Patents
Literature
900results about How to "Reduce diffuse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
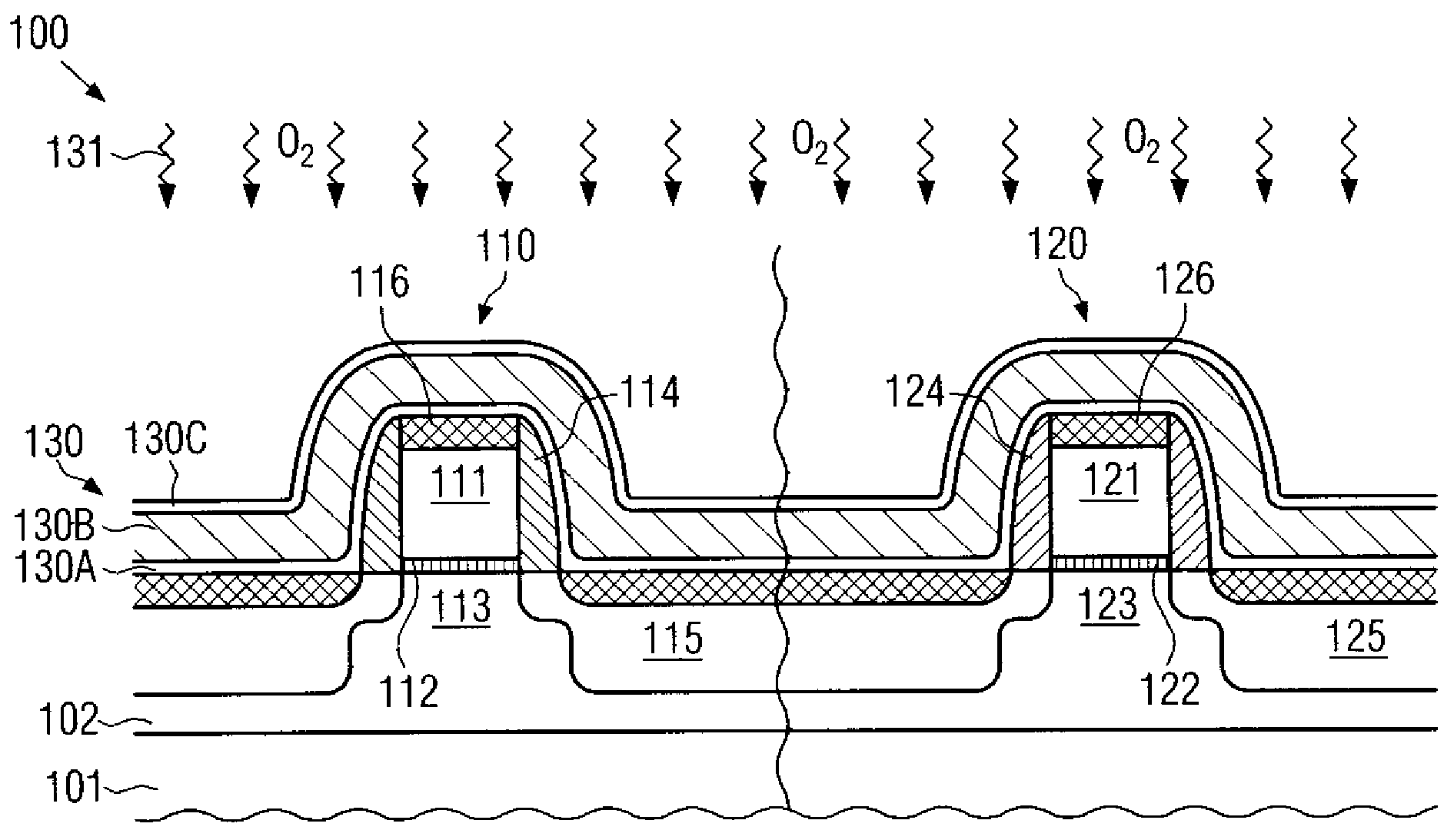
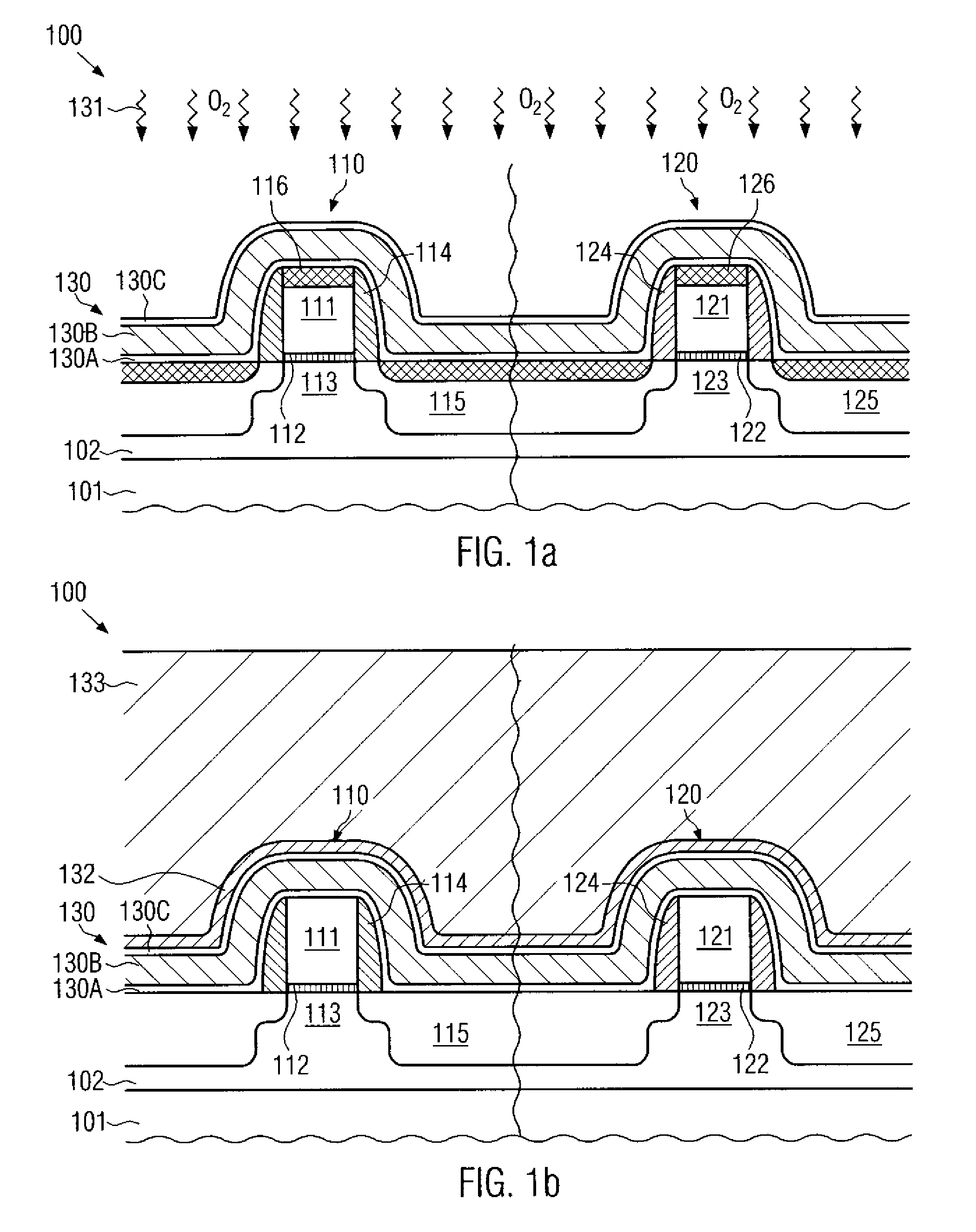
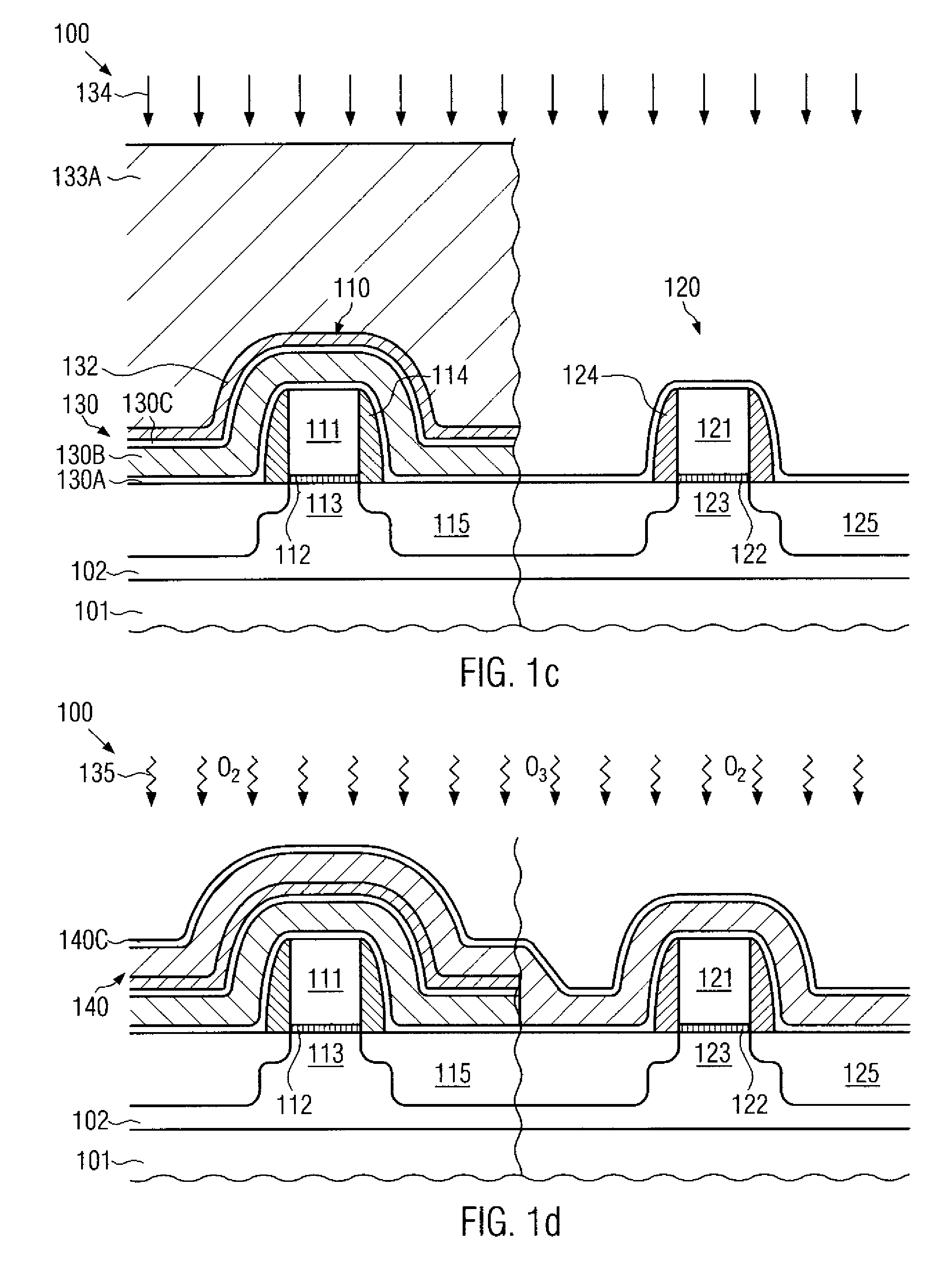
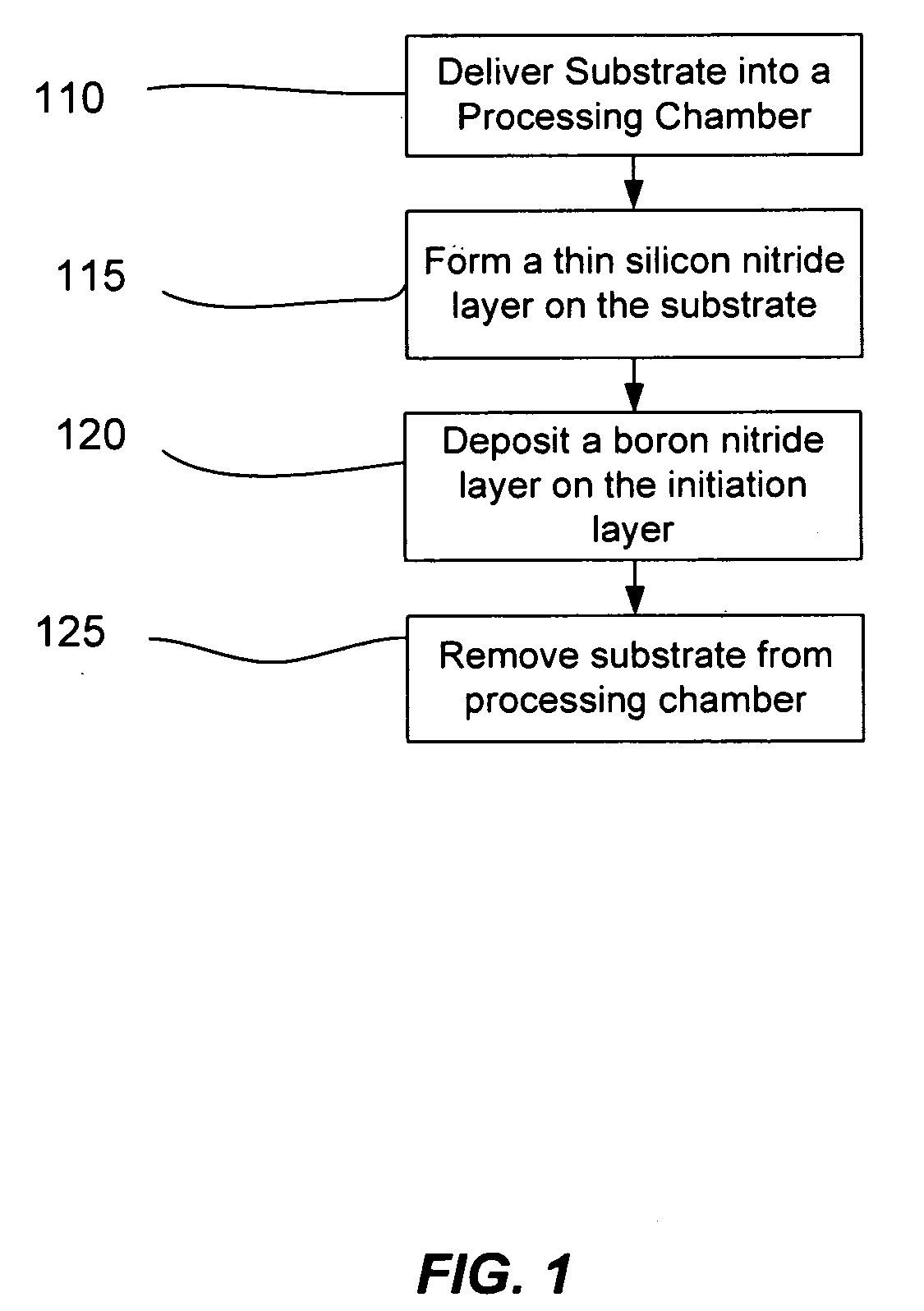
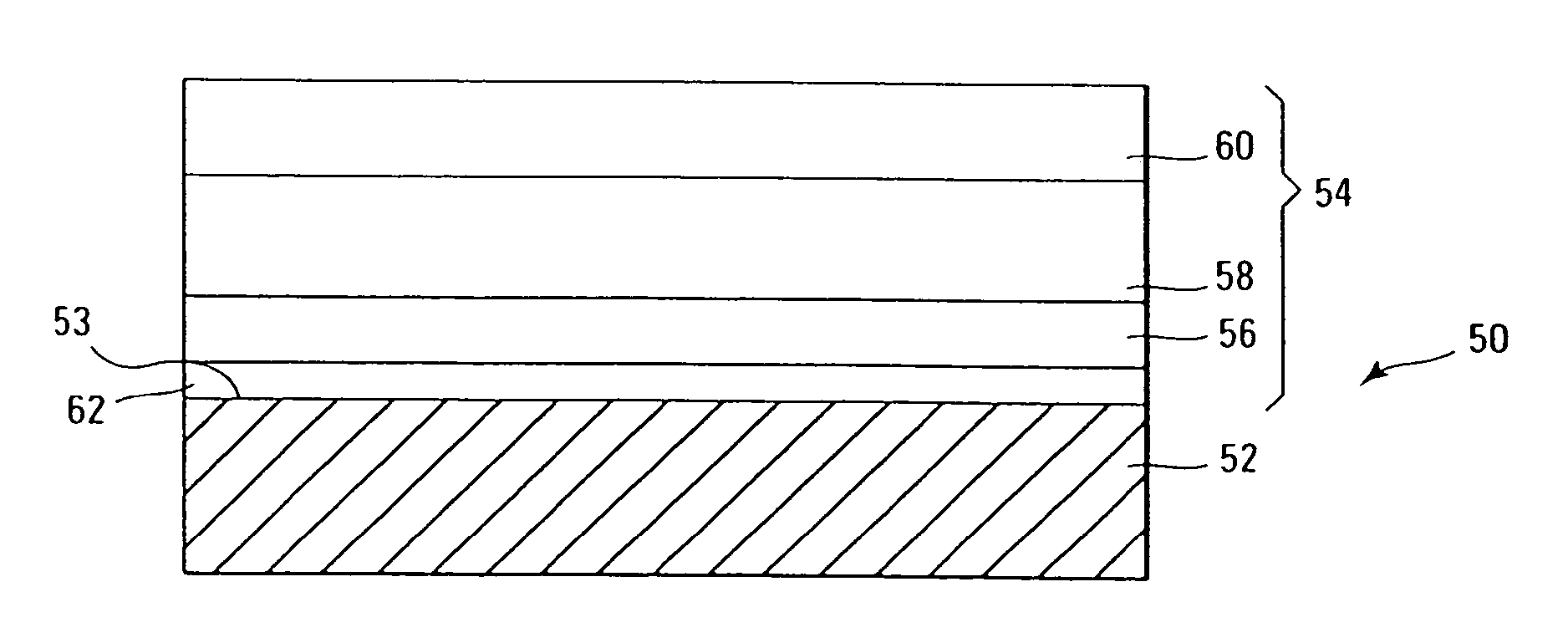
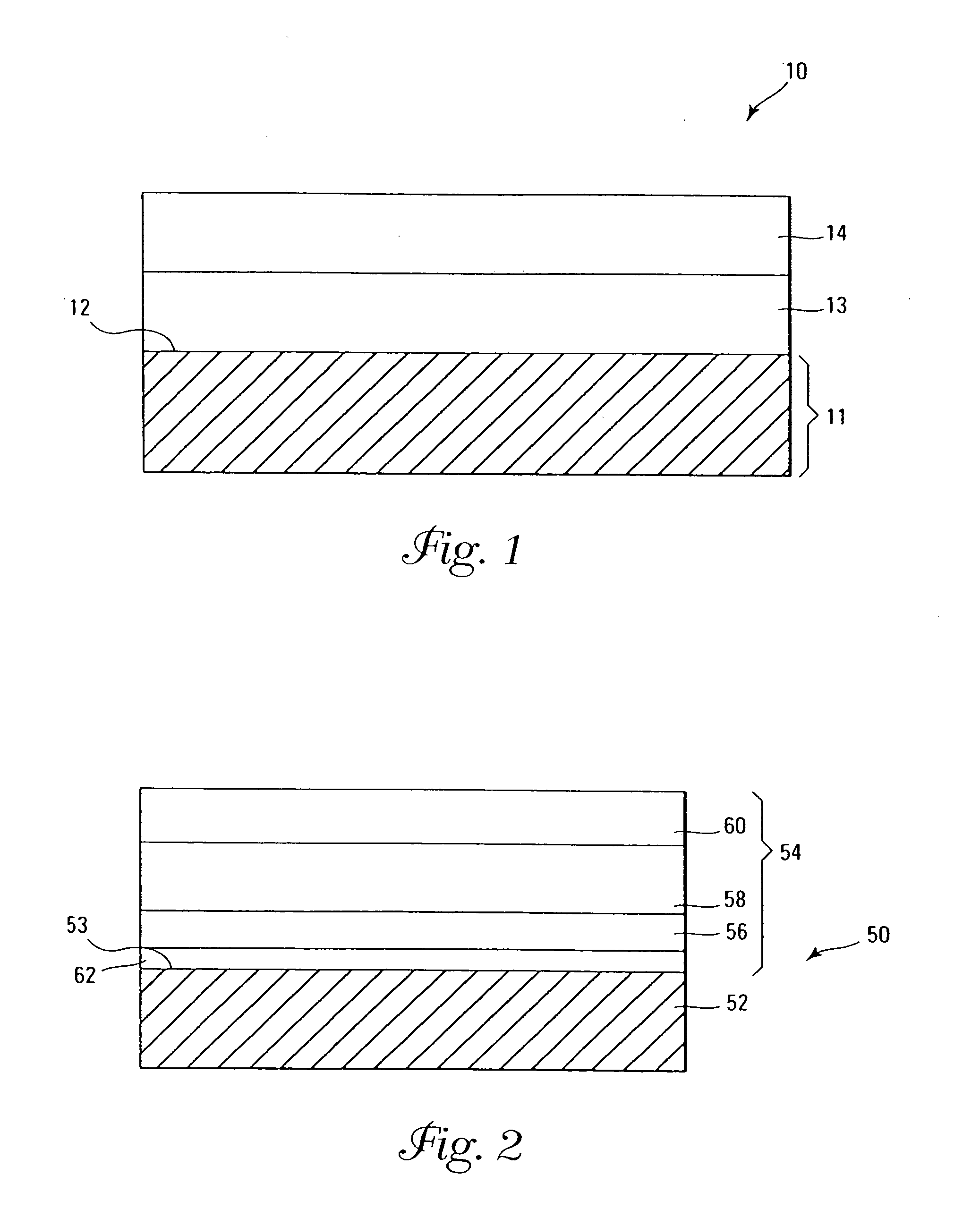
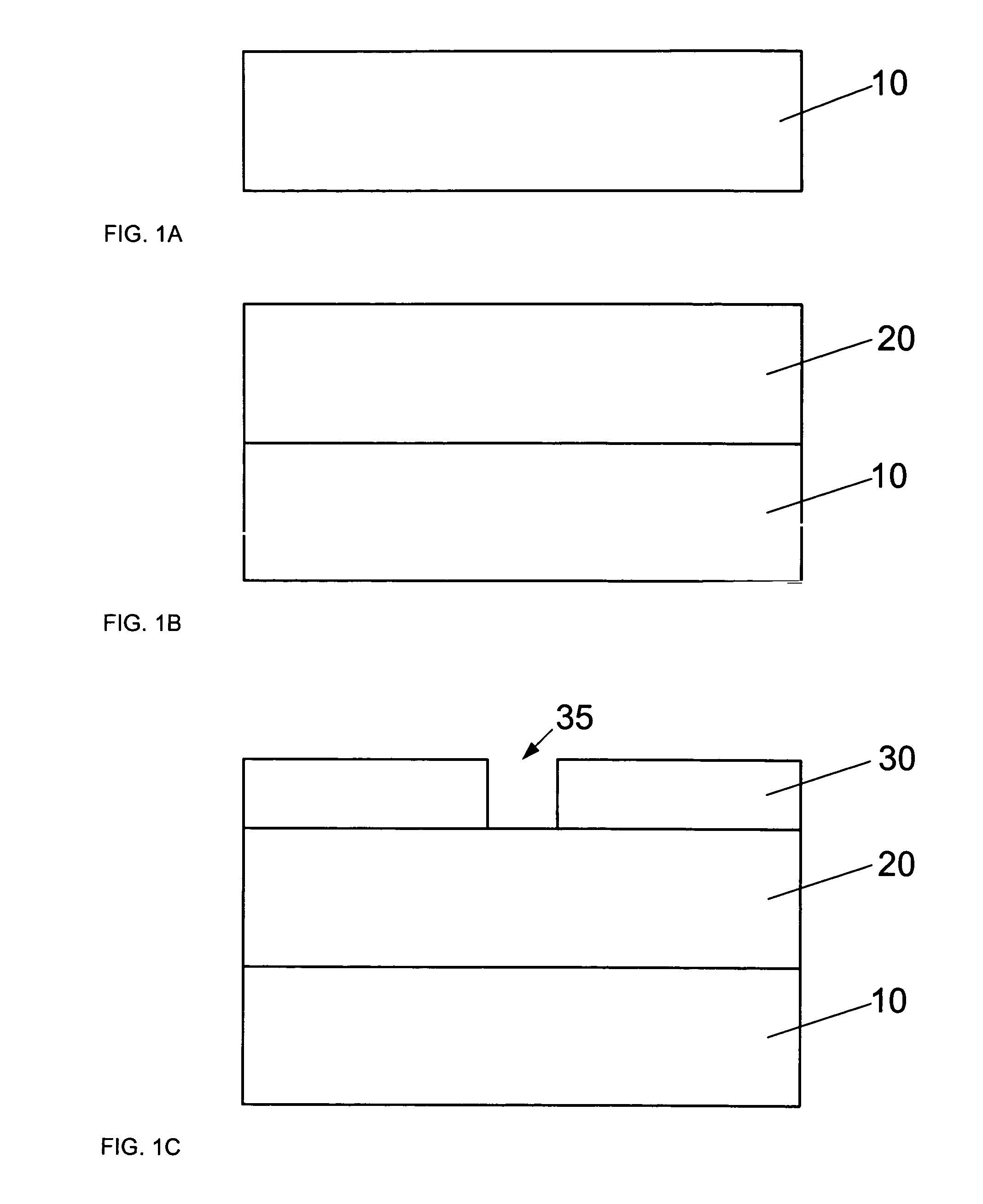
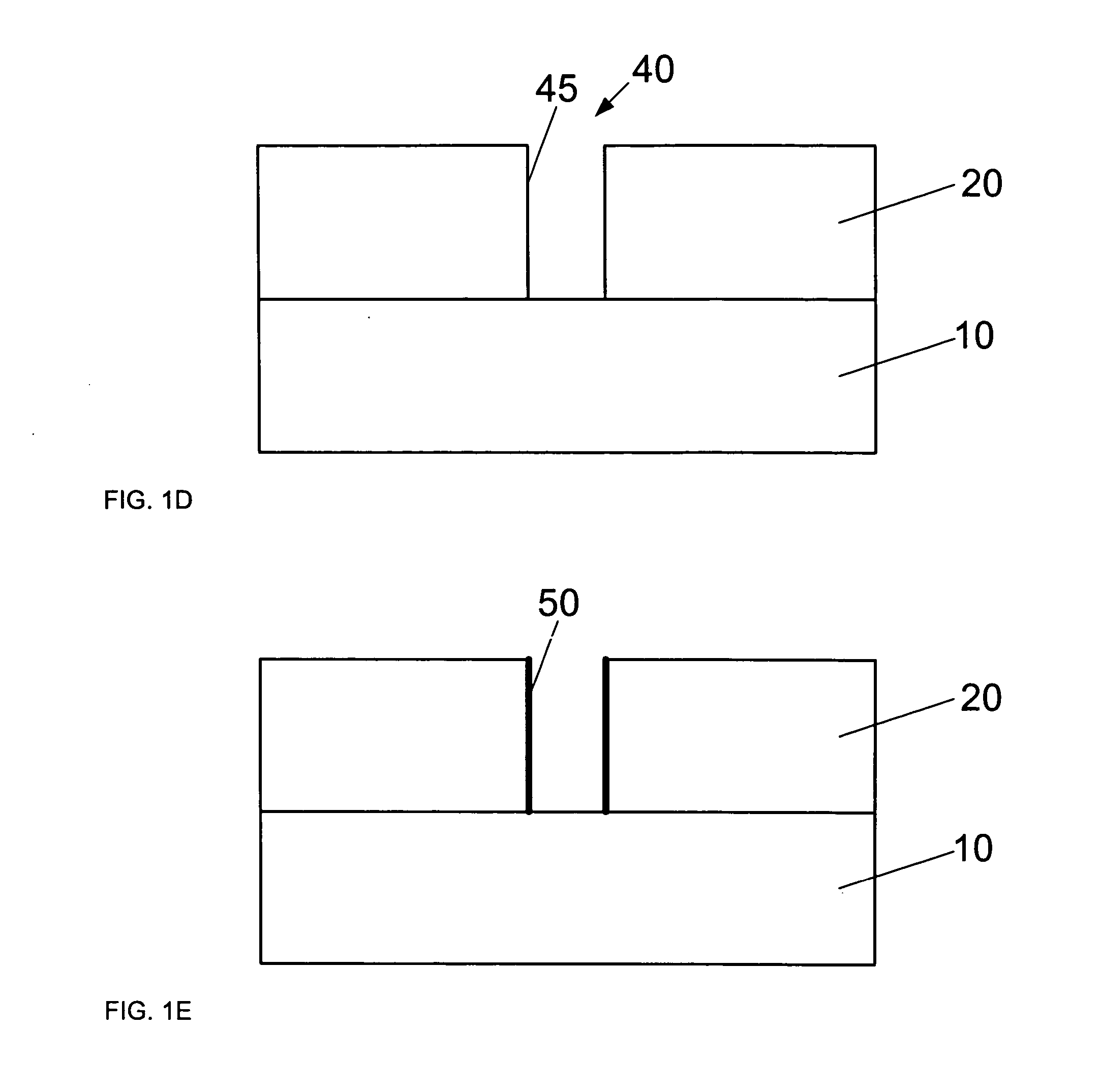
Method for reducing resist poisoning during patterning of silicon nitride layers in a semiconductor device
ActiveUS7550396B2Improve performanceReduce diffuseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesResistNitrogen
By performing a plasma treatment for efficiently sealing the surface of a stressed dielectric layer containing silicon nitride, an enhanced performance during the patterning of contact openings may be achieved, since nitrogen-induced resist poisoning may be significantly reduced during the selective patterning of stressed layers of different types of intrinsic stress.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
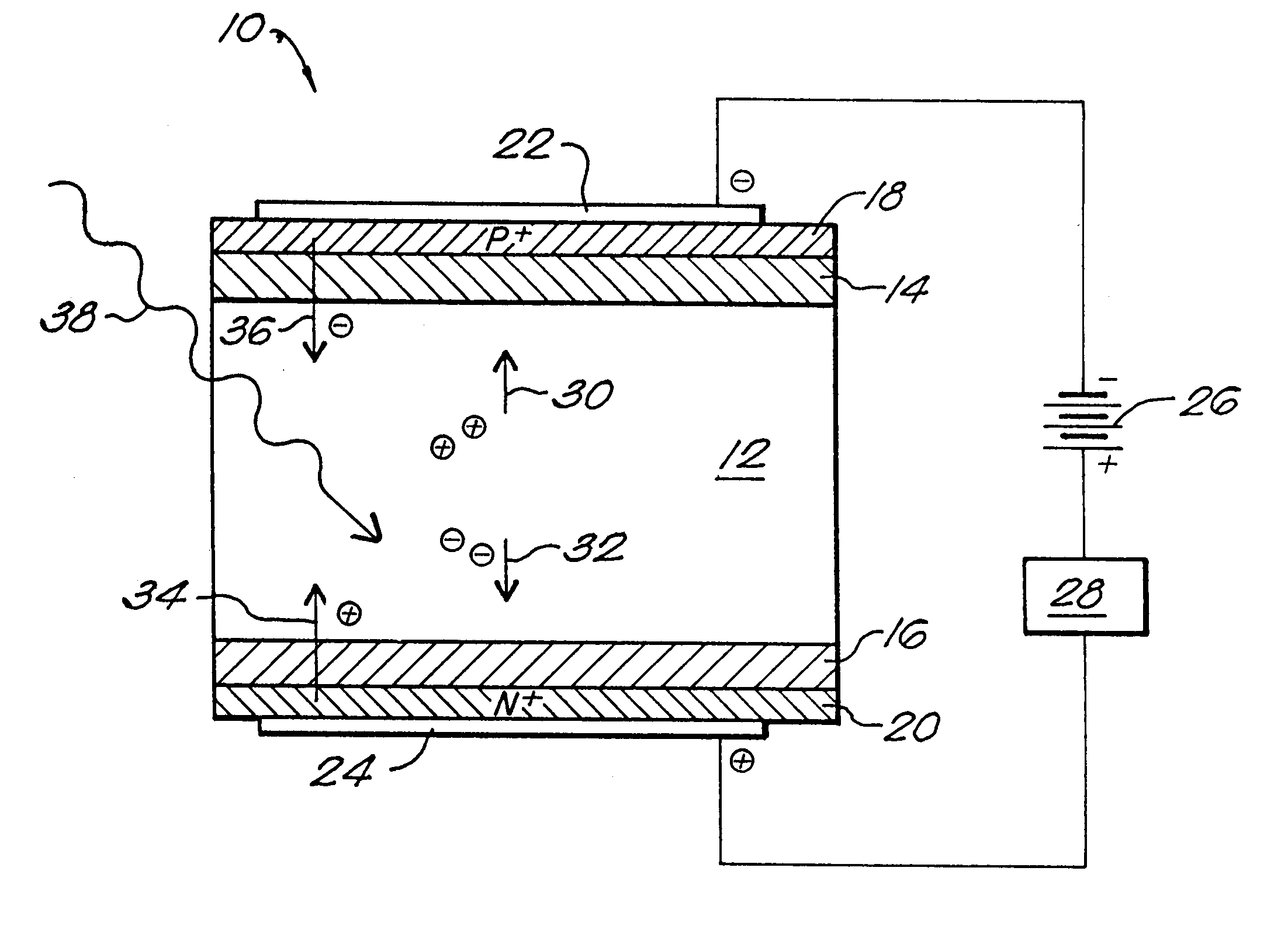
Semiconductor P-I-N detector
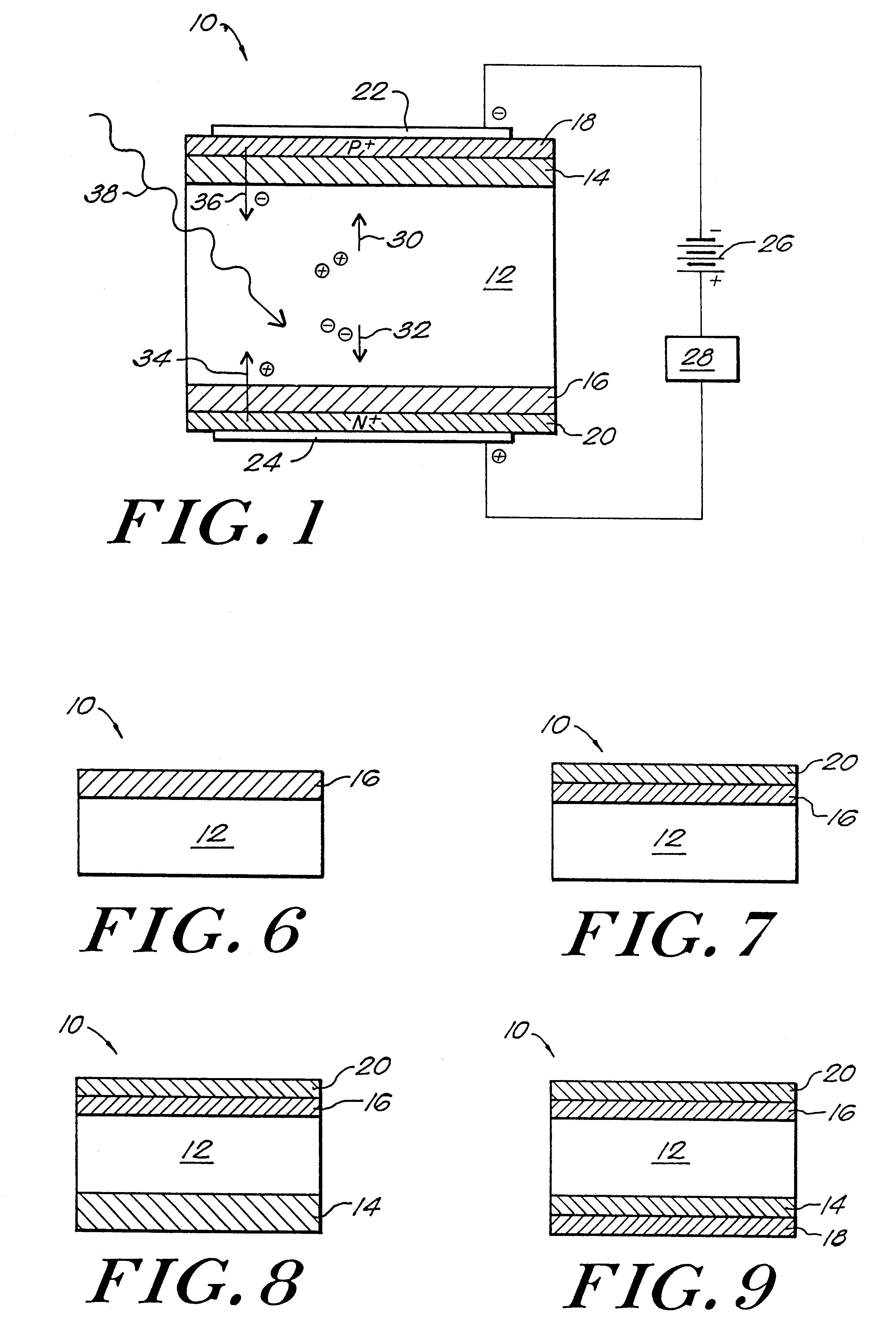
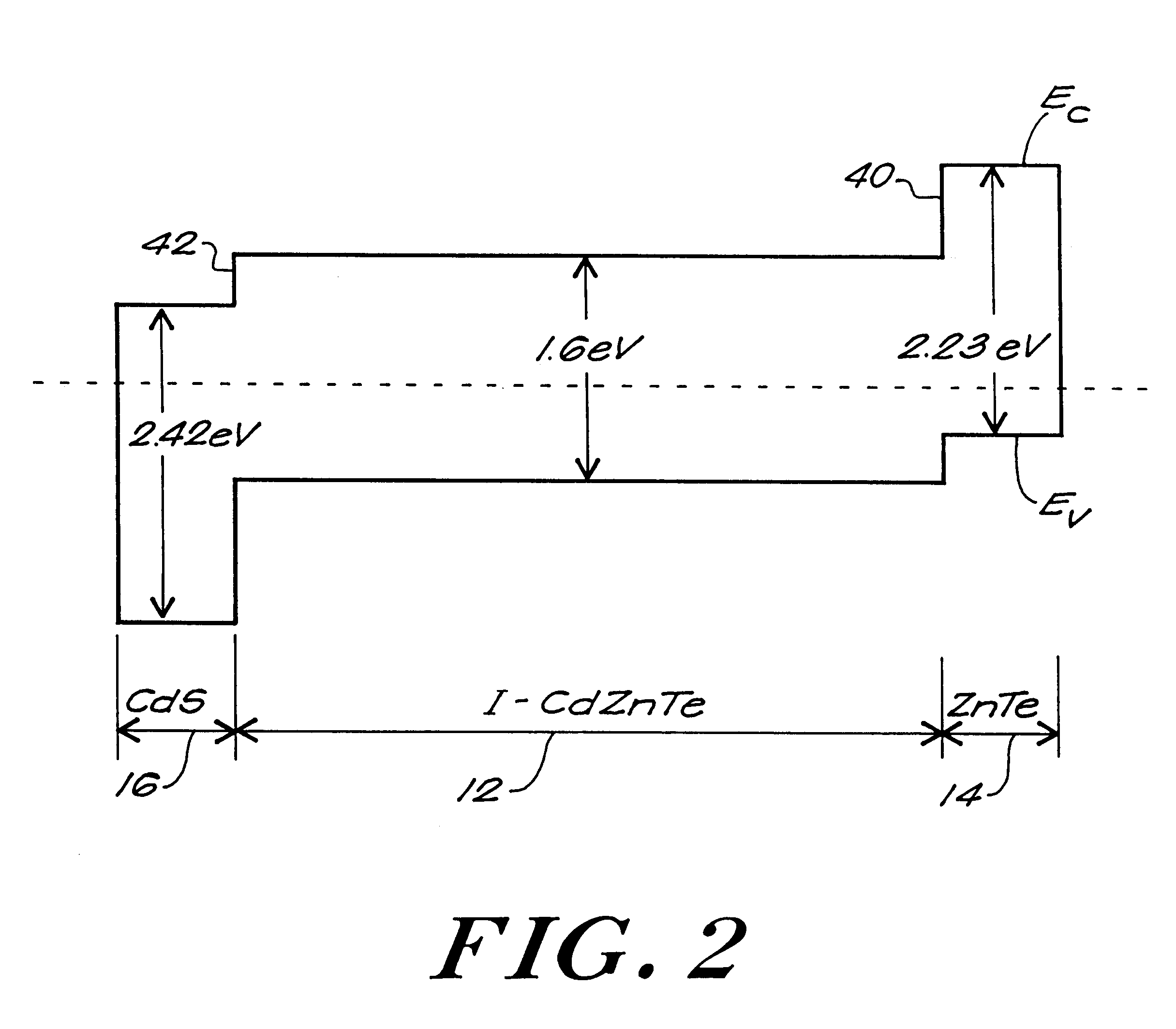
InactiveUS6255708B1Reduce leakage currentMitigating dopant diffusionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantIndium
A semiconductor P-I-N detector including an intrinsic wafer, a P-doped layer, an N-doped layer, and a boundary layer for reducing the diffusion of dopants into the intrinsic wafer. The boundary layer is positioned between one of the doped regions and the intrinsic wafer. The intrinsic wafer can be composed of CdZnTe or CdTe, the P-doped layer can be composed of ZnTe doped with copper, and the N-doped layer can be composed of CdS doped with indium. The boundary layers is formed of an undoped semiconductor material. The boundary layer can be deposited onto the underlying intrinsic wafer. The doped regions are then typically formed by a deposition process or by doping a section of the deposited boundary layer.
Owner:MASIMO SEMICON +2
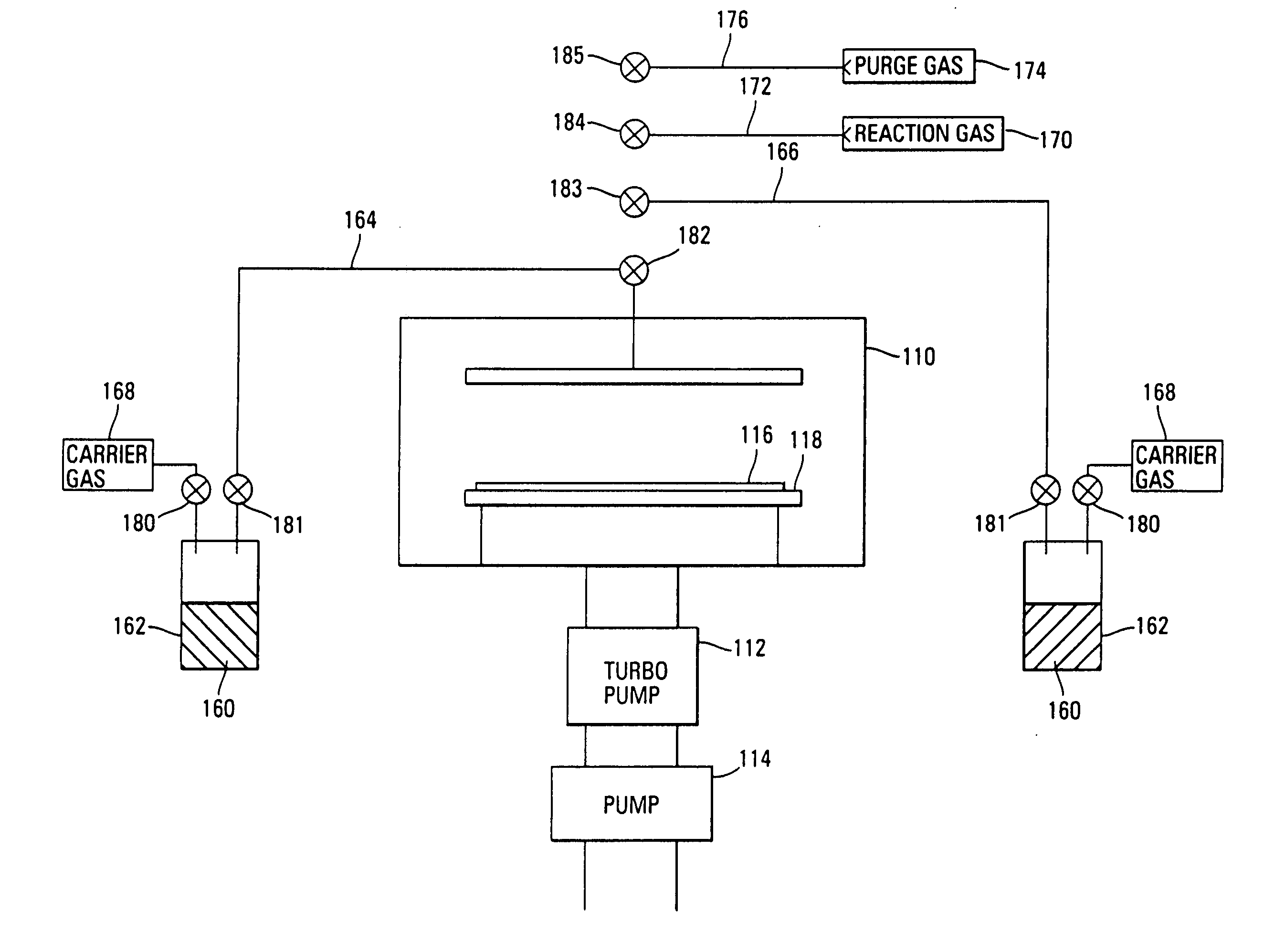
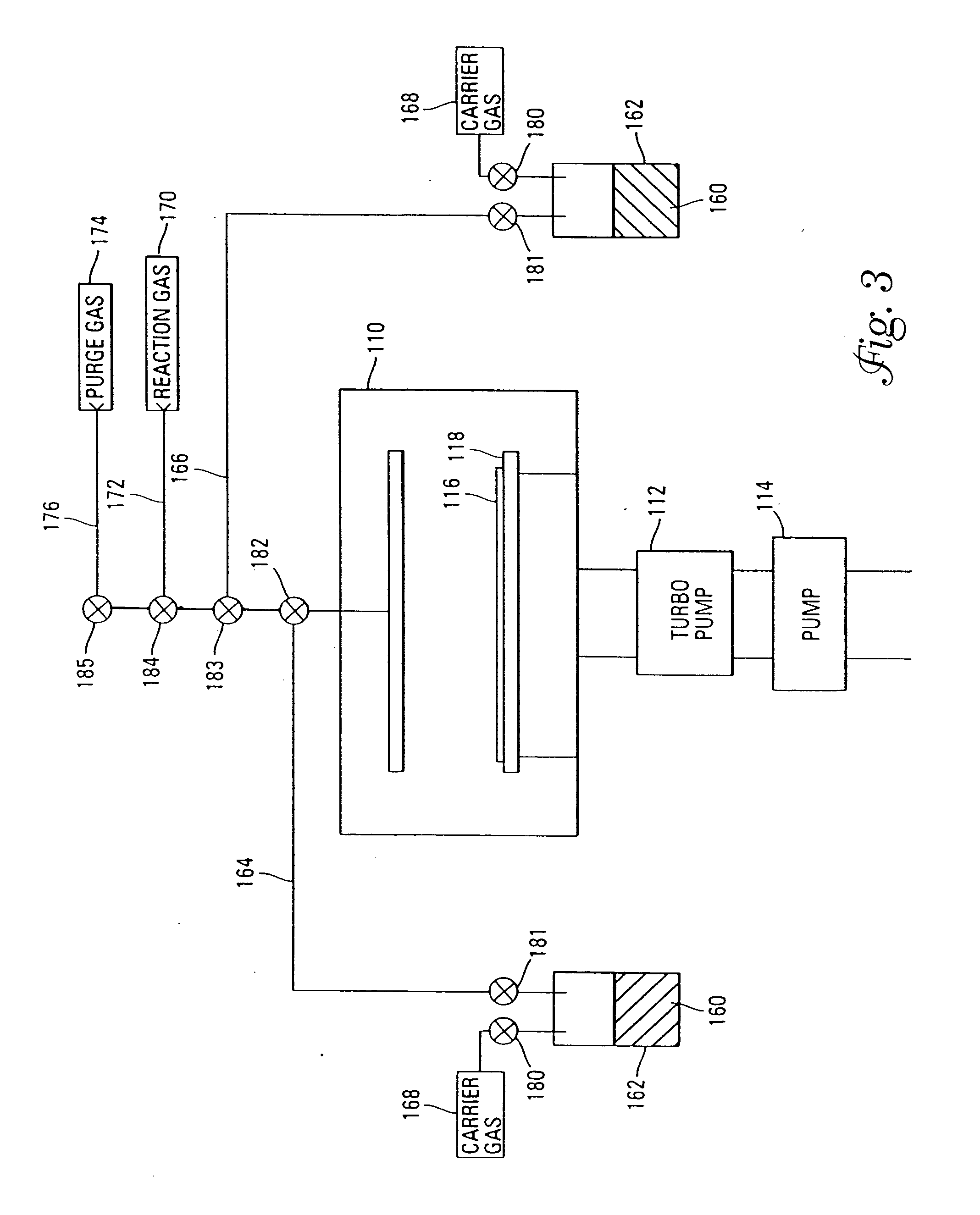
Systems and methods of forming refractory metal nitride layers using disilazanes
InactiveUS7122464B2Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseDeposition process
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum (silicon) nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a refractory metal precursor compound, a disilazane, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Self-aligned double-gate MOSFET by selective epitaxy and silicon wafer bonding techniques
InactiveUS6365465B1Controlled diffusionReduce diffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
A structure and a method of manufacturing a double-gate metal oxide semiconductor transistor includes forming a laminated structure having a single crystal silicon channel layer and insulating oxide and nitride layers on each side of the single crystal silicon channel, forming openings in the laminated structure, forming drain and source regions in the openings, doping the drain and source regions, forming a mask over the laminated structure, removing portions of the laminated structure not protected by the mask, removing the mask and the insulating oxide and nitride layers to leave the single crystal silicon channel layer suspended from the drain and source regions, forming an oxide layer to cover the drain and source regions and the channel layer, and forming a double-gate conductor over the oxide layer such that the double-gate conductor includes a first conductor on a first side of the single crystal silicon channel layer and a second conductor on a second side of the single crystal silicon channel layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Control of dopant diffusion from buried layers in bipolar integrated circuits
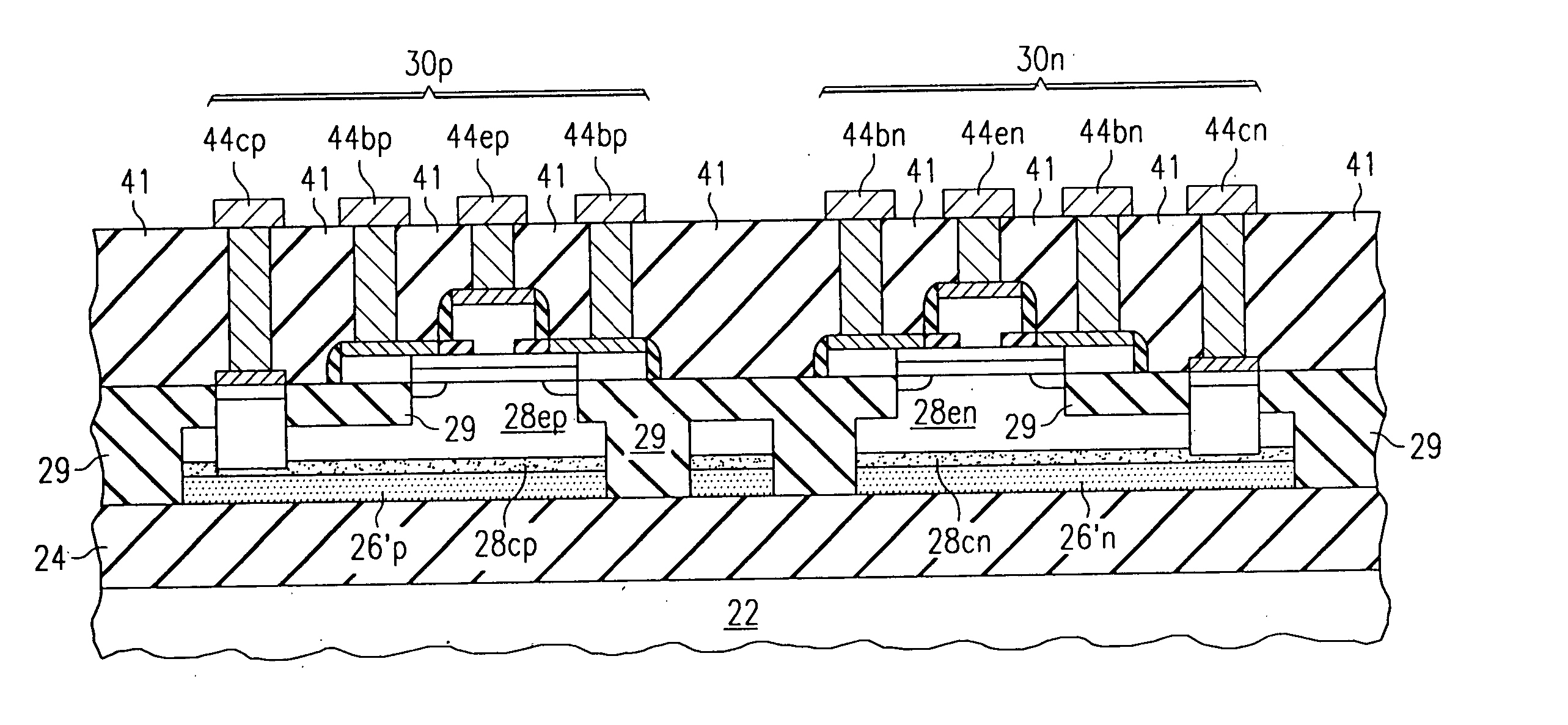
InactiveUS20050250289A1Mitigating dopant diffusionReduce diffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantDiffusion
An integrated circuit and method of fabricating the integrated circuit is disclosed. The integrated circuit includes vertical bipolar transistors (30, 50, 60), each having a buried collector region (26′). A carbon-bearing diffusion barrier (28c) is disposed over the buried collector region (26′), to inhibit the diffusion of dopant from the buried collector region (26′) into the overlying epitaxial layer (28). The diffusion barrier (28c) may be formed by incorporating a carbon source into the epitaxial formation of the overlying layer (28), or by ion implantation. In the case of ion implantation of carbon or SiGeC, masks (52, 62) may be used to define the locations of the buried collector regions (26′) that are to receive the carbon; for example, portions underlying eventual collector contacts (33, 44c) may be masked from the carbon implant so that dopant from the buried collector region (26′) can diffuse upward to meet the contact (33). MOS transistors (70, 80) including the diffusion barrier (28) are also disclosed.
Owner:BABCOCK JEFFREY A +5
Systems and methods for forming refractory metal nitride layers using organic amines
InactiveUS6967159B2Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsTantalum nitrideDeposition process
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using an atomic layer deposition process (a vapor deposition process that includes a plurality of deposition cycles) with a refractory metal precursor compound, an organic amine, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Structure and method for manufacturing MOSFET with super-steep retrograded island
InactiveUS20060068555A1Reduce morbidityReduce diffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingKryptonDopant
The present invention comprises a method for forming a semiconducting device including the steps of providing a layered structure including a substrate, a low diffusivity layer of a first-conductivity dopant; and a channel layer; forming a gate stack atop a protected surface of the channel layer; etching the layered structure selective to the gate stack to expose a surface of the substrate, where a remaining portion of the low diffusivity layer provides a retrograded island substantially aligned to the gate stack having a first dopant concentration to reduce short-channel effects without increasing leakage; growing a Si-containing material atop the recessed surface of the substrate; and doping the Si-containing material with a second-conductivity dopant at a second dopant concentration. The low diffusivity layer may be Si1-x-yGexZy, where Z can be carbon (C), xenon (Xe), germanium (Ge), krypton (Kr), argon (Ar), nitrogen (N), or combinations thereof.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High performance CMOS device structure with mid-gap metal gate
InactiveUS6916698B2Improve performanceReduce diffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSWork function
High performance (surface channel) CMOS devices with a mid-gap work function metal gate are disclosed wherein an epitaxial layer is used for a threshold voltage Vt adjust / decrease for the PFET area, for large Vt reductions (˜500 mV), as are required by CMOS devices with a mid-gap metal gate. The present invention provides counter doping using an in situ B doped epitaxial layer or a B and C co-doped epitaxial layer, wherein the C co-doping provides an additional degree of freedom to reduce the diffusion of B (also during subsequent activation thermal cycles) to maintain a shallow B profile, which is critical to provide a surface channel CMOS device with a mid-gap metal gate while maintaining good short channel effects. The B diffusion profiles are satisfactorily shallow, sharp and have a high B concentration for devices with mid-gap metal gates, to provide and maintain a thin, highly doped B layer under the gate oxide.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for forming tantalum silicide layers
InactiveUS6995081B2Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseNitrogen
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) tantalum suicide layers (including tantalum silicon nitride layers), which are typically useful as diffusion barrier layers, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a tantalum halide precursor compound, a silicon precursor compound, and an optional nitrogen precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
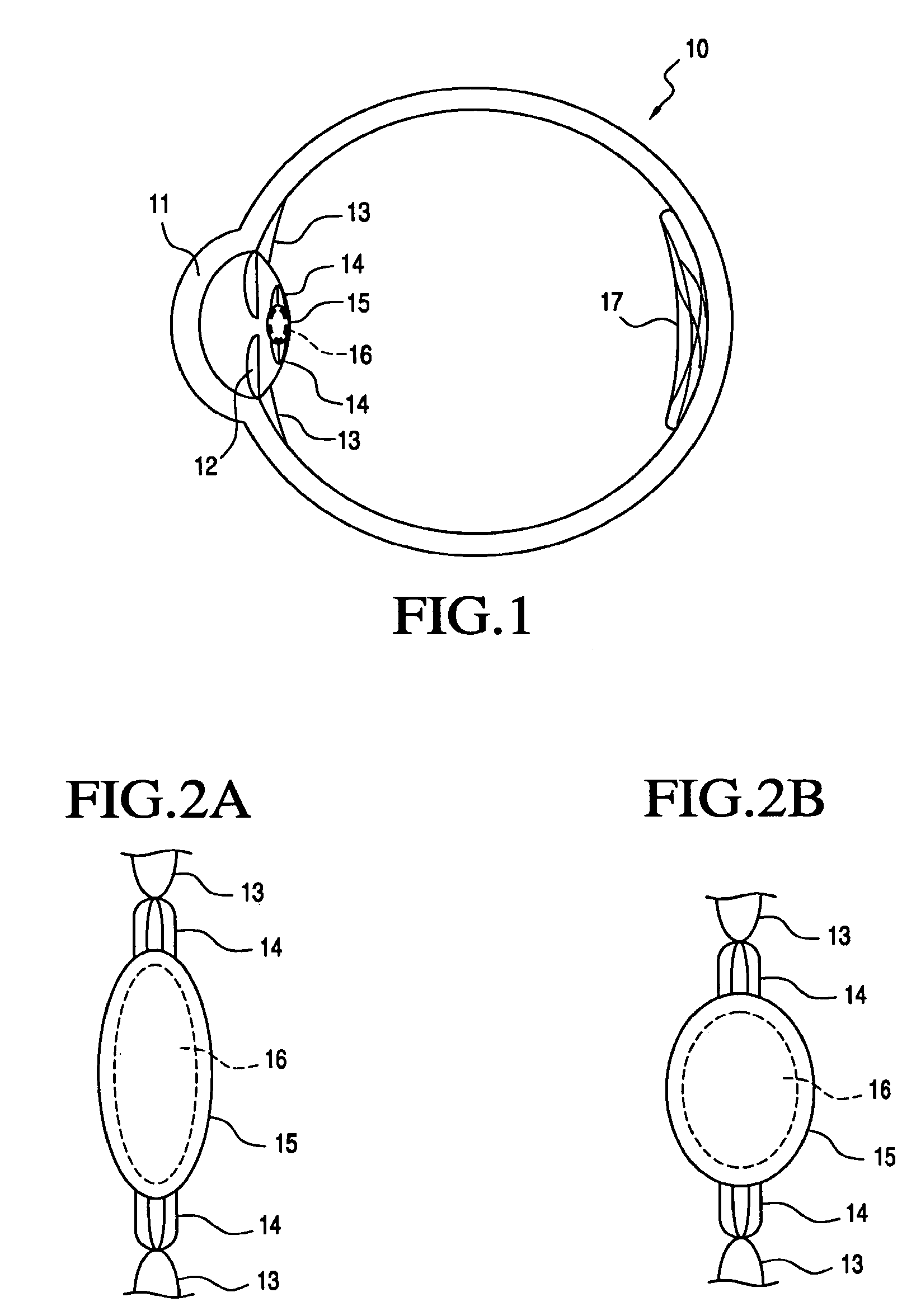
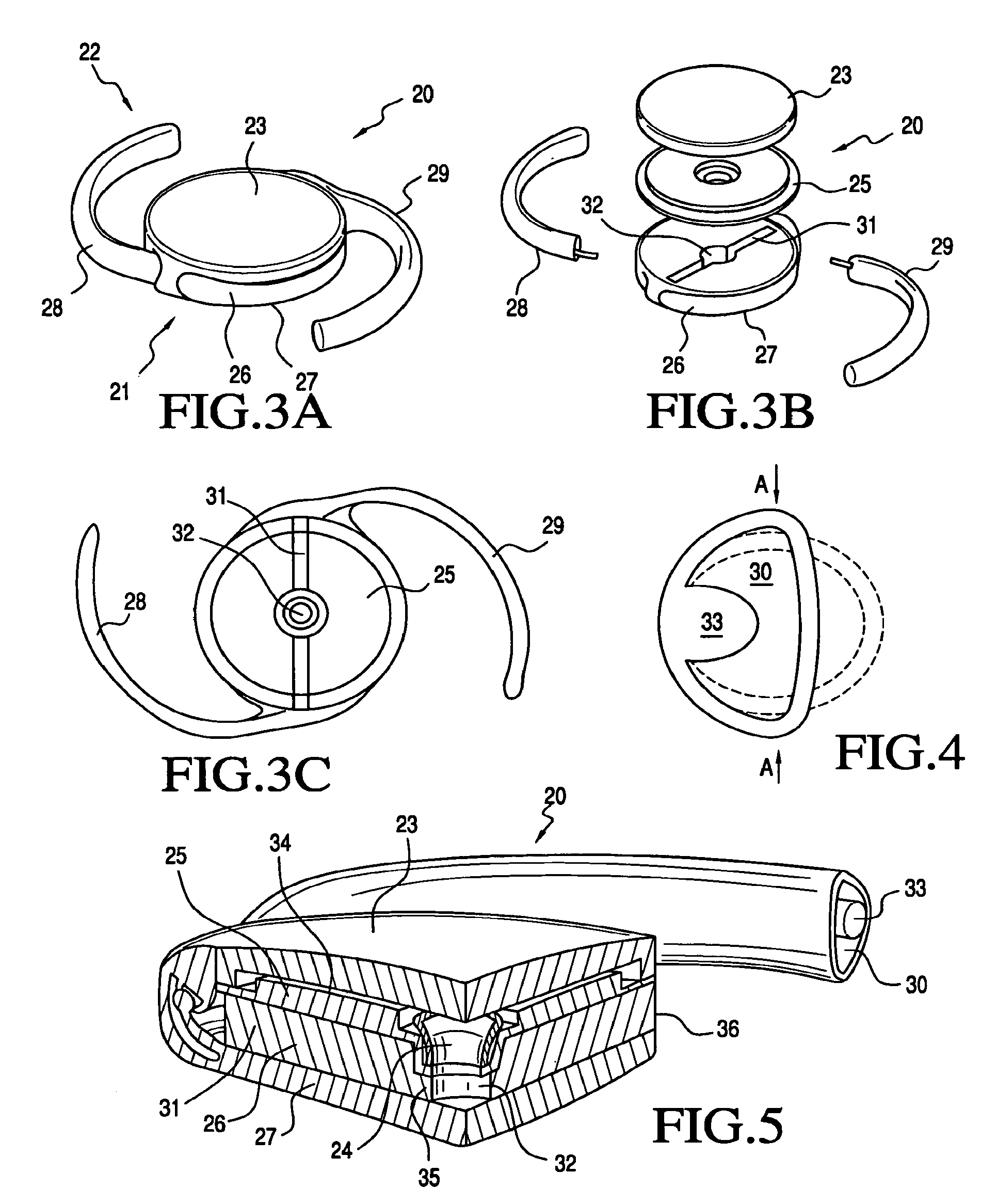
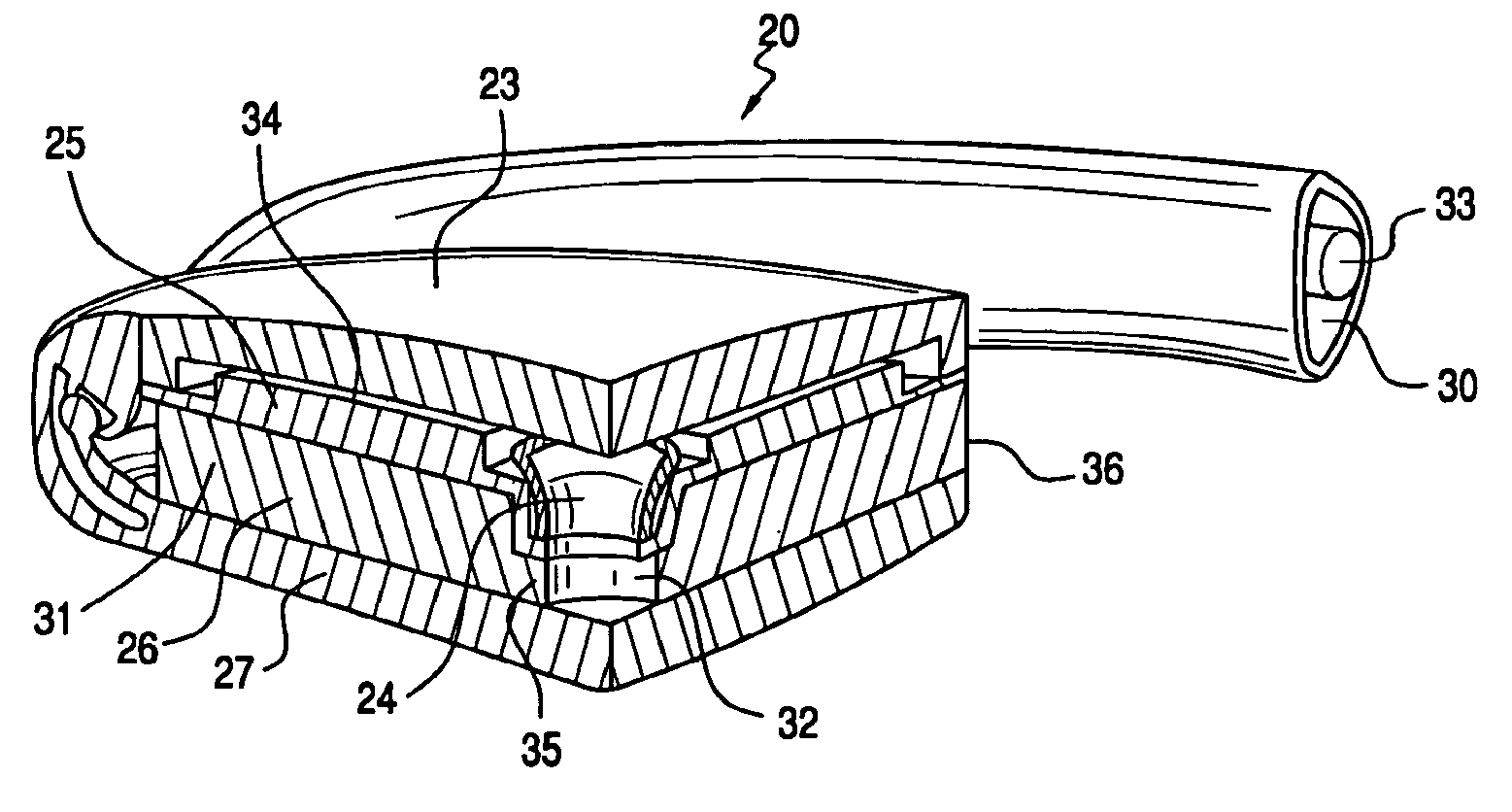
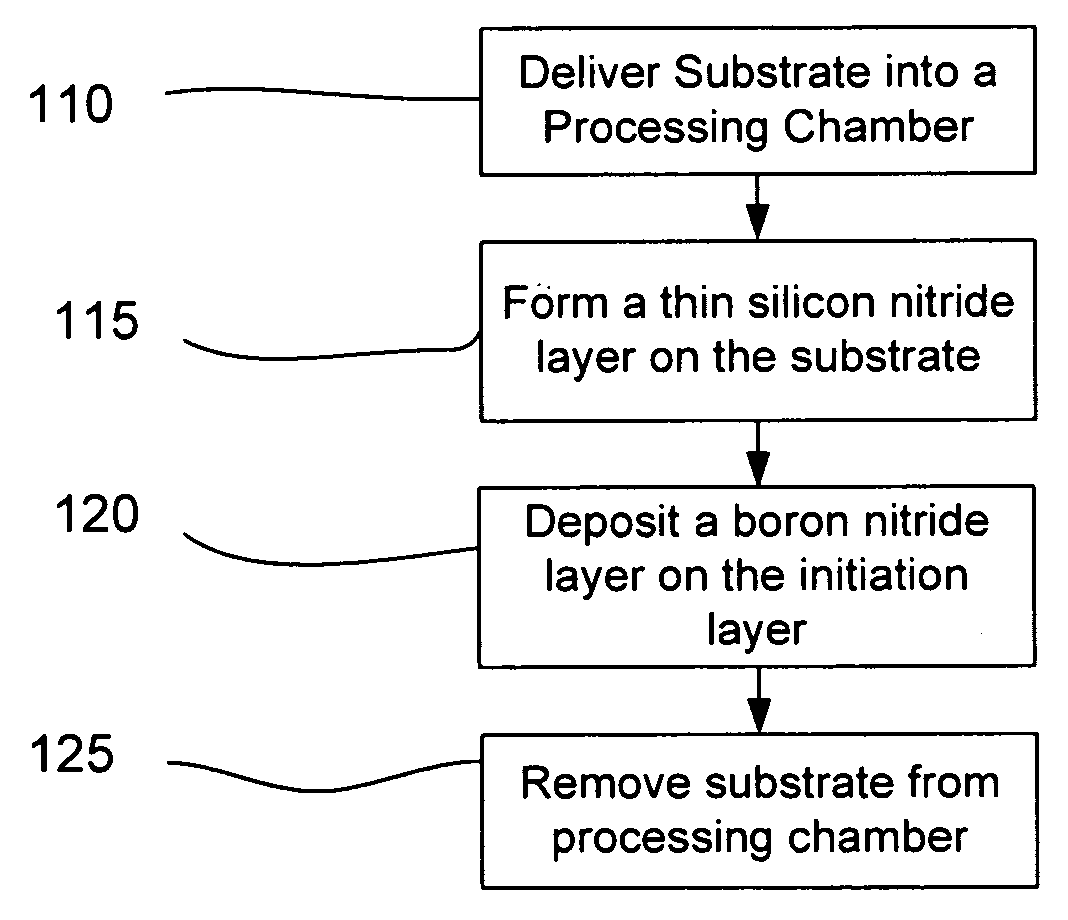
Accommodating intraocular lens system and method
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided having optical parameters that are altered in-situ, wherein an optic portion of the lens includes an actuator that deflects a lens element to alter the optical power of the lens, responsive to forces applied to a haptic portion to the lens by contraction of the ciliary muscles. Forces applied to the haptic portion may result in fluid displacements from or to the haptic portion from the actuator. Displacement of fluid to the actuator may either increase or reduce the degree of deflection imposed on the lens element by the actuator.
Owner:ALCON INC
Systems and methods of forming refractory metal nitride layers using disilazanes
InactiveUS20050028733A1Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseDeposition process
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum (silicon) nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a refractory metal precursor compound, a disilazane, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods of forming tantalum silicide layers
InactiveUS20060048711A1Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseNitrogen
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) tantalum silicide layers (including tantalum silicon nitride layers), which are typically useful as diffusion barrier layers, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a tantalum halide precursor compound, a silicon precursor compound, and an optional nitrogen precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Accommodating intraocular lens system and method
ActiveUS20060041307A1Efficiently manipulatedReduce diffuseIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical power
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided having optical parameters that are altered in-situ, wherein an optic portion of the lens includes an actuator that deflects a lens element to alter the optical power of the lens, responsive to forces applied to a haptic portion to the lens by contraction of the ciliary muscles. Forces applied to the haptic portion may result in fluid displacements from or to the haptic portion from the actuator. Displacement of fluid to the actuator may either increase or reduce the degree of deflection imposed on the lens element by the actuator.
Owner:ALCON INC
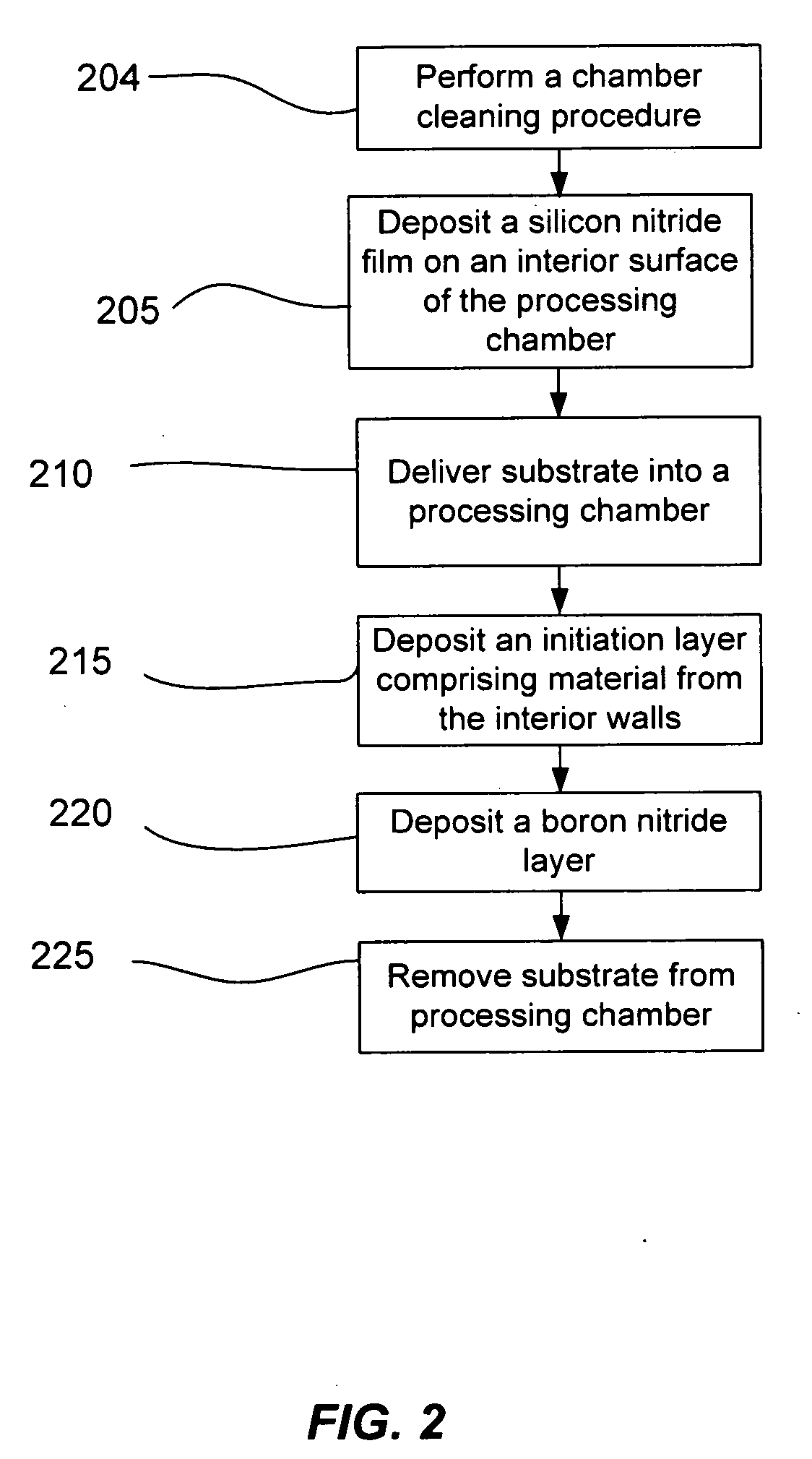
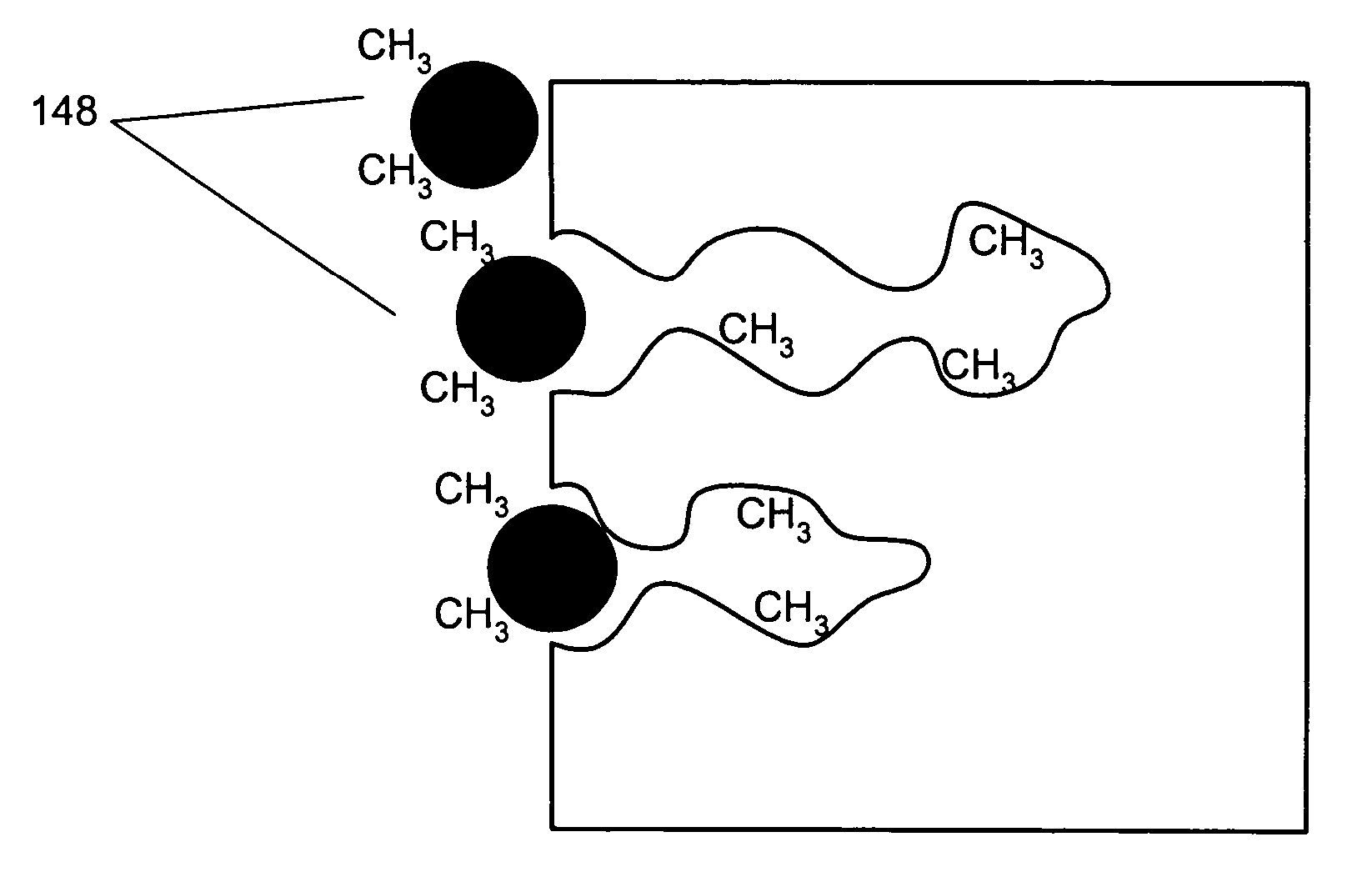
Boron film interface engineering
ActiveUS20100098884A1Reduce diffuseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesInterface engineeringBoron
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
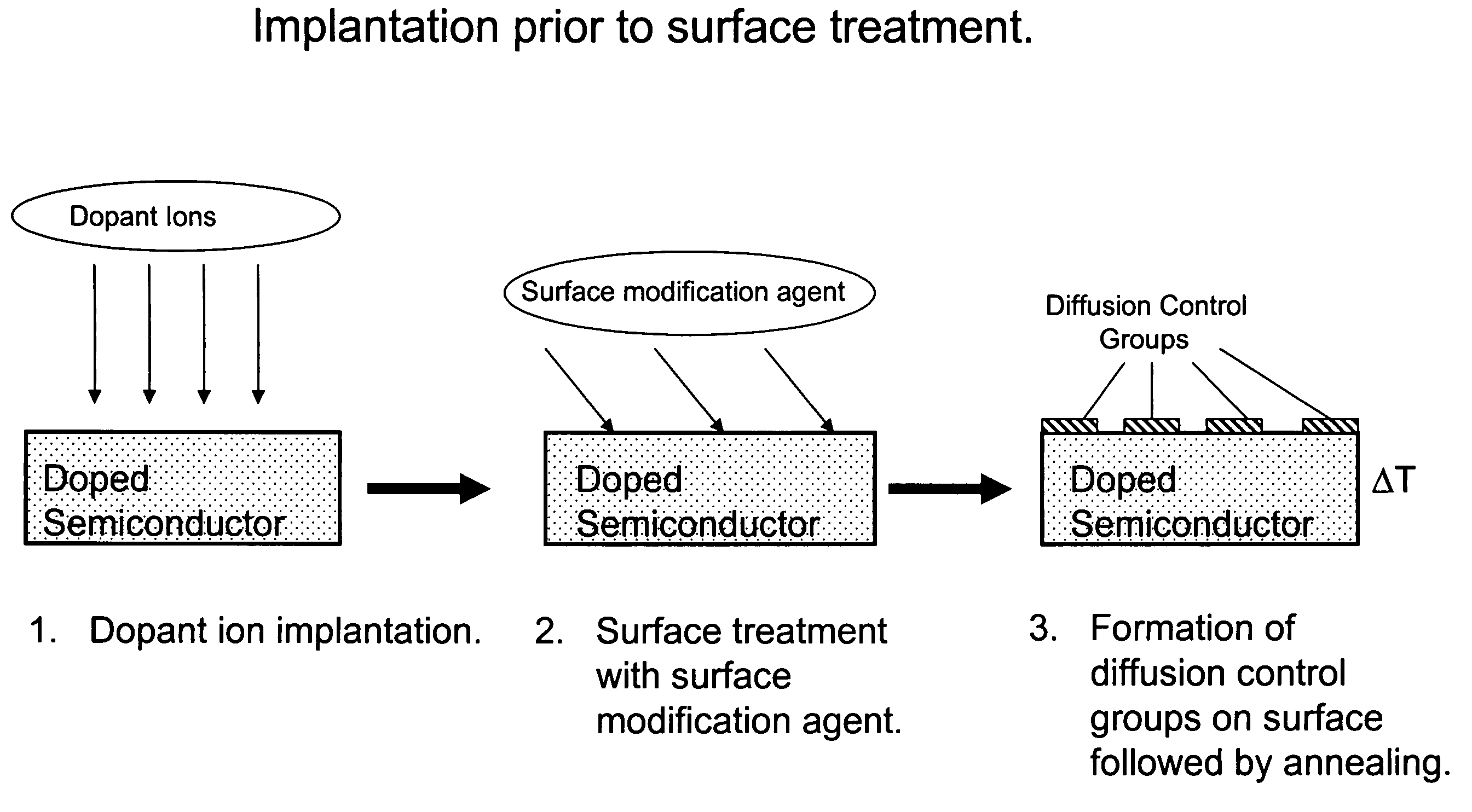
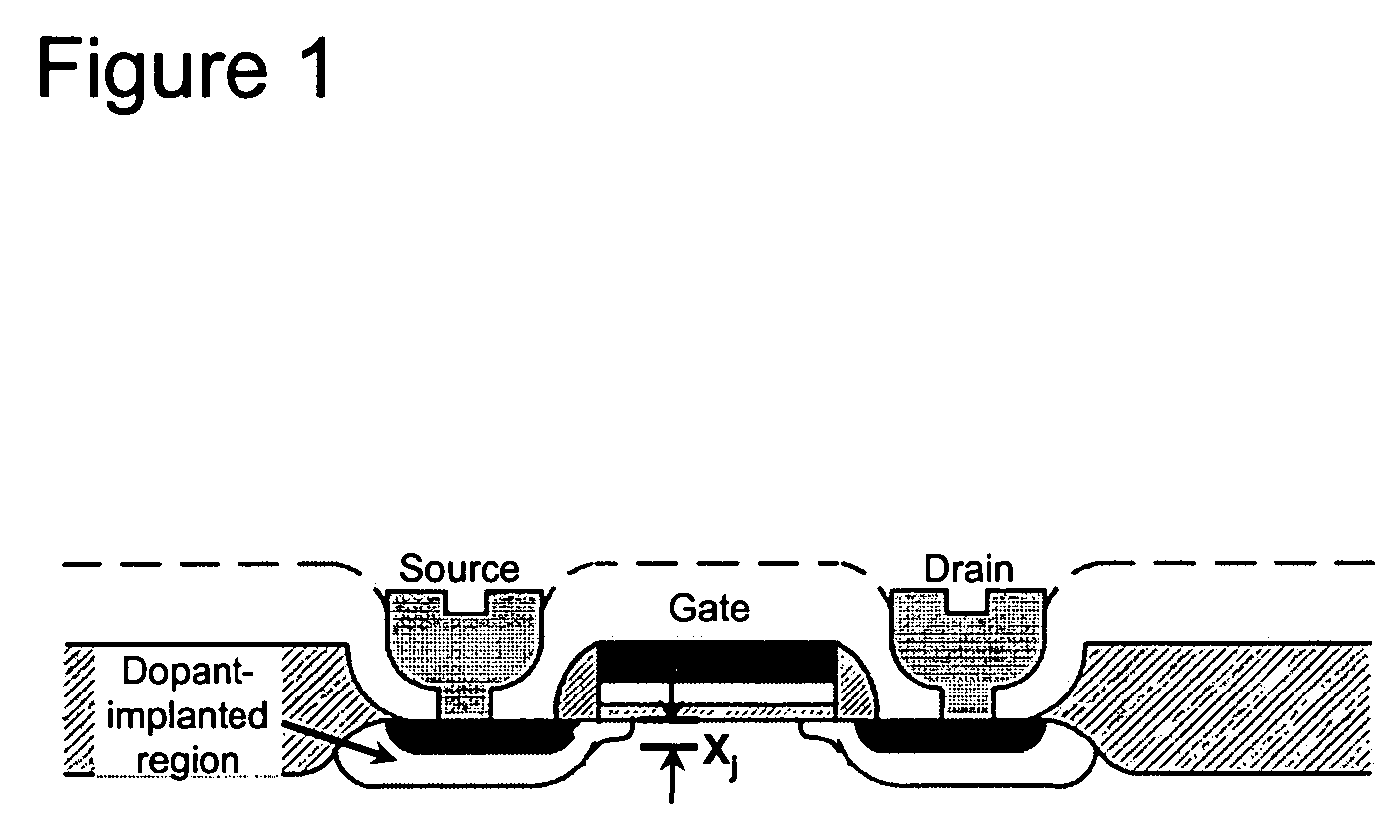
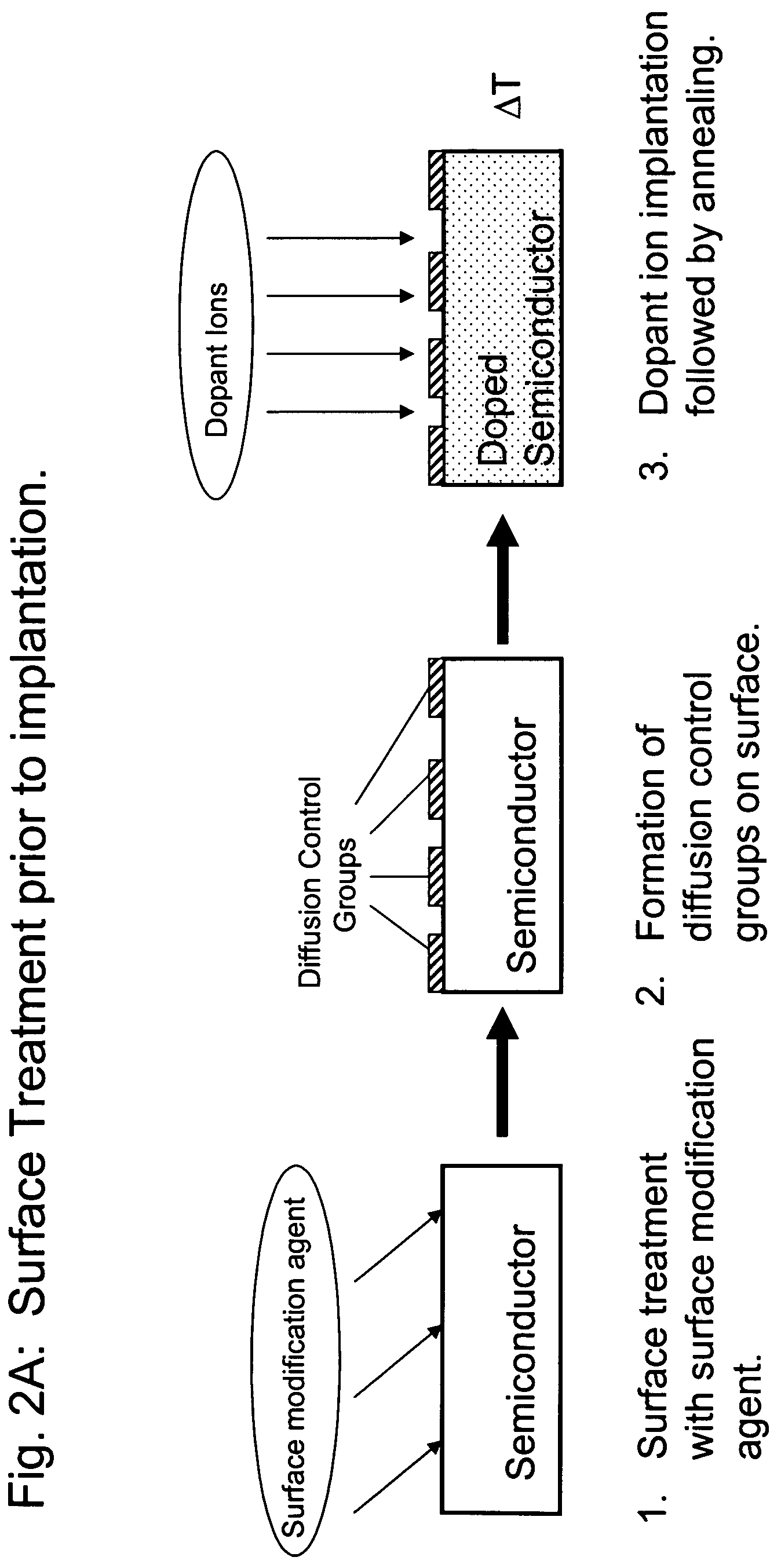
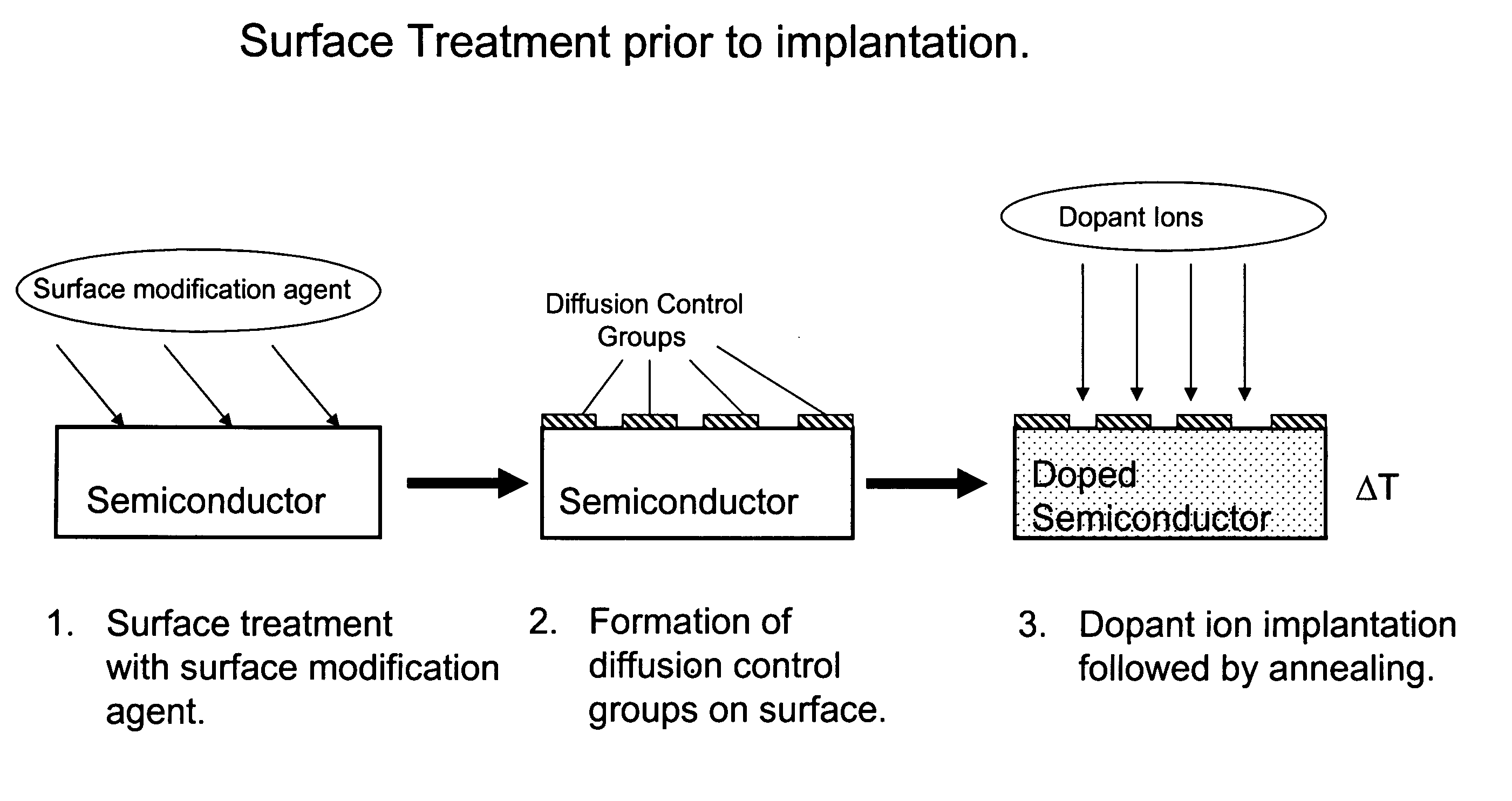
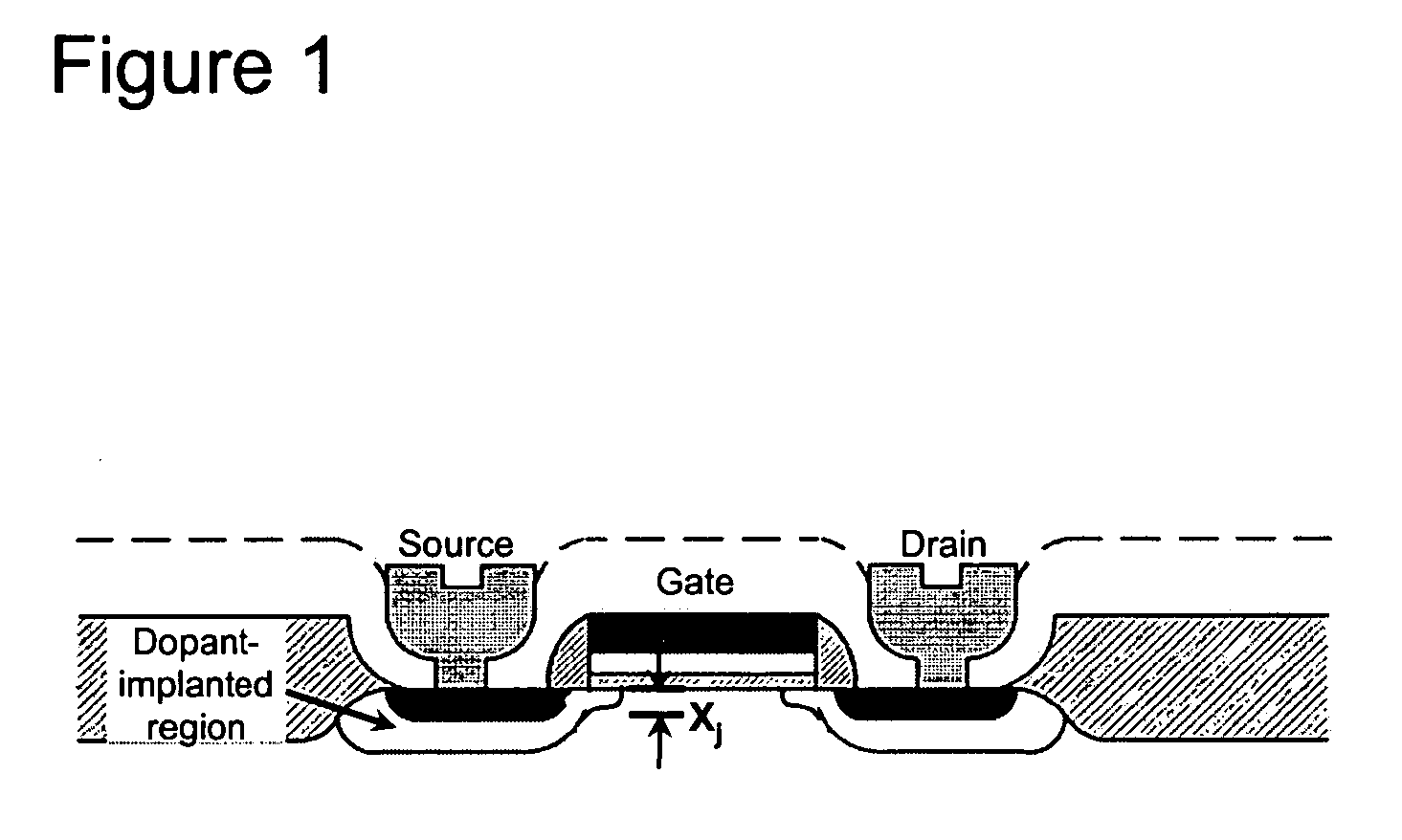
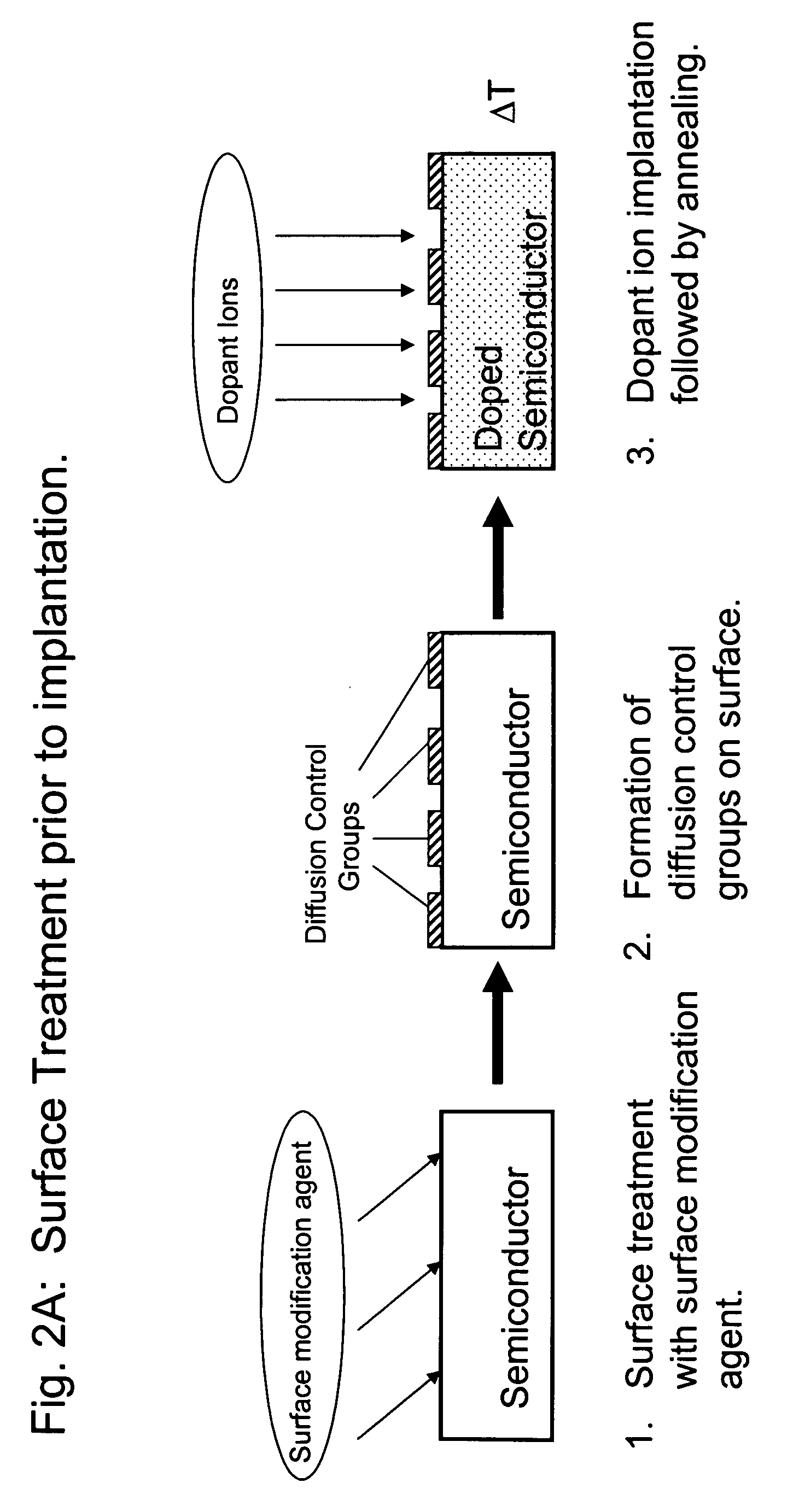
Methods for controlling dopant concentration and activation in semiconductor structures
InactiveUS7846822B2Easy to integrateLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantSemiconductor materials
The present invention provides methods for fabricating semiconductor structures and devices, particularly ultra-shallow doped semiconductor structures exhibiting low electrical resistance. Methods of the present invention use modification of the composition of semiconductor surfaces to allow fabrication of a doped semiconductor structure having a selected dopant concentration depth profile, which provides useful junctions and other device components in microelectronic and nanoelectronic devices, such as transistors in high density integrated circuits. Surface modification in the present invention also allows for control of the concentration and depth profile of defects, such as interstitials and vacancies, in undersaturated semiconductor materials.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Systems and methods of forming refractory metal nitride layers using disilazanes
InactiveUS20060292788A1Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseDeposition process
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum (silicon) nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a refractory metal precursor compound, a disilazane, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods of forming refractory metal nitride layers using organic amines
InactiveUS20050287804A1Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseTantalum nitride
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using an atomic layer deposition process (a vapor deposition process that includes a plurality of deposition cycles) with a refractory metal precursor compound, an organic amine, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
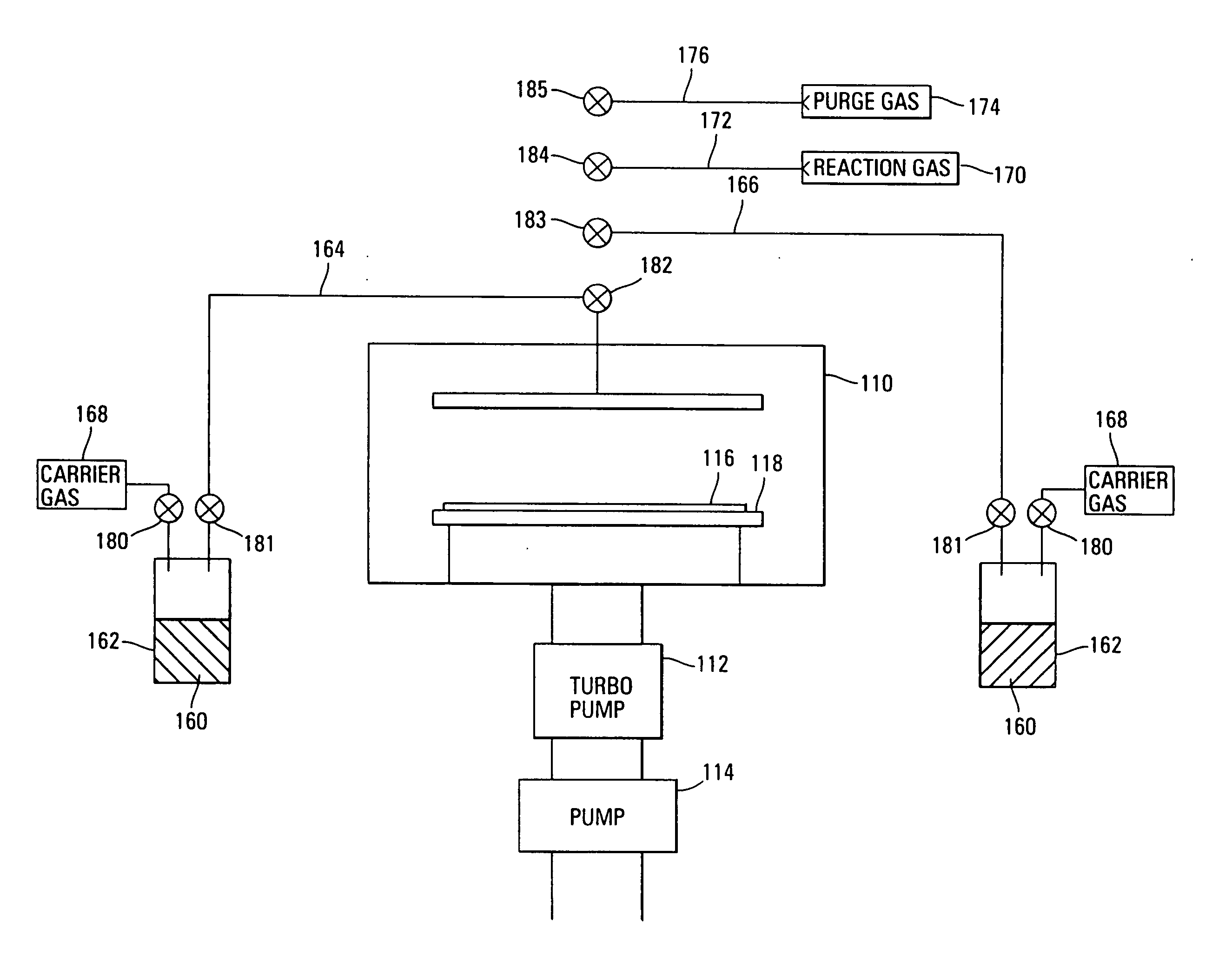
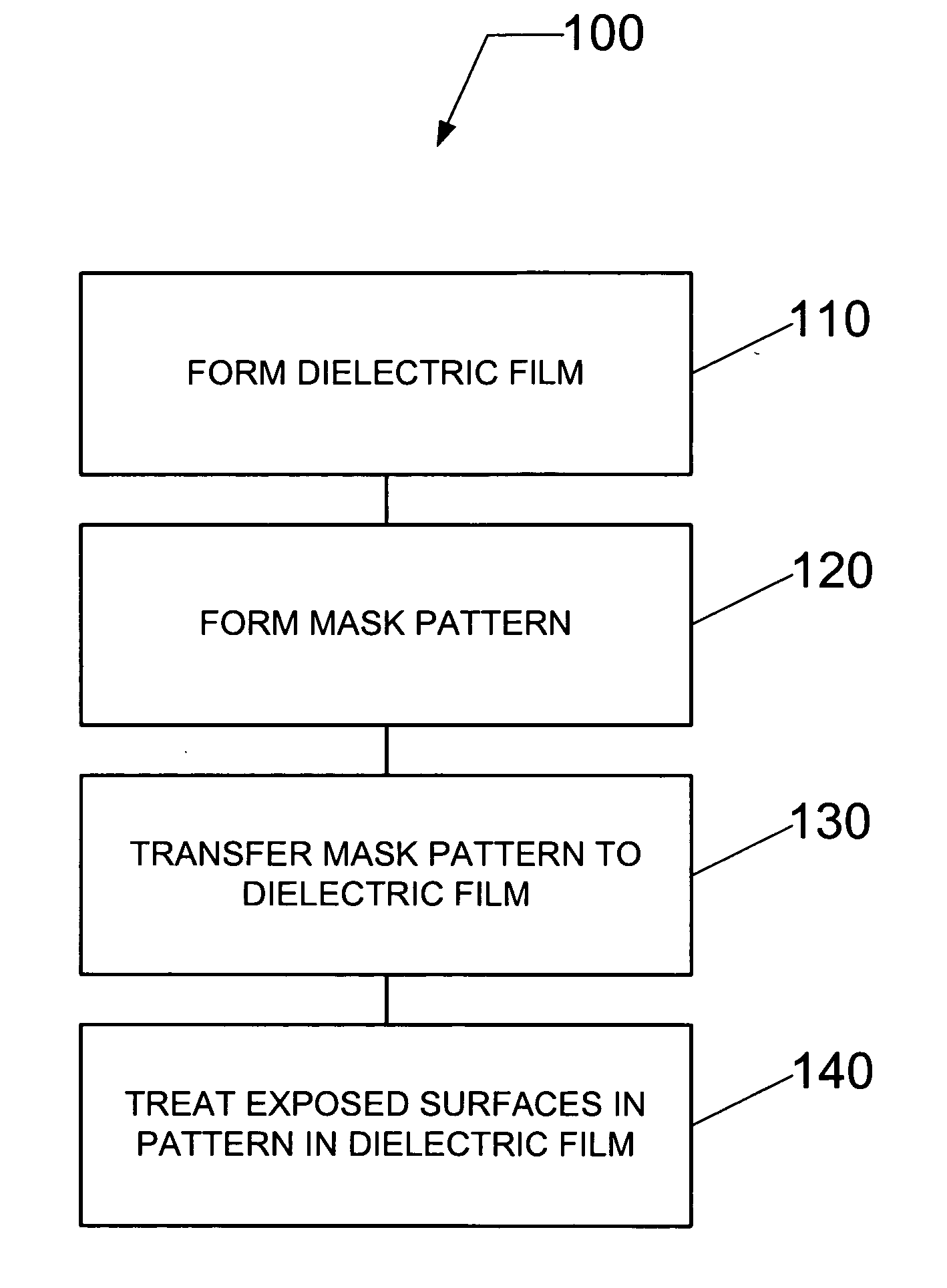
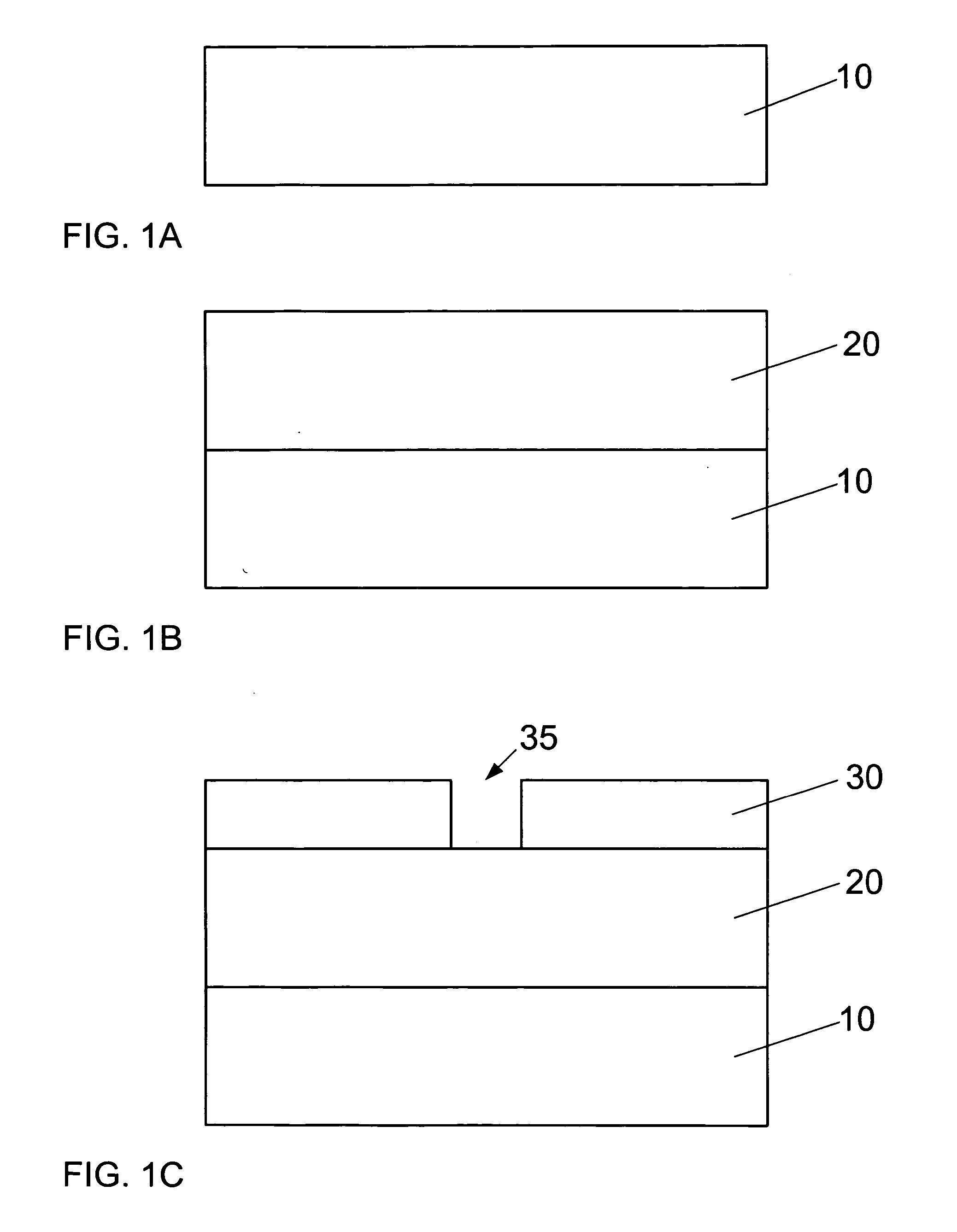
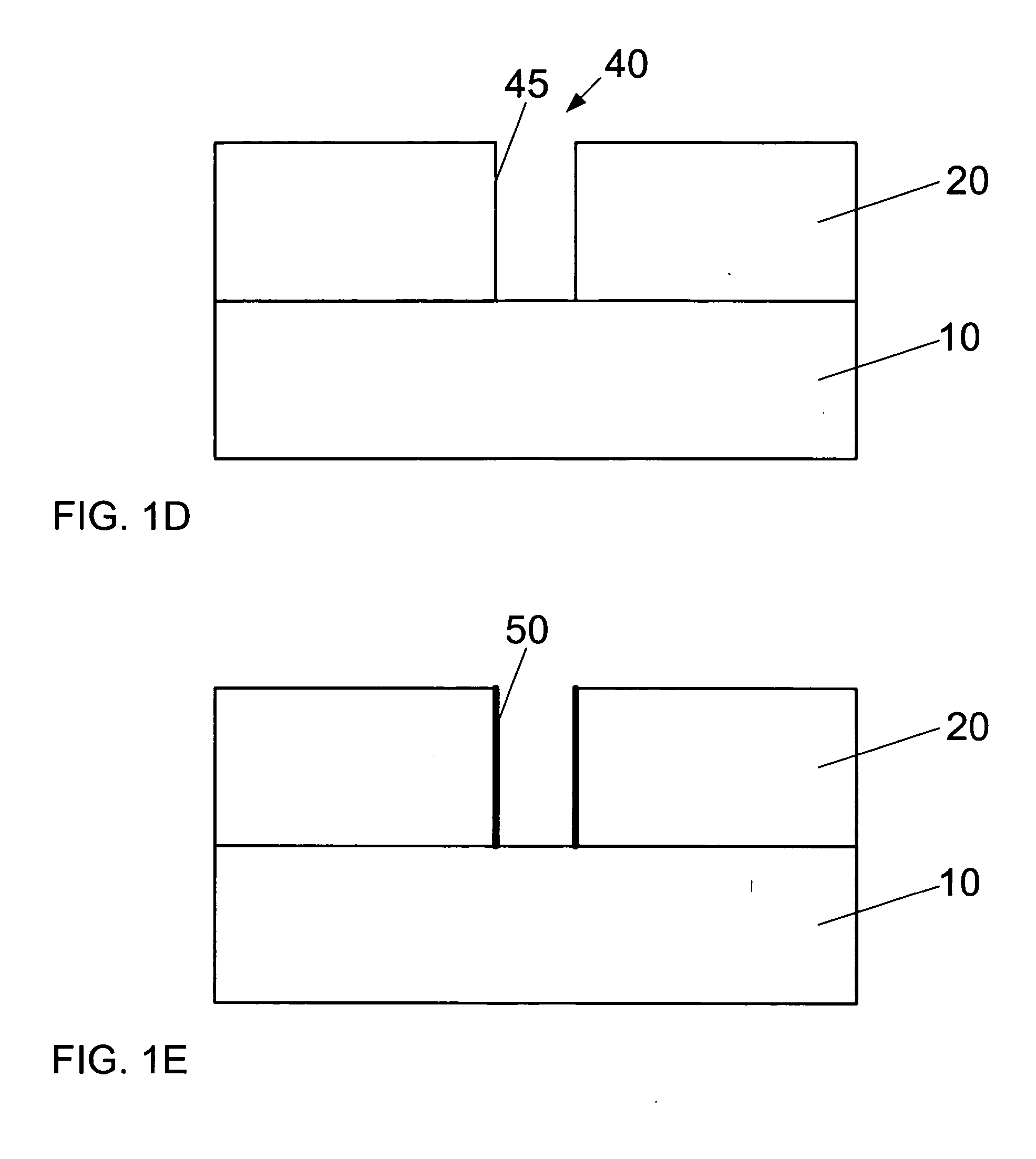
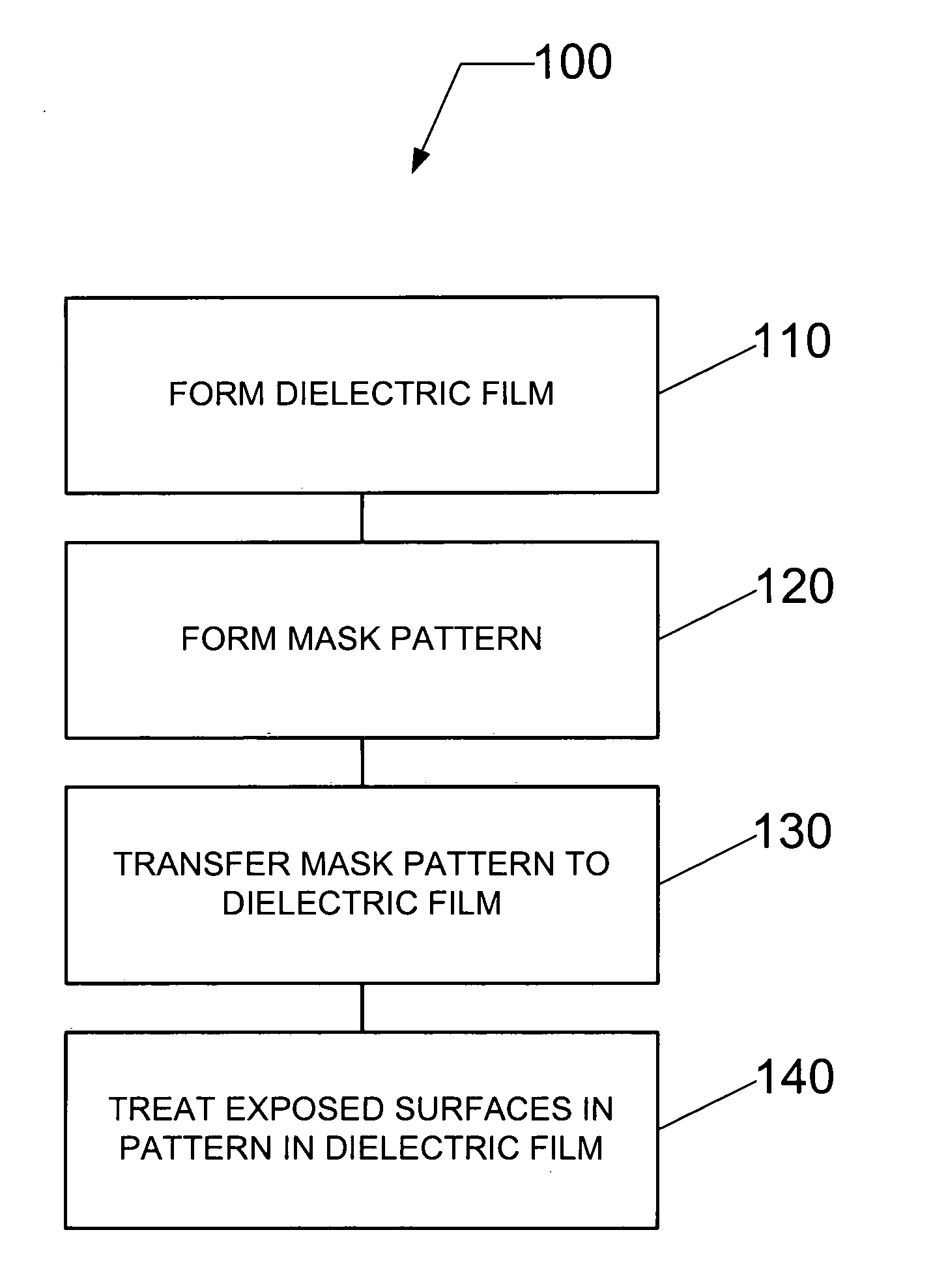
Method and system for treating a dielectric film
InactiveUS20050077597A1Reduce diffuseImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringDielectric permittivity
A method and system for treating a dielectric film includes exposing at least one surface of the dielectric film to a CxHy containing material, wherein x and y are each integers greater than or equal to a value of unity. The dielectric film can include a low dielectric constant film with or without pores having an etch feature formed therein following dry etch processing. As a result of the etch processing or ashing, exposed surfaces in the feature formed in the dielectric film can become damaged, or activated, leading to retention of contaminants, absorption of moisture, increase in dielectric constant, etc. Damaged surfaces, such as these, are treated by performing at least one of healing these surfaces to, for example, restore the dielectric constant (i.e., decrease the dielectric constant) and cleaning these surfaces to remove contaminants, moisture, or residue. Moreover, preparation for barrier layer and metallization of features in the film may include treating by performing sealing of sidewall surfaces of the feature to close exposed pores and provide a surface for barrier film deposition.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
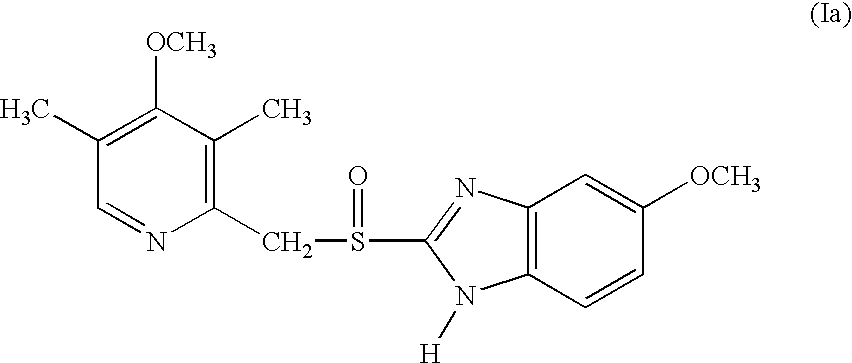
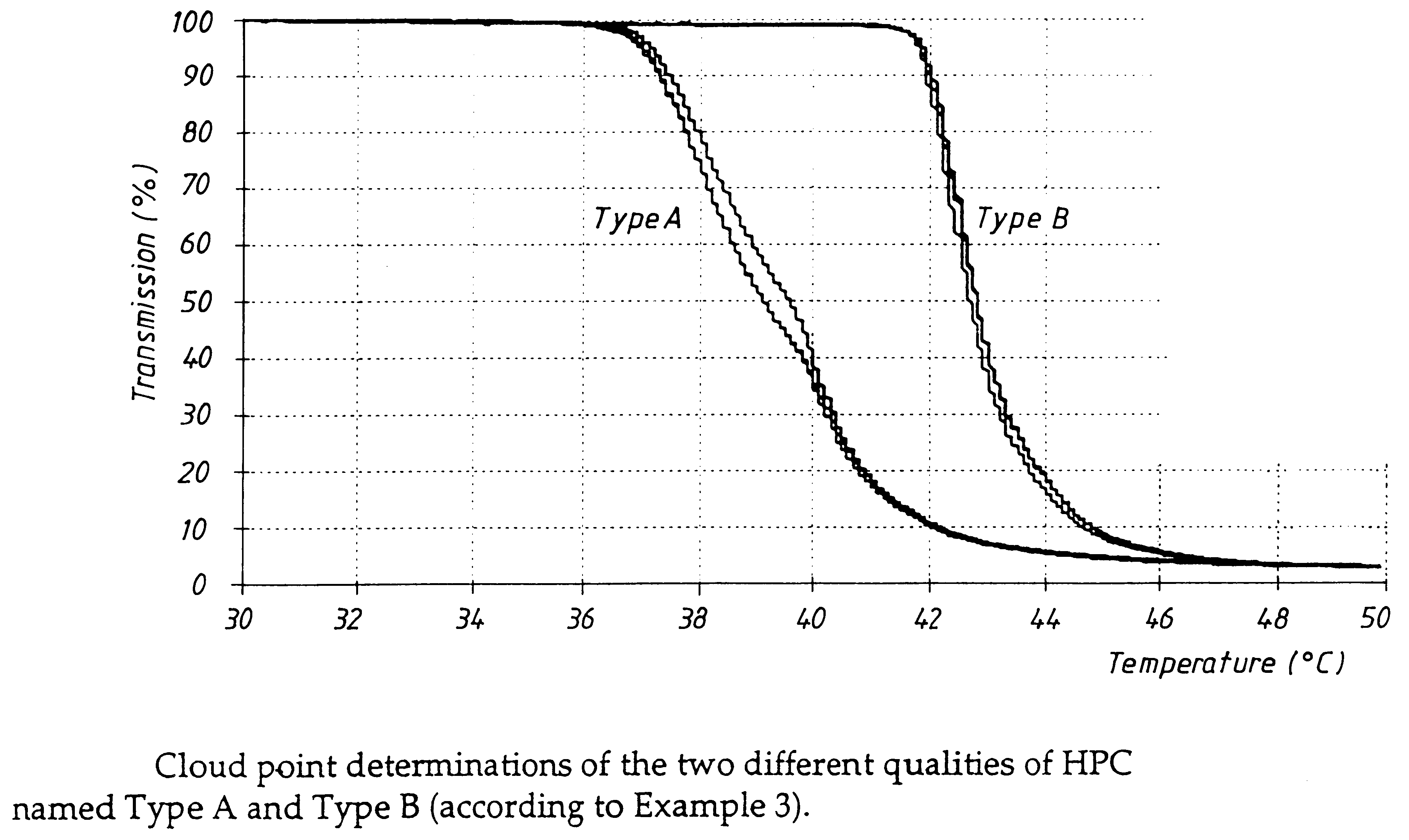
Pharmaceutical formulation comprising omeprazole
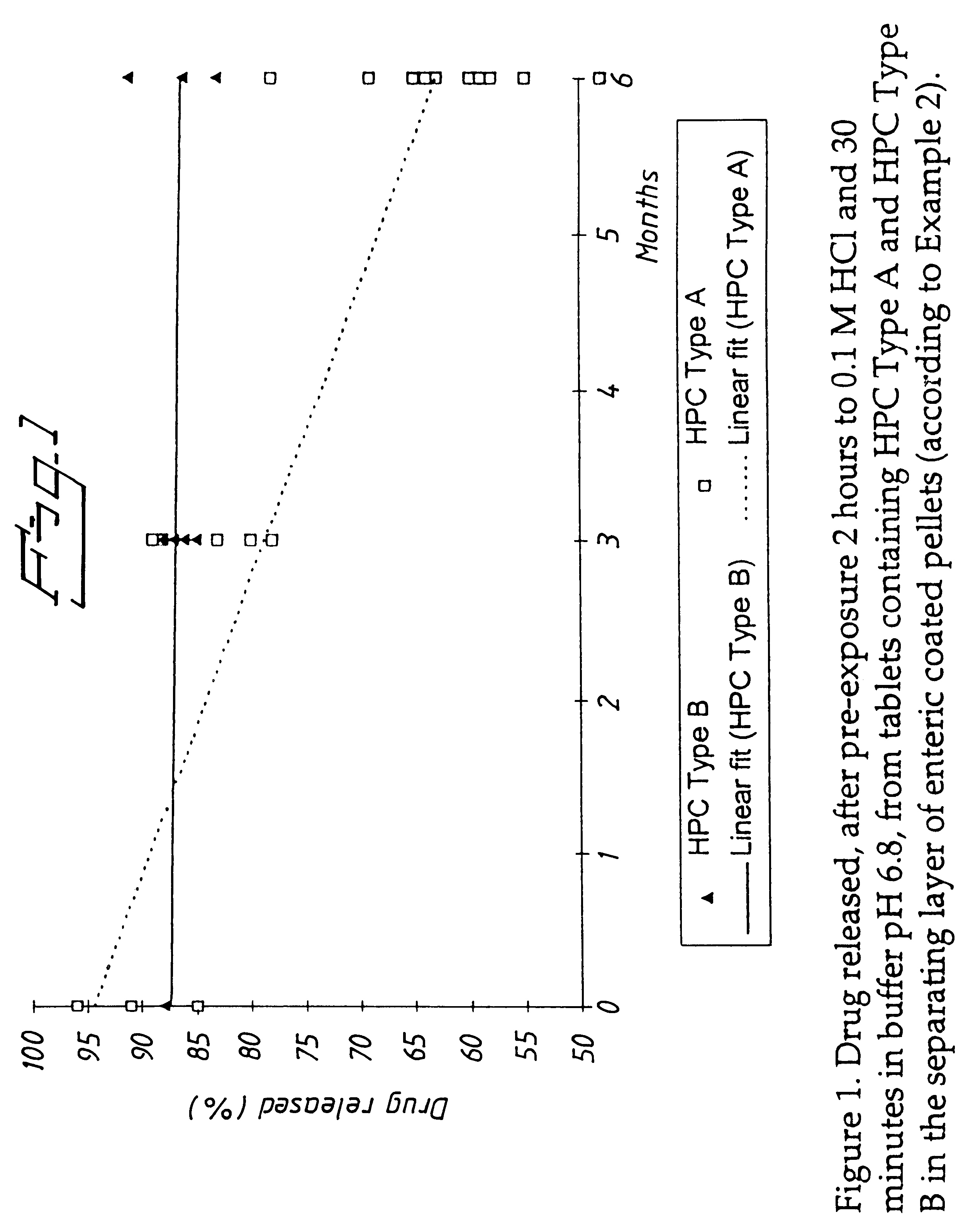
InactiveUS6428810B1Reduce diffuseHigh film thicknessOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryEnantiomerOmeprazole
An enteric coated oral pharmaceutical formulation comprising as active ingredient a compound selected from the group of omeprazole, an alkaline salt of omeprazole, one of the single enantiomers of omeprazole and an alkaline salt of one of the single enantiomers of omeprazole, wherein the formulation comprises a core material that comprises the active ingredient and optionally an alkaline reacting compound, the active ingredient is in admixture with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, such as for instance a binding agent, and on said core material a separating layer and an enteric coating layer. A hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) with a specific cloud point is used in the manufacture of the claimed pharmaceutical formulations. Furthermore, the application describes the processes for their preparation and the use of the claimed formulations in medicine.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Treatment of low dielectric constant films using a batch processing system
ActiveUS20070077782A1Reduce diffuseImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBatch processingOptoelectronics
A method and system for treating a dielectric film in a batch processing system includes exposing at least one surface of the dielectric film to a treating compound including a CxHy containing compound, where x and y represent integers greater than or equal to unity. The plurality of wafers are heated when the treating compound is introduced. The dielectric film can include a low dielectric constant film with or without pores having an etch feature formed therein following dry etch processing.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Touch surface with variable refractive index
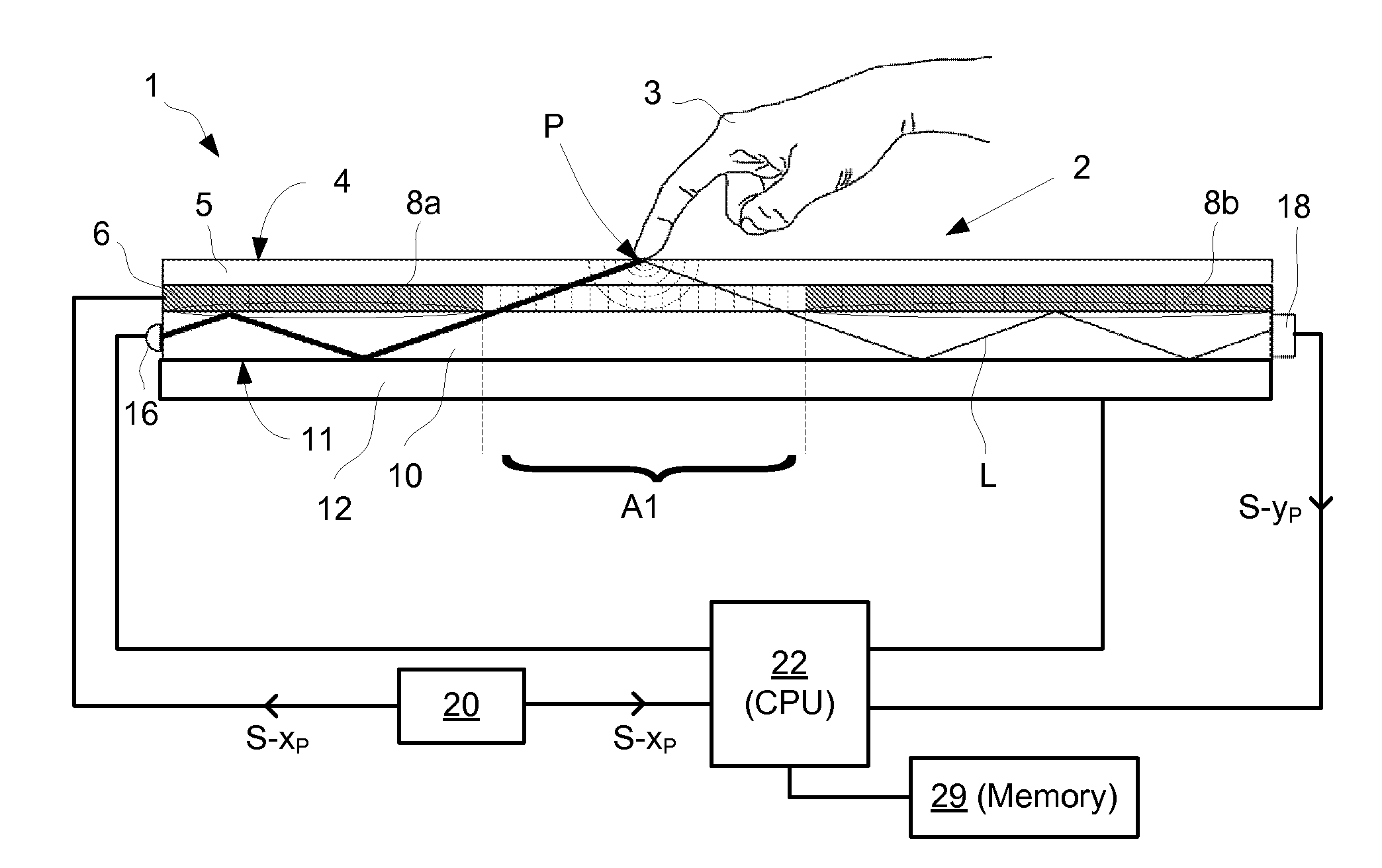
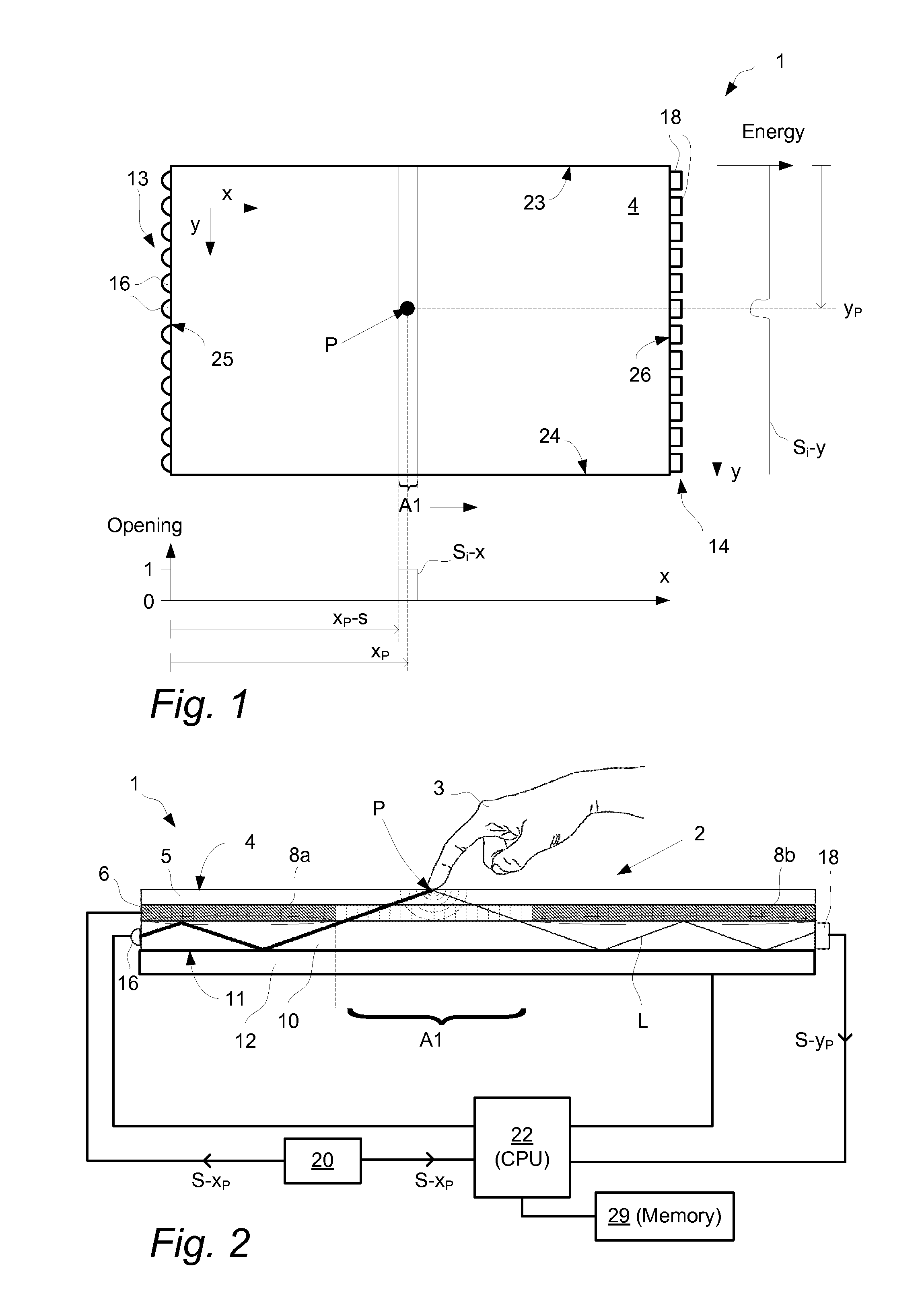
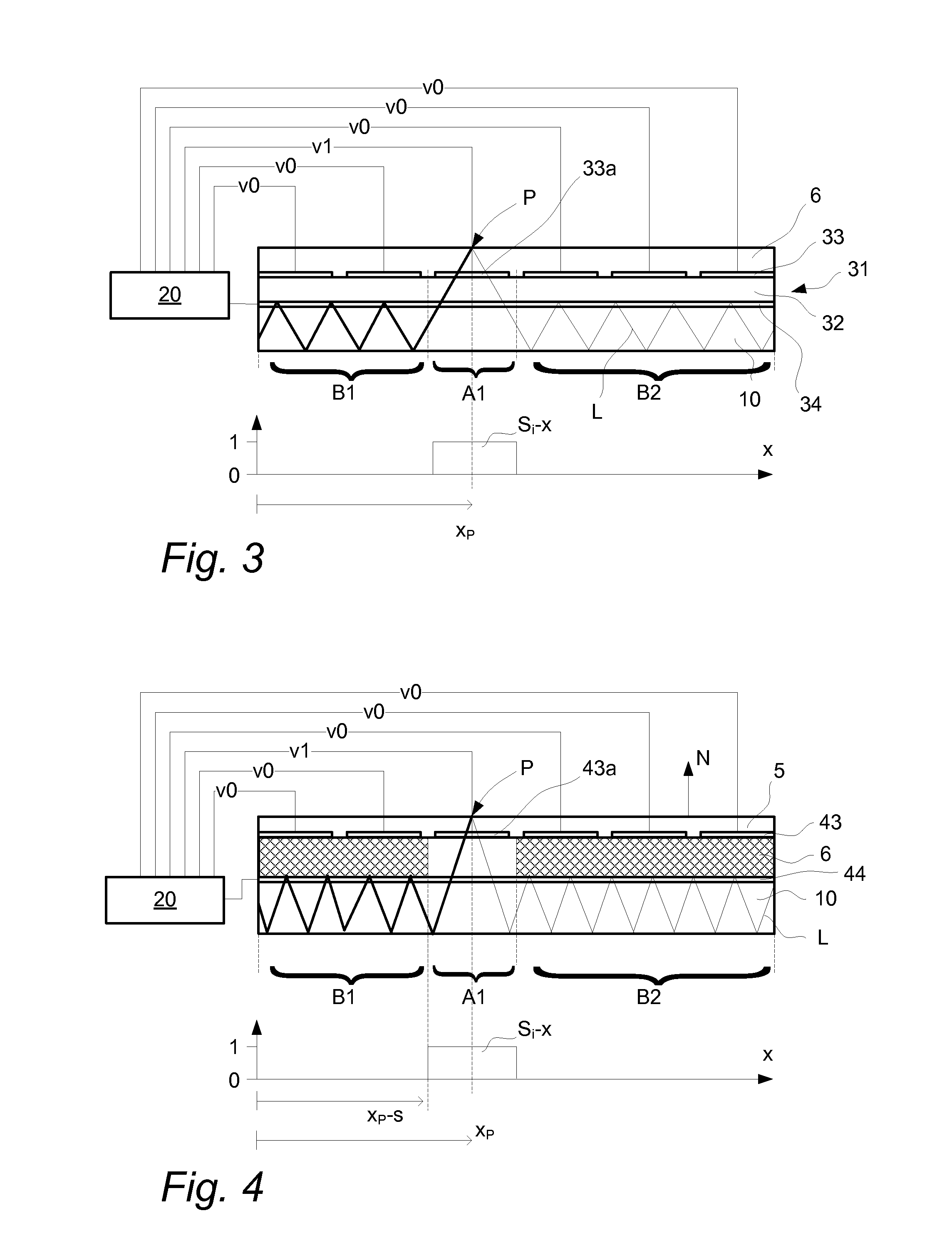
InactiveUS20120169672A1Reduce the numberOvercome limitationsInput/output processes for data processingRefractive indexSelective control
An apparatus for determining a location of at least one object on a touch surface, comprising: a light transmissive panel defining the touch surface and including a controllable reflective boundary; an illumination arrangement configured to introduce light into the panel; a control device configured to selectively control the reflective boundary such that the light may pass between a first layer and a second layer via an opening in the reflective boundary; a light detection arrangement configured to measure the light passed via the opening and impinged on the touch surface; and a processor unit configured to determine the location as a function of the measured light passed via the opening and the selective control of the reflective boundary. A method and computer readable medium is also described.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Method and system for treating a dielectric film
InactiveUS20050215072A1Reduce diffuseImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesArylSilanes
A method and system for treating a dielectric film includes exposing at least one surface of the dielectric film to an alkyl silane, an alkoxysilane, an alkyl siloxane, an alkoxysiloxane, an aryl silane, an acyl silane, a cyclo siloxane, a polysilsesquioxane (PSS), an aryl siloxane, an acyl siloxane, or a halo siloxane, or any combination thereof. The dielectric film can include a low dielectric constant film with or without pores having an etch feature formed therein following dry etch processing. As a result of the etch processing or ashing, exposed surfaces in the feature formed in the dielectric film can become damaged, or activated, leading to retention of contaminants, absorption of moisture, increase in dielectric constant, etc. Damaged surfaces, such as these, are treated by performing at least one of healing these surfaces to, for example, restore the dielectric constant (i.e., decrease the dielectric constant) and cleaning these surfaces to remove contaminants, moisture, or residue. Moreover, preparation for barrier layer and metallization of features in the film may include treating by performing sealing of sidewall surfaces of the feature to close exposed pores and provide a surface for barrier film deposition.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Stable fragrance microcapsule suspension and process for using same
InactiveUS20050227907A1Improve performanceReduce diffuseCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsDeodorantNon ionic
Described is a stable initial impact and continuous impact fragrance and / or benefit agent-imparting aqueous suspension of microencapsulated fragrance and / or benefit agent, e.g., malodour counteractant suspended in a non-confined fragrance-containing and / or benefit agent-containing liquid phase oil-in-water emulsion. On storage, the viscosity of the suspension undergoes a minimal increase over an extended period of time thereby avoiding undesirable agitation resistance during the blending of the suspension with other materials. The suspension is thus useful for imparting a benefit or an aroma to a consumable material such as a liquid anionic, cationic, non-ionic or zwitterionic detergent, a shampoo, a bodywash, liquid soaps, hair conditioners, skin lotions, anti-perspirants, deodorants or liquid fabric softener and / or conditioner compositions. Also described is a process for preparing such stable suspensions and apparatus for carrying out such process.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Polypropylene foam and foam core structure
InactiveUS20050159496A1Reduce the probability of spreadingReduce diffuseLayered product treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsPolystyrenePolypropylene
One or more external surfaces of an extruded foam are coated by co-extruding a skin of polymer on the surface to reduce the diffusion the foaming gases out of the cells of the solidifying polymer foam. The sealing effect can involve coating one side of the extruded foam (AB foam) or both sides (ABA form). The skins can be solid or foamed. Alternatively, a cylinder is formed from an annular die and, preferably, a cylindrical cooling mandrel. By extruding and drawing the cylinder of foam onto a cooled cylindrical mandrel, which expands the diameter of the cylinder, the optimum physical properties of the structure can be achieved. This is because the foam structure is stretched in longitudinal and lateral directions. Preferable, the foaming polymer has “inherent melt strength” and “strain hardening” so that the foam cells are more consistent in size and shape. The preferred polymers are polypropylene or polystyrene.
Owner:ARMACELL ENTERPRISE GMBH & CO KG
Copper technology for ULSI metallization
InactiveUS6919266B2Reduce diffuseFew process stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTungsten nitrideElectroless deposition
A copper damascene structure formed by direct patterning of a low-dielectric constant material is disclosed. The copper damascene structure includes a tungsten nitride barrier layer formed by atomic layer deposition using sequential deposition reactions. Copper is selectively deposited by a CVD process and / or by an electroless deposition technique.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Heat-treating methods and systems
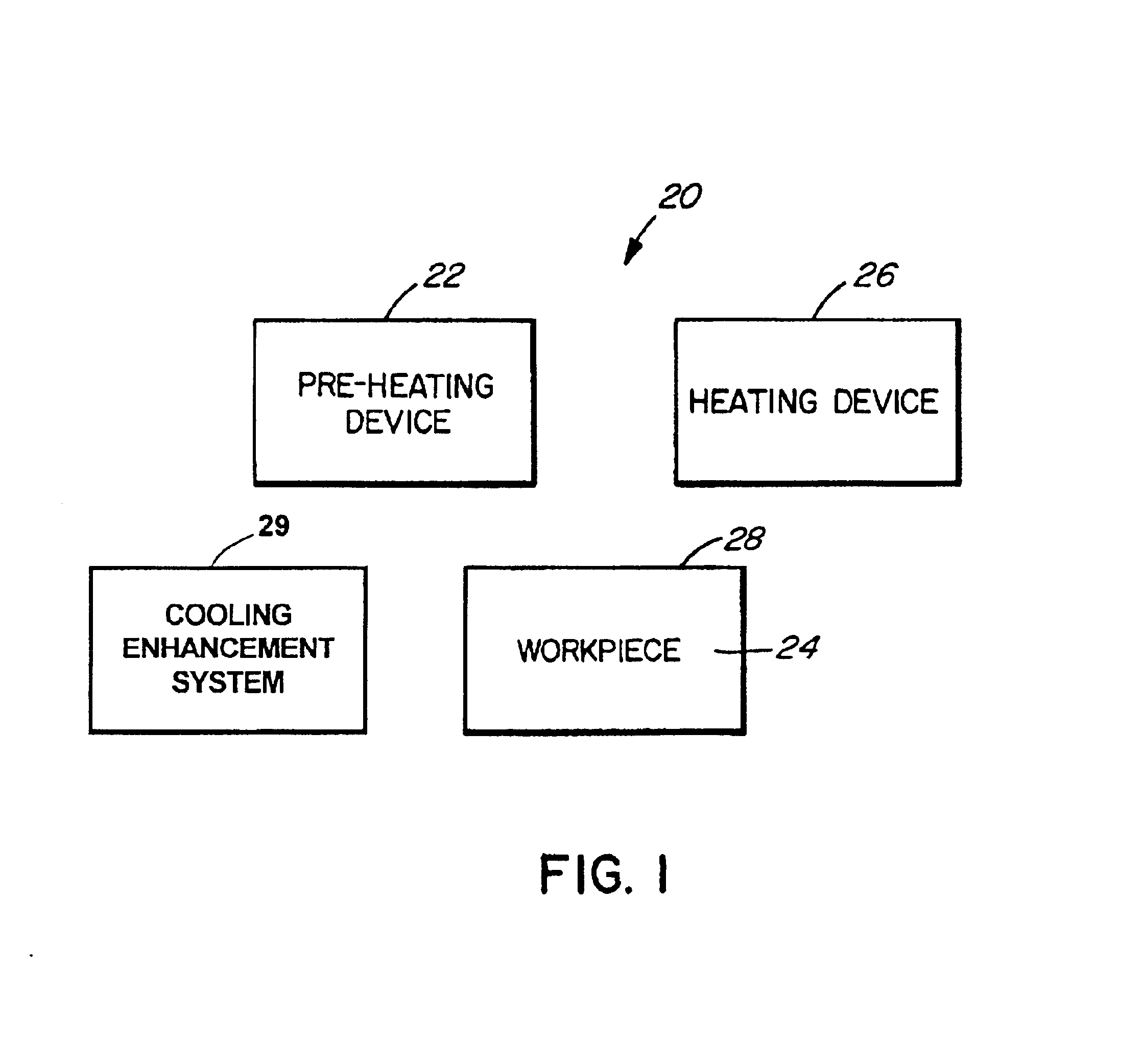
InactiveUS6941063B2Improve cooling effectWeakening rangeMechanical apparatusDrying solid materials with heatThermal radiationSemiconductor
A method involves pre-heating a workpiece to an intermediate temperature, heating a surface of the workpiece to a desired temperature greater than the intermediate temperature, and enhancing cooling of the workpiece. Enhancing cooling may involve absorbing radiation thermally emitted by the workpiece. An apparatus includes a first heating source for heating a first surface of a semiconductor wafer, a second heating source for heating a second surface of the semiconductor wafer, and a first cooled window disposed between the first heating source and the semiconductor wafer.
Owner:MATTSON TECHNOLOGY +1
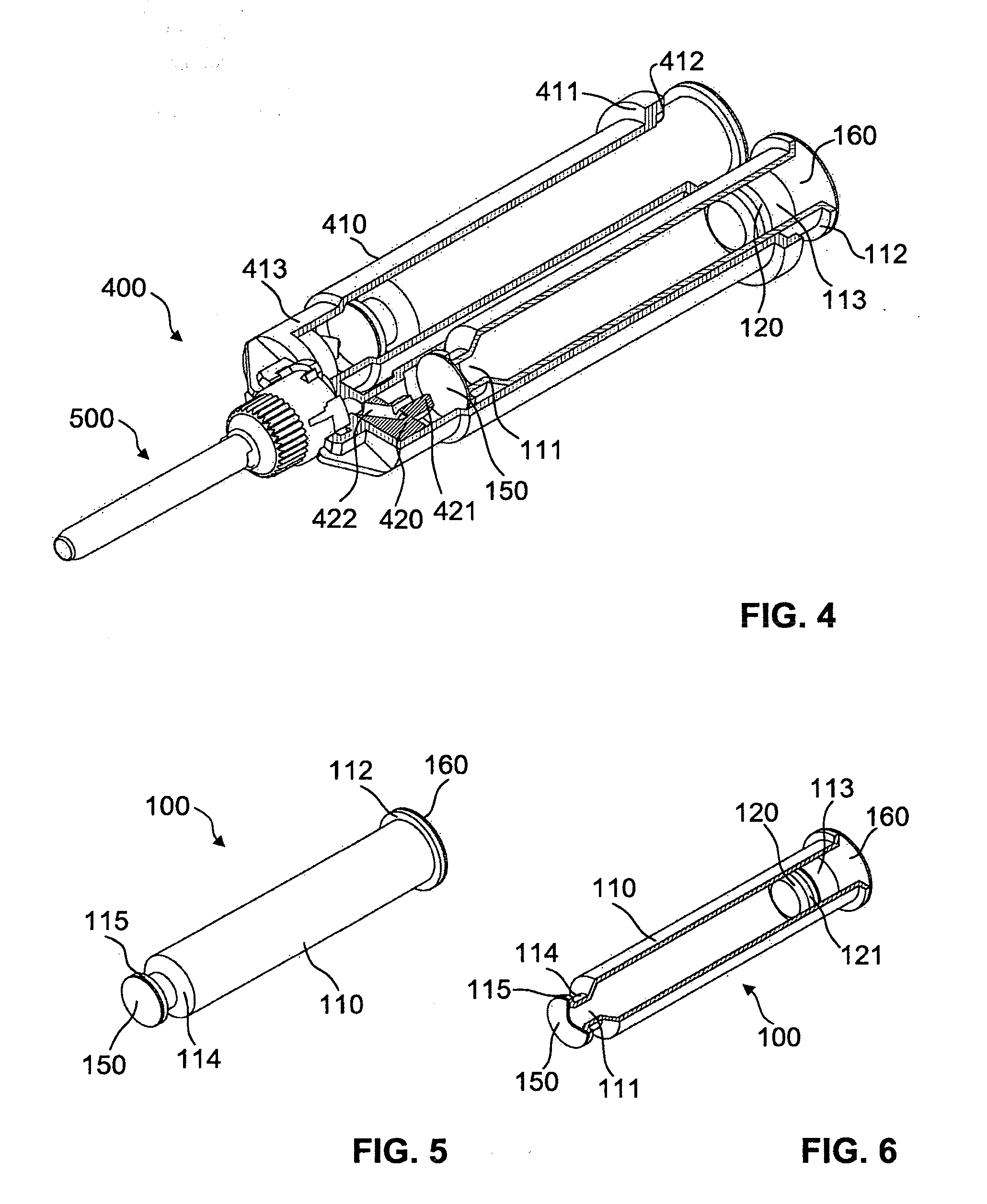
Sealed container comprising a displaceable piston
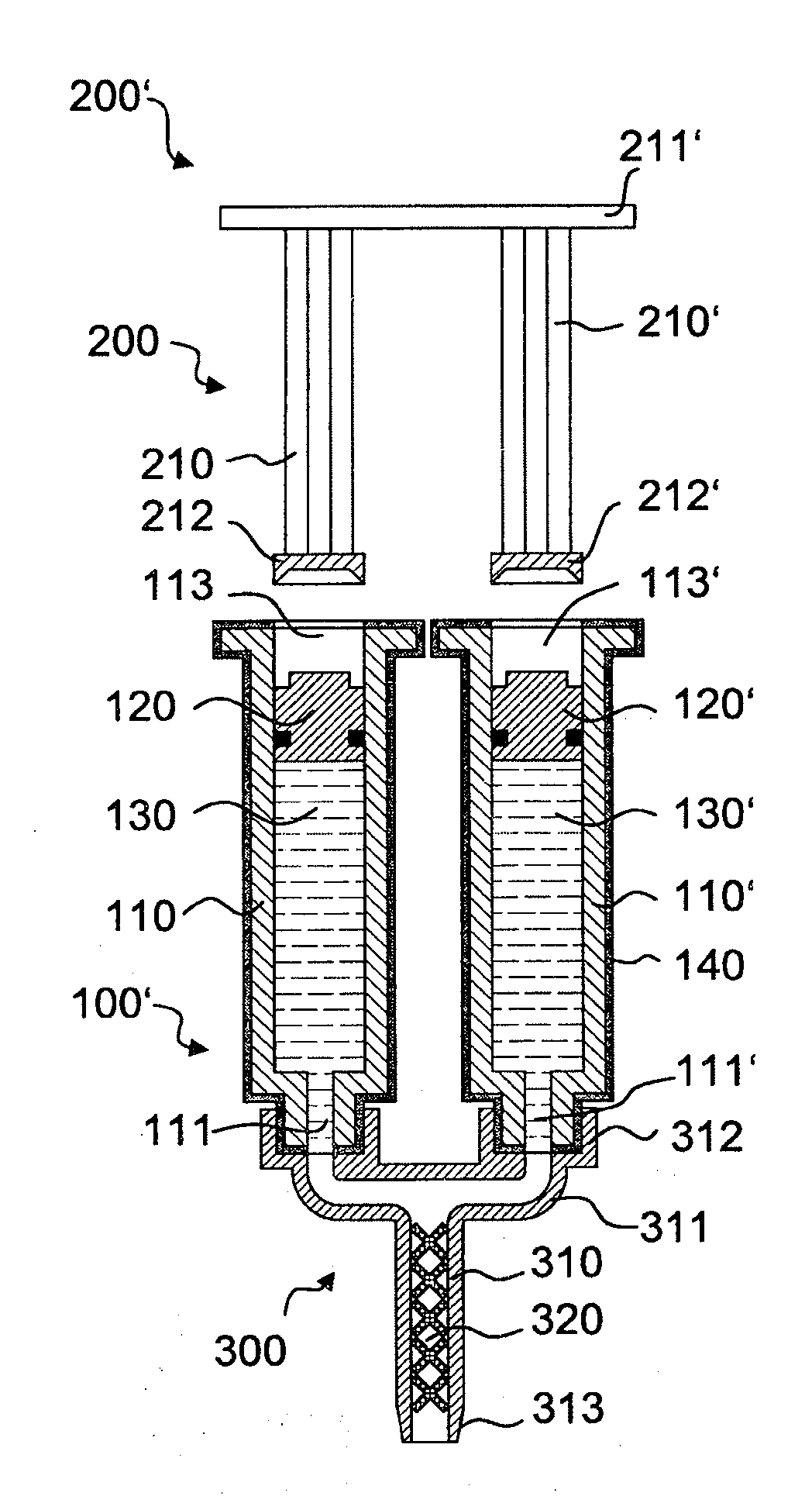
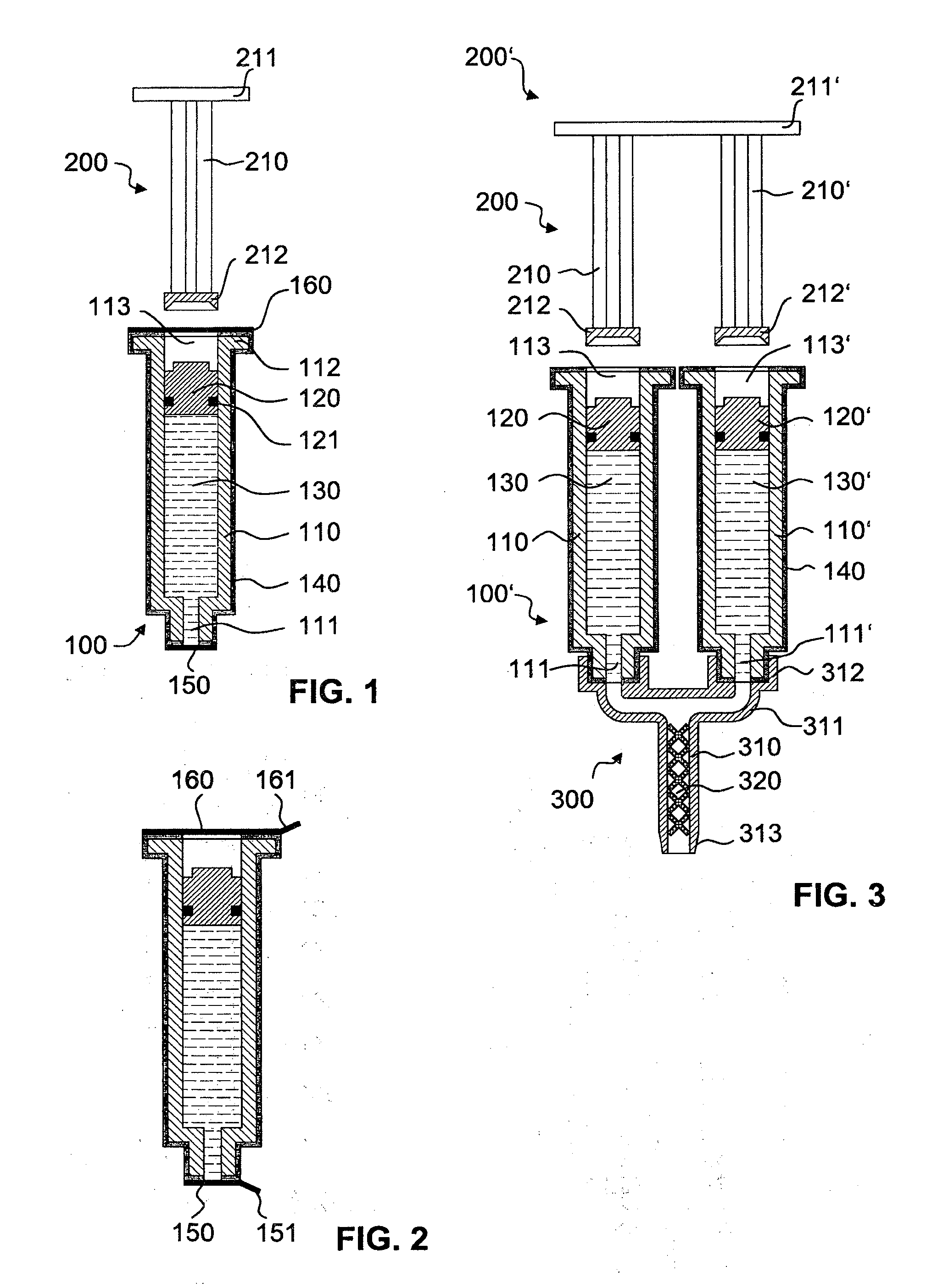
InactiveUS20120175384A1Reduce penetrationImprove tightnessInfusion syringesClosure using stoppersEngineeringPiston
A syringe-type container comprising a hollow main body with a distal outlet opening and a proximal actuation opening for inserting an actuation element. A piston is displaceably arranged inside the main body for discharging a flowable product from the container. To reduce the permeability of the container, the main body has a diffusion-reducing layer. The outlet opening is closed with a first removable or severable seal, and the actuation opening is closed with a second seal.
Owner:MEDMIX SYST
Methods for controlling dopant concentration and activation in semiconductor structures
InactiveUS20060024928A1Easy to integrateLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention provides methods for fabricating semiconductor structures and devices, particularly ultra-shallow doped semiconductor structures exhibiting low electrical resistance. Methods of the present invention use modification of the composition of semiconductor surfaces to allow fabrication of a doped semiconductor structure having a selected dopant concentration depth profile, which provides useful junctions and other device components in microelectronic and nanoelectronic devices, such as transistors in high density integrated circuits. Surface modification in the present invention also allows for control of the concentration and depth profile of defects, such as interstitials and vacancies, in undersaturated semiconductor materials.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Organic Light Emitting Display Device
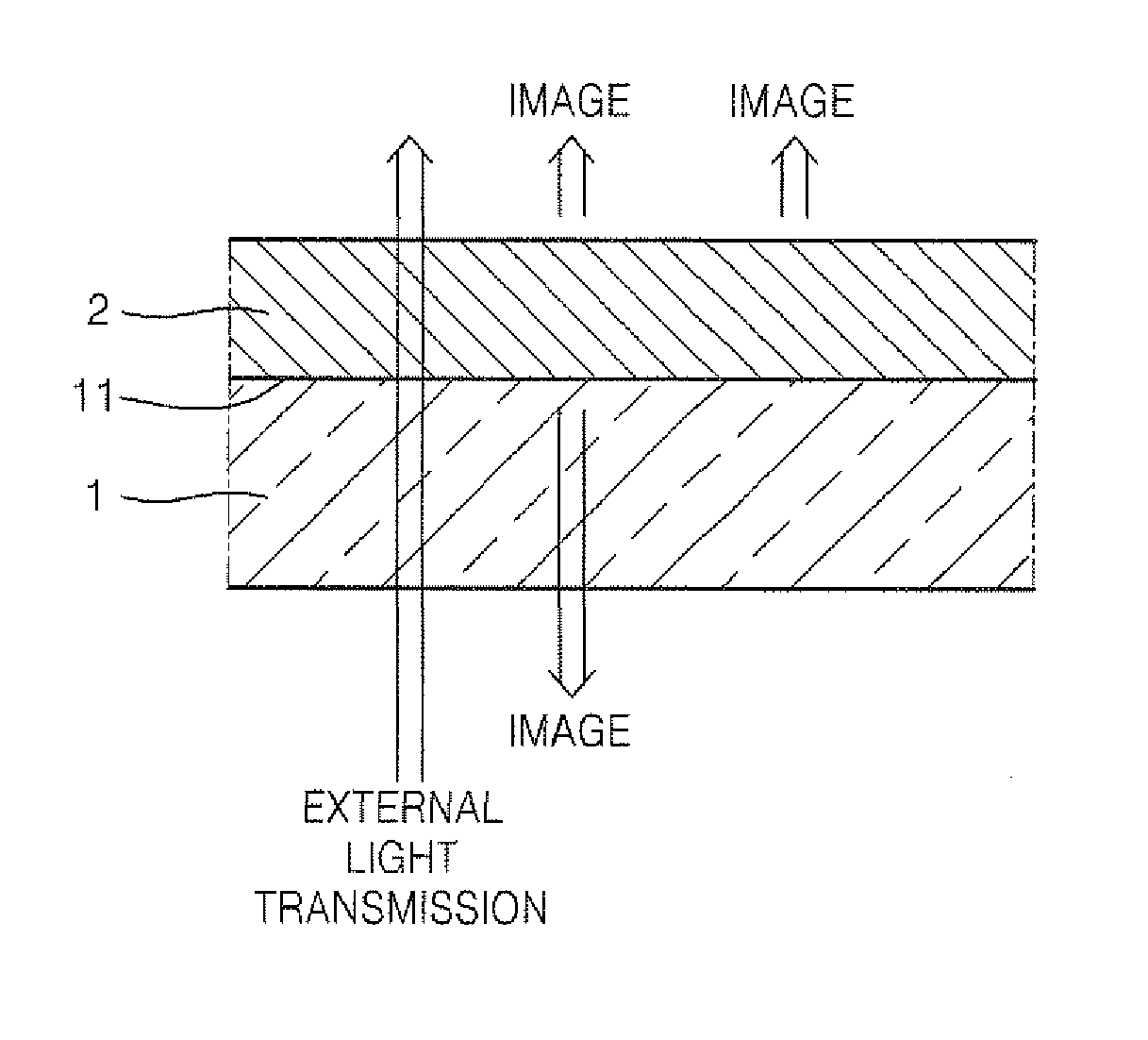
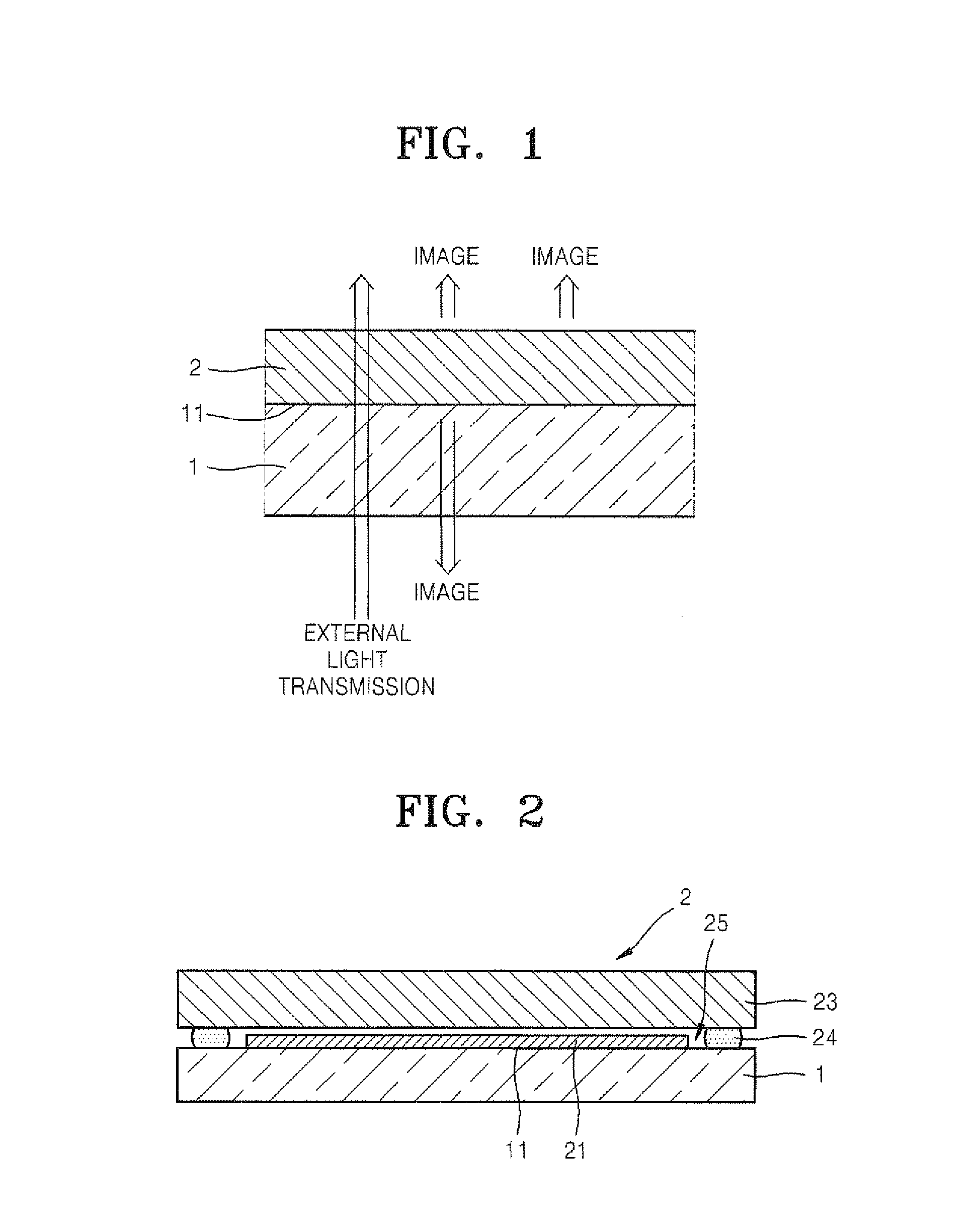
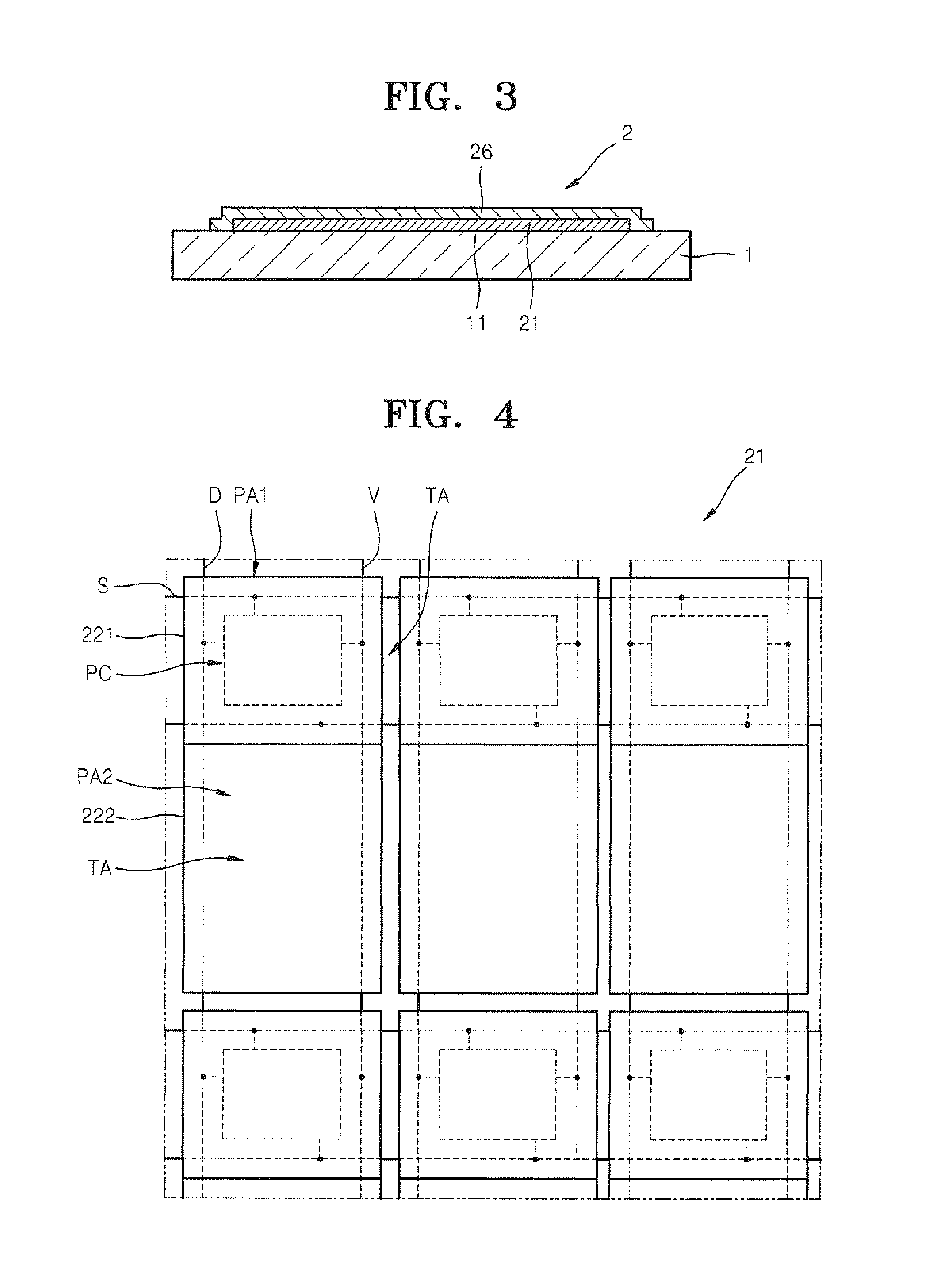
ActiveUS20110205198A1Improve transmittanceImprove Outcoupling EfficiencyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesTransmittanceOrganic layer
An organic light emitting display device comprises: a substrate; a plurality of thin film transistors (TFTs) formed on a first surface of the substrate; a passivation layer covering the plurality of TFTs; a plurality of first pixel electrodes formed on the passivation layer and respectively electrically connected to the plurality of TFTs, and overlapping with the plurality of TFTs so as to cover the plurality of TFTs, and including a reflection layer formed of a light-reflecting conductive material; a second pixel electrode formed of a light-transmitting conductive material and disposed on the passivation layer so as to be electrically connected to the plurality of first pixel electrodes; an opposite electrode formed such that light is transmitted or reflected therethrough, and disposed opposite the plurality of first pixel electrodes and the second pixel electrode; and an organic layer interposed between the plurality of first pixel electrodes and the second pixel electrode, and including an emission layer. Accordingly, transmittivity of the organic light emitting display device is increased, and optical outcoupling efficiency of the organic light emitting display device is also increased during double-sided emission.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Lithium-sulfur battery and cathode therefore
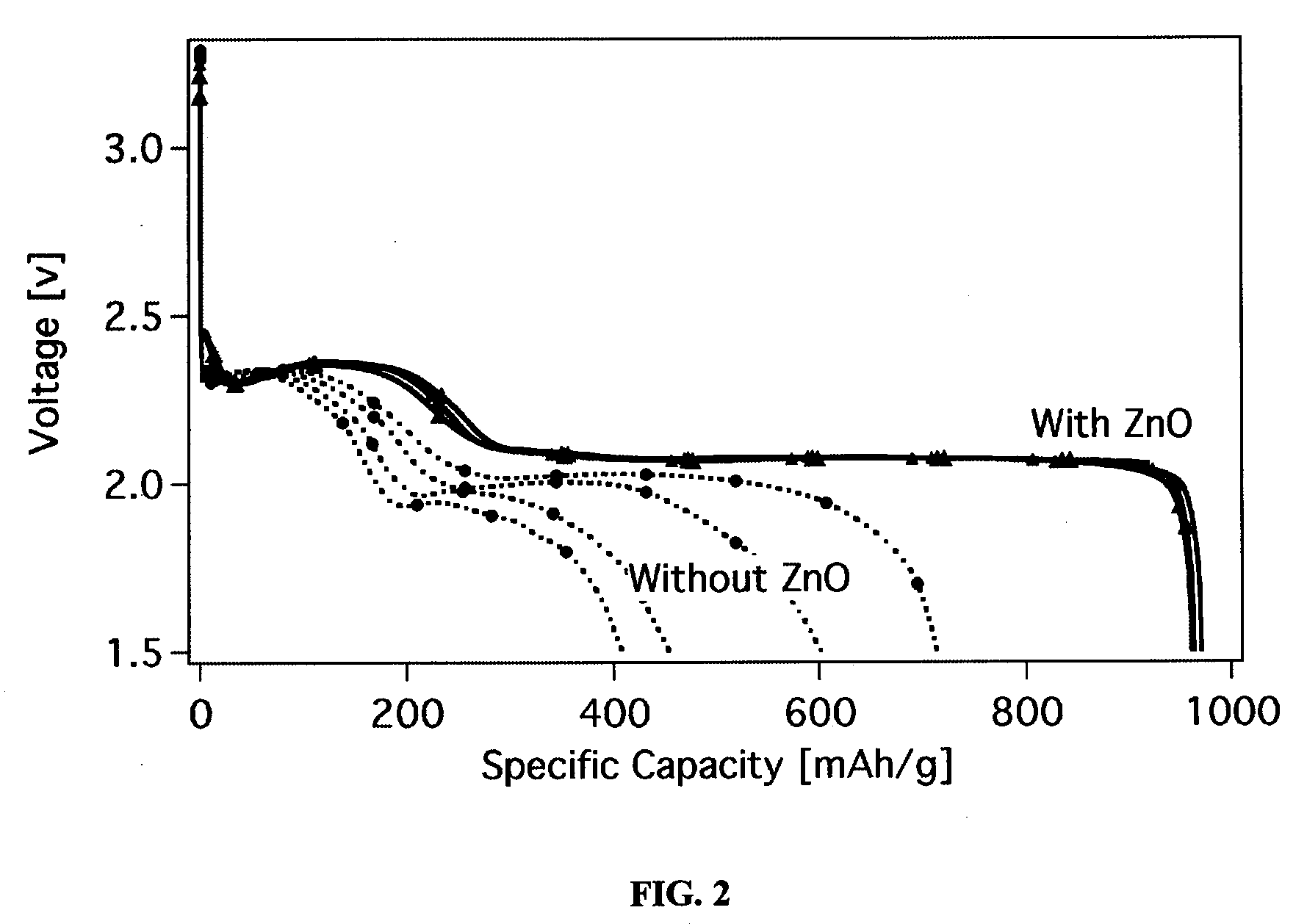
ActiveUS20090226809A1Increase energy densityIncrease specific energyDeferred-action cellsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersHigh energyLithium sulfur
An improved cathode suitable for lithium-sulfur batteries, a battery including the cathode, and a battery including a separator containing inorganic fillers are disclosed. The cathode includes sulfur and a metal oxide and optionally includes an additional polymeric material. The metal oxide reduces dissolution of sulfur at the cathode and reduces sulfur-containing deposits on the battery anode, thereby providing a battery with relatively high energy density and good partial discharge performance. The separator also reduces unwanted diffusion of sulfur species.
Owner:EAGLE PICHER TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com