Patents
Literature
246 results about "Cataract surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
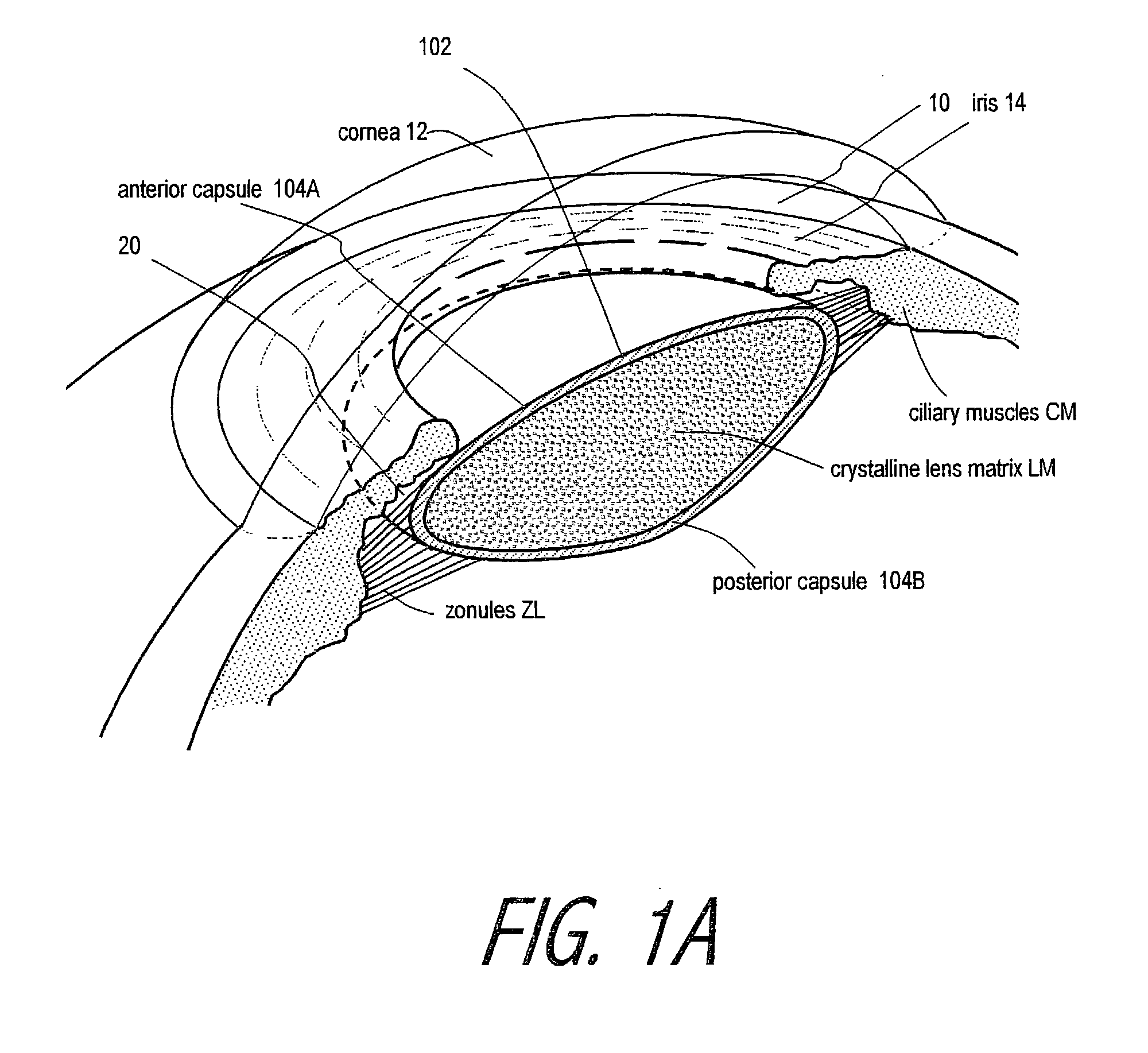
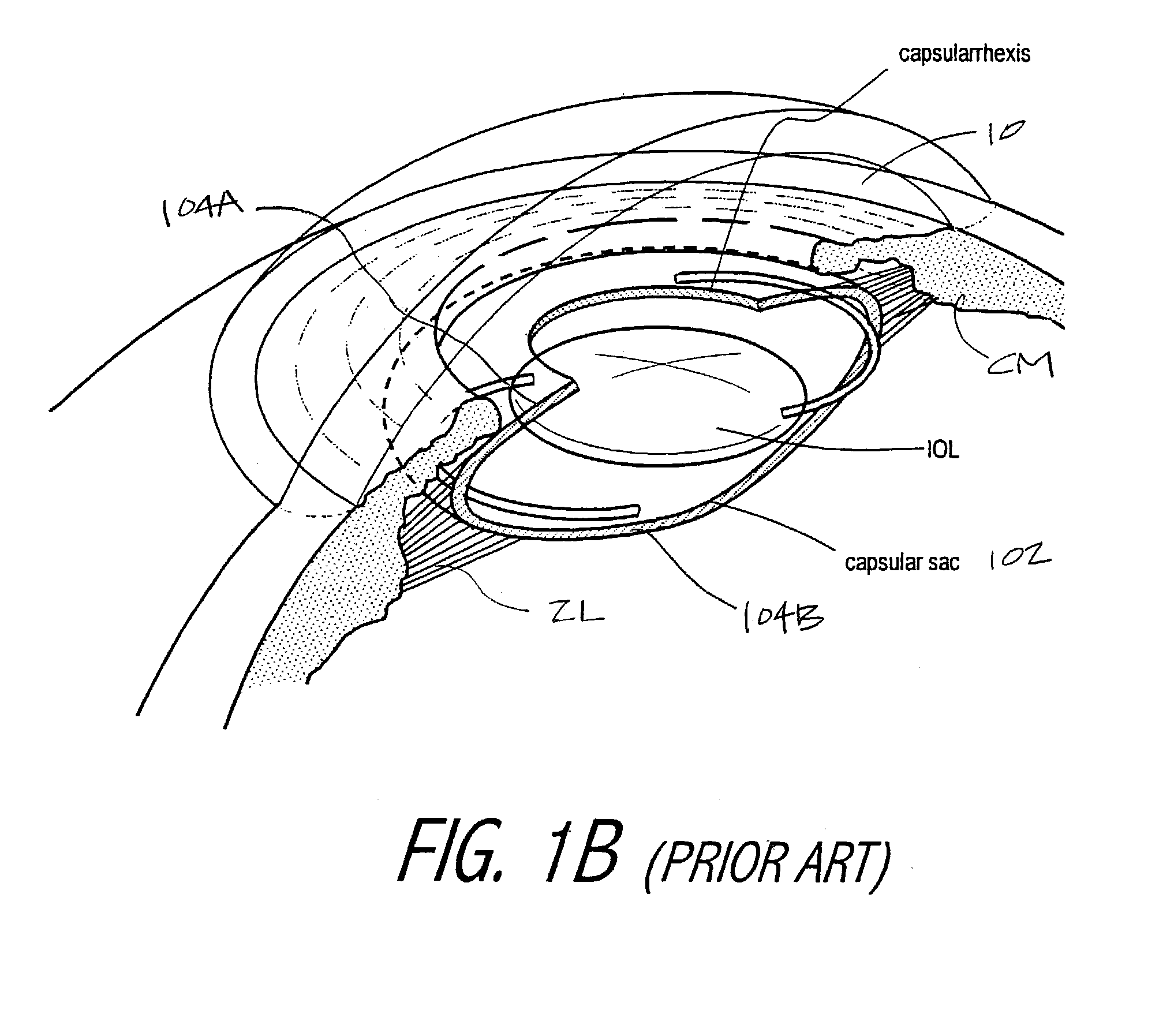
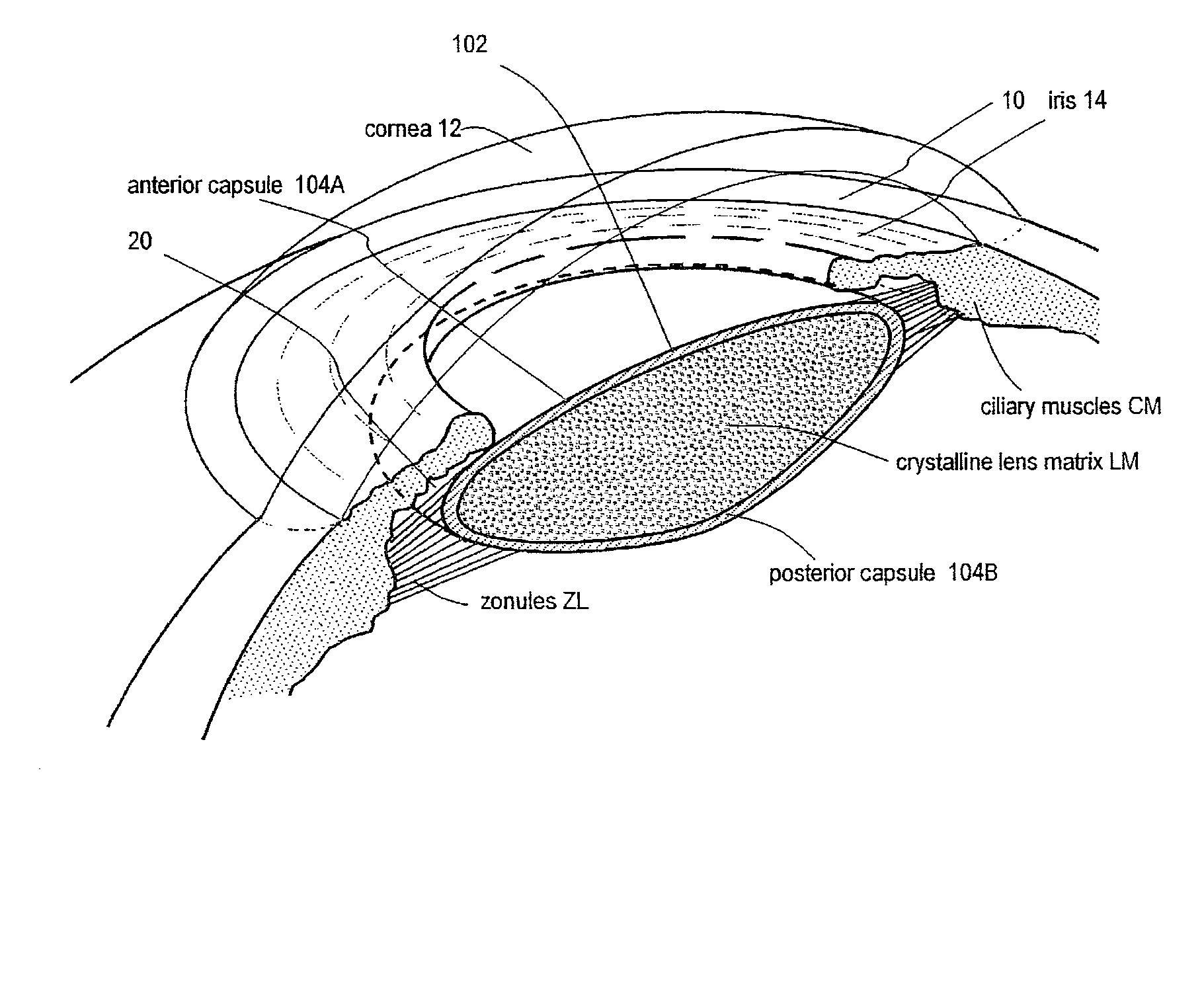
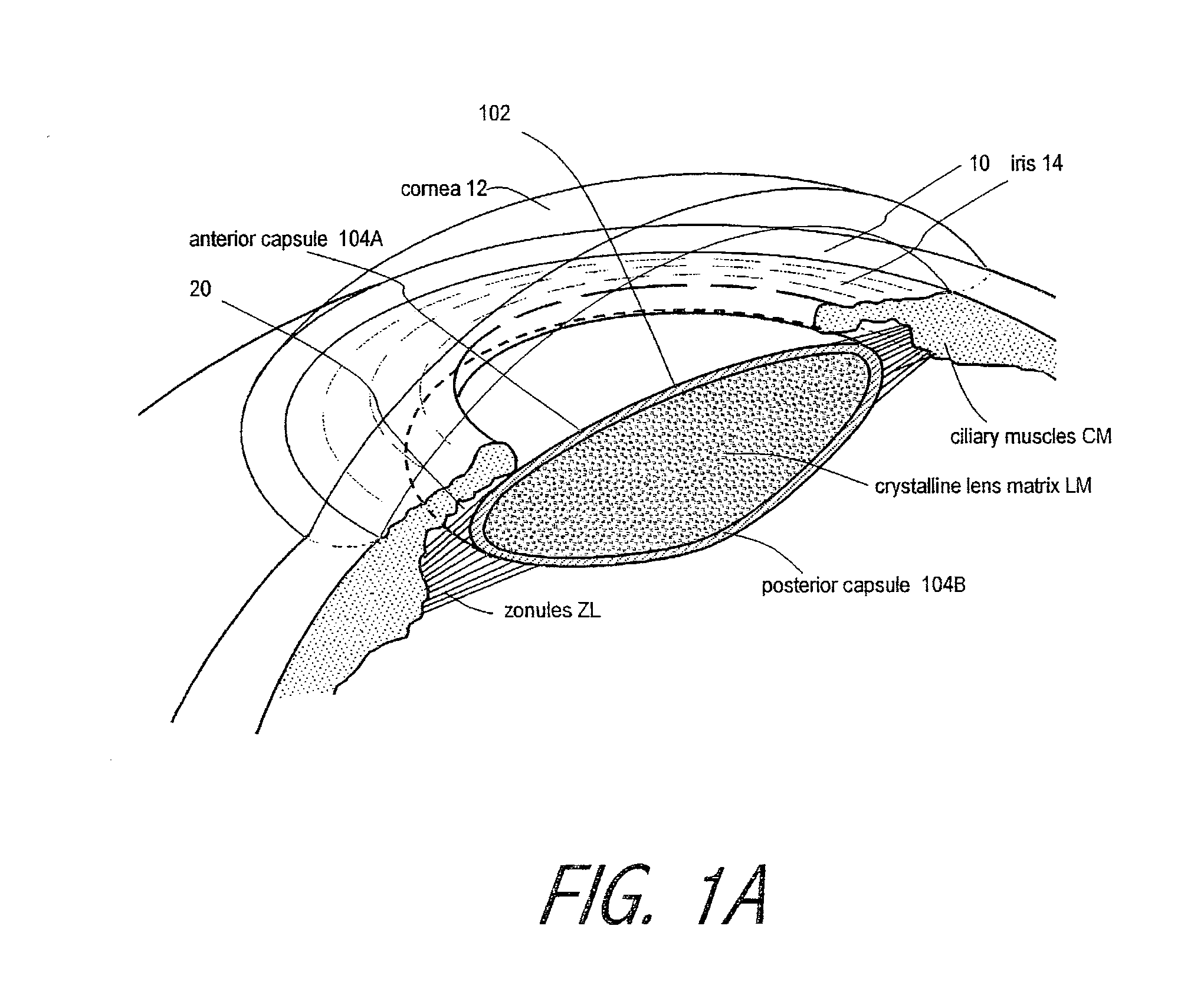
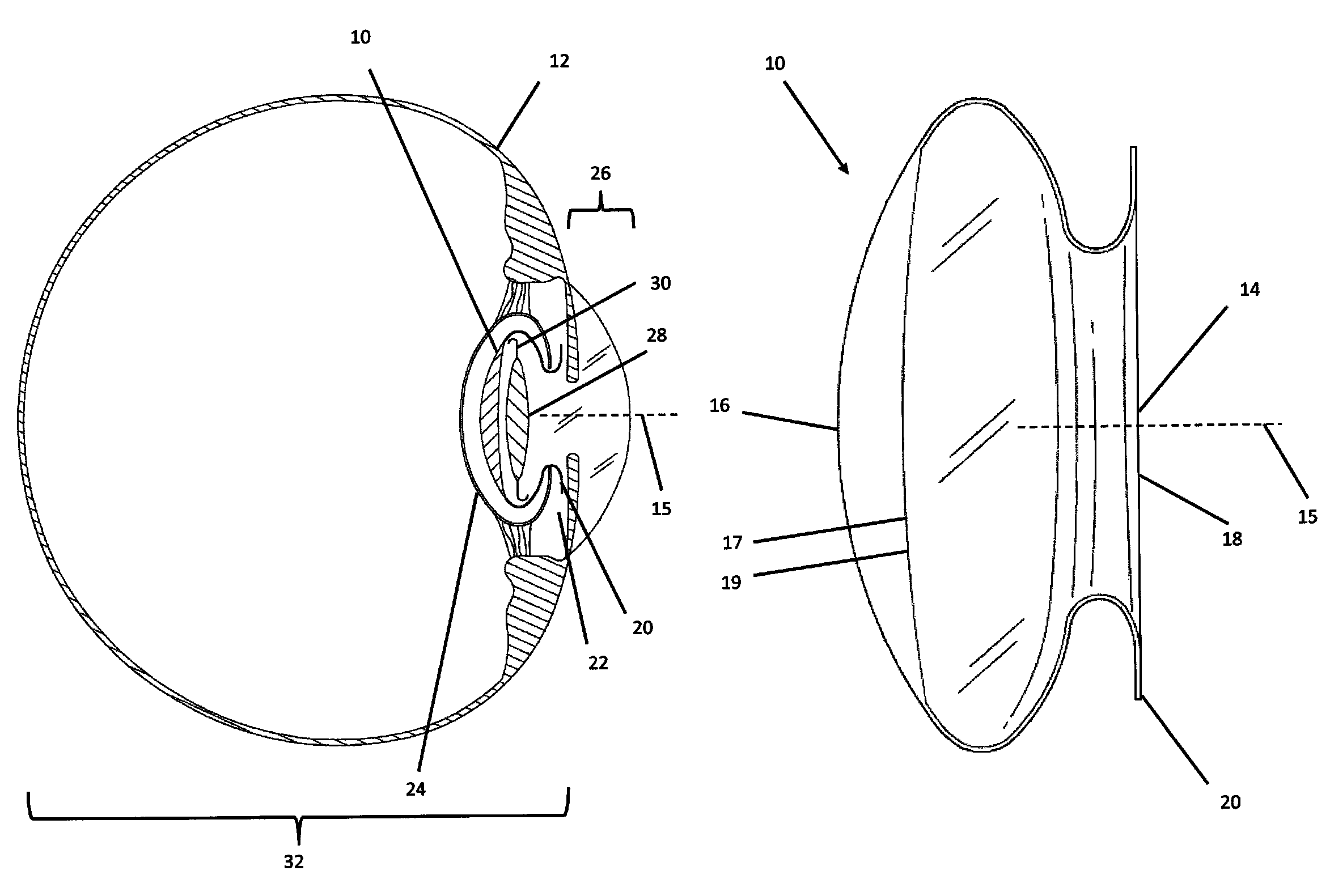
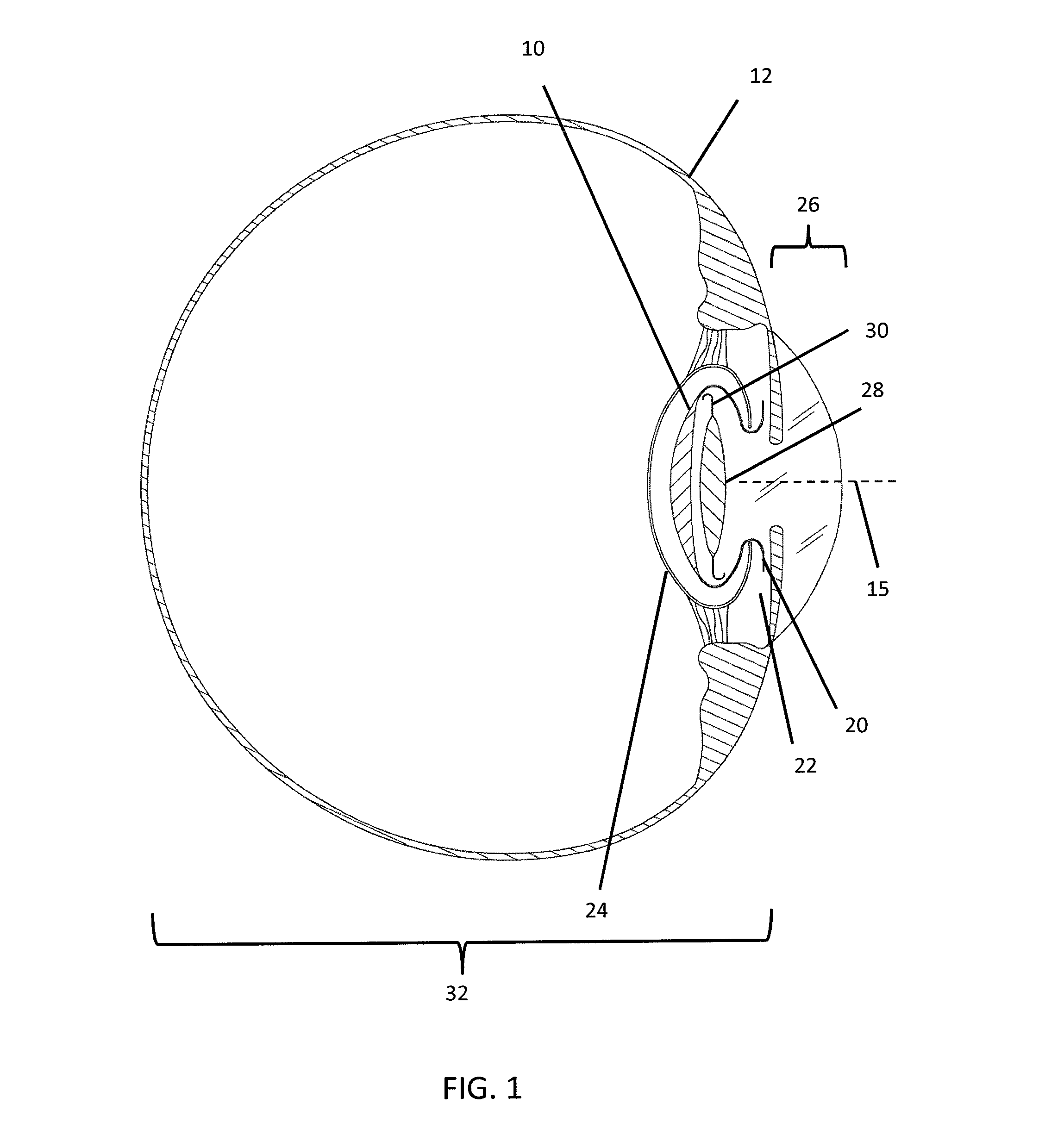
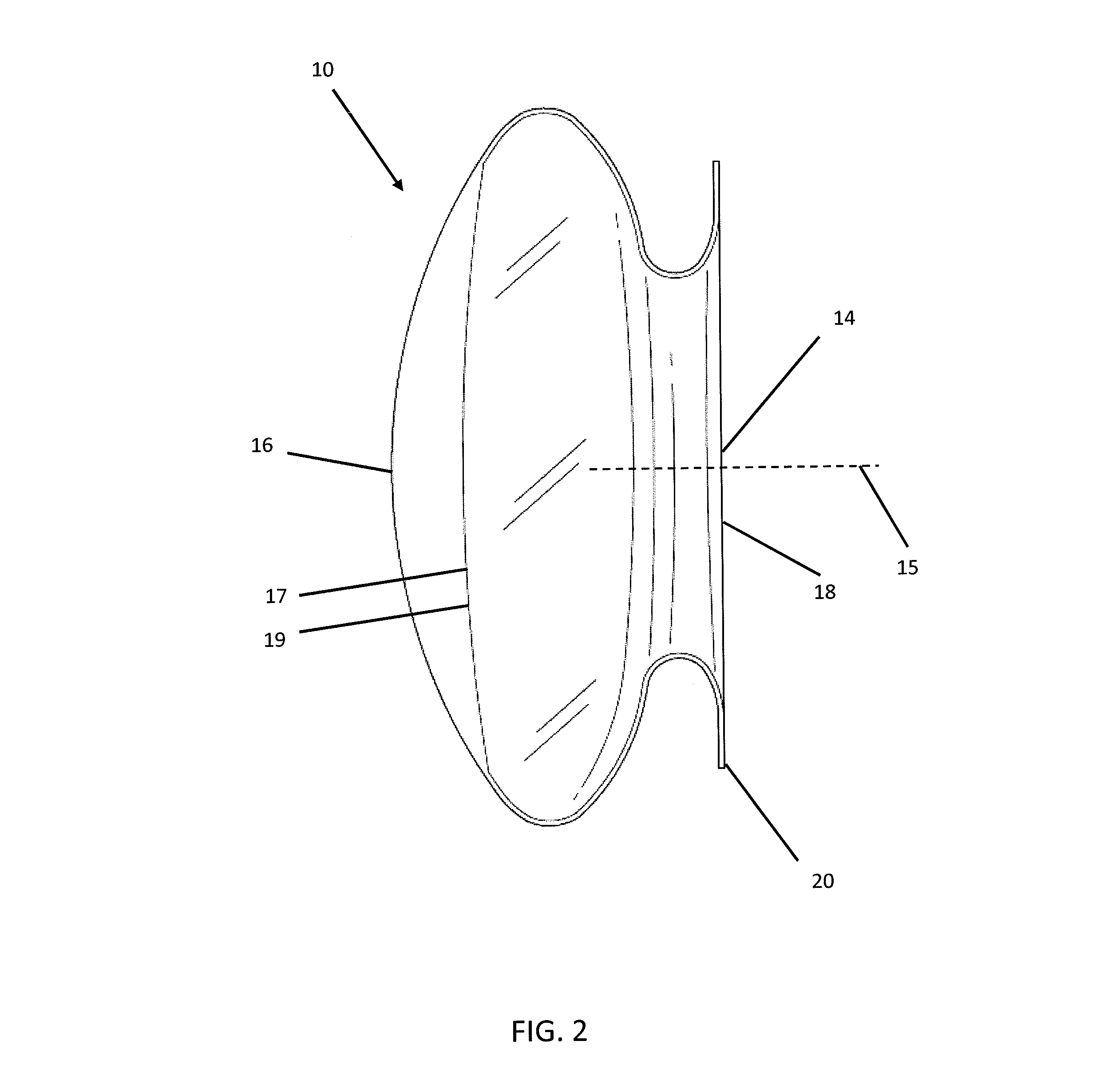
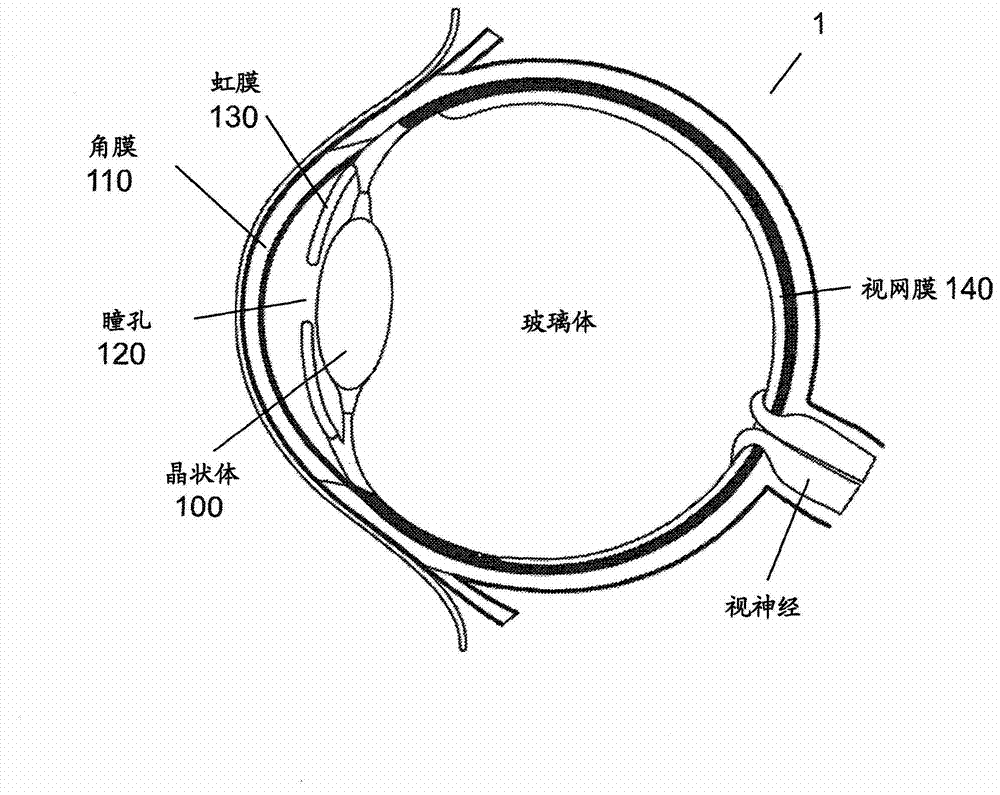
Cataract surgery, also called lens replacement surgery, is the removal of the natural lens of the eye (also called "crystalline lens") that has developed an opacification, which is referred to as a cataract, and its replacement with an intraocular lens. Metabolic changes of the crystalline lens fibers over time lead to the development of the cataract, causing impairment or loss of vision. Some infants are born with congenital cataracts, and certain environmental factors may also lead to cataract formation. Early symptoms may include strong glare from lights and small light sources at night, and reduced acuity at low light levels.
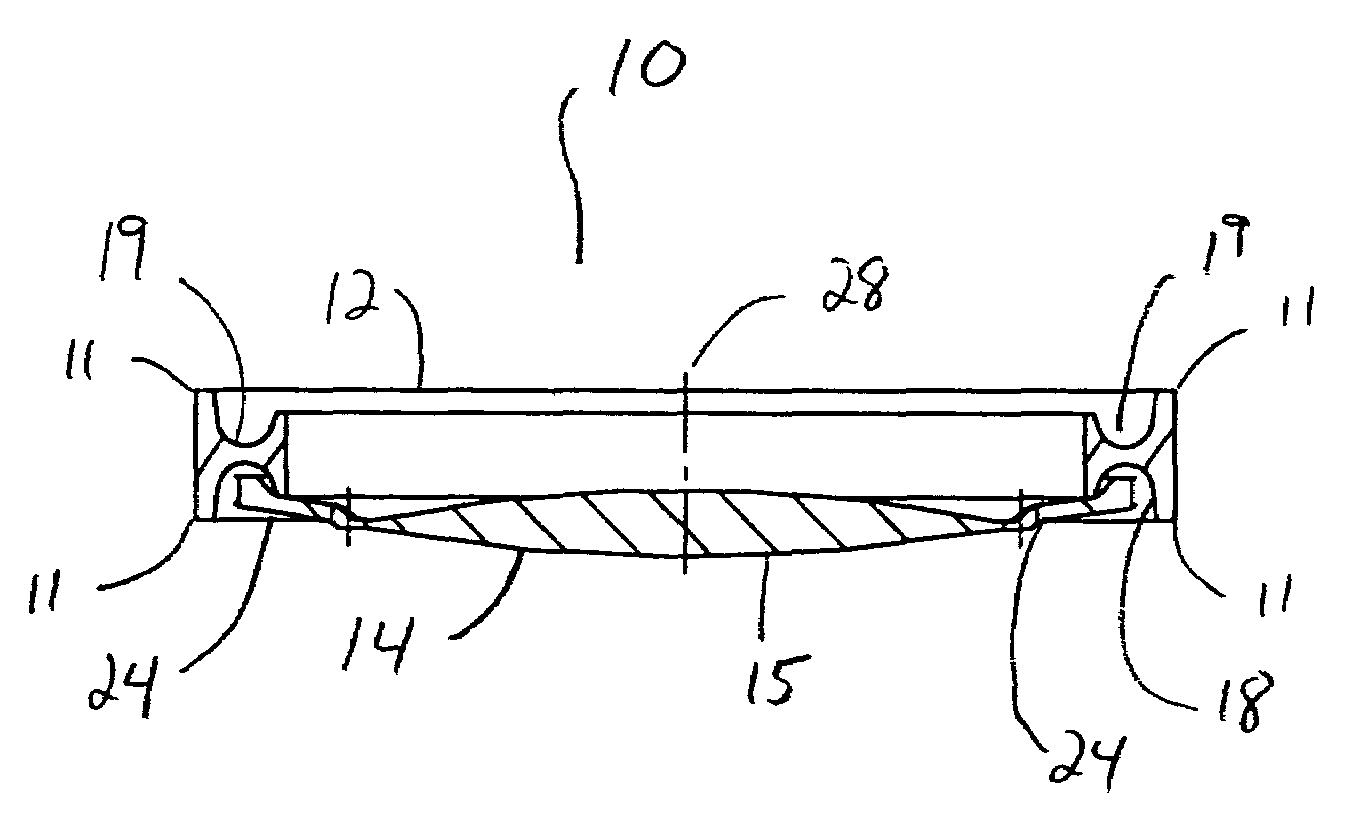
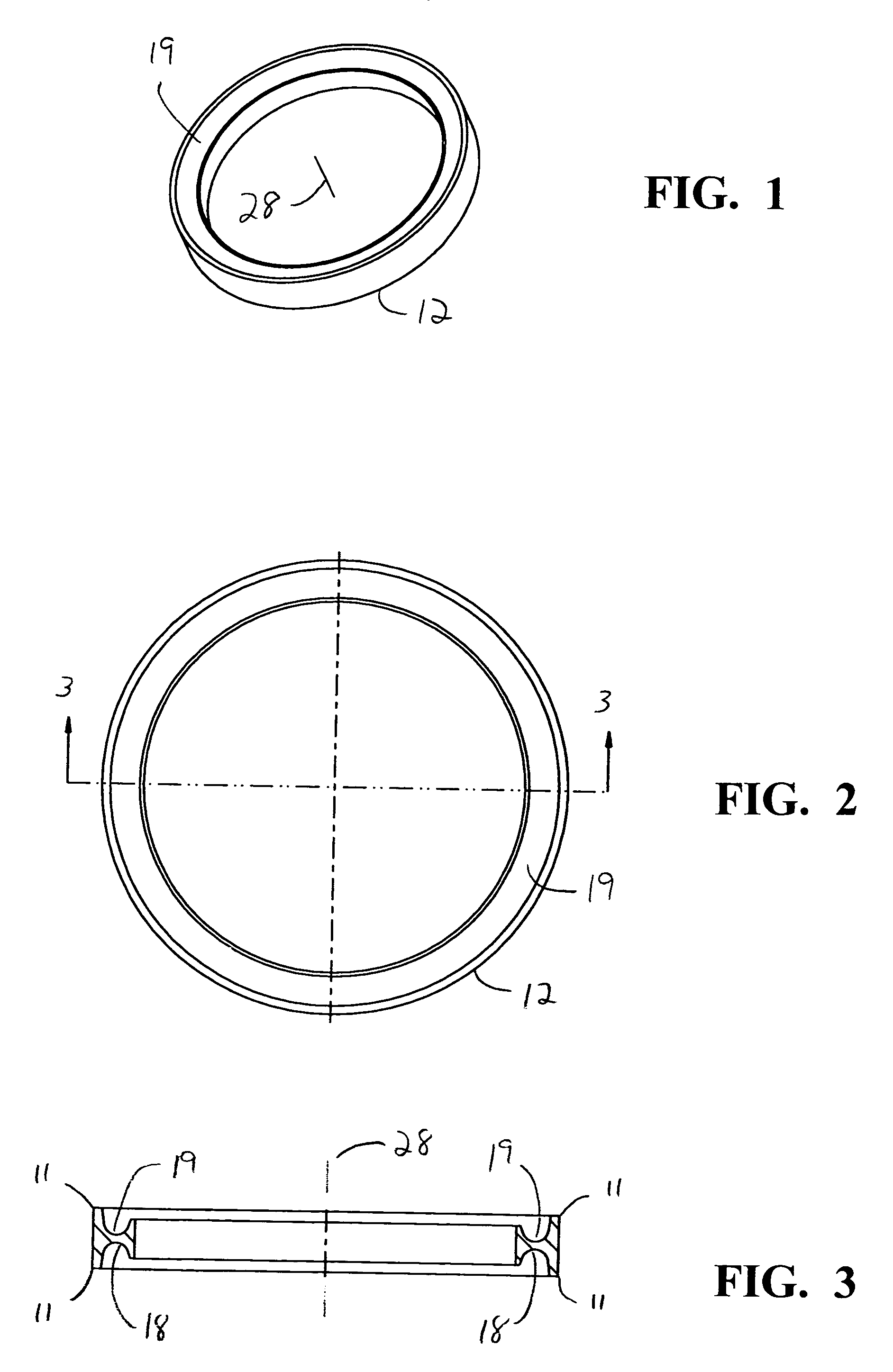
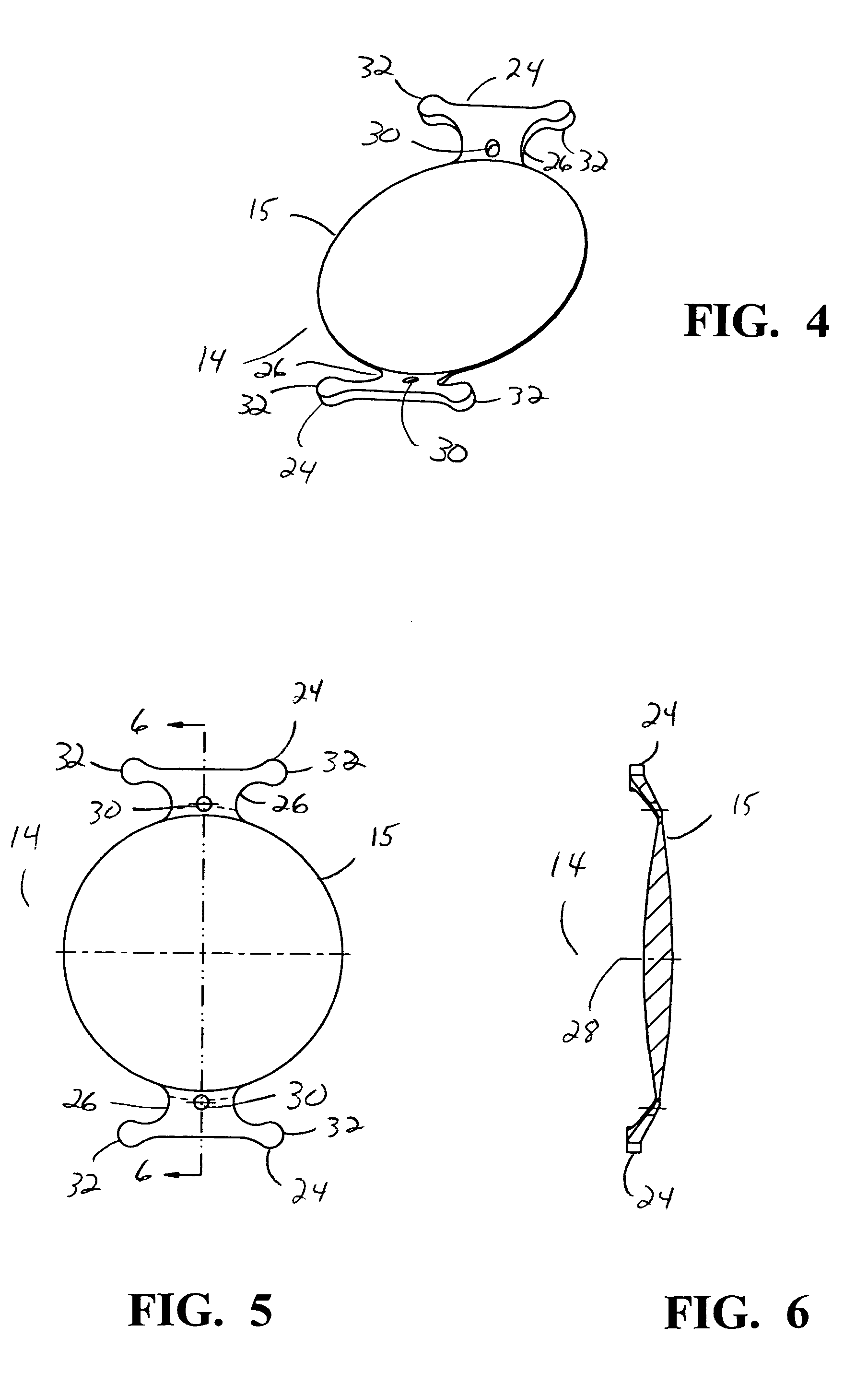
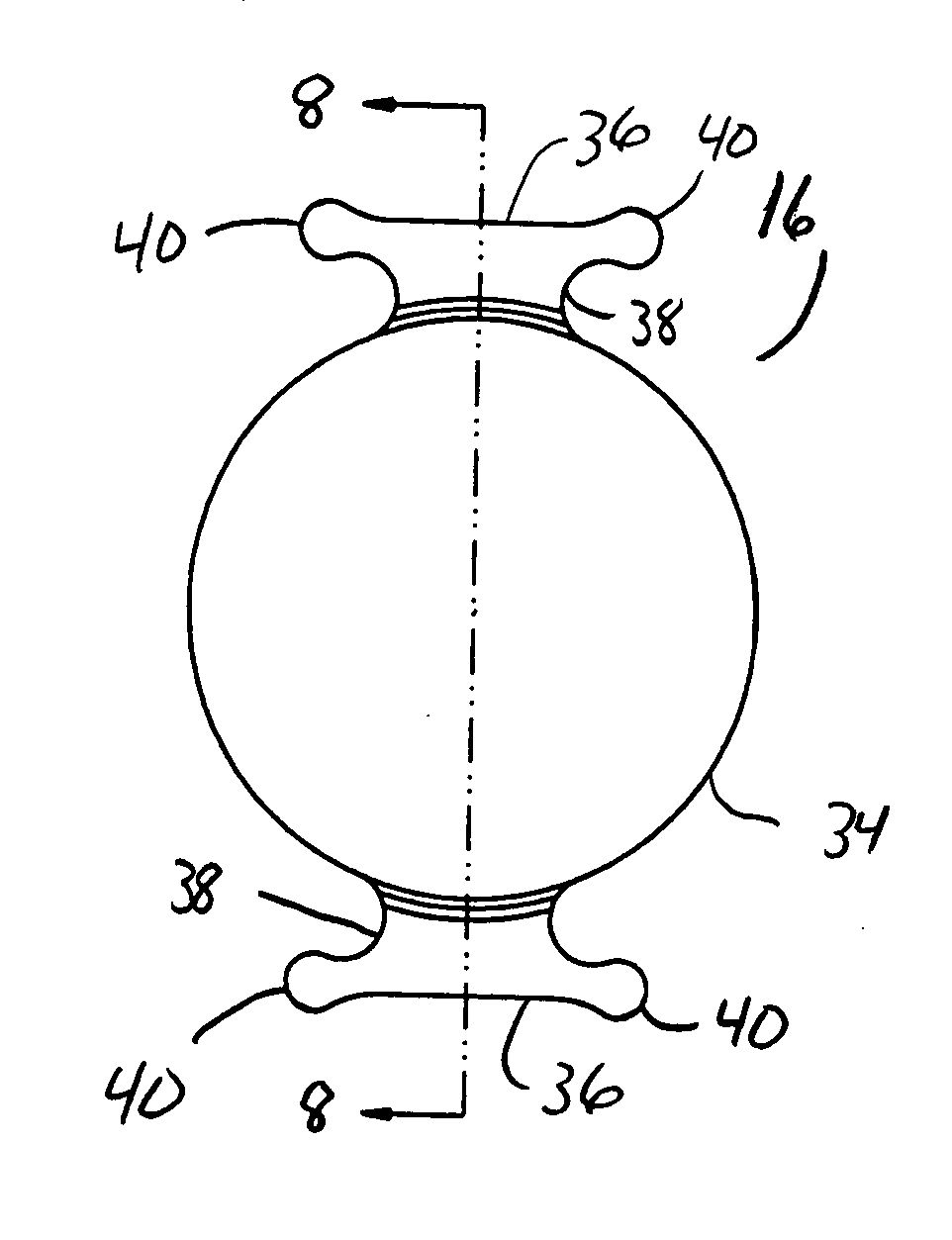
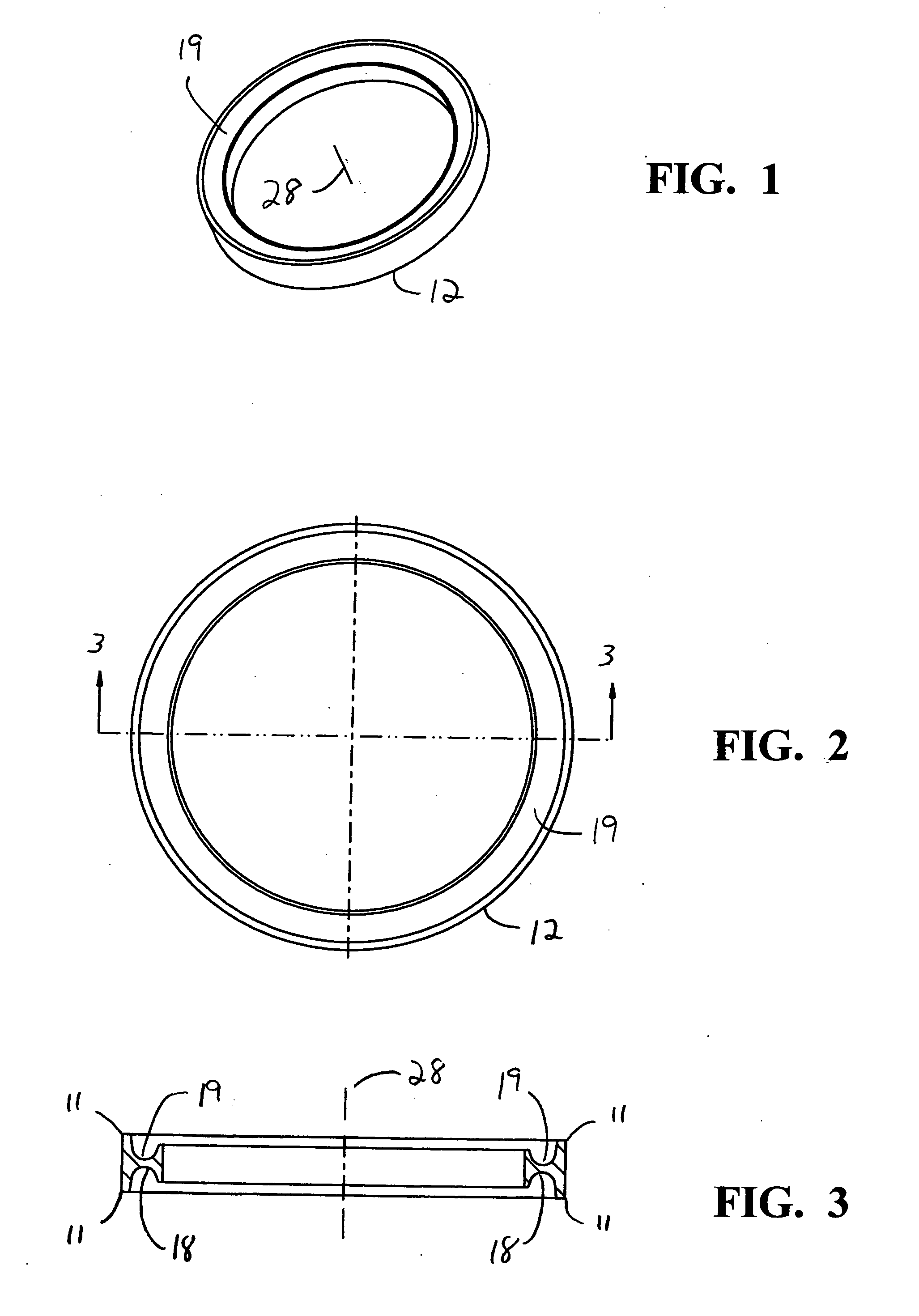
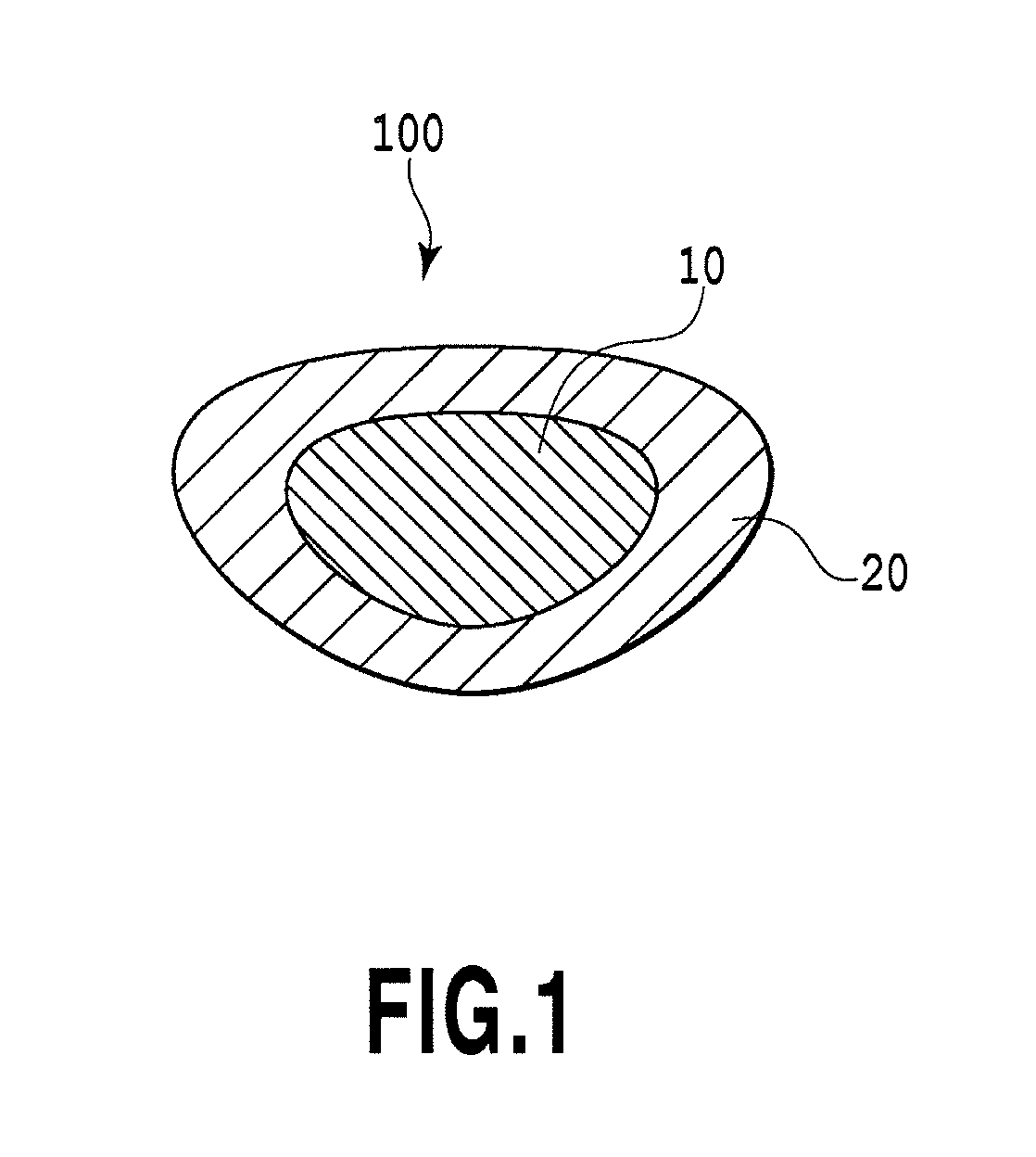
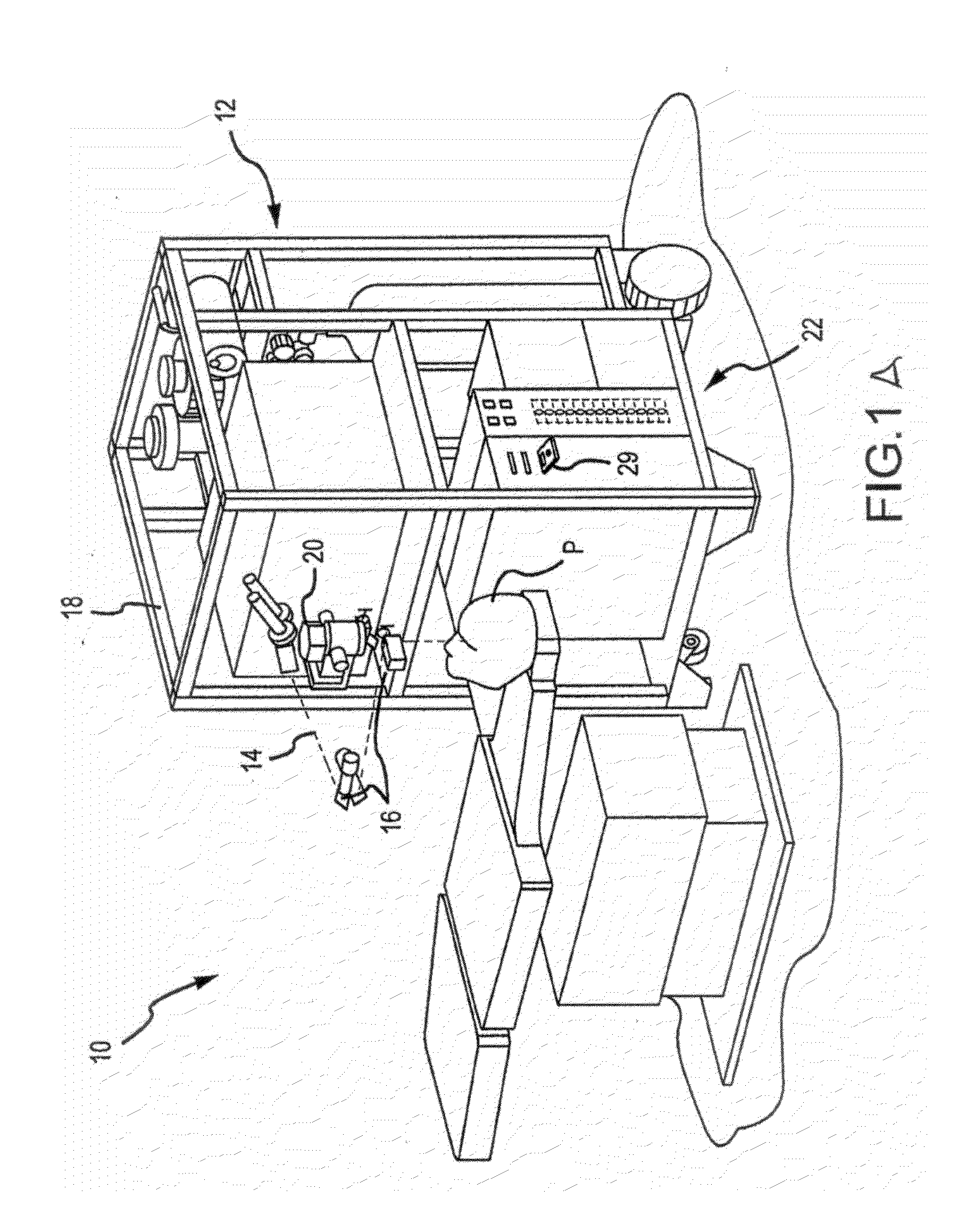
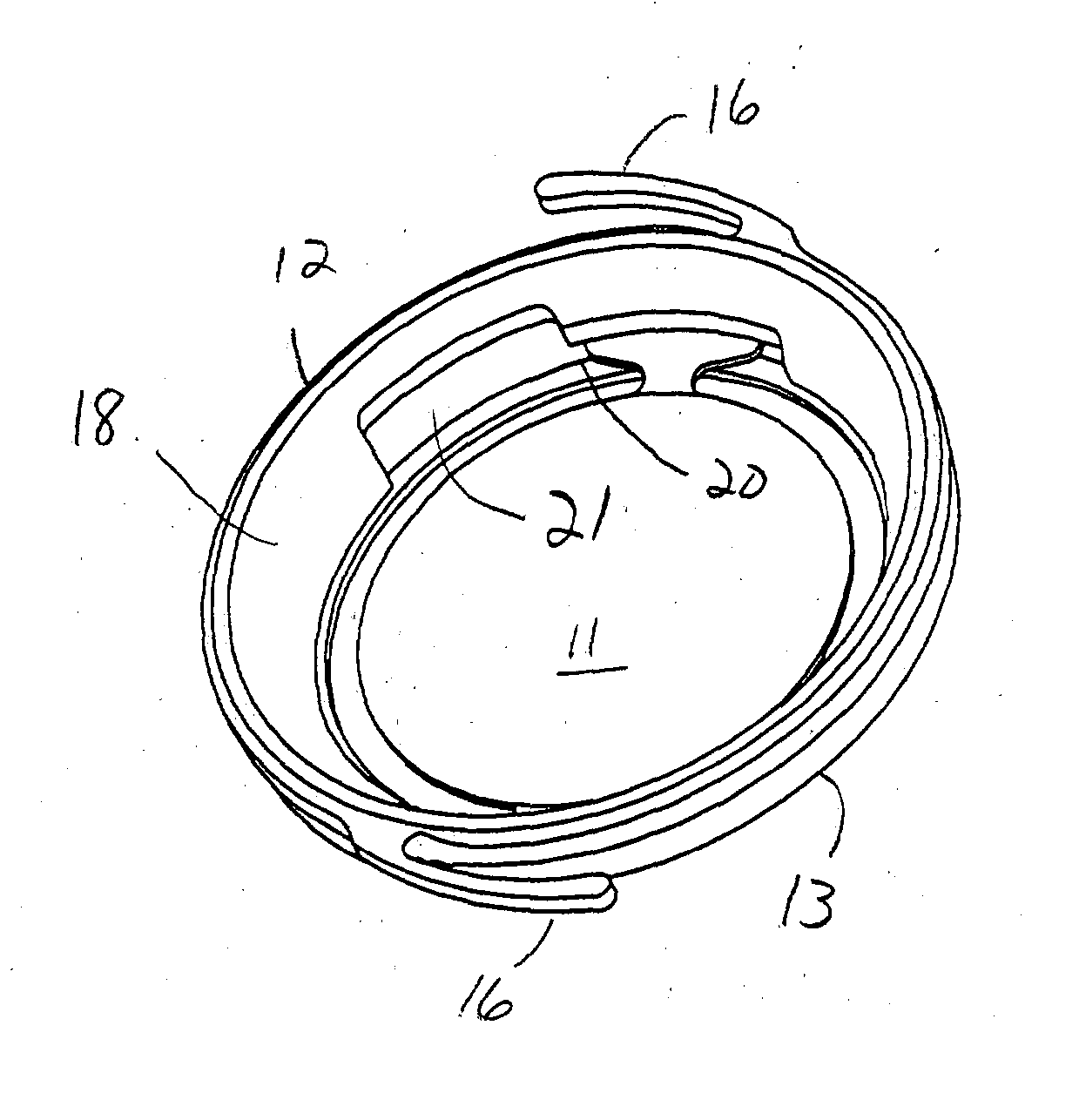
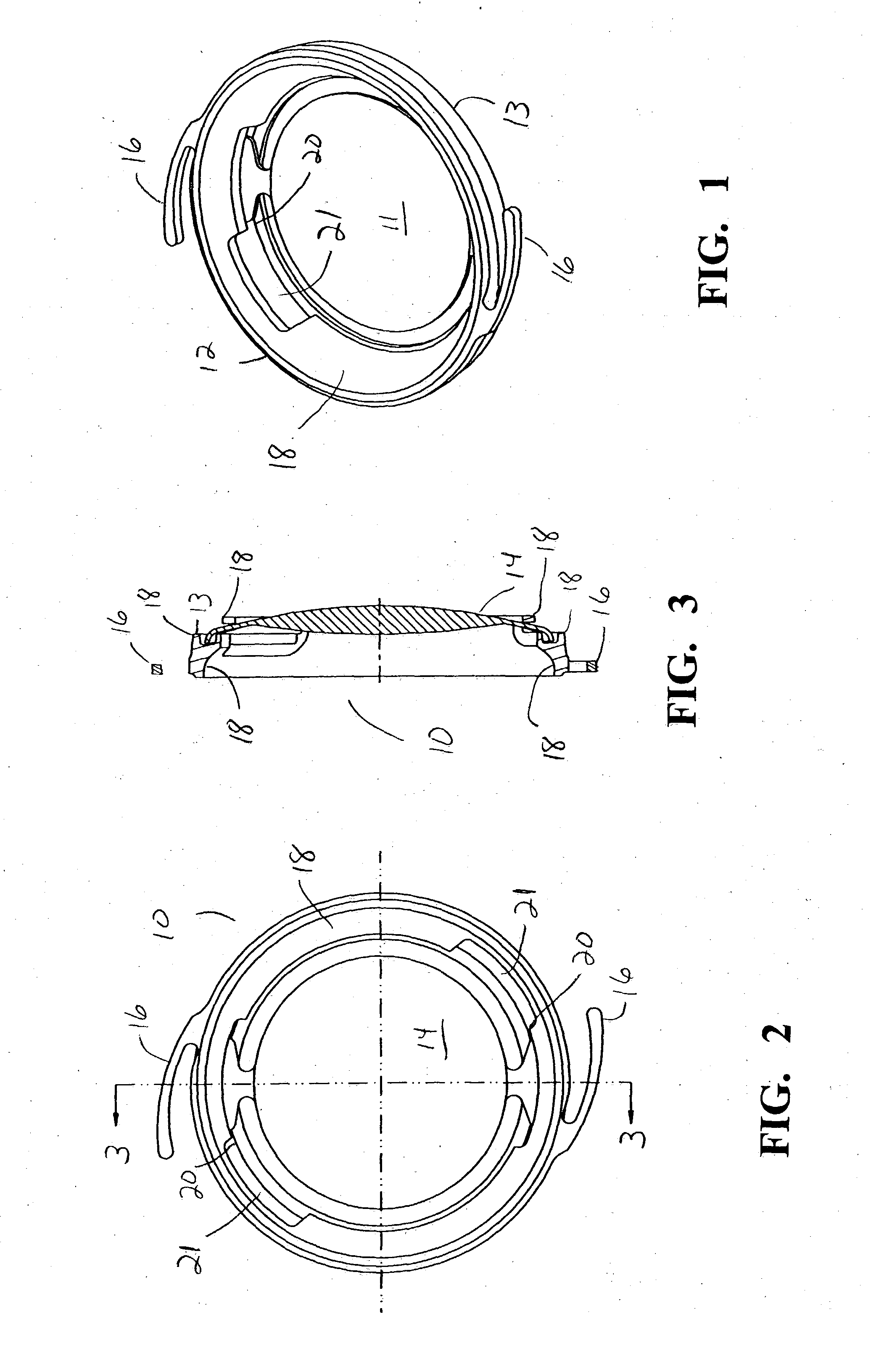
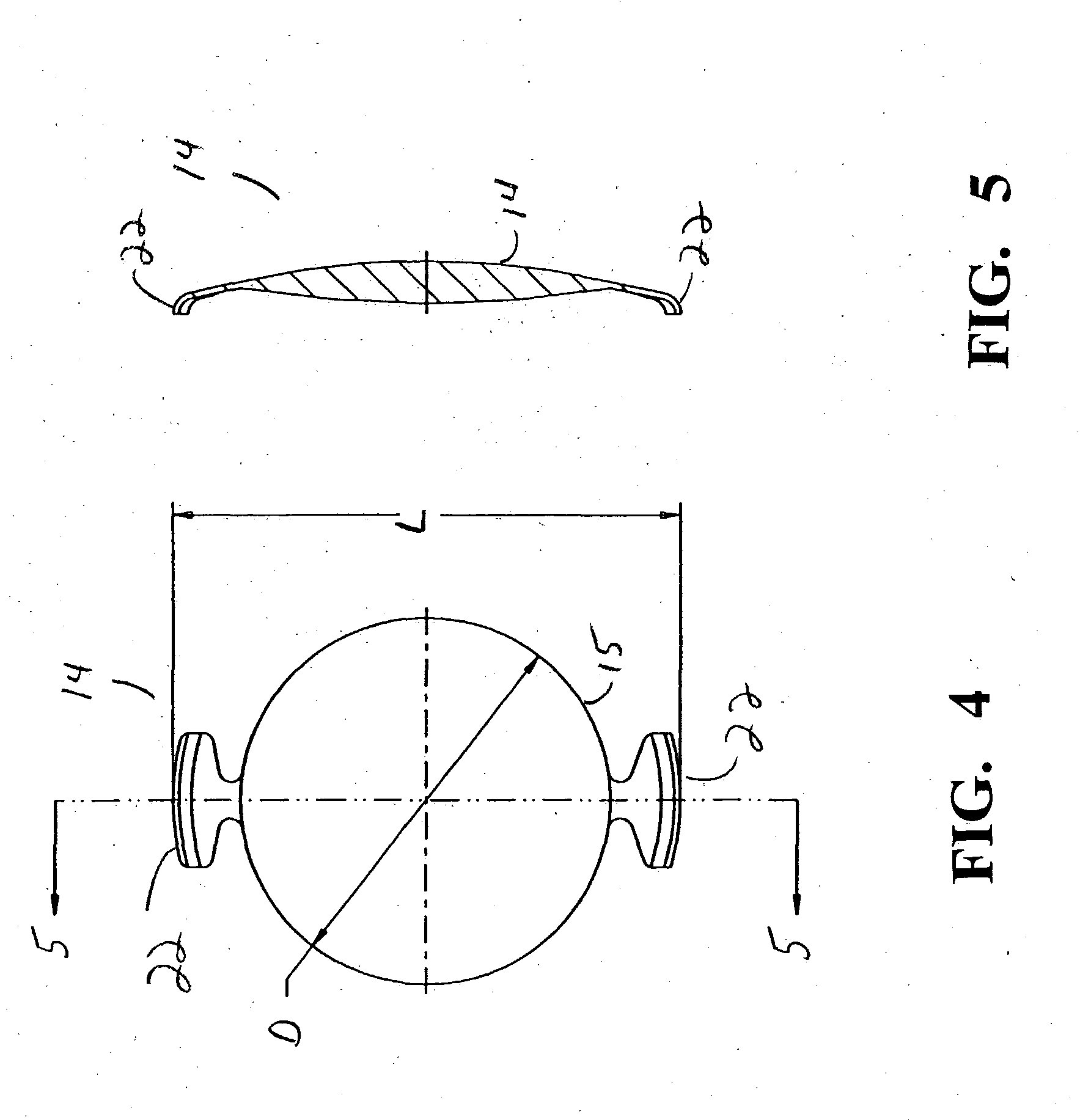
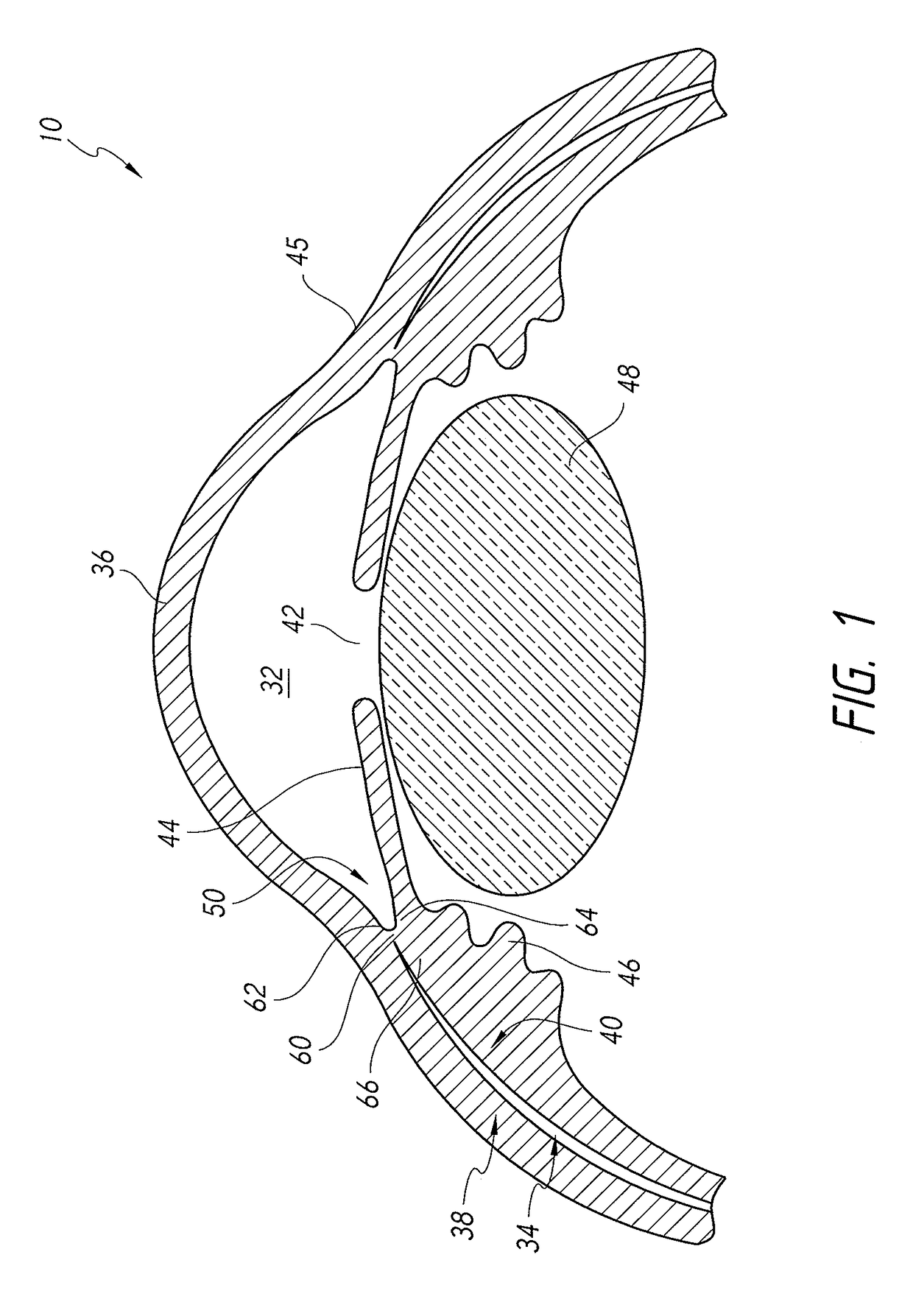
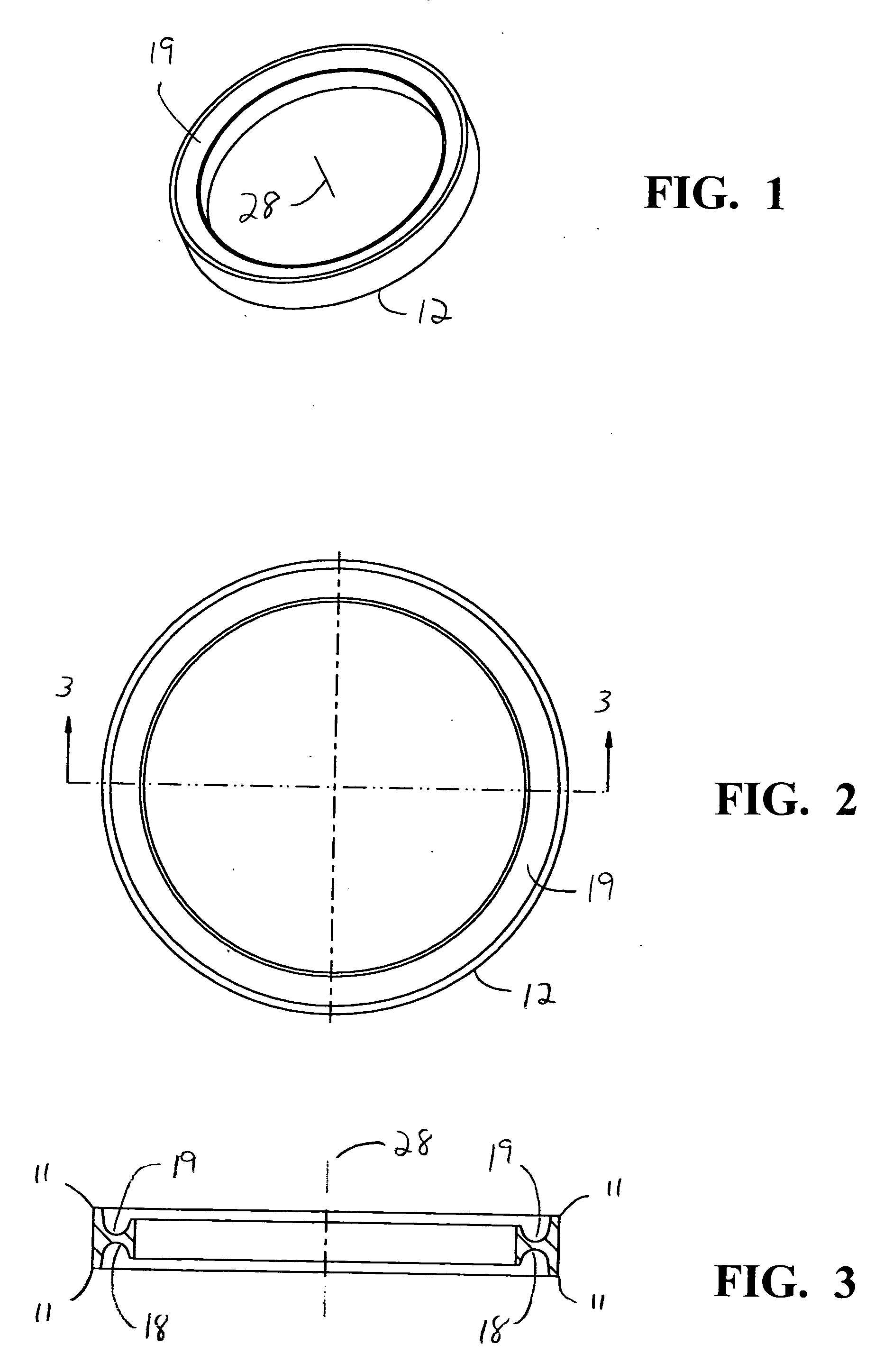
Modular intraocular implant
An adjustable ocular insert to be implanted during refractive cataract surgery and clear (human) crystalline lens refractive surgery and adjusted post-surgically. The implant comprises relatively soft but compressible and resilient base annulus designed to fit in the lens capsule and keep the lens capsule open. Alternatively the annulus may be placed in the anterior or posterior chamber. The annulus can include a pair of opposed haptics for secure positioning within the appropriate chamber. A rotatable annular lens member having external threads is threadedly engaged in the annulus. The lens member is rotated to move the lens forward or backward so to adjust and fine-tune the refractive power and focusing for hyperopia, myopia and astigmatism. The intraocular implant has a power range of approximately +3√0π−3 diopters.
Owner:EGGLESTON HARRY C
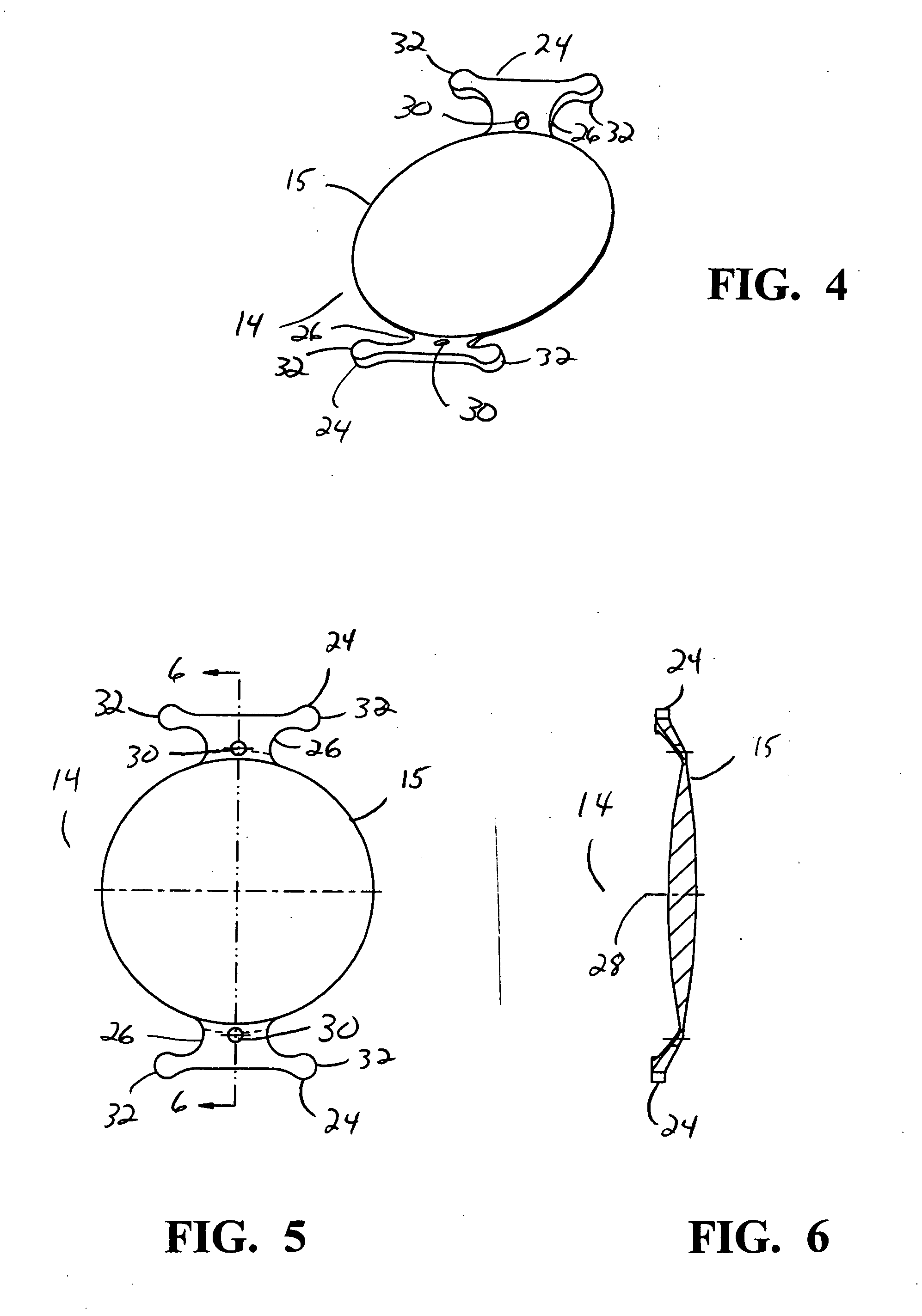
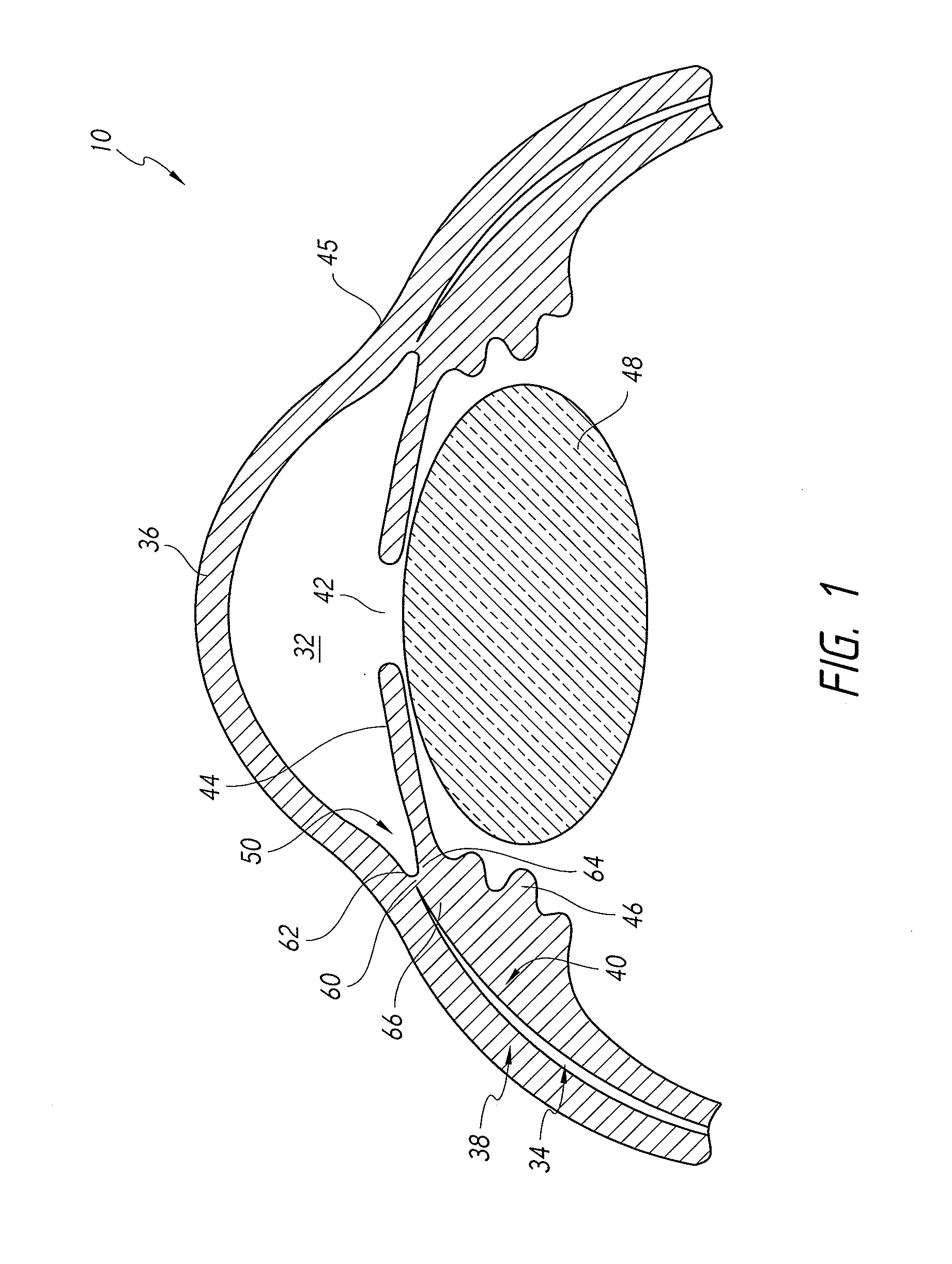
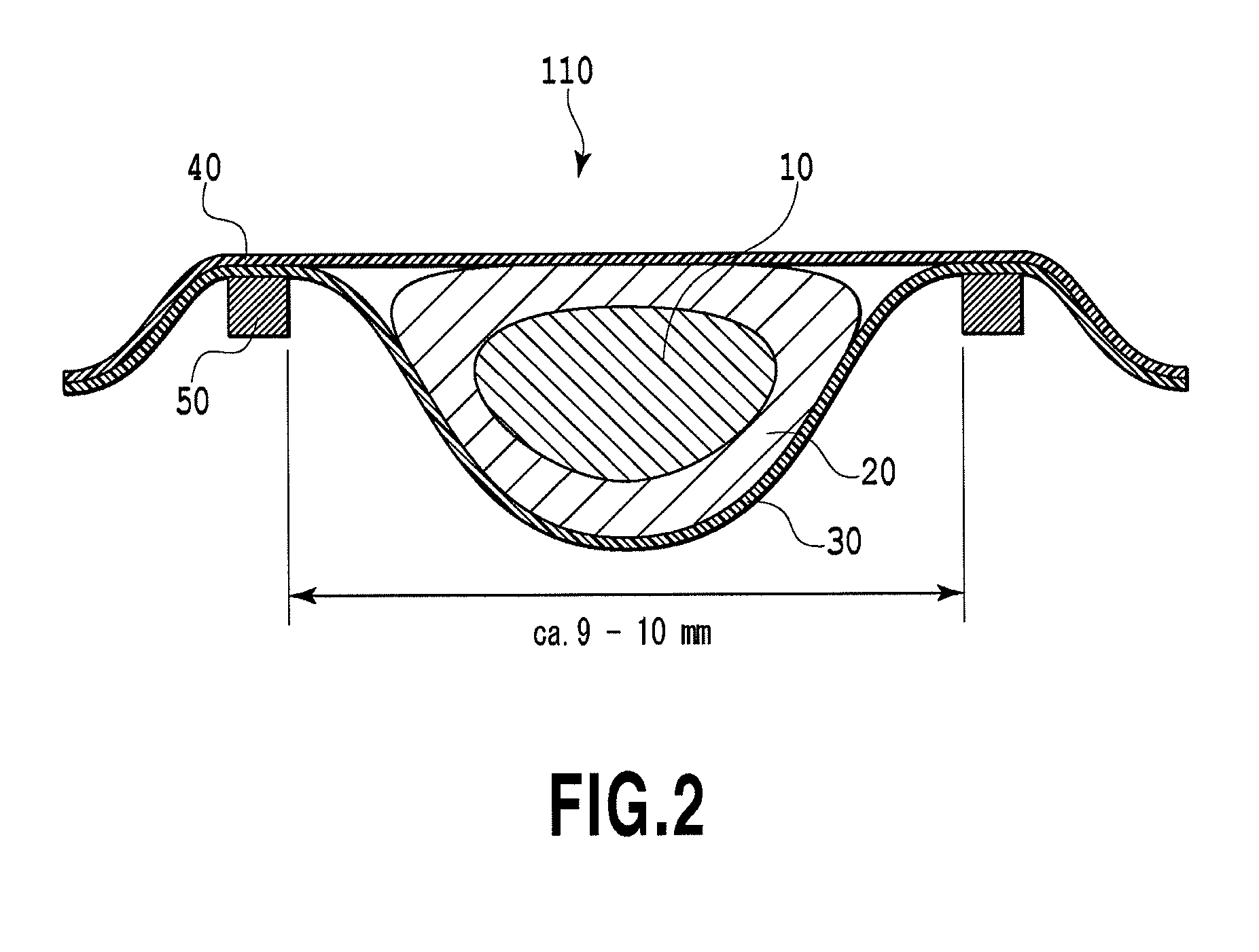
Intraocular implant devices
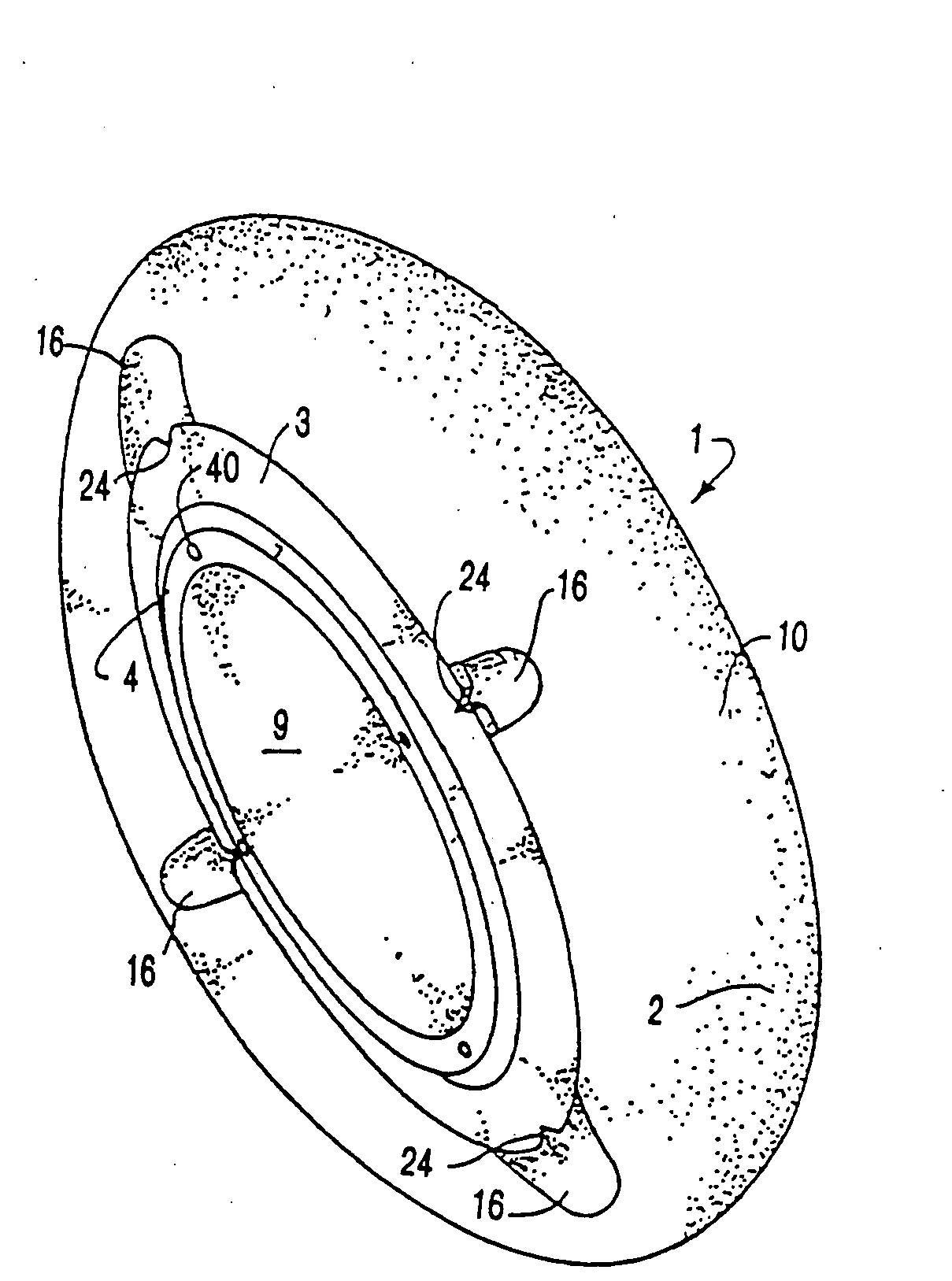
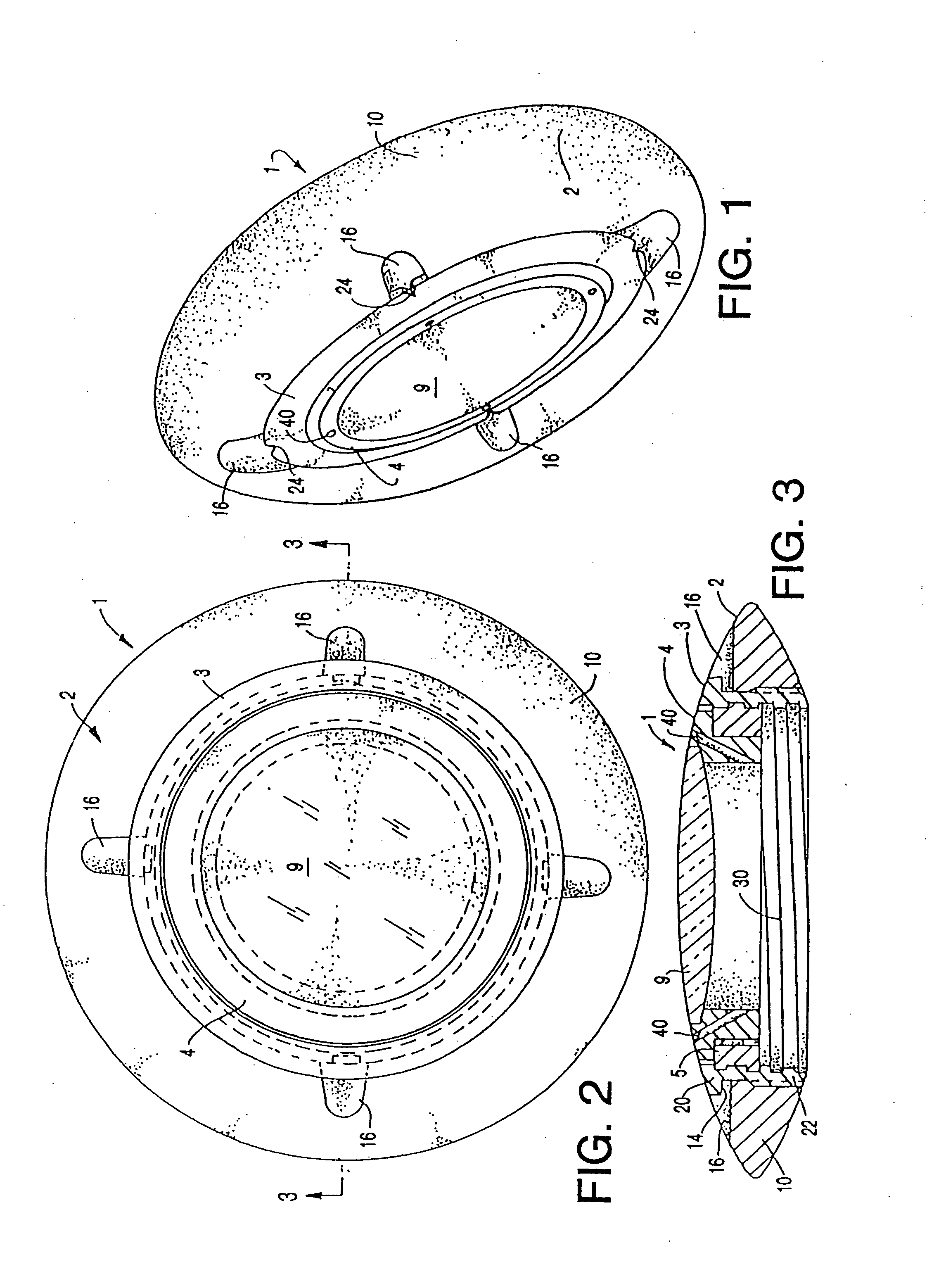
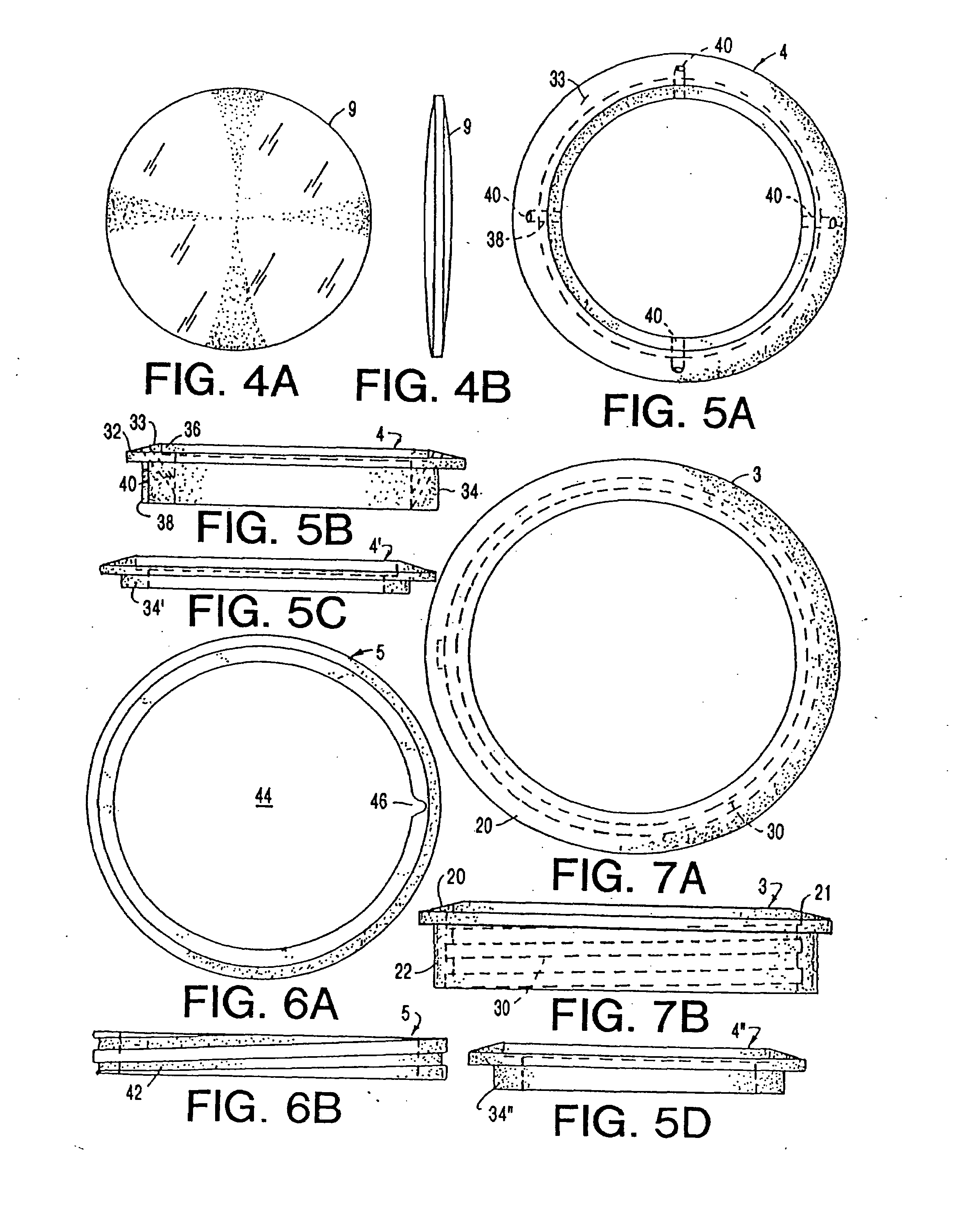
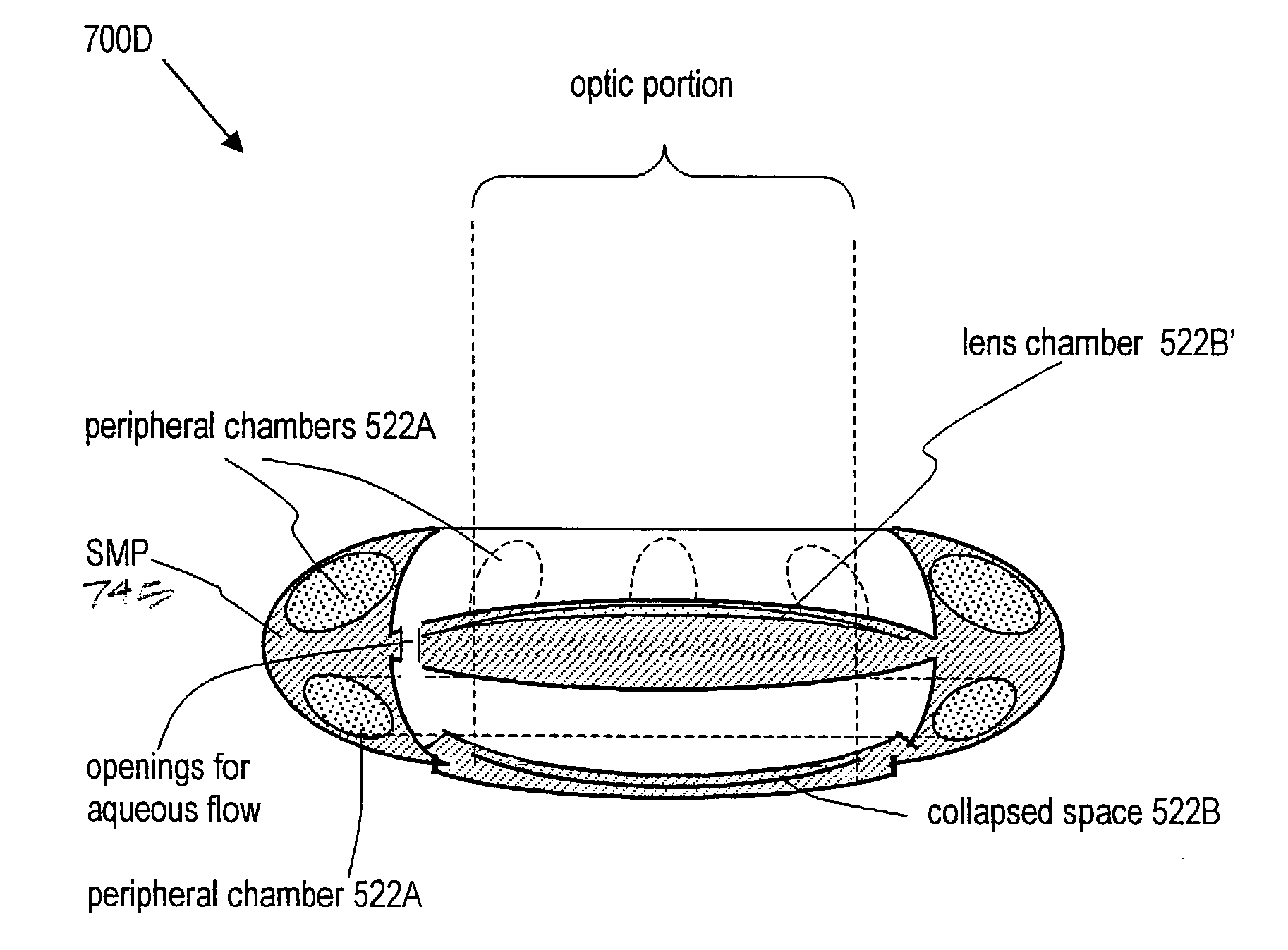
A deformable intracapsular implant device for shaping an enucleated lens capsule sac for use in cataract procedures and refractive lensectomy procedures. In one embodiment, the intraocular implant devices rely on thin film shape memory alloys and combine with the post-phaco capsular sac to provide a biomimetic complex that can mimic the energy-absorbing and energy-releasing characteristics of a young accommodative lens capsule. In another embodiment, the capsular shaping body is combined with an adaptive optic. The peripheral capsular shaping body carries at least one fluid-filled interior chamber that communicates with a space in a adaptive optic portion that has a deformable lens surface. The flexing of the peripheral shaping body in response to zonular tensioning and de-tensioning provides an inventive adaptive optics mechanism wherein fluid media flows between the respective chambers “adapts” the optic to increase and decrease the power thereof. In one embodiment, the capsular shaping body carries a posterior negative power adaptive optic that can be altered in power during accommodation to cooperate with an independent drop-in exchangeable intraocular lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Accommodating Intraocular Lens
InactiveUS20100228344A1Minimal incisionSimplified lens exchangeIntraocular lensIntraocular lensCataract surgery
A deformable intracapsular implant device for shaping an enucleated lens capsule sac for use in cataract procedures and refractive lensectomy procedures. In one embodiment, the intraocular implant devices rely on thin film shape memory alloys and combine with the post-phaco capsular sac to provide a biomimetic complex that can mimic the energy-absorbing and energy-releasing characteristics of a young accommodative lens capsule. In another embodiment, the capsular shaping body is combined with an adaptive optic. The peripheral capsular shaping body carries at least one fluid-filled interior chamber that communicates with a space in a adaptive optic portion that has a deformable lens surface. The flexing of the peripheral shaping body in response to zonular tensioning and de-tensioning provides an inventive adaptive optics mechanism wherein fluid media flows between the respective chambers “adapts” the optic to increase and decrease the power thereof. In one embodiment, the capsular shaping body carries a posterior negative power adaptive optic that can be altered in power during accommodation to cooperate with an independent drop-in exchangeable intraocular lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
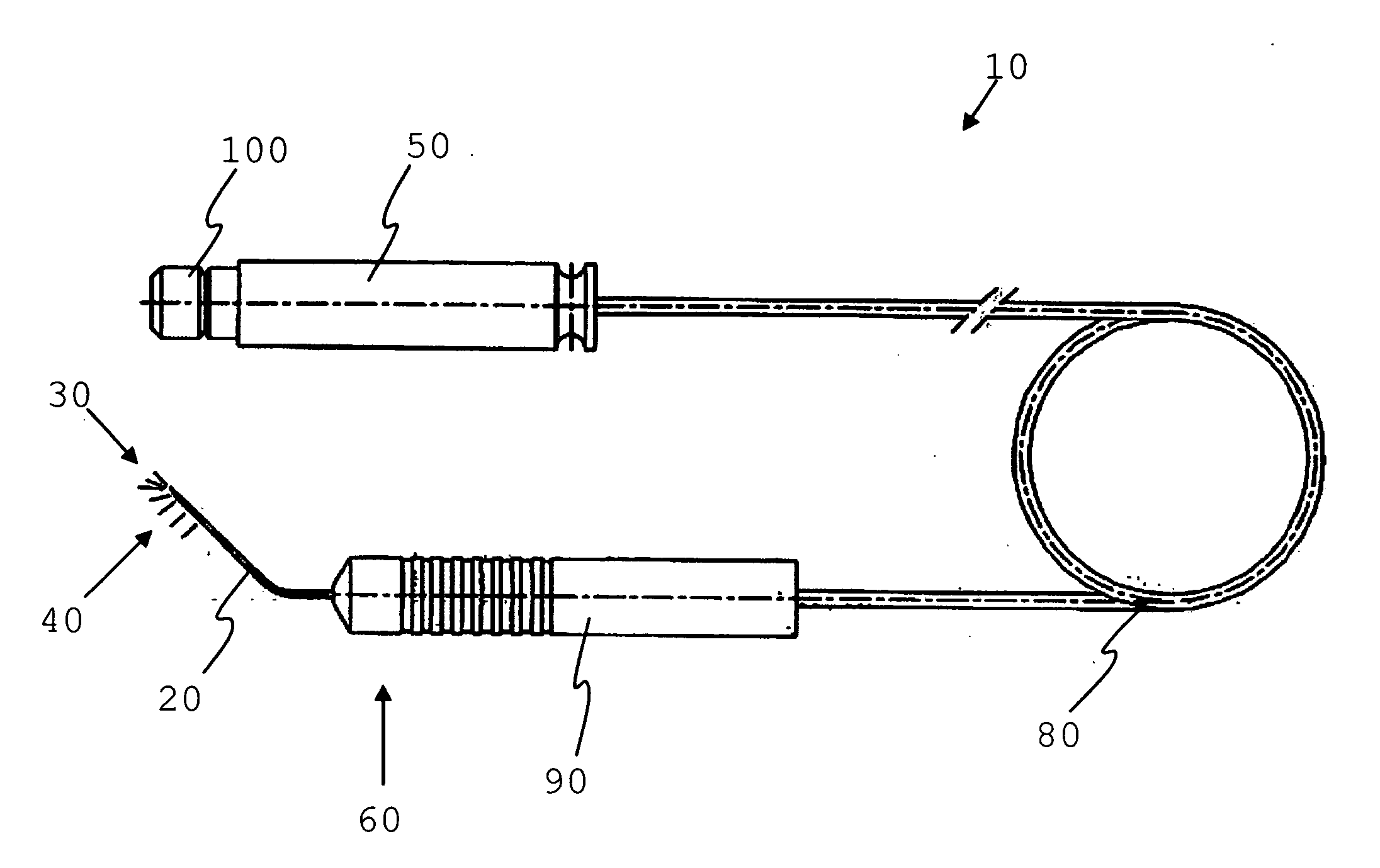
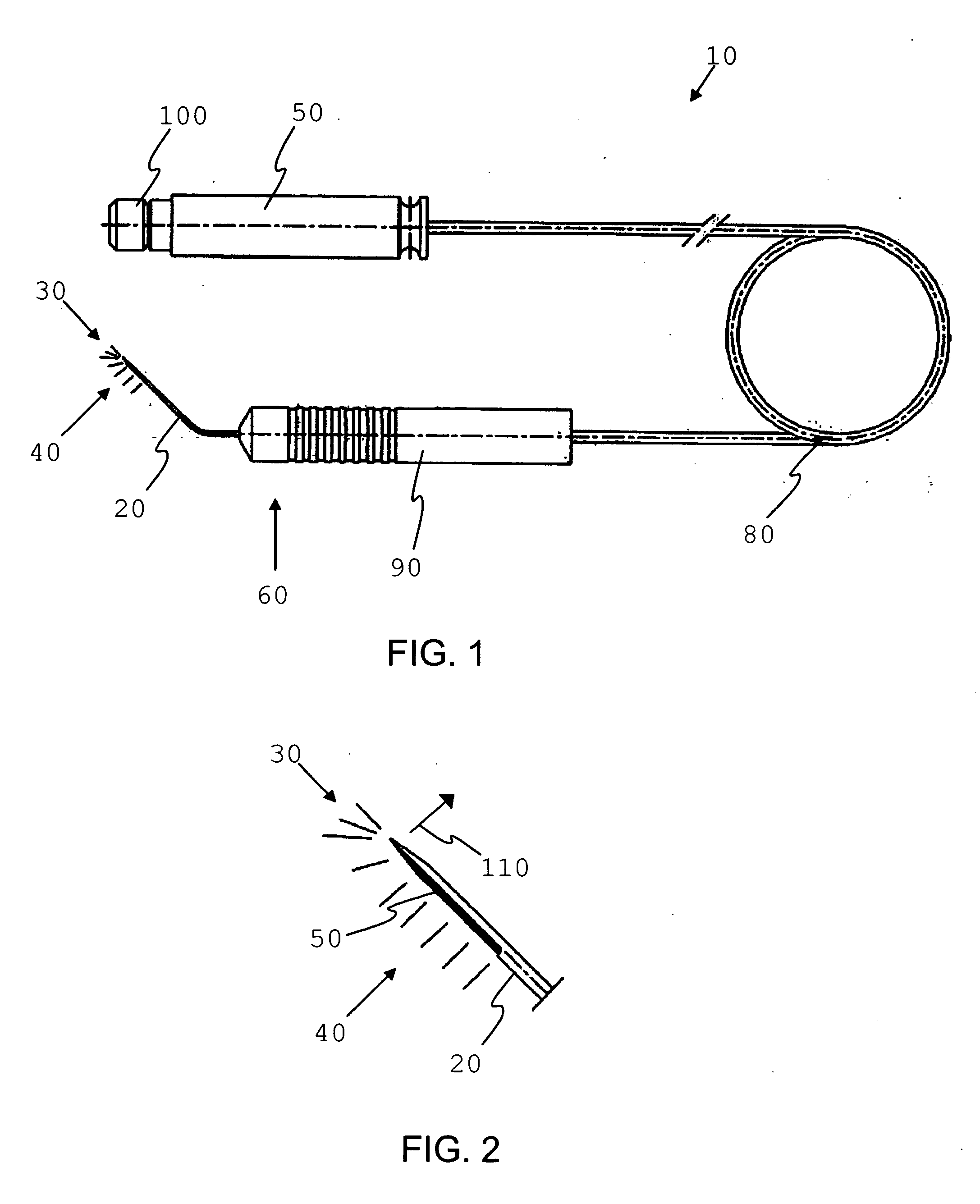
Method and apparatus for laser assisted cataract surgery
Devices and methods for use in laser-assisted surgery, particularly cataract surgery. Specifically, the use of an optical fiber with a proximal and distal end, wherein the distal end has a non-orthogonal angle with the diameter of the optical fiber, to create an off-axis steam bubble for cutting and removing tissue in an operative region. Where the optical fiber is bent, rotating the fiber creates a circular cutting path for the steam bubble, allowing access to tissues that may normally be blocked by obstructions and obstacles.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
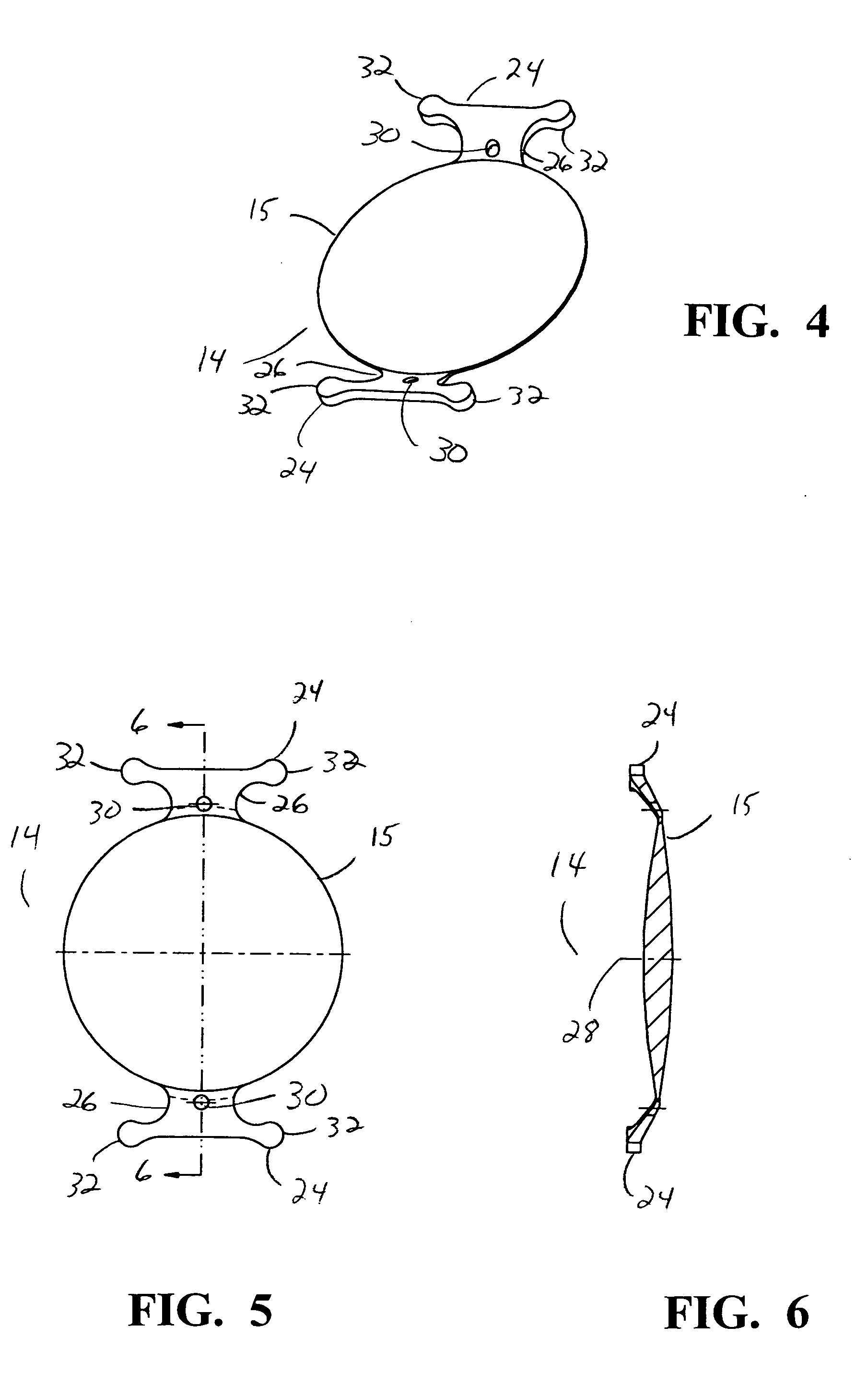
Intraocular lens
A two or three component lens system. The first component is a ring-like supporting component that is implanted in the capsular bag following cataract surgery. The first component is a non-optical component and does not correct for any refractive errors. The first component may contains features to help reduce or eliminate PCO. The second component is an optical component that may contain all of the corrective optical power of the lens system. The second component has a pair of tabs for locking the second component within the first component. The third component is optional and is similar to second component and contains some optical power to correct for any residual optical error not corrected by the second component. The second and third components may also be implanted so as to move relative to one another, thereby providing some accommodation.
Owner:ALCON INC
Intraocular lens system
A two or three component lens system. The first component is a ring-like supporting component that is implanted in the capsular bag following cataract surgery. The first component is a non-optical component and does not correct for any refractive errors. The first component may contain features to help reduce or eliminate PCO. The second component is an optical component that may contain all of the corrective optical power of the lens system. The second component has a pair of tabs for locking the second component within the first component. The first component includes a feature that allows the surgeon to change the position of the second component along the optical axis of the lens system. The third component is optional and is similar to second component and contains some optical power to correct for any residual optical error not corrected by the second component. The second and third components may also be implanted so as to move relative to one another, thereby providing some accommodation.
Owner:ALCON INC
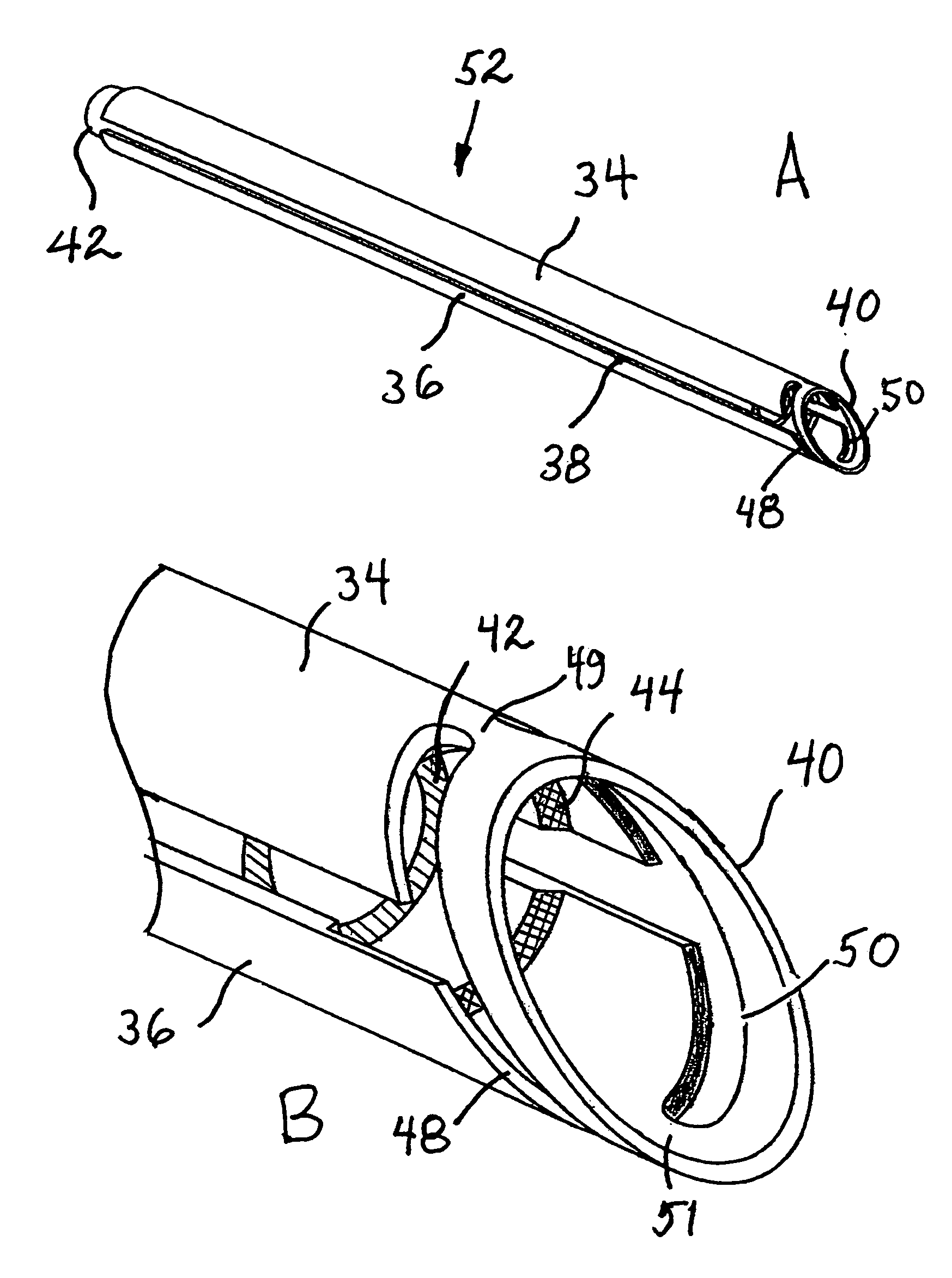
Thermal airflow tool and system
A combination pressurized airflow and thermal cutting tool constructed as a dual-use thermal airflow tool for directed heating and drying of a specific area in surgical procedures, such as, by way of example, in eye cataract surgery where it is primarily used for needs related to the operation of a thermal cutting tool. The thermal airflow tool comprises a probe having an elongated, hollow body adapted to provide electrical power to a burning ring formed at a distal end thereof, and an air channel for conducting pressurized airflow to the distal end of the probe, with at least two apertures radially disposed at the distal end of the probe. The thermal airflow tool is in physical and electrical connection with an air pressure unit and thermal power unit, respectively, for directing and concentrating at least one of the pressurized airflow and heat at the distal end of the thermal airflow tool onto a surgical area when electrical power is applied to the thermal airflow tool.
Owner:VALENS ASSOC INC
Shielded intraocular probe for improved illumination or therapeutic application of light
ActiveUS20050245916A1Diminishes unwanted glareLaser surgeryEndoscopesKeratorefractive surgeryForceps
An intraocular light probe has a mask or shield affixed at its distal end thereof which forms a directed light beam for intraocular illumination of target tissues or intraocular application of therapeutic light. The mask or shield serves to more fully focus, intensify and direct the beam toward the target tissues. The mask or shield also helps direct light away from other tissues and away from the eyes of the surgeon. This lessens unwanted glare. By placing a light probe beneath a surgical instrument such as a phacoemulsifier or vitrector, laser, cutting instrument (e.g., scissors or knife), forceps or probe / manipulator, whether as part of or separate from an infusion sleeve, a mask or shield effect is created. This has the same benefits of directing the beam toward target tissues, away from other tissues and away from the eyes of the surgeon. The mask or shield is opaque or semi-opaque and made of a soft, semi-rigid or rigid material. The shield can be rigid enough to serve as the shaft of an instrument with a probe or manipulator at its distal tip. It may also be reflective on the side adjacent to the fiber bundle to help direct, magnify, and intensify the beam of light. The shape of the shield can be flat, curved or circular with an opening along one side. The mask / shield can be removed from the fiberoptic light for sterilization. The device of the invention is preferably introduced into the eye via the primary or side-port incision to provide intraocular cross-lighting of tissues during surgical procedures such as cataract surgery, corneal surgery, vitrectomy, intraocular lens implantation, refractive surgery, glaucoma surgery and vitreo / retinal surgery.
Owner:CONNOR CHRISTOPHER S
Prosthetic capsular bag and method of inserting the same
ActiveUS8900300B1Stabilizing effective lens positionPromote resultsIntraocular lensCataract surgeryLens placode
The present invention relates to a prosthetic capsular bag and method for inserting the same. The prosthetic capsular bag helps to maintain the volume of the natural capsular bag, thereby stabilizing the effective lens position of an IOL so that refractive outcomes may be improved with cataract surgery. The prosthetic capsular bag further provides an integrated refractive surface, providing a means for experimentally determining an effective lens position prior to inserting an IOL.
Owner:OMEGA OPHTHALMICS
System for calculating IOL power
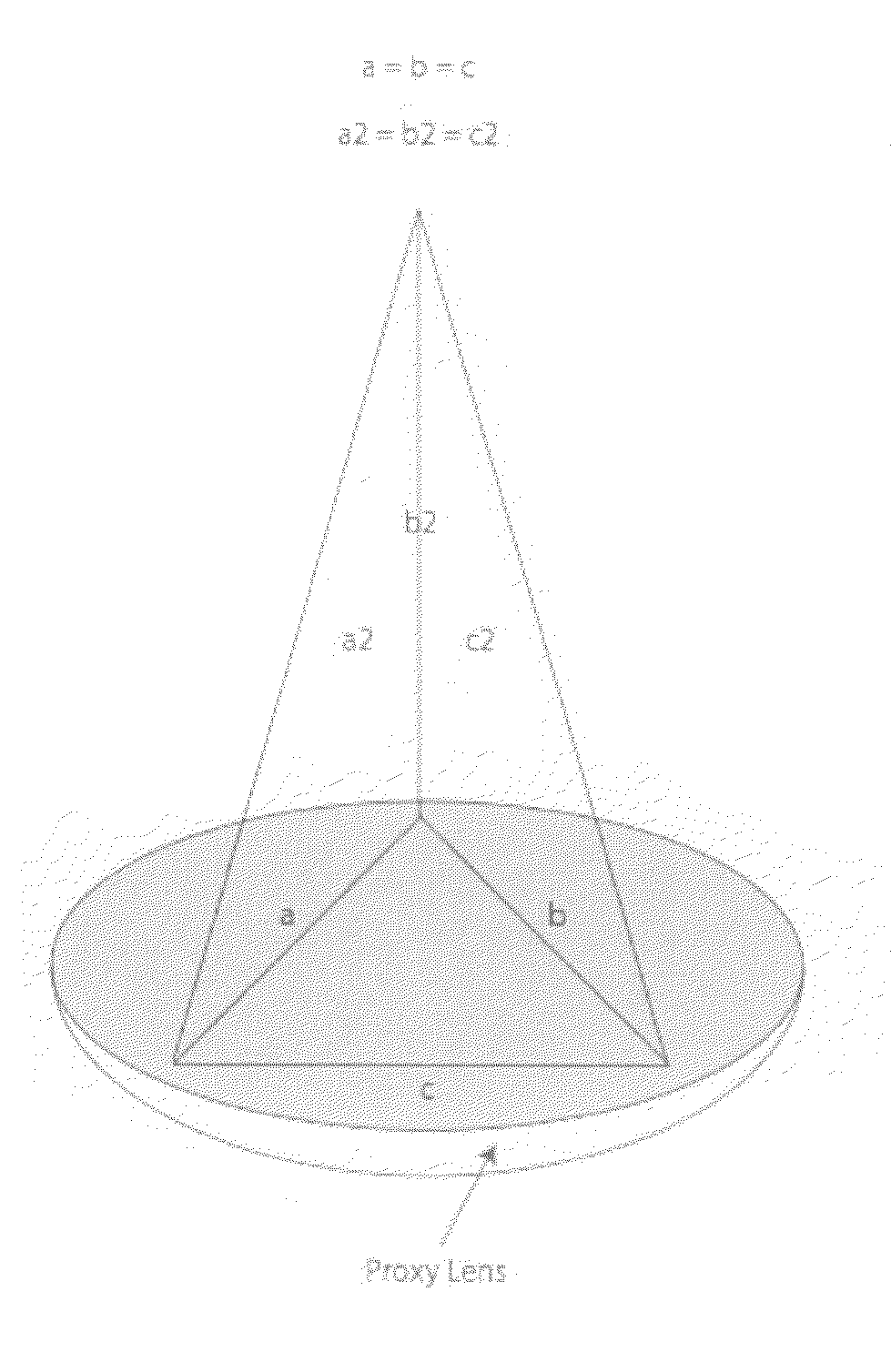
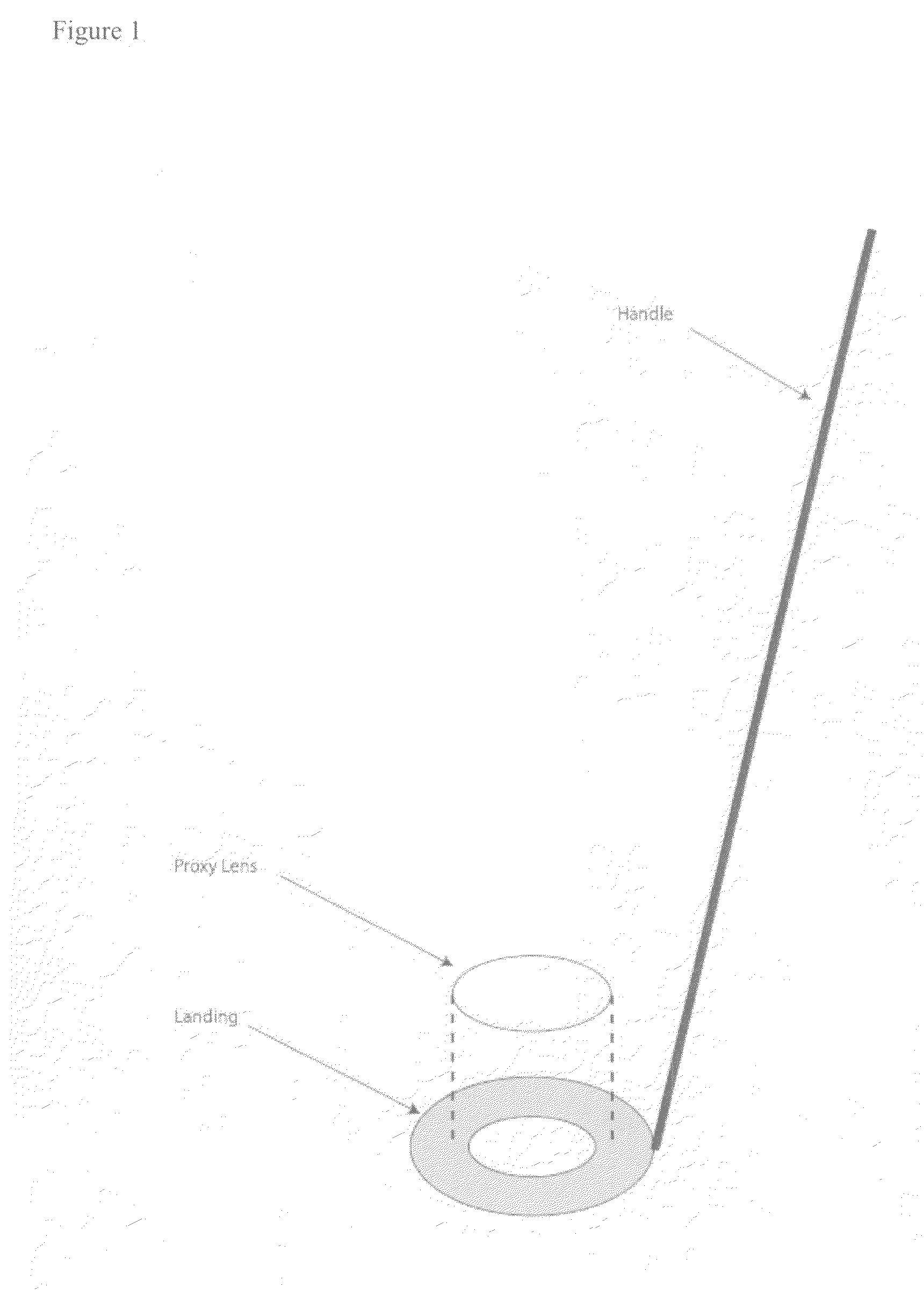
InactiveUS20080004610A1Improve human ophthalmic surgery patient wellnessReduce probabilityEye surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive measurementsCamera lens
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus to improve human ophthalmic surgery patient wellness and surgical procedural outcome of both indicated cataract surgery and elective surgeries with the implantation of permanent standard intraocular lens (IOL) and new technology intraocular lens (NTIOL). The present invention further relates to measurement of refraction intra-operatively to validate or obviate the pre-operative calculations and thus selection of the IOL or NTIOL and allow for a correction to be made intra-operatively before the permanent IOL or NTIOL is implanted. Specifically, several embodiments of the invention pertain to a disposable, temporary Proxy Lens apparatus that are used for in situ refractive measurements, an Insertion Tool apparatus to manipulate the Proxy Lens within the optical path for the refractive measurement and a Refractometer apparatus to perform the refractive measurements.
Owner:MILLER DAVID +4
Systems and methods for delivering an ocular implant to the suprachoroidal space within an eye
Delivery devices, systems and methods are provided for inserting an implant into an eye. The delivery or inserter devices or systems can be used to dispose or implant an ocular stent or implant, such as a shunt, in communication with the suprachoroidal space, uveal scleral outflow pathway, uveoscleral outflow path or supraciliary space of the eye. The implant can drain fluid from an anterior chamber of the eye to a physiologic outflow path of the eye, such as, the suprachoroidal space, uveal scleral outflow pathway, uveoscleral outflow path or supraciliary space. Alternatively, or in addition, the implant can elute a drug or therapeutic agent. The delivery or inserter devices or systems can be used in conjunction with other ocular surgery, for example, but not limited to, cataract surgery through a preformed corneal incision, or independently with the inserter configured to make a corneal incision. The implant can be preloaded with or within the inserter to advantageously provide a sterile package for use by the surgeon, doctor or operator.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Methods and compositions usable in cataract surgery
The invention relates to a method of performing ocular surgery, after an anterior capsulotomy has been made, by forming a sealed expanded capsular bag. The method includes sealing the capsular bag with a viscoelastic material to provide a gas tight seal to prevent leakage into the anterior chamber of the eye during the surgical process; expanding the capsular bag by introducing a gas capable of exerting a pressure on the inner surface of the capsular bag wall; inspecting and / or treating the capsular bag with one or several devices and / or agents suitable for performing inspection and / or treatment. The inspection and / or treatment can comprise any of visual inspection, estimation of capsular bag volume; labeling any residual epithelial cells to detect the presence thereof; removing residual epithelial cells, implanting one or more intracapsular implants; injecting a lens forming material for molding a lens in situ; drying the lens capsule; alone or in any combination. Use of a viscoelastic compound for the preparation of a temporary intraocular seal capable of sealing the capsular bag is also provided.
Owner:PHACO TREAT
Artificial lens for cataract surgery practice
InactiveUS8821166B2Easiness of beingEfficient learning processOptical articlesEducational modelsFiberCataract surgery
An object is to provide an artificial lens for use in an artificial eye device for cataract surgery practice. The artificial lens includes an artificial nucleus corresponding to a human eye lens nucleus and an artificial cortex corresponding to a human eye lens cortex. The artificial nucleus is formed of an agar gel of agar concentration 1.0 wt % to 5.0 wt %. The artificial cortex is formed of an agar gel of agar concentration 0.5 wt % to 1.5 wt % which is lower than the agar concentration of an agar gel forming the artificial nucleus. In another embodiment, an artificial lens includes an artificial nucleus corresponding to a human eye lens nucleus and an artificial cortex corresponding to a human eye lens cortex. The artificial nucleus is formed of cheese or a cheese-like substance, and the artificial cortex is formed of pulp fiber.
Owner:FRONTIER VISION
Free-form progressive multifocal refractive lens for cataract and refractive surgery
InactiveUS20140135919A1Improve acuityIncrease distanceIntraocular lensOptical partsPresent dayKeratorefractive surgery
A new type of multi-focal lens that has a free-form progressive multifocal front surface consisting of a 16th order polynomial superimposed on a standard conic base surface is described. The center region of the lens is optimized for distance vision, while simultaneously optimizing the rest of the lens for near vision. The resulting free-form even asphere polynomial surface is smooth, unlike present day diffractive multifocal designs. Additionally, this lens design is suitable for both refractive and cataract surgeries.
Owner:STAAR SURGICAL COMPANY INC
Lenticular capsule-expanding device
InactiveUS20150289970A1High precisionAdjustment function can be effectivelyIntraocular lensCataract surgeryEngineering
A lenticular capsule-expanding device is arranged in a lens capsule in a cataract surgery, etc. The device includes a front supporting section to be arranged in contact with an inner surface of an anterior capsule, the front supporting section, a rear supporting section to be arranged in contact with an inner surface of a posterior capsule, the rear supporting section being arranged behind the front supporting section, and a connecting section that connects the front and rear supporting sections in a manner as to have an urging force for separating the front and rear supporting sections in a separating direction. By the urging force of the connecting section, the front supporting section presses against the inner surface of the anterior capsule and the rear supporting section presses against the inner surface of the posterior capsule.
Owner:XLENS TECH INC
Therapeutic contact lens for pseudo-aphakic eyes and/or eyes with retinal neuro-degeneration
The object of the invention is a contact lens for pseudo-aphakic eyes and / or eyes with macular and retinal degeneration, its main characteristic being the application of a yellow filter to a standard contact lens, with the purpose of protecting the eye from the short wavelength radiation of the visible spectrum (lower than 500 nm).This invention avoids the difficulties and risks of existing techniques, providing protection to the cataract-operated eye and improving natural protection in eyes with retinal neuro-degeneration, through the simple application of a contact lens.The invention consists of the combination of a standard contact lens and yellow filter, which absorbs short wavelengths of 350 / 500 nm, both its components being appropriate for use in the human eye.
Owner:UNIV COMPLUTENSE DE MADRID
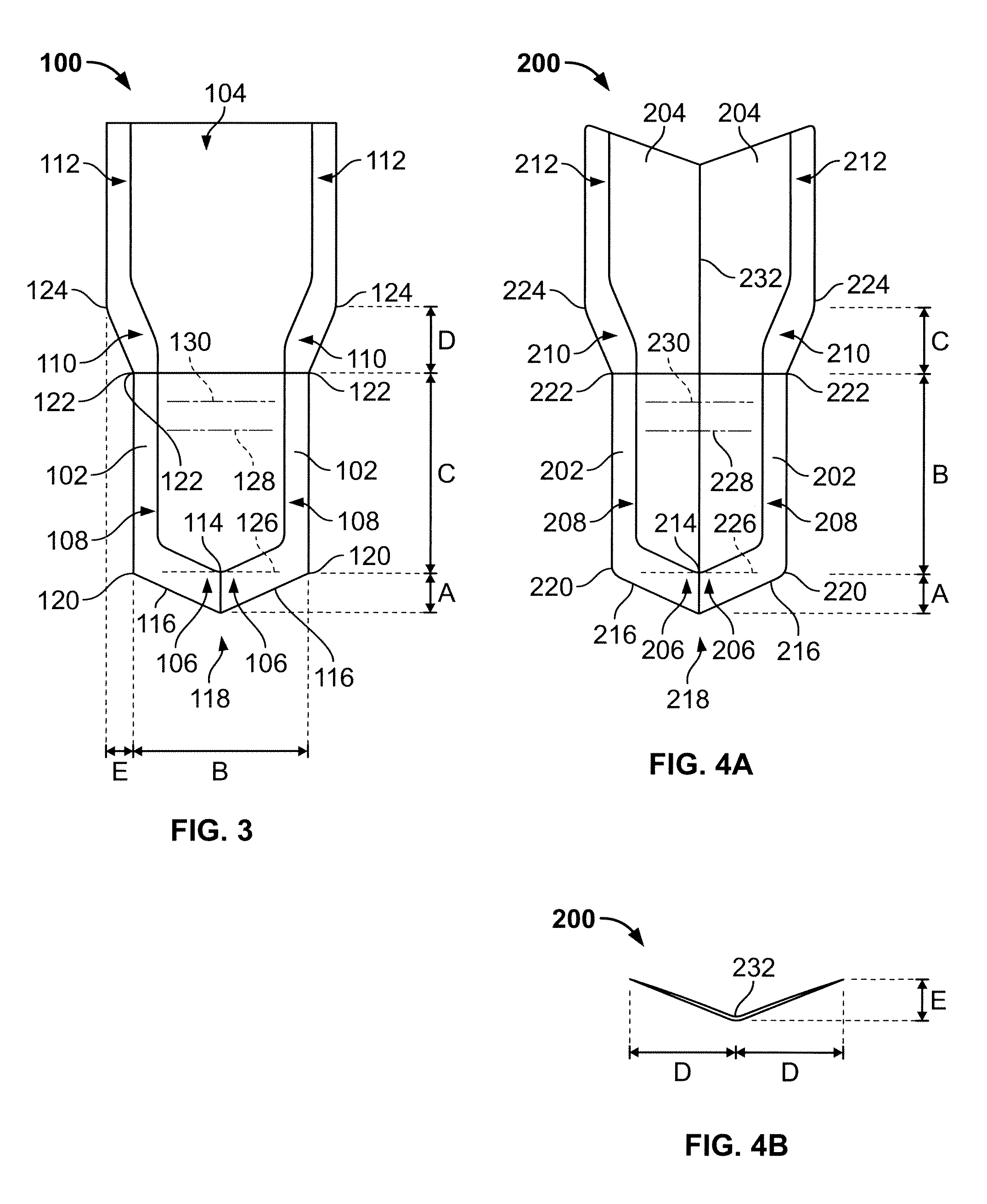
Surgical blade and trocar system
InactiveUS20080215078A1Minimize bendingEasily and rapidly removedEye surgeryCannulasEye SurgeonSurgical blade
The present invention provides an improved surgical blade and trocar system for accessing the retina and other parts of the eye while doing vitreo-retinal and cataract surgeries, including surgeries for macular degeneration. The eye surgeon uses an improved surgical blade for vitreo-retinal and cataract surgeries having a generally flat, V-shaped, W-shaped, or “extended W” shaped cross-section. Using the improved surgical blade, the surgeon creates a multi-planar, self-sealing surgical wound, first by directing the surgical blade substantially perpendicular to the eye surface, then redirecting the blade to follow the general curvature of the eye globe, and finally redirecting the blade to enter the interior of the eye. The improved surgical blade is used with an improved trocar system having two main parts-a relatively rigid, wide-mouthed outer segment and a generally thin-walled, collapsible plastic polymer or metal mesh sleeve that spans the surgical wound and substantially molds to its contour. The improved surgical blade and trocar system can be adapted for use in either vitreo-retinal or cataract surgeries.
Owner:BENNETT MICHAEL D
Prosthethic capsular bag and method of inserting the same
ActiveUS20150127102A1Stabilizing effective lens positionPromote resultsIntraocular lensCataract surgeryCapsular bag
The present invention relates to a prosthetic capsular bag and method for inserting the same. The prosthetic capsular bag helps to maintain the volume of the natural capsular bag, thereby stabilizing the effective lens position of an IOL so that refractive outcomes may be improved with cataract surgery. The prosthetic capsular bag further provides an integrated refractive surface, providing a means for experimentally determining an effective lens position prior to inserting an IOL.
Owner:OMEGA OPHTHALMICS
Method and system for eye measurements and cataract surgery planning using vector function derived from prior surgeries
ActiveUS20160150952A1Good curative effectImproved refractive correctionsLaser surgeryComputer-aided planning/modellingCorrective surgeryIntraocular lens
Improved devices, systems, and methods for planning cataract surgery on an eye of a patient incorporate results of prior corrective surgeries into a planned cataract surgery of a particular patient by driving an effective surgery vector function based on data from the prior corrective surgeries. The exemplary effective surgery vector employs an influence matrix which may allow improved refractive corrections to be generated so as to increase the overall efficacy of a cataract surgery by specifying one or more parameters of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted during the cataract surgery.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Intraocular lens system
ActiveUS20050015144A1Easy to implantReduce morbidityIntraocular lensIntraocular lensCataract surgery
A two part lens system. The first part is a ring-like supporting component that is implanted in the capular bag following cataract surgery. The first component is a non-optical component and contains a pair of haptics for fixating the first component within the capular bag. The second component is an optical component that contains all of the corrective optical power of the lens system. The second component has a pair of tabs for locking the second component within the first component.
Owner:ALCON INC
Systems and methods for delivering an ocular implant to the suprachoroidal space within an eye
Delivery devices, systems and methods are provided for inserting an implant into an eye. The delivery or inserter devices or systems can be used to dispose or implant an ocular stent or implant, such as a shunt, in communication with the suprachoroidal space, uveal scleral outflow pathway, uveoscleral outflow path or supraciliary space of the eye. The implant can drain fluid from an anterior chamber of the eye to a physiologic outflow path of the eye, such as, the suprachoroidal space, uveal scleral outflow pathway, uveoscleral outflow path or supraciliary space. Alternatively, or in addition, the implant can elute a drug or therapeutic agent. The delivery or inserter devices or systems can be used in conjunction with other ocular surgery, for example, but not limited to, cataract surgery through a preformed corneal incision, or independently with the inserter configured to make a corneal incision. The implant can be preloaded with or within the inserter to advantageously provide a sterile package for use by the surgeon, doctor or operator.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Intraocular lens system
A two or three component lens system. The first component is a ring-like supporting component that is implanted in the capsular bag following cataract surgery. The first component is a non-optical component and does not correct for any refractive errors. The first component may contains features to help reduce or eliminate PCO. The second component is an optical component that may contain all of the corrective optical power of the lens system. The second component has a pair of tabs for locking the second component within the first component. The third component is optional and is similar to second component and contains some optical power to correct for any residual optical error not corrected by the second component. The second and third components may also be implanted so as to move relative to one another, thereby providing some accommodation.
Owner:ALCON INC
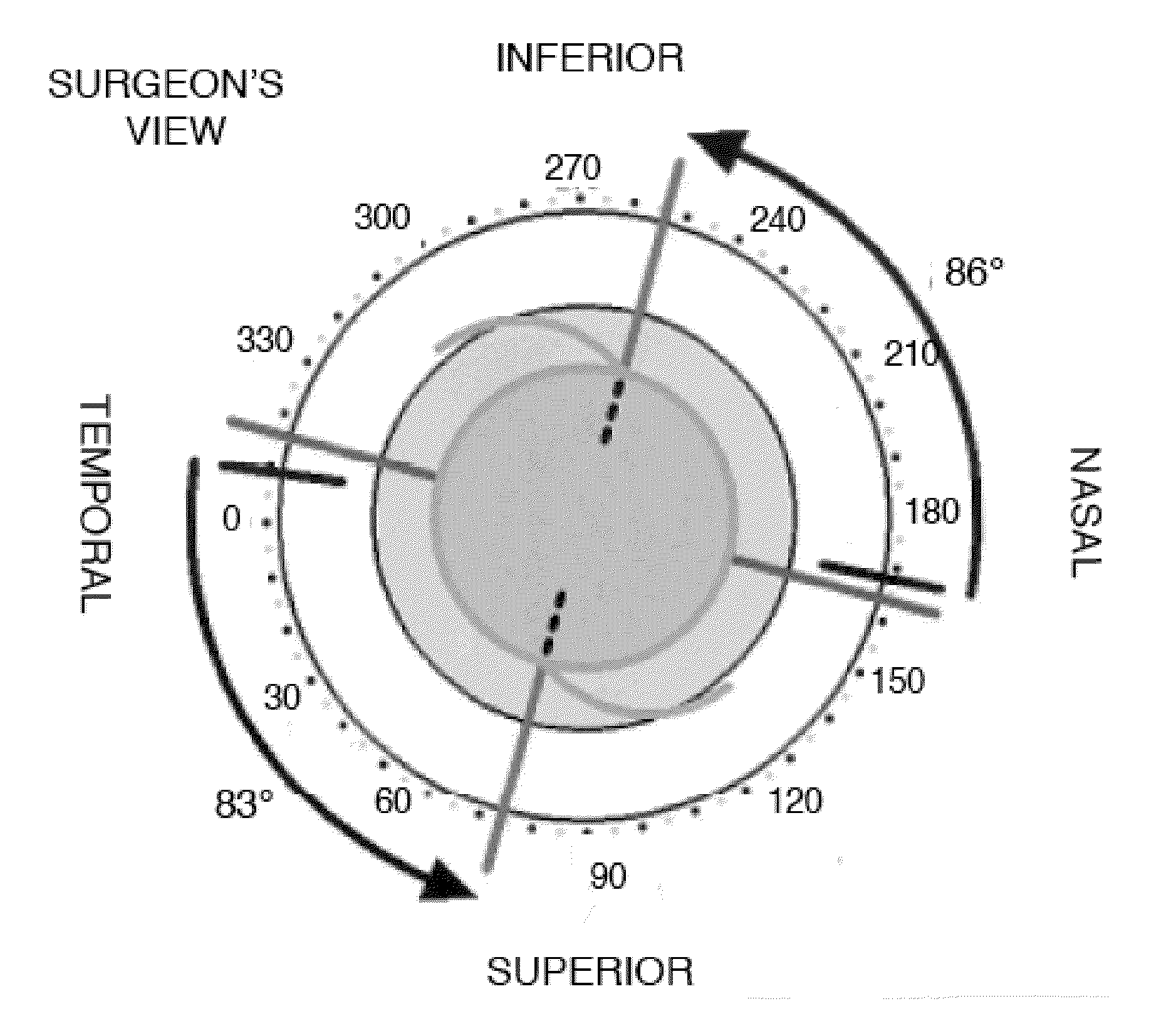
Tools and methods for the surgical placement of intraocular implants
InactiveUS20130018276A1Optimal astigmatic correctionMinimize and eliminate post-operative residual astigmatismDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVisual acuityCataract surgery
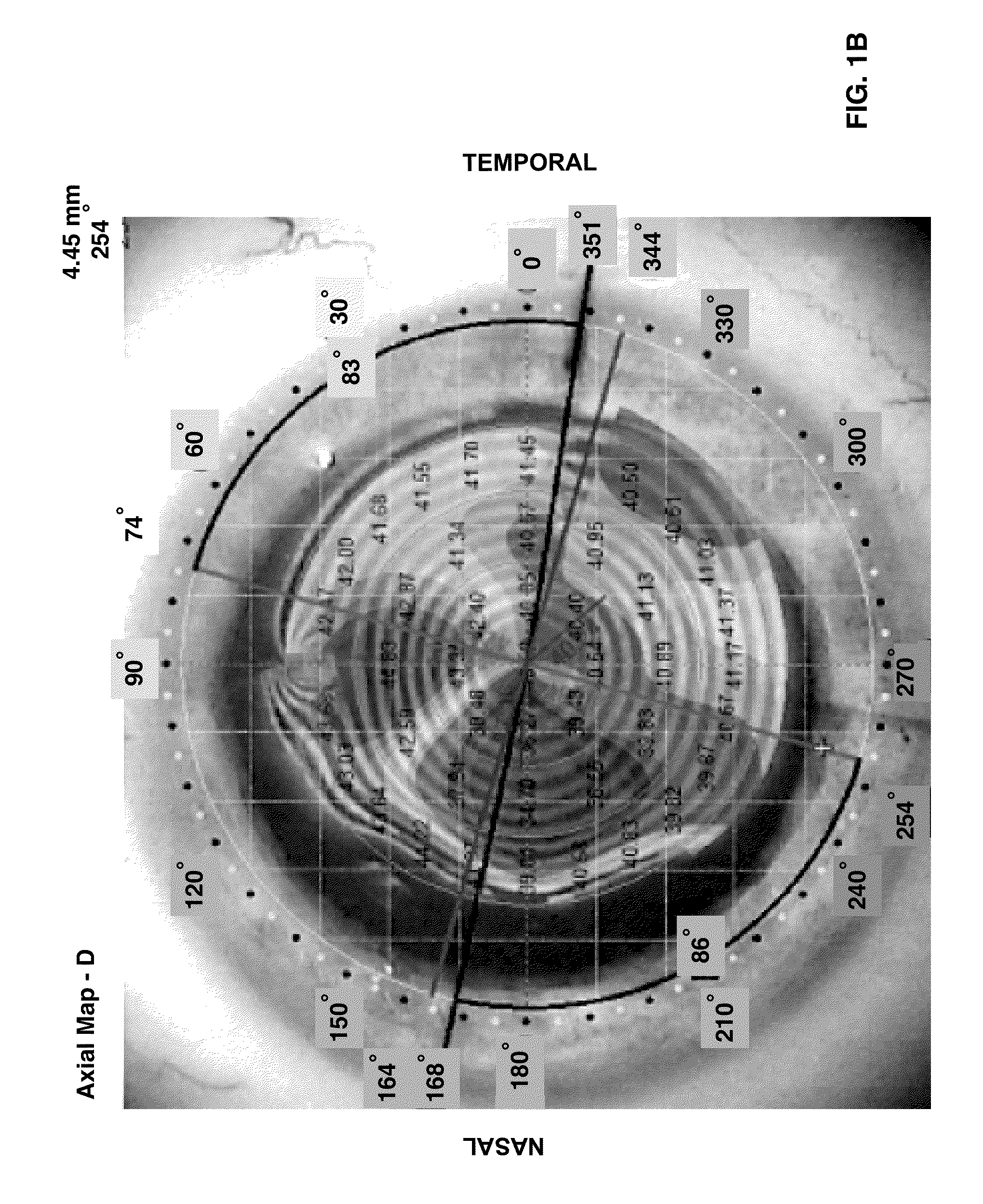
Provided herein is a measurement tool for implantable non-spherical asymmetric optics comprising a viewable, rotatable angular caliper superimposable over an image of an eye. Also provided are methods for optimally placing non-spherical asymmetric optics in an eye of a patient and for correcting post-operative astigmatism in a patient having cataract surgery. The measurement tool is useful to plan the optimal correct surgical placement of a non-spherical asymmetric optic, e.g., a toric intraocular implant or a toric intraocular contact lens, in the eye. By superimposing the measurement tool over a corneal topographic image, an optimal positioning of the non-spherical asymmetric optic can be effected in an optical zone of interest. Correct placement or re-placement at least minimizes astigmatism in post-operative vision. Also provided are computer program products and computer readable media comprising modules and methods for data entry, lens selection and surgical planning utilized to practice the methods provided herein.
Owner:ZALDIVAR ROBERTO +2
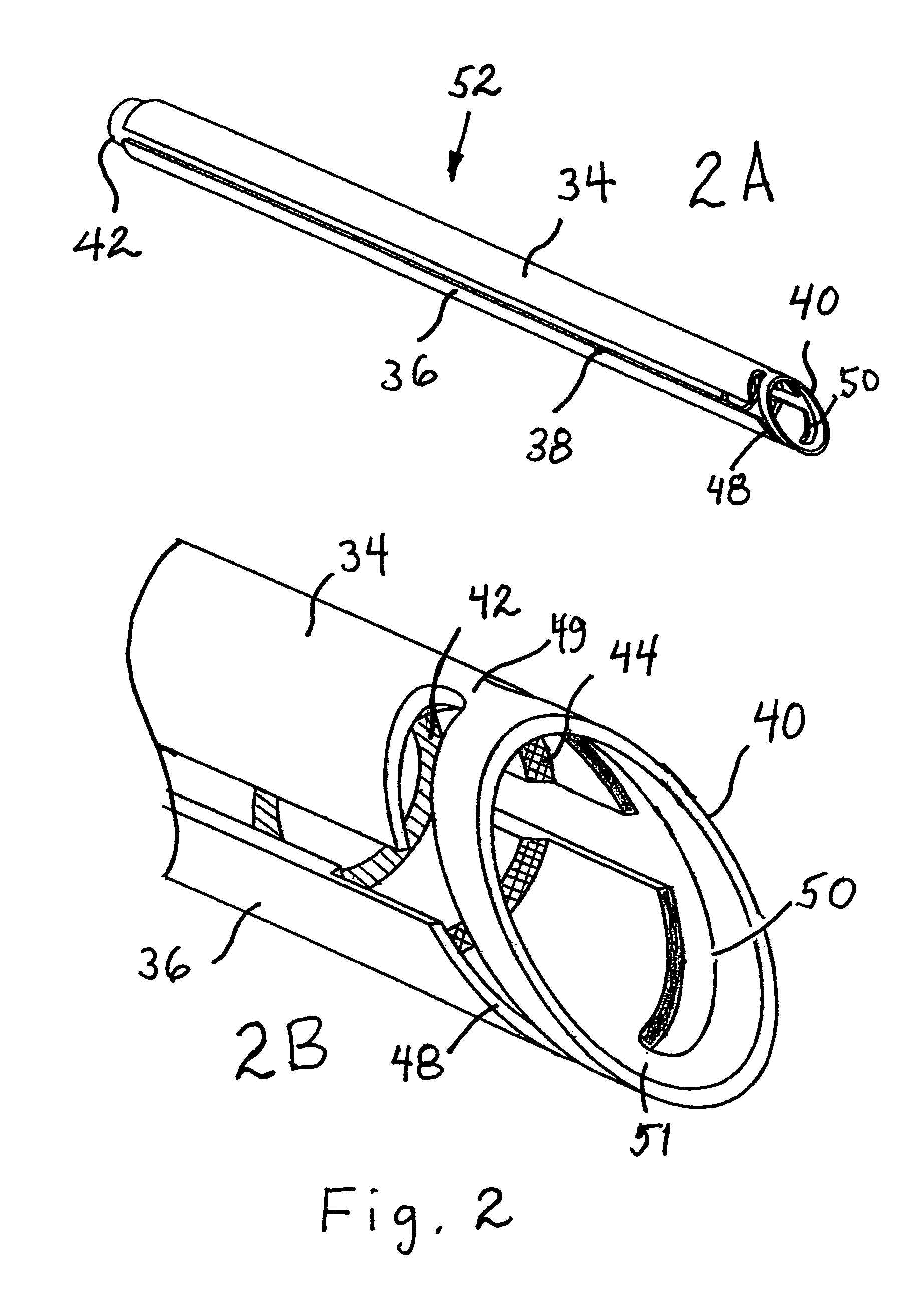
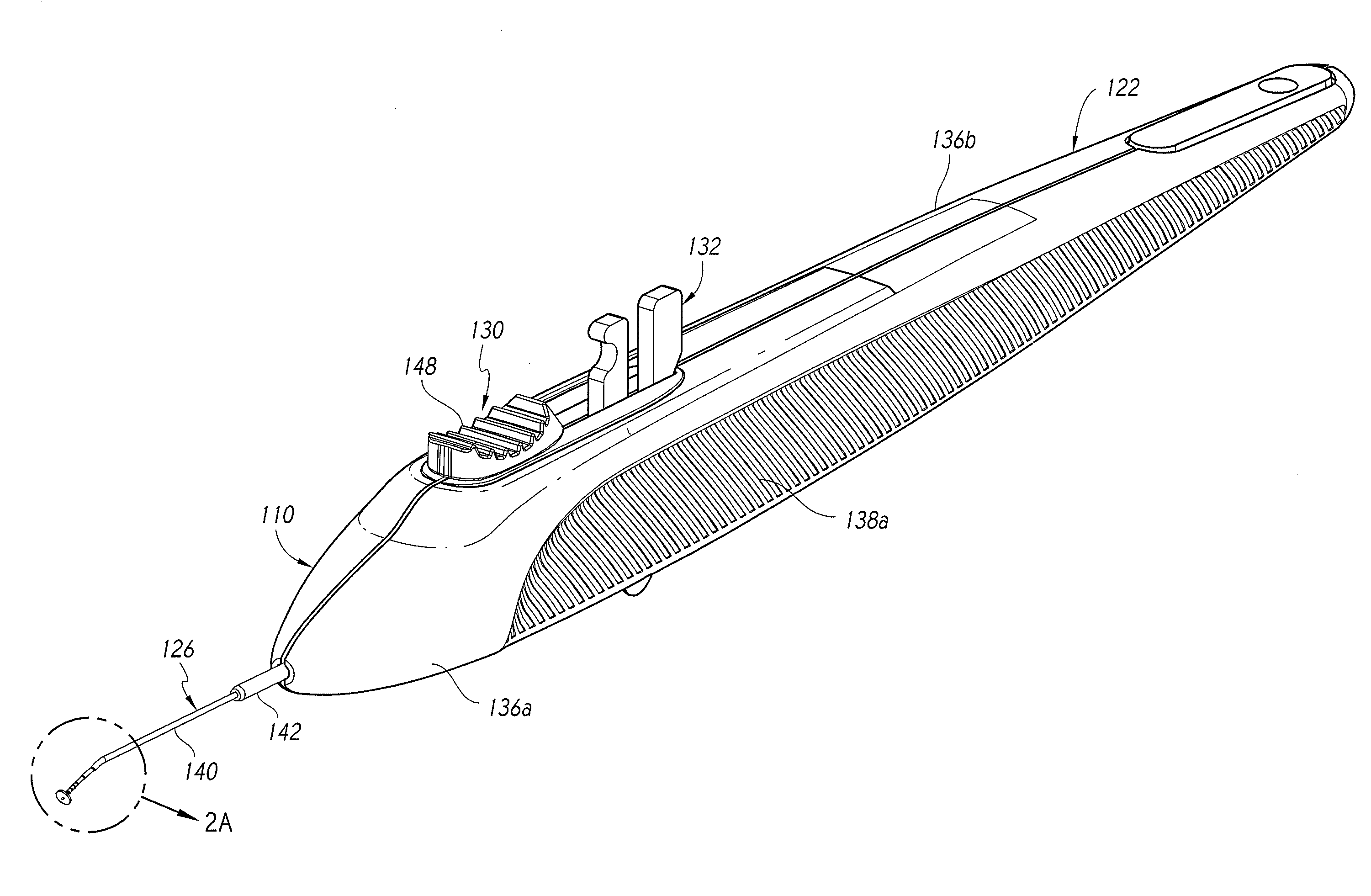
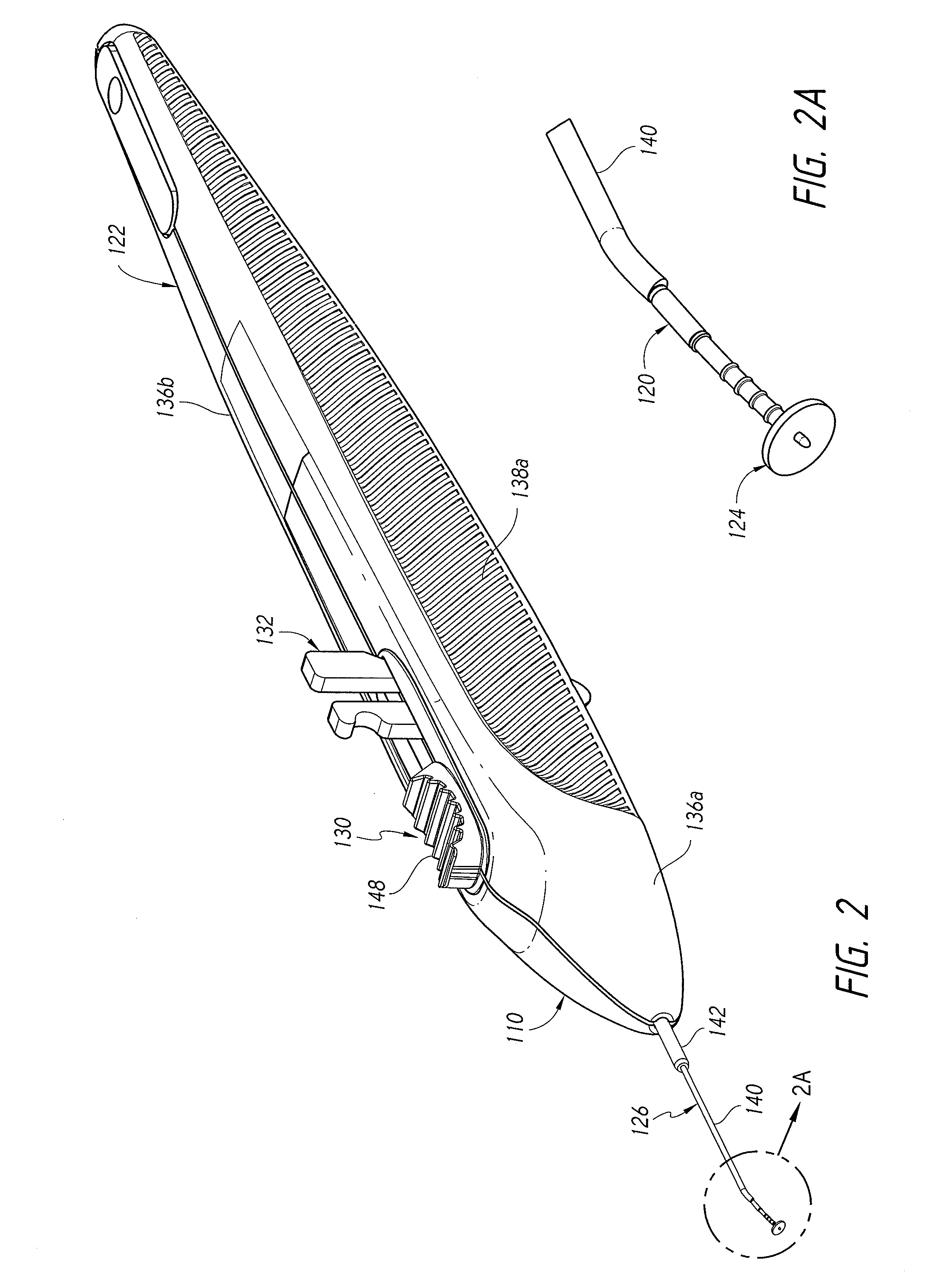
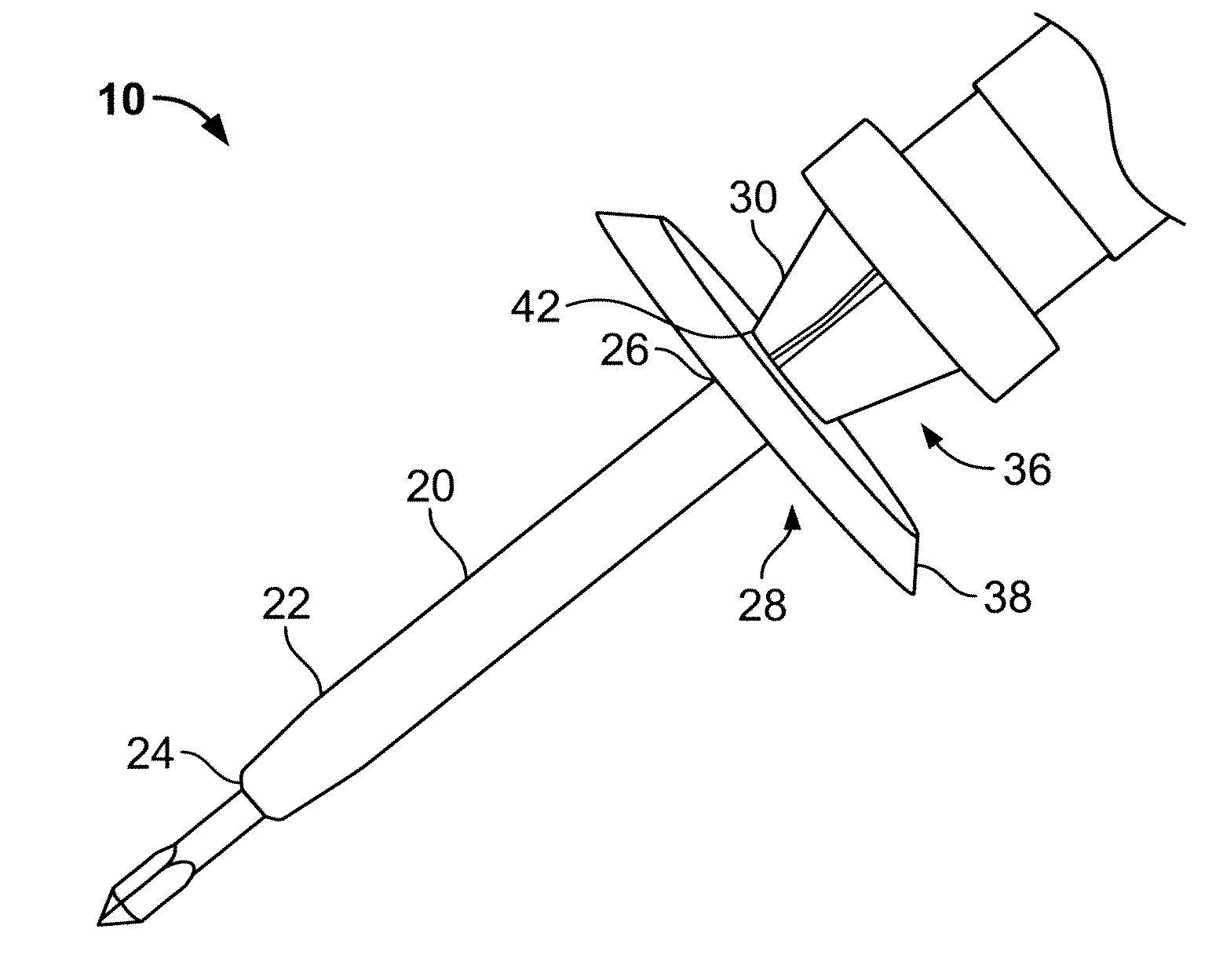
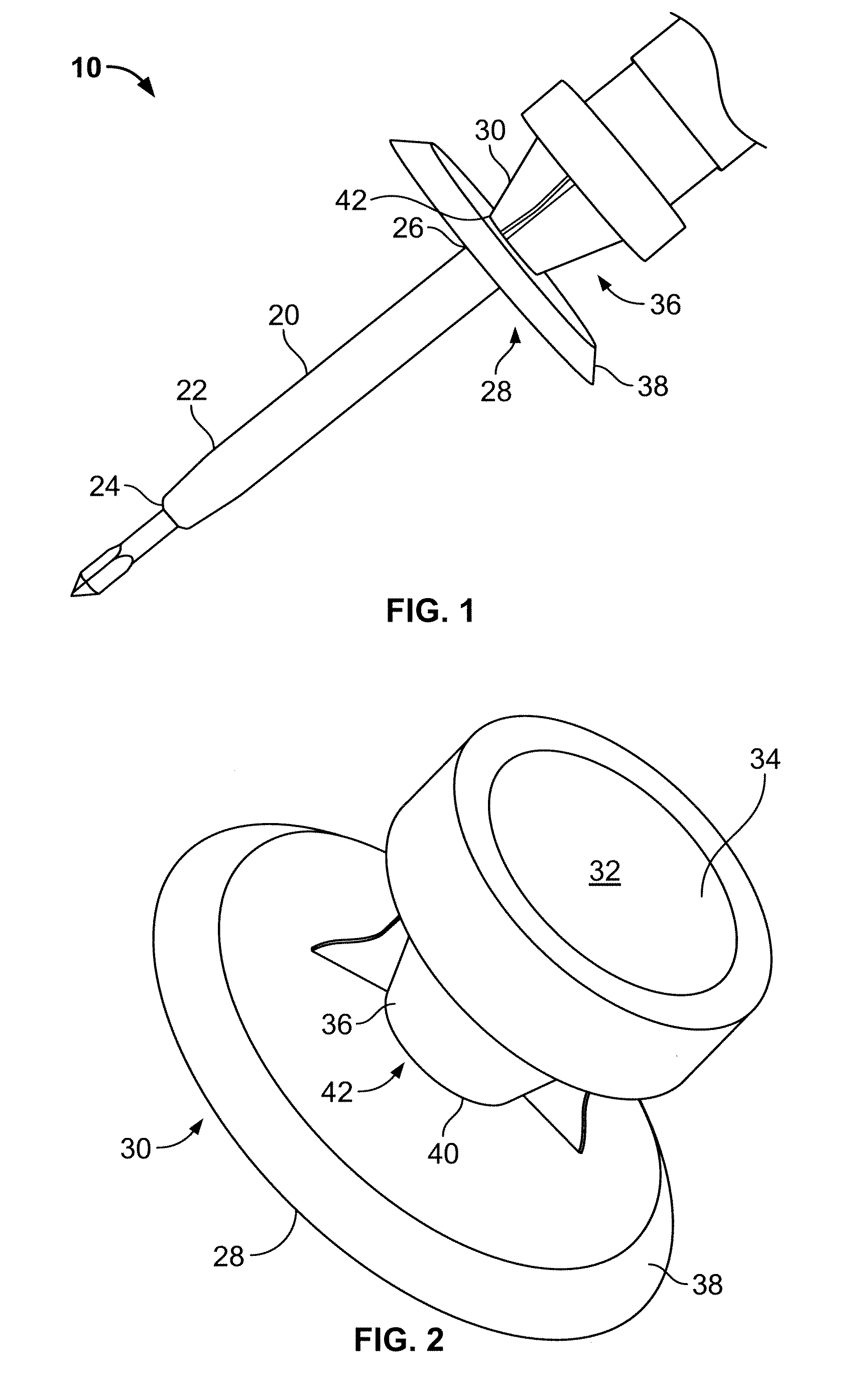
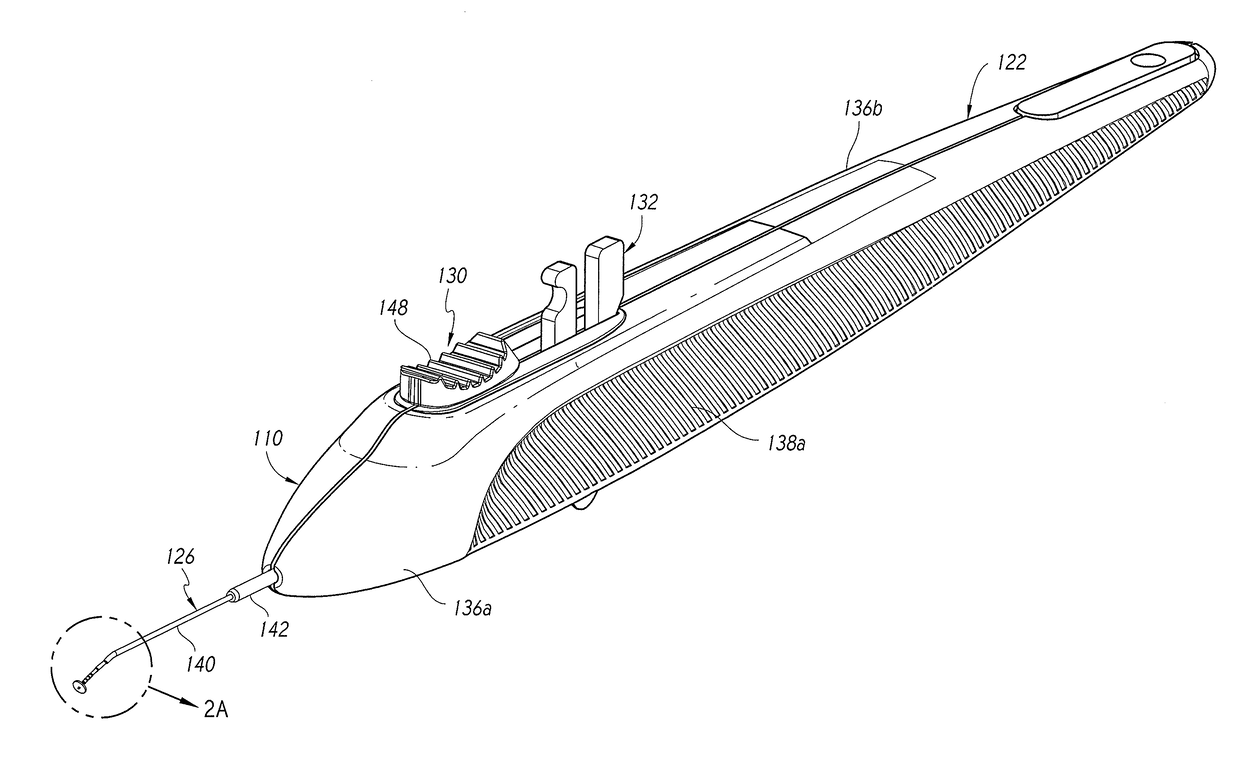
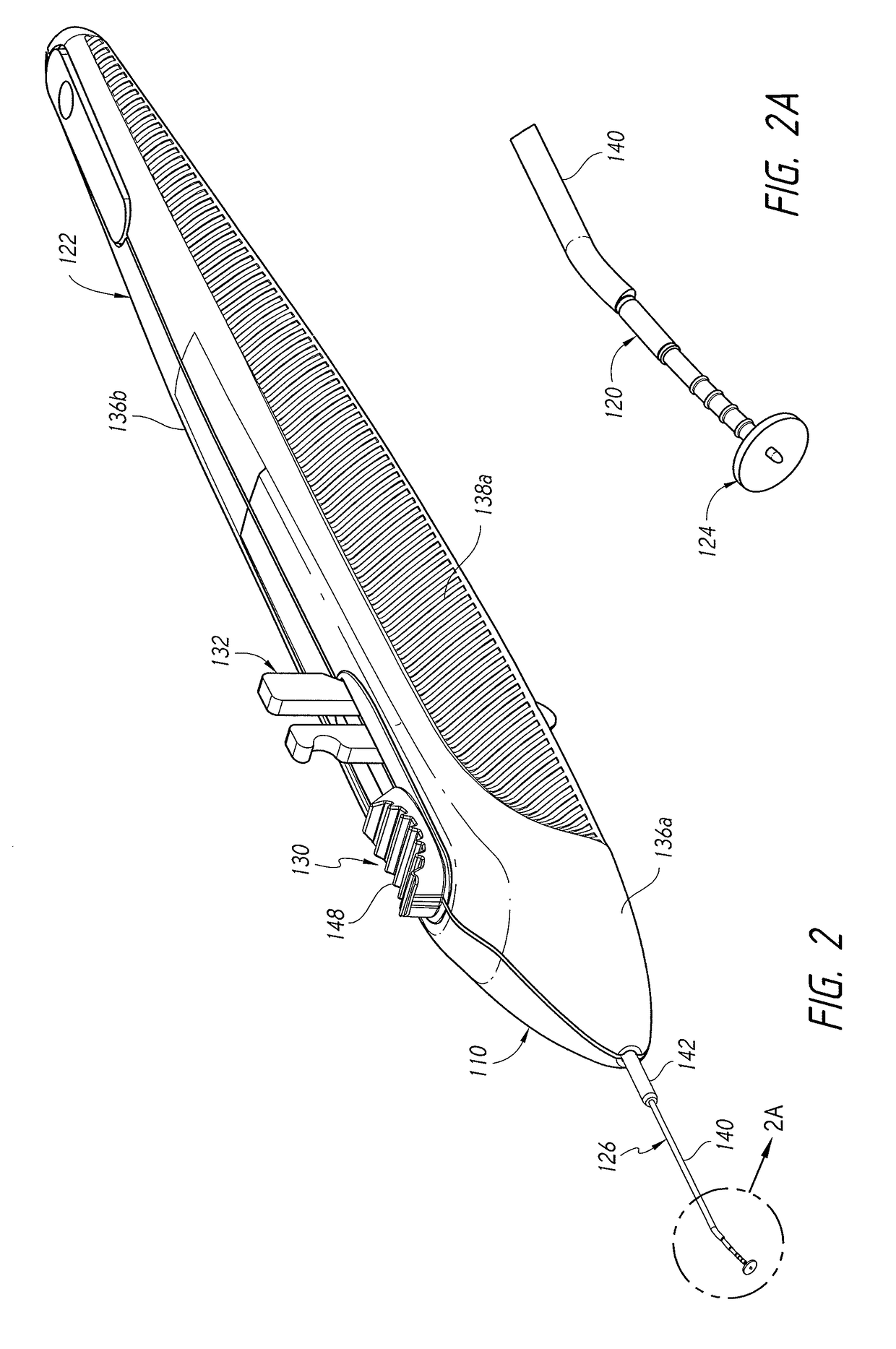
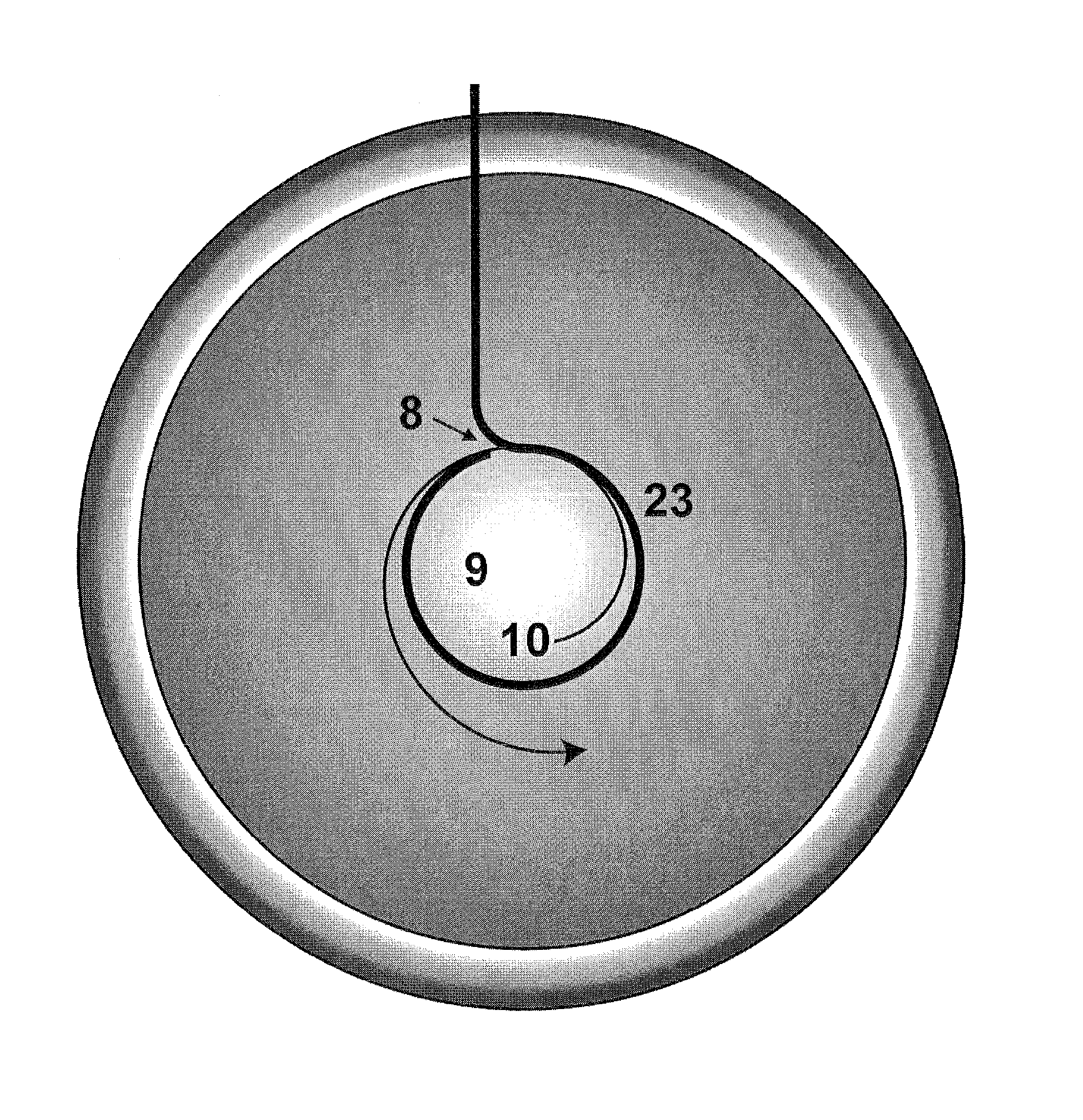
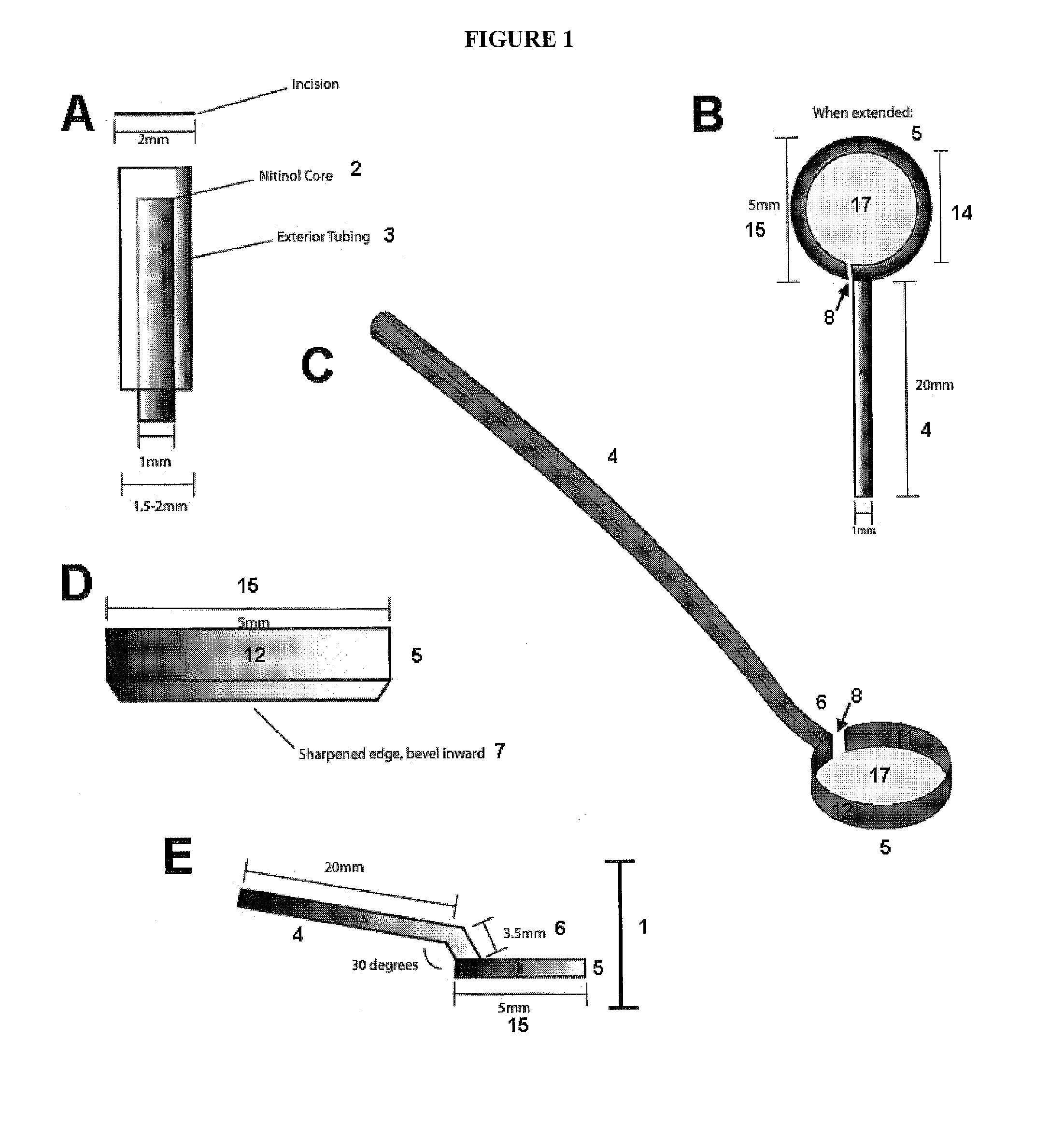
Incising apparatus for use in cataract surgery
InactiveUS7011666B2Safe and simple and inexpensive deviceLess complexEye surgerySurgeryCataract surgeryCataracts
An incising apparatus for cataract surgery is provided. The incising apparatus includes a handle having a proximal end and a distal end. A circular cutting band is adapted to slide along the handle. At least one stopper element is provided in the vicinity of the proximal end of the handle. The at least one stopper element is positioned within the interior of the circular band so as to restrict the motion of the circular band relative to the handle.
Owner:FEINSOD MATTHEW
Element for use on the transparent surfaces of buildings for eye protection and therapy
Element for the protection and therapy of eyes applied to the transparent vertical surfaces of buildings. The invention is prepared by applying a yellow pigmented filter to the transparent or translucent surfaces of a building in which a subject may be found, and is designed to protect the eyes from the short wavelengths of the visible spectrum in the range 500 to 380 nm. The invention avoids the difficulties and risks of existing ways of protecting healthy eyes or eyes subjected to cataract surgery, and improves the protection of eyes suffering neurodegeneration, simply by applying a filter to the transparent or translucent surfaces of any building in which a subject may be found to provide protection against the neurodegenerative components of light (short wavelengths).
Owner:UNIV COMPLUTENSE DE MADRID
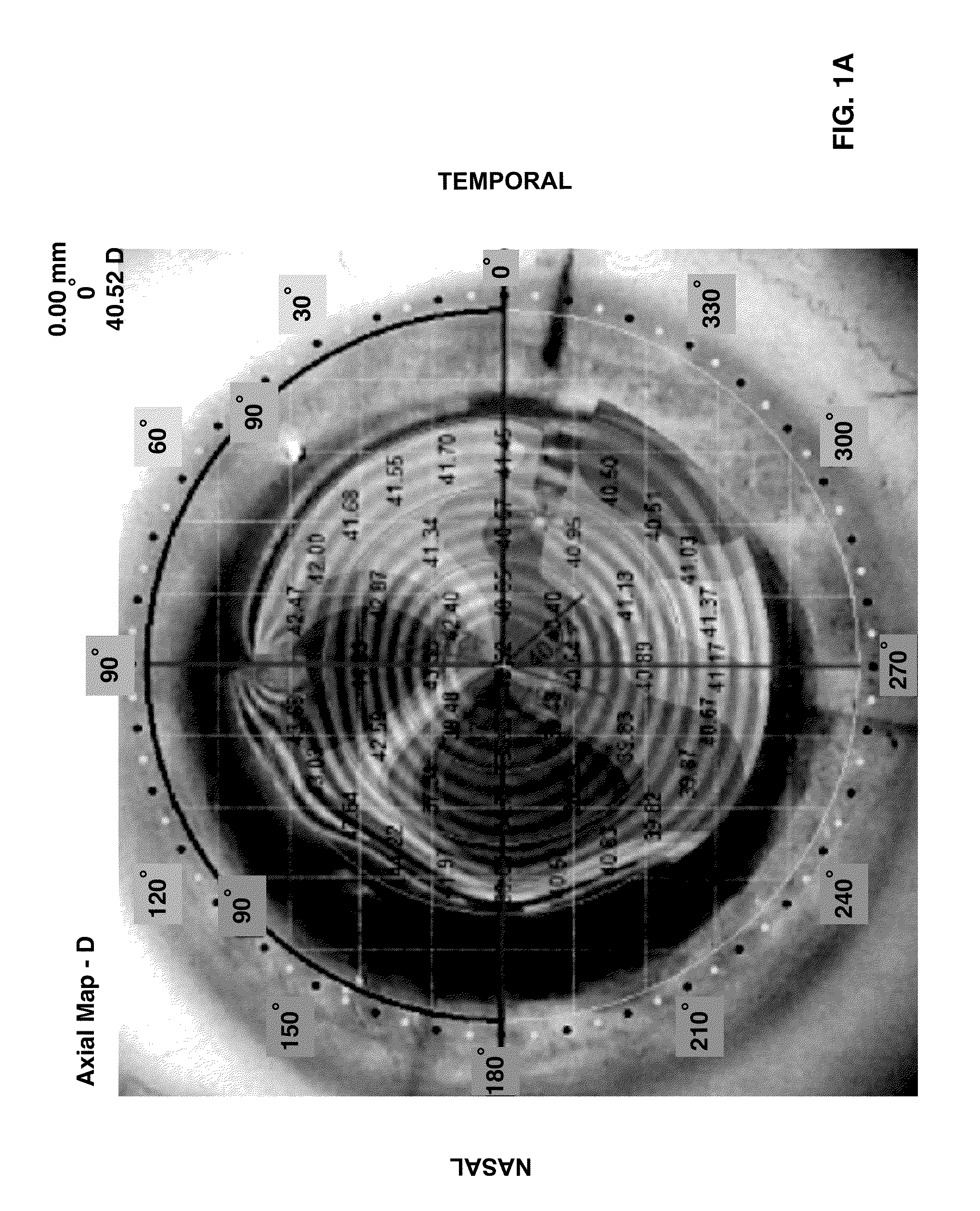
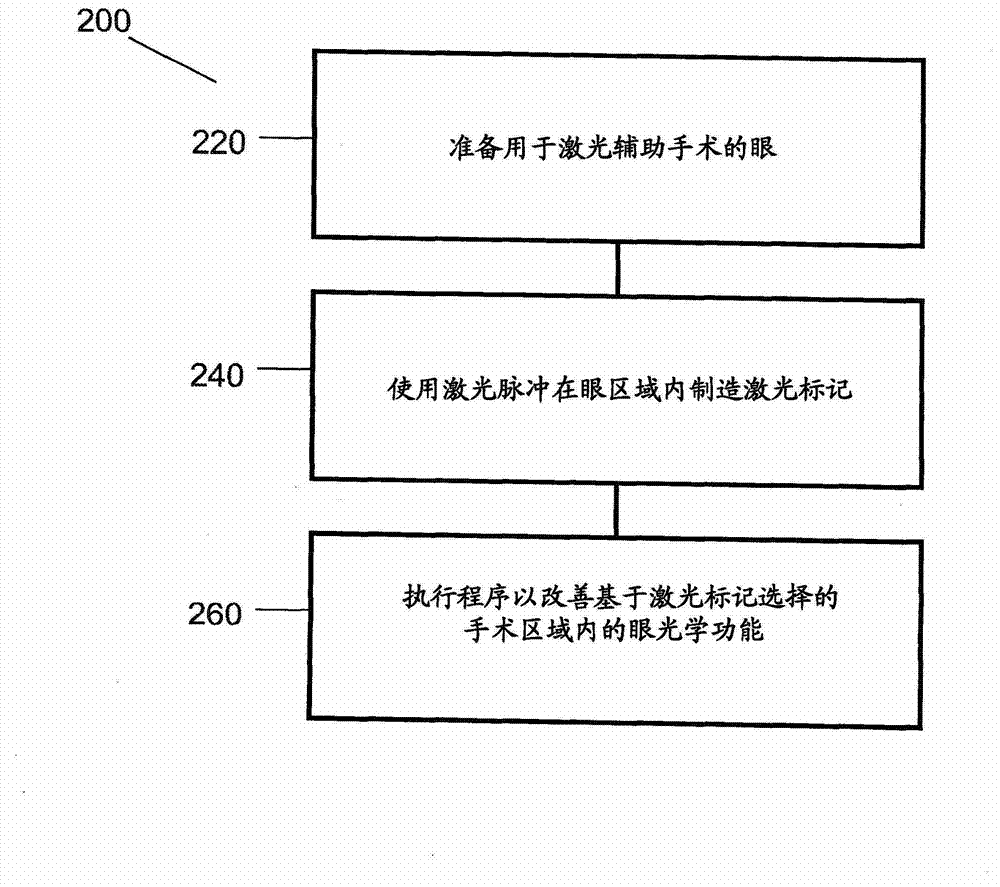
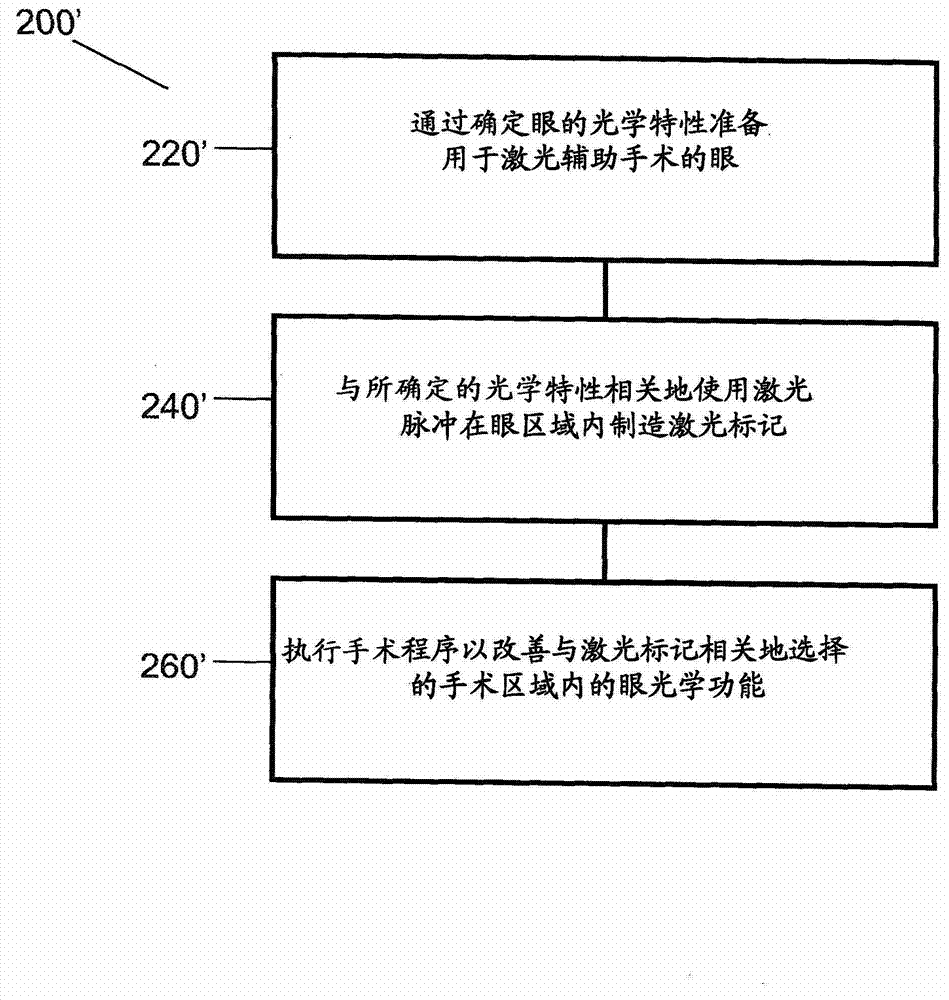
Method to guide a cataract procedure by corneal imaging
A method of performing a cataract procedure may include the steps of: imaging one or more corneal marks created by a corneal procedure, determining corneal location information regarding a location of a treatment region of the corneal procedure based on the imaged corneal marks, and placing laser pulses for a cataract surgery using the corneal location information. A corresponding ophthalmic laser system may include an imaging system to image a corneal region of an eye, an image analyzer to facilitate a determination of corneal location information based on one or more image provided by the imaging system, and a surgical laser system to place laser pulses into a lens of the eye using the corneal location information. The imaging system may include an ophthalmic coherence tomographic (OCT) system.
Owner:ALCON LENSX
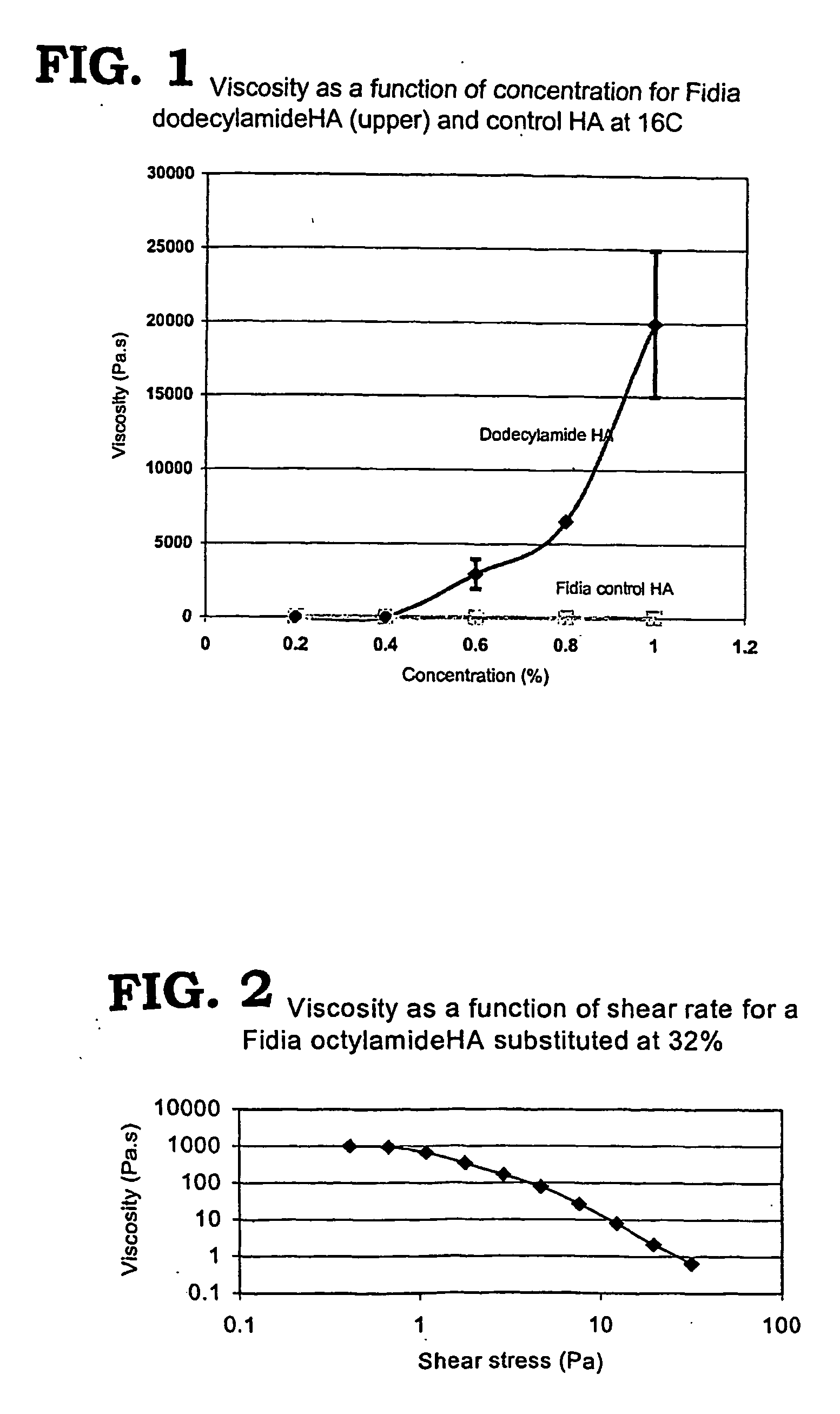
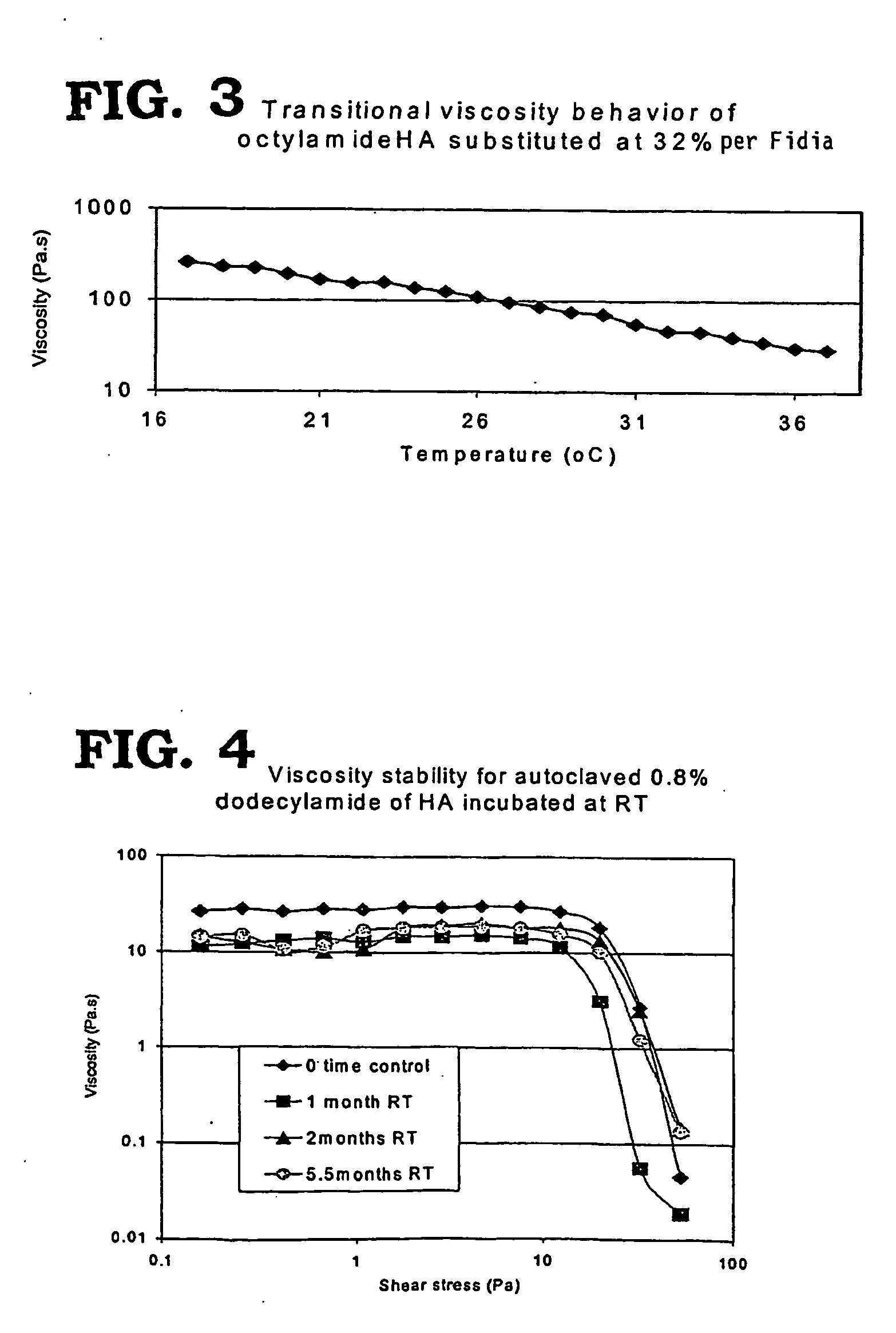
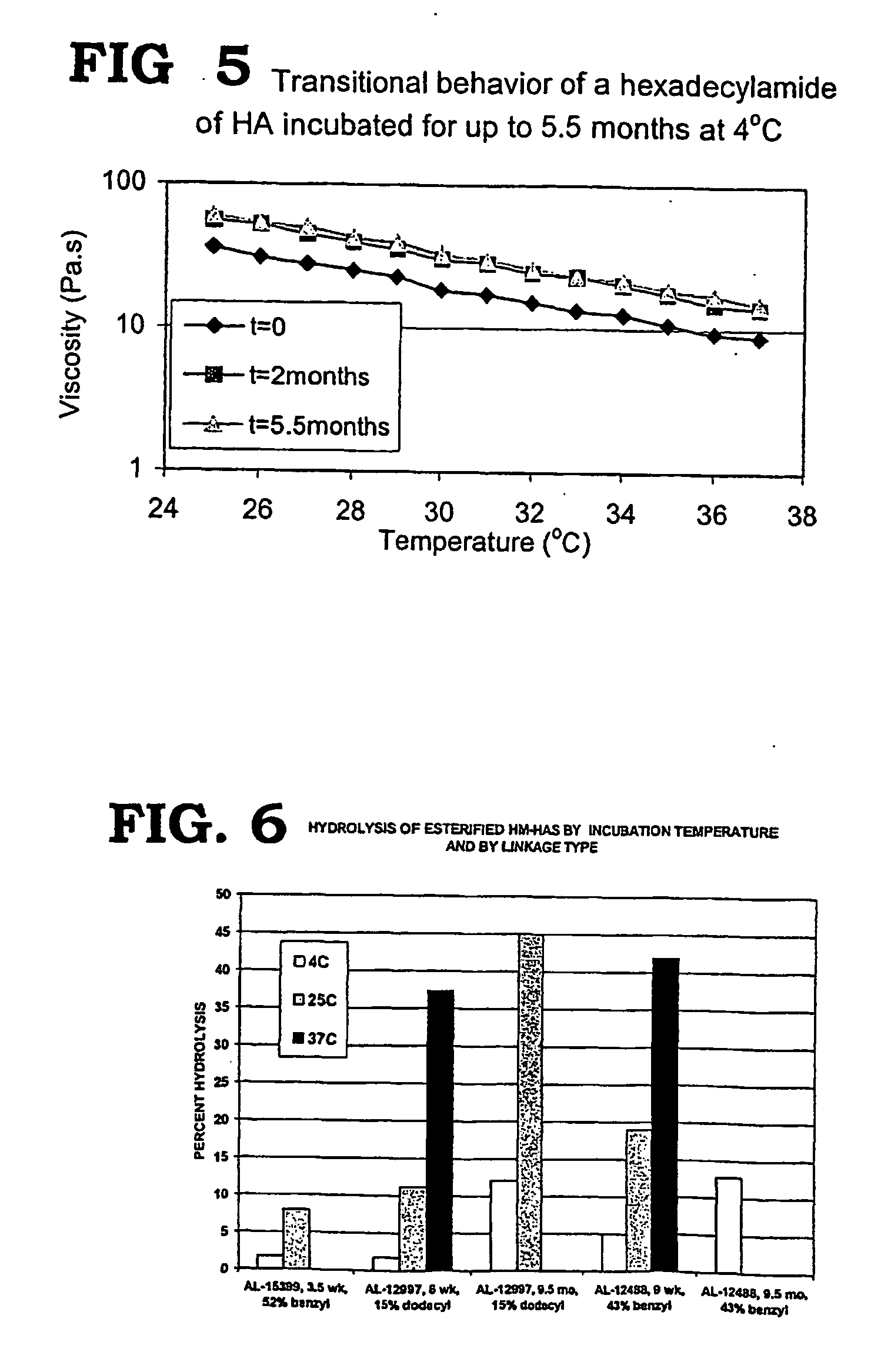
Non-aspirating transitional viscoelastics for use in surgery
InactiveUS20050281862A1Easy to optimizeReduce and avoid occurrenceBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSurgical operationCataract surgery
Non-aspirating viscoelastics, compositions, and methods of use are disclosed. The non-aspirating, transitional viscoelastics possess sufficient viscosity to be useful in ophthalmic viscosurgery, but may be left in the eye with little or no resulting IOP spike. The compositions are particularly useful in cataract surgery.
Owner:KARAKELLE MUTLU +4
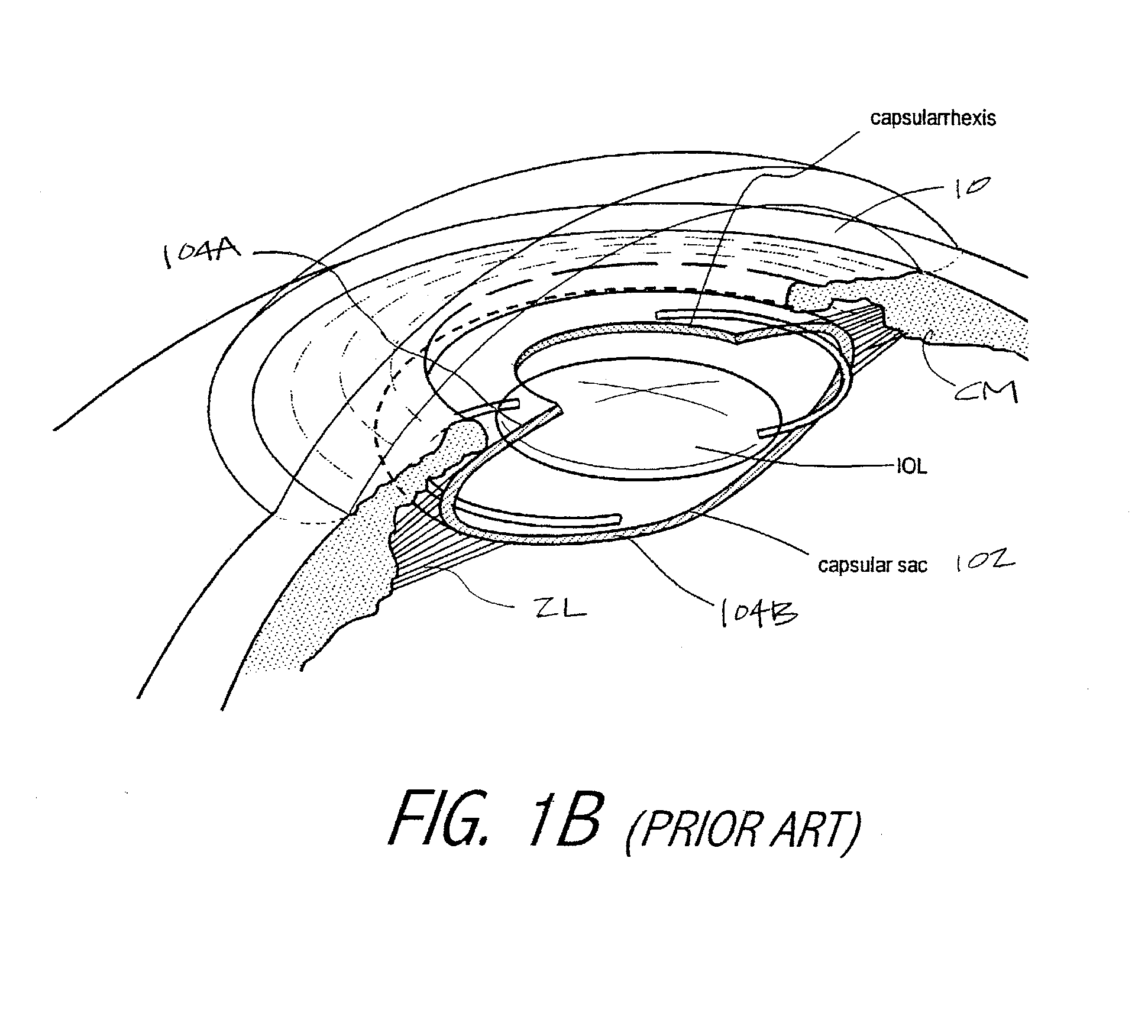
Devices and Methods for Creating a Predictable Capsulorhexis of Specific Diameter
The present invention relates generally to the field of cataract surgery and more particularly to methods and apparatus for performing a capsulorhexis. This invention is in the field of medical devices. The present invention relates to a device constructed from metals, polymers or other materials that are amenable to precise surface modifications and methods for its use, wherein (1) the device assists in capsulorhexis and (2) a patterned surface having milli-, micron-, and / or nano-sized micropatterning characteristics that imparts surface stabilizing and self-adhesive properties.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
System and method for axis identification in astigmatic cataract surgery
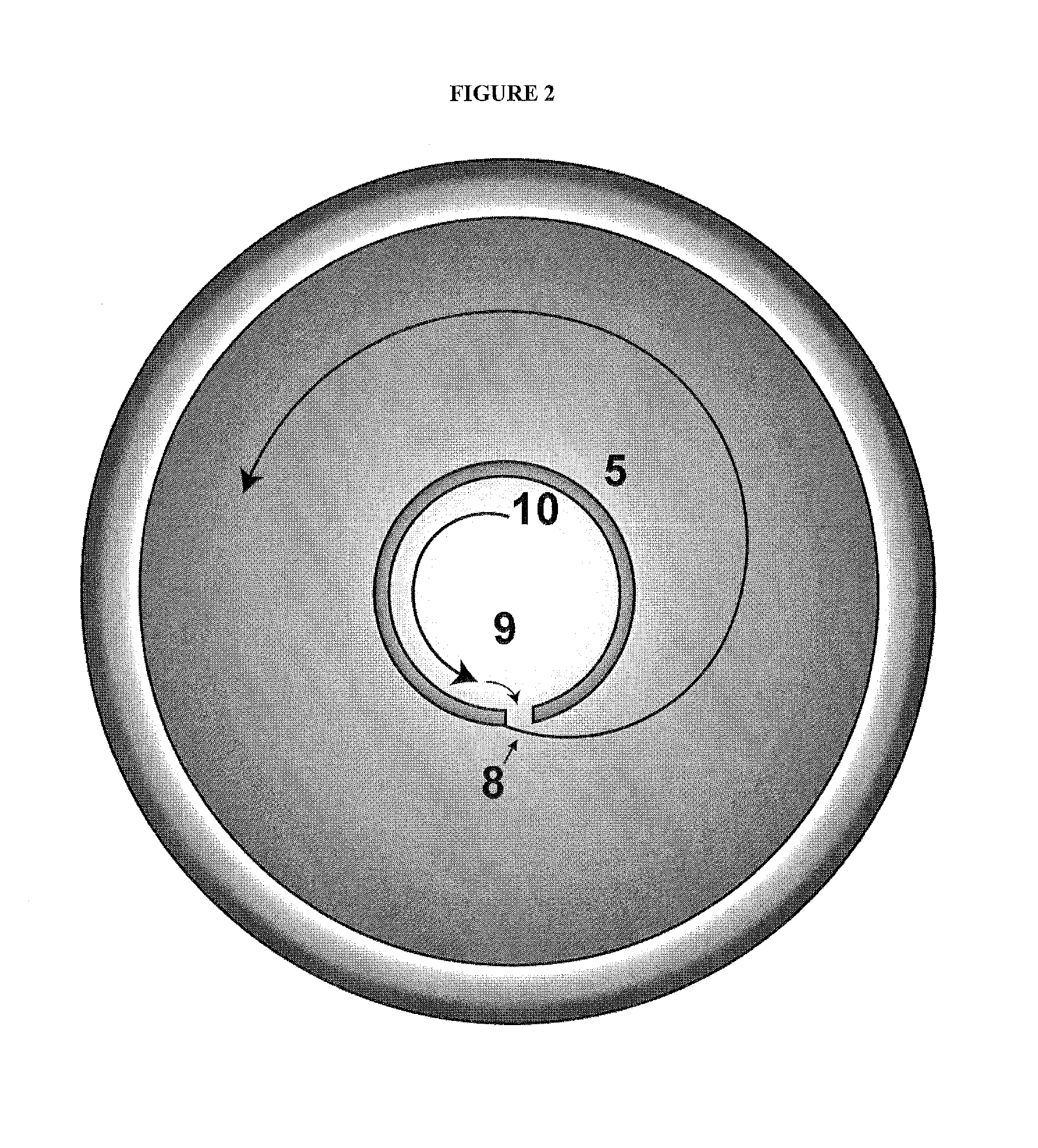
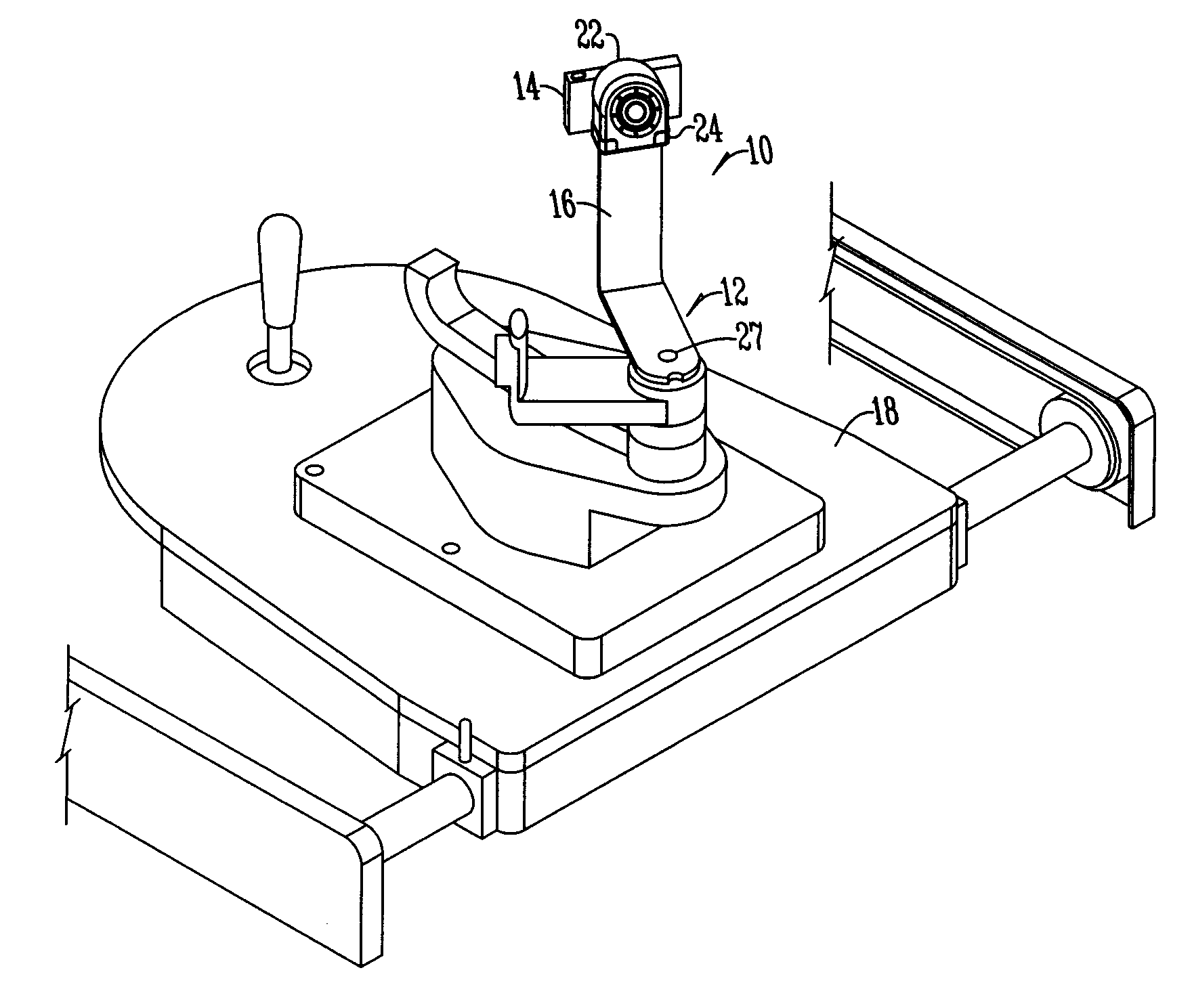
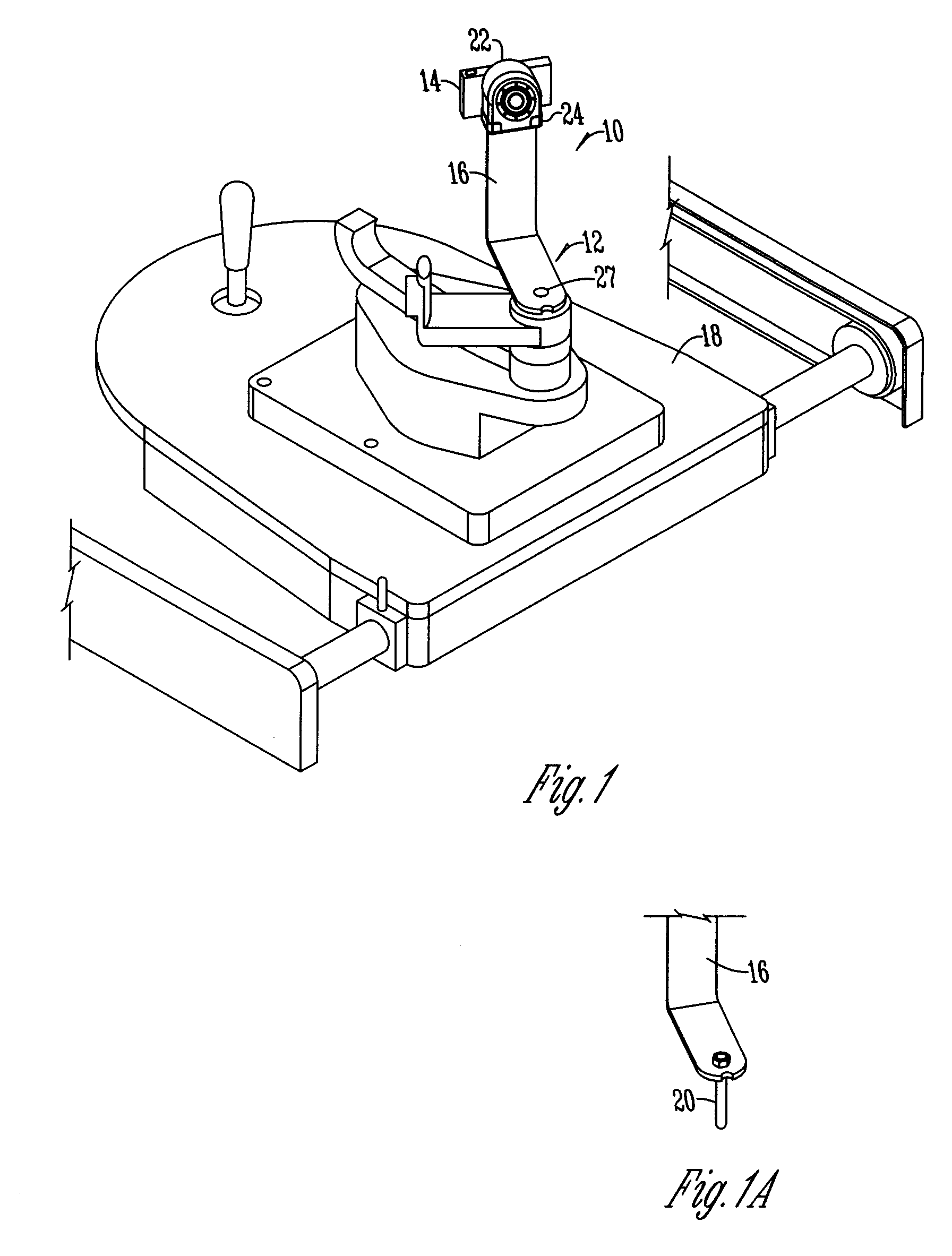
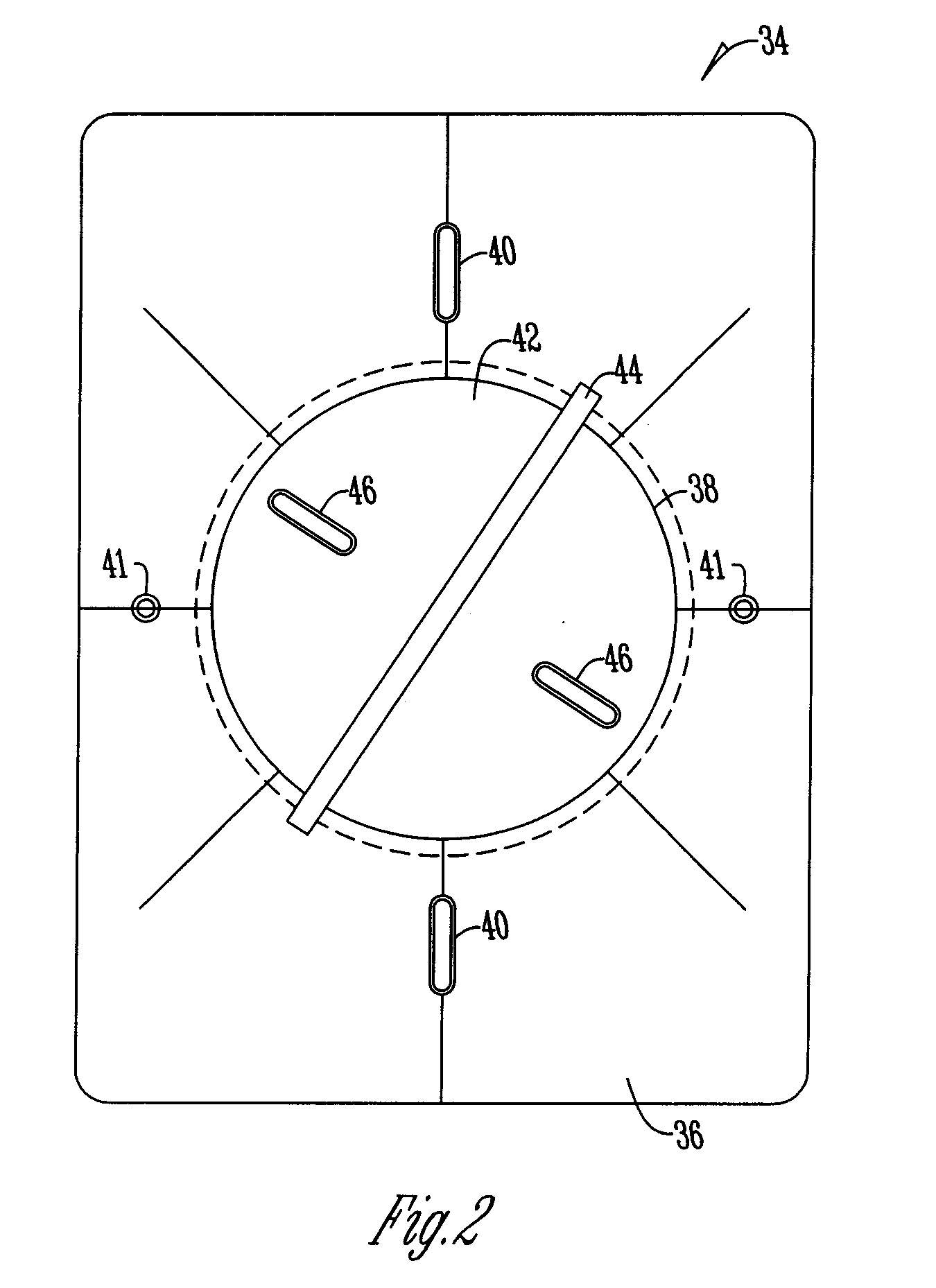
A method and system for identifying an astigmatic axis having a camera and light mounted to a slit lamp for taking a photo of a patient's eye. A template having a rotatable dial is set using a schematic diagram. The template is transferred to the photo and the correct axis is marked through slots on the template.
Owner:OCULOCAM
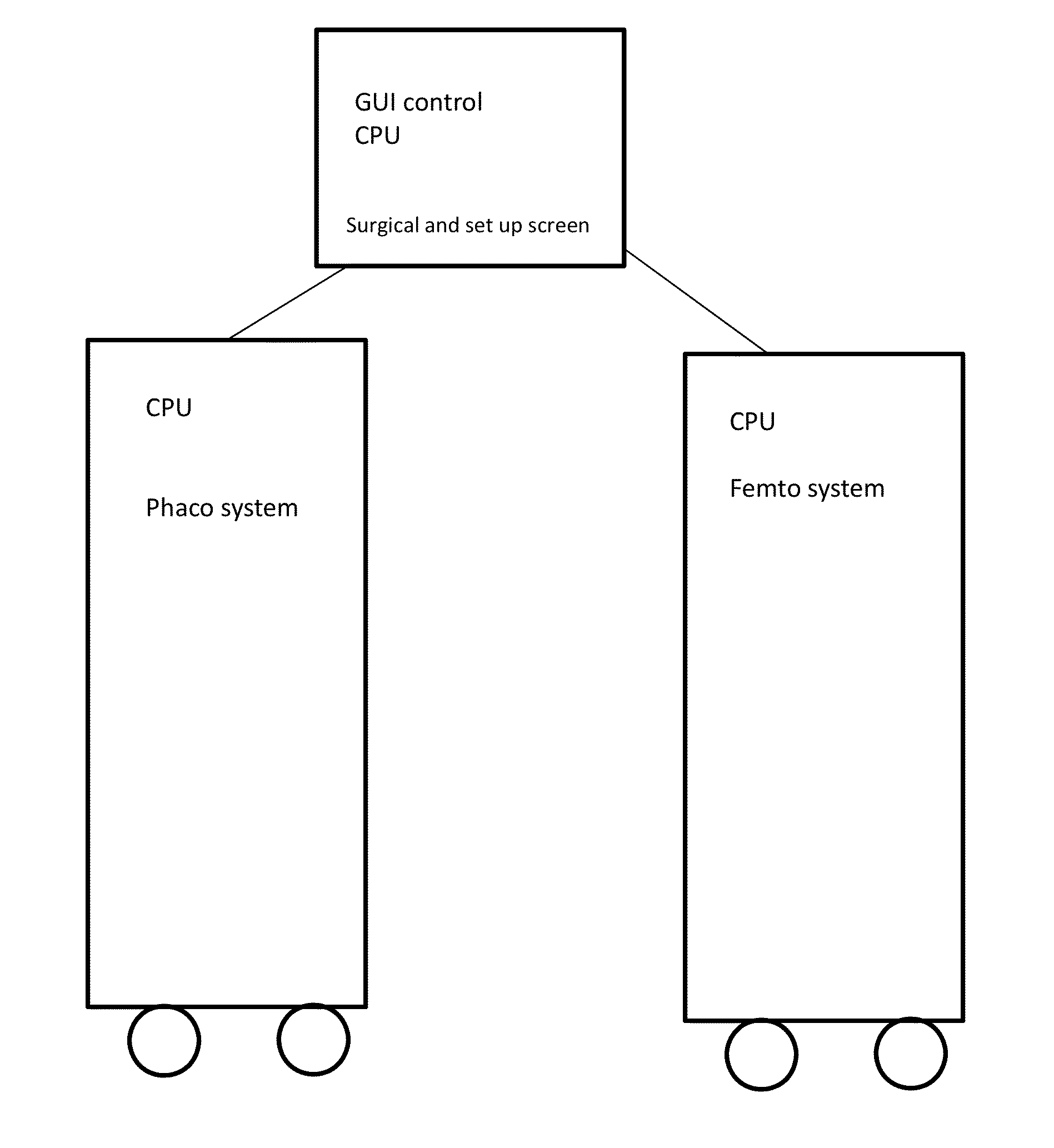
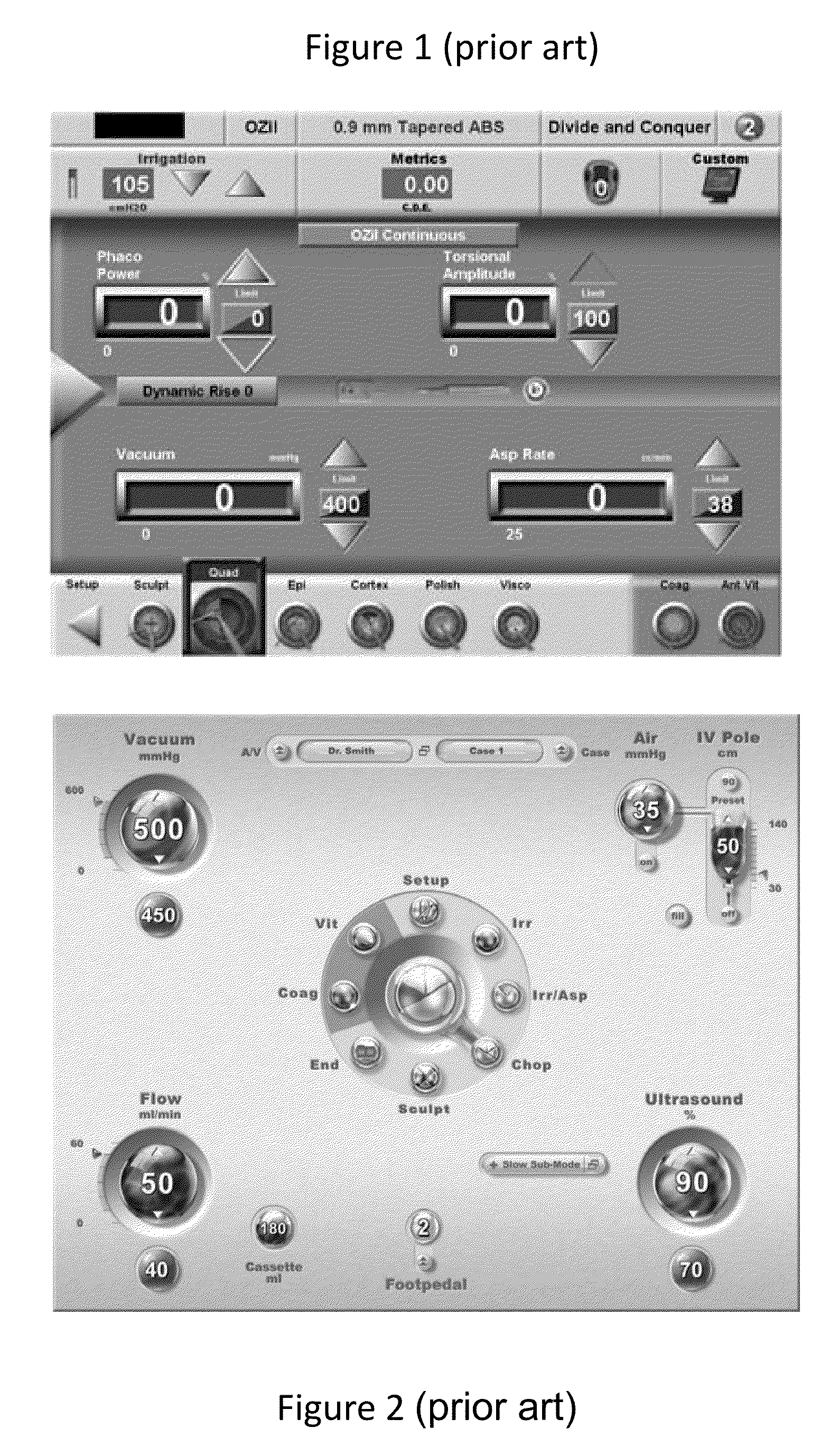
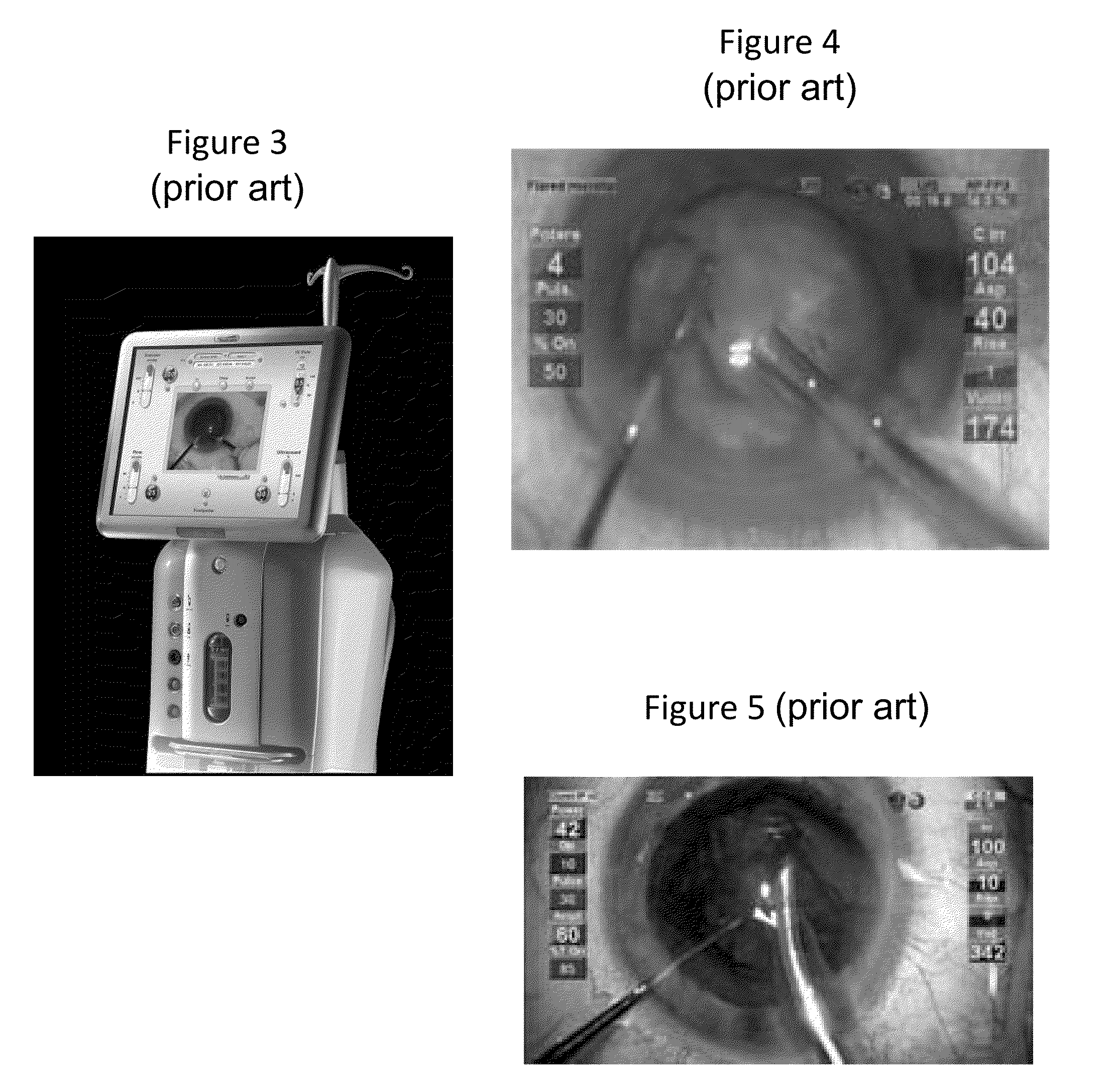
Systems and methods for combined femto-phaco cataract surgery
Devices to perform femtolaser ablation and phacoemulsification are physically and / or operationally combined. In some embodiments the femtolaser ablation and phacoemulsification are housed together, and in other embodiments they are housed separately, but operated through a common display screen. At least some software can be shared by the femtolaser ablation and phacoemulsification functionalities. A non-transitory computer-readable memory can provide data that can be used to operate each of at least one femtolaser ablation functionality and at least one phacoemulsification functionality.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com