Patents
Literature
106results about "Hydrogen bromide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
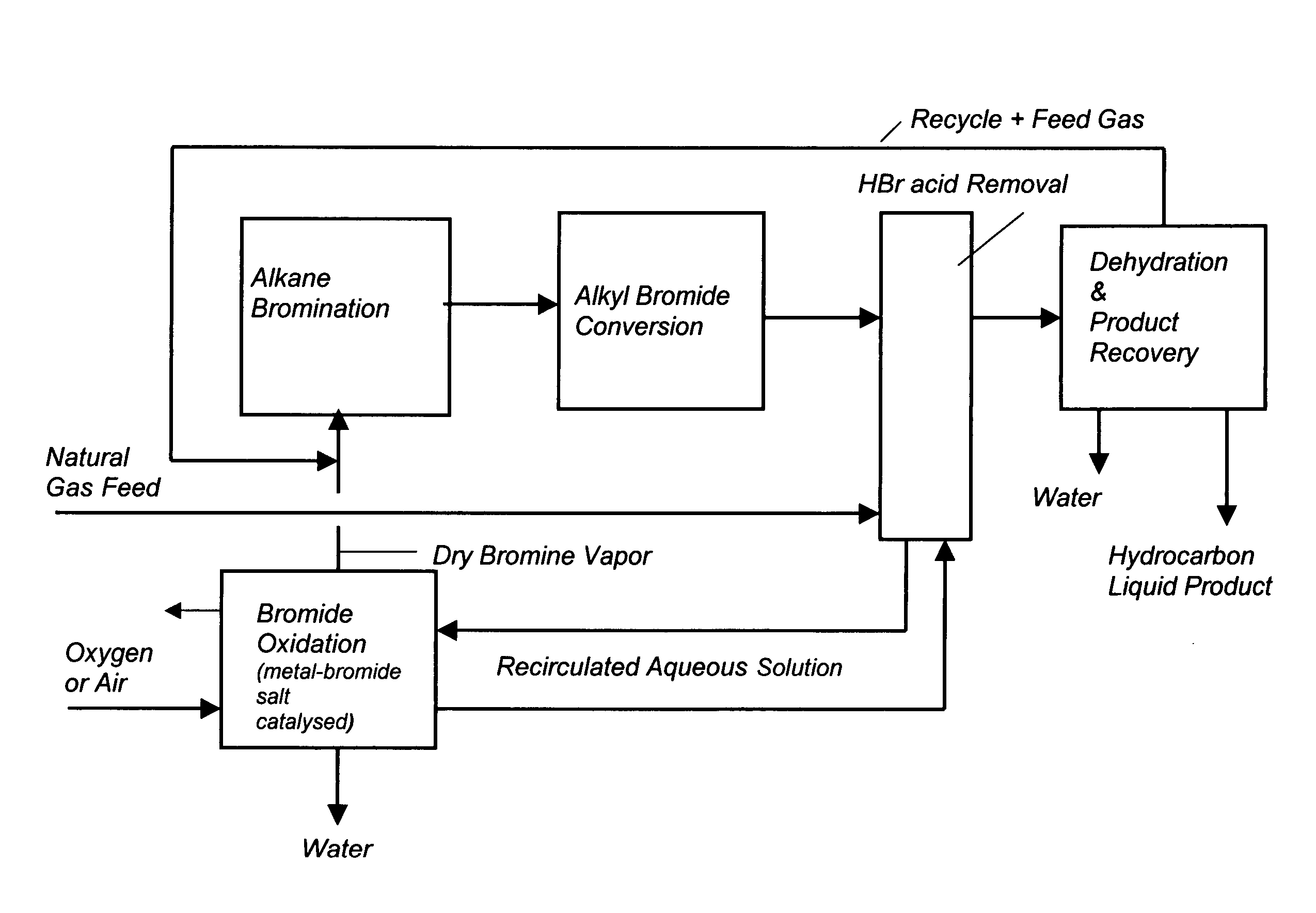
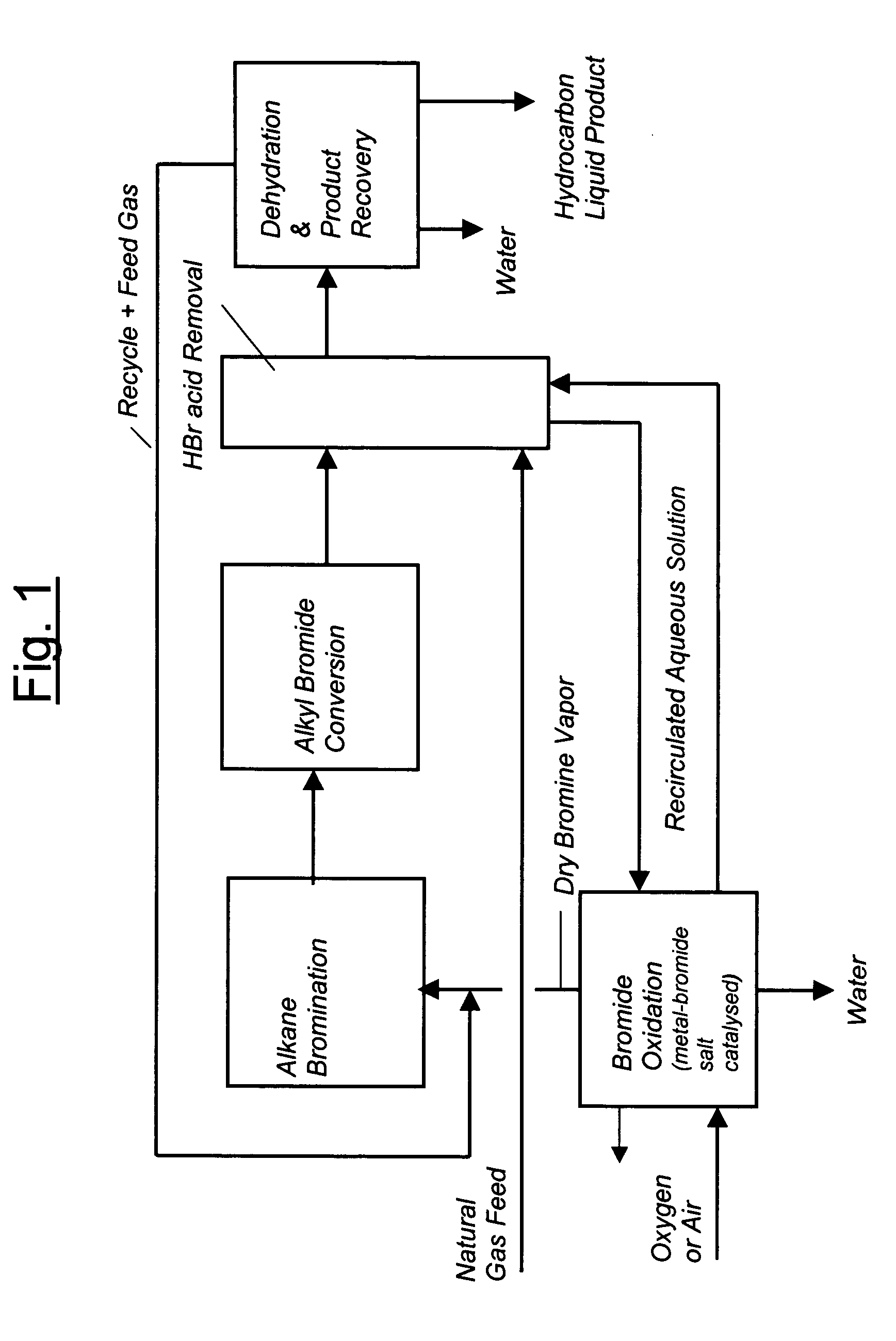
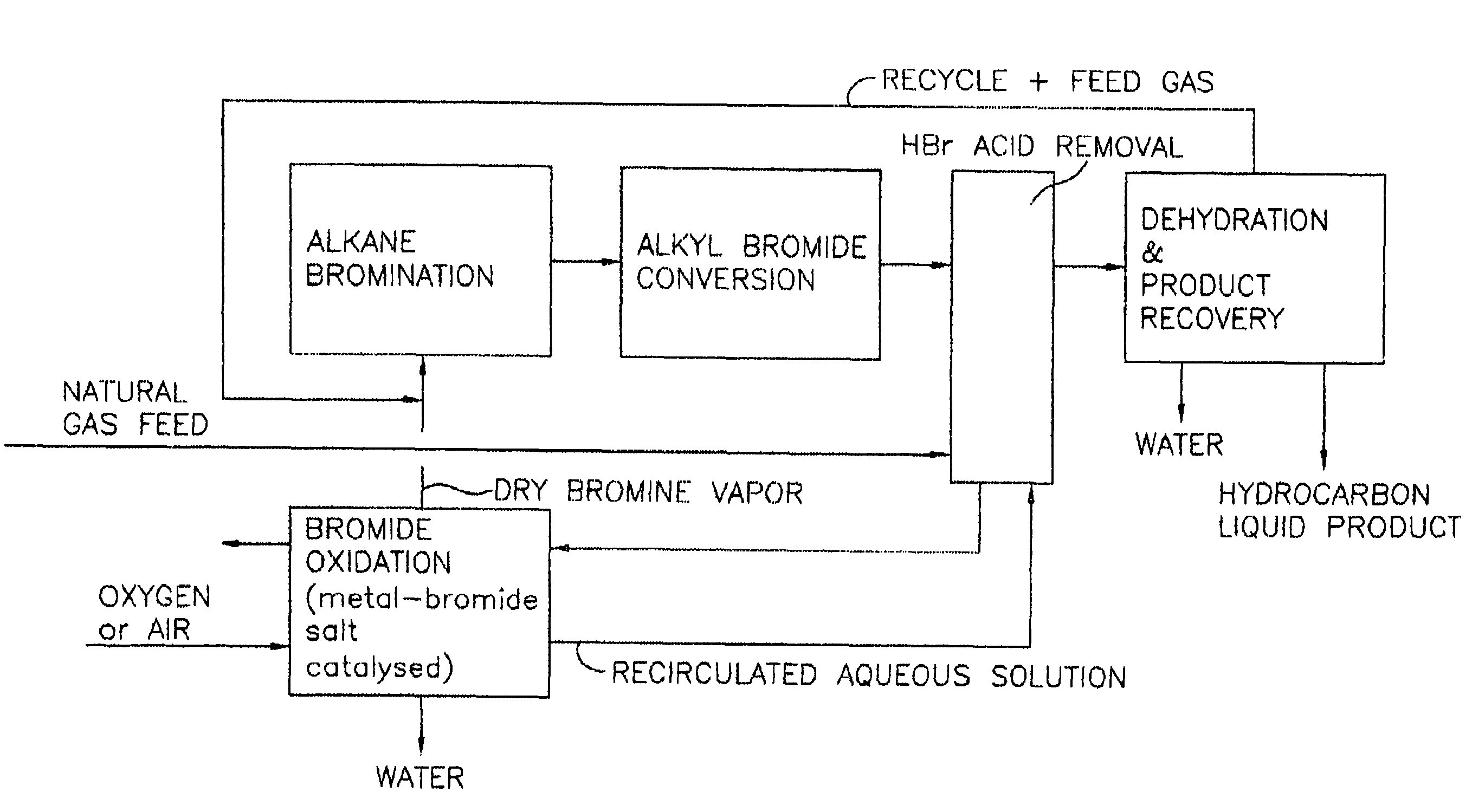
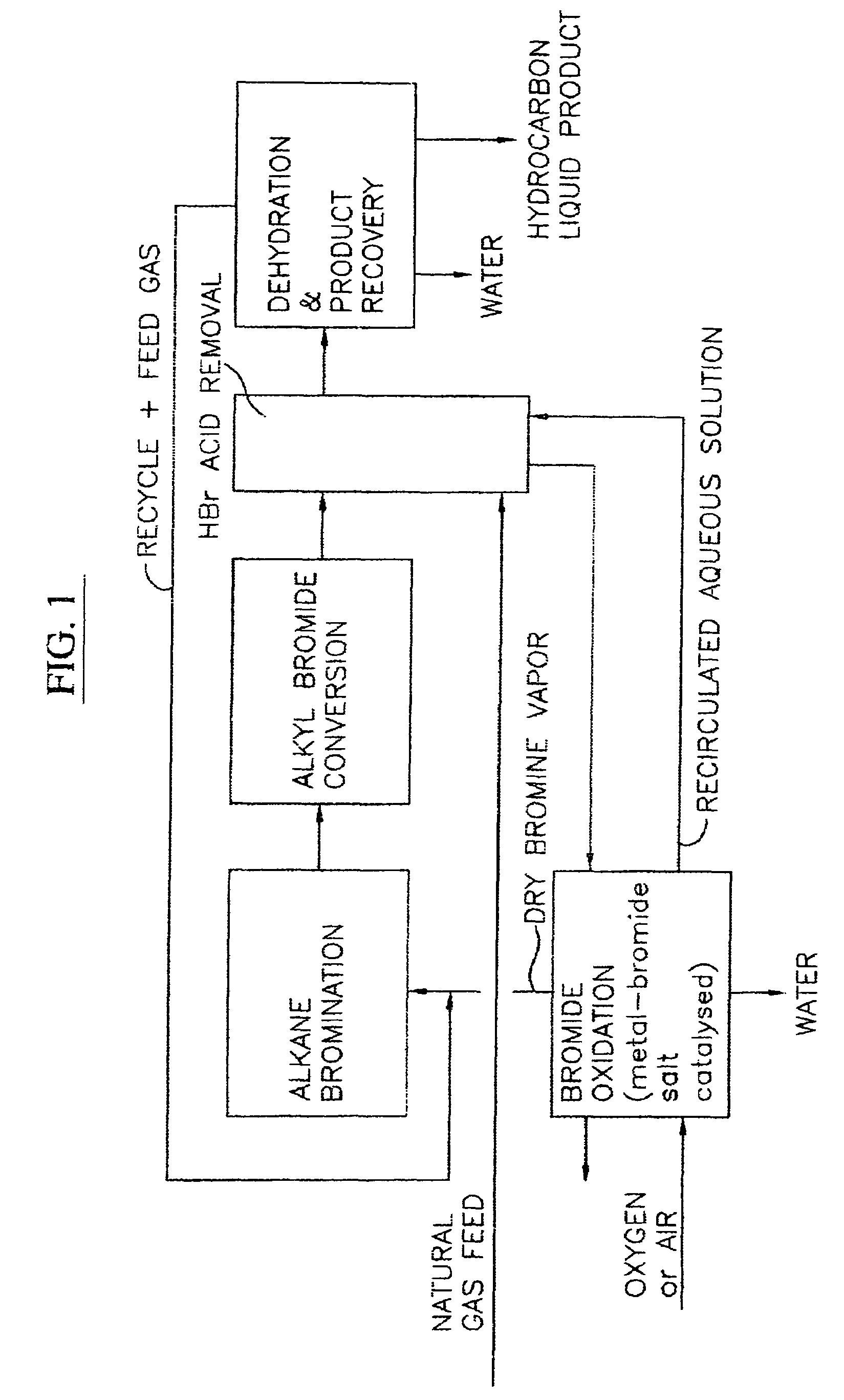
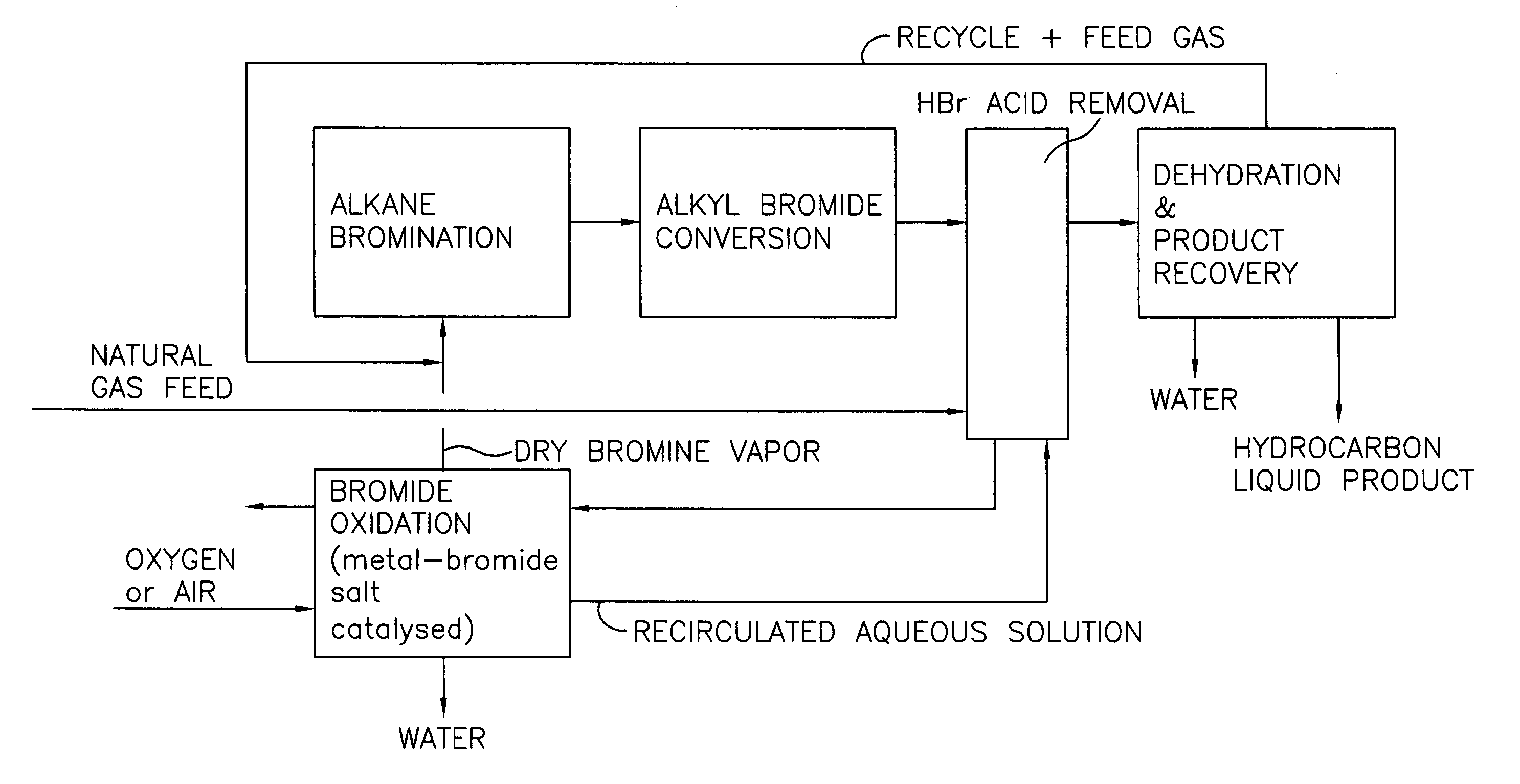
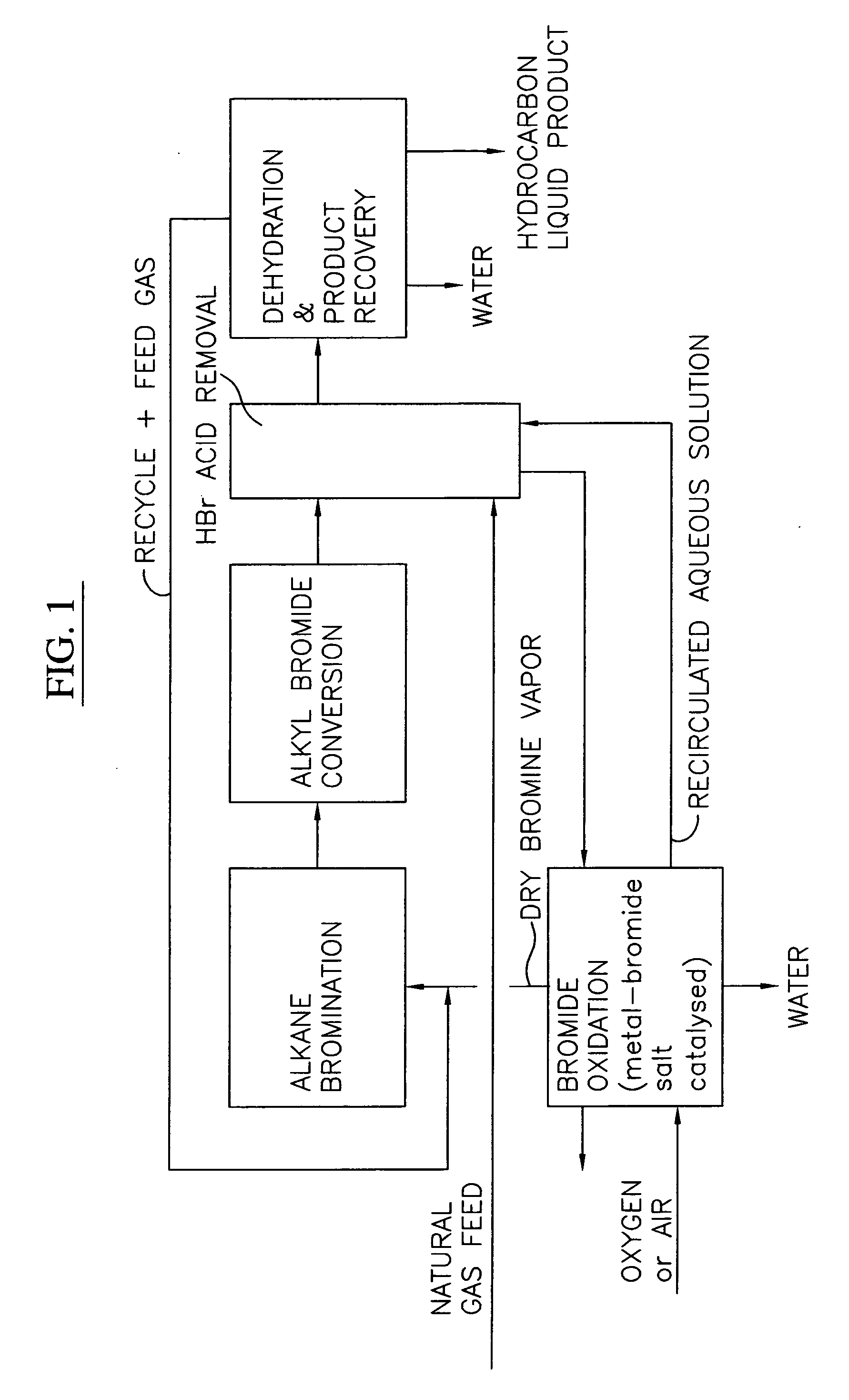
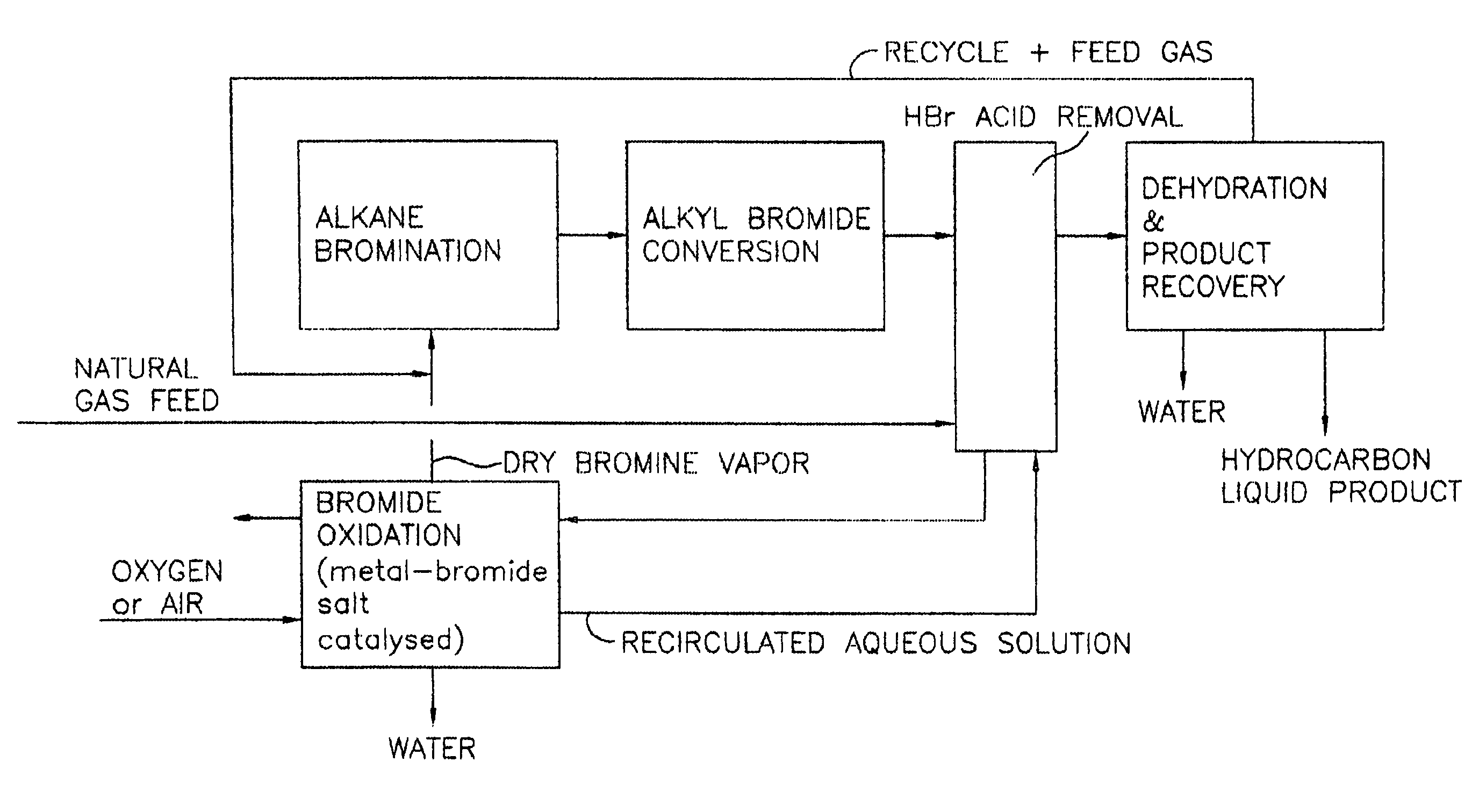
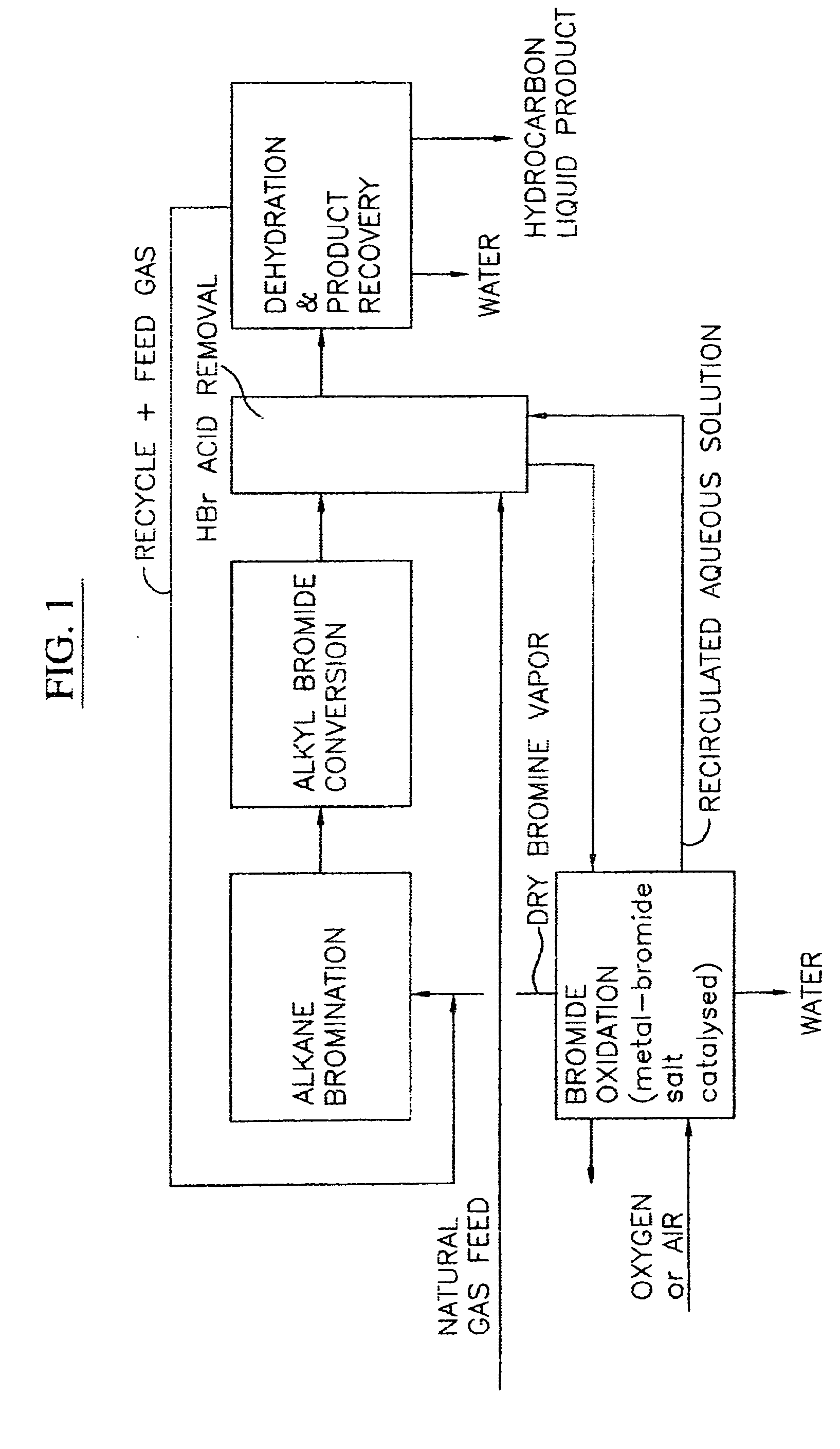
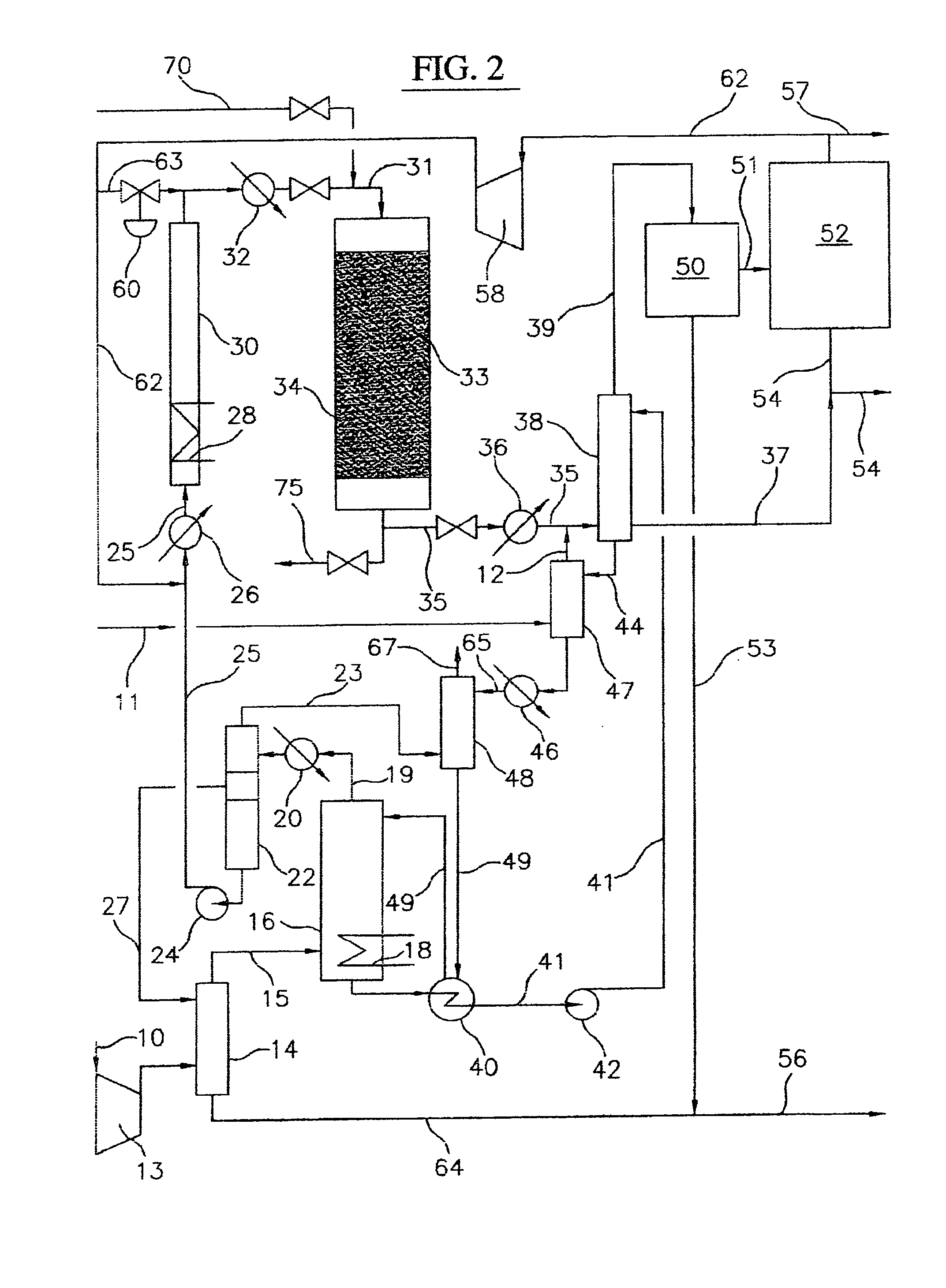
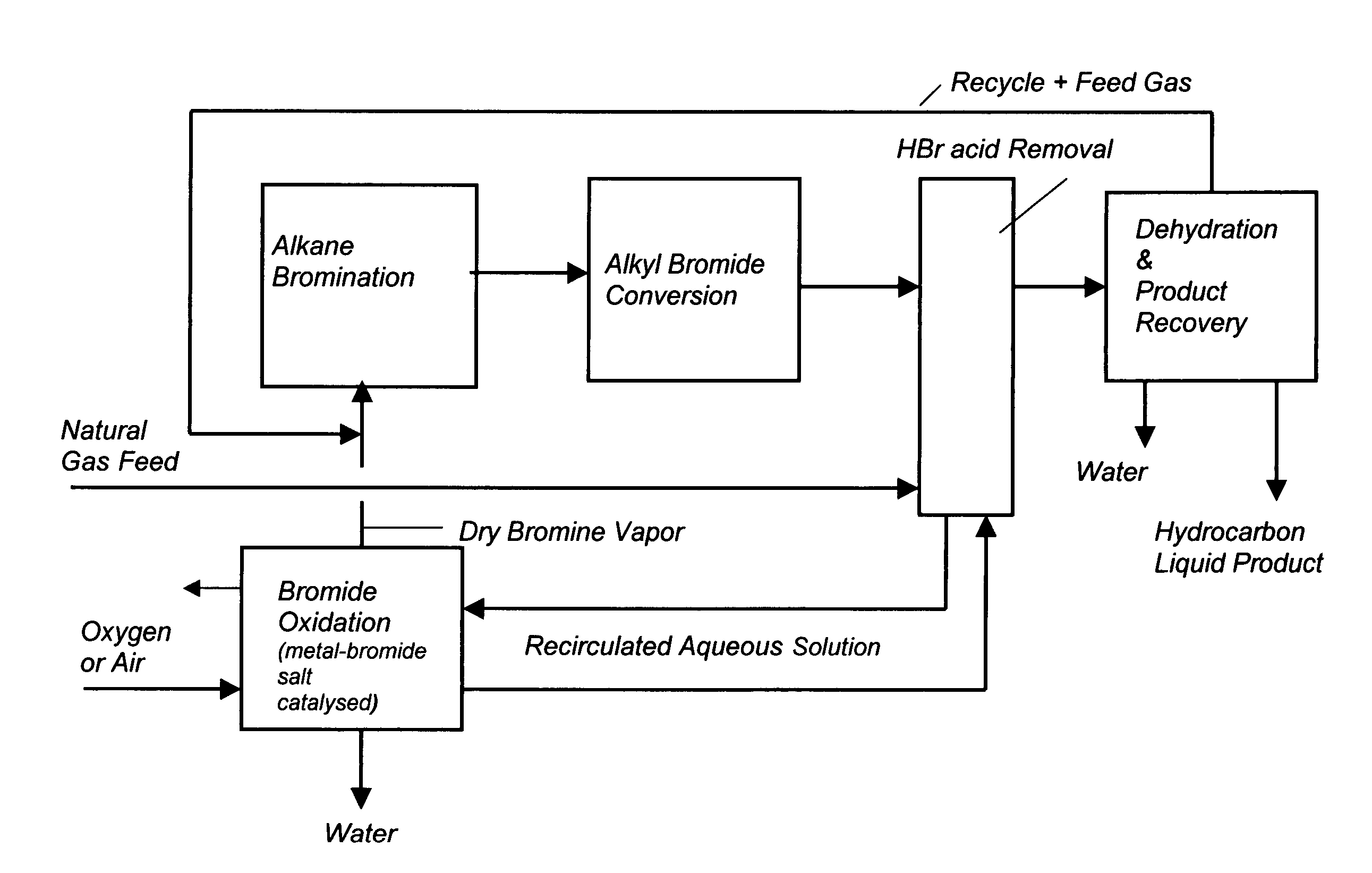
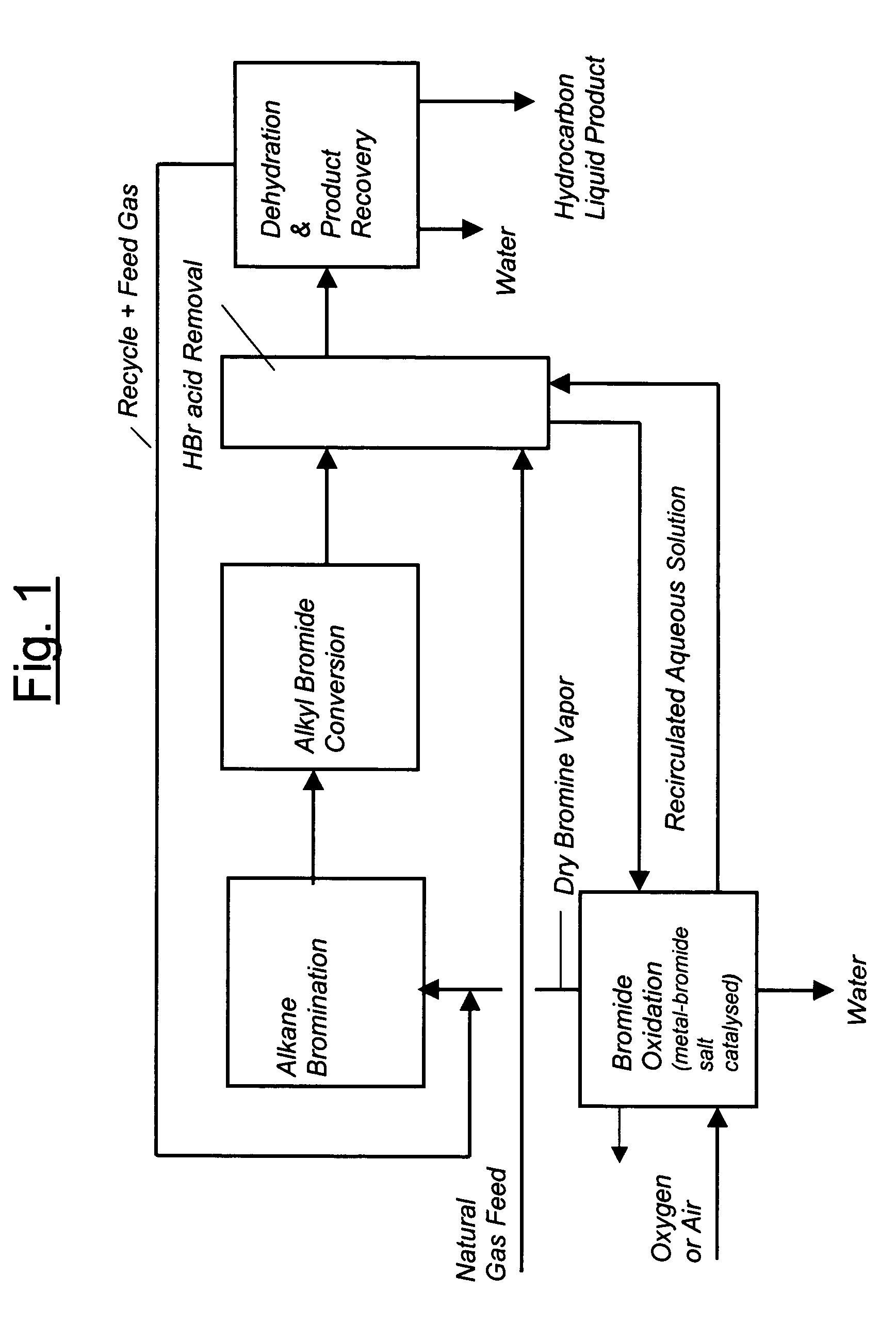
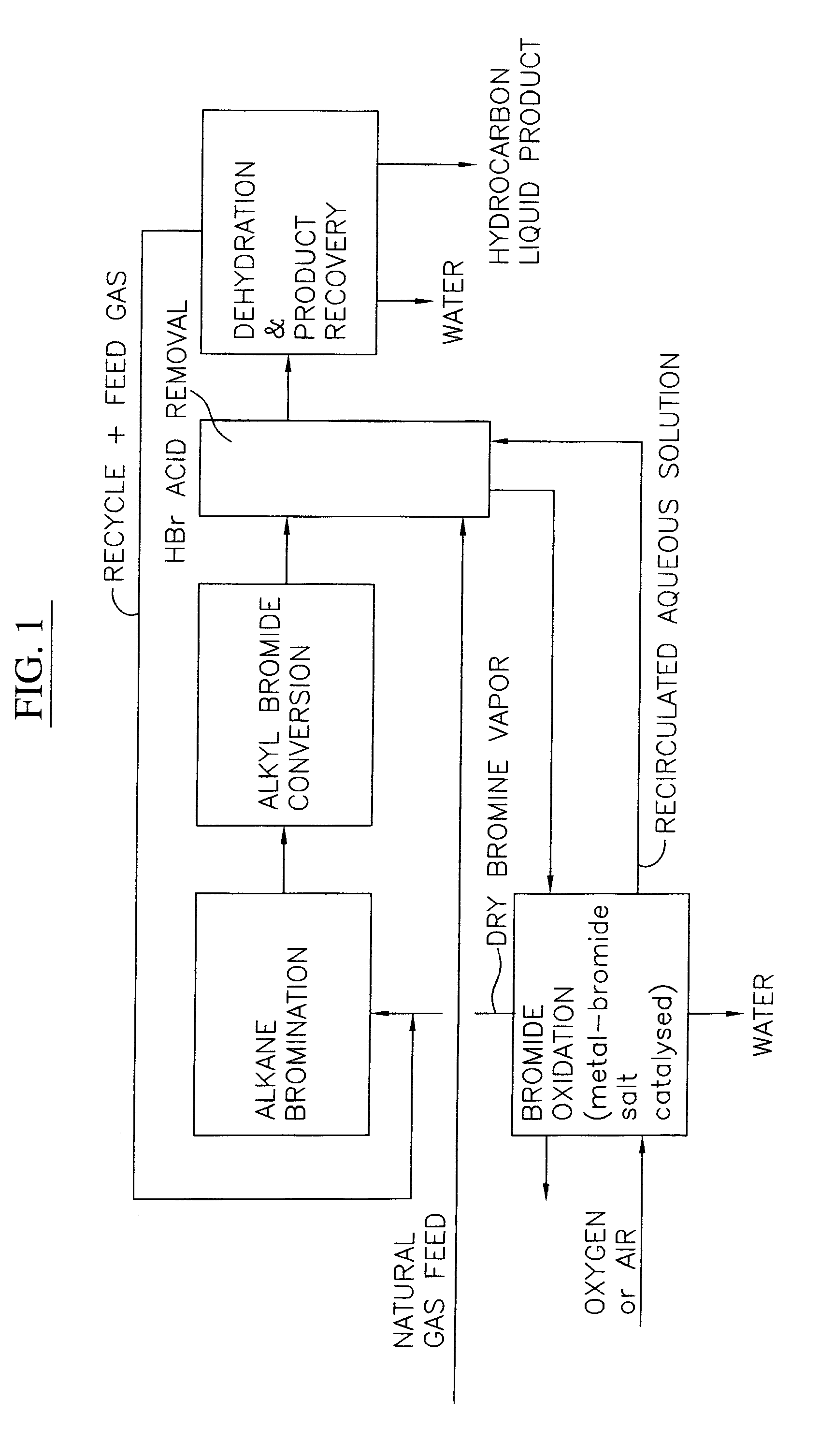
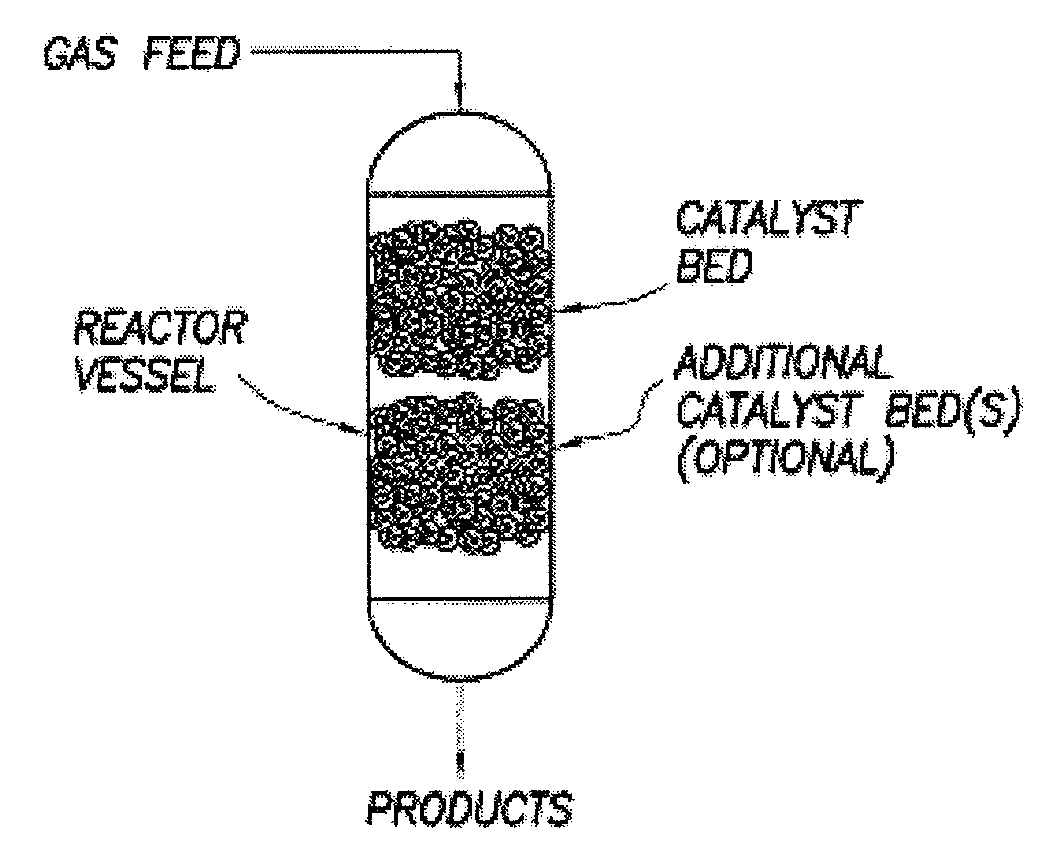
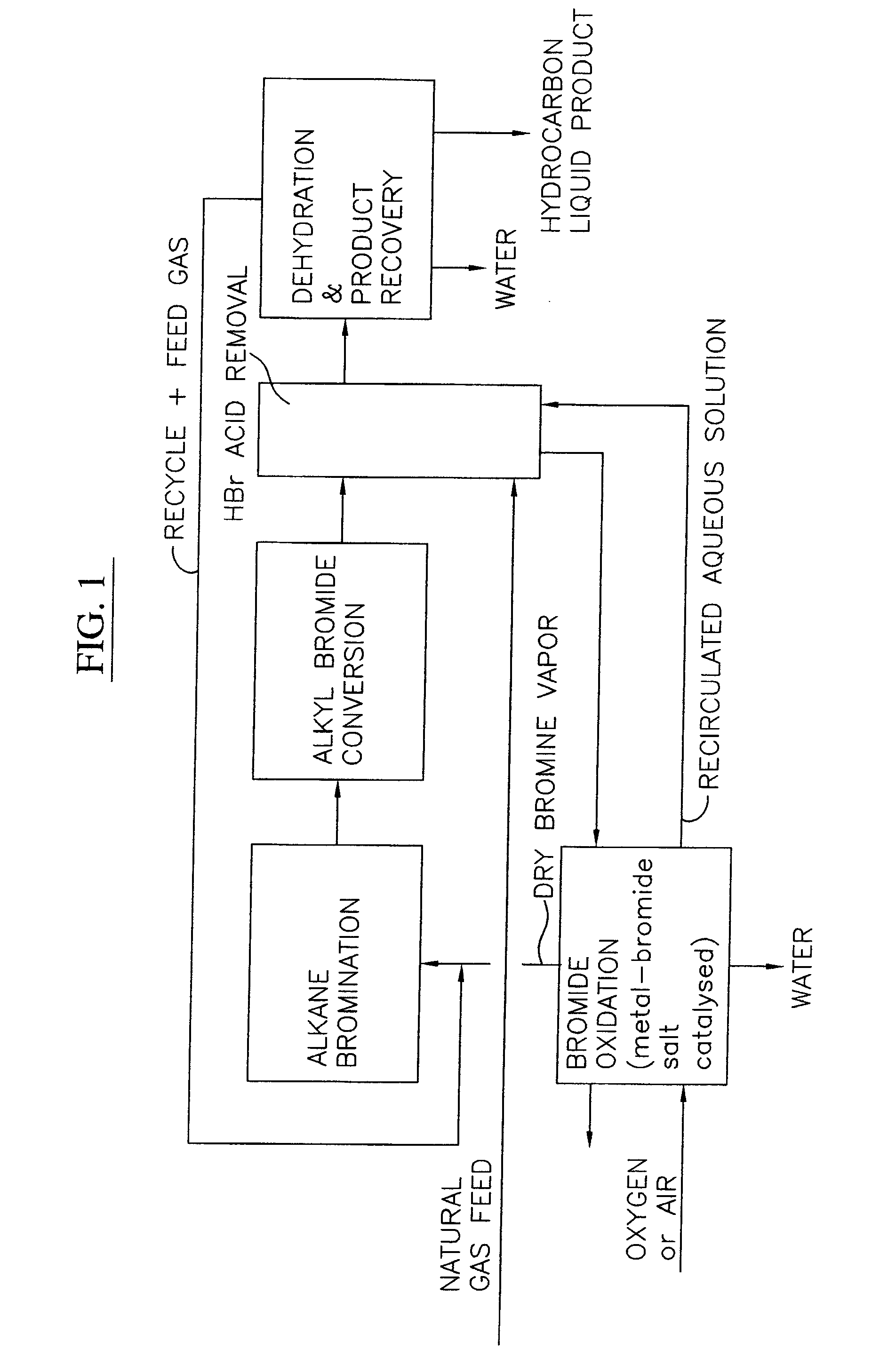
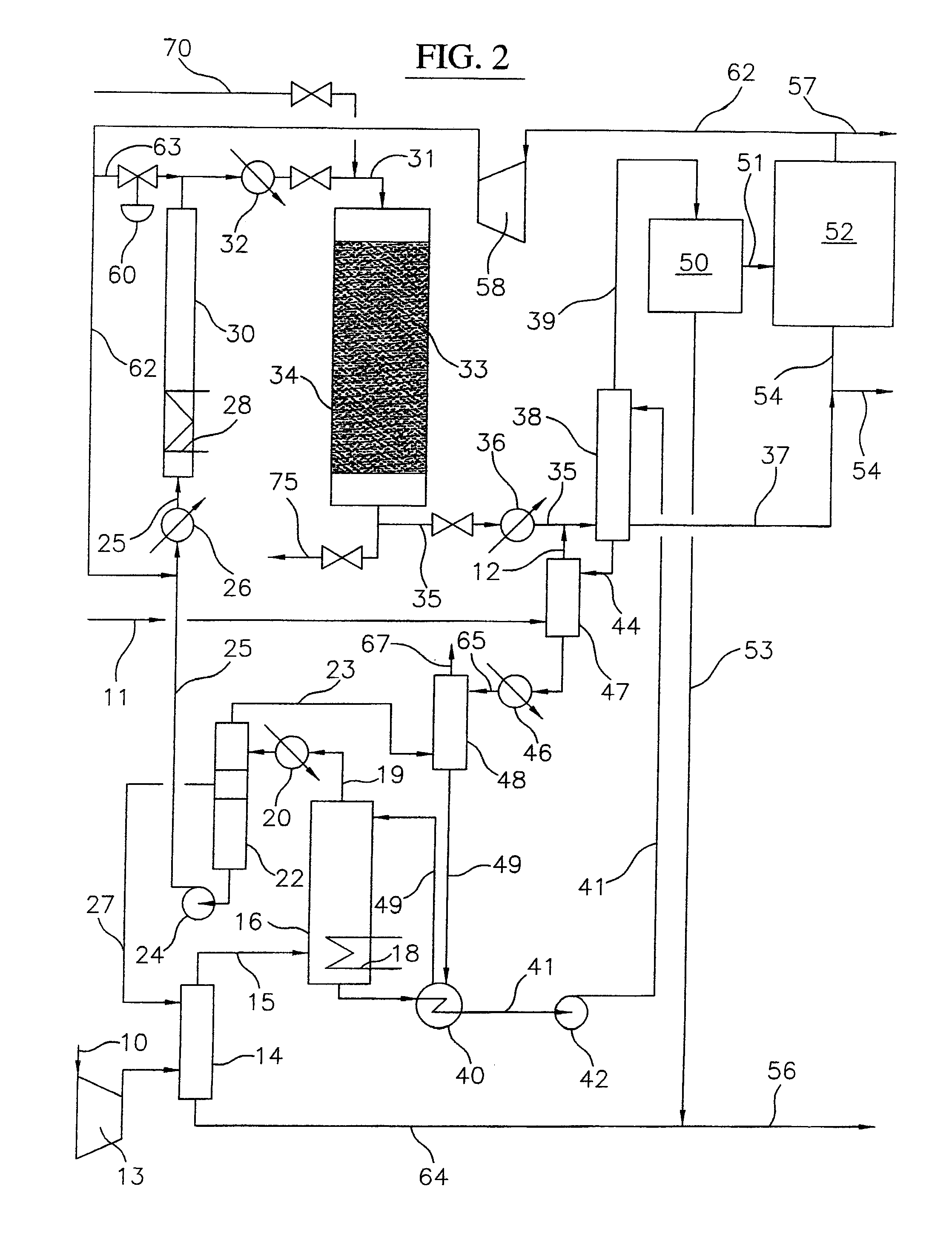
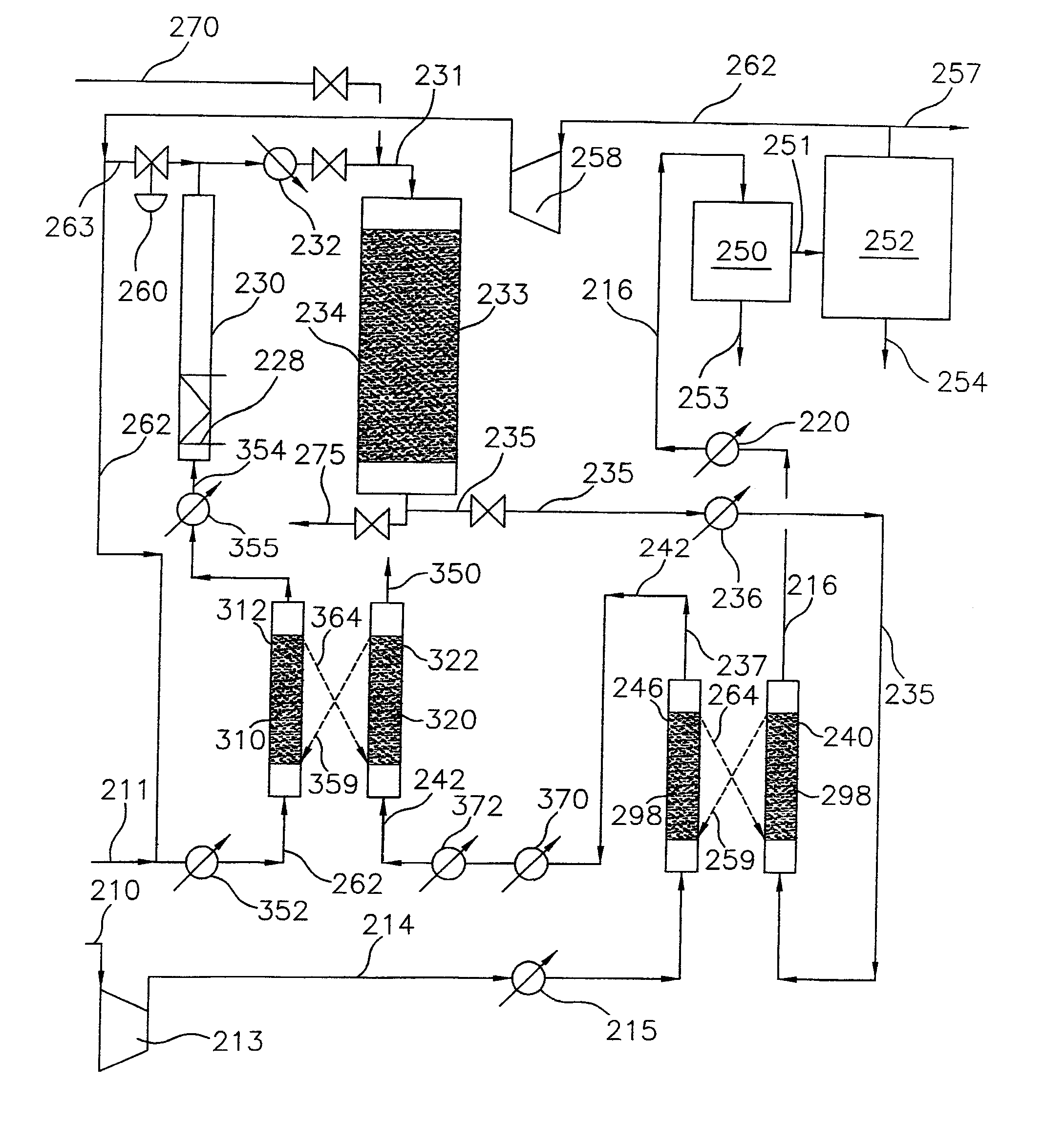
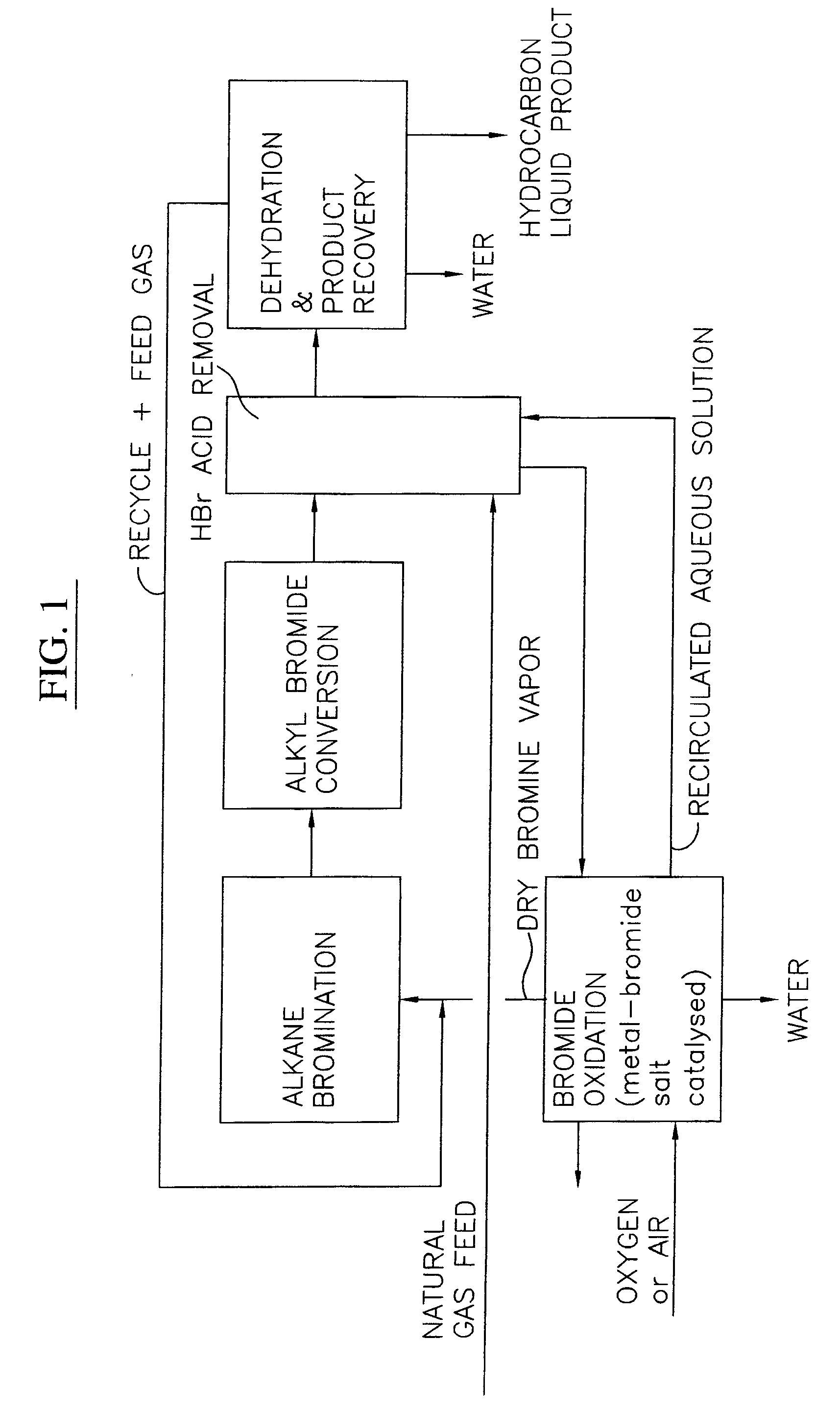
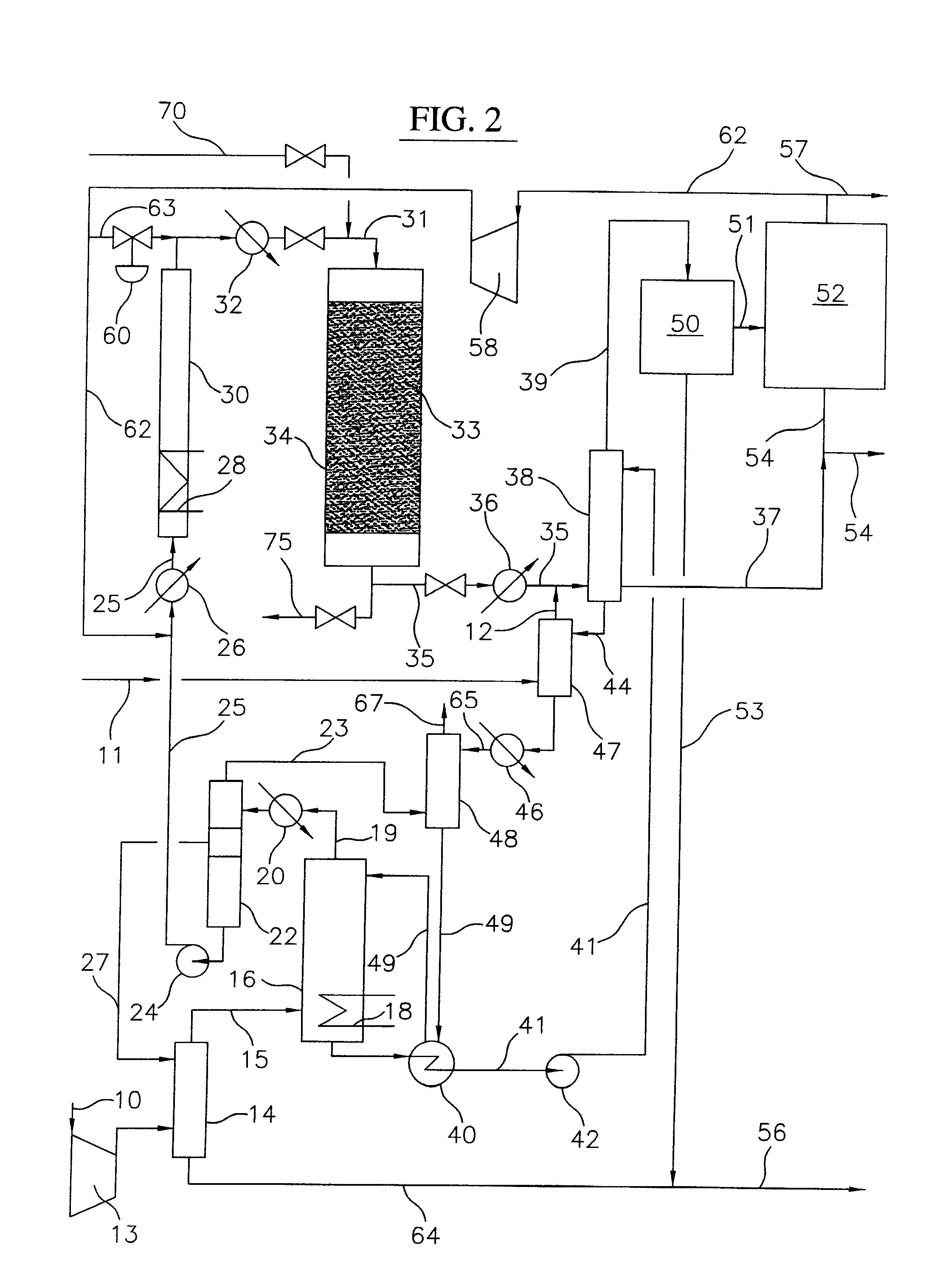
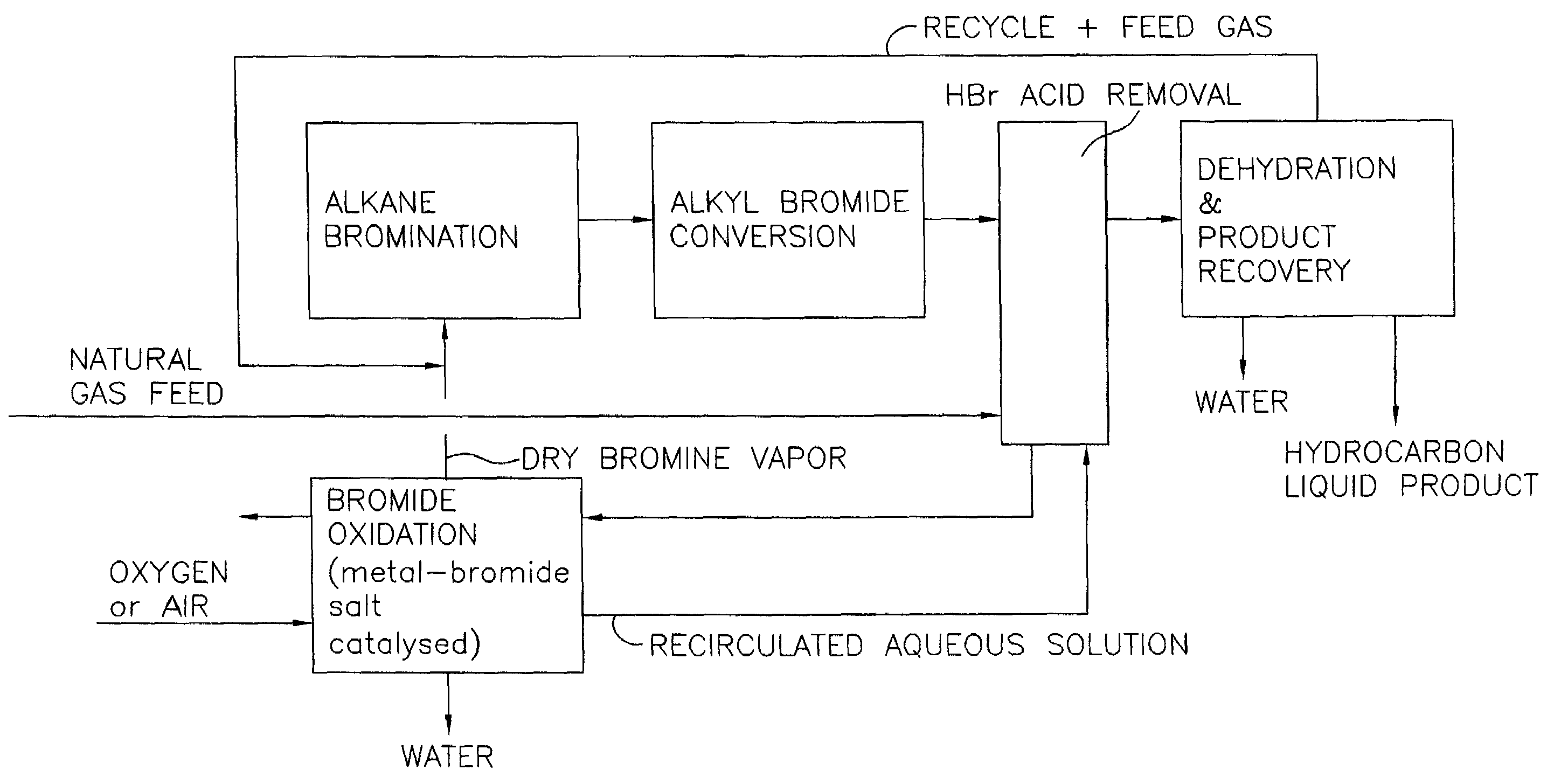
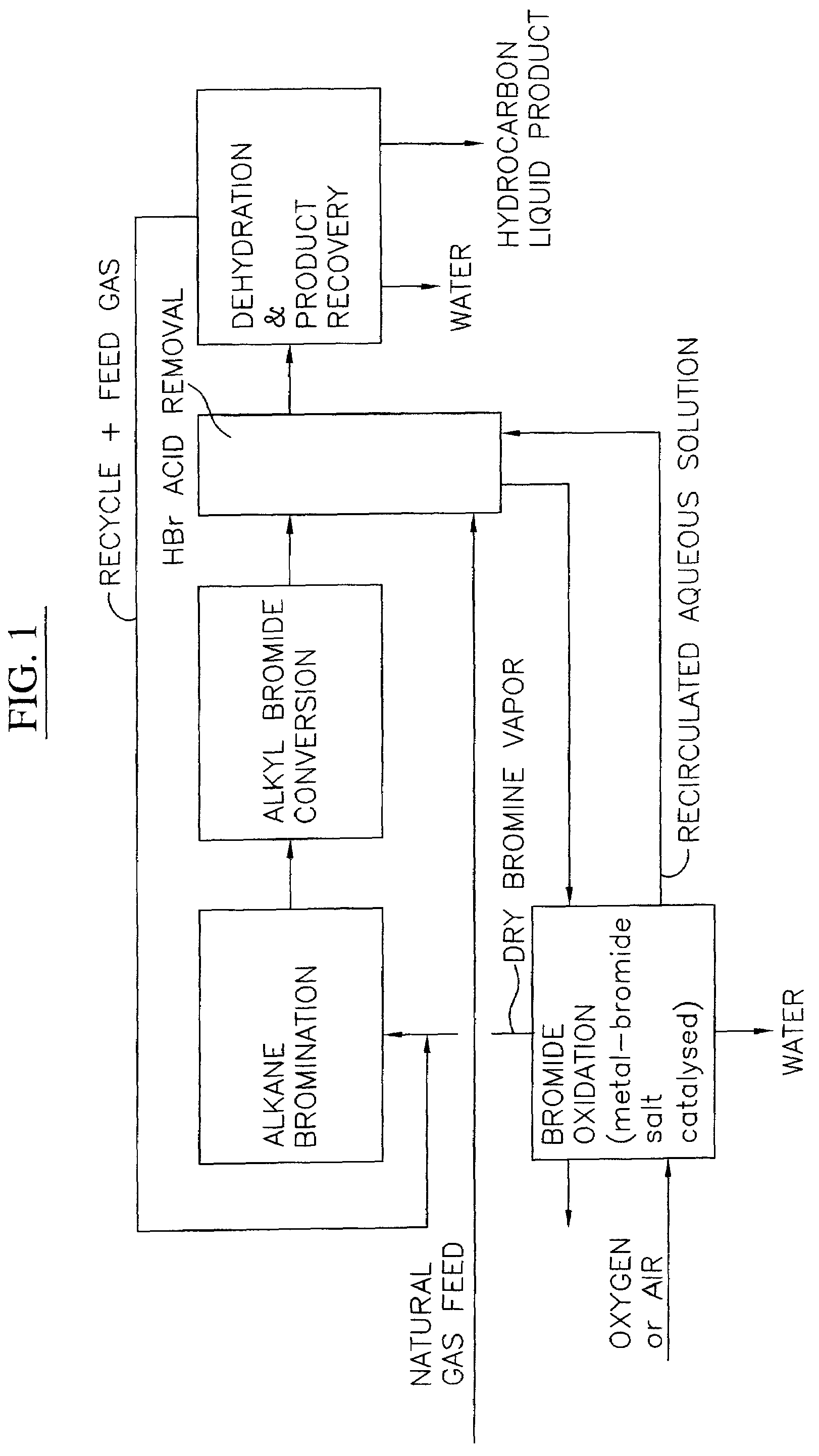
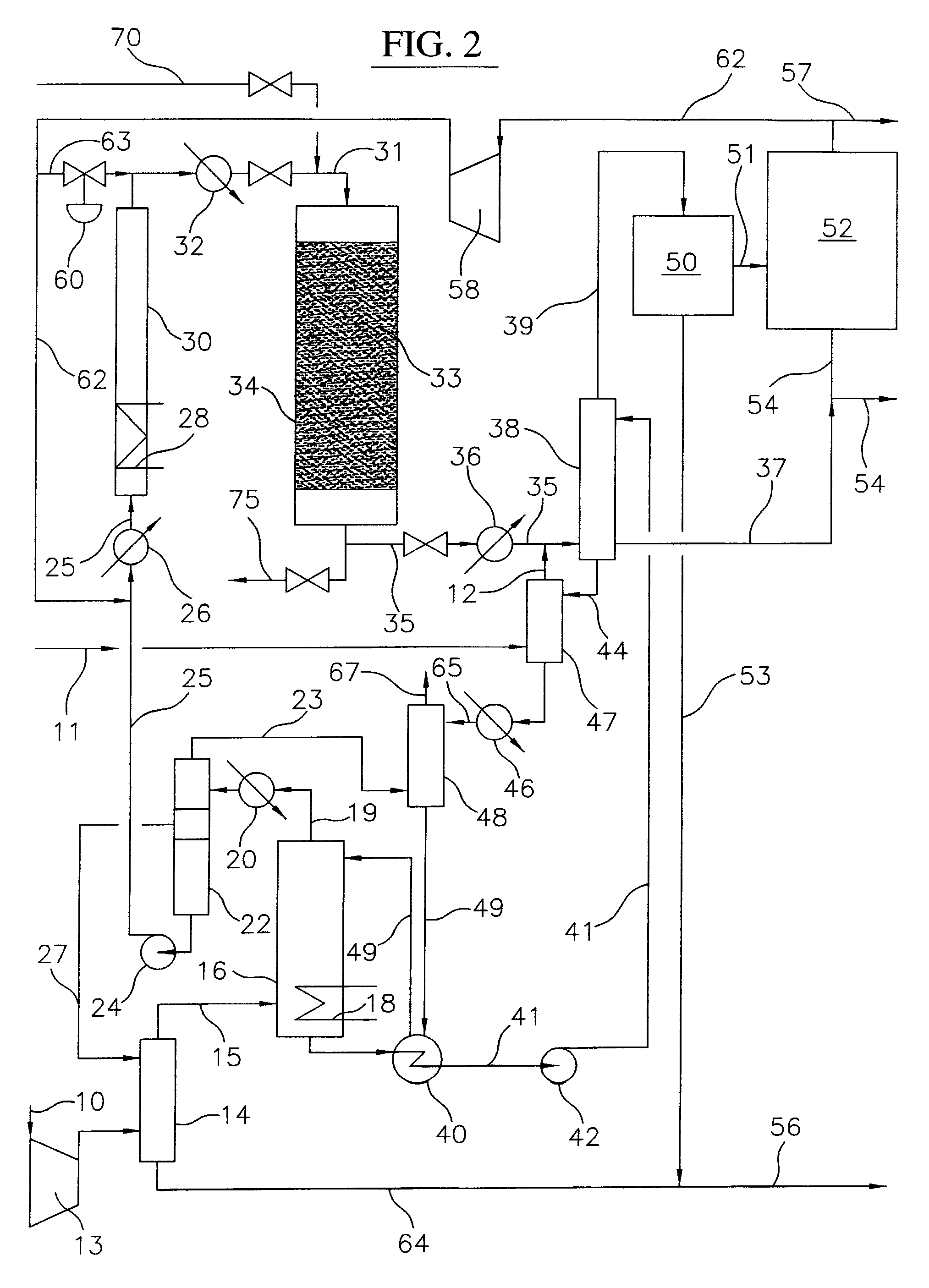
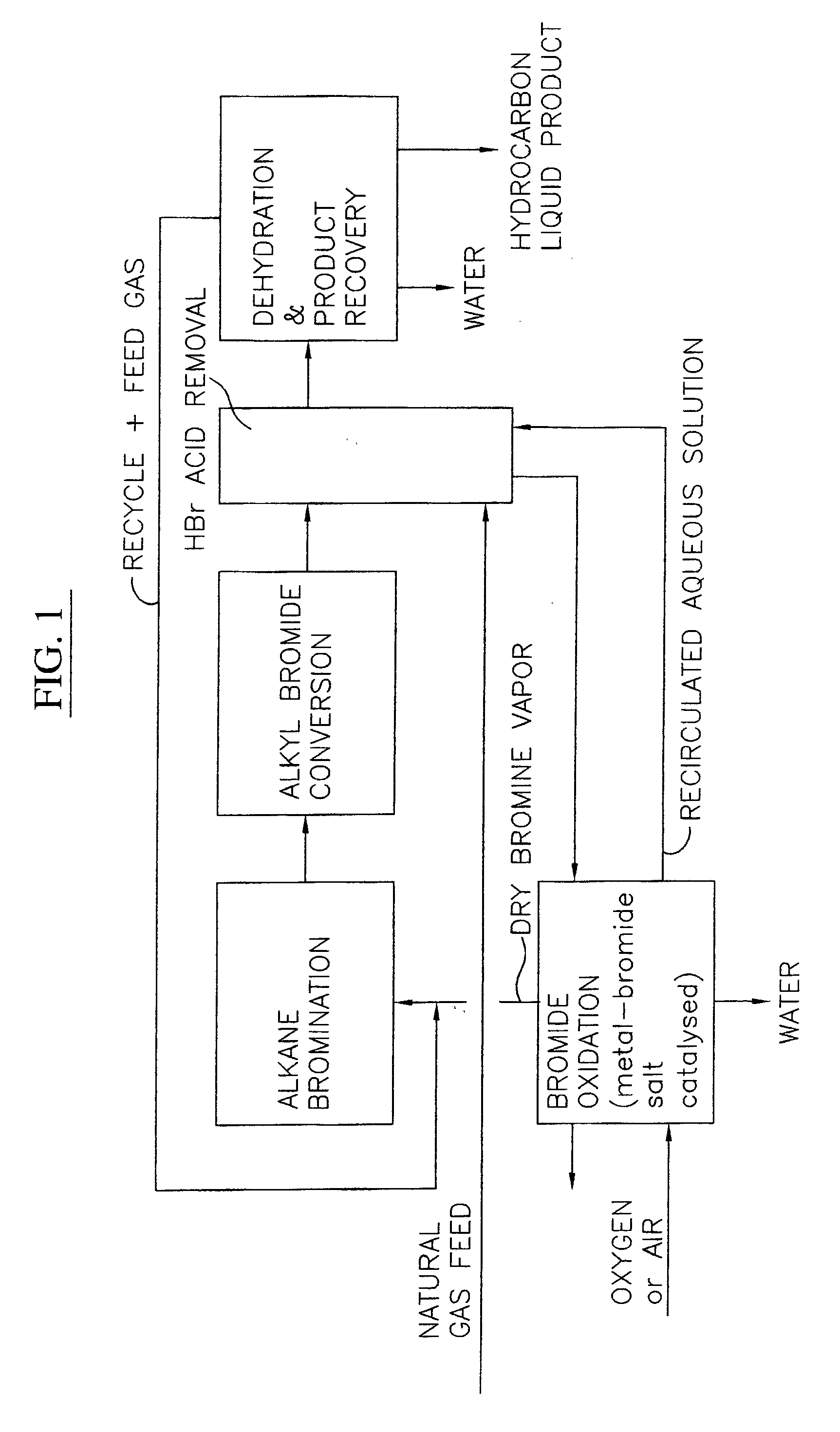
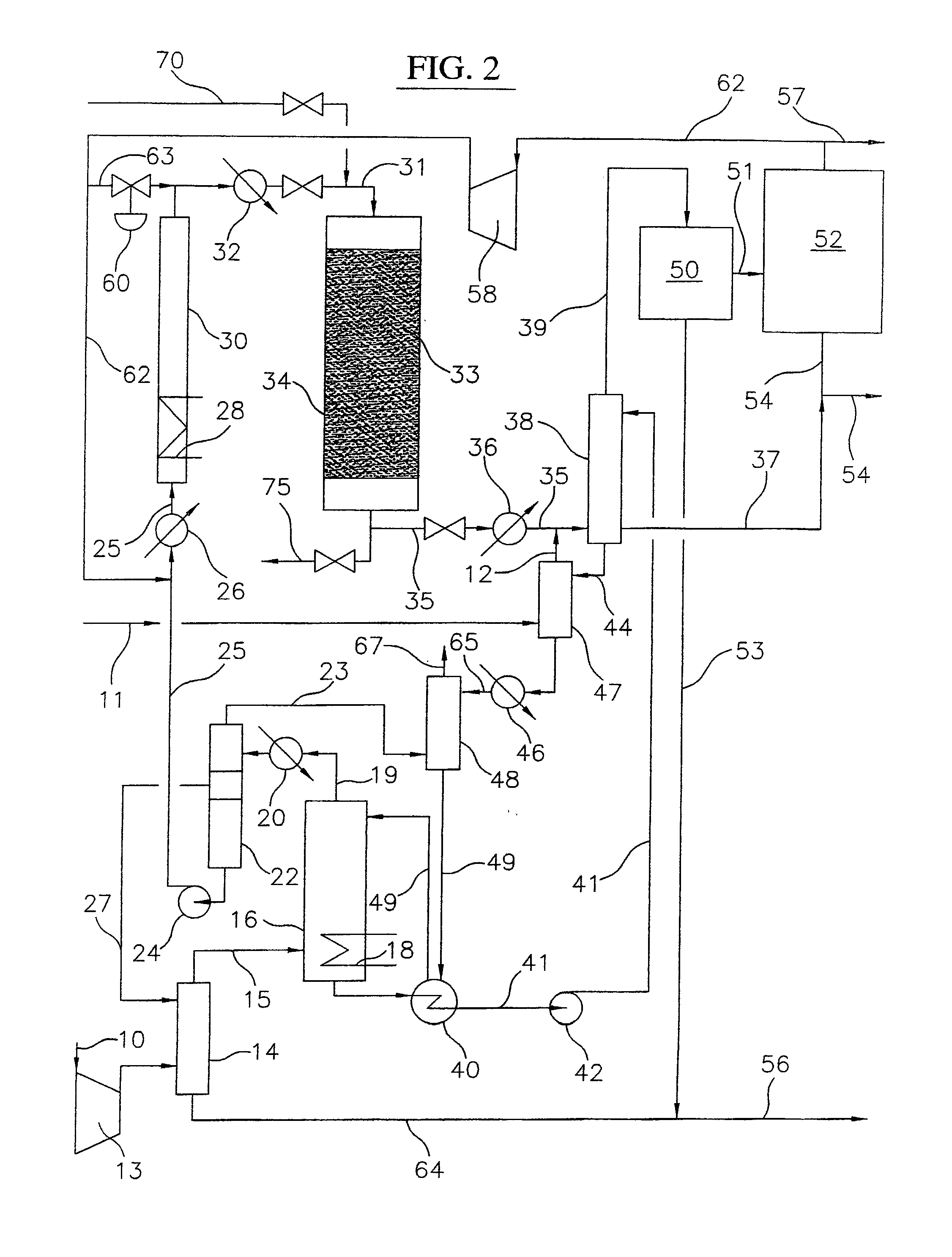
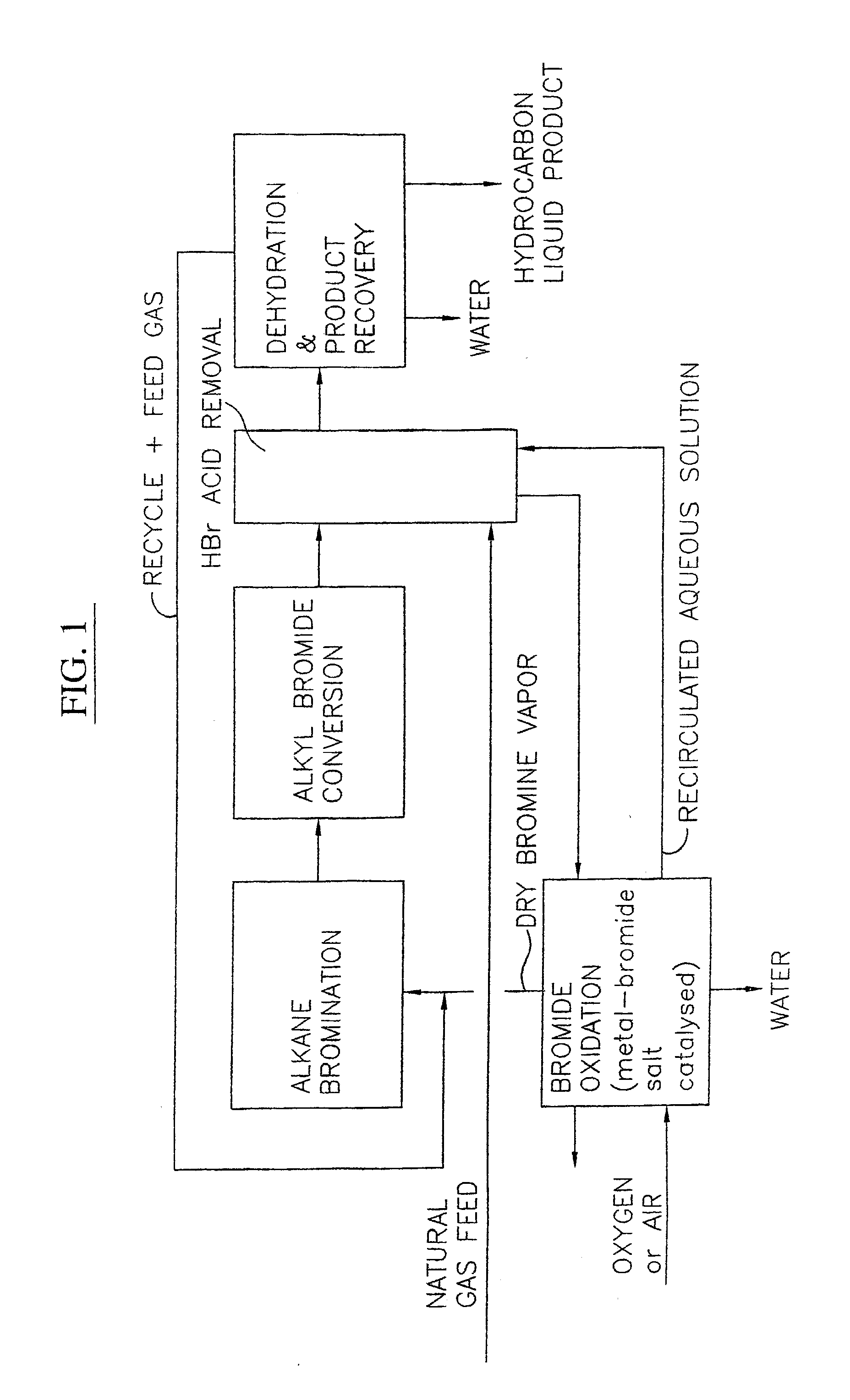
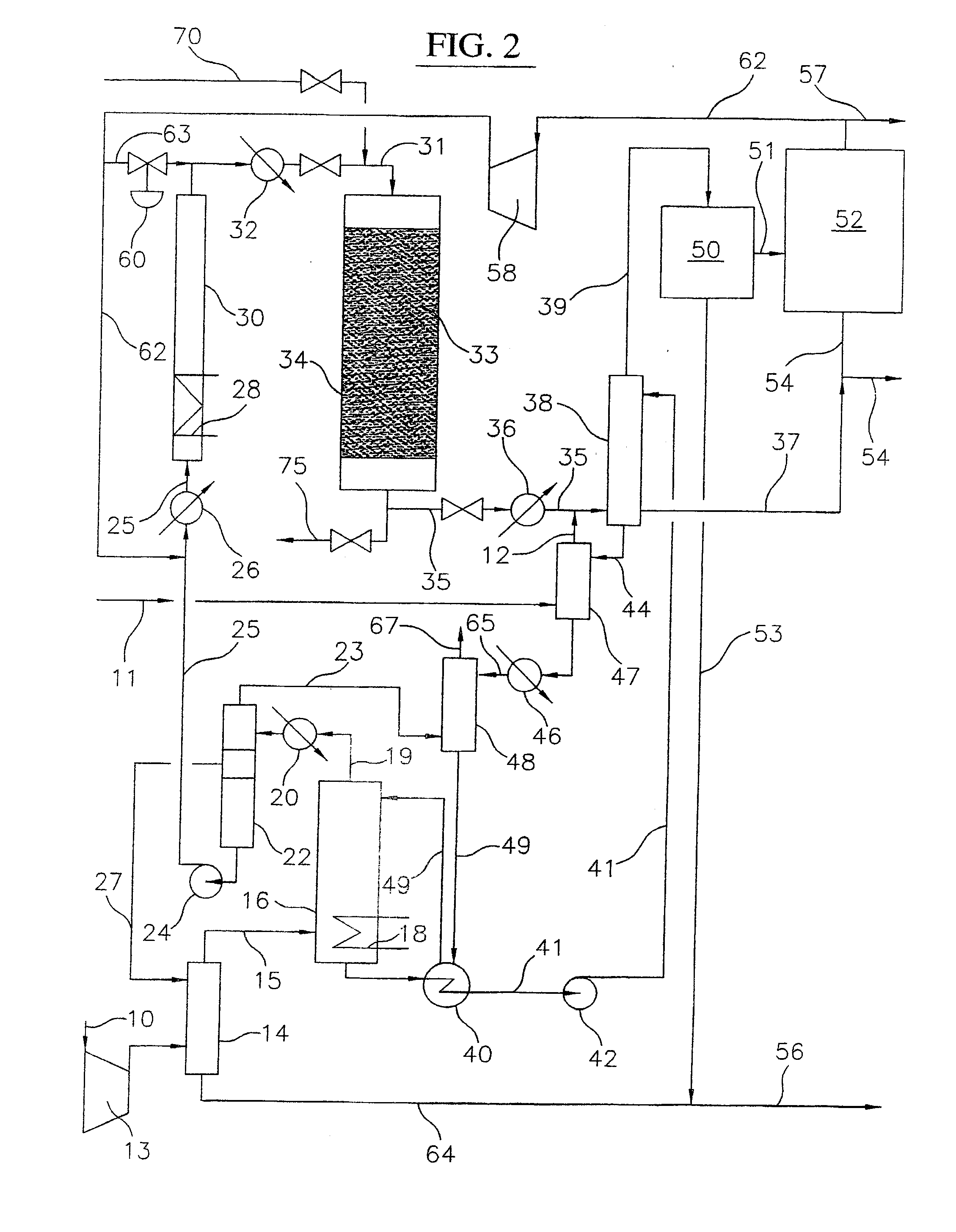
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
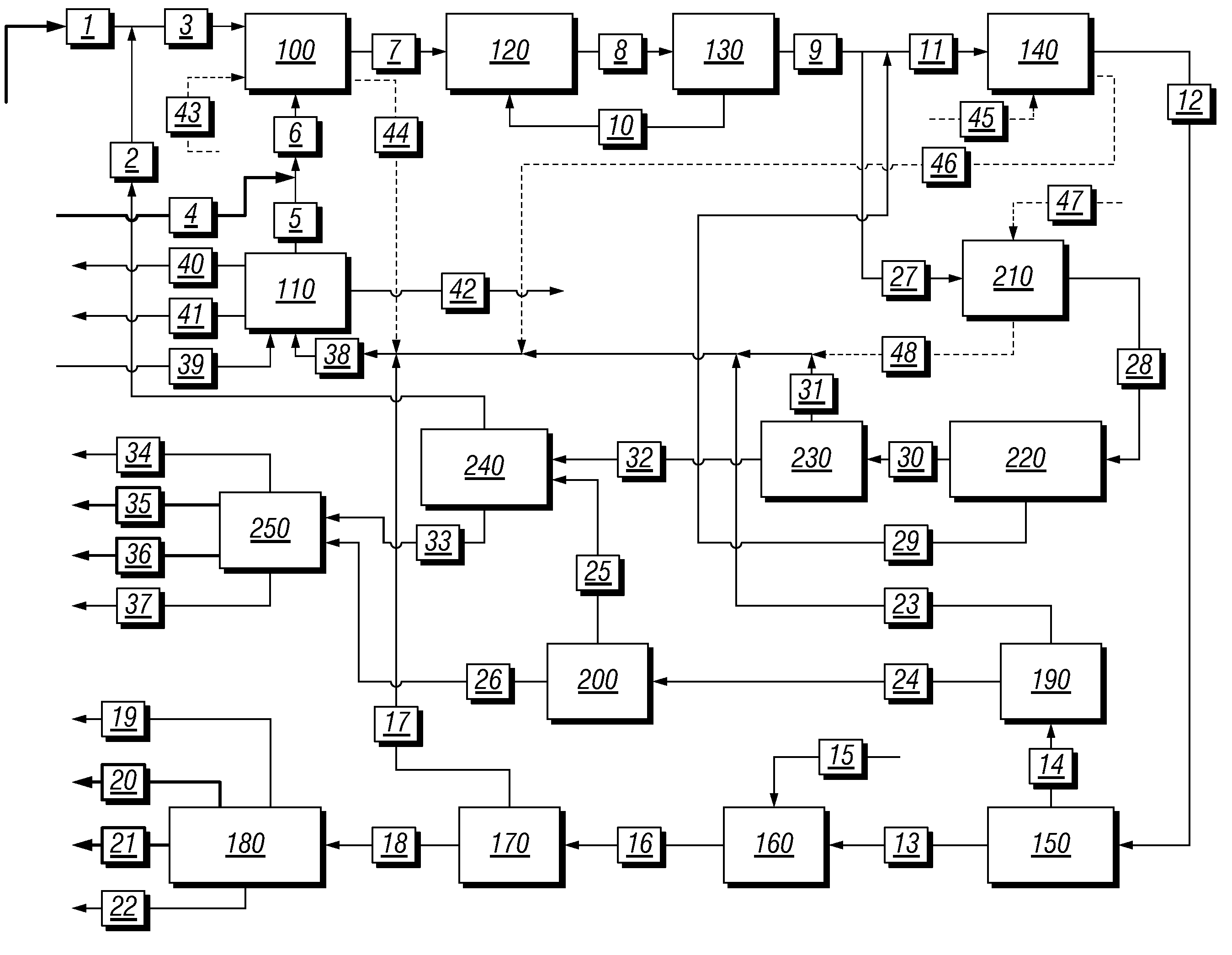
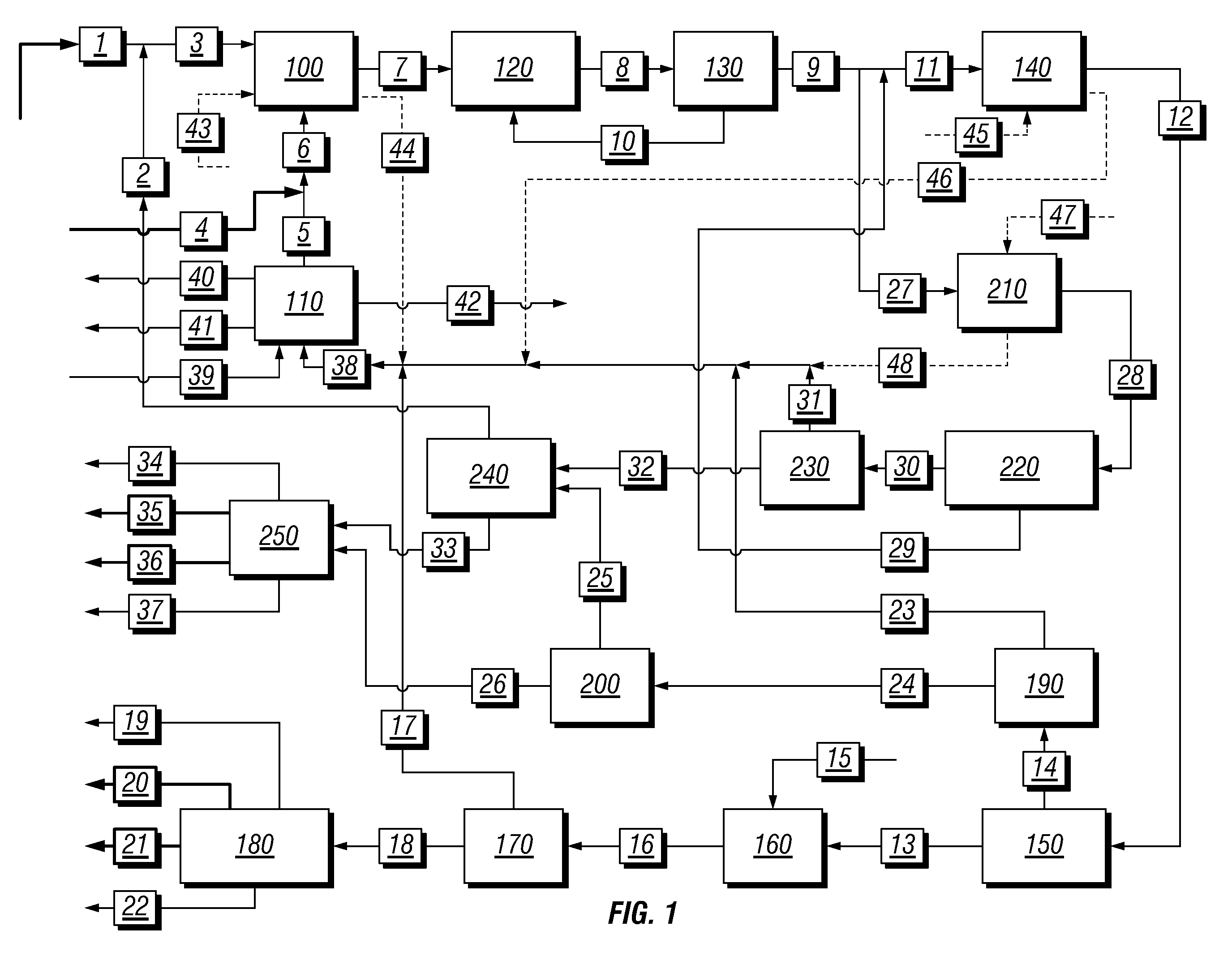
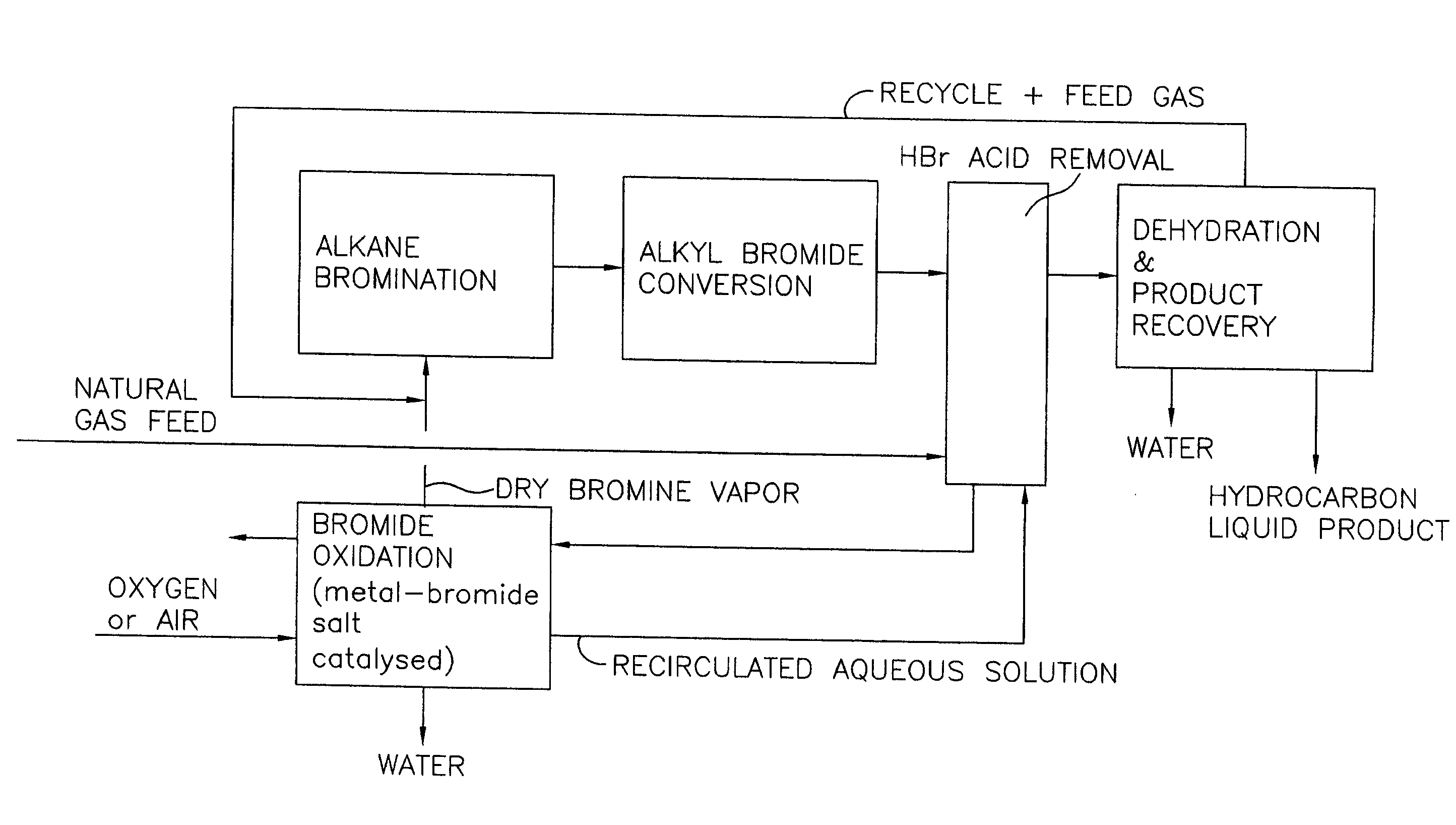
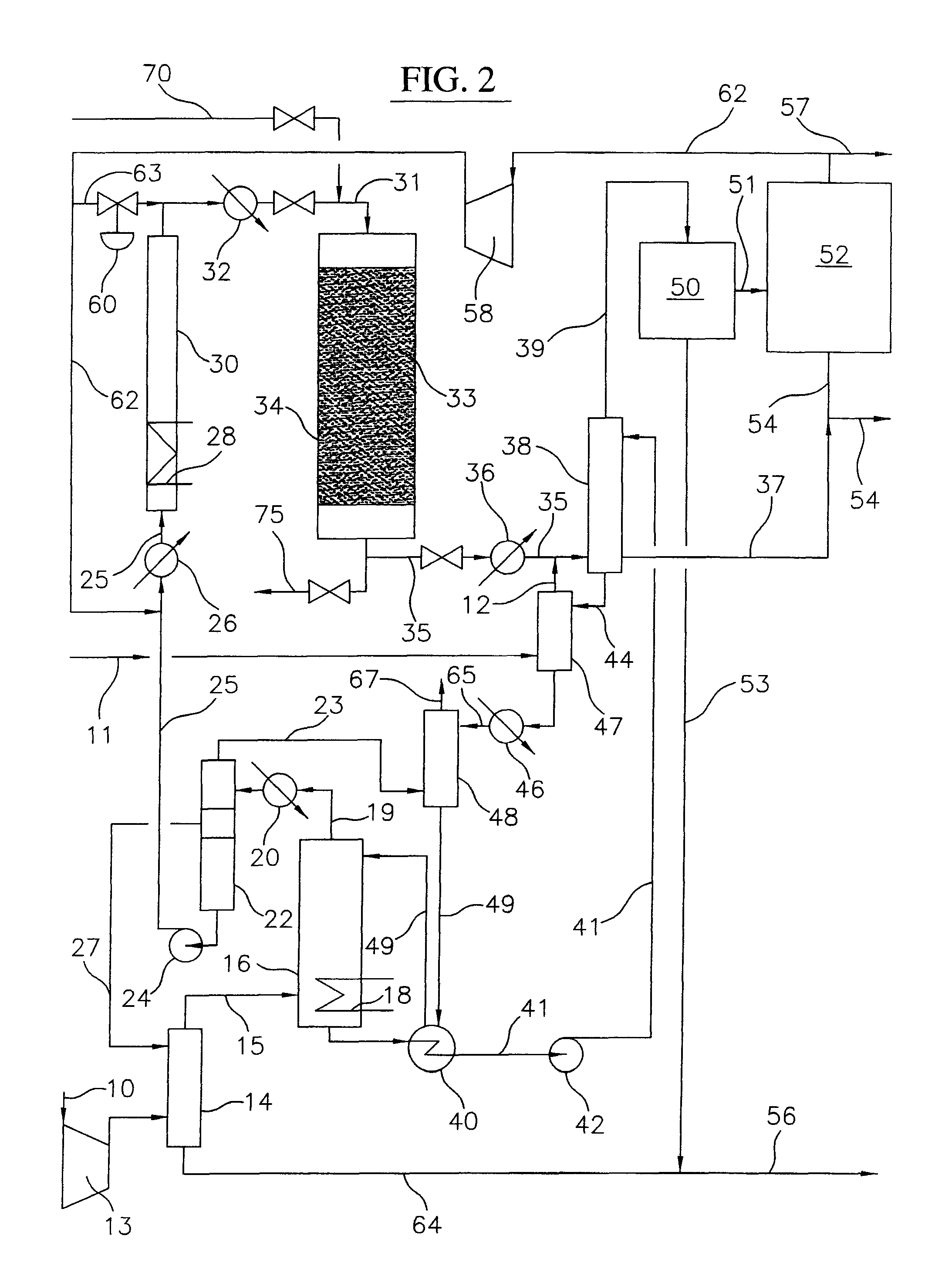
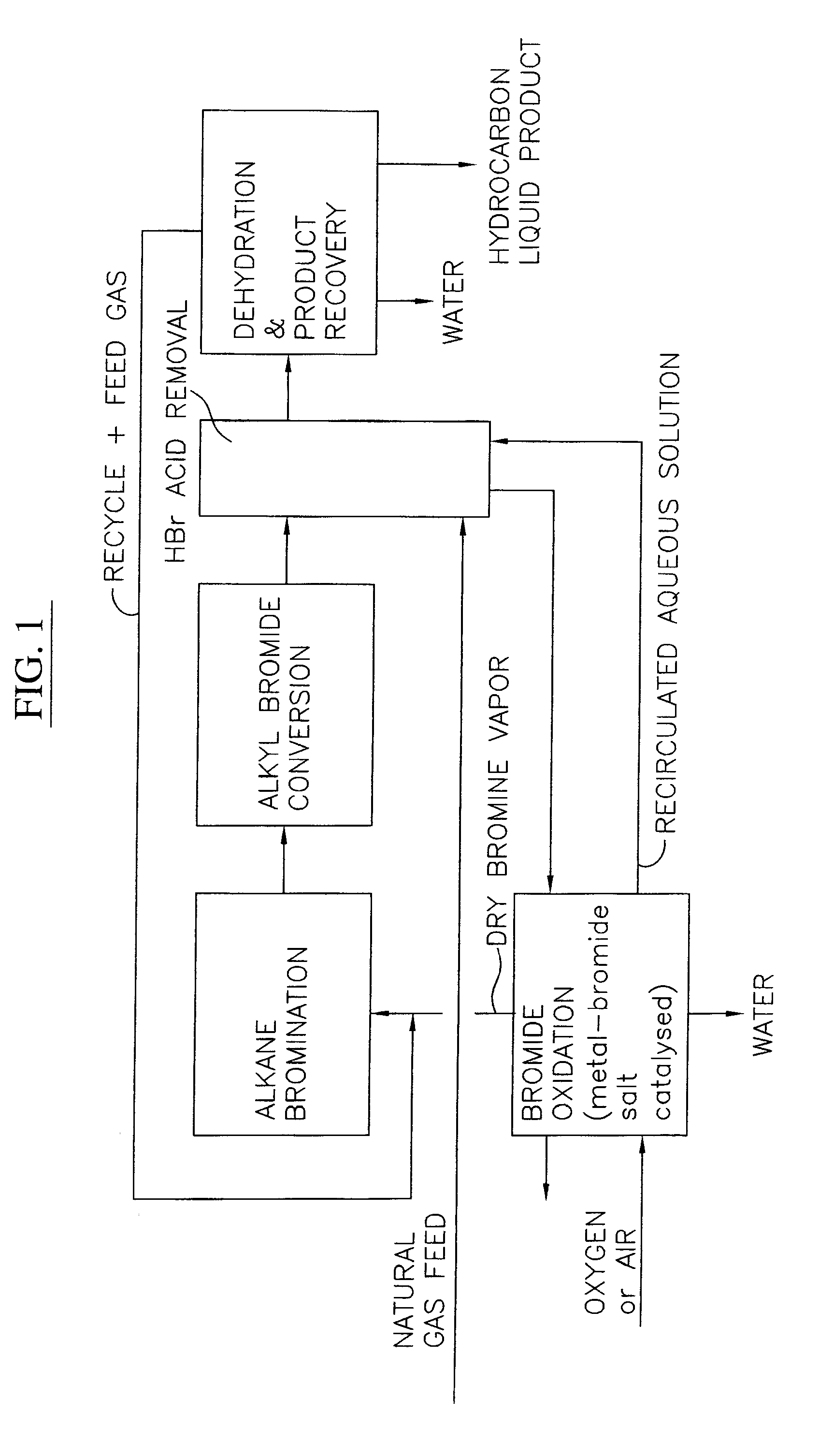
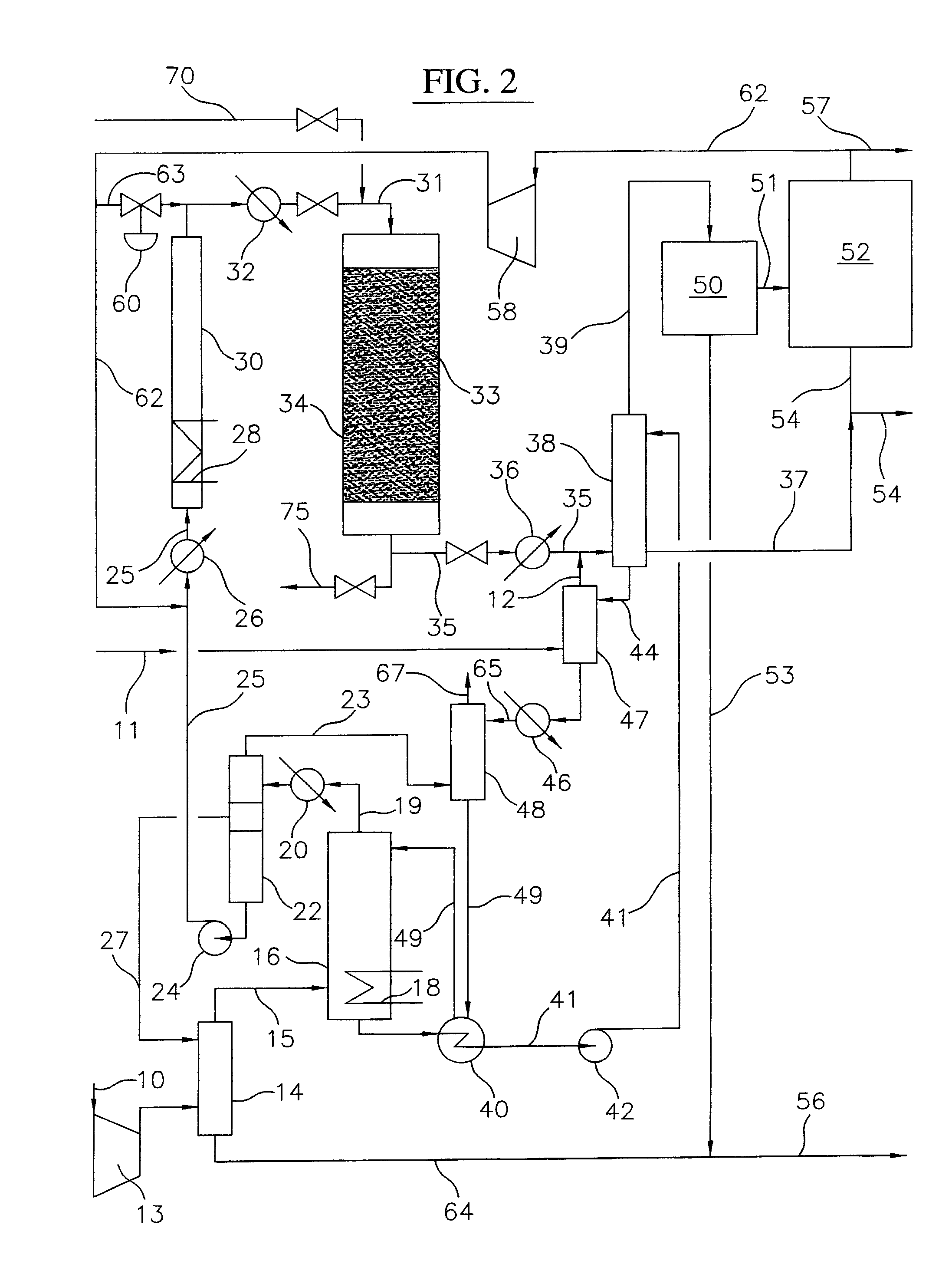
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 zeolite, at a temperature of from about 150° C. to about 400° C. so as to form higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Hydrobromic acid vapor is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons. A portion of the propane and butane is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and reacted with the mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid over the synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst to form C5+ hydrocarbons.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
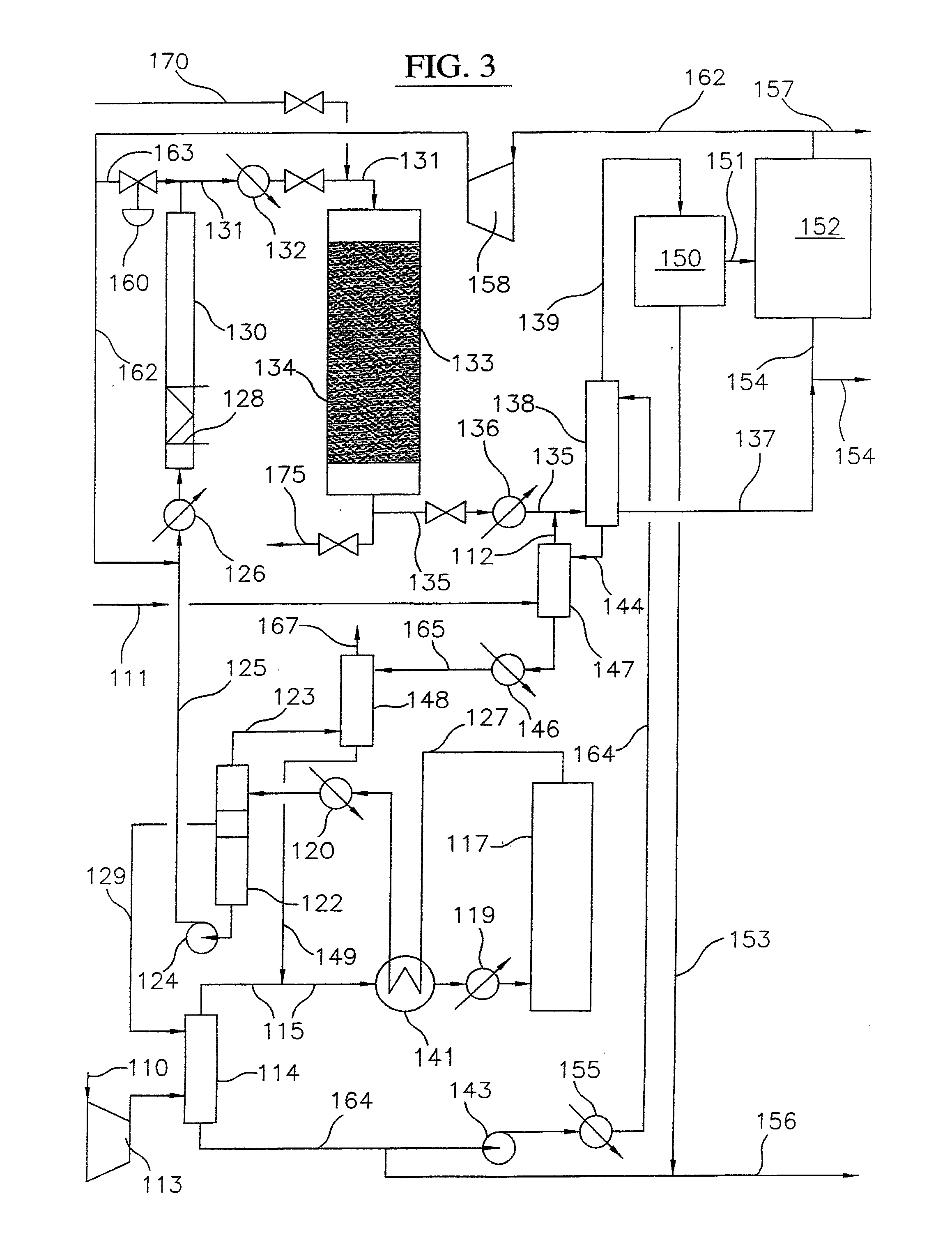
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
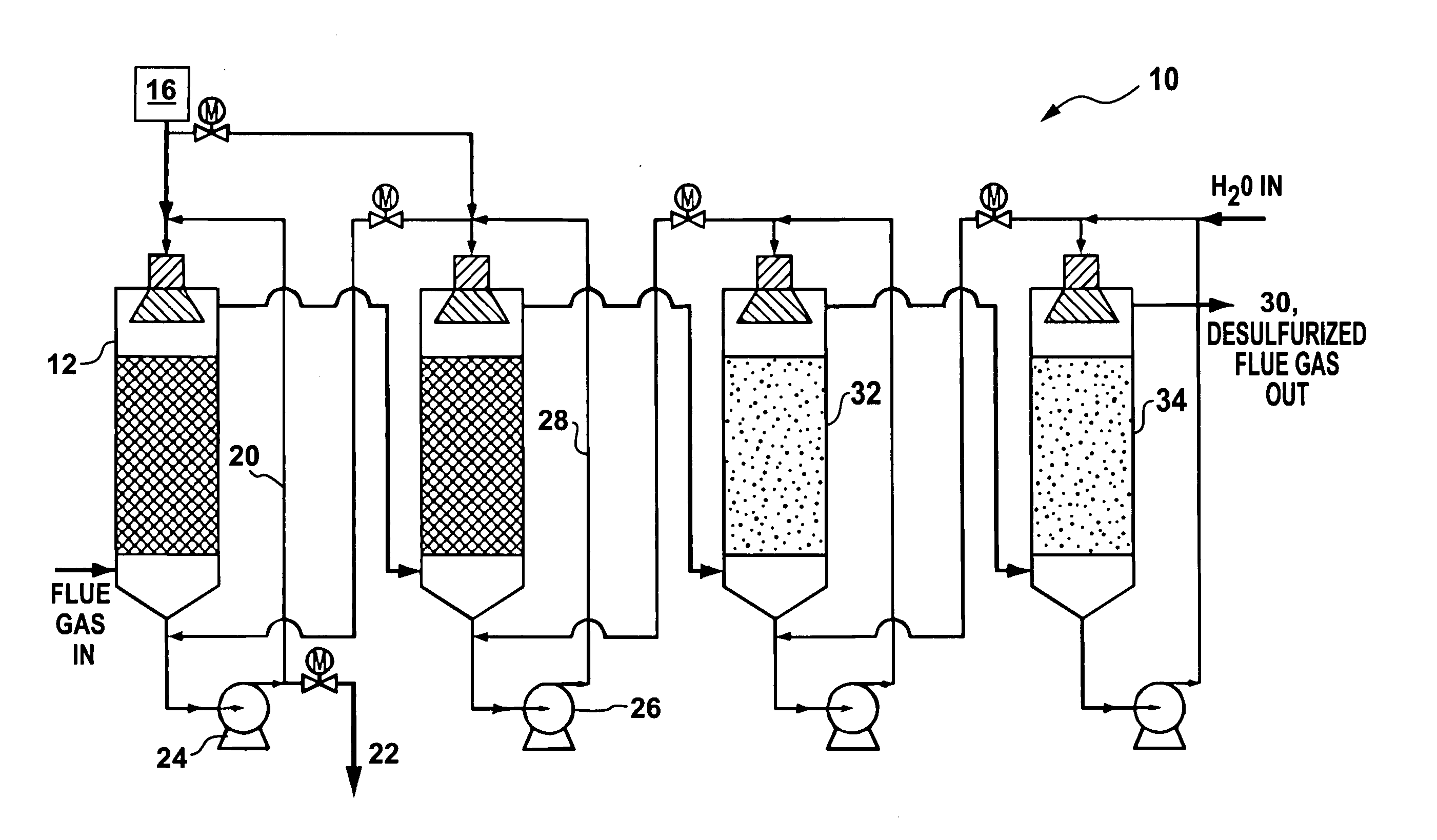
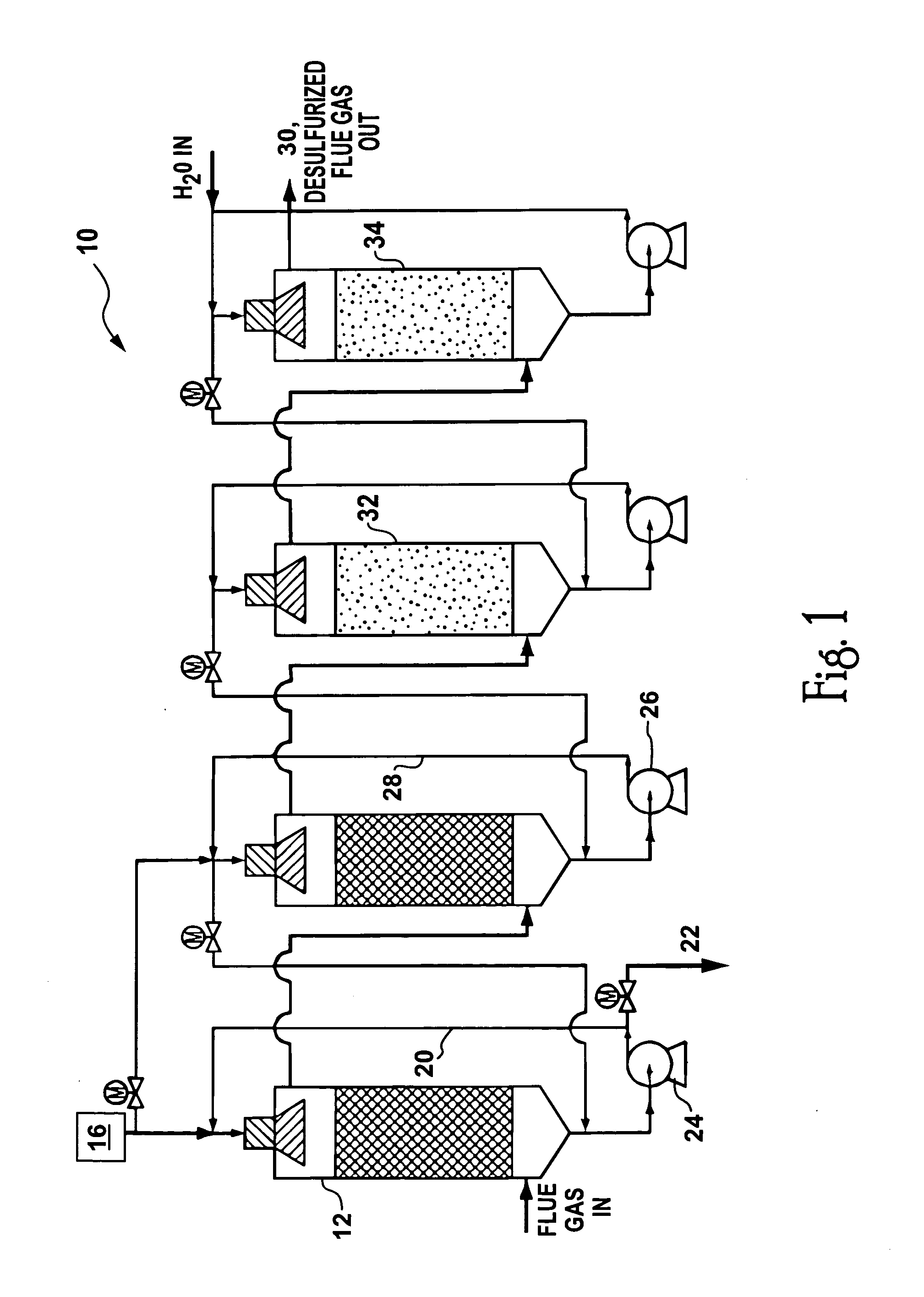
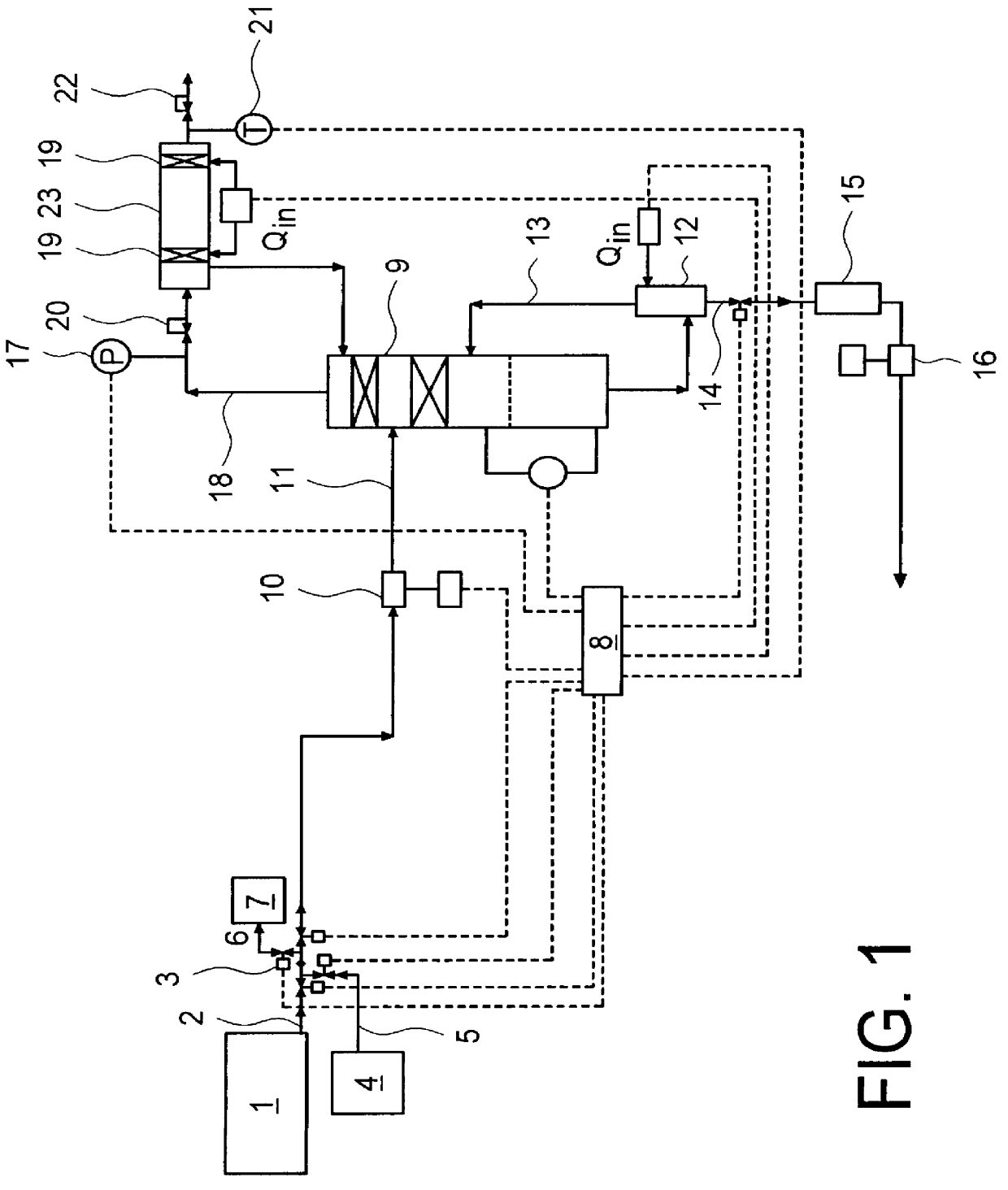
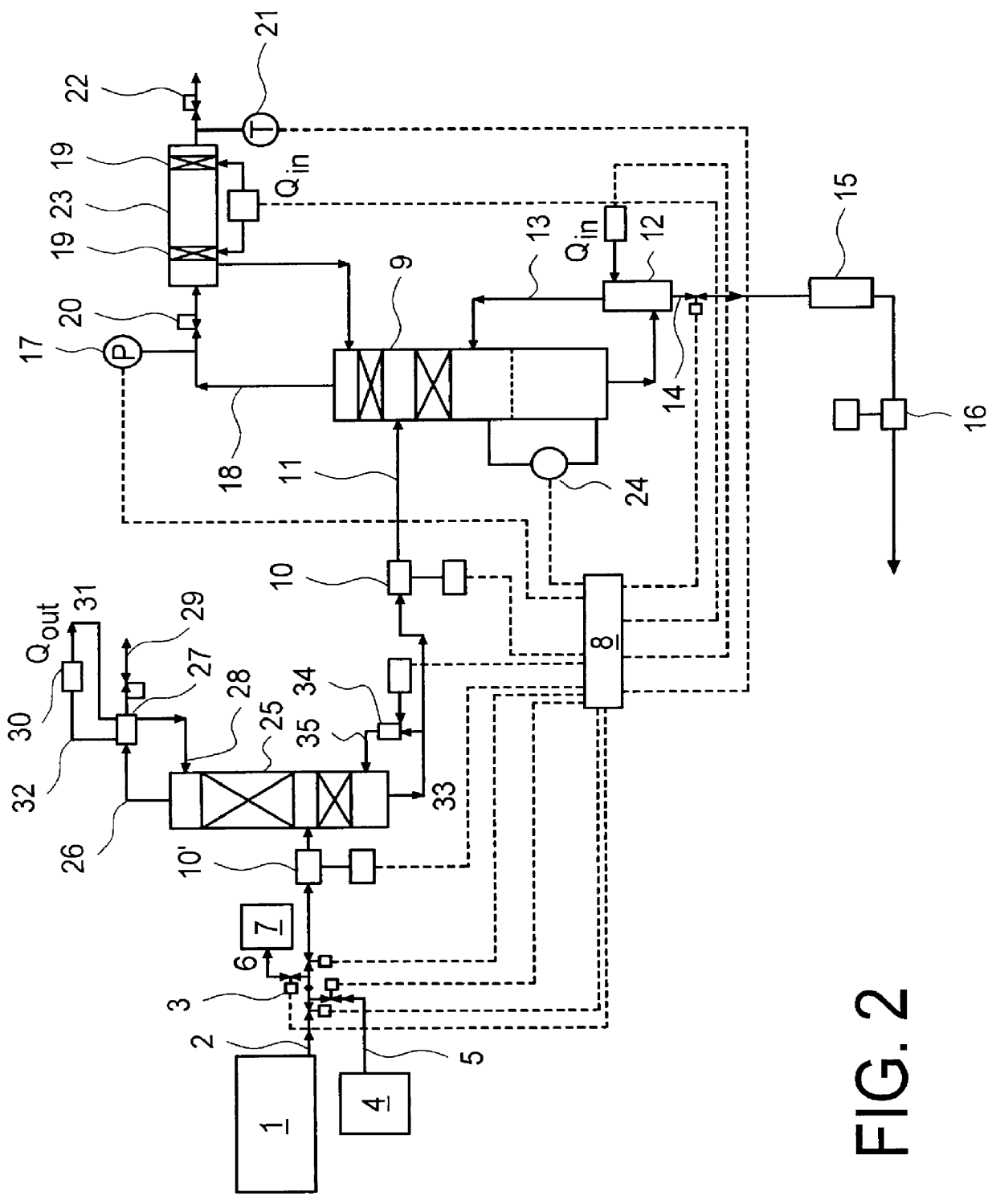
Method for processing stack gas emissions
Apparatus and methods for augmenting the Mark 13a process of Van Zelzen et al., by providing for the addition of dispatchable energy storage and / or additional waste stream treatments. Sulfur-containing stack gas emissions from the burning of fossil fuels for electricity production are cleaned, removing the sulfur by use of the Bunsen reaction. The process produces hydrogen and sulfuric acid as byproducts. The hydrogen output of the process can be used to co-produce electricity in a reversible fuel cell, and optionally can be stored so that electricity can be produced during periods of high demand. Optionally the hydrogen can be reacted with air-nitrogen or nitrogen from the combustion gasses to produce ammonia. The sulfuric acid can optionally be reacted with iron or aluminum to produce iron or aluminum sulphates and additional electricity. In addition, mercury removal from the gas emissions from burning fossil fuels (primarily coal) can be performed.
Owner:SOLAR REACTOR TECH
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20060100469A1High selectivityAvoid disadvantagesBromide preparationRefining with non-metalsAlkaneBromine
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:MARATHON GTF TECH
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 zeolite, at a temperature of from about 150° C. to about 450° C. so as to form higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Propane and butane which comprise a portion of the products may be recovered or recycled back through the process to form additional C5+ hydrocarbons. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 zeolite, at a temperature of from about 150° C. to about 400° C. so as to form higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Hydrobromic acid vapor is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons. A portion of the propane and butane is removed from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and reacted with the mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid over the synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst to form C5+ hydrocarbons.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
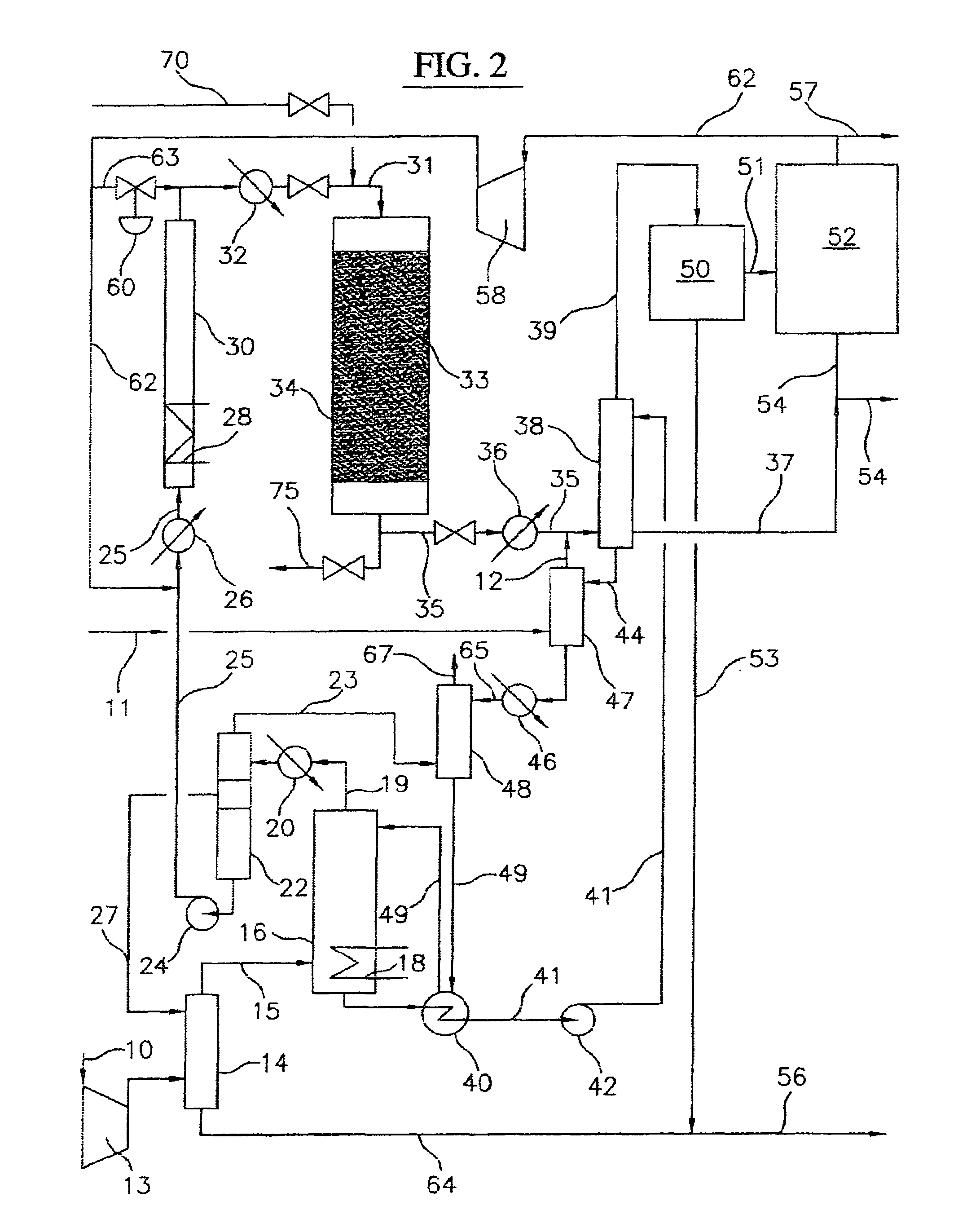
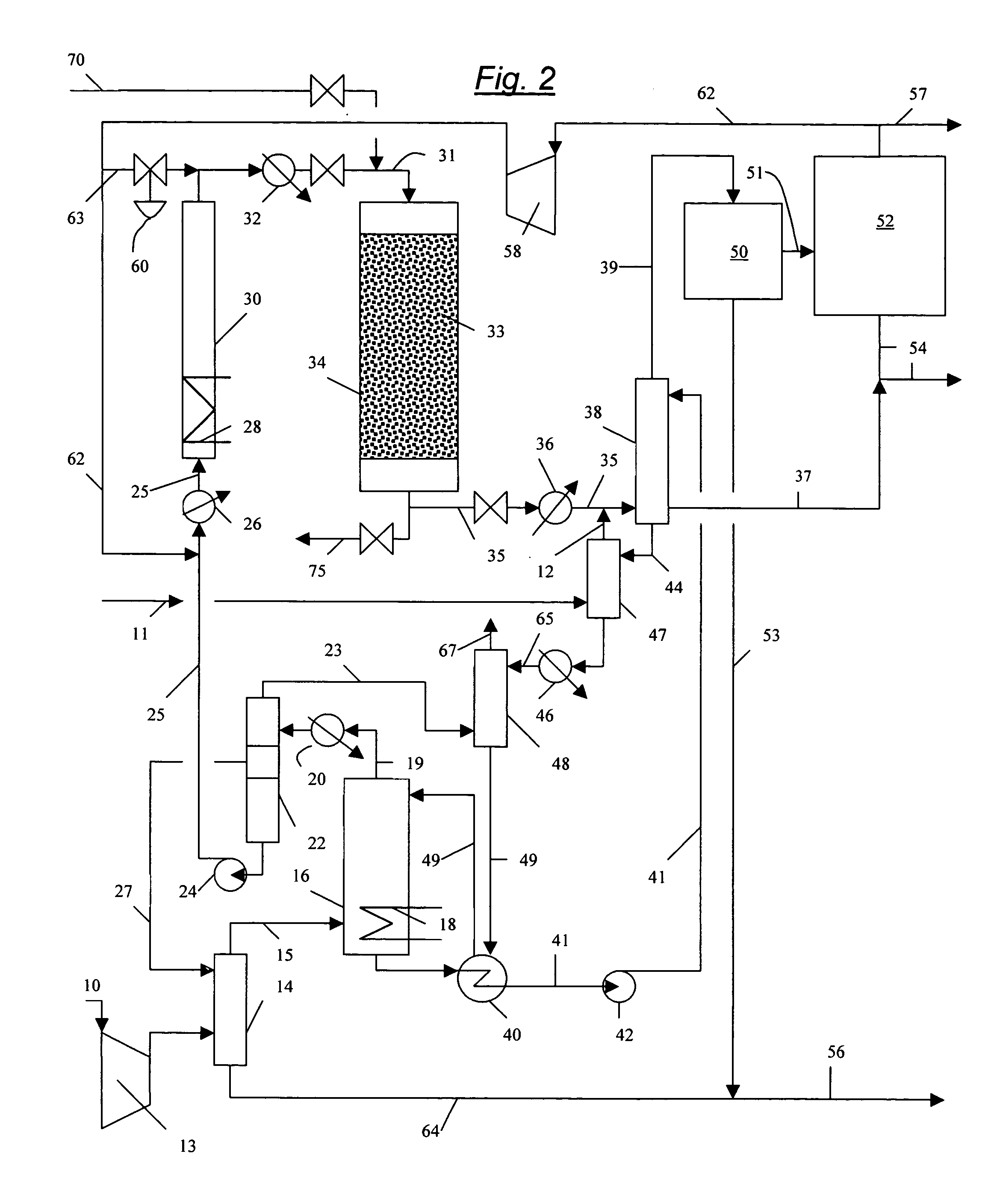
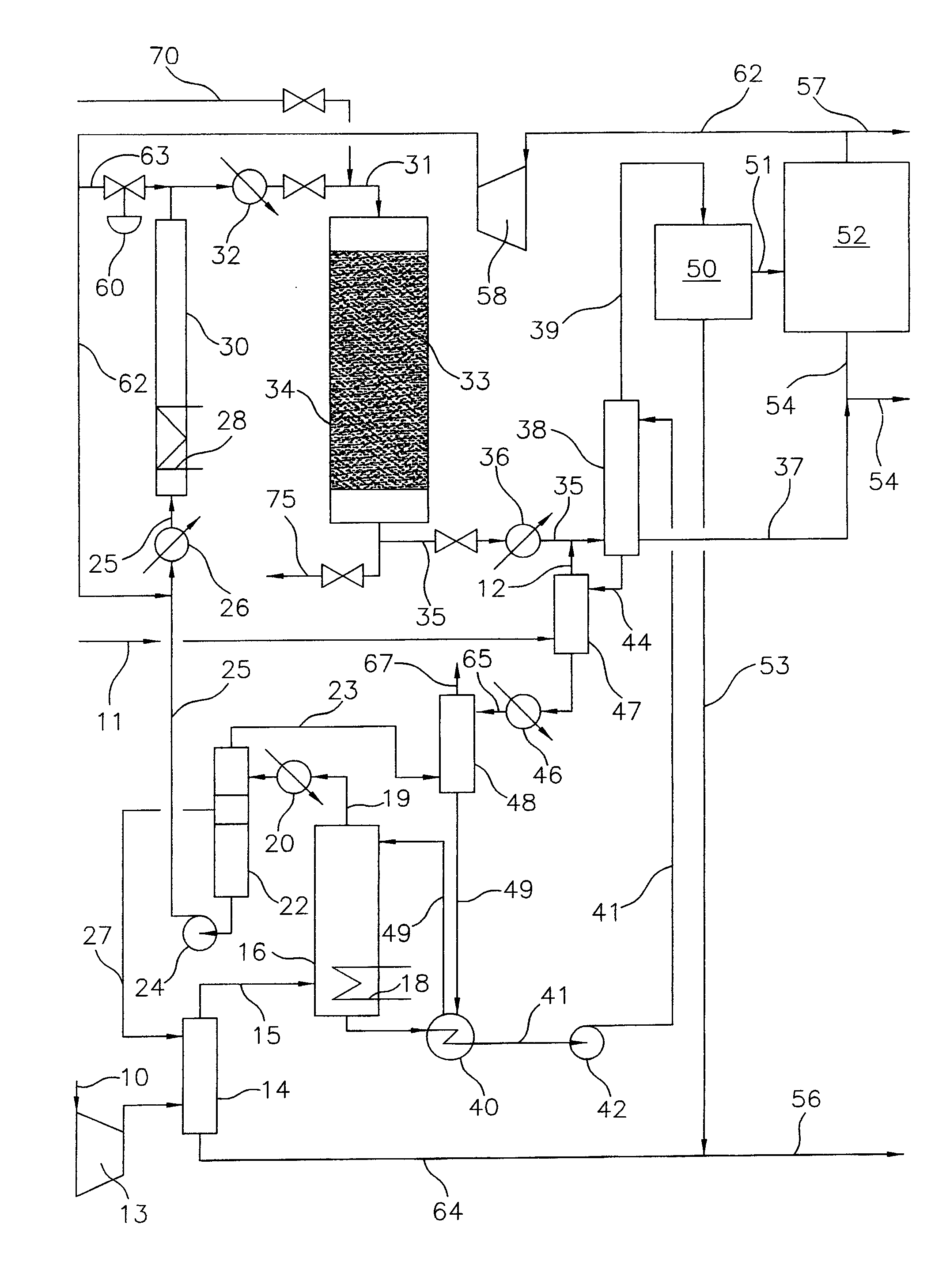
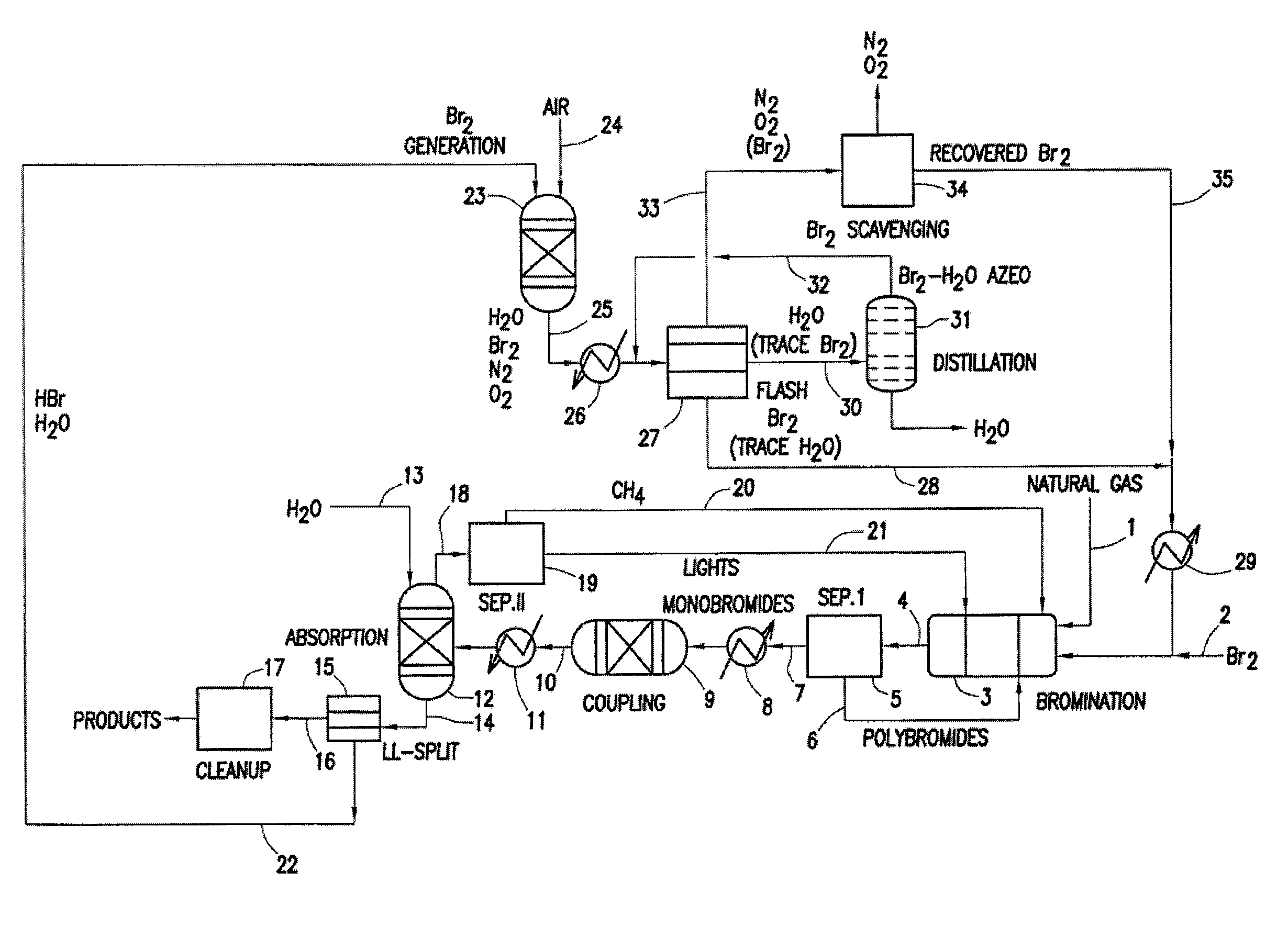
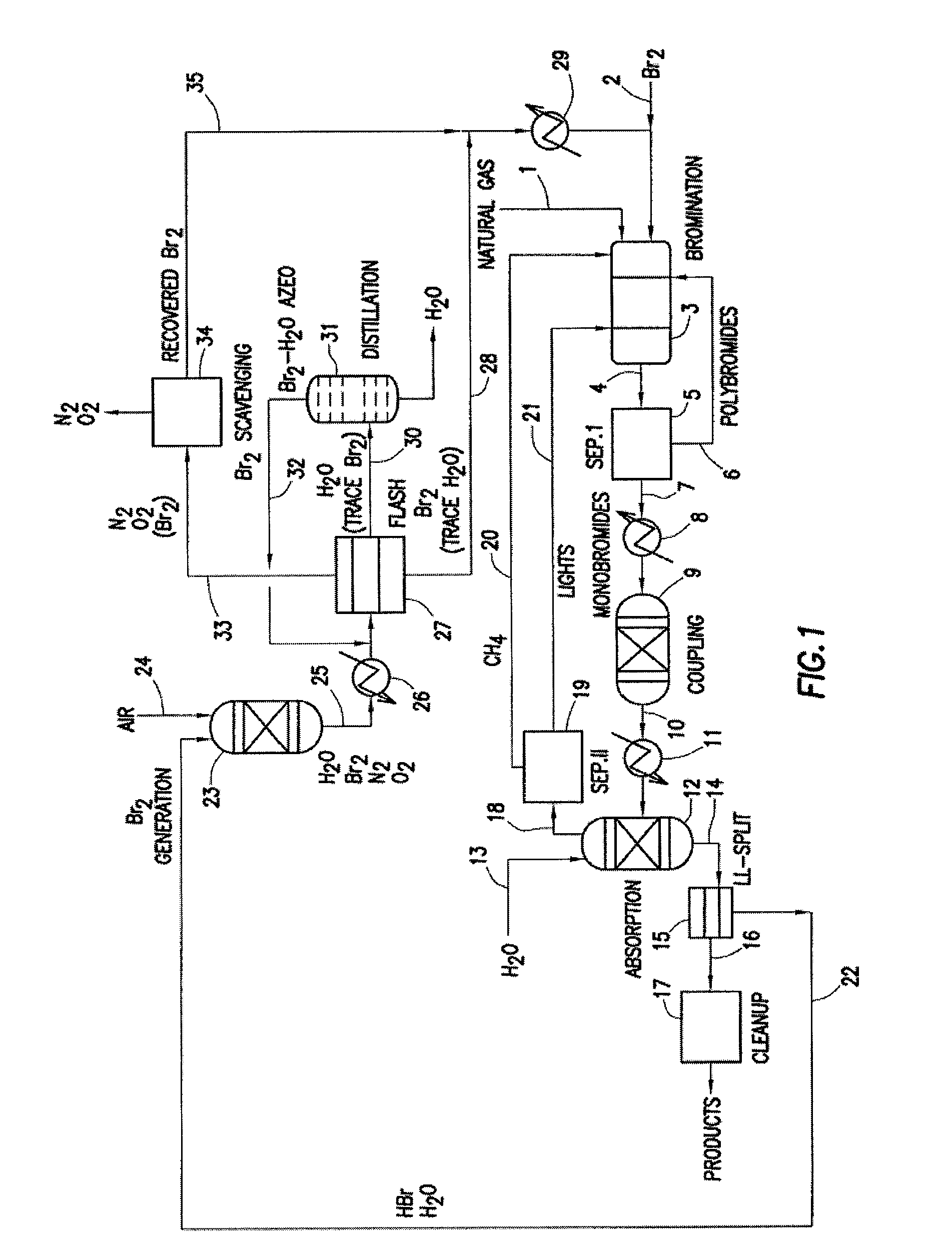
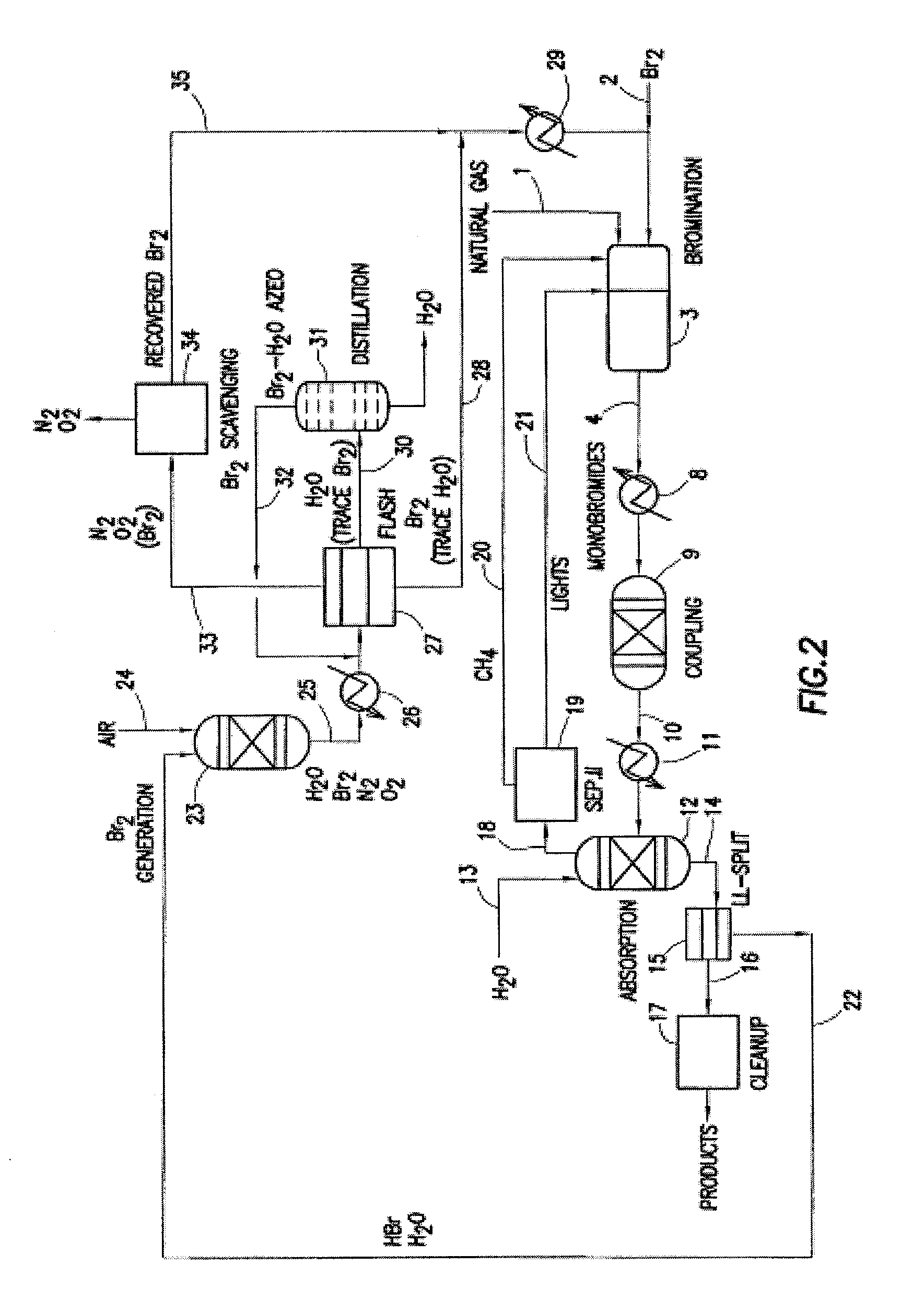
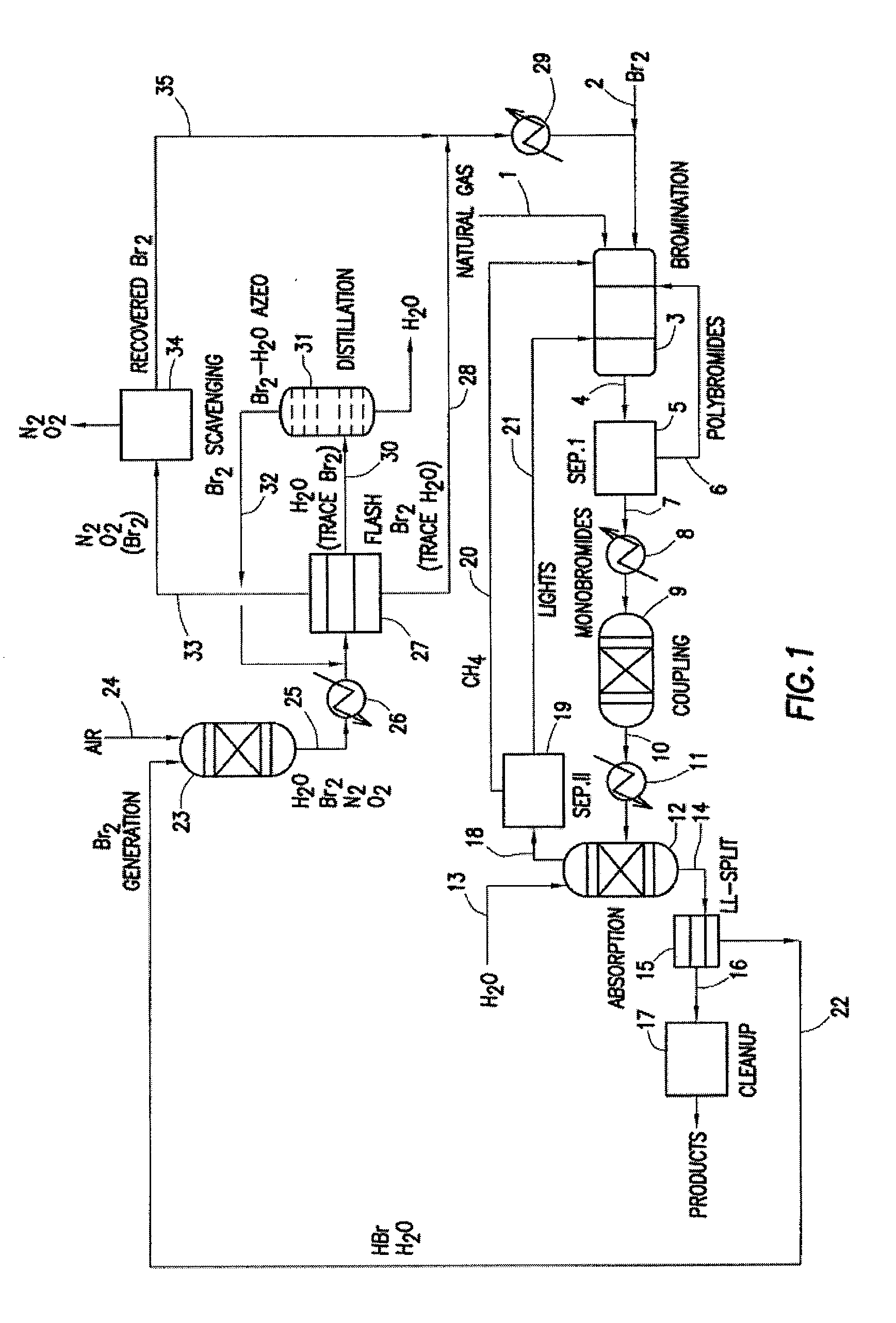
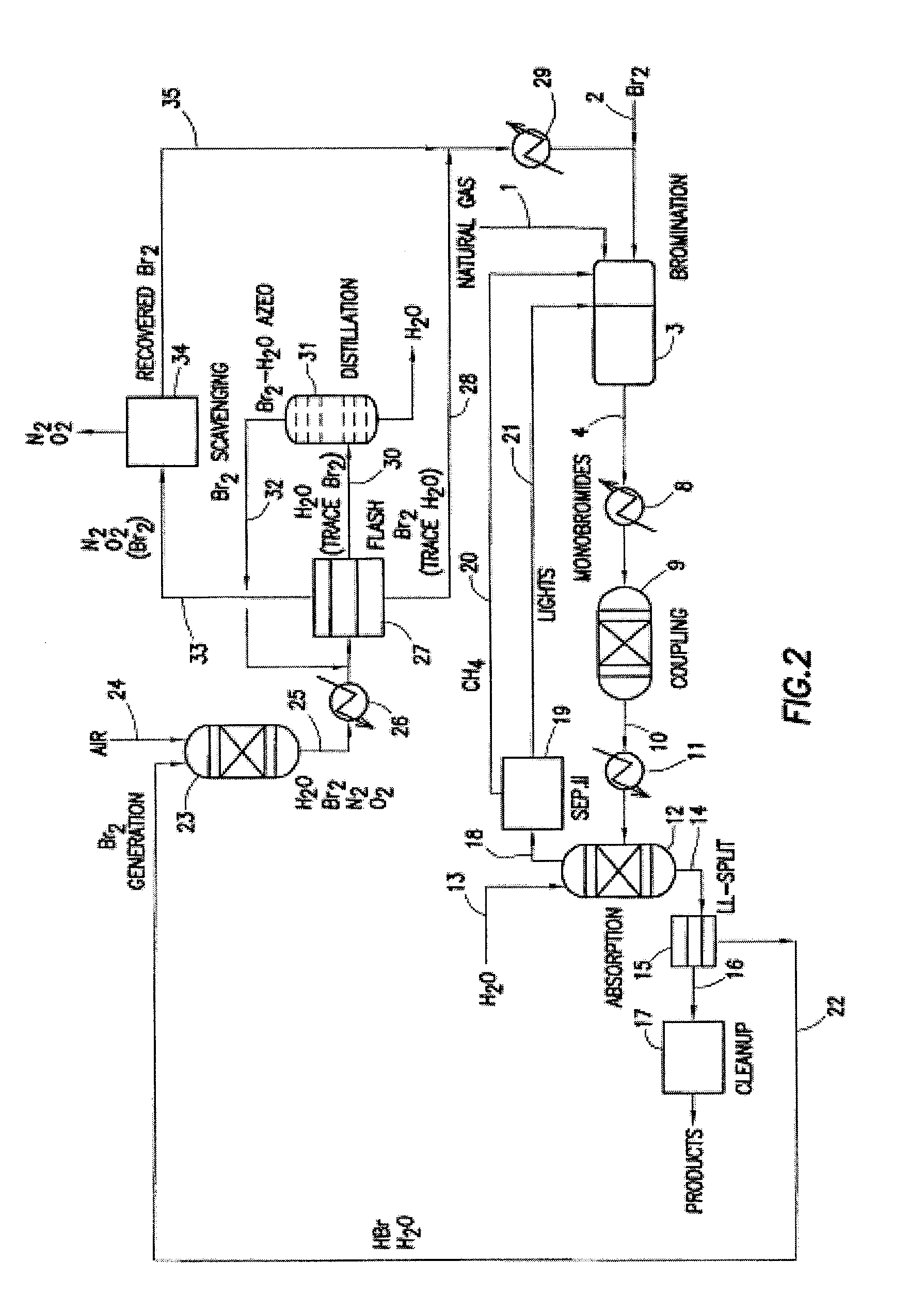
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
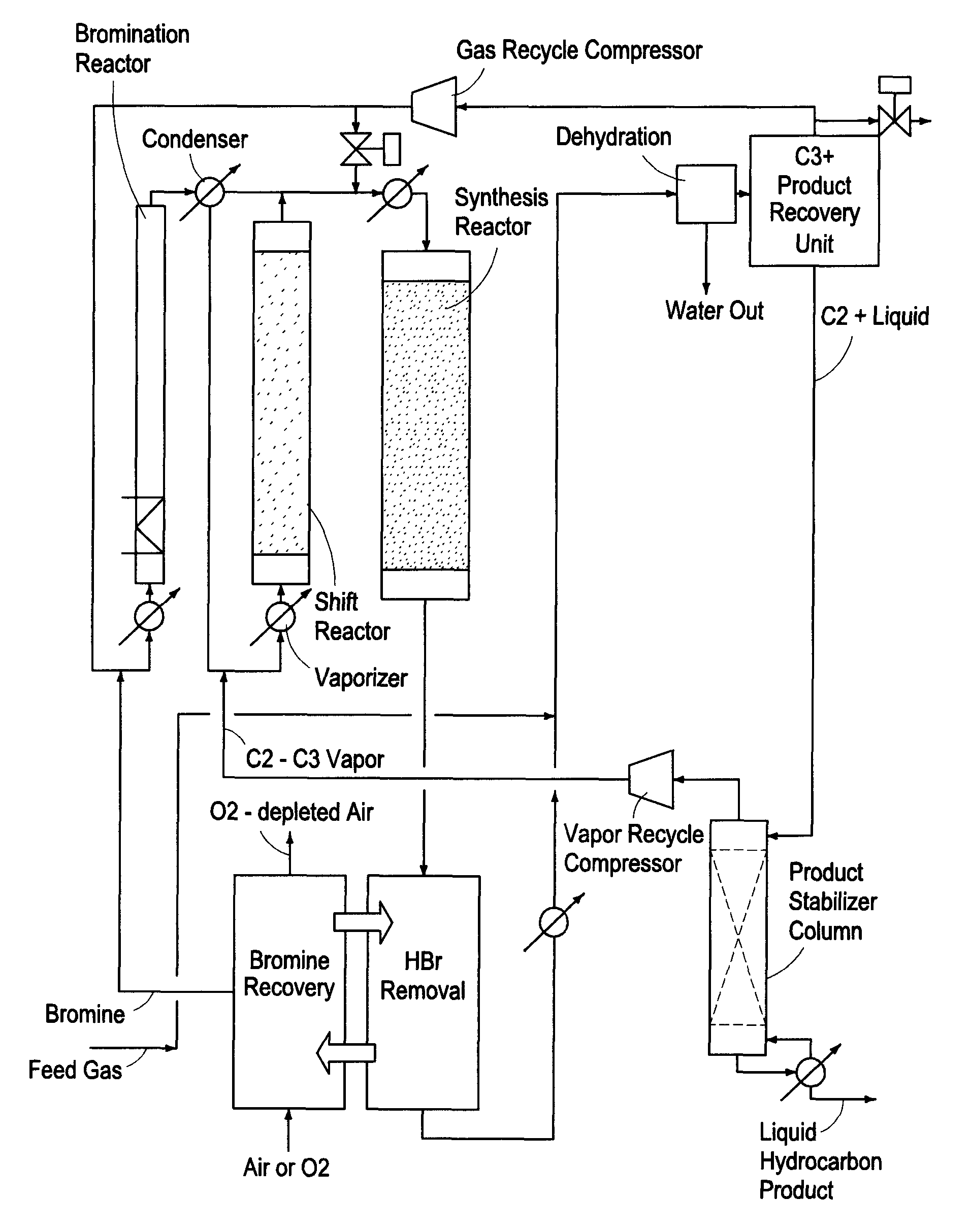
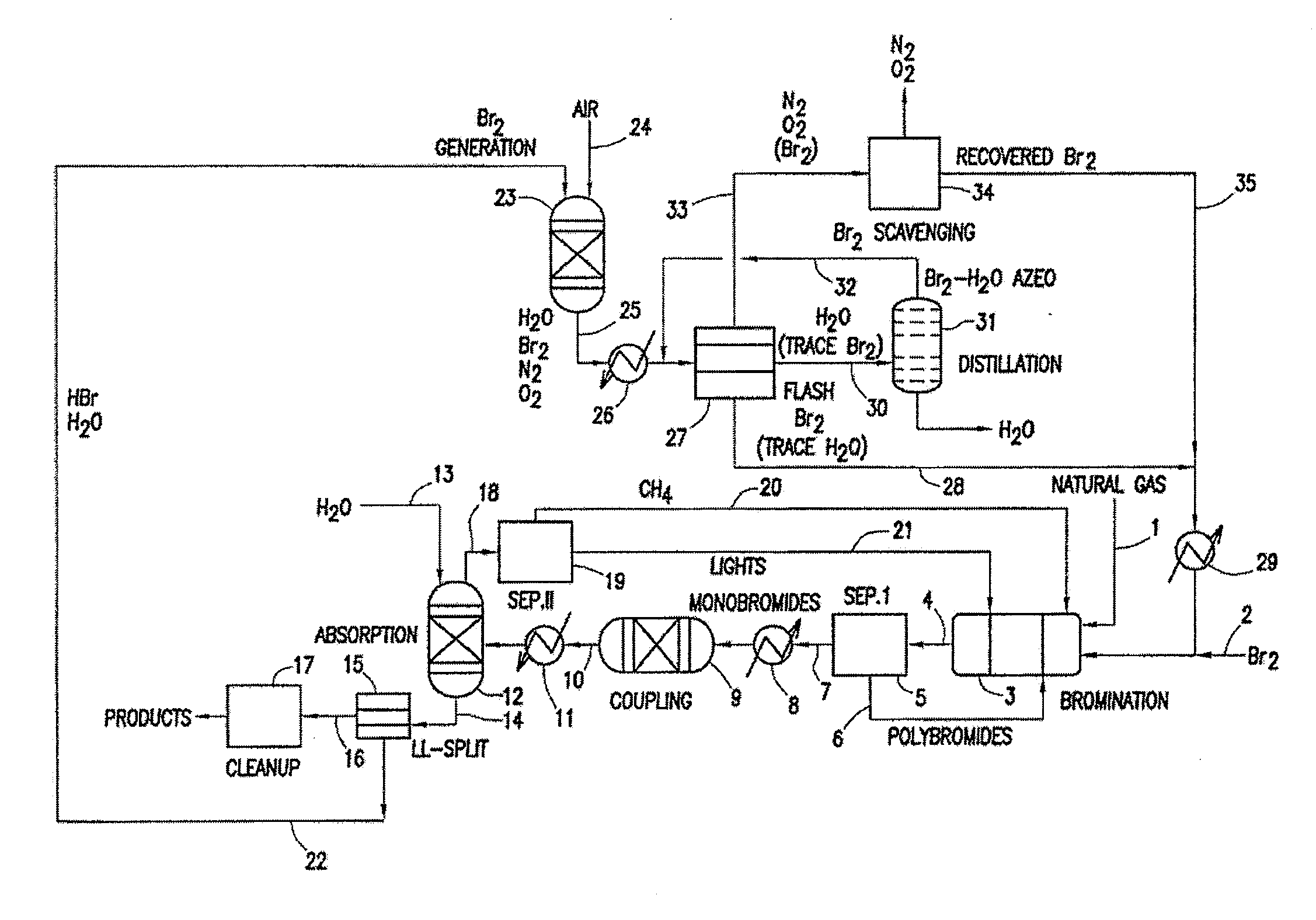
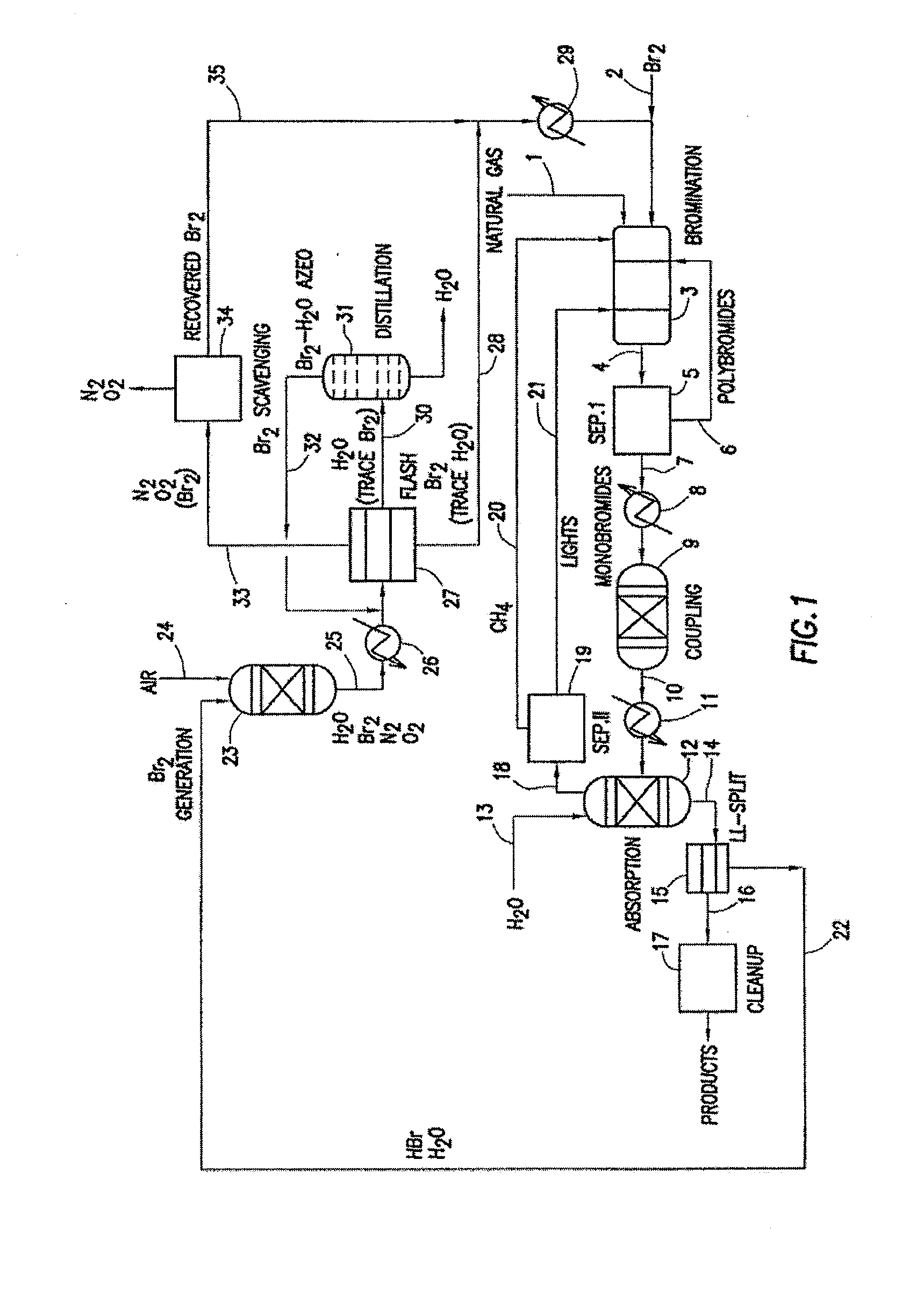
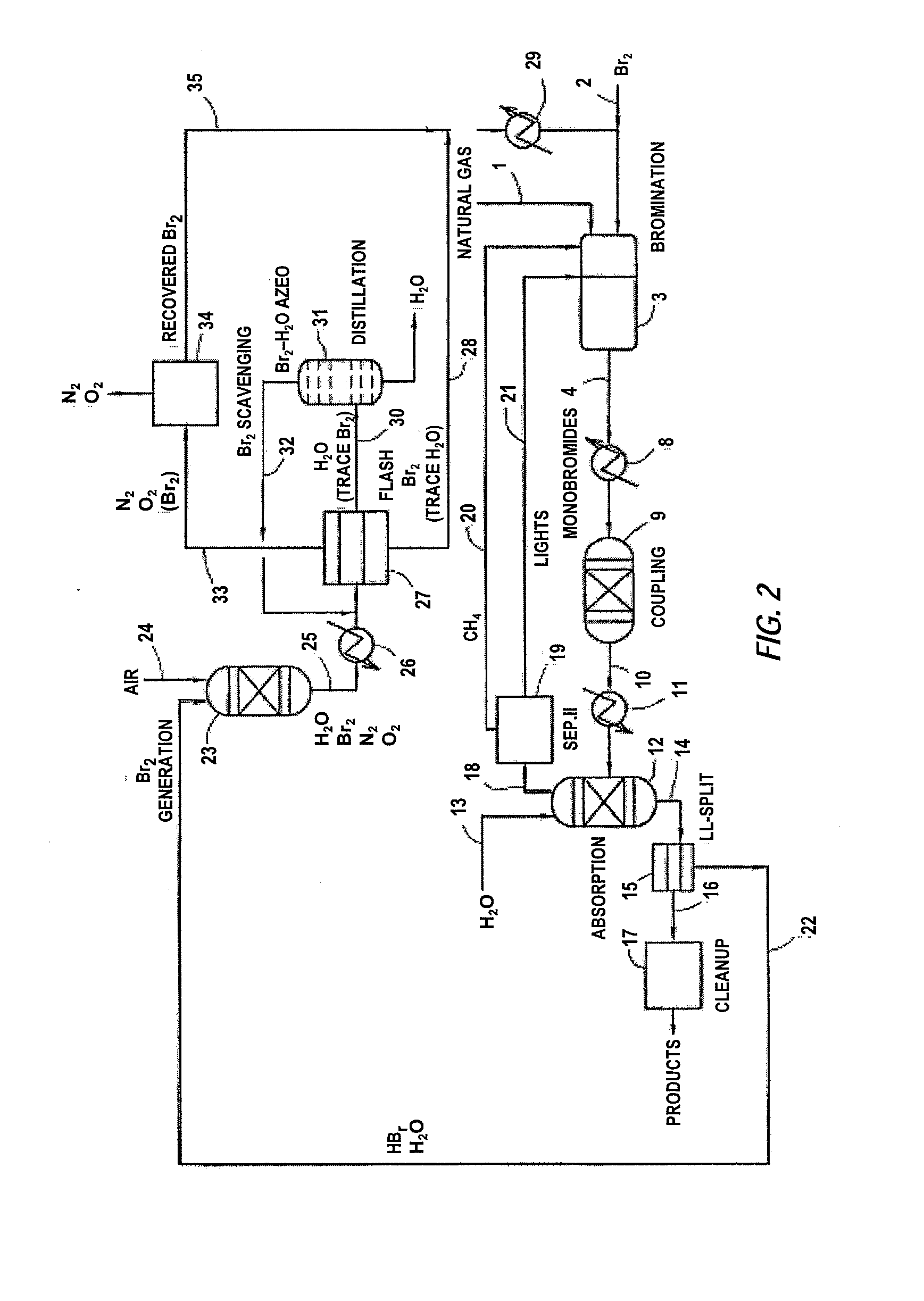
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is thermally reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide. Poly-brominated alkanes present in the alkyl bromides are further reacted with methane over a suitable catalyst to form mono-brominated species. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrogen bromide. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrogen bromide from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrogen bromide for use in the process, and to selectively form mono-brominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
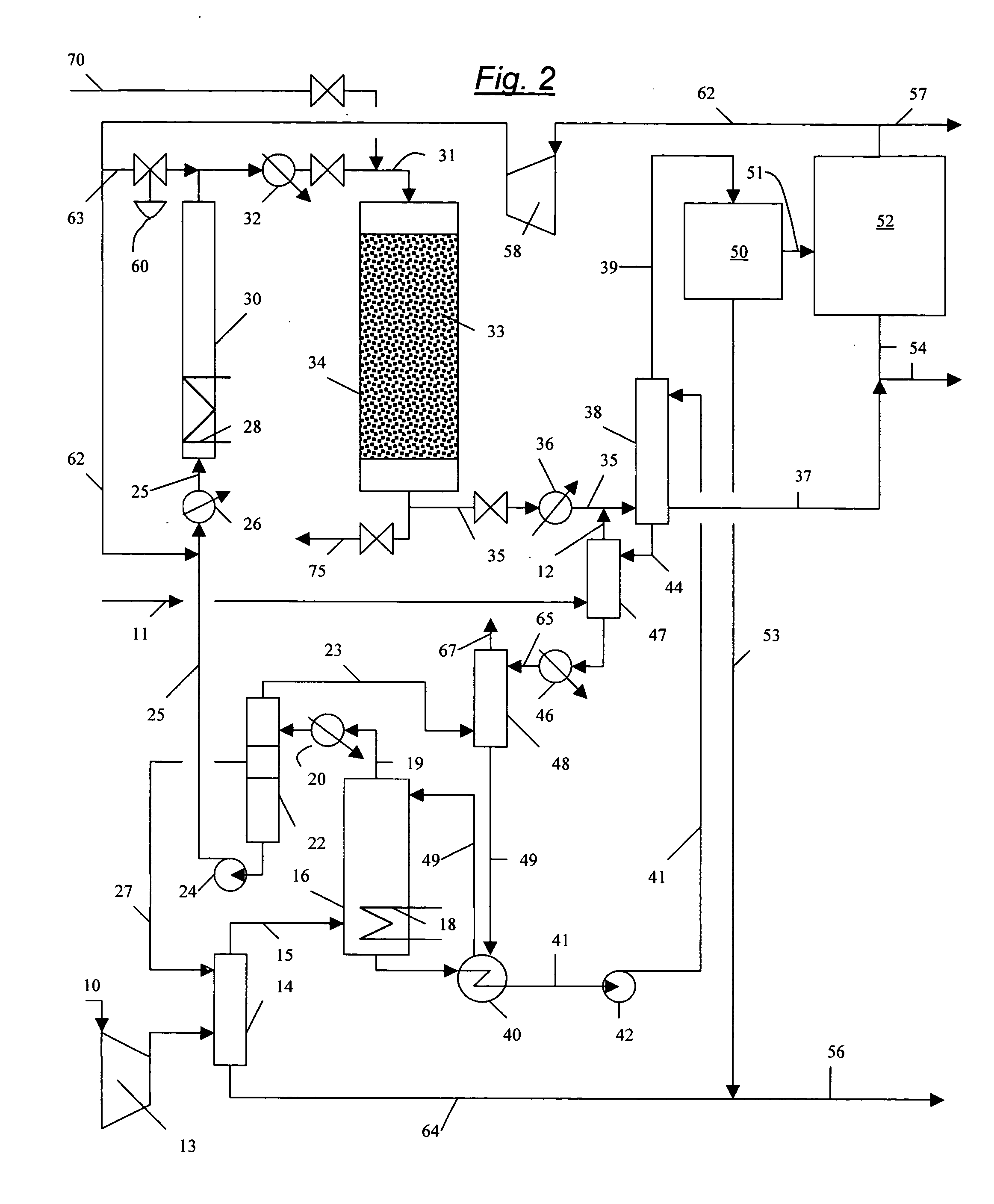
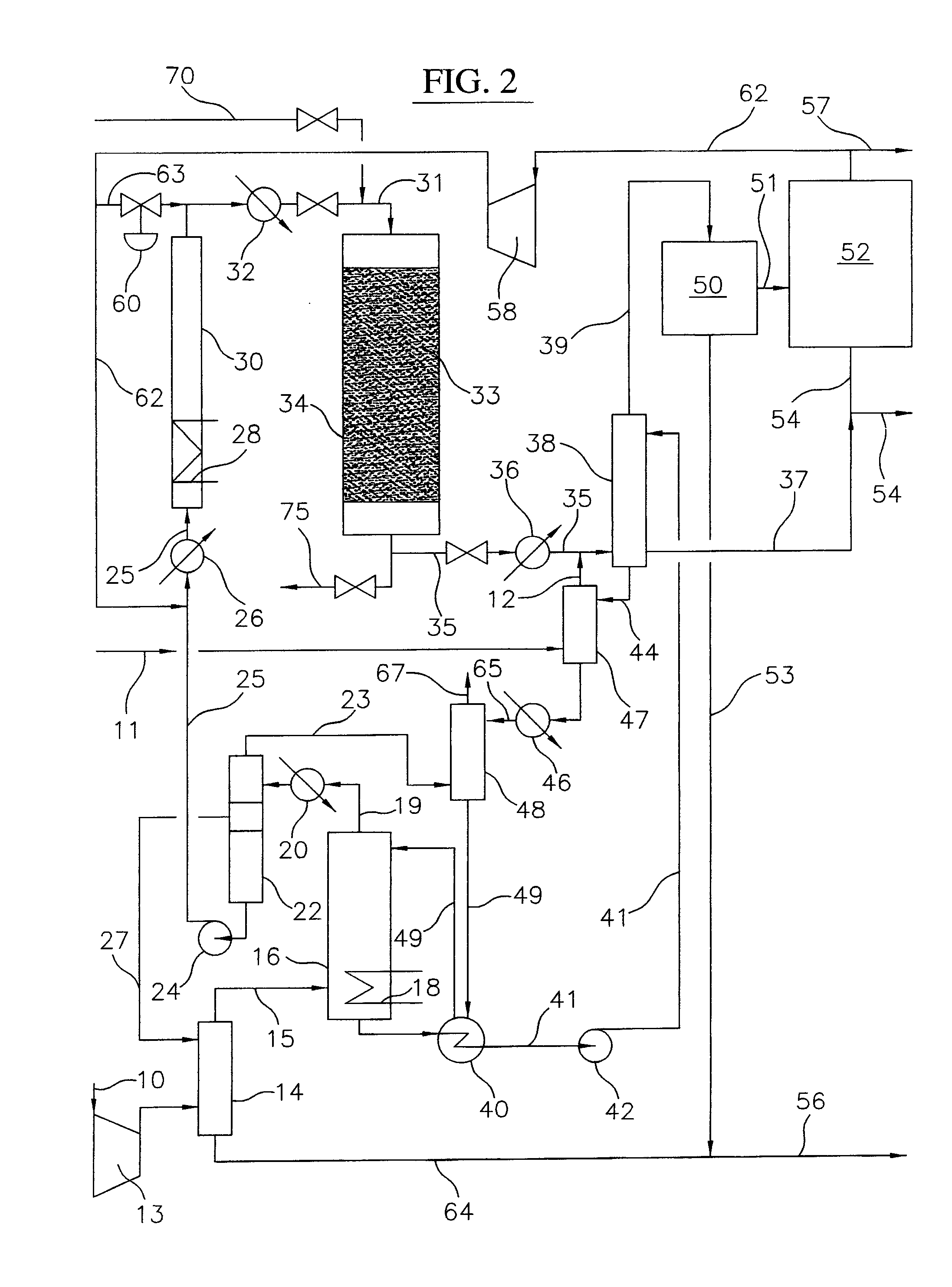
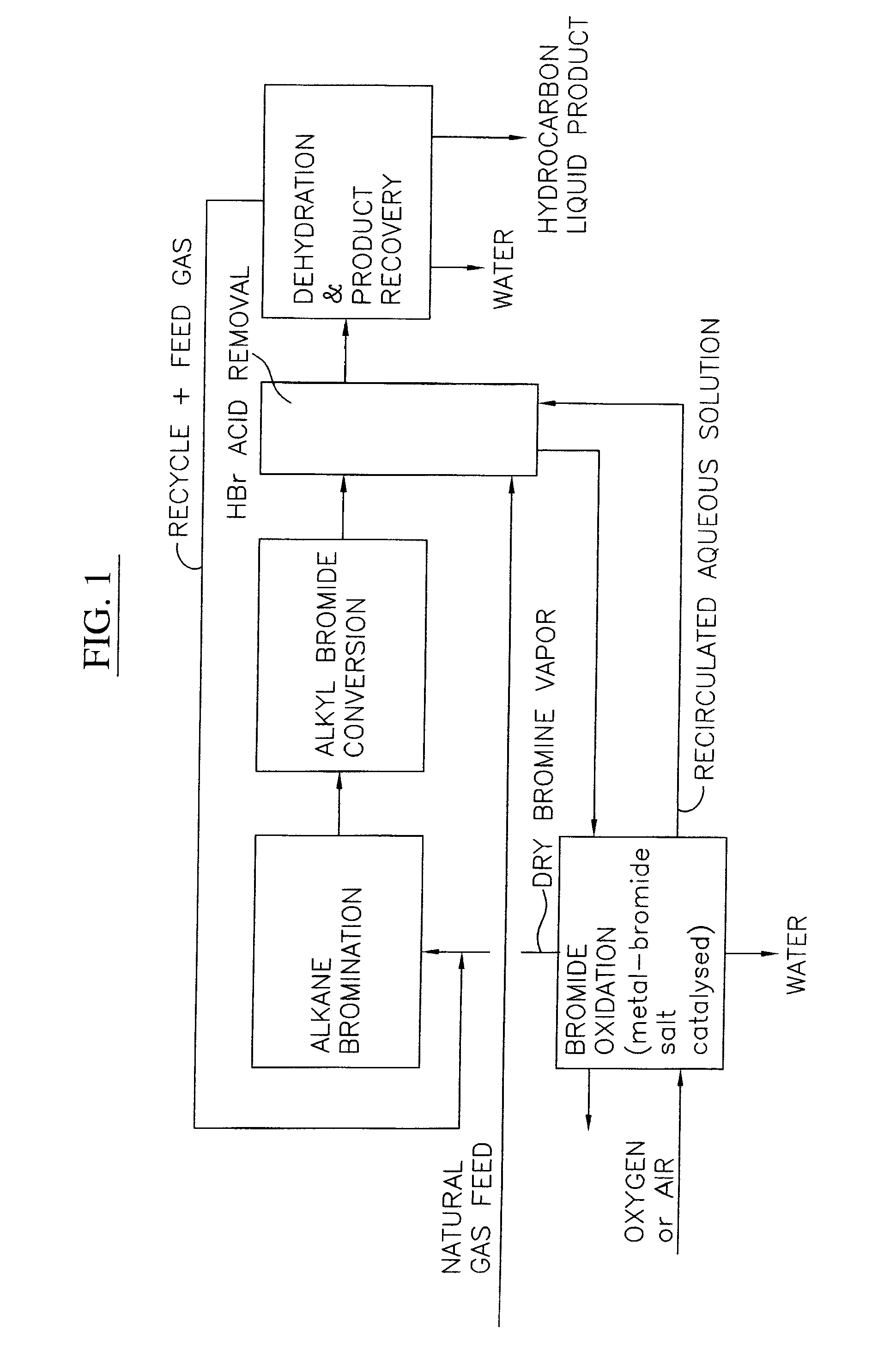
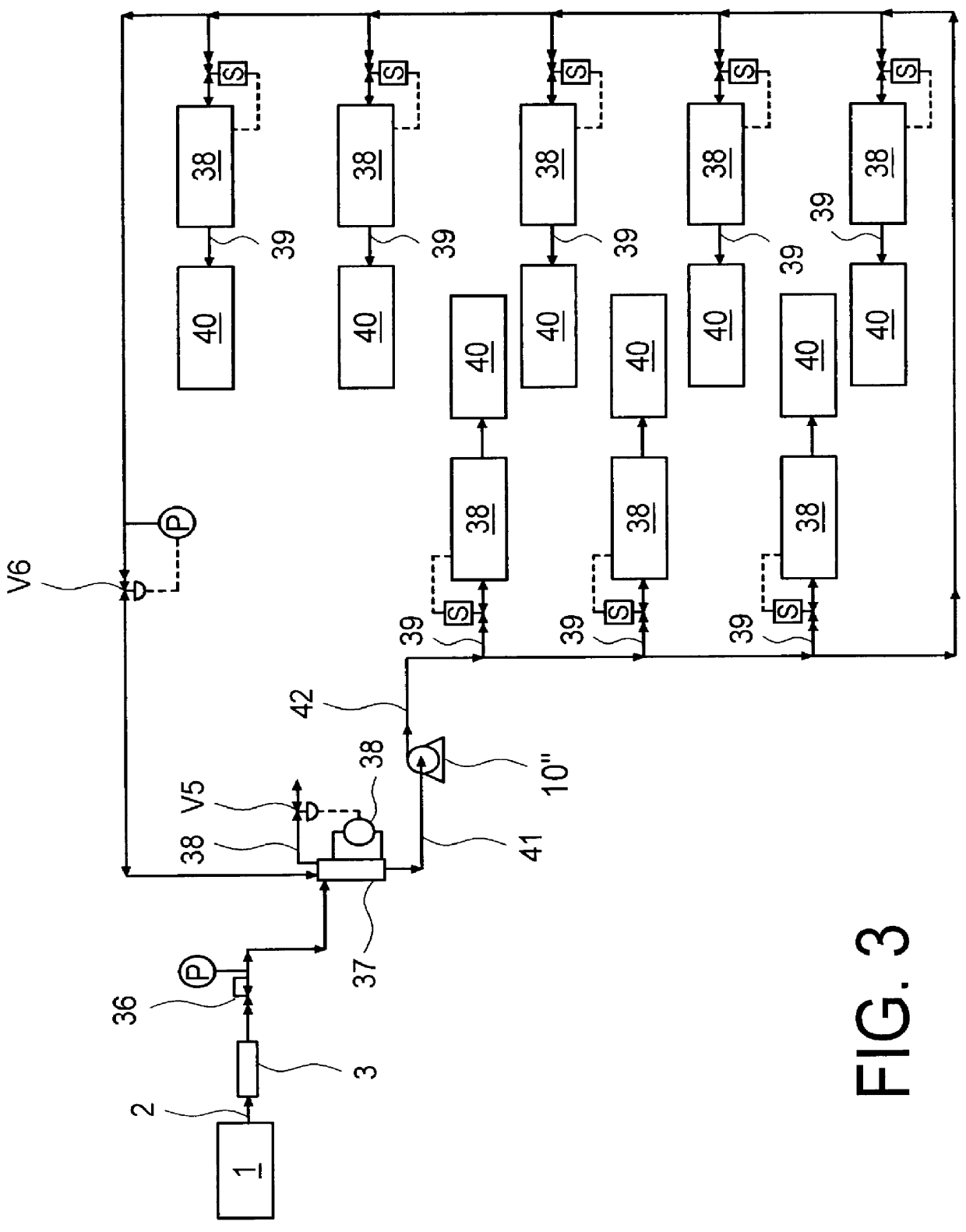
Continuous Process for Converting Natural Gas to Liquid Hydrocarbons
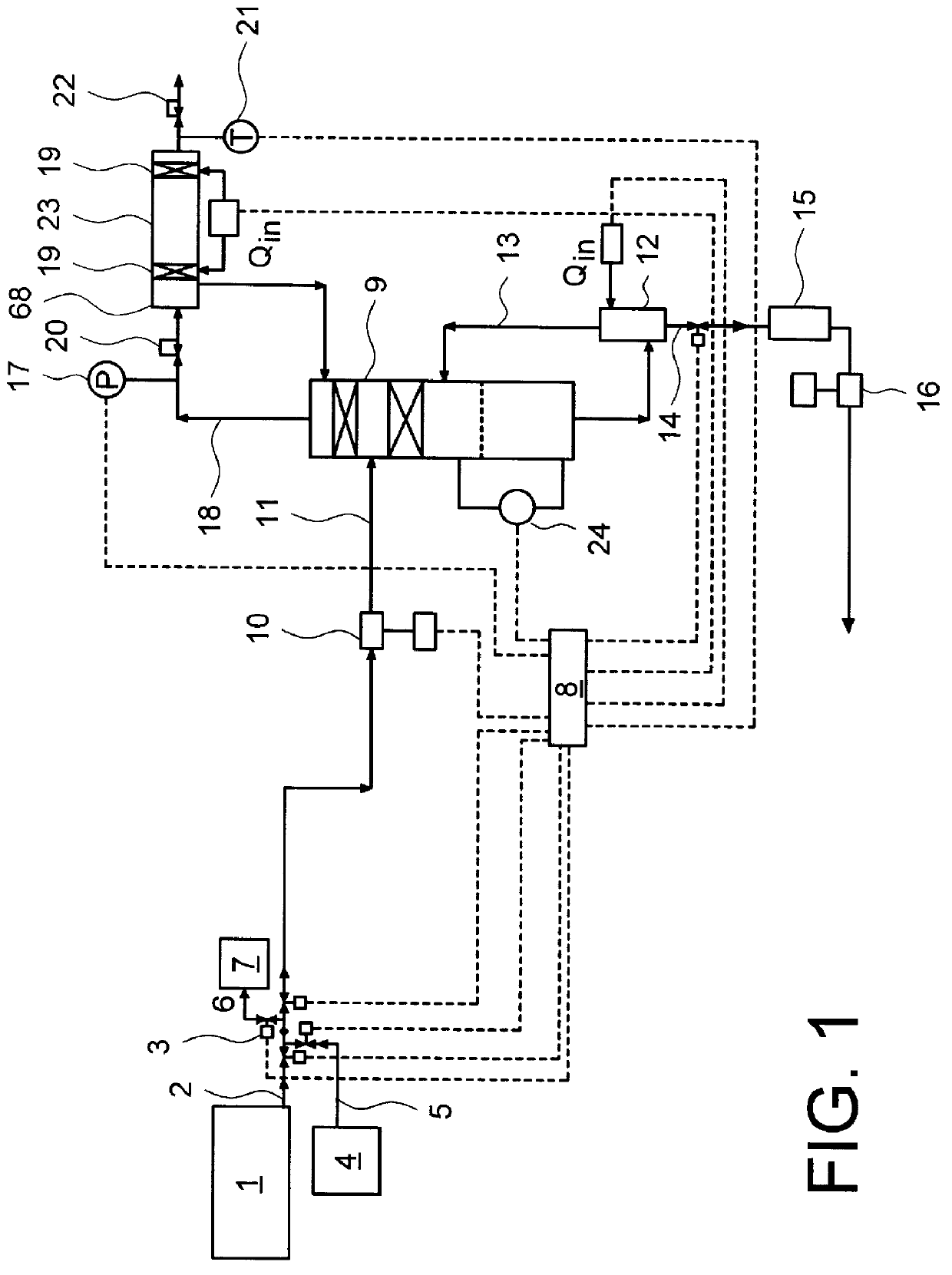
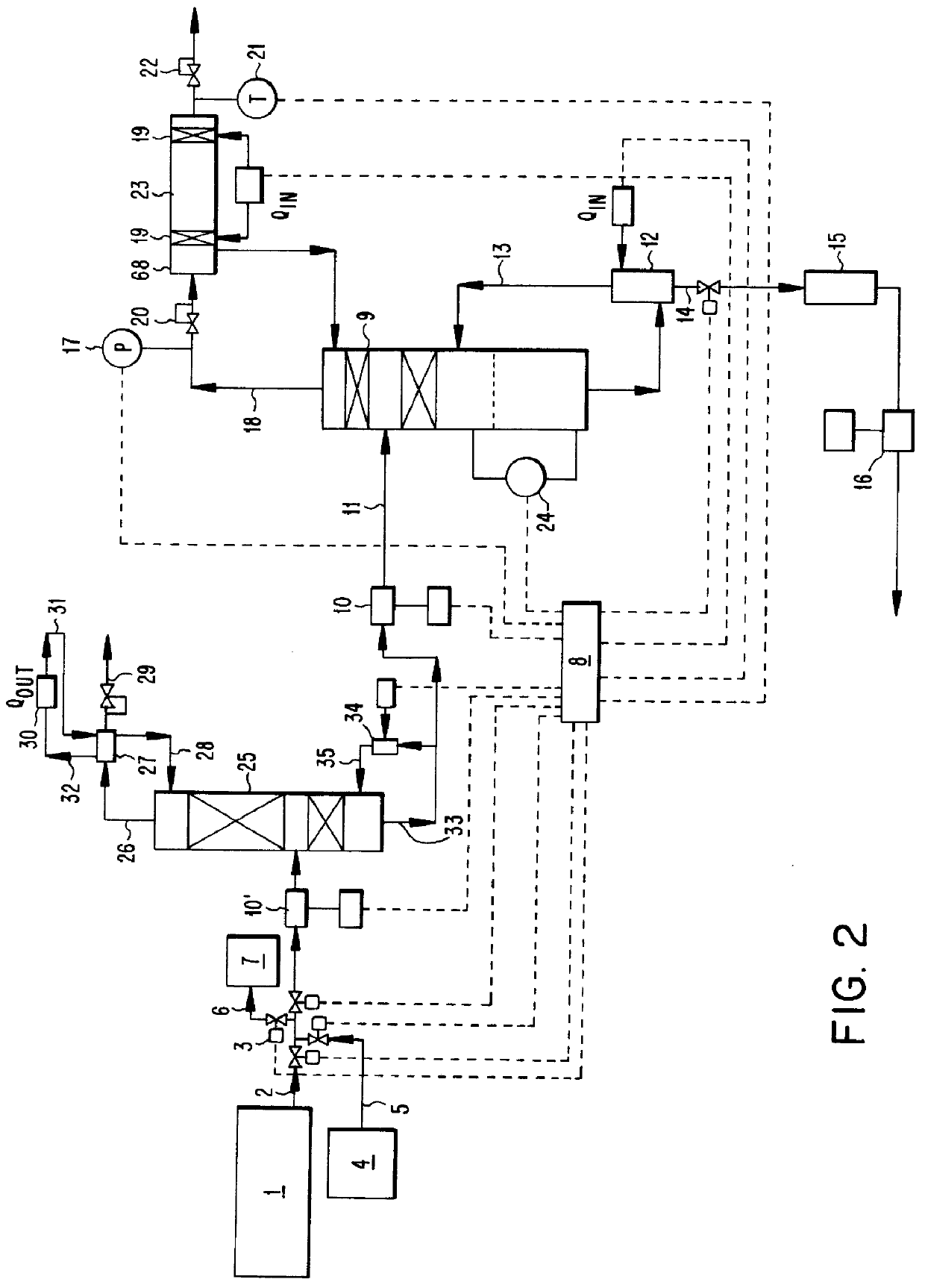
A method comprising: providing an alkyl halide stream; contacting at least some of the alkyl halides with a coupling catalyst to form a product stream comprising higher hydrocarbons and hydrogen halide; contacting the product stream with a solid reactant to remove at least a portion of the hydrogen halide from the product stream; and reacting the solid reactant with a source of oxygen to generate a corresponding halogen.
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process, and to selectively form monobrominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
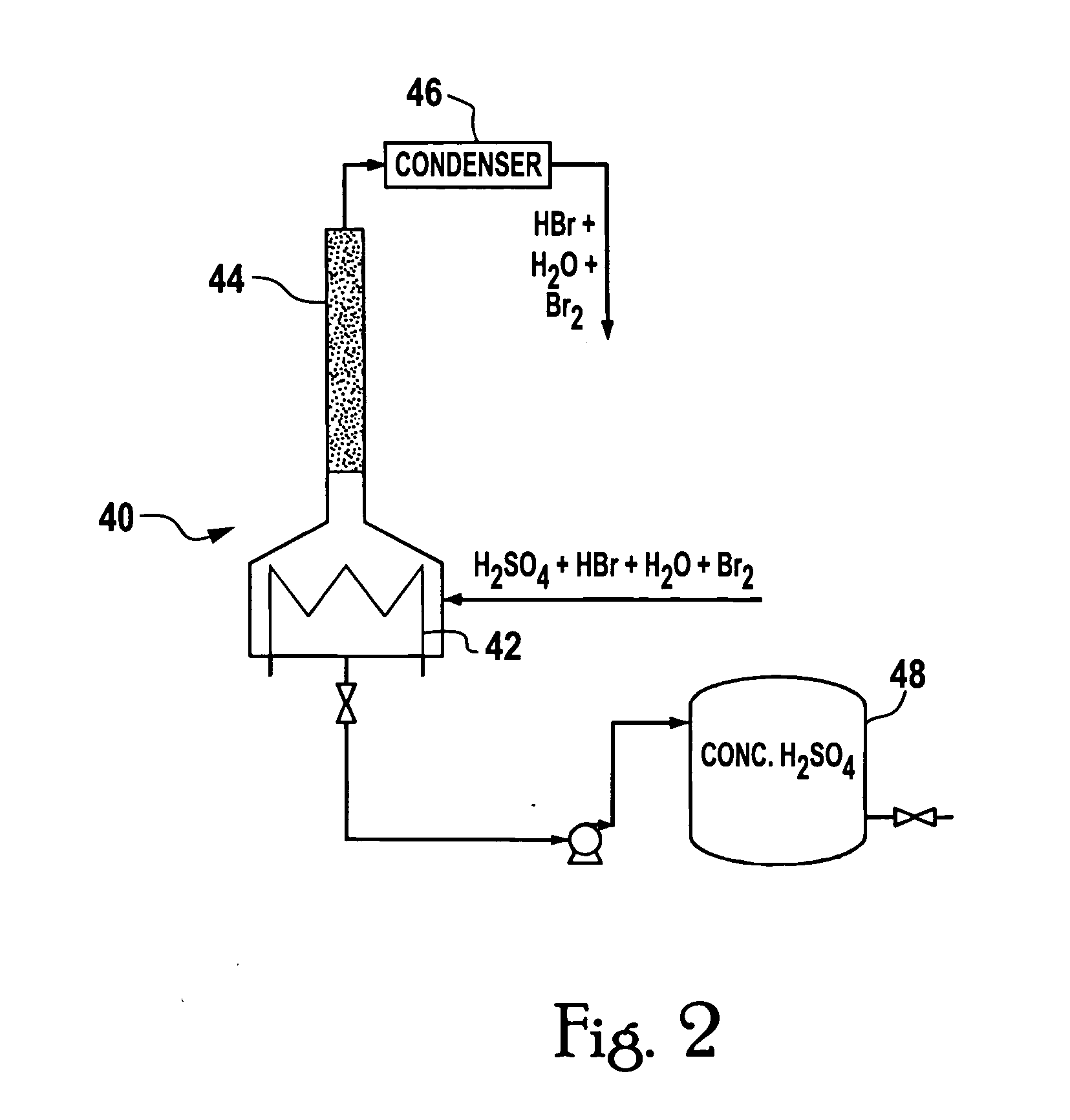
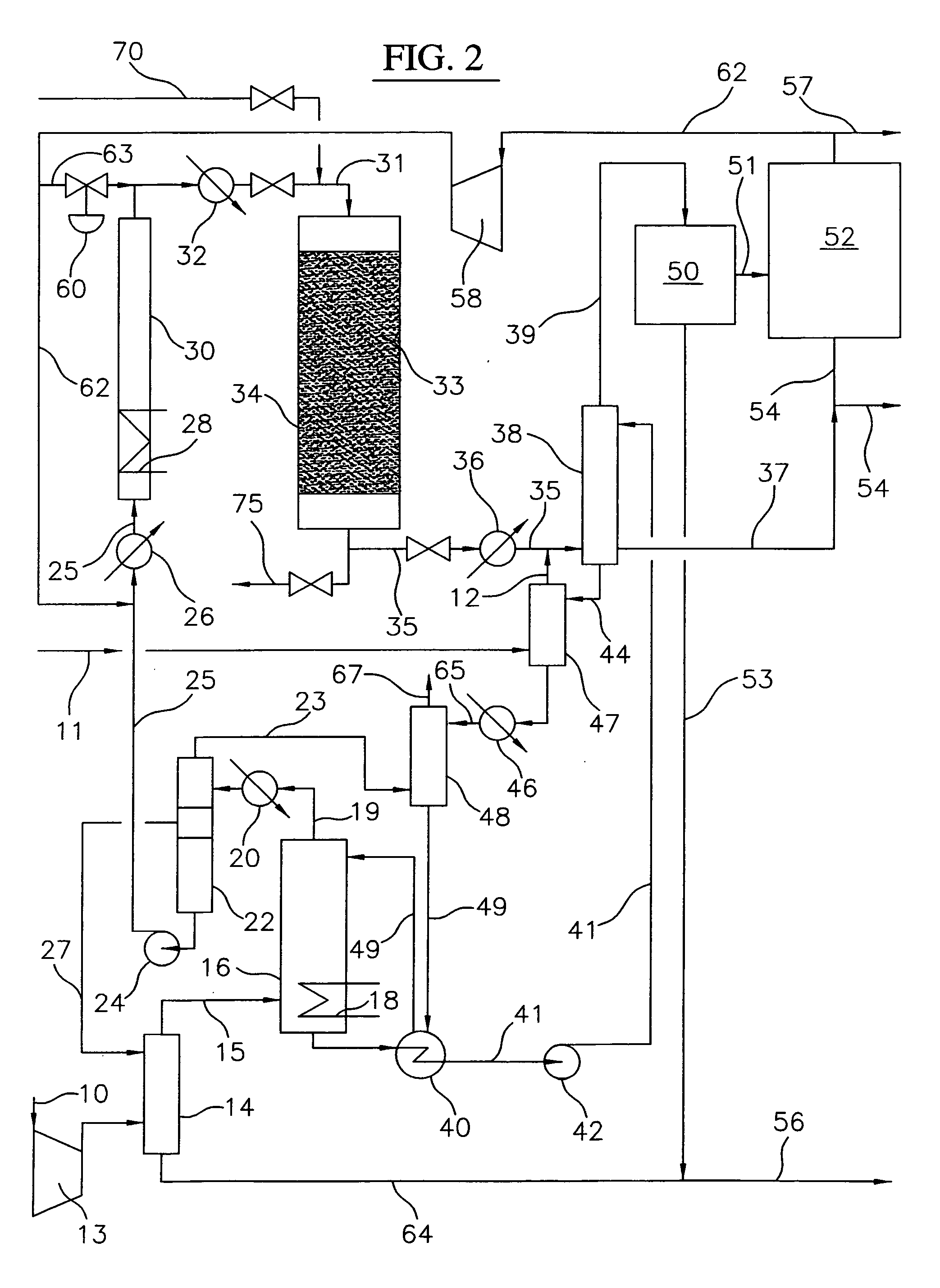
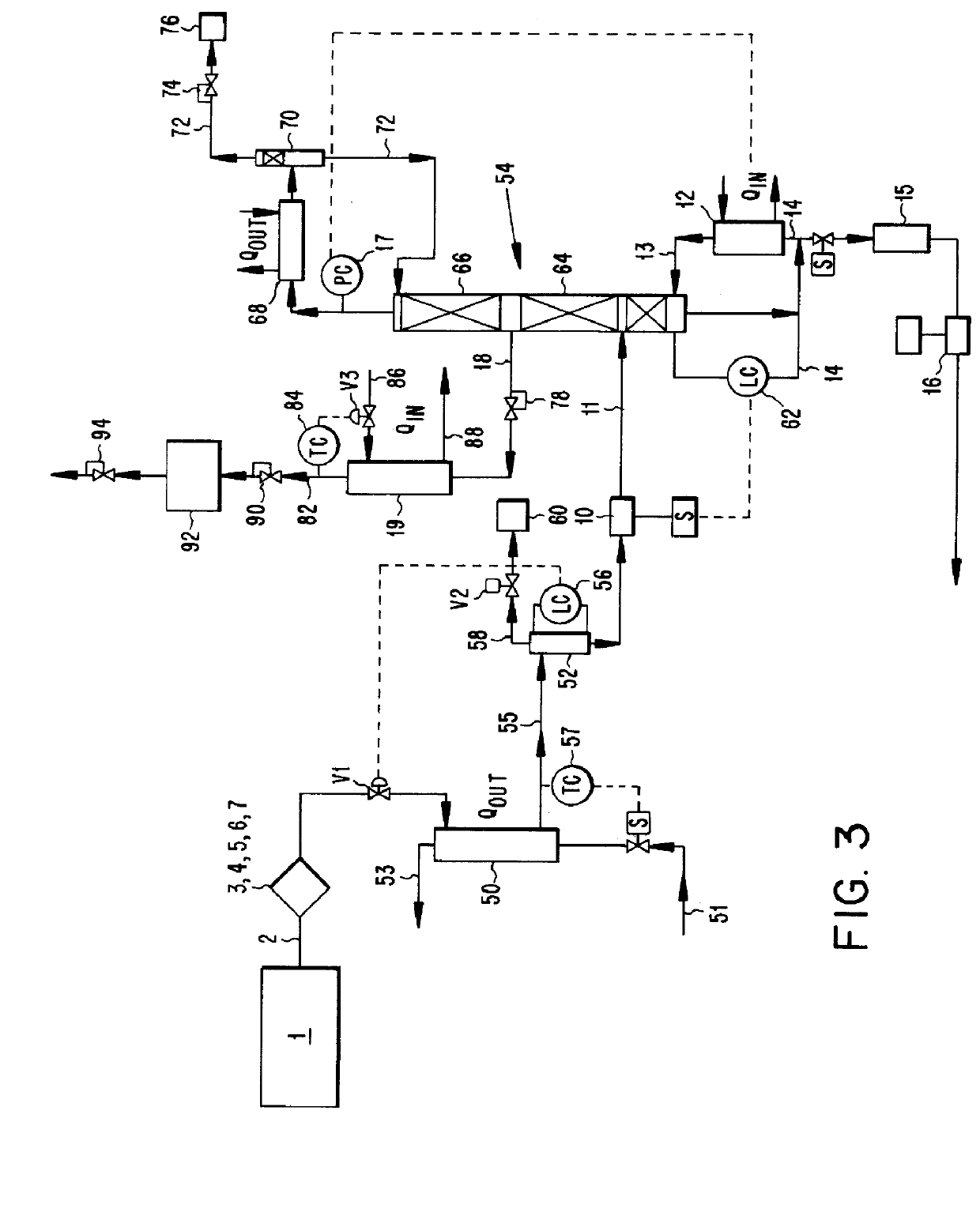
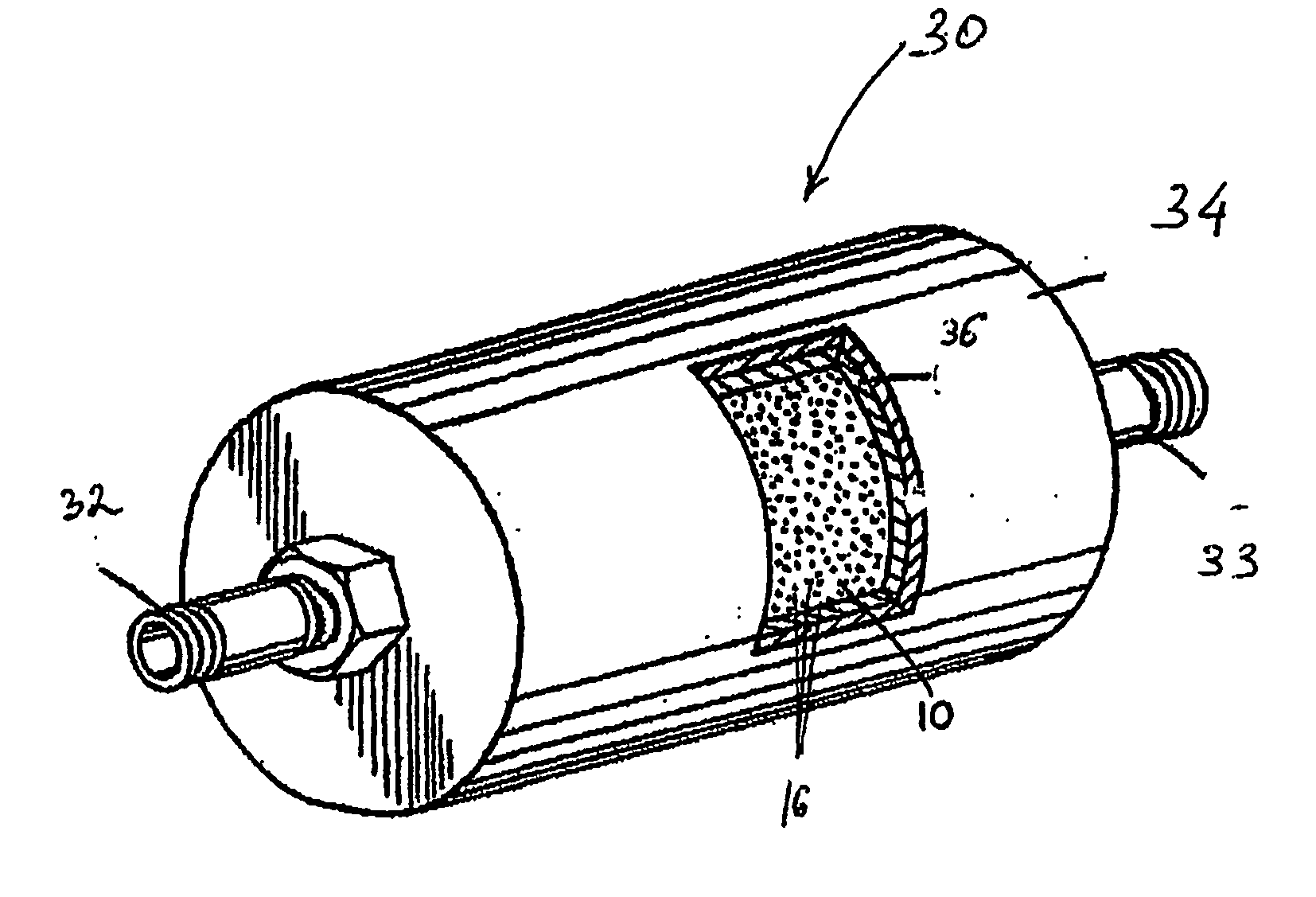
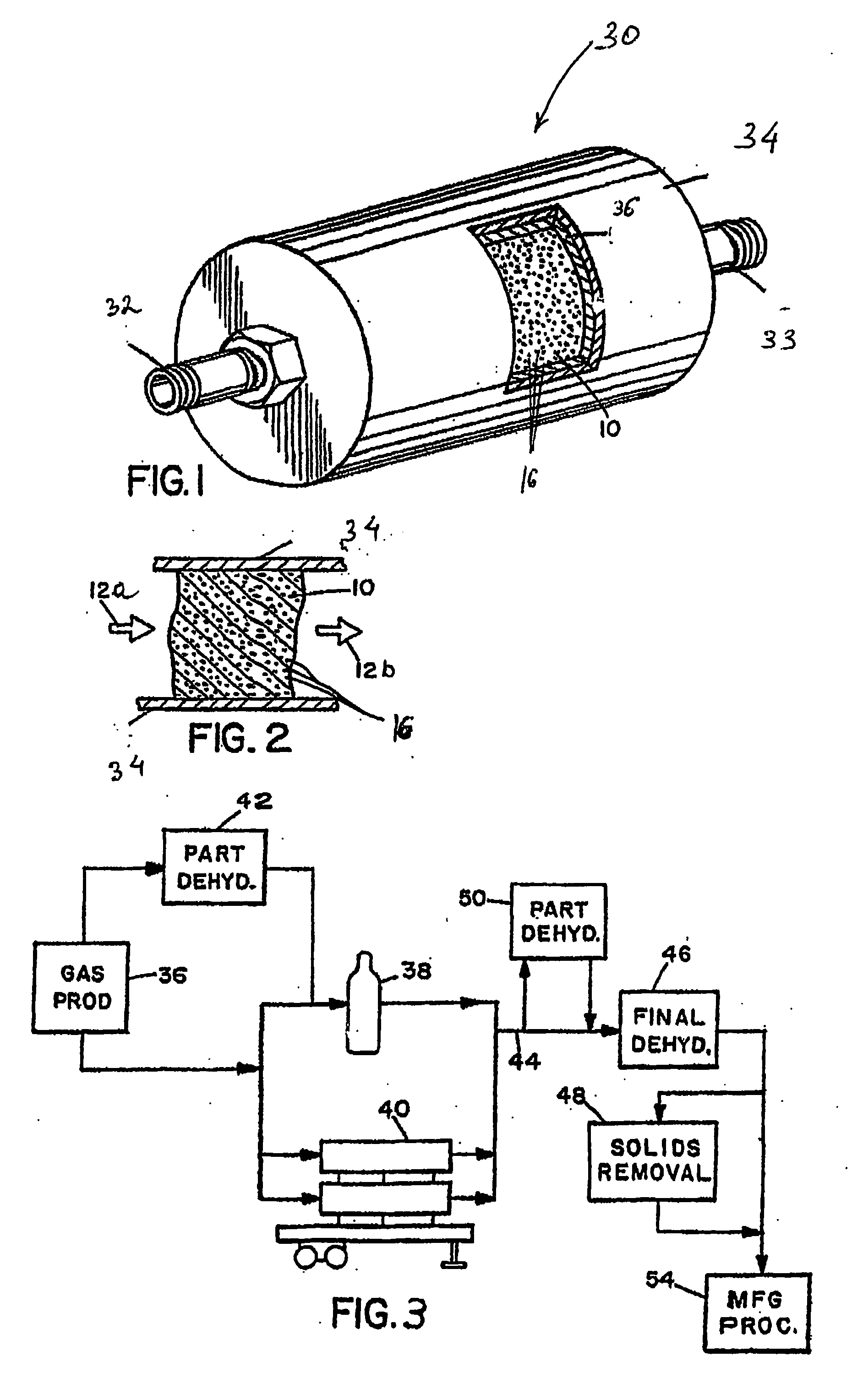
System and method for delivery of a vapor phase product to a point of use
Provided are a novel system and method for delivery of a vapor phase product to a point of use, as well as a novel on-site chemical distribution system and method. The system for delivery of a vapor phase product includes a storage vessel containing a liquid chemical under its own vapor pressure, a column connected to receive the chemical in liquified state from the storage vessel, wherein the chemical is fractionated into a contaminated liquid heavy fraction and a purified light vapor fraction and a conduit connected to the column for removing the purified light vapor fraction therefrom. The system is connected to the point of use for introducing the purified vapor fraction thereto. Particular applicability is found in semiconductor manufacturing in the delivery of electronic specialty gases to one or more semiconductor processing tools.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
Hydrogen sulfide abatement with scale control and/or well acidizing
InactiveUS6375907B1Avoid disadvantagesLow costHydrogen bromideLiquid degasificationHydrogen halidePower station
The emissions of hydrogen sulfide during the production of natural gas, oil or geothermal fluids from subterranean formations and the subsequent processing of these fluids is reduced by converting the hydrogen sulfide into a hydrogen halide or a halogen acid and then using the hydrogen halide or halogen acid for scale control and / or well acidizing. In a preferred embodiment, hydrogen sulfide produced with geothermal fluids is converted into hydrochloric acid, which is then used to reduce pH and control scale formation during the extraction of energy from geothermal fluids in a geothermal power plant.
Owner:UNION OIL OF CALIFORNIA
Integrated process to coproduce aromatic hydrocarbons and ethylene and propylene
An integrated process for producing aromatic hydrocarbons and ethylene and / or propylene and optionally other lower olefins from low molecular weight hydrocarbons, preferably methane, which comprises: (a) contacting one or more low molecular weight alkanes, preferably methane, with a halogen, preferably bromine, under process conditions sufficient to produce a monohaloalkane, preferably monobromomethane, (b) reacting a first portion of the monohaloalkane in the presence of a coupling catalyst under process conditions sufficient to produce aromatic hydrocarbons and C2-5 alkanes, (c) separating the aromatic hydrocarbons from the product mixture of step (b) to produce aromatic hydrocarbons, (d) reacting a second portion of the monohaloalkane in the presence of a coupling catalyst under process conditions sufficient to produce ethylene and / or propylene.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
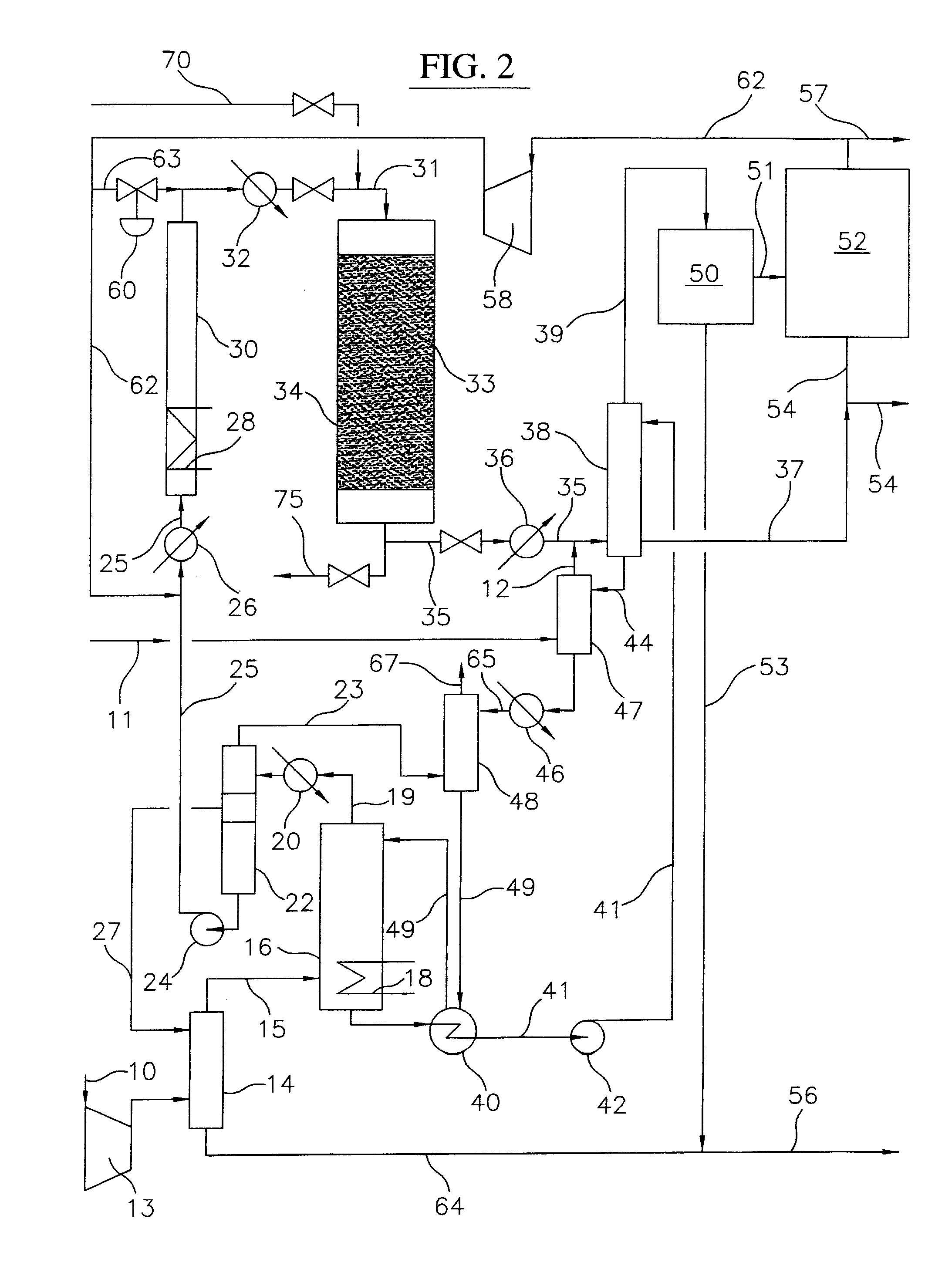
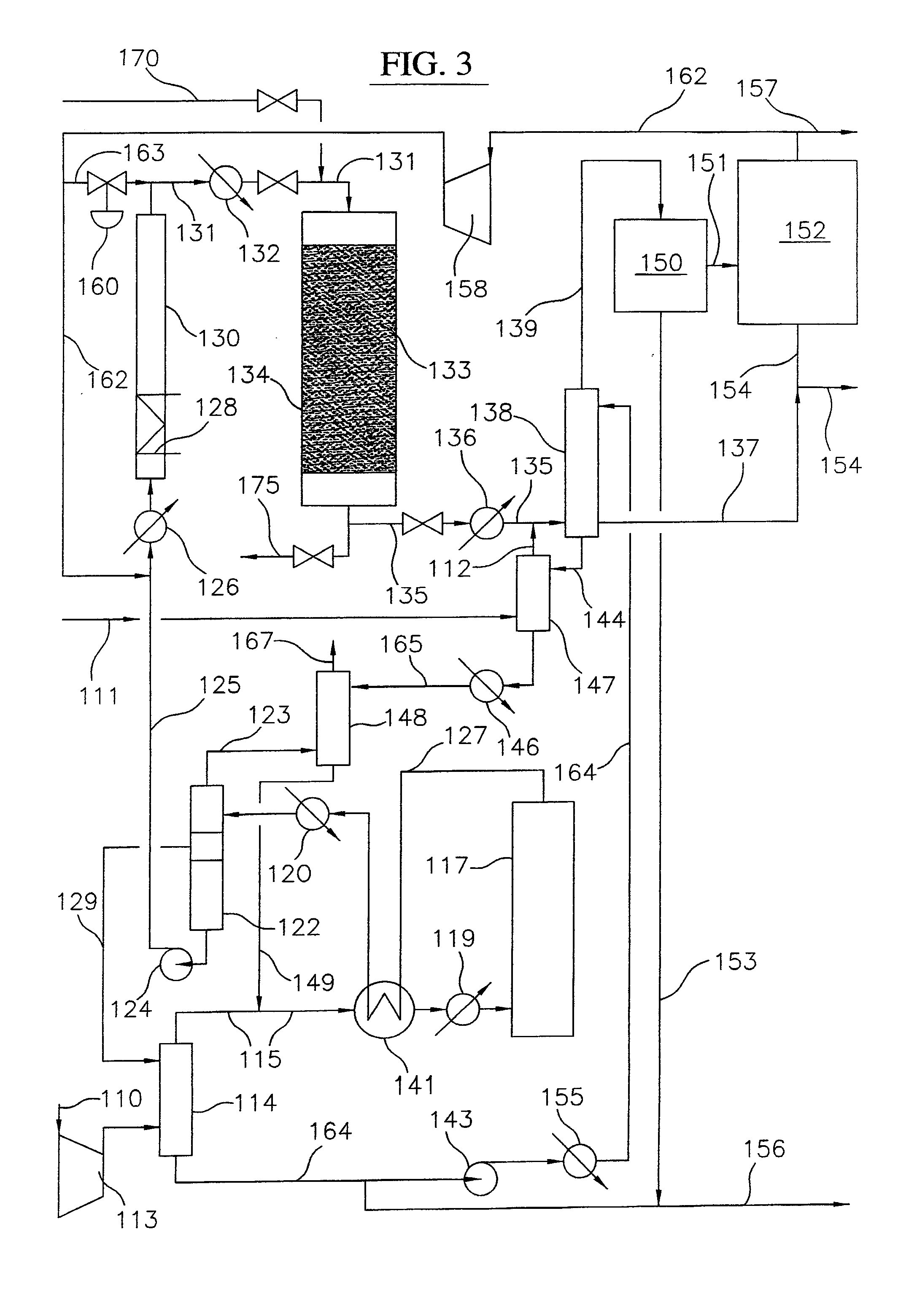
Embodiments disclose a process for converting gaseous alkanes to higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereofs wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes may be reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid then may be reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 or an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form hydrobromic acid vapor and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:MARATHON GTF TECH
System and method for delivery of a vapor phase product to a point of use
Provided are a novel system and method for delivery of a vapor phase product to a point of use, as well as a novel on-site chemical distribution system and method. The system for delivery of a vapor phase product includes a storage vessel containing a liquid chemical under its own vapor pressure, a column connected to receive the chemical in liquified state from the storage vessel, wherein the chemical is fractionated into a contaminated liquid heavy fraction and a purified light vapor fraction and a conduit connected to the column for removing the purified light vapor fraction therefrom. The system is connected to the point of use for introducing the purified vapor fraction thereto. Particular applicability is found in semiconductor manufacturing in the delivery of electronics specialty gases to one or more semiconductor processing tools.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080200740A1High selectivityAvoid disadvantagesHydrogen bromideBromide preparationAlkaneBromine
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process, and to selectively form monobrominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
Embodiments disclose a process for converting gaseous alkanes to higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereofs wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes may be reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid then may be reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as a ZSM-5 or an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form hydrobromic acid vapor and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, olefins or mixtures thereof and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:MARATHON GTF TECH
Process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and liquid hydrocarbons
ActiveUS8008535B2High selectivityAvoid disadvantagesBromide preparationHydrogen bromideAlkaneAlkyl bromide
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid vapor. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrobromic acid are then reacted over a synthetic crystalline alumino-silicate catalyst, such as an X or Y type zeolite, at a temperature of from about 250° C. to about 500° C. so as to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and hydrobromic acid vapor. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrobromic acid vapor from the olefins and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons and to generate bromine from the hydrobromic acid for use in the process.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes is thermally reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide. Poly-brominated alkanes present in the alkyl bromides are further reacted with methane over a suitable catalyst to form mono-brominated species. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide is then reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrogen bromide. Various methods are disclosed to remove the hydrogen bromide from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrogen bromide for use in the process, and to selectively form mono-brominated alkanes in the bromination step.
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Continuous process for converting natural gas to liquid hydrocarbons
A method comprising: providing an alkyl halide stream; contacting at least some of the alkyl halides with a coupling catalyst to form a product stream comprising higher hydrocarbons and hydrogen halide; contacting the product stream with a solid reactant to remove at least a portion of the hydrogen halide from the product stream; and reacting the solid reactant with a source of oxygen to generate a corresponding halogen.
Owner:GRT INC
Processes for converting gaseous alkanes to liquid hydrocarbons using microchannel reactor
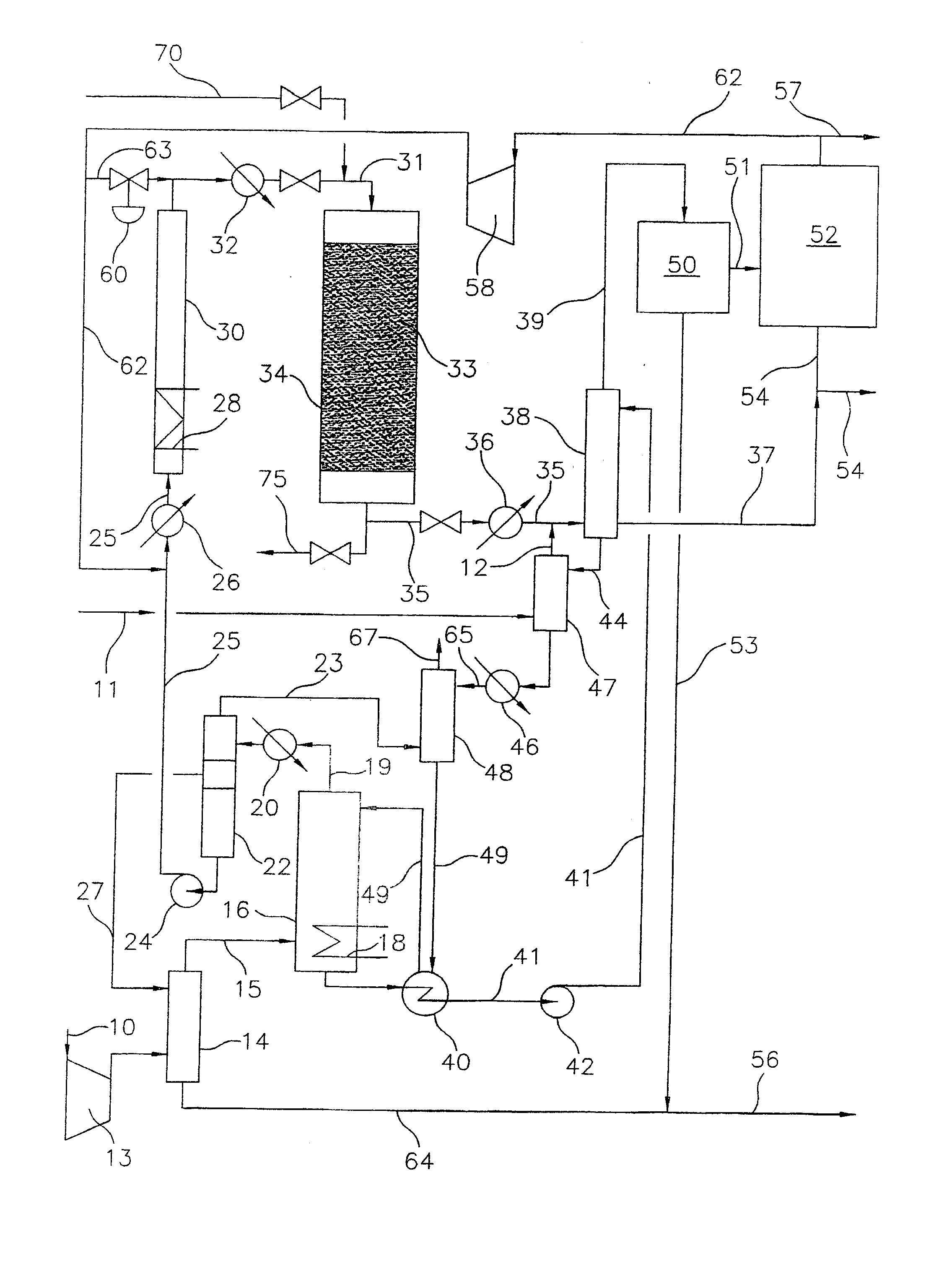
A process for converting gaseous alkanes to olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof wherein a gaseous feed containing alkanes may be thermally or catalytically reacted with a dry bromine vapor to form alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide. Poly-brominated alkanes present in the alkyl bromides may be further reacted with methane over a suitable catalyst to form mono-brominated species. The mixture of alkyl bromides and hydrogen bromide may then be reacted over a suitable catalyst at a temperature sufficient to form olefins, higher molecular weight hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof and hydrogen bromide. Various methods and reactions are disclosed to remove the hydrogen bromide from the higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, to generate bromine from the hydrogen bromide for use in the process, to store and subsequently release bromine for use in the process, and to selectively form mono-brominated alkanes in the bromination step. One or more of the reactions of the processes of the present invention may be conducted in a microchannel reactor.
Owner:GTC TECHNOLOGY US LLC
Apparatus and method for purification of corrosive gas streams
InactiveUS20070031321A1Reduce moistureWater contentMagnesium fluoridesHydrogen bromideParticulatesHalogen
A process, composition and apparatus for the removal of impurities from corrosive gases, particularly halogen-containing gases, down to about 100 ppb concentration are described. The critical component is zirconia (ZrO2), which in a variety of physical forms is capable of dehydrating such gases. The zirconia can be in the form of a coating on a substrate, as a granular bulk material, or deposited within the pores of a porous body. The zirconia is retained in a simple container which is easily installed in a gas supply line, such as to a gas- or vapor-deposition manufacturing unit. The purification process can be operated for long periods of time in the presence of these gases. The invention provides final purification to gas streams intended for gas- or vapor-deposition formation of high purity electronic, prosthetic or similar products, and can be used in combination with a preliminary dehydration process or a solid particulate removal unit upstream.
Owner:MYKROLIS CORP +1
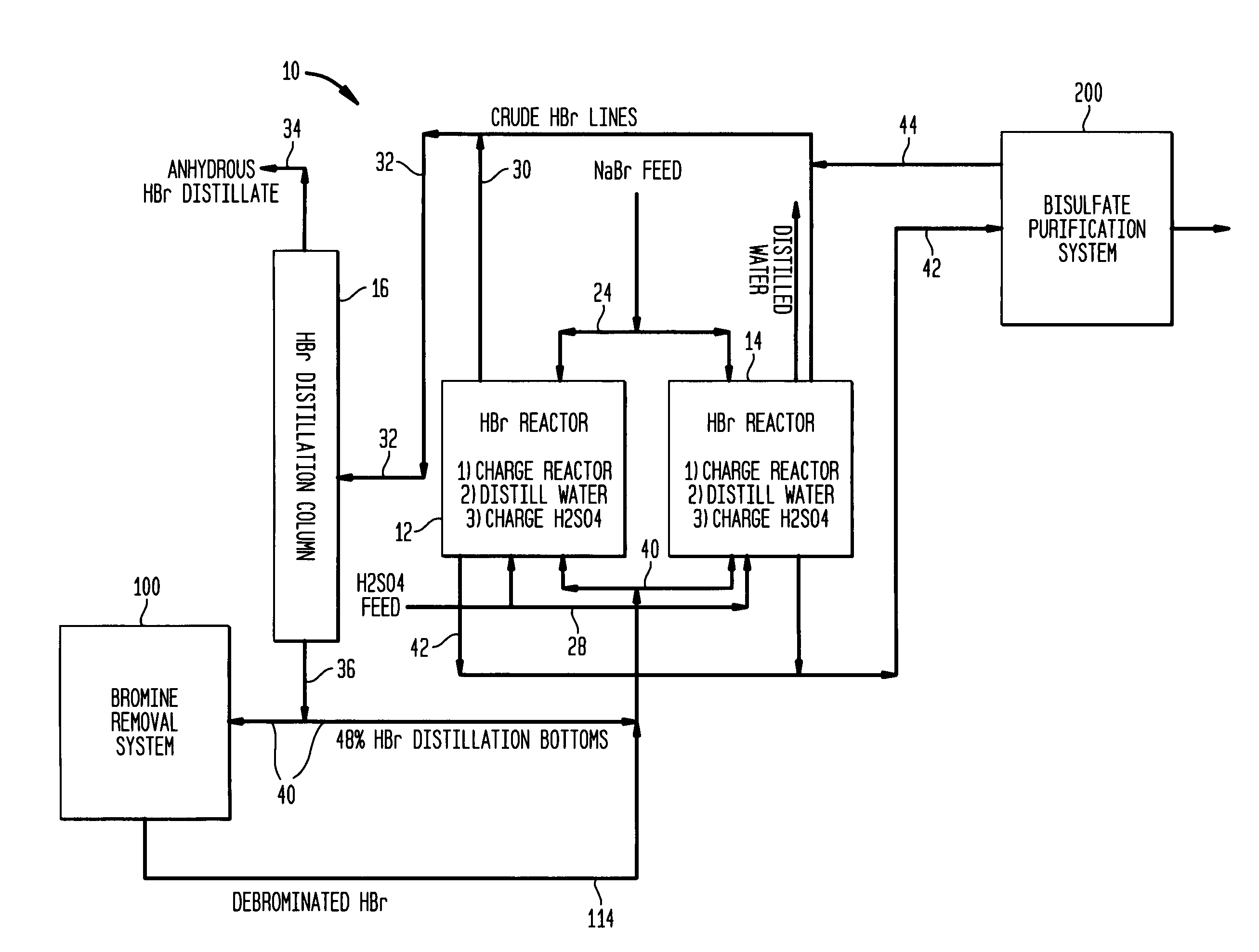
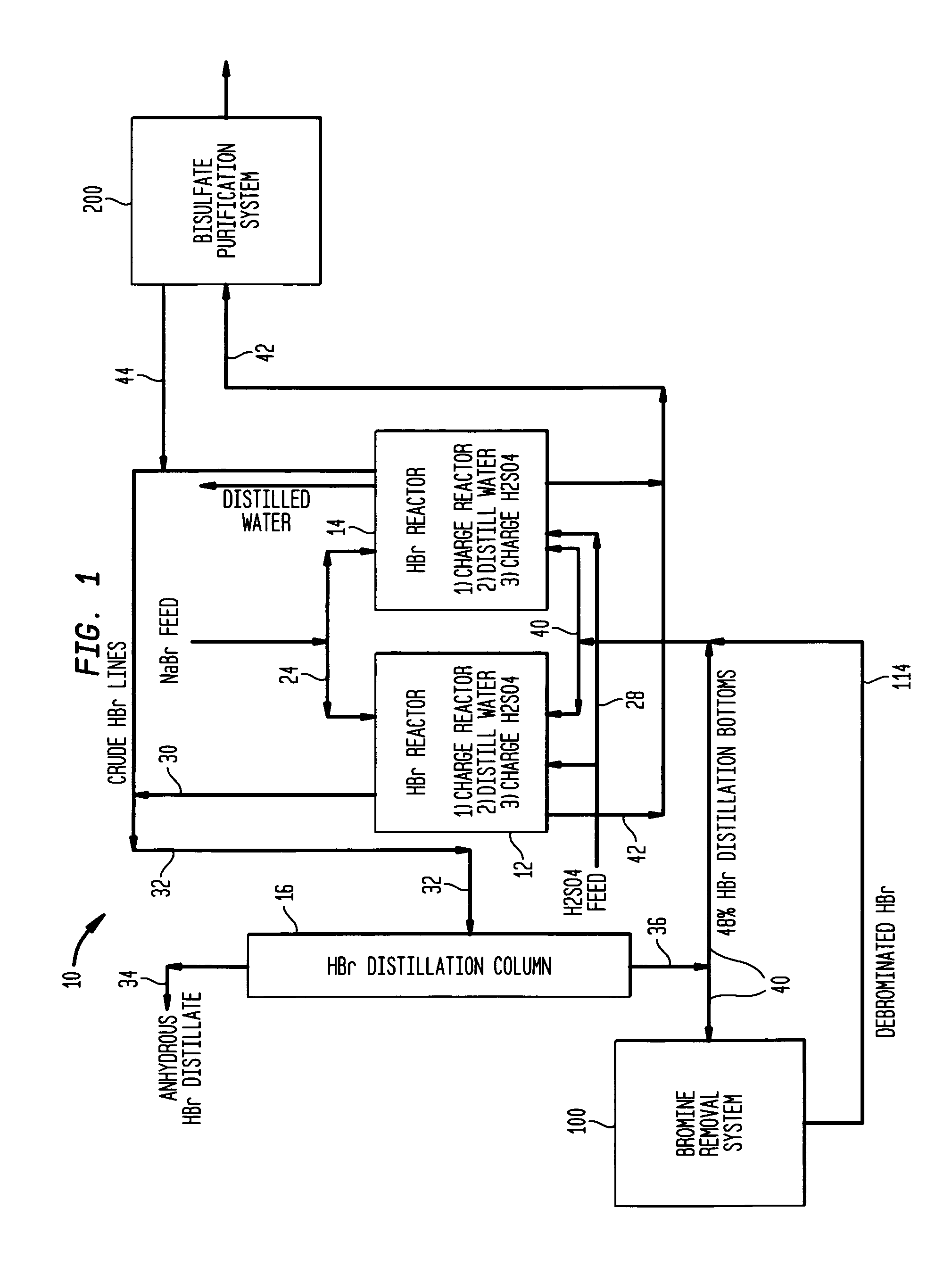
Conversion of sodium bromide to anhydrous hydrobromic acid and sodium bisulfate
InactiveUS20050135990A1Hydrogen bromideChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationSodium bisulfateSodium bromide
Process for the conversion of sodium bromide to anhydrous hydrobromic acid and sodium bisulfate, said process with the following sequential steps: reaction of sodium bromide and sulfuric acid in a solution of water to produce hydrobromic acid and sodium bisulfate wherein the conversion of sodium bromide is greater than about 99%; adsorption of iron bromide onto a solid adsorbent; separation of hydrobromic acid and water from the sodium bisulfate; separation and drying of hydrobromic acid; and solidification of the sodium bisulfate into a flaked or granular form.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
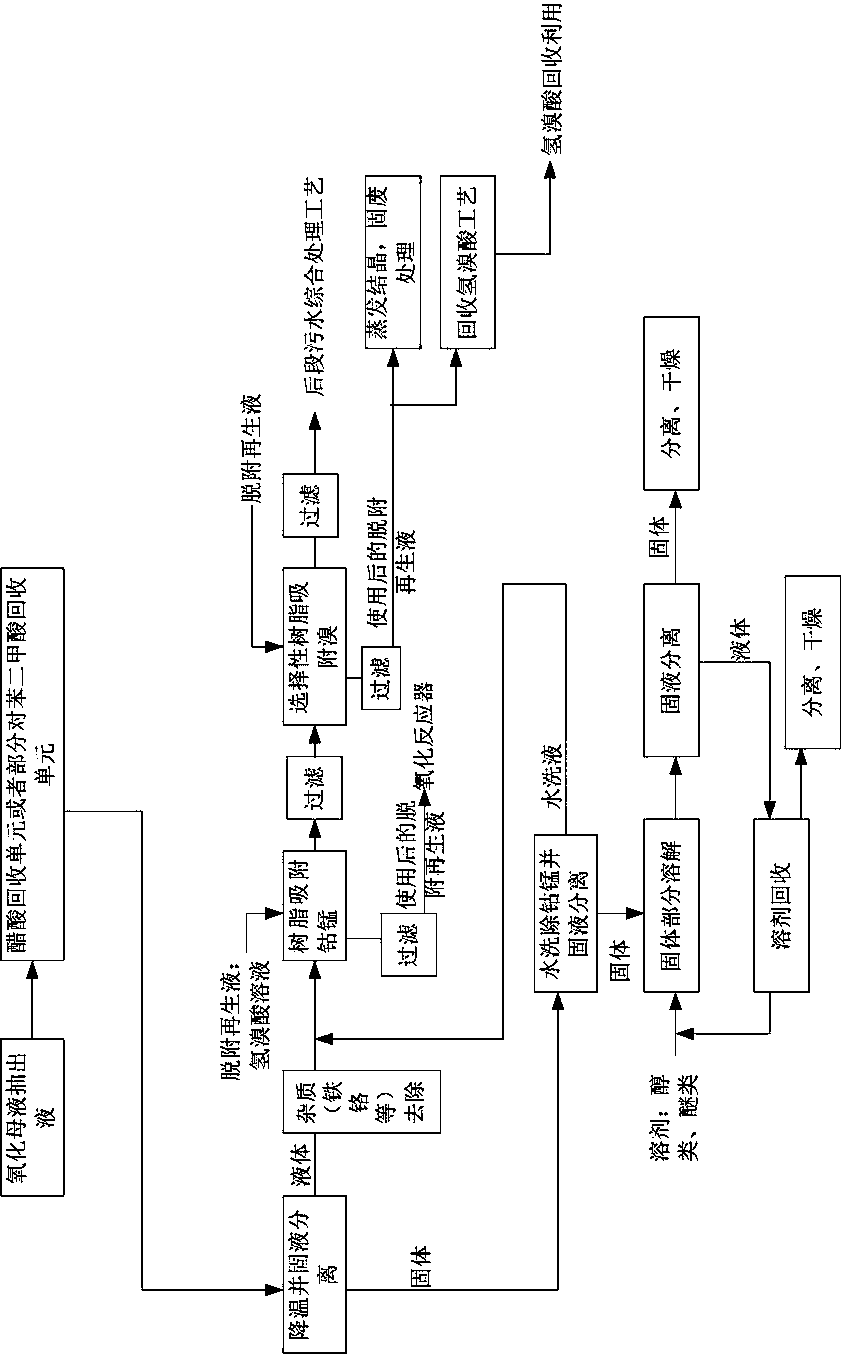
Treatment process for mother liquor extraction liquid of purified terephthalic acid oxidation unit
InactiveCN109776307AReduce processing difficultyReduce consumptionHydrogen bromideCarboxylic compound separation/purificationBenzoic acidSludge
The invention relates to a treatment process for a mother liquor extraction liquid of a purified terephthalic acid oxidation unit, and belongs to the field of industrial wastewater treatment. The process comprises the steps that the oxidized mother liquor extraction liquid is treated by an acetic acid recovery unit or a terephthalic acid partial recovery unit and a temperature-reducing solid-liquid separation unit. A separation liquid passes through an impurity removal unit, a resin cobalt and manganese adsorption unit for recovering cobalt and manganese and a bromine removal unit for recovering bromine, and finally, waste liquid is directly discharged to a comprehensive sewage treatment unit; solids are washed with water at first, a water washing liquid is conveyed to the resin cobalt andmanganese adsorption unit to recover the cobalt and manganese, and the remaining solids are recovered and extracted and purify terephthalic acid and benzoic acid, and economic value is generated. Theconcentration of bromine, benzoic acid, phthalic acid and other benzene-series compounds in the oxidized mother liquor extraction liquid is reduced, the adverse effects on the activity of biochemicalsludge are avoided, the difficulty of treating wastewater is reduced, and the efficiency of later comprehensive sewage treatment is improved; the consumption quantity of alkaline substances is reduced, the resources are saved, the enterprise cost is reduced, and the utilization rate is increased.
Owner:佰仕邦水处理环保科技(大连)有限公司
Apparatus and method for purification of corrosive gas streams
InactiveCN1809412ALess susceptible to corrosionReduce moisture contentHydrogen bromideBromineHalogenPhysical chemistry
A process, composition and apparatus for the removal of impurities from corrosive gases, particularly halogen-containing gases, down to about 100 ppb concentration are described. The critical component is zirconia (ZrO2), which in a variety of physical forms is capable of dehydrating such gases. The zirconia can be in the form of a coating on a substrate, as a granular bulk material, or deposited within the pores of a porous body. The zirconia is retained in a simple container which is easily installed in a gas supply line, such as to a gas- or vapor-deposition manufacturing unit. The purification process can be operated for long periods of time in the presence of these gases. The invention provides final purification to gas streams intended for gas- or vapor-deposition formation of high purity electronic, prosthetic or similar products, and can be used in combination with a preliminary dehydration process or a solid particulate removal unit upstream.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
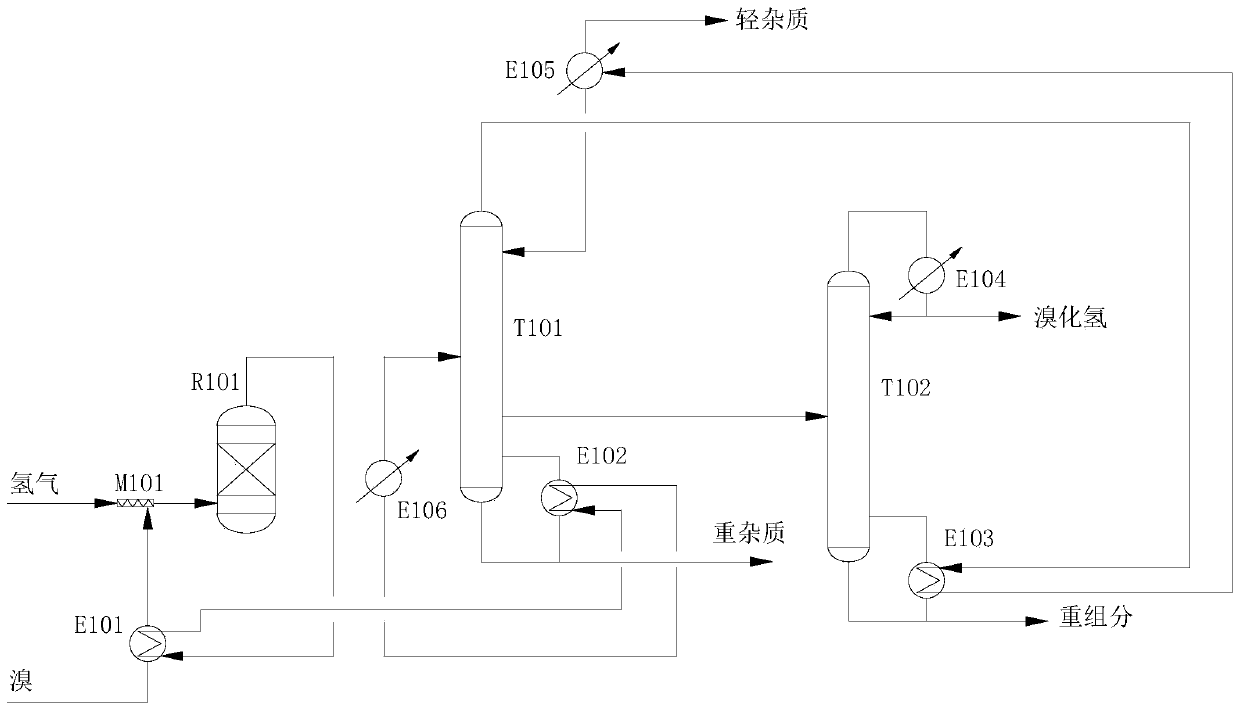
Preparation method of electronic grade hydrogen bromide
PendingCN110562924AReduce energy consumptionReduce cooling consumptionHydrogen bromideHydrogenGas phase
The invention discloses a preparation method of electronic grade hydrogen bromide, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, bromine is gasified by a preheater, and mixed with hydrogen toenter a reactor for catalytic combustion reaction to generate hydrogen bromide; reaction products are extracted from the top of the reactor and then enter the preheater to exchange heat with the bromine and then enter a reboiler to exchange heat with materials in the bottom of a light removal tower; and the heat-exchanged reaction products enter the light removal tower after being cooled by a cooler. The gas phase extracted from the top of the light removal tower enters the reboiler to exchange heat with the materials in the bottom of a heavy removal tower, and enters a condenser to be condensed and cooled, the liquid phase returns to the light removal tower to be extracted as light component impurities; crude hydrogen bromide extracted from the side line of the light removal tower entersthe heavy removal tower, and heavy impurities are extracted from the tower bottom; a 6N electronic grade hydrogen bromide product is extracted from the top of the heavy removal tower, and heavy components are extracted from the tower bottom. According to the invention, heat generated by the reaction and a double-effect rectification process are fully utilized, no external heat source is needed, and liquid nitrogen can be saved by more than 45 percent; the bromine and hydrogen are selected as reaction raw materials, the reaction product has less impurities and high bromine selectivity, and canbe 100% converted into hydrogen bromide.
Owner:TIANJIN ZHONGKE TUOXIN TECH CO LTD
Purifying method for hydrogen bromide
Owner:SUZHOU JINHONG GAS CO LTD
High yield co-production of anhydrous hydrogen bromide and sodium bisulfate
InactiveUS7045111B1Hydrogen bromideChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationHydrogen SulfateDistillation
A process for co-producing anhydrous hydrogen bromide and a purified bisulfate salt by (a) reacting a bromide salt with sulfuric acid to produce crude hydrogen bromide and crude bisulfate salt; (b) purifying the crude hydrogen bromide to produce anhydrous hydrogen bromide; and (c) removing bromide from the crude bisulfate salt to form a purified bisulfate salt. There are also provided improvements in the bisulfate purification and bromine removal, whereby bromine is removed from the system by a distillation process and the bromide is removed from the crude bisulfate via a spray drying process.
Owner:SHELLEF HLDG
Method for separating gas
InactiveCN101048340AAdvantages of reprocessingEasy to separateHydrogen bromideGas treatmentProduct gasCarboxylic acid
Gas mixtures, which contain HF, HCl or HBr and other constituents, particularly gas mixtures, which contain carboxylic acid fluorides, C(O)F2 or phosphorus pentafluoride as well as HCl and, optionally, HF, can be separated into their individual constituents by using ionic liquids.
Owner:SOLVAY FLUOR GMBH DE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com