Systems and methods for forming metal oxides using metal organo-amines and metal organo-oxides
a technology of metal organoamines and metal oxides, which is applied in the direction of coatings, transistors, chemical vapor deposition coatings, etc., can solve the problems of forming an undesirable siosub>2 /sub>interfacial layer, the traditional use of integrated circuit technology is approaching its performance limits, and the layer no longer effectively functions as an insulator
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
Example 1
Atomic Layer Deposition of (Hf,Ti)O2
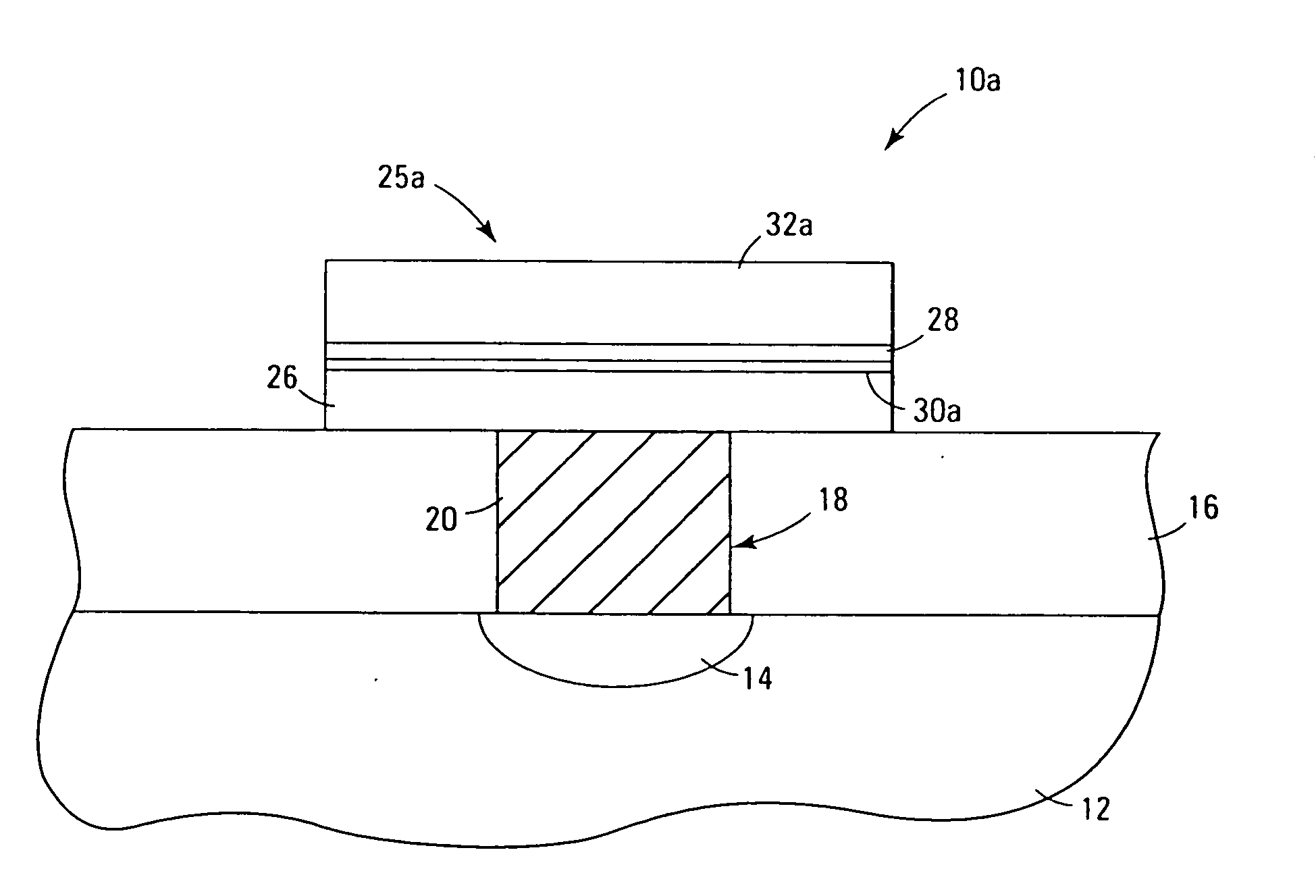
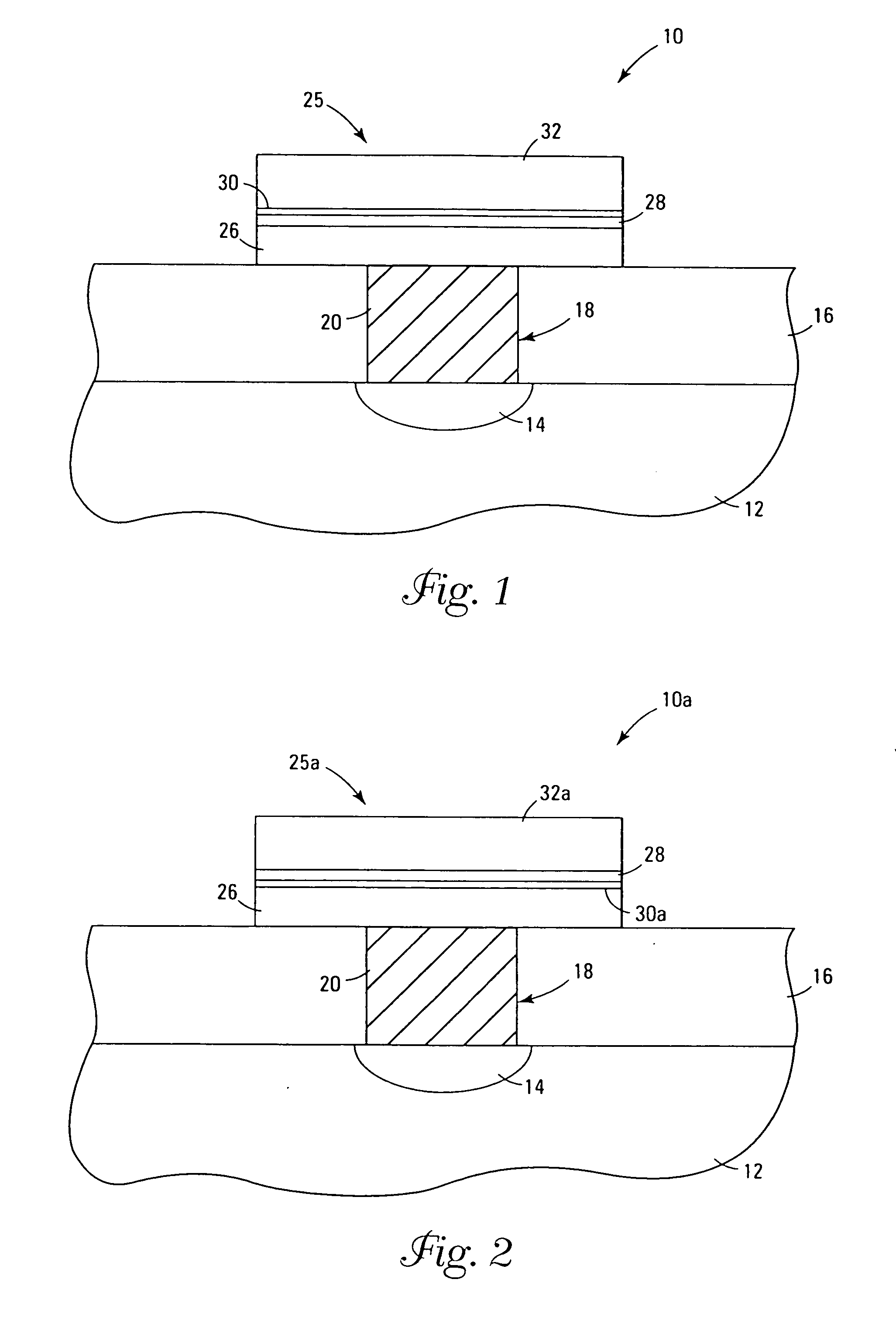
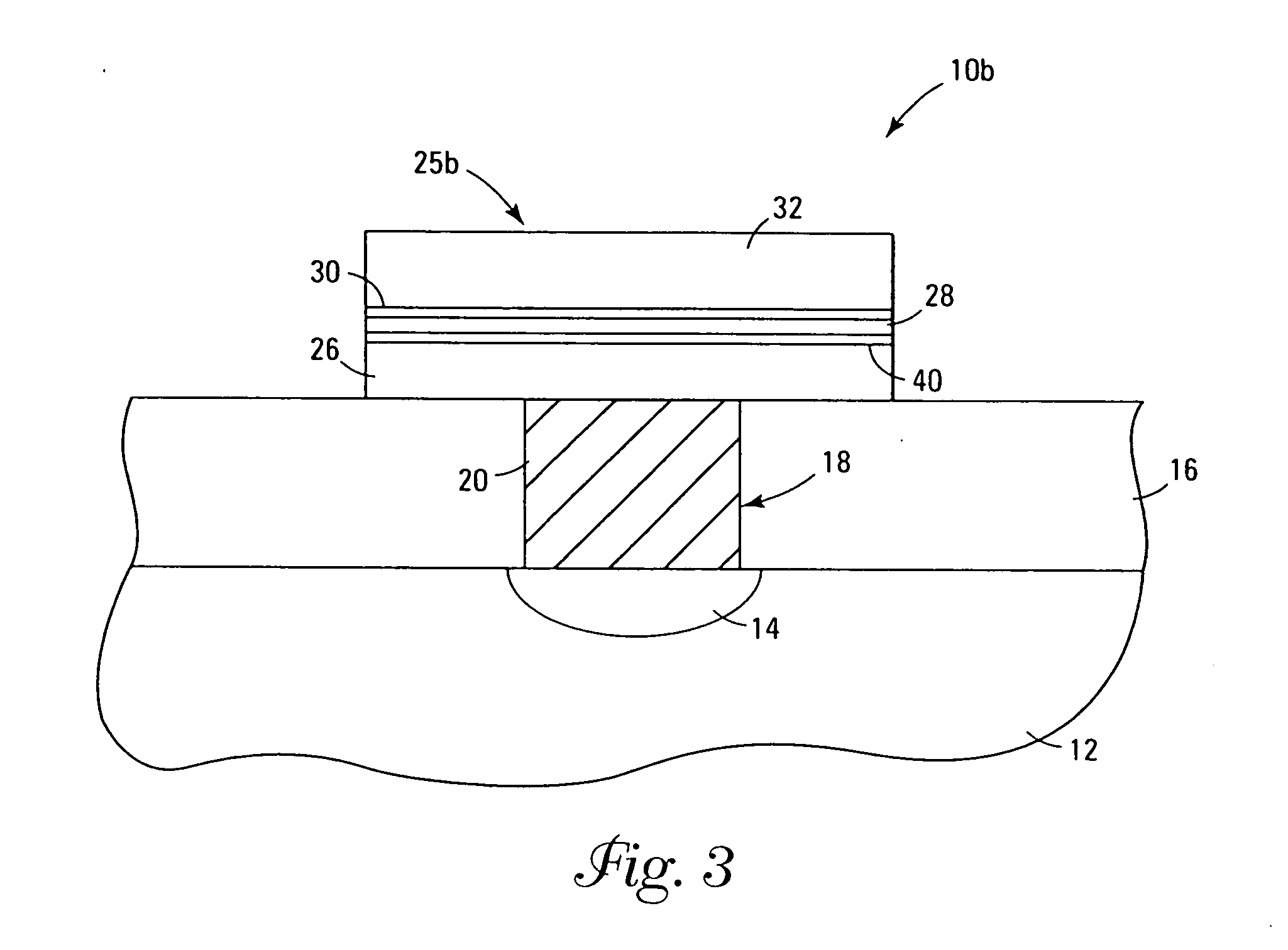
[0071] A chamber of configuration shown in FIG. 4 was set up with pneumatic valves under computer control to pulse the valves open in sequential manner. Two reservoirs connected to the chamber contained Ti(NMe2)4 and Hf(OC(CH3)3)4 (Strem Chemical, Newburyport, Mass.). The substrate was a silicon wafer having doped poly-silicon as a top layer and was maintained at 150° C. for the deposition.
[0072] Each cycle involved a 5-second pulse of Hf(OC(CH3)3)4 and a 5-second pulse of Ti(NMe2)4, each separated by a 10-second purge with argon and a 20-second pump down under dynamic vacuum. The precursors were introduced with helium carrier gas, using mass flow controllers set at 5 sccm. After 400 cycles a (Hf,Ti)O2 film 180 Å thick was obtained. The film was nearly 50 / 50 Hf / Ti based on x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and had no detectable nitrogen or carbon.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com