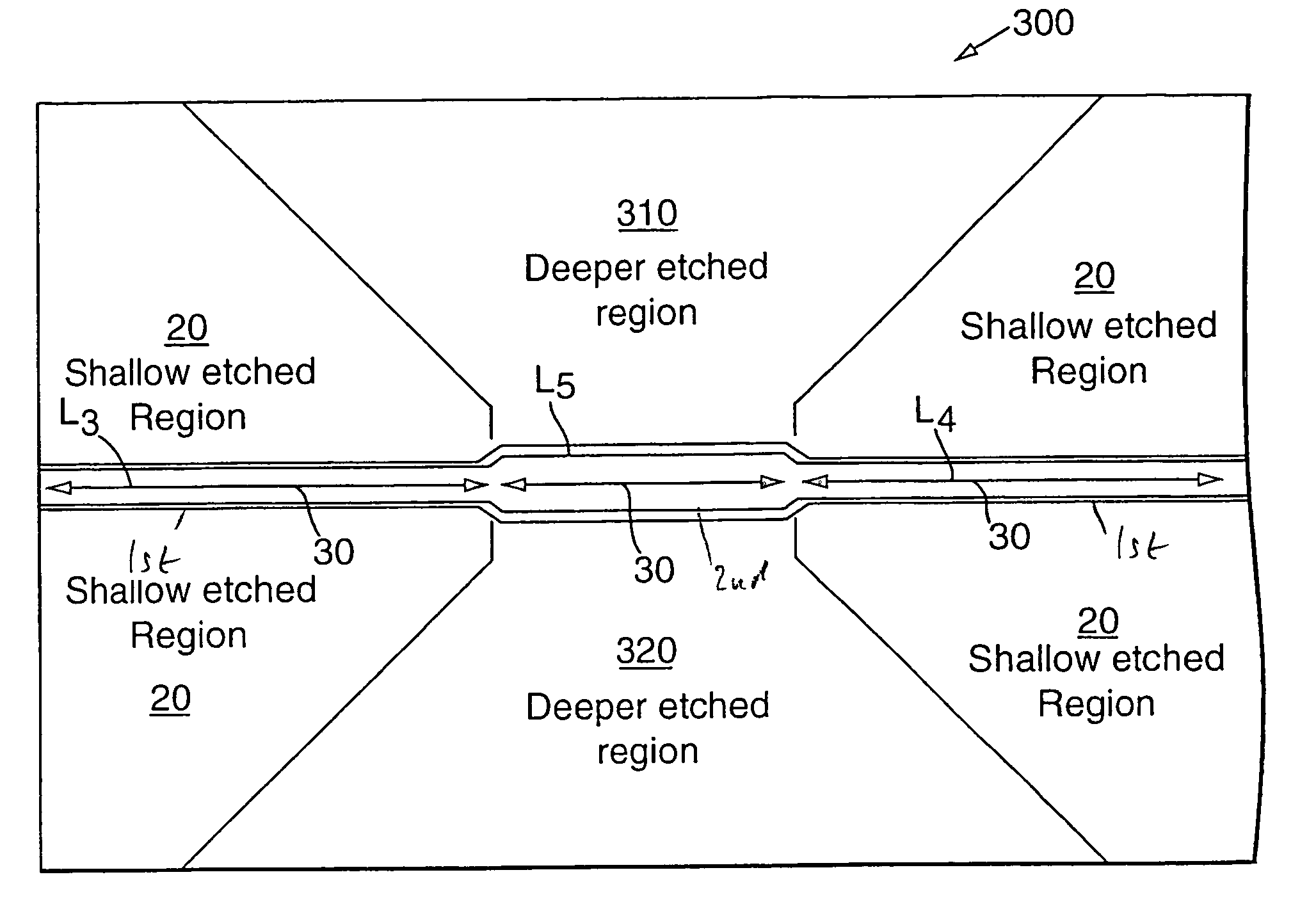
The invention concerns a guided wave spatial filter (300) for receiving input radiation and outputting corresponding filtered output radiation, the filter comprising first and second waveguide sections (30, L3, L5) connected in series, the sections: (a) mutually matched for transmitting fundamental mode radiation components present in the input radiation therethrough to provide the output radiation; and (b) mutually mismatched for hindering higher-order mode radiation components present in the input radiation from propagating therethrough and contributing to the output radiation. The spatial filter (300) is implemented using rib waveguides (30) for the sections with associated relatively deeply and relatively shallowly etched structures (20, 310, 320) for imparting to the sections their radiation mode filtration characteristics. The spatial filter according to the invention can be incorporated into optical splitters and optical modulators to enhance their performance and desensitise them to higher-order mode radiation injected thereinto.
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD
Silicon-based electro-optic device
ActiveUS8532440B2Efficient connectionReduced propagation lossOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsZeroth orderMetal electrodes
In an electro-optic device, a stack structure including a first silicon layer of a first conductivity type and a second silicon layer of a second conductivity type has a rib waveguide shape so as to form an optical confinement area, and a slab portion of a rib waveguide includes an area to which a metal electrode is connected. The slab portion in the area to which the metal electrode is connected is thicker than a surrounding slab portion. The area to which the metal electrode is connected is set so that a range of a distance from the rib waveguide to the area to which the metal electrode is connected is such that when the distance is changed, an effective refractive index of the rib waveguide in a zeroth-order mode does not change.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FOUNDRY PTE LTD +1
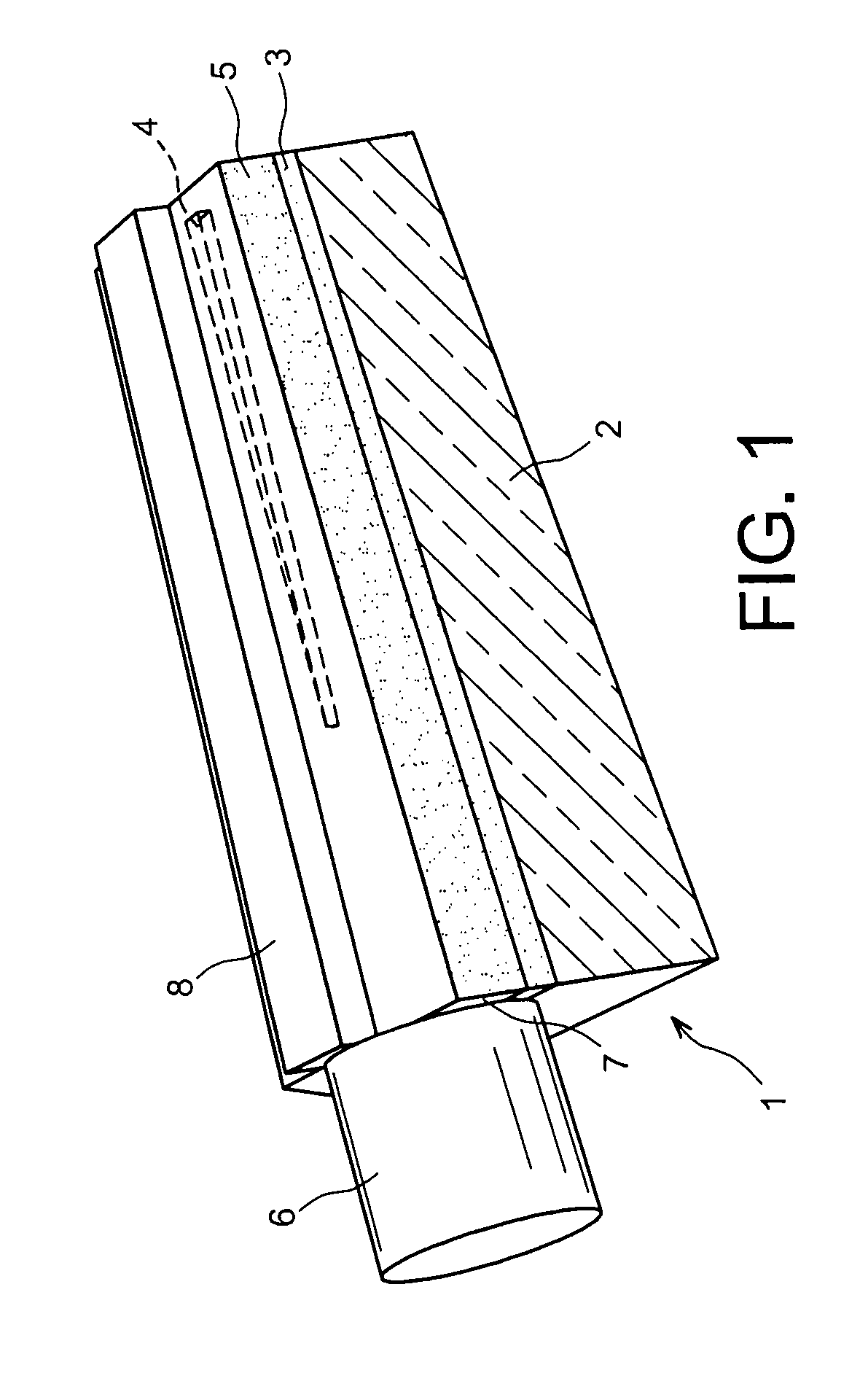
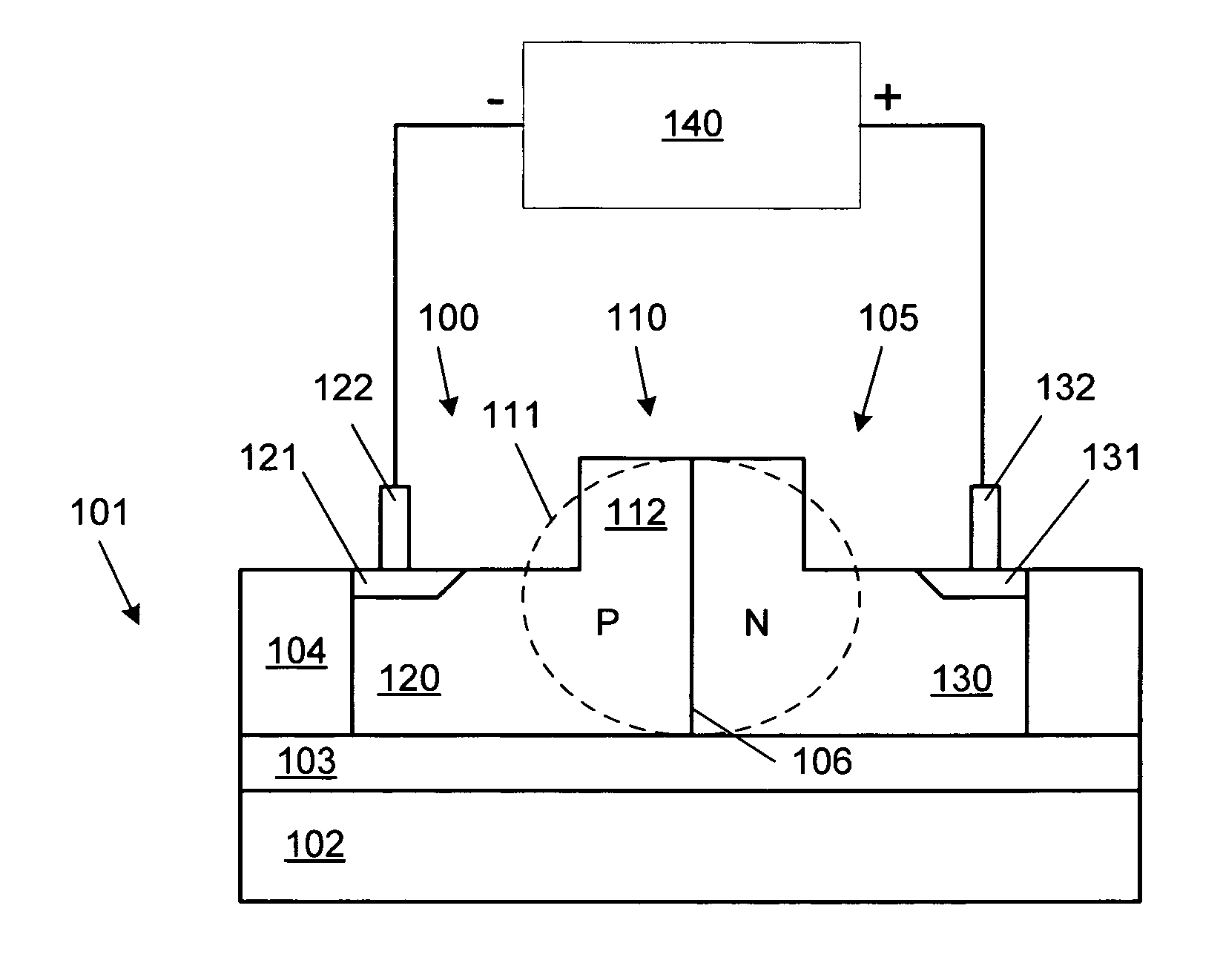
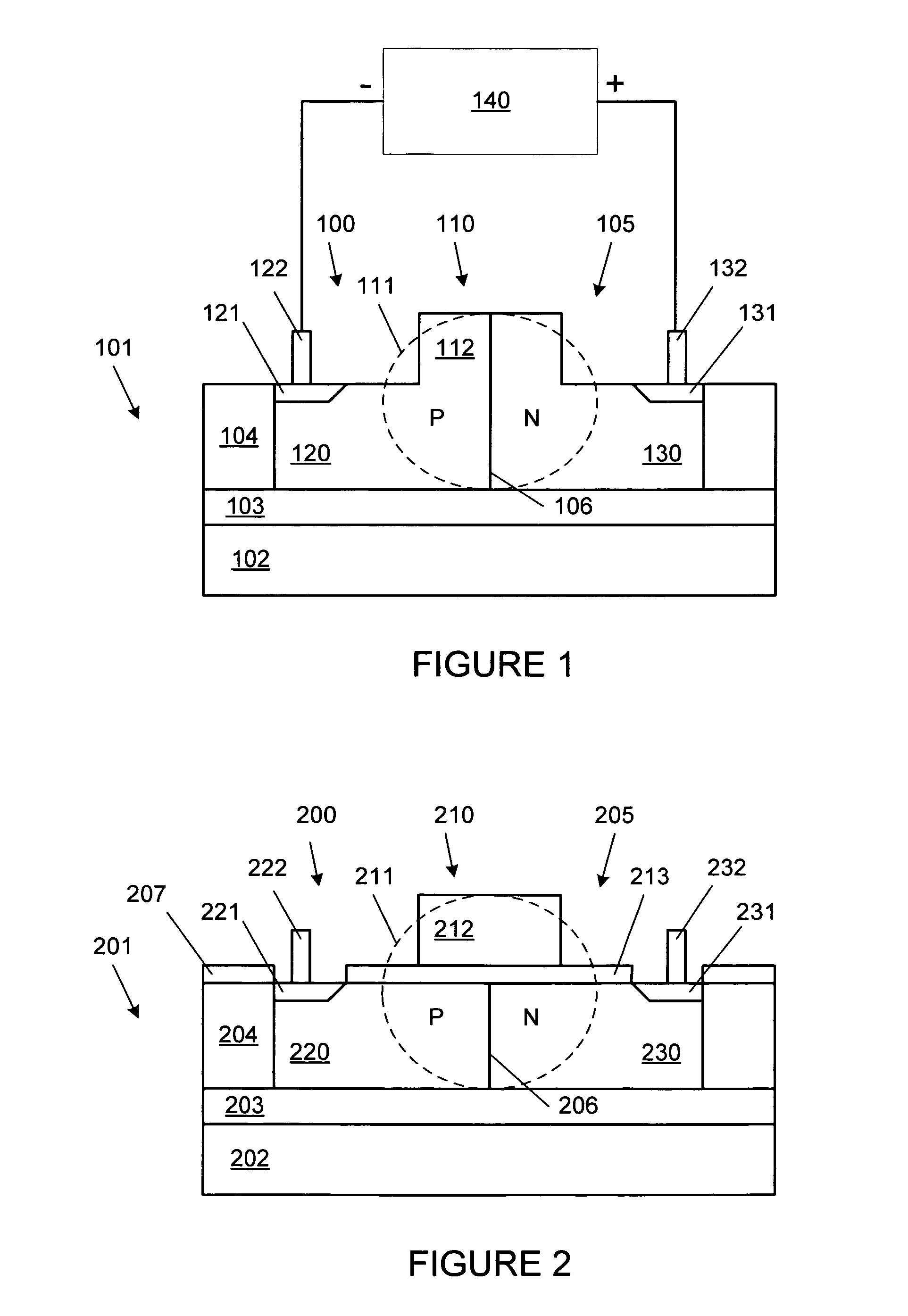
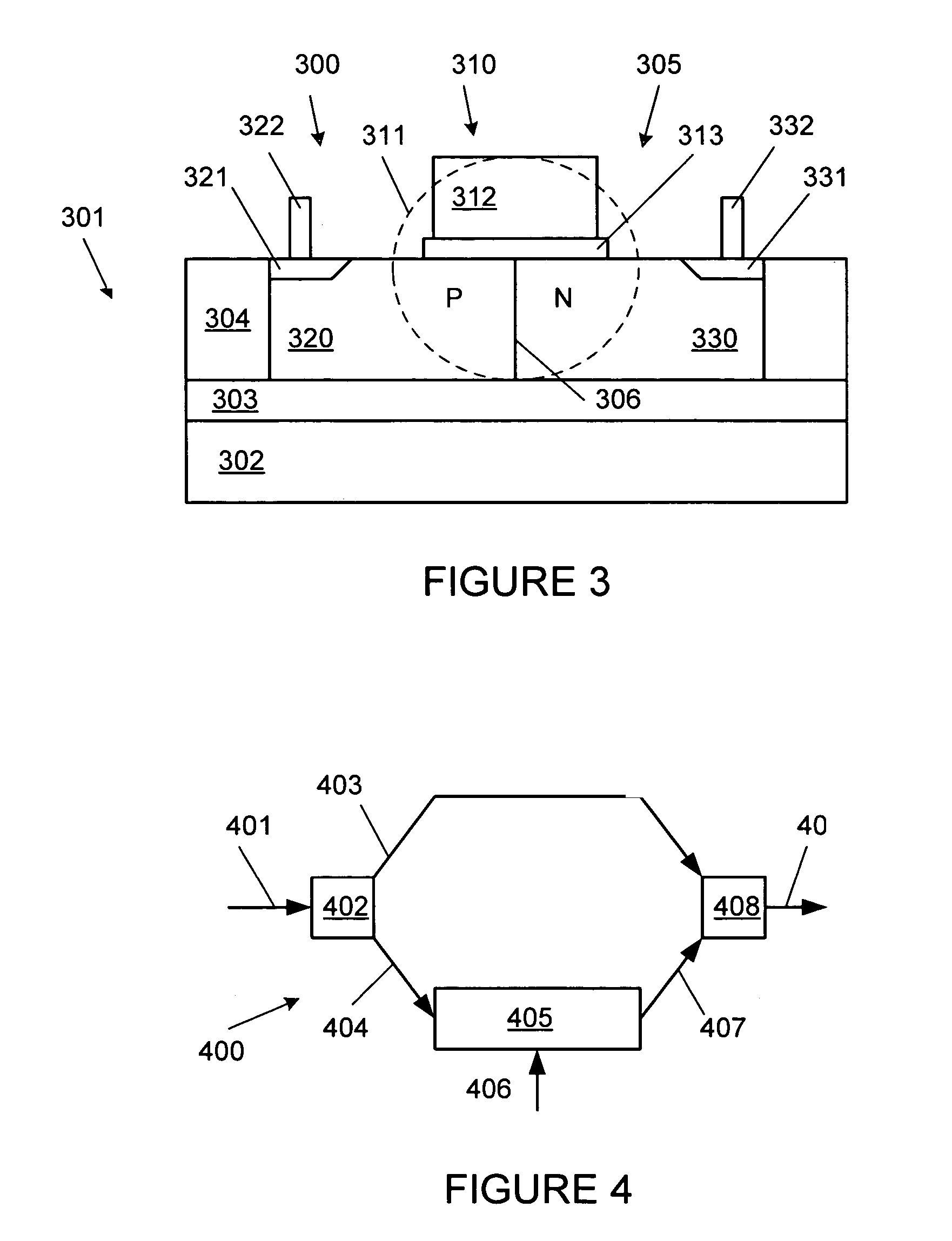
Method And System For A Silicon-Based Optical Phase Modulator With High Modal Overlap
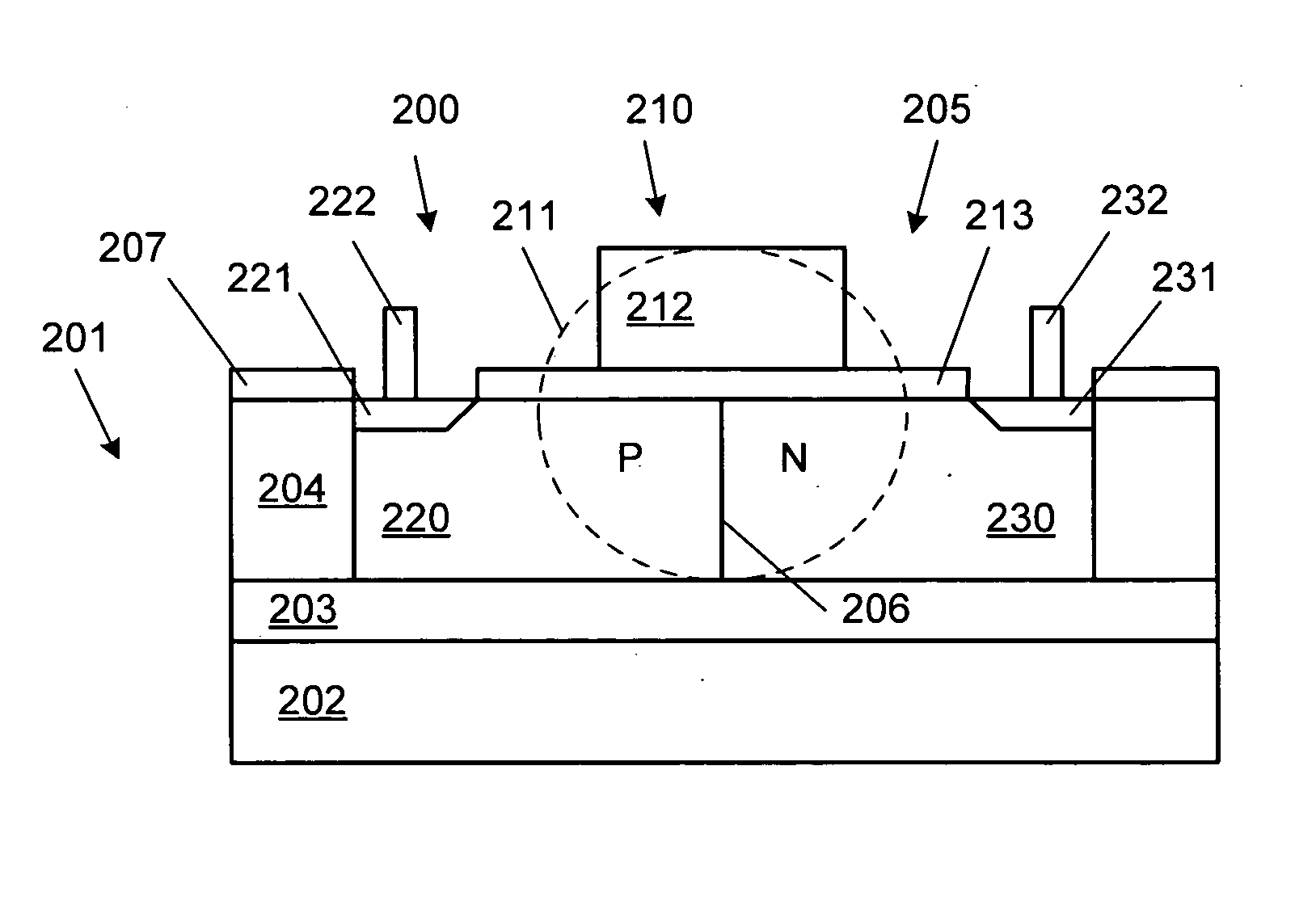
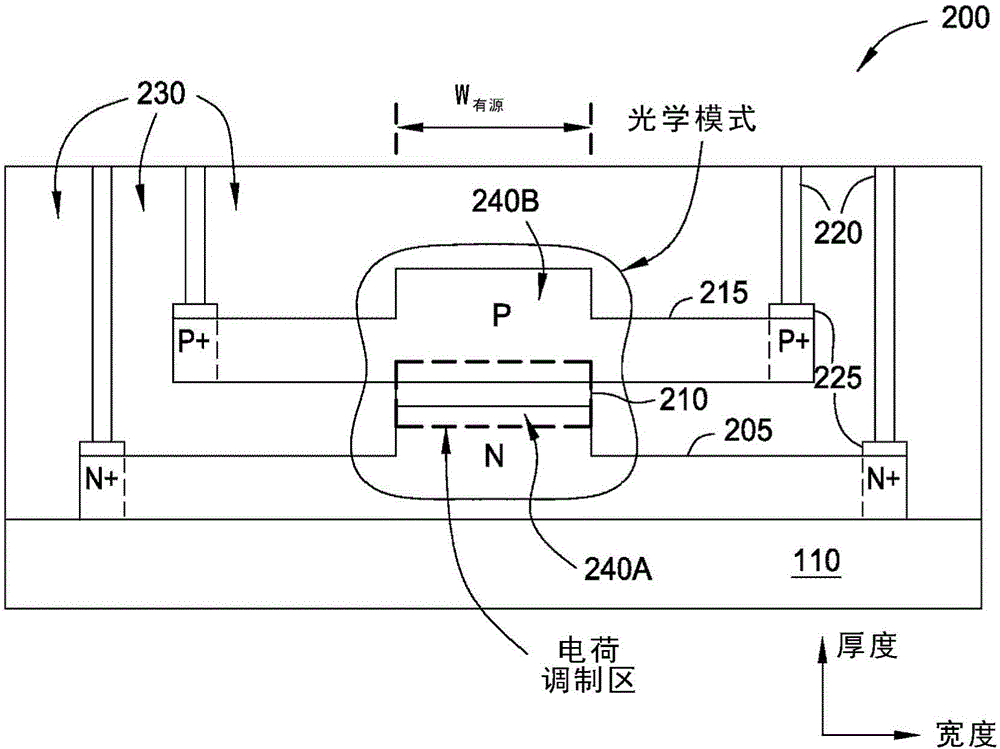
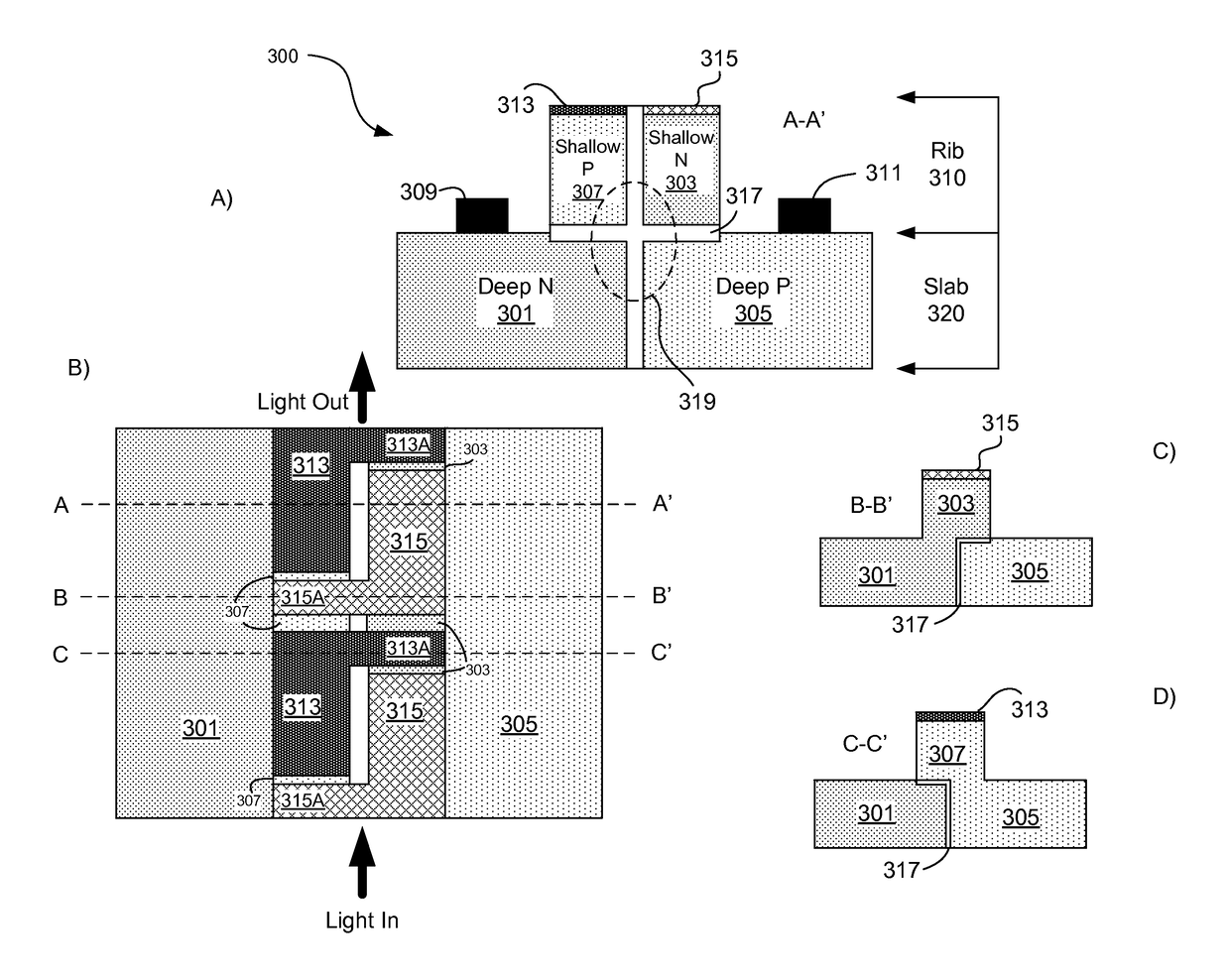
Methods and systems for a silicon-based optical phase modulator with high modal overlap are disclosed and may include, in an optical modulator having a rib waveguide in which a cross-shaped depletion region separates four alternately doped sections: receiving an optical signal at one end of the optical modulator, modulating the received optical signal by applying a modulating voltage, and communicating a modulated optical signal out of an opposite end of the modulator. The modulator may be in a silicon photonically-enabled integrated circuit which may be in a complementary-metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) die. An optical mode may be centered on the cross-shaped depletion region. The four alternately doped sections may include: a shallow depth p-region, a shallow depth n-region, a deep p-region, and a deep n-region. The shallow depth p-region may be electrically coupled to the deep p-region periodically along the length of the modulator.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
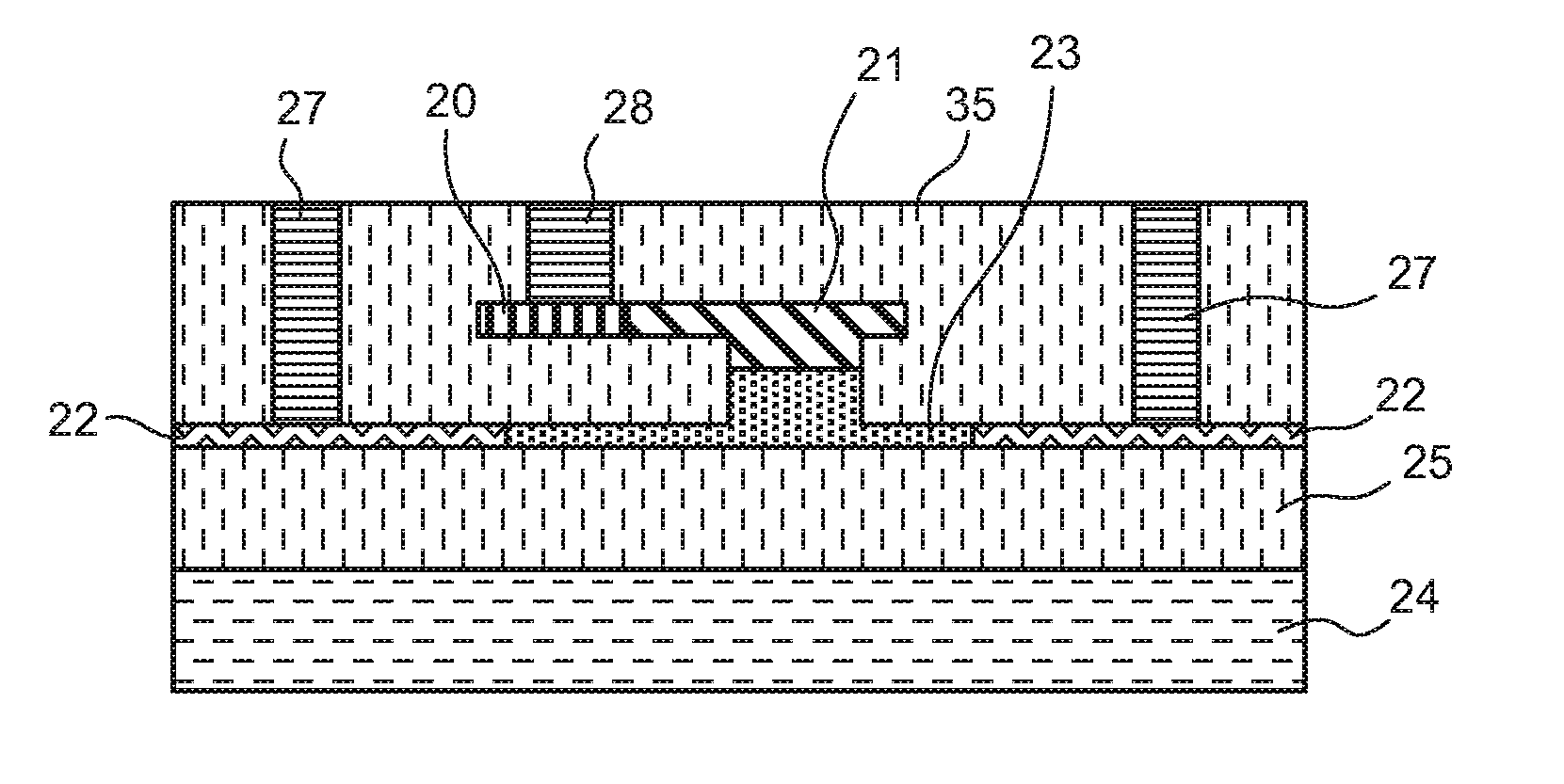
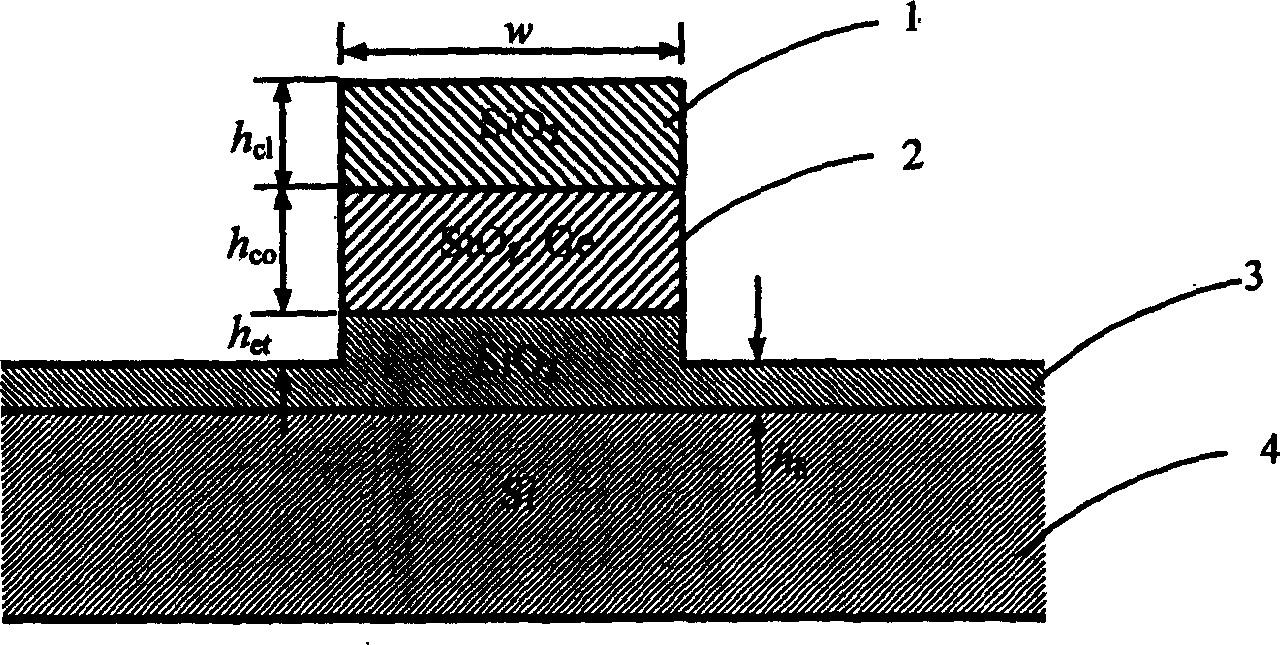
Deep-etched SiO2 ridge waveguide and its preparing process
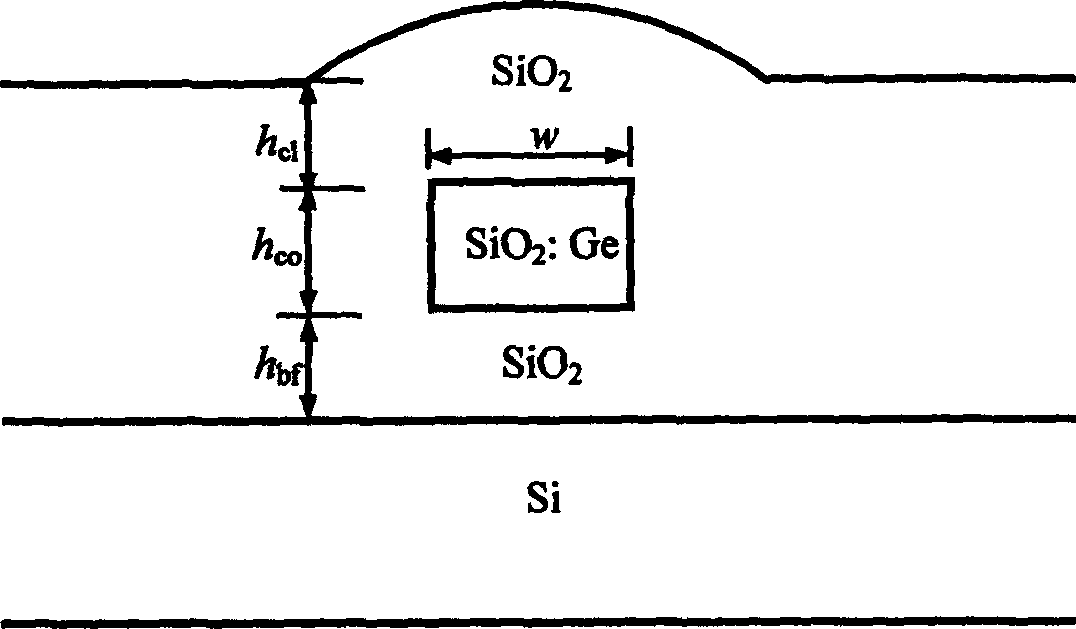
InactiveCN1743880AStrengthen restrictionsSmall bending radiusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWaveguideSilicon dioxide
This invention discloses deep etched silicon dioxide rib waveguides and preparation thereof, which contains in turn depositing lower cladding, core cladding and upper cladding on substrate by silicon dioxide film deposition technology, etching penetrating upper cladding and core cladding by deep etching technology, etching part or all lower cladding, In said invention, the light field limitation is increased with reduced curve semidiameter and raised light integrity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
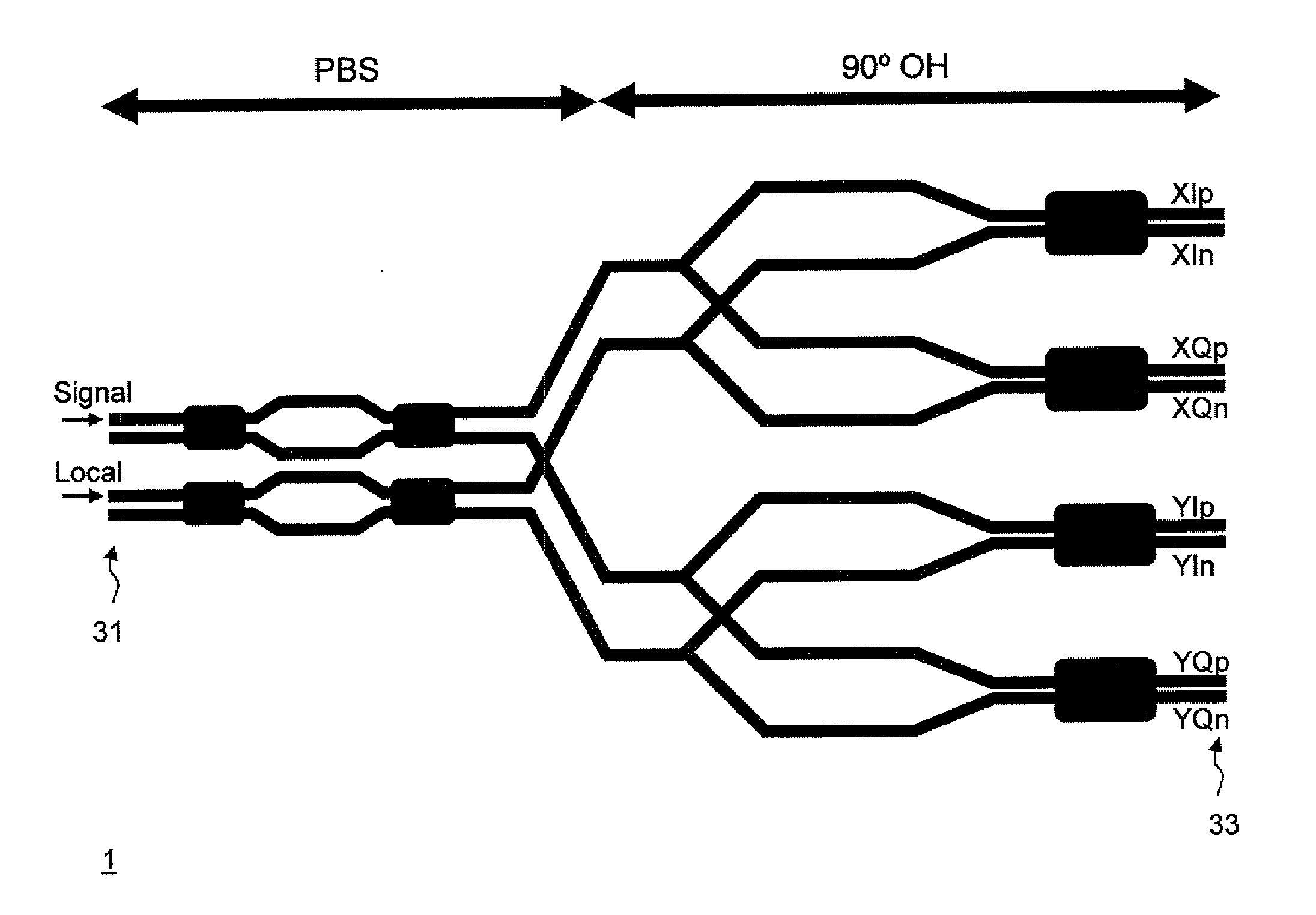
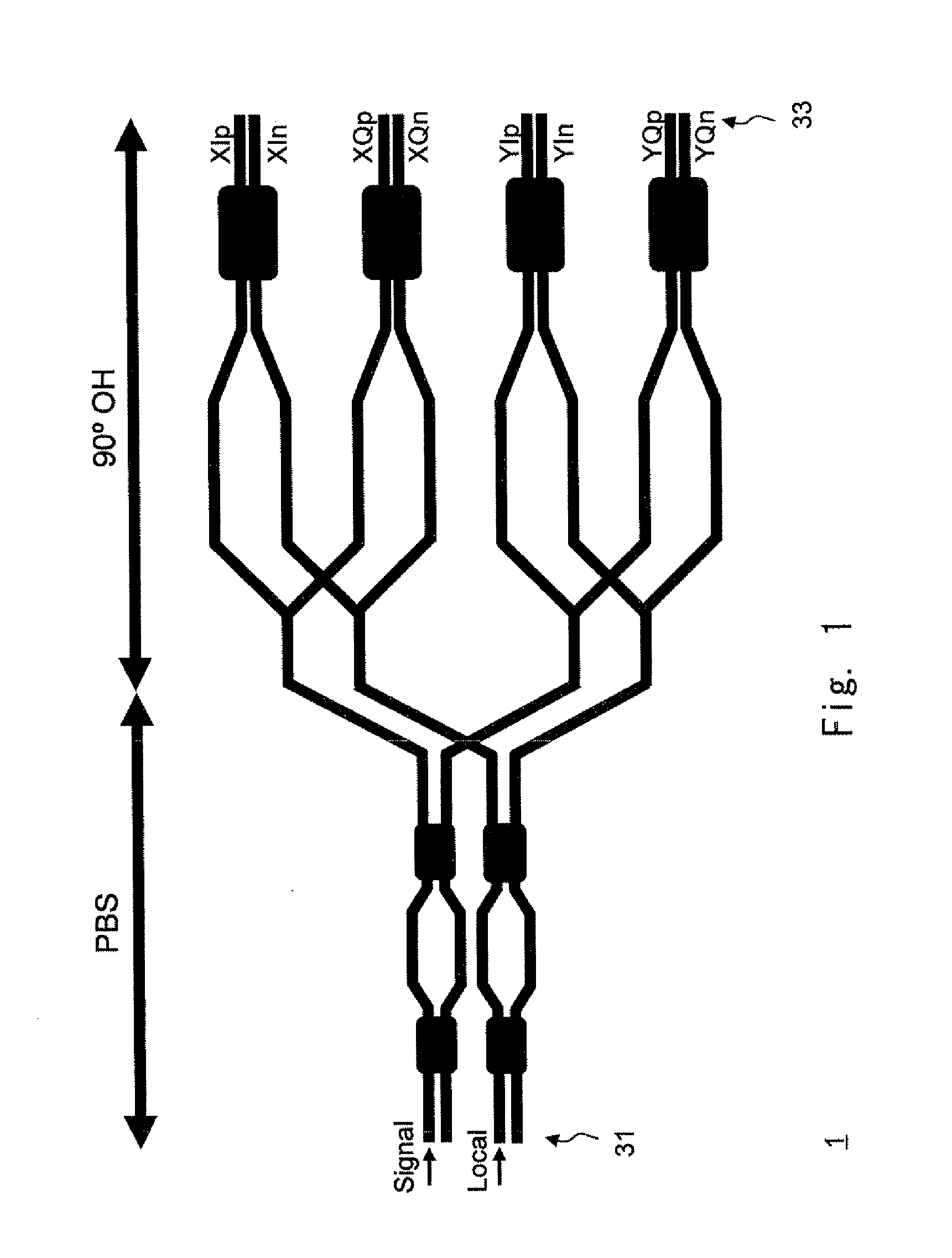
Polarization beam splitter and optical device
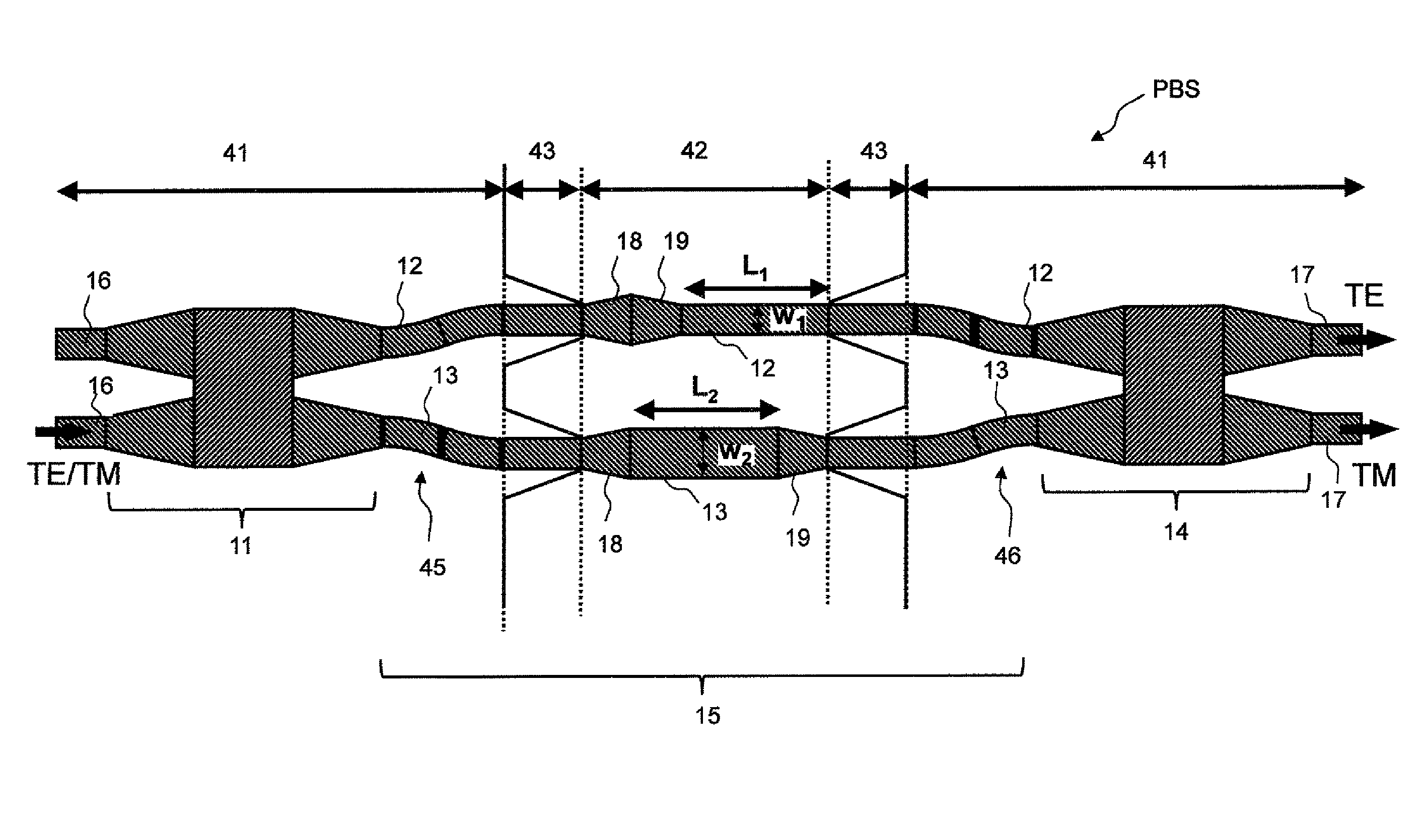
ActiveUS20150378098A1Improve productivityOptical measurementsUsing optical meansProduction rateMultiplexing
Provided are a polarization beam splitter and an optical device with high productivity. A polarization beam splitter (PBS) according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes: a demultiplexer (11) that is formed of a rib waveguide (50) and demultiplexes input light into first input light and second input light; a multiplexer (14) that is formed of the rib waveguide (50) and multiplexes the first input light and the second input light that are obtained by demultiplexing the input light by the demultiplexer (11); a first arm waveguide (12) that is formed of a channel waveguide (51) and guides the first input light to the multiplexer (11); and a second arm waveguide (13) that is formed of the channel waveguide (51), generates a phase difference in the first input light propagating through the first arm waveguide, and guides the second input light to the multiplexer (14).
Owner:NEC CORP
Electro-optical modulator using ribbed waveguides
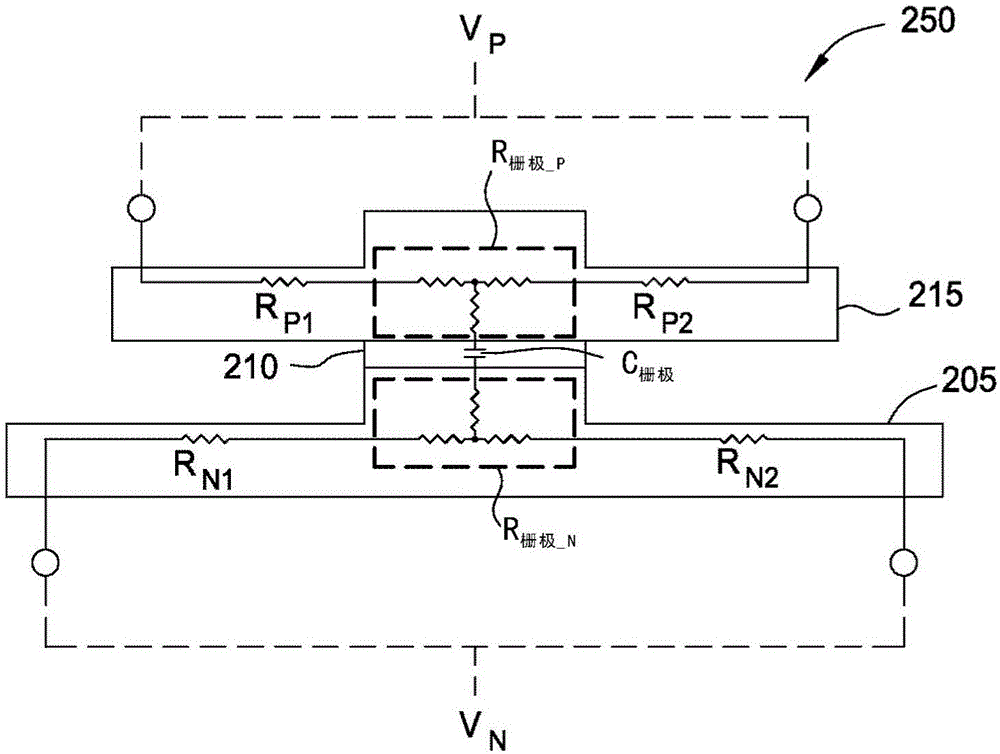
The invention discloses an electro-optical modulator using ribbed waveguides. An optical modulator may include a lower waveguide, an upper waveguide, and a dielectric layer disposed therebetween. When a voltage potential is created between the lower and upper waveguides, these layers form a silicon-insulator-silicon capacitor (also referred to as SISCAP) guide that provides efficient, high-speed optical modulation of an optical signal passing through the modulator. In one embodiment, at least one of the waveguides includes a respective ridge portion aligned at a charge modulation region which may aid in confining the optical mode laterally (e.g., in the width direction) in the optical modulator. In another embodiment, ridge portions may be formed on both the lower and the upper waveguides. These ridge portions may be aligned in a vertical direction (e.g., a thickness direction) so that ridges overlap which may further improve optical efficiency by centering an optical mode in the charge modulation region.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for a silicon-based optical phase modulator with high modal overlap
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Polarization beam splitter and optical device
ActiveUS9459406B2Improve productivityOptical measurementsOptical waveguide light guideProduction rateMultiplexing
Provided are a polarization beam splitter and an optical device with high productivity. A polarization beam splitter (PBS) according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes: a demultiplexer (11) that is formed of a rib waveguide (50) and demultiplexes input light into first input light and second input light; a multiplexer (14) that is formed of the rib waveguide (50) and multiplexes the first input light and the second input light that are obtained by demultiplexing the input light by the demultiplexer (11); a first arm waveguide (12) that is formed of a channel waveguide (51) and guides the first input light to the multiplexer (11); and a second arm waveguide (13) that is formed of the channel waveguide (51), generates a phase difference in the first input light propagating through the first arm waveguide, and guides the second input light to the multiplexer (14).
Owner:NEC CORP
Waveguide optoelectronic device
PendingCN110325900AReduce capacitanceHigh bandwidthOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsSemiconductor materialsEngineering physics
A waveguide optoelectronic device comprising a rib waveguide region, and method of manufacturing a rib waveguide region, the rib waveguide region having: a base of a first material, and a ridge extending from the base, at least a portion of the ridge being formed from a chosen semiconductor material which is different from the material of the base wherein the silicon base includes a first slab region at a first side of the ridge and a second slab region at a second side of the ridge; and wherein: a first doped region extends along: the first slab region and along a first sidewall of the ridge,the first sidewall contacting the first slab region; and a second doped region extends along: the second slab region and along a second sidewall of ridge, the second sidewall contacting the second slab region.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS INC
Optical waveguide device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9880404B2Reduce light lossReduce the driving voltageOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsWaveguideRib waveguides
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FOUNDRY PTE LTD
Polarization rotator
The disclosure discloses a polarization rotator and a polarization stabilizer. The polarization rotator includes a rib waveguide. The rib waveguide includes: a slab portion; and a ridge portion, whichis disposed along a surface of the slab portion. The slab portion has a first slab region whose width, as measured in a direction perpendicular to a guiding direction of the waveguide, increases froma first slab width to a second slab width along a first length, and the ridge portion has a first ridge region whose width, as measured in the same direction as the slab widths, decreases from a first ridge width to a second ridge width along the same first length; such that the rotator is configured to rotate the polarization of light during its transmission through the rib waveguide.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS INC
Optoelectronic device
The invention discloses an optoelectronic device which includes a rib waveguide, the rib waveguide including a ridge portion, incorporating a temperature-sensitive optically active region. The rib waveguide further includes a slab portion, which is positioned adjacent to the ridge portion. The device further includes a heater, which is disposed on top of the slab portion. The part of the heater closest to ridge portion is at least 2 micrometres away from the ridge portion. The device may also have a heater provided in an epitaxial crystalline cladding. In other embodiments the device also includes a bottom cladding layer, and may also include various thermal insulation enhancing cavities.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com