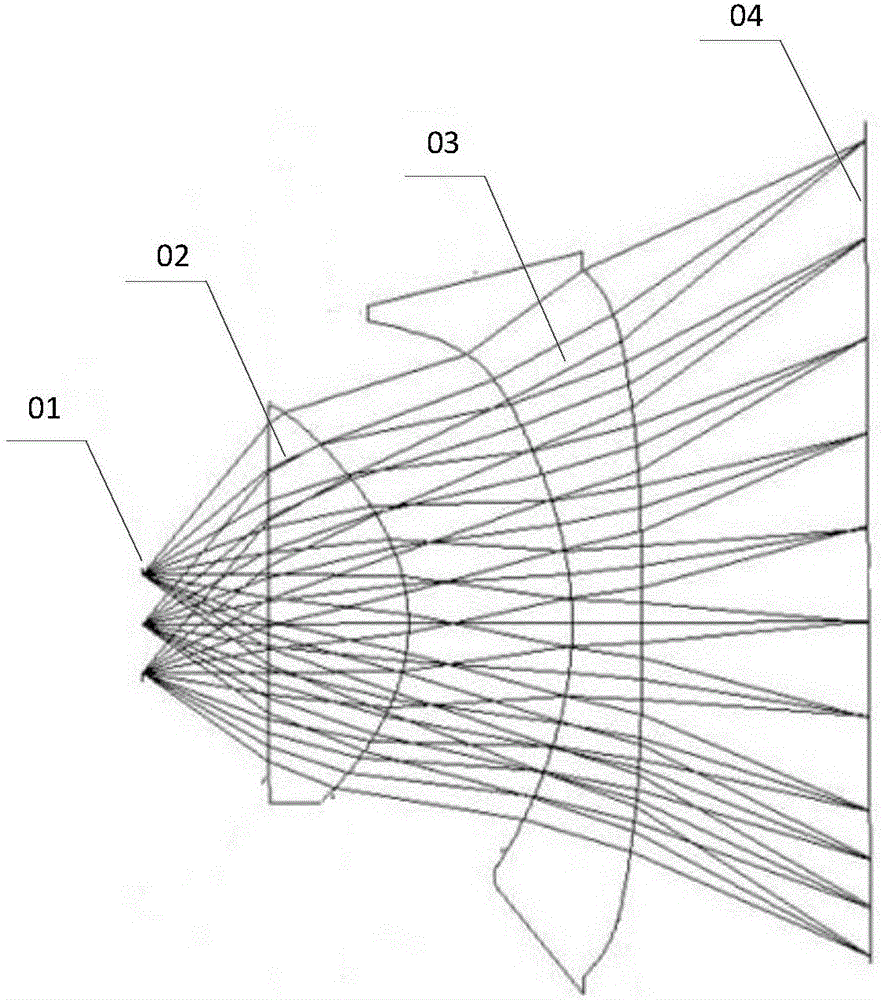
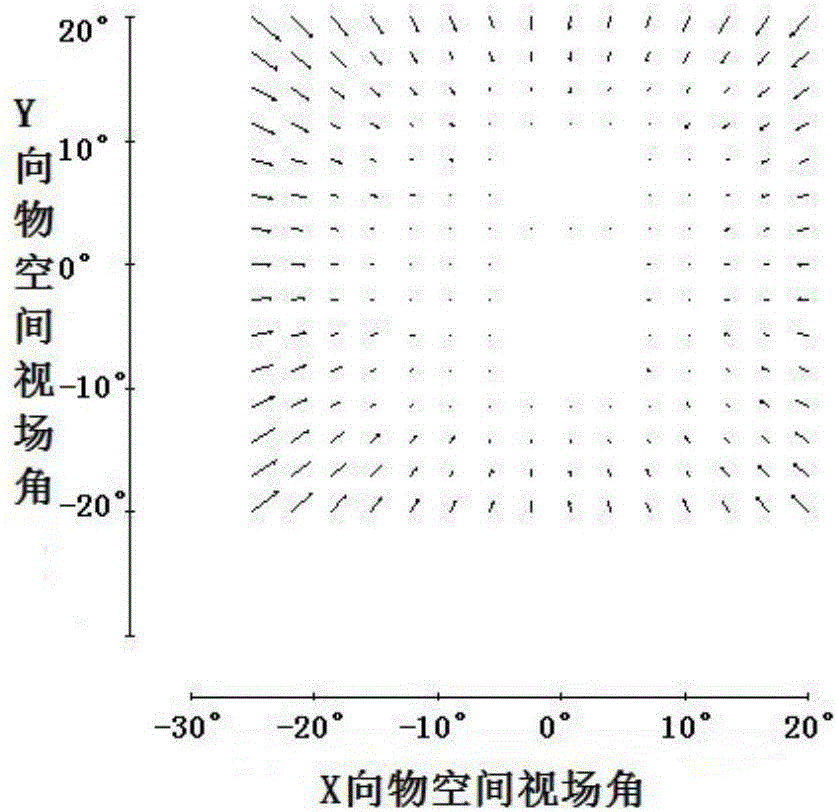
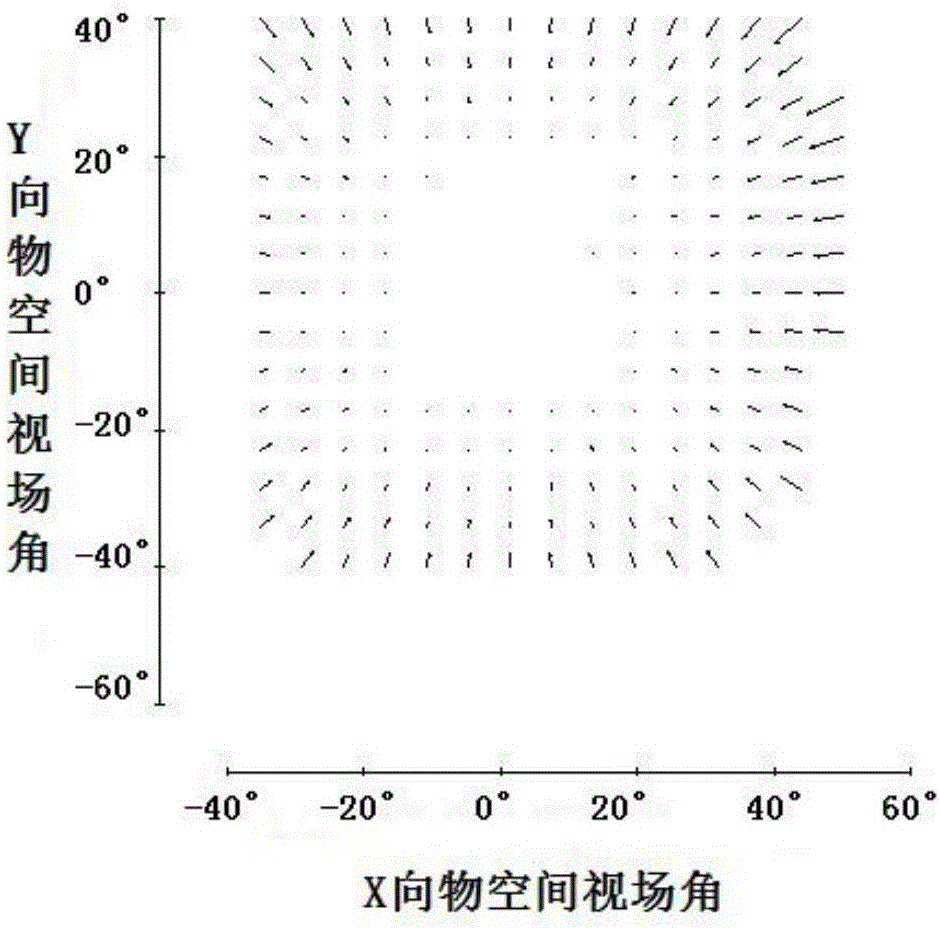
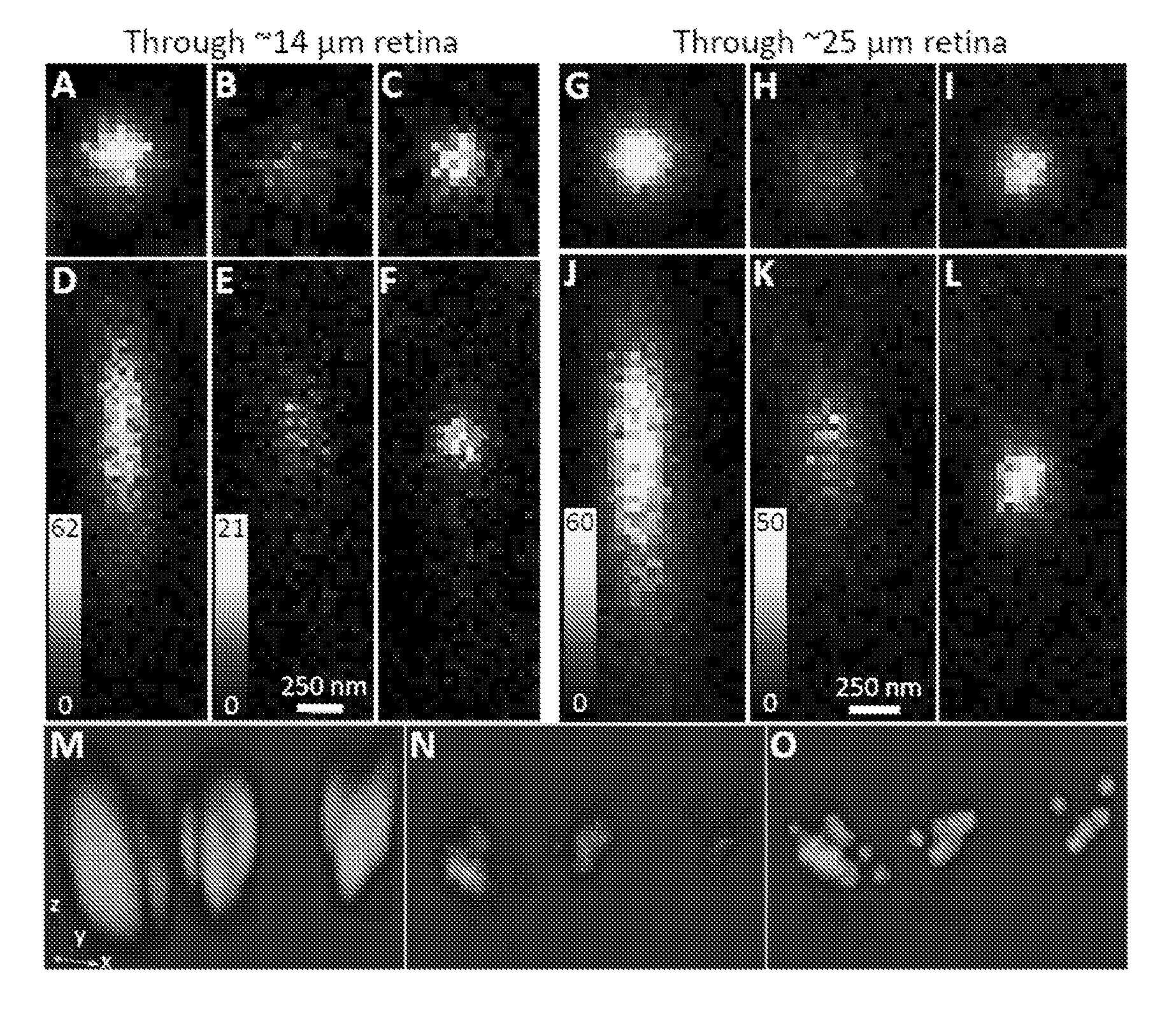
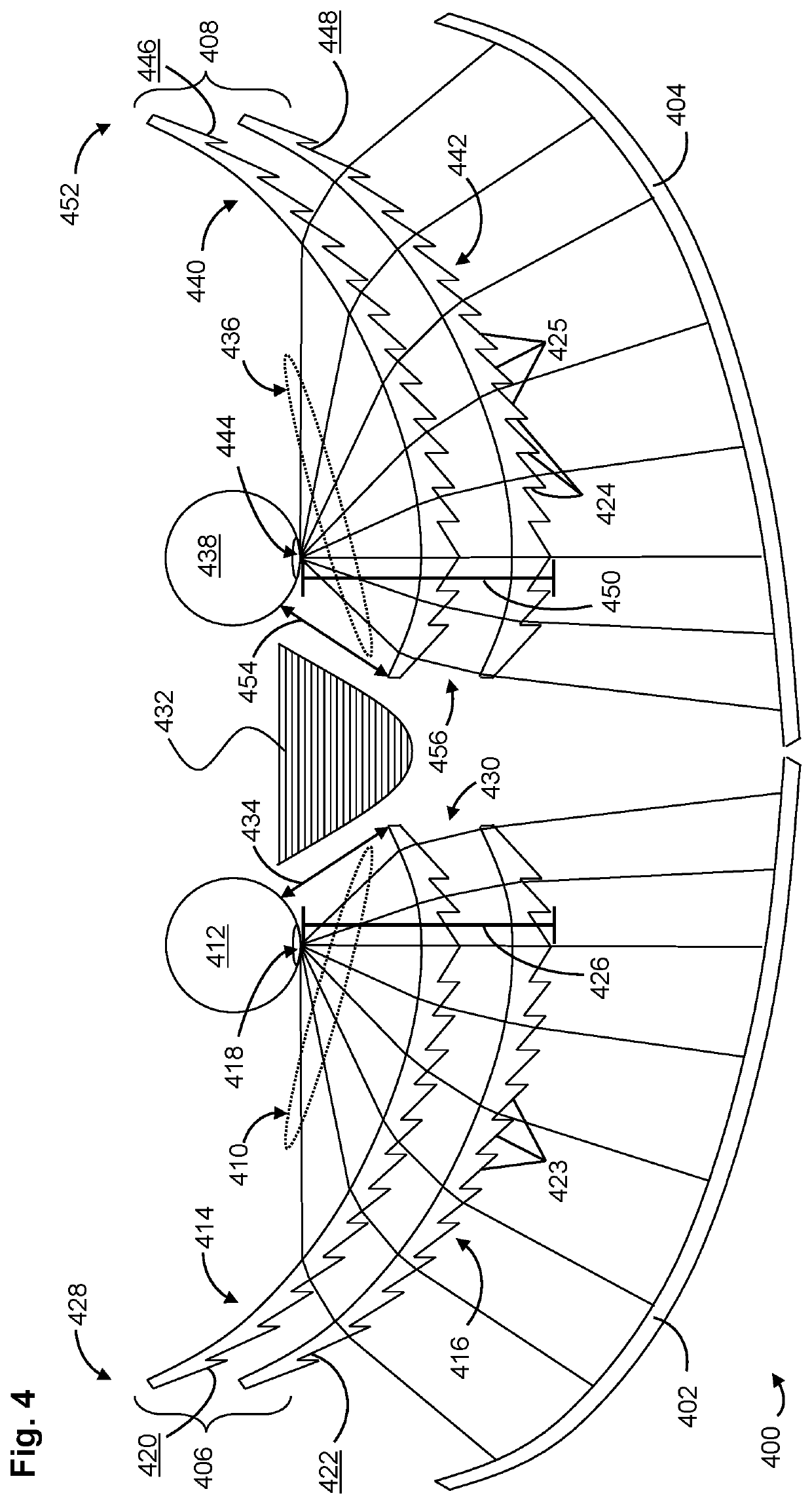
Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Reduce optical aberration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ophthalmic lens combinations
InactiveUS20060238702A1Enhance degree of accommodationLow in optical aberrationIntraocular lensOptical partsOptical powerOptometry
Owner:ABBOTT MEDICAL OPTICS INC
Ophthalmic devices, system and methods that improve peripheral vision
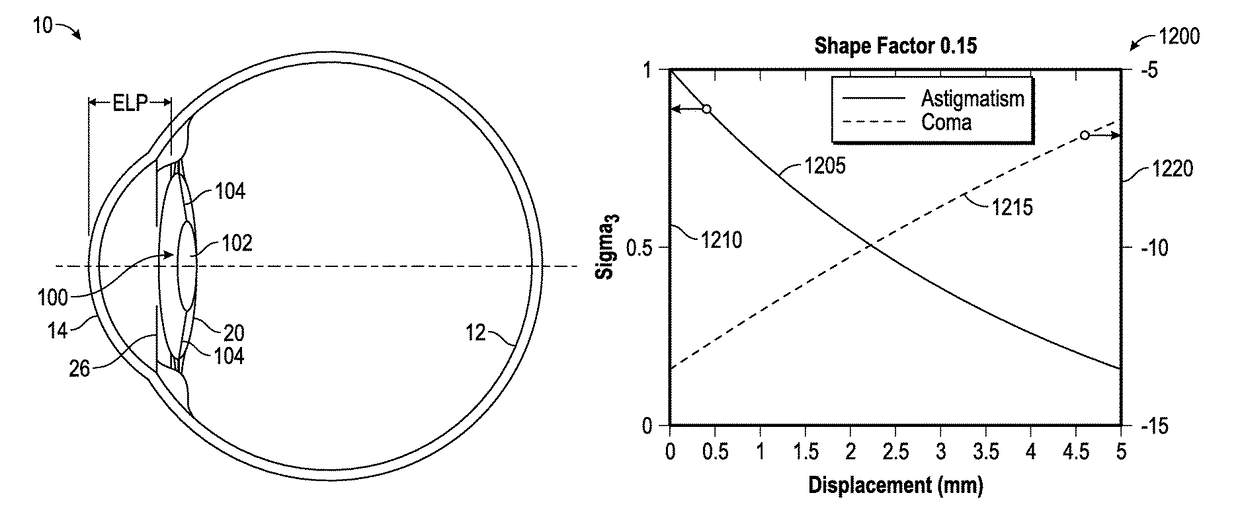
ActiveUS20150320547A1Improve image qualityReduce optical aberrationEye diagnosticsIntraocular lensRetinaVisual perception
The present disclosure relates to devices, systems, and methods for improving or optimizing peripheral vision. In particular, methods are disclosed which include utilizing particular characteristics of the retina in improving or optimizing peripheral vision. Additionally, various IOL designs, as well as IOL implantation locations, are disclosed which improve or optimize peripheral vision.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Perceived Image Depth for Autostereoscopic Displays
InactiveUS20150015946A1Reduce optical aberrationMore field of viewOptical elementsDisplay designDisplay device
An autostereoscopic display provides an extremely deep projection area by observing a relationship between a desired depth of projection and an autostereoscopic display design that includes a focal length of lenticles of a lenticular array and a number of views. The relationship specifies a projected depth at which lenticular crossover can occur for a given autostereoscopic with the specific lenticular focal length and number of views. Approximations can be used to simplify the relationship such that the projected depth is directly related to a product of the focal length and the number of views. To reduce optical aberrations, lenticles of the lenticular array include meniscus-cylinder lenses.
Owner:SOLIDDD
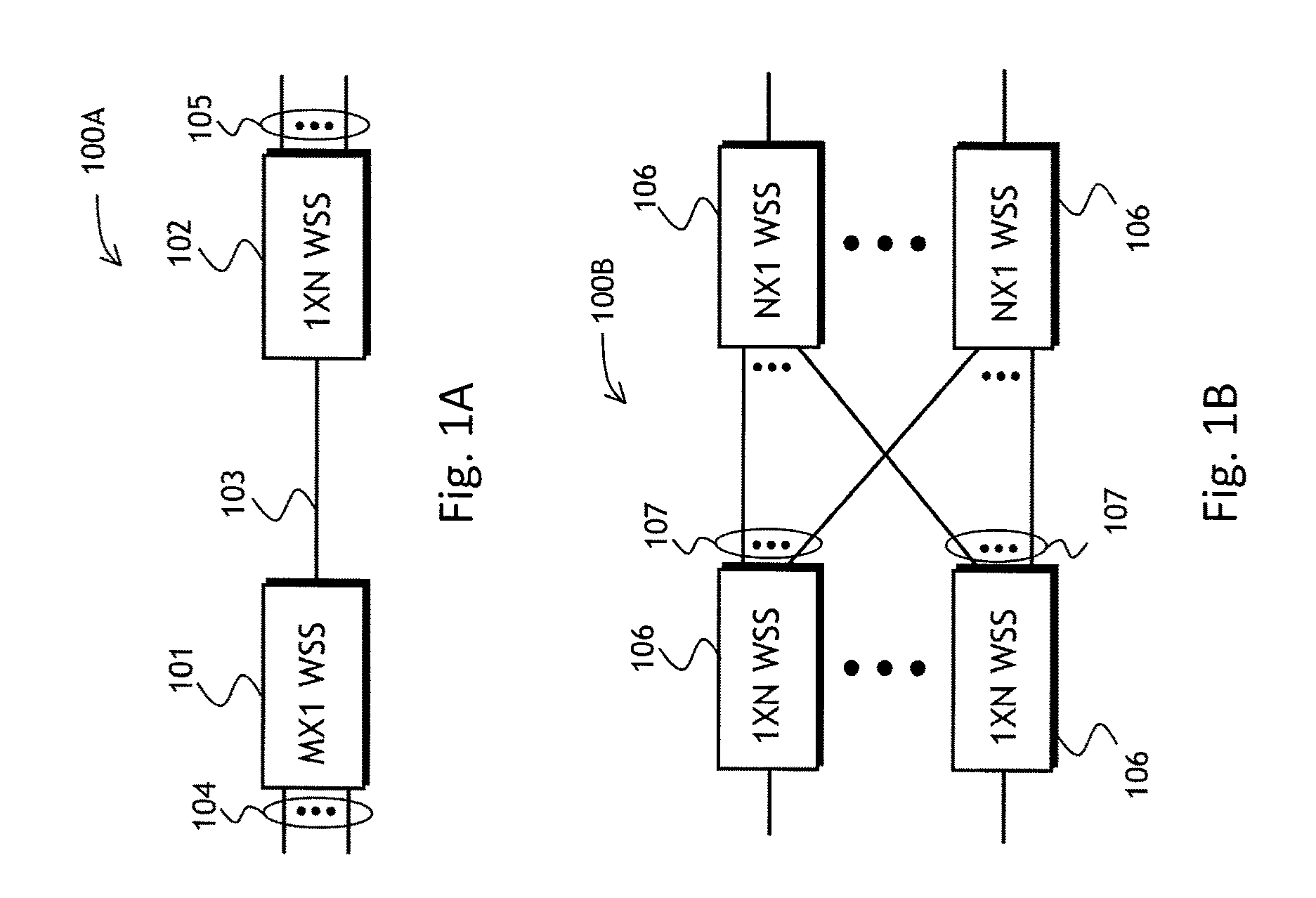
M x n wss with reduced optics size
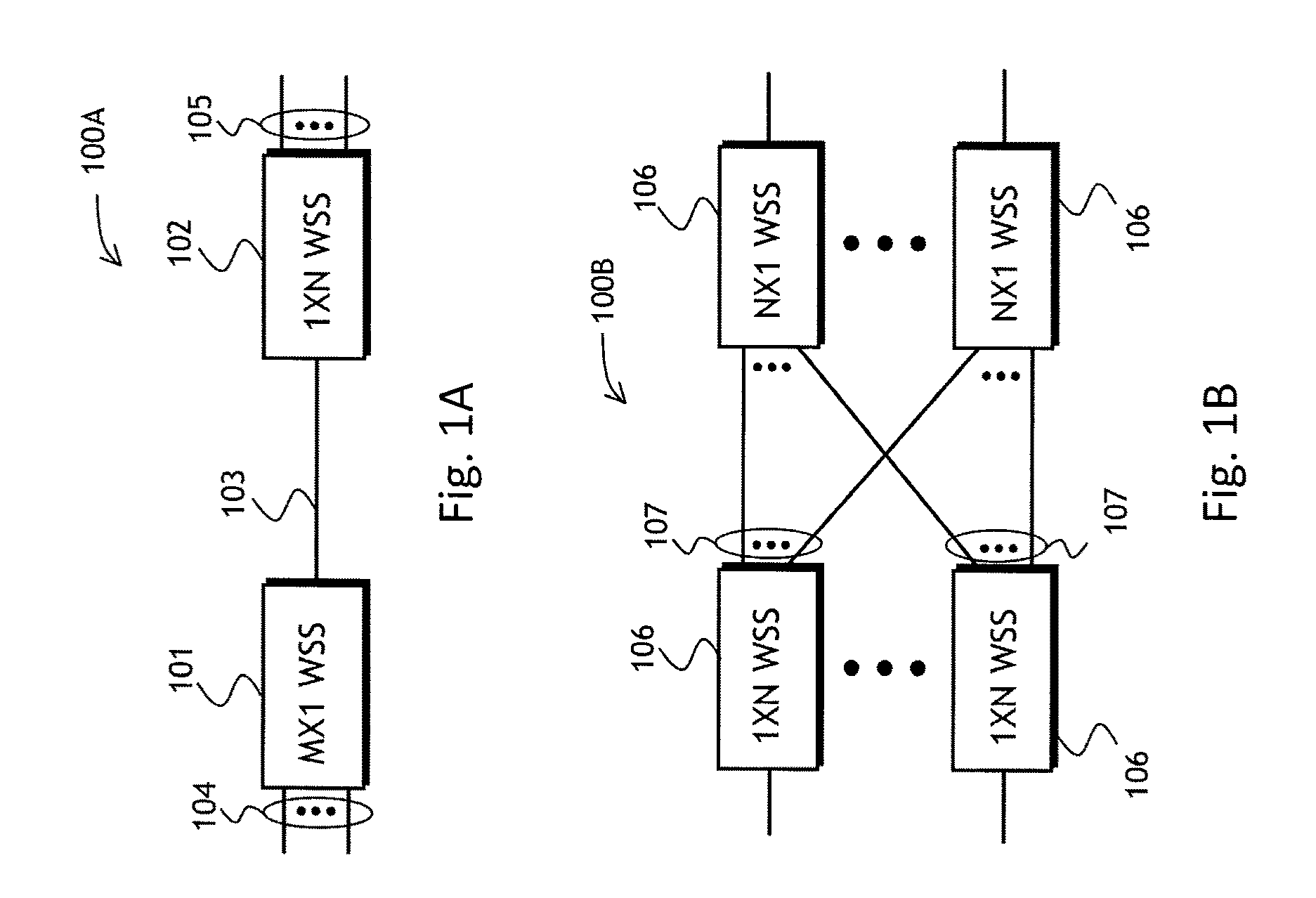
A M×N wavelength selective switch (WSS) module capable of independently routing any wavelength channel from any input port to any output port is provided. The M×N WSS includes a first beam relayer including first and second elements having optical power, each of which is disposed such that light transmitted to or from a first plurality of ports passes through a common point. The M×N WSS also includes a wavelength dispersive element, a first switching array having M rows including K switching elements, a second beam relayer, and a second switching array including N switching elements. The second switching array includes an optical by-pass disposed at the common point, which provides means for separating the input and output beams of light, and which allows both the input and output optical beams to traverse similar paths throughout the optical train.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Fiber coupled artificial compound eye
InactiveUS7376314B2Sharpen imageReduce optical aberrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCoupling light guidesDistortion freeDetector array
A multiple aperture array, wide angle imaging system incorporates compound refractive optics modeled after the eyes of insects. The system channels light through the apertures of a convex spatial filter and a pair of lenslet arrays hot press molded on a positive meniscus form. The lenslets act as afocal Keplerian telescopes to superpose light from hundreds of adjacent channels to a common point on the convex surface of a fiber optic imaging taper. The superposed light from all the channels form a curved, high intensity image that is transformed by the taper into a flat format for readout by a mosaic detector array. The image is upright and distortion free with an infinite depth of field. Ghost images are blocked by a honeycomb louver baffle positioned between the lenslets and the imaging taper. The system is conformable to the geometry of any convex mounting surface, whether spherical, aspherical, or cylindrical.
Owner:SPECTRAL IMAGING LAB
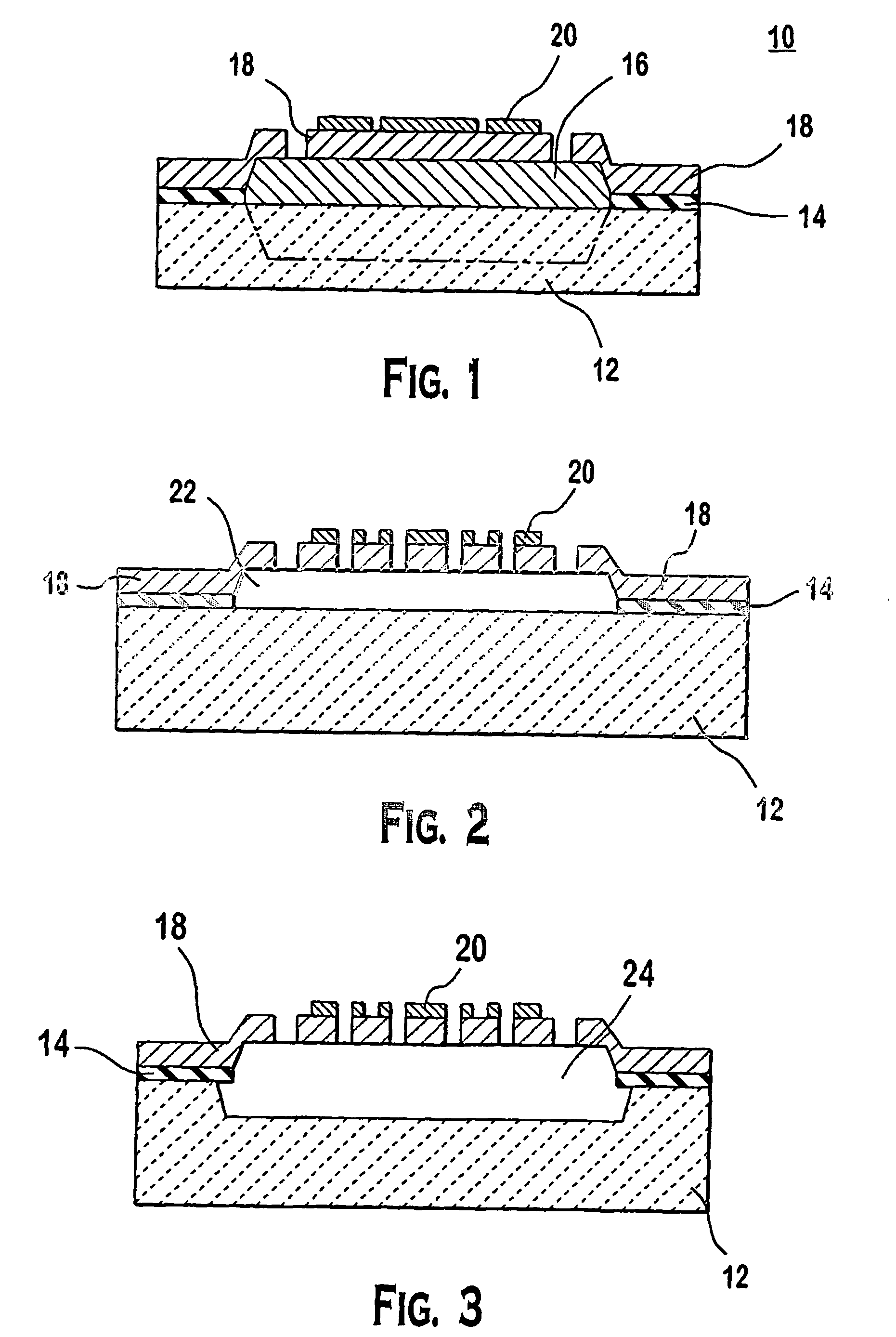
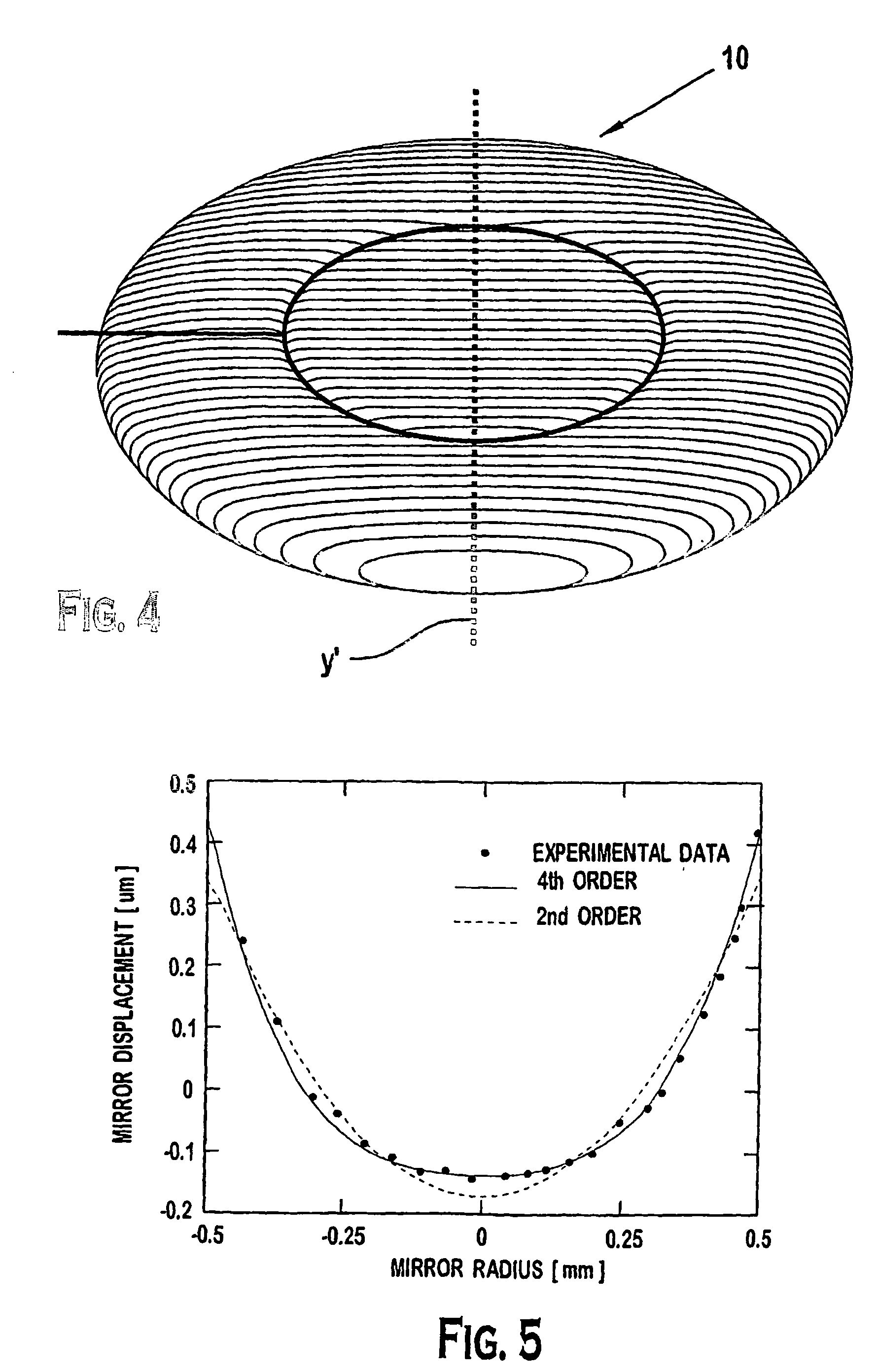
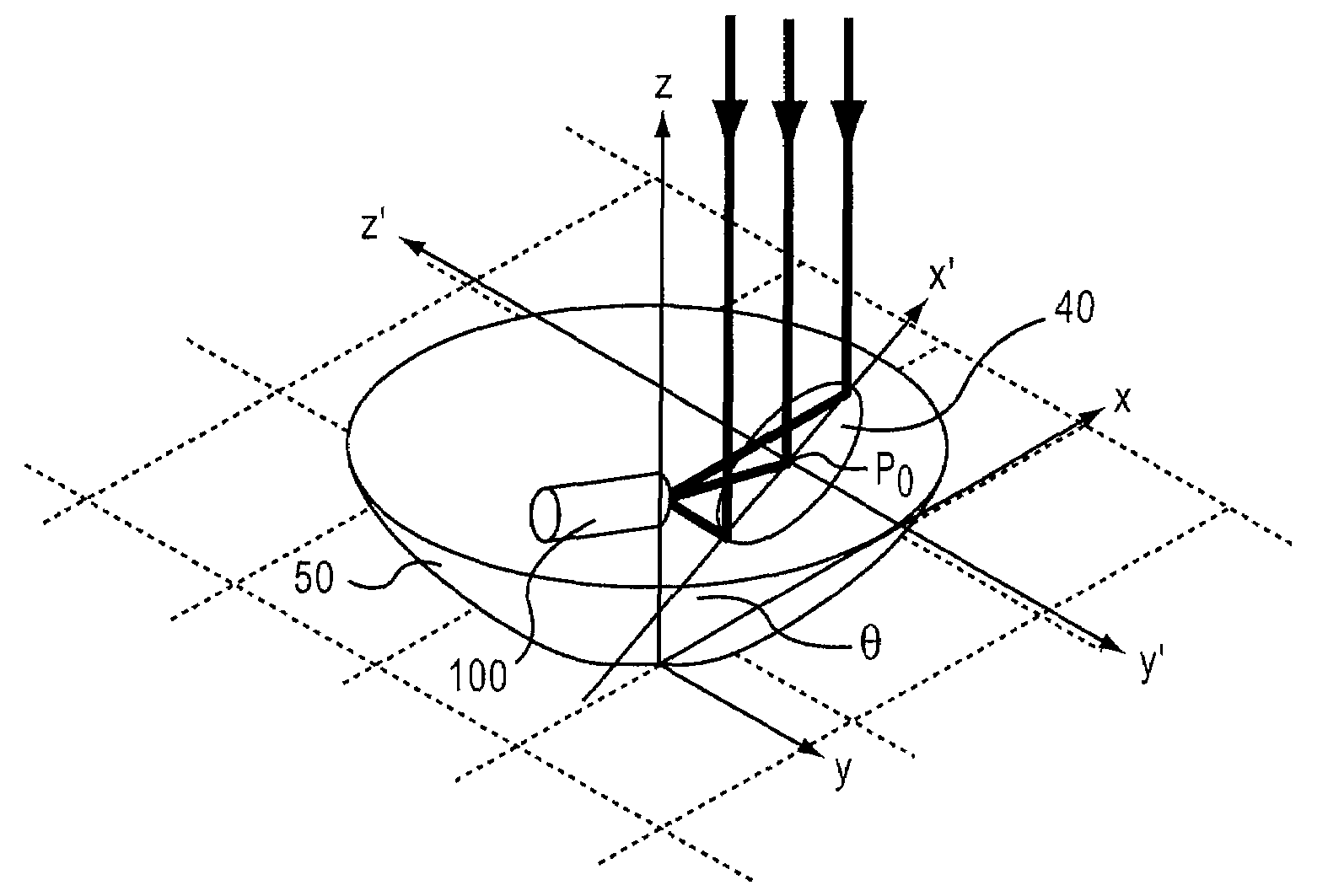
Off-axis variable focus and aberration control mirrors and method
ActiveUS20060232846A1Reduce optical aberrationOptical aberrations in the image formed by the reflected light beam is reducedMirrorsMountingsOptical aberrationPhysics
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
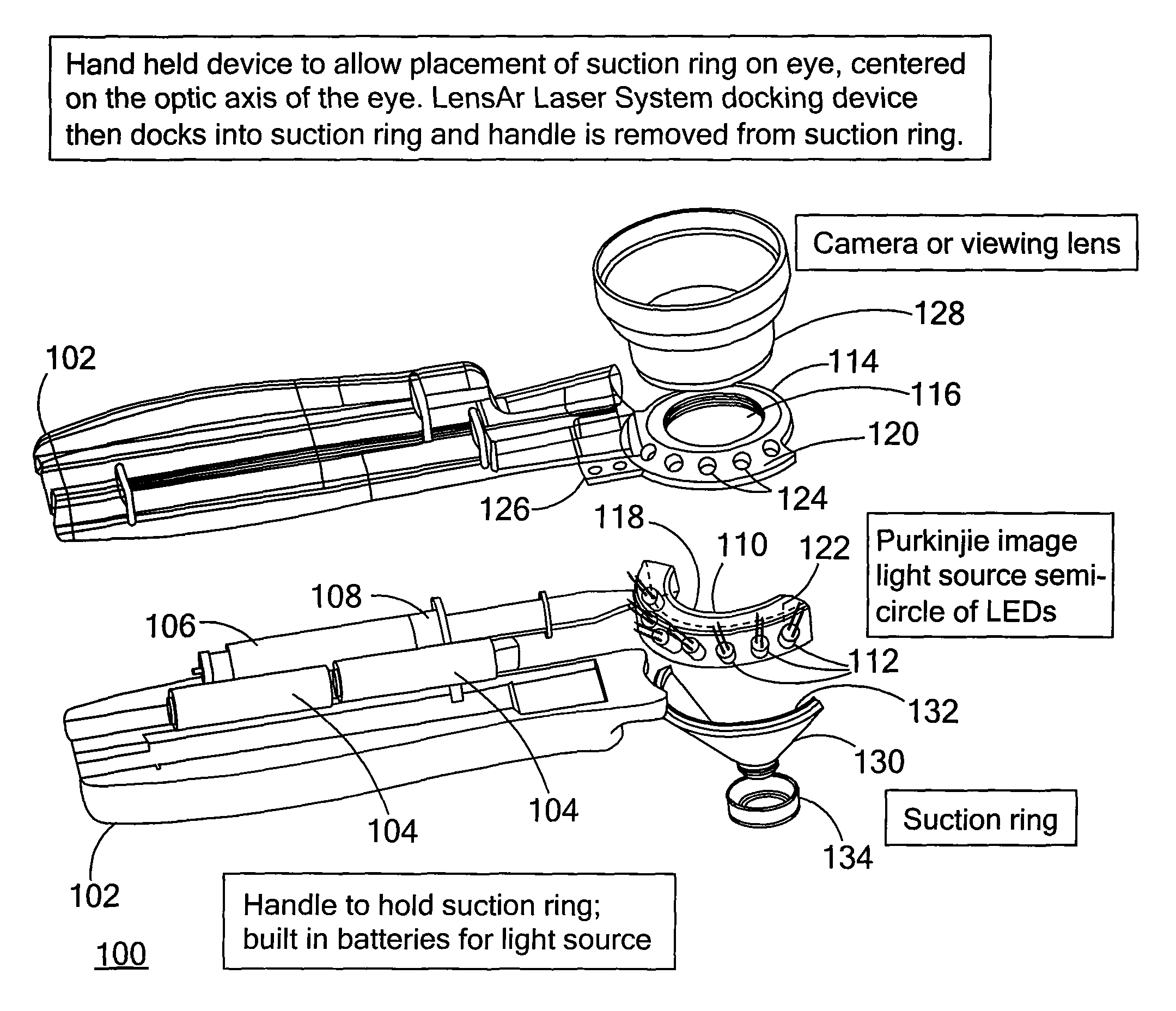
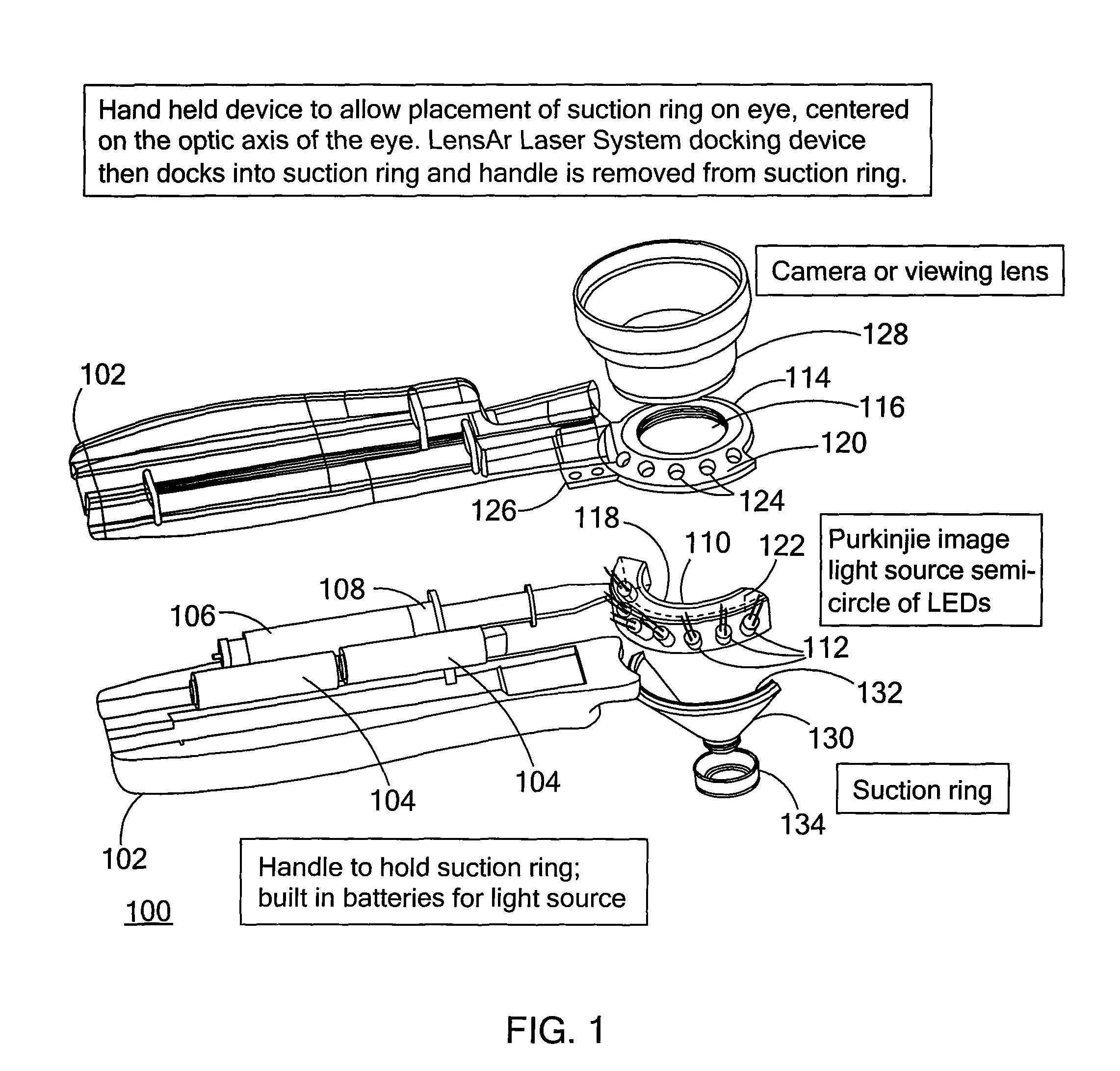
Purkinjie image-based alignment of suction ring in ophthalmic applications
ActiveUS8556425B2Improved visual outcomeAccurate and stabile placementLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsOptometryImage based
Owner:LENSAR LLC
Beam Optical Component Having a Charged Particle Lens
InactiveUS20080230694A1Reduce optical aberrationImprove spatial resolutionThermometer detailsElectrode and associated part arrangementsLight beamAtomic physics
The present invention relates to a beam optical component including a charged particle lens for focusing a charged particle beam, the charged particle lens comprising a first element having a first opening for focusing the charged particle beam; a second element having a second opening for focusing the charged particle beam and first driving means connected with at least one of the first element and the second element for aligning the first opening with respect to the second opening. With the first driving means, the first opening and the second opening can be aligned with respect to each other during beam operation to provide a superior alignment of the beam optical component for a better beam focusing. The present invention also relates to a charged particle beam device that uses said beam optical component for focusing the charged particle beam, and a method to align first opening and second opening with respect to each other.
Owner:ICT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TESTING GESELLSCHAFT FUER HALBLEITERPRUEFTECHNIK GMBH
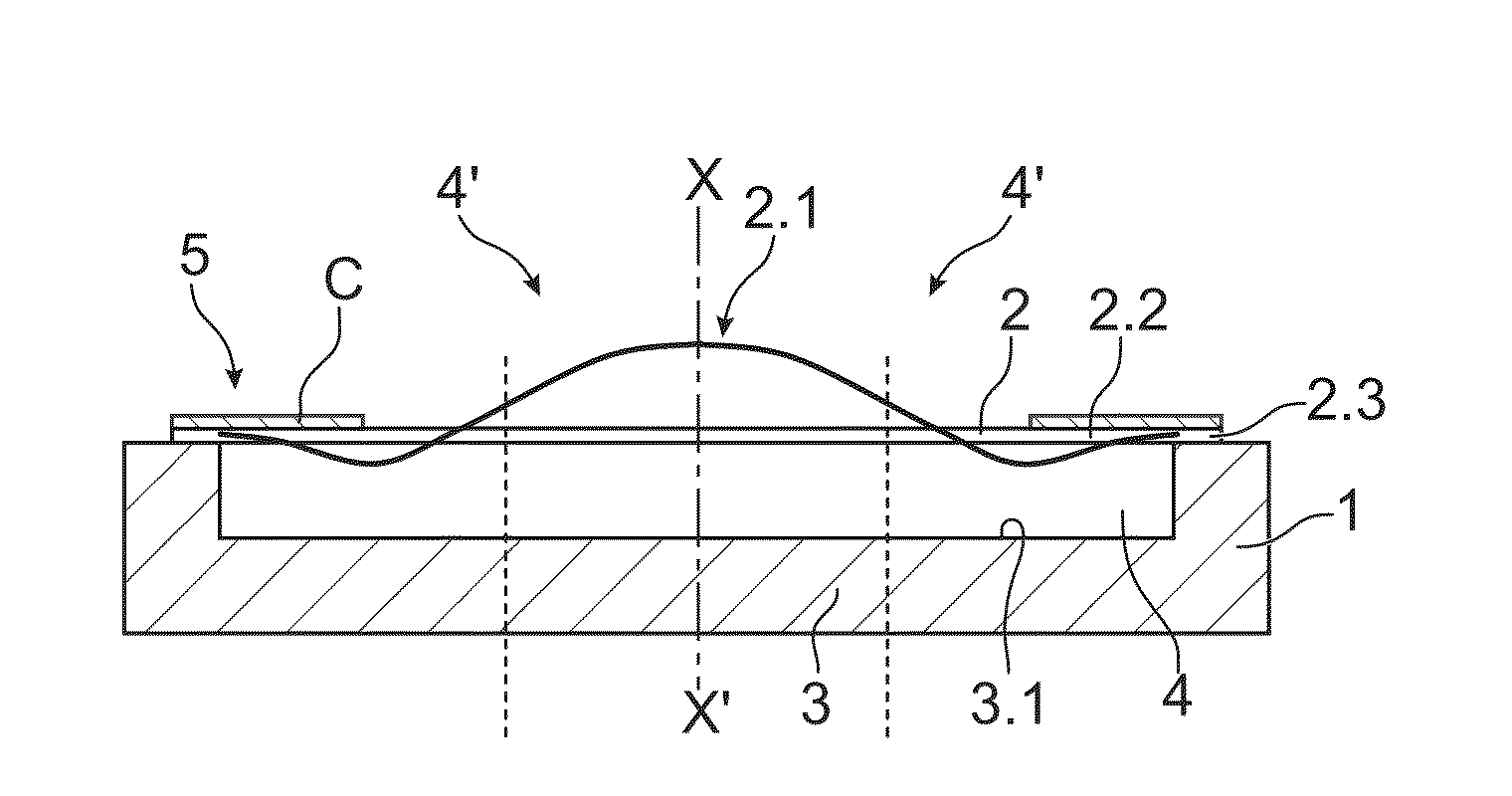
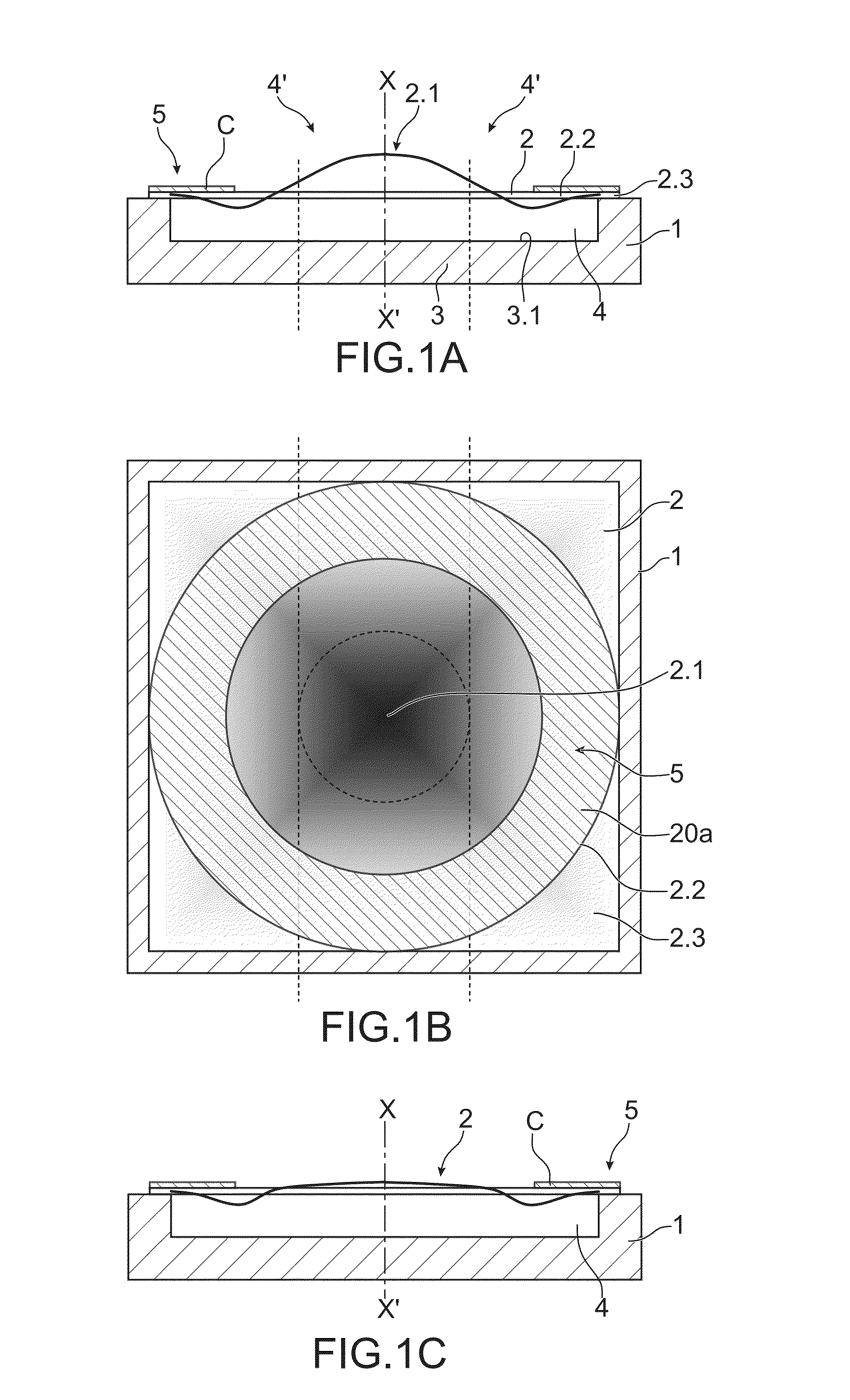
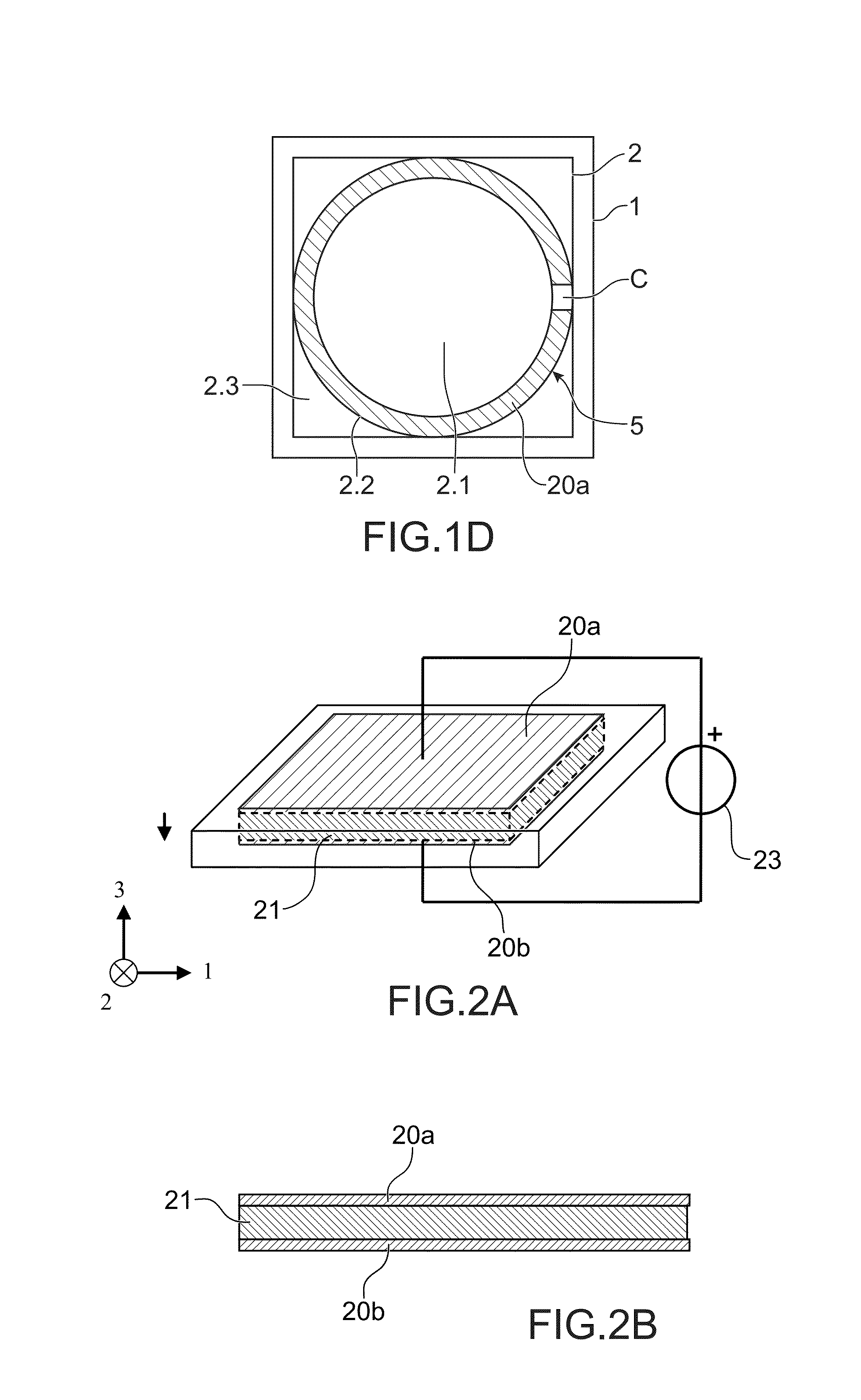
Optical device with a piezoelectrically actuated deformable membrane shaped as a continuous crown
Owner:WEBSTER CAPITAL LLC
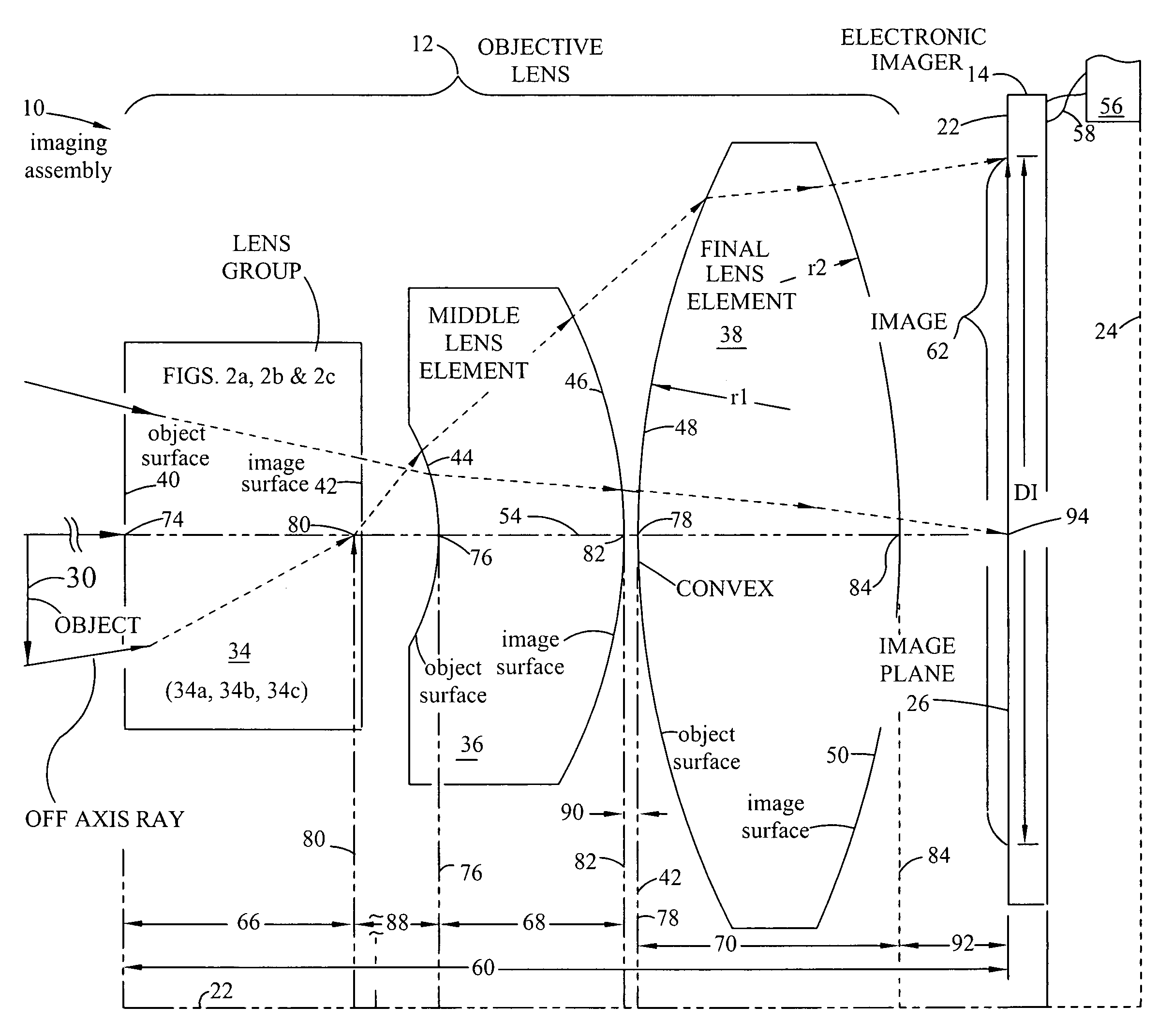
Objective lens
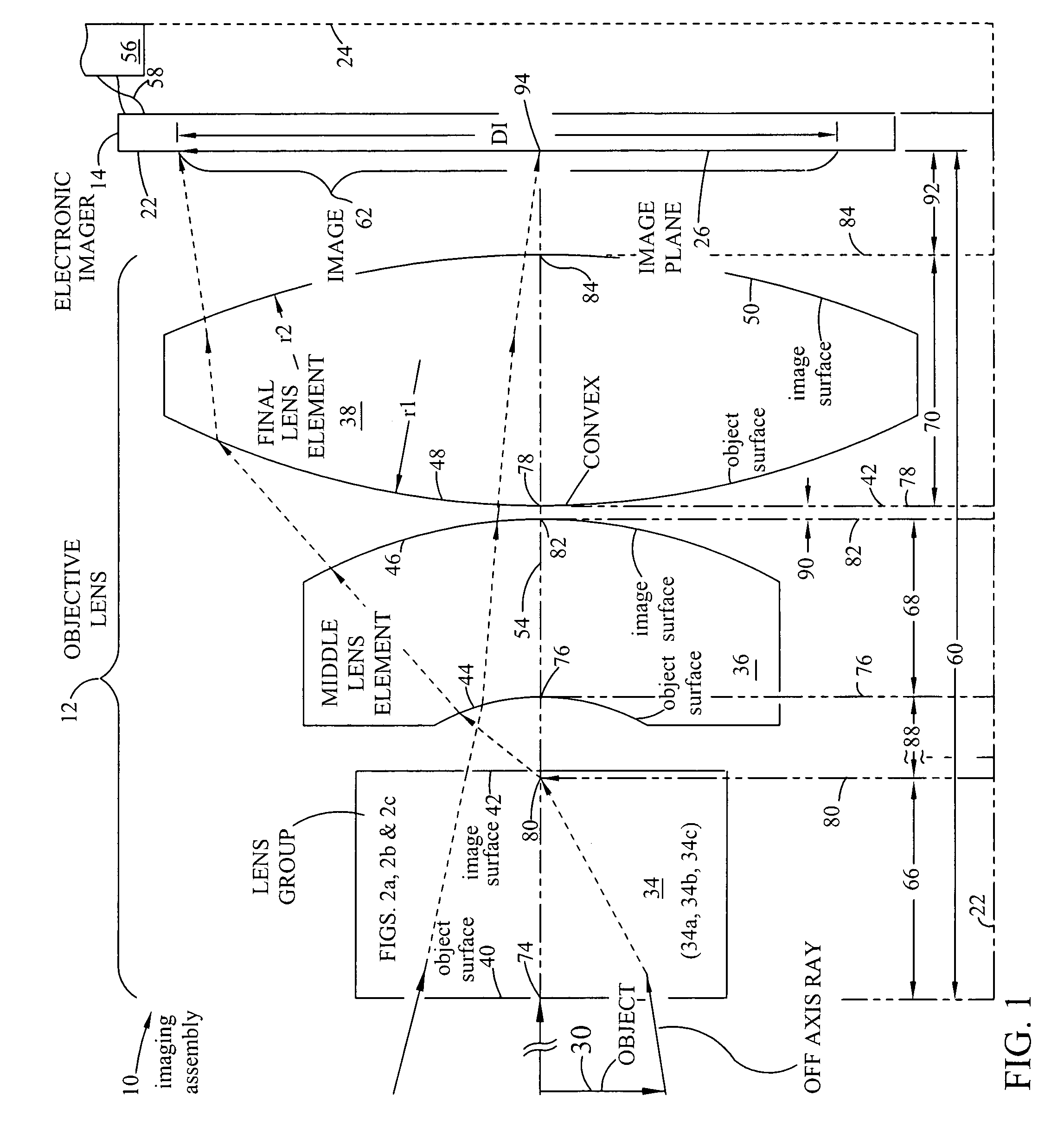
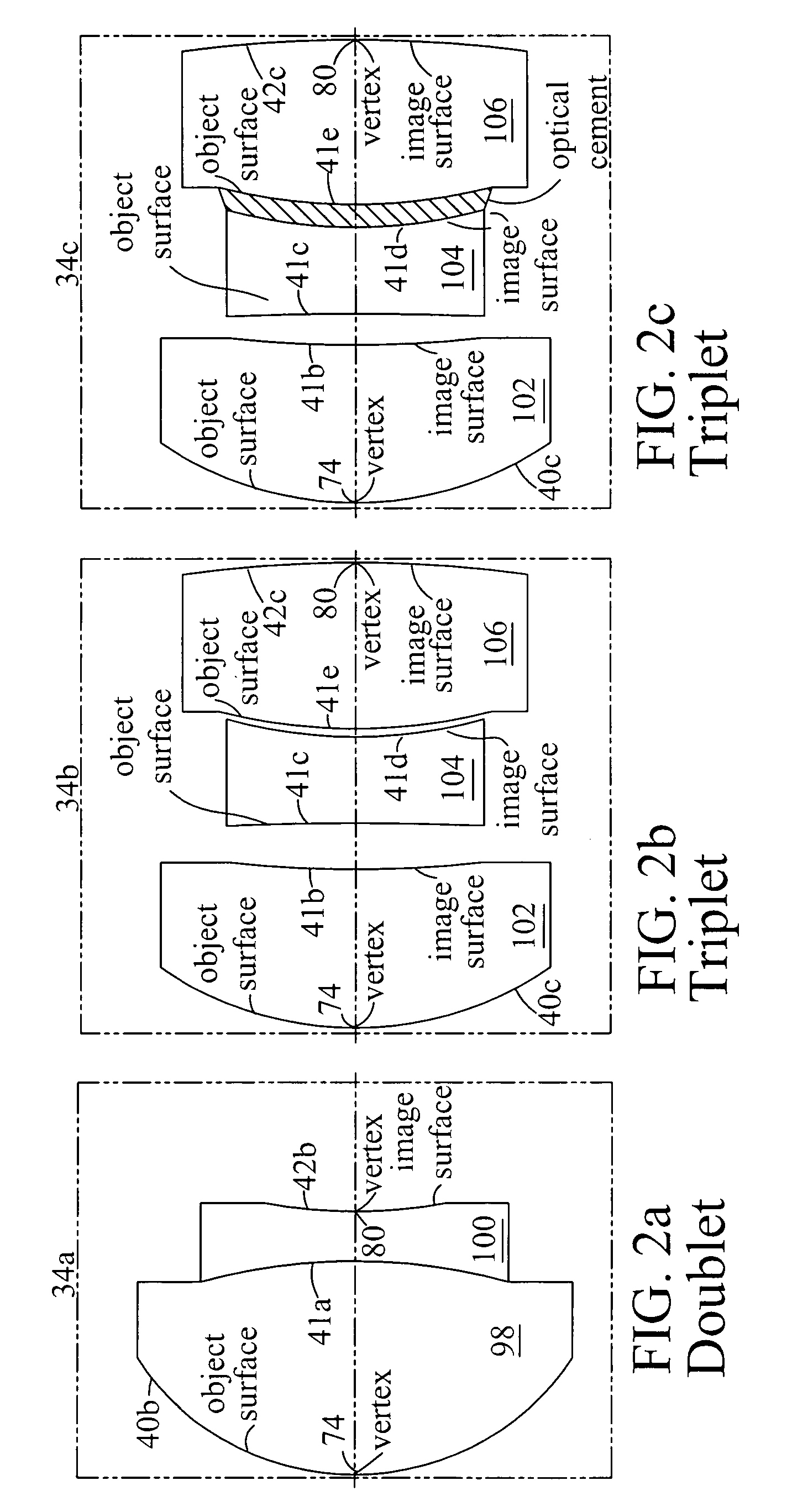
The compact imaging assembly has an electronic imager and an objective lens with a focal length fo. The objective lens receives light and forms an image of the object on the imager's image plane. The image plane has a maximum effective dimension DI. The objective lens has a first lens group comprising two to three elements with an object surface facing the object and an image surface facing an image plane. The objective lens also has a middle lens element with a concave object surface that is facing the lens group image surface, and a final lens element that has a positive power. The distance from the lens group object surface to the image plane is TT. The lens group, the middle lens and the final lens elements are coaxially aligned and on an optical axis normal to the image plane.
Owner:NING ALEX
M X N WSS with reduced optics size
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Non-Round Fluid Filled Lens Optic
InactiveUS20110085243A1Reduce optical aberrationSimple designEye diagnosticsOptical partsOptical powerOptic disk
An optical and mechanical design of a sealed, non-round fluid-filled lens capable of providing variation of optical power. The fluid lens includes at least three optical components: at least one mostly rigid optical disc, at least one mostly flexible optical membrane and a layer of a transparent fluid that is in communication via a fluid channel with a reservoir of excess fluid contained in a reservoir that can be accessed to augment the fluid volume inside the fluid lens to change the power of the fluid lens. The fluid lens is capable of providing correction of spherical and astigmatic errors, and utilizes contoured membranes to minimize image aberrations.
Owner:ADLENS BEACON INC
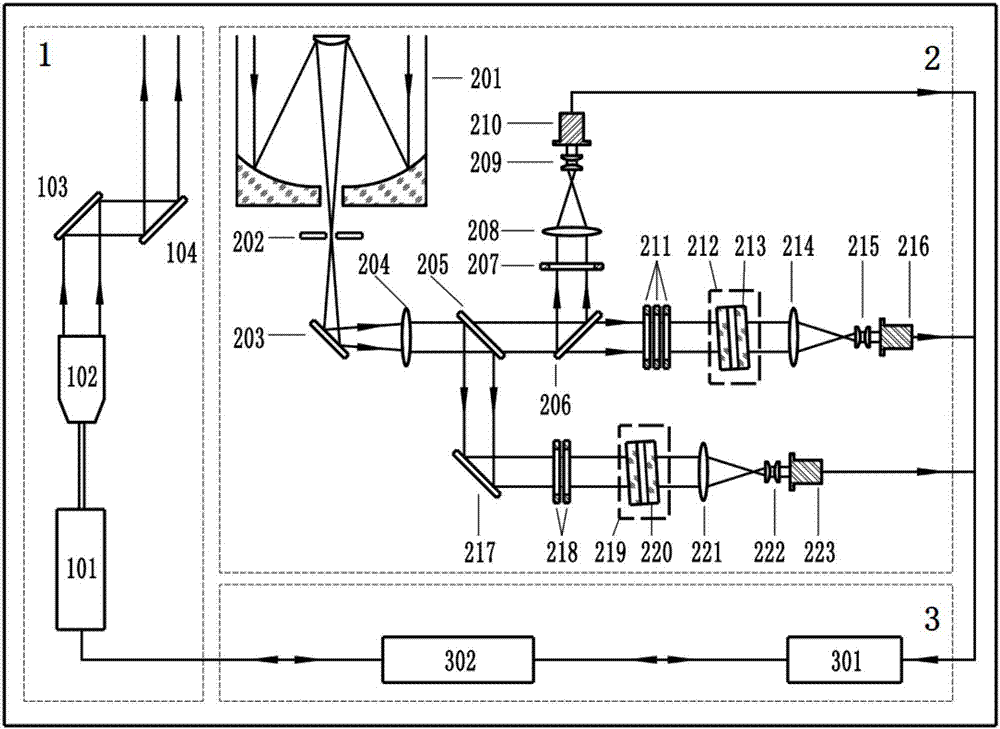
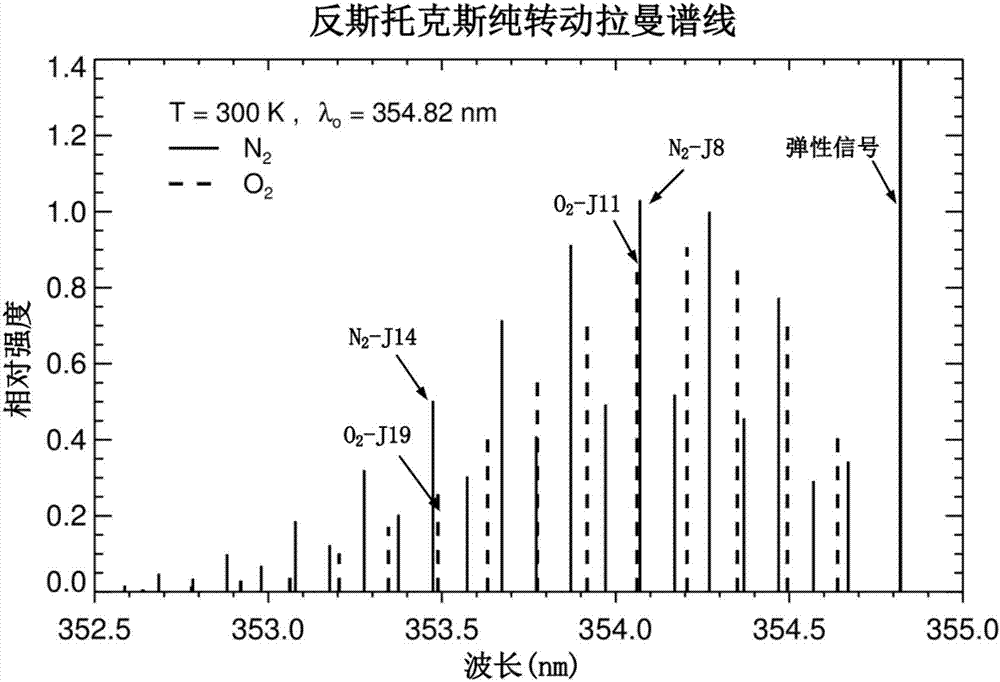
Ultraviolet quasi-single pure-rotation Raman spectrum extraction-based all-day temperature measurement laser radar
ActiveCN107024699AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove working environmentThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsAtmospheric temperature
The present invention discloses an ultraviolet quasi-single pure-rotation Raman spectrum extraction-based all-day temperature measurement laser radar. The laser radar comprises a laser emitting unit, an optical receiving unit and a signal acquisition and control unit. The laser emitting unit emits the ultraviolet laser of 354. 82 nm in wavelength and the ultraviolet laser is adopted as a detection light source. The laser emitting unit sends a pulse laser beam to the atmosphere. The pulse laser beam and atmospheric particles interact to generate a series of discrete spectrum line scattering signals. The optical receiving unit receives the scattering signals through a telescope and then respectively and simultaneously extracts elastic scattering signals and quasi-single-branched anti-stoke pure-rotation Raman spectral line signals through three channels. The signal acquisition and control unit realizes the real-time acquisition and the inversion of signals, so that the normal and orderly operation of the entire laser radar system is ensured. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the signal-to-noise ratio of the system is enhanced, and the light-receiving path is optimized. The system stability is improved. The all-day detection of the atmospheric temperature, the aerosol space distribution and time evolution parameters is implemented.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
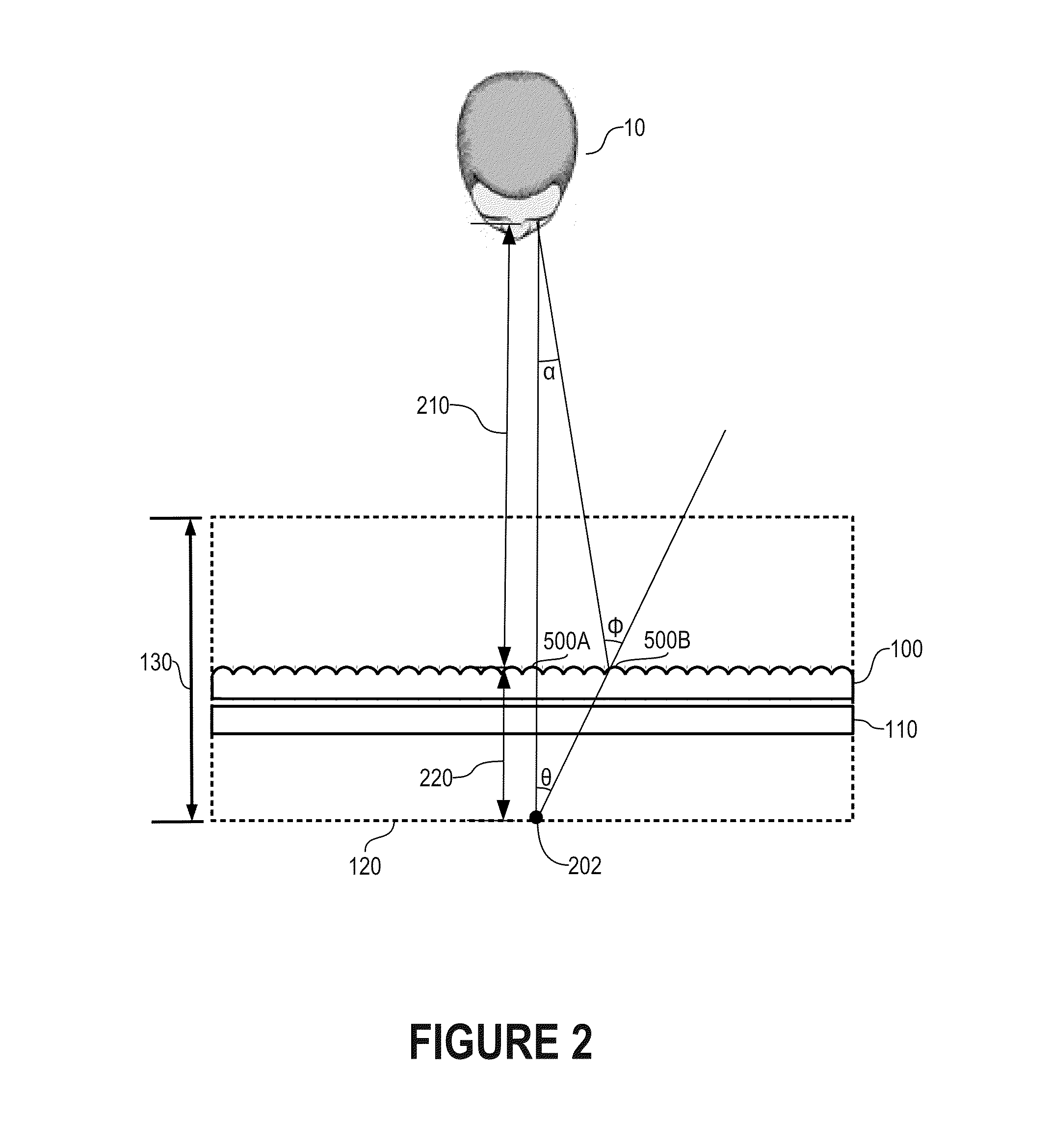
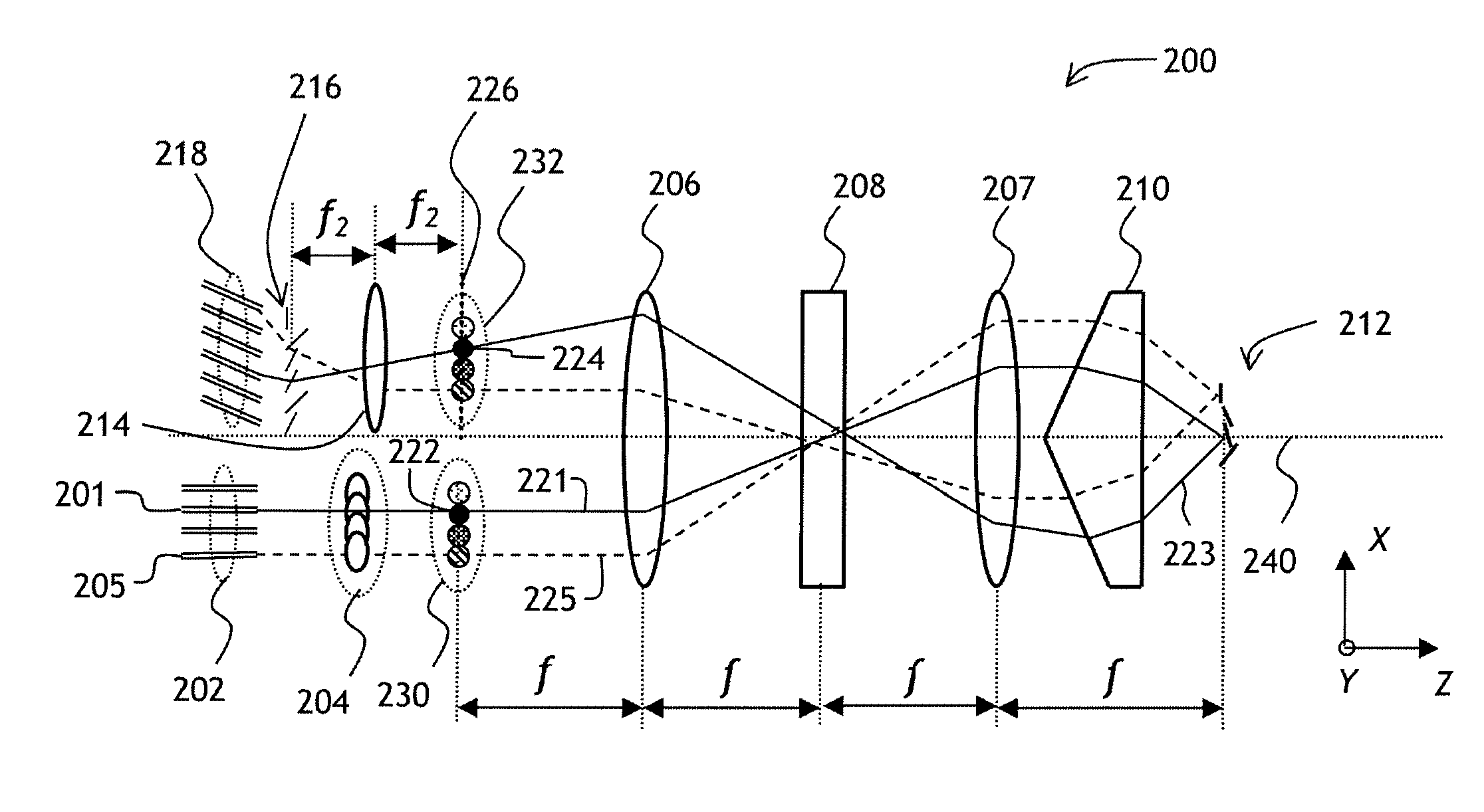
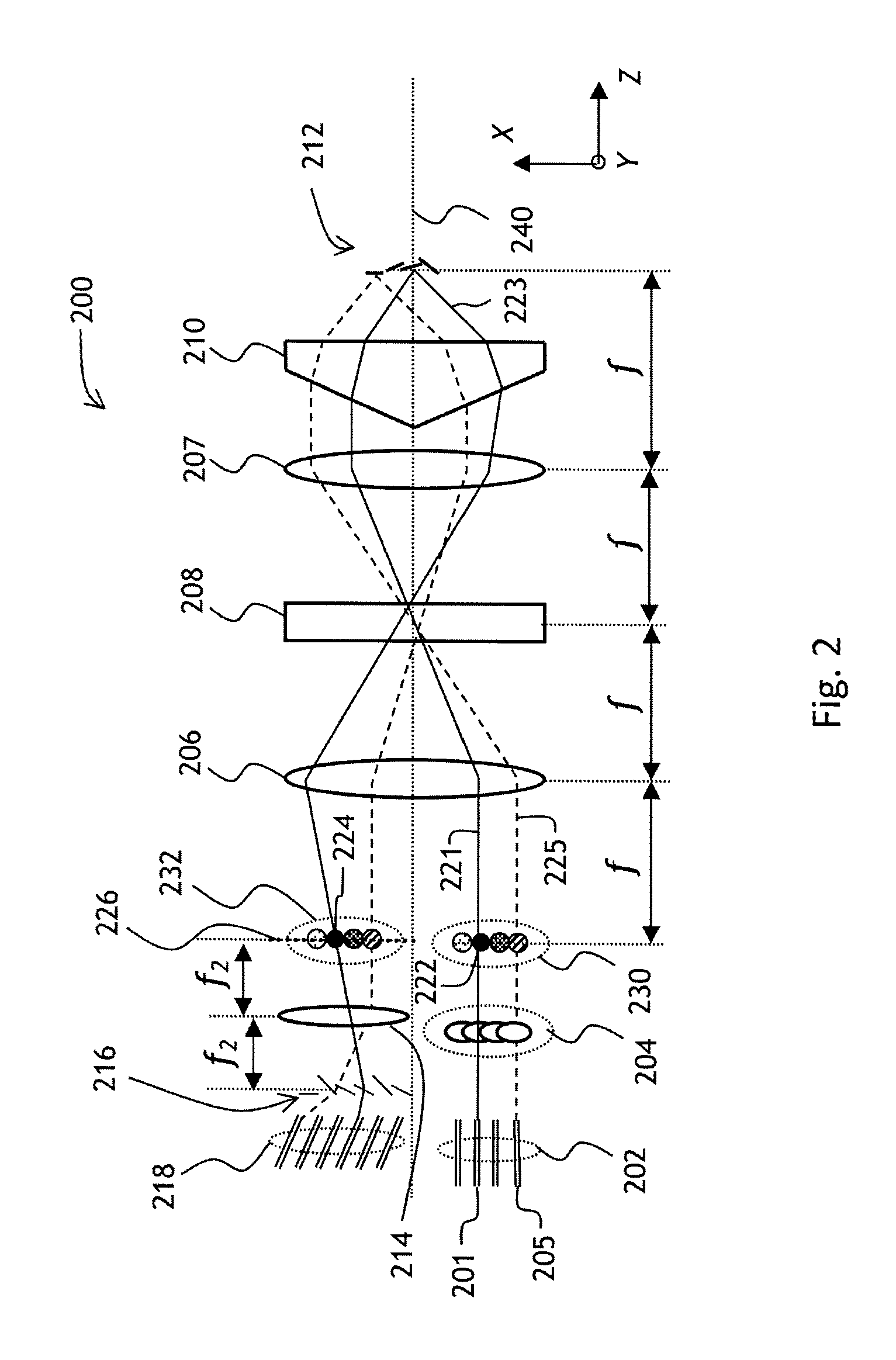
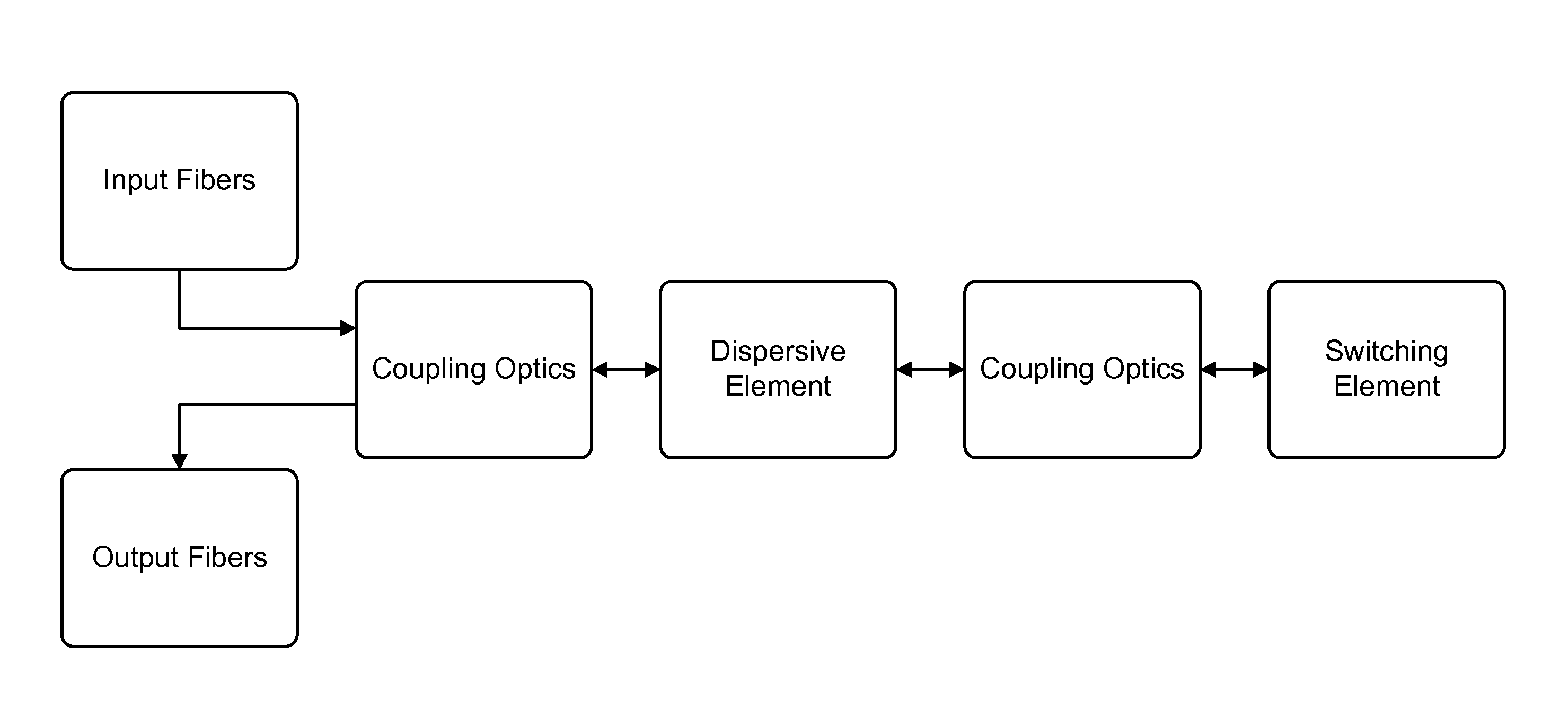
Systems And Methods For Reducing Off-Axis Optical Aberrations In Wavelength Dispersed Devices
ActiveUS20130177272A1Reducing off-axis optical aberrationReduce polarizationCoupling light guidesFiberGrism
Through its higher refractive index, a silicon grism can be used to reduce the Described herein are systems and methods for reducing optical aberrations in an optical system to decrease polarization dependent loss. Embodiments are provided particularly to define beam trajectories through an optical switching system which reduce off-axis aberrations. In one embodiment, a silicon grism is provided for reducing the curvature of the focal plane at an LCOS device in a wavelength selective switch (WSS) such that the separated polarization states converge at the LCOS at substantially the same point along the optical axis for all wavelengths. In this embodiment, an axial offset at the LCOS device will not produce large PDL at the coupling fibers. In another embodiment, a coupling lens having an arcuate focusing region is provided to address an offset in the optical beams, such that the separated polarization states couple symmetrically to respective output fibers.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Adaptive optical devices with controllable focal power and aspheric shape
A fluidic lens may include an optical surface configured for deflection dominated by bending stress. An adjustable concentric load may be applied to the optical surface to cause a clear aperture region of the optical surface to deflect with generally spherical curvature. Adjusting the concentric load controls the radius of curvature. An adjustable uniformly-distributed load may be applied to the optical surface by fluid pressure that causes the clear aperture region to deflect with an aspheric shape. Adjusting the pressure controls the asphericity of curvature. First and second fluids having similar densities and different refractive indexes may be disposed on either side of a deflectable optical surface to help balance gravitational loading on either side of the optical surface, thereby reducing gravity-associated aberrations.
Owner:HOLOCHIP
Add/drop module using two full-ball lenses
InactiveUS7006728B1Lower requirementReduce optical aberrationCoupling light guidesCamera lensEngineering
An optical device has a housing for receiving a plurality of optical fibers adapted to carry optical signals. A filter is disposed within the housing for transmitting specific optical signals having a predetermined wavelength range. A first ball lens is coupled to the housing and is positioned relative to the filter and the optical fibers to selectively collimate and focus the optical signals. A second ball lens is coupled to the housing and is also positioned relative to the filter and optical fibers to selectively collimate and focus the optical signals. Both ball lenses are optically coupled to the filter.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Virtual-reality display optics system
InactiveCN106291939AEasy to correctReduce optical aberrationMagnifying glassesImaging qualityDisplay device
The invention discloses a virtual-reality display optics system which comprises a liquid display screen, a lens combination and diaphragm which are sequentially arranged along the optic axis. Light rays sent out through the liquid crystal screen enter human eye pupils via the diaphragm after refraction of the lens combination, the lens combination comprises a convex lens and a meniscus lens, the front surface, opposite to the diaphragm, of the convex lens is of a Fresnel surface while the rear surface of the same is of an aspheric surface, and both the front surface and the rear surface of the convex lens are provided with preset inclined angles relative to the pitching direction perpendicular to the optic axis of the eye pupils; the front surface of the meniscus lens is opposite to the rear surface of the convex lens while the rear surface of the meniscus lens is opposite to the liquid crystal display. By the arrangement, optical aberration can be well corrected and reduced, small optical aberration is good in imaging quality, and imaging quality is improved; meanwhile, light paths are formed through the lens combination of the optics system with the Fresnel and aspheric surfaces, and field is enlarged through optimal design of software.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stimulated emission depletion microscopy
ActiveUS9575302B2Reduce optical aberrationPhotometryMicroscopesStimulated emissionBrightness perception
Aberrations in stimulated emission depletion microscopy are corrected using an adaptive optics approach using a metric which combines both image sharpness and brightness. Light modulators (22,32) are used to perform aberration correction in one or more of the depletion path (10), the excitation path (12), or the emission path from sample to detector.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Offset aperture gimbaled optical system with optically corrected conformal dome
ActiveUS20150022873A1Increase profitReduce optical aberrationDirection controllersOptical elementsAxis of symmetryOptical correction
An offset aperture gimbaled optical system comprises a gimbal and an optics assembly that is mounted on an inner gimbal and offset radially from an axis of symmetry (and rotation axis) of a conformal dome. An optical corrector adjacent the inner surface of the conformal dome encompasses the field-of-view of the optics assembly as the inner gimbal rotates about its rotation axis. The corrector is fixed with respect to the inner gimbal's rotation axis while it rotates about the axis of symmetry. The optical corrector comprises an aspheric transparent arch having an optical corrector shape and position responsive to a shape of the conformal dome at the offset position of the optics assembly. In different applications, the offset aperture provides for reduced optical aberrations and improved utilization of the available packaging volume to accommodate multiple offset aperture optics assemblies.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Optical lens system with a wide field of view
An optical lens system with a wide field of view includes, in order from the object side to the image side: a stop, a first lens element with a positive refractive power, a second lens element with a negative refractive power, and a third lens element with a positive refractive power. A focal length of the first lens element and the second lens element combined is f12, a focal length of the third lens element is f3, and they satisfy the relation: 0.3<f12 / f3<0.9, so that the optical lens system has a wide field of view, high resolution, short length and less distortion.
Owner:NEWMAX TECH
Ophthalmic devices that improve peripheral vision
The present disclosure relates to devices, systems, and methods for improving or optimizing peripheral vision. In particular, methods are disclosed which include utilizing particular characteristics of the retina in improving or optimizing peripheral vision. Additionally, various IOL designs, as well as IOL implantation locations, are disclosed which improve or optimize peripheral vision.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Offset aperture gimbaled optical system with optically corrected conformal dome
ActiveUS9335126B2Increase profitReduce optical aberrationDirection controllersSelf-propelled projectilesAxis of symmetryOptical correction
An offset aperture gimbaled optical system comprises a gimbal and an optics assembly that is mounted on an inner gimbal and offset radially from an axis of symmetry (and rotation axis) of a conformal dome. An optical corrector adjacent the inner surface of the conformal dome encompasses the field-of-view of the optics assembly as the inner gimbal rotates about its rotation axis. The corrector is fixed with respect to the inner gimbal's rotation axis while it rotates about the axis of symmetry. The optical corrector comprises an aspheric transparent arch having an optical corrector shape and position responsive to a shape of the conformal dome at the offset position of the optics assembly. In different applications, the offset aperture provides for reduced optical aberrations and improved utilization of the available packaging volume to accommodate multiple offset aperture optics assemblies.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Compact high field of view display
ActiveUS20210033865A1Reduce scattered lightFocal length is lowPolarising elementsLensWide fieldDisplay device
A wide field of view display device employs curved optical components for enhanced performance with a compact arrangement. A wide field of view display includes a curved display device; a first curved lens having a display side and an exit side, wherein the display side is facing the curved display device; a first plurality of Fresnel facets disposed on the display side of the first curved lens; a second curved lens having a display side and an exit side, wherein the display side is facing the exit side of the first curved lens; and a second plurality of Fresnel facets disposed on the display side of the second curved lens, wherein the first plurality of Fresnel facets is configured to focus light from the curved display device on the second plurality of Fresnel facets, and wherein the second plurality of Fresnel facets is configured to focus light from the first plurality of Fresnel facets on a central image point.
Owner:SHARP KK
Perceived image depth for autostereoscopic displays
ActiveUS20180321501A1Reduce optical aberrationMore field of viewOptical elementsDisplay designDisplay device
An autostereoscopic display provides an extremely deep projection area by observing a relationship between a desired depth of projection and an autostereoscopic display design that includes a focal length of lenticles of a lenticular array and a number of views. The relationship specifies a projected depth at which lenticular crossover can occur for a given autostereoscopic with the specific lenticular focal length and number of views. Approximations can be used to simplify the relationship such that the projected depth is directly related to a product of the focal length and the number of views. To reduce optical aberrations, lenticles of the lenticular array include meniscus-cylinder lenses.
Owner:SOLIDDD
Beam optical component having a charged particle lens
InactiveUS8445846B2Reduce optical aberrationImprove spatial resolutionThermometer detailsElectrode and associated part arrangementsLight beamAtomic physics
The present invention relates to a beam optical component including a charged particle lens for focusing a charged particle beam, the charged particle lens comprising a first element having a first opening for focusing the charged particle beam; a second element having a second opening for focusing the charged particle beam and first driving means connected with at least one of the first element and the second element for aligning the first opening with respect to the second opening. With the first driving means, the first opening and the second opening can be aligned with respect to each other during beam operation to provide a superior alignment of the beam optical component for a better beam focusing. The present invention also relates to a charged particle beam device that uses said beam optical component for focusing the charged particle beam, and a method to align first opening and second opening with respect to each other.
Owner:ICT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TESTING GESELLSCHAFT FUER HALBLEITERPRUEFTECHNIK GMBH
Quantum dot-based polarization built-in color liquid crystal display and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN110632784AReduce optical aberrationReduce interferenceNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceLiquid crystal
A quantum dot-based polarization built-in color liquid crystal display according to the present invention comprises: a light source; a liquid crystal optical unit which is positioned above the light source and controls the phase delay of light incident from the light source; a polarizing functional layer that is positioned above the liquid crystal optical unit and that adjusts the transmittance oflight; and a quantum dot light-emitting section that is positioned above the polarizing functional layer and includes a plurality of quantum dot patterns having different light-emitting characteristics in a visible light region in accordance with the intensity of transmitted light. According to the embodiment, the quantum dot patterns and the polarizing functional layer are formed in the display,therefore, the characteristics of high color purity, low optical aberration, low interference effect and the like can be realized at the same time without a color filter; ; the polarizing functionallayer can be manufactured through a solution process, so that the advantages of low cost, simplified process and large area can be realized, and the limitation of a conventional color display technology based on quantum dots can be overcome.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
Offset aperture dual-gimbaled optical system
ActiveUS9347743B2Increase profitReduce optical aberrationDirection controllersOptical elementsEngineeringOptical aberration
An offset aperture two-axis gimbaled optical system comprises a two-axis gimbal and an optics assembly that is mounted on the inner gimbal and offset radially from the rotation axis of the outer gimbal. The optics assembly is suitably offset so that its optical aperture does not overlap the rotation axis of the outer gimbal and its optical aperture is symmetric about the rotation axis of the inner gimbal. In different applications, the offset aperture provides for reduced optical aberrations and improved utilization of the available packaging volume to accommodate multiple offset aperture optics assemblies.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
System and method for using diffractive elements for changing the optical pathway
InactiveUS20090180187A1Reduce aberrationReduce optical aberrationDiffraction gratingsHalographic mechanical componentsManipulatorDiffraction optics
An apparatus for adjusting an optical pathway, comprising a diffractive optics element configured for diffracting a plurality of light waves passing in the optical pathway, and a diffractive optics element (DOE) manipulator configured for manipulating said diffractive optics element, thereby changing the optical pathway.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Off-axis variable focus and aberration control mirrors and method
ActiveUS7494233B2Reduce optical aberrationOptical aberrations in the image formed by the reflected light beam is reducedMirrorsMountingsOptical aberrationPhysics
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
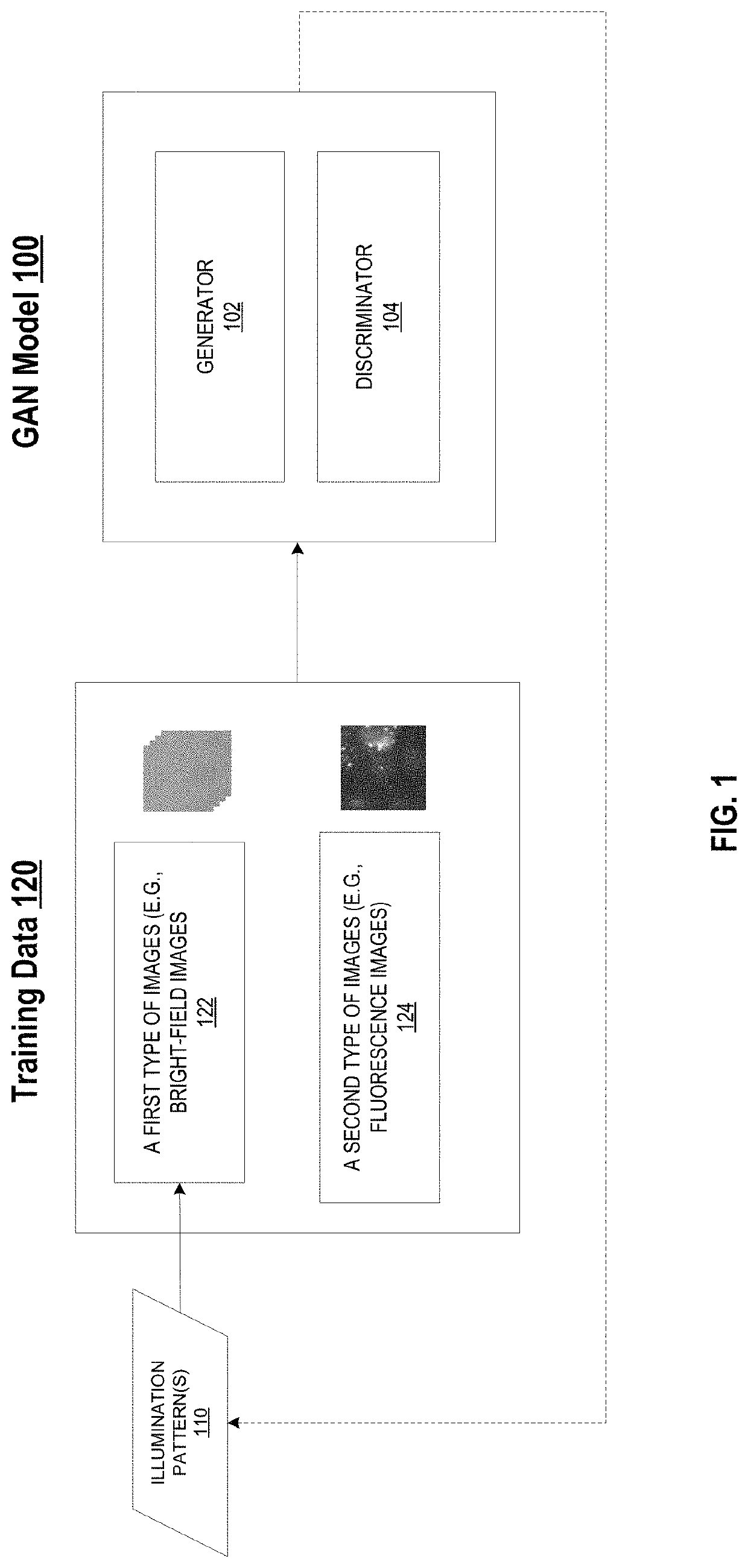
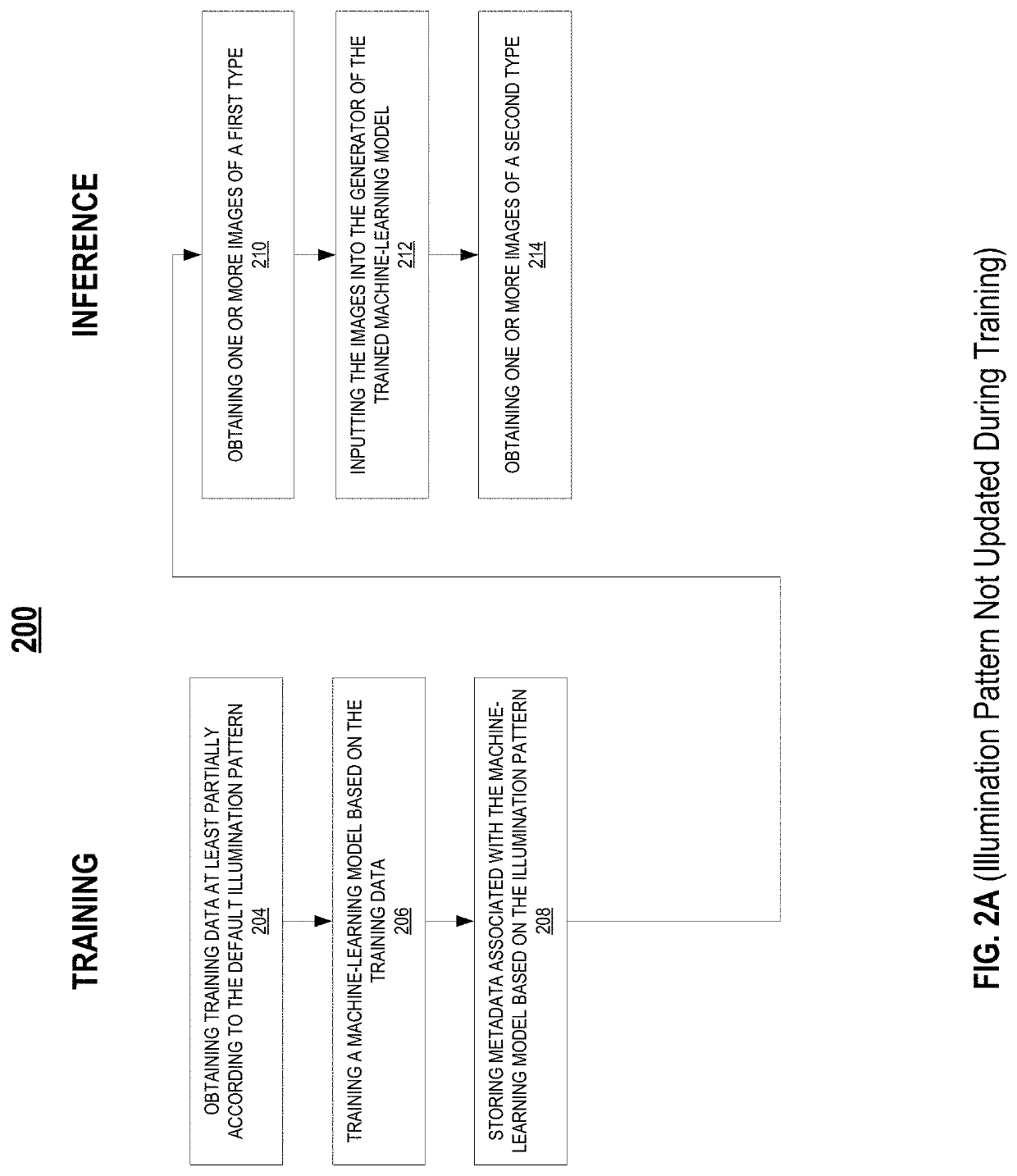
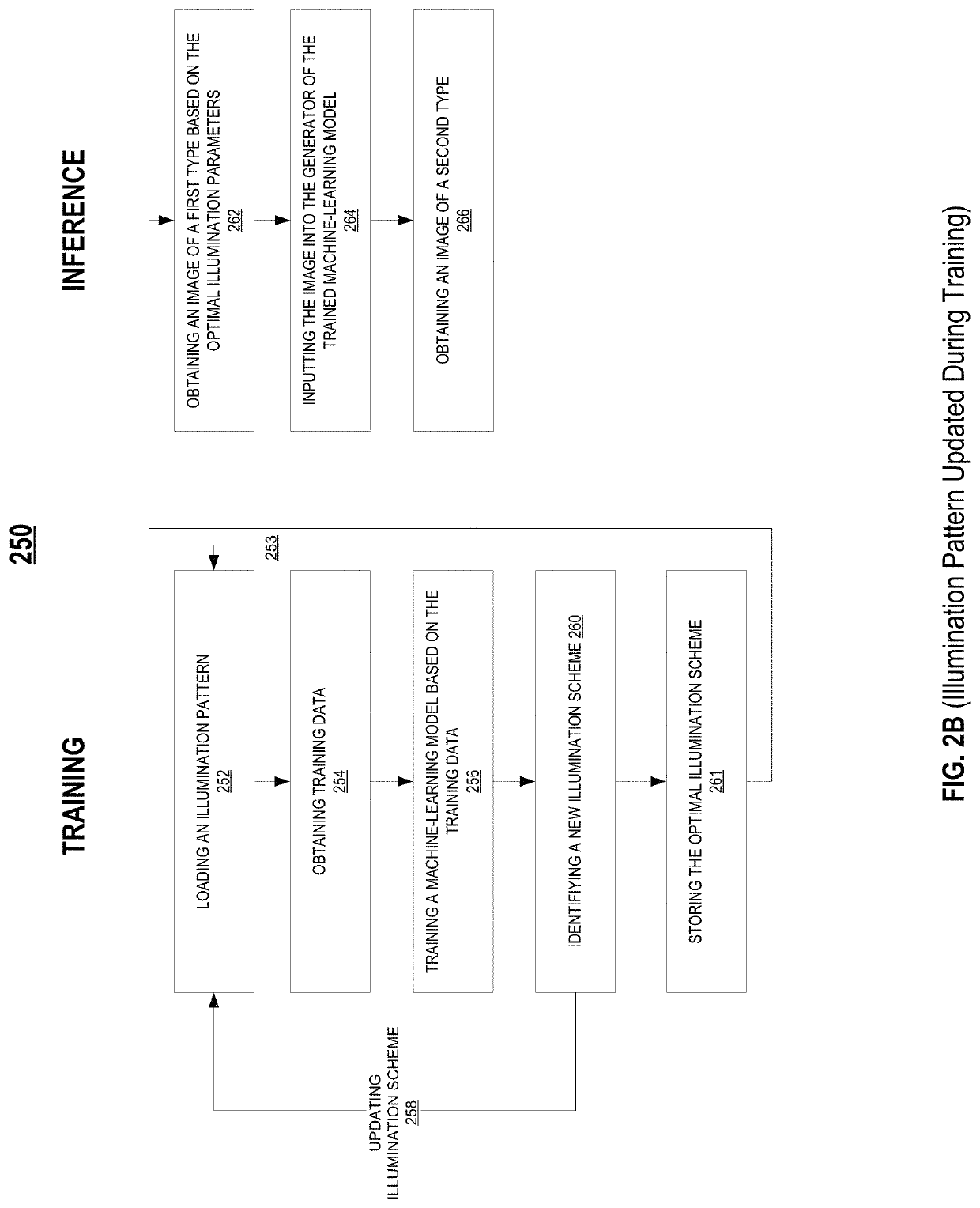
Biological image transformation using machine-learning models
ActiveUS11423256B2Add featureReduce optical aberrationImage enhancementImage analysisBiologyMachine learning
Described are systems and methods for training a machine-learning model to generate image of biological samples, and systems and methods for generating enhanced images of biological samples. The method for training a machine-learning model to generate images of biological samples may include obtaining a plurality of training images comprising a training image of a first type, and a training image of a second type. The method may also include generating, based on the training image of the first type, a plurality of wavelet coefficients using the machine-learning model; generating, based on the plurality of wavelet coefficients, a synthetic image of the second type; comparing the synthetic image of the second type with the training image of the second type; and updating the machine-learning model based on the comparison.
Owner:INSITRO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com