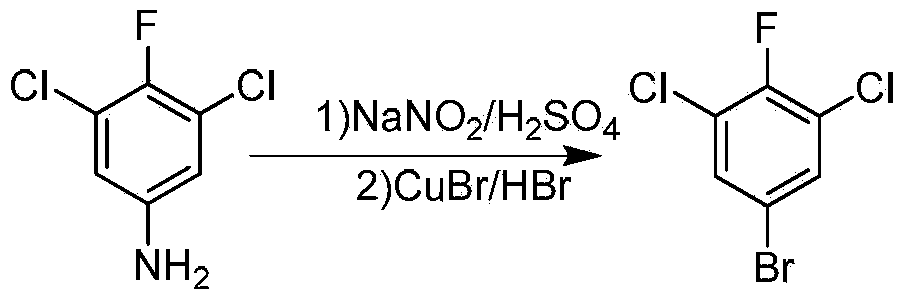Patents
Literature
1082 results about "Hydrobromic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydrobromic acid is a strong acid formed by dissolving the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. "Constant boiling" hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution that distills at 124.3 °C and contains 47.6% HBr by mass, which is 8.89 mol/L. Hydrobromic acid has a pKₐ of −9, making it a stronger acid than hydrochloric acid, but not as strong as hydroiodic acid. Hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids known.
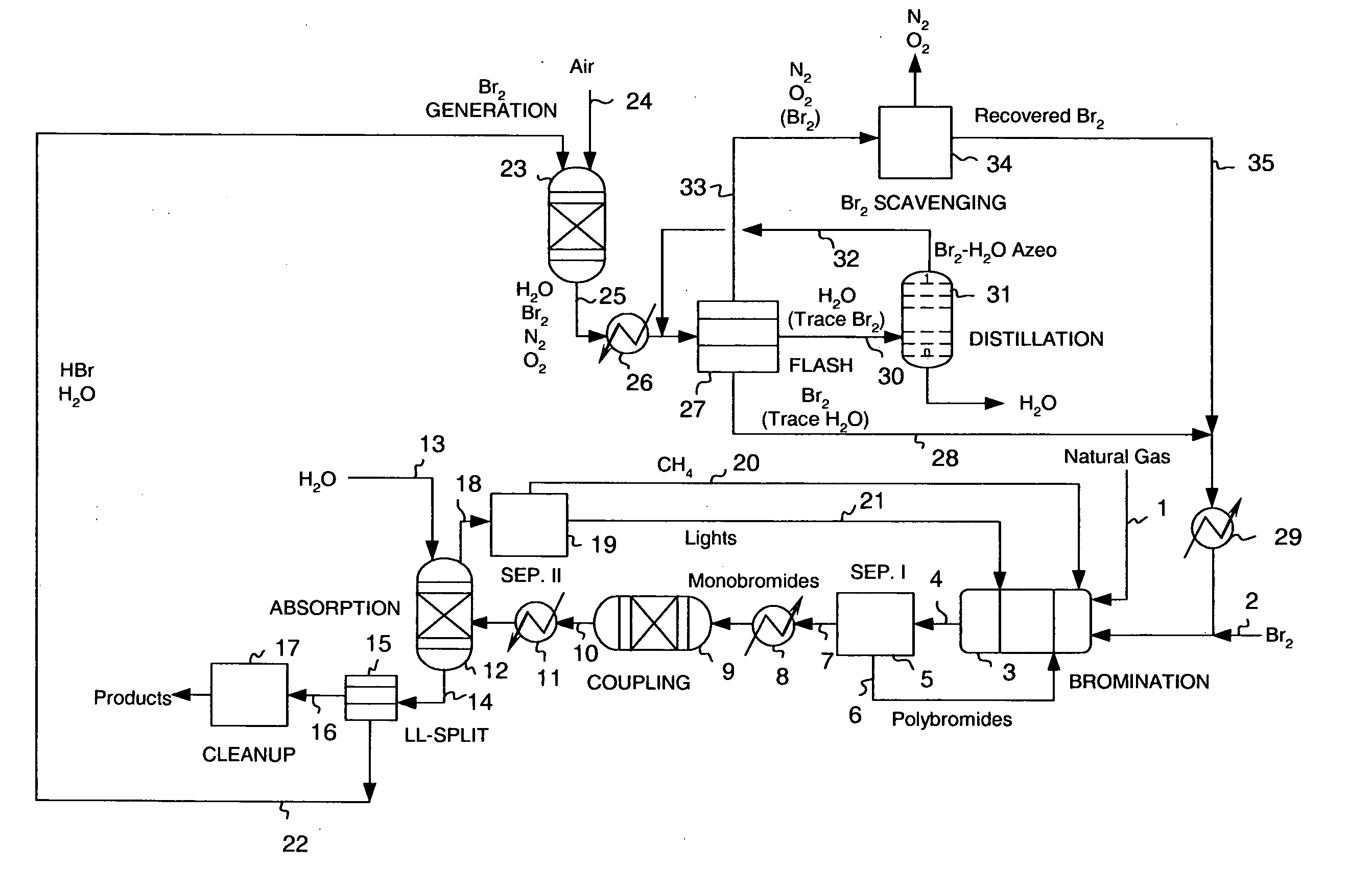
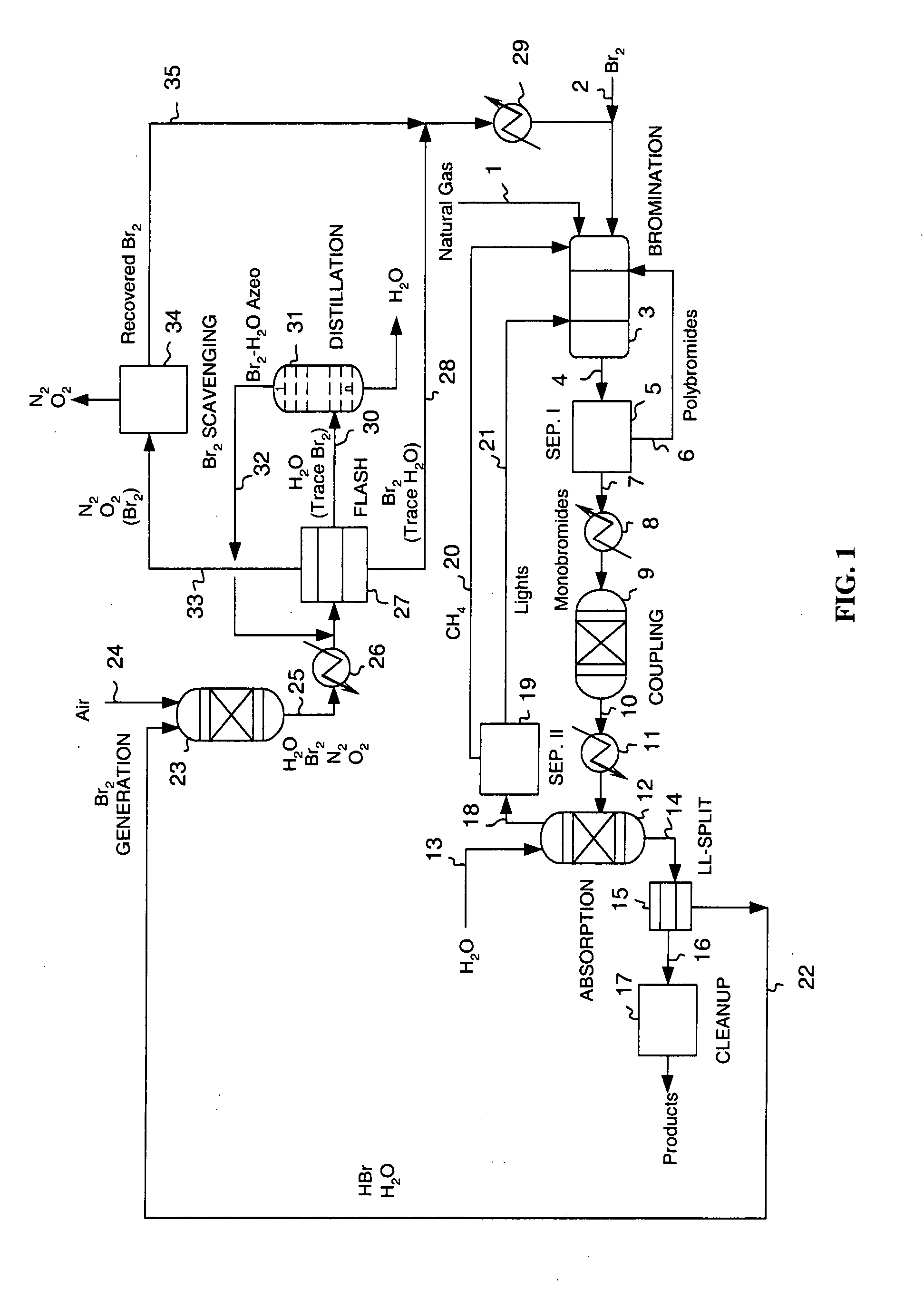
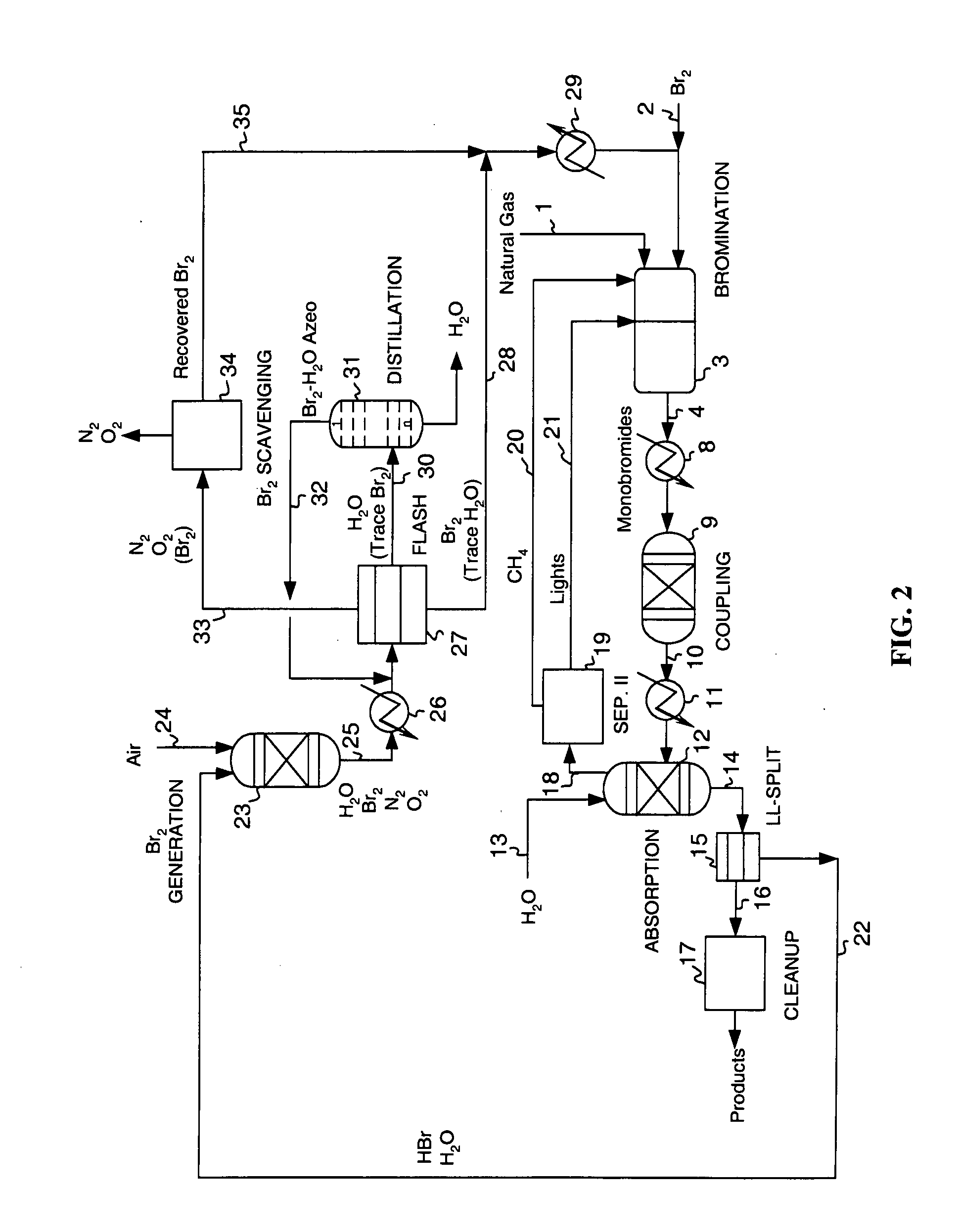
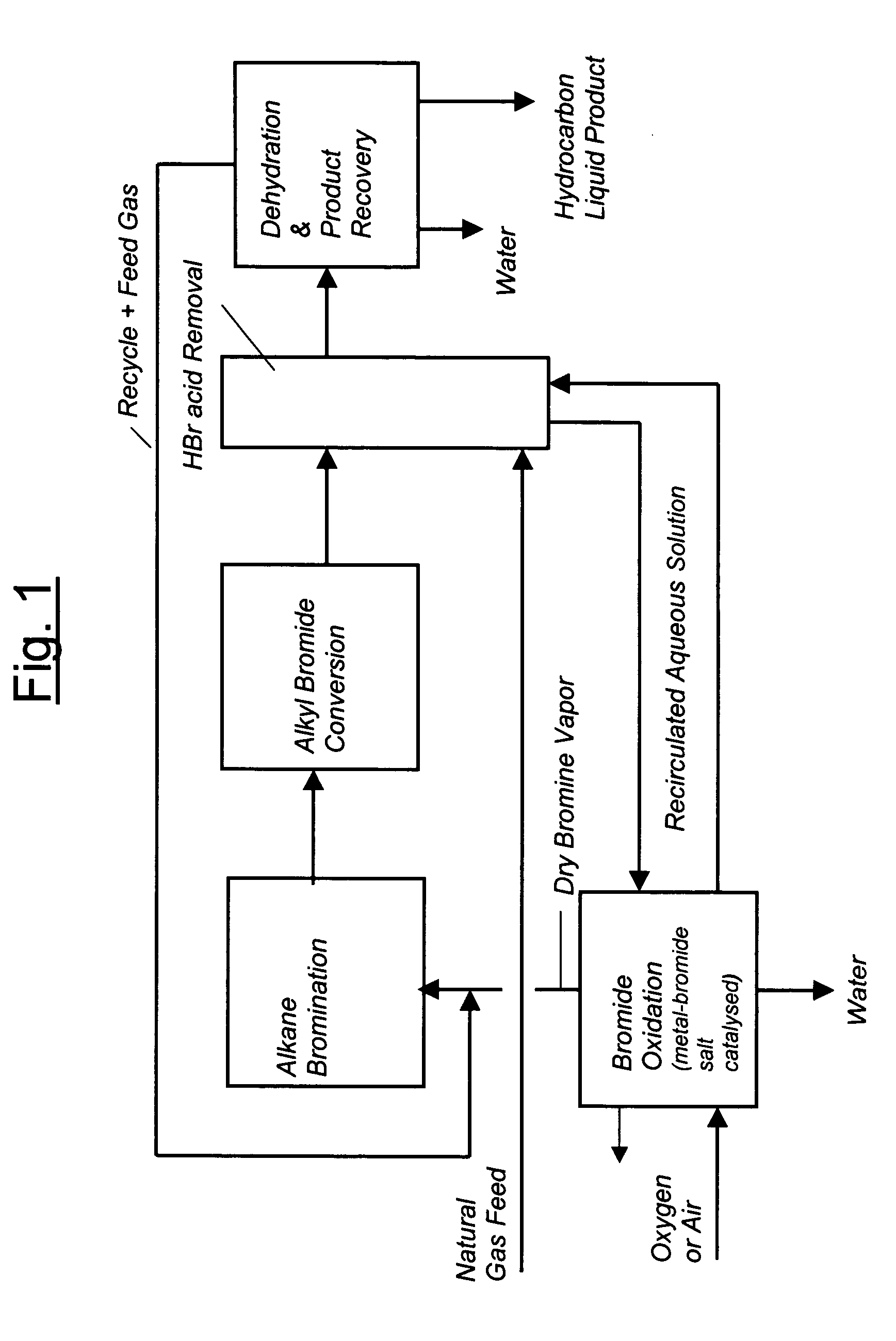
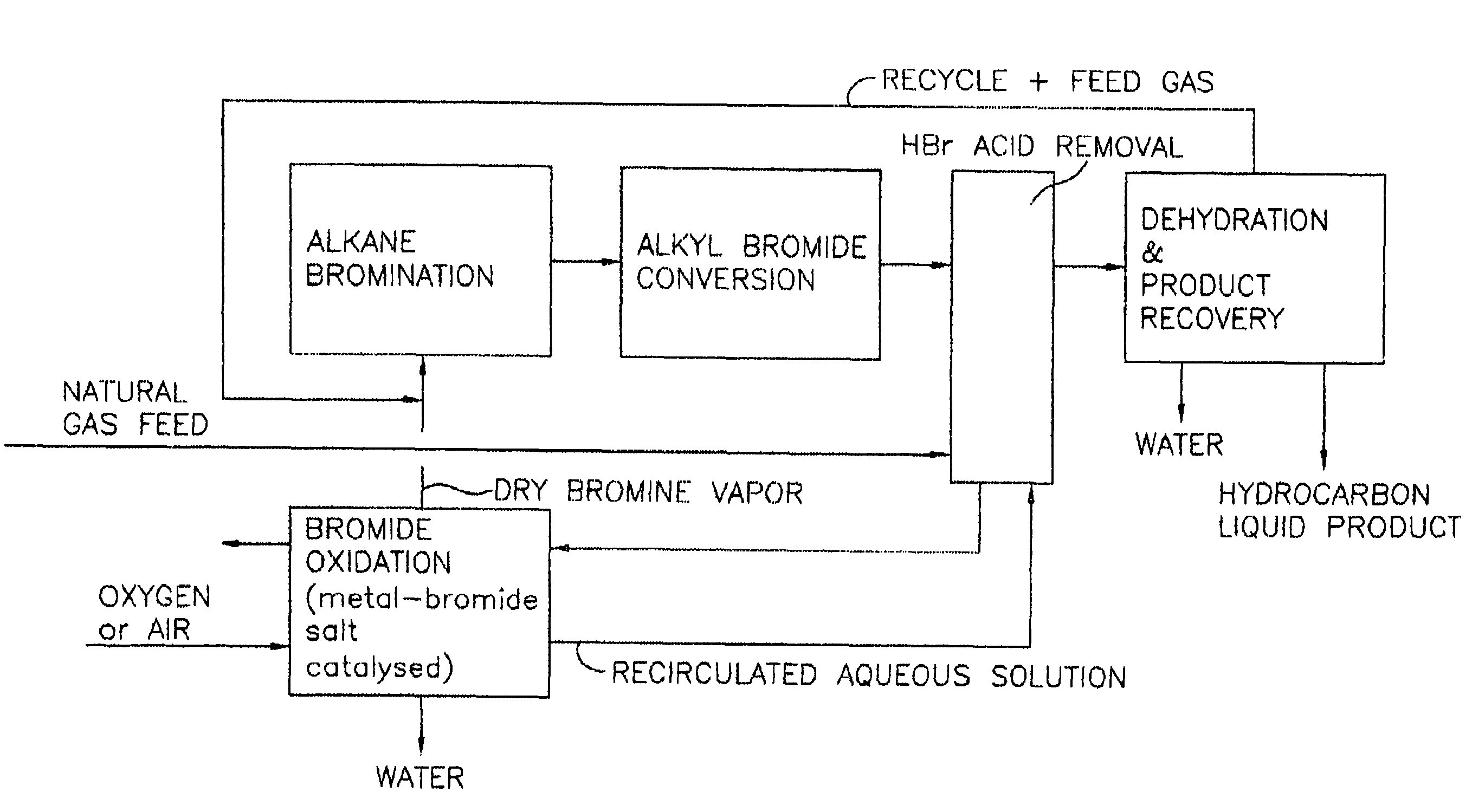
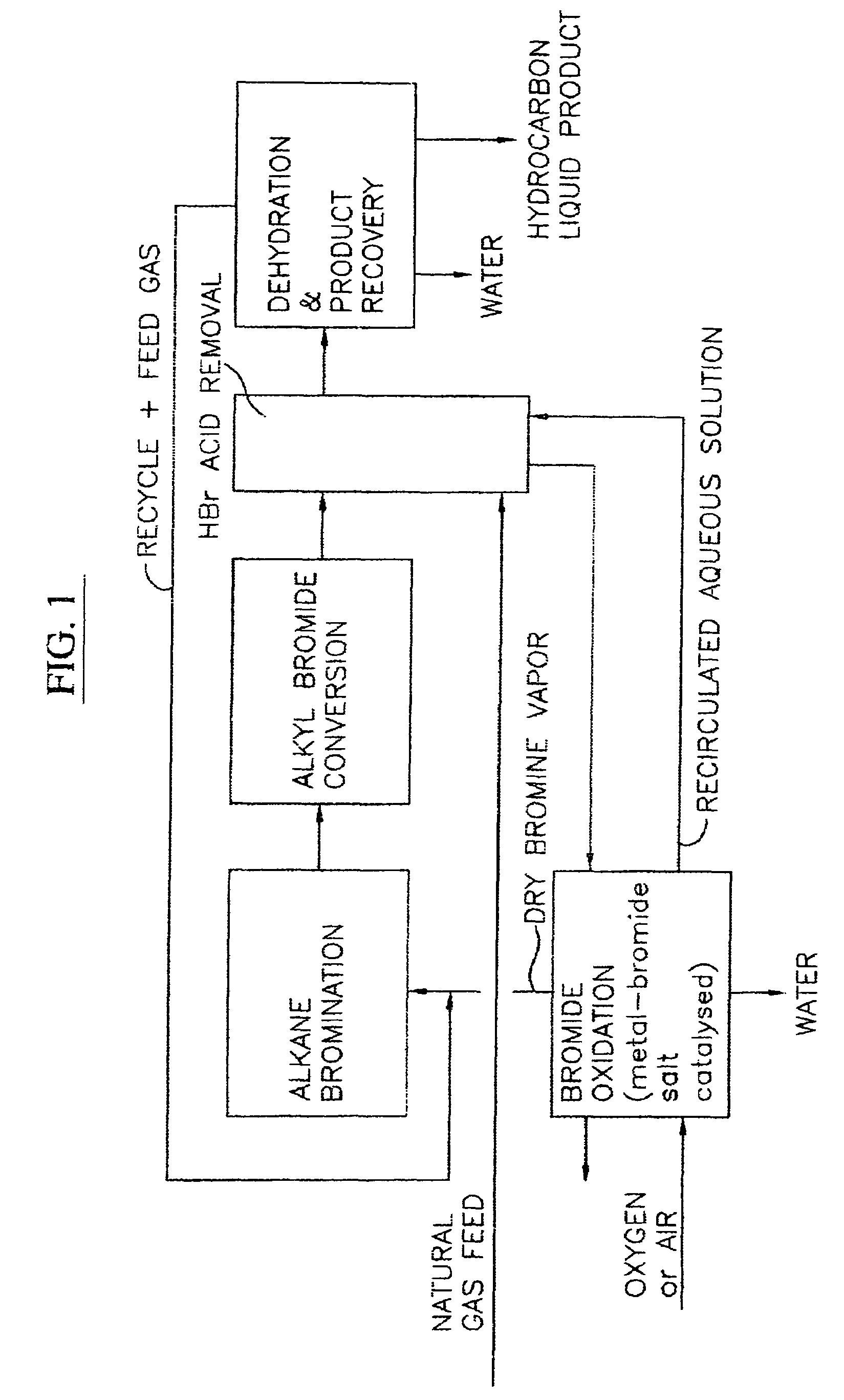
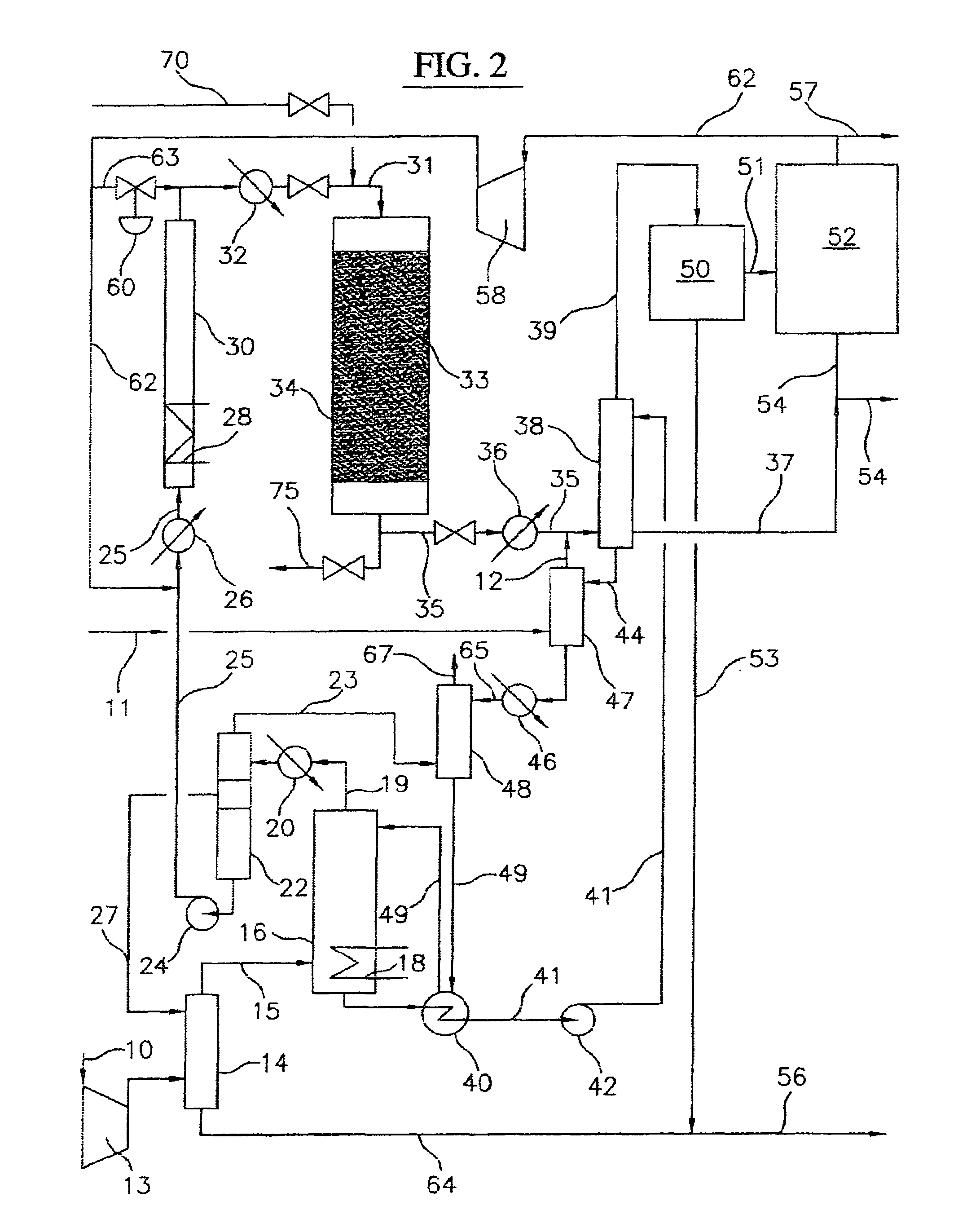
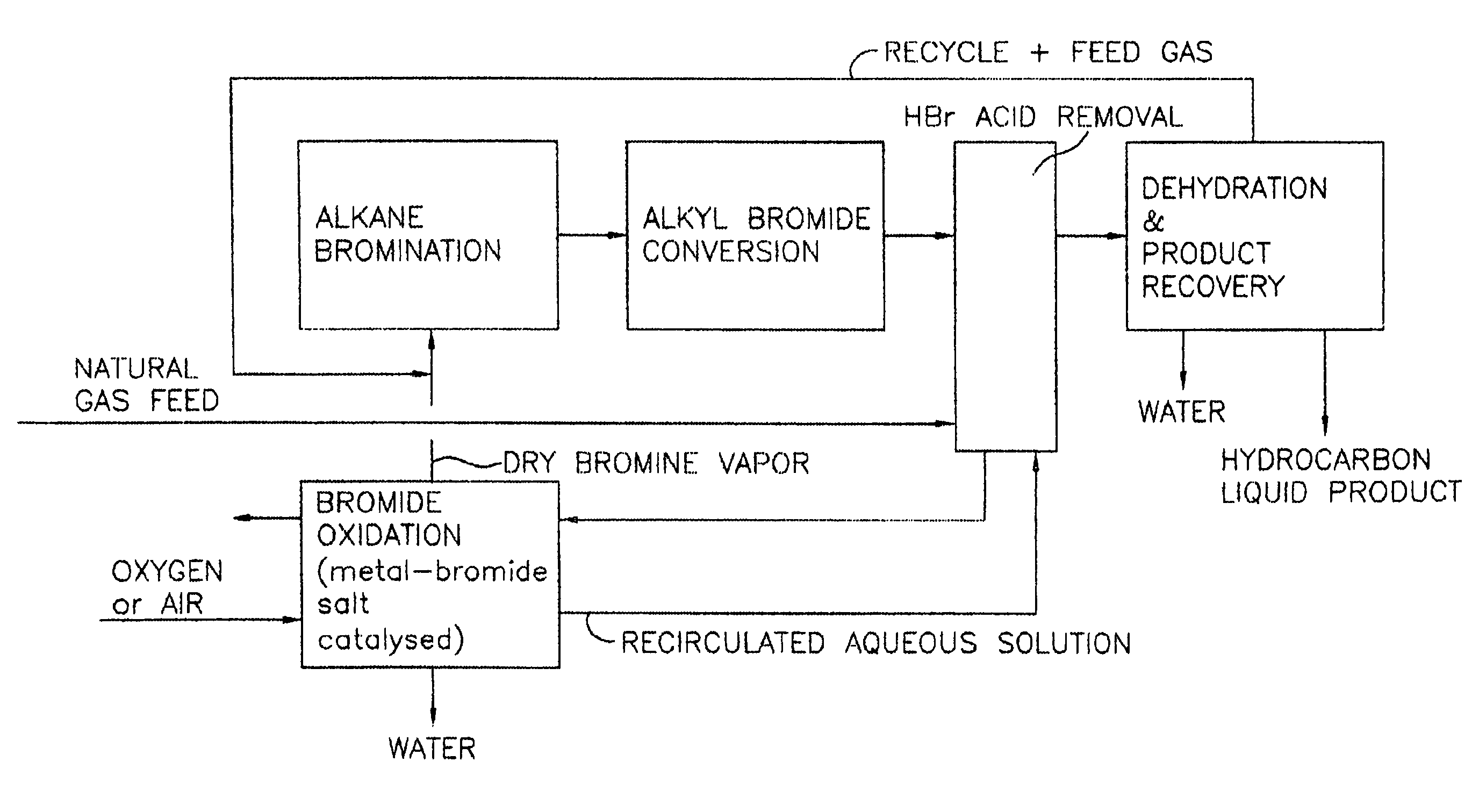
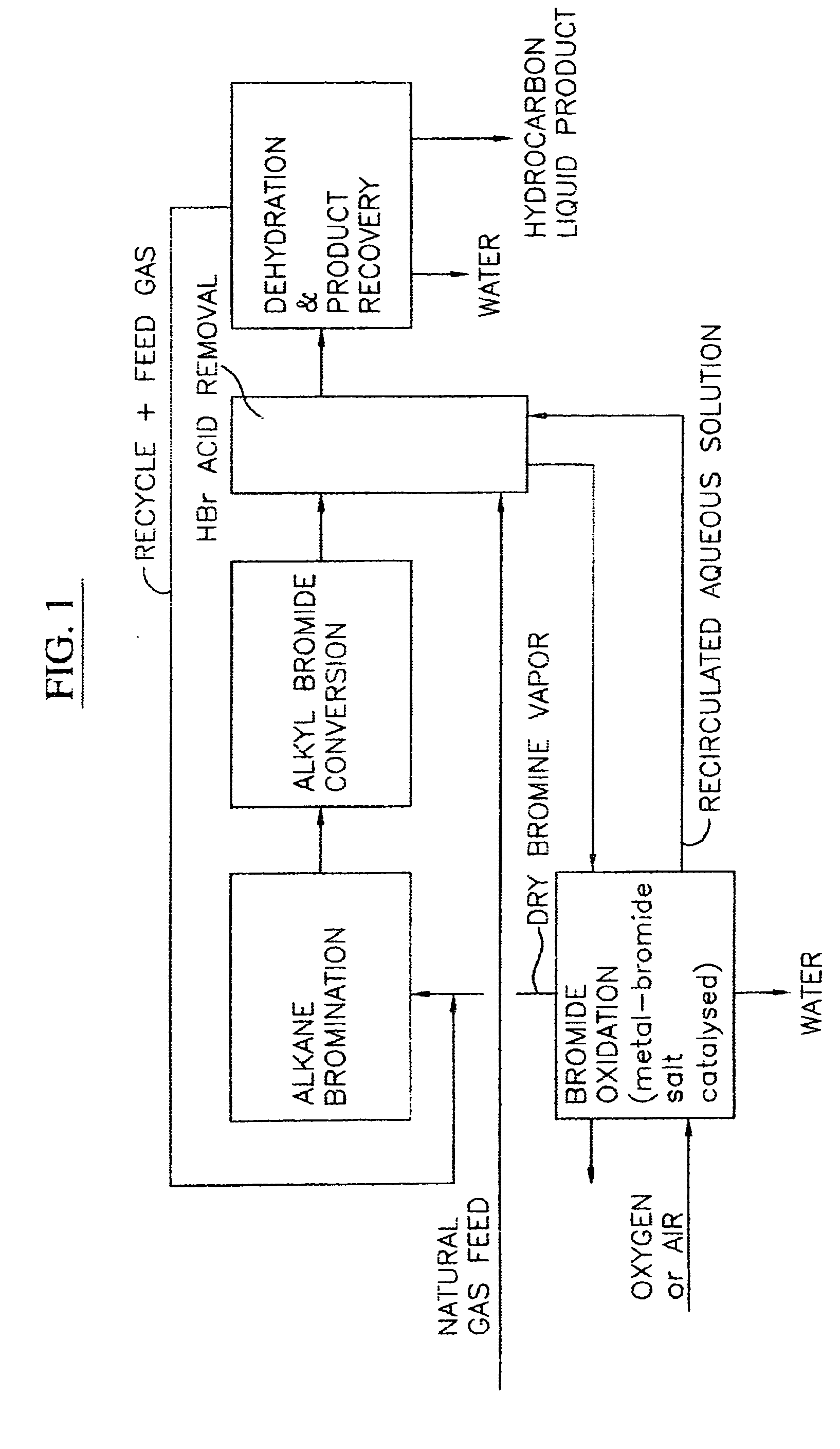
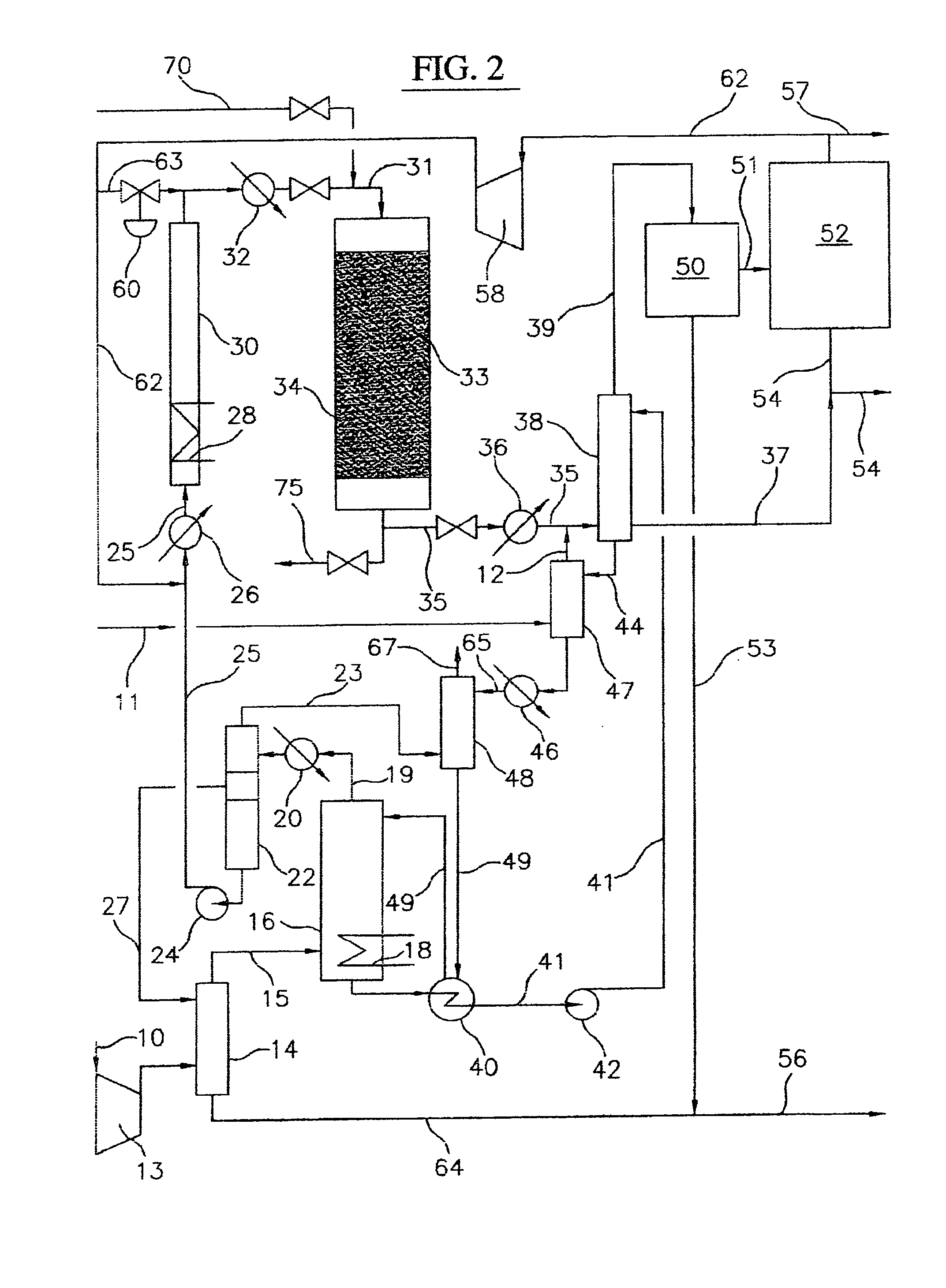
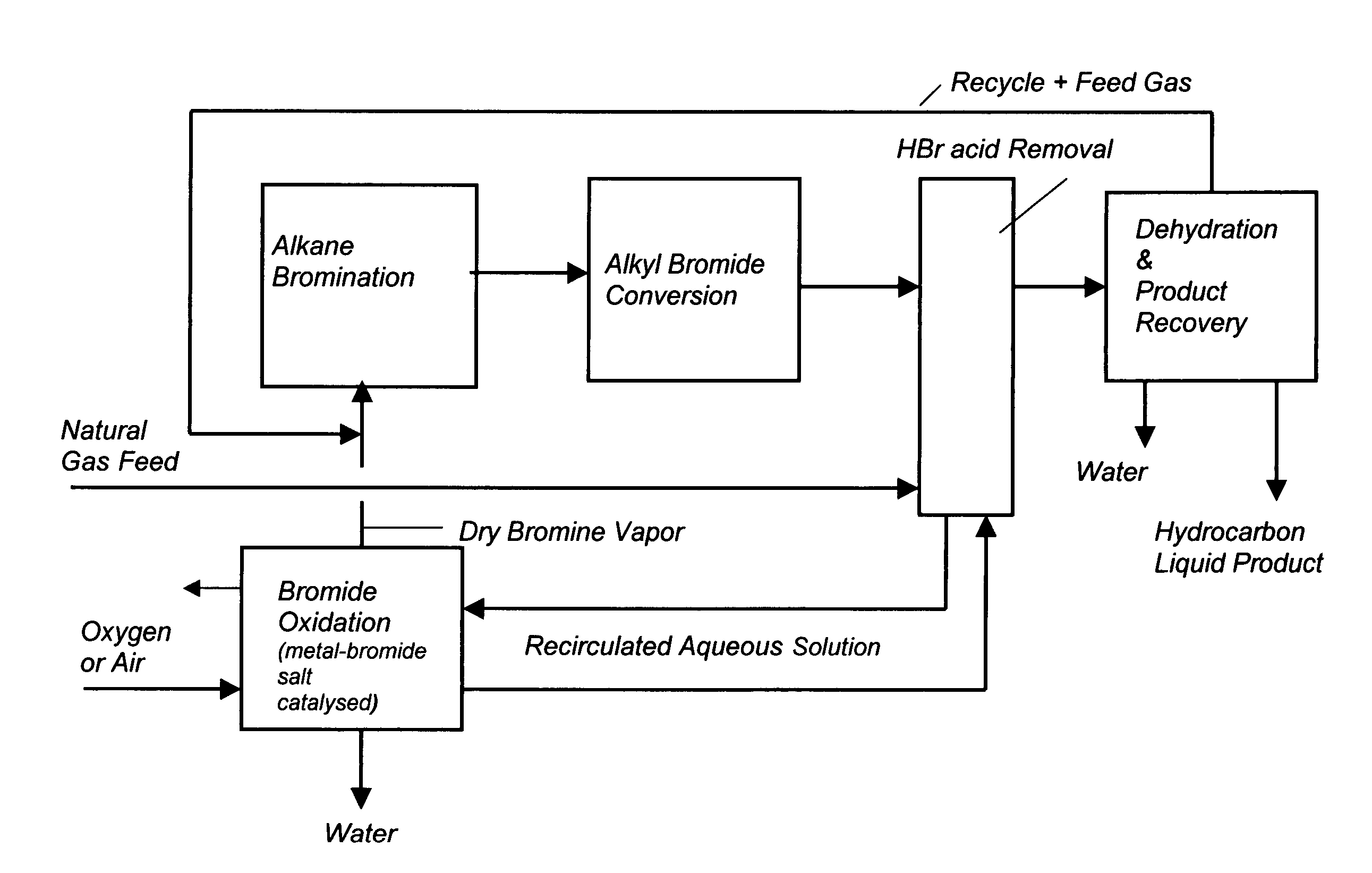
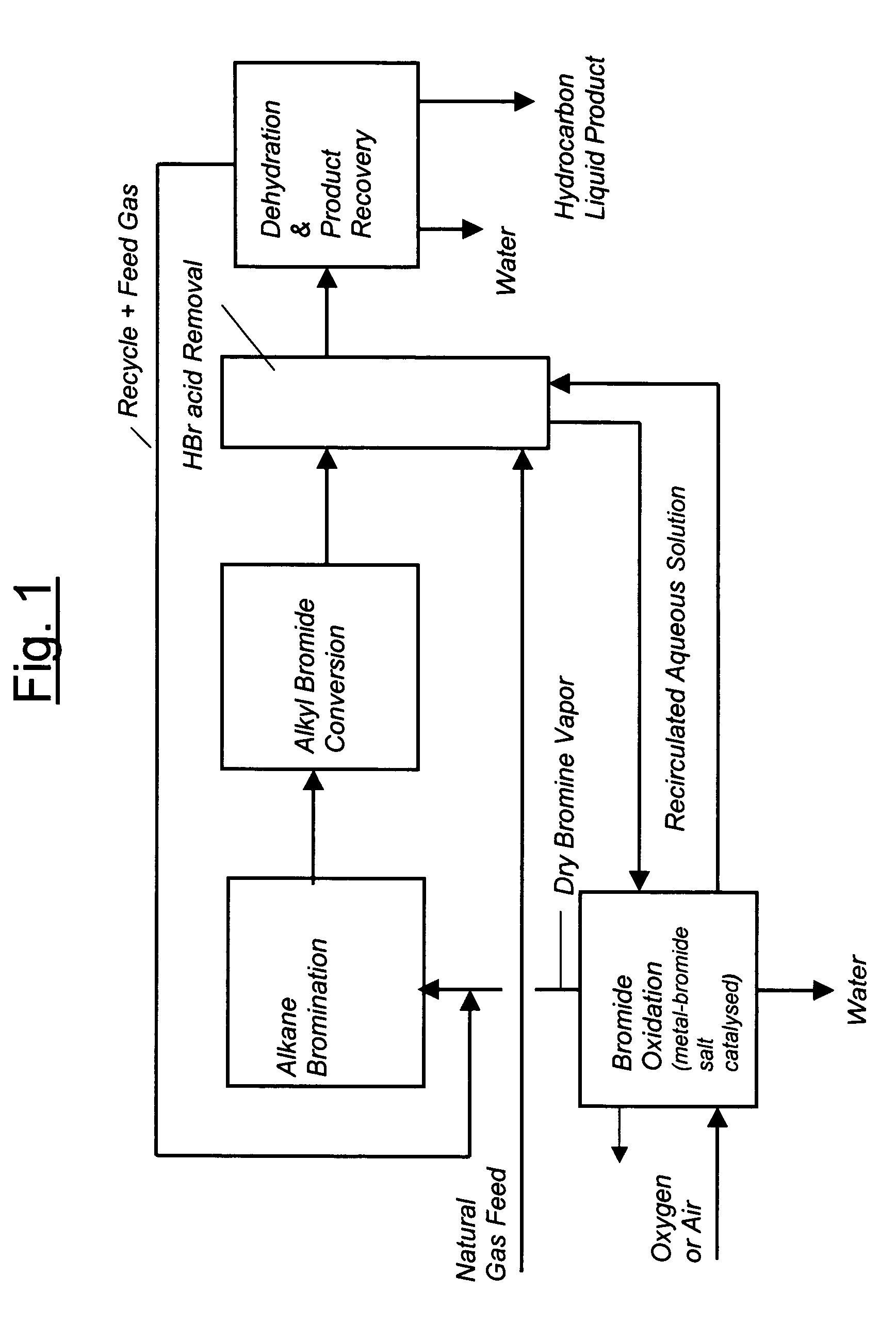
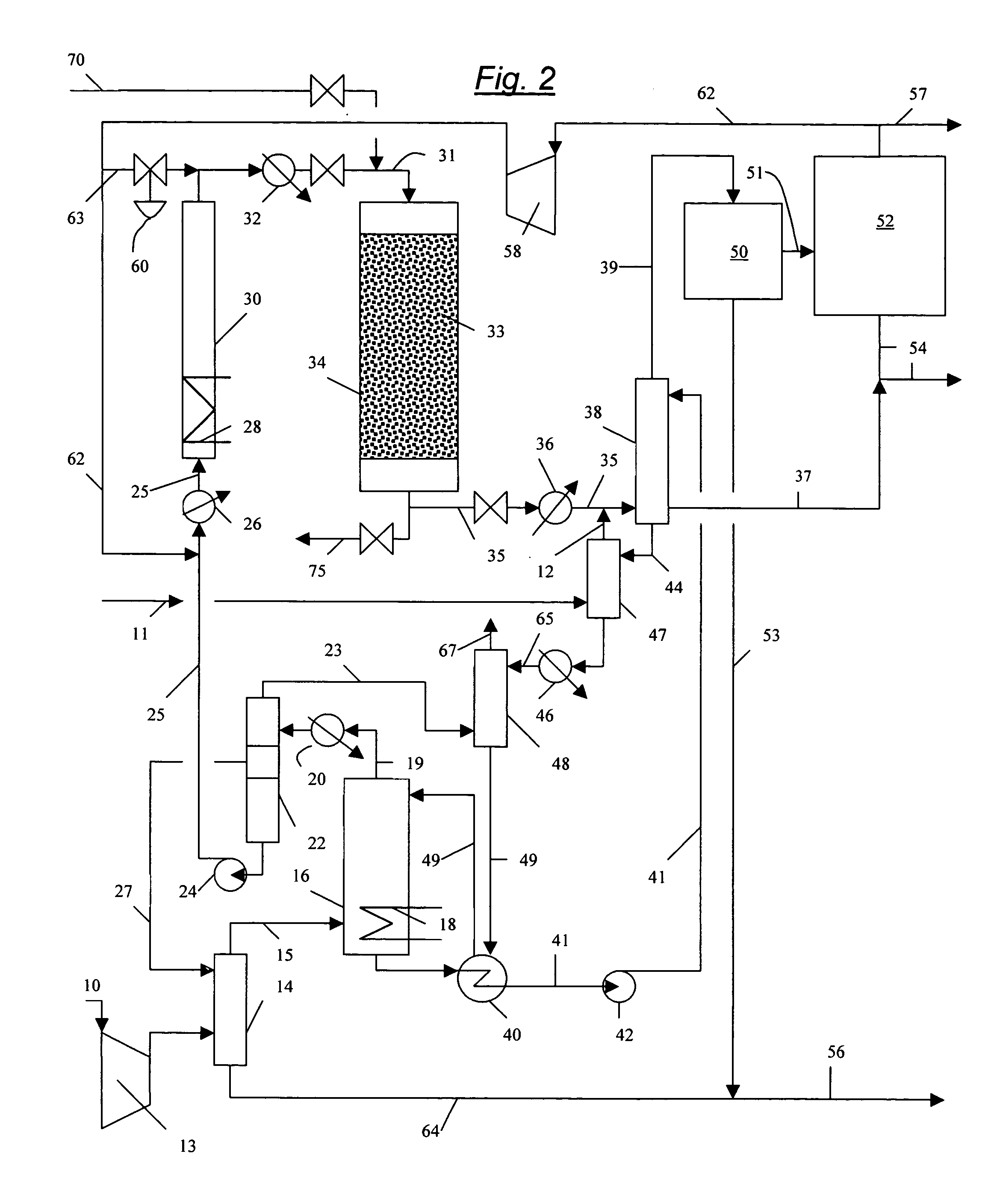
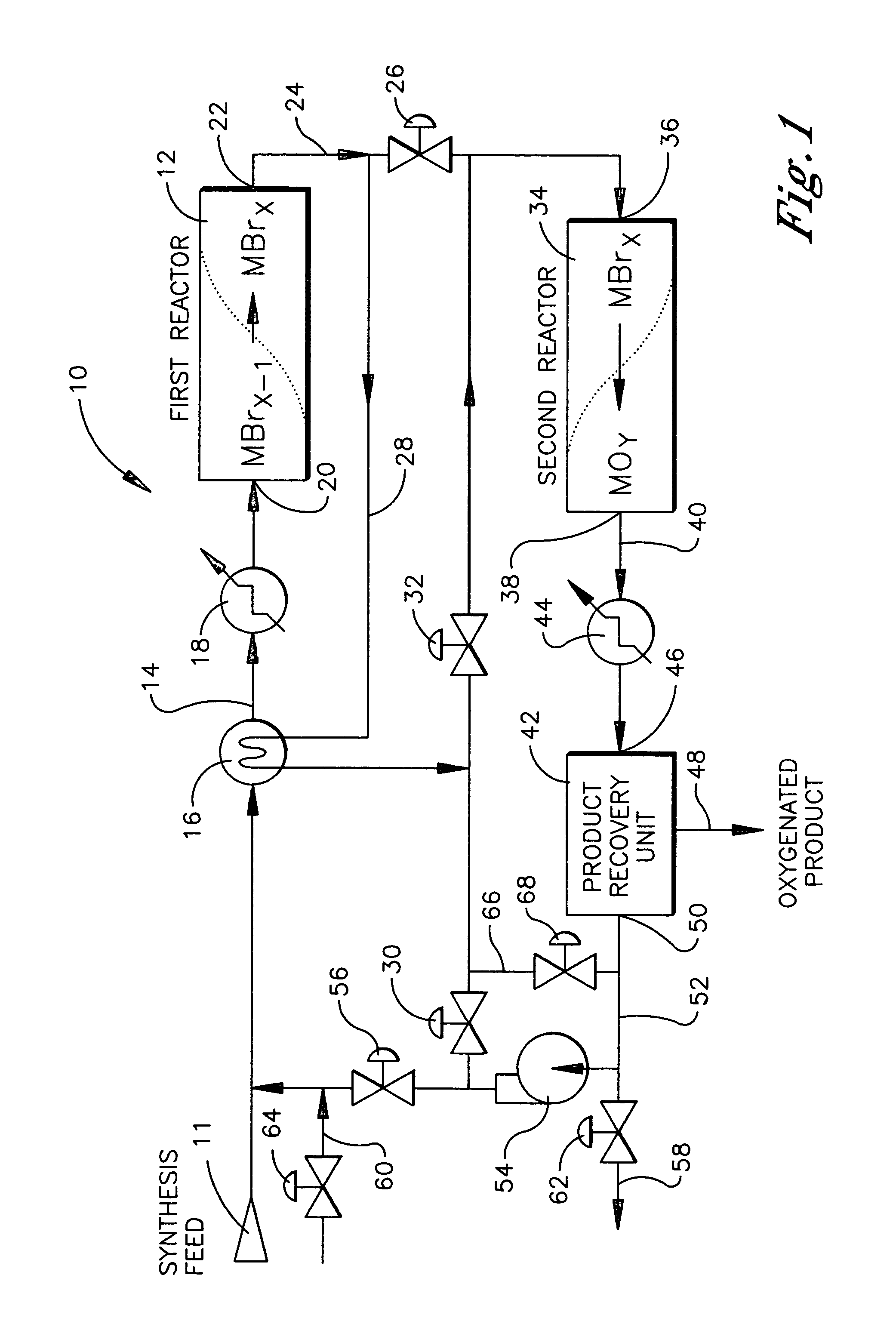
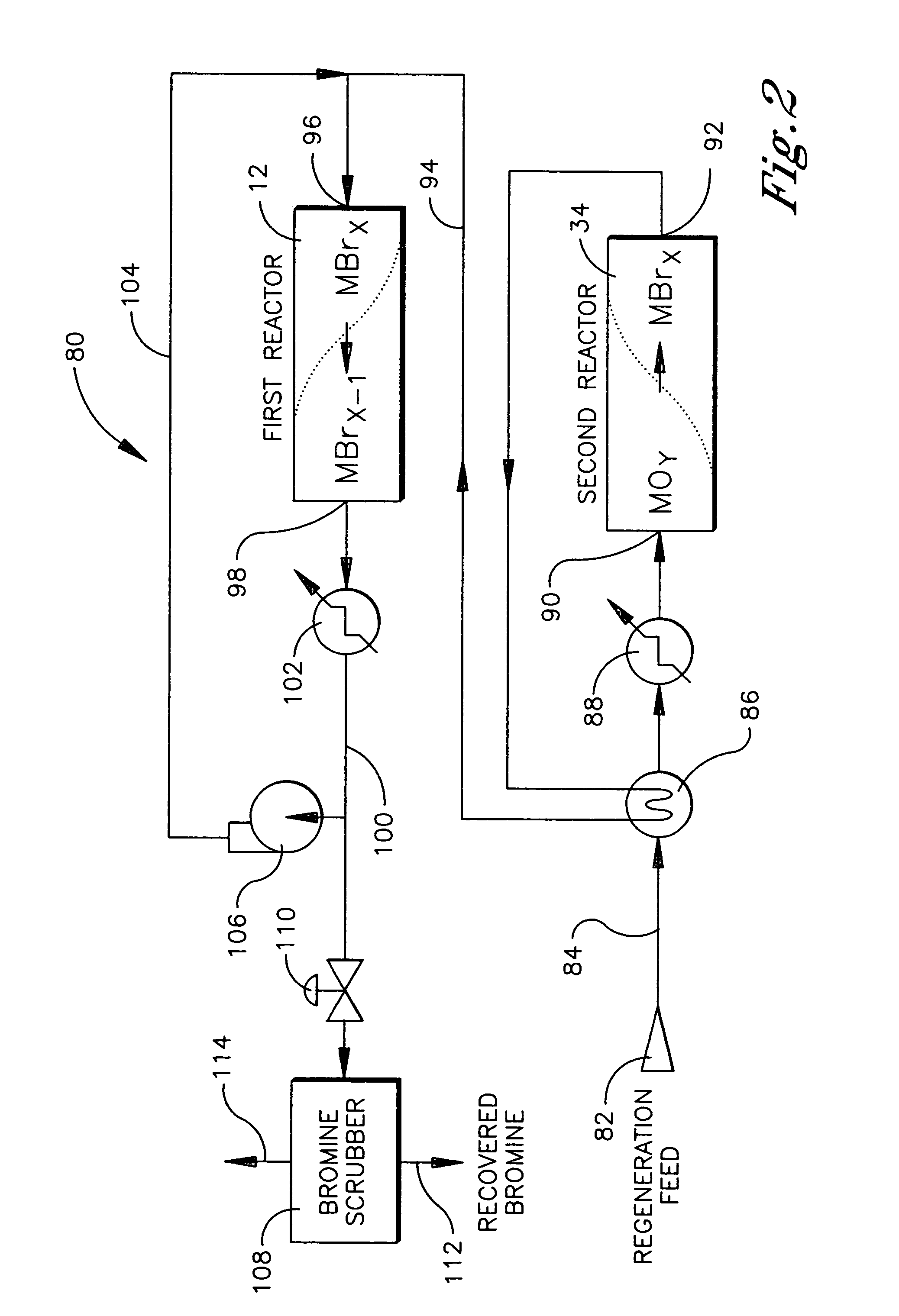
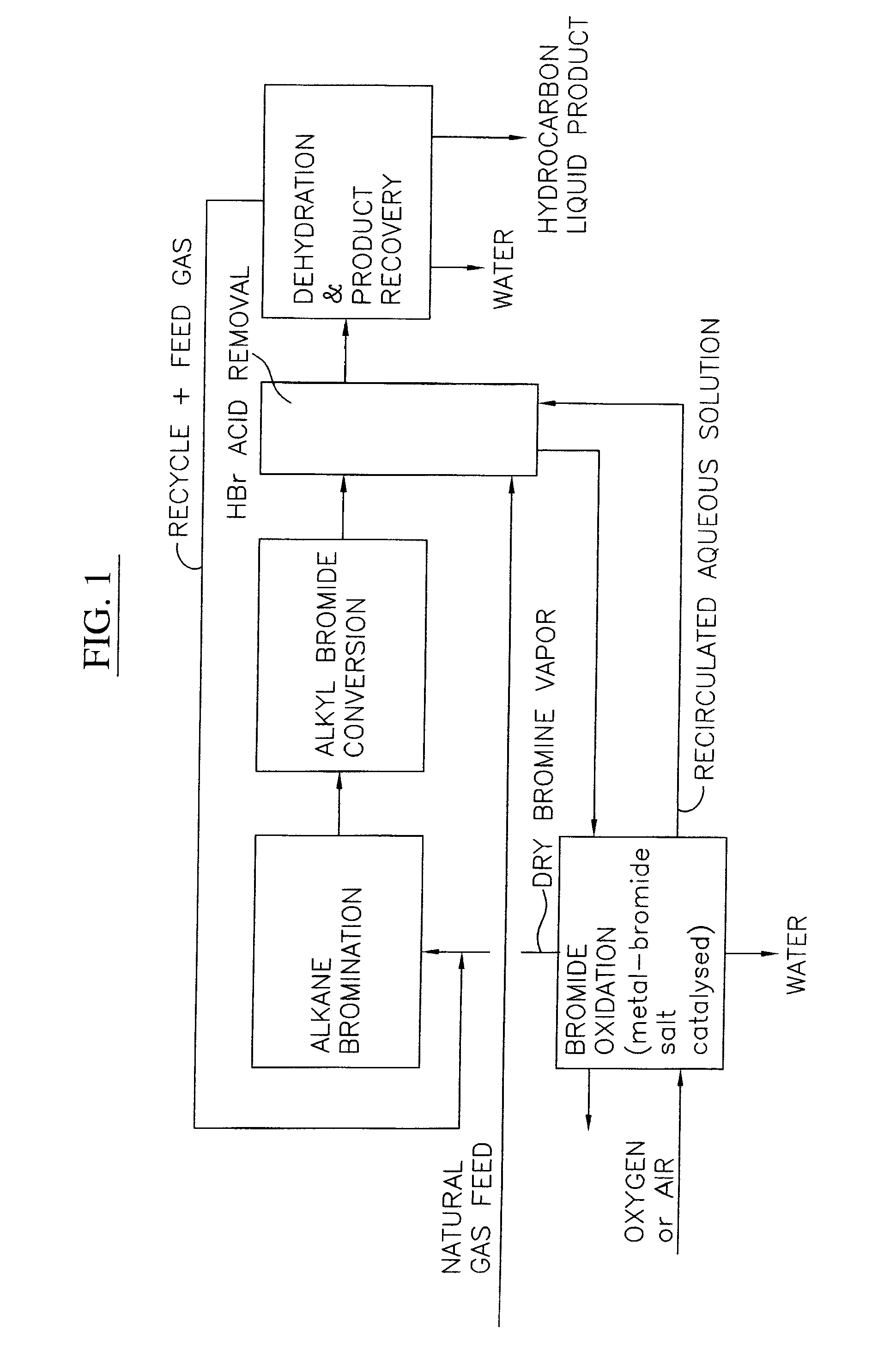
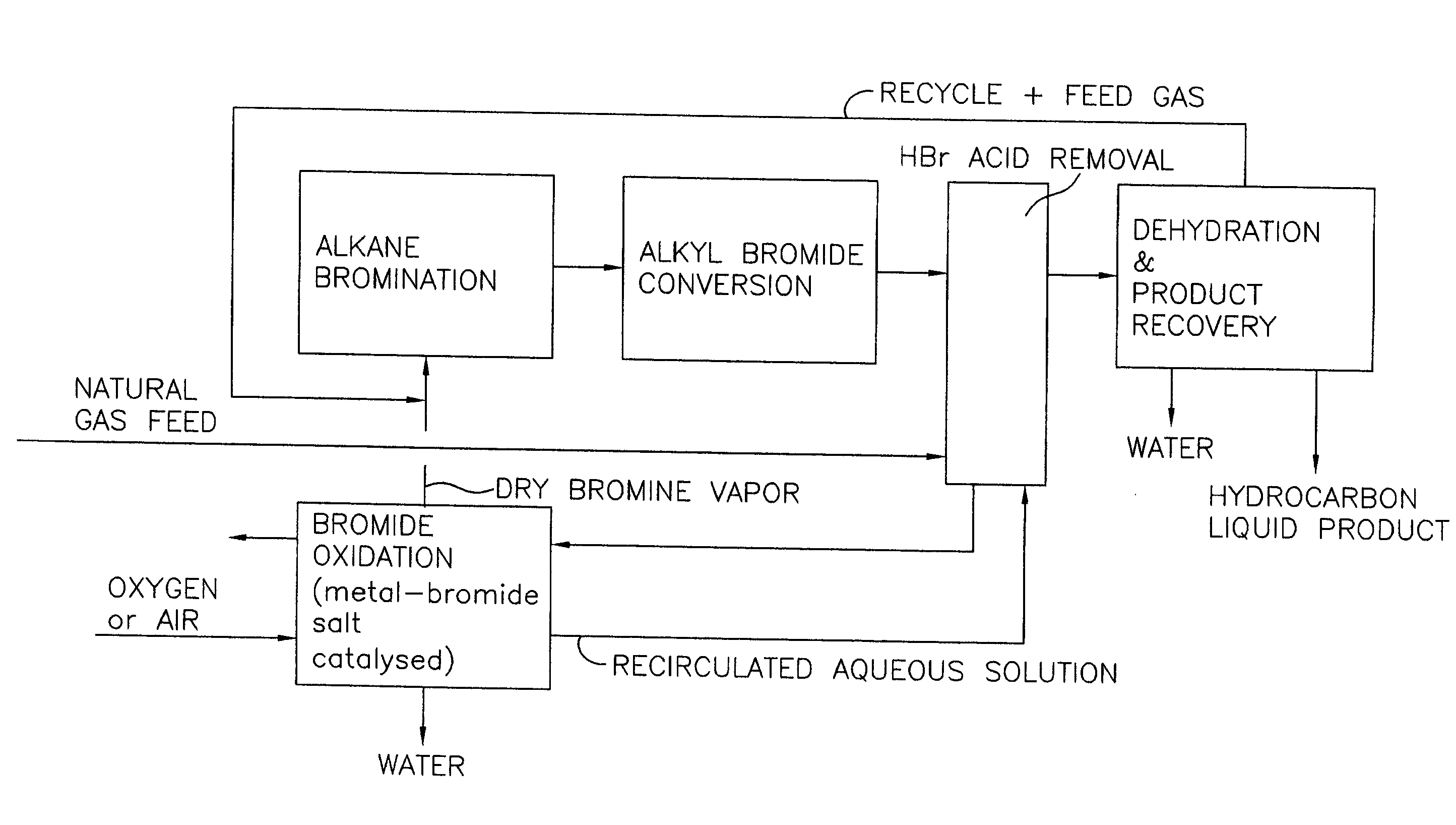
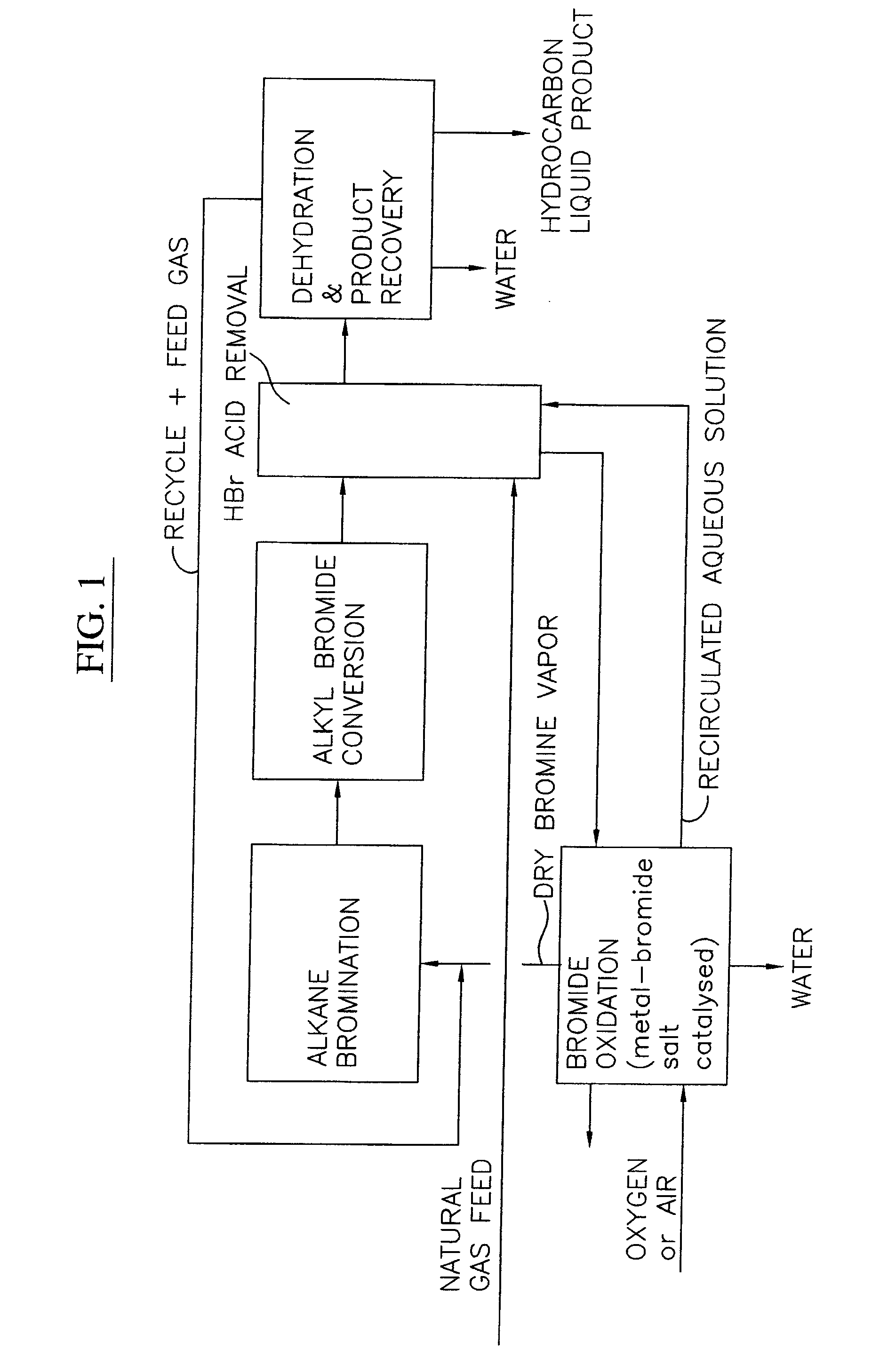
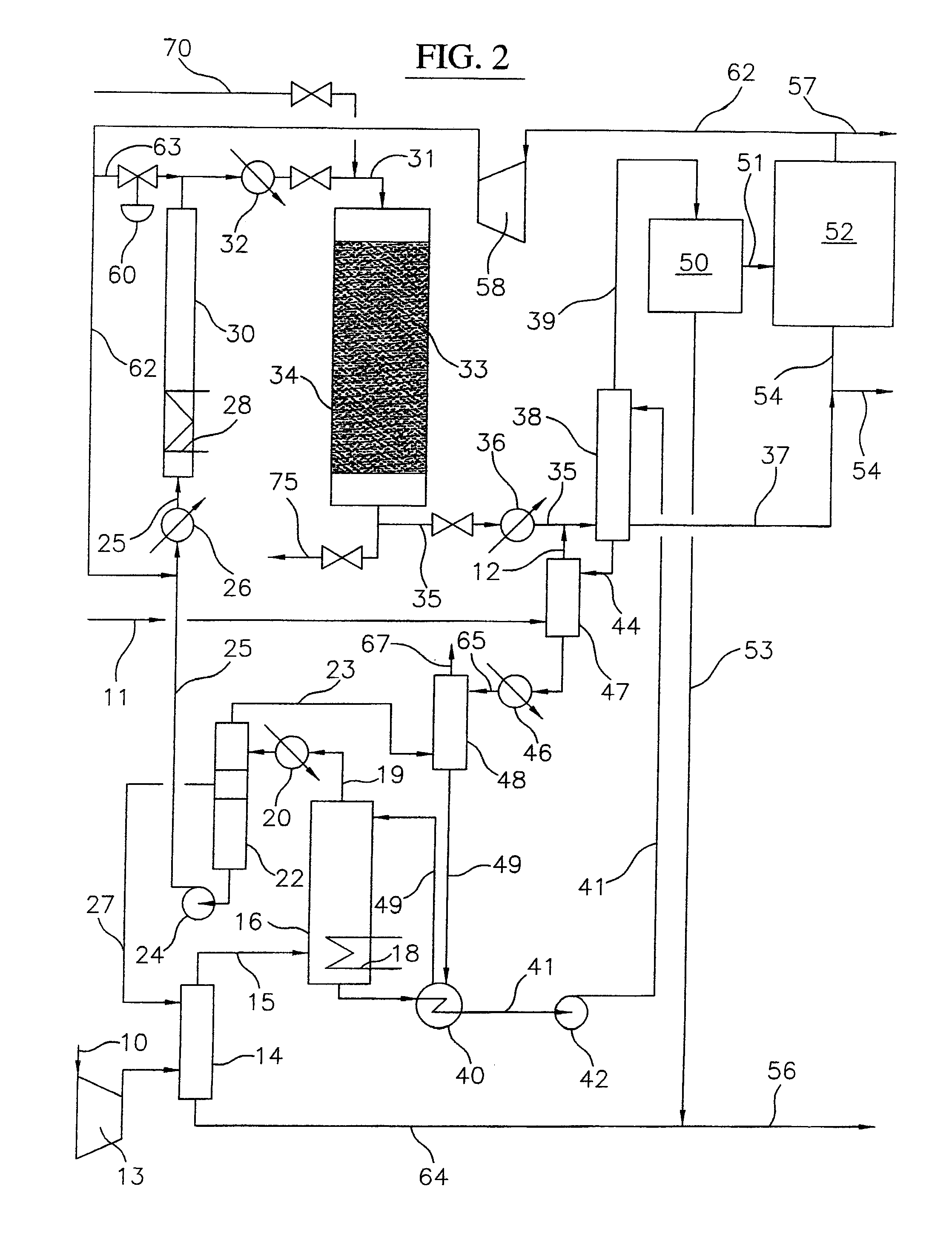
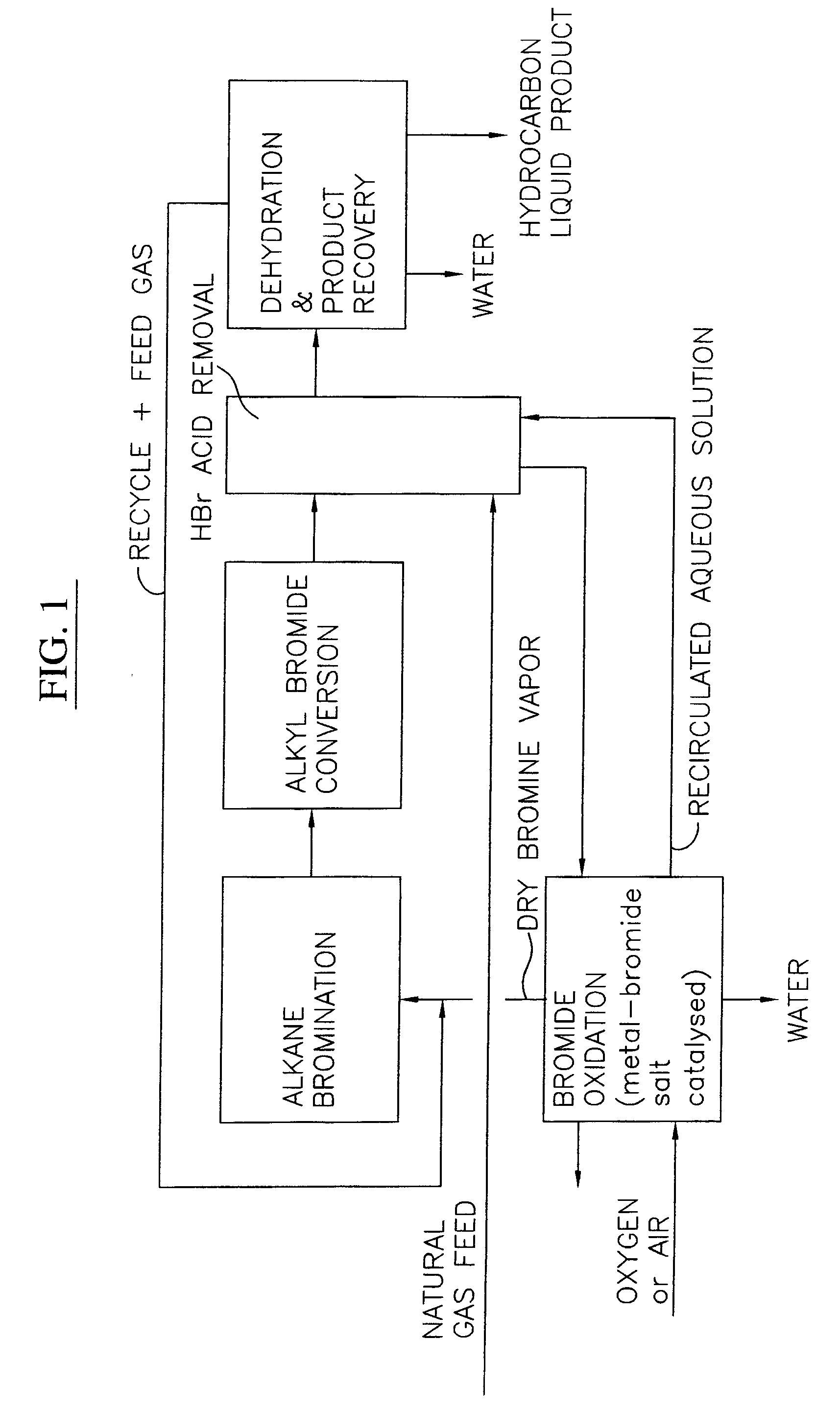
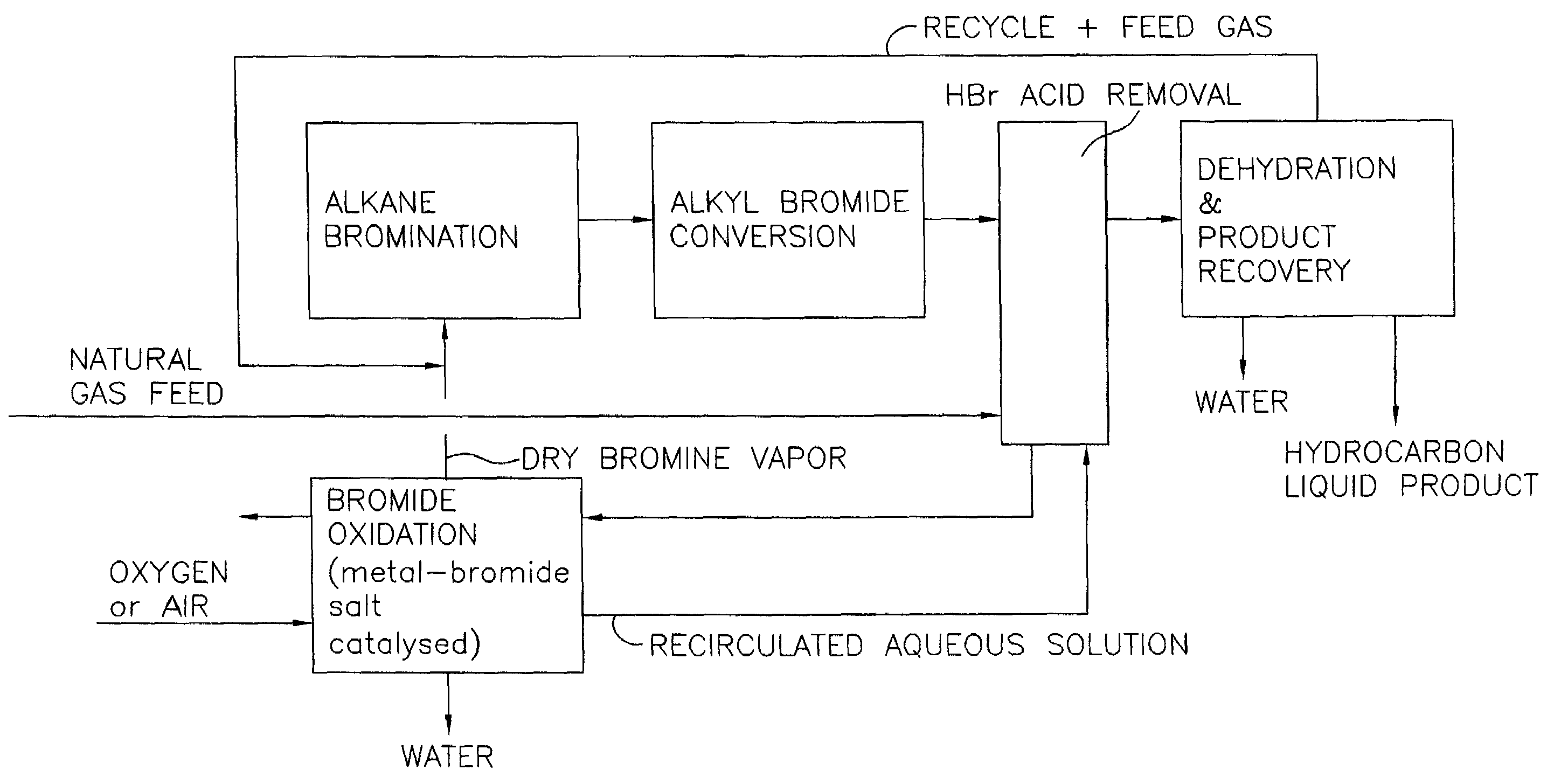
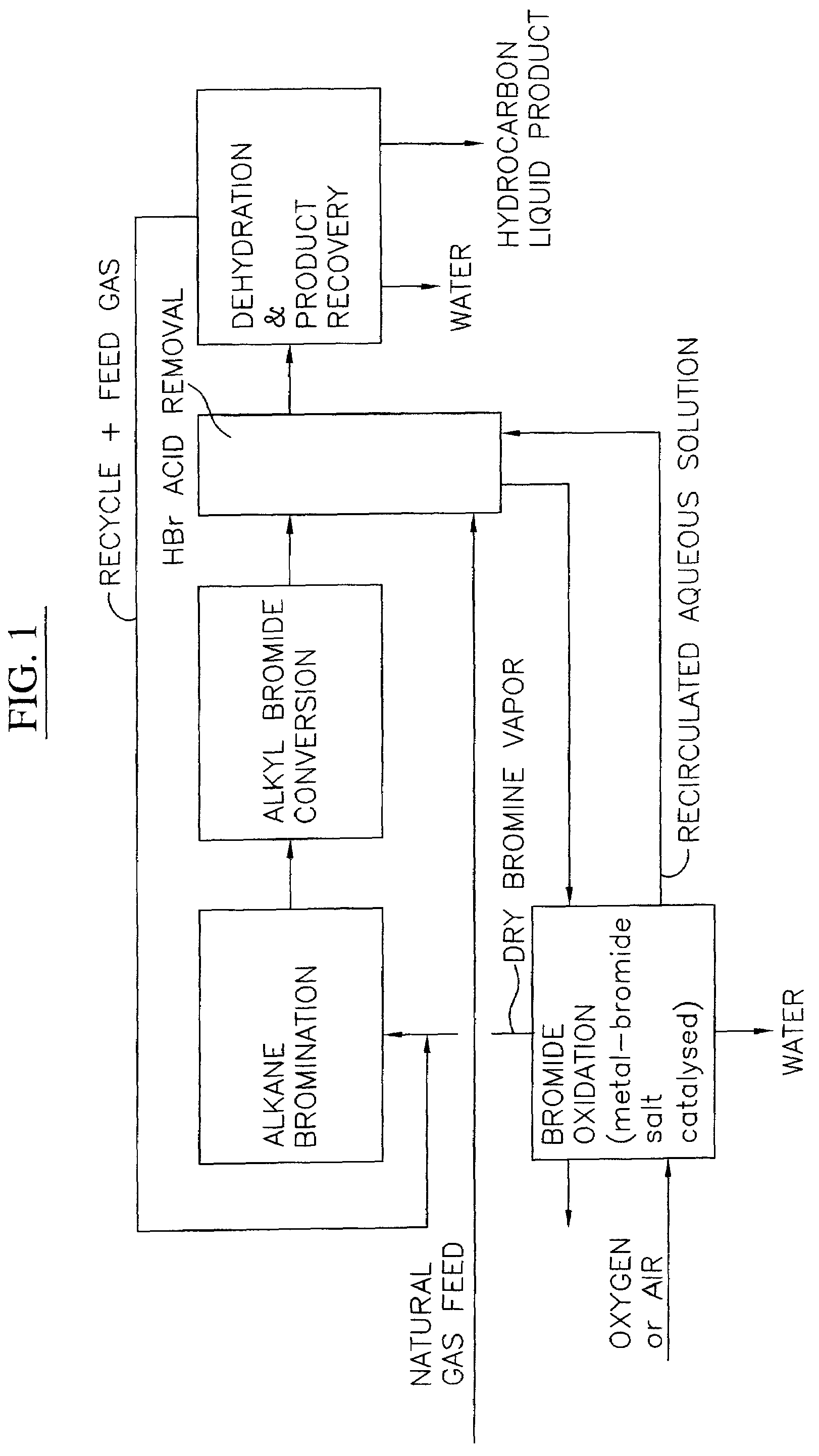
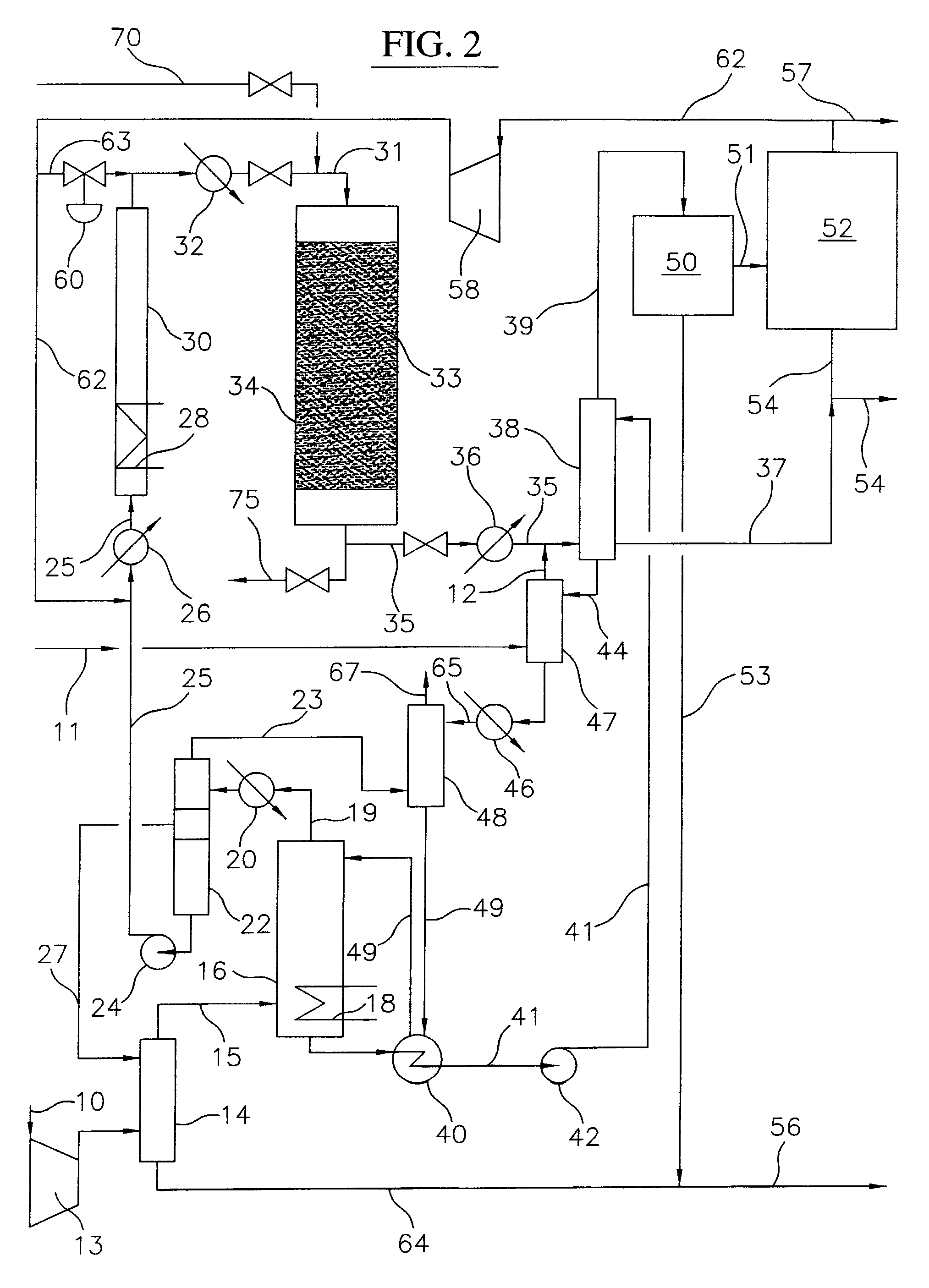
Continuous process for converting natural gas to liquid hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20070238909A1Easily toleratedContinuous regenerationMolecular sieve catalystLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryAlkaneOxygen
An improved continuous process for converting methane, natural gas, or other hydrocarbon feedstocks into one or more higher hydrocarbons or olefins by continuously cycling through the steps of alkane halogenation, product formation (carbon-carbon coupling), product separation, and regeneration of halogen is provided. Preferably, the halogen is continually recovered by reacting hydrobromic acid with air or oxygen. The invention provides an efficient route to aromatic compounds, aliphatic compounds, mixtures of aliphatic and aromatic compounds, olefins, gasoline grade materials, and other useful products.
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
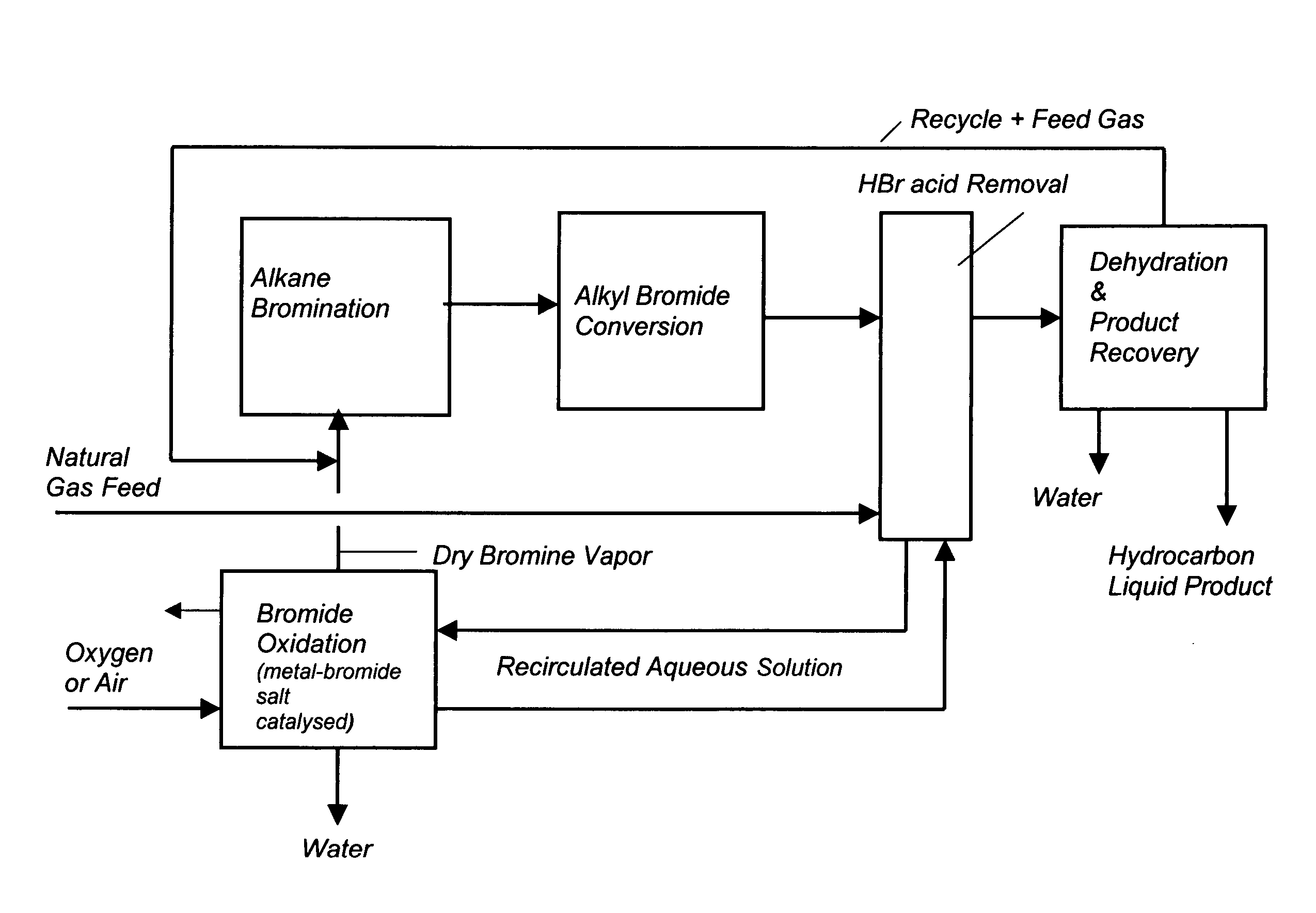
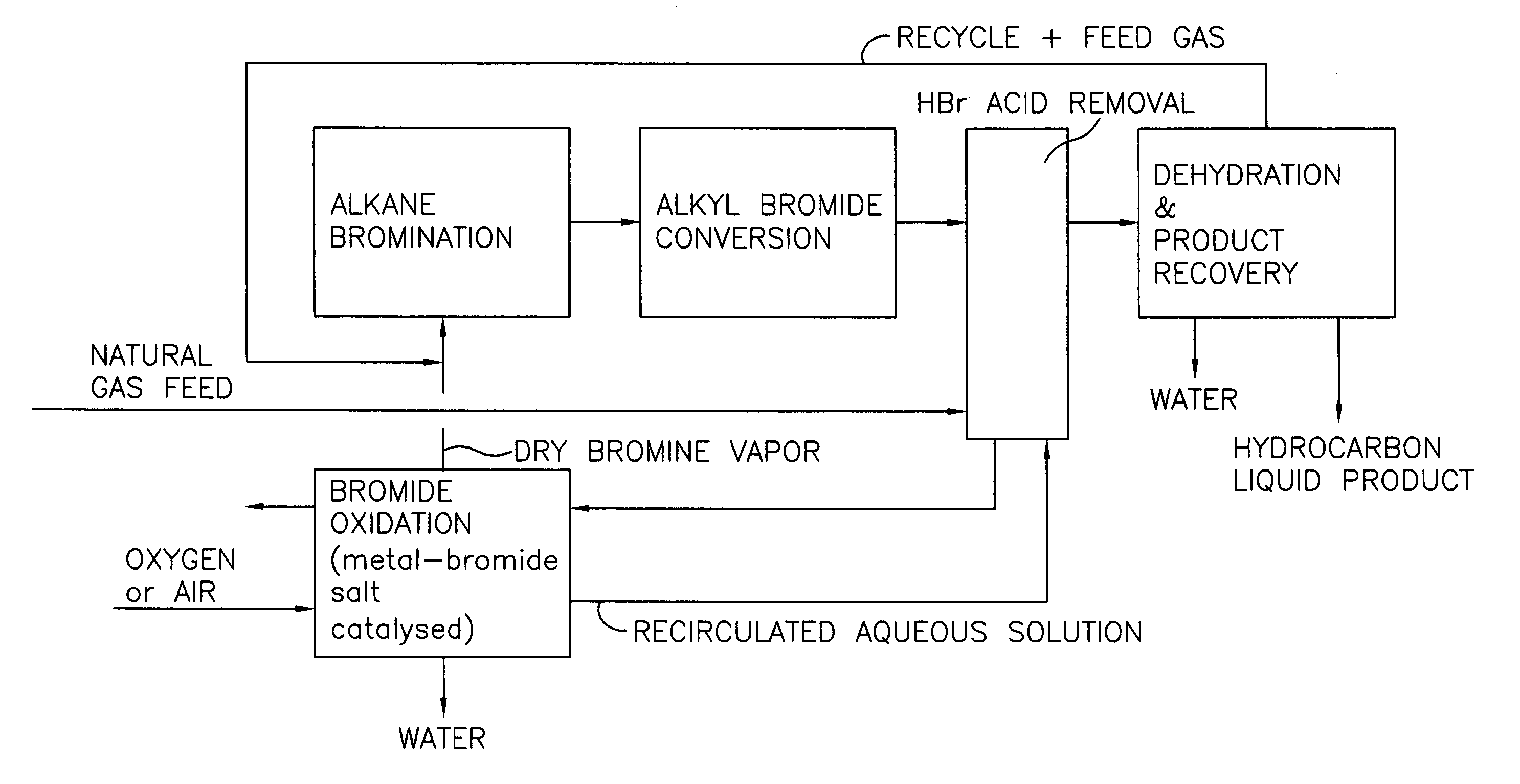
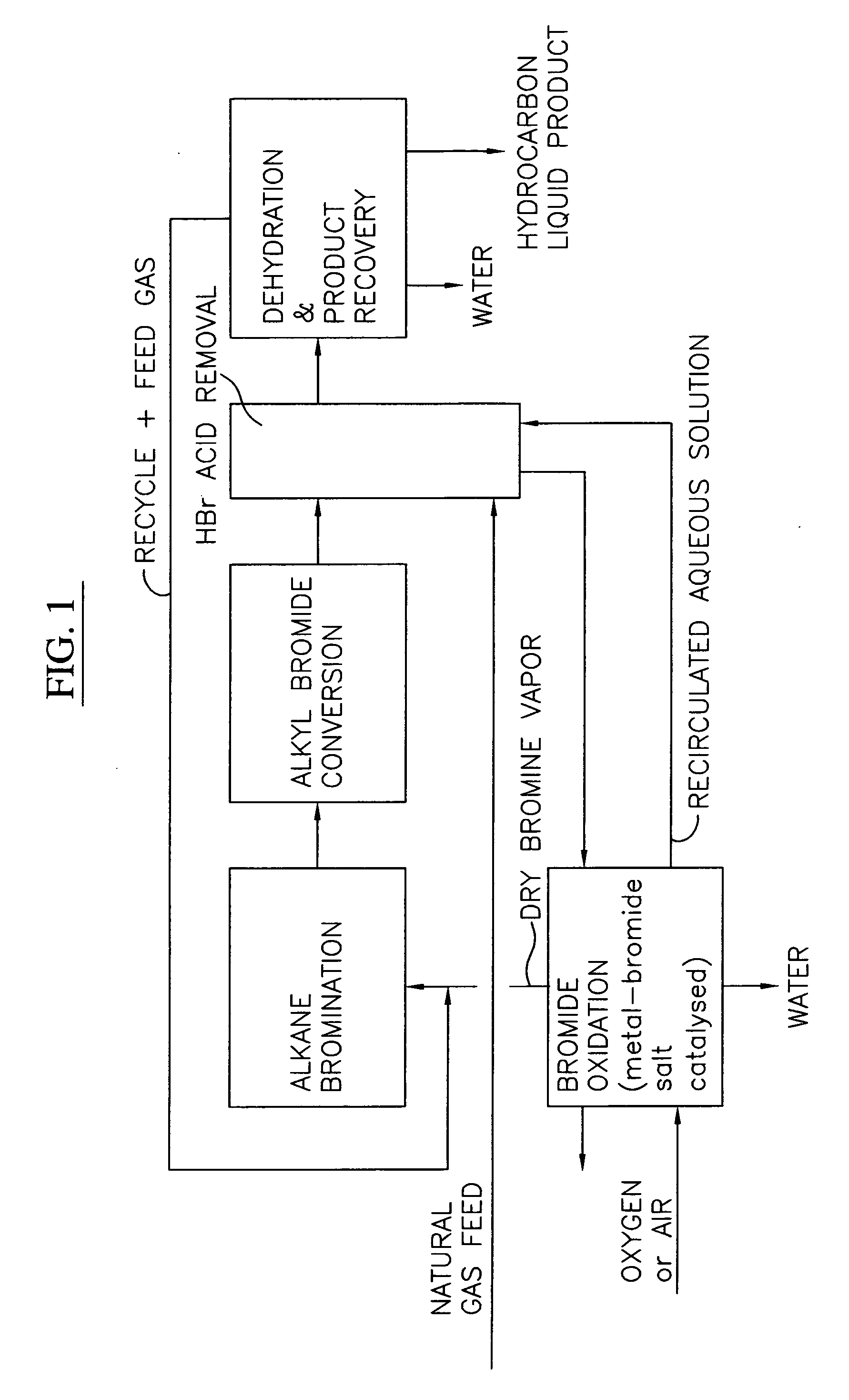
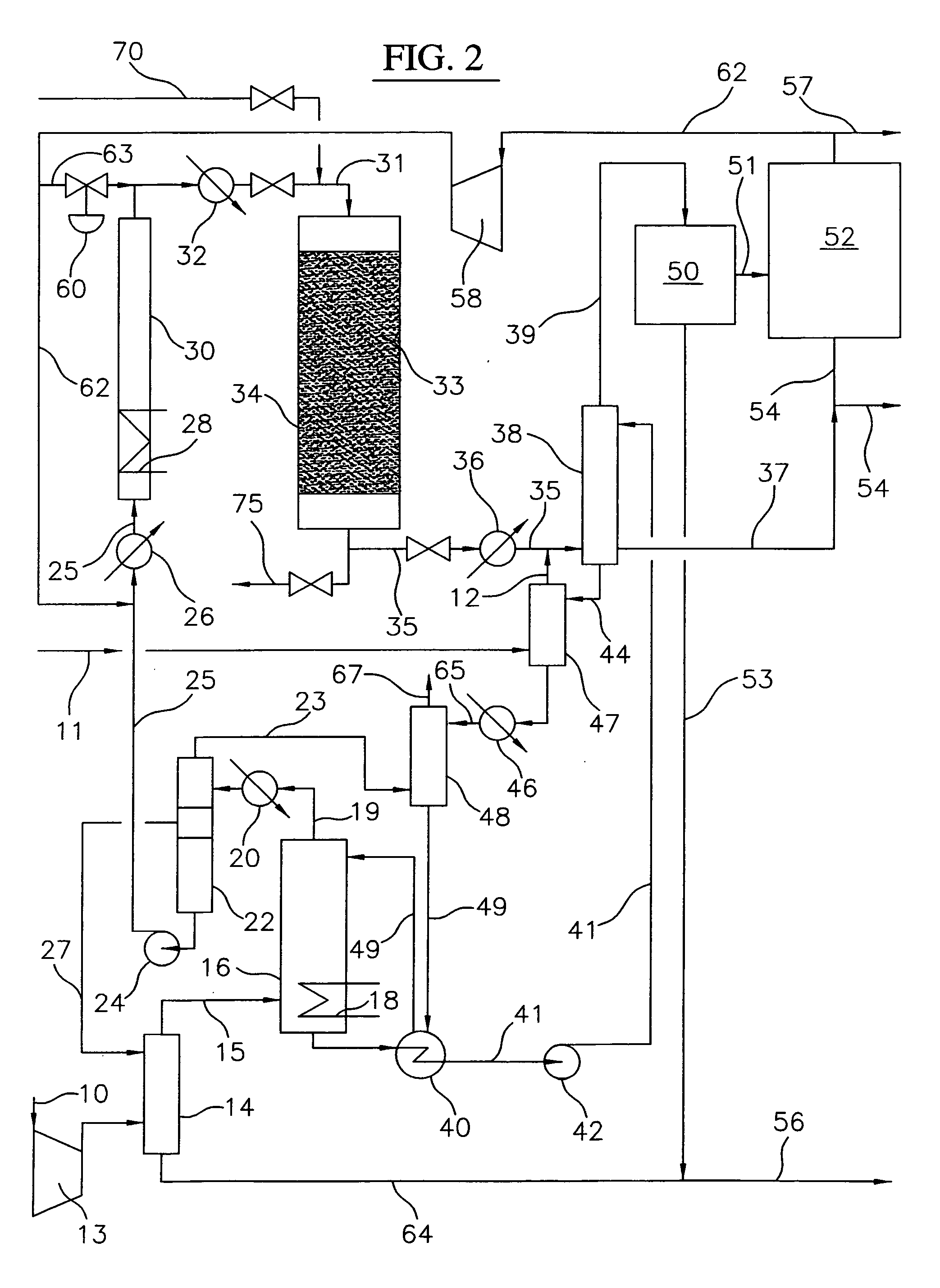
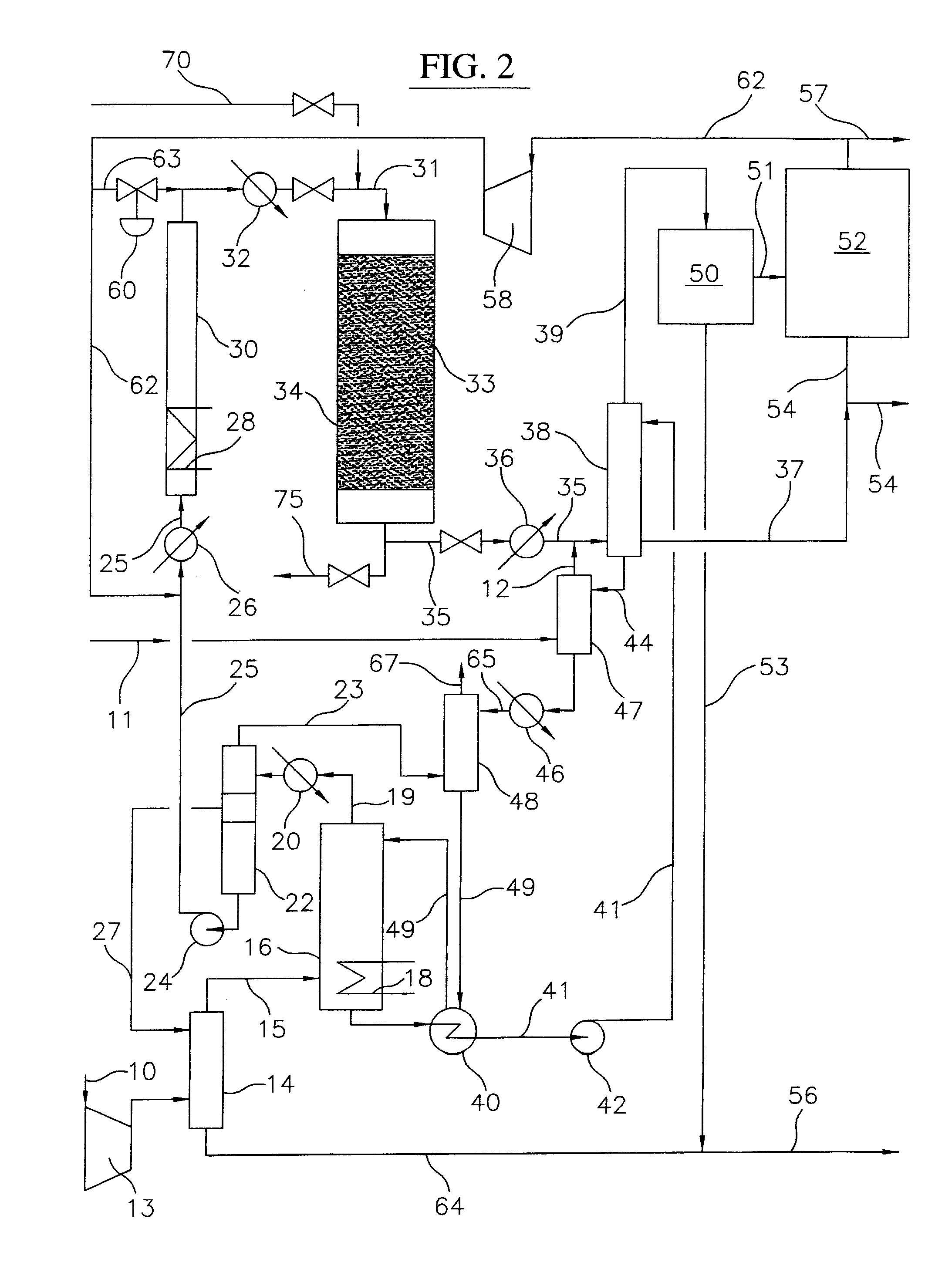
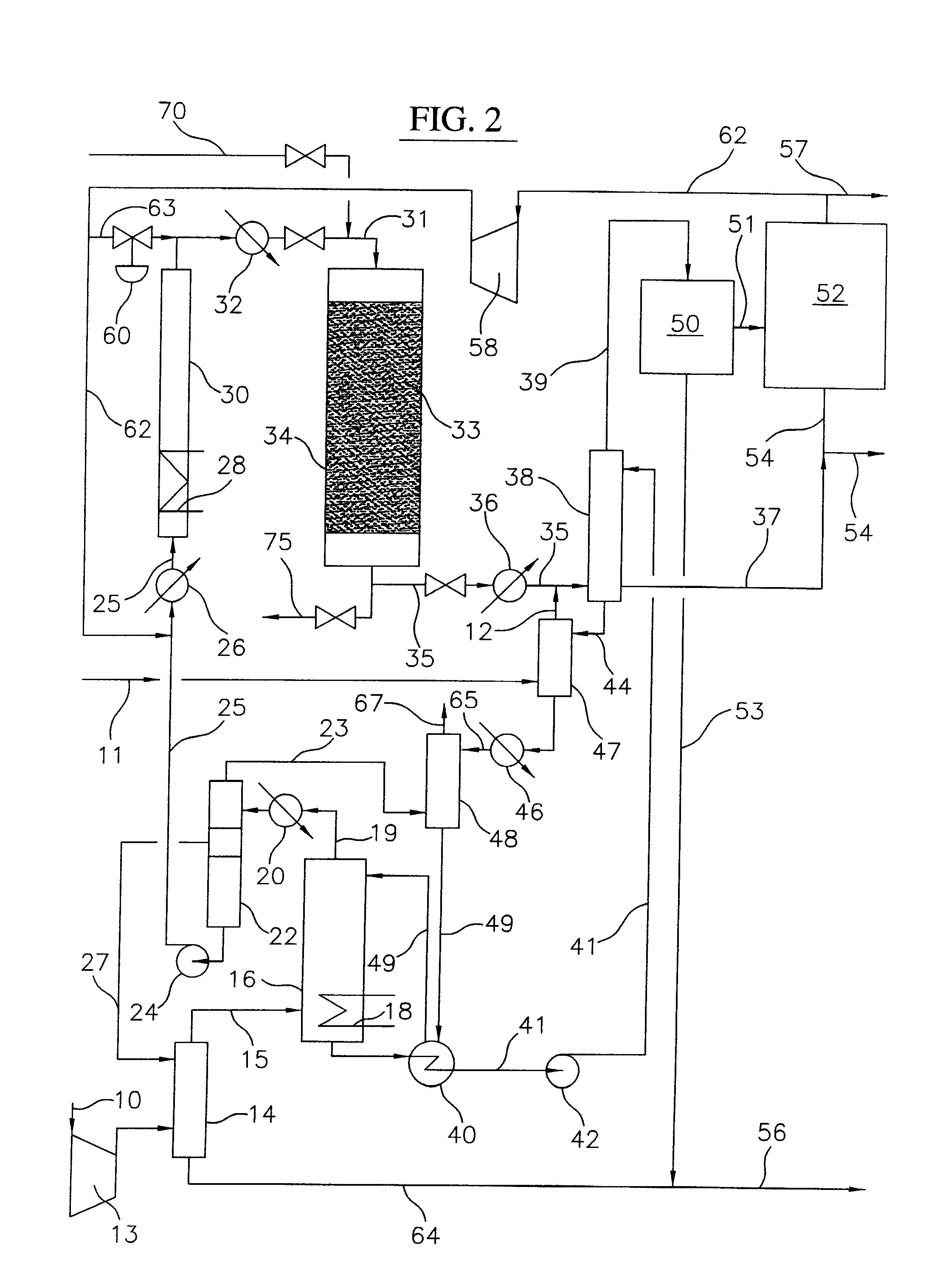
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 zeolite, at a temperature of from about 150° C. to about 400° C. so as to form higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Hydrobromic acid vapor is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons. A portion of the propane and butane is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and reacted with the mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid over the synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst to form C5+ hydrocarbons.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
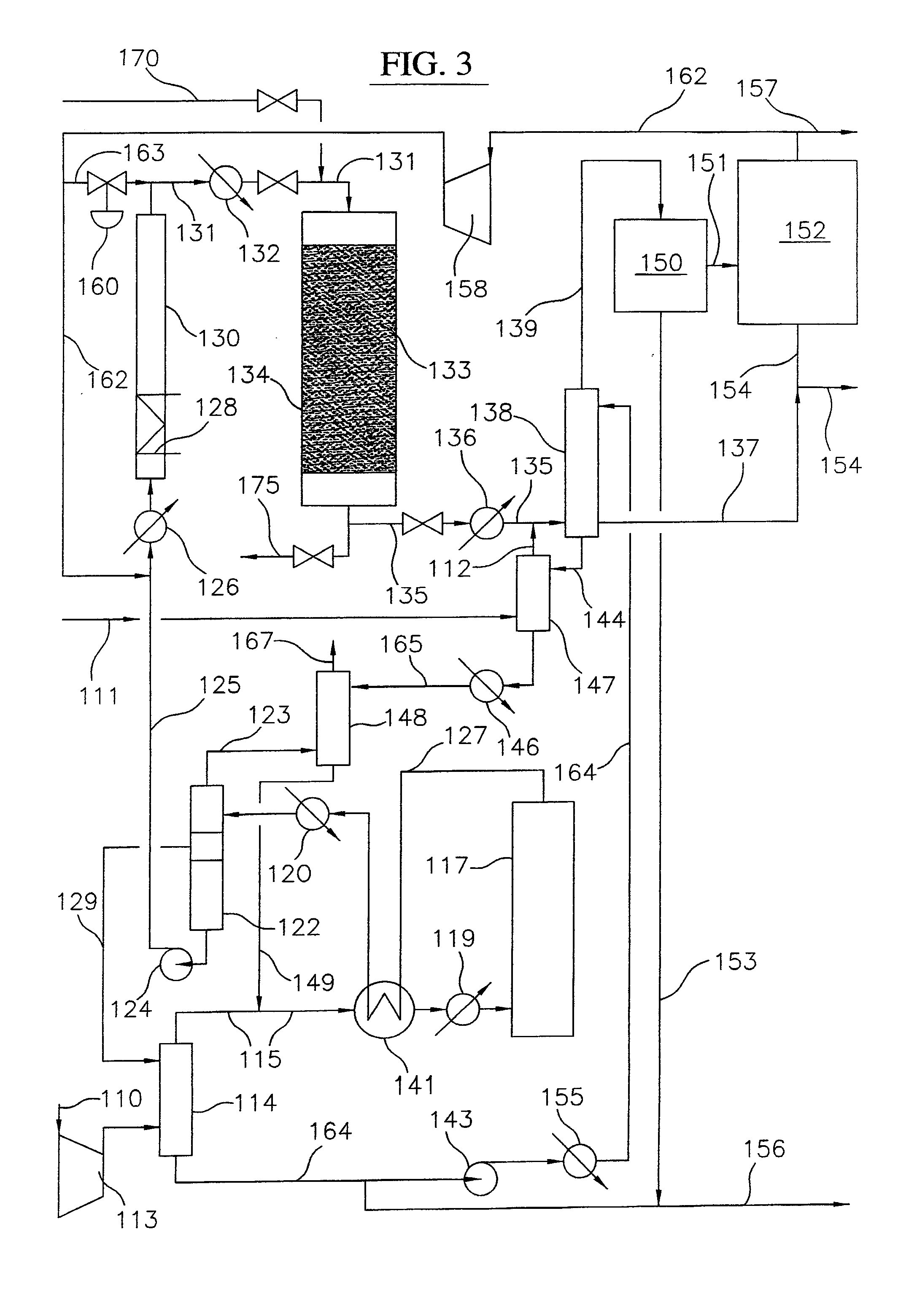
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20060100469A1High selectivityAvoid disadvantagesBromide preparationRefining with non-metalsAlkaneBromine
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:MARATHON GTF TECH
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 zeolite, at a temperature of from about 150° C. to about 450° C. so as to form higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Propane and butane which comprise a portion of the products may be recovered or recycled back through the process to form additional C5+ hydrocarbons. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 zeolite, at a temperature of from about 150° C. to about 400° C. so as to form higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Hydrobromic acid vapor is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons. A portion of the propane and butane is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and reacted with the mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid over the synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst to form C5+ hydrocarbons.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
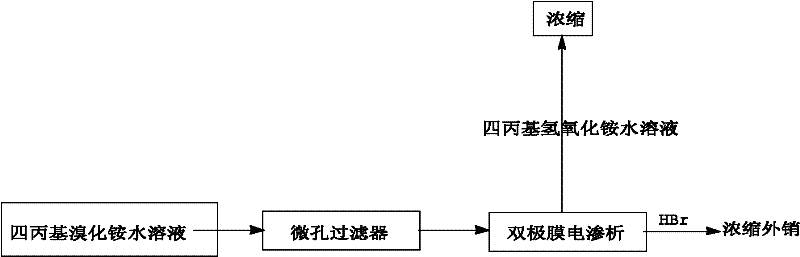
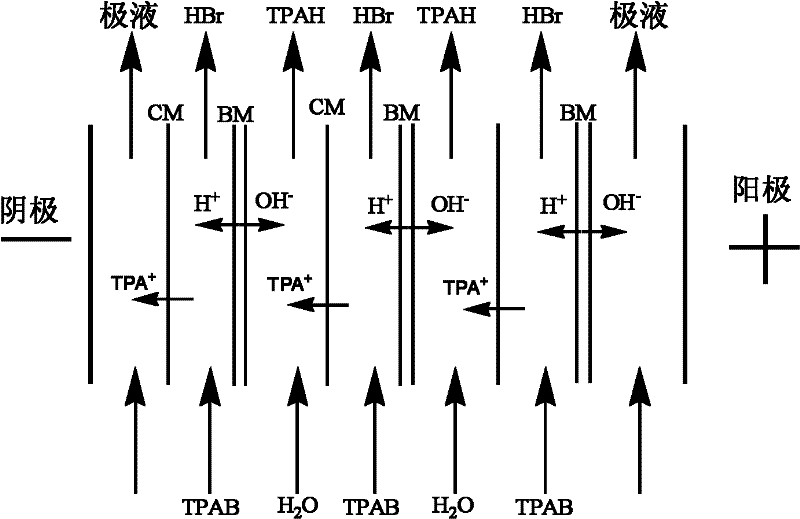
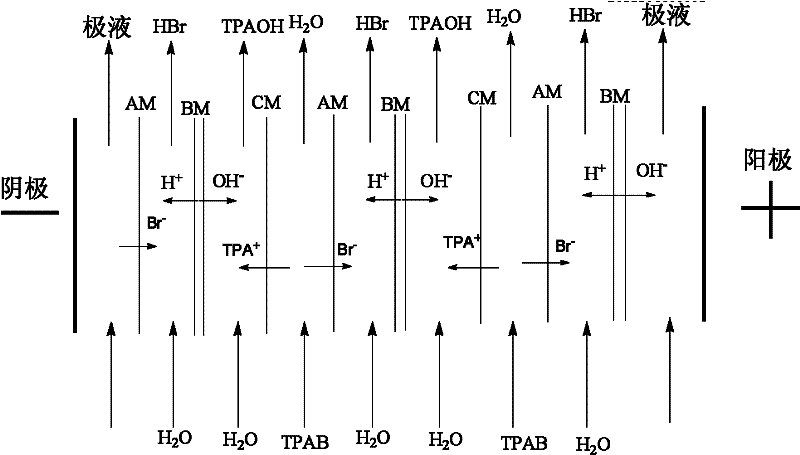
Method for preparing tetrapropyl ammonium hydroxide by utilizing bipolar membrane electrodialysis
InactiveCN102531927AHigh purityLow costSemi-permeable membranesOrganic compound preparationSodium sulfateElectrodialysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing tetrapropyl ammonium hydroxide by utilizing bipolar membrane electrodialysis, and the method comprises the following steps of: using a tetrapropyl ammonium bromide aqueous solution as a raw material, processing the tetrapropyl quaternary ammonium salt aqueous solution through a microporous filter, and then enabling the processed tetrapropyl quaternary ammonium salt aqueous solution to enter a material liquid room of a bipolar membrane electrodialyzing device, respectively adding water in an acid room and an alkali room, respectively adding a sodium sulfate solution in pole liquid rooms, controlling the current density, the voltage and the temperature of the bipolar membrane electrodialyzing device to be 150-600 A / M2, 20-300 V and 5-45DEG C respectively, carrying out circulating cooling through chilled saline water in a circulating coil pipe by using an electrodialyzing compartment in a running process, stopping running when the conductivity of the material liquid room is decreased to below 2000 [mu]s / cm, obtaining a tetrapropylammonium hydroxide solution in the alkali room, and recycling a hydrobromic acid solution in the acid room. By using the method, the raw material cost is low; the selectivity is multiple; the purity of the tetrapropyl ammonium hydroxide is high; hydrobromic acid further can be recovered; and the generation of a pollutant in the process is effectively avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
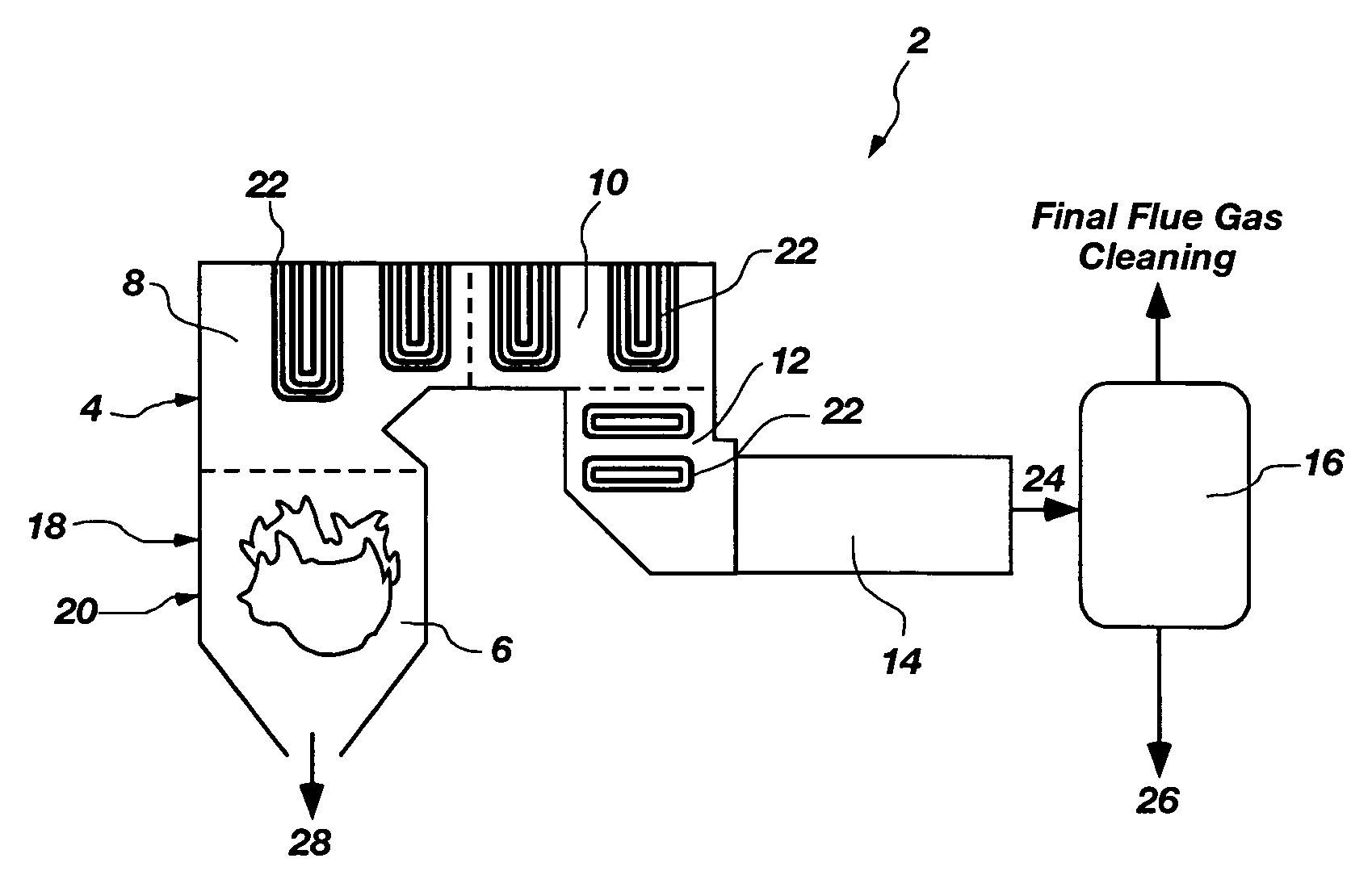
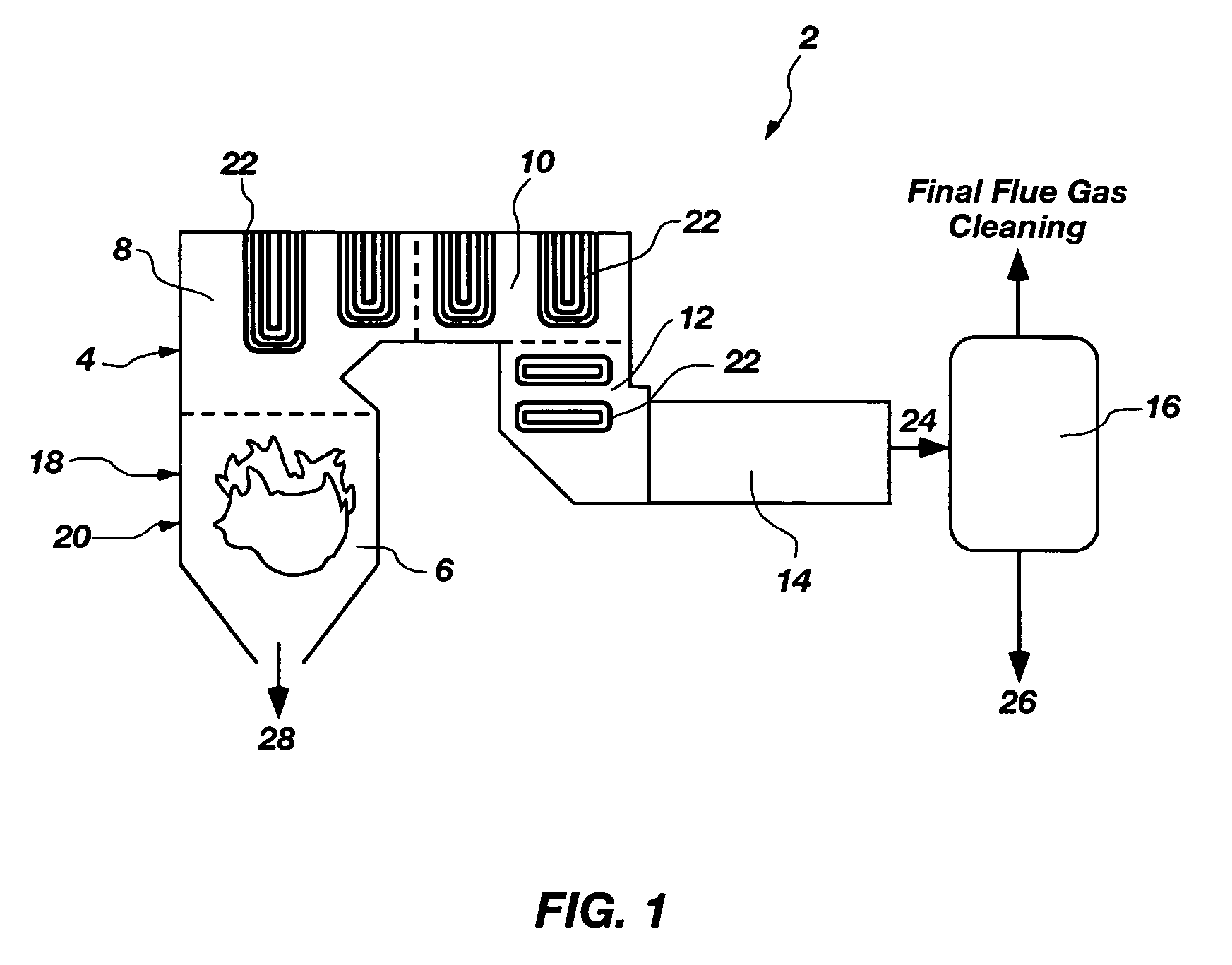
Method for oil shale pollutant sorption/NOx reburning multi-pollutant control
A method of decreasing pollutants produced in a combustion process. The method comprises combusting coal in a combustion chamber to produce at least one pollutant selected from the group consisting of a nitrogen-containing pollutant, sulfuric acid, sulfur trioxide, carbonyl sulfide, carbon disulfide, chlorine, hydroiodic acid, iodine, hydrofluoric acid, fluorine, hydrobromic acid, bromine, phosphoric acid, phosphorous pentaoxide, elemental mercury, and mercuric chloride. Oil shale particles are introduced into the combustion chamber and are combusted to produce sorbent particulates and a reductant. The at least one pollutant is contacted with at least one of the sorbent particulates and the reductant to decrease an amount of the at least one pollutant in the combustion chamber. The reductant may chemically reduce the at least one pollutant to a benign species. The sorbent particulates may adsorb or absorb the at least one pollutant. A combustion chamber that produces decreased pollutants in a combustion process is also disclosed.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Novel flow chart for preparing acetic acid, methanol and dimethyl ether from methane by non synthetic gas process
ActiveCN1640864APreparation by oxidation reactionsOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidGas composition
The new process of synthesizing acetic acid with methane consists of two reaction steps, including the first step of reacting methane, oxygen and hydrogen bromide or hydrobromic acid on catalyst to produce CH3Br, CO and H2O; and the second step of reacting CH3Br, CO and H2O on catalyst to prepare acetic acid. During the reaction of synthesizing methanol and dimethyl ether, the first step of oxybromizing reaction may have the reacting gas composition regulated and different catalyst adopted to reach the aim of creating CH3Br and H2O in high selectivity; and methanol and dimethyl ether may be then produced through hydrolysis on one other kind of catalyst. In the process of preparing acetic acid or methanol and dimethyl ether, HBr as the circular reaction medium is regenerated and returned to the reactor for reuse.
Owner:MICROVAST POWER SYST CO LTD
Preparation method of 5-bromo-1,3-dichloro-2-fluorobenzene
ActiveCN103664511AEasy to operateHigh purityHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationDecompositionSide reaction
The invention discloses a preparation method of 5-bromo-1,3-dichloro-2-fluorobenzene, which comprises the following steps: (1) simultaneously feeding ammonium salt and a sodium nitrite aqueous solution into a tubular reactor for tubular diazotization reaction so as to obtain a diazonium salt intermediate, wherein the ammonium salt is prepared through dissolving 3,5-dichloro-4-fluoroaniline in sulfuric acid; (2) dissolving cuprous bromide in hydrobromic acid, heating to 100-130 DEG C, dropwise adding the diazonium salt intermediate prepared in the step (1) for reaction, and after the complete reaction, performing after-treatment to obtain the 5-bromo-1,3-dichloro-2-fluorobenzene. According to the preparation method, the tubular diazotization reaction technology is adopted to prepare diazonium salt, so that the side reaction including diazonium salt coupling and decomposition and the like can be reduced, the diazotization reaction is enabled to be more stable, and the final yield is improved; in addition, the tubular diazotization reaction technology has a series of advantages of continuity in production, safety, short reaction time, energy saving and the like, and is relatively suitable for industrial production in the future.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LINJIANG CHEM
Conversion of alkanes to oxygenates
Owner:MARATHON OIL CO
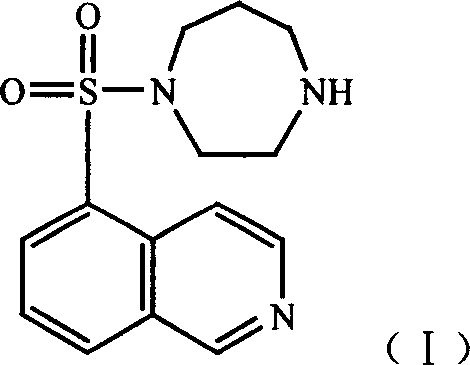
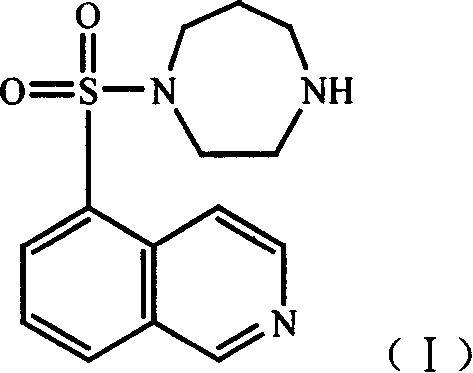
Hydrate of medicinal salt of Fasudil
InactiveCN101092413AImprove stabilityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHydrobromideDisease
This invention discloses hydrates of pharmaceutical salts of hexahydro-1-(5-sulfonylisoquinoline)-1H-1,4-diaza, i.e., fasudil, especially semi-hydrates of nitrate, sulfate, hydrobromide and mesylate of fasudil, their preparation method, and their application in drugs for preventing and / or treating cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. The hydrates of pharmaceutical salts of fasudil have such advantages as high stability and high solubility, and can be manufactured into various preparations with other active components and / or pharmaceutically acceptable carriers. The method has such advantages as simple process, high drug purity, high yield, and stable product quality, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG XUANZHU PHARMA TECH CO LTD
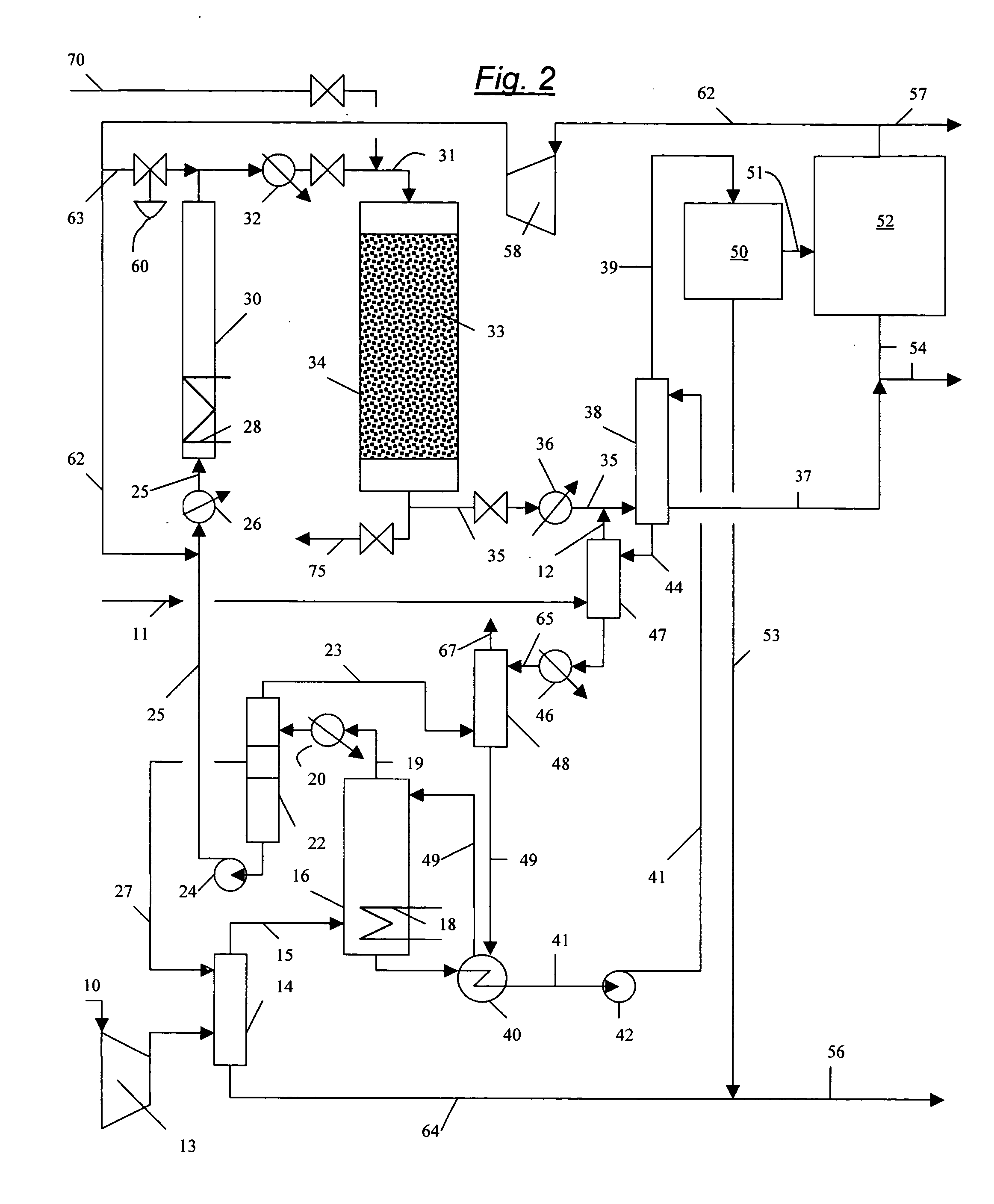
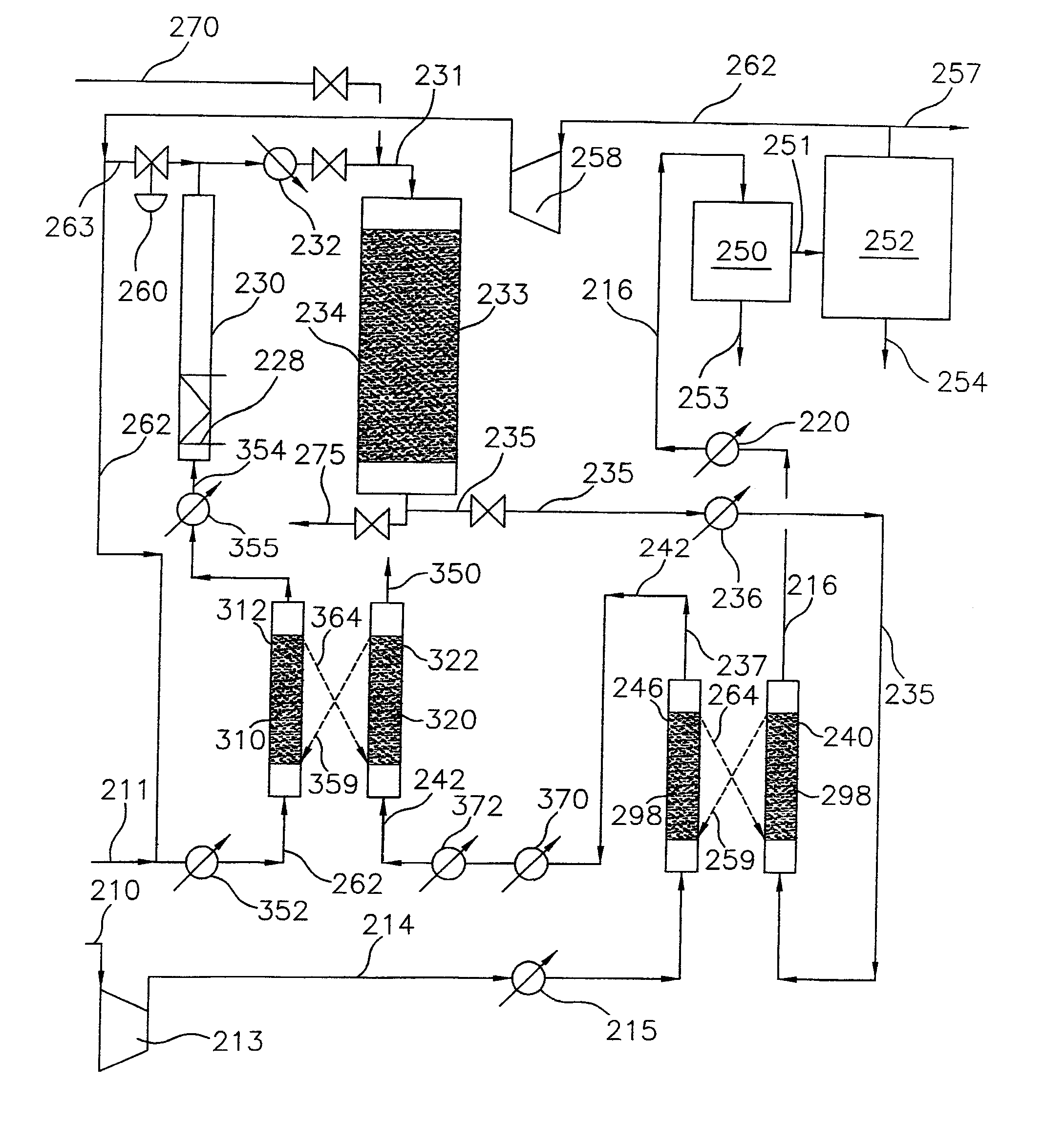
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process, and to selectively form monobrominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Method for salt preparation
InactiveUS20100204470A1High yieldAmino preparation from aminesOrganic compound preparationHydrobromideBiochemical engineering
The present invention provides a new method for preparation and crystallization of hydrochlorides, hydrobromides or hydroiodides of pharmaceutical compounds or their intermediates in which the base or its acid addition salt is reacted in a solvent with a Trialkylsilylhalogenide.
Owner:SANDOZ AG
Treating method of metallic titanium material
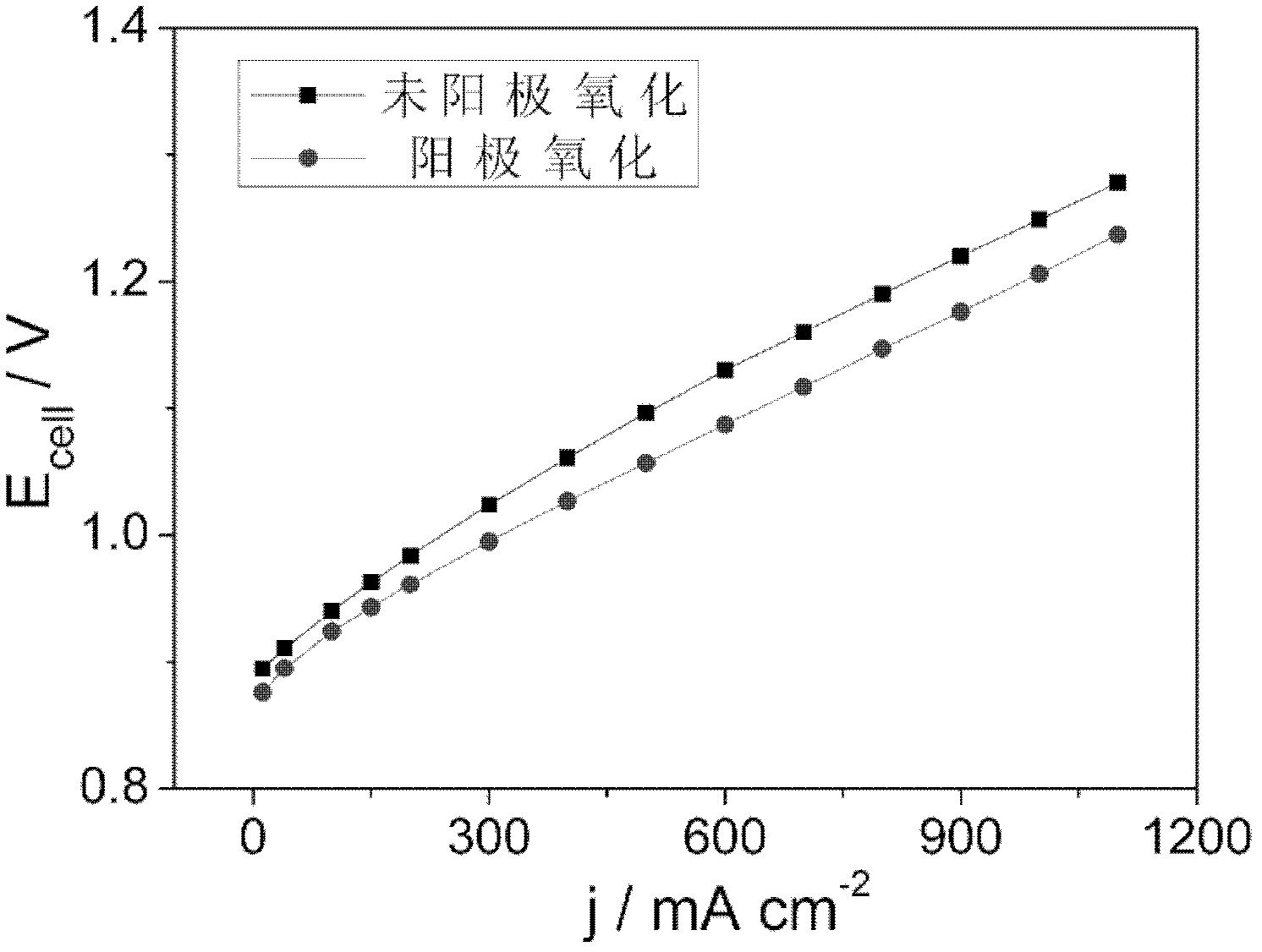
ActiveCN103173835ASimple preparation processNo complex equipment requiredElectrolytic inorganic material coatingCell electrodesAnodizingFuel cells
The invention provides a treating method of a metallic titanium material. The metallic titanium material is sintered porous titanium, a titanium felt, a titanium mesh or foaming titanium. The treating method of the metallic titanium material comprises the following steps of: purifying the surface of the titanium material; taking the titanium material after purification as an anode to carry out anodizing; and electro-depositing a layer of catalyst or coating a catalyst precursor on the surface of the titanium material after oxidation, and carrying out high-temperature roasting to obtain the titanium material with high catalytic activity. The prepared titanium material with the catalytic activity can be used as a diffusion layer and also an electrode, has the advantages that the preparation method is simple, the catalytic activity is high, the decomposition voltage is greatly lowered, the energy utilization ratio is increased, and the like, is applied to a hydrobromic acid electrolytic cell and can also be used as the diffusion layer or the electrode in a hydrobromic fuel cell and a hydrobromic reproducible energy storage cell.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
Embodiments disclose a process for converting gaseous alkanes to higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereofs wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes may be reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid then may be reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 or an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form hydrobromic acid vapor and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:MARATHON GTF TECH
Cogeneration method for sugar and acetylpropionic acid by utilizing lignocellulose-like biomass
The present invention is process of co-producing sugar and levulic acid solution with lignocellulose material, and belongs to the field of biomass resource utilizing technology. Agricultural and forestry waste as reaction material is dilute acid hydrolyzed in a two-step process at certain temperature and in the presence of 0.01-0.2 mol concentration hydrochloric acid solution, hydroiodic acid solution, sulfuric acid solution or other inorganic acid solution as catalyst to produce both sugar solution and levulic acid solution in the total conversion rate over 20 wt%. The present invention provides one new way for utilizing lignocellulose comprehensively.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080200740A1High selectivityAvoid disadvantagesHydrogen bromideBromide preparationAlkaneBromine
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
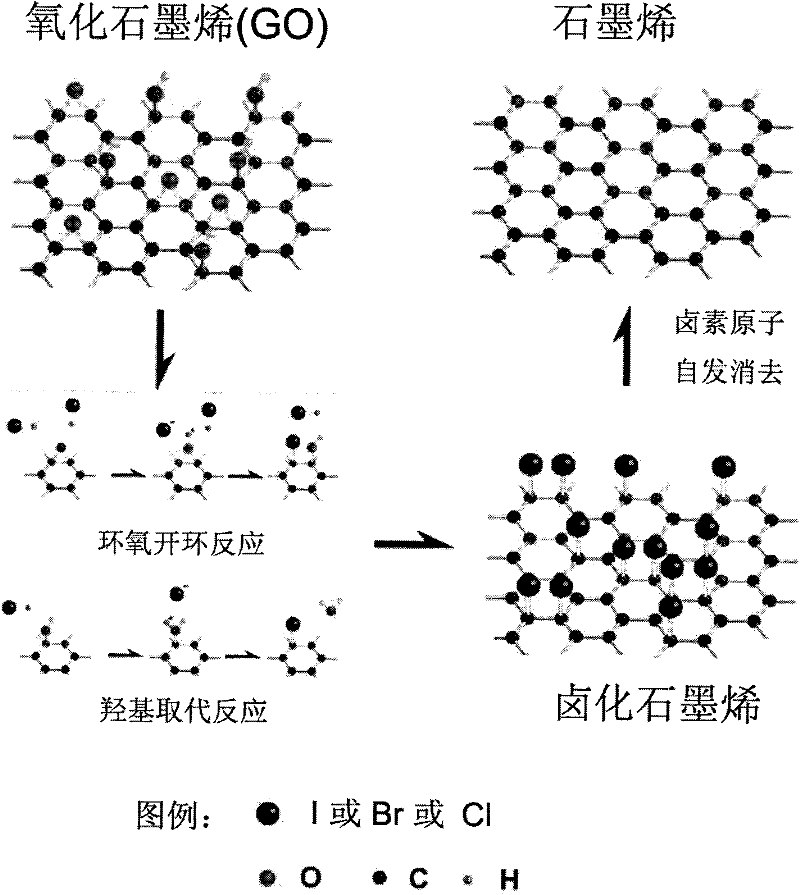
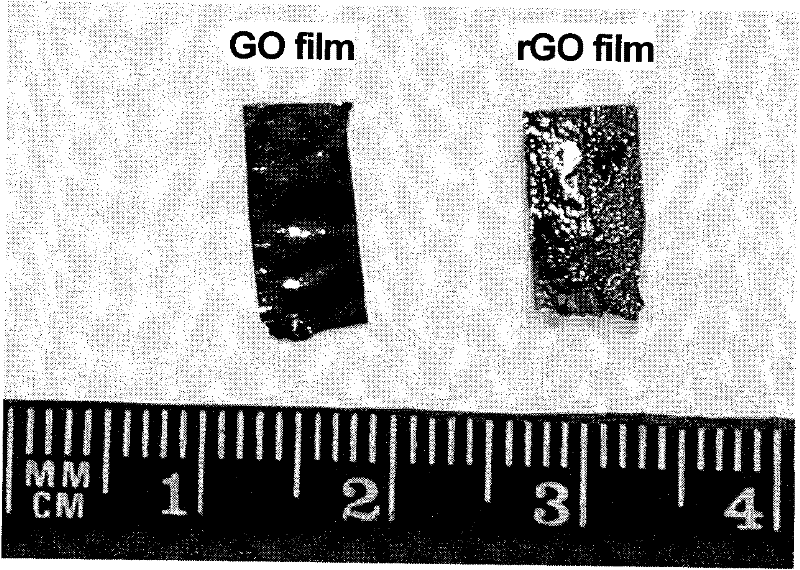
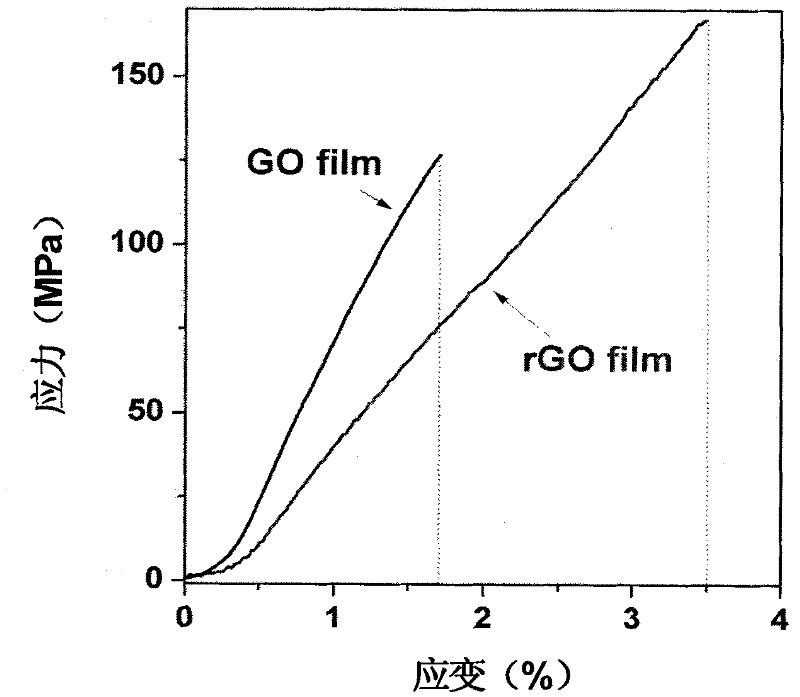
A kind of method that graphene oxide reduction prepares graphene material
The invention relates to the field of graphene materials, in particular to a novel method for preparing a graphene material by reducing graphene oxide (GO). The method is suitable for reducing various graphene-oxide-based powder and thin-film materials. In the method, a graphene oxide product is soaked for 10 seconds-24 hours in a halogenating reagent, such as hydroiodic acid, hydrobromic acid, sulfoxide chloride and the like, in a temperature range from minus 5 DEG C to 140 DEG C, and is taken out and dried, thereby the reduction of the graphene oxide material is completed; and the graphene material obtained after reduction has an excellent electric conduction performance and can maintain the flexibility of thin-film products. The method is simple and is easy to control, can realize the reduction on lots of graphene materials at low temperature with high efficiency and low cost and is beneficial to solving of the problems of environment pollution, high cost and the like in the prior art.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for recovering organic acid and cobalt-manganese metal in terephthalic acid oxidized residues
ActiveCN102503813AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemical recyclingMANGANESE ACETATEBenzoic acid
The invention belongs to the technology for recovering organic acid and catalyst from terephthalic acid oxidized residues, which includes the steps of firstly, discharging high-temperature oxidized residues from a pure terephthalic acid (PTA for short) production device, controlling the solid content within the range from 20% to 45% and implementing primary filtering separation within the temperature range from 55 DEG C to 90 DEG C, and directly vending separated solid for manufacturing resin or paint or returning the separated solid to an oxidation reactor for use, wherein primary filtrate is treated according to the process: (I) adding oxalic acid to obtain cobalt-manganese oxalate precipitation, obtaining cobalt-manganese oxalate by means of filtering separation, further cooling the filtrate by means of filtering separation, utilizing the separated solid for extracting benzoic acid and delivering the filtrate to a waste water treating device; or (II) directly cooling the primary filtrate for secondary filtering separation, utilizing the separated solid for extracting benzoic acid, adding oxalic acid into secondary filtrate to obtain cobalt-manganese oxalate precipitation, obtaining cobalt-manganese oxalate by means of filtering separation and delivering the filtrate to a waste water treating device; and secondly, carrying out reaction of the cobalt-manganese oxalate obtained from (I) or (II) with oxidant such as hydrogen peroxide, peroxyacetic acid, bromine, manganate, permanganic acid, manganese dioxide or / and hydrobromic acid, utilizing cobalt acetate aqueous liquor, cobalt bromide aqueous liquor, manganese acetate aqueous liquor, manganese bromide aqueous liquor, acetic acid or / and pure water as dissolvent, then carrying out reaction of the cobalt-manganese oxalate with metallic cobalt, metallic manganese or / and hydrobromic acid after the cobalt-manganese oxalate is completely dissolved, and obtaining homogeneous phase liquor containing cobalt-manganese bromide ions by means of purification and filtration, wherein the mixed liquor can be directly mixed with cobalt acetate, manganese acetate, cobalt bromide, manganese bromide, acetic acid or water to serve as oxidation catalyst for the terephthalic acid.
Owner:浙江上虞利星化工有限公司
Preparation method of antiviral medicine
ActiveCN103374038ARaw materials are easy to getSimple process routeGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCarboxylic acid salt preparationAntiviral drugBenzenesulfonates
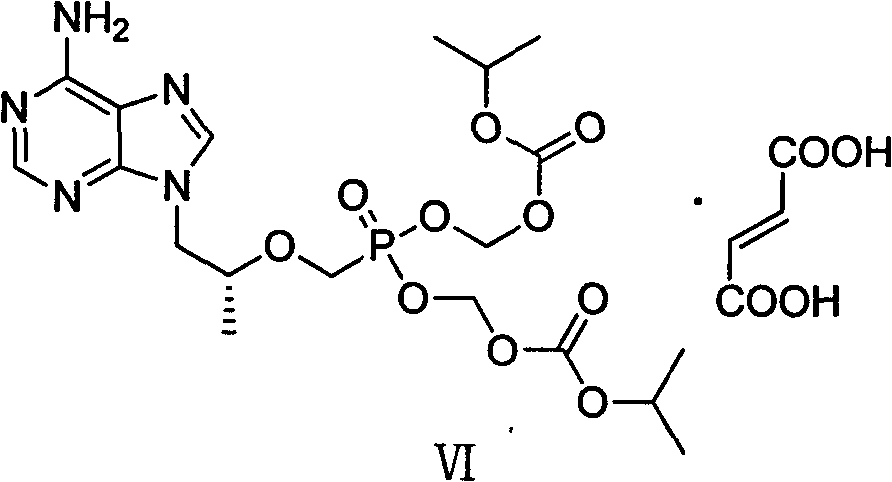
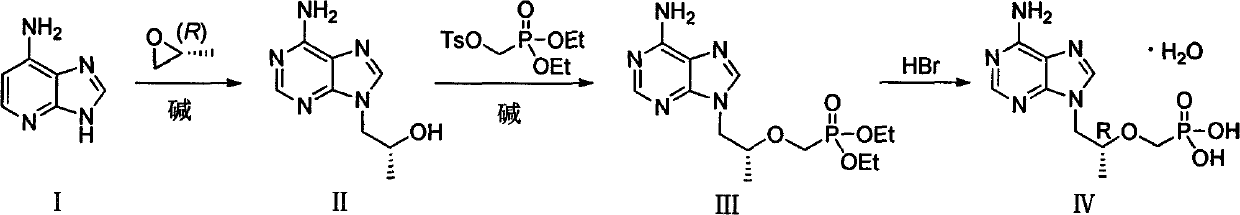
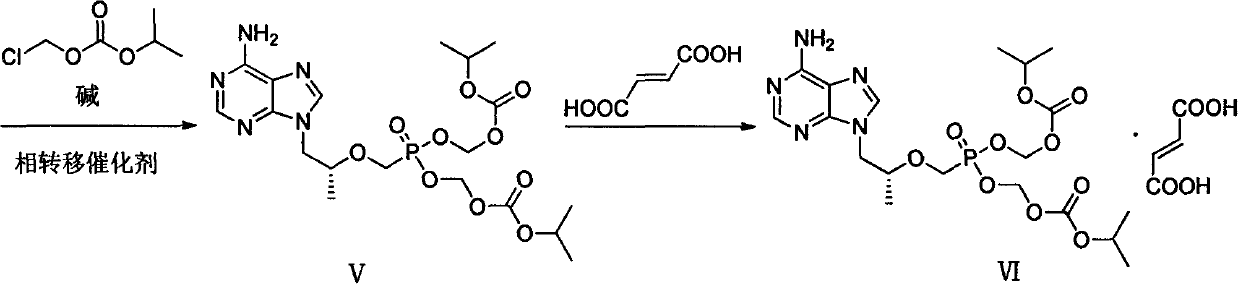
The invention discloses a preparation method of anantiviral medicine tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: performing addition reaction on adenine serving as raw material and (R)-epoxypropane in the presence of alkali; then, performing substitution reaction with (diethyoxyl phosphoracyl) methyl-4-methyl benzenesulfonate; then, hydrolyzing by using a hydrobromic acid solution; crystallizing to obtain tenofovir monohydrate; and reacting the product tenofovir monohydrate with chloromethyl isopropyl carbonate and fumaric acid to obtain tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate. The selected initial raw material is low in cost and easily available, and the synthetic line is simplified and the utilization ratio of the raw material and the total yield are improved. The intermediate obtained in the reaction is purified by the recrystallization method, so that the yield is high, less three-wastes are generated in the reaction process, and the cost is low; therefore, the preparation method is favorable for industrial production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIYUNSHAN PHARMA HLDG CO LTD BAIYUNSHAN PHARMA GENERAL FACTORY
Eco-friendly method of preparation of high purity tetrabromobisphenol-A
InactiveUS6365786B1High yieldMost efficientOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationTetrabromobisphenol AOrganic layer
A highly pure and colorless tetrabromobisphenol-A (TBBPA) possessing melting point in the range of 178-182° C. is prepared in yields of 50-70% in first batch and 90-100% when the spent organic layer is recycled. In this method, the corrosive liquid bromine is displaced by sodium bromide / hydrobromic acid as brominating agent. Further, sodium bromate is used as an oxidizing as well as brominating agent to utilize the hydrobromic acid that is produced during the bromination of bisphenol-A (BPA). The reaction is conducted at 10-15° C. in a mixture of methylene chloride-water or carbon tetrachloride-water in the presence of hydrochloric acid and sodium lauryl sulfate. The crystalline product settled at the bottom of the reaction vessel is filtered, washed, dried and weighed. The spent organic layer is recycled in subsequent batches to maximize the overall yield of product recovered directly as solid and to minimize generation of organic effluent.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process, and to selectively form monobrominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Cardiac glycoside compounds and antitumor application thereof
InactiveCN102219821AStrongly inhibits proliferative activityOrganic active ingredientsGlycoside steroidsBenzoic acidO-Phosphoric Acid
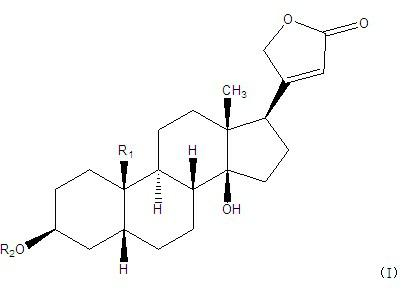
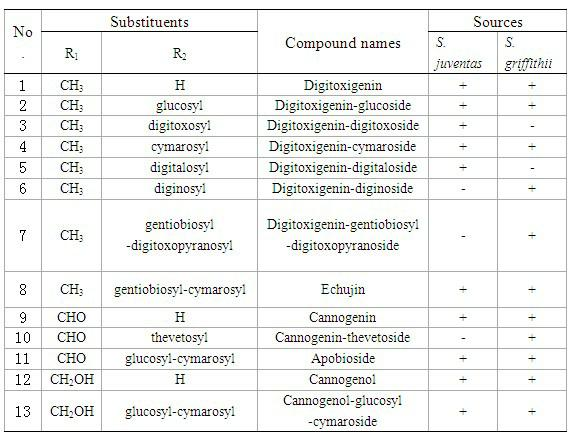
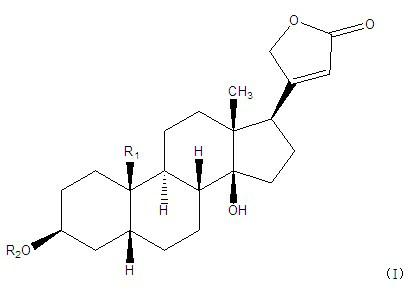
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicaments and in particular relates to cardiac glycoside compounds with a general formula (I), as well as derivatives, stereoisomers, a racemic mixture or a non-racemic mixture of the stereoisomers and pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts or solvates, wherein R1 is CH3, CHO or CH2OH; R2 is H or a linear saccharide chain or a branched saccharide chain, the linear saccharide chain or the branched saccharide chain is formed by saccharides; and these acids comprise inorganic acids like hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, hydrobromic acid, phosphoric acid, nitric acid, carbonic acid and the like as well as organic acids like methanoic acid, acetic acid, succinic acid, citric acid, lactic acid, fumaric acid, tartaric acid, benzoic acid, p-methyl-benzenesulfonic acid, methylsulphonic acid, naphthalenesulfonic acid, gluconic acid and the like. The cardiac glycoside compounds can be obtained by separation from plants, in particular Streptocaulon plant juventas or Streptocaulon griffithii, by using multiple conventional separating means or obtained through synthesis, semisynthesis or bioconversion means. These compounds have excellent inhibiting and treatment effects on multiple tumor cells.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for bromoalkane
InactiveCN102826954AReduce corrosionExtended service lifeHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationAlcoholProduct gas
The invention discloses a preparation method for bromoalkane. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing lower alcohol with hydrobromic acid; heating a mixture to a reflow state; enabling the lower alcohol and the hydrobromic acid in the mixture to fully react to obtain a product mixed solution A; distilling the product mixed solution A; condensing the distilled gas to obtain a product mixed solution B; standing the product mixed solution B for layering; taking a lower-layer liquid to obtain a bromoalkane crude product C; rectifying the bromoalkane crude product C; and condensing the rectified gas to obtain liquid bromoalkane. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity in process and reaction control, no need of catalyst, low production cost, less pollution, favorable quality of products and high purity.
Owner:SHANDONG TIANYI CHEM
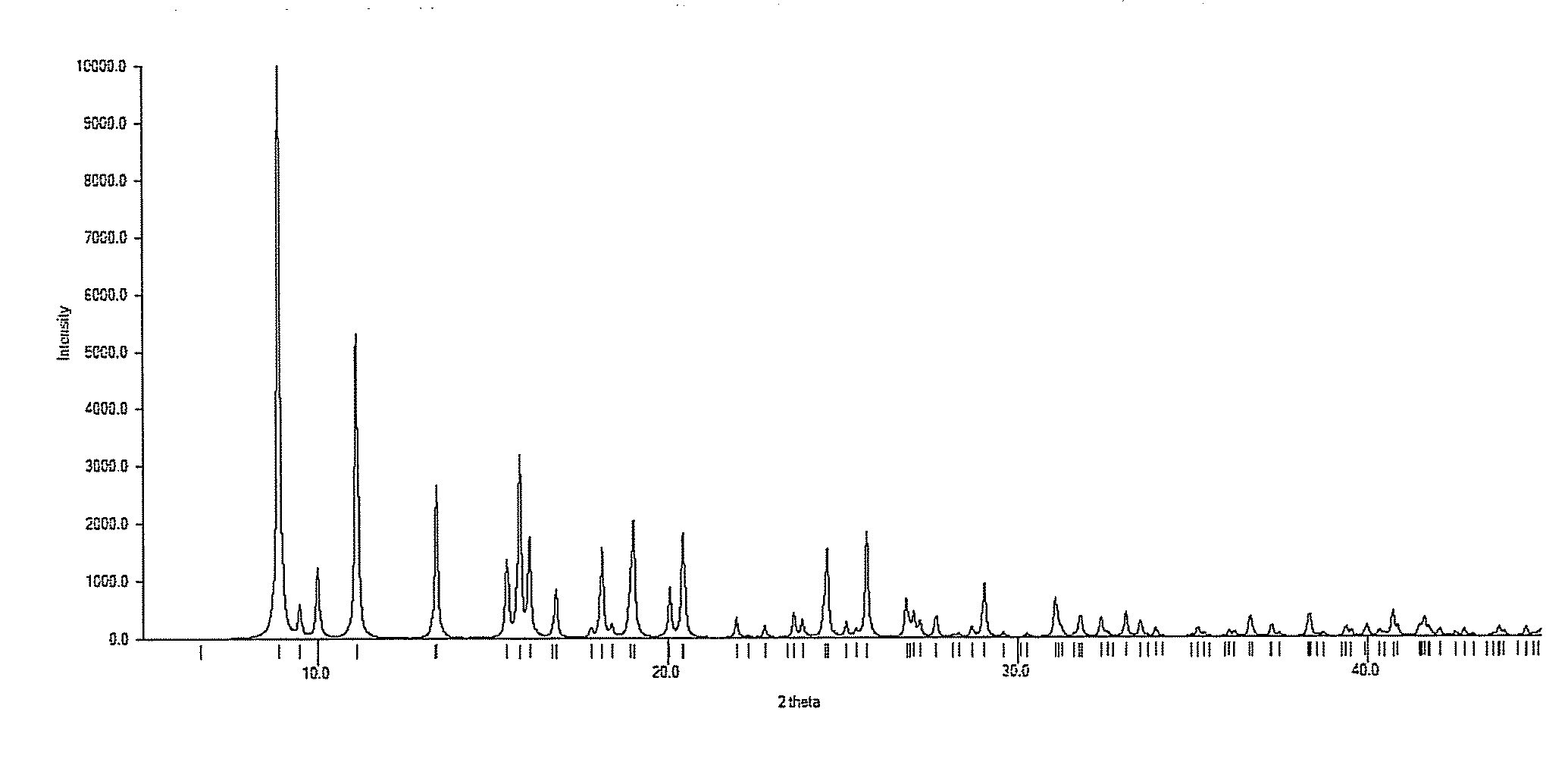
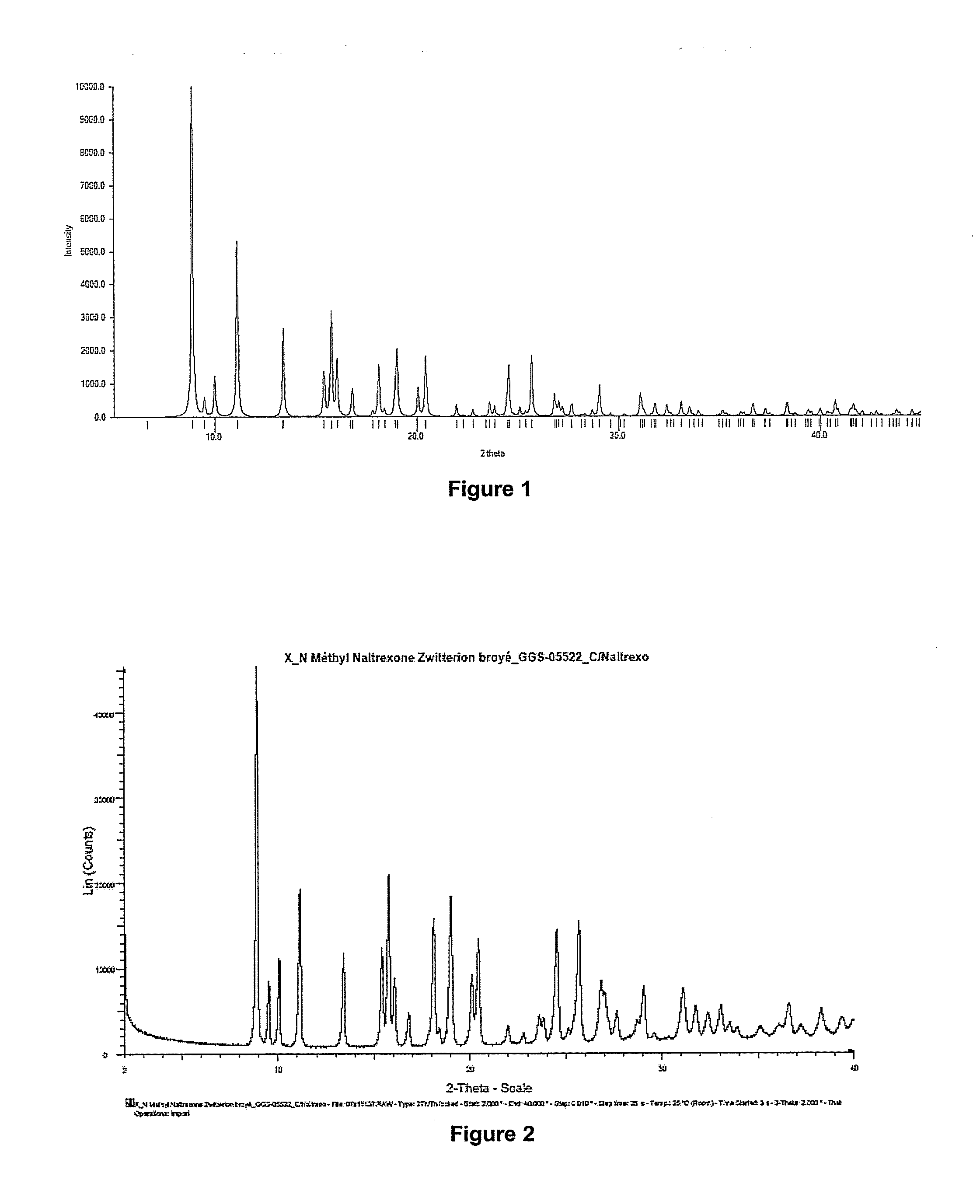
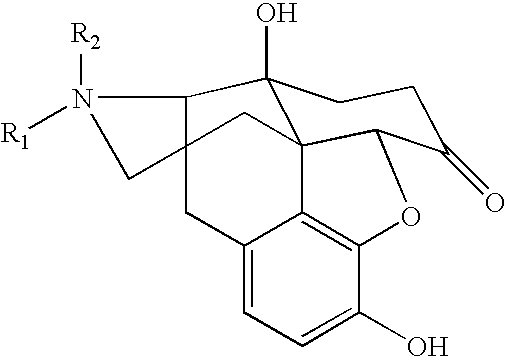
Process for preparing n-alkylnaltrexone halides
The invention relates to a novel process for preparing N-methylnaltrexone bromide, comprising at least the steps consisting in:(i) reacting N-methylnaltrexone methyl sulfate in aqueous solution with an alkaline agent chosen from the group constituted by sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, cesium carbonate, strontium carbonate and mixtures thereof, for a pH of the aqueous reaction medium of between 7 and 10, and then in(ii) reacting the product thus obtained with hydrobromic acid, which is added for a pH of the aqueous reaction medium of between 0.5 and 5, in order thus to obtain the N-methylnaltrexone bromide.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Synthesis method of 5-bromo-2-chloro benzoic acid
ActiveCN105622382AEasy to operateHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationBenzoic acidChlorobenzilate
The invention provides a synthesis method of 5-bromo-2-chloro benzoic acid.The method includes the following steps of A, making 2-chlorine benzotrichloride and bromide reagents react under the effect of a catalyst to obtain 2-chloro-5-bromine benzotrichloride, wherein bromide reagents include one or more of bromine, N-bromosuccinimide, dibromohydantoin and hydrobromic acid; B, conducting hydrolysis reaction on 2-chloro-5-bromine benzotrichloride in the step A under the acid condition to obtain 5-bromo-2-chloro benzoic acid.According to the method, 2-chlorine benzotrichloride which is low in price and easy to obtain is adopted as the raw material, operation is easy, intermediates do not need to be purified, 5-bromo-2-chloro benzoic acid is synthesized through a one-pot method, purity is high, yield is high, three-waste emission is little, and production cost is low.It is shown through experiment results that 2-chloro-5-benzoic acid obtained according to the synthesis method has yield larger than 95% and purity of 80-92%.
Owner:苏州正济药业有限公司
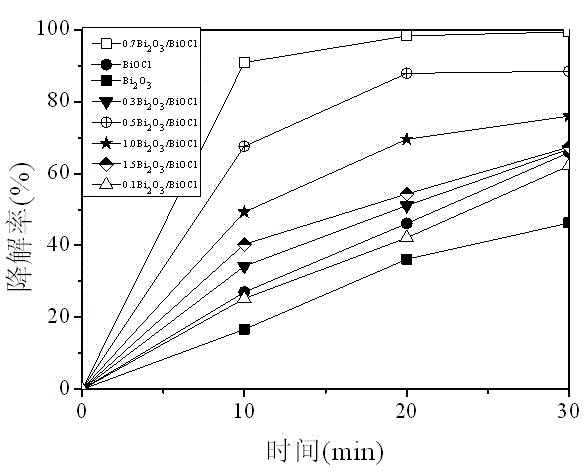
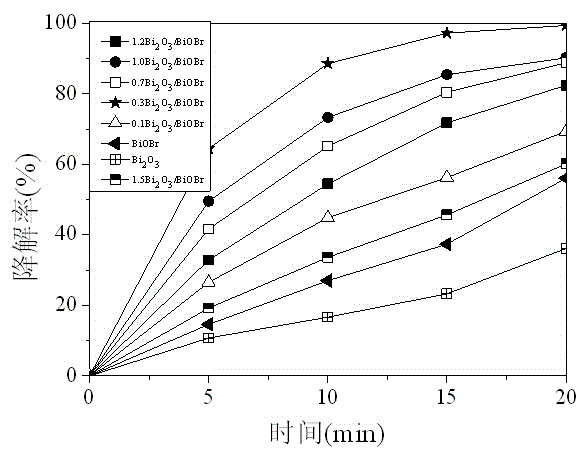
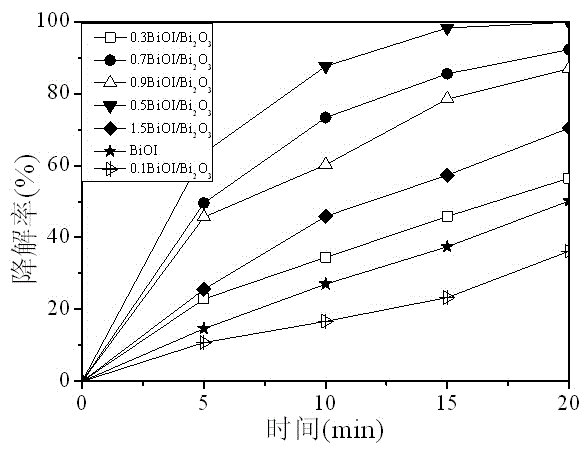
Preparation method of bismuth oxyhalide/bismuth oxide visible-light photocatalyst
InactiveCN104525225AReduce recombination rateNo pollution in the processPhysical/chemical process catalystsCharge carrierRoom temperature
The invention relates to a preparation method of a bismuth oxyhalide / bismuth oxide visible-light photocatalyst and belongs to the field of visible-light photocatalyst preparation. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving bismuth nitrate in a salpeter solution, adjusting pH with alkali lye, stirring, filtering, washing, drying, calcining at high temperature of 300-600 DEG C for 3-10 hours to prepare yellow bismuth oxide; adding a proper amount of hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid or hydroiodic acid with a certain concentration into the prepared bismuth oxide, carrying out an ultrasonic reaction, carrying out centrifugal separation, and drying at constant temperature of 50-100 DEG C for 4-10 hours to obtain the bismuth oxyhalide / bismuth oxide photocatalyst. The method can be carried out at room temperature and at normal pressure. Equipment is simple and easy to operate, can be put into practical use and has a potential application in industrial production. According to the prepared bismuth oxyhalide / bismuth oxide visible-light photocatalyst, the problem of high photo-generated electron and carrier recombination rate is solved effectively, and photocatalytic performance is greatly enhanced.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Etching composition and method for fabricating semiconductor device by using the same
ActiveUS20180148645A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingO-Phosphoric AcidPropanoic acid
An etching composition selectively removes a titanium nitride film from a stacked conductive film structure including a titanium nitride (TiN) film and a tantalum nitride (TaN) film. The etching composition configured to etch titanium nitride (TiN) includes 5 wt % to 30 wt % of hydrogen peroxide, 15 wt % to 50 wt % of acid compound, and 0.001 wt % to 5 wt % of corrosion inhibitor, with respect to a total weight of the etching composition, wherein the acid compound includes at least one of phosphoric acid (H3PO4), nitric acid (HNO3), hydrochloric acid (HCl), hydroiodic acid (HI), hydrobromic acid (HBr), perchloric acid (HNO4), silicic acid (H2SiO3), boric acid (H3BO3), acetic acid (CH3COOH), propionic acid (C2H5COOH), lactic acid (CH3CH(OH)COOH), and glycolic acid (HOCH2COOH).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Orally disintegrating pharmaceutical composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103989650AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderOrally disintegrating tabletFiller Excipient
The invention relates to an orally disintegrating pharmaceutical composition and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of pharmaceutical preparations. Considering the characteristic of bitter taste of hydrobromic acid vortioxetine, the invention provides a method for preparing orally disintegrating tablets which are small in particle size and can cover the bitter taste. The method is realized by mainly adopting the technical scheme, namely the composition is prepared by granulating or directly tabletting pharmaceutical microcapsules, 20-80 weight percent of filling agent, 5-10 weight percent of disintegrating agent, 0.5-2 percent of flavoring agent and 1-2 percent of lubricating agent. The orally disintegrating tablets do not have a grit feeling, sweetening agents such as saccharin sodium salt and Aspartame are not needed to be added into a subsequent tablet prescription, or the flavor of the tablets can be increased by adding a small amount of sweetening agent or essence and flavor according to market requirements, and the medicine content and encapsulation efficiency can meet the industrial large-scale production requirements.
Owner:李雪梅
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com