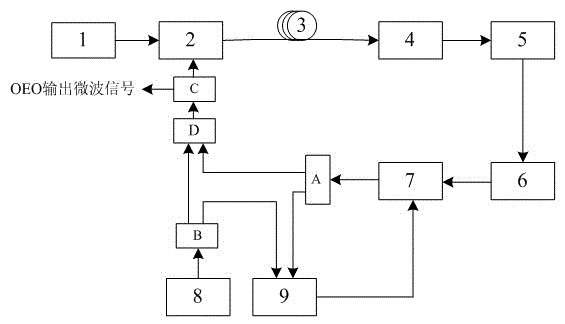
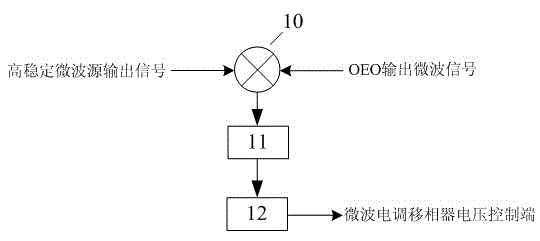
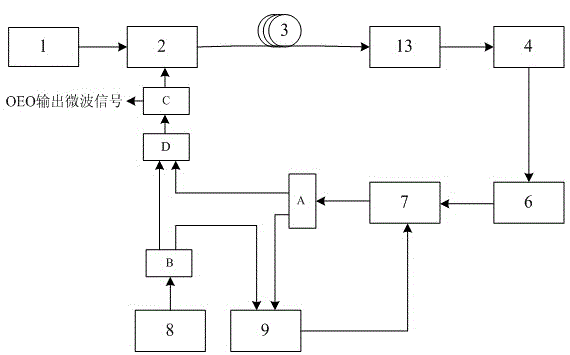
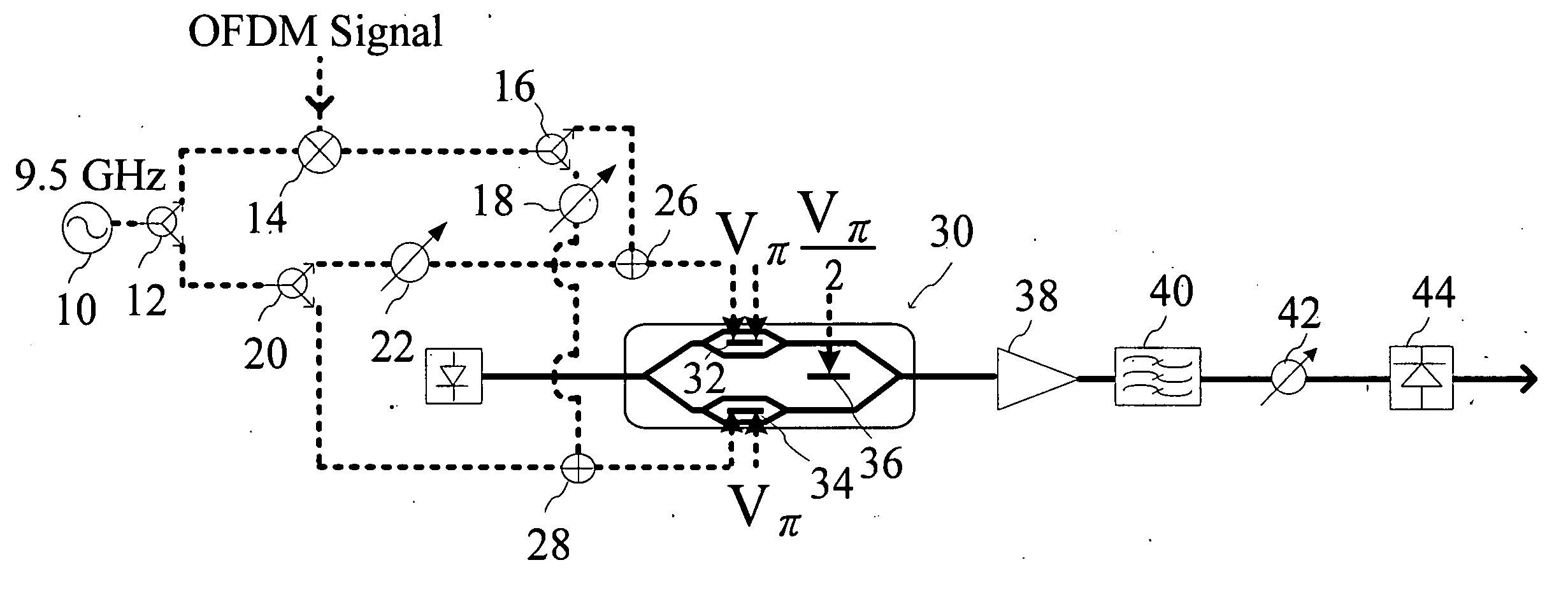
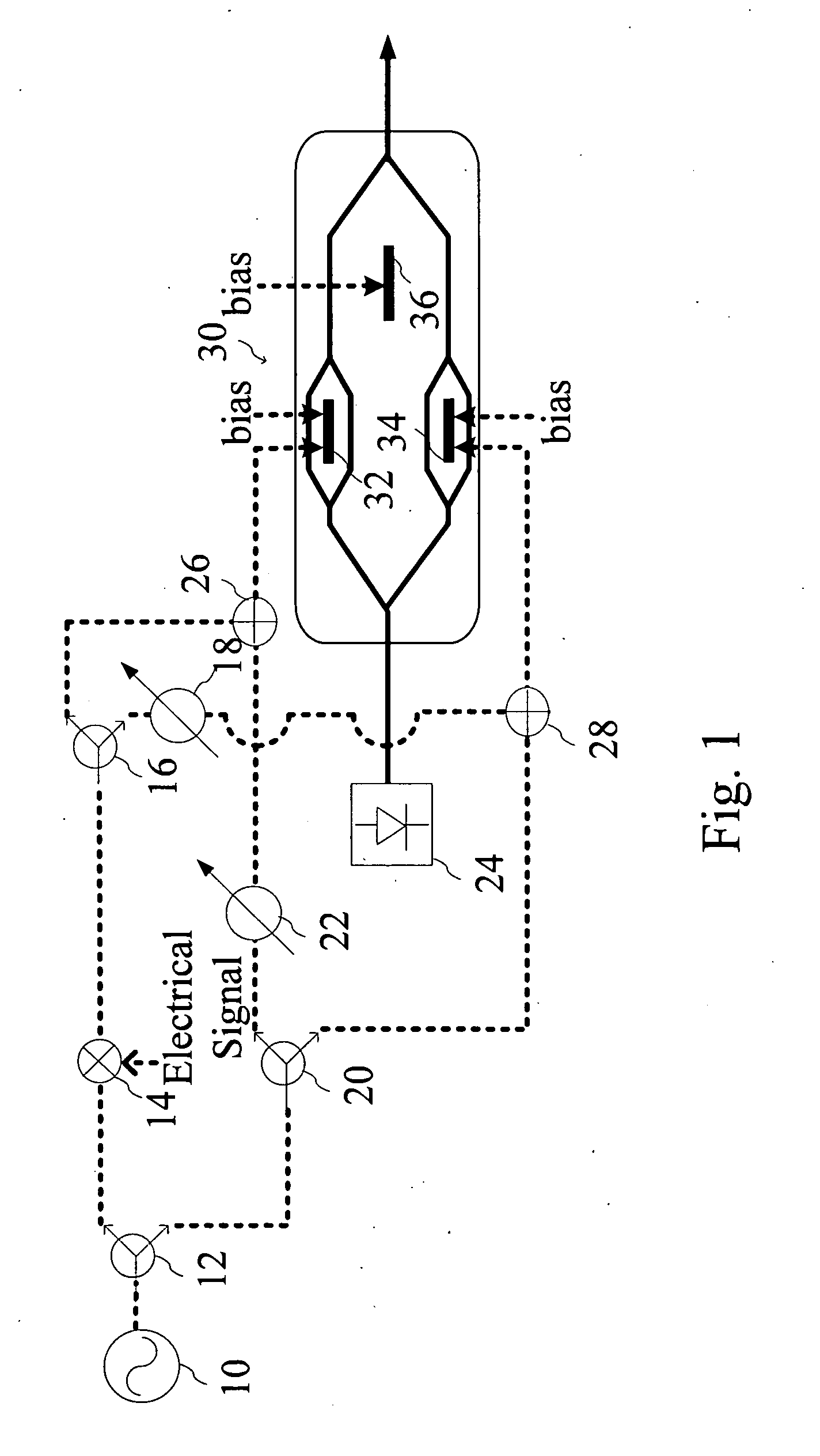
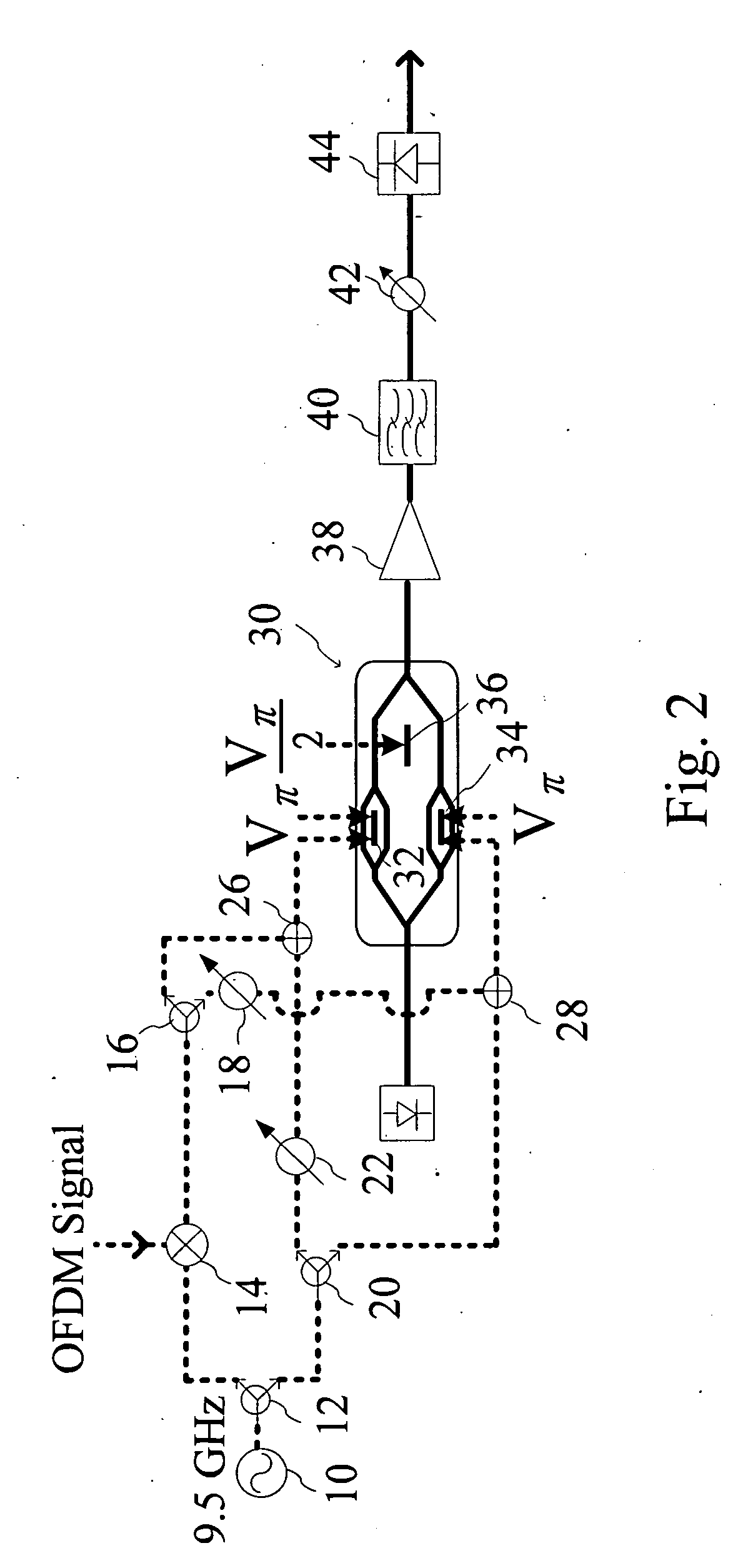
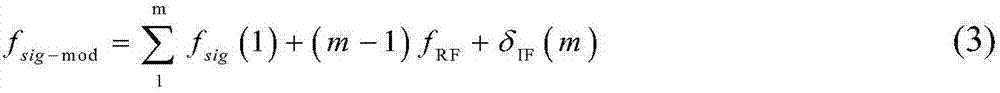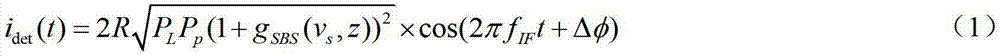Patents
Literature
1626 results about "Electro-optic modulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
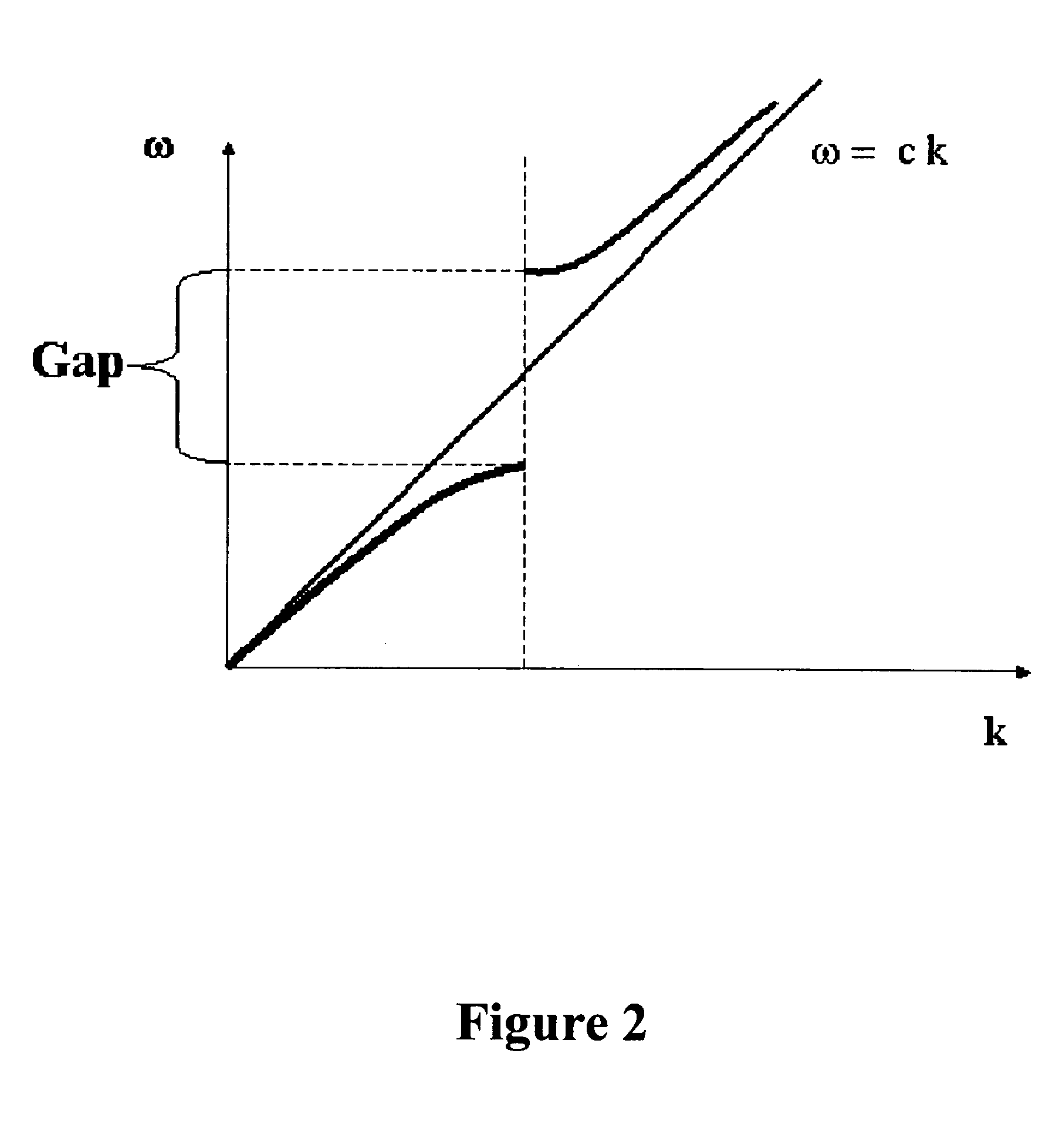
An electro-optic modulator (EOM) is an optical device in which a signal-controlled element exhibiting an electro-optic effect is used to modulate a beam of light. The modulation may be imposed on the phase, frequency, amplitude, or polarization of the beam. Modulation bandwidths extending into the gigahertz range are possible with the use of laser-controlled modulators. The electro-optic effect is the change in the refractive index of a material resulting from the application of a DC or low-frequency electric field.
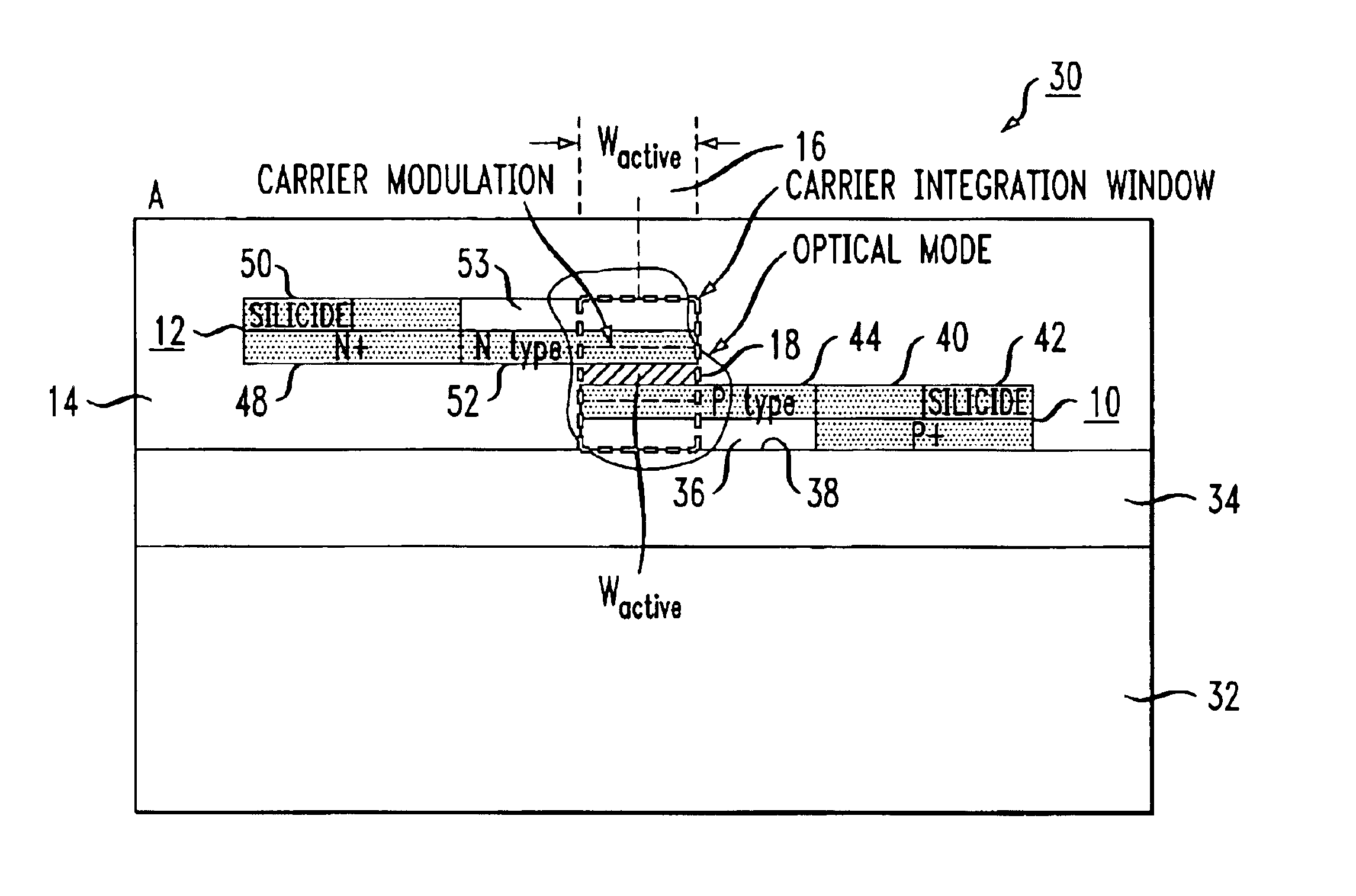
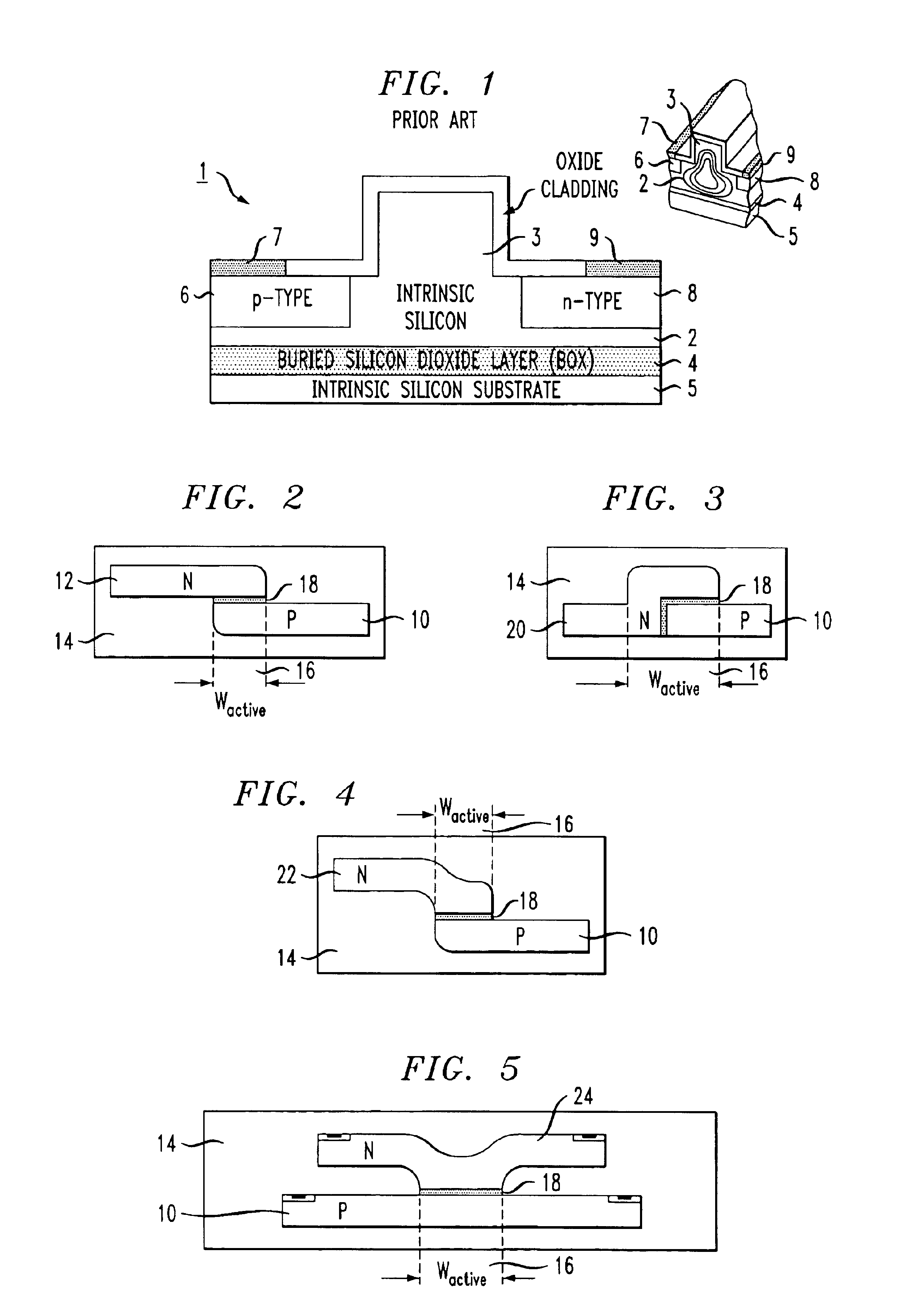
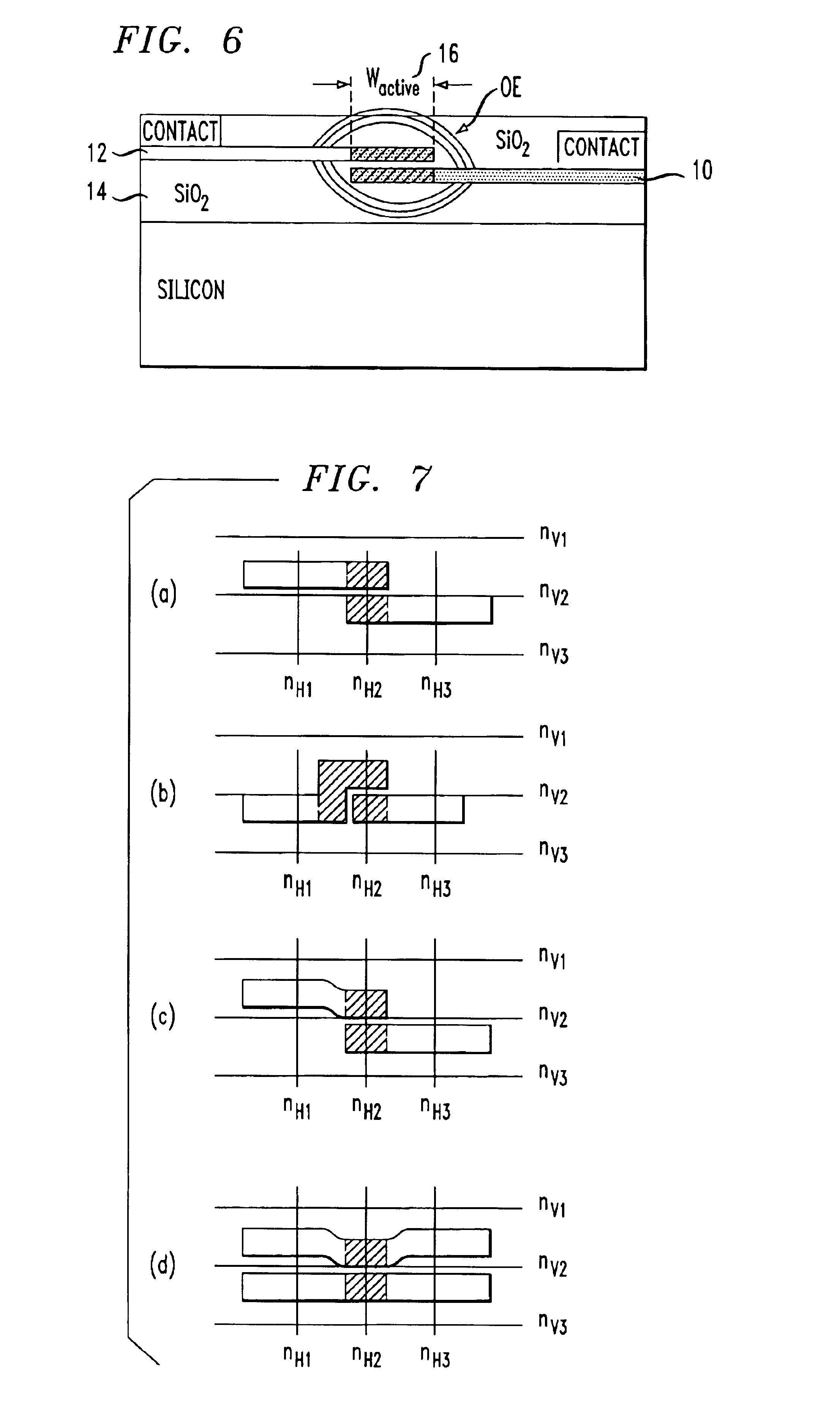
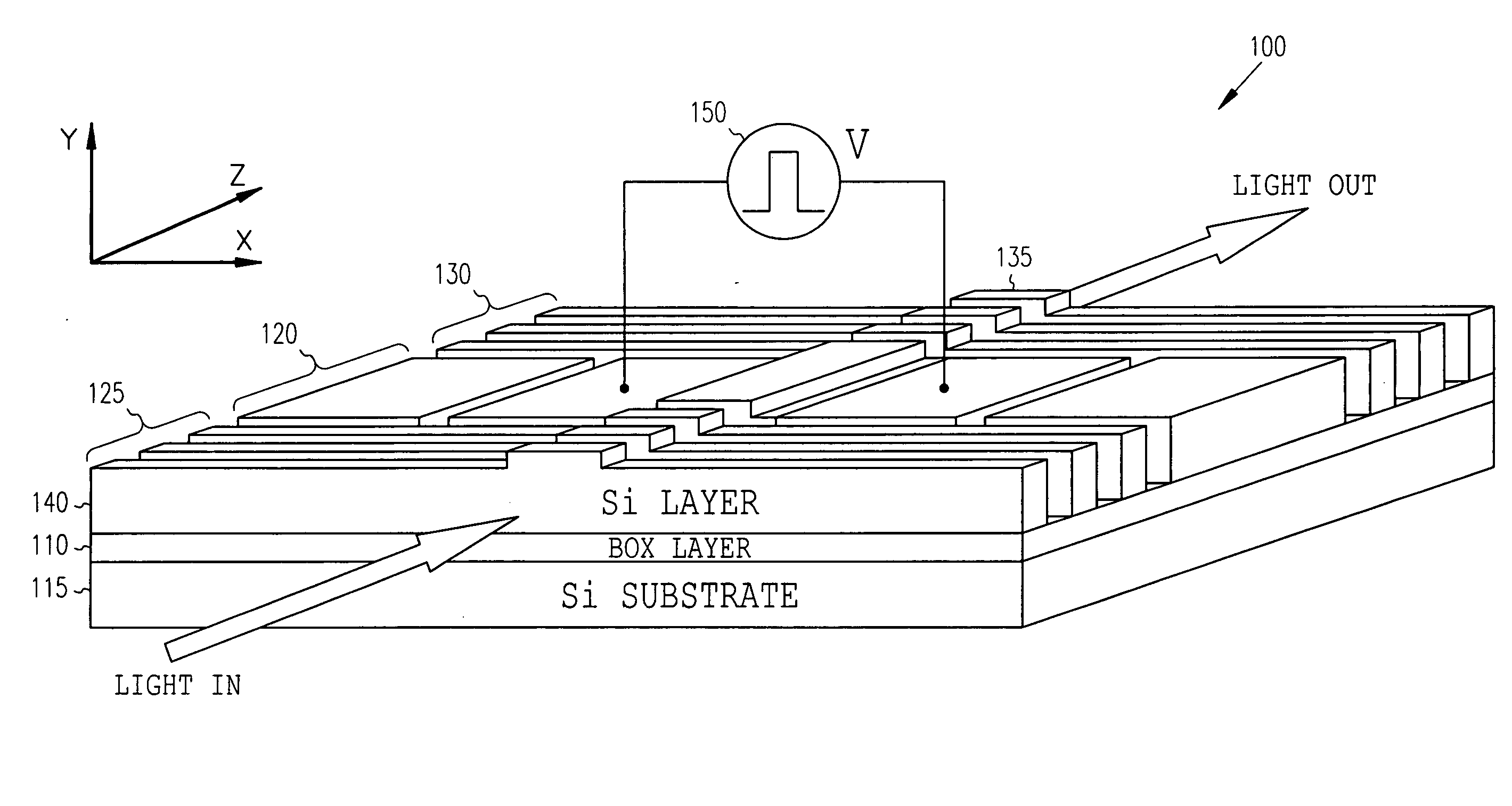
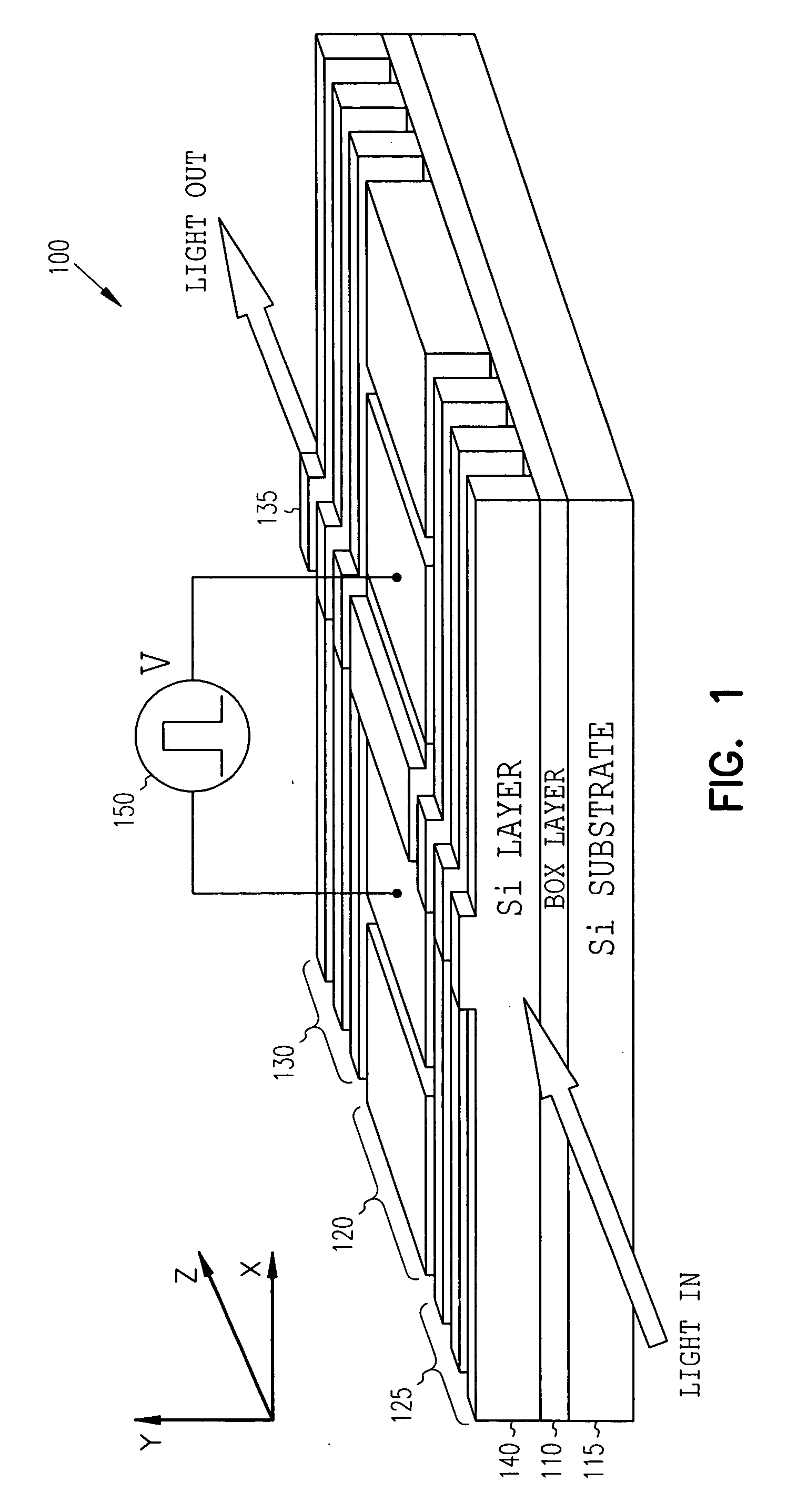
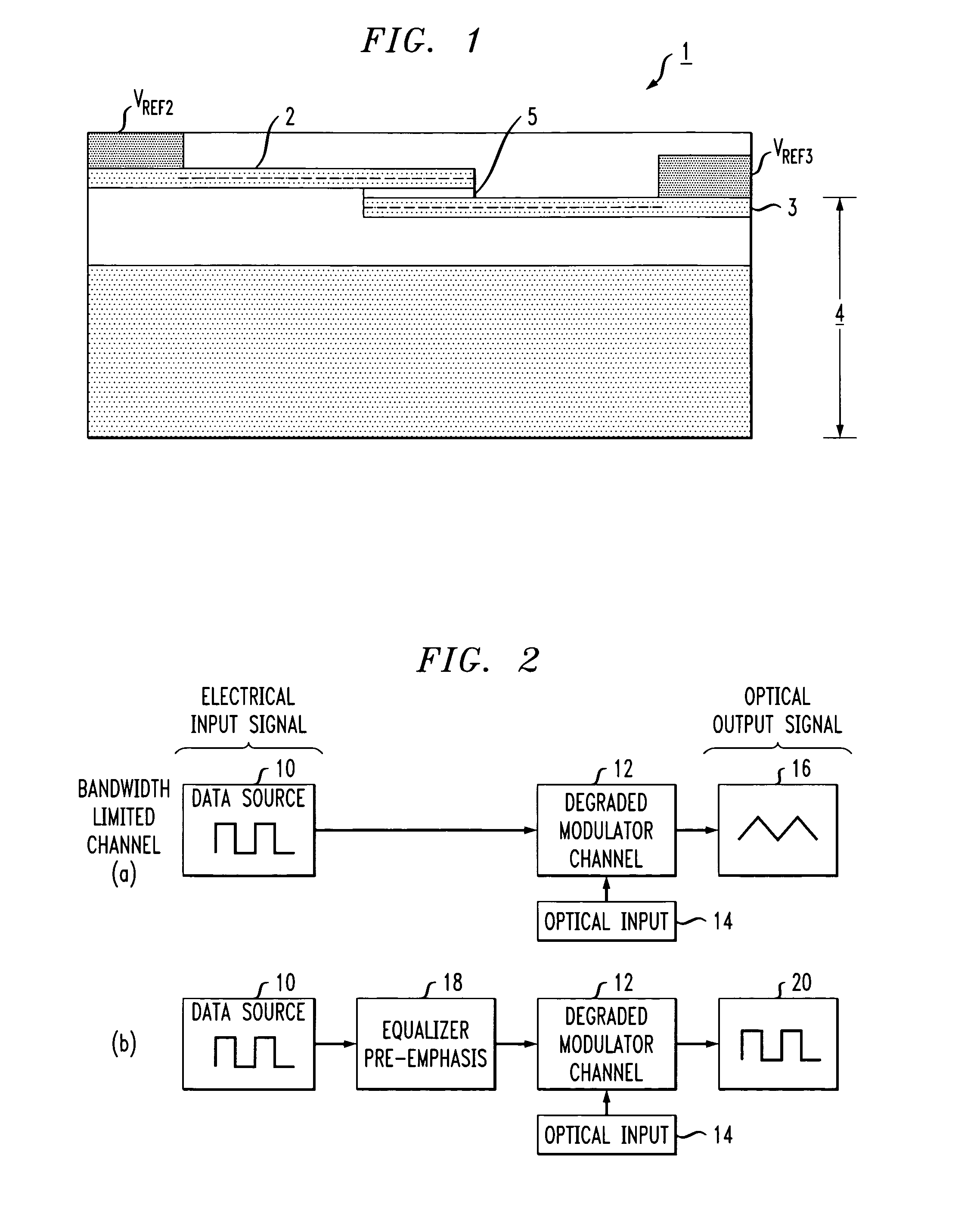
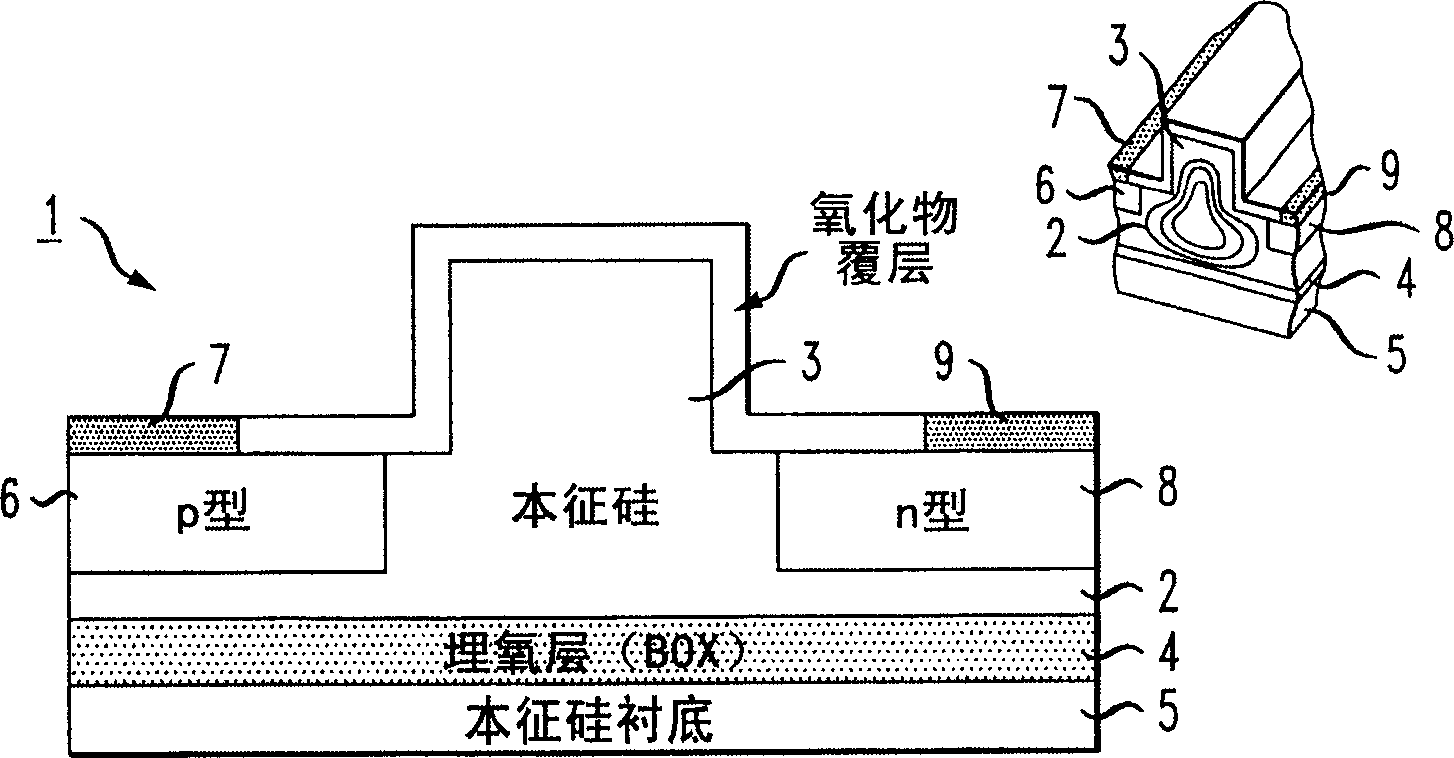
High-speed silicon-based electro-optic modulator
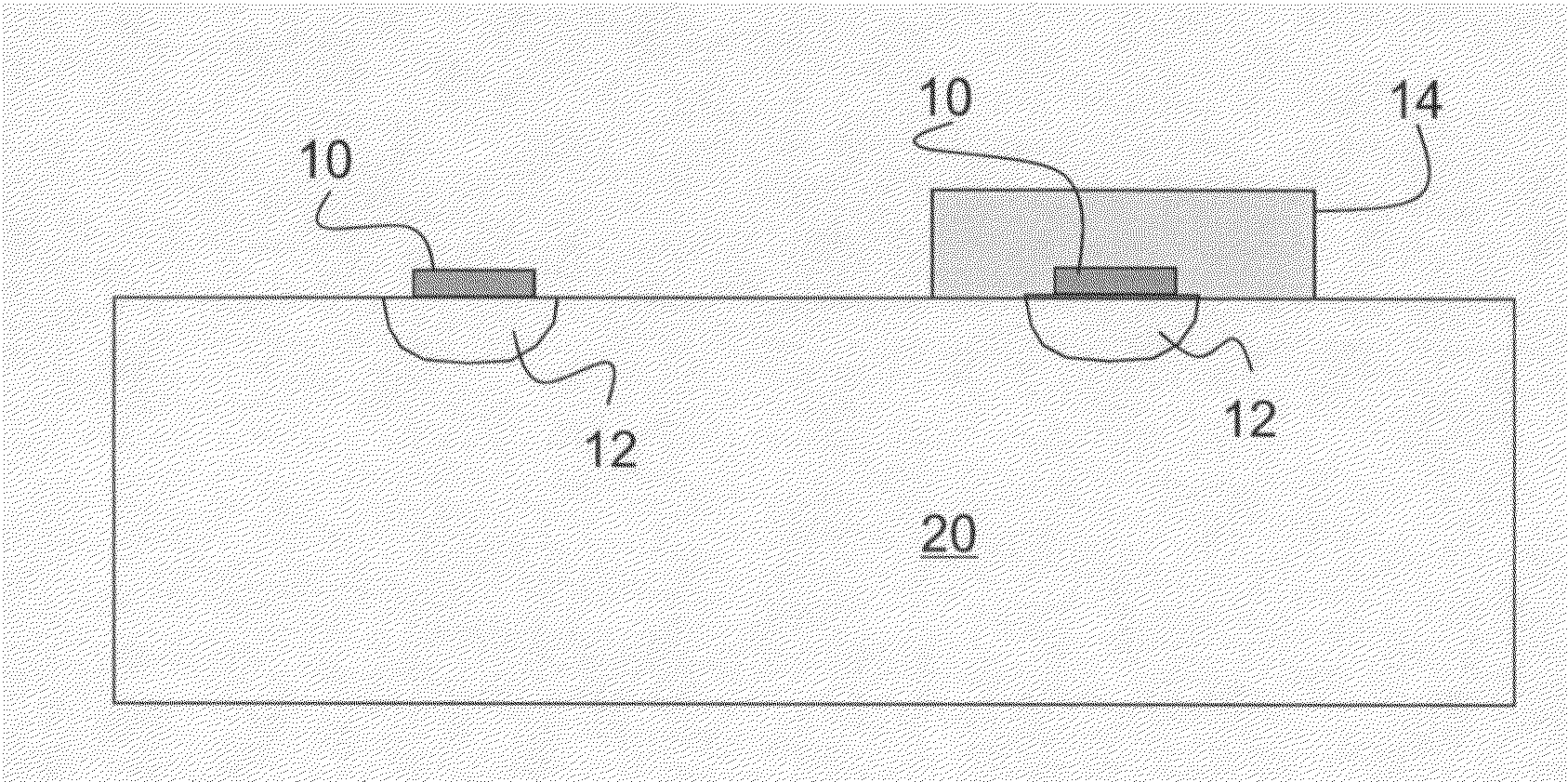
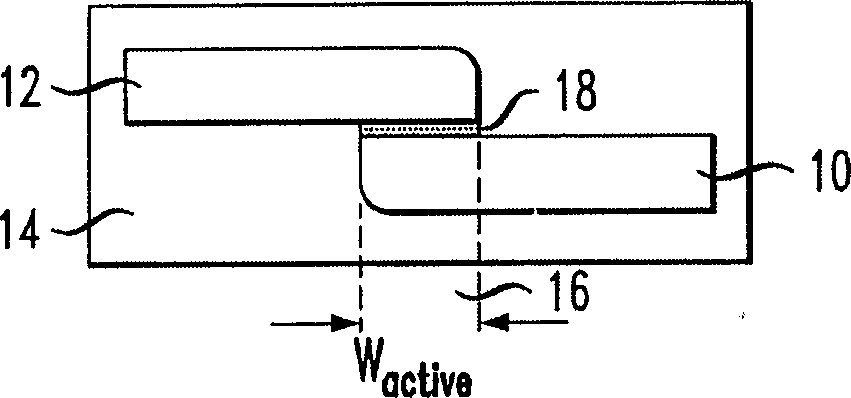
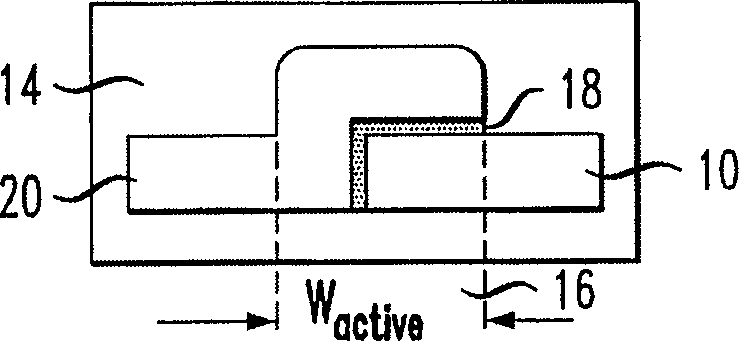
ActiveUS6845198B2Series resistance is minimizedLower optical lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideElectricitySurface layer
A silicon-based electro-optic modulator is based on forming a gate region of a first conductivity to partially overly a body region of a second conductivity type, with a relatively thin dielectric layer interposed between the contiguous portions of the gate and body regions. The modulator may be formed on an SOI platform, with the body region formed in the relatively thin silicon surface layer of the SOI structure and the gate region formed of a relatively thin silicon layer overlying the SOI structure. The doping in the gate and body regions is controlled to form lightly doped regions above and below the dielectric, thus defining the active region of the device. Advantageously, the optical electric field essentially coincides with the free carrier concentration area in this active device region. The application of a modulation signal thus causes the simultaneous accumulation, depletion or inversion of free carriers on both sides of the dielectric at the same time, resulting in high speed operation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Laser cutting of stents and other medical devices
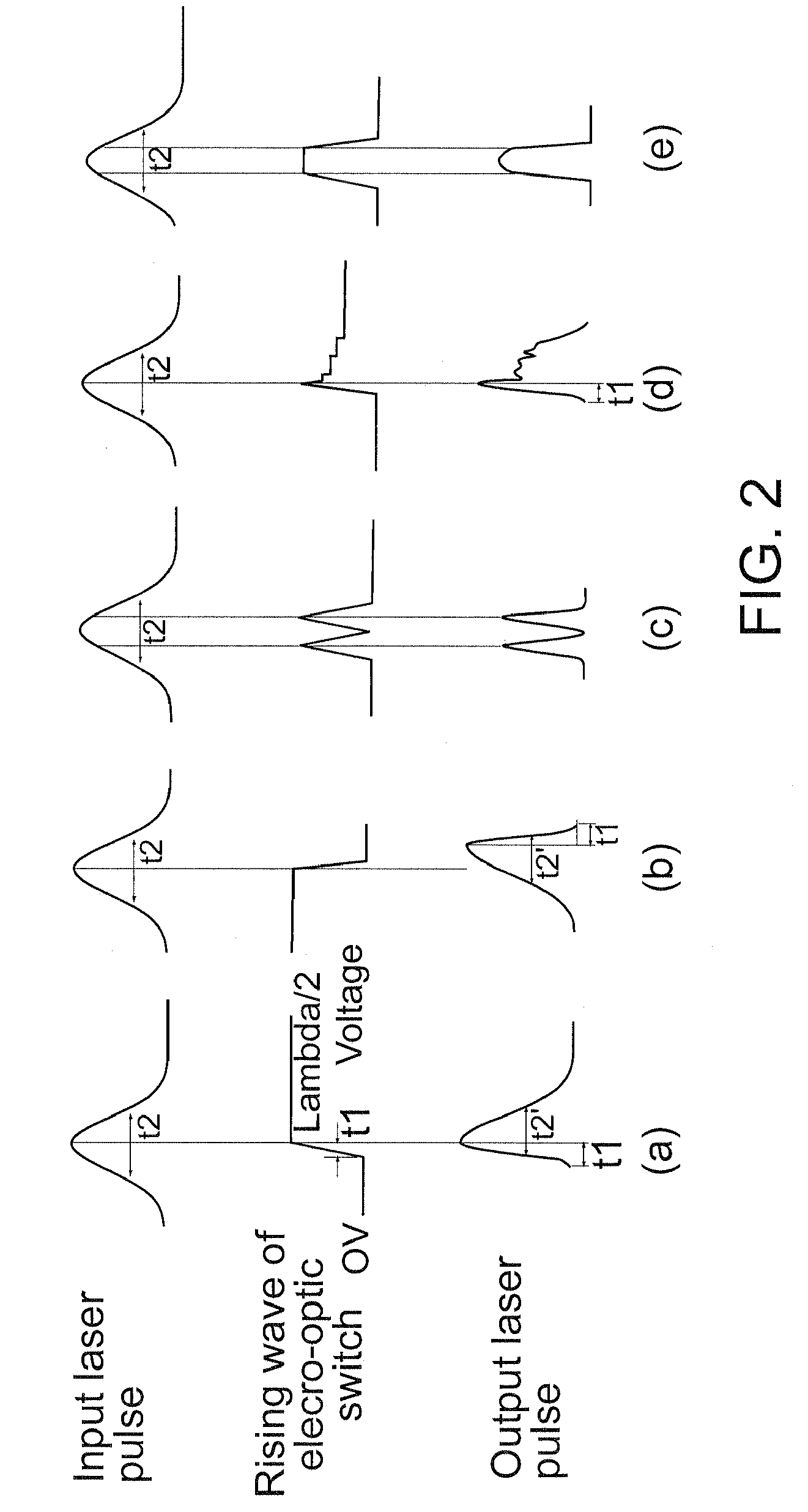
A desired pattern may be cut into a stent preform by impinging a laser beam onto the stent preform. The laser beam is formed using a laser system comprising a resonator cavity for resonating laser radiation, a gain medium contained in the resonator cavity, a pump for periodically pumping the gain medium and an electro-optical modulator in communication with the resonator cavity. The laser system produces a radiation pulse for each pump period. Each radiation pulse is conditioned by suppressing at least a portion of the pulse. The pulse may also be modulated with an electro-optical modulator to produce a pulse train of ordered pulses of radiation. Each pulse train is output from the optical cavity as an output laser beam which is directed at the stent preform to cut a desired pattern in the stent preform.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
System for transmitting optical data
InactiveUS6563623B1Flexible useEasy to optimizeDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersPhase shiftedOptical power
The transmission system includes a first electro-optical modulator adapted to supply in response to an input electrical signal a controlled phase optical signal having an optical power modulated between low levels and high levels and a phase shift within each time cell that contains a low power level. To make it more flexible to use, the system includes a second electro-optical modulator controlled by the input signal and optically coupled to the first electro-optical modulator to apply to said controlled phase optical signal complementary power and / or phase modulation so as respectively to modify its extinction ratio and / or to apply a transient "chirp" to it.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Steady state surface mode device for stereoscopic projection
A modulator and system used to display motion pictures is provided. The design comprises a sheet polarizer and a SMD electro-optical modulator configured to operate in a steady state (non-switching) mode. The modulator is formed from two substantially parallel relatively clear plates, such as glass, two coatings of a transparent conductor, such as indium tin oxide, located between the two substantially parallel relatively clear plates, two polyamide layers located between the two coatings of the transparent conductor, and a film of liquid crystal material located between the two polyamide layers.
Owner:REAID INC
Multiple mode display device
An apparatus comprising a selection device and a multiple mode display device is disclosed. The multiple mode display device comprises a lens sheet comprising a plurality of individual lenticules forming a lenticular surface, an electro-optical modulator positioned adjacent the lens sheet, and a display device comprising a display surface. Alternatively, a multiple mode display arrangement is disclosed, comprising a lens sheet comprising a plurality of individual lenticules forming a lenticular surface and a display device comprising a display surface. The display device is positioned behind the lens sheet, thereby enabling viewing images transmitted in at least a planar mode and a stereoscopic mode.
Owner:REAID INC
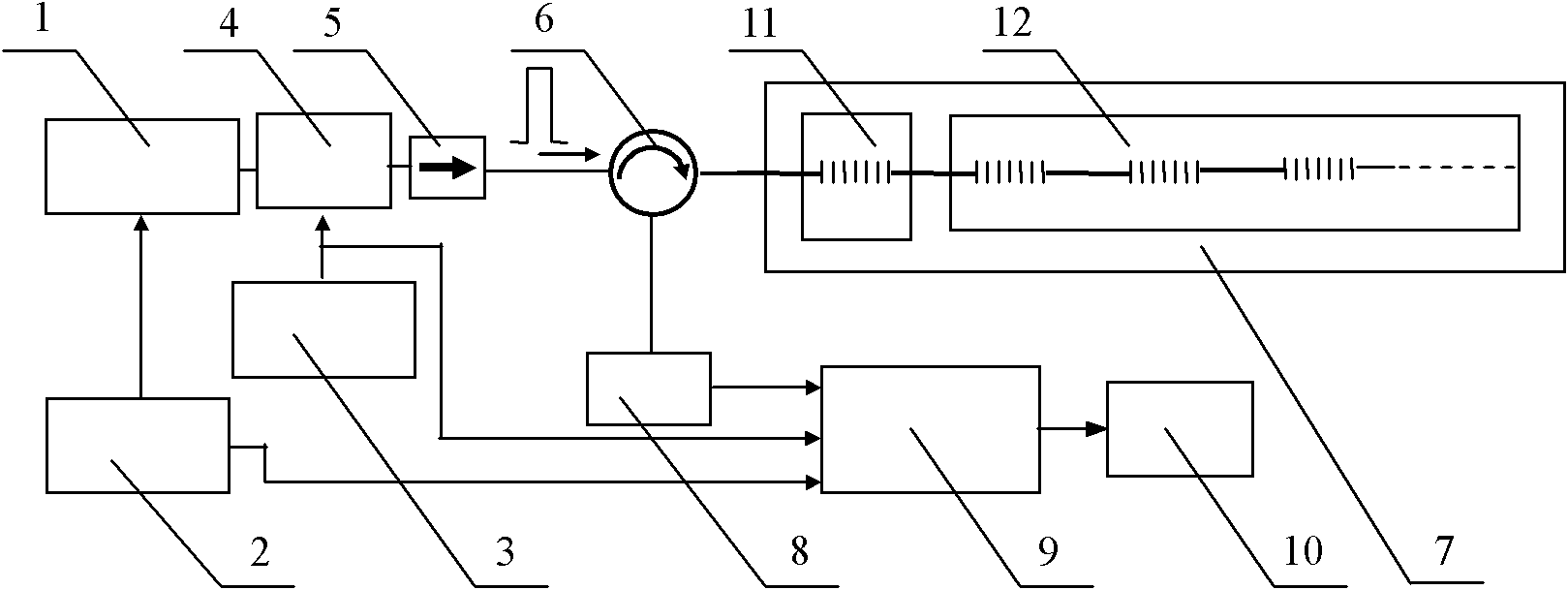
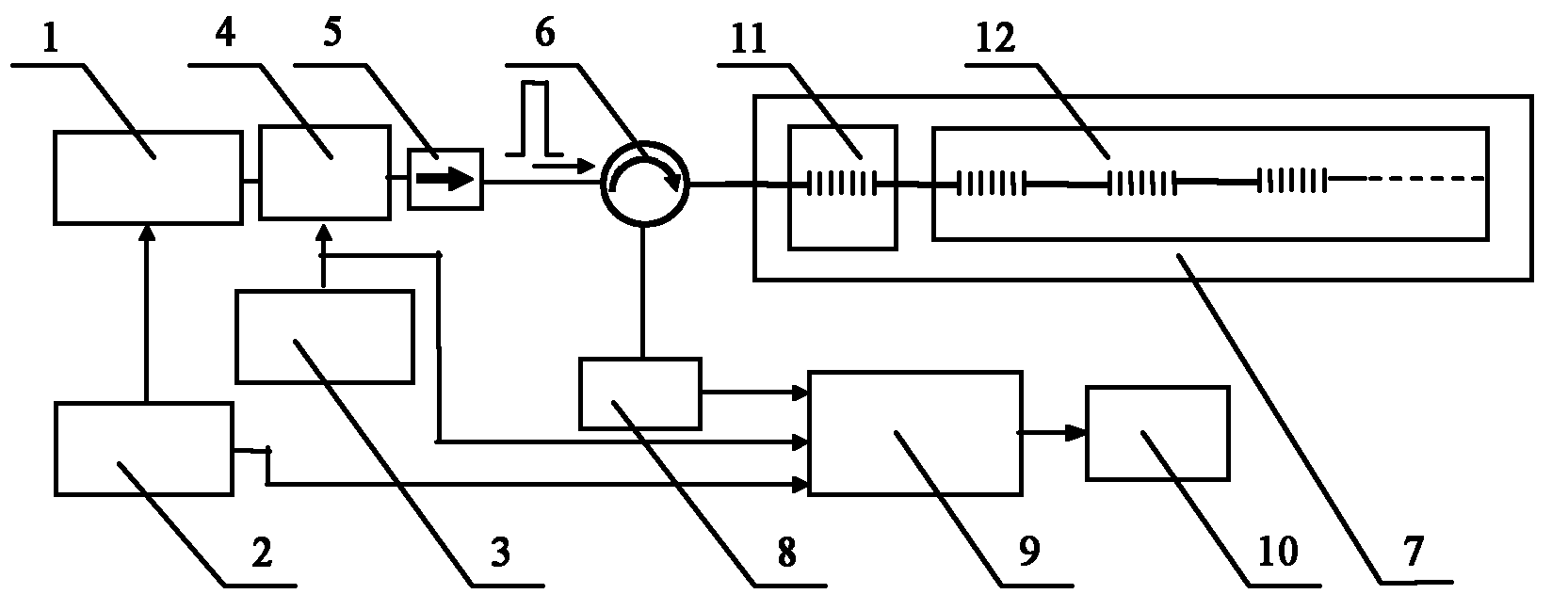
COTDR (coherent detection based optical time-domain reflectometry) fused long-distance coherent detection brilouin optical time-domain analyzer
InactiveCN102759371AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove dynamic rangeThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansSpectrum analyzerLine width
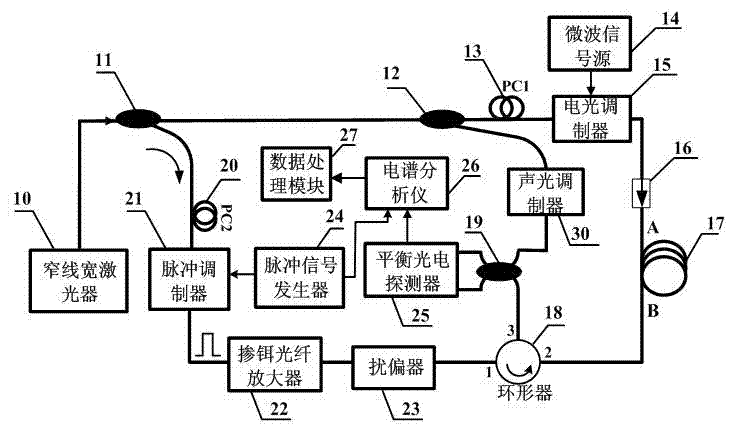
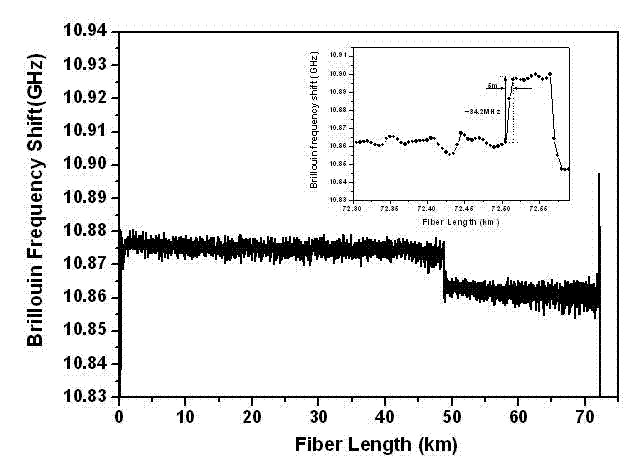
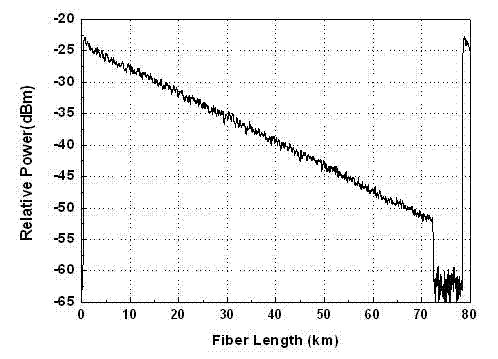
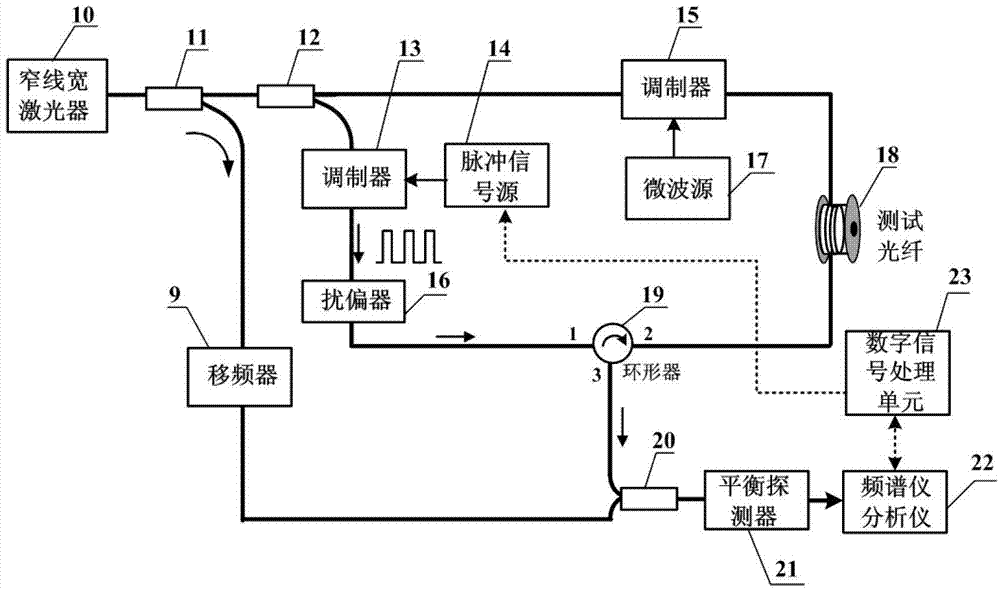
The invention discloses a COTDR (coherent detection based optical time-domain reflectometry) fused long-distance coherent detection brilouin optical time-domain analyzer which comprises a narrow-linewidth laser, two couplings, a microwave signal source, an electro-optic modulator, an isolator, a long-distance sensing optical fiber, an optical circulator, a 3 db coupling, a pulse modulator, an Er-doped fiber amplifier, a scrambler, a pulse signal generator, a balancing photoelectric detector, an electrical frequency spectrum analyzer, a data processing module and an acousto-optic modulator. According to the invention, the signal-to-noise ratio of BOTDA (brilouin optical time domain analysis) is improved by using a coherent detection method, a non-local effect of a BOTDA system is reduced in a double-sideband detection mode, and the sensing distance is more than 70 km under the condition of no light amplification such as raman; and according to the invention, the COTDR is fused to a coherent detection based BOTDA system, and the system can run in a breakpoint testing mode, so that the defect that the traditional BOTDA can not run when a sensing fiber has breakpoints and can not carry out positioning on breakpoints is effectively overcome, thereby enhancing the adaptability and practicability of the sensing system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
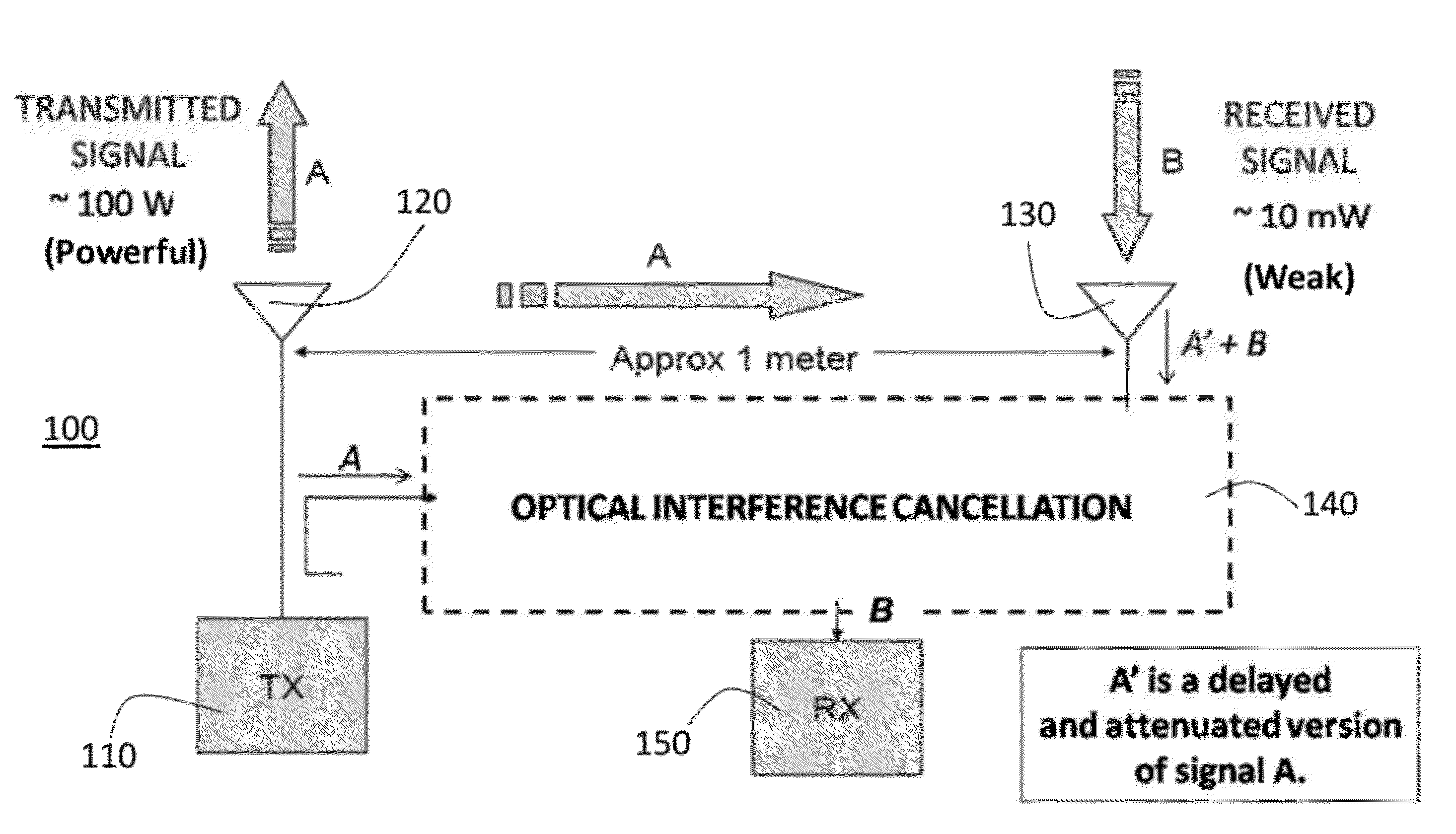
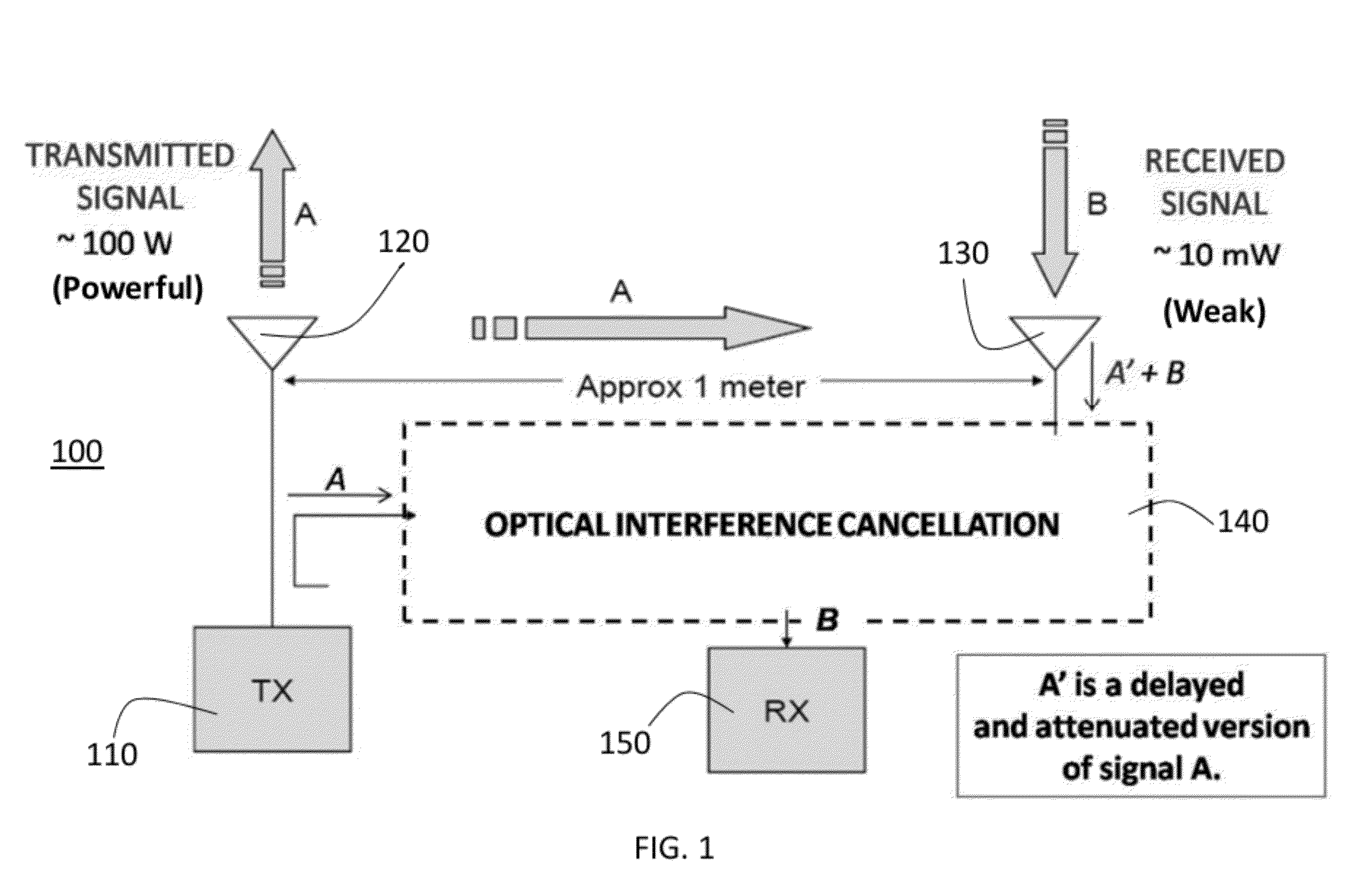
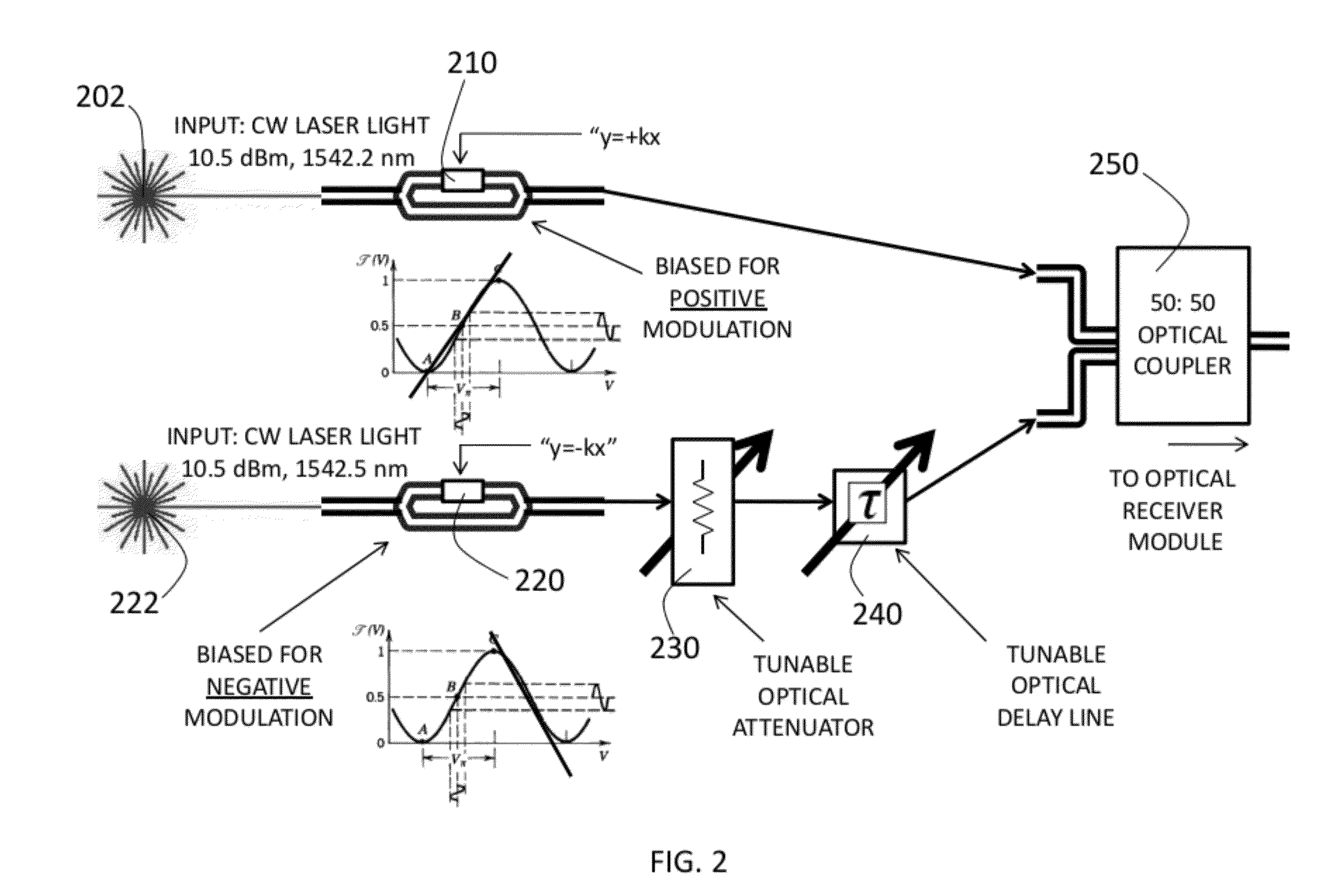
Optical Counter-Phase System And Method Of RF Interference Cancellation
ActiveUS20120251031A1Improve dynamic rangeReduce signalingLight demodulationTransmissionCarrier signalBroadband
A system and method for cancellation of RF interference in the optical domain. The system and method utilize two Mach-Zehnder electrooptic modulators biased for parallel counter-phase modulation. The method of signal subtraction is referred to as incoherent optical subtraction, since two independent laser sources serve as the optical carrier waves. The system has produced the broadband cancellation result while simultaneously recovering a 50 dBm signal which was initially “buried” under the broadband interference. The cancellation depths achieved by the system are due to the accurate channel tracking and precise time delays attainable with modern optical devices—unattainable with state-of-the-art electronic devices at the time of this writing.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
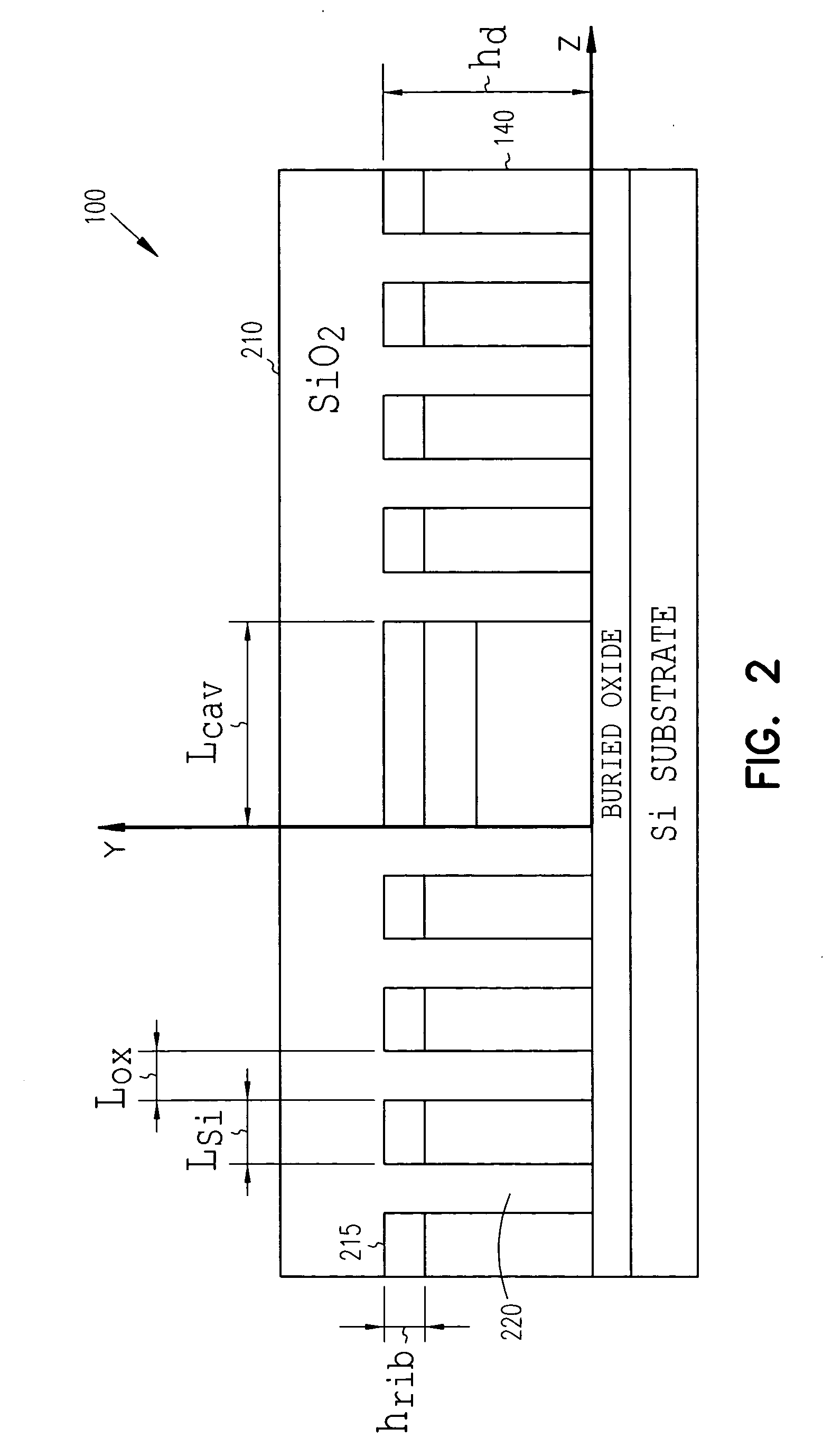
Electro-optic modulator on rib waveguide
InactiveUS20050089257A1Refractive index variesOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsCharge carrierRefractive index
An electro-optic modulator is formed on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) rib waveguide. An optical field in the modulator is confined by using an electrically modulated microcavity. The microcavity has reflectors on each side. In one embodiment, a planar Fabry-Perot microcavity is used with deep Si / SiO2 Bragg reflectors. Carriers may be laterally confined in the microcavity region by employing deep etched lateral trenches. The refractive index of the microcavity is varied by using the free-carrier dispersion effect produced by a p-i-n diode formed about the microcavity. In one embodiment, the modulator confines both optical field and charge carriers in a micron-size region.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
High confinement waveguide on an electro-optic substrate
InactiveUS20090324163A1Reduce mode sizeMode size matchingNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guideGratingActive component
The invention relates to an optical device including a passive high confinement waveguide, such as of silicon-rich silicon nitride, on an electro-optic substrate, like lithium niobate, optically coupled to a waveguide in the electro-optic substrate. A wide range of electro-optic devices are enabled by this high confinement waveguide structure, including: directional couplers, compact tap couplers, folded electro-optic devices, electro-optic modulators including ring resonators, electro-optic gratings. Further applications enabled by the present invention include hybrid passive planar lightwave circuits (PLC) integrated with electro-optically active waveguides, using the high confinement waveguide as an intermediary waveguide to transfer optical power between the passive and active components.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Sensing method of optical-fiber Bragg grating laser device
InactiveCN101793570AReduced spectral rangeHigh precisionThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansGratingFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a sensing method with an optical-fiber Bragg grating laser device. An optical-fiber Bragg grating is used as a reflector of the resonant cavity, an active optical fiber capable of generating sufficient gains is added, and a double wavelength / multiple wavelength optical-fiber Bragg grating laser device is formed under the action of a pump light source and used as a sensor. When the outside strain, temperature and other physical quantities act on the sensing system, the beat signal frequency among the double wavelength or multiple wavelength laser can shift, and counter stress, temperature and other physical parameters can be measured precisely by detecting the beat signal frequency information. The invention has the advantages of simple manufacture, stable and reliable operation, stable measurement result and high precision, and is free from the interference of light intensity, polarization and other optical information quantities. The multipoint distribution sensing measurement can be realized in a frequency-division multiplexing mode. An electrooptical modulator is added before the spectrum analyzer starts detection so as to randomly adjust the beat signal frequency, thereby greatly reducing the spectral range of the spectrum analyzer and reducing the detection cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Nanophotonic devices based on quantum systems embedded in frequency bandgap media
InactiveUS20050185686A1Add nonlinearityImprove efficiencyQuantum computersLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonicsBinding state
The present invention describes nanophotonic materials and devices for both classical and quantum optical signal processing, transmission, amplification, and generation of light, which are based on a set of quantum systems having a discrete energy levels, such as atoms, molecules, or quantum dots, embedded in a frequency bandgap medium, such as artificial photonic crystals (photonic bandgap materials) or natural frequency dispersive media, such as ionic crystals, molecular crystals, or semiconductors, exhibiting a frequency (photonic) bandgap for propagating electromagnetic modes coupled to optical transitions in the quantum systems. If the frequency of one of optical transitions, called the working transition, lies inside the frequency bandgap of the medium, then spontaneous decay of the working transition into propagating photon modes is completely suppressed. Moreover, the excitation of the working transition and a photon form a photon-quantum system bound state lying inside the photonic bandgap of the medium, in which radiation is localized in the vicinity of the quantum system. In a quantum system “wire” or a quantum system “waveguide”, made of spatially disordered quantum systems, or in a chain quantum system waveguide made of a periodically ordered identical quantum systems, wave functions of the photon-quantum system bound states localized on different quantum systems overlap each other and develop a photonic passband lying inside bandgap of the photonic bandgap medium. Photons with frequencies lying inside the photonic passband propagate along the quantum system waveguide. Since the working transition cannot be excited twice, the passband photons interact with each other extremely strongly both in one waveguide and in different waveguides that are located sufficiently close to each other. These unique nonlinear properties of the quantum system waveguides are proposed to use for engineering key nanophotonic devices, such as all-optical and electro-optical switches, modulators, transistors, control-NOT logic gates, nonlinear directional couplers, electro-optical modulators and converters, generators of entangled photon states, passband optical amplifiers and lasers, as well as all-optical integrated circuits for both classical and quantum optical signal processing, including quantum computing.
Owner:ALTAIR CENT
System and method utilizing an electrooptic modulator
A system and method utilize an array of dynamically controllable optical elements to adjust one or more portions of a beam propagating therethrough. For example, the adjustments can be to change a ratio of horizontally and vertically polarized light in the portions of the beam. The adjustments can be made through application of an appropriate electric field to each of the optical elements, which forms an electrooptic modulator. In one example, a polarizer / analyzer is positioned after the array, such that only desired orientations are transmitted. The polarizing provides a desired light intensity profile, which can, for example, make the intensity inform across the beam or be used to partially or fully attenuate (e.g., block) the beam.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
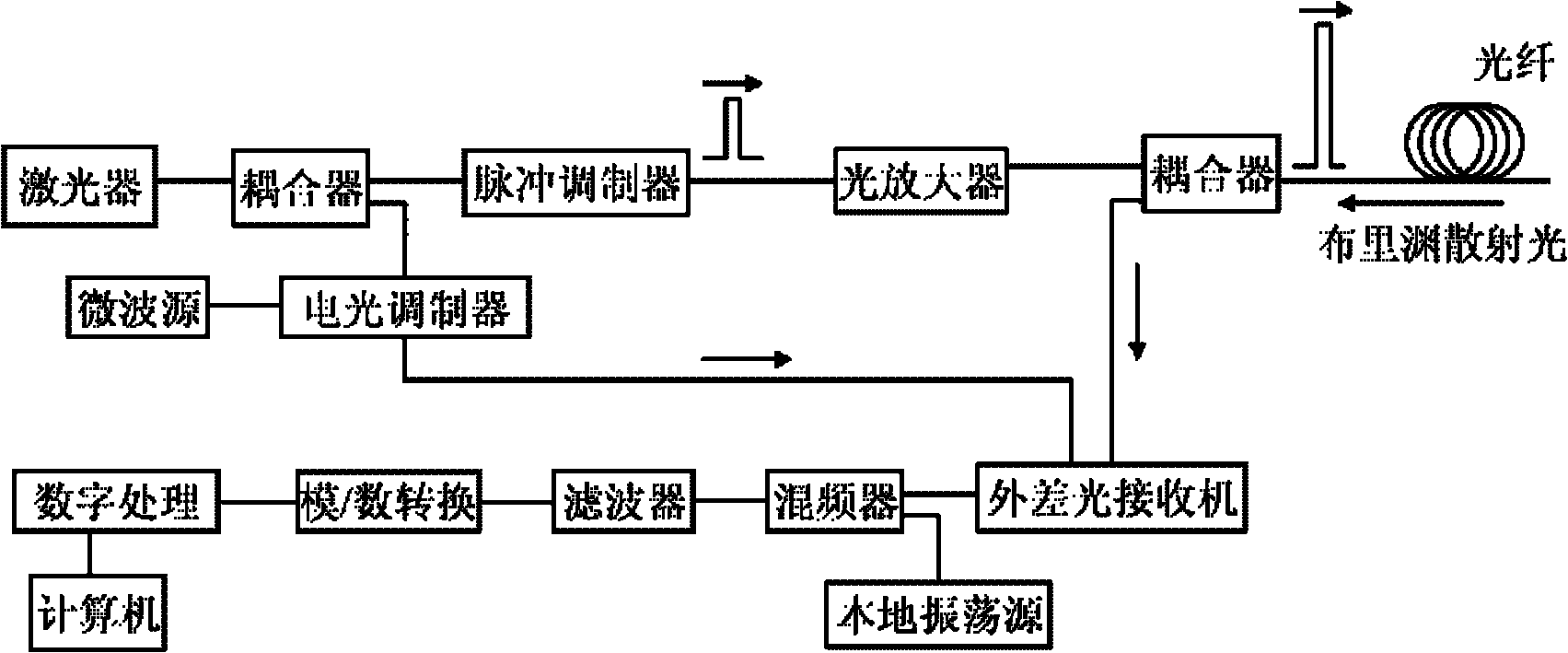
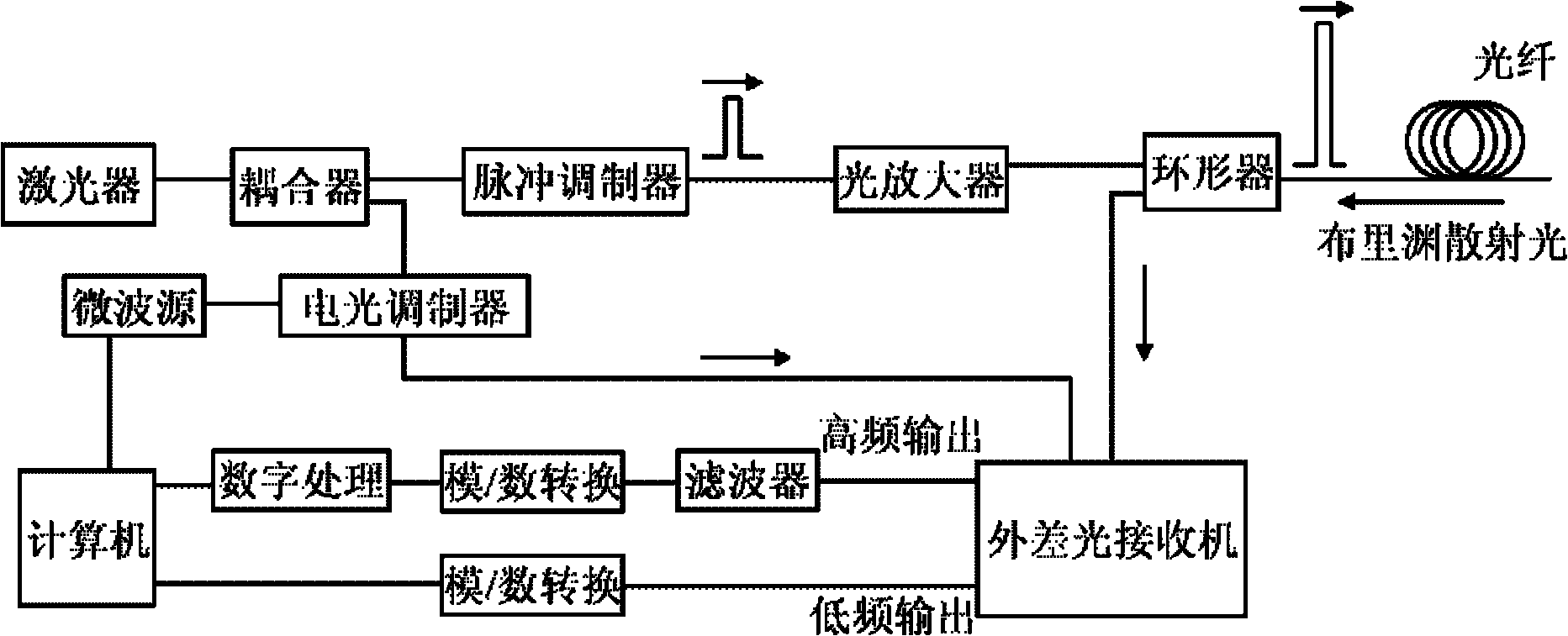
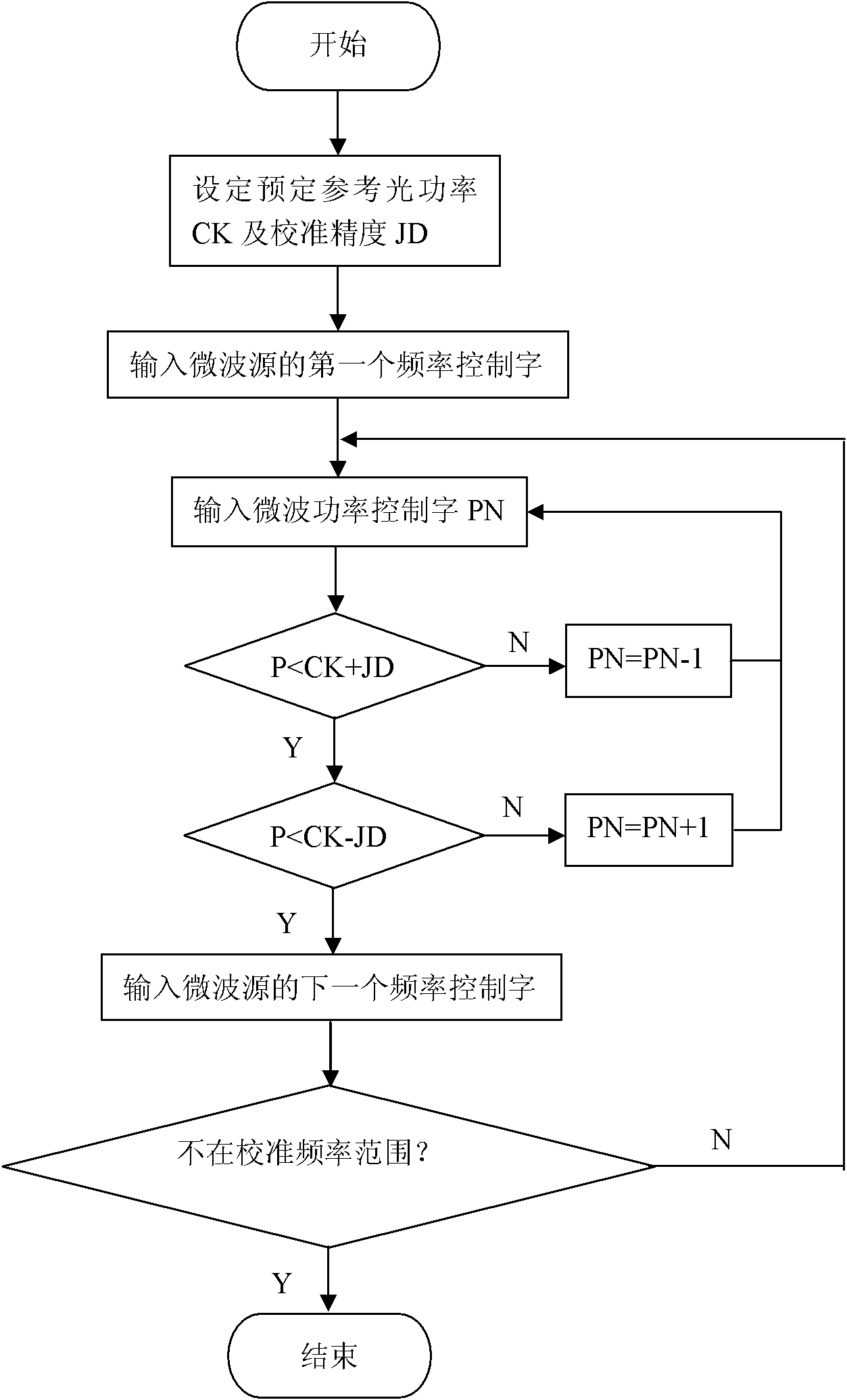
BOTDR (Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) for calibrating optical power of reference light and calibrating method thereof
InactiveCN101839698AAccurate measurementHigh measurement accuracyThermometers using physical/chemical changesThermometer testing/calibrationTime domainOptical power
Owner:NANJING UNIV
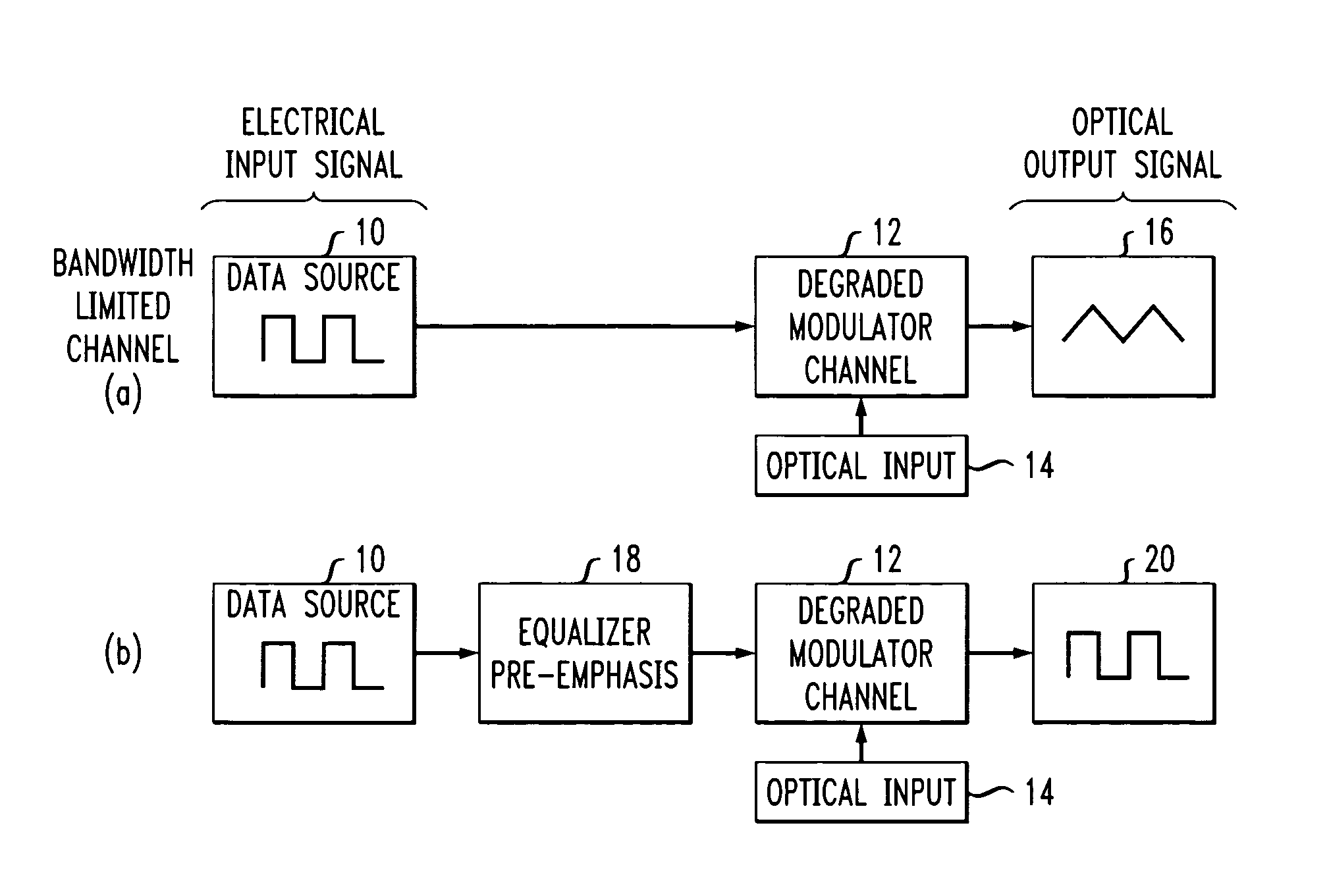
High speed, silicon-based electro-optic modulator
ActiveUS7065301B2Fast switching speedReduce fallsElectromagnetic transmittersOptical light guidesCarrier signalRefractive index
An electro-optic modulator arrangement for achieving switching speeds greater than 1 Gb / s utilizes pre-emphasis pulses to accelerate the change in refractive index of the optical waveguide used to form the electro-optic modulator. In one embodiment, a feedback loop may be added to use a portion of the modulated optical output signal to adjust the magnitude and duration of the pre-emphasis pulses, as well as the various reference levels used for modulated. For free carrier-based electro-optic modulators, including silicon-based electro-optic modulators, the pre-emphasis pulses are used to accelerate the movement of free carriers at the transitions between input signal data values.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
Laser micromachining using programmable pulse shapes
InactiveUS20090245301A1Improve throughputAvoid damageLaser detailsNon-linear opticsLeading edgeNanosecond
Laser pulse shaping techniques produce tailored laser pulse spectral output. The laser pulses can be programmed to have desired pulse widths and pulse shapes (such as sub-nanosecond to 10 ns-20 ns pulse widths with 1 ns to several nanoseconds leading edge rise times). Preferred embodiments are implemented with one or more electro-optical modulators receiving drive signals that selectively change the amount of incident pulsed laser emission to form a tailored pulse output. Triggering the drive signal from the pulsed laser emission suppresses jitter associated with other stages of the link processing system and substantially removes jitter associated with pulsed laser emission build-up time.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
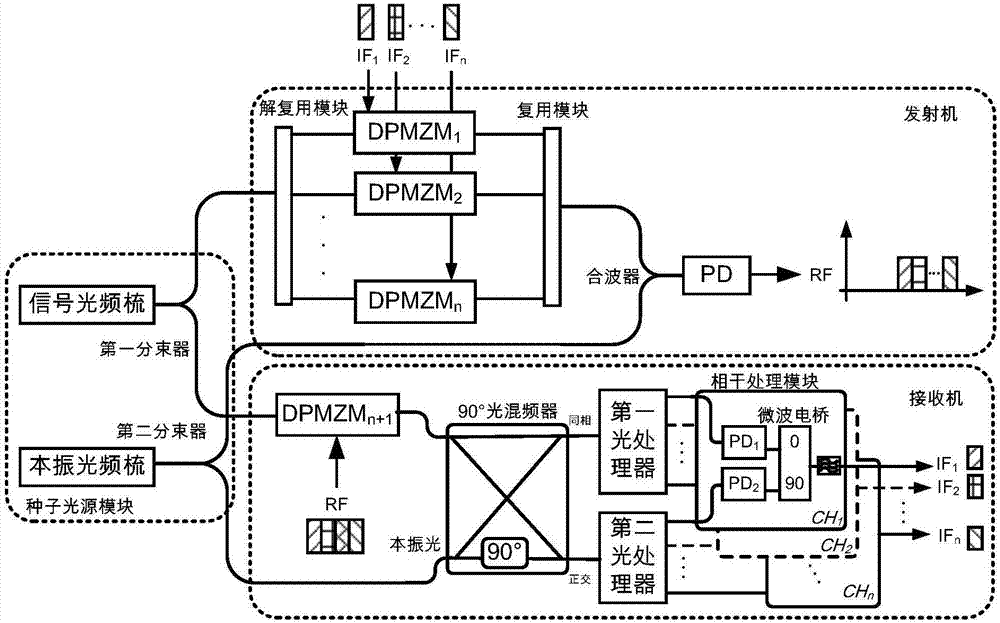
Microwave photonic transceiver based on coherent optical frequency combs
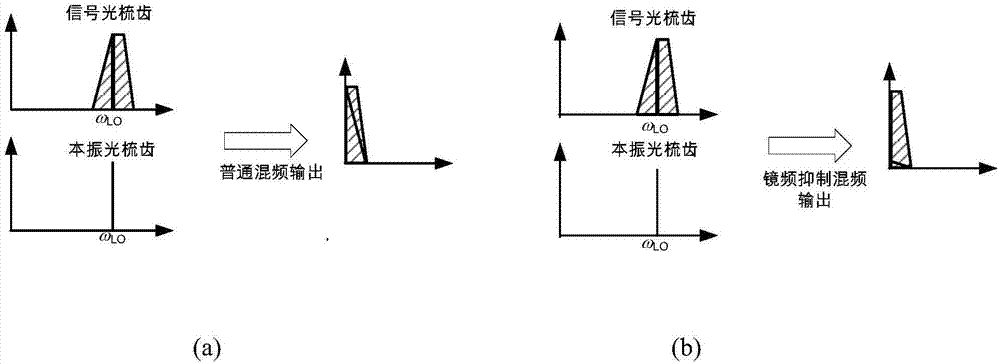
ActiveCN107222263ALarge real-time processing bandwidthLarge dynamic rangeElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsElectromagnetic receiversBeam splitterTransceiver
The invention discloses a microwave photonic transceiver based on coherent optical frequency combs. A signal optical frequency comb and a local oscillator optical frequency comb which are coherent are generated through a seed light source module and are each divided into two paths through two beam splitters; for a transmitting module, one path of the signal optical frequency comb is taken and each comb tooth is separated through a de-multiplexing module, a to-be-transmitted intermediate frequency signal is loaded through electro-optical modulation, the modulated signal optical frequency comb and one path of the local oscillator optical frequency comb are combined, and a high-frequency transmitting signal is obtained through photo-electric detection; for a receiving module, the other path of the signal optical frequency comb directly loads a receiving signal through an electro-optical modulator and sends the receiving signal to a signal light input end of an optical mixer, the other path of the local oscillator optical frequency comb is input into a local oscillator light input end of the same optical mixer, and two paths of orthogonal output light signals of the optical mixer are taken to carry out channel cut and coherent detection respectively. The microwave photonic transceiver disclosed by the invention has large real-time processing bandwidth and large dynamic range, and the system consumption is effectively reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Photonic channelized RF receiver employing dense wavelength division multiplexing
ActiveUS7245833B1Reliable detectionHigh sensitivity and reliabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingLight beamPhotonics
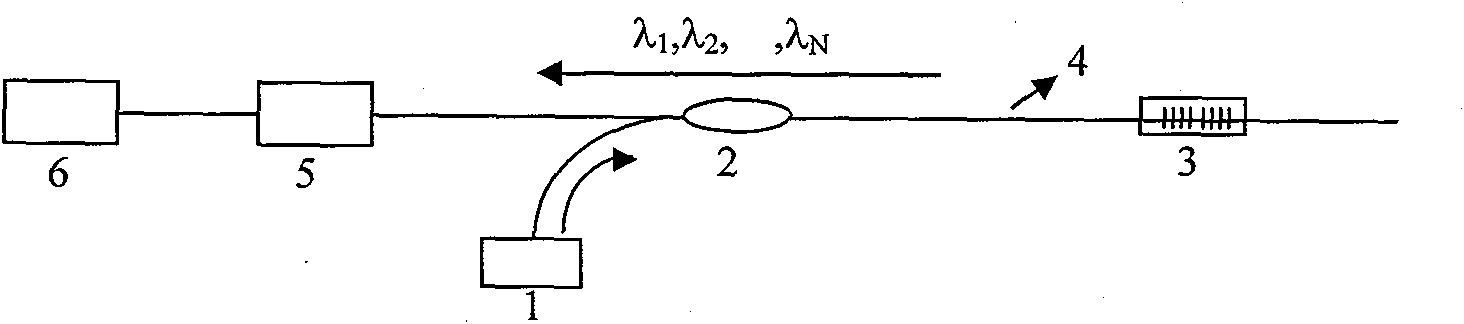
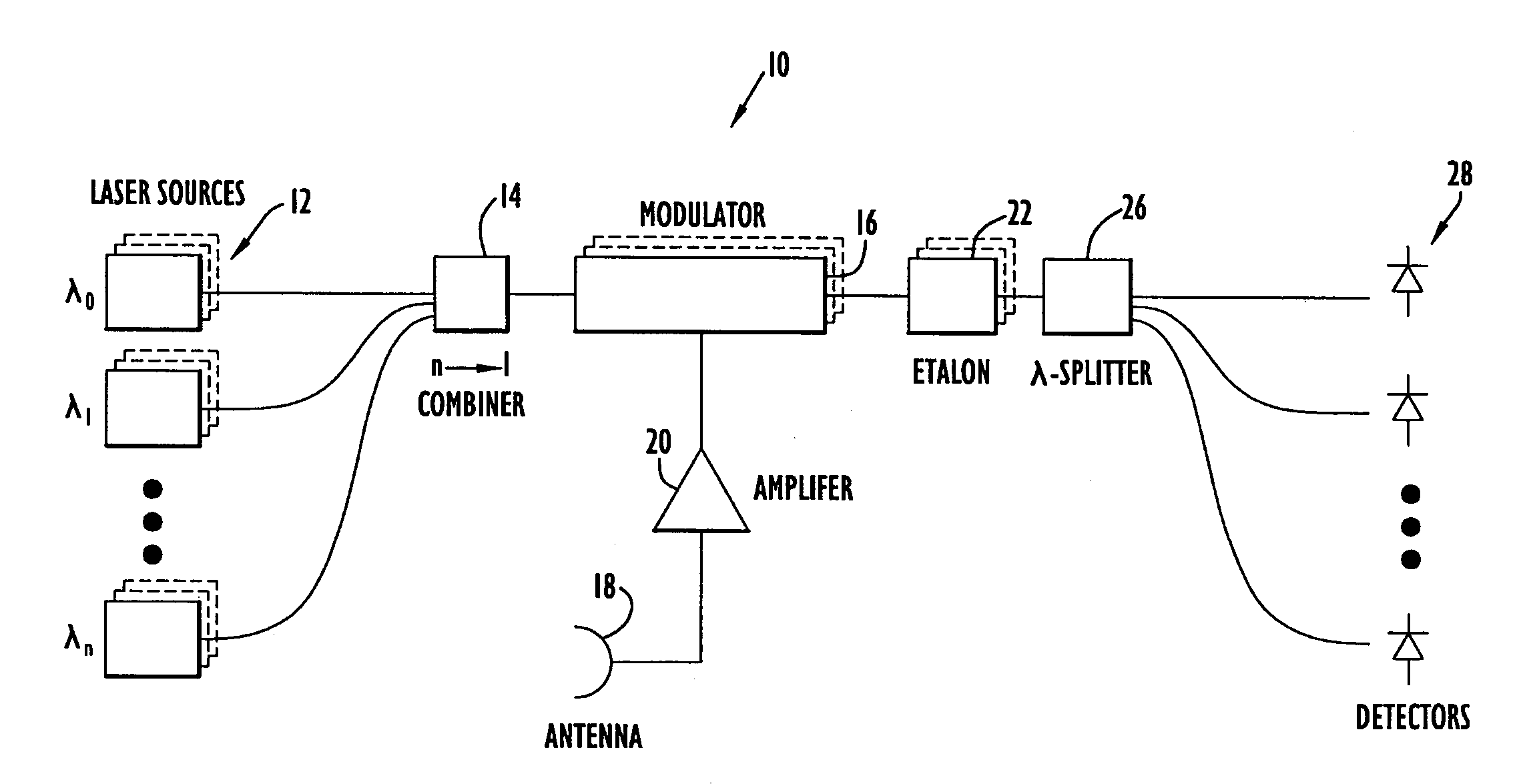
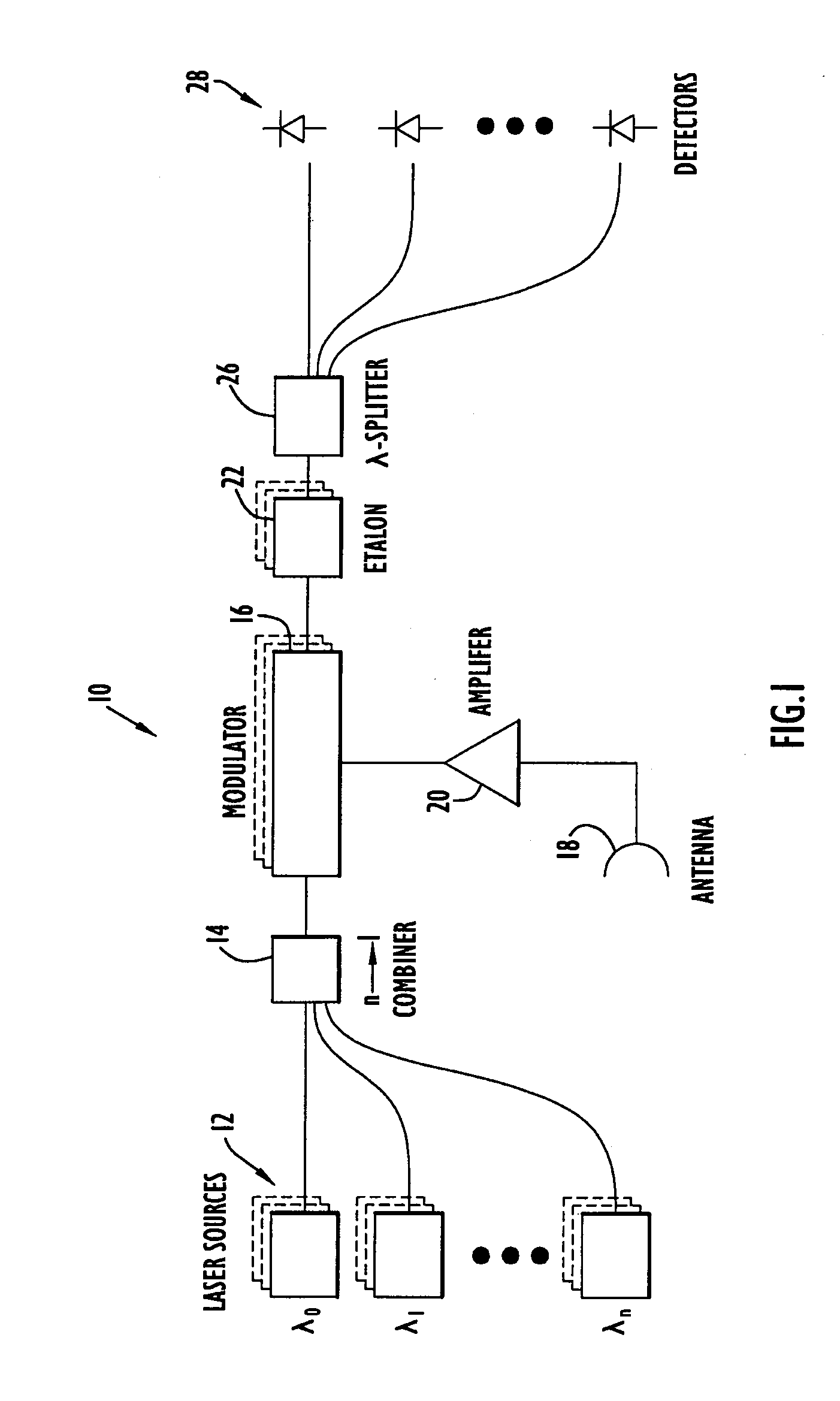
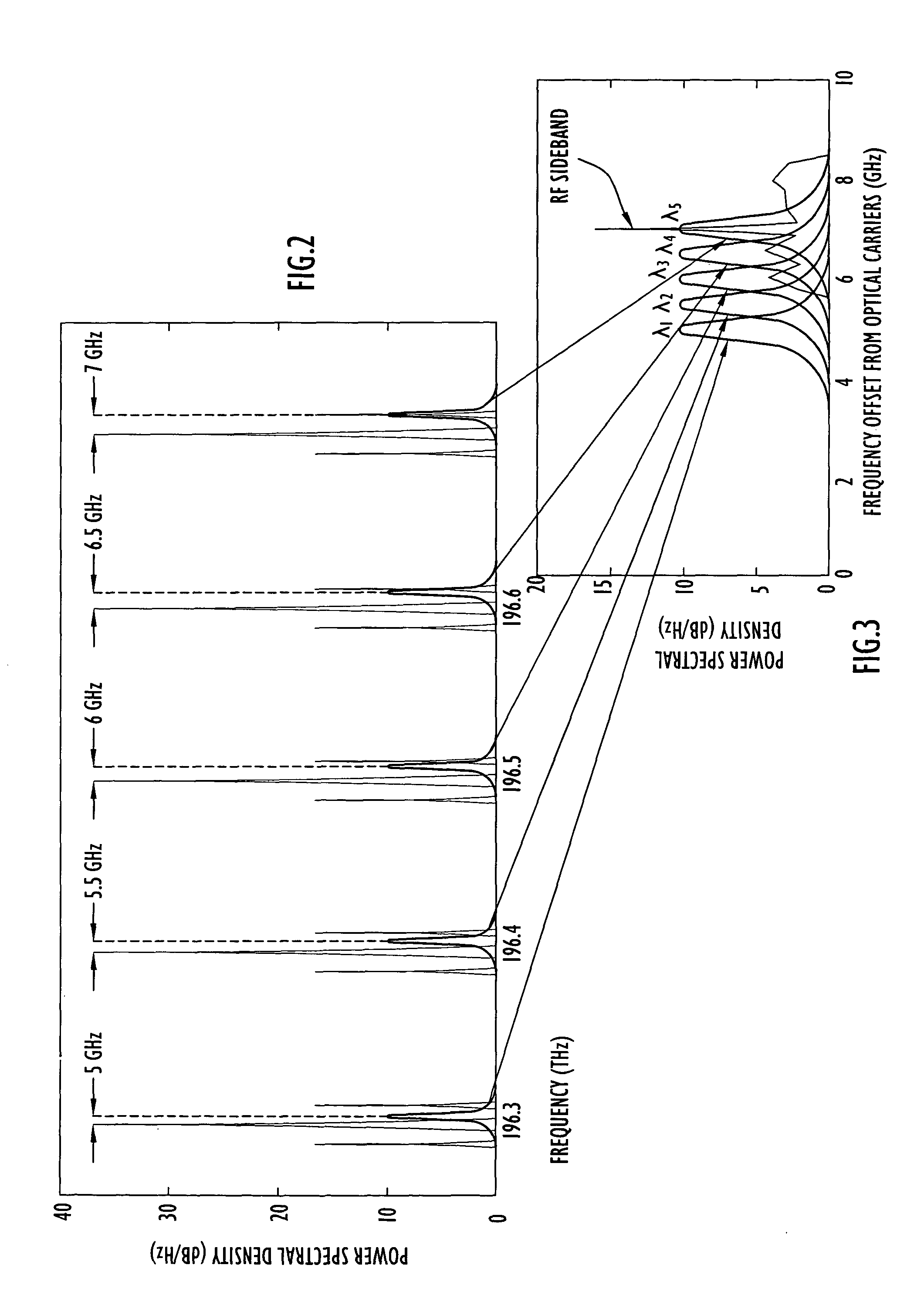
A photonic channelized receiver includes: an optical source, an optical combiner, an electro-optical modulator, an etalon, a wavelength splitter, and a set of detectors. The optical source produces a set of optical signals at spaced wavelengths, and the optical combiner combines the optical signals into a common beam. The electro-optical modulator modulates the common beam with an RF signal to produce sidebands offset from frequencies of the optical signals by the RF signal frequency. The etalon has a periodic transfer function that filters the modulated common beam such that the signals in the filtered, modulated common beam function as receiver channels corresponding to respective RF frequencies. The wavelength splitter separates the common beam into channel output signals whose intensities are a function of the frequency of the RF signal. The detectors measure the intensities of the channel output signals to determine the frequency of the RF signal.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
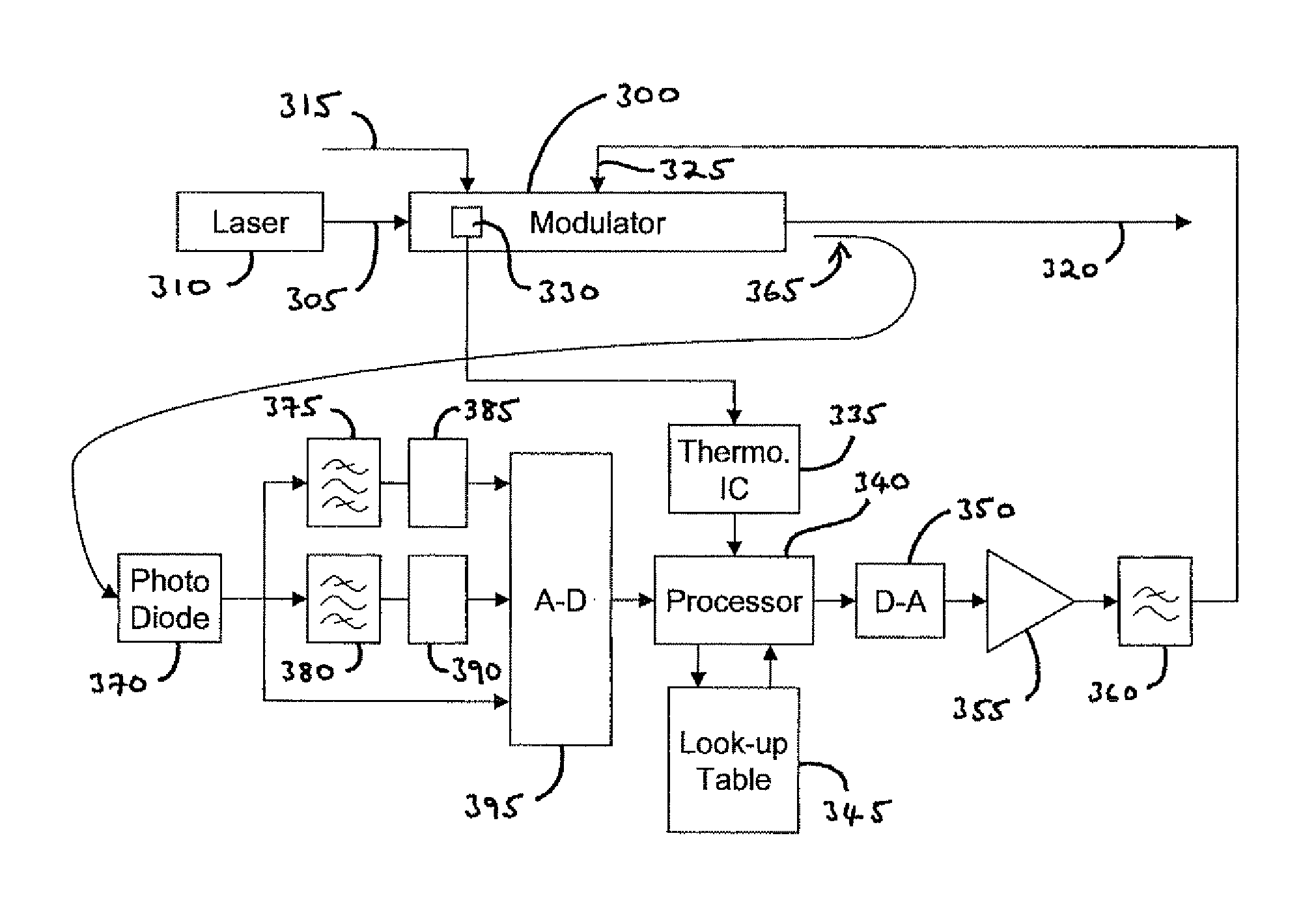
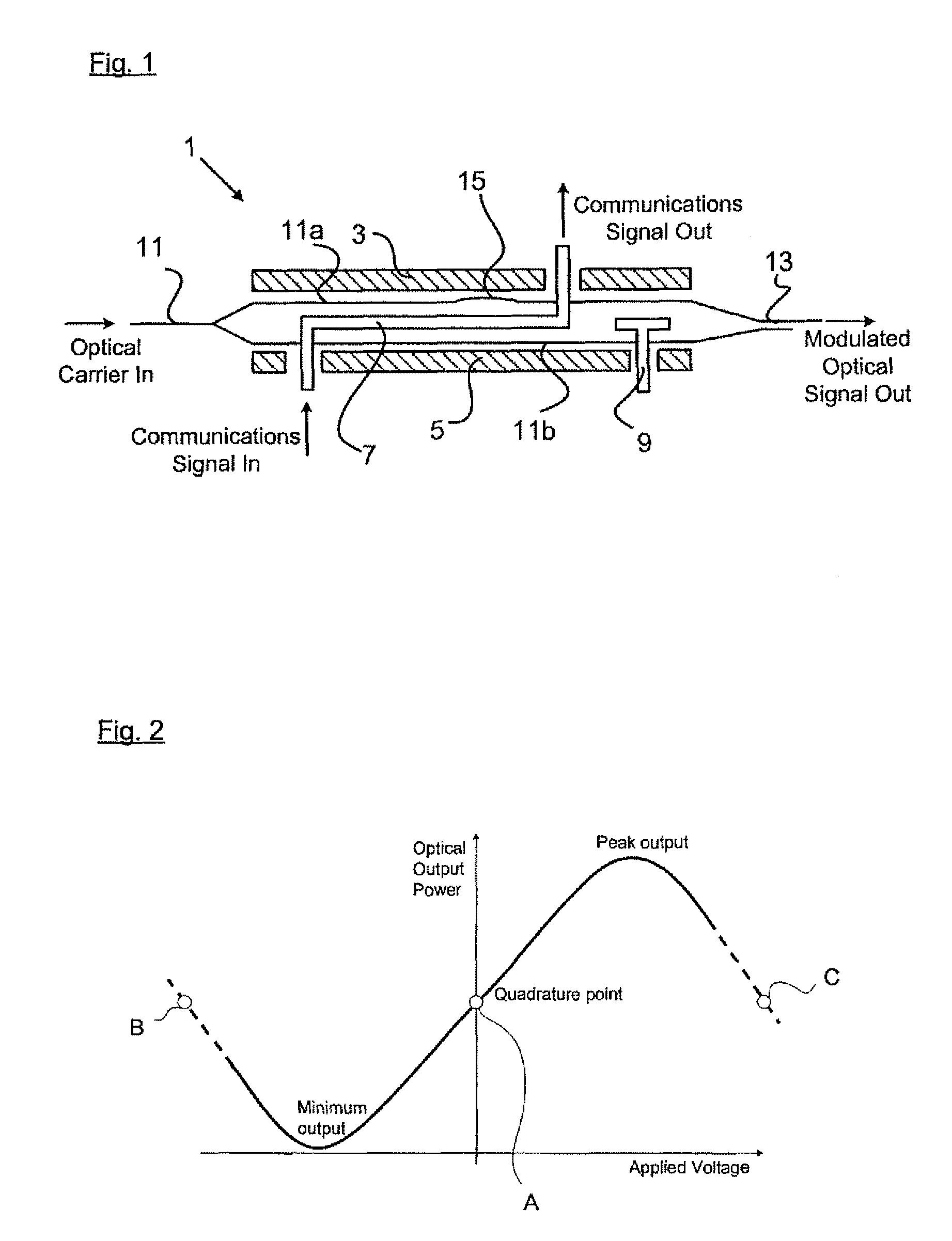
Bias controller
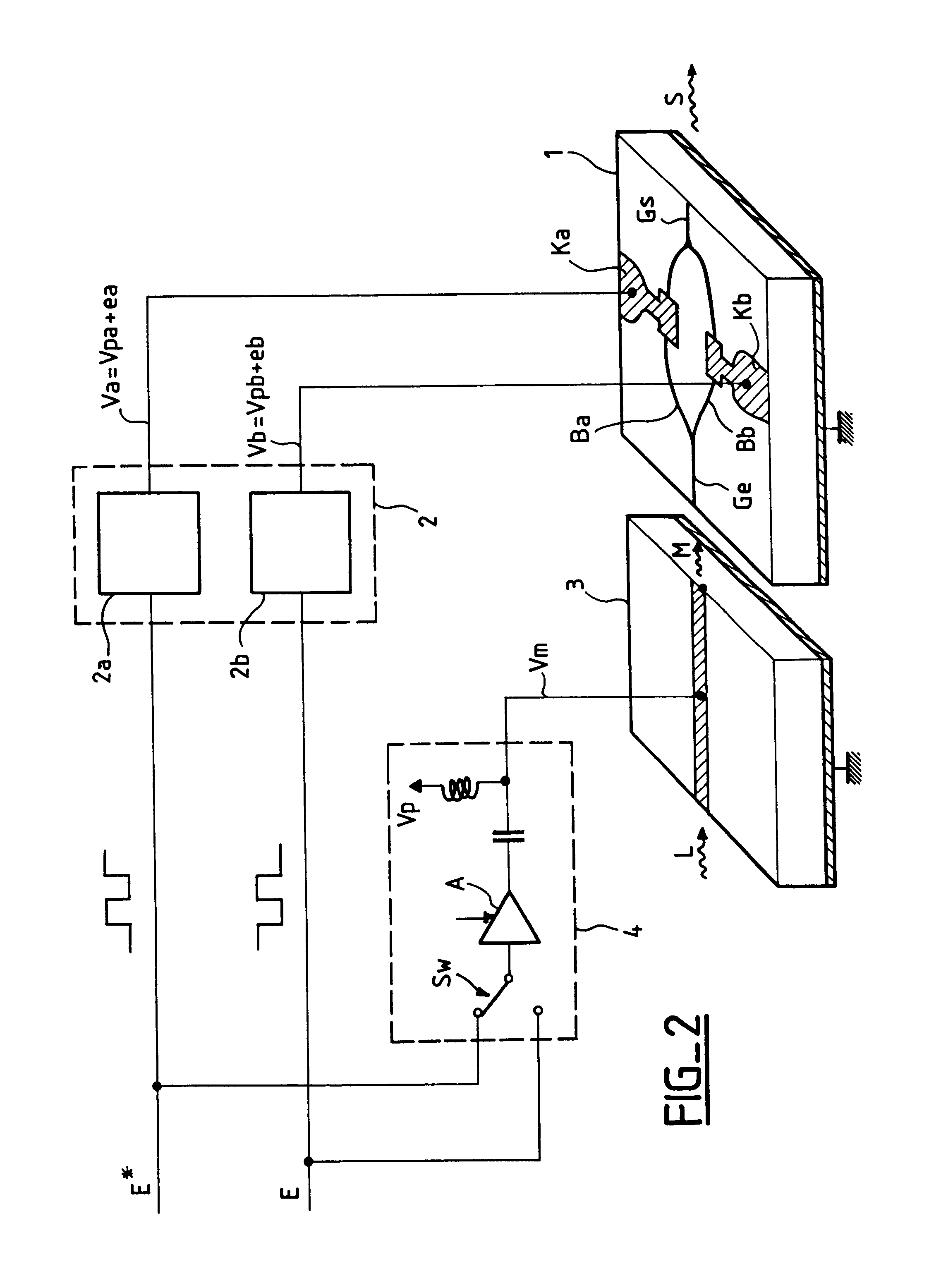
A bias controller and a method for controlling the bias of an electro-optic modulator are provided. In the method, for a received indication of modulator temperature, steps are provided for accessing a look-up table to determine a corresponding value of bias voltage, for a required bias point, to apply to the modulator. If no such value is stored, additional steps are provided to generate a pilot tone for input to the modulator and to recognize, from the signal content of a modulated optical signal output by the modulator, operation of the modulator at the required bias point, adjusting the value of bias voltage being applied to the modulator as required. When operation at the required bias point is recognized, the respective value of bias voltage for that modulator temperature is stored in the look-up table. The same method is provided to configure a bias controller in respect of a given modulator, if necessary ab initio.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Electro-optical modulator based on carrier depletion or carrier accumulation in semiconductors with advanced electrode configuration
ActiveUS20140248019A1Reduce crosstalkHigh on-chip device densityElectromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsMach–Zehnder interferometerEngineering
An electro-optical modulator with two electrodes as part of a transmission line of a first phase modulator and two electrodes as part of a transmission line of a second phase modulator included in two arms of a Mach-Zehnder-interferometer. An electrical controller applies a first electrical high-frequency-modulated voltage signals between the first and second electrodes and applies a second electrical high-frequency-modulated signals between the fourth and third electrodes. The electrical controller applies signals such that voltages applied to the first and fourth electrodes have substantially a same high-frequency content, and voltages applied to the second and third electrodes have substantially the same high-frequency content. In such configuration, a constant voltage offset is produced by either the voltages applied to the first and fourth electrodes or, the second and third electrodes. Thereby, cross-talk between electrodes, electrical losses, device size and fabrication costs may be reduced.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIV
Circuit architecture for electro-optic modulation based on free carrier dispersion effect and the waveguide capacitor structures for such modulator circuitry using CMOS or Bi-CMOS process
ActiveUS20070292073A1Improve performanceOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsHemt circuitsElectro-optic modulator
New circuit architecture for electro-optic modulator based on free-carrier dispersion effect is invented, in which the waveguide capacitor of the modulator is embed in the circuits and physically layout together with transistors, the switching of the modulator occurs in transistors, and as the result, the electro-optical modulation occurs in the waveguide capacitor. The invented modulator is not one physical device, it is actually a circuit. Several circuit design techniques are imported, leading to several new modulator circuits that have very high operation speed and very small power consumption. Several new waveguide capacitor structures are also invented that allow high efficient modulator circuits to be built.
Owner:LI BING
Distributed optical fiber sensor based on roman and brillouin scattering
InactiveUS20130020486A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioRealize measurementRadiation pyrometryForce measurementMechanical engineeringMaterials science
A distributed optical fiber sensor based on Raman and Brillouin scattering is provided. The distributed optical fiber sensor includes a semiconductor FP cavity pulsed wideband optical fiber laser (11), a semiconductor external-cavity continuous narrowband optical fiber laser (12), a wave separator (13), an electro-optic modulator (14), an isolator (15), an Er-doped optical fiber amplifier (16), a bidirectional coupler (17), an integrated wavelength division multiplexer (19), a first photoelectric receiving and amplifying module (20), a second photoelectric receiving and amplifying module (21), a direct detection system (22), a narrowband optical fiber transmission grating (23), a circulator (24) and a coherence detection module (25). The temperature and the strain can be measured simultaneously, and the signal-to-noise ratio of the system is enhanced.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
BOTDA (Brillouin Optical Time-Domain Analysis) system based on pulse coding and coherent detection
InactiveCN103245370AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove adaptabilityConverting sensor output opticallyContinuous lightDigital signal processing
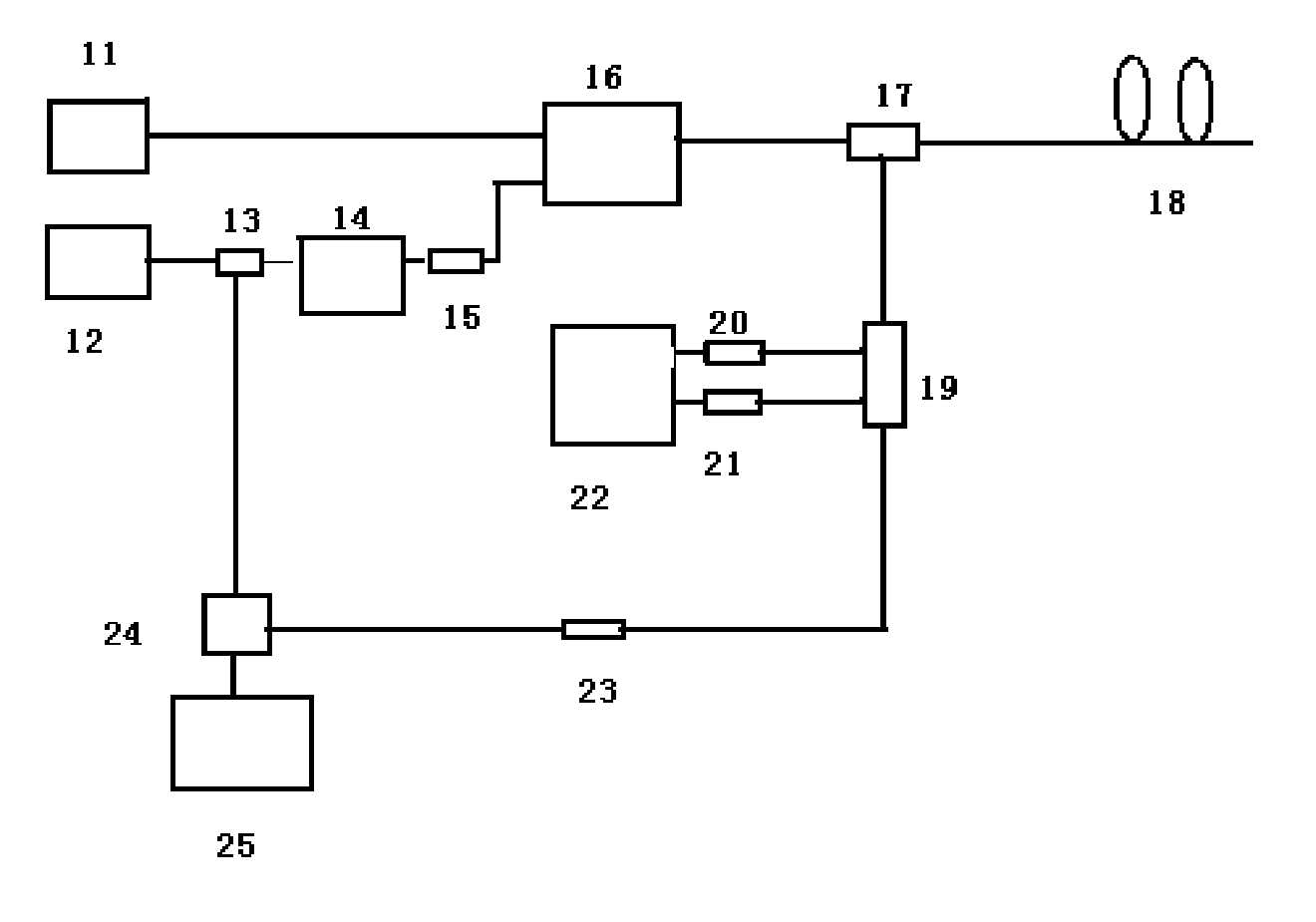
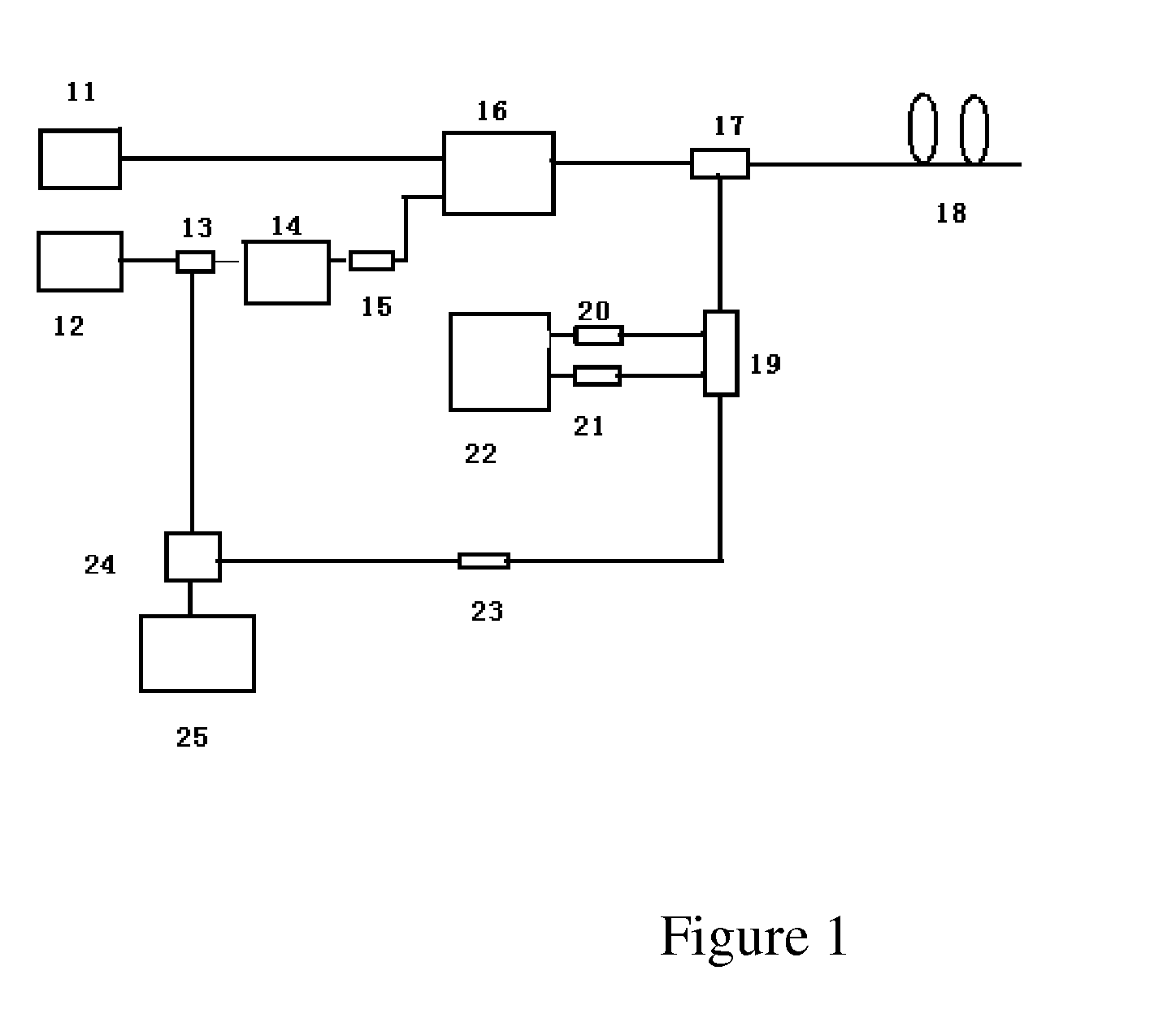
A BOTDA system based on pulse coding and coherent detection comprises a narrow linewidth laser device (10), a first polarization-maintaining coupler (11), a second polarization-maintaining coupler (12), a microwave signal source (17), testing optical fibers (18), an optical circulator (19), a 3dB coupler (20), a balance photoelectric detector (21), a scrambler (16), a spectrum analyzer (22) and a digital signal processing unit (23), wherein continuous light emitted by the arrow linewidth laser device (10) is divided into two channels of continuous light, namely, a first channel of the continuous light and a second channel of the continuous light, through the first polarization-maintaining coupler (11); and the system further comprises a frequency shifter (9), a first electrooptical modulator (13), a pulse signal source (14) and a second electrooptical modulator (15). The system adopts a pulse coding technology and a coherent detection method, so that the signal to noise ratio of the BOTDA and the measurement accuracy can be improved, the sensing distance is increased, and the system has the function of breakpoint detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Stable microwave oscillator
InactiveCN103560380AHigh spectral purityStable Single Mode OscillationSolid masersMicrowave phase shifterBand-pass filter
The invention discloses a stable photoelectric oscillator. The stable photoelectric oscillator comprises a laser device, an electro-optical modulator, a long optical fiber, a photoelectric detector, an amplifier, an electric band-pass filter, an electrically-controlled microwave phase shifter, a high-stability microwave source, a 2*1 wave combiner or directional coupler, a first 1*2 power divider or directional coupler, a second 1*2 power divider or directional coupler, a third 1*2 power divider or directional coupler and a phase locking control module, wherein the phase locking control module comprises a frequency mixer, an electric low pass filter and a servo control module, the output end of the frequency mixer is connected to the input end of the electric low pass filter, and the output end of the electric low pass filter is connected to the input end of the servo control module. According to the stable photoelectric oscillator, an electric injection of the external high-stability microwave source and a phase locking control mechanism are added based on a traditional single-loop OEO structure. Compared with the prior art, the stable photoelectric oscillator has the advantages that insertion loss of an optical link in a resonant cavity is not increased, the high signal to noise ratio of the photoelectric resonant cavity is maintained, and the structural complexity of the stable photoelectric oscillator is lower than that of an existing scheme. The stable photoelectric oscillator is easy to obtain.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Optical modulating device with frequency multiplying technique for electrical signals
The present invention relates to an optical modulating device with frequency multiplying technique for electrical signals, which primary comprises a mixer, which generates a mixed data signal from a first electrical signal and a second electrical signal. The mixed data signal is then received by a first phase shift device to have its phase shifted and becomes a first shifted signal. The first electrical signal is further received by a second phase shift device to have its phase shifted and becomes a second shifted signal. The present invention further comprises an integrated electro-optic modulator (Mach-Zehnder modulator), which is used to receive an input optical signal, the mixed data signal, the first shifted signal, the second shifted signal and the first electrical signal mentioned above, the integrated electro-optic modulator will then modulates the input optical signal into a frequency multiplying output optical signal that carries the first electrical signal and the second electrical signal. The present invention can carry and transmit amplitude shift keying signals and vector modulation signals, thereby provides a more advanced optical communication transmission service.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
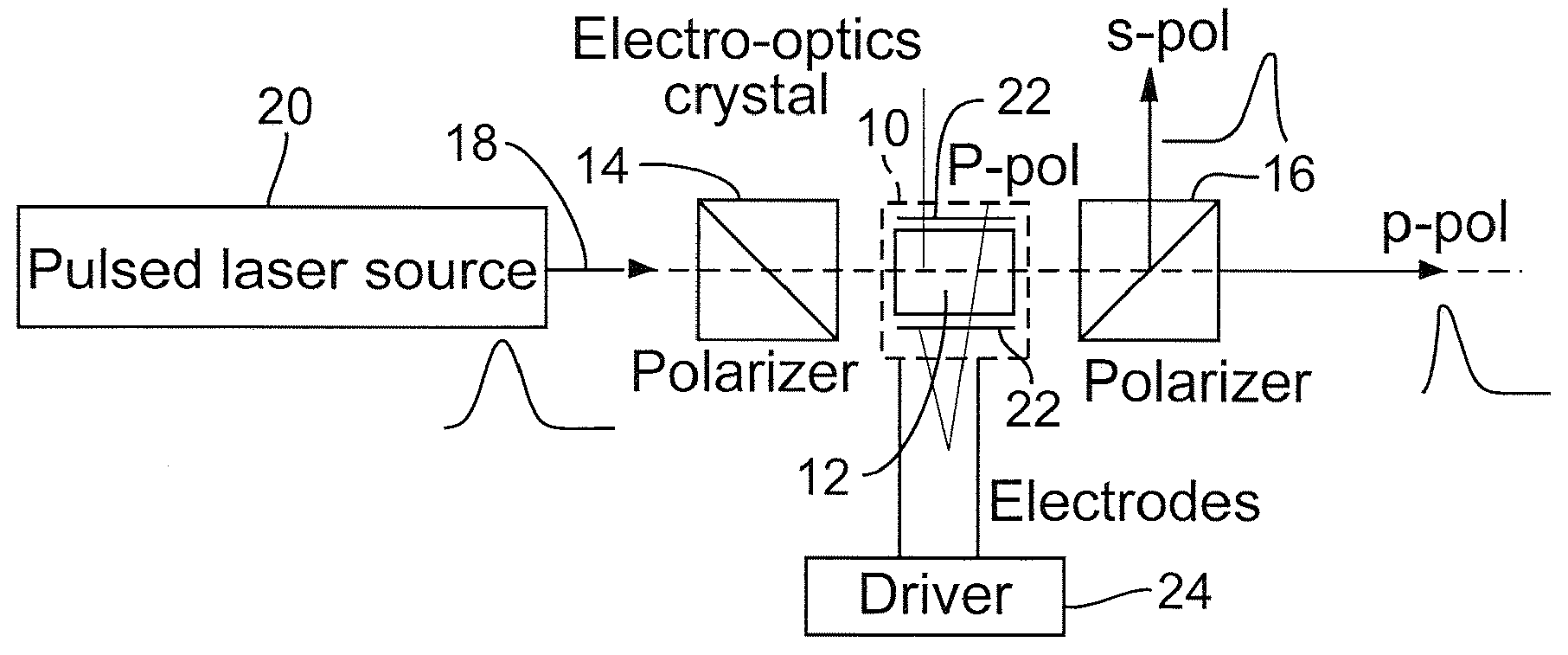
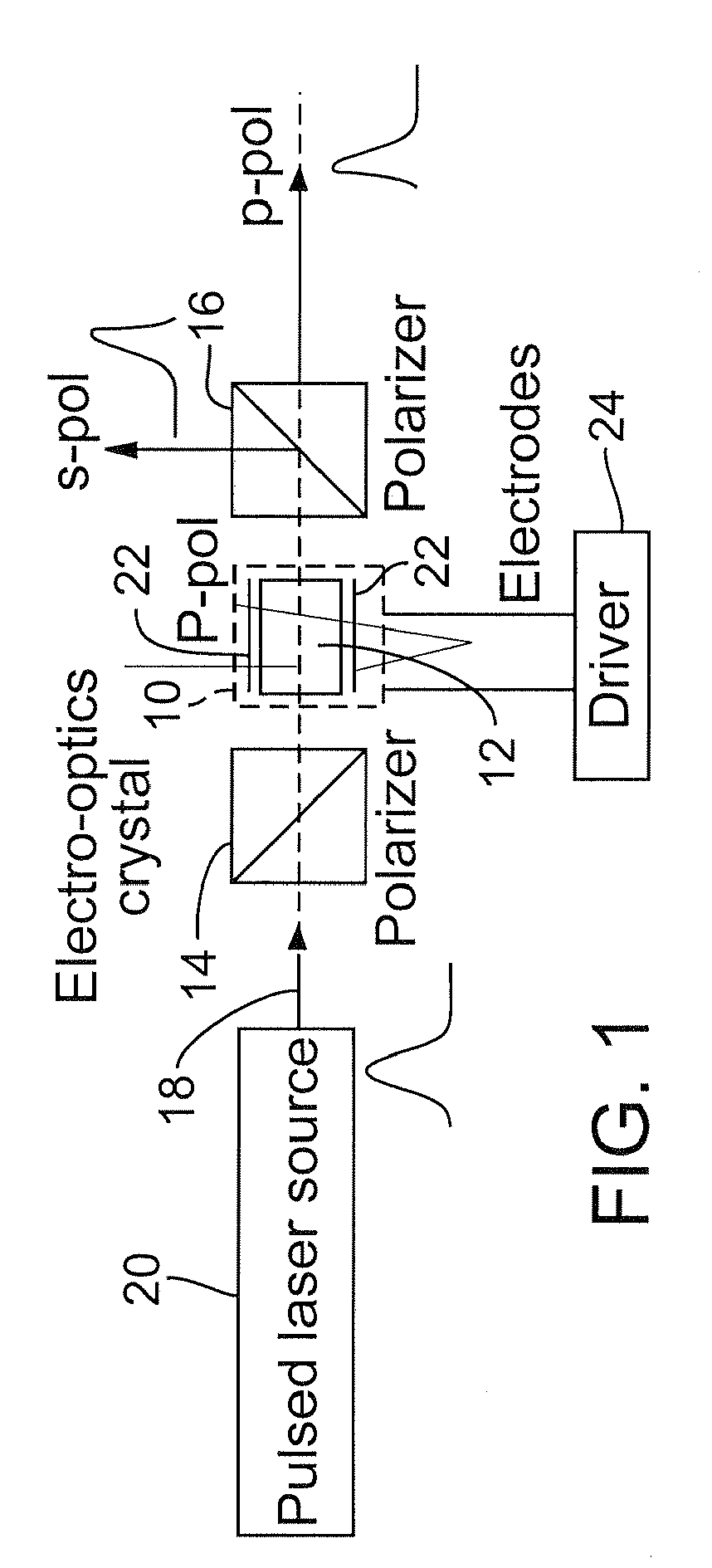
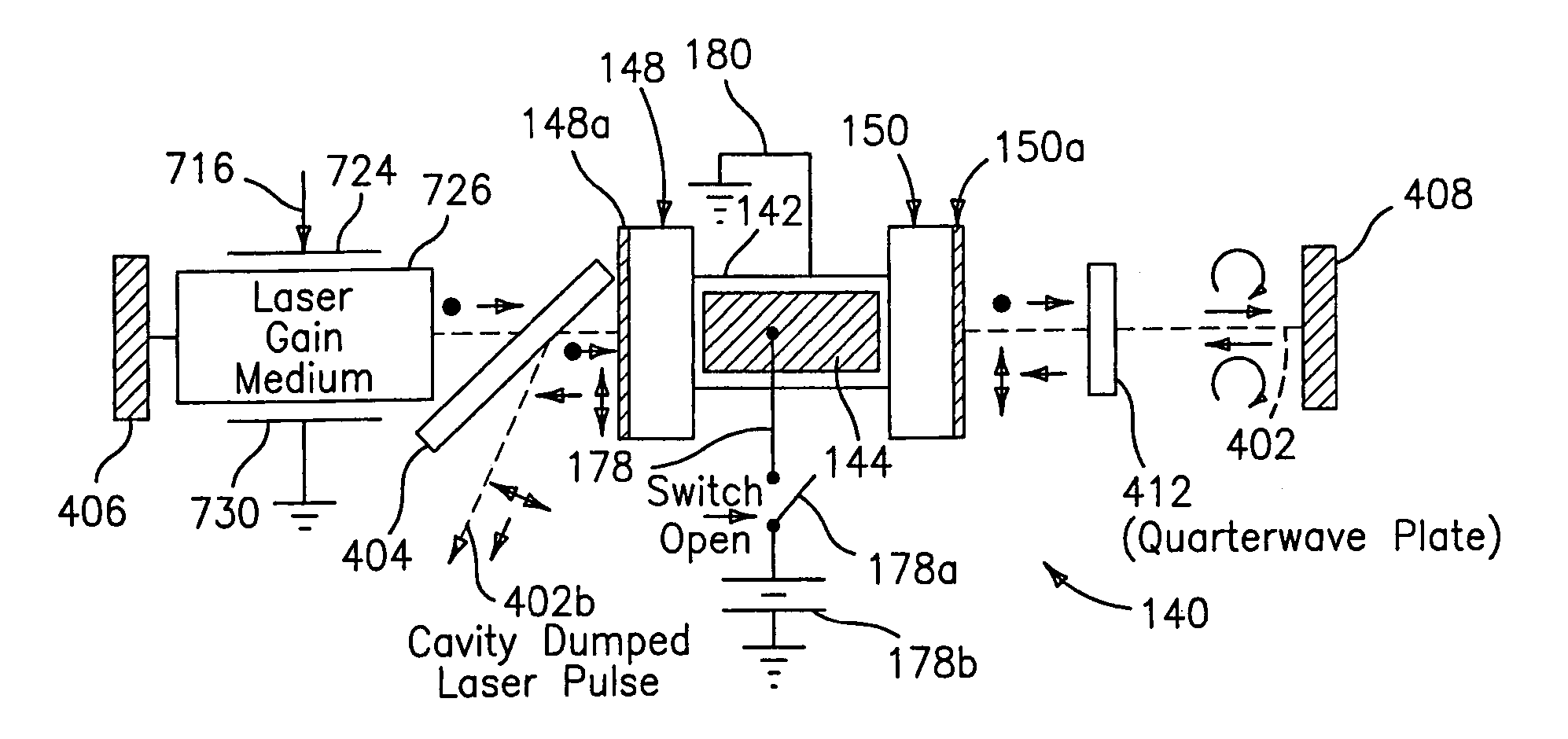
Q-switched, cavity dumped laser systems for material processing
InactiveUS7058093B2High strengthLow powerActive medium materialGas laser constructional detailsEngravingPeak value
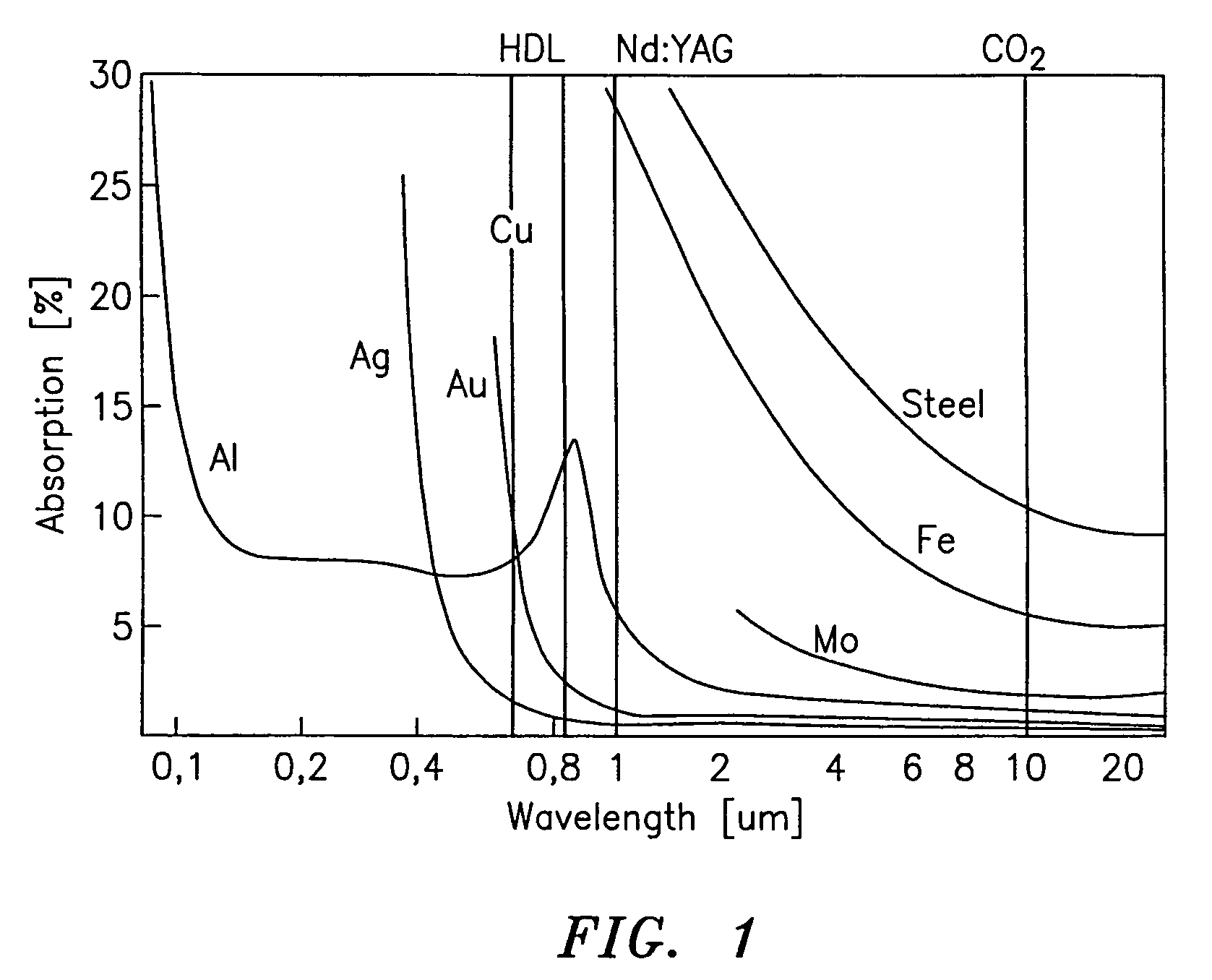
This disclosure discusses techniques for obtaining wavelength selected simultaneously super pulsed Q-switched and cavity dumped laser pulses utilizing high optical damage threshold electro-optic modulators, maintaining a zero DC voltage bias on the CdTe electro-optic modulator (EOM) so as to minimize polarization variations depending on the location of the laser beam propagating through the CdSe EOM crystal, as well as the addition of one or more laser amplifiers in a compact package and the use of simultaneous gain switched, Q-switched and cavity dumped operation of CO2 lasers for generating shorter pulses and higher peak power for the hole drilling, engraving and perforation applications.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Method for manufacturing PDLC-based electro-optic modulator using spin coating
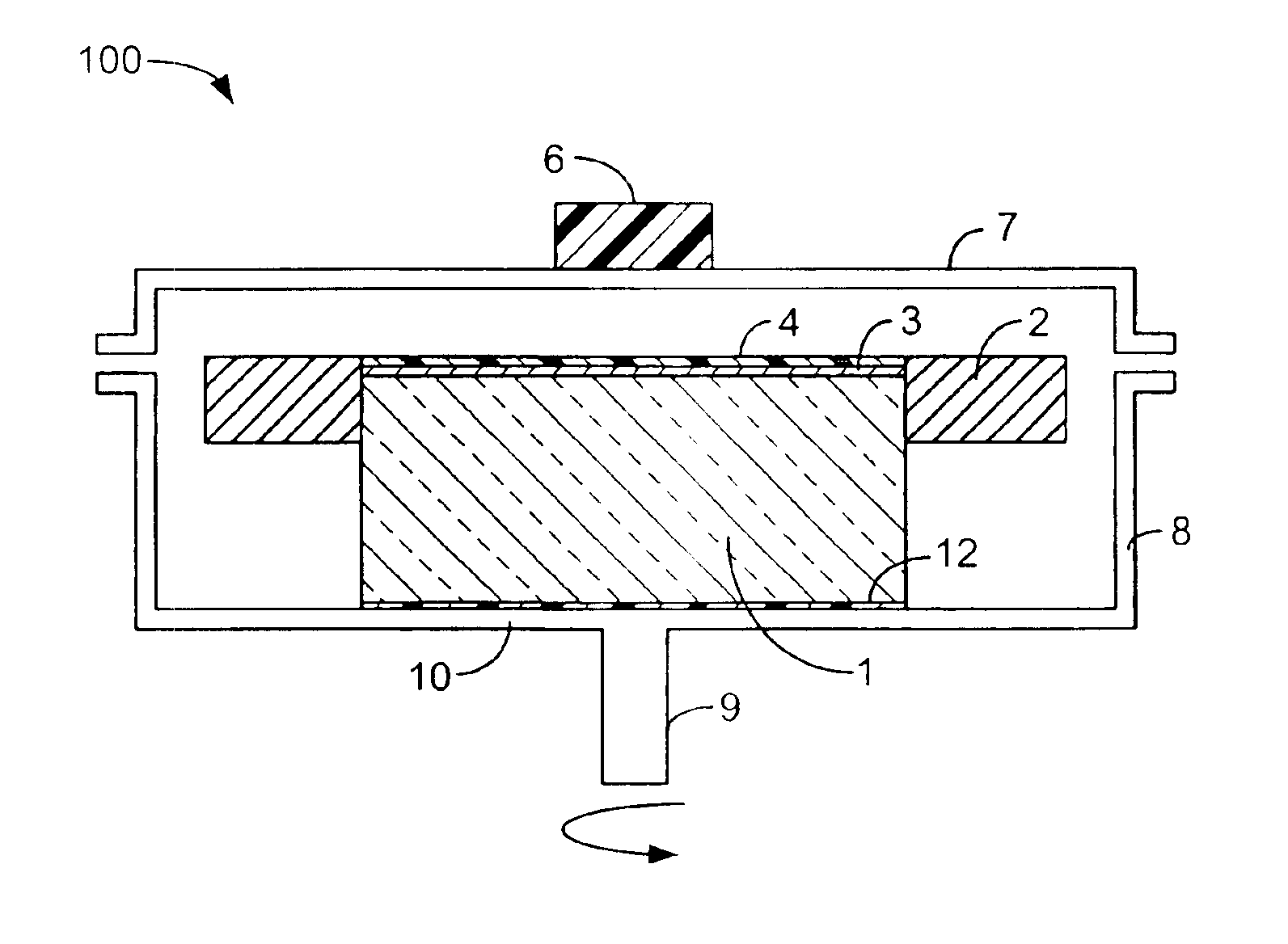
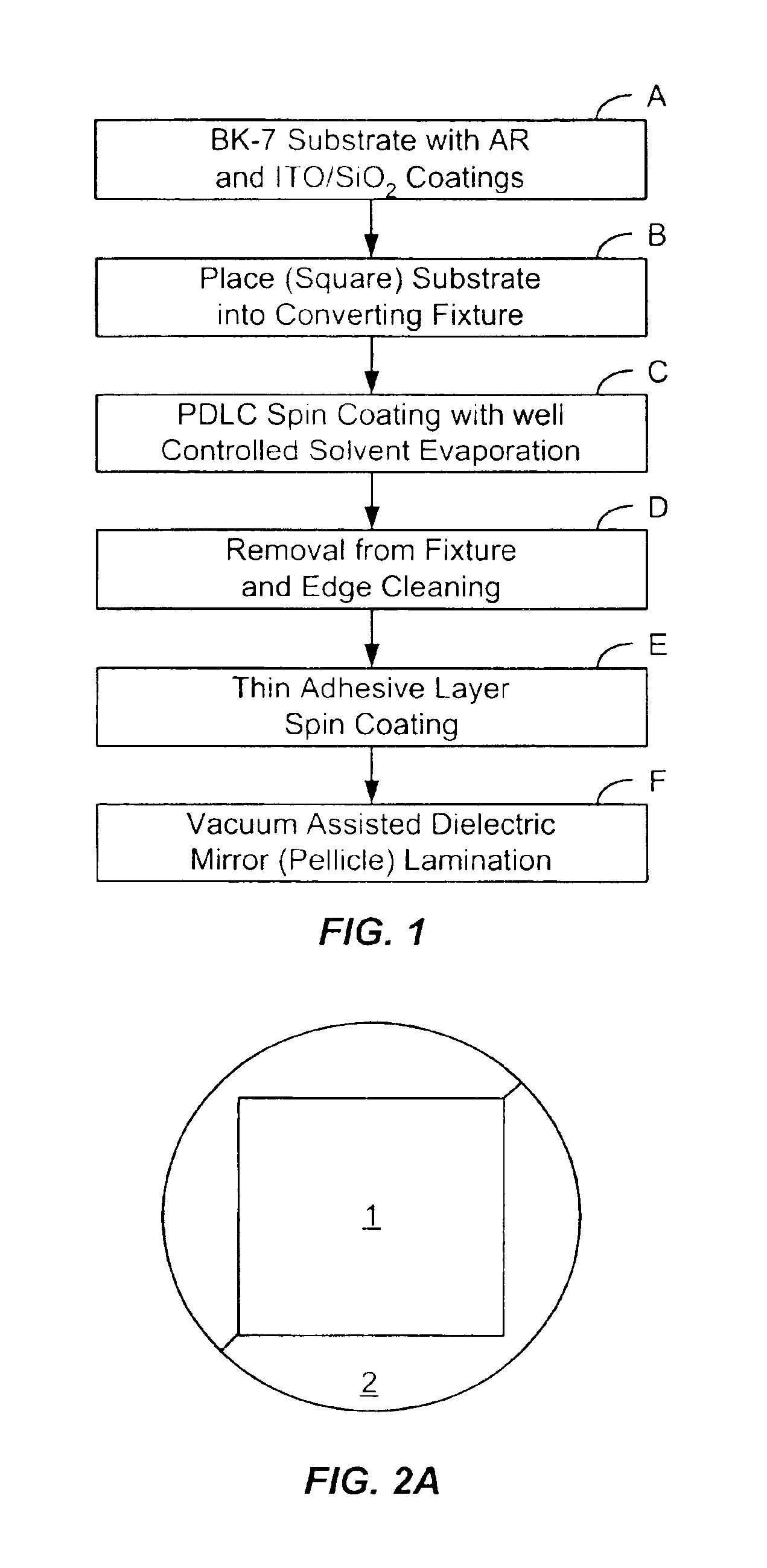
InactiveUS6866887B1Reduce and eliminate thickness and electro-optical variationSpraying apparatusLaminationWater basedEmulsion
Electro-optic structures are constructed by spin coating water based emulsions or solvent based sensor materials, preferably a solvent-based polymer dispersed liquid crystal (PDLC), onto a substrate under conditions of controlled solvent evaporation. In a particular process, the uniformity of the PDLC coating is achieved by 1) spin coating in a semi-sealed chamber, 2) “converting” a square substrate into round substrate by using a fixture; 3) providing a controllable distance between the substrate and a spin coater top cover; and 4) providing a controllable solvent evaporation rate.
Owner:PHOTON DYNAMICS
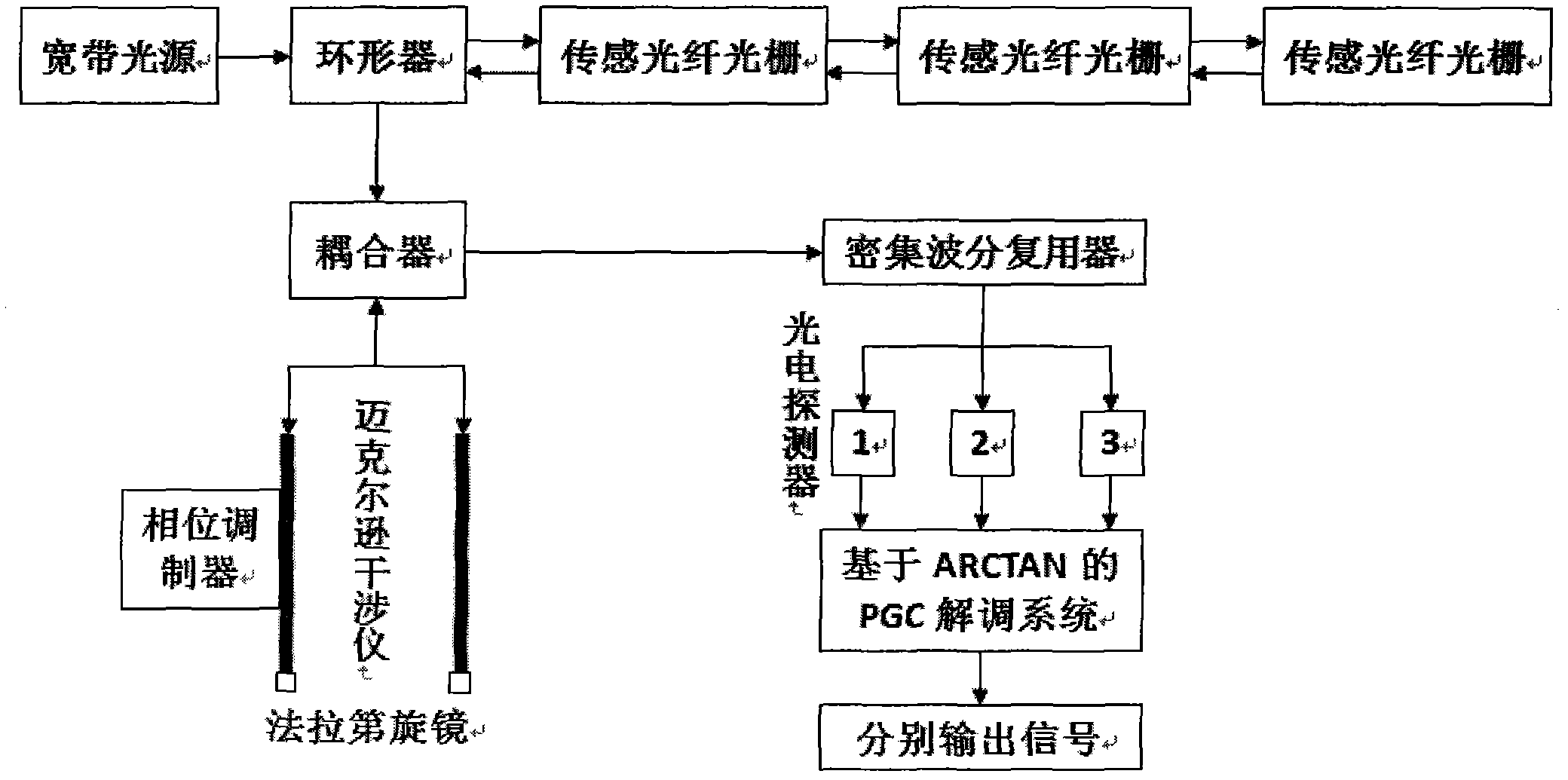
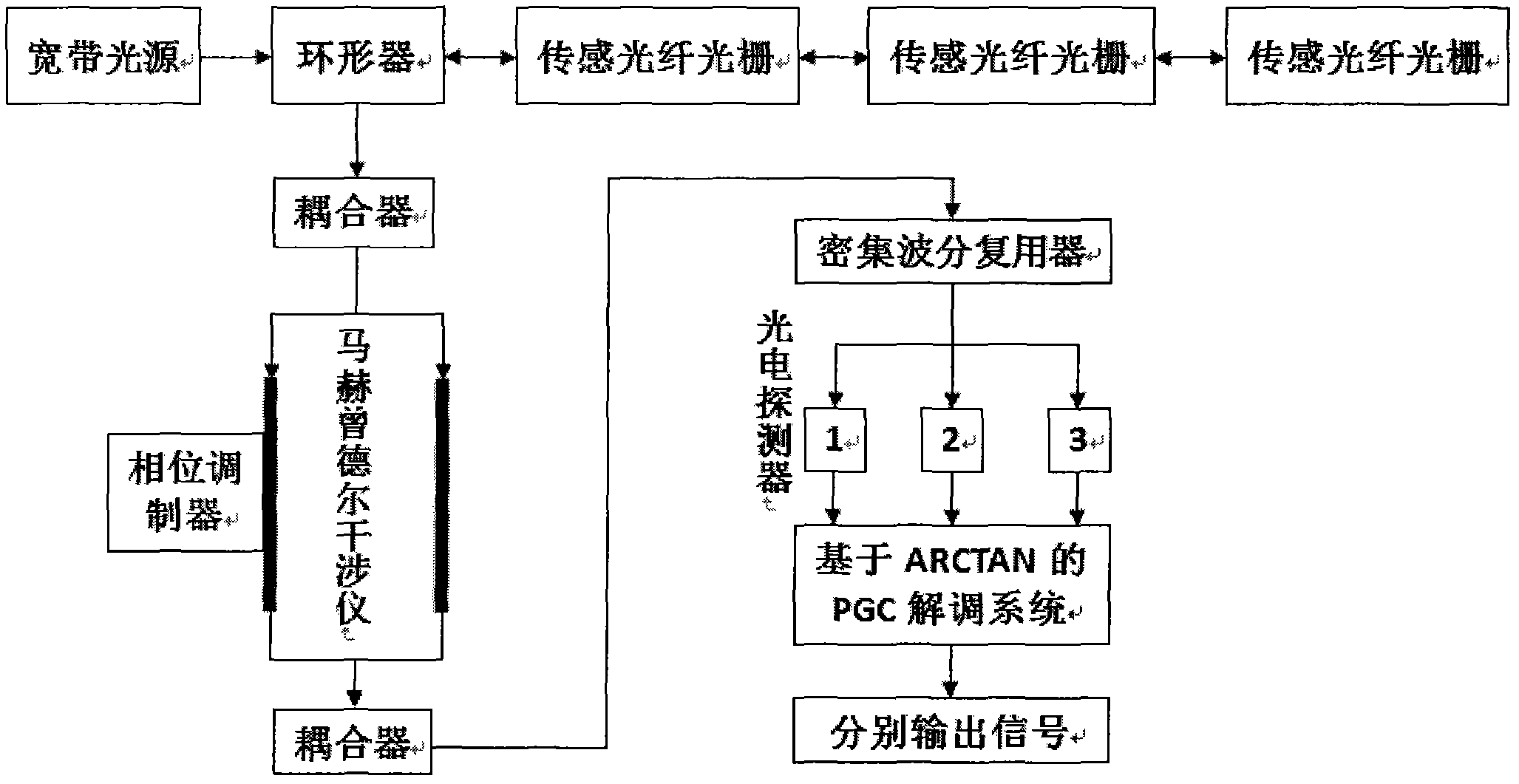
Unbalanced interferometer based fiber bragg grating (FBG) demodulation system and method
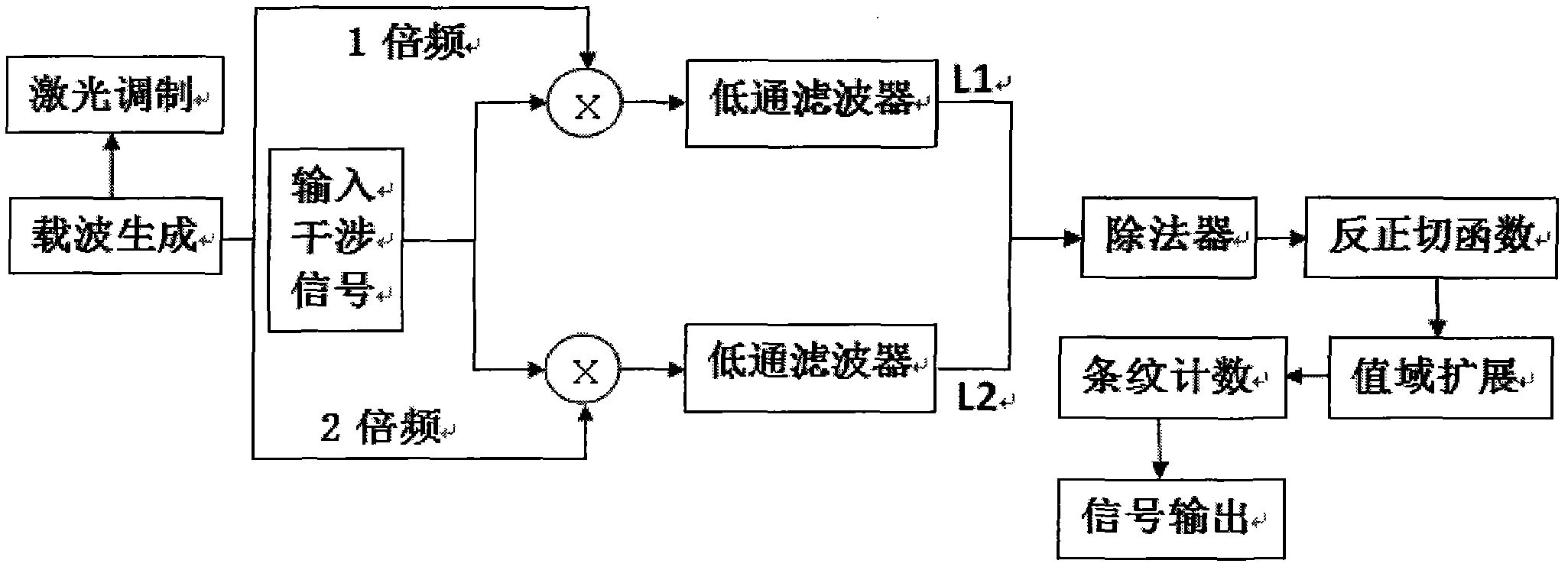
InactiveCN102147552AResponsiveHigh sensitivityLight demodulationConverting sensor output opticallyGratingAcousto-optics
The invention relates to an unbalanced interferometer based fiber bragg grating (FBG) demodulation system and method, belonging to the technical field of fiber optic sensing. The system sequentially passes through a superluminescent diode (SLD) or an amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) broadband light source, an optic isolator, a circulator or a coupler, and a fiber bragg grating and returns back to the circulator or the coupler, and then passes through the coupler, an unbalanced Michelson interferometer with two channels and a Faraday rotator mirror and returns back to an interferometer and the coupler or passes through a Mach-Zehnder interferometer with two channels and the coupler, wherein one channel of the interferometer is wound around a piezoelectric ceramic or an electrooptical modulator, and an acousto-optic modulator, finally passes through a dense wave division multiplexer and a photoelectric detector and is connected with an ARCTAN based PGC (Phase Generation Carrier) signal response demodulation module. The invention has the advantages; by adopting the combination of the an FBG sensor and ARCTAN-based PGC phase modulation, the system has high sensitivity, large dynamic range and good linearity, good response to an abrupt signal and easiness of multiplexing, low cost and easiness of implementing.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
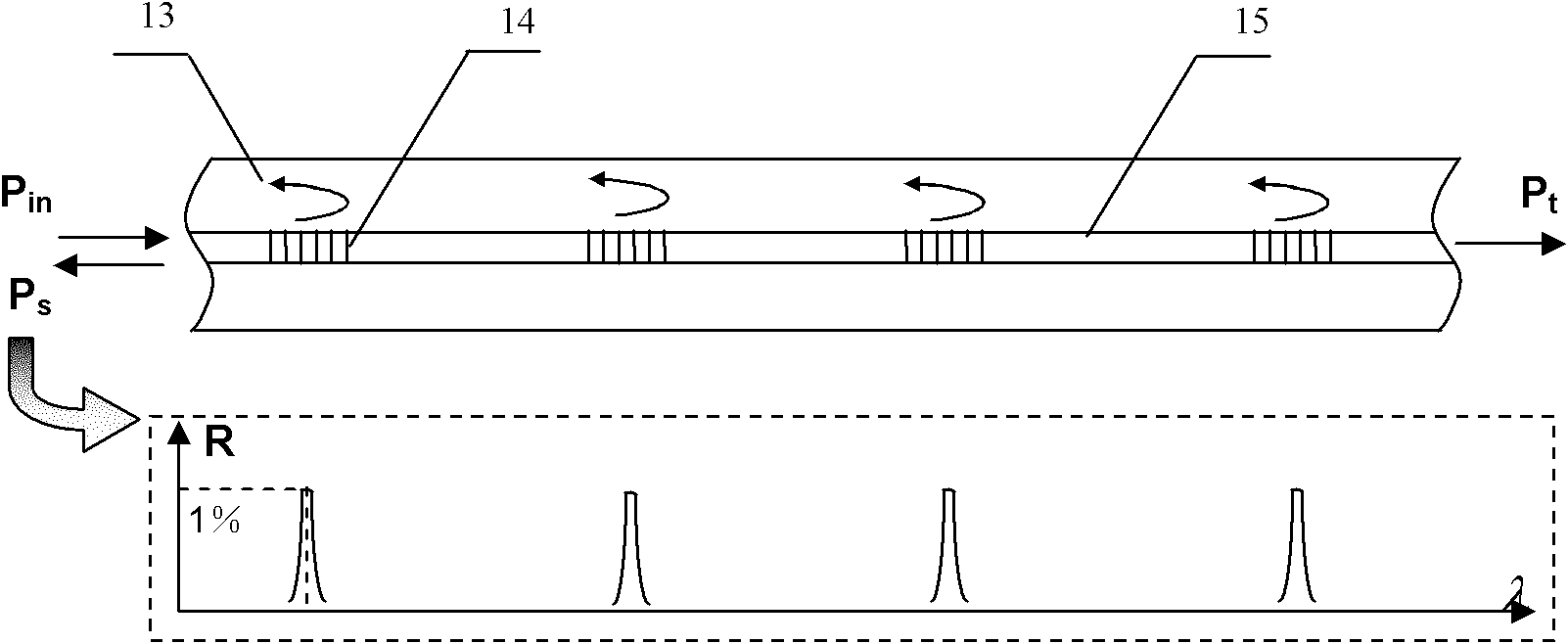
Distributed sensing system based on weak Bragg reflection structure
InactiveCN102102998AImprove reflectivityHigh measurement accuracyConverting sensor output opticallyControl signalDistributed Bragg reflector
The invention discloses a distributed sensing system based on a weak Bragg reflection structure. The distributed sensing system comprises a SG-DBR (Screen Grid-Distributed Bragg Reflector) tunable laser (1), an electrooptic modulator (4), an opto-isolator (5), an optical circulator (6), and weak Bragg reflection cycle structural optical fibers (7), which are connected in turn; wherein the SG-DBR tunable laser (1) is controlled by a wavelength tuning control circuit (2), the electrooptic modulator (4) is controlled by an impulse function generator (3), a photo-detector (8) is connected with the optical circulator (6), control signals outputted by the wavelength tuning control circuit (2) and the electrooptic modulator (4) and electric signals outputted by the photo-detector (8) enter a data acquisition card (9) jointly, and are processed and then transmitted to a data processing device (10). The distributed sensing system realizes the long-distance distributed sensing alarm for parameters such as temperature, stress and vibration, and has the characteristics of higher detection sensitivity and positioning precision, easiness for realization, lower cost and reliability for operation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-speed silicon-based electro-optic modulator
ActiveCN1764863AReduce light lossReduce power consumptionCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideElectricitySurface layer
A silicon-based electro-optical modulator (30) based on a gate region of the first conductivity formed to partially cover the body region of the second conductivity type, having interposed between the contact portions of the gate region and the body region (12, 10) A relatively thin dielectric layer (10). The modulator may be formed on an SOI platform with a body region formed in a relatively thin silicon surface layer of the SOI structure and a gate region formed with a relatively thin silicon layer (10) overlying the SOI structure. The doping of the control gate and body regions is used to form lightly doped regions above and below the dielectric layer, thereby defining the active region of the device (16). Advantageously, the photoelectric field in the active device region is substantially identical to the free carrier concentration region. Therefore, the application of the modulation signal causes the free carriers on both sides of the dielectric layer to accumulate, deplete or invert simultaneously, resulting in high-speed operation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Device and method for controlling bias voltage of electrooptical modulator
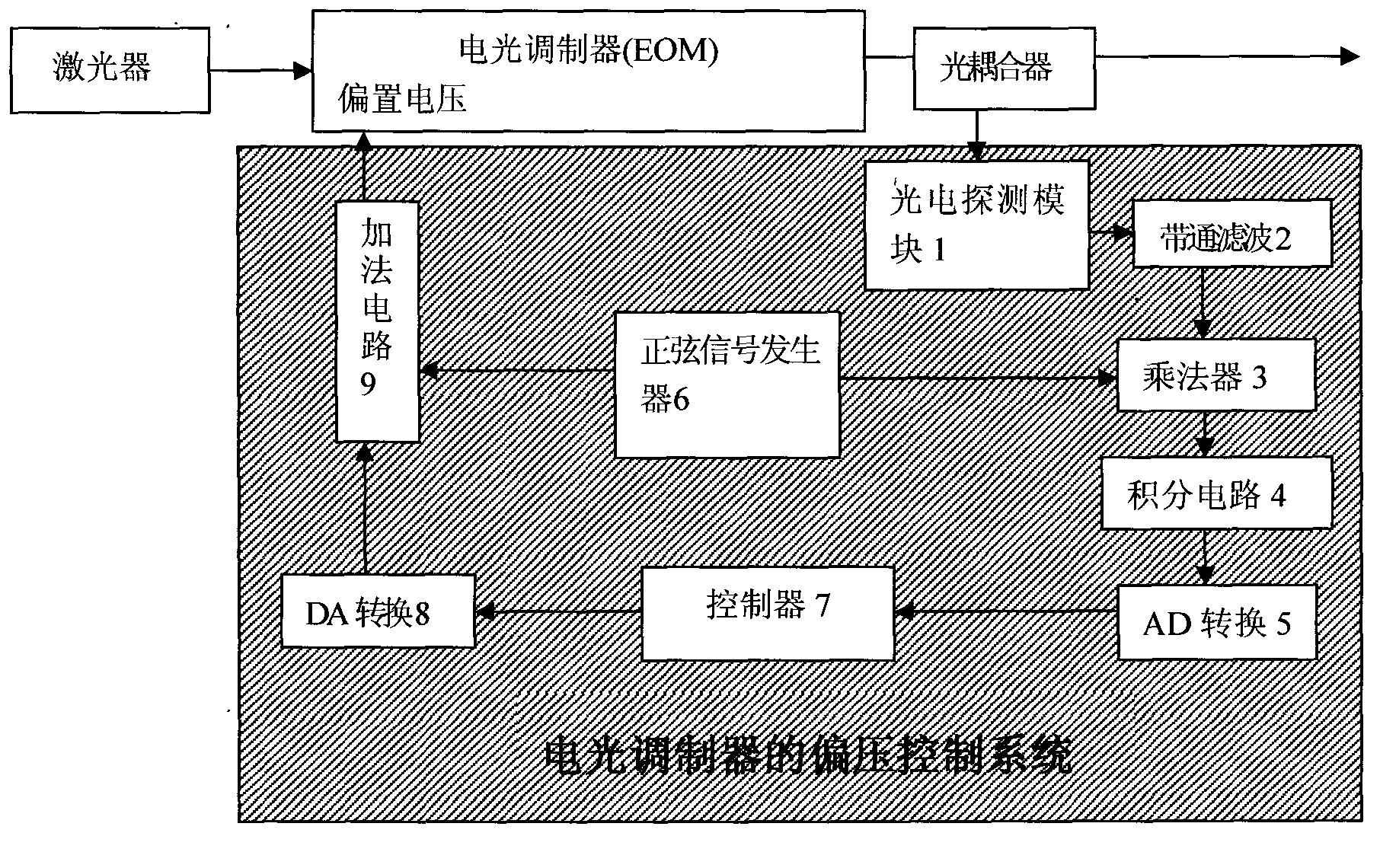
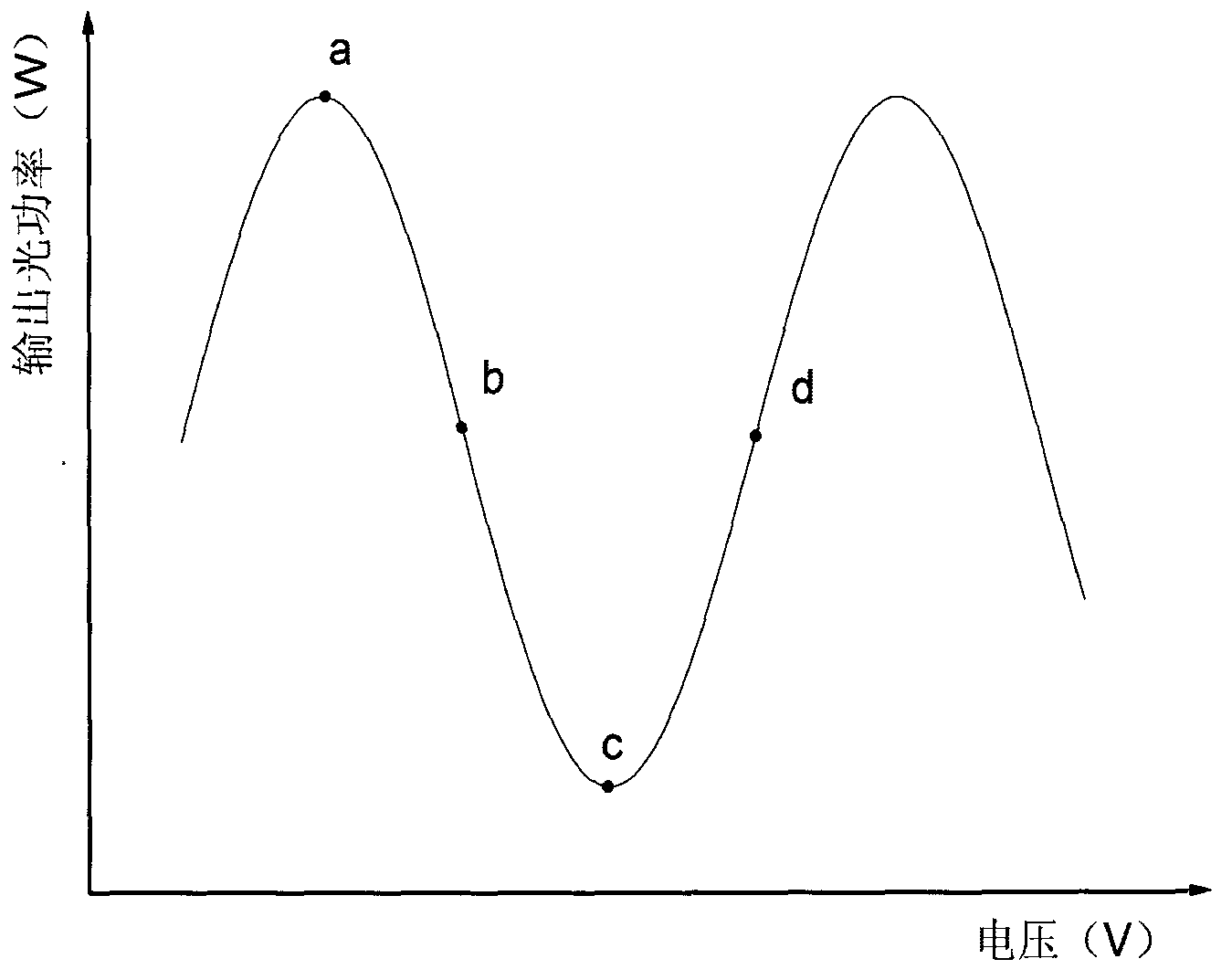
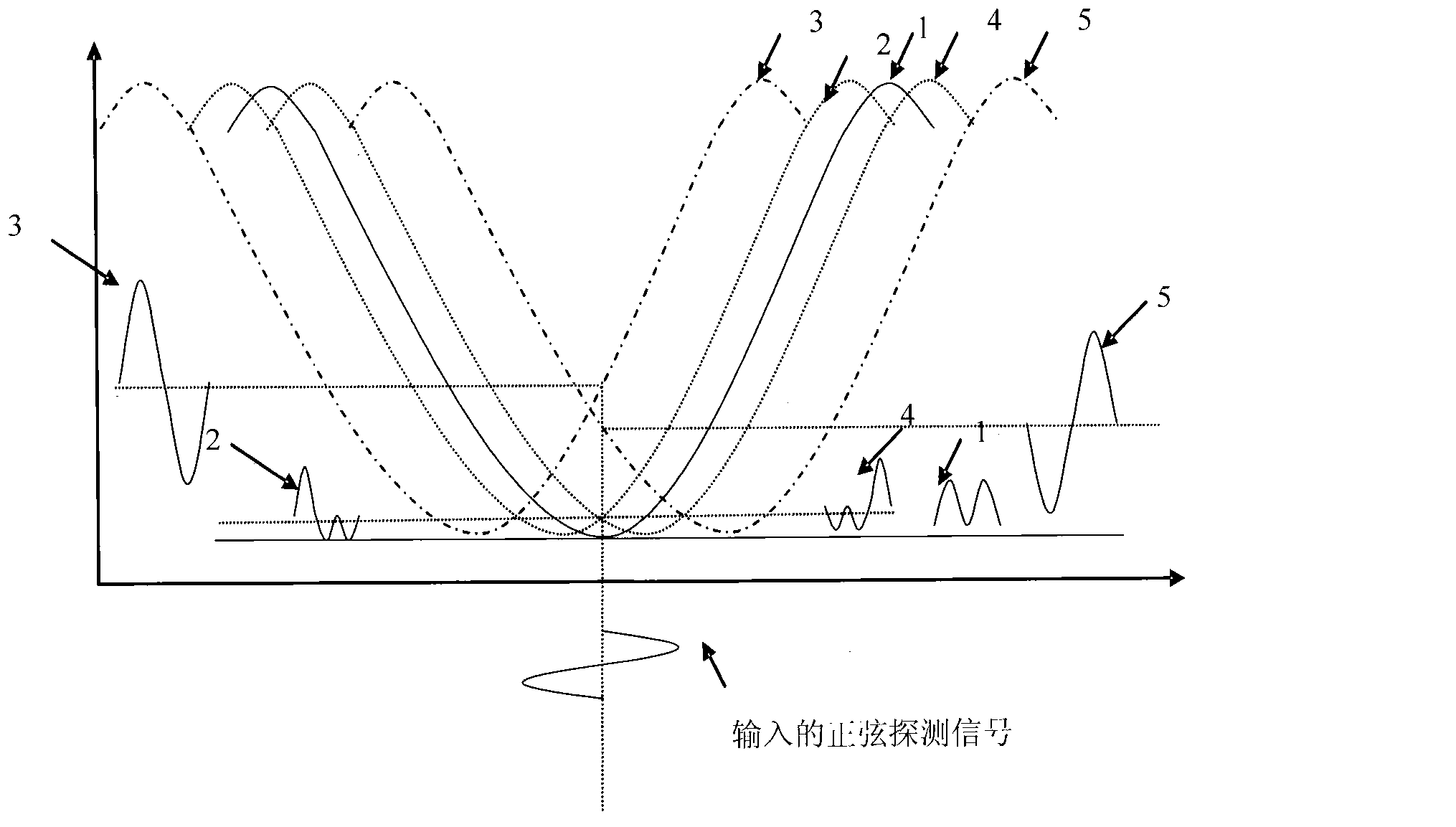
InactiveCN103019286AStable jobChange the size of the optical power at willNon-linear opticsElectric variable regulationEngineeringElectro-optic modulator
The invention discloses a device and method for controlling the bias voltage of an electrooptical modulator. The device and method are used for controlling the bias voltage of the electrooptical modulator, not only can enable the stable working of the electrooptical modulator to resist the external interference, but also can control the electrooptical modulator to work in different states according to the need. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting a continuous-sine bias voltage signal with the known period into the electrooptical modulator, then demodulating the response of the electrooptical modulator to the signal to judge and determine the working point of the electrooptical modulator and the drift of the working point caused by external influence, and finally adjusting the bias voltage of the electrooptical modulator and enabling the electrooptical modulator to work on the set working point stably.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com