Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Reaction become bad" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
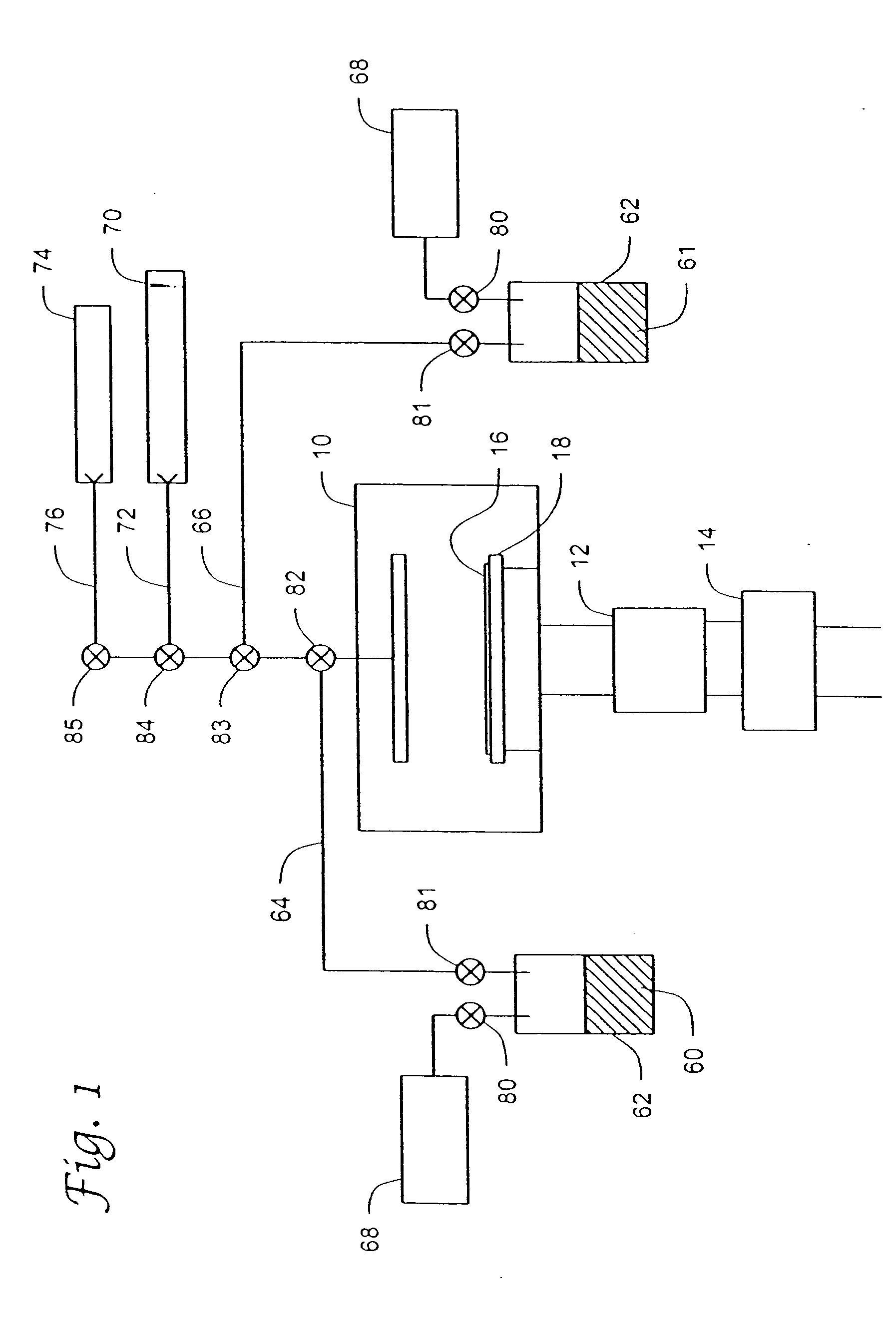
Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using alcohols
InactiveUS7041609B2Reduce decreaseAvoid problemsTransistorSolid-state devicesAlcoholDeposition process
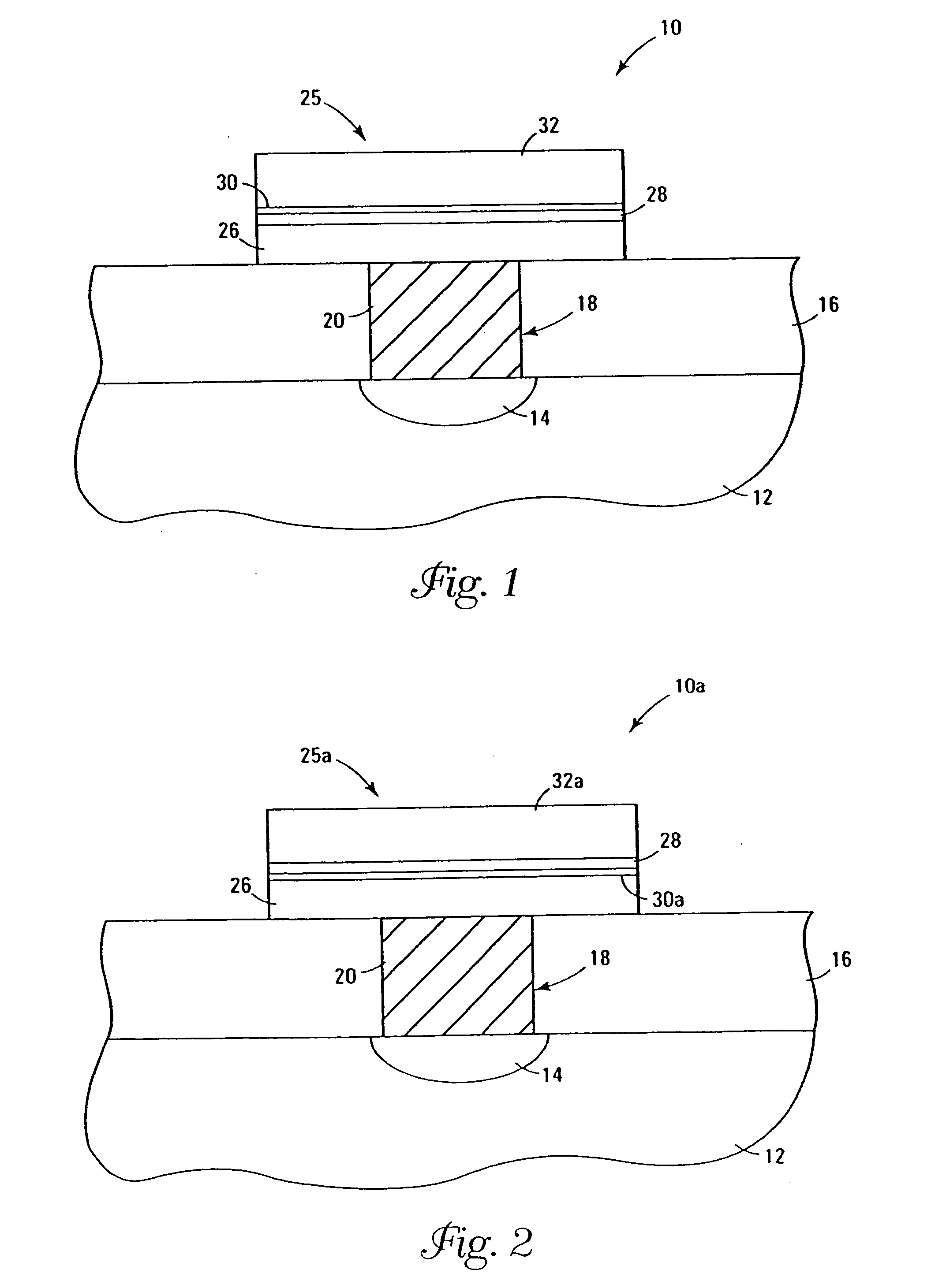
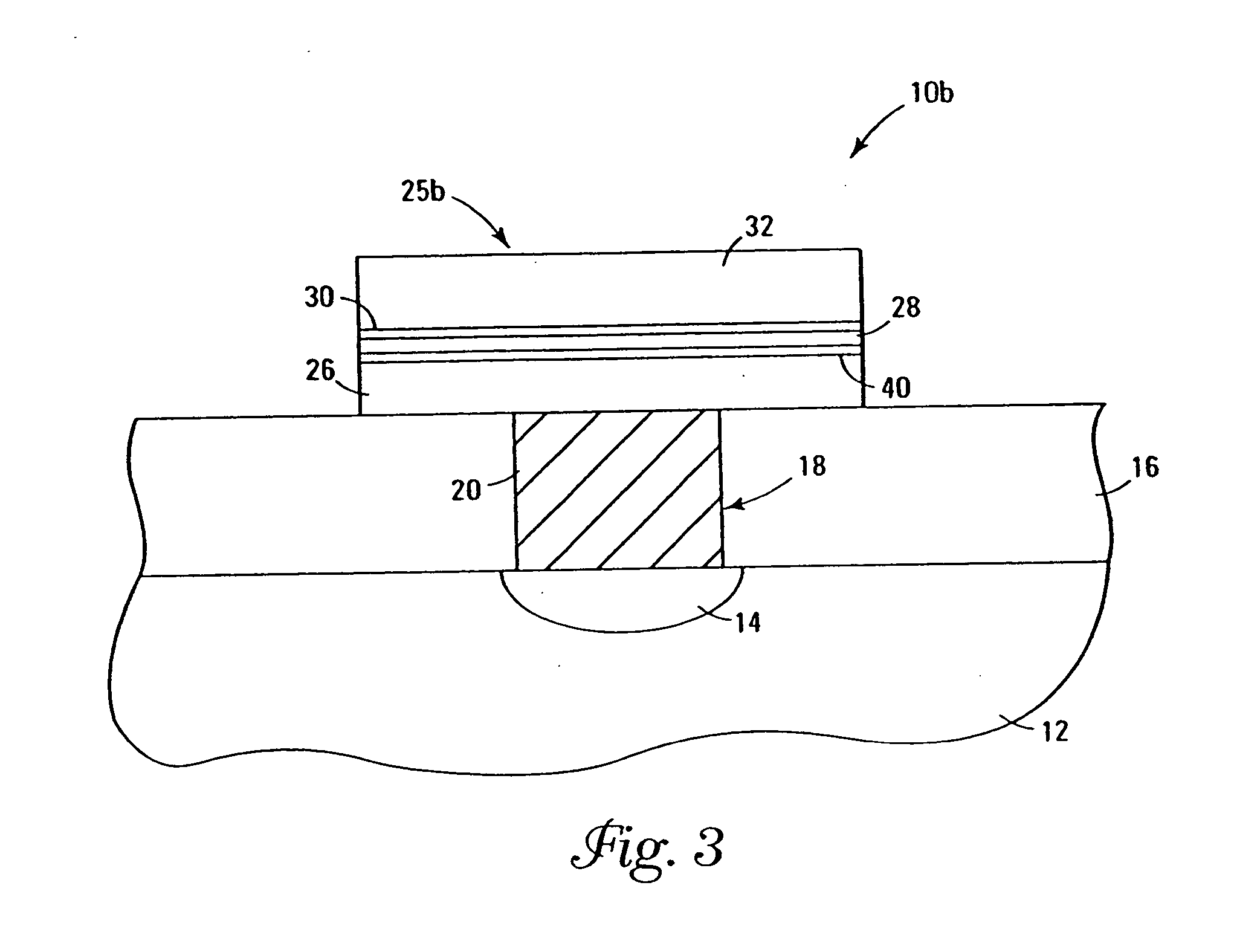
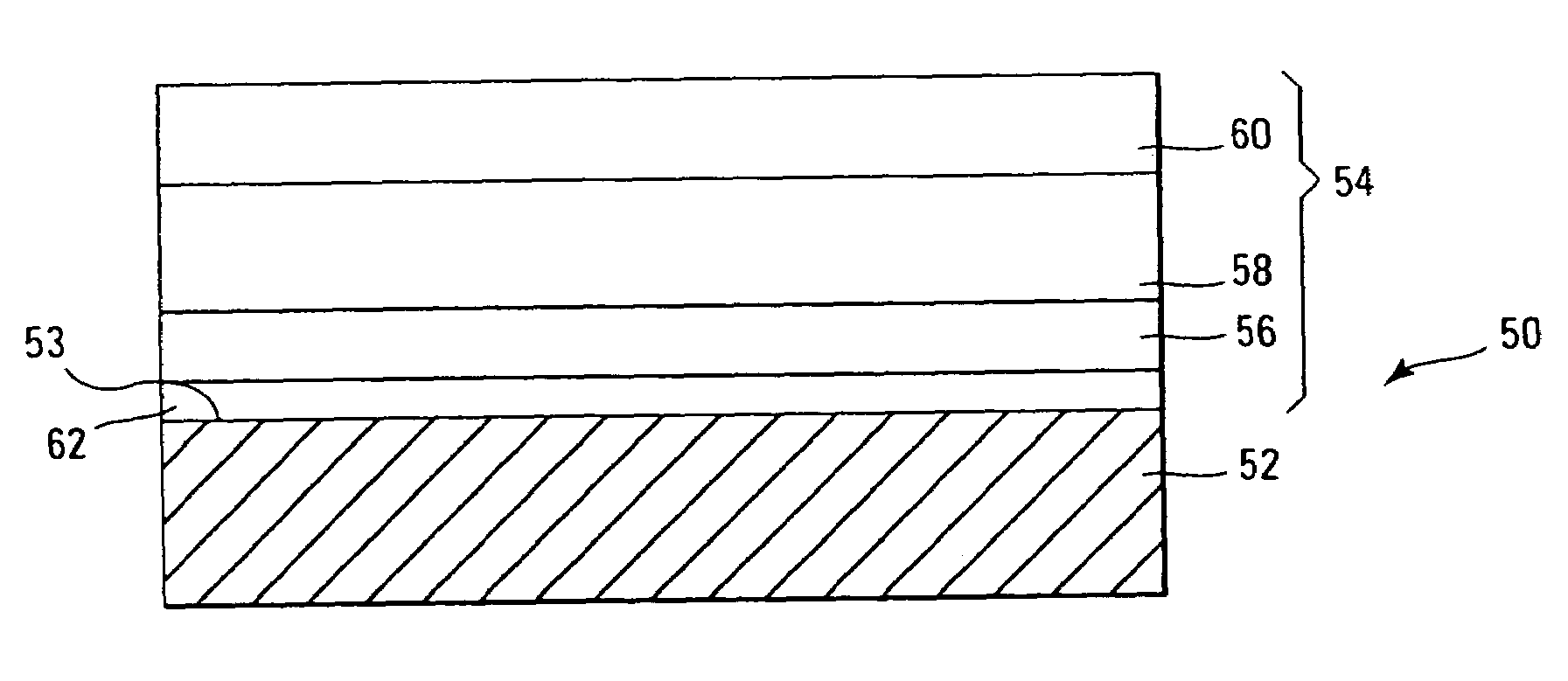
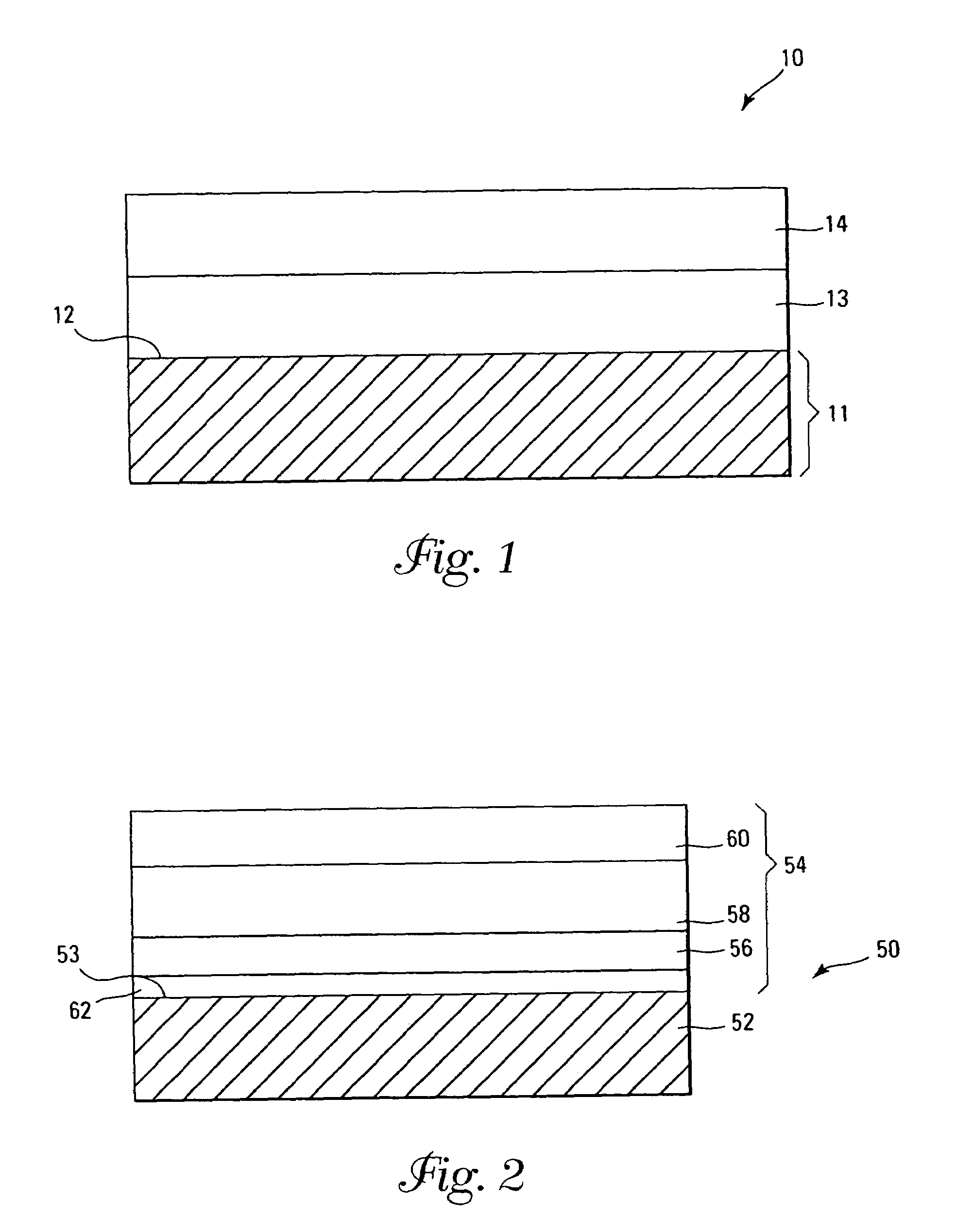
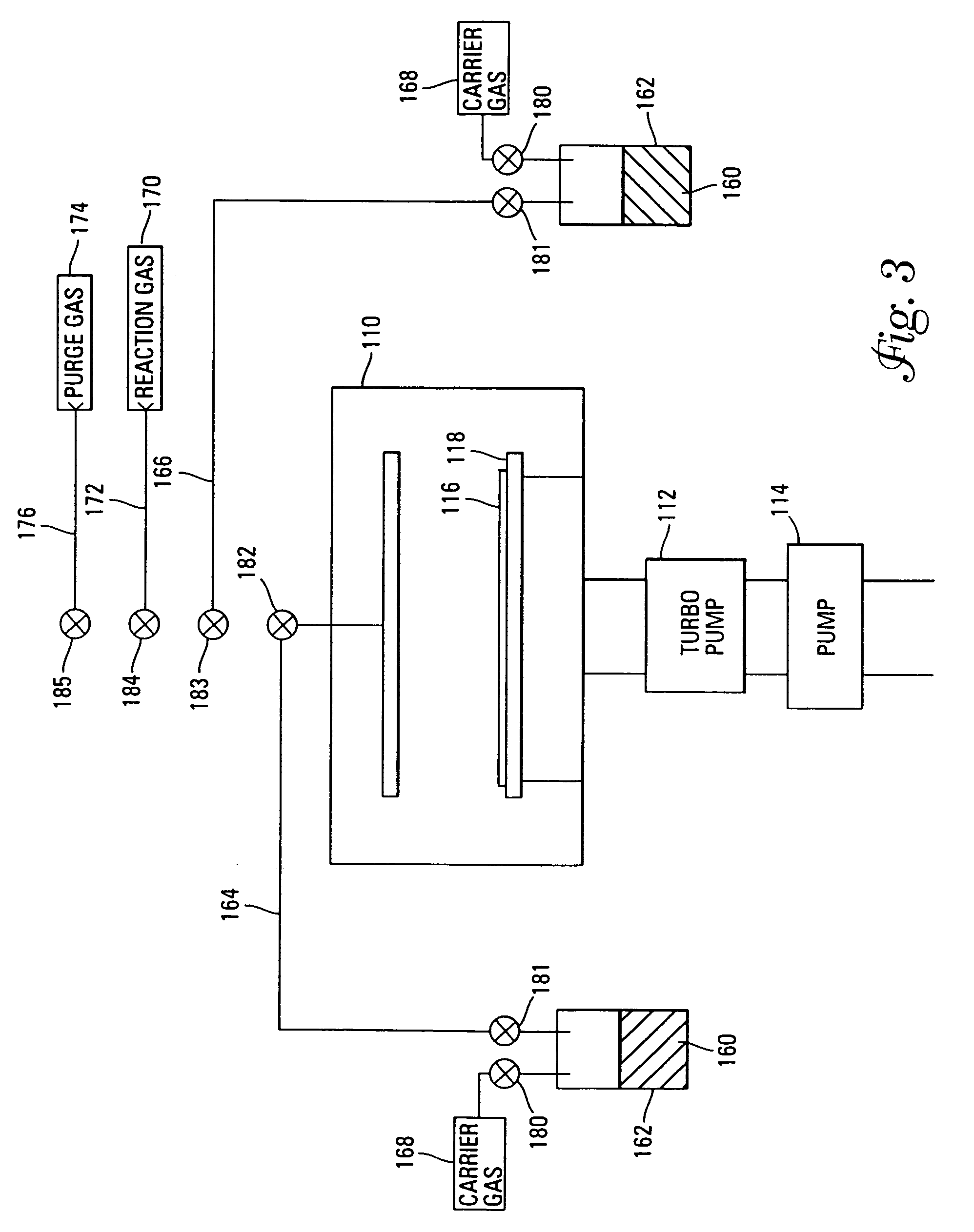
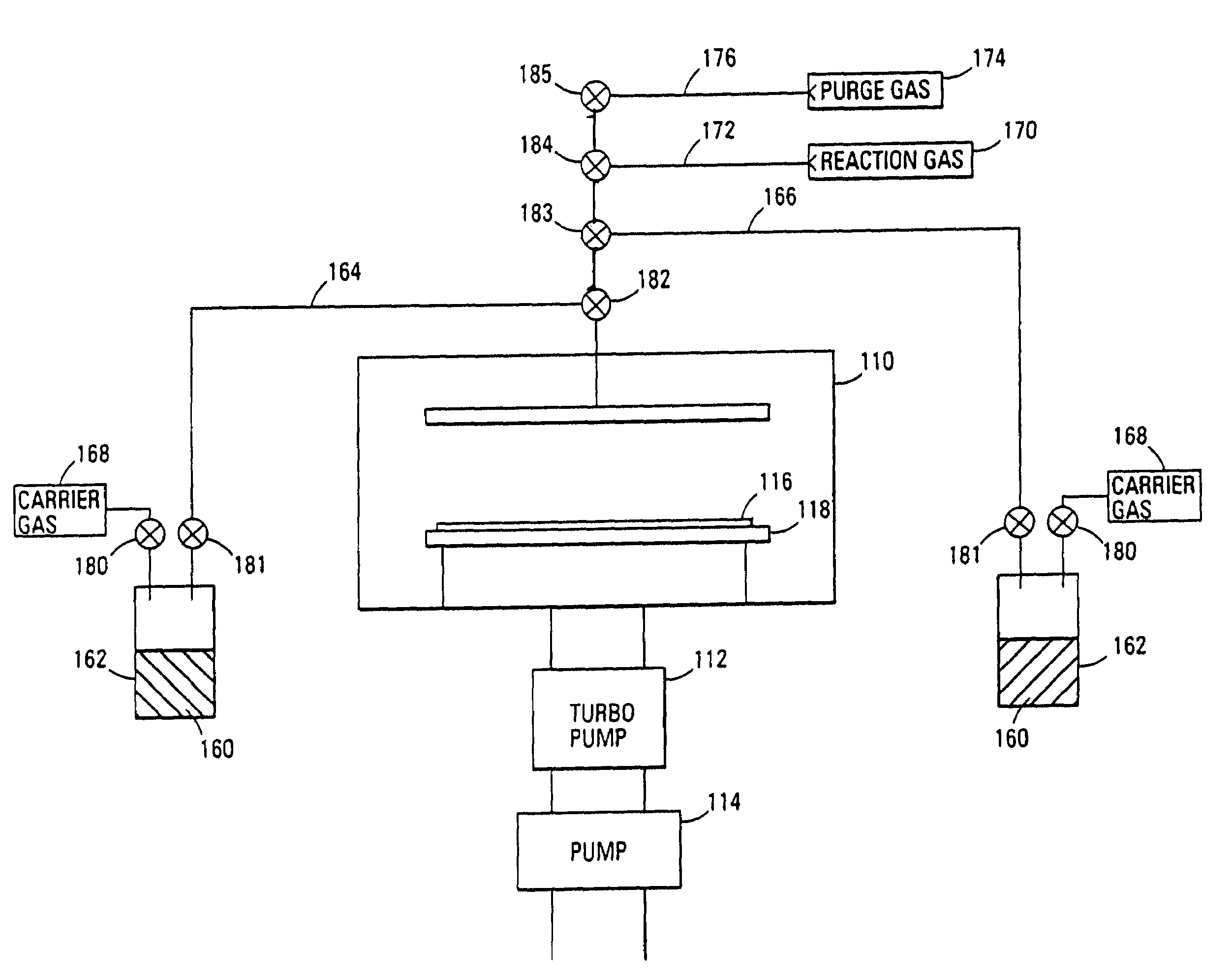
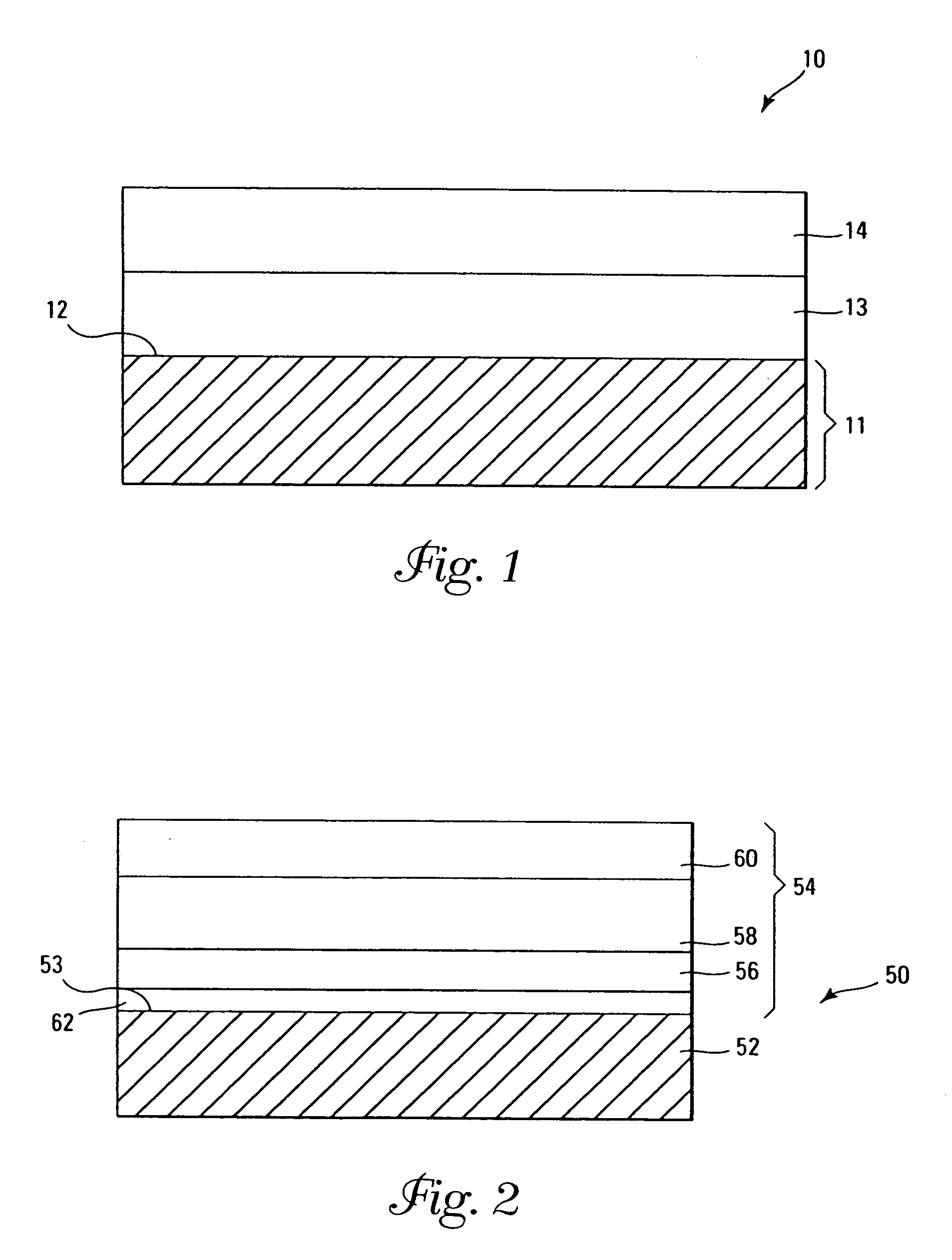
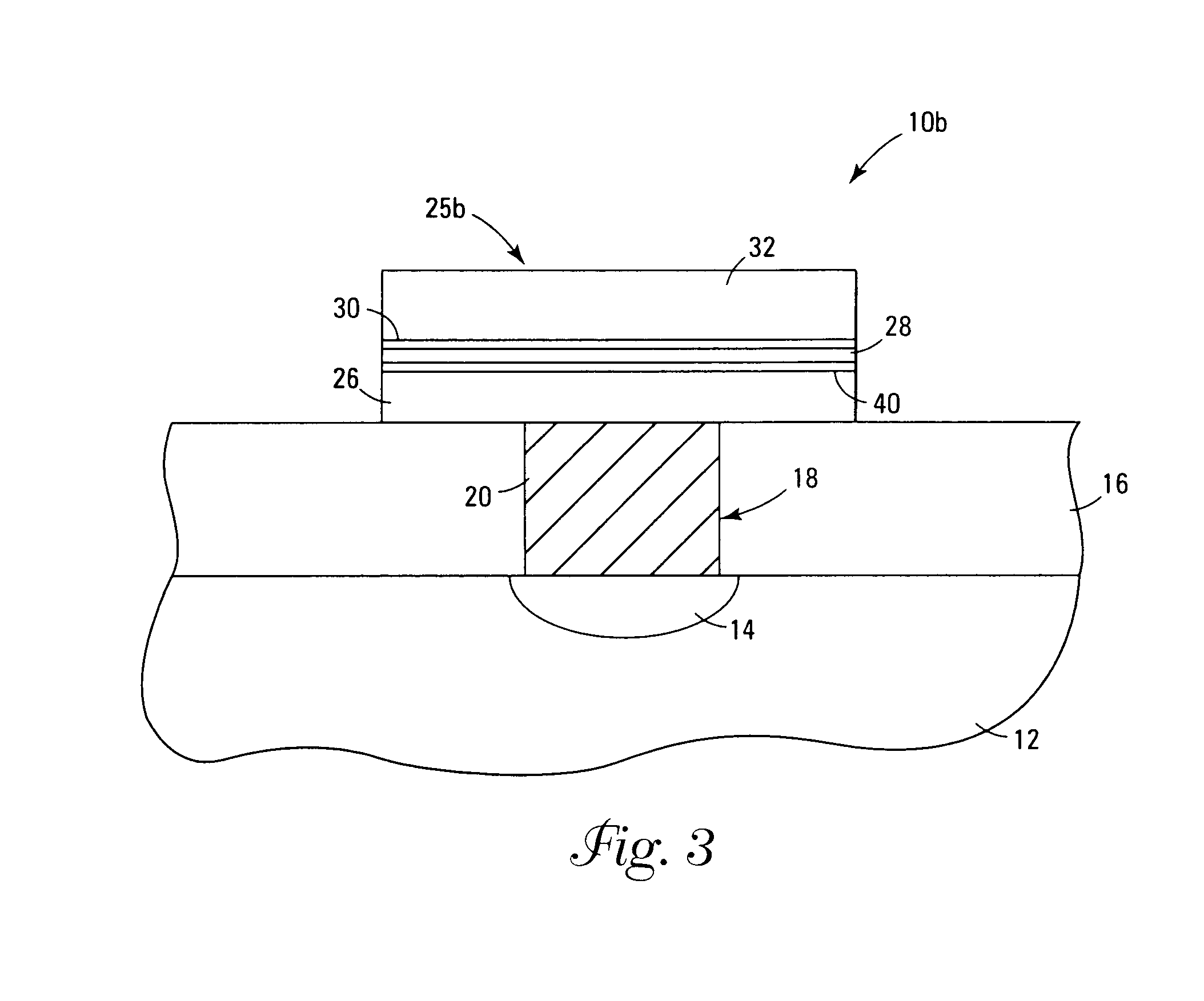
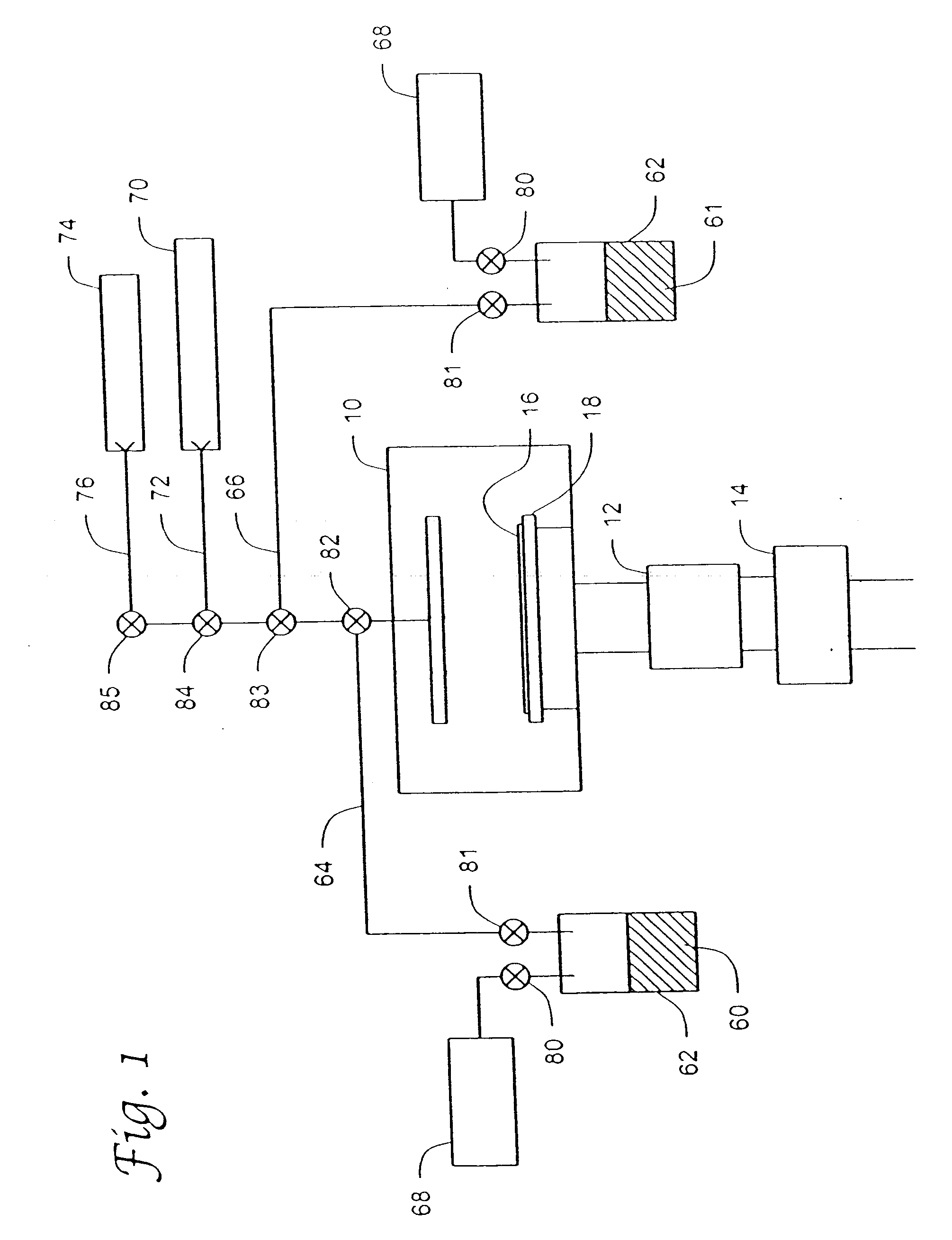
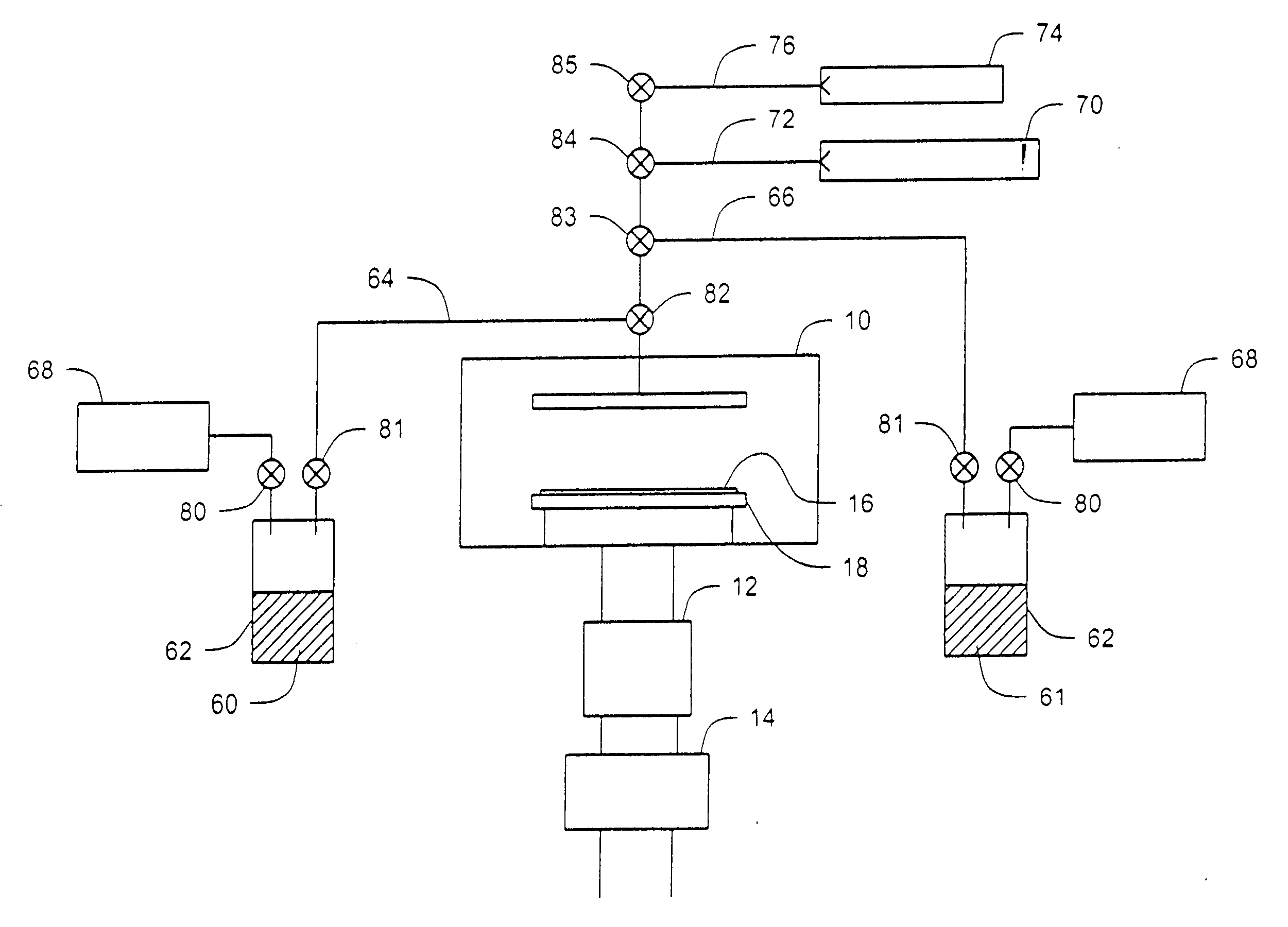
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process, one or more alcohols, and one or more metal-containing precursor compounds.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming metal oxide layers
InactiveUS20060252244A1Reducing (Easy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseDeposition process
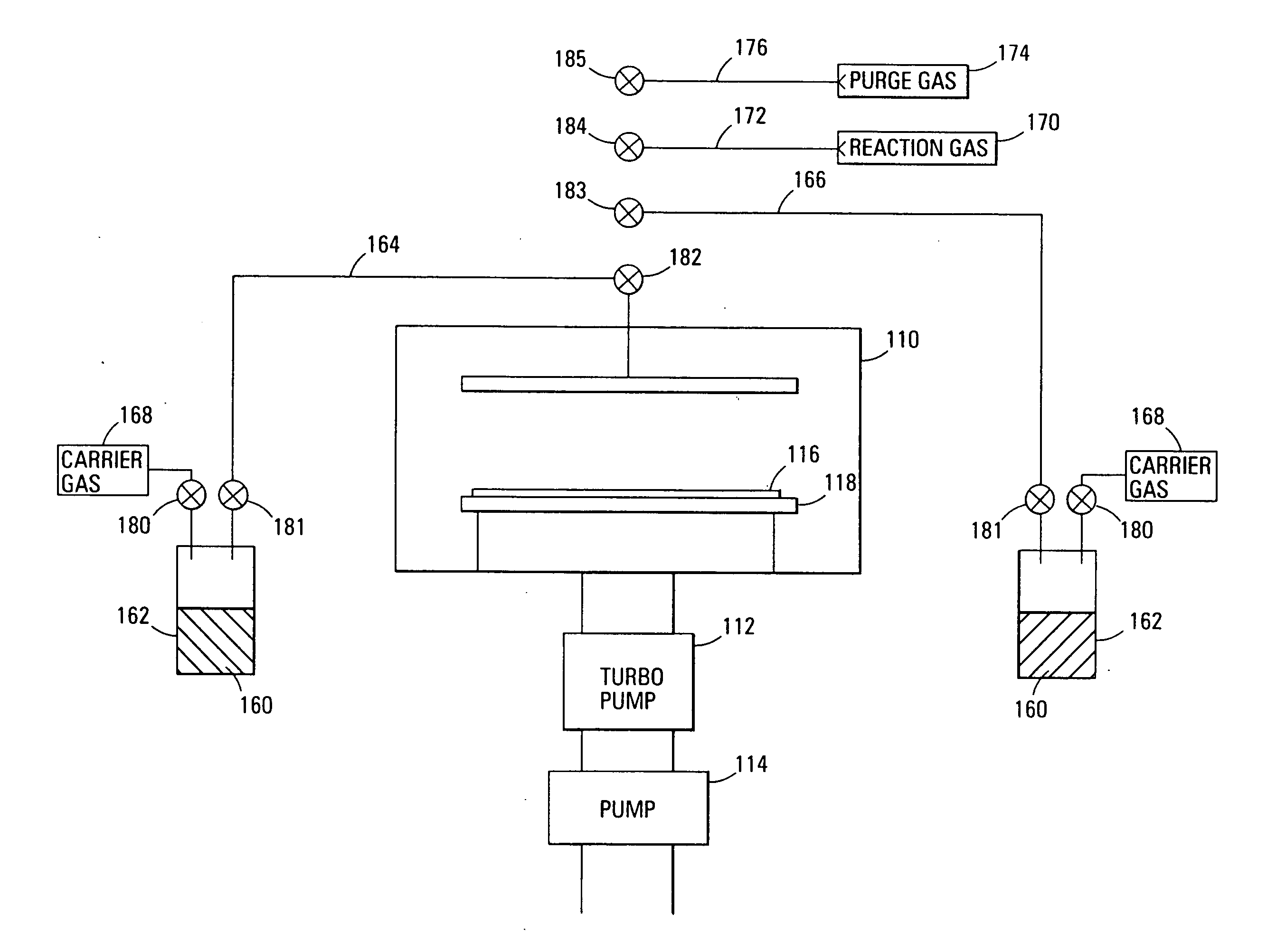
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer, preferably a dielectric layer, on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and ozone with one or more metal organo-amine precursor compounds.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods of forming refractory metal nitride layers using disilazanes
InactiveUS7122464B2Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseDeposition process
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum (silicon) nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a refractory metal precursor compound, a disilazane, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and method for forming silicon oxide layers
InactiveUS7115528B2Reduce decreaseEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseSilicon oxide
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer, preferably a dielectric layer, on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and ozone with one or more metal organo-amine precursor compounds.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming refractory metal nitride layers using organic amines
InactiveUS6967159B2Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsTantalum nitrideDeposition process
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using an atomic layer deposition process (a vapor deposition process that includes a plurality of deposition cycles) with a refractory metal precursor compound, an organic amine, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming metal-doped alumina
InactiveUS6984592B2Reduce decreaseEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phaseOptoelectronics
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal-doped aluminum oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using metal organo-amines and metal organo-oxides
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and one or more precursor compounds that include organo-amine ligands and one or more precursor compounds that include organo-oxide ligands.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming refractory metal oxide layers
InactiveUS20050009266A1Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseEther
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal oxide layers, such as tantalum pentoxide layers, on substrates by using vapor deposition processes with refractory metal precursor compounds and ethers.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming tantalum silicide layers
InactiveUS6995081B2Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseNitrogen
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) tantalum suicide layers (including tantalum silicon nitride layers), which are typically useful as diffusion barrier layers, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a tantalum halide precursor compound, a silicon precursor compound, and an optional nitrogen precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming strontium- and/or barium-containing layers
InactiveUS7115166B2Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesStrontium titanateBarium strontium titanate
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
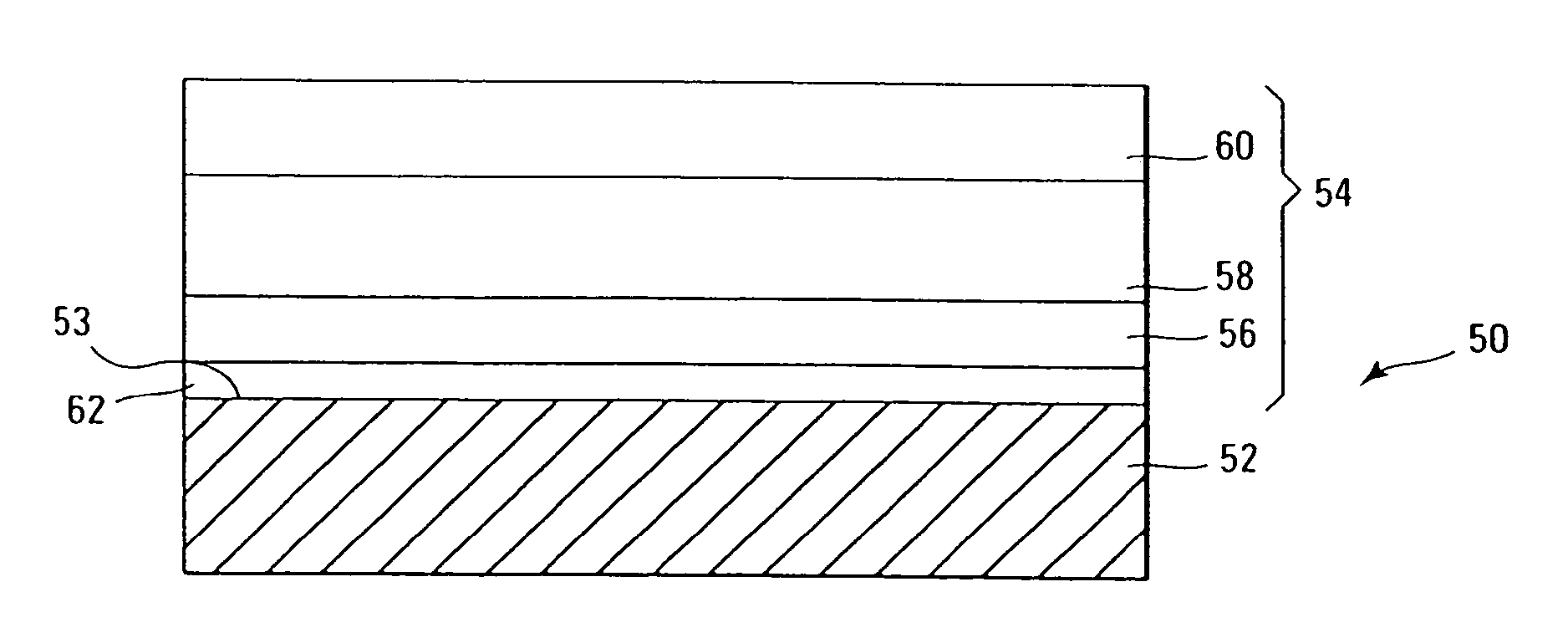
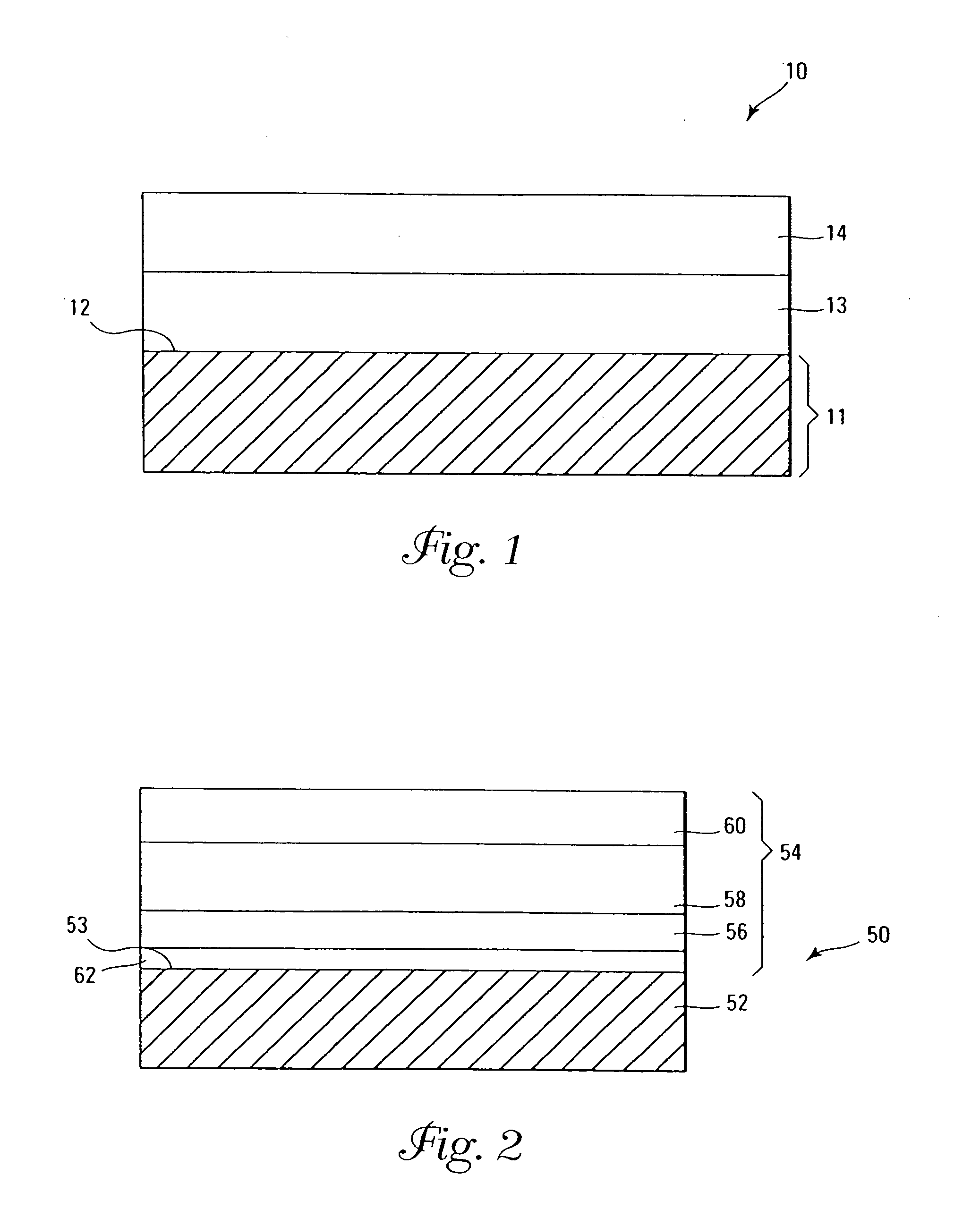
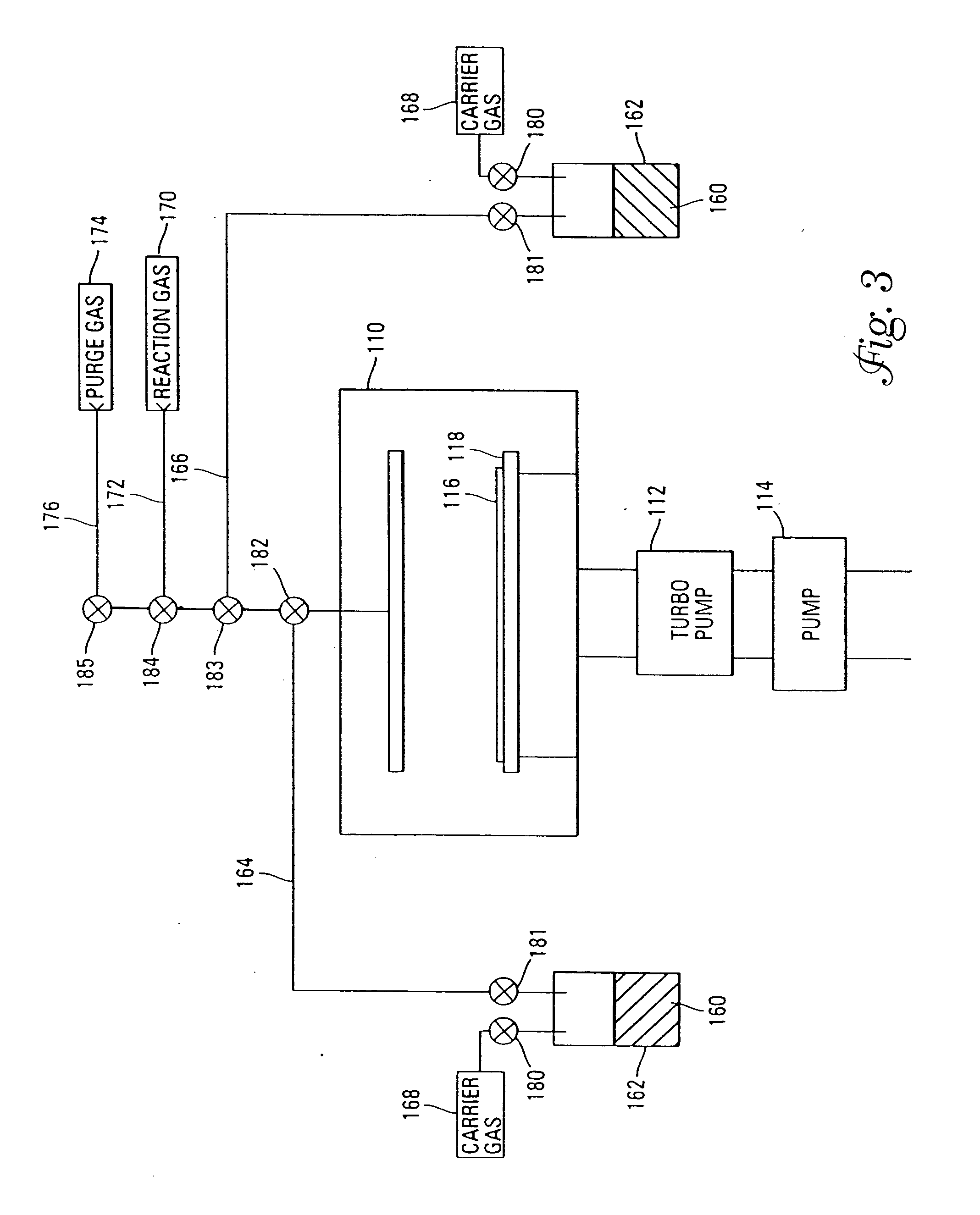
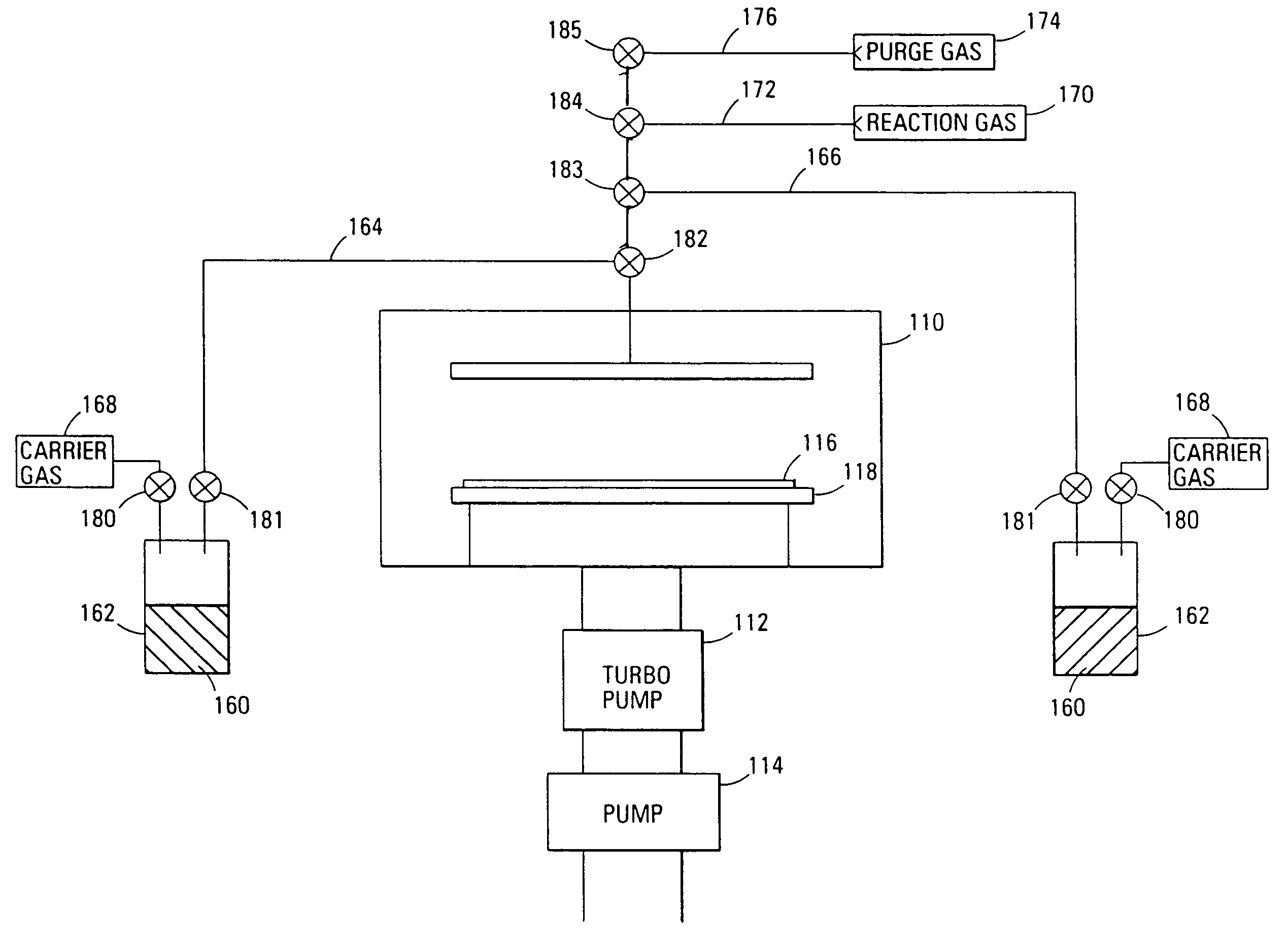
Systems and methods for forming tantalum oxide layers and tantalum precursor compounds
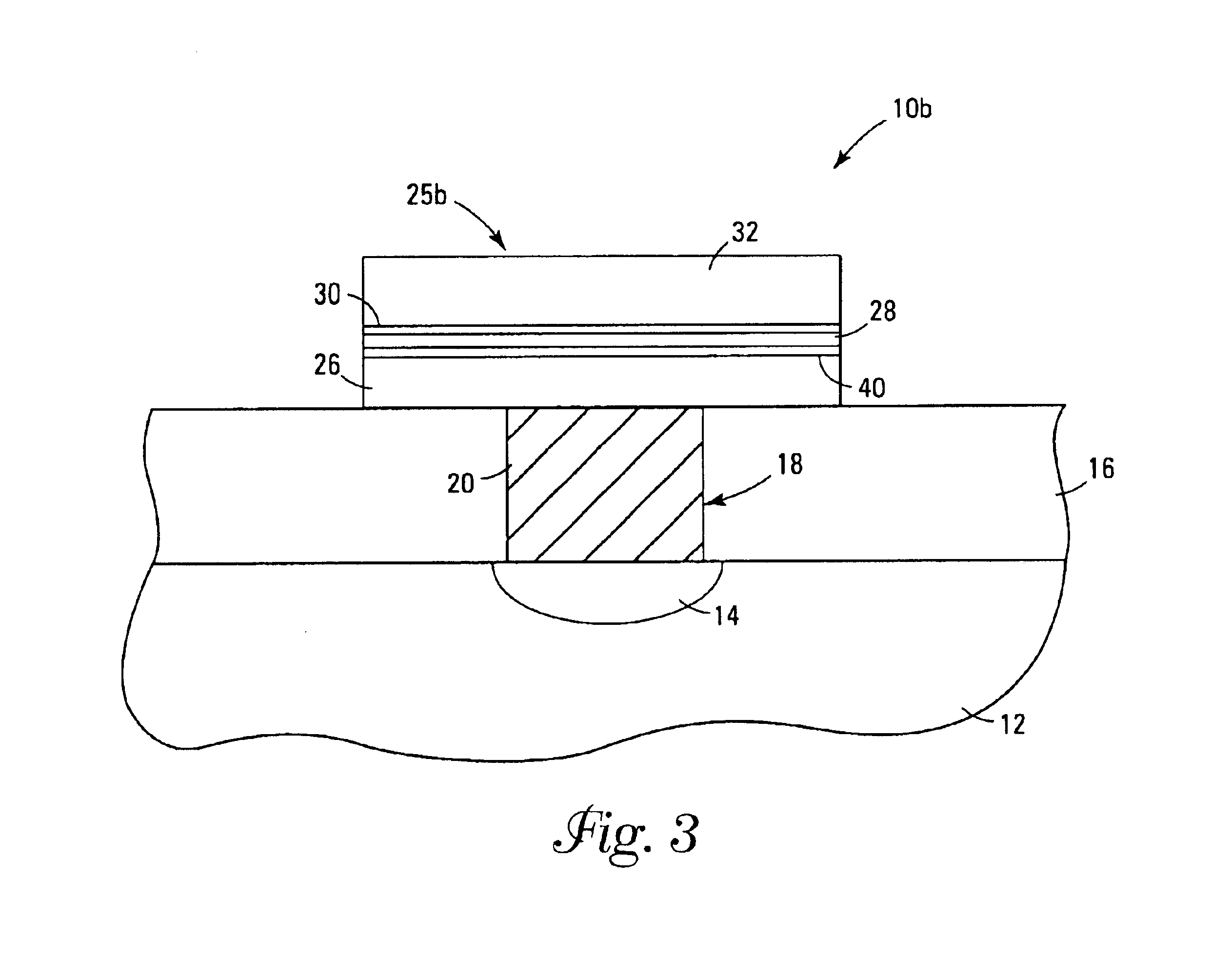
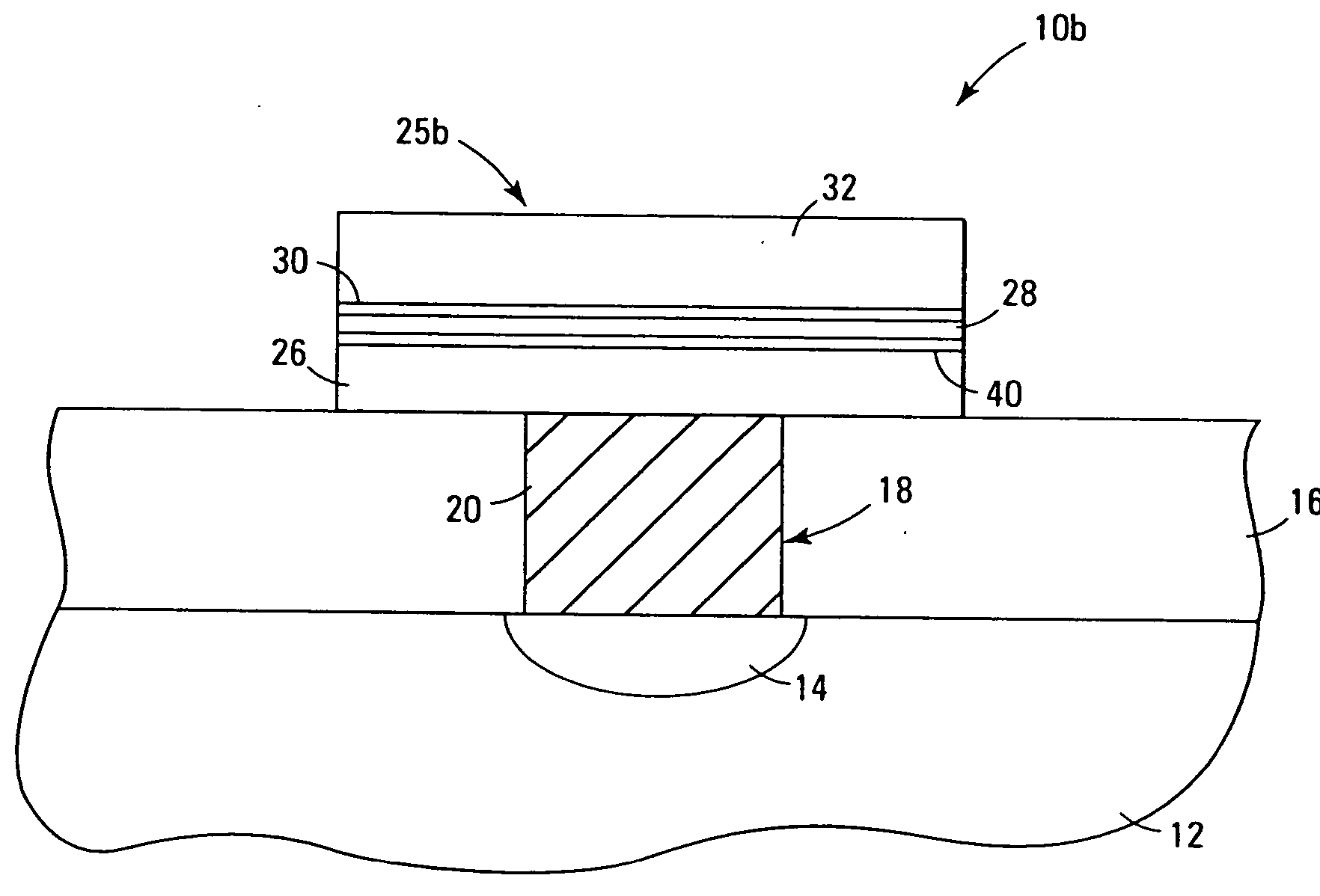
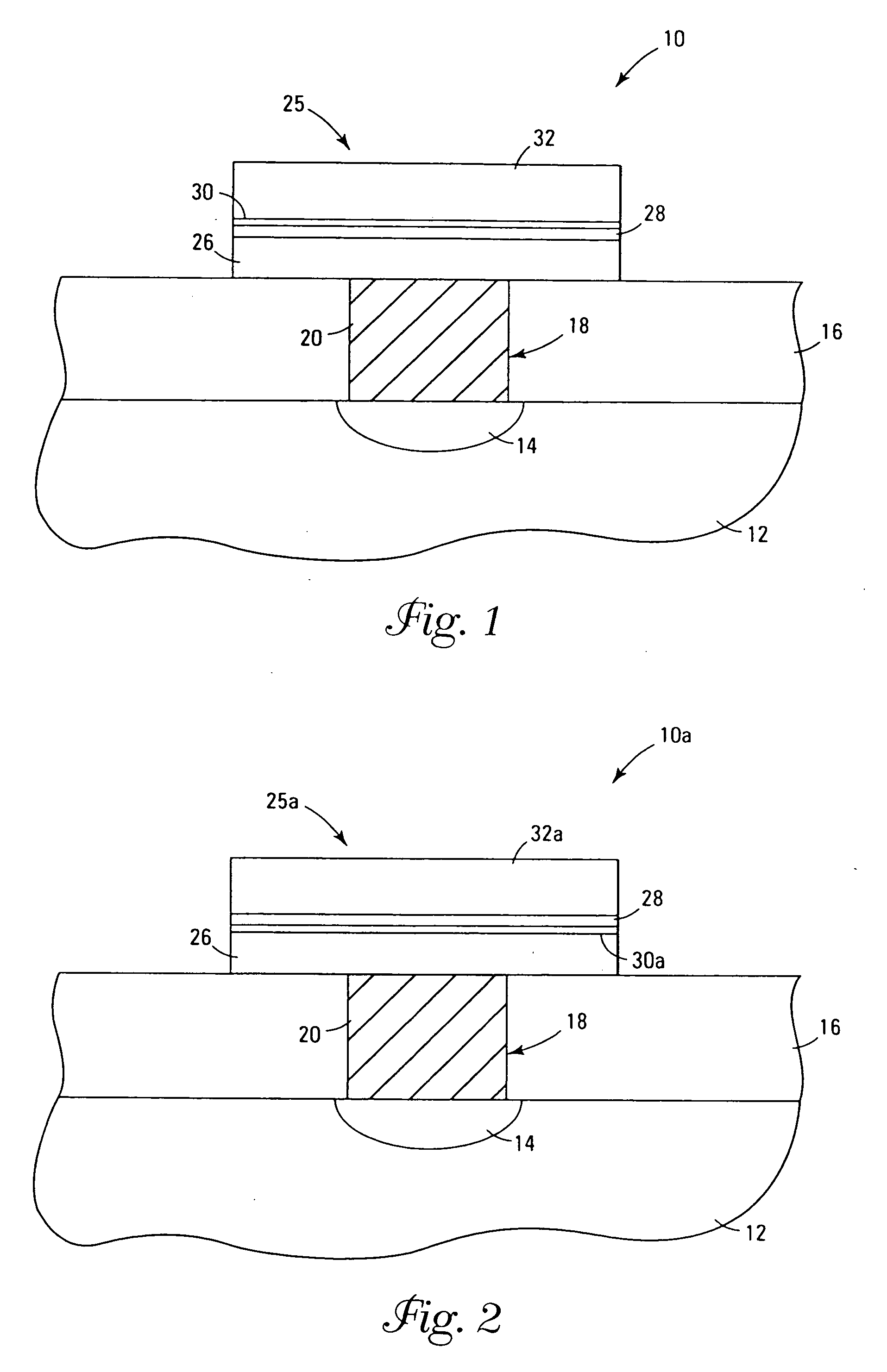
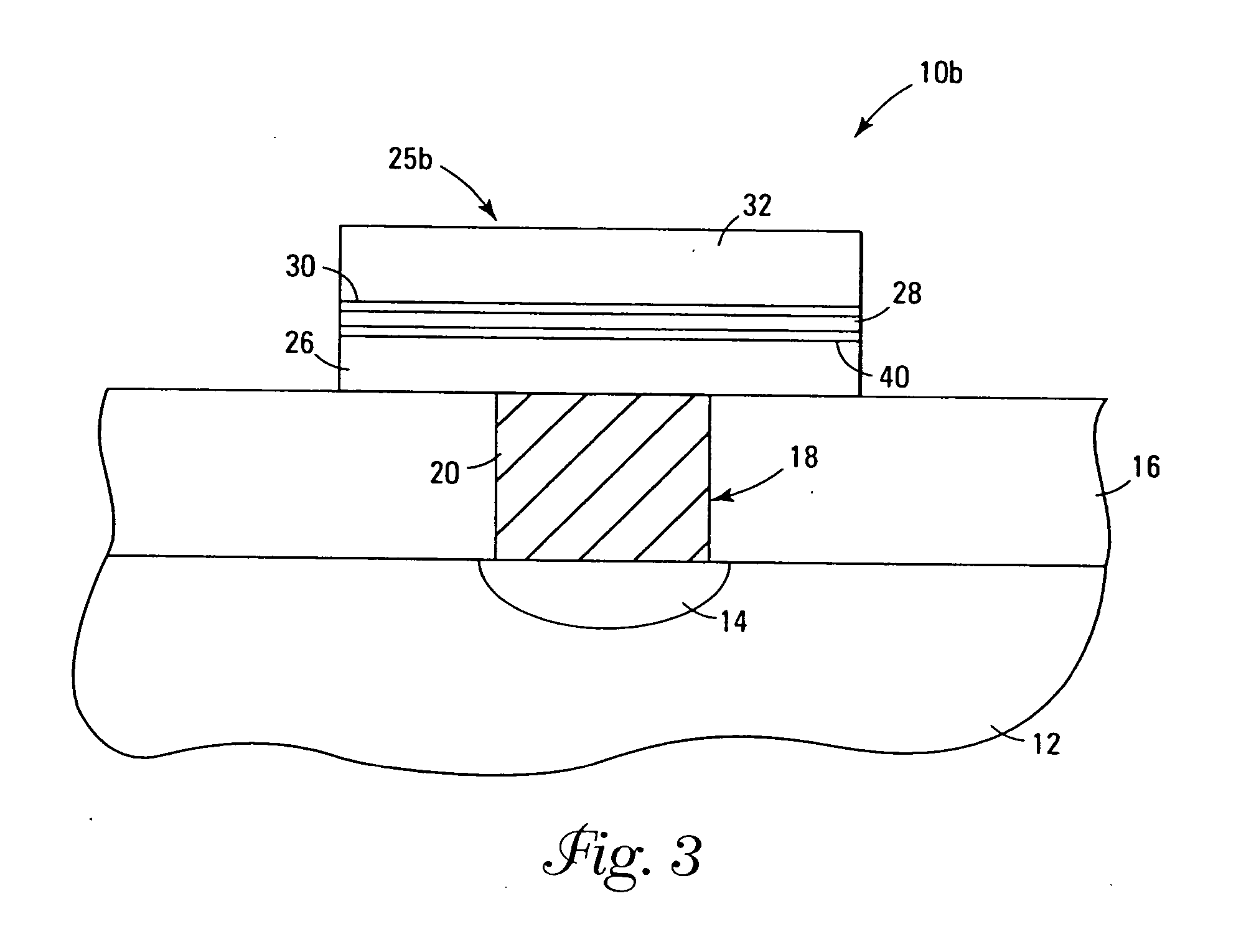
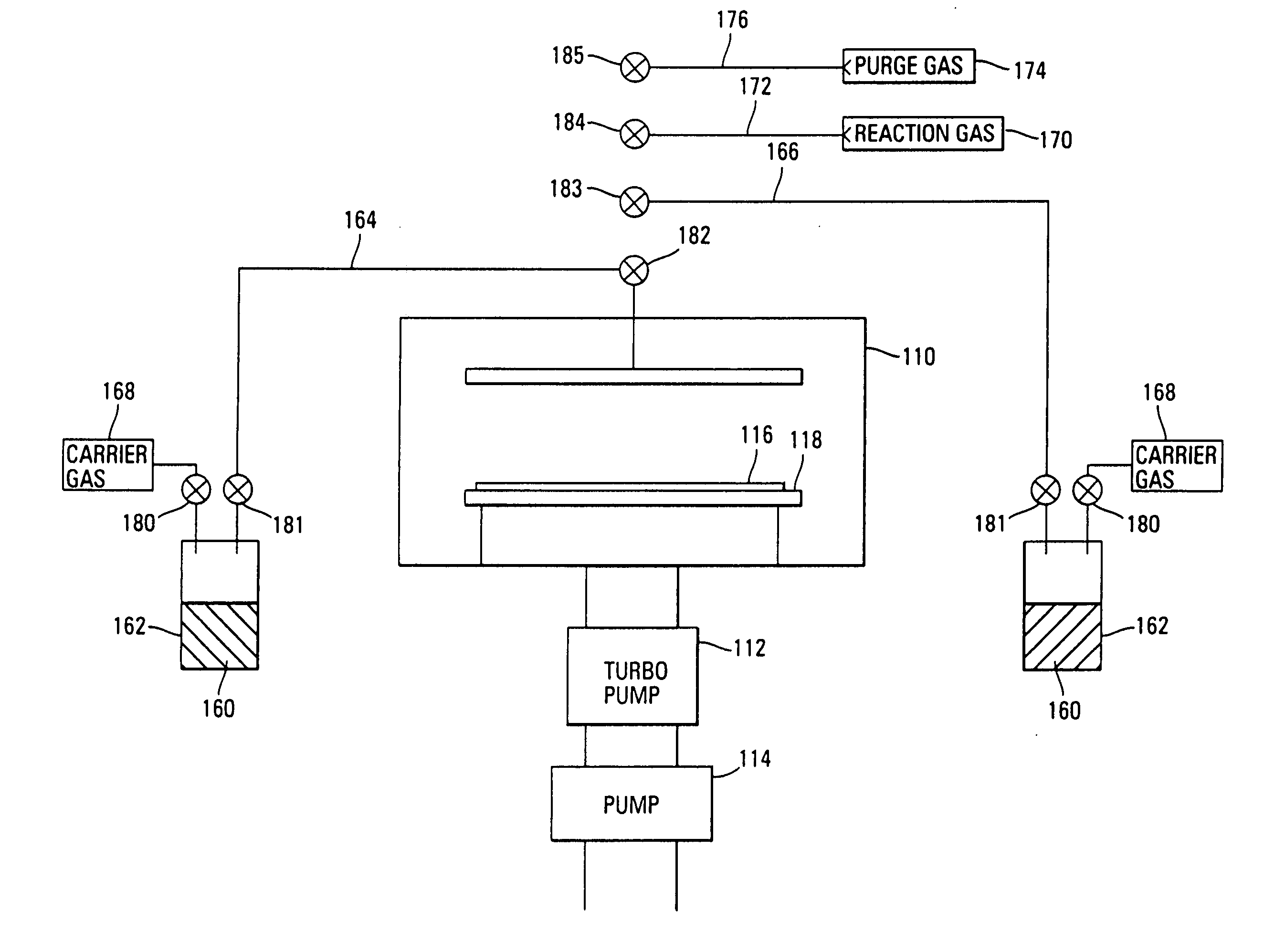
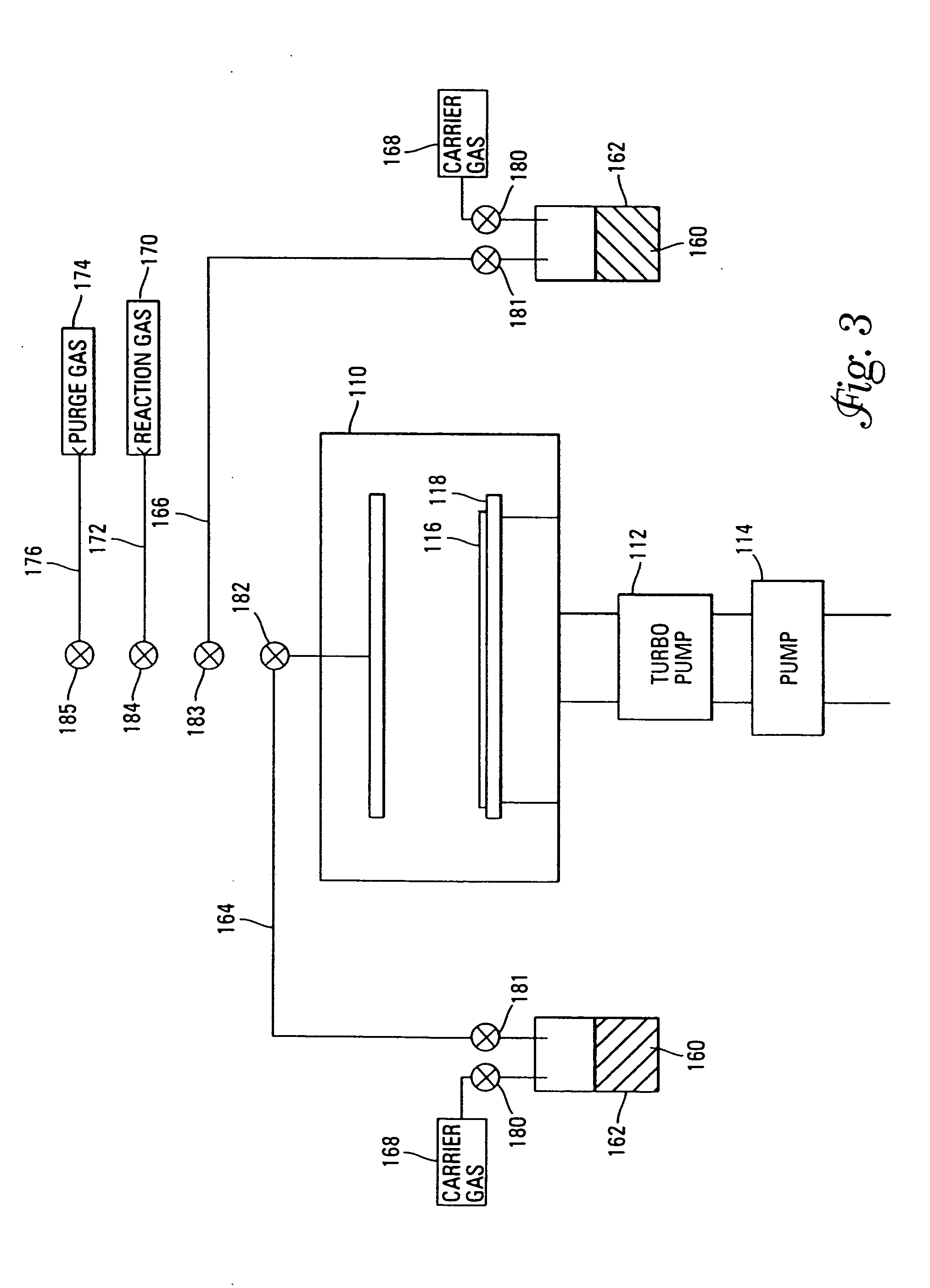
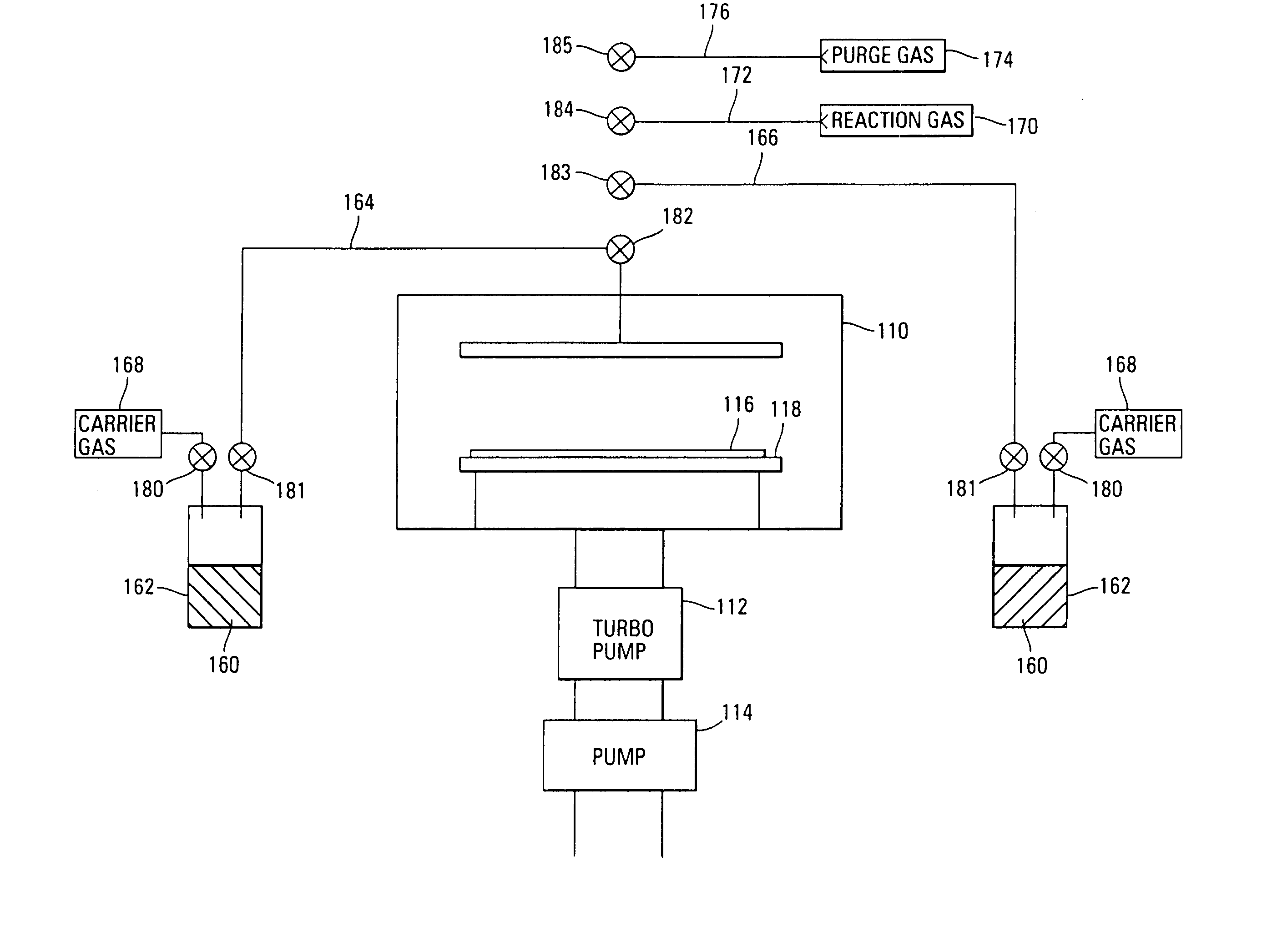
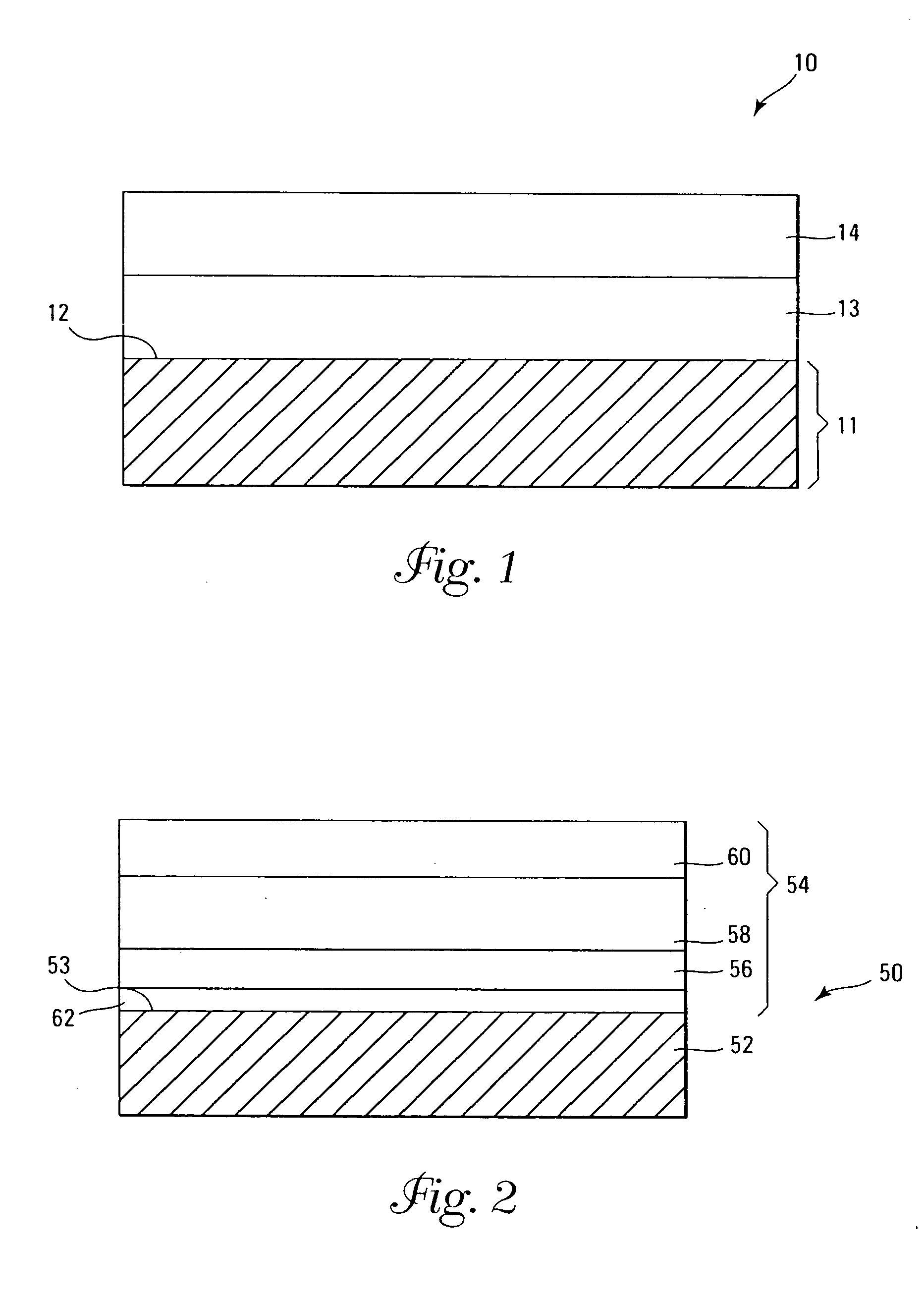
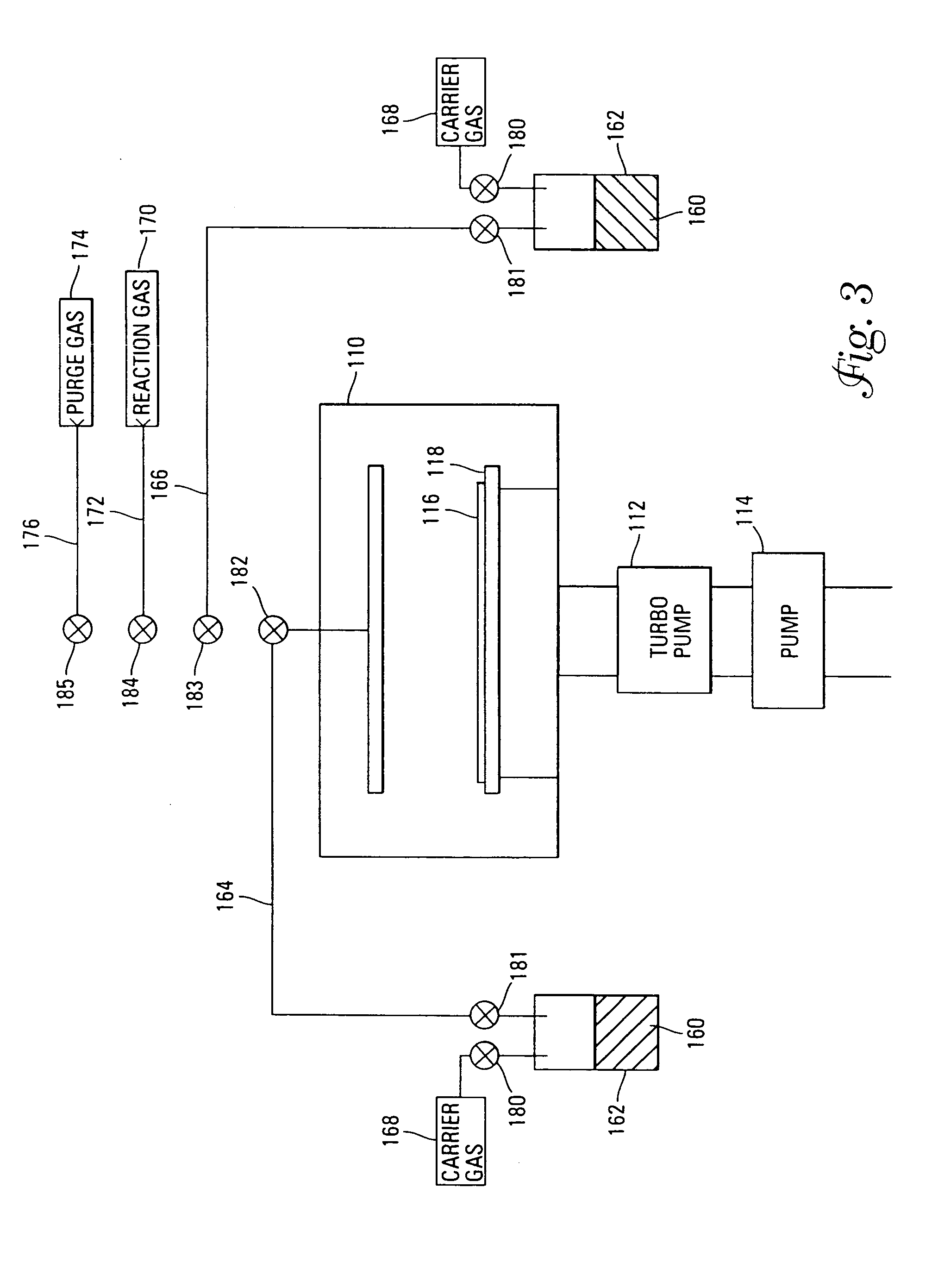
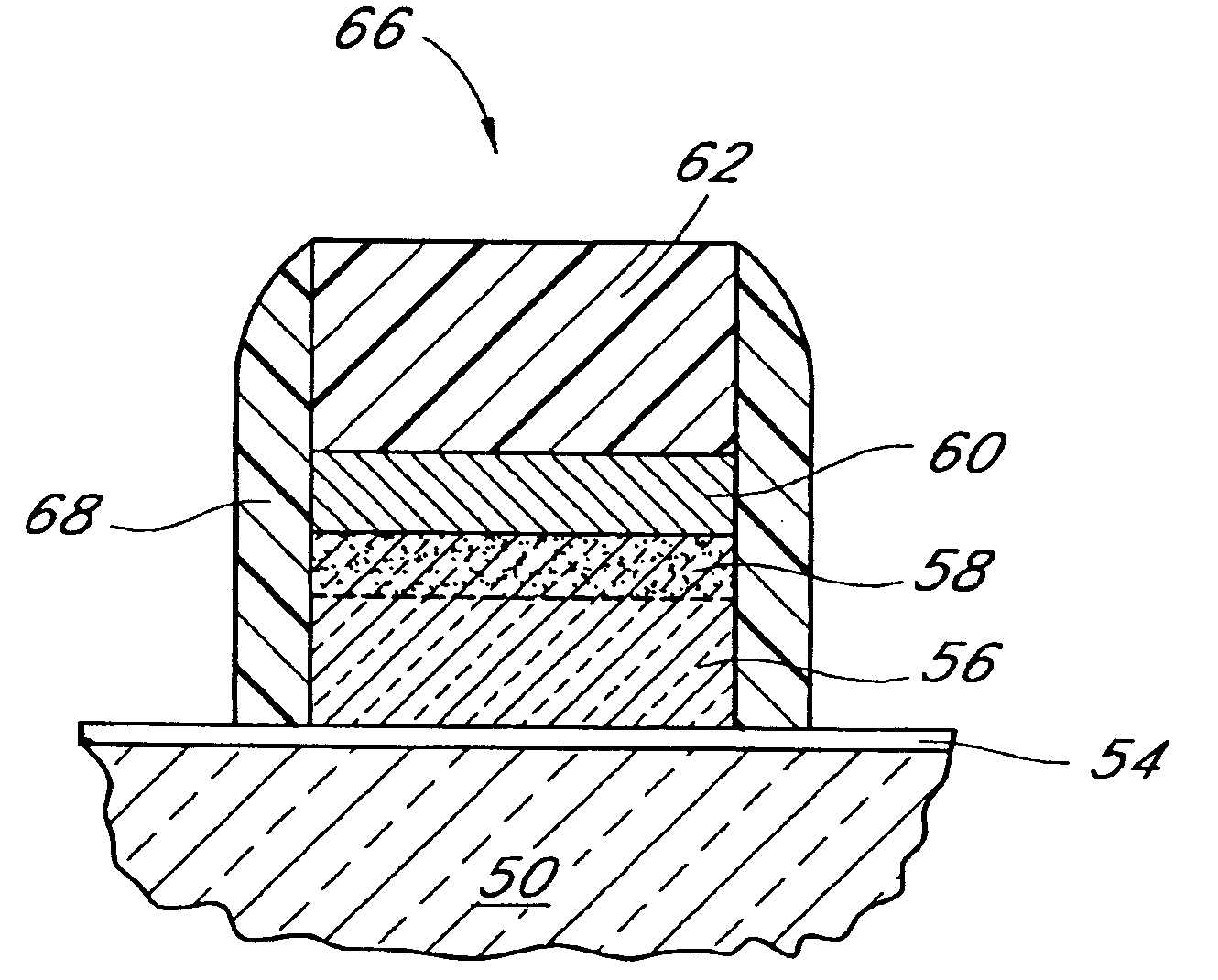
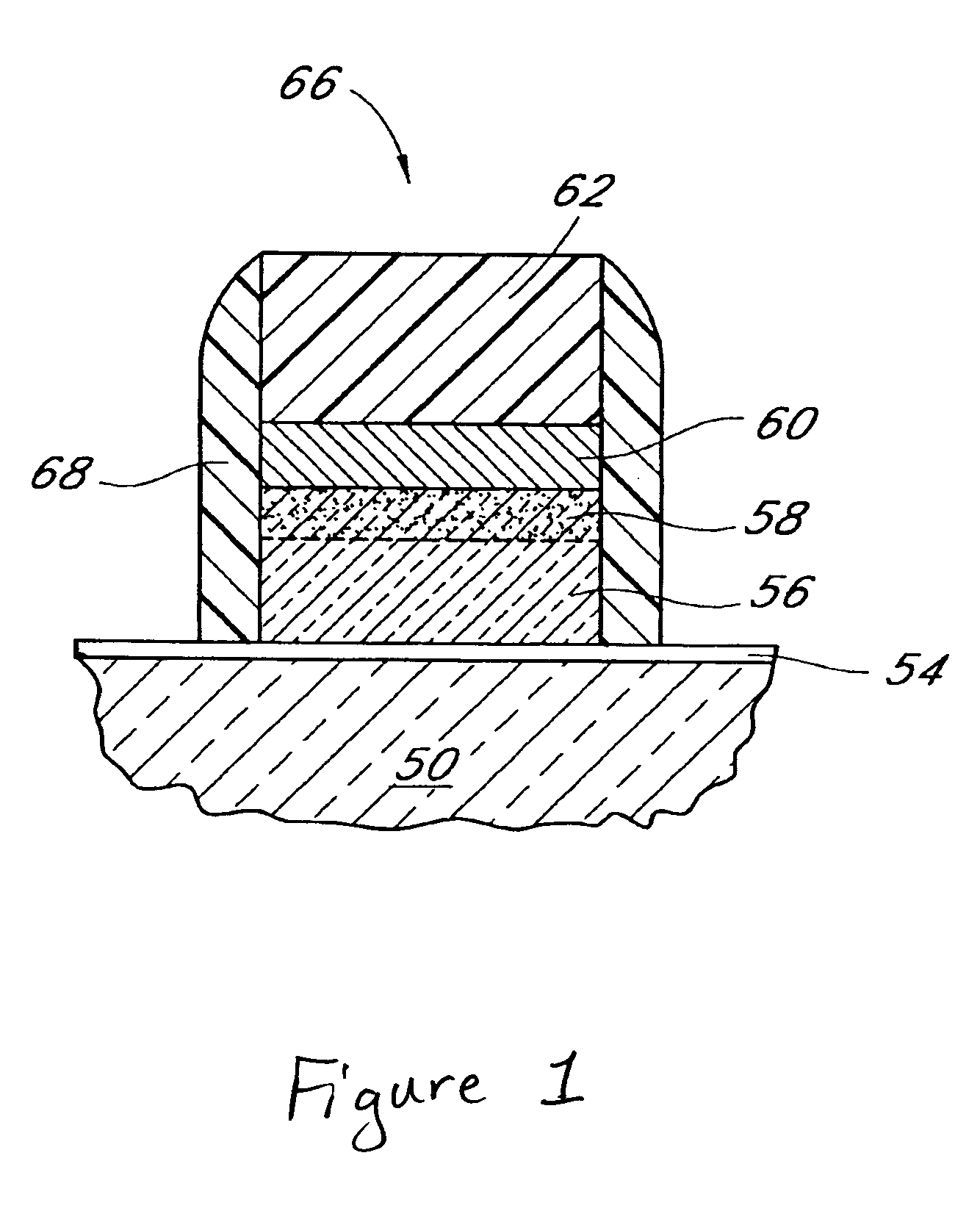
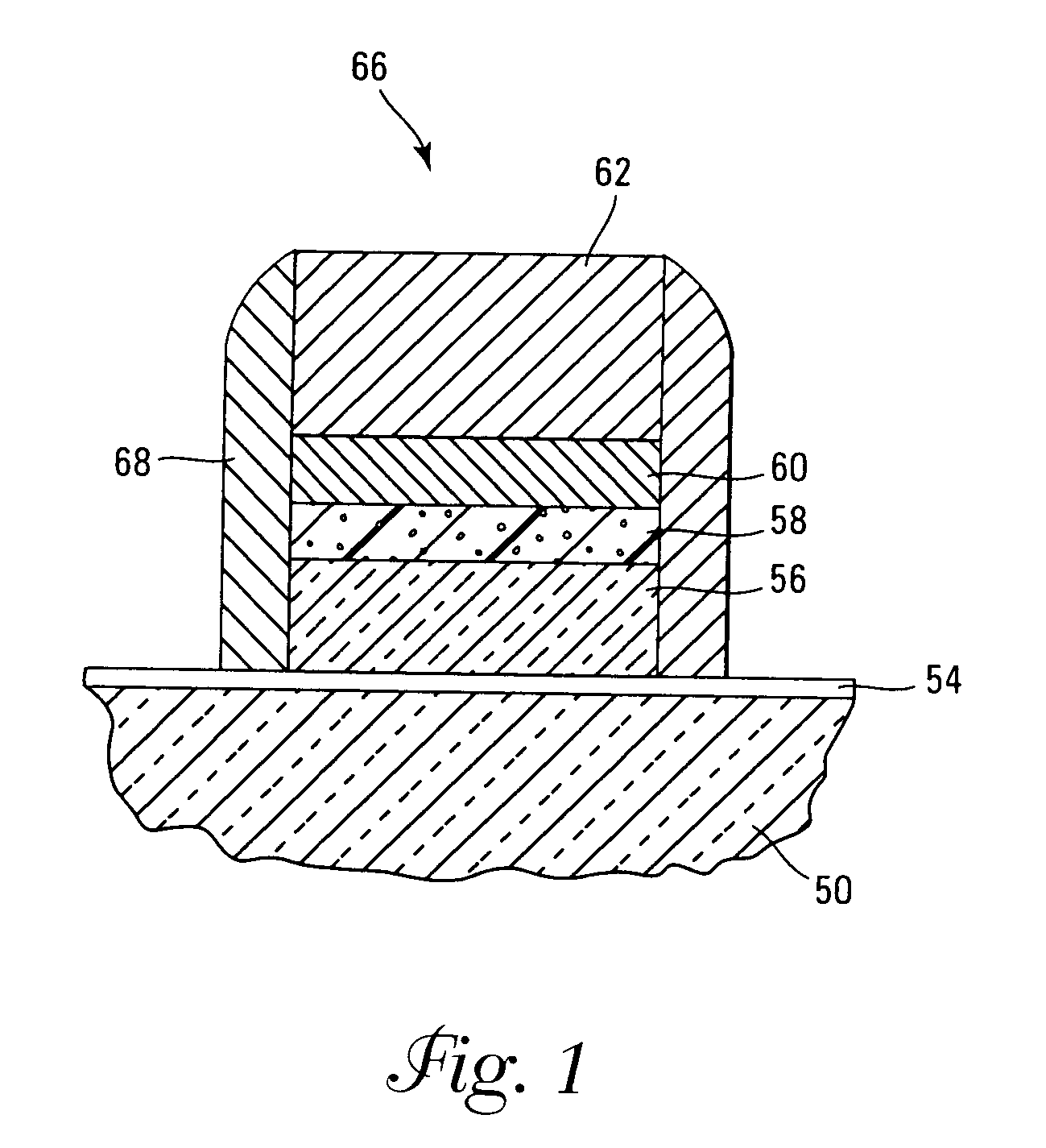
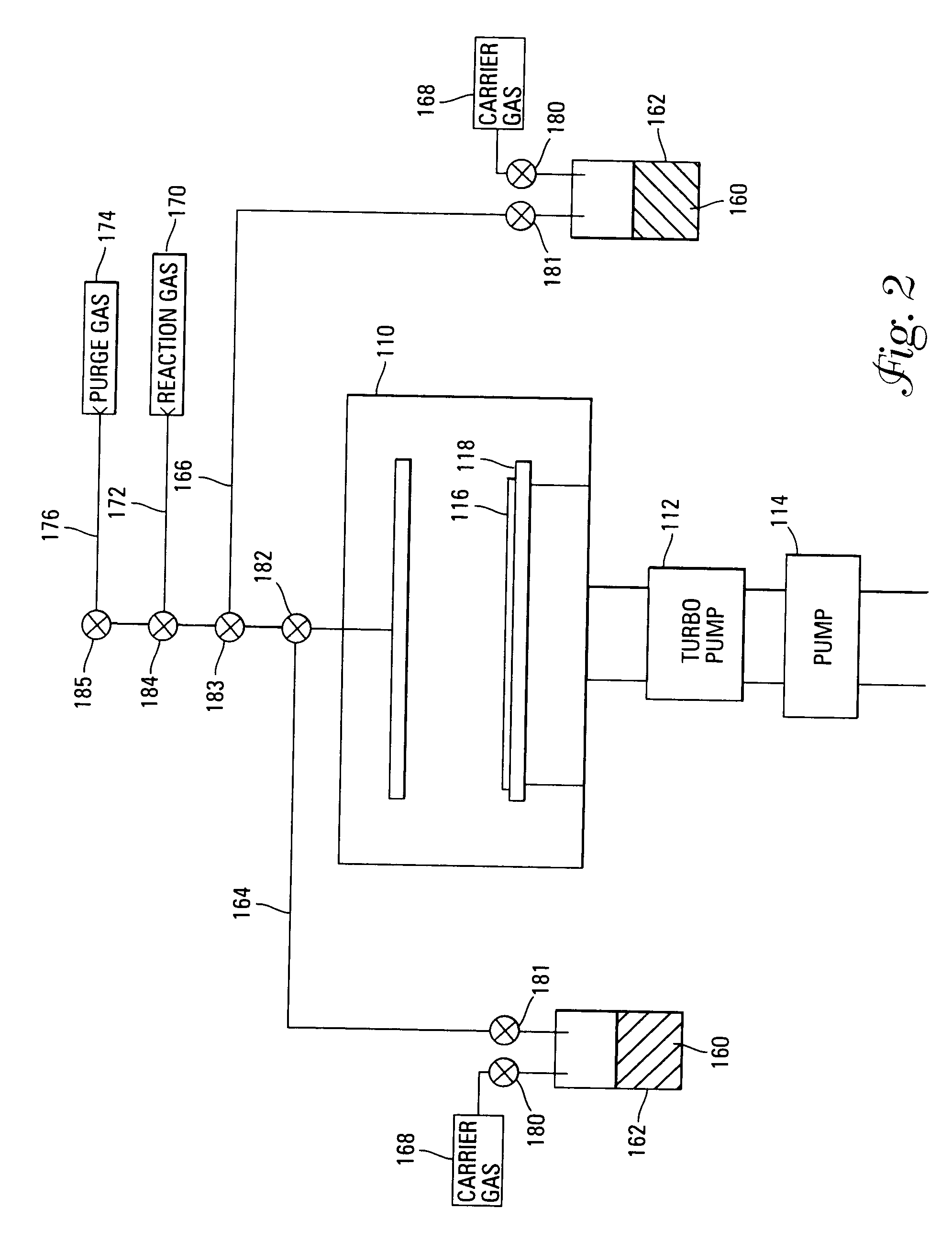
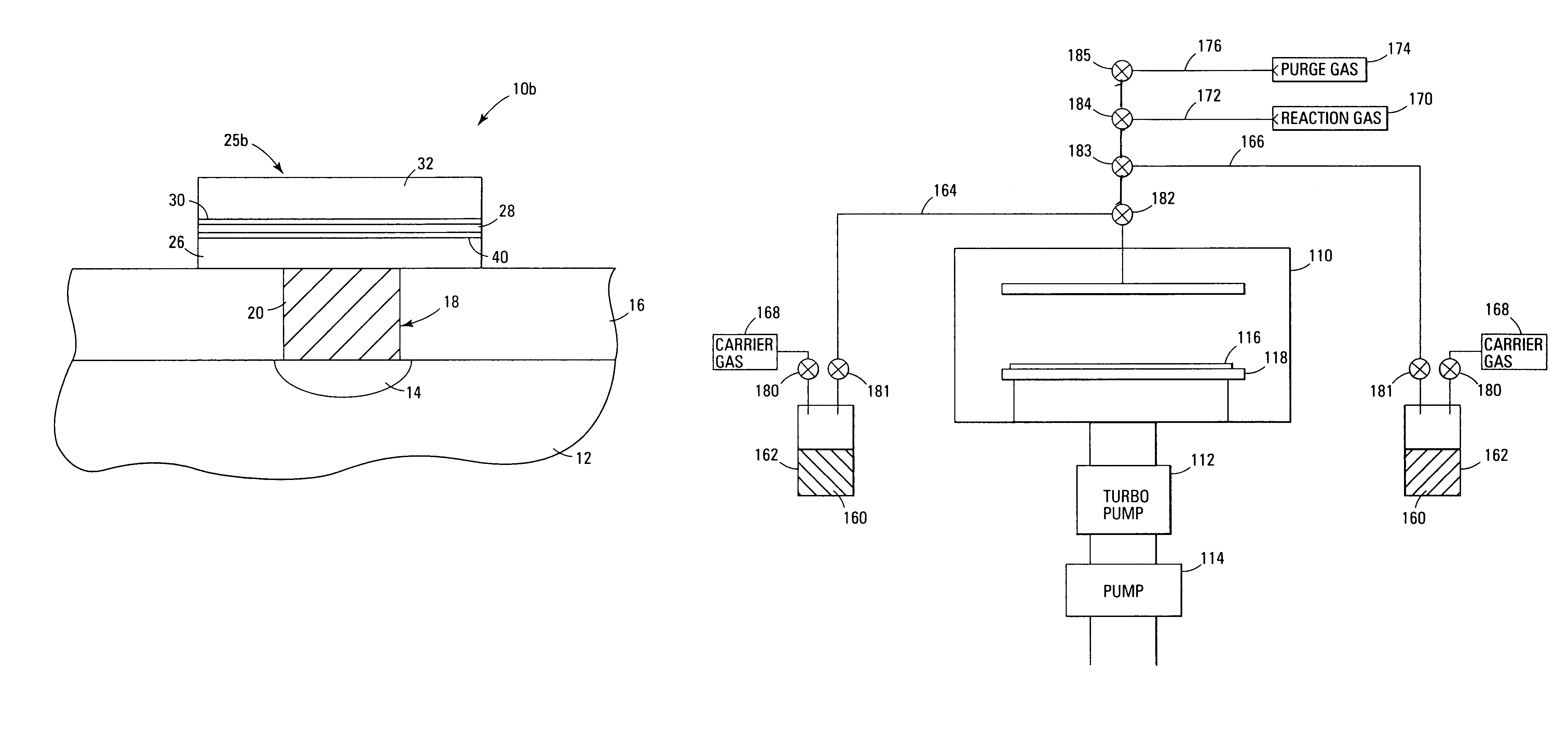
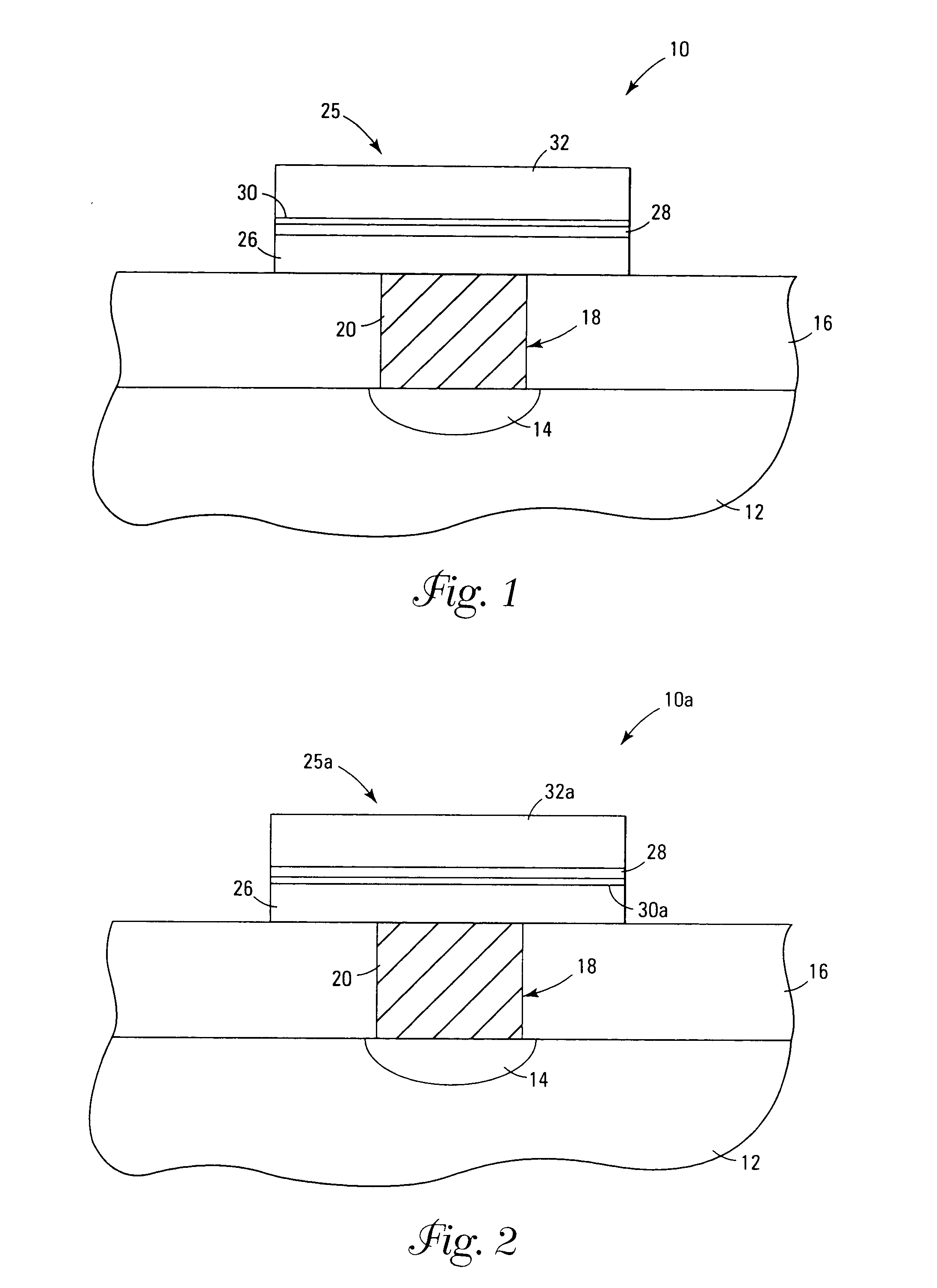
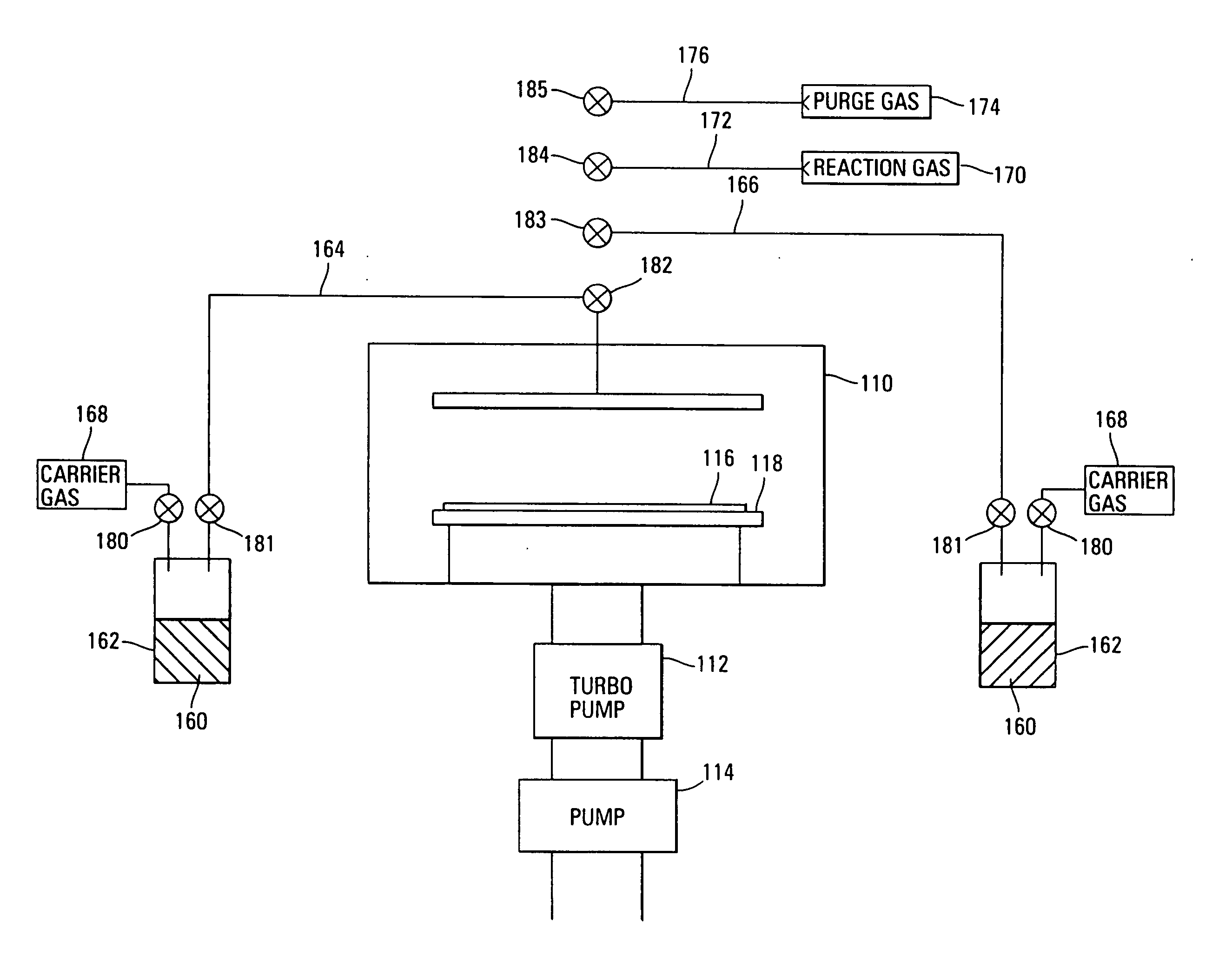
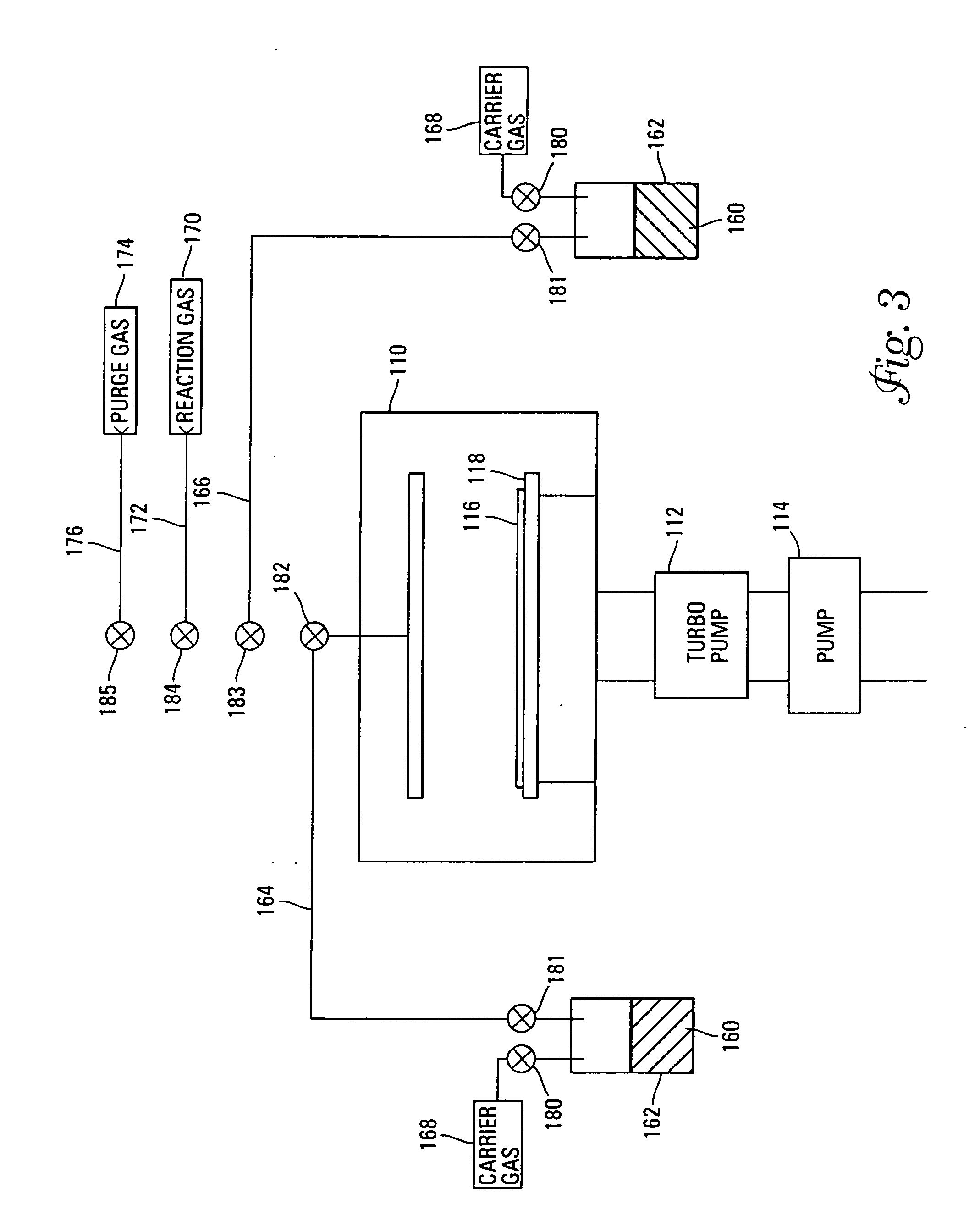
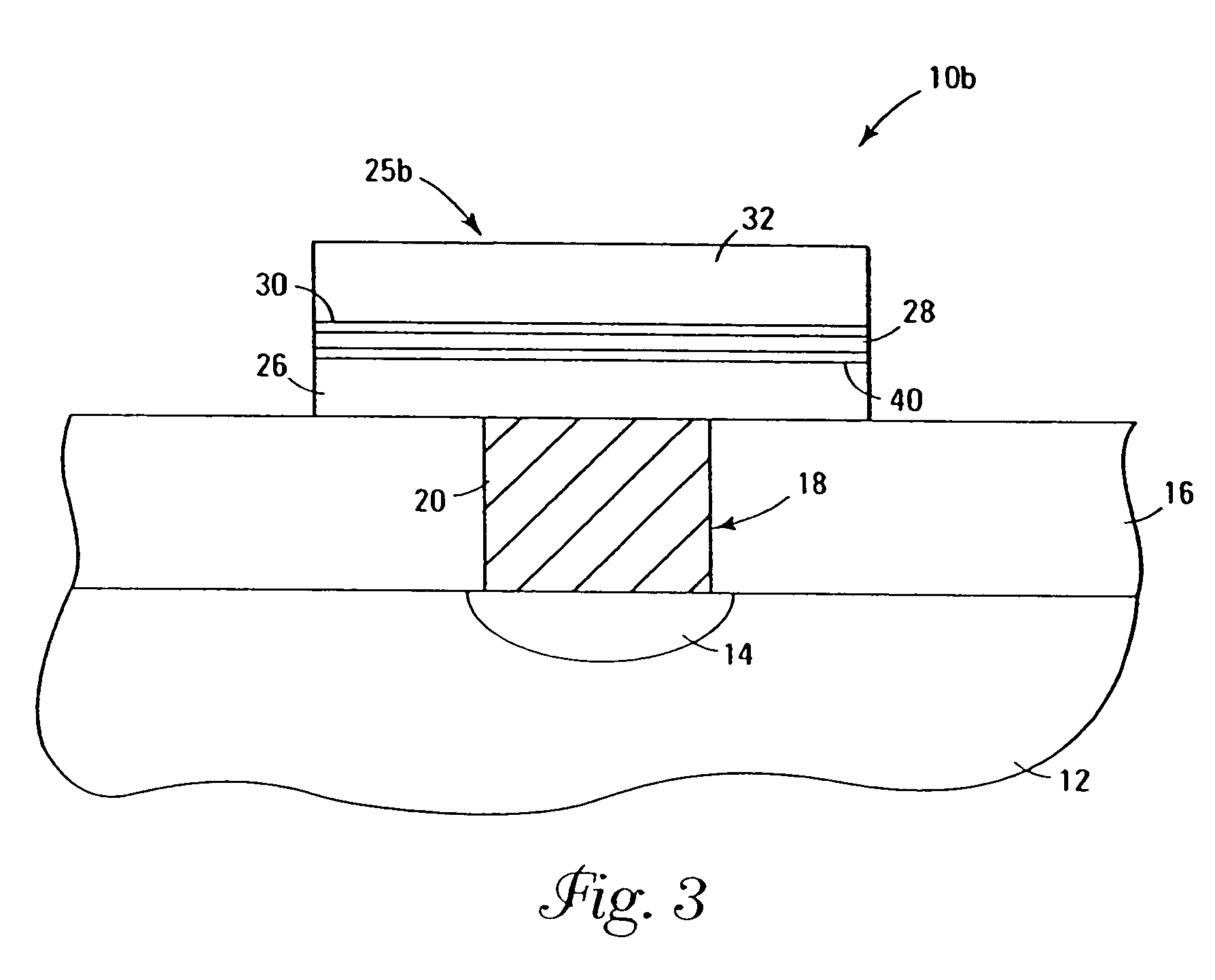
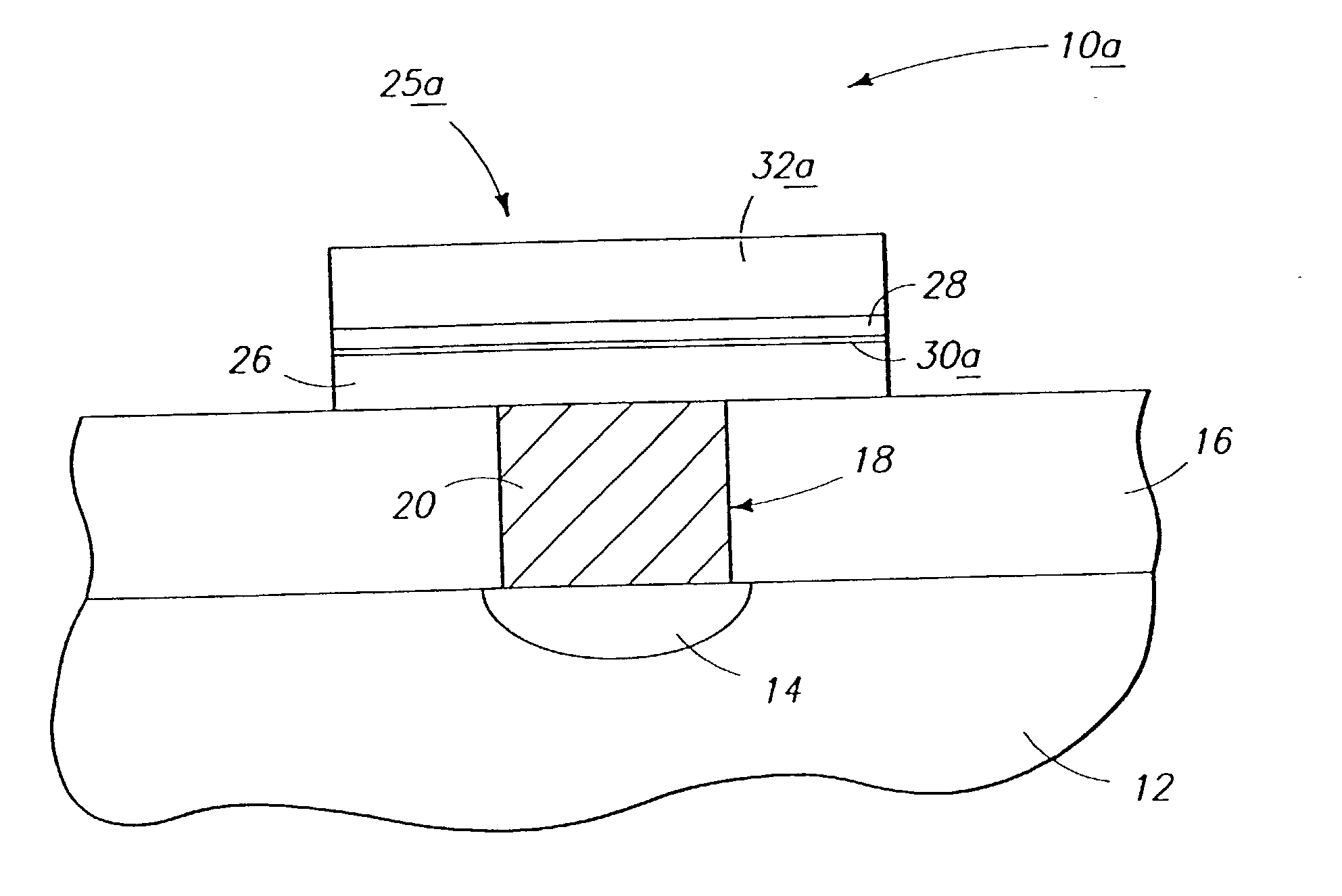
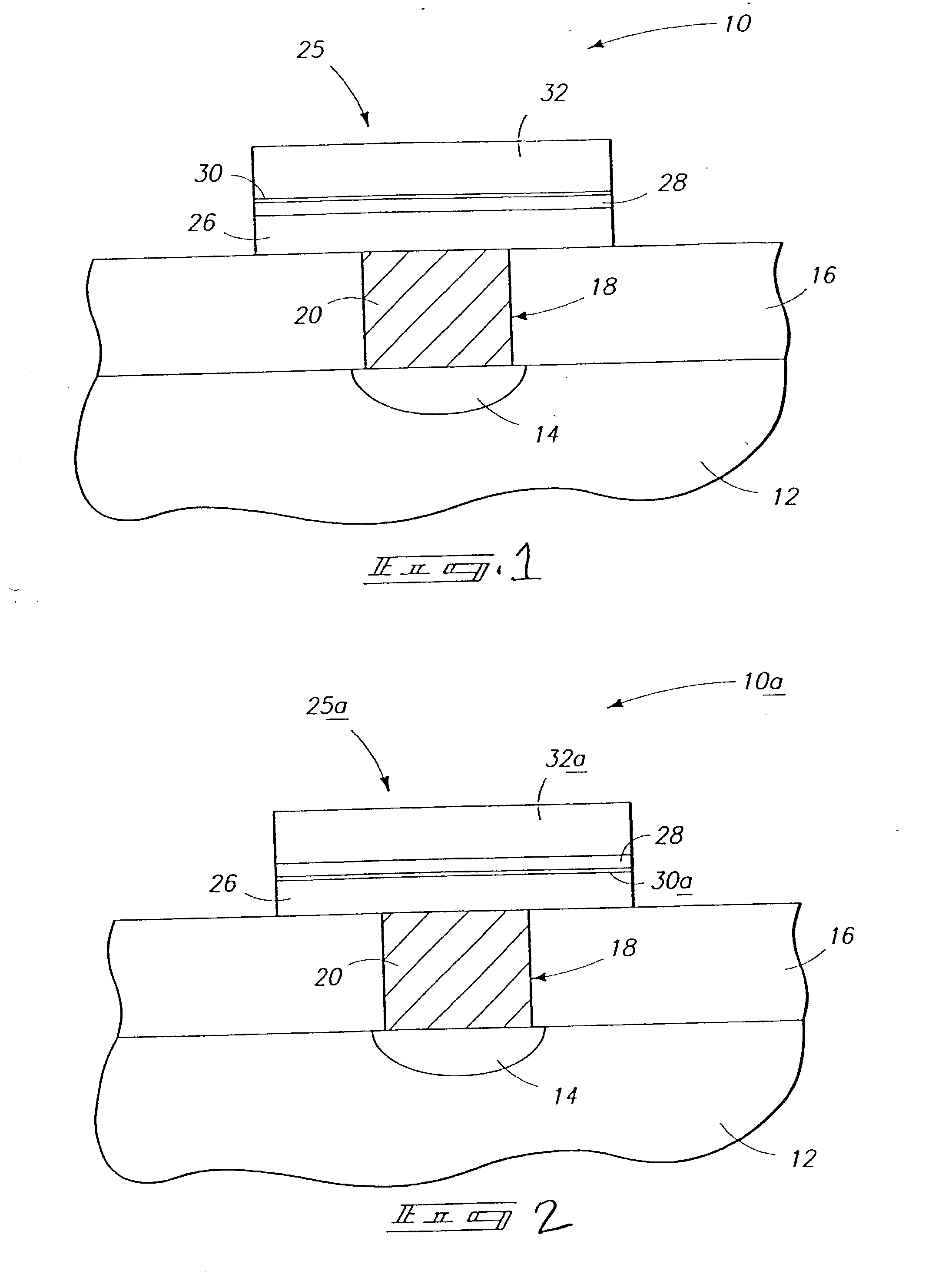
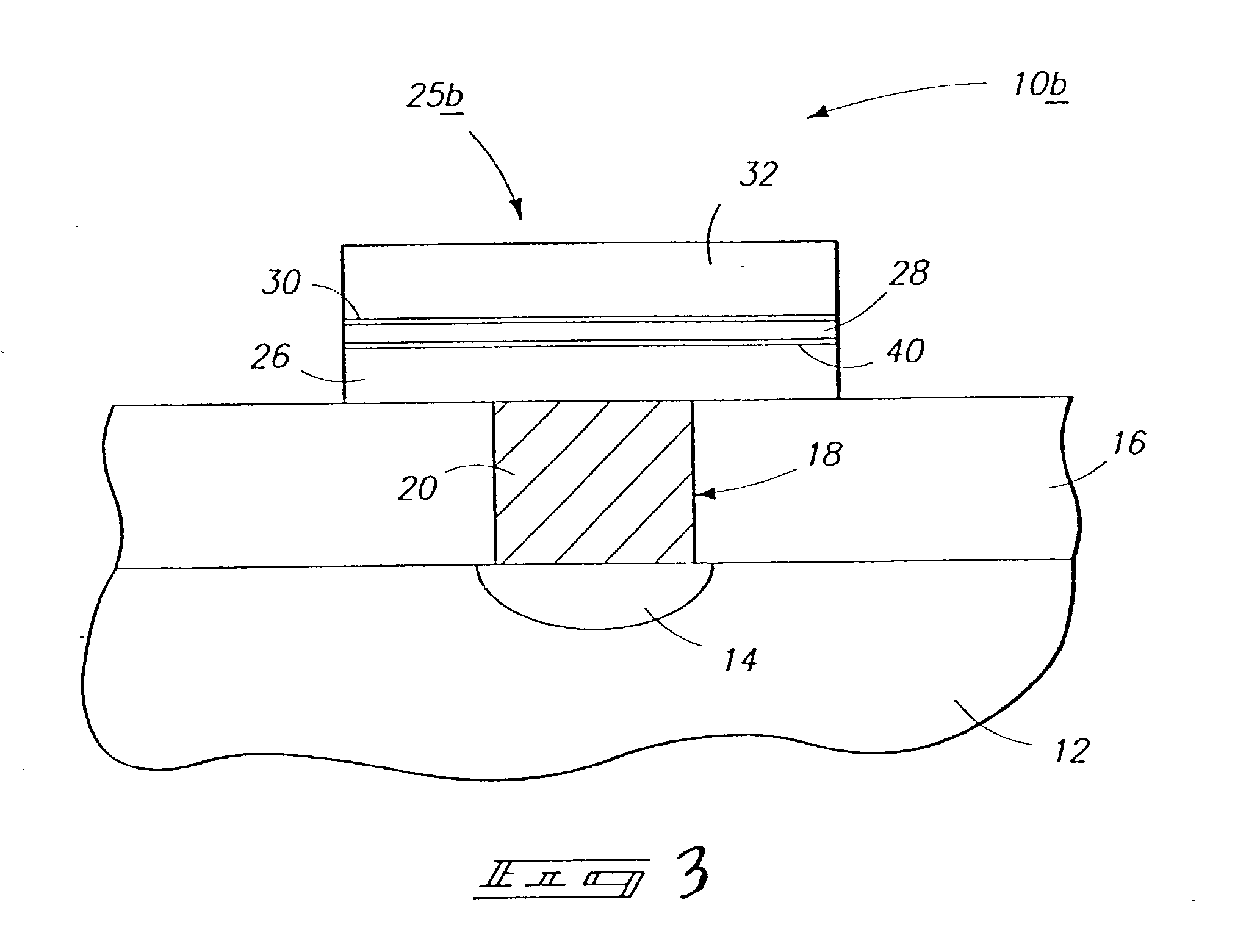
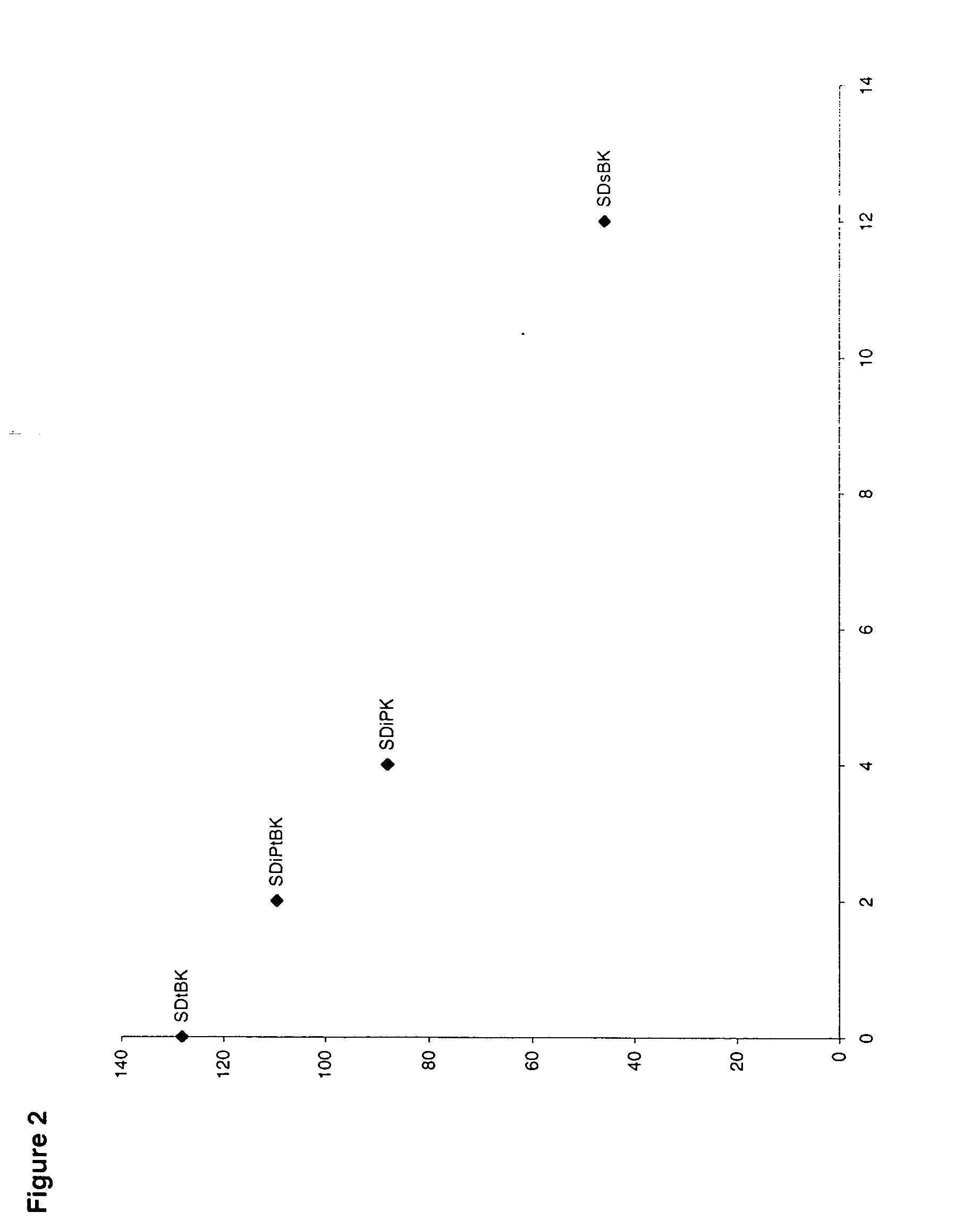
InactiveUS7030042B2Easy to controlReaction become badSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGroup 5/15 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesCompound aGas phase
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming tantalum oxide layers and tantalum precursor compounds
InactiveUS20050019978A1Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompound aGas phase
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) a tantalum oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and a tantalum precursor compound that includes alkoxide ligands, for example.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods of forming refractory metal nitride layers using disilazanes
InactiveUS20050028733A1Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseDeposition process
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum (silicon) nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a refractory metal precursor compound, a disilazane, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods of forming tantalum silicide layers
InactiveUS20060048711A1Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseNitrogen
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) tantalum silicide layers (including tantalum silicon nitride layers), which are typically useful as diffusion barrier layers, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a tantalum halide precursor compound, a silicon precursor compound, and an optional nitrogen precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming zirconium and/or hafnium-containing layers
InactiveUS7112485B2Reduce decreaseEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseOrganic group
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) a zirconium and / or hafnium-containing layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and one or more silicon precursor compounds of the formula Si(OR)4 with one or more zirconium and / or hafnium precursor compounds of the formula M(NR′R″)4, wherein R, R′, and R″ are each independently an organic group and M is zirconium or hafnium.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using metal organo-amines and metal organo-oxides
InactiveUS20050287819A1Reduce decreaseAvoid problemsTransistorSolid-state devicesGas phaseChemical compound
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposit ion process and one or more precursor compounds that include organo-amine ligands and one or more precursor compounds that include organo-oxide ligands.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using metal compounds containing aminosilane ligands
InactiveUS7087481B2Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsChemical compoundDeposition process
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and one or more precursor compounds that include aminosilane ligands.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming zirconium and/or hafnium-containing layers
InactiveUS20050160981A9Reduce decreaseEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseOrganic group
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) a zirconium and / or hafnium-containing layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and one or more silicon precursor compounds of the formula Si(OR)4 with one or more zirconium and / or hafnium precursor compounds of the formula M(NR′R″)4, wherein R, R′, and R″ are each independently an organic group and M is zirconium or hafnium.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using metal diketonates and/or ketoimines
InactiveUS7253122B2Reduce decreaseEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseKetone
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and one or more precursor compounds that include diketonate ligands and / or ketoimine ligands.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using metal diketonates and/or ketoimines
InactiveUS20060252279A1Reduce decreaseEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseKetone
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and one or more precursor compounds that include diketonate ligands and / or ketoimine ligands.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods of forming refractory metal nitride layers using disilazanes
InactiveUS20060292788A1Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseDeposition process
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum (silicon) nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using a vapor deposition process with a refractory metal precursor compound, a disilazane, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using metal compounds containing aminosilane ligands
InactiveUS20060258175A1Easy to controlReaction become badSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseDeposition process
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and one or more precursor compounds that include aminosilane ligands.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Metal-doped alumina and layers thereof
InactiveUS20050221006A1Reduce problemReduce decreaseSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition processSemiconductor
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal-doped aluminum oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
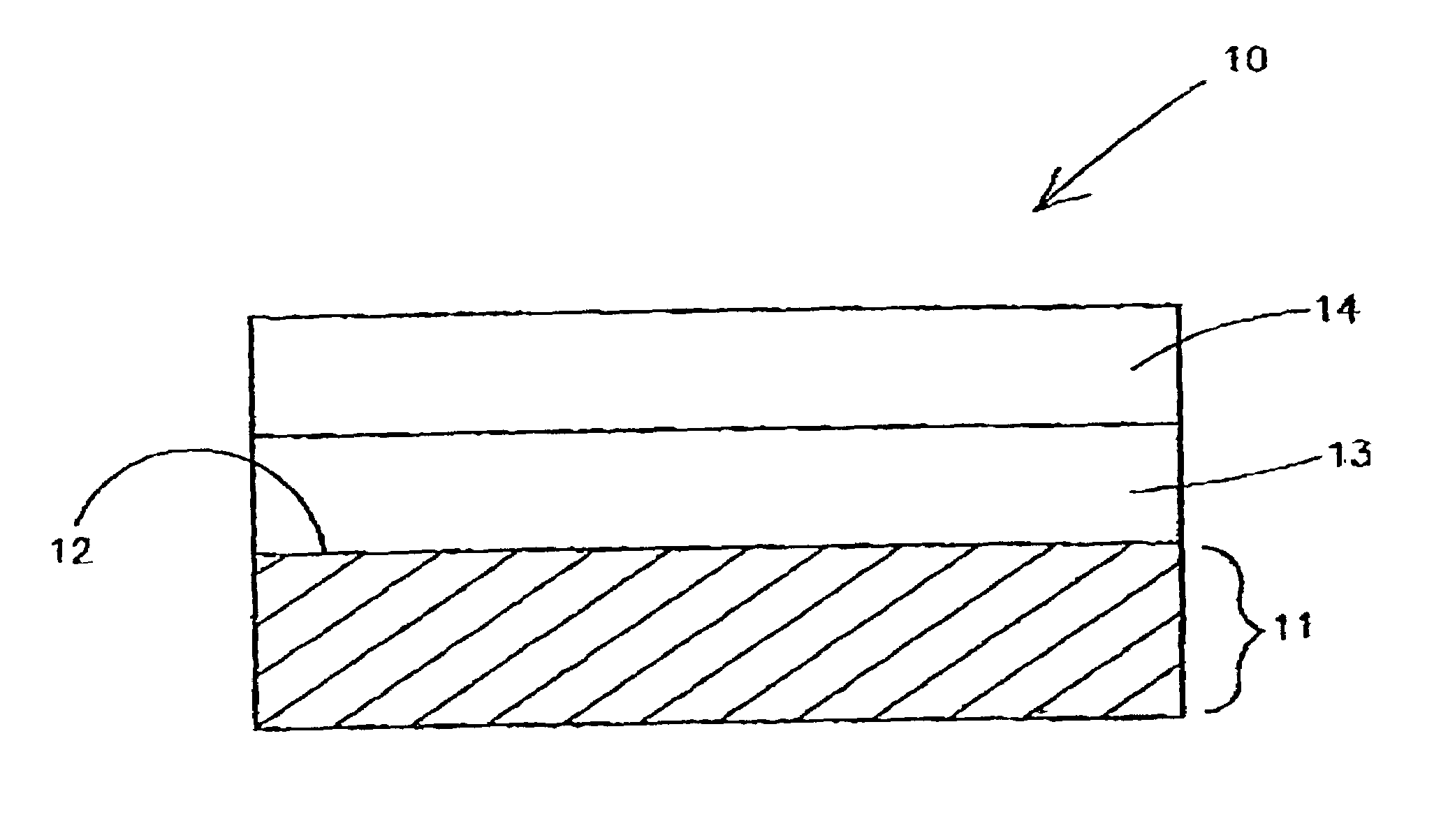
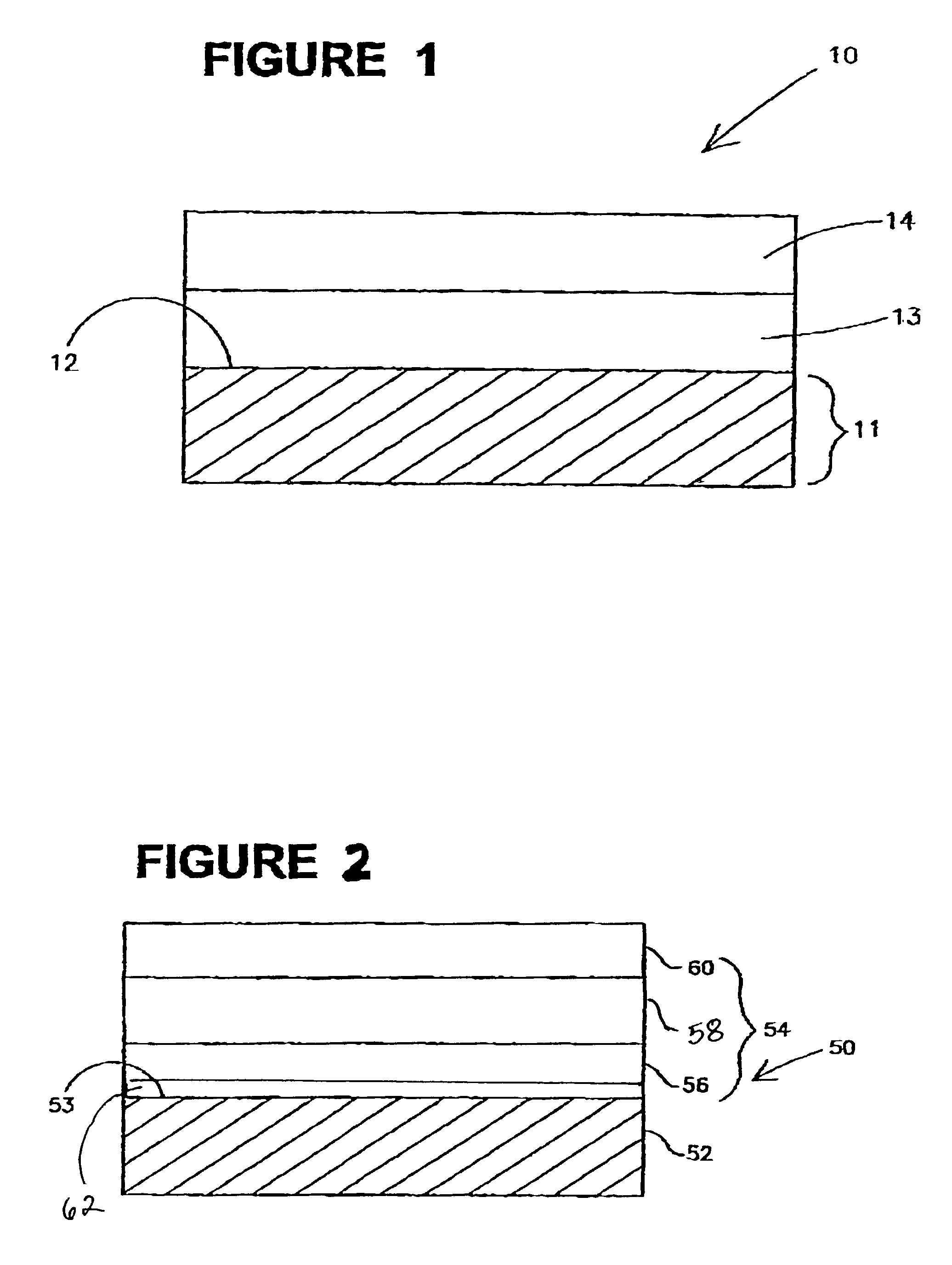
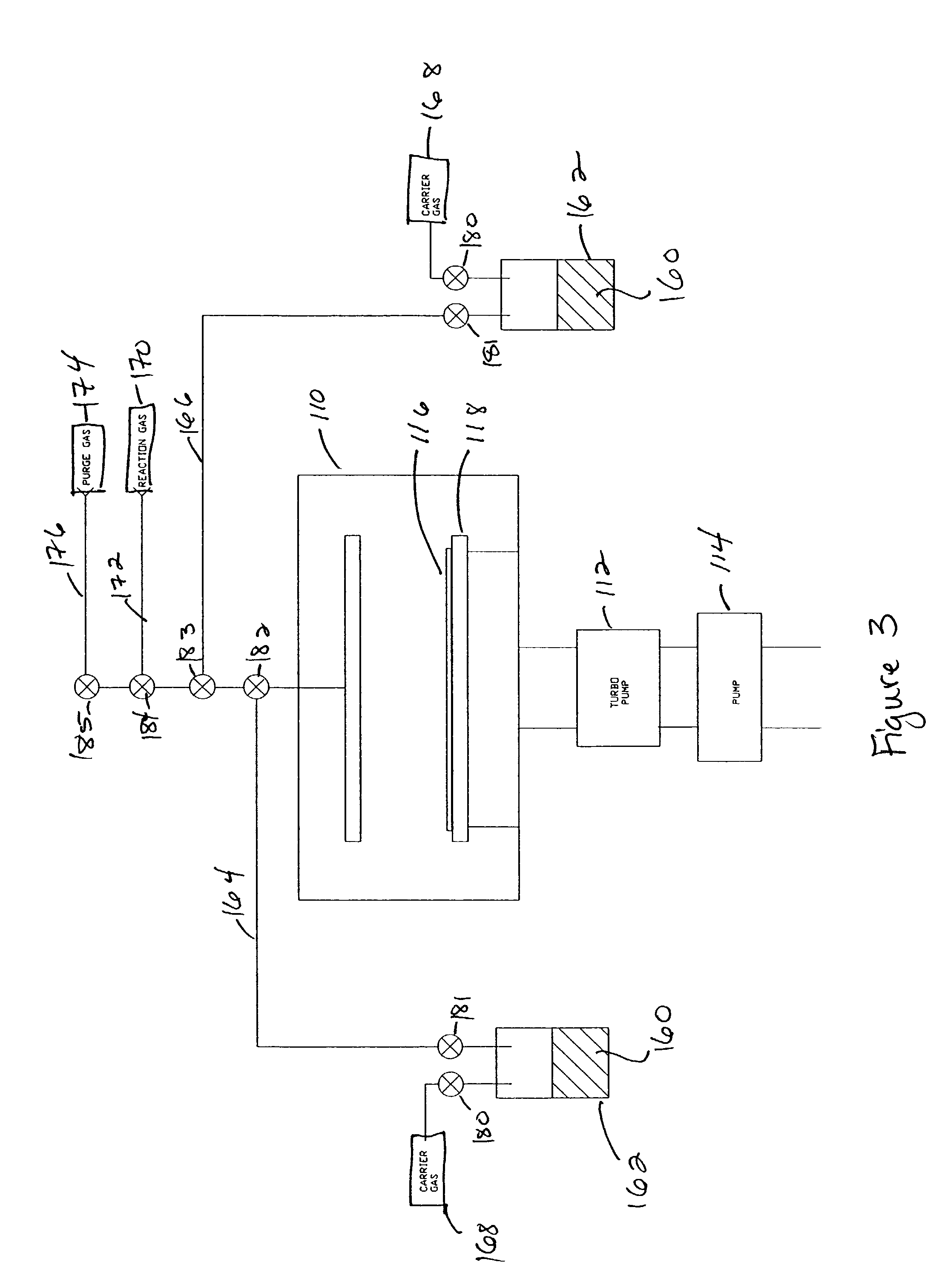
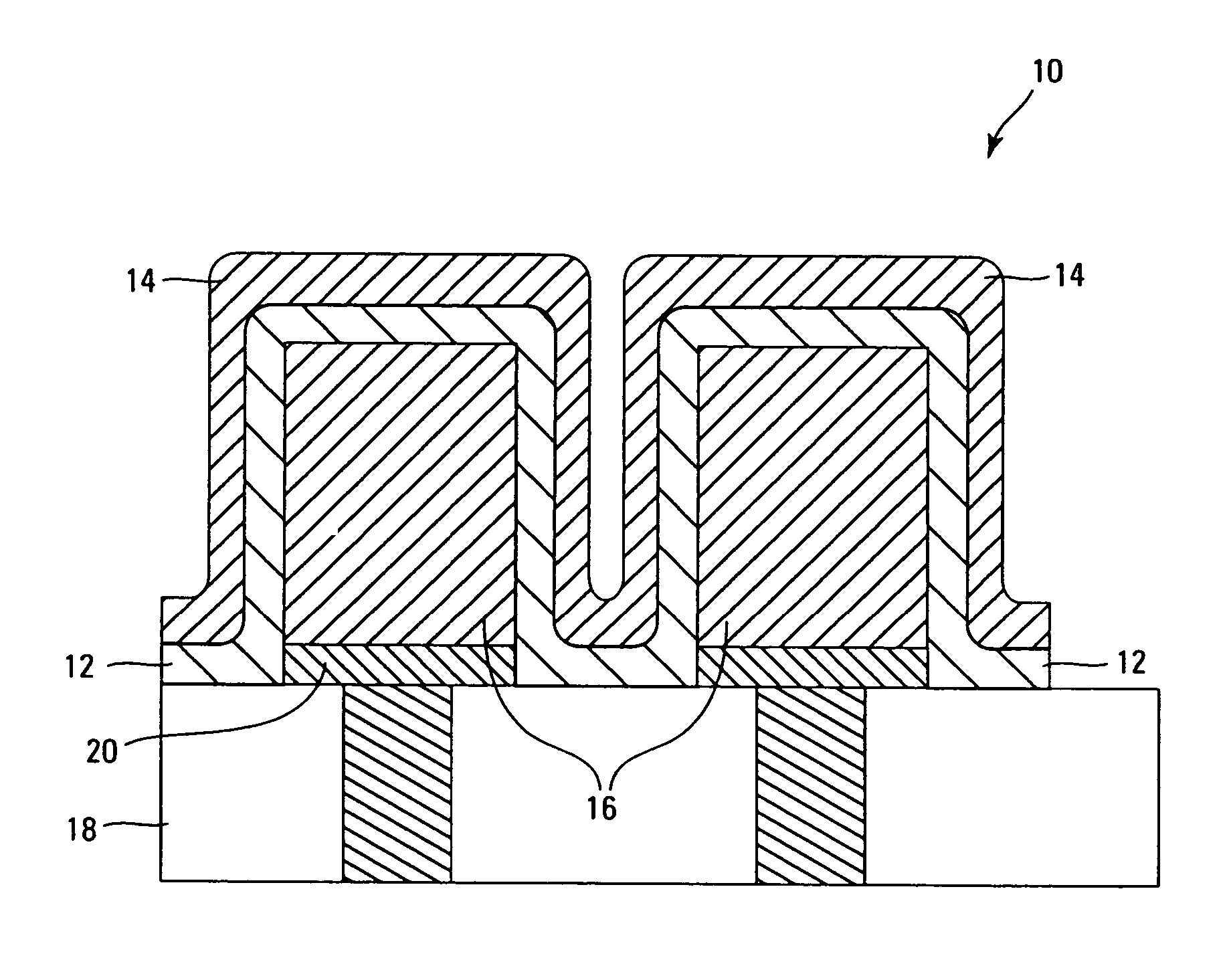
Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using alcohols
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process, one or more alcohols, and one or more metal-containing precursor compounds.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods of forming refractory metal nitride layers using organic amines
InactiveUS20050287804A1Reduce diffuseReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseTantalum nitride
A method of forming (and apparatus for forming) refractory metal nitride layers (including silicon nitride layers), such as a tantalum nitride barrier layer, on a substrate by using an atomic layer deposition process (a vapor deposition process that includes a plurality of deposition cycles) with a refractory metal precursor compound, an organic amine, and an optional silicon precursor compound.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using metal diketonates and/or ketoimines
InactiveUS20070295273A1Reduce decreaseEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsGas phaseKetone
A method of forming (and an apparatus for forming) a metal oxide layer on a substrate, particularly a semiconductor substrate or substrate assembly, using a vapor deposition process and one or more precursor compounds that include diketonate ligands and / or ketoimine ligands.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
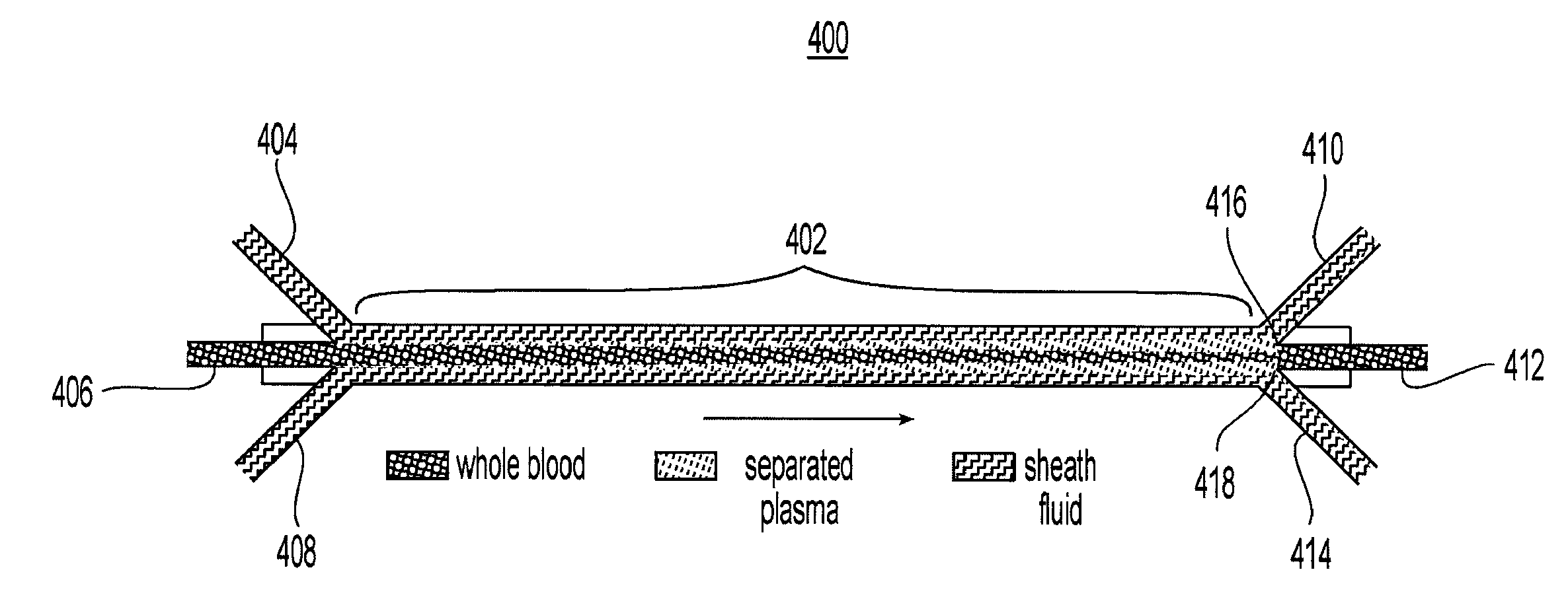
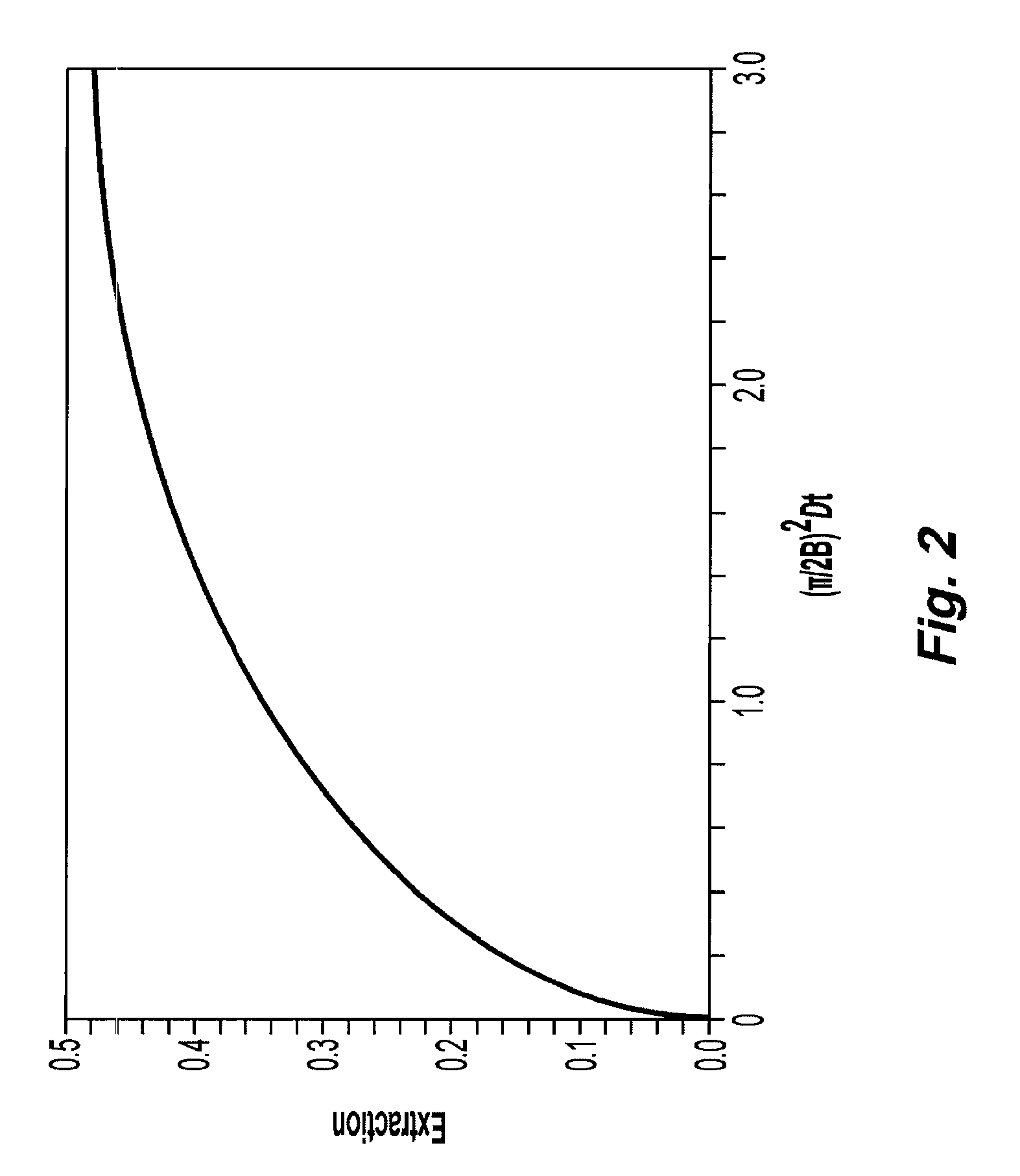
Systems and methods of blood-based therapies having a microfluidic membraneless exchange device
InactiveUS20080009780A1PreventsMinimize bioincompatibilitiesSamplingOther blood circulation devicesAmount of substanceThin layer
The present invention is directed to devices, systems and methods for removing undesirable materials from a sample fluid by contact with a second fluid. The sample fluid flows as a thin layer adjacent to, or between, concurrently flowing layers of the second fluid, without an intervening membrane. In various embodiments, a secondary separator is used to restrict the removal of desirable substances and effect the removal of undesirable substances from blood. The invention is useful in a variety of situations where a sample fluid is to be purified via a diffusion mechanism against an extractor fluid. Moreover, the invention may be used for the removal of components from a sample fluid that vary in size. When blood is the sample fluid, for example, this may include the removal of ‘small’ molecules, ‘middle’ molecules, macromolecules, macromolecular aggregates, and cells, from the blood sample to the extractor fluid.
Owner:COLUMBIA UNIV (US)
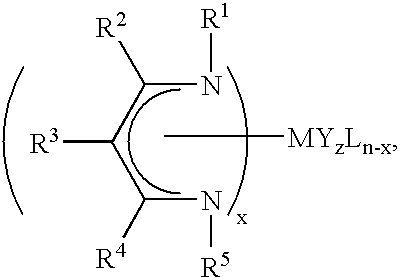
Atomic layer deposition systems and methods including metal beta-diketiminate compounds
ActiveUS20060292841A1Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDiketoneChemical compound
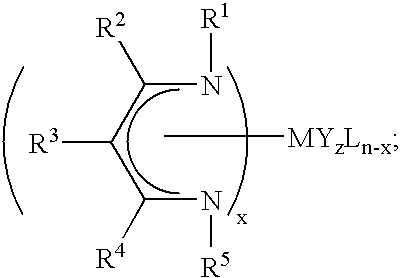
The present invention provides atomic layer deposition systems and methods that include metal compounds with at least one β-diketiminate ligand. Such systems and methods can be useful for depositing metal-containing layers on substrates.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Beta-diketiminate ligand sources and metal-containing compounds thereof, and systems and methods including same
InactiveUS20060292303A1Increase vapor pressureLow melting pointSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCobalt organic compoundsGas phaseΒ diketiminate
The present invention provides metal-containing compounds that include at least one β-diketiminate ligand, and methods of making and using the same. In certain embodiments, the metal-containing compounds include at least one β-diketiminate ligand with at least one fluorine-containing organic group as a substituent. In other certain embodiments, the metal-containing compounds include at least one β-diketiminate ligand with at least one aliphatic group as a substituent selected to have greater degrees of freedom than the corresponding substituent in the β-diketiminate ligands of certain metal-containing compounds known in the art. The compounds can be used to deposit metal-containing layers using vapor deposition methods. Vapor deposition systems including the compounds are also provided. Sources for β-diketiminate ligands are also provided.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Unsymmetrical ligand sources, reduced symmetry metal-containing compounds, and systems and methods including same
ActiveUS20060292873A1Good step coverageDetrimental to reactionGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsGroup 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesStereochemistryMetal
The present invention provides metal-containing compounds that include at least one β-diketiminate ligand, and methods of making and using the same. In some embodiments, the metal-containing compounds are homoleptic complexes that include unsymmetrical β-diketiminate ligands. In other embodiments, the metal-containing compounds are heteroleptic complexes including at least one β-diketiminate ligand. The compounds can be used to deposit metal-containing layers using vapor deposition methods. Vapor deposition systems including the compounds are also provided. Sources for β-diketiminate ligands are also provided.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com