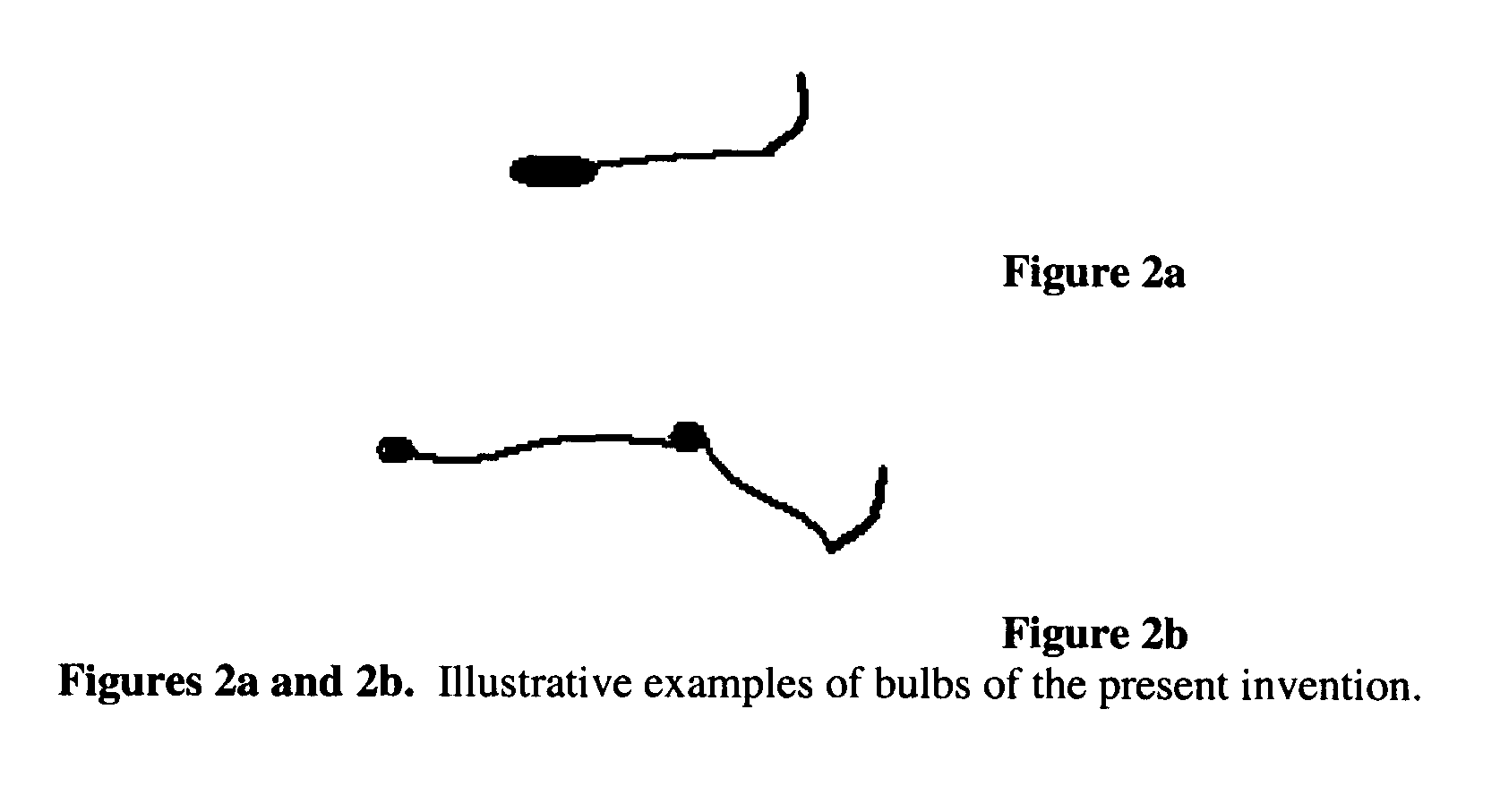
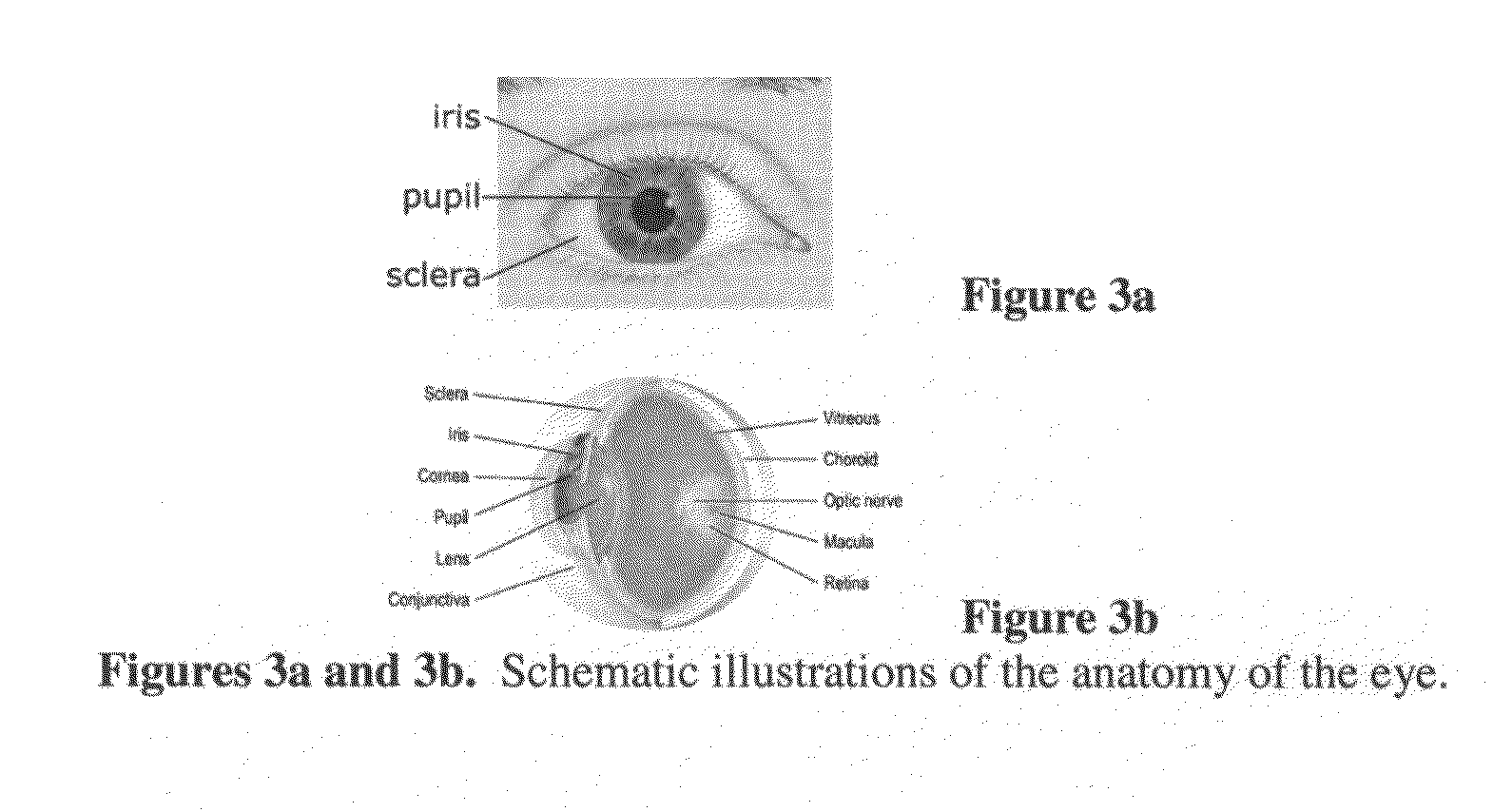
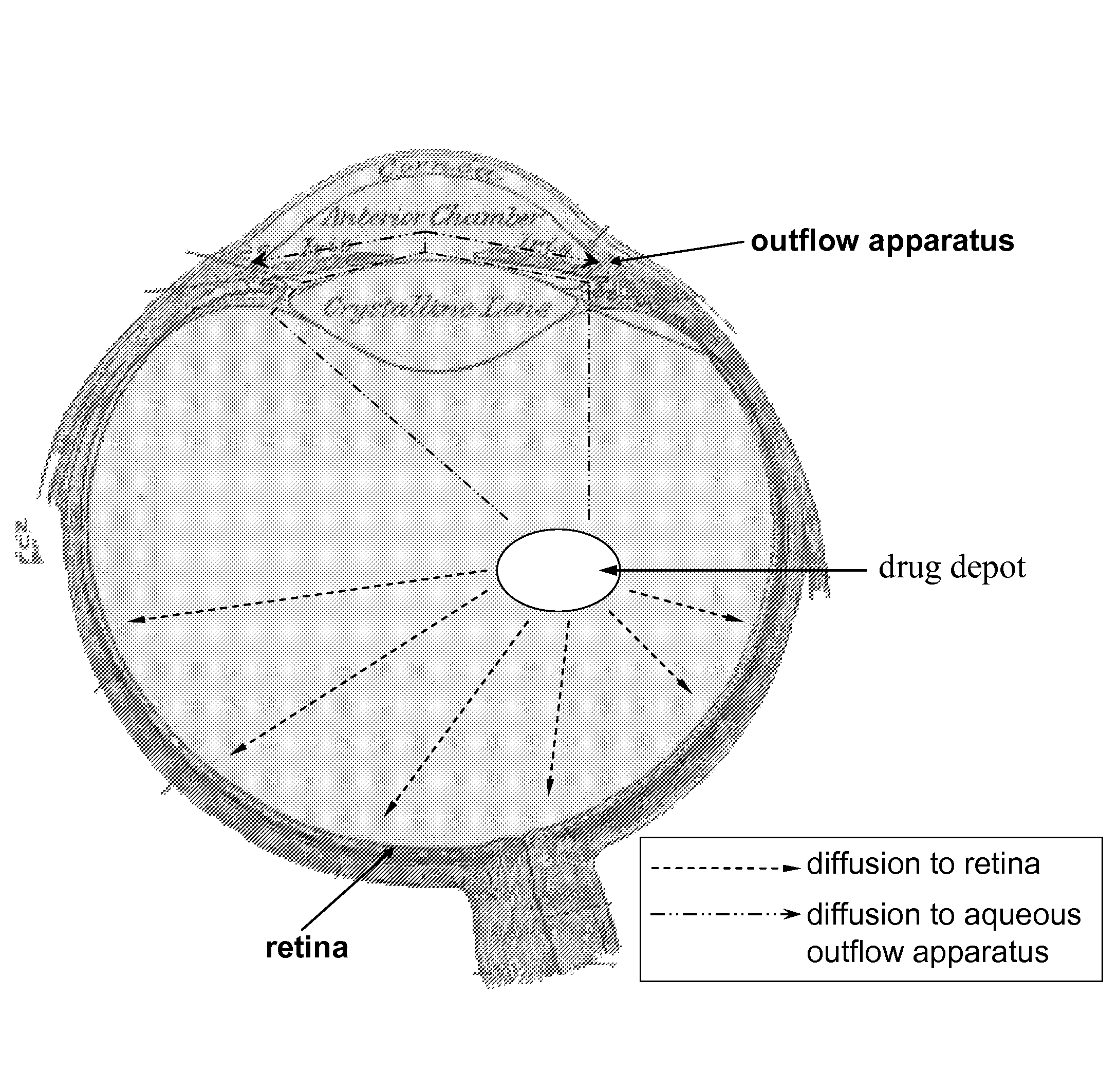
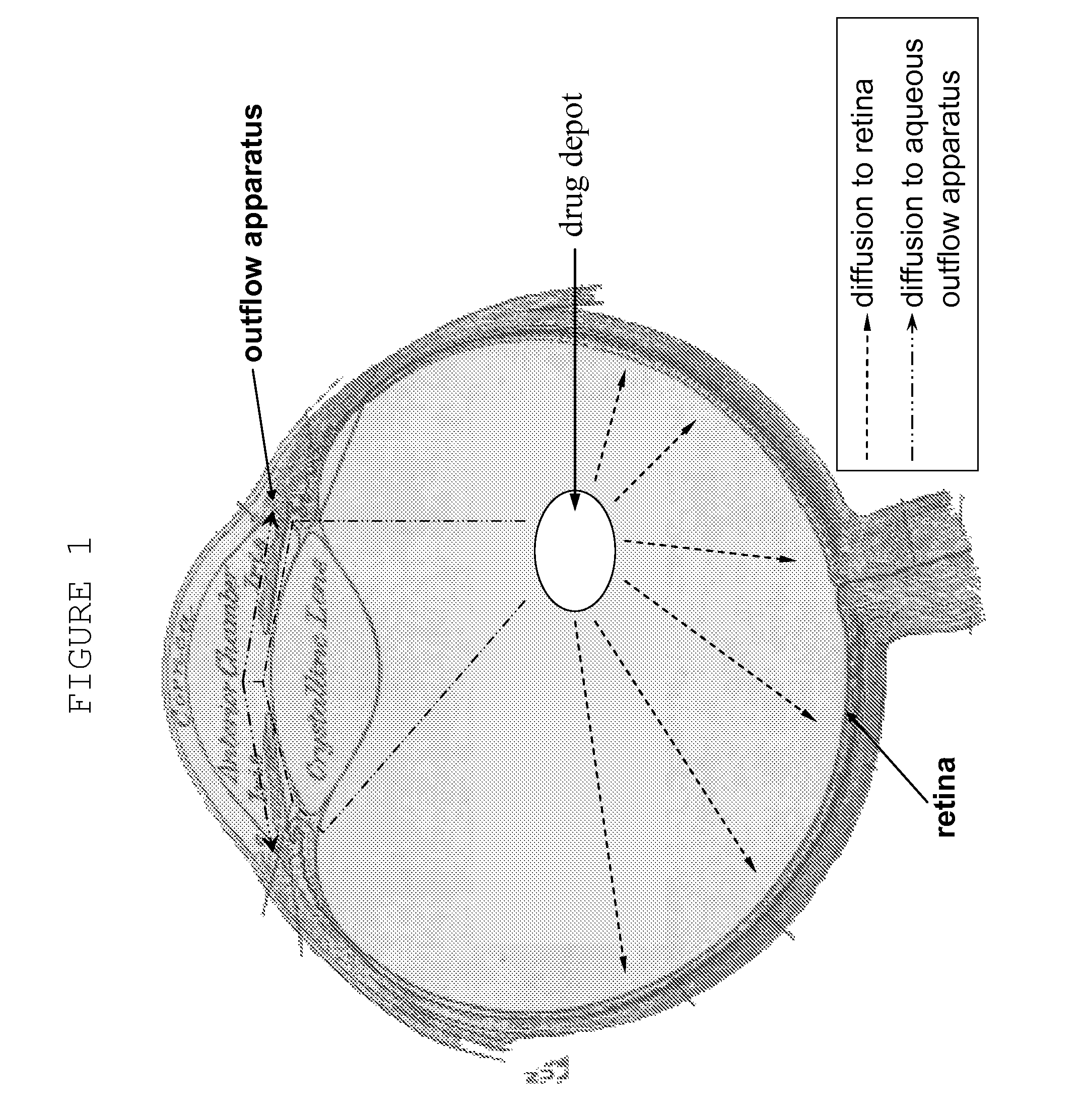
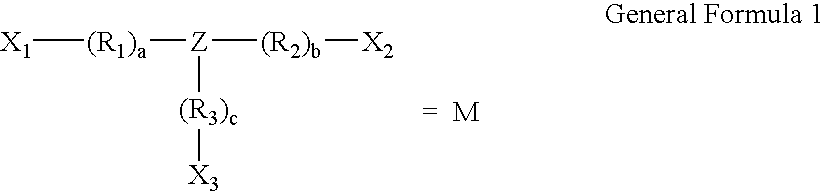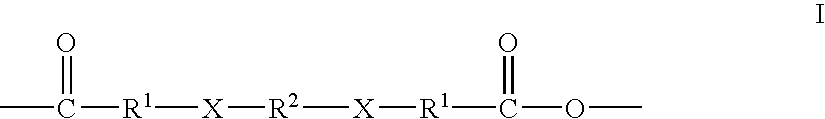Patents
Literature
173 results about "Polymeric drug" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
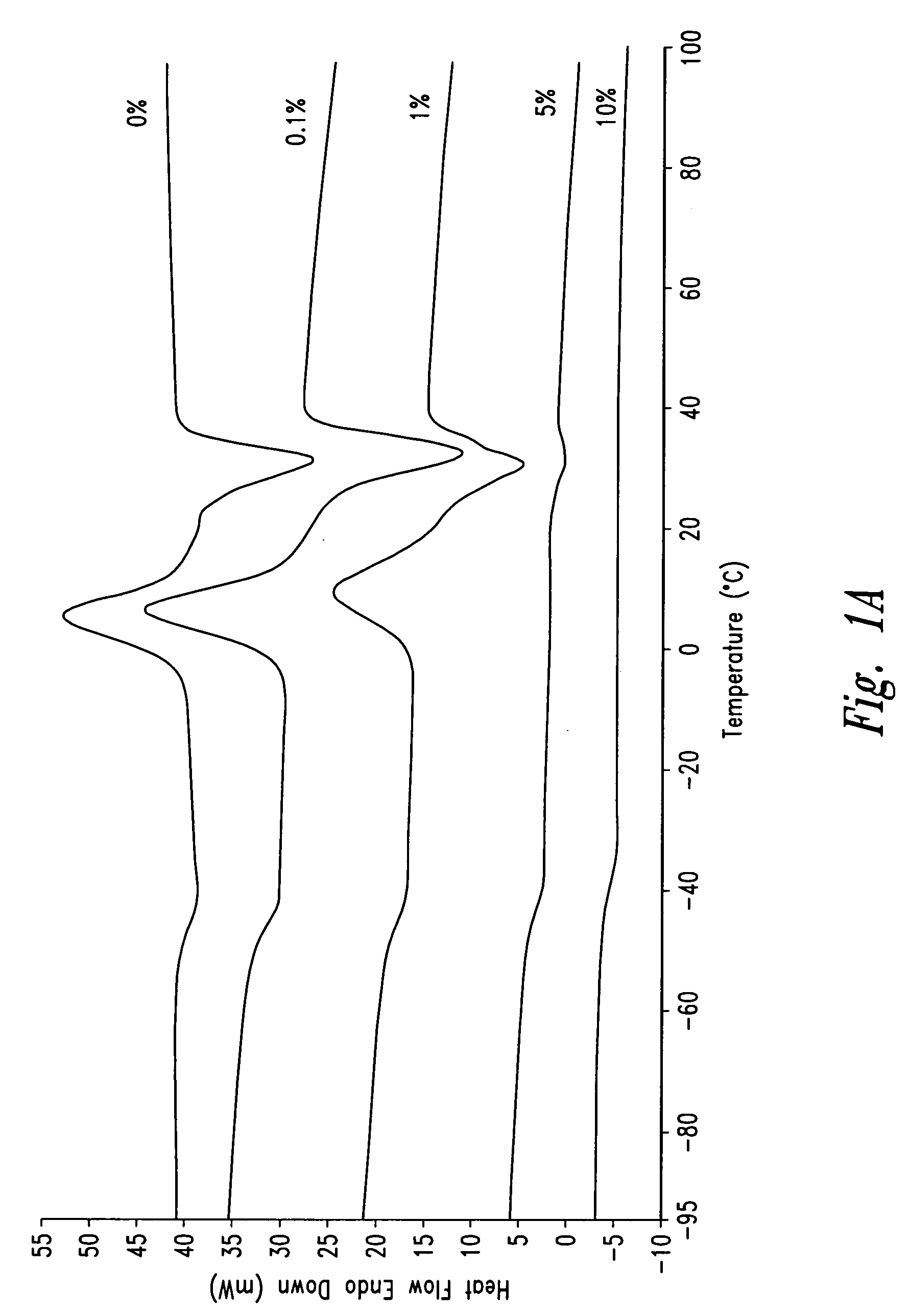
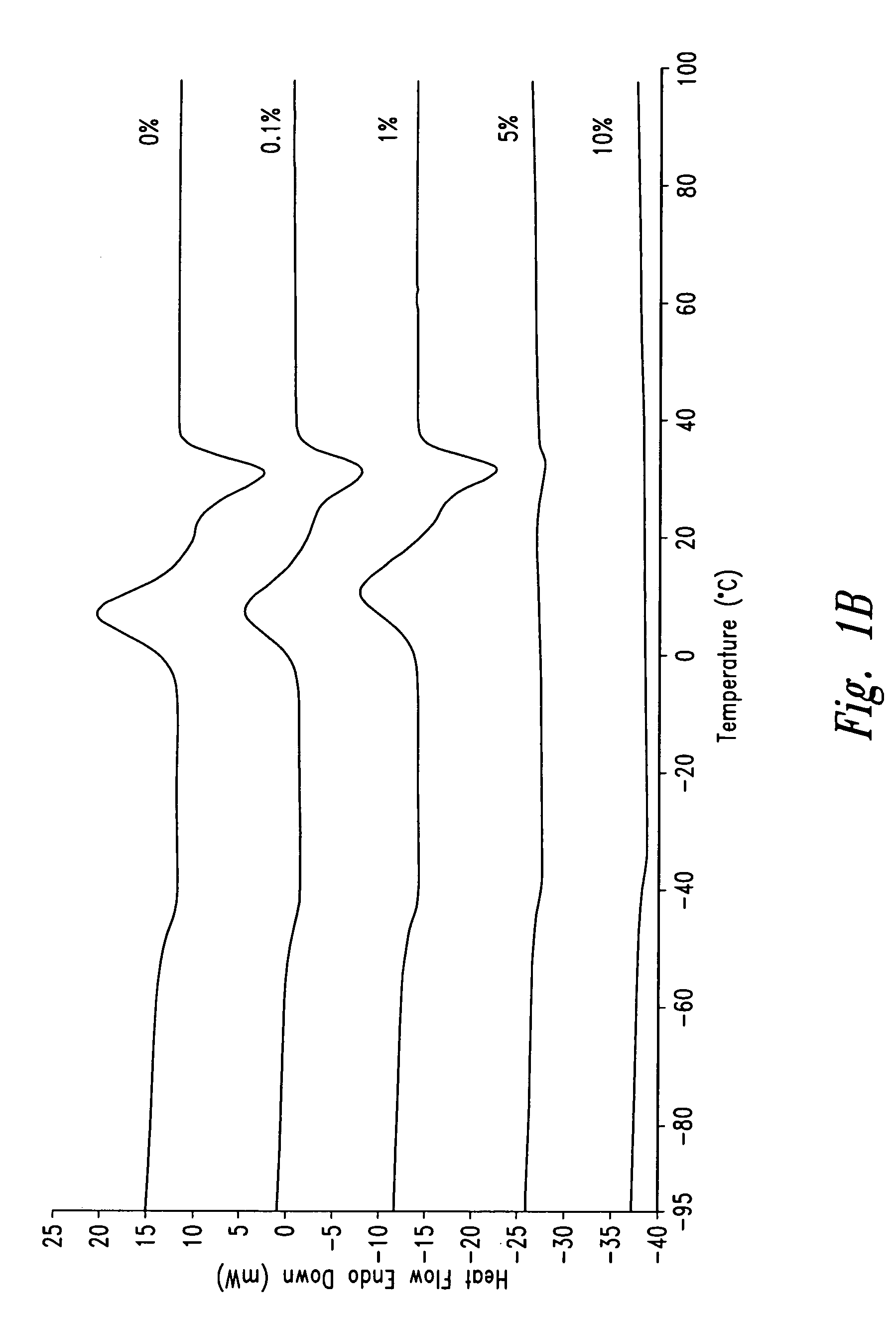
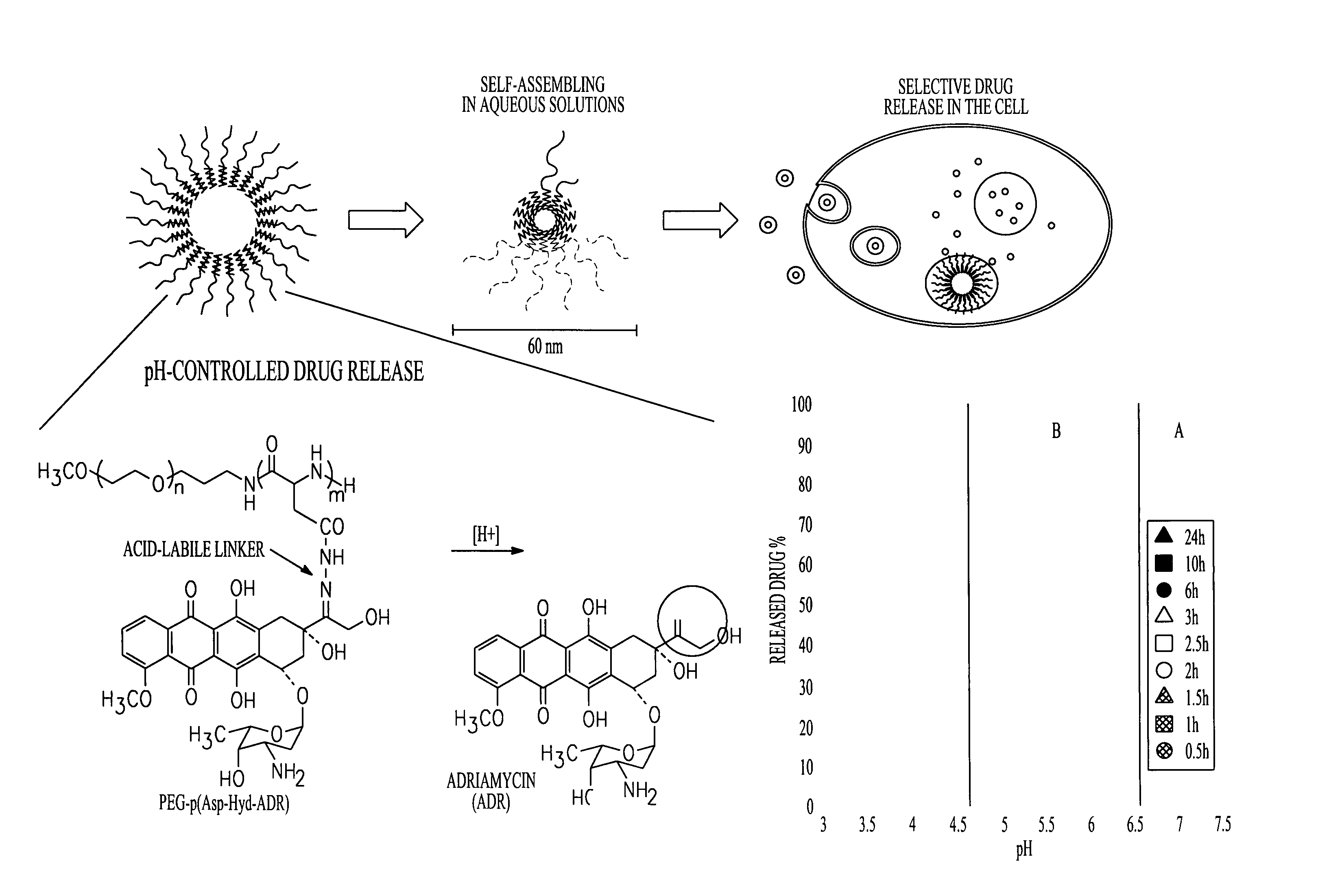
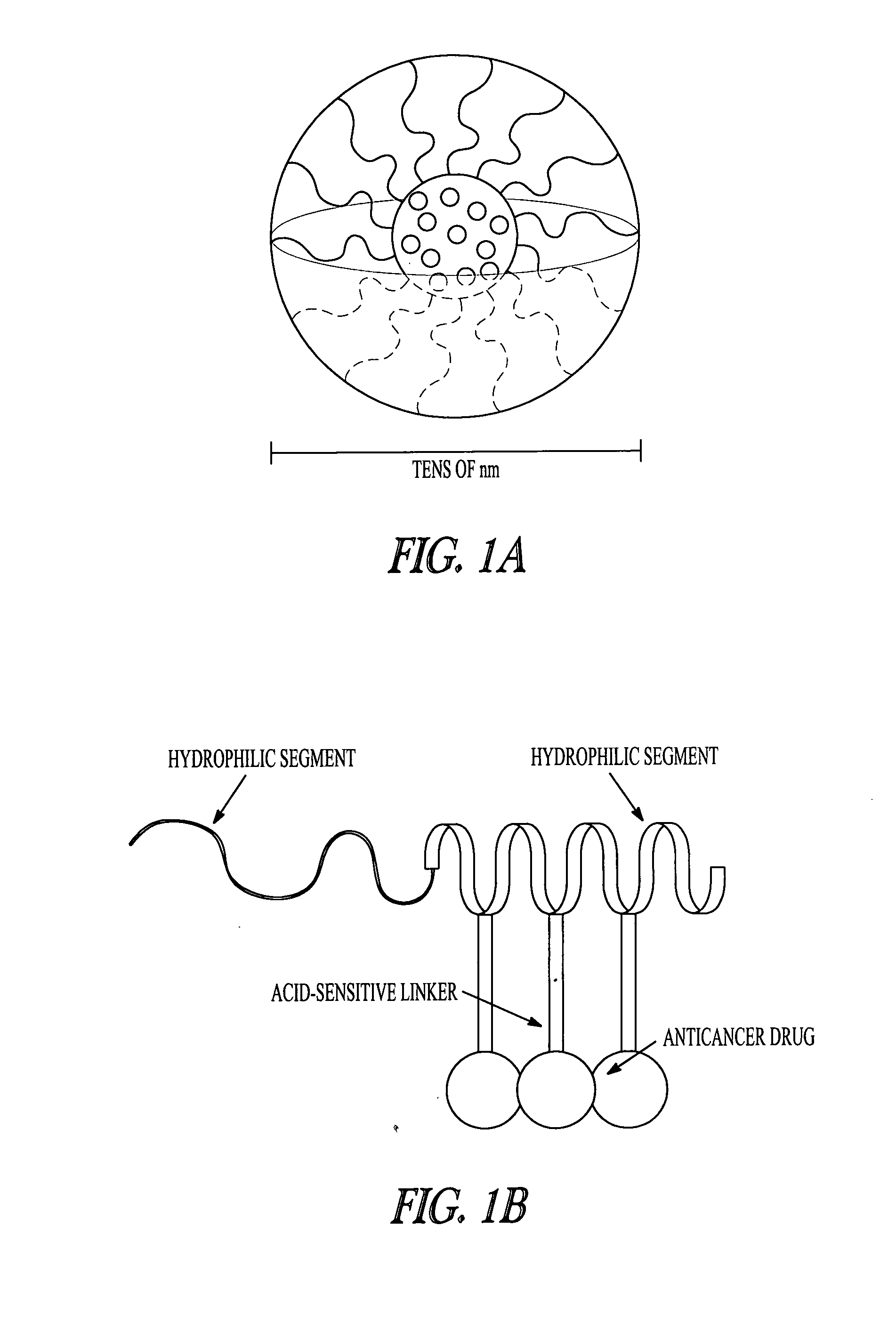
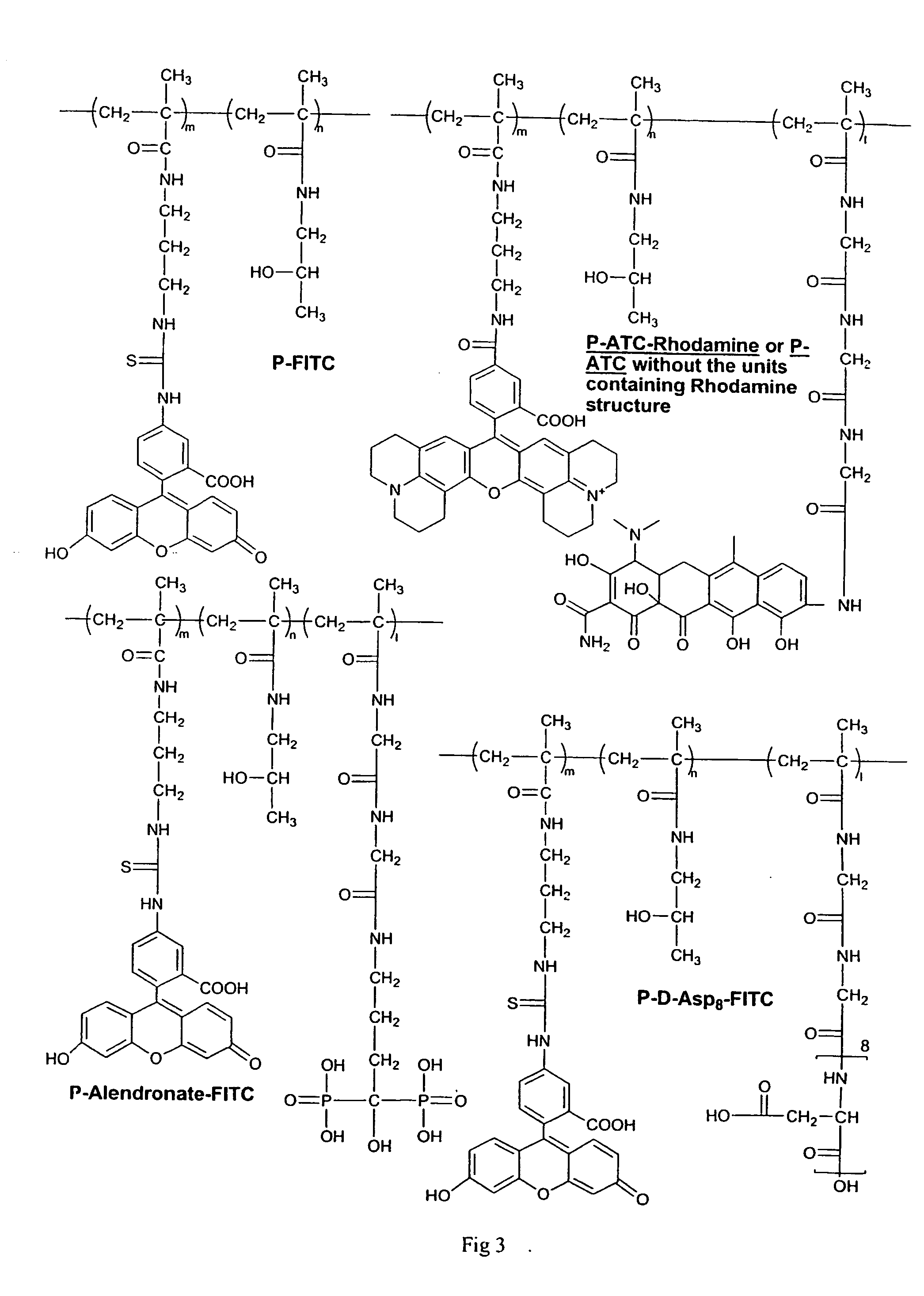
Polymeric drugs are defined as polymers that are active pharmaceutical ingredients, i.e., they are neither drug carriers nor prodrugs.
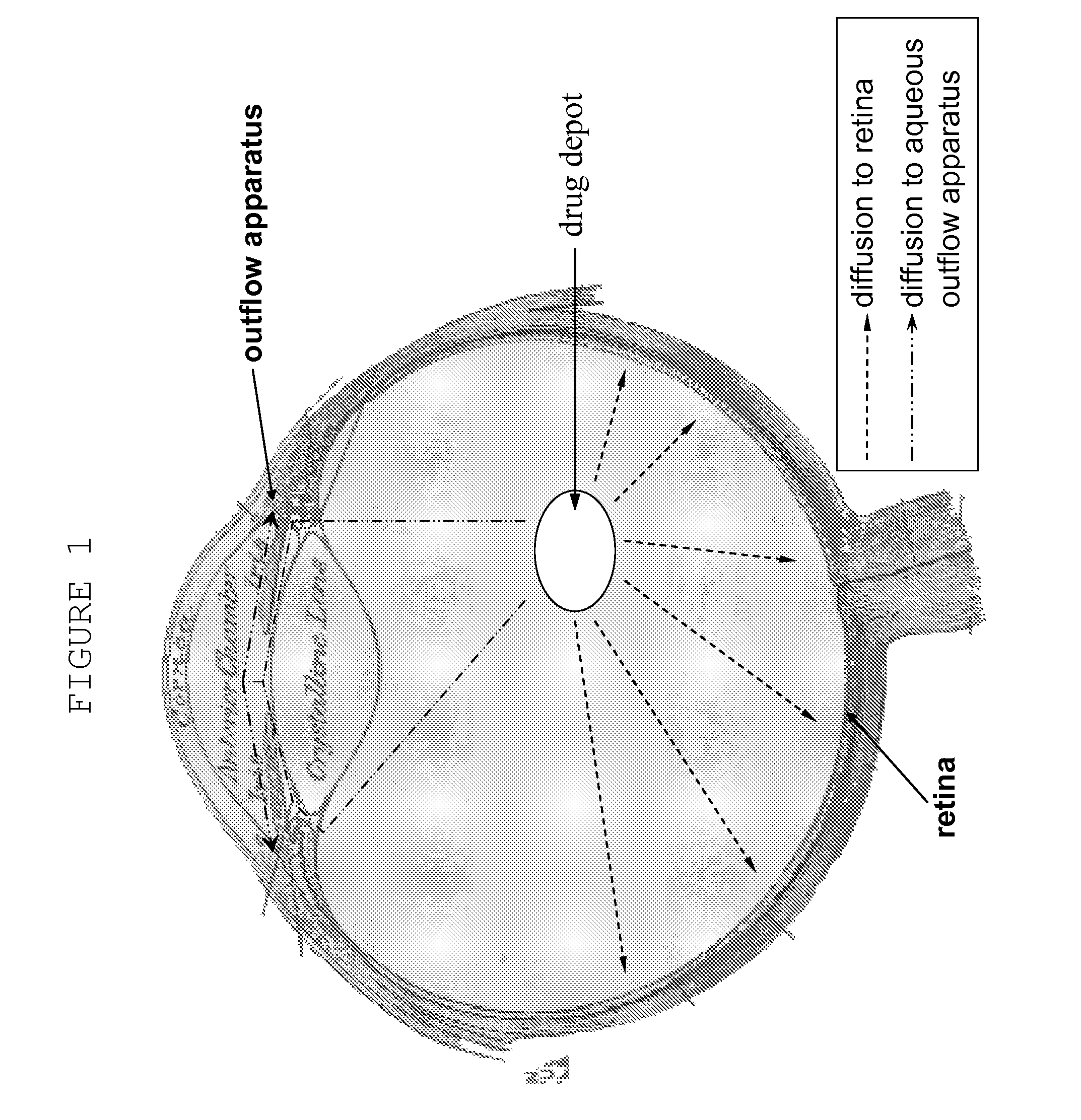
Hydrogels used to deliver medicaments to the eye for the treatment of posterior segment diseases
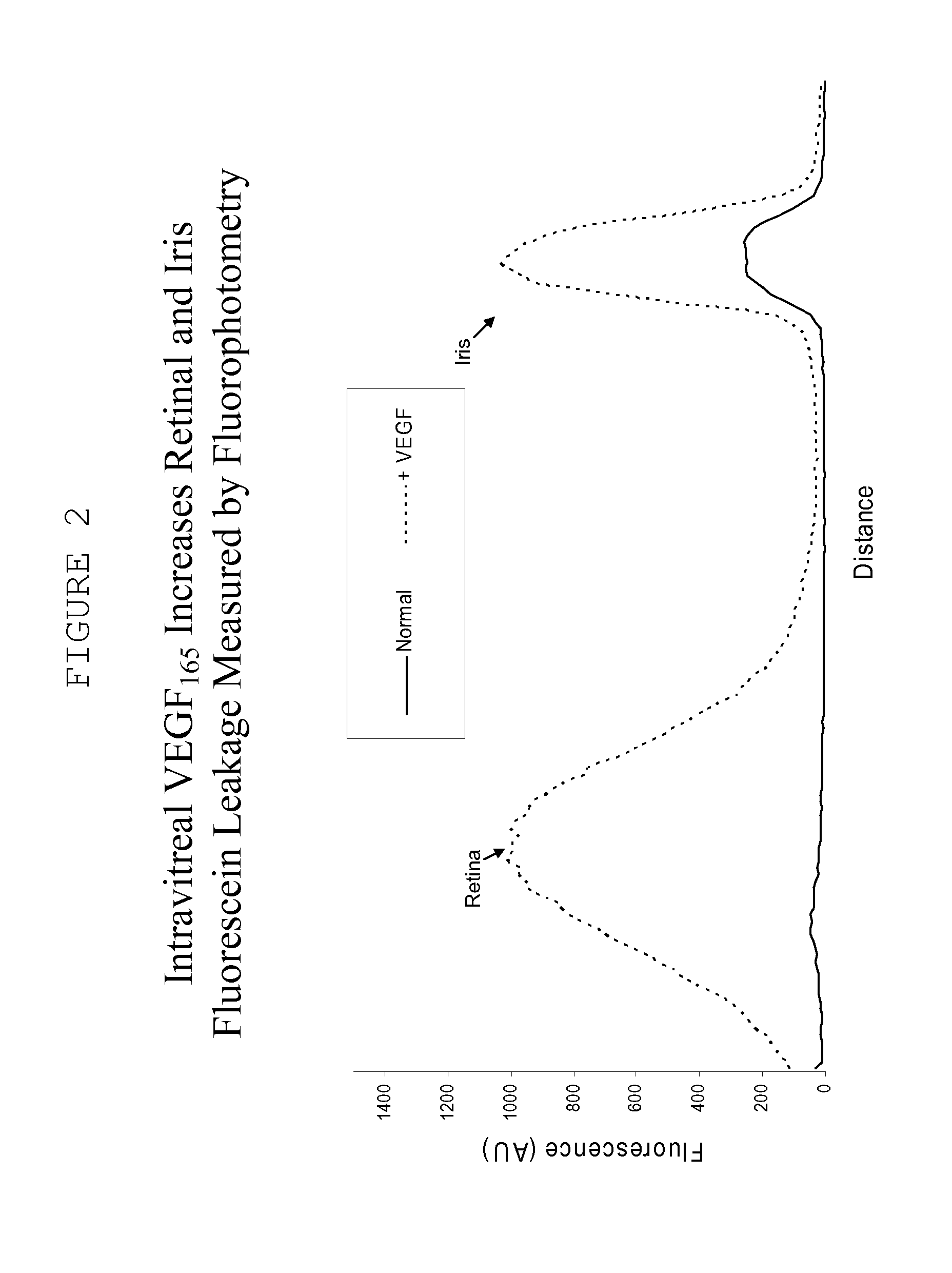
This invention provides a polymeric drug delivery system including a hydrogel containing one or more drugs for the treatment of a posterior segment disease. Exemplary drugs are anti-angiogenesis compounds for the treatment of macular degeneration. Allowing passive transference of this drug from a dilute solution into the hydrogel produces the delivery system. The hydrogel, when placed in contact with the eye, delivers the drug. The delivery of the drug is sustained over an extended period of time, which is of particular utility in the eye, which is periodically flushed with tears. This sustained delivery accelerates the treatment process while avoiding potential damaging effects of localized delivery of high concentrations of compounds, e.g., from eye drops.
Owner:DIRECTCONTACT
Protein-Polymer-Drug Conjugates
ActiveUS20130101546A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsDrug conjugationPharmaceutical drug
A drug conjugate is provided herein. The conjugate comprises a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) and a polymeric carrier substituted with one or more -LD-D, the protein based recognition-molecule being connected to the polymeric carrier by LP. Each occurrence of D is independently a therapeutic agent having a molecular weight≦5 kDa. LD and LP are linkers connecting the therapeutic agent and PBRM to the polymeric carrier respectively. Also disclosed are polymeric scaffolds useful for conjugating with a PBRM to form a polymer-drug-PBRM conjugate described herein, compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Polymeric conjugates for tissue activated drug delivery
InactiveUS20040228831A1Simple methodAbsorption bioactivityPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChemical MoietyActive agent
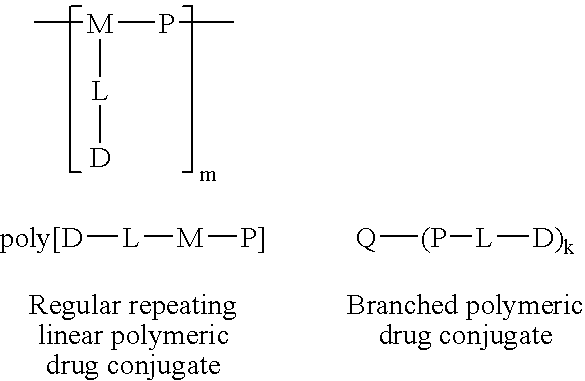
The present invention relates to a polymeric drug conjugate with one or more biologically active agents conjugated via an enzymatically cleavable linker to either a regular repeating linear unit comprising a water soluble polymer segment and a multifunctional chemical moiety, or a branched polymer comprising two or more water soluble polymer segments each bound to a common multifunctional chemical moiety, as well as to methods of making such conjugates. The present invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such conjugates and to the use of such conjugates to treat pathological conditions.
Owner:VECSTREETCARED
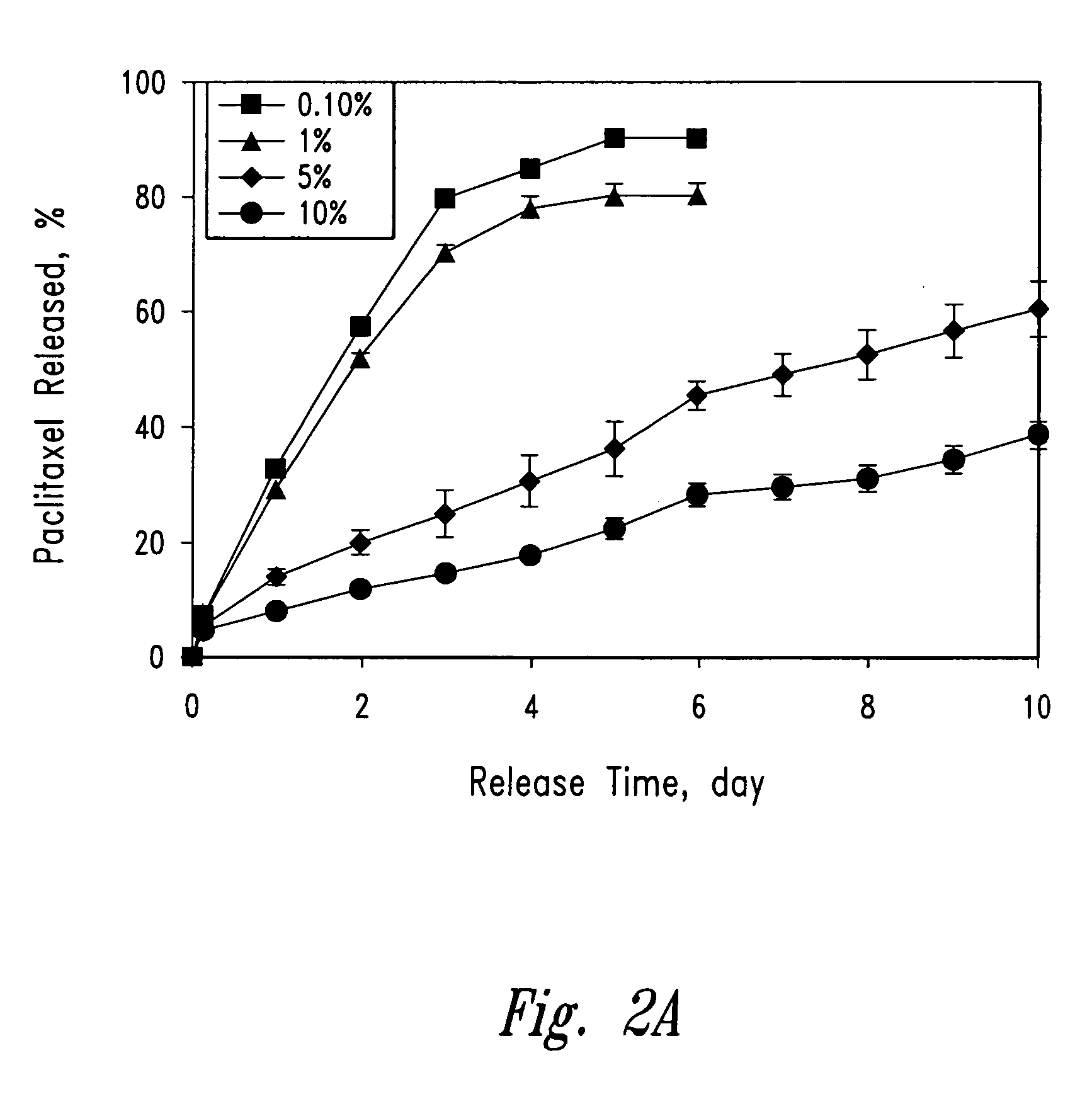
Polymeric drug delivery system for hydrophobic drugs
InactiveUS20050249799A1Low oral bioavailabilityStable against aggregationAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryHydrophobic polymerImmediate release
An oral delivery system for Class II drugs that have low oral bioavailability due to their insolubility in water and slow dissolution kinetics and method for making such a drug delivery system are disclosed herein. The formulation may be a controlled release or immediate release formulation. The immediate release formulation contains a Class II drug, together with a hydrophobic polymer, preferably a bioadhesive polymer. In one embodiment, the drug and polymer are co-dissolved in a common solvent. The solution is formed into small solid particles by any convenient method, particularly by spray drying. The resulting particles contain drug dispersed as small particles in a polymeric matrix. The particles are stable against aggregation, and can be put into capsules or tableted for administration. The controlled release formulations contain a BCS Class II drug and a bioadhesive polymer. The controlled release formulations may be in the form of a tablet, capsules, mini-tab, microparticulate, or osmotic pump. Enhancement of oral uptake of the drug from use of bioadhesive polymers occurs through (1) increased dissolution kinetics due to stable micronization of the drug, (2) rapid release of the drug from the polymer in the GI tract; and (3) prolonged GI transit due to bioadhesive properties of the polymers. The combination of these effects allows the preparation of a compact, stable dosage form suitable for oral administration of many class II drugs.
Owner:SPHERICS
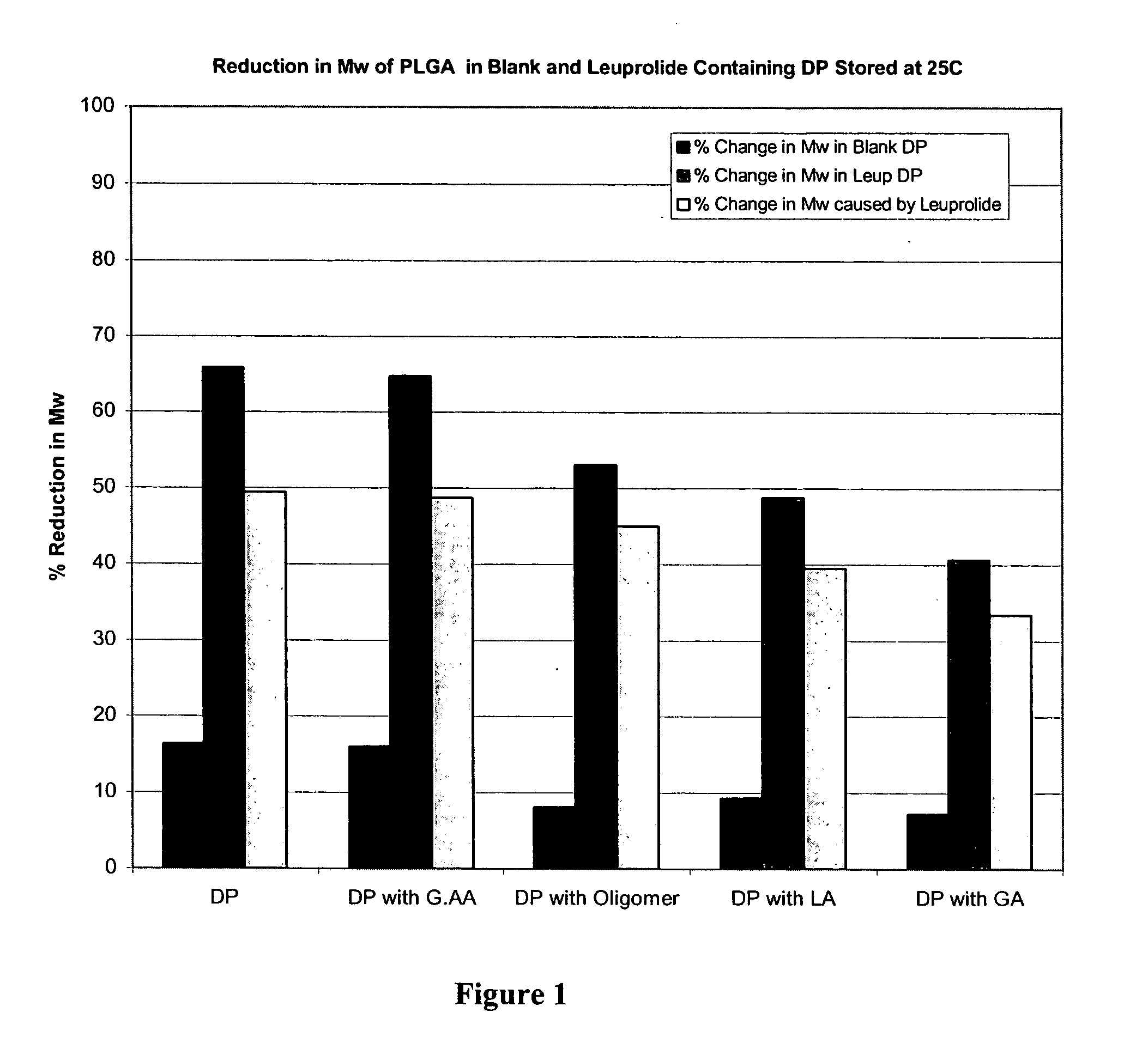
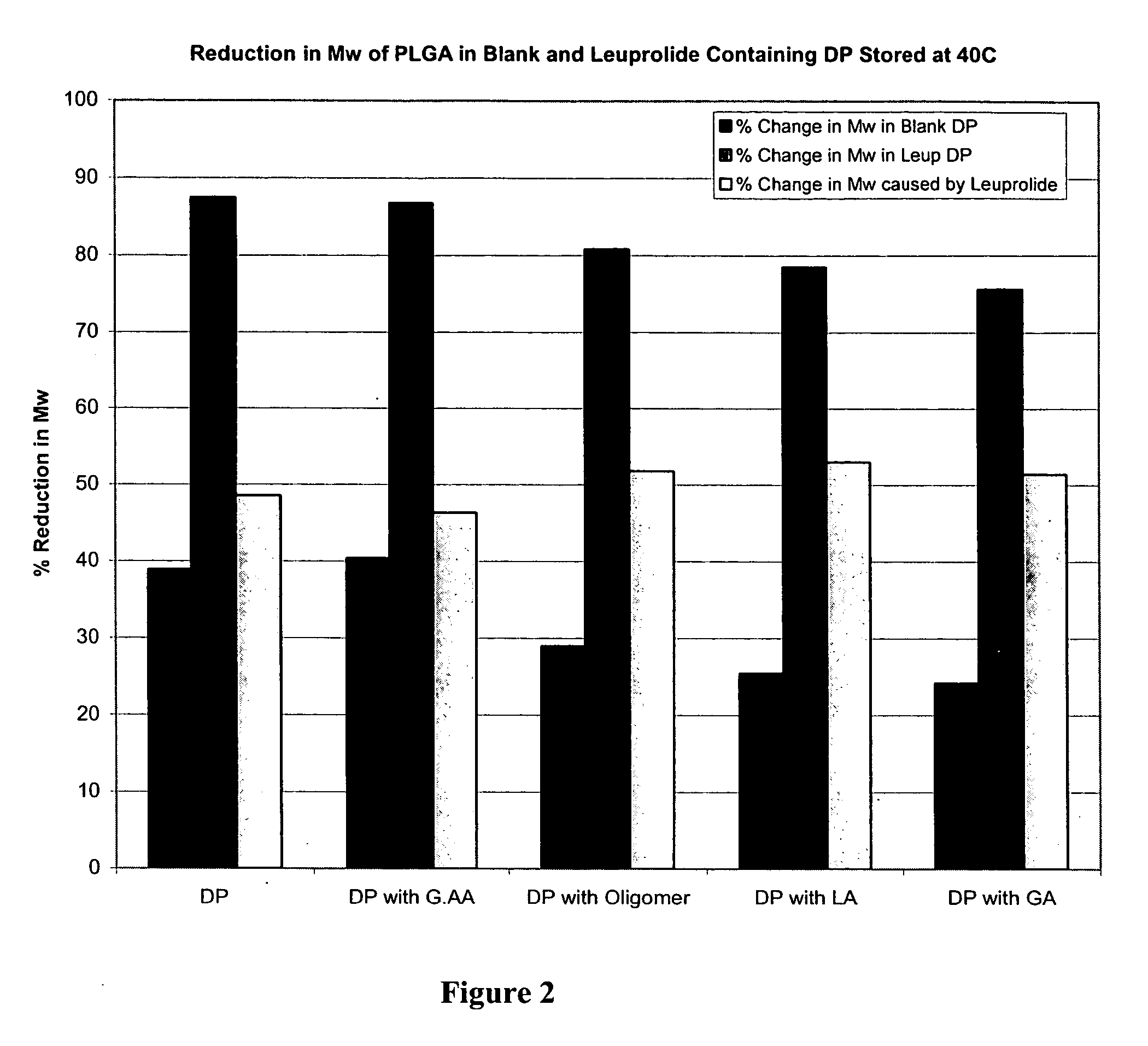
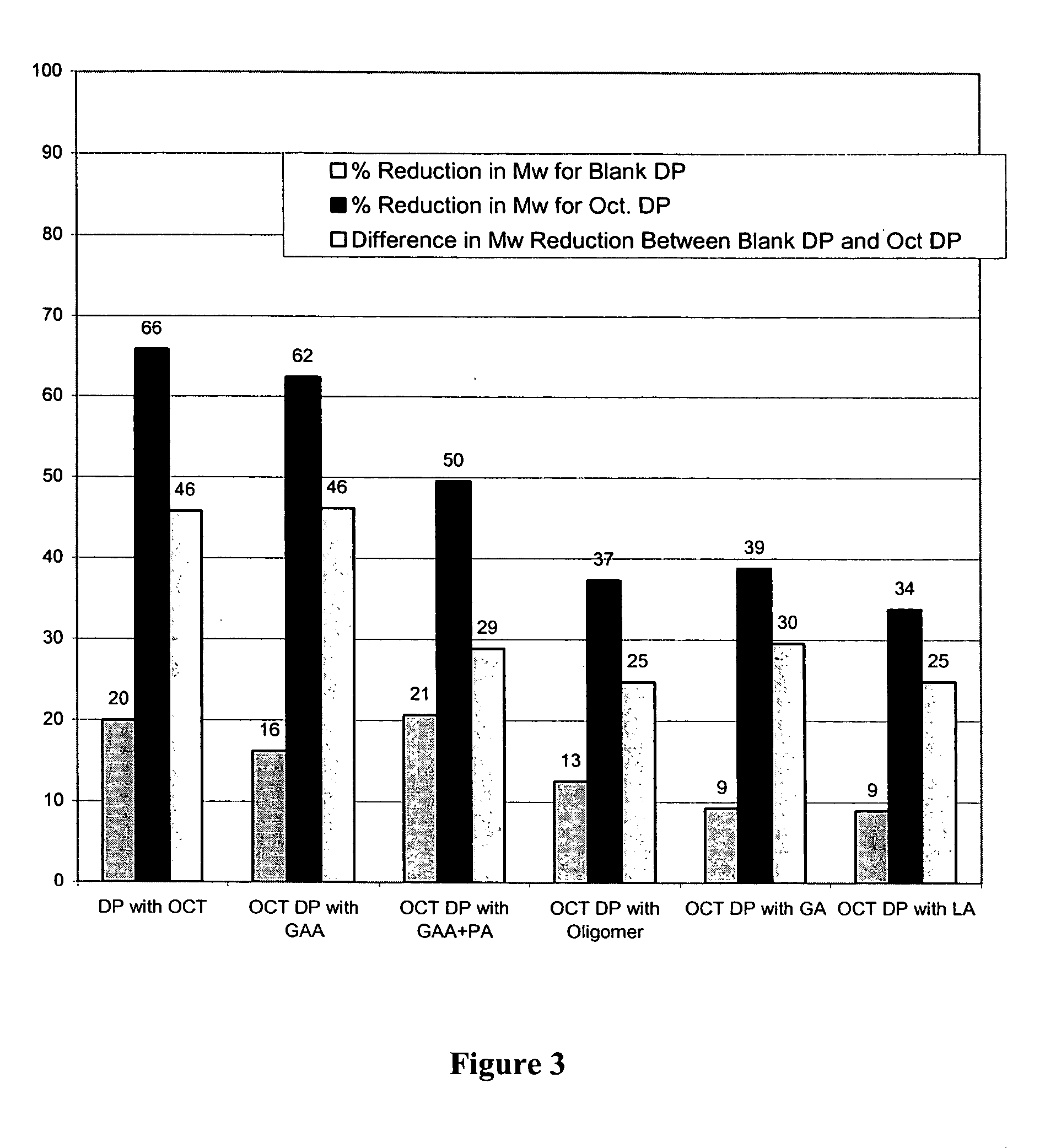
Prevention of molecular weight reduction of the polymer, impurity formation and gelling in polymer compositions
ActiveUS20050042294A1Reduce and eliminate molecular weight reductionReduce molecular weightPowder deliveryBiocideSolubilityActive agent
Polymer and drug containing compositions and method of preparing such compositions are disclosed. The dispersed phase formulation has a polymer, a pharmaceutically or biologically active agent and a small fraction of low pKa acid additive. Stable, filter sterilizable, non-gelling solutions containing GnRH analogues at least at levels typically used in sustained release formulations and a method of increasing solubility of a high level of a GnRH analogue or a freeze-dried antgonist of GnRH in a polymer containing solution are also disclosed. The amount of the acid additive in the polymer solution is such that it is sufficient to increase the solubility of the high level of the GnRH analogue in the polymer solution without affecting the release characteristics of the microspheres prepared therefrom.
Owner:OAKWOOD LAB LLC
Polymeric drug formulations
InactiveUS7005454B2Reduce the formation of blood clotsPrevent thrombosisPowder deliveryBiocideWater insolubleMedicine
Polymeric drug formulations containing a non-releasing single-phase dispersion of a water-soluble drug in a water-insoluble tissue-compatible polymer matrix. Polymeric drug formulations are also disclosed containing a single-phase dispersion of a water-soluble drug and a water-insoluble tissue-compatible polymer matrix, and a second, phase-disrupting polymer that is non-miscible with the tissue-compatible polymer and is present in an amount sufficient to form phase-separated microdomains of the second polymer in the tissue-compatible polymer matrix, so that the release rate of the water-soluble drug from the tissue-compatible polymer matrix is related to the amount of the second polymer. Methods of preparing the polymeric drug formulations are also described, as well as methods for site-specific drug delivery utilizing the polymeric drug formulations.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
Polymeric systems for drug delivery and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050042293A1Precise moldingMore solid formPowder deliveryKetone active ingredientsWater insolubleIn vivo
Biodegradable polymeric implants can provide a safe and efficient means to deliver drugs in the treatment of various diseases. Although a polymeric drug delivery system can be implanted as a solid device within a subject, it is also possible to administer such a system as an injectable liquid which solidifies in vivo. An improved formulation of a polymeric drug delivery system comprises a water insoluble copolymer that is a solid or wax at 37° C., a water soluble polymer that is a liquid at 25° C., and a hydrophobic drug. These drug delivery systems can be administered by injection, and do not require the use of a toxic curing agent or inconvenient temperature manipulations.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Polymeric drug formulations
InactiveUS7101840B2Improve performanceTrend downPowder deliverySaccharide peptide ingredientsNon solventWater insoluble
A method of forming a polymeric drug formulation in which a water-soluble drug is blended with a water-insoluble tissue-compatible polymer that is miscible in the solid phase with the drug, and with a poly(alkylene oxide), in a solvent system capable of forming a homogeneous solution of the drug, the tissue-compatible polymer and the poly(alkylene oxide), after which the solution is added to a non-solvent for the drug, the tissue-compatible polymer and the poly(alkylene oxide), so that a microdomain-separated solid co-precipitate of the drug, the tissue-compatible polymer and the poly(alkylene oxide) is formed, wherein the poly(alkylene oxide) is blended in an amount effective to form phase-separated microdomains in said co-precipitate.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
Therapeutic polyanhydride compounds for drug delivery
InactiveUS20060013851A1Enhanced solubility and processabilityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderThiolPHENOL LIQUID
Polyanhydrides which link low molecular weight drugs containing a carboxylic acid group and an amine, thiol, alcohol, or phenol group within their structure into polymeric drug delivery systems are provided. Also provided are methods of producing polymeric drug delivery systems via these polyanhydride linkers as well as methods of administering low molecular weight drug to a host via the polymeric drug delivery systems. Medical implants based on the polymeric drug delivery system of the invention are also provided.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Molecularly imprinted phosphate binders for therapeutic use
InactiveUS20050276781A1Increase surface areaSpecific binding capacityOrganic dyesSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsPhosphateCalcium Binder
Methods for synthesizing molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) having an affinity for dietary phosphates, resulting polymers, pharmaceutical compositions and modes of administration are disclosed. The MIP compounds are useful for binding excess dietary phosphates in a patient in need thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Barrier coatings for fluids contacting medical devices
The invention relates to methods and materials that, for example, function to increase the barrier properties of containers including polymeric drug medication reservoirs and related containers such as infusion set tubing. Embodiments of the invention include aqueous container systems having containers coated with a composition selected to have one or more material properties including an ability to reduce the diffusion or permeation of compounds such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and preservatives (e.g. phenol, benzyl alcohol and m-cresol) into or through a wall of the container.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Protein-polymer-drug conjugates
ActiveUS20150104407A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDrug conjugationPharmaceutical drug
A polymeric scaffold useful for conjugating with a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) to form a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate is described herein. The scaffold includes one or more terminal maleimido groups. Also disclosed is a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate prepared from the scaffold. Compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions are also described.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
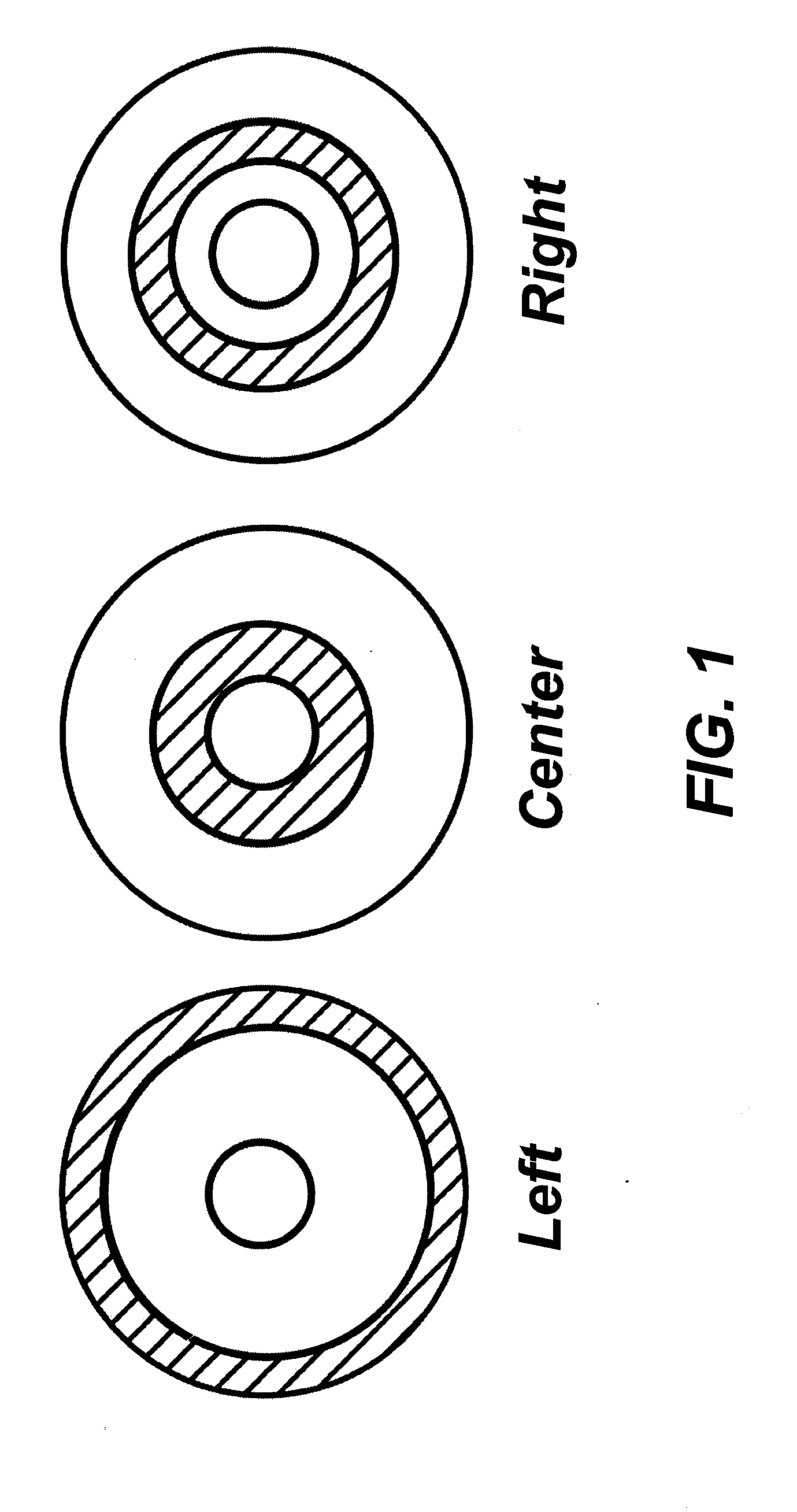
Ocular therapy using glucocorticoid derivatives selectively penetrating posterior segment tissues
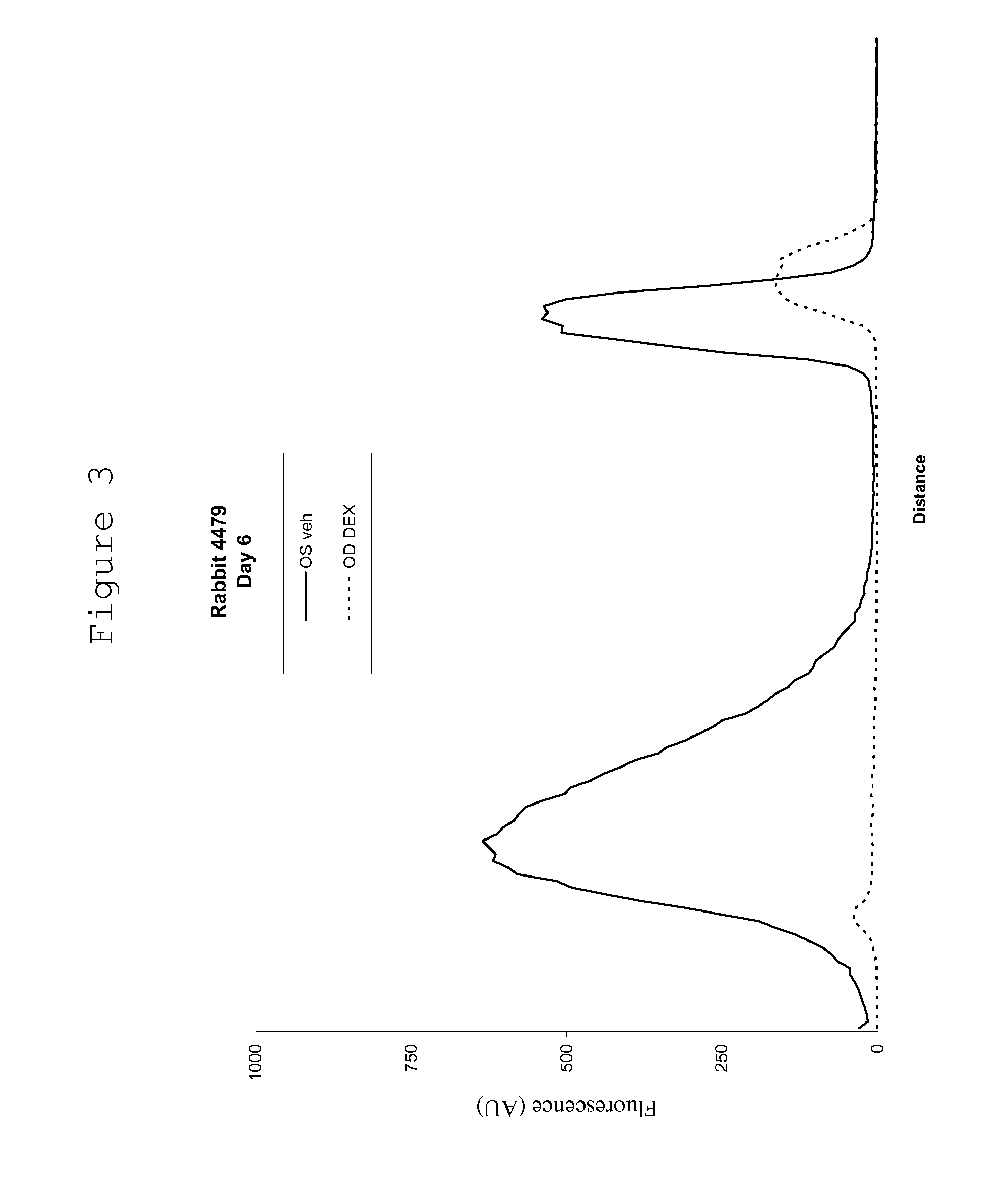
Ophthalmically therapeutic materials, such as liquid-containing compositions and polymeric drug delivery systems, include a therapeutic component that includes an Glucocorticoid Derivative which, upon delivery to the posterior segment of a mammalian eye, does not significantly diffuse to the anterior segment of said eye. Methods of making and using the present materials are also described.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Protein-Polymer-Drug Conjugates
ActiveUS20120321583A1High drug loadingImprove bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDrug conjugationPharmaceutical drug
A drug conjugate is provided herein. The conjugate comprises a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) and a polymeric carrier substituted with one or more -LD-D, the protein based recognition-molecule being connected to the polymeric carrier by LP. Each occurrence of D is independently a therapeutic agent having a molecular weight ≦5 kDa. LD and LP are linkers connecting the therapeutic agent and PBRM to the polymeric carrier respectively. Also disclosed are polymeric scaffolds useful for conjugating with a PBRM to form a polymer-drug-PBRM conjugate described herein, compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Polymeric micelles for combination drug delivery
InactiveUS20080248097A1Low water solubilityLower effective doesBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsCancer cellCombination drug therapy
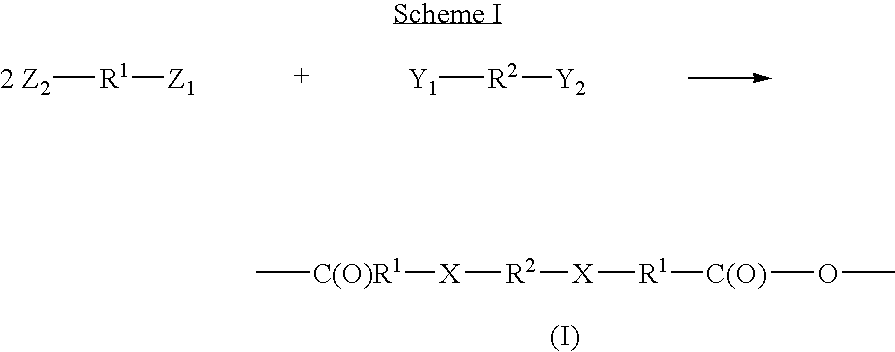
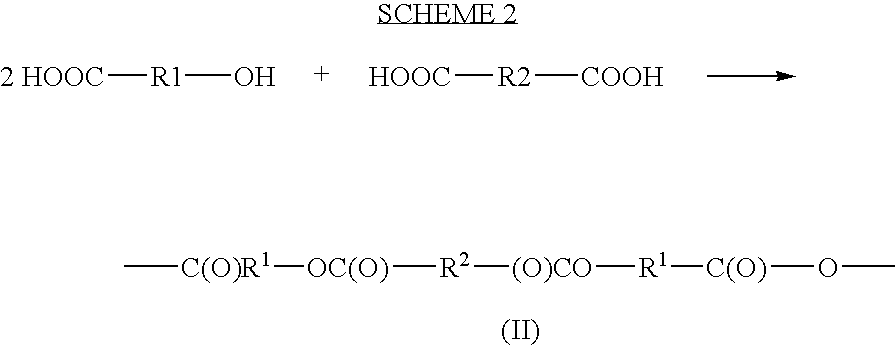
The invention provides block polymers, micelles, and micelle formulations for combination drug therapy. Polyamide block polymers, such as those of formulas I and II are useful, for example, for preparation of mixed drug micelles, including simply mixed micelles, physically mixed micelles, and chemically mixed micelles. The invention further provides methods of treating cancer, and inhibiting and killing cancer cells. Also provided are methods for the preparation of polymer drug conjugates and intermediates for their synthesis.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Hyaluronic acid containing bioconjugates:targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs to cancer cells
A cell-targeted polymeric drug delivery system was designed based on the specific interaction between hyaluronic acid (HA) and its cell surface receptors overexpressed on cancer cell surface. The invention relates to compounds composed of a carrier molecule, 5 wherein the carrier molecule contains at least one residue of an anti-cancer agent and at least one residue of a hyaluronic acid. The invention also relates to methods of making and using the compounds thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Water-soluble polymeric bone-targeting drug delivery system
InactiveUS20050287114A1Good water solubilityImproved pharmacokinetic parametersBiocideOrganic chemistryWater solubleBone targeting
The present invention provides bone-targeting polymeric drug delivery systems based on HPMA and related copolymers and methods of making thereof. The water-soluble bone-targeting polymeric conjugates of the present invention comprise water-soluble copolymer backbones (P) which are linked, via a first spacer (S1), with a bone-related therapeutic agents or drug (D) and, via a second spacer (S2), with a bone-targeting moiety (T).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Therapeutic polyanhydride compounds for drug delivery
InactiveUS20050053577A1Enhanced solubility and processabilityAntibacterial agentsSuture equipmentsAlcoholThiol
Polyanhydrides which link low molecular weight drugs containing a carboxylic acid group and an amine, thiol, alcohol or phenol group within their structure into polymeric drug delivery systems are provided. Also provided are methods of producing polymeric drug delivery systems via these polyanhydride linkers as well as methods of administering low molecular weight drugs to a host via the polymeric drug delivery systems.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method and apparatus for making polymeric drug delivery devices having differing morphological structures
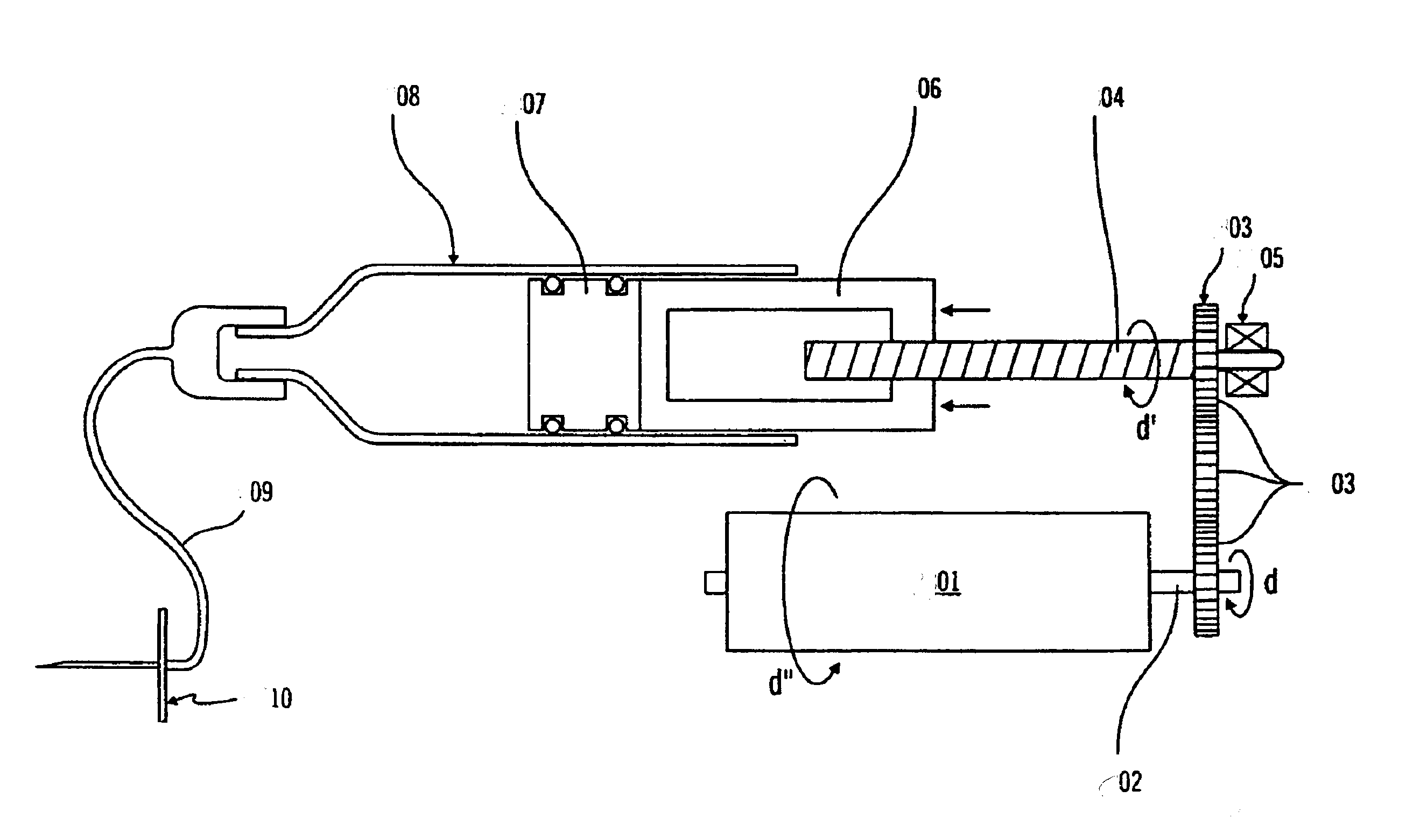
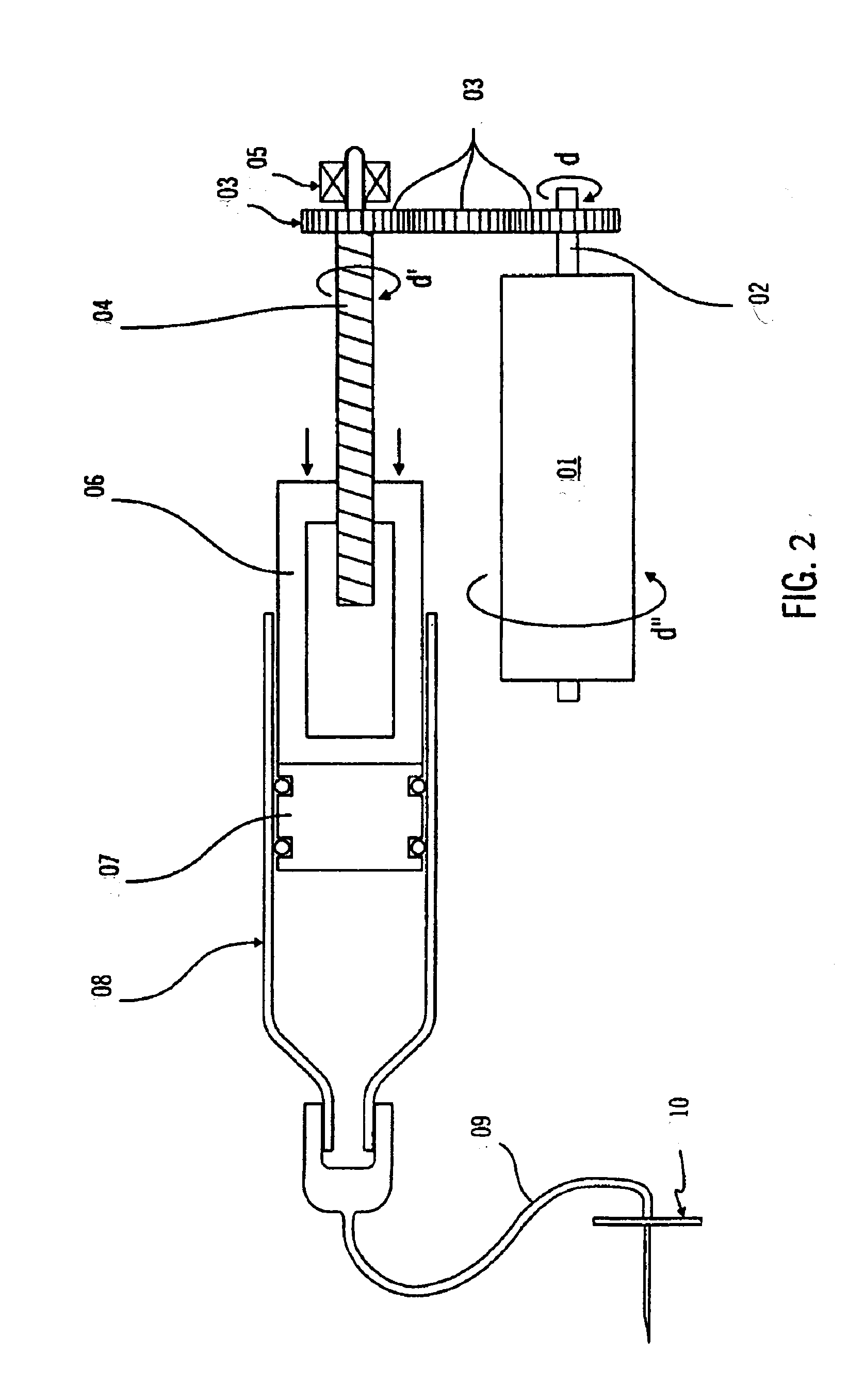
InactiveUS20080169582A1Wide rangeEasy to manufactureWood working apparatusDomestic articlesAnatomical conduitPlasticizer
A polymeric medical device is constructed from bioabsorbable polymers. The device is constructed from a tube comprised of at least one polymer. The polymer is treated at pre-determined heating and cooling temperatures to obtain a desired morphology. The morphology or arrangement of the polymeric structure ensures that the device maintains its shape characteristics to ensure proper modeling of the vessel. In particular, the crystallinity of the polymeric structure is adjusted so as to resist recoil. The device can also contain a therapeutic agent dispersed throughout the structure or coated on the structure in such a manner as to elute the therapeutic agent when implanted in an anatomical conduit. The device can also be constructed from a blend of polymers and other agents such as plasticizers.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
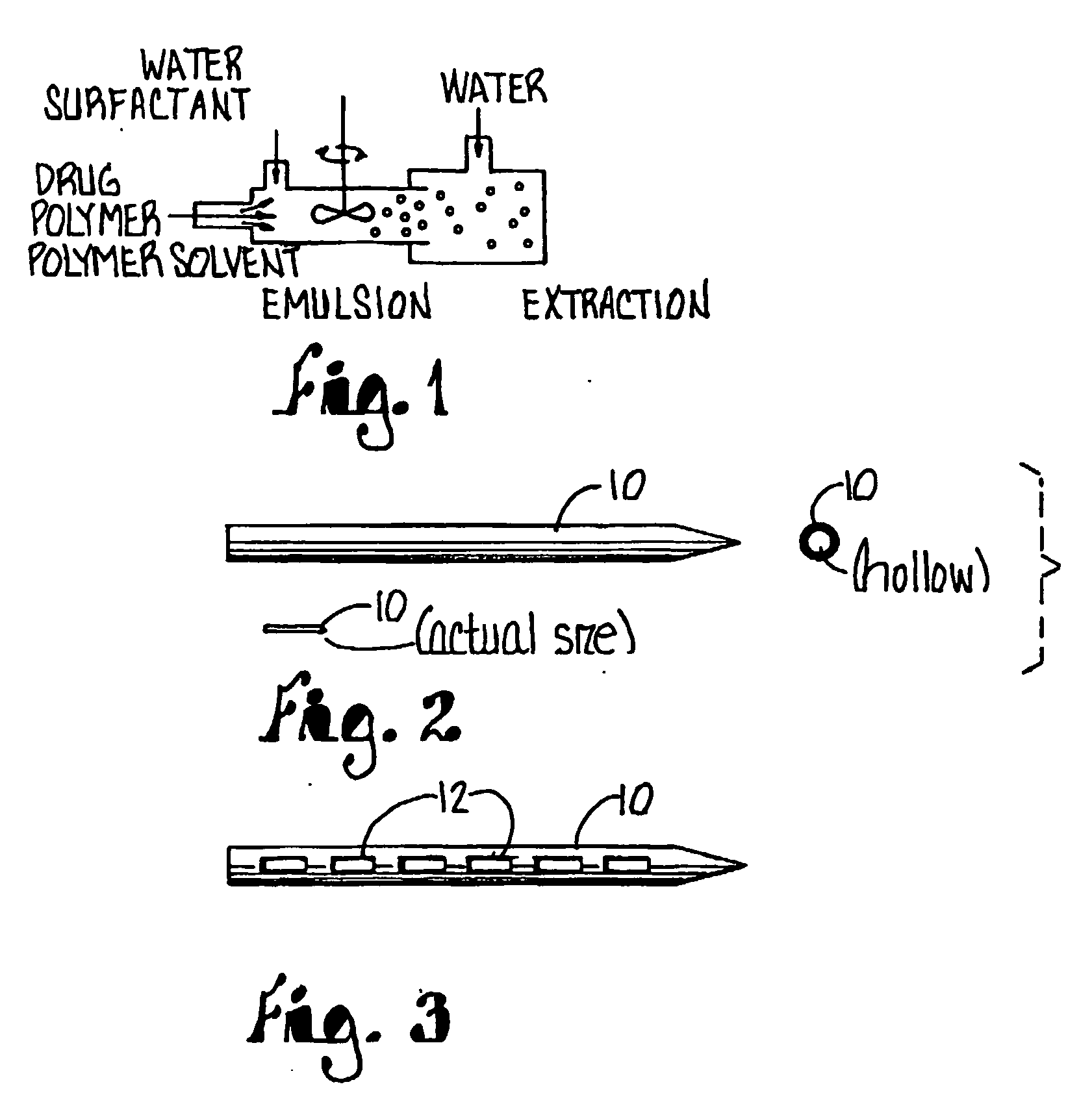
Biodegradable drug-polymer delivery system
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Ocular therapy using glucocorticoid derivatives selectively penetrating posterior segment tissues
Ophthalmically therapeutic materials, such as liquid-containing compositions and polymeric drug delivery systems, include a therapeutic component that includes an Glucocorticoid Derivative which, upon delivery to the posterior segment of a mammalian eye, does not significantly diffuse to the anterior segment of said eye. Methods of making and using the present materials are also described.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
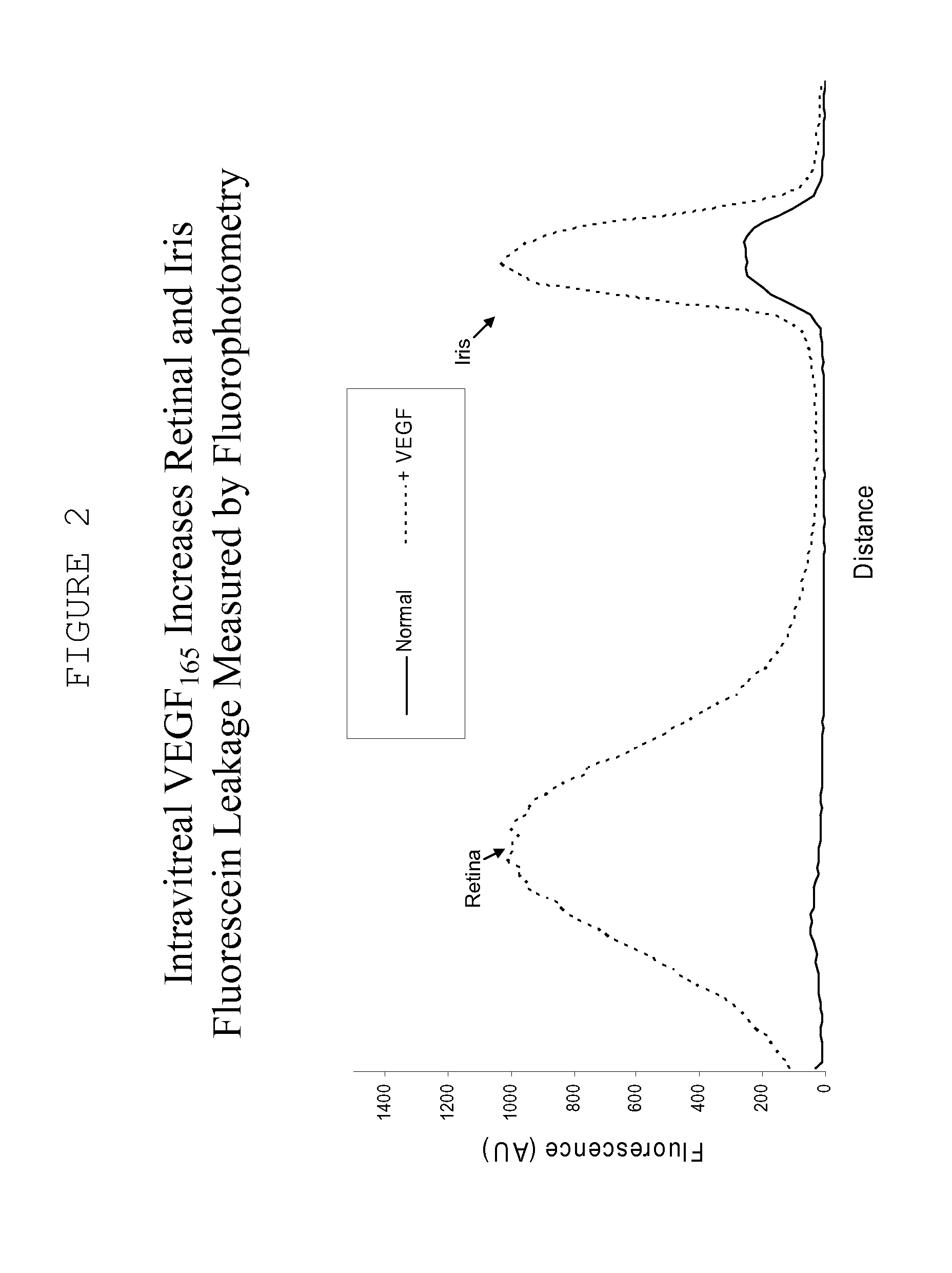
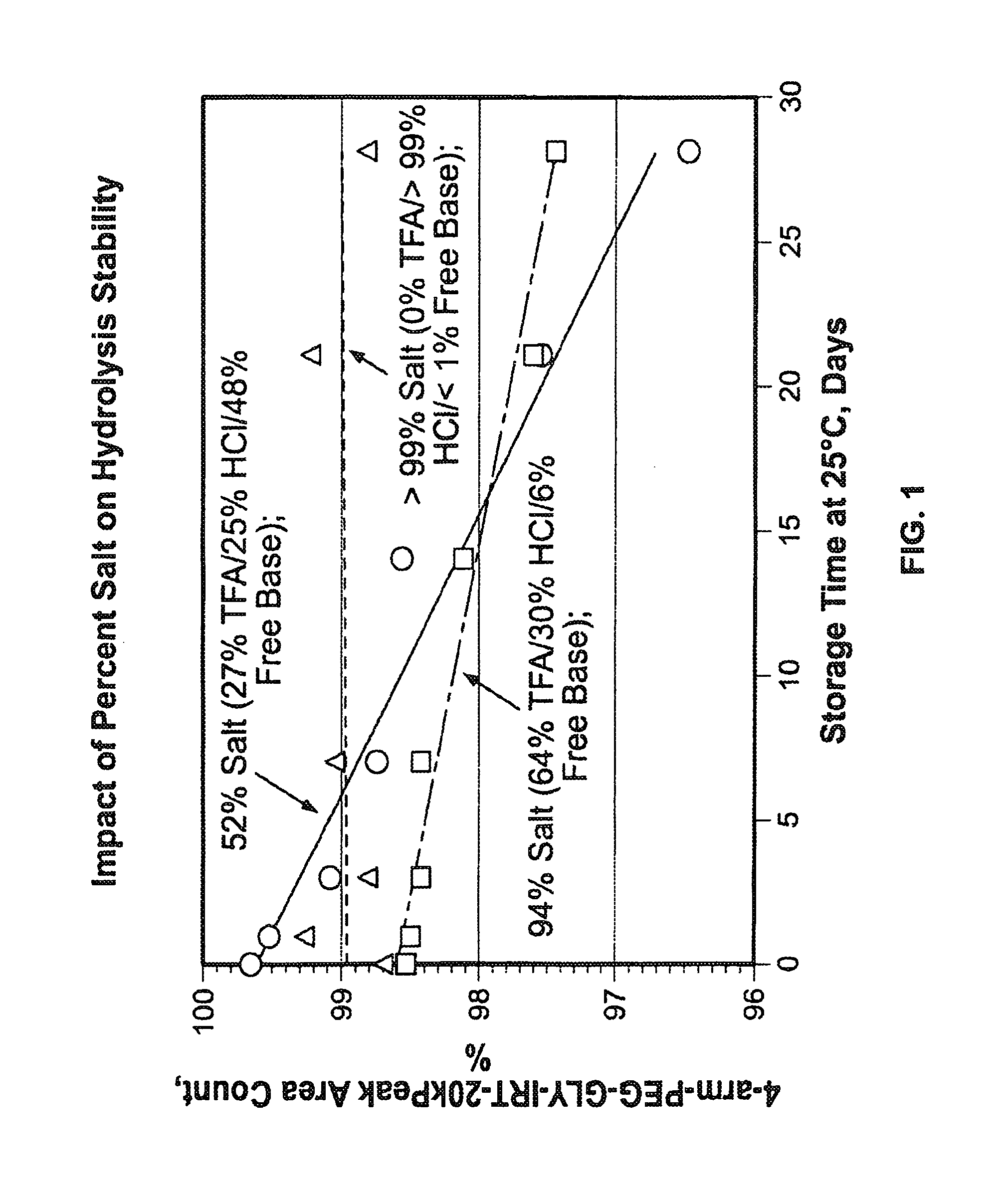
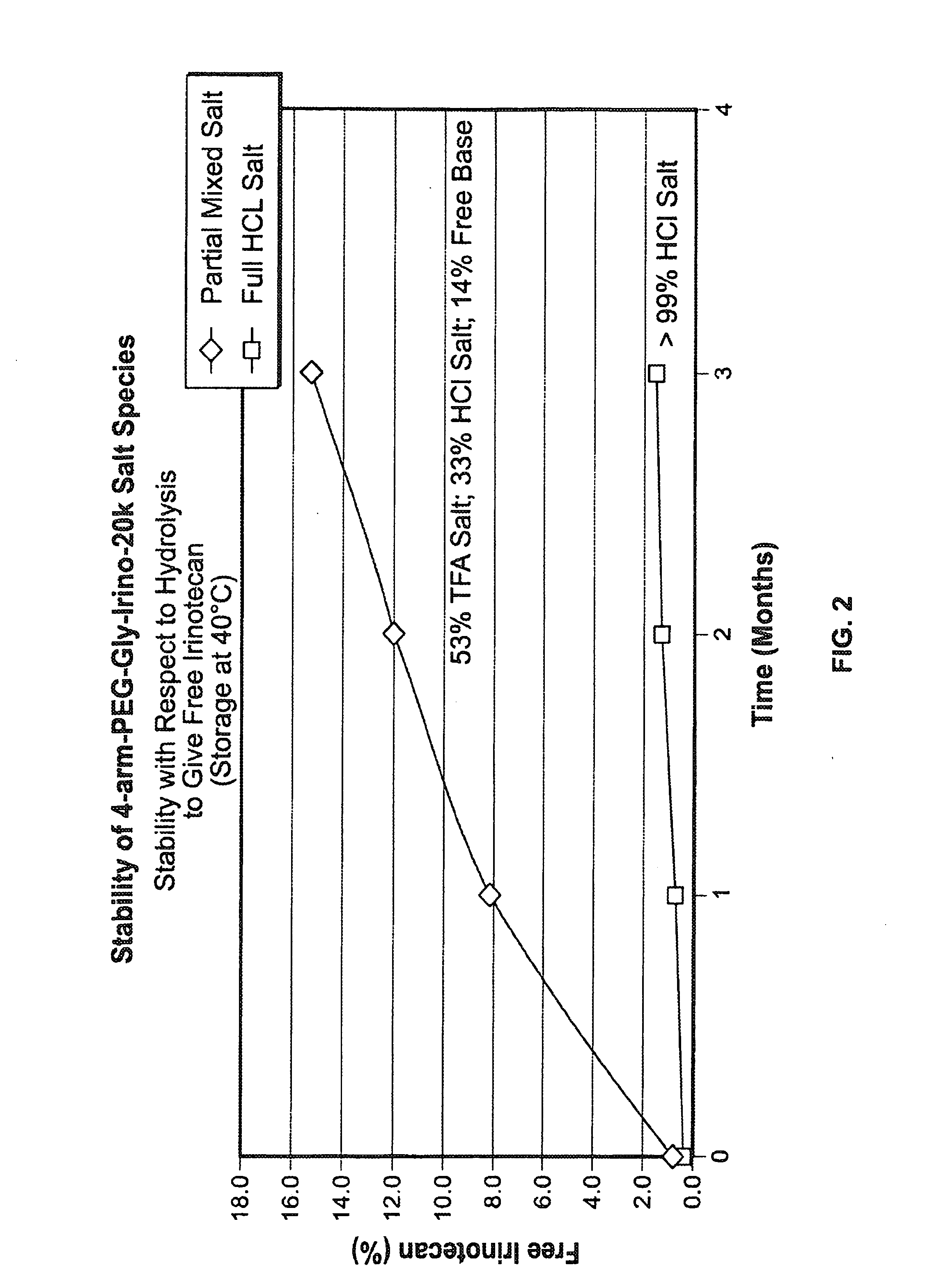
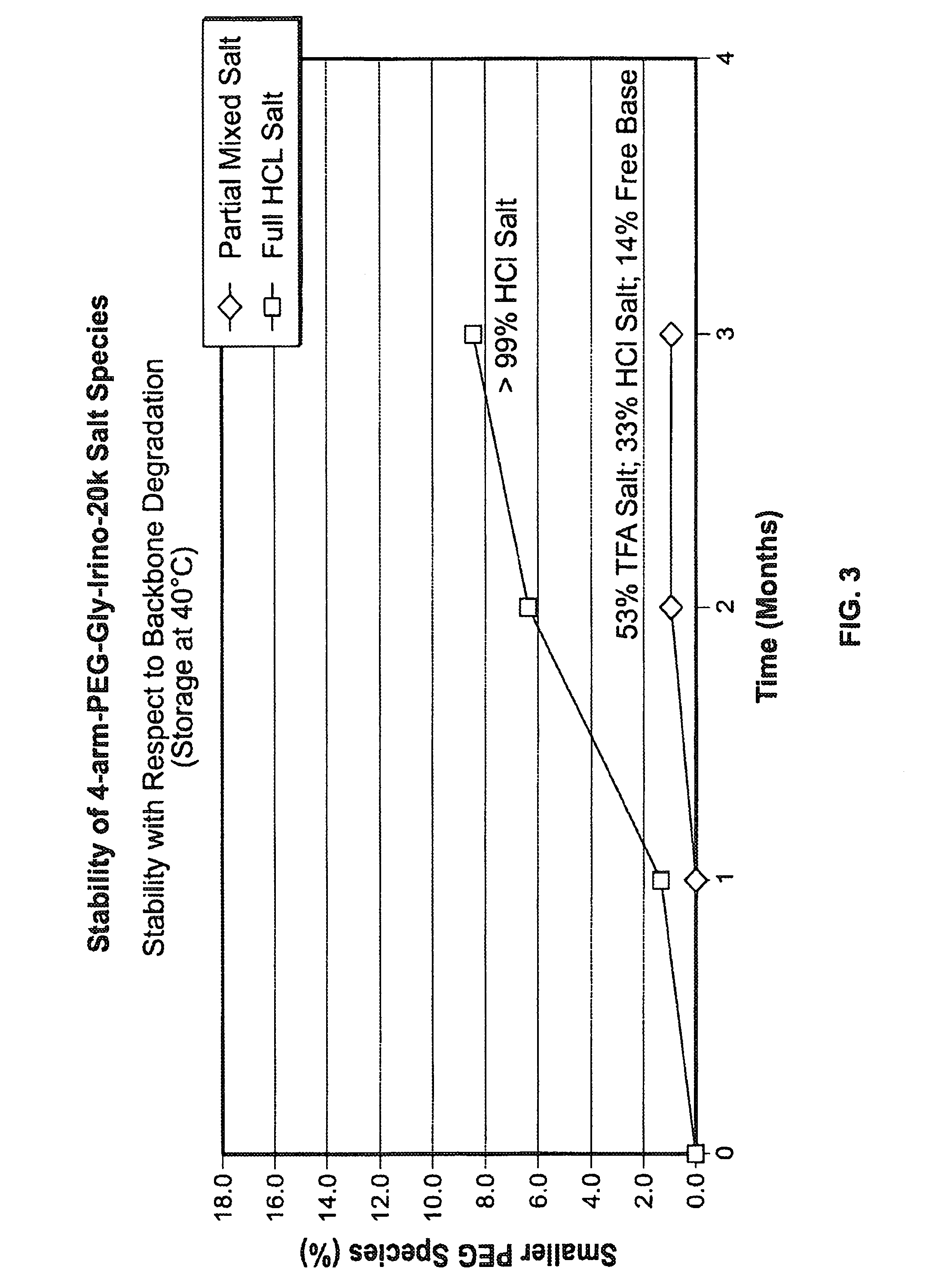
Acid Salt Forms of Polymer-Drug Conjugates and Alkoxylation Methods
Among other aspects, provided herein is a mixed-acid salt of a water-soluble polymer-drug conjugate, along with related methods of making and using the same. The mixed-salt acid salt is stably formed, and appears to be more resistant to hydrolytic degradation than the corresponding predominantly pure acid salt or free base forms of the polymer-drug conjugate. The mixed acid salt is reproducibly prepared and recovered, and provides surprising advantages over non-mixed acid salt forms of the water-soluble polymer drug conjugate.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Preparation method and application of degradable hyperbranched polyamidoamine
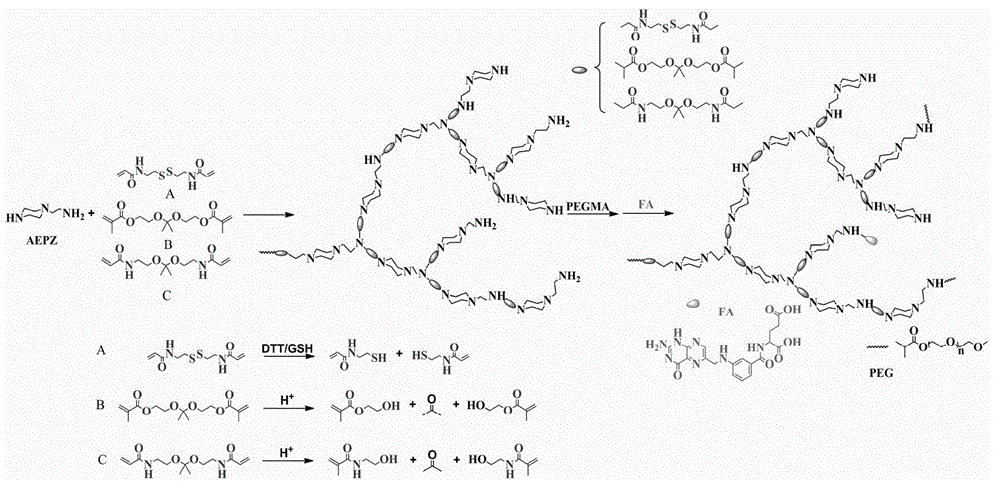
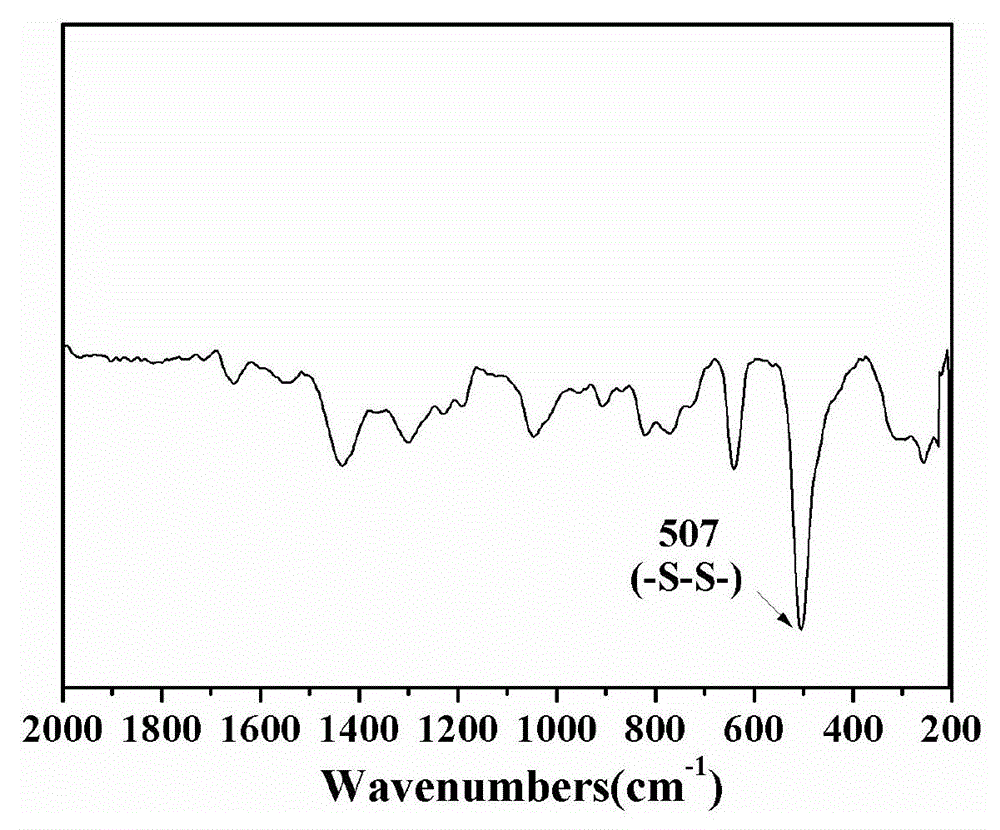
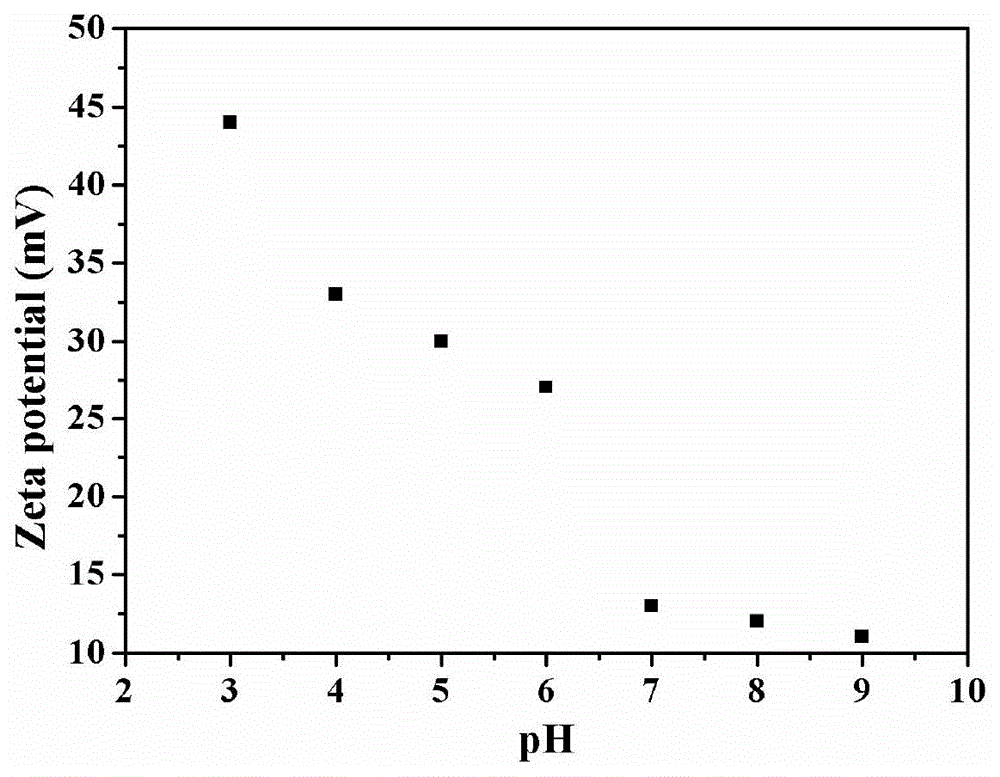
ActiveCN104004196AWith environmentDegradableGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityPolymer science
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of degradable hyperbranched polyamidoamine. Degradable hyperbranched polyamidoamine is prepared by taking a bifunctional monomer containing a disulfide bond or a ketal bond and an amino-containing trifunctional monomer N-aminoethylpiperazine (AEPZ) or diethylenetriamine (DETA) as main raw materials and employing a one-pot method to perform Michael addition polymerization reaction. By coupling polyethylene glycol (PEG) and folic acid (FA) with degradable hyperbranched polyamidoamine, folic-acid-targeted PEGylated degradable hyperbranched polyamidoamine is obtained. The raw materials are easily available, the preparation method is simple, and the prepared polymer medicine carrier has the advantages of hyperbranched polyamidoamine, such as three-dimension branching structure, a lot of cavities at the interior of molecules, low viscosity, a lot of functional groups, simple preparation method, biodegradability, and the like. Additionally, the water solubility and the stability of the carrier material are improved by grafting a PEG chain segment to the terminal, and the carrier is endowed with active targeting property on tumor cells through coupling of FA.
Owner:SUZHOU CHIEN SHIUNG INST OF TECH
Combined polymer-medicine micelle and its prepn process
InactiveCN1416902AAvoid Molecular WeightAvoid limitationsPowder deliverySolution deliveryPolymer scienceFreeze-drying
The present invention provides one kind of combined polymer-medicine micelle to control the release of hydrophobic medicine. The micelle contains two or more kinds of amphiphilic block copolymer and one or more kinds of hydrophobic medicine. The amphiphilic block copolymer includes hydrophilic segment of copolymer of ethanediol or ethylene epoxide and epoxypropane; and hydrophobic segment selected from biodegradable PDLLA, PDLA, PLGA and PCL or their mixture. The micelle exists in the state of water dispersing liquid or freeze dried powder. The combined poloymer-medicine may be prepared via solid phase melting and dispersing process, solvent evaporating process or dialysis process. The present invention makes it possible to control the release of medicine effectively.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Polymeric pharmaceutical dosage form in sustained release
This invention relates to a polymeric pharmaceutical dosage form for the delivery, in use, of at least one pharmaceutical composition in a rate-modulated and site-specific manner. The dosage form comprises a biodegradable, polymeric, scaffold incorporating loaded with at least one active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). The polymer or polymers making up the scaffold degrade in a human or animal body in response to or in the absence of specific biological stimuli and, on degradation, release the API or APIs in an area where said stimuli are encountered. Preferably the polymeric scaffold is formed from poly (D1L-lactide) (PLA) and polymethacrylate (Eudragit S100 / ES100) polymers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
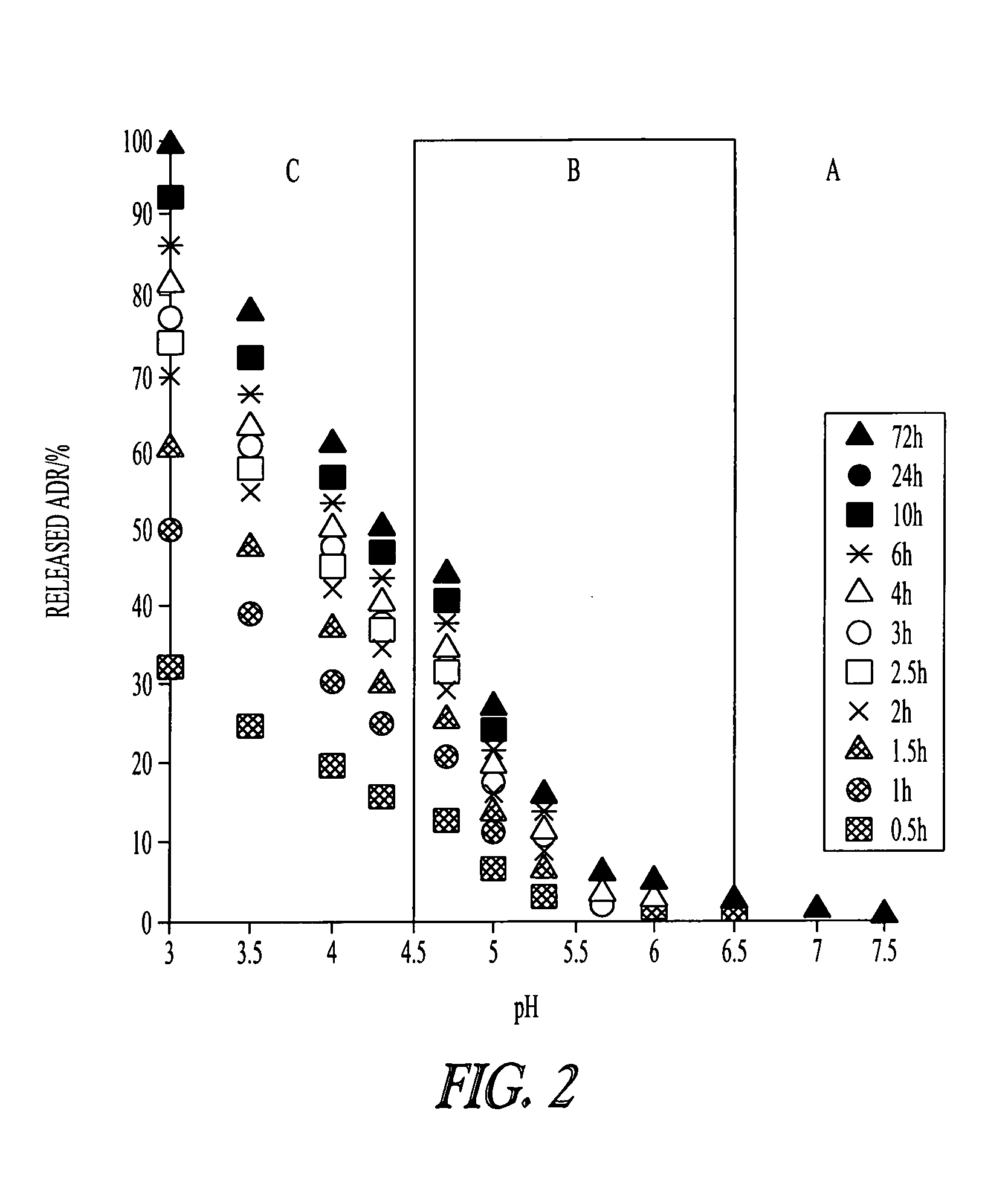
Acid sensitive polymer prodrug, nanoparticles of prodrug and application of nanoparticles
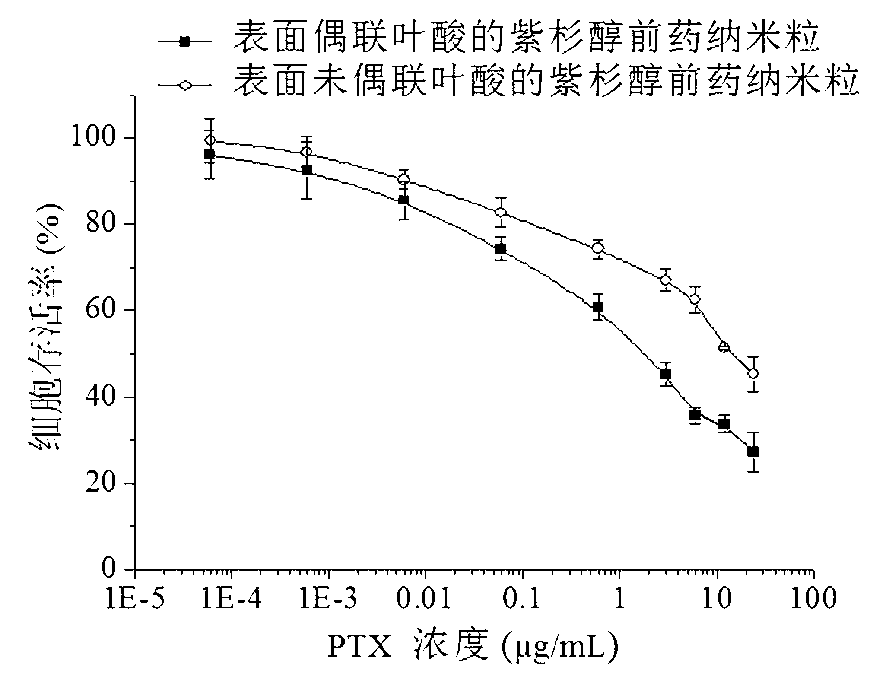
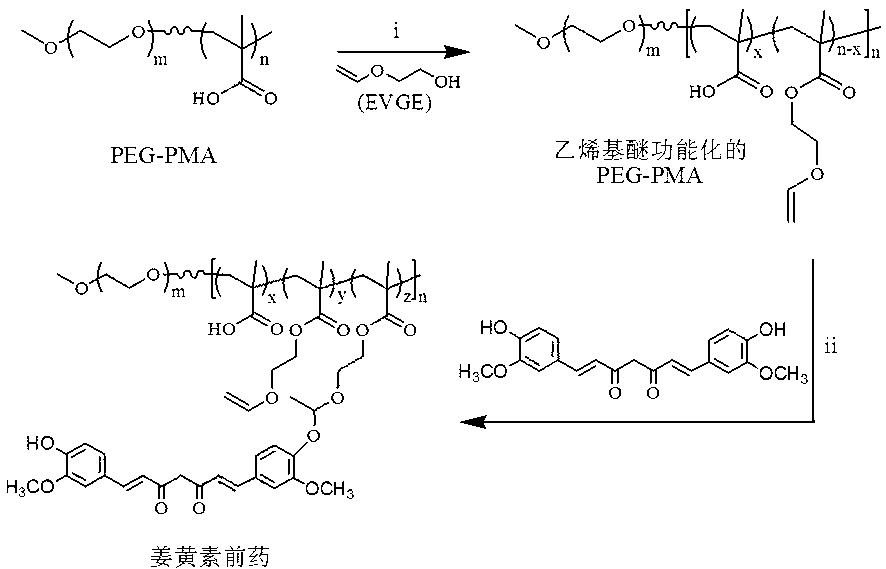
ActiveCN103285400APowerful killingBeneficial for combination therapyPowder deliveryKetone active ingredientsVinyl etherCancer cell
The invention discloses an acid sensitive polymer prodrug, nanoparticles of the prodrug and application of the nanoparticles. In the acid sensitive polymer prodrug, a polymer precursor is a vinyl ether-functionalized water-soluble A-B type two-block polymer; drug molecules are linked with the A-B type two-block polymer through an acetal bond; the acid sensitive polymer prodrug is self-assembled in water solution to form predrug micellar nanoparticles in which a polyethylene glycol hydrophilic chain segment serves as an outer surface and an anti-cancer drug bound to a polymer main chain through the acetal bond serves as a hydrophobic core. The pH sensitive prodrug and the nanoparticles of he prodrug are simple in preparation method, and good in tumor inhibitory effect; the nanoparticles also can efficiently encapsulate another hydrophobic anticancer drug; the kill capability to the cancer cell is enhanced; and the efficiency of endocytosis of the cell to the nanoparticles can be enhanced by coupling specific target molecules onto the surfaces of the nanoparticles. Thus, the inhibitory effect on the tumor cell is enhanced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Protein-polymer-drug conjugates and methods of using same
InactiveUS20150366982A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsHer2 expressionMedicine
A polymeric scaffold useful for conjugating with a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) to form a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate is described herein. The scaffold includes one or more terminal maleimido groups. Also disclosed is a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate prepared from the scaffold. Compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders, such as cancer in a subject having low HER2 expression with the conjugates or their compositions are also described.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Therapeutic AZO-compounds for drug delivery
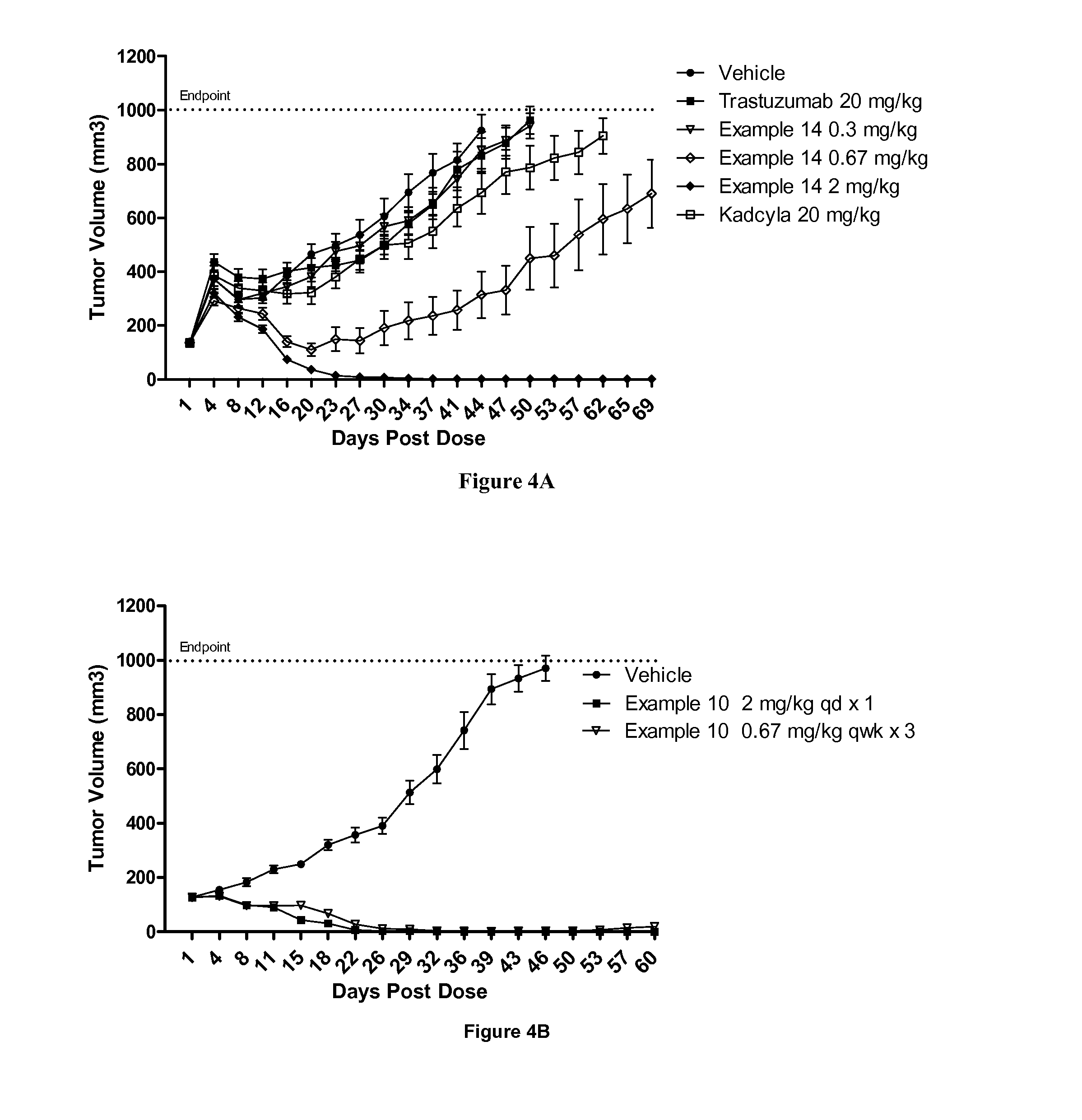
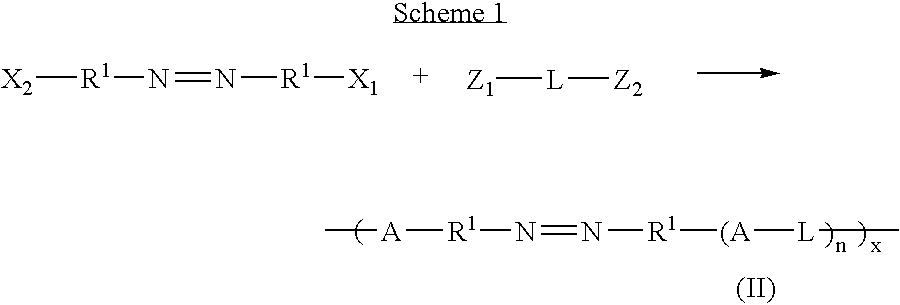
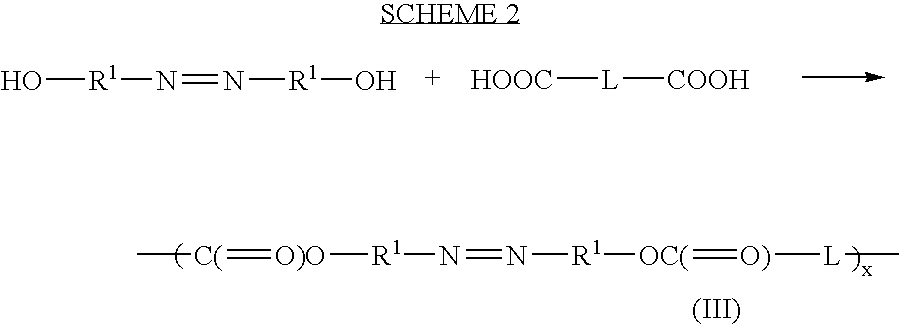
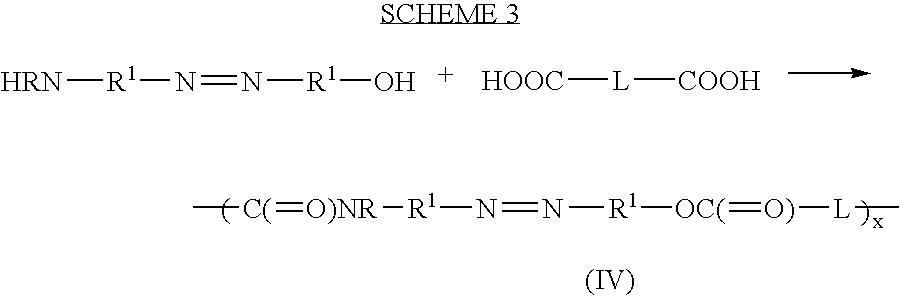
Polyazo compounds, which include low molecular weight drugs having a carboxylic acid group and an amine, thiol, alcohol or phenol group within their structure, formed into polymeric drug delivery systems are provided. Also provided are methods of producing polymeric drug delivery systems having these polyazo compounds as well as methods of administering low molecular weight drugs to a host via the polymeric drug delivery system.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
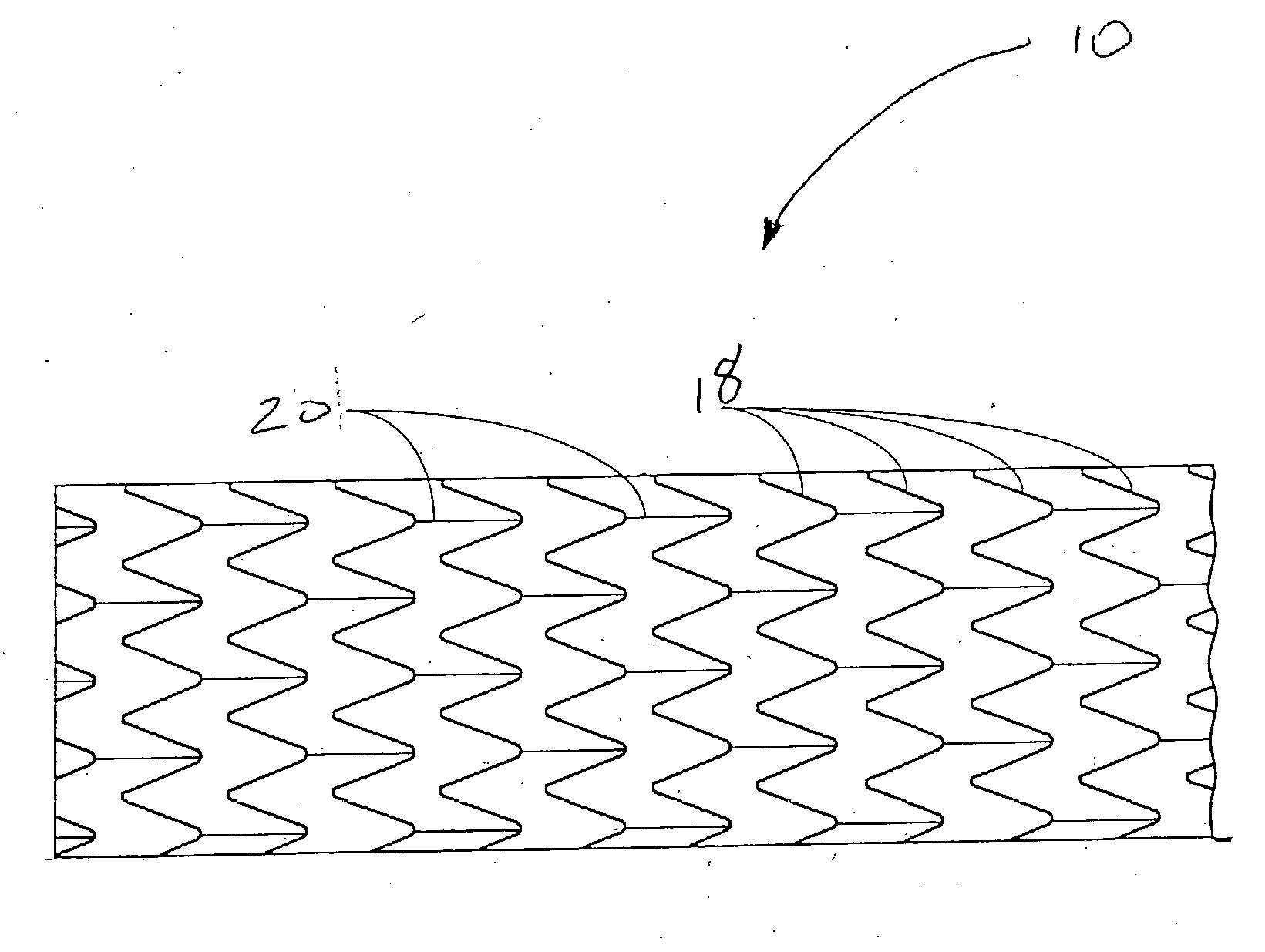
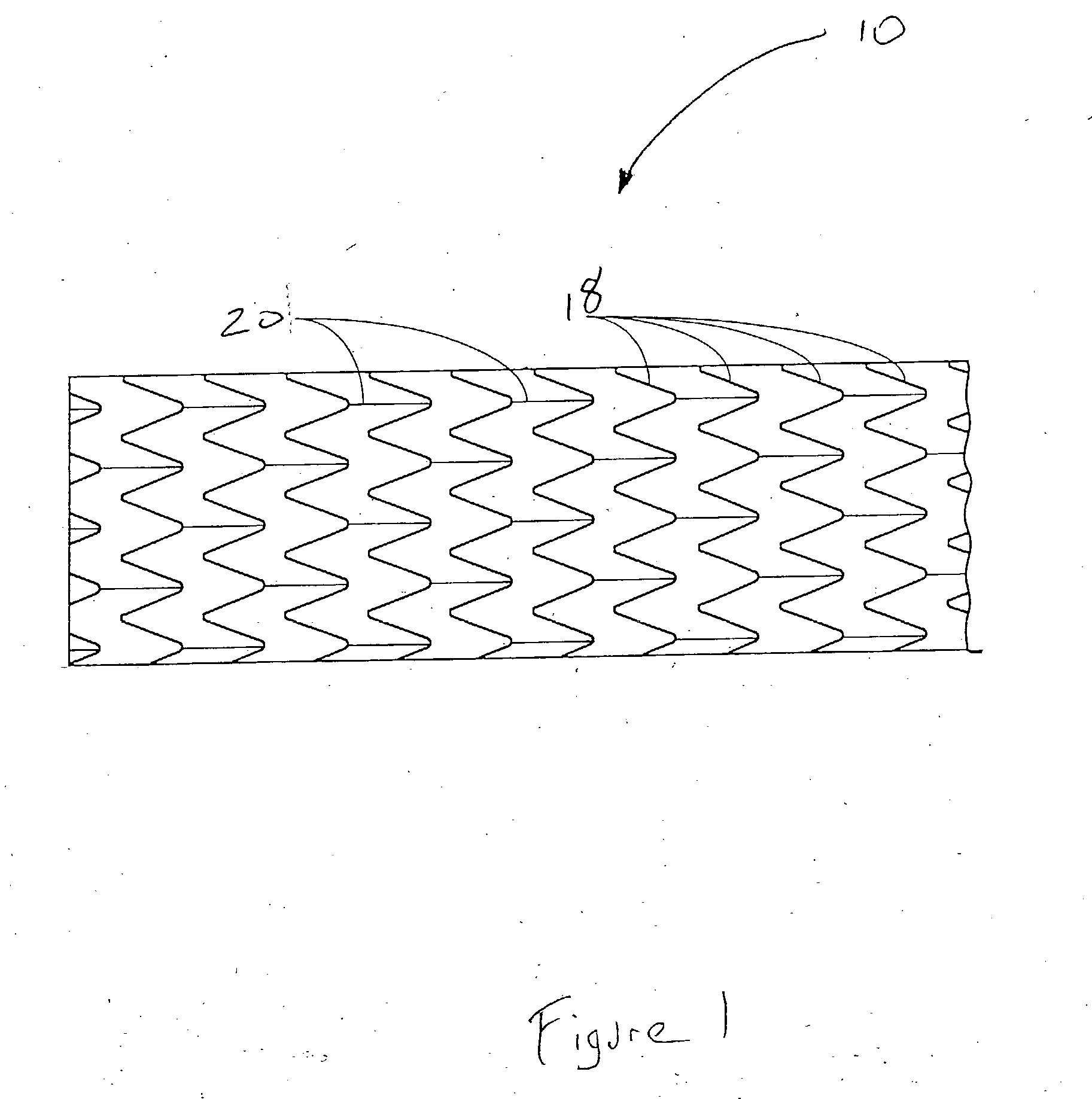
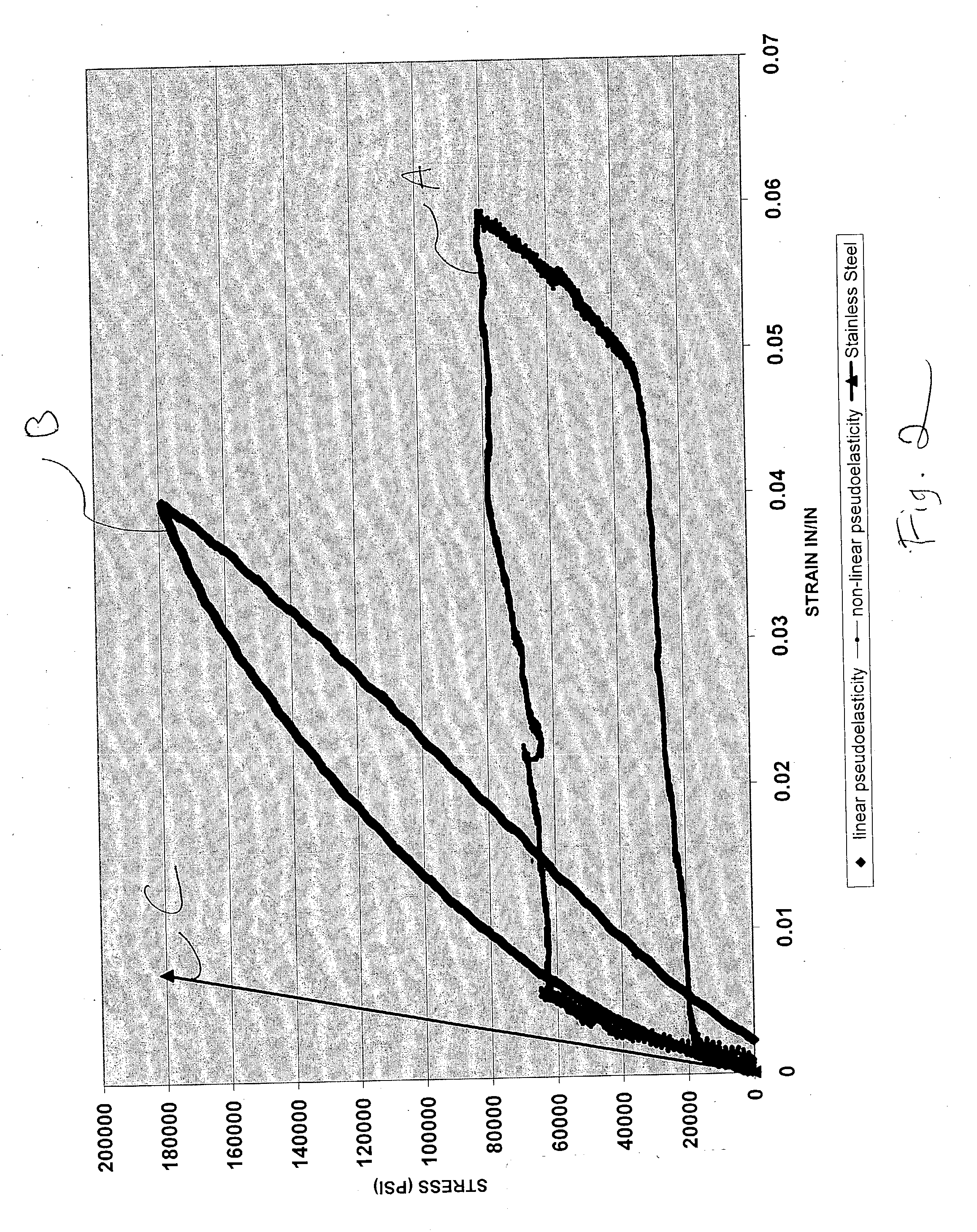
Pseudoelastic stents having a drug coating and a method of producing the same
An implantable medical device, such as a stent, having linear pseudoelastic behavior and a polymeric drug coating is disclosed. A method of producing an implantable medical device having linear pseudoelastic behavior and a polymeric drug coating is also disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com