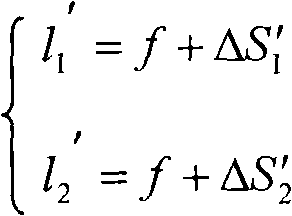Patents
Literature
218 results about "Refractometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from Snell's law while for mixtures, the index of refraction can be calculated from the composition of the material using several mixing rules such as the Gladstone–Dale relation and Lorentz–Lorenz equation.
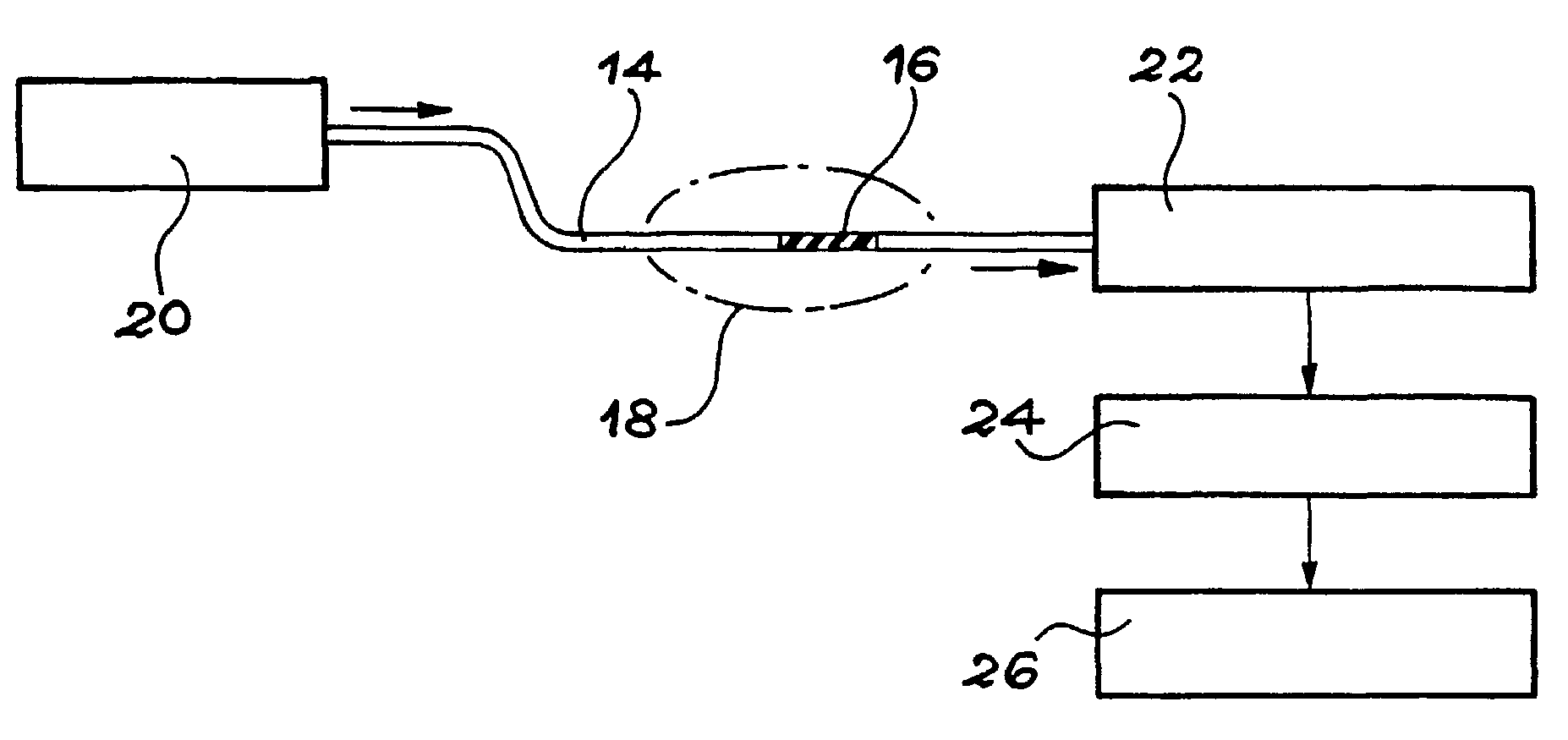
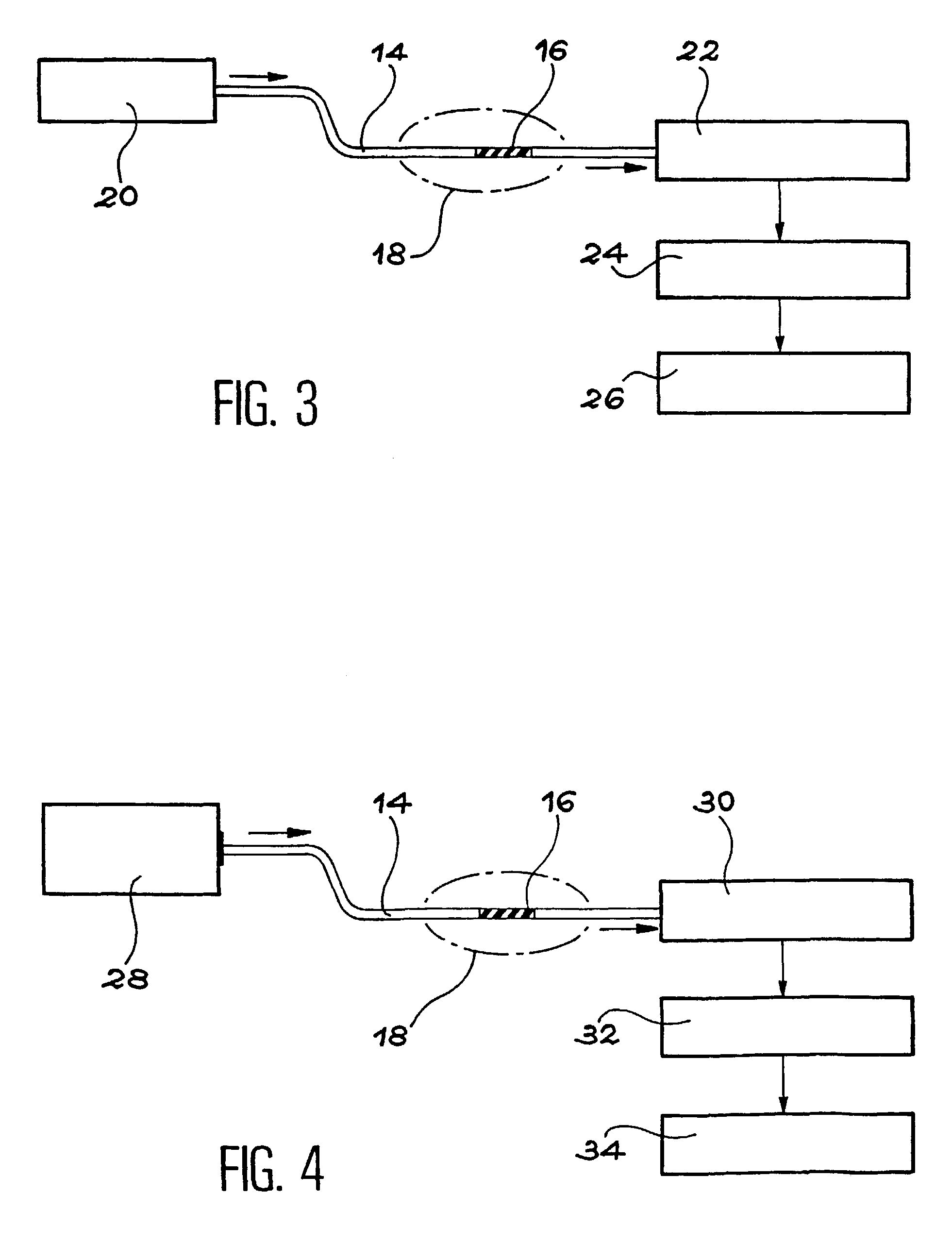
System for calculating IOL power
InactiveUS20080004610A1Improve human ophthalmic surgery patient wellnessReduce probabilityEye surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive measurementsCamera lens
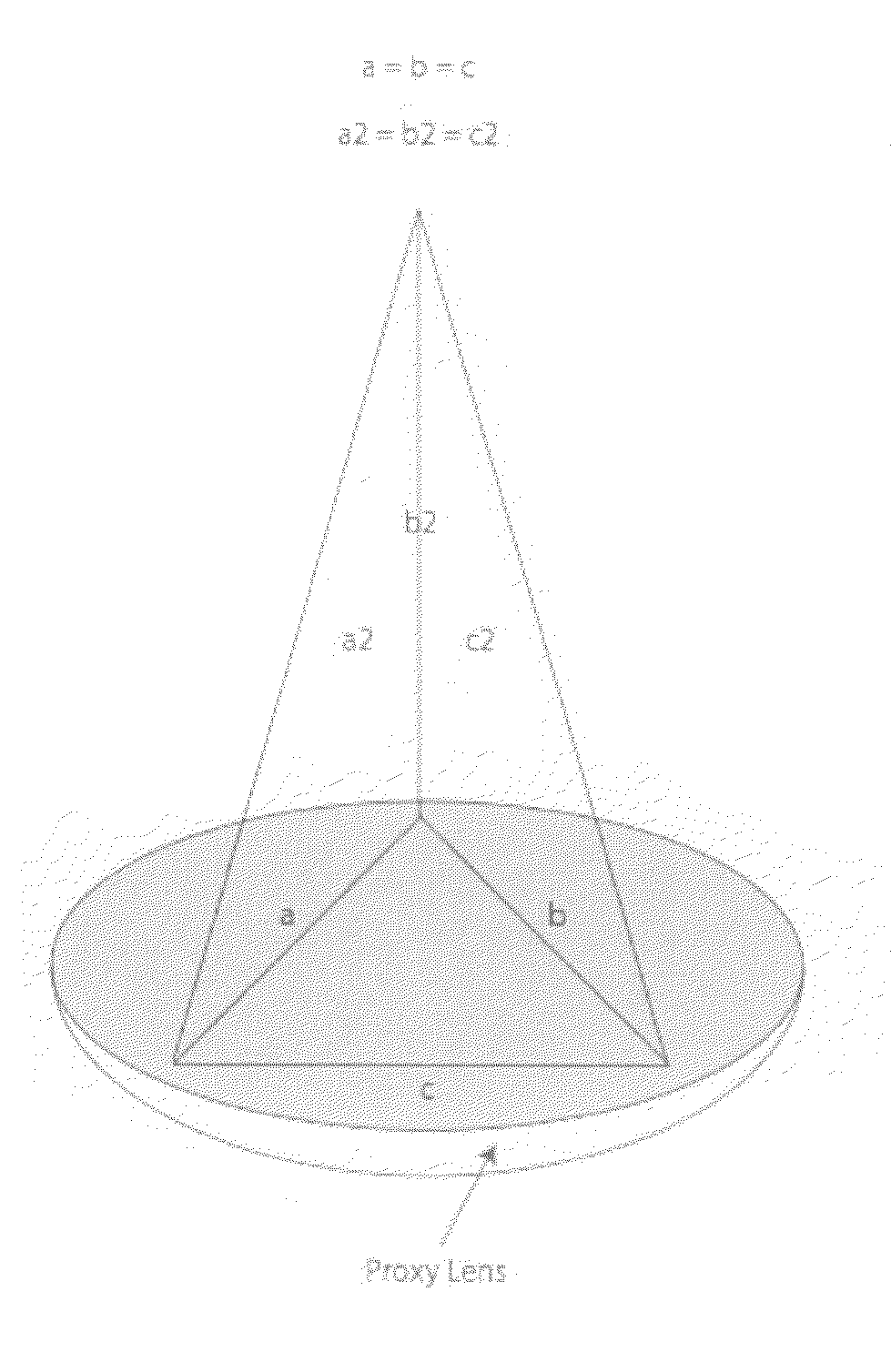
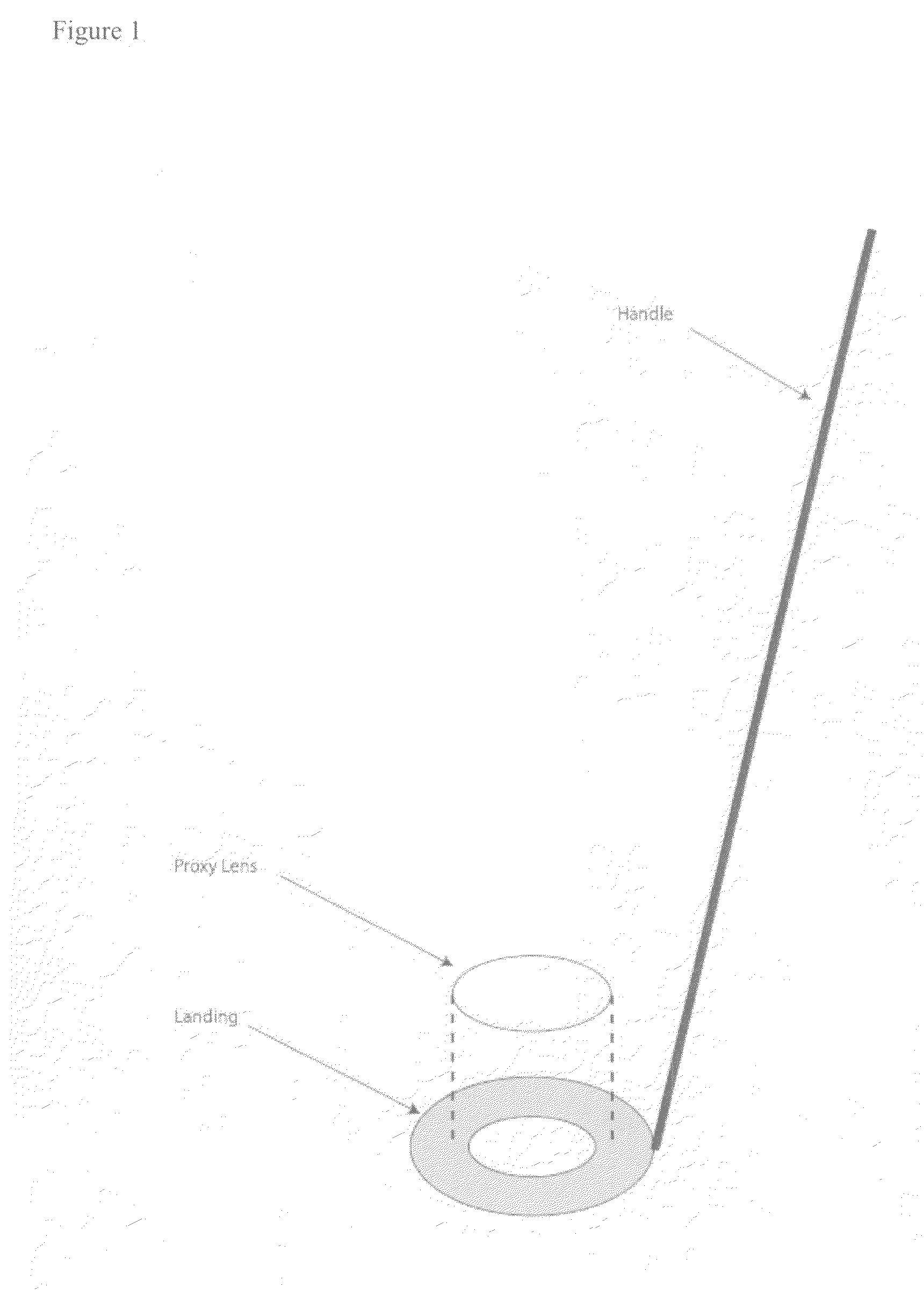
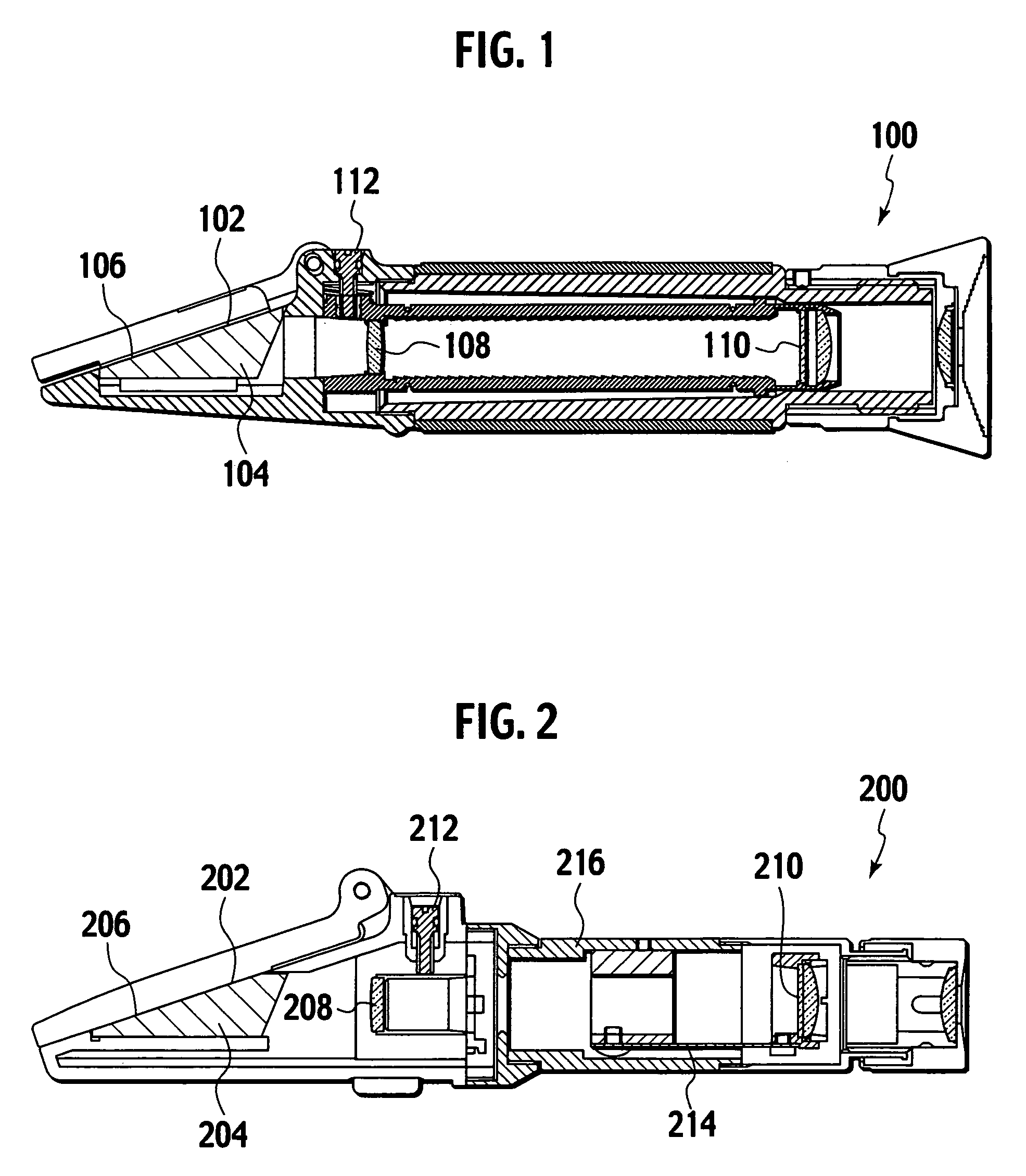
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus to improve human ophthalmic surgery patient wellness and surgical procedural outcome of both indicated cataract surgery and elective surgeries with the implantation of permanent standard intraocular lens (IOL) and new technology intraocular lens (NTIOL). The present invention further relates to measurement of refraction intra-operatively to validate or obviate the pre-operative calculations and thus selection of the IOL or NTIOL and allow for a correction to be made intra-operatively before the permanent IOL or NTIOL is implanted. Specifically, several embodiments of the invention pertain to a disposable, temporary Proxy Lens apparatus that are used for in situ refractive measurements, an Insertion Tool apparatus to manipulate the Proxy Lens within the optical path for the refractive measurement and a Refractometer apparatus to perform the refractive measurements.
Owner:MILLER DAVID +4
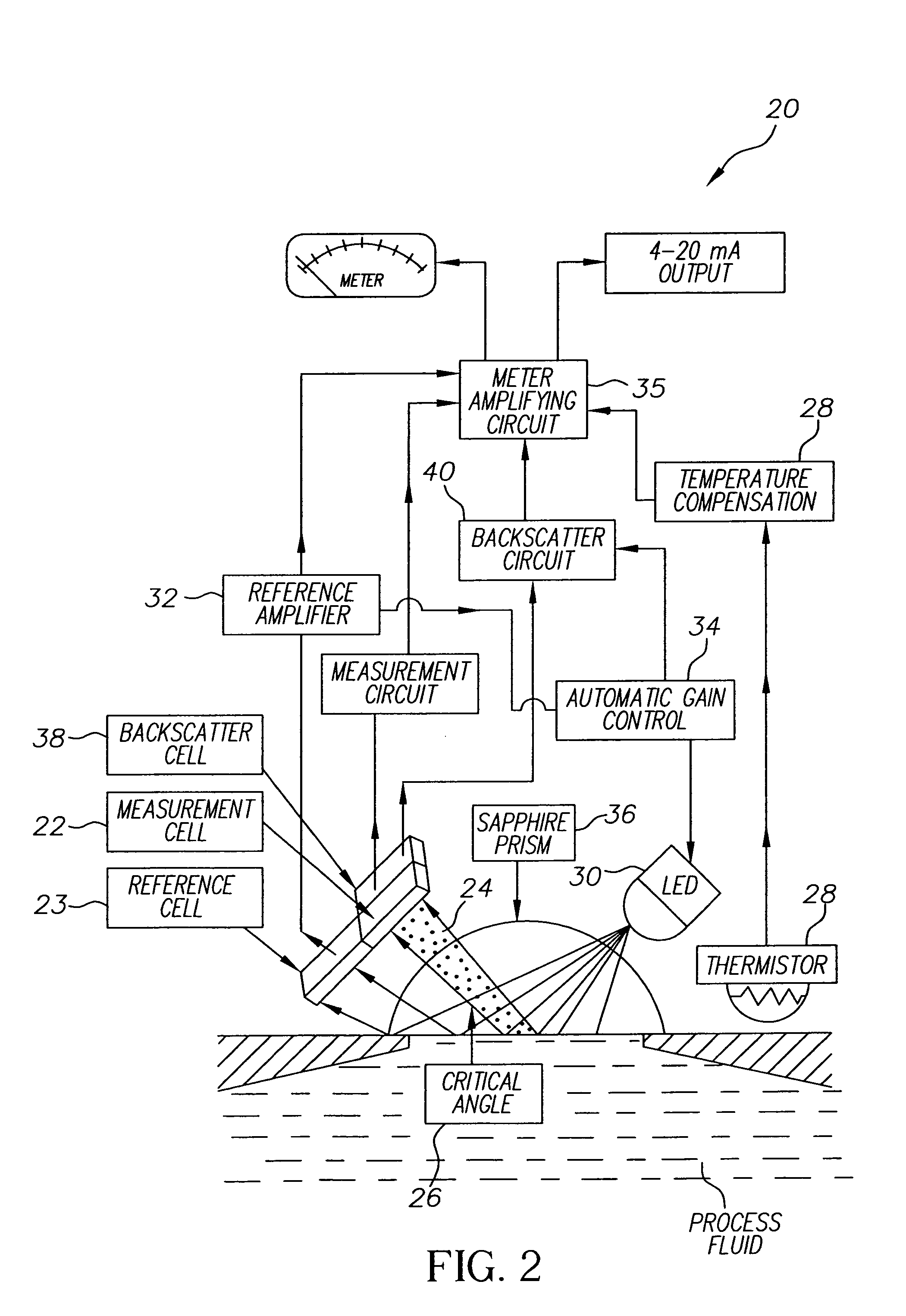
System and method for controlling ink concentration using a refractometer
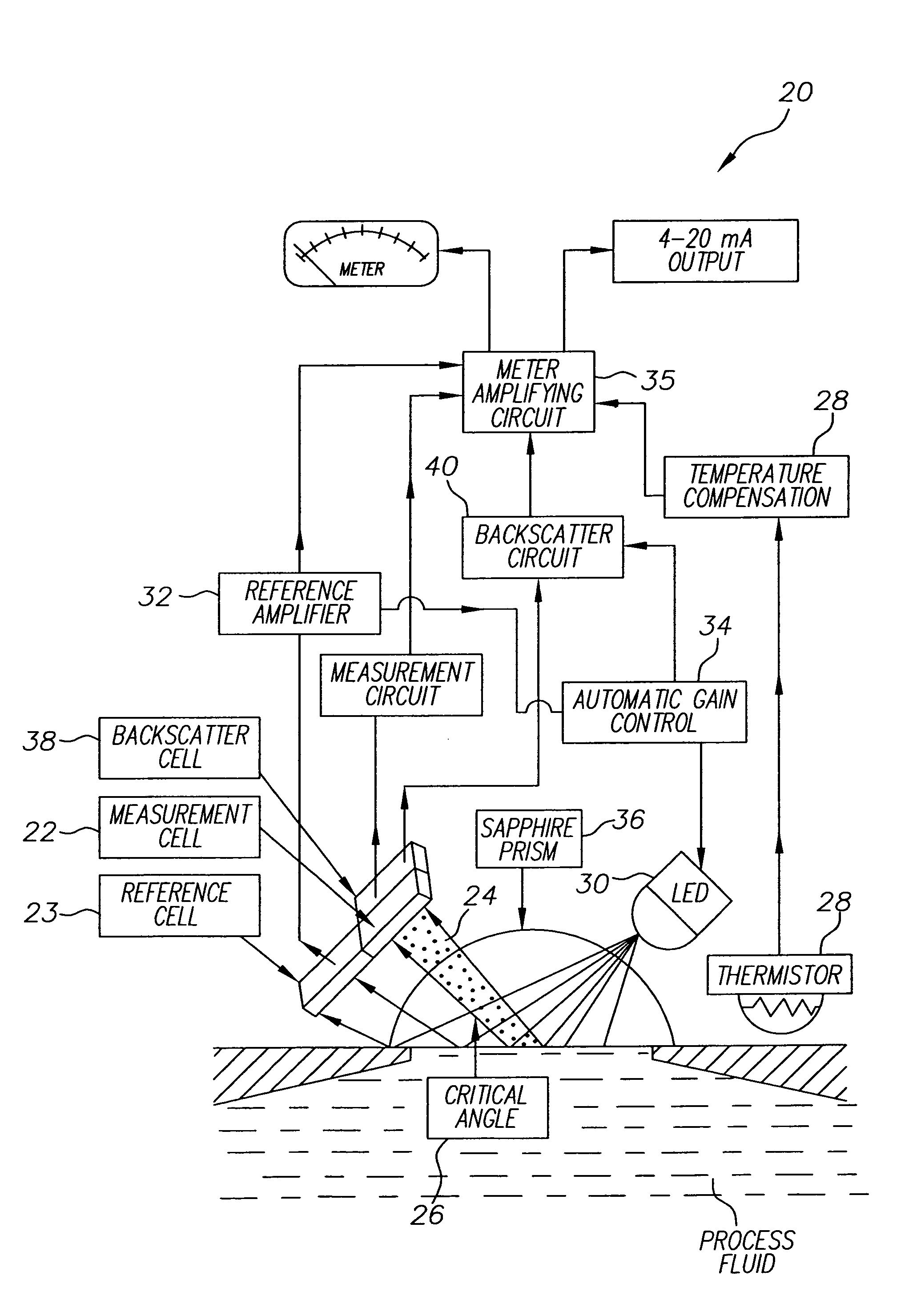
The present invention relates to ink output in ink jet printing systems. A refractometer is used to control the concentration of inks used in continuous ink jet printers. A concentration detector measures the total amount of light reflected from a surface. Changes in the ink cause a definite change in sensor output. As the refractive index is changed, shifting the critical angle for internal reflection, more or less light is reflected to the sensor. The index of refraction can be determined from the sensor once corrections are made to account for temperature dependencies of the sensor and light source and baseline measurement of reflected light amplitude. These dependencies are carried out in the refractometer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
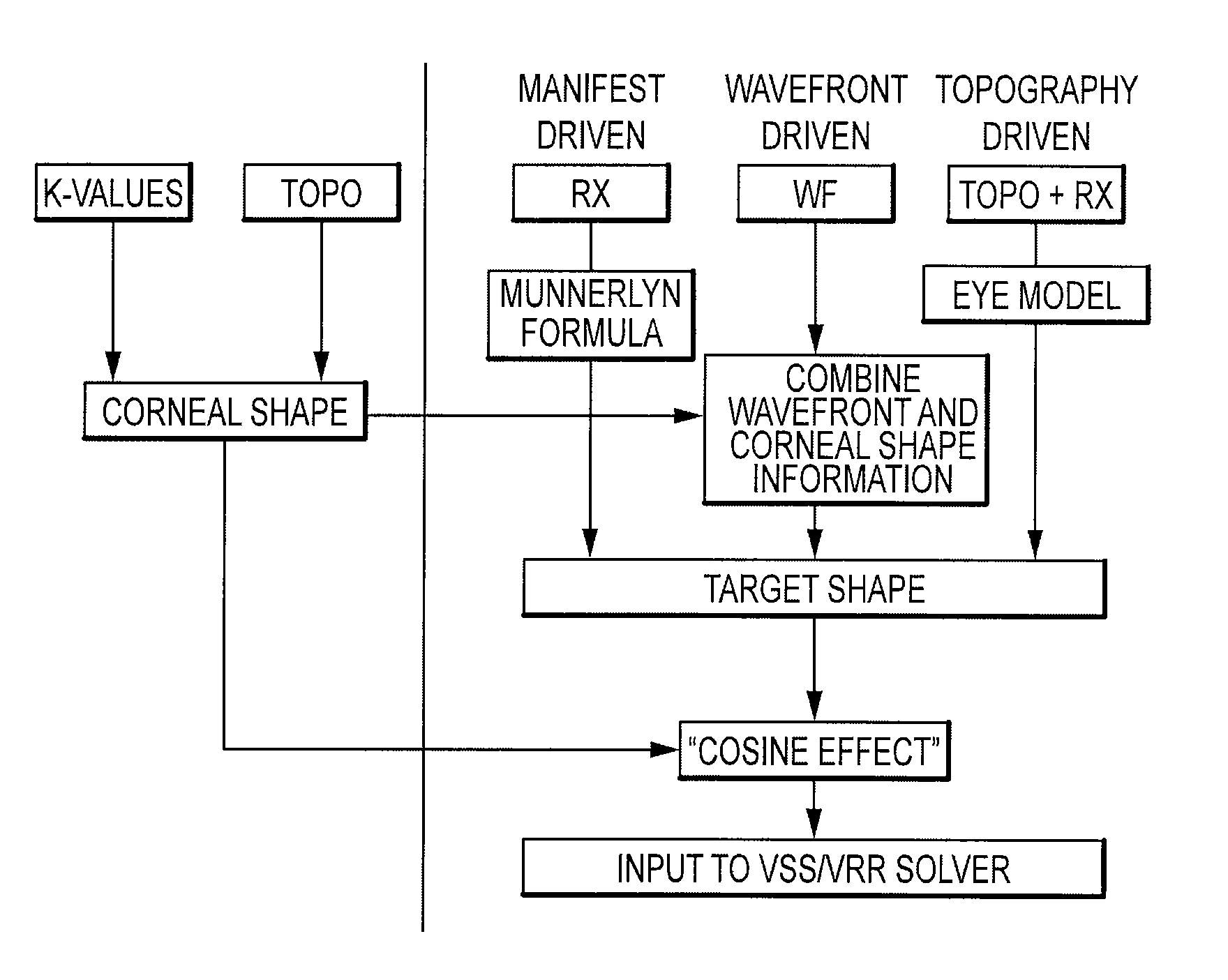
Combined wavefront and topography systems and methods
ActiveUS20080281304A1Easy to implementLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsWavefrontCorneal shape
Methods, software, and systems are provided for determining an ablation target shape for a treatment for an eye of a patient. Techniques include determining wavefront information from the eye of the patient with a wavefront eye refractometer, determining anterior corneal shape information from the eye with a corneal topography device, and combining the wavefront information and the anterior corneal shape information to determine the ablation target shape.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
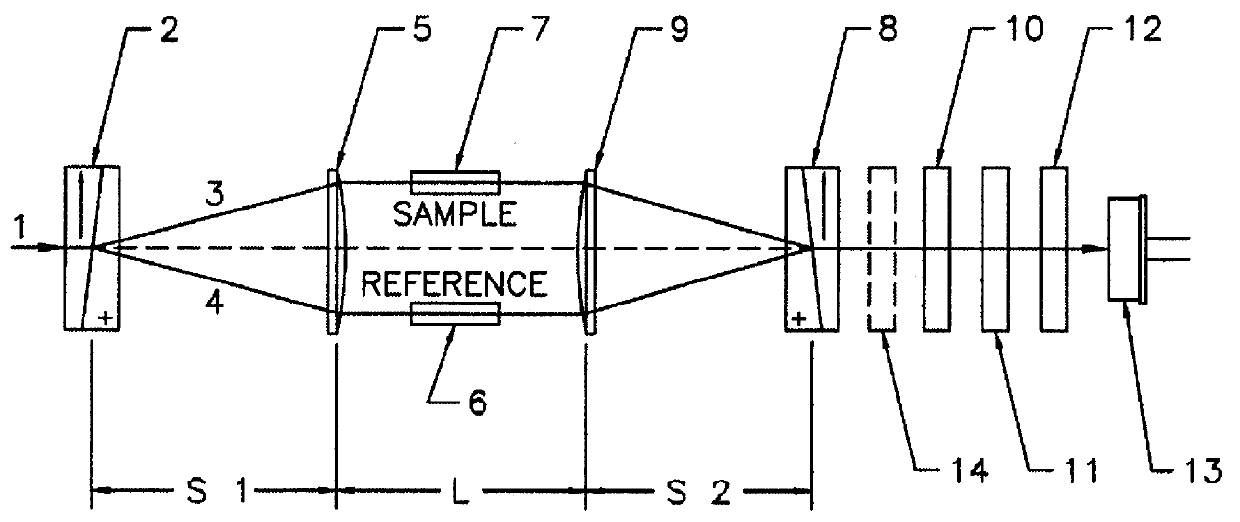
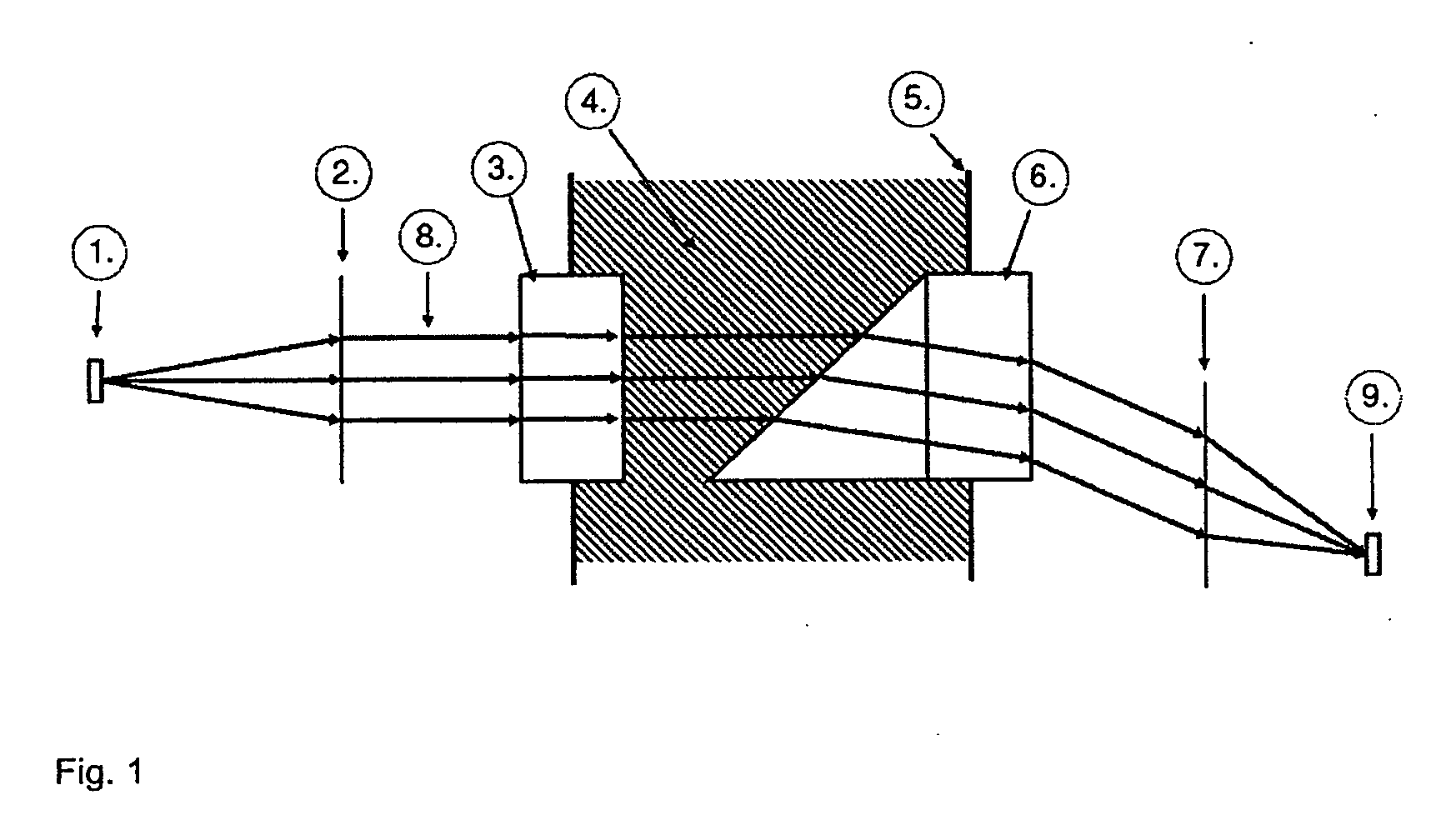
Extended range interferometric refractometer
A method and apparatus is disclosed for measuring the refractive index difference between a reference and sample liquid based on an interferometric design. The resultant device has an almost unlimited range of operation in contrast to a conventional interferometric refractometer of the so-called polarization type whose dynamic range is restricted to a relatively narrow range of refractive indices. The measurement of the refractive index difference between a sample and reference cell is achieved by measuring the angle through which the plane of polarization of a combined beam has rotated. For the conventional device, this angle is restricted to about pi radians which corresponds to a half wavelength shift between the reference and sample components of said combined beam. The extended range device disclosed permits this angle to be tracked and measured accurately over many rotations. The rotation tracking is achieved by one of three embodiments, the preferred of which involves the use of a liquid crystal retarder. The other two techniques incorporate, respectively, a rotating polarizer and a doubly split beam. All three embodiments permit the measurement of both the sine and cosine of the rotation angle and, thereby, allows a four quadrant arctangent calculation to yield the rotation angle directly. The error associated with such measurements is not a function of the rotation angle of the combined beams.
Owner:WYATT TECH
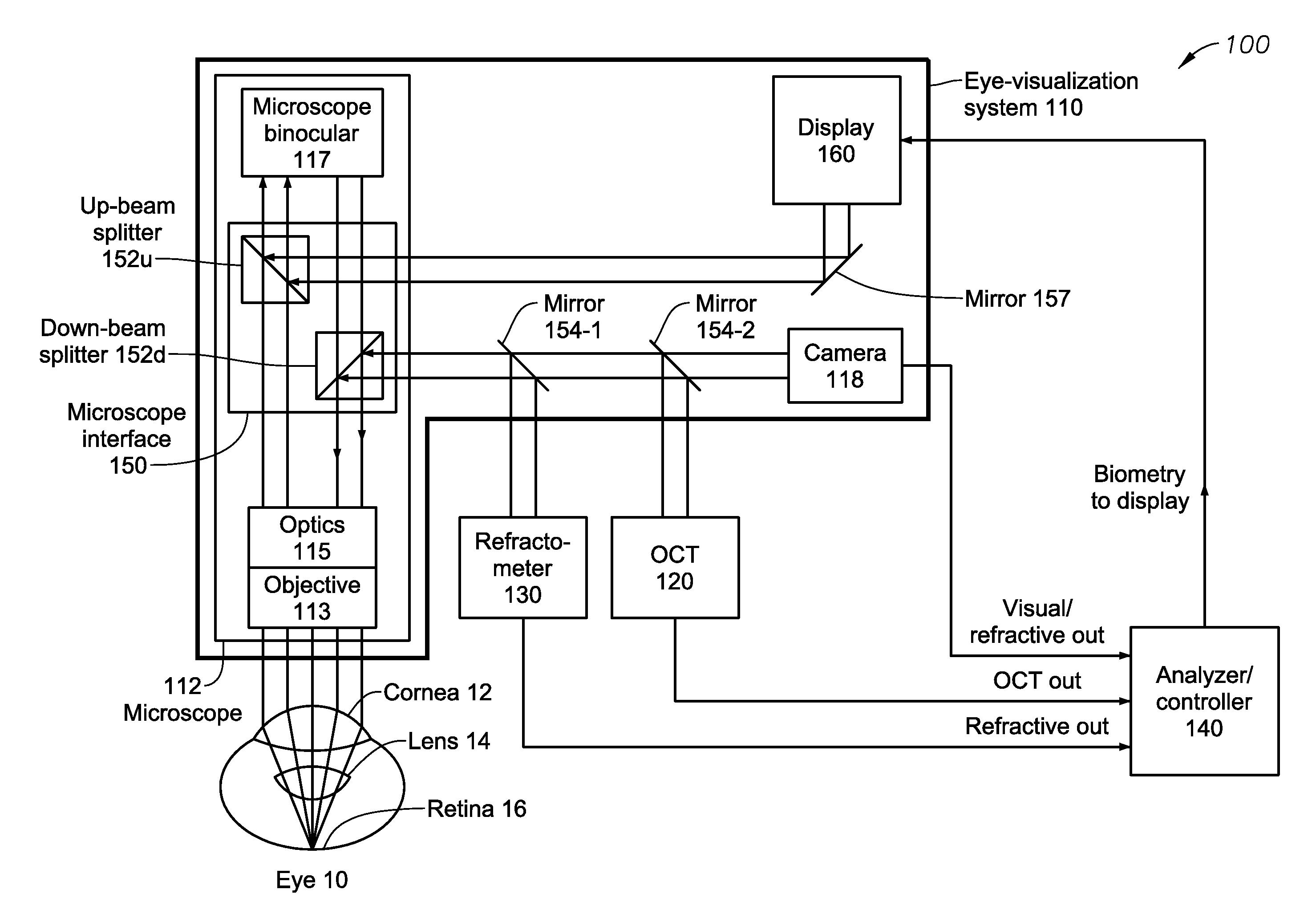
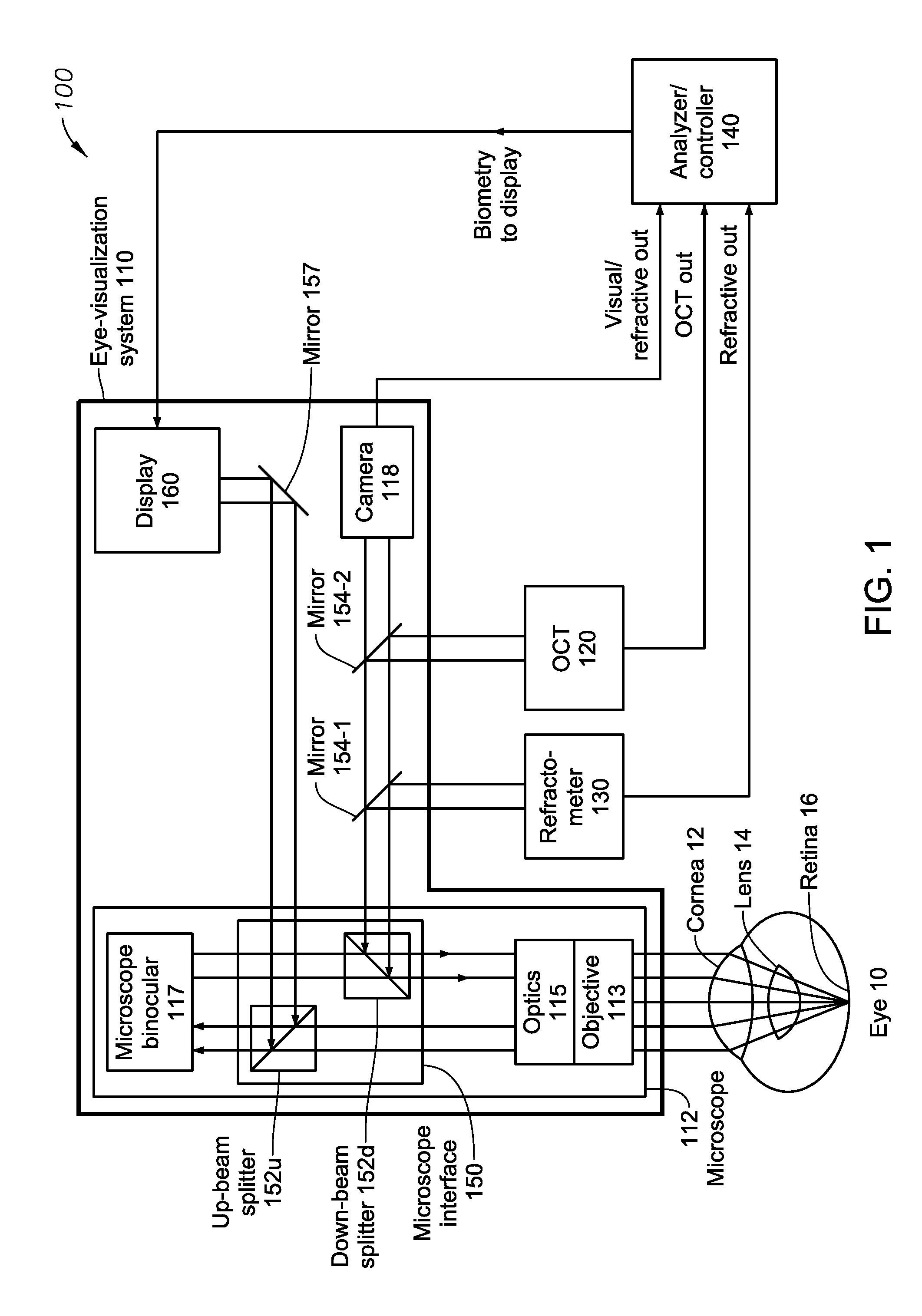
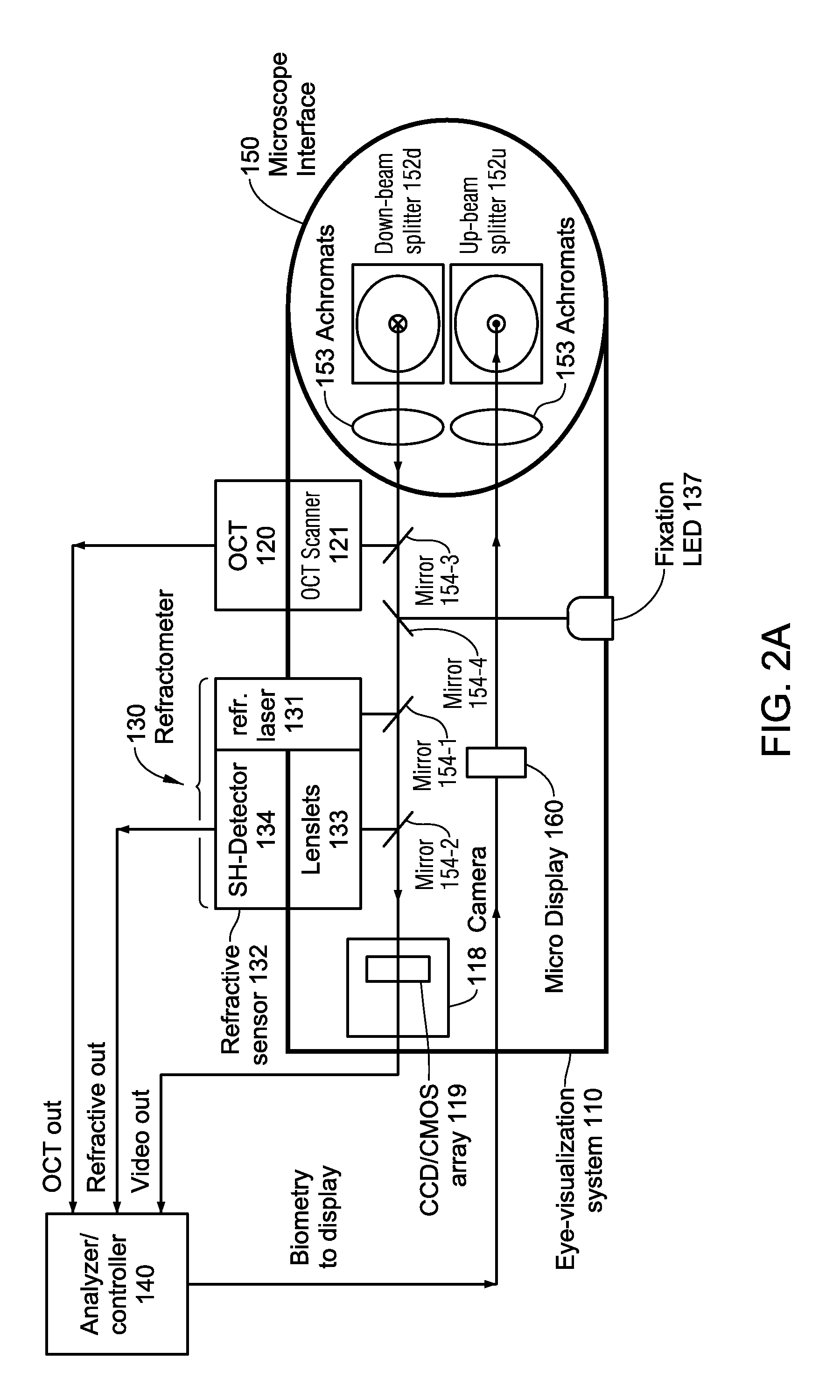
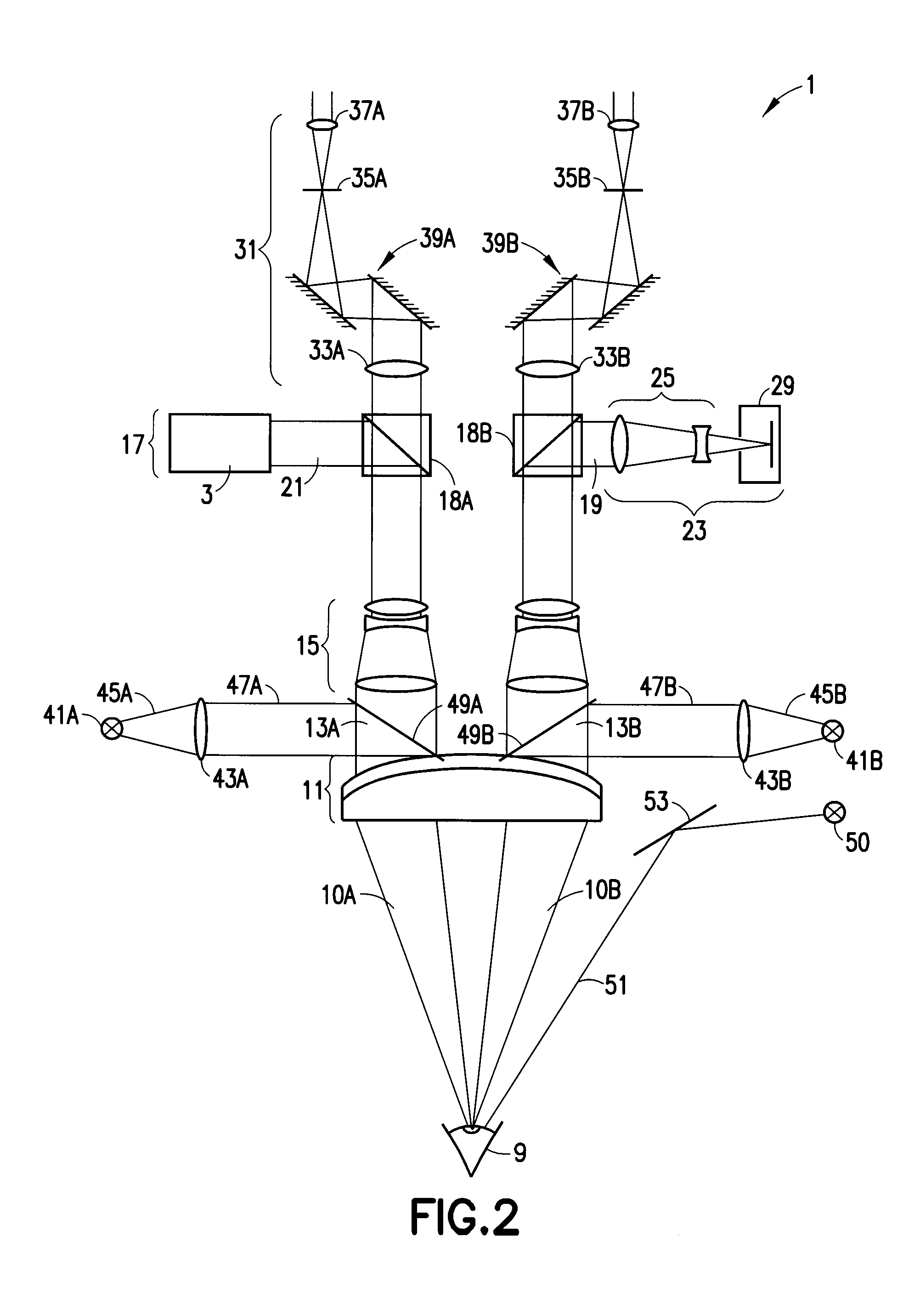
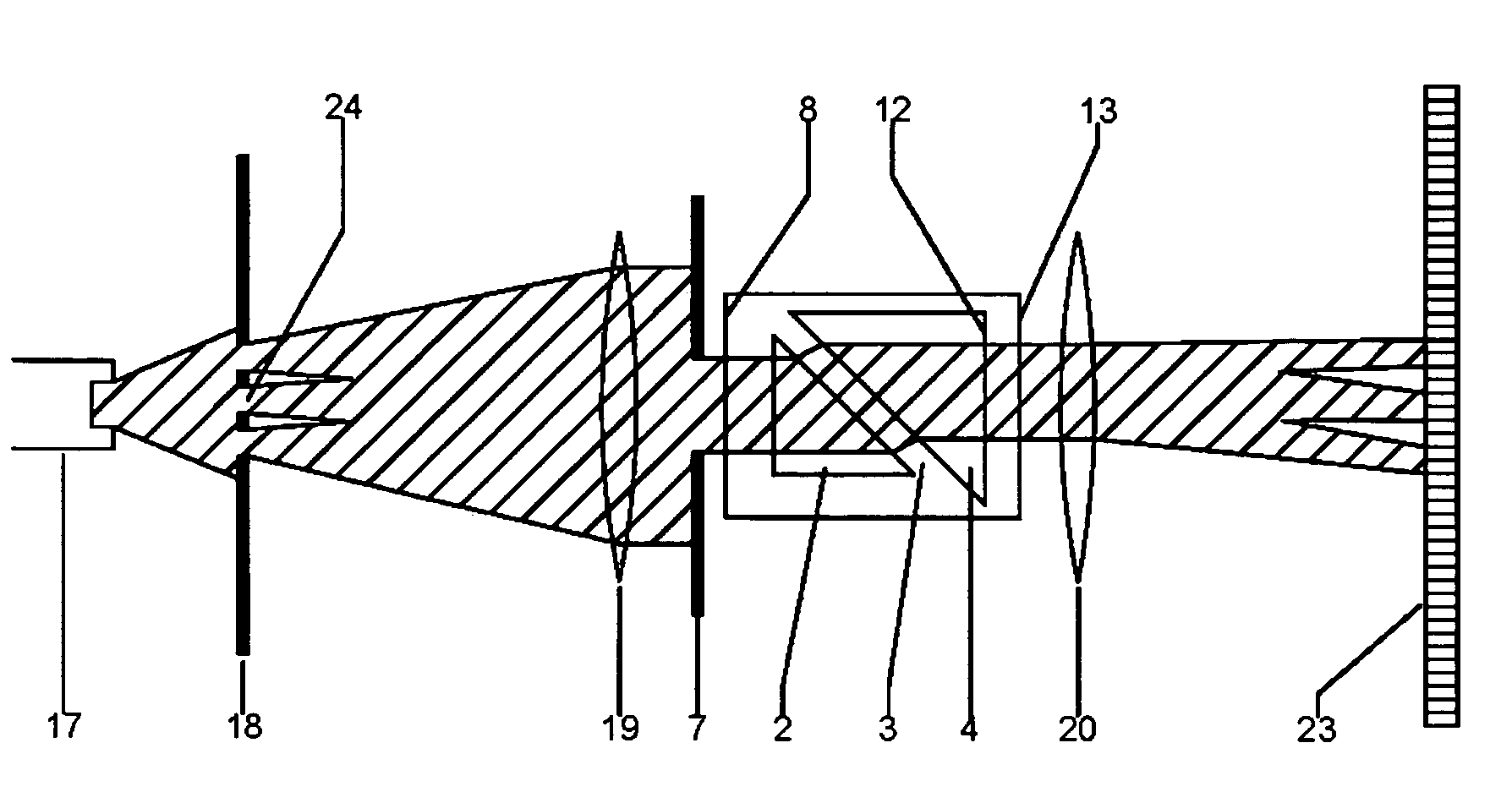
Integrated OCT-Refractometer System for Ocular Biometry
ActiveUS20150077705A1Improve accuracyIncrease choiceLaser surgeryRefractometersSlit lampVisual perception
A Slit-lamp-or-Microscope-Integrated-OCT-Refractometer system includes an eye-visualization system, configured to provide a visual image of an imaged region in an eye; an Optical Coherence Tomographic (OCT) imaging system, configured to generate an OCT image of the imaged region; a refractometer, configured to generate a refractive mapping of the imaged region; and an analyzer, configured to determine refractive characteristics of the eye based on the OCT image and the refractive mapping, wherein the refractometer and the OCT imaging system are integrated into the eye visualization system.
Owner:ALCON INC
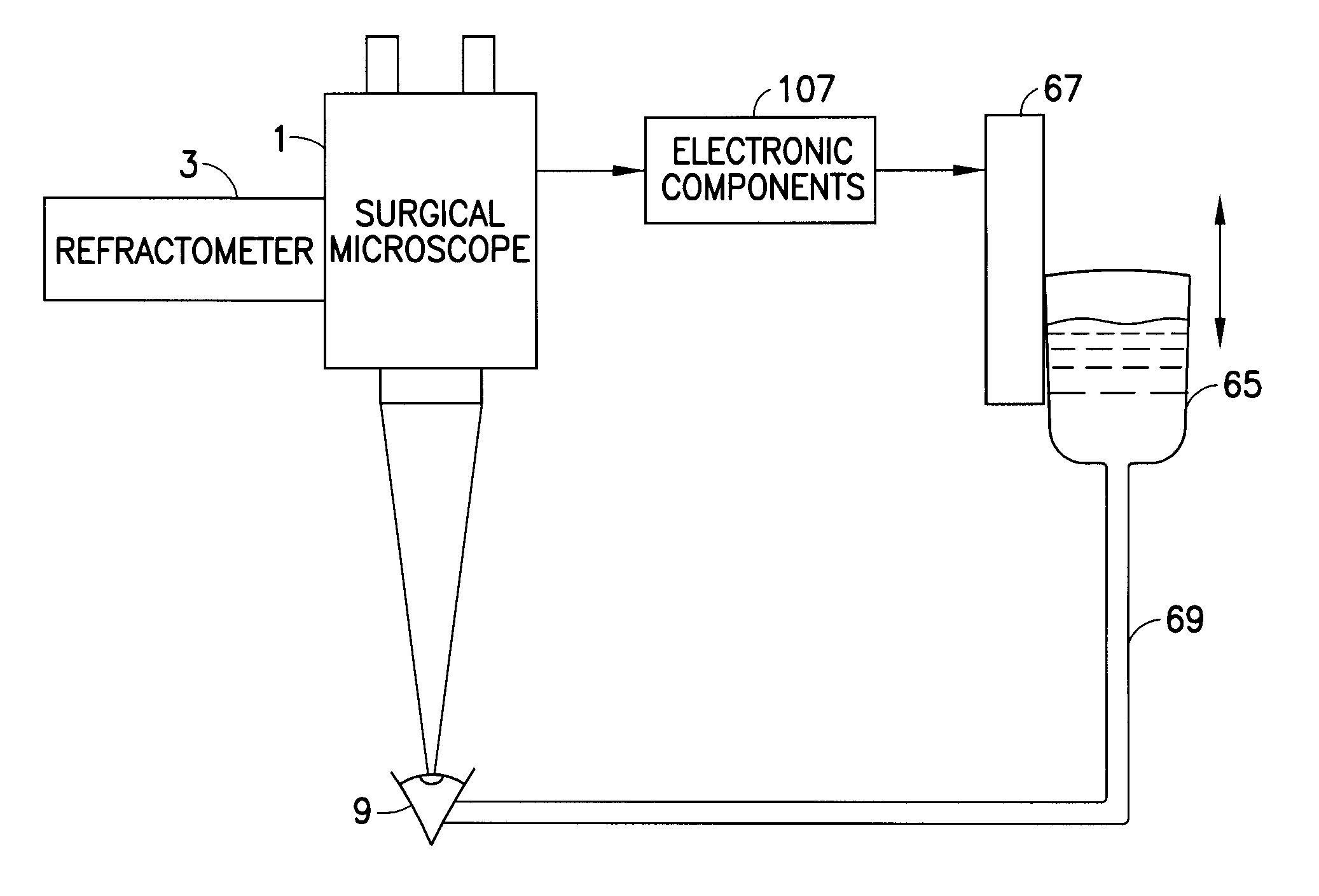
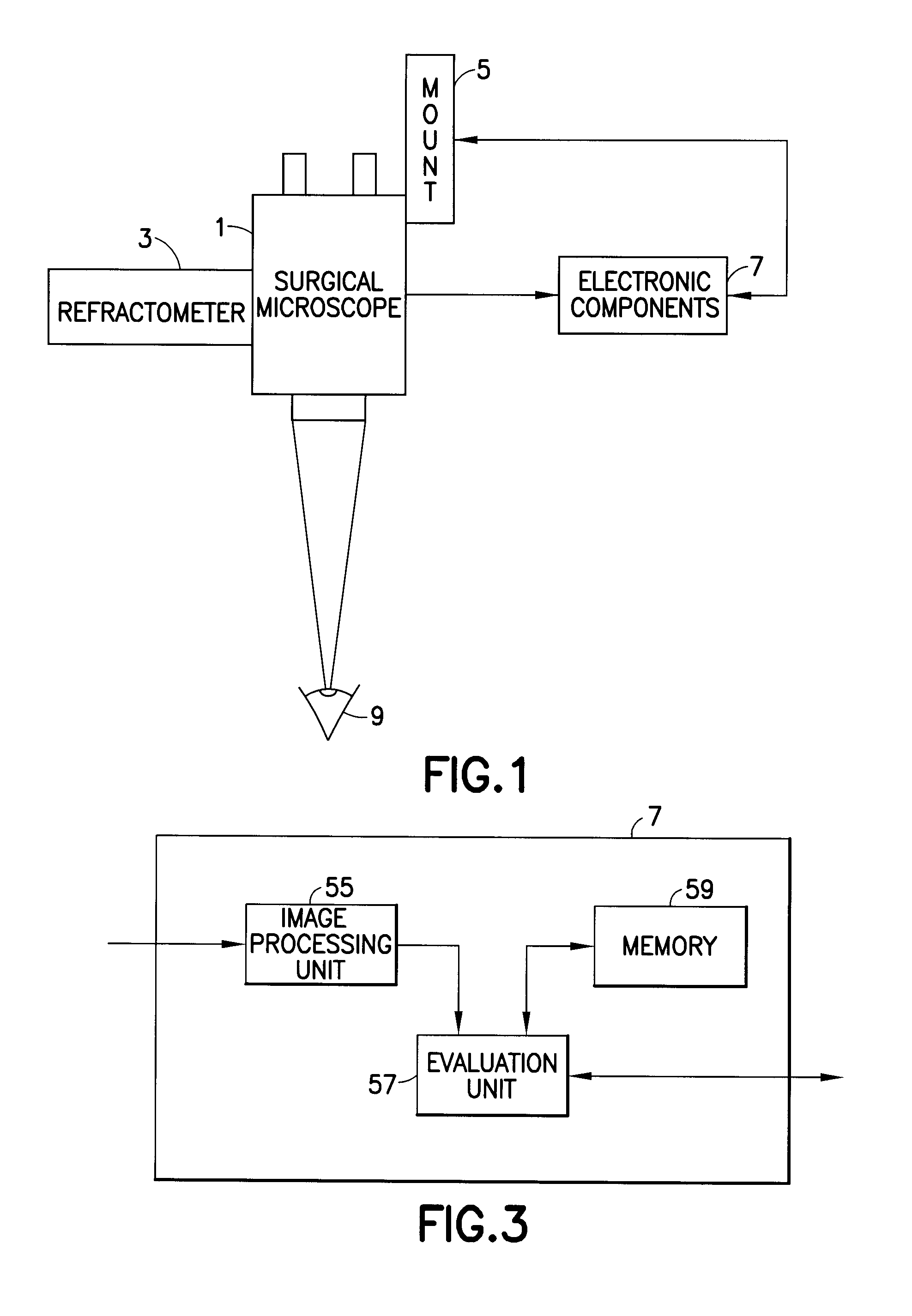
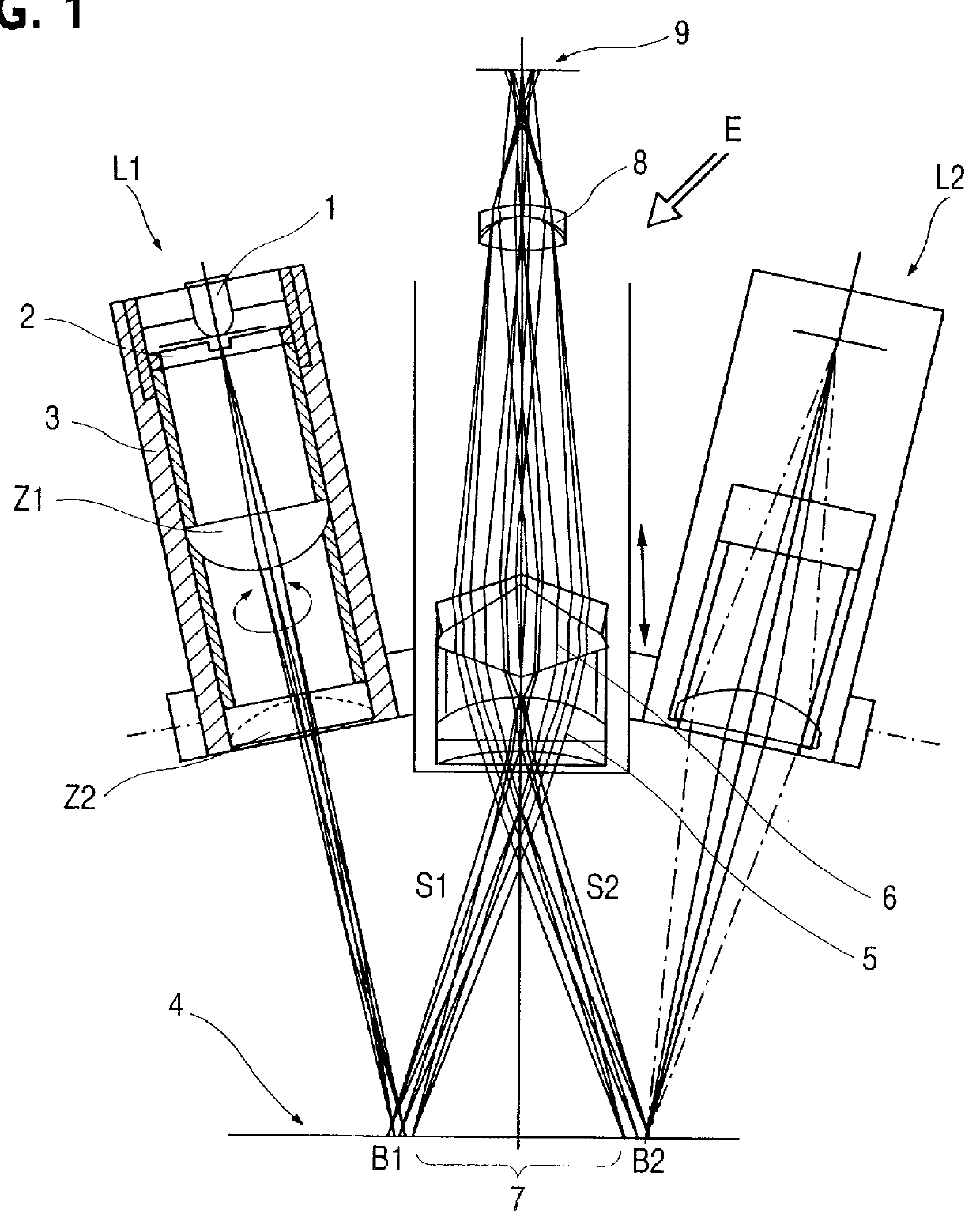
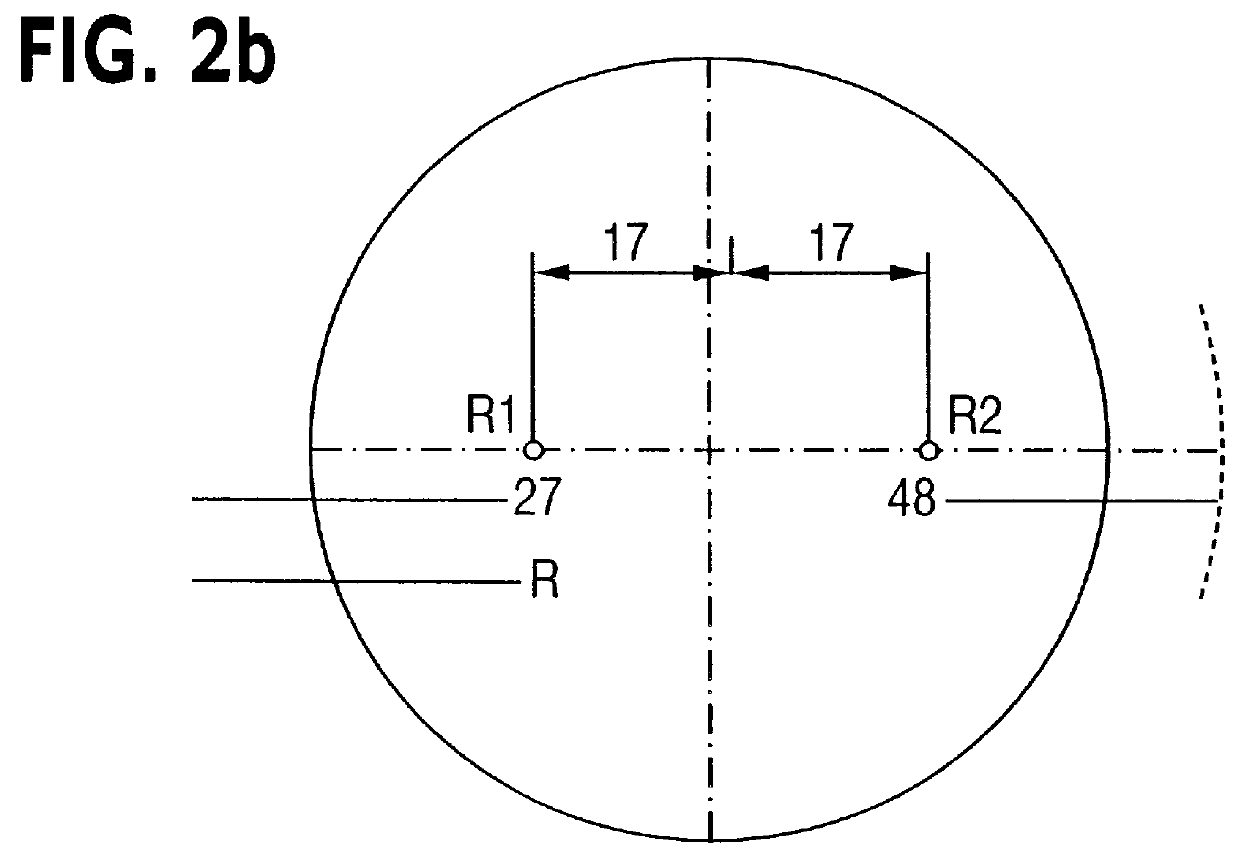
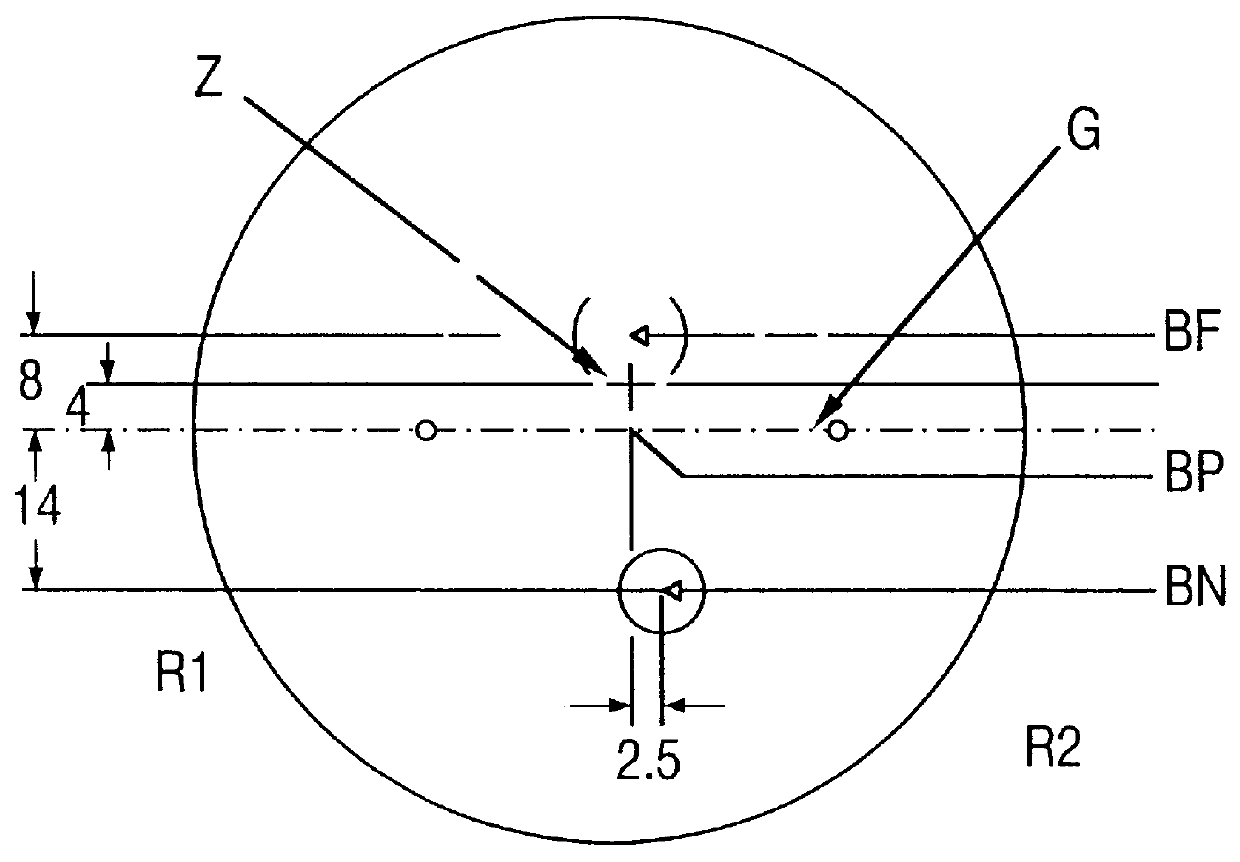
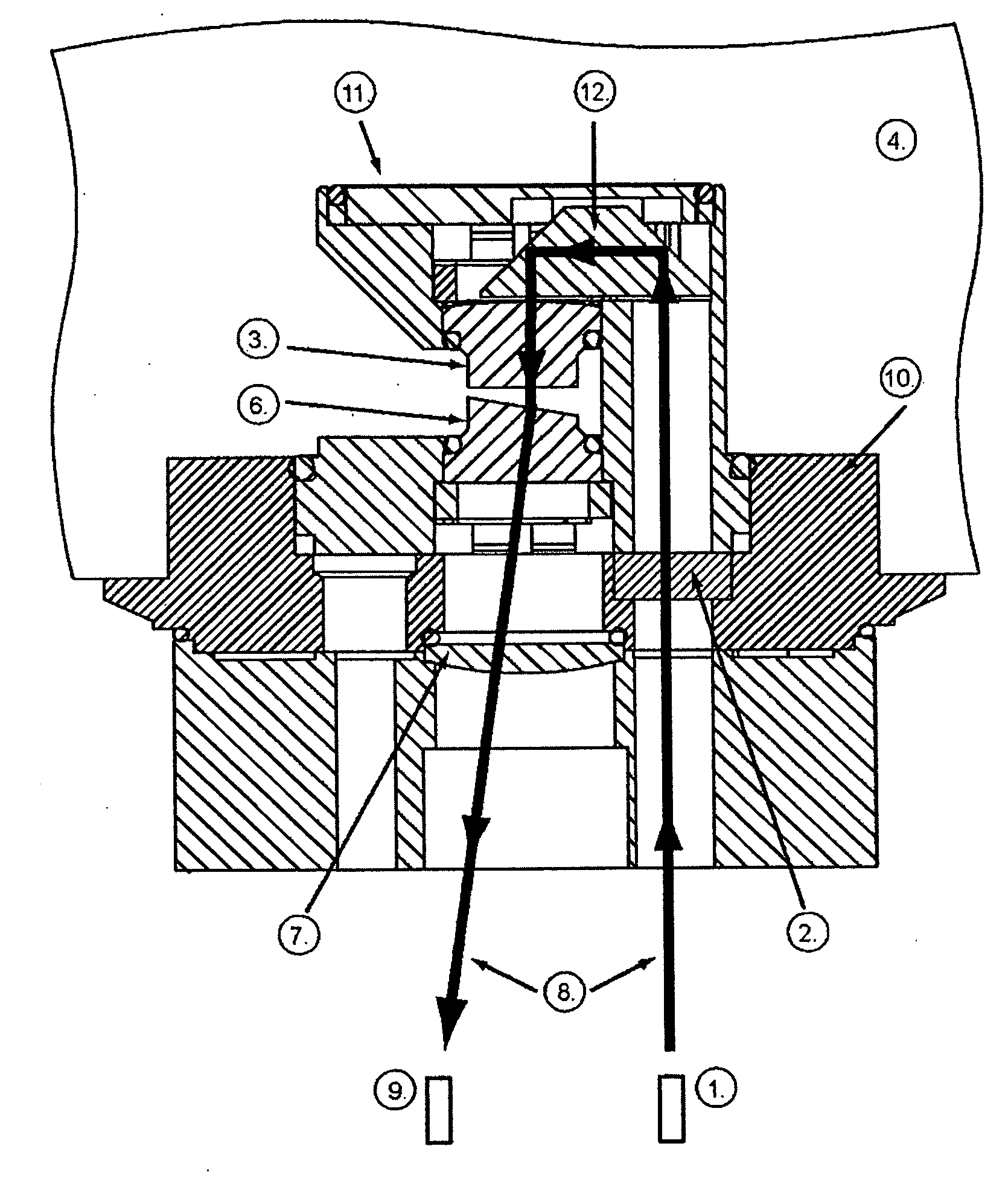
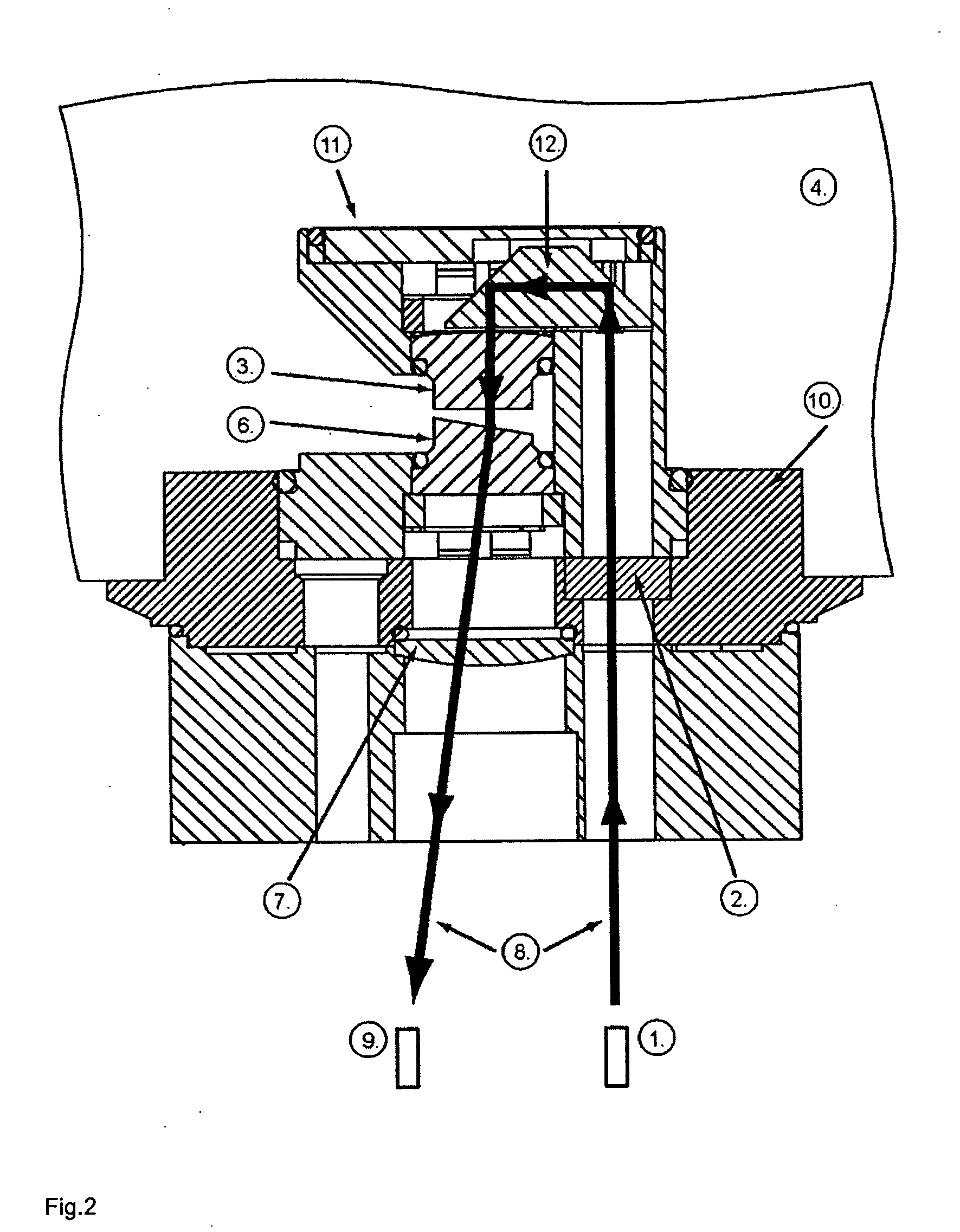
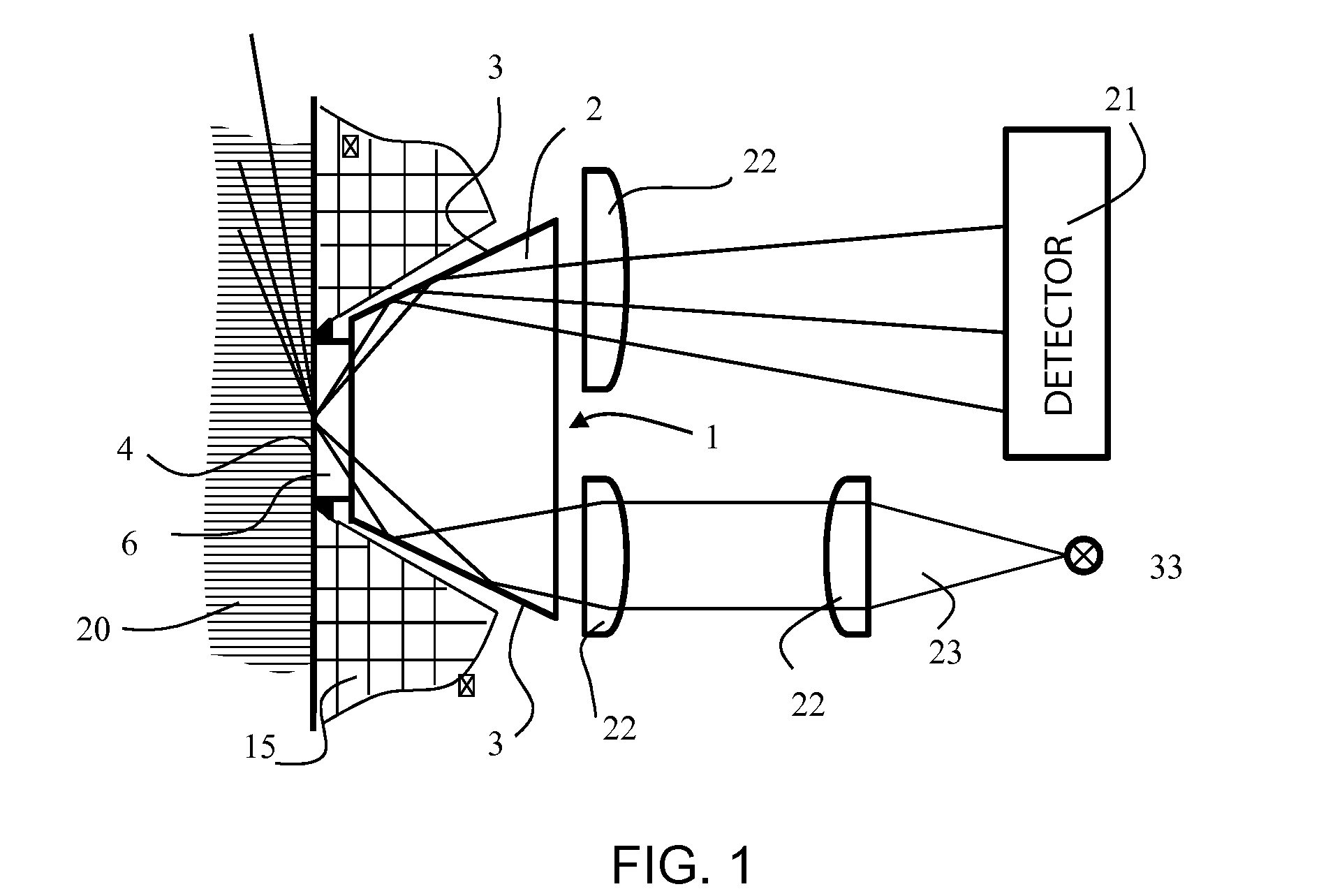
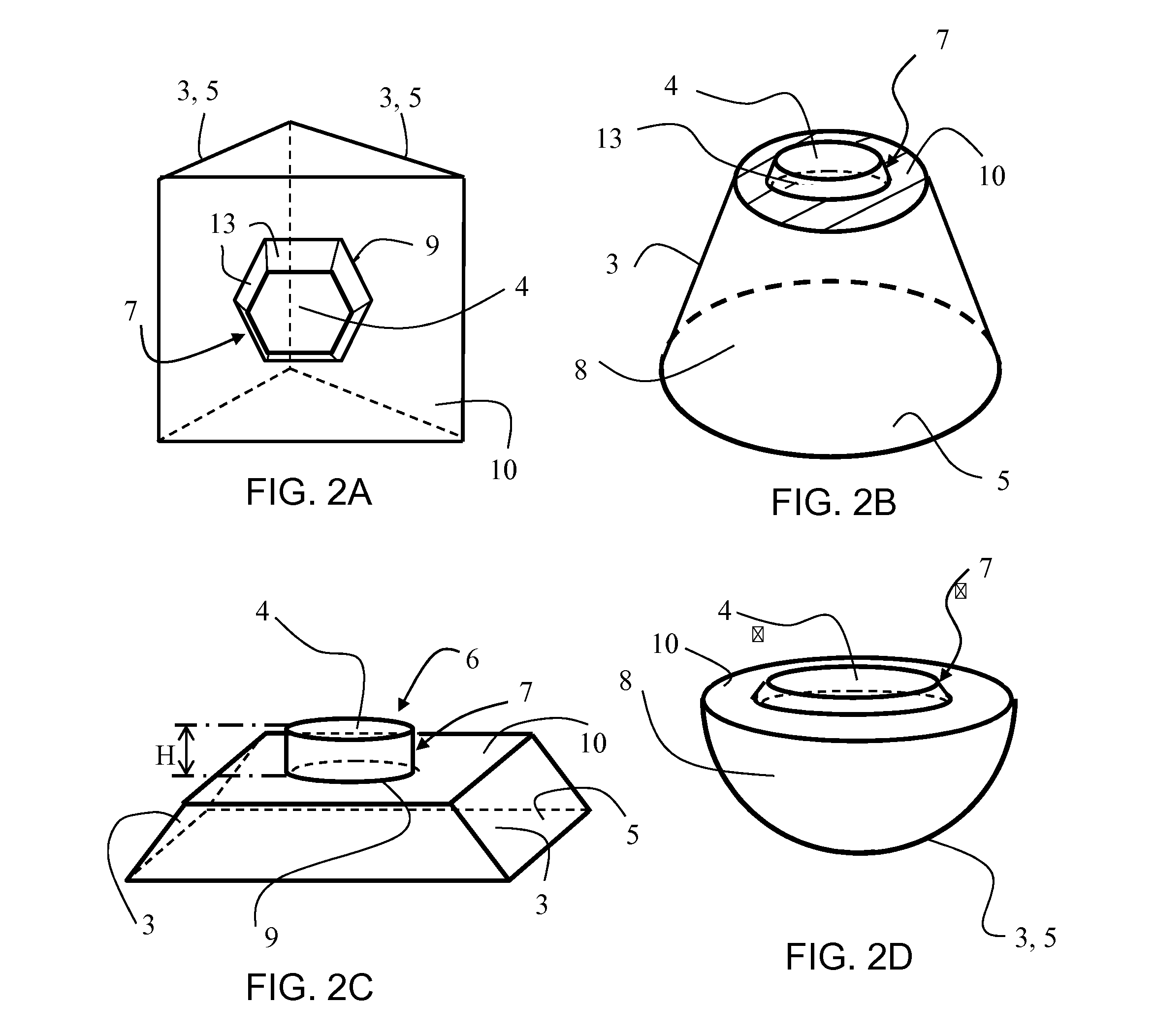
Measurement system and method for establishing the refraction of an eye, the radius of curvature of the cornea or the internal pressure of an eye
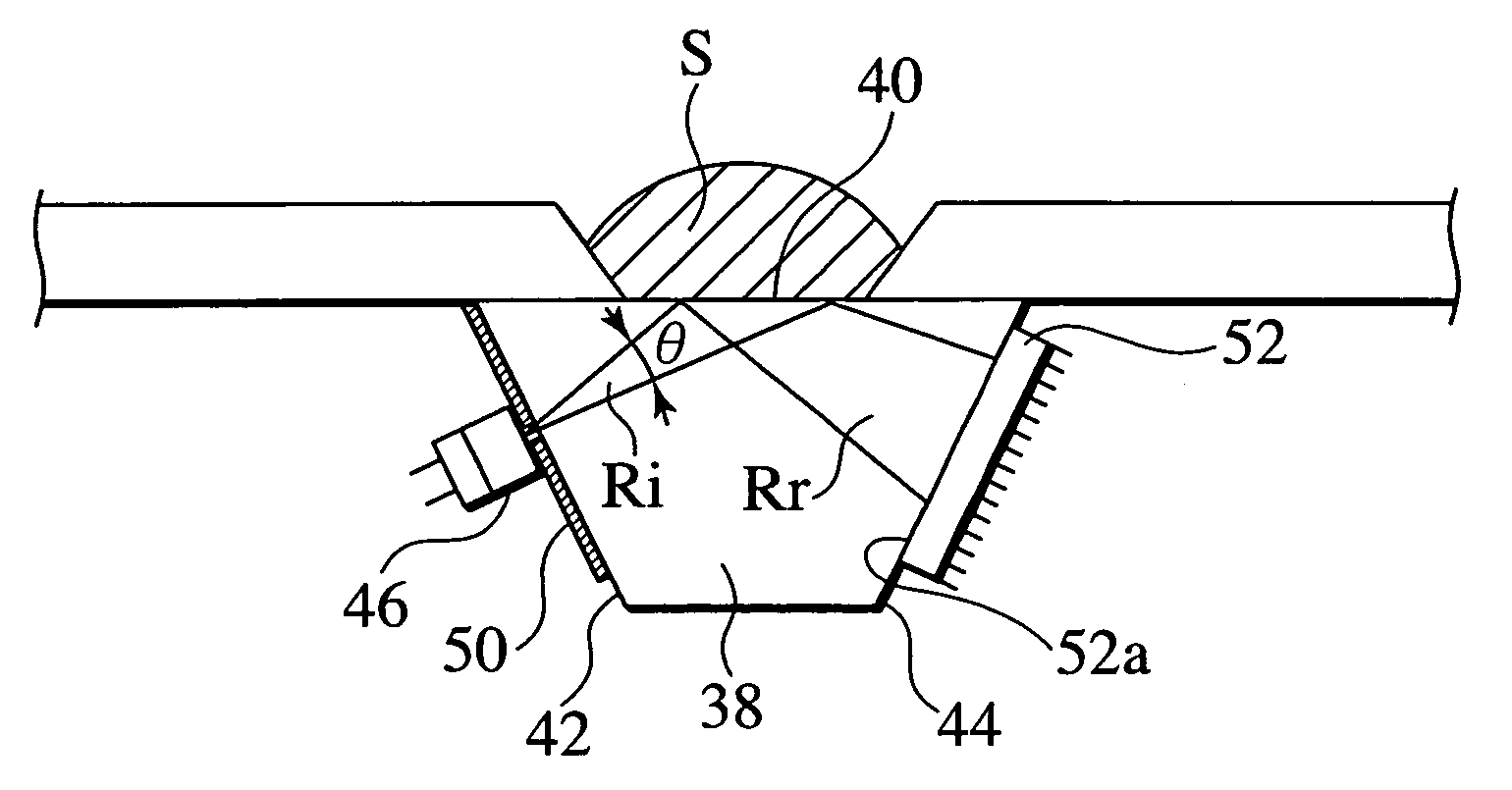
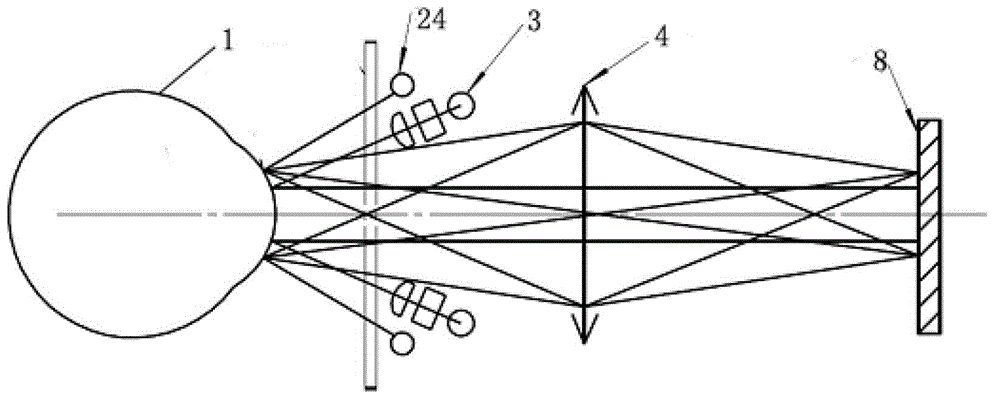
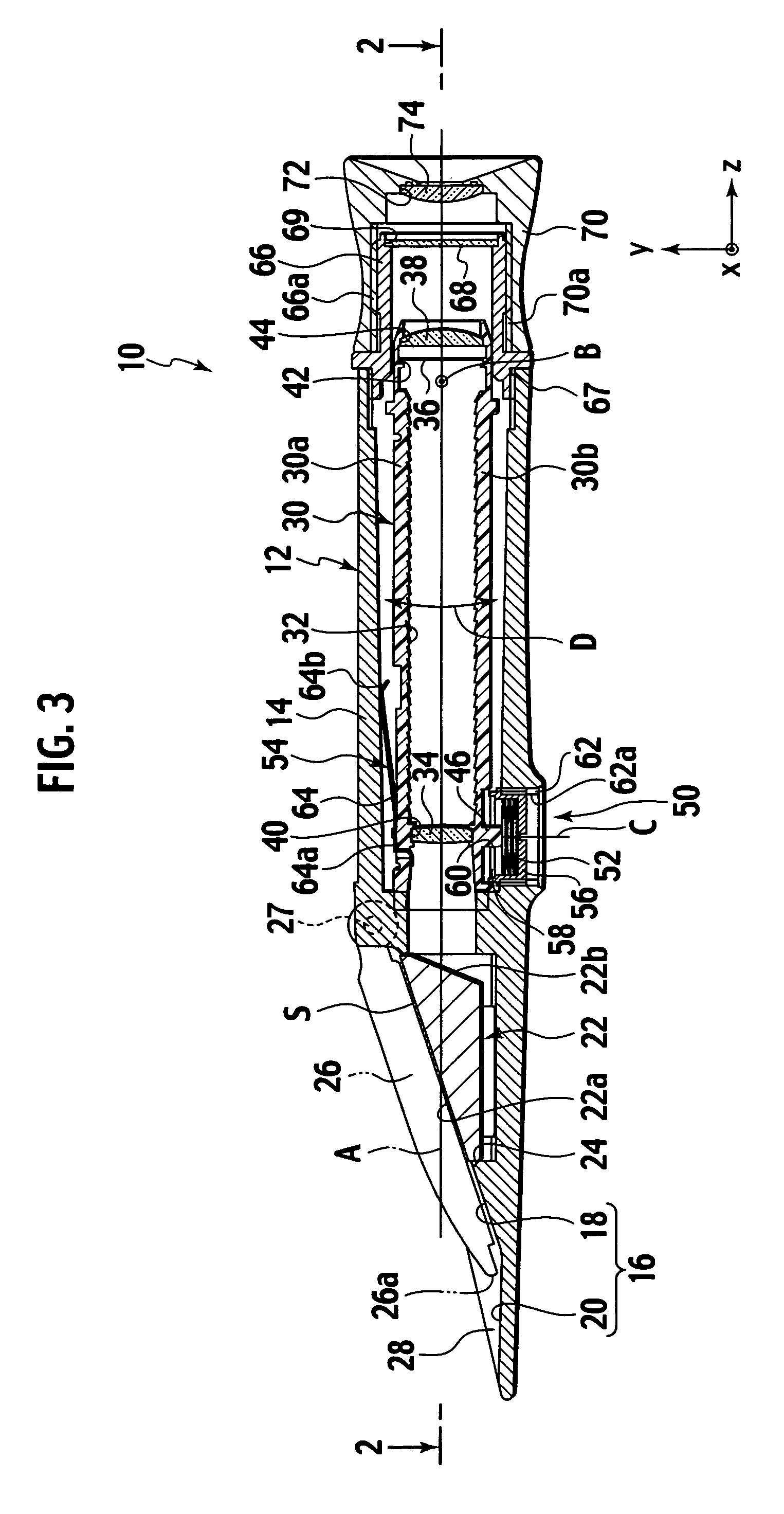
A method for establishing the refraction of an eye (9) by means of a refractometer (3) is provided, in which the current visual axis (S) of the eye (9) is established before establishing the refraction, the refractometer (3) is aligned with respect to the visual axis (S) of the eye (9) and the refraction is established after the alignment. The visual axis (S) of the eye (9) is established on the basis of the position of a Purkinje image of at least one light source (41, 50) used to illuminate the eye and a relationship between the position of the Purkinje image and the visual axis (S).
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
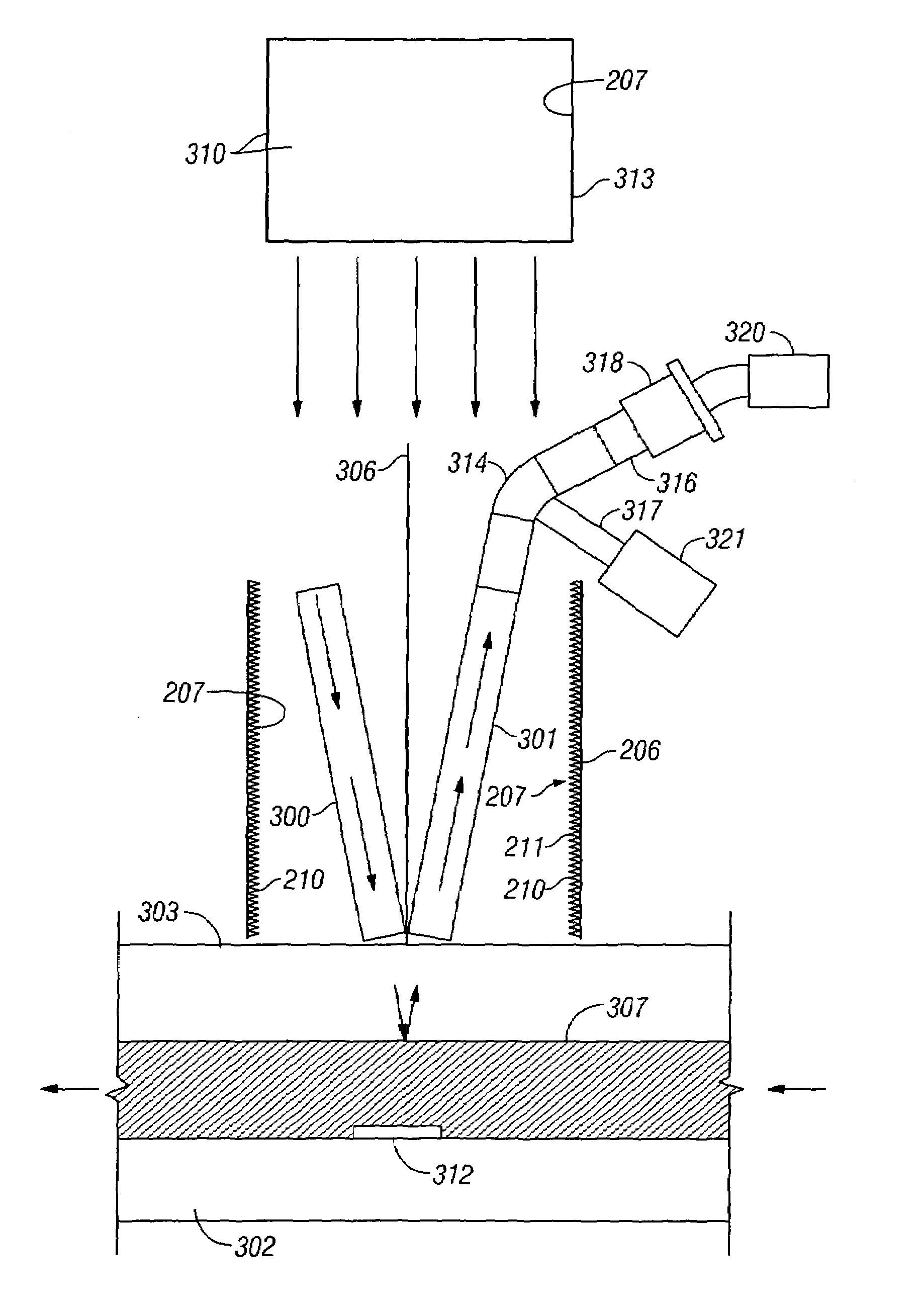
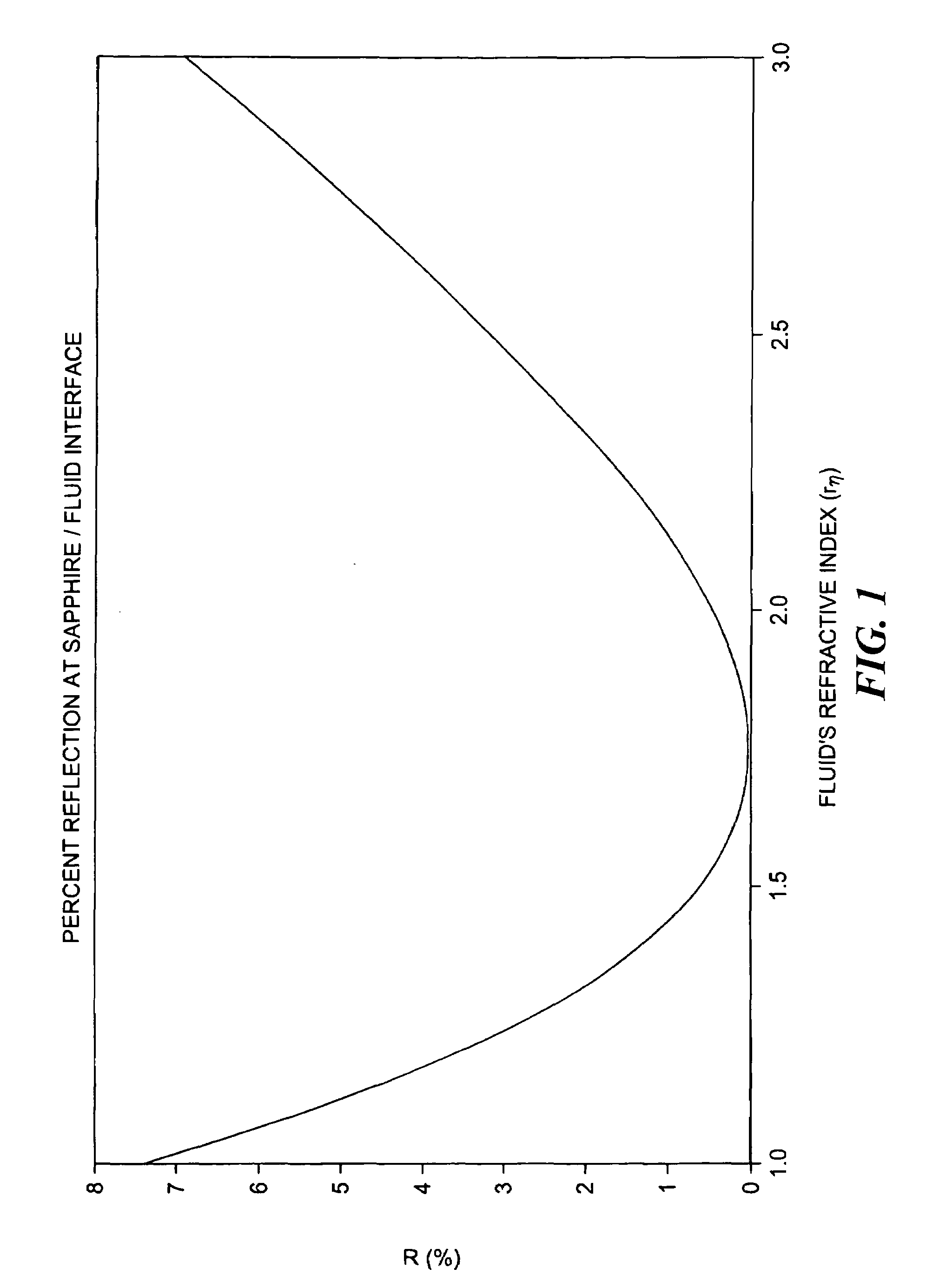
Method and apparatus for a downhole refractometer and attenuated reflectance spectrometer
InactiveUS7016026B2Increase brightnessLess sensitiveRadiation pyrometrySamplingReflection spectroscopySpectrometer
The invention relates to refractometry and attenuated reflectance spectrometry in a wellbore environment. Specifically, it pertains to a robust apparatus and method for measuring refractive index of fluids along a continuum (rather than in steps), and for measuring attenuated reflectance spectra, and for interpreting the measurements made with this apparatus to determine a variety of formation fluid parameters. The present invention provides a method and apparatus to distinguish between gas and liquid based on the much lower index of refraction of gas. It can also be used to monitor fluid sample clean up over time. The refractive index of a wellbore fluid is determined from the fraction, R, of light reflected off the interface between a transparent window that has a known refractive index and this fluid. Preferably, the refractive index is measured at some wavelength of light for which the fluid is not highly attenuating but is optimally attenuating. The adjacent transmission spectrometer can be used to correct the refractive index measurement for attenuation at those wavelengths, which it monitors. Also, this reflection-based refractometer design can be used as an attenuated reflectance spectrometer at highly attenuating wavelengths.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
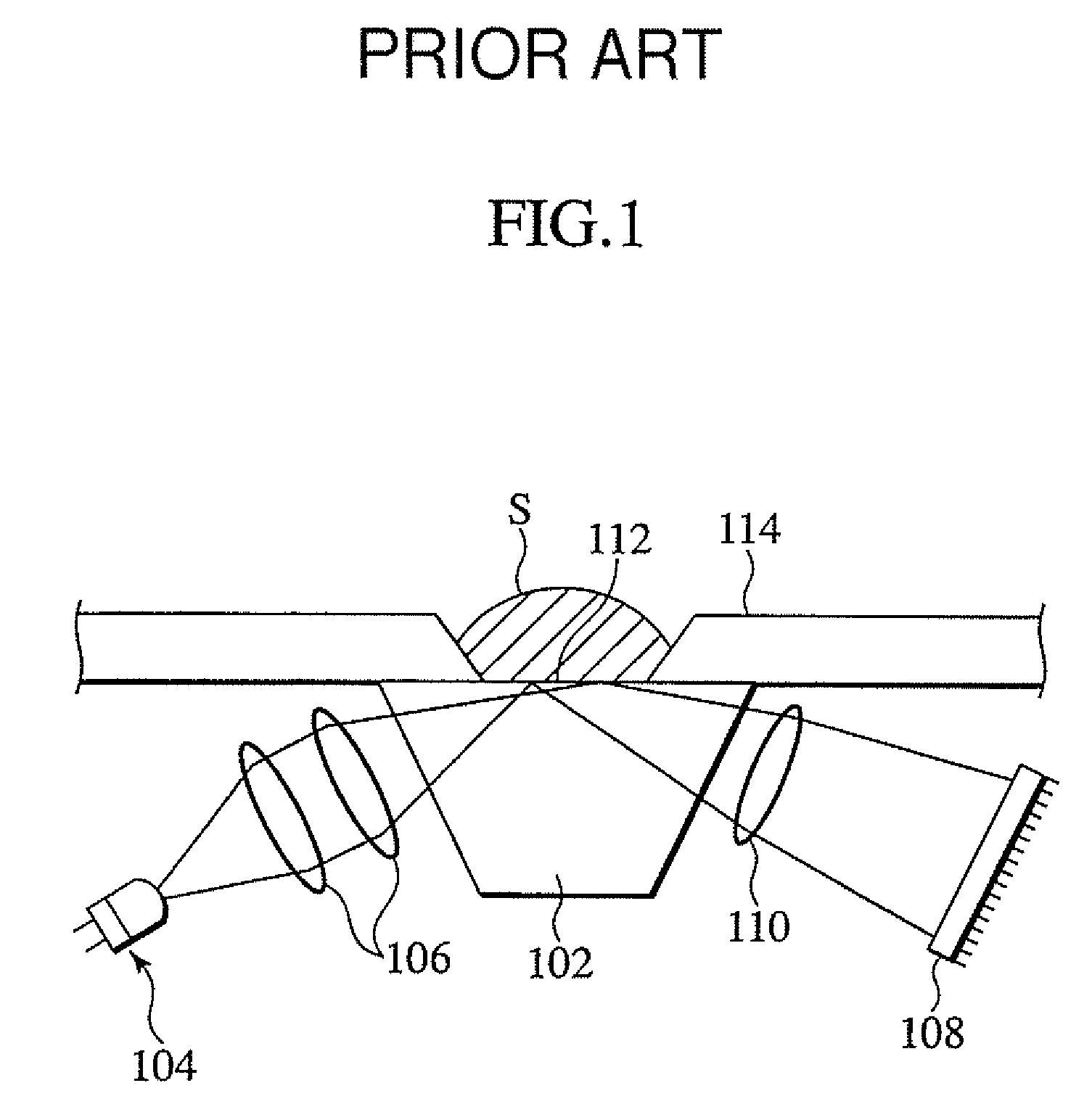
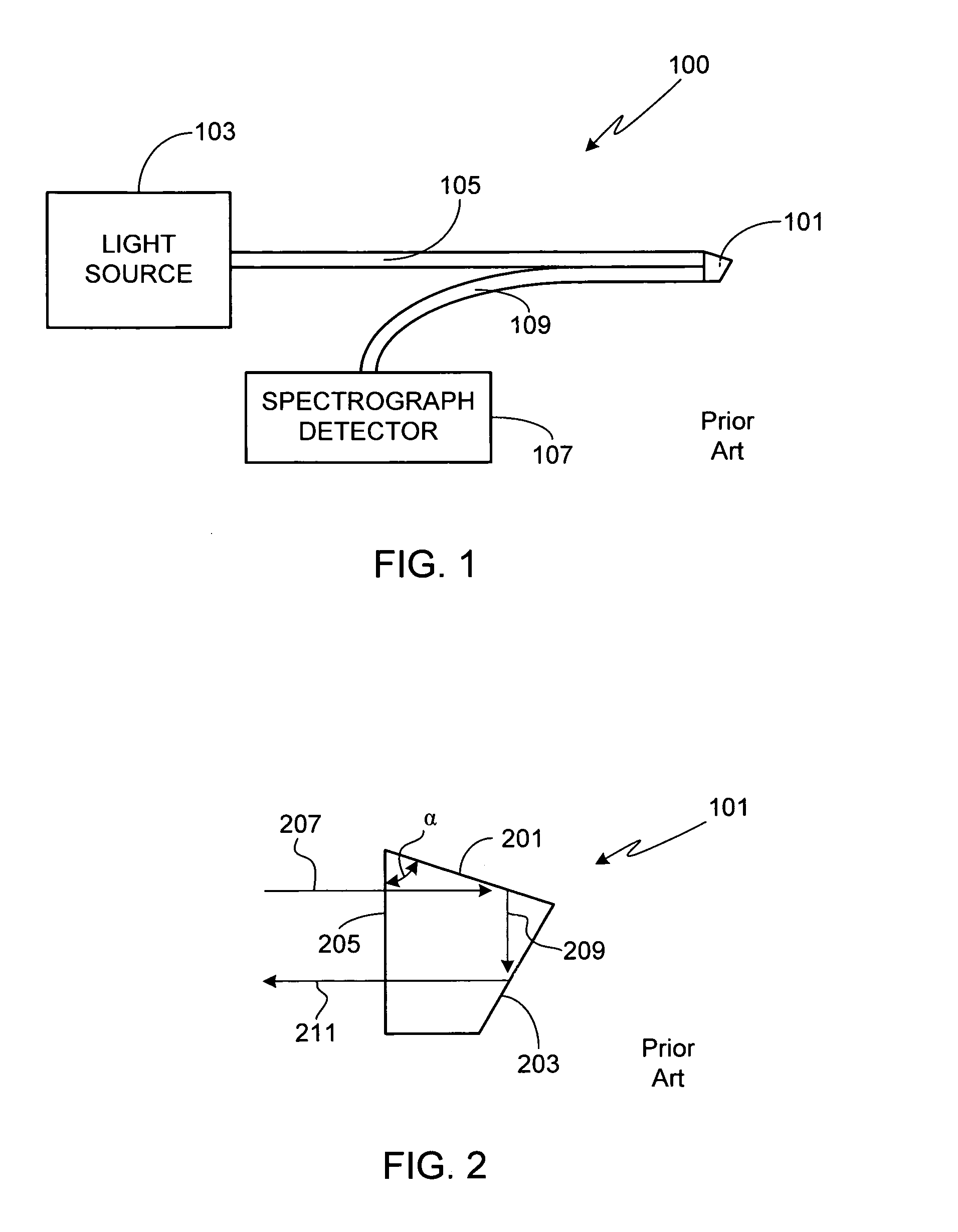
Refractometer
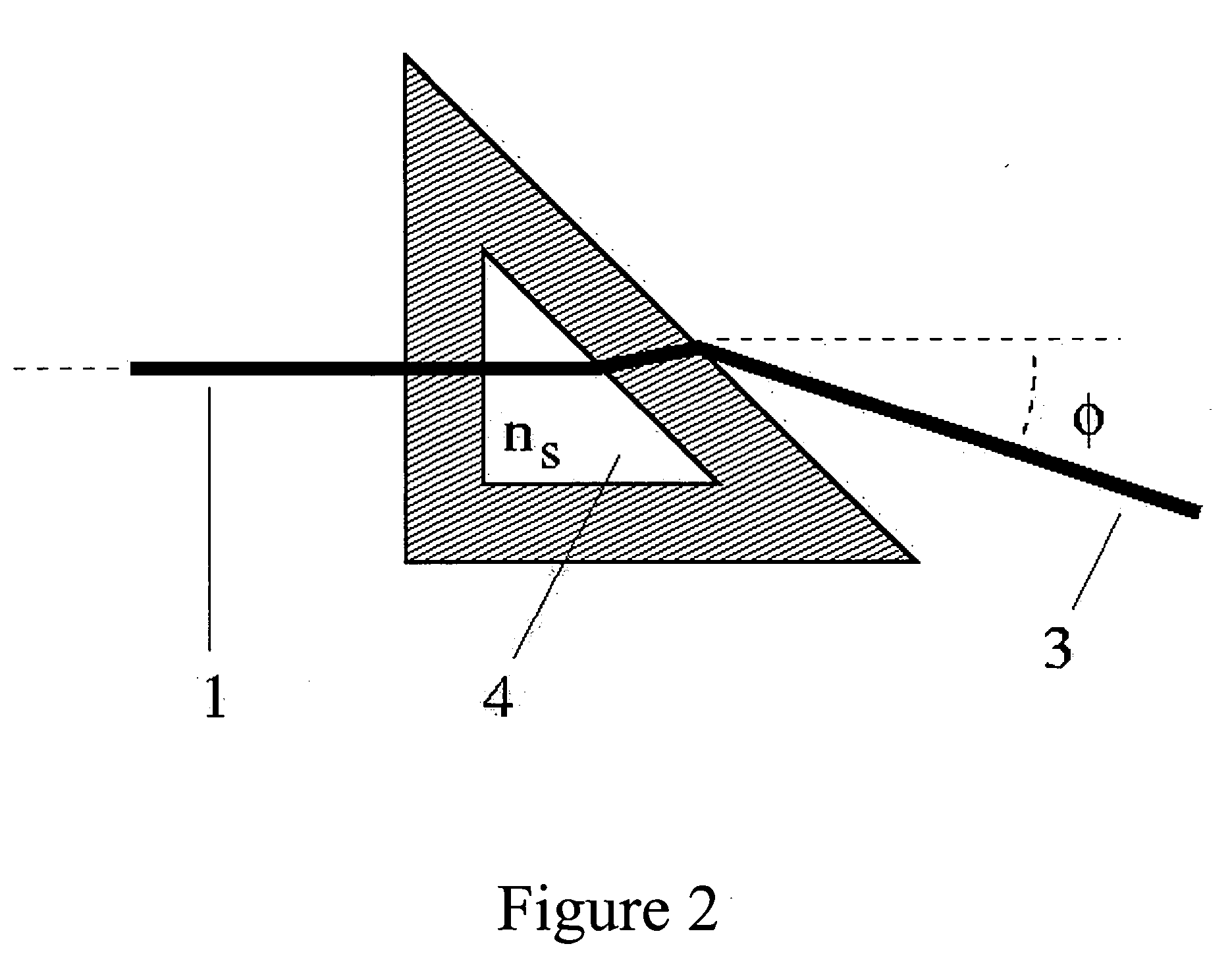
InactiveUS7492447B2Low production costEfficient measurementPhase-affecting property measurementsWavelength filterPrism
A refractometer for measuring refractive index of a sample comprising a prism having an interface contacting the sample, a light source that radiates light towards the interface from an entrance face of the prism, and a photoelectric sensor for receiving light reflected at the interface and directed outward from an exit face of the prism. The light source and the photoelectric sensor are secured to the prism. The refractometer comprises a sample stage arranged surrounding the interface surface. This sample stage provides a non-adhesive coating formed on the surface thereof. The refractometer comprises filter means arranged between the interface surface and the photoelectric sensor. This filter means includes a wavelength filter that selectively allows transmission of light having a wavelength within a prescribed region, including a wavelength of light of the light source.
Owner:ATAGO
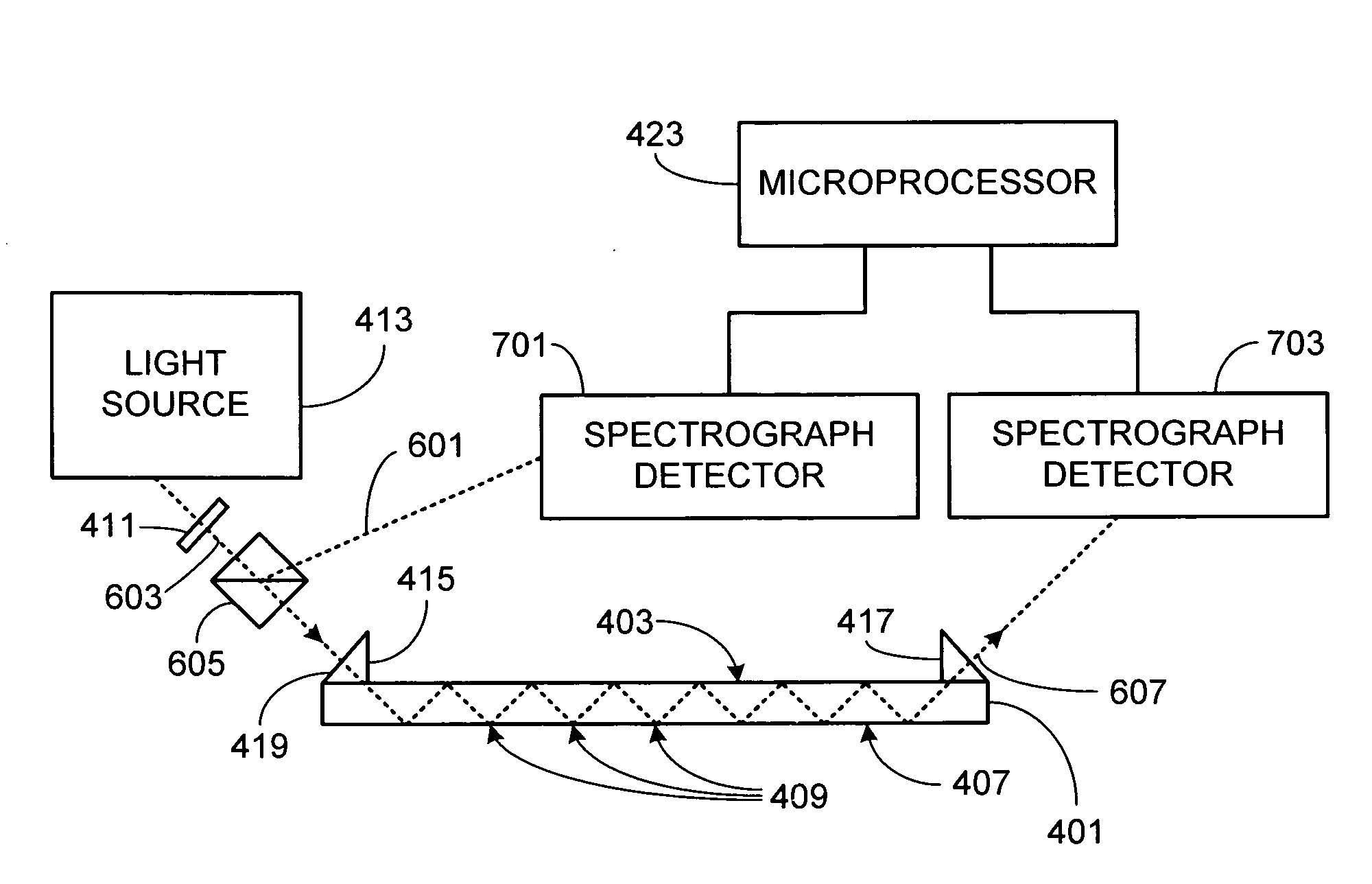
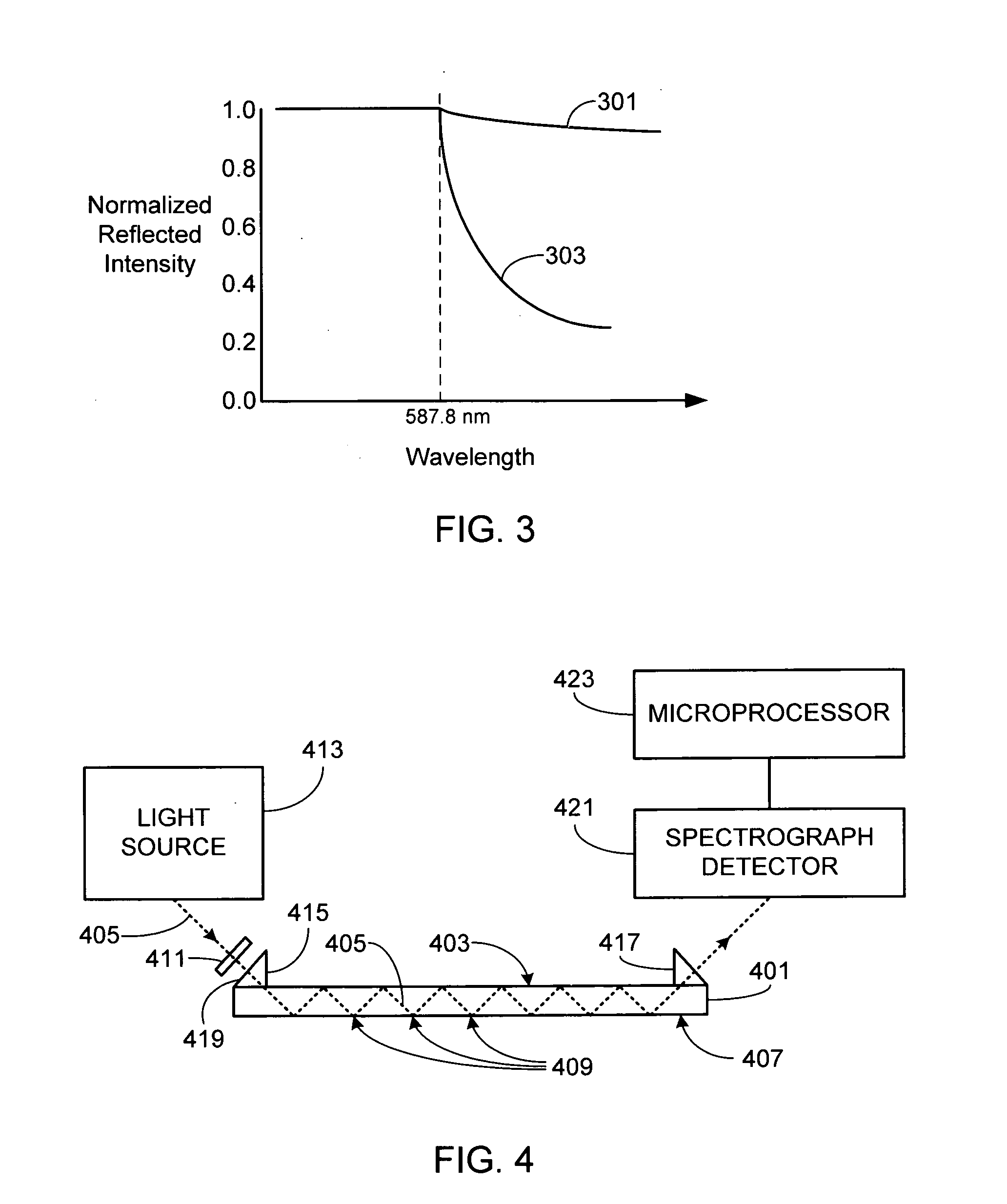
Optically amplified critical wavelength refractometer
InactiveUS20090279074A1High sensitivityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTotal internal reflectionBroadband light source
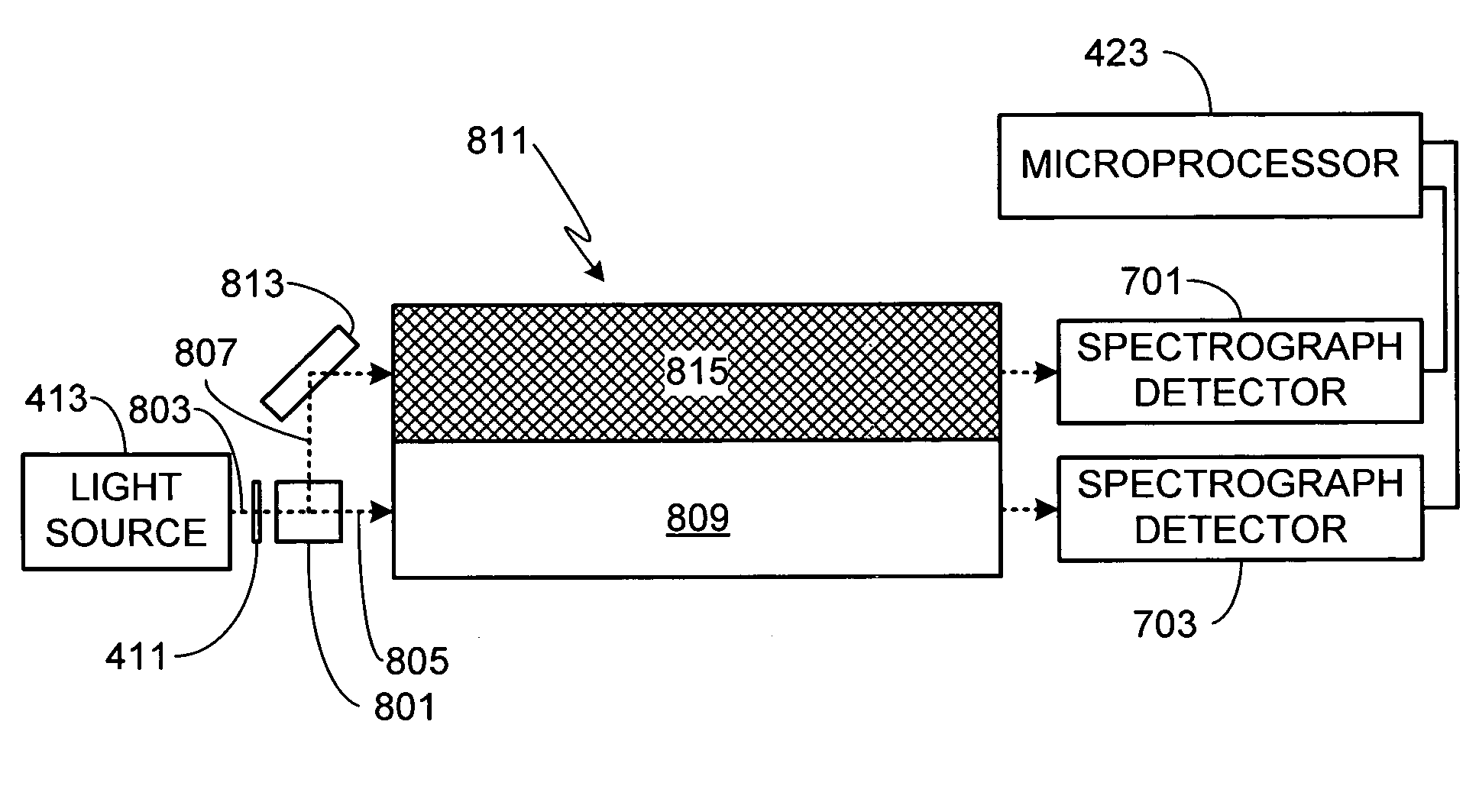
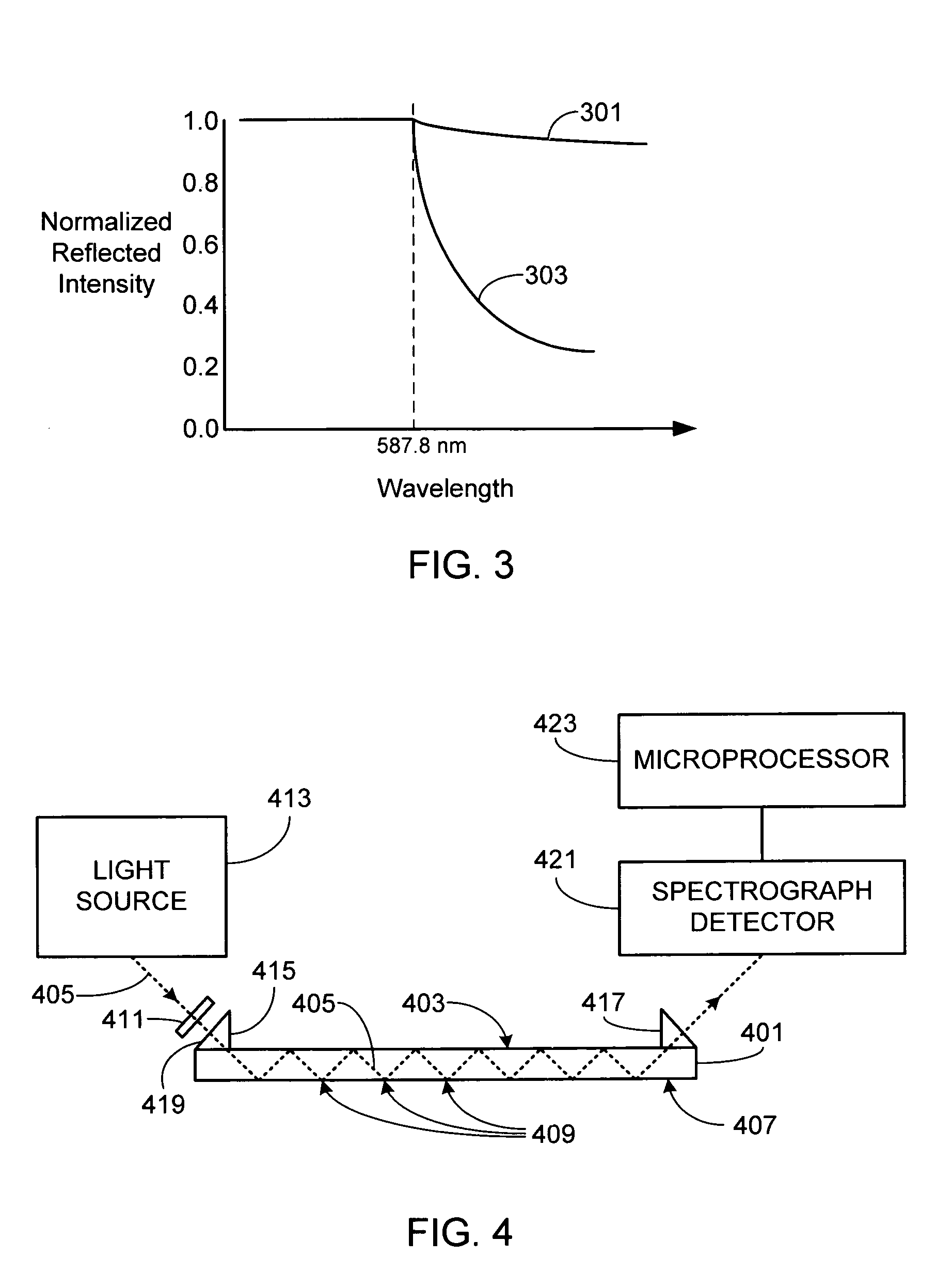
A critical wavelength refractometer is provided. A broadband light source (413) is optically coupled to a sensor (401), the sensor having at least one sensing surface (407). As the light from the broadband light source passes through the sensor, it undergoes multiple internal reflections against the sensing surface. Due to the index of refraction of the material in contact with the sensing surface, a portion of the light passing through the sensor is reflected while a second portion of the light is transmitted through the sensing surface and into the material. A detector (421) coupled to the sensor measures the spectral intensity of the light that passes completely through the sensor after having undergone the multiple internal reflections against the sensing surface. A microprocessor (423) coupled to the detector determines the critical wavelength based on the spectral intensity measurement, thereby allowing the index of refraction of the material to be determined.
Owner:SEALITE ENG
Computerized refractometer capable of automatically compensating corneal curvature measuring accuracy and corneal curvature calculation method
The invention relates to a computerized refractometer capable of automatically compensating the corneal curvature measuring accuracy and a corneal curvature calculation method. The traditional refractometer can not accurately measure the human eye corneal curvature radius. The computerized refractometer capable of automatically compensating the corneal curvature measuring accuracy comprises a main imaging device, wherein the main imaging device consists of an eyepieces lens, a diaphragm, a first imaging objective and an image sensor which are linearly arranged. The computerized refractometer capable of automatically compensating the corneal curvature measuring accuracy is characterized by also comprising two groups of collimation illumination devices, wherein each collimation illumination device consists of a first light emitting diode (LED) lamp, a pinhole plate and a collimating mirror, and the collimation illumination devices and the main imaging device form two paths of collimation light path systems. The computerized refractometer also comprises two groups of annular light sources, wherein the two groups of annular light sources and the main imaging device form two paths of non-collimation light path systems. The computerized refractometer disclosed by the invention consists of a corneal curvature measuring system and an eye diopter measuring system, the corneal curvature can be accurately measured, and the eye diopter can be accurately measured.
Owner:NINGBO MING SING OPTICAL R & D
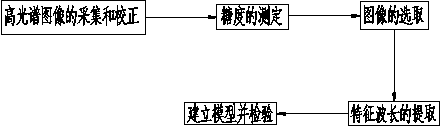
Navel orange sugar degree detection method based on hyper-spectral imaging technology
InactiveCN103472031AEasy to measureNo damagePhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsPattern recognitionSugar
The invention relates to a navel orange sugar degree detection method based on a hyper-spectral imaging technology. The navel orange sugar degree detection method based on the hyper-spectral imaging technology comprises the following steps: collecting spectra of a navel orange through a hyper-spectral imaging system, and performing black-white calibration to eliminate the noise influence; measuring the sugar degree of the navel orange through a digital refractometer; establishing a relationship between the spectra and the sugar degree so as to facilitate subsequent measurement of the sugar degree and nondestructive detection of the sugar degree of the navel orange. Compared with a conventional detection method, the navel orange sugar degree detection method based on the hyper-spectral imaging technology is high in detection speed, easy and convenient to operate and harmless to fruits. Compared with a near infrared spectrum detection method, the navel orange sugar degree detection method based on the hyper-spectral imaging technology has the advantages that more information is obtained and a detection result is more accurate and stable.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Process and device for measuring the optical properties of spectacle lenses by means of an optical detector of engravings in the spectacle lenses
InactiveUS6088089AMeasure quickly and accuratelyQuickly and accurately approachedOptical surface grinding machinesUsing optical meansEngravingOptical property
PCT No. PCT / DE97 / 01347 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 12, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 12, 1998 PCT Filed Jun. 27, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 00693 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 8, 1998An apparatus for detecting parameters of an ophthalmic lens including a vertex refractometer having a lens support for the ophthalmic lens and a detection device for optical detection of at least one engraved marking on at least one predetermined surface area of the ophthalmic lens. The vertex refractometer has a measurement beam path which passes through the ophthalmic lens when the ophthalmic lens is lying on the lens support and the detection device has at least one light source, an imaging optical system for directing light from the at least one light source onto the at least one predetermined surface area of the ophthalmic lens with at least one engraved marking, and an optical receiver system having a light sensor which is connected to an evaluation and representation unit. The optical receiver system images light beams from the imaging optical system which are reflected from the at least one predetermined surface area of the ophthalmic lens. The vertex refractometer and the detection device are disposed so that a spacing between an axis of the measurement beam path of the vertex refractometer and an axis of the optical receiving system of the detection device is selected so that with the ophthalmic lens being positioned relative to the measuring beam path passing through the ophthalmic lens, the at least one predetermined surface area with the at least one engraved marking of the ophthalmic lens is illuminated by the at least one light source.
Owner:G RODENSTOCK INSTR
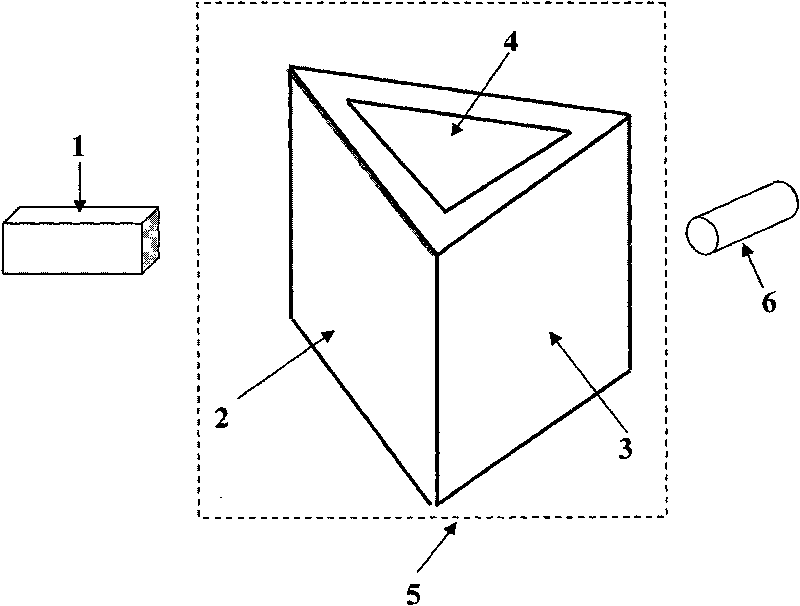
Liquid prism refractometer
InactiveCN101706425AWide range of refractive index measurementSimple structurePhase-affecting property measurementsSpecific gravity measurementRough surfaceMeasuring instrument
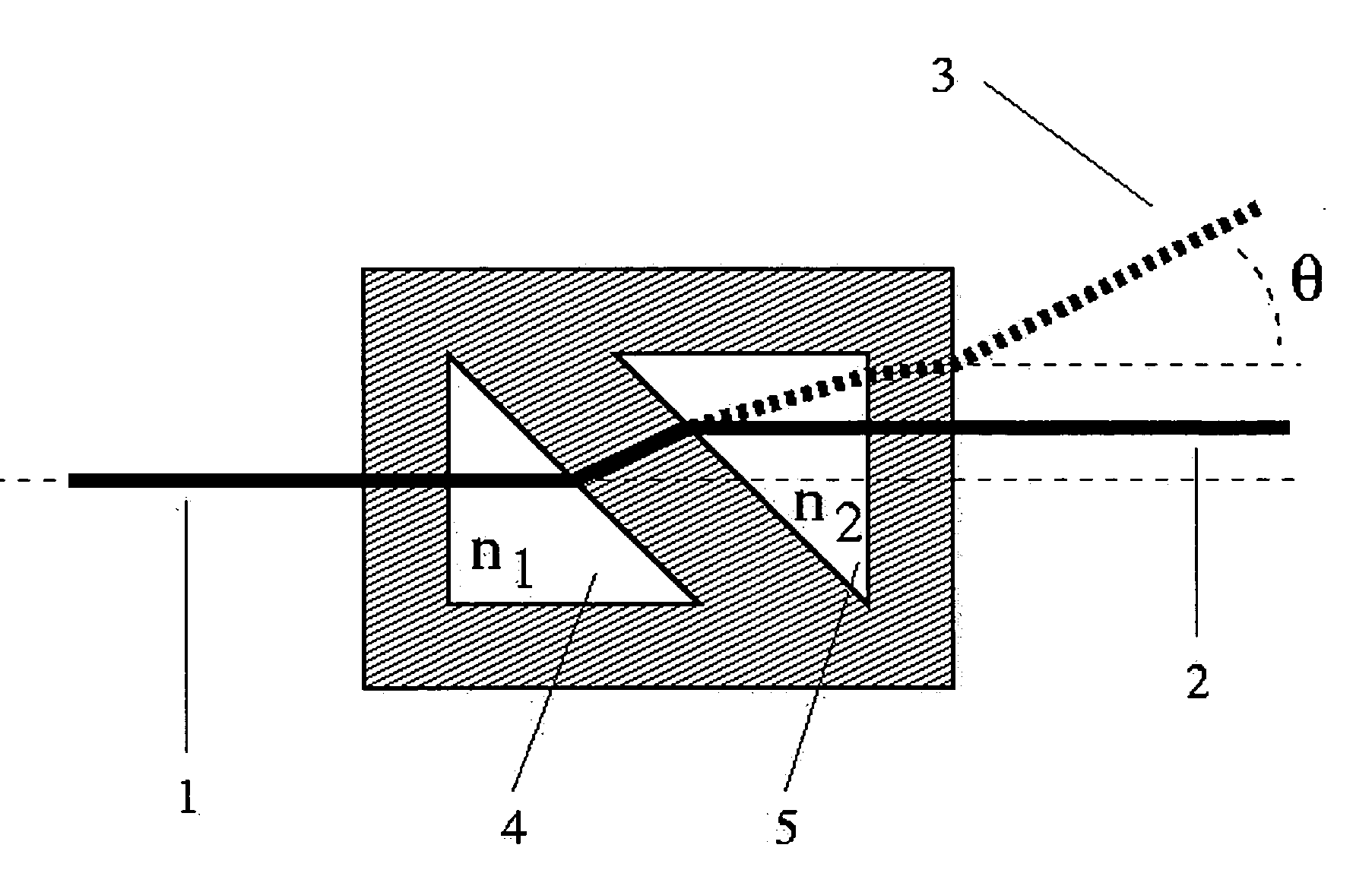
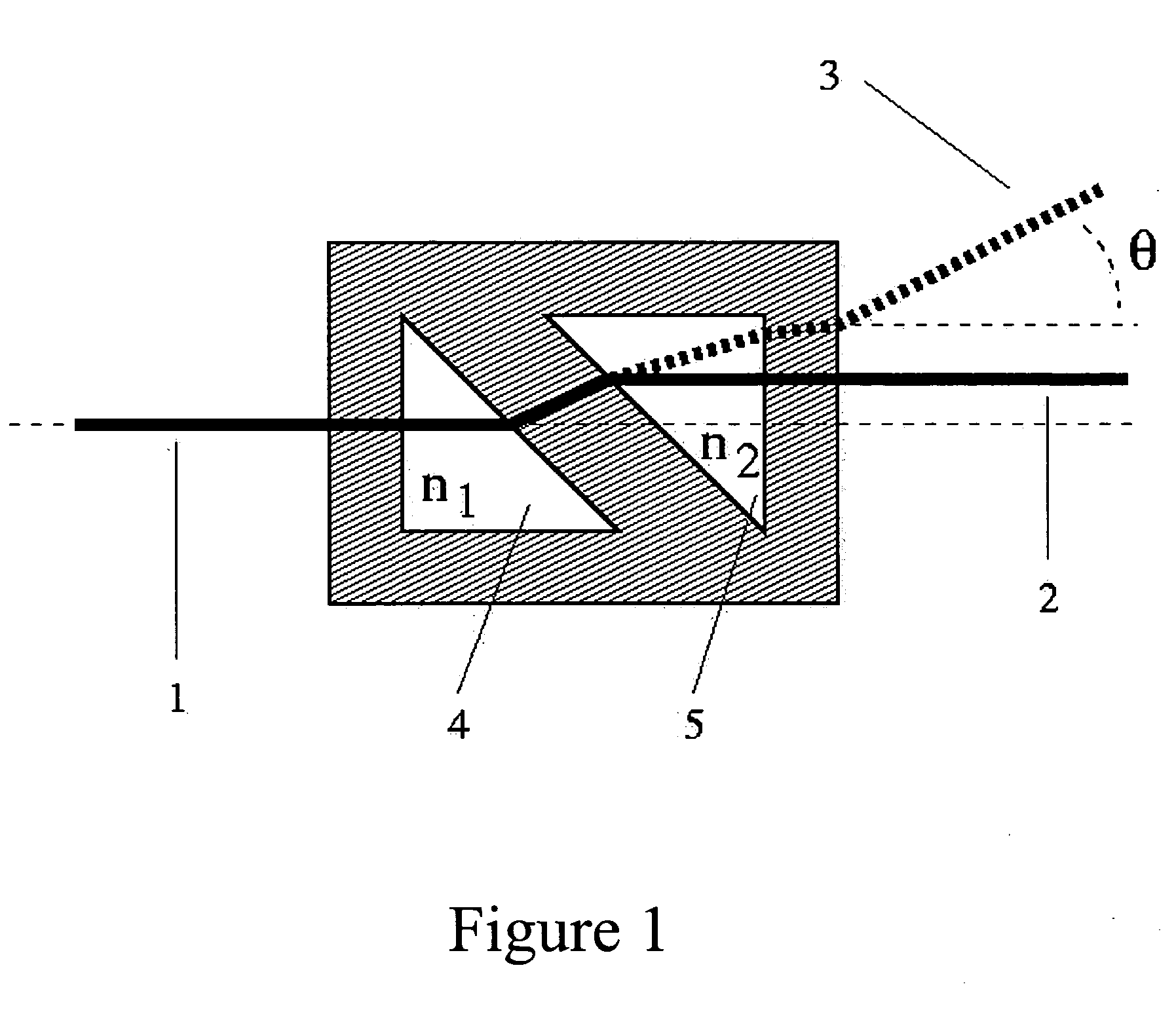
The invention relates to a liquid prism refractometer, in particular to a novel structure of the liquid prism refractometer used for measuring liquid refractive index and a work principle thereof, belonging to the technical field of devices for measuring the refractive index, concentration and density of liquid. The refractometer comprises a monochromatic light source (1), a hollow triple prism (5) and an optical receiving device (6), wherein the hollow triple prism (5) is made of transparent material without limitation of the refractive index, the outer side of a light incidence surface (2) is ground to be a rough surface, and an included angle between the light incidence surface (2) and a light-emitting surface (3) is 60 degrees; an upper bottom surface (4) is provided with a movable cover which is used for canning and pouring the liquid; and a liquid prism can be formed when the liquid is filled. Therefore, the refractive index, the concentration value and the density value of the liquid to be measured can be measured by utilizing the measurement principle of a glancing incidence method. Compared with the existing common prism measuring instruments such as Abbe refractometer and the like, the liquid prism refractometer has wider refractive index measuring range, and simple structure, easy manufacturing, lower cost and higher accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Dynamic scene real time double face refraction drafting method based on image mapping space
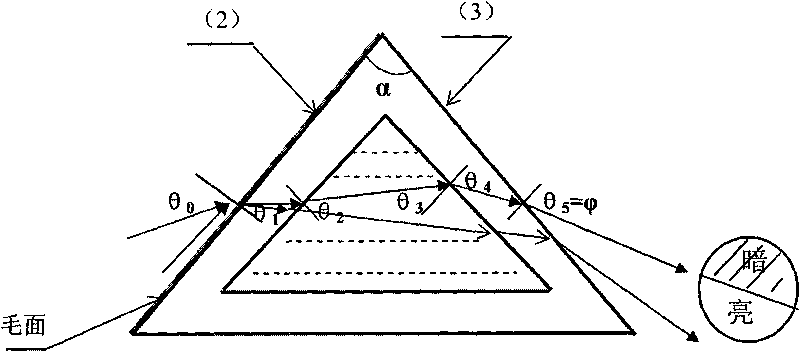
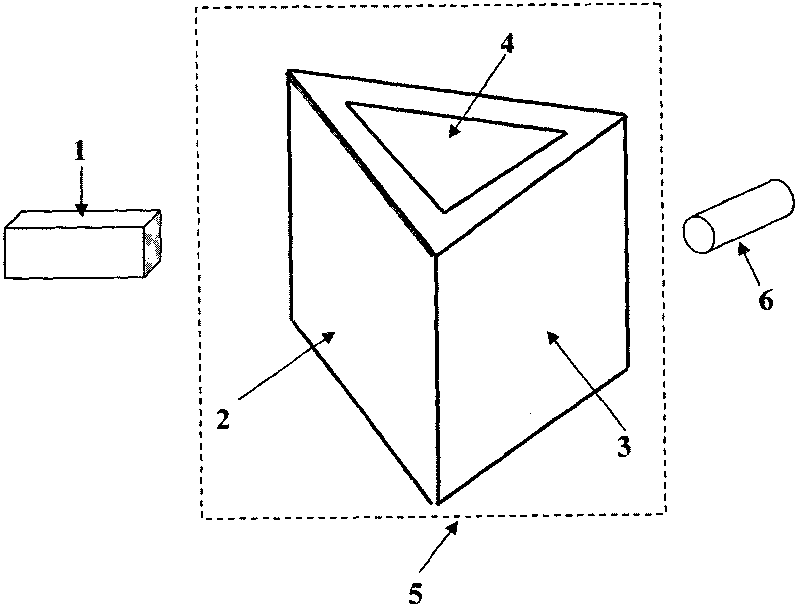
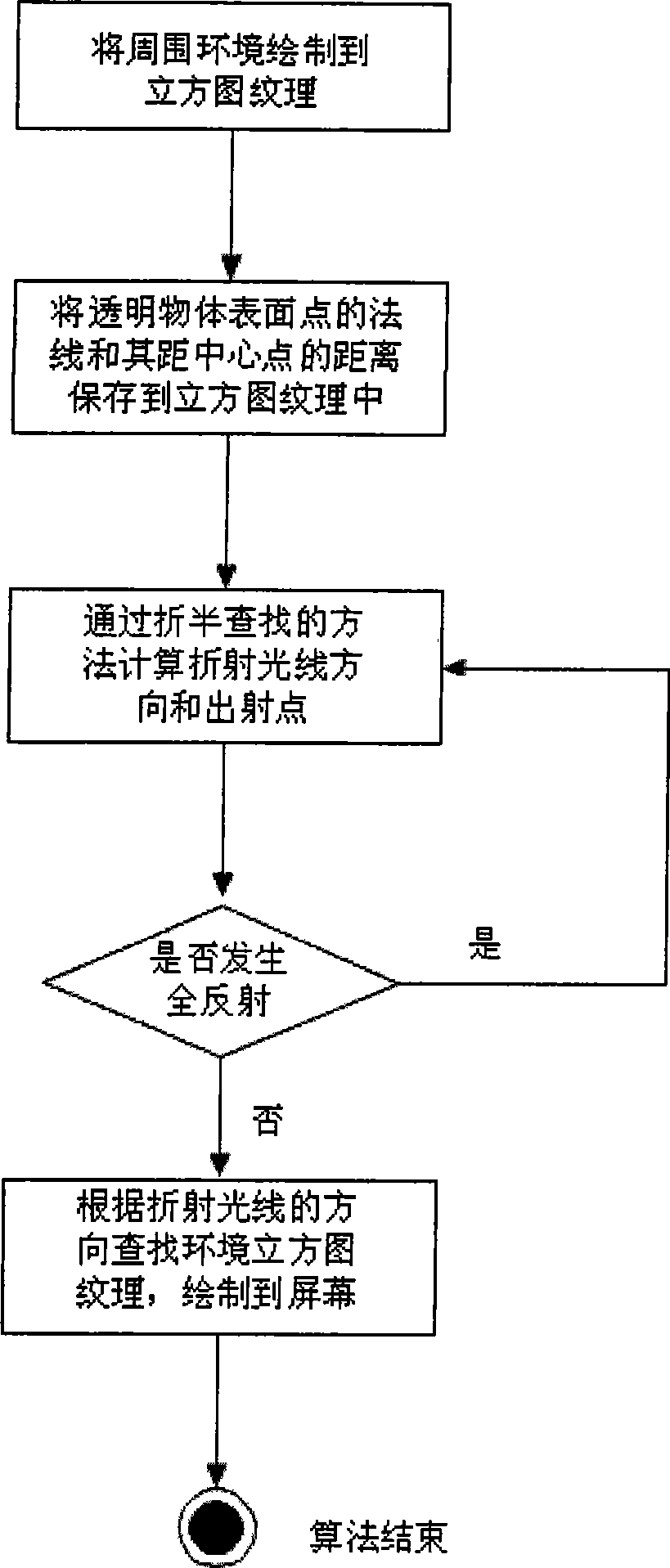
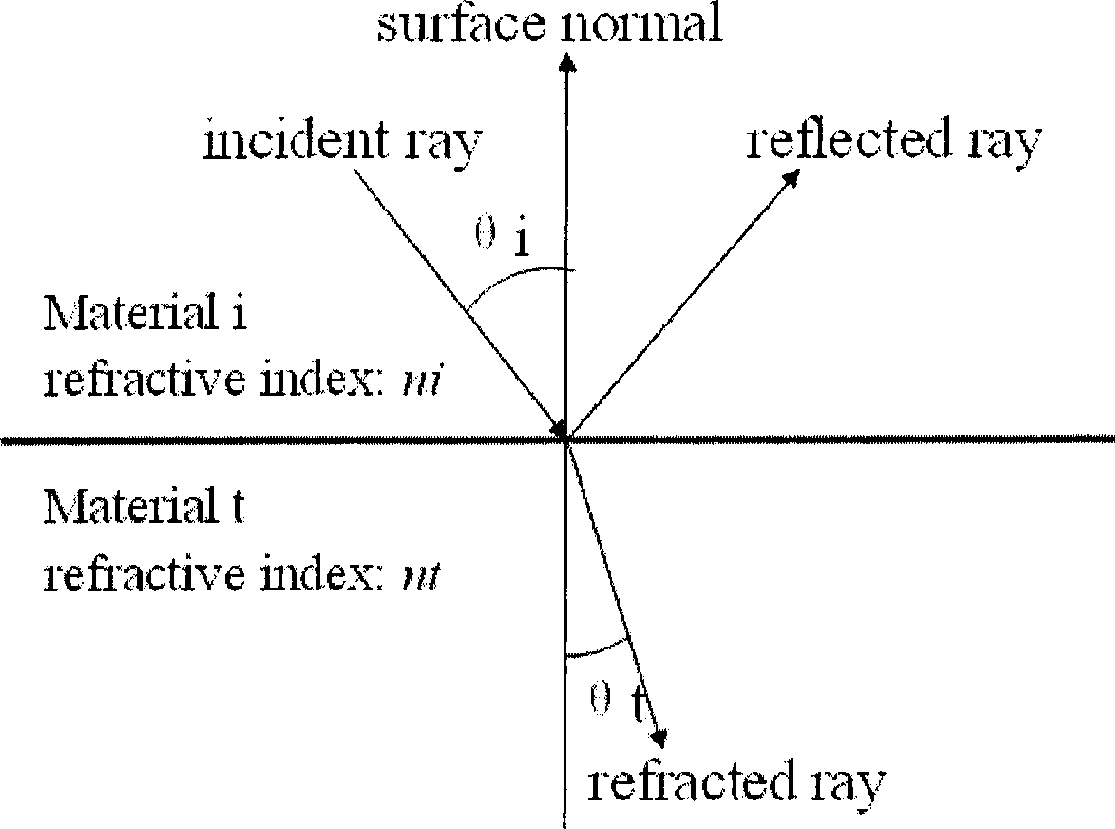
InactiveCN101441774AImprove the speed of refraction renderingReduce time complexity3D-image renderingGraphicsViewpoints
The invention relates to a method for drawing a dynamic scene through double-face refraction in real time based on an image mapping space, which comprises the following steps: using the center of a transparent object as a viewpoint to draw surface color information and depth information of other circumferential objects except the transparent object to the veins of a cubic image; using the center of the transparent object as the viewpoint to draw the distances between the external surface normal line and the center of the transparent object and between the surface vertex and the center of the transparent object to the veins of one cubic image; generating a first refraction on the surface of the transparent object, calculating the direction of the refracted ray of the time, and using the veins of the cubic image as an input to approximately calculate the position of an intersection point of the light of the next time and the surface of the transparent object through a bisearch mode on an image hardware; if a total reflection happens, searching the next intersection point, and if the total reflection does not happen, performing a second time refraction at the intersection point so that the light passes out of the transparent body; and calculating the refraction of the refracted ray to other circumferential objects on the image hardware, and finding out a first lighting color of the surface position of an object intersecting with the refracted ray along the refracted ray, which serves as a screen pixel color corresponding to the refracted ray. The method can satisfy the real-time requirement on frame rate, and can obtain quite vivid light refraction drawing effect simultaneously.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
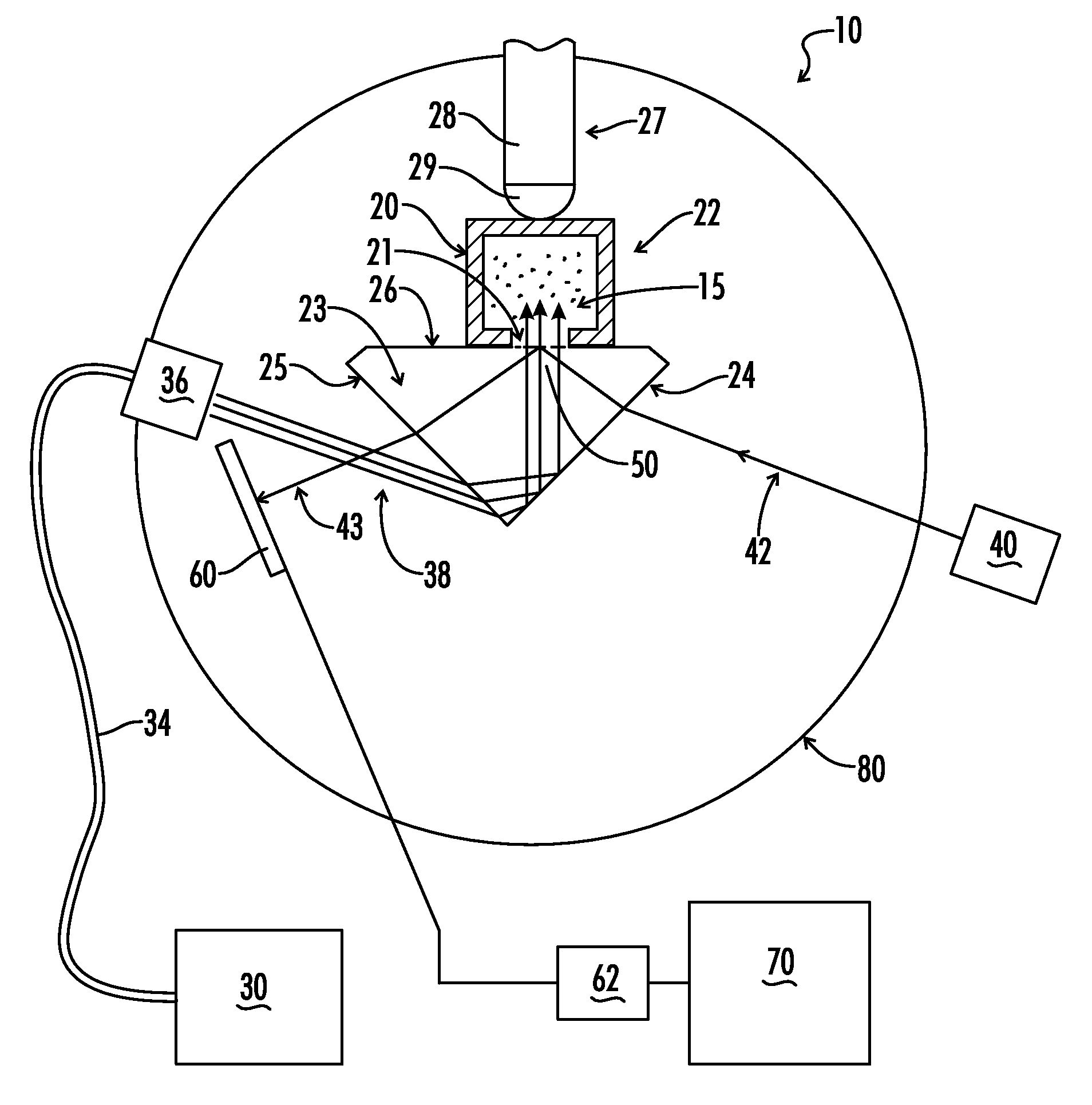
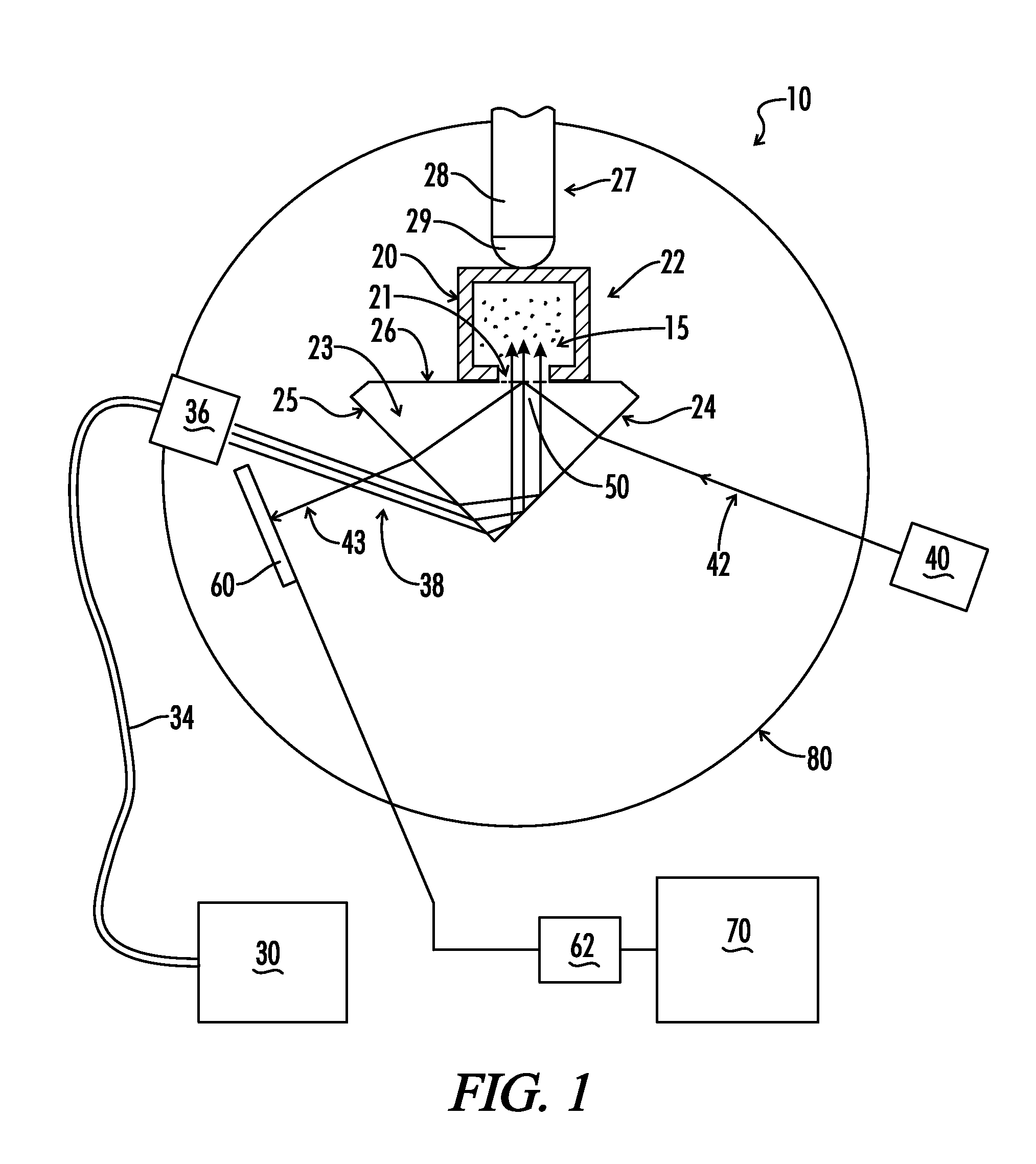
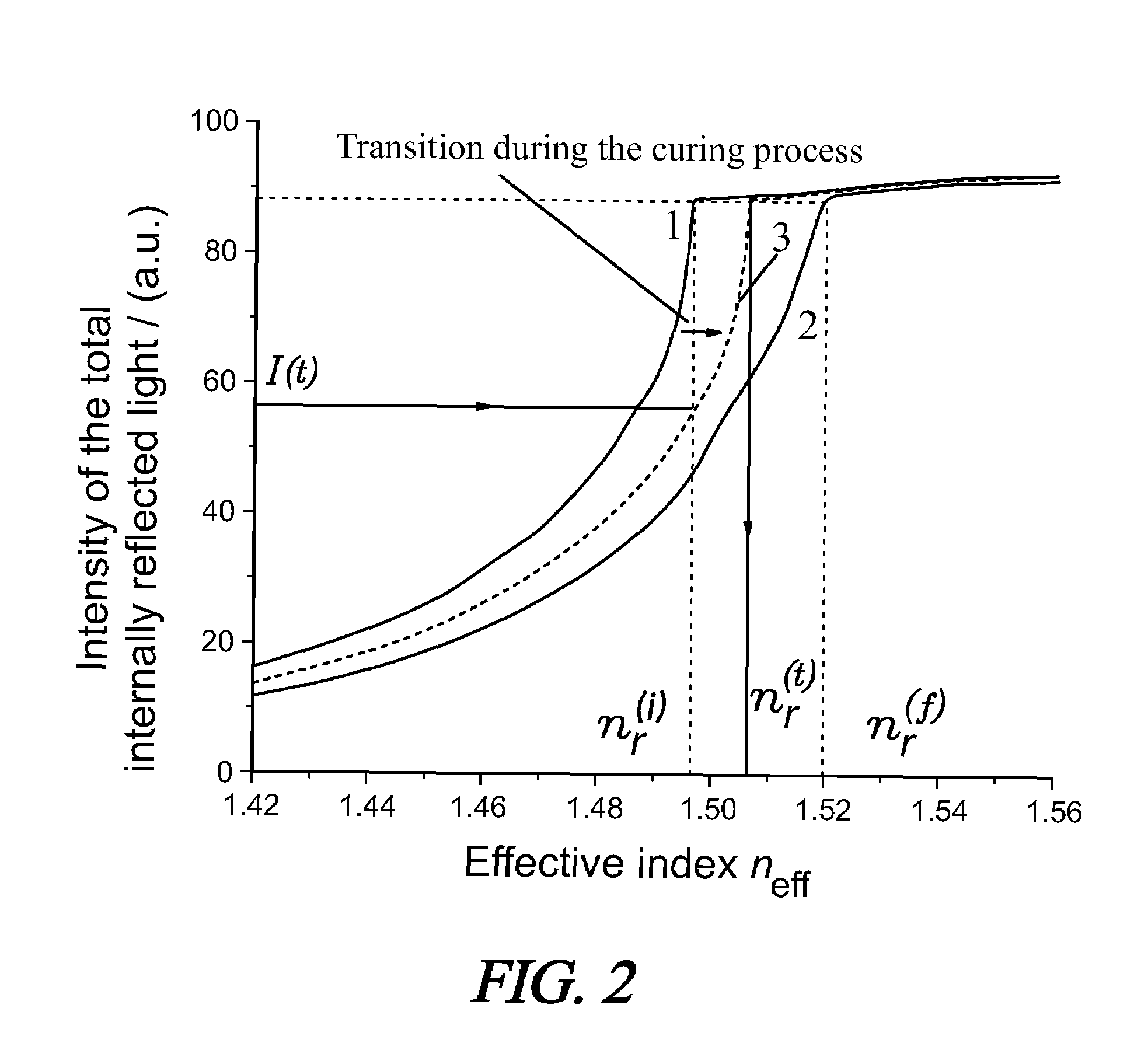
Dynamic refractometer
A refractometer computer controls the rotation of a rotary plate upon which are mounted a prism optically coupled via an optical window to a spectroscopic cell holding a resin exhibiting a dynamic refractive index during photocuring. The computer system positions the prism and spectroscopic cell relative to a visible light laser which illuminates the prism-resin interface at selected incidence angles. A photodetector mounted on the plate generates a signal to the computer proportional to intensity of an internally reflected light beam. A curing light is selectively transmitted through the prism and into the photocurable resin. The refractometer determines the intensity of the internally reflected beam a selected incidence angles and determines the effective refractive index curve of the resin at an uncured state and, optionally, at a completely cured state. Next, an amount of uncured resin and selected optical components to be joined by the resin is placed in the spectroscopic cell and irradiated with the UV light. The refractometer is fixed at a selected incidence angle and measures the intensity of an internally reflected light beam of light throughout the cure cycle. The refractometer determines the resin's refractive index of the polymeric mixture by means of extrapolation of a horizontal shift in the effective refractive index curve of the resin from an uncured state to a selected point in the cure cycle.
Owner:CURLEY MICHAEL J +1
Transmitted light refractometer
ActiveUS20090103076A1Compact structureHigh measurement accuracyPhase-affecting property measurementsLight beamPrism
A transmitted light refractometer allows high measurement accuracy across a broad measurement range, even under difficult measuring conditions. The transmitted light refractometer can be connected to a process simply via a single access. In accordance with advantageous features, the transmitted light refractometer covers a measurement range for all practically relevant media and includes integrated temperature compensation. A deflecting optics unit is arranged relative to an illumination optics unit such that the deflecting optics unit deflects a parallel beam through the process liquid and a measurement prism into the transmitted light refractometer back to the side from which it was radiated. The illumination optics unit, an imaging optics unit, and a detector plane are arranged on the light radiation side such that only one process access is needed.
Owner:FLEXIM FLEXIBLE INDMESSTECHN
Portable refractometer
InactiveUS7369221B2Accurate temperature compensationFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesPhase-affecting property measurementsRotational axisPrism
A portable refractometer is provided that includes a lens barrel having a lens barrel axis. A prism is secured to one end of the lens barrel, the prism having an entry face that provides a boundary surface between the prism and a substance to be measured. A tube shaped optical chassis is inside the lens barrel, and is rotatably supported about a predetermined rotational axis perpendicular to the lens barrel axis. An objective lens is arranged in the optical chassis, and is positioned in relation to the optical chassis. An optical scale is arranged inside the optical chassis, at the focal point of the objective lens. A mover moves the objective lens relatively in relation to the optical scale in response to changes in temperature by turning the optical chassis about the rotational axis.
Owner:ATAGO
Refractometer cell for both absolute and differential refractive index measurement of fluids
An improved cell for a walk-off refractometer is disclosed that permits measurement of the differential refractive index, DRI, between a sample fluid and a reference fluid. In addition, the new cell design permits the measurement of the refractive index, RI, of a fluid relative to the refractive index of the material comprising or surrounding the flow cell. Thus a single instrument may be used to measure separately the RI of a sample fluid and the DRI between a sample fluid and a reference fluid. The new flow cell contains two chambers, typical of a DRI instrument, but an asymmetric internal angle in either the sample or the reference chamber. By the provision of this unique structure, it is an objective of this invention to be able to measure the refractive index of a fluid relative to the refractive index of the material comprising the flow cell or relative to the medium surrounding the flow cell, either of which may be considered a measurement of the RI of the fluid. With the addition of mirror means, it is the further objective of this invention to improve its sensitivity. A further objective of the invention is to measure the asymmetric internal angle of the flow cell using well-characterized reference fluids.
Owner:WYATT TECH
Apparatus and method for determination of tear osmolarity
InactiveUS20110211189A1Reduce the impactLarge massPhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsPrismTear osmolarity
An apparatus comprises a spectrophotometer system configured to measure light absorbance by a tear sample, a refractometer system configured to measure refractive index of the tear sample, and an evaluation unit programmed to calculate an osmolarity of the tear sample based on the measured absorbance and refractive index and stored calibration curves. The spectrophotometer and refractometer systems may share a common prism contacted by the tear sample during measurement. The evaluation unit may be programmed to carry out steps of a method for determining osmolarity of the tear sample in accordance with the invention. The osmolarity of the tear sample may be used as an indicator in diagnosing dry eye.
Owner:REICHERT
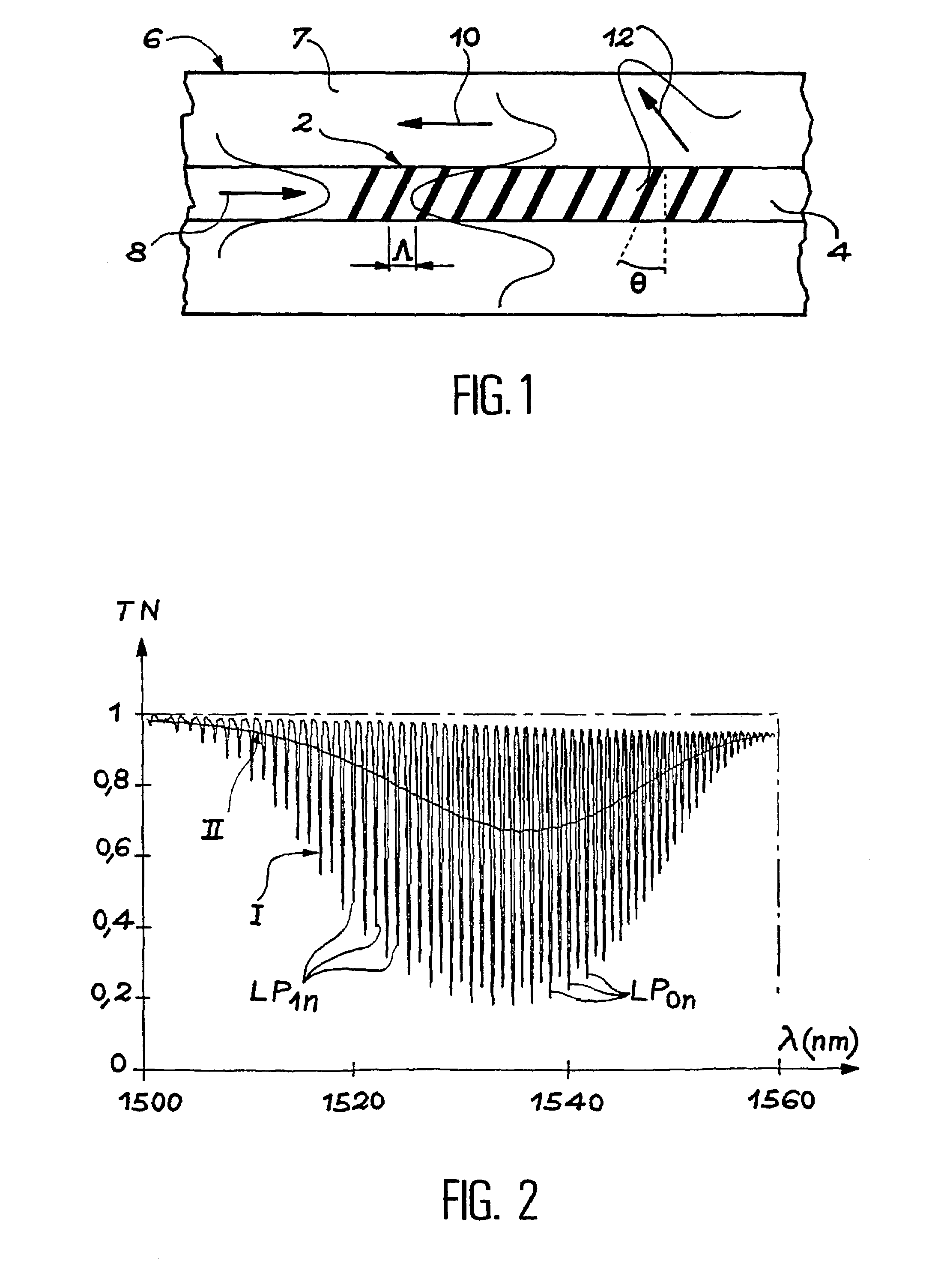
Refractometer with blazed bragg gratings
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Enhanced sensitivity differential refractometer incorporating a photodetector array
ActiveUS7027138B2Optimization rangeAccurate detectionWithdrawing sample devicesPhase-affecting property measurementsPhotodetectorDetector array
An improved differential refractometer incorporating a photodetector array is disclosed. Using a multi-element photo array provides the basis for measurement of differential refractive index values with a heretofore unattainable combination of sensitivity of measurement and concurrent range of measurement. Within the large dynamic range attainable, the detector structure provides equal sensitivity irrespective of deflection within the range. The transmitted light beam is tailored to provide a spatial variation of the light intensity at the array improving thereby the precision of measurement of its displacement. This in turn results in improved precision in the reported differential refractive index and in the calculation of the differential refractive index increment dn / dc. Integrating the detector array into the flow cell structure of the parent case results in a detector of exceptional sensitivity and range for sample quantities far smaller than required by conventional differential refractometers.
Owner:WYATT TECH
Dispersion speckle refractometer and method for testing myopic, hyperopic and astigmatic degrees
The invention discloses a dispersion speckle refractometer and a method for testing myopic, hyperopic and astigmatic degrees. The dispersion speckle refractometer comprises a laser, a half-reflecting half-transparent prism, a two-dimensional rotary reflecting mirror capable of rotating around a horizontal rotating shaft and a vertical rotating shaft, and a diffuser screen; the half-reflecting half-transparent prism and the diffuser screen are positioned in a laser transmitting direction of the laser along an optical path, and the two-dimensional rotary reflecting mirror is positioned in a reflected light transmitting direction of the half-reflecting half-transparent prism; a circular pupil sheet is arranged between the diffuser screen and an eyeball of a human body to be tested; and a light-transmitting diameter of the pupil sheet is 4 + / - 0.5mm, and a distance from the pupil sheet to a cornea is smaller than 6mm. The invention has the advantages that: the cost is low, and the operability and the practicability are good; the precision of testing parameters such as the myopic degree, the hyperopic degree, the astigmatic degree and the like is quite reliable; and inferential analysis on a patient glasses situation is facilitated.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Optically amplified critical wavelength refractometer
InactiveUS7619725B1High sensitivityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTotal internal reflectionBroadband light source
A critical wavelength refractometer is provided. A broadband light source (413) is optically coupled to a sensor (401), the sensor having at least one sensing surface (407). As the light from the broadband light source passes through the sensor, it undergoes multiple internal reflections against the sensing surface. Due to the index of refraction of the material in contact with the sensing surface, a portion of the light passing through the sensor is reflected while a second portion of the light is transmitted through the sensing surface and into the material. A detector (421) coupled to the sensor measures the spectral intensity of the light that passes completely through the sensor after having undergone the multiple internal reflections against the sensing surface. A microprocessor (423) coupled to the detector determines the critical wavelength based on the spectral intensity measurement, thereby allowing the index of refraction of the material to be determined.
Owner:SEALITE ENG
Combined wavefront and topography systems and methods
Methods, software, and systems are provided for determining an ablation target shape for a treatment for an eye of a patient. Techniques include determining wavefront information from the eye of the patient with a wavefront eye refractometer, determining anterior corneal shape information from the eye with a corneal topography device, and combining the wavefront information and the anterior corneal shape information to determine the ablation target shape.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Preparation method of high-purity fudosteine
ActiveCN104418779ASteady improvement in qualityGood effectSulfide preparation1-PropanolReaction step
The invention provides a preparation method of a novel antitussive phlegm-eliminating drug high-purity fudosteine, wherein the preparation method includes the steps: (1) synthesizing an intermediate 3-bromo-1-propanol; (2) carrying out a reaction of cysteine hydrochloride with 3-bromo-1-propanol to obtain a crude product; and (3) carrying out crystallization refining on the obtained crude product to obtain the high-purity fudosteine. The domestic cheap easily-available raw materials of cysteine hydrochloride, hydrobromic acid and 1,3-propylene glycol materials are utilized, monitoring of a gas chromatograph, a liquid chromatograph and a refractometer is used for tracking a catalytic reaction process and a reaction terminal point. The preparation method has the advantages of less reaction steps, high selectivity, low pollution, low cost and stable quality, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:TOPFOND PHARMA CO LTD
Method for detecting cutting fluid concentration during use
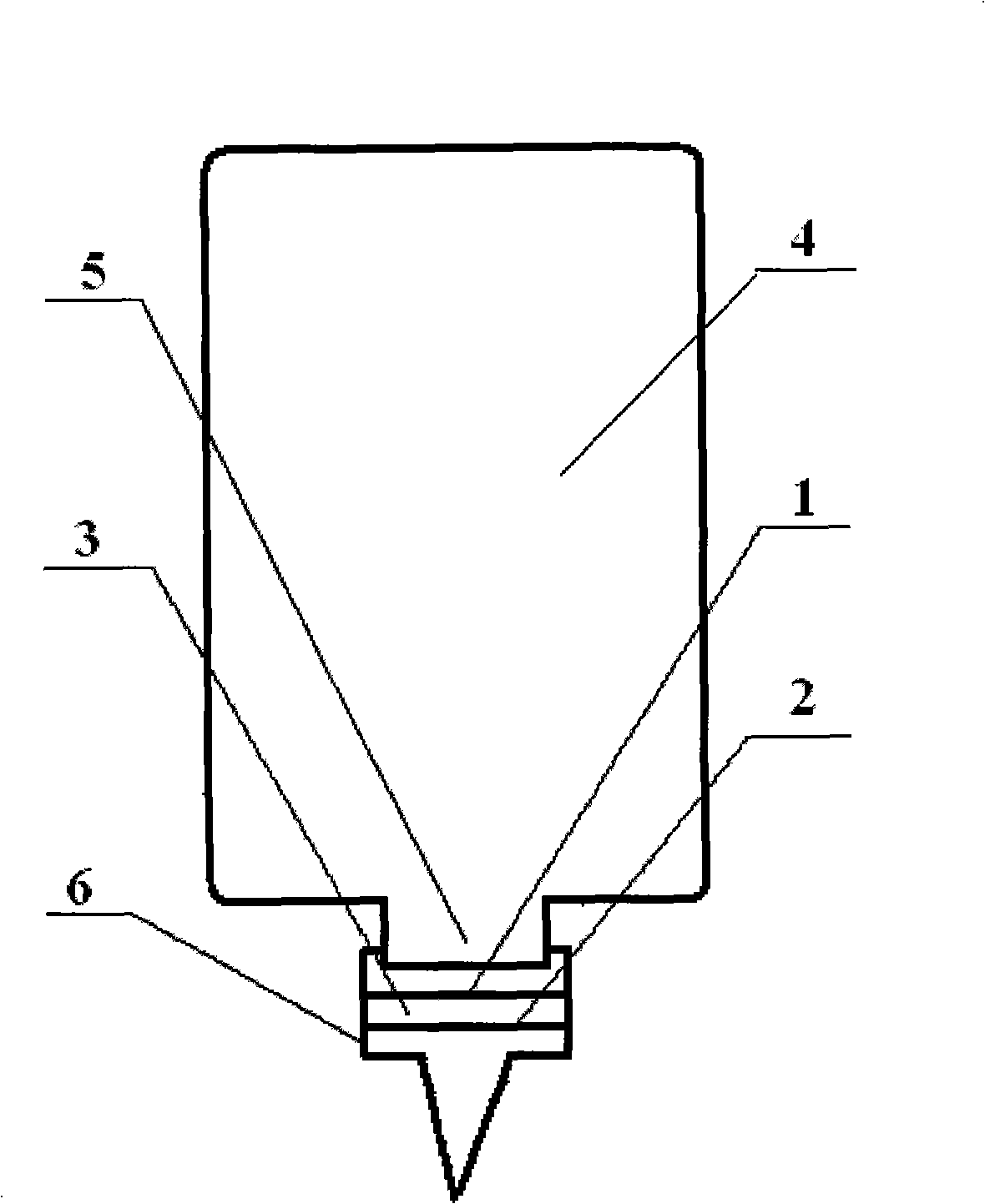
ActiveCN101329272AEfficient removalPreparing sample for investigationPhase-affecting property measurementsBiochemical engineeringEngineering
The invention relates to a detection method of the consistency of cutting liquid in use, which mainly solves the problem that the prior art can not exactly measure the effective consistency of the dirty cutting liquid in use. The method of the invention uses the cutting liquid in use to be stored in a sample pre-processor; the sample pre-processor comprises a container (4), an outlet (5) and a sample outlet head (6); the sample outlet head (6) is provided with at least two layers of filter films; wherein, in the direction from the container (4) to the sample outlet head (6), the first filter film (1) layer is normal qualitative or quantitative filter paper and the other filter film (2) layer is a micro-hole filter film with the aperture of 0.1-10 microns; the cutting liquid which is processed by the pre-processor is dropped onto a refractometer; the problem of the prior art is well solved by the technical proposal that the refractive index is tested by the refractometer and the sample consistency is obtained by converting the cutting liquid consistency-refractive index standard curve; therefore, the method of the invention can be used for the site management on the cutting liquid consistency.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Method for on-line measuring microbe film thickness by optical fibre bragg grating sensor
The invention discloses an on-line measuring method of microbial film thickness by using a Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) sensor, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: step one: the microbial film thickness d and a microbial film refractive index n2 are calibrated by the Abell refractometer and an optical microscope, thus determining the relational function f(n2) between the microbial film refractive index n2 and the microbial film thickness, namely, determining that d is equal to f(n2); step two: a given D type FBG sensor is placed in a trickling biofilter; and step three, a broadband laser light source emits broadband laser with the wavelength of 1450nm to 1590nm, the broadband laser is injected into photosensitive single-mode fiber by a fiber optic isolator and transmitted to the D type FBG along the optical fiber after passing through a fiber optic coupler; the laser with the wavelength of Lambda0 positioned at a resonant center is intensely reflected in the D type FBG, the reflected laser is output into a spectrum analyzer by the fiber optic isolator after passing through the fiber optic coupler, and the spectrum analyzer displays the size of the wavelength at the resonant center so as to obtain the refractive index of the microbial film at the moment.
Owner:重庆工学院
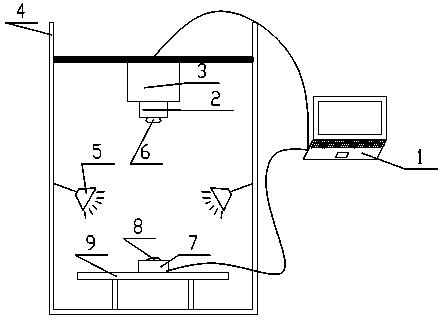
Automatic observation apparatus for detecting mineral samples
InactiveUS20160187255A1Maximum efficiencyBig errorPhase-affecting property measurementsInvestigating jewelsControl systemEngineering
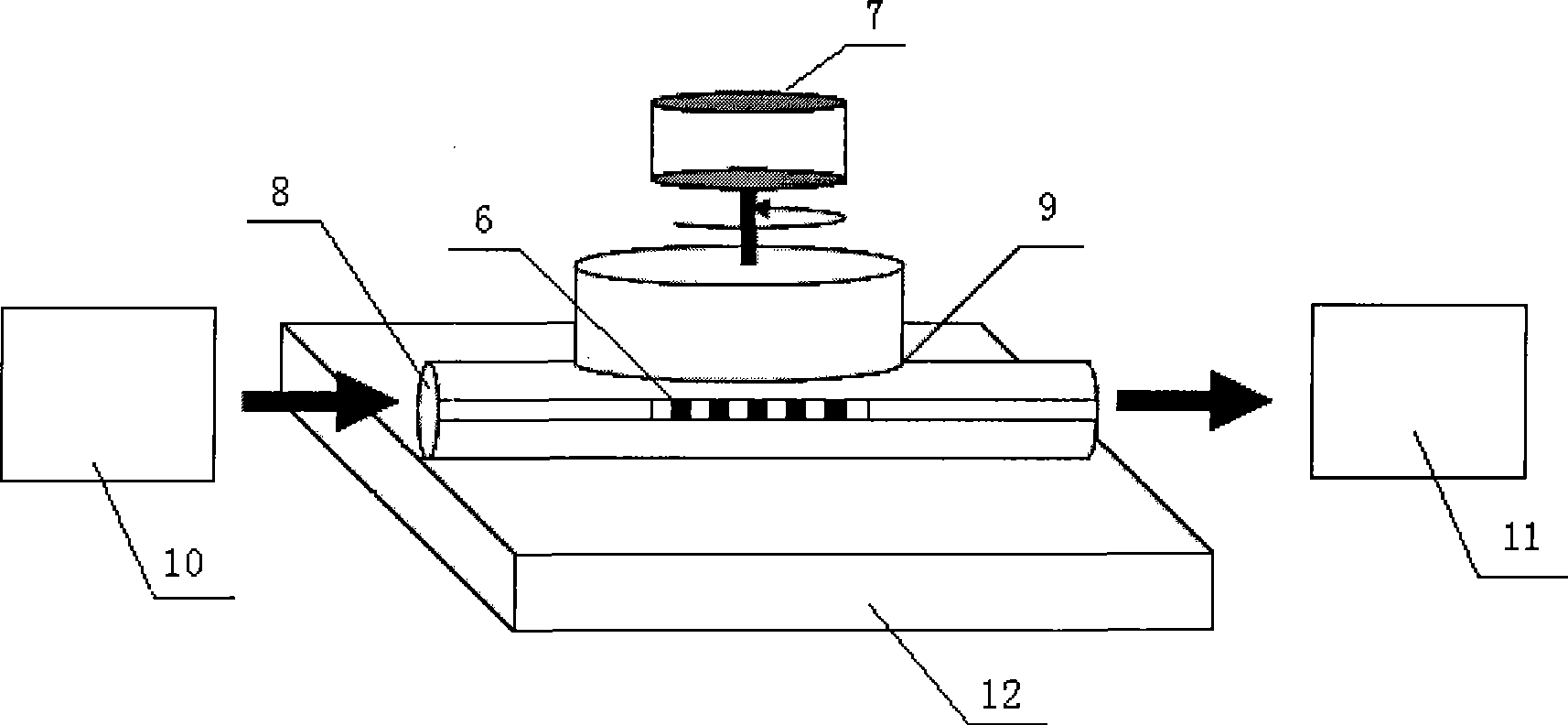
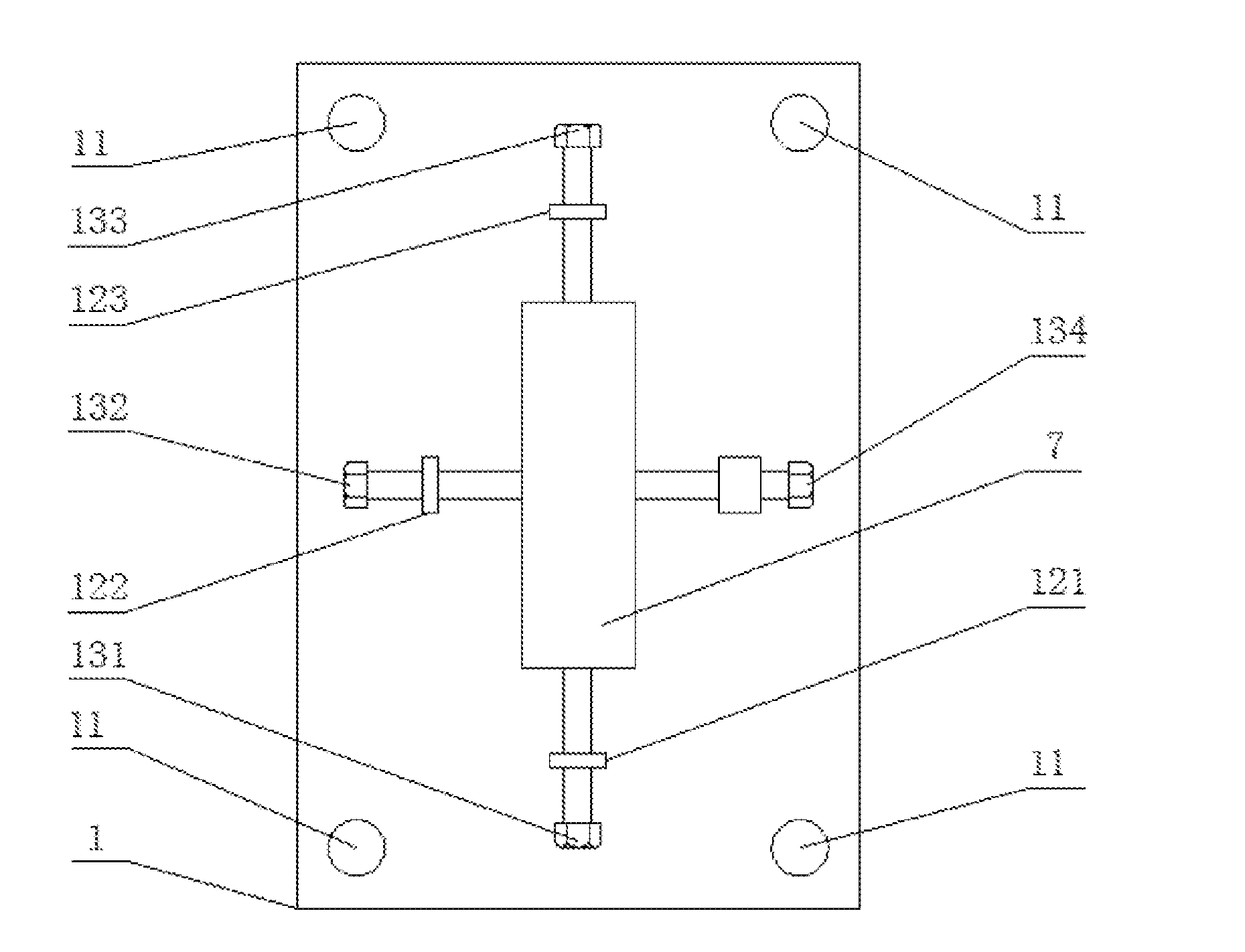
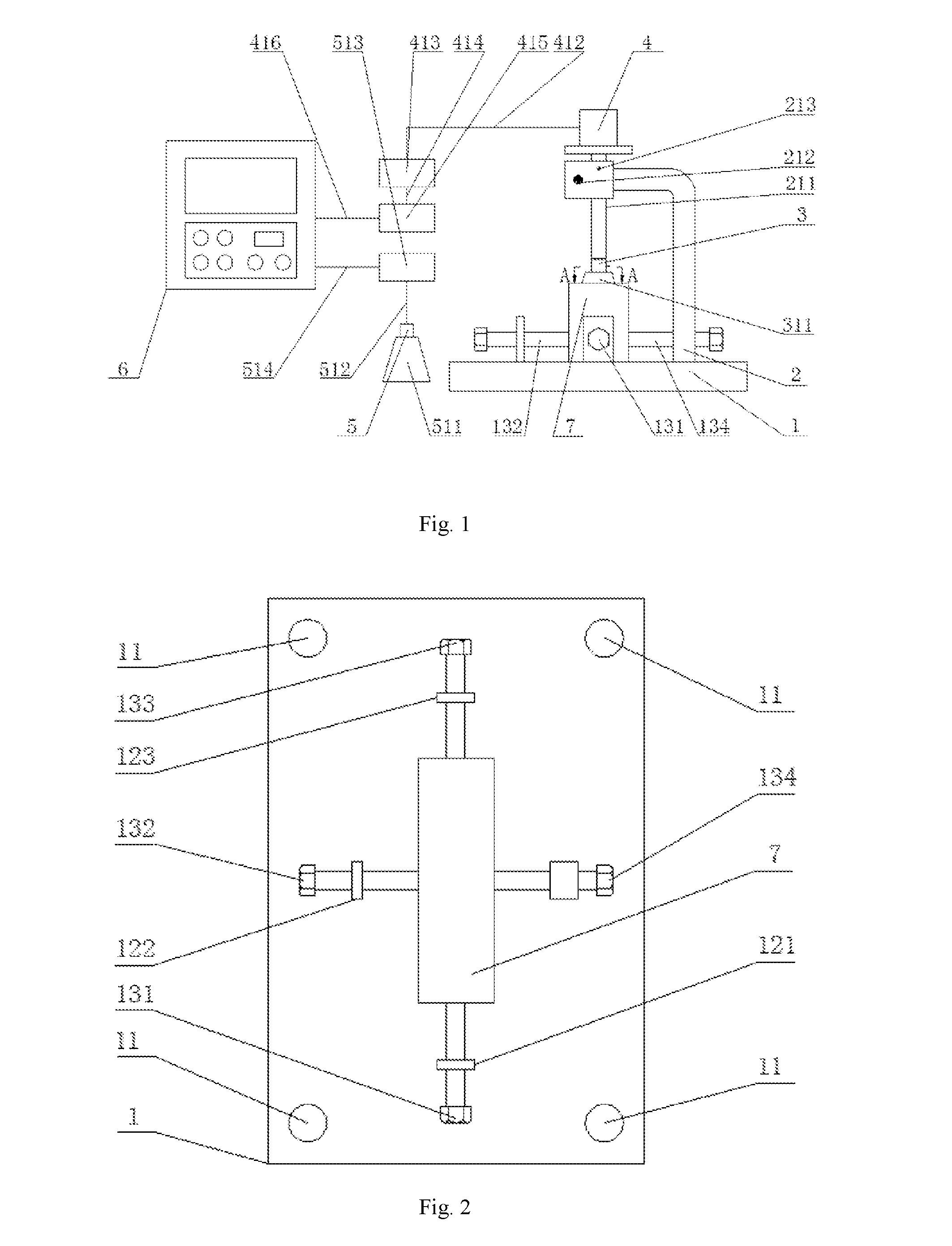
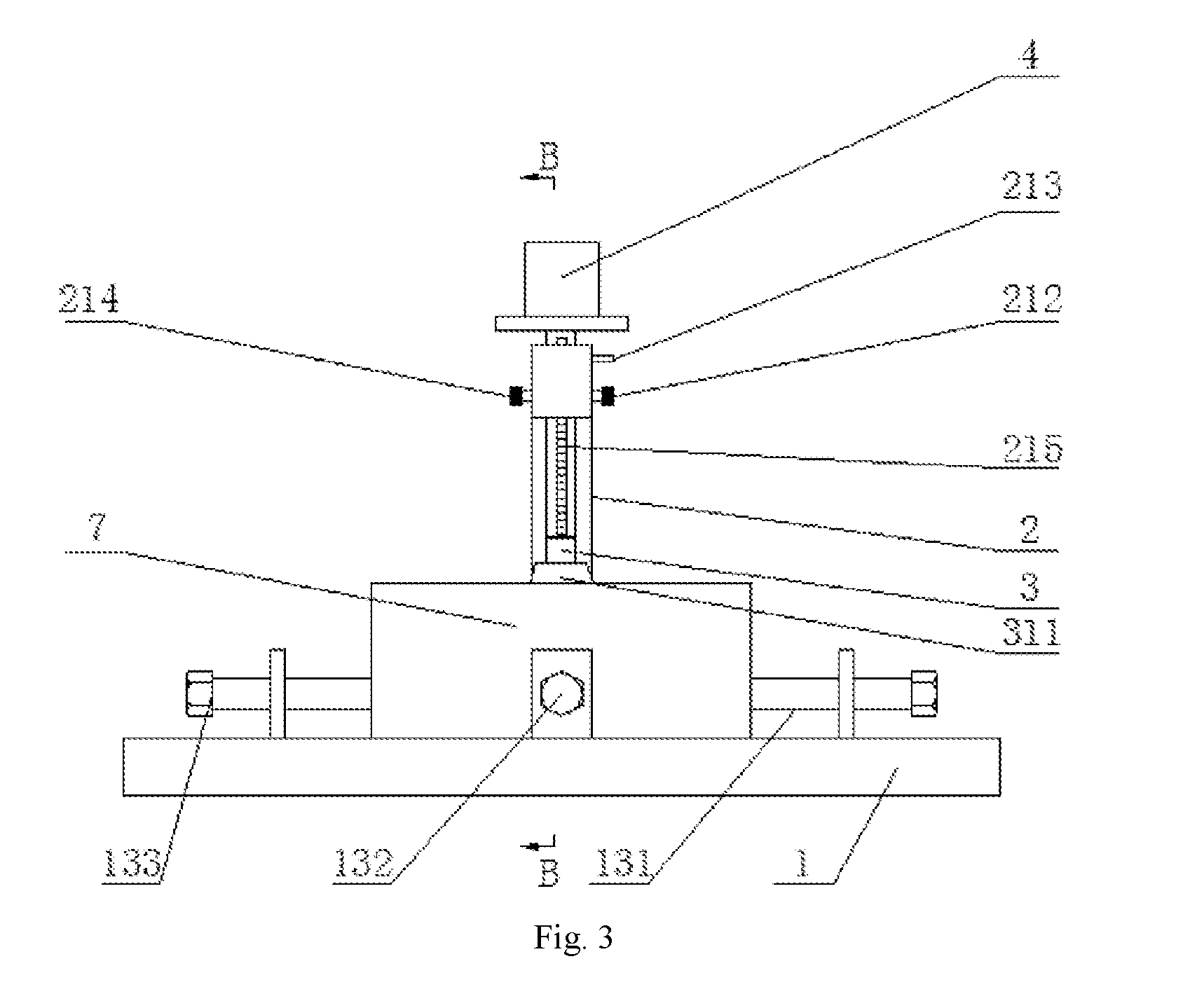
An automatic observation apparatus for detecting mineral samples comprises a base (1), a supporting arm (2), a sample fixing device (3), a stepper motor (4), a high-definition camera (5) and a control system (6). A refractometer is fixed on the base (1). A vertical through hole is formed at the top end of the supporting arm (2), and a lifting rod (211) penetrates through the vertical through hole and is matched with the vertical through hole in shape. A cavity is formed at the top end of the supporting arm (2), a gear (216) is mounted in the cavity, and the gear (216) is meshed with a rack (215) of the lifting rod (211). The sample fixing device (3) is a right-hexagonal-prism shell with the top end sealed, a spring (312) is arranged in a vertical hole of the sample fixing device, a sample locating head fixing device (314) is arranged at the lower end of the spring (312), a blind hole is formed in the lower end of the sample locating head fixing device (314), and a sample locating head (316) is matched with the blind hole in the lower end of the sample locating head fixing device (314). The apparatus can conveniently and efficiently fix samples, stray light interference is avoided, mineral samples can be rotated to be observed from different angles, and mineral sample detection accuracy is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Device and method for detecting refractive index of optical flat based on displacement sensor
InactiveCN102175644ASimple structureEasy to detectPhase-affecting property measurementsVertical planeObject point
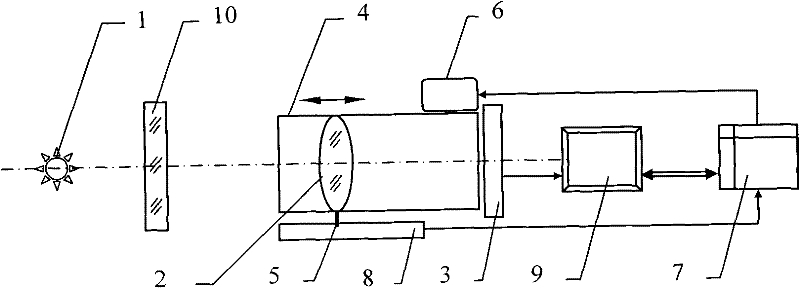
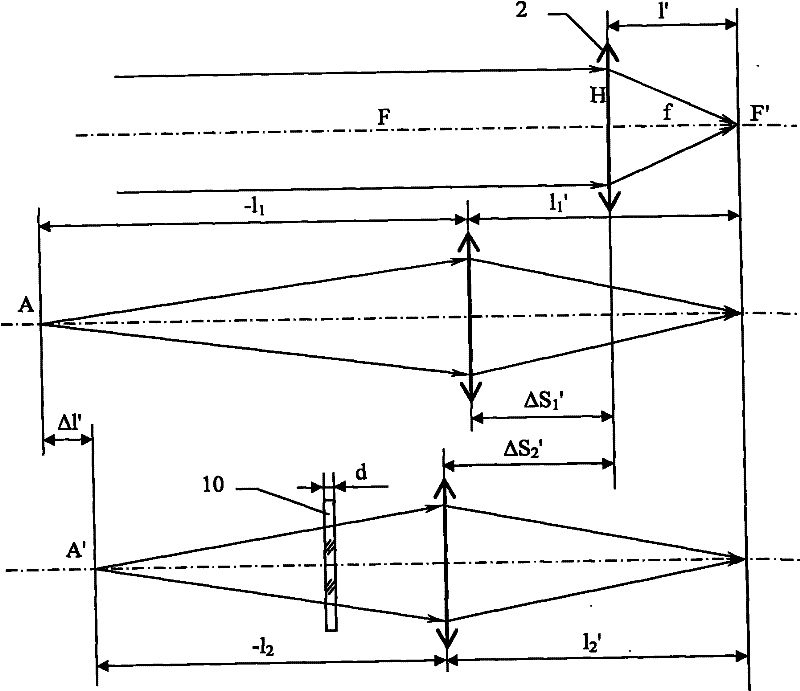
The invention relates to a device and method for detecting the refractive index of an optical flat based on a displacement sensor, belonging to the technical field of optical measurement. When he existing automatic V-prism refractometer is adopted for detection, two vertical planes are needed to be processed on a measured piece, and the structure of the detection device is complicated. The detection device provided by the invention comprises a light source, an optical imaging system and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) image sensor which are optically, coaxially and sequentially ranked, wherein the optical imaging system is positioned in a cam cylinder and is in slide pin connection with the displacement sensor; a motor drives the cam cylinder to rotate and controls a processing circuit to be respectively electrically connected with the motor and the displacement sensor and connected with the serial port of an upper computer; and the CCD image sensor is also electrically connected with the upper computer. The detection method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: processing a material to be detected into the measured piece of the optical flat; clearly imaging the infinite distance through the optical imaging system; clearly imaging a close object point A and obtaining the displacement delta S1' of the main surface H of the optical imaging system; adding the measured piece of the optical flat and clearly imaging the refractive image A' of the measured piece of the optical flat in the close object point A to obtain the displacement delta S2'; and computing the refractive index n of the material to be detected according to the displacement delta S1' and the displacement delta S2'.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Deflecting prism and measuring assembly
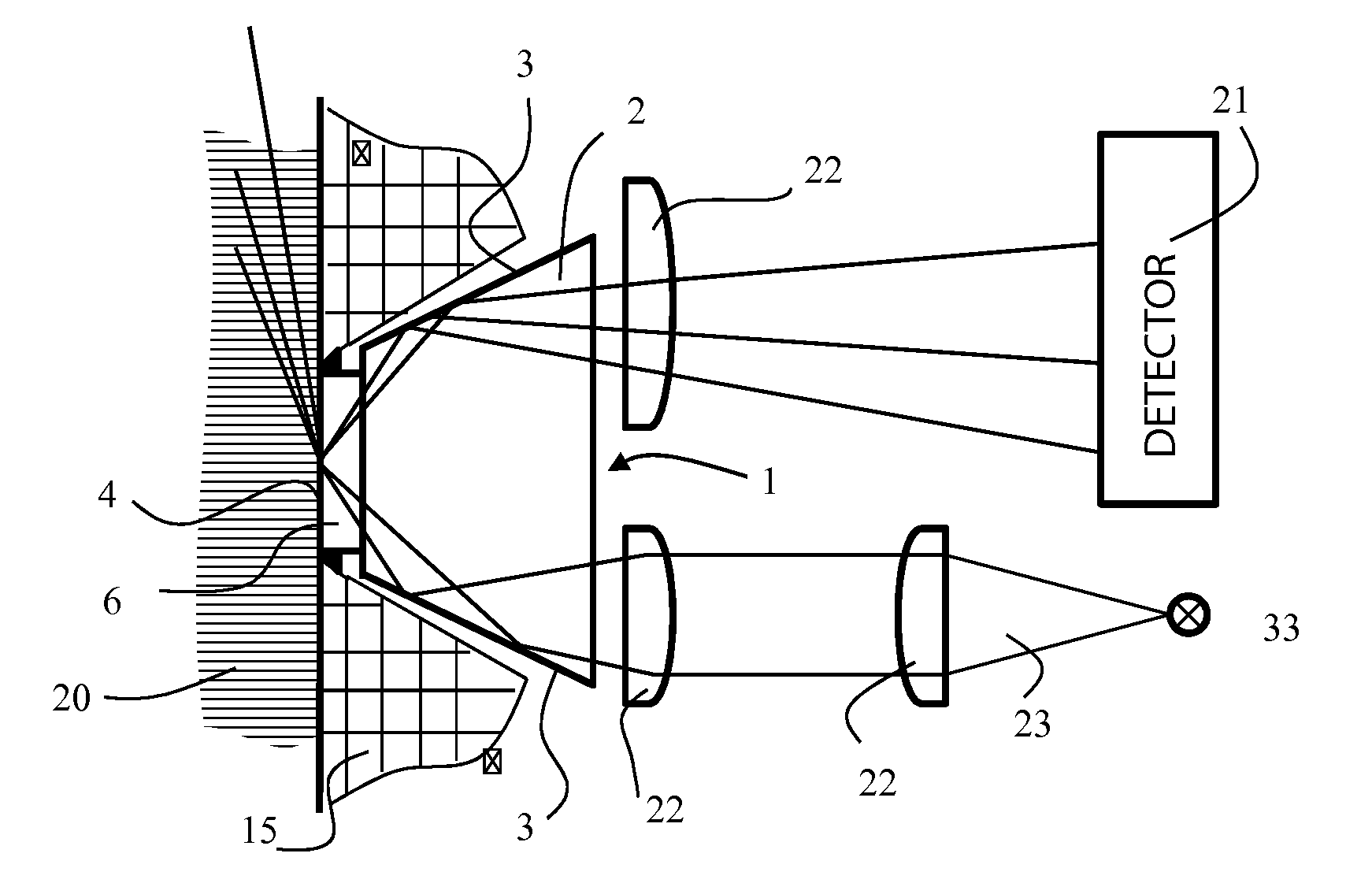
A deflecting prism for electromagnetic radiation, in particular for refractometer- and / or ATR-measurements, is part of a measuring configuration. The deflecting prism has a body produced in one piece from a mono-crystal. The body has at least two beam conductive surfaces on a side of the body opposite each other or circumferentially about the body and a measuring surface lying between the beam conductive surfaces or surrounded by the latter. The body further has at least one beam entry surface or a beam exit surface. Accordingly, the measuring surface lies on an elevation formed on the body, which crosses over via a ledge surrounding the elevation into the remaining part of the body. On the remaining part, the beam conductive surfaces and / or the beam entry surface or exit surface lie.
Owner:ANTON PAAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com