Patents
Literature
59 results about "Photoablation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photoablation is the use of light or lasers to destroy tissues. The excimer laser of deep ultra-violet light is mainly used in Photoablation.The wavelength of laser used in photoablation is approximately 200 nm.
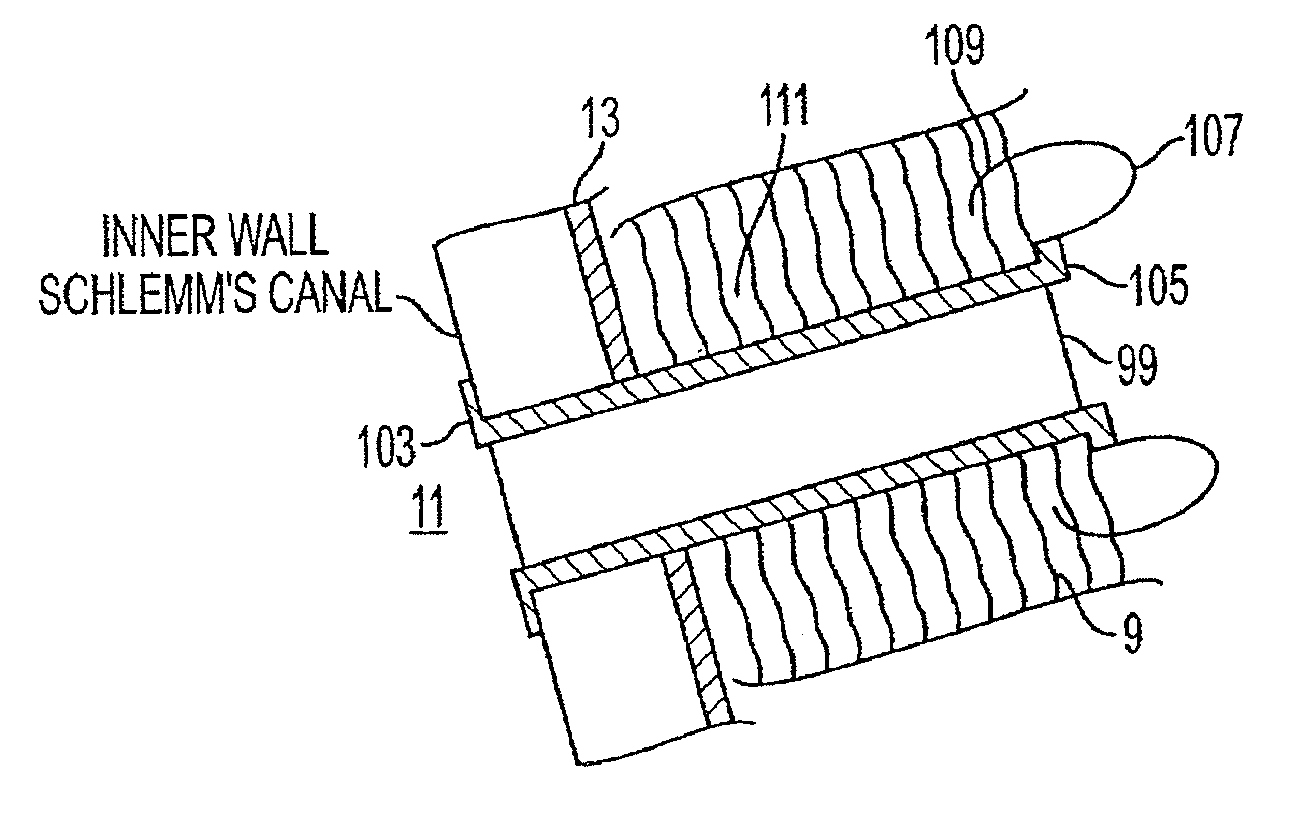
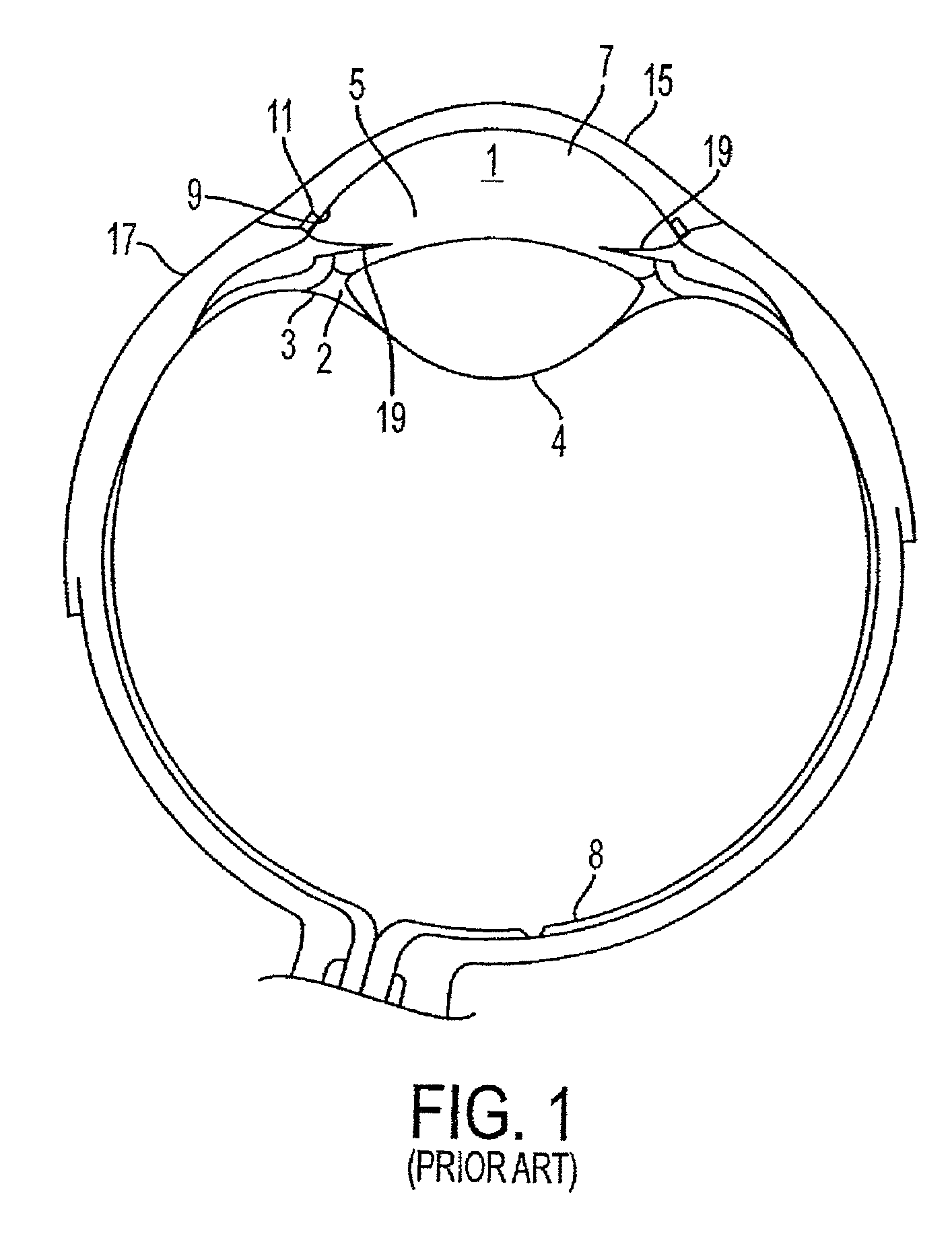
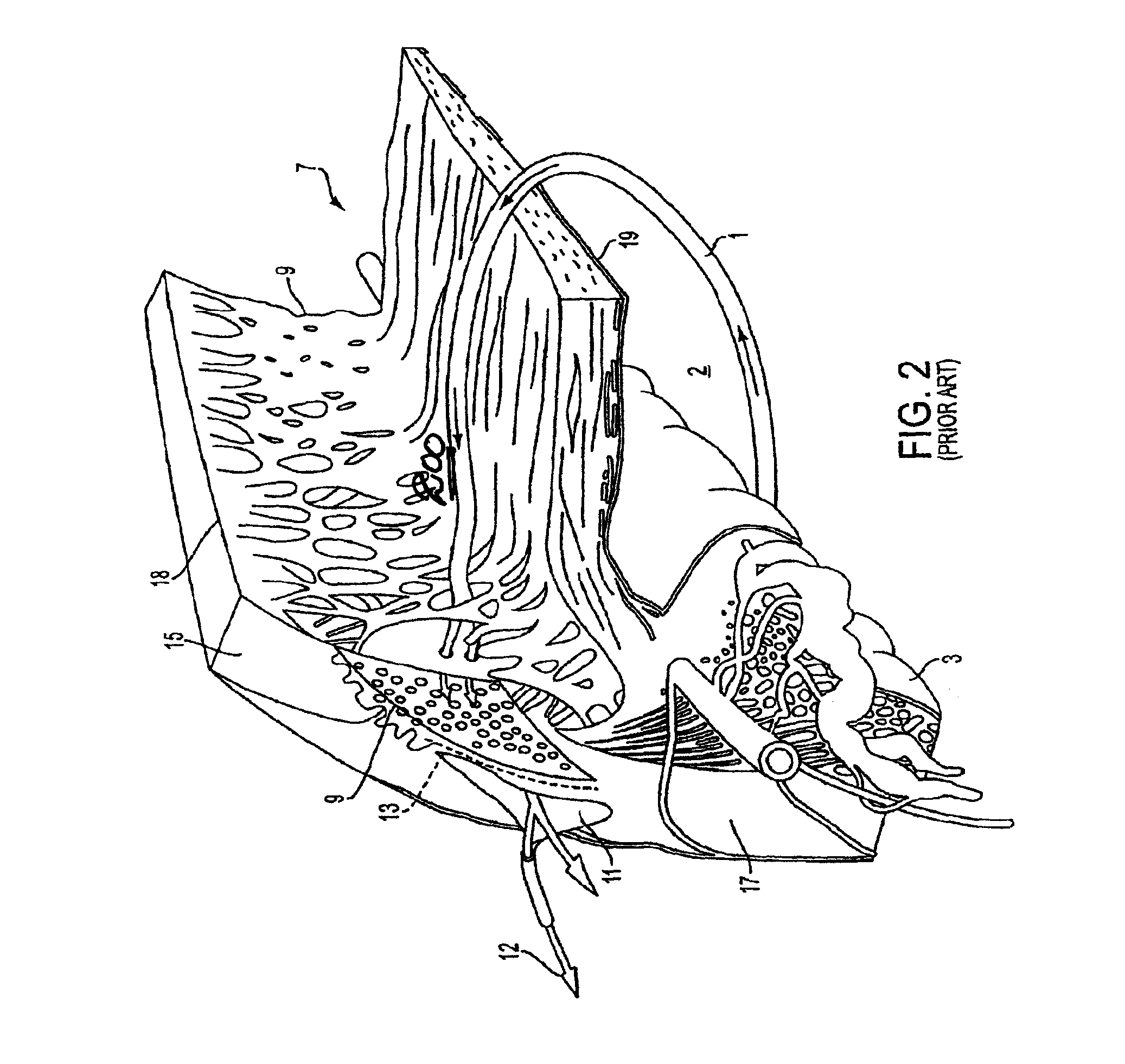
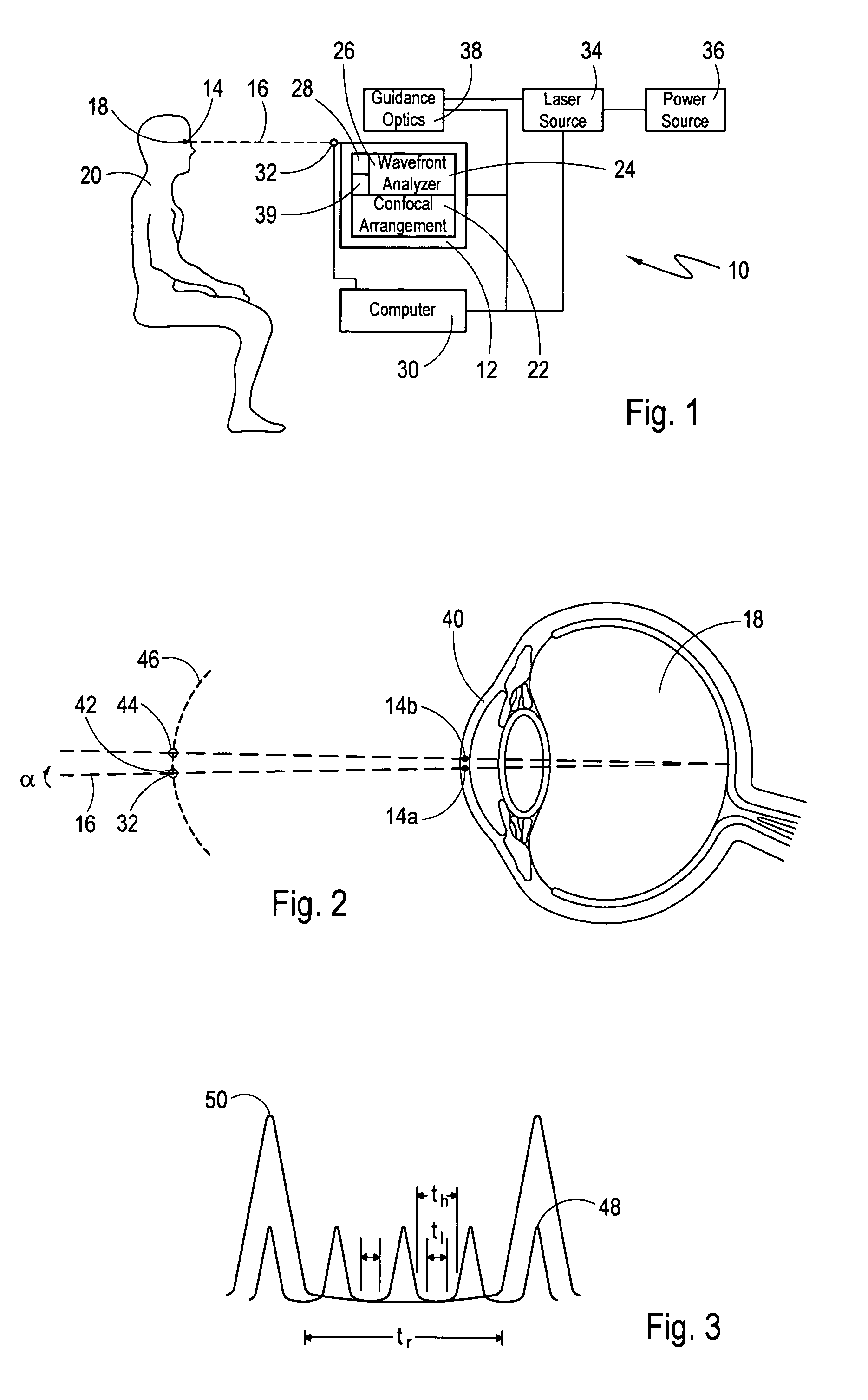
Delivery system and method of use for the eye
InactiveUS8540659B2Minimal thermal effectLower eye pressureLaser surgeryEye implantsFiberPhotoablation
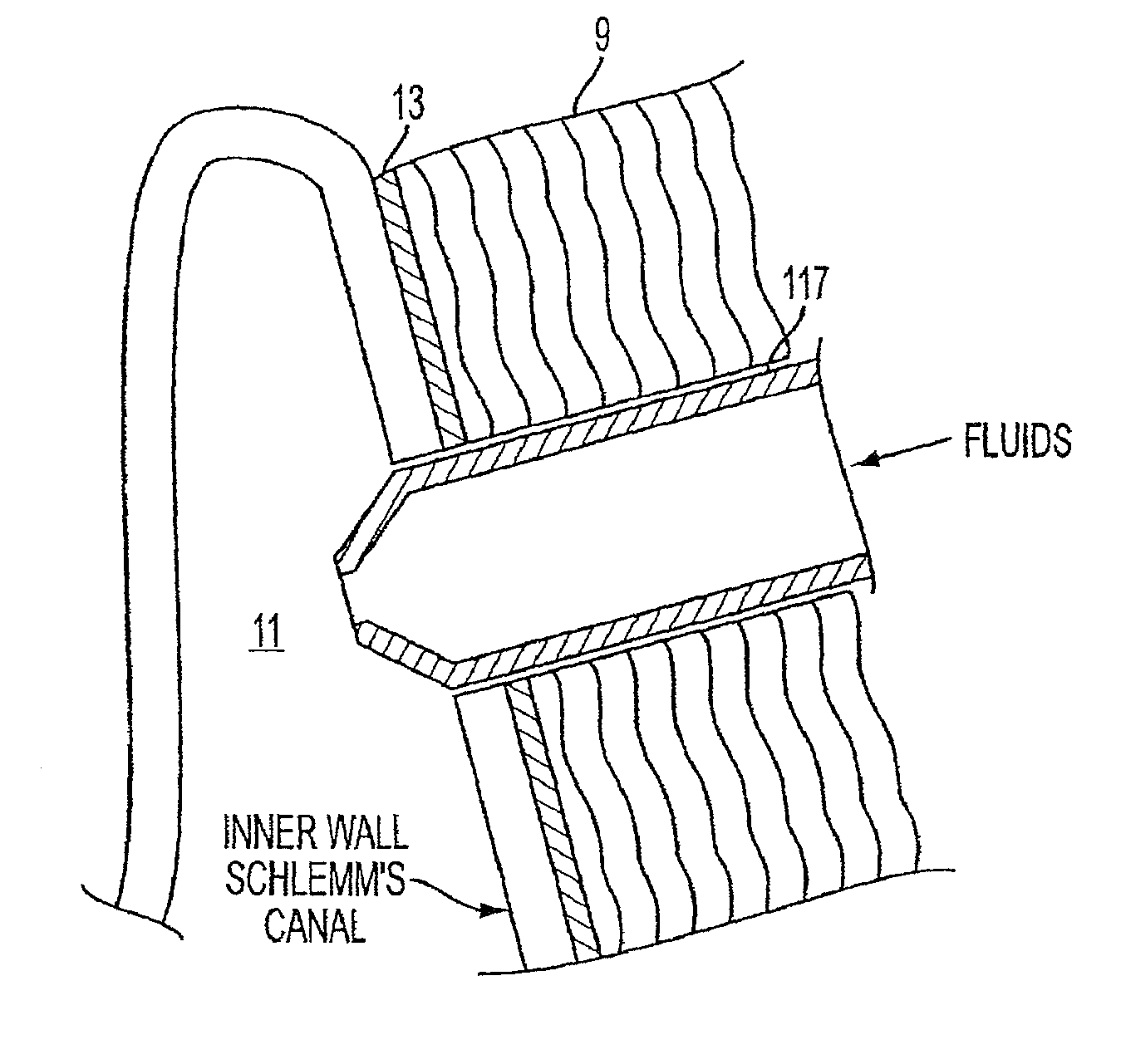
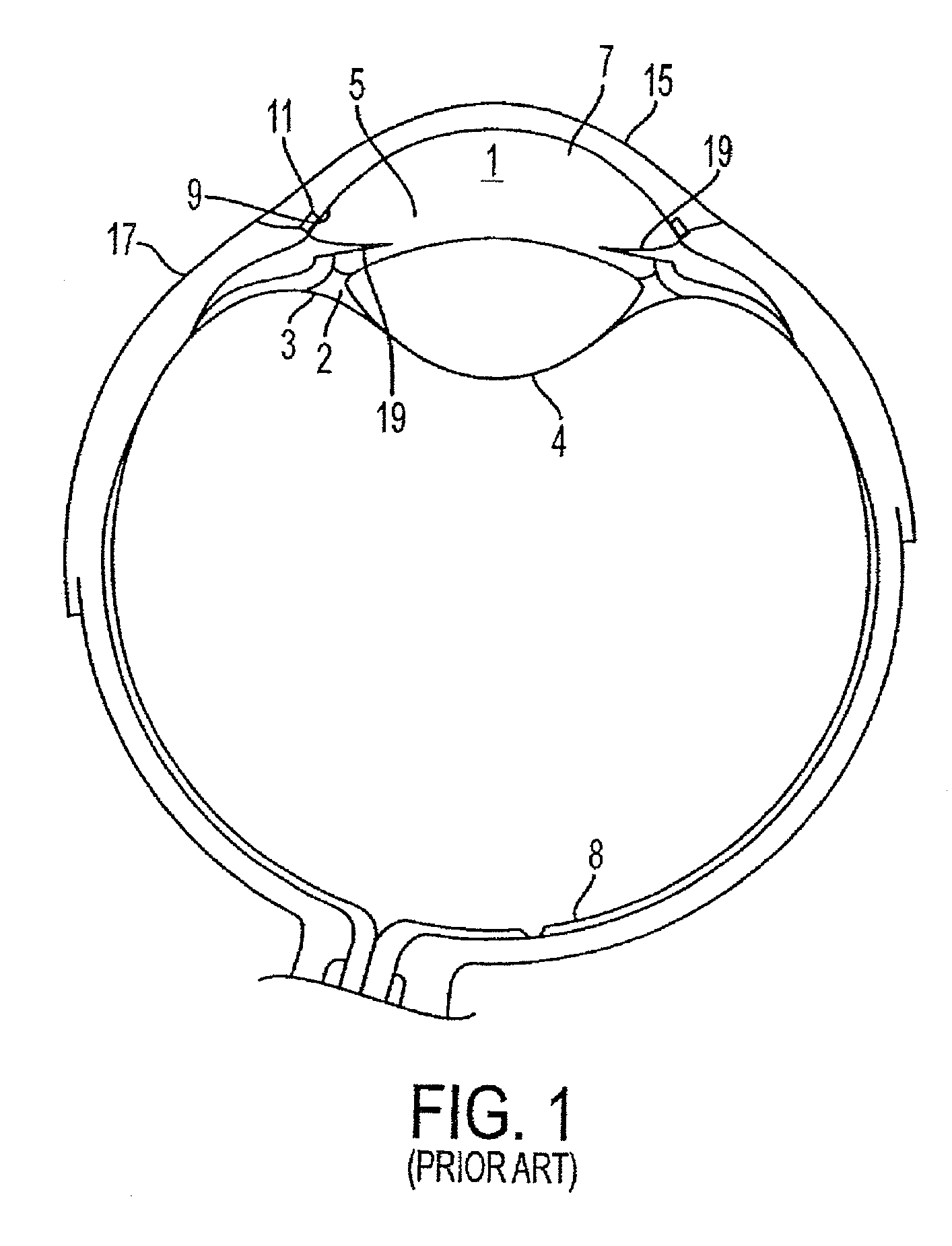
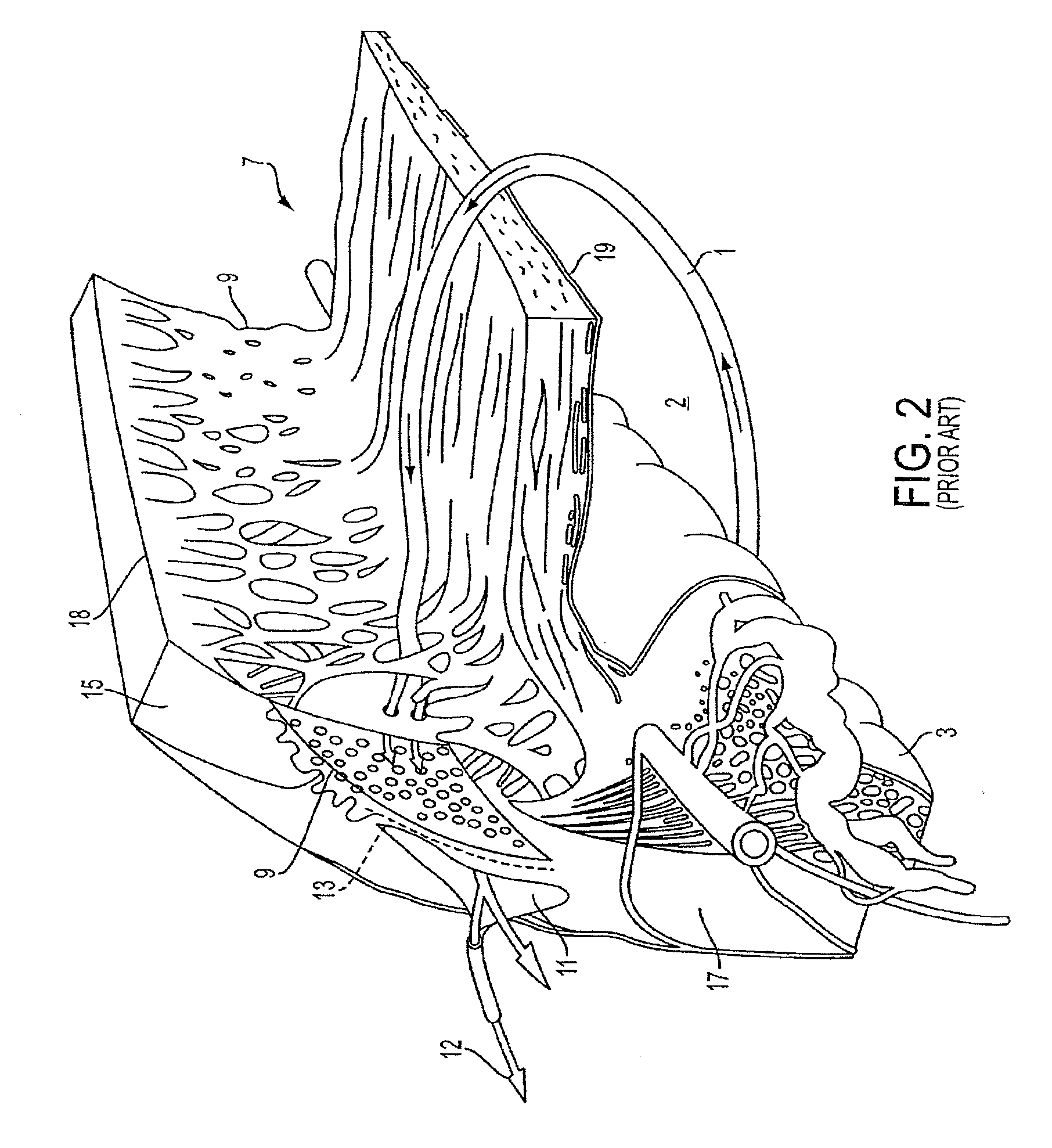
A method and delivery system are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Pulsed laser radiation is delivered from the distal end of a fiber-optic probe sufficient to cause photoablation of selected portions of the trabecular meshwork, the juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and an inner wall of Schlemm's canal in the target site. The fiber-optic probe may be advanced so as to create an aperture in the inner wall of Schlemm's canal in which fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye flows. The method and delivery system may further be used on any tissue types in the body.
Owner:IVANTIS INC
Collagen modulators for use in photoablation eximer laser keratectomy
A method of smoothing irregular corneal surfaces and removing protuberances from corneal surfaces by photoablative eximer laser keratectomy is provided. Collagen compositions for use in making collagen modulators useful in photoablative procedures are described. These compositions are applied to irregular corneal surfaces in sufficient amounts to at least fill in depressions or other irregularities on a corneal surface and are converted into a modulator, as a gel or polymerized film, prior to photoablation. The collagen modulators facilitate the photoablative smoothing of irregular corneal surfaces and protect adjacent corneal tissue from undesired photoablation.
Owner:EUCLID SYST CORP
Excimer laser unit and relative control method for performing cornea ablation to reduce presbyopia
ActiveUS20060195074A1Mitigates presbyopiaLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPhotoablationHyperopic astigmatism
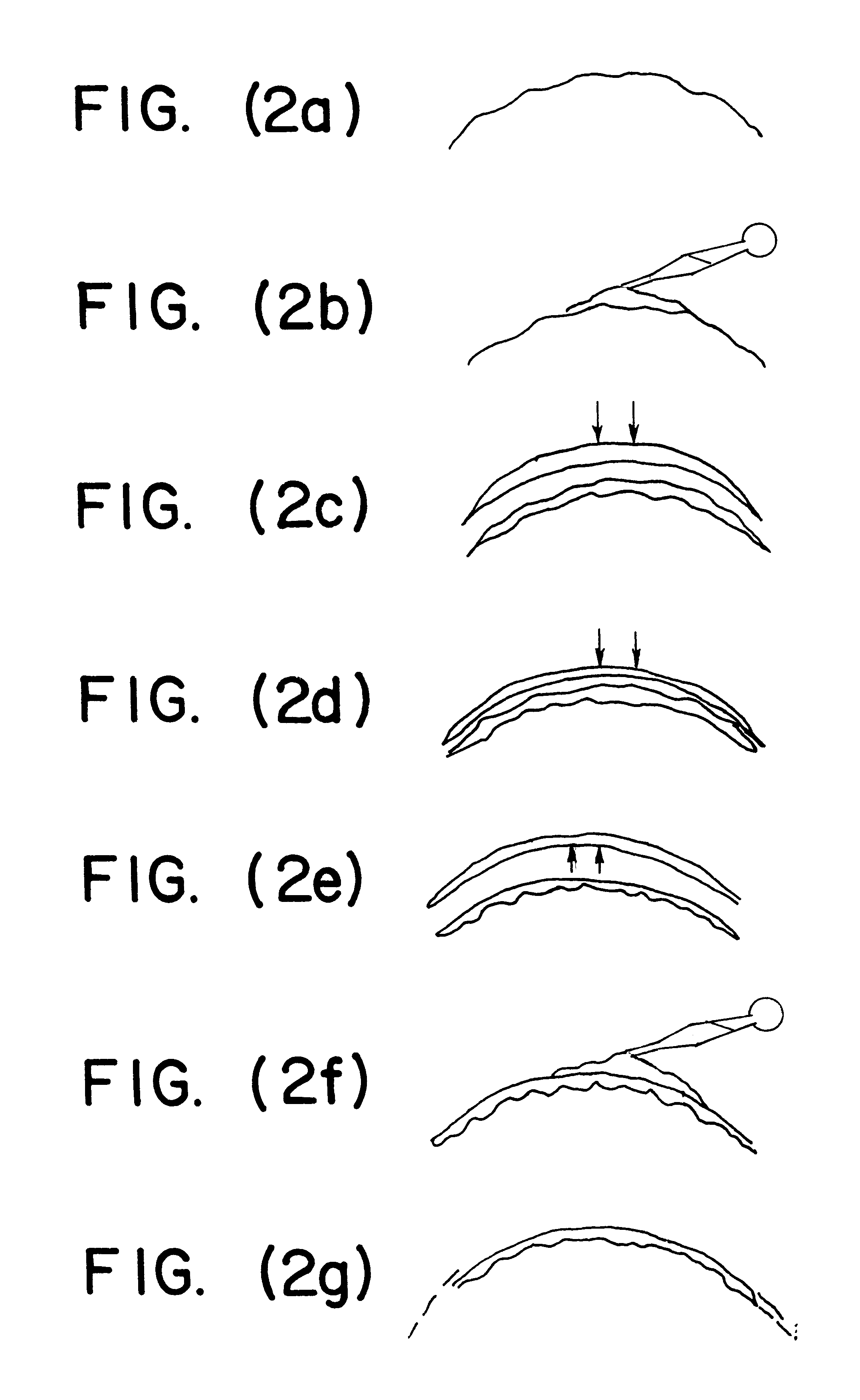
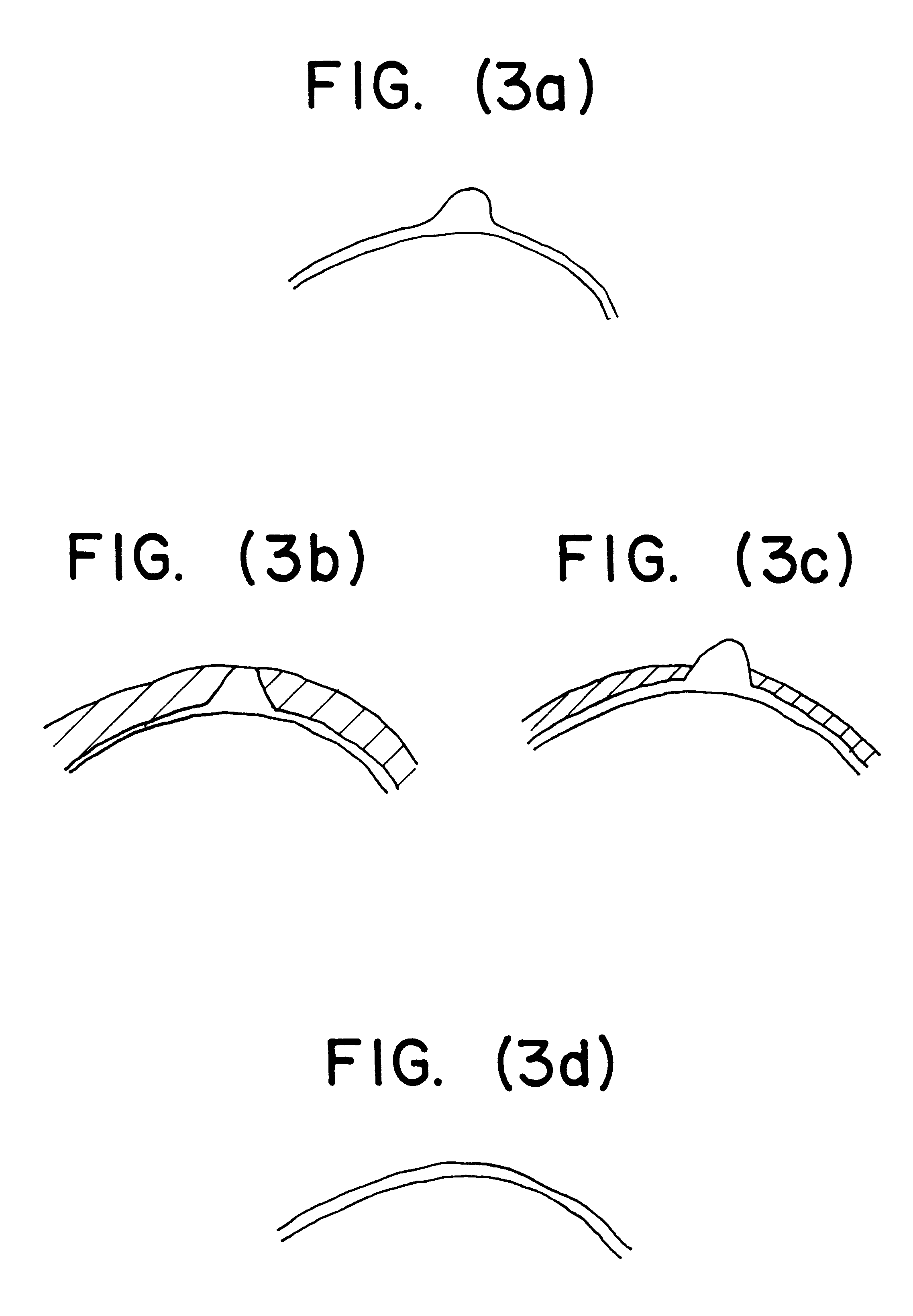
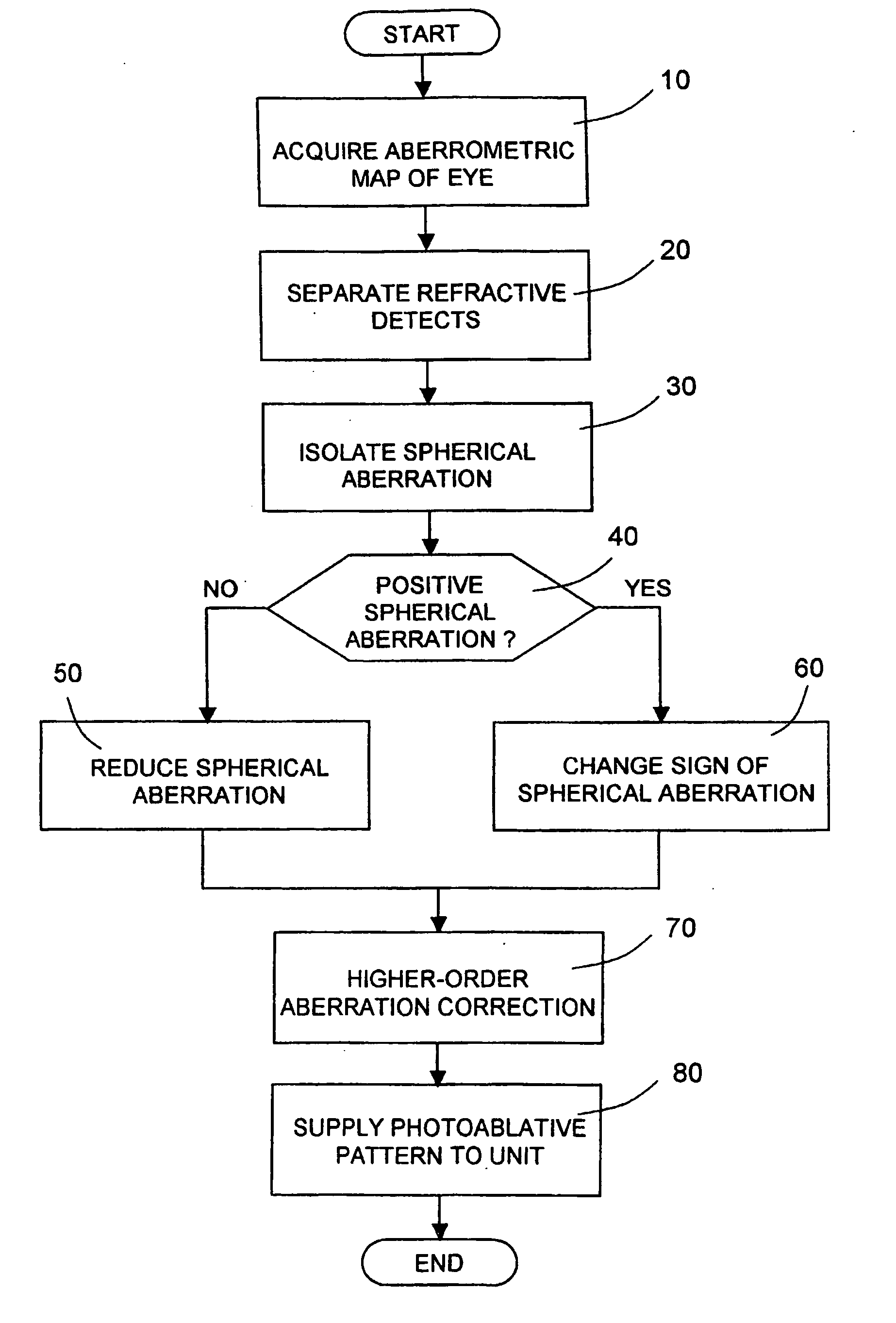
There are described an excimer laser unit and a method of controlling the unit to perform cornea ablation to reduce presbyopia, wherein the excimer laser unit is controlled to form on the cornea a photoablative pattern inducing a fourth-order ocular aberration, in particular a positive spherical aberration. More specifically, an aberrometric map of the eye is first acquired indicating the visual defects of the eye, which include second-order visual defects such as hypermetropia, astigmatism, and myopia, and higher-order visual defects such as spherical aberration; if the detected spherical aberration is negative, it is reduced by numerically increasing its absolute value to obtain an overcorrect photoablative inducing positive spherical aberration; conversely, if the detected spherical aberration is positive, its sign is changed and its absolute value increased numerically to obtain an overcorrect photoablative pattern inducing positive spherical aberration; and the photoablative pattern so generated is supplied to the excimer laser unit for implementation on the cornea.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Closed loop control for intrastromal wavefront-guided ablation
InactiveUS6887232B2Accurate compensationEasy to controlLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPhotoablationClosed loop
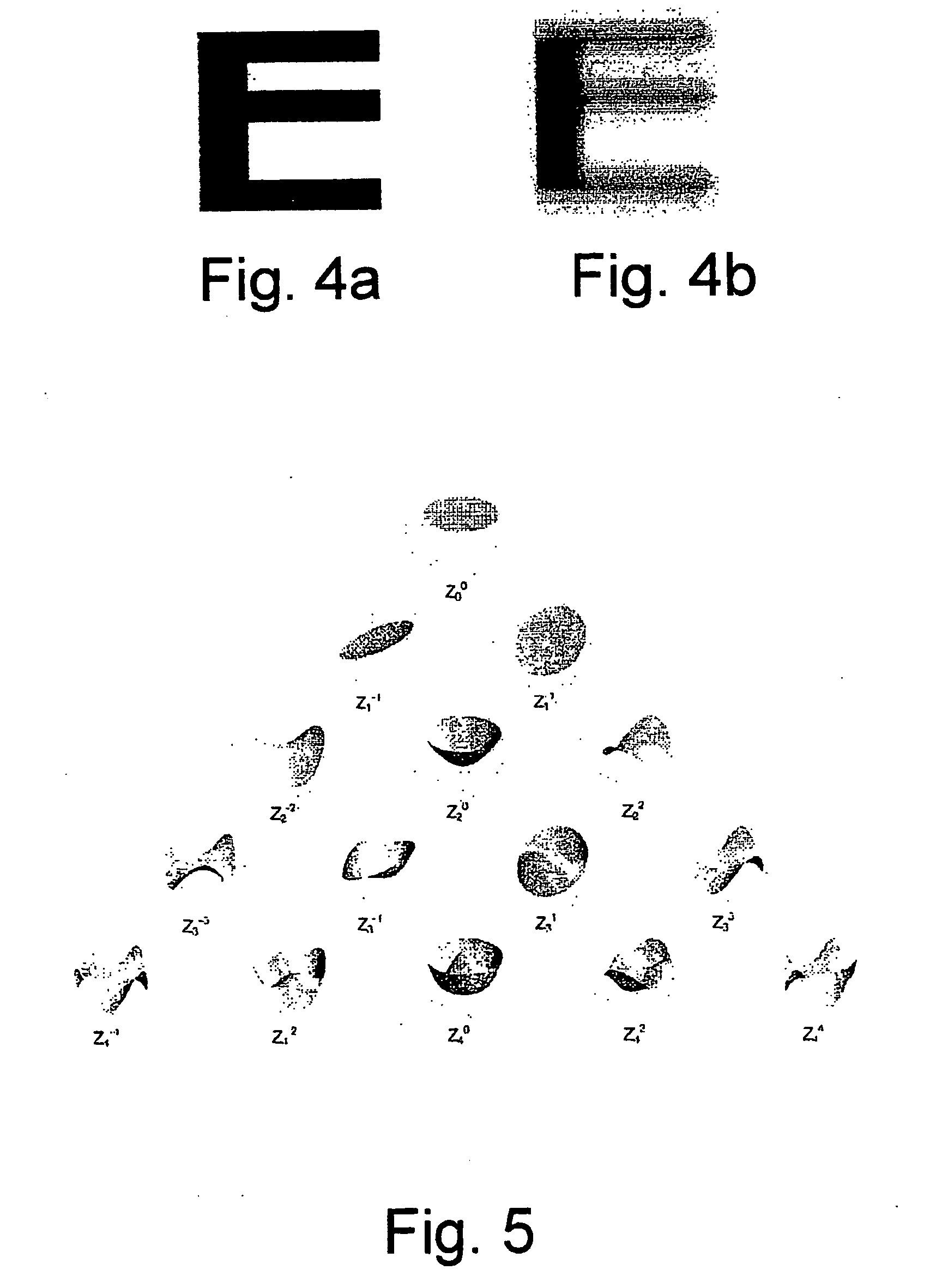
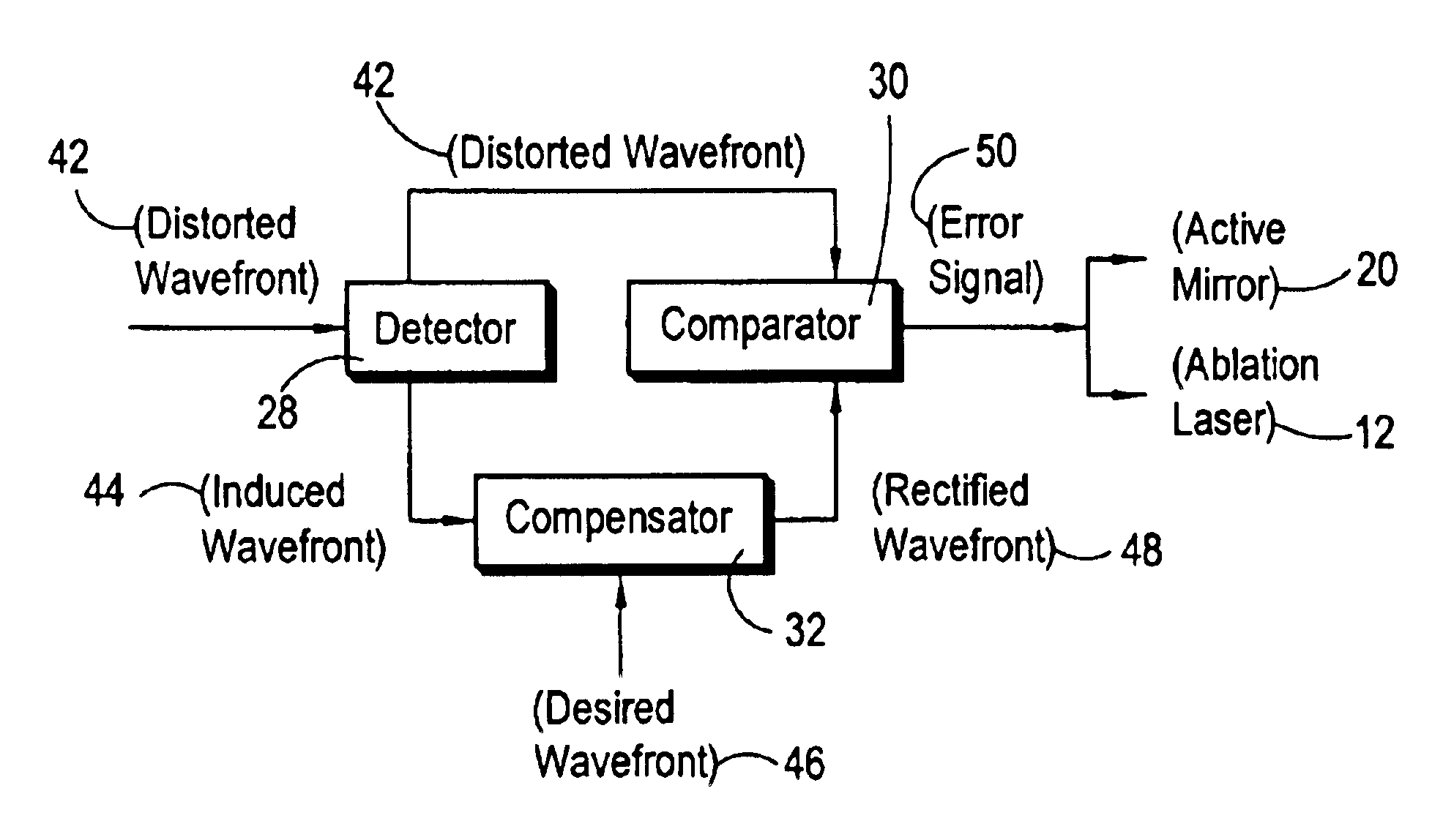
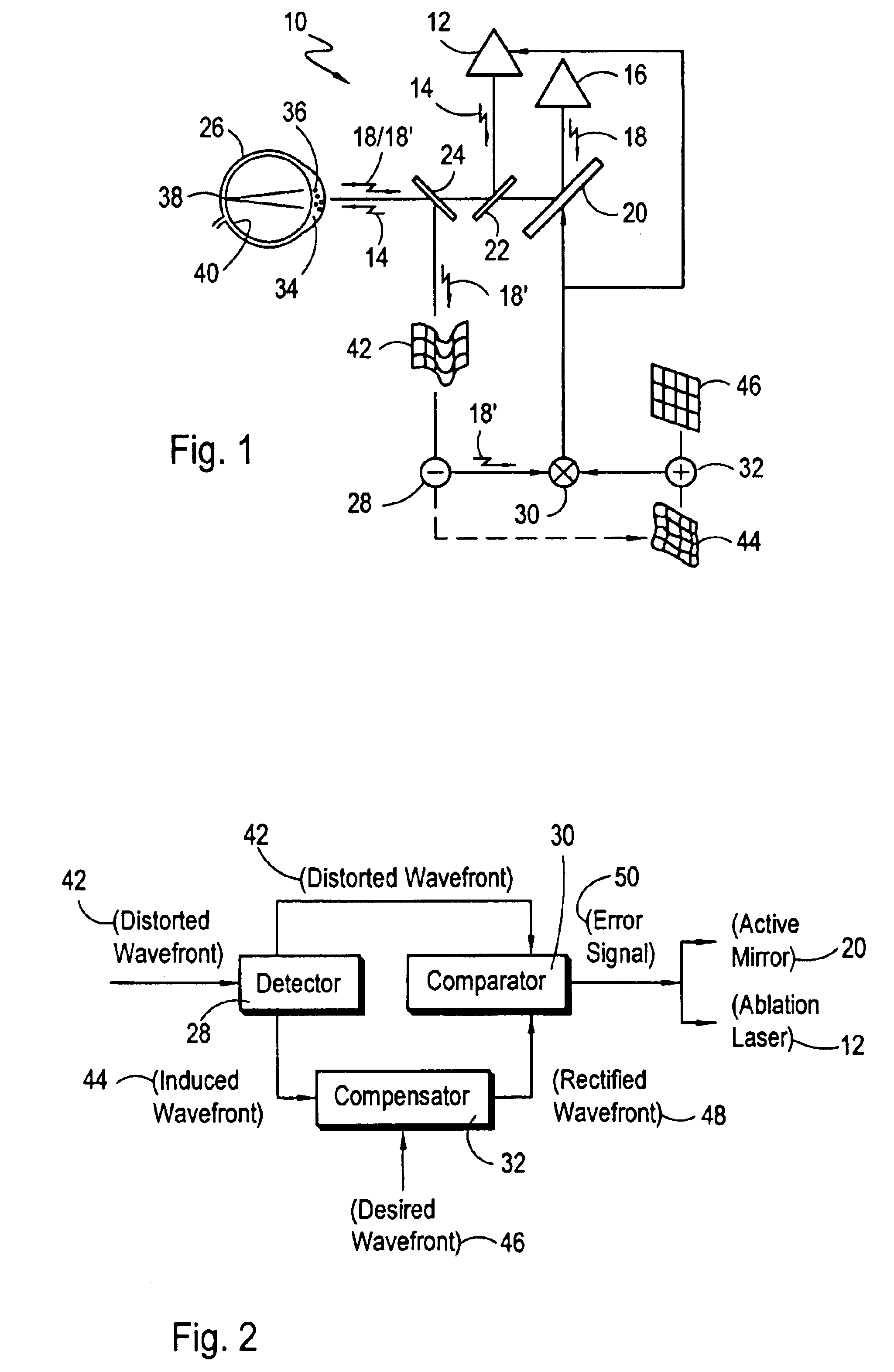
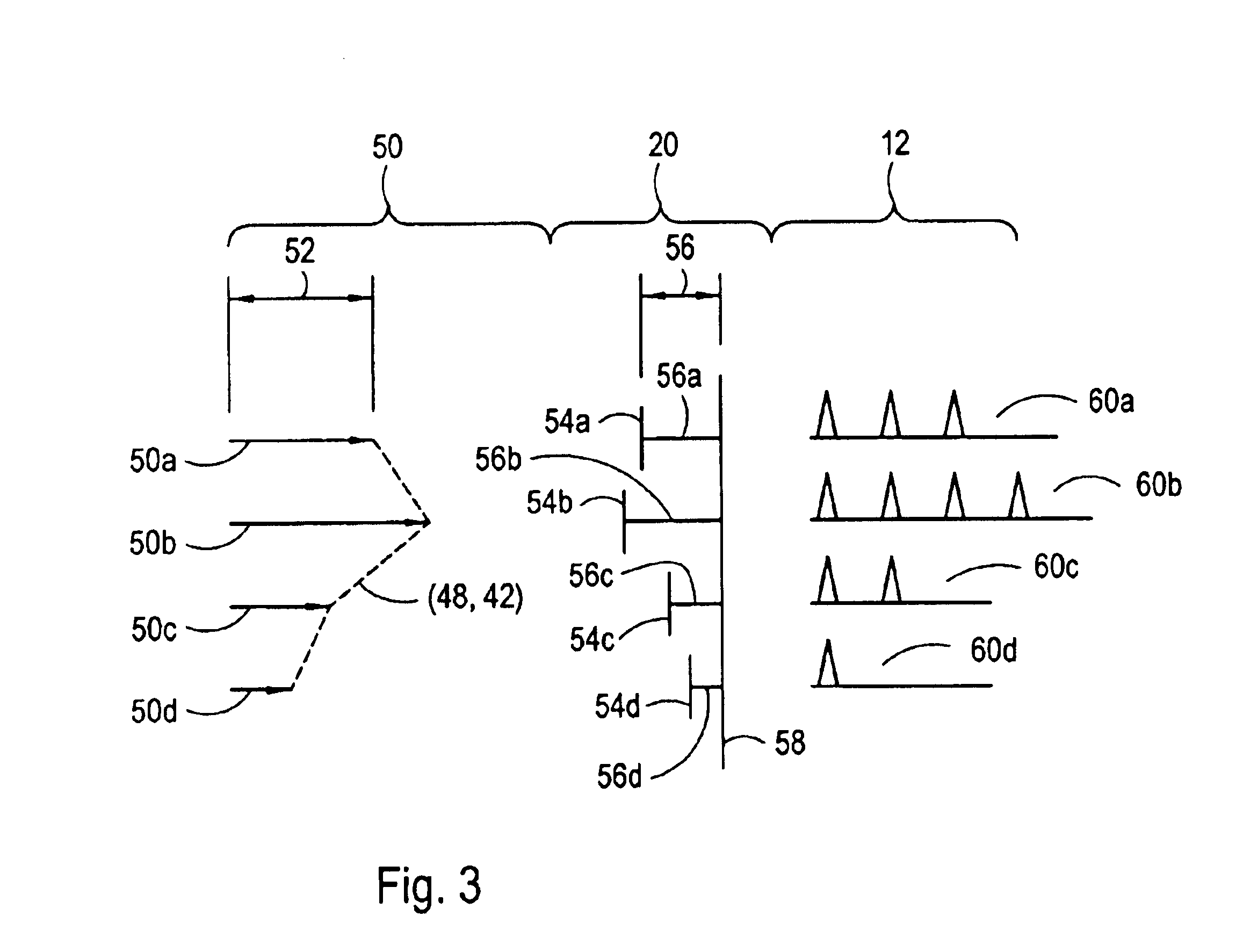
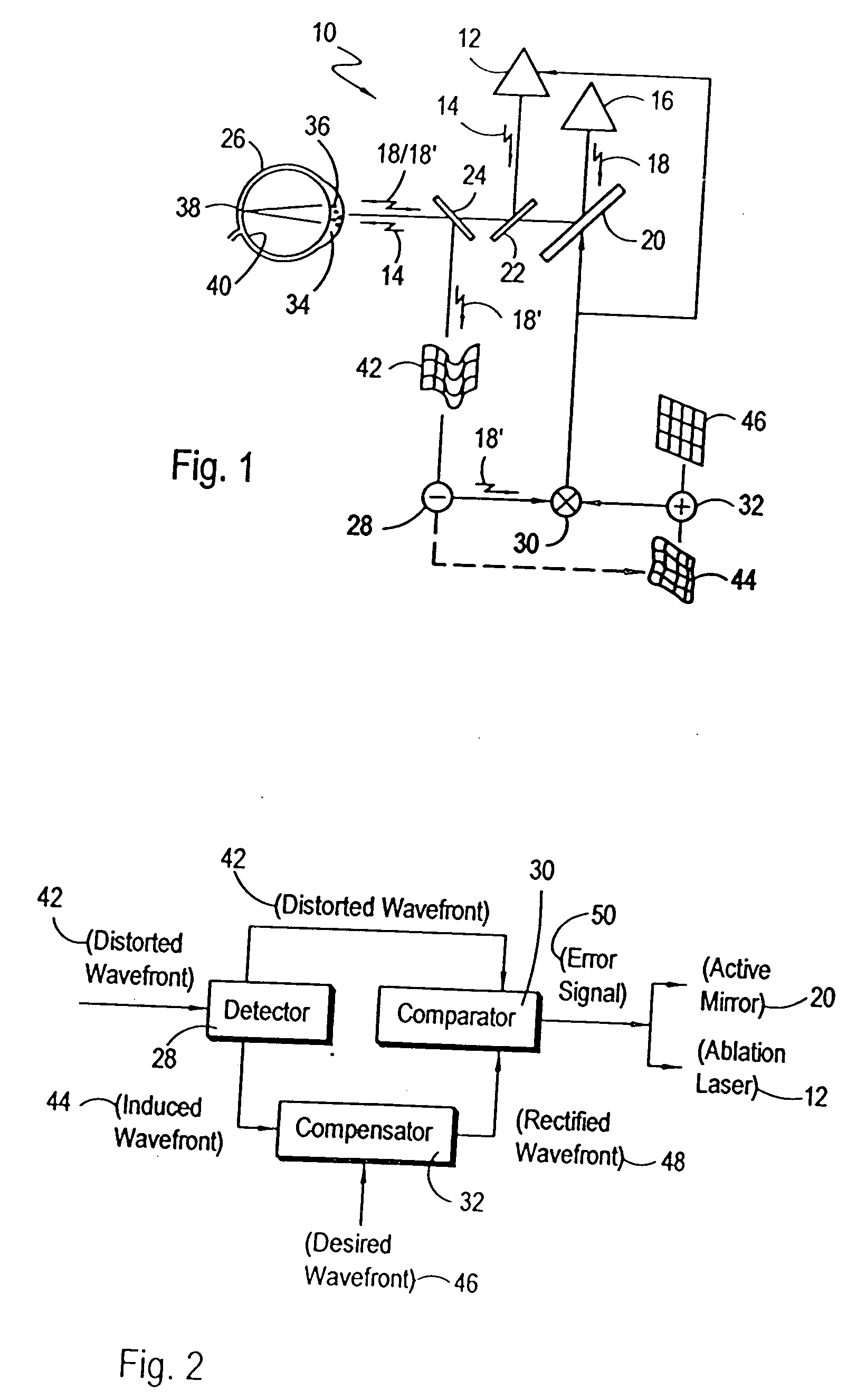
A closed-loop control system for the intrastromal photoablation of tissue includes an active mirror for individually directing the component beams of a diagnostic laser beam to a focal point on the retina of an eye. The reflected beam is analyzed to identify a distorted wavefront indicative of required corneal corrections, and an induced wavefront indicative of optical aberrations introduced by bubbles formed during tissue ablation. A comparator alters the induced wavefront with a desired wavefront to create a rectified wavefront, and a comparator compares the rectified wavefront with the distorted wavefront to create error signals. The error signals are then used to operate the active mirror and to control an ablation laser until the absence of error signals indicate the required stromal tissue has been photoablated.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Delivery system and method of use for the eye
InactiveUS20080108934A1Reduce elevated intraocular pressureMinimal thermal effectLaser surgeryEye implantsPhotoablationFiber
A method and delivery system are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Pulsed laser radiation is delivered from the distal end of a fiber-optic probe sufficient to cause photoablation of selected portions of the trabecular meshwork, the juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and an inner wall of Schlemm's canal in the target site. The fiber-optic probe may be advanced so as to create an aperture in the inner wall of Schlemm's canal in which fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye flows. The method and delivery system may further be used on any tissue types in the body.
Owner:IVANTIS INC
Devices and methods for separating layers of materials having different ablation thresholds
ActiveUS20070078447A1Avoids and minimizes inadvertent photoablationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPhotoablationBeam energy
A method and device for photoablation is disclosed wherein photoablation occurs along the interface between a material having a lower energy ablation threshold and a material having a higher energy ablation threshold. The method and device utilize a laser beam having a beam energy density which is less than the higher energy ablation threshold and greater than or equal to the lower energy ablation threshold. By directing such a laser beam to the interface, the material having the lower energy threshold is photoablated while the material having the higher energy threshold is largely unaffected.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Carlo-computer assisted and robot guided laser-osteotome
ActiveUS20120220992A1High osteotomic precisionImprove securityDiagnosticsControlling energy of instrumentPhotoablationRobotic arm
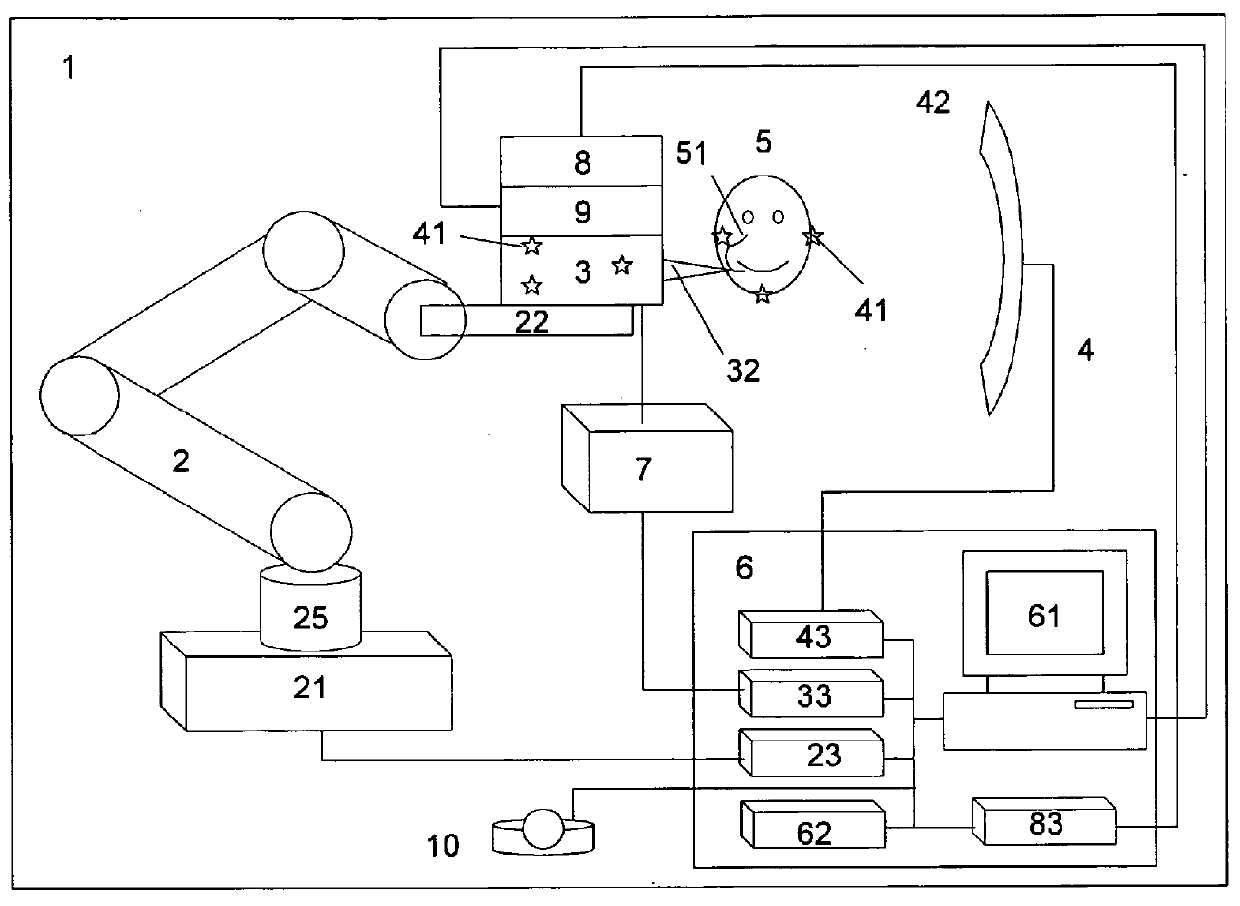
A Computer Assisted and Robot-Guided Laser Osteotome (CARLO) medical device (1) for perforating hard tissue, having a photoablation laser source (31) mounted in a robotic arm (2), and optical system (37) for focusing a laser beam in a target plane of the ostetomy line featuring an autotracking navigation system (8).
Owner:ADVANCED OSTEOTOMY TOOLS - AOT
Controlled ocular lens regeneration
The present invention addresses the treatment of ocular conditions by the enhancement of lens regeneration. This is accomplished by the administration of a high viscosity composition including a hyaluronic acid compound and laser photoablation. Excess high viscosity composition may be removed by focal laser photophacoablation. Additionally, a collagen product may be injected within the lens capsule to improve lens cell proliferation and differentiation, and to improve the configuration, shape and structure of regenerated lenses. Various embodiments involving the enhancement of lens regeneration are described. For example, lens regeneration may be enhanced by filling the lens capsule bag with the inventive hyaluronic acid compound; by inserting at least one collagen patch in the lens capsule; and / or by injecting a collagen-based product into the lens capsule.
Owner:GWON ARLENE E
Method for preparing monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots based on electronic dynamic regulation and control
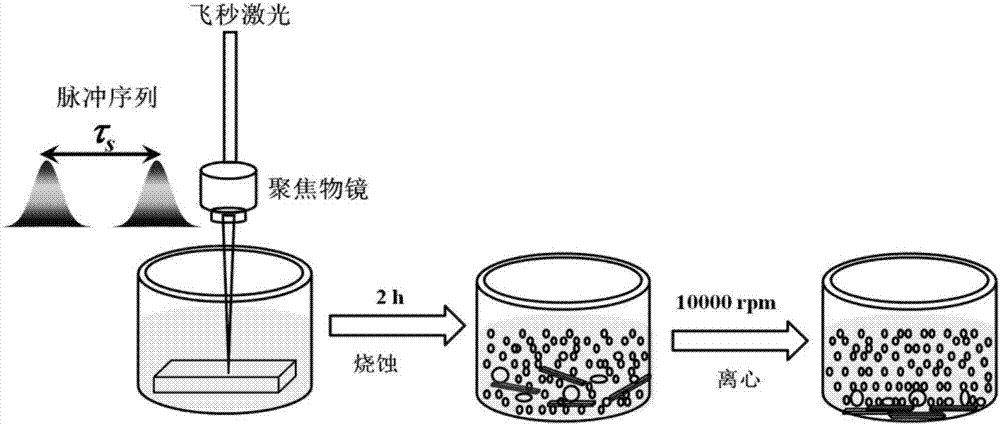
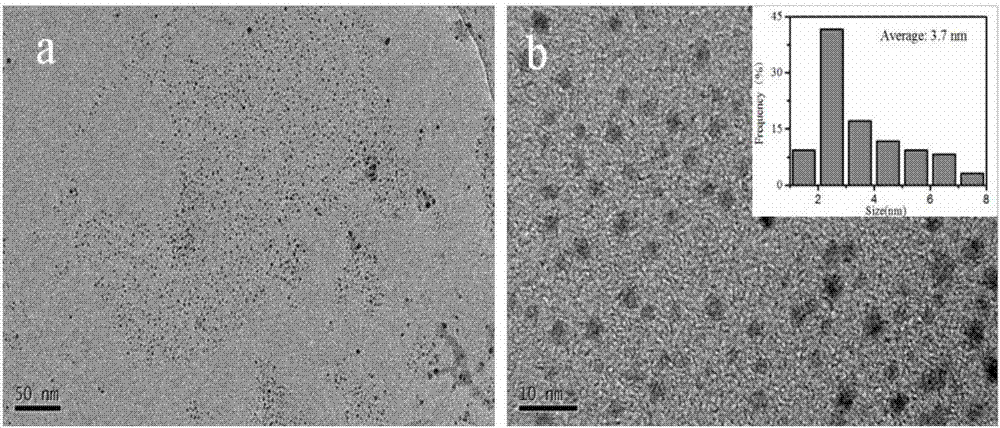
ActiveCN106905966AHigh yieldPromote absorptionCatalyst activation/preparationNanotechnologyPhotoablationLaser scanning
The invention relates to a method for preparing monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots based on electronic dynamic regulation and control, in particular to a method for obtaining the monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots with uniform particle sizes by obtaining molybdenum disulfide suspension and then centrifugally separating and belongs to the field of femtosecond laser application. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: aiming at the characteristics of a molybdenum disulfide material, carrying out pulse shaping on traditional femtosecond laser monopulse by using a Michelson interferometer to form a pulse sequence; adjusting energy of the pulse sequence, delay among sub pulses, laser scanning speed and scanning intervals; ablating blocky molybdenum disulfide in water and further regulating and controlling local transient electronic dynamics in the interaction process of laser and the material to form multistage photoablation monolayer molybdenum, and obtaining the monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots with the uniform particle sizes; carrying out laser-induced water dissociation to enhance light absorption and improve the yield of the molybdenum disulfide quantum dots. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of no need of special chemical environment or chemical reagent, greenness, no pollution, and simple and flexible operation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
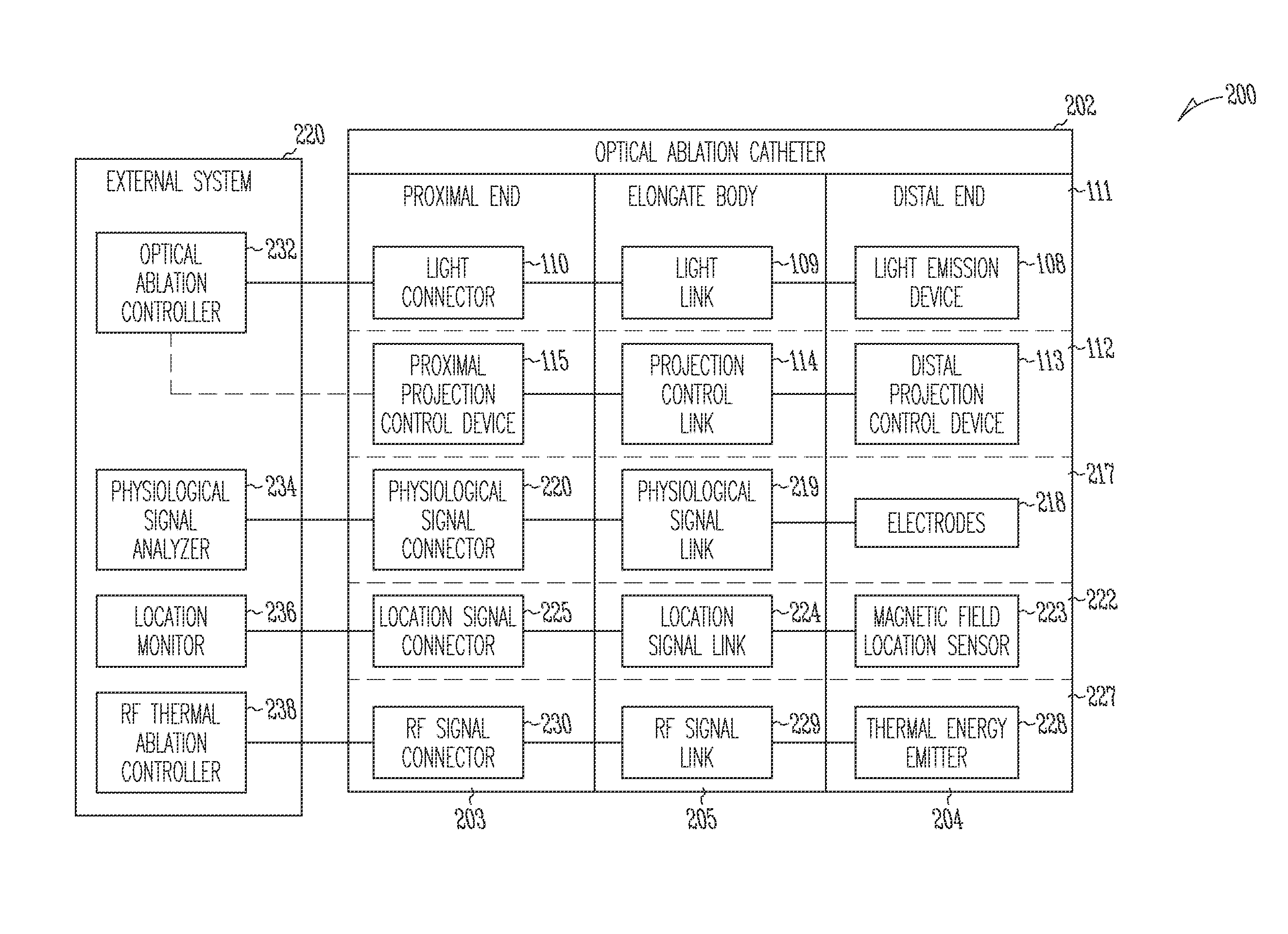
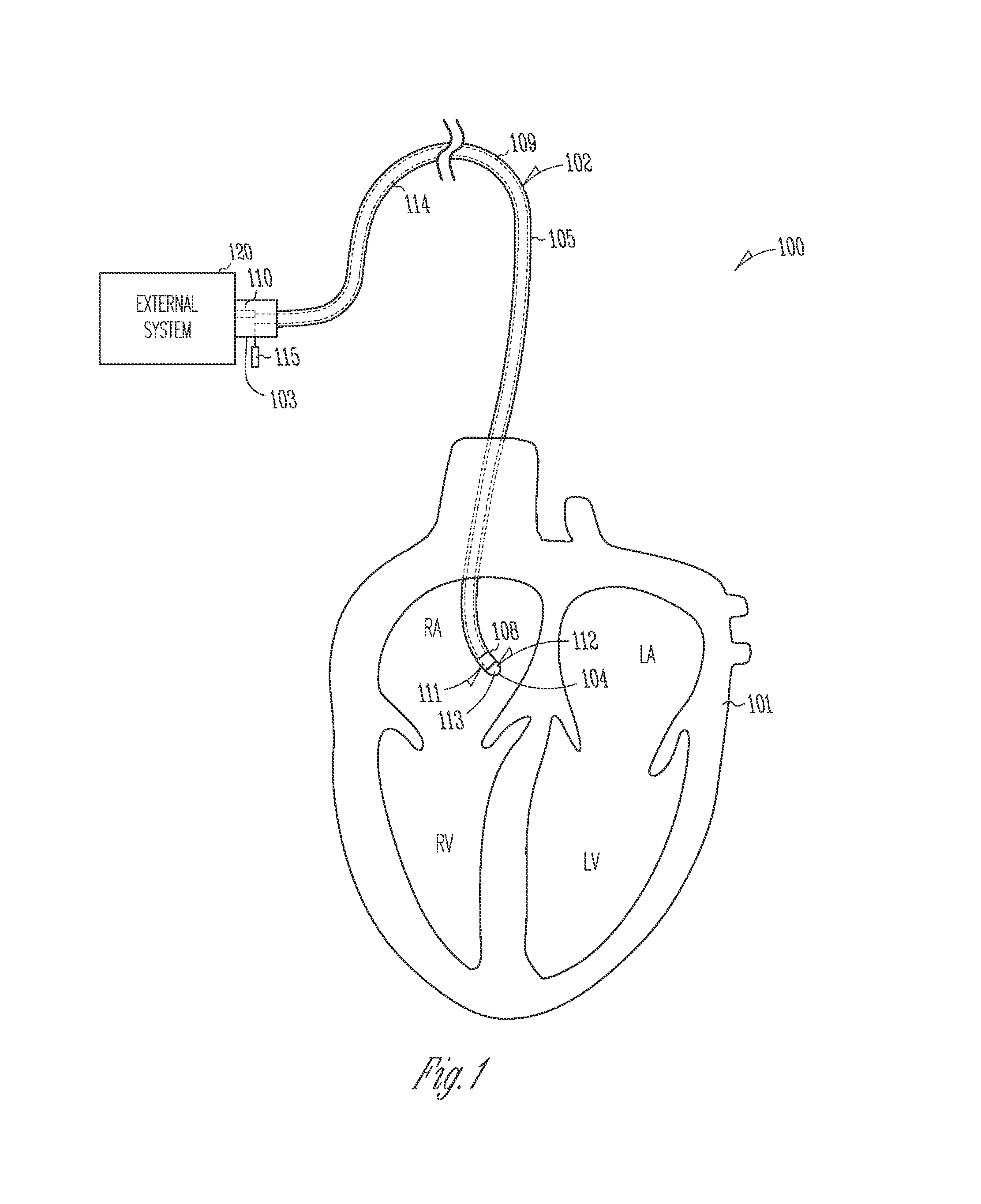
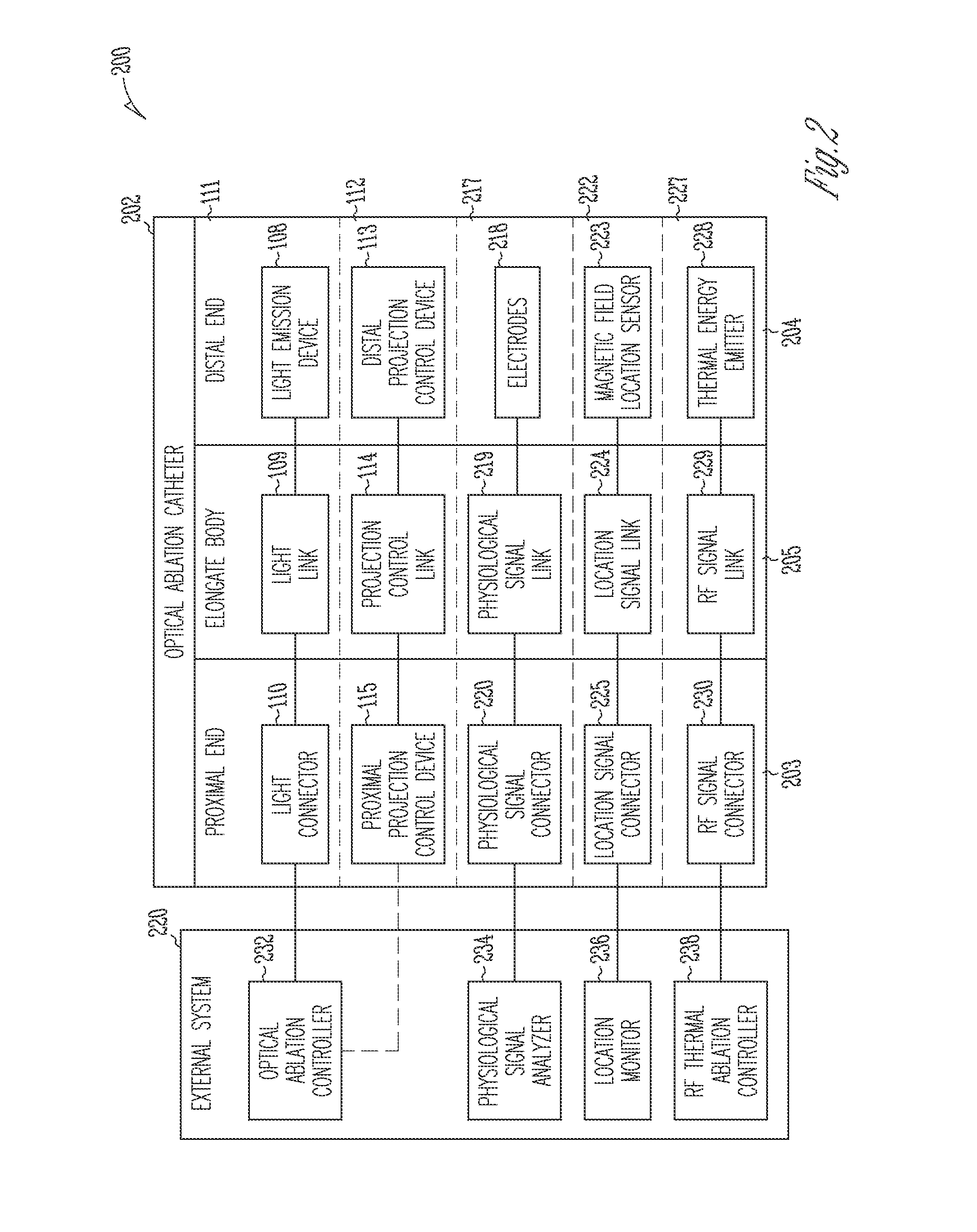
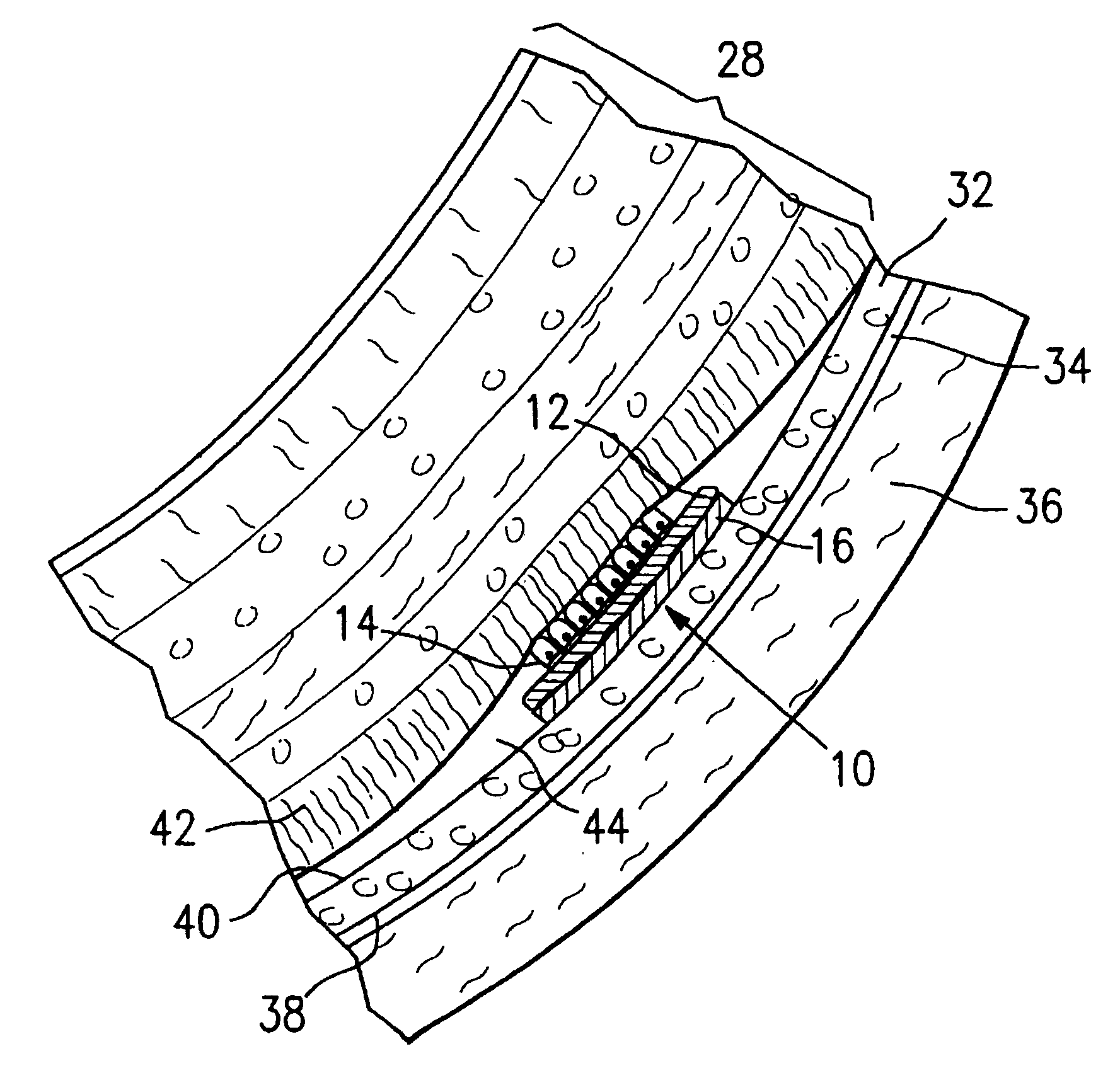
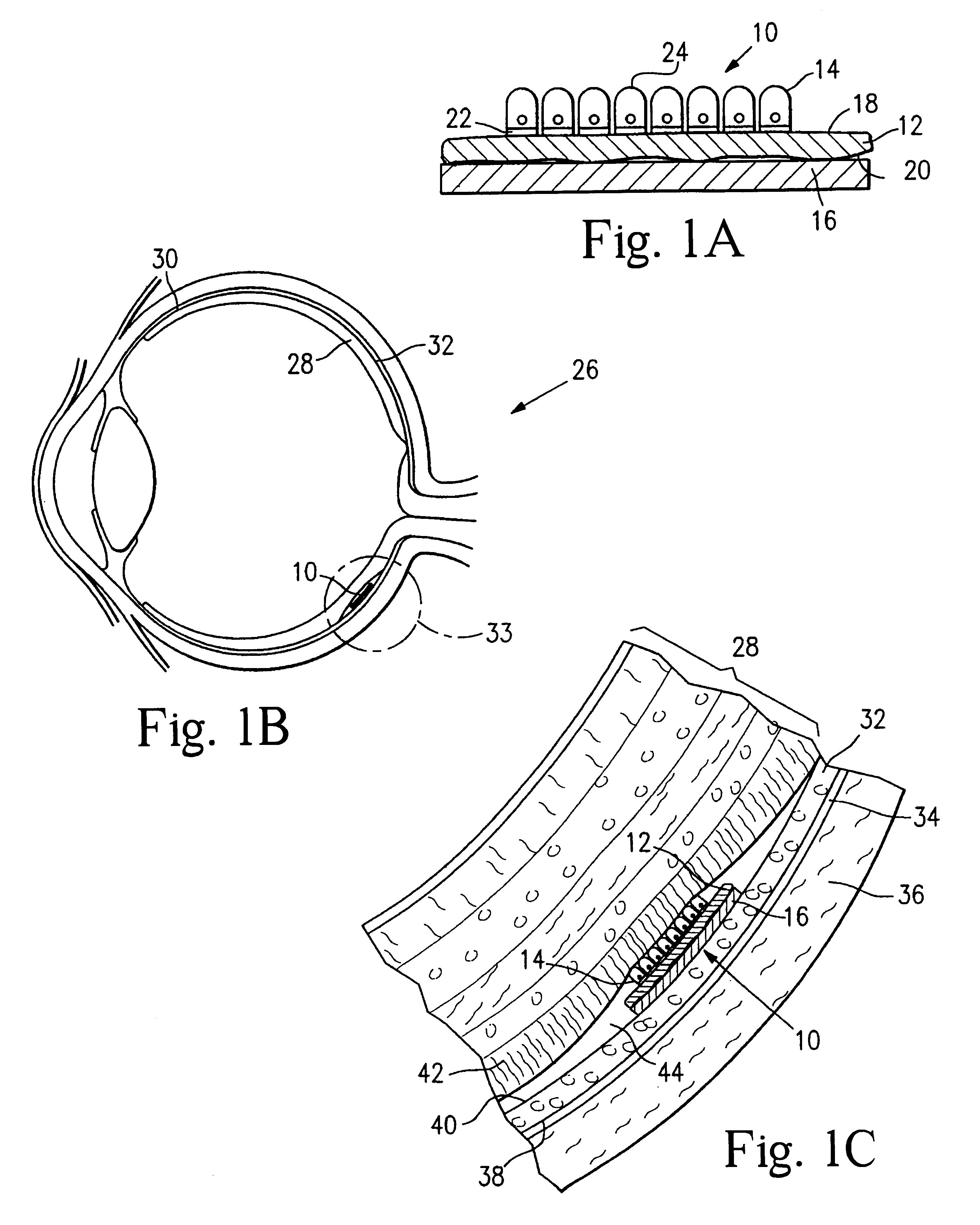
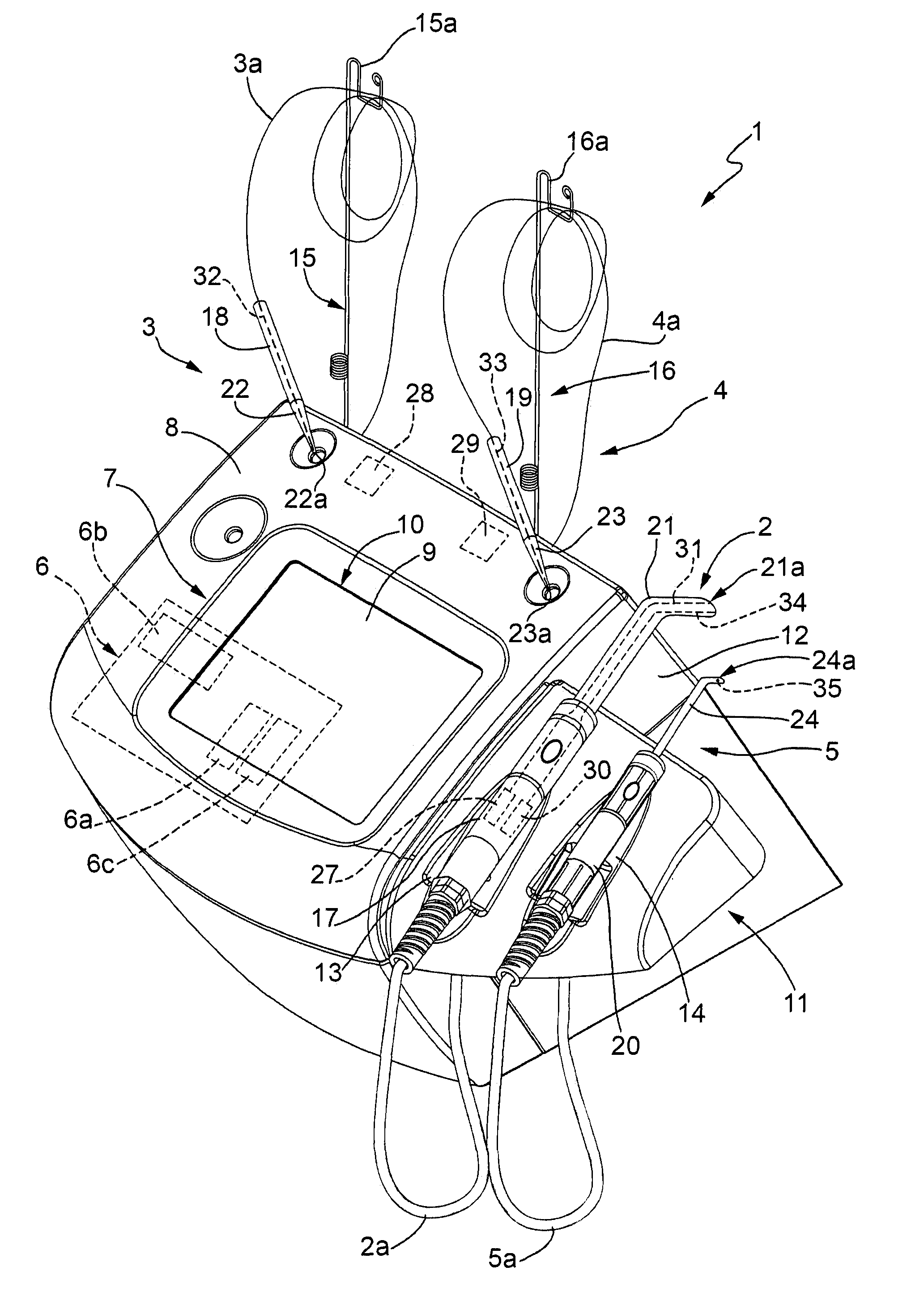
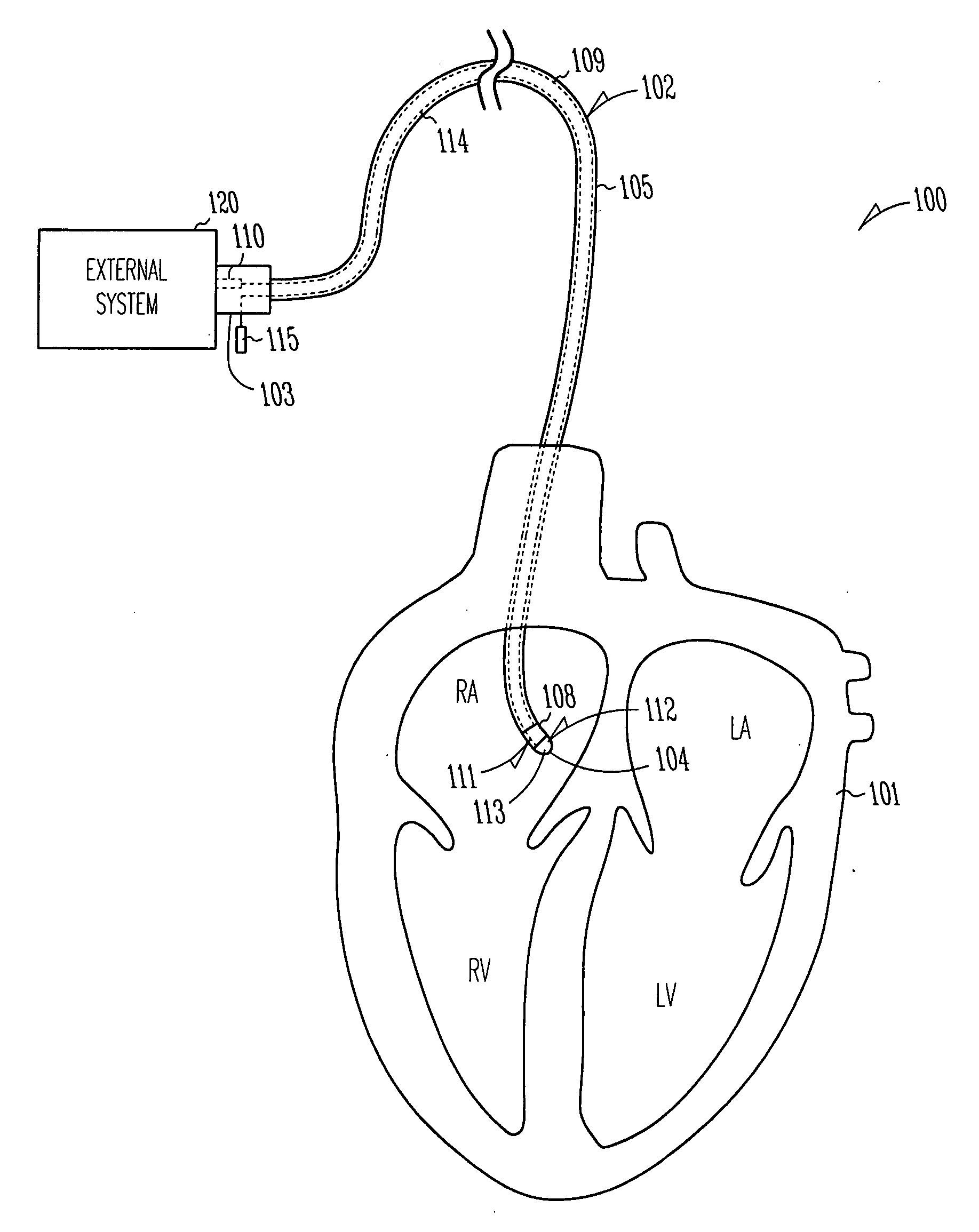
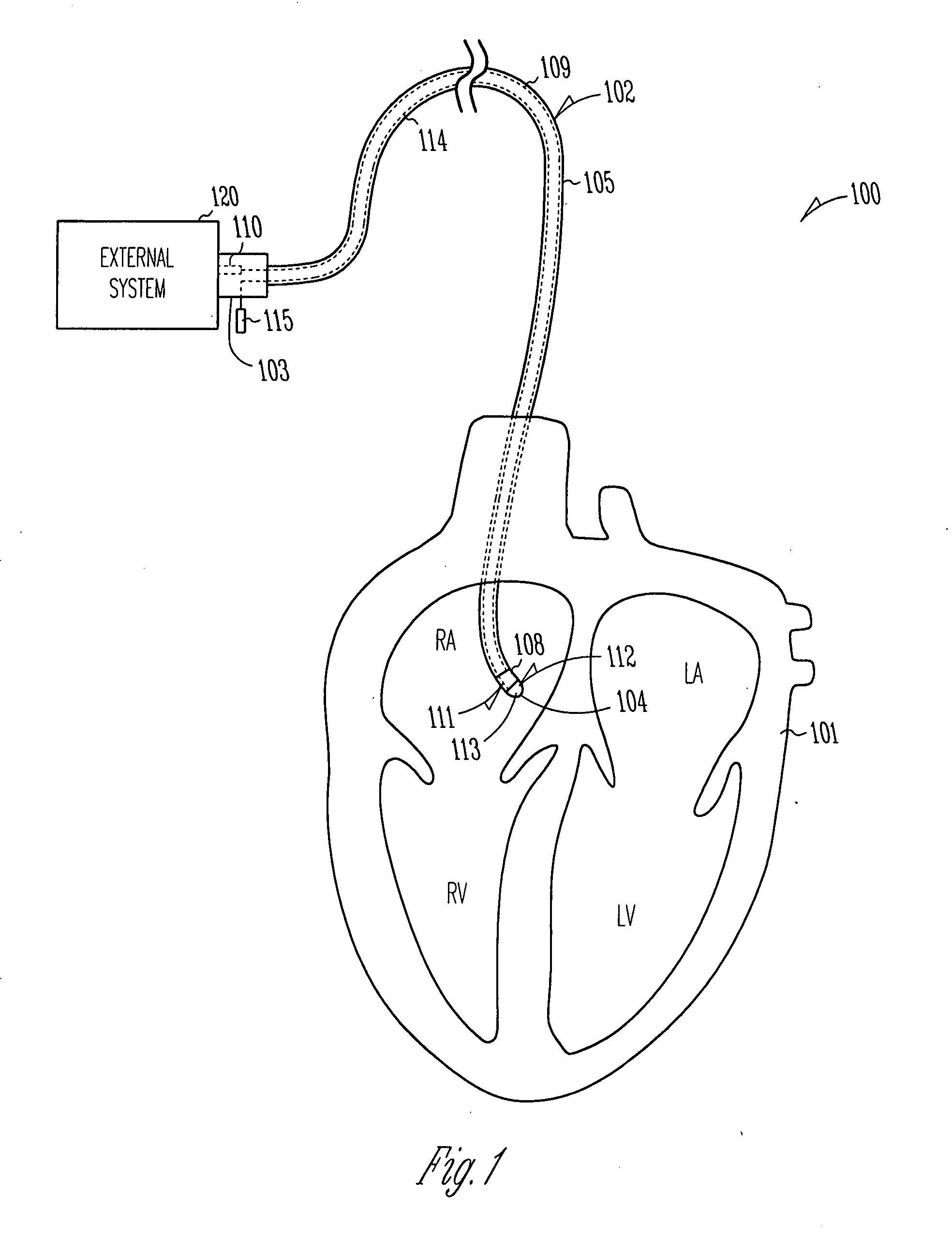
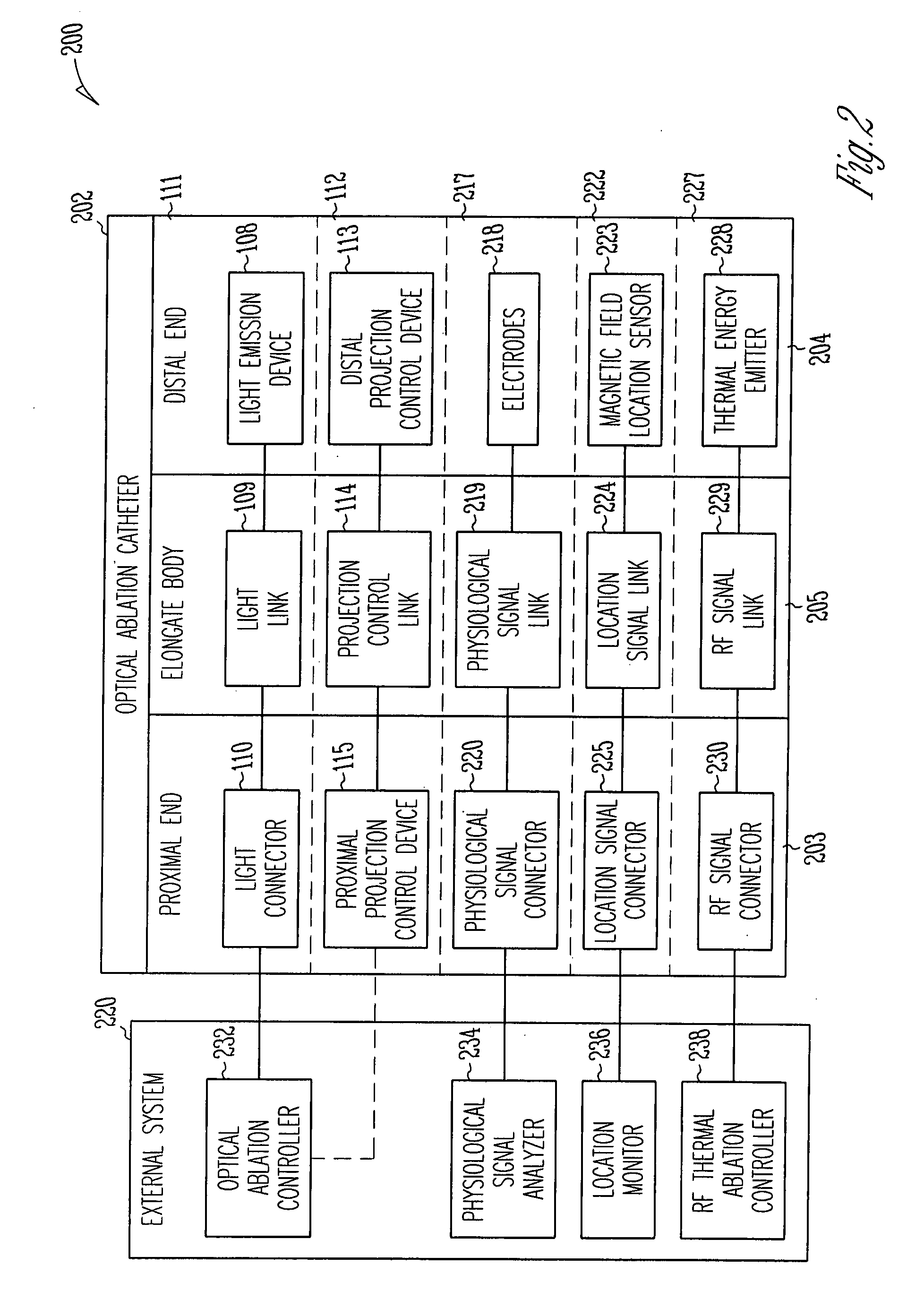
Systems and devices for photoablation
ActiveUS8480662B2Reduce the risk of blood clotsPrevent, inhibit or treat cardiac arrhythmiasSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyPhotoablationLight emission
The invention provides a catheter for optical ablation of tissue in a living body, the catheter including: a distal end; a proximal end; an elongate catheter body coupled between the distal end and the proximal end; a light emission device at the distal end and configured to emit an ablation light having characteristics selected to regulate an optically regulatable transcription control element operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence for a gene product, the expression of which gene product in cells directly or indirectly kills cells; and a projection control mechanism coupled to the light emission device and configured to control an effectively illuminated area where the optically regulatable transcription control element is effectively regulatable by the ablation light projected from the light emission device. Also provided is a system which includes the catheter, and methods to prevent, inhibit or treat AF which employ an expression cassette and / or one or more selected wavelengths of light.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Microfabricated tissue as a substrate for pigment epithelium transplantation
InactiveUS6939378B2Improve adaptabilityImprove abilitiesHeart valvesArtificially induced pluripotent cellsPhotoablationEpithelium
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
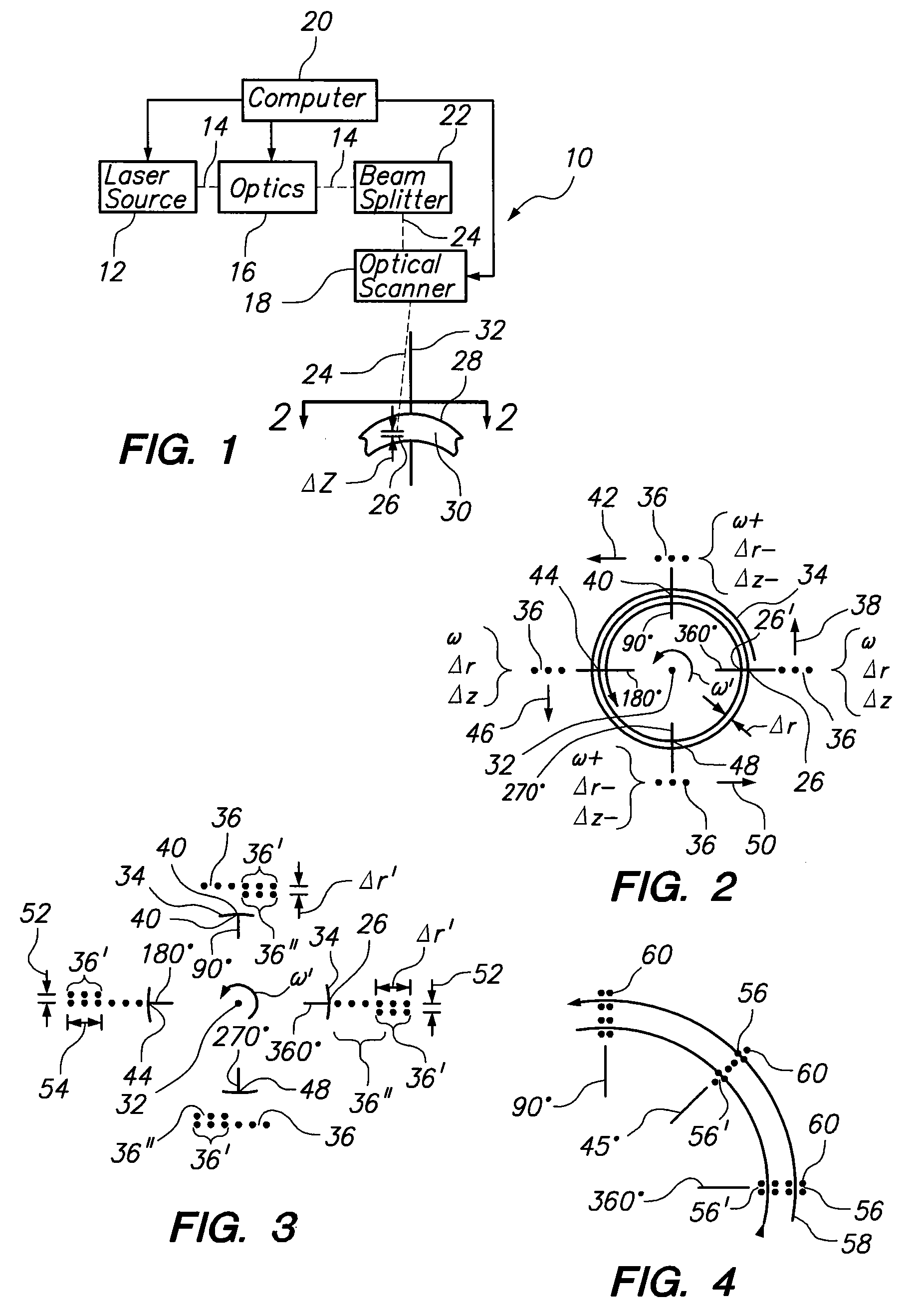
System and Method for Photoablation Using Multiple Focal Points with Rotating Beam Splitter
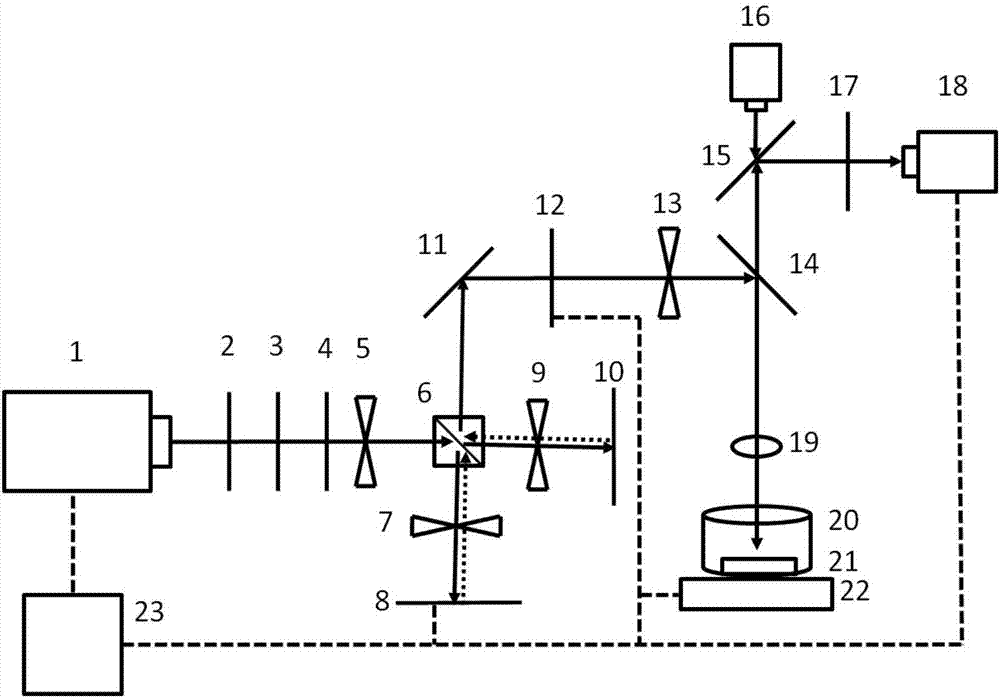
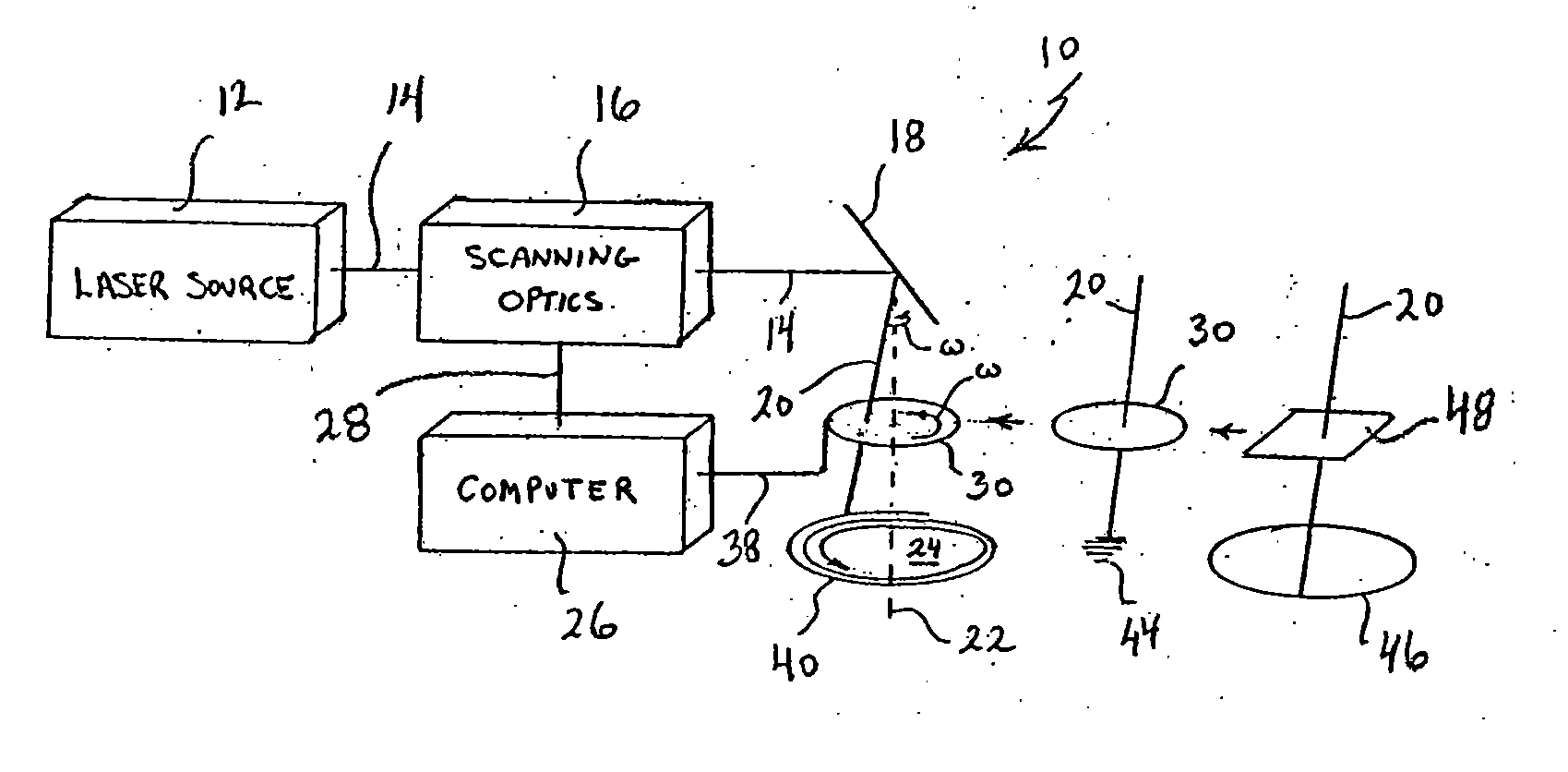
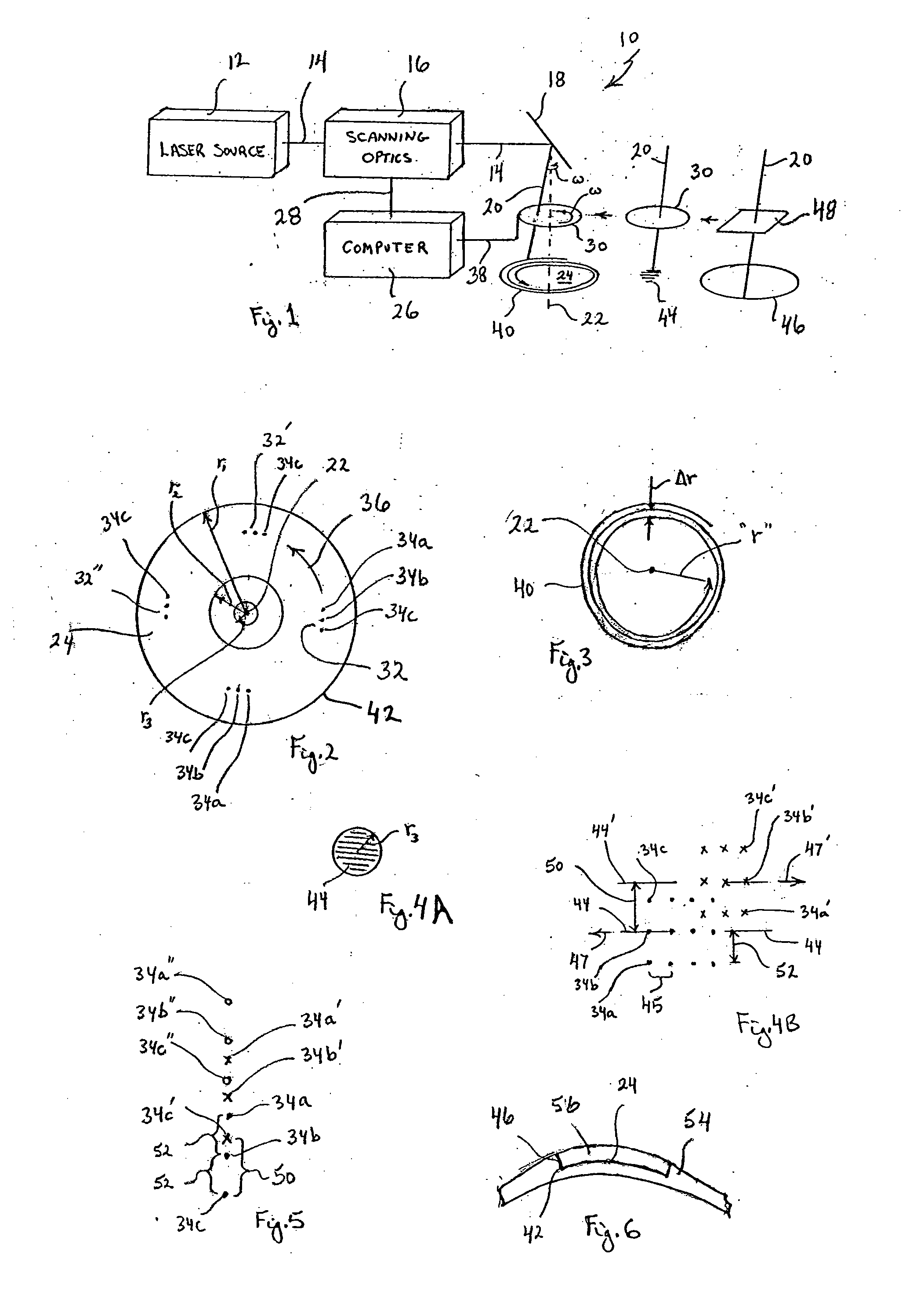
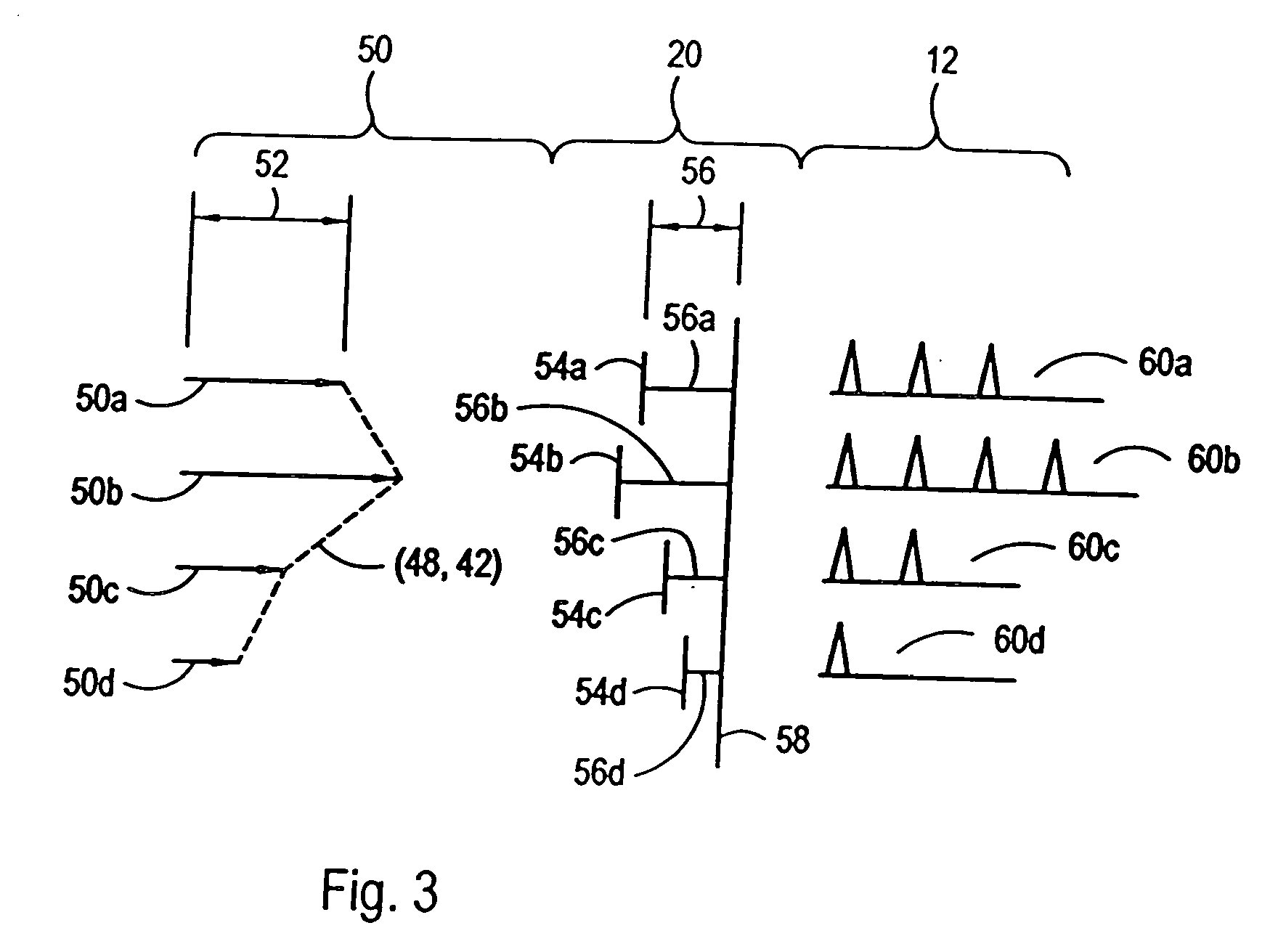
A system and method for performing ophthalmic surgery requires splitting a laser beam into a pattern having a plurality of focal points. The pattern is then moved along a spiral path according to a predetermined, two-phase protocol. In the first phase, a radial spacing “Δr” between spiral lines, and the velocity of the pattern “rω” are held constant as the radius “r” is decreased from r1 to r2. In the second phase the angular velocity “ω” is held constant and the radial spacing “Δr” is proportionally increased as “r” is further decreased from r2 to r3. Additional LIOB is required both inside r3, as r is reduced to zero and, then, along the periphery of the treatment area for a rim cut at r1.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
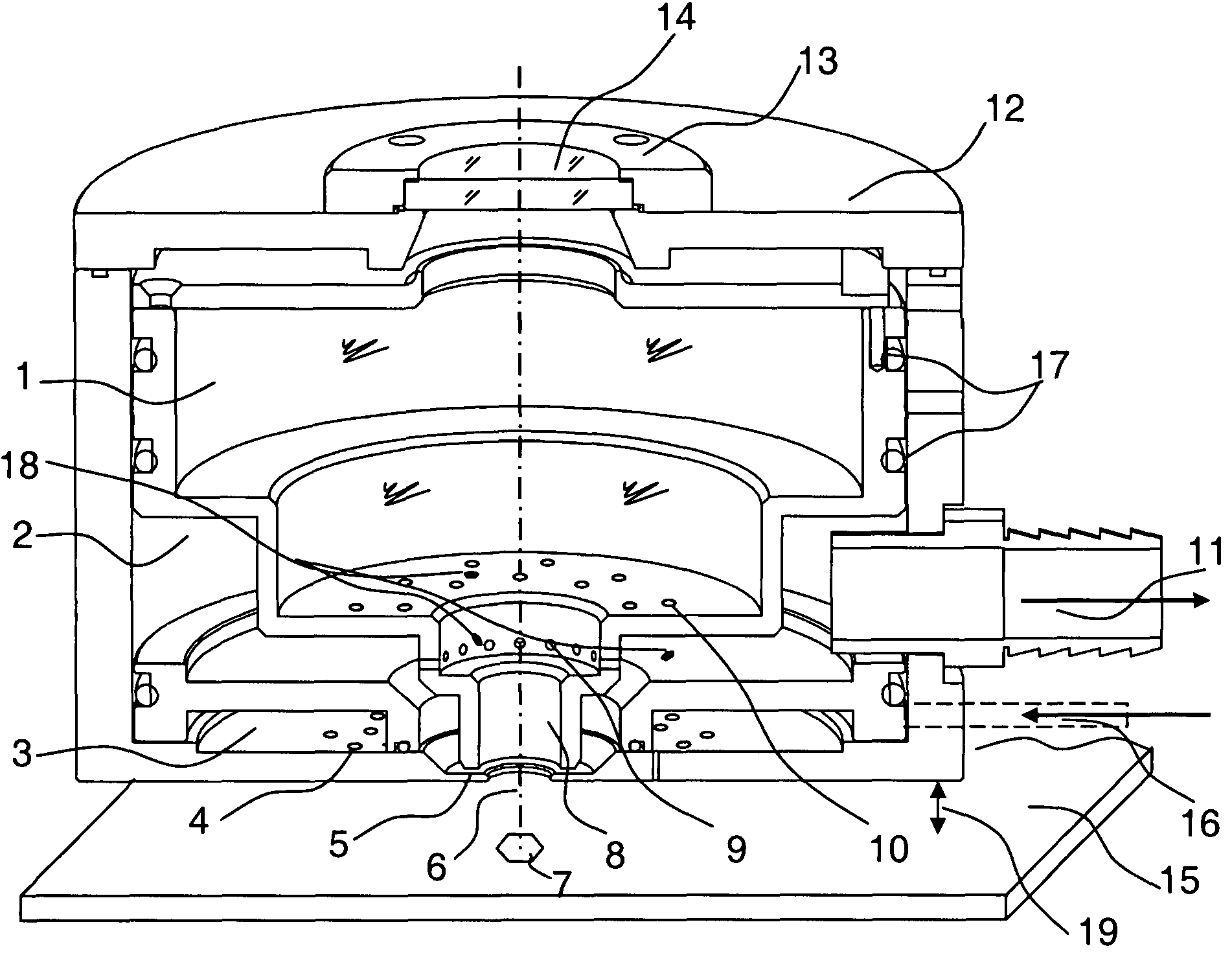
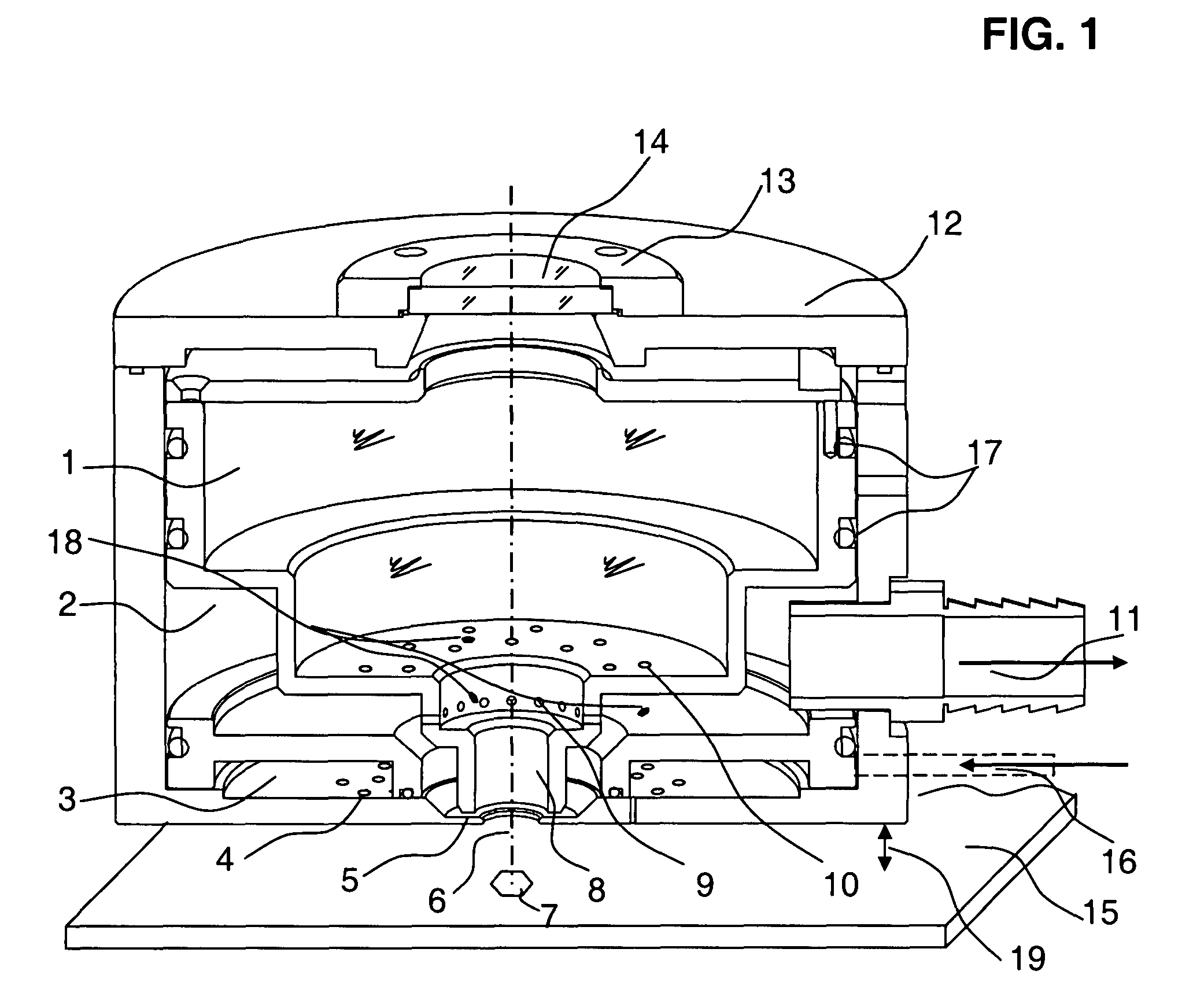
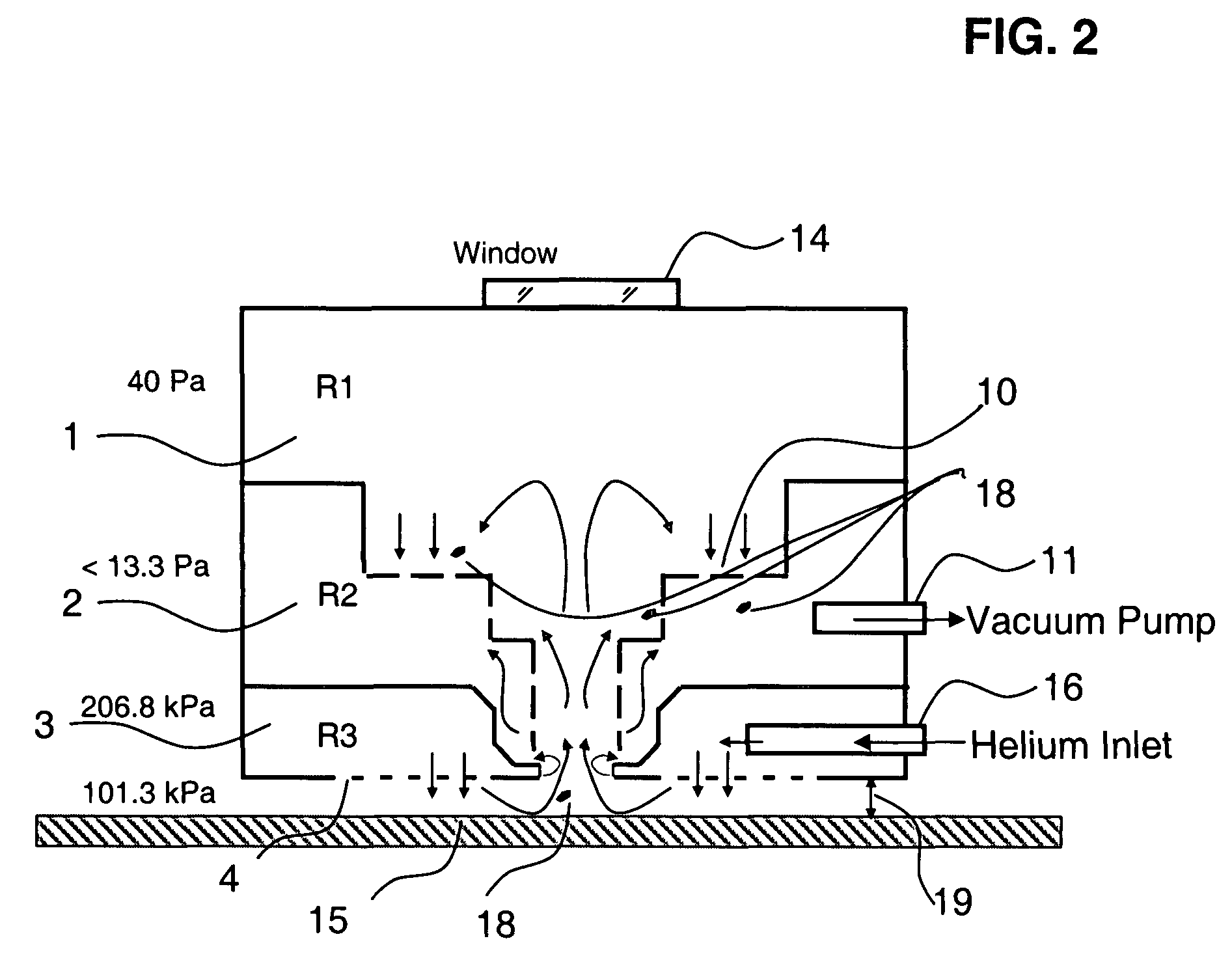
Vacuum debris removal system
InactiveUS20090107966A1Rapid debris removalEffective material removalWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPhotoablationParticulates
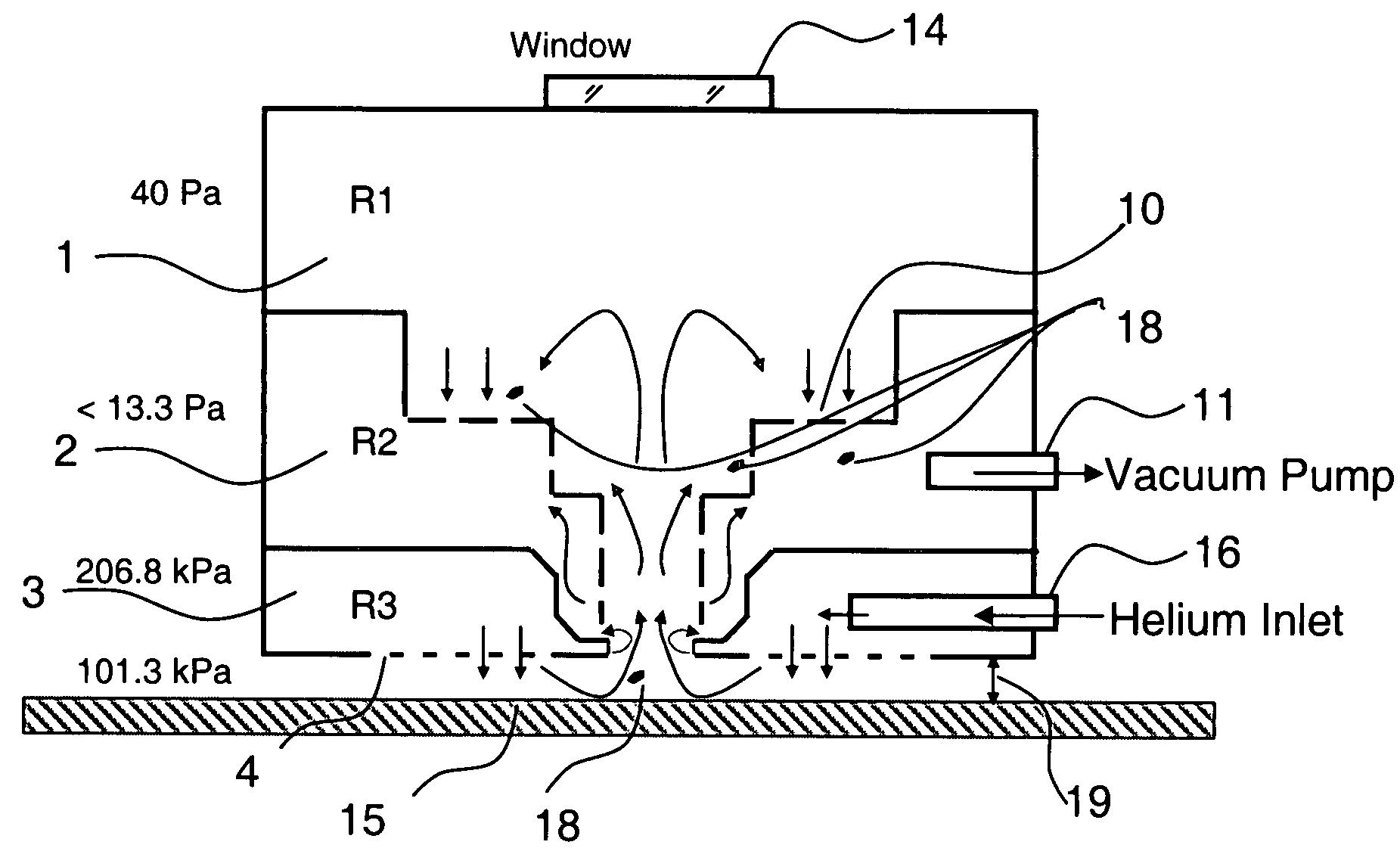
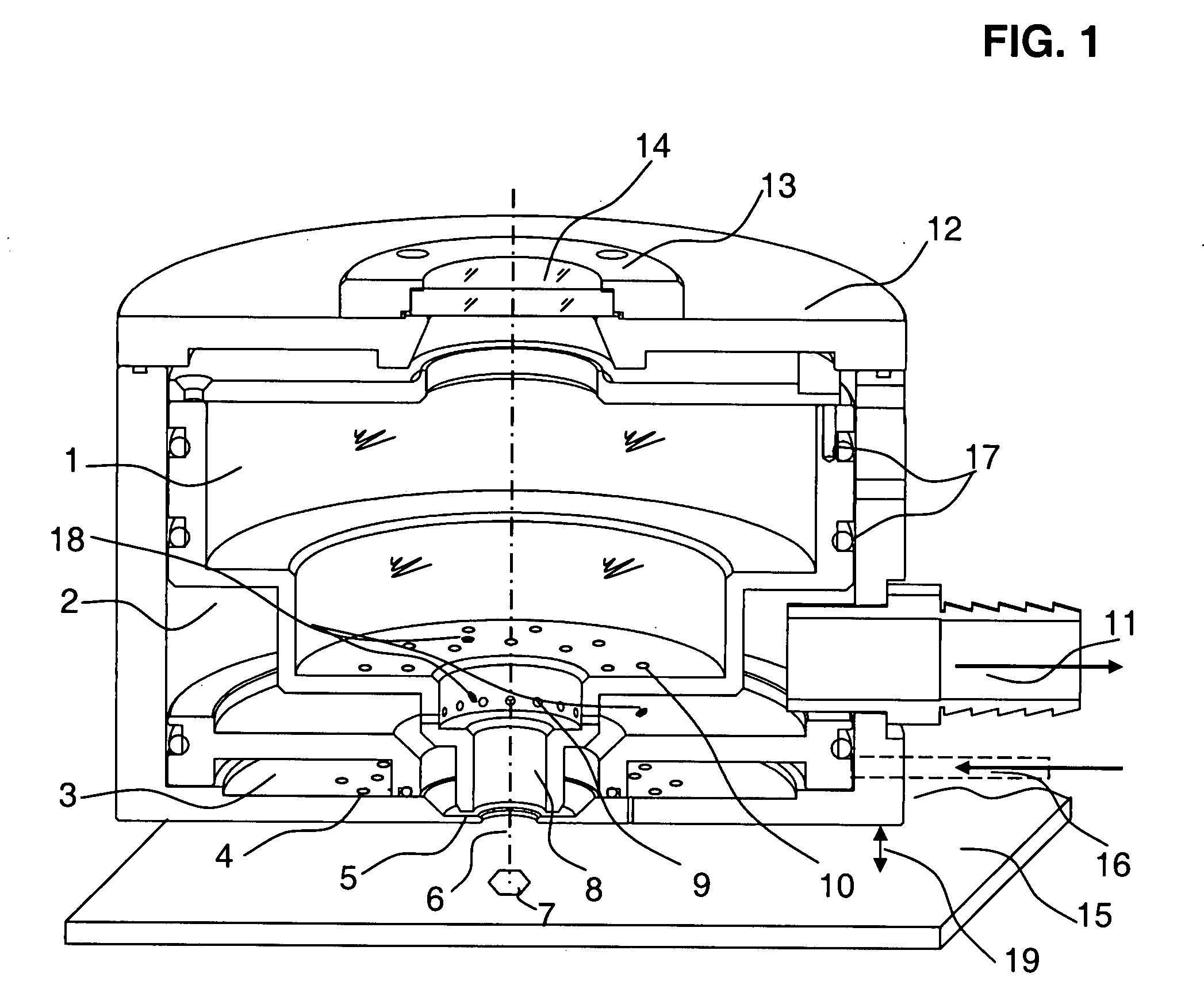
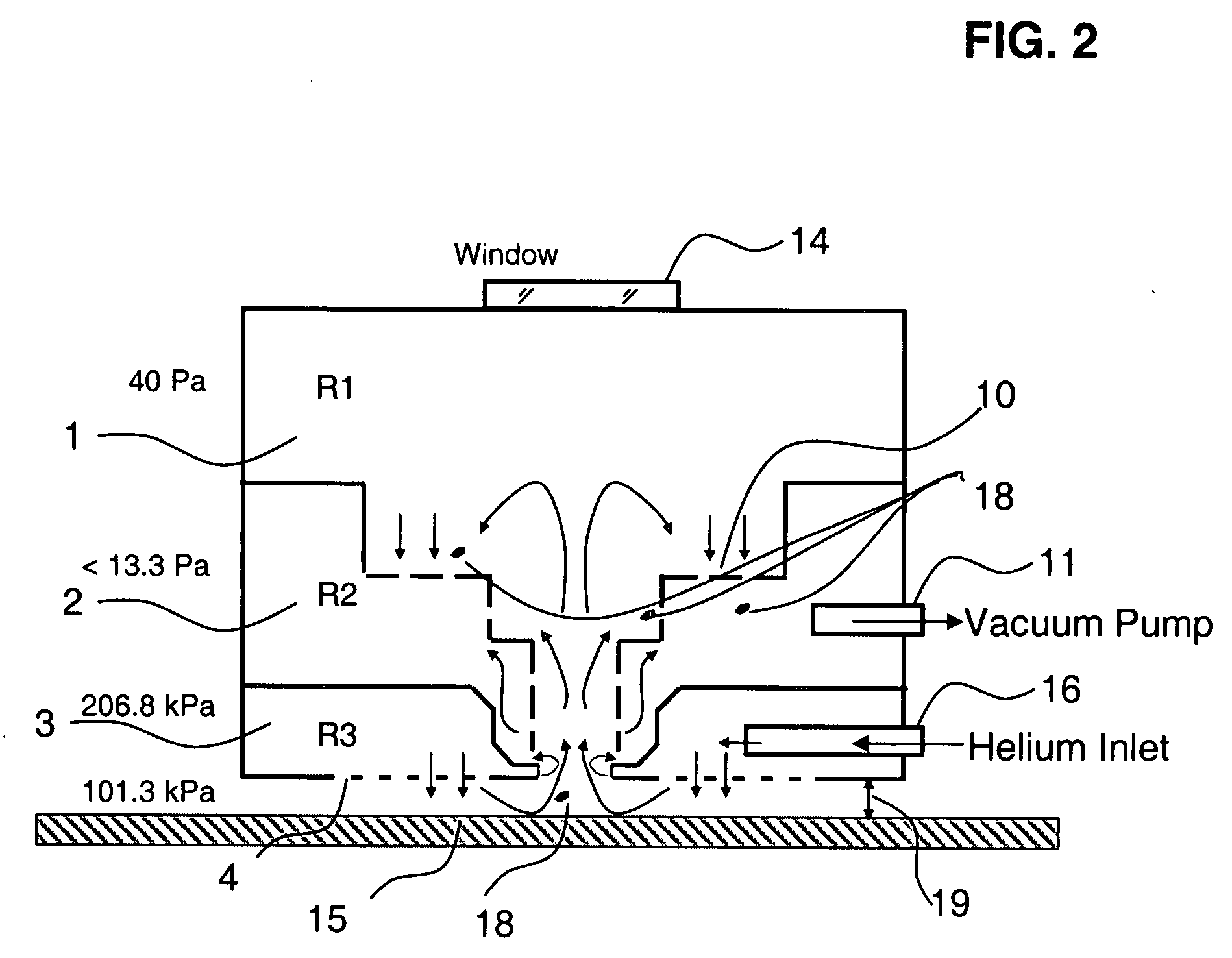
A turbulence-controlled vacuum debris removal subsystem safely exhausts particles ejected during photoablation. Nested interconnected chambers provide diminishing sweeping gas partial pressure and diminishing turbulence, ejecting particles from the ablation beam path between pulses, without compromising continuing particle conductance. Removal rate (debris generation rate) depends on conductance and particle sizes. The chambers interconnect through metering holes which enable optimization of partial pressure differentials. Controlled flow accomplishes debris removal, reducing turbulence of the mixture of debris and sweeping gases. A preferred embodiment uses a nest of concentric chambers, providing a clear light path. Another preferred embodiment uses orifices on chamber faces for removal and forming an envelope of gas around the processing region for dynamically containing the ejected particulate matter from the ablation site to the exhaust.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
A method and a system for laser photoablation within a lens
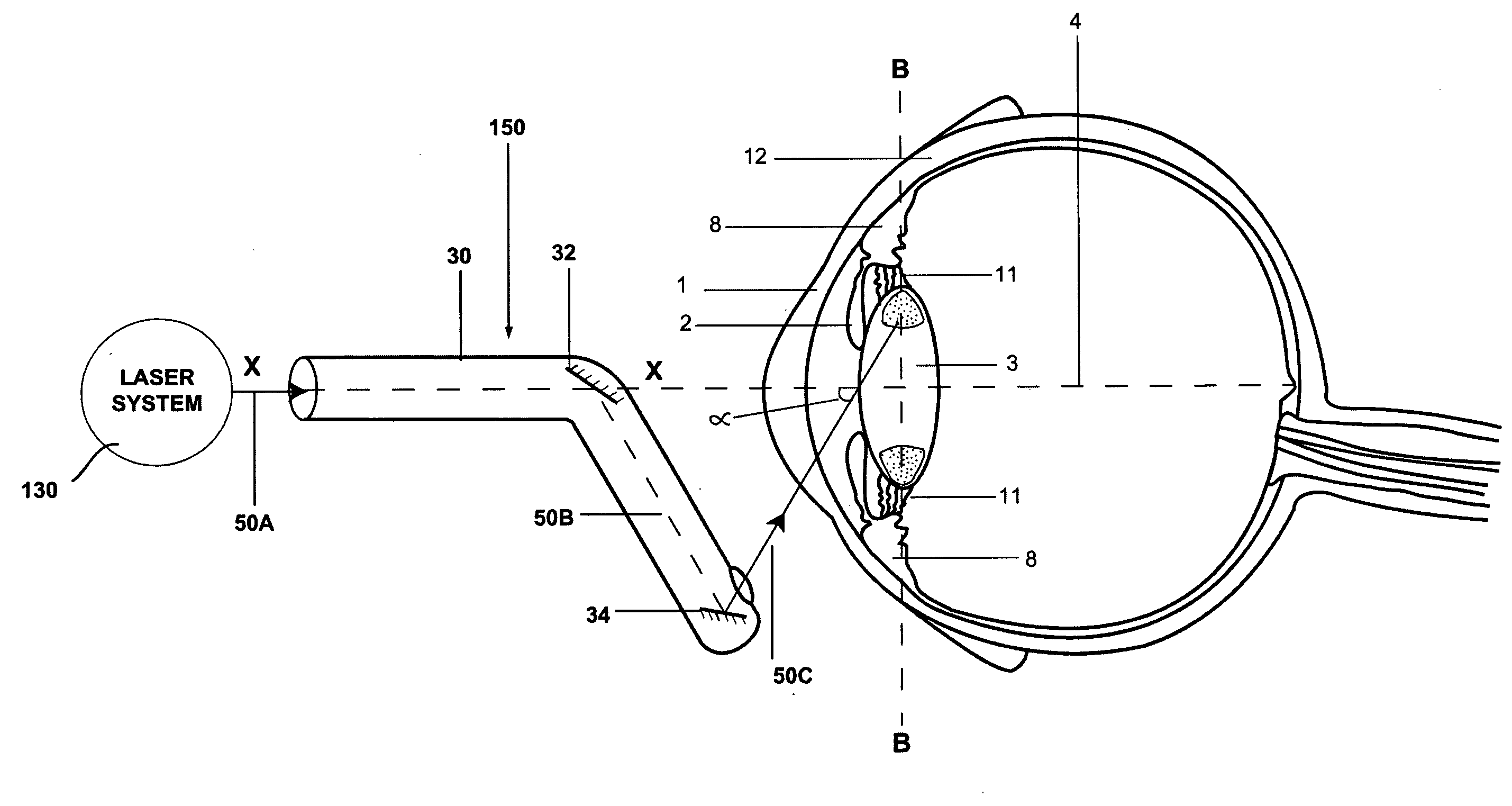
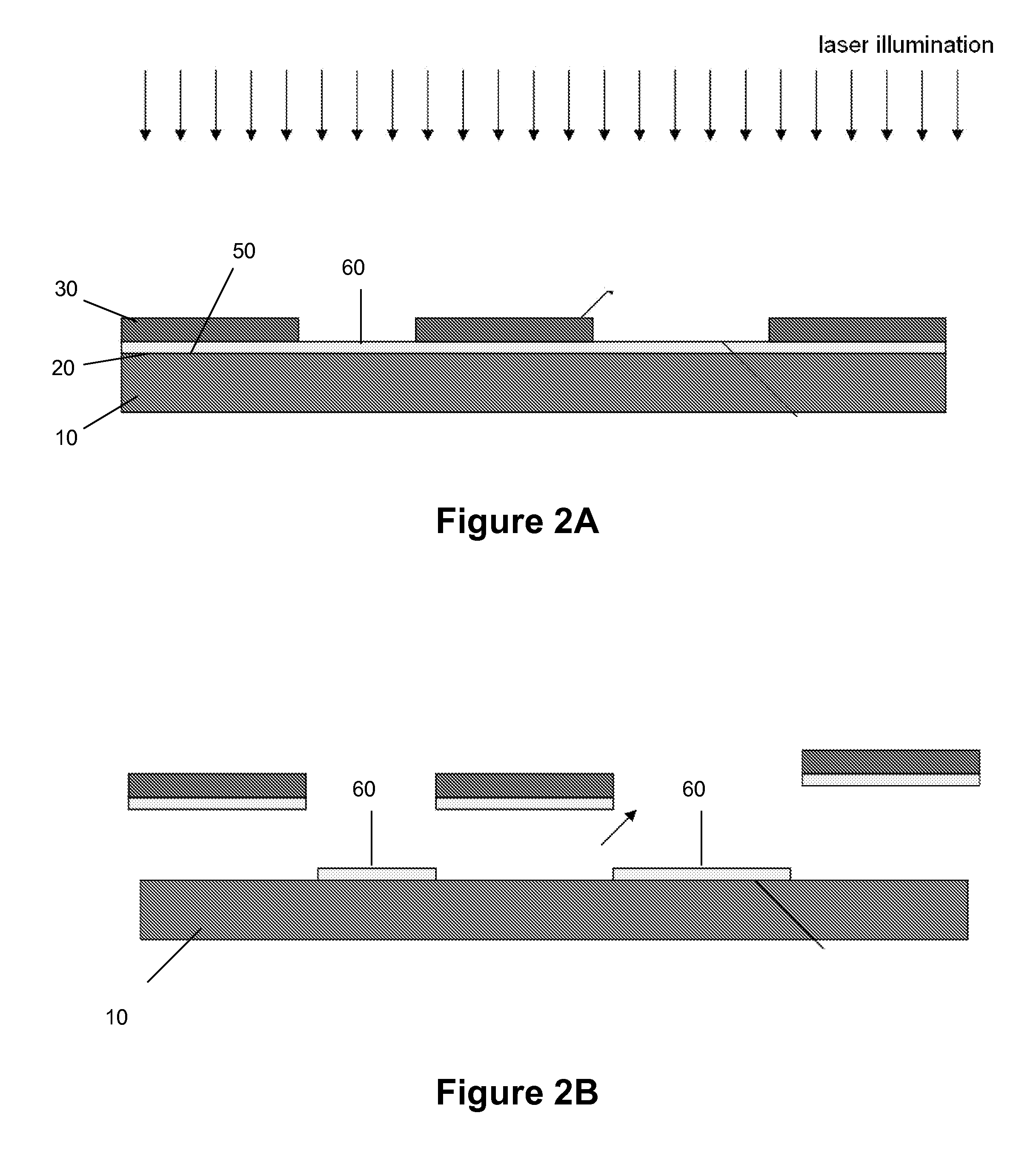
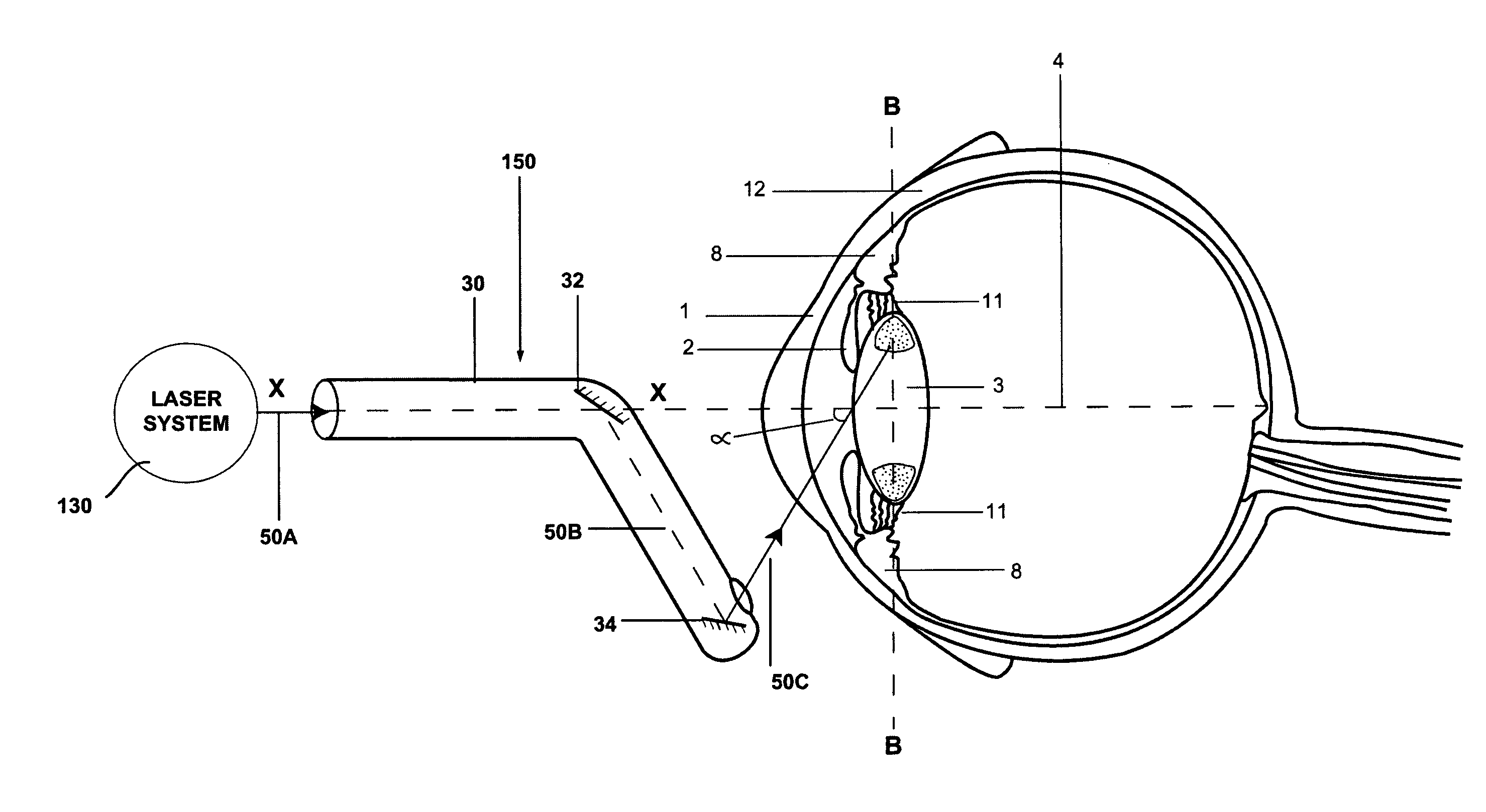
InactiveUS20100312231A1Reduce coronal diameter of lensEnhancement/improvement of abilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPhotoablationLaser beams
The present invention provides a method for ablating a presbyopic lens for restoring accommodation in human eye and a system thereof wherein a laser beam is directed obliquely to carry out multiple photoablations in circular way within the lens behind the iris and preferably near the edge or equator of the lens and / or in the vicinity of zonules to re-establish accommodation of the lens lost due to presbyopia.
Owner:SINGH AJOY I
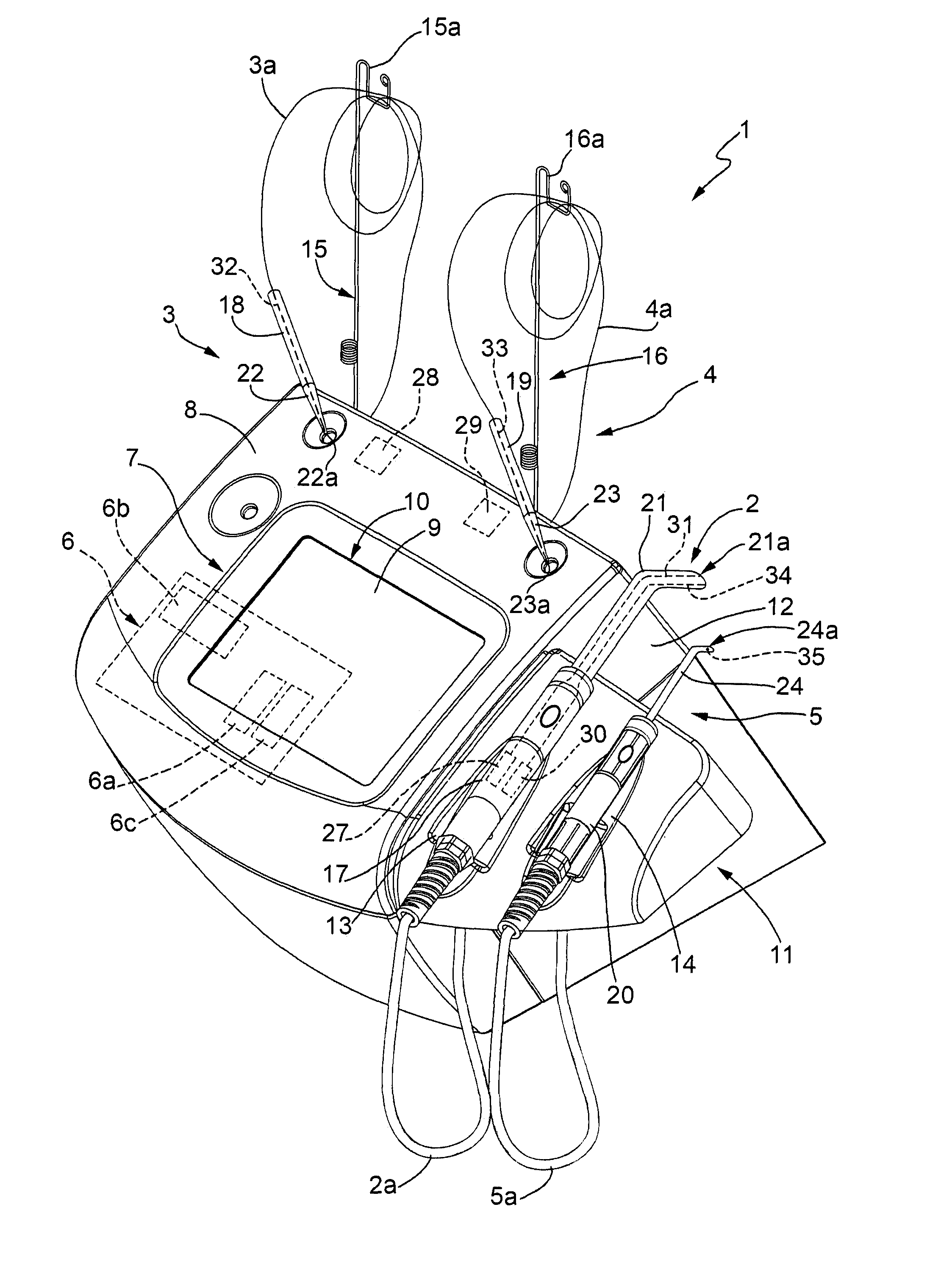
Device for Dentistry Treatments
InactiveUS20140147802A1Effective treatmentEasy and inexpensive to produceEndoscopesDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionPhotoablationPhototherapy unit
Device for dentistry treatments having a photodiagnosis unit for performing photodiagnosis of a portion of gingival tissue, a temperature measurement unit for measuring the temperature of the portion of gingival tissue, a photoablation unit for performing photoablation of part of the portion of gingival tissue, a phototherapy unit for performing photodynamic and / or photoinductive therapy of the portion of gingival tissue, a control unit configured to acquire, by means of the photodiagnosis unit and the temperature measurement unit, information relative to the state of the portion of gingival tissue, and to control operation of the photoablation and phototherapy units according to the information acquired.
Owner:GP INVESTIMENTI
Systems and devices for photoablation
ActiveUS20090054883A1Avoid photolysisReduce the risk of blood clotsSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyPhotoablationLight emission
The invention provides a catheter for optical ablation of tissue in a living body, the catheter including: a distal end; a proximal end; an elongate catheter body coupled between the distal end and the proximal end; a light emission device at the distal end and configured to emit an ablation light having characteristics selected to regulate an optically regulatable transcription control element operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence for a gene product, the expression of which gene product in cells directly or indirectly kills cells; and a projection control mechanism coupled to the light emission device and configured to control an effectively illuminated area where the optically regulatable transcription control element is effectively regulatable by the ablation light projected from the light emission device. Also provided is a system which includes the catheter, and methods to prevent, inhibit or treat AF which employ an expression cassette and / or one or more selected wavelengths of light.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
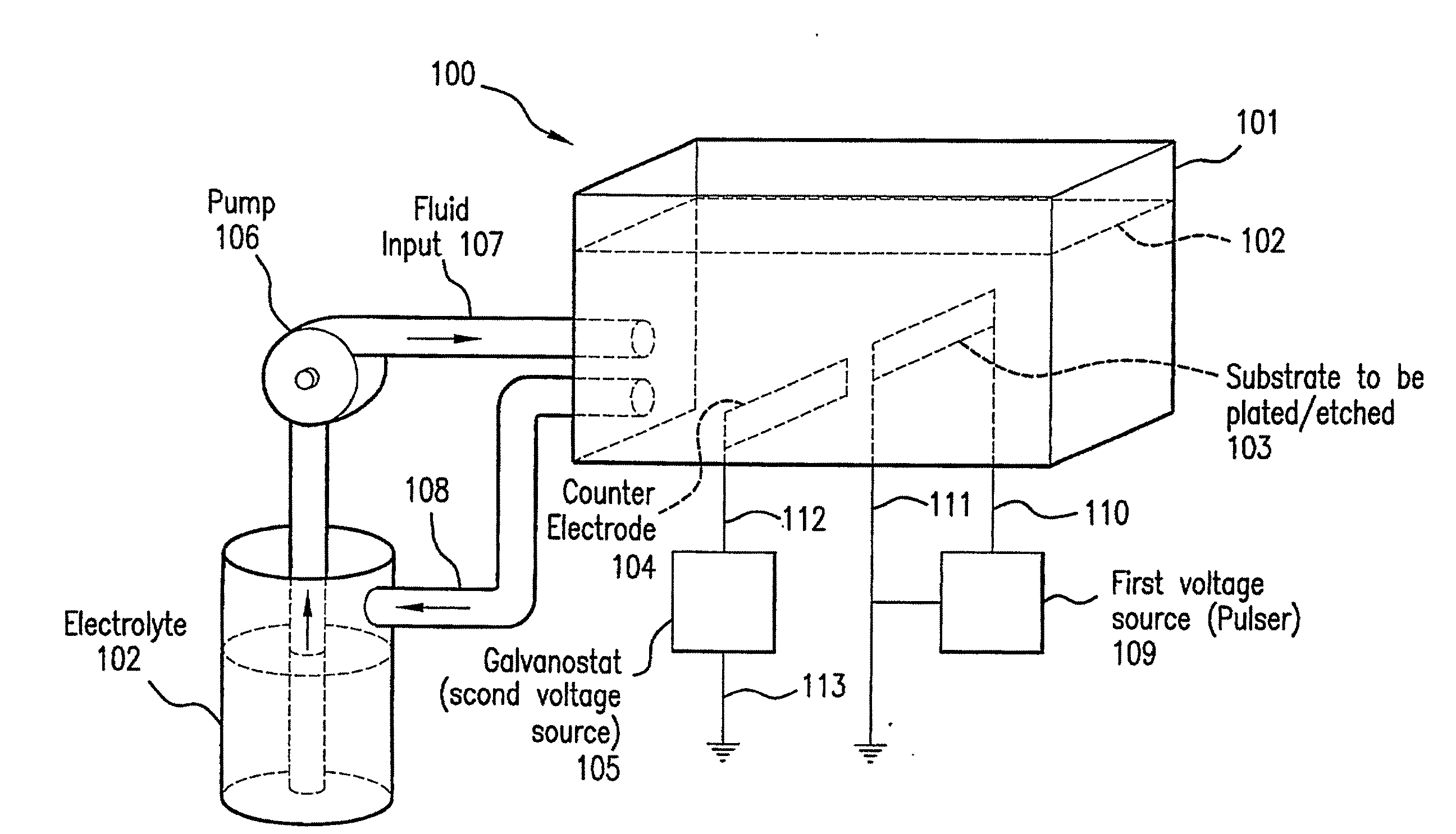
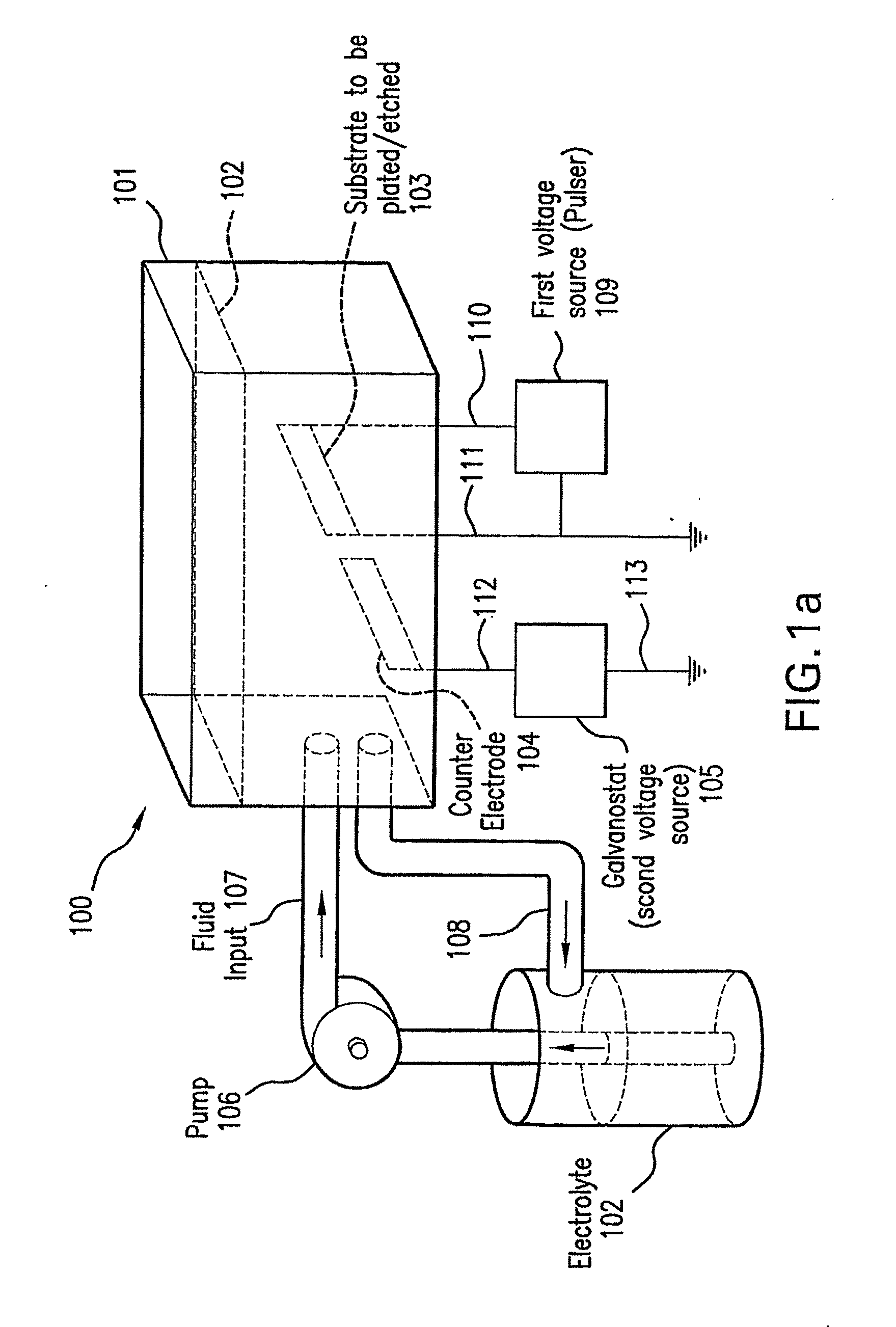
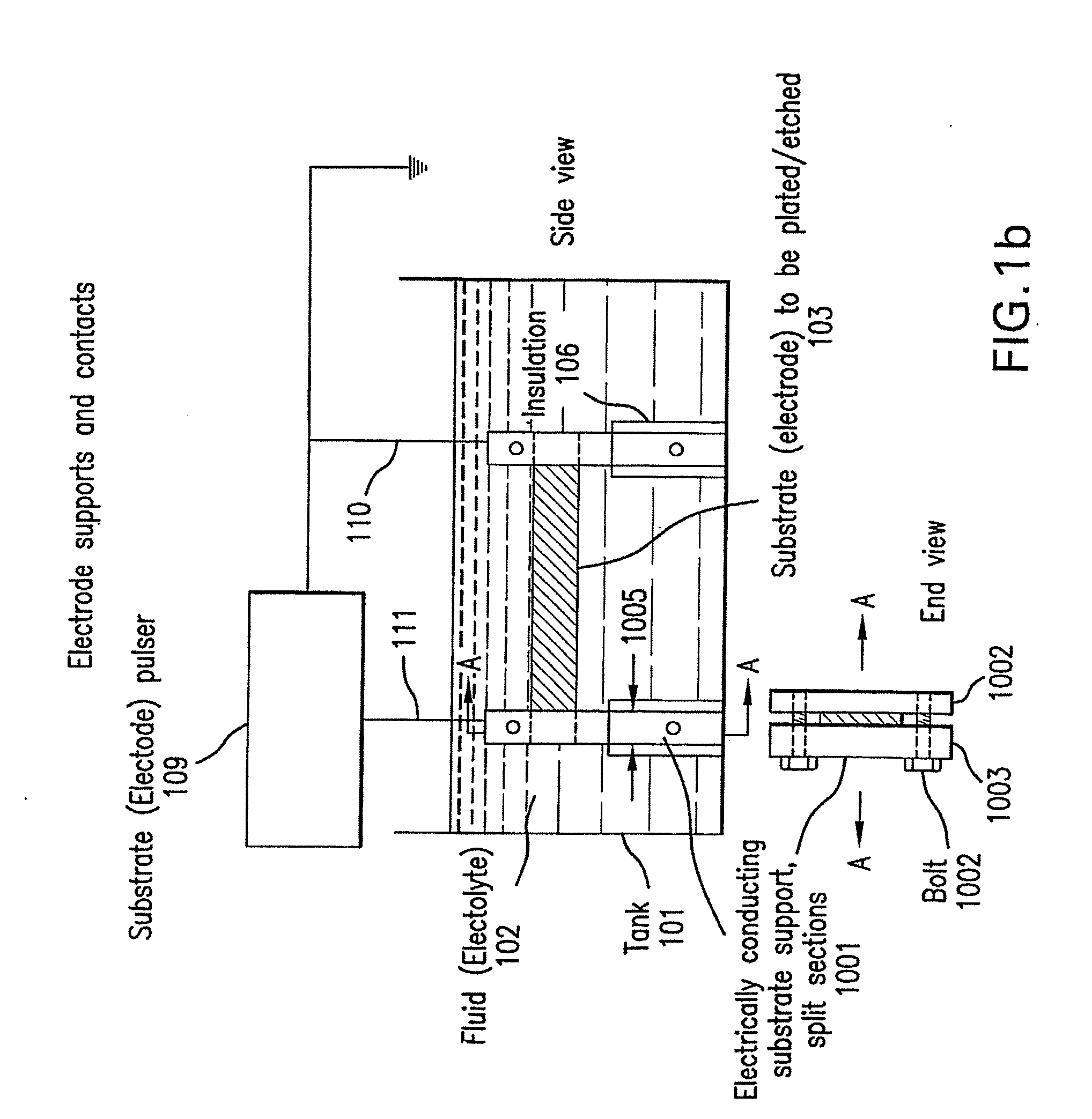
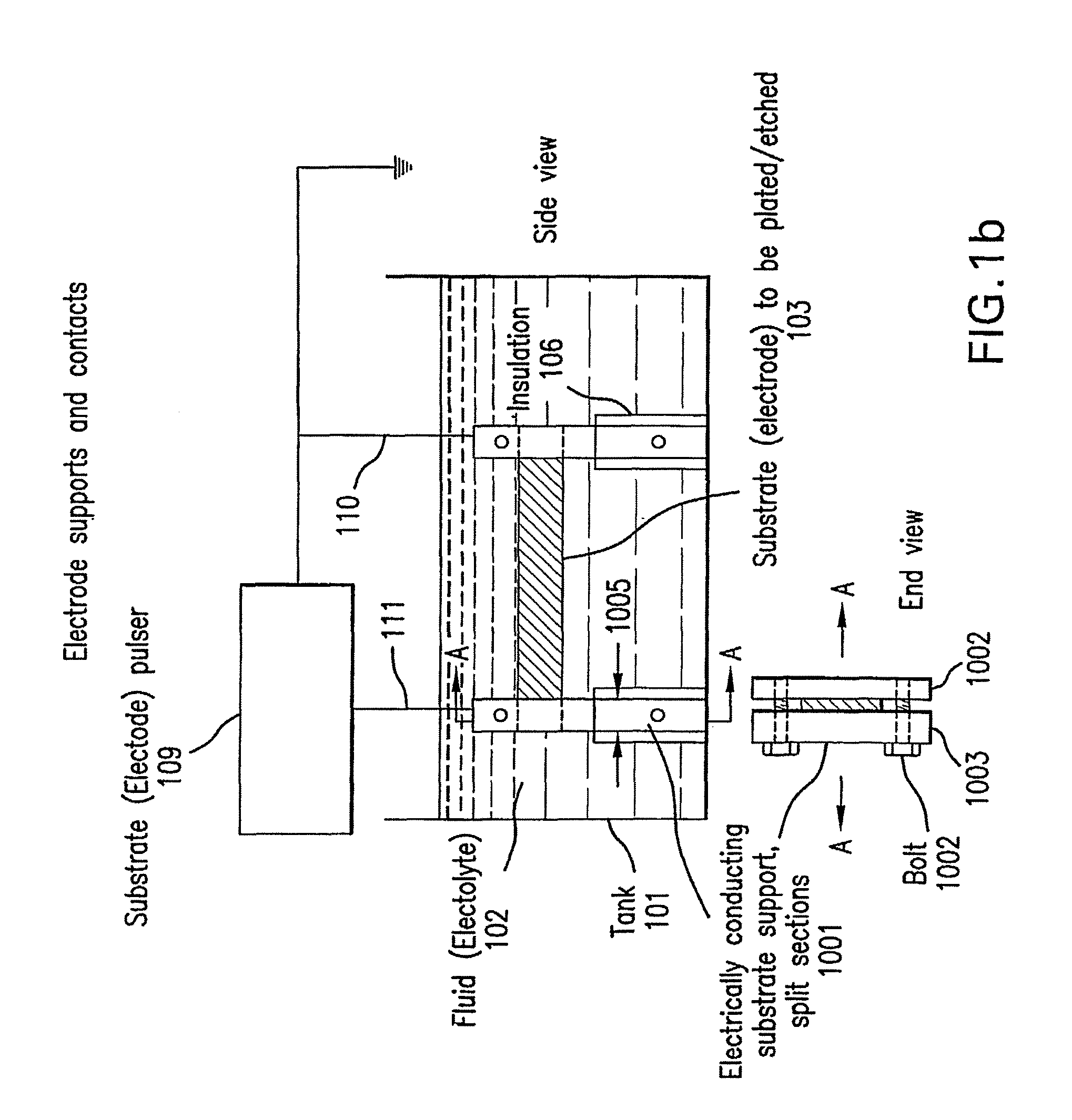
In situ plating and etching of materials covered with a surface film
Systems and methods for plating and / or etching of hard-to-plate metals are provided. The systems and methods are designed to overcome the deleterious effect of superficial coating or oxide layers that interfere with the plating or etching of certain metal substrates. The systems and methods involve in situ removal of coating materials from the surfaces of the metal substrates while the substrates are either submerged in plating or etching solutions, or are positioned in a proximate enclosure just prior to submersion in the plating or etching solutions. Further, the substrates can be in contact with a suitable patterning mask to obtain patterned oxide-free regions for plating or etching. This in situ removal of coating layers may be achieved by pulse heating or photoablation of the substrate and the inhibiting coating layers. Electrical energy or laser light energy may be used for this purpose. Additionally or alternatively, the coating materials may be removed by mechanical means.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
System and method for photoablation using multiple focal points using cyclical phase modulation
InactiveUS20080287935A1Faster angular speedIncrease ωLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEye laser surgeryPhotoablation
A system and method for performing ophthalmic laser surgery requires directing a laser beam through a stationary beam splitter to create a pattern of multi-focal spots. Also, a beam scanner is used to move this pattern along a substantially spiral path in a target area of tissue. To compensate for cyclical changes in orientation of the pattern relative to its spiral path, a computer is used to phase modulate pattern movement. Specifically, this phase modulation is expressed as:v′=v(1+F sin(nθ))where v is a variable (e.g. angular speed, line spacing, or z-spacing), v′ is the phase modulated variable, F is a magnitude factor for phase modulation control, n is an integer, and θ is an angular position of the pattern during phase modulation.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Delivery System and Method of Use for the Eye
A method and delivery system are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Pulsed laser radiation is delivered from the distal end of a fiber-optic probe sufficient to cause photoablation of selected portions of the trabecular meshwork, the juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and an inner wall of Schlemm's canal in the target site. The fiber-optic probe may be advanced so as to create an aperture in the inner wall of Schlemm's canal in which fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye flows. The method and delivery system may further be used on any tissue types in the body.
Owner:IVANTIS INC
Illumination system optimized for throughput and manufacturability
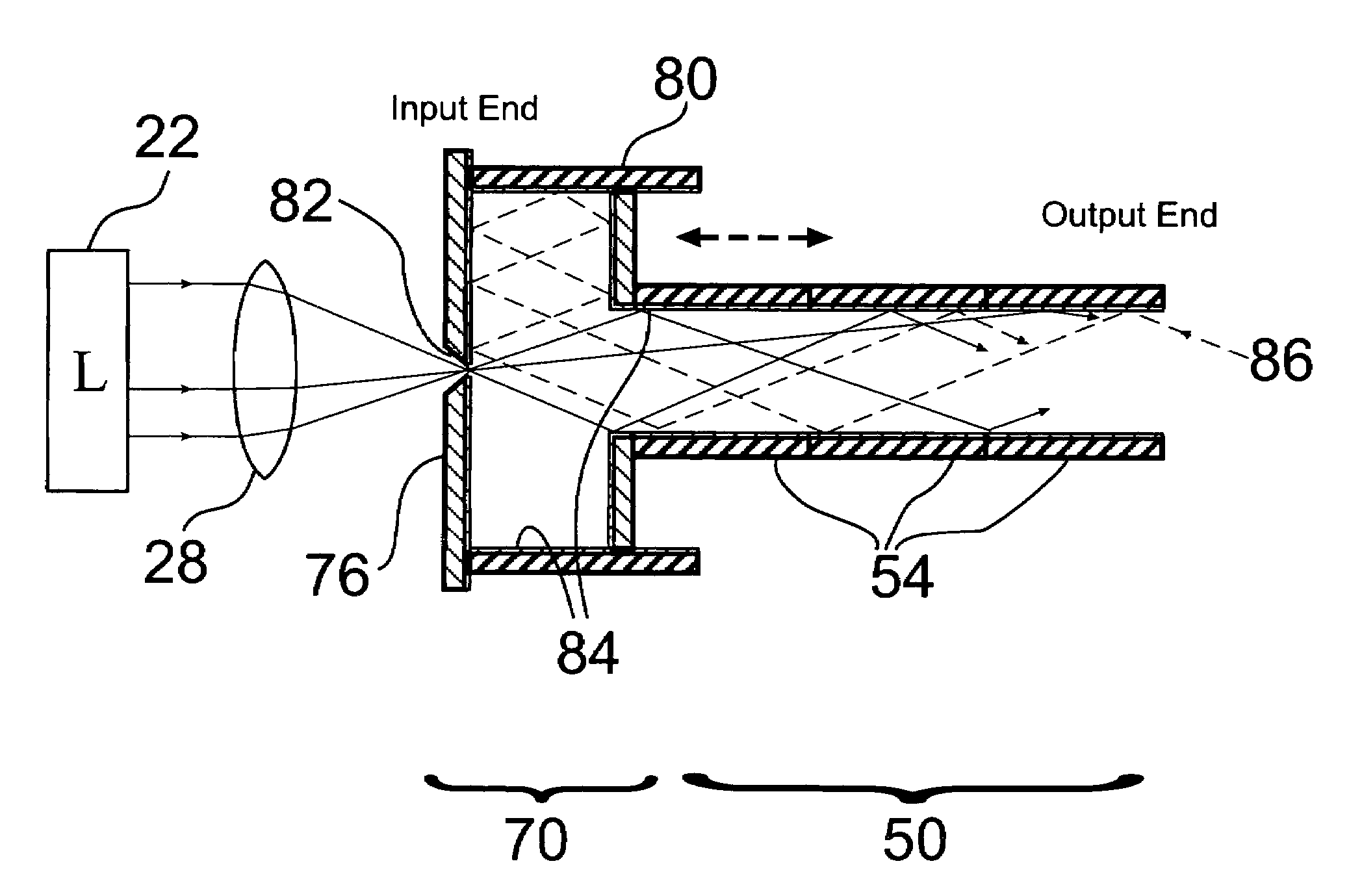
InactiveUS20060001845A1Raise the ratioImprove recycling efficiencyDiffusing elementsPhotomechanical apparatusPhotoablationProjection image
An optimized illumination system that efficiently produces uniform illumination for exposure, photoablation, and laser crystallization systems. The illumination system includes a homogenizer that uniformizes and shapes a light beam, which is directed onto a mask by condenser optics. The illumination system recycles radiation by directing light reflected by the mask back into the illumination system, where an apertured mirror situated at the input end re-directs it back toward the mask. The relative areas of the mirror and aperture affect recycling efficiency and system throughput, so the system features a larger-diameter recycling segment enabling greater mirror-to-aperture area ratios. An added segment at the output end of the homogenizer matches the homogenizer diameter to the projection imaging system object field size. This standardizes the homogenizer and condenser lens integration, reducing the need for customized parts and thus reducing manufacturing time and expense.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Closed loop control for intrastromal wavefront-guided ablation with fractionated treatment program
InactiveUS20050149005A1Improve accuracyImprove the effect of surgeryLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsInitial treatmentPhotoablation
A closed-loop control system for altering the optical characteristics of a patient's cornea includes an algorithm for predicting the shape of the cornea after one or more gas bubbles resulting from intrastromal photoablation have collapsed. Patient data can be used as an input for the algorithm, which is then run to prepare an initial treatment plan for a corneal alteration. The initial plan typically includes a plurality of intrastromal photoablation locations and corresponding ablation energies. After photoablation of plan location(s) and before the resulting bubbles collapse, a real-time wavefront shape for light passing through the cornea is measured. The wavefront is then used in the algorithm to predict a post bubble collapse cornea shape and to generate an updated treatment plan. The procedure then continues by ablating location(s) identified in the updated treatment plan. Wavefront measurement and plan updating can be repeated as many times as desired.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
In situ plating and etching of materials covered with a surface film
Systems and methods for plating and / or etching of hard-to-plate metals are provided. The systems and methods are designed to overcome the deleterious effect of superficial coating or oxide layers that interfere with the plating or etching of certain metal substrates. The systems and methods involve in situ removal of coating materials from the surfaces of the metal substrates while the substrates are either submerged in plating or etching solutions, or are positioned in a proximate enclosure just prior to submersion in the plating or etching solutions. Further, the substrates can be in contact with a suitable patterning mask to obtain patterned oxide-free regions for plating or etching. This in situ removal of coating layers may be achieved by pulse heating or photoablation of the substrate and the inhibiting coating layers. Electrical energy or laser light energy may be used for this purpose. Additionally or alternatively, the coating materials may be removed by mechanical means.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Highly-integrated low-mass solar sail
InactiveUS20050274849A1Substantial weight savingHinders its propagationCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusPhotoablationSolar sail
Low mass-per-unit-area plastic film, preferably polyimide, prepared by a process of controlled treating of a supply of plastic film, possibly with one surface reflectively coated, at a microlithography workstation with included photoablation optics. This treatment achieves significant controlled removal of material in a selected pattern by providing relative motion between untreated plastic film and the workstation's photoablation optics while controlling photoablation of a pattern in the film. The material has a significant quantity of the mass of its plastic removed by photoablation, leaving a tessellated pattern of ridges surrounding individual wells. The resulting low-mass, rip-resistant film retains the general attributes of a large-area plastic film. The treated film also retains its reflective surface, on which amorphous silicon may be deposited. The silicon may be thereafter crystallized, utilizing the same optics, and used for fabrication of microelectronics.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Illumination system optimized for throughput and manufacturability
InactiveUS7158305B2Increase the area ratioImprove recycling efficiencyDiffusing elementsPhotomechanical apparatusPhotoablationOptoelectronics
Owner:ANVIK CORP
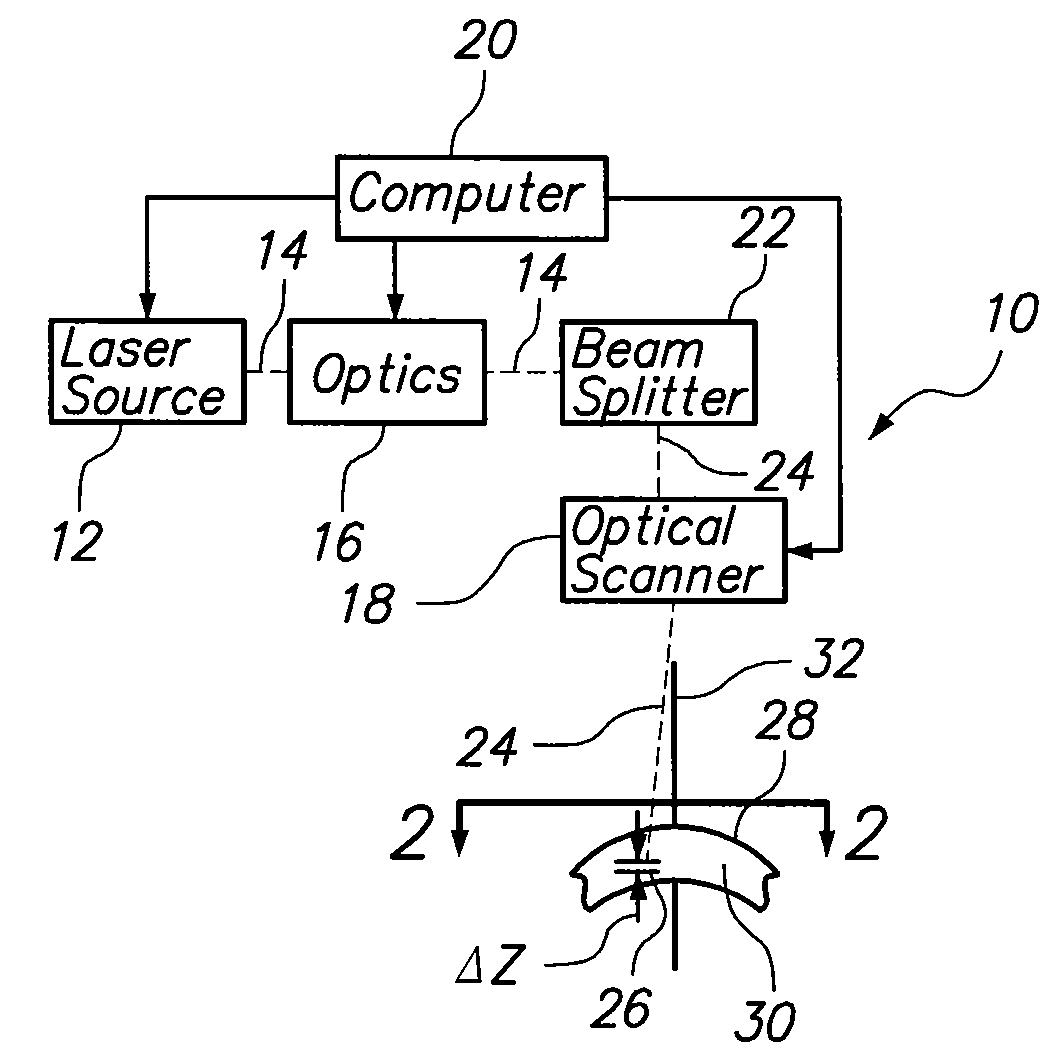
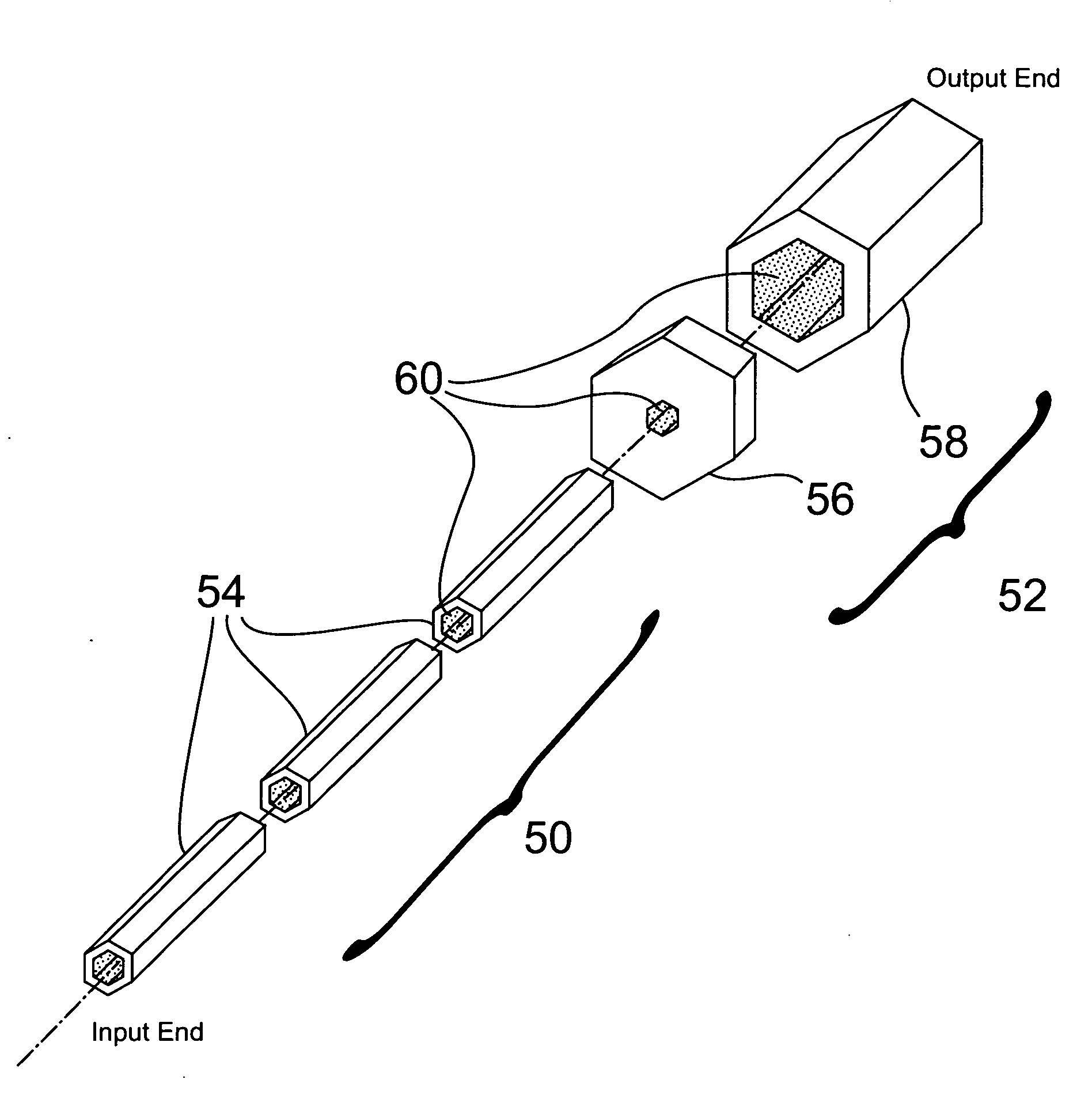
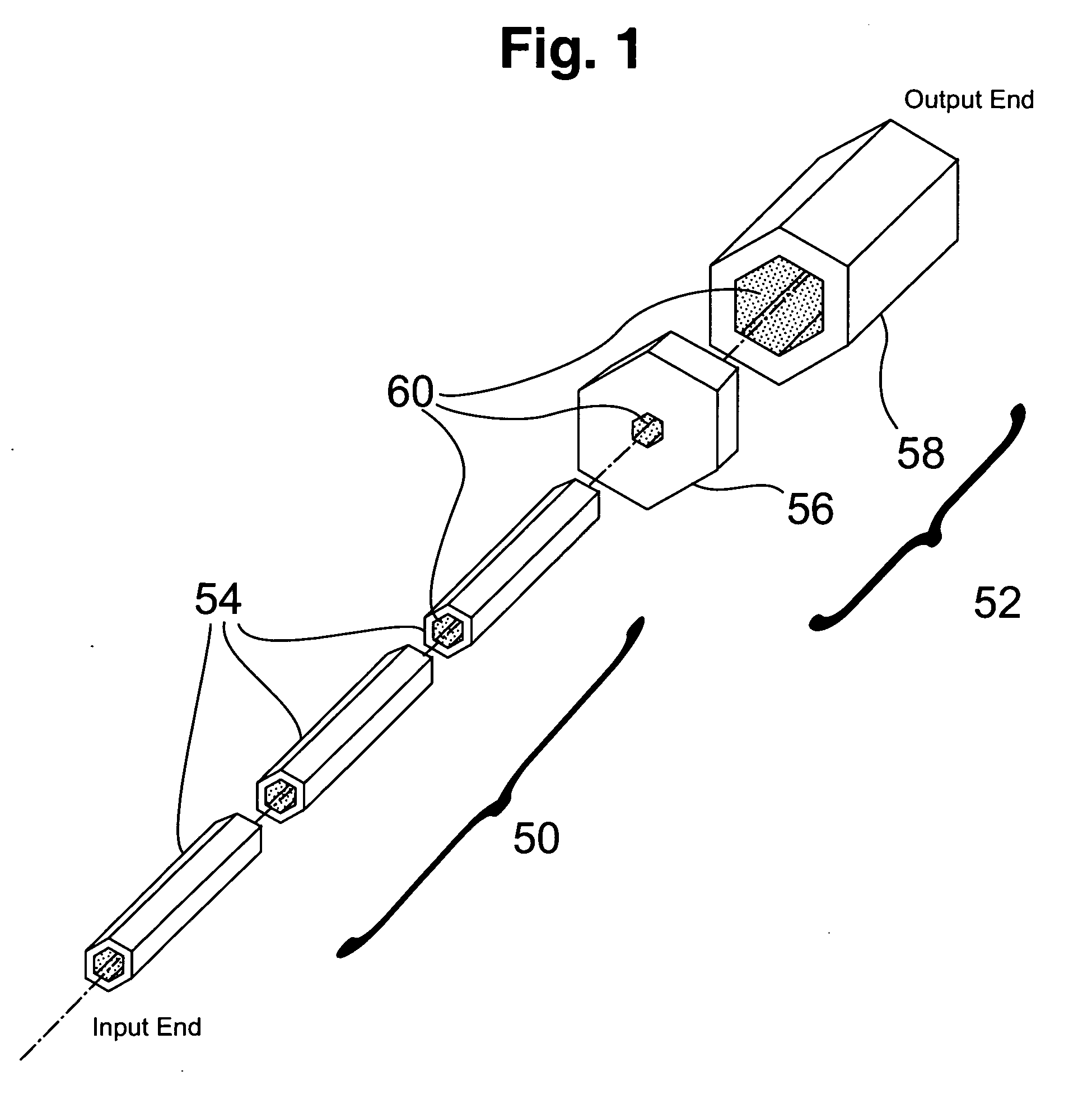
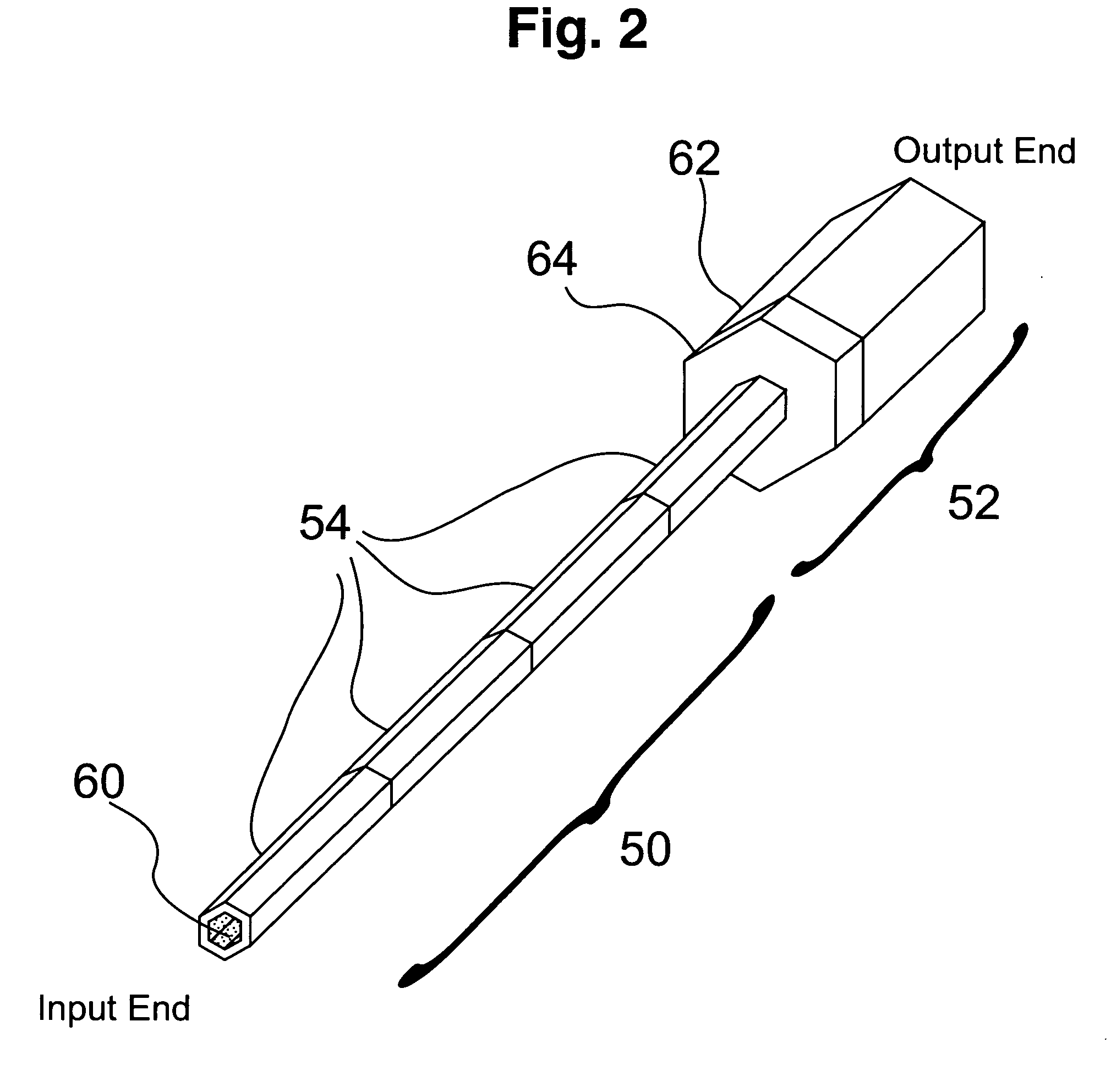
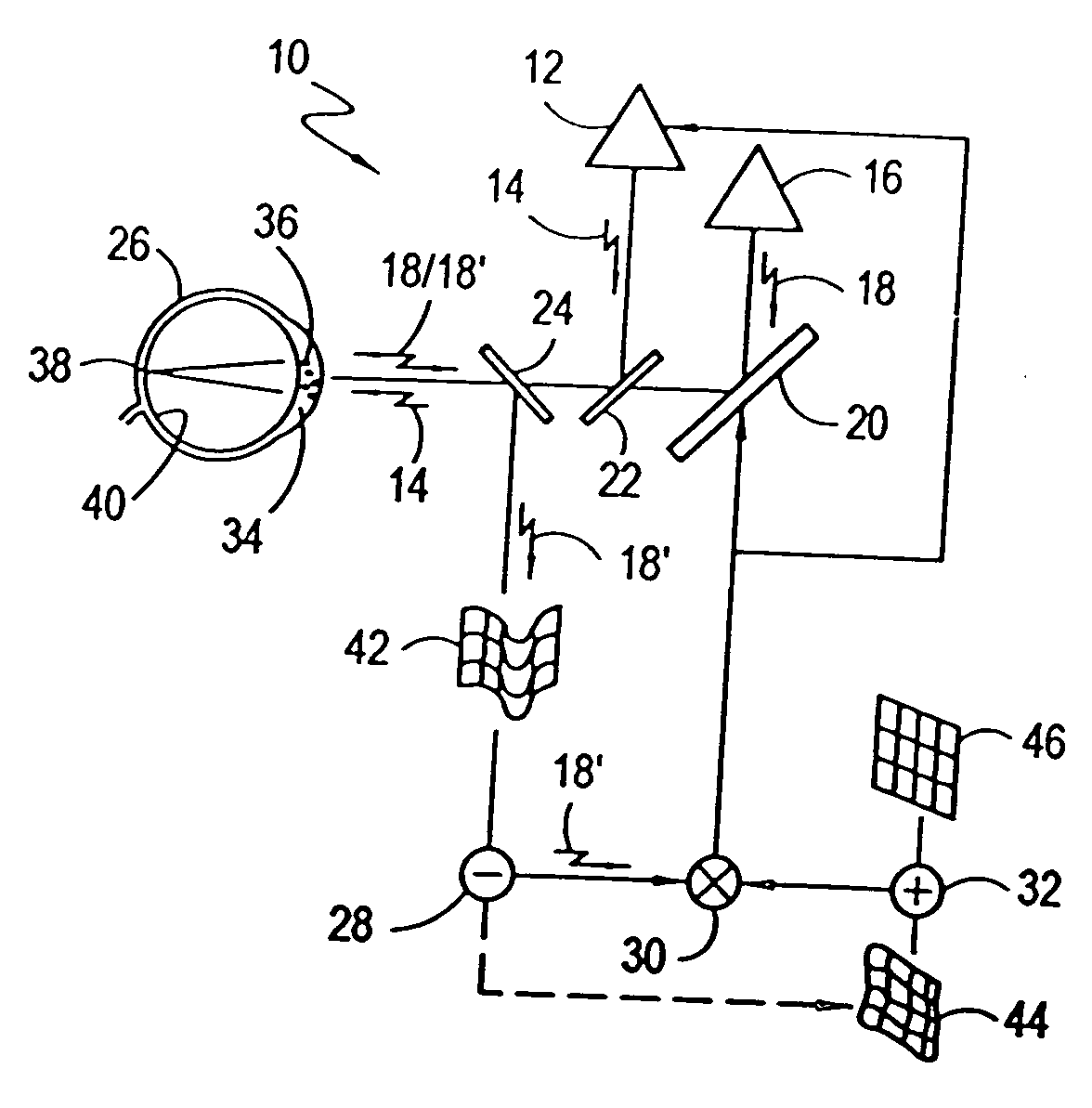
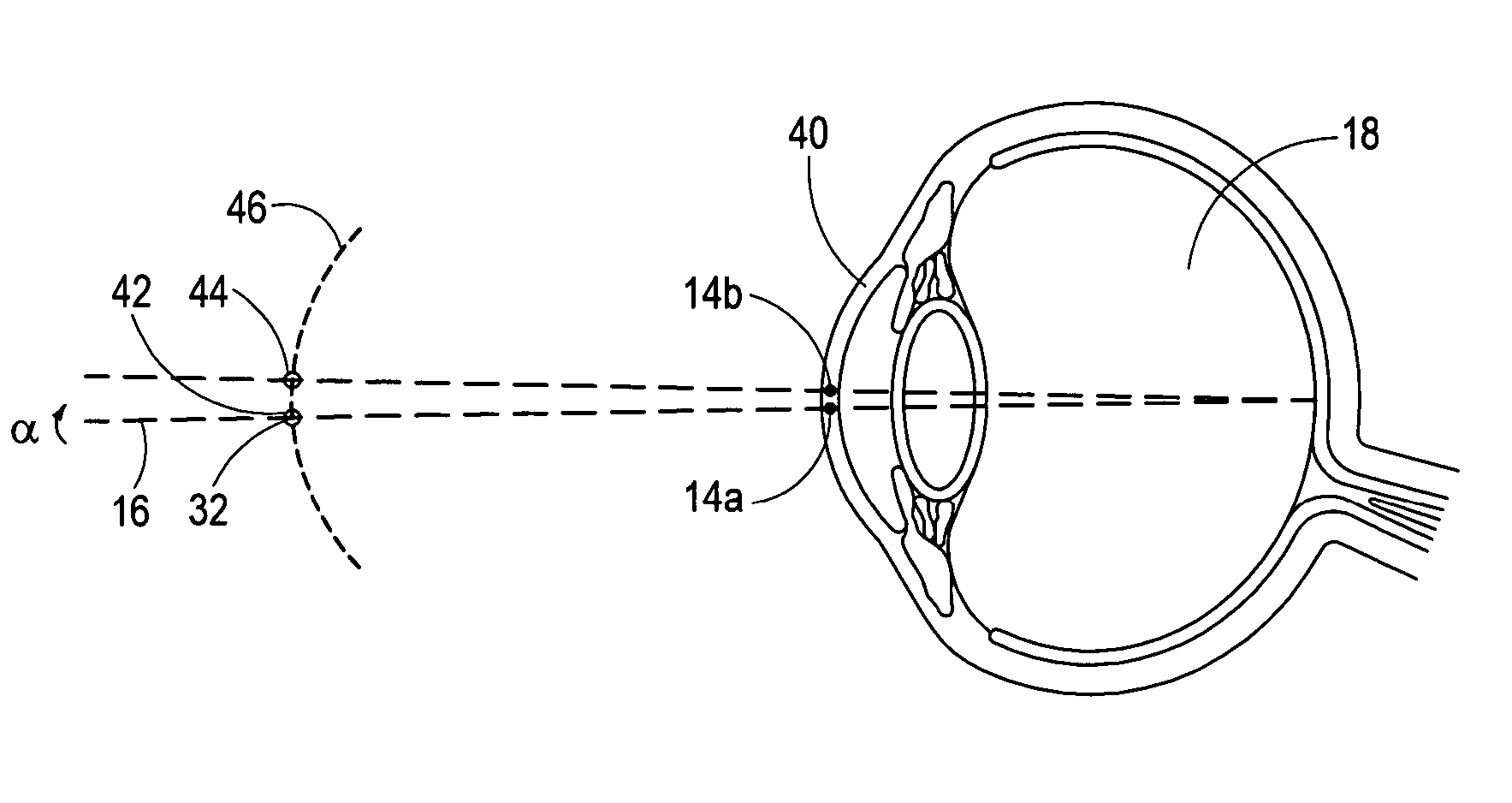
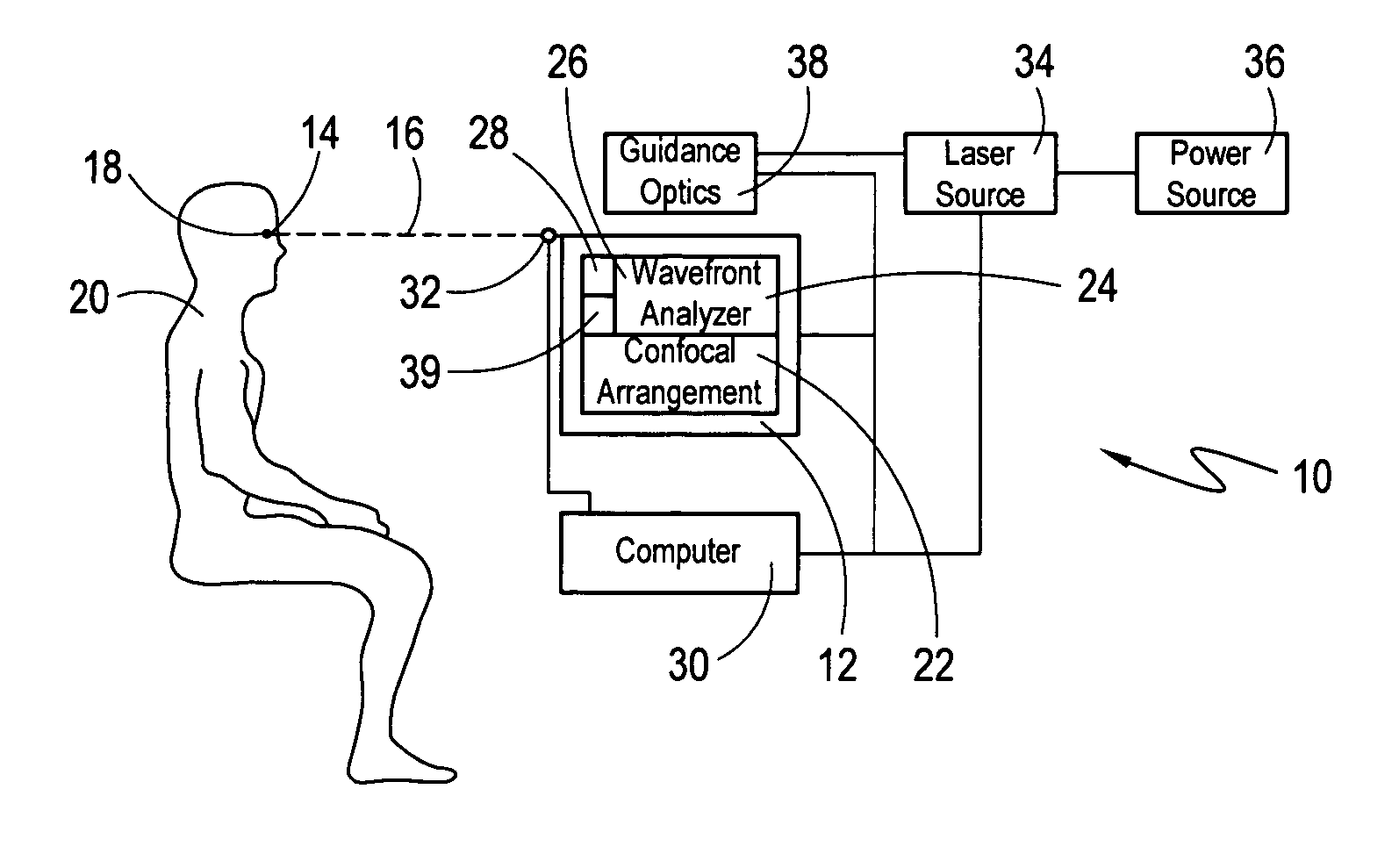
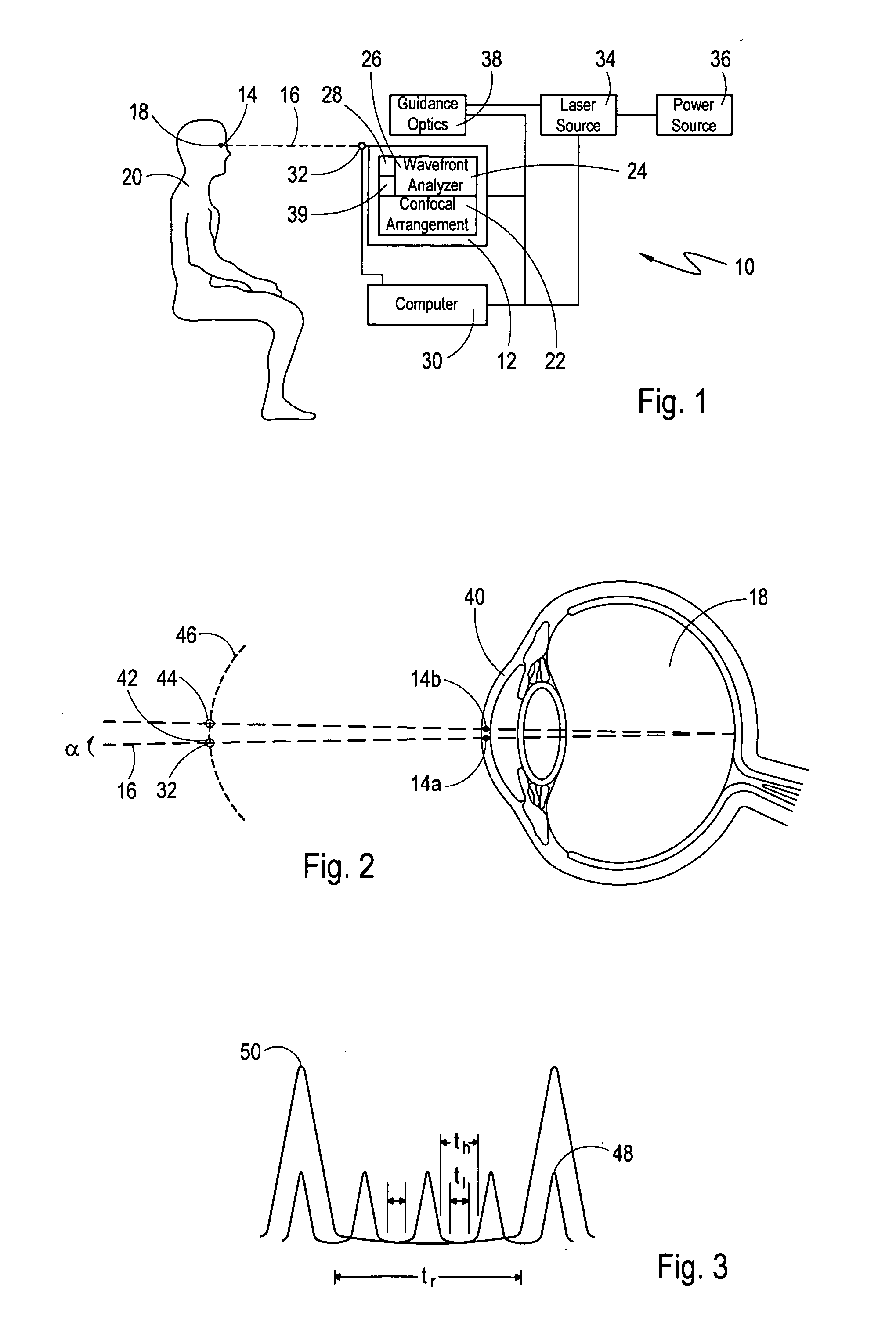
Eye position control monitor for laser vision correction
InactiveUS6966905B2Precise alignmentAccurately determineLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPhotoablationFixation point
A system for spatially stabilizing a base point on the optical axis of a patient's eye, for photoablation of the cornea, includes an optical element for identifying the base point. The system also includes an illumination source which is a fixation point for the eye. Movement of the illumination source induces a saccadic movement of the eye wherein the optical axis of the eye moves from a first orientation to a second orientation. Following the saccadic movement of the eye there is a latency period during which the base point, and hence the eye, is substantially stabilized. Movement of the light source is timed to coincide the latency period with the resting period of the patient's heartbeat sequence, and the relaxation period of the patient's respiration cycle. During the latency period, photoablation is accomplished by directing a train of laser pulses from a laser source into the corneal tissue.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Vacuum debris removal system
InactiveUS7795559B2Quick removalEfficient removalWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusControl flowPhotoablation
Owner:ANVIK CORP
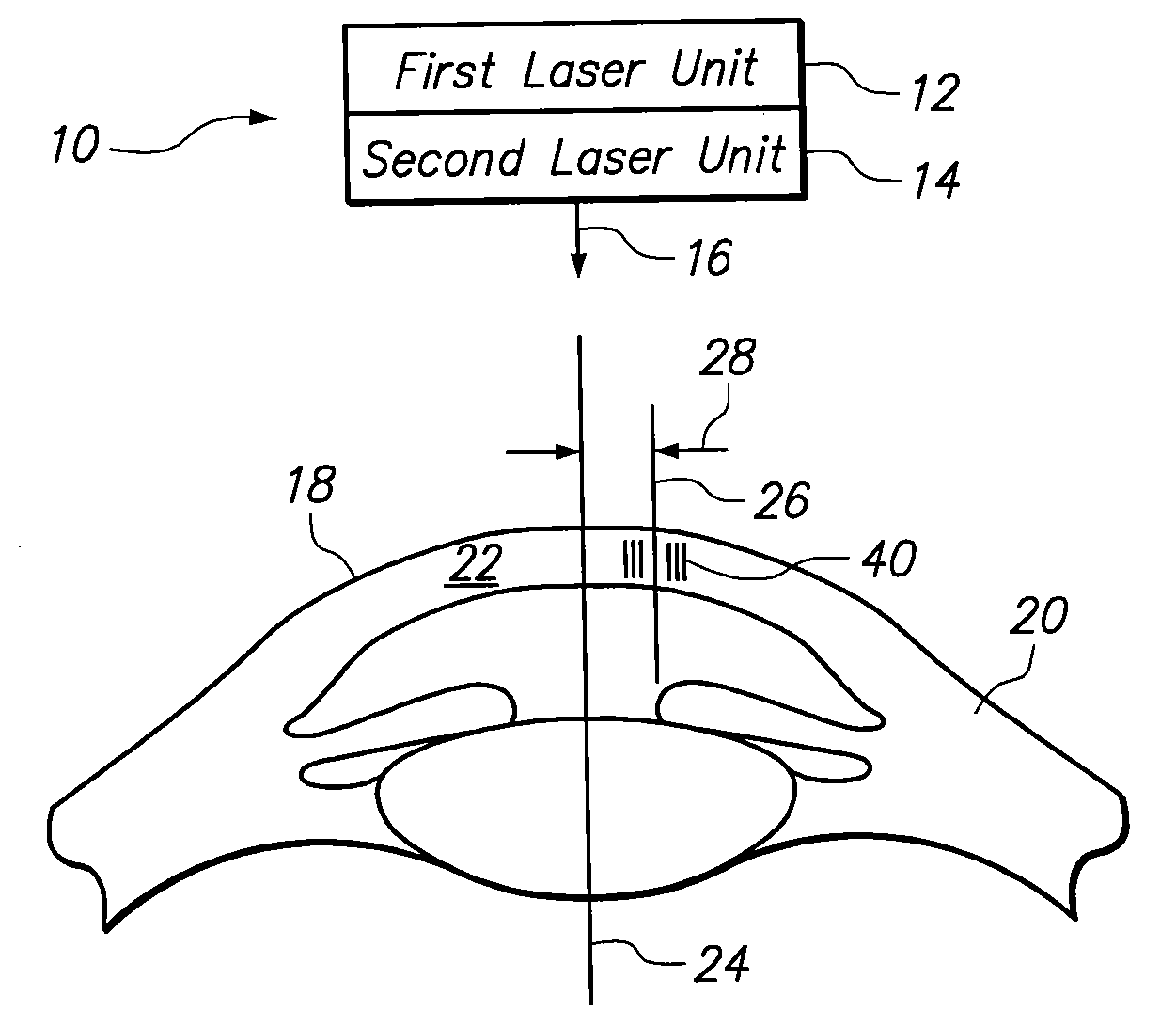
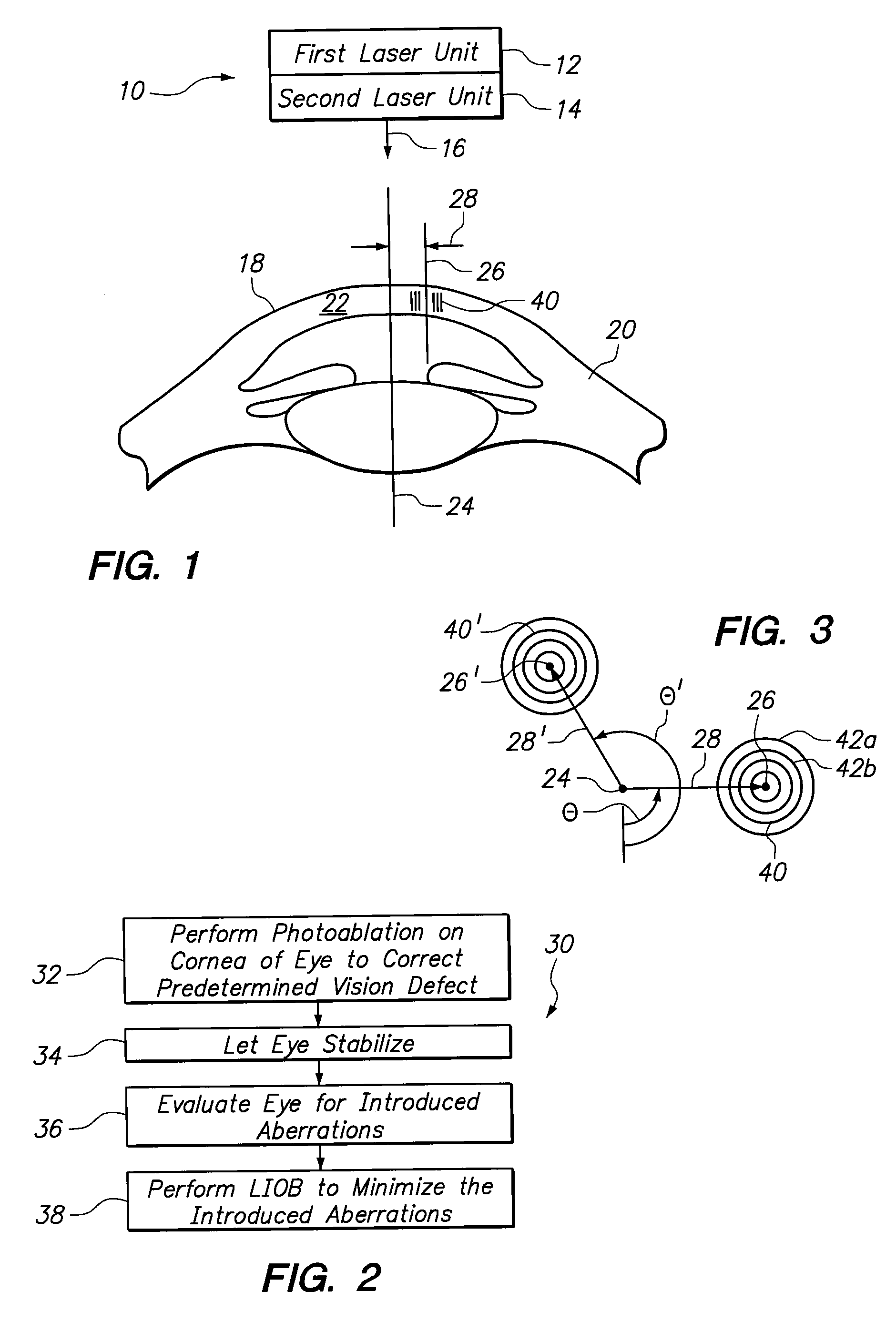
System and Methods for Minimizing Higher Order Aberrations Introduced During Refractive Surgery
InactiveUS20100217247A1Minimized optical aberrationMinimize aberrationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPhotoablationRefractive surgery
A system and method are provided for minimizing the adverse effects of any optical aberrations, and particularly higher order aberrations, that may be introduced into an eye during the correction of a visual defect by photoablation (i.e. removal) of corneal tissue. In accordance with the present invention, after a predetermined time interval following the photoablation of tissue (e.g. about two weeks), the eye is evaluated for aberrations. Laser Induced Optical Breakdown (LIOB) is then performed on intrastromal tissue, as needed, to correct for the introduced aberrations.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Material assisted laser ablation
ActiveUS8546067B2Low costGood chemical stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsPhotoablationMicroelectromechanical systems
This invention provides photoablation—based processing techniques and materials strategies for making, assembling and integrating patterns of materials for the fabrication of electronic, optical and opto-electronic devices. Processing techniques of the present invention enable high resolution and / or large area patterning and integration of porous and / or nano- or micro-structured materials comprising active or passive components of a range of electronic devices, including integrated circuits (IC), microelectronic and macroelectronic systems, microfluidic devices, biomedical devices, sensing devices and device arrays, and nano- and microelectromechanical systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method and a system for laser photoablation within a lens
InactiveUS8435233B2Reduce coronal diameter of lensEnhancement/improvement of abilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPhotoablationLens plate
A method for ablating a presbyopic lens for restoring accommodation in human eye and a system thereof wherein a laser beam is directed obliquely to carry out multiple photoablations in circular way within the lens behind the iris and preferably near the edge or equator of the lens and / or in the vicinity of zonules to re-establish accommodation of the lens lost due to presbyopia.
Owner:SINGH AJOY I
Eye position control monitor for laser vision correction
ActiveUS20050113813A1Precise alignmentAccurately determineLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPhotoablationFixation point
A system for spatially stabilizing a base point on the optical axis of a patient's eye, for photoablation of the cornea, includes an optical element for identifying the base point. The system also includes an illumination source which is a fixation point for the eye. Movement of the illumination source induces a saccadic movement of the eye wherein the optical axis of the eye moves from a first orientation to a second orientation. Following the saccadic movement of the eye there is a latency period during which the base point, and hence the eye, is substantially stabilized. Movement of the light source is timed to coincide the latency period with the resting period of the patient's heartbeat sequence, and the relaxation period of the patient's respiration cycle. During the latency period, photoablation is accomplished by directing a train of laser pulses from a laser source into the corneal tissue.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com