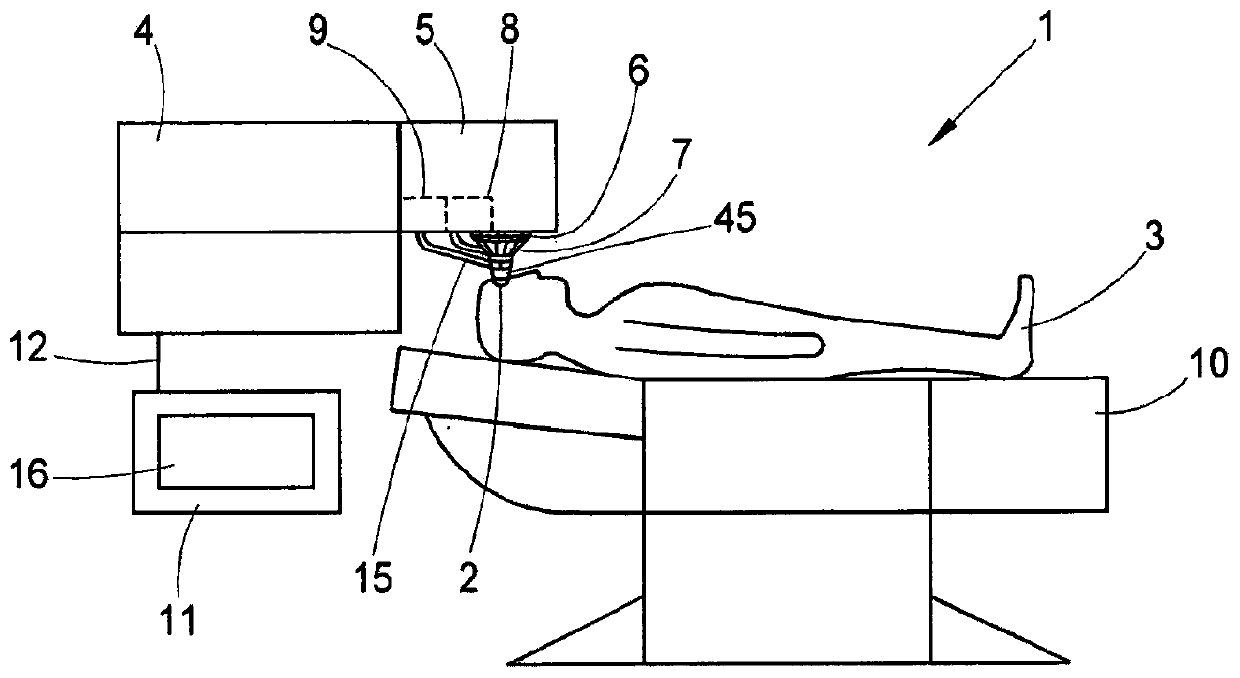
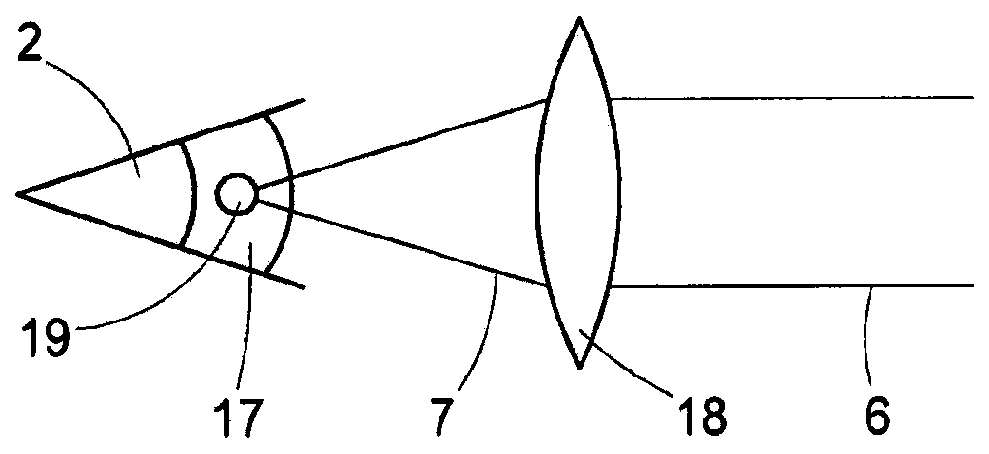
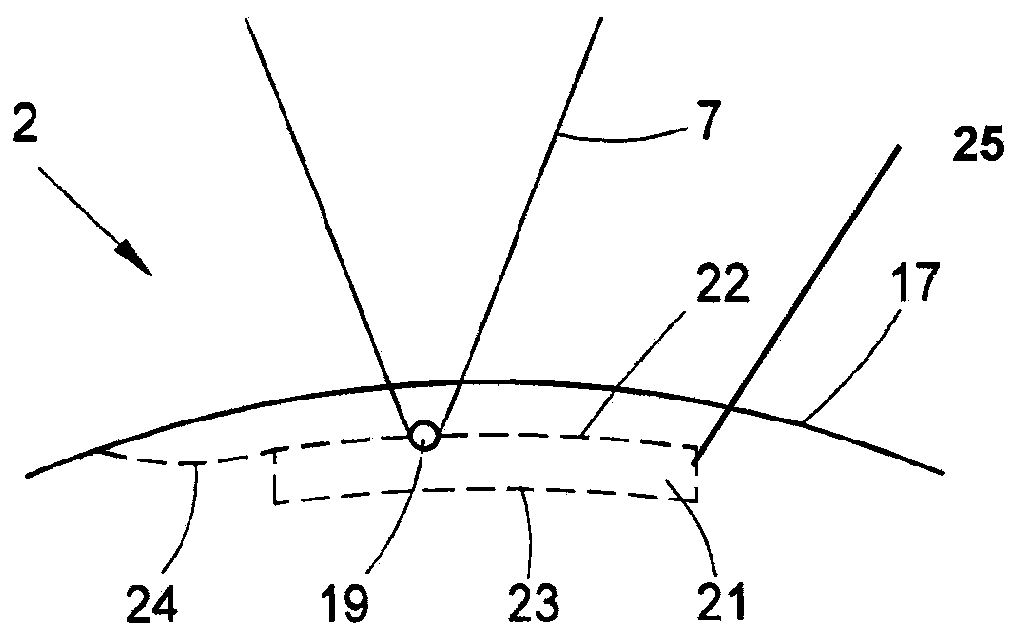
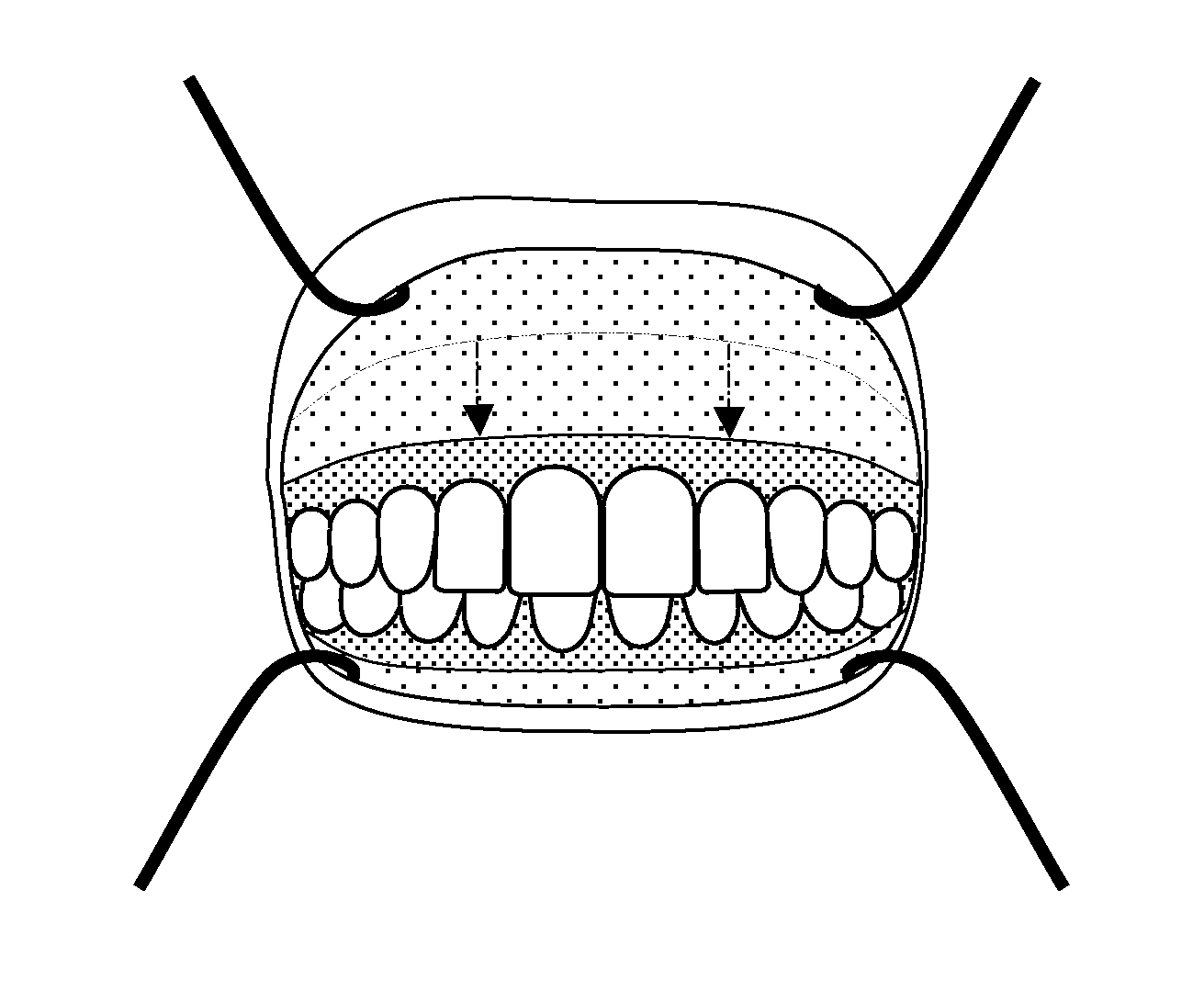
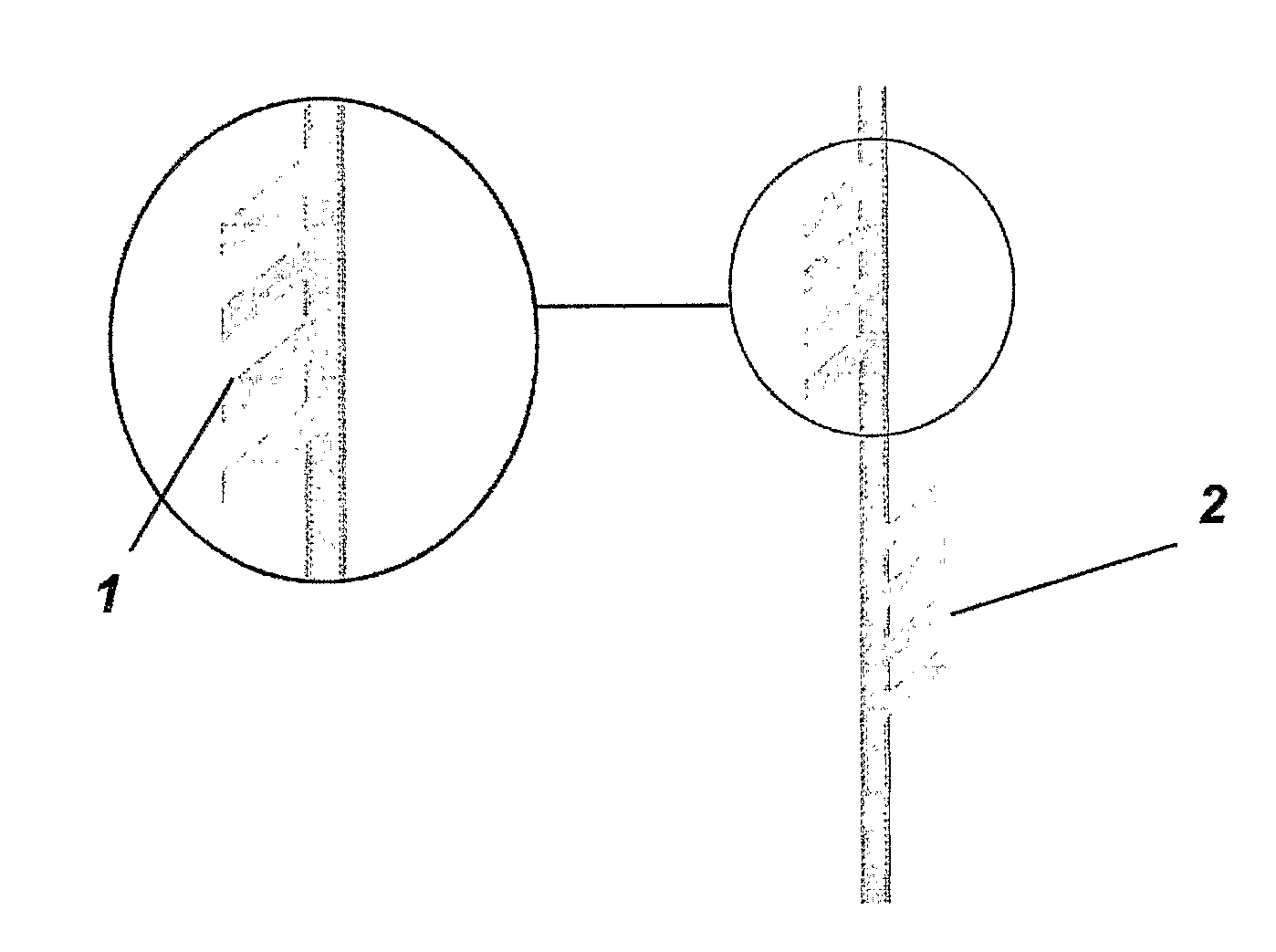Patents
Literature
39 results about "Corrective surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
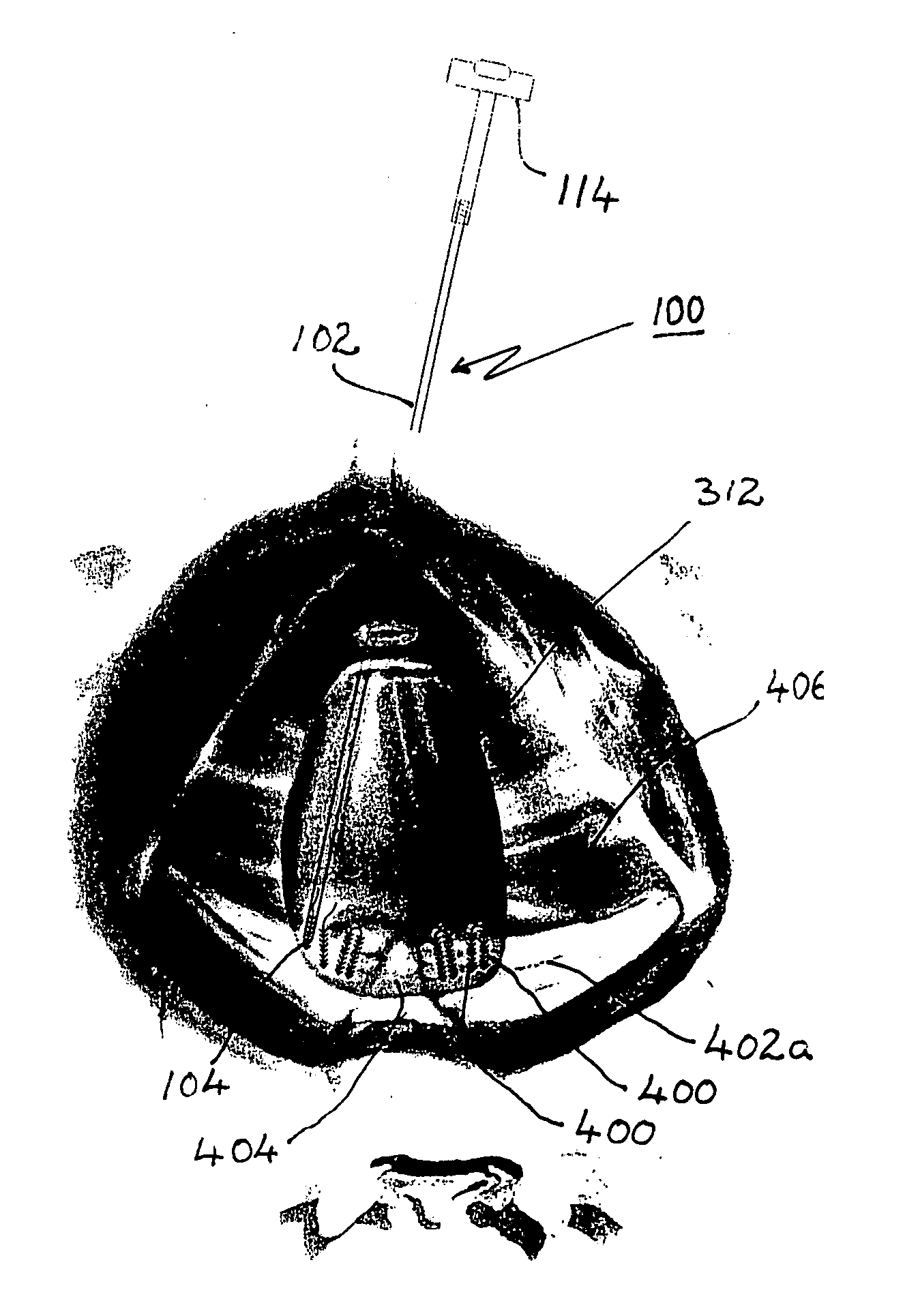
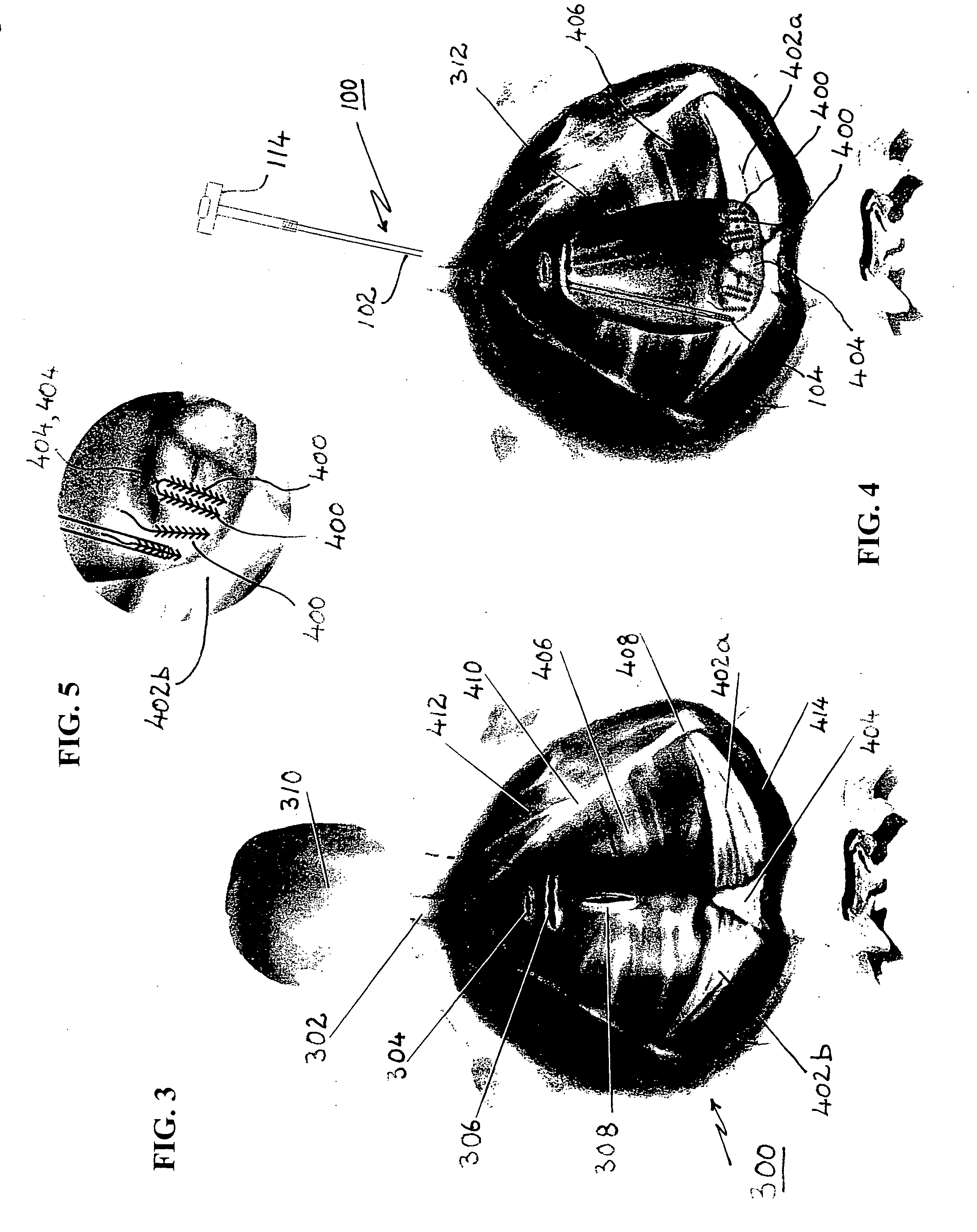
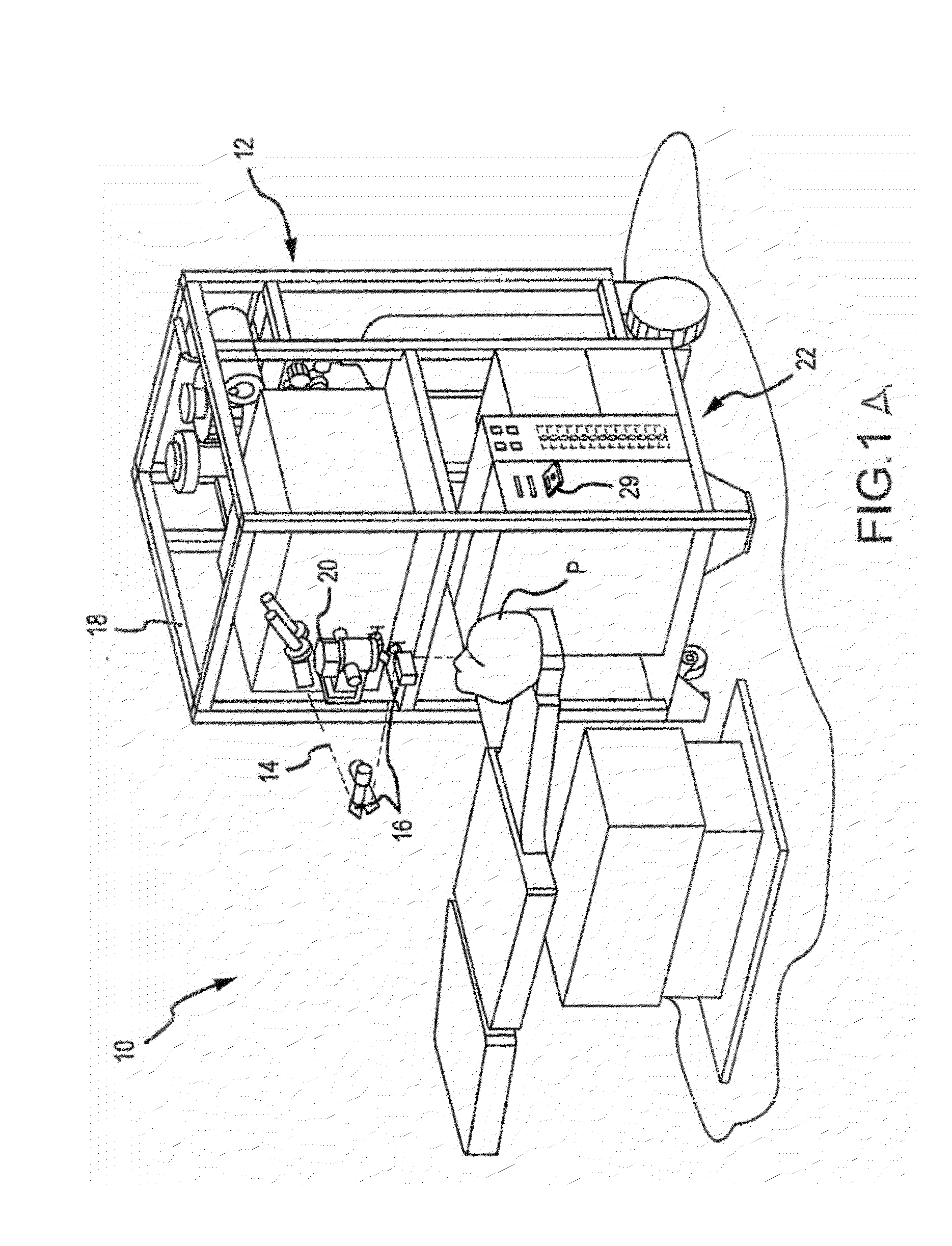
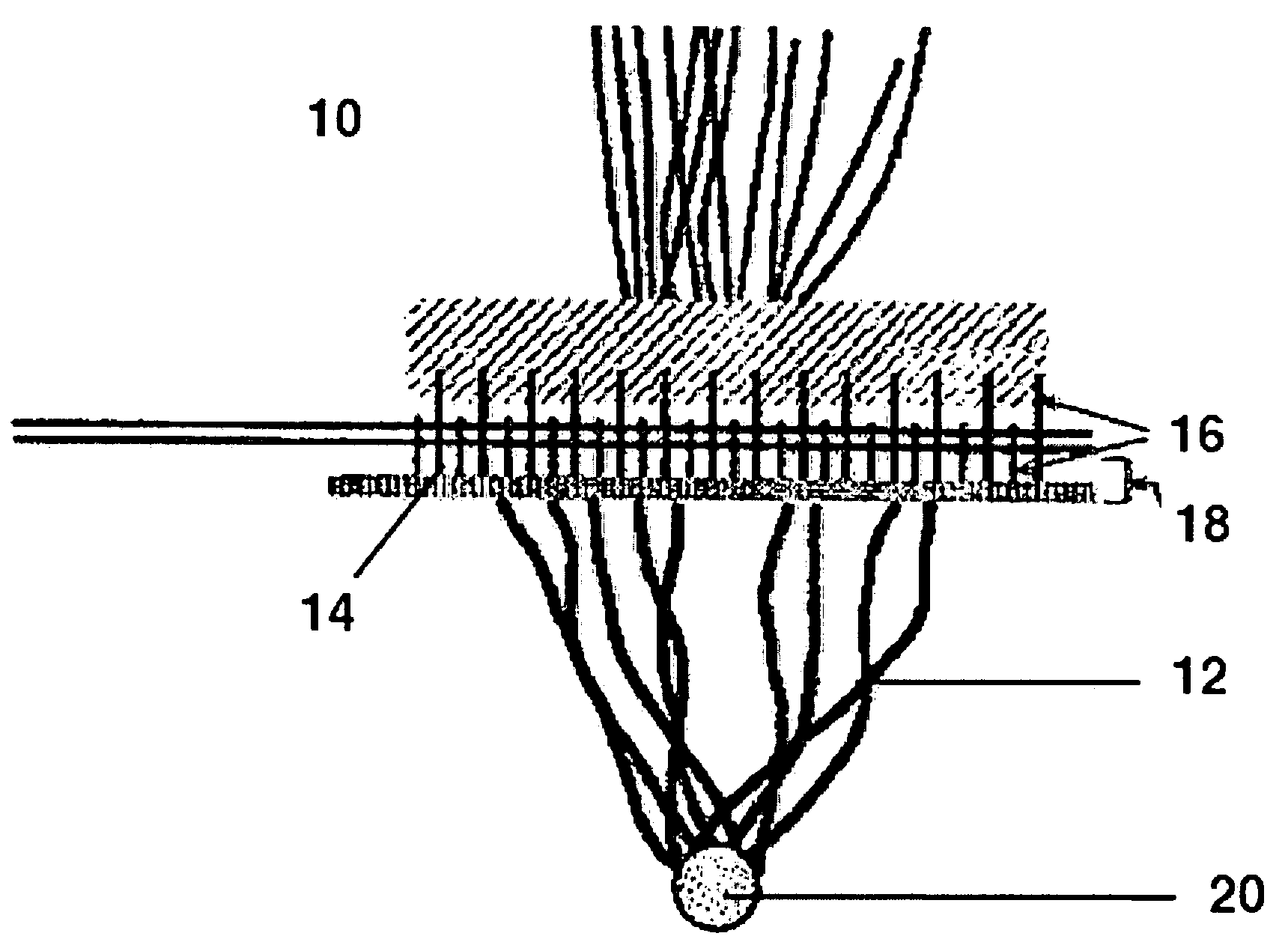
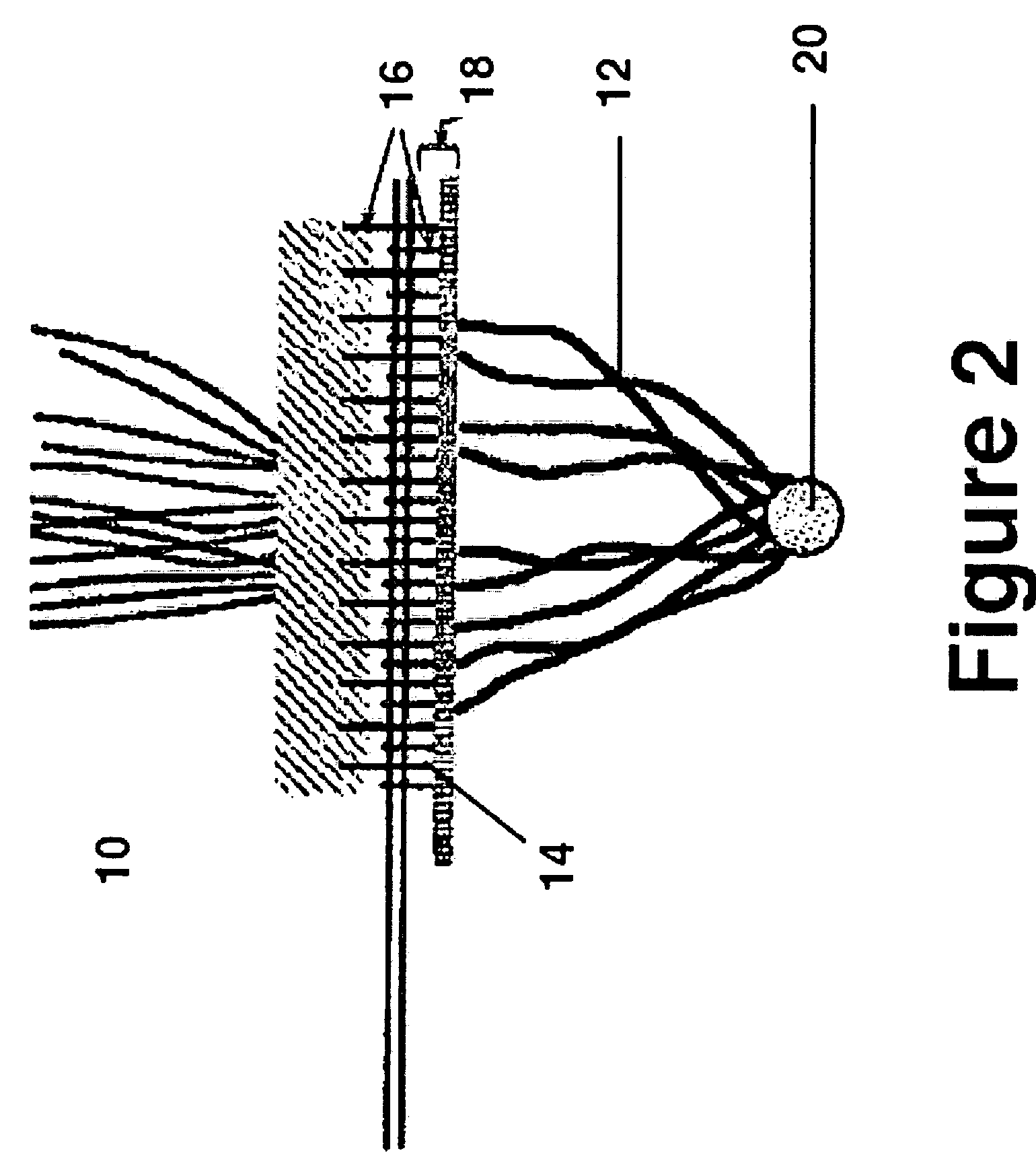
Apparatus and method for incision-free vaginal prolapse repair
InactiveUS20050199249A1Simple, minimally invasive and inexpensiveQuick fixSuture equipmentsBed wetting preventionVaginal ProlapsesDistressing
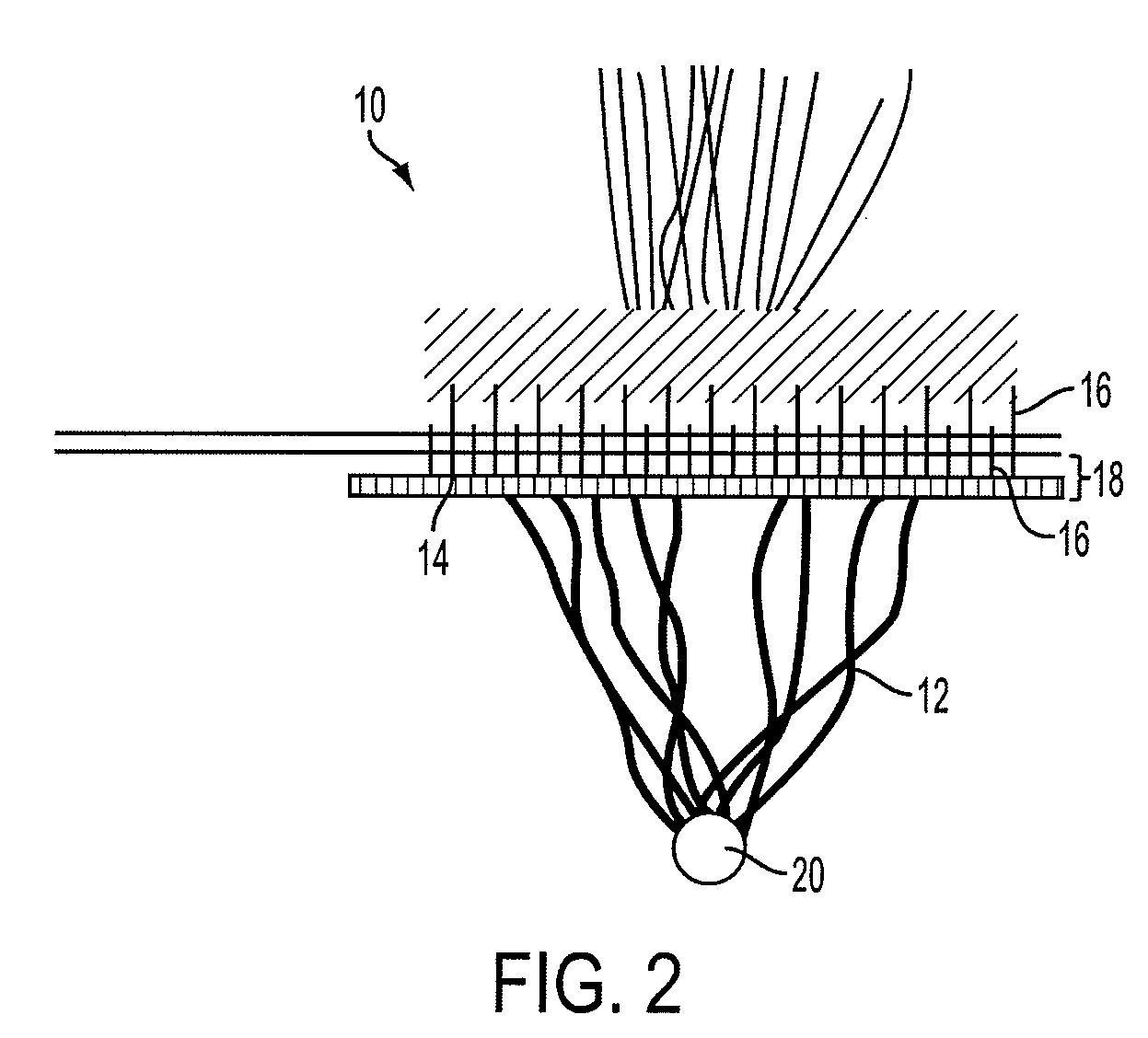
In a preferred application, e.g., the repair of vaginal prolapse after relocation of the vagina and any organs displaced by the prolapse, corrective surgery is initiated by applying a hollow tubular element, formed to forcibly insert a barbed anchor attached to a distal end of a first length of suture, without any incision, from the inside of the vagina through the vaginal wall (the supported tissue) into selected support tissue within a patient's pelvis. This involves puncturing and thus locally severe physical distressing of both the supported tissue and the support tissue. The barbed anchor is left in the support tissue as the tubular element is then withdrawn from the support tissue and out of the vagina, leaving the proximate end portion of the suture extending through the vaginal wall into the vagina. A second such anchor, with a second length of suture attached thereto, is similarly inserted adjacent to the first anchor. The proximate end portions of the sutures are tied to each other inside the vagina, to thereby secure the vaginal wall to the support tissue with corresponding punctures formed in each by the insertions of the two anchors being thereby held in respective, precisely aligned, intimate contact during healing. This results in a pair of fused scars that cooperate to permanently bond the vaginal wall locally to the support tissue. If the sutures and / or the anchors are made of absorbable material they will all eventually disappear and the fused scars will provide the permanent bonding. If the anchors are made of non-absorbable material they may remain where located. A plurality of such paired fused-scar bonds may be generated, at the surgeon's discretion, to ensure adequate support for the repaired vagina. The apparatus and method can be readily adapted to similarly effect deliberate, local, beneficial bonding between other adjacent living tissues in a patient.
Owner:KARRAM MICKEY M
Bone fixation device and method
In a method and system for corrective surgery of a bone, a bone is cut into a first bone segment and a second bone segment. A plate is positioned over the first bone segment and the second bone segment such that at least one member of the plate is positioned to engage the second bone segment. The at least one member of the plate is inserted into the second bone segment. At least one bone screw is screwed into the first bone segment through at least one compression slot of the plate causing an application of compressive force to secure the first bone segment and the second bone segment to form a corrective construct. The at least one member is positioned at an angle or an offset from the second plate segment
Owner:ZIMMER INC
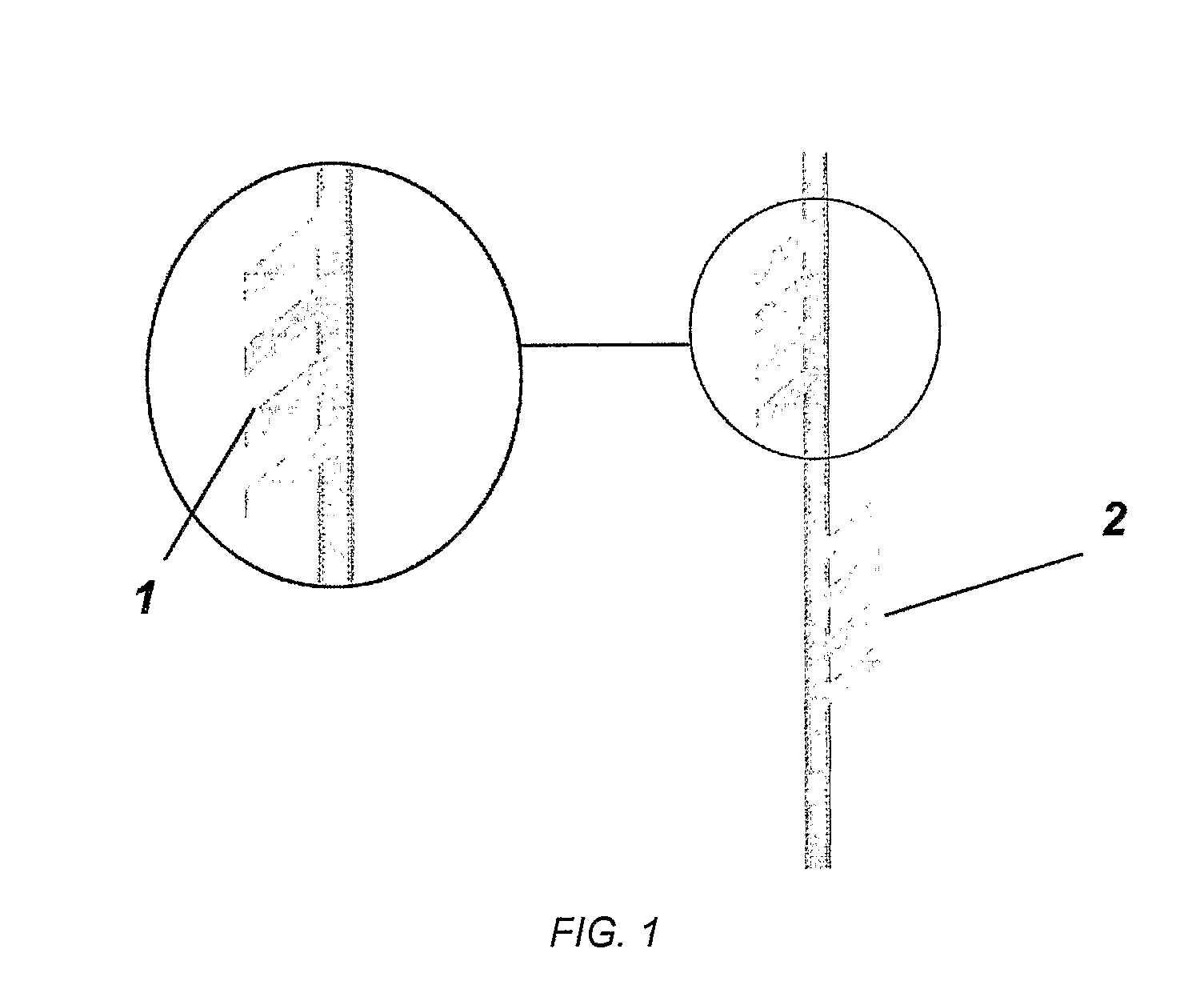
Surgery thread
The present invention refers to surgery threads which are flexible, made of resistant inert plastic material and being employed in aesthetic surgeries in the cases of skin ageing prevention and / or correction surgeries for motion injury signals, wherein the threads comprise a previous defined sequence of a tissue support arrangement having a number of fixing claws placed alongside of the thread surface and wherein an arrangement of an upstream claw (1) set and a downstream claw (2) set is provided.
Owner:BERAMENDI JOSE ANTONIO ENCINAS
Bone fixation device and method
In a method and system for corrective surgery of a bone, a bone is cut into a first bone segment and a second bone segment. A plate is positioned over the first bone segment and the second bone segment such that at least one member of the plate is positioned to engage the second bone segment. The at least one member of the plate is inserted into the second bone segment. At least one bone screw is screwed into the first bone segment through at least one compression slot of the plate causing an application of compressive force to secure the first bone segment and the second bone segment to form a corrective construct. The at least one member is positioned at an angle or an offset from the second plate segment.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Apparatus and method for performing presbyopia corrective surgery
InactiveUS6843787B2Prevent edemaAccurate contourLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorrective surgeryNose
A process and system for addressing presbyopia of an eye is disclosed and features the resecting of an eye to expose a corneal stroma and system and method for determining an eye sculpturing center point found in a nasal-superior region of the eye. Sculpturing through use of an ablation laser is then carried out relative to the determined eye sculpturing centerpoint which sculpturing includes leaving a central optic zone unable relative to the presbyopic corrective process. Following sculpturing the resected portion of the eye is returned to cover over the sculptured region. The sculpturing profile is also formed with ablation control to define an advantageous (e.g., aspherical) ablation profile in the stroma.
Owner:RUIZ LUIS ANTONIO
Augmentation and repair of vocal cord tissue defects
InactiveUS7412978B1Reduce the possibilityLower potentialBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCorrective surgeryTissue defect
A method for corrective surgery in a human subject of a vocal cord defect amenable to rectification by the augmentation of tissue subadjacent to the vocal cord defect, the method comprising: placing an effective amount of autologous in vitro cultured cells into a vocal cord tissue of the subject in a position subadjacent to the vocal cord defect, wherein the vocal cord tissue is selected from the group consisting of a scar, Reinke's space, a muscle of the vocal cord, and the lamina propria, wherein the in vitro cultured cells are obtained by culturing a plurality of viable cells retrieved from the subject, and wherein the cultured cells are suspended in a collagen or modified collagen solution prior to injection of the cultured cells. The in vitro cultured cells can be fibroblasts, e.g., fibroblasts derived from dermis, fascia, connective tissue, or lamina propria.
Owner:CASTLE CREEK BIOSCIENCES LLC
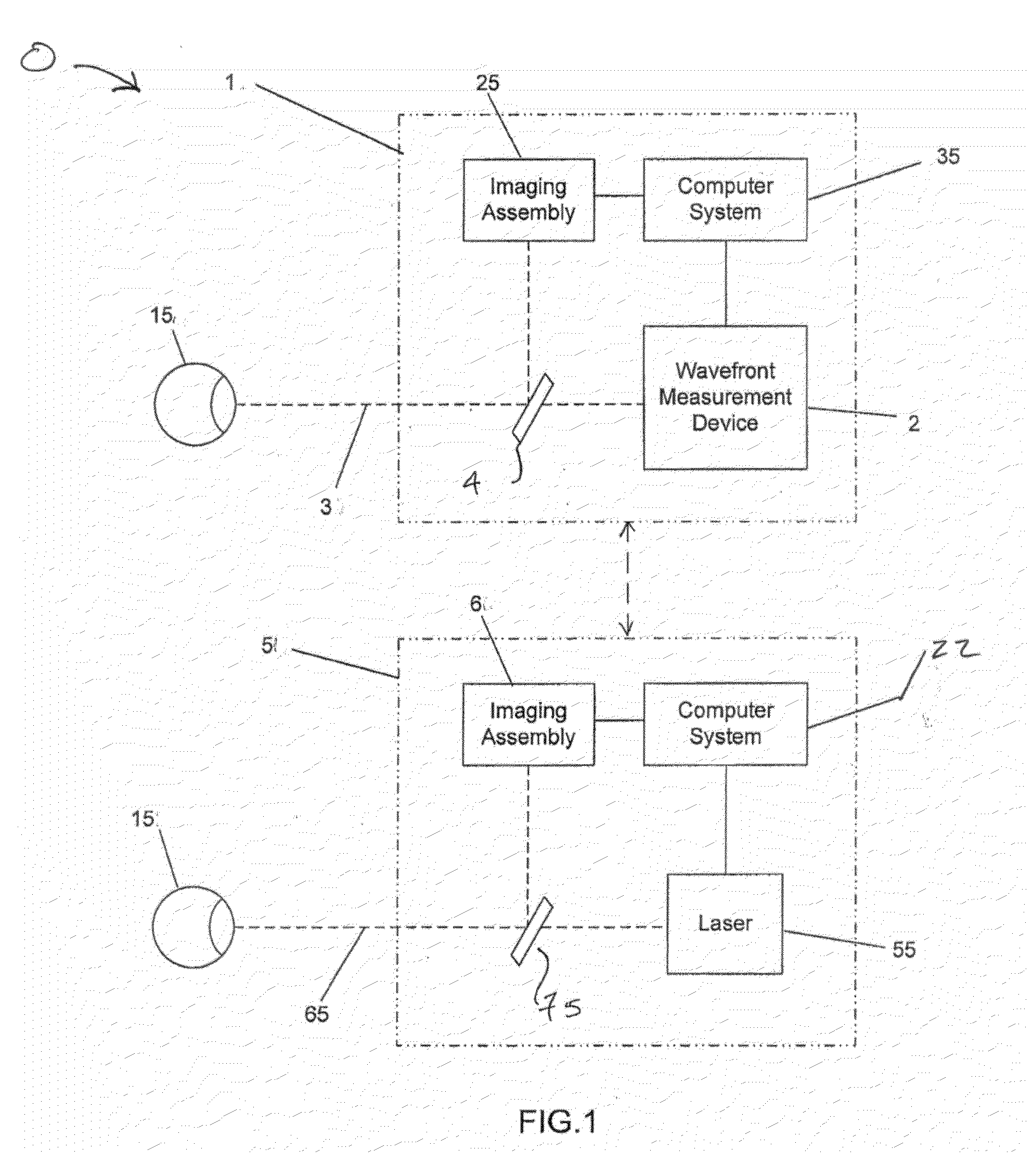
Method and system for eye measurements and cataract surgery planning using vector function derived from prior surgeries
ActiveUS20160150952A1Good curative effectImproved refractive correctionsLaser surgeryComputer-aided planning/modellingCorrective surgeryIntraocular lens
Improved devices, systems, and methods for planning cataract surgery on an eye of a patient incorporate results of prior corrective surgeries into a planned cataract surgery of a particular patient by driving an effective surgery vector function based on data from the prior corrective surgeries. The exemplary effective surgery vector employs an influence matrix which may allow improved refractive corrections to be generated so as to increase the overall efficacy of a cataract surgery by specifying one or more parameters of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted during the cataract surgery.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
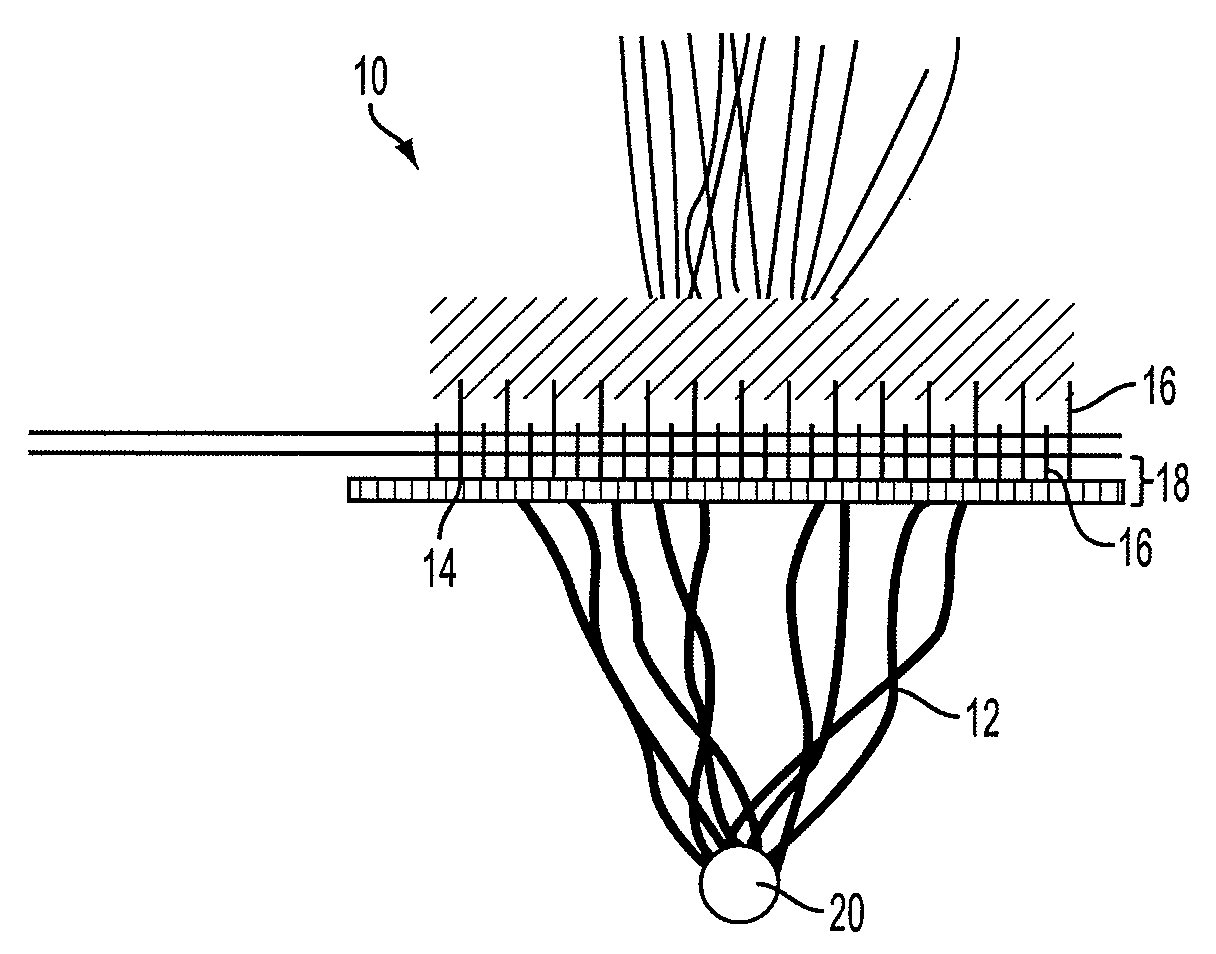
Apparatus and method for incision-free vaginal prolapse repair
InactiveUS20090023982A1Simple, minimally invasive and inexpensiveQuick fixSuture equipmentsTubular organ implantsVaginal ProlapsesDistressing
In a preferred application, e.g., the repair of vaginal prolapse after relocation of the vagina and any organs displaced by the prolapse, corrective surgery is initiated by applying a hollow tubular element, formed to forcibly insert a barbed anchor attached to a distal end of a first length of suture, without any incision, from the inside of the vagina through the vaginal wall (the supported tissue) into selected support tissue within a patient's pelvis. This involves puncturing and thus locally severe physical distressing of both the supported tissue and the support tissue. The barbed anchor is left in the support tissue as the tubular element is then withdrawn from the support tissue and out of the vagina, leaving the proximate end portion of the suture extending through the vaginal wall into the vagina. A second such anchor, with a second length of suture attached thereto, is similarly inserted adjacent to the first anchor. The proximate end portions of the sutures are tied to each other inside the vagina, to thereby secure the vaginal wall to the support tissue with corresponding punctures formed in each by the insertions of the two anchors being thereby held in respective, precisely aligned, intimate contact during healing. This results in a pair of fused scars that cooperate to permanently bond the vaginal wall locally to the support tissue. If the sutures and / or the anchors are made of absorbable material they will all eventually disappear and the fused scars will provide the permanent bonding. If the anchors are made of non-absorbable material they may remain where located. A plurality of such paired fused-scar bonds may be generated, at the surgeon's discretion, to ensure adequate support for the repaired vagina. The apparatusand method can be readily adapted to similarly effect deliberate, local, beneficial bonding between other adjacent living tissues in a patient.
Owner:KARRAM MICKEY M
System and Method for Refractive Surgery with Augmentation by Intrastromal Corrective Procedures
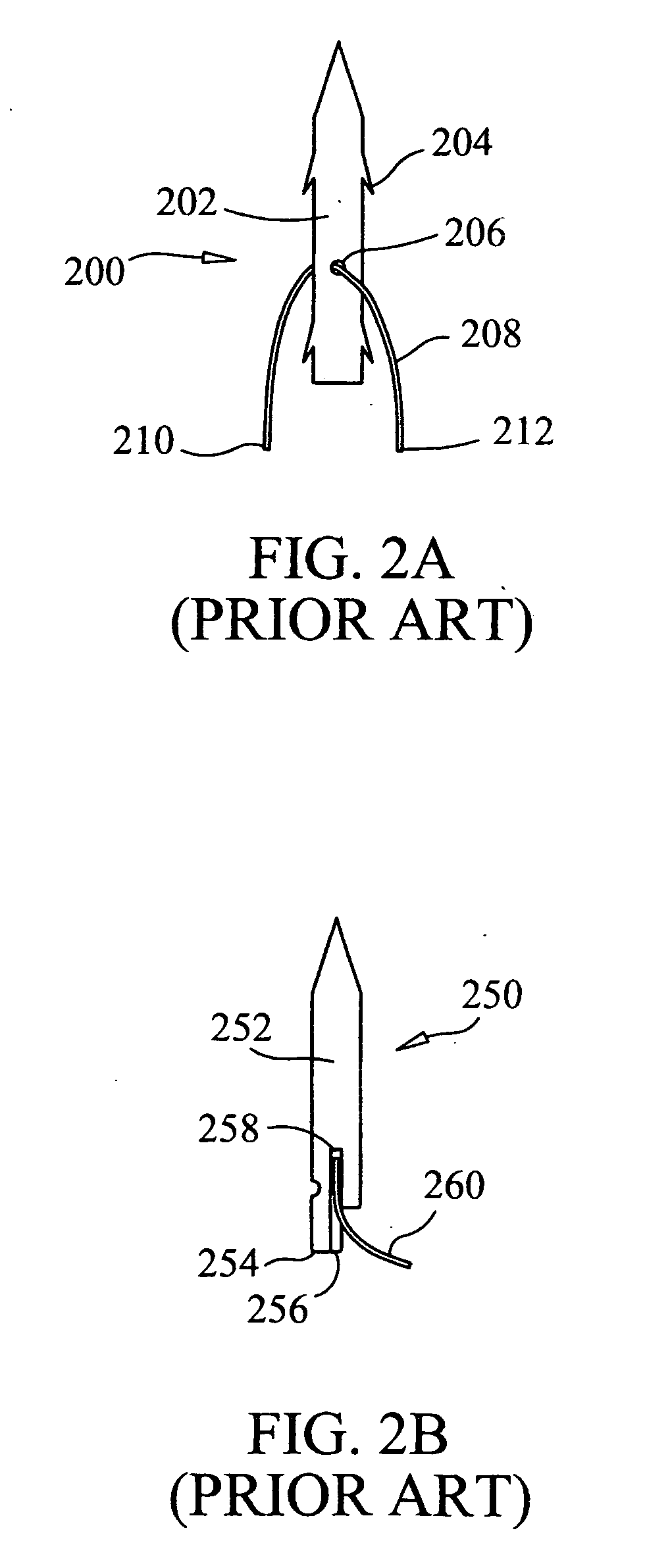
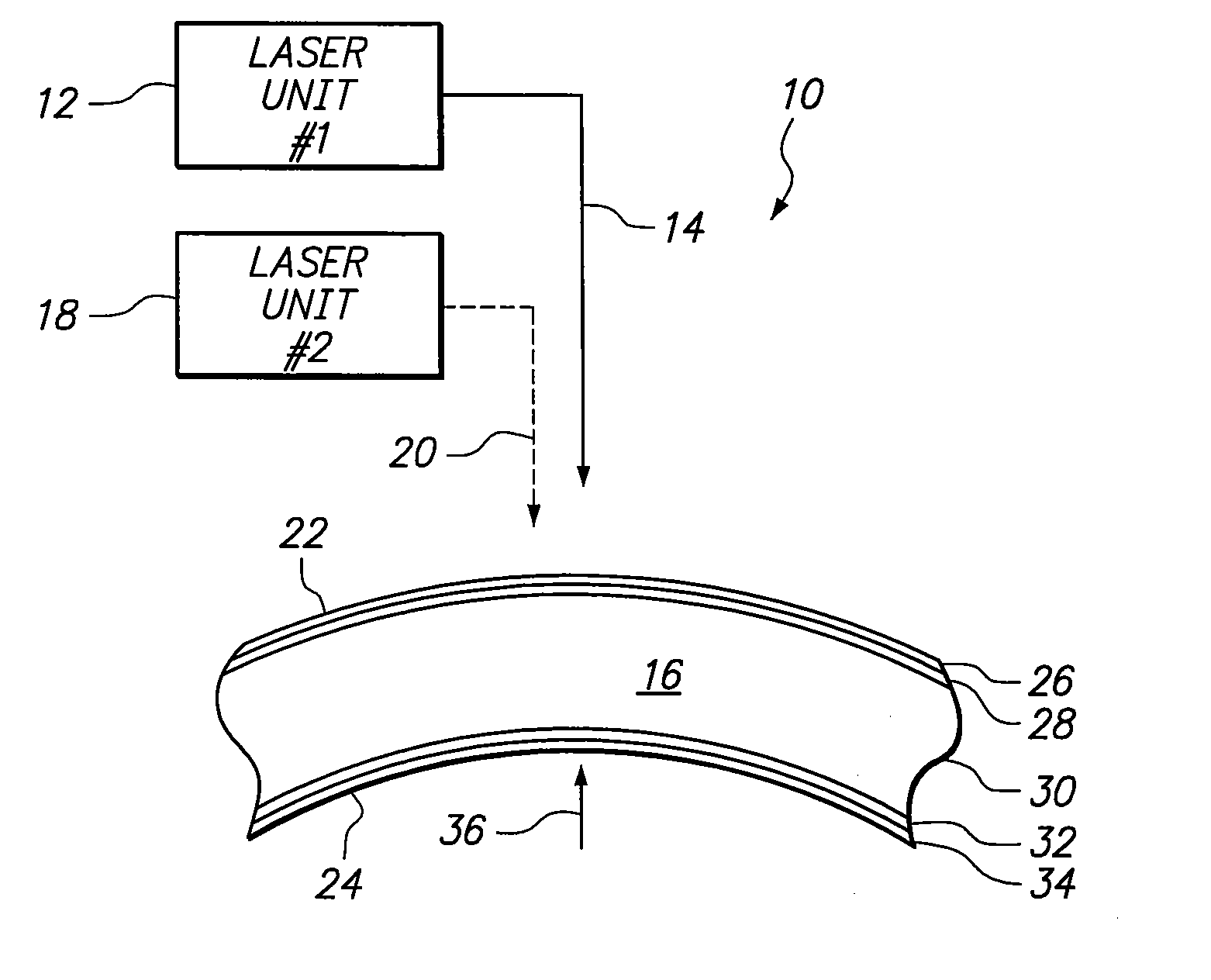
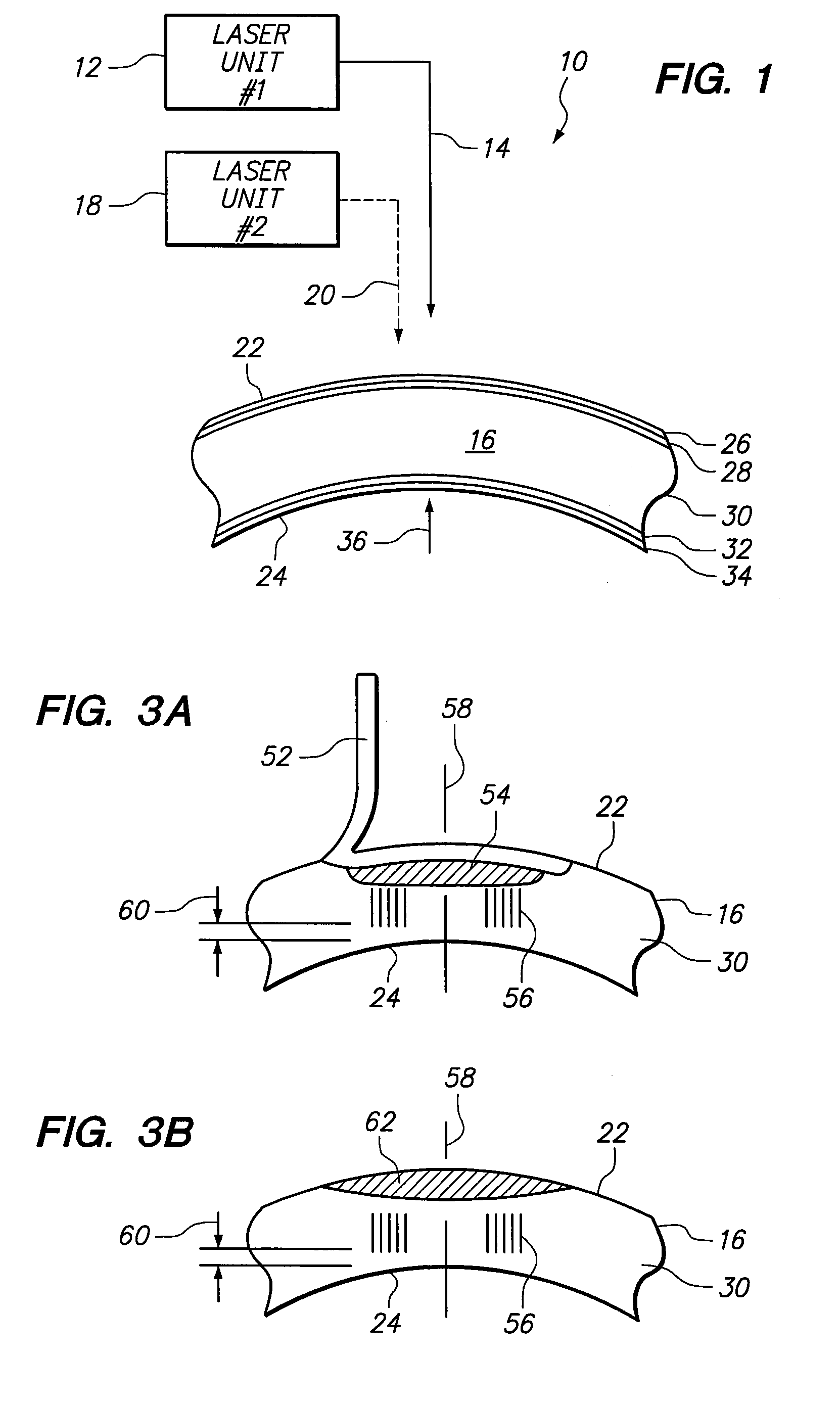
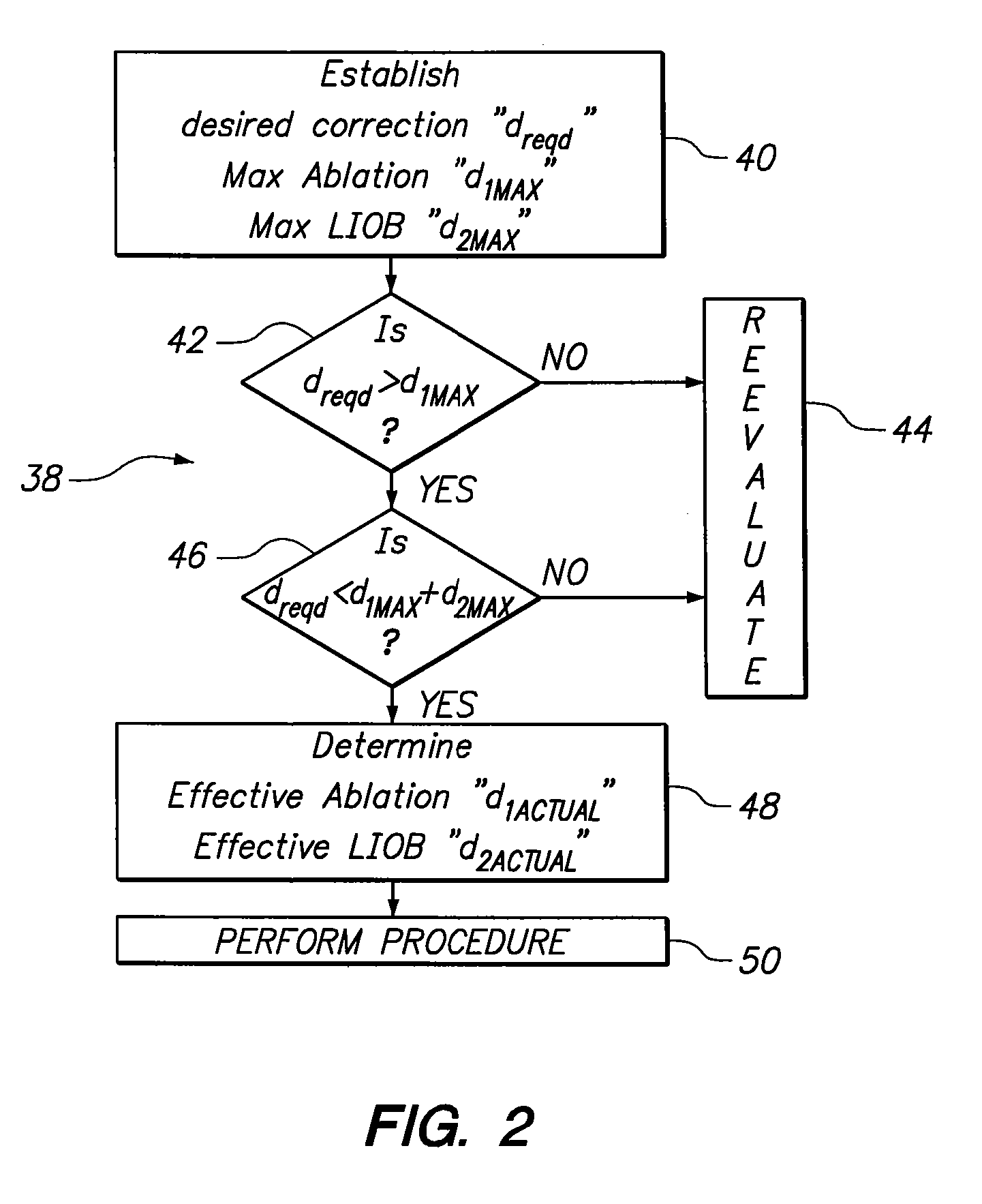
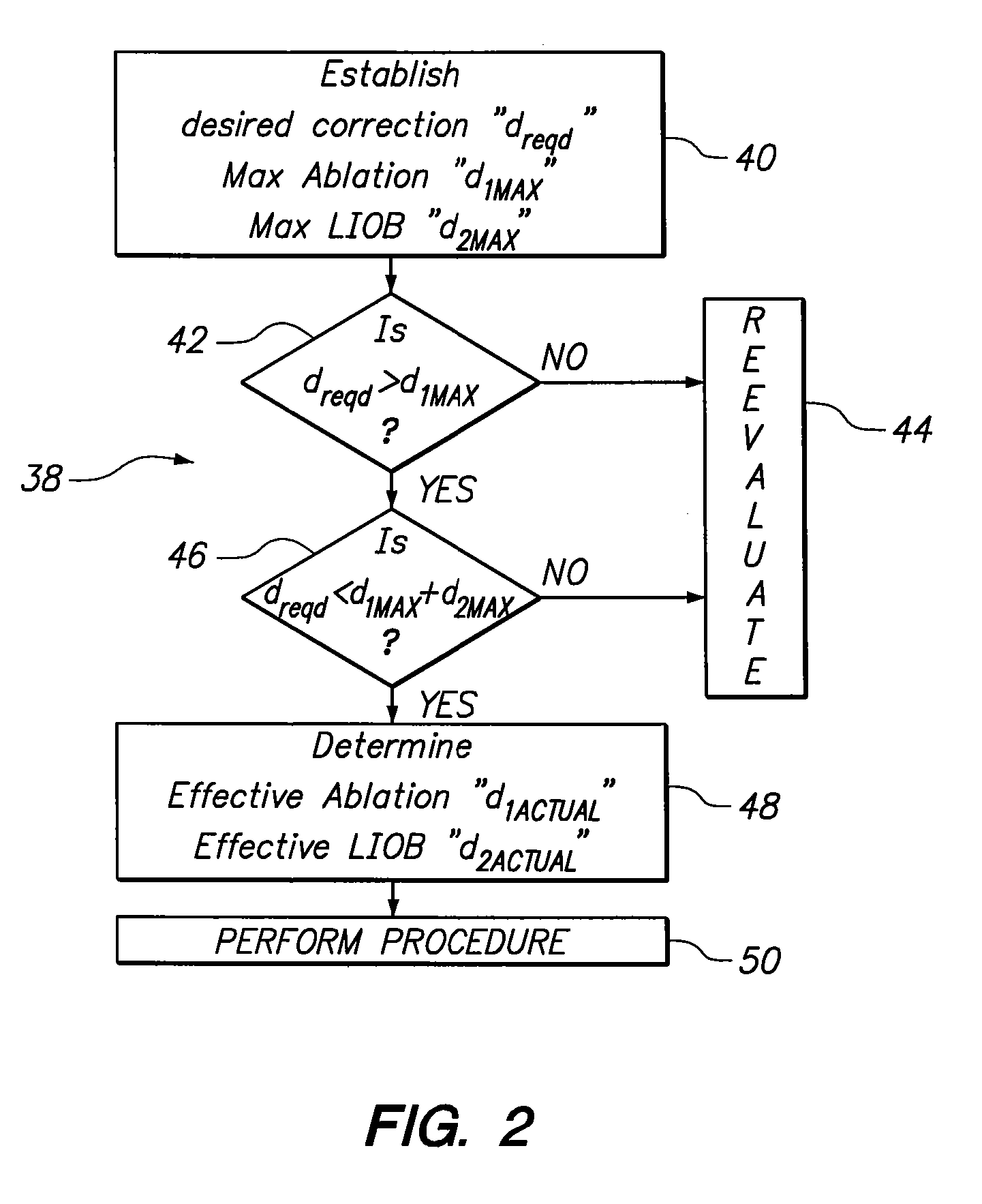
A system and method are provided for an ophthalmic surgical procedure to provide a refractive correction for an eye. Specifically, the procedure is indicated when the desired refractive correction “dreqd” exceeds the capability of a correction achievable when corneal tissue is only ablated. In accordance with the present invention, an optimized refractive correction “d1” is accomplished by the ablation of corneal tissue (e.g. by a PRK or LASIK procedure). The optimized correction is then followed by a complementary refractive correction “d2” wherein stromal tissue is weakened with Laser Induced Optical Breakdown (LIOB). Together, the optimized refractive correction (ablation) and the complementary refractive correction (LIOB) equal the desire refractive correction (dreqd=d1+d2).
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
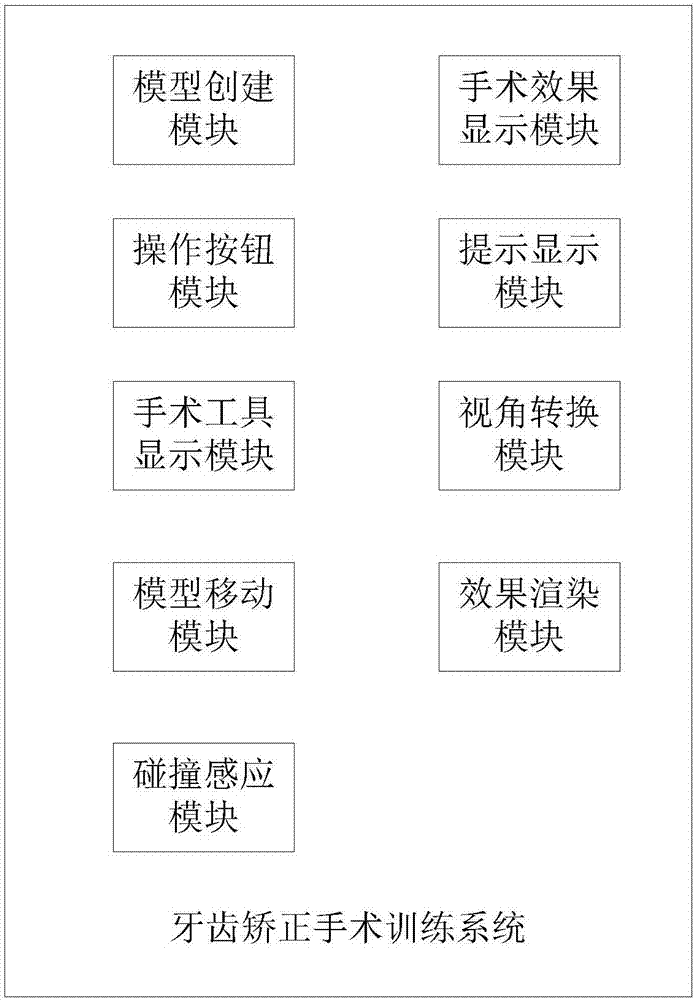
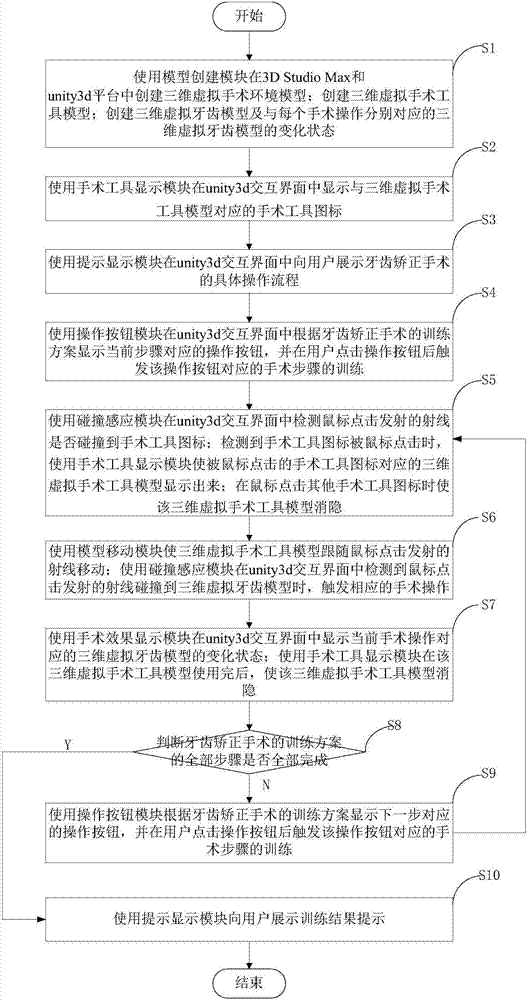
Orthodontic surgery training system and training method
ActiveCN107240343ASave teaching resourcesImprove learning efficiencyEducational modelsVirtual realityTraining methods
The present invention discloses an orthodontic surgery training system, which relates to the field of virtual reality technology and comprises a model creating module, an operation button module, a surgical tool display module, a model moving module, a collision sensing module, a surgical effect display module and a prompt display module, Inventing 3D Virtual Operating Room and Patient Models, 3D Virtual Surgical Tool Models, and 3D Virtual Dental Models Using the Model Creation Module in 3D Studio Max and Unity3d Platforms Using the Action Button Module, Surgical Tool Display Module, Model Mobility Module, Collision Sensing Module , The operation effect display module and the prompt display module realize the virtual surgery training according to the orthodontic training program. With each operation of the user, the three-dimensional virtual surgical tool model and the three-dimensional virtual dental model may move or change correspondingly. The invention also discloses a dental orthodontic training method.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Method and system for eye measurements and cataract surgery planning using vector function derived from prior surgeries
ActiveUS20160074125A1Good curative effectImproved refractive correctionsLaser surgeryDiagnosticsCorrective surgeryIntraocular lens
Improved devices, systems, and methods for planning cataract surgery on an eye of a patient incorporate results of prior corrective surgeries into a planned cataract surgery of a particular patient by driving an effective surgery vector function based on data from the prior corrective surgeries. The exemplary effective surgery vector employs an influence matrix which may allow improved refractive corrections to be generated so as to increase the overall efficacy of a cataract surgery by specifying one or more parameters of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted during the cataract surgery.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Methods and compositions for optimizing the outcomes of refractive laser surgery of the cornea
InactiveUS20090099557A1Laser surgeryHydroxy compound active ingredientsSide effectCorrective surgery
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for use in surgical procedures for refractive ablation of the cornea to achieve vision correction with a minimum of undesirable side effects and for a broad range of optical conditions such myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatism. Specifically disclosed are compositions, and methods involving their use, wherein the compositions act as agents for the reversible removal of corneal epithelial layers to provide access for UV radiation in manipulation of the refractive properties of the cornea. The methods and compositions of the present invention are capable of achieving desirable results in corrective surgery not possible with current methods for exposing the corneal stroma to far-UV laser radiation.
Owner:SEDAREVIC OLIVIA N
Methods and Compositions for Optimizing the Outcomes of Refractive Laser Surgery of the Cornea
InactiveUS20080161780A1Laser surgeryHydroxy compound active ingredientsCorrective surgerySide effect
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for use in surgical procedures for refractive ablation of the cornea to achieve vision correction with a minimum of undesirable side effects and for a broad range of optical conditions such myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatism. Specifically disclosed are compositions, and methods involving their use, wherein the compositions act as agents for the reversible removal of corneal epithelial layers to provide access for UV radiation in manipulation of the refractive properties of the cornea. The methods and compositions of the present invention are capable of achieving desirable results in corrective surgery not possible with current methods for exposing the corneal stroma to far-UV laser radiation.
Owner:SERDAREVIC OLIVIA N
Non-blending spinal side bending corrector
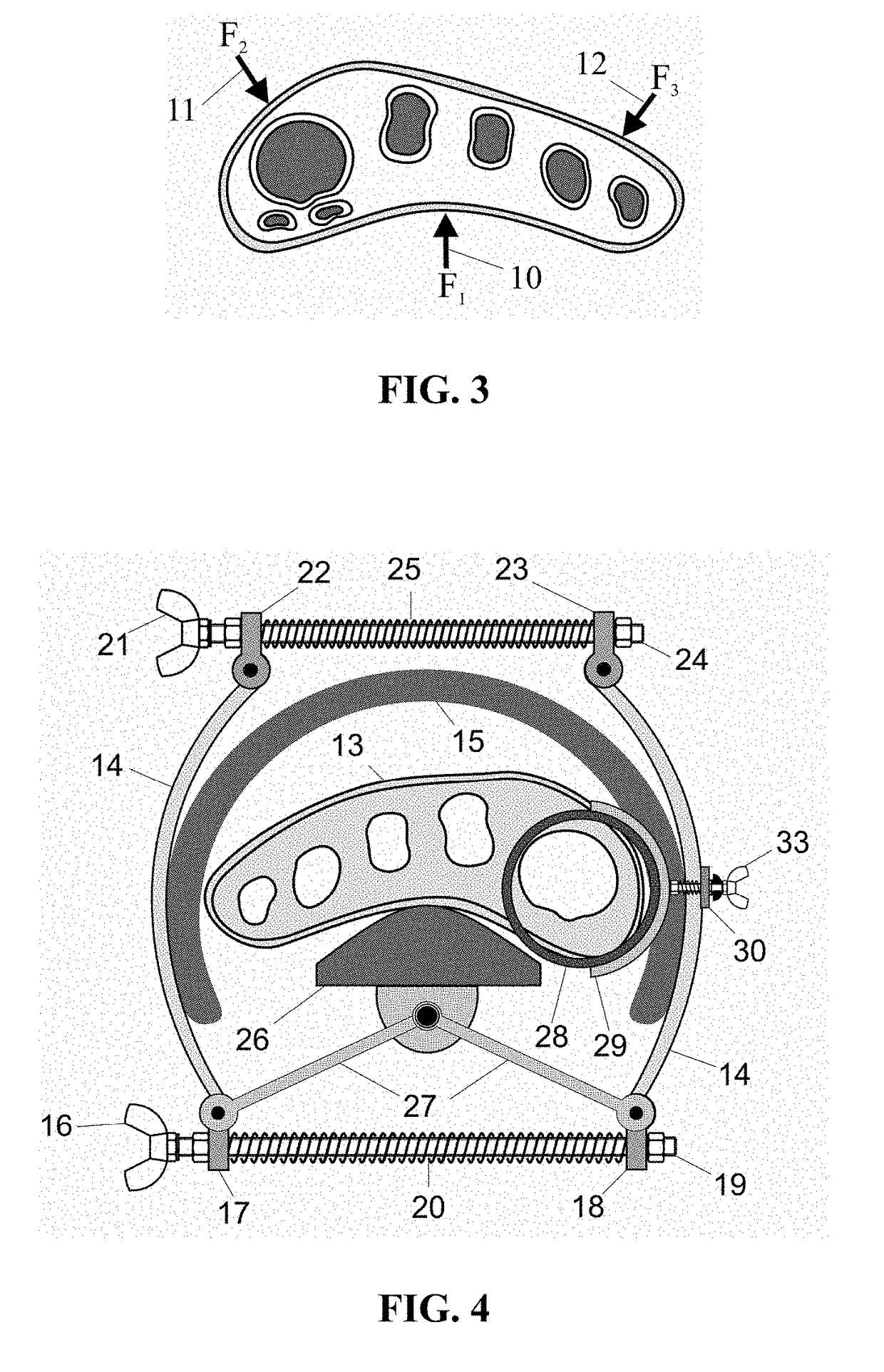
InactiveCN1745723AAvoid damageGuaranteed translation correction forceInternal osteosythesisCorrective surgeryScoliosis
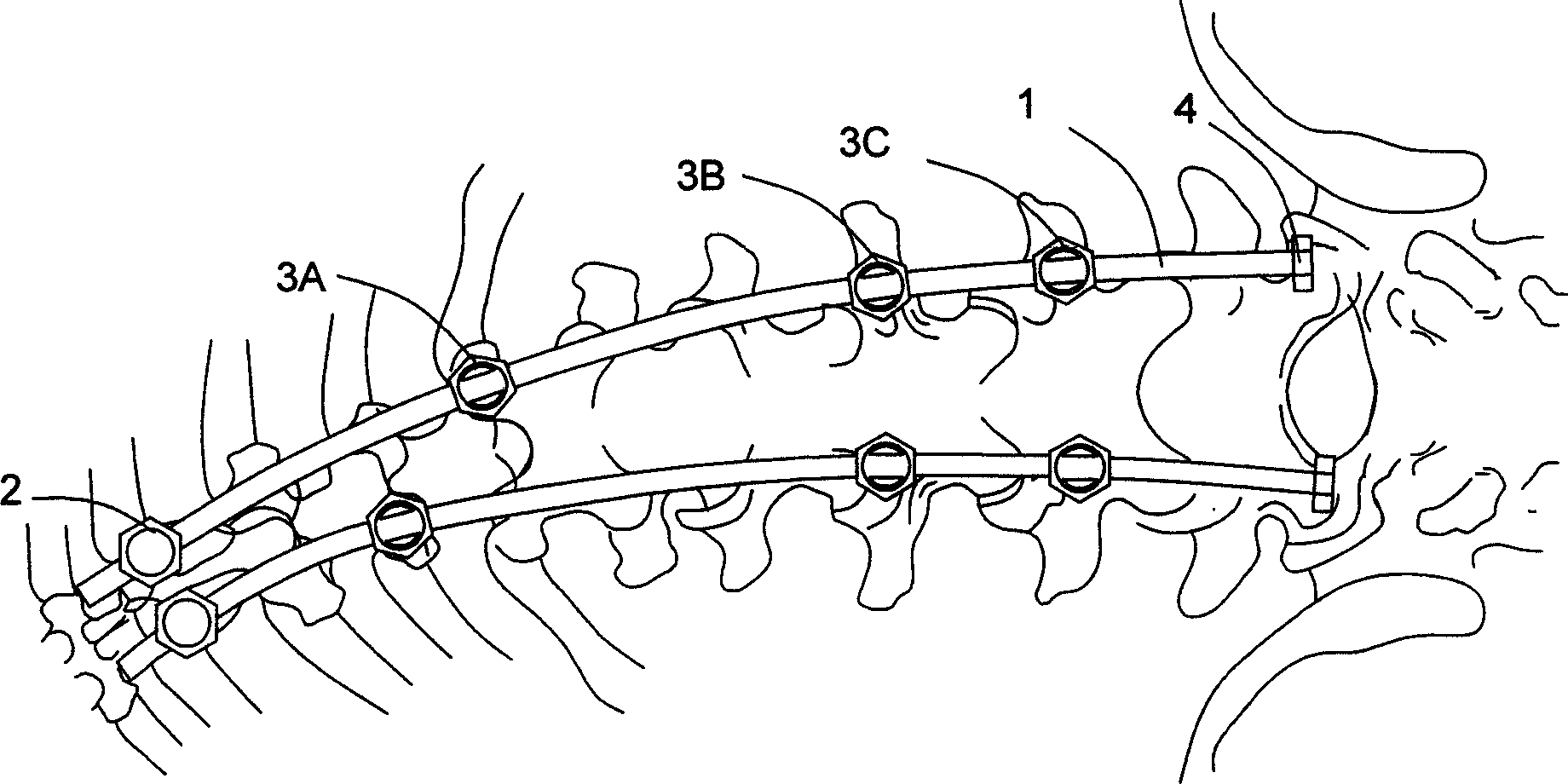
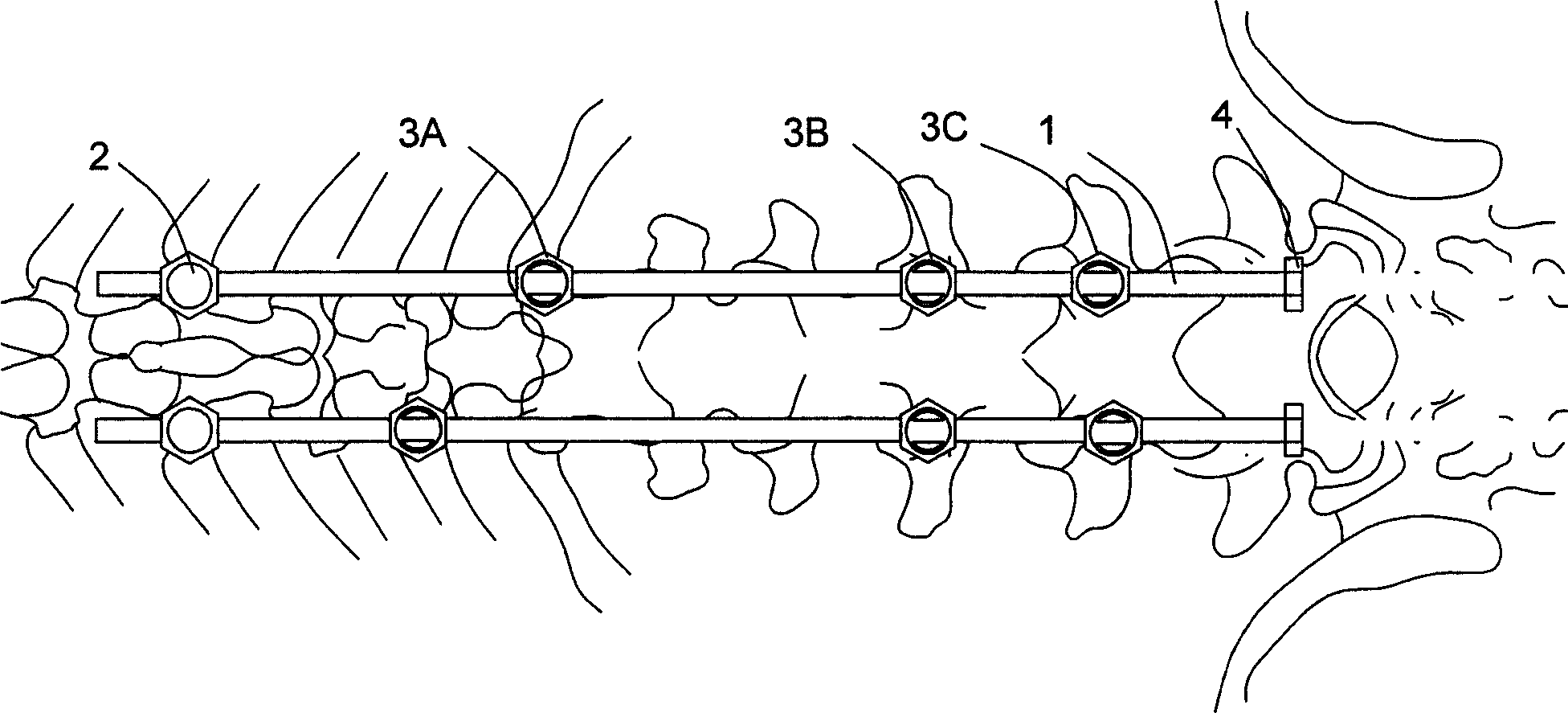
A device for correcting the non-fusion scoliosis is composed of a correcting rod, the fixing nail fixed to the curved spine and locked to the said correcting rod, and multiple nails for pediculus arcus vertebrae, which are linked with said correcting rod in slide mode. Its advantage is 3D correcting effect.
Owner:王岩 +2
Method and system for eye measurements and cataract surgery planning using vector function derived from prior surgeries
ActiveUS20160073868A1Good curative effectImproved refractive correctionsLaser surgeryRefractometersIntraocular lensCorrective surgery
Improved devices, systems, and methods for planning cataract surgery on an eye of a patient incorporate results of prior corrective surgeries into a planned cataract surgery of a particular patient by driving an effective surgery vector function based on data from the prior corrective surgeries. The exemplary effective surgery vector employs an influence matrix which may allow improved refractive corrections to be generated so as to increase the overall efficacy of a cataract surgery by specifying one or more parameters of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted during the cataract surgery.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Method of maintaining the structure of an opening in the anterior or posterior capsule
ActiveUS20130013061A1Rigid enoughReduces and minimizes glareIntraocular lensCorrective surgeryIntraocular lens insertion
A method of maintaining the structure of an opening in the anterior or posterior capsule formed by a capsulorhexis whereby a device is inserted into opening in the anterior or posterior capsule, the device having a main body including a peripheral portion and an opening therethrough, wherein the peripheral portion engages with the inside peripheral edge of the opening in the anterior or posterior capsule, wherein the device is inserted into the opening in the anterior or posterior capsule after an intraocular lens has been inserted into the capsular bag of an eye during cataract corrective surgery.
Owner:CORONEO MINAS THEODORE
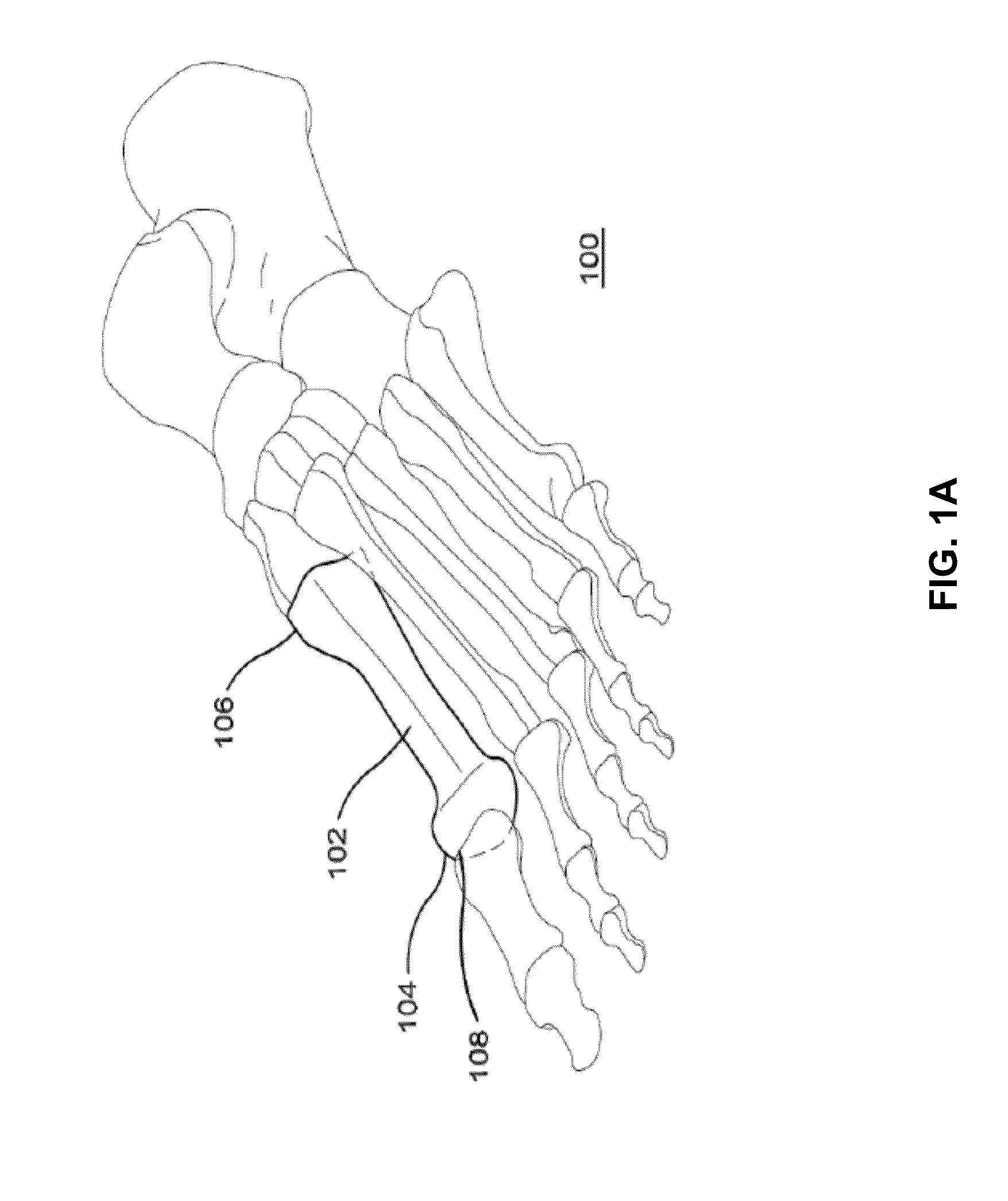
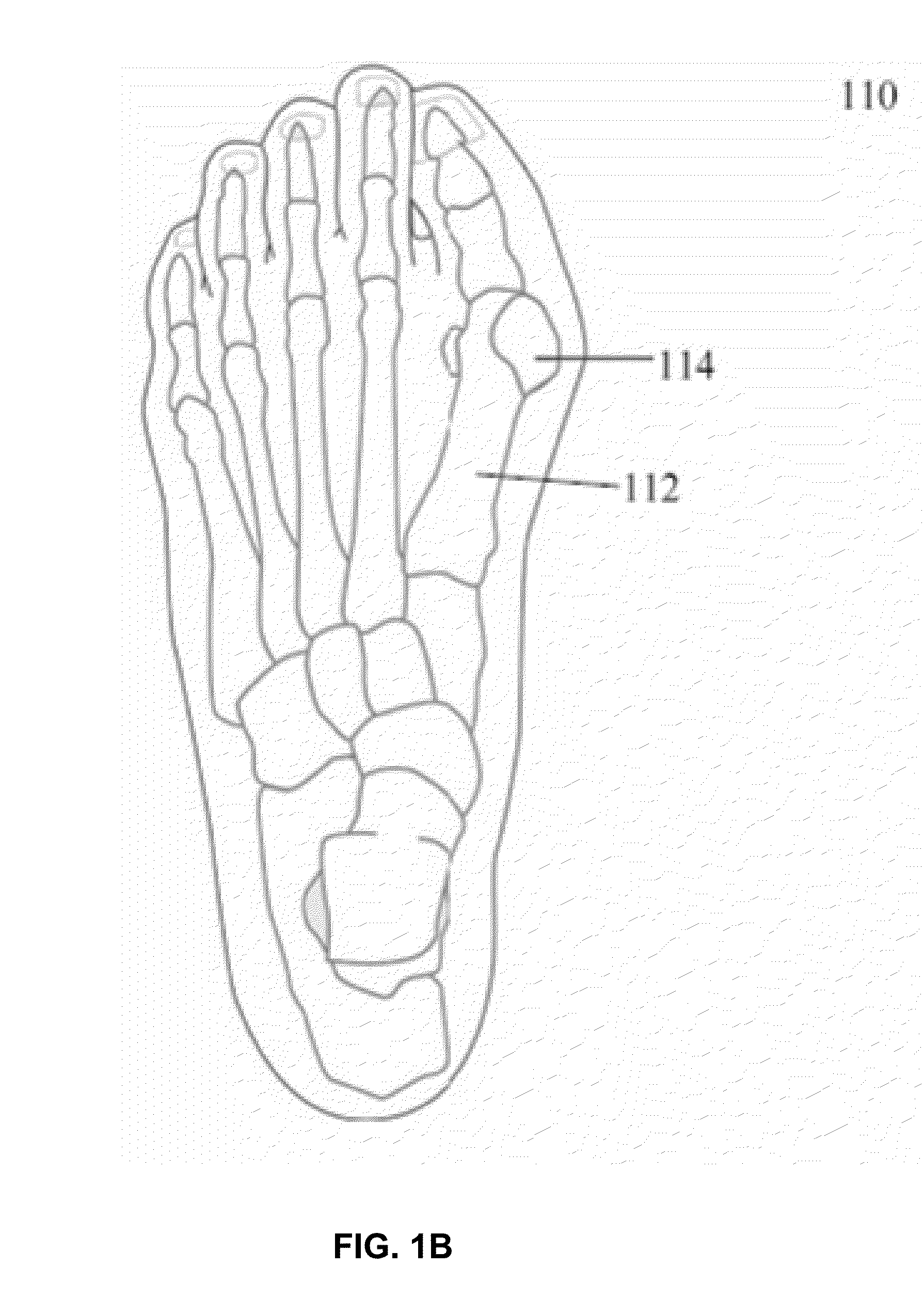
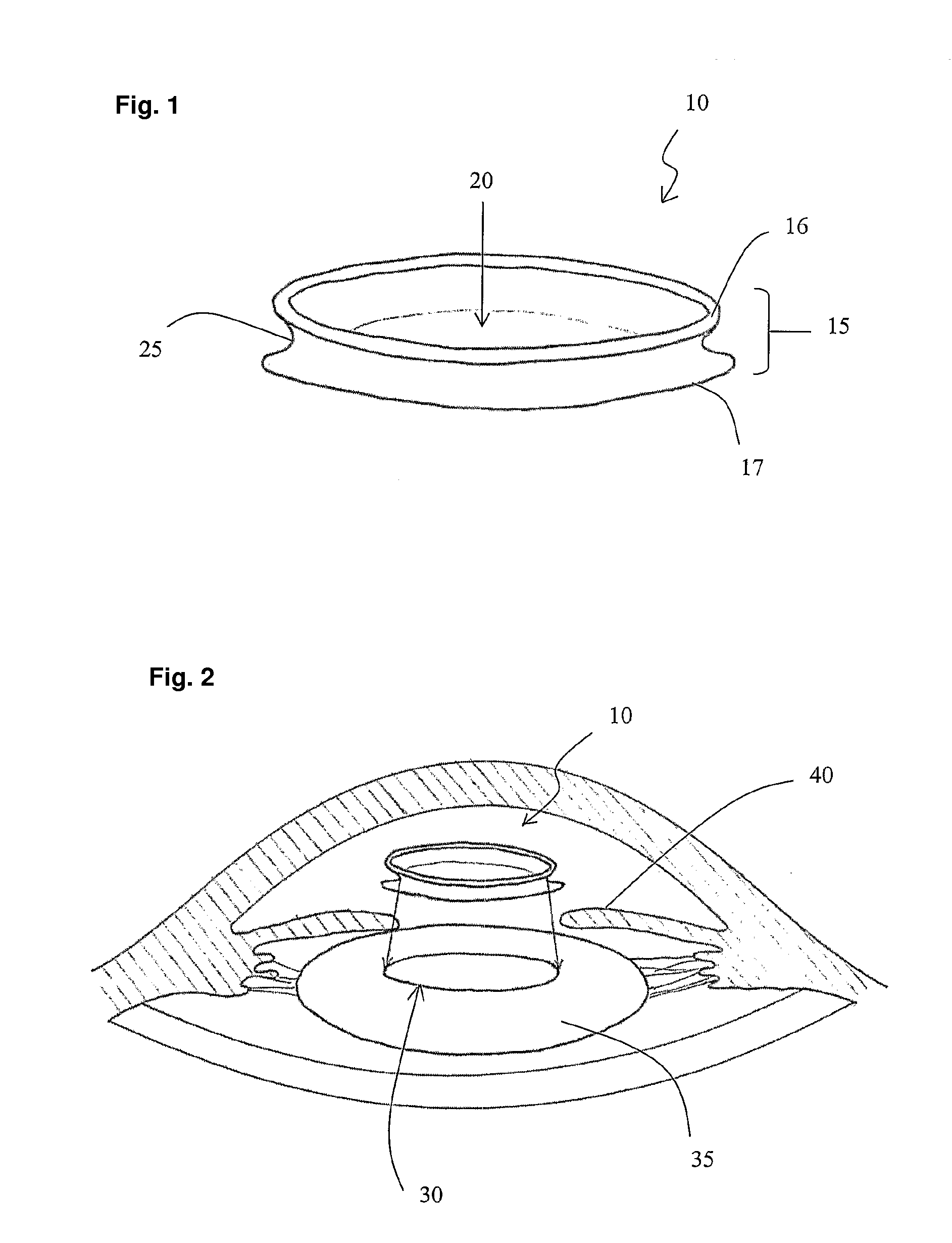
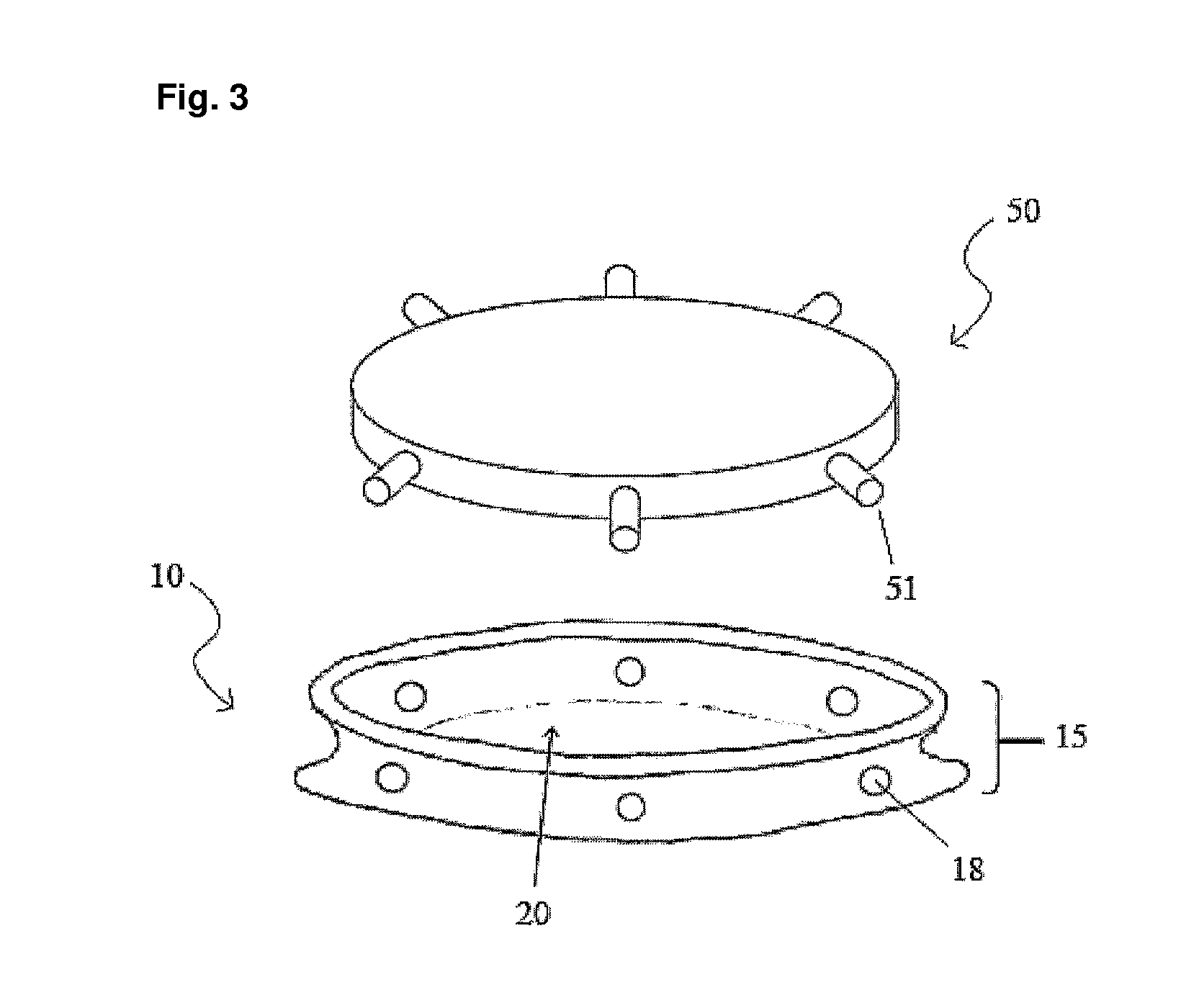
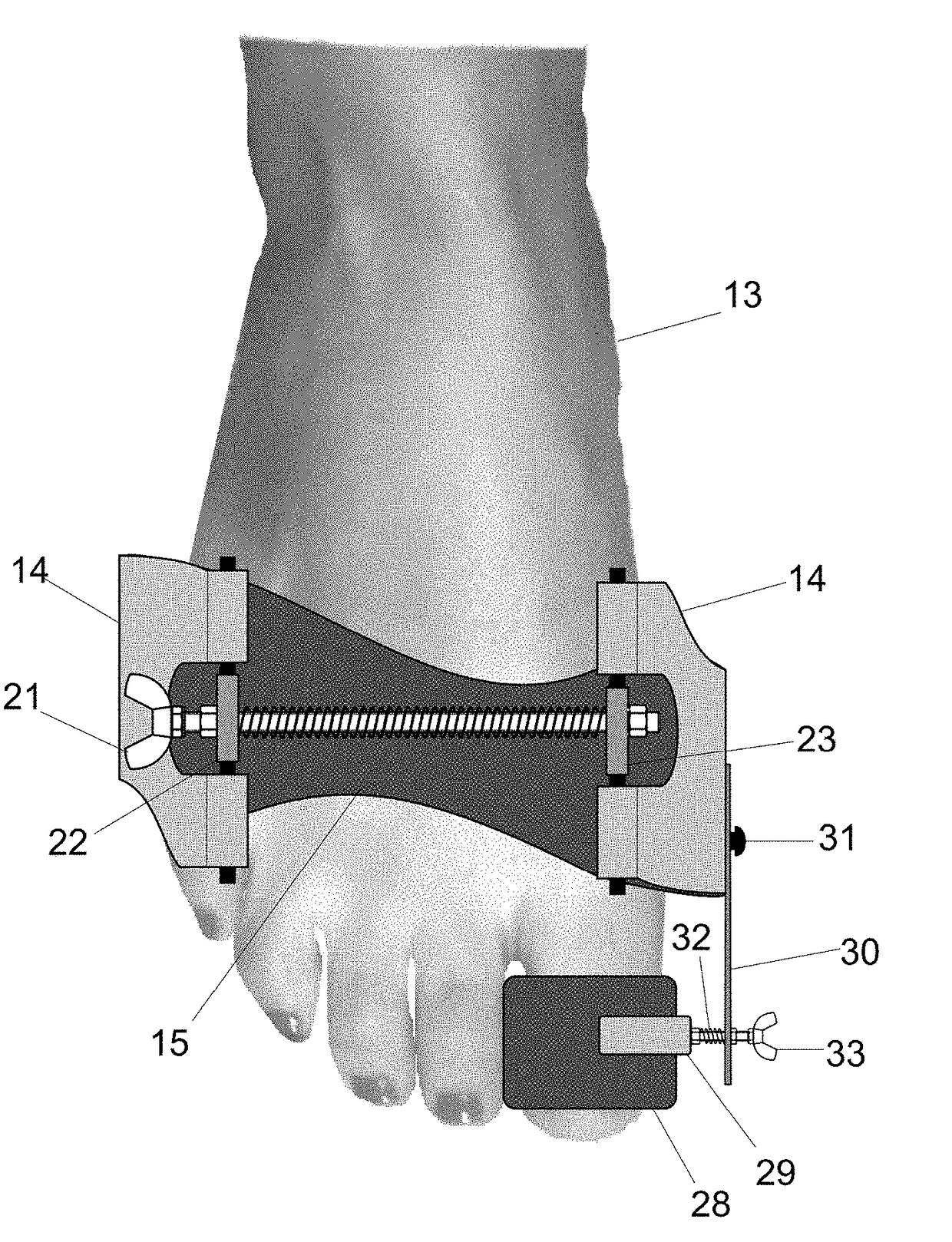
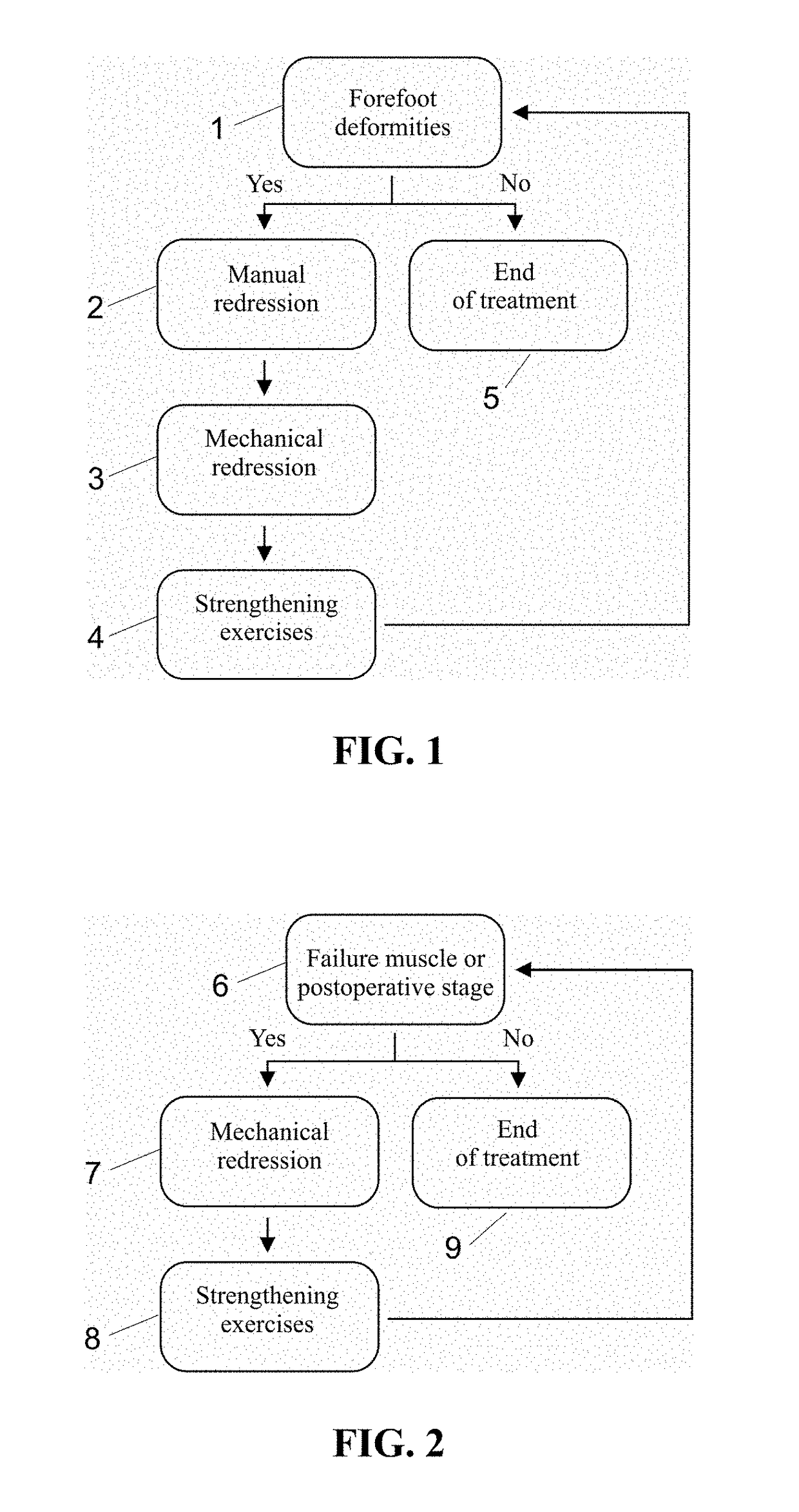
Foot orthosis with comprehensive method for correcting deformities of the transverse arch of the foot in cases of static transverse flatfoot compounded by hallux valgus, with possible preventive and post-operative applications.
InactiveUS20180243121A1Strengthen foot muscleGood effectChiropractic devicesCorrective surgeryOrthopedic department
The proposed method is an innovative approach to correcting orthopedic deformities. It involves gradual manual mobilization of contracture soft tissues and diminutive foot joints by a physiotherapist, followed by mechanical reinforcement of the resulting effect by an orthosis which depresses and push the Ist, IVth and Vth metatarsal bones while elevating or actually blocking the fall the immobile IInd and IIIrd metatarsal bones according to the “three forces” rule. Correction transverse arch foot runs simultaneously with the correction of hallux valgus (if necessary). The propose method comprises sequentially applied passive redression (manual treatment), and a follow-up with the use of a specially designed orthosis (mechanical treatment). The method is suitable for patients undergoing preparation for corrective HV surgery and for post-operative HV. Method can be used preventively e.g. in women who frequently wear high-heel shoes and in for those who need to remain standing for prolonged periods of time.
Owner:DYGUT JACEK MAREK +1
Method and system for eye measurements and cataract surgery planning using vector function derived from prior surgeries
ActiveUS10583039B2Good curative effectImproved refractive correctionsLaser surgeryIntraocular lensCorrective surgeryCataract surgery
Improved devices, systems, and methods for planning cataract surgery on an eye of a patient incorporate results of prior corrective surgeries into a planned cataract surgery of a particular patient by driving an effective surgery vector function based on data from the prior corrective surgeries. The exemplary effective surgery vector employs an influence matrix which may allow improved refractive corrections to be generated so as to increase the overall efficacy of a cataract surgery by specifying one or more parameters of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted during the cataract surgery.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Plasminogen activator to prevent corneal and subepithelial haze after laser vision correction surgery
InactiveUS7179461B2Preventing and reducing postoperative corneal subepithelial hazePrevents hazeSenses disorderElectrotherapyUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorCorrective surgery
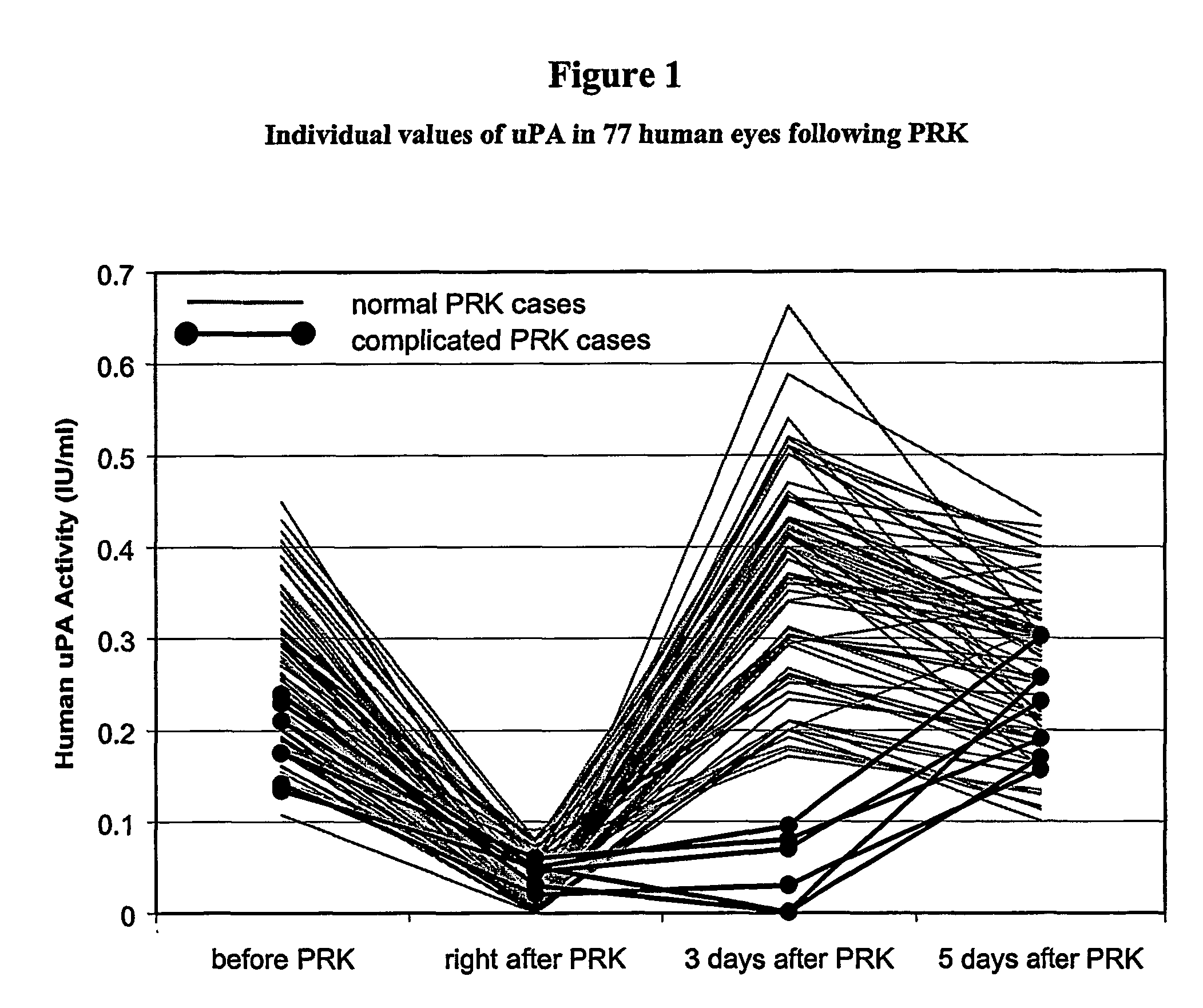
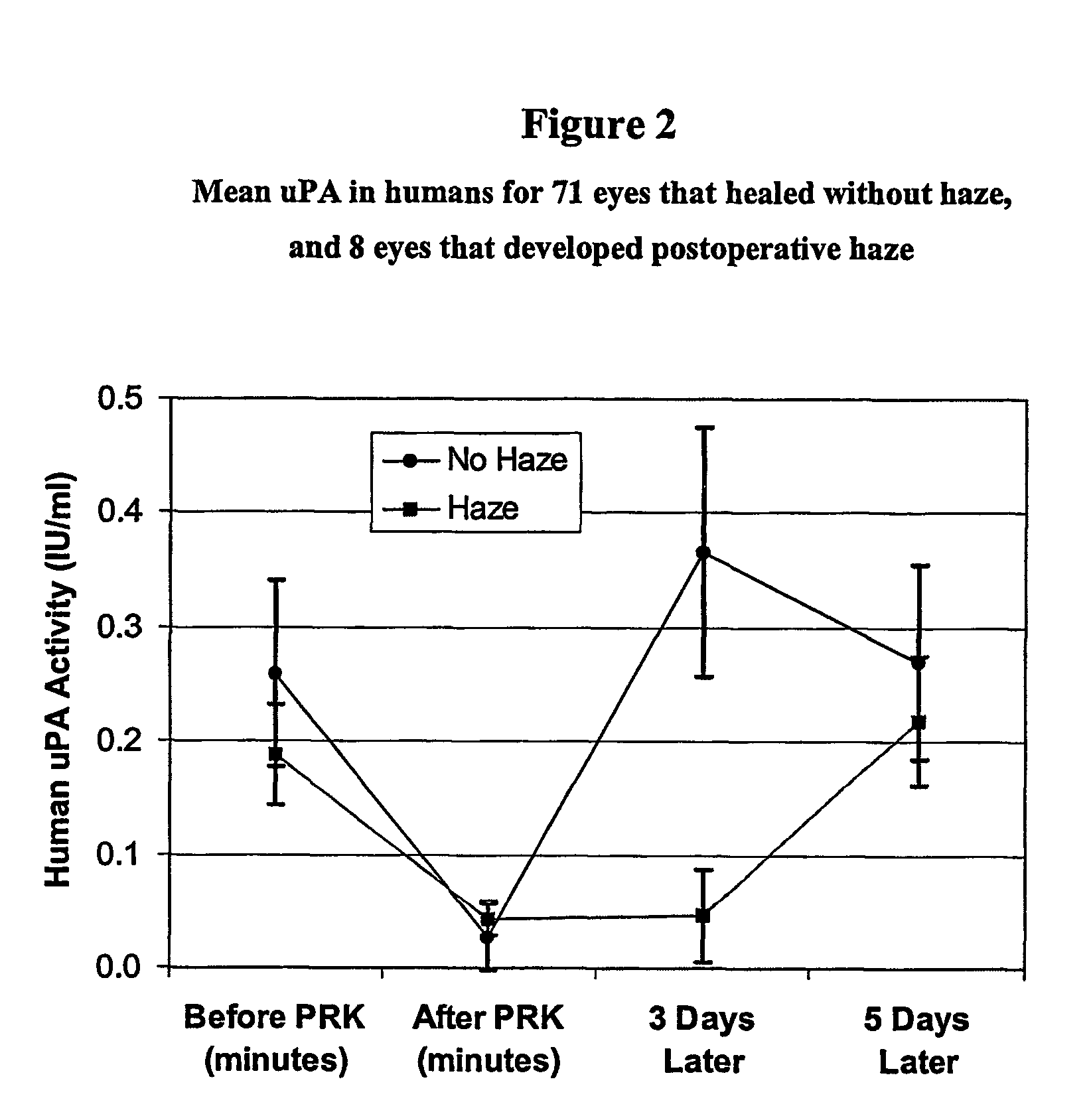
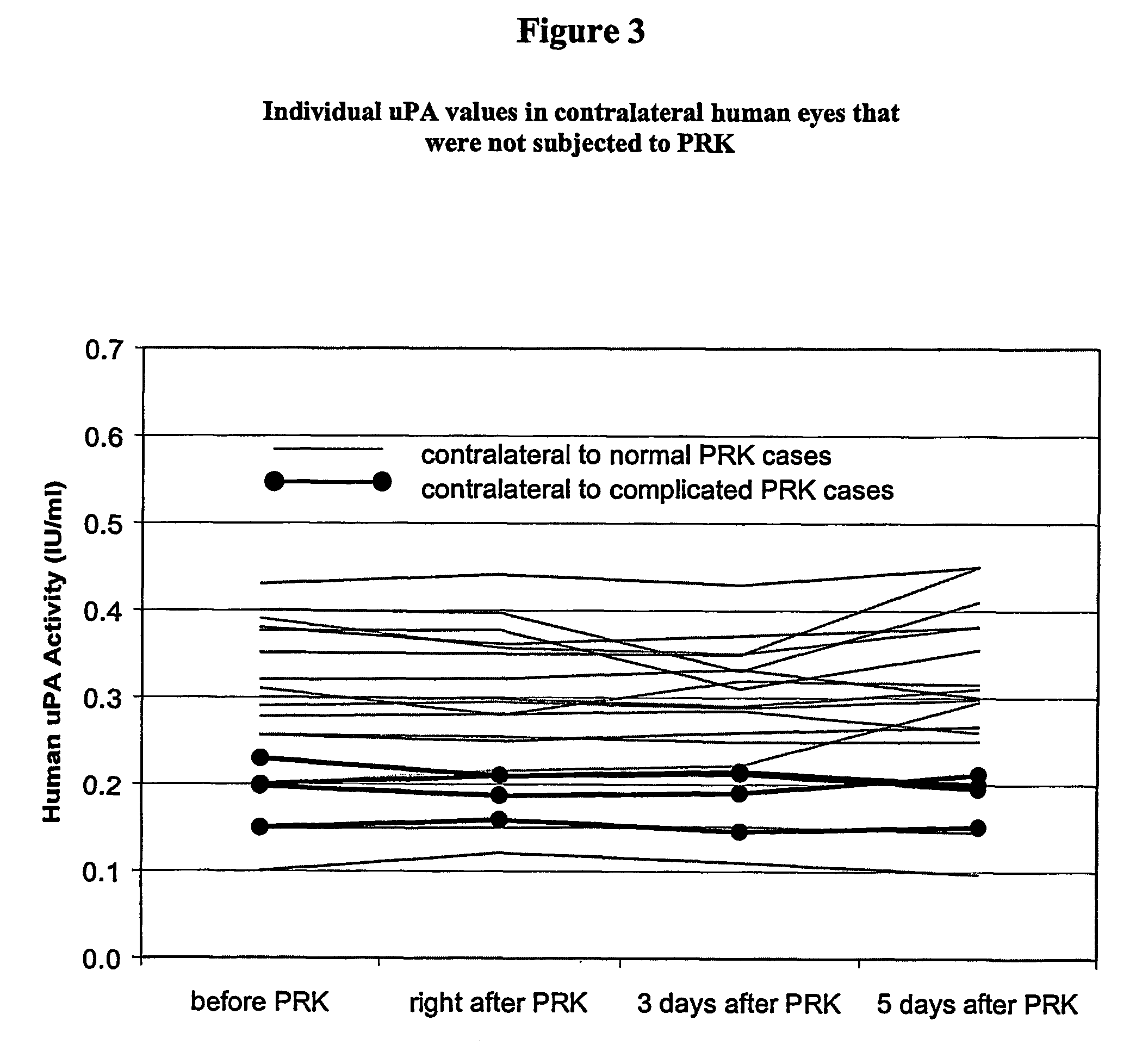
The present invention is directed to a method to prevent or reduce postoperative corneal subepithelial haze after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy (PRK), laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) surgery. According to the method, a therapeutically effective amount of one or more plasminogen activators, most preferably urokinase (uPA), is administered topically to the surface of the affected eye at levels between 0.1 and 2,500 IU / ml, about eight to twelve times on the day of surgery, and four to eight times per day for about the next six to twelve days thereafter. The most preferred therapeutic amount is from about 0.1–1 IU uPA / ml, and also 1–10 IU / ml. Plasminogen activators that can be used in the inventions include urokinase, prourokinase, streptokinase and mutants thereof. The invention also covers topical ophthalmic compositions that include one or more plasminogen activators, most preferably uPA, to prevent or reduce postoperative corneal subepithelial haze.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Spinal deformity correcting instrument
InactiveCN103040512AEasy to operateSimplify the installation processInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnSurgical operation
A spinal deformity correcting instrument is made of shape memory alloy capable of being implanted into the spinal column of a human body, and comprises a hook, universal heads and longitudinal bars. The universal heads and the hook are integrated, the universal heads on two sides of the hook are respectively arranged on a left shoulder and a right shoulder of the hook and are hollow cylinders, U-shaped grooves are arranged on the cylinders, and threads are arranged on inner side surfaces of the U-shaped grooves; the longitudinal bars are solid cylinders and are fixedly placed in the U-shaped grooves of the universal heads, and diameters of the longitudinal bars are matched with sizes of the U-shaped grooves arranged on the universal heads; and the hook is arched, bent hooks are arranged at two ends of the hook, and a longitudinal groove is arranged on the arched top of the hook. During usage, a doctor can operate the spinal deformity correcting instrument on a transverse process or vertebral plate without implanting a pedicle screw into the human body or opening the spinal canal of the human body, advantages of the bent hooks, the longitudinal bars and the universal heads which are made of the memory alloy can be sufficiently played, complicated surgical operation is simplified, surgical risks are greatly reduced, and the spinal deformity correcting instrument can be widely applied to various spinal deformity correcting surgeries and can be easily popularized in primary hospitals.
Owner:陆晓生
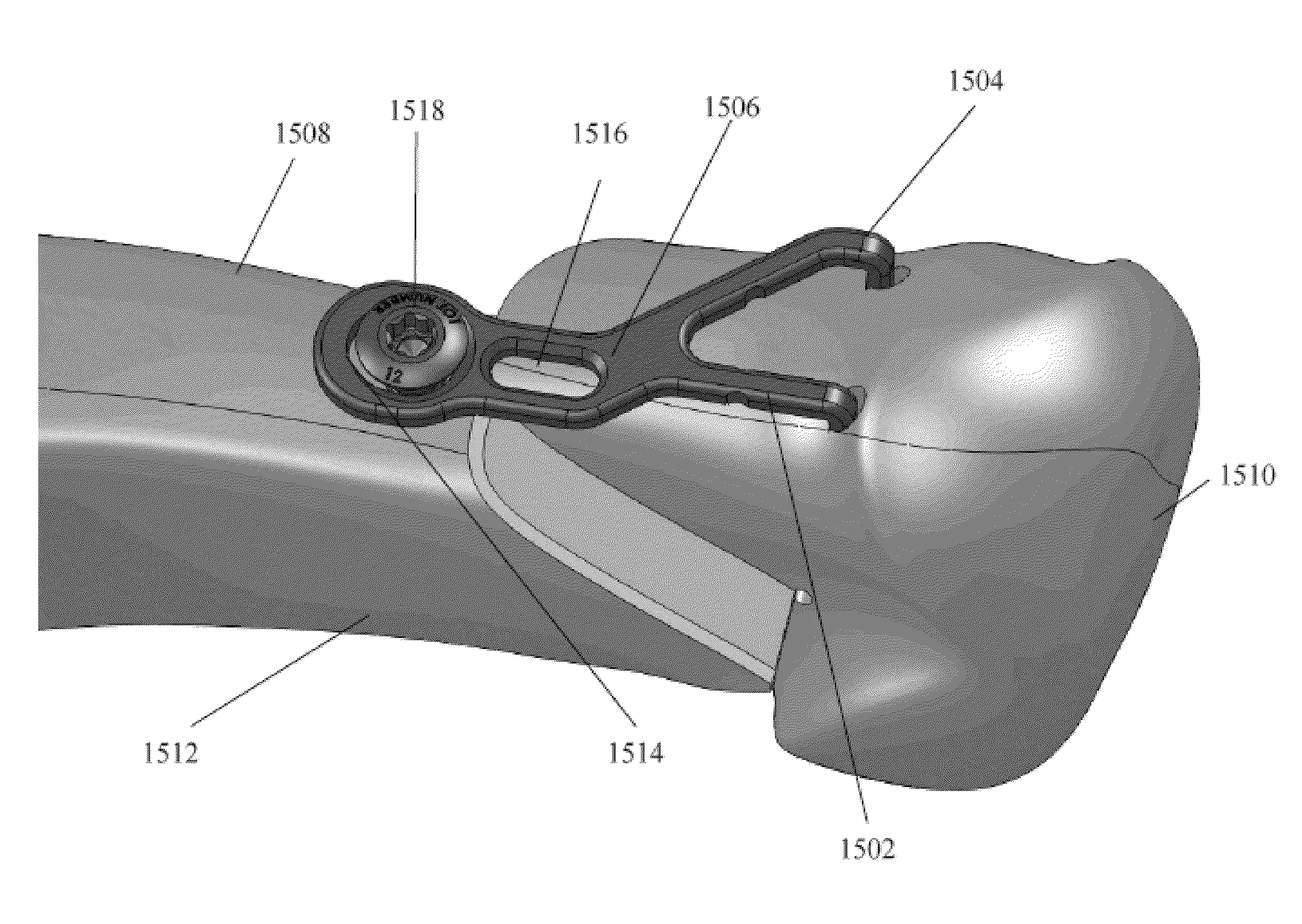
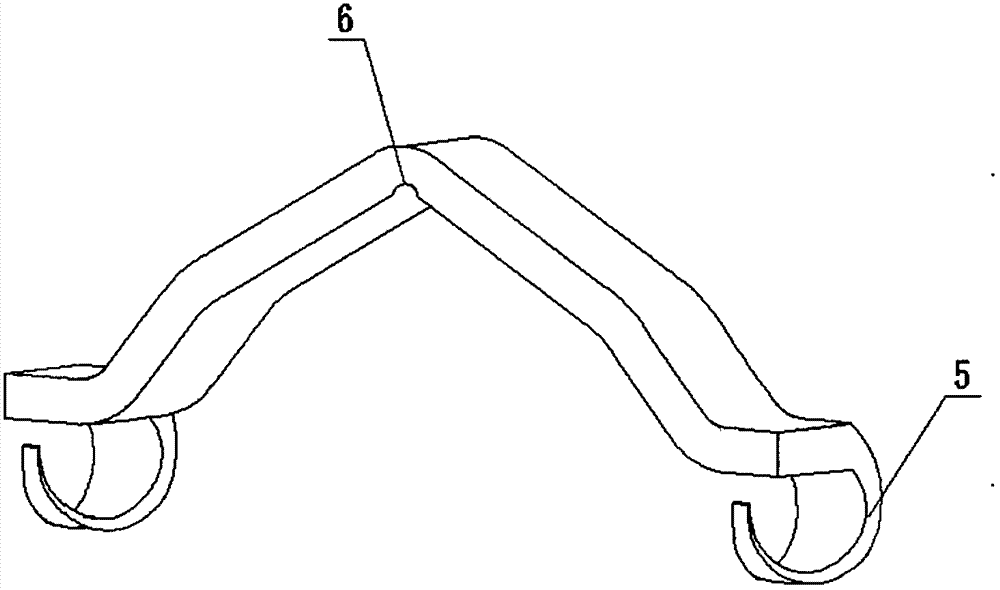
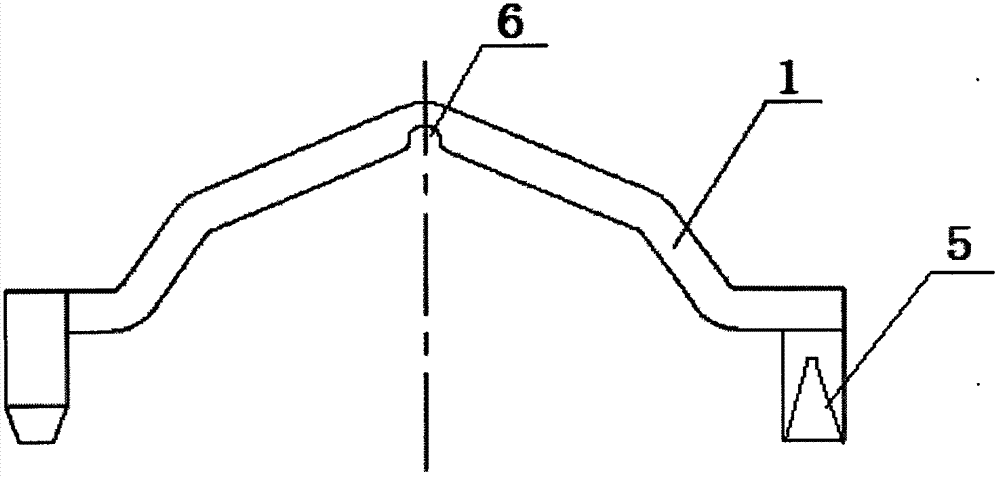
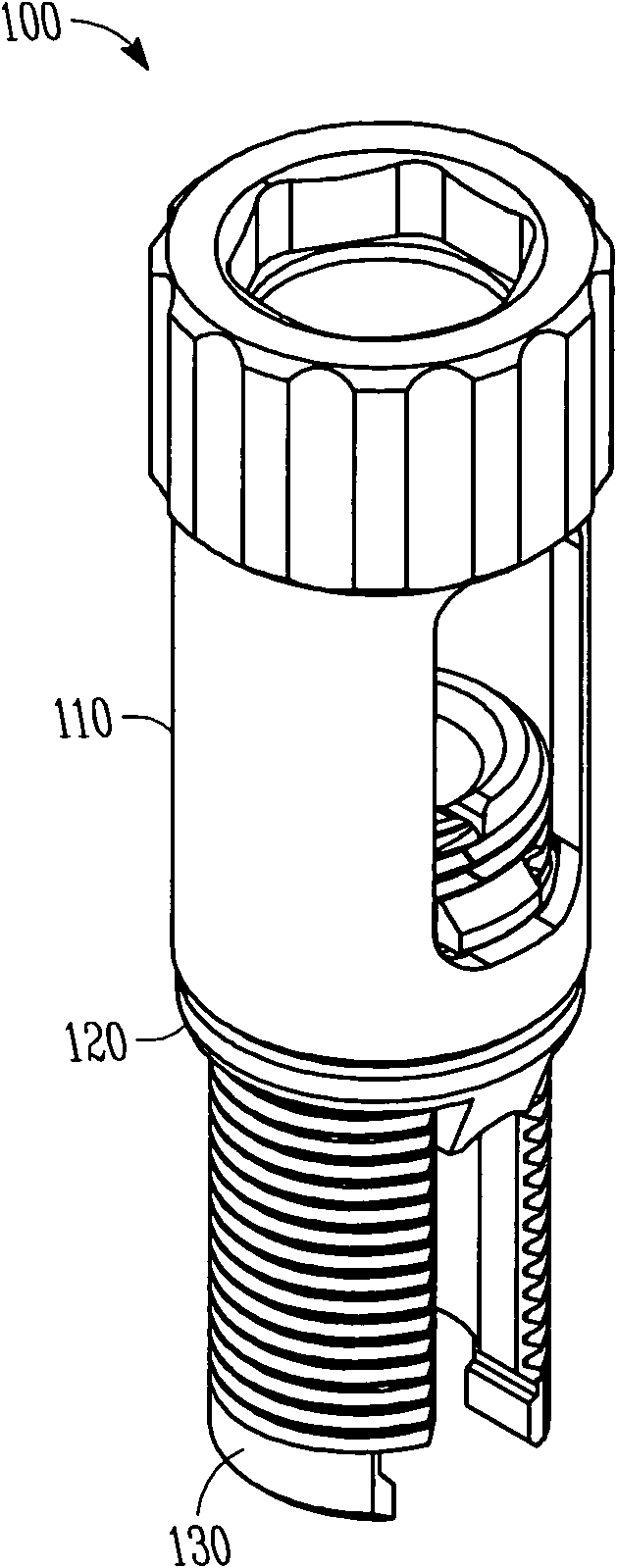
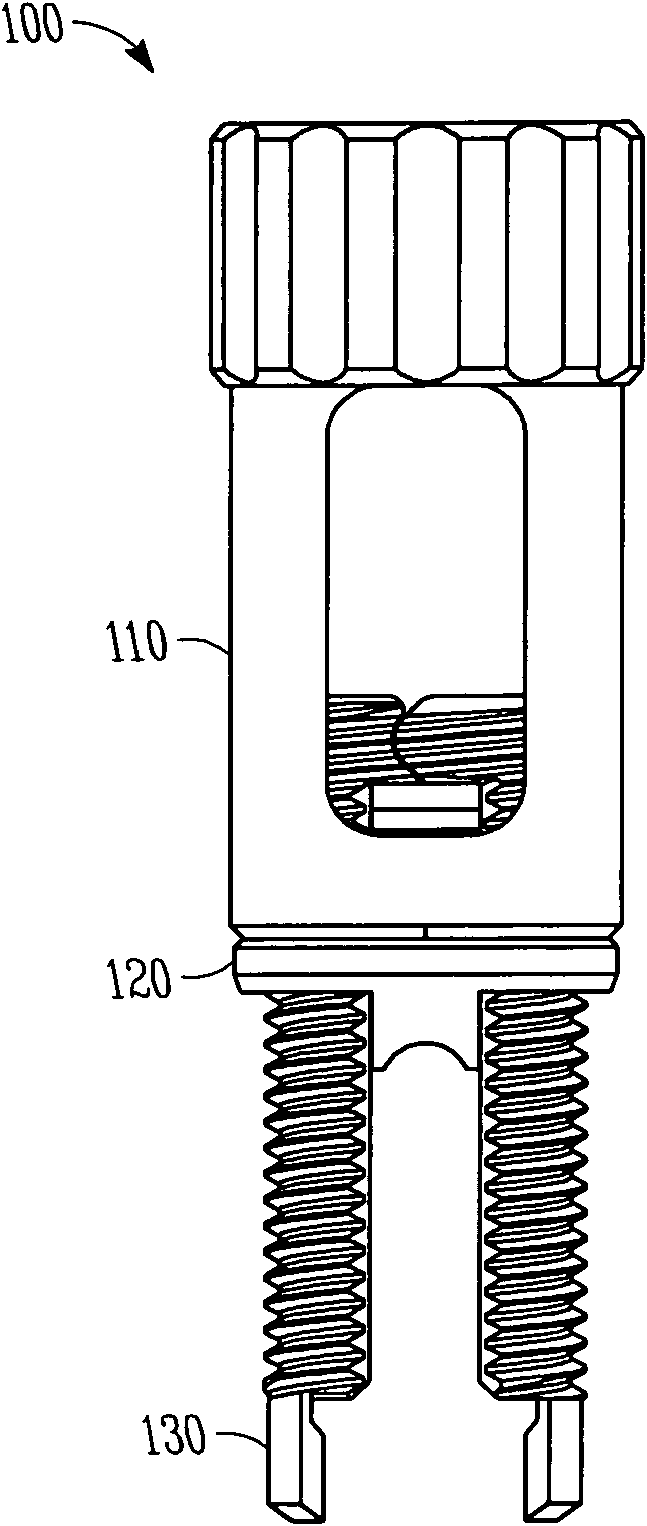
Rod reducer apparatus for spinal corrective surgery
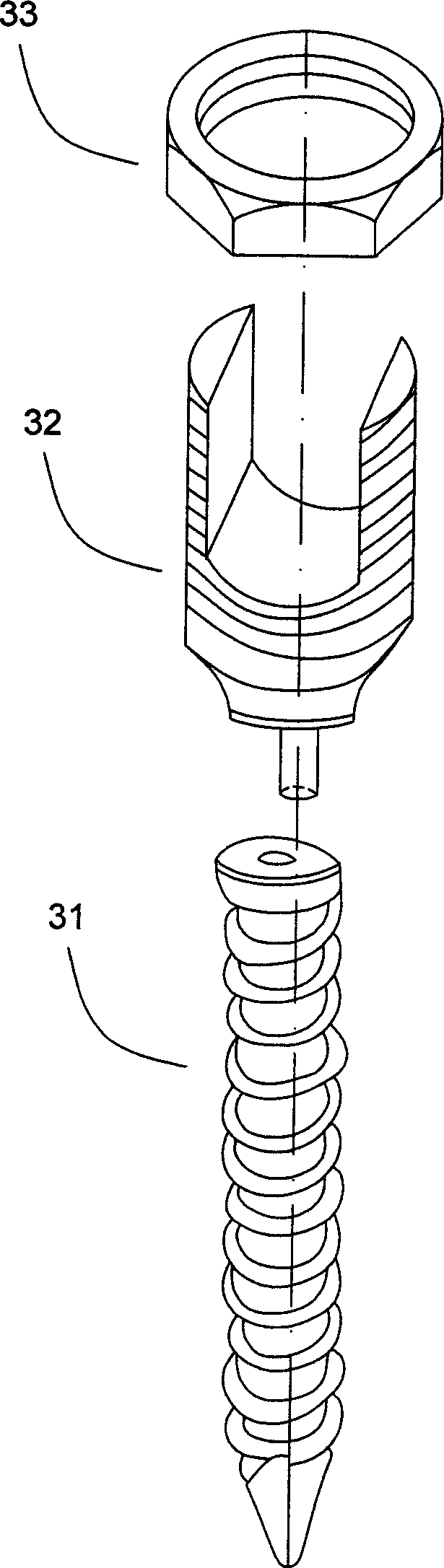
Spinal rod reduction apparatuses, systems, and methods are provided. In various examples, a rod reduction apparatus includes a first threaded member (130, 210, 330) including an engagement feature (138A, 138B, 220, 332, 334) configured to selectively anchor the first threaded member to the implantable screw assembly. A second threaded member (110, 230, 310) is configured to threadably engage with the first threaded member. The second threaded member is axially movable with respect to the first threaded member with rotation of the second threaded member. A spinal rod urging member (120, 240, 320) is axially movable with the second threaded member. The urging member includes a bearing surface (126, 242, 320) that is configured to selectively abut the spinal rod and selectively urge the spinal rod toward the implantable screw assembly with rotation of the second threaded member in a first rotational direction.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
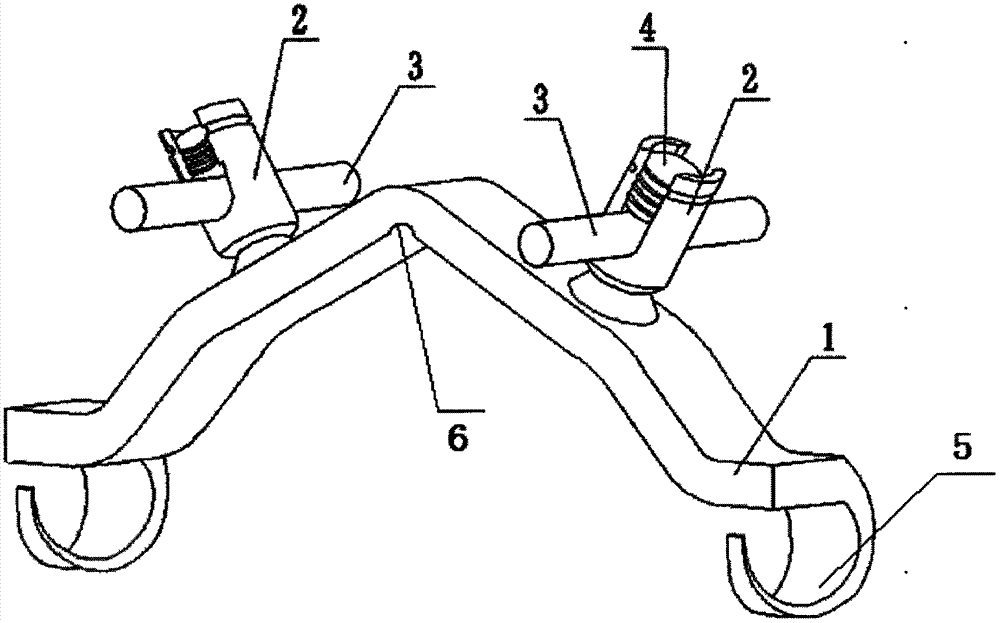
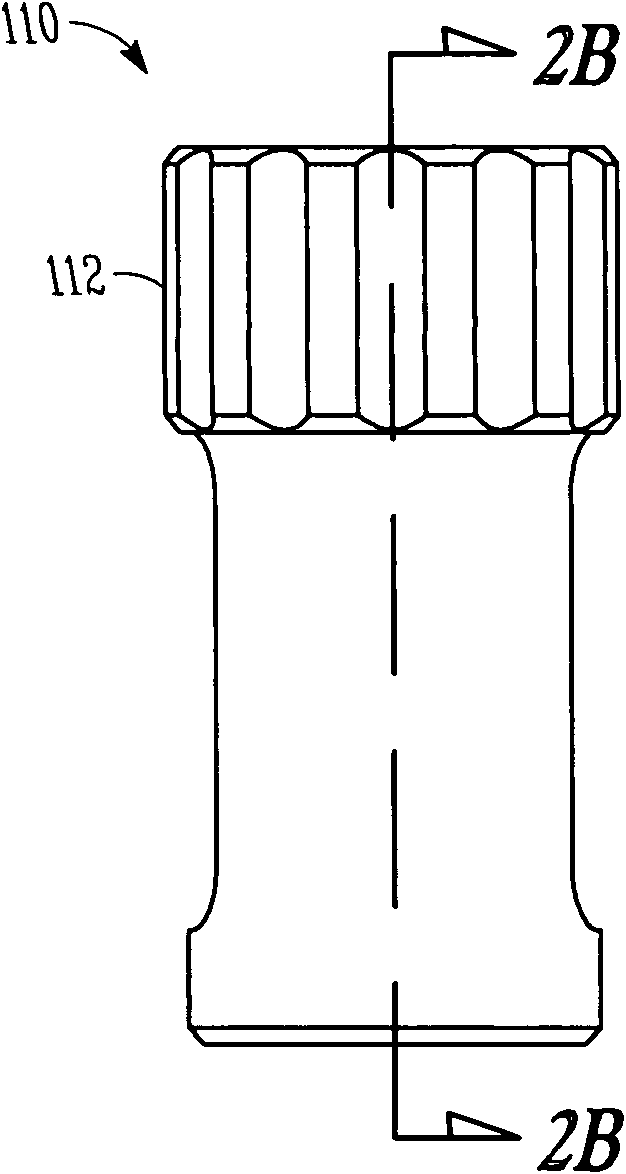
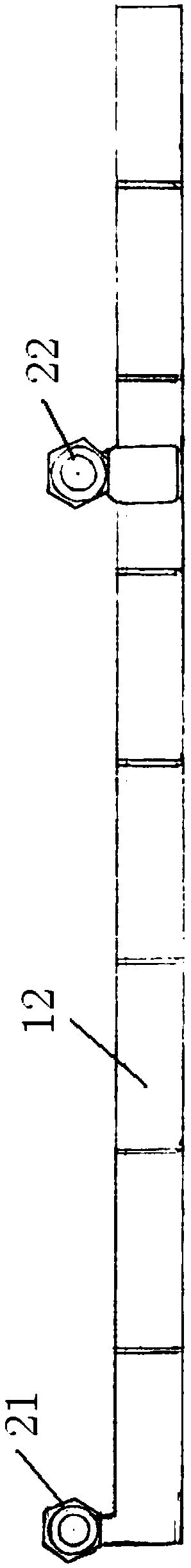
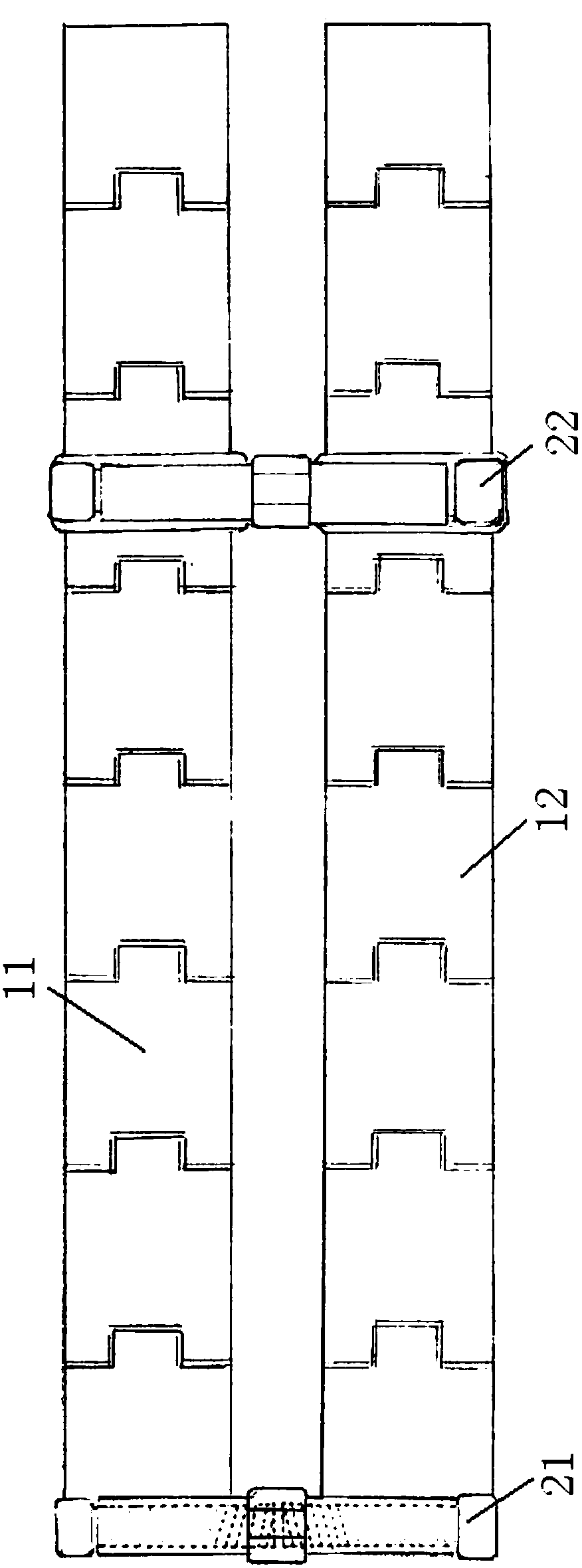
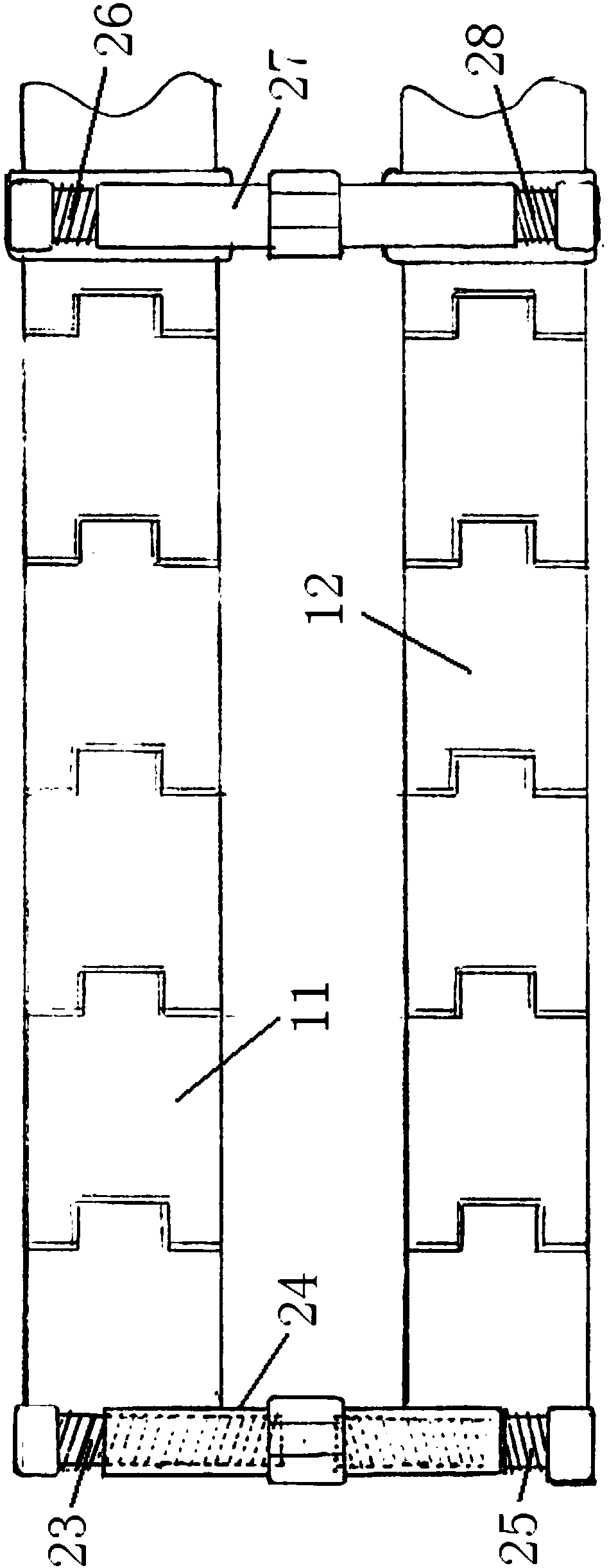
Scoliosis posterior correction surgery field full-view stable exposure device
PendingCN107647889AFull use of orthopedic skillsGuarantee smooth implementationSurgeryScoliosisAnatomical structures
The invention discloses a scoliosis posterior correction surgery field full-view stable exposure device which comprises a first track bar (11) and a second track bar (12) which can be bent freely. Thefirst track bar (11) and the second track bar (12) are connected through a first distance adjusting assembly (21) and a second distance adjusting assembly (22), the first distance adjusting assembly(21) and the second distance adjusting assembly (22) can adjust the distance between the first track bar (11) and the second track bar (12), and the first track bar (11) and the second track bar (12)are each provided with a hook assembly (31). The hook assemblies (31) can transversely pull each local soft tissue to open, the compression hemostasis effect is effectively achieved, the surgery fieldcan be fully, completely and stably exposed, it is ensured that the anatomical structure inside the surgery field is clear, and the device is accurate to operate and convenient and safe to use.
Owner:邹德威
Retreatment in ophthalmic refractive surgery
The invention relates to a planning device for generating control data, a treatment device for refractive ophthalmic surgery and a method for generating control data for such a treatment device which enables better Complementary refractive correction. In this case, the planning device includes a calculation unit for determining the corneal cutting plane for the retreatment, wherein the calculation unit is designed to take into account changes in the thickness of the epithelium, which are mainly caused by previous treatments, during the calculation. .
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
High lip-line smile corrective surgical method
ActiveUS8857442B1Low implementation costRetaining its effectivenessDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsCorrective surgeryEngineering
A high lip-line smile corrective surgical method. A first incision is made above a mucogingival junction to define a first edge. A second incision is made on attached gingiva above a gum line to define a second edge. Lift a section defined by the first and second incisions and remove the section with a micro scalp without affecting or contacting periosteum. Separate elevator muscles of the upper lip attached to the upper alveolar ridge with angulated gingevectomy scissors in reverse motion with release of tension so that the first and second edges meet. Seal the first and second edges with suture, individual stitches, or polypropylene; and cauterize the sealed the first and second edges.
Owner:OSPINA GLORIA A
System and method for refractive surgery with augmentation by intrastromal corrective procedure
A system and method are provided for an ophthalmic surgical procedure to provide a refractive correction for an eye. Specifically, the procedure is indicated when the desired refractive correction “dreqd” exceeds the capability of a correction achievable when corneal tissue is only ablated. In accordance with the present invention, an optimized refractive correction “d1” is accomplished by the ablation of corneal tissue (e.g. by a PRK or LASIK procedure). The optimized correction is then followed by a complementary refractive correction “d2” wherein stromal tissue is weakened with Laser Induced Optical Breakdown (LIOB). Together, the optimized refractive correction (ablation) and the complementary refractive correction (LIOB) equal the desire refractive correction (dreqd=d1+d2).
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Method and system for eye measurements and cataract surgery planning using vector function derived from prior surgeries
ActiveUS10582847B2Good curative effectImproved refractive correctionsLaser surgeryComputer-aided planning/modellingCorrective surgeryCataract surgery
Improved devices, systems, and methods for planning cataract surgery on an eye of a patient incorporate results of prior corrective surgeries into a planned cataract surgery of a particular patient by driving an effective surgery vector function based on data from the prior corrective surgeries. The exemplary effective surgery vector employs an influence matrix which may allow improved refractive corrections to be generated so as to increase the overall efficacy of a cataract surgery by specifying one or more parameters of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted during the cataract surgery.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Method and system for eye measurements and cataract surgery planning using vector function derived from prior surgeries
ActiveUS10582846B2Good curative effectImproved refractive correctionsLaser surgeryRefractometersCorrective surgeryCataract surgery
Improved devices, systems, and methods for planning cataract surgery on an eye of a patient incorporate results of prior corrective surgeries into a planned cataract surgery of a particular patient by driving an effective surgery vector function based on data from the prior corrective surgeries. The exemplary effective surgery vector employs an influence matrix which may allow improved refractive corrections to be generated so as to increase the overall efficacy of a cataract surgery by specifying one or more parameters of an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted during the cataract surgery.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Special installation tool of internally-installed splayed plate in orthopaedic corrective surgery
InactiveCN101940494AImprove accuracyImprove installation efficiencySurgeryCorrective surgeryEngineering
The invention relates to a special installation tool of an internally-installed splayed plate in an orthopaedic corrective surgery, comprising a positioning needle, a splayed template, a double-guide hole meter and an inclinometer of the double-guide hole meter, wherein one guide hole pillar of the double-guide hole meter is fixedly connected with the inclinometer of the double-guide hole meter; the bottom of the guide hole pillar is connected with the splayed template; and the positioning needle is inserted between the inclinometer of the double-guide hole meter and the splayed template. When drilling hole, the front end of the splayed template is fixed by using a splayed plate tongs, wherein when the splayed plate tongs clamp, two grips positioned on the head of the splayed plate tongs are parallel, the distance between the two grips is the distance between two clamped surfaces of the splayed template, and two bulges positioned on the head of the splayed plate tongs support against grooves positioned on the two clamped surfaces of the splayed template. The special installation tool designed according to the dimensions of the splayed plate and the splayed template greatly enhances the installation position accuracy rate and the installation efficiency of the splayed plate; and in addition, the invention has compatibility with the splayed plate and can reduce the workload of a doctor, enhance the accuracy and reduce the bone injury of a patient by using the tool in the installation process.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
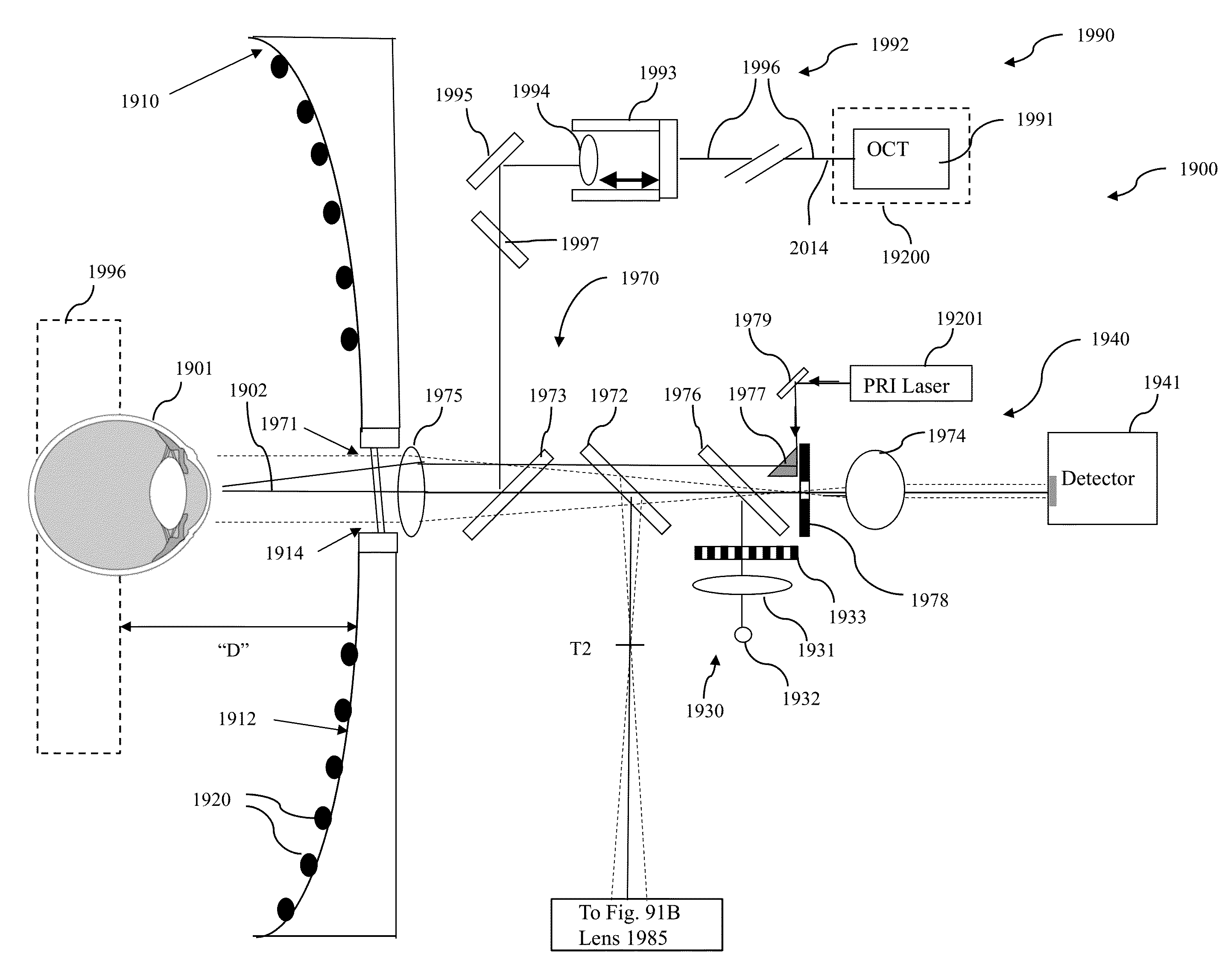
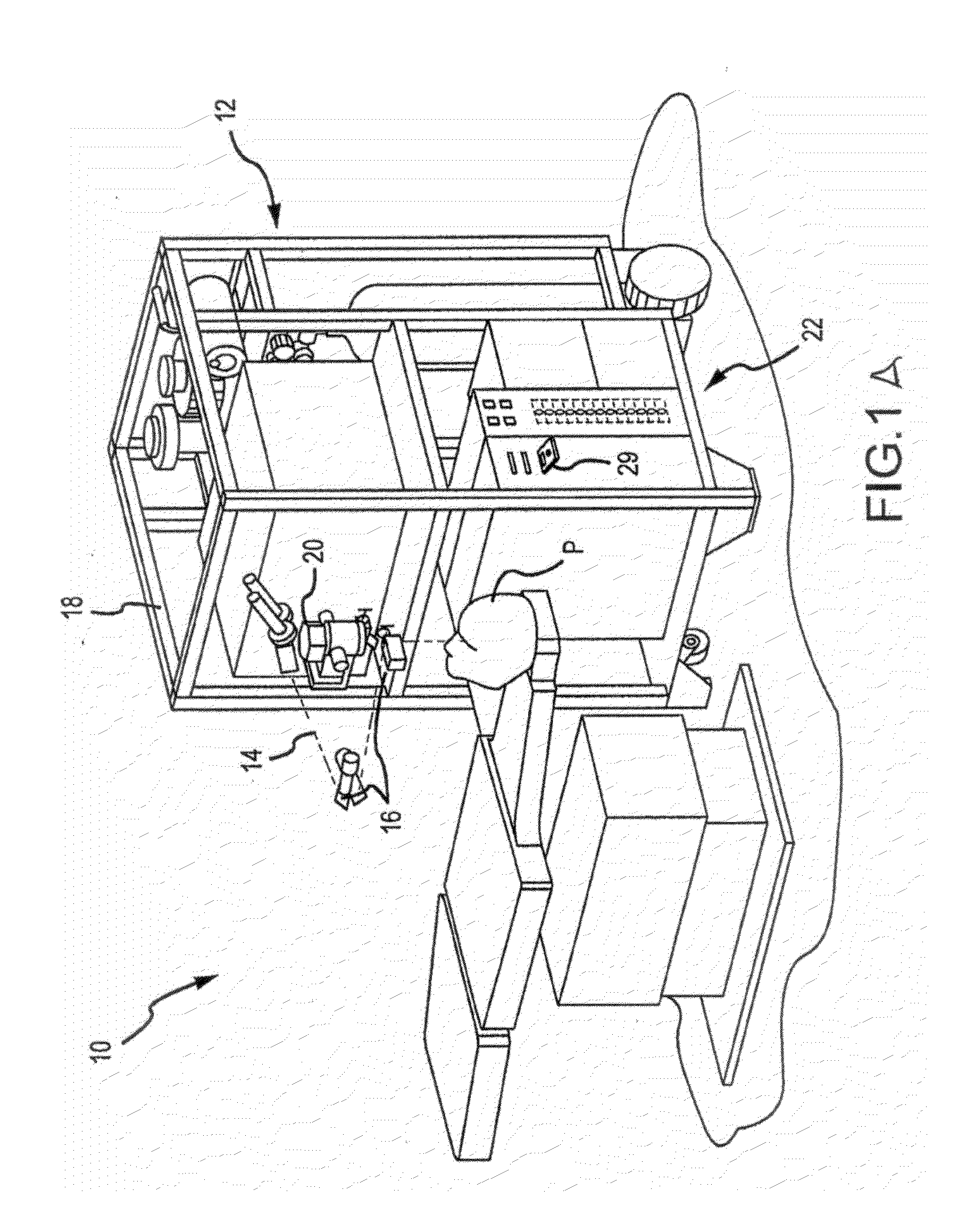
Optical coherence tomography-augmented surgical instruments and systems and methods for correcting undesired movement of surgical instruments
An OCT-augmented surgical instrument able to correct for undesired movement, as well as a system for use with such a surgical instrument and a method of correcting for undesired movement during surgery using OCT.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Rod shearing instrument used in spinal surgical incision
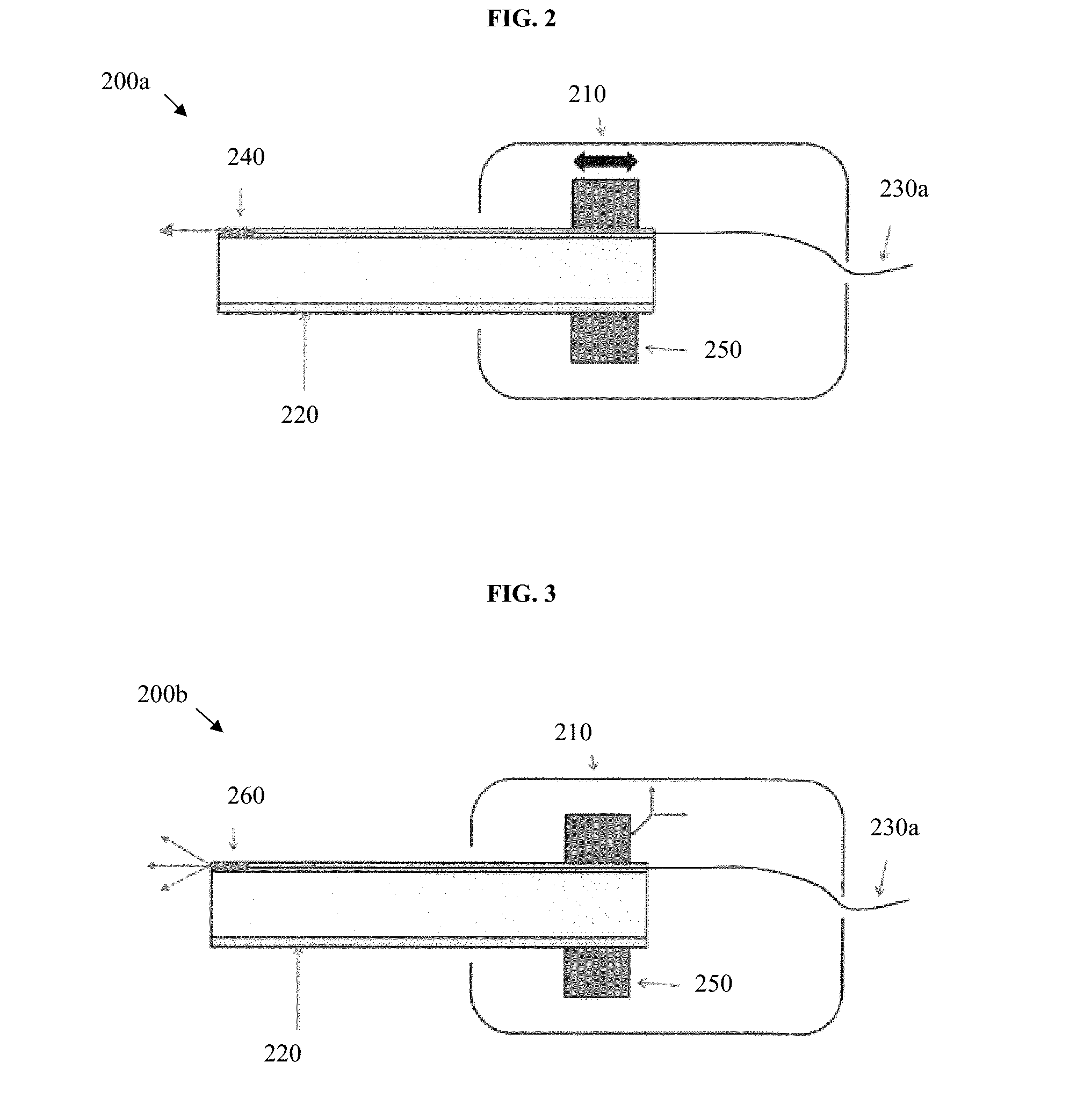
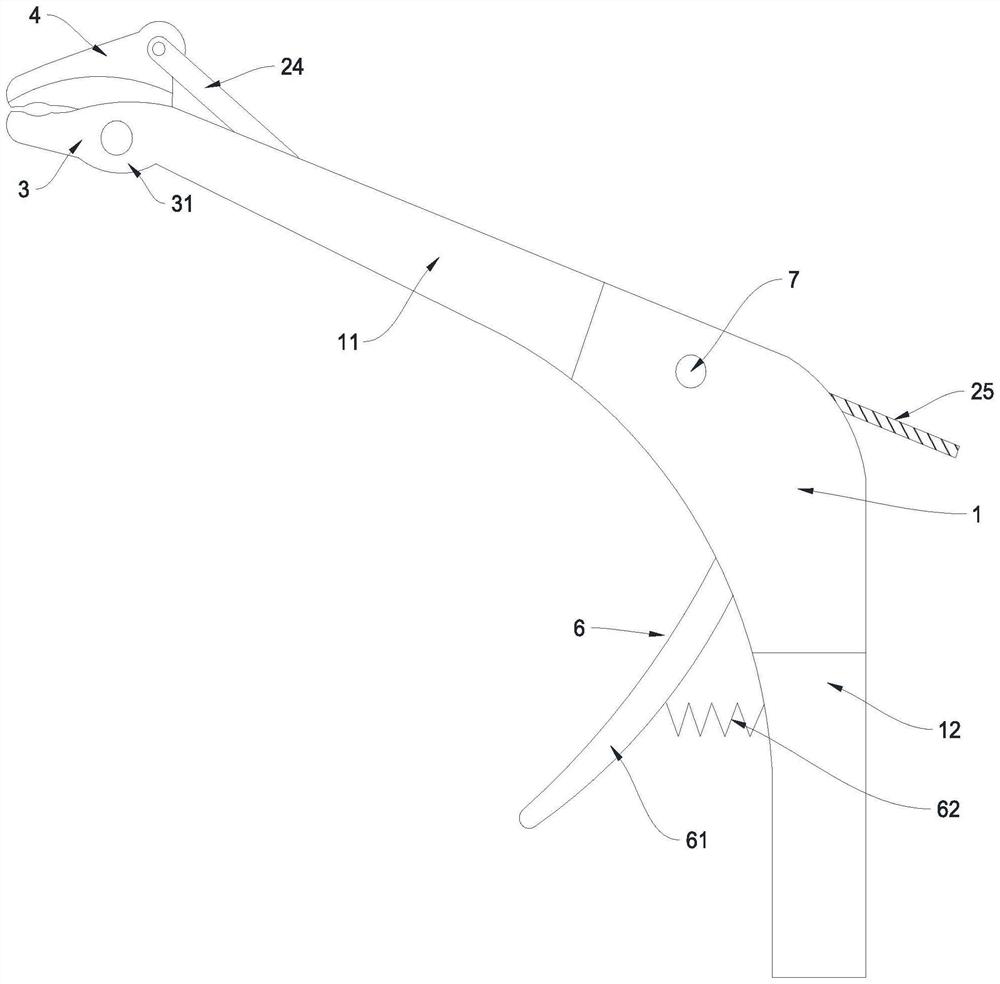
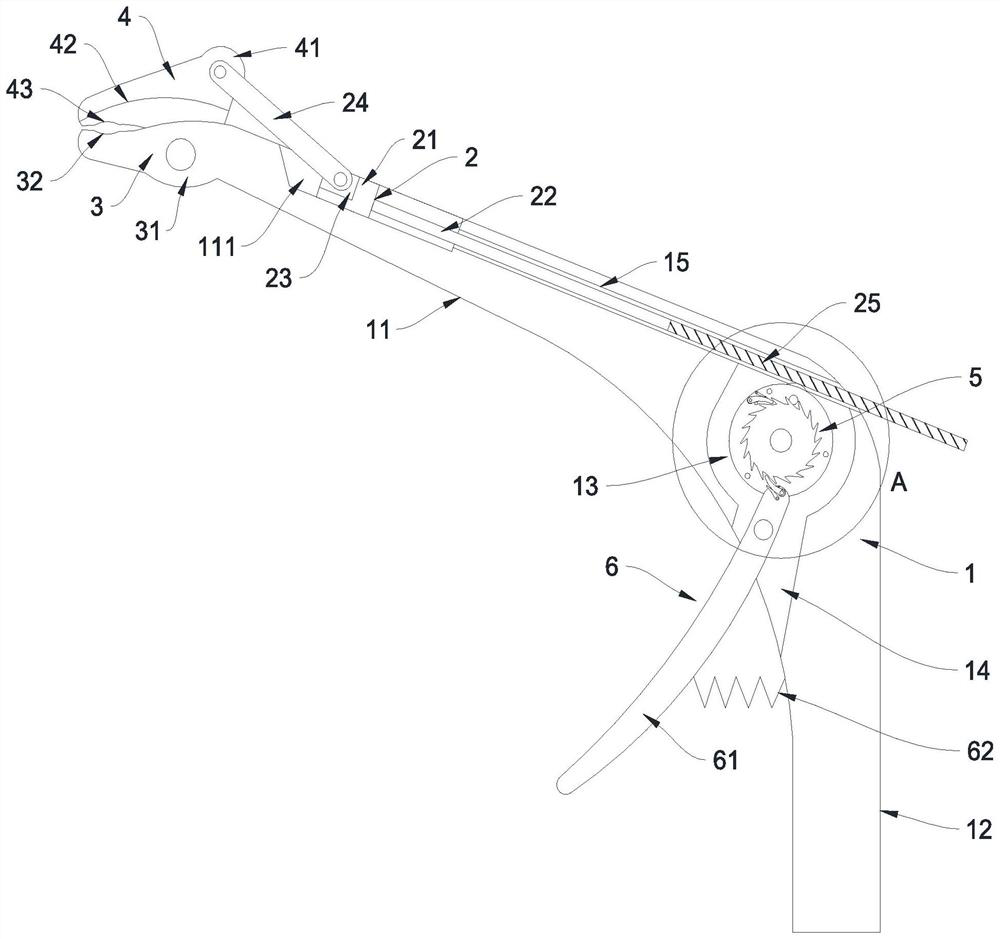
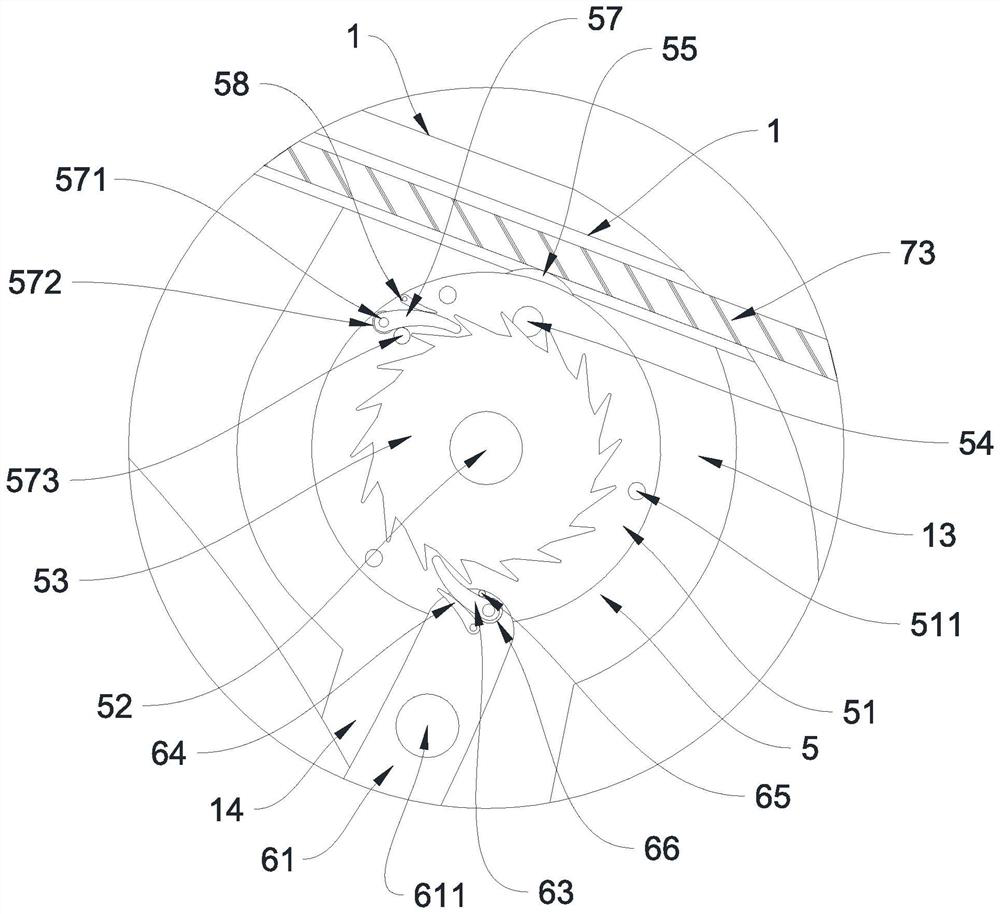
PendingCN114176753AEasy and efficient cuttingSave powerInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnSurgical risk
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, and discloses a rod cutting instrument used in a spinal surgical incision, the rod cutting instrument comprises a seat body, a pushing mechanism, a fixed forceps knife, a movable forceps knife, a linkage mechanism and a driving mechanism, the seat body is in a 7-shaped bent shape, one end of the seat body is provided with a handle, the other end of the seat body is provided with a forceps arm, the fixed forceps knife and the movable forceps knife are arranged at the end of the forceps arm, and the linkage mechanism is connected with the linkage mechanism. A sliding groove is formed in the clamp arm, the pushing mechanism is located in the sliding groove, and the pushing mechanism is connected with the movable clamp knife; a linkage cavity is formed in the seat body, a driving groove is formed in the lower side of the driving cavity in a communicating mode, a guide sliding hole is formed in the upper side of the linkage cavity in a communicating mode, the linkage mechanism is located in the linkage cavity, the driving mechanism is located in the driving groove, and the linkage mechanism is connected between the driving mechanism and the pushing mechanism; the problems that in the scoliosis deformity correction operation process, due to limitation of a cutting tool, a fixing rod needs to be taken down for cutting, time and labor are wasted in the cutting process, and operation risks exist are solved.
Owner:杭州知橙生物科技有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com