Patents
Literature
123 results about "Pulsed laser radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for laser machining transparent materials
ActiveUS8350183B2Short wavelengthLonger laser pulse durationLaser surgeryWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLight beamLasing wavelength
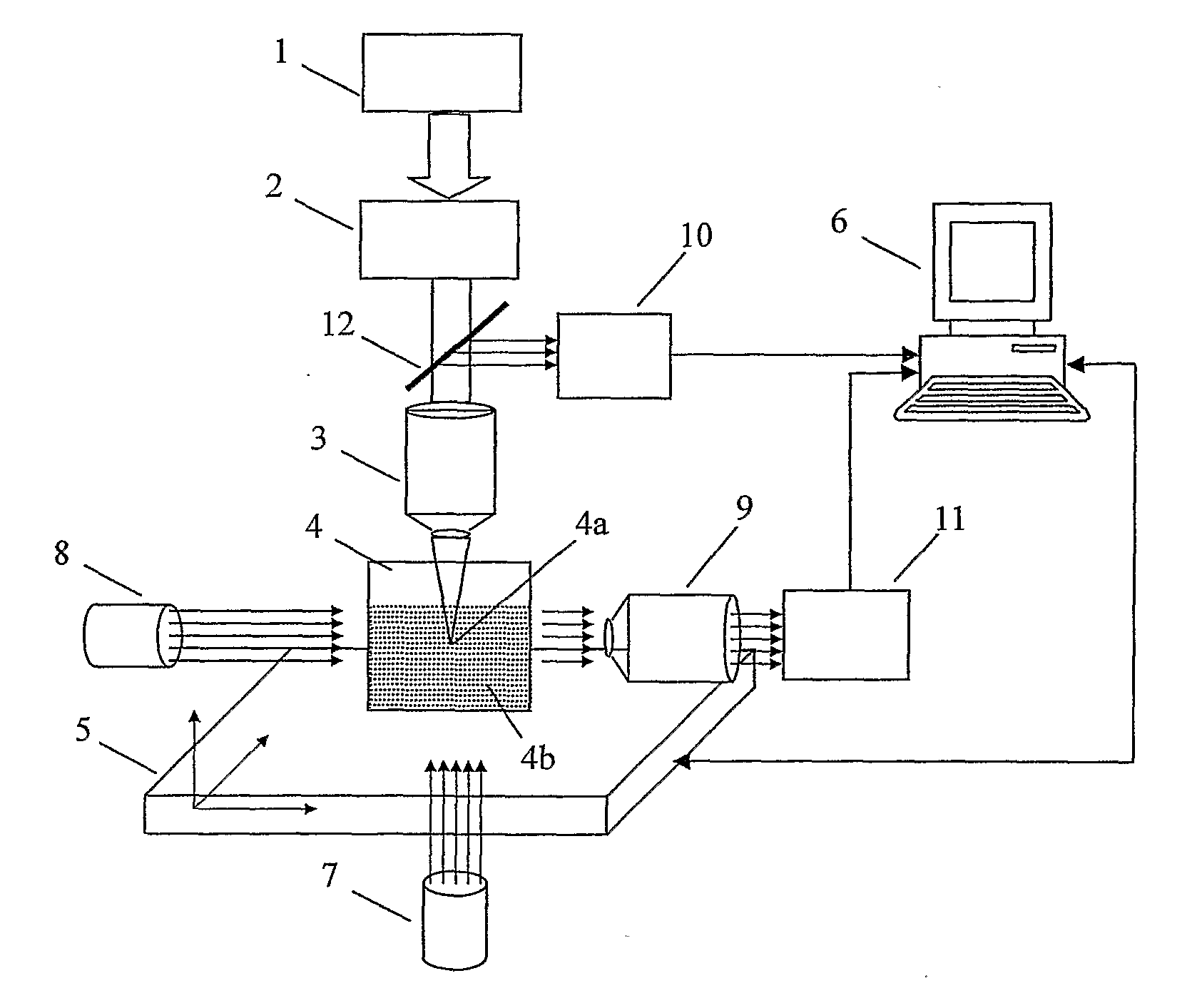
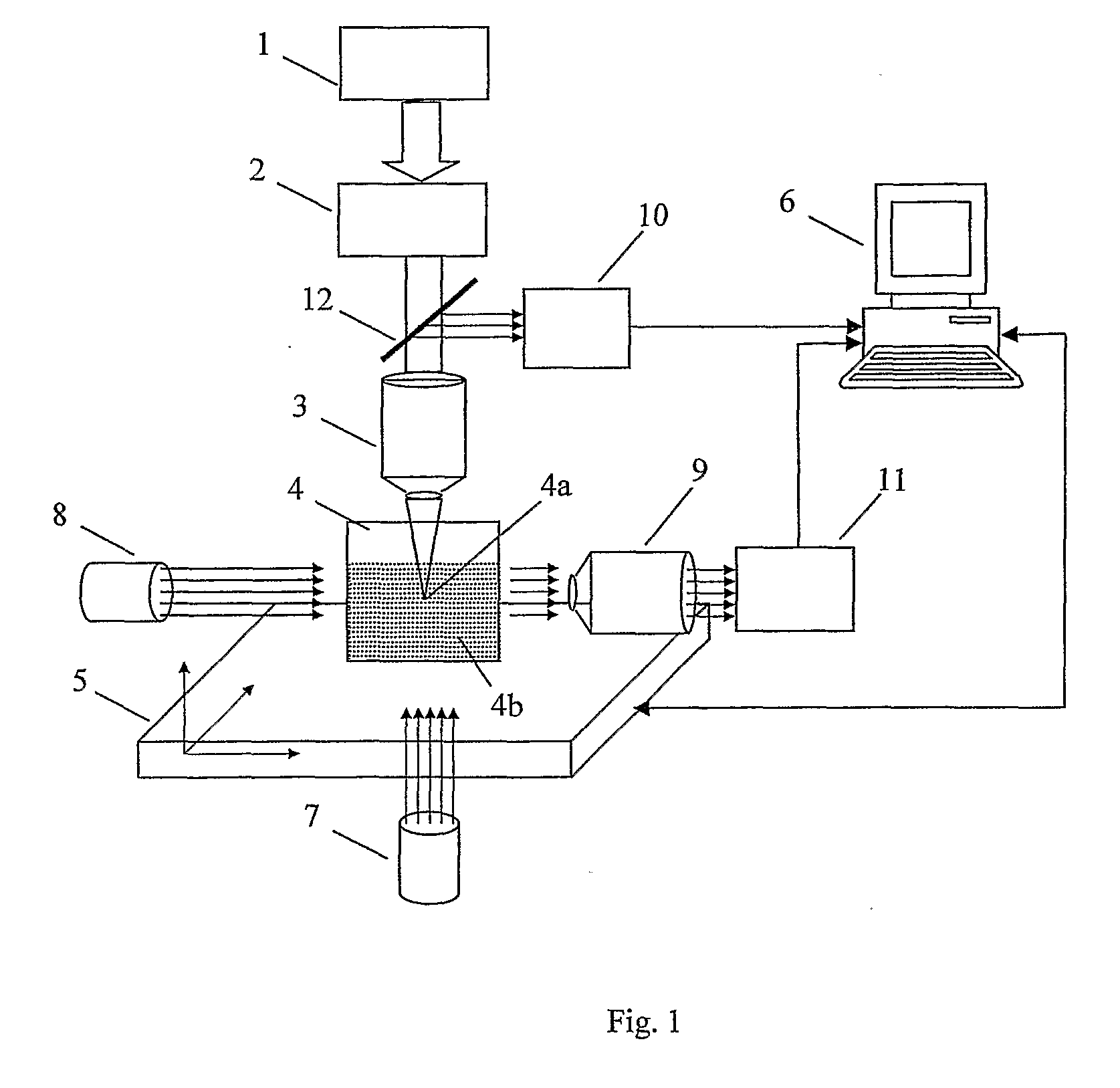
A method for machining a transparent material by the non-linear absorption of pulsed laser radiation, in the region of a laser focus, includes the following steps: a laser wavelength of between 300 and 1000 μm is selected; and laser impulses having a temporally flat beam profile are applied. The method is characterized in that the irradiation intensity is selected from an interval pre-determined for the material to be machined, in which plasma is formed without plasma luminescence. An apparatus for laser treating a transparent material includes structure to set an irradiance and inspect the treatment as being within a defined interval.
Owner:GERRSHEIMER REGENSBURG GMBH
Laser-assisted placement of veiled composite material
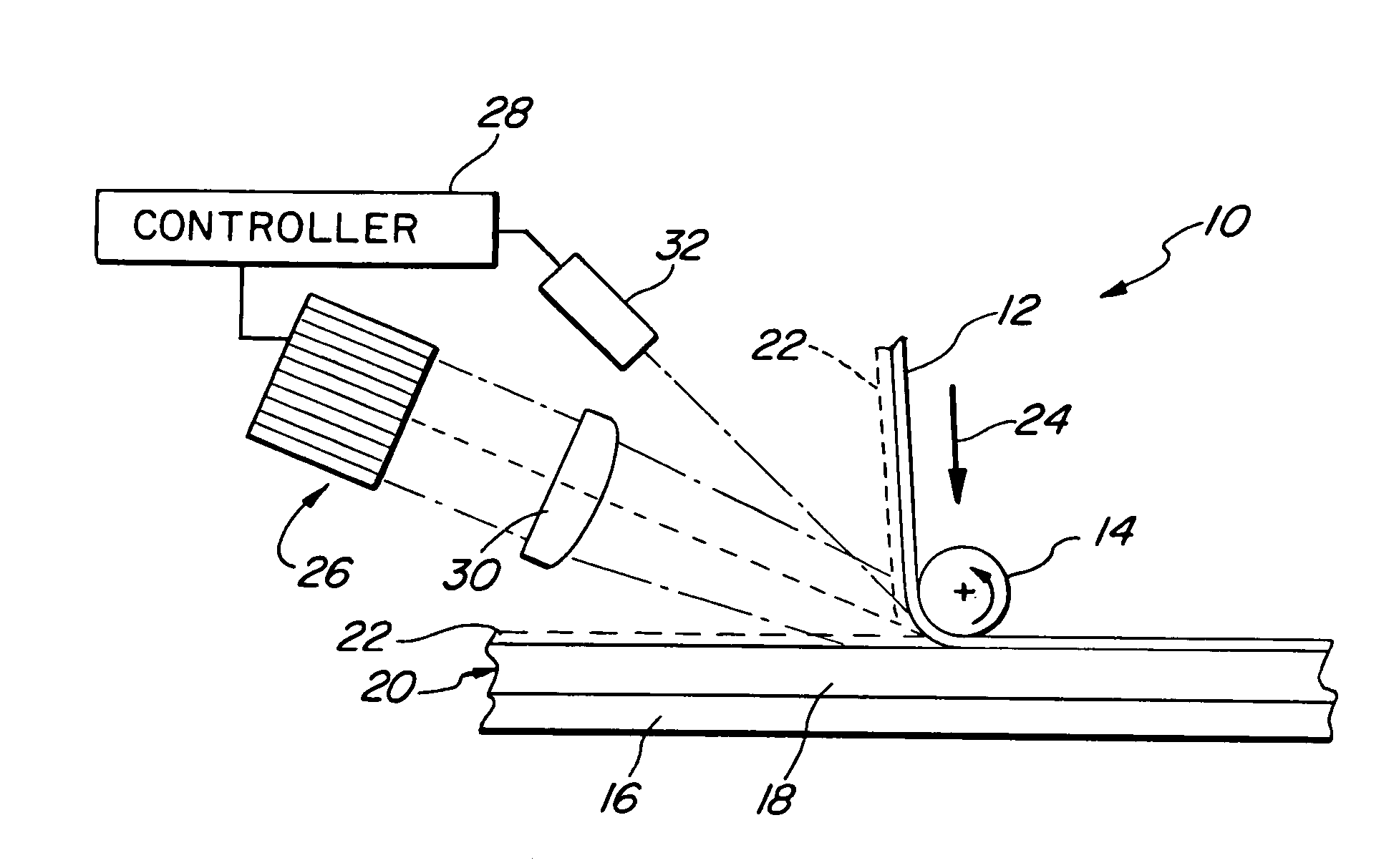
InactiveUS20060048881A1Easy to controlLamination ancillary operationsLaminationThermoplasticOptoelectronics
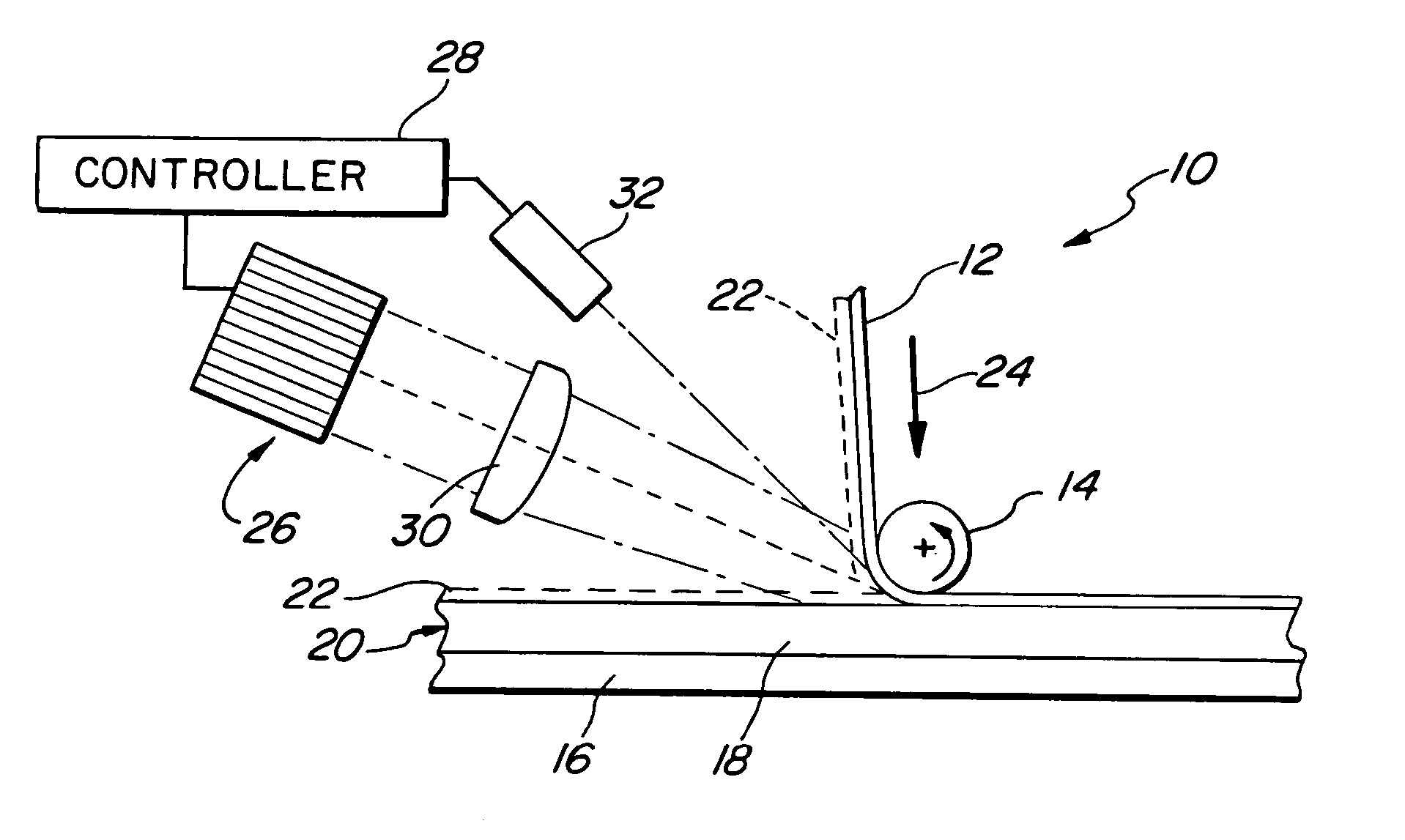
A method of forming preform structures from fiber composite materials in an automated tape placement process, for subsequent resin infusion and heating. Pulsed laser radiation is directed into a nip region of a compaction roller during formation of a composite preform structure to selectively heat discrete areas on a resin veil of thermoplastic to an incoming fiber tape material and a surface of a substrate, to more precisely control tacking of the resin veil of thermoplastic to the fiber tape and the surface of a substrate in predetermined locations.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Delivery system and method of use for the eye
InactiveUS8540659B2Minimal thermal effectLower eye pressureLaser surgeryEye implantsFiberPhotoablation
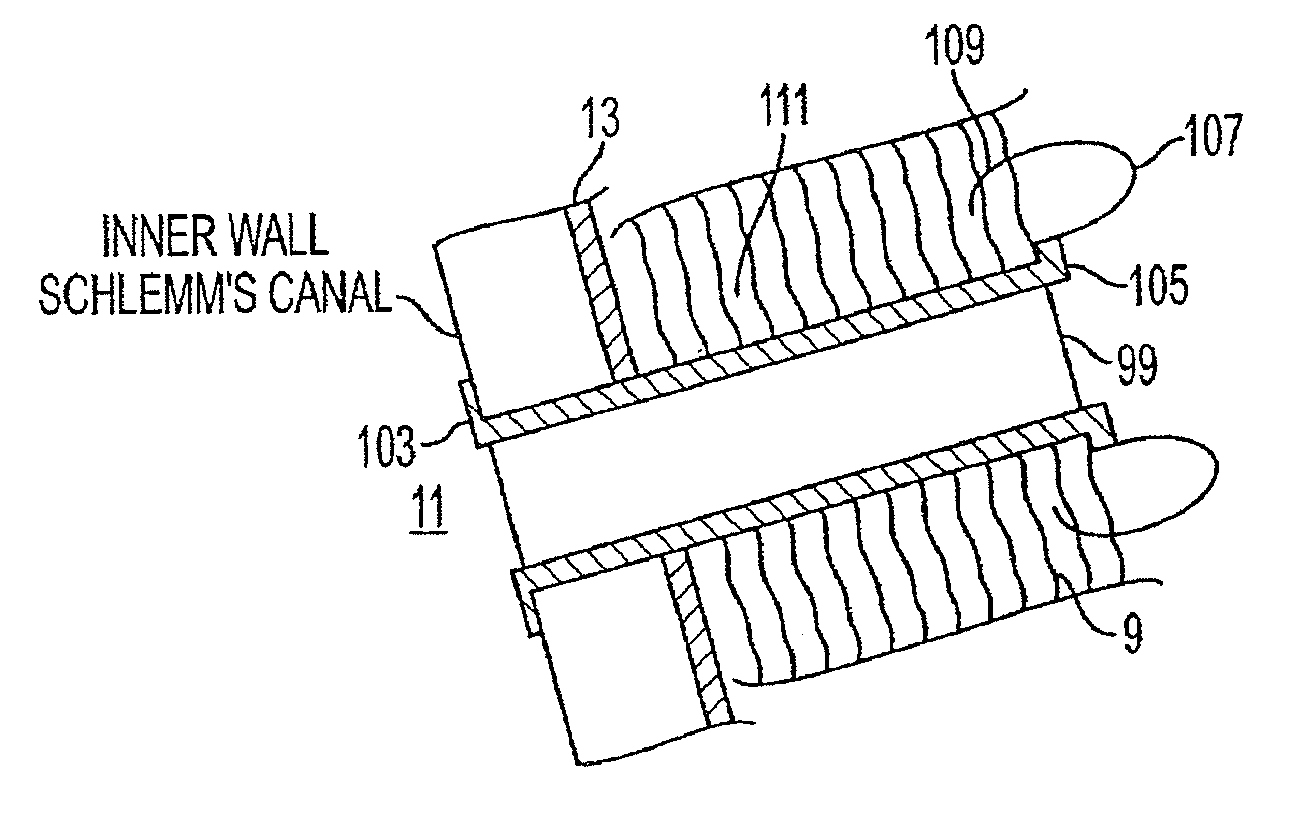
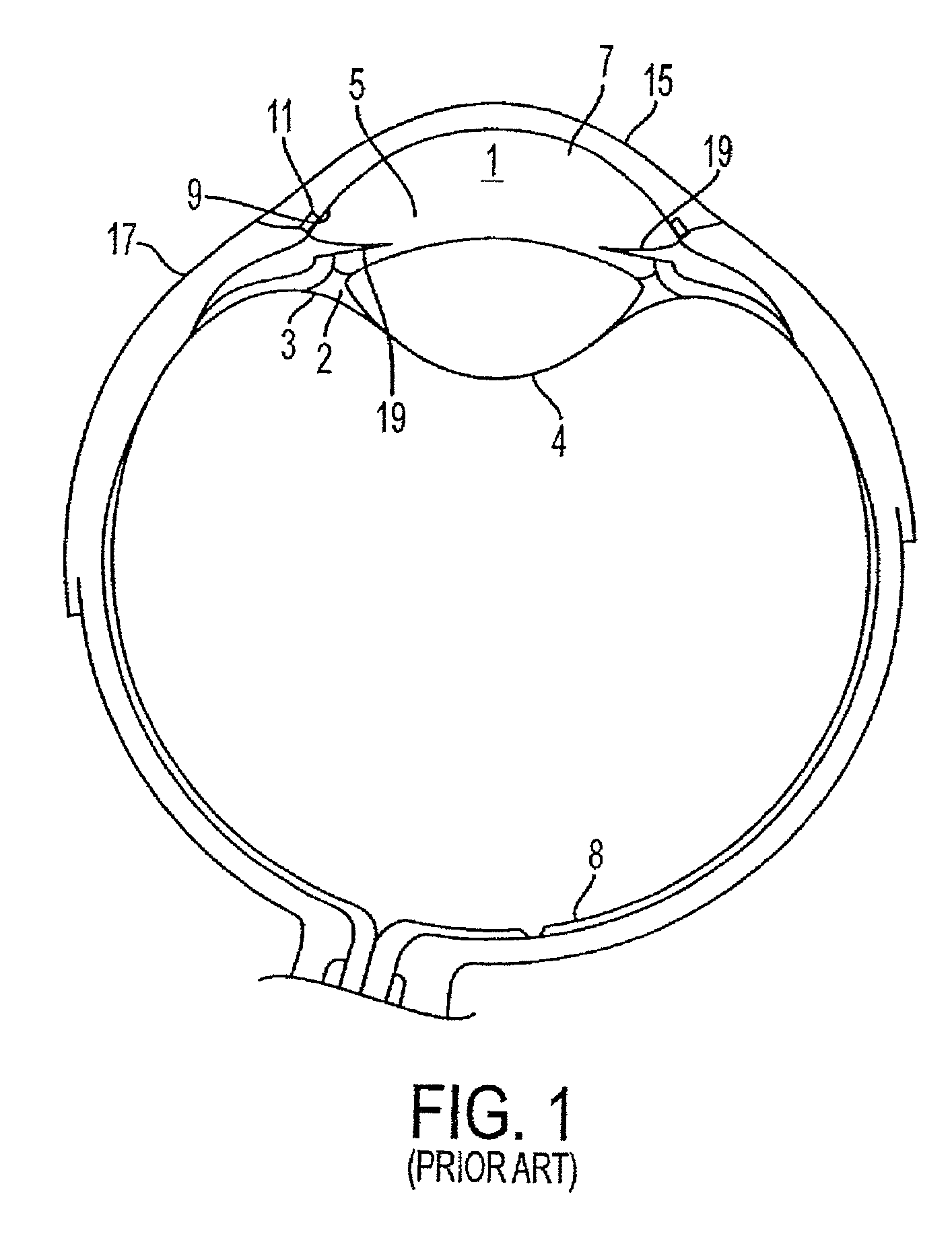
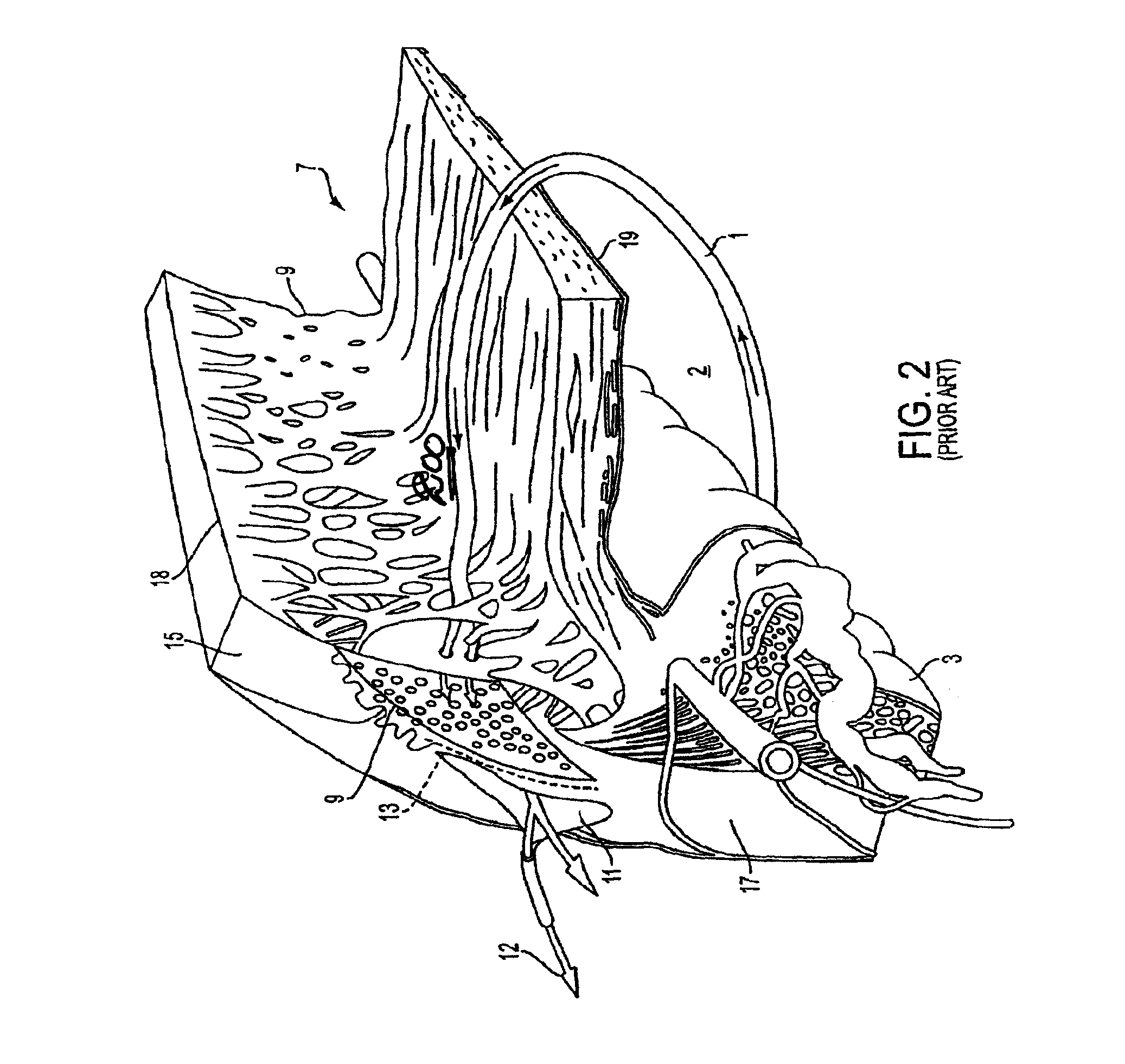
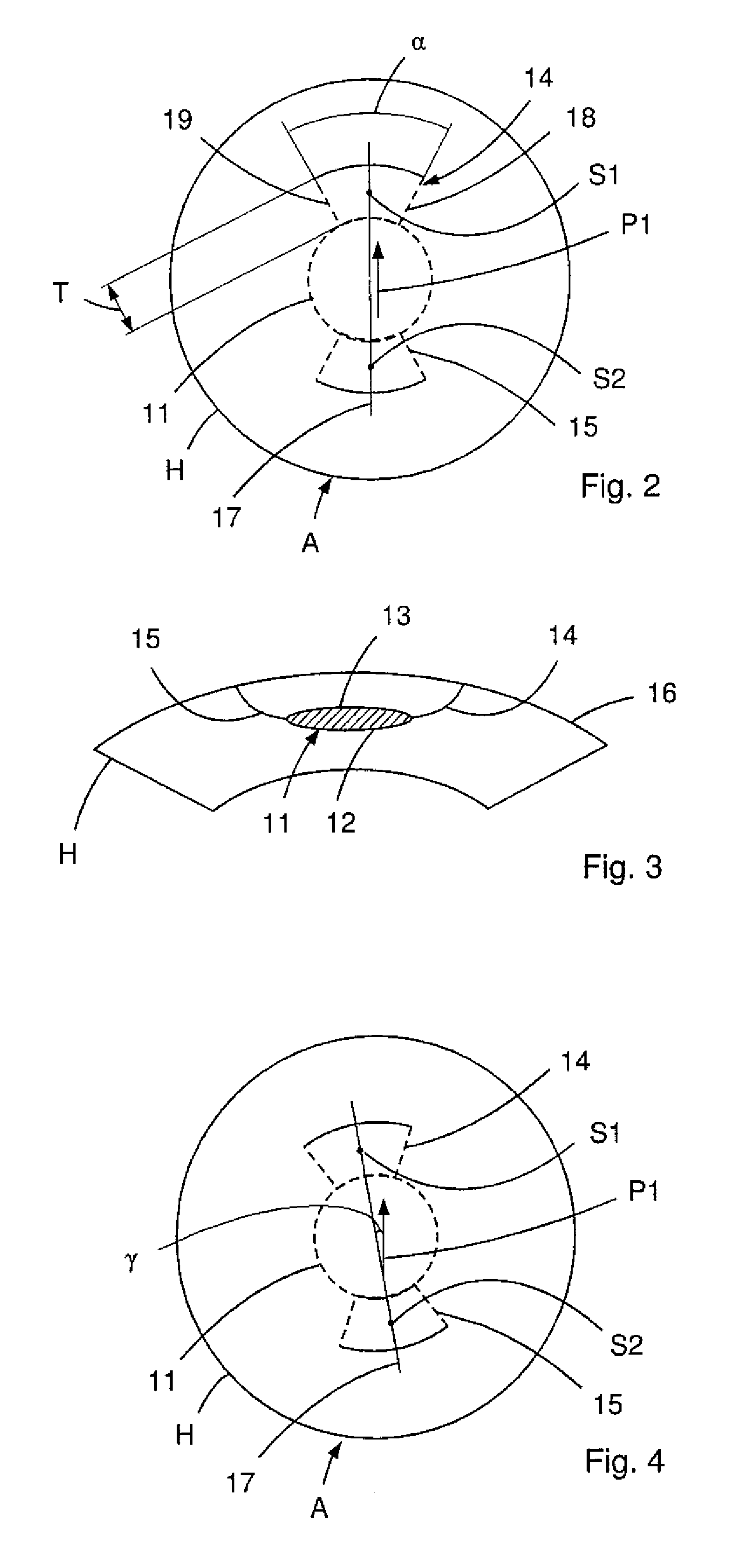
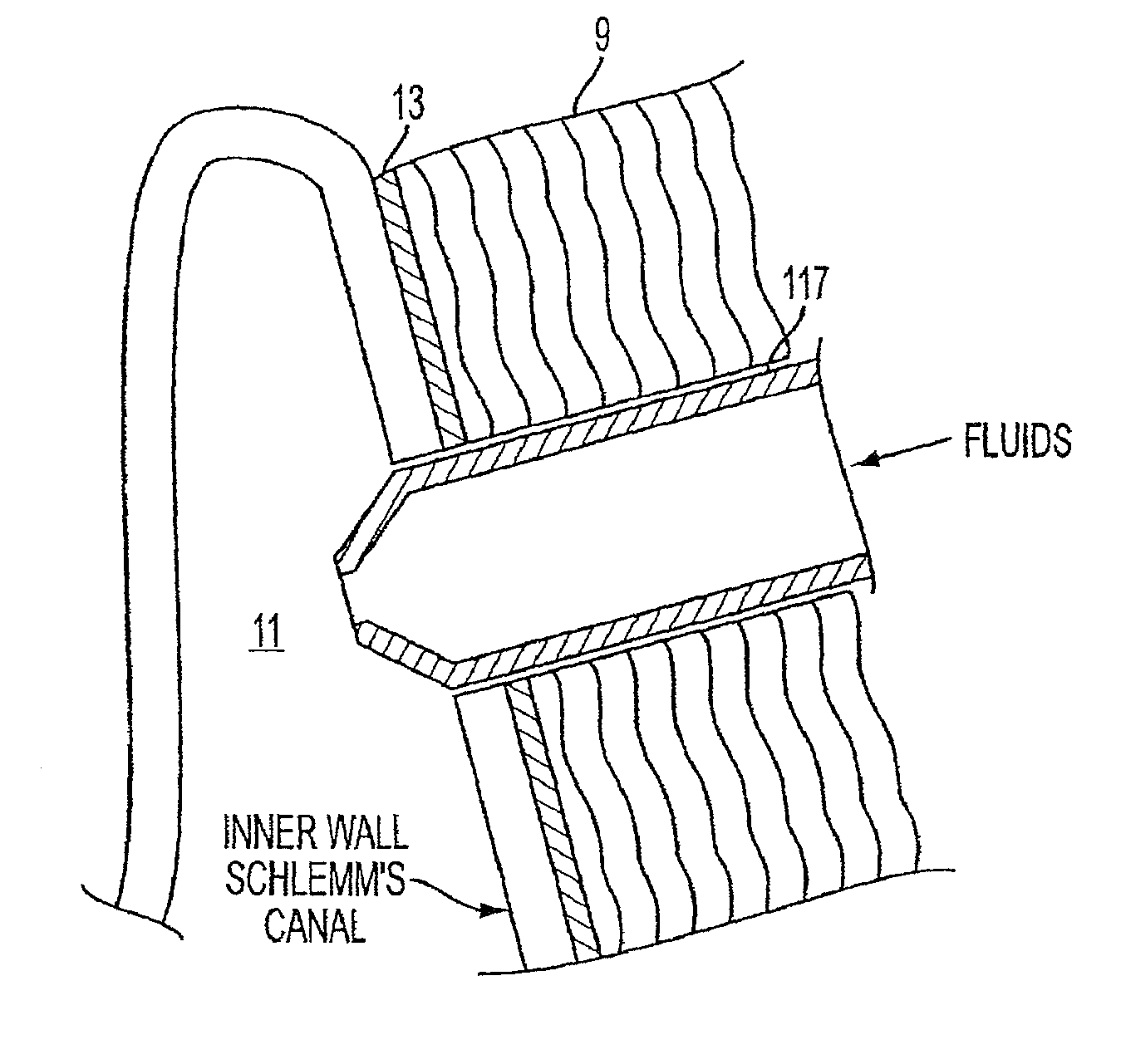
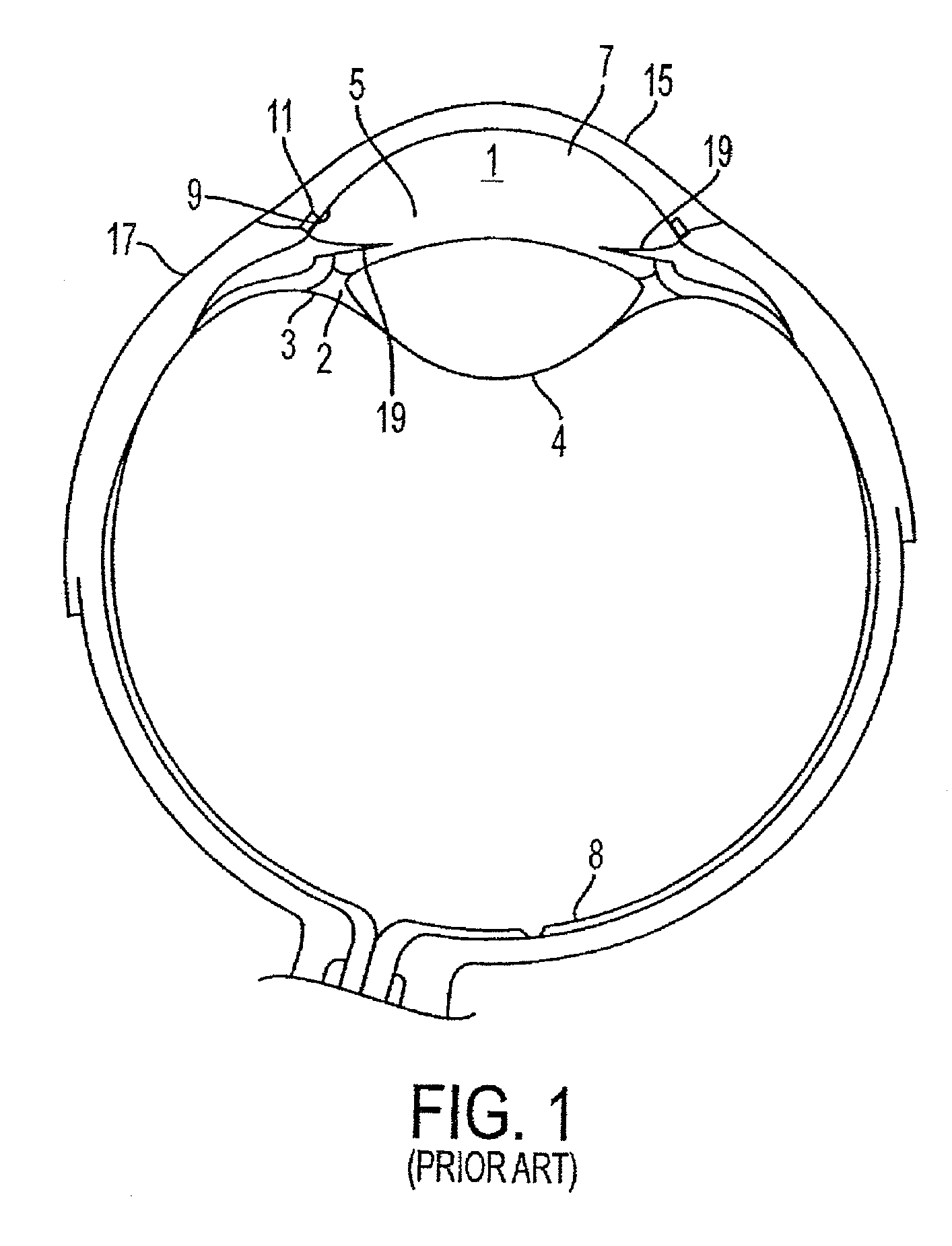
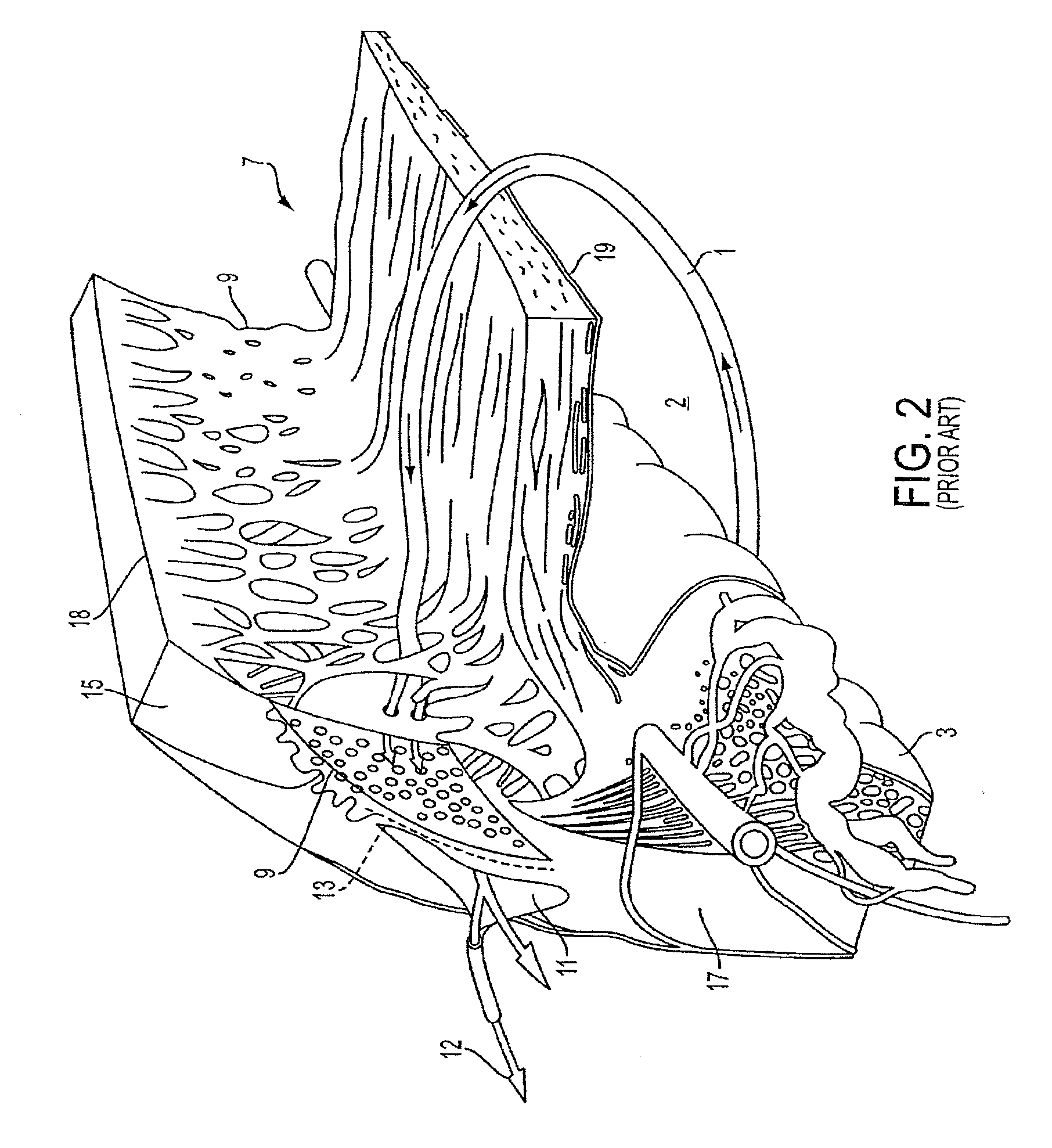
A method and delivery system are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Pulsed laser radiation is delivered from the distal end of a fiber-optic probe sufficient to cause photoablation of selected portions of the trabecular meshwork, the juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and an inner wall of Schlemm's canal in the target site. The fiber-optic probe may be advanced so as to create an aperture in the inner wall of Schlemm's canal in which fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye flows. The method and delivery system may further be used on any tissue types in the body.
Owner:IVANTIS INC
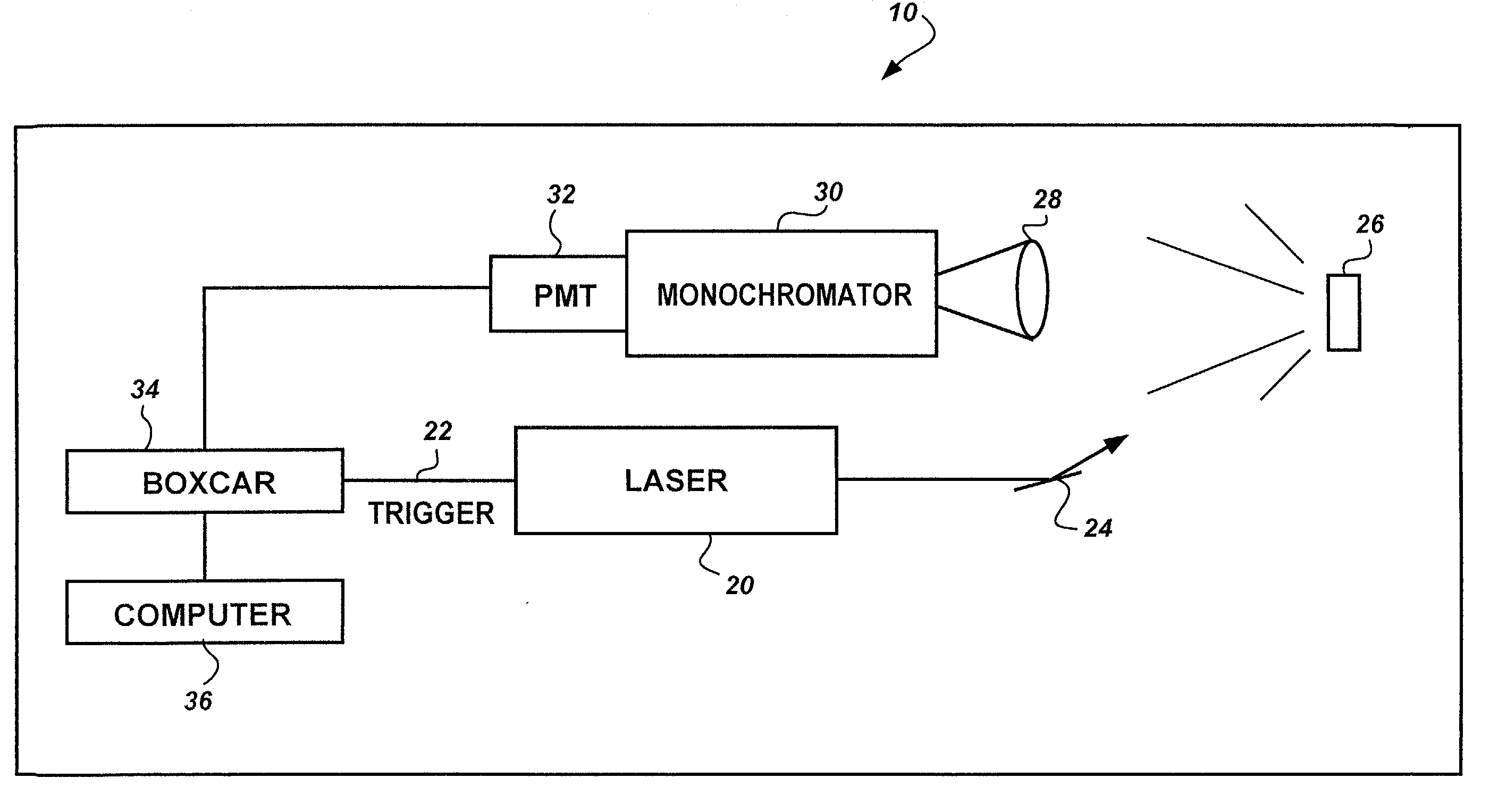
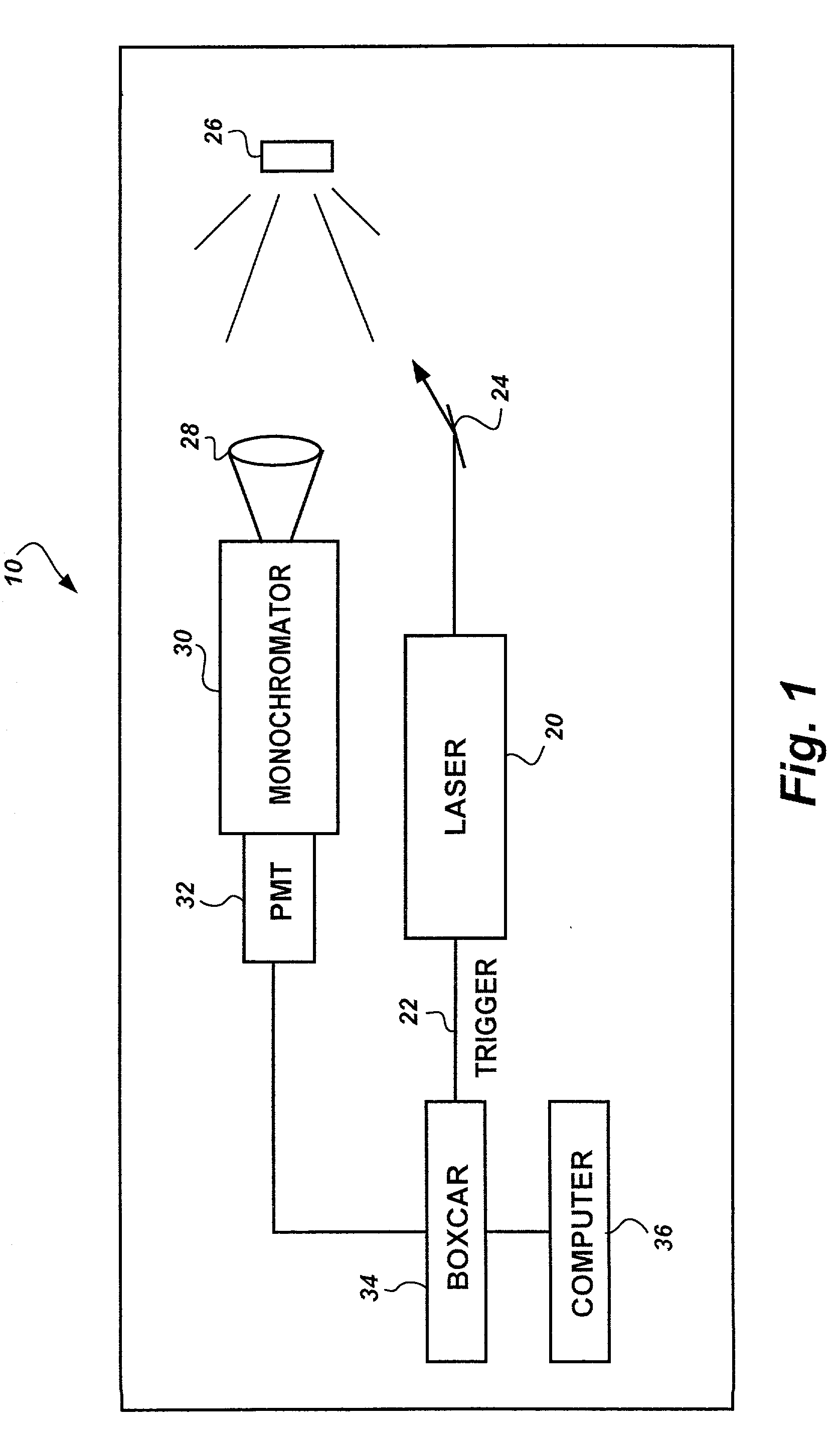
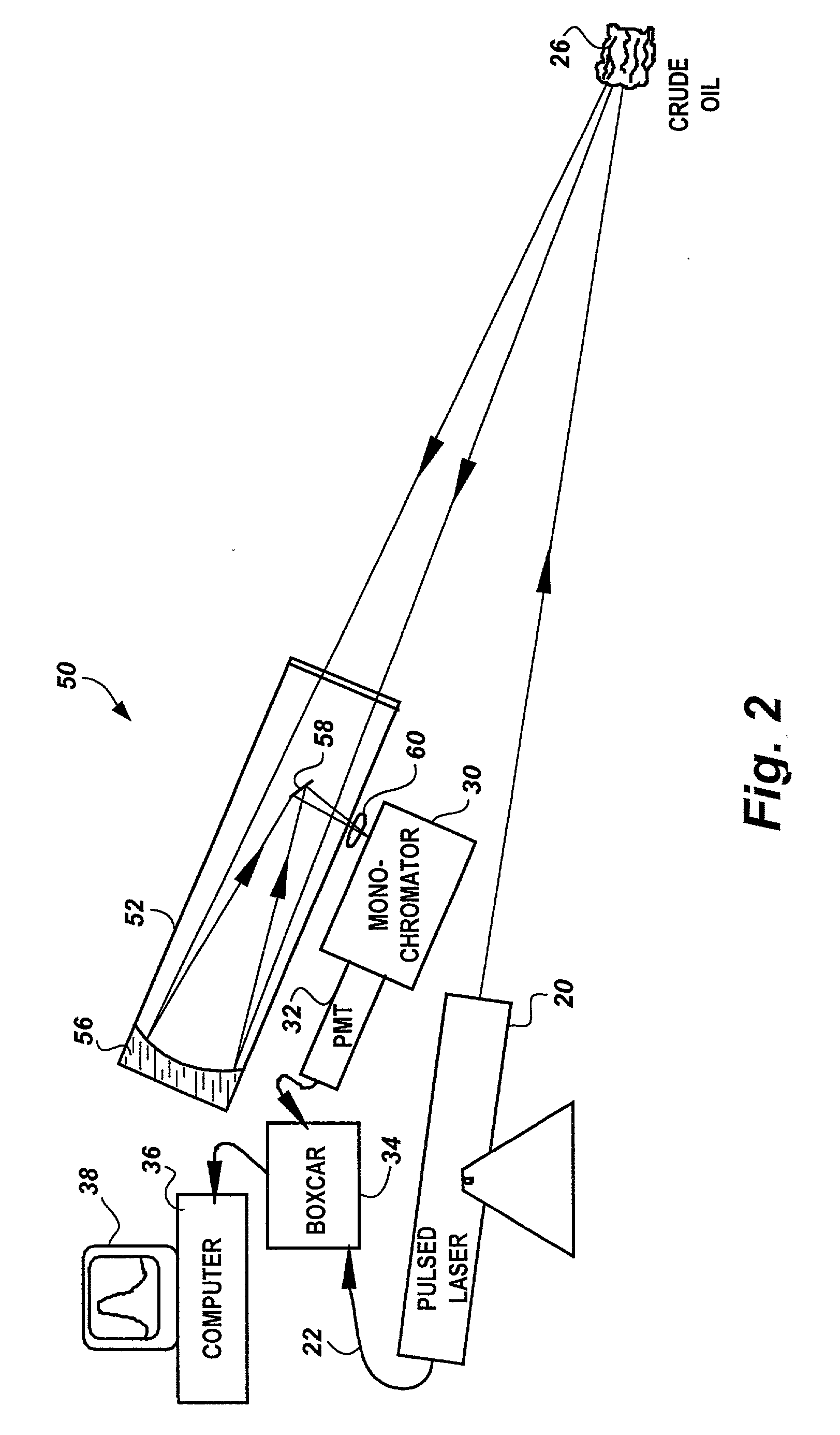
Method for characterization of petroleum oils using normalized time-resolved fluorescence spectra
A method based on time-resolved, laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy for the characterization and fingerprinting of petroleum oils and other complex mixtures. The method depends on exciting the wavelength-resolved fluorescence spectra of samples using ultraviolet pulsed laser radiation, measuring them at specific time gates within the temporal response of the excitation laser pulse, and comparing them in terms of their shapes alone without taking into account their relative intensities. The method provides fingerprints of crude oils without resorting to any kind of approximation, for distinguishing between closely similar crude oils of the same grade, and is useful in remote and non-remote setups, along with applications in fingerprinting blended and non-blended crude oils using different ultraviolet excitation wavelengths. Applications include estimating °API gravity of crude oils and monitoring degradation of mineral oils.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
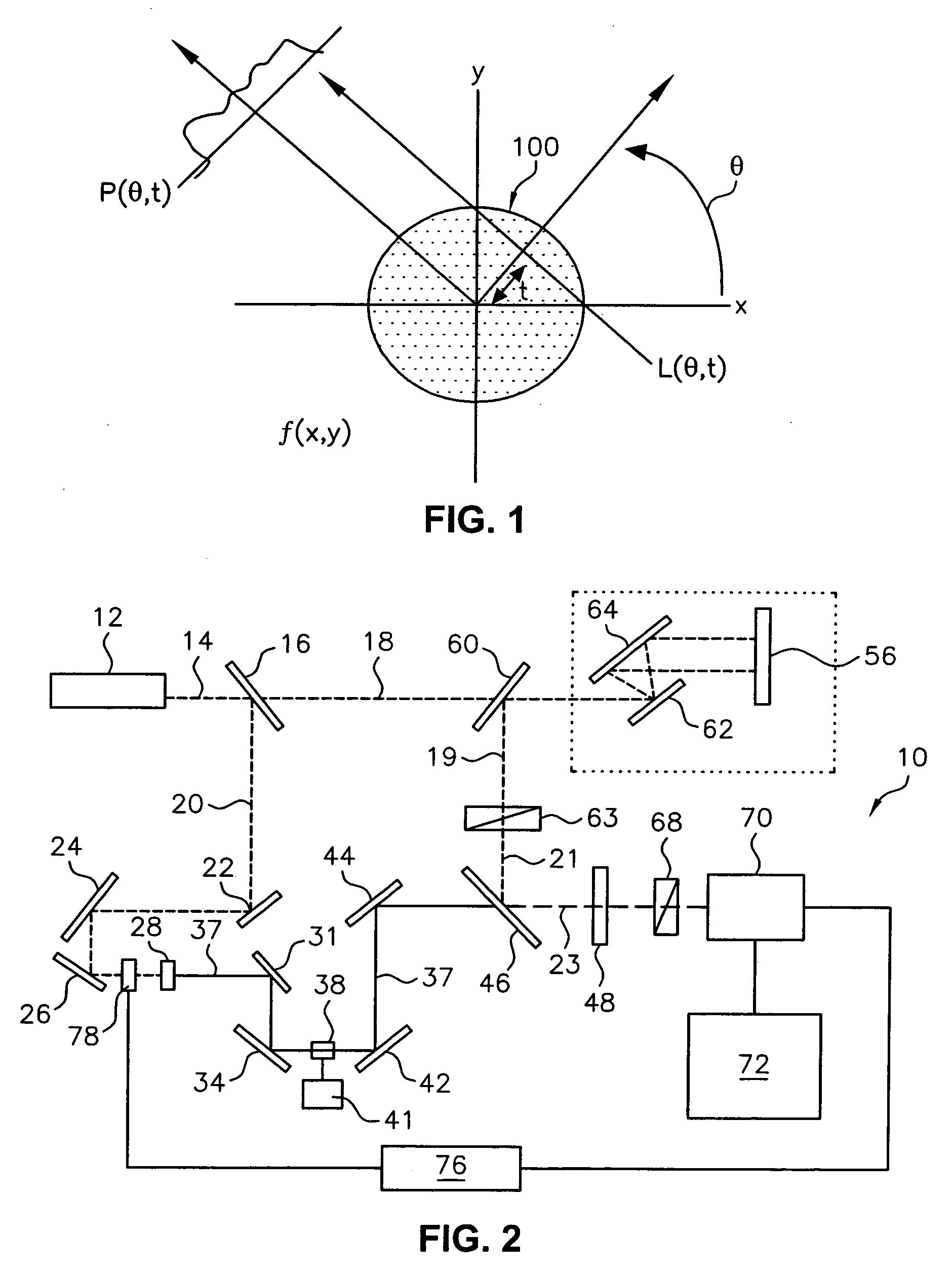
Transmission mode terahertz computed tomography
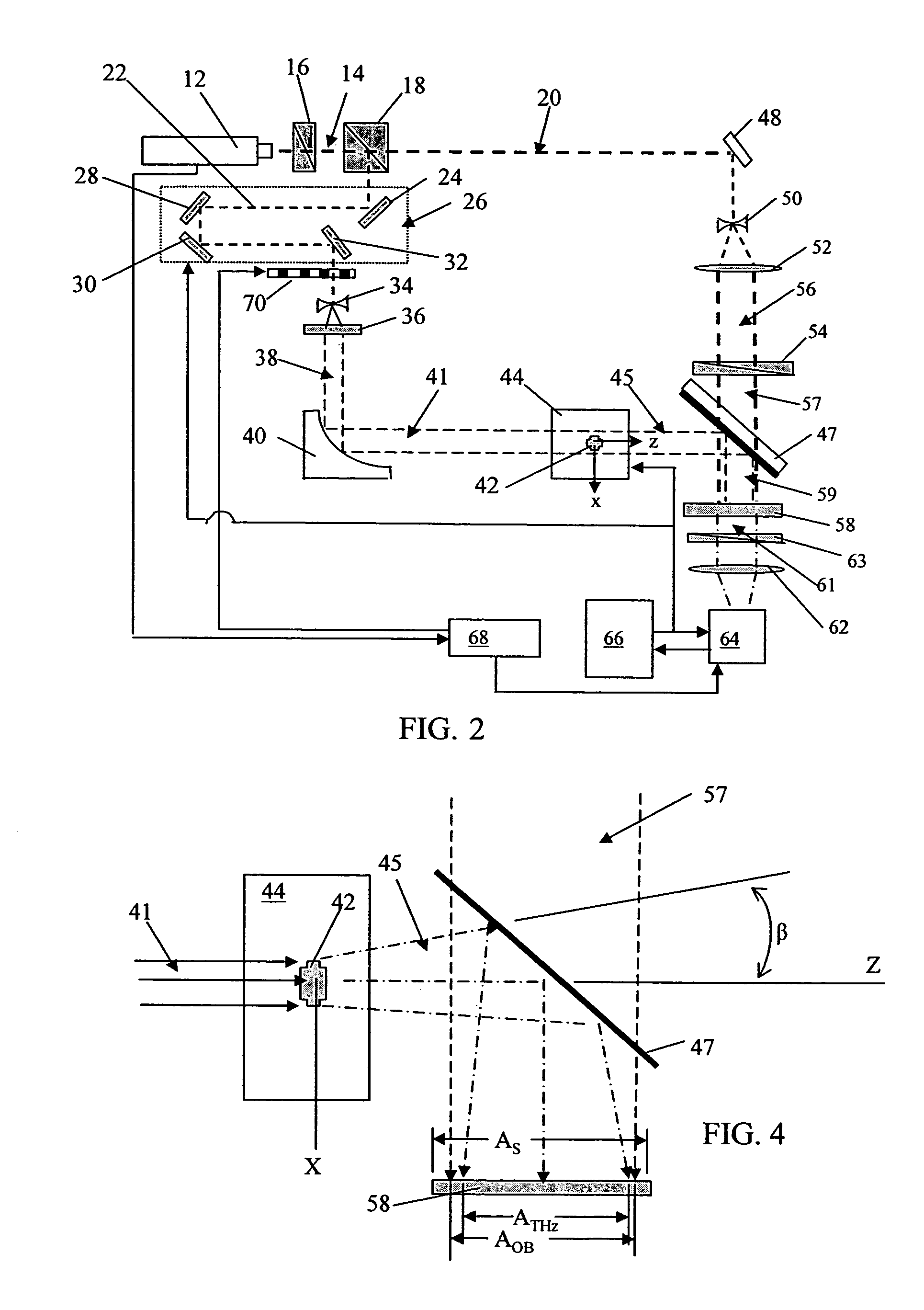
A method of obtaining a series of images of a three-dimensional object by transmitting pulsed terahertz (THz) radiation through the entire object from a plurality of angles, optically detecting changes in the transmitted THz radiation using pulsed laser radiation, and constructing a plurality of imaged slices of the three-dimensional object using the detected changes in the transmitted THz radiation. The THz radiation is transmitted through the object as a scanning spot. The object is placed within the Rayleigh range of the focused THz beam and a focusing system is used to transfer the imaging plane from adjacent the object to a desired distance away from the object. A related system is also disclosed.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
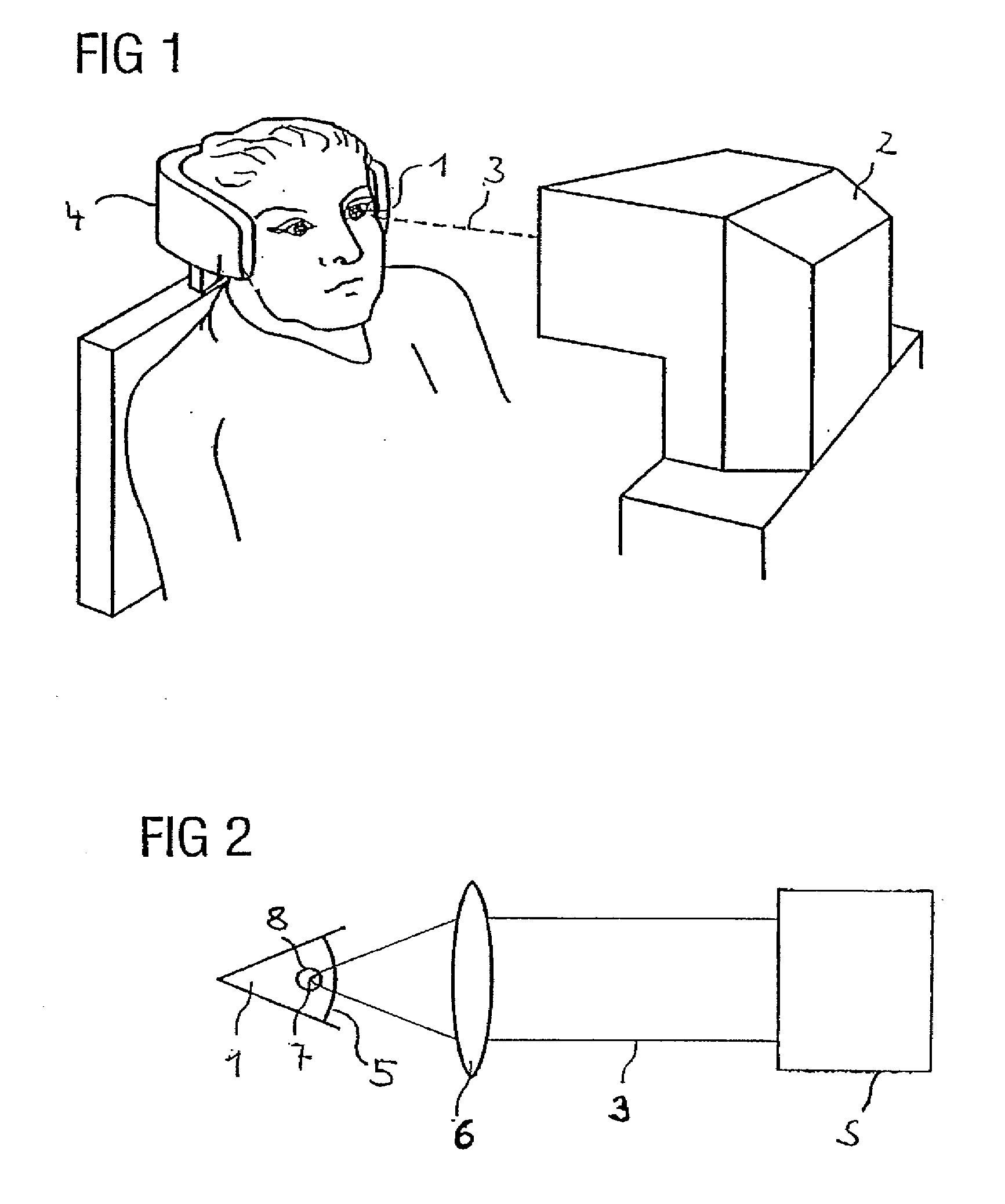
Apparatus and method for generating cut surfaces in the cornea of an eye for correction of ametropia
ActiveUS20080275433A1Cut surface smoothOpening cuts can be preventedLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal surfaceRefractive error
An apparatus for generating cut surfaces in the cornea of an eye in order to correct ametropia is provided, said apparatus comprising a laser unit, which can focus pulsed laser radiation into the cornea and move it therein in order to generate cut surfaces, and a control unit, which controls the laser unit for generating cut surfaces such that a predetermined lenticle to be removed is separated from the surrounding corneal material in the cornea by at least one cut surface, and that at least two mutually spaced apart cut surfaces are formed as opening cuts, each extending from the lenticle to the anterior corneal surface, the position and shape of the opening cuts being selected such that the opening cuts contribute to the correction of the ametropia of the eye or do not counteract the correction of the ametropia of the eye.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Delivery system and method of use for the eye
InactiveUS20080108934A1Reduce elevated intraocular pressureMinimal thermal effectLaser surgeryEye implantsPhotoablationFiber
A method and delivery system are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Pulsed laser radiation is delivered from the distal end of a fiber-optic probe sufficient to cause photoablation of selected portions of the trabecular meshwork, the juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and an inner wall of Schlemm's canal in the target site. The fiber-optic probe may be advanced so as to create an aperture in the inner wall of Schlemm's canal in which fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye flows. The method and delivery system may further be used on any tissue types in the body.
Owner:IVANTIS INC
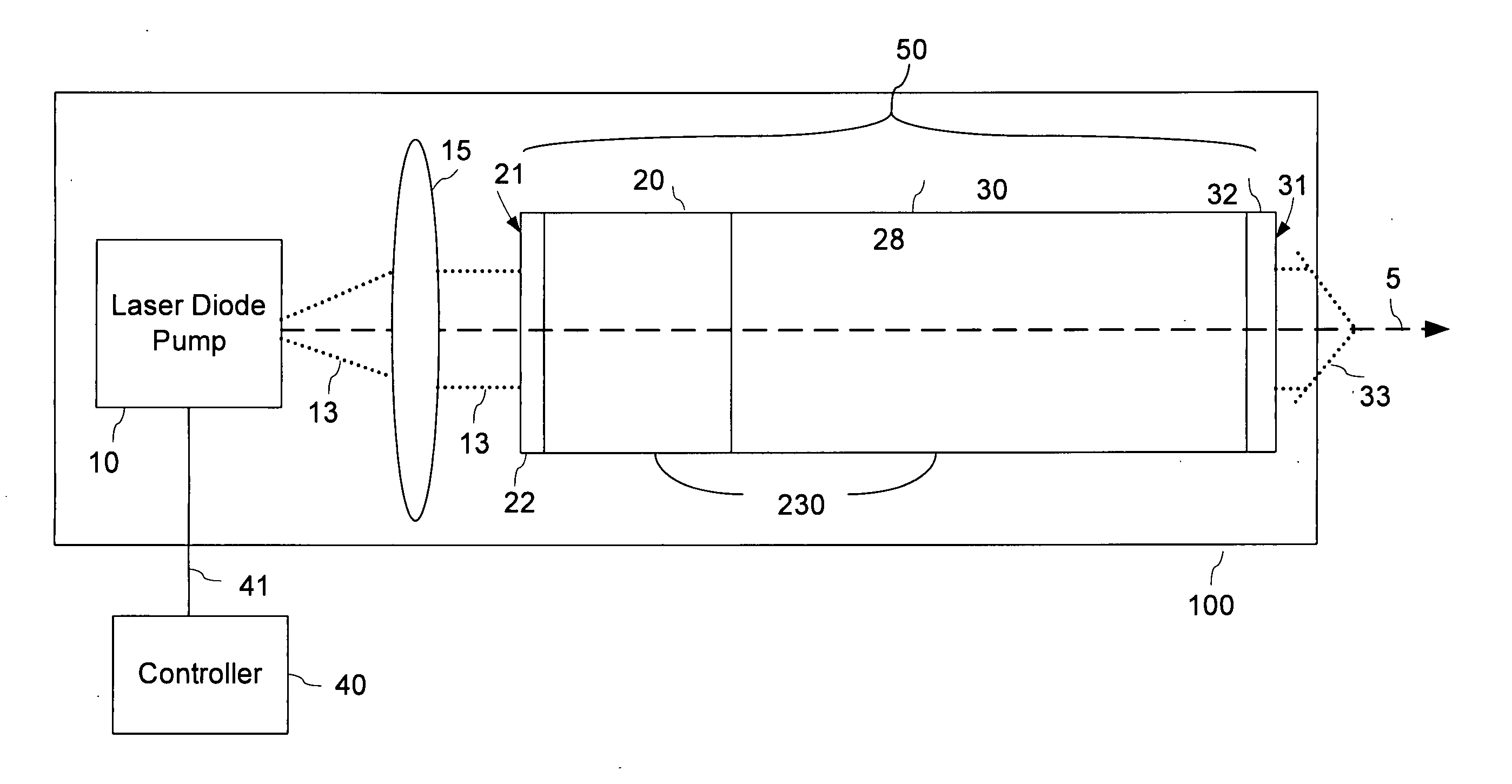
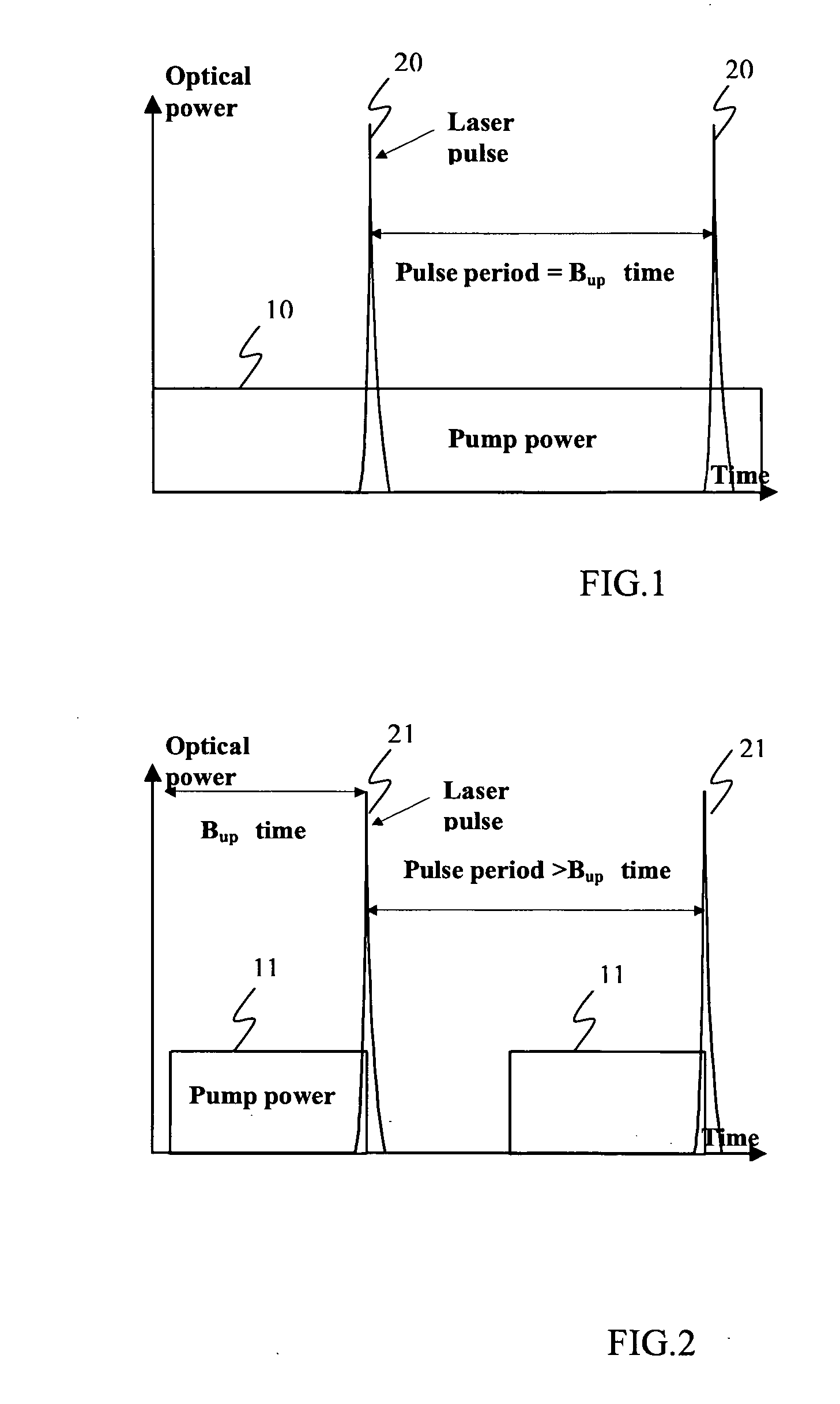
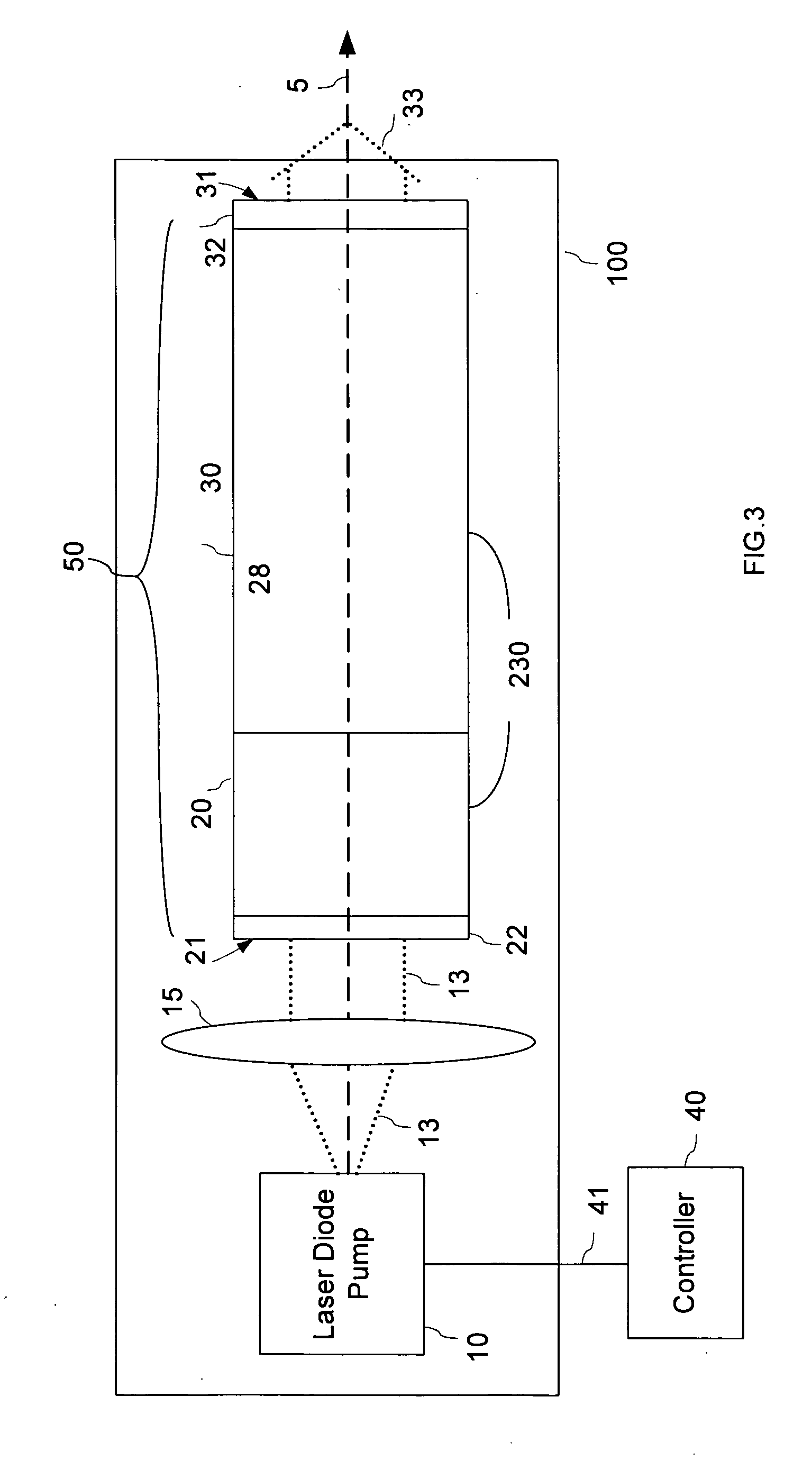
Passively Q-switched laser with adjustable pulse repetition rate
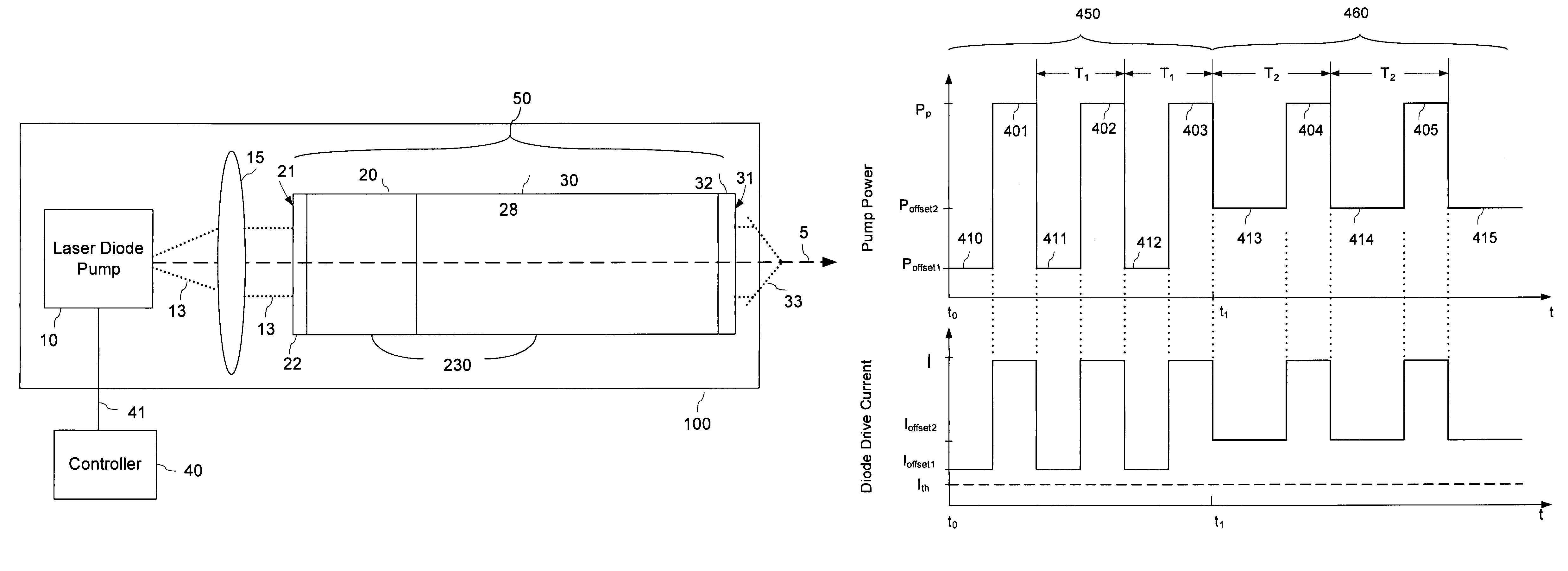
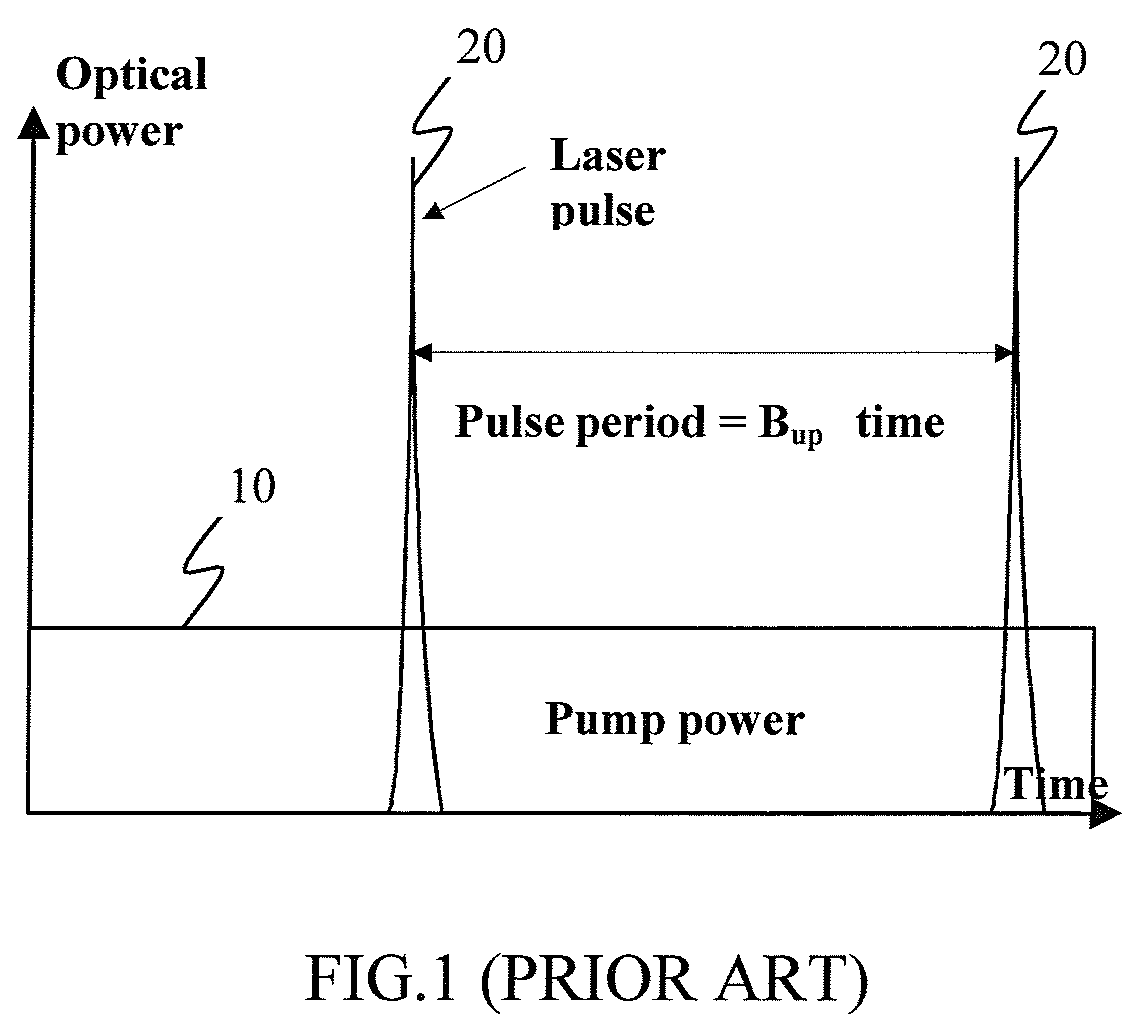
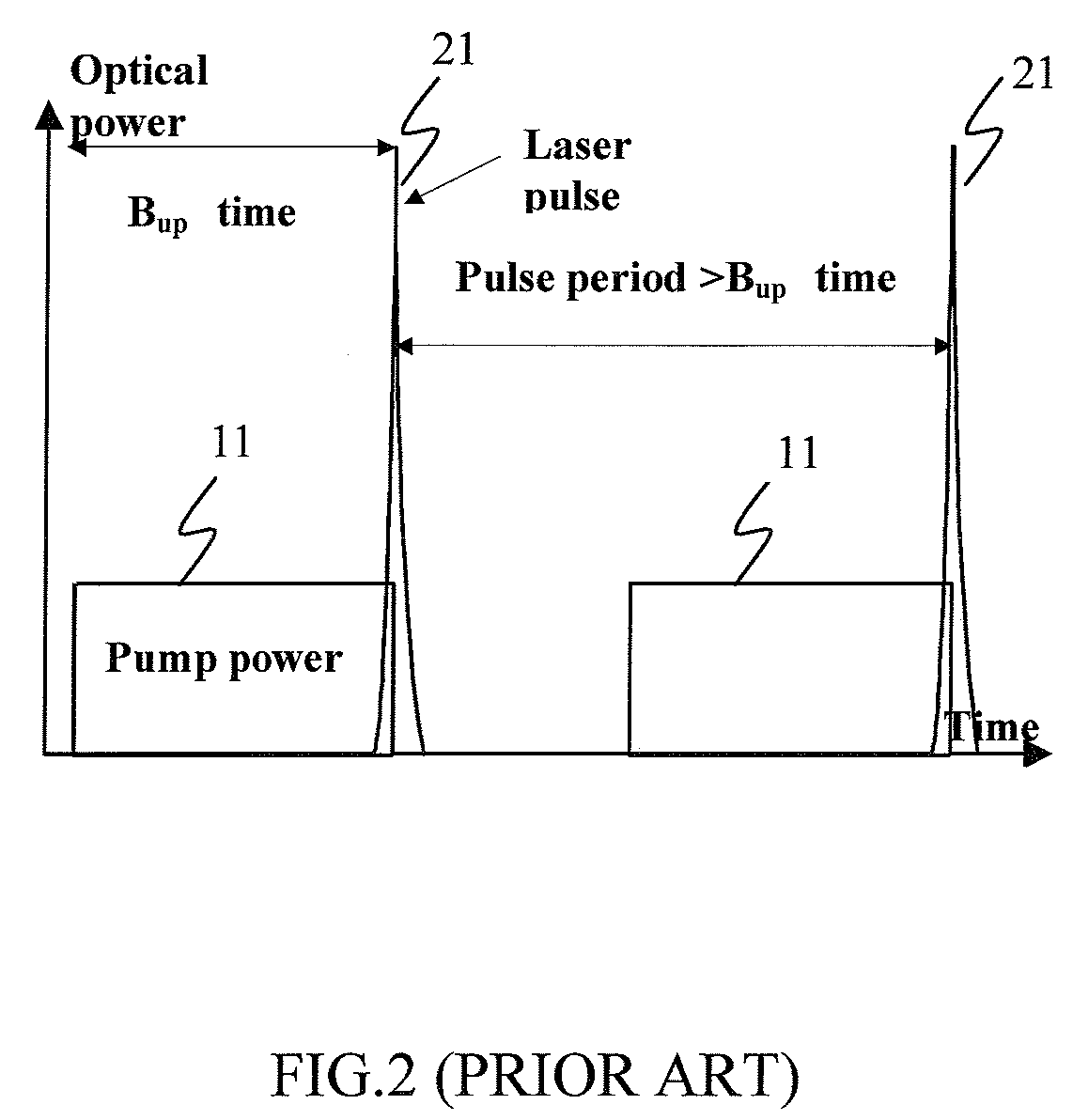
A method is disclosed for varying a pulse repetition rate of a passively q-switched laser while maintaining other characteristics of the laser radiation. The laser is optically pumped with a sequence of pump pulses which includes alterations between non-zero power levels and is characterized by two adjustable parameters. By simultaneously changing the adjustable parameters, the pulse repetition rate of the laser can be changed while maintaining the laser pulse energy, divergence of the pulsed laser radiation, and optical spectrum of the pulsed laser radiation at constant levels. In one embodiment, the sequence of pump pulses includes pump power offset which magnitude and / or duration is adjusted when the laser repetition rate is changed.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Methods and devices for laser desorption chemical ionization
InactiveUS6838663B2Growing populationSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansDesorptionGas phase
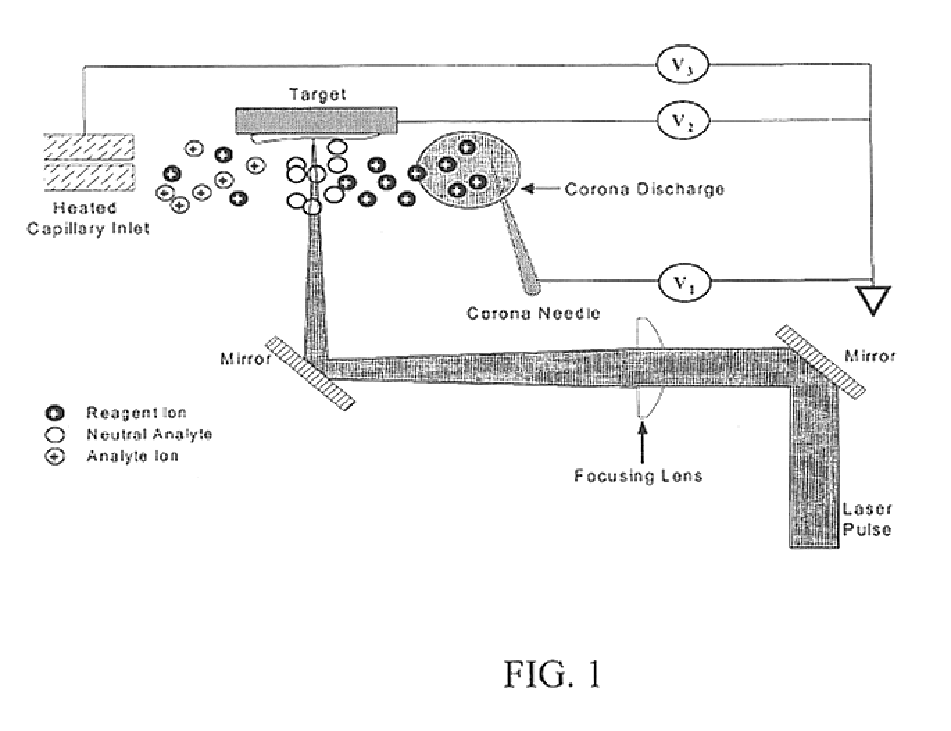
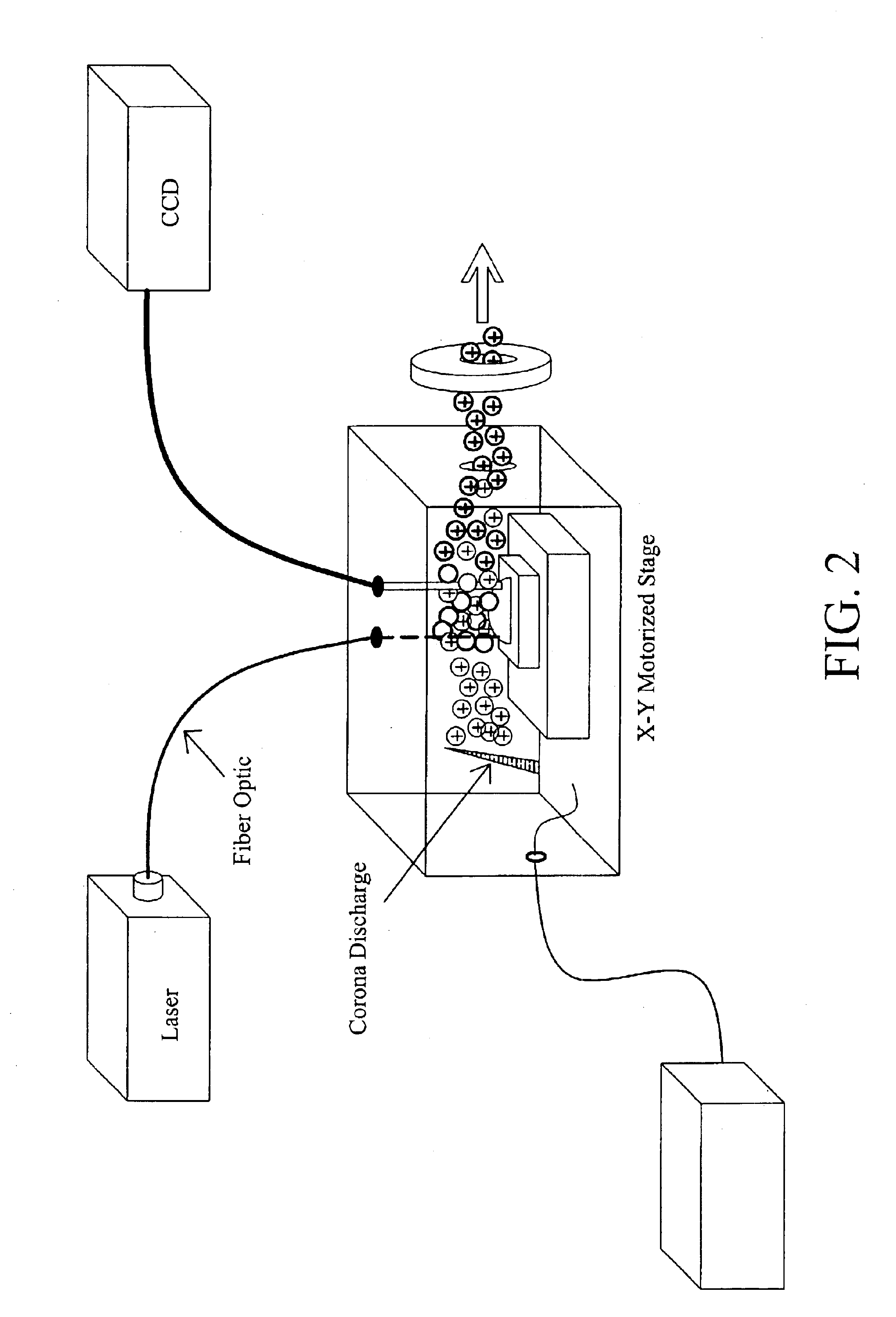
The subject invention pertains to a methods and devices for ionizing a sample material. The subject invention also relates to an ionization source and to a method of sampling gas-phase ions from a sample. An ionization source in accordance with the subject invention can be used in conjunction with mass spectrometry or other sampling techniques. The subject invention can utilize a means for desorbing gas-phase ions and neutral molecules from a sample and a means to generate reagent ions where the reagent ions ionize the desorbed neutral molecules so as to increase the population of gas-phase ions. The subject invention can incorporate laser radiation for desorbing gas-phase ions and neutral molecules from a sample. In a specific embodiment, the subject invention provides an ionization source that uses a pulsed laser for desorption, so as to produce a population of desorbed neutral molecules from a sample, as well as a number of gas-phase sample ions. In a further specific embodiment, the pulsed laser radiation can be adjusted such that neutral molecules are desorbed without the production of gas-phase sample ions by the laser radiation.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA
Method and apparatus for delivery of pulsed laser radiation
InactiveUS20070224768A1Improve throughputSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning processes and apparatusSurface reactionTotal dose
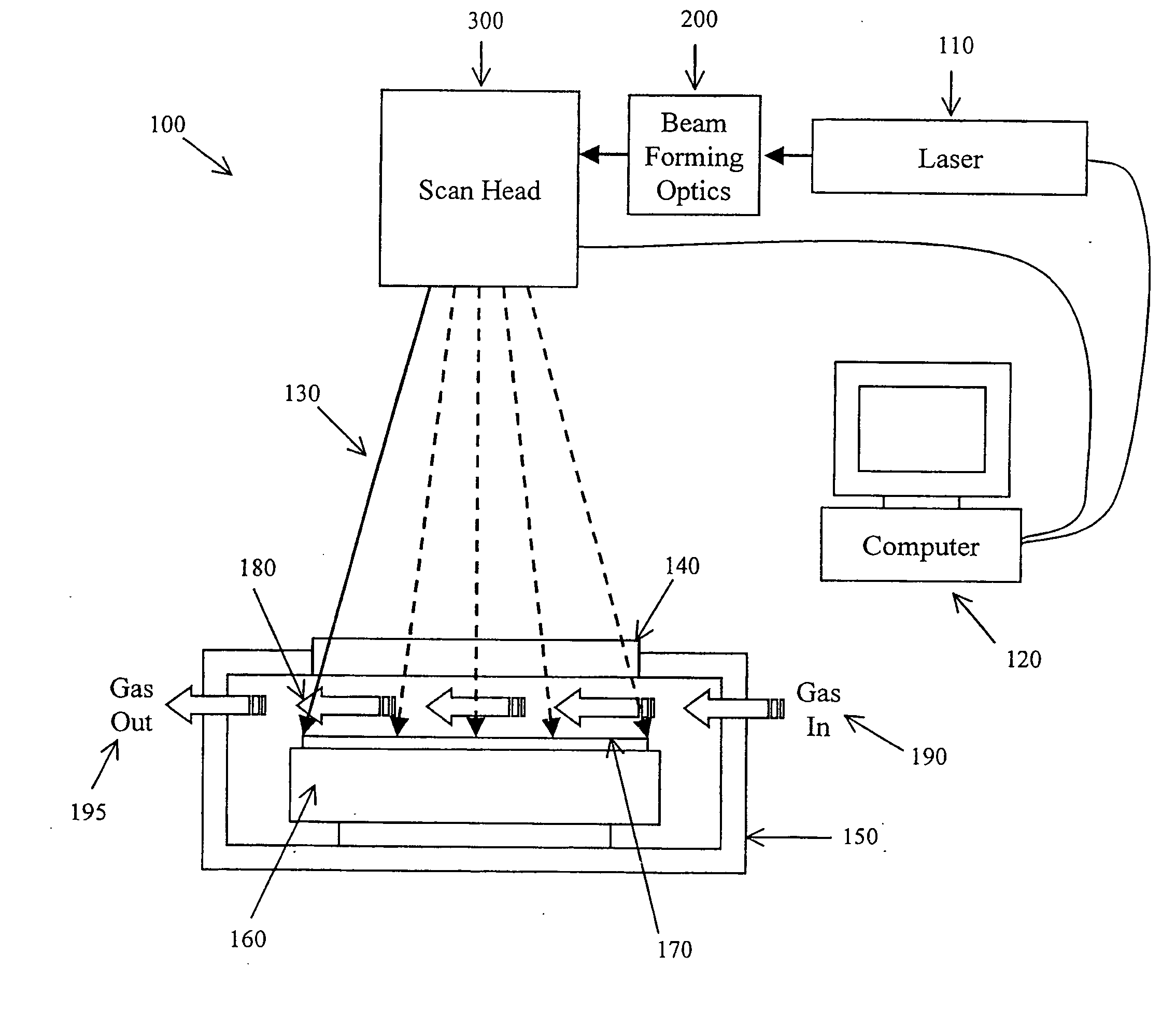
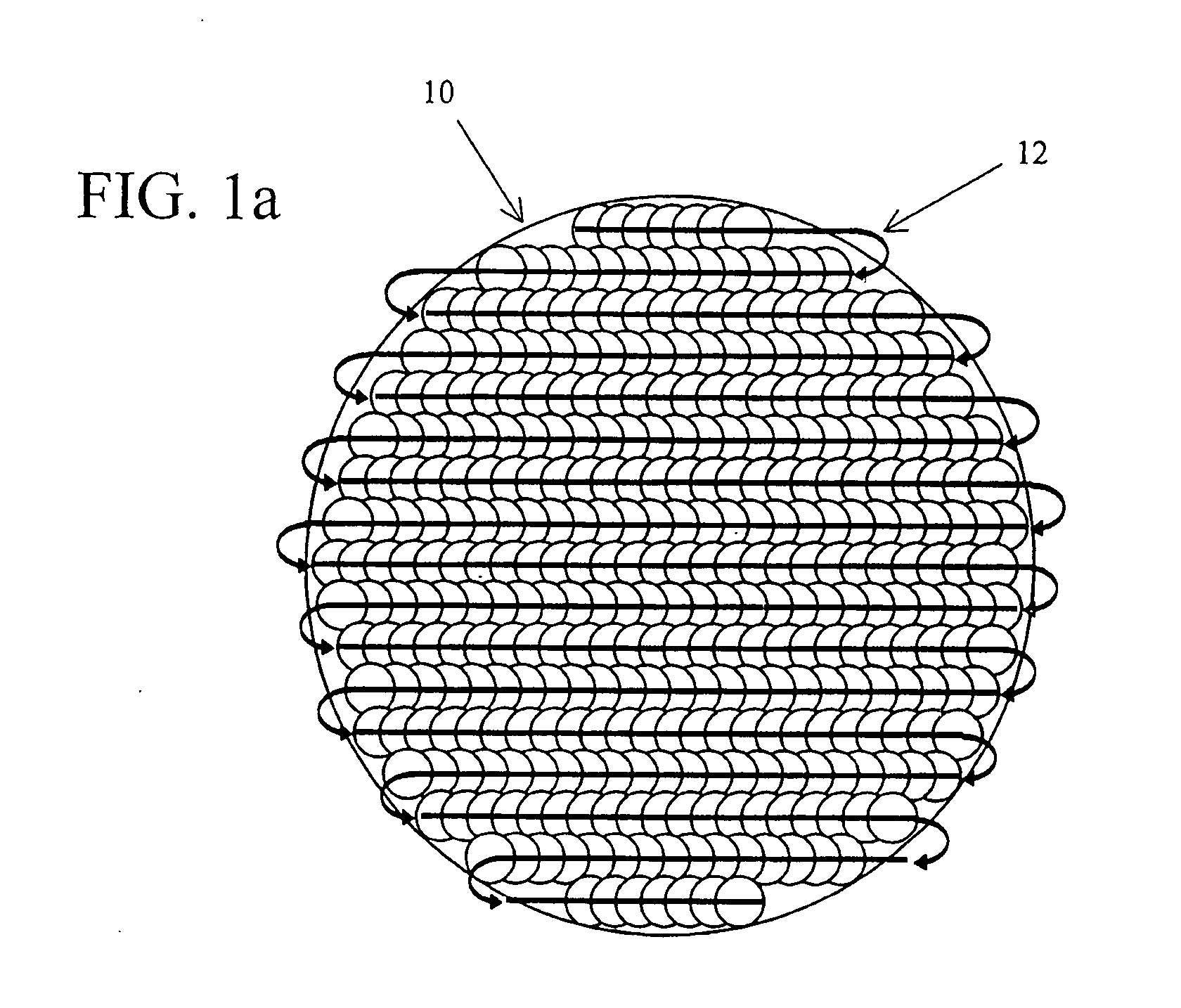
A method and apparatus delivers pulsed laser energy to a damage-sensitive surface. The pulse scanning method and apparatus allow for the deposition of a total dose of laser radiation that could not be attained by any conventional means without damaging the substrate being exposed. Using a solid-state diode pumped YAG laser and an enclosure with a gas ambient, laser pulses are scanned across a substrate according to one of several programmed approaches. Pulses are deposited that are non-adjacent in time, or non-adjacent in space, or both; conventional methods have the pulses adjacent in both time and space. Using the various approaches of the invention, the degree of spatial and temporal adjacency can be precisely controlled to permit significant laser radiation doses without causing any substrate damage. The present invention novel method and apparatus can be carried out by integrating a computer, laser and scan head with a small chamber into which gas can flow to permit a variety of surface reactions on damage-sensitive substrates that could otherwise not be conducted with conventional methods and systems.
Owner:UVTECH SYST
Transmission mode terahertz computed tomography
A method of obtaining a series of images of a three-dimensional object by transmitting pulsed terahertz (THz) radiation through the entire object from a plurality of angles, optically detecting changes in the transmitted THz radiation using pulsed laser radiation, and constructing a plurality of imaged slices of the three-dimensional object using the detected changes in the transmitted THz radiation. The THz radiation is transmitted through the object as a scanning spot. The object is placed within the Rayleigh range of the focused THz beam and a focusing system is used to transfer the imaging plane from adjacent the object to a desired distance away from the object. A related system is also disclosed.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
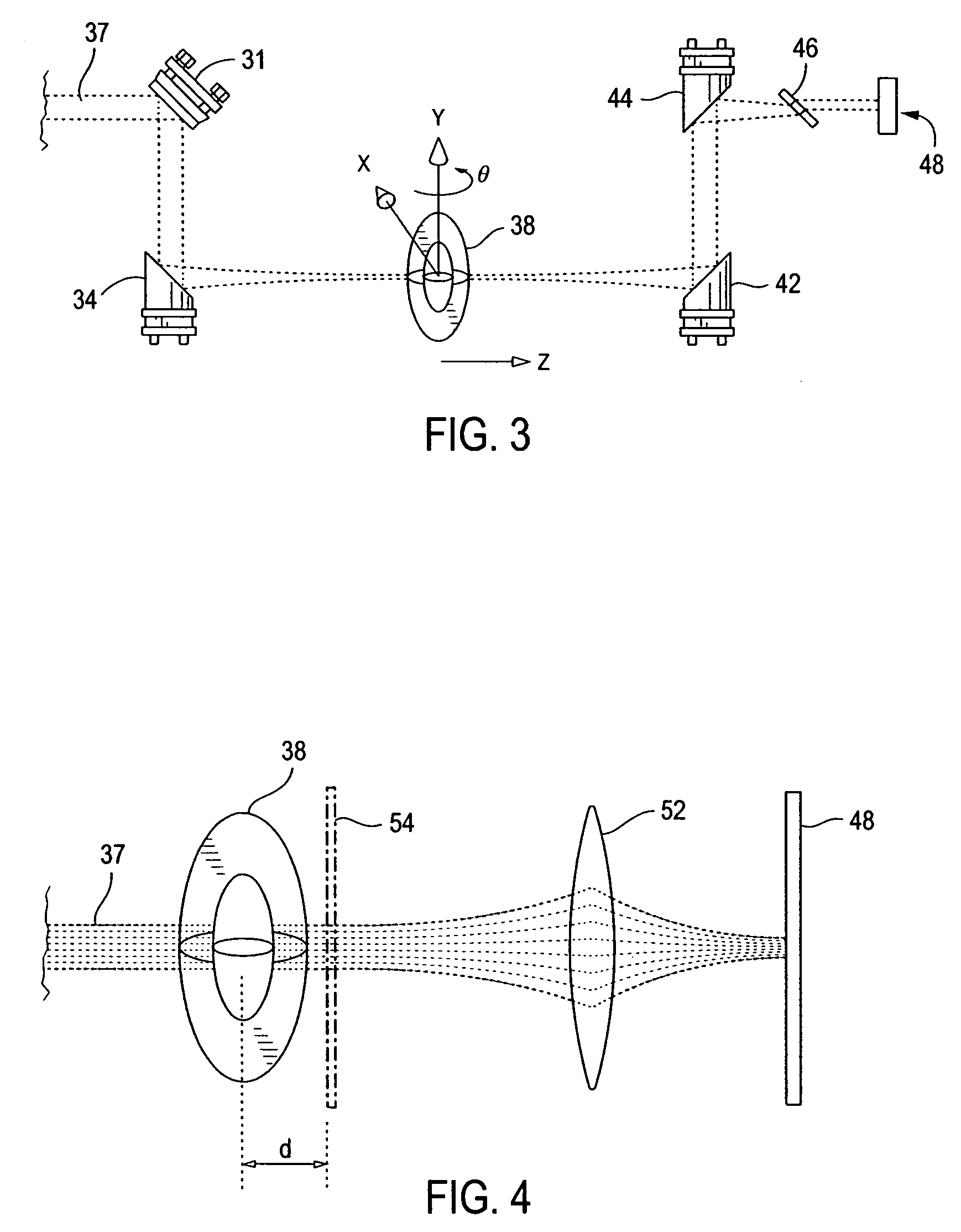
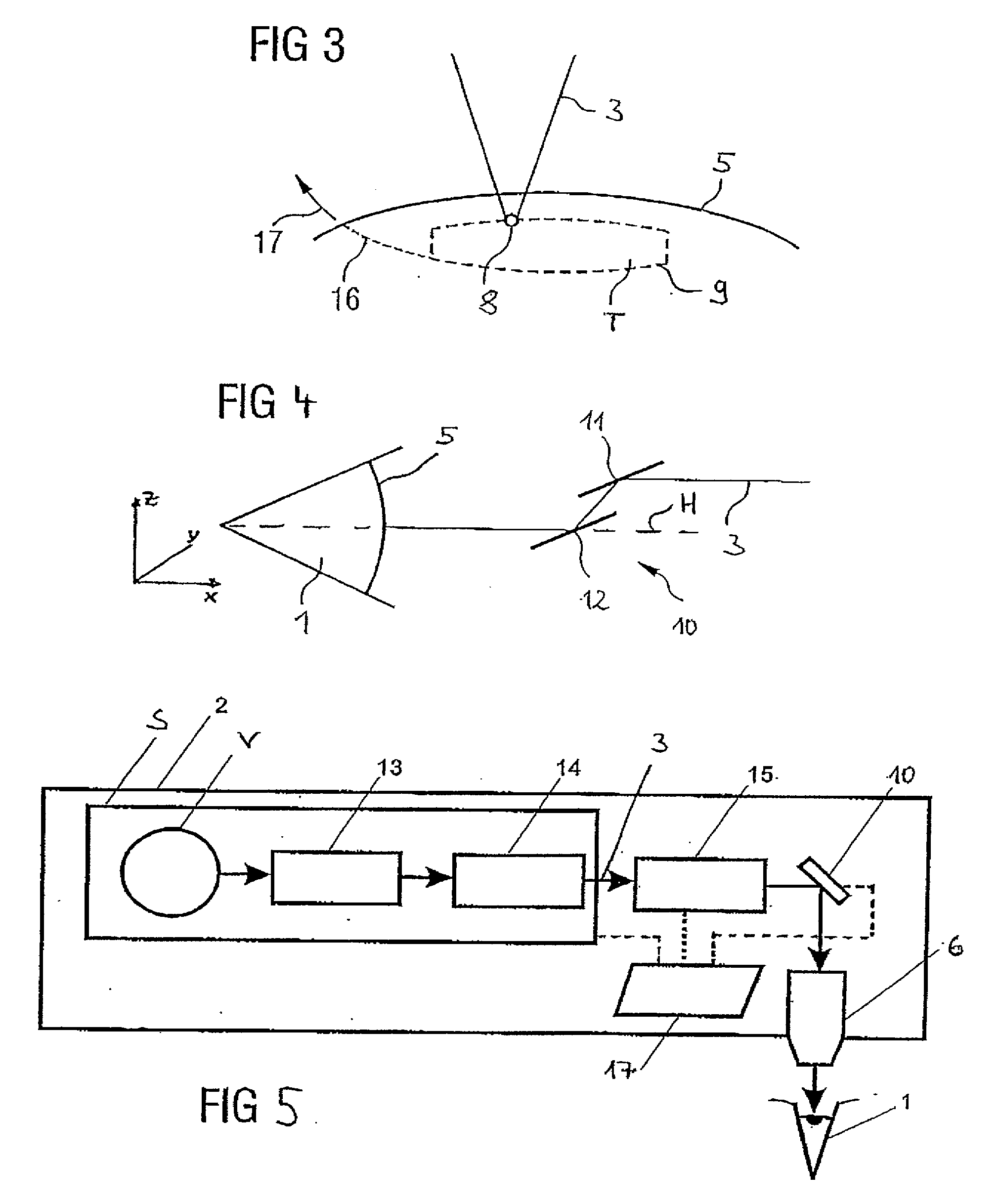
Device and method for material processing by means of laser radiation
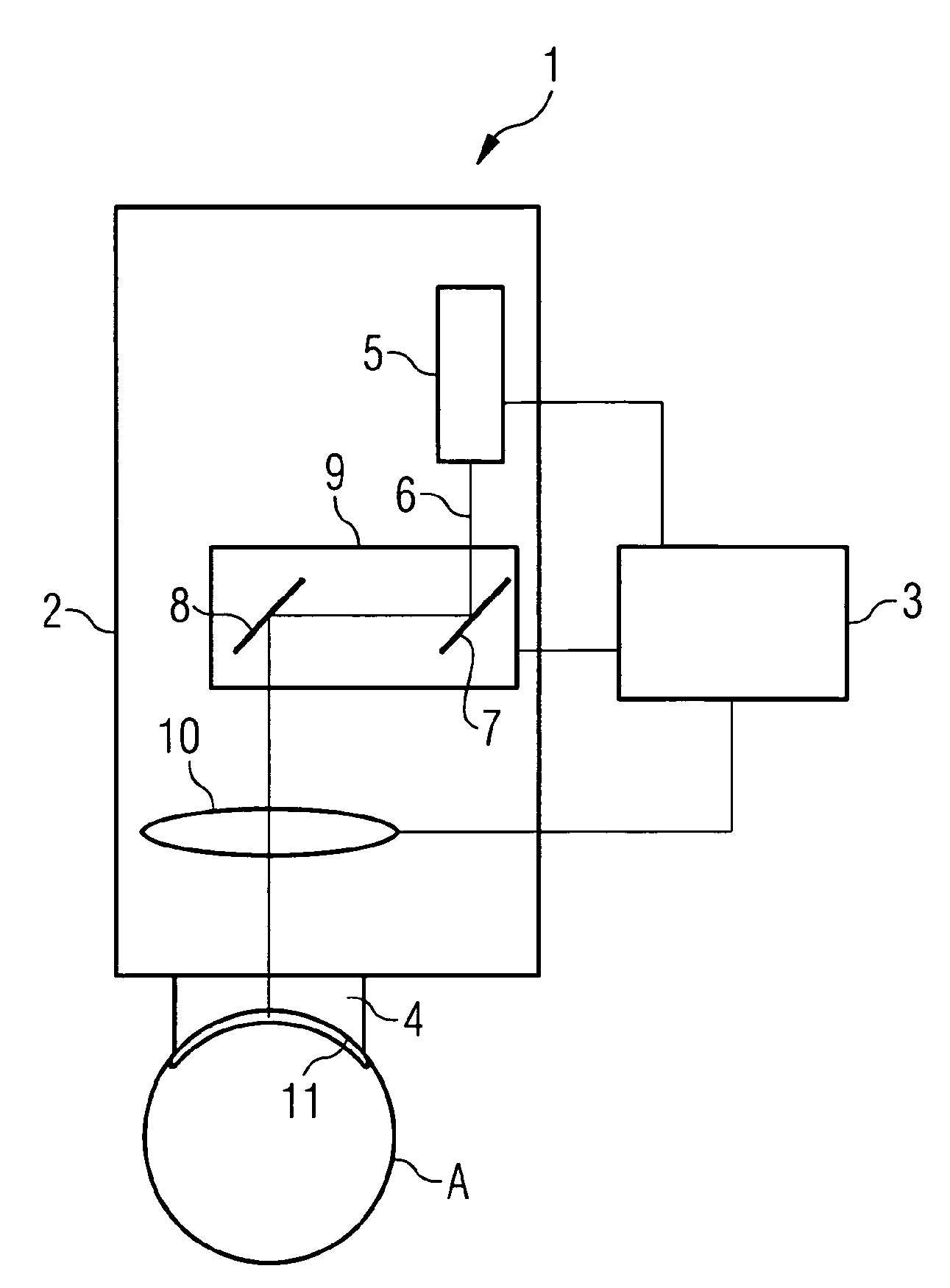
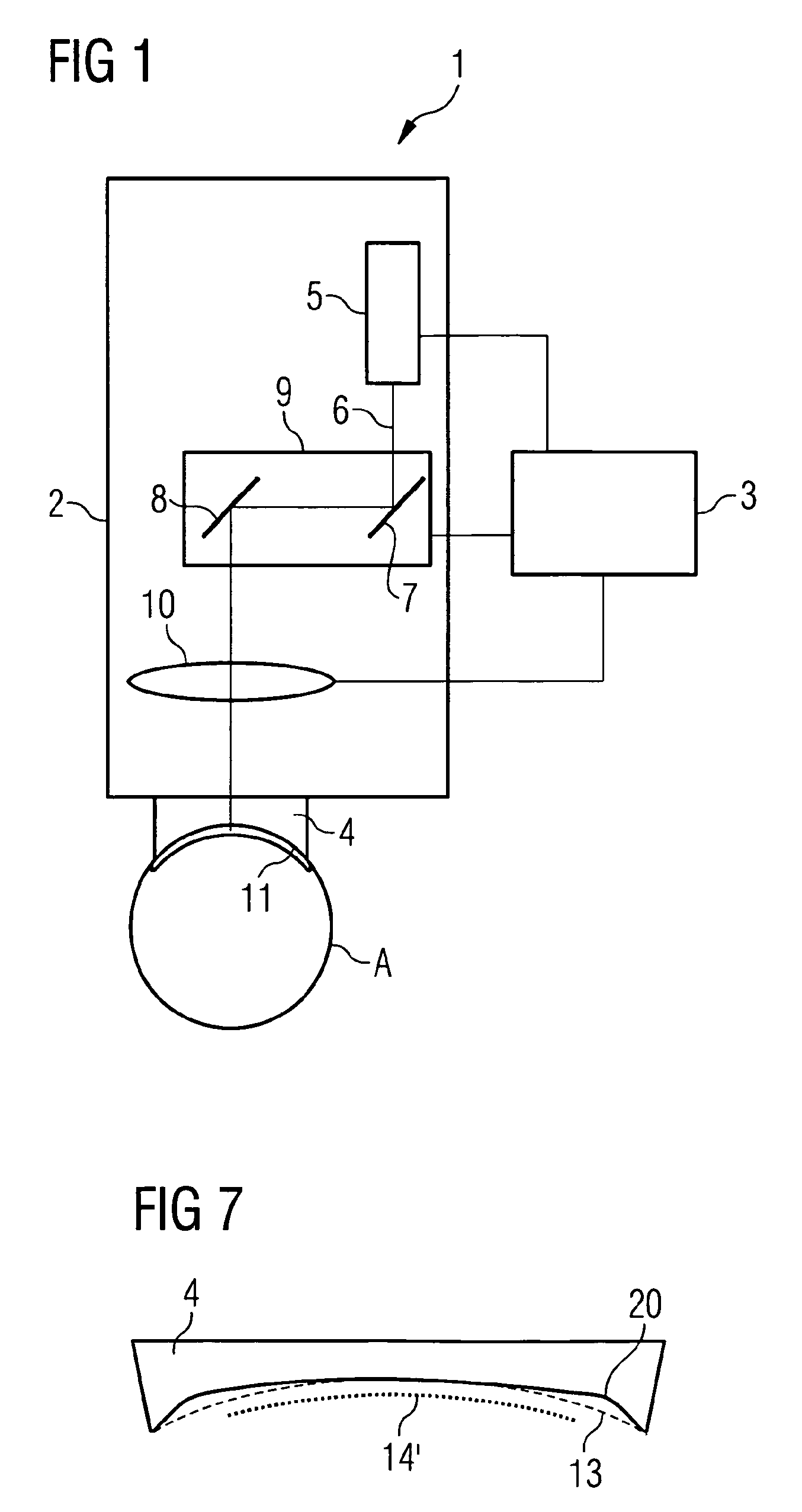
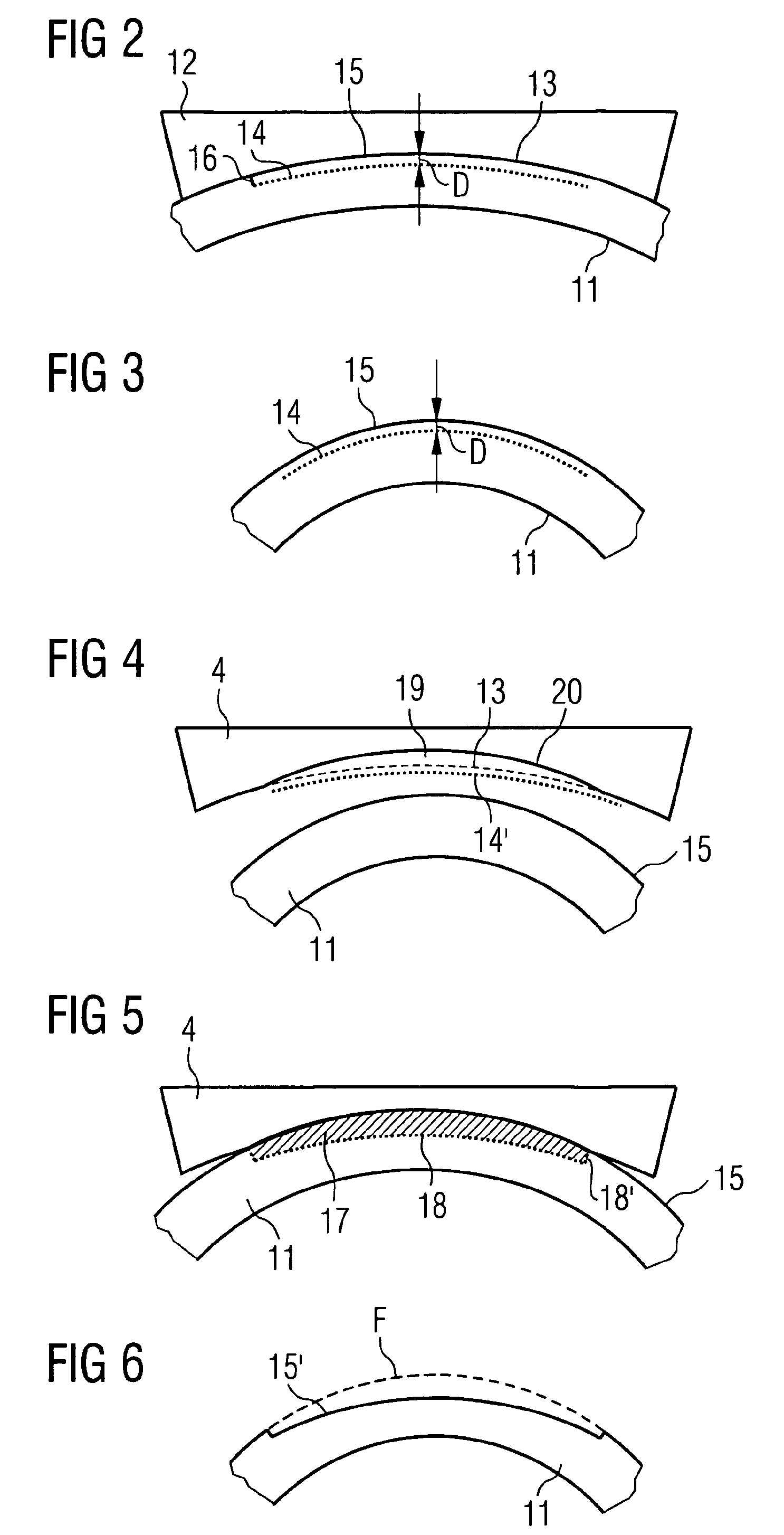
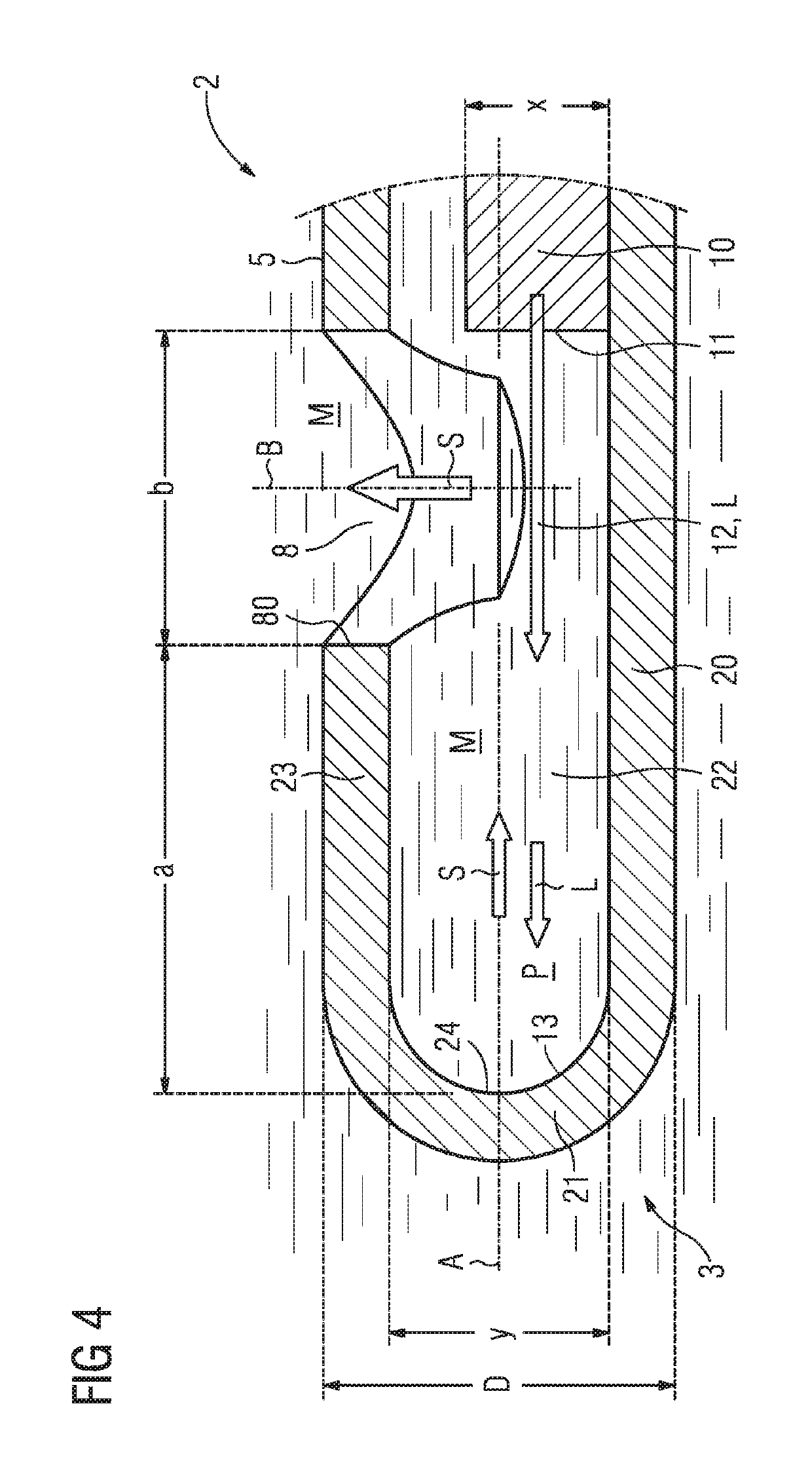
ActiveUS20070088409A1Weaken energyReduce impactLaser surgeryDiagnosticsMaterials processingPulsed laser radiation
In a device for material processing by laser radiation, including a source of laser radiation emitting pulsed laser radiation for interaction with the material; optics focusing the pulsed processing laser radiation to a center of interaction in the material and a scanning unit shifting the positions of the center of interaction within the material. Each processing laser pulse interacts with the material in a zone surrounding the center of interaction assigned to the laser pulse so that material is separated in the zones of interaction. A control unit controls the scanning unit and the source of laser radiation such that a cut surface is produced in the material by sequential arrangement of zones of interaction. The control unit controls the source of laser radiation and the scanning unit such that adjacent centers of interaction are located at a spatial distance a ≦10 μm from each other.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Photoemissive ion mobility spectrometry in ambient air
InactiveUS20070114395A1Avoids photochemistryIncrease currentTube electron sourcesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansUltravioletPrism
A photoemissive ion mobility spectrometer is disclosed for of chlorinated hydrocarbons and nitro-organic materials. Backside illumination of a thin gold film by pulsed laser radiation, pulsed ultraviolet xenon flashlamp, or like UV source, is used to produce bursts of low energy photo-emitted electrons. These swarms of thermalized electrons are directly attached by electronegative analytes or by reactant molecules, followed by charge transfer to the more electronegative analyte. Total internal reflection is incorporated for the backside illumination using optical elements such as a fused silica prism. The spectrometer allows for the direct vaporization of adsorbed explosive molecules from surfaces followed by direct injection into the photoemissive ion mobility spectrometer through a heated inlet.
Owner:NORTH DAKOTA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Laser apparatus for cutting brittle material
ActiveUS20180133837A1Glass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesOptical axisAspheric lens
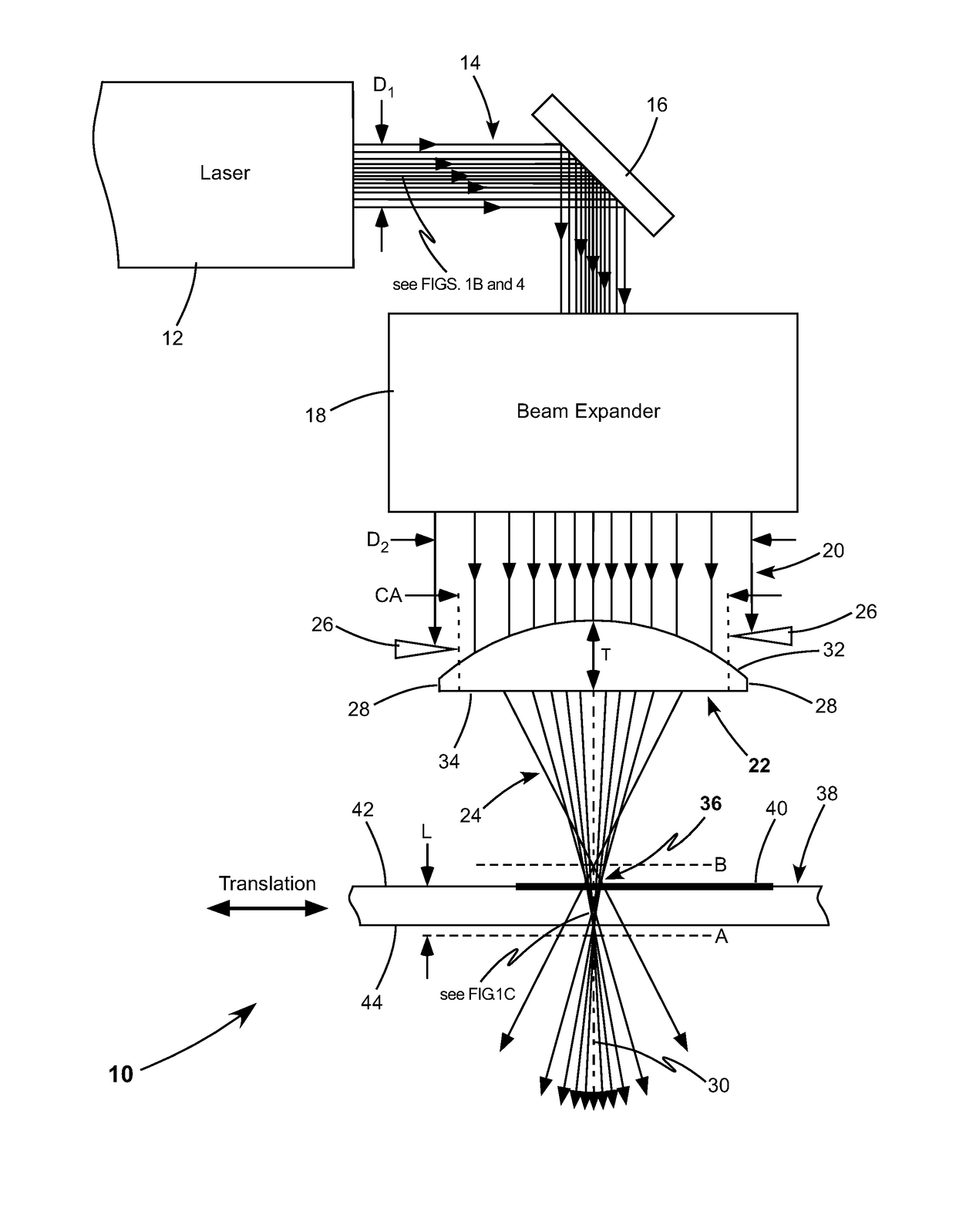
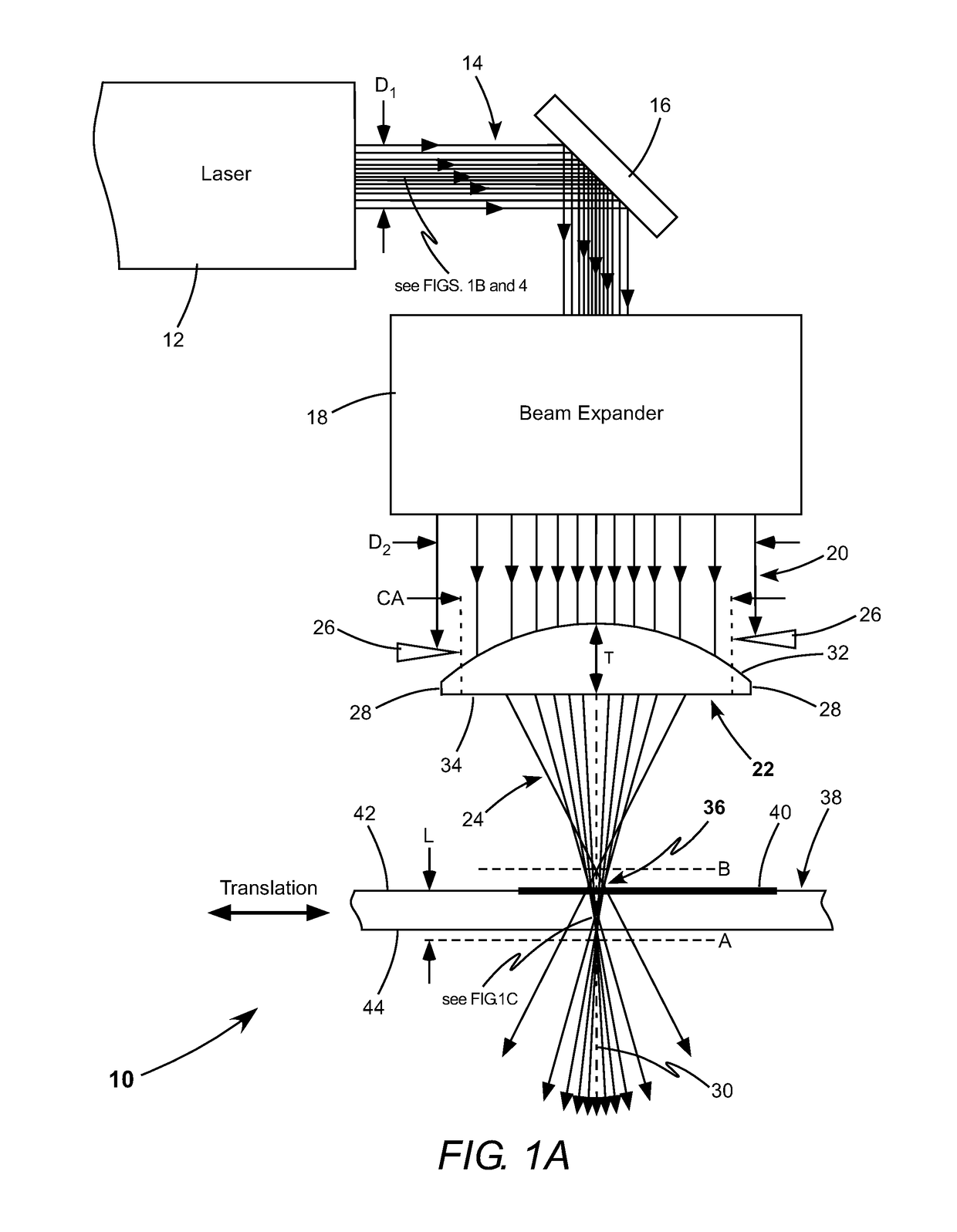
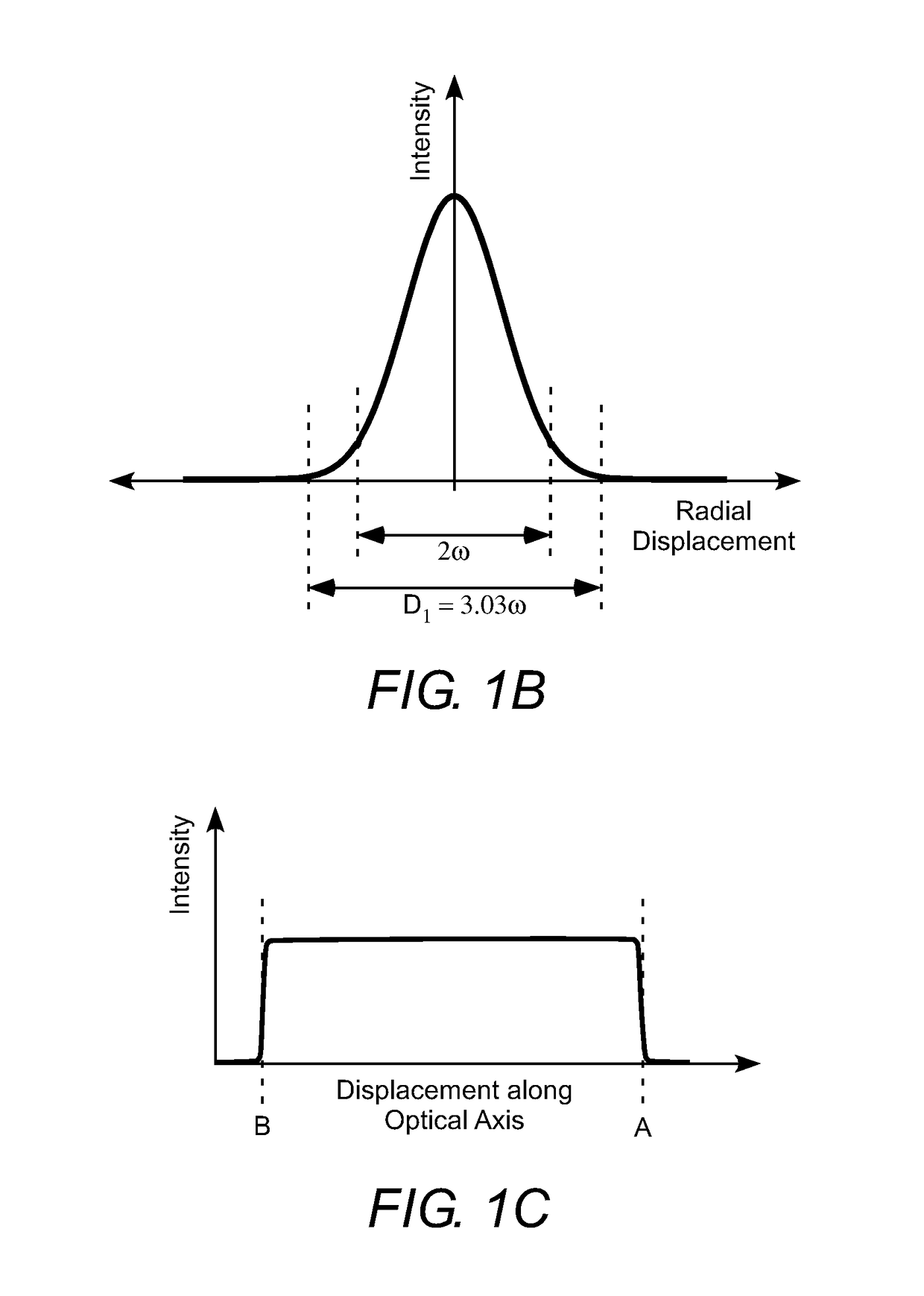
An apparatus for cutting brittle material comprises an aspheric focusing lens, an aperture, and a laser-source generating a beam of pulsed laser-radiation. The aspheric lens and the aperture form the beam of pulsed laser-radiation into an elongated focus having a uniform intensity distribution along the optical axis of the aspheric focusing lens. The elongated focus extends through the full thickness of a workpiece made of a brittle material. The workpiece is cut by tracing the optical axis along a cutting line. Each pulse or burst of pulsed laser-radiation creates an extended defect through the full thickness of the workpiece.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Apparatus for generating a correcting cut surface in the cornea of an eye so as to correct ametropia as well as a contact element for such apparatus
InactiveUS20100049174A1Correcting ametropiaThe instrument is easy to operateLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorCorneal surface
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
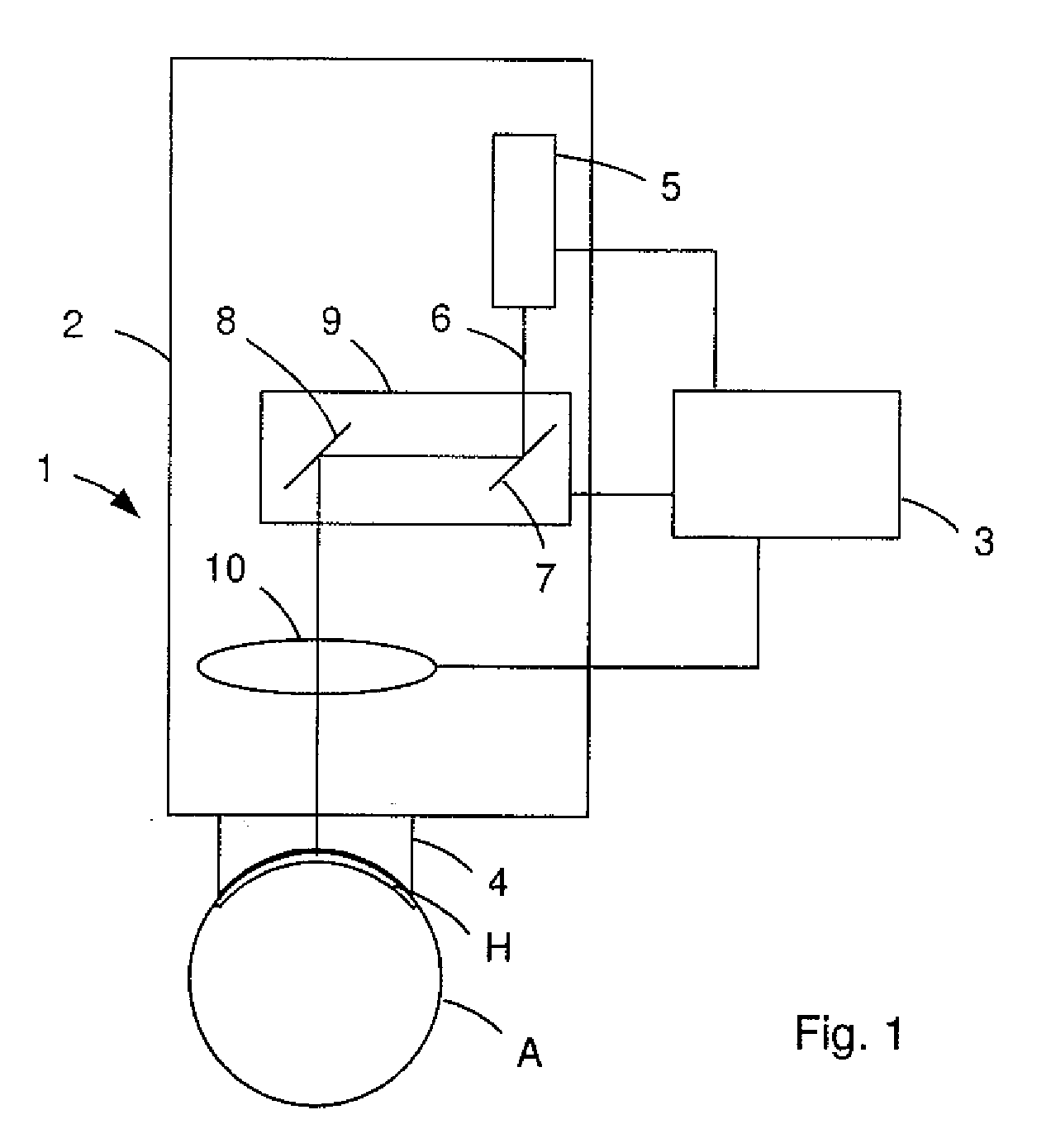
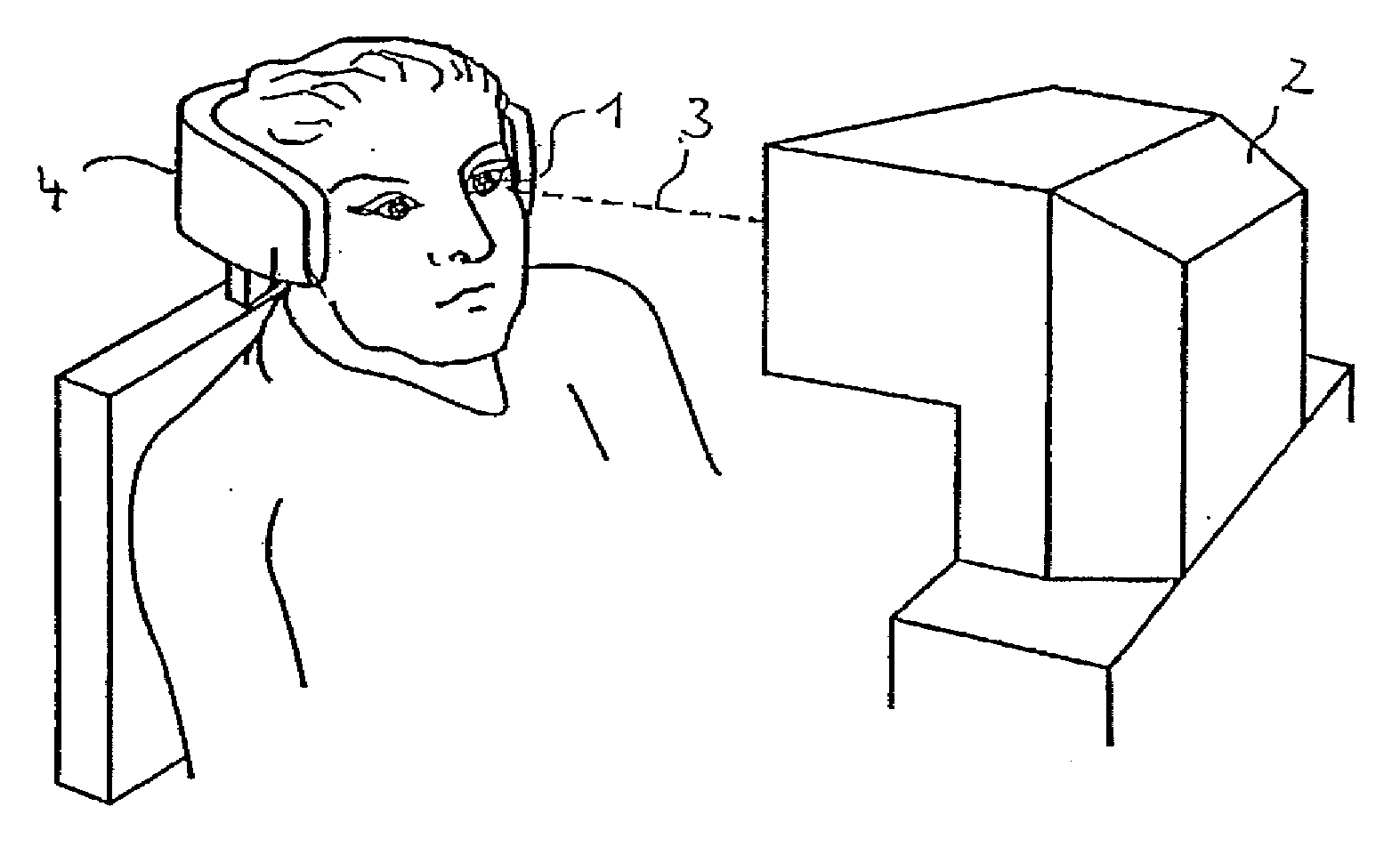
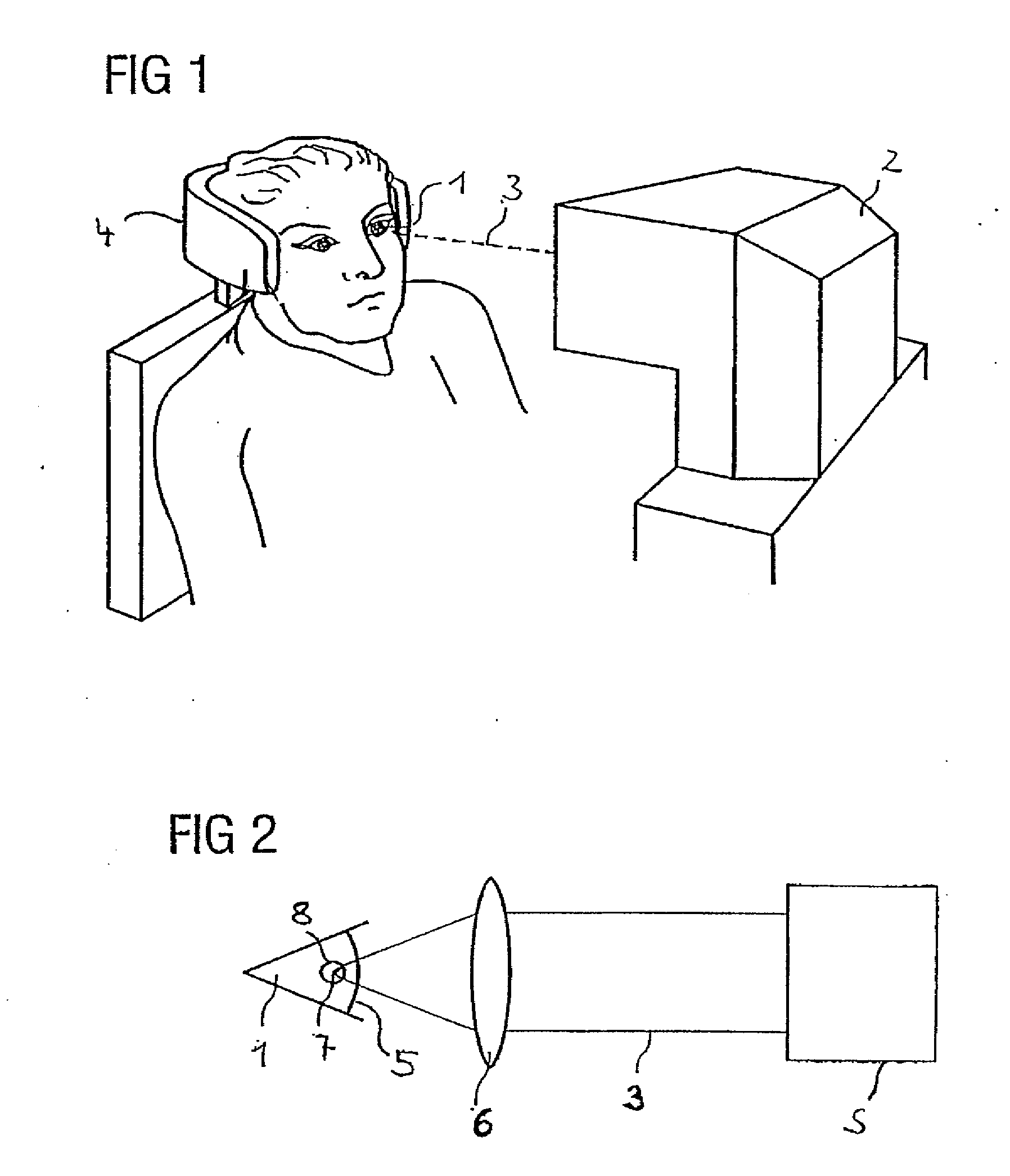
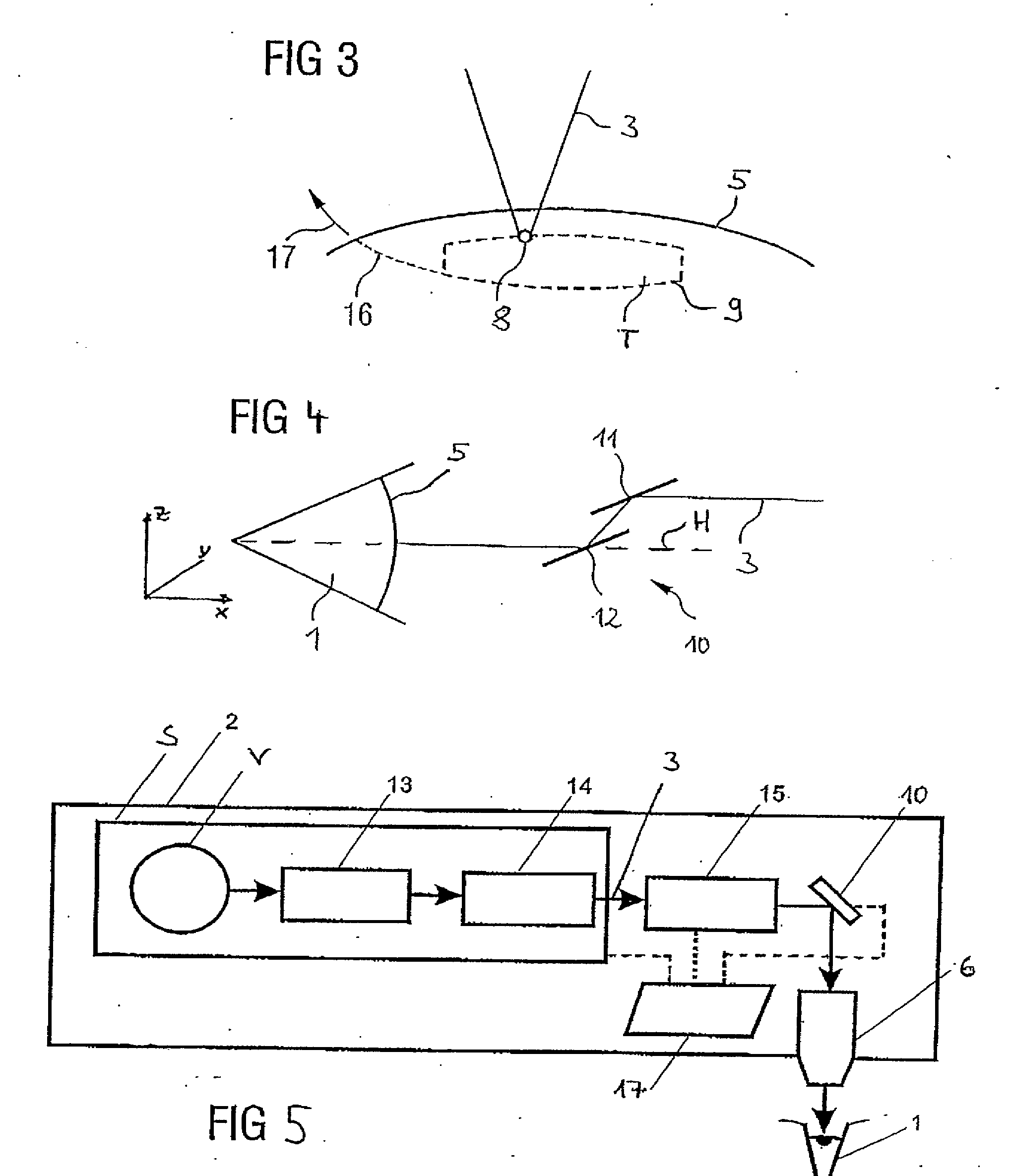
Electro-optical range finder
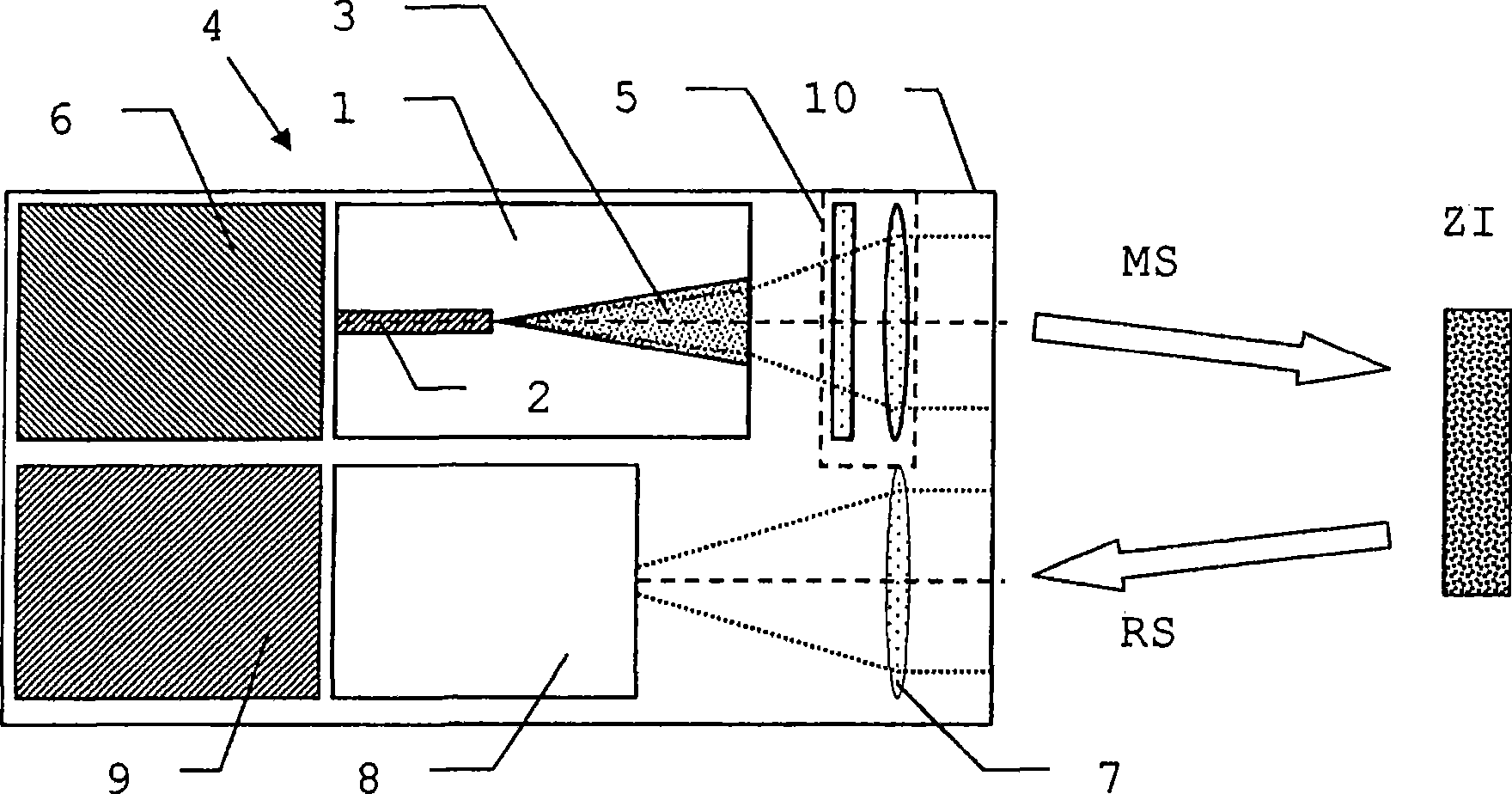
InactiveCN101490503AExpand the scope of workHigh measurement accuracyOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationWaveguidePulsed laser radiation
An electro-optical range finder (4) has a trapezoidal laser (1) as a laser source, a laser source controller (6) for generating pulsed laser radiation, receiving optics (7) and a detector (8) with an evaluation unit (9) for receiving and evaluating the measuring radiation (RS) reflected by a target (ZI), in order to measure distance, has a separate supply for the guided waveguide region (2) and the trapezoidal region (3) as well as transmitting optics (5) with astigmatism compensation and for collimating the laser radiation.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
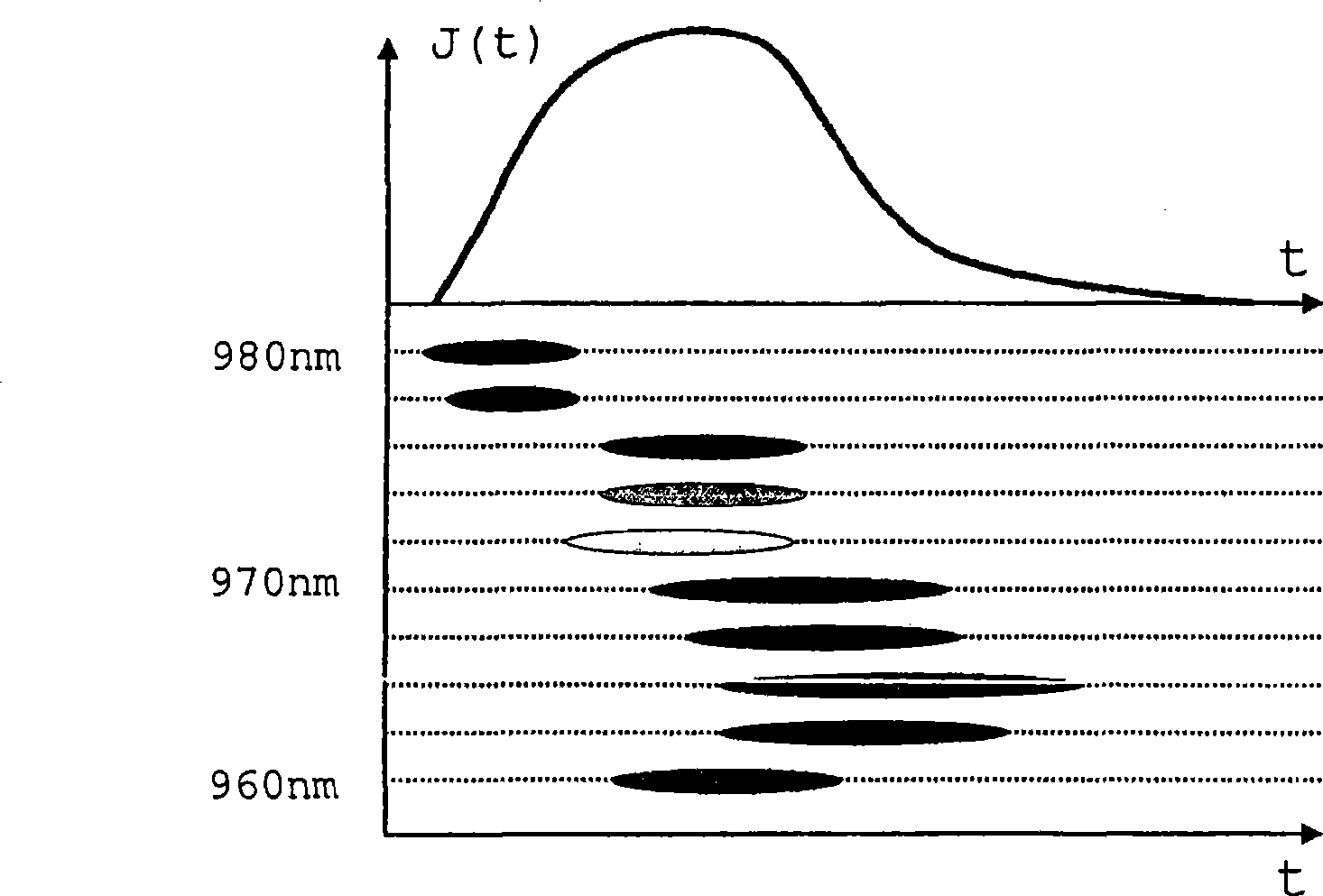
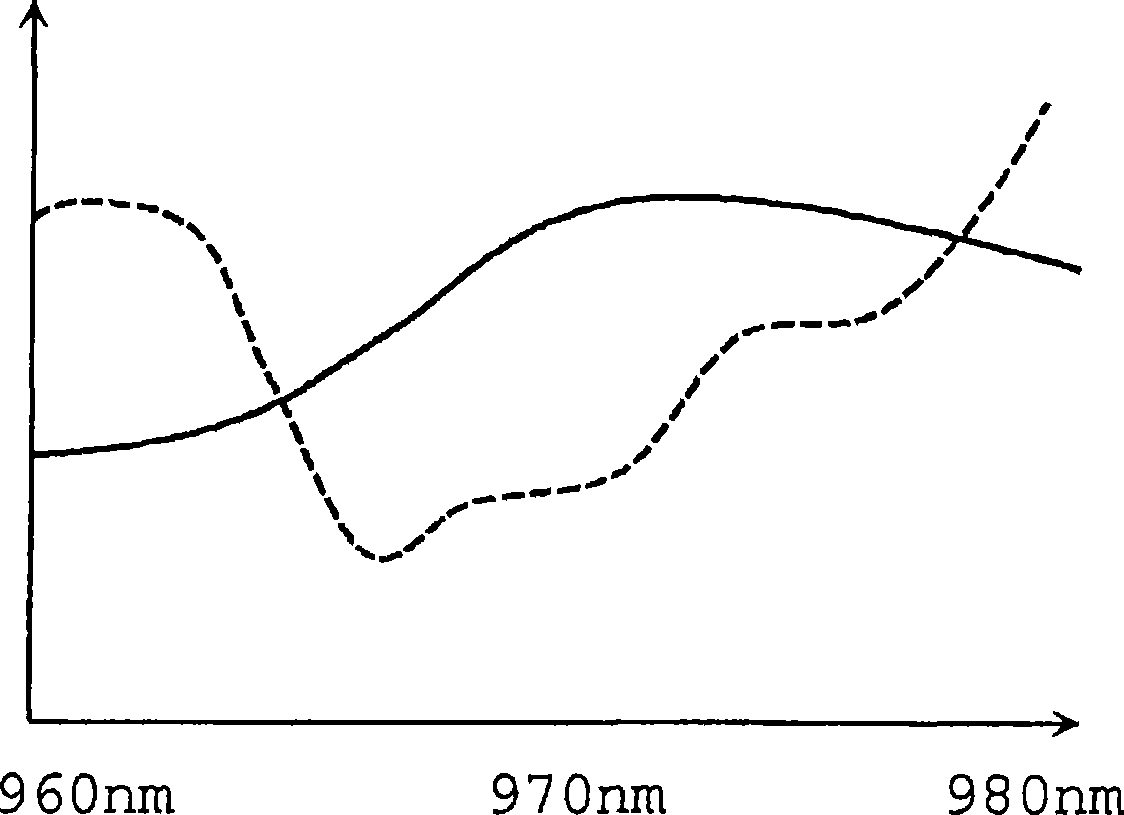
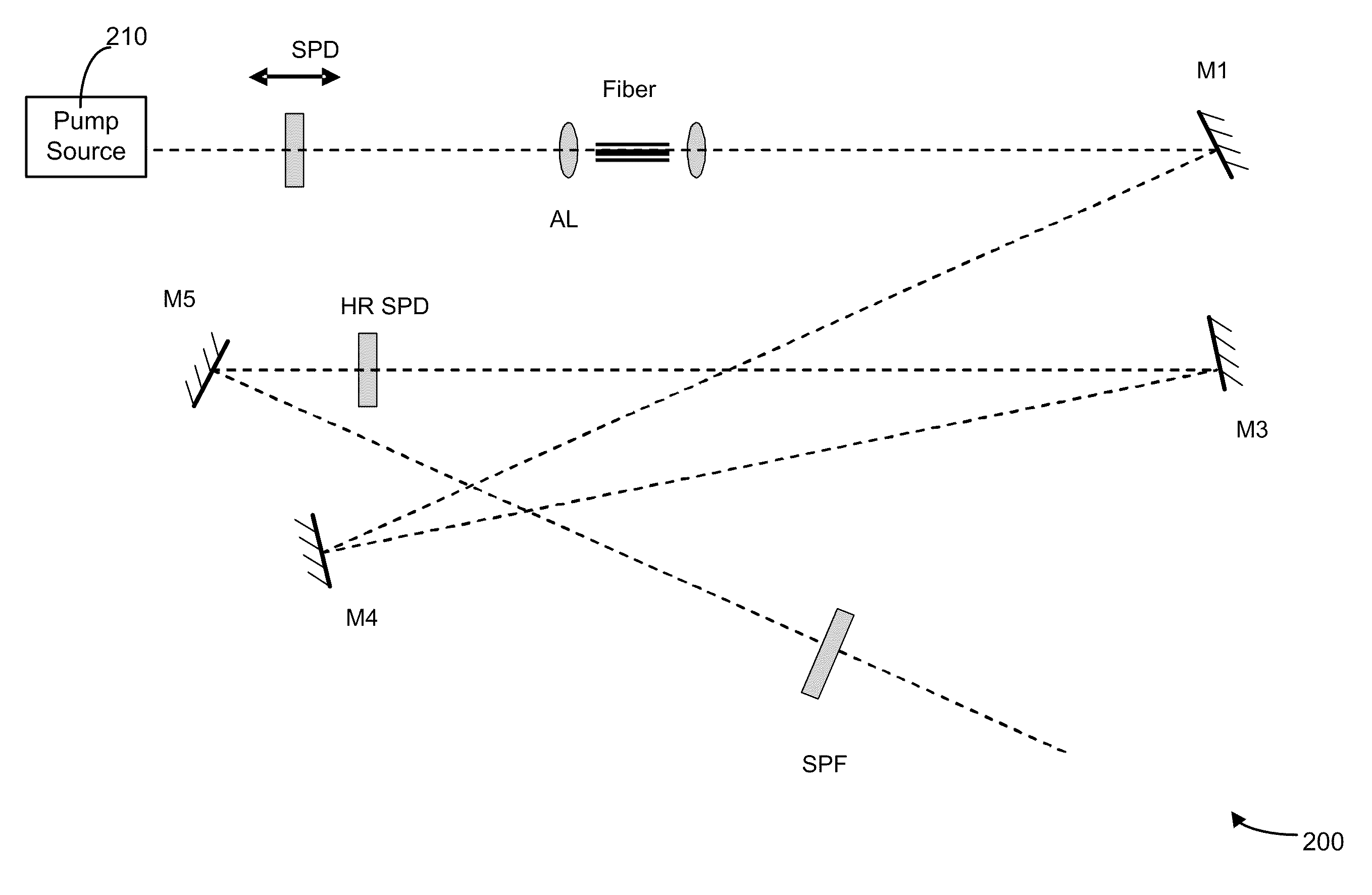
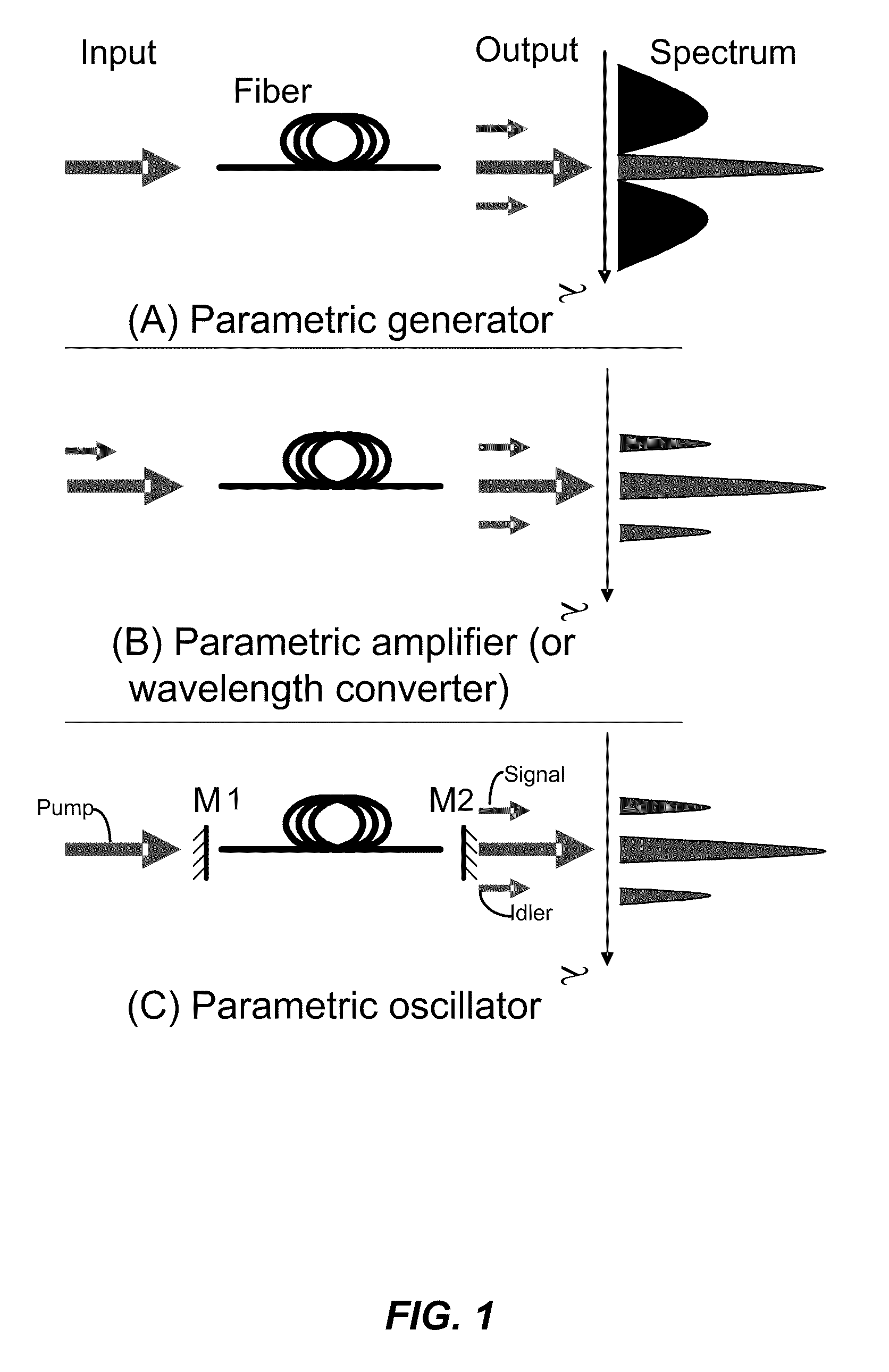
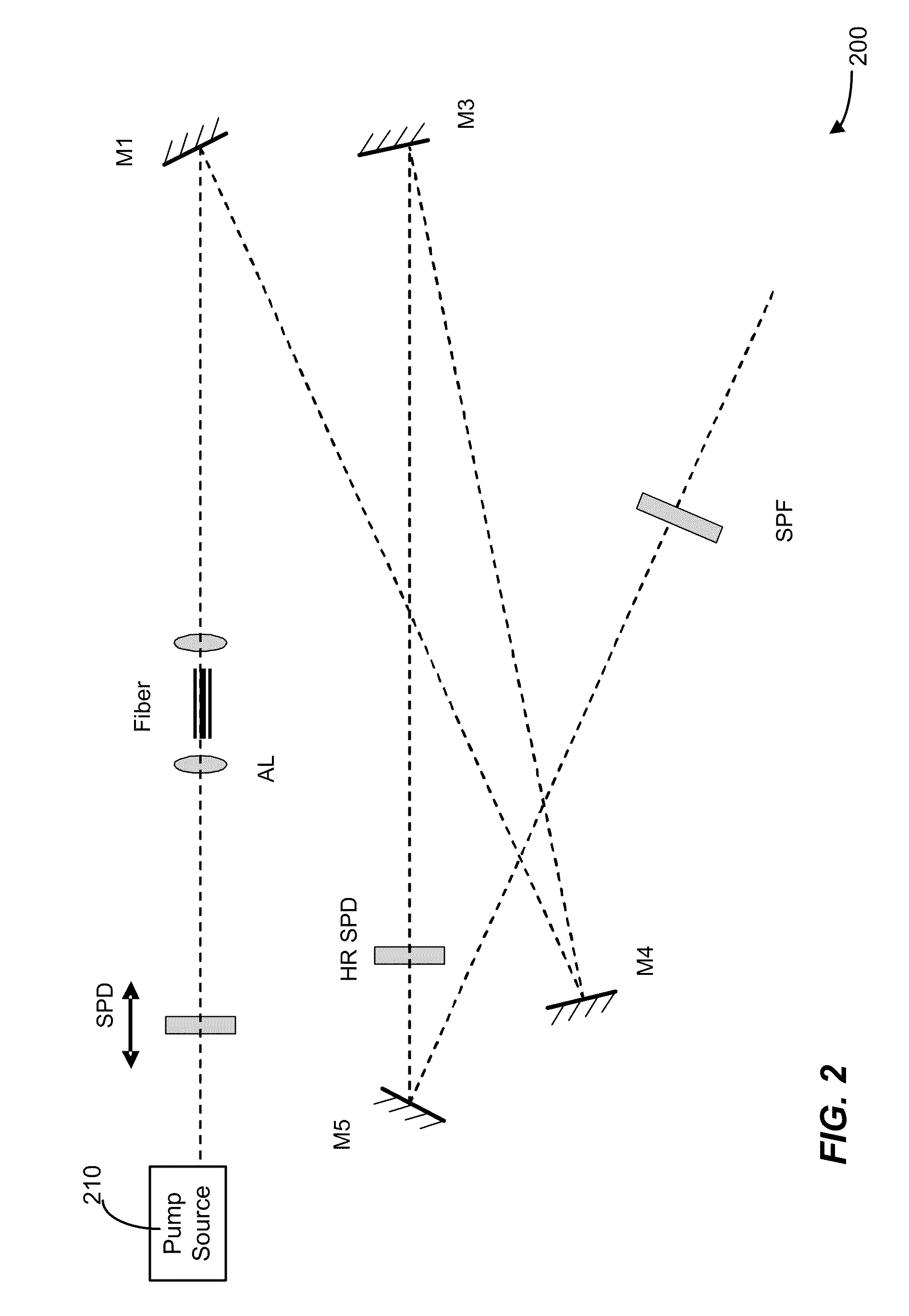
Fiber optical parametric oscillator with high power and bandwidth
InactiveUS20090141340A1Great power widthImprove performanceFibre transmissionActive medium shape and constructionFiberLength wave
The present invention provides methods, systems, and apparatus of improved fiber-based optical parametric oscillators (FOPOs). These oscillators can be used in the creation of short pulsed laser radiation, which are useful in numerous applications, such as characterization of materials and molecules. A relationship between fiber length and performance is realized, where shorter lengths counterintuitively provide greater power and width of output bands. This relationship is used to develop improved FOPOs. For example, fibers of 10 cm or less may be used to obtain superior performance in terms of wavelength tunability (e.g. bandwidth of 200 nm and greater) and output power (e.g. pulse power of 1 nJ). Other realized relationships between length and wavelength position of output bands are also used to select the wavelength range output from the FOPO. The diameter of the fiber may be selected to provide positioning (e.g. a centering) of the range of attainable output wavelengths.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Delivery System and Method of Use for the Eye
A method and delivery system are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Pulsed laser radiation is delivered from the distal end of a fiber-optic probe sufficient to cause photoablation of selected portions of the trabecular meshwork, the juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and an inner wall of Schlemm's canal in the target site. The fiber-optic probe may be advanced so as to create an aperture in the inner wall of Schlemm's canal in which fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye flows. The method and delivery system may further be used on any tissue types in the body.
Owner:IVANTIS INC
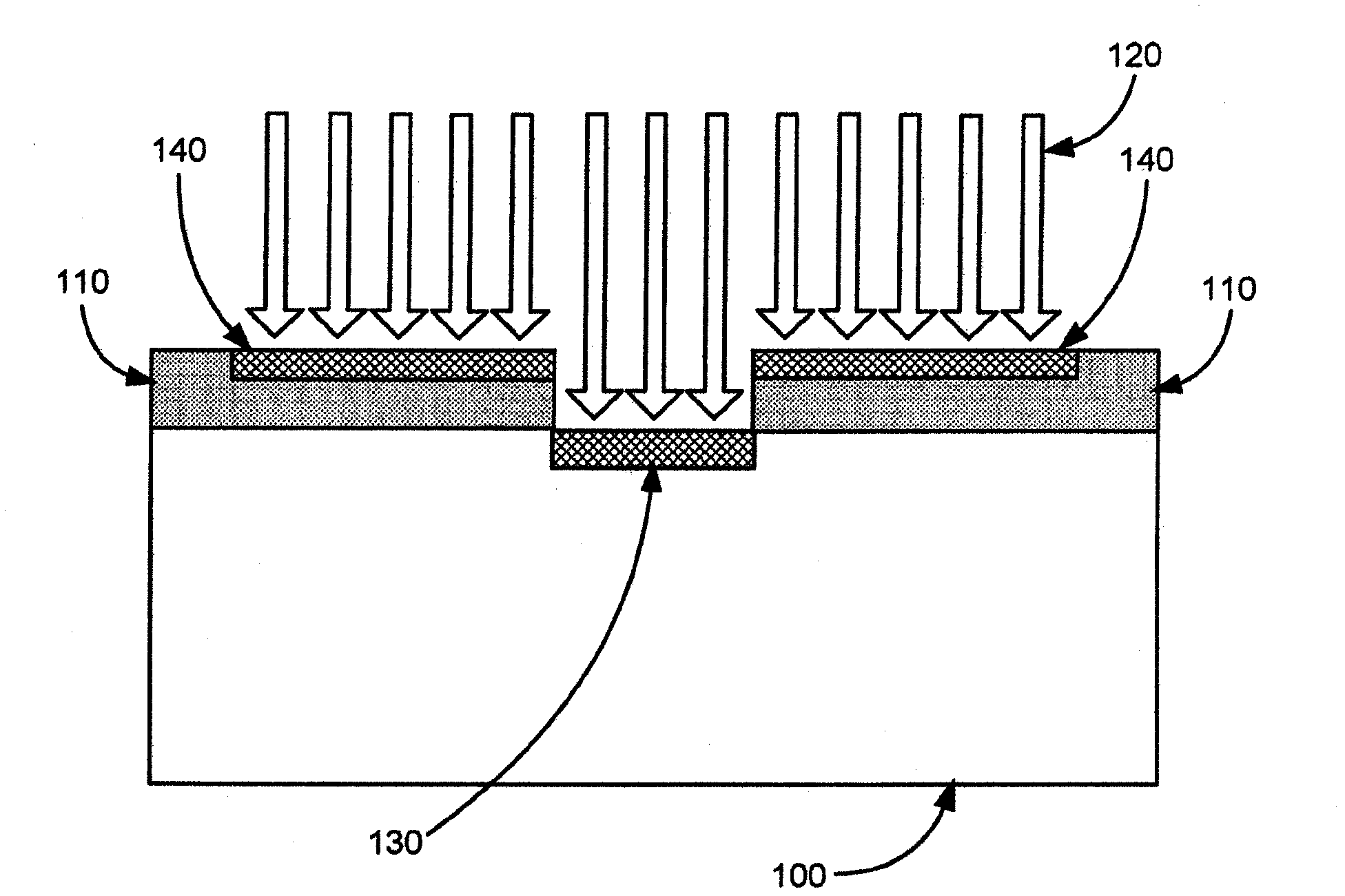
Thin sacrificial masking films for protecting semiconductors from pulsed laser process
InactiveCN102099898ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser processingPulsed laser radiation
The present disclosure is directed to systems and methods for protecting a semiconductor product or material from harmful effects of pulsed laser irradiation. In some embodiments, a thin sacrificial protective mask layer that expires after one laser processing operation is applied to the surface of the product or material to be laser-treated. The thin protective mask layer reflects, absorbs, or otherwise protects the underlying product or material from the energy of the laser.
Owner:SIONYX
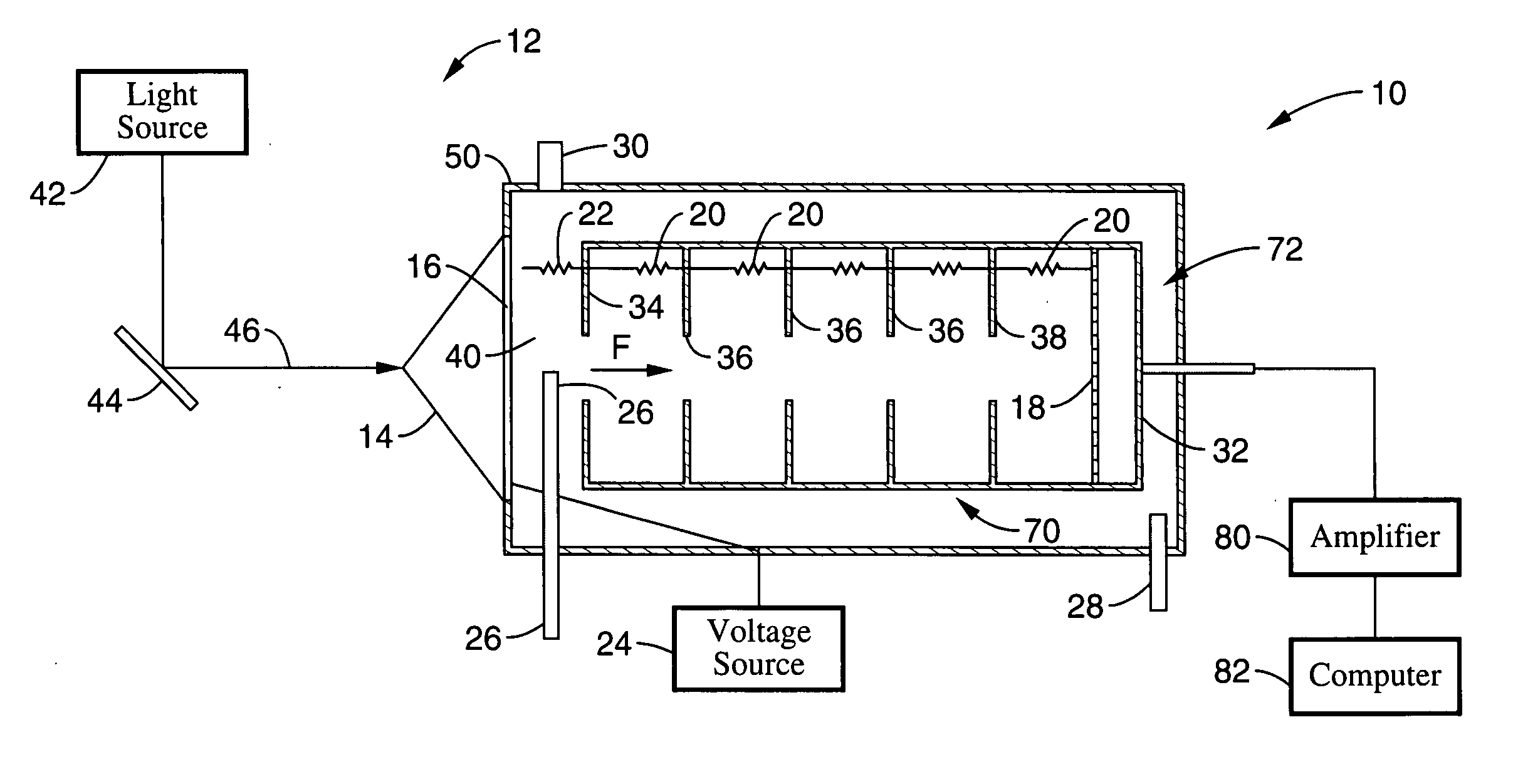
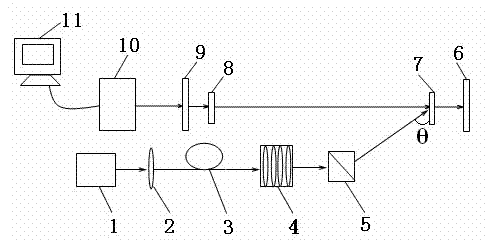
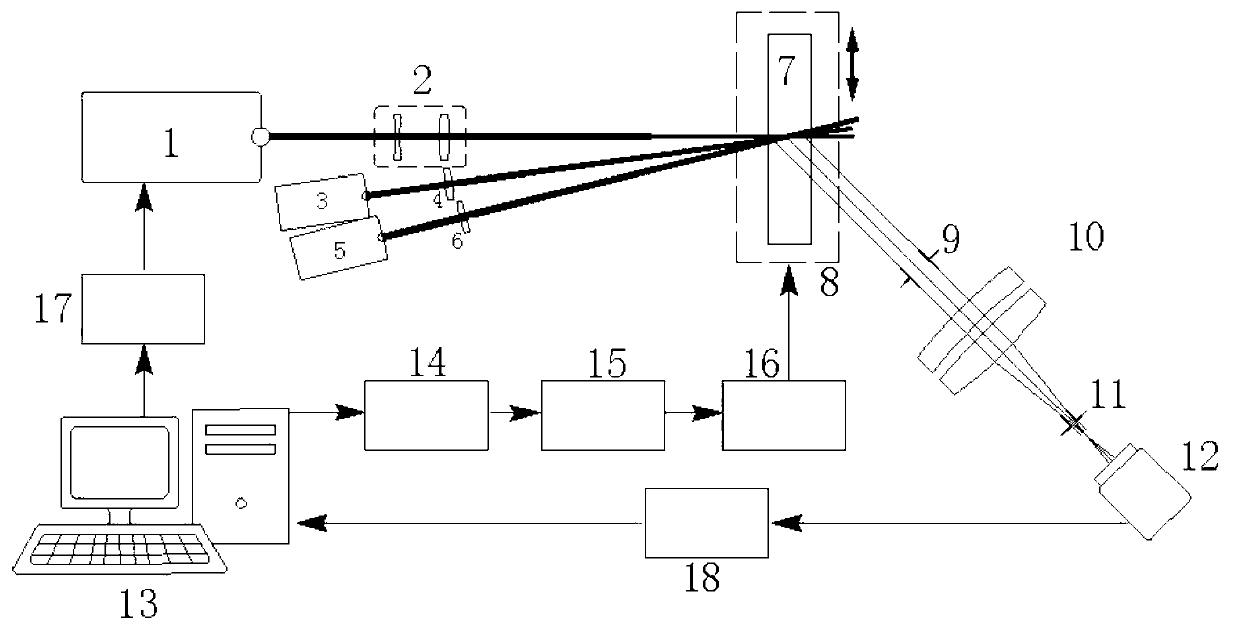
Device and method for measuring thermal distortion of polarized beam splitter mirror
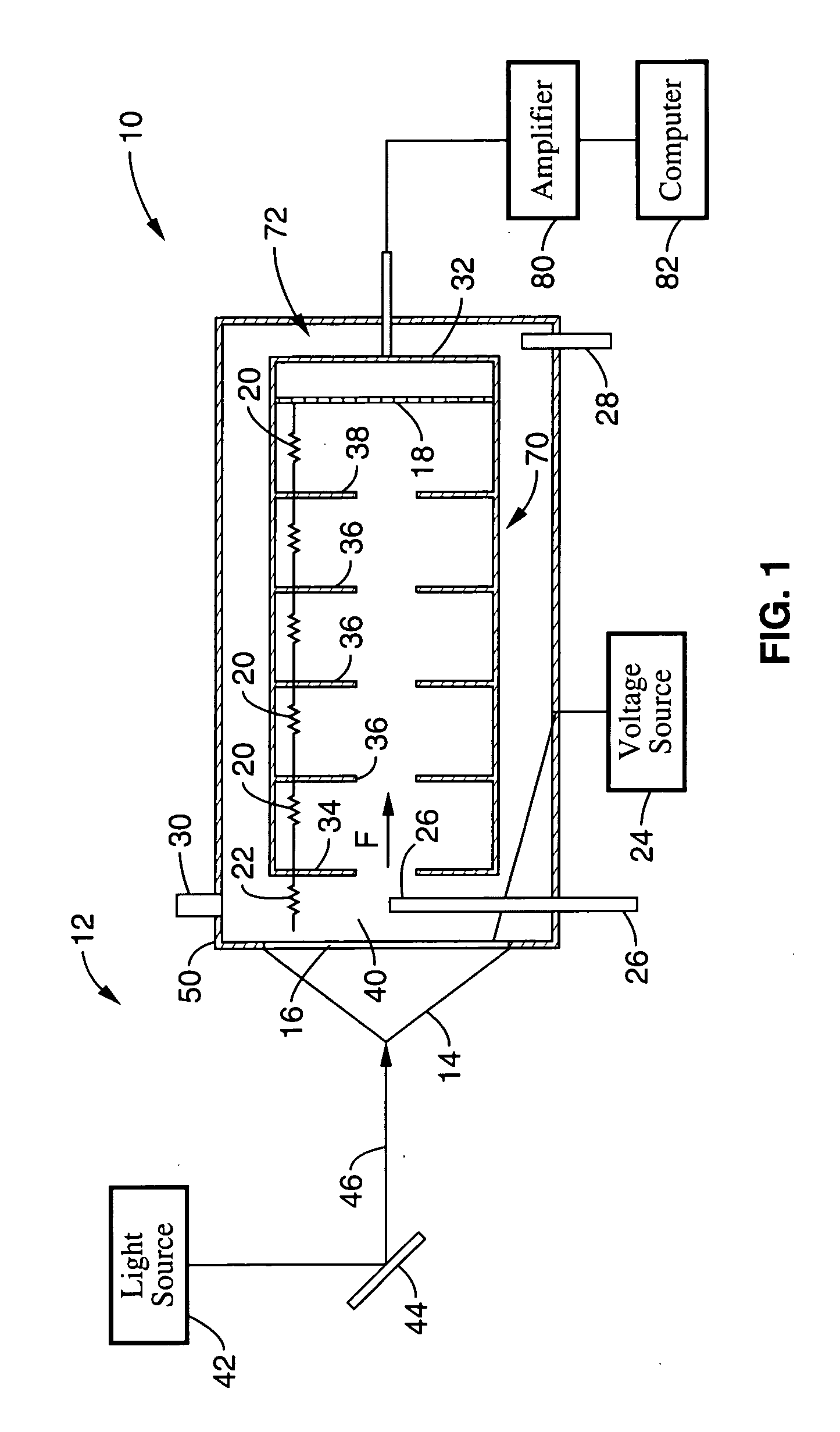
The invention provides a device and a method for measuring the thermal distortion of a polarized beam splitter mirror. The device comprises a solid laser, a focusing lens, an energy optical fiber, an optical fiber shaping lens group, a beam splitter prism, a transmission plane mirror, a polarized beam splitter mirror, a zero-degree color filter, an attenuation light filter, a Fizeau interferometer and a computer, wherein the laser emitted from the solid laser is coupled to the energy optical fiber through the focusing lens, transmitted into a measuring room through the energy optical fiber, and is further radiated to the surface of the polarized beam splitter mirror in a theta angle through the optical fiber shaping lens group and the beam splitter prism; and the light emitted from the Fizeau interferometer is vertically radiated to the polarized beam splitter mirror through the light attenuation light filter and the zero-degree color filter. The device for measuring the thermal distortion of the polarized beam splitter mirror has the characteristics of simple structure, good stability and strong interference resistance, wavefront distortion of an optical film element under a laser radiation can be measured without contact, and moreover, the measurement can be carried out in continuous, single pulse or repeated pulse laser radiation.
Owner:RES INST OF PHYSICAL & CHEM ENG OF NUCLEAR IND
Fiber optical parametric oscillator with high power and bandwidth
InactiveUS7898731B2Great power widthImprove performanceFibre transmissionActive medium shape and constructionFiberLength wave
The present invention provides methods, systems, and apparatus of improved fiber-based optical parametric oscillators (FOPOs). These oscillators can be used in the creation of short pulsed laser radiation, which are useful in numerous applications, such as characterization of materials and molecules. A relationship between fiber length and performance is realized, where shorter lengths counterintuitively provide greater power and width of output bands. This relationship is used to develop improved FOPOs. For example, fibers of 10 cm or less may be used to obtain superior performance in terms of wavelength tunability (e.g. bandwidth of 200 nm and greater) and output power (e.g. pulse power of 1 nJ). Other realized relationships between length and wavelength position of output bands are also used to select the wavelength range output from the FOPO. The diameter of the fiber may be selected to provide positioning (e.g. a centering) of the range of attainable output wavelengths.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for creating, trapping and manipulating a gas bubble in liquid
InactiveUS20110036991A1Scattering properties measurementsSurgical instrument detailsFocal zoneOptical breakdown
A method for producing, trapping and manipulating a gas microbubble in liquid is disclosed. The method includes providing a pulsed laser source for generating a pulsed laser radiation and focusing optics; and focusing a pulsed laser radiation to a focal zone within the liquid, with energy exceeding the threshold of optical breakdown in the liquid at the focal zone. It is also suggested to use focusing optics to focus the laser beam to a focal point at a depth close to the compensation depth of the focusing optics for spherical aberration.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMS GMBH
Device and method for material processing by means of laser radiation
InactiveUS20080065052A1Weaken energyIncrease demandLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsOptoelectronicsMaterials processing
A device for material processing by laser radiation, including a source of laser radiation emitting pulsed laser radiation for interaction with the material, optics focusing the pulsed processing laser radiation to a center of interaction in the material, and a scanning unit shifting the positions of the center of interaction within the material. Each processing laser pulse interacting with the material in a zone surrounding the center of interaction assigned to the laser pulse so that material is separated in the zones of interaction. A control unit controls the scanning unit and the source of laser radiation such that a cut surface is produced in the material by sequential arrangement of zones of interaction. The control unit controls the source of laser radiation and the scanning unit such that adjacent centers of interaction are located at a spatial distance a ≦10 μm from each other.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
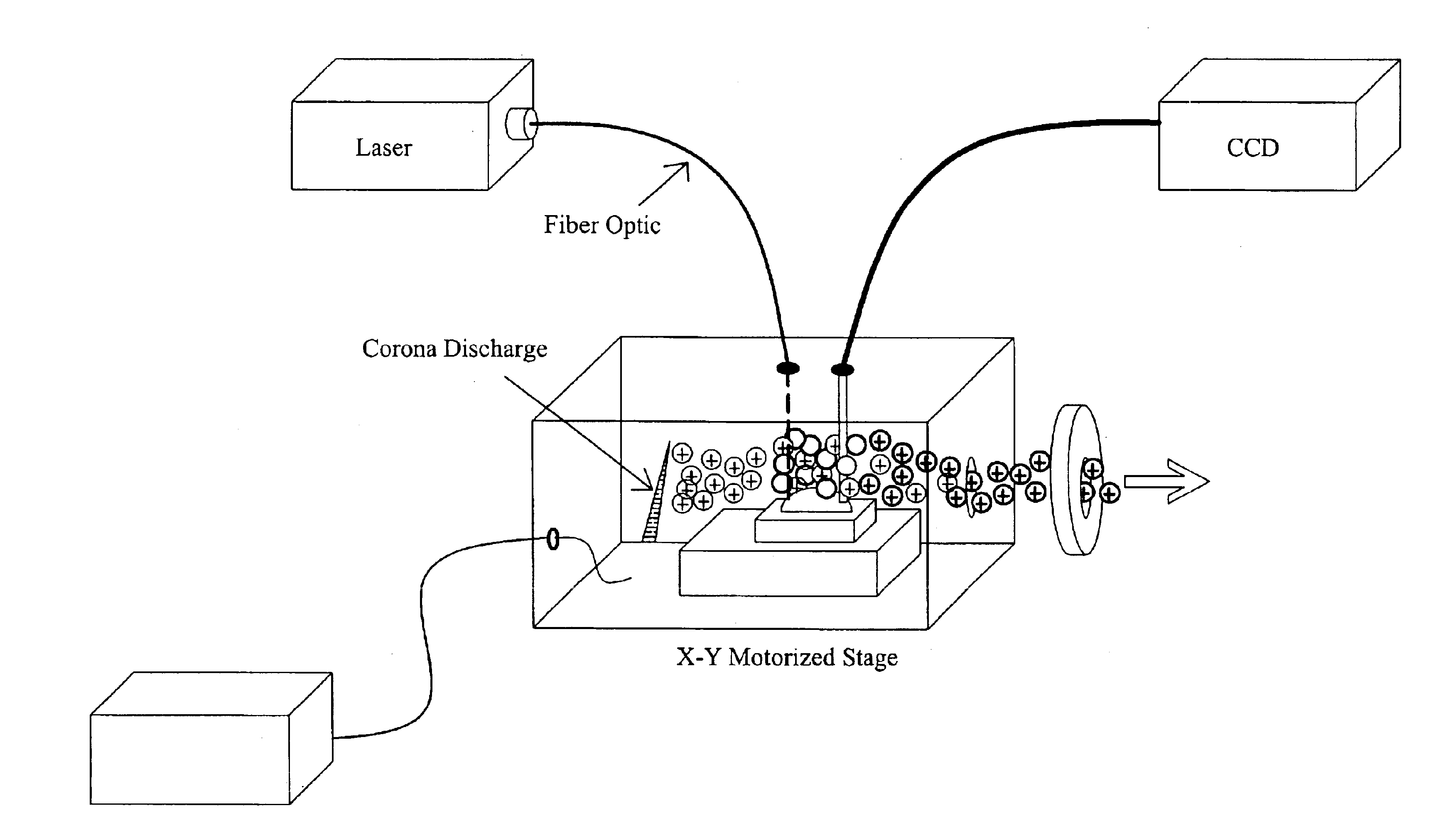
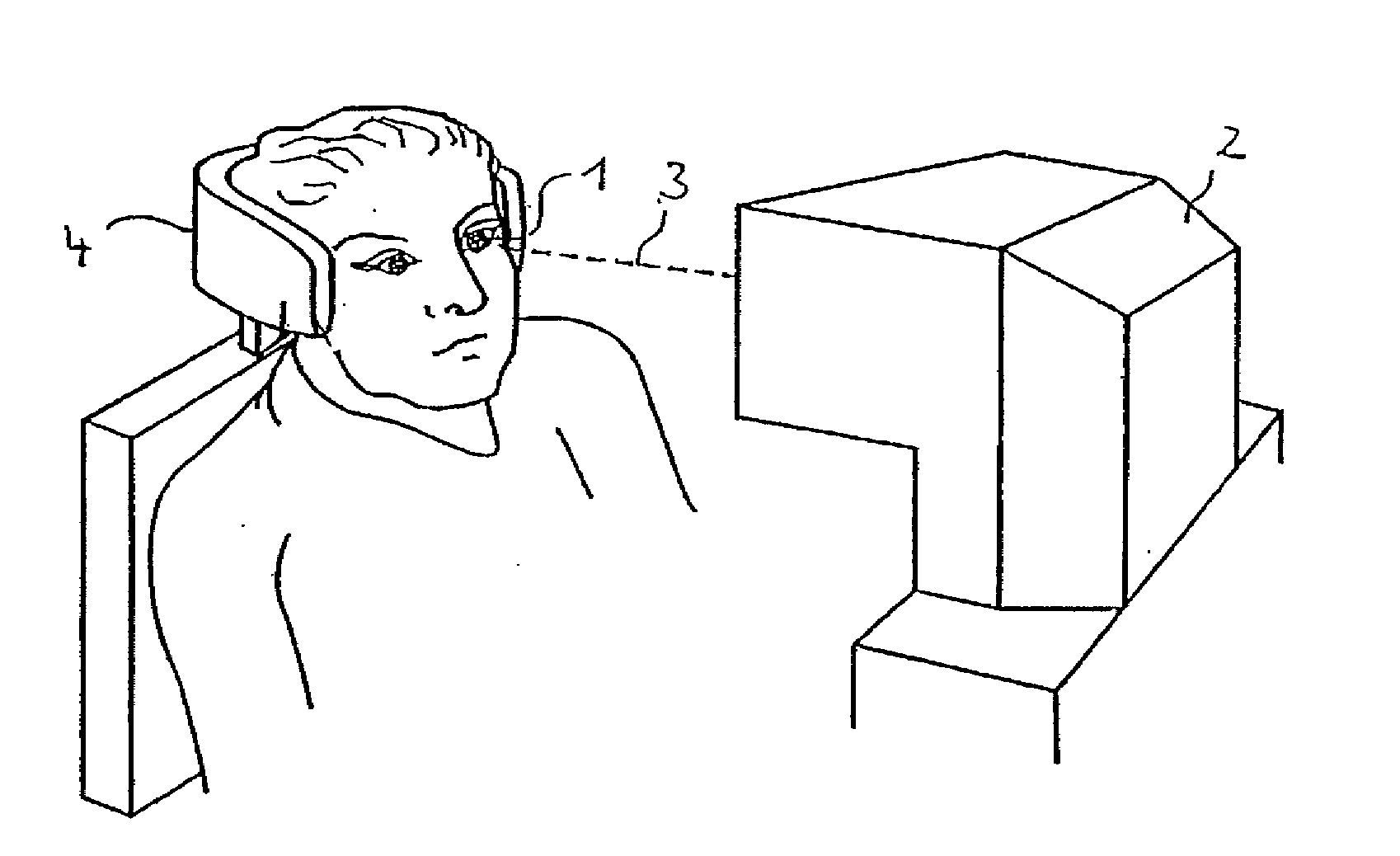
In-vivo laser damage automatic and quick detection device for optical element
ActiveCN103278309AStable and reliable in vivo injuryReduce judgment errorTesting optical propertiesVisual field lossPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses an in-vivo laser damage automatic and quick detection device for an optical element. The in-vivo laser damage automatic and quick detection device comprises the optical element to be detected arranged on a mobile platform, a pulse laser radiation system consisting of an Nd:YAG laser device and a first focusing lens which are sequentially arranged, an HeNe laser lighting system consisting of a first HeNe continuous laser device, a second focusing lens, a second HeNe laser device and a third focusing lens, and a damage detection system consisting of an aperture diaphragm, a scattered light collection lens group, a visual field diaphragm and a photoelectric detector which are coaxial sequentially, wherein the output end of the photoelectric detector is connected with the input end of a computer; and the output end of the computer is connected with the control ends of the Nd:YAG laser device and the mobile platform through a data output card. The in-vivo laser damage automatic and quick detection device is suitable for automatic and quick detection and judgment for in-vivo damages of optical elements of various types.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Space variant polarization converter
This patent describes an optical element, which converts incident linearly or circularly polarized visible light into radially or azimuthally polarized light beam. The polarization converter is a single optical element, produced by direct laser writing technique in an optically transparent substrate. Direct laser writing based on ultra-short pulsed laser radiation forms form birefringence self-assembled nanogratings in optically transparent material, such as fused silica. The period of gratings is smaller than wavelengths of a visible light.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Diffraction mode terahertz tomography
InactiveUS7129491B2Radiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsThz radiationPulsed laser radiation
A method of obtaining a series of images of a three-dimensional object. The method includes the steps of transmitting pulsed terahertz (THz) radiation through the entire object from a plurality of angles, optically detecting changes in the transmitted THz radiation using pulsed laser radiation, and constructing a plurality of imaged slices of the three-dimensional object using the detected changes in the transmitted THz radiation. The THz radiation is transmitted through the object as a two-dimensional array of parallel rays. The optical detection is an array of detectors such as a CCD sensor.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Passively Q-switched laser with adjustable pulse repetition rate
A method is disclosed for varying a pulse repetition rate of a passively q-switched laser while maintaining other characteristics of the laser radiation. The laser is optically pumped with a sequence of pump pulses which includes alterations between non-zero power levels and is characterized by two adjustable parameters. By simultaneously changing the adjustable parameters, the pulse repetition rate of the laser can be changed while maintaining the laser pulse energy, divergence of the pulsed laser radiation, and optical spectrum of the pulsed laser radiation at constant levels. In one embodiment, the sequence of pump pulses includes pump power offset which magnitude and / or duration is adjusted when the laser repetition rate is changed.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Applicator and device for cell treatment
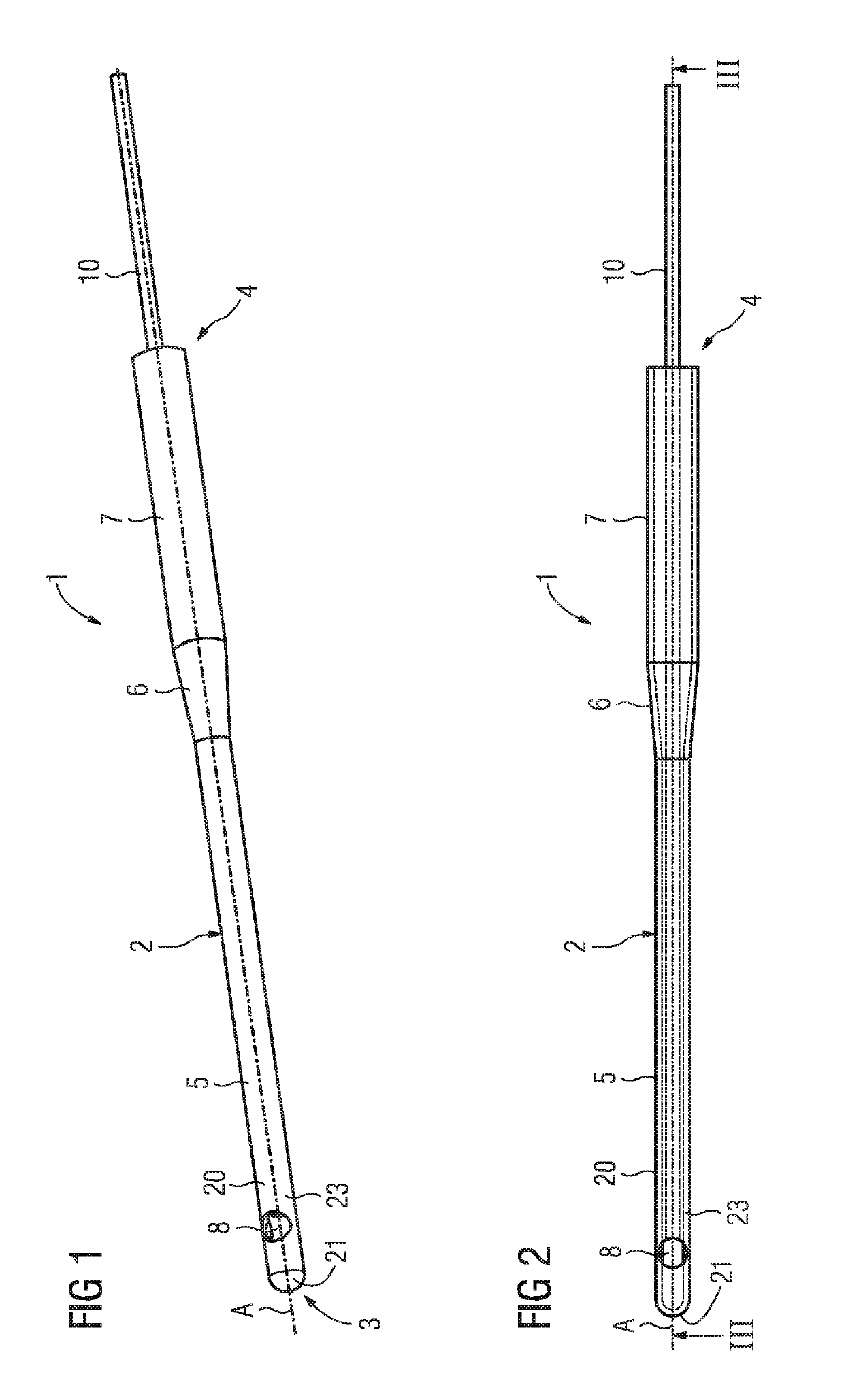
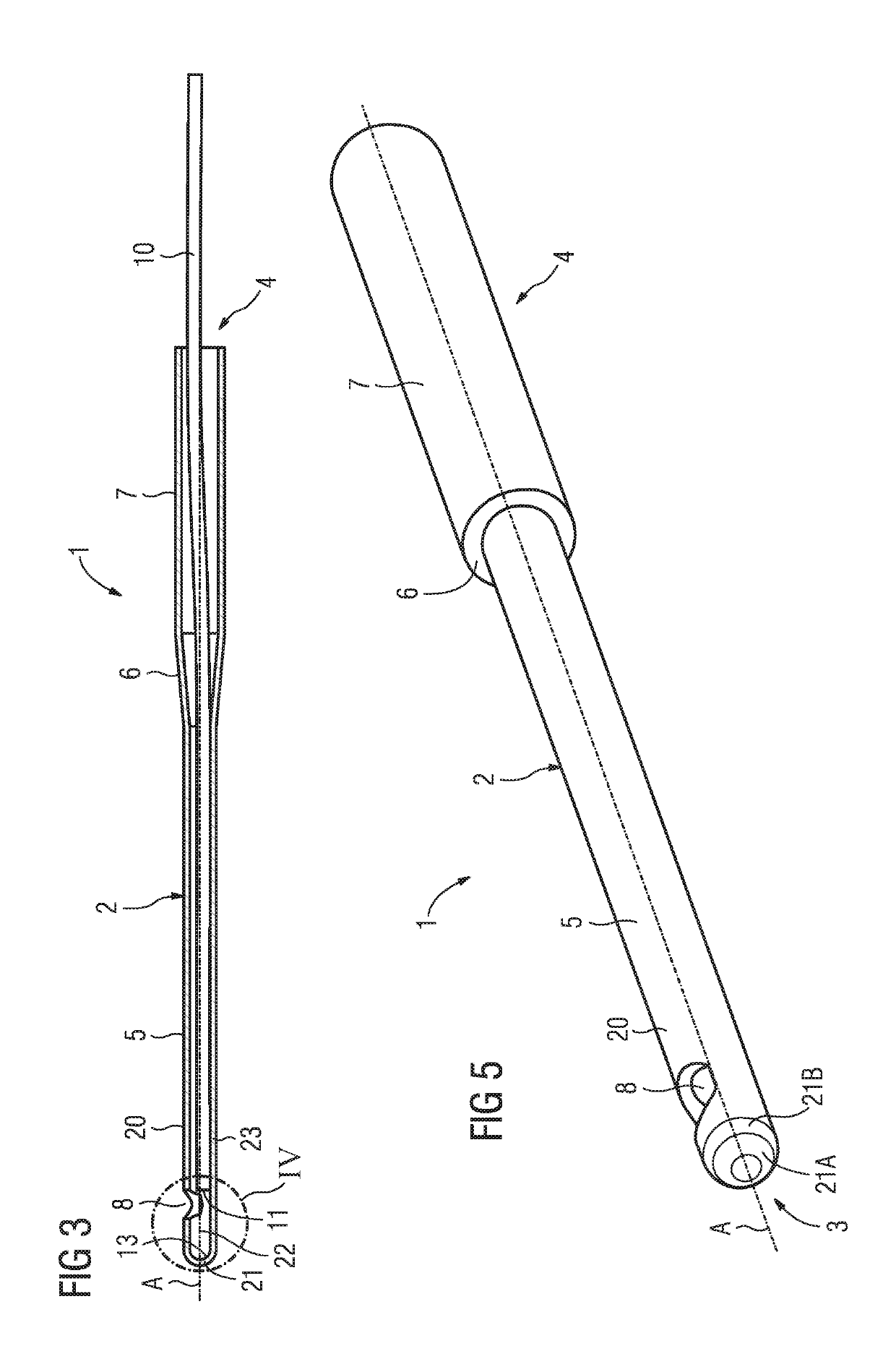
An applicator configured for cell treatment with pressure pulses has a hollow needle with a wall, which encloses a cavity and has a closed-off design at a closed-off end. A target is arranged or formed at the closed-off end on the inner side of the wall and a laser radiation emitter for emitting preferably pulsed laser radiation is arranged in the cavity of the hollow needle, at a distance from the target. The laser radiation emitter is arranged so that the emerging laser radiation impinges directly on the target through an interspace situated between the laser radiation emitter and the target. Under the formation of a plasma, at least one pressure pulse can be generated at the target by the target being impinged upon by laser radiation from the laser radiation emitter. The wall of the hollow needle has a lateral emergence opening for the emergence of the pressure pulse.
Owner:A R C LASER
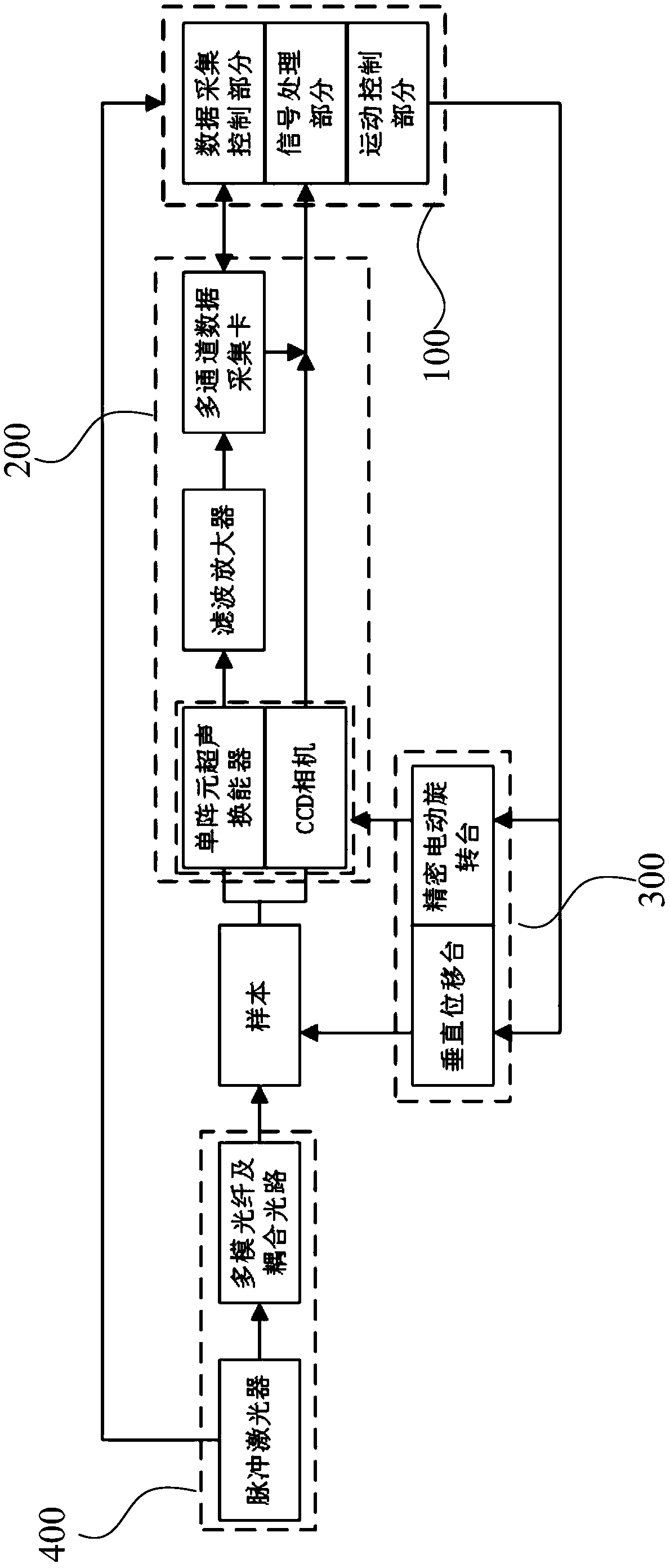
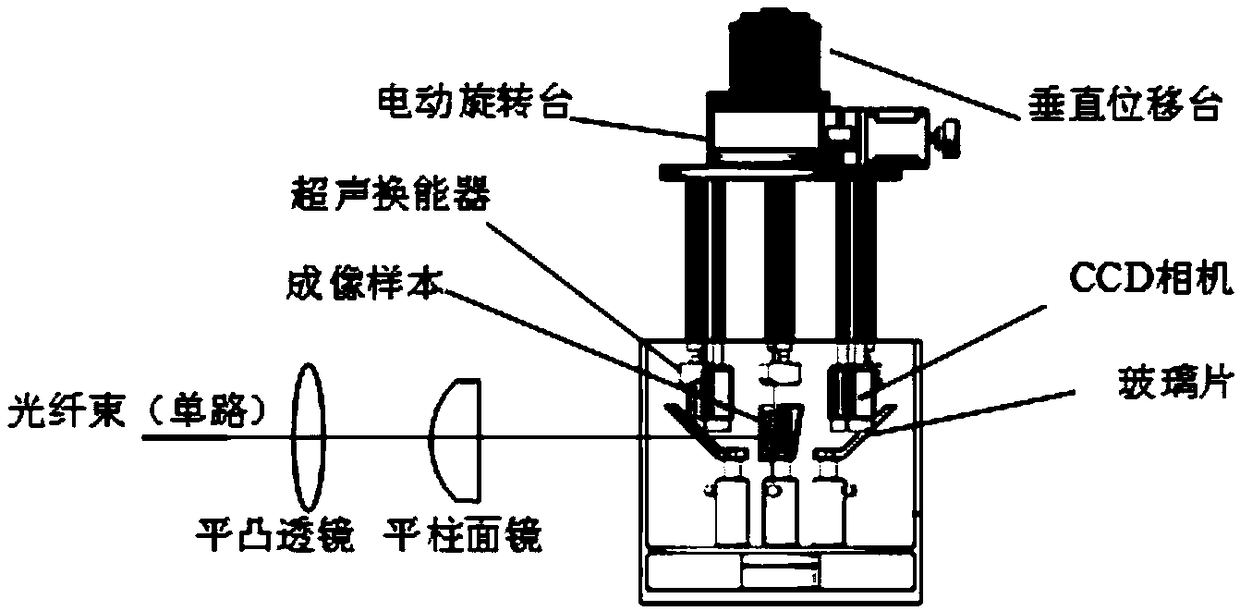
Ultrasonic, photoacoustic and fluorescent three-mode imaging system
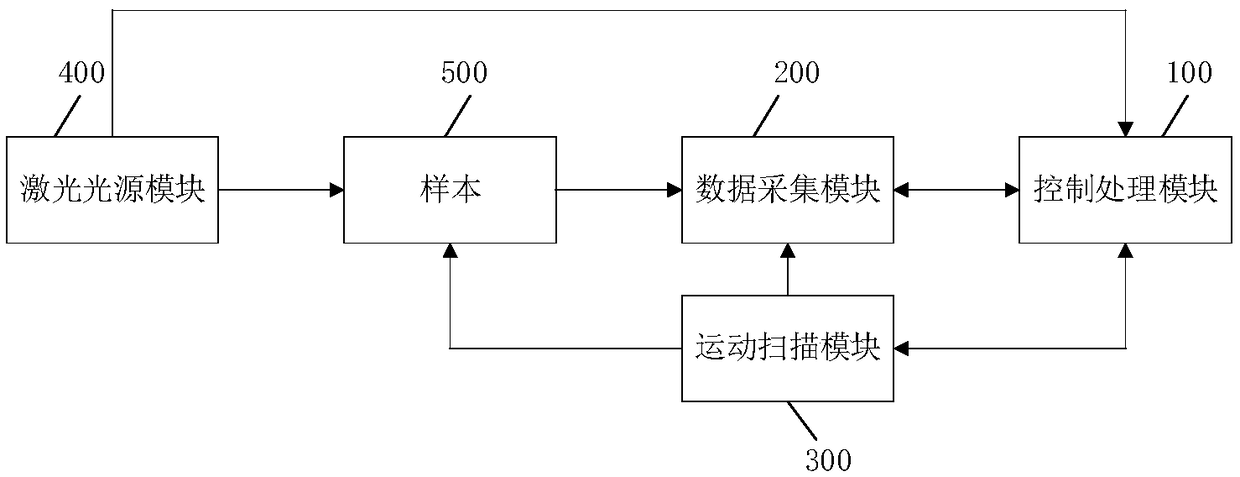
InactiveCN108717045AImprove imaging resolutionUniform Laser IrradiationFluorescence/phosphorescenceSonificationFluorescence
The invention provides an ultrasonic, photoacoustic and fluorescent three-mode imaging system. The ultrasonic, photoacoustic and fluorescent three-mode imaging system comprises a laser light source module, a motion scanning module, a data acquisition module and a control processing module; the laser light source module is used for providing pulsed laser radiation to an imaging sample and enablingthe imaging sample to generate photoacoustic and fluorescent signals and sending synchronous trigger signals to the data acquisition module and the control processing module; the motion scanning module is used for performing three-dimensional scanning on the sample according to preset motion parameters; the data acquisition module is used for acquiring the photoacoustic / ultrasonic / fluorescent signals generated from the sample; the control processing module is used for receiving trigger pulse signals of a pulsed laser light source, enabling a motion scanning device to scan a target sample according to control instruments, processing received data of the target sample and fusing photoacoustic / ultrasonic / fluorescent images to acquire multimodal reconstructed images. By the arrangement, scanning time in imaging is reduced, and imaging resolution and imaging speed of the imaging system are increased.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
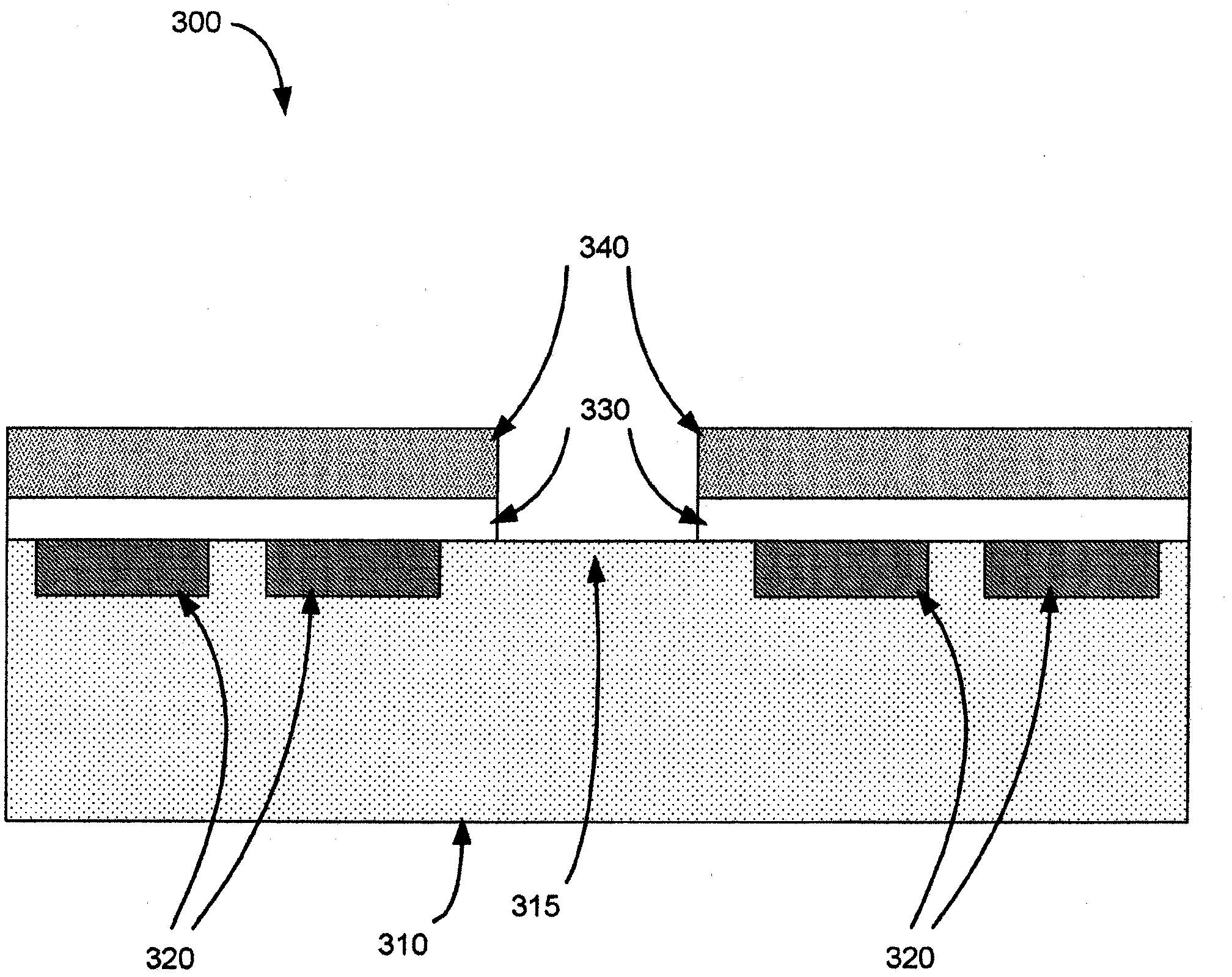
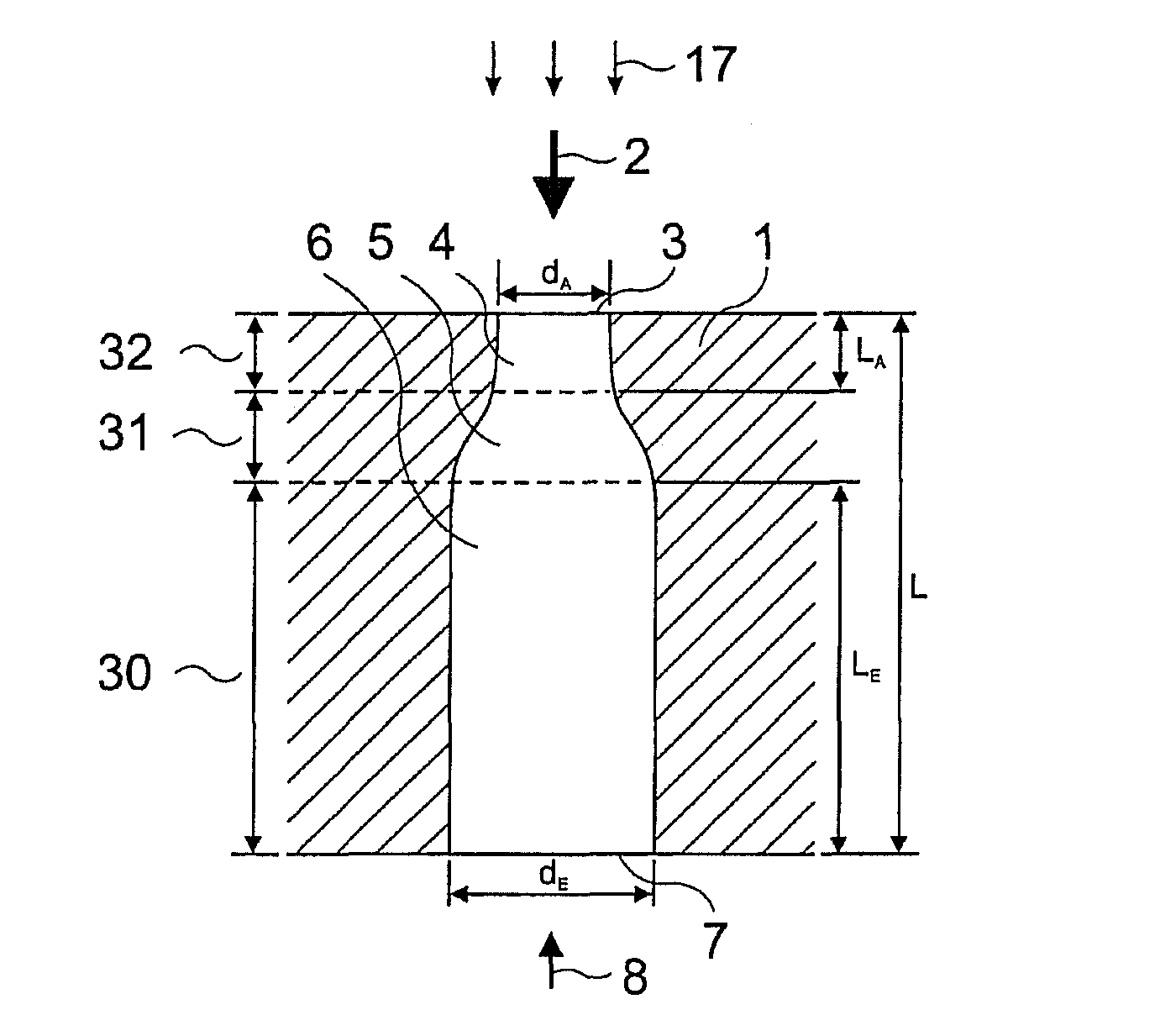
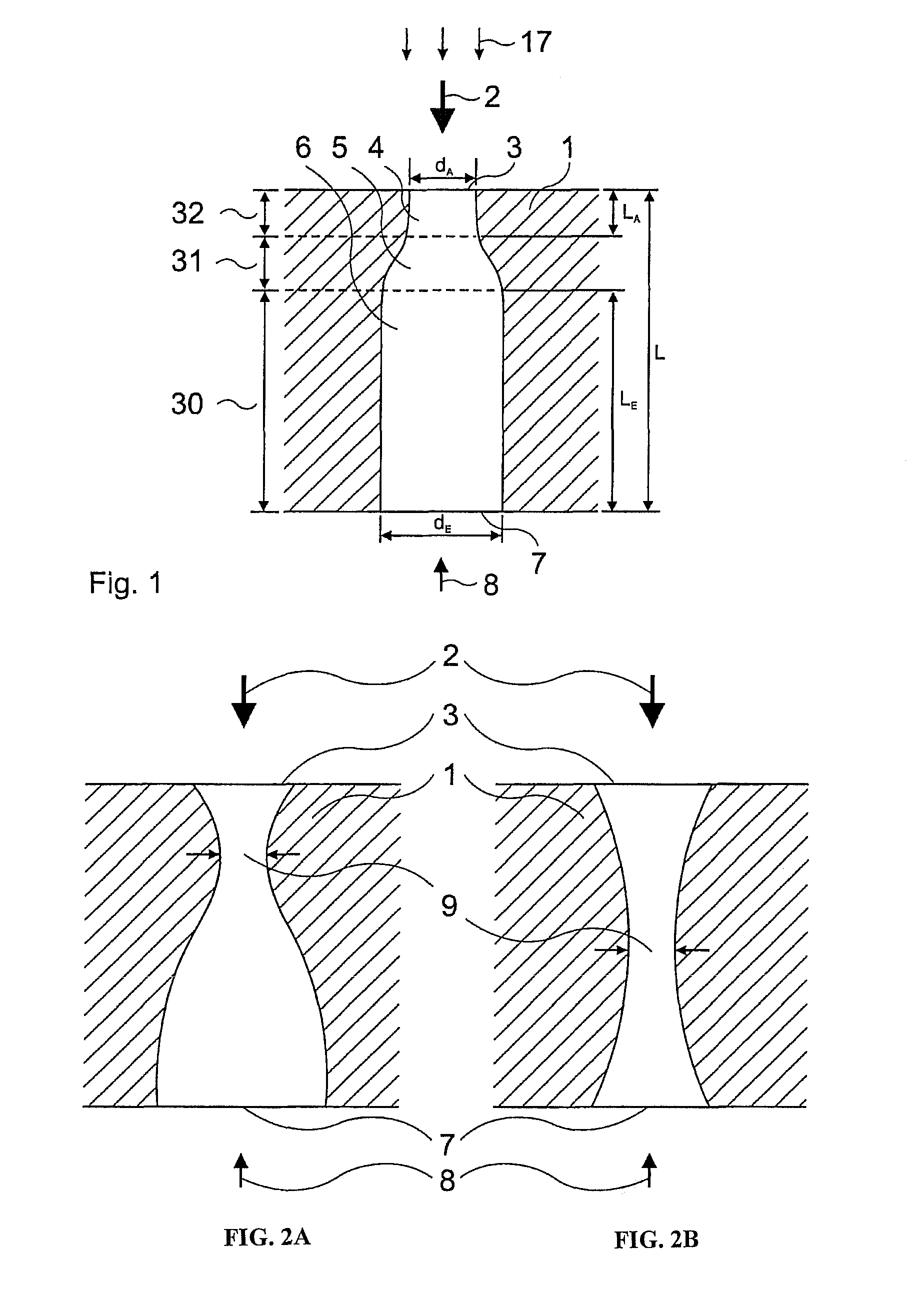
Method for boring bottle-like holes having a defined geometry by means of pulsed laser radiation
InactiveUS8237083B2SwiftlySmall diameterFuel injection apparatusMachines/enginesBeam diameterLight beam
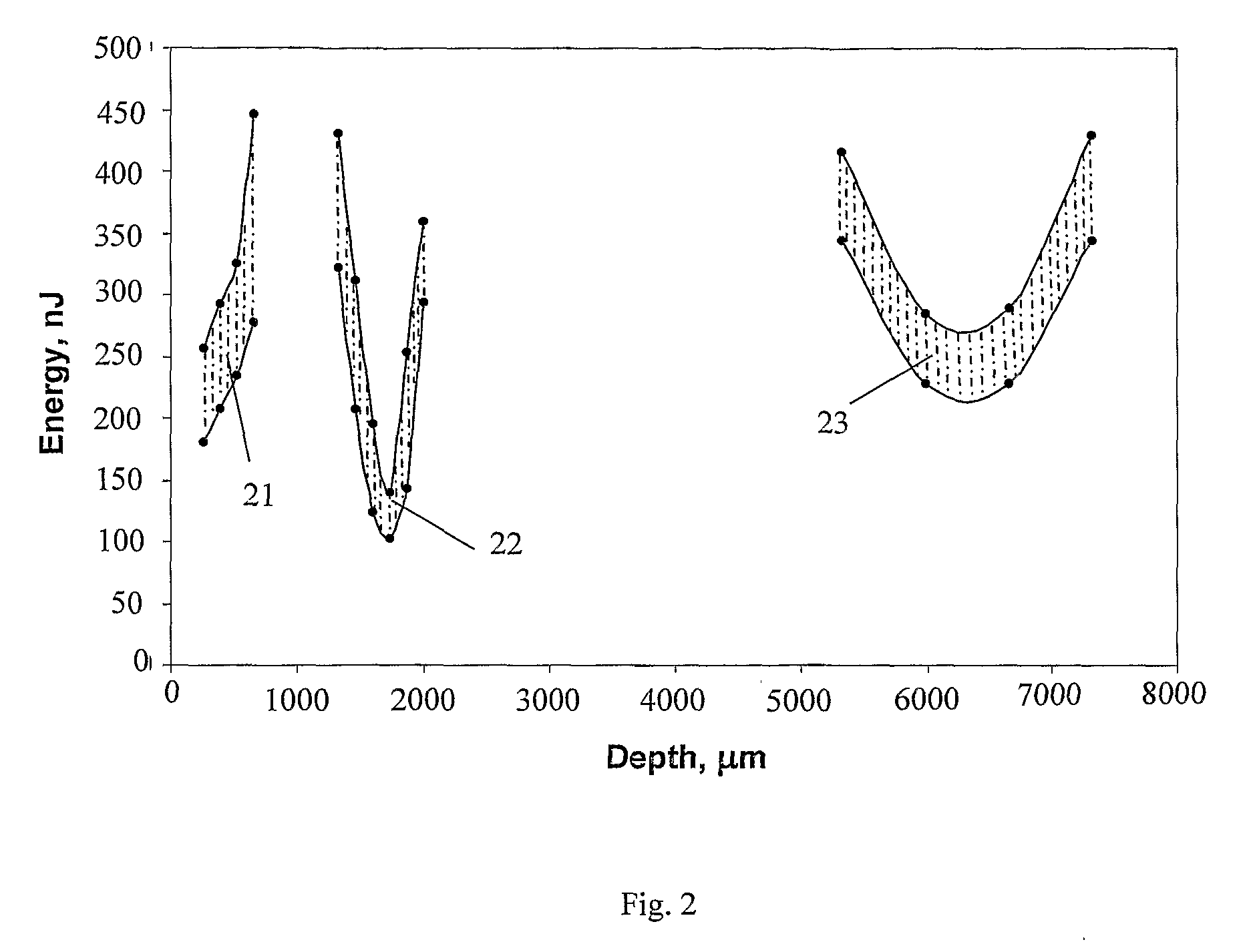
The present invention is a method and system for the drilling of holes in a workpiece within a diameter range of 20 μm to 500 μm by means of laser radiation. The invention utilizes the beam quality of a laser beam as well as: the polarization of the laser radiation; the parameters of the impulses of the laser used; and, the type and pressure of the process gas used. The method and system utilize means for focusing laser radiation, in particular the ratio of the beam diameter at the site of the focusing element and its focal distance, and wherein the focusing is done in coordination with the beam quality number and wave length and other factors. A first working gas supports the formation of the hole shape and accelerates the drilling process; and, a second working gas is utilized to improve the surface quality of the drilling walls.
Owner:PRELATEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com