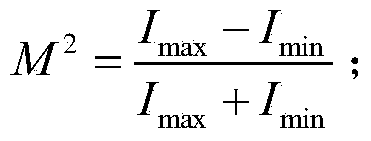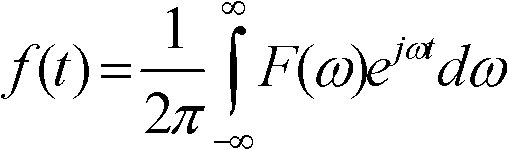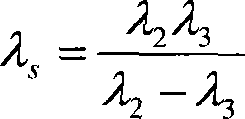Patents
Literature
602 results about "Michelson interferometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
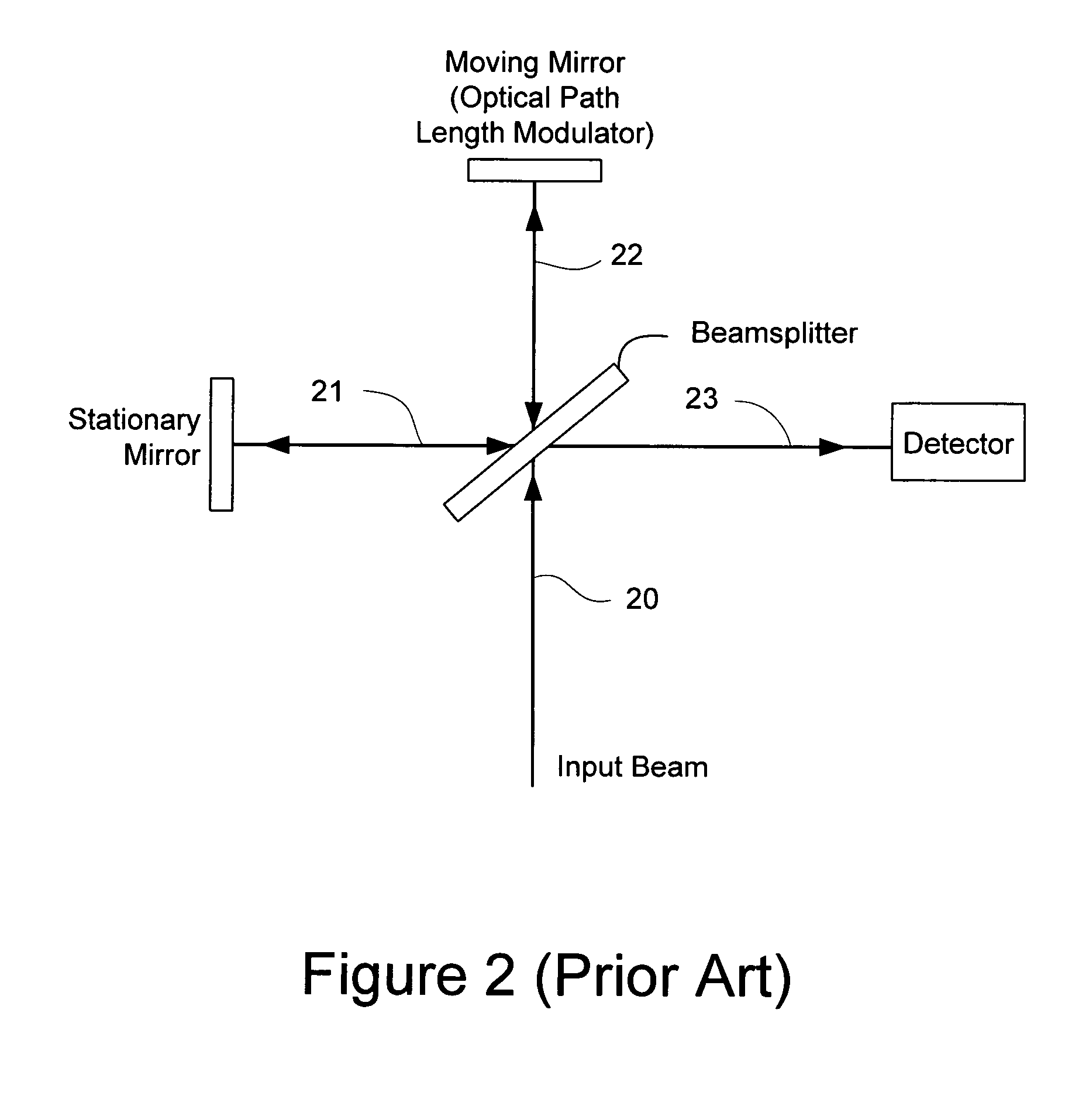
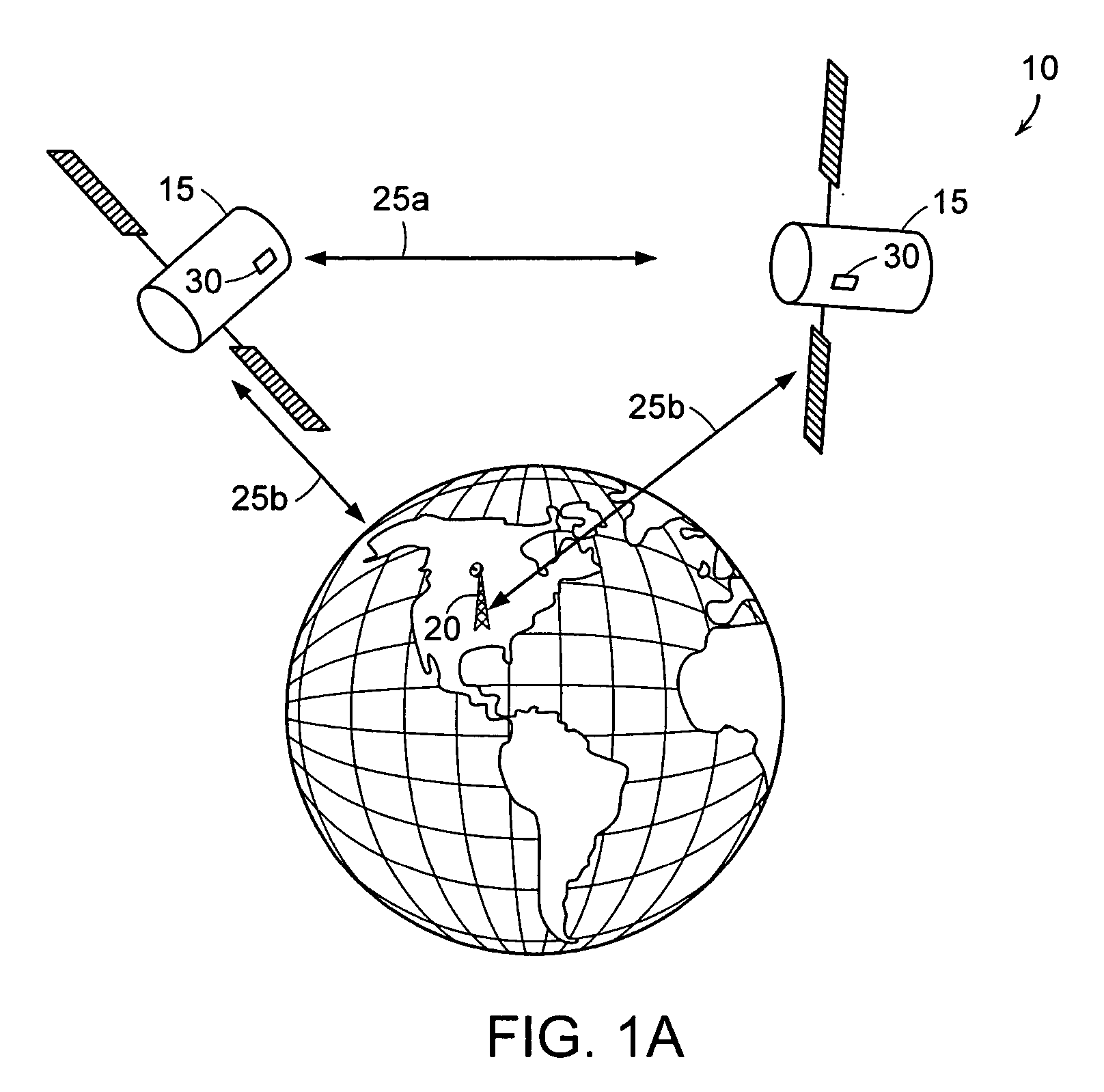
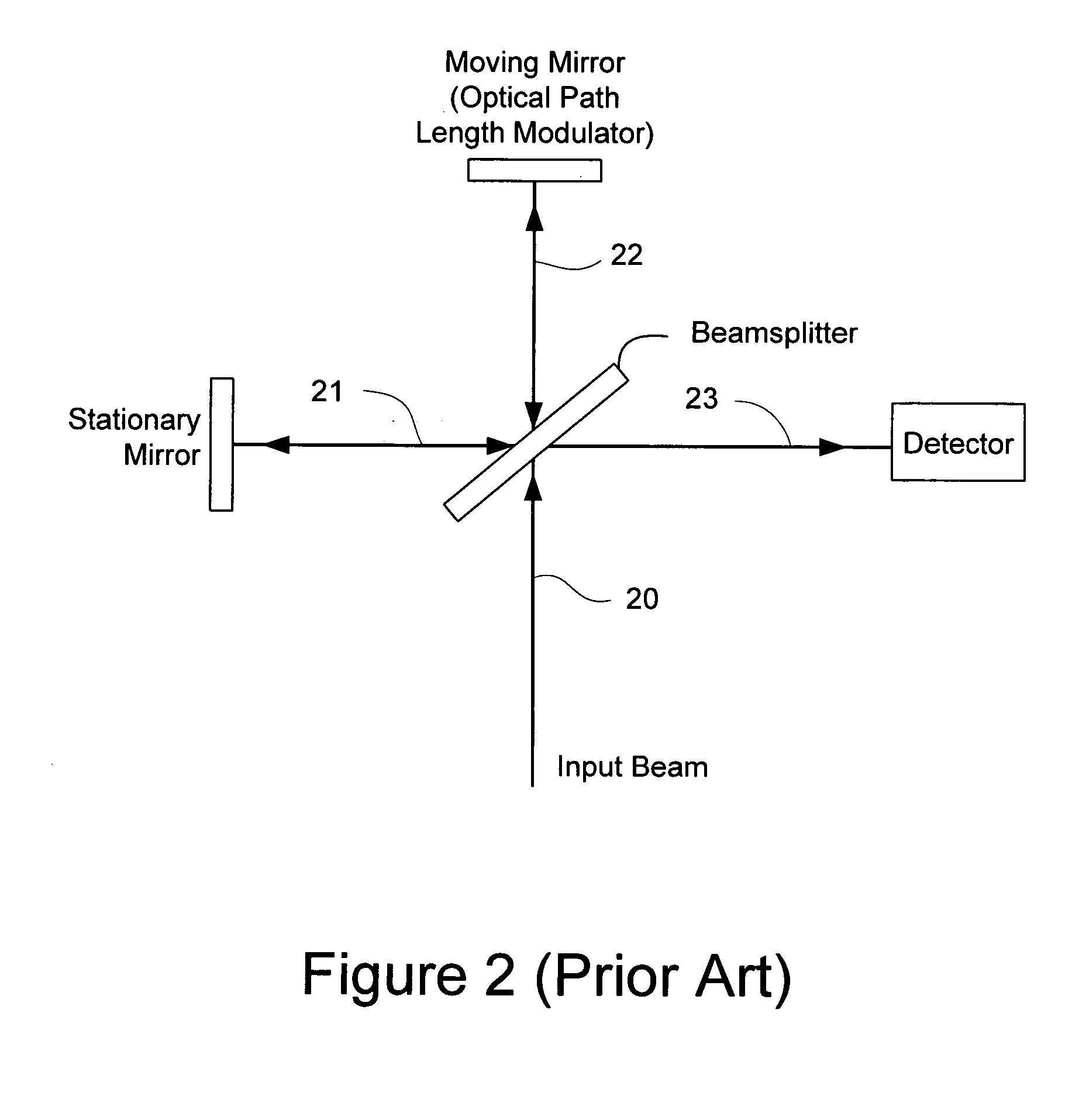
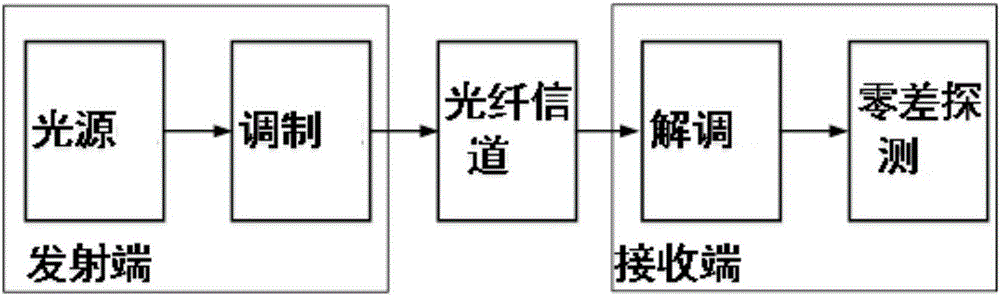
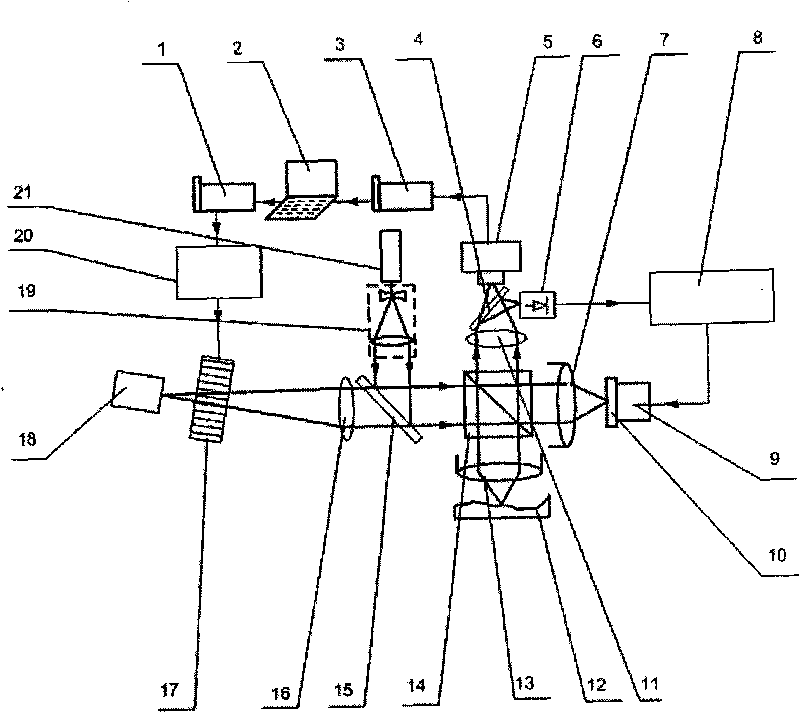
The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by Albert Abraham Michelson. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light beams is reflected back toward the beamsplitter which then combines their amplitudes using the superposition principle. The resulting interference pattern that is not directed back toward the source is typically directed to some type of photoelectric detector or camera. For different applications of the interferometer, the two light paths can be with different lengths or incorporate optical elements or even materials under test.
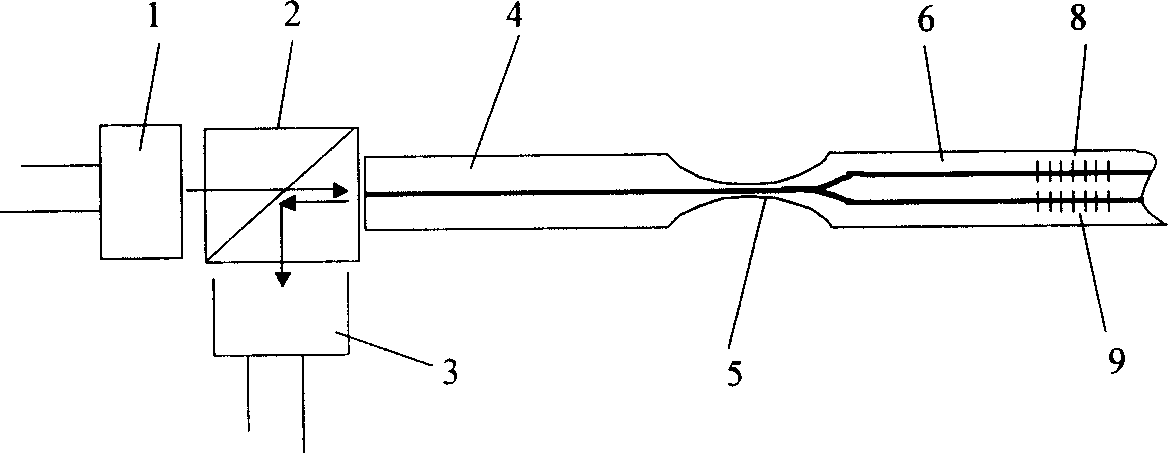
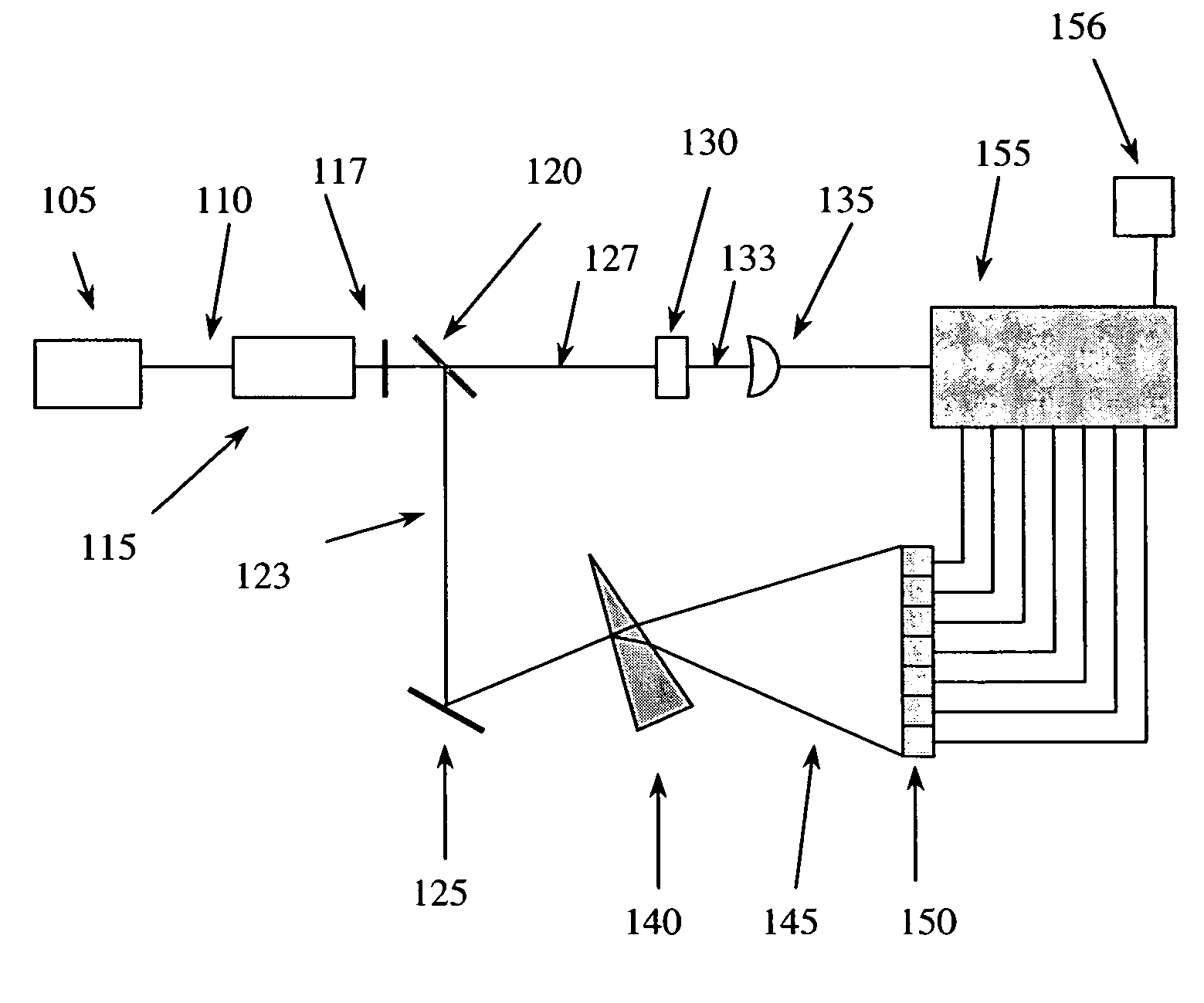
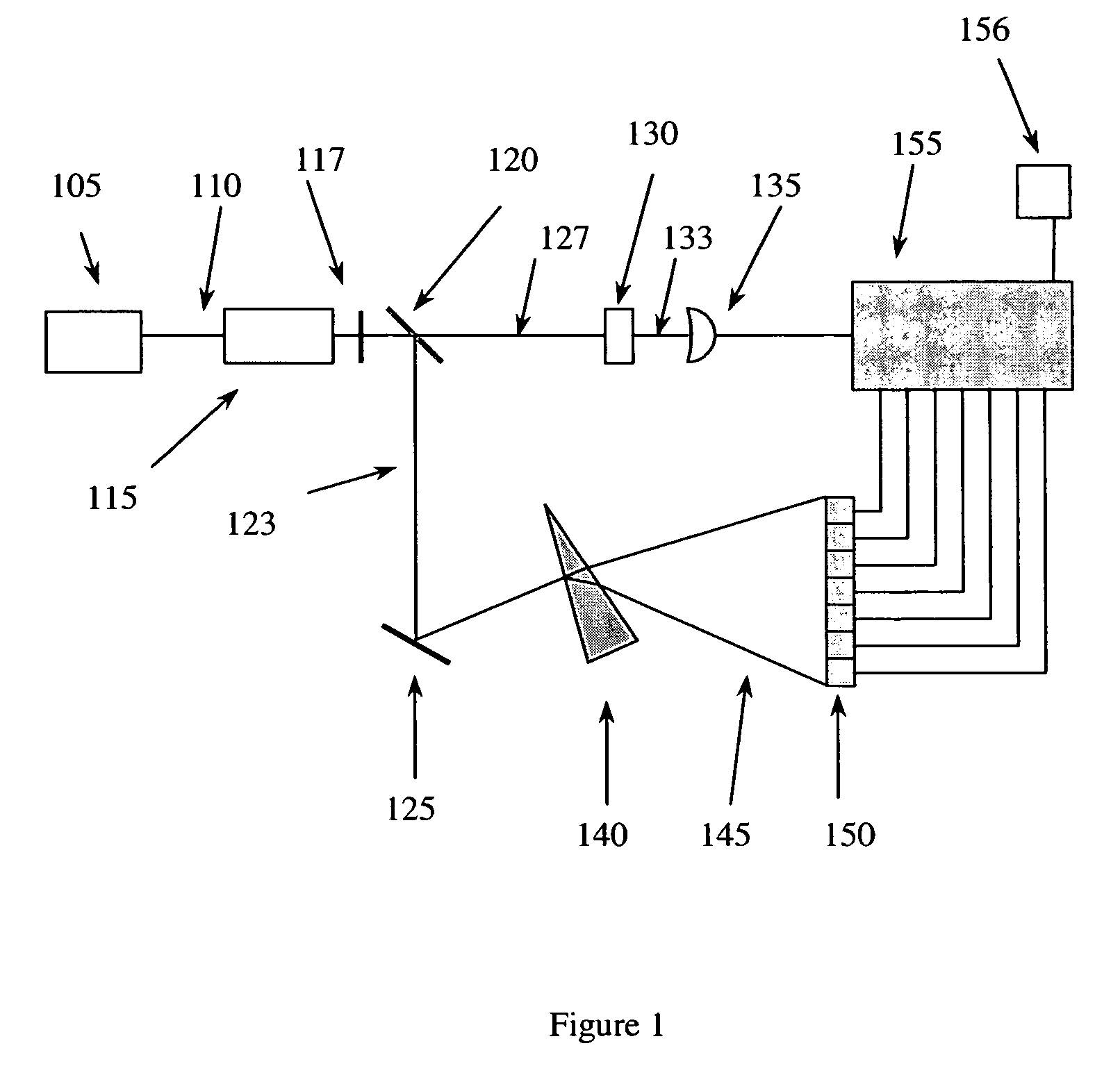
Miniature fourier transform spectrophotometer
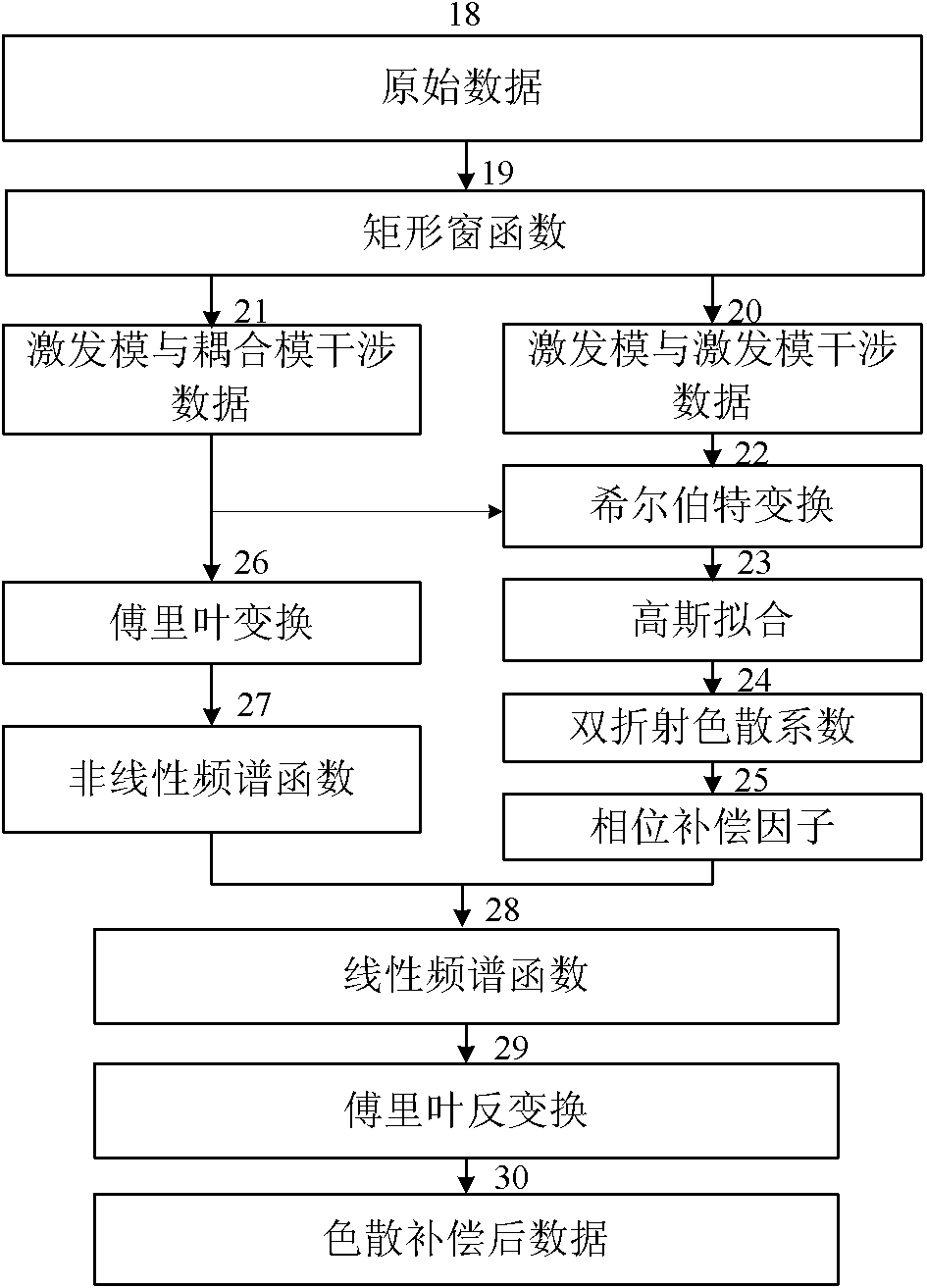
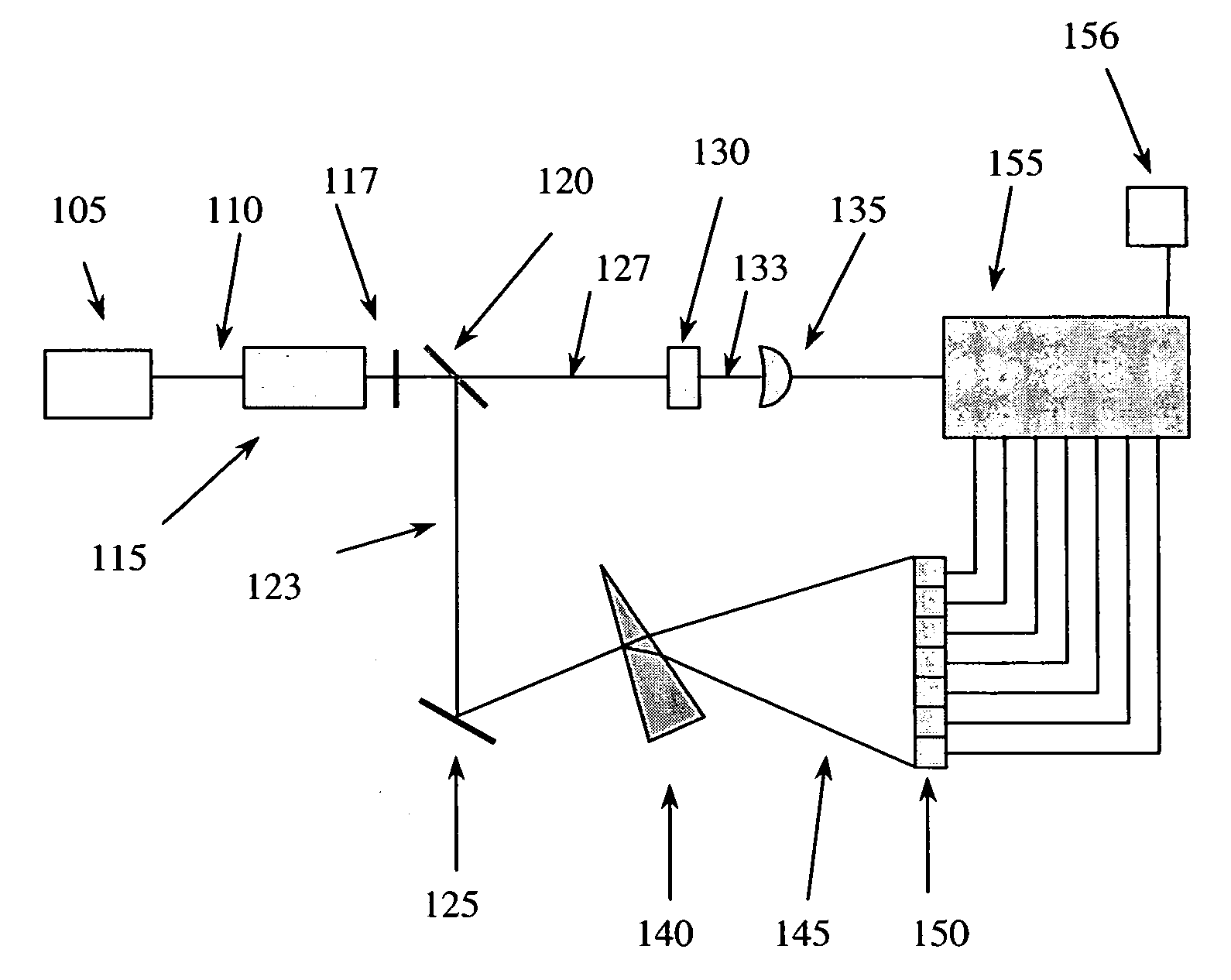
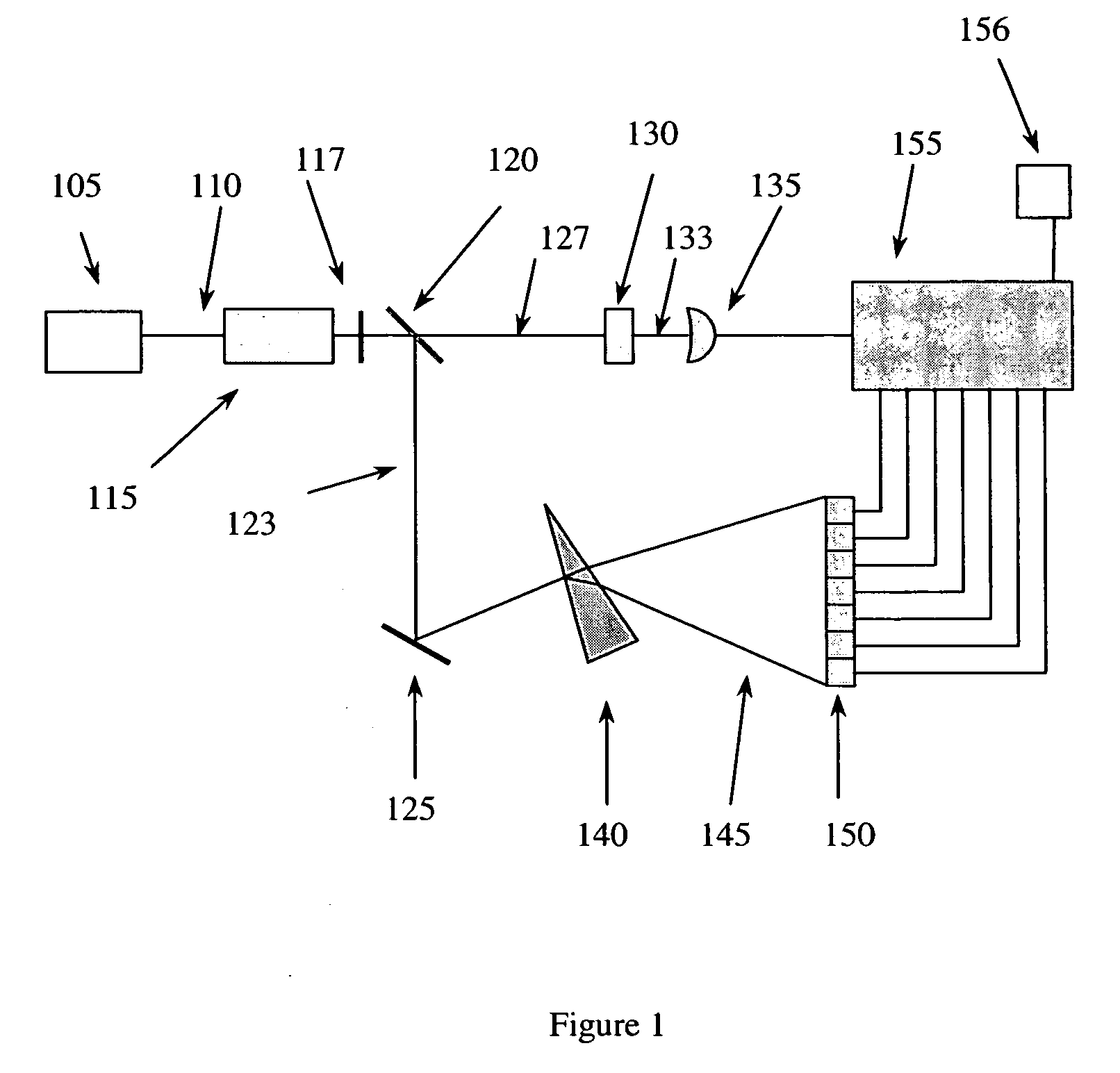
ActiveUS7359058B2Decreased wavelengthRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryMichelson interferometerOptical path length
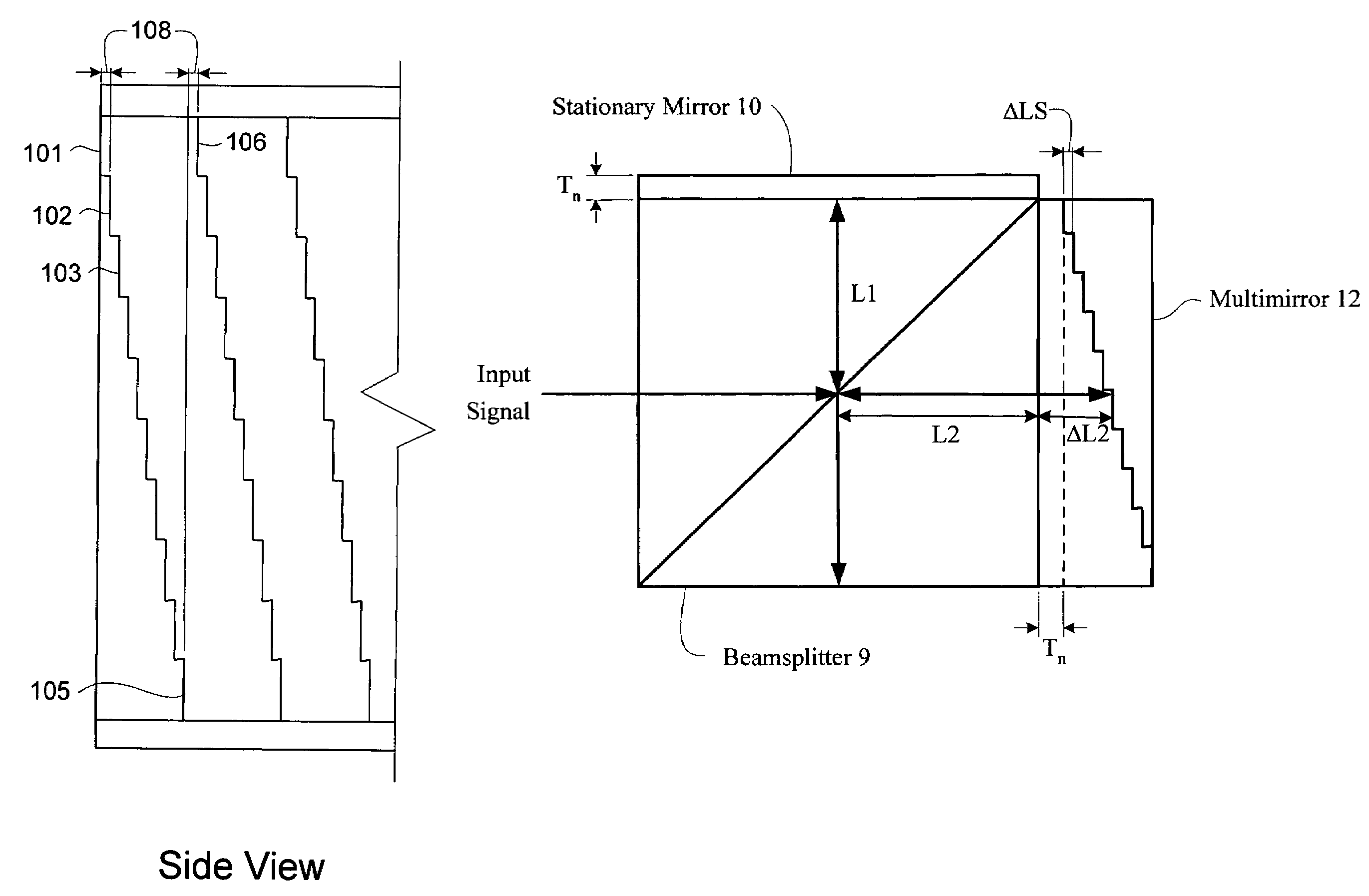
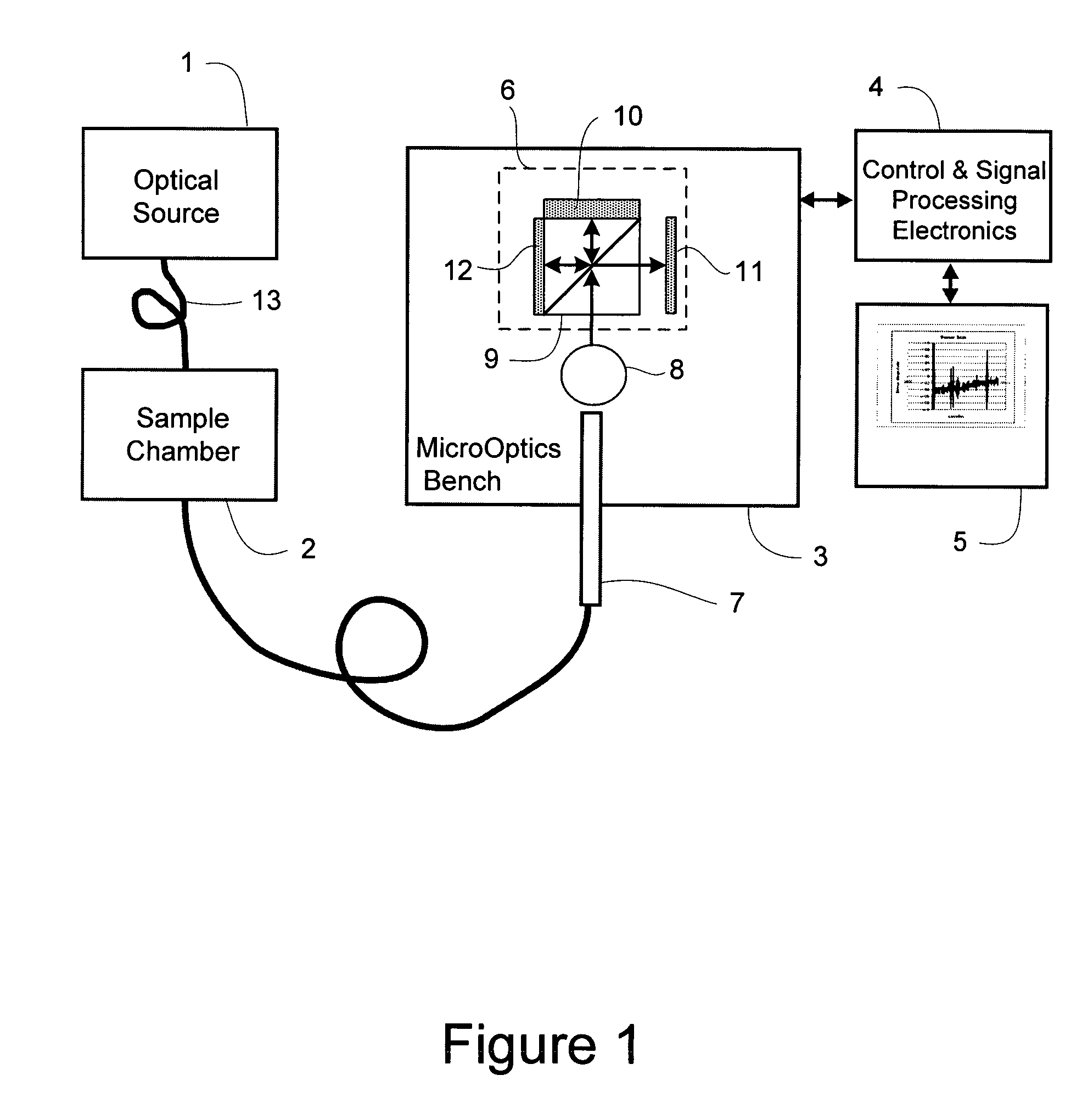
The Miniature Fourier Transform Spectrophotometer provides the capability, in a miniaturized device, of determining the light absorption / transmission spectra of a collected sample of gas or liquid though Fourier Transform spectroscopy techniques. The device takes an optical input from an optical fiber, manipulates that light through miniature optical components, and launches it into a miniaturized Michelson interferometer with a scanning mirror that acquires the interferogram of the optical input. The interferogram can be processed to retrieve the spectrum of the input light. A novel multi-stepped micro-mirror operates as the optical path length modulator in the miniaturized interferometer. A unique monolithic beamsplitter / mirror combination provides for accurate alignment of the components and greatly simplifies product integration. The device is designed to cover various optical spectra of interest. During operation, the precision and accuracy of the microfabricated components in the device allow operation and resolution even at extremely low wavelengths. In addition, the miniaturized nature of the device allows it to be used in new and extremely space-constrained applications.
Owner:MORGAN RES CORP
Reconfigurable polarization independent interferometers and methods of stabilization
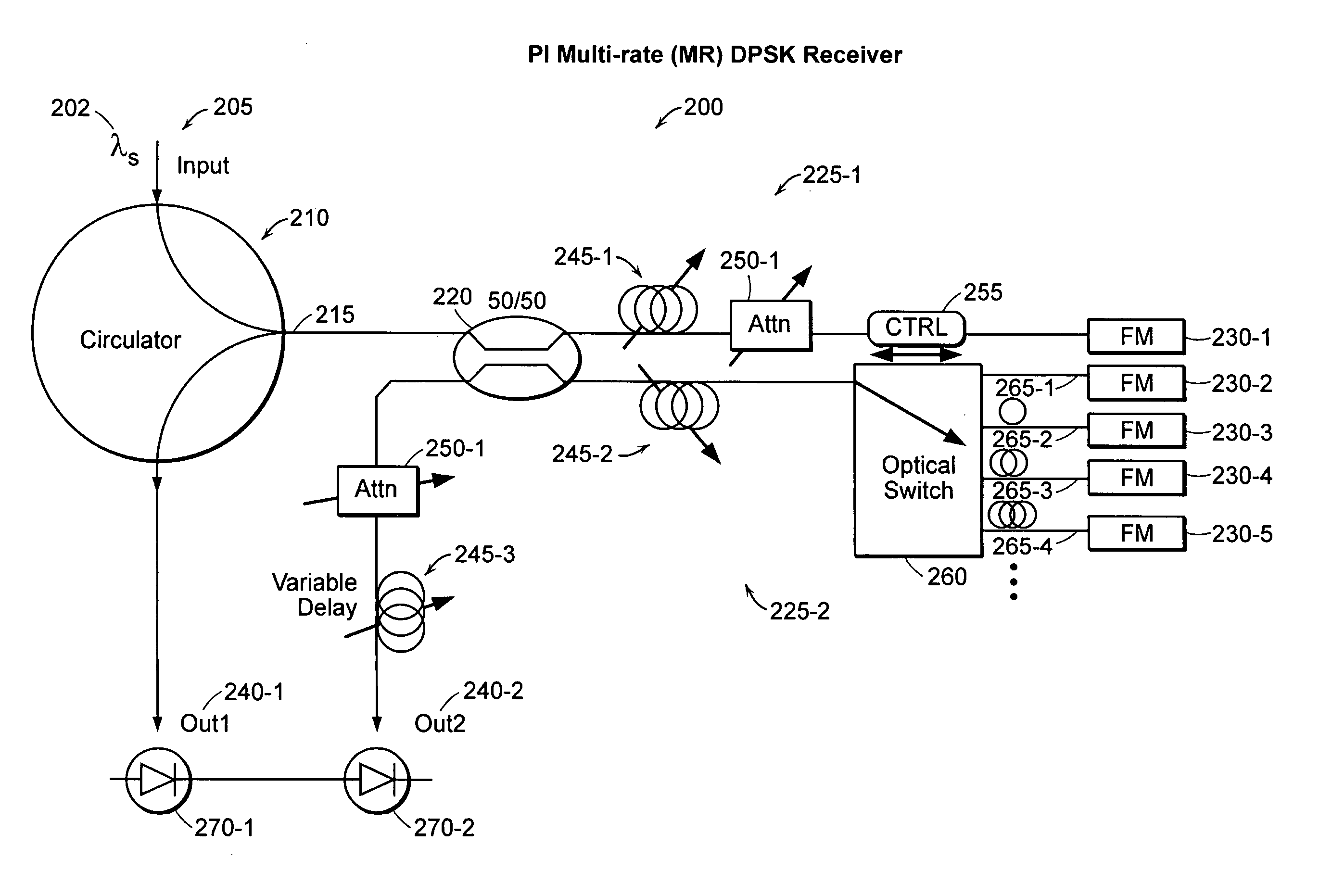
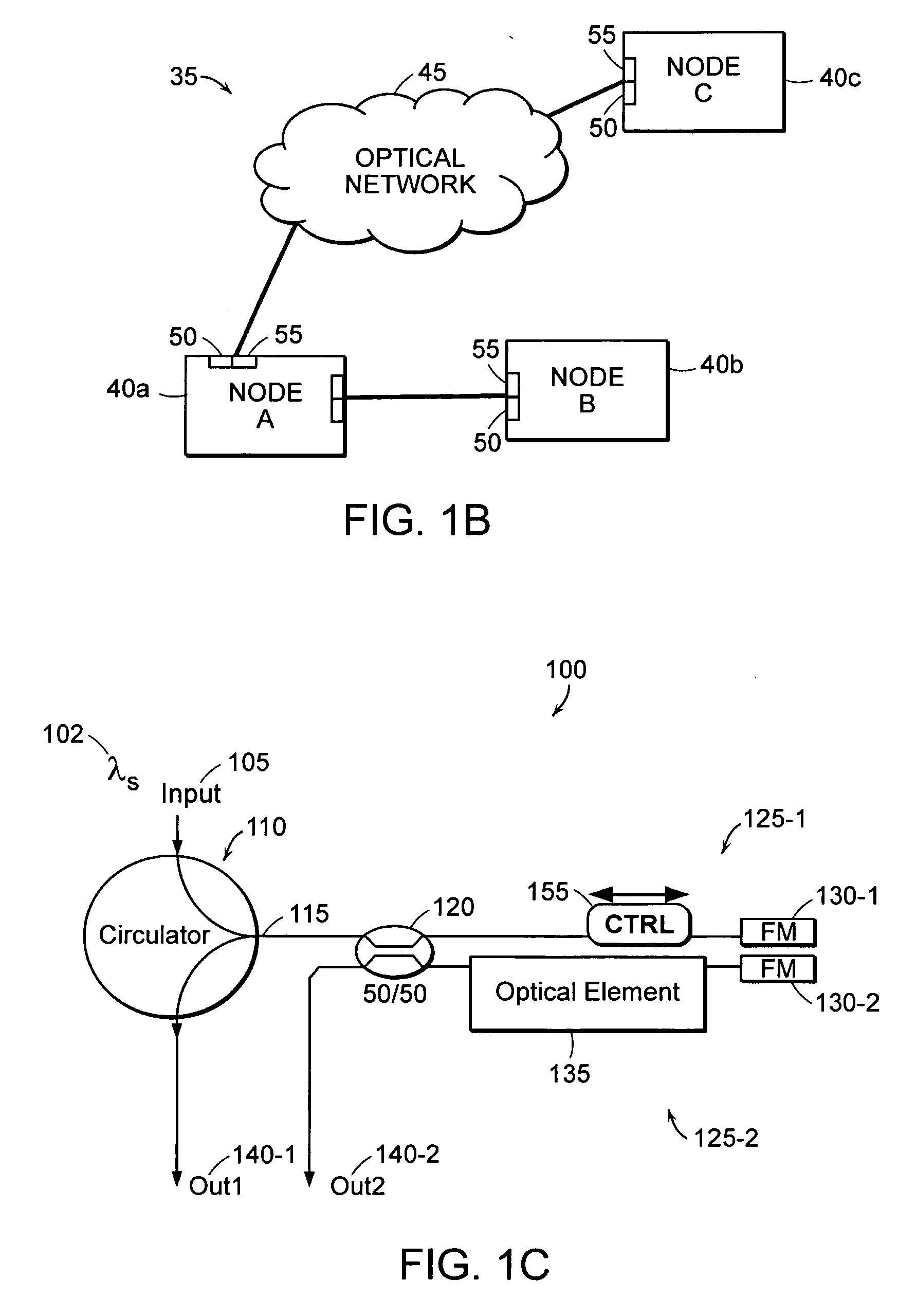
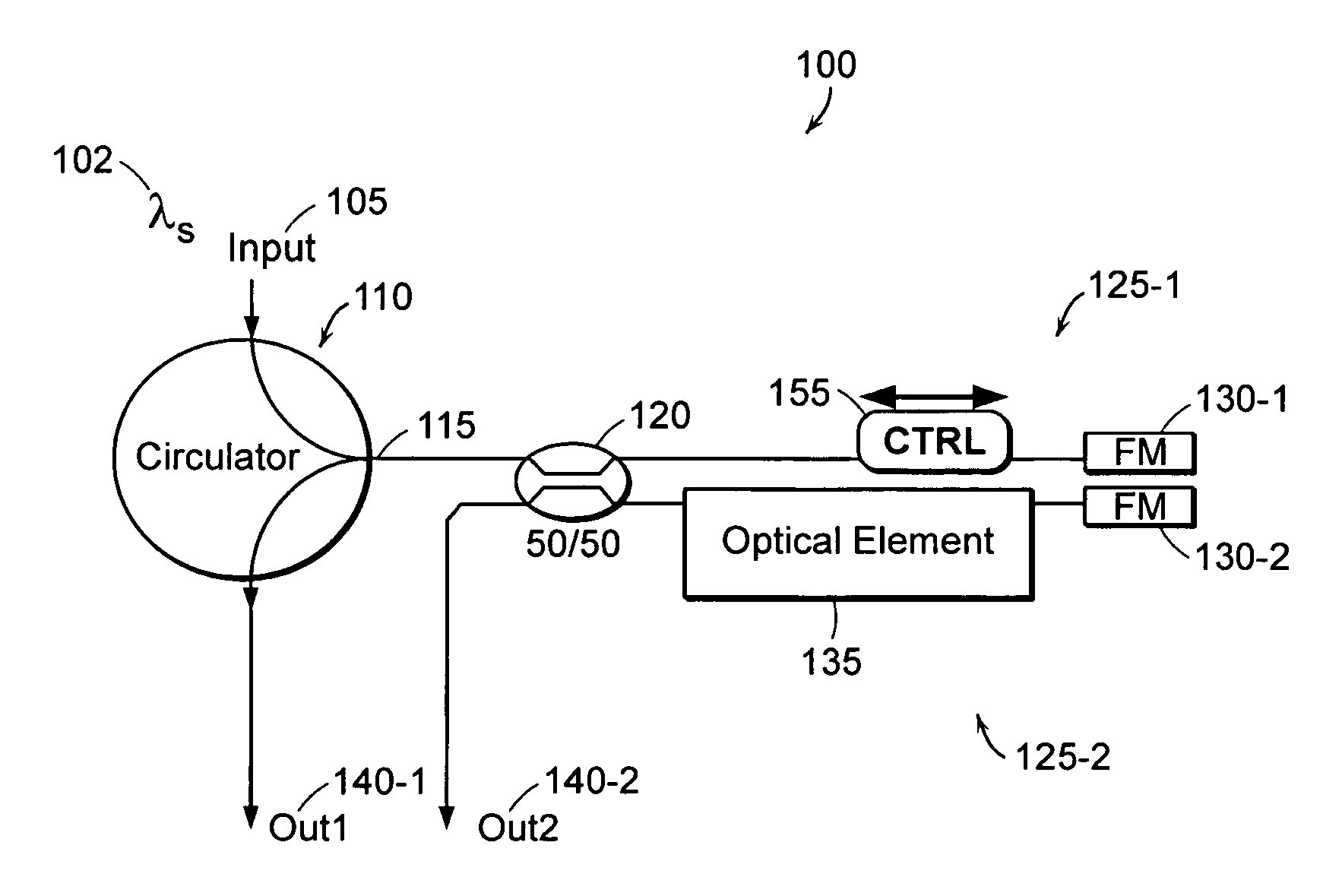
A polarization independent (PI) interferometer design that can be built from standard optical components is described. Based upon a Michelson interferometer, the PI interferometer uses a 50 / 50 splitter and Faraday Rotator Mirrors (FM's). The interferometer achieves good optical characteristics, such as high extinction ratio (ER) and low insertion loss (IL). Lack of polarization sensitivity reduces interferometer construction tolerances and cost, enhances performance and utility, and expands the scope of interferometric based devices. Such characteristics can be used to construct flexible, high performance, polarization insensitive, multi-rate, self-calibrating, optical DPSK receivers, power combiners, optical filters and interleavers, all-optical switches, and cascaded interferometers. Since polarization is not maintained in standard fiber optic networks, a PI-DPSK receiver allows for use of more sensitive DPSK communications over fiber, without need for costly polarization control hardware. Other applications of PI interferometers include optical CDMA, secure communications, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and temporal gratings with ultra-precise timing.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Nonlinear optical device
InactiveUS20050047702A1Enhanced optical confinementEasy to integrateOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsAudio power amplifierMichelson interferometer
There is provided a non-linear optical device for enhancing the bandwidth accessible in the nonlinear generation of an optical signal. The device comprises a planar optical waveguide, the planar optical waveguide being operative to generate an optical output from an optical input having an input bandwidth by means of a non-linear optical process, the optical output having a wavelength within an accessible bandwidth, wherein the planar optical waveguide is operative to enhance the accessible bandwidth such that the ratio of the accessible bandwidth to the input bandwidth is at least 4. The device is particularly applicable to broad optical continuum generation, but may also be used in a parametric oscillator or amplifier arrangement with broad tuning range. The planar waveguide geometry permits easy integration in more complex photonic integrated circuits such as a Michelson interferometer for low coherence interferometry based optical coherence tomography.
Owner:MESOPHOTONICS LTD
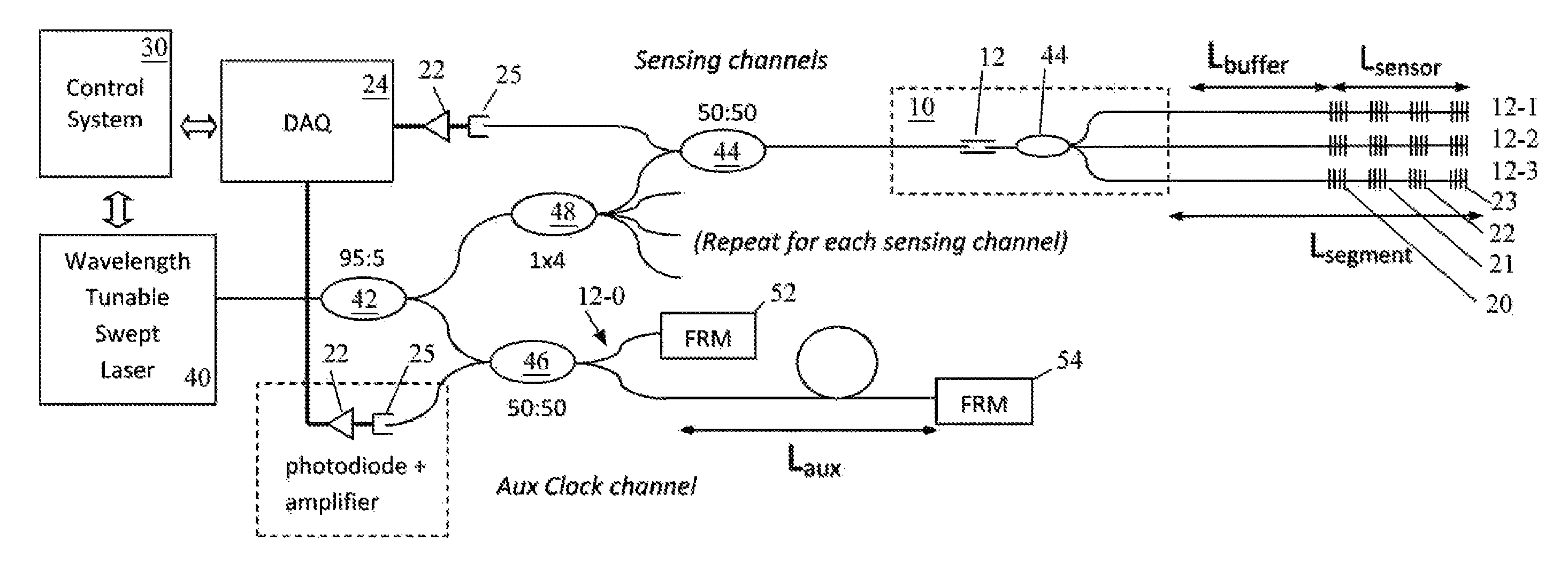
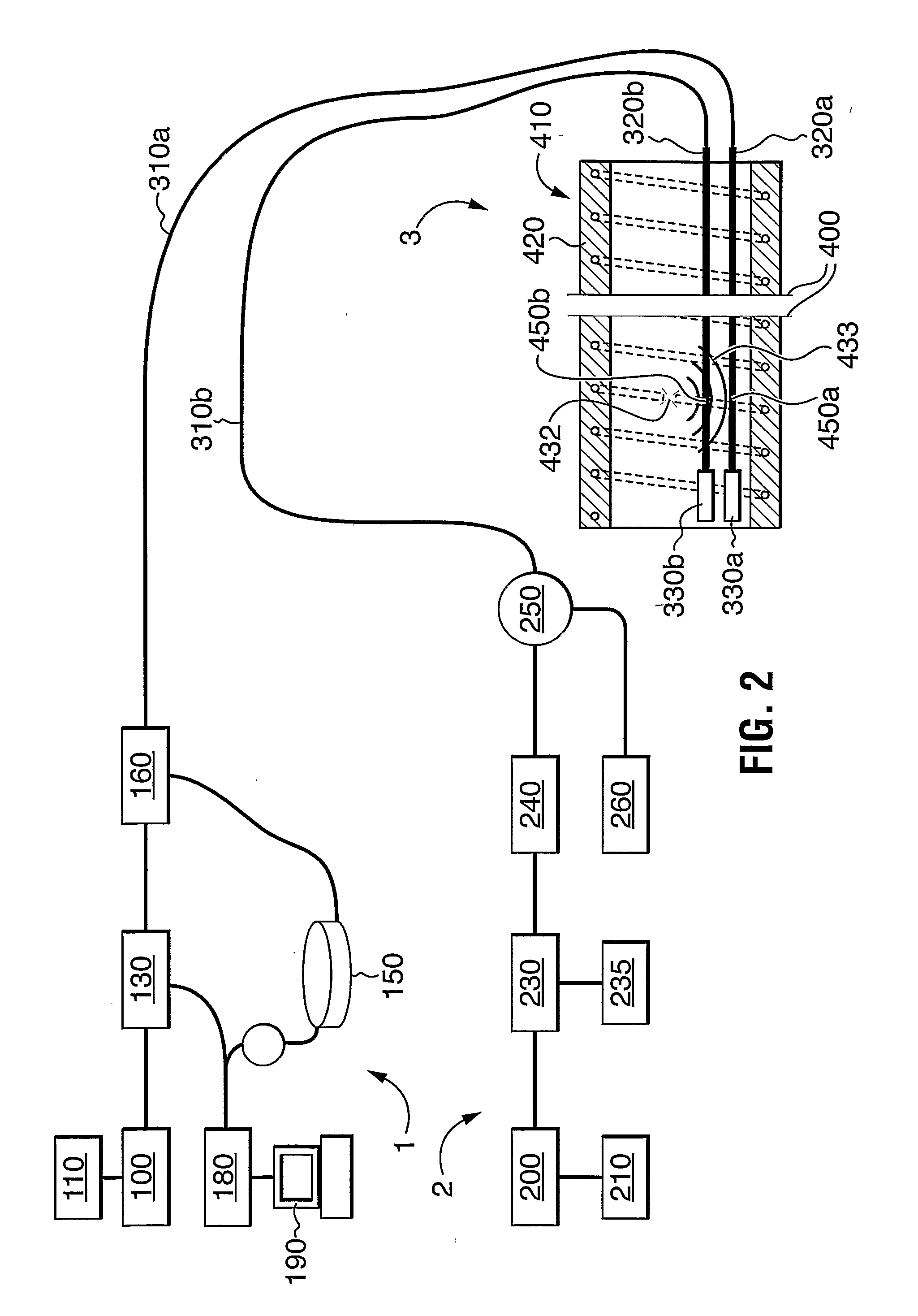
Method and apparatus of multiplexing and acquiring data from multiple optical fibers using a single data channel of an optical frequency-domain reflectometry (OFDR) system
ActiveUS8909040B1Simplifies opticalSimplifies electronicWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingMeasurement point
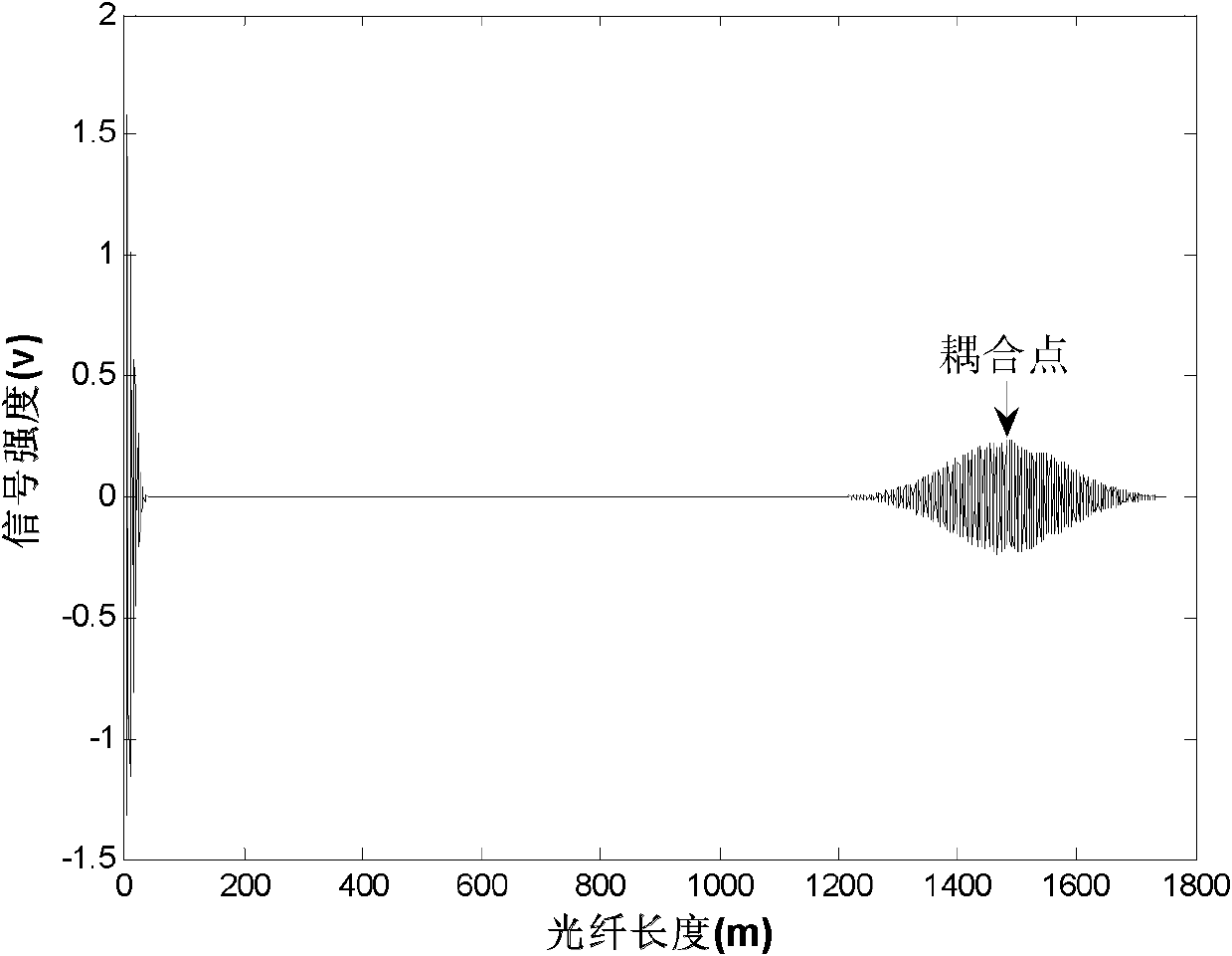
A method and system for multiplexing a network of parallel fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensor-fibers to a single acquisition channel of a closed Michelson interferometer system via a fiber splitter by distinguishing each branch of fiber sensors in the spatial domain. On each branch of the splitter, the fibers have a specific pre-determined length, effectively separating each branch of fiber sensors spatially. In the spatial domain the fiber branches are seen as part of one acquisition channel on the interrogation system. However, the FBG-reference arm beat frequency information for each fiber is retained. Since the beat frequency is generated between the reference arm, the effective fiber length of each successive branch includes the entire length of the preceding branch. The multiple branches are seen as one fiber having three segments where the segments can be resolved. This greatly simplifies optical, electronic and computational complexity, and is especially suited for use in multiplexed or branched OFS networks for SHM of large and / or distributed structures which need a lot of measurement points.
Owner:NASA
Distributed optical fiber sensing system based on phase generated carrier technology
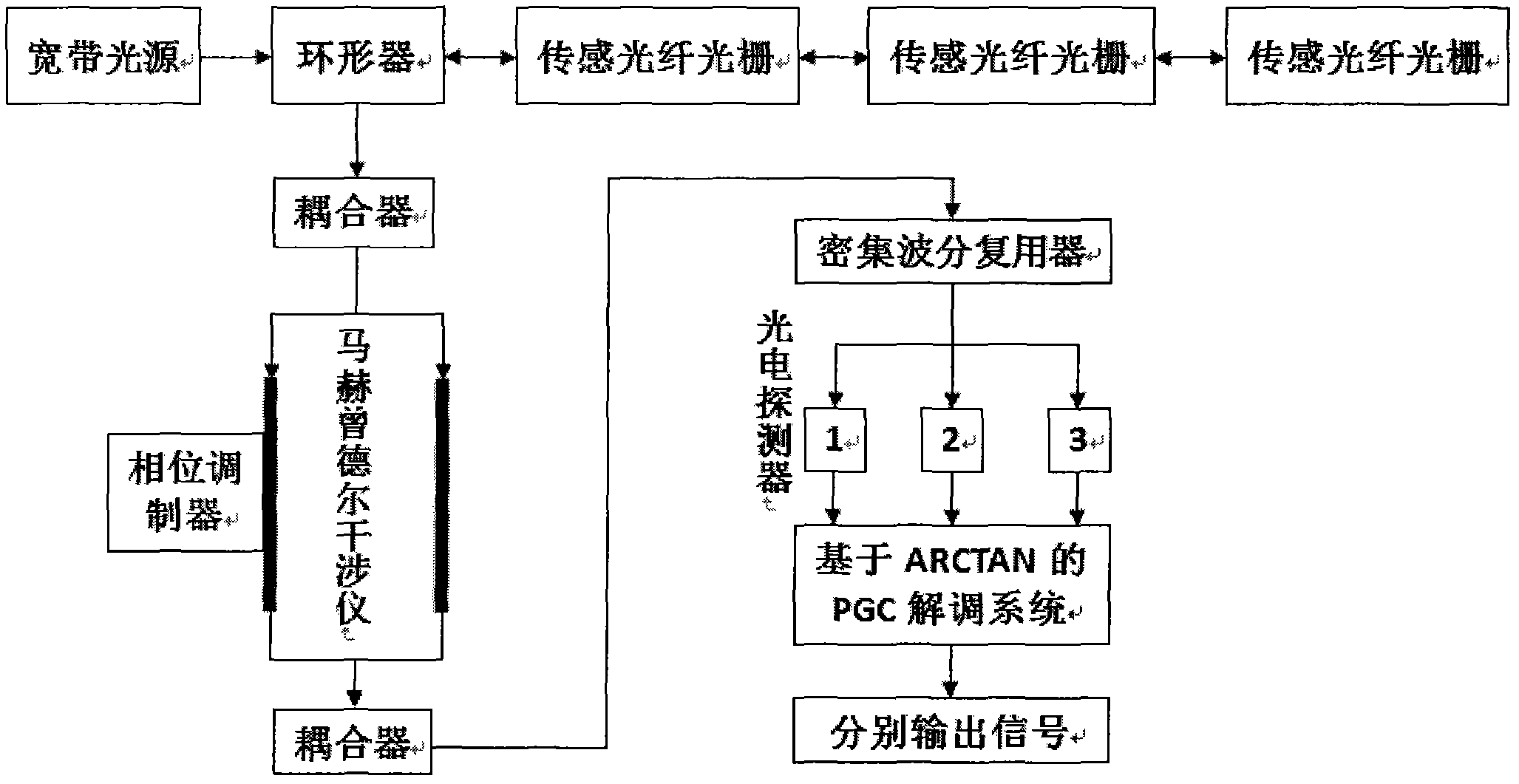
ActiveCN103759750ARealize dynamic measurementEliminate phase destructive fading problemsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFiberGrating
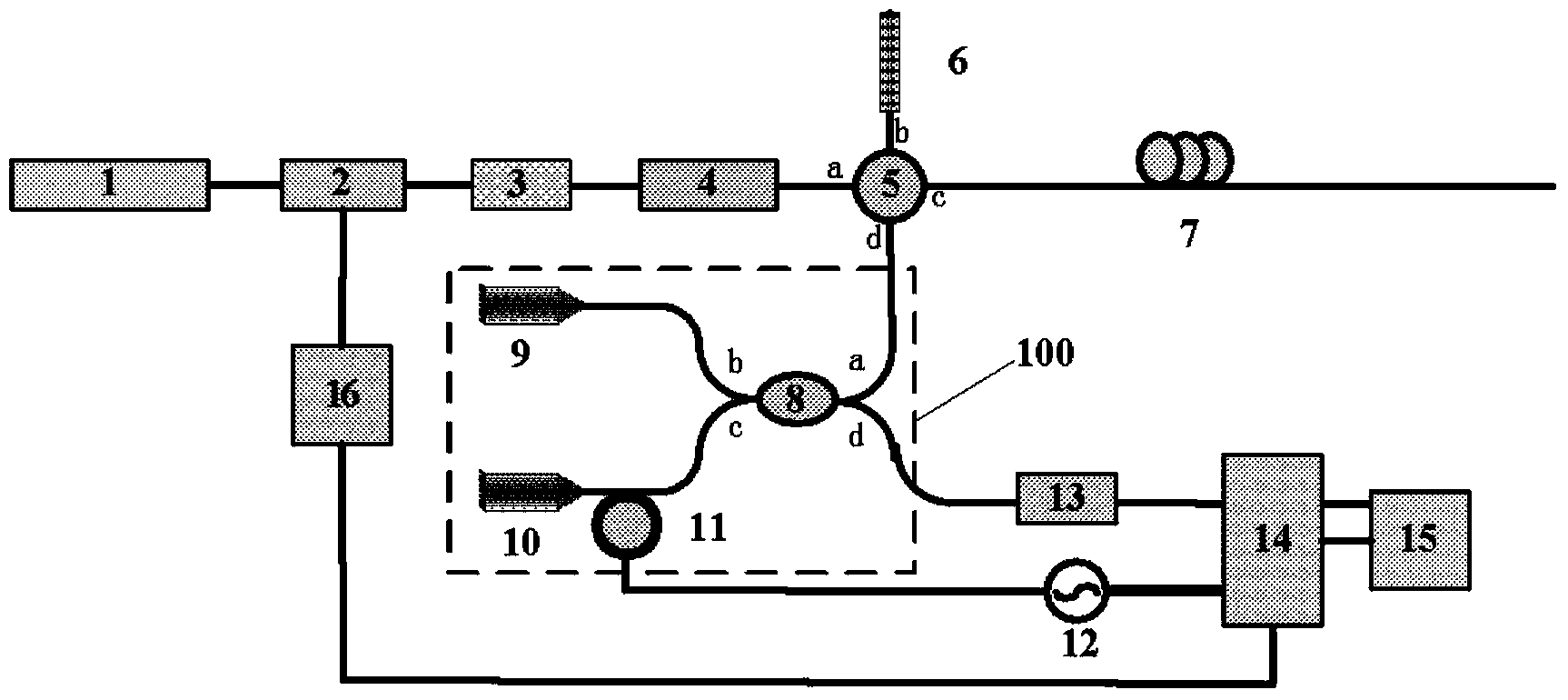
A distributed optical fiber sensing system based on the phase generated carrier technology comprises a narrow-linewidth laser device, a modulator, an optoisolator, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, an optical circulator, a fiber grating, a sensing fiber, a Michelson interferometer, a carrier circuit, a photoelectric detector, a data acquisition card, a signal processor and a pulse generator. The input end of the modulator is connected with the output end of the narrow-linewidth laser device. The input end of the optoisolator is connected with the output end of the modulator. The input end of the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier is connected with the output end of the optoisolator. A port a of the optical circulator is connected with the output end of the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier. The fiber grating is connected with a port b of the optical circulator. The output end of the carrier circuit is connected with an electrical interface of the Michelson interferometer. The input end of the photoelectric detector is connected with the output end of the Michelson interferometer. One input end of the data acquisition card is connected with the output end of the photoelectric detector, and the other input end of the data acquisition card is connected with the output end of the carrier circuit. The input end of the signal processor is connected with the output end of the data acquisition card. The input end of the pulse generator is connected with the trigger input end of the data acquisition card, and the output end of the pulse generator is connected with an electrical interface of the modulator.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
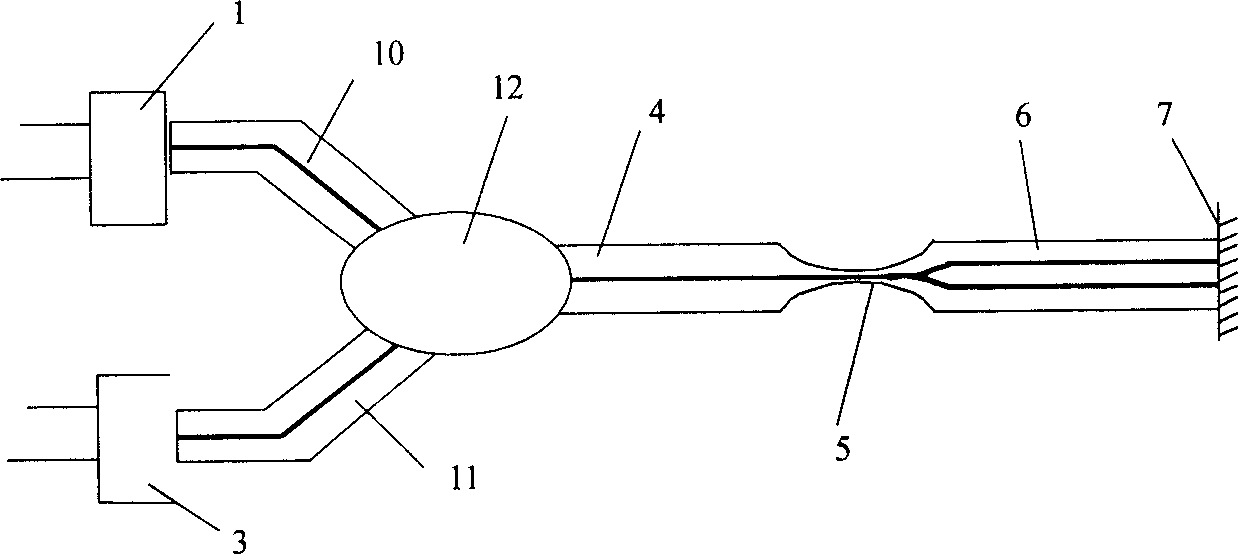
Combination measuring instrument of optical fiber Mach-Zehnder and Michelson interferometer array
InactiveCN101329184ASolving Multiplexing ProblemsRealize inquiryCoupling light guidesConverting sensor output opticallyMeasuring instrumentMultiple sensor
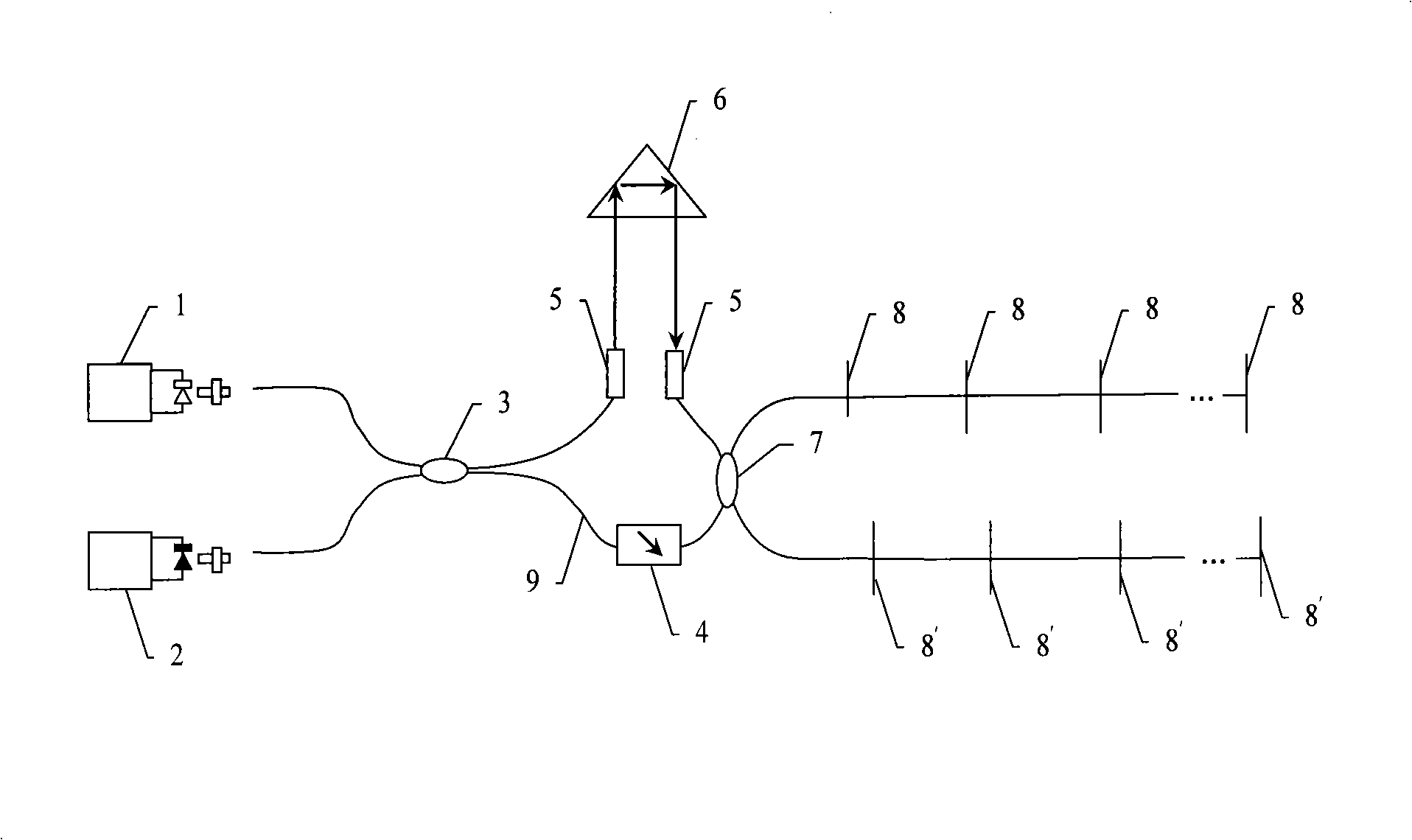
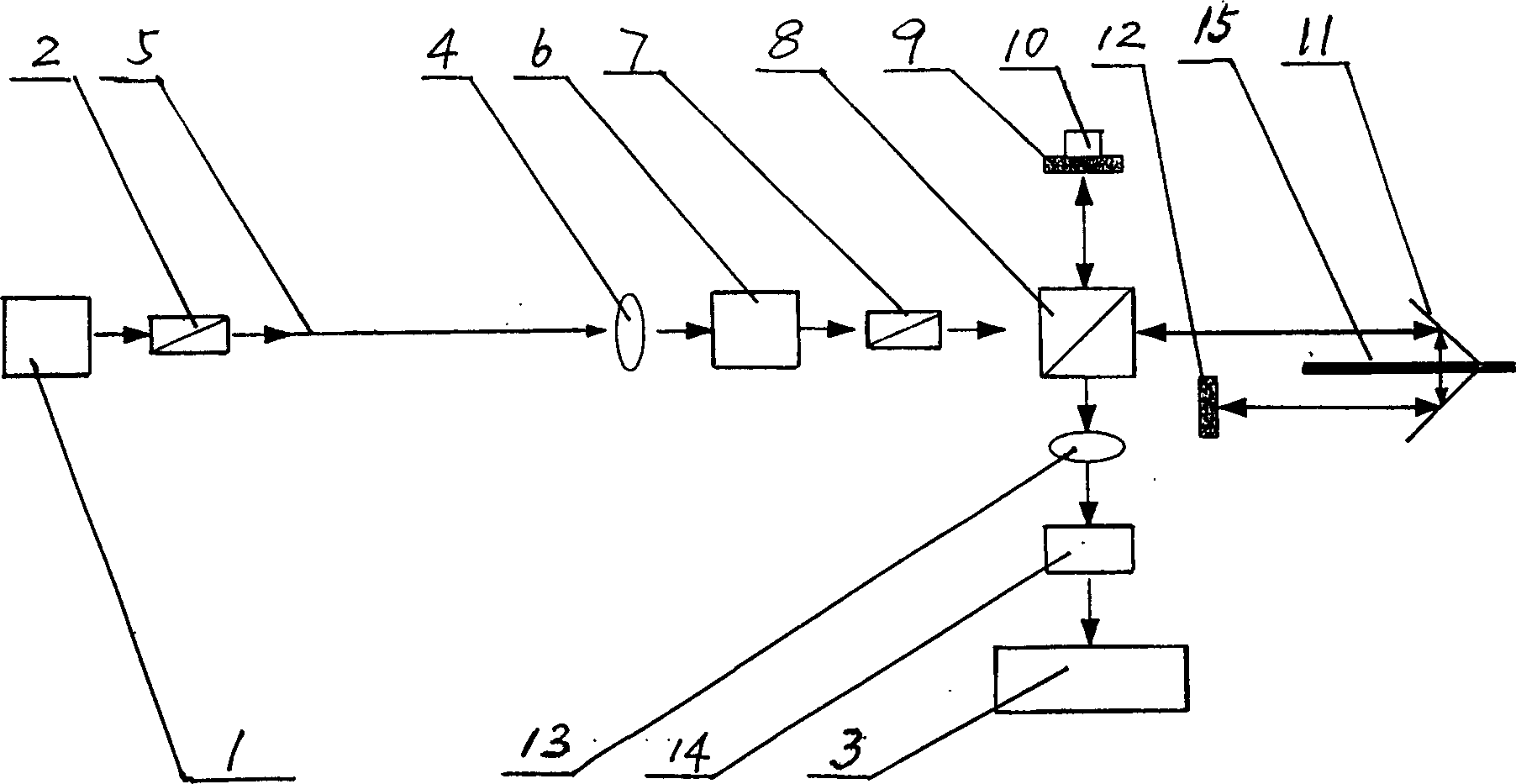
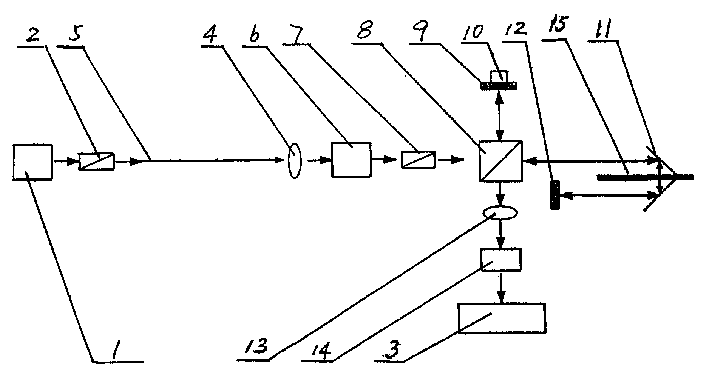
The invention provides a measuring instrument with an optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer and optical fiber Michdson interferometer arrays, which comprises a broad-band light source 1, a photoelectric detector 2, a 3dB optical fiber 2 multiplied by 2 coupler 3, the optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer, a transposed 3dB optical fiber 2 multiplied by 2 coupler 7, optical fiber Michdson interferometers arrays 8 and 8', and a single-mode connecting optical fiber 9, wherein, the optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer consists of an attenuator 4, a self-focusing lens 5, an axicon lens 6 with total reflection angle, and the connecting optical fiber 9. The measuring instrument with the optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer and the optical fiber Michdson interferometer arrays utilizes a technique that measures strain and temperature at the same time, realizes the temperature compensation technique and the array arrangement of optical fiber sensors, realizes absolute measurement under the situation that the multiple sensors are not interfered by each other, lowers the cost of single-point measurement and ensures real-time measurement; furthermore, the measuring instrument has simple techniques and easy implementation, and as standard optical fiber communication elements are adopted as the optical fiber materials and devices, the measuring instrument has low cost, easy acquisition of the optical fiber materials and devices and easy popularization.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Unbalanced interferometer based fiber bragg grating (FBG) demodulation system and method
InactiveCN102147552AResponsiveHigh sensitivityLight demodulationConverting sensor output opticallyGratingAcousto-optics
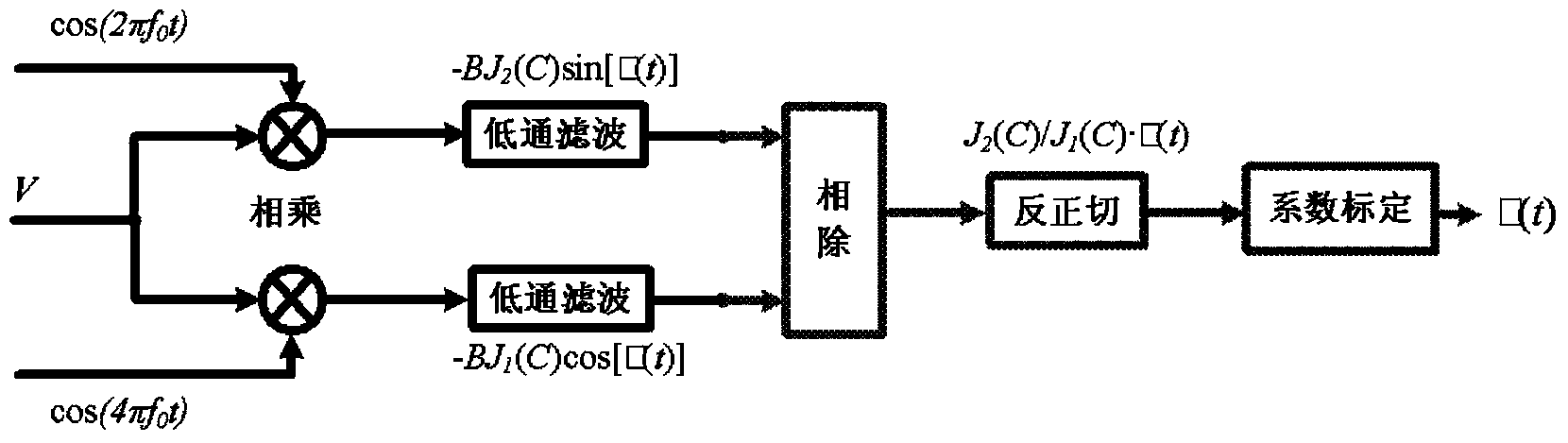
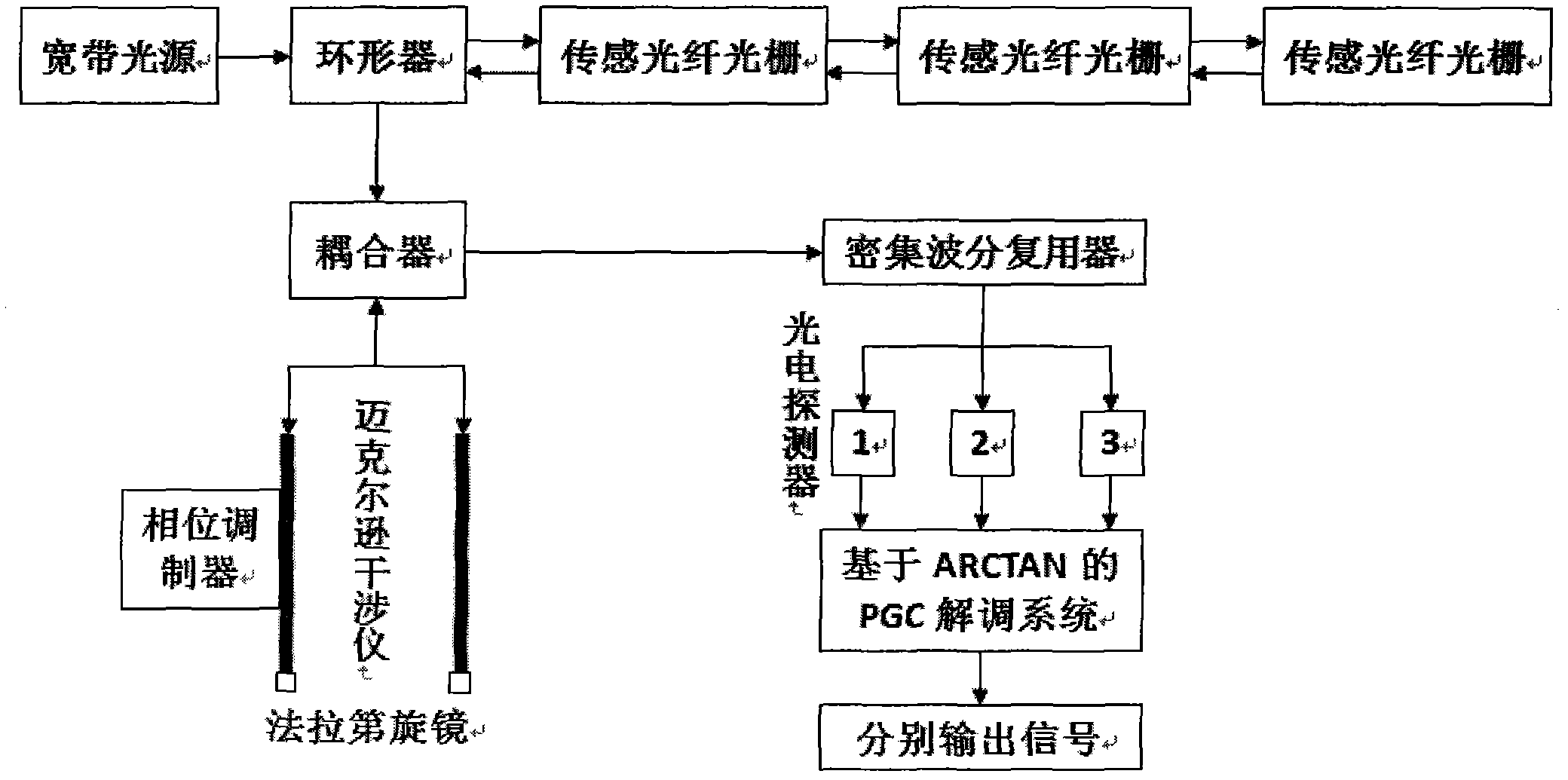
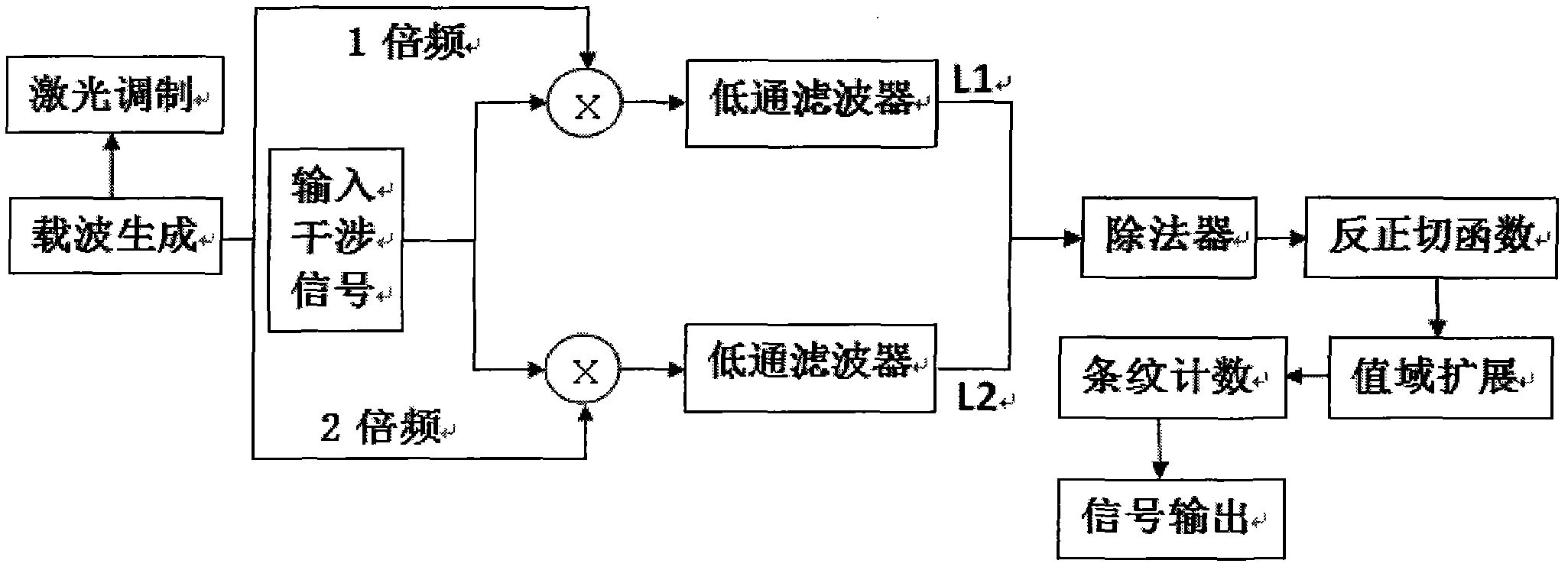
The invention relates to an unbalanced interferometer based fiber bragg grating (FBG) demodulation system and method, belonging to the technical field of fiber optic sensing. The system sequentially passes through a superluminescent diode (SLD) or an amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) broadband light source, an optic isolator, a circulator or a coupler, and a fiber bragg grating and returns back to the circulator or the coupler, and then passes through the coupler, an unbalanced Michelson interferometer with two channels and a Faraday rotator mirror and returns back to an interferometer and the coupler or passes through a Mach-Zehnder interferometer with two channels and the coupler, wherein one channel of the interferometer is wound around a piezoelectric ceramic or an electrooptical modulator, and an acousto-optic modulator, finally passes through a dense wave division multiplexer and a photoelectric detector and is connected with an ARCTAN based PGC (Phase Generation Carrier) signal response demodulation module. The invention has the advantages; by adopting the combination of the an FBG sensor and ARCTAN-based PGC phase modulation, the system has high sensitivity, large dynamic range and good linearity, good response to an abrupt signal and easiness of multiplexing, low cost and easiness of implementing.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Fibre Optic Sensor Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20070247631A1Good indicationDetection of fluid at leakage pointForce measurement by measuring optical property variationEngineeringMichelson interferometer
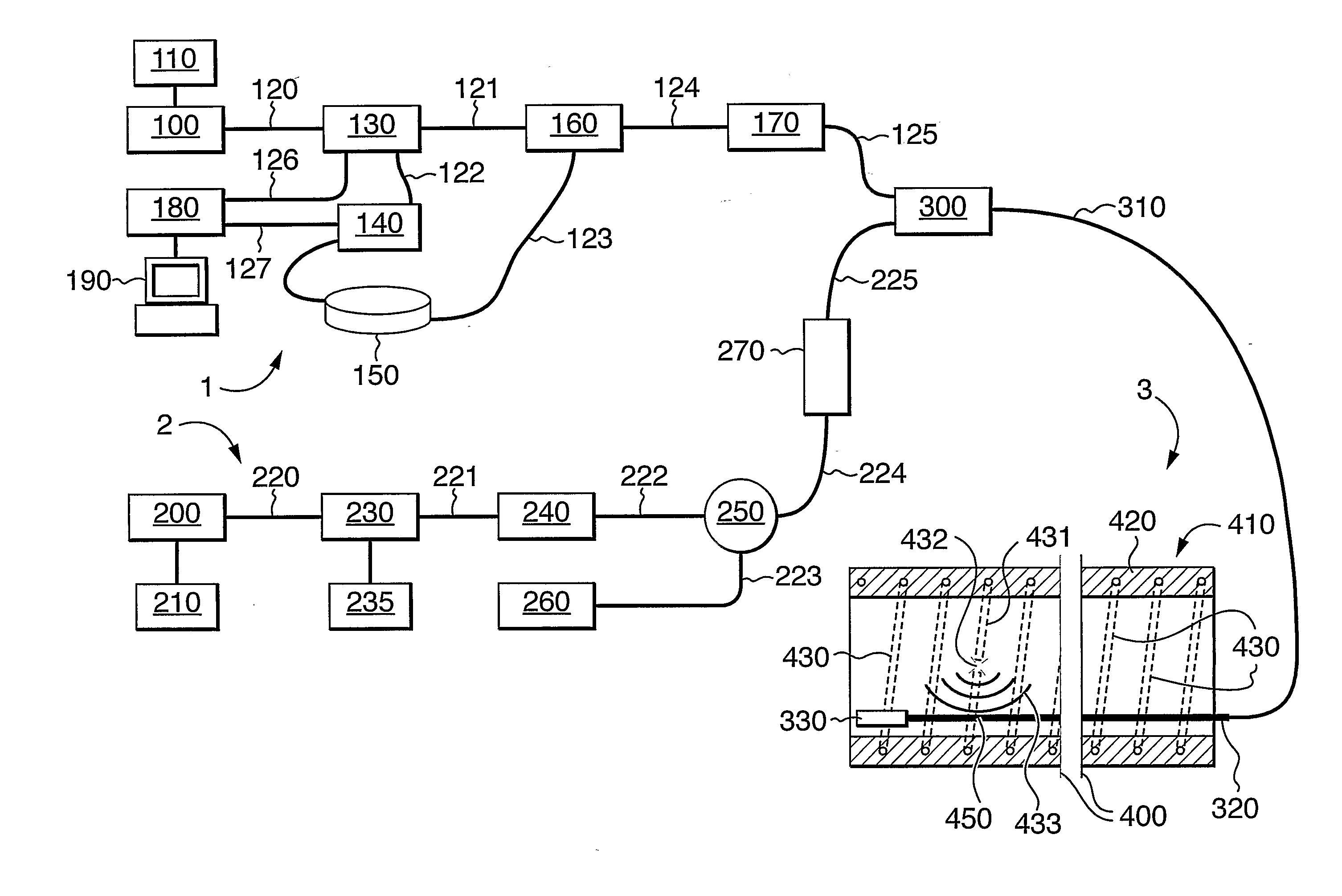
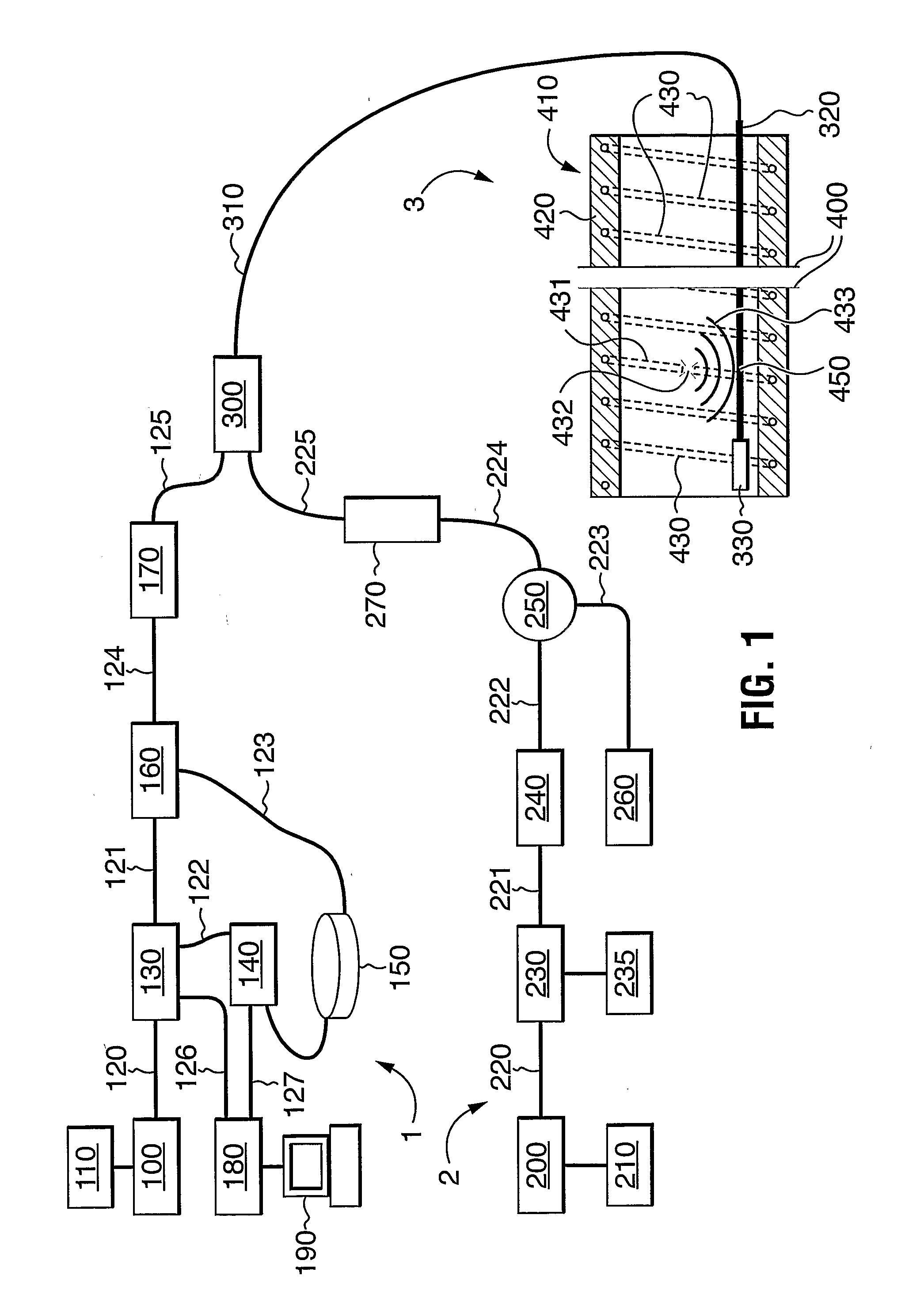
This invention uses an interferometric fibre optic sensor, particularly a Sagnac or Michelson interferometer, in a first fibre to monitor a sensing length of the first fibre and to detect disturbances. Signals indicating disturbances are classified as being of interest or not of interest, depending on predetermined criteria. Disturbances of interest can be, for example, the breaking of reinforcement wires in concrete pipe, the breaking of wires in suspension cables, a fire, a pipeline leak, or an intrusion. A location sensor system is used to determine the location of disturbances of interest, and to confirm the interferometer signal to reduce noise. The location sensor system is a fibre optic sensor, such as a phase OTDR sensor or a Brillouin effect sensor, which can detect the location of events it senses. It is present either in the first fibre or in a separate fibre laid adjacent the first fibre along its sensing length, as for example in the same optical cable.
Owner:PURETECH VENTURES
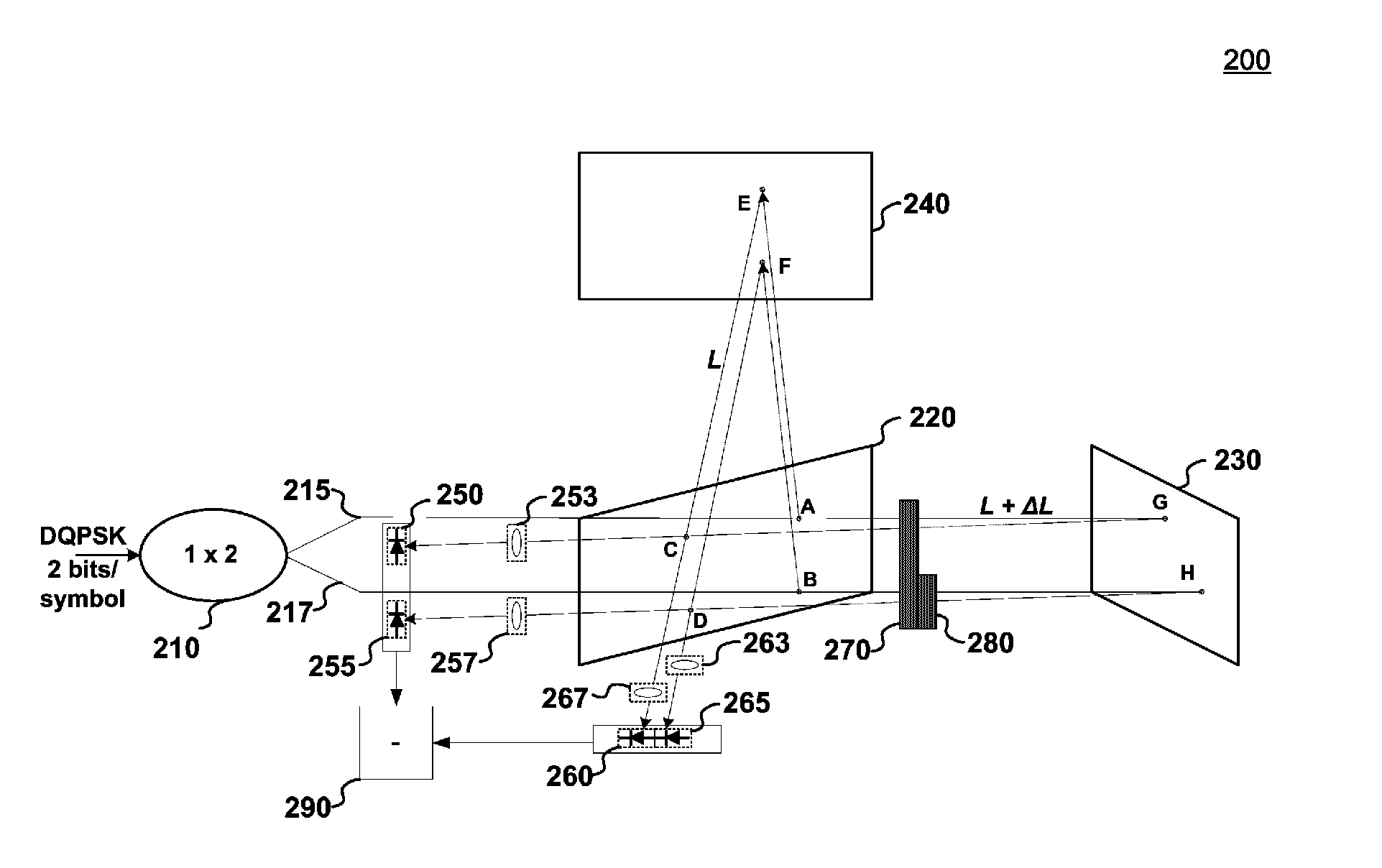
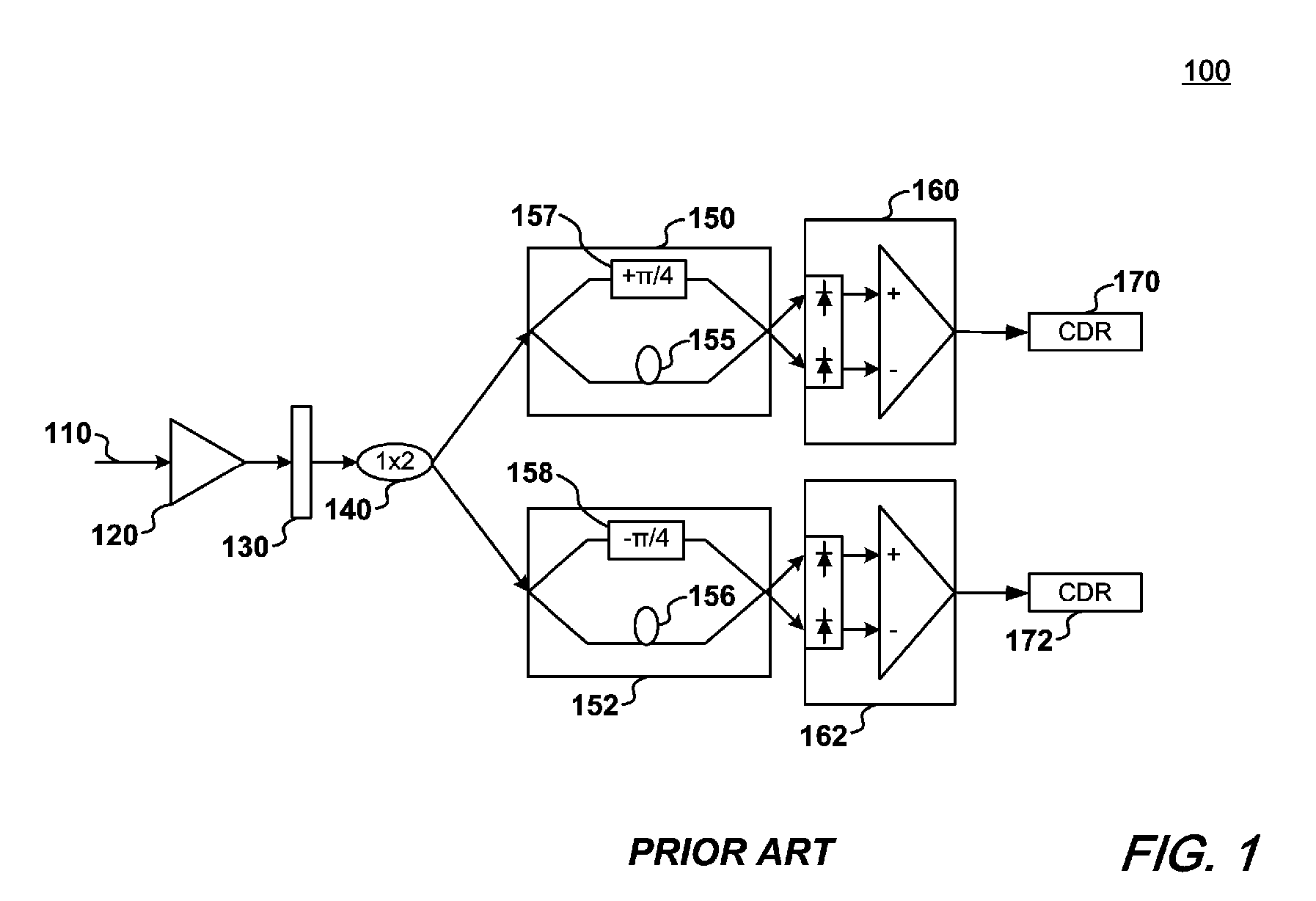
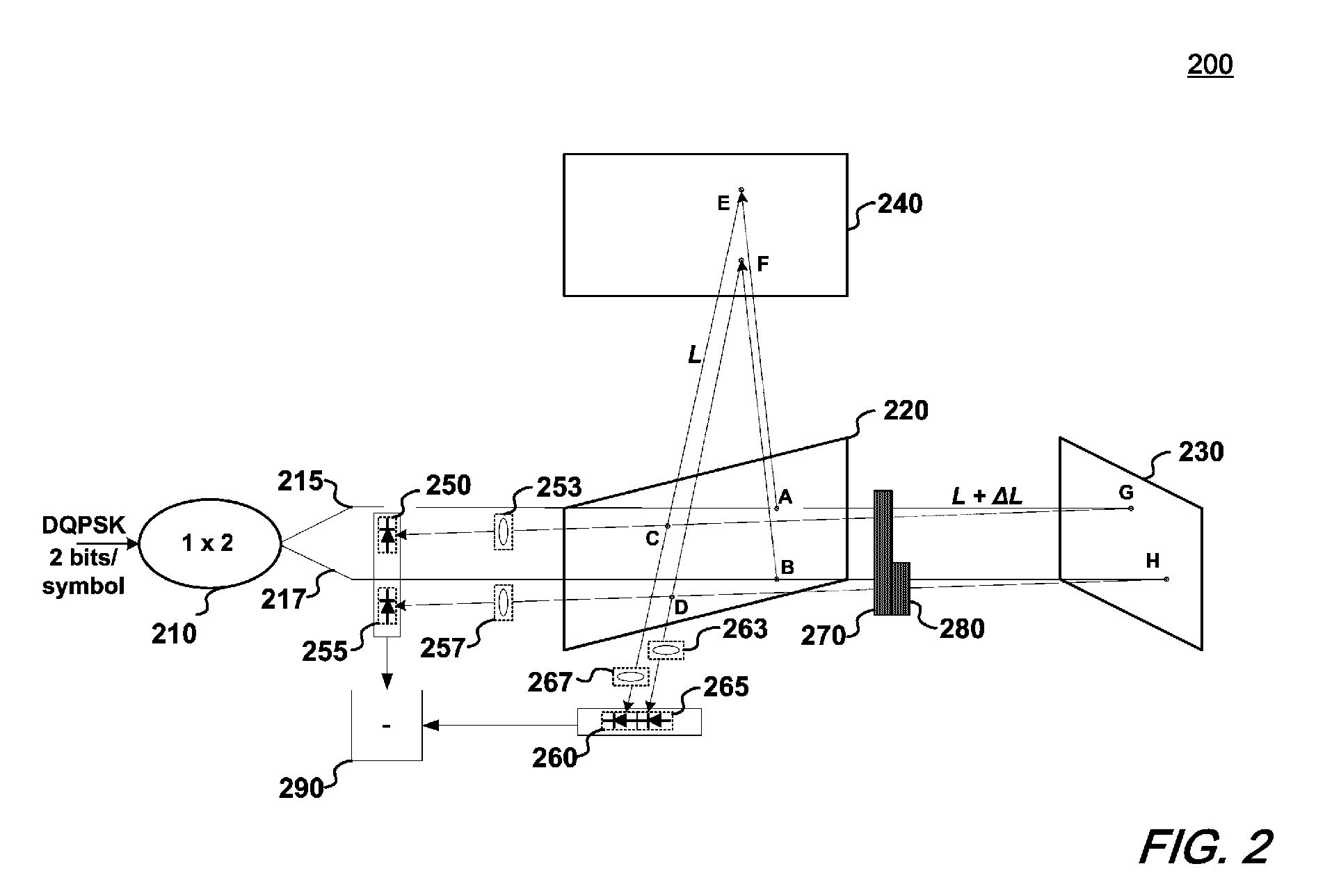
Optical demodulating apparatus and method
ActiveUS7526210B2Electromagnetic transmittersLight demodulationPhase differenceMichelson interferometer
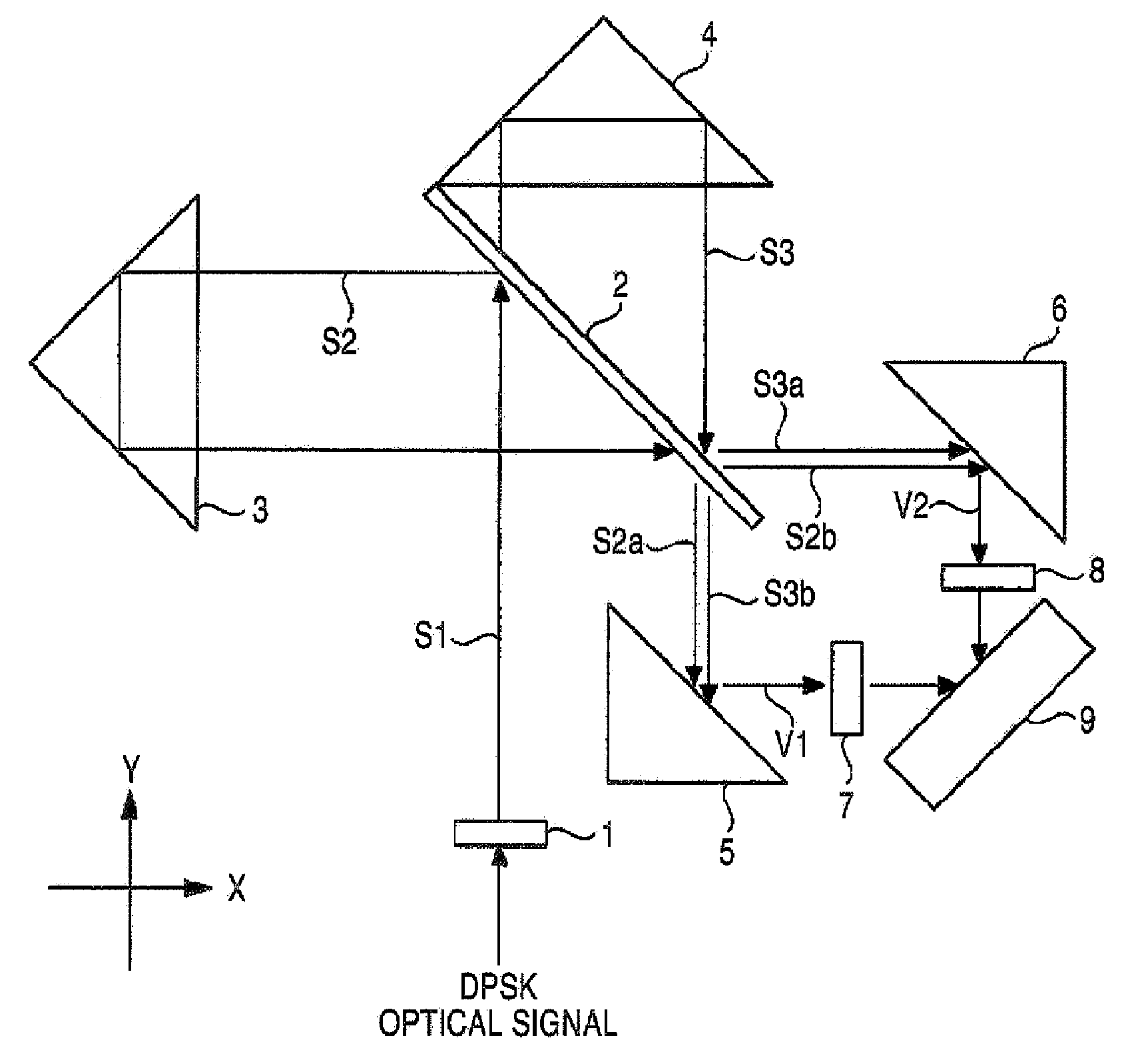
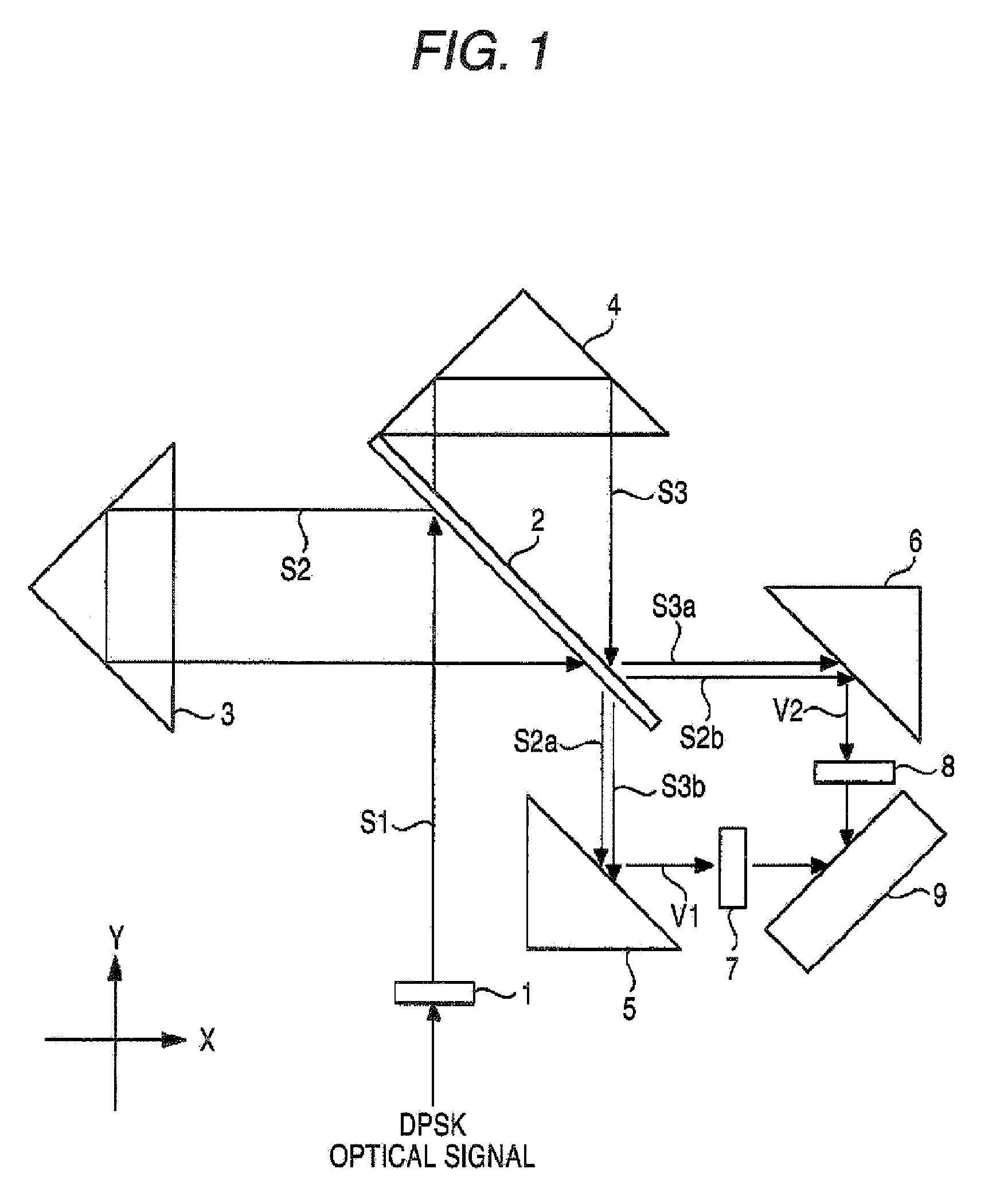
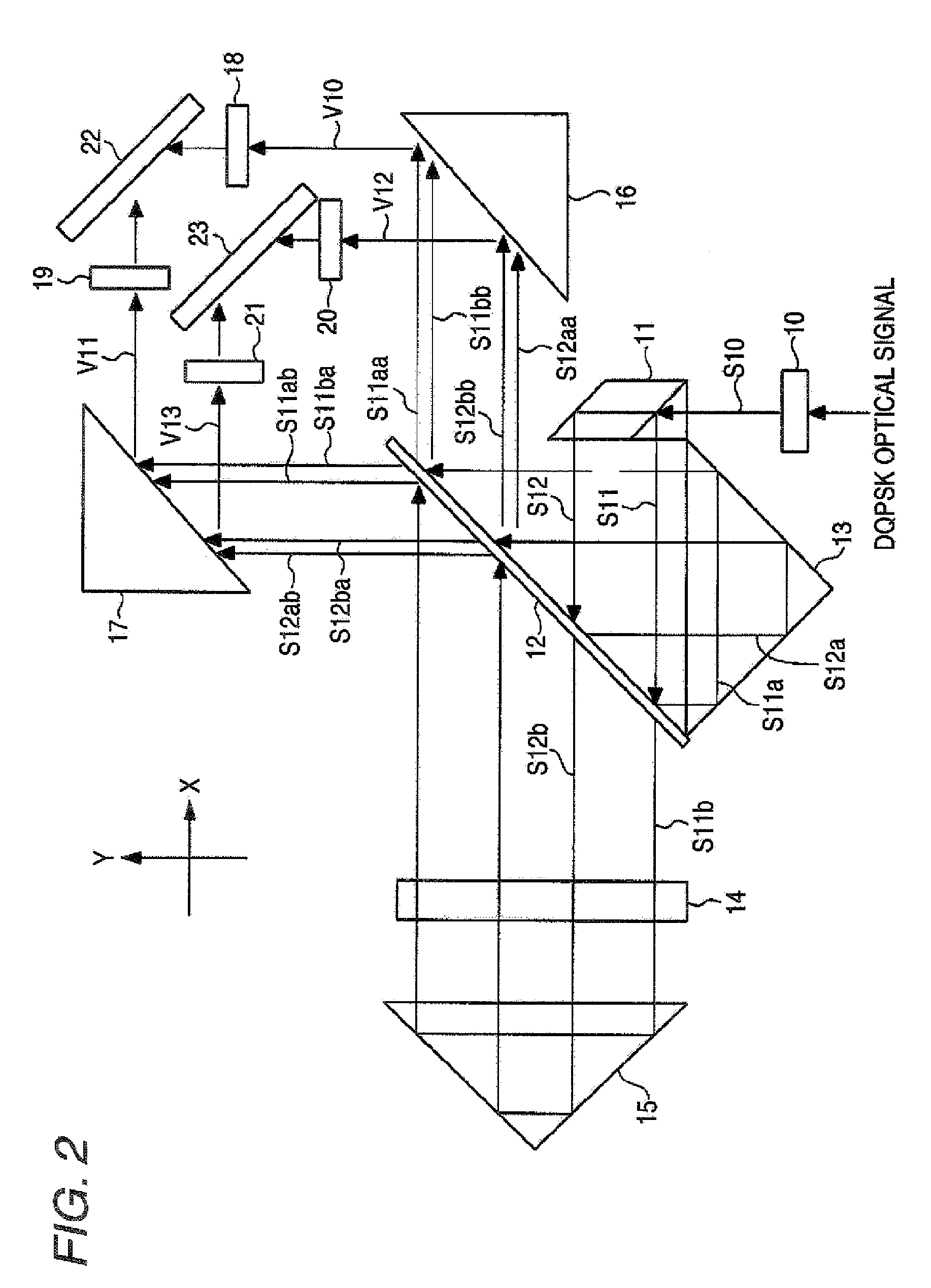
An optical demodulator and accompanying method(s) that demodulates a DQPSK signal employing a single optical delay interferometer comprising a free-space Michelson interferometer having two optical paths, connected to a 1×2 coupler. Positioned within an arm of the Michelson interferometer is a phase shifter that produces a phase difference of π / 2 between the two paths. The resulting demodulator is compact, reliable, and may be constructed to be substantially immune from undesirable thermal sensitivities.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
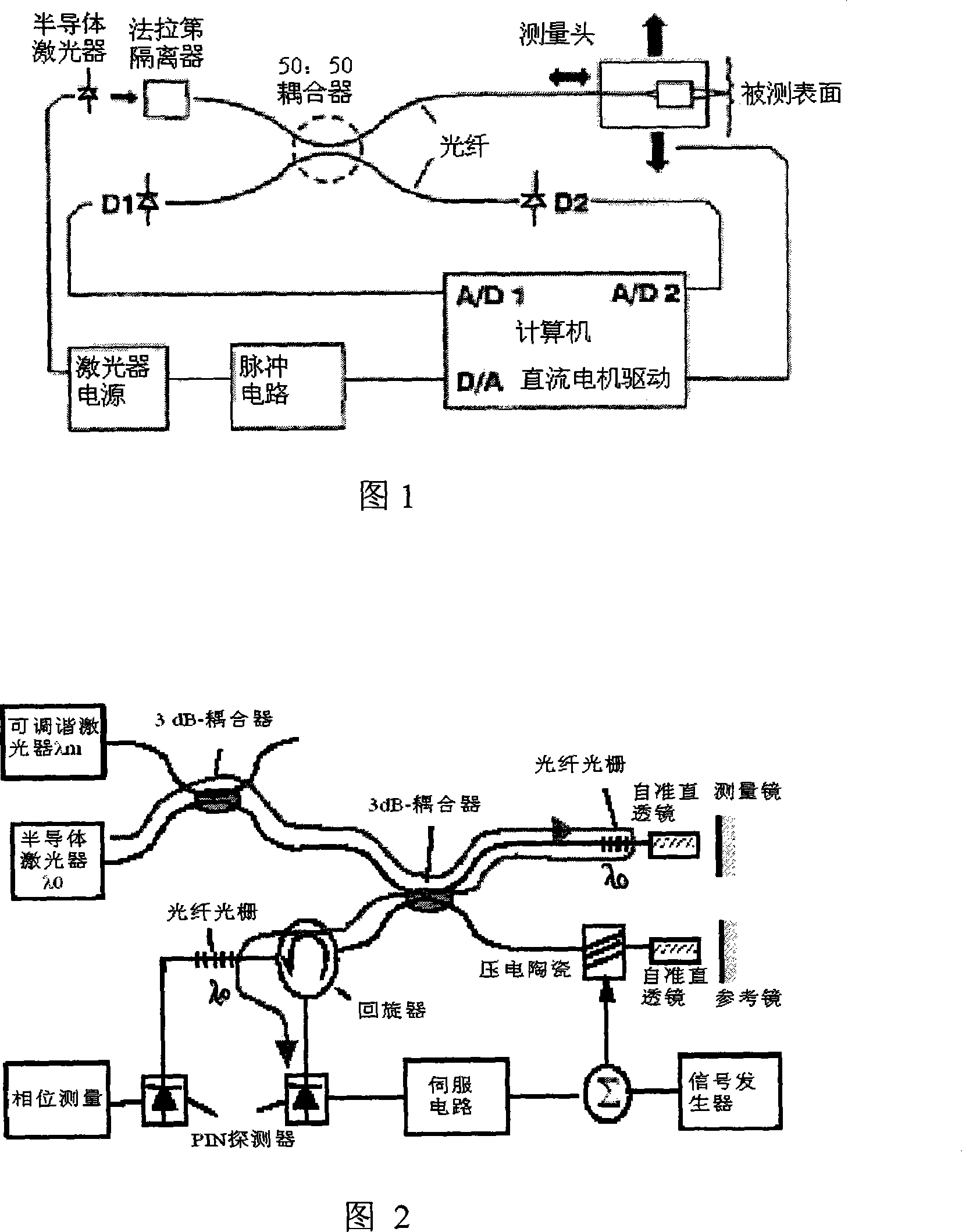
Optical fiber interference type on-line micro-displacement measuring system using fibre grating
InactiveCN101013025ALow costConvenient automatic measurementUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyFiberGrating
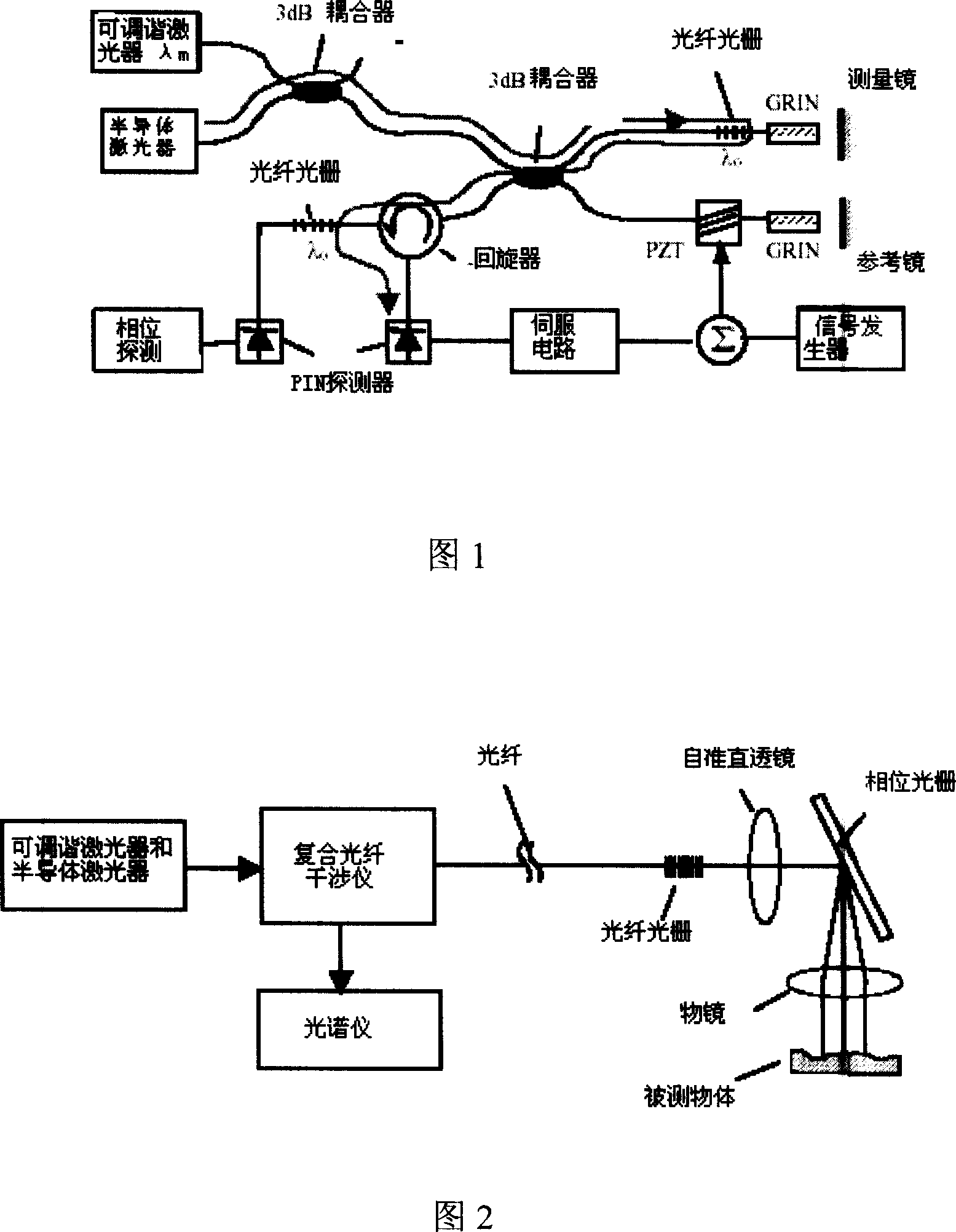
The invention discloses a micro-displacement measuring system, especially the micro-displacement measuring system applied for the online measurement. It uses the fiber grating nature and WDM technology to compose Michelson interferometer, and the interferometer contains two fibers Michelson interferometers with separate mirrors but almost overlap optical road. One interferometer is used for measurement, while another interferometer through feedback control to compensate the measurement impact for the environmental interference, thereby allowing the system to apply to on-line measurement. The invention only using the light emitted by a semiconductor laser with 1.5nm spectrum wide and 1550nm center wavelength to function the two interferometers at the same time, it not only lowers the system cost, but also conveniently implements the automatic measurement, and the feedback control circuit has no effect to the measurement with piezoelectric ceramic discharge, making the measurement continuously processing.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Reconfigurable polarization independent interferometers and methods of stabilization
A polarization independent (PI) interferometer design that can be built from standard optical components is described. Based upon a Michelson interferometer, the PI interferometer uses a 50 / 50 splitter and Faraday Rotator Mirrors (FM's). The interferometer achieves good optical characteristics, such as high extinction ratio (ER) and low insertion loss (IL). Lack of polarization sensitivity reduces interferometer construction tolerances and cost, enhances performance and utility, and expands the scope of interferometric based devices. Such characteristics can be used to construct flexible, high performance, polarization insensitive, multi-rate, self-calibrating, optical DPSK receivers, power combiners, optical filters and interleavers, all-optical switches, and cascaded interferometers. Since polarization is not maintained in standard fiber optic networks, a PI-DPSK receiver allows for use of more sensitive DPSK communications over fiber, without need for costly polarization control hardware. Other applications of PI interferometers include optical CDMA, secure communications, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and temporal gratings with ultra-precise timing.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for efficiently processing high-quality micro hole with large ratio of pit-depth to pit-diameter through femtosecond laser
InactiveCN103878496AAspect ratioQuality improvementWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusUltrasound attenuationMichelson interferometer
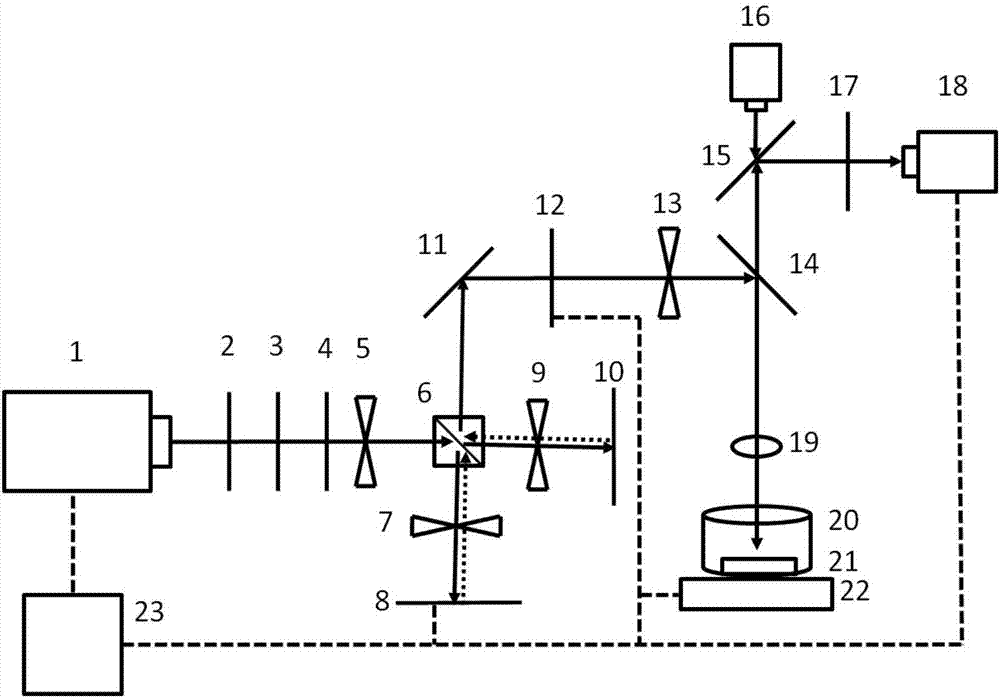
The invention relates to the field of laser application, in particular to a method for efficiently processing a high-quality micro hole with a large ratio of pit-depth to pit-diameter through a femtosecond laser. According to the method, the wavelength of a near-infrared femtosecond laser monopulse is regulated by a femtosecond laser optical parameter amplifier, so that the near-infrared femtosecond laser monopulse becomes visible light. Afterwards, an optical path of a Michelson interferometer is used for modulating the visible light to be laser double impulses and the overall energy of the laser double impulses is regulated with a continuous attenuation sheet. The obtained visible light double impulses penetrate through an optical shutter and are perpendicularly focused on the upper surface of a sample to be processed through an objective lens. Finally, the optical shutter is used for controlling the exposure time of the visible light double impulses and therefore the number of laser impulses which irradiates the surface of the sample to be processed is regulated until the depth of the processed hole is saturated. According to the processing method, the ratio of pit-depth to pit-diameter and the quality in processing the micro hole can be effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Michelson's interferometer integrated into single optical fiber
InactiveCN1908577AImprove stabilityReduce volumeUsing optical meansDual coreMichelson interferometer
The related Michelson interferometer with only one optical fiber comprises: integrating the co-light-path part of source input and signal output and two interference arms into one optical fiber; and using the integrated optical fiber with one segment as mono-core fiber and one segment as dual-core fiber to replace the conventional product. The advantages of this invention include: 1. well stability; 2. small size and compact structure; 3. low requirement to source coherence; and 4. automatic compensation for light path difference.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
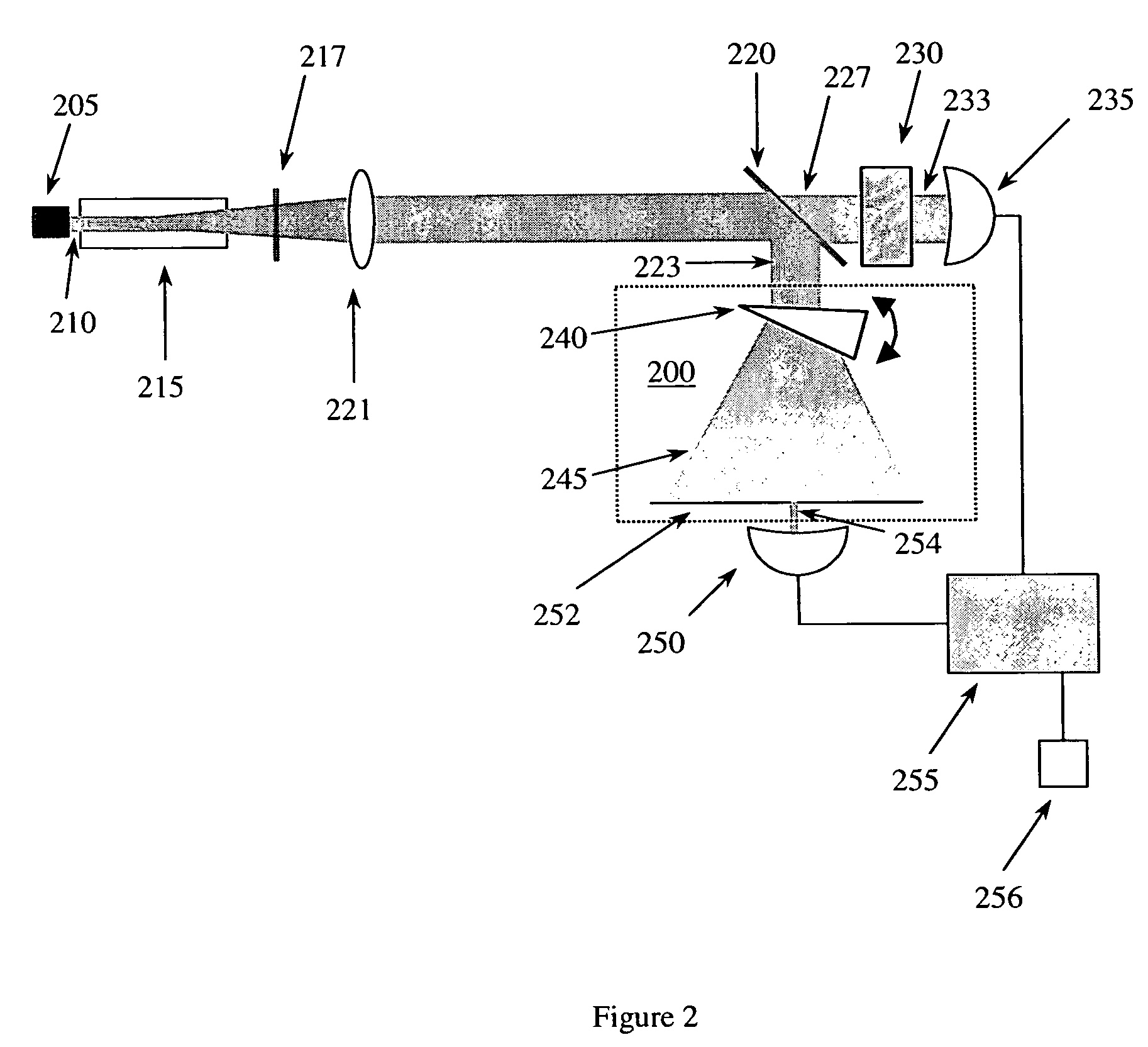
Miniature fourier transform spectrophotometer
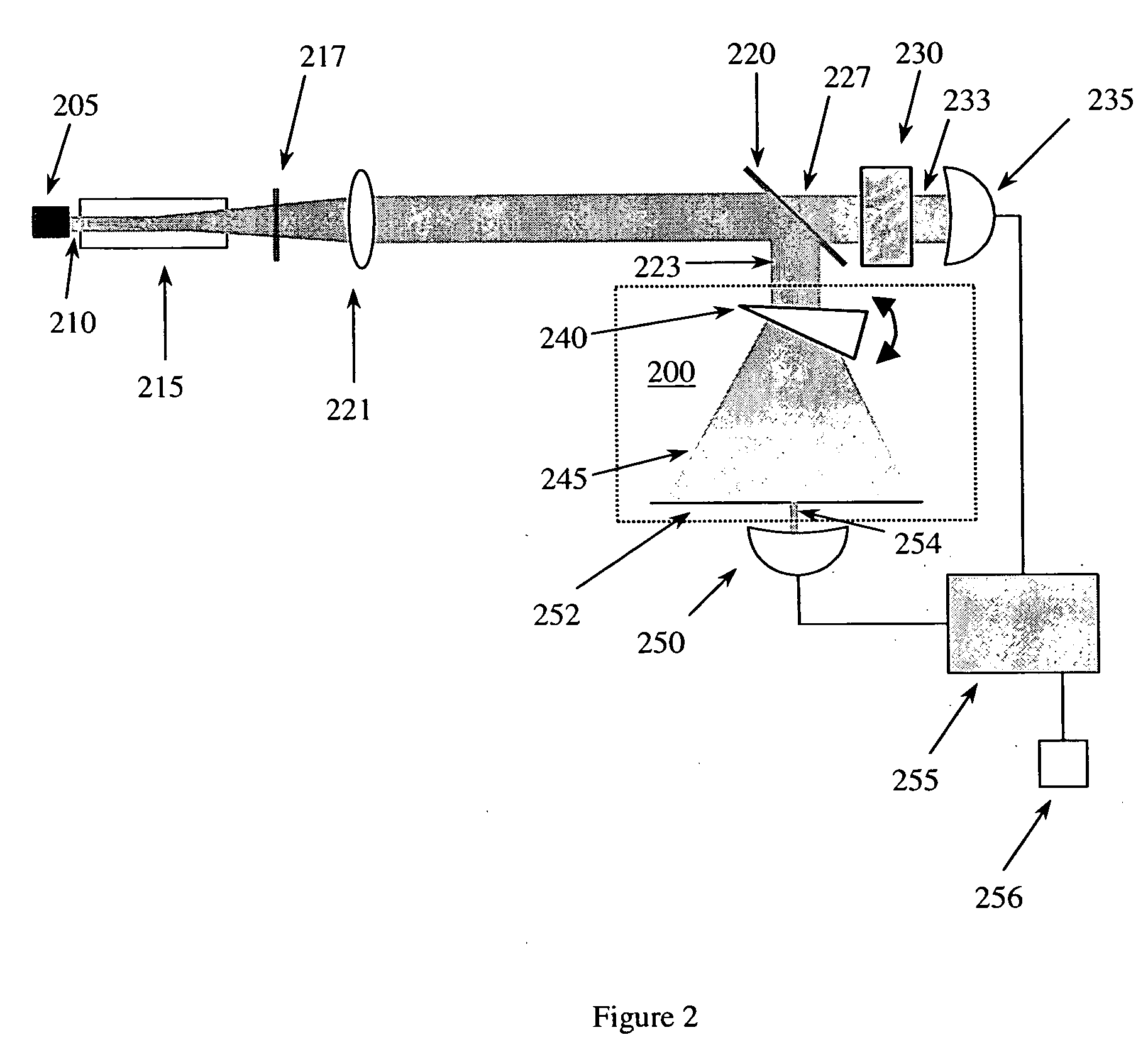
ActiveUS20060232781A1Low wavelengthDecreased wavelengthRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryImage resolutionMiniaturization
The Miniature Fourier Transform Spectrophotometer provides the capability, in a miniaturized device, of determining the light absorption / transmission spectra of a collected sample of gas or liquid though Fourier Transform spectroscopy techniques. The device takes an optical input from an optical fiber, manipulates that light through miniature optical components, and launches it into a miniaturized Michelson interferometer with a scanning mirror that acquires the interferogram of the optical input. The interferogram can be processed to retrieve the spectrum of the input light. A novel multi-stepped micro-mirror operates as the optical path length modulator in the miniaturized interferometer. A unique monolithic beamsplitter / mirror combination provides for accurate alignment of the components and greatly simplifies product integration. The device is designed to cover various optical spectra of interest. During operation, the precision and accuracy of the microfabricated components in the device allow operation and resolution even at extremely low wavelengths. In addition, the miniaturized nature of the device allows it to be used in new and extremely space-constrained applications.
Owner:MORGAN RES CORP
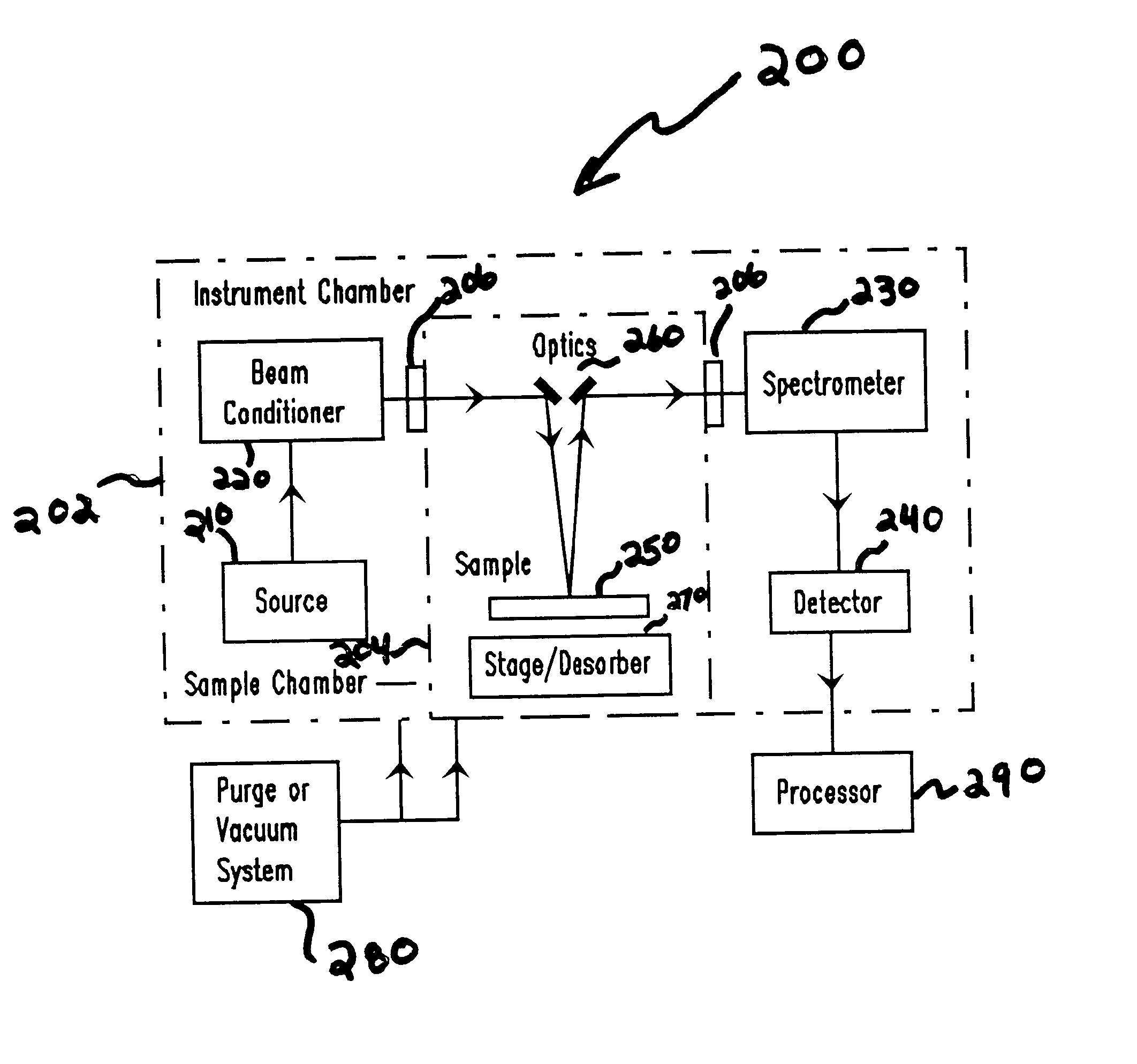
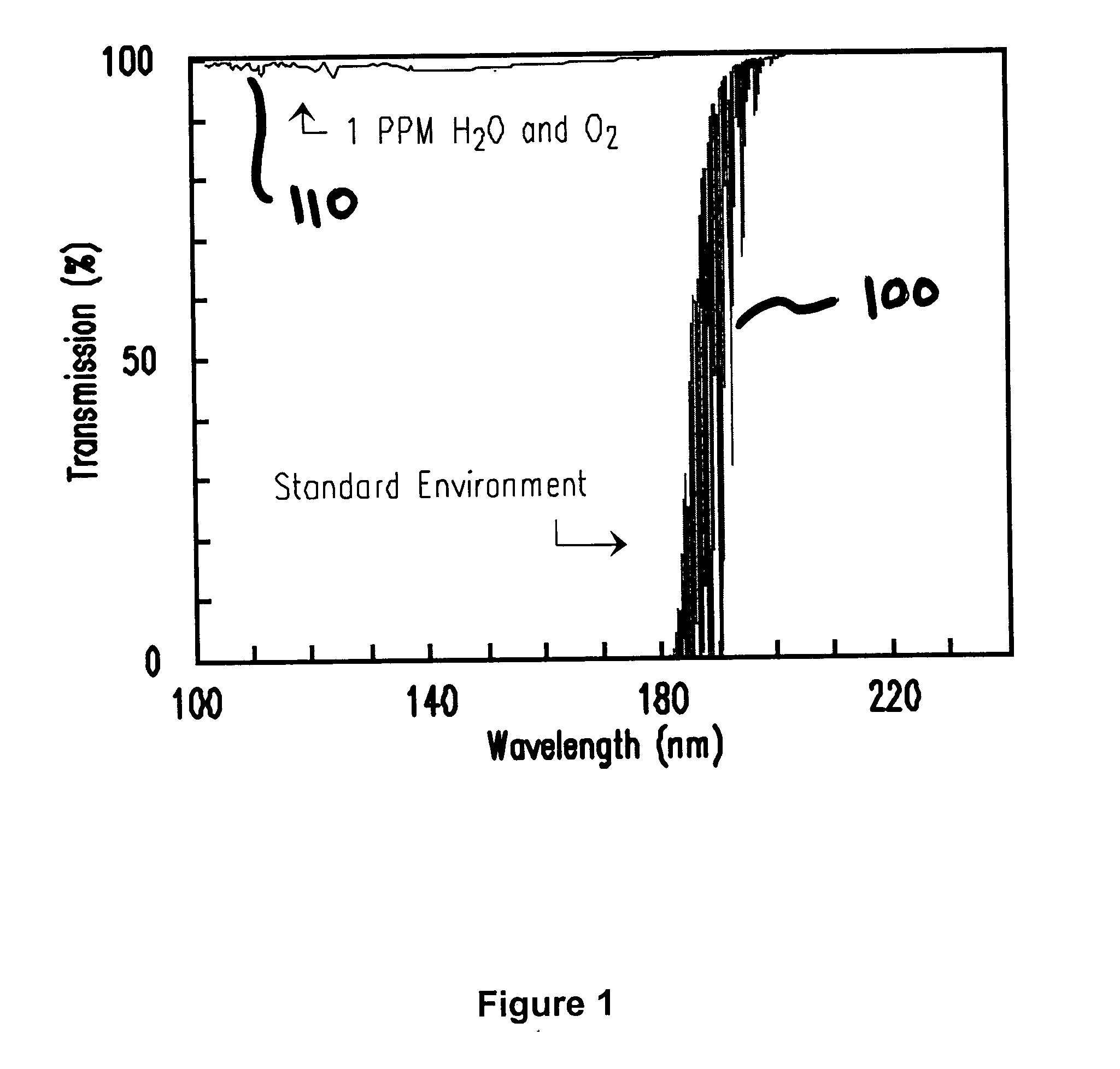
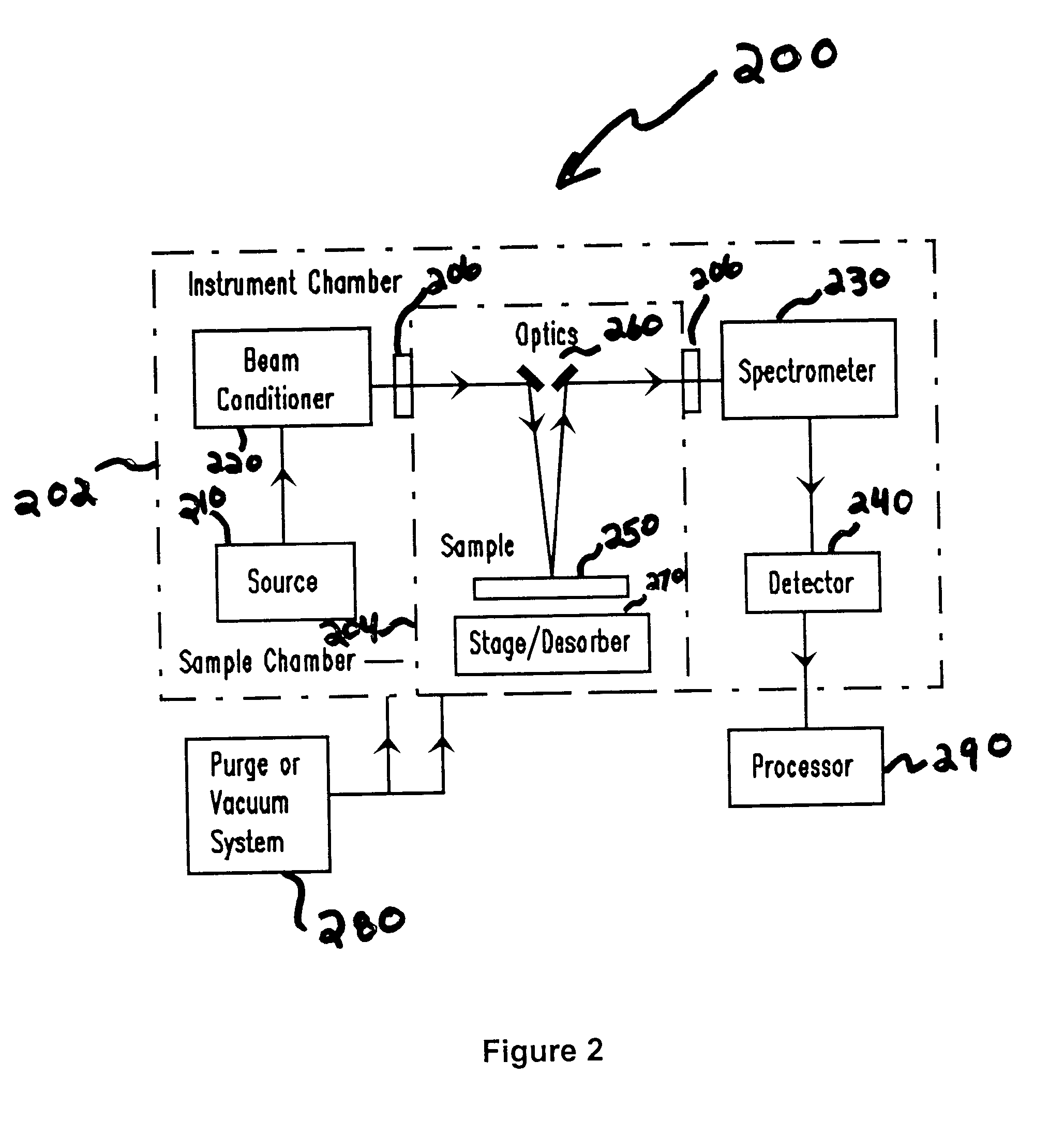
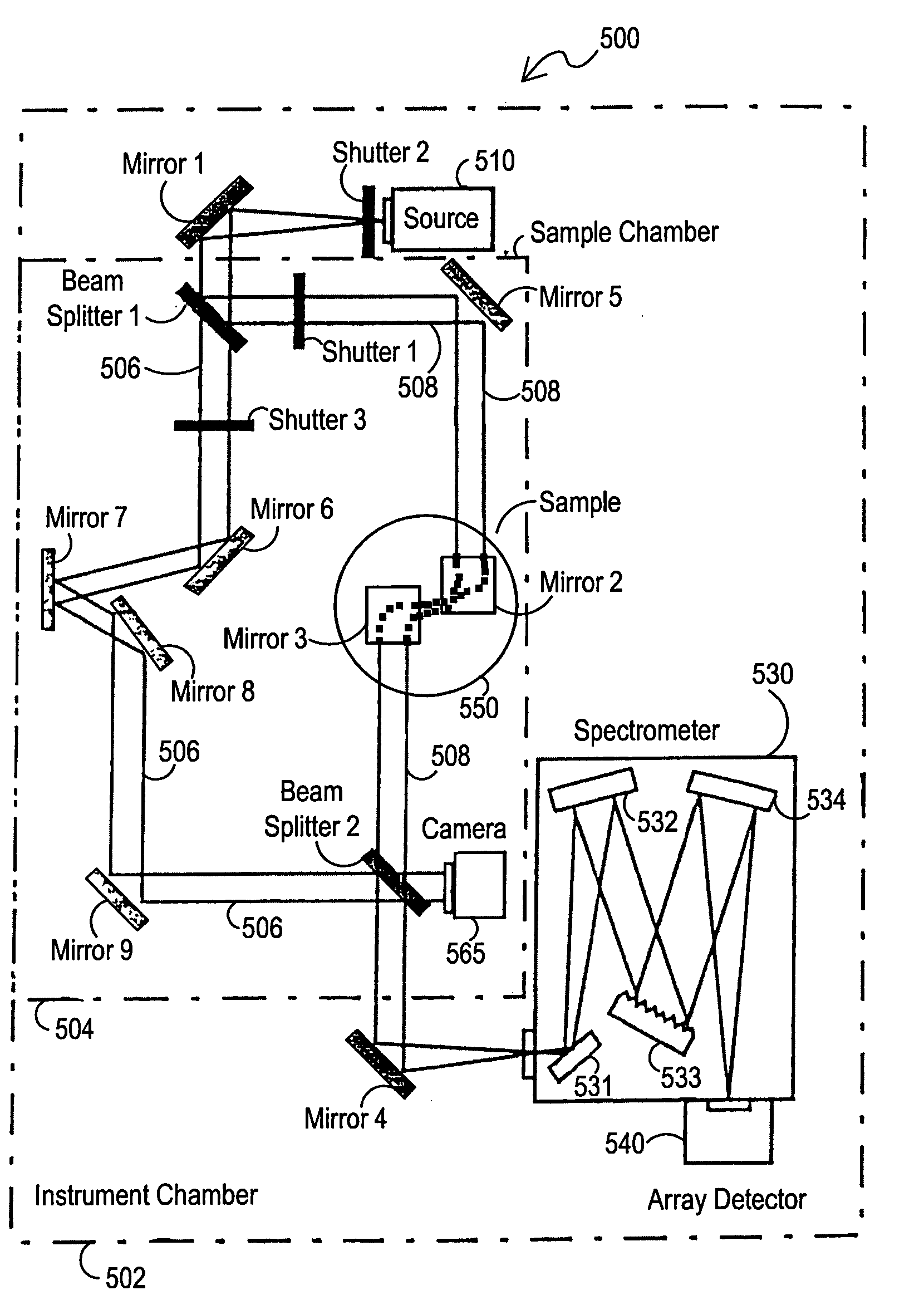
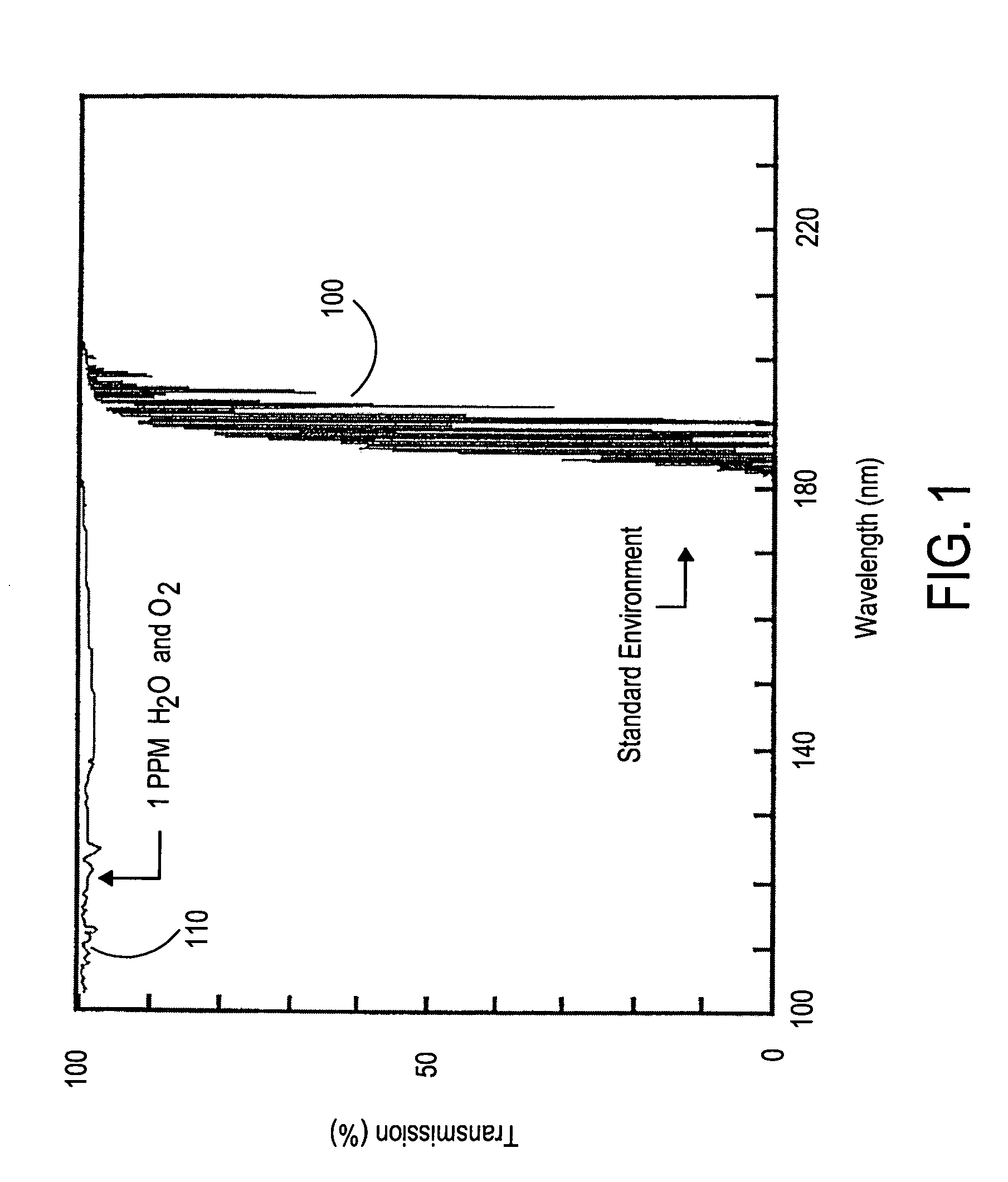
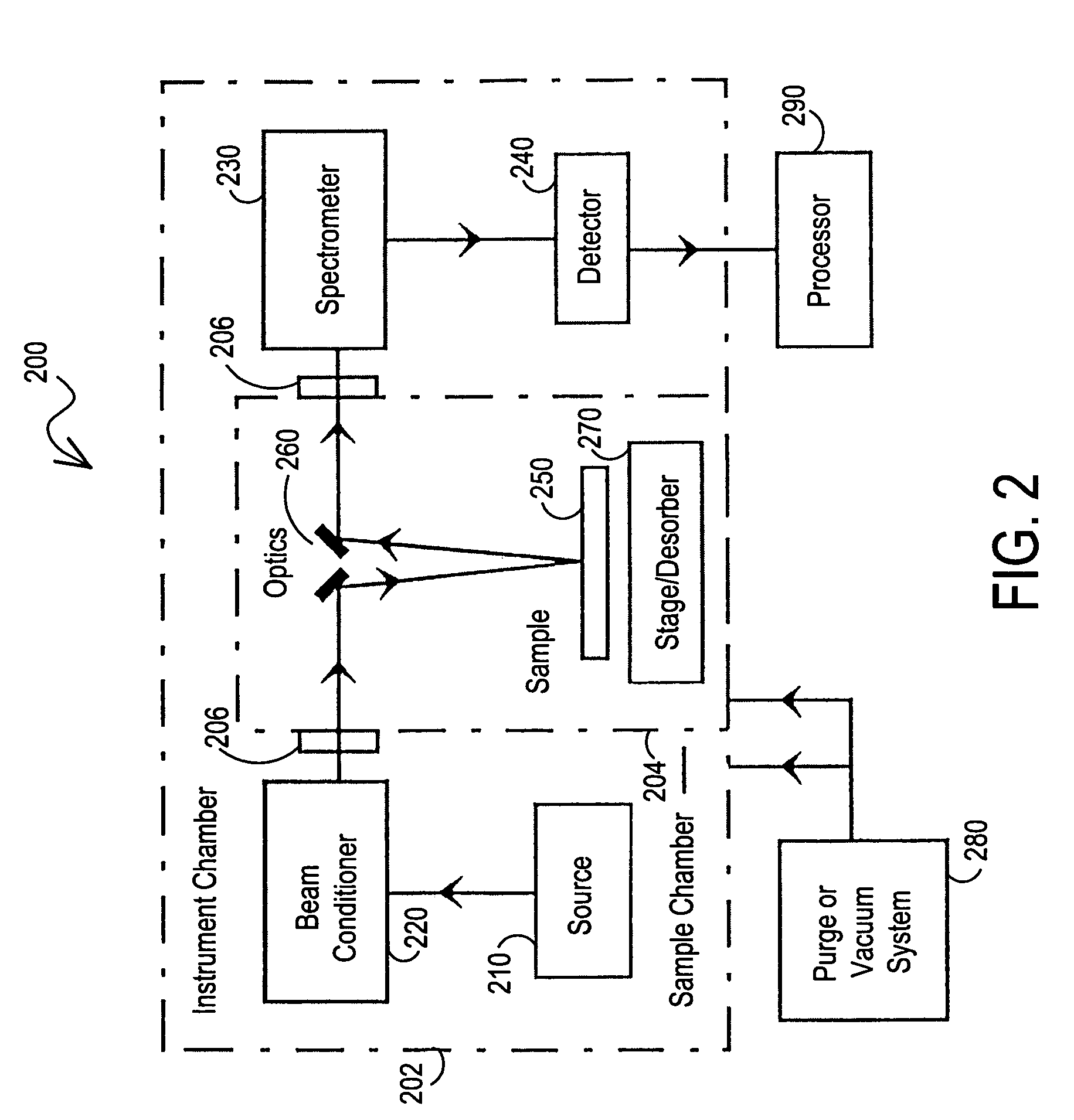
Vacuum ultraviolet referencing reflectometer
ActiveUS20050002037A1Thin layerSmall featureSpectrum investigationPolarisation-affecting propertiesBeam splitterMetrology
A spectroscopy system is provided which operates in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum. More particularly, a system utilizing reflectometry techniques in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum is provided for use in metrology applications. To ensure accurate and repeatable measurement, the environment of the optical path is controlled to limit absorption effects of gases that may be present in the optical path. To account for absorption effects that may still occur, the length of the optical path is minimized. To further account for absorption effects, the reflectance data may be referenced to a relative standard. Referencing is particularly advantageous in the VUV reflectometer due to the low available photon flux and the sensitivity of recorded data to the composition of the gaseous medium contained with the optical path. Thus, errors that may be introduced by changes in the controlled environment may be reduced. In one exemplary embodiment, the VUV reflectometer may utilize a technique in which a beam splitter is utilized to create a sample beam and a reference beam to form the two arms of a near balanced Mach Zehnder interferometer. In another exemplary embodiment, the reference channel may be comprised of a Michelson interferometer.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
Method for preparing monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots based on electronic dynamic regulation and control
ActiveCN106905966AHigh yieldPromote absorptionCatalyst activation/preparationNanotechnologyPhotoablationLaser scanning
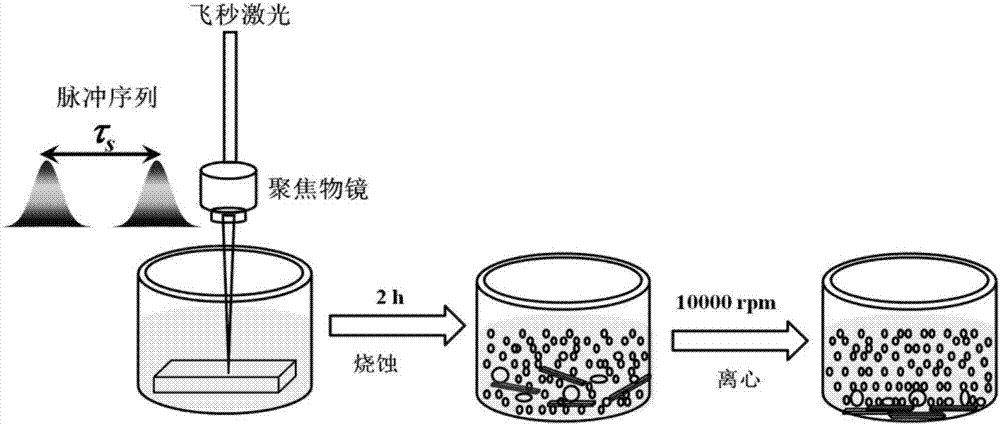
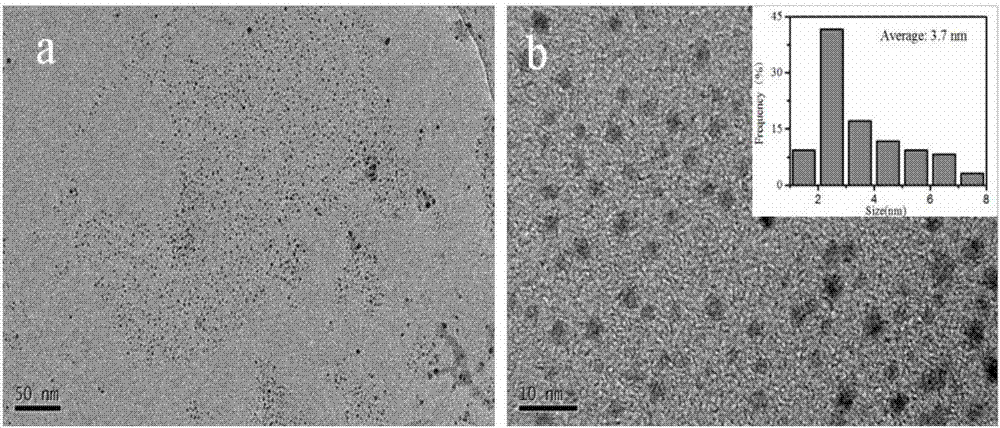
The invention relates to a method for preparing monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots based on electronic dynamic regulation and control, in particular to a method for obtaining the monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots with uniform particle sizes by obtaining molybdenum disulfide suspension and then centrifugally separating and belongs to the field of femtosecond laser application. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: aiming at the characteristics of a molybdenum disulfide material, carrying out pulse shaping on traditional femtosecond laser monopulse by using a Michelson interferometer to form a pulse sequence; adjusting energy of the pulse sequence, delay among sub pulses, laser scanning speed and scanning intervals; ablating blocky molybdenum disulfide in water and further regulating and controlling local transient electronic dynamics in the interaction process of laser and the material to form multistage photoablation monolayer molybdenum, and obtaining the monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots with the uniform particle sizes; carrying out laser-induced water dissociation to enhance light absorption and improve the yield of the molybdenum disulfide quantum dots. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of no need of special chemical environment or chemical reagent, greenness, no pollution, and simple and flexible operation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Optical signal demodulator
InactiveUS7411725B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersOptoelectronicsMichelson interferometer
A demodulator includes: a Michelson interferometer having: a half-mirror which splits an optical signal, emits a first split light to a first optical path, and emits a second split light to a second optical path; a first reflector which reflects the first split light to the half-mirror; and a second reflector which reflects the second split light to the half-mirror, wherein the half-mirror recombines the first split light and the second split light, and emits a recombined optical signal while splitting the recombined optical signal; and an balanced optical detector which receives the recombined optical signals from the Michelson interferometer, and generates a demodulated signal based on the two recombined optical signals. The length difference between the first optical path and the second optical path is set so that the second split light has a delay time equal to a one-bit period, with respect to the first split light.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
CCD chip modulation transfer function test device and method
InactiveCN103592108AReflect image qualityUnaffected by stray lightTesting optical propertiesMichelson interferometerHe ne laser
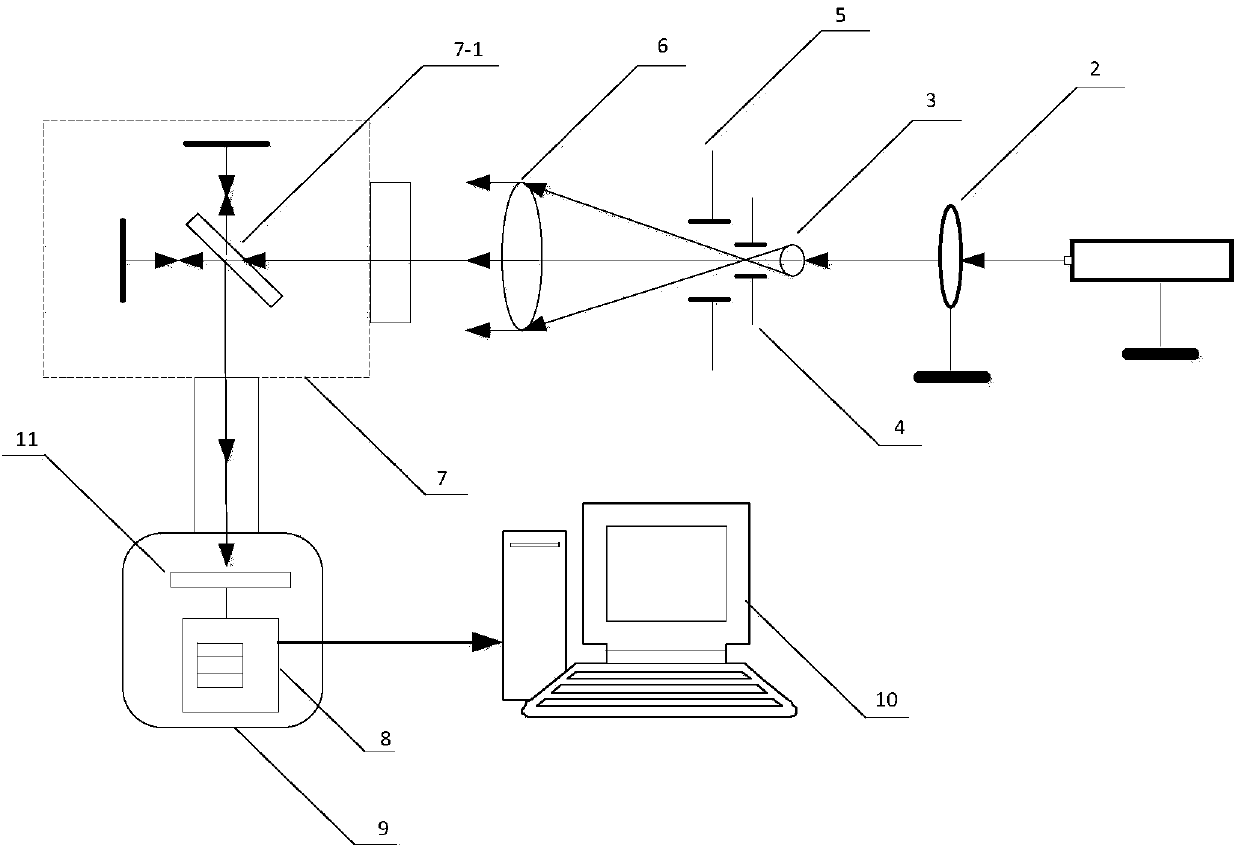
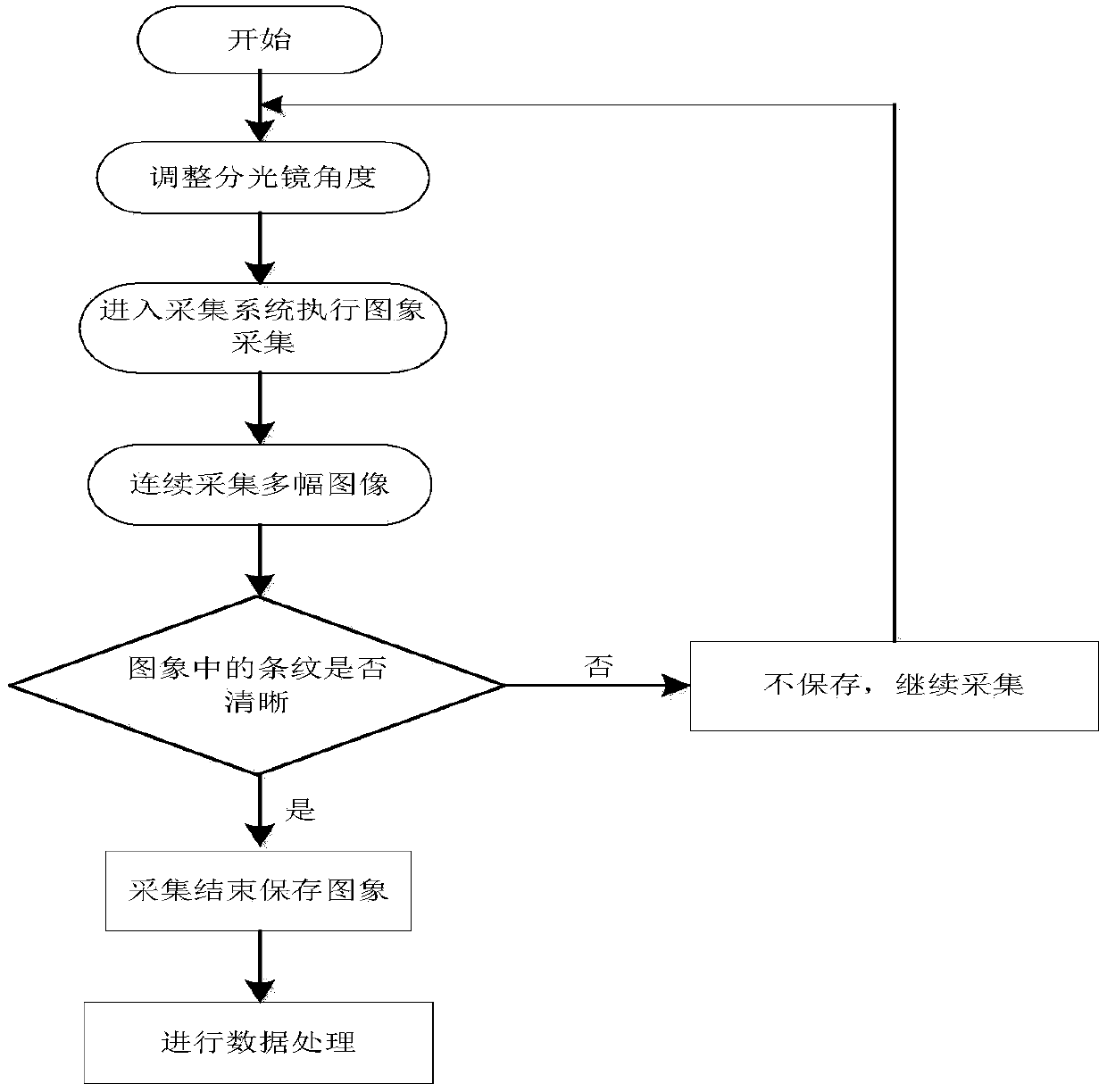
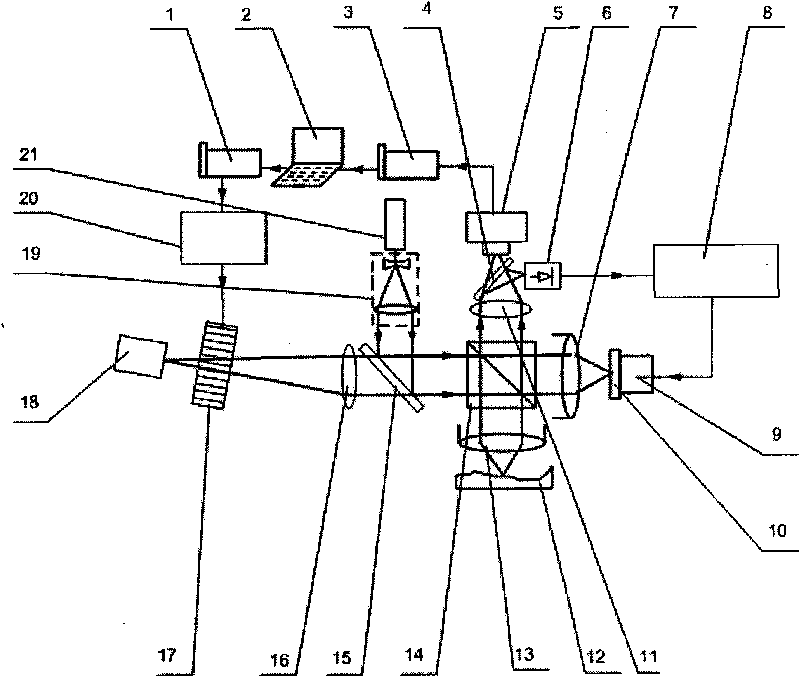
The invention discloses a CCD chip modulation transfer function test device and method. The CCD chip modulation transfer function test device mainly comprises a He-Ne laser, an adjustable attenuator, a beam expander, a pinhole filter, a diaphragm, a collimating lens, an improved Michelson interferometer, a camera obscura, an image capture card and a PC data processing system, wherein the He-Ne laser, the adjustable attenuator, the beam expander, the pinhole filter, the diaphragm and the collimating lens are arranged on the incident light path of the improved Michelson interferometer in sequence, and the optical axis of the He-Ne laser, the optical axis of the adjustable attenuator, the optical axis of the beam expander, the optical axis of the pinhole filter, the optical axis of the diaphragm and the optical axis of the collimating lens are arranged on the same straight line, the camera obscura is arranged on the emergent light path of the improved Michelson interferometer, and the PC data processing system is connected with the image capture card which is arranged in the camera obscura and is connected with a CCD. Incident light is processed through the CCD chip modulation transfer function test device to form parallel light, and goes out in a sine interference fringe mode through the improved Michelson interferometer, a sine interference fringe pattern is used as a target, imaging is carried out through the CCD, and a modulation transfer function of the CCD is obtained through a test by using the method of the ratio between the sine interference fringe contrast and the image contrast.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) apparatus, methods, and applications
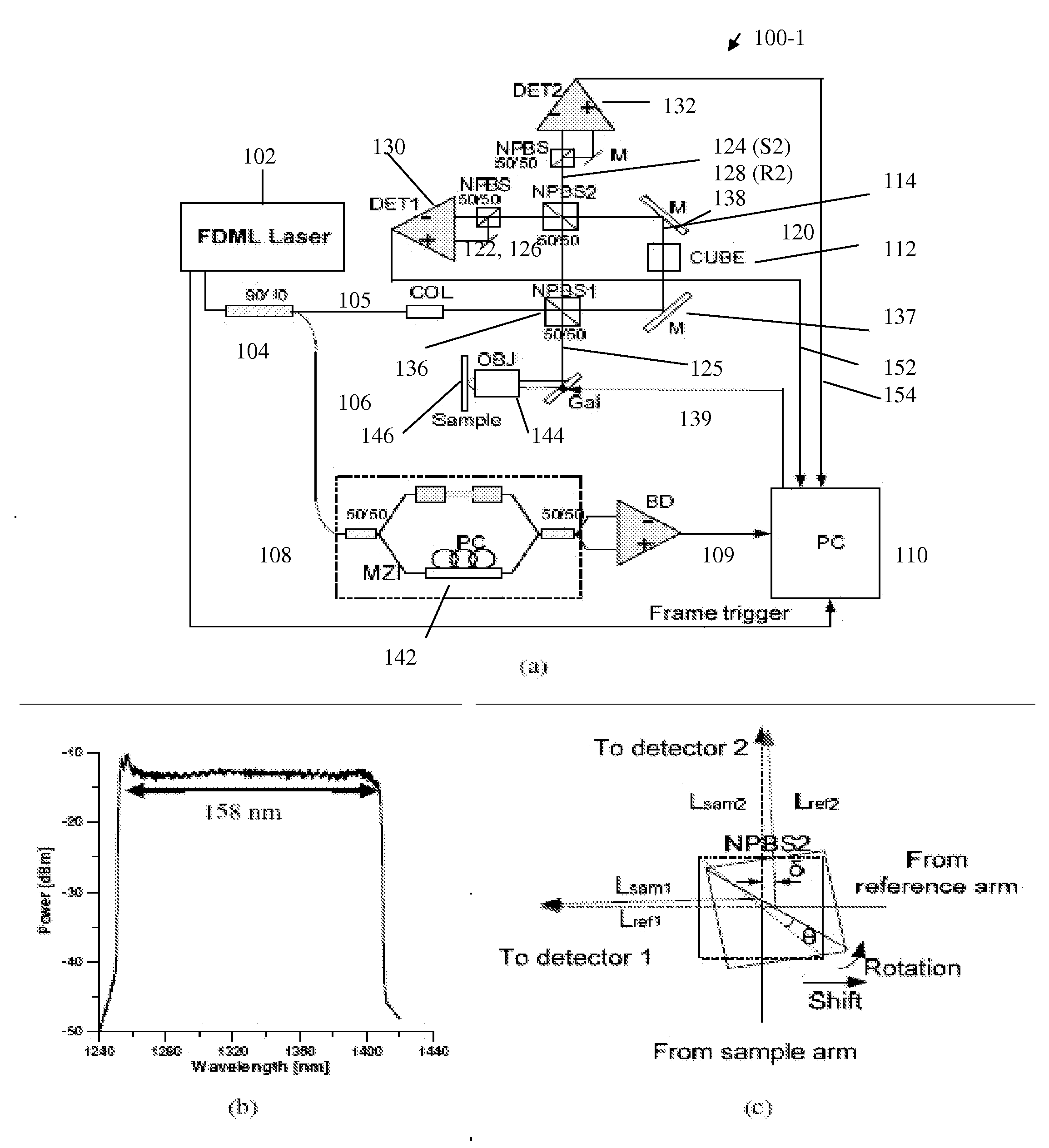
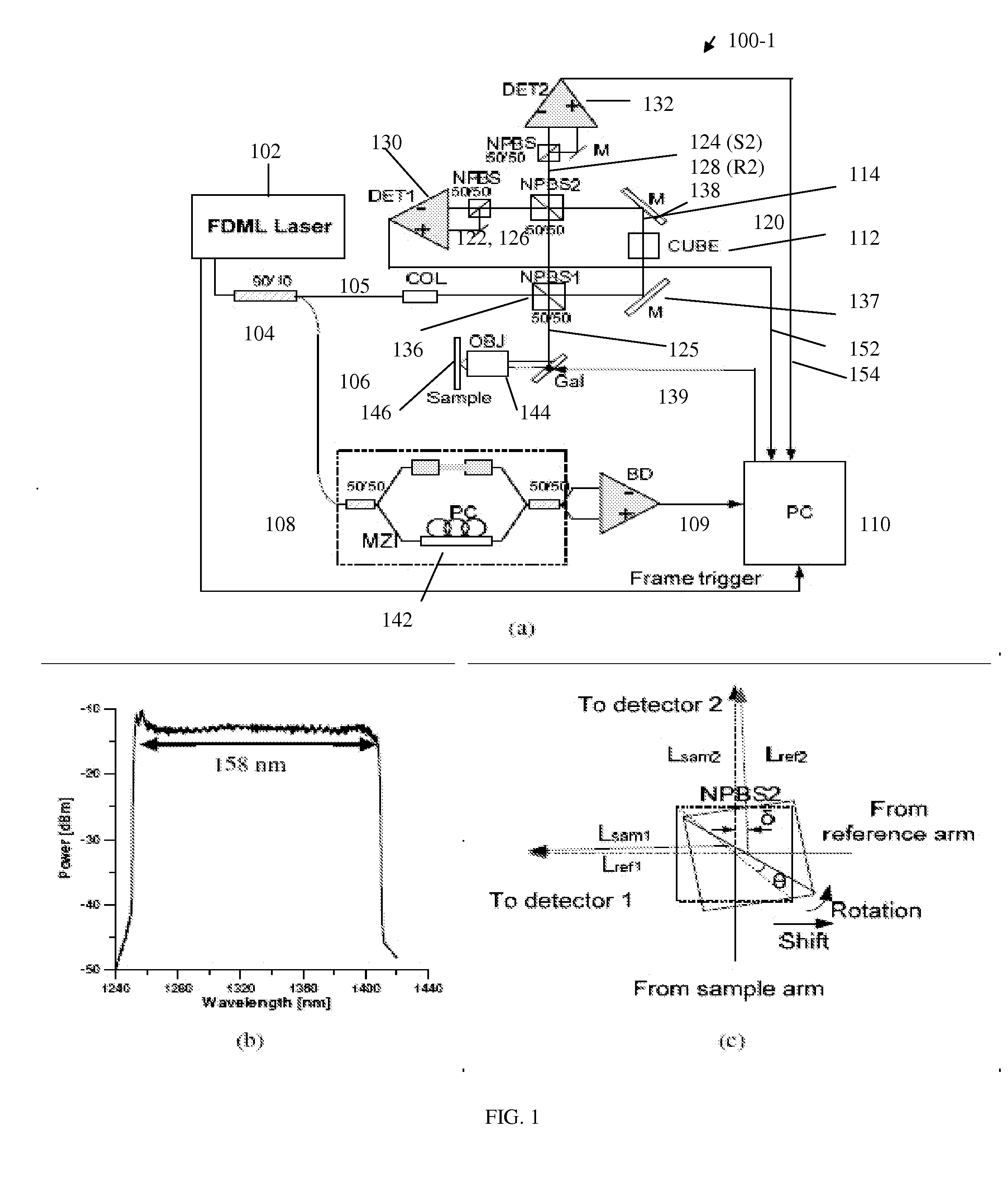
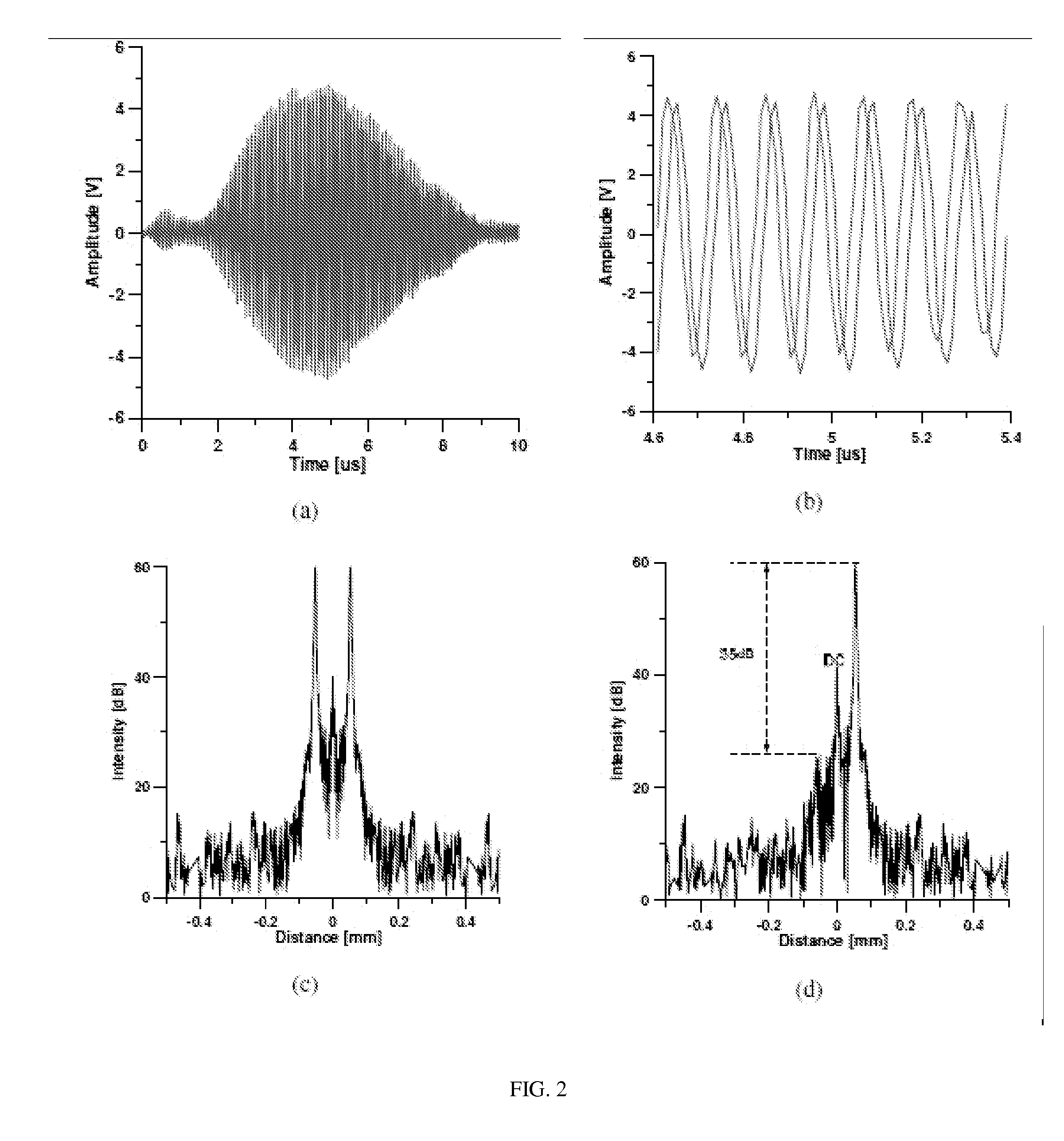
A free-space Michelson Interferometer-based Dual Detection Frequency Domain-Optical Coherency Tomography (DD-FD-OCT) apparatus includes a non-polarizing beam splitter that can be used to misalign sample and reference beam paths to provide a stable π / 2 phase shift between simultaneously detected interfering sample and reference beams to eliminate the mirror image created by Fourier transformation during image reconstruction. A hybrid fiber system Mach Zehnder Interferometer- and free-space Michelson Interferometer-based Dual Detection Frequency Domain-Doppler Optical Coherency Tomography (DD-FD-DOCT) apparatus provides higher power efficiency and thus better sensitivity compared to the free-space DD-FD-OCT. Both DD-FD-OCT systems enable functional imaging with the contrasts of Doppler and that of polarization, in addition to full range images simultaneously.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on Faraday-Michelson interference
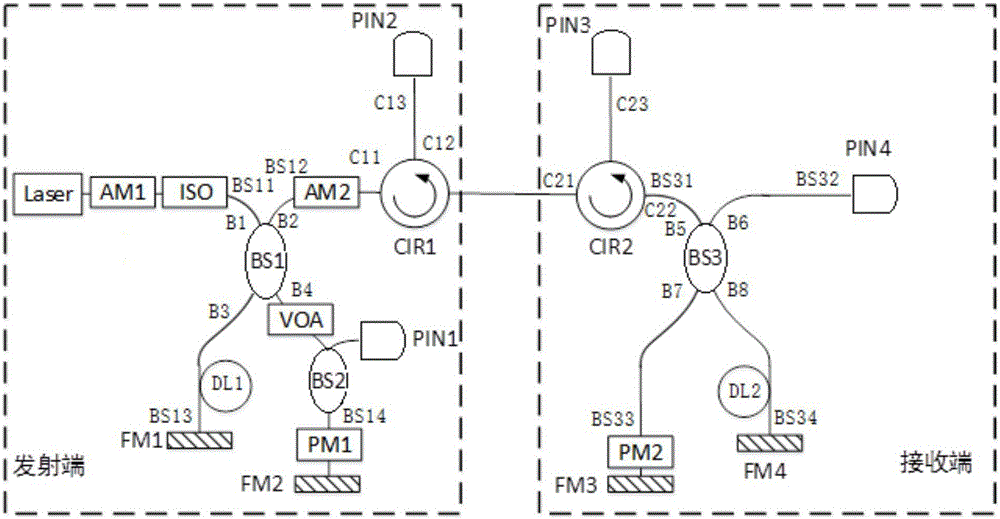
ActiveCN105897414ASmooth transmissionImprove stabilityKey distribution for secure communicationSignal lightMichelson interferometer
The invention discloses a continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on Faraday-Michelson interference. A transmitting end is used for generating a pulse light source which is in accordance with the parameters such as repetition frequency, pulse width and so on, and modulating regular components X and P of a signal light; a communication channel is a light propagation channel, and used for transmitting the signal light modulated by the transmitting end and an unmodulated local oscillation light to a receiving end; a receiving end demodulation module realizes measurement and component selection: X or P; and a receiving end zero-difference detection module is used for performing detection processing, and acquiring modulation information data of a signal. The continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on the Faraday-Michelson interference provided by the invention introduces two unequal-arm Faraday-Michelson interference rings, and with the help of a Faraday polarization rotating mirror, the polarization scrambling in a pulse round trip process can be self-compensated, which is beneficial to improving the stability of the system and not easily interfered by polarization; and besides, long distance stable quantum key distribution can be realized in combination with an existing detection technology and a post-processing algorithm.
Owner:ANHUI QASKY QUANTUM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Dispersion compensation method for broadband light source
ActiveCN102332956AImprove test accuracyHigh precisionElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumMichelson interferometer
The invention discloses a dispersion compensation method for a broadband light source. A polarization-preserving fiber polarization coupling testing system based on a Michelson interferometer is formed by the broadband light source, and the Michelson interferometer compensates the optical path difference between an excitation mode and a coupling mode in the polarization-preserving fiber, and a detector acquires an interference signal; specifically, the method comprises the following steps of: intercepting the initial data acquired by the detector through a window function, and taking out the interference data Imain between the excitation modes and the interference data Icoupling between the excitation mode and the coupling mode; respectively executing Hilbert transformation and Gaussian fitting on the Imain and the Icoupling, obtaining envelopes (I)main and (I)coupling of the interference signal, getting a birefringence dispersion coefficient Delta D according to a ratio Eta of the width of the (I)main to the width of the (I)coupling at a 1 / e part, obtaining a phase factor needed for the dispersion compensation, and then multiplying the phase factor by a nonlinear frequency spectrum function with dispersion information to eliminate nonlinear phase items causing the widening of the interference signal envelopes; and finally, obtaining the dispersion compensated interference signal Icomp by executing Fourier inversion on the obtained linear frequency spectrum function.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Entangled photon fourier transform spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050206904A1High resolutionHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryMichelson interferometerElectron
Novel spectroscopy techniques using entangled photons are disclosed. In one technique, entangled photons are directed to a sample of interest, while the photons with which they are entangled are resolved according to frequency. The photons transmitted by or reflected from the sample and the frequency-resolved photons are detected. Such detection may be by way of an electronic coincidence counter or a biphoton sensitive material, which absorbs entangled photons while allowing other photon pairs to pass. Detection information is used to derive spectroscopic properties of the sample. In another technique, a Fourier transform spectroscopy technique using entangled photons is disclosed. Entangled photons are directed to a sample, while the photons with which they are entangled are directed to a Michelson interferometer. The photons transmitted by or reflected from the sample and the photons leaving the Michelson interferometer are detected. Such detection may be by way of an electronic coincidence counter or a biphoton sensitive material. Detection information is used to derive spectroscopic properties of the sample.
Owner:MDA INFORMATION SYST
Broad-band light source signal detection method and its detector
InactiveCN1412538AGuaranteed accuracyHigh precisionPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsPolarization-maintaining optical fiberPhotoelectric conversion
The method for detecting wideband light source signal includes the following steps: 1. laying the polarization-protecting optical fibre on the tested body; 2. one end of the polarization-protecting optical fibre is inputted into wideband detection light source; 3. using polarizing spectroscopic system to divide the wideband detection light source outputted by another end of the polarization-protecting optical fibre into linear polarized light, reflecting and transmission, feeding the linear polarized light into Michelson interferometer; and 4. making the interference light signal undergo the processes of collection, photoelectric conversion, A / D conversion, etc. to output the detection parameters of said tested body. Said invented detector is formed from detection light source system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
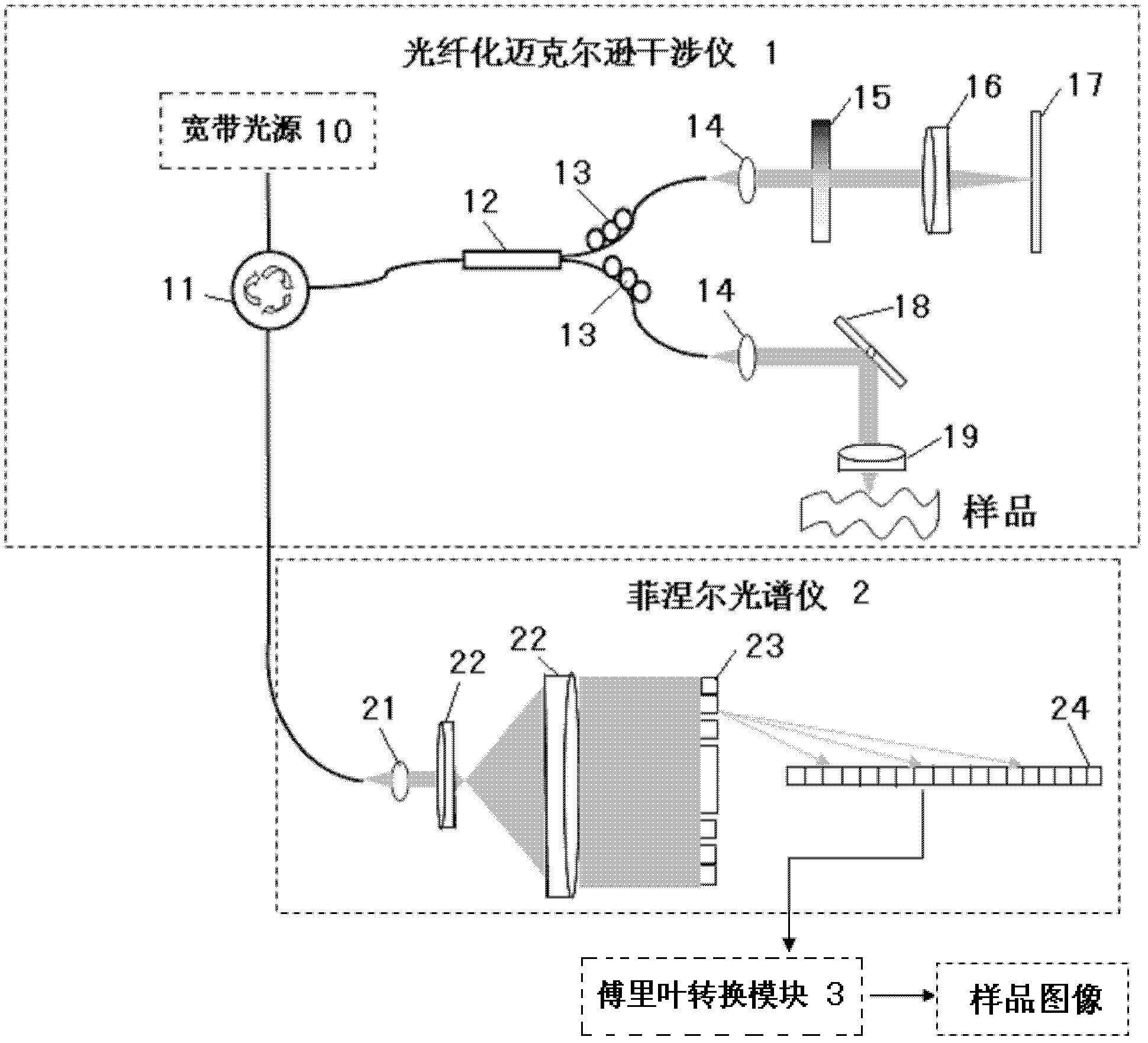
Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography imaging system based on Fresnel spectrometer
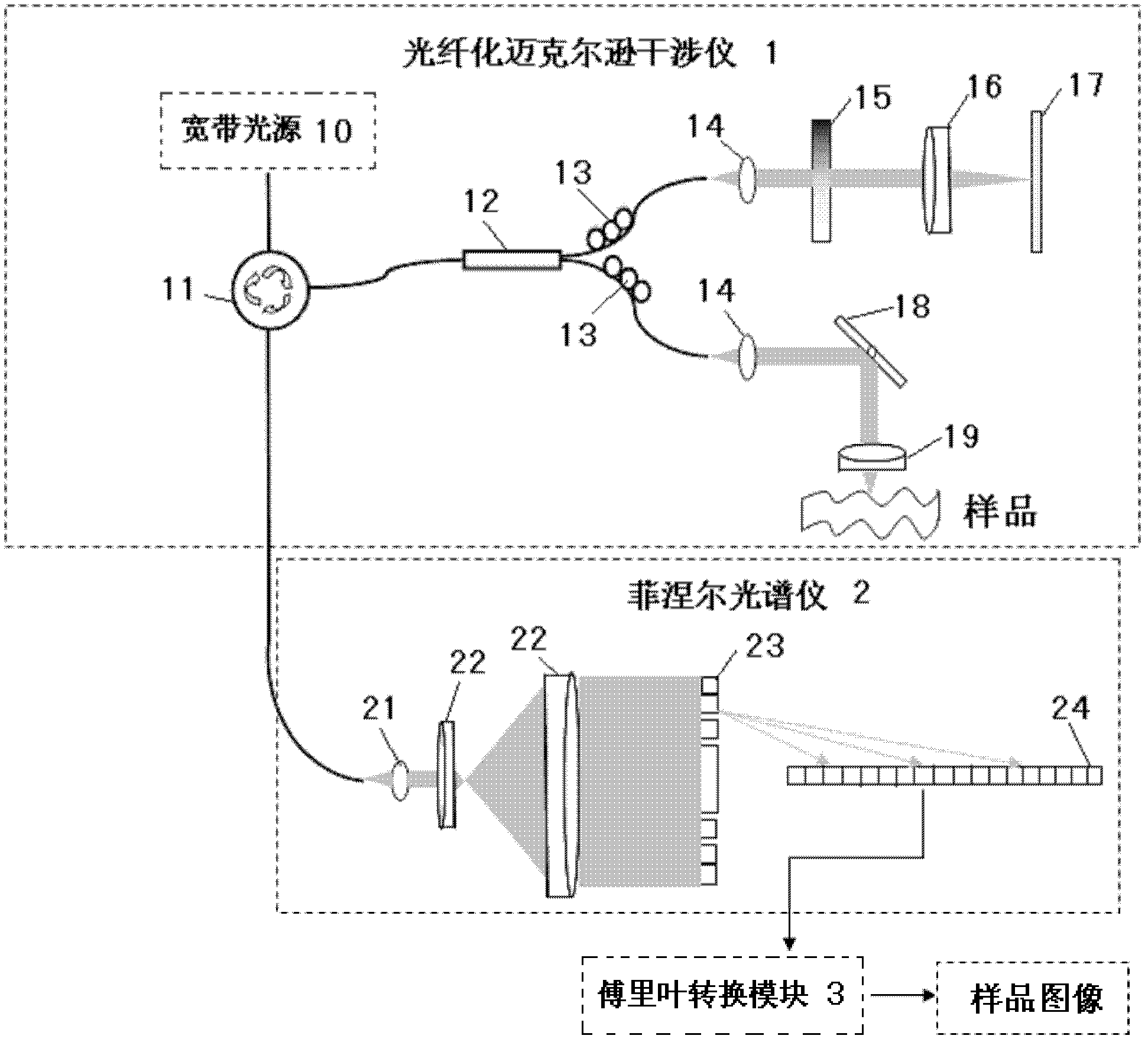
ActiveCN102499648AQuick extractionReduced post-processing timePhase-affecting property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumMichelson interferometer
The invention relates to a spectral-domain optical coherence tomography imaging system based on a Fresnel spectrometer, which is characterized by comprising a Michelson interferometer, the Fresnel spectrometer and a Fourier transformation module. The Michelson interferometer sends coherent light which is formed by superposing sample light returned from various layers of a sample with reference light into the Fresnel spectrometer, the coherent light is emitted onto a Fresnel zone plate parallelly through a collimating lens and an expanded beam lens respectively, and is expanded at the same interval according to the wave number and then projected to a linear array CCDs (charge coupled devices) by the Fresnel zone plate, frequency spectrum data of the coherent light are read by the linear array CCDs and sent to the Fourier transformation module, and then recovered into information of spatial position of the sample by means of discrete Fourier transformation through the Fourier transformation module. The spectral-domain optical coherence tomography imaging system based on the Fresnel spectrometer can be applied to not only spectral-domain optical coherence tomography imaging but also spectral analysis having requirements for wavelength-wave number conversion and resampling for imaging or detecting and required to be expanded uniformly according to the wave number, and especially can be applied to the biomedical imaging process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
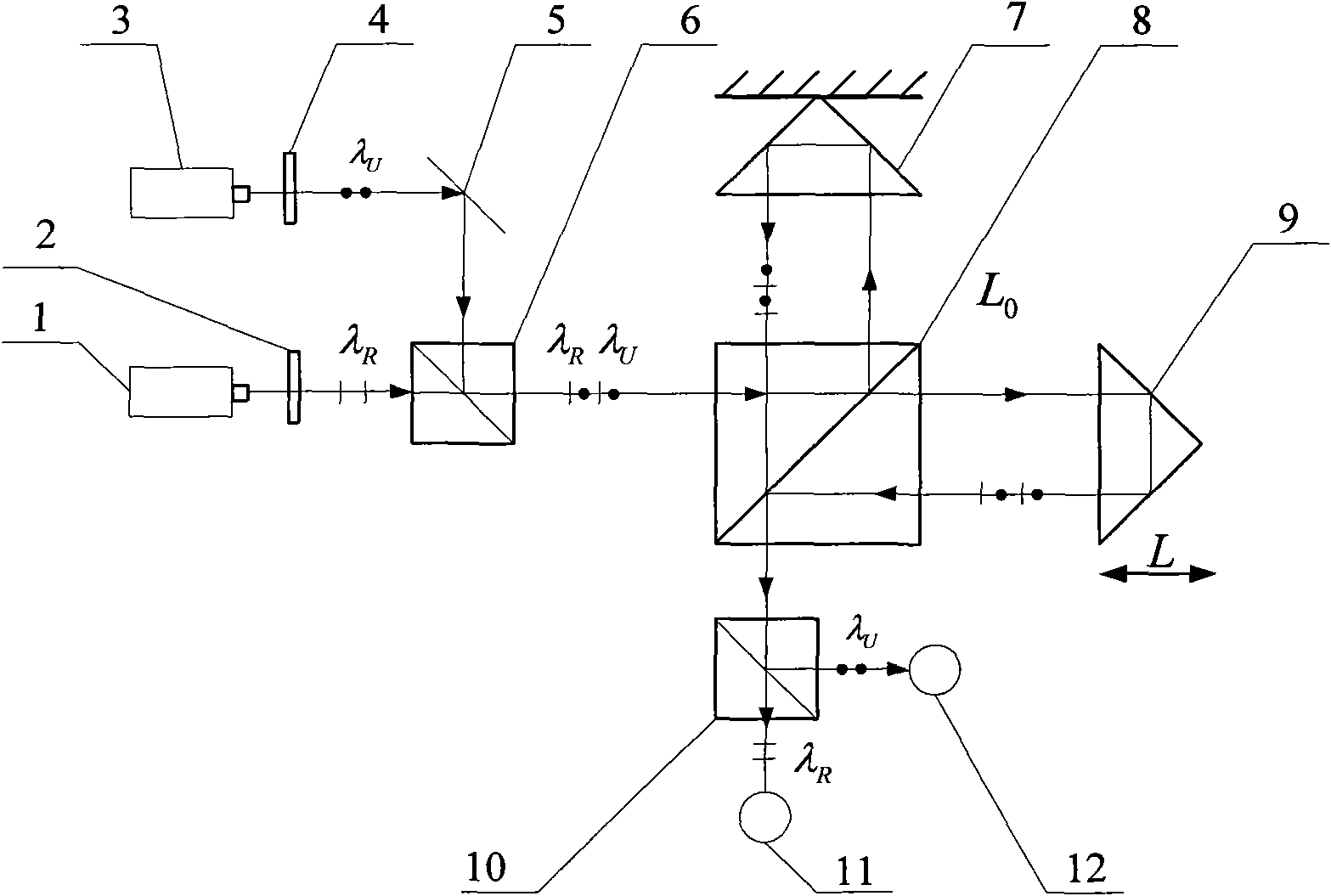
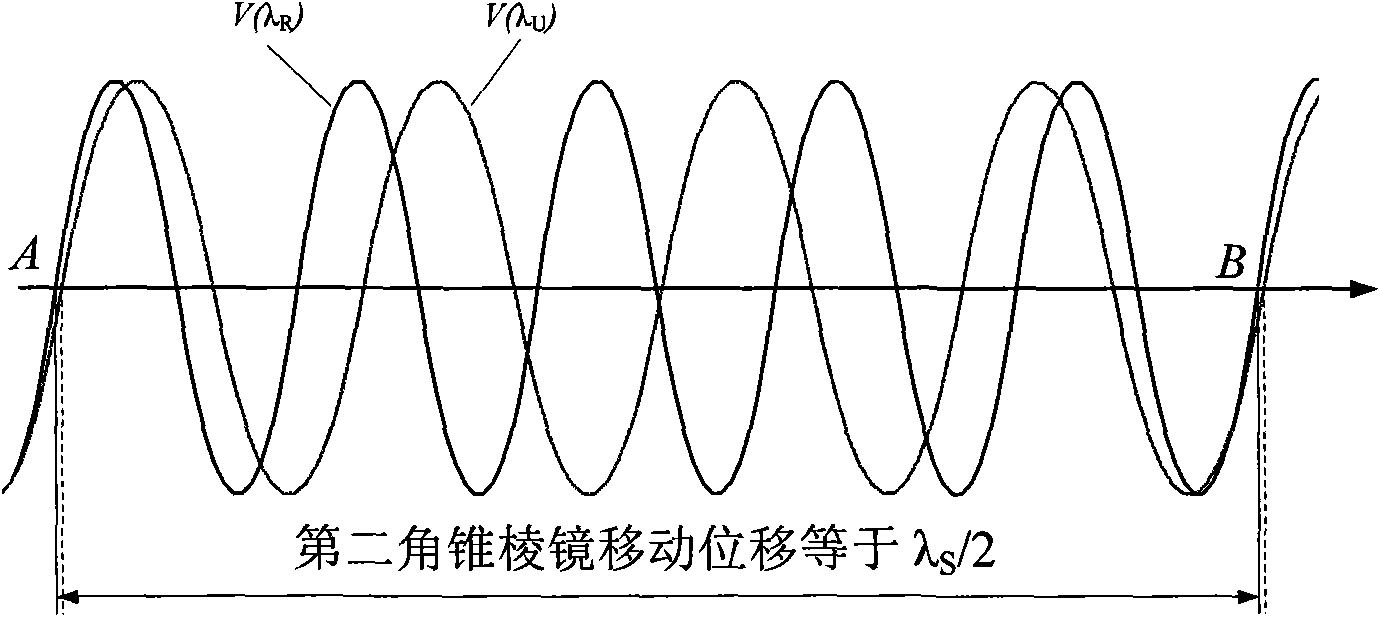
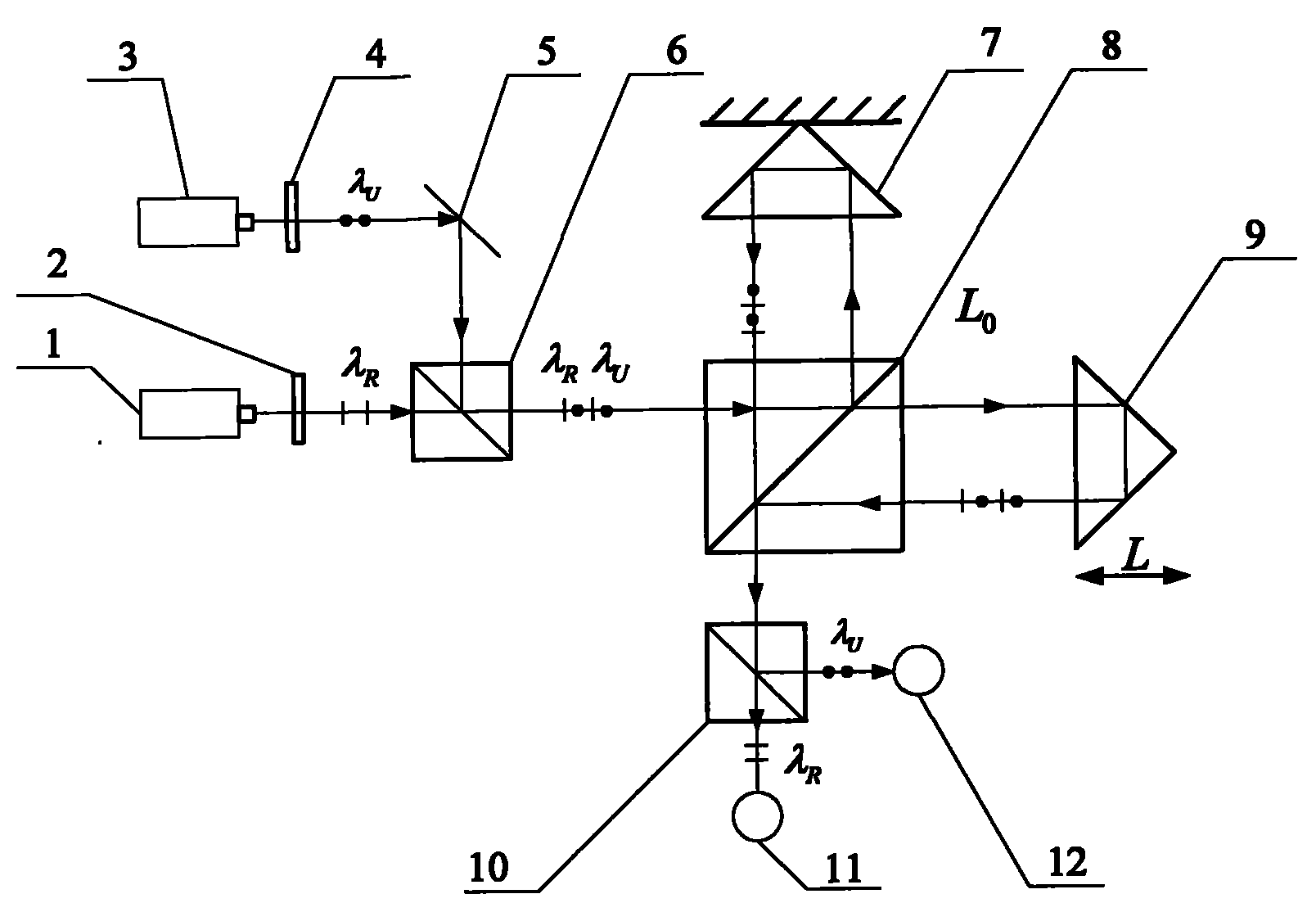
Method and device for measuring laser wavelength based on bound wavelength
InactiveCN101832821AInhibition effectStrong anti-interference ability in the environmentOptical measurementsInterference resistancePhase difference
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring laser wavelength based on bound wavelength, and the method has the following steps: adopting a laser with higher wavelength stability as a reference laser, modulating beam of the reference laser and beam of a laser to be measured into orthogonal linear polarized light, and entering in the same Michelson interferometer to form respective interference signals, wherein the measuring arm of the Michelson interferometer moves, the phase relations of the interference signals of the reference light and light to be measured change; and when the phase difference of the two paths of interference signals is 2pi, half displacement of the bound wavelength formed by the reference light and the light to be measured is moved corresponding to the measuring arm. The bound wavelength value can be measured by detecting the zero crossing point positions of the two paths of interference signals twice, and the wavelength value of the laser to be measured can be obtained according to the relationship between the laser wavelength to be measured, the reference laser wavelength and the bound wavelength. The invention has strong environment interference resistance, low cost and easy practicability, and the wavelength measurement precision can be above 10-8.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method and assembly for measuring a dispersion in transparent media
InactiveUS20060244972A1Reliable and accurate measurementEasy to useDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBeam splitterGlucose Measurement
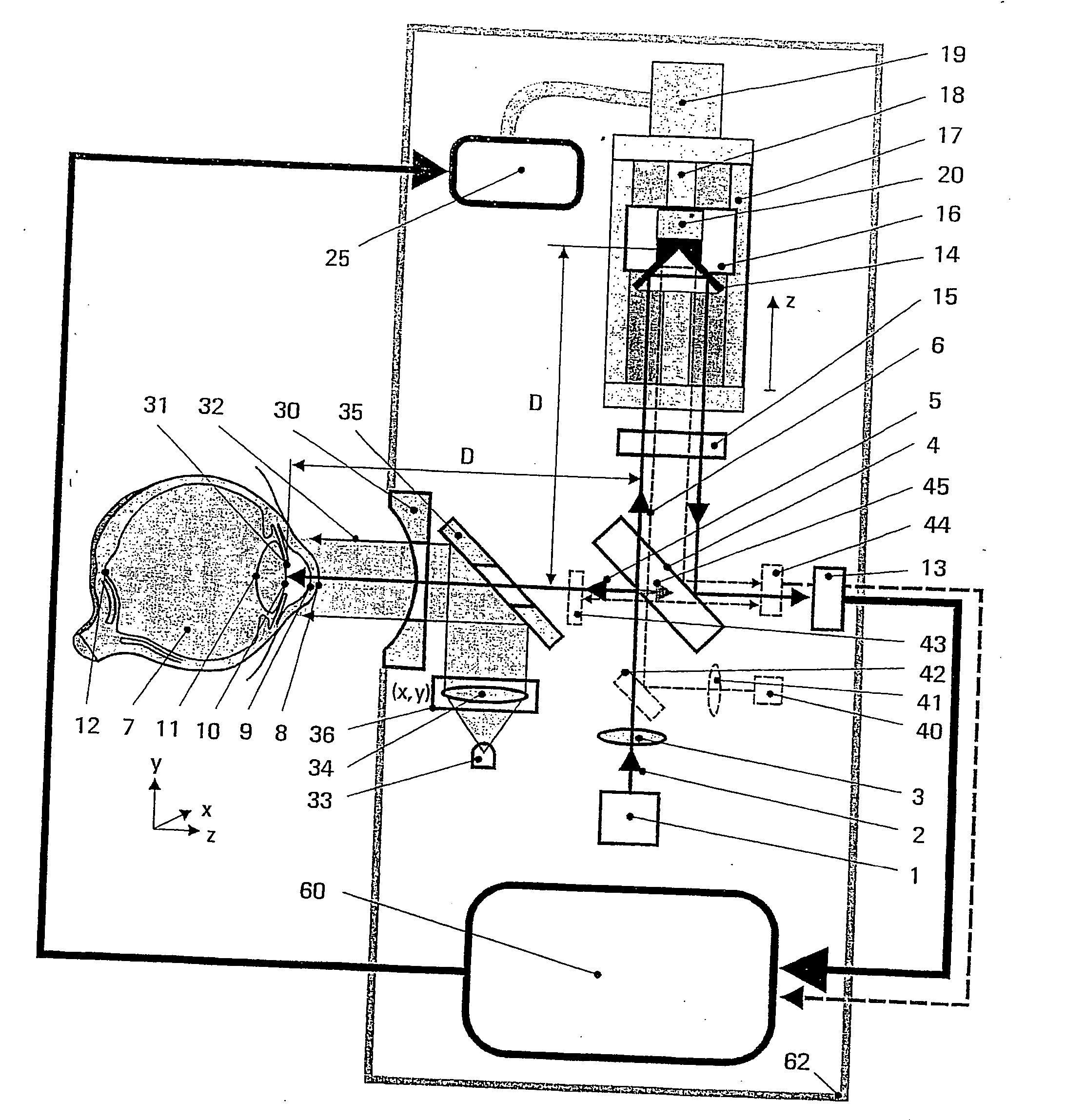
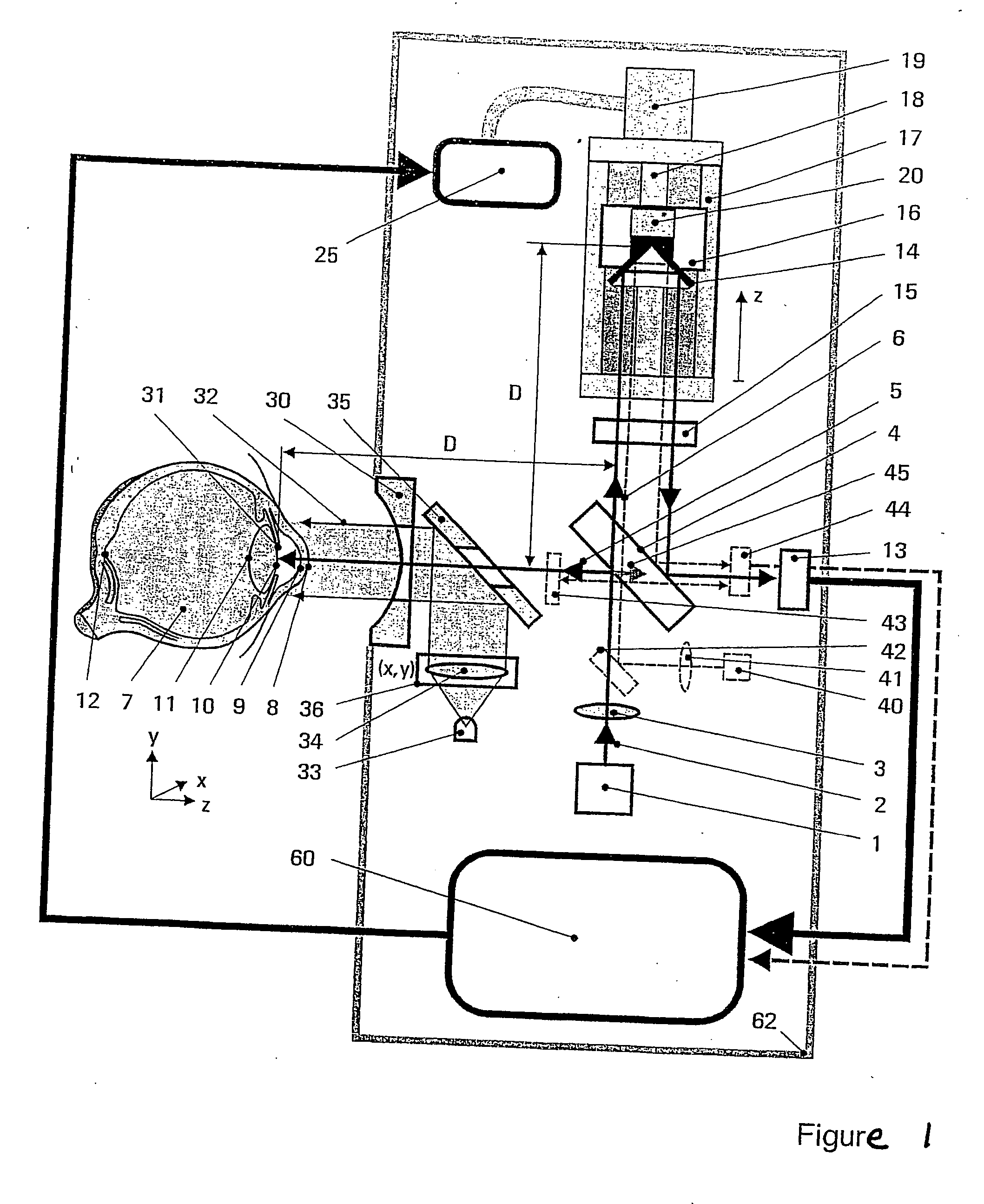
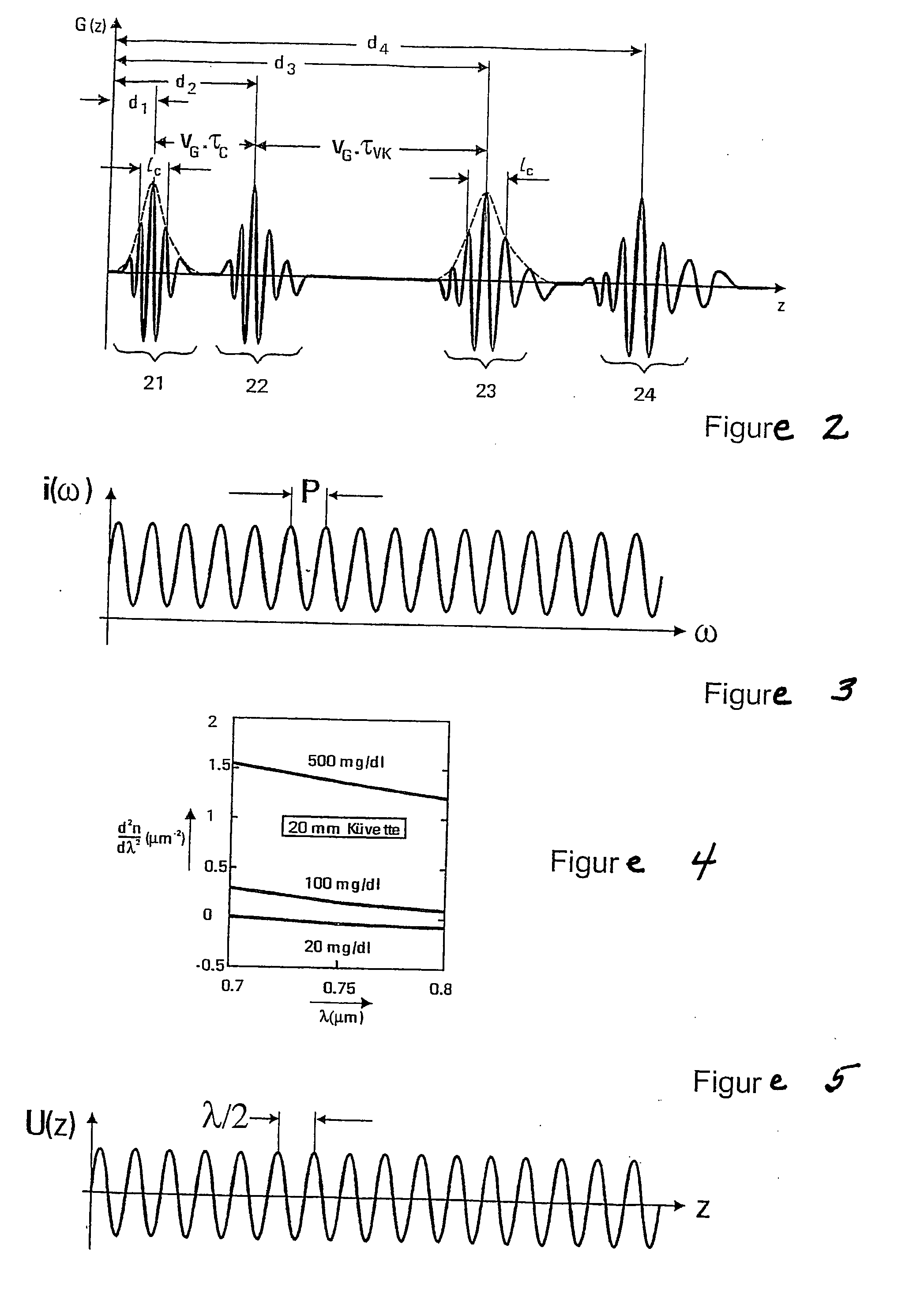
Spatially localized dispersion measurement and glucose measurement by means of optical short-coherence interference refractometry. This application is directed to methods and arrangements for the measurement of the dispersion and of the glucose content in transparent and partially transparent tissues and body fluids. Methods of short-coherence interferometry and spectral interferometry are modified for the measurement of tissue thickness and for the measurement of local dispersion. In the technique based on short-coherence interferometry, partial interferograms from the short-coherence interferogram G(τ) are used for the dispersion measurement. In the technique based on spectral interferometry, partial areas from the ω-spectrum of the spectral interferogram are used for the dispersion measurement. FIG. 6 shows an arrangement based on spectral interferometry. A temporally short-coherence light source illuminates the modified Michelson interferometer. The beam splitter splits the illuminating beam into a measurement beam and a reference beam. The light waves and reflected from the interferometer impinges on the spectrometer at the interferometer output. The registered spectral interferogram i(ω) forms the basis for the calculation of the dispersion of different orders. The viewing direction of the eye of the subject is fixated by means of a target beam.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
System for quickly measuring surface quality
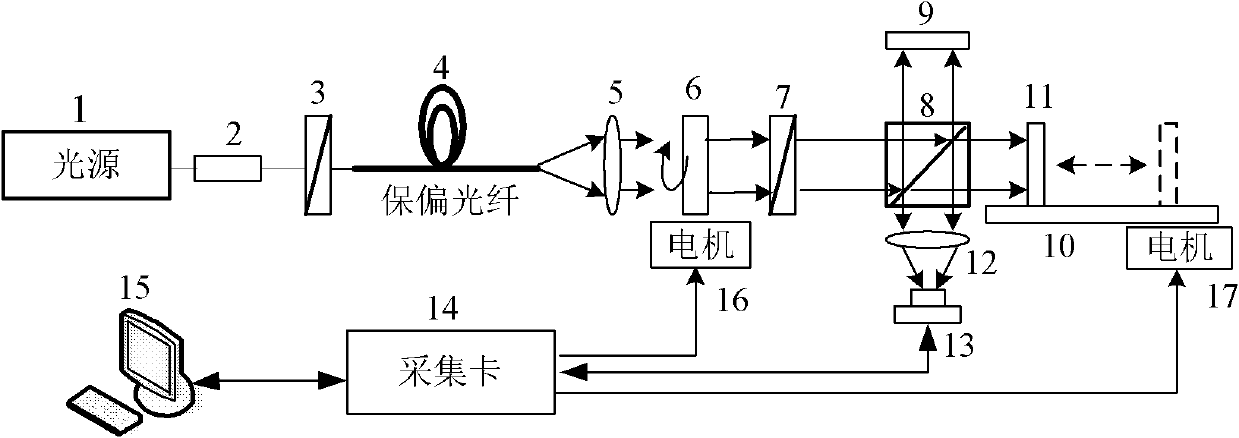
InactiveCN101718520AShort reaction timeFast measurementUsing optical meansEnvironmental noiseAcousto-optics
The invention discloses a system for quickly measuring surface quality. The system comprises two sets of common-path interferometers, wherein one set of reference interferometer for noise compensation is specially used for detecting noises such as vibration, air disturbance and the like in environment, and eliminating the influence of interference of the background noises through negative feedback; and the other set of main interferometer for measurement controls wavelength of optical wave incident to the interferometers by using an acousto-optic filter, and can quickly acquire a three-dimensional feature of a surface to be measured by processing a generated interference signal by using large-scale parallel computation based on GPGPU. The system can measure the surface quality in real time, does not need mechanical light path scanning in the process of measurement, and can reach a high measurement speed. The system can be updated one time in 1 to 2 seconds on average, and can be updated more frequently after being optimized. The system can reduce influence of environmental noise on the measurement by adding the active optical path compensation technology, achieves measurement accuracy of sub-nano range, reduces cost, saves a usually expensive high-precision translation stage and can be used for processing workshops with more interference.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Entangled photon fourier transform spectroscopy
InactiveUS7292342B2High sensitivityEasy to operateRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryMichelson interferometerElectron
Owner:MDA INFORMATION SYST
Vacuum ultraviolet referencing reflectometer
ActiveUS7394551B2Change levelThin layerSpectrum investigationPolarisation-affecting propertiesBeam splitterMetrology
A spectroscopy system is provided which operates in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum. More particularly, a system utilizing reflectometry techniques in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum is provided for use in metrology applications. To ensure accurate and repeatable measurement, the environment of the optical path is controlled to limit absorption effects of gases that may be present in the optical path. To account for absorption effects that may still occur, the length of the optical path is minimized. To further account for absorption effects, the reflectance data may be referenced to a relative standard. Referencing is particularly advantageous in the VUV reflectometer due to the low available photon flux and the sensitivity of recorded data to the composition of the gaseous medium contained with the optical path. Thus, errors that may be introduced by changes in the controlled environment may be reduced. In one exemplary embodiment, the VUV reflectometer may utilize a technique in which a beam splitter is utilized to create a sample beam and a reference beam to form the two arms of a near balanced Mach Zehnder interferometer. In another exemplary embodiment, the reference channel may be comprised of a Michelson interferometer.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
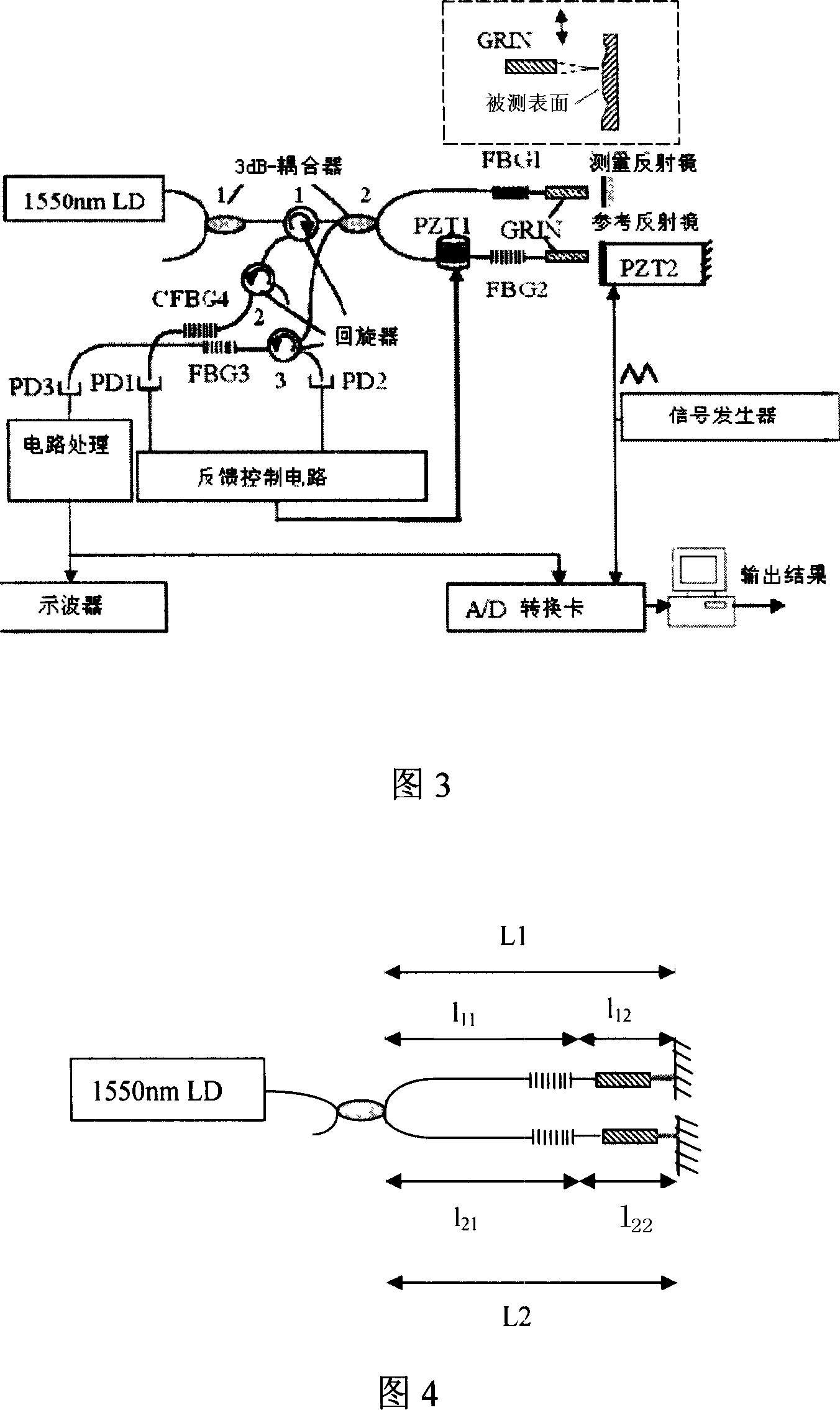
On-line measuring system using optical fiber grating synthetic wave for interfering step height
InactiveCN101126629AMeasurement stabilitySuitable for online measurementUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyGratingMichelson interferometer
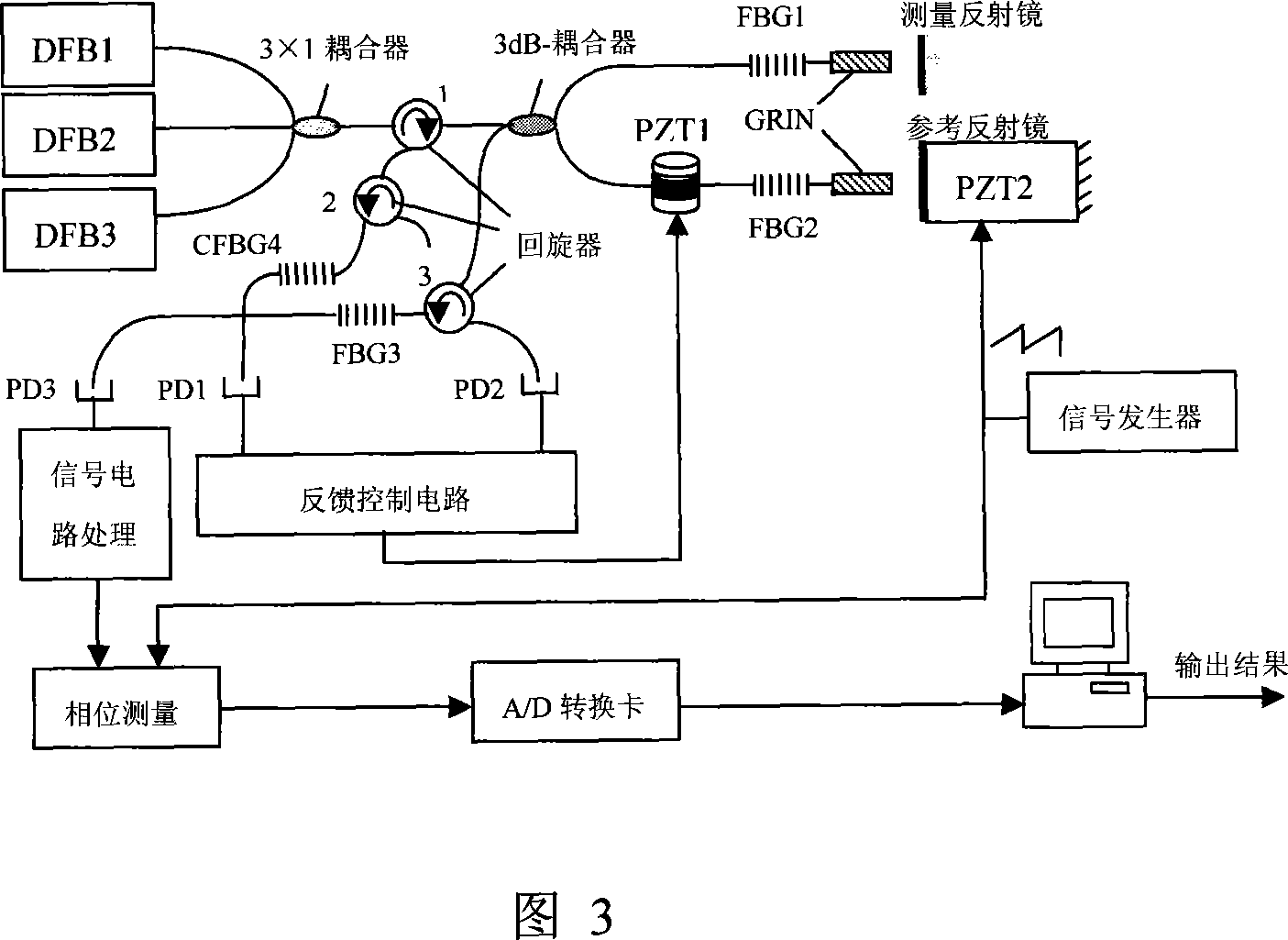
The utility model discloses an on-line measuring system for interference step height in composite wave from optical fiber raster. A composite optical fiber interferometer is built by making use of the Bragg wavelength reflective property in the optical fiber raster. The composite interferometer comprises two optical fiber Michelson interferometers with almost coincident light paths. A Michelson interferometer is used for measuring, and the other is used for stabilizing the system. The impact on the measuring system brought by the environmental interference is corrected through the feedback control compensation, so that the system is applicable to online measuring. Three lasers emit lights of slightly different wavelength but within 1550nm waveband. Because of the effects of the optical fiber raster reflecting Bragg wavelength and self-chirped optical fiber raster reflecting the specific spectrum, a wavelength acts on the stabilizing interferometer for stabilizing the measuring system, and the other two wavelengths act on the measuring interferometer to produce composite wave interference for actual measurement. Different composite wavelengths can be gained by regulating the two wavelengths acting on the measuring interferometer; and the measurement of different step heights can be carried out.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com