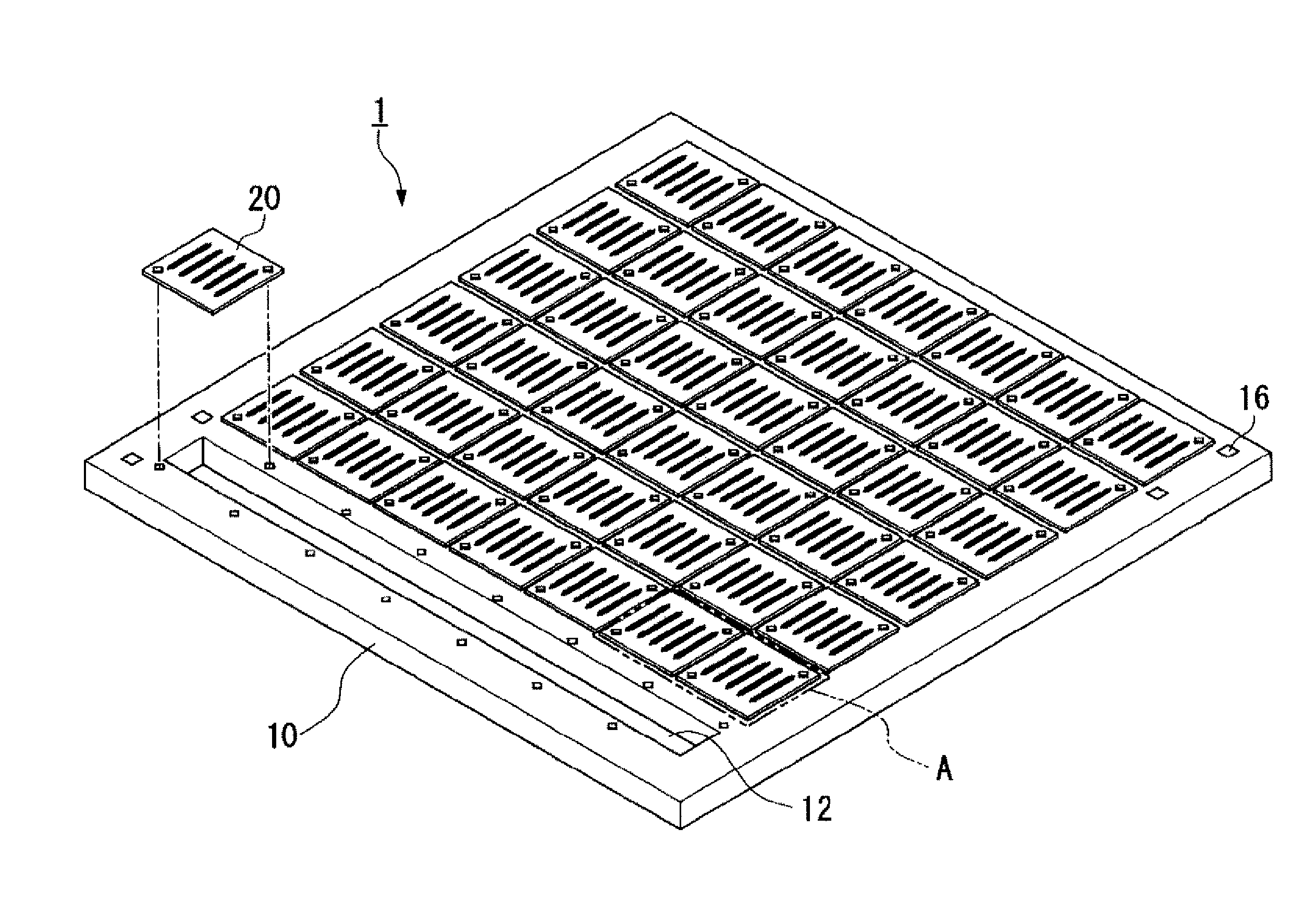
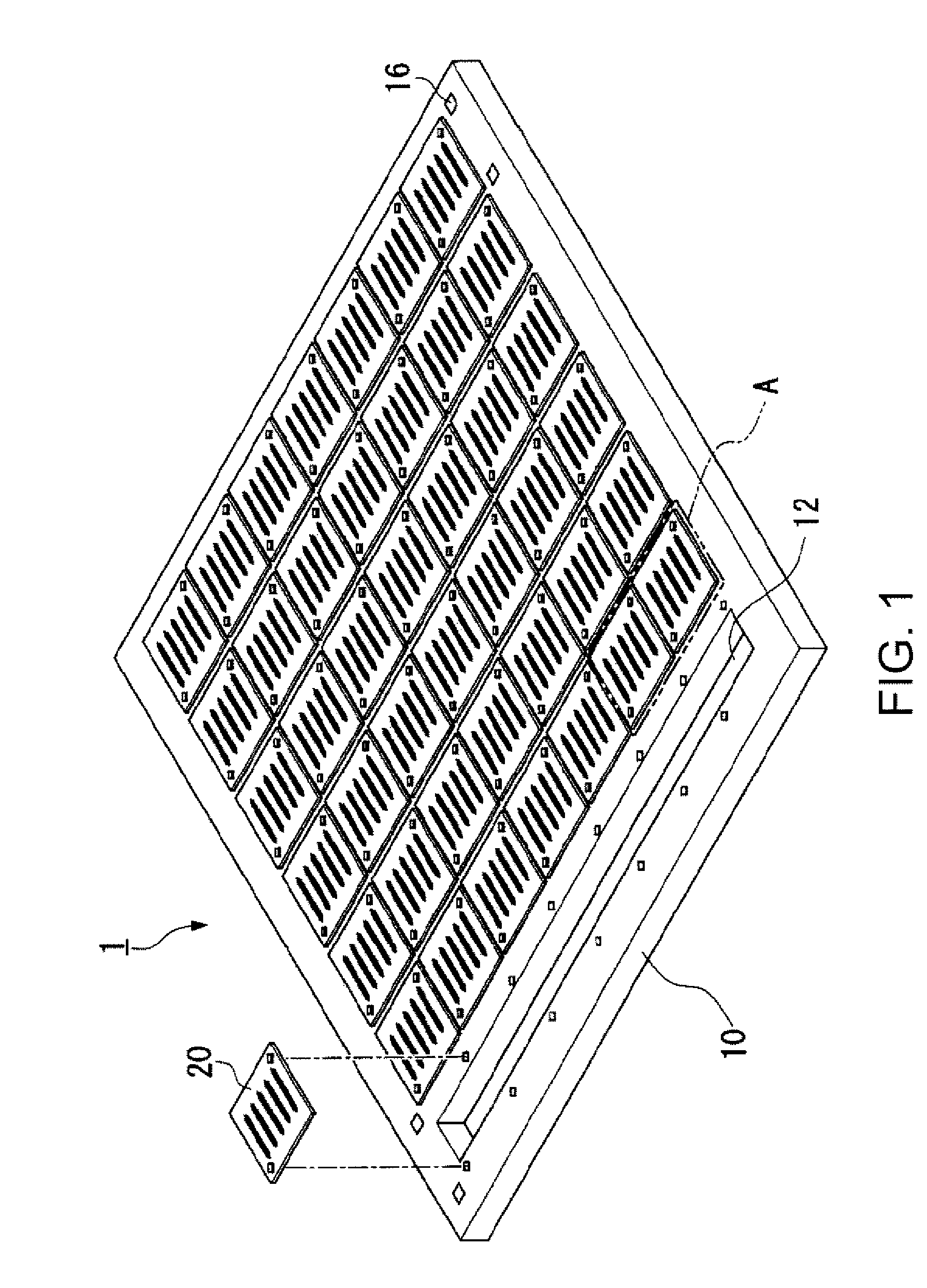
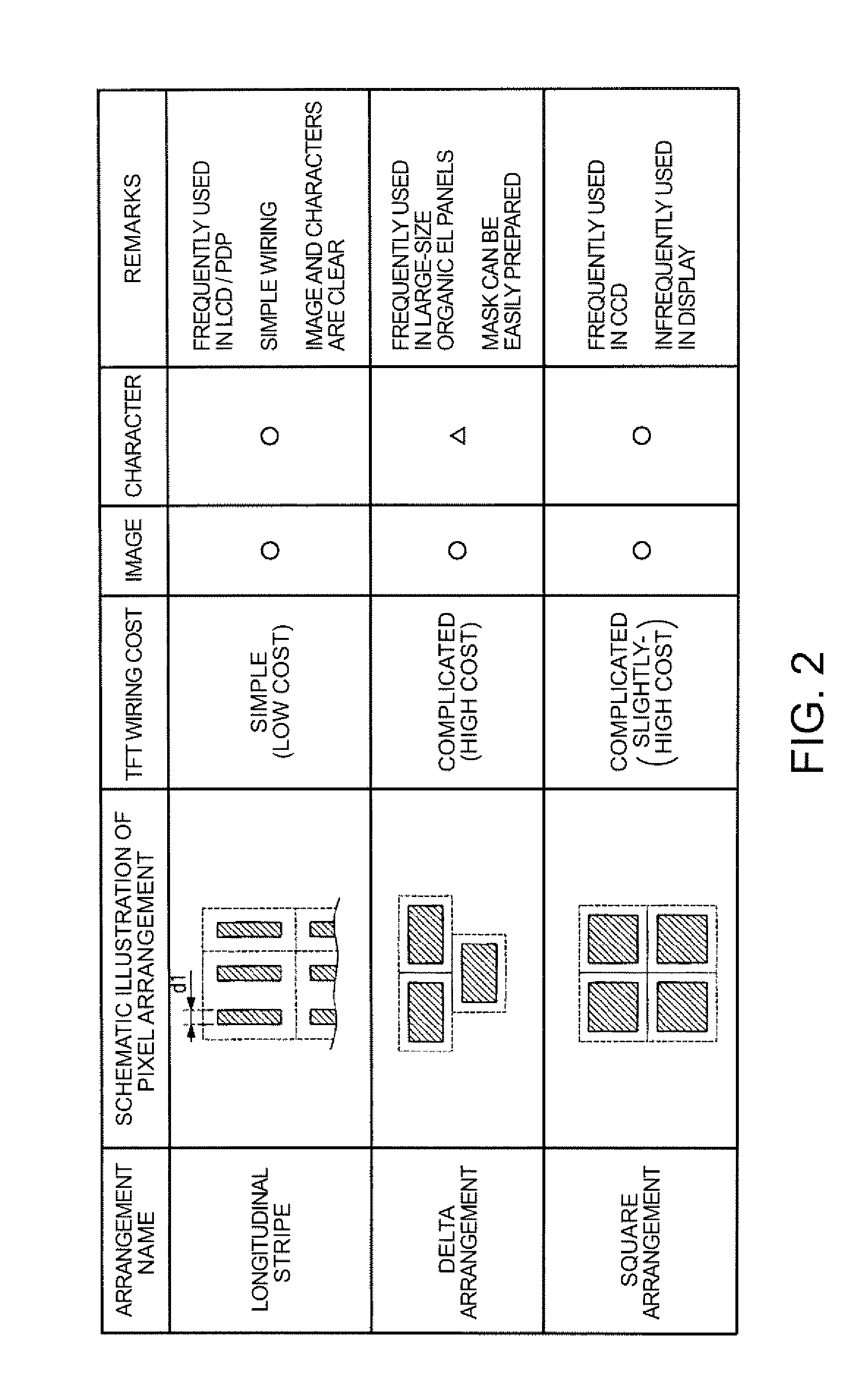
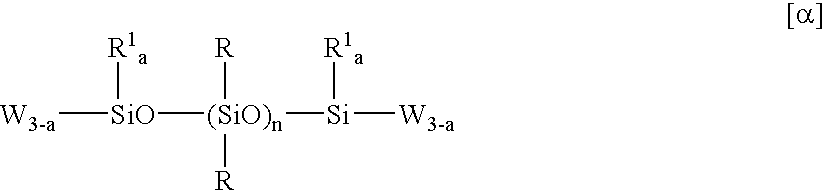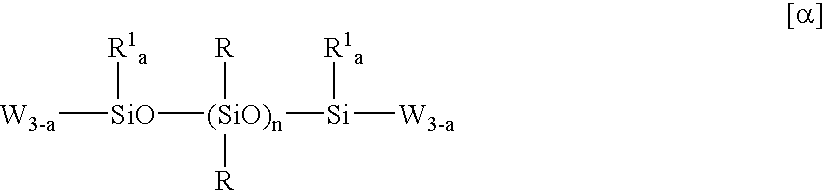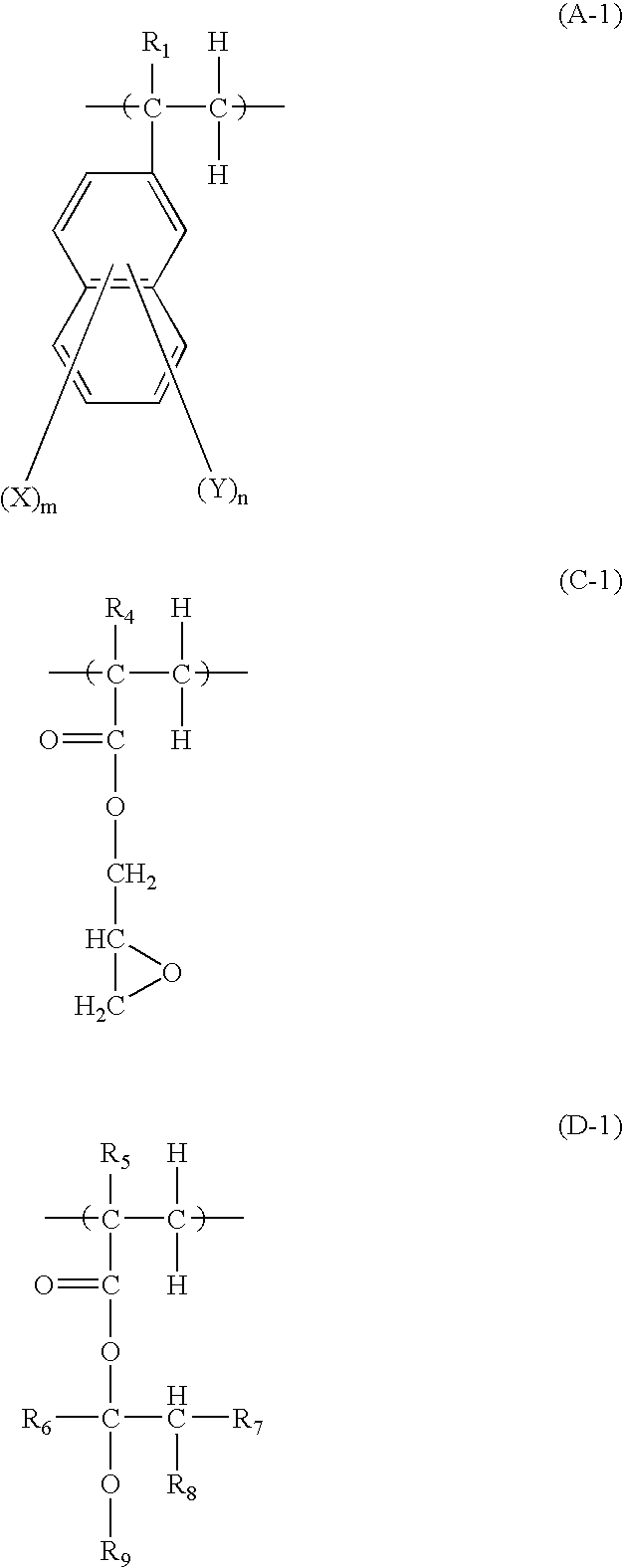Patents
Literature
237results about How to "High film thickness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for forming dielectric film in trenches by PEALD using H-containing gas
ActiveUS9455138B1Increase deposition rateHigh film thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical physicsNoble gas
A method for forming a dielectric film in a trench on a substrate by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) performs one or more process cycles, each process cycle including: (i) feeding a silicon-containing precursor in a pulse; (ii) supplying a hydrogen-containing reactant gas at a flow rate of more than about 30 sccm but less than about 800 sccm in the absence of nitrogen-containing gas; (iii) supplying a noble gas to the reaction space; and (iv) applying RF power in the presence of the reactant gas and the noble gas and in the absence of any precursor in the reaction space, to form a monolayer constituting a dielectric film on a substrate at a growth rate of less than one atomic layer thickness per cycle.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Laminated semiconductor substrate process for producing the same
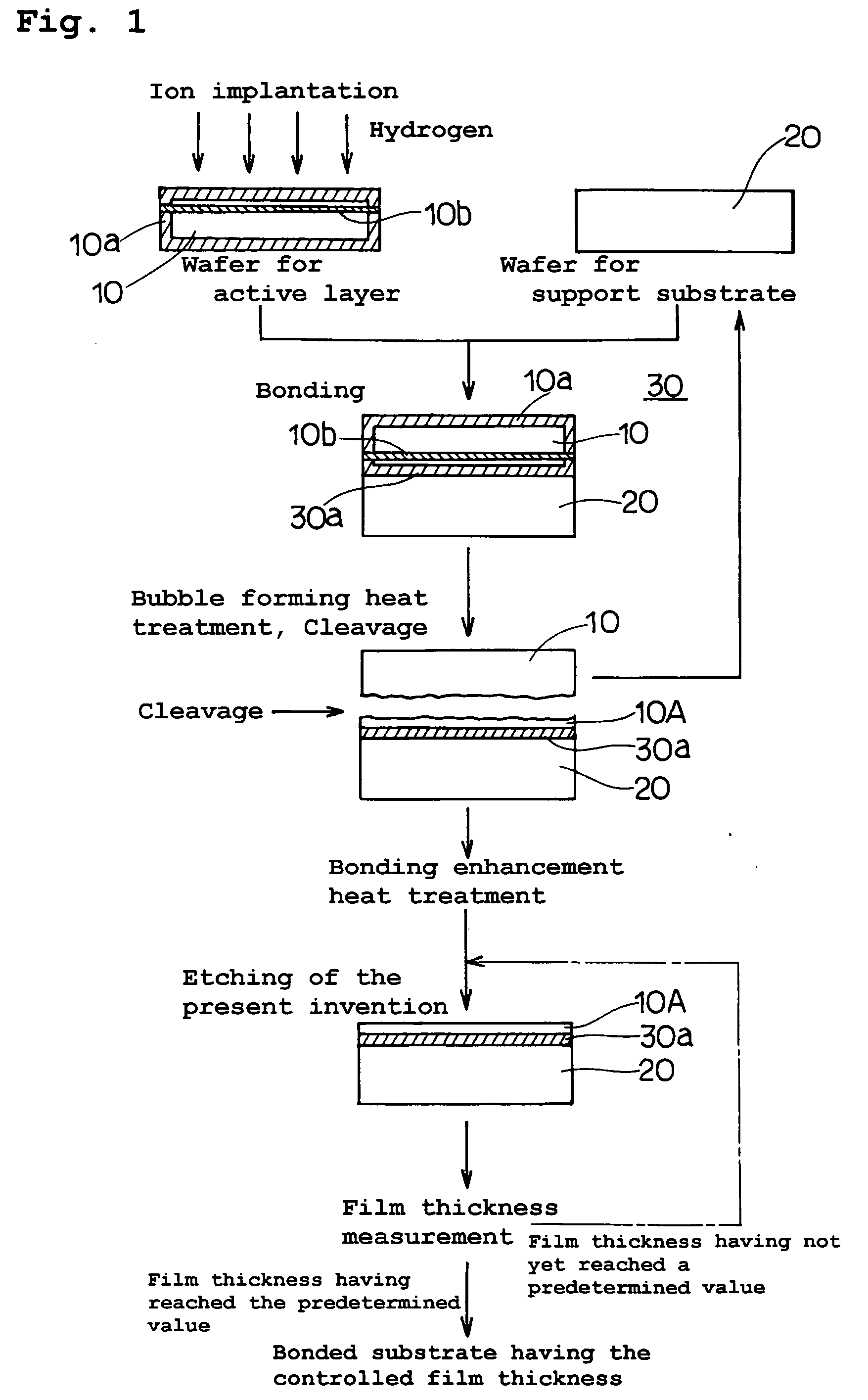
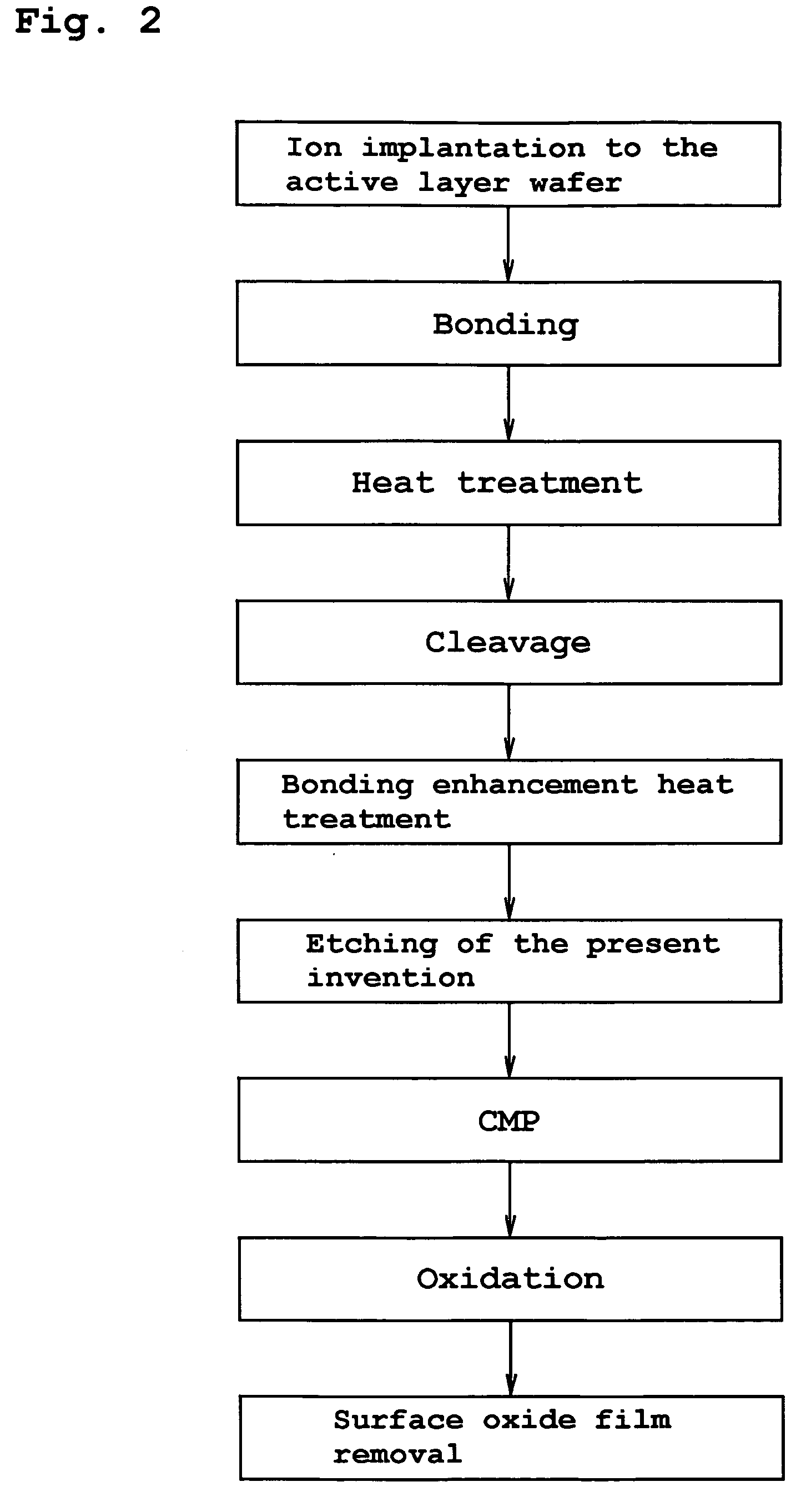
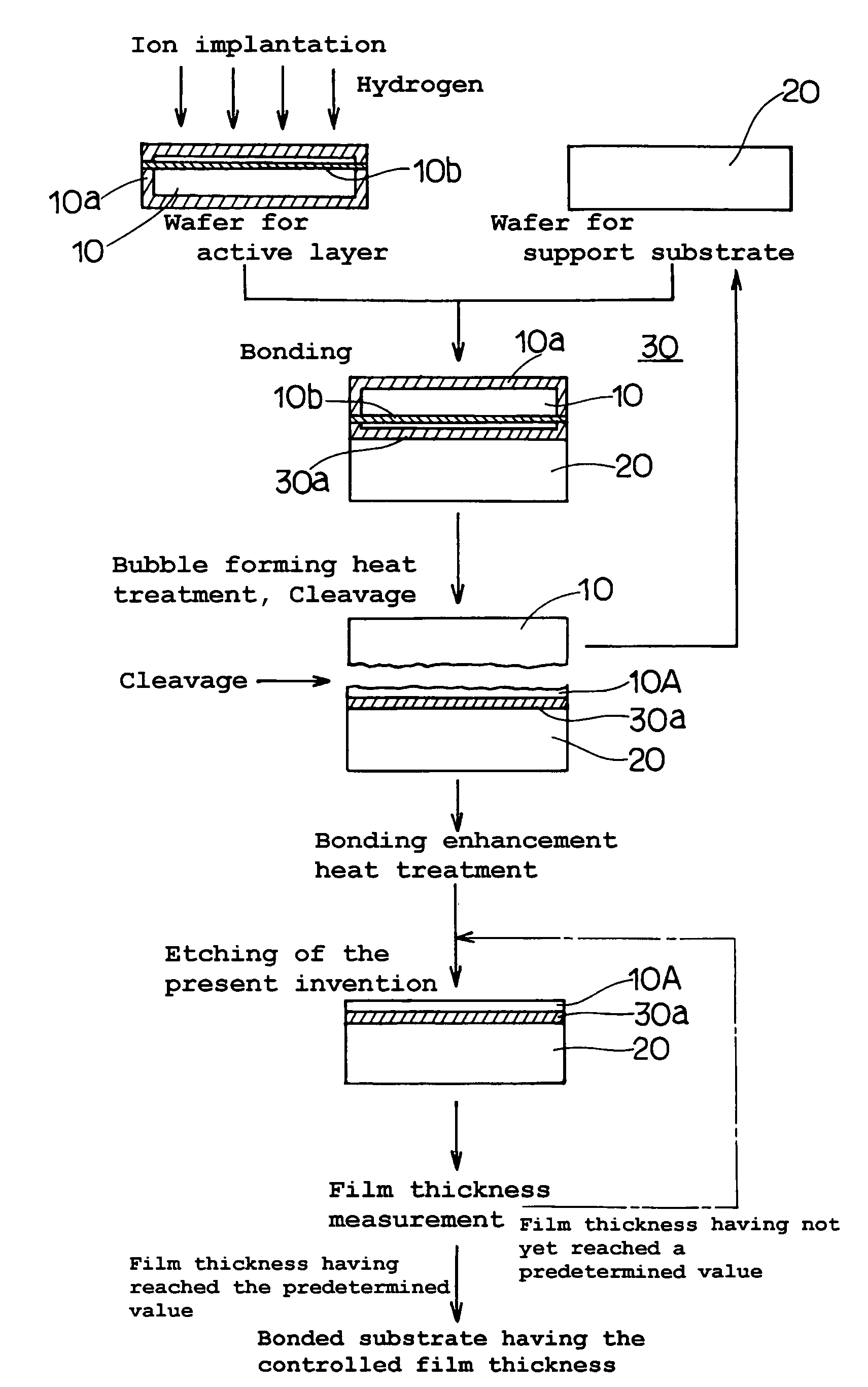
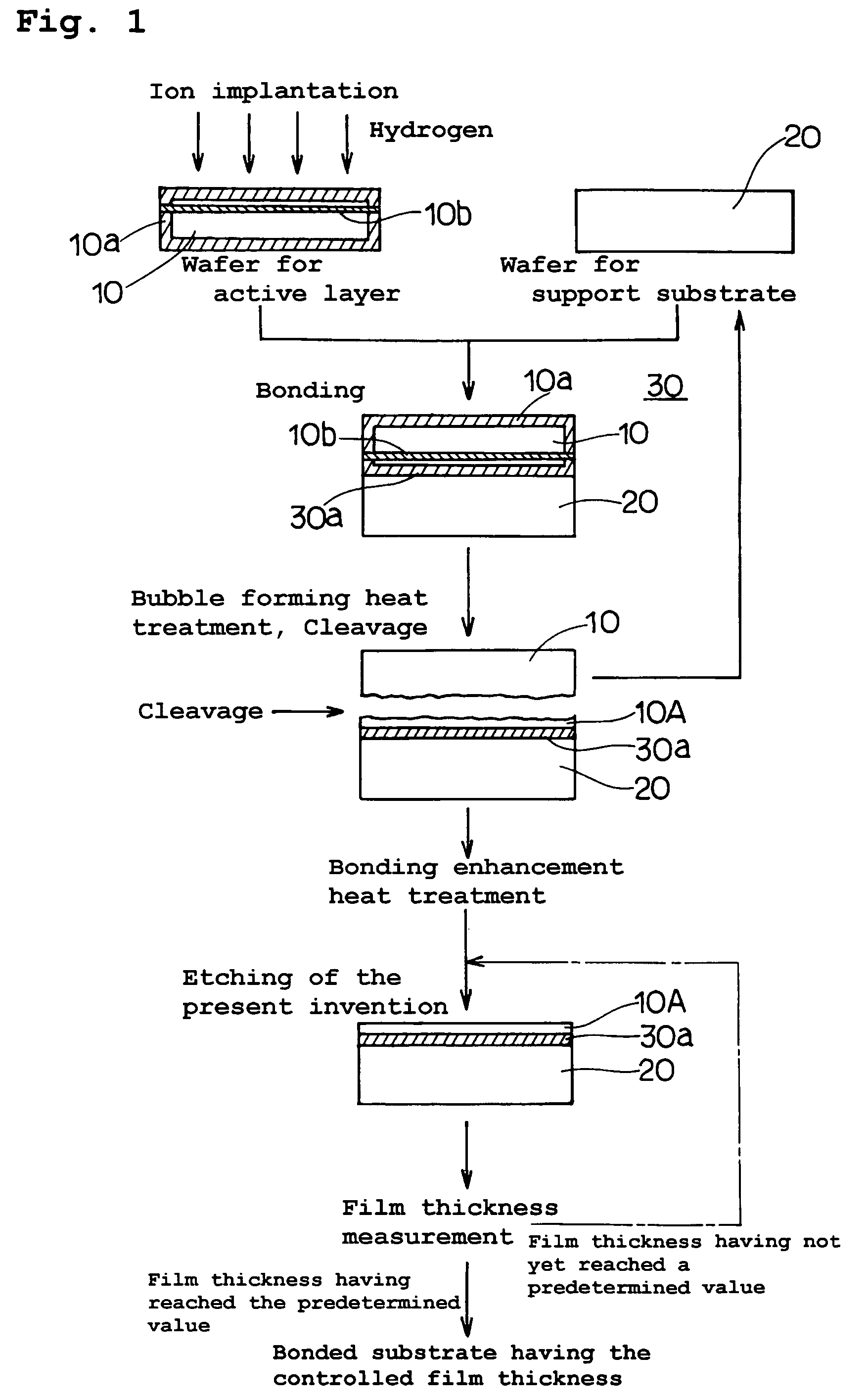
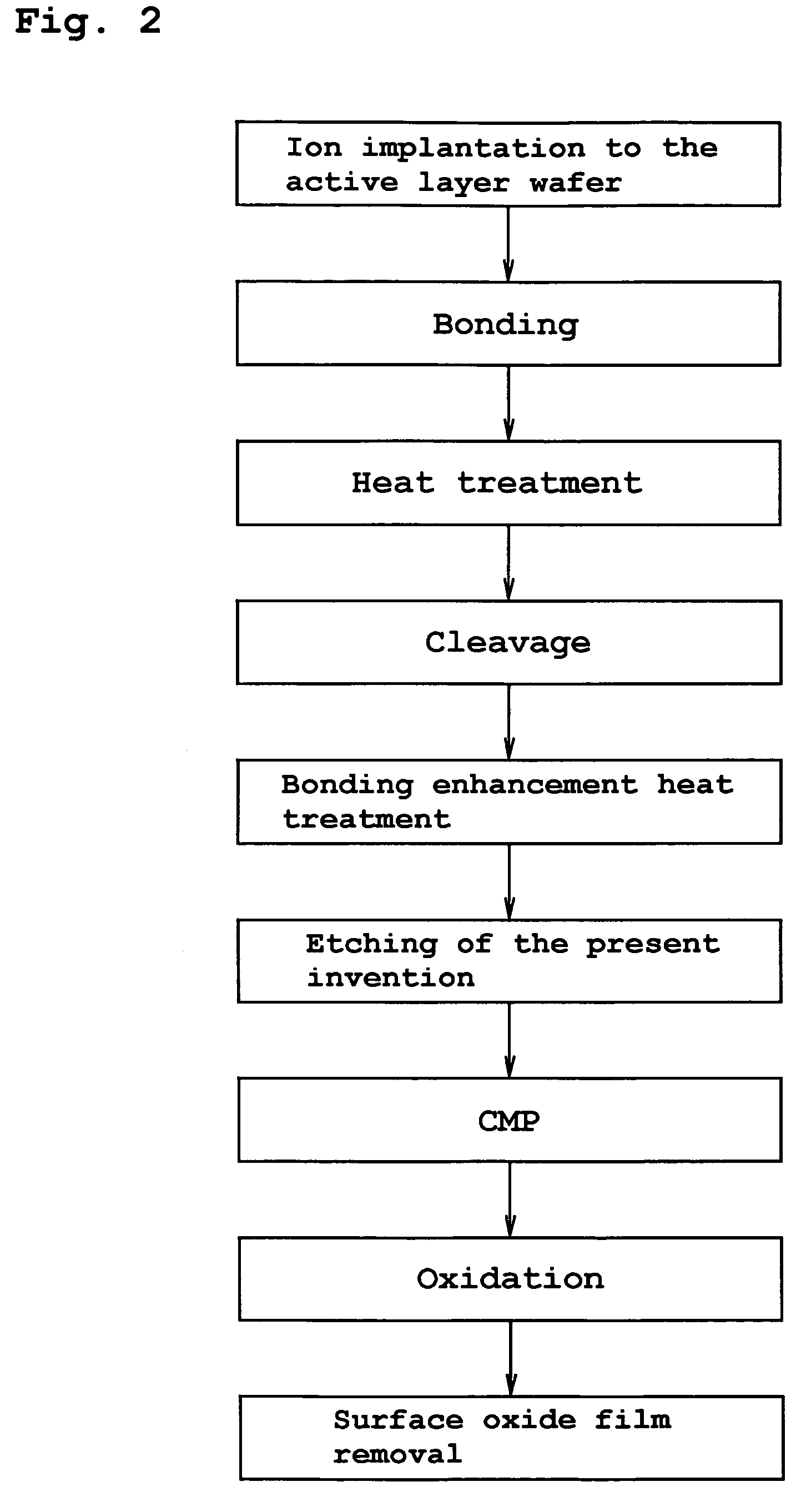
InactiveUS20060118935A1Simple processReduce surface roughnessDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEtchingSurface roughness
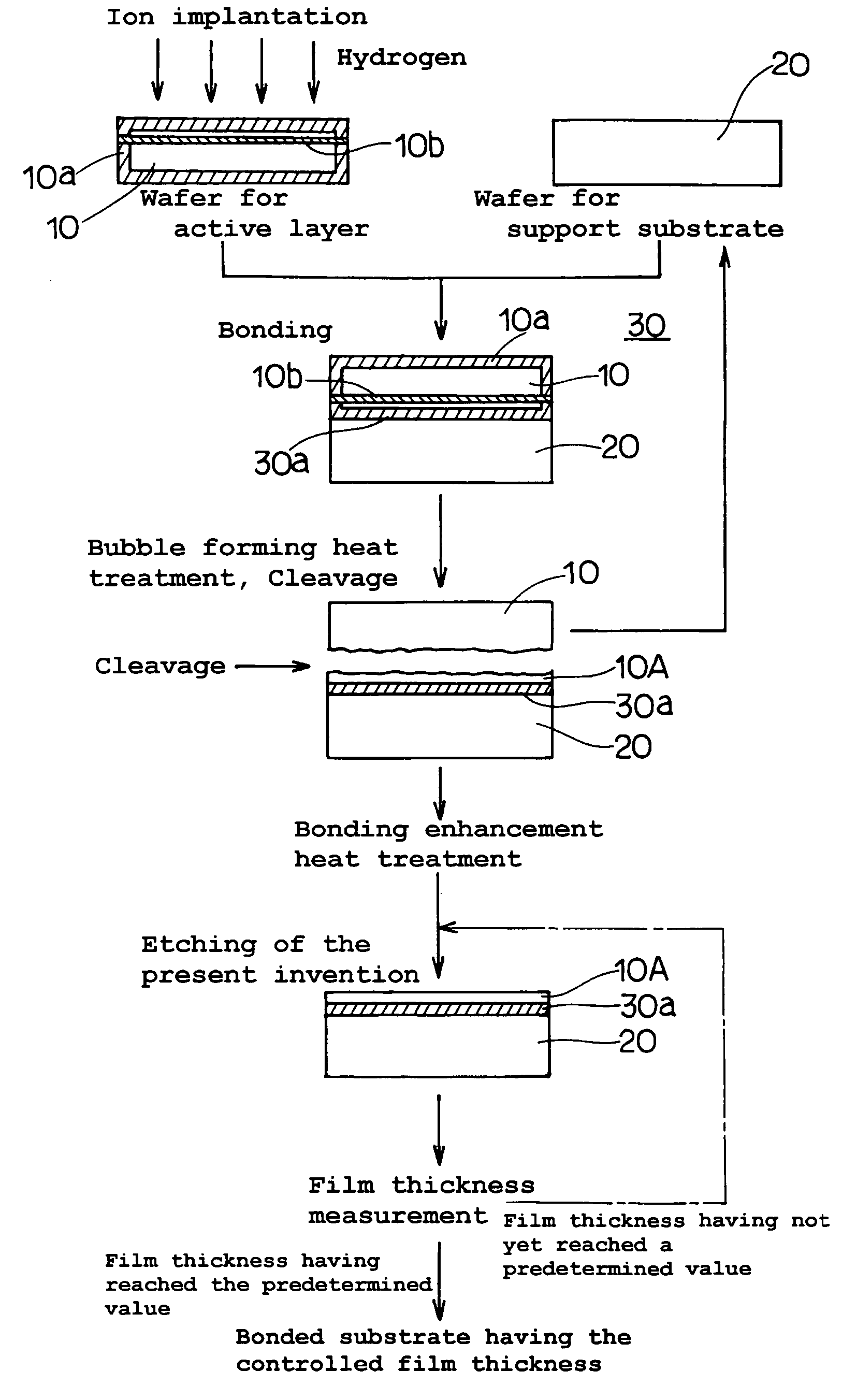
The present invention provides a bonded substrate fabricated to have its final active layer thickness of 200 nm or lower by performing the etching by only 1 nm to 1 μm with a solution having an etching effect on a surface of an active layer of a bonded substrate which has been prepared by bonding two substrates after one of them having been ion-implanted and then cleaving off a portion thereof by heat treatment. SC-1 solution is used for performing the etching. A polishing, a hydrogen annealing and a sacrificial oxidation may be respectively applied to the active layer before and / or after the etching. The film thickness of this active layer can be made uniform over the entire surface area and the surface roughness of the active layer can be reduced as well.
Owner:SUMCO CORP +1
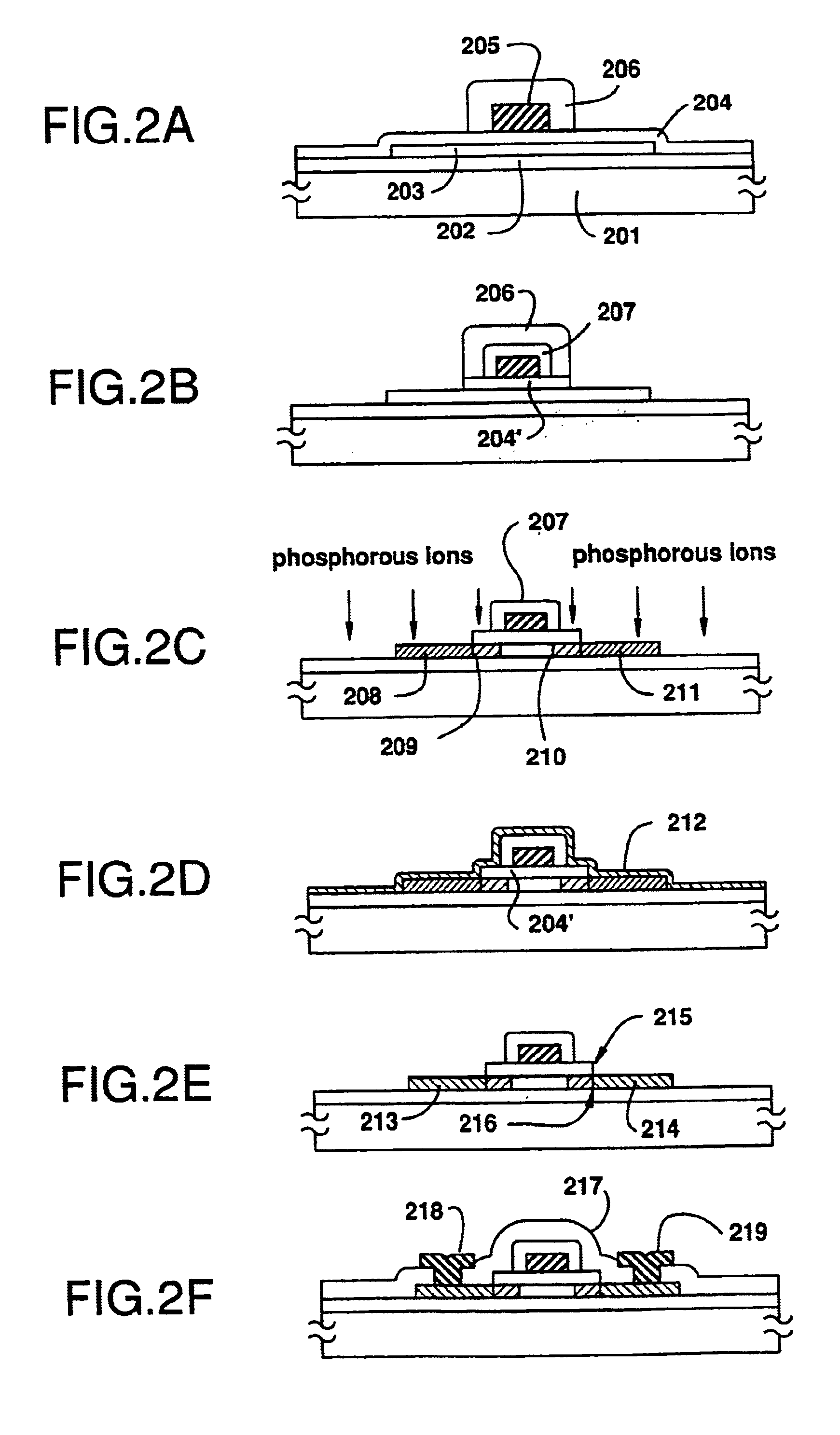
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
A TFT formed on an insulating substrate source, drain and channel regions, a gate insulating film formed on at least the channel region and a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film. Between the channel region and the drain region, a region having a higher resistivity is provided in order to reduce an Ioff current. A method for forming this structure comprises the steps of anodizing the gate electrode to form a porous anodic oxide film on the side of the gate electrode; removing a portion of the gate insulating using the porous anodic oxide film as a mask so that the gate insulating film extends beyond the gate electrode but does not completely cover the source and drain regions. Thereafter, an ion doping of one conductivity element is performed. The high resistivity region is defined under the gate insulating film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
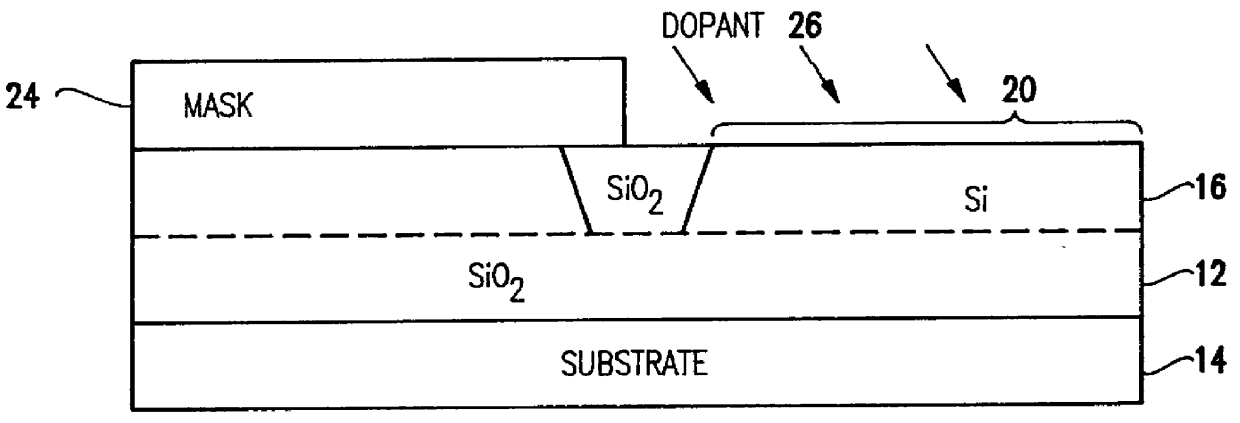
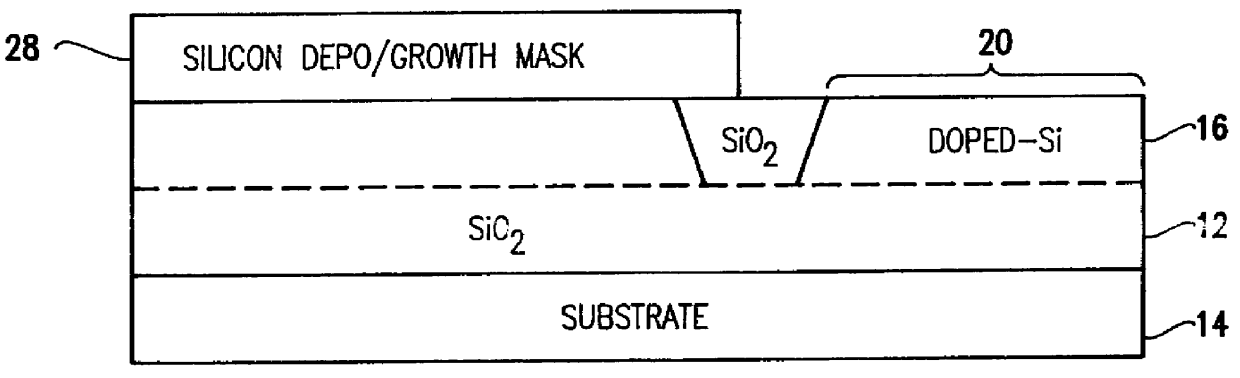
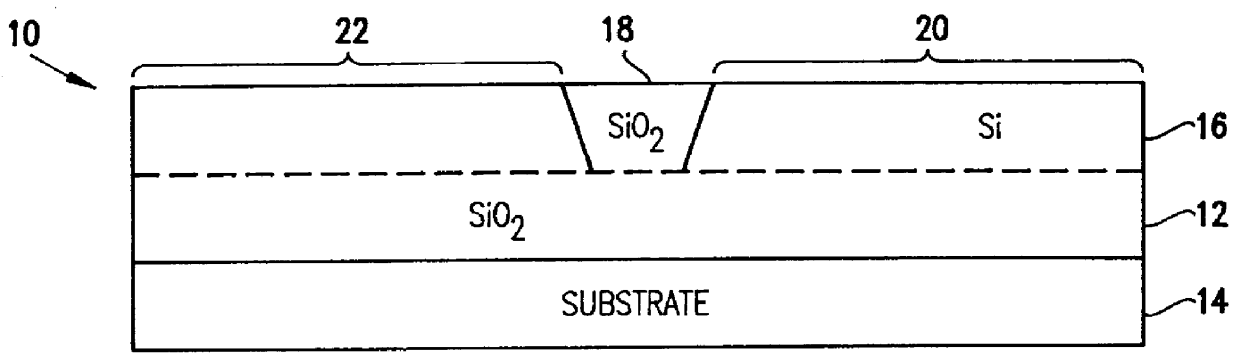
Silicon-on-insulator and CMOS-on-SOI double film fabrication process with a coplanar silicon and isolation layer and adding a second silicon layer on one region
InactiveUS6096584AHigher power-to-failure thresholdImprove protectionTransistorSolid-state devicesIsolation layerElectronic component
Silicon is formed at selected locations on a silicon-insulator (SOI) substrate during fabrication of selected electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, and diodes. The silicon location is defined using a patterned, removable mask, and the silicon may be applied by deposition or growth and may take the form of polysilicon or crystalline silicon. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) characteristics of the SOI device is significantly improved by having a thick double layer of silicon in selected regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Dielectric resonator, dielectric filter, dielectric duplexer, and communication device
InactiveUS6556101B1Reducing losses in dielectric resonatorsReduce conduction lossResonatorsWaveguidesElectrical conductorDielectric resonator
A small-sized low-loss dielectric resonator, dielectric filter, and dielectric duplexer, and a communication device using such an element. Through-holes are formed in a dielectric block. The inner surface of each through-hole is covered with a thin-film multilayer electrode consisting of an outermost conductive layer and a multilayer region including thin-film conductive layers and thin-film dielectric layers. An outer conductor having a similar thin-film multilayer electrode structure is formed on the outer surface of the dielectric block. An outer conductor in the form of a single-layer electrode is formed on a short-circuited end face of the dielectric block thereby connecting together the thin-film conductive layers of the inner and outer conductors.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Adaptive optical devices with controllable focal power and aspheric shape
ActiveUS20130176628A1Limit ability to control optical propertyReduce optical aberrationLensRefractive indexEngineering
A fluidic lens may include an optical surface configured for deflection dominated by bending stress. An adjustable concentric load may be applied to the optical surface to cause a clear aperture region of the optical surface to deflect with generally spherical curvature. Adjusting the concentric load controls the radius of curvature. An adjustable uniformly-distributed load may be applied to the optical surface by fluid pressure that causes the clear aperture region to deflect with an aspheric shape. Adjusting the pressure controls the asphericity of curvature. First and second fluids having similar densities and different refractive indexes may be disposed on either side of a deflectable optical surface to help balance gravitational loading on either side of the optical surface, thereby reducing gravity-associated aberrations.
Owner:HOLOCHIP
Fluidic lens with reduced optical aberration
ActiveUS20100208357A1Increased complexityHigh film thicknessAdditive manufacturing apparatusOptical filtersEngineeringActuator
A fluidic lens device capable of providing variable focal power with reduced optical aberration is disclosed. The device includes a lens member and an actuator. The lens member comprises one or more elastic optical surfaces, a compliant support member in communication with the optical surfaces, and a fluid-filled chamber. The optical surfaces have a high value of elastic modulus, reducing coma and other aberrations associated gravity and acceleration. The support member may provide a compliant fluid seal and allow the edges of the optical surfaces to pivot, reducing spherical and other aberrations. One or more piezoelectric ring-bender actuators may provide the force required for compressing the support ring and deflecting the optical surfaces. The actuators may be configured to provide the fluidic lens device with reduced sensitivity to changes in temperature.
Owner:HOLOCHIP
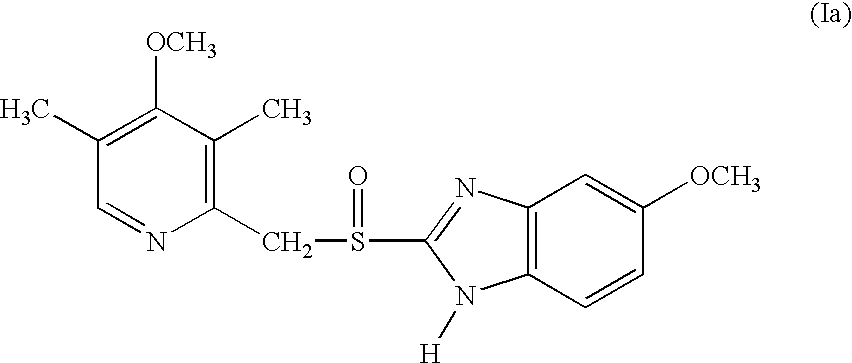
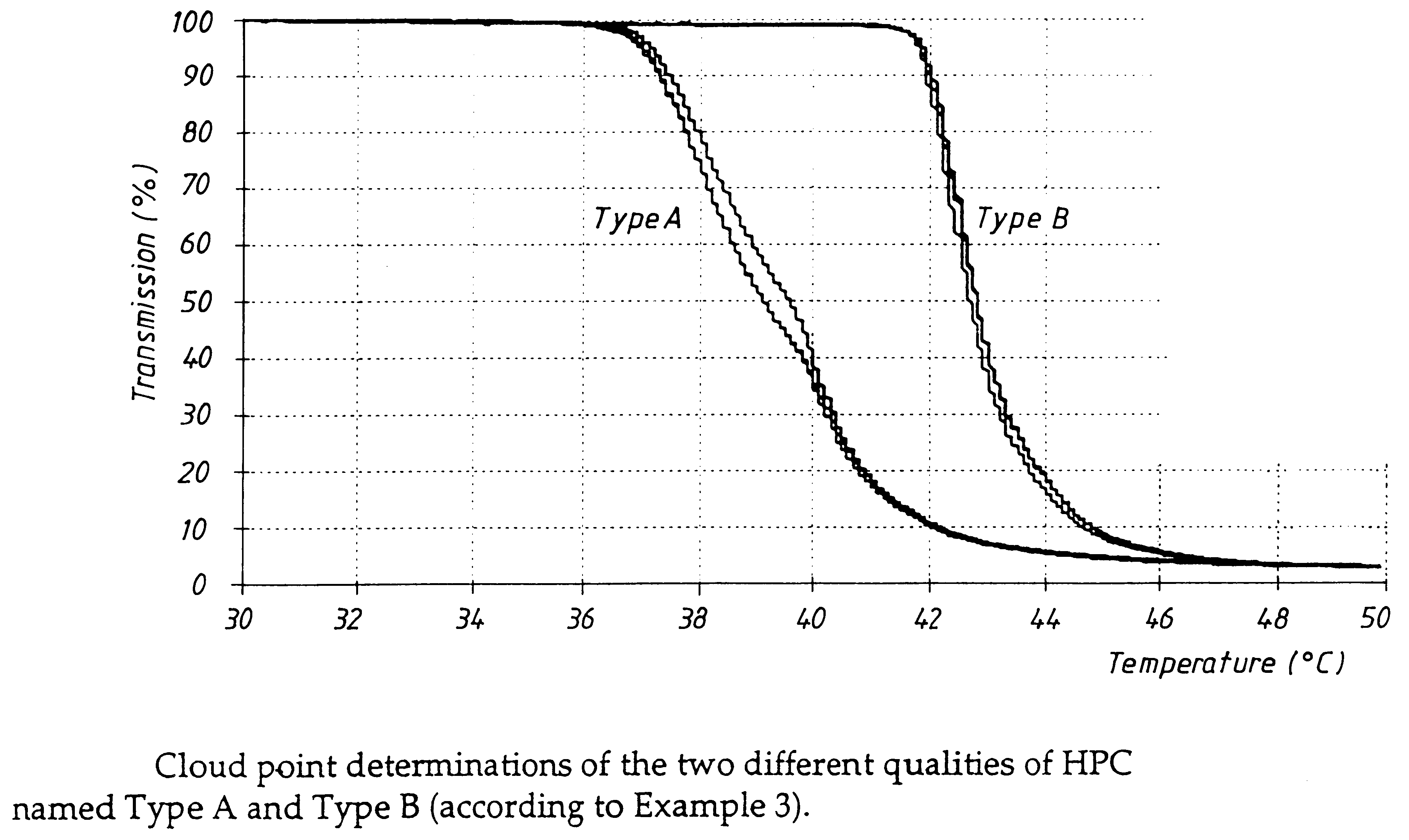
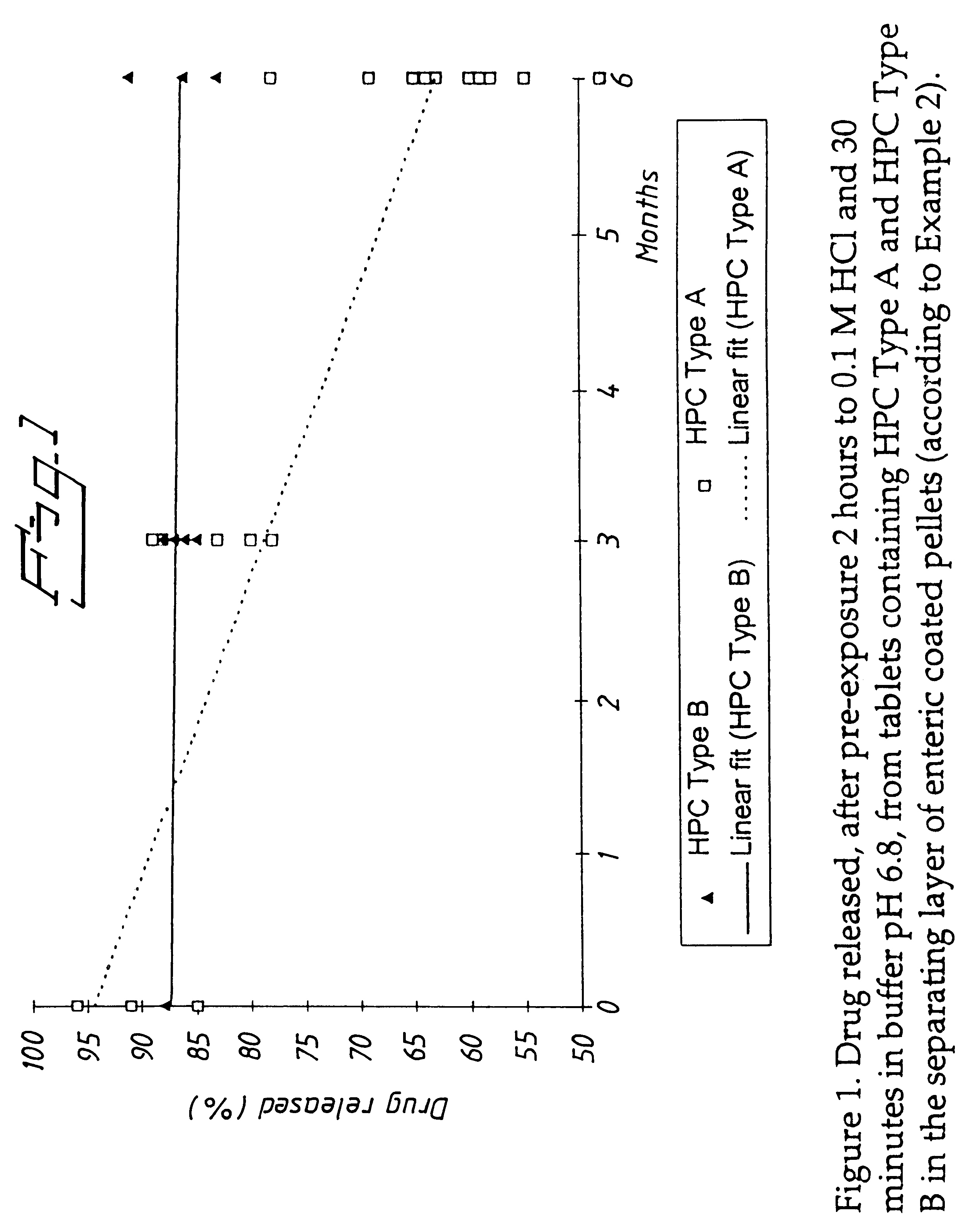
Pharmaceutical formulation comprising omeprazole
InactiveUS6428810B1Reduce diffuseHigh film thicknessOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryEnantiomerOmeprazole
An enteric coated oral pharmaceutical formulation comprising as active ingredient a compound selected from the group of omeprazole, an alkaline salt of omeprazole, one of the single enantiomers of omeprazole and an alkaline salt of one of the single enantiomers of omeprazole, wherein the formulation comprises a core material that comprises the active ingredient and optionally an alkaline reacting compound, the active ingredient is in admixture with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, such as for instance a binding agent, and on said core material a separating layer and an enteric coating layer. A hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) with a specific cloud point is used in the manufacture of the claimed pharmaceutical formulations. Furthermore, the application describes the processes for their preparation and the use of the claimed formulations in medicine.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050142705A1High regionImprove uniformityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringHigh resistivity
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Hologram element, production method thereof, and optical header
InactiveUS20060055993A1High film thicknessImprove productivityHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesRecord information storageProduction rateLight beam
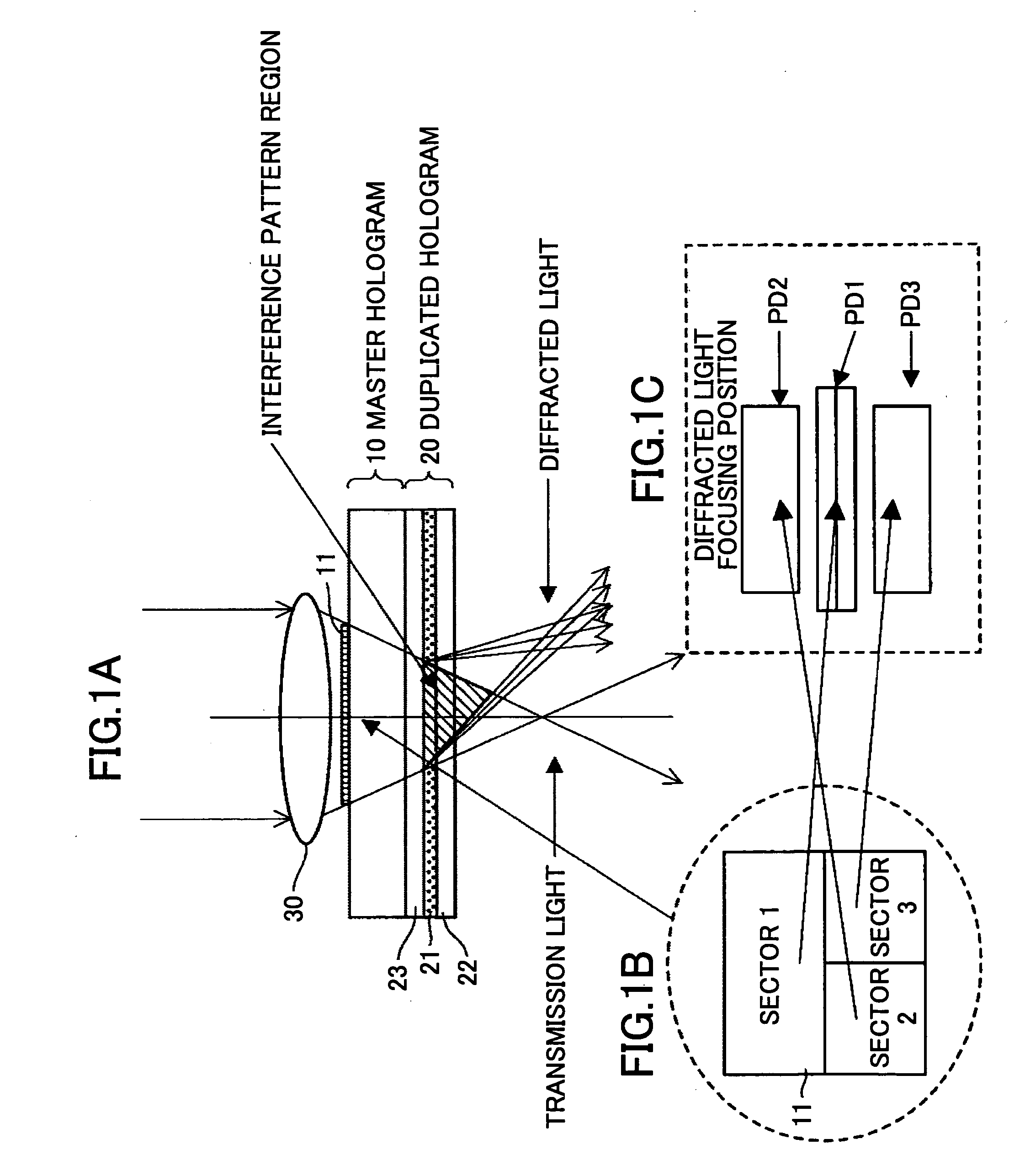
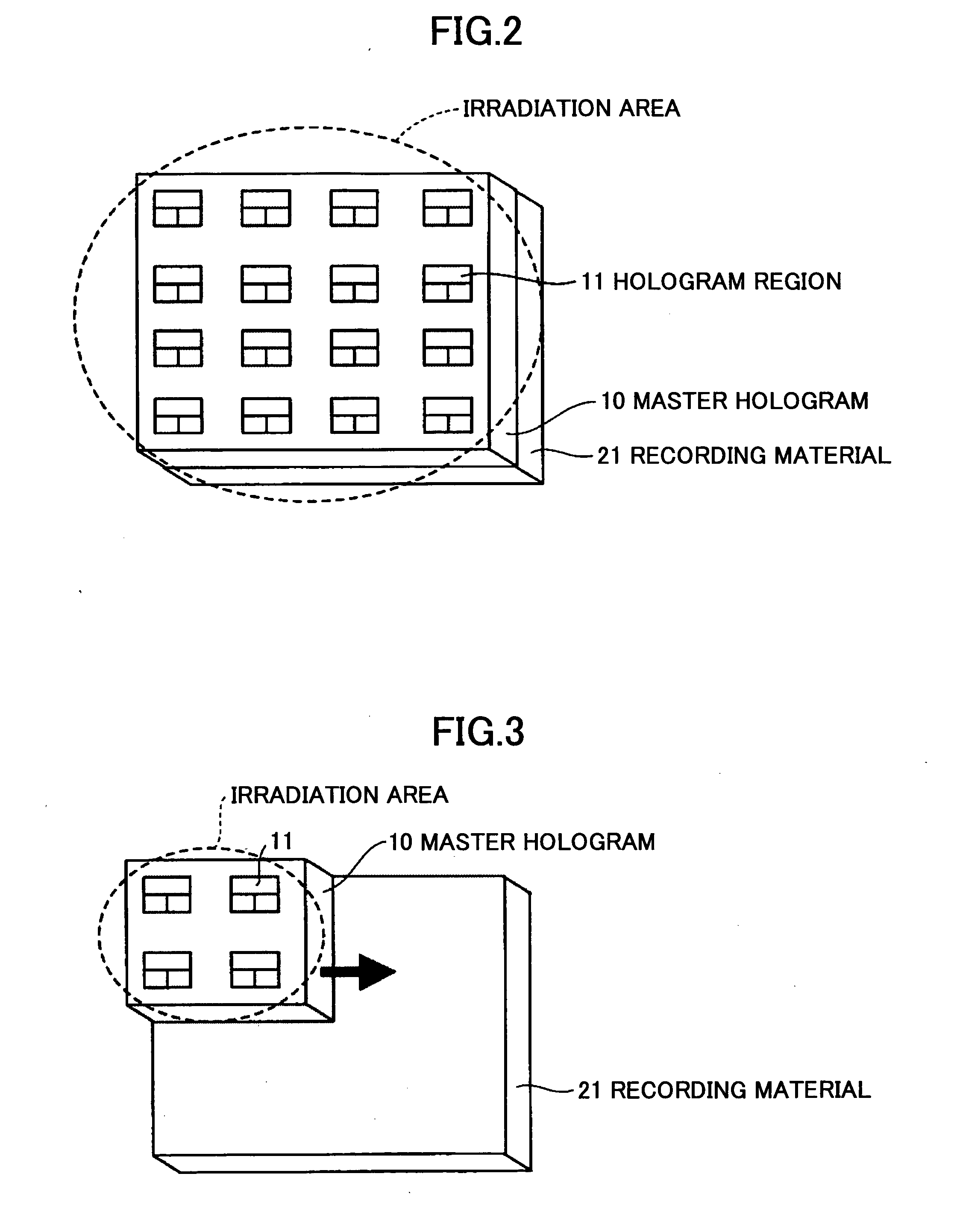
A method of producing a hologram element is disclosed that is able to prevent spread of a polymerization reaction and light leakage during exposure with interference light, and improve productivity in mass production. The hologram element is for transmitting, reflecting, diffracting, or scattering incident light, and includes a pair of substrates, an isolation member between the substrates that forms an isolated region, and a photo-sensitive recording material sealed in the isolated region. The hologram element includes a periodic structure formed by exposing the recording material to interference light. The interference light is generated by two or more light beams, or by using a master hologram. The recording material is formed from a composite material including a polymerized polymer or a polymerized liquid crystal. The periodic structure is formed by exposing the recording material to the interference light to induce the polymerization reaction and phase separation in the composite material.
Owner:RICOH KK
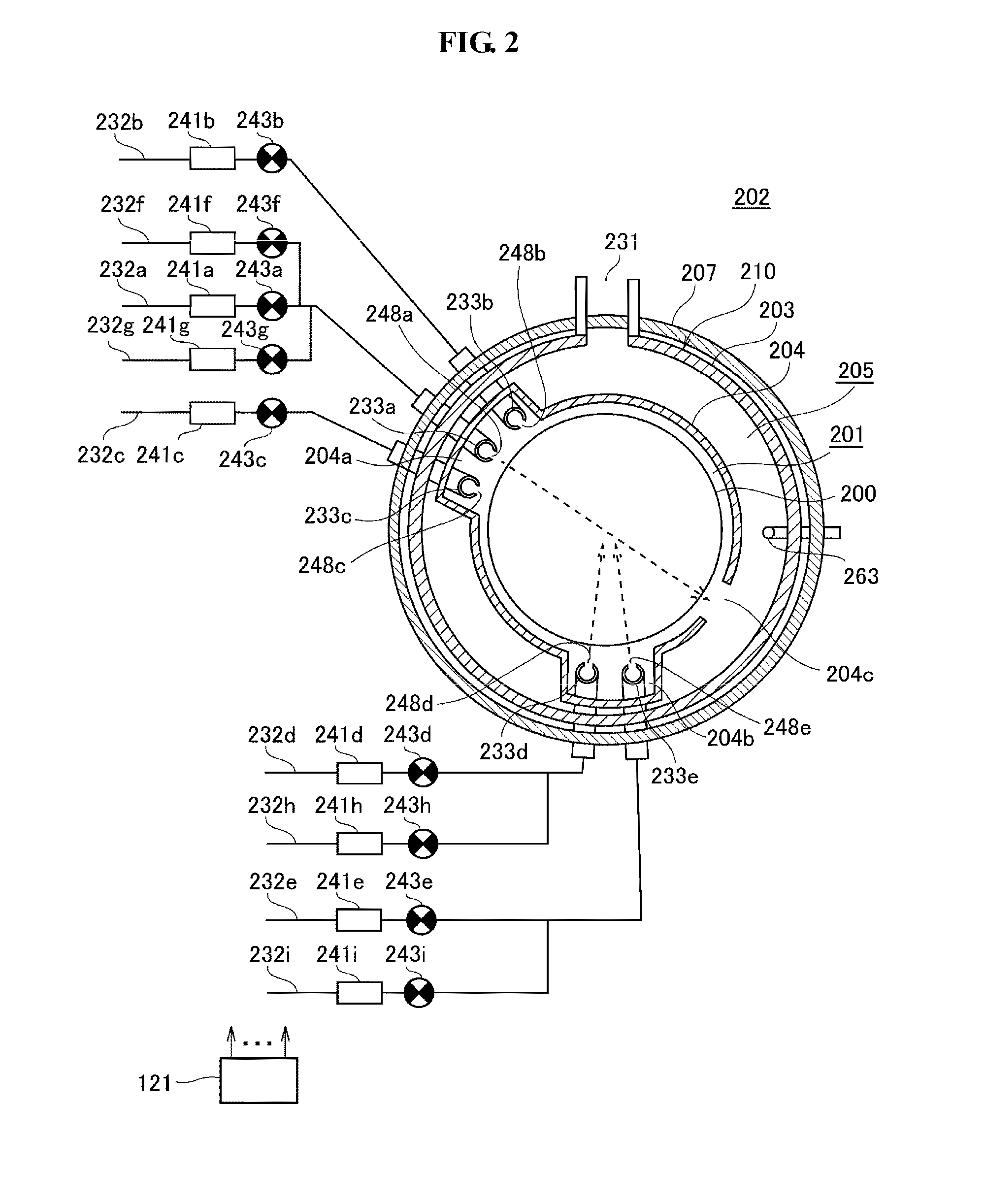
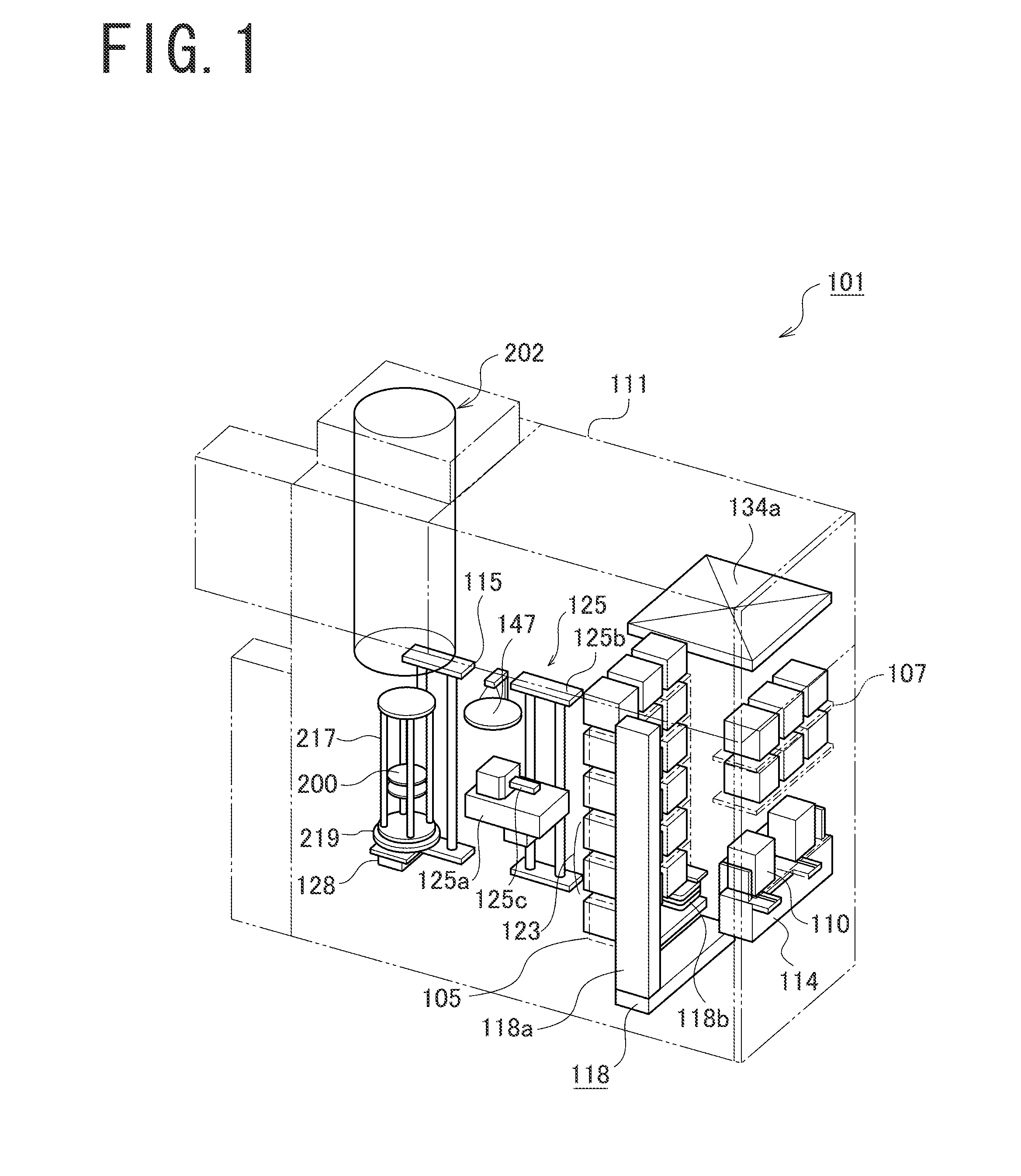
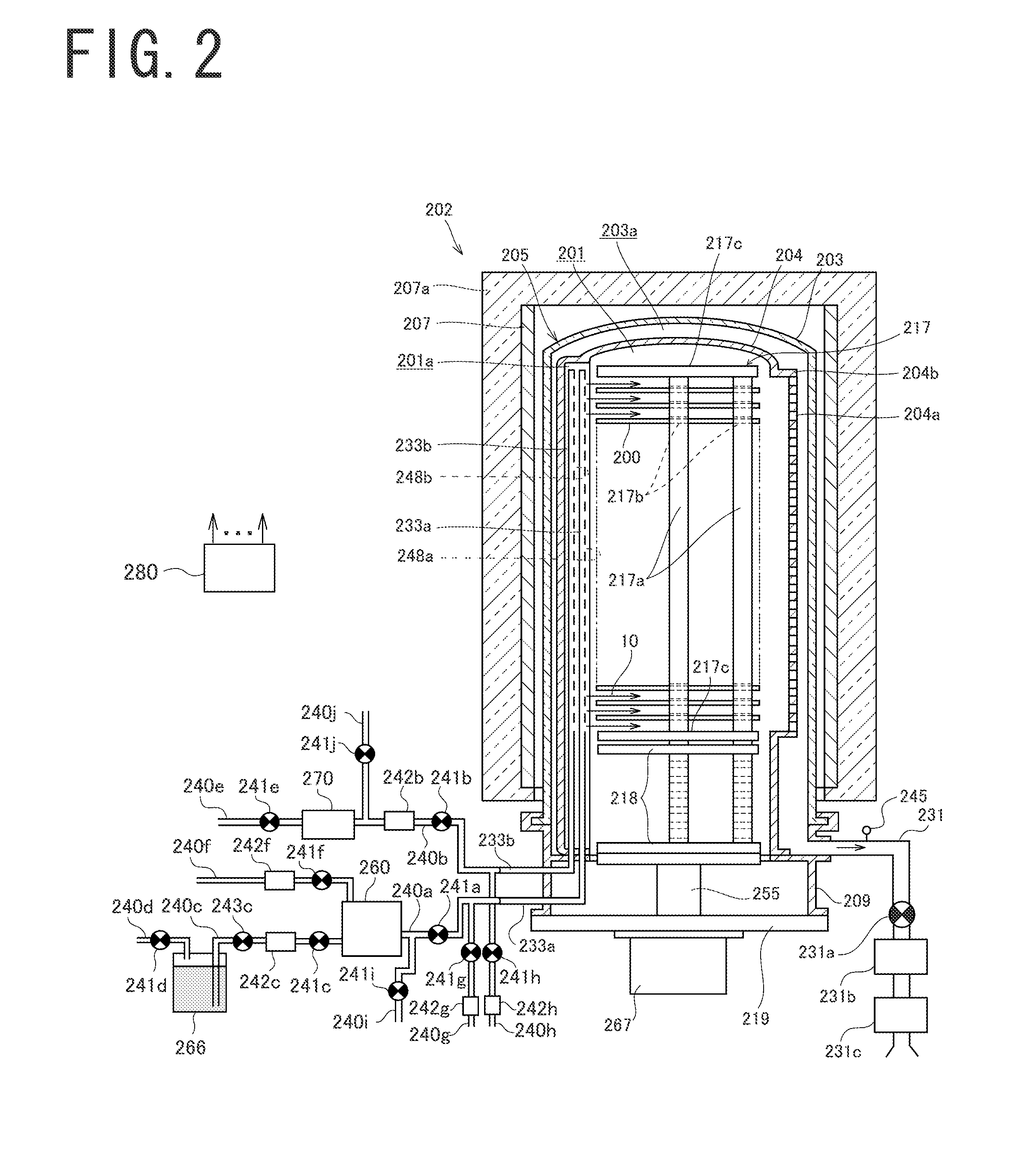
Substrate processing apparatus, method of manufacturing semiconductor device, and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium
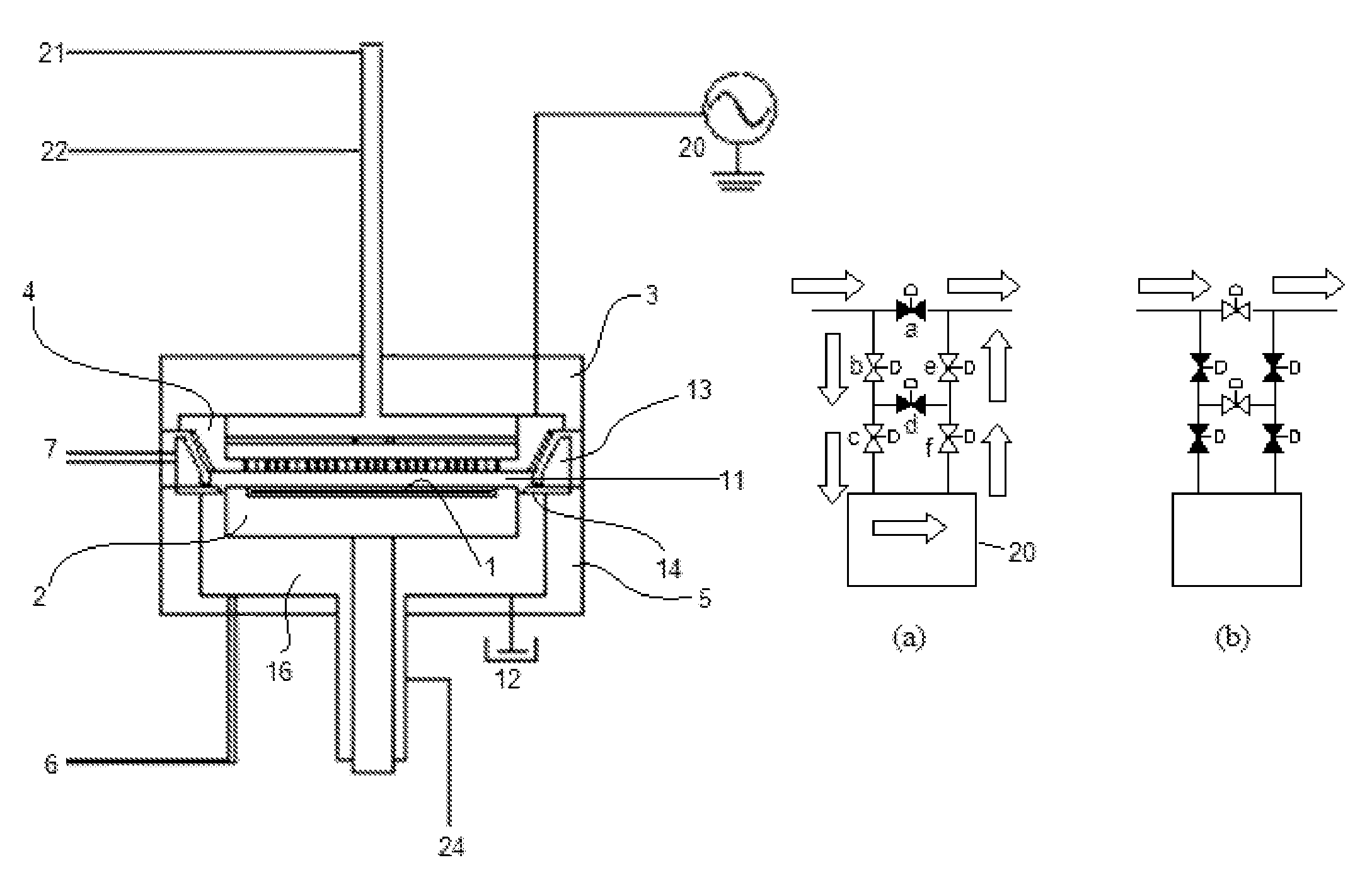
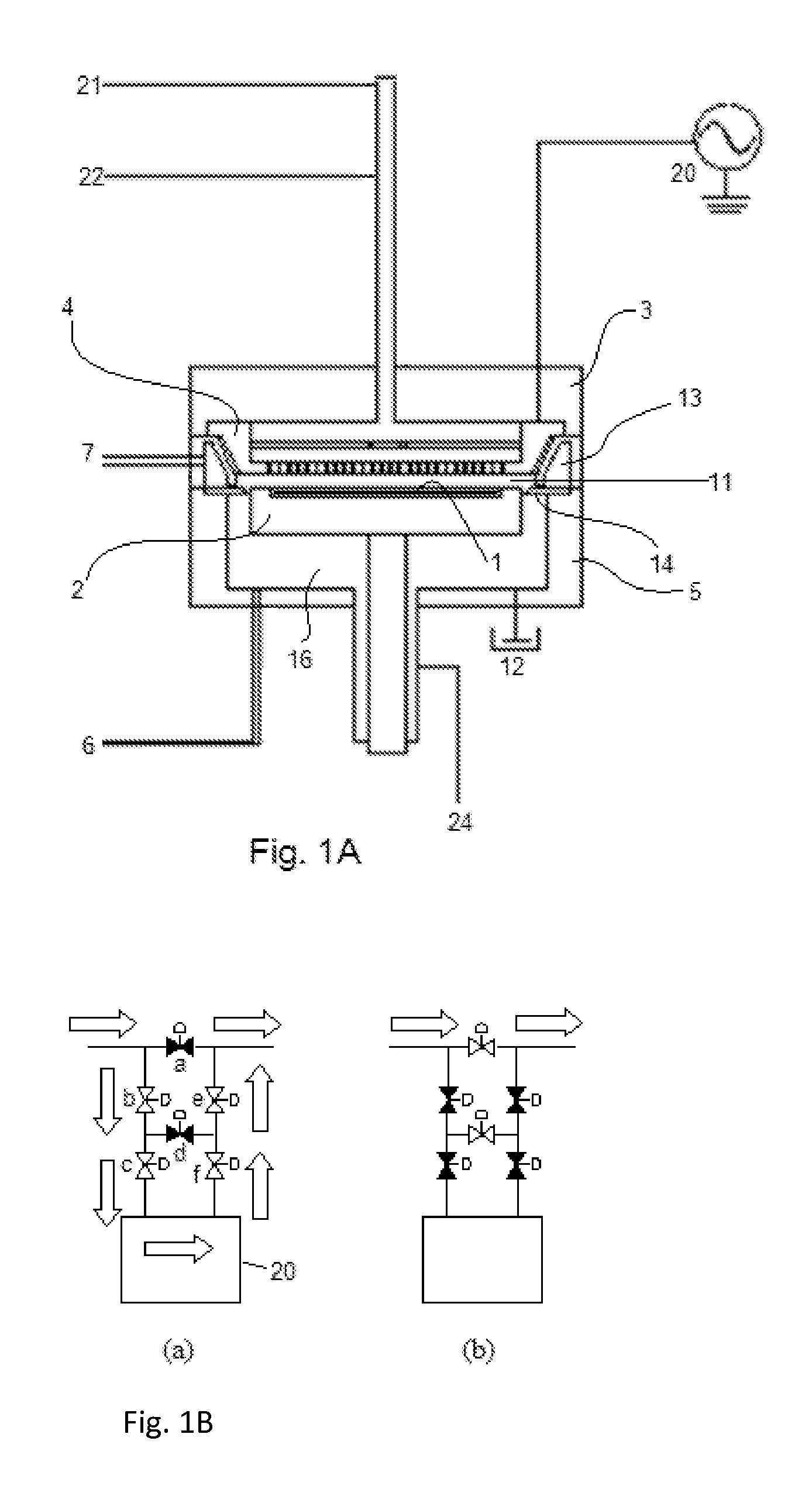
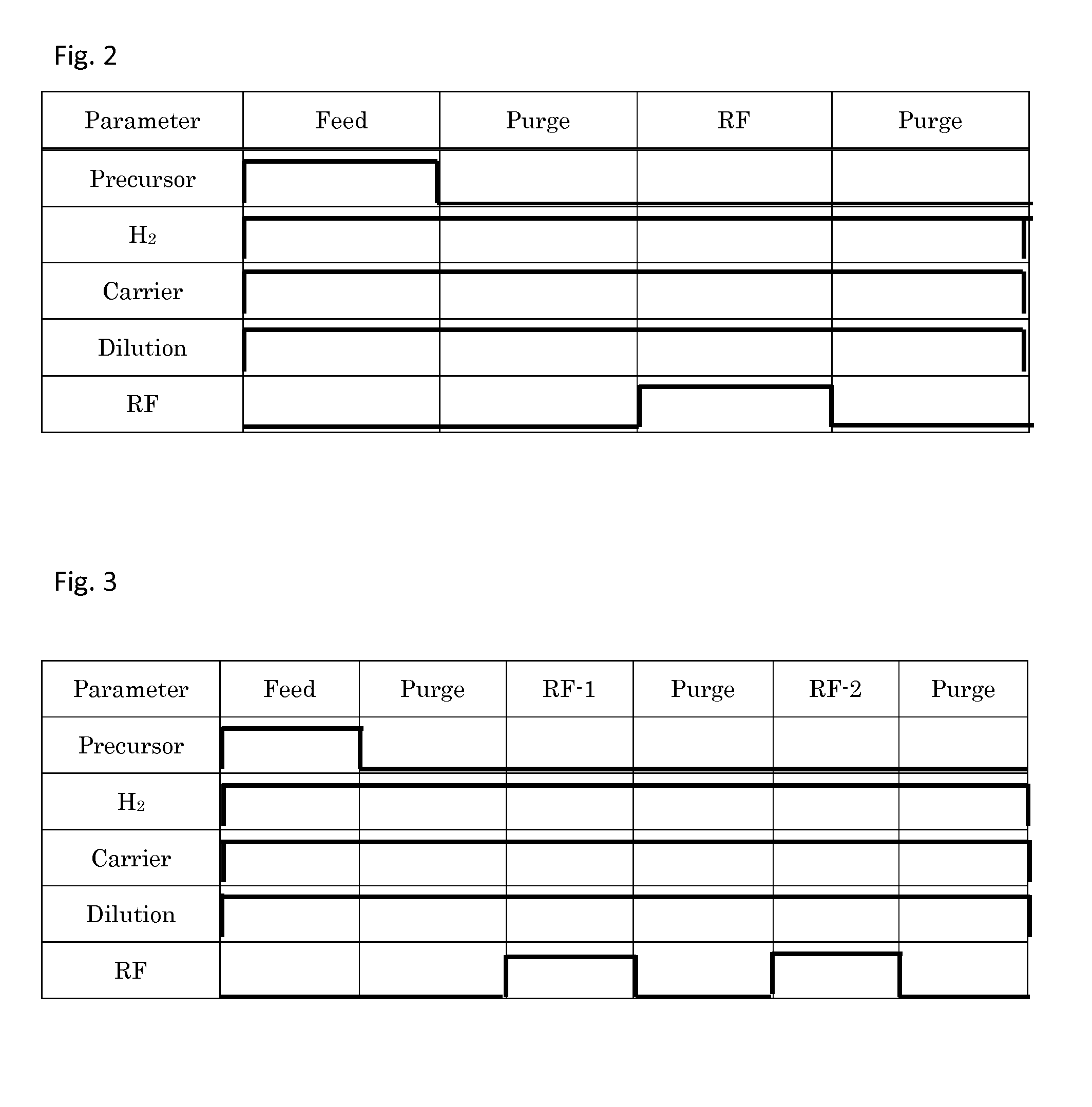
ActiveUS20140357058A1Improve inter-plane uniformity and in-plane uniformity of film thicknessDecrease productivityLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesHydrogenDevice material
There is provided a substrate processing apparatus including: a process chamber configured to accommodate and process a plurality of substrates arranged with intervals therebetween; a first nozzle extending along a stacking direction of the substrates and configured to supply a hydrogen-containing gas into the process chamber; and a second nozzle extending along the stacking direction of the substrates and configured to supply an oxygen-containing gas into the process chamber, wherein the first nozzle includes a plurality of first gas supply holes disposed in a region extending from an upper portion to a lower portion of the first nozzle corresponding to a substrate arrangement region where the substrates are arranged, and the second nozzle includes a plurality of second gas supply holes disposed at an upper portion and a lower portion of the second nozzle to correspond to upper substrates and lower substrates of the substrates.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Display and method for manufacturing display
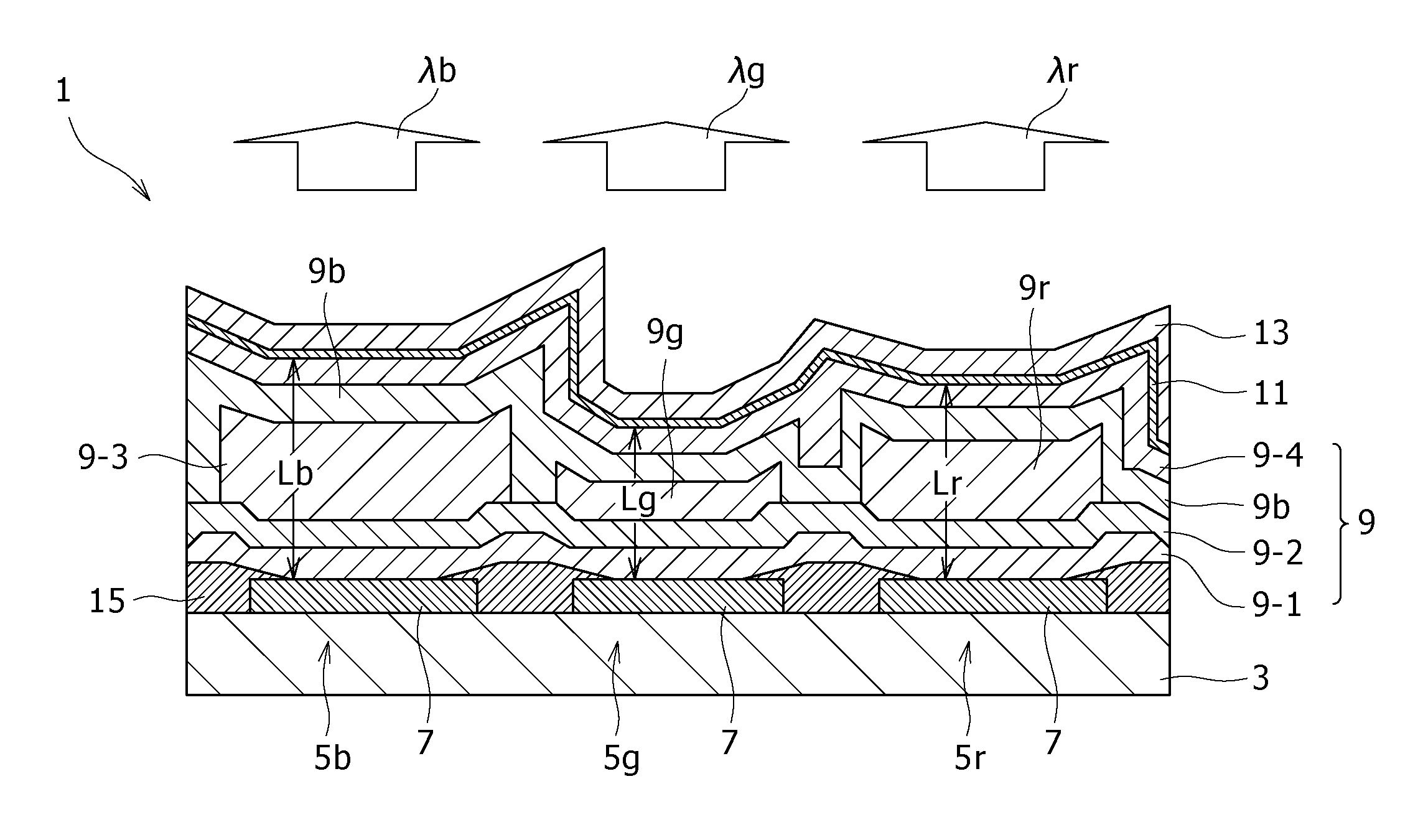
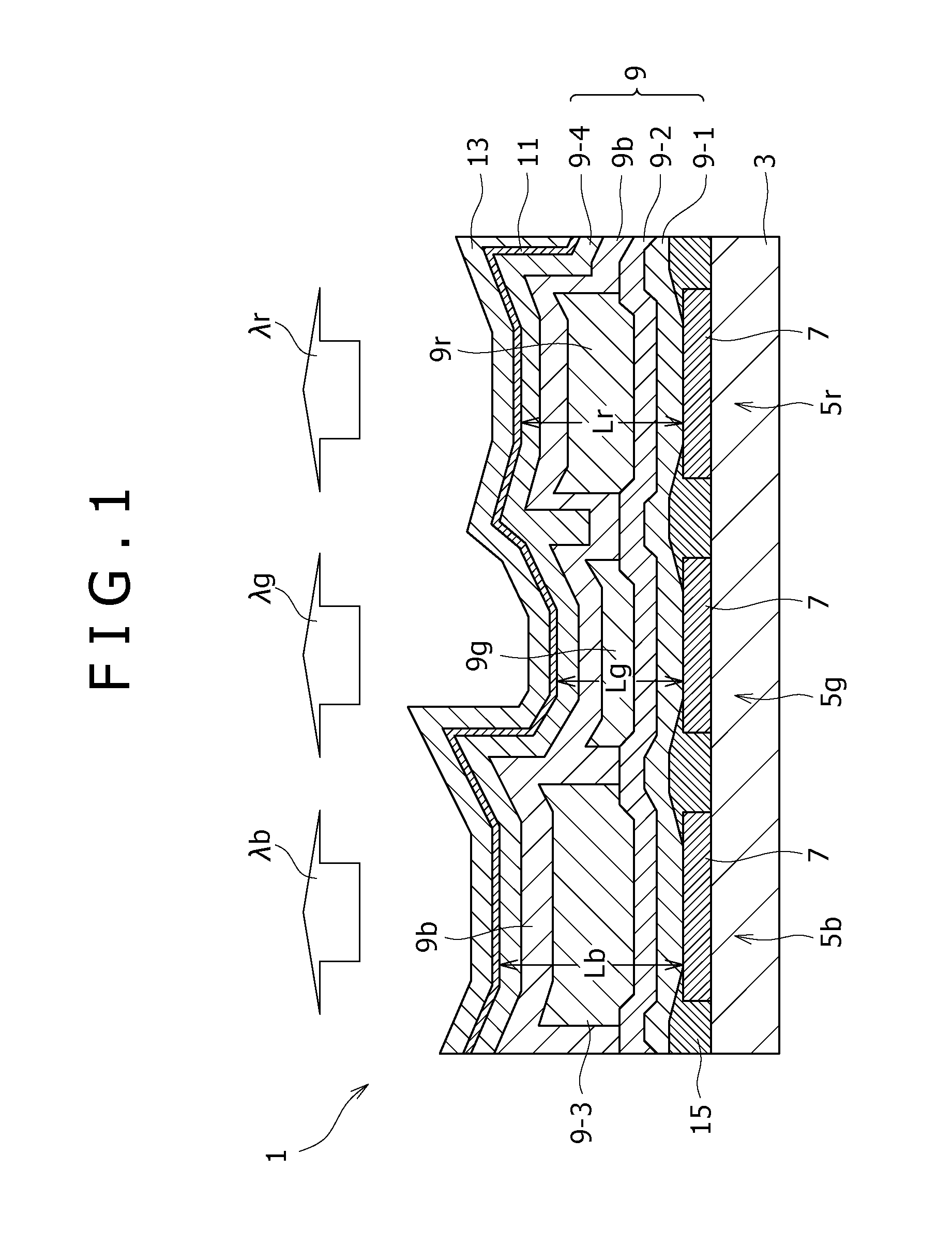
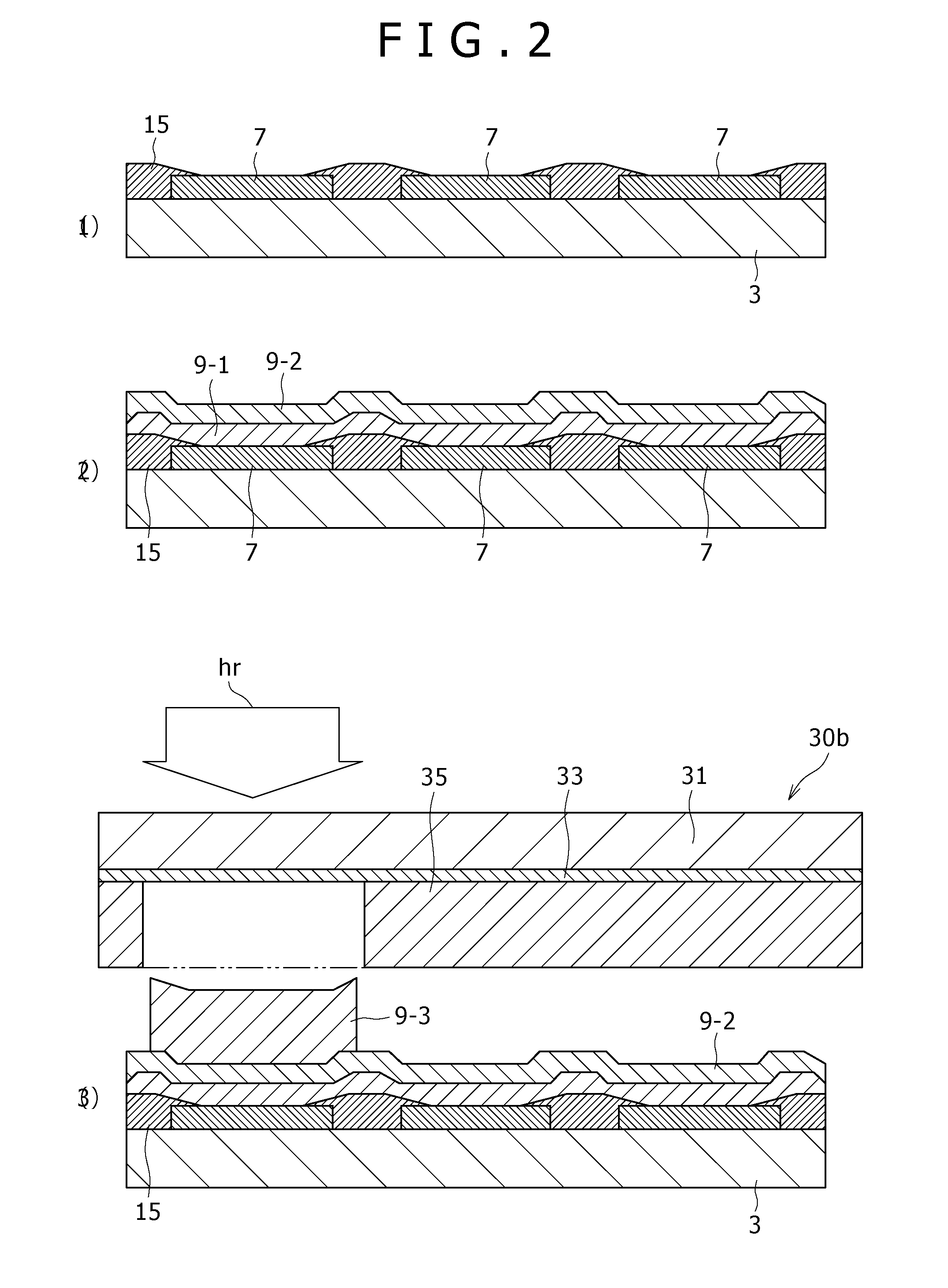
InactiveUS20080018239A1Reduce defectsEnsure controllabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesResonanceOrganic layer
Disclosed herein a display including: a plurality of organic electroluminescent elements configured to be arranged over a substrate and be each obtained by depositing a lower electrode, an organic layer including at least a light-emitting layer, and an upper electrode in that order, the organic layer of each of the organic electroluminescent elements being adjusted to have a film thickness that allows resonance of a wavelength of luminescent light generated in the light-emitting layer, wherein the film thickness of the organic layer in a first organic electroluminescent element that generates luminescent light having a shortest wavelength among the plurality of organic electroluminescent elements is set larger than the film thickness of the organic layer in a second organic electroluminescent element that generates luminescent light having a wavelength longer than the shortest wavelength of luminescent light generated in the first organic electroluminescent element.
Owner:SONY CORP
Light-emitting element and light emitting device using the same
ActiveUS7564052B2Less-increase in driving voltageLess-increase in resistance valueElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesEngineeringLight emission
The present invention provides a light-emitting element having less increase in driving voltage with the accumulation of light-emission time, and provides a light-emitting element having less increase in resistance value with the increase in film thickness. A light-emitting element includes a first layer, a second layer and a third layer between a first electrode and a second electrode. The first layer is provided to be closer to the first electrode than the second layer, and the third layer is provided to be closer to the second electrode than the second layer. The first layer is a layer including an aromatic amine compound and a substance showing an electron accepting property to the aromatic amine compound. The second layer includes a substance of which an electron transporting property is stronger than a hole transporting property, and a substance showing an electron donating property to the aforementioned substance.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Substrate processing apparatus
InactiveUS20100083898A1Improve film thickness uniformityLong distanceLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas supplyElectrical and Electronics engineering
There are provided an inner tube in which a substrate is stored; an outer tube surrounding the inner tube; a gas nozzle disposed in the inner tube; a gas ejection hole opened on the gas nozzle; a gas supply unit supplying gas into the inner tube through the gas nozzle; a gas exhausts hole opened on the side wall of the inner tube; and an exhaust unit exhausting a space between the outer tube and the inner tube and generating a gas flow in the inner tube toward the gas exhaust hole from the gas ejection hole, wherein the side wall of the inner tube is constituted, so that a distance between an outer edge of the substrate and the gas exhaust hole is set to be longer than a distance between the outer edge of the substrate and the gas ejection hole.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Light-shielding film for optical element and optical element having light-shielding film
InactiveUS20110200810A1Relieve pressureReduce distortionPrismsOther chemical processesWavelength range
A light-shielding film for optical element includes at least a resin and a colorant. The light-shielding film for optical element has an average extinction coefficient of 0.03 or more and 0.15 or less as an average of extinction coefficients of the whole light-shielding film for light having wavelengths ranging from 400 to 700 nm.
Owner:CANON KK
Organic electroluminescent device, method of manufacture thereof and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20050237780A1Easy to controlReduce voltage dropElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesEngineeringOrganic electroluminescence
An organic electroluminescent device includes electrodes, an organic functional layer formed between facing electrodes, and separators for separating one of the electrodes into a strip, wherein the one electrode includes the first film formed with a vapor deposition method and the second film formed into a strip on the first film between the separators, and wherein the separators have dividing sections provided therein for electrically dividing the vapor deposited films formed on the top surfaces of the separators when the first film is formed.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
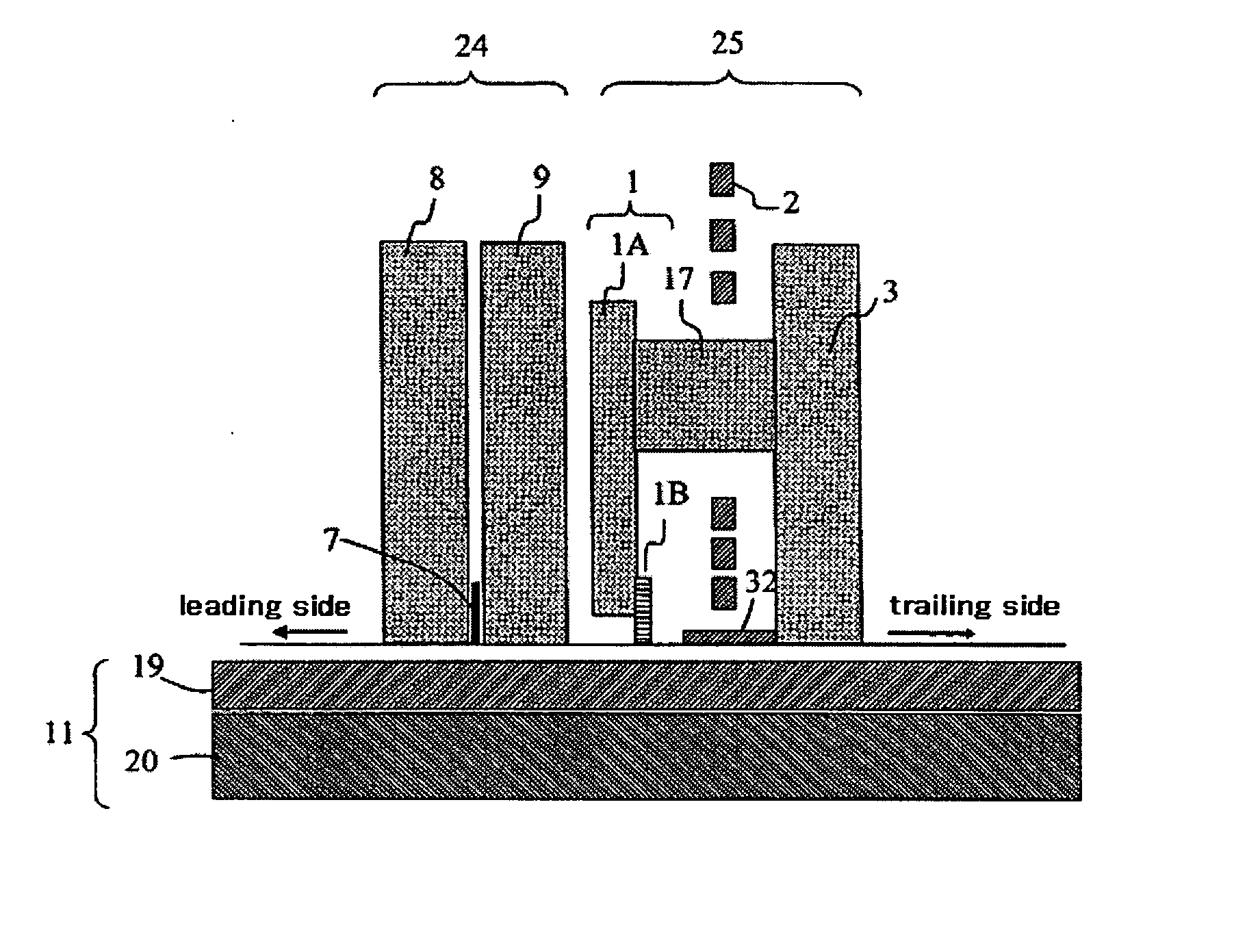
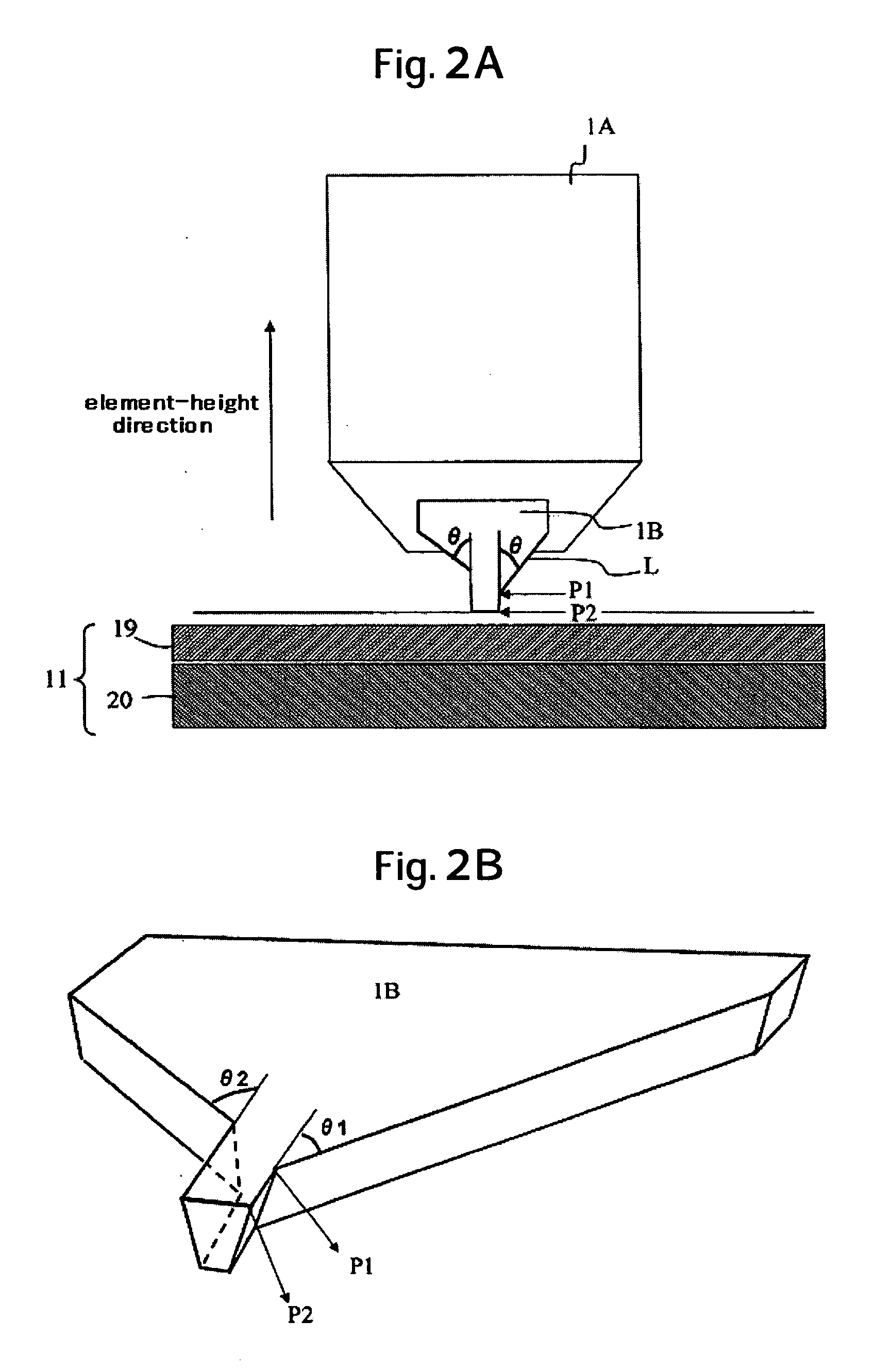
Magnetic recording head and magnetic disk storage apparatus mounting the magnetic head
InactiveUS20060262453A1High write-field intensityImprove recording densityRecord information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsMagnetic polesUltimate tensile strength
Embodiments of the invention provide a magnetic head which can suppress broadening of the magnetic field distribution in the track-width direction without reducing the magnetic field intensity. In one embodiment, a main pole is composed of a pole tip having a part providing a write-track width, and a yoke part recessed from the air bearing surface in the element-height direction, where the trailing side surface of the pole tip is made as an asymmetric structure with respect to the track center.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Method for forming a block copolymer pattern
InactiveUS20110206905A1High film thicknessIncrease feature densityMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsVolumetric Mass DensityNanostructure
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA +1
Bonded semiconductor substrate manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7491342B2Simple processReduce surface roughnessDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEtchingSurface roughness
The present invention provides a bonded substrate fabricated to have its final active layer thickness of 200 nm or lower by performing the etching by only 1 nm to 1 μm with a solution having an etching effect on a surface of an active layer of a bonded substrate which has been prepared by bonding two substrates after one of them having been ion-implanted and then cleaving off a portion thereof by heat treatment. SC-1 solution is used for performing the etching. A polishing, a hydrogen annealing and a sacrificial oxidation may be respectively applied to the active layer before and / or after the etching. The film thickness of this active layer can be made uniform over the entire surface area and the surface roughness of the active layer can be reduced as well.
Owner:SUMCO CORP +1
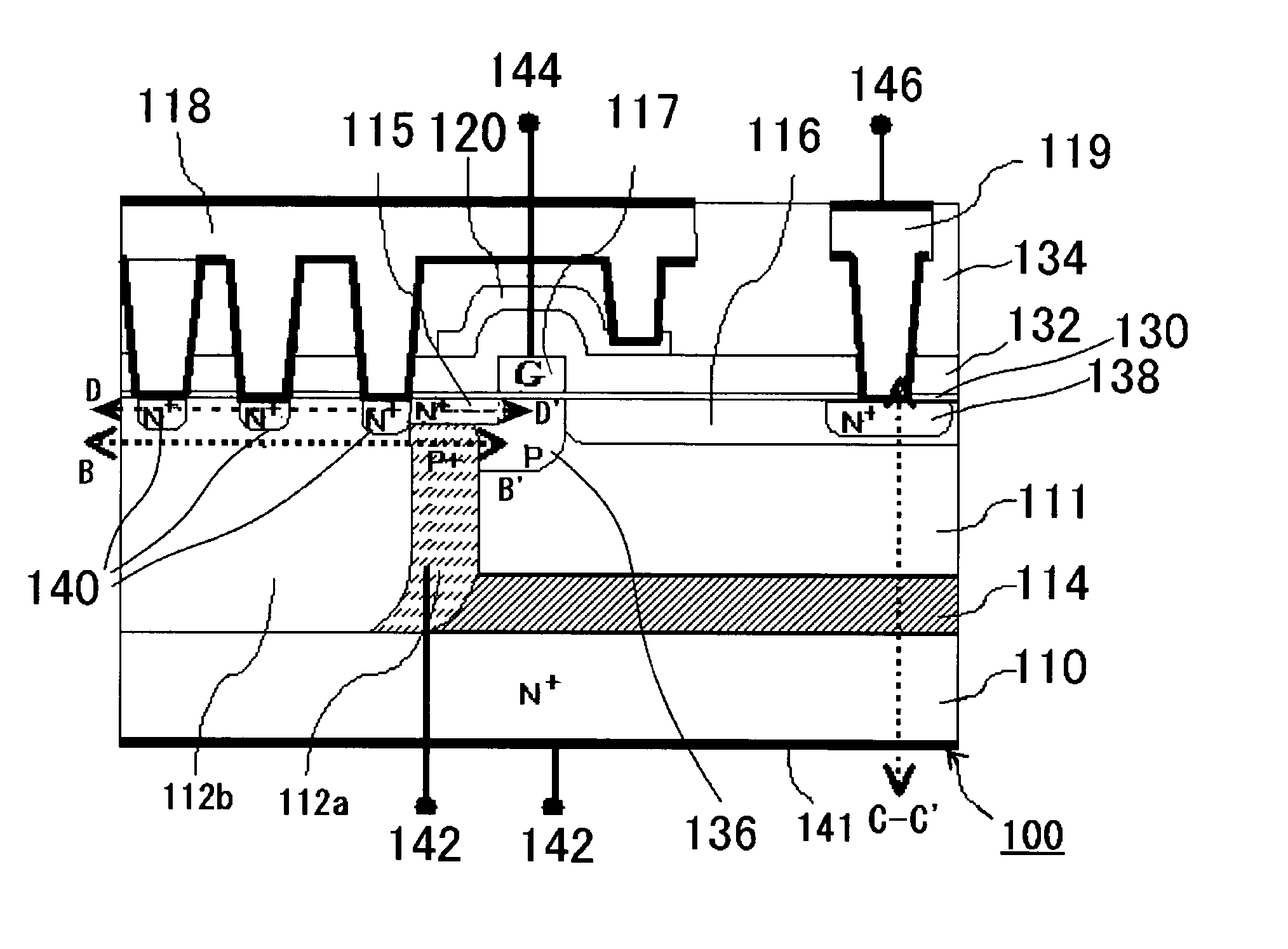
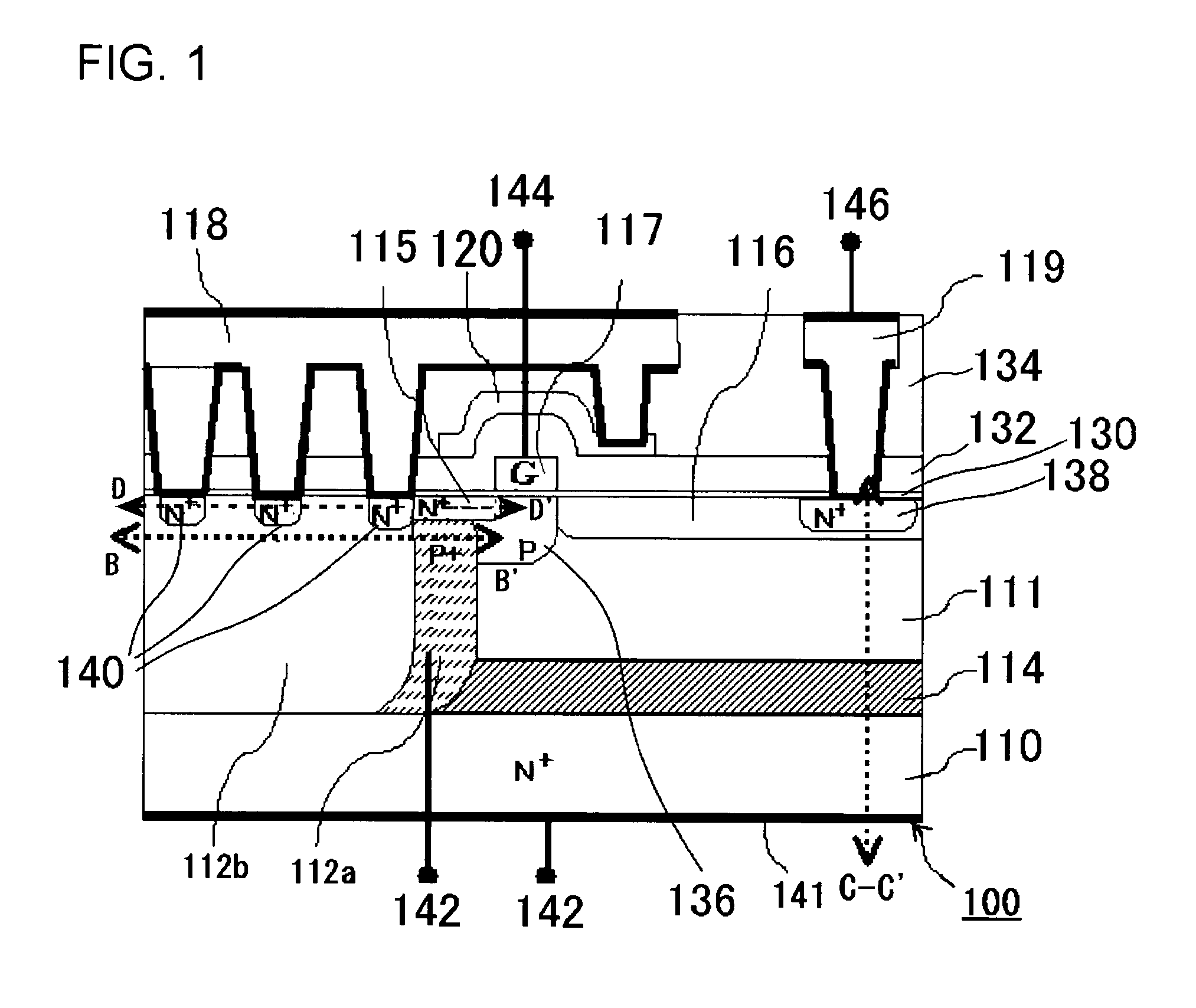
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050269601A1Extending of the semiconductor substrate can be preventedHigh film thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETHigh concentration
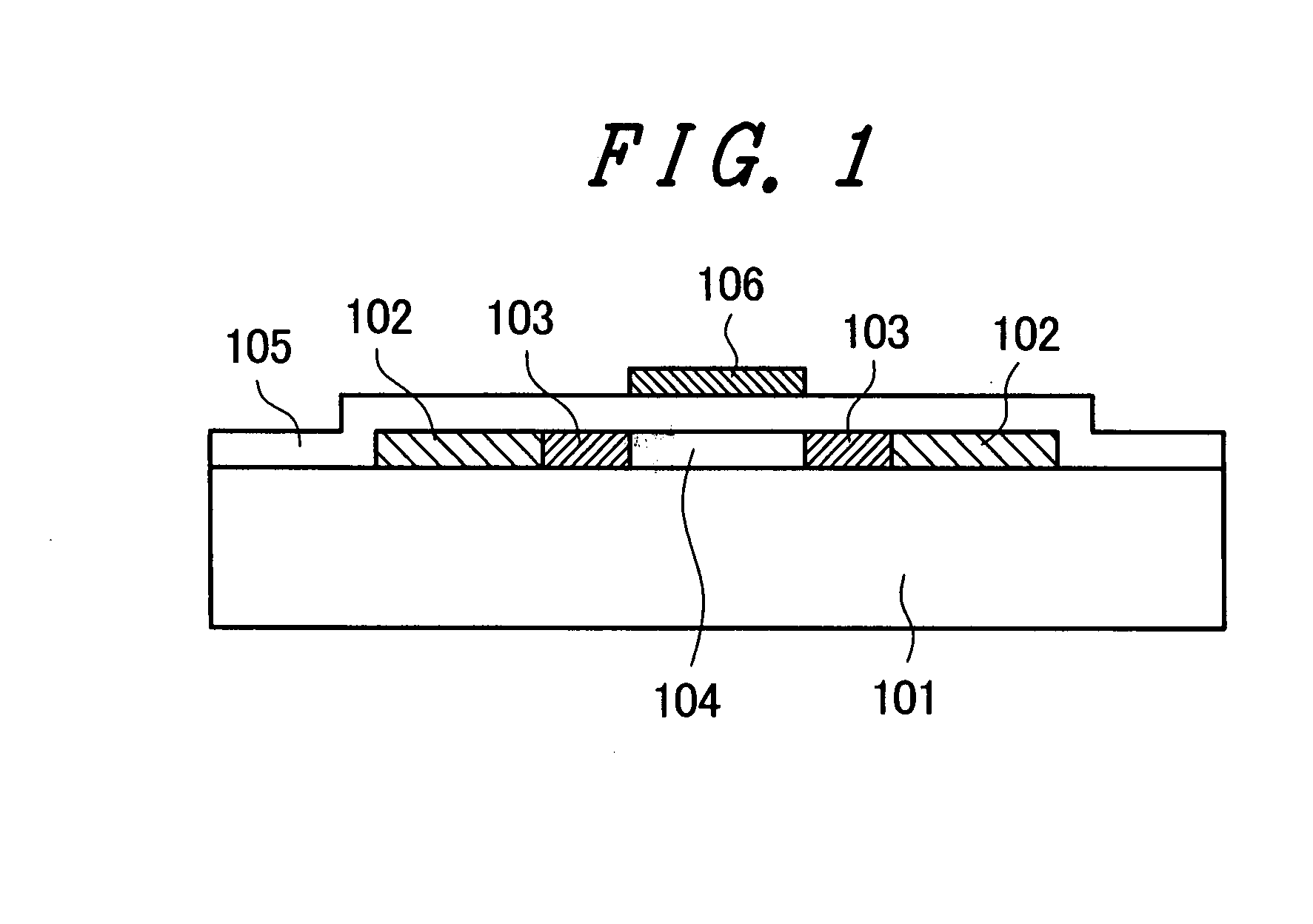
The semiconductor device comprises: a semiconductor substrate (N+ substrate 110) containing a first conductivity type impurity implanted therein; a second conductivity type impurity-implanted layer (P+ implanted layer 114) at relatively high concentration, formed on the semiconductor substrate (N+ substrate 110); a second conductivity type impurity epitaxial layer (P− epitaxial layer 111) at relatively low concentration, formed on the second conductivity type impurity-implanted layer (P+ implanted layer 114); and a field effect transistor 100 (N-channel type lateral MOSFET 100)composed of a pair of impurity diffusion regions (N+ source diffusion layer 115 and N− drain layer 116) provided in the second conductivity type impurity epitaxial layer (P− epitaxial layer 111) and a gate electrode 117 provided over a region sandwiched with the pair of impurity diffusion regions (N+ source diffusion layer 115 and N− drain layer 116).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Mask, mask chip, manufacturing method of mask, manufacturing method of mask chip, and electronic device
InactiveUS20070017895A1Precise patternEasy to provideDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectronElectrical and Electronics engineering
A mask in which a plurality of mask chips are connected to one another via a supporting member, includes: a plurality of first opening sections that are provided in the plurality of mask chips and that correspond to a pattern to be formed; a cutout section provided at at least one of side faces opposing to each other of the mask chips adjacent to each other; a gap section provided at a connected section connecting the mask chips adjacent to each other, the gap section being composed of the cutout section and including a second opening section corresponding to a pattern to be formed; and a block section that is provided at at least one of the mask chips adjacent to each other and that covers the gap section other than the second opening section.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Resist pattern, process for producing same, and utilization thereof
InactiveUS20040063025A1High wiring densityHigh resolutionPhotosensitive materialsElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisResistChemical compound
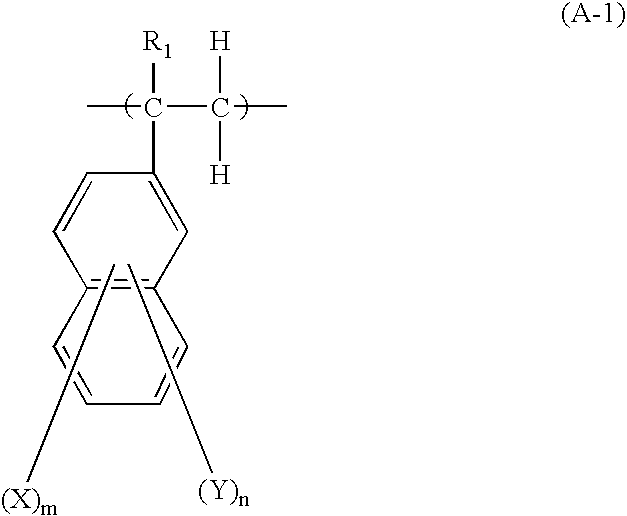
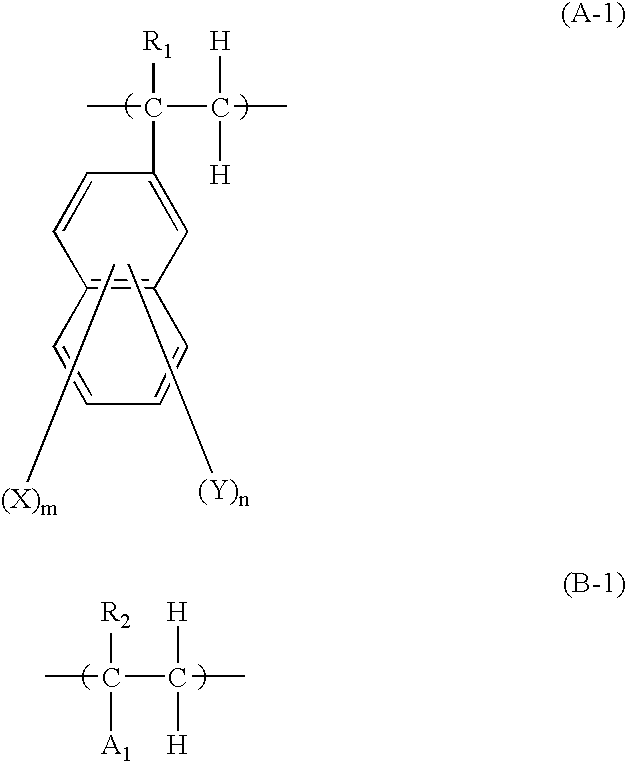
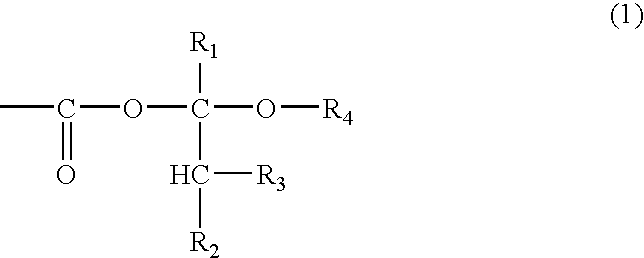
A resist pattern having a film thickness of 1 to 100 mum and an aspect ratio (ratio of the line width to the film thickness of the resist pattern) of 3.5 or higher is provided in accordance with the present invention, the resist pattern being useful for increasing the density of a semiconductor package substrate circuit, and use of the resist pattern enabling a low conductor resistance to be maintained in fine wiring. This resist pattern can be produced using, for example, a photosensitive resin composition that includes (A) a binder polymer, (B1) a photopolymerizable compound having three ethylenically unsaturated bonds per molecule, (C) a photopolymerization initiator, and (D) either or both of a compound represented by general formula (I): (in the formula, m is an integer of 2 to 6) or a compound represented by general formula (II).
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Tei Coat for Organopolysiloxane Antifouling Coat, Composite Coats, and Ships and Underwater Structures Covered with the Composite Coats
InactiveUS20090042042A1Big burden to solveWell formedAntifouling/underwater paintsSynthetic resin layered productsEpoxyBond properties
Disclosed is a tie coat which is formed on a surface of a base or an undercoating film prior to formation of an organopolysiloxane-based antifouling coating film and is formed from a moisture-curing organopolysiloxane-based composition comprising (b1) organopolysiloxane having condensing functional groups at both ends of a molecule and / or (b2) a curing composition formed by subjecting the component (b1) and an extender pigment selected from the group consisting of silica, calcium carbonate, talc, mica, clay, kaolin and barium sulfate to contact treatment with heating or without heating. Also disclosed is a composite coating film wherein on a surface of the above tie coat is formed a finish coat formed from a three-pack type organopolysiloxane-based curing composition comprising (c1) a main agent comprising the component (b1), (c2) a curing agent component comprising tetraalkoxysilicate or its condensate and (c3) a curing accelerator component comprising a metallic compound. Further disclosed is a composite coating film wherein an epoxy-based sealer coat, the tie coat and the finish coat are formed in this order on a surface of an old antifouling coating film (G). There is provided by the invention a tie coat capable of forming a composite coating film having excellent interlaminar bond property. The composite coating film is favorably formed on a surface of a base, an undercoating film, an old antifouling coating film or the like, has excellent interlaminar bond strength and antifouling property and is preferably used for coating outer surfaces of ships, submerged parts of marine structures, water supply / drainage channels of atomic power plant, etc.
Owner:CHUGOKU MARINE PAINTS
Fluidic lens with reduced optical aberration
ActiveUS8064142B2Increased complexityHigh film thicknessAdditive manufacturing apparatusOptical filtersEngineeringOptical aberration
A fluidic lens device capable of providing variable focal power with reduced optical aberration is disclosed. The device includes a lens member and an actuator. The lens member comprises one or more elastic optical surfaces, a compliant support member in communication with the optical surfaces, and a fluid-filled chamber. The optical surfaces have a high value of elastic modulus, reducing coma and other aberrations associated gravity and acceleration. The support member may provide a compliant fluid seal and allow the edges of the optical surfaces to pivot, reducing spherical and other aberrations. One or more piezoelectric ring-bender actuators may provide the force required for compressing the support ring and deflecting the optical surfaces. The actuators may be configured to provide the fluidic lens device with reduced sensitivity to changes in temperature.
Owner:HOLOCHIP
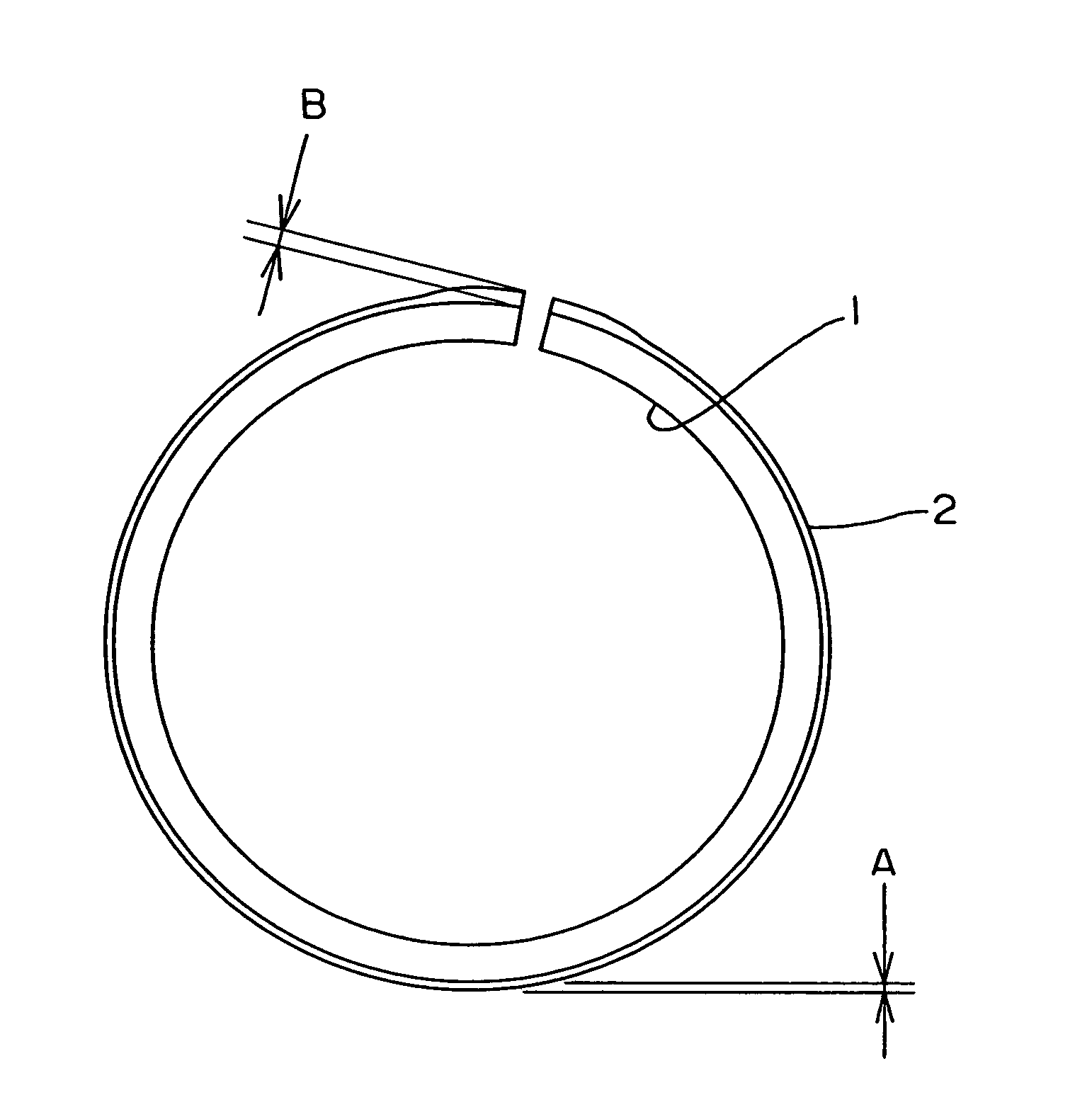
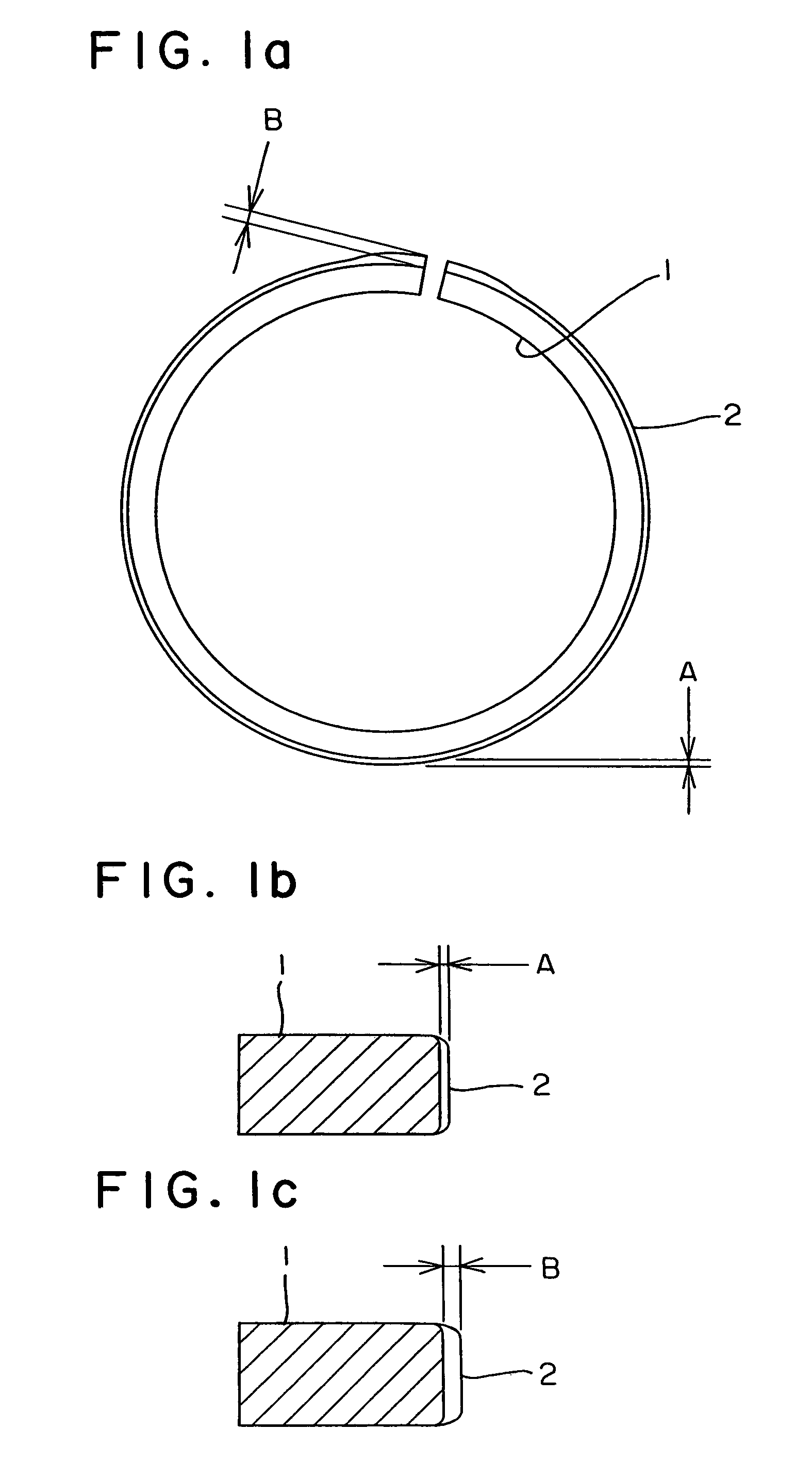
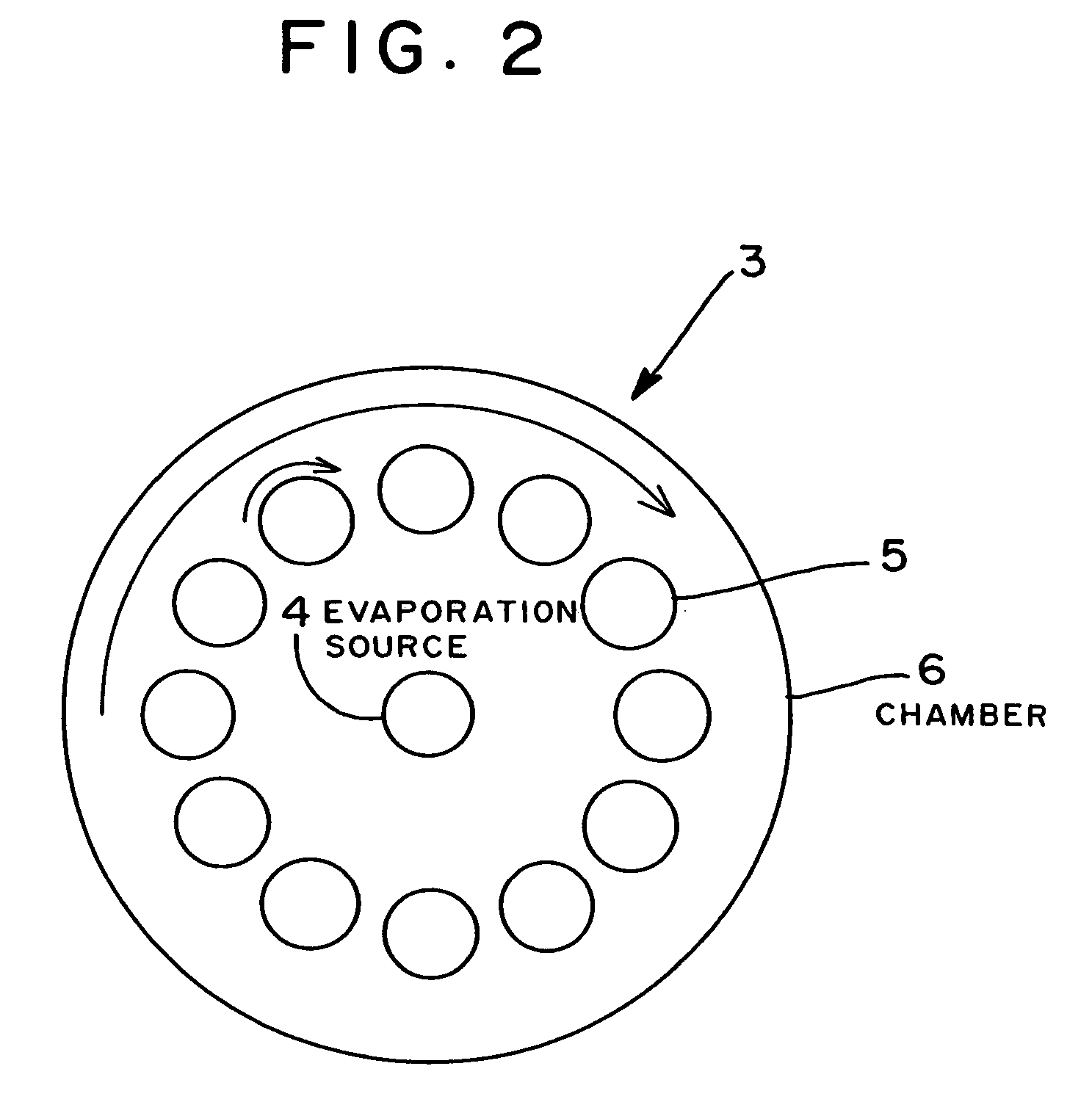
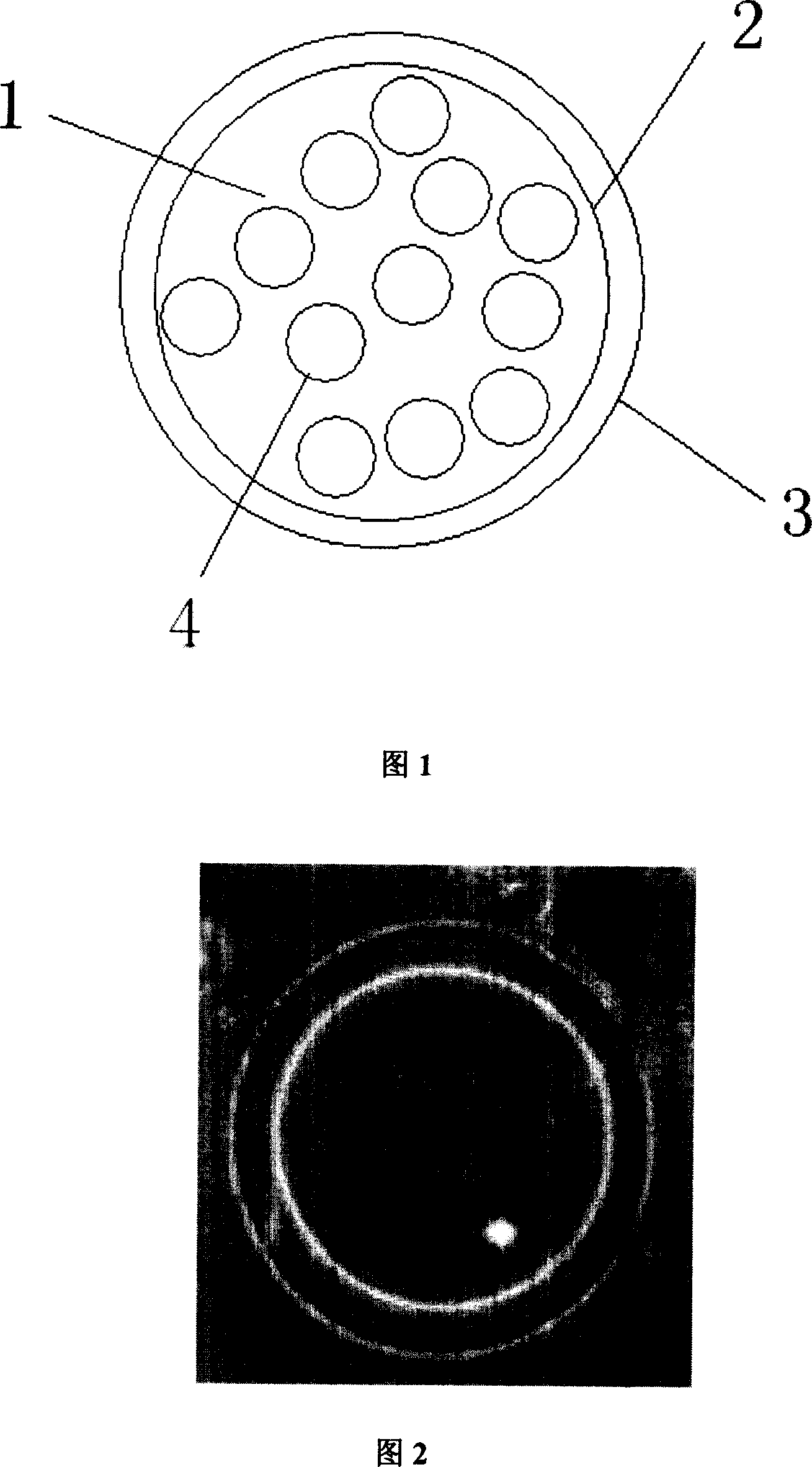
Piston ring and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7052019B2Improve wear resistancePrevent peelingPiston ringsBraking action transmissionCountermeasurePiston ring
A manufacturing method of a piston ring is developed, wherein the method provides a countermeasure for wear of butt ends of the ion plating film coated piston ring and a countermeasure for breakage of the piston ring and the piston ring manufactured at a low cost. A thickness of the film (2) in the vicinity of butt ends (7) of a piston ring (1) is made greater than the thickness of the film (2) at other outer peripheral surface. Piston ring blanks (5) are rotated around their own axes toward an evaporation source (4) and a speed is lowered when the butt ends (7) face the evaporation source (4).
Owner:RIKEN CO LTD
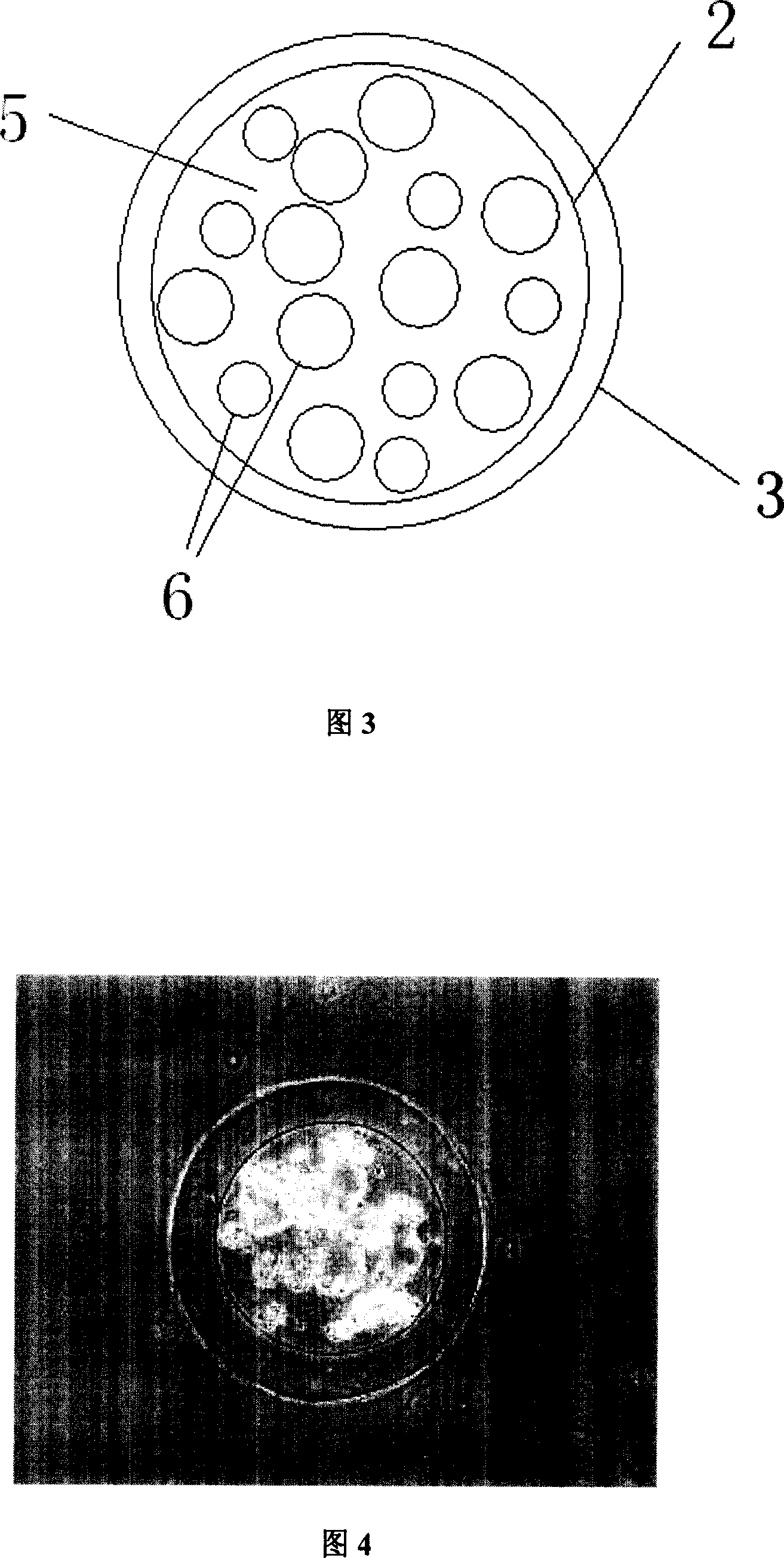
Method for producing liquid core microcapsule by electrostatic spraying
InactiveCN101152623AUniform particle sizeGood encapsulation performanceMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationCelluloseSprayer
The invention provides a method for preparation of liquid core microcapsule with static sprayer: calcium chloride solution of 2-3 percent is mixed with thickening agent and then is uniformly mixed with core material substance; a certain amount of mixed solution is taken out and then is put into solution containing sodium alginate of 0.6-1.5 percent with static sprayer while adopting a flat needle for adhesive deposite or an injection needle as a nozzle; after capsulated, liquid core sodium alginate microcapsule is filtered and then is cleaned with purified water; then liquid core sodium alginate microcapsule is put into calcium chloride solution for continuous solidification of 5-10 minutes; then microcapsule is filtered and then is cleaned with purified water; at last microcapsule is stored in storage solution with calcium ion concentration of 0.05-0.01 percent. High viscosity malt dextrin or sodium carbonxymethyl cellulose or xanthan gum is adopted as thickening agent. Microcapsule prepared with the invention has liquid core, with uniform particle size, good sacculation performance, simple process and high membrane thickness, therefore, microcapsule has high mechanical strength and can be widely used in the field of pharmaceutical chemical engineering, artificial organ implantation and food processing, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH +1
Underlayer Coating Forming Composition for Lithography Containing Naphthalene Ring Having Halogen Atom
ActiveUS20070238029A1Effective absorptionExcellent underlayer coatingPhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSolvent
There is provided an underlayer coating forming composition for lithography, and an underlayer coating having a high dry etching rate compared with photoresist, and causing no intermixing with the photoresist, which are used in lithography process of manufacture of semiconductor device. Concretely, it is an underlayer coating forming composition comprising a polymer having a structural unit containing naphthalene ring substituted with halogen atom in a molar ratio of 0.3 or more in the structural units constituting the polymer, a solvent.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Anti-reflective film and optical element having anti-reflective film
InactiveUS20050280890A1Effective lightingHigh film thicknessMirrorsOptical filtersRefractive indexLength wave
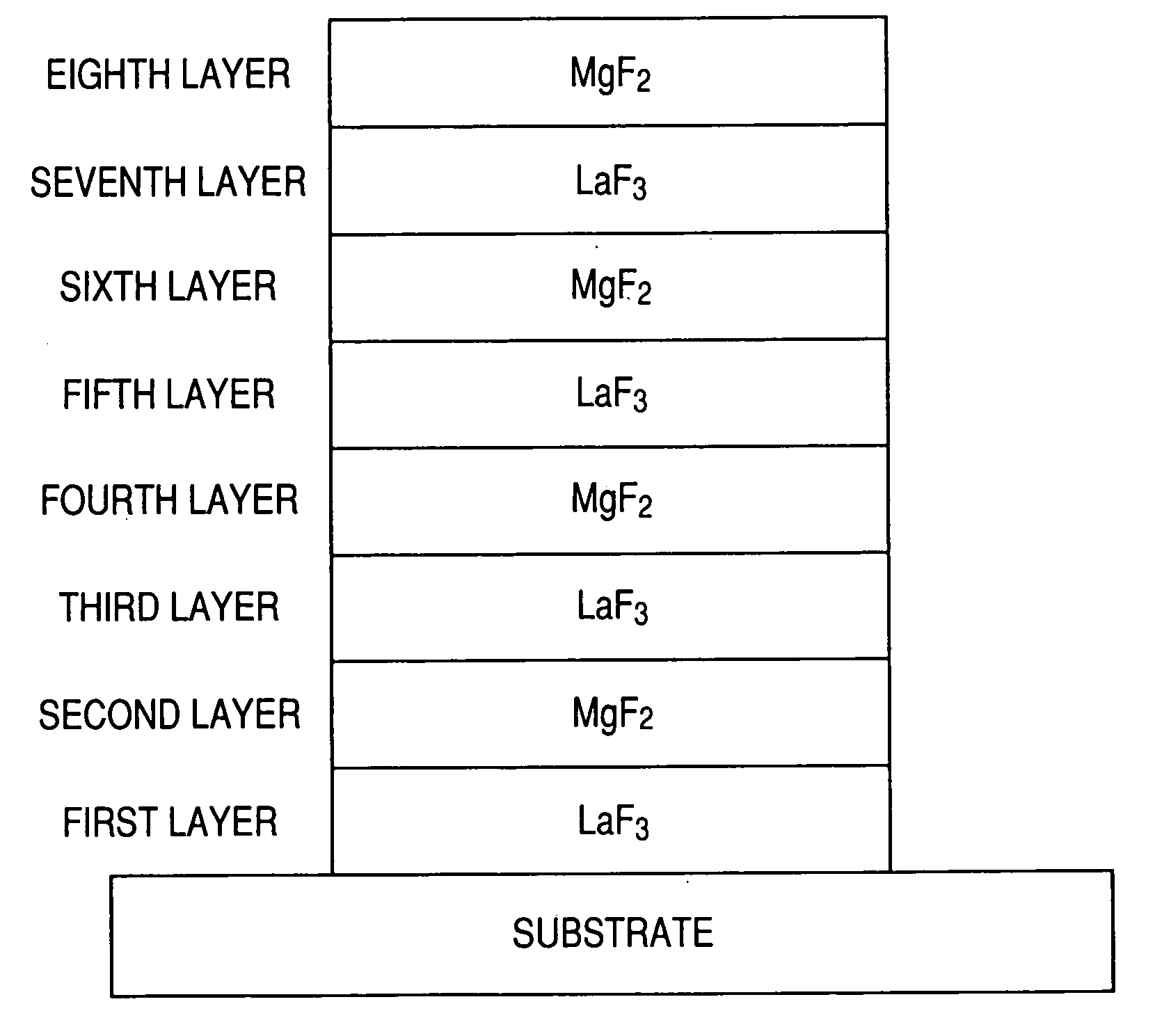
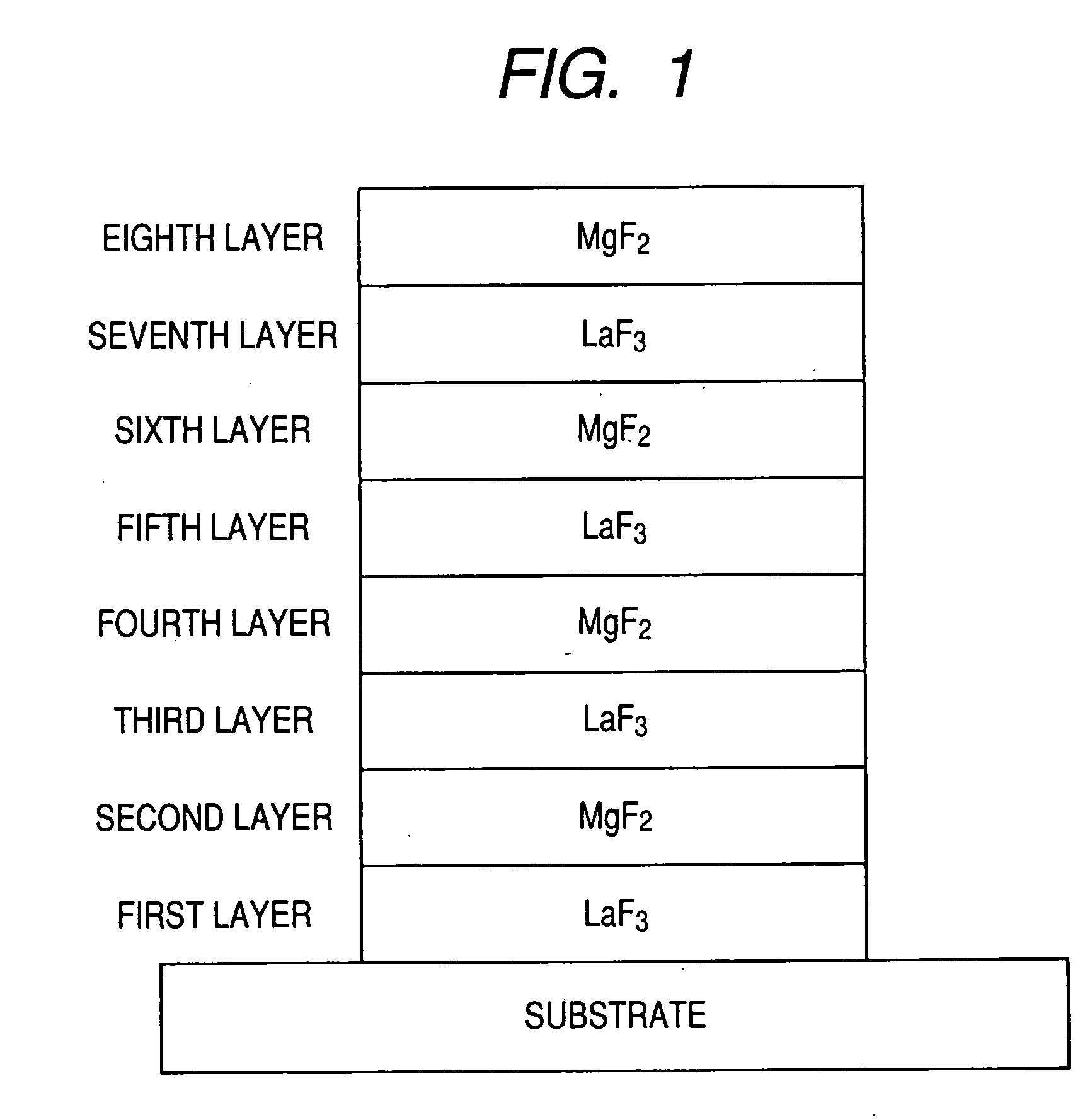
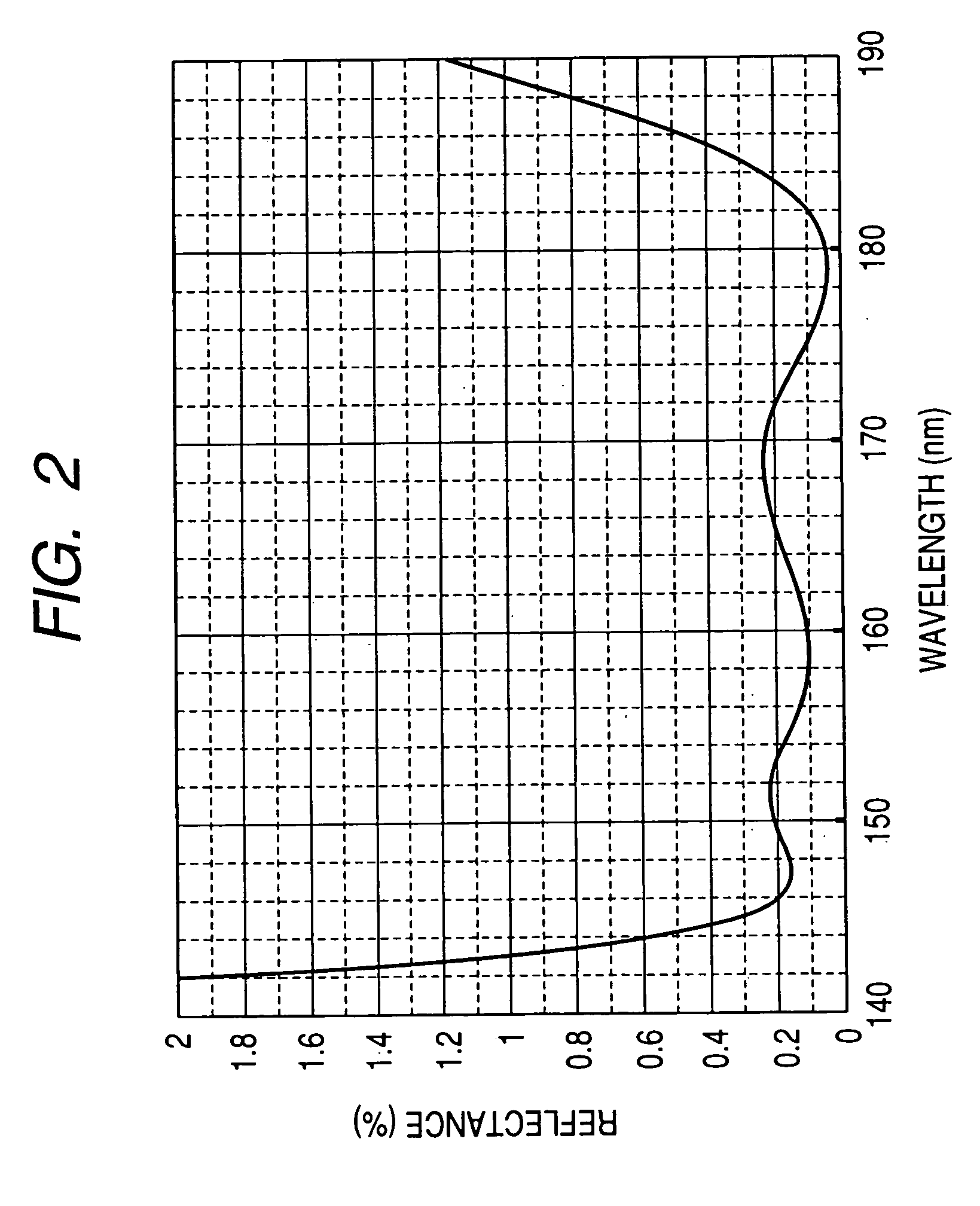
In an anti-reflective film comprising alternating layers of high refractive-index layers and low refractive-index layers, by designing such that a designed central wavelength λ0 is within a wavelength range of 141 nm to 189 nm, and that when the first to eighth layers as counted from a substrate have optical film thicknesses d1 to d8 respectively, the equations of: 0.45λ0≦d1≦0.65λ0; 0.05λ0≦d2≦0.20λ0; 0.29λ0≦d3≦0.49λ0; 0.01λ0≦d4≦0.15λ0; 0.05λ0≦d5≦0.20λ0; 0.23λ0≦d6≦0.28λ0; 0.23λ0≦d7≦0.28λ0; and 0.23λ0≦d8≦0.28λ0 are satisfied, the anti-reflective film can be formed so as to have a low reflectance for a light incident at such a large angle as 30 degrees or more, without increasing the whole thickness of the film.
Owner:CANON KK
Composition for forming lower layer film for lithography comprising compound having protected carboxyl group
ActiveUS20060210915A1Increased shelf stabilityReduce sublimation substance producedRadiation applicationsPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersLithography processDevice material
There is provided an underlayer coating forming composition for lithography, and an underlayer coating having a high dry-etching rate compared with photoresist, and causing no intermixing with the photoresist, which are used in lithography process of manufacture of semiconductor device. Concretely it is an underlayer coating forming composition comprising a compound having a protected carboxyl group, a compound having a group capable of reacting with a carboxyl group and a solvent, and an underlayer coating forming composition comprising a compound having a group capable of reacting with a carboxyl group and a protected carboxyl group and a solvent.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Display device and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20080073654A1Improve featuresPhotoconductivity is reducedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceSingle crystal
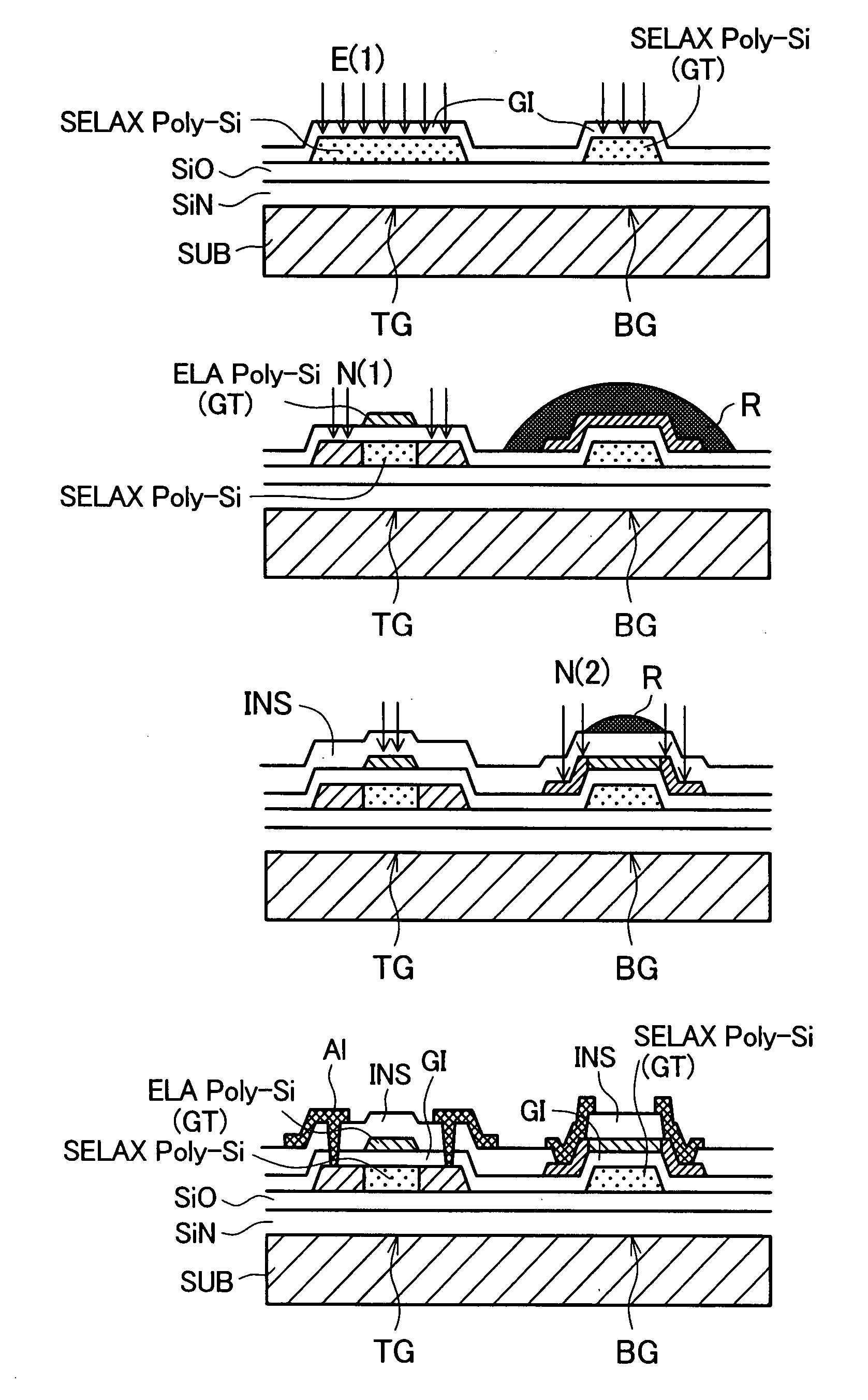
Improvement in characteristics of a SELAX-TFT and throughput of ELA crystallization is achieved. When a thin film transistor using pseudo single crystal semiconductor and a thin film transistor using particulate polysilicon semiconductor are formed on a single substrate, the film thickness of an amorphous semiconductor film before crystallization in the pseudo single crystal semiconductor portion is greater than that in the polysilicon semiconductor portion.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com