Patents
Literature
1005 results about "Hydrogen Sulfate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
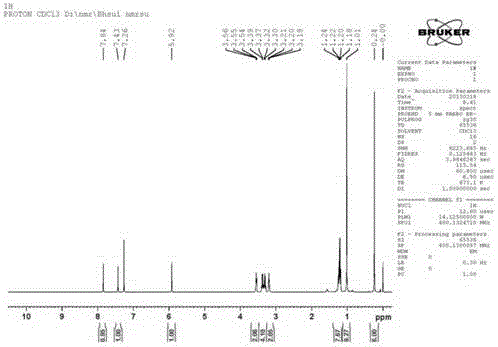
Hydrogen sulfate, also known as bisulfate, is an ion. Its chemical formula is HSO4-. It is formed as part of sulfuric acid, H2SO4. Chemical compounds containing this ion are known as bisulfates or hydrogen sulfates. An example would be sodium bisulfate.
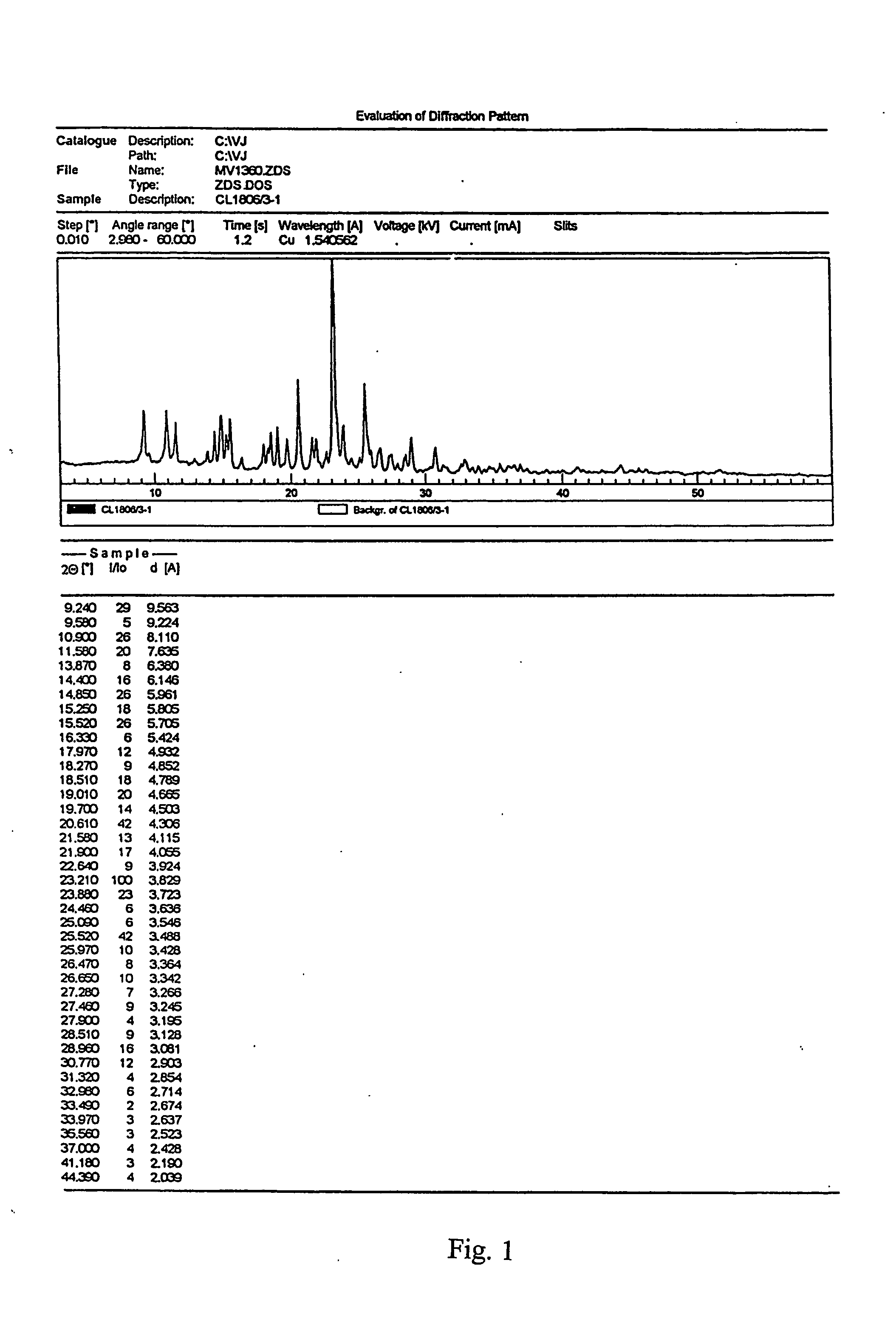
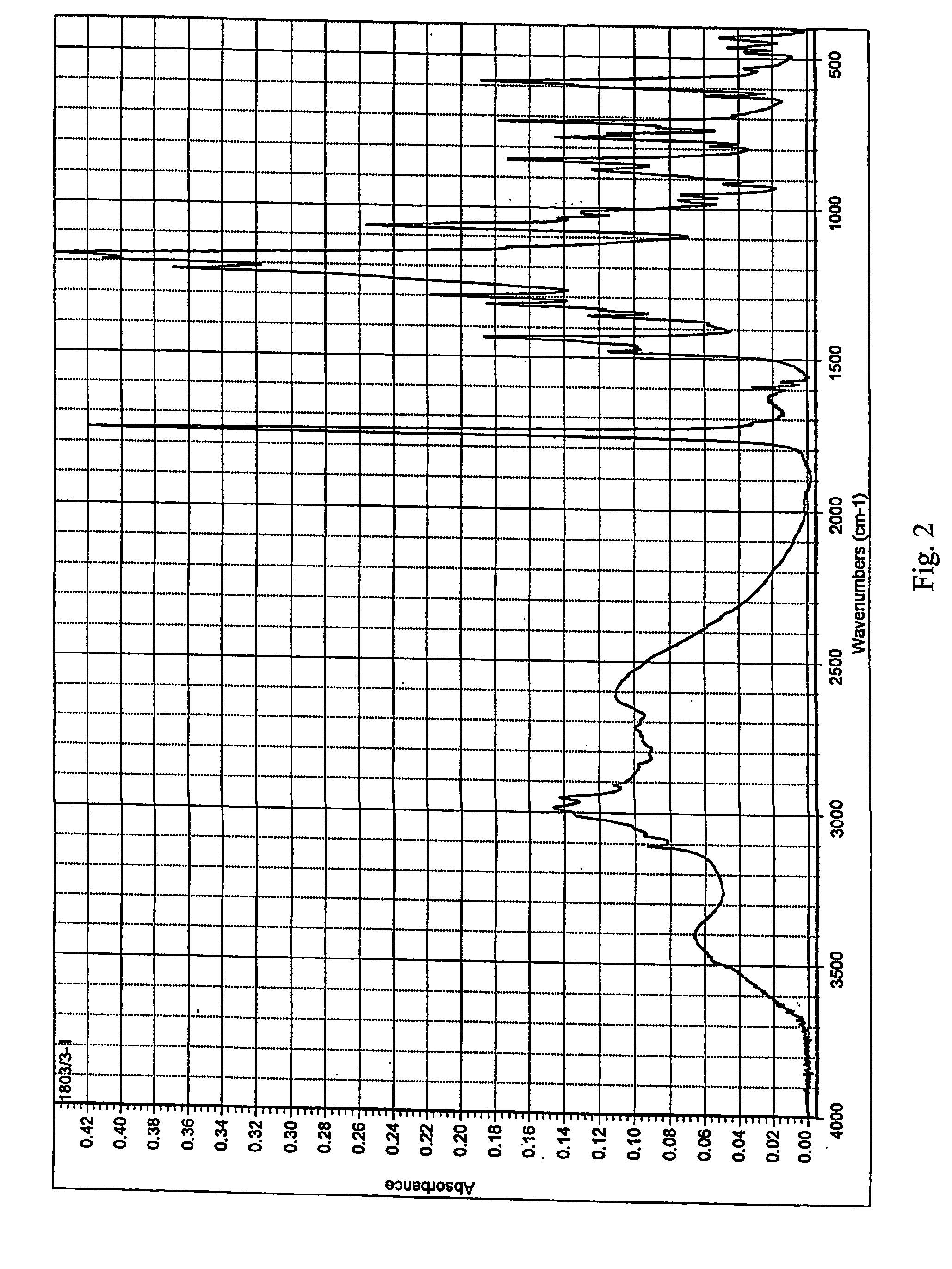
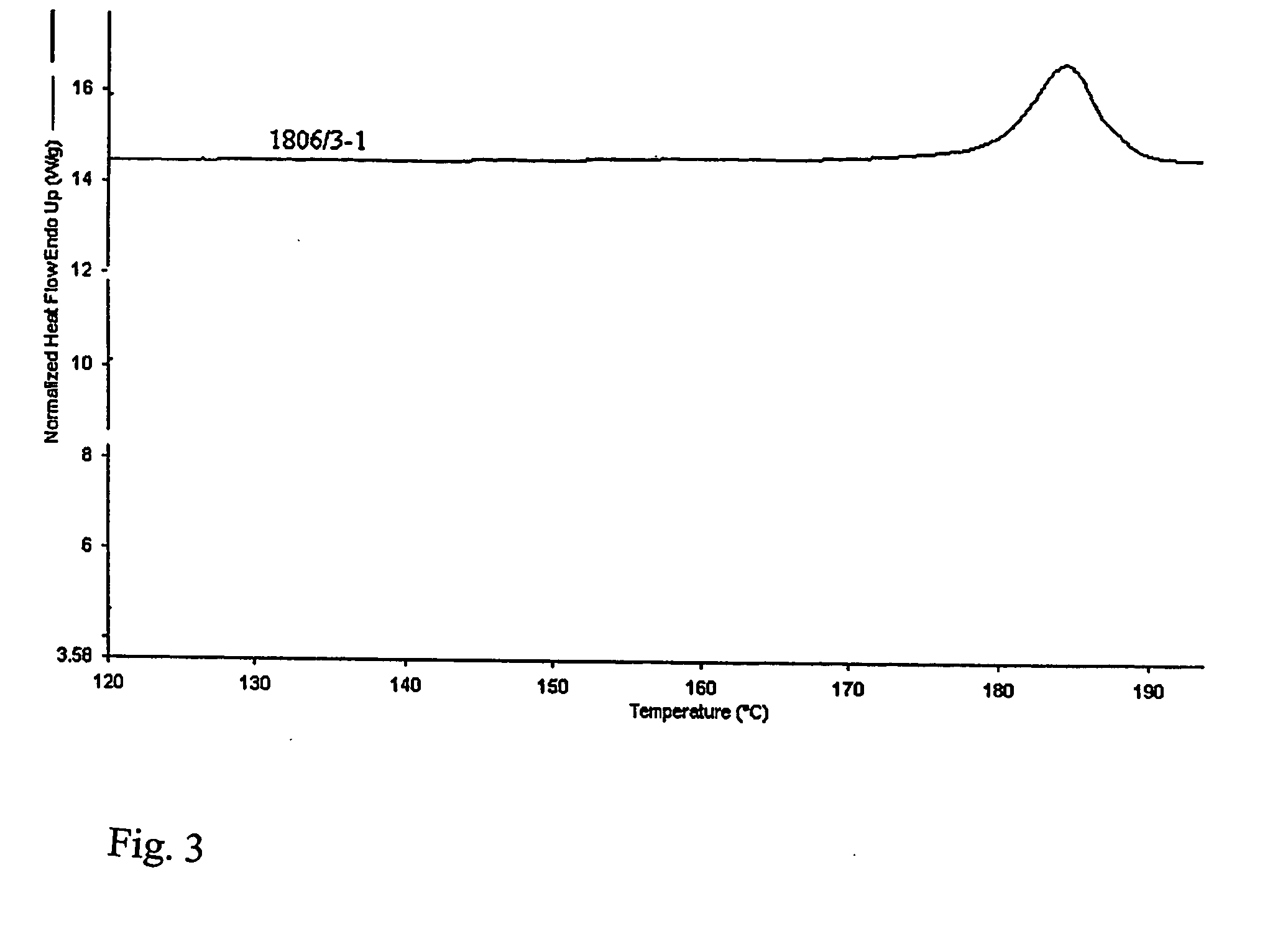
Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate
A novel crystalline form of (S)—N-(5-((R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide, pharmaceutical compositions containing said crystalline form and the use of said crystalline form in the treatment of pain, cancer, inflammation, neurodegenerative disease or Trypanosoma cruzi infection are disclosed. In some embodiments, the novel crystalline form comprises a stable polymorph of (S)—N-(5-((R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate. The present invention is further directed to a process for the preparation of the novel crystalline form.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA
Method for recycling metal in waste LiMn1-x-yNixCoyO2 battery and preparing LiMn1-x-yNixCoyO2
ActiveCN104538695AImprove performanceReduce recycling costsCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingHydrogen SulfateFiltration
A method for recycling metal in a waste LiMn1-x-yNixCoyO2 battery and preparing LiMn1-x-yNixCoyO2 comprises the steps that a waste lithium ion battery is discharged and dismantled, or positive electrode leftover materials and positive electrode fragments are collected, and waste positive plates are obtained; waste LiMn1-x-yNixCoyO2 powder is obtained through the calcinations, water dissolution and the filtration of the waste positive plates; the waste LiMn1-x-yNixCoyO2 powder and potassium pyrosulfate are mixed according to a certain proportion and calcinated, the calcinated products are leached by water, a potassium carbonate solution is added into the solution, then the filtration is carried out, the proportion of Li, Ni, Co and Mn in filter residues is adjusted by supplying carbonate, ball-milling, compressing and the calcinating are carried out on the Li, the Ni, the Co and the Mn, and LiMn1-x-yNixCoyO2 positive materials are regained. Composition adjustment is carried out on filtrate with sulfuric acid, and potassium hydrogen sulfate is obtained after the crystallization treatment is carried out.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Sterilization powder, and preparation method.
InactiveCN101049107AImprove permeabilityImprove effectivenessBiocideDisinfectantsHydrogen SulfateNuclear chemistry
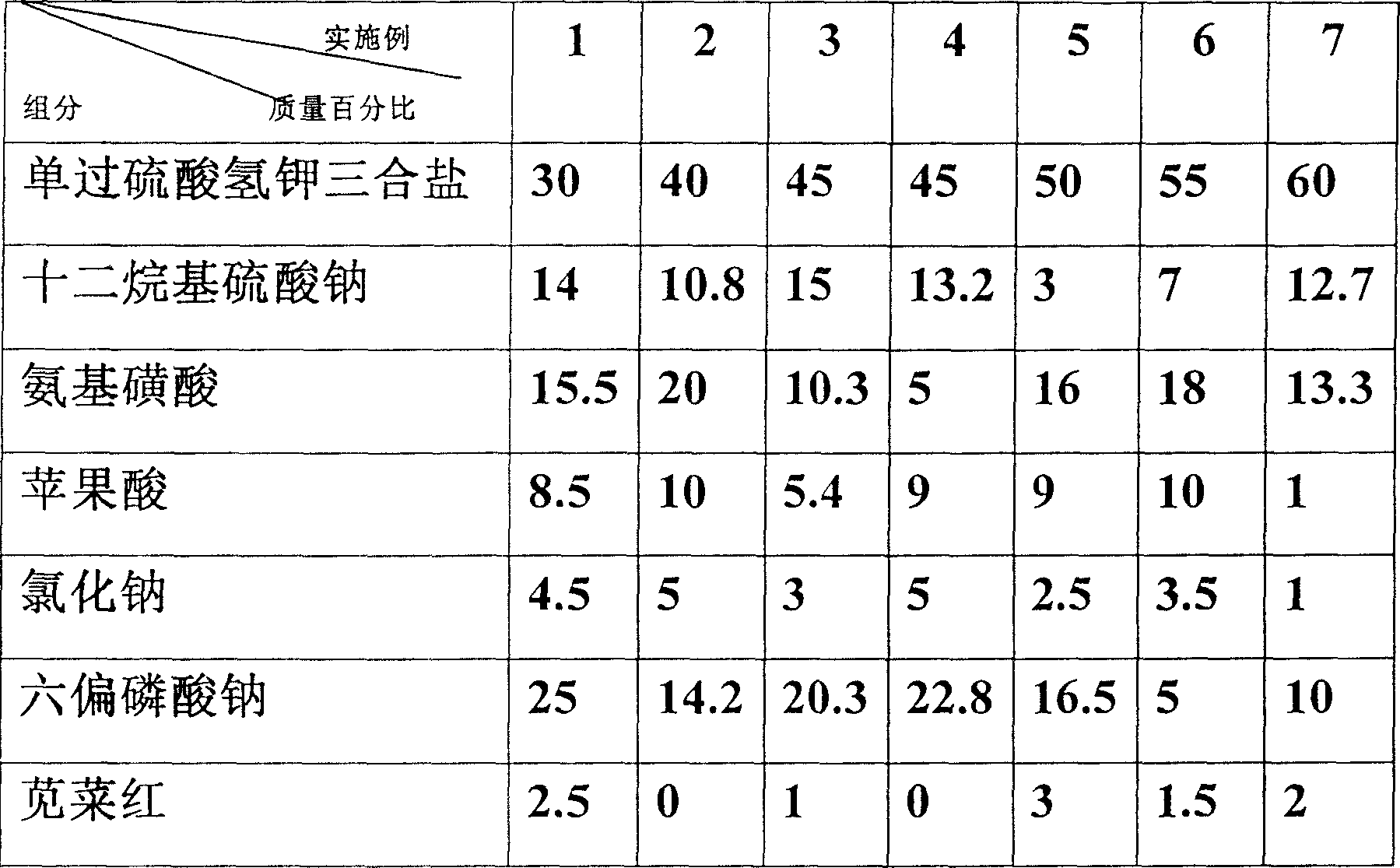
A disinfecting powder with high killing power to virus is proportionally prepared from the mixture of potassium hydrogen monosulfate, potassium hydrogen persulfate and potassium hydrogen sulfate, sodium laurylsulfate, sodium hexametaphosphate, aminosulfonic acid, malic acid and sodium chloride. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:CHENGDU ROSUN DISINFECTION PHARMA
Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA INC
Method for comprehensively recovering aluminum and potassium from vanadium extraction from stone coal
InactiveCN102424914AHigh recovery rateEfficient recyclingProcess efficiency improvementHydrogen SulfateAluminium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering aluminum and potassium from vanadium extraction from stone coal. The technical process of the method mainly comprises: crystallizing pentaphyllum potassium aluminum sulfate in sulfuric acid leachate of stone coal; purifying pentaphyllum potassium aluminum sulfate recrystals, or adding water to dissolve the pentaphyllum potassium aluminum sulfate recrystals and adding a potassium-containing pH regulator to precipitate aluminum; filtering to obtain aluminum hydroxide and a potassium sulfate or potassium hydrogen sulfate solution; transforming the potassium sulfate or potassium hydrogen sulfate solution by lime to obtain potassium carbonate or potassium hydroxide; and thus, effectively separating and recovering aluminum and potassium. The method has the advantages that: the aluminum and potassium recovery rates are high; the products are diversified; impurities harmful to the recycling of water from vanadium extraction from stone coal are not introduced in the aluminum and potassium recovery technical process; the reagent consumption is small; the production cost is low; environment pollution is avoided; and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Quaternary ammonium ionic liquid as well as preparation and application method thereof
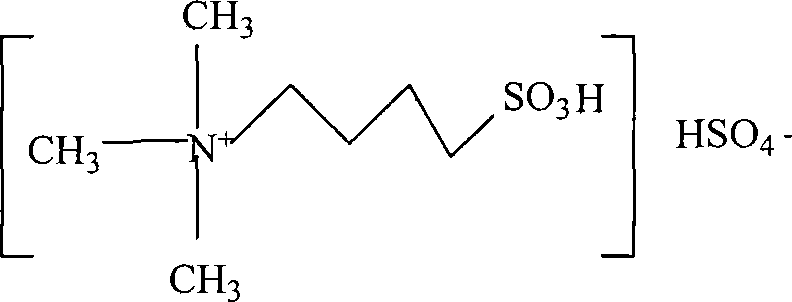
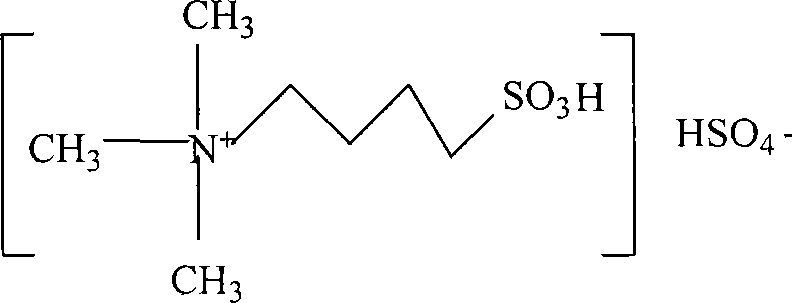
InactiveCN101182300AUnique physical and chemical propertiesReduce corrosionOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMolecular compositionHydrogen Sulfate
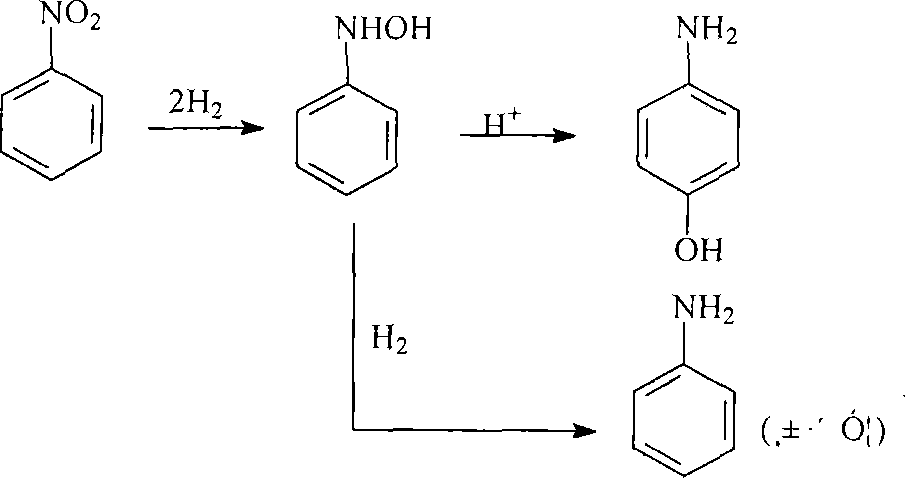
A quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid of the present invention and its preparation and application methods belong to quaternary ammonium compounds, and its molecular composition is N, N, N-trimethyl-N-sulfobutyl-ammonium bisulfate, and its molecular formula is [HSO3-b -N(CH3)3]HSO4, the structural formula is as follows: the quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid of the present invention is non-corrosive equipment and environment-friendly, and the quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid catalyst of the present invention is used for nitrobenzene catalytic hydrogenation to synthesize p-amino The phenol reaction is a liquid phase method, the reaction temperature is 60-130° C., and the PAP yield reaches 19.5-88%.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
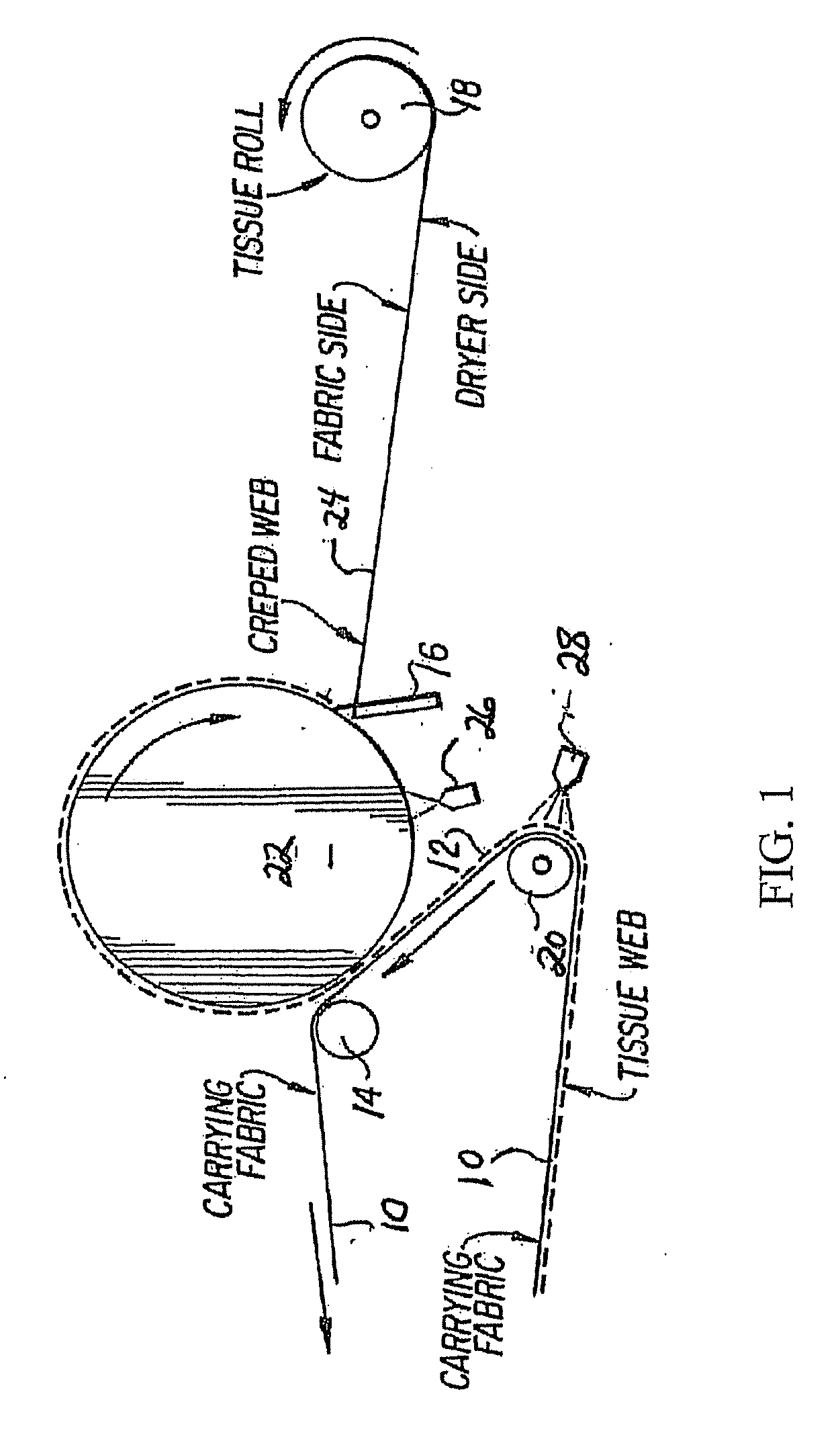
Acidified polyamidoamine adhesives, method of manufacture, and use for creping and ply bond applications
InactiveUS20080257507A1Excellent crepingExcellent plyNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperAdhesiveIodide
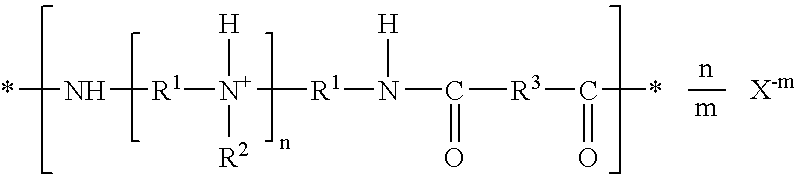
A paper adhesive composition includes a cationic non-crosslinked acidified solution of a polyamidoamine with the repeating unitswherein n≧1; m=1 or 2; X−m is chloride, bromide, iodide, sulfate, bisulfate, nitrate, oxalate, alkyl carboxylate, aryl carboxylate, hydrogen phosphate, dihydrogen phosphate, alkyl sulfonate, aryl sulfonate, or a combination comprising at least one of the foregoing anions; R1 is a divalent aliphatic, cycloaliphatic, or araliphatic group having from 1 to 24 carbon atoms; R2 is hydrogen or a monovalent aliphatic, cycloaliphatic, or araliphatic group having from 1 to 24 carbon atoms; and R3 is a divalent hydrocarbon radical derived from a dibasic carboxylic acid.
Owner:KEMIRA CHEM
Method for regenerating positive electrode active material in LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 waste lithium ion battery
ActiveCN104466295AImprove performanceReduce recycling costsWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingHydrogen SulfateSodium bisulfate
The invention discloses a method for regenerating a positive electrode active material in a LiNi1 / 3Co1 / 3Mn1 / 3O2 waste lithium ion battery. The method includes the steps that the waste lithium ion battery is subjected to discharging and dismantling or positive pole leftover materials and positive electrode fragments are collected to obtain waste positive plates, and the waste positive plates are subjected to roasting, water dissolving and filtering to obtain waste LiNi1 / 3Co1 / 3Mn1 / 3O2 powder; the waste LiNi1 / 3Co1 / 3Mn1 / 3O2 powder and sodium pyrosulfate are roasted after being mixed according to a certain proportion, roasted products are leached by water, then a sodium carbonate solution is added into liquor, filtering is conducted, after the proportion of Li, Ni, Co and Mn in carbonate modulation filter residues is supplemented, the Li, Ni, Co and Mn are subjected to ball milling, compressing and roasting, and accordingly the LiNi1 / 3Co1 / 3Mn1 / 3O2 positive electrode material is obtained again. Components of filter liquor are adjusted through sulfuric acid, crystallization processing is carried out, and then sodium hydrogen sulfate is obtained.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for recovering cobalt lithium metal from waste lithium ion battery of lithium cobalt oxide positive material
ActiveCN104466292AHigh recovery rateShort processWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementHydrogen SulfateLithium metal
The invention discloses a method for recovering cobalt lithium metal from a waste lithium ion battery of a lithium cobalt oxide positive material. The method comprises the following steps: discharging and disassembling the waste lithium ion battery to obtain a waste positive plate, roasting the waste positive plate, dissolving with water and filtering to obtain waste lithium cobalt oxide powder; mixing the waste lithium cobalt oxide powder and sodium hydrogen sulfate according to a certain proportion and then roasting; leaching the roasting product with water; adding sodium carbonate solution into the solution and then filtering; supplementing a certain quantity of lithium carbonate into filter residue and then performing ball milling, pressing and placing in a resistance furnace to roast to newly obtain the lithium cobalt oxide positive material with good electrochemical performance, wherein the ingredients of the filter liquor are adjusted by using sulfuric acid and the sodium hydrogen sulfate obtained after the crystallization treatment is performed can be reutilized.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of hydroxyapatite
InactiveCN1631773AReduce manufacturing costWide variety of sourcesPhosphorus compoundsHydrogen SulfateApatite
The invention is preparation of hydroxyl group apatite at middle and low temperature direct by conch one step process. The invention uses the conch powder as rough material mixed with hydrogen sulfate solution and pyrolyzes 6 to 48 hours at temperature of 90 to 105 deg C. After the reaction collate and dry to obtain the hydroxyl group apatite powder. The rough material shell in the invention has a broad source and low price. The preparation is very simple which is just one step to convert shell directly to hydroxyl group apatite so to greatly lower the prepare cost of the hydroxyl group apatite.
Owner:NINGBO ECONOMIC & TECH DEV ZONE JINGGE NEW MATERIAL DEV
Complex catalyst for synthesizing carbonate ester by using homogeneous oxidation carbonylation of alcohol (S), its prepn. tech. and use
InactiveCN1792453ASimple preparation processHigh activityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsQuaternary ammonium cationProtein carbonyl
A complex catalyst for preparing carbonate from alcohol by homogeneous oxidizing-carbonylating reaction has a chemical formula MXnLm, where M is metal, X is chosen from halogen, SO4 (or HSO4) radical, CO3 (or HCO3) radical, etc, L is chosen from RN4 ion, RP4 ion, pyridine, etc, and m=1-12. It is prepared through complex reaction between quaternary ammonium (or phosphorus) salt and metal salt. Its application method is also disclosed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for recovering cobalt lithium aluminum from positive pole plate of scrap lithium ion battery
ActiveCN104103870AHigh recovery rateReduce recycling costsWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingHydrogen SulfateLithium carbonate
The invention discloses a method for recovering cobalt lithium aluminum from the positive pole plate of a scrap lithium ion battery. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, discharging and disassembling the scrap lithium ion battery, calcinating the scrap positive pole plate in a chamber electric furnace, and dissolving and filtering with water so as to obtain scrap lithium cobalt oxides powder and aluminum foil; secondly, mixing the scrap lithium cobalt oxides powder and sodium hydrogen sulfate or sodium purosulfate according to a certain proportion, and then placing the mixture in a ball mill for ball milling; thirdly, placing the mixture obtained after the ball milling in the chamber electric furnace for calcinating at low temperature; fourthly, leaching a product obtained after the calcination with water for generating a leaching liquid to be subjected to operations of cobalt sedimentation and lithium sedimentation so as to obtain cobalt oxalate and lithium carbonate.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing ultrafine high-whiteness active barite powder
ActiveCN102616824AConserve waterFully washedCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEHydrogen Sulfate
The invention relates to the field of mineral materials, in particular to a method for preparing ultrafine high-whiteness active barite powder. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing pulp from 325-mesh barite powder, and performing wet ultrafine grinding until the particle size is less than 10mu m; (2) filtering the barite pulp subjected to wet ultrafine grinding, and drying; (3) adding mixed acid into the dried ultrafine barite powder, and performing oxidation leaching reaction with stirring, wherein the mixed acid is a mixed solution of sulfuric acid, hydrofluoric acid and oxalic acid; (4) filtering the barite powder subjected to oxidation leaching reaction by the mixed acid, and washing until the pH is 6 to 7; and (5) performing pressure filtration, and drying to obtain the ultrafine high-whiteness active barite powder. The preparation method is simple and controllable and easy to popularize, equipment can be localized completely, over 99 percent of prepared barite product has the particle size of -10mu m, and the whiteness is over 90 percent.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Composite flocculant for water treatment and its preparing process
InactiveCN100406396CNo secondary pollutionLow toxicityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationHydrogen SulfateSilicic acid
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
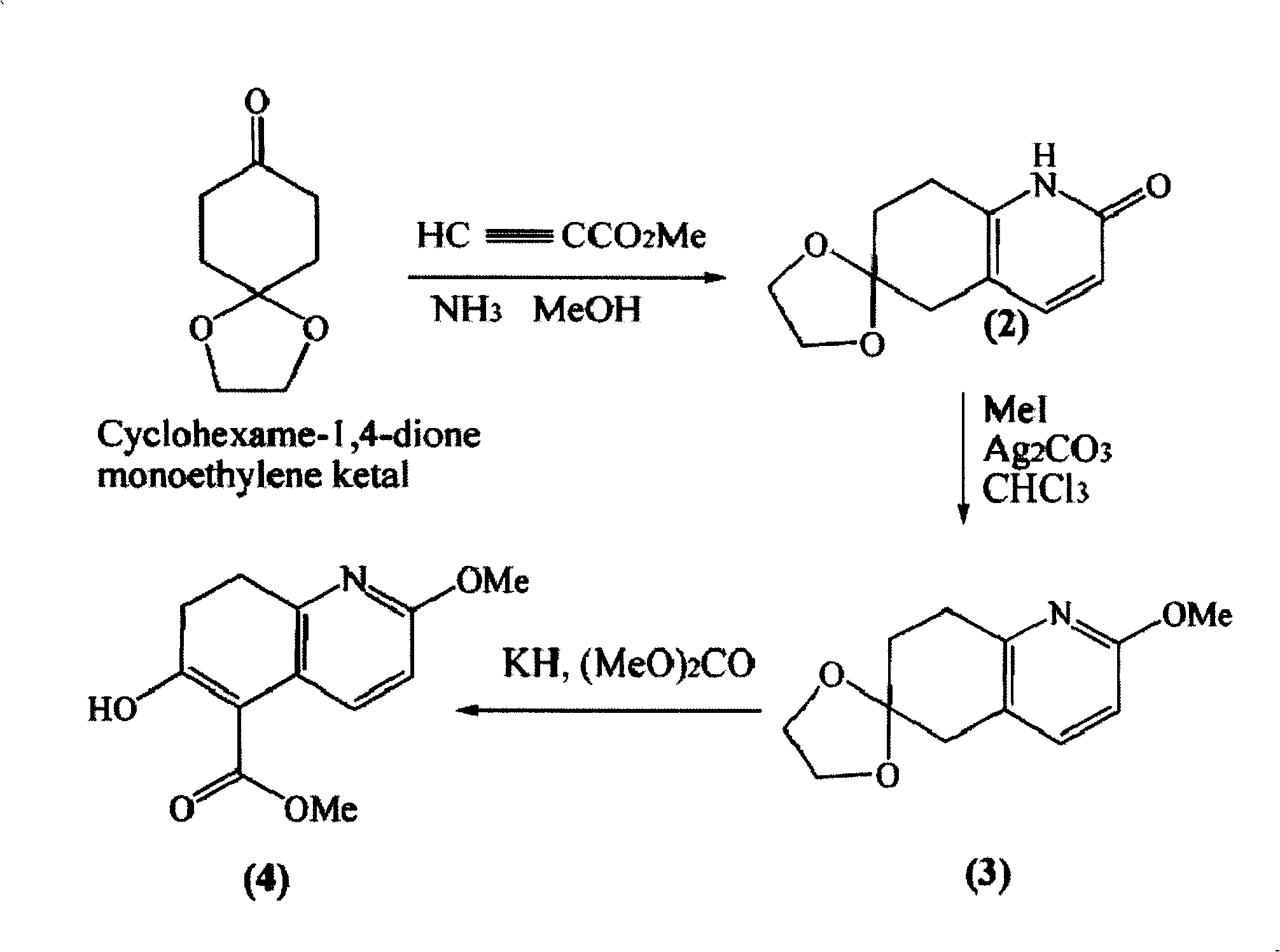
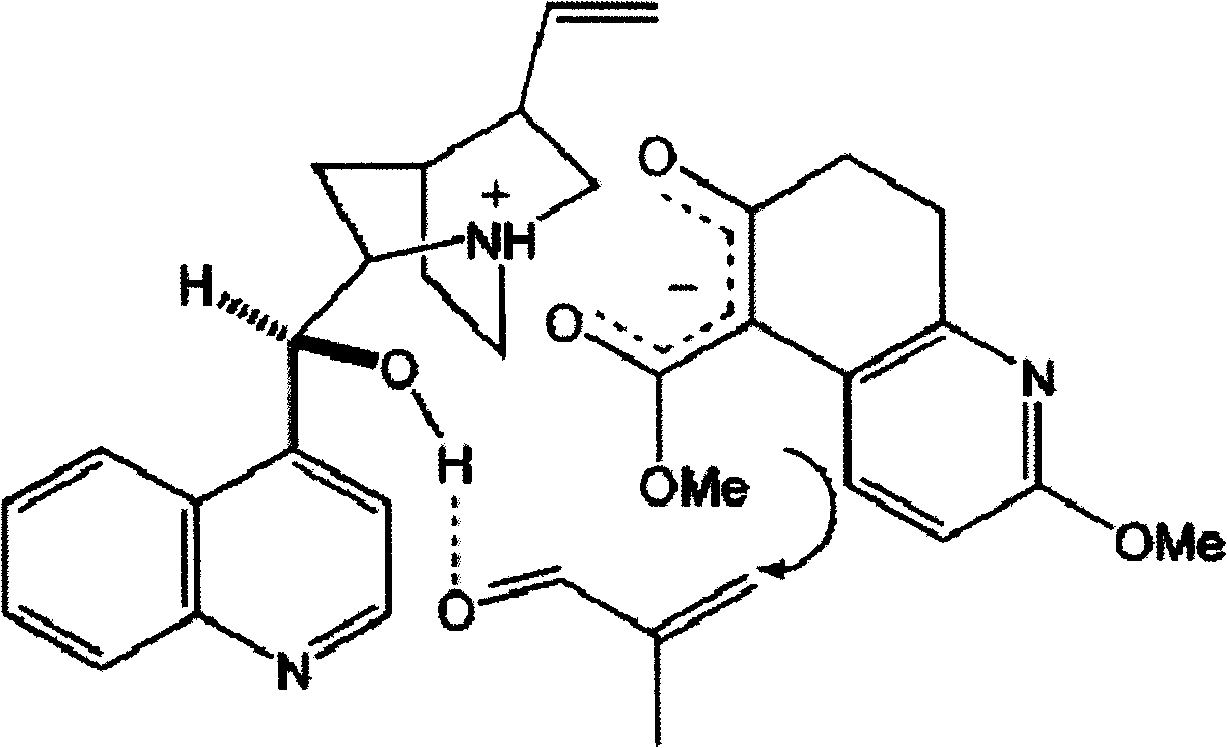
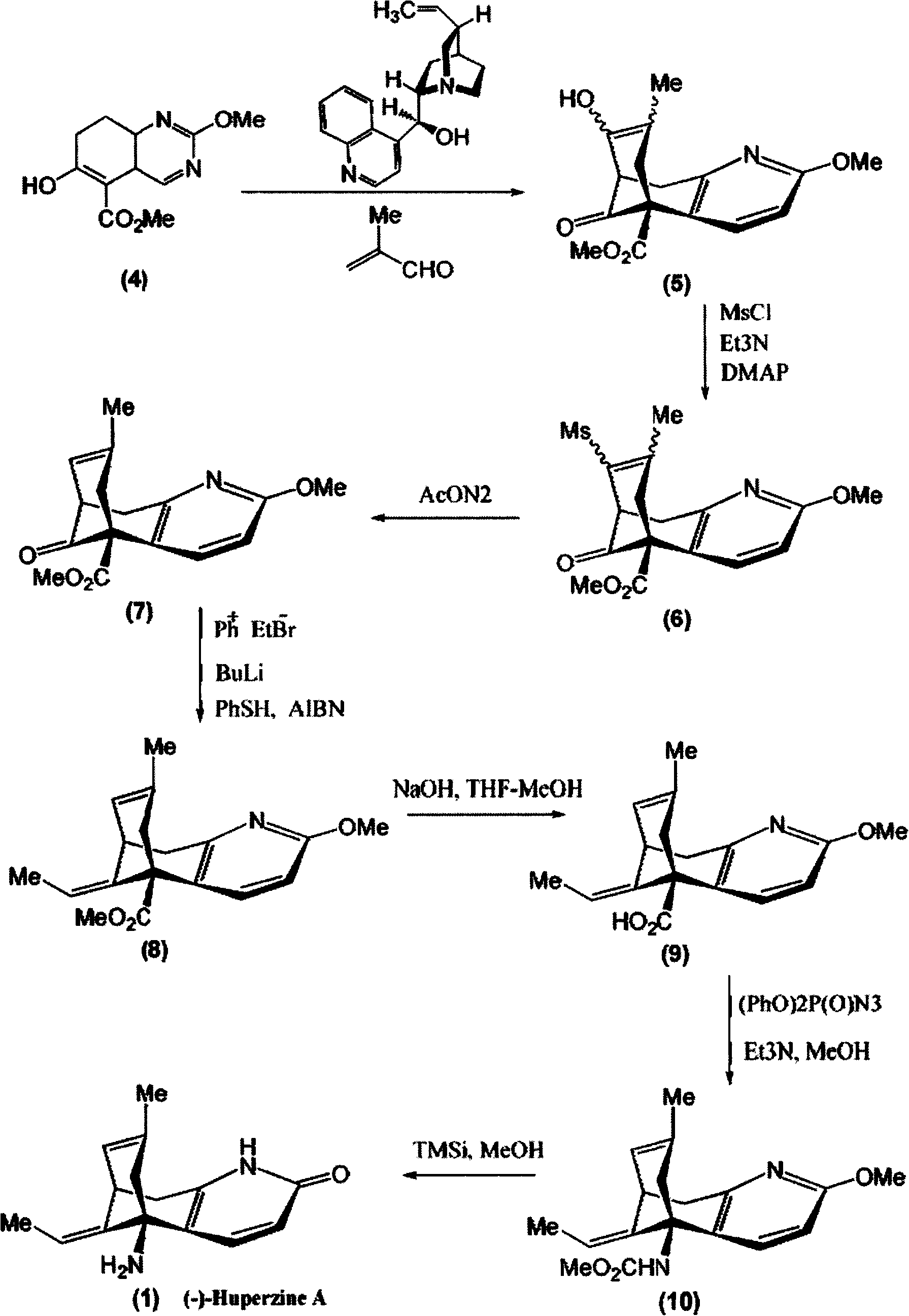
Asymmetric synthesis for chiral huperzine A
Disclosed is an asymmetric total-synthesis method for chiral huperzine a. The method takes 1,4-dihydro-spiro (4,5) -8 -decanone as starting material to get benzoate through hydroxymethylation and the treatment of benzoyl chloride and K2CO3; the benzoate is reacted with hydrogen sulfate O-methyl iso urea to get quinazoline; after the ketal is eliminated, Mander reagent is used for methyl esterification reaction so as to obtain beta-keto ester. Chiral ammonia, such as cinchona alkaloid, is used to promote the tandem asymmetric Michael addition / aldol condensation reaction of beta-keto esters and methyl acrolein. The compound carboxylate of diastereoisomer is reacted with MsCl, triethylamine and DMAP to get transformed. Through TMSI and MeOH processing, the protective group is removed so as to obtain optically pure-chiral huperzine a.
Owner:京山瑞生制药有限公司 +1
Method of treating livestock footbath solutions
This invention relates to a method of treating a livestock footbath solution comprising adding an alkali metal bisulfate to the solution. The invention also relates to a method of treating a livestock footbath solution comprising adding to the solution a blend of an alkali metal bisulfate and a material to treat a bacterial disease. The invention also relates to a method of treating a livestock footbath solution comprising rotating the addition to the solution of an alkali metal bisulfate and a material to treat a bacterial disease.
Owner:JONES HAMILTON
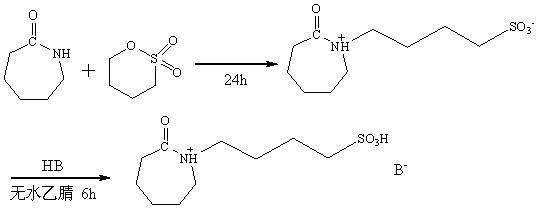
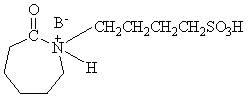
Sulfonic- functionalized caprolactam acidic ion liquid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102120728ACheap and easy to getThe synthesis steps are simpleOrganic chemistryHydrogen SulfateSulfate radicals
The invention relates to a chemical product and a preparation technology thereof, in particular to sulfonic-functionalized caprolactam acidic ion liquid and a preparation method thereof. The ion liquid has the following structural general formula shown in the specification, wherein B<-> is selected from the following anions: hydrogen sulfate radicals, p-toluene sulfate radicals, formate radicals, phosphate radicals, and acetate radicals. The preparation method comprises the steps of: firstly, mixing a caprolactam water solution with the concentration of 5-10mol / L with 1,4-butane sultone in the molar ratio of 1:1.1 for reaction for 6-24 h at the temperature of 25-80 DEG C; and then, reacting a reaction product with conjugate acid of the paired anion B<-> in the molar ratio of 1:1 for 4-6h. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages that the raw materials are cheap and are easy to obtain and the synthesis steps are simple and convenient and are easy to popularize and apply; the varieties of anions can be adjusted as required so as to satisfy requirements on different acidities so that stronger adjustability is achieved; and the synthesized ion liquid is more degradable than ion liquid of imidazole and pyridine, and is more environmental-friendly and recyclable.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
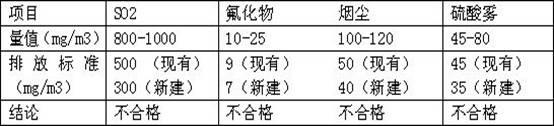
Novel comprehensive utilization technique of industrial waste sulfuric acid
InactiveCN101200439AImprove qualityIncrease profitOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSocial benefitsHydrogen Sulfate
The invention relates to a method for recycling the waste sulfuric acid of the second separation during the production process of the industrial sulfanilamide. The invention method is the novel process of first recycling the organic matter and second treating the waste sulfuric acid, and hydrochloric acid and ammonium hydrogen sulfate or ammonium sulfate with wide application by the treatment of the waste sulfuric acid. The invention not only reduces the environmental pollution and but also decreases the production cost of the industrial sulfanilamide, and has the good environmental protection benefit, the social benefit and the enormous economic benefit.
Owner:BEIJING ZIGUANG YINGLI CHEM TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing solid-state calcium magnesium titanium iron sulfur nitrogen silicon composite fertilizer by using water to quench titanium-containing blast furnace slag
InactiveCN101265136ASolve pollutionMeet needsAmmonium salt fertilisersFertilizer mixturesAir atmosphereHydrogen Sulfate
The invention belongs to a method for producing plant fertilizers, more particularly to a method for producing a solid-state Ca / Mg / Ti / Fe / S / N / Si compound fertilizer from water-quenched blast furnace slag. The invention is characterized in that: the raw materials include titanium oxide-containing water-quenched blast furnace slag, ammonium sulfate, ammonium hydrogen sulfate, ammonium pyrosulfate and ammonium persulfate; the method comprises the following steps: ball-milling Ti-containing water-quenched blast furnace slag to obtain powder of particle size of 60-160 micrometers, mixing the furnace slag powder with 3-20 times of one substance selected from ammonium sulfate, ammonium hydrogen sulfate, ammonium pyrosulfate, ammonium persulfate, or a mixture thereof, heating the resulting mixture up to 200-500 DEG C and maintaining the temperature for 10-65 min, and crushing clinkers to small pieces of 4-12 mm diameter. The invention utilizes Ti-containing water-quenched blast furnace slag and other raw materials to produce plant fertilizers, and thereby realizes environmental protection, Ti resource utilization and nutrient supplementation to plants.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
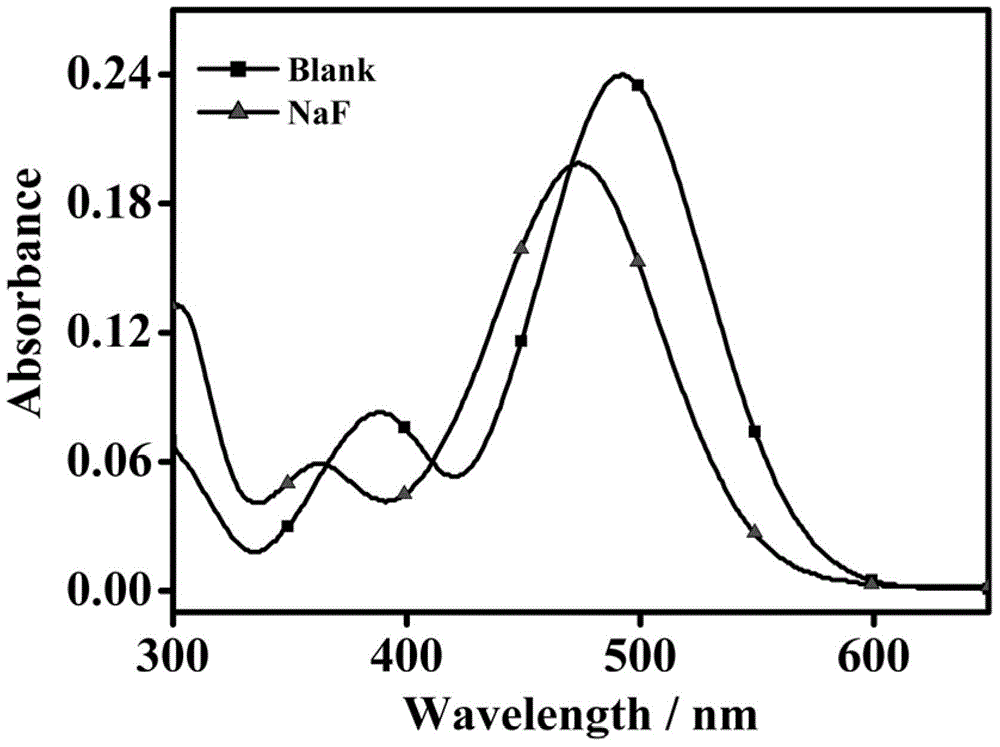
Fluorescent molecular probe for detecting fluoride ions in aqueous solutions as well as synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN104418874AEasy to synthesizeMild reaction conditionsGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceHydrogen SulfateSulfate radicals
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fluorescent molecular probe for detecting fluoride ions in aqueous solutions through fluorescence enhancement and an application of the fluorescent molecular probe to detecting fluoride ions. The fluorescent molecular probe is prepared by protecting 1,4-diethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-7-hydroxyquinoxaline-6-aldehyde taken as a raw material with silane and then condensing the raw material and malononitrile. The fluorescent molecular probe is simple and convenient to synthesize, and reaction conditions are mild. The fluorescent molecular probe has the specific characteristics that the probe molecule has stable optical properties and higher synthetic yield; the probe molecule has high sensitivity of detection of fluoride ions in the aqueous solutions and low lower limit of detection, and the limit of detection is 5.4mu M; the response range is 0-1mM and the detection range is wide; the probe molecule has good selectivity and has no responses to anions, such as chloride ions, bromide ions, iodide ions, tetrabutylammonium cyanide, nitrates radicals, hydrosulfate radicals, perchlorate radicals, acetate radicals, thiocyanate radicals, azide radicals, cysteine, bovine serum albumin, carbonate radicals, sulfate radicals and reduced glutathione; the fluorescent molecular probe has practical application values in the fields of biochemistry, environmental sciences and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU ROWLAND BIOTECH
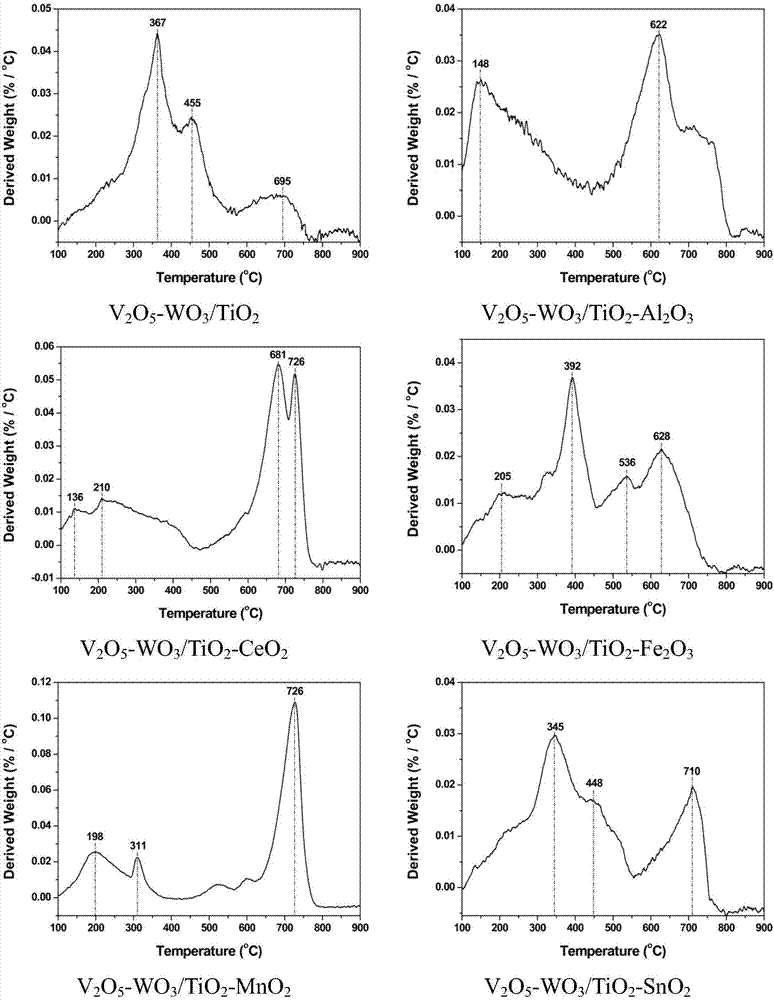
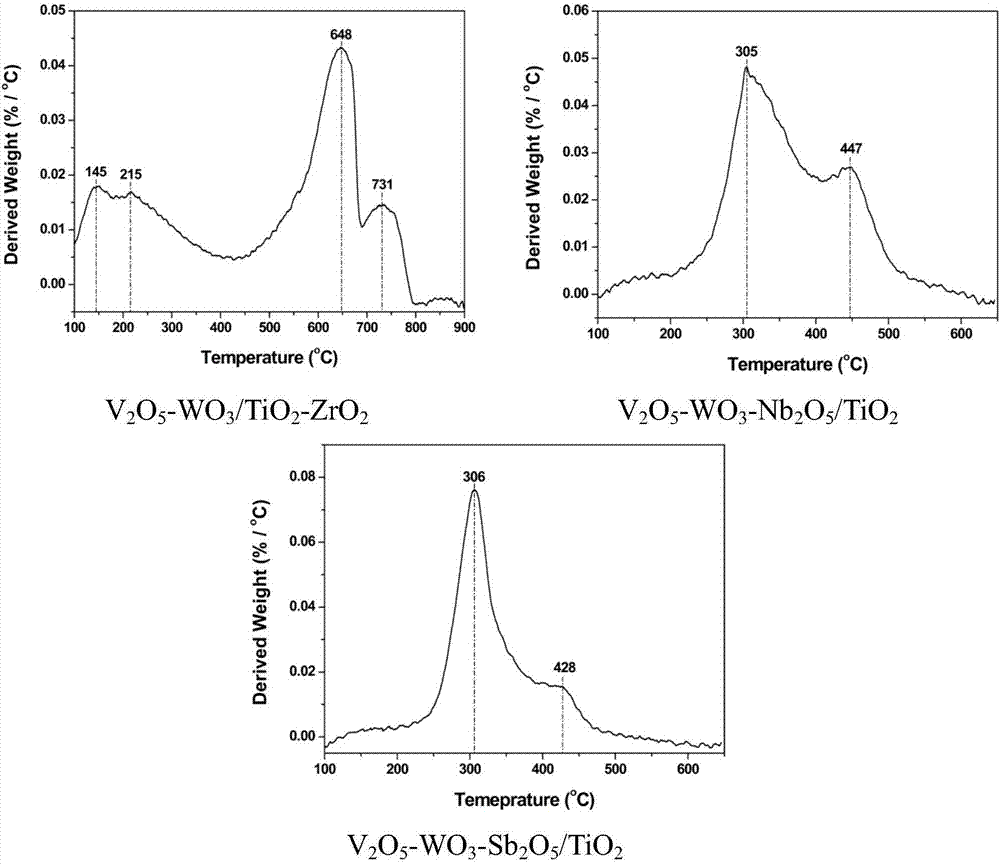
SCR (selective catalytic reduction) denitration catalyst for accelerating ammonium hydrogen sulfate decomposition by low-temperature flue gas, preparation method and application
ActiveCN107262086APromote low temperature decompositionFacilitate decomposition behaviorDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrogen SulfateDecomposition
The invention relates to an SCR (selective catalytic reduction) denitration catalyst, in particular to an SCR (selective catalytic reduction) denitration catalyst for accelerating ammonium hydrogen sulfate decomposition by low-temperature flue gas, a preparation method and an application. The SCR denitration catalyst takes composite oxides formed by titanic oxides and transition metal oxides as carriers, vanadium oxides as active components and tungsten oxides as co-catalysts, the molar ratio of transition metal elements to titanium elements in the catalyst is (0.1-0.5):1, and the transition metal oxides include one or more of MnO2, Fe2O3, CeO2, ZrO2, Al2O3, SnO2, Nb2O5 and Sb2O5. An appropriate quantity of transition metal oxides are added into the catalyst, the SCR denitration catalyst for accelerating low-temperature decomposition of ammonium hydrogen sulfate is prepared, and the catalyst accelerates the ammonium hydrogen sulfate to decompose at the temperature lower than 350 DEG C.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for manufacturing crystalline form I of clopidogrel hydrogen sulphate
InactiveUS20060041136A1Powder deliveryOrganic chemistryClopidogrel hydrogen sulphateHydrogen Sulfate
A method for manufacturing hydrogen sulphate (alpha S) of the alpha-(2-chlorophenyl)-6,7dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4H)-acetic acid methyl ester (clopidogrel hydrogen sulphate) of formula I, in crystalline Form I, wherein the compound of formula is separated out of a solution of clopidogrel in the form of the free base or salt in a solvent selected from the series of primary, secondary or tertiary C1-C5 alcohols, their esters with C1-C4 carboxylic acids, or optionally of mixtures thereof.
Owner:ZENTIVA AS
Method for recycling metal from waste lithium ion battery with Ni-Co lithium manganite positive electrode materials
ActiveCN104538696AHigh recovery rateReduce recycling costsWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementHydrogen SulfateFiltration
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Resource recycling method of industrial phosphogypsum waste residues
ActiveCN104211099AResource conservationHigh chemical puritySulfate/bisulfate preparationCalcium/strontium/barium oxides/hydroxidesHydrogen SulfateSilicic acid
The invention discloses a resource recycling method of industrial phosphogypsum waste residues and relates to the technical field of inorganic chemical industry. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out a reaction on gypsum calcium sulfate and concentrated sulfuric acid to generate calcium hydrogen sulfate; carrying out a reaction on calcium hydrogen sulfate which is 1 time and a sodium hydroxide NaOH or potassium hydroxide KOH aqueous solution which is 4 times; filtering or precipitating and separating to recover calcium hydroxide, limonite, silicic acid and calcium fluoride and CaHPO4; and obtaining sodium sulfate / potassium sulfate, sodium aluminate or potassium aluminate and calcium acetate Ca(CH3COO)2. The method is mainly applied to resource recycling of industrial phosphogypsum waste residues.
Owner:济宁理工思源商务服务有限公司
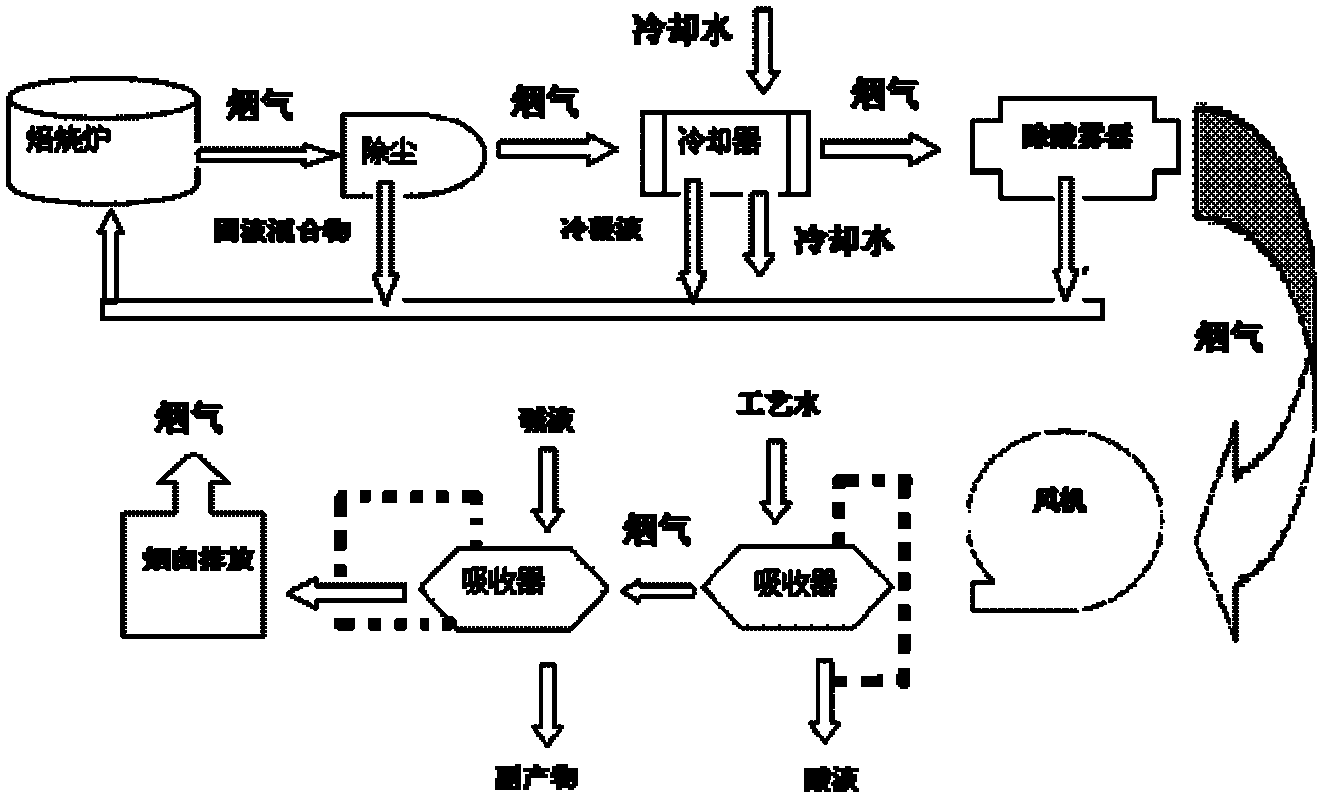
Process for treating tail gas of rare earth mineral powder and concentrated sulphuric acid roasting process
ActiveCN102247708AAvoid energy consumptionAvoid investmentDispersed particle separationVapor condensationHydrogen SulfateHexafluorosilicic acid
The invention relates to a process for treating tail gas of a rare earth mineral powder and concentrated sulphuric acid roasting process. The process comprises the following steps of: introducing the tail gas of 300 DEG C of the process into a dust remover for dust removal with a machine; then introducing the tail gas into a condenser for cooling, condensing massive sulphuric acid fog and water vapour in the smoke and recycling acid liquor; introducing the cooled smoke into an acid fog collector, collecting acid fog and water fog in the smoke for recycling; boosting the treated smoke by a fan, introducing the treated smoke into a first absorber, washing by diluted acid liquor or process water to remove residual sulphuric acid fog, hydrofluoric acid and fluosilicic acid from the smoke; andthen introducing the smoke into a second absorber, washing the smoke by an alkali washing tower to remove residual sulphuric acid fog, hydrofluoric acid and SO2 gas from the smoke, and discharging the smoke out after defogging. The process provided by the invention can save massive smoke cooling water, produce less waste water, reduce waste water treatment cost, and recycle the side product fluoric acid produced by solid mineral substances, sulphuric acid, hydrofluoric acid and the like in the tail gas as a raw material for recycling fluorine.
Owner:北京鸿源龙嘉环保科技有限公司
Method for preparing monopotassium phosphate from fertilizer grade calcium hydrophosphate
The invention relates to a method for preparing monopotassium phosphate from fertilizer grade calcium hydrophosphate. The method comprises the following steps of: slowly adding the fertilizer grade calcium hydrophosphate used as a material into a reaction tank containing potassium hydrogen sulfate solution at 60-68 DEG C, controlling the reaction solid-to-liquid ratio at (1:3)-(1:5) and the reaction time at 6.5-8 hours; controlling the sulphur and phosphorus mass ratio of the potassium hydrogen sulfate to the calcium hydrophosphate in reaction to S to P being (1-1.2):(1-1.4); adjusting the pH value of the filtrate by use of 85% industrial phosphoric acid; generating byproduct calcium sulfate whisker by filtering after the reaction is finished, adjusting the pH value of the filtrate to 4.5-5.5, and preparing the monopotassium phosphate product of meeting the top-quality goods of the national industry standard from the filtrate by purifying, concentrating, crystallizing, dewatering and drying, and controlling the drying temperature at 80-100 DEG C. By adopting the method, the technological process of producing the monopotassium phosphate is simple in flow, low in production cost, free of the three wastes, and easy for realization of large-scale and industrial production.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
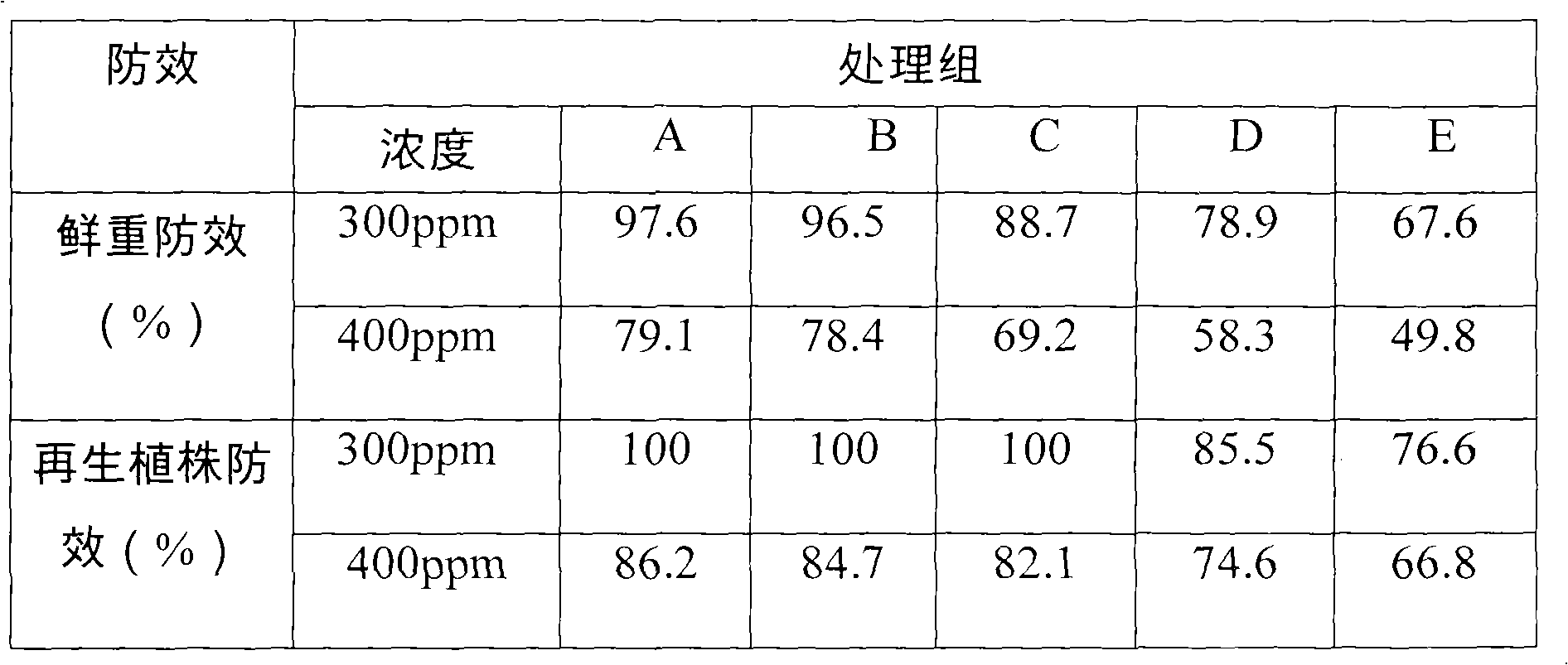
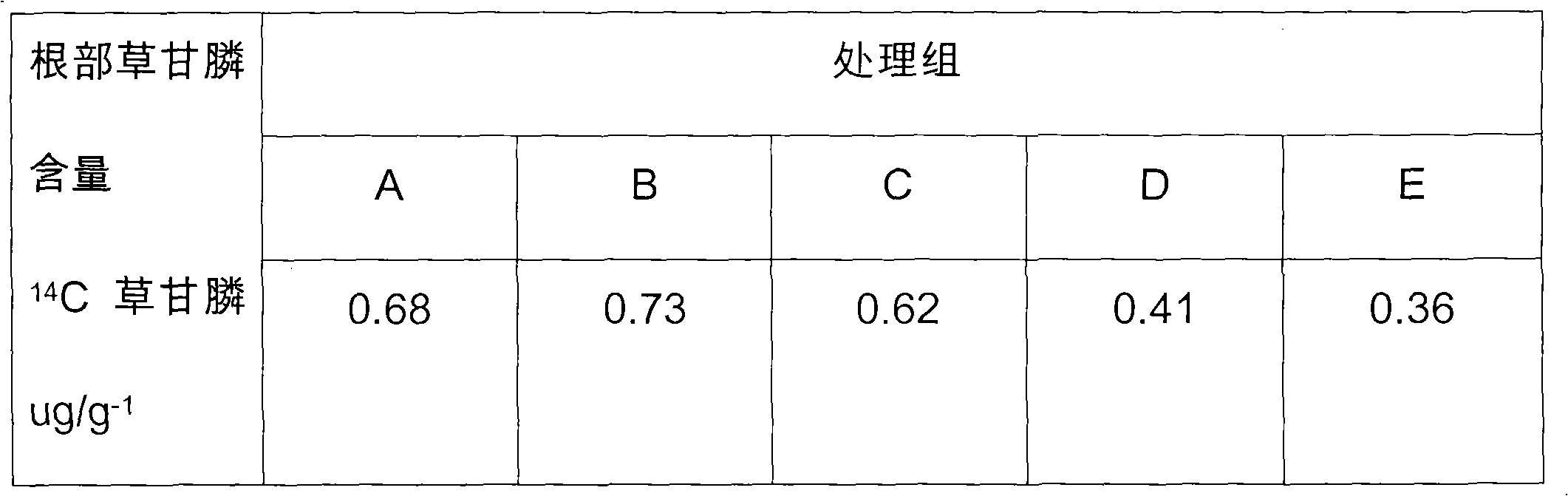
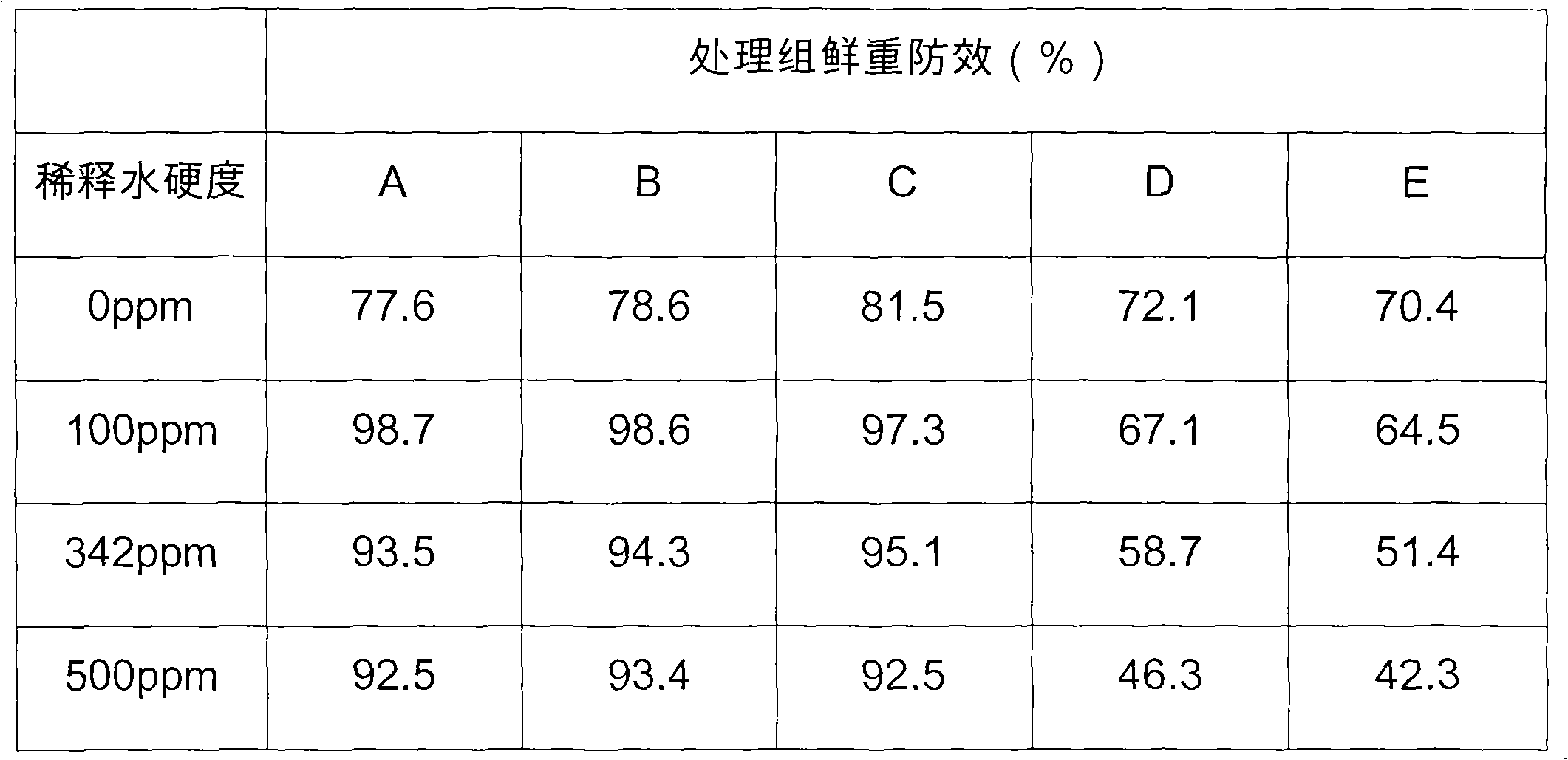
Glyphosate water-based composition
ActiveCN101796964AImprove hard water resistanceSignificant synergyBiocideAnimal repellantsWater basedNoxious weed
The invention relates to a glyphosate water-based composition. The glyphosate water-based composition is characterized in that: the weight percentage of the glyphosate (based on glyphosate acid) in the composition is more than or equal to 20 percent; and the weight percentage of sulfate ions or hydrogen sulfate ions is more than or equal to 20 percent. The glyphosate water-based composition can be processed into an aqueous agent and a suspending agent. The composition has the advantages of promoting plants to adsorb and transmit the glyphosate, enhancing the herbicidal activity of the glyphosate, reducing the using amount of the glyphosate and having special effect of weeding noxious weed such as cogongrass, alligator alternanthera, scandent hop and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPOSION AGROCHEM
Method of dissolving scale
InactiveUS7048803B2Hollow article cleaningTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsHydrogen SulfateAlkali metal
A method of dissolving scale comprises contacting the scale with a solution of an alkali metal bisulfate. Another method of dissolving scale comprises contacting the scale with a solution of an alkali metal bisulfate and a strong mineral acid. A further method of dissolving scale comprises contacting the scale with a solution of an alkali metal bisulfate and an inorganic oxidizer.
Owner:JONES HAMILTON
Method for producing nitrate-and-sulfur-based compound fertilizer and co-producing gypsum by utilizing potassium hydrogen sulfate
InactiveCN102126737ARealize comprehensive utilizationHigh removal rateCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesFertilizer mixturesHydrogen SulfatePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for producing a nitrate-and-sulfur-based compound fertilizer and co-producing gypsum by utilizing potassium hydrogen sulfate, belonging to the technical field of compound fertilizers. The method comprises the following steps: decomposing phosphrite with nitric acid; filtering and removing acid-insoluble substances and organic suspended matters; adding industrial ammonium sulfate or sulfuric acid in the purified acidolysis solution for decalcification; filtering so as to obtain decalcified byproduct high-purity gypsum; producing the nitrate-and-sulfur-based compound fertilizer by using the decalcified acidolysis solution; directly carrying out neutralization reaction on the decalcified acidolysis solution and gas ammonia so as to obtain nitrophosphate fertilizer slurry containing ammonium nitrate and monoammonium phosphate; evaporating the slurry, and then adding potassium hydrogen sulfate; and then granulating and drying so as to obtain the nitrate-and-sulfur-based compound fertilizer. In the invention, the calcium in the acidolysis solution generated after the phosphrite is decomposed by phosphoric acid is removed by using the ammonium sulfate or sulfuric acid, and other impurity ions are not added; and as a nutrient, the ammonia in the ammonium sulfate is remained in a finished product when the calcium is removed by using the ammonium sulfate. The removal rate of the calcium in the acidolysis solution is up to above 95%.
Owner:KINGENTA ECOLOGICAL ENG GRP
Chemical mechanical polishing aqueous dispersion and chemical mechanical polishing method for semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090325383A1Sufficient and almost equal polishing rateDesired thicknessNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingColloidal silicaHydrogen Sulfate
A chemical mechanical polishing aqueous dispersion according to the invention includes (A) 0.1 to 4 mass % of colloidal silica having an average particle diameter of 10 to 100 nm, and (B) 0.1 to 3 mass % of at least one ammonium salt selected from ammonium phosphate, diammonium phosphate, and ammonium hydrogen sulfate, the chemical mechanical polishing aqueous dispersion having a mass ratio (A) / (B) of the component (A) to the component (B) of 1 to 3 and a pH of 4 to 5 and being able to simultaneously polish at least two films that form a polishing target surface and are selected from a polysilicon film, a silicon nitride film, and a silicon oxide film.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/188b02b2-acff-4d2c-ba88-4c922a659078/US20160137654A1-20160519-D00001.PNG)
![Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/188b02b2-acff-4d2c-ba88-4c922a659078/US20160137654A1-20160519-D00002.PNG)
![Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/188b02b2-acff-4d2c-ba88-4c922a659078/US20160137654A1-20160519-D00003.PNG)
![Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/dd488455-105a-4fe6-9198-3f70269ed7d6/US20170165267A1-20170615-D00000.png)
![Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/dd488455-105a-4fe6-9198-3f70269ed7d6/US20170165267A1-20170615-D00001.png)
![Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate Crystalline form of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide hydrogen sulfate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/dd488455-105a-4fe6-9198-3f70269ed7d6/US20170165267A1-20170615-D00002.png)