Patents
Literature
767 results about "Laser assisted" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
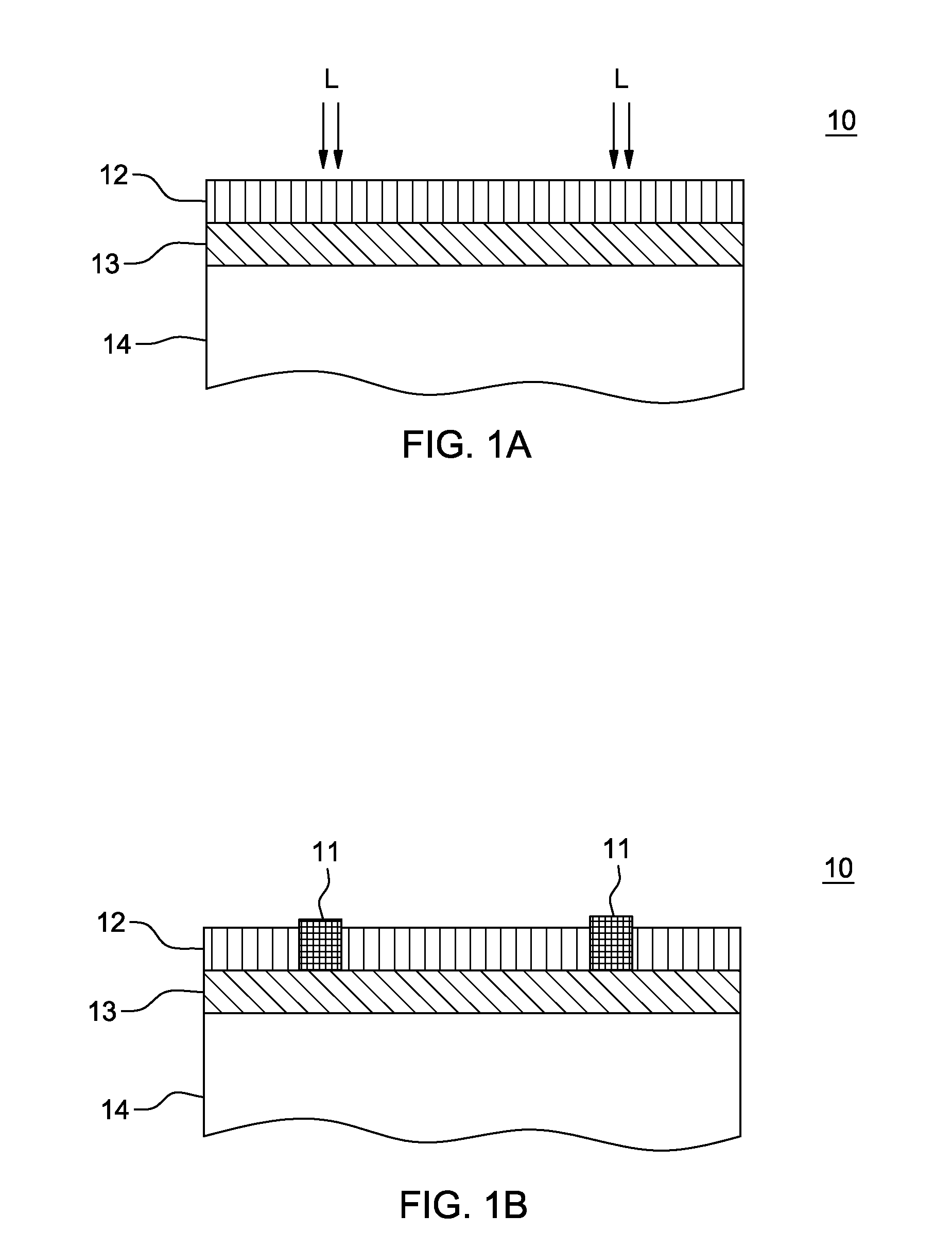
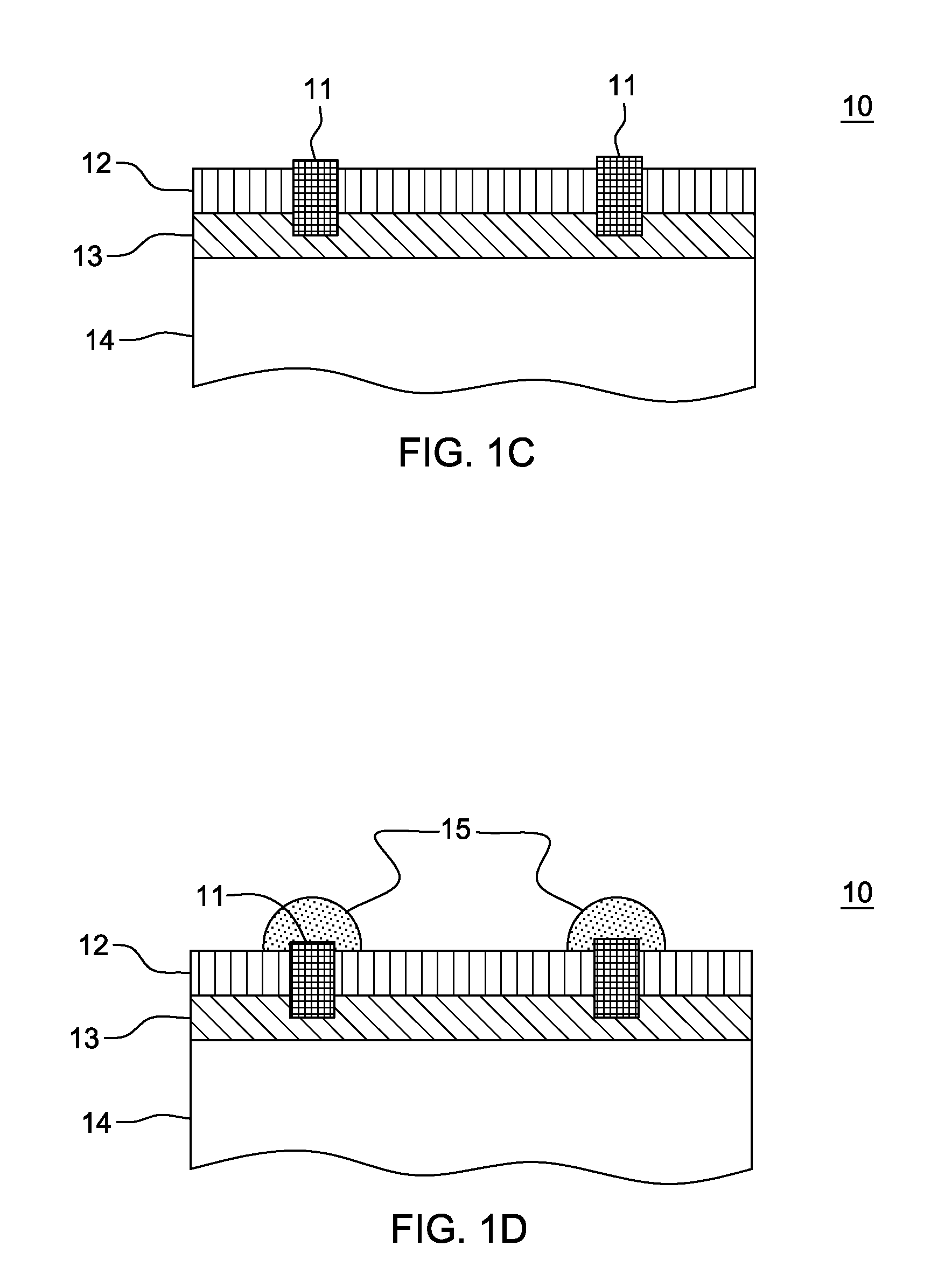
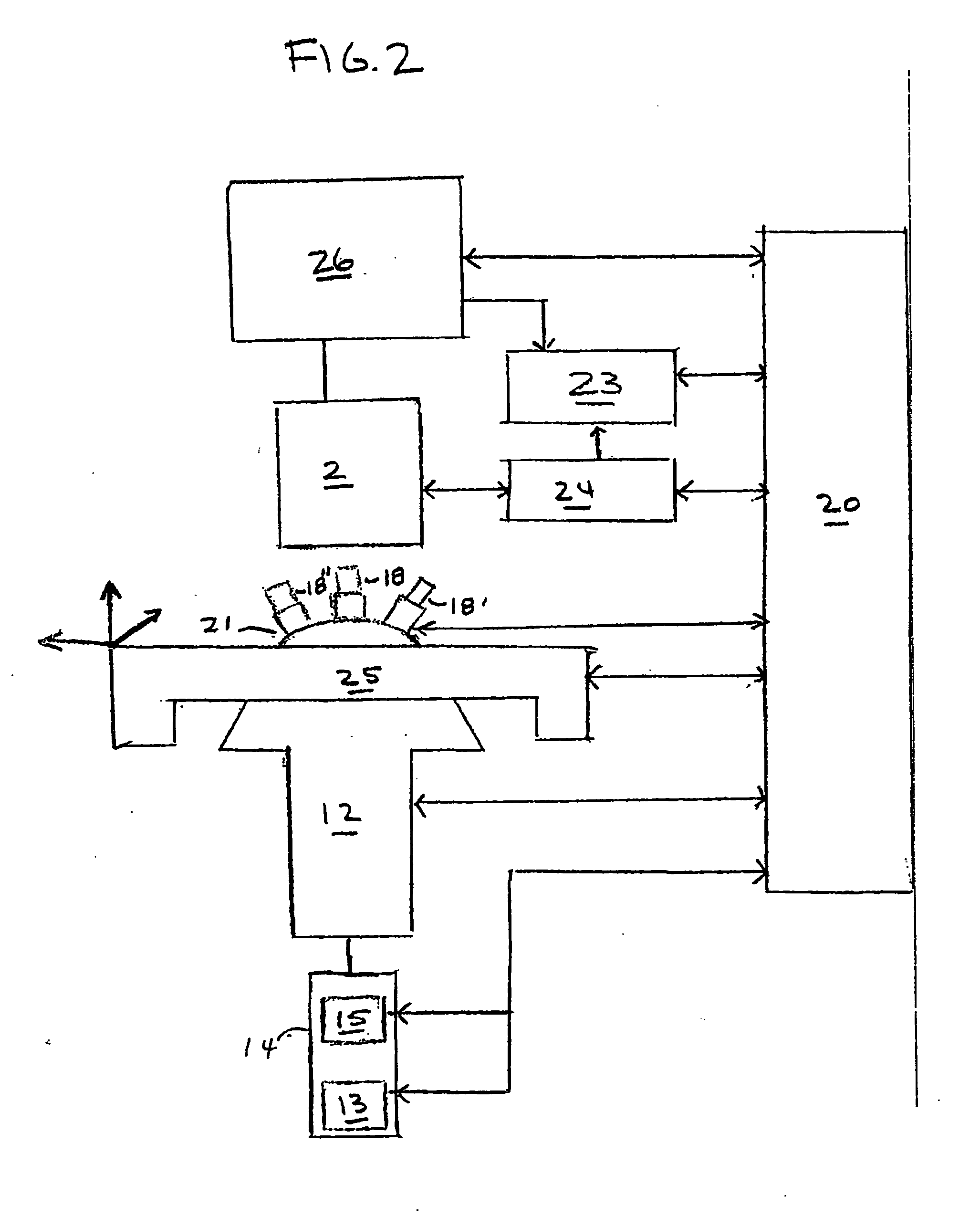
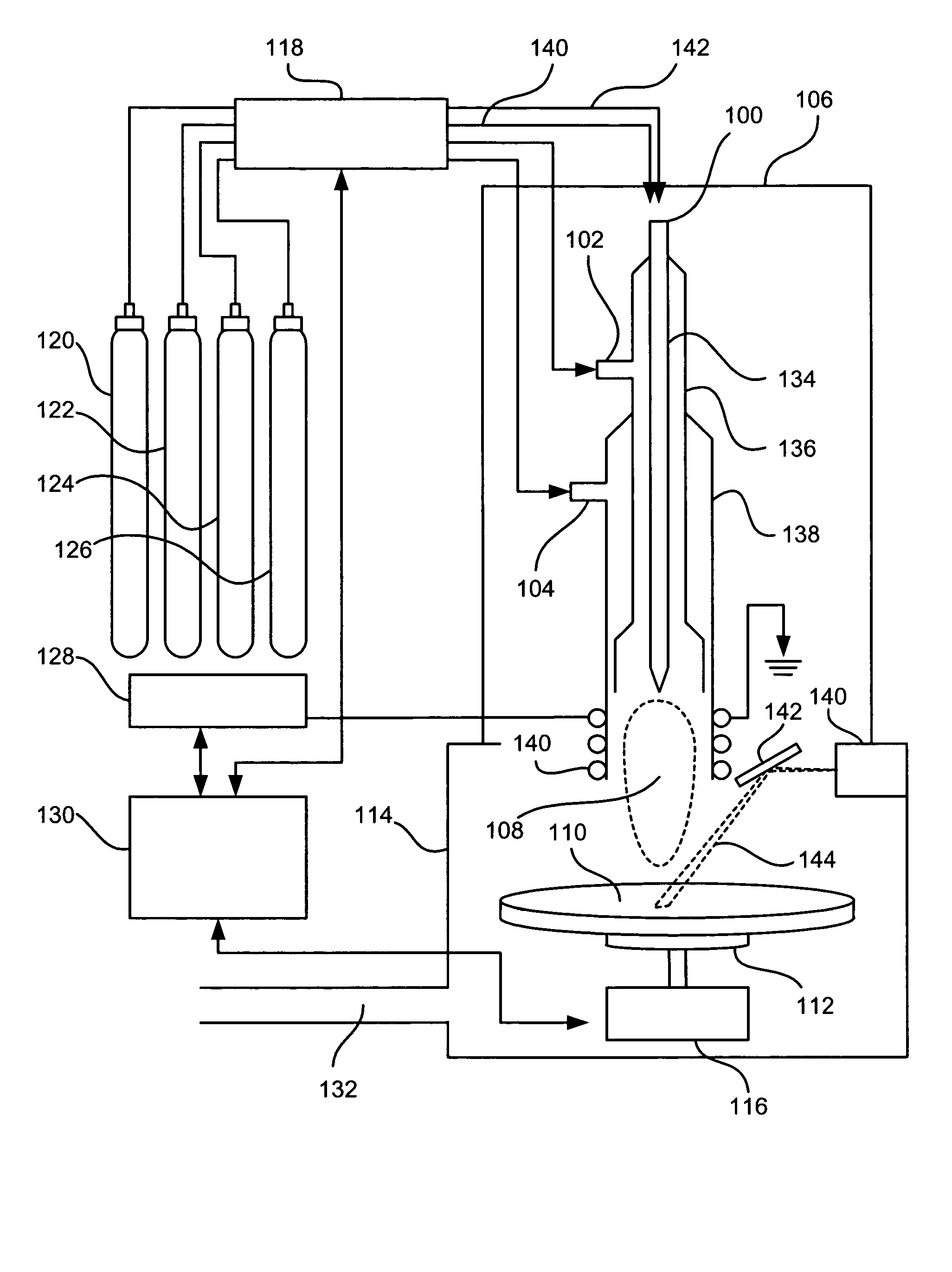
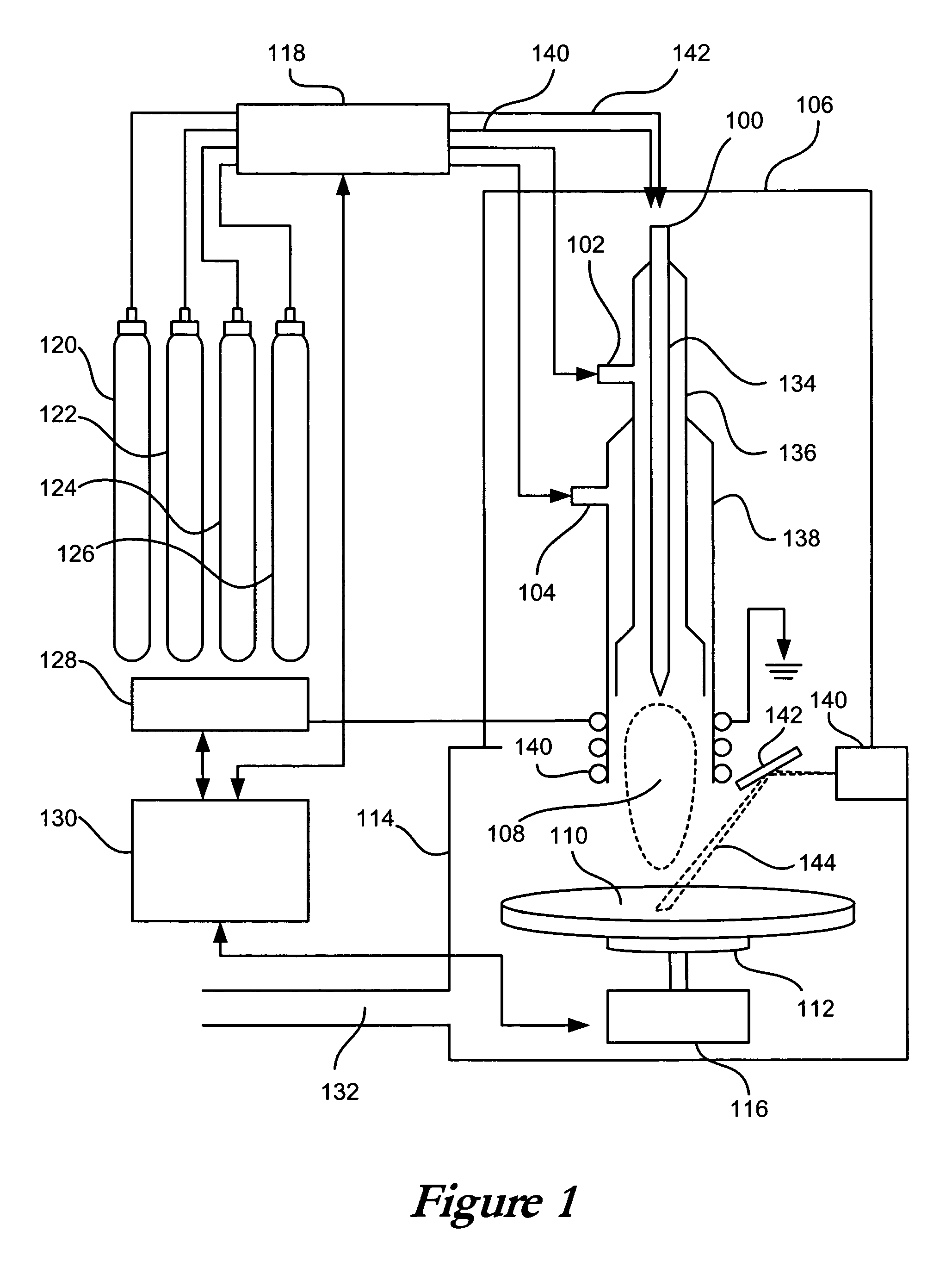
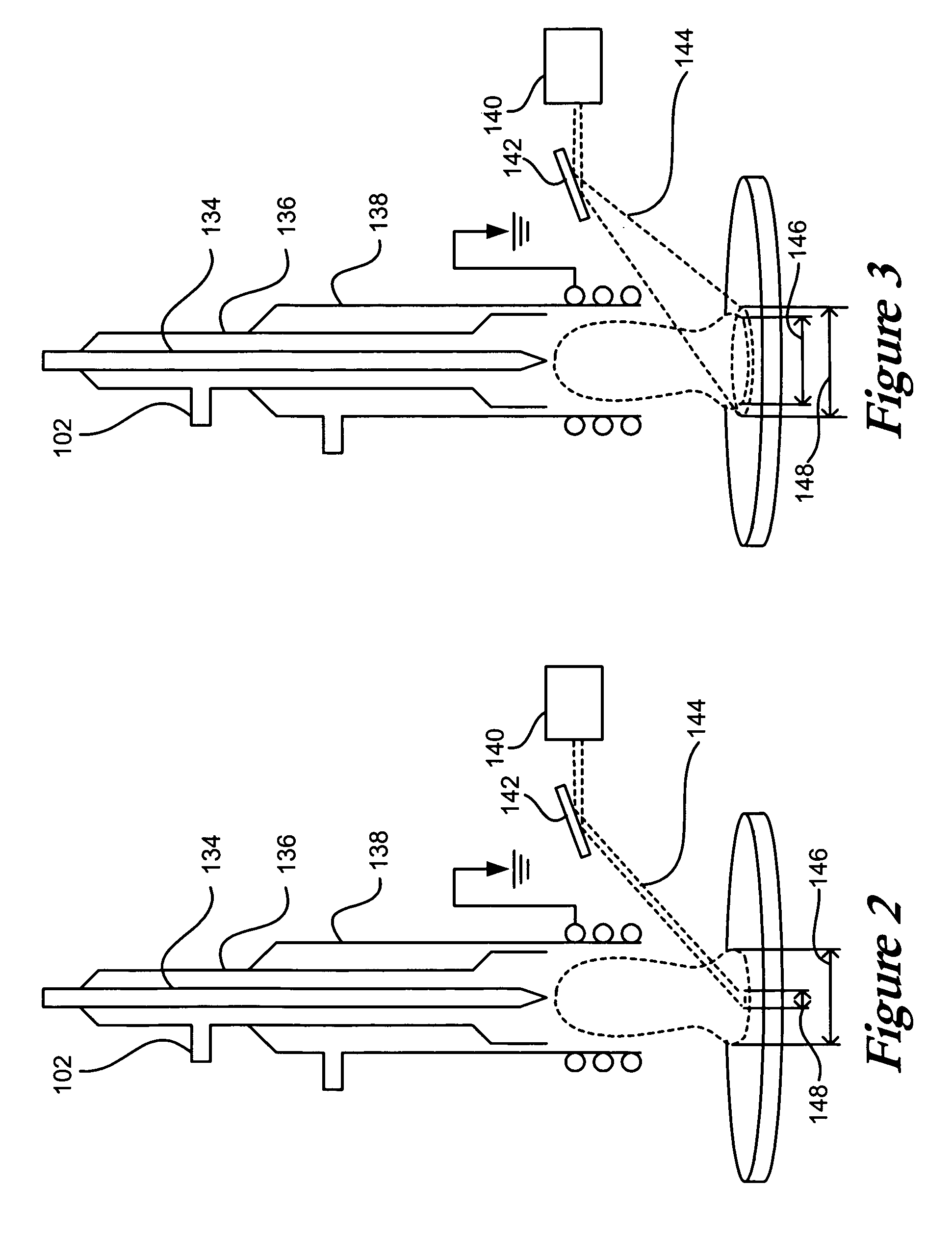
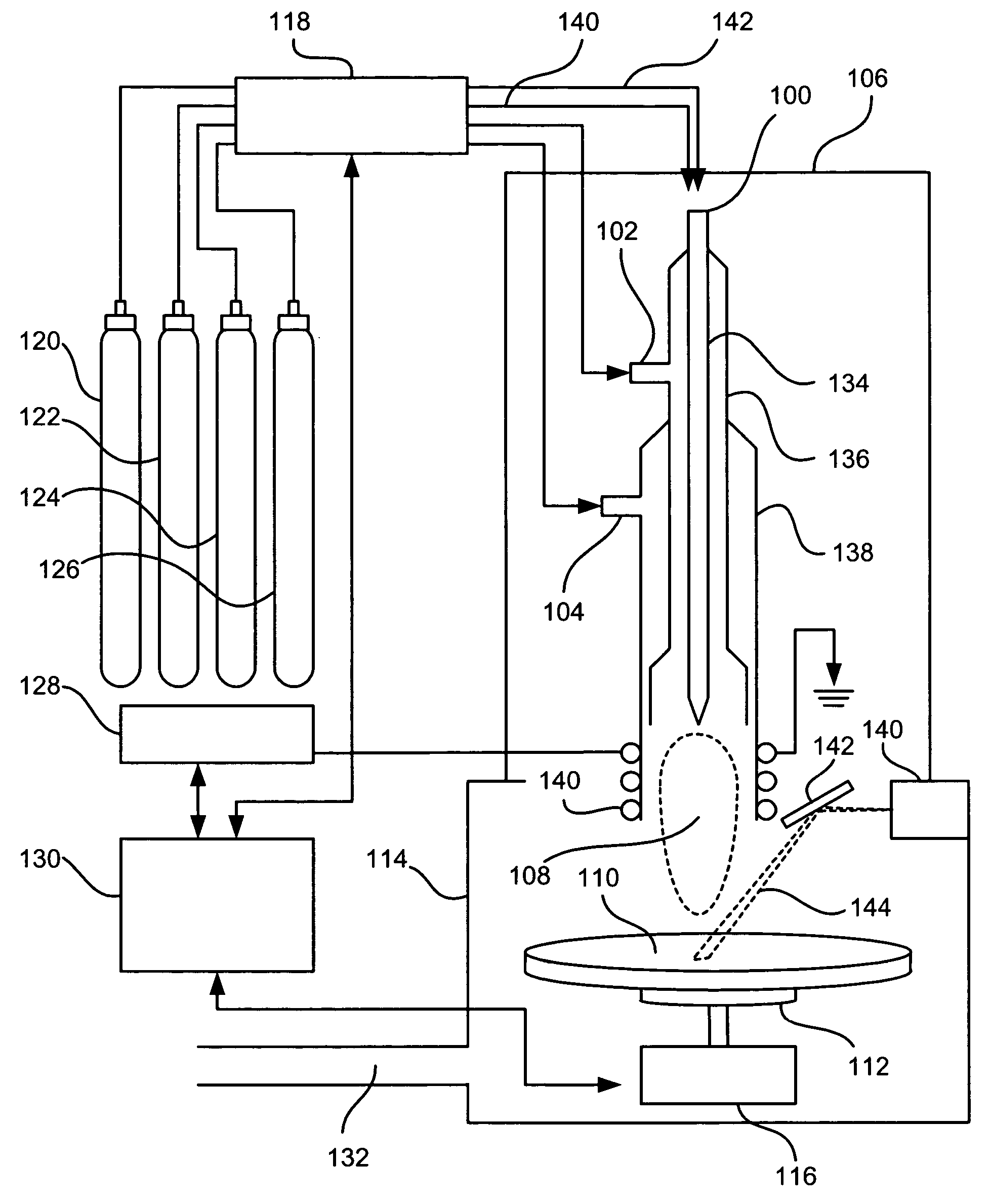
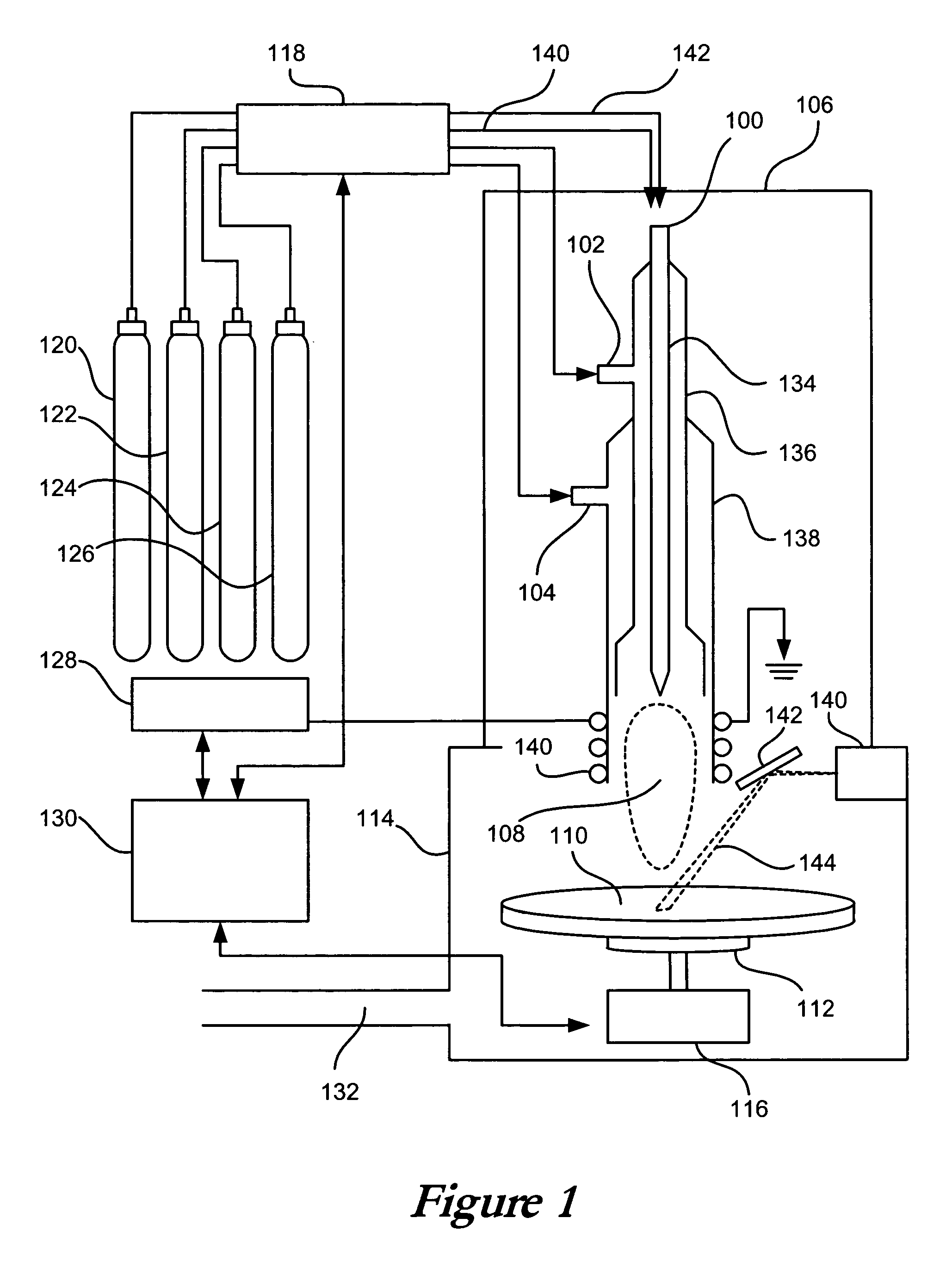
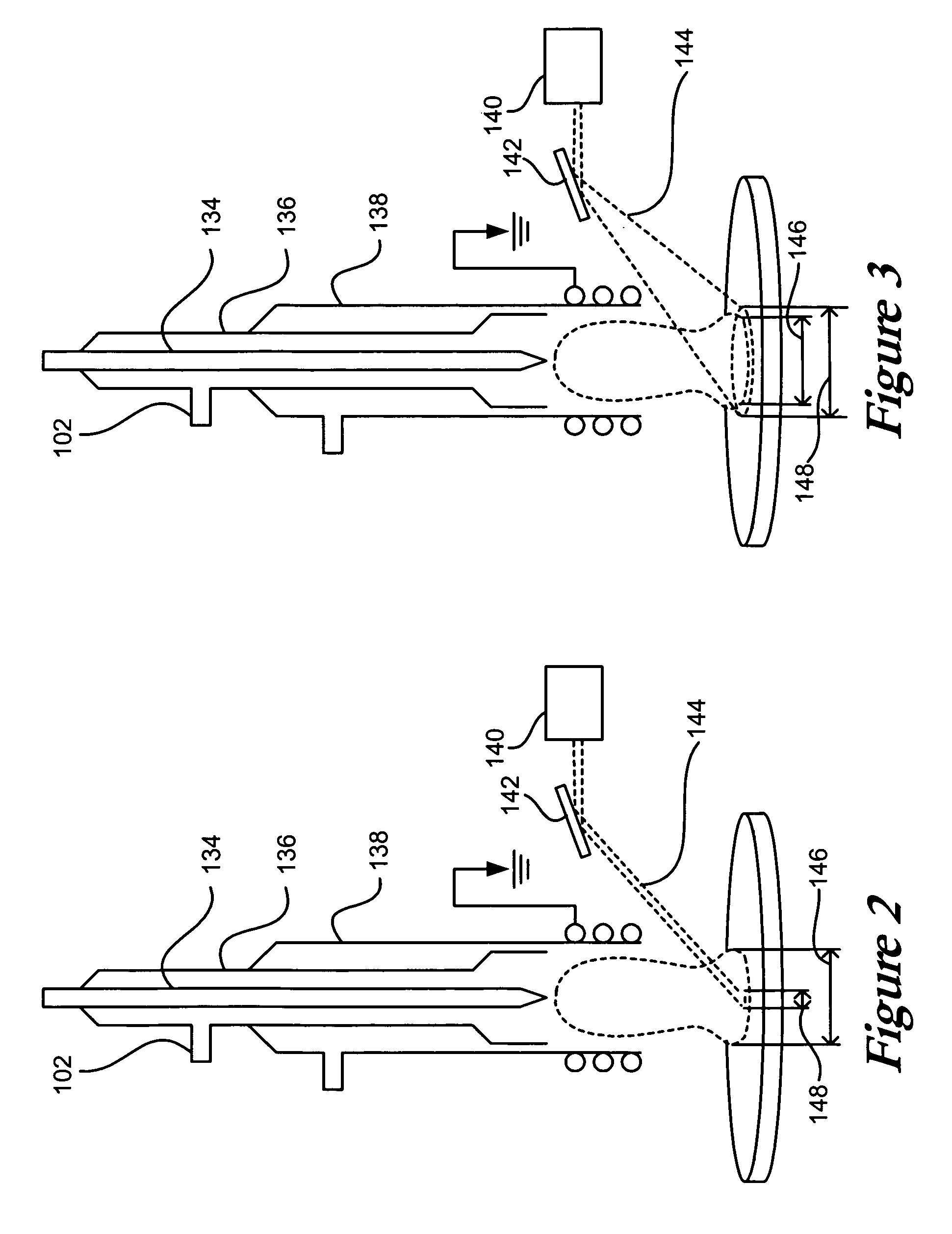
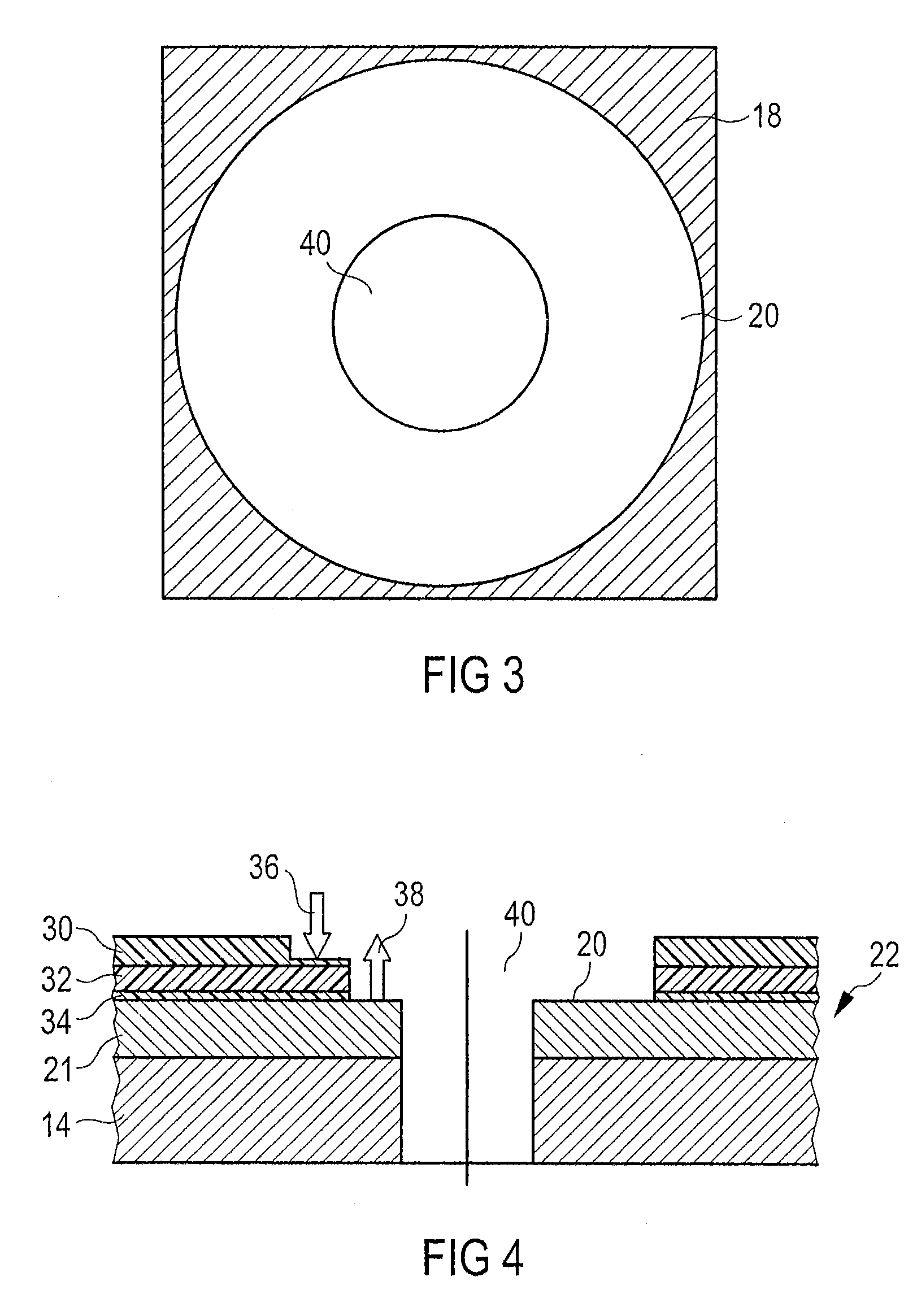
Method and apparatus for laser assisted cataract surgery
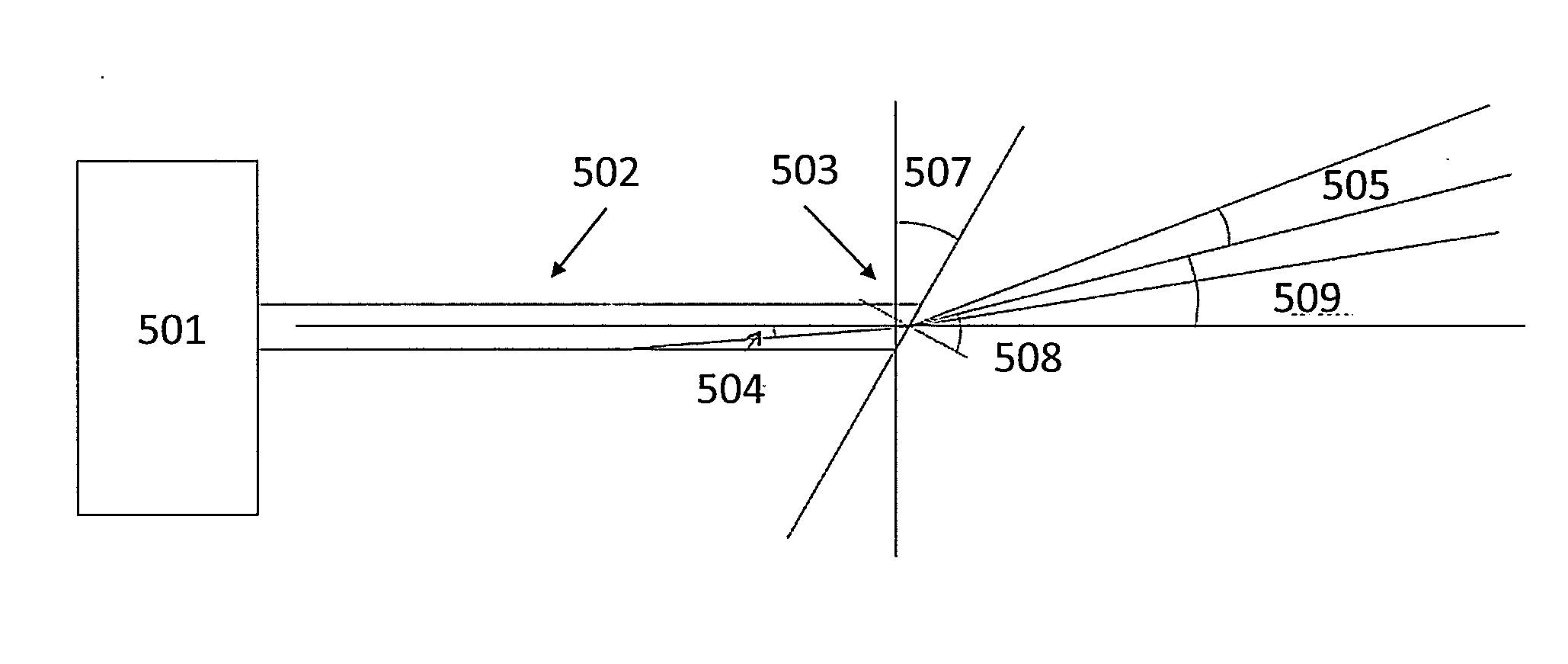
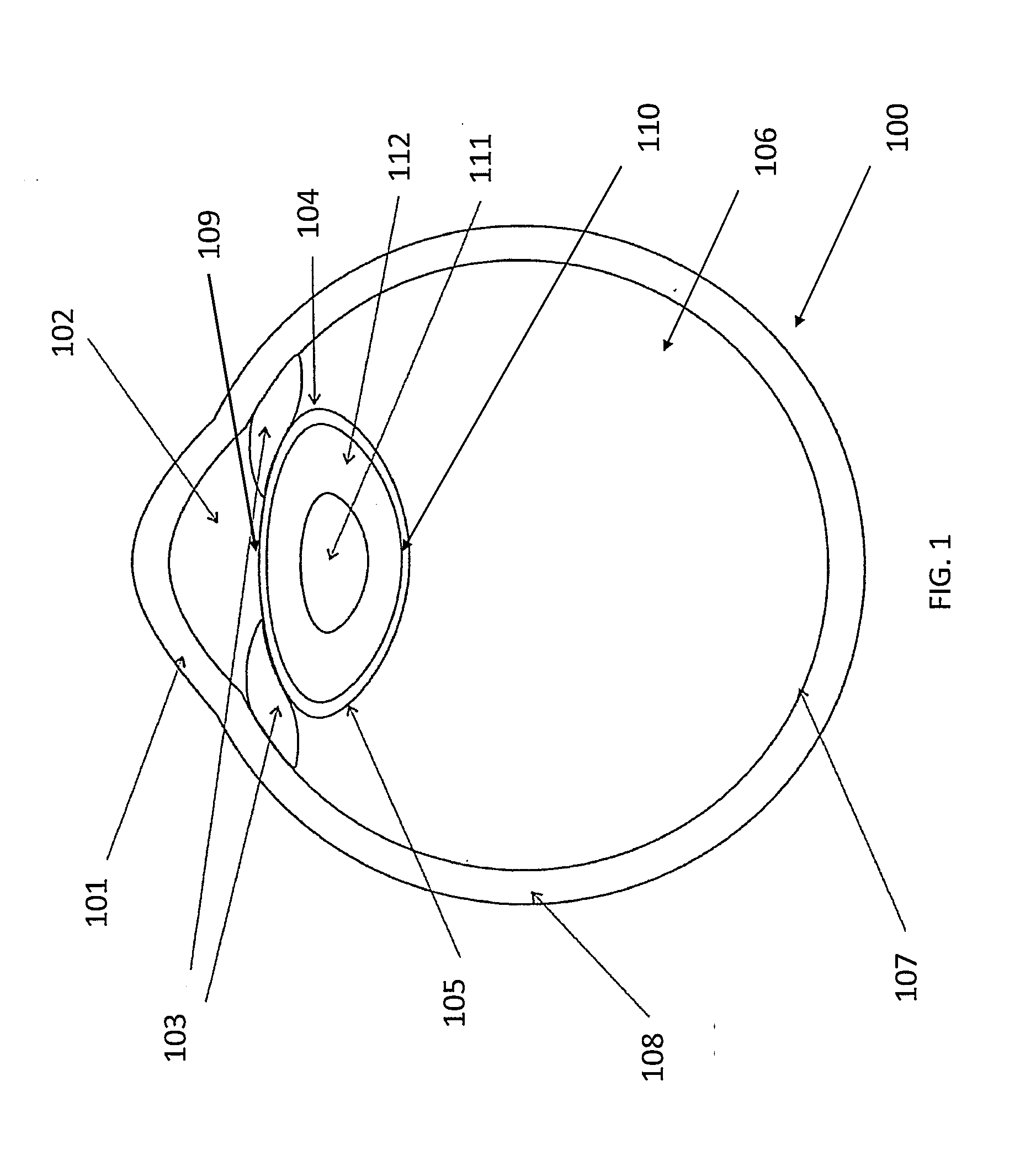
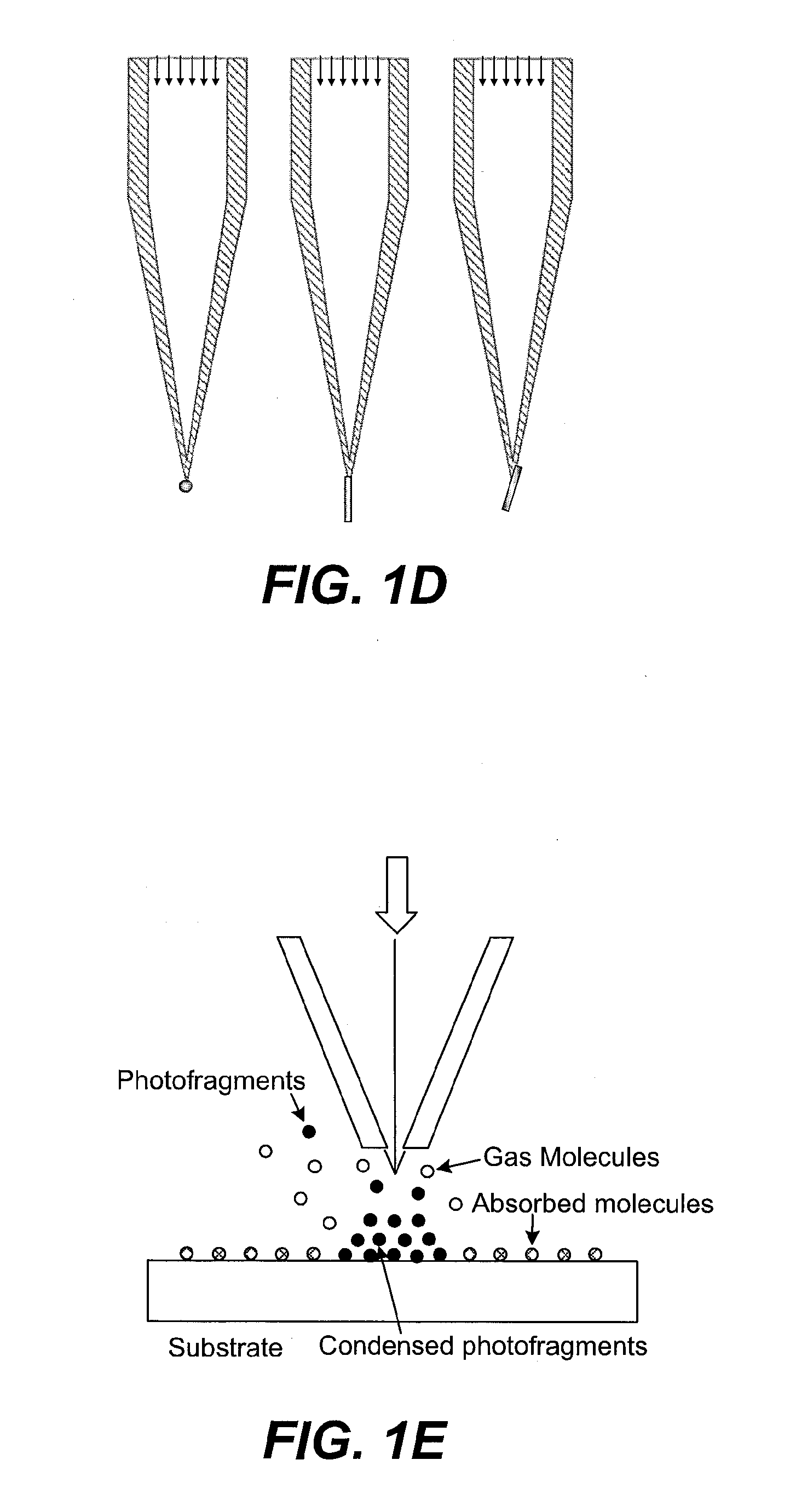
Devices and methods for use in laser-assisted surgery, particularly cataract surgery. Specifically, the use of an optical fiber with a proximal and distal end, wherein the distal end has a non-orthogonal angle with the diameter of the optical fiber, to create an off-axis steam bubble for cutting and removing tissue in an operative region. Where the optical fiber is bent, rotating the fiber creates a circular cutting path for the steam bubble, allowing access to tissues that may normally be blocked by obstructions and obstacles.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Laser-assisted placement of veiled composite material
InactiveUS20060048881A1Easy to controlLamination ancillary operationsLaminationThermoplasticOptoelectronics
A method of forming preform structures from fiber composite materials in an automated tape placement process, for subsequent resin infusion and heating. Pulsed laser radiation is directed into a nip region of a compaction roller during formation of a composite preform structure to selectively heat discrete areas on a resin veil of thermoplastic to an incoming fiber tape material and a surface of a substrate, to more precisely control tacking of the resin veil of thermoplastic to the fiber tape and the surface of a substrate in predetermined locations.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
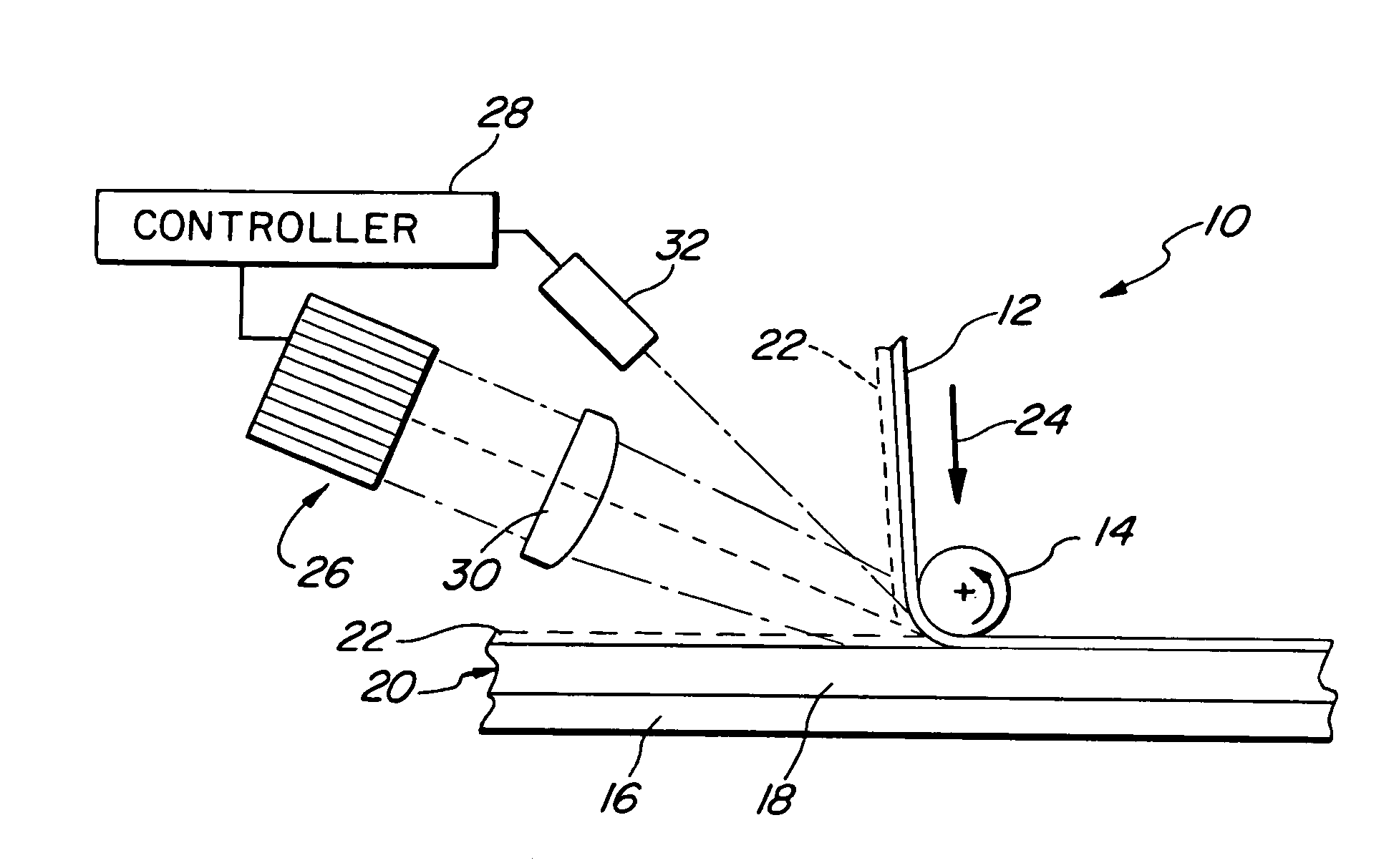
Laser assisted drilling
An apparatus for drilling underground having at least one optical fiber for transmitting light energy from a laser energy source disposed above ground to an underground drilling location and a mechanical drill bit having at least one cutting surface and forming at least one light transmission channel aligned to transmit light from the at least one optical fiber through the mechanical drill bit by way of the at least one light transmission channel.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Systems and Methods of Laser Texturing and Crystallization of Material Surfaces
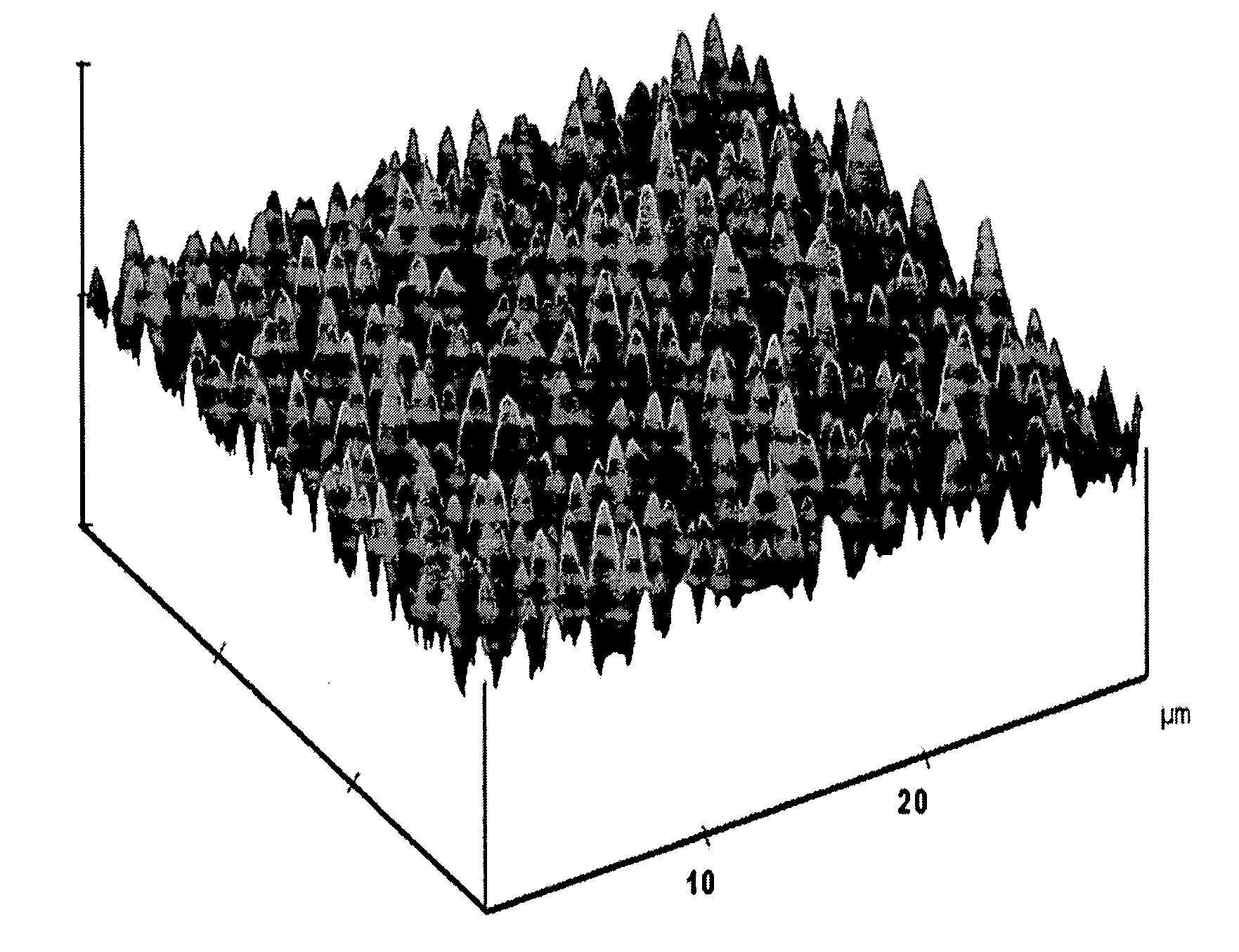
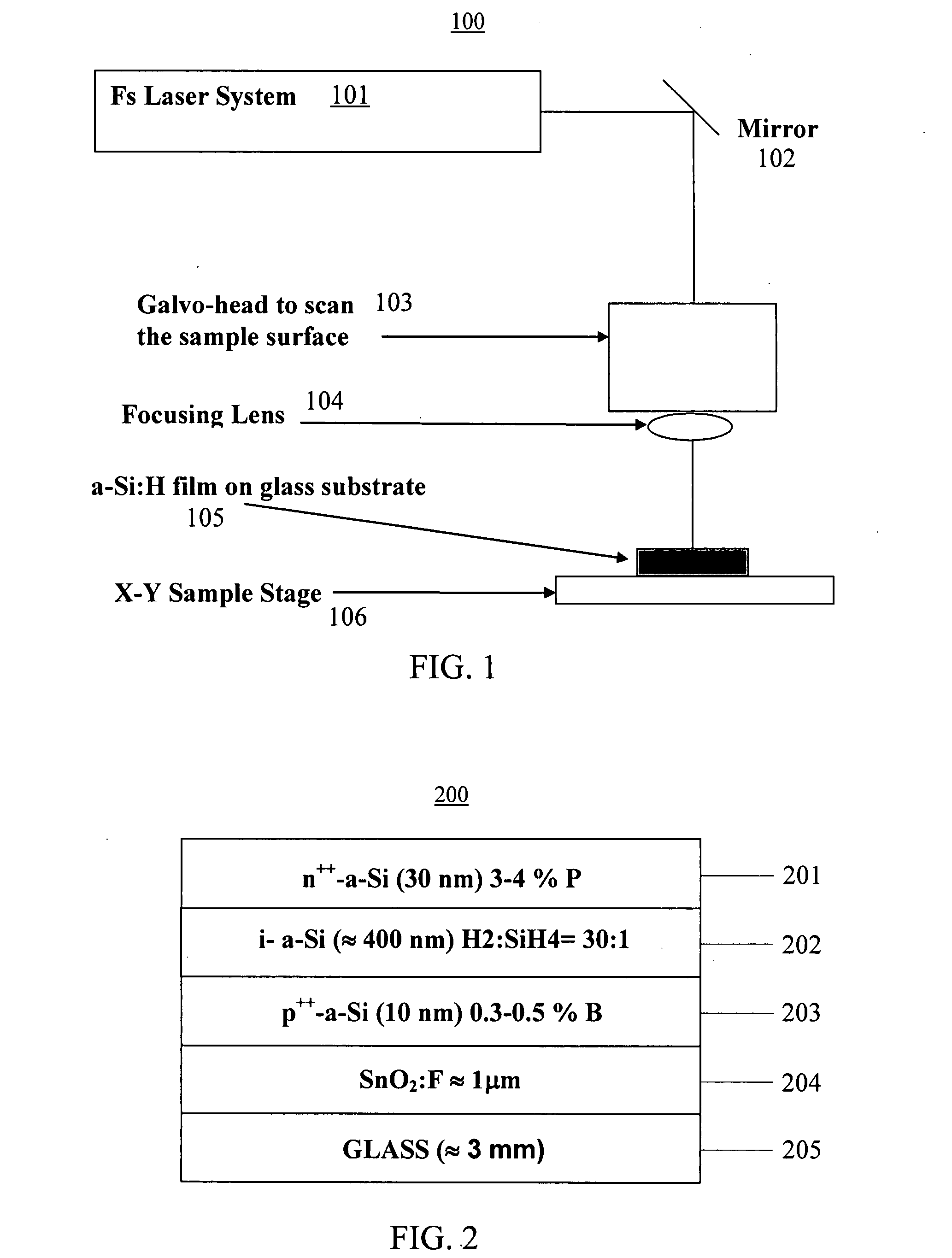
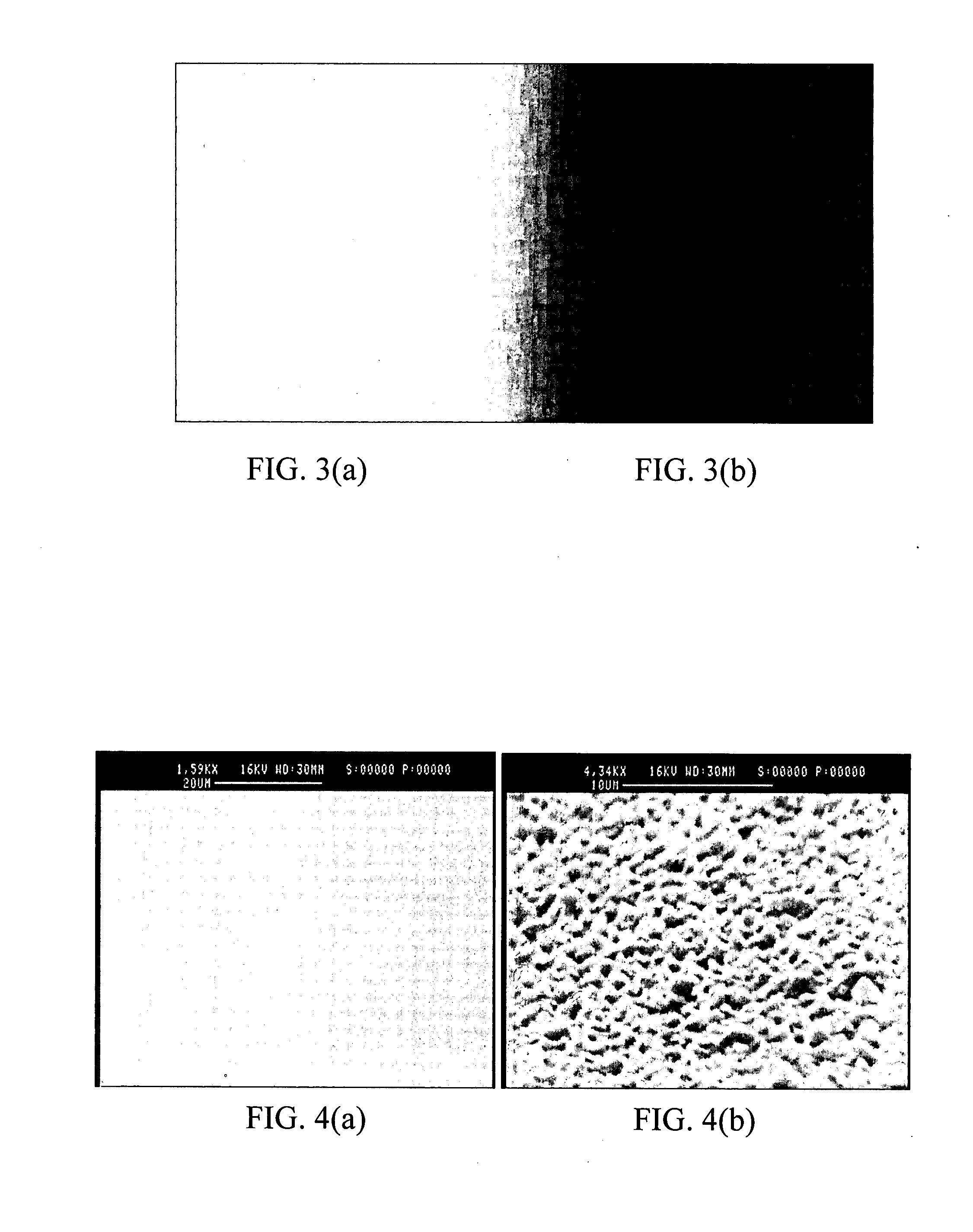
The surface of a material is textured and crystallized in a single step by exposing the surface to pulses from an ultrafast laser. The laser treatment causes pillars to form on the treated surface. These pillars provide for greater light absorption. The crystallization of the material provides for higher electric conductivity and changes in optical properties of the material. The method may be performed in a gaseous environment, so that laser assisted chemical etching will aid in the texturing of the surface. This method may be used on various material surfaces, such as semiconductors, metals, ceramics, polymers, and glasses.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method and apparatus for laser assisted cataract surgery
Devices and methods for use in laser-assisted surgery, particularly cataract surgery. Specifically, the use of an optical fiber with a proximal and distal end, wherein the distal end has a non-orthogonal angle with the diameter of the optical fiber, to create an off-axis steam bubble for cutting and removing tissue in an operative region. Where the optical fiber is bent, rotating the fiber creates a circular cutting path for the steam bubble, allowing access to tissues that may normally be blocked by obstructions and obstacles.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
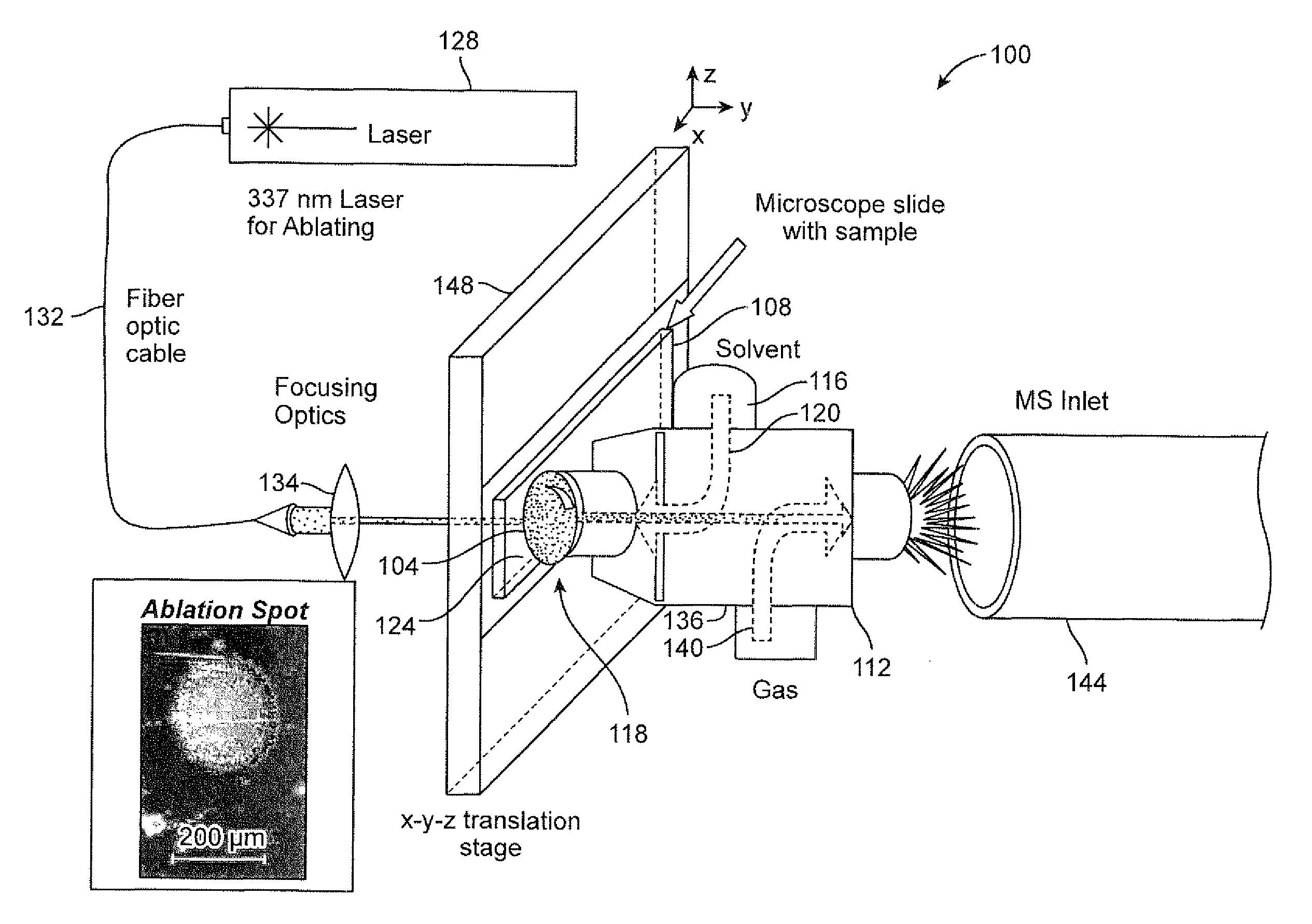
Systems and methods for laser assisted sample transfer to solution for chemical analysis
ActiveUS20120079894A1Stop the flowParticle separator tubesWithdrawing sample devicesAtomic force microscopyAnalyte
Systems and methods are described for laser ablation of an analyte from a specimen and capturing of the analyte in a dispensed solvent to form a testing solution. A solvent dispensing and extraction system can form a liquid microjunction with the specimen. The solvent dispensing and extraction system can include a surface sampling probe. The laser beam can be directed through the surface sampling probe. The surface sampling probe can also serve as an atomic force microscopy probe. The surface sampling probe can form a seal with the specimen. The testing solution including the analyte can then be analyzed using an analytical instrument or undergo further processing.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Silicon chip carrier with through-vias using laser assisted chemical vapor deposition of conductor
ActiveUS20050082676A1High aspect ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesControl mannerGas phase
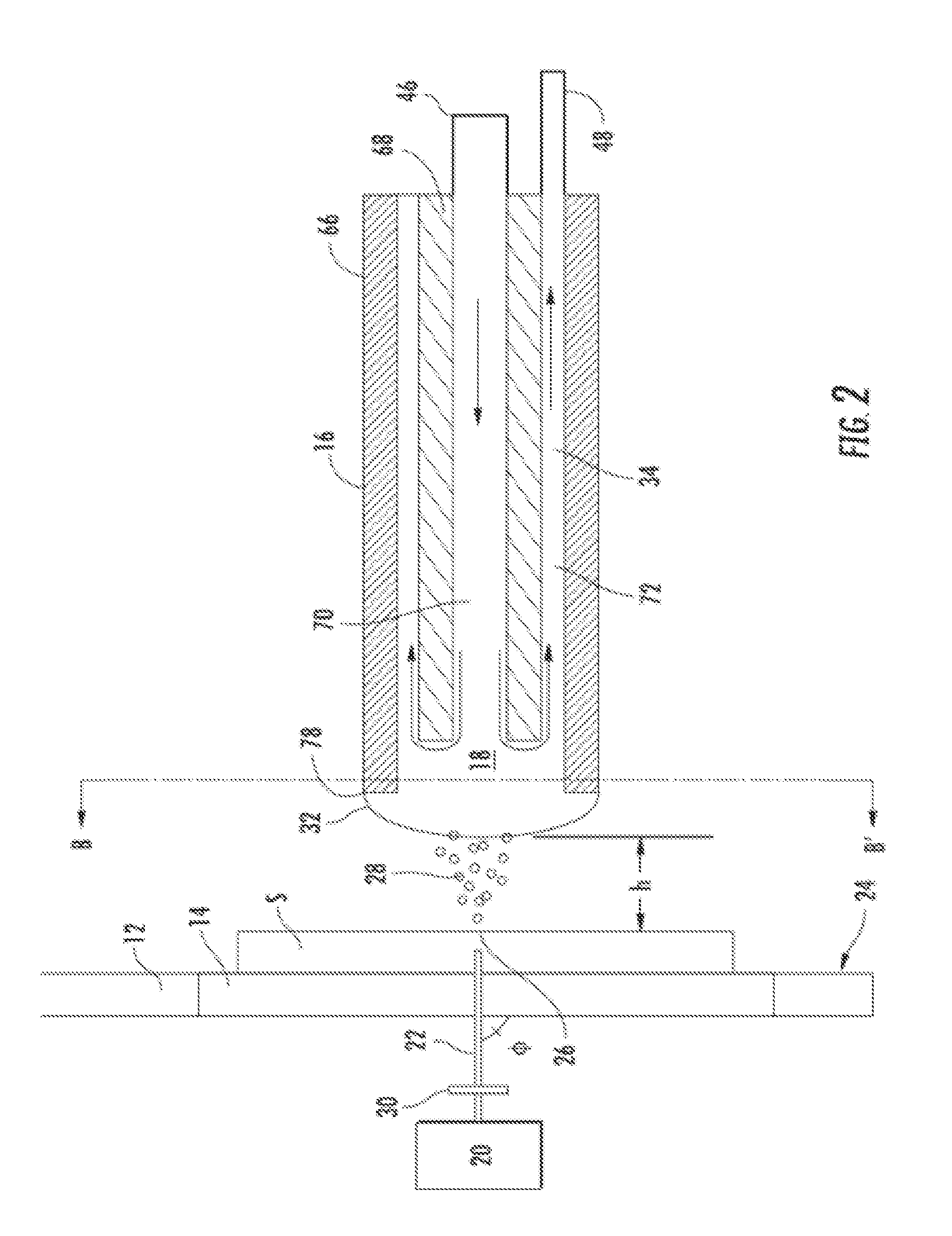
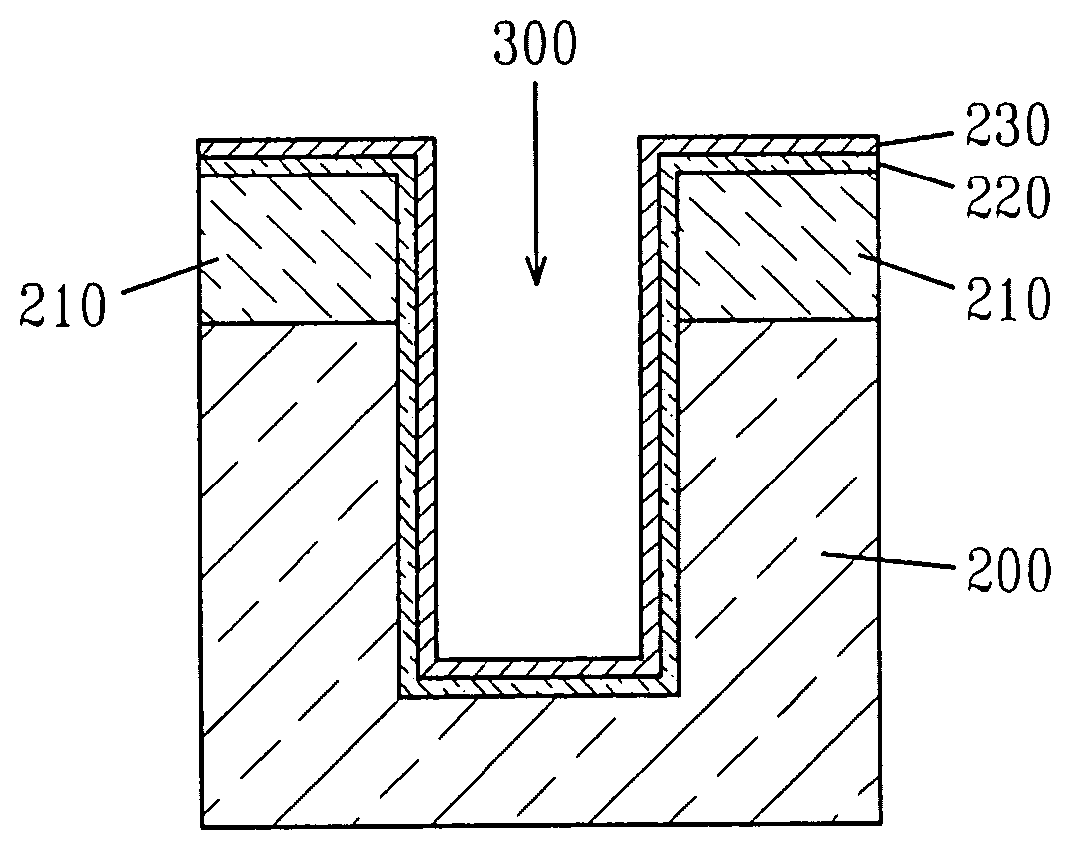
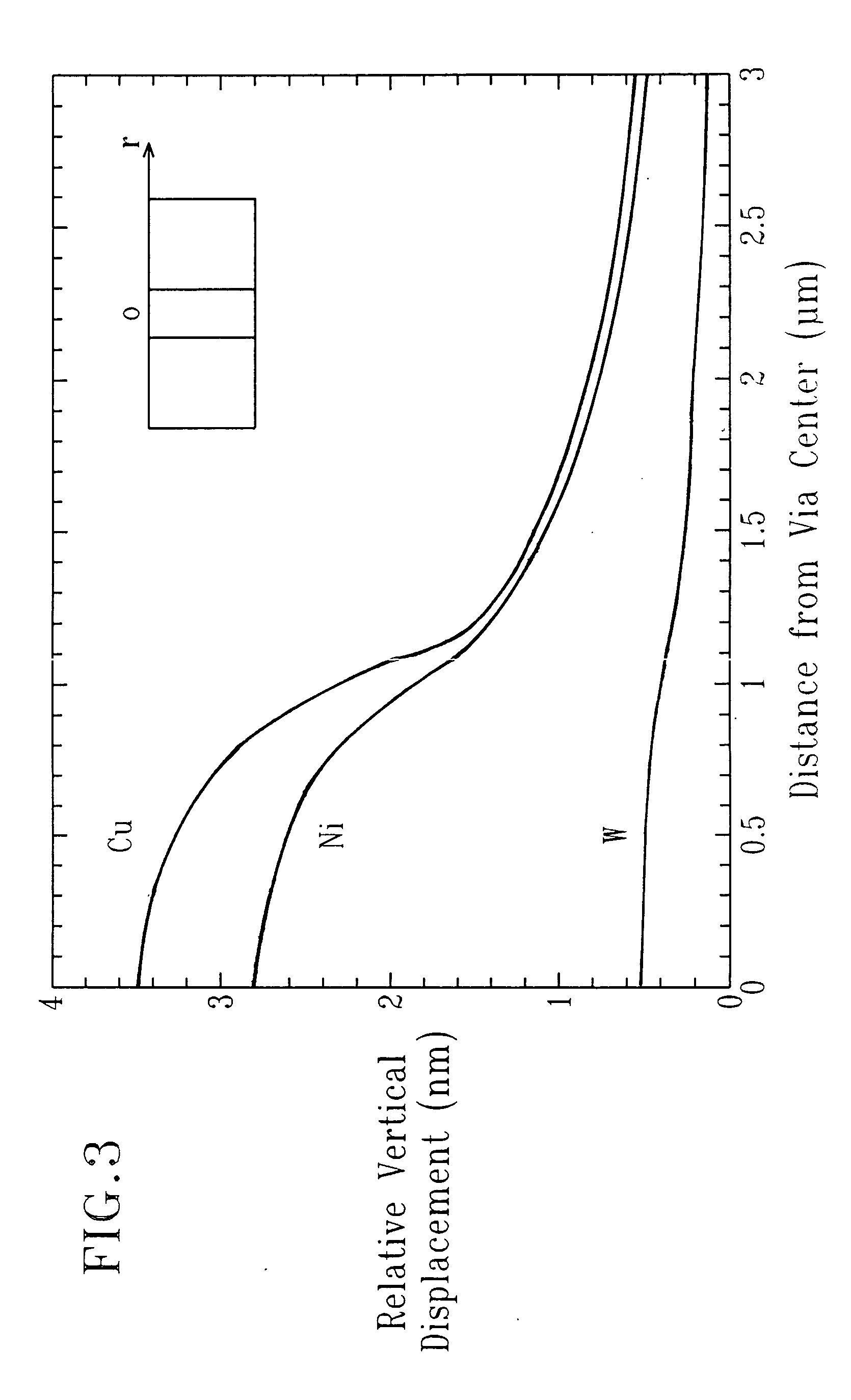
This disclosure teaches a method of filling deep vias or capping deep conducting paste filled vias in silicon or glass substrate using laser assisted chemical vapor deposition of metals. This method uses a continuous wave or pulsed laser to heat the via bottom and the growing metal fill selectively by selecting the laser wavelength such that silicon and / or glass do not absorb the energy of the laser in any appreciable manner to cause deposition in the field. Alternatively holographic mask or an array of micro lenses may be used to focus the laser beams to the vias to fill them with metal. The substrate is moved in a controlled manner in the z-direction away from the laser at about the rate of deposition thus causing the laser heating to be focused on the surface region of the growing metal fill.
Owner:ELPIS TECH INC
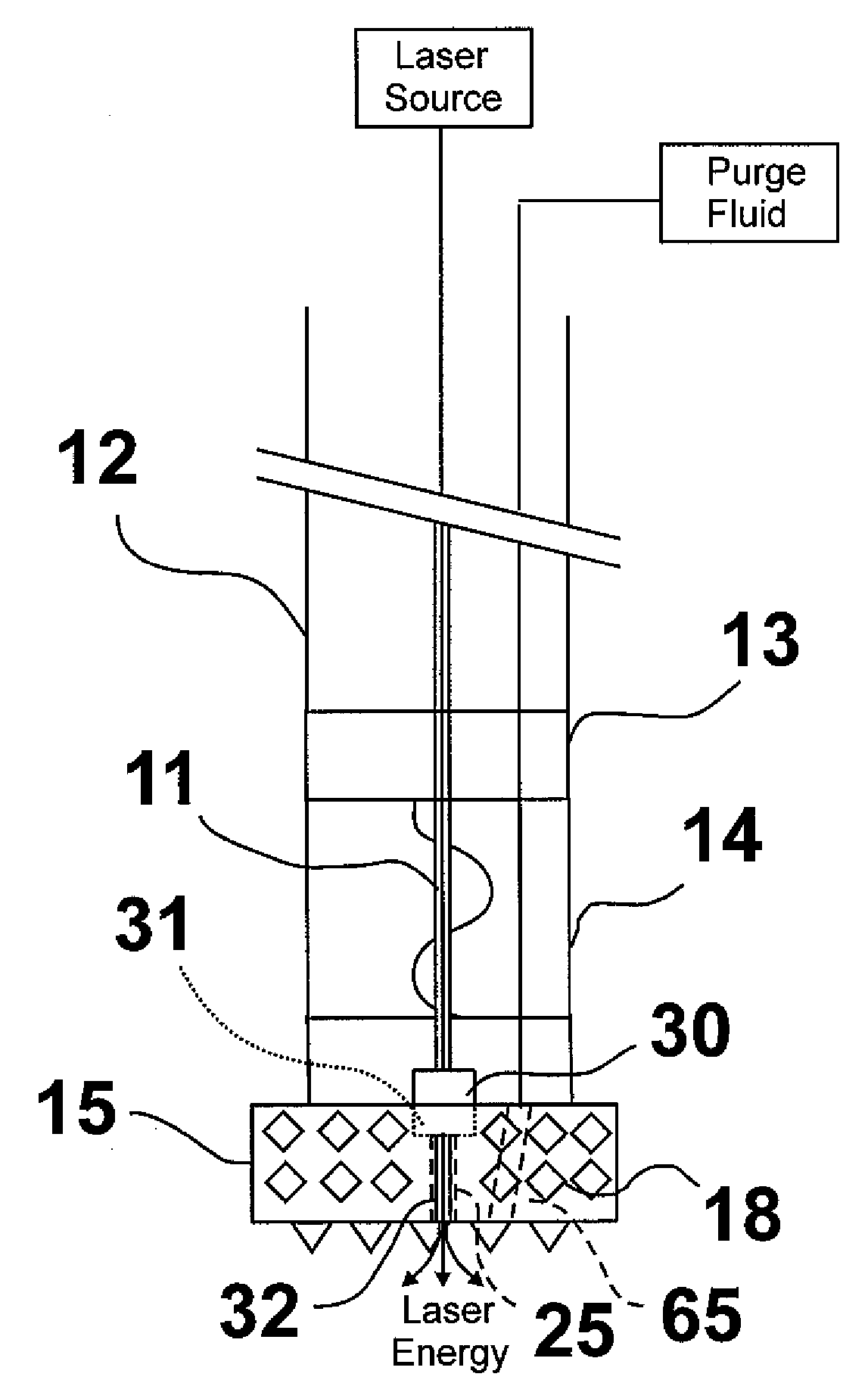
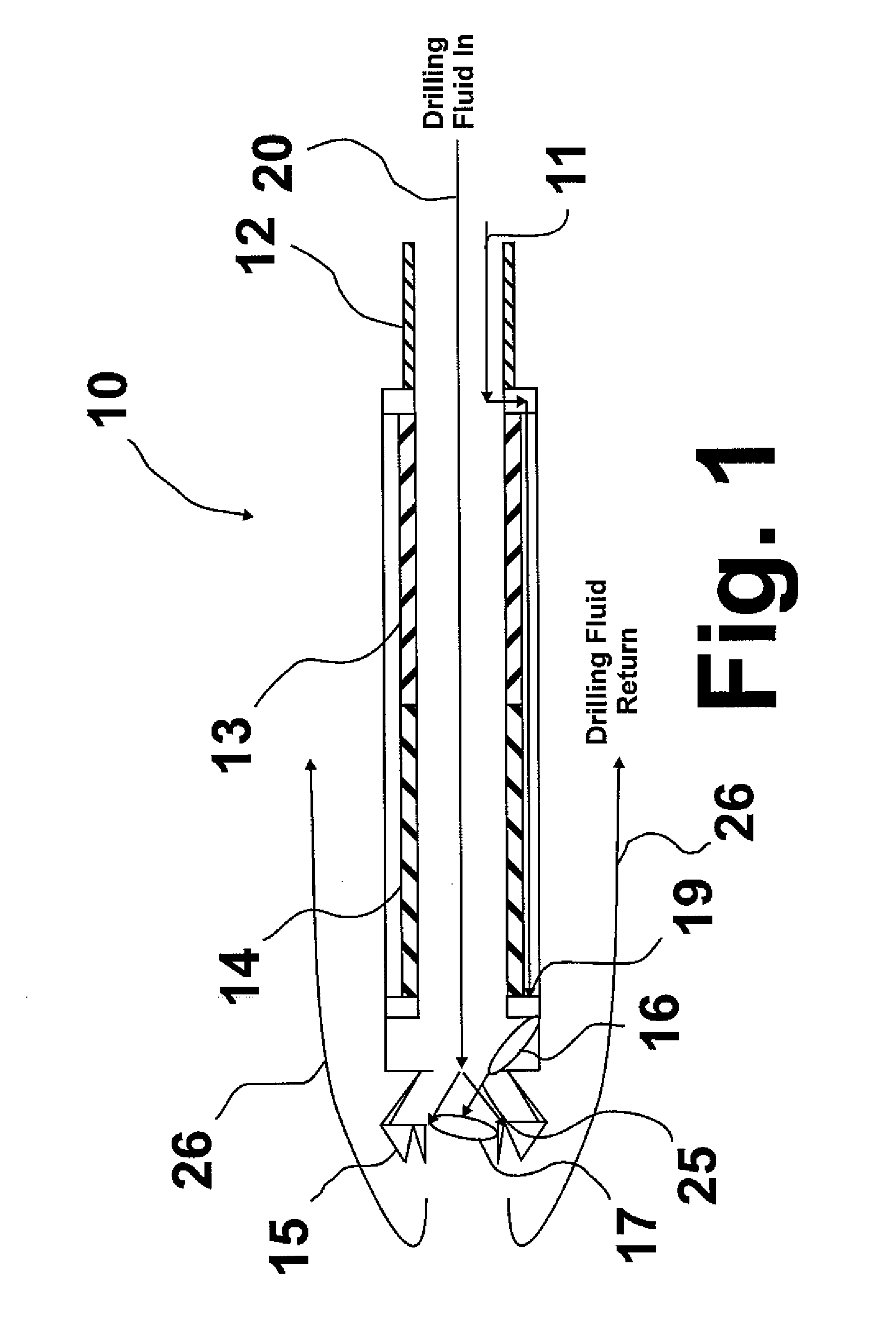
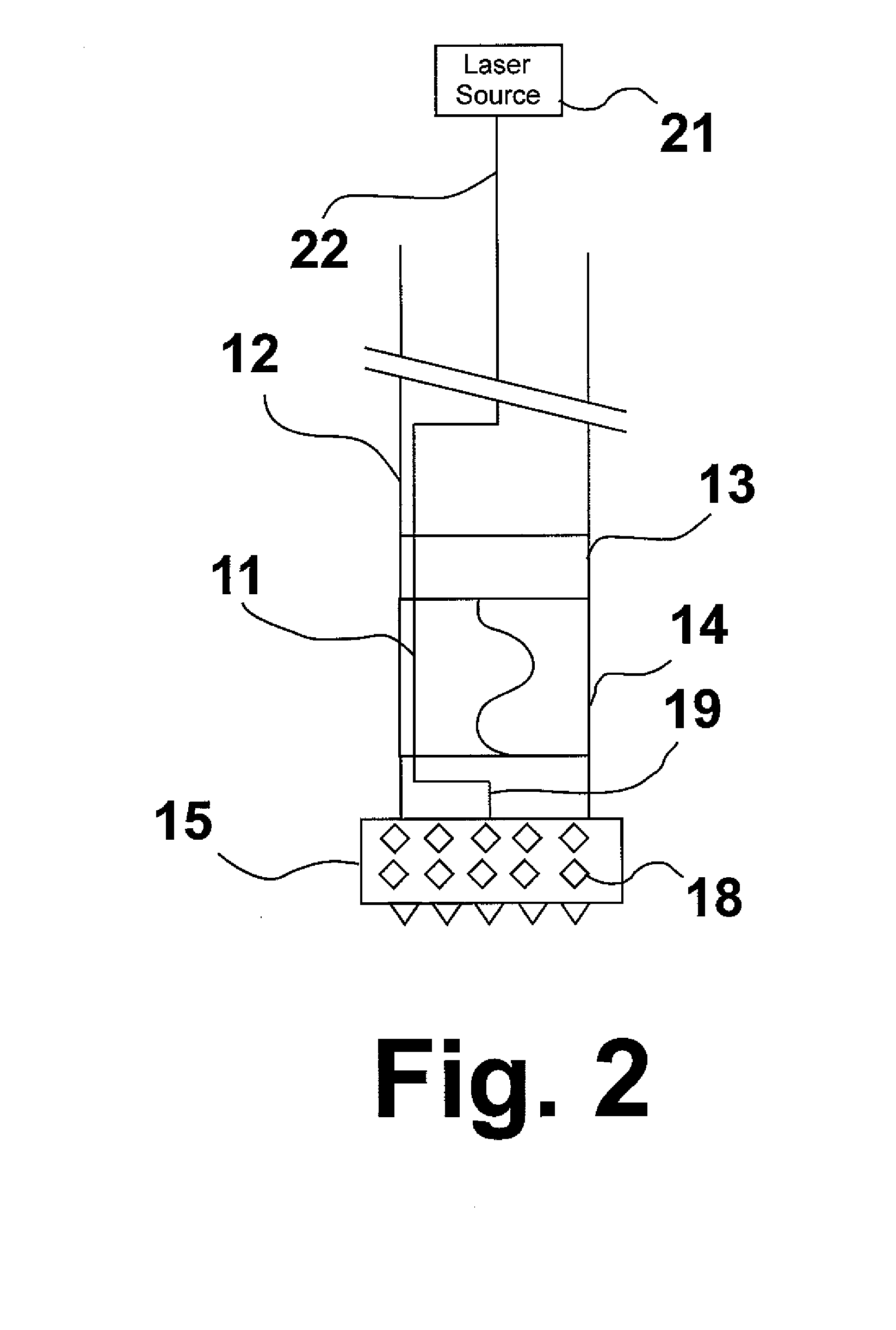
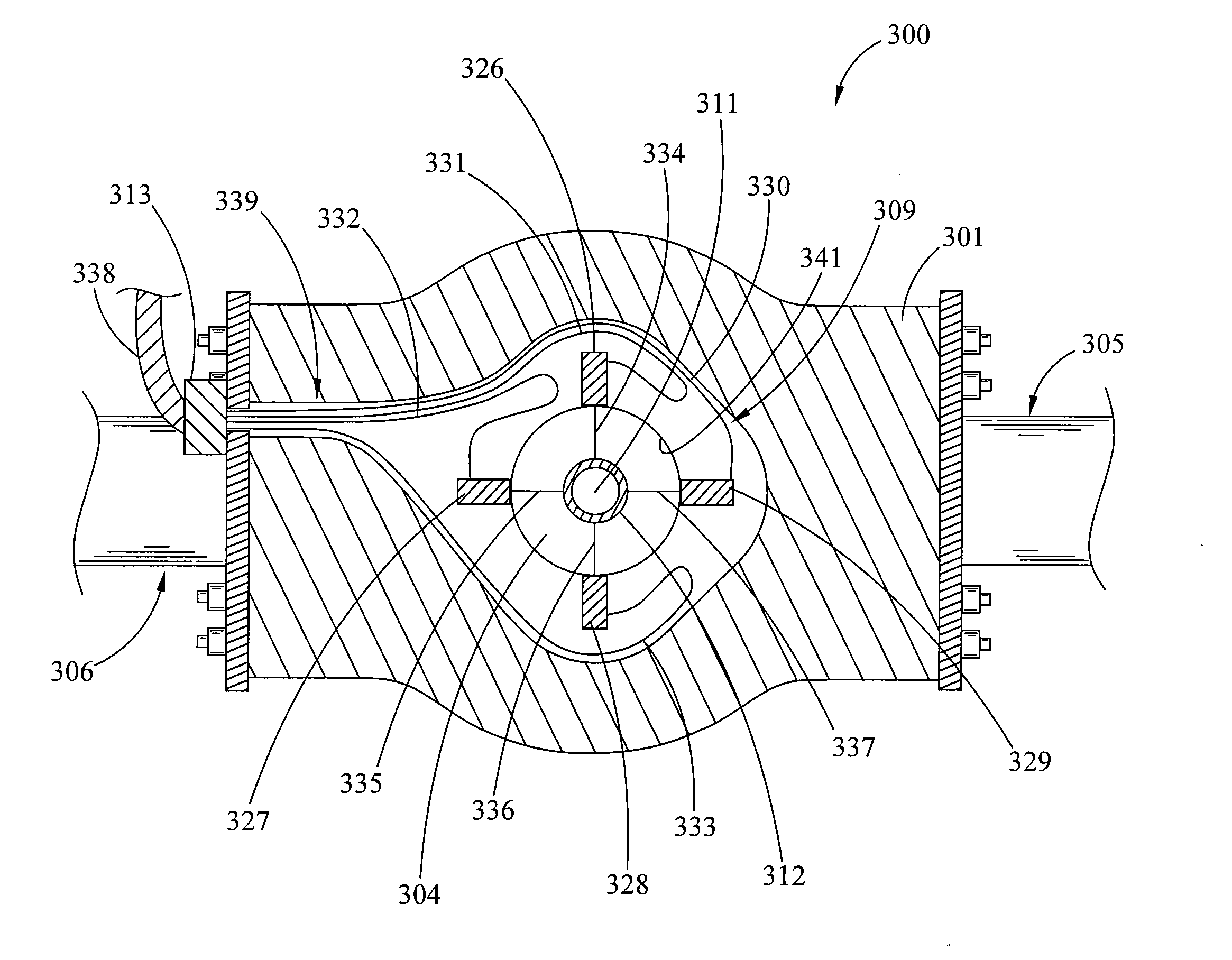
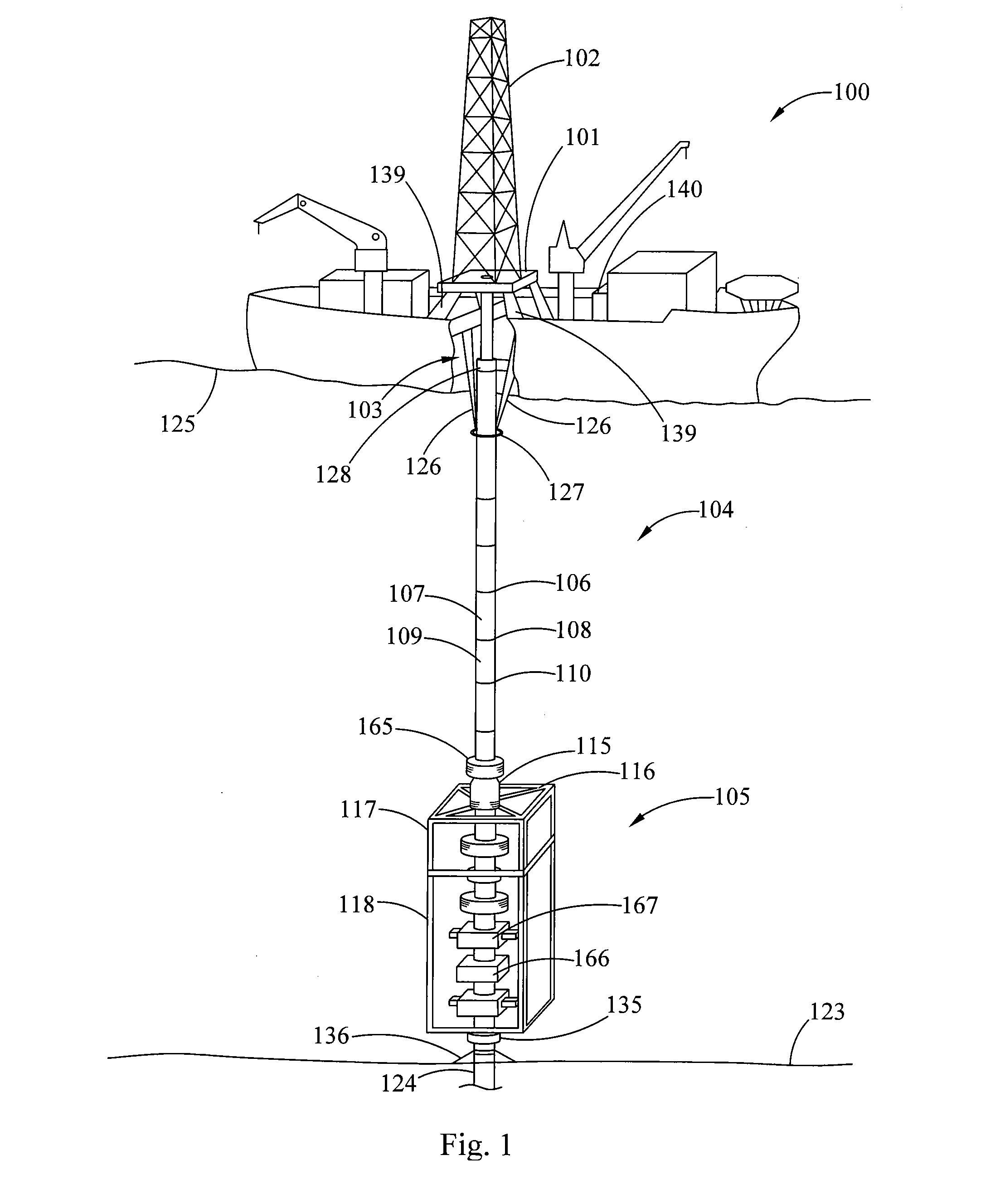
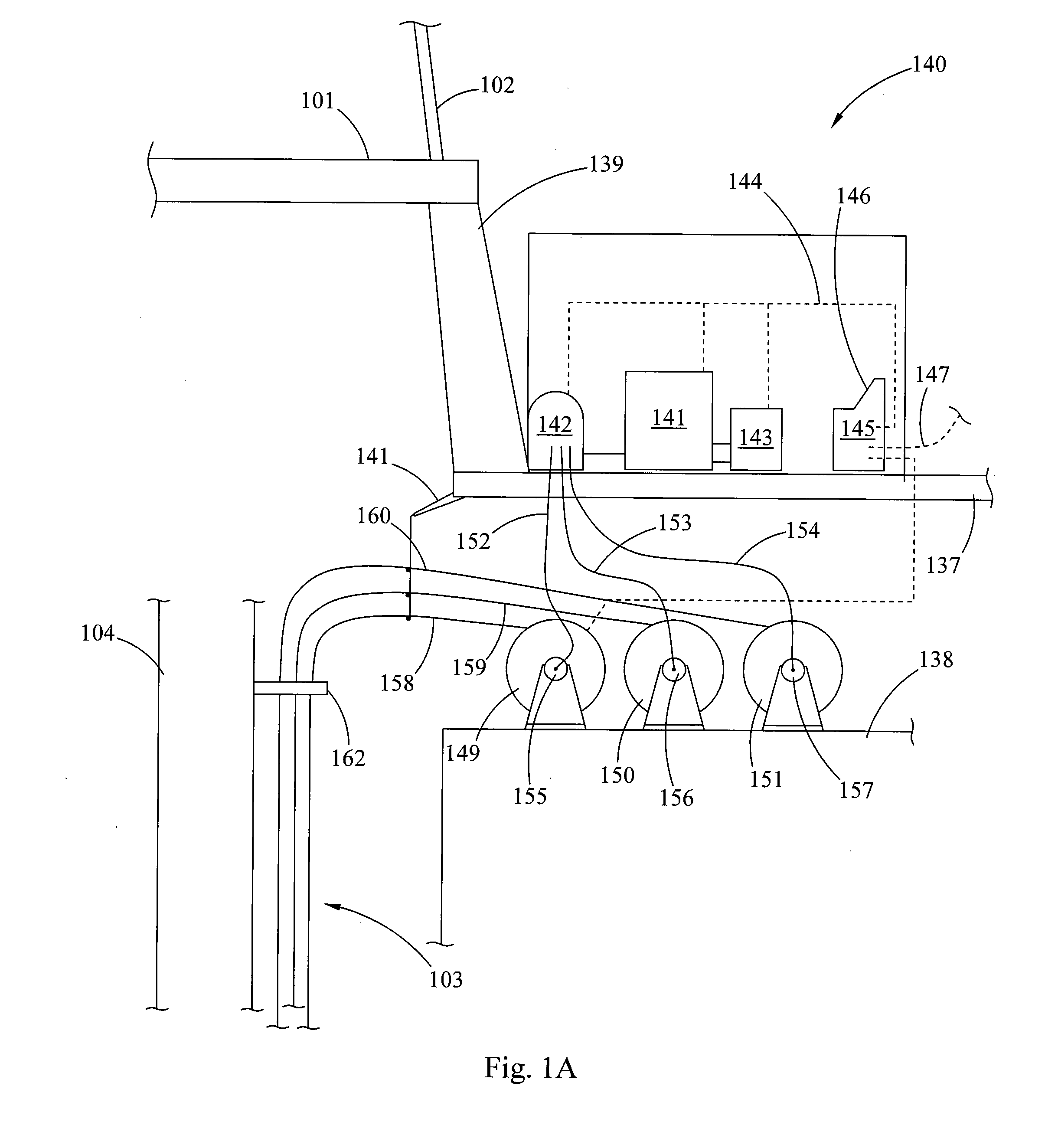
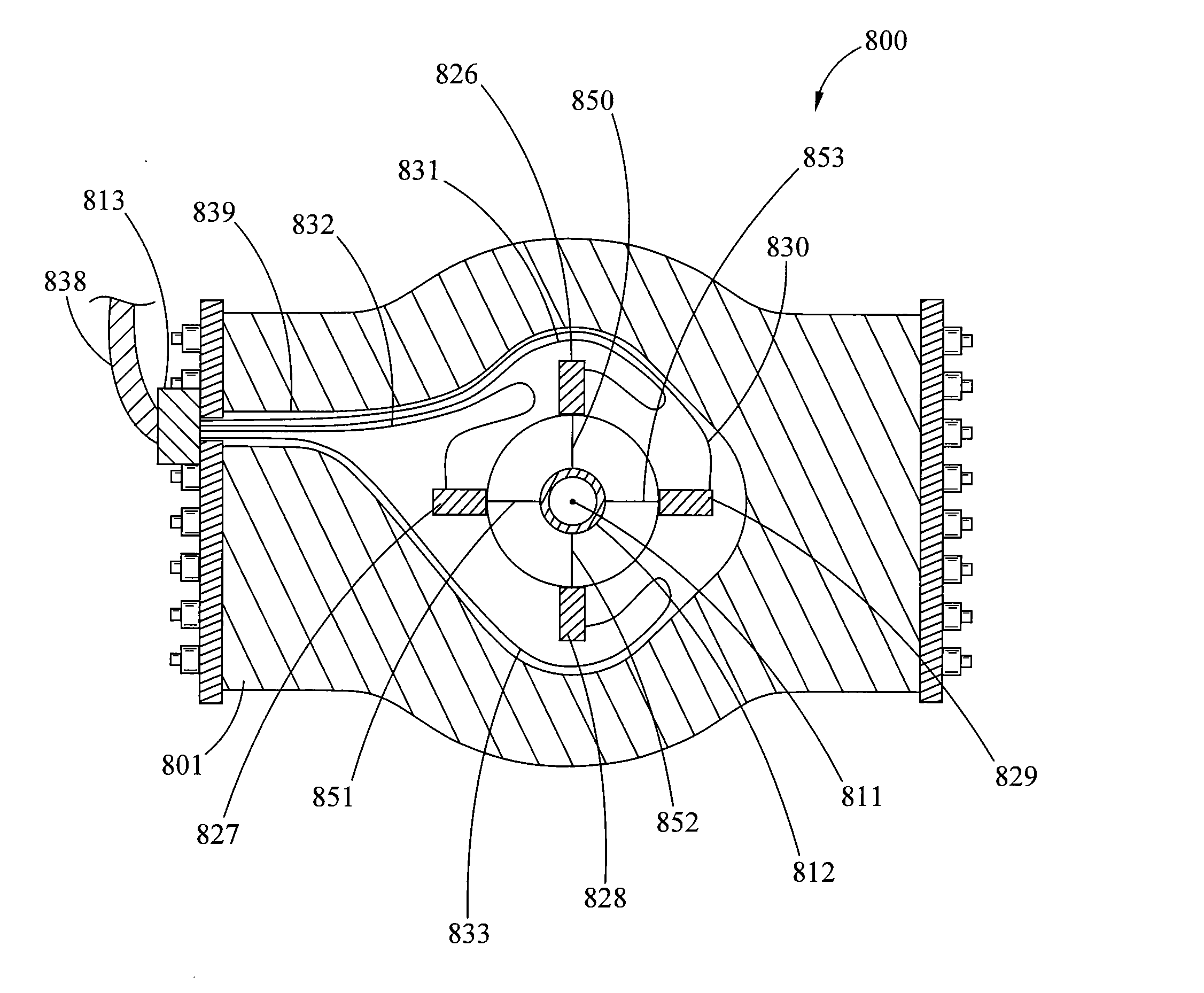
Laser assisted system for controlling deep water drilling emergency situations
There is provided a high power laser riser blowout preventer system and controller for operation thereof. The system utilizes high power laser cutters that are associated with the riser and the blowout preventer to provided an integrated operation to quickly weaken or cut tubulars to address potential emergency and emergency situations that can arise during deep sea drilling.
Owner:FORO ENERGY
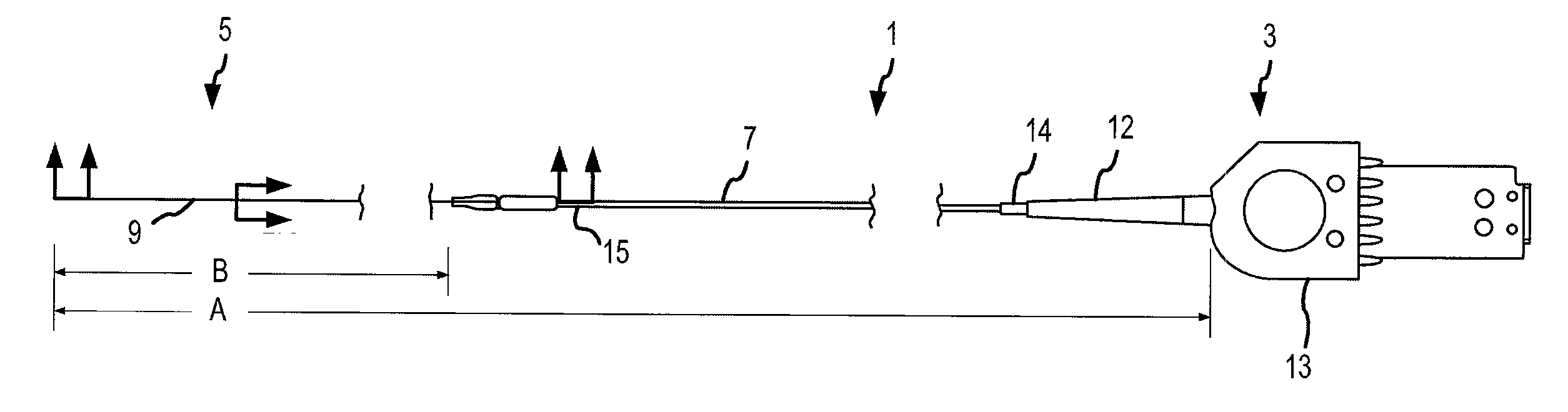
Laser-assisted guidewire having a variable stiffness shaft
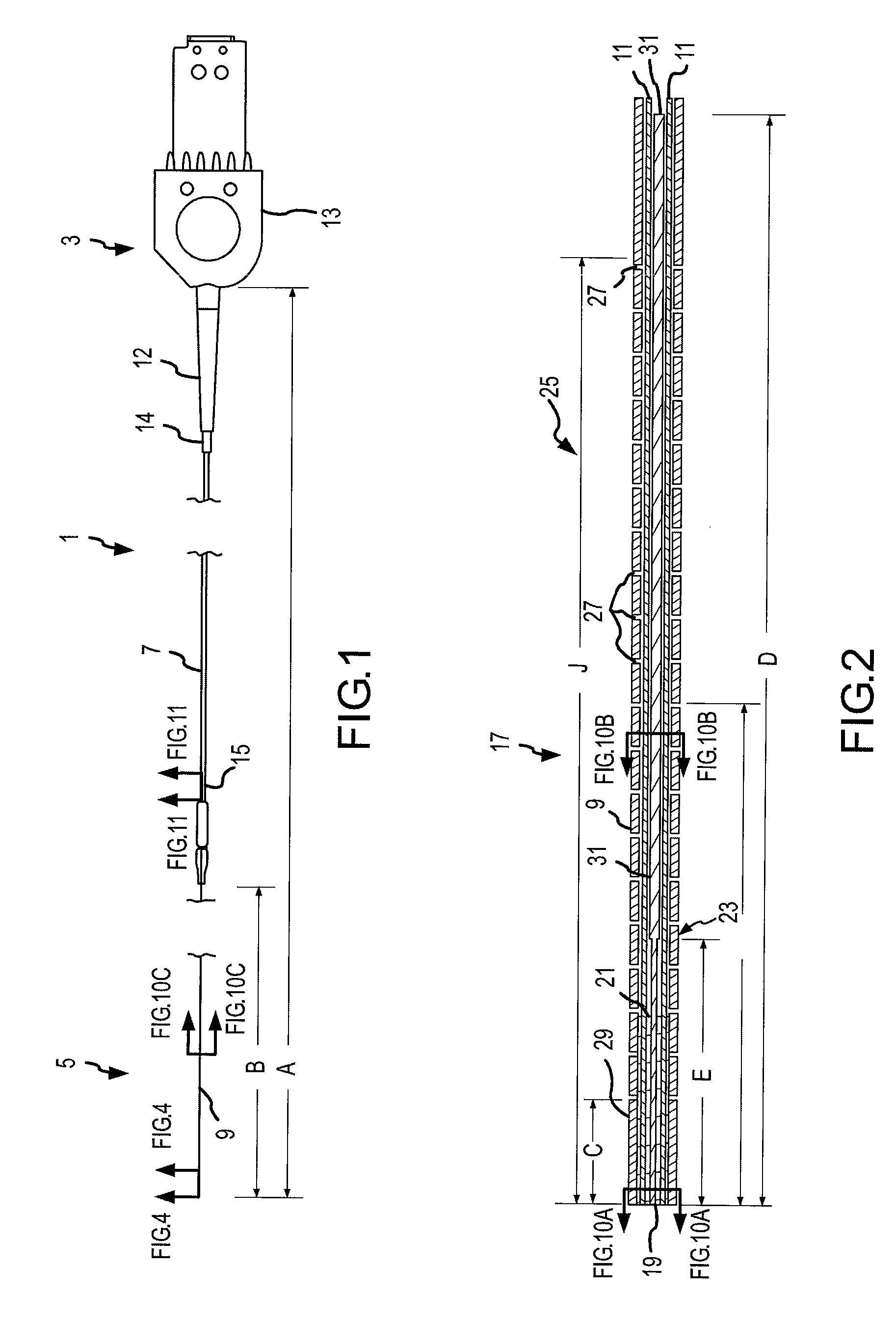
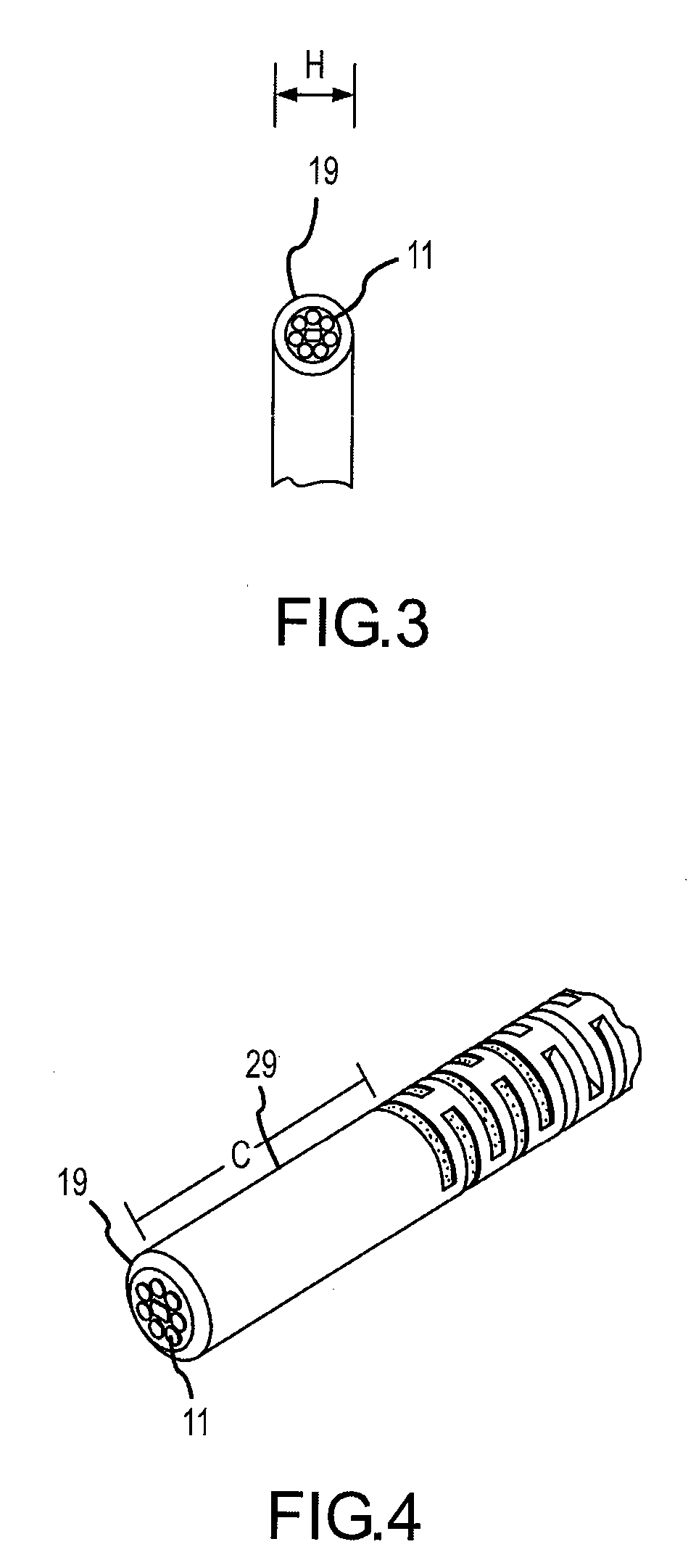
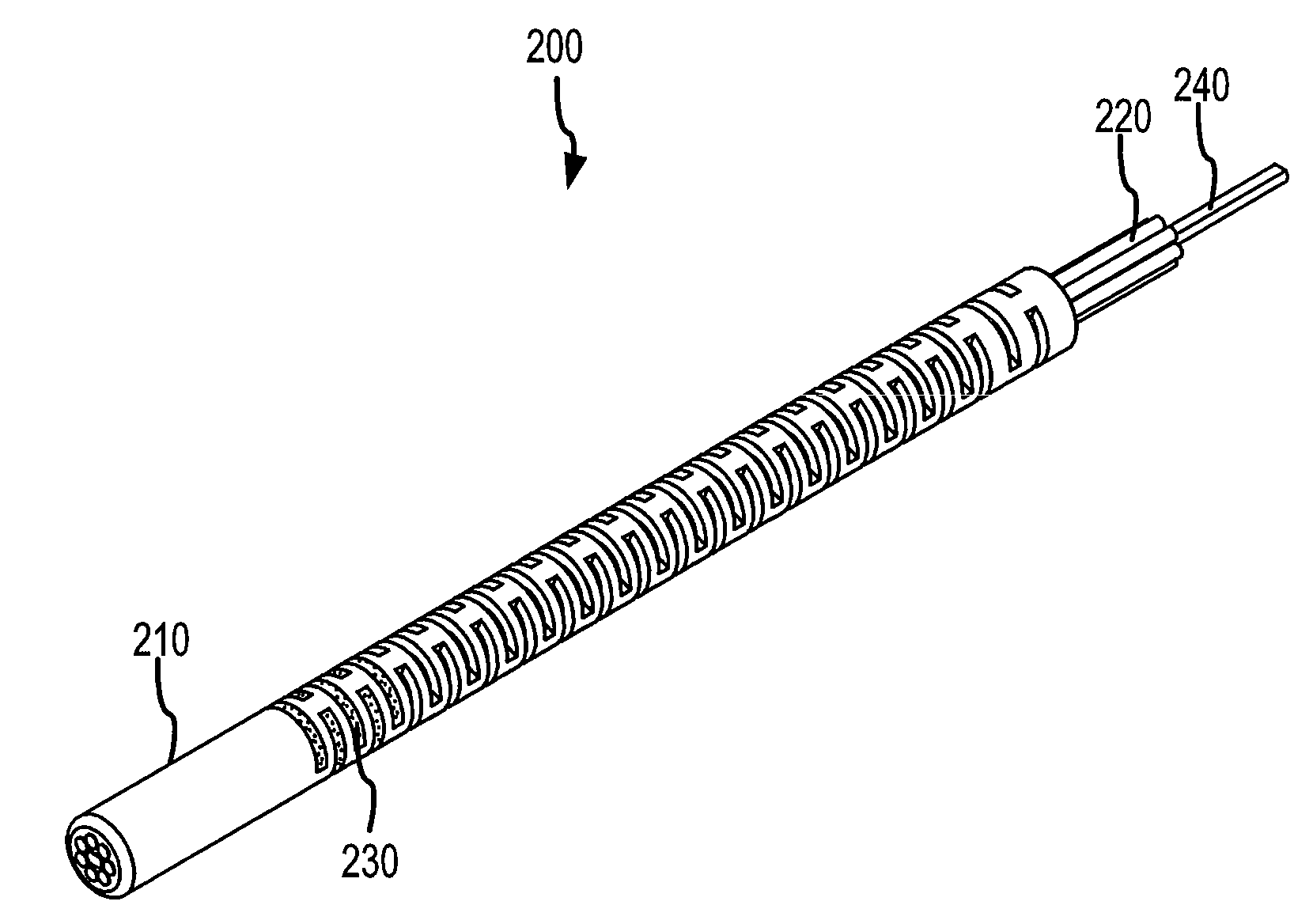
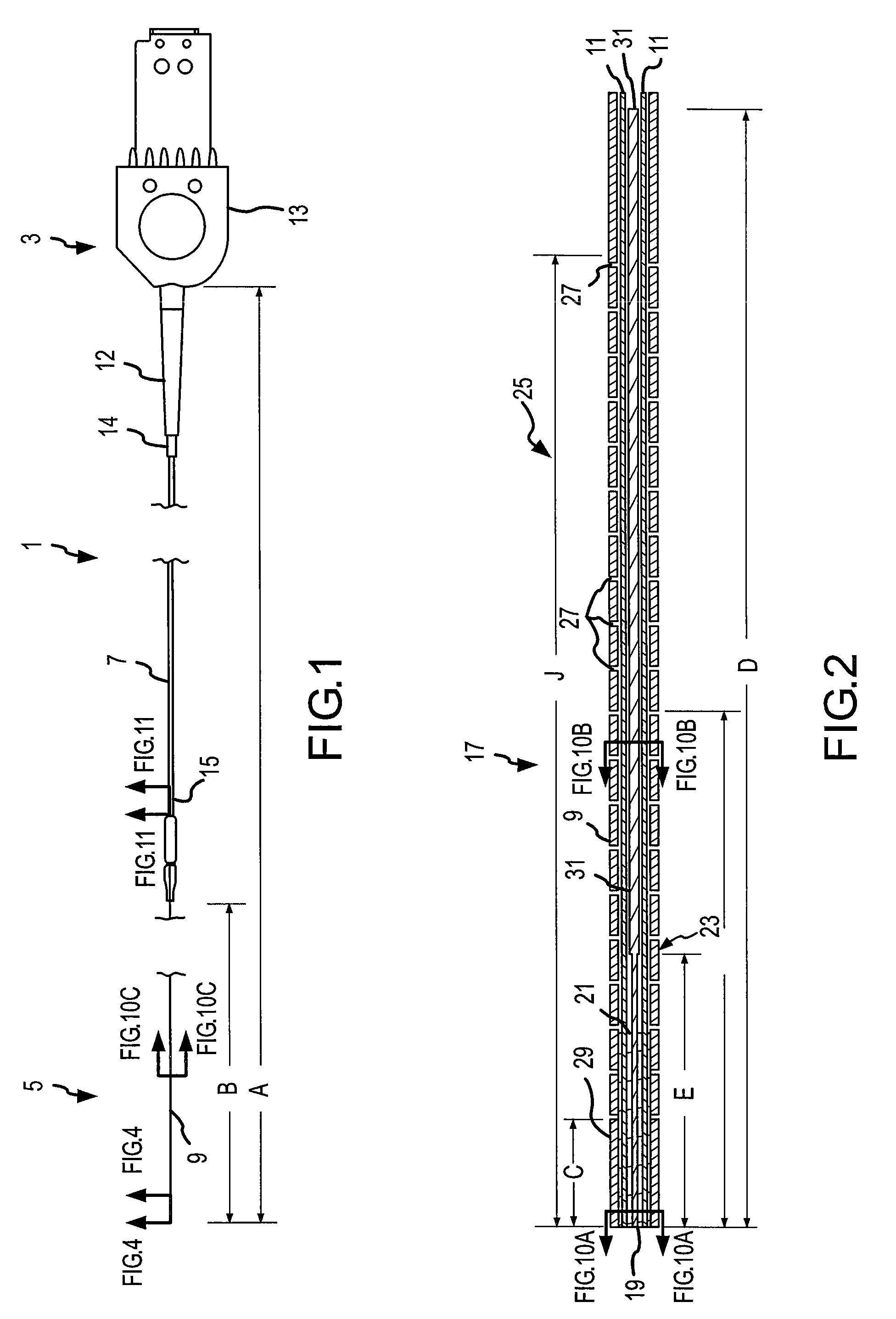
Embodiments of the present invention comprise a fiber optic guidewire having a hypotube with a plurality of openings that provide variable stiffness and tracking characteristics between at least one proximal segment and one distal segment of the guidewire. In some embodiments, the guidewire further comprises a mandrel disposed within the hypotube, the mandrel cooperating with the optical fibers to permit the distal end of the hypotube to be shaped as desired by a user. Methods of manufacturing and using the guidewire are also disclosed.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Laser-assisted guidewire having a variable stiffness shaft
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Laser assisted blowout preventer and methods of use
ActiveUS20120217018A1Quick cutProtection from damageDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsHigh power lasersLaser assisted
There is provided a high power laser assisted blowout preventer and methods of use. In particular, there are provided systems and assemblies for utilizing high power laser energy within a blowout preventer to cut tubulars that are present within the bore of the blowout prevent, reducing the risk that such tubulars will inhibit the ability of the blowout preventer to seal a well.
Owner:FORO ENERGY
Laser assisted riser disconnect and method of use
There is provided a high power laser-riser blowout preventer package and laser module for use with a subsea riser. The laser module and laser-riser package use high power laser energy to quickly cut the riser permitting an offshore drilling rig to quickly, and in a controlled manner disconnect from a blowout preventer.
Owner:FORO ENERGY
Localized metal contacts by localized laser assisted conversion of functional films in solar cells
InactiveUS20120060908A1Reduce shadowsImprove conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationElectricityTransparent conducting film
A solar cell, including contact metallization formed using selective laser irradiation. An upper layer is formed in the solar cell including a material which can be selectively modified to electrical contacts upon laser irradiation. Selective laser irradiation is applied to at least one region of the upper layer to form at least one electrical contact in the layer. A remaining region of the upper layer may be a functional layer of the solar cell which need not be removed. The upper layer may be, e.g., a transparent, conductive film, and anti-reflective film, and / or passivation. The electrical contact may provide an electrically conductive path to at least one region below the upper layer of the solar cell.
Owner:TETRASUN
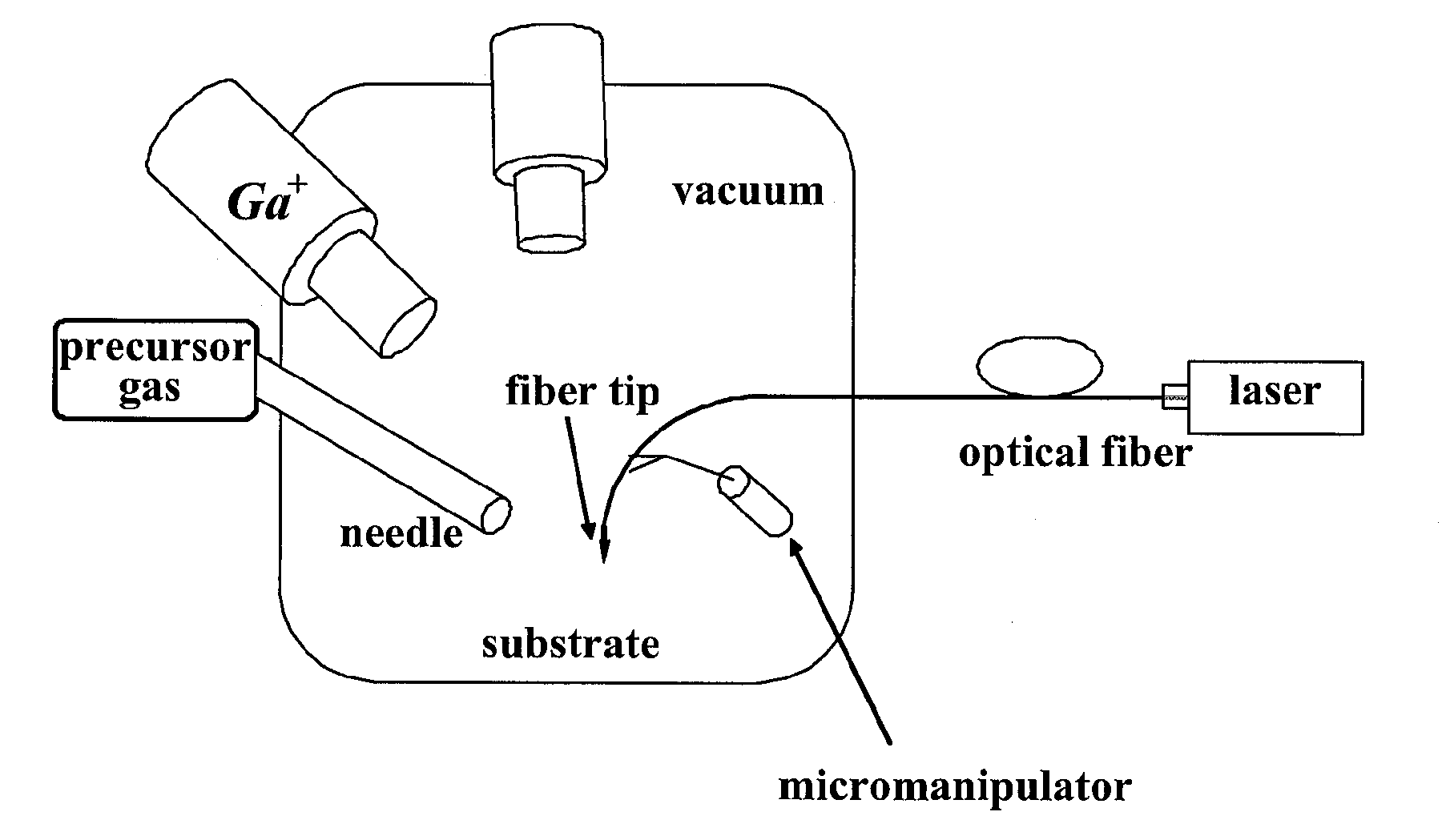
Laser-assisted nanomaterial deposition, nanomanufacturing, in situ monitoring and associated apparatus
Laser-assisted apparatus and methods for performing nanoscale material processing, including nanodeposition of materials, can be controlled very precisely to yield both simple and complex structures with sizes less than 100 nm. Optical or thermal energy in the near field of a photon (laser) pulse is used to fabricate submicron and nanometer structures on a substrate. A wide variety of laser material processing techniques can be adapted for use including, subtractive (e.g., ablation, machining or chemical etching), additive (e.g., chemical vapor deposition, selective self-assembly), and modification (e.g., phase transformation, doping) processes. Additionally, the apparatus can be integrated into imaging instruments, such as SEM and TEM, to allow for real-time imaging of the material processing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Laser assisted material deposition
Apparatus is provided for a method of forming a film on a substrate that includes activating a gas precursor to deposit a material on the substrate by irradiating the gas precursor with electromagnetic energy at a frequency tuned to an absorption frequency of the gas precursor. The electromagnetic energy can be provided by an array of lasers. The frequency of the laser beam is selected by switching from one laser in the array to another laser in the array. The laser array may include laser diodes, one or more tunable lasers, solid state lasers, or gas lasers. The frequency of the electromagnetic energy is selected to impart specific amounts of energy to a gas precursor at a specific frequency that provides point of use activation of the gas precursor.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
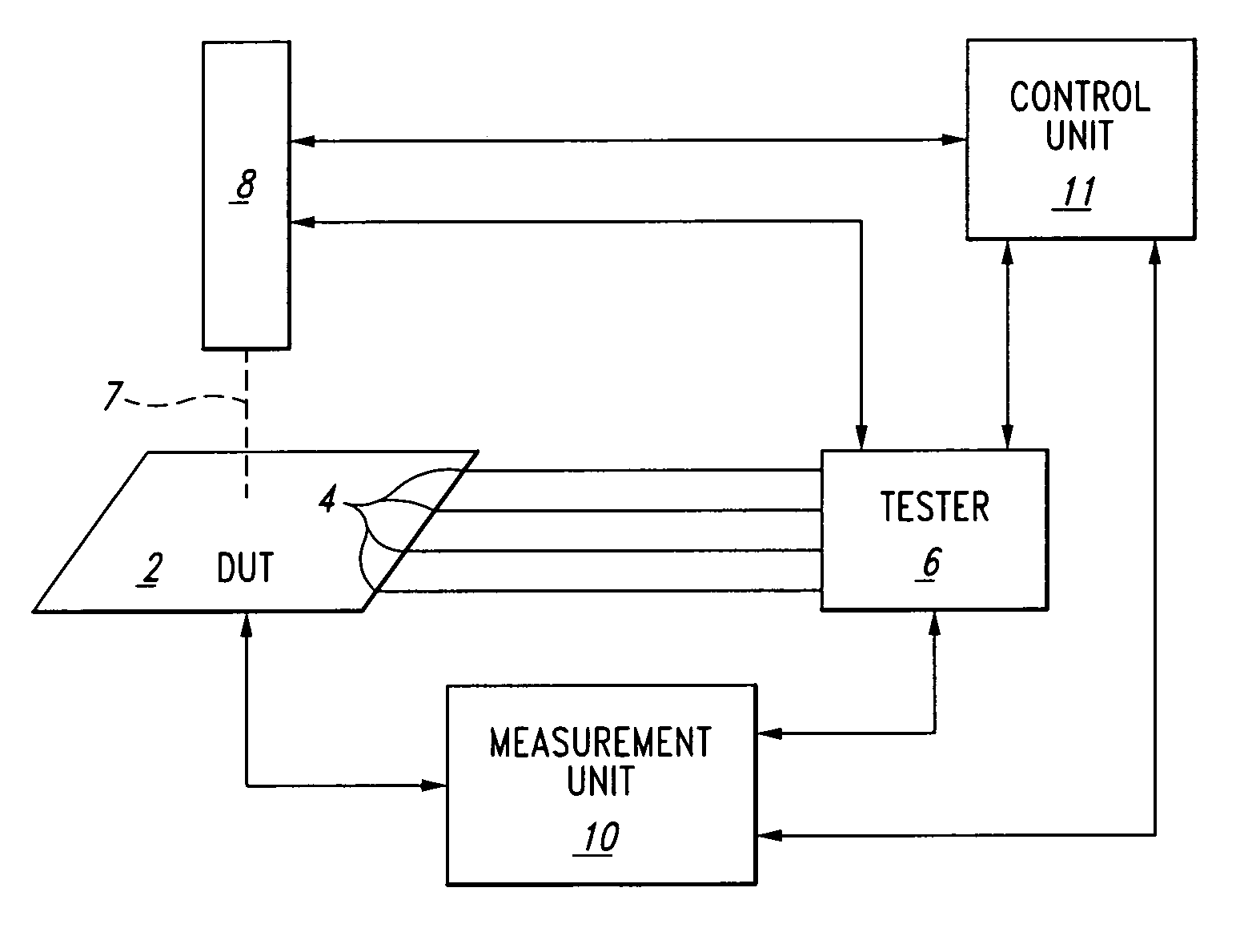
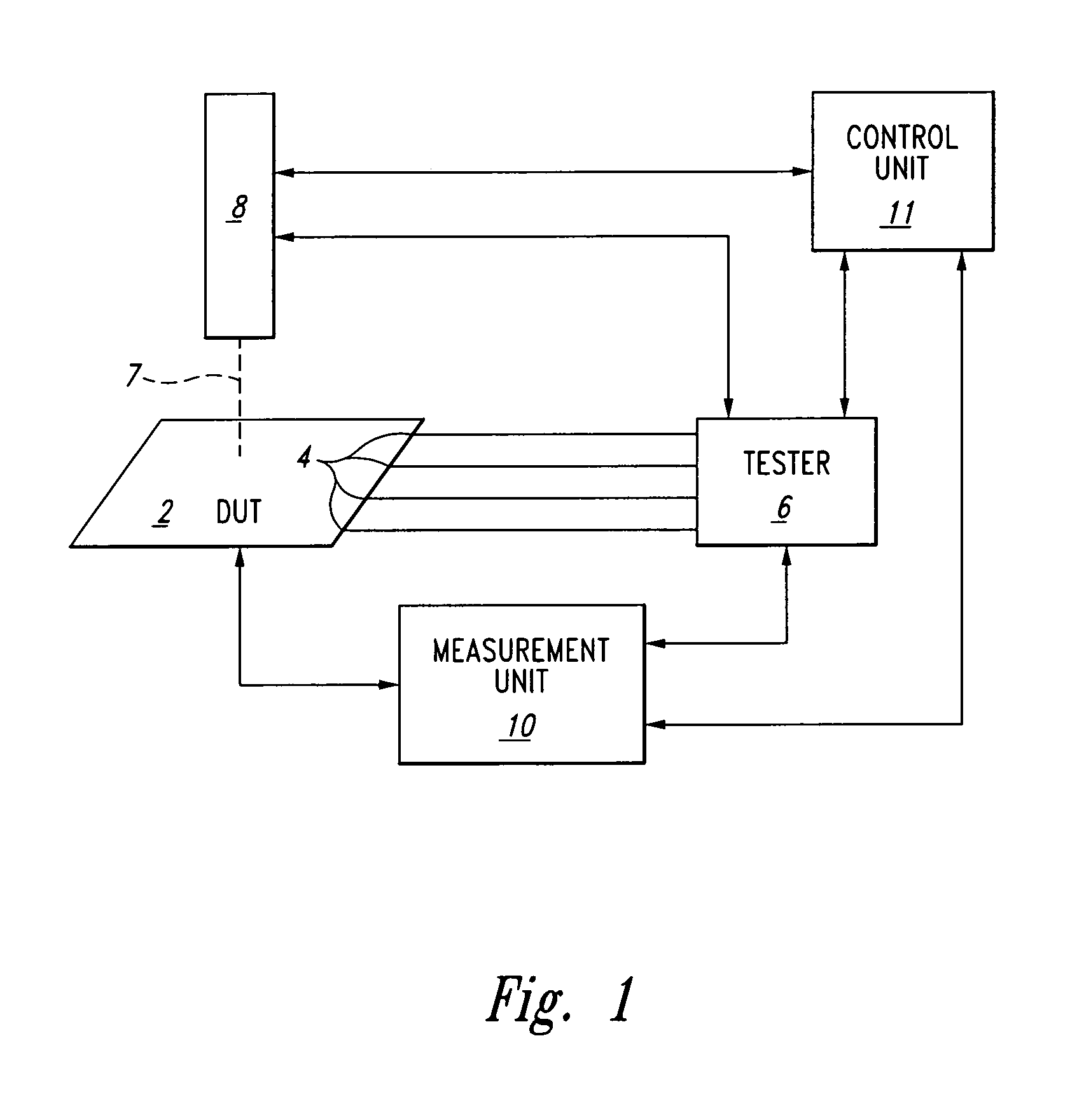
Spatial and temporal selective laser assisted fault localization
ActiveUS6967491B2Electric discharge tubesSpecial data processing applicationsSpecific testLaser assisted
A method and apparatus for laser-assisted fault mapping which synchronizes the laser control with the tester unit. The inventive method provides for laser-assisted pseudo-static fault mapping to localize defects in a device whose inputs are being stimulated dynamically by a tester. It further provides for laser-assisted dynamic soft error mapping, to localize in terms of location and to correlate with respect to a specific test vector, sensitive areas in a device by utilizing device performance criteria such as pass-fail status outputs. The apparatus includes a fully controllable dynamic laser stimulation apparatus connected to a control unit that provides complete synchronization with a tester unit.
Owner:DCG SYST
Selective laser-assisted transfer of discrete components
InactiveUS20140238592A1Easy to packDifficult to handleMechanical working/deformationLamination ancillary operationsEngineeringLaser assisted
Electronic components are often assembled using robotic equipment, such as pick-and-place machines, that is not optimized for components such as ultra-thin semiconductor bare dice. Selective laser-assisted die transfer is described based on the unique blistering behavior of a multilayer dynamic release layer when irradiated by low energy focused laser pulse(s) in which the blister creates translation of the article being placed. Accurate placement results are provided with negligible lateral and angular displacement.
Owner:NORTH DAKOTA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
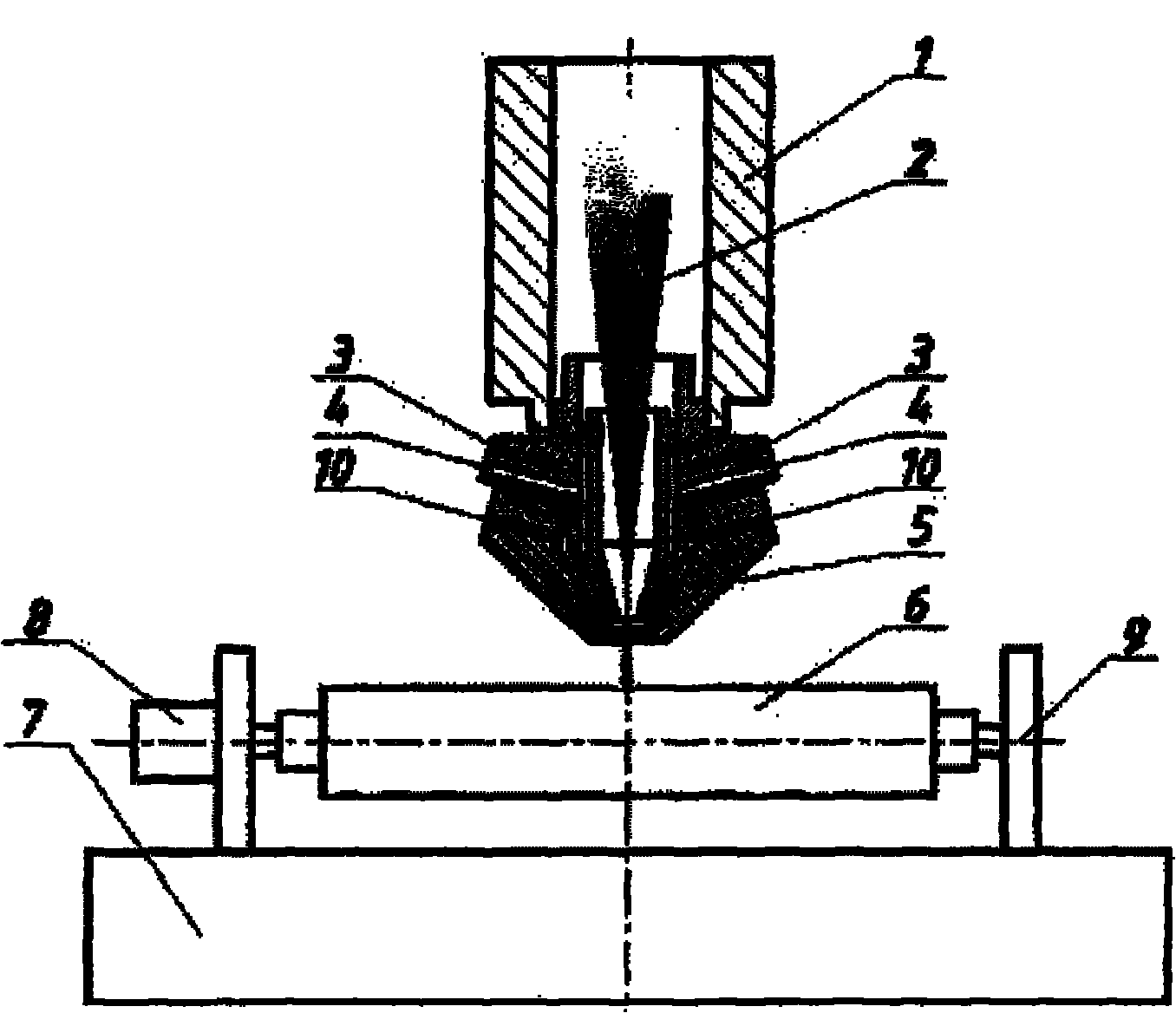
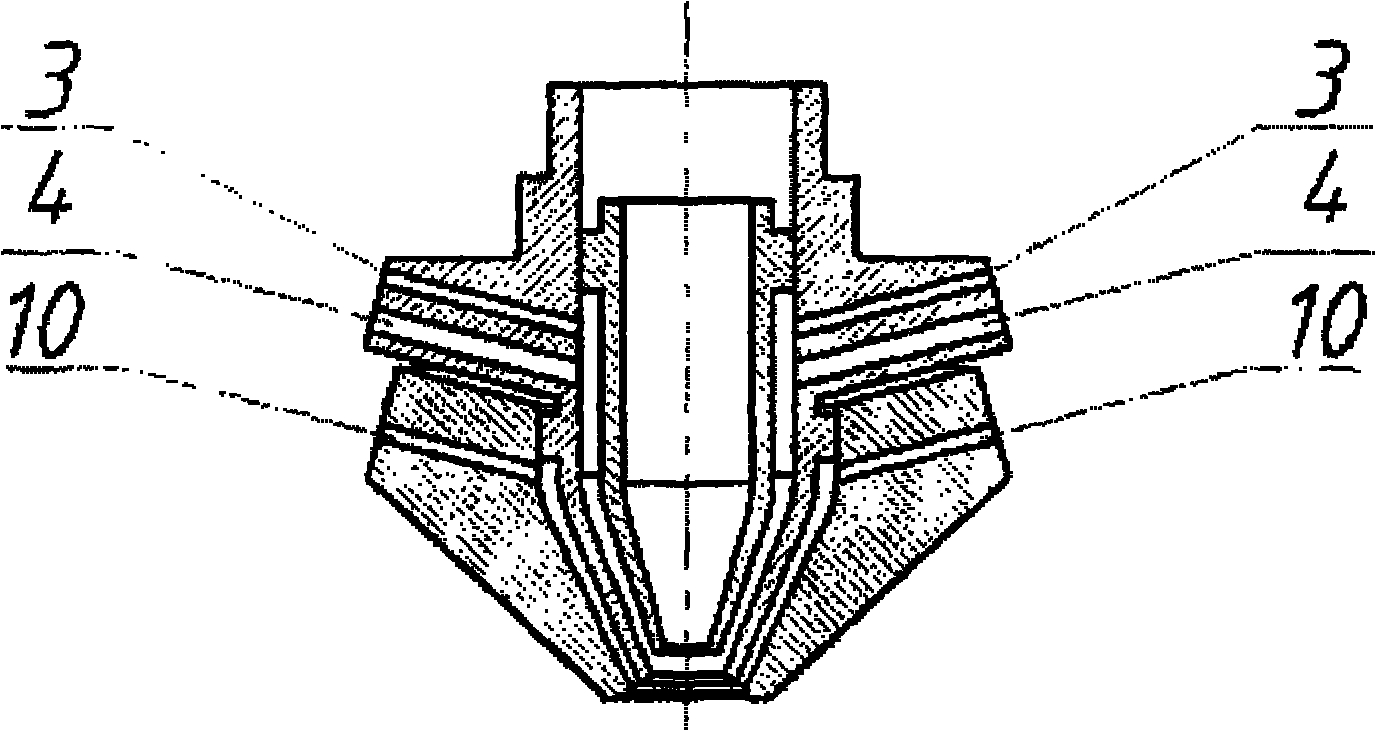
Device and method for laser shot blasting reinforcement of hard and brittle material
The invention discloses a device and a method for laser shot blasting reinforcement of a hard and brittle material, and relates to the field of mechanical manufacture of hard and brittle material processing and laser application. The device comprises a laser aid heating system, a laser shot blasting reinforcement system, a workpiece clamp system, a computer numerical control system, a measurement feedback system and a protective gas circulating system. The method comprises a laser aid heating stage and a laser shot blasting reinforcement stage, namely performing aid heating treatment on the area to be reinforced by adopting high-power continuous laser, wherein for most metal materials, the plastic performance is improved along with the rise of temperature; and after the temperature of the heating area reaches a predetermined heating temperature, implementing laser shot blasting reinforcement treatment by adopting high-power pulse laser. The device and the method can implement the laser shot blasting reinforcement on the hard and brittle material so as to broaden the application range of the laser shot blasting reinforcement technology, and meanwhile compound the advantages of continuous laser and pulse laser so as to broaden the application field and the application prospect of laser manufacture.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
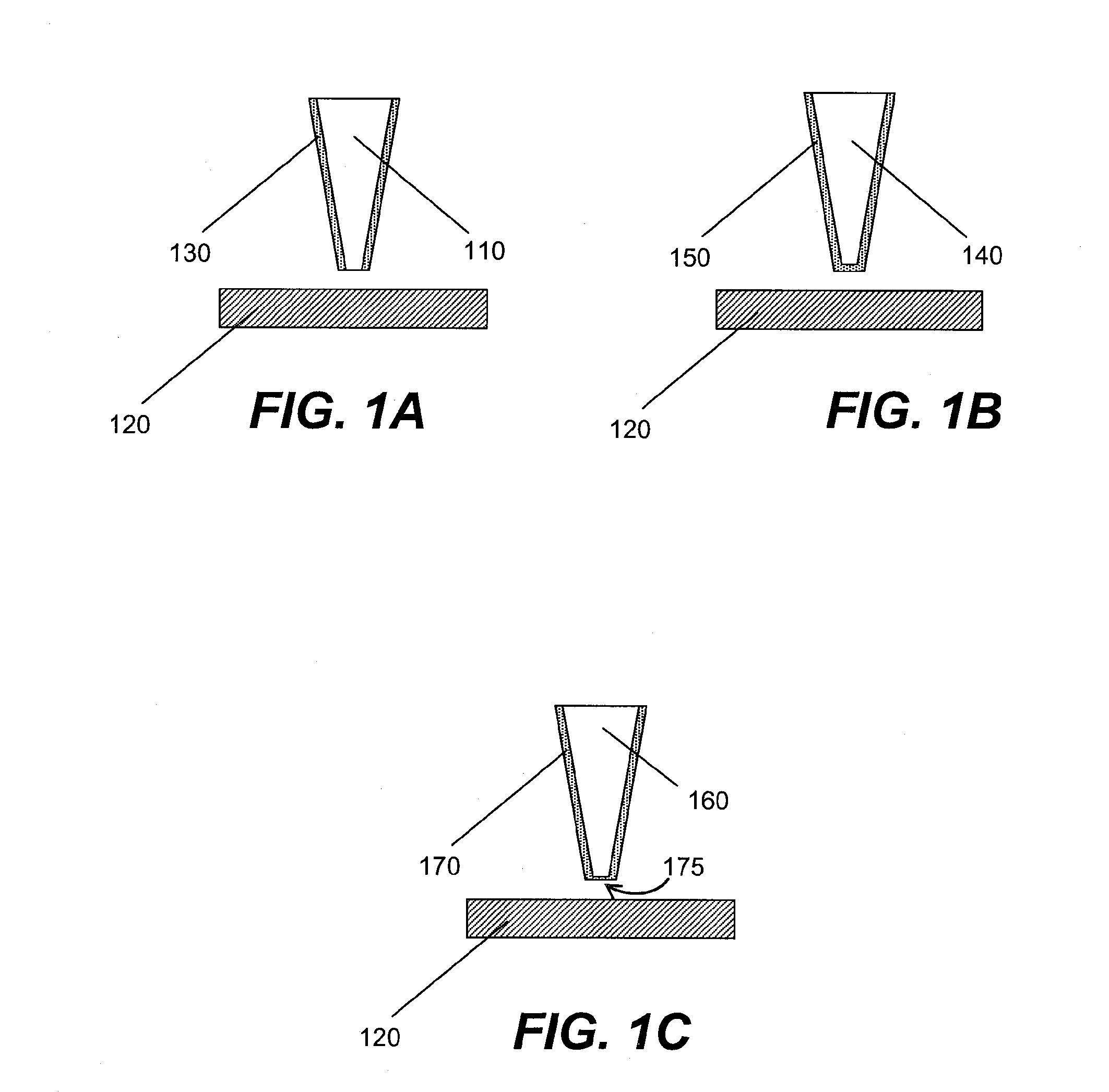
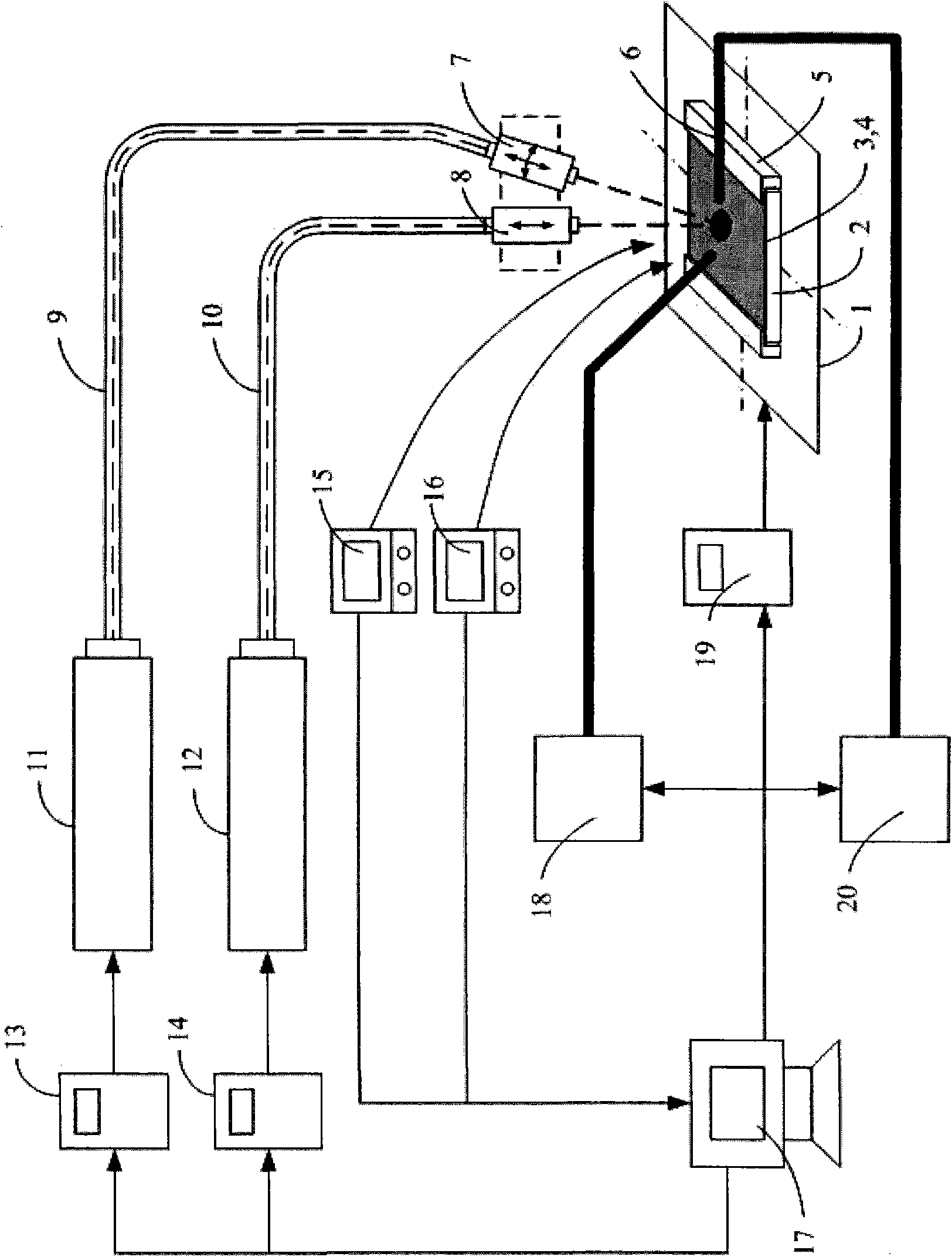
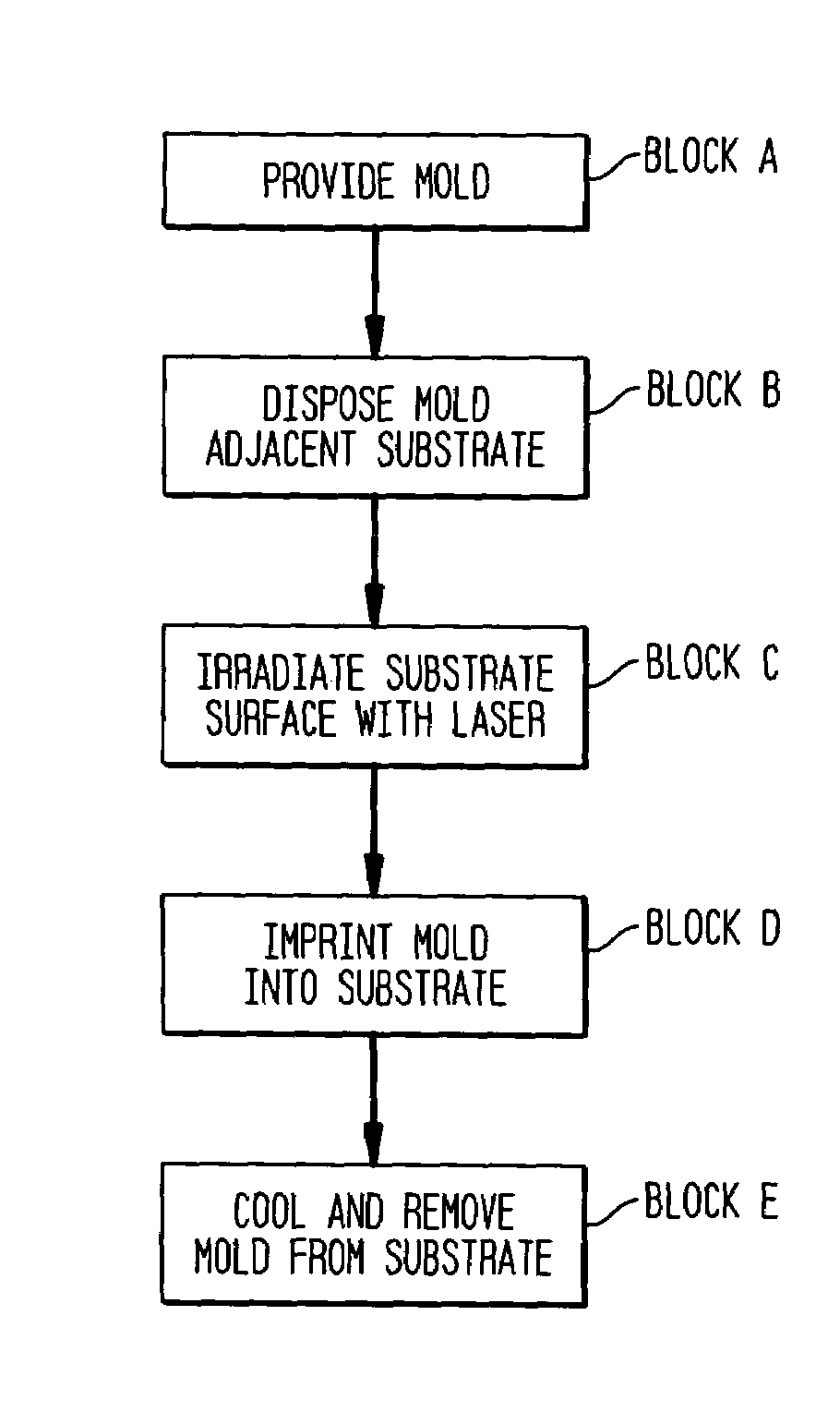
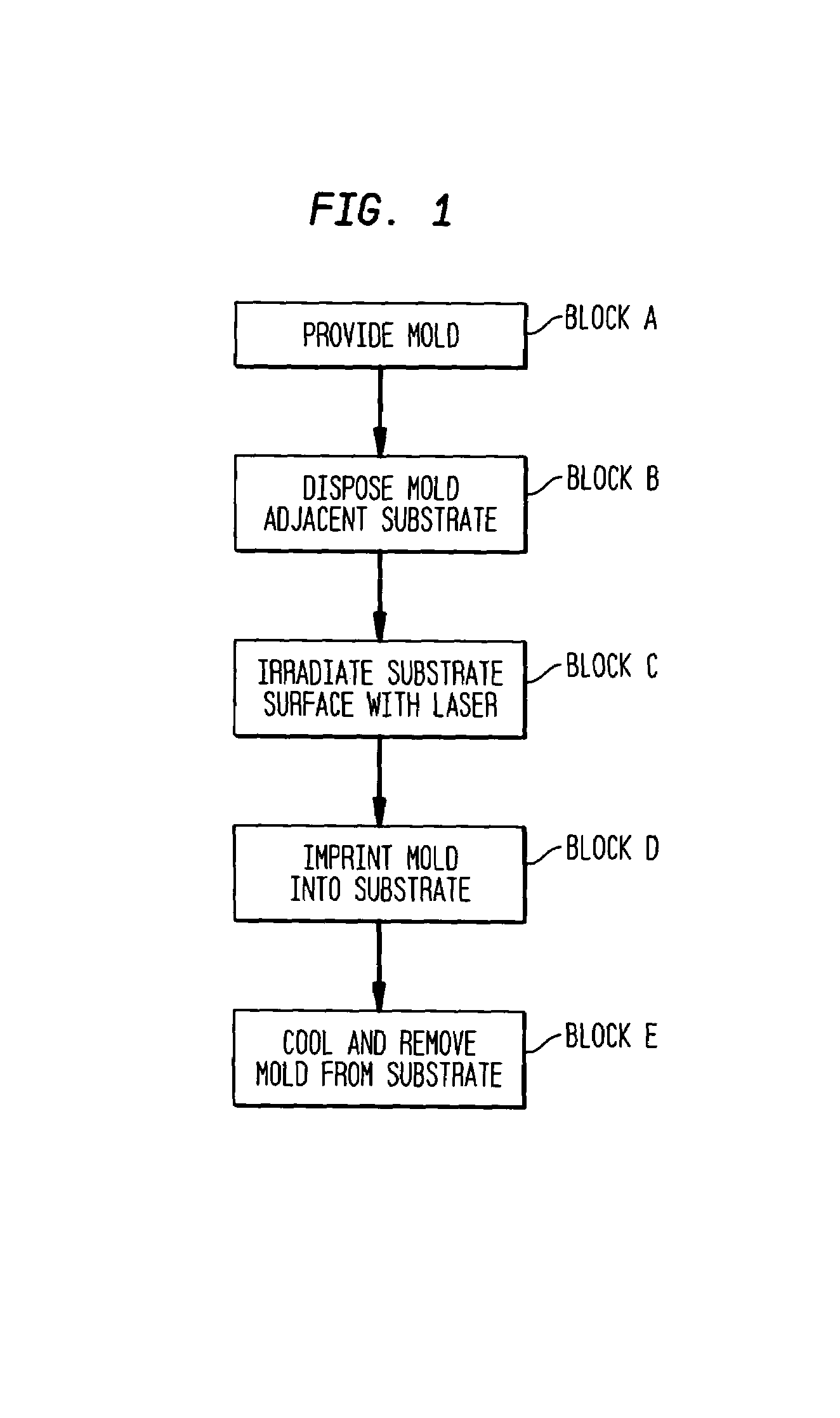
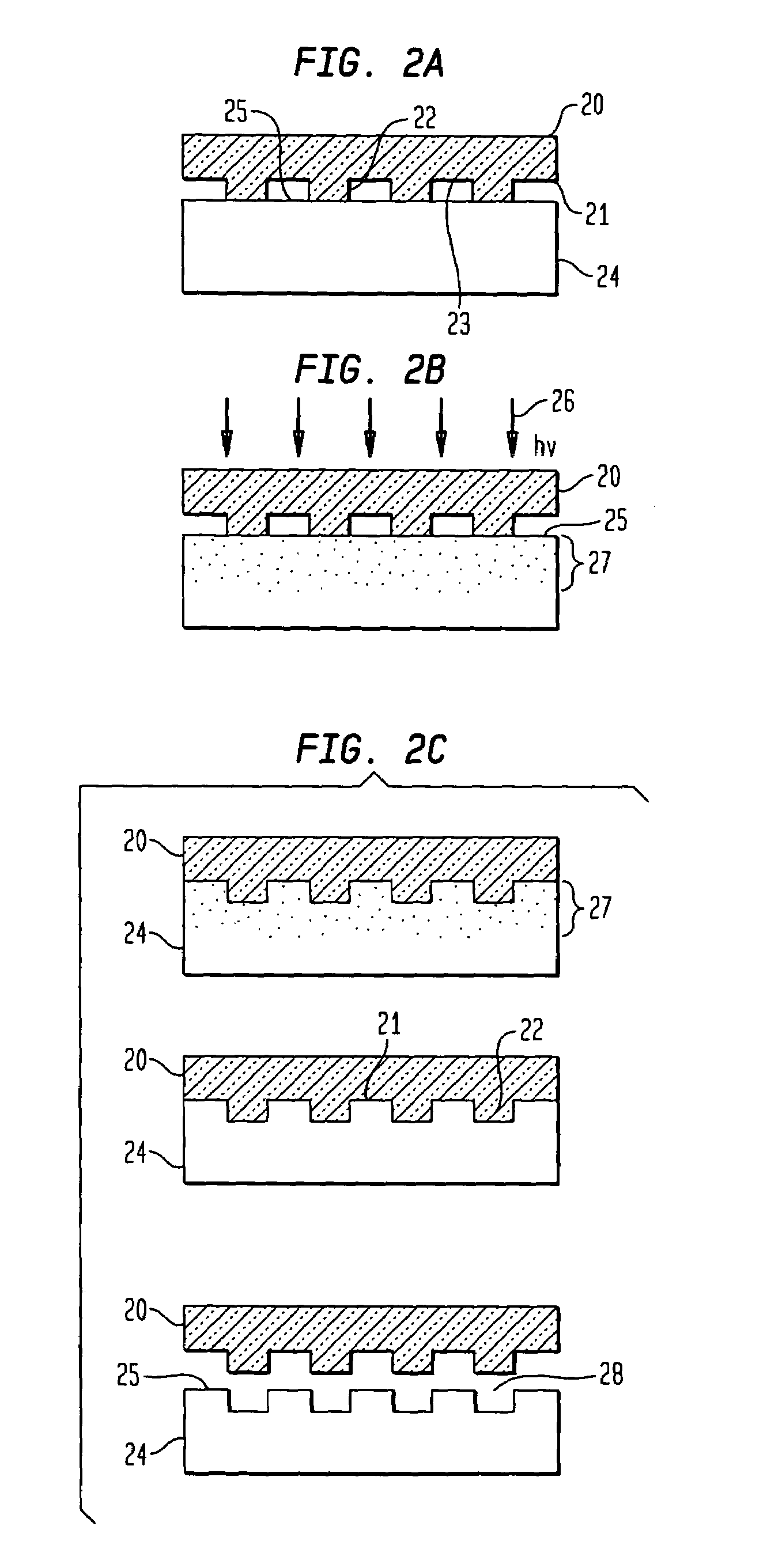
Laser assisted direct imprint lithography
In accordance with the invention, features can be directly imprinted into the surface of a solid substrate. Specifically, a substrate is directly imprinted with a desired pattern by the steps of providing a mold having a molding surface to imprint the pattern, disposing the molding surface adjacent or against the substrate surface to be imprinted, and irradiating the substrate surface with radiation to soften or liquefy the surface. The molding surface is pressed into the softened or liquefied surface to directly imprint the substrate. The substrate can be any one of a wide variety of solid materials such as semiconductors, metals, or polymers. In a preferred embodiment the substrate is silicon, the laser is a UV laser, and the mold is transparent to the UV radiation to permit irradiation of the silicon workpiece through the transparent mold. Using this method, applicants have directly imprinted into silicon large area patterns with sub-10 nanometer resolution in sub-250 nanosecond processing time. The method can also be used with a flat molding surface to planarize the substrate.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
Method and device for preparing working layer of metallurgical hot roll by laser direct deposition
InactiveCN101818342ARealize direct manufacturingReduce flyingMetallic material coating processesLaser technologyAlloy composite
The invention discloses a method and a device for preparing a working layer of a metallurgical hot roll by laser direct deposition, which belong to the field of the application of laser technology. The method is characterized in that high speed steel-like powder and Co-based alloy composite powder are used as the materials for the working layer of the roll. Concretely, the method comprises: filling high speed steel-like powder or mechanically mixed powder which uses Co-based alloy and the like as a substrate material and is added with reinforcing and toughening submicron grains with different amounts into a powder supply system; and performing laser-assisted direct metal deposition on the surface of a roll core, of which the travel is controlled by a worktable, with synchronous powder supply to manufacture the working layer of the roll. A deposition method adopts an alternate deposition mode. The corresponding deposition thickness is determined according to the requirements on the thickness of the working layer. The hard phase content of the powder, in which the Co-based alloy is added as a hard phase, is increased layer by layer so as to form a gradient deposited layer. In the method, the reinforced, toughened and wear-resistance working layer is prepared on the surface of a cheap hot roll core part material by laser-assisted metal direct deposition technology under specific process conditions.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
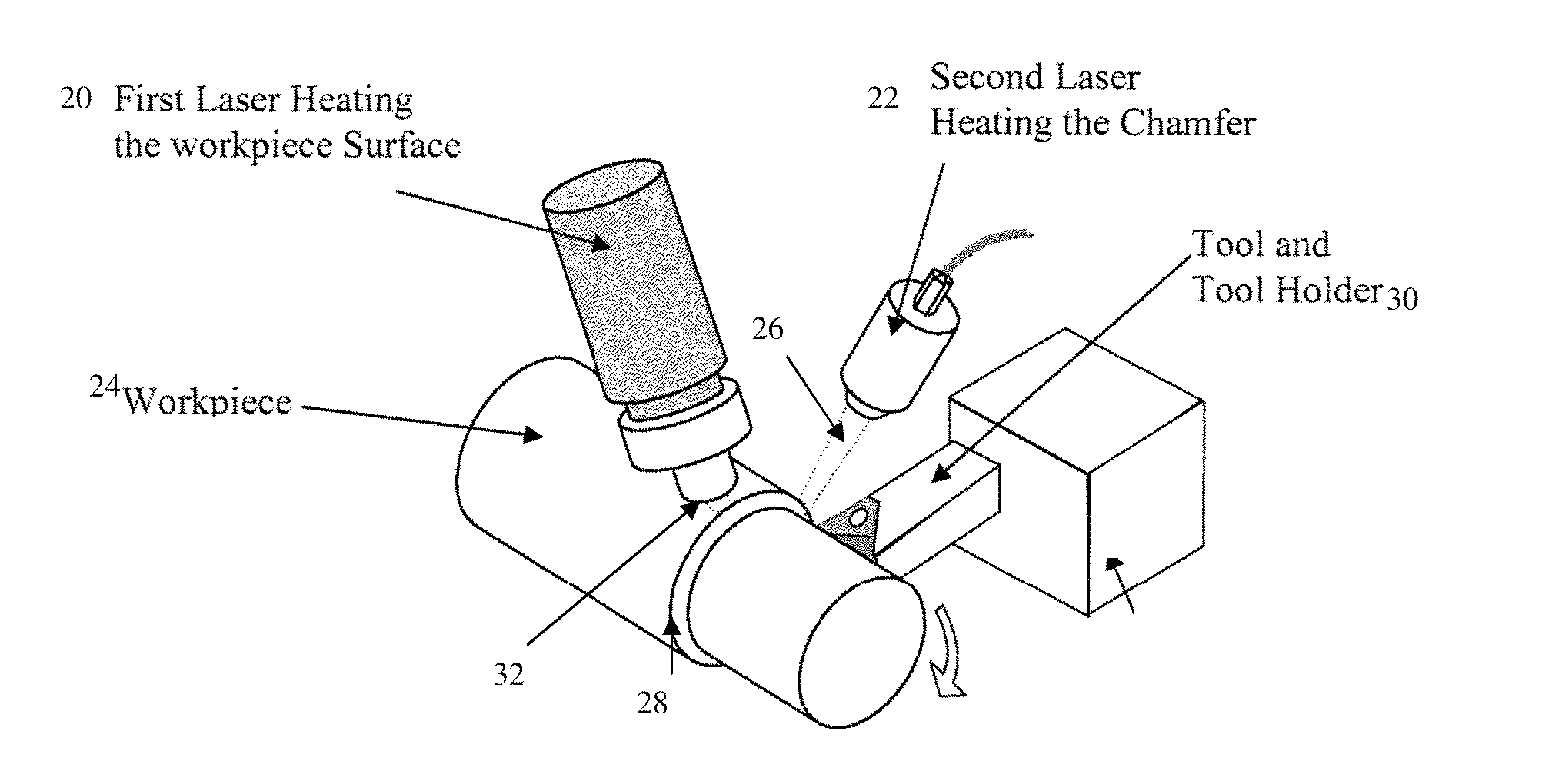
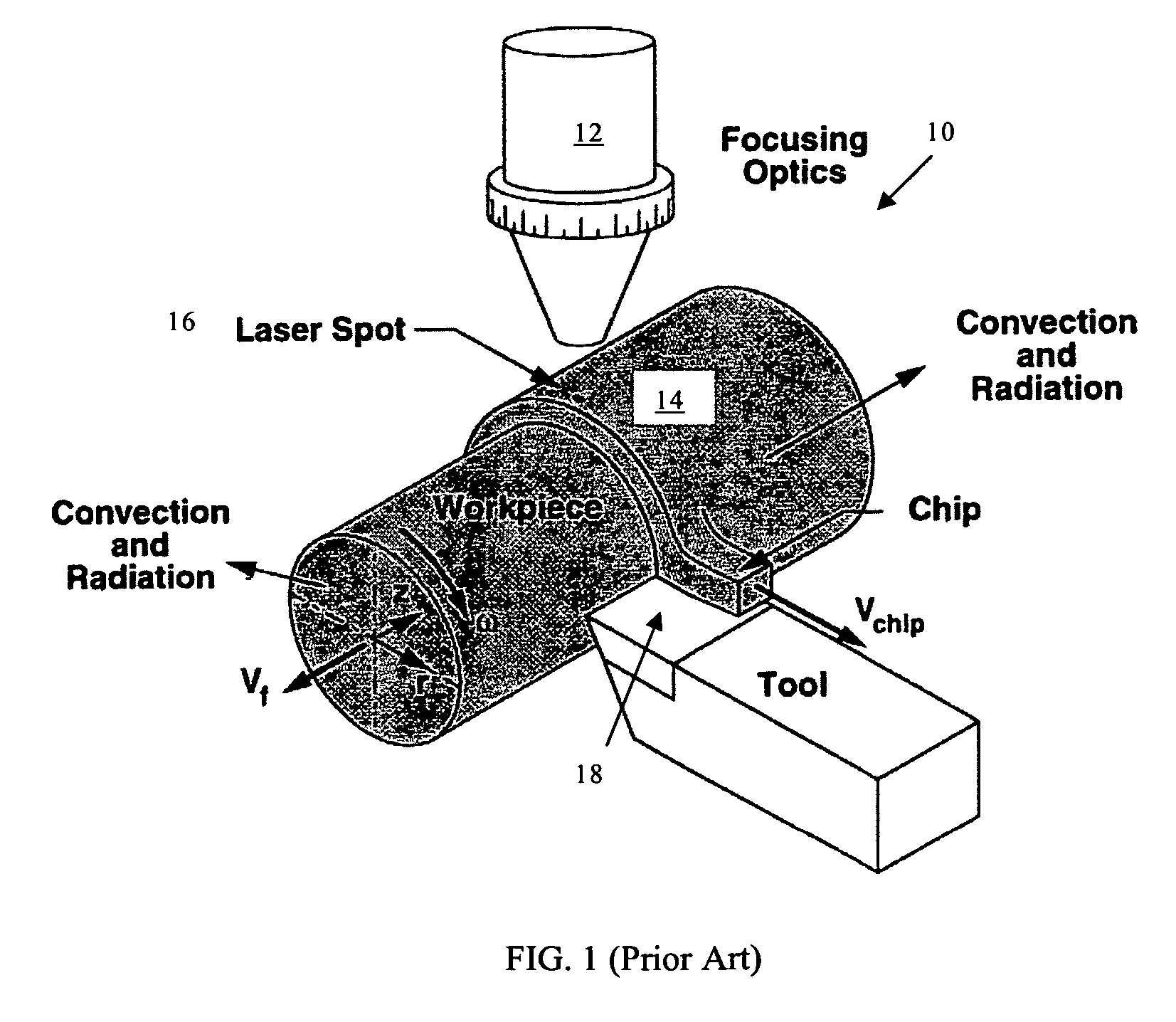
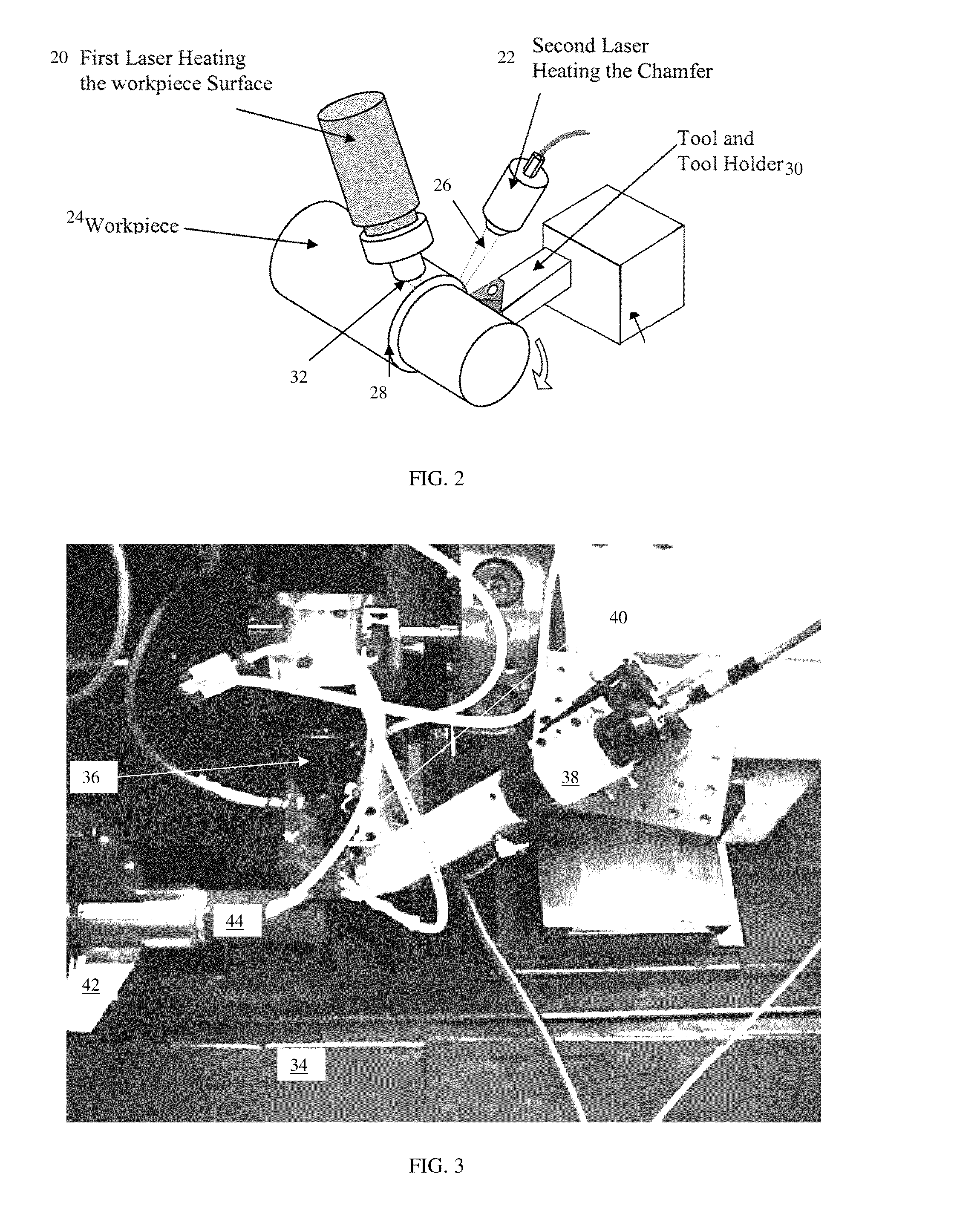
Laser assisted machining process with distributed lasers
Laser assisted machining process and machine utilizing multiple distributed laser units that are strategically distributed around the workpiece being machined to simultaneously heat the workpiece, creating a desired temperature distribution for laser assisted machining. Sequential incremental heating from different directions and positions are used, resulting in longer tool life and shorter machining time.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Spatial and temporal selective laser assisted fault localization
ActiveUS20050006602A1Electric discharge tubesSpecial data processing applicationsSpecific testTester device
A method and apparatus for laser-assisted fault mapping which synchronizes the laser control with the tester unit. The inventive method provides for laser-assisted pseudo-static fault mapping to localize defects in a device whose inputs are being stimulated dynamically by a tester. It further provides for laser-assisted dynamic soft error mapping, to localize in terms of location and to correlate with respect to a specific test vector, sensitive areas in a device by utilizing device performance criteria such as pass-fail status outputs. The apparatus includes a fully controllable dynamic laser stimulation apparatus connected to a control unit that provides complete synchronization with a tester unit.
Owner:DCG SYST
Systems and methods for laser-assisted plasma processing
InactiveUS7297892B2Speed up the processHighly controllableArc welding apparatusOptical light guidesTorchLaser assisted
A controllable heat source, such as a laser or flame torch, can be used to pre-heat a portion of the surface of a workpiece, such as a glass optic or semiconductor wafer. Reactive atom plasma (RAP) processing can be used to modify the pre-heated surface portion, as the pre-heated material will more readily chemically combine with the atomic radicals of the precursor in the plasma. A RAP torch, such as an ICP plasma torch, MIP plasma torch, or flame torch, can be used to shape, polish, etch, planarize, deposit, chemically modify and / or redistribute material on the surface of the workpiece. The material modified by the torch can substantially correspond to the pattern or portion of the surface that was pre-heated by the heat source. This description is not intended to be a complete description of, or limit the scope of, the invention. Other features, aspects, and objects of the invention can be obtained from a review of the specification, the figures, and the claims.
Owner:IMREAL ENTERPRISES
Systems and methods for laser-assisted plasma processing
InactiveUS20050061783A1Speed up the processFootprint is small and preciseArc welding apparatusPlasma welding apparatusLaser assistedTorch
A controllable heat source, such as a laser or flame torch, can be used to pre-heat a portion of the surface of a workpiece, such as a glass optic or semiconductor wafer. Reactive atom plasma (RAP) processing can be used to modify the pre-heated surface portion, as the pre-heated material will more readily chemically combine with the atomic radicals of the precursor in the plasma. A RAP torch, such as an ICP plasma torch, MIP plasma torch, or flame torch, can be used to shape, polish, etch, planarize, deposit, chemically modify and / or redistribute material on the surface of the workpiece. The material modified by the torch can substantially correspond to the pattern or portion of the surface that was pre-heated by the heat source. This description is not intended to be a complete description of, or limit the scope of, the invention. Other features, aspects, and objects of the invention can be obtained from a review of the specification, the figures, and the claims.
Owner:IMREAL ENTERPRISES
Method and apparatus for a printed circuit board using laser assisted metallization and patterning of a substrate
InactiveUS20070144769A1Printed electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOptoelectronicsLaser assisted
A printed circuit is made by laser projection patterning a metal panel of a substrate, laminating a dielectric layer on the metal panel, laser irradiating the substrate to form vias in the substrate, laser activating a seed coat on the substrate, washing the seed coat from an unpatterned portion of the substrate, forming a patterned build-up layer on the substrate, and etching away a metal plating forming metal protrusions.
Owner:INTEL CORP
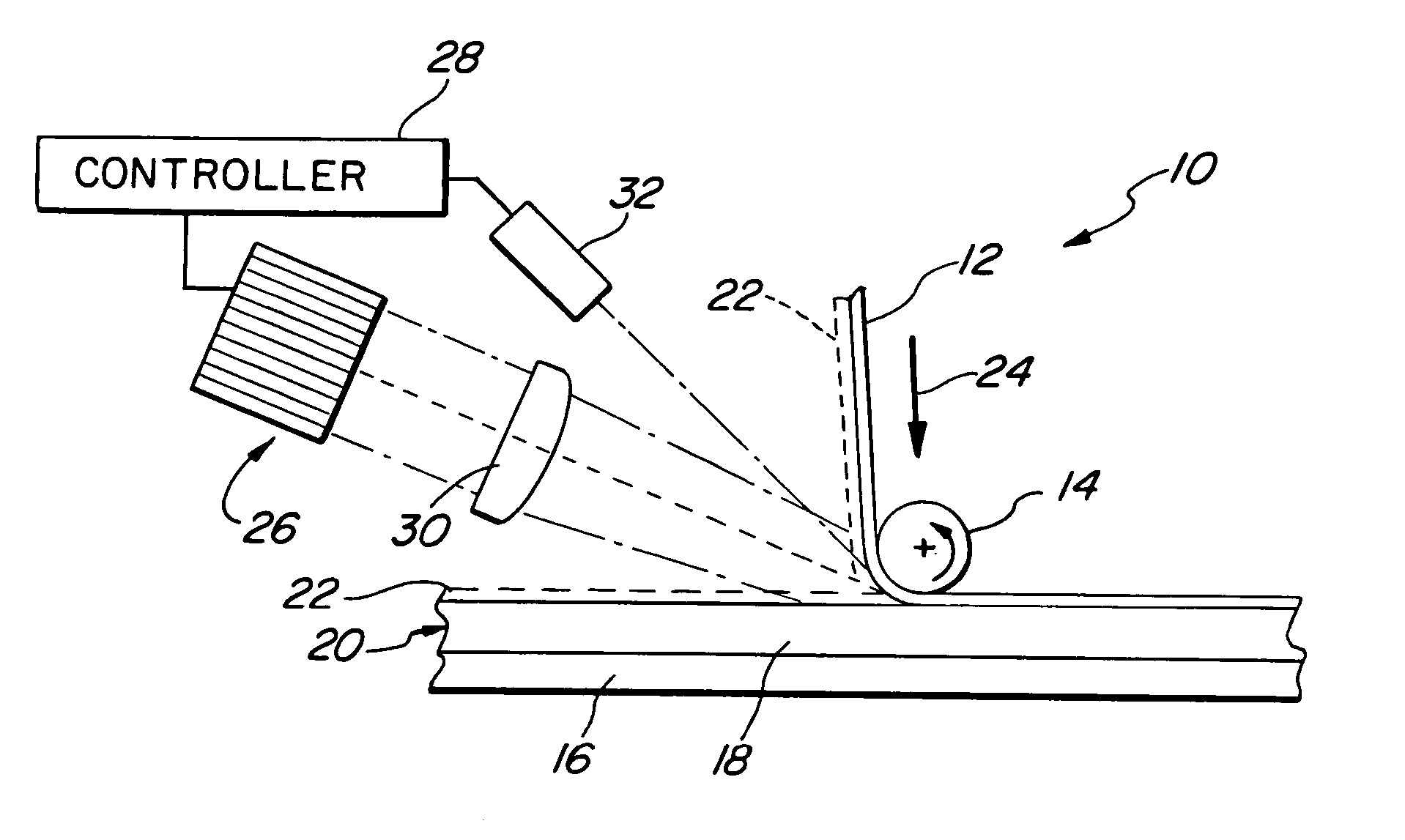
Laser-assisted coating removal method
InactiveUS7525065B2Improve the level ofNegative effectWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusLight beamLaser assisted
Stripping is accomplished with a pulsed laser beam that targets the material and area to be stripped. The wavelength laser beam may be selected or adjusted to the absorption behavior of the material to be stripped without damaging the underlying base material. A control unit may operably adjust an optical system to guide the laser beam over the surface to be treated. a coating. This makes it possible to improve the surface stripping process.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
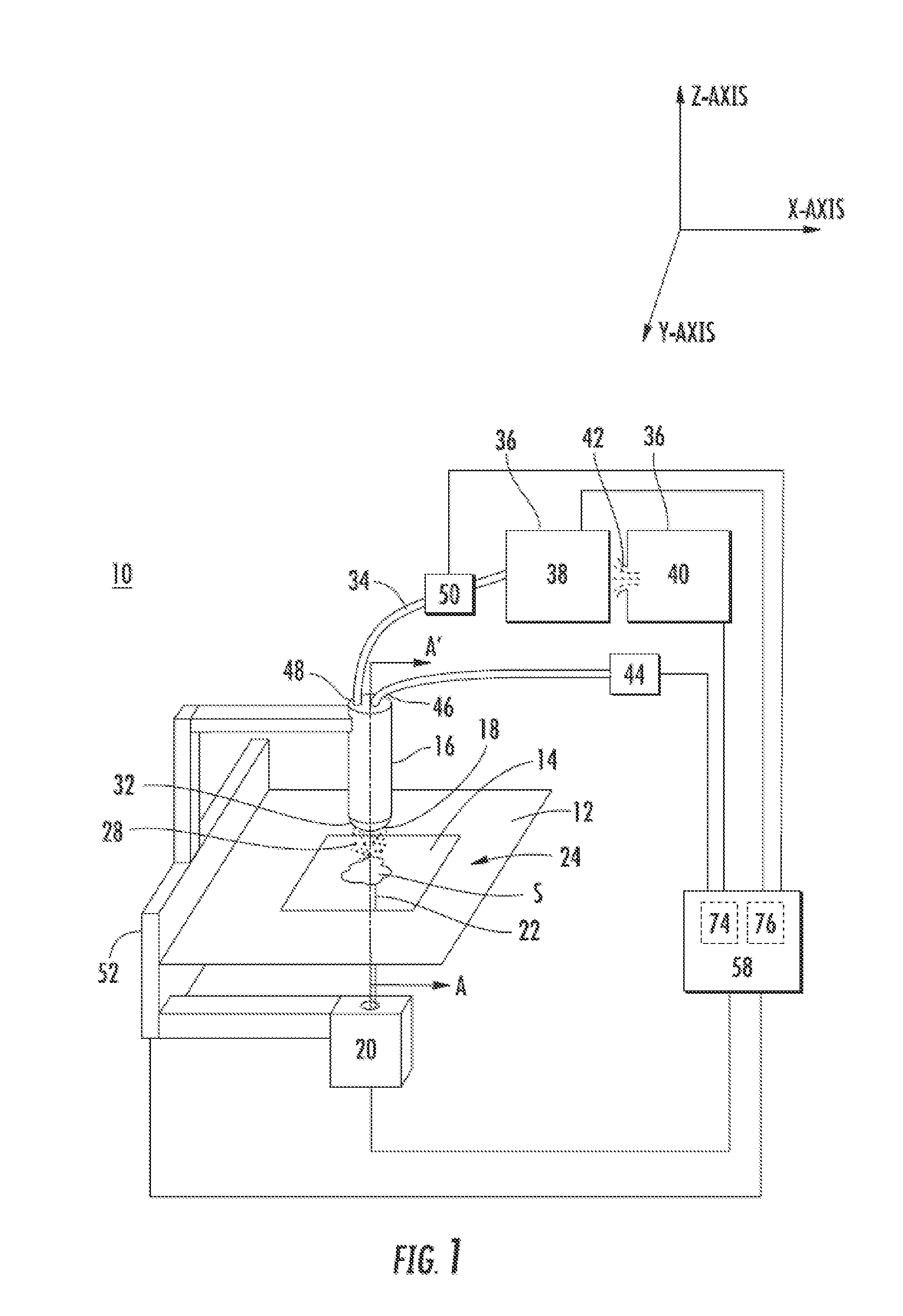
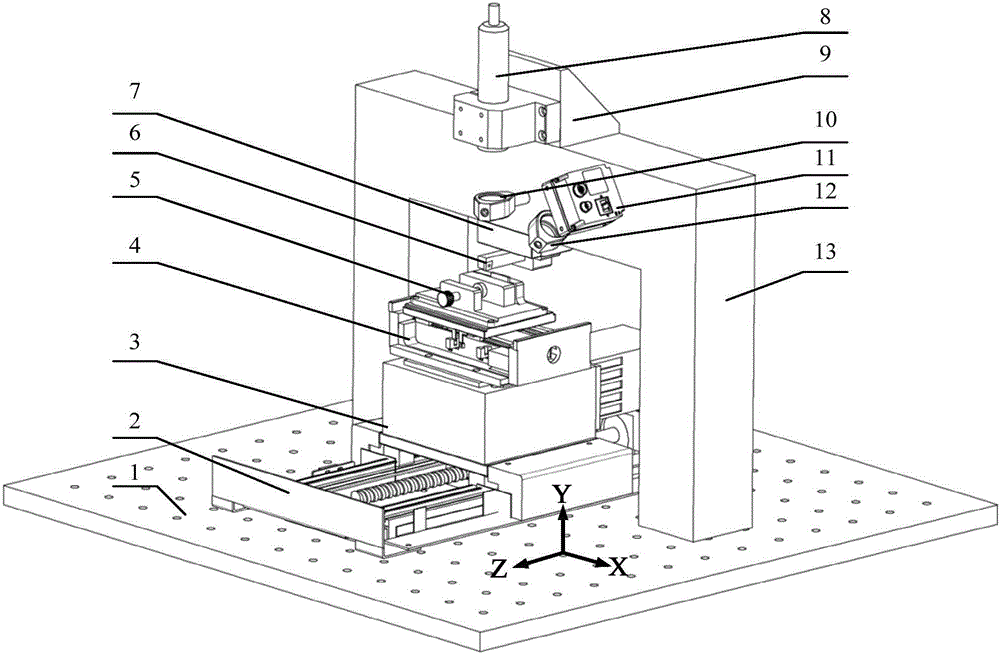
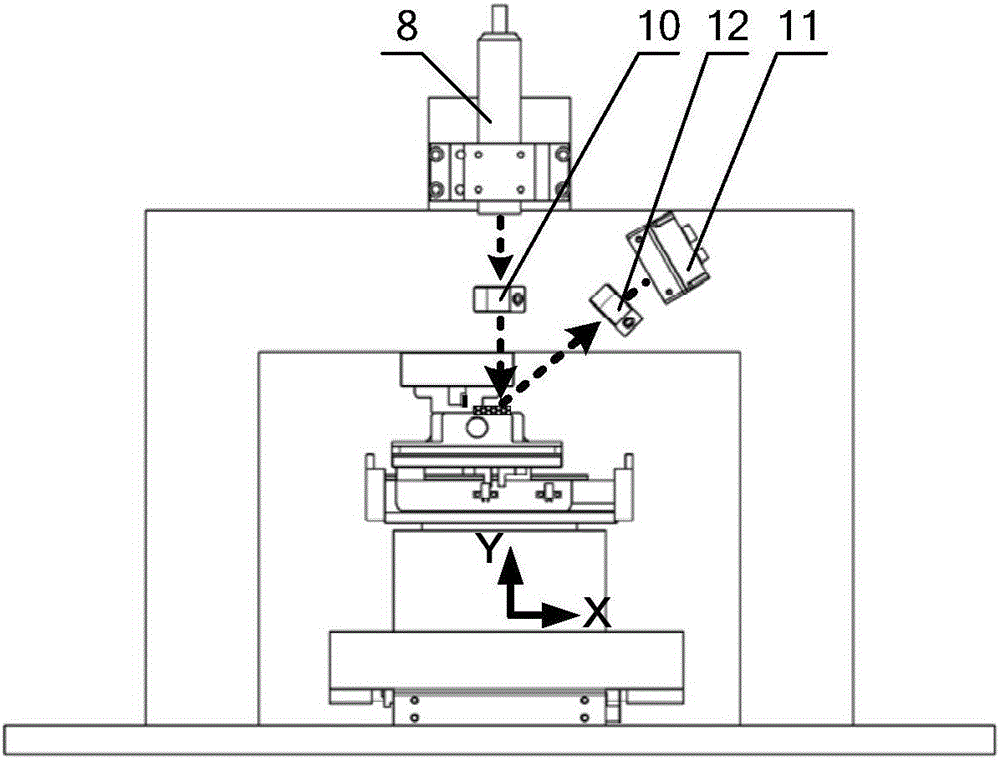
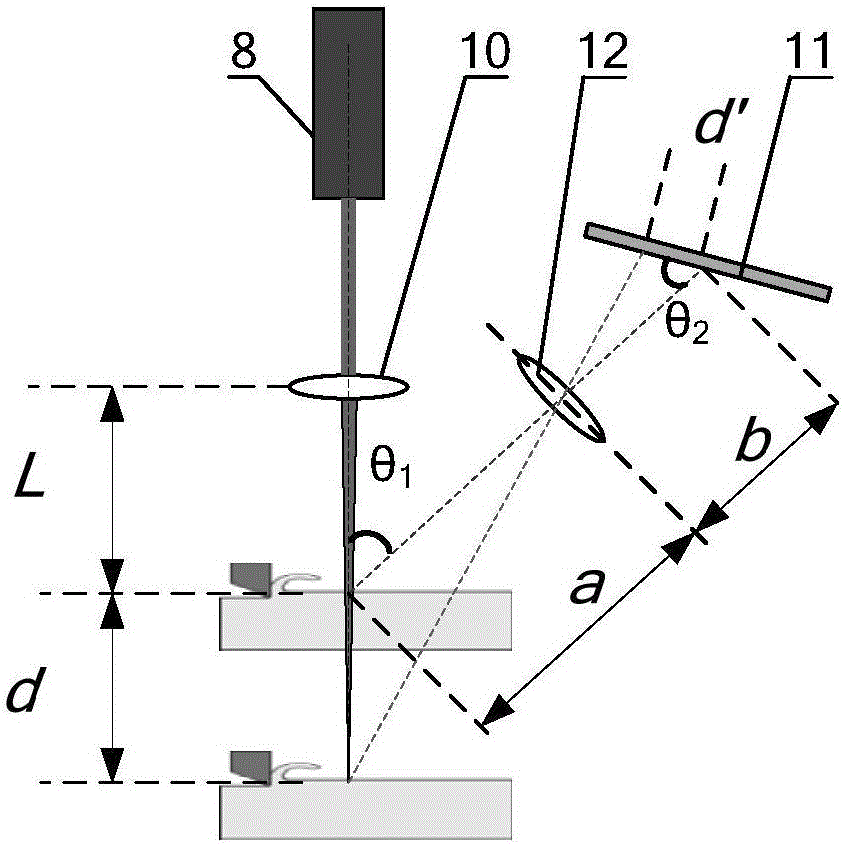
Laser-assisted orthogonal micro-cutting device and method having automatic laser focus following function
ActiveCN106312567AIncreased durabilityExtend your lifeOther manufacturing equipments/toolsLaser beam welding apparatusMachined surfaceLight beam
The invention discloses a laser-assisted orthogonal micro-cutting device and method having an automatic laser focus following function, belongs to the technical field of machining equipment and aims to solve the problem that height changes of to-be-machined surfaces cannot be monitored in real time in laser-assisted micro-cutting processes in the prior art. A motion unit and a laser-assisted machining unit of the device are mounted on a shock-absorbing platform; an optical automatic following unit is arranged on the laser-assisted machining unit and comprises a lens A, a lens B and a linear array charge coupled device (CCD) sensor; laser emitted by a laser light source of the laser-assisted machining unit irradiates a to-be-machined surface via the lens A, and a laser beam reflected by the to-be-machined surface is focused on the linear array CCD sensor via the lens B; and the to-be-machined surface is mounted on the motion unit, and a computer control unit adjusts displacement of the to-be-machined surface in the direction X, the direction Y and the direction Z in real time by the aid of the motion unit according to the laser action range fed back by the linear array CCD sensor.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Copper-clad laminate-based method for micro-removing copper film from selected area by assistance of laser
InactiveCN102202466AAchieve preparationHigh precisionConductive material chemical/electrolytical removalLaser beam welding apparatusOptoelectronicsCopper foil
The invention discloses a copper-clad laminate-based method for micro-removing copper film from a selected area by assistance of laser, belonging to the field of micromachining. The method comprises the following steps of: applying a layer of coating material on the surface of a copper foil of the copper-clad laminate; making a pattern to be removed through drawing software; respectively connecting a laser with a laser motion control system and a computer, wherein laser parameters and a laser motion path are controlled through laser control software; placing and clamping the coated copper-clad laminate on a processing platform, and keeping a coated surface of the copper-clad laminate and the focal point of a laser beam within a same plane; importing the pattern to be removed into the laser control software, positioning the pattern in the position where the copper film is required to be removed by indicating light, and adjusting the laser parameters so that the laser beam acts on the copper-clad laminate for selectively removing the coated layer; placing the scanned copper-clad laminate into an etching agent to be etched; and putting and rinsing the etched sample in clean water to remove the coating. The invention has the advantages of high precision and efficiency, good controllability, and controllable shape of the selected area, and can realize FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit)wiring and masking as well as manufacturing of exquisite handicraft articles.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Laser-assisted cold spray coating method and nozzle apparatus
ActiveCN103920626AFacilitate depositionAvoid cloggingLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid spraying apparatusTransmittanceSpray coating
The present invention discloses a laser-assisted cold spray coating method and a nozzle apparatus. According to the nozzle apparatus, one side of the nozzle throat portion is a nozzle constriction section, the other side of the nozzle throat portion is a nozzle expansion section, the nozzle side on the nozzle constriction section is provided with a high pressure gas inlet and a light transmittance window for entering of a laser beam, the light transmittance window deviates from the axis line of the nozzle, the nozzle on the nozzle constriction section is provided with a reflecting mirror A, the nozzle side on the nozzle expansion section is provided with a powder inlet, a reflecting mirror B, a reflecting mirror C and a reflecting mirror D, a laser beam entering from the light transmittance window sequentially passes through the reflecting mirror A, the reflecting mirror D, the reflecting mirror B and the reflecting mirror C in the nozzle and then is emitted from the nozzle expansion section, and the powder inlet is positioned between the reflecting mirror D and the reflecting mirror B; and according to the technical scheme, the laser is incident onto the reflecting mirror in the nozzle in a certain angle forming with the nozzle axis line, and the light beam is subjected to multiple reflections through the reflecting mirrors on the inner wall of the nozzle and finally irradiates on the substrate, such that the gas, the powder and the substrate inside the nozzle can be uniformly pre-heated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Position determination system using radio and laser in combination
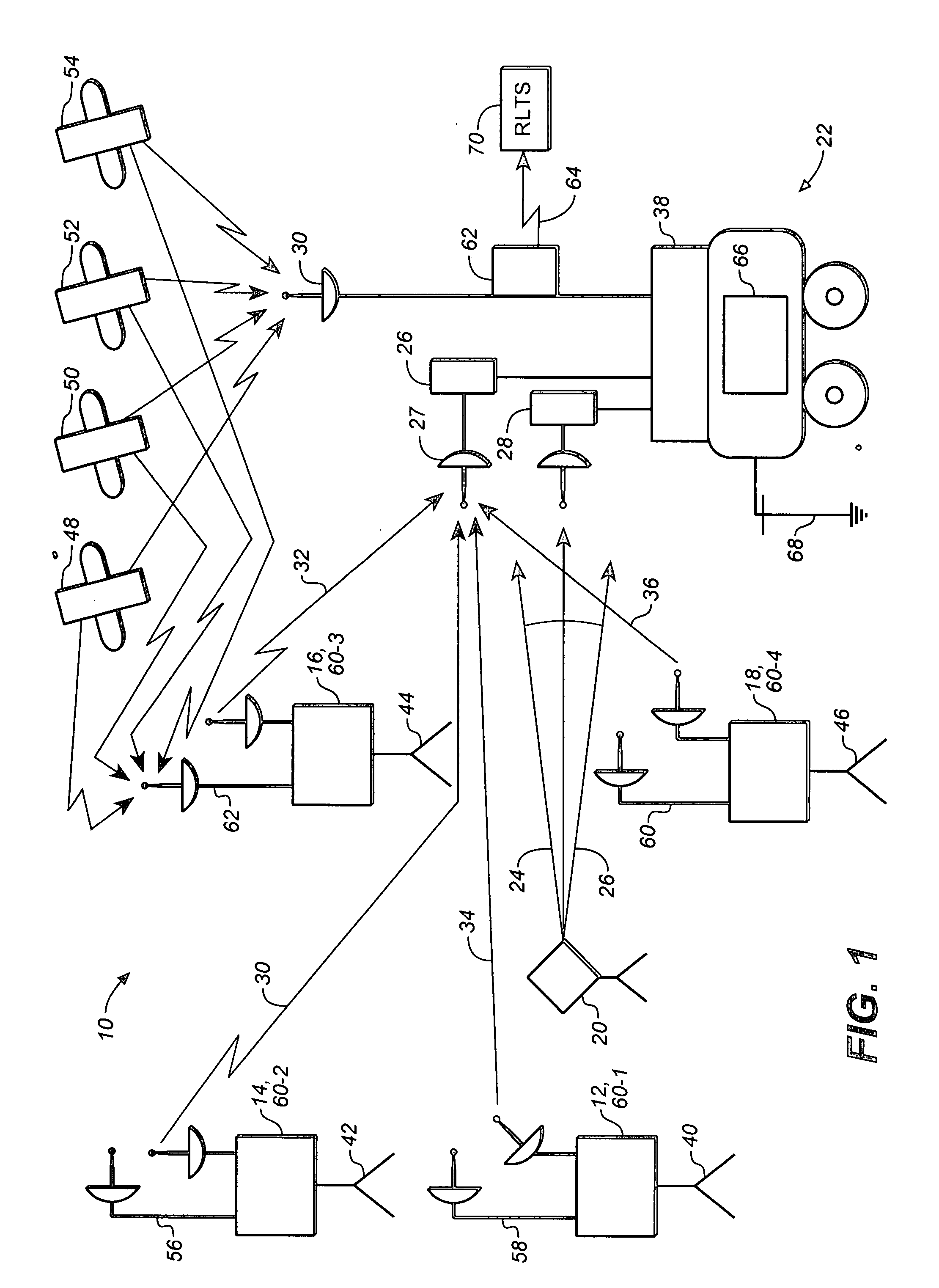
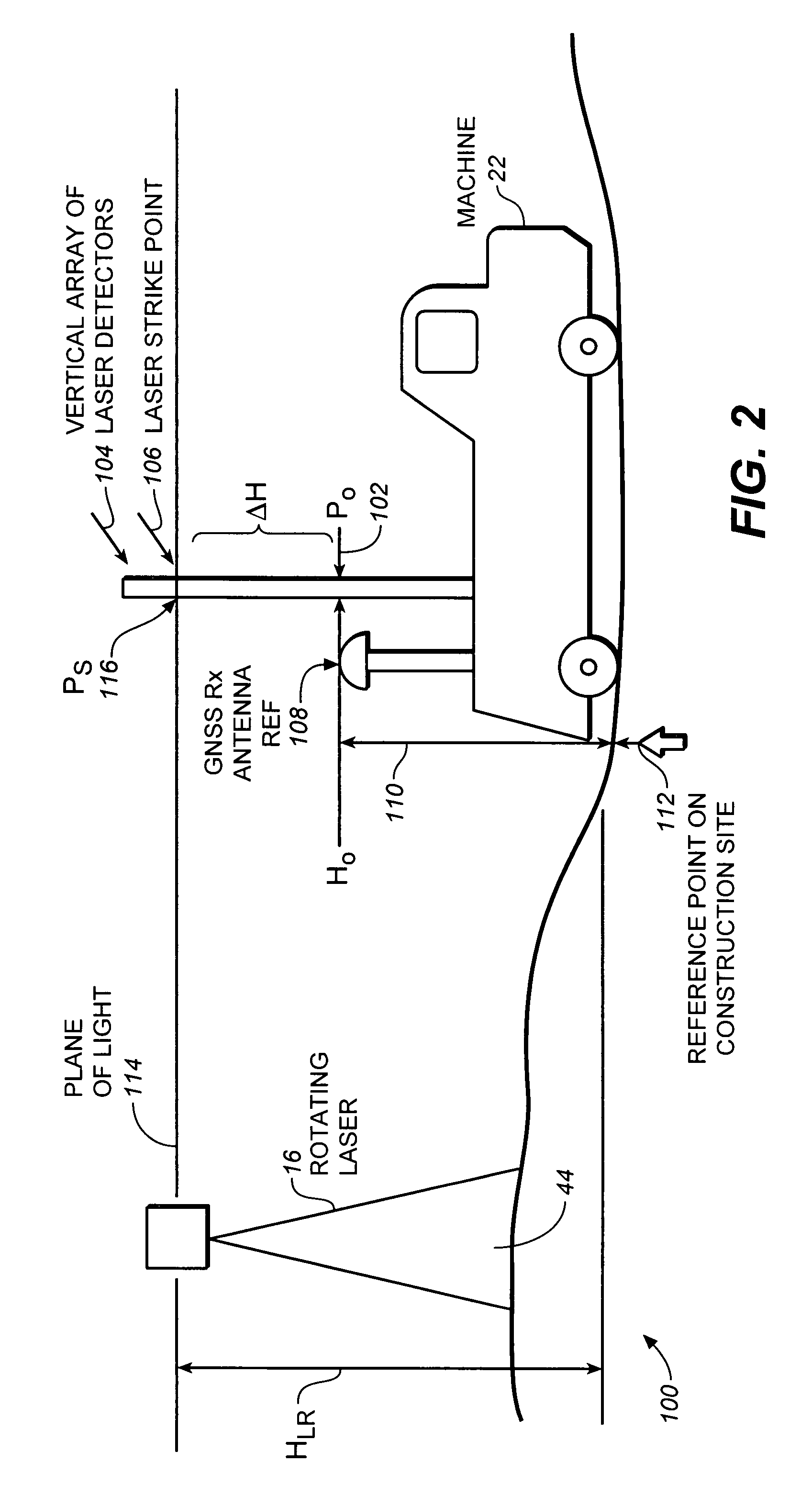
ActiveUS20080247758A1Improve abilitiesDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationLaser transmitterRadio reception
A combined radio and laser positioning system comprising: a network of ground based radio communication devices, a laser transmitter configured to generate at least one laser beam, and at least one user unit. Each user unit comprises a radio receiver configured to receive at least one ranging radio signal transmitted by at least one ground based radio communication device, a laser detector configured to receive at least one laser beam generated by the laser transmitter, and a processor configured to convert a set of data including: {a set of data transmitted by at least one ranging radio signal, and a set of data transmitted by said at least one laser beam} into position coordinates of the user unit, wherein a set of vertical coordinates of the user unit is obtained with a laser-assisted (LA) accuracy.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com