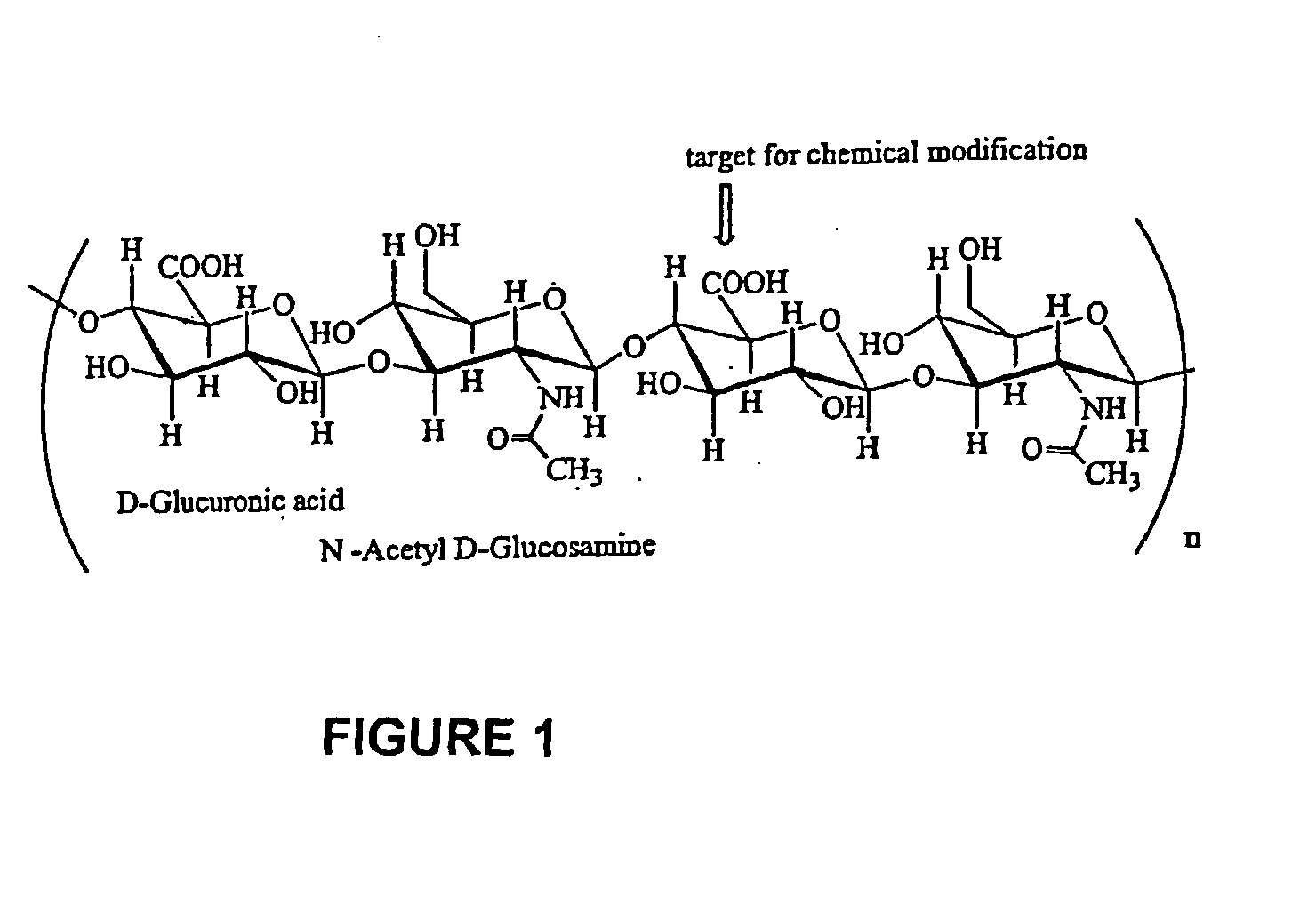
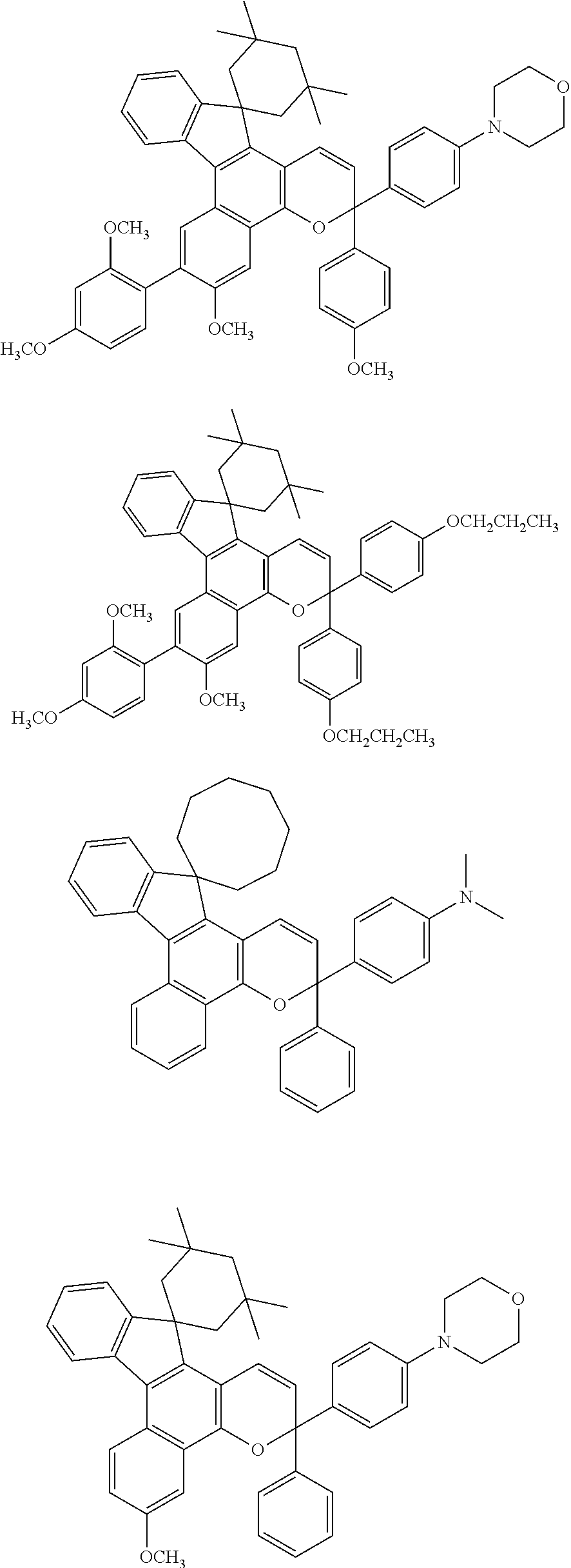
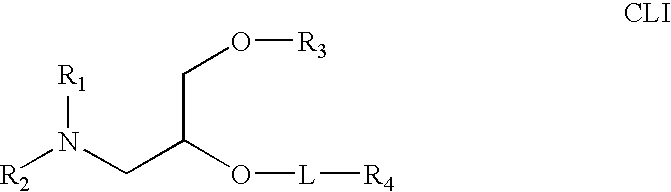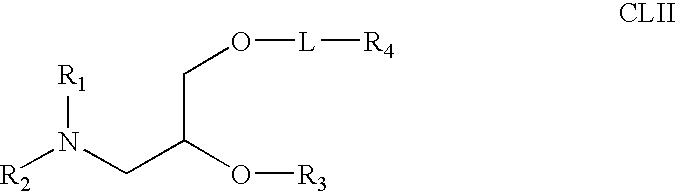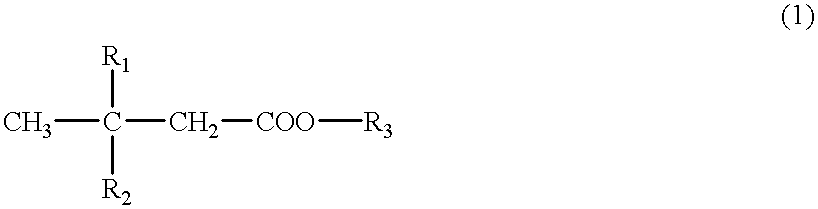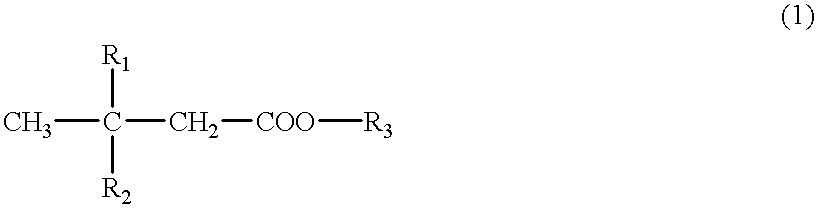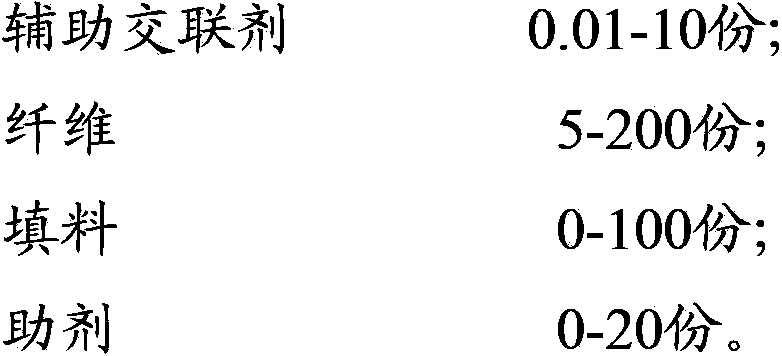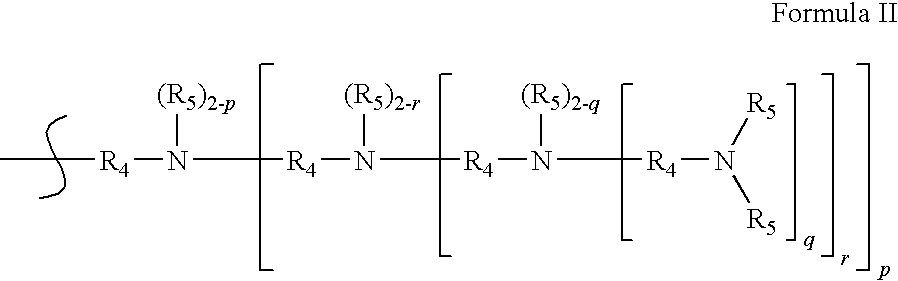Patents
Literature
287 results about "Molecular composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Molecular Composition of Cells. Cells are composed of water, inorganic ions, and carbon-containing (organic) molecules. Water is the most abundant molecule in cells, accounting for 70% or more of total cell mass.
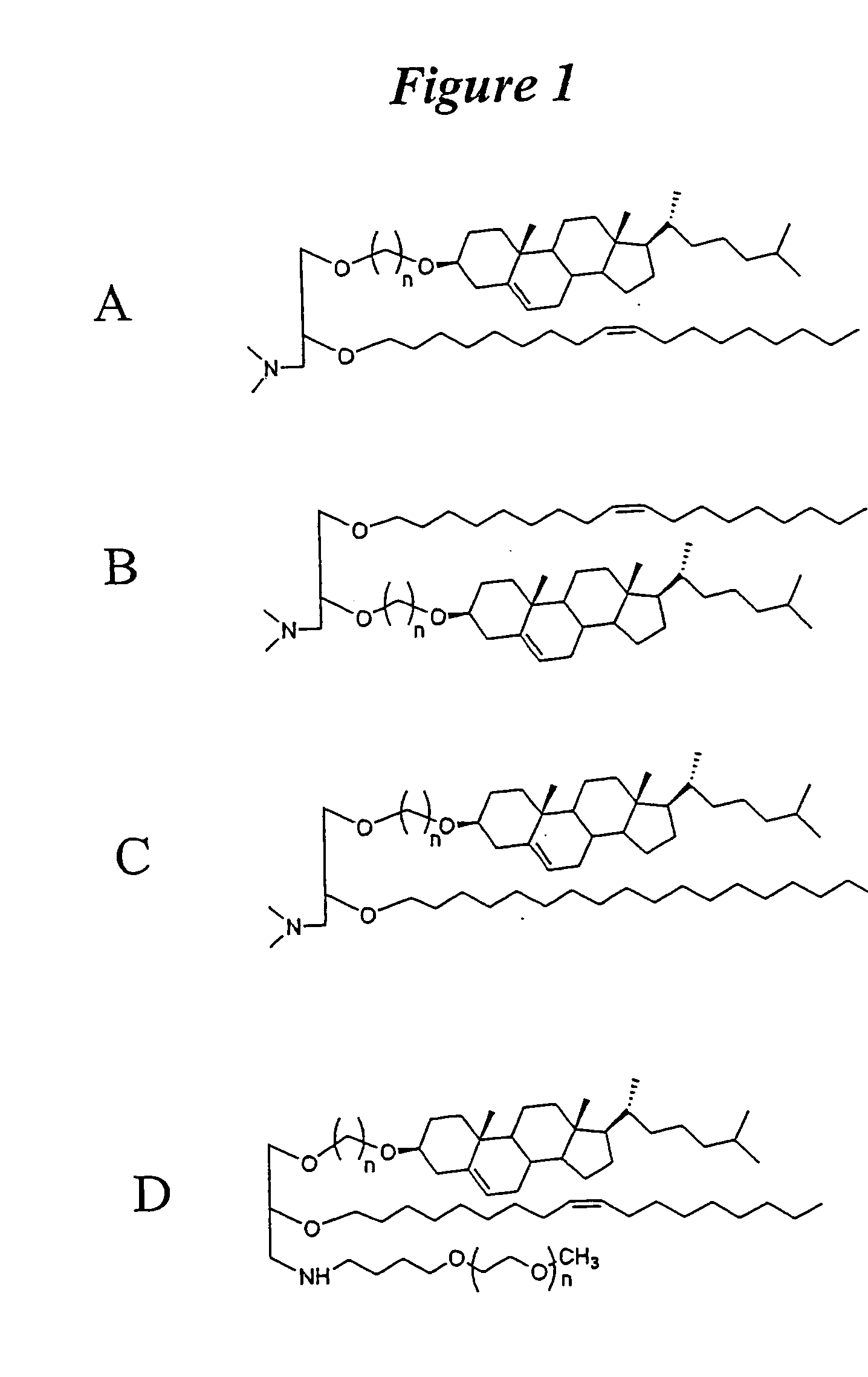
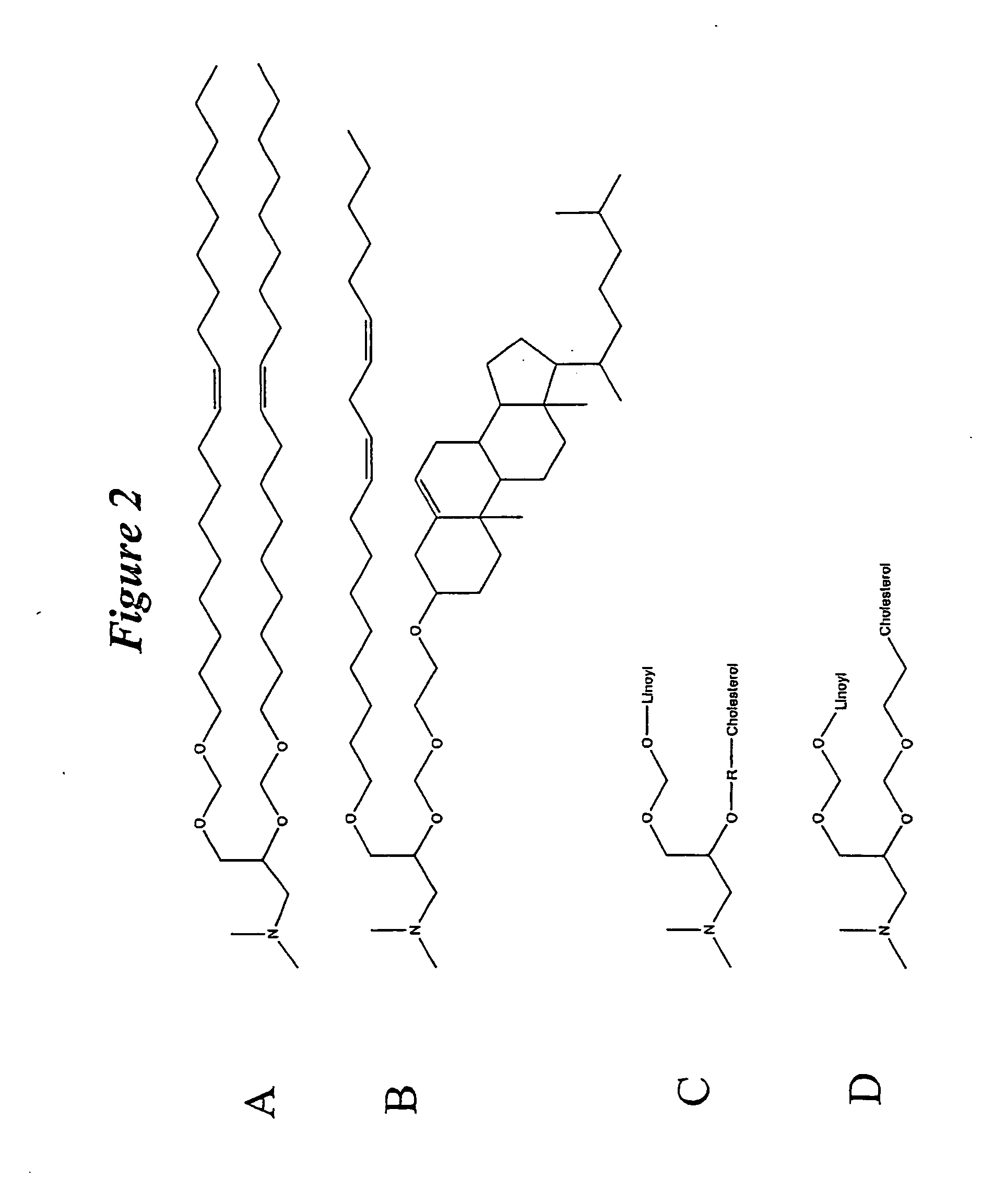
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
ActiveUS7404969B2Reduce deliveryAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationMolecular composition
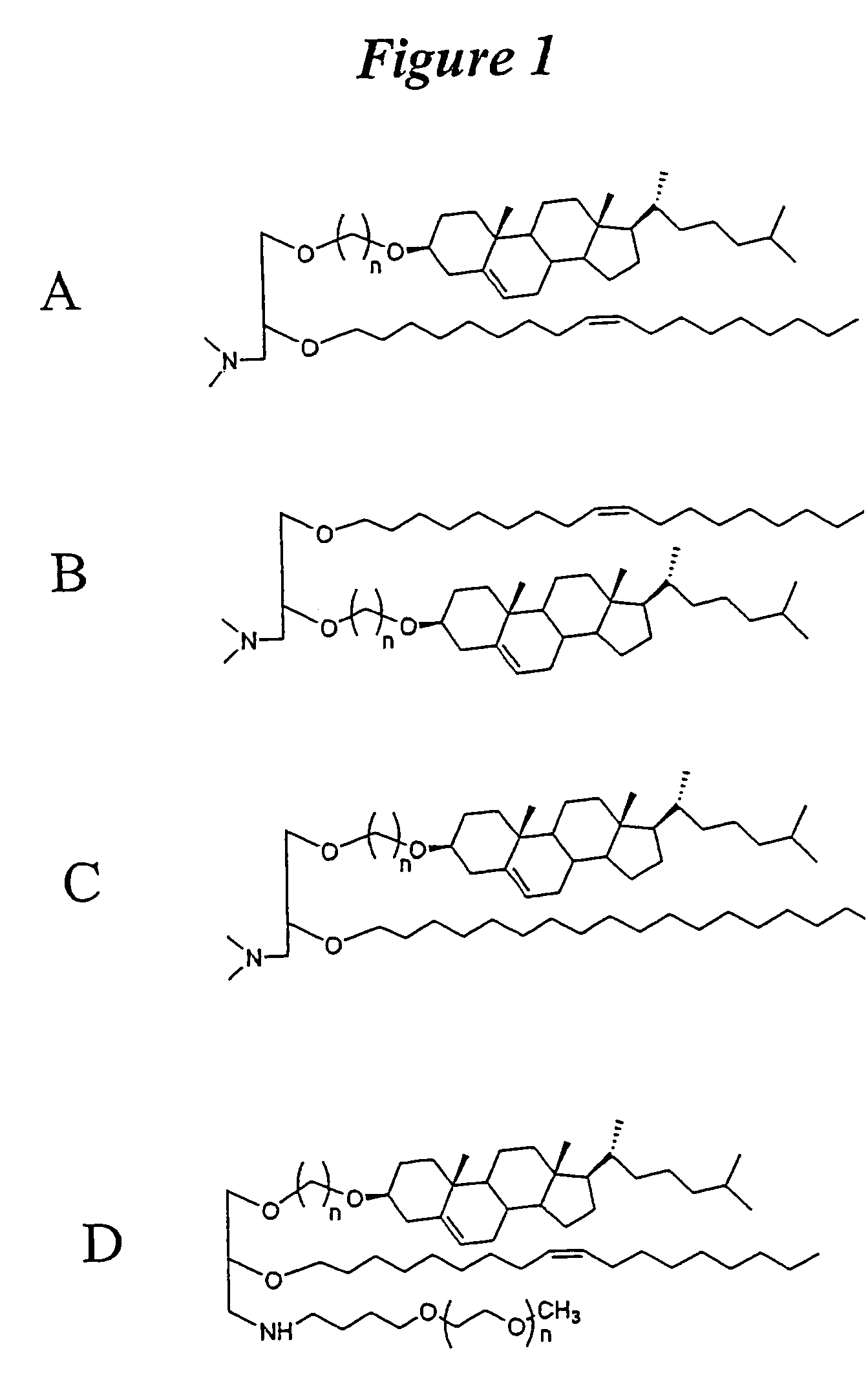
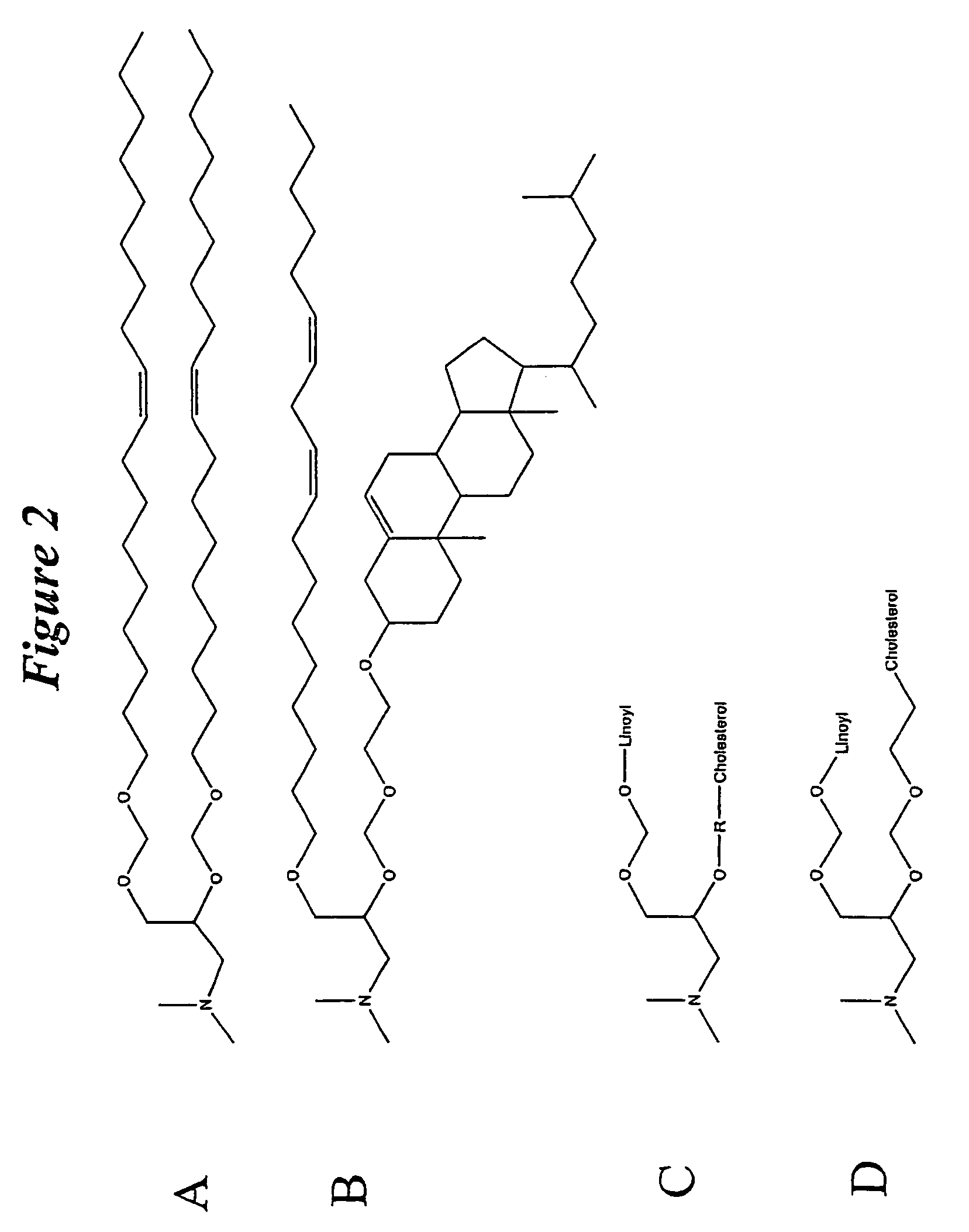
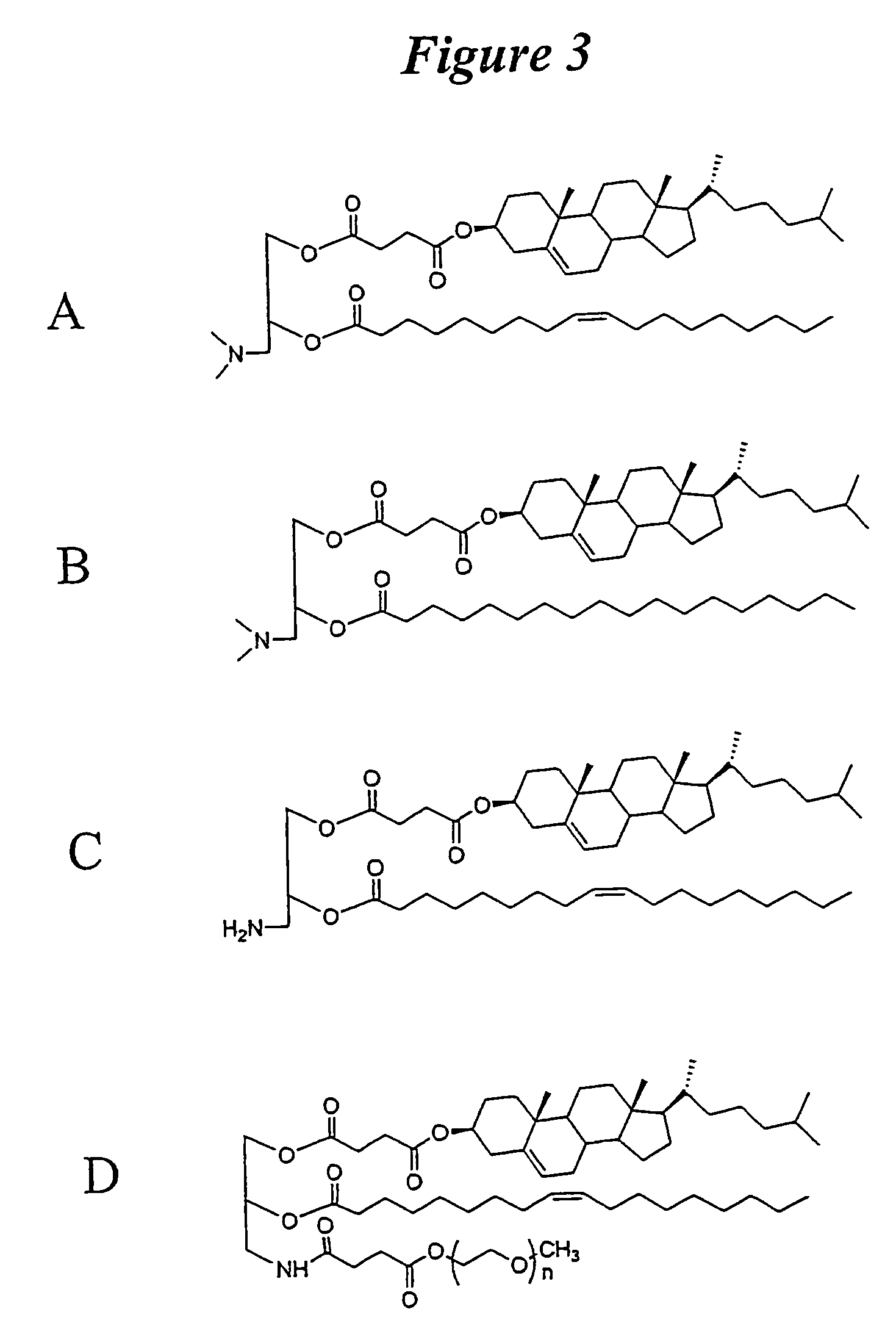
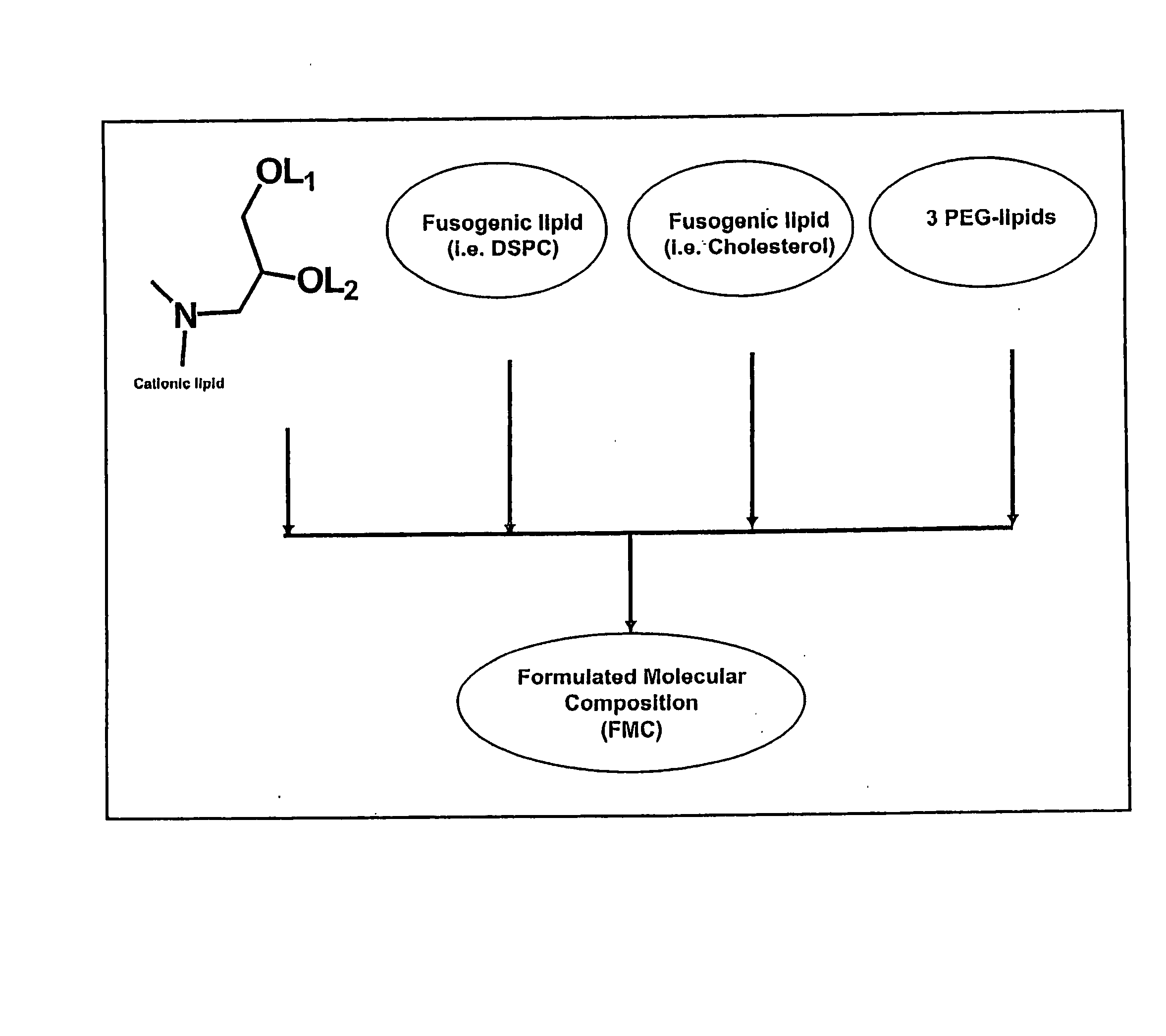
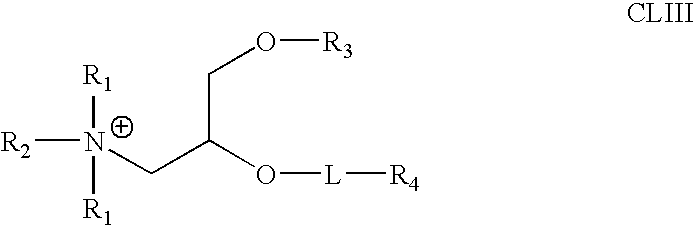
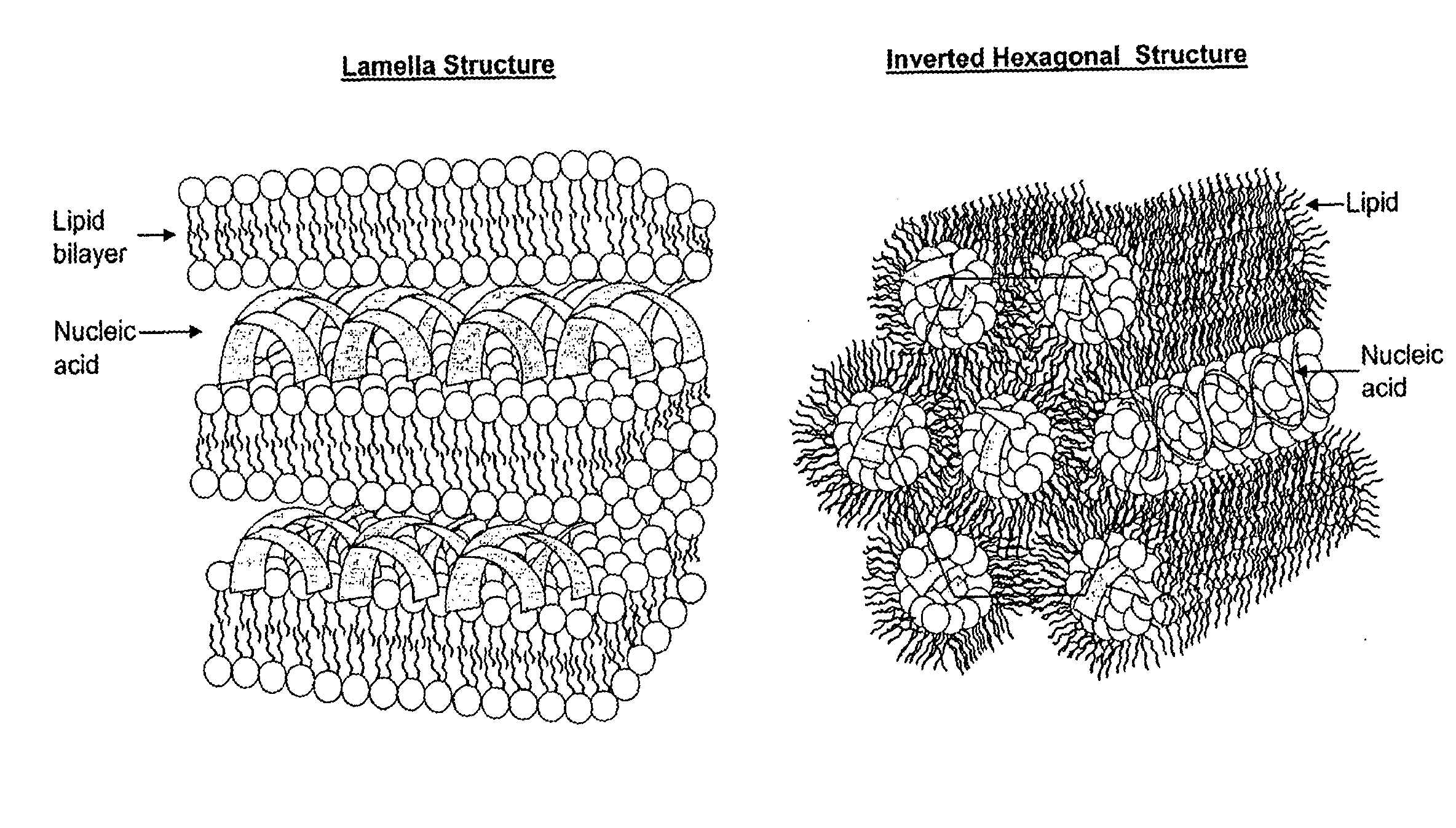
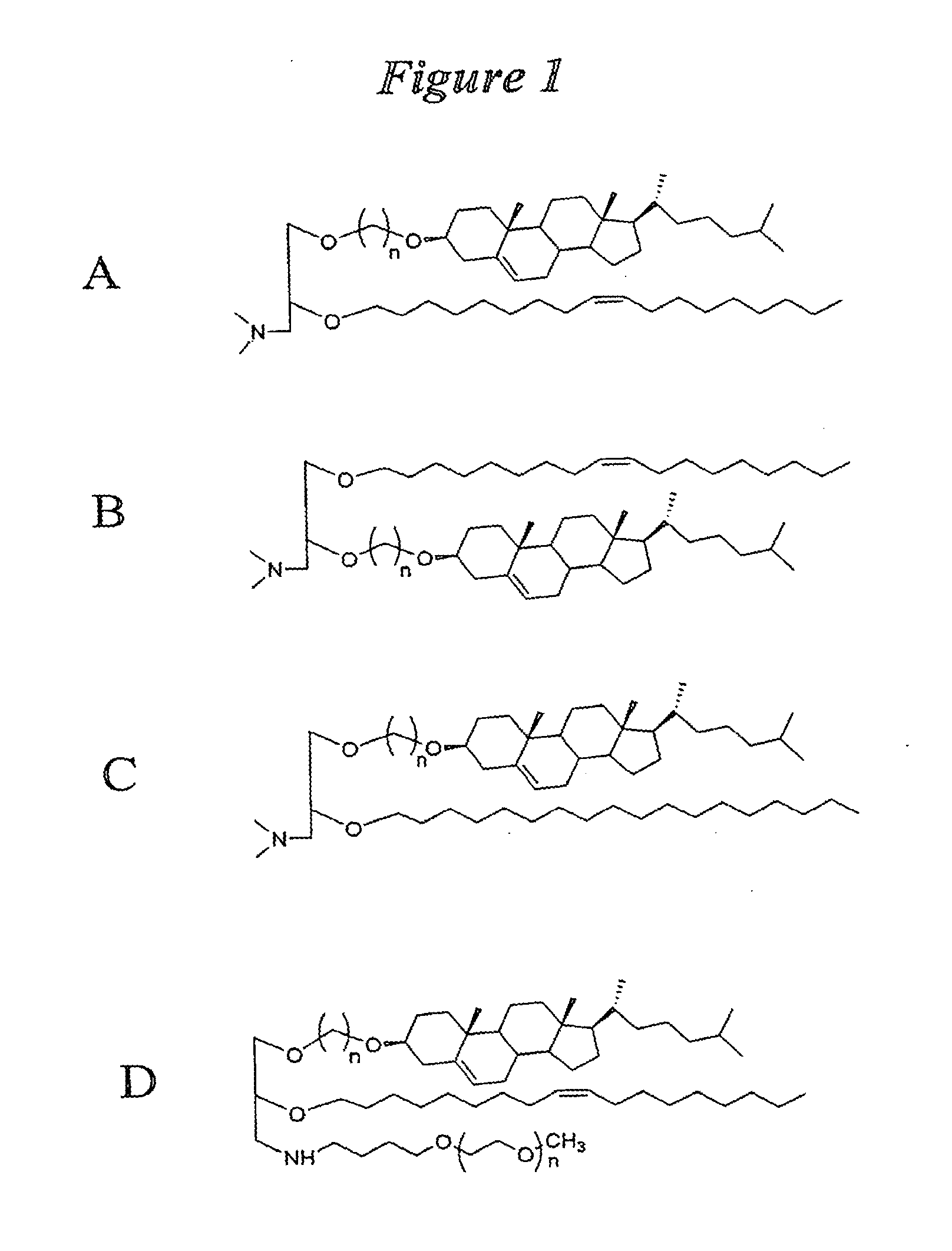
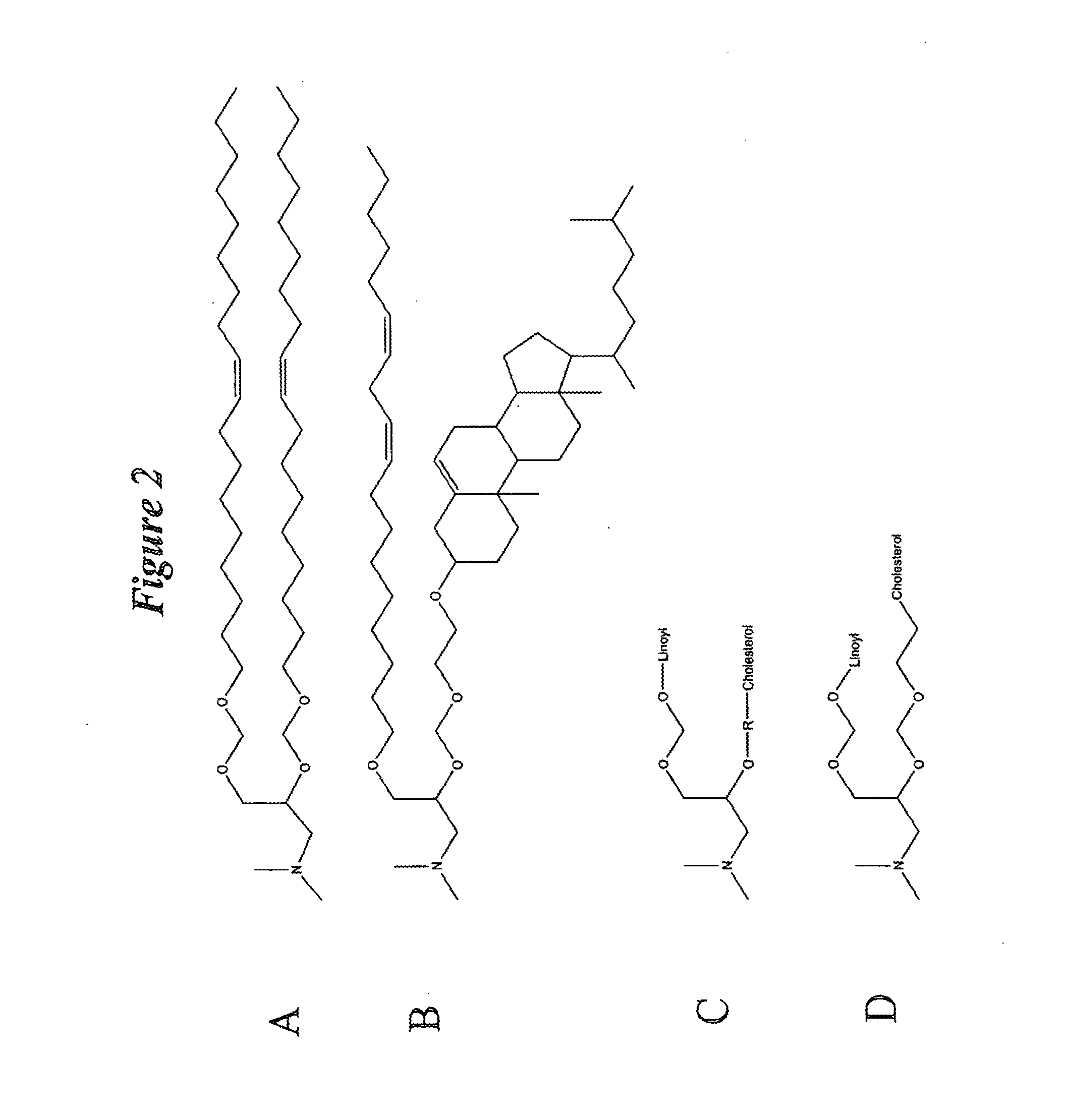
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver short interfering nucleic acid (siNA). The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
ActiveUS20080020058A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryLipid formationCholesterol
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), short hairpin RNA (shRNA), and RNAi inhibitor molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Glucagon-like insulinotropic peptides, compositions and methods
The present invention provides novel complexes consisting of certain GLP-1 molecules associated with a divalent metal cation that is capable of co-precipitating with a GLP-1 molecule. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of using such complexes for enhancing the expression of insulin in B-type islet cells is claimed, as is a method for treating maturity onset diabetes mellitus in mammals, particularly humans.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
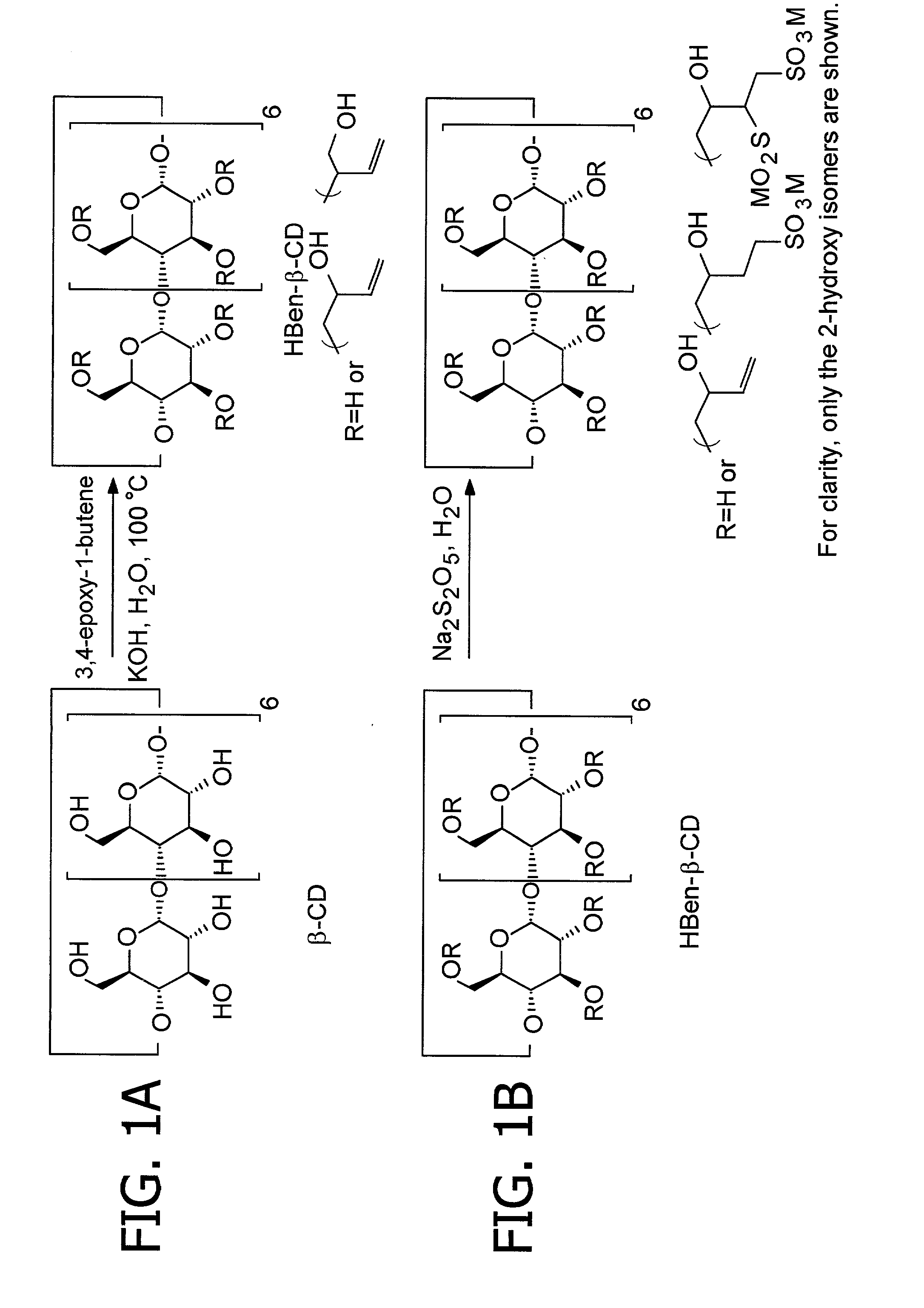
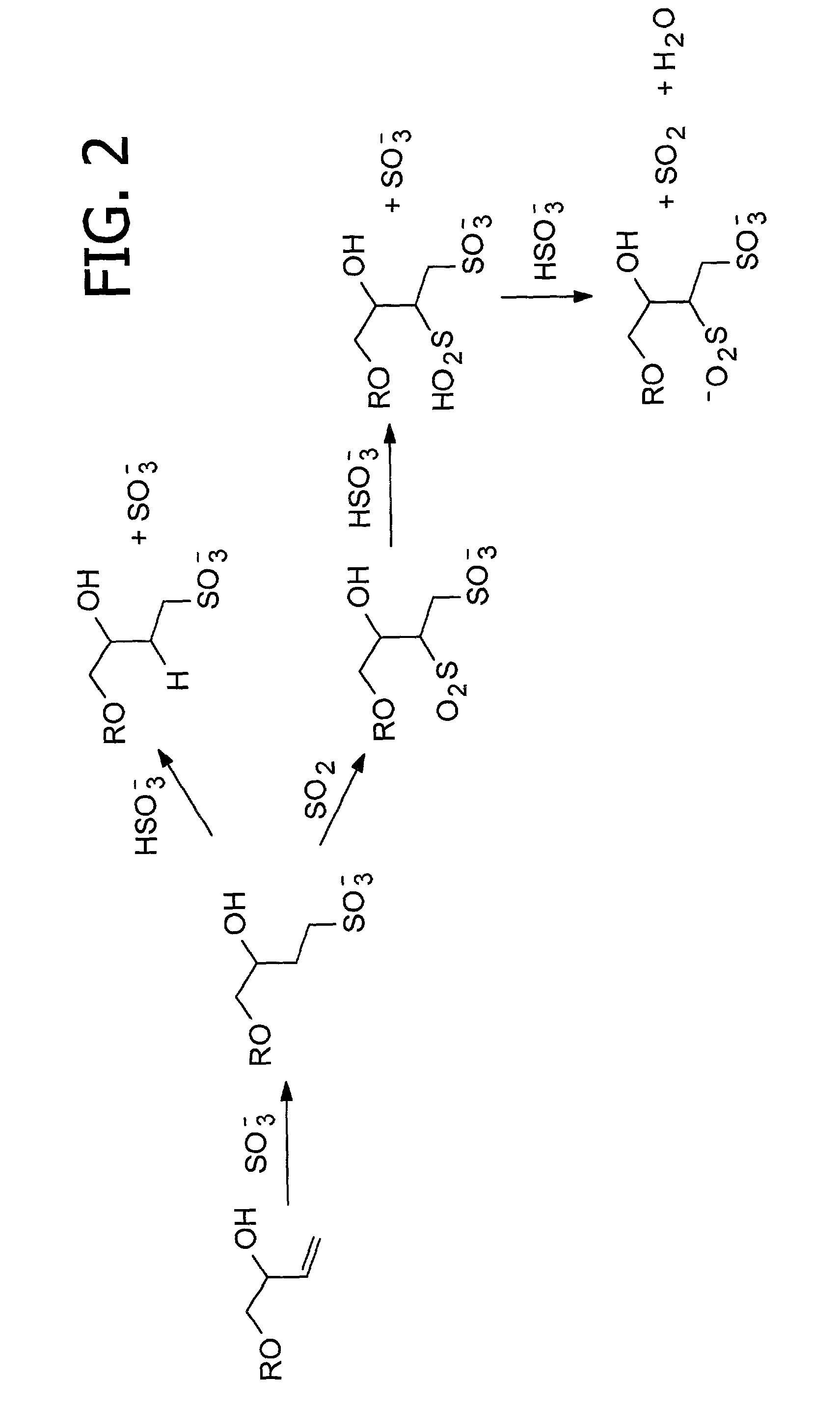
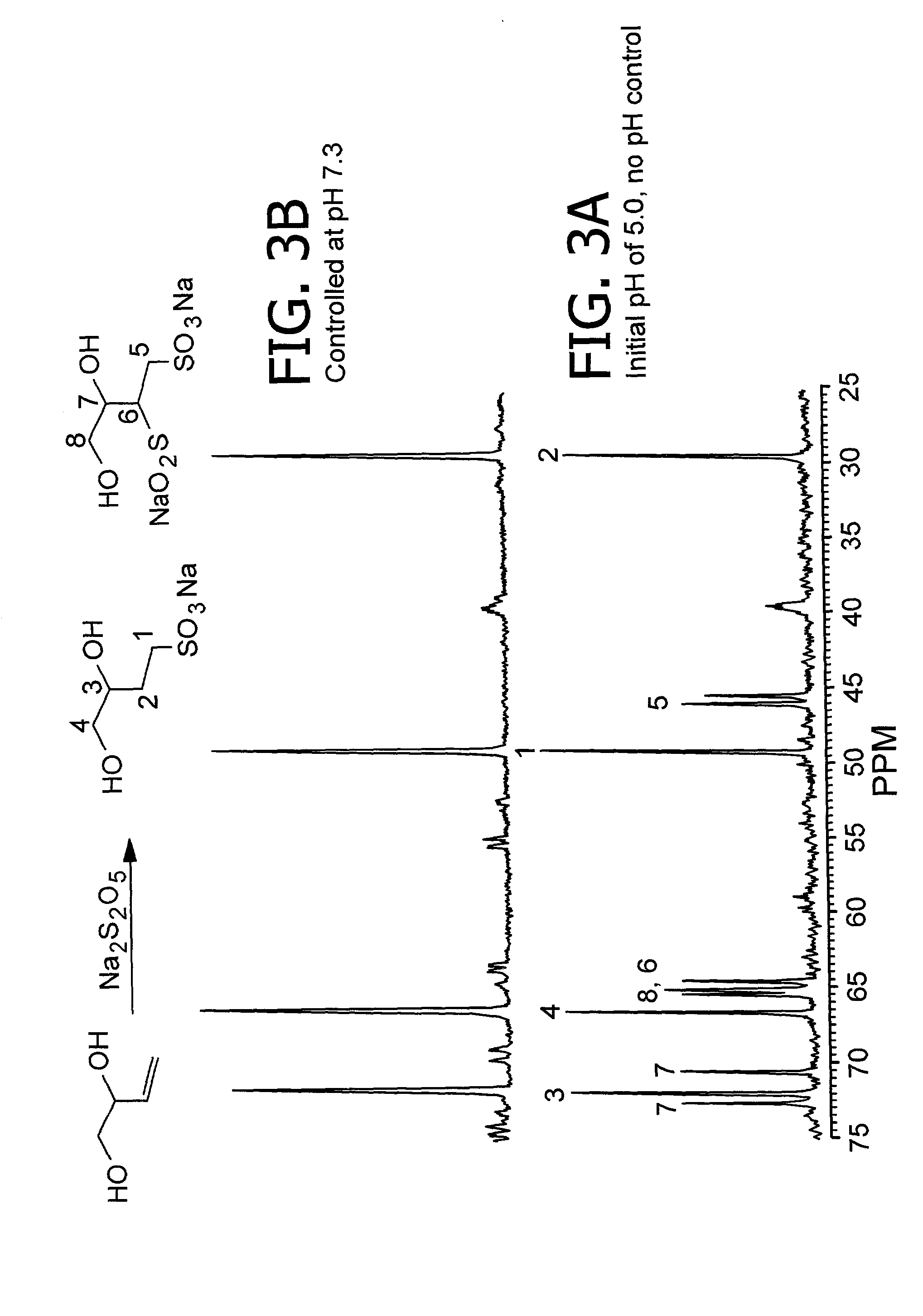
Cyclodextrin sulfonates, guest inclusion complexes methods of making the same and related materials
InactiveUS20020128468A1Organic chemistryOther chemical processesMolecular compositionCyclodextrin derivative
This invention relates to new cyclodextrin derivatives, processes for producing these cyclodextrin derivatives, and inclusion complexes comprised of the new cyclodextrin derivatives and guest molecules, as well as methods of making such materials and related materials and methods of using the same.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Cerebral function improving agents
A cerebral function improving agent containing as the active ingredient a compound represented by the following formula:wherein R2 represents a hydrogen atom when R1 is a hydroxyl group;or R1 and R2 in combination represent an oxo group;R3 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkali metal, or a monohydric,dihydric or trihydric alcohol residue;which may be an oligomer composed of 2-10 molecules when R1 represents a hydroxyl group and R2 and R3 represent hydrogen atoms.The agent supresses cerebral edema, protects cerebral function, activates cerebral metabolisms and reduces the extent of cerebral infarction.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Multiplex composite bone tissue engineering bracket material capable of degrading gradiently and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a multiplex composite engineering scaffold material capable of gradually decomposing bone tissue and a preparation method thereof. The composite scaffold material consists of calcium phosphate bone cement, biological compatible degradable synthetic high polymer and biological compatible degradable natural high polymer, has better mechanical property and gradient degradation characteristic, and can achieve the aim of regenerating and repairing bone tissue defect by implanting a bone growth factor to induce in-vivo stem cells to be differentiated into bone cells, thereby obviously improving initial strength and toughness of the scaffold material, and ensuring enough strength and toughness of the scaffold material during operating and implanting. After compounded with the high polymer material, the scaffold has excellent flexibility, so that the scaffold can be subjected to certain machining, such as cutting and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
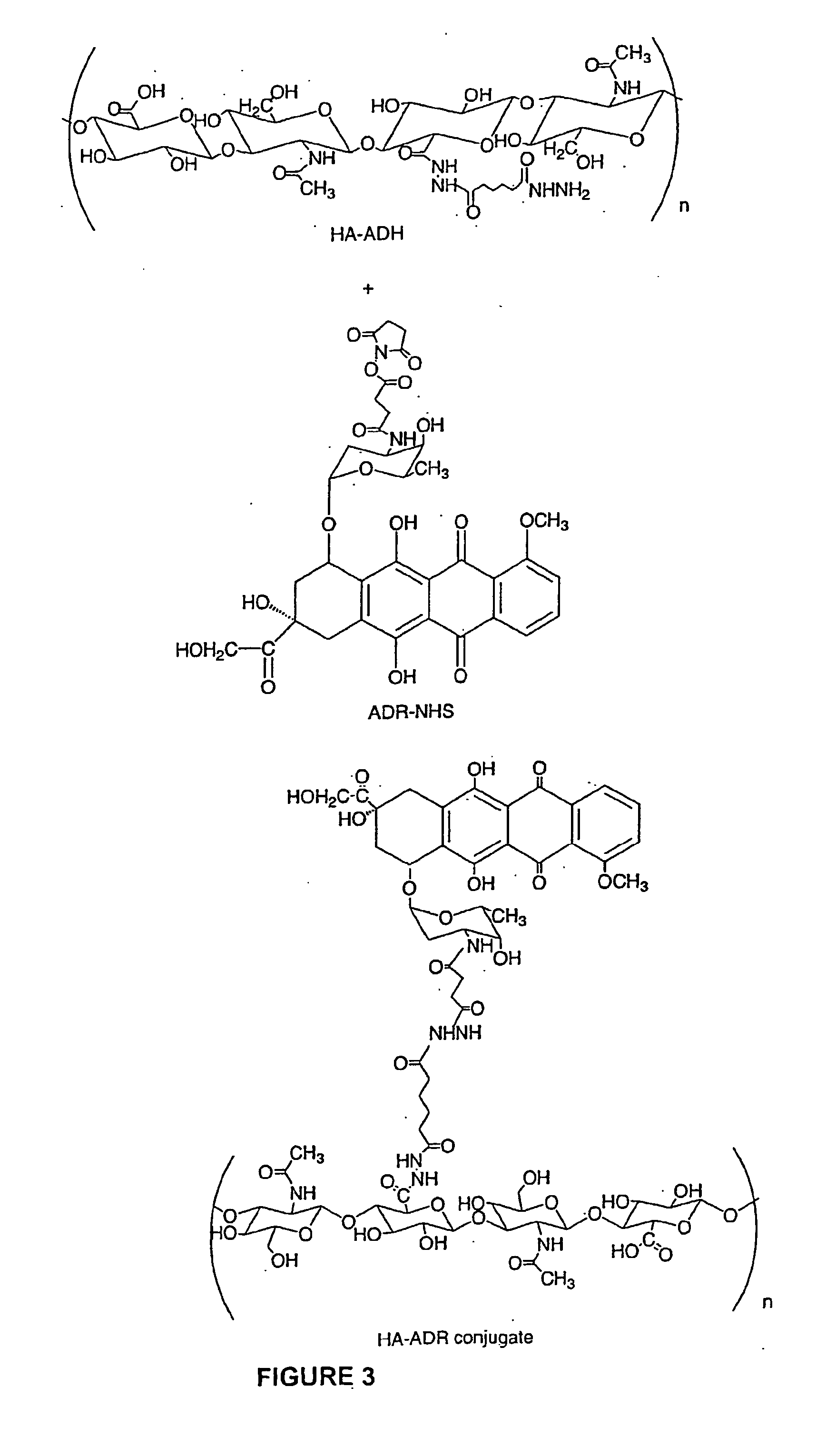
Hyaluronic acid containing bioconjugates:targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs to cancer cells
A cell-targeted polymeric drug delivery system was designed based on the specific interaction between hyaluronic acid (HA) and its cell surface receptors overexpressed on cancer cell surface. The invention relates to compounds composed of a carrier molecule, 5 wherein the carrier molecule contains at least one residue of an anti-cancer agent and at least one residue of a hyaluronic acid. The invention also relates to methods of making and using the compounds thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Magnelium base layer-shaped double-hydroxide ultraviolet barrier material used in anti-aging asphalt
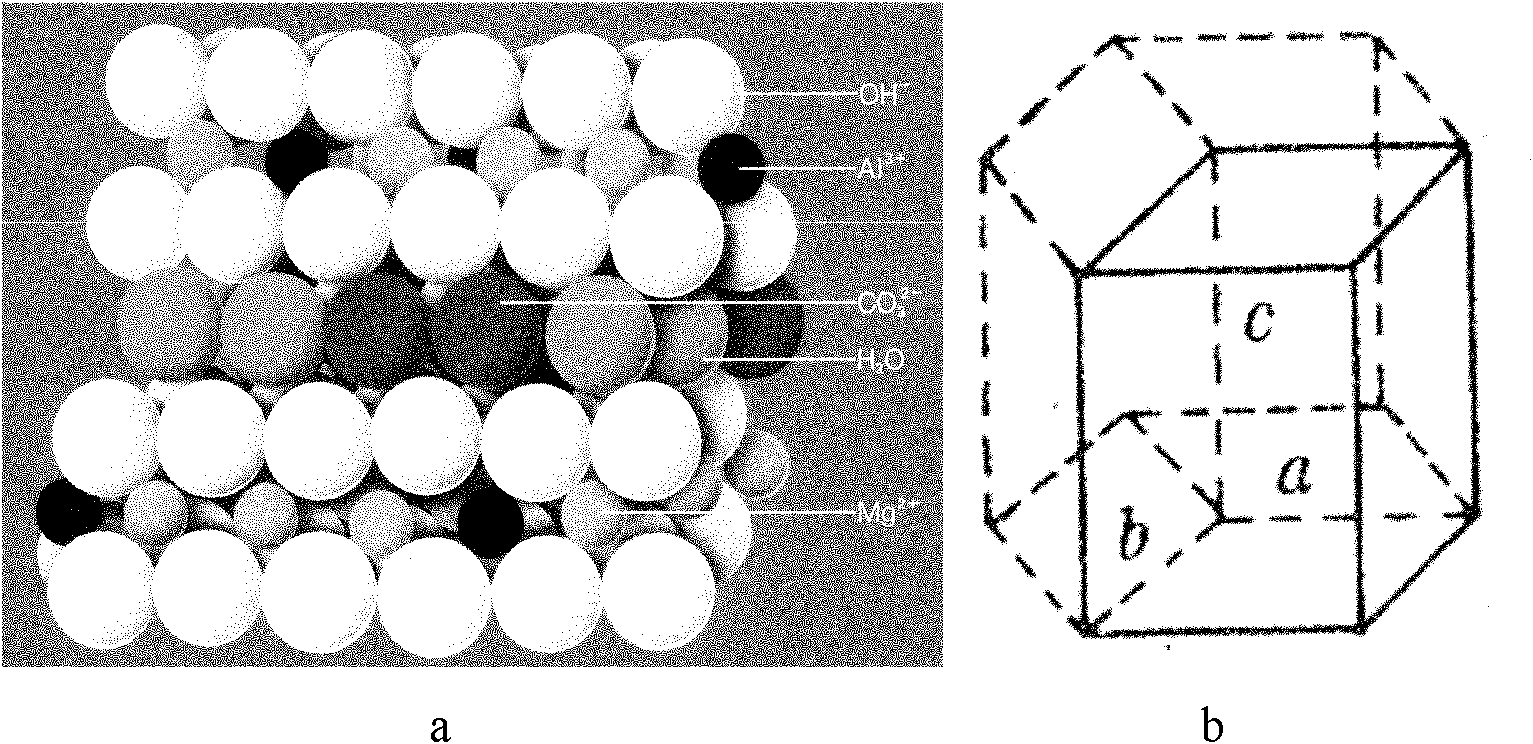
ActiveCN102180614AImproved performance against UV agingExtended service lifeMolecular compositionAging resistance
The invention relates to a magnelium base layer-shaped double-hydroxide ultraviolet barrier material used in anti-aging asphalt and a preparation method thereof. The magnelium base layer-shaped double-hydroxide ultra-violet barrier material has a laminated structure formed by magnelium double-hydroxide plywoods and interlayer carbonate through multi-stage superposition, and molecular composition is as follows: Mg1-xAlx (OH) 2 (CO3) x / 2 . mH2O. The inorganic plywoods of the material can play a role in physically shielding ultraviolet rays, and metal elements on the plywoods and interlayer anions can play a role in chemically absorbing the ultraviolet rays; in addition, by controlling the size and number of layers of the plywoods, multi-stage reflection and refraction occur on interfaces of the plywoods when the ultraviolet rays pass through the multi-stage plywoods, and multi-stage absorption occurs on the plywoods and interlayers, so as to play a role in blocking the ultraviolet rays. Due to the multi-stage multiple chemical absorption and physical shielding effect, the material has good ultraviolet blocking effect, and remarkably improves the ultraviolet aging resistance of asphalt when the material is used for preparing the anti-aging asphalt.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
Small ultraviolet frequency sweeping laser-based resonance Raman spectrum detection system and method
ActiveCN104849257AMiniaturizationAchieving high-sensitivity detectionRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringRaman lineUltraviolet
The invention discloses a small ultraviolet frequency sweeping laser-based resonance Raman spectrum detection system method. The small ultraviolet frequency sweeping laser based resonance Raman spectrum detection system comprises a small ultraviolet frequency sweeping laser, a main controller and a data analysis system, wherein the small ultraviolet frequency sweeping laser is composed of a pulse semiconductor laser assembly, an optical fiber laser assembly and an ultraviolet frequency sweeping optical assembly; the testing point of a detected object is located in a molecular composition of a material, has the intensity of a stokes Raman line of molecules with the ultraviolet frequency sweeping wavelength corresponding to the resonance Raman excitation wavelength is enhanced by tens of thousands to millions of times, and thus, multiple molecules of a sample, having extremely low concentration, can be detected. The system has the beneficial effects that an electronic-optical fiber integrated structure is adopted, so that an ultraviolet frequency sweeping laser source is miniaturized; an acousto-optic tunable filter is adopted, and thus, the ultraviolet laser frequency can be rapidly adjusted; and according to the ultraviolet frequency sweeping resonance Raman method, fluorescence interference is eliminated, the high-sensitivity resonance Raman detection of the multiple molecules of the sample can be achieved through fast frequency sweeping.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quaternary ammonium ionic liquid as well as preparation and application method thereof
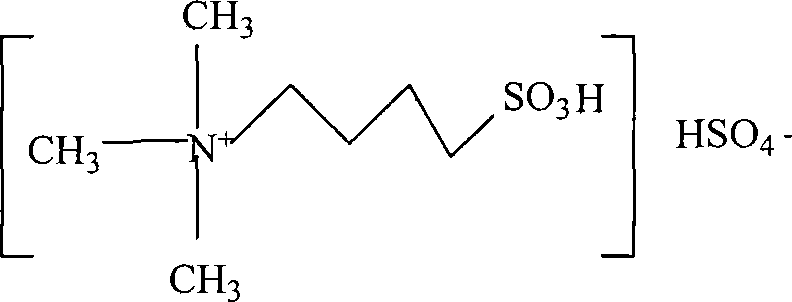
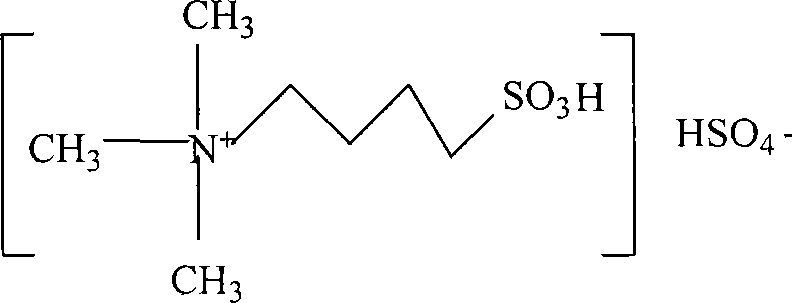
InactiveCN101182300AUnique physical and chemical propertiesReduce corrosionOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMolecular compositionHydrogen Sulfate
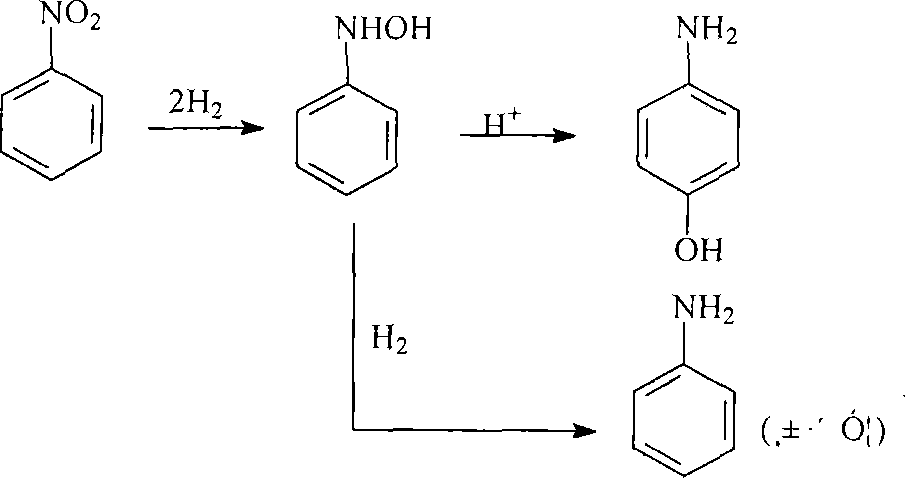
A quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid of the present invention and its preparation and application methods belong to quaternary ammonium compounds, and its molecular composition is N, N, N-trimethyl-N-sulfobutyl-ammonium bisulfate, and its molecular formula is [HSO3-b -N(CH3)3]HSO4, the structural formula is as follows: the quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid of the present invention is non-corrosive equipment and environment-friendly, and the quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid catalyst of the present invention is used for nitrobenzene catalytic hydrogenation to synthesize p-amino The phenol reaction is a liquid phase method, the reaction temperature is 60-130° C., and the PAP yield reaches 19.5-88%.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor device having improved insulation film and manufacturing method thereof
A semiconductor device which has an interlayer insulating film comprised of molecules with silicon-oxygen bonds and silicon-fluorine bonds and contains a rare gas in concentration higher than 1011 atoms per cm2. The interlayer insulating film is preferably a fluorine-containing silicon oxide film which contains a rare gas. In a manufacturing process, an interlayer insulating is formed by a chemical vapor deposition from a material gas including a silicon-containing gas, a fluorine compound gas, a rare gas, and oxygen. The silicon-containing gas is preferably SiH4 gas, and the fluorine compound gas is preferably SiF4 gas. The flow rate of the rare gas is greater than three times the total flow rate of the SiH4 gas and SiF4 gas. The rare gas is at least one type of gas selected from neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), and xenon (Xe).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Photochromic composition
ActiveUS20160222285A1Improved color developabilityIncrease speedSpectales/gogglesLayered productsMolecular compositionPolyrotaxane
A photochromic composition comprising (A) a polyrotaxane having a composite molecular structure composed of an axial molecule and a plurality of cyclic molecules clathrating the axial molecule and (B) a photochromic compound.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Minimally invasive blood glucose monitoring microneedle and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102512181AKeep activeEasy to store for a long timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsWater insolubleIn vivo
The invention discloses a minimally invasive blood glucose monitoring microneedle which comprises a needle handle, a needle body and a needle point which are sequentially connected, wherein after one of an amino group, an aldehyde group, a hydroxide radical and a carboxyl group is modified on the surfaces of the needle body and needle point of the microneedle, and the microneedle can be covered by a metal nano material layer modified by a Ph response molecule, the microneedle is inserted in a solution consisting a water-soluble polymer and a water-insoluble polymer, a porous polymer material layer is coated on the metal nano material layer, and then the microneedle is inserted in a glucose oxidase solution, so that the water-soluble polymer is dissolved and a plurality of pores are formed in a polymer layer; and glucose oxidase is absorbed on the surface of the porous polymer layer or in the holes, and the metal nano material has a grain size of 20-1000nm. By using the characteristic that the minimally invasive blood glucose monitoring microneedle has different intensities of Raman signals for different concentrations of glucose, the purpose of minimally invasively detecting the glucose in vivo and in vitro can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Systems and methods for characterization of molecules
InactiveUS20060269964A1Molecular entity identificationBiological testingMolecular compositionLiquid liquid partition
The present invention generally provides systems and methods for the detection, identification, or characterization of differences between properties or behavior of corresponding species in two or more mixtures comprised of molecules, including biomolecules and / or molecules able to interact with biomolecules, using techniques such as partitioning. The experimental conditions established as distinguishing between the mixtures of the molecules using the systems and methods of the invention can also be used, in some cases, for further fractionation and / or characterization of the biomolecules and / or other molecules, using techniques such as single-step or multiple-step extraction, and / or by liquid-liquid partition chromatography. The methods could also be used for discovering and identifying markers associated with specific diagnostics, and can be used for screening for such markers once discovered and identified during diagnostics screening.
Owner:ANALIZA
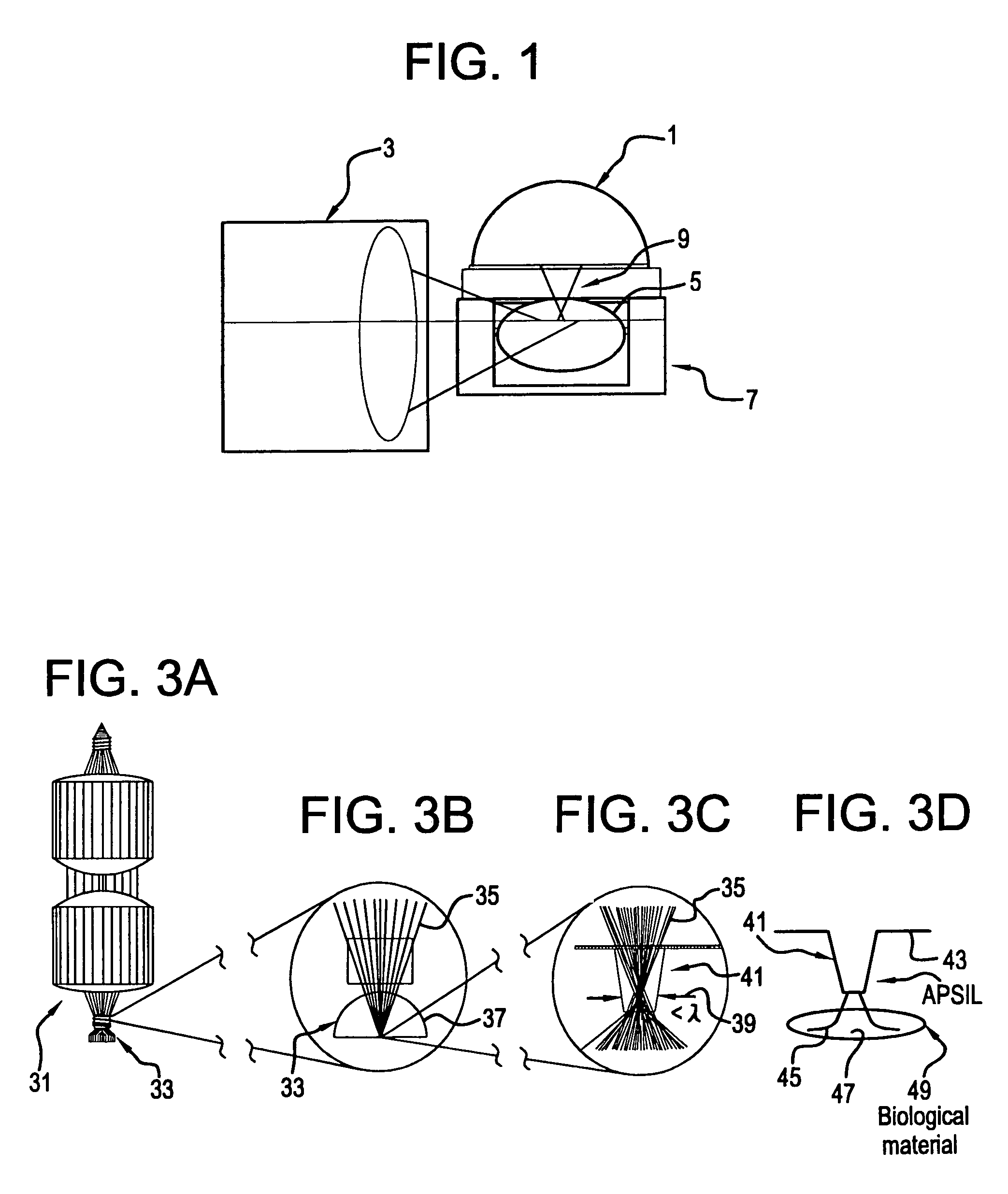
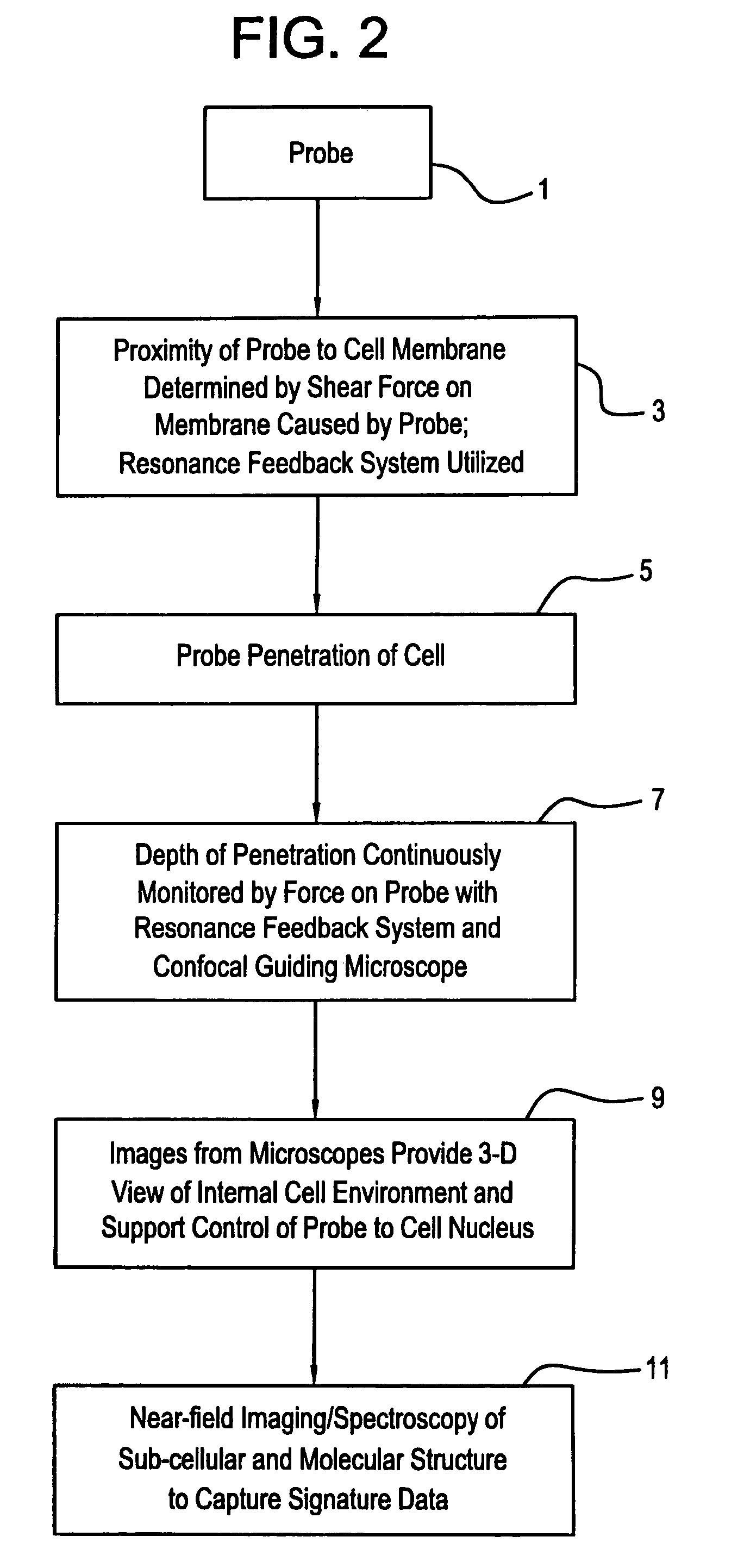
Precision optical intracellular near field imaging/spectroscopy technology
InactiveUS7129454B2Facilitates molecular analysisMore powerSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseaseMolecular analysis
A Precision Optical Intracellular Near Field Imaging / Spectroscopy Technology (POINT / NANOPOINT) is a high-resolution instrument for analyzing and comparing molecular characteristics of cells. A nanosensor array is provided which is capable of imaging inner regions of living cells without destroying its natural environment and providing new information about molecular makeup of cells. The POINT probe collects data from high-resolution imagery, providing an imaging tool for investigating cells at sub-cellular and molecular levels. Data are then incorporated into a signature facilitating molecular analysis of diseases. The POINT probe non-invasively penetrates cell membranes to image insides of intact cells allowing the POINT probe to collect data without destroying cell structures. The probe provides cellular imaging to enable the viewing of both imaging and spectroscopy of internal regions of cells. The POINT system may be attached to existing microscopes to achieve a very high resolution.
Owner:NANOPOINTS
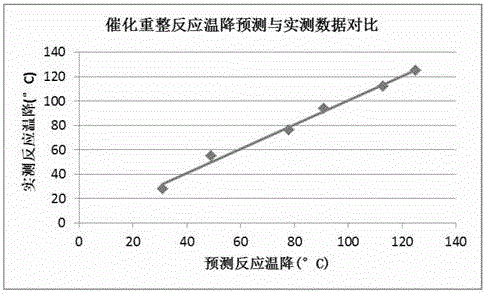
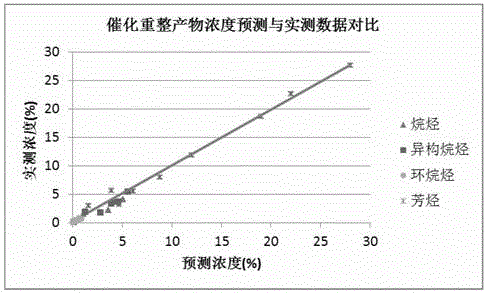
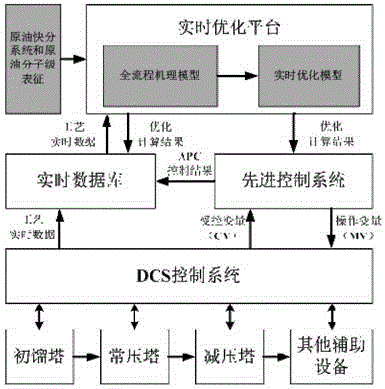
Molecular-level real time optimization (RTO) method for oil refining and petrochemical device
PendingCN106444672AThe optimization direction is accurateEffective optimization planTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlMolecular compositionEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a molecular-level RTO method for an oil refining and petrochemical device. The method mainly comprises the steps that molecular composition and physicochemical properties of a product are predicted according to molecular compositions of raw materials, a model is optimized, and a production scheme is optimized. The method can be used to optimize the oil refining and petrochemical device in real time, maintain the device in the optimal state always, improve economic benefits, and reduce energy consumption.
Owner:SYSPETRO TECH CO LTD +2
Superhydrophobic coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104559622AMolecular weight controllableNarrow molecular weight distributionPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyester coatingsMolecular compositionOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a superhydrophobic coating. The superhydrophobic coating comprises the following ingredients by mass percent: 5-15% of fluorine-containing segmented copolymer, 65-85% of an amino nanometer or micron material, and 10-20% of resin, wherein the fluorine-containing segmented copolymer is a copolymer containing a monomer and a fluorine-containing acrylic acid monomer; the monomer is a mixture of an epoxy acrylate monomer or an epoxy acrylate monomer and an acrylate monomer. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the superhydrophobic coating. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing the fluorine-containing segmented copolymer, preparing the amino nanometer or micron material, and preparing the superhydrophobic coating. The superhydrophobic coating and the preparation method disclosed by the invention have the following benefits: (1) the molecular weight of the fluorine-containing segmented copolymer is controllable, the molecular weight is narrow in distribution, and the molecular structure and the molecular composition are controllable; (2) the chemical bond interaction between the polymer and the nanoparticles is provided, so that the superhydrophobic coating has the advantages of the nanoparticles and the high molecular compound, and the dispersibility and the stability in the organic solvent are high; (3) the superhydrophobic coating is good in hydrophobicity, and high in comprehensive paint film property.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
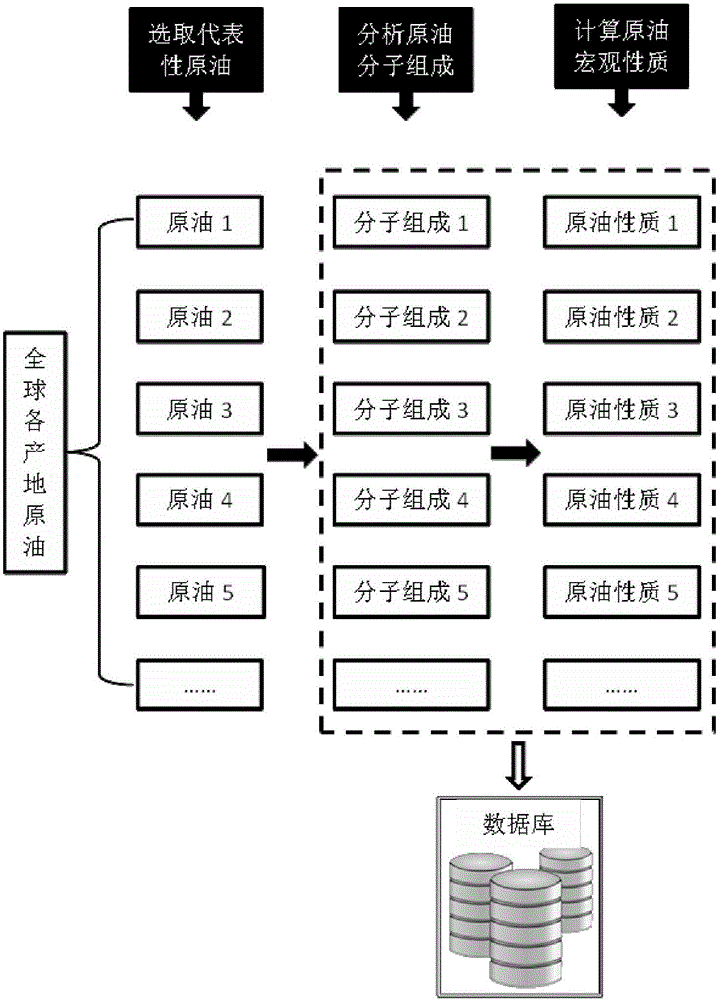
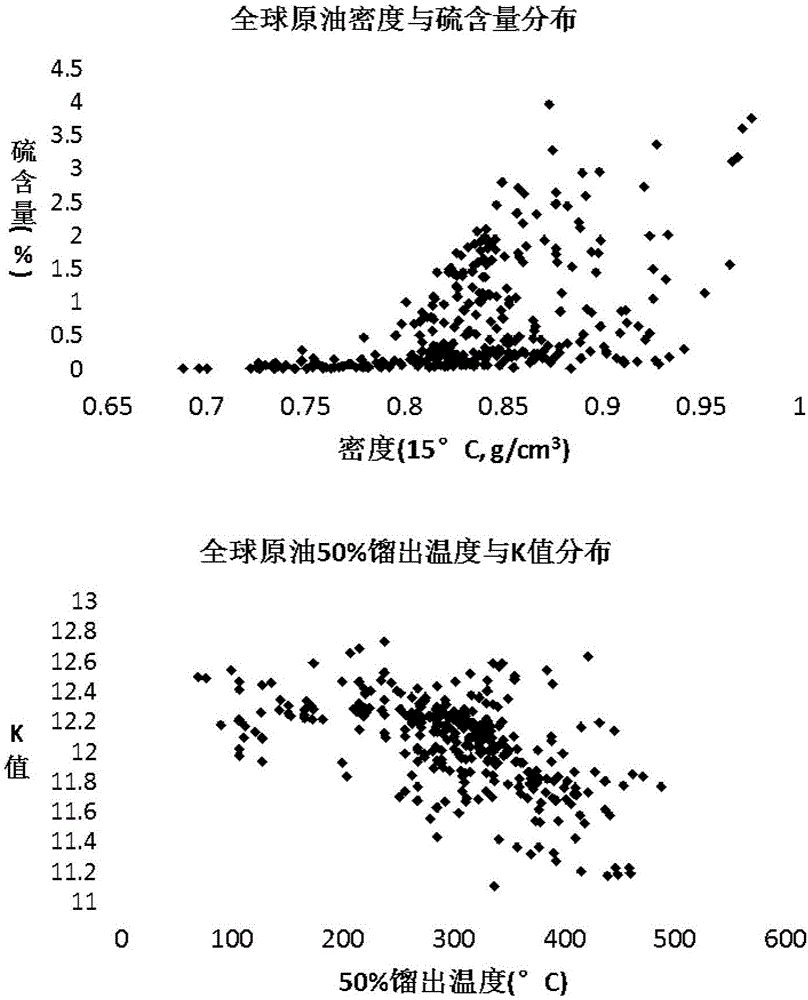
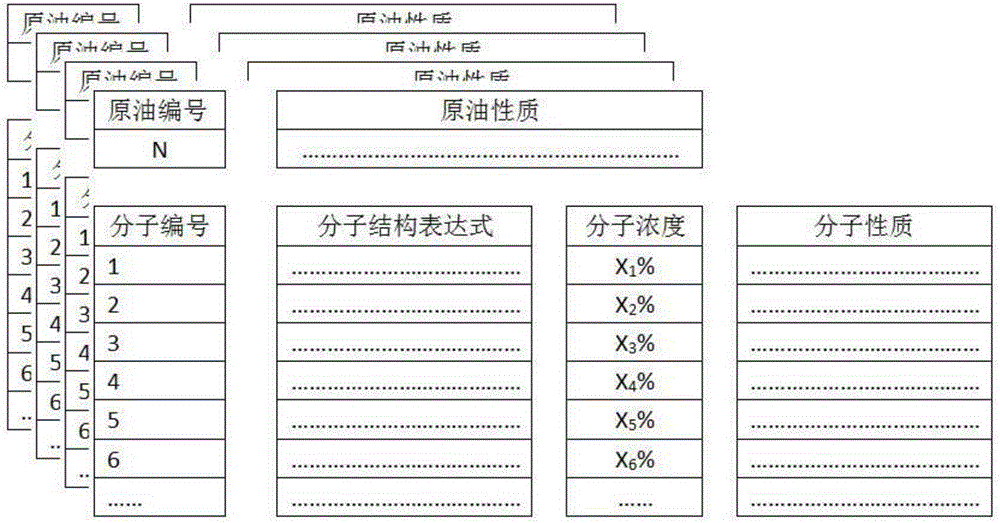
Method used for determining molecular composition of crude oil based on crude oil macroscopic properties
ActiveCN106568924ALow costEasy accessFlow propertiesAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMolecular compositionData retrieval
The invention discloses a method used for determining molecular composition of crude oil based on crude oil macroscopic properties. The method comprises following steps: a database of crude oil macroscopic properties and molecular composition data is established, the macroscopic properties of crude oil to be detected are measured and similar data retrieval in the database is carried out, and the detailed molecular composition of the crude oil to be detected is determined based on similar crude oil molecular composition.
Owner:SYSPETRO TECH CO LTD
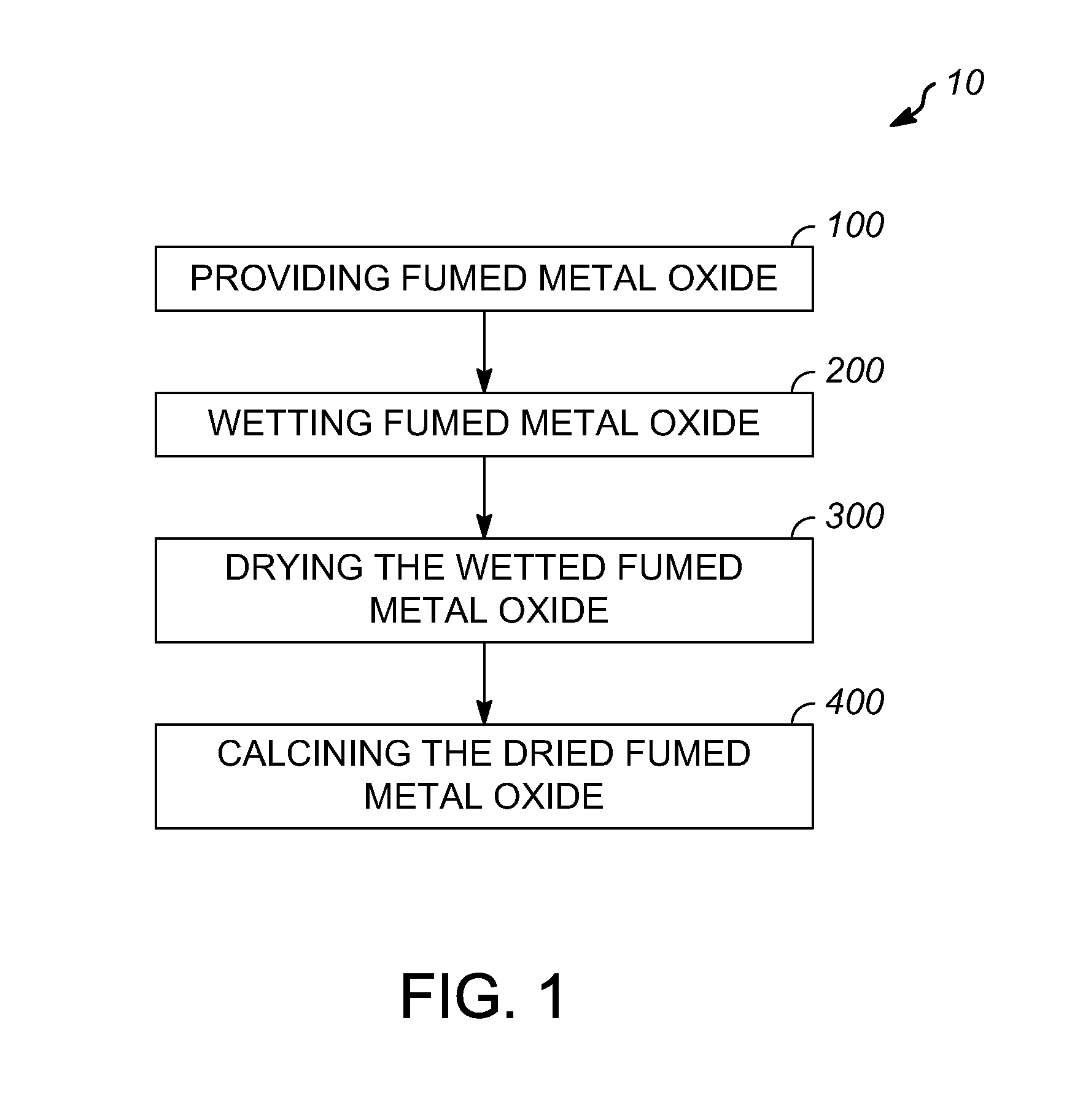
Densified fumed metal oxides and methods for producing the same
A method for producing a densified fumed metal oxide having an increased bulk density and substantially the same surface area as an undensified fumed metal oxide with the same molecular composition is provided. The fumed metal oxide is wetted with a solvent to form a wetted fumed metal oxide. The wetted fumed metal oxide is dried to form a dried fumed metal oxide. The dried fumed metal oxide is calcined.
Owner:UOP LLC
Polypeptide derivatives for generating stable micro-molecular hydrogel
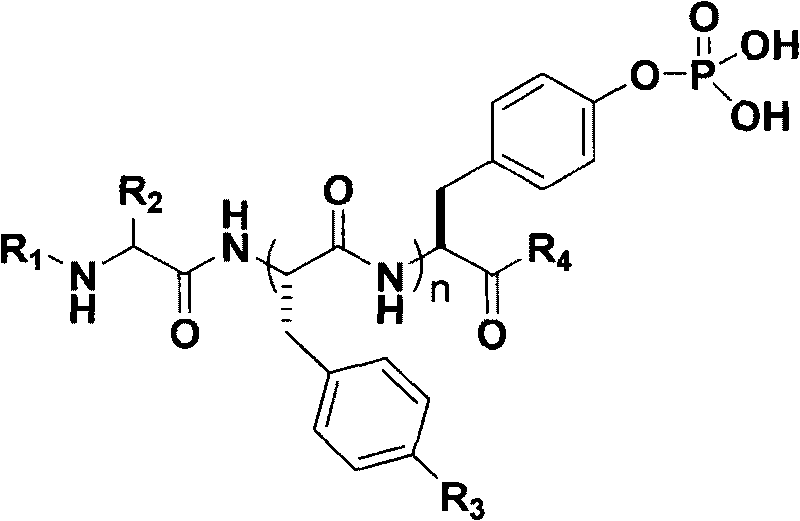
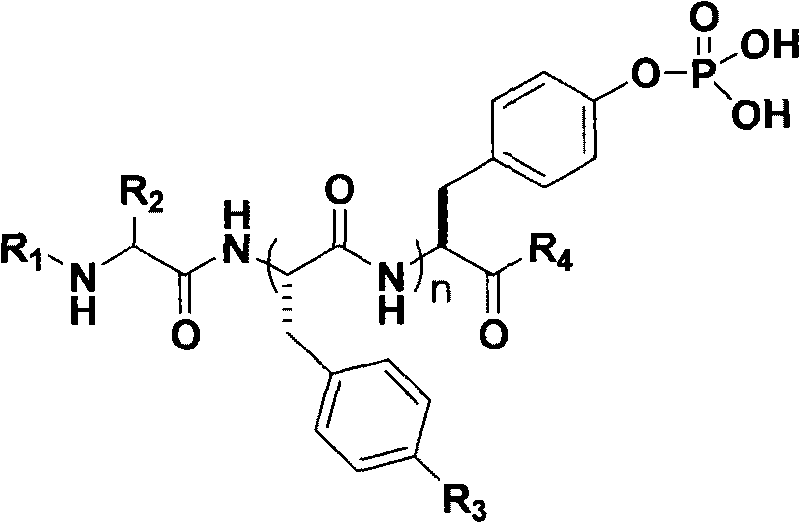
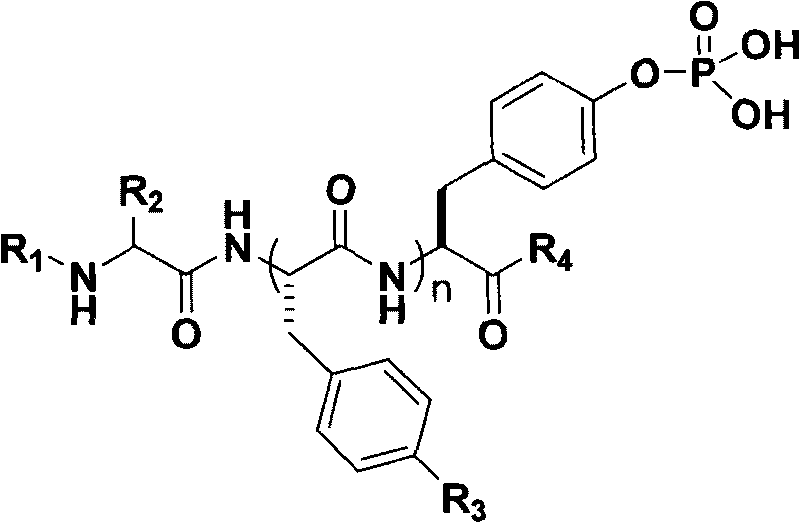
The invention discloses polypeptide derivatives for generating stable micro-molecular hydrogel and relates to a compound library containing polypeptides. The molecular composition and structure are represented by a compound structural formula below, wherein in the formula, R1 represents aromatic ring derivatives, R2 represents one side chain group of 20 natural amino acids, R3 may be any of H and halogen, R4 may be OMe group or NHMe group, and n is 0 to 3. The micro-molecular hydrogel generated by the polypeptide derivatives can exist stably in a large amount of an aqueous solution, the shape can be well maintained, the micro-molecular hydrogel has high biocompatibility and is widely applied in the fields of tissue engineering, cosmetic, and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Waterproof and breathable bionic artificial skin and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a bionic artificial skin. The artificial skin comprises a protective layer, an epidermal layer, and a corium layer, and is characterized in that the protective layer is composed of polymer films, which contain micro pores, are non-degradable, or have a low degrading speed; the epidermal layer is composed of biopolymer, which contains a micro pore structure and can be degraded and absorbed; and the corium layer is composed of biopolymer sponge that can be degraded and absorbed. The protective layer has a waterproof and moisture permeable function; the material of the epidermal layer is the same as the human epidermis and has a micro pore structure, thus the artificial skin has a similar oxygen and moisture permeable function as that of human skin, the artificial skin is enabled to have a breathable function, the epidermal layer and corium layer of the artificial skin can be degraded, and moreover, because the components of the epidermal layer and corium layer are similar to human skin, and degradation products can promote the regeneration of epidermal cells and fibroblast. The invention also provides a preparation method of the bionic artificial skin.
Owner:BEIJING PAISHENG BIOTECH CO LTD
Asphalt analysis discriminating method
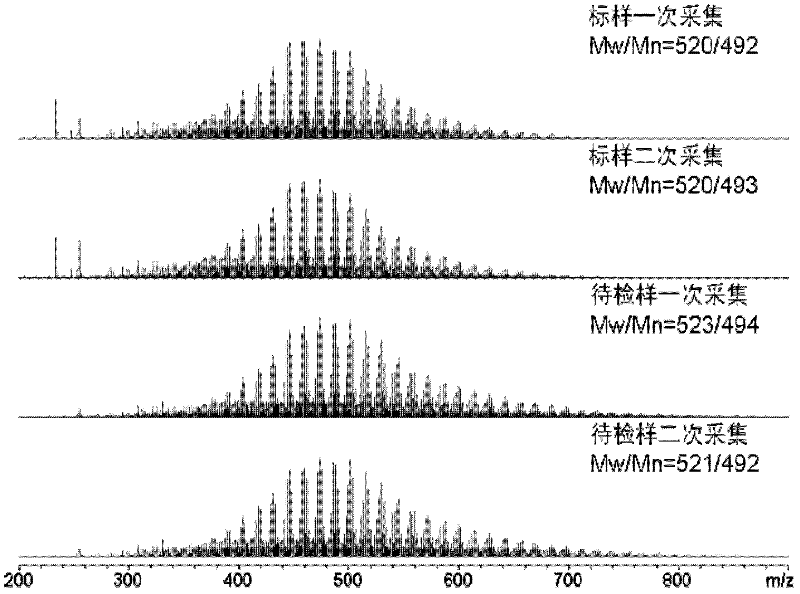
ActiveCN102507718AQuality improvementGuaranteed accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectral ratioPetroleum
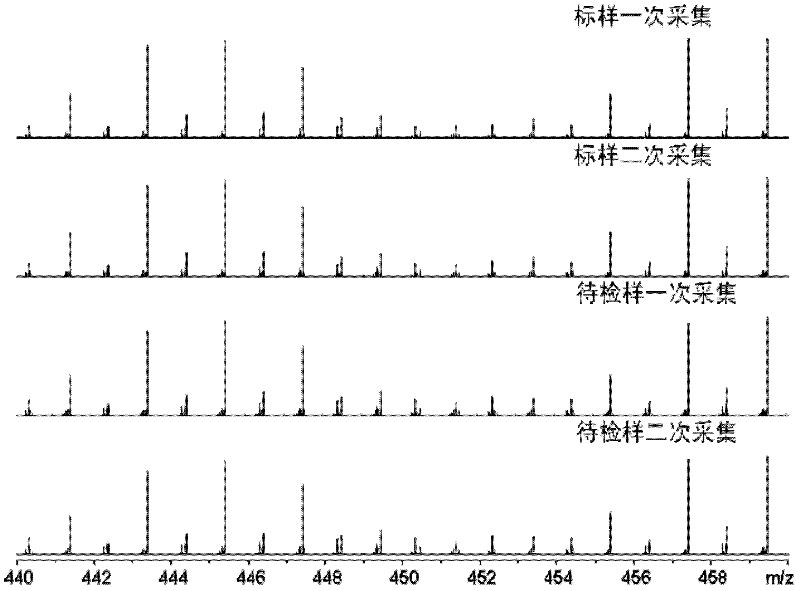
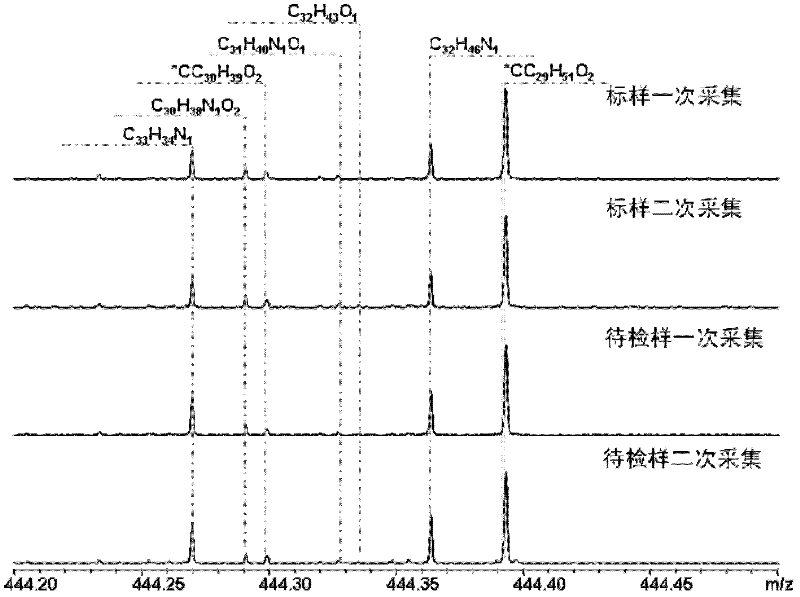
The invention relates to an asphalt analysis discriminating method by utilizing an electronic spray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry technology. The asphalt analysis discriminating method comprises the following steps of: (1) detecting a standard sample in an electronic spray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer to determine molecular composition, molecular weight and distributed mass spectrometric data of a polar compound in the standard sample; (2) detecting a sample to be detected in the electronic spray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer to determine the molecular composition, molecular weight and distributed mass spectrometric data of another polar compound in the sample to be detected; and (3) evaluating differences of the molecular compositions, molecular weights and distribution of the sample to be detected and the standard sample, detected in a wide band mode and a narrow band mode, by utilizing a spectral ratio method and a repeatability limit method to obtain an asphalt fingerprint identification result. Through the asphalt analysis discriminating method disclosed by the invention, the characteristics of the obtained asphalt fingerprint are remarkable and have very high representativeness and reliability; and the variety discrimination and product identification of petroleum asphalt, coal pitch, natural asphalt (consisting of rock asphalt and lake asphalt) can be realized by comparison of asphalt fingerprint mass spectrometric data of the standard sample and the sample to be detected.
Owner:RES INST OF HIGHWAY MINIST OF TRANSPORT
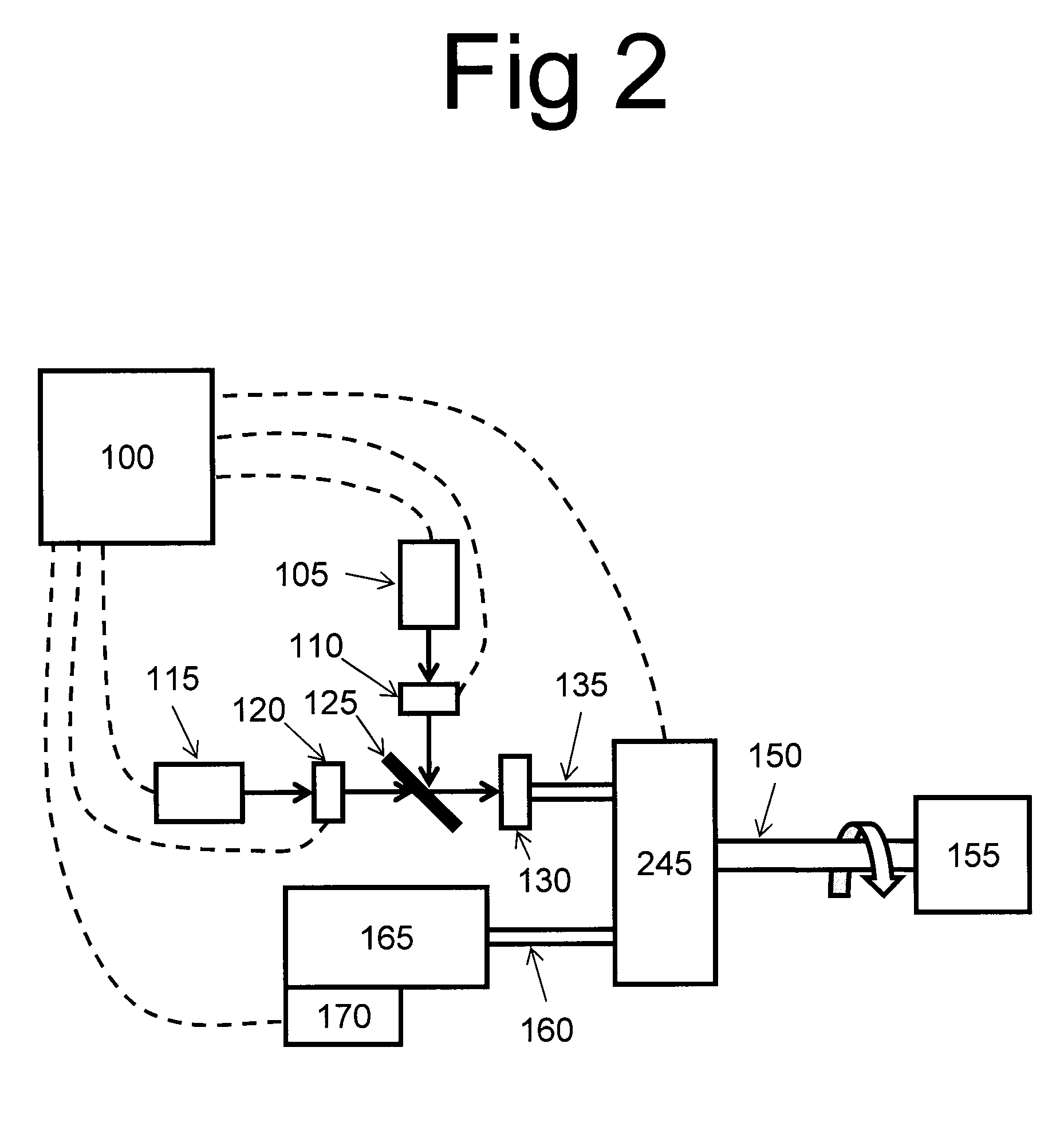
Apparatus, computer-accessible medium and method for measuring chemical and/or molecular compositions of coronary atherosclerotic plaques in anatomical structures
InactiveUS20090073439A1Reduce absorptionReduce scatterDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnalogue computers for chemical processesInelastic scatteringAnatomical structures
Exemplary apparatus and method can be provided for controlling at least one electro-magnetic radiation. For example, it is possible to rotate and / or translate at least one optical waveguide. At least one of the optical waveguide(s) can receive a first radiation at a first wavelength and transmit the first radiation to at least one sample. Such optical waveguide and / or another optical waveguide may receive a second radiation at a second wavelength that is different from the first wavelength. For example, the second radiation may be produced based on an inelastic scattering of the first radiation. In addition, exemplary apparatus and method can be provided which can also be used to receive data associated with the second radiation, determine at least one characteristic of the at least one sample based on the data, and generate the image and / or the map of a portion of the arterial sample based on the at least one characteristic. Further, exemplary computer-accessible medium can be provided which includes a software arrangement thereon. When a processing arrangement executes the software arrangement, the processing arrangement is configured to modify at least one characteristic of an arrangement using certain procedures. These exemplary procedures include simulating at least one electro-magnetic radiation provided into and out of the arrangement, simulating an inelastic scattering radiation from at least one simulated sample, receiving the simulated inelastic scattering radiation into and out of the simulated arrangement, and determining a simulated characteristic of the simulated arrangement as a function of the simulated inelastic scattering radiation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
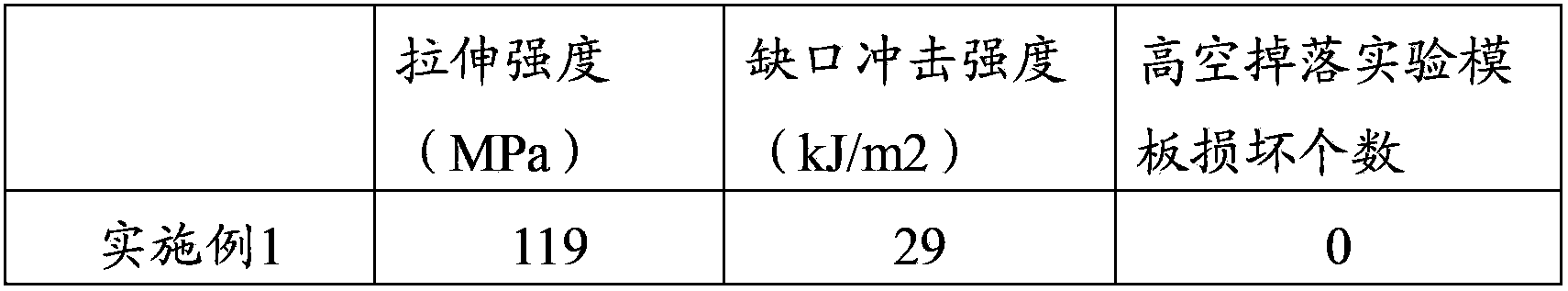
High-molecular composition used for plastic building template and its preparation method
The invention relates to the building material field, and especially relates to a high-molecular composition used for plastic building template and its preparation method. The high-molecular composition used for plastic building template comprises the following ingredients by weight: 100 parts of polyolefin feed back, 0.01-2 parts of cross-linking agent, 0.01-10 parts of auxiliary cross-linking agent, 5-200 parts of fiber, 0-100 parts of filling material and 0-20 parts of auxiliary agent. Compared with a prior art, the addition of the cross-linking agent and the auxiliary cross-linking agent in the high-molecular composition raw material can greatly increase the mechanical property of the building template, so that the building template has high strength and good shock resistance, the building template is not damaged while falling off from high altitude, and is difficultly scratched by hard objects, and the usage efficiency and life of the building template can be obviously increased.
Owner:HEFEI GENIUS NEW MATERIALS
Composition and preparation method of targeting liposome-cyclic dinucleotide and application of targeting liposome-cyclic dinucleotide to anti-tumor
ActiveCN106667914AProlong metabolic cycleEnhance the effect of anti-tumor therapyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderTumor targetCholesterol
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly discloses a composition and a preparation method of cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP (cyclic Guanosine Adenosine Monophosphate) encapsulated by a targeting liposome and application of the cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP to anti-tumor. The targeting liposome consists of lecithin, cholesterol, polyethylene glycol and the like as well as a link targeting molecule of the targeting liposome; a cGAMP slow release drug encapsulated by the targeting liposome can be used for enhancing the intensifying cell osmosis action, enhancing an immune reaction, effectively targeting drug delivery and intensifying the inhibition on the growth of multiple tumor cells. Therefore, the cGAMP encapsulated by the targeting liposome can be used for preparing an anti-tumor targeting slow release drug, and has important potential application in the field of targeting immune anti-tumor.
Owner:HANGZHOU XINGAO BIOTECH CO LTD
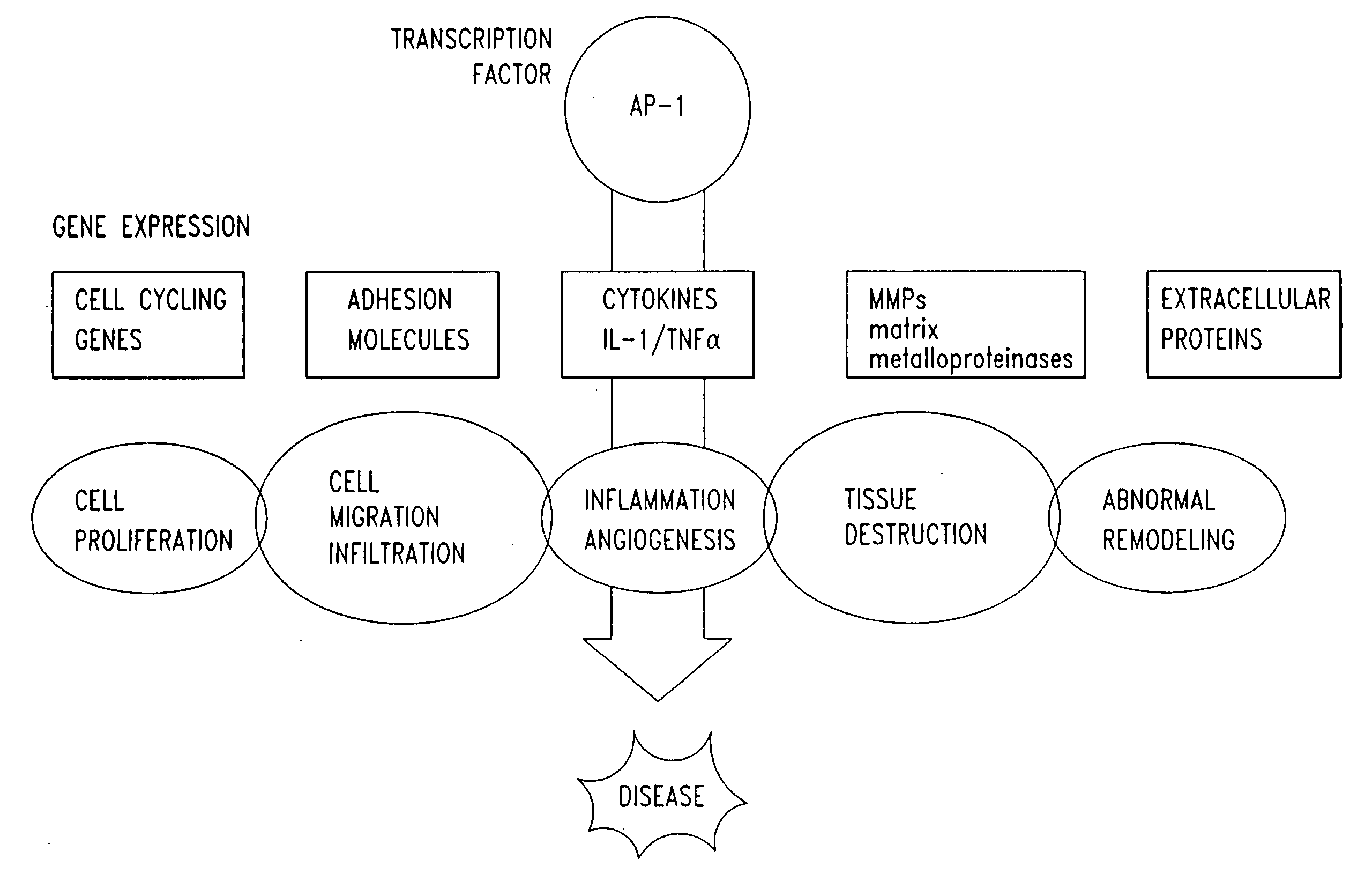
Compositions and methods for treating cellular response to injury and other proliferating cell disorders regulated by hyaladherin and hyalurons
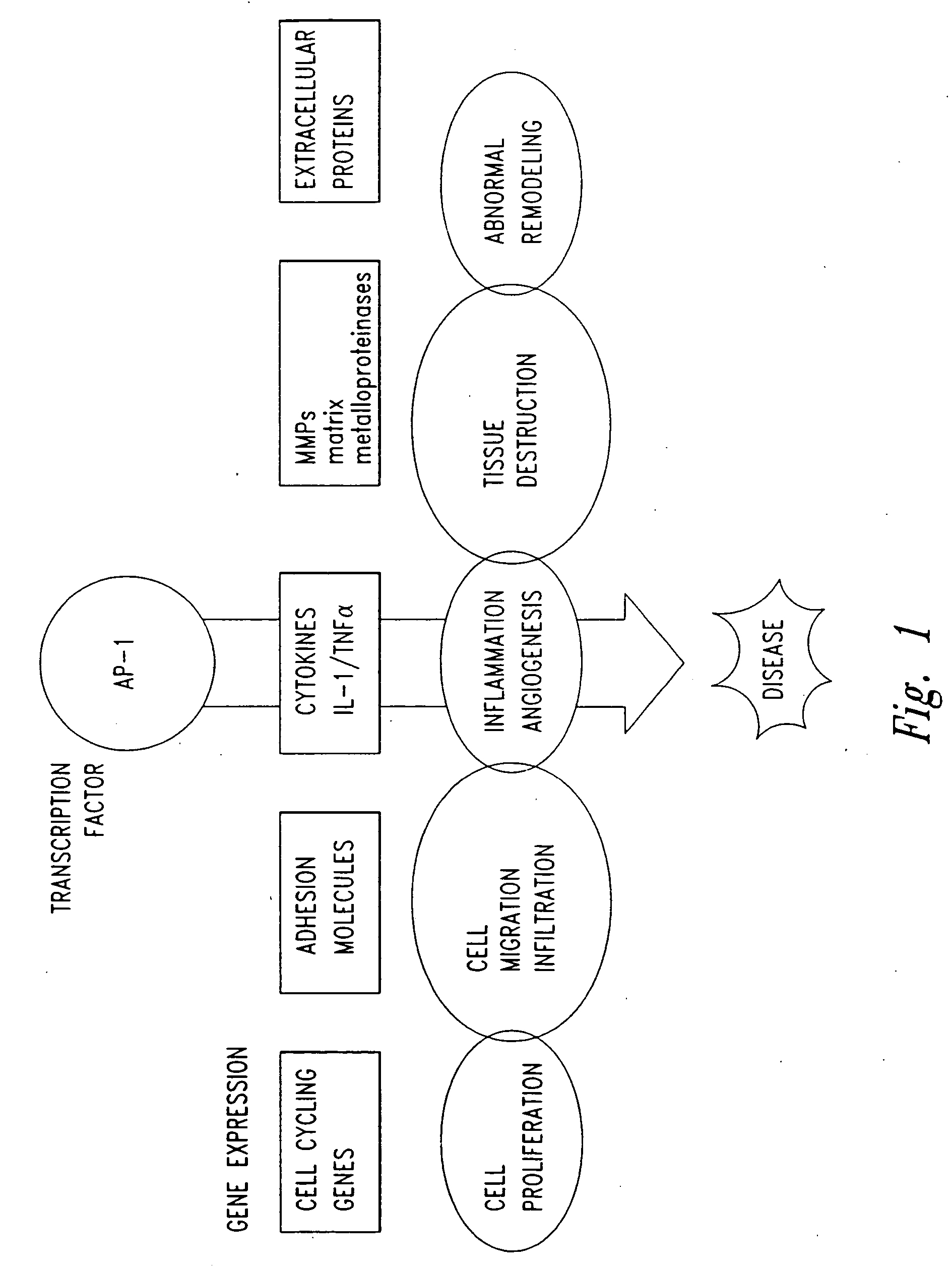
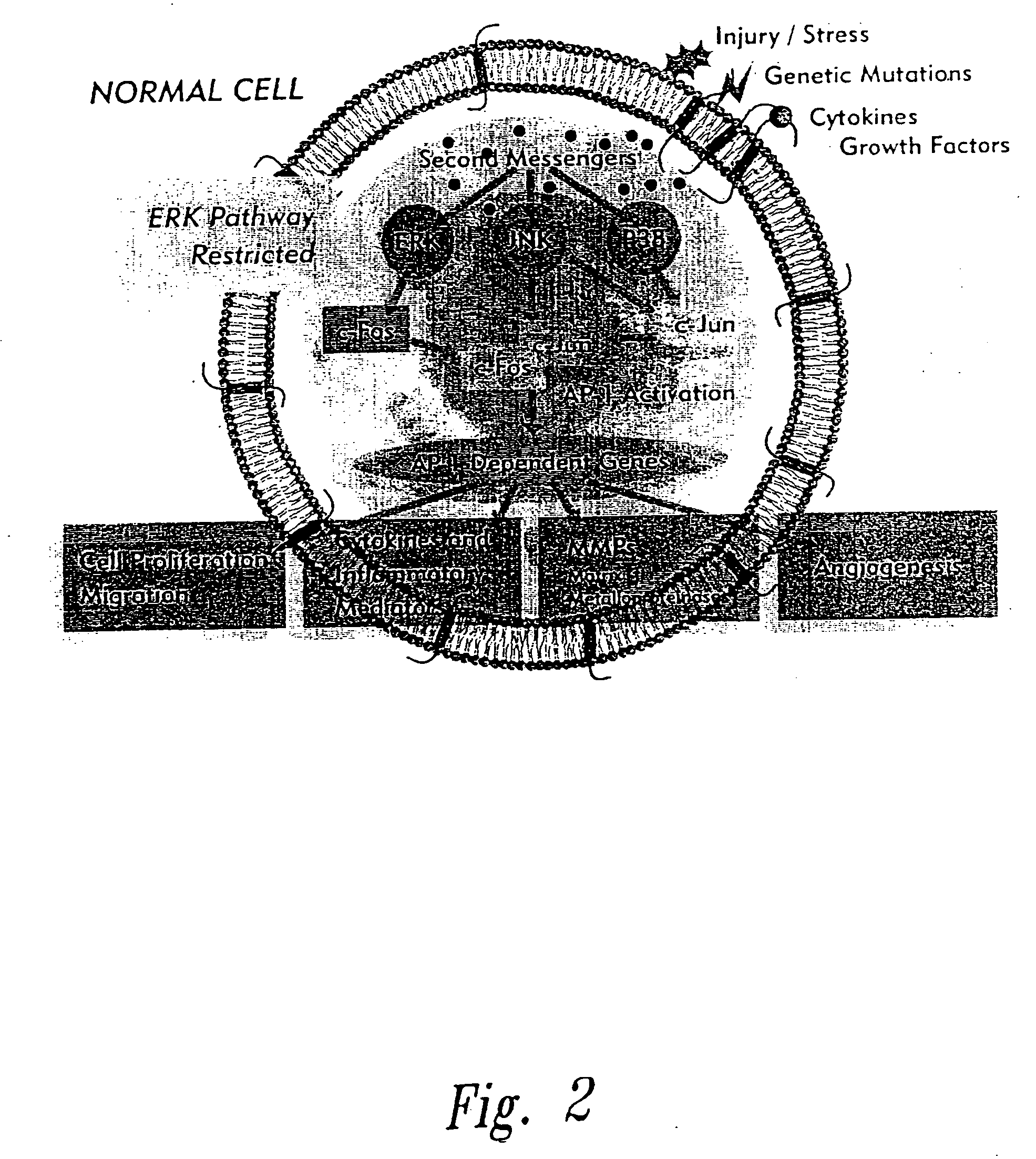
InactiveUS20050058646A1Inhibit cell proliferationPrevent proliferationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCancer cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating a tissue disorder associated with a response-to-injury process or proliferating cells in a mammal. These tissue disorders are associated with a novel cellular phenotype designated as “transition cells” which are described herein. This cellular phenotype is characterized in having an activated erk kinase signaling activity, a stimulated AP-1 binding activity, and at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of: (a) increased podosome formation, (b) increased flux of intracellular or extracellular hyaluronans or hyaladherins, (c) increased expression of a hyaladherin, (d) an inability to form focal adhesions, (e) increased metalloproteinase activity, and (f) increased expression of a hyaladherin. Example tissue disorders include fibrosis, inflammation, degeneration and invasive disorders such as occur in cancerous cells. The methods provided herein include administering to the mammal, an effective amount of a composition that alters the activity of transition molecules within a cell Transition molecules are shown to be comprised of hyaladherins, hyaluronans and associated molecules that regulate the transitional phenotype. A novel cell culture comprising transition cells is also provided, as well as compositions comprising particular peptides, polypeptides, and antibodies that affect the transitional phenotype.
Owner:TURLEY EVA +1
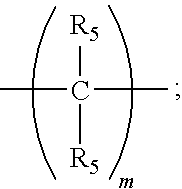
Dendrimer Compositions
Amine compounds, amine polymers, crosslinked amine polymers and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same may include polyhydroxy-containing cores that may be substituted with amine groups and may be used to treat hyperphosphatemia or to remove ions from the gastrointestinal tract of animals, including humans.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Thermoplastic high-molecular composition interpenetrated network structure and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a thermoplastic high-molecular composition interpenetrated network structure and a preparation method thereof. More particularly, the invention relates to the thermoplastic high-molecular composition interpenetrated network structure obtained by adopting a supercritical process to process a thermoplastic high-molecular composition.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com